Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Avoid reallocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
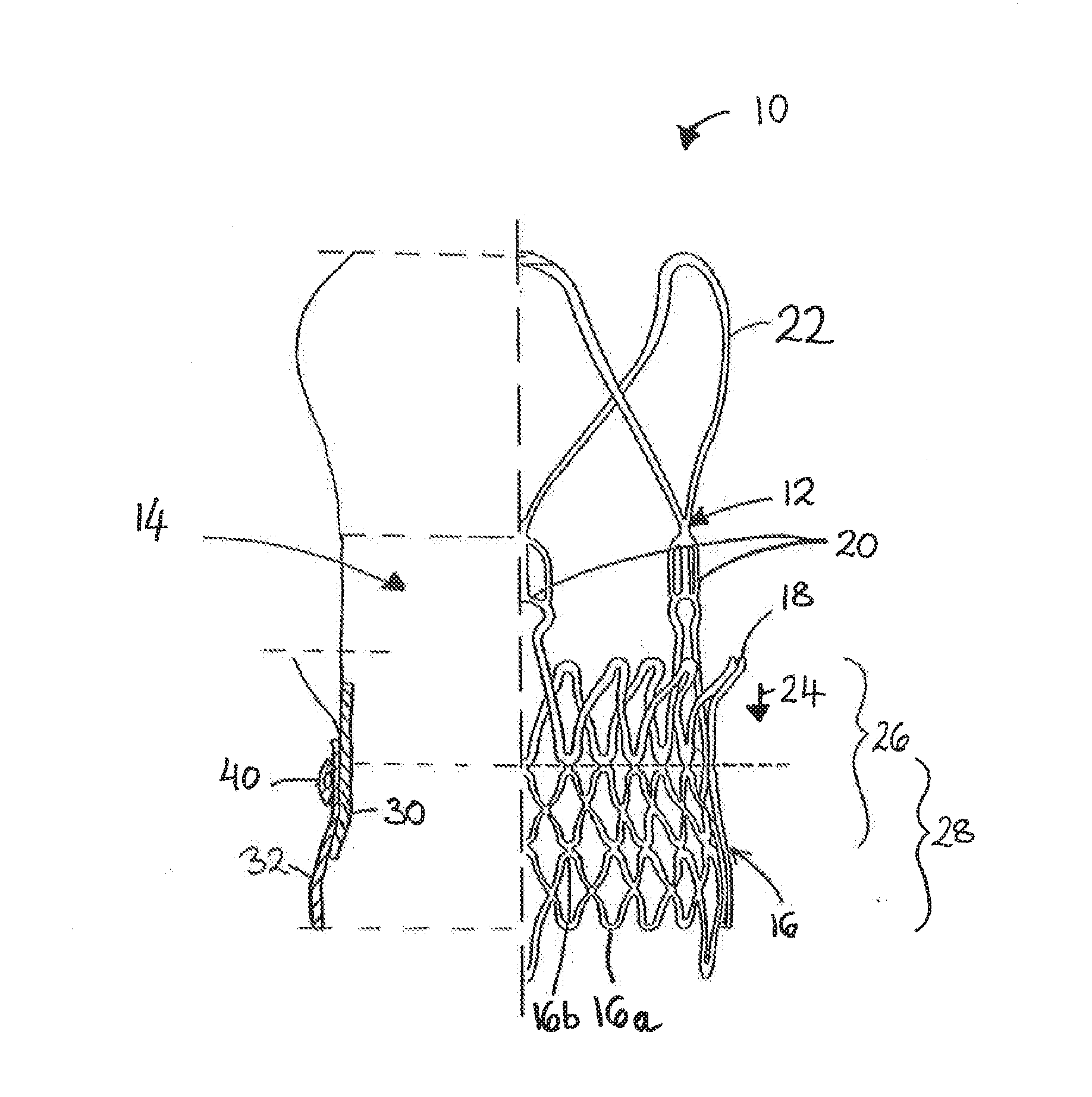
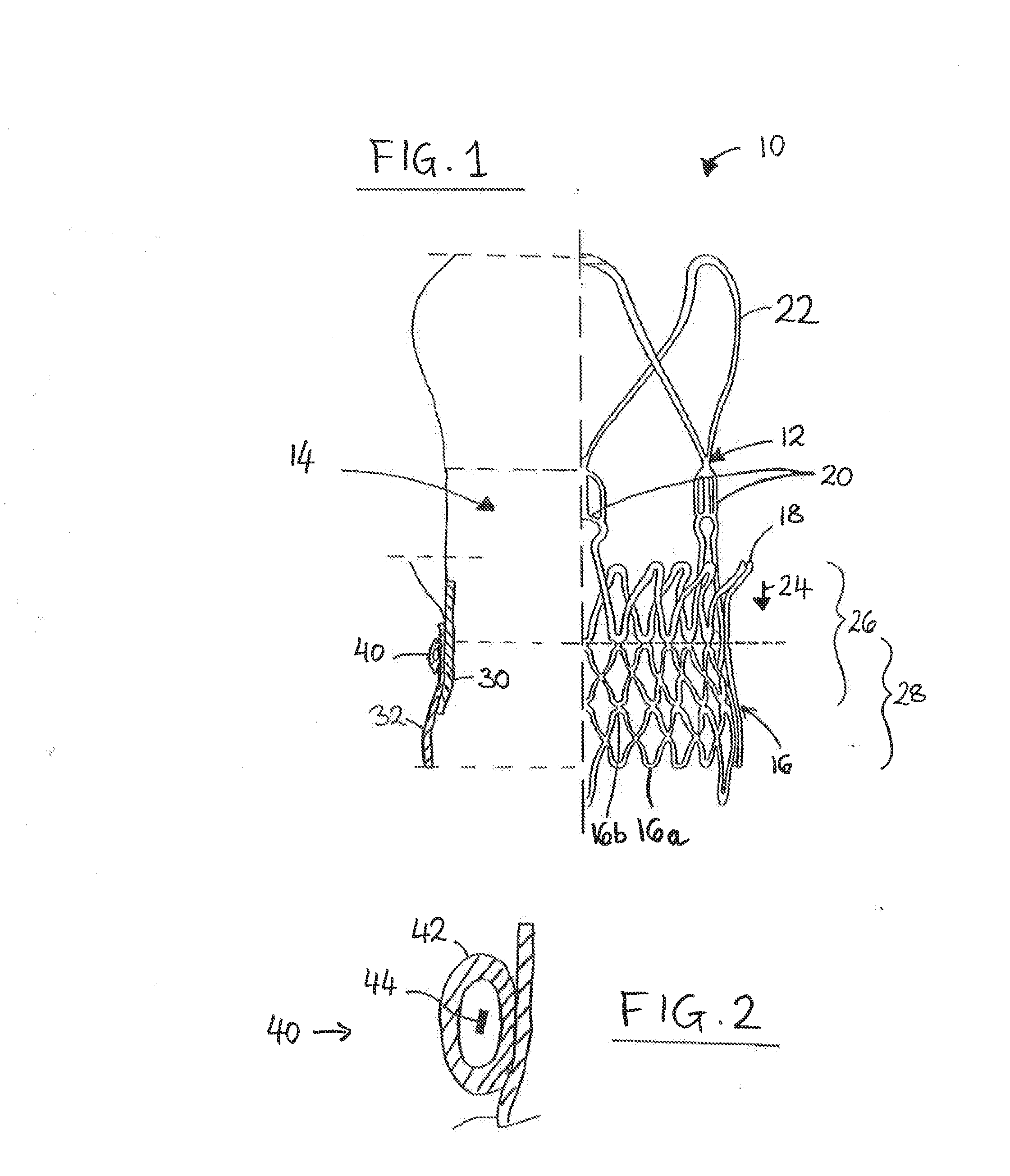
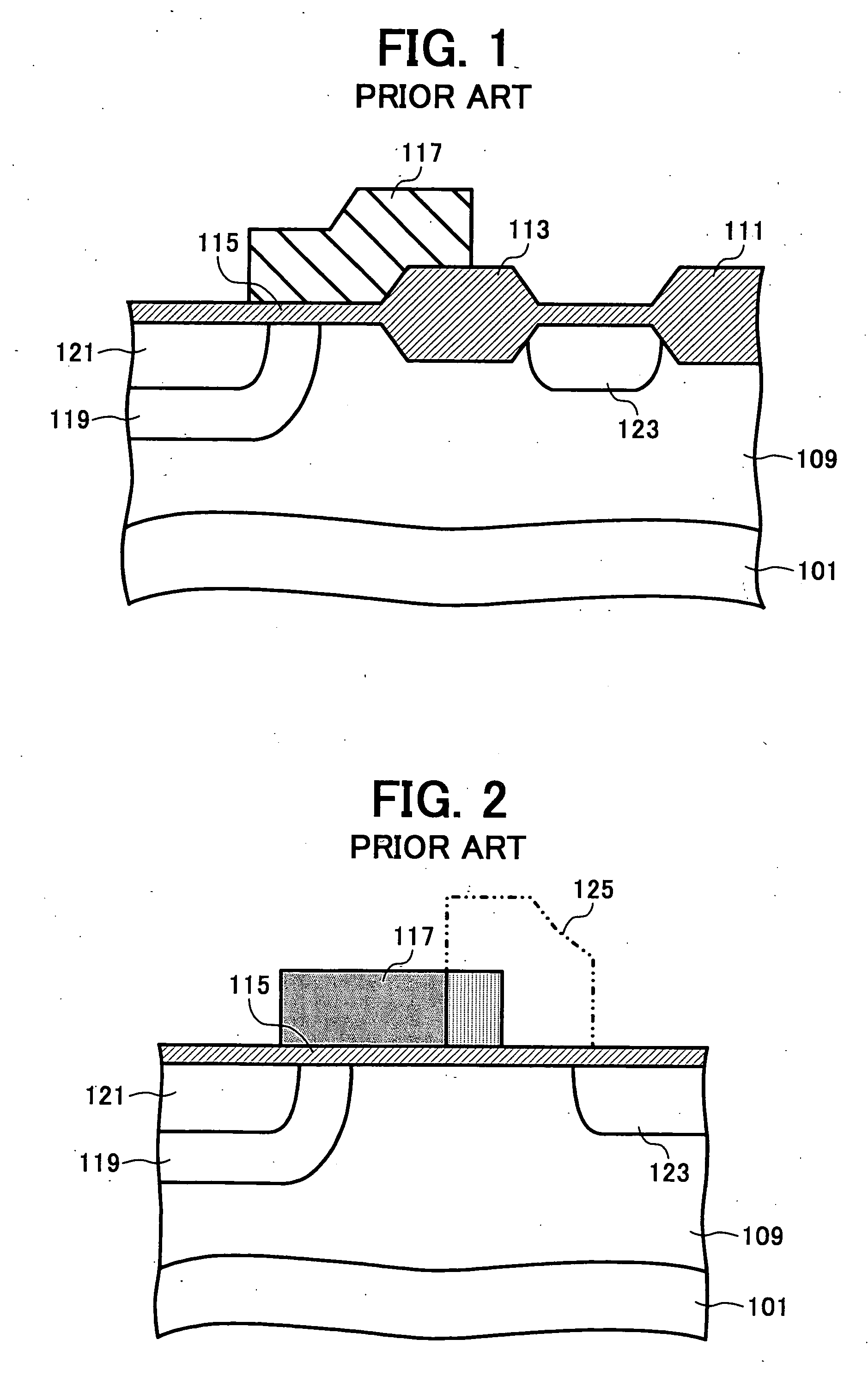
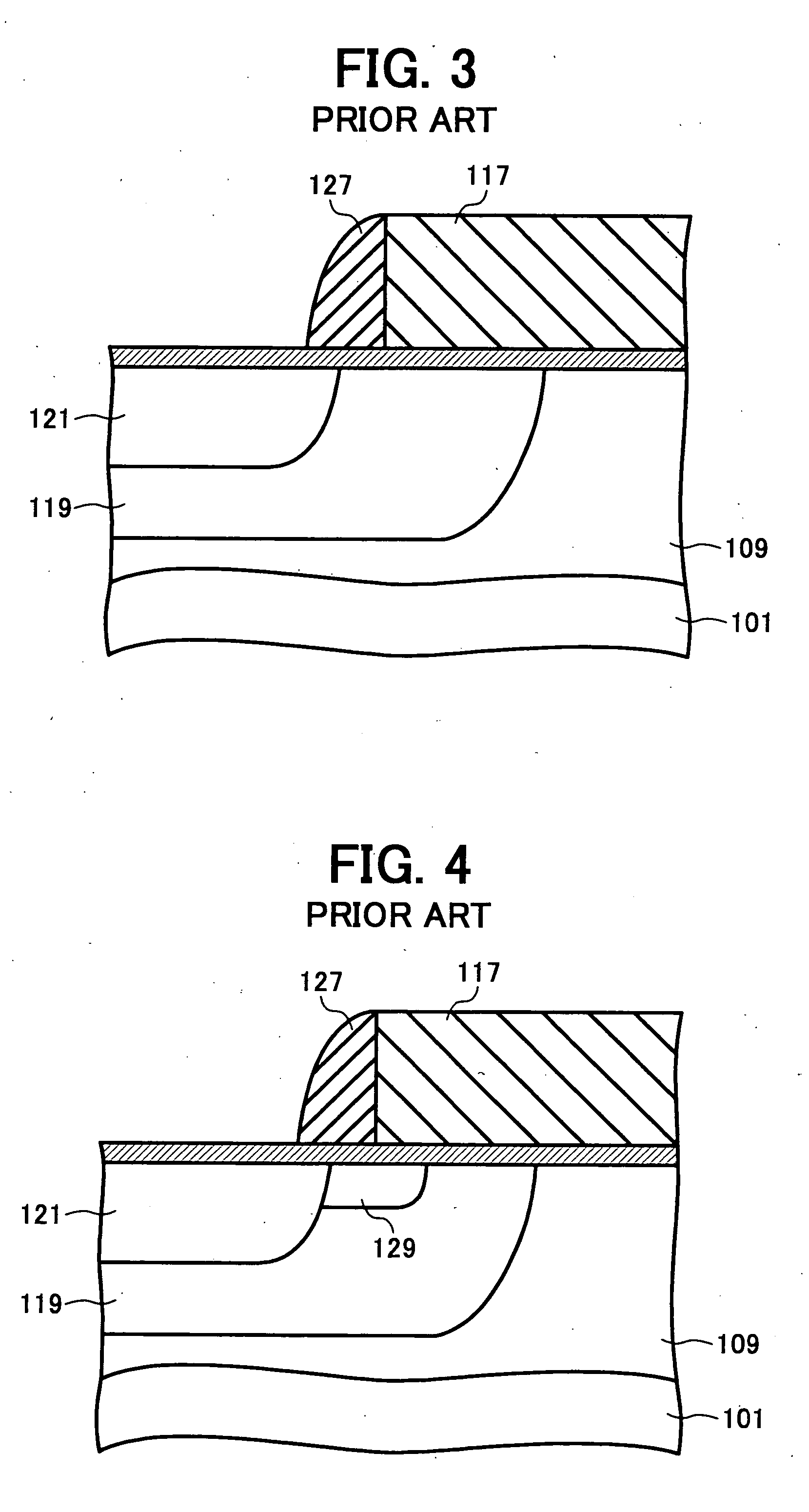
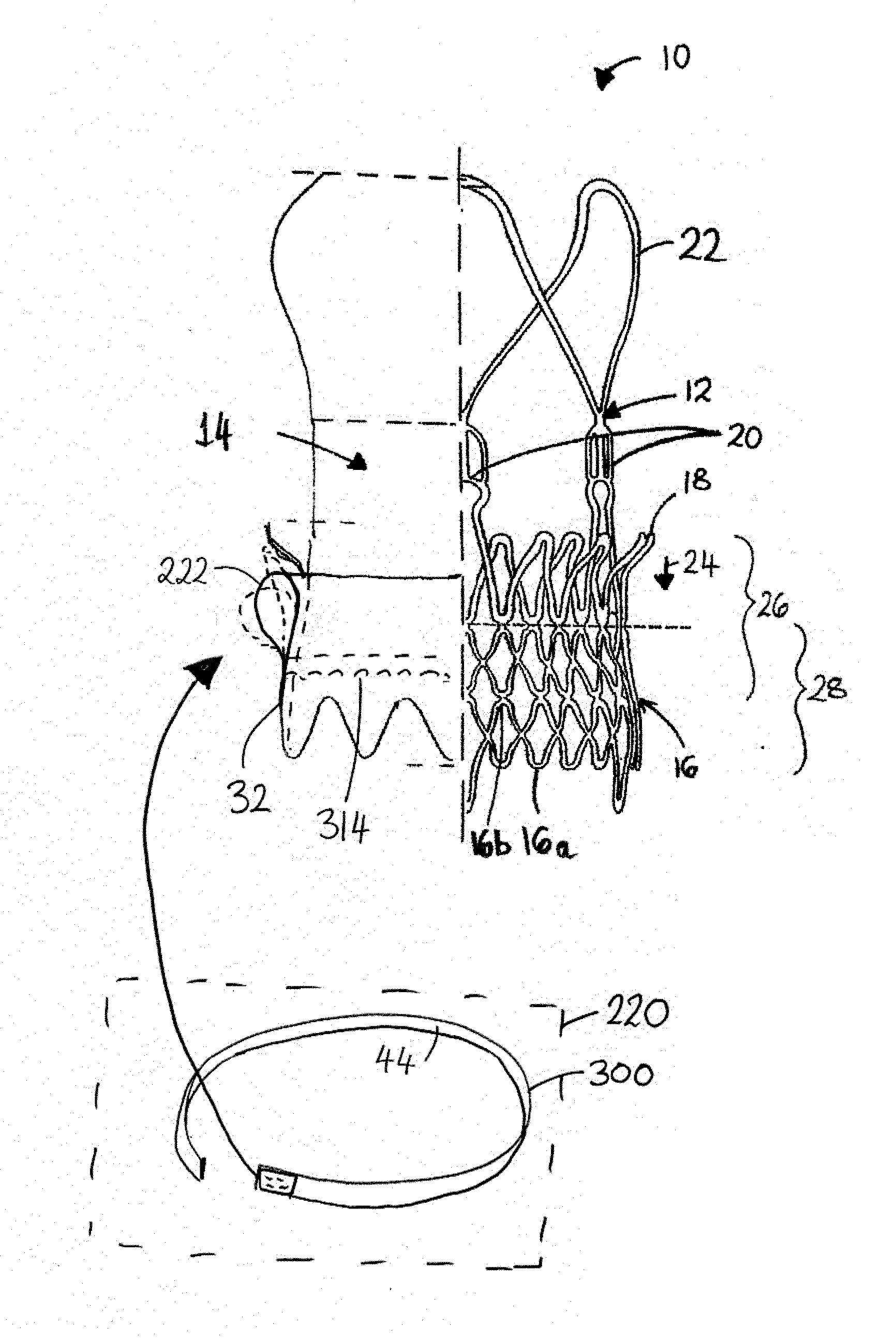
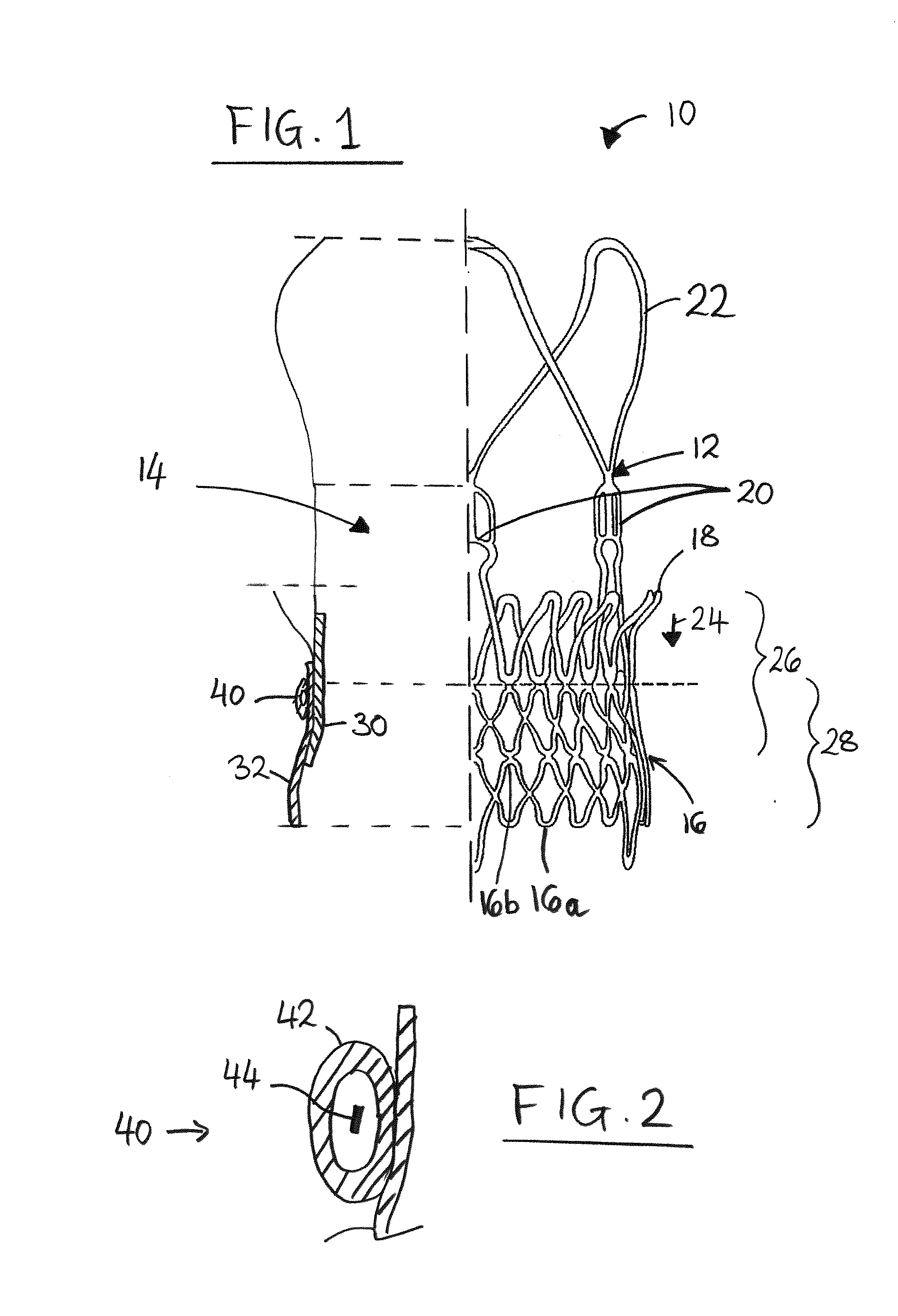
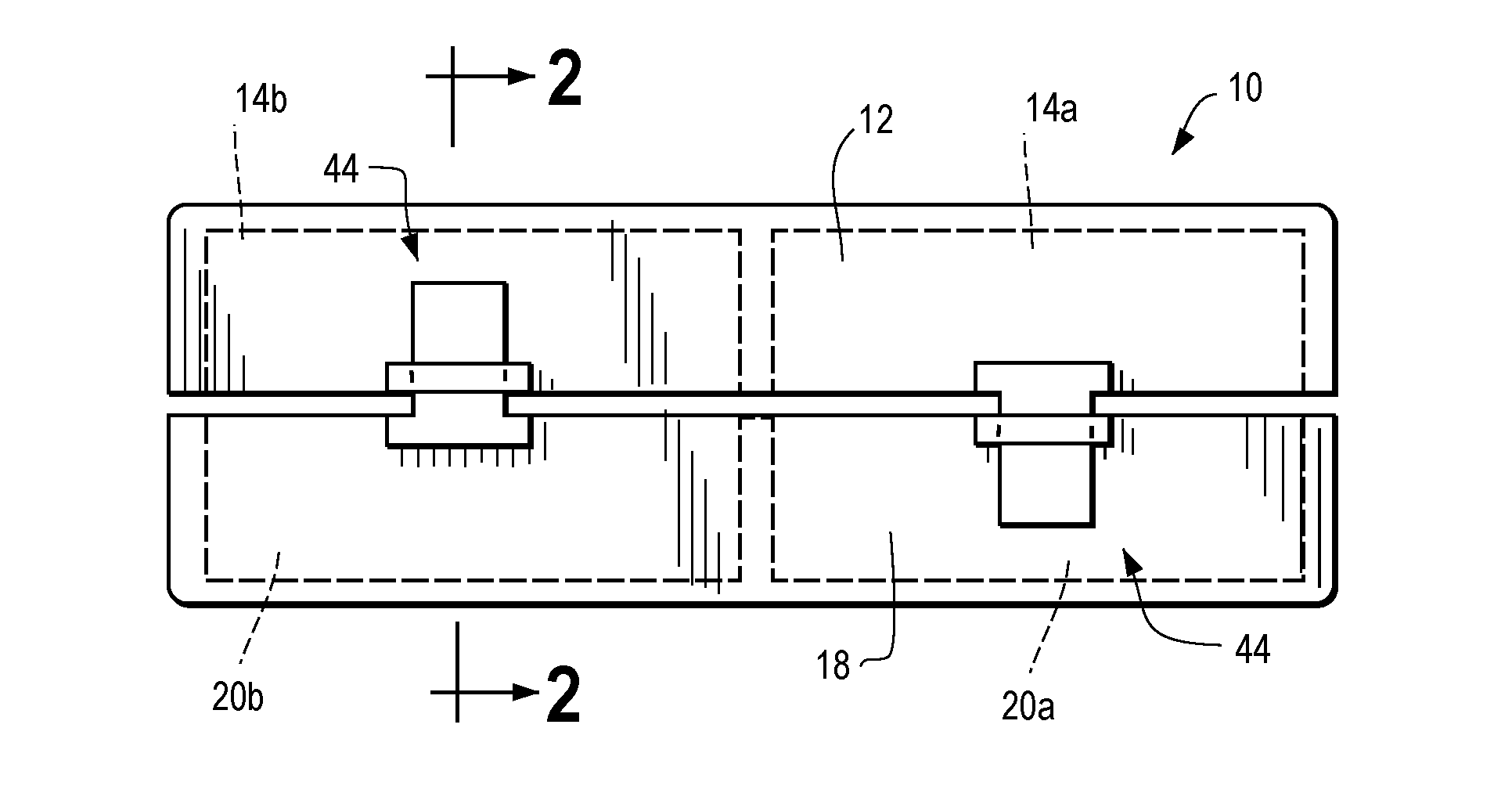
Prosthesis Seals and Methods for Sealing an Expandable Prosthesis
InactiveUS20140350668A1Good strength against burstingHigh riskStentsHeart valvesInsertion stentProsthesis
Embodiments of the present disclosure are related to devices and techniques for para-valve sealing of an expandable stent-valve implanted using a catheter. In some embodiments, a stent-valve is provided which comprises a seal sleeve / cuff containing material that swells when contacted by blood. A piercing tool may be included and used to permit a user to puncture the sleeve / cuff prior to introduction into a patient's body. In some embodiments, the sleeve / cuff has an integral tubular structure configured to withstand balloon expansion of the stent-valve during or after implantation.
Owner:SYMETIS
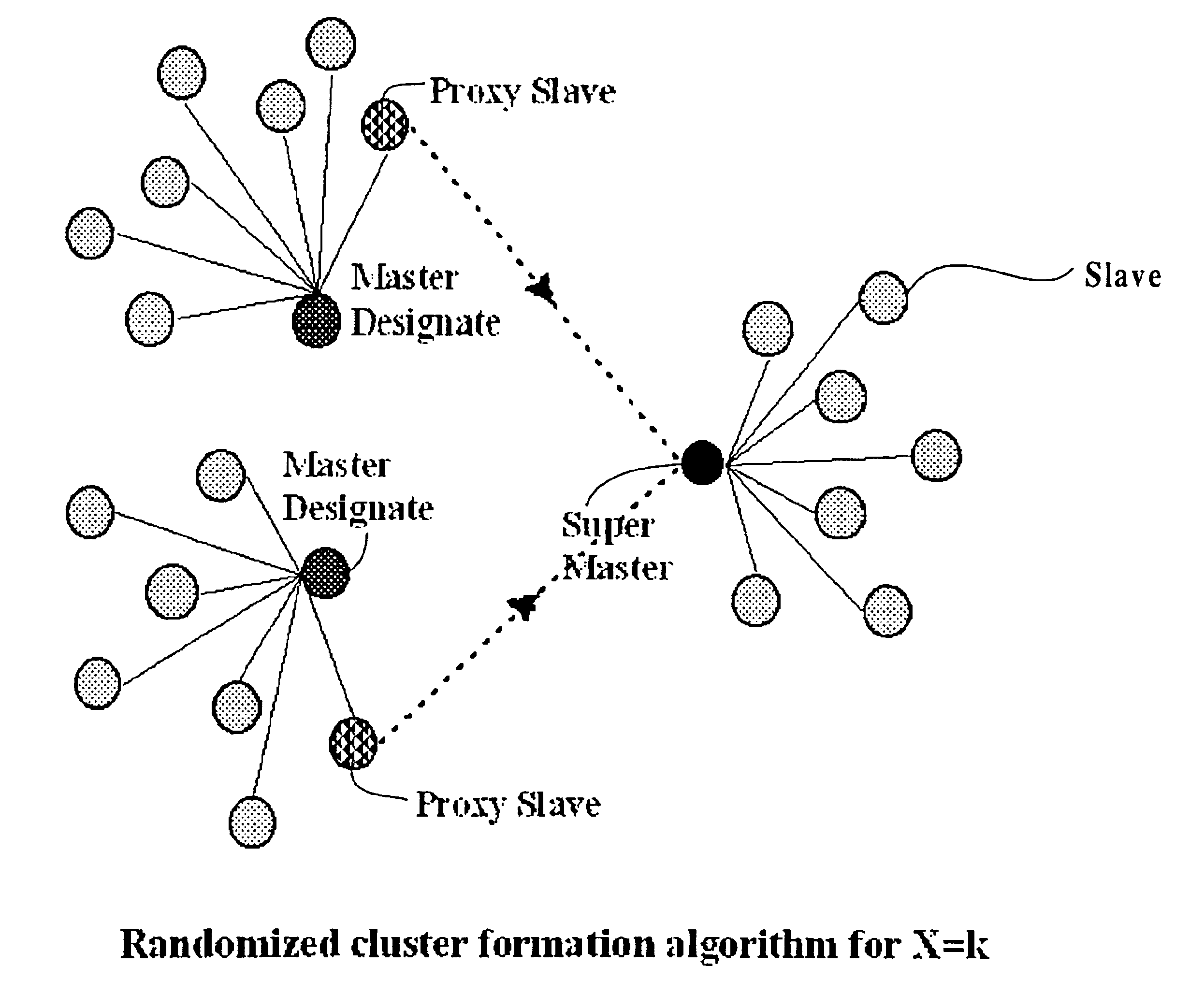
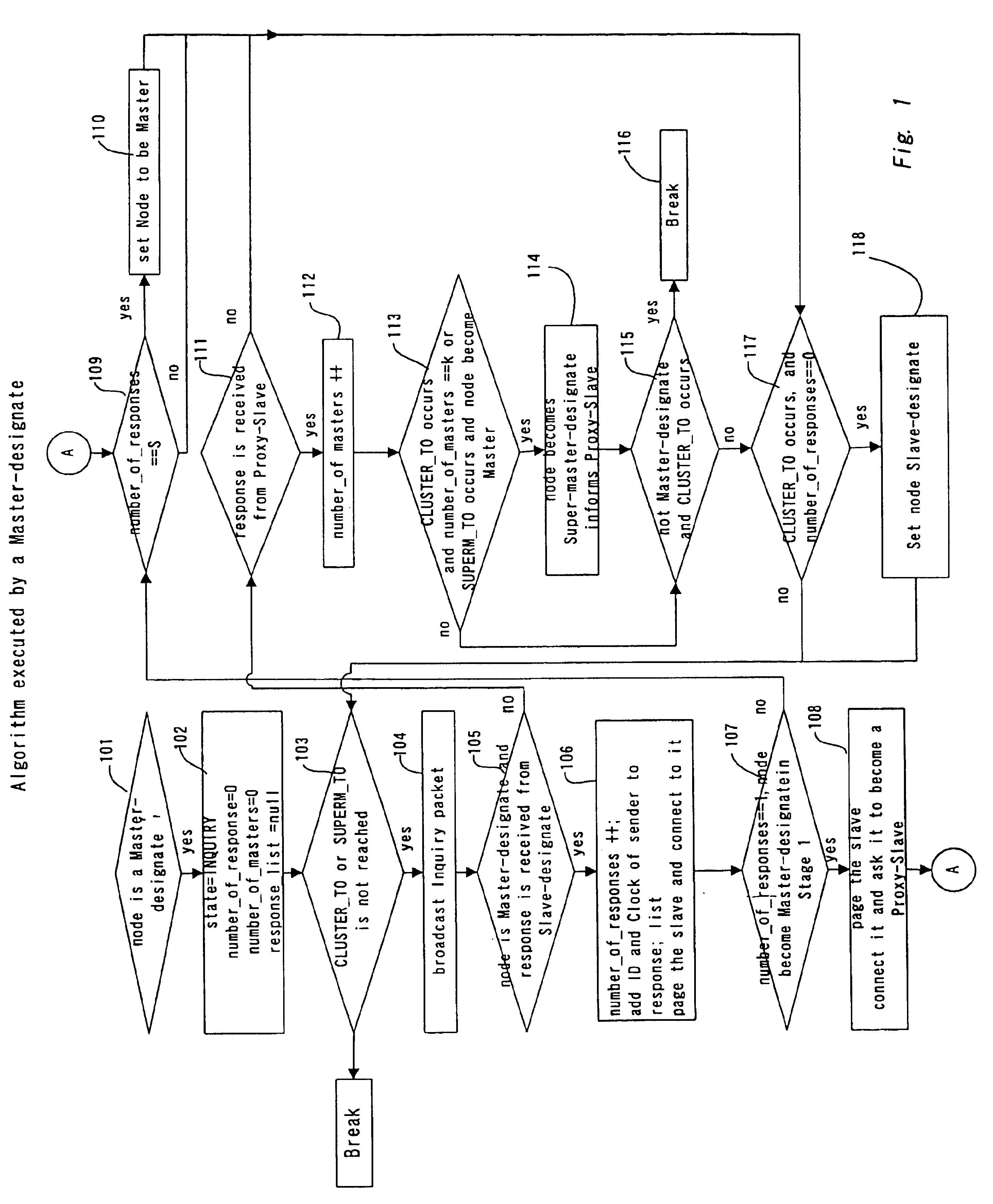
Clustering in wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS6876643B1SpeedLess timeNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless transmissionComputer program
A method, system, and computer program product for organizing a set of nodes into a minimum number of connected clusters of bounded size in a wireless transmission system, wherein the method comprises using of bits in packets used in the initial stages of the device discovery procedure, to include information relating to a state of device discovery to achieve the separation of the nodes into those in the transmit-state and the receive-state; defining a Master-designate among the nodes through a statistical procedure and defining remaining nodes as a Slave-designate; defining a cluster including the Master-designate and at least one the Slave-designate, wherein the Slave-designate continuously scans for the inquiry message transmitted from the Master-designate and the Slave-designate transmits the inquiry response to the Master-designate.
Owner:IBM CORP
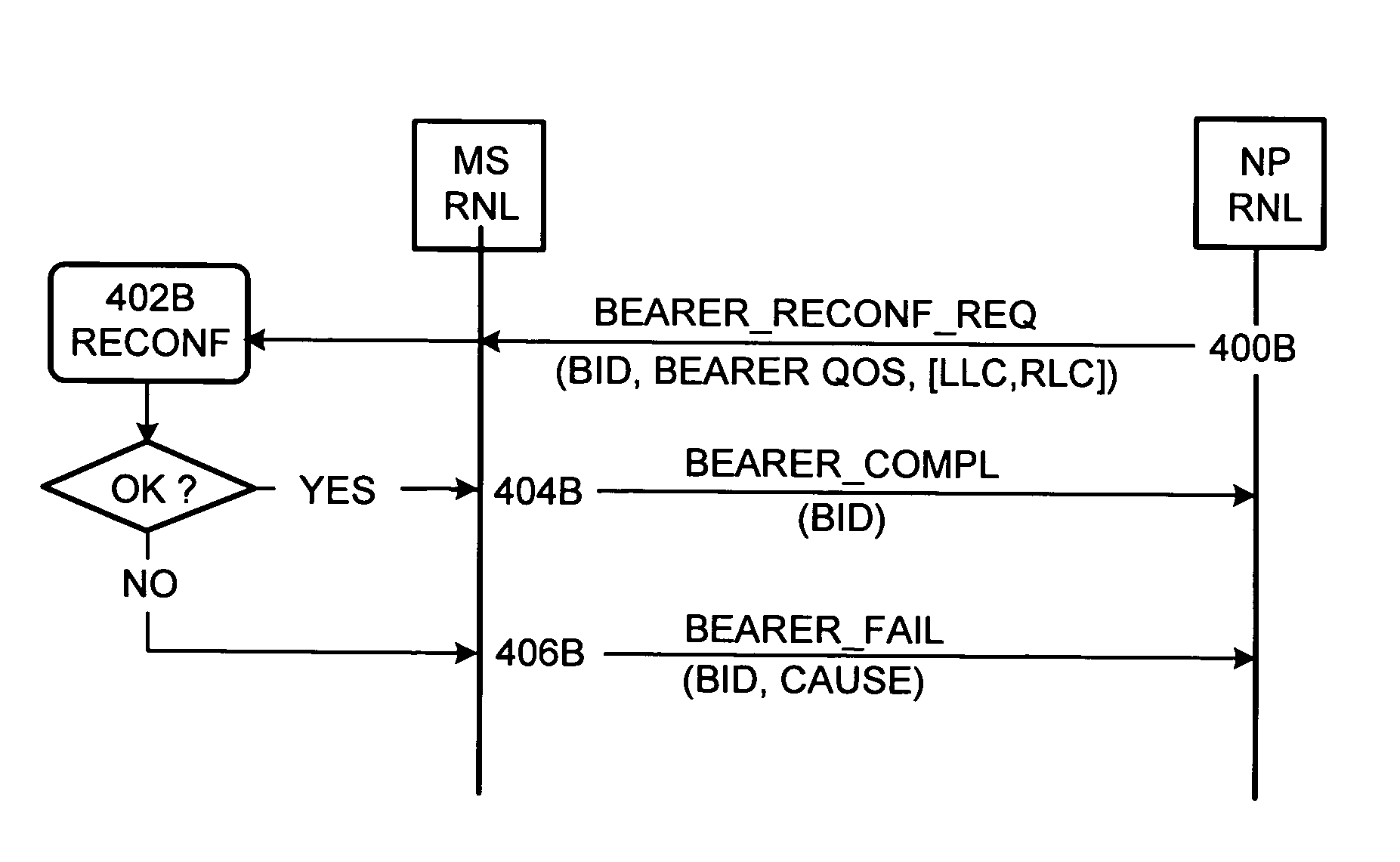
Method for connection reconfiguration in cellular radio network
InactiveUS7599384B2Reduce loadReduce in quantityNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceCellular radio
Owner:SISVEL INT
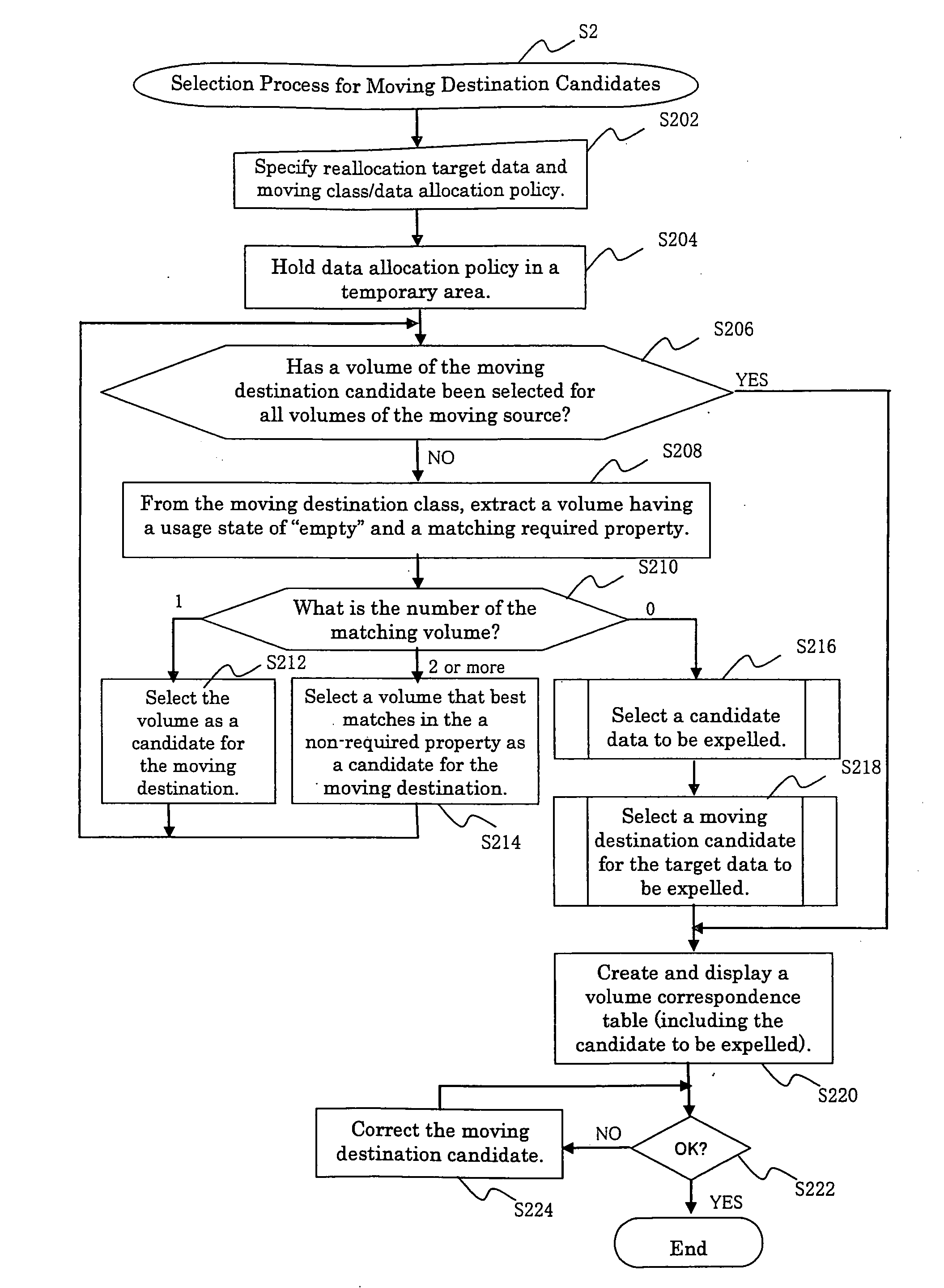
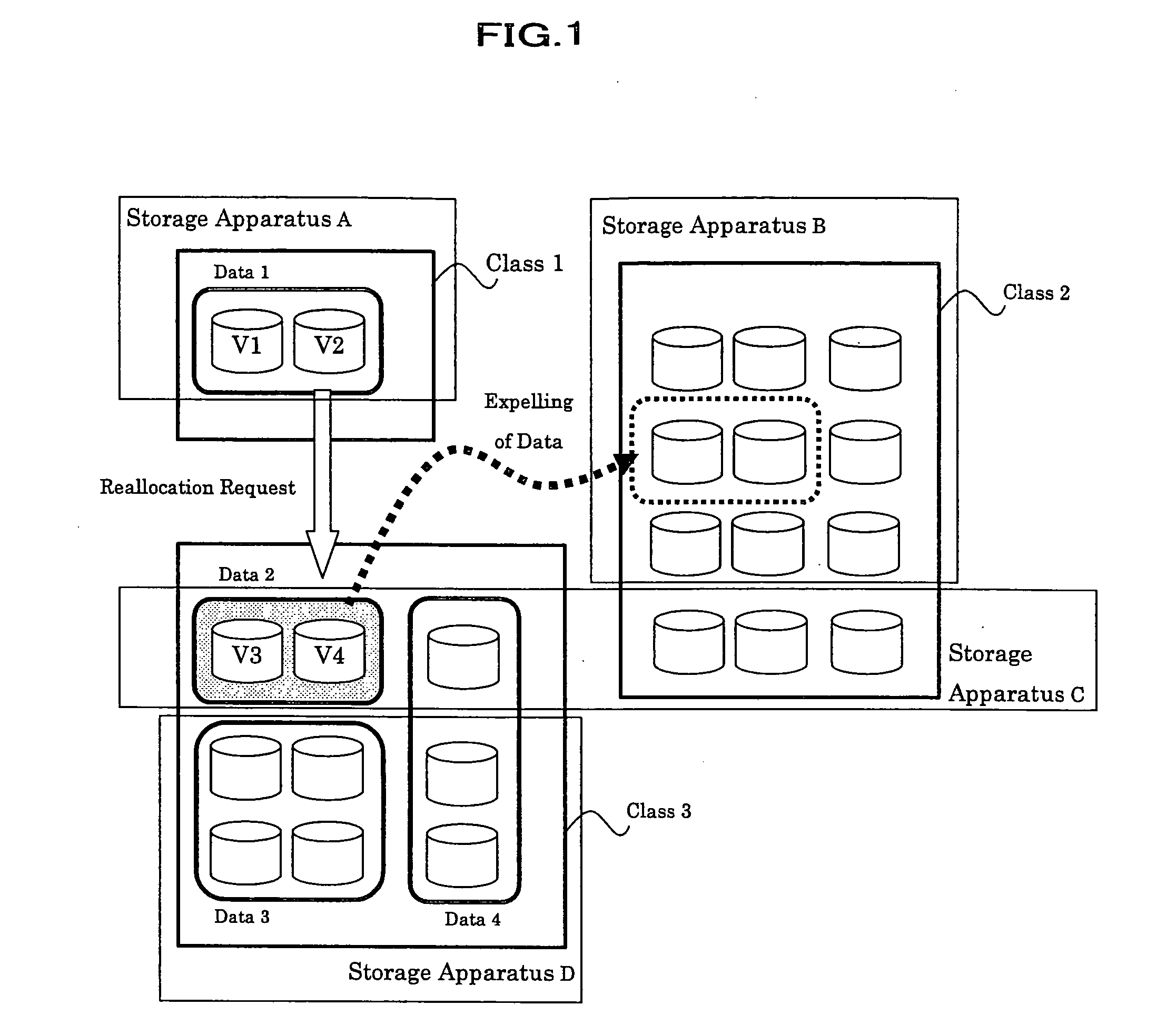
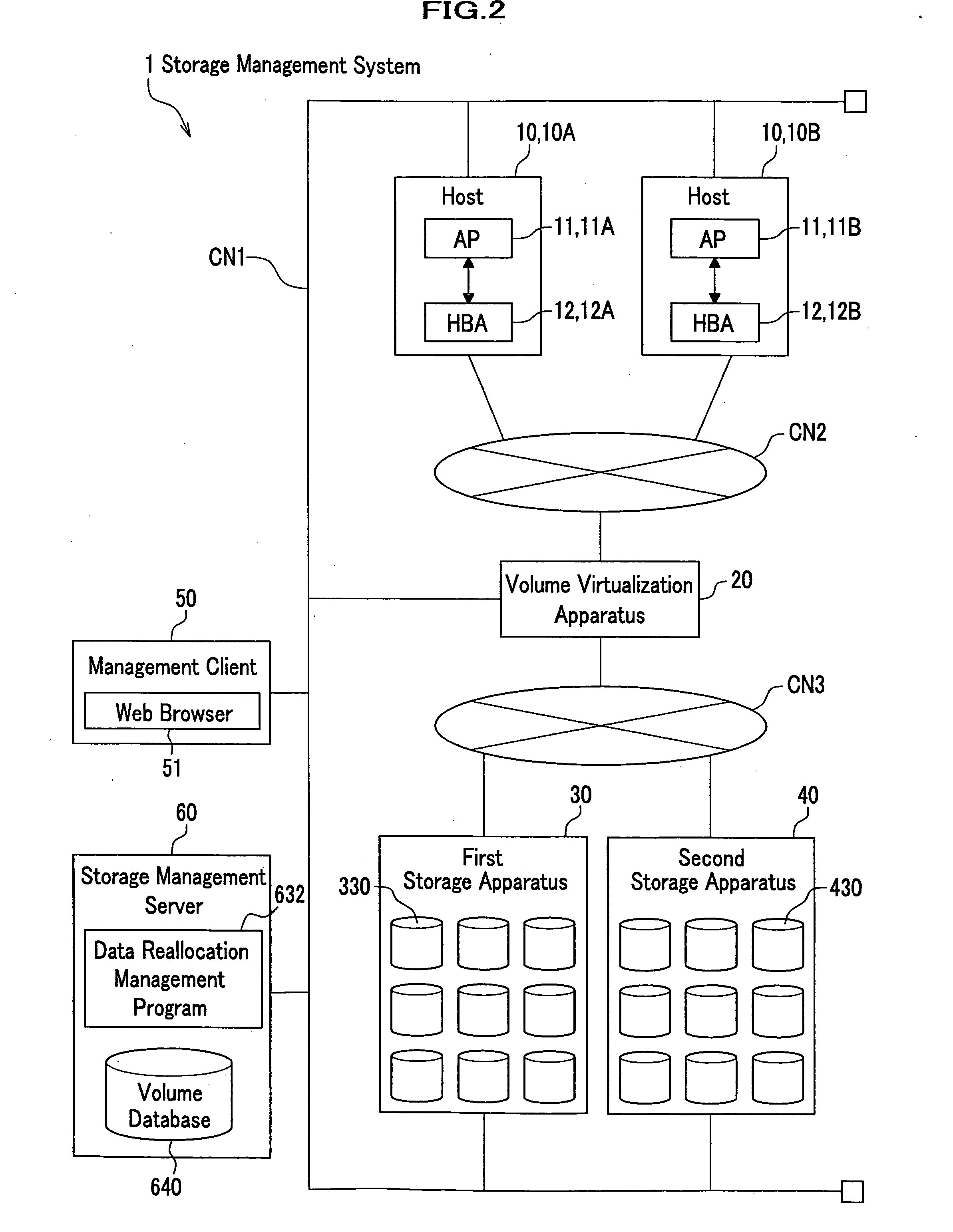
Storage management system, storage management server, and method and program for controlling data reallocation
InactiveUS20060242377A1Easy to operateAvoid reallocationMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingControl dataStorage management
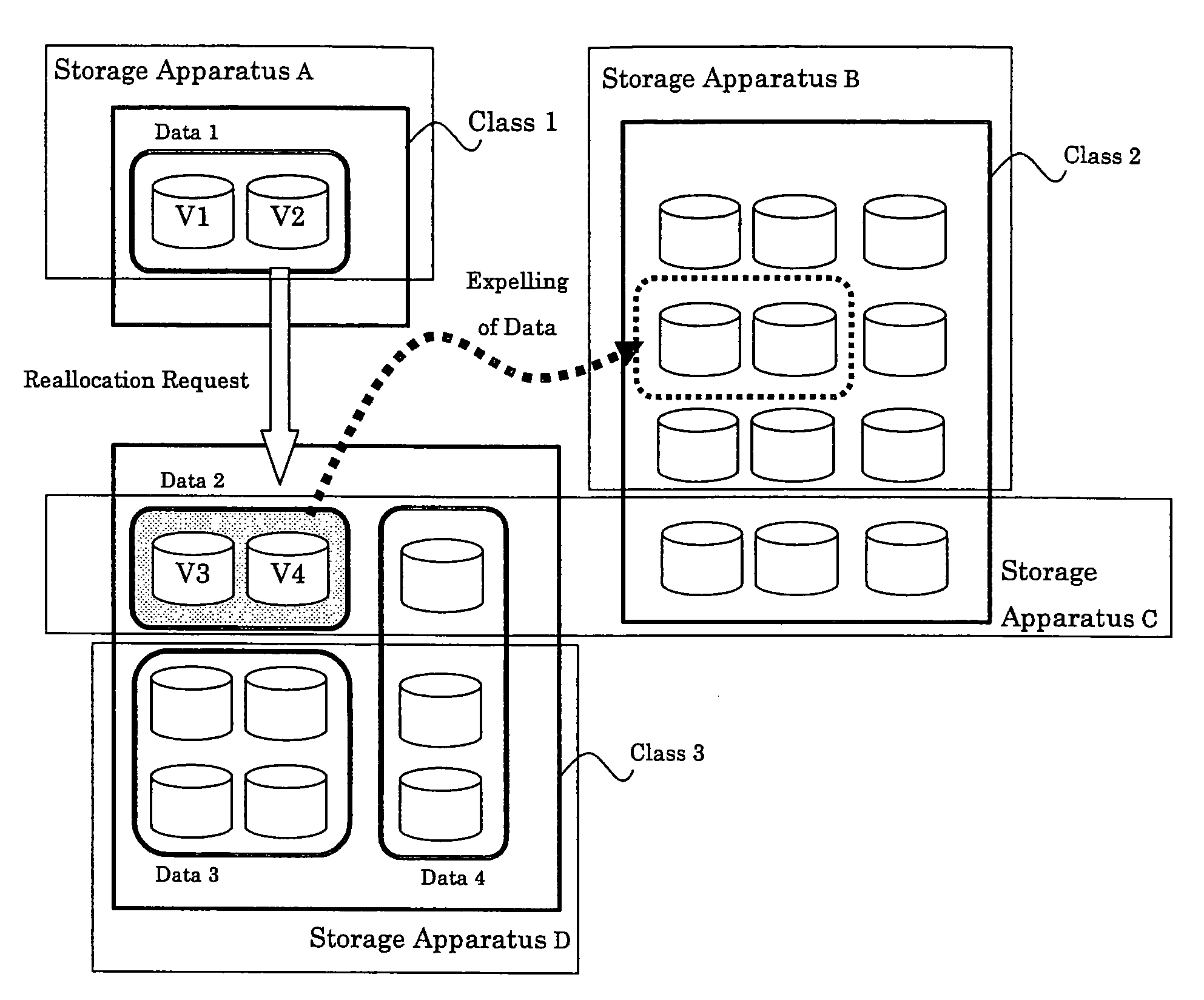
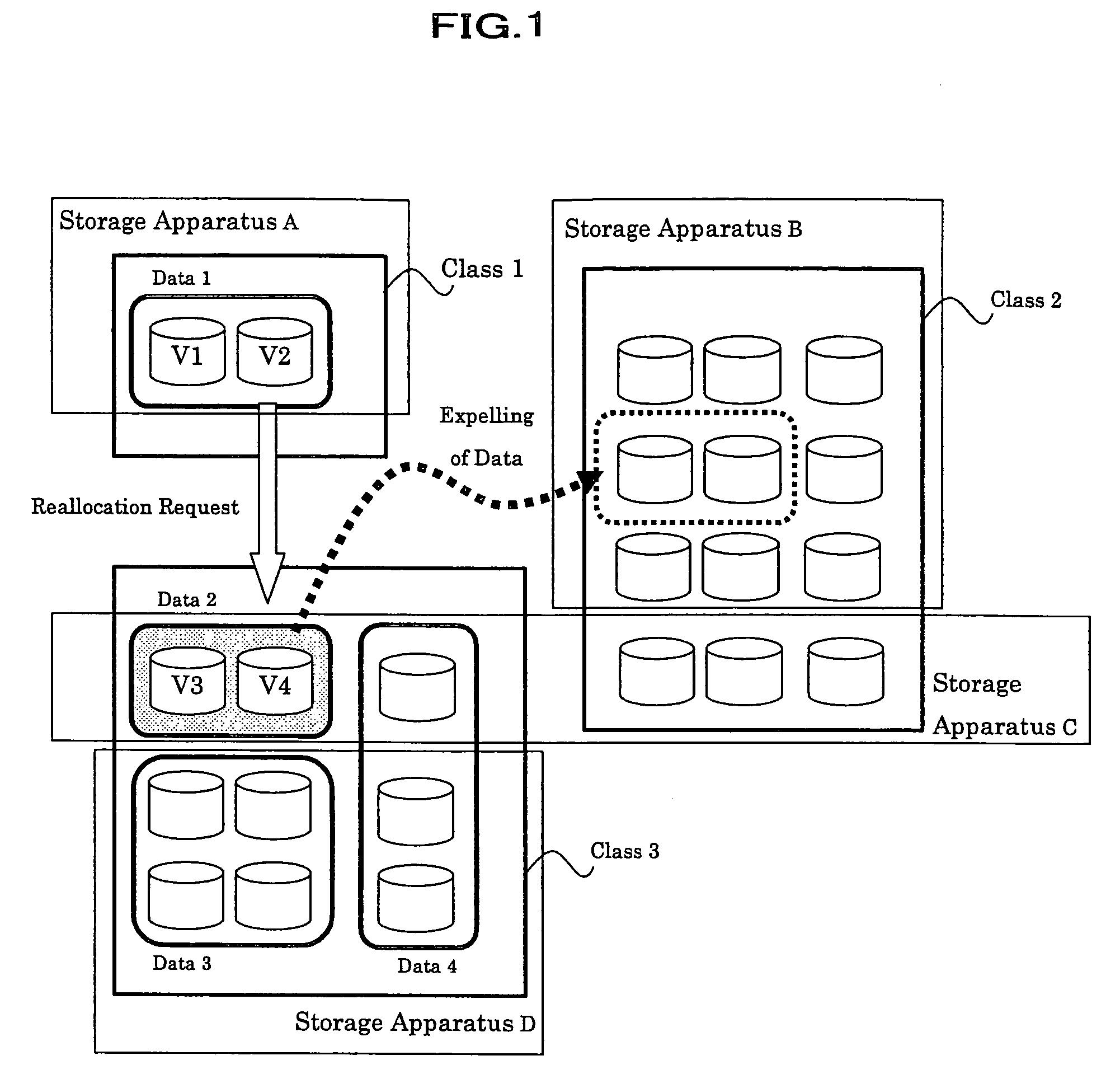
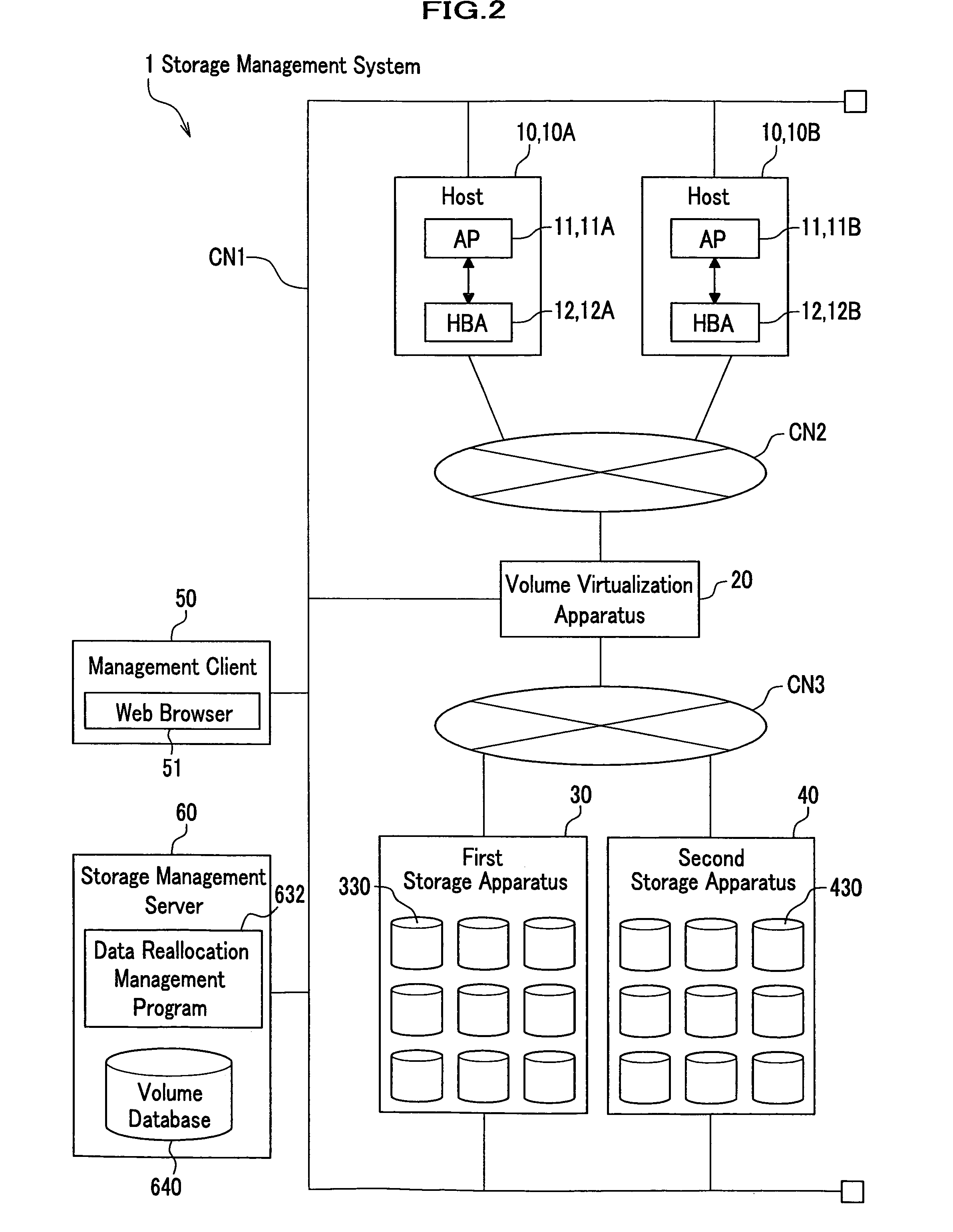
In a storage management system, a host recognizes a plurality of storage apparatuses as one virtual storage apparatus. The user divides each of the volumes that the storage apparatuses have into a plurality of classes in accordance with a policy. When a user specifies moving target data and a class or a policy of a moving destination, the data is reallocated to a class that meets it. The class or policy is held as a data allocation policy. If a sufficient empty space is not present in the moving destination class, by finding out from allocated data, data that also complies with a policy of other class, target data to be expelled and a class of expelling destination are determined for expelling data, so as to ensure a sufficient empty space for reallocation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
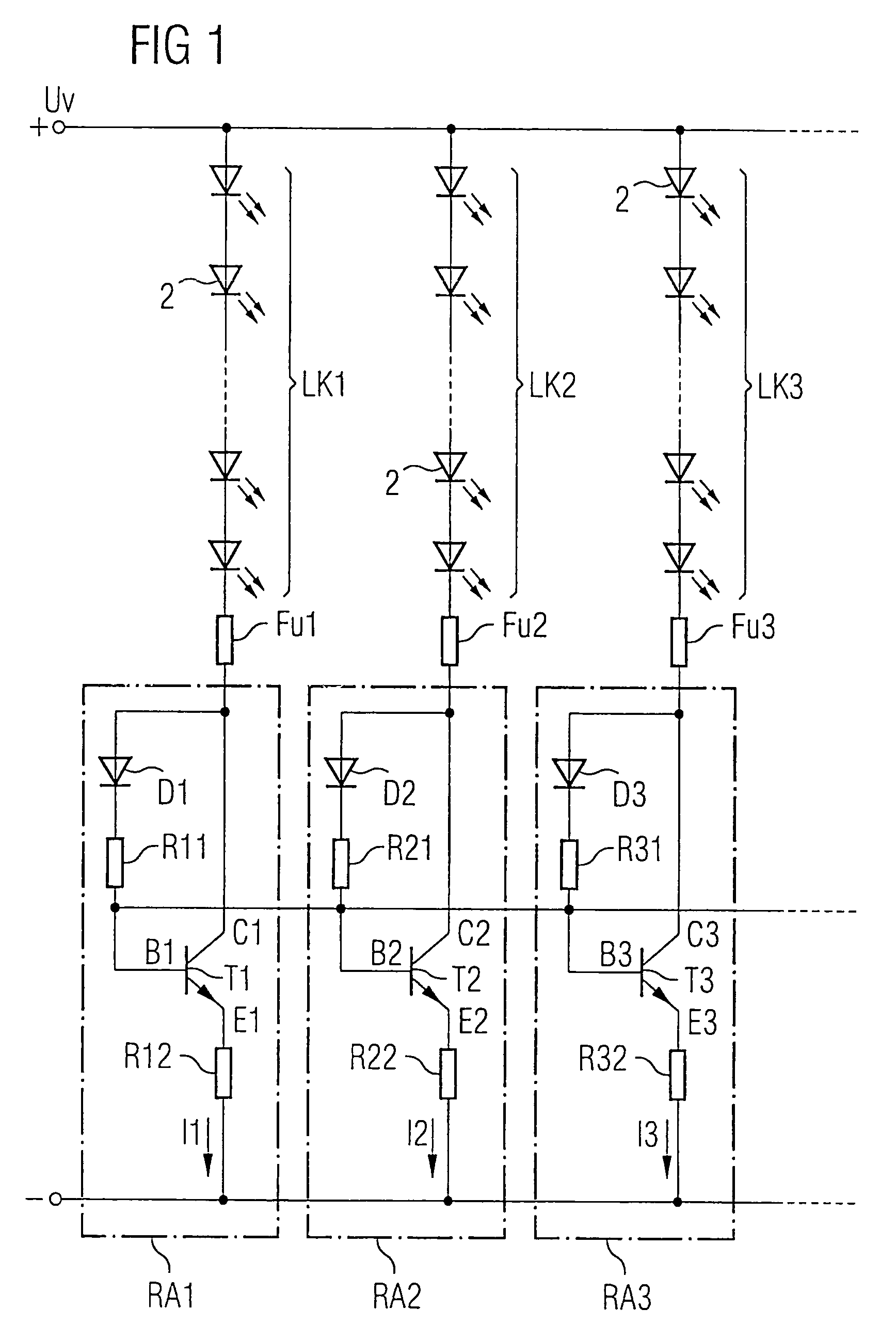
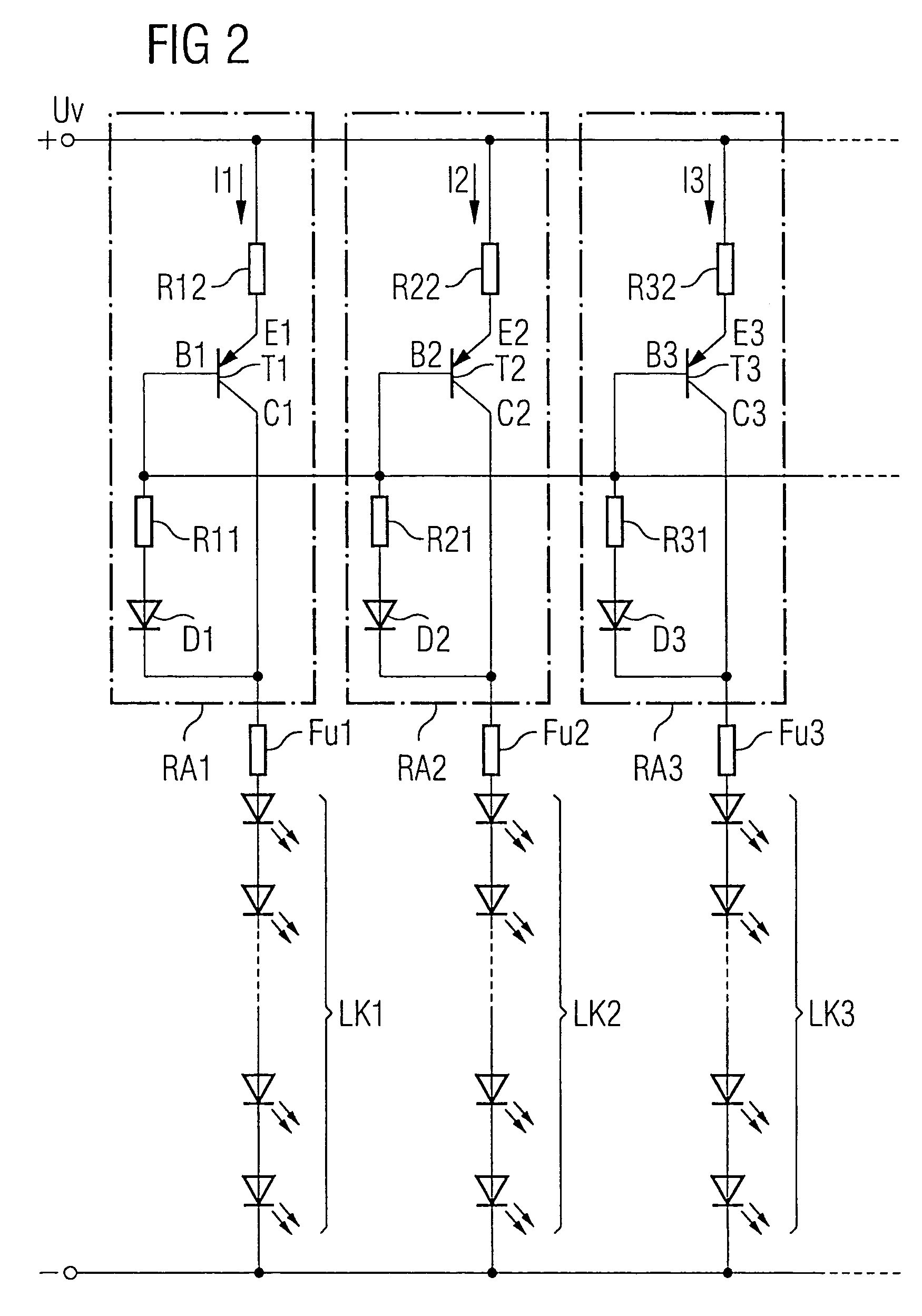
Circuit for an LED array
InactiveUS7317287B2Small currentMaintain distributionElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementVoltageCathode
Owner:OSRAM OPTO SEMICON GMBH & CO OHG
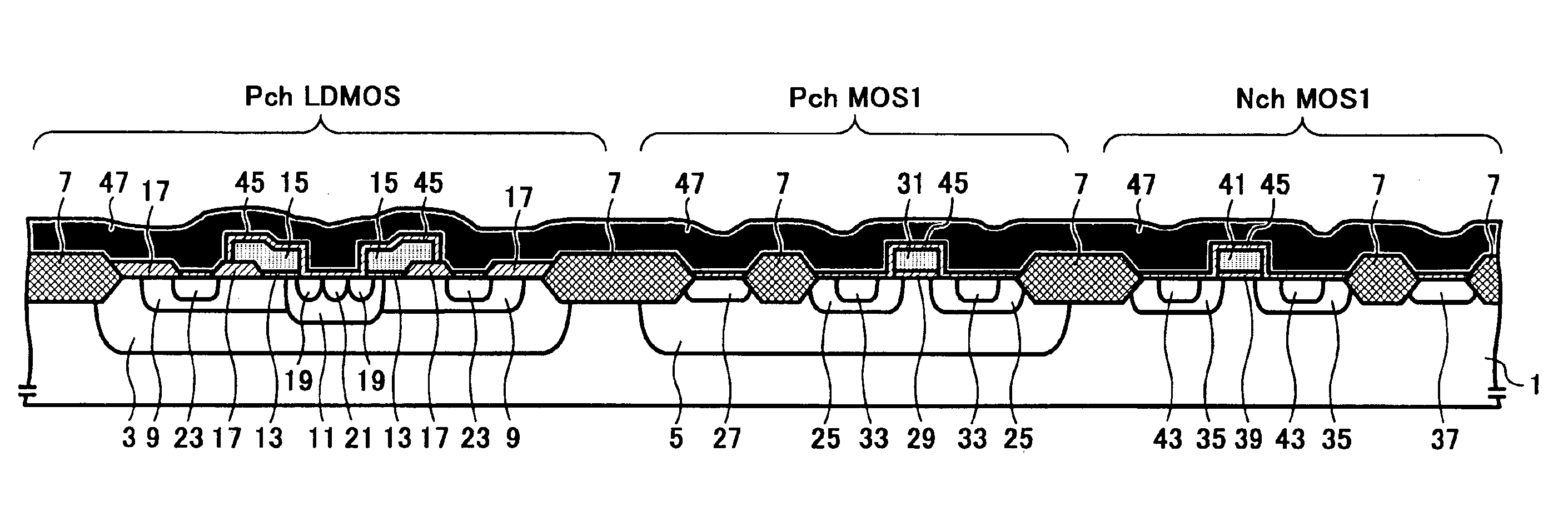
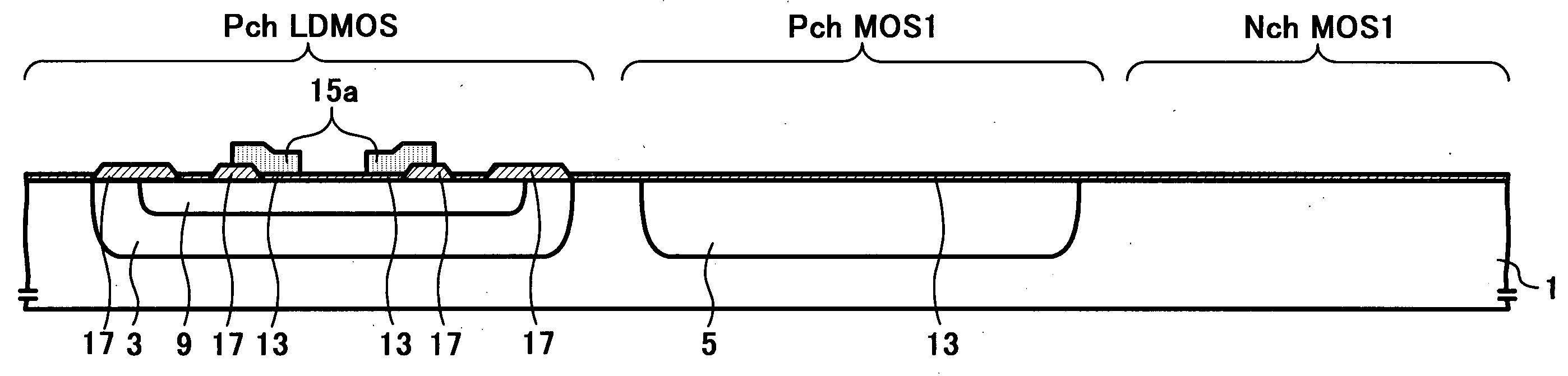
LDMOS transistor capable of attaining high withstand voltage with low on-resistance and having a structure suitable for incorporation with other MOS transistors
ActiveUS6894350B2Lower on-resistanceRedistribution of the channel well region is preventedTransistorSolid-state devicesLDMOSGate oxide
Owner:RICOH KK
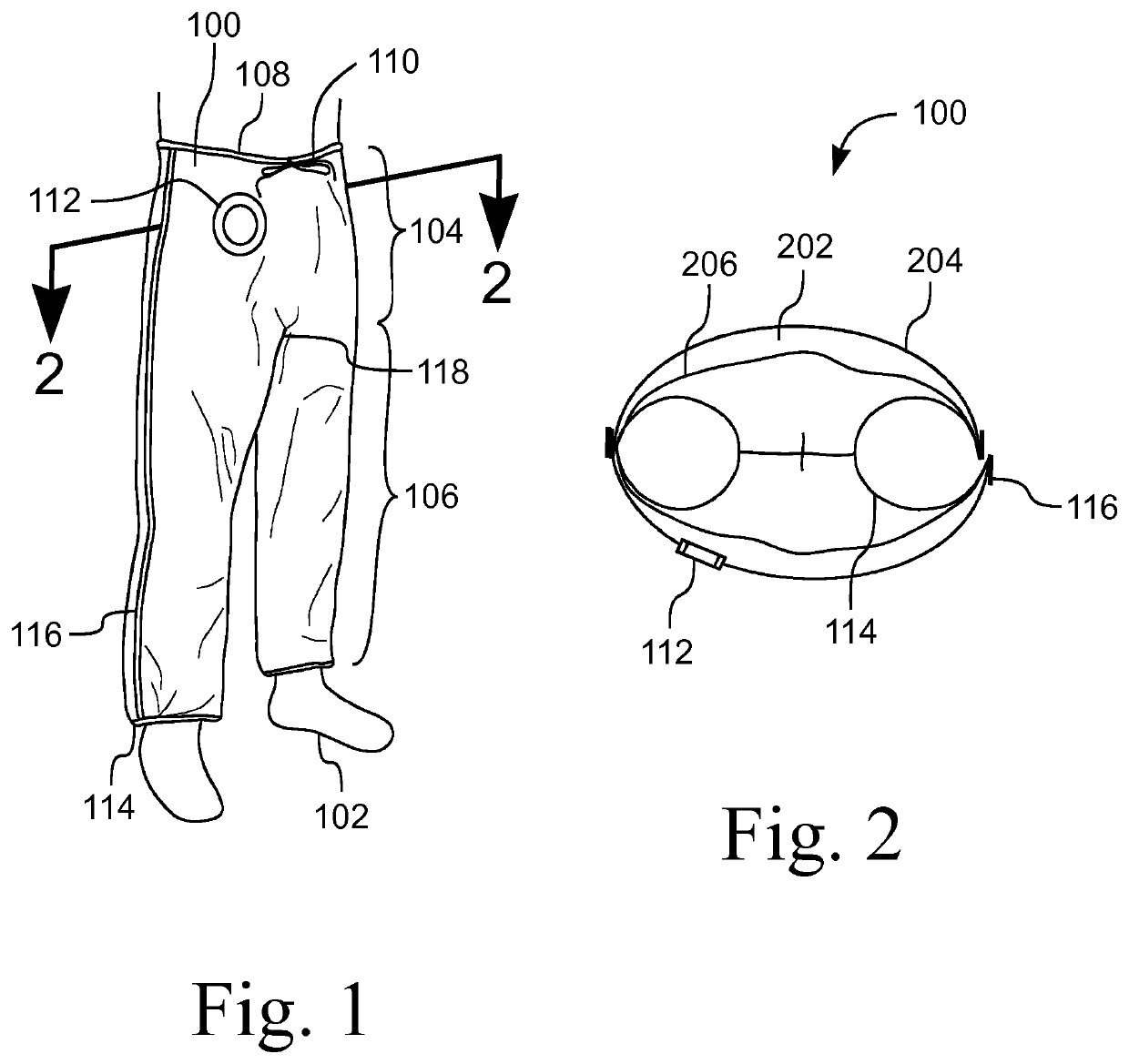
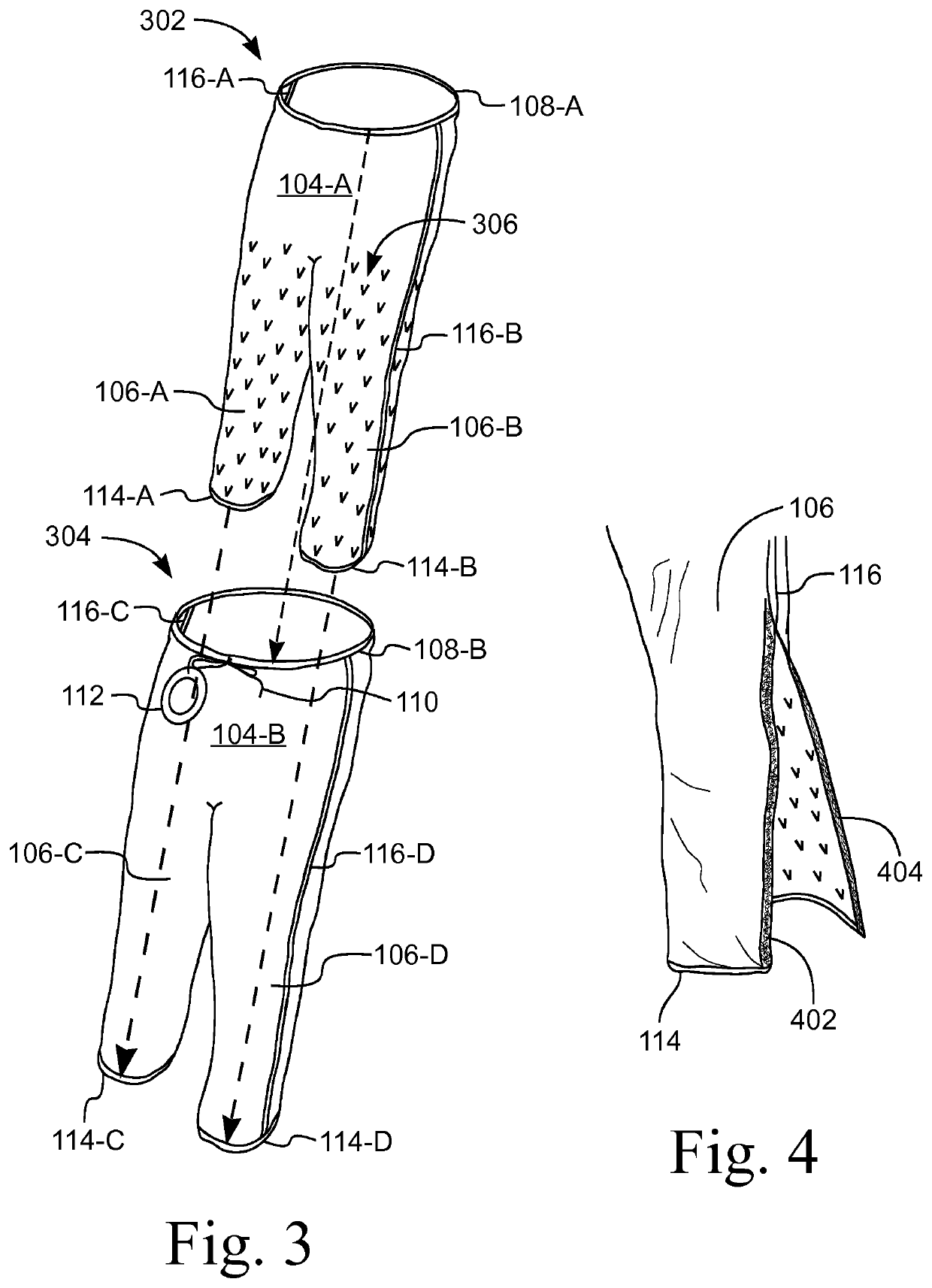
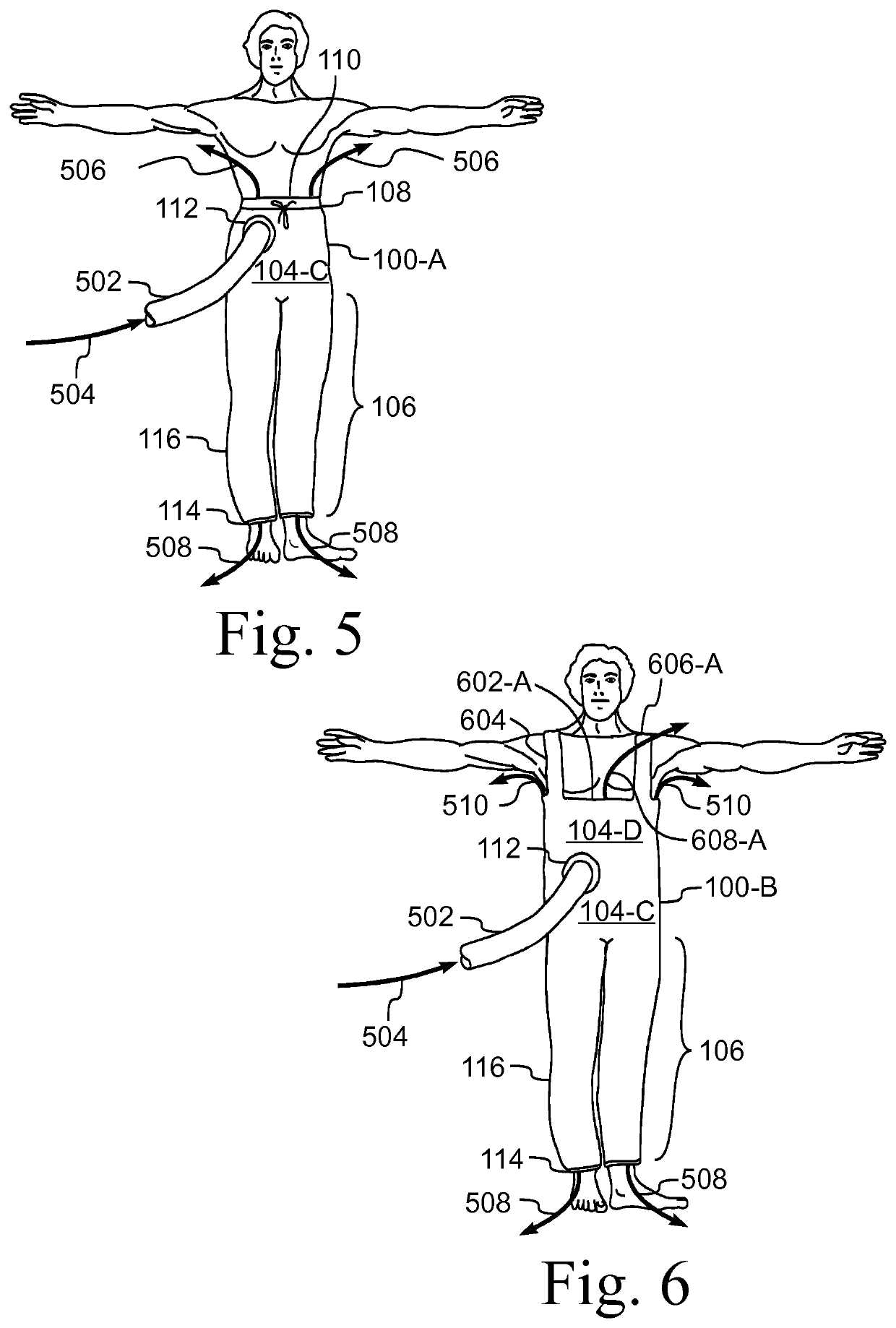
Prewarming Gown
ActiveUS20120047623A1Avoid areaMaintain air temperatureTherapeutic coolingPyjamasHuman bodyEngineering
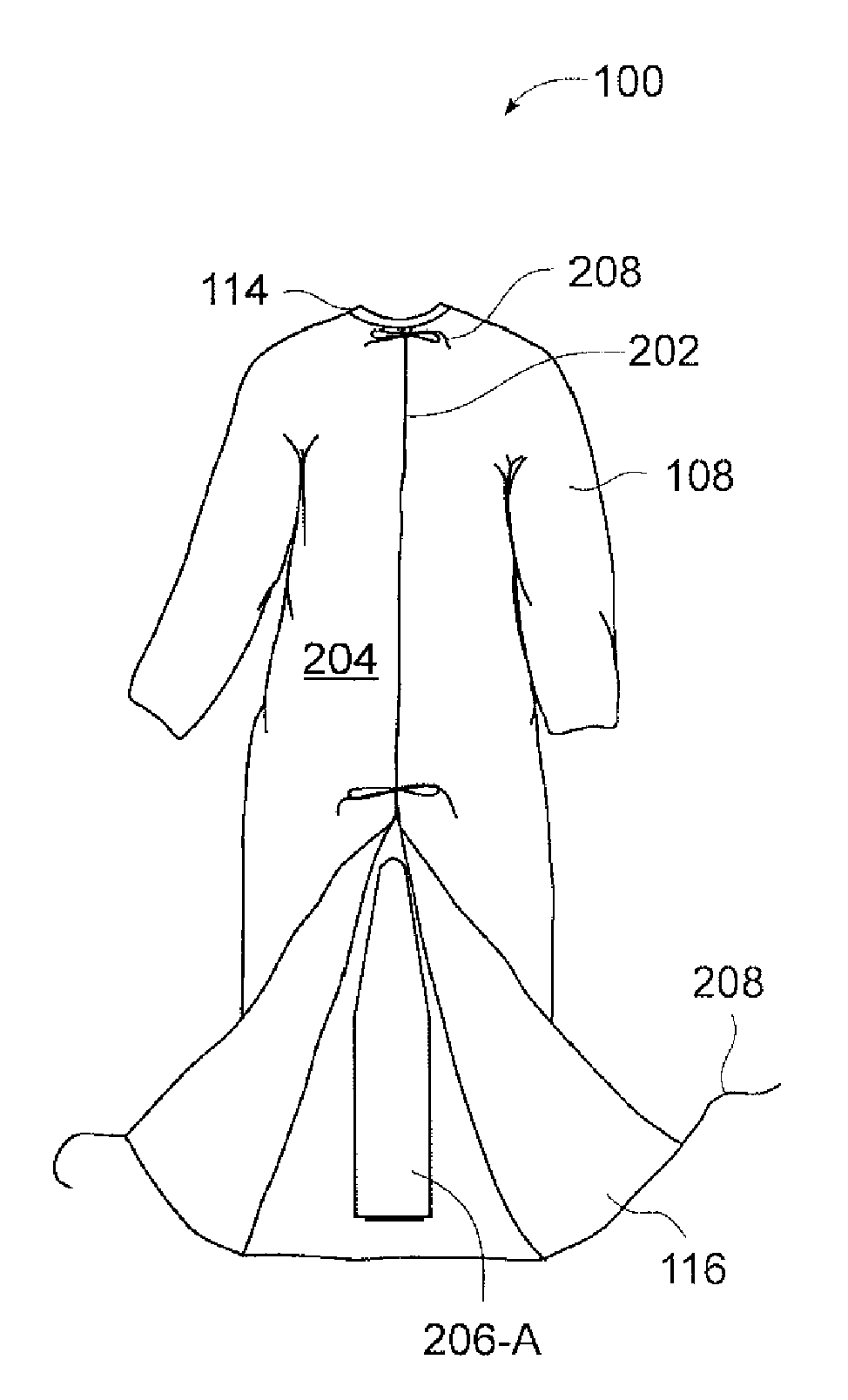
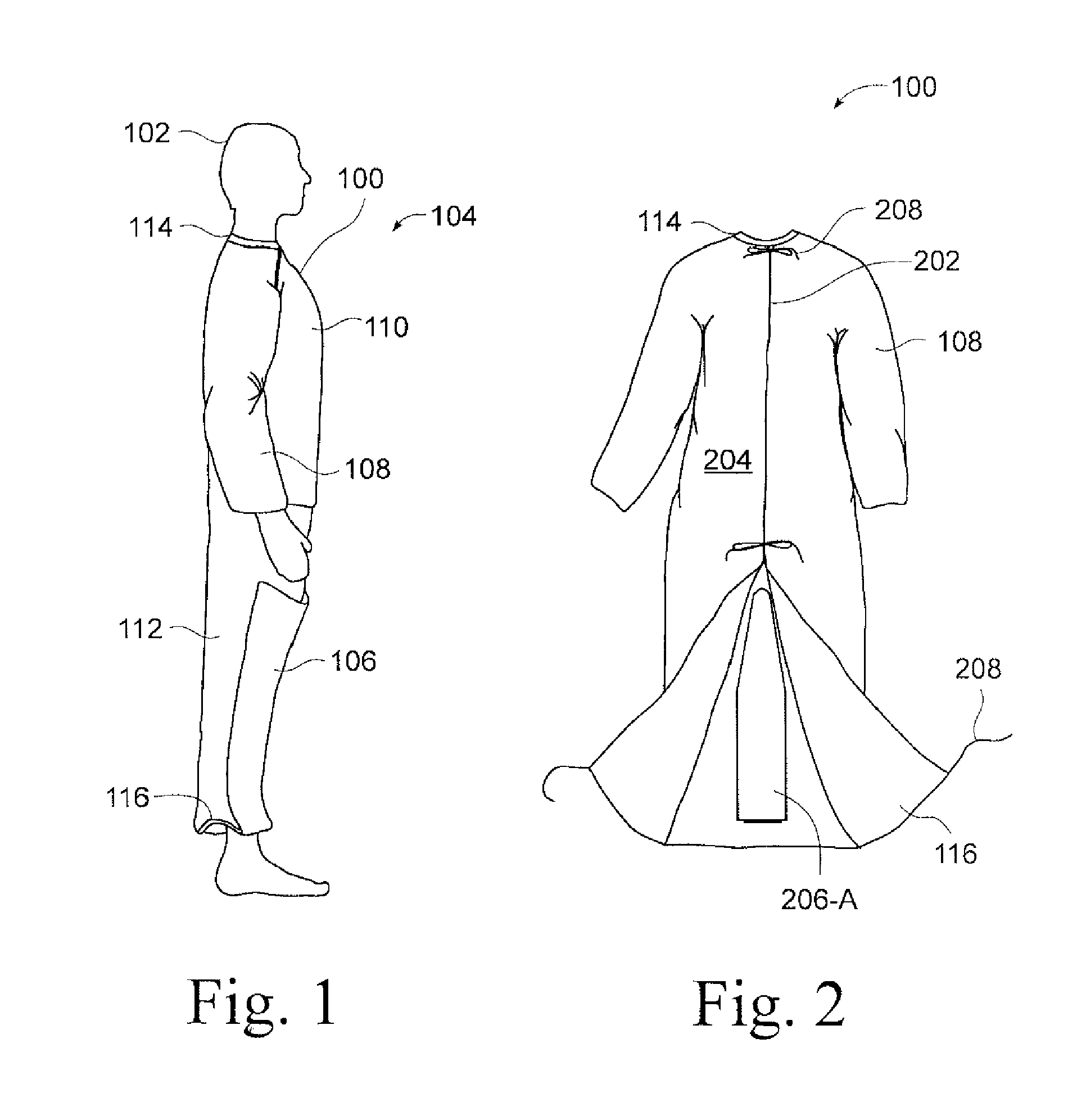
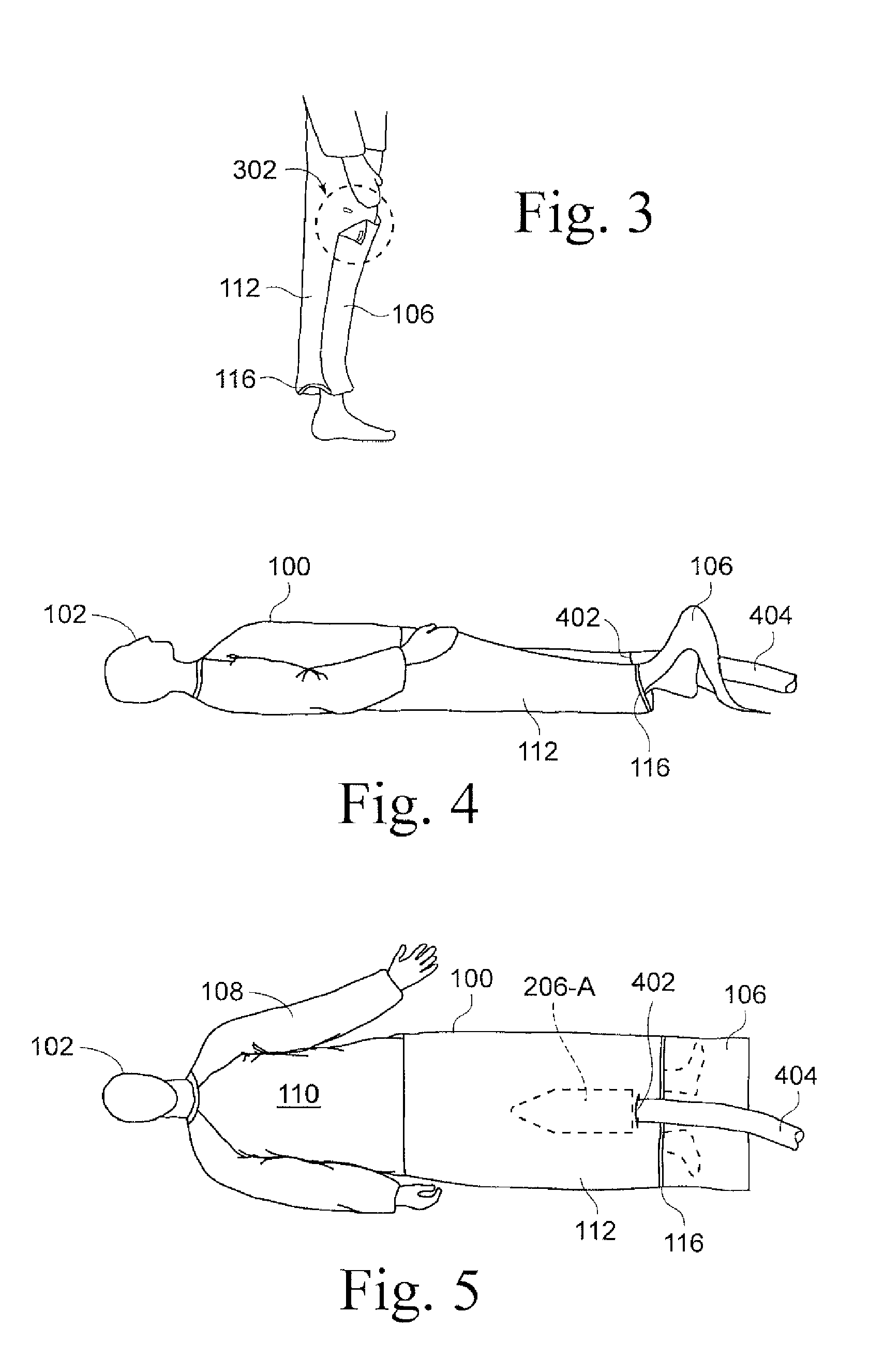
A device for warming a human body. The device is a gown that has a body with a thorax portion and a leg portion. One embodiment prevents redistribution hypothermia with a distributor attached to the inside of the leg portion. The sleeves, leg portion, and posterior of the gown are heat reflective. The anterior of the thorax portion of the gown is non-reflective. The distributor inflates when heated air is supplied. The distributor exhausts air into the gown. Temperature is maintained at a desired level for the extremities, while preventing the thorax area from being elevated to an uncomfortable level. Another embodiment is a perioperative warming device. The device is a gown that has a thorax portion and a leg portion. Each portion has an independent air chamber and inlet. The two portions are releasably connected. The sleeves, leg portion, and anterior of the gown are heat reflective.
Owner:THE SURGICAL INT
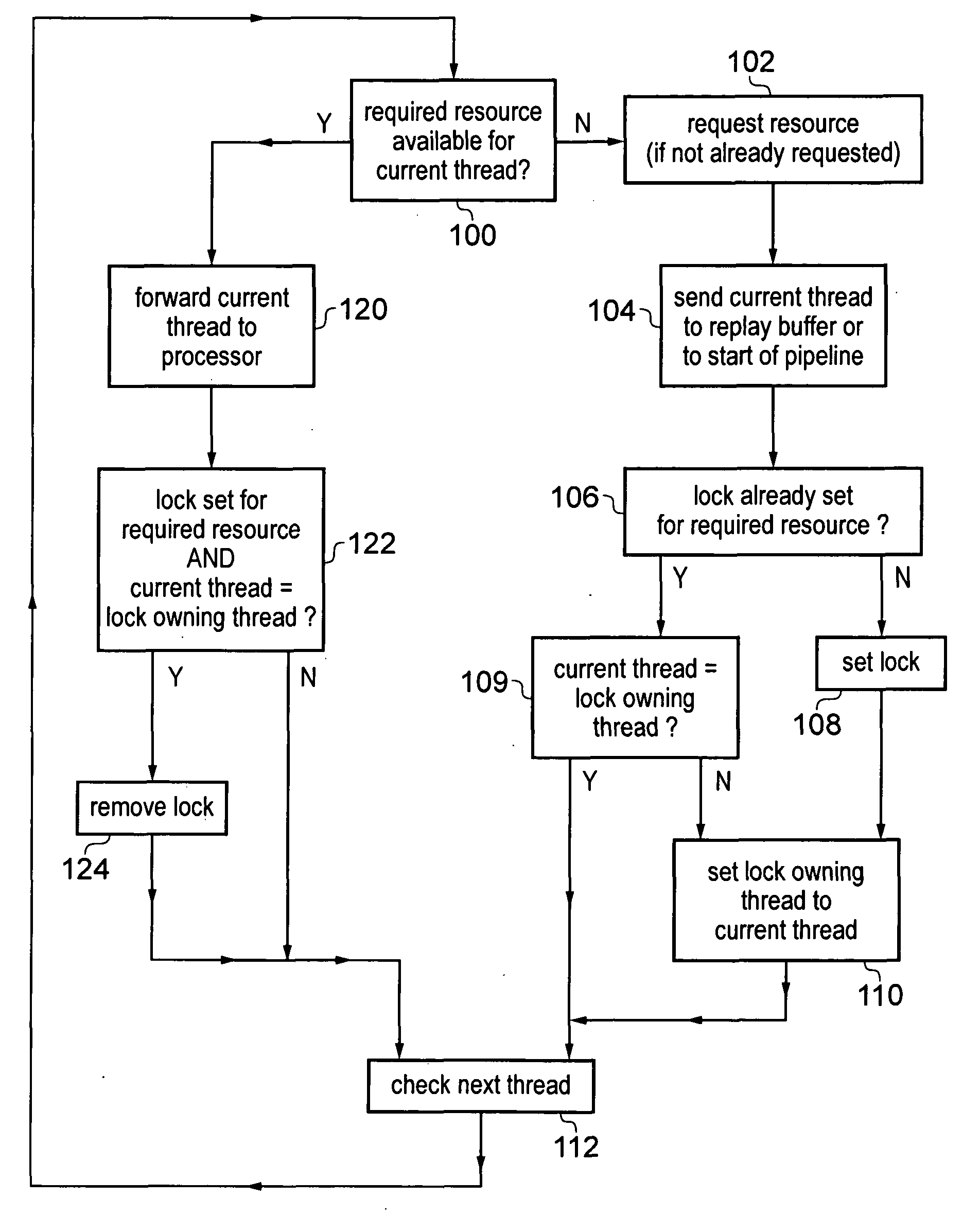
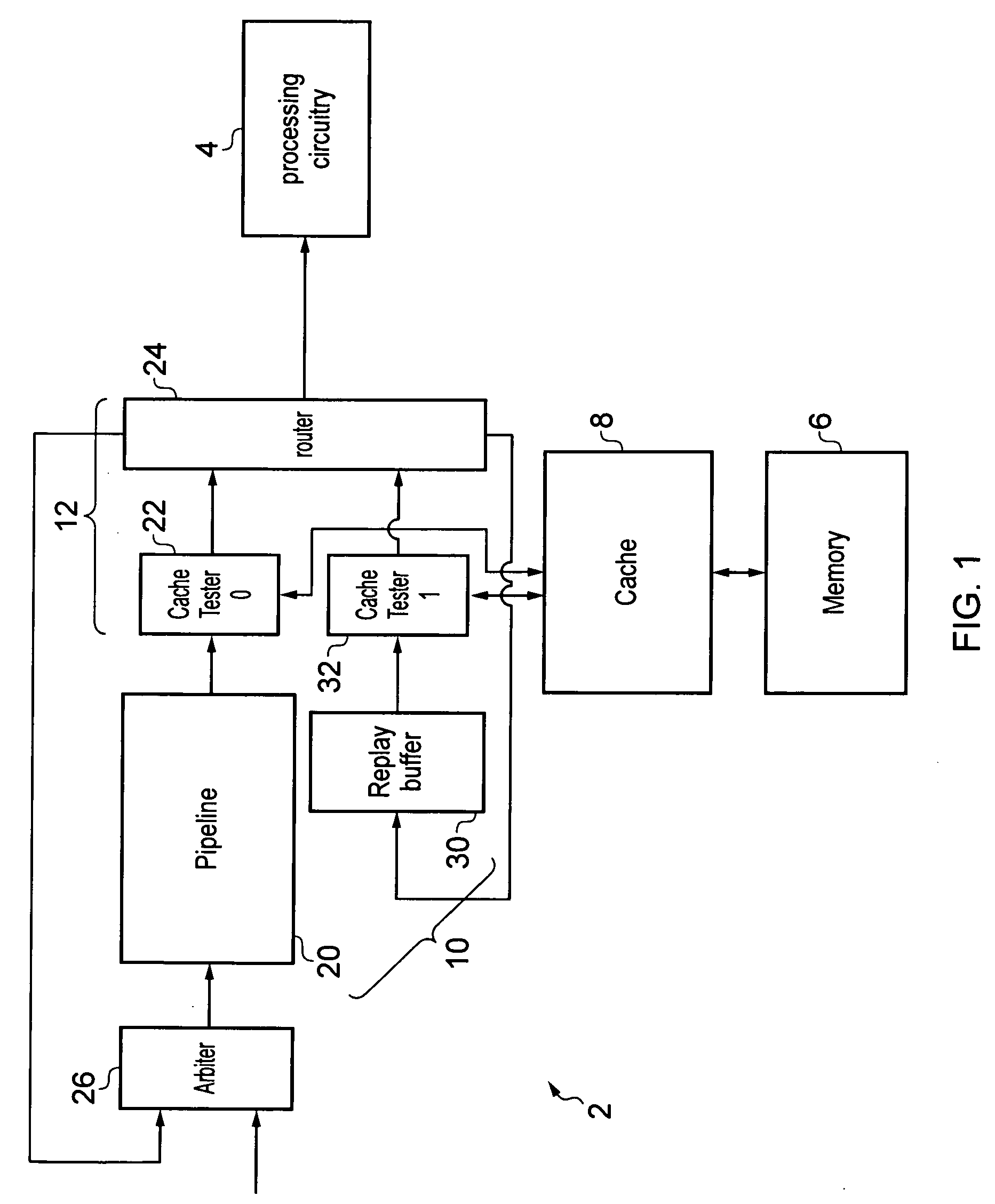
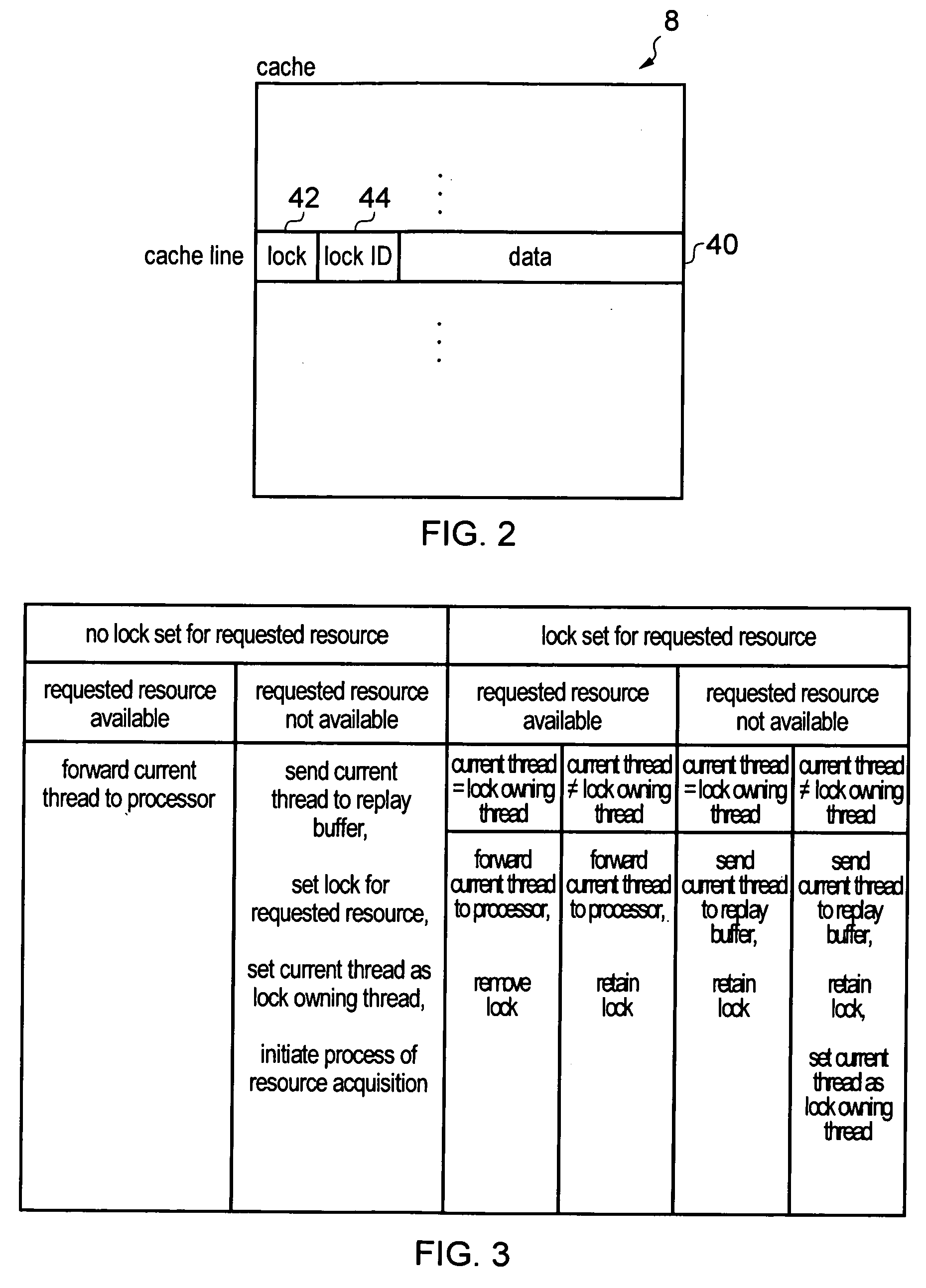
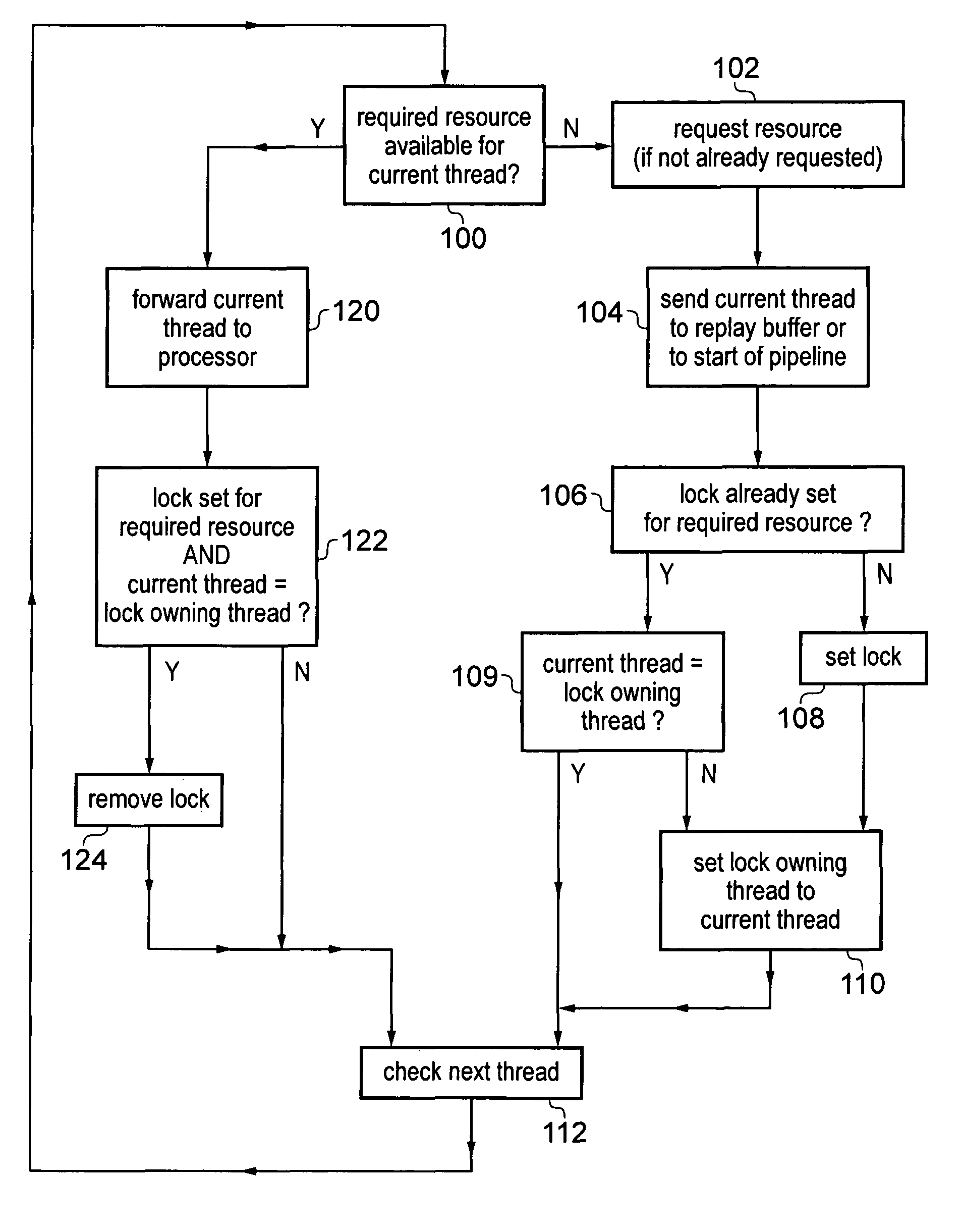
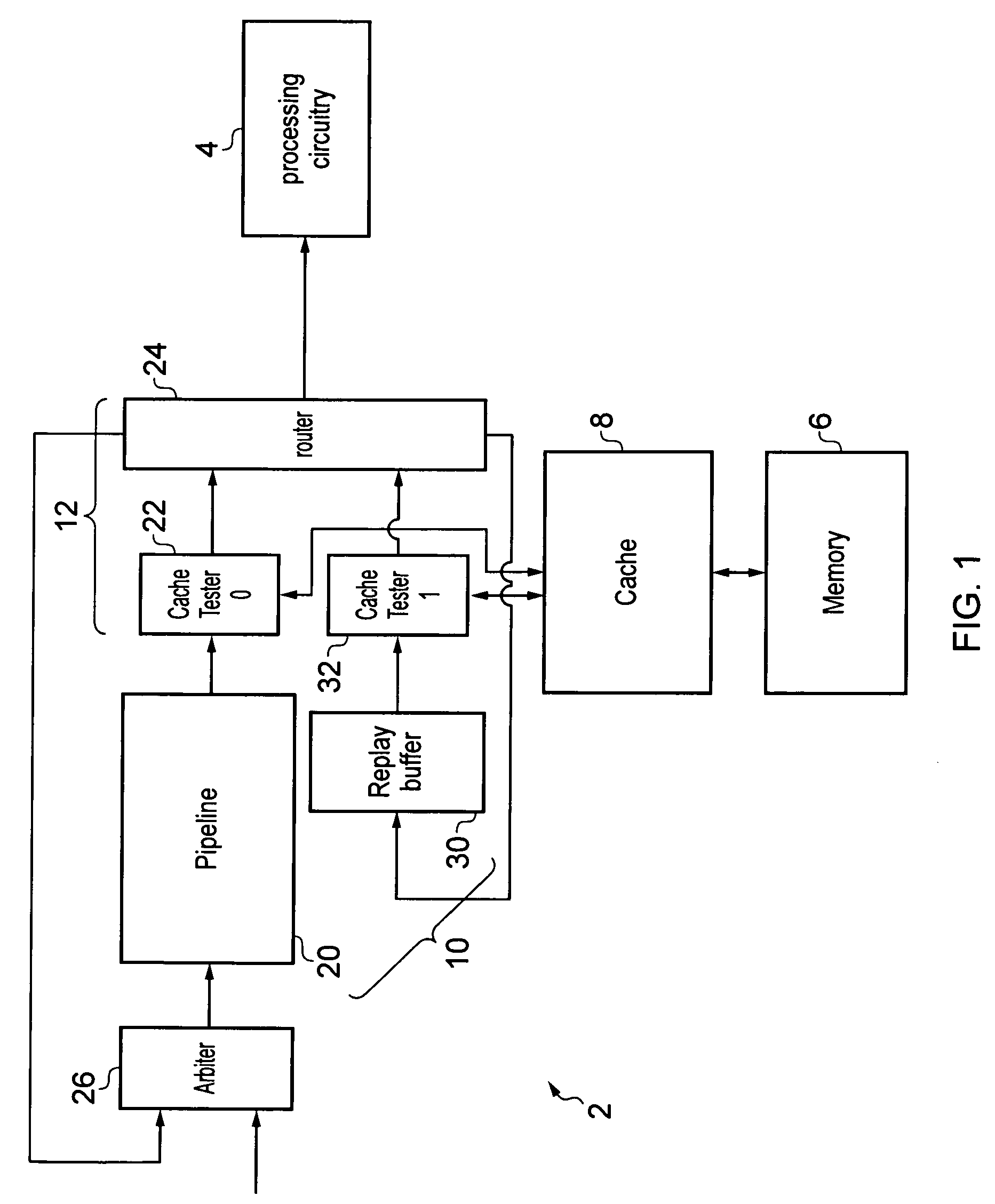
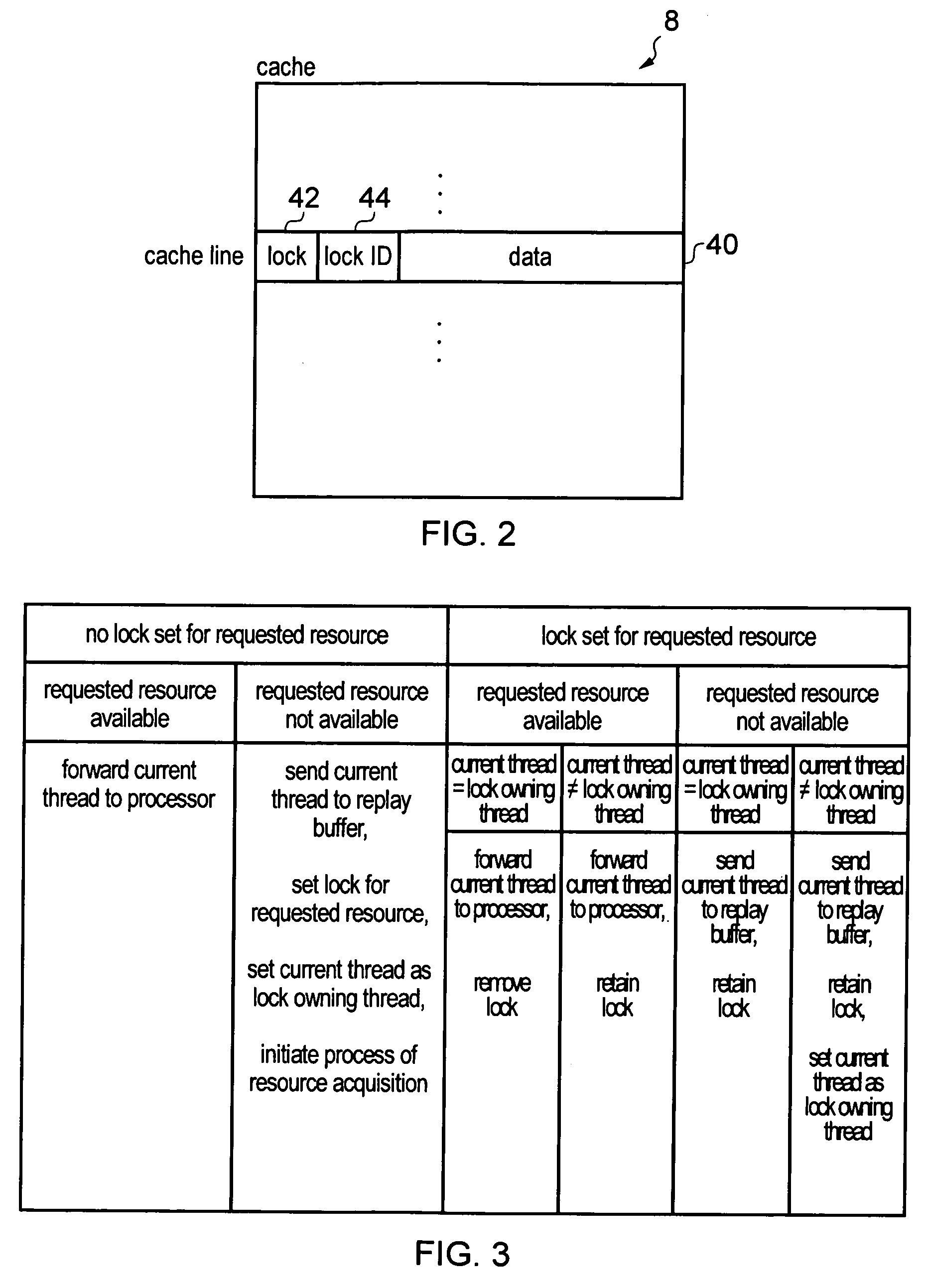
Apparatus and method for processing threads requiring resources
ActiveUS20130247060A1Efficient processingAvoid reconfigurationResource allocationMemory systemsOperating systemData processing
A data processing apparatus has processing circuitry for processing threads using resources accessible to the processing circuitry. Thread handling circuitry handles pending threads which are waiting for resources required for processing. When a request is made for a resource which is not available, a lock is set to ensure that once the resource becomes available, the resource remains available until the lock is removed. This prevents other threads reallocating the resource. When a subsequent pending thread requests access to the same locked unavailable resource, the lock is transferred to that subsequent thread so that the latest thread accessing that resource is considered the lock owning thread. The lock is removed once the lock owning thread is ready for processing.
Owner:ARM LTD
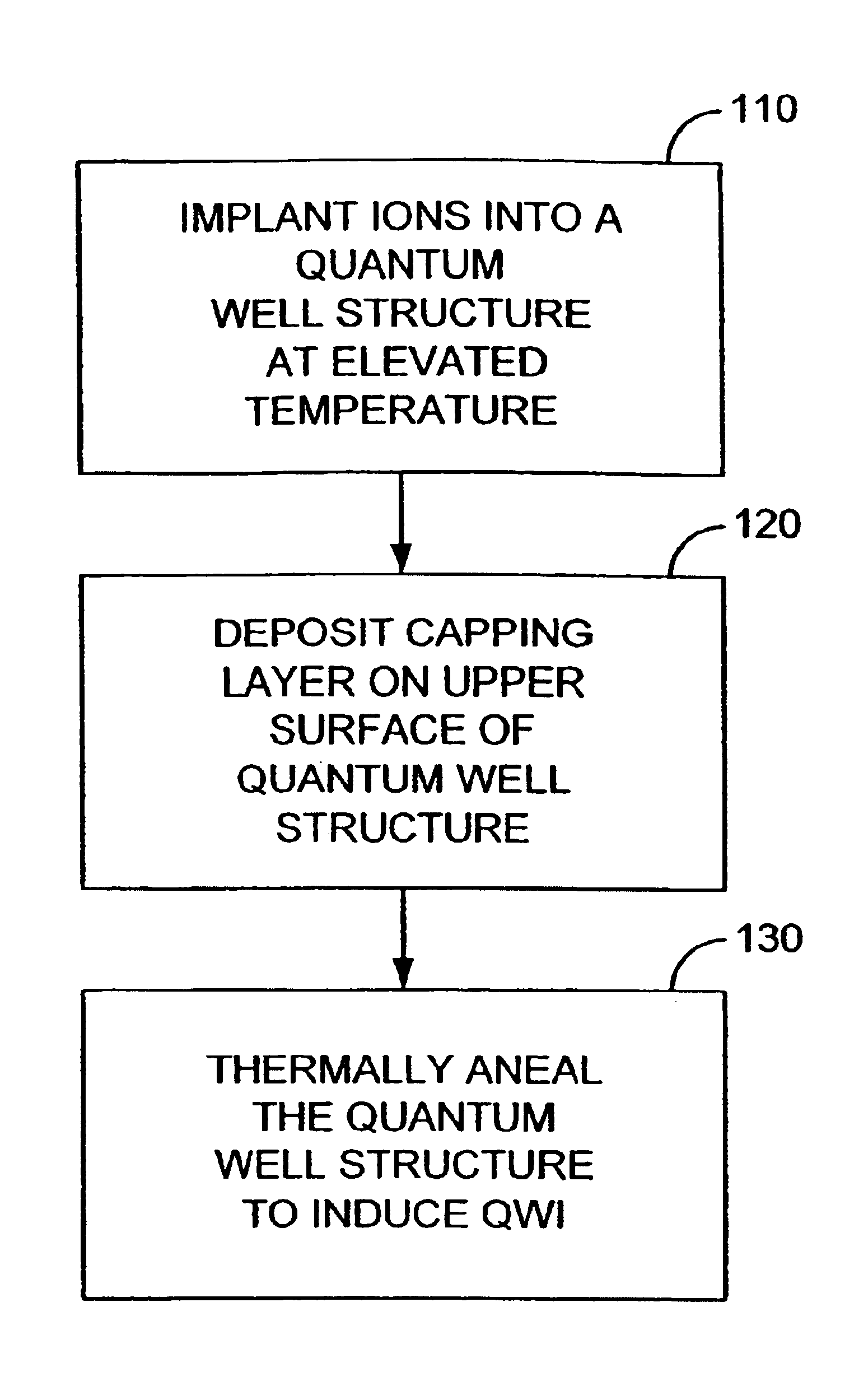
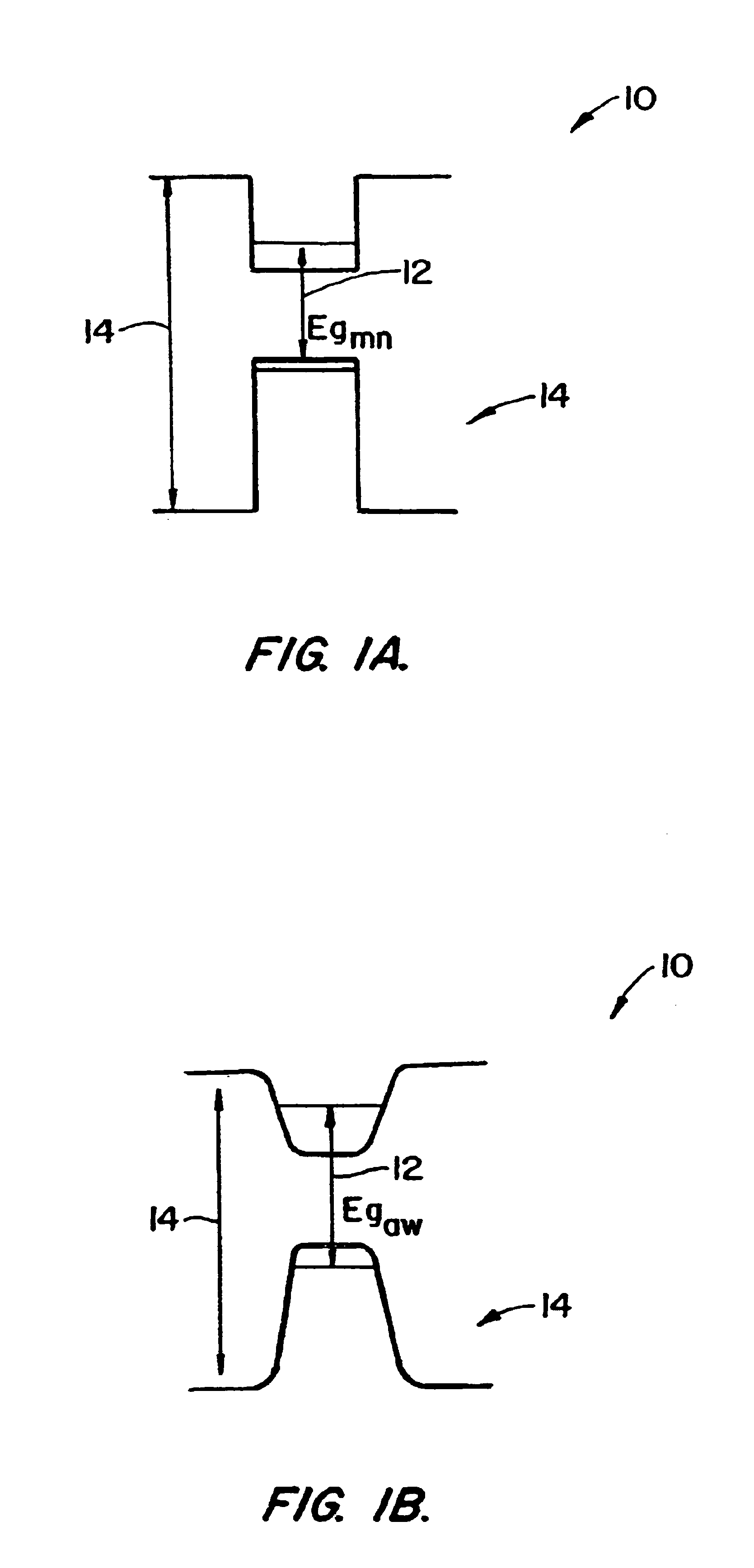
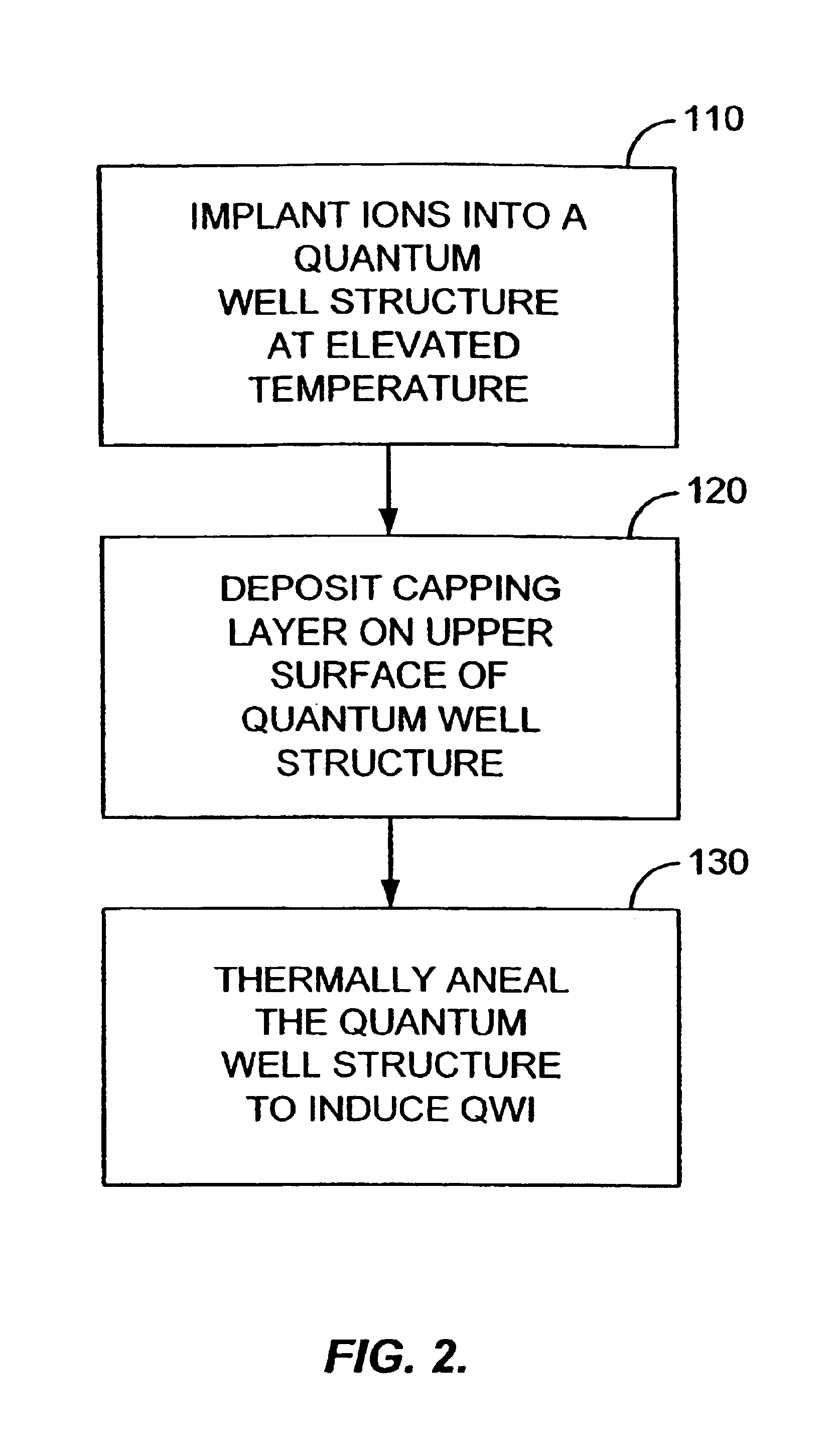
Method for shifting the bandgap energy of a quantum well layer
InactiveUS6878562B2Reduce formationAvoid reallocationLaser detailsLaser active region structureQuantum wellPhotonics
A process for shifting the bandgap energy of a quantum well layer (e.g., a III-V semiconductor quantum well layer) without inducing complex crystal defects or generating significant free carriers. The process includes introducing ions (e.g., deep-level ion species) into a quantum well structure at an elevated temperature, for example, in the range of from about 200° C. to about 700° C. The quantum well structure that has had ions introduced therein includes an upper barrier layer, a lower barrier layer and a quantum well layer. The quantum well layer is disposed between the upper barrier layer and the lower barrier layer. The quantum well structure is then thermally annealed, thereby inducing quantum well intermixing (QWI) in the quantum well structure and shifting the bandgap energy of the quantum well layer. Also, a photonic device assembly that includes a plurality of operably coupled photonic devices monolithically integrated on a single substrate using the process described above.
Owner:HO SENG TIONG
Semiconductor device, method for manufacturing the semiconductor device, and integrated circuit including the semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050017297A1Lower on-resistanceImprove stabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesLDMOSDevice material
A semiconductor device, methods for manufacturing the semiconductor device, and an integrated circuit including the semiconductor device are disclosed. The semiconductor device includes an LDMOS transistor and a MOS transistor, both formed simultaneously on a same substrate. The gate electrodes and the gate oxide layers of the LDMOS and the MOS are formed independently from one another. The source and drain regions of the LDMOS and the MOS are respectively formed in a self-aligned manner. In this way, the LDMOS and the MOS can be formed, in an effective manner, while sustaining the respective desired characteristics.
Owner:RICOH KK
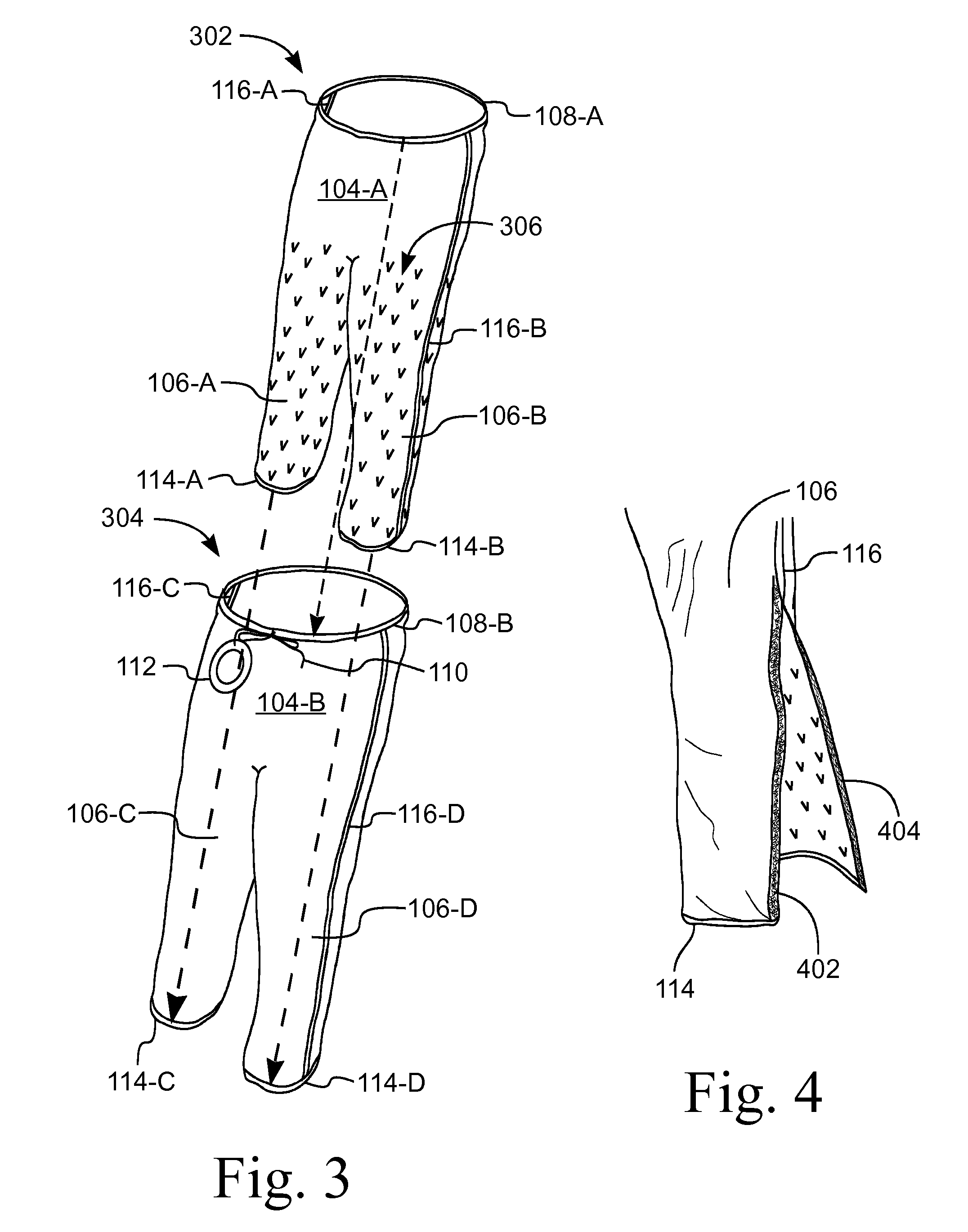
Garment For Preventing Redistribution Hypothermia
ActiveUS20120047622A1Prevent hypothermiaComfort levelChemical protectionHeat protectionEngineeringTemperature gradient
A thermal therapy garment that covers at least the lower extremities of a patient. The garment has an air impermeable outer layer and an air permeable inner layer. An inflatable air chamber is defined between the inner and outer layers. An inlet port connects to the chamber to allow inflation with conditioned air, which is exhausted through the inner layer over a selected region of the patient's lower body. A gown has a length sufficient to overlap a waist portion of the garment, The gown has an opening that coincides with the inlet port, thereby allowing a hose to pass through the gown and connect to the inlet port. In one embodiment, the gown has sleeves and / or a posterior portion that are heat reflective whereby the extremities are warmed to minimize the core to peripheral temperature gradient.
Owner:THE SURGICAL INT
Prosthesis seals and methods for sealing an expandable prosthesis
Embodiments of the present disclosure are related to devices and techniques for para-valve sealing of an expandable stent-valve implanted using a catheter. In some embodiments, a stent-valve is provided which comprises a seal sleeve / cuff containing material that swells when contacted by blood. A piercing tool may be included and used to permit a user to puncture the sleeve / cuff prior to introduction into a patient's body. In some embodiments, the sleeve / cuff has an integral tubular structure configured to withstand balloon expansion of the stent-valve during or after implantation. In some embodiments, the seal is provided as a separate component from the stent-valve.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
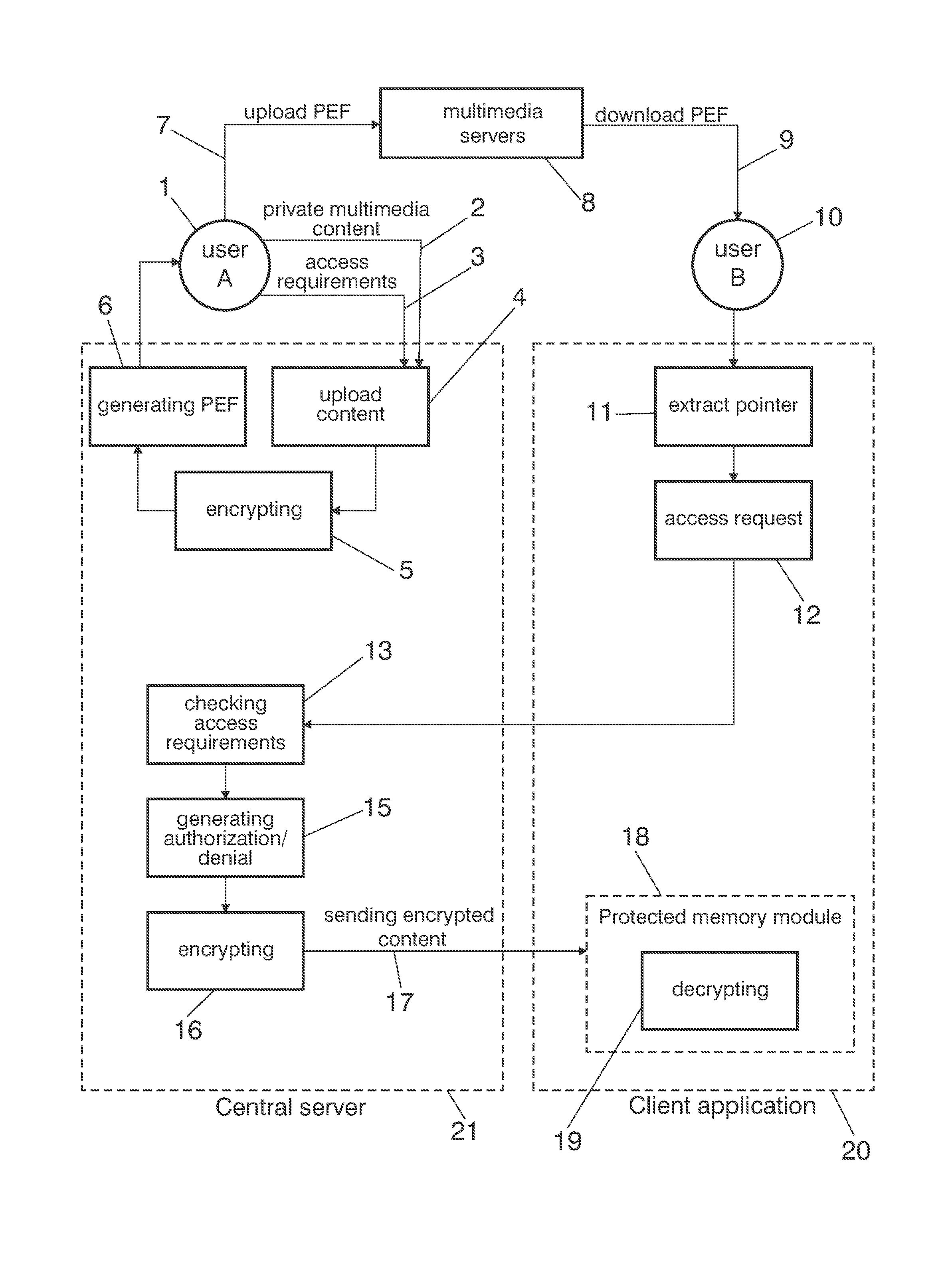
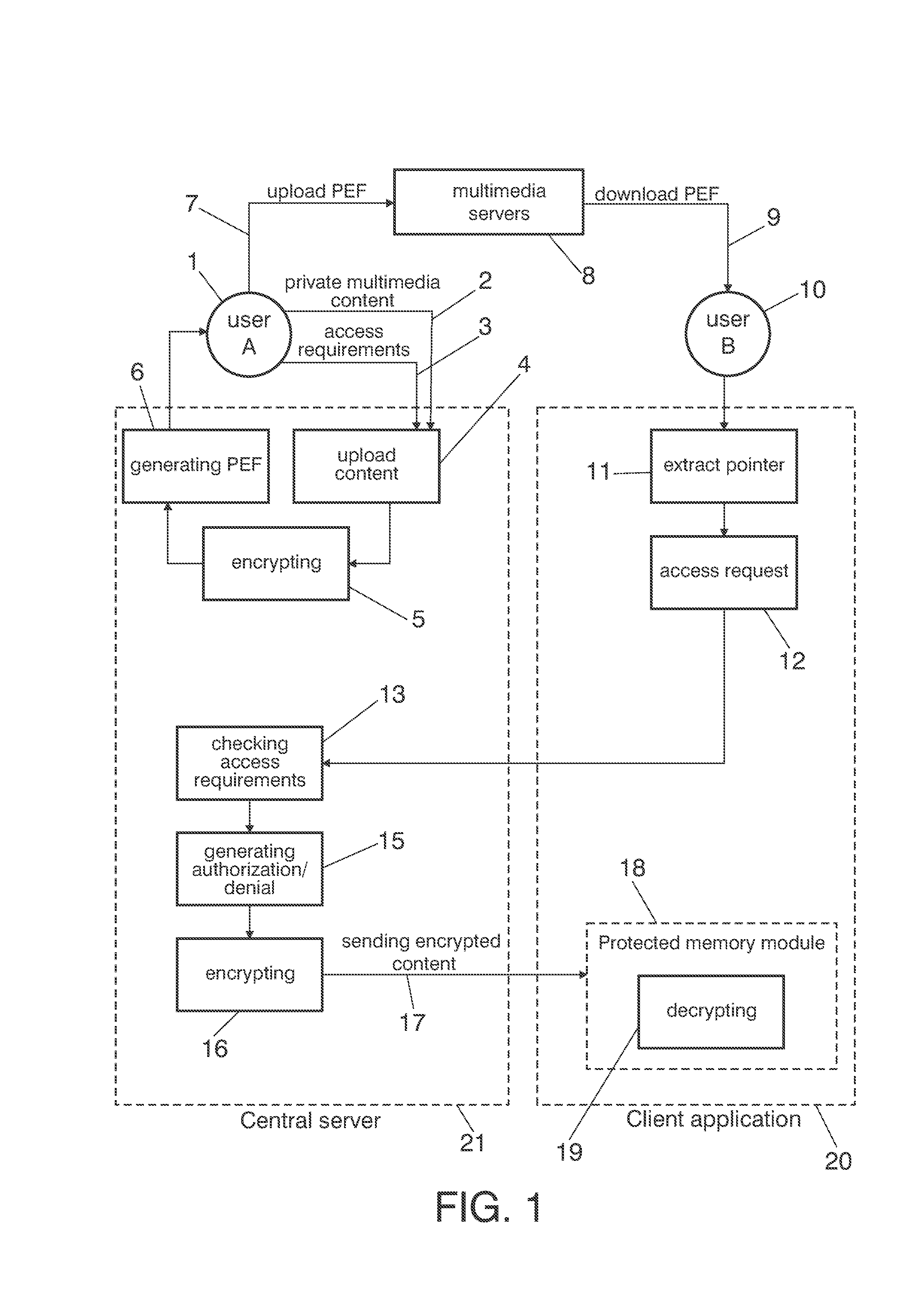
Multimedia privacy enhancer
InactiveUS20130166904A1Avoid reallocationUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionWeb browserMultimedia servers
The disclosure relates to a method and a system for protecting private multimedia content which comprises a central server in communication with a client application, characterized in that a user uploads a private multimedia content to the central server and a reference file is generated including a pointer to the private multimedia content and access requirements associated. The reference file is uploaded to multimedia servers and other users of the network download it through a web browser. The client application extracts the pointer from the reference file and sends a request to the central server, where it is checked if the request fulfils the access requirements associated for the private multimedia content requested.
Owner:TELEFONICA SA
Electronic mail distribution system for permitting the sender of electronic mail to control the redistribution of sent electronic mail messages
InactiveUS20060031320A1Avoid reallocationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet privacyDistribution system
A system that will enable the sender of the E-mail to control the redistribution of the message tasks that are to be redistributed by the receiver of the E-mail. More particularly, the present invention comprises enabling the sender of E-mail to specify conditions for the redistribution of an E-mail message sent to a receiving display terminal in combination with an implementation enabling this sender to track the redistribution of the sent E-mail message and apparatus enabling the sender to change the redistribution of the E-mail message. According to the invention, initially, there is an implementation enabling a user at the terminal receiving the sent E-mail message to redistribute the sent E-mail message subject to the conditions specified by the sender. The sent E-mail message specifies tasks divided out of the sent E-mail message to be assigned, respectively, to subsequent receivers of the redistribution messages by such messages.
Owner:IBM CORP
Unmanned aerial vehicle one-station multi-machine system air-ground data link channel distribution method
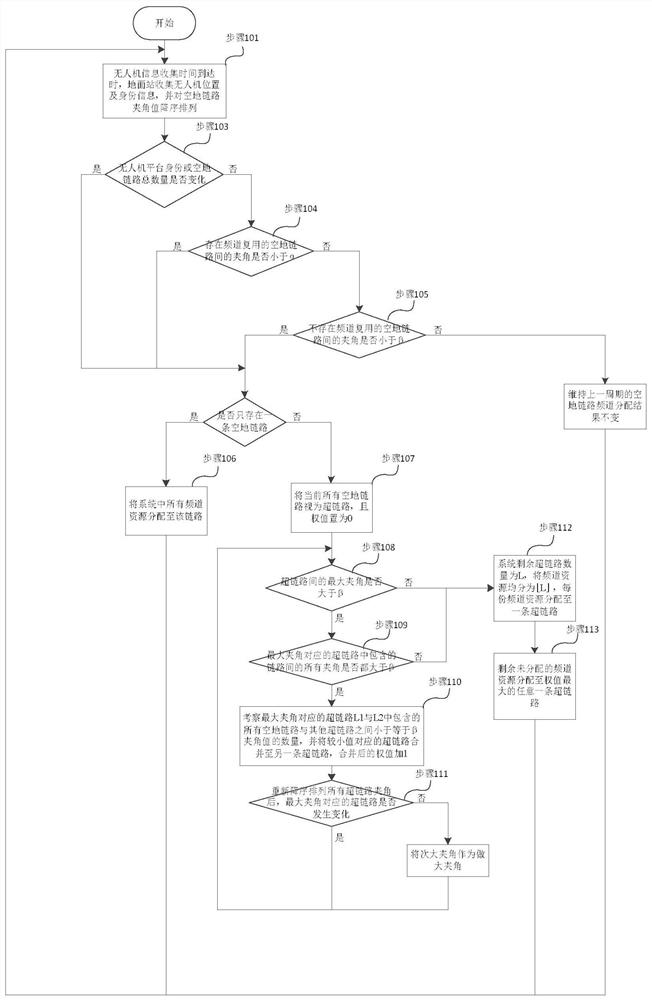
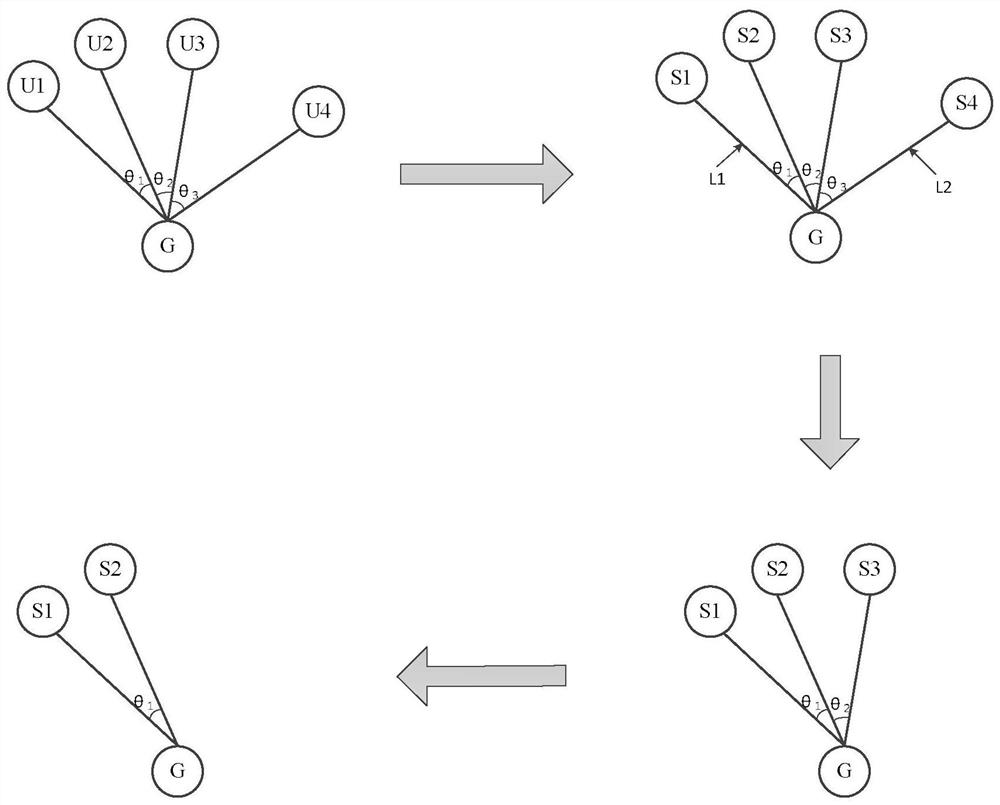
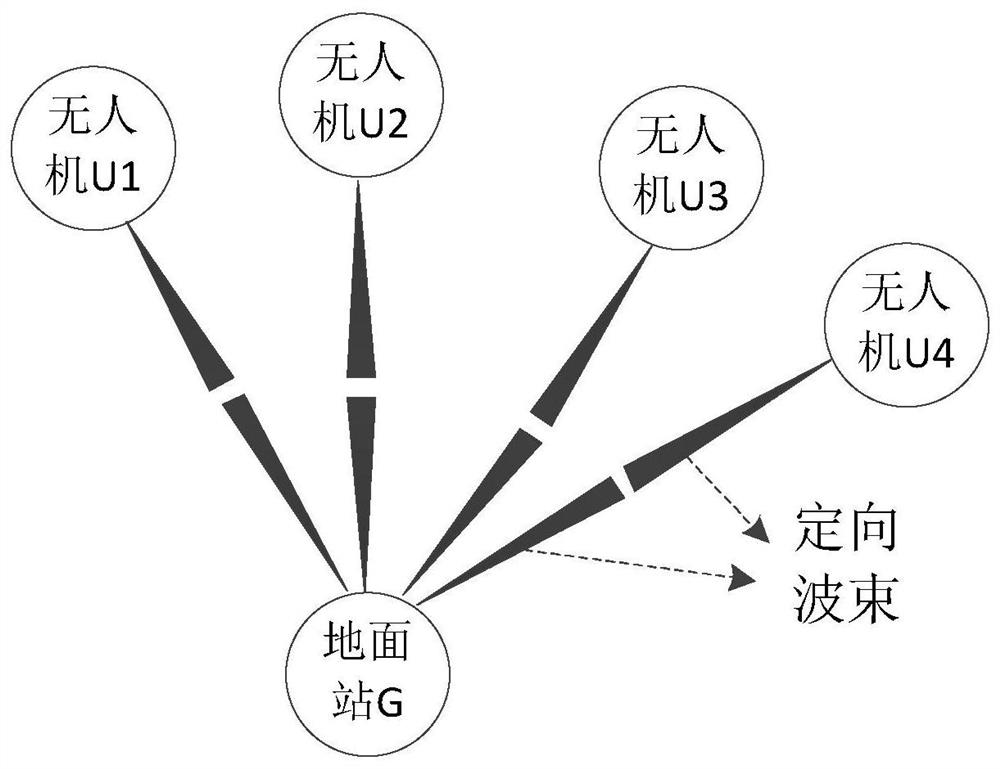
ActiveCN110022545AEnhanced resource reuse capabilityImprove resource utilizationParticular environment based servicesVehicle infrastructure communicationMultiplexingMulti machine system
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle one-station multi-machine system air-ground data link channel allocation method, and aims to provide a link channel allocation method capable of reducing the operation complexity and improving the channel resource reuse degree. The method is realized through the following technical scheme: a ground control station obtains unmanned aerial vehicle platform position information, counts the number of air-ground data links, calculates included angles between every two air-ground data links, and performs descending order arrangement on all includedangle values; then, starting from the air-ground data link corresponding to the maximum included angle, a 'super link' is constructed according to the relation between the included angle between the links and a 'multiplexing threshold', and the number of the air-ground data links contained in the super link is taken as the weight of the super link; the ground control station iteratively performs the super link merging process until no super link which can be further merged exists, and the channel resources are evenly distributed to each super link; and after the distribution process is finished, the channel distribution result is sent to the unmanned aerial vehicle platform through the uplink air link.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Apparatus and method for processing threads requiring resources
ActiveUS8966494B2Avoid reallocationReduce amountProgram synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer scienceData processing
A data processing apparatus has processing circuitry for processing threads using resources accessible to the processing circuitry. Thread handling circuitry handles pending threads which are waiting for resources required for processing. When a request is made for a resource which is not available, a lock is set to ensure that once the resource becomes available, the resource remains available until the lock is removed. This prevents other threads reallocating the resource. When a subsequent pending thread requests access to the same locked unavailable resource, the lock is transferred to that subsequent thread so that the latest thread accessing that resource is considered the lock owning thread. The lock is removed once the lock owning thread is ready for processing.
Owner:ARM LTD
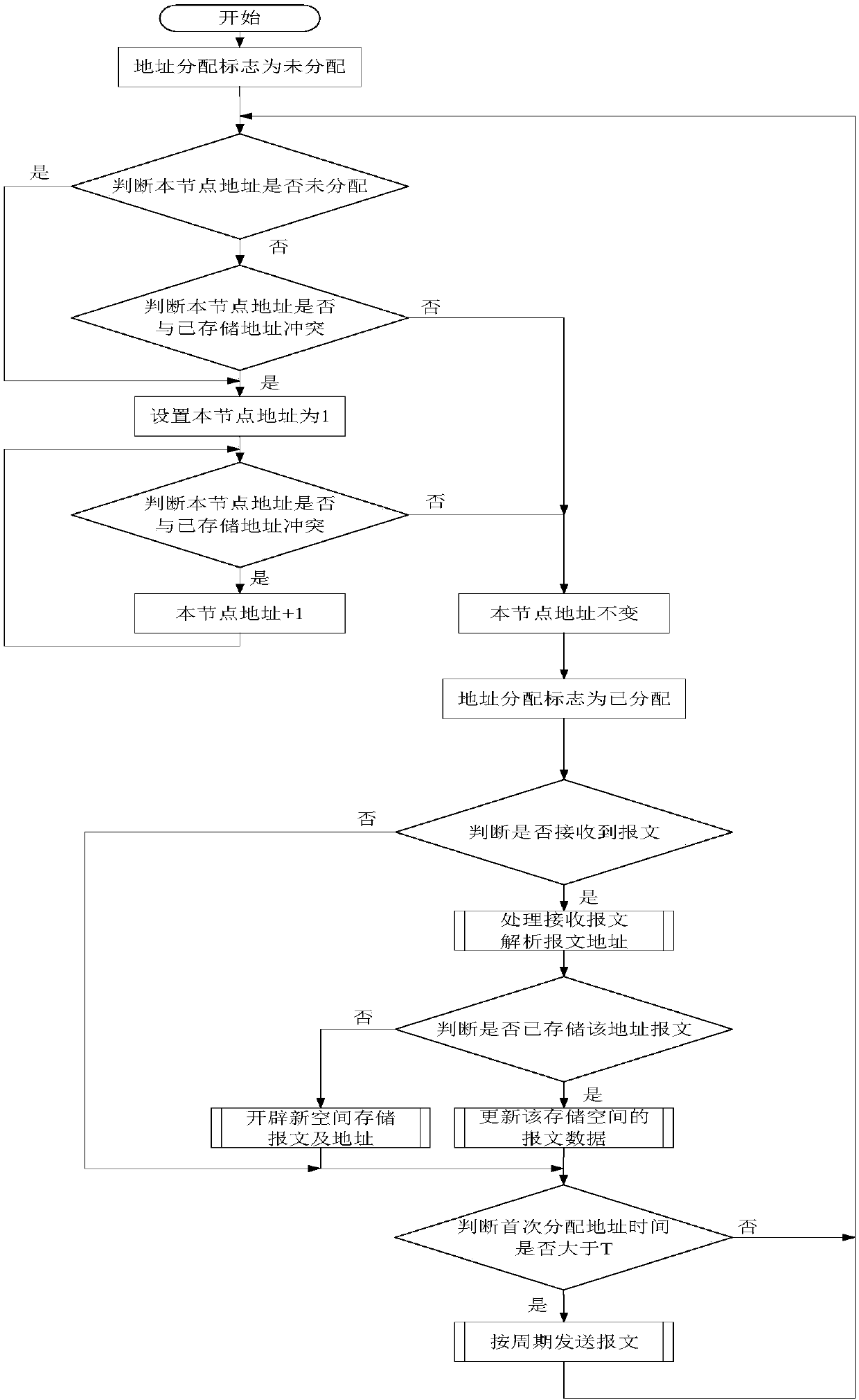
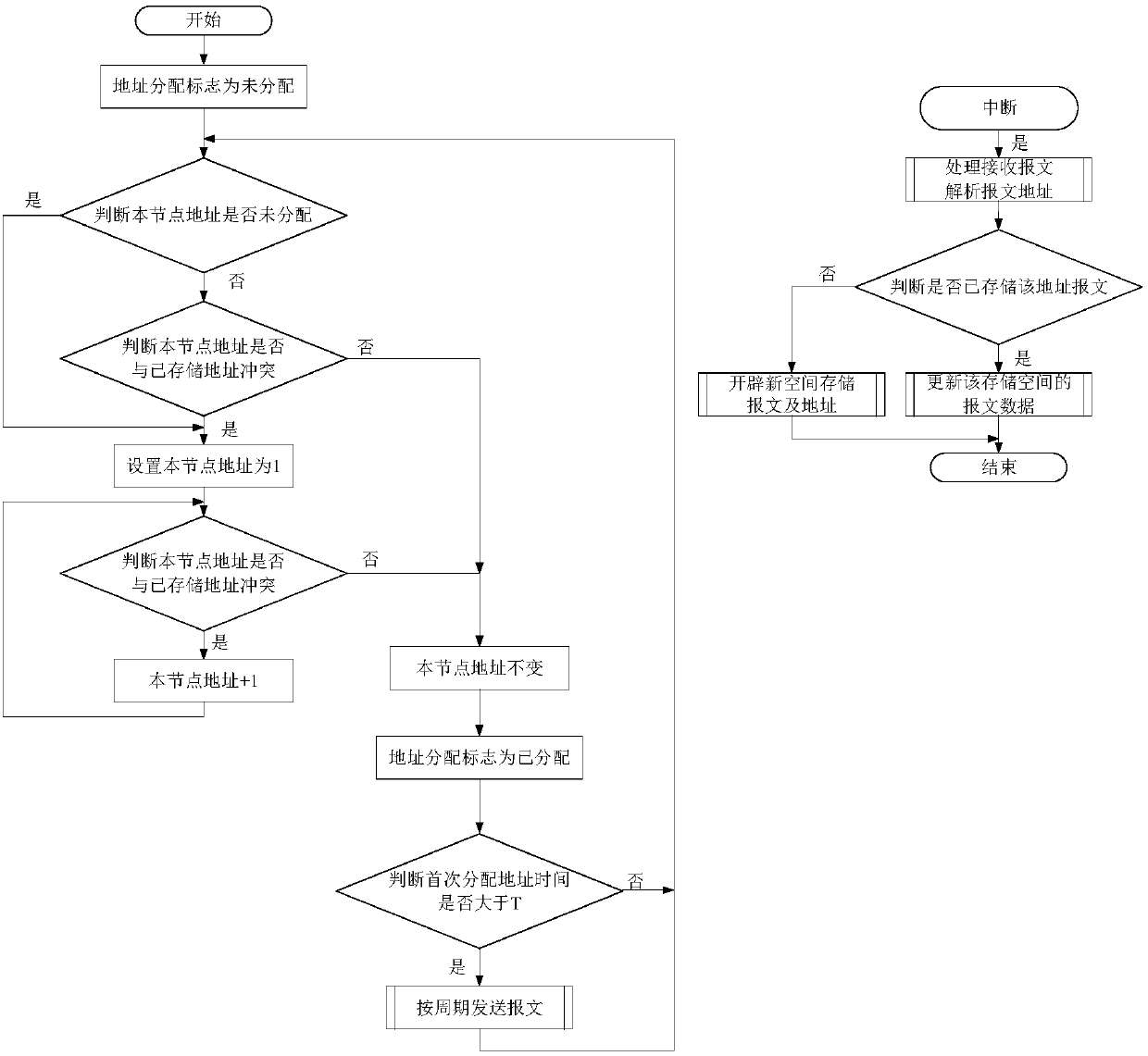
Method for automatically allocating address to same node on communication bus
ActiveCN107835266AAvoid reallocationReduce manual operationsData switching networksData errorComputer science
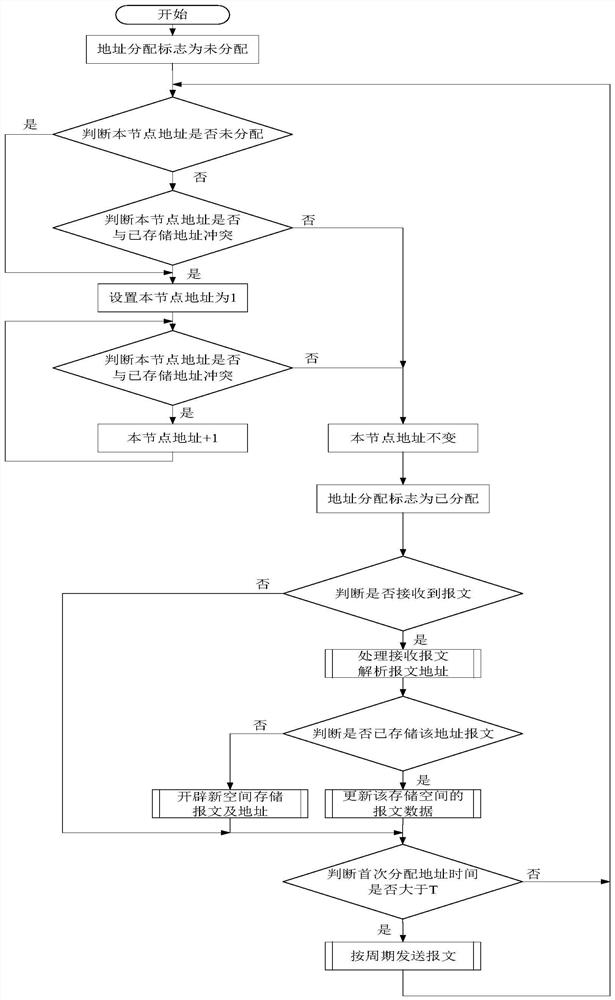
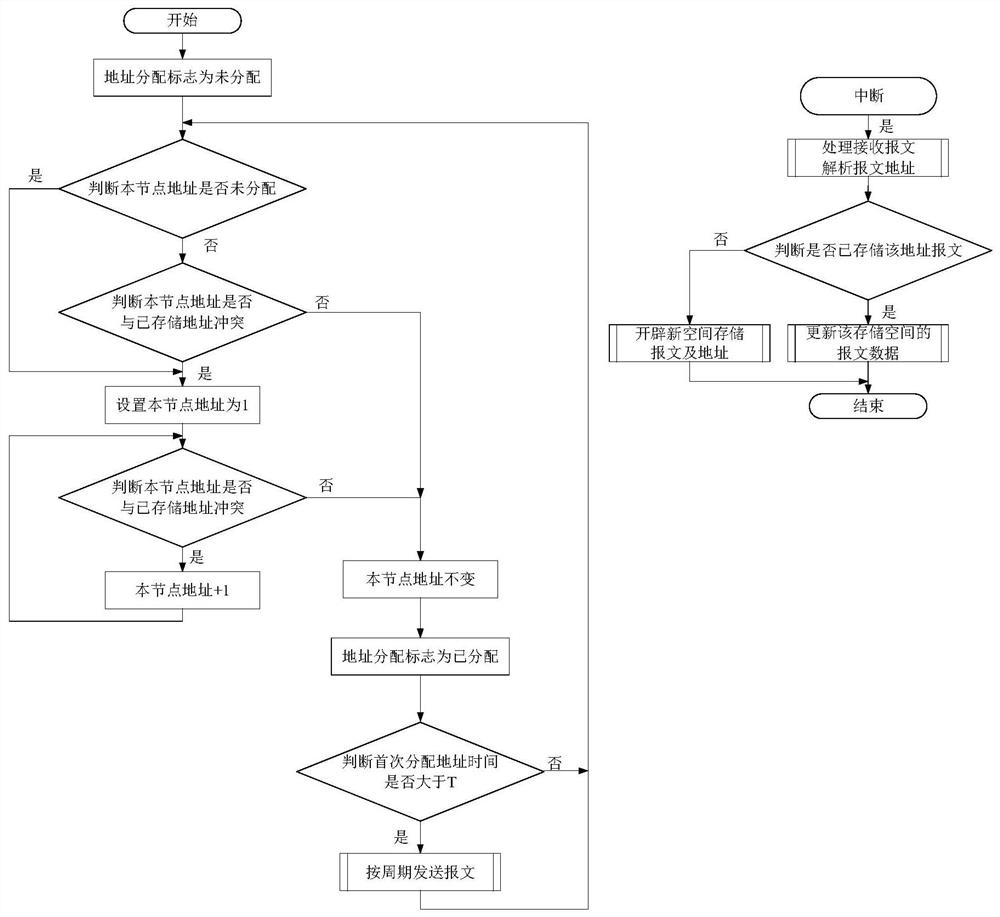
The invention relates to a method for automatically allocating an address to the same node on a communication bus. The method includes the following steps: step S1, setting a global variable address allocation tag, initializing the address allocation tag as an address unallocated state, judging whether the address allocation tag of a current node is unallocated, if not, executing the step S2, andif yes, executing the step S3; step S2, judging whether an address of the current node conflicts with a stored address, if yes, executing the step S3, and if not, executing the step S5; step S3, allocating an initial address that is a minimum address number '1' on the bus to the current node; step S4, judging whether the address of the current node conflicts with the stored address, if not, executing the step S5, and if yes, adding 1 to the address of the current node, and re-executing the step S4; and step S5, switching the address allocation tag to an address allocated state and remaining unchanged. According to the method disclosed by the invention, when equipment replaces a CAN bus due to the movement of the node, the reallocation of the address can be avoided, repeated addresses can be automatically rearranged in time, and bus data errors caused by the repeated addresses can be avoided.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
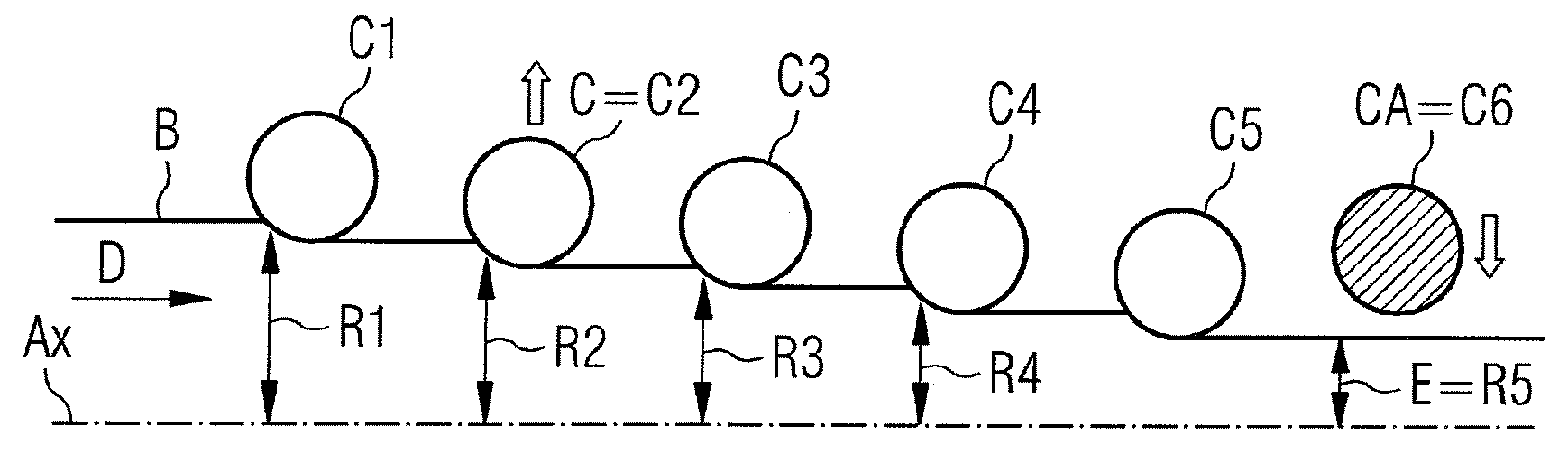
Method for changing a roller in a roll mill for a continuously running steel strip
InactiveCN102066015AAvoid reallocationGet rid of specsRoll force/gap control deviceMetal rolling stand detailsEngineeringSteel belt
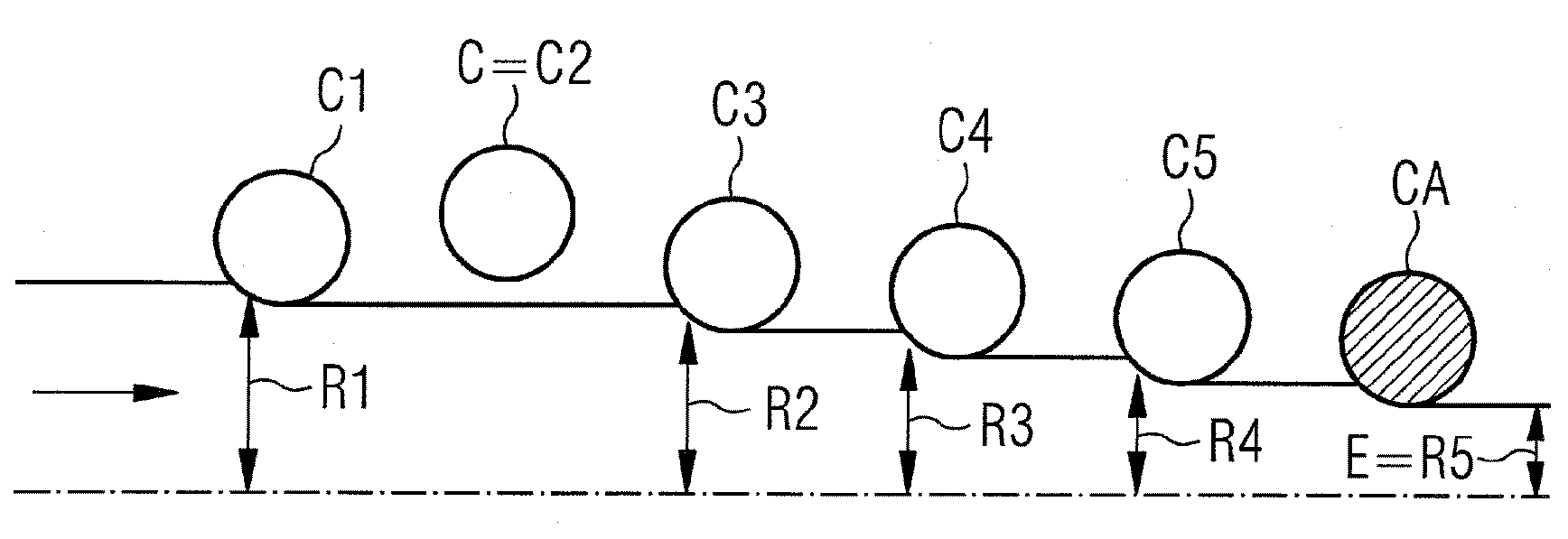
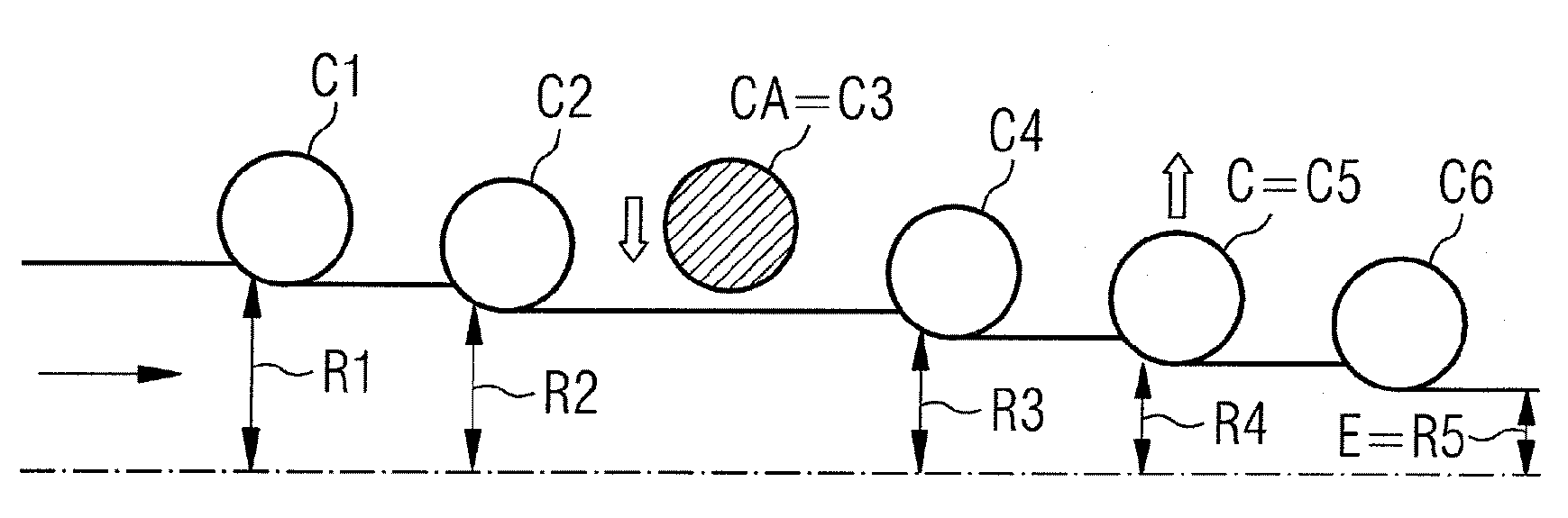
The invention relates to a method for changing rollers in a roll stand (C) adapted for bearing at least one working roller for a continuously-running steel-strip roll mill, wherein said stand (C) is part of a plurality (N) of roll stands arranged in series along the roll mill in the continuous running direction (D), wherein a rolling standby function in a free clamping position of the roller (s) is allocated to at least one dedicated stand (CA) among the plurality (N) of stands, origin setpoint values controlling an adjustment of the roller clamping are individually allocated to the other stands in an active rolling position, and in the case of a roller change when passing into the free clamping position of the cage (C), the origin setpoint value of said cage (C) and the origin setpoint values of the cages remaining in an active rolling position are redistributed individually among each of said cages, including the dedicated cage (CA).
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH FRANCE
Prewarming gown
ActiveUS20130231723A1Avoid areaMaintain air temperatureTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingEngineeringHypothermia
A device for warming a human body. The device is a gown (100, 1500) that has a thorax portion (110, 1502) and a leg portion (112, 1504). One embodiment prevents redistribution hypothermia with a distributor (206) attached to the inside of the leg portion (112). The sleeves (108), leg portion (112), and posterior of the gown (100) are heat reflective. The anterior of the thorax portion (110) of the gown is non-reflective. The distributor (206) inflates when heated air is supplied and exhausts air into the gown (100). Temperature is maintained at a desired level for the extremities, while preventing the thorax area from being elevated to an uncomfortable level. Another embodiment is a perioperative warming device. The device is a gown (1500) that has a thorax portion (1502) and a leg portion (1504). Each portion has an independent air chamber and inlet. The two portions are releasably connected. The sleeves (1508), leg portion (1504), and anterior of the gown (1500) are heat reflective.
Owner:THE SURGICAL INT
Storage management system, storage management server, and method and program for controlling data reallocation
InactiveUS7409496B2Easy to operateAvoid reallocationMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingControl dataStorage management
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Solid state image pickup device capable of suppressing smear
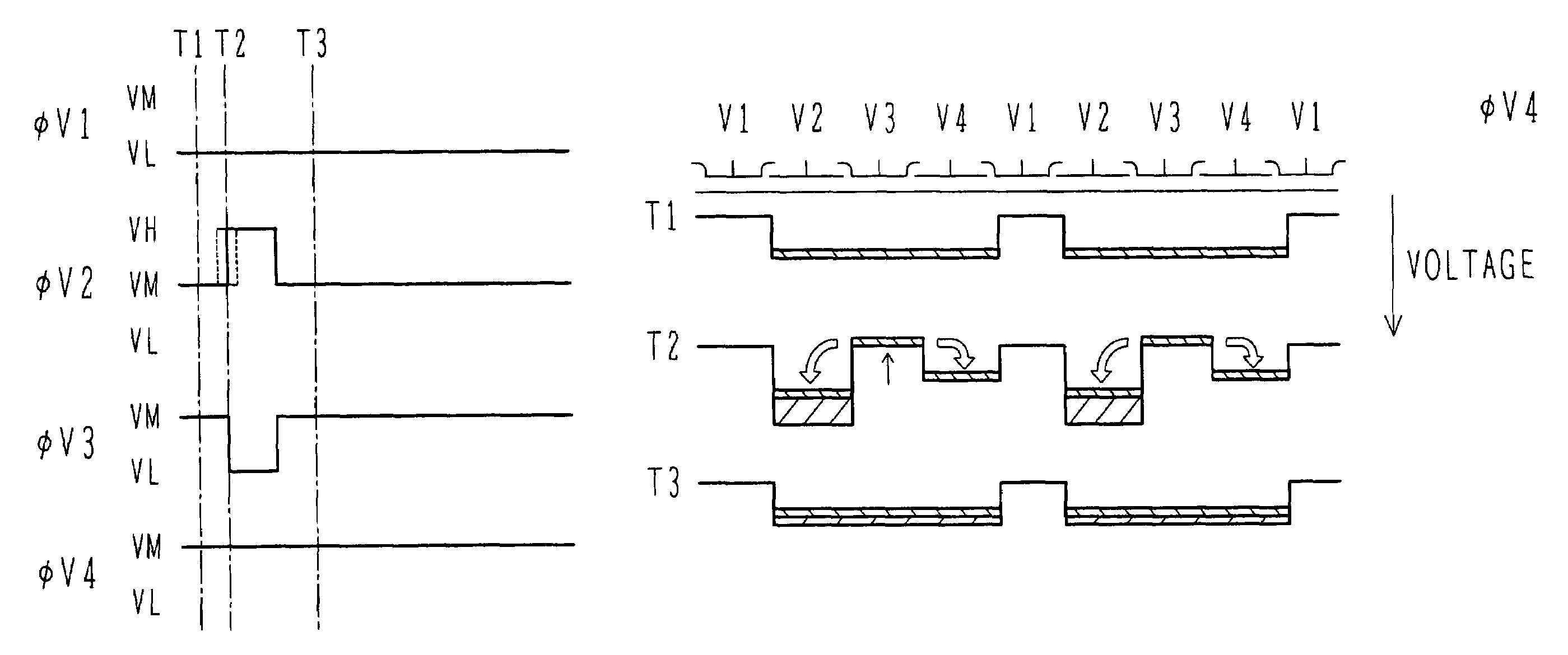
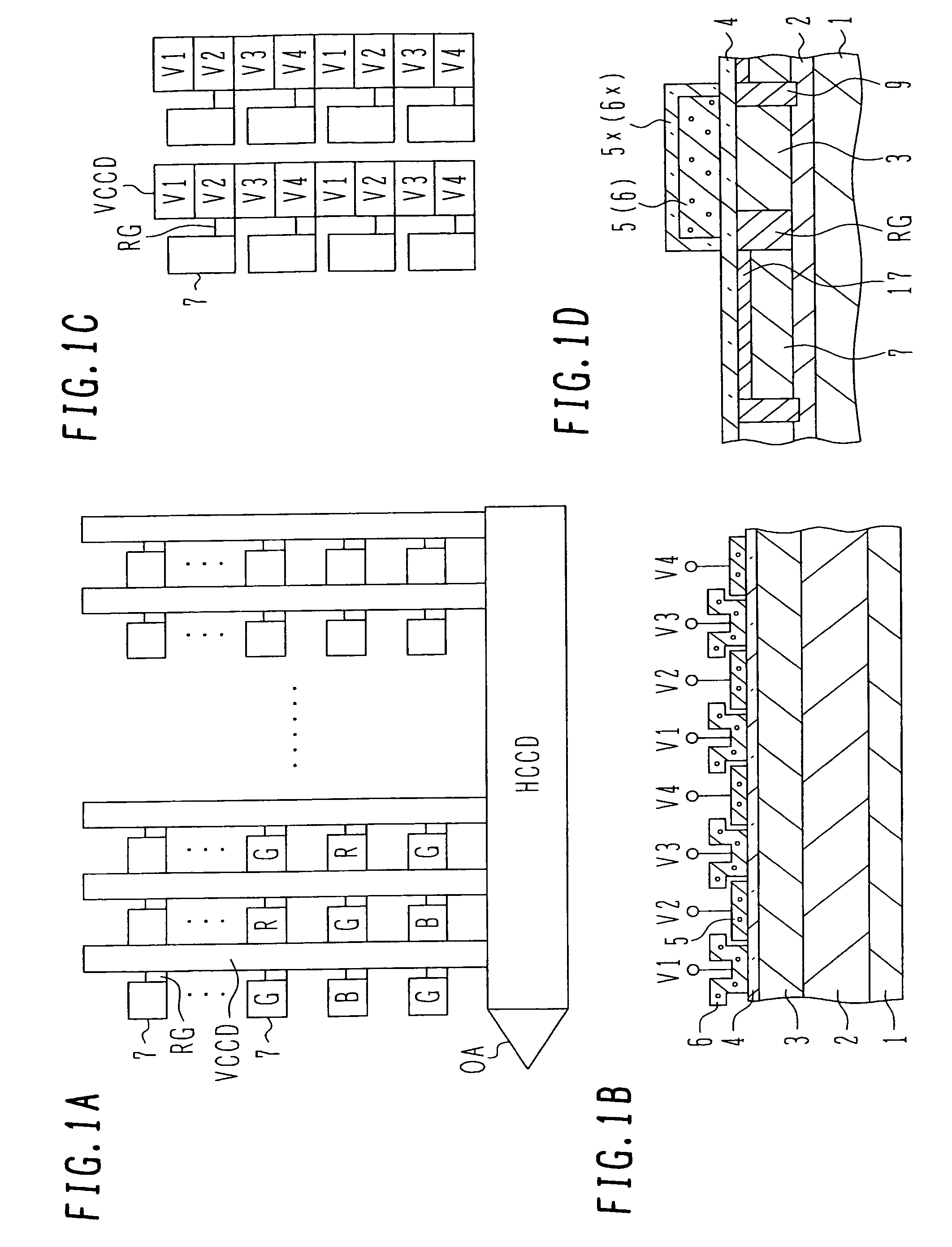
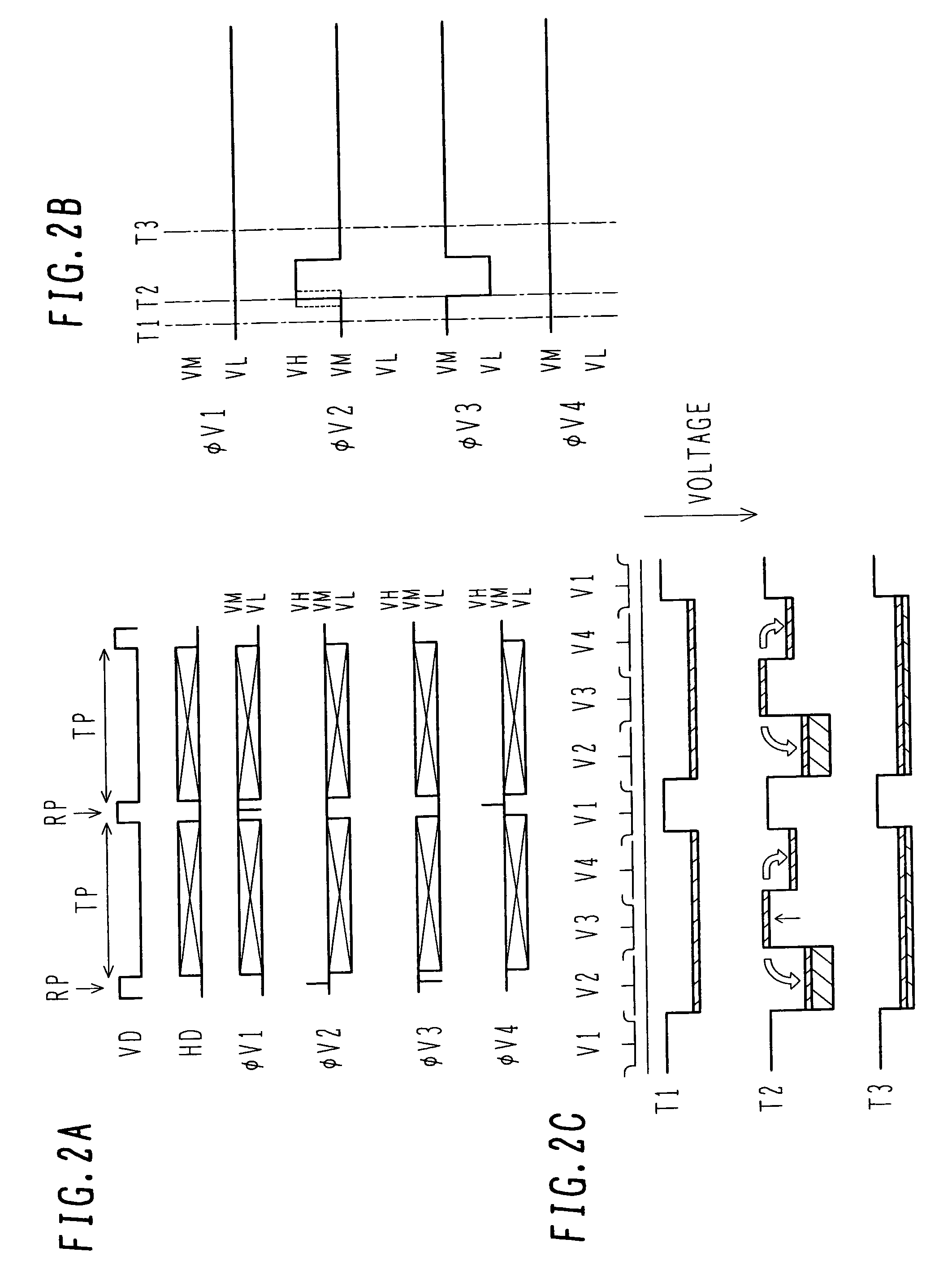
InactiveUS7052929B2Avoid reallocationReduce voltageTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPotential changeEngineering
A driving method for a solid state image pickup device, having four or more transfer stages as one transfer unit, includes reading signal charge from the charge accumulation regions to the vertical charge transfer channels. The reading step includes (b-1) applying the barrier forming voltage to a first transfer electrode to form a barrier of at least one stage per the transfer unit; (b-2) applying the read pulse to a second transfer electrode to read signal charge from a corresponding charge accumulation region to a corresponding vertical charge transfer channel; and (b-3) applying a cancellation pulse to a third transfer electrode spaced by at least one transfer stage from the first transfer electrode, the cancellation pulse cancelling out a potential change in the charge accumulation region to be caused by the read pulse.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and system to optimize distributed charging station efficiency and user experience
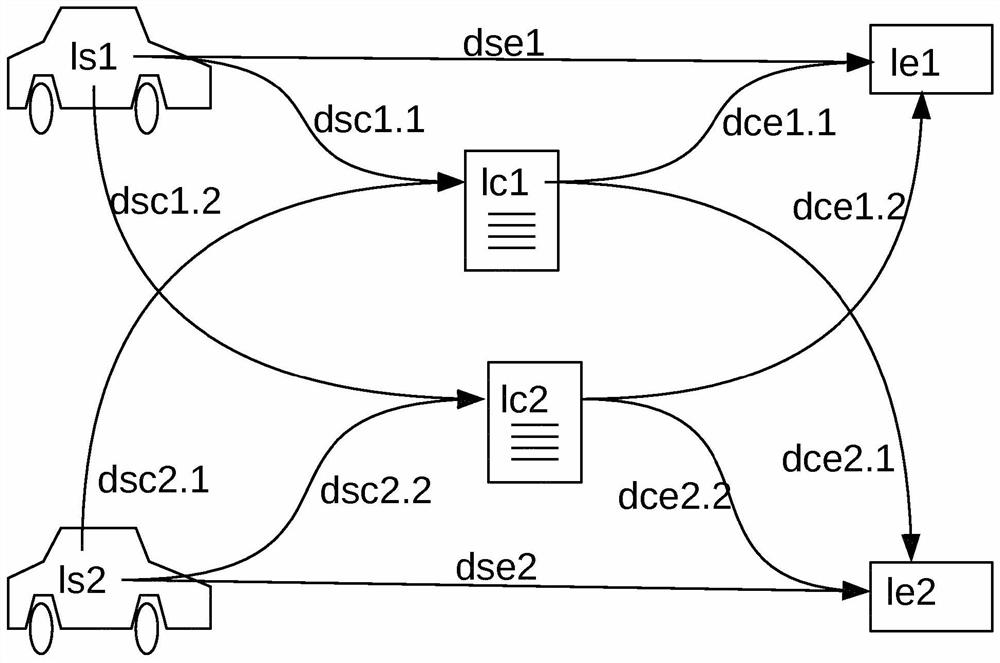
PendingCN113195299AReduce usageAvoid reallocationData processing applicationsCharging stationsSimulationCharging station
Provided a computer-implemented method for optimizing highly distributed charging stations efficiency and user experience, it is an objective of the present invention to optimally allocate charging stations. The objective is solved by the steps: a) receiving charging station data, the charging station data identifying one or more charging stations and charging station locations (lc1, lc2); b) receiving one or more requests (R) to charge one or more requesting vehicles, each request comprising data identifying a departure location (ls1, ls2) and an arrival location (le1, le2) of the respective requesting vehicle, being able to know feasible routes; c) receiving and / or determining detours data, the detours data indicating at least one charging station detour distance for a plurality of vehicles, the plurality of vehicles including the requesting vehicles; d) identifying charging station candidates for the requesting vehicles by optimizing an objective function (F) with linear constraints; and e) allocate at least some of the charging station candidates to the requesting vehicles; wherein optimizing the objective function (F) with linear constraints includes reducing a waiting time in the queue, price, a total detour distance for the requesting vehicles.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
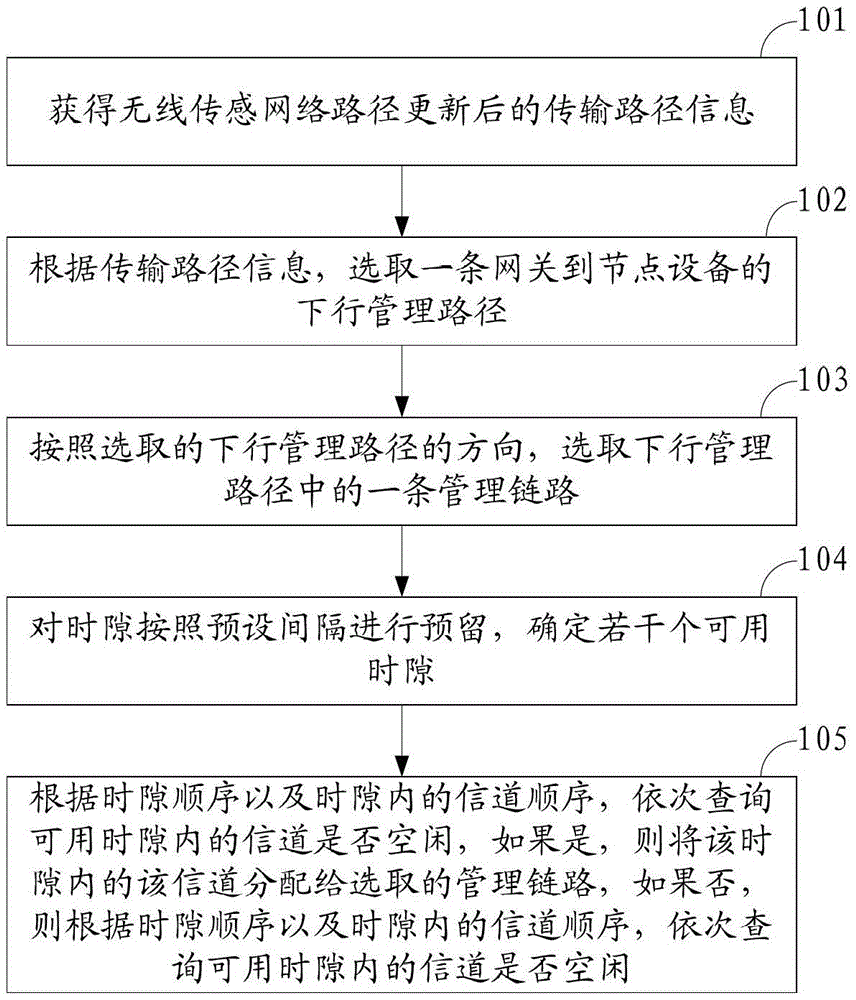
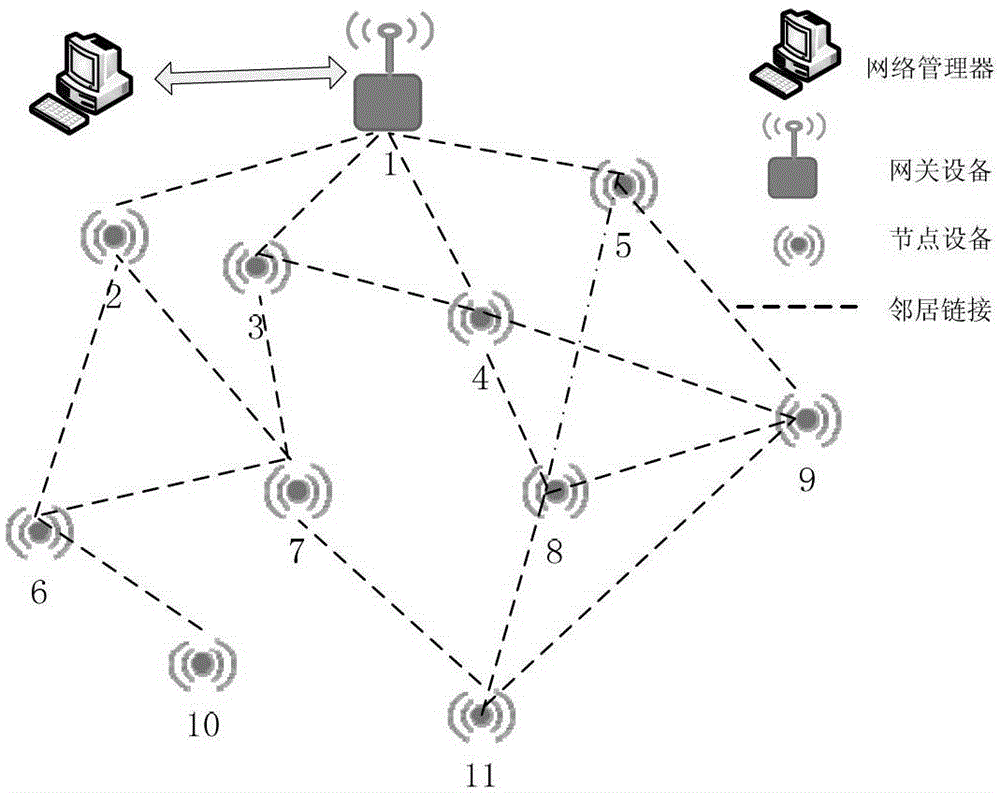
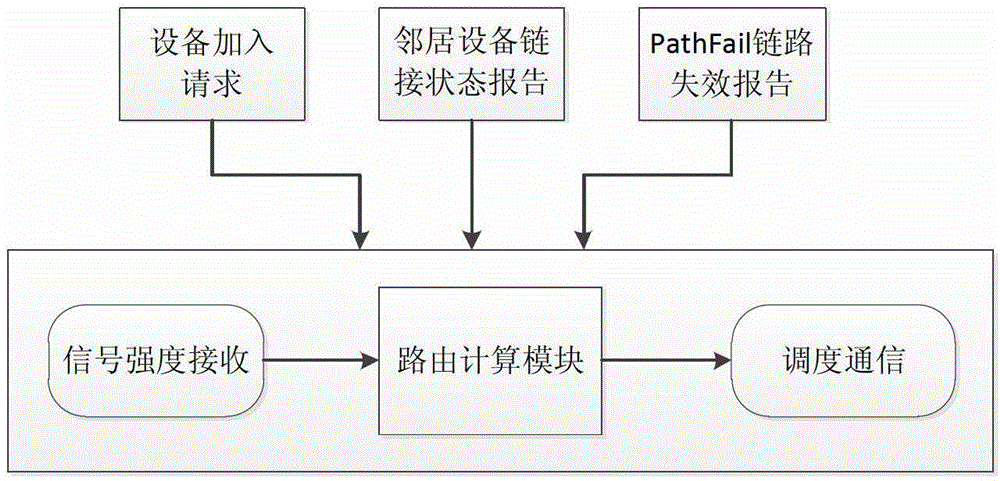
Dispatching communication method and device in industrial wireless sensing network
ActiveCN103052127BTake advantage ofImprove real-time performanceNetwork topologiesCommunication deviceResource distribution
The invention discloses a dispatching communication method in an industrial wireless sensing network and aims at realizing the dispatching communication and the resource distribution in the industrial wireless sensing network. The method comprises the following steps that the updated transmission route information of an industrial wireless sensing network route is obtained; a downward management route from a gateway to node equipment is selected according to the transmission route information; one management link in the downward management route is selected according to the direction of the selected downward management route; time slots are reserved according to preset intervals, and a plurality of available time slots are determined; and whether channels in the available time slots are idle or not are sequentially inquired according to the time slot sequences and the channel sequences in the time slots, if so, the channels in the time slots are distributed to the selected management link, and if not, whether the channels in the available time slots are idle or not are sequentially inquired according to the time slot sequences and the channel sequences in the time slots. The invention also discloses a dispatching communication device in the industrial wireless sensing network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUPCON TECH
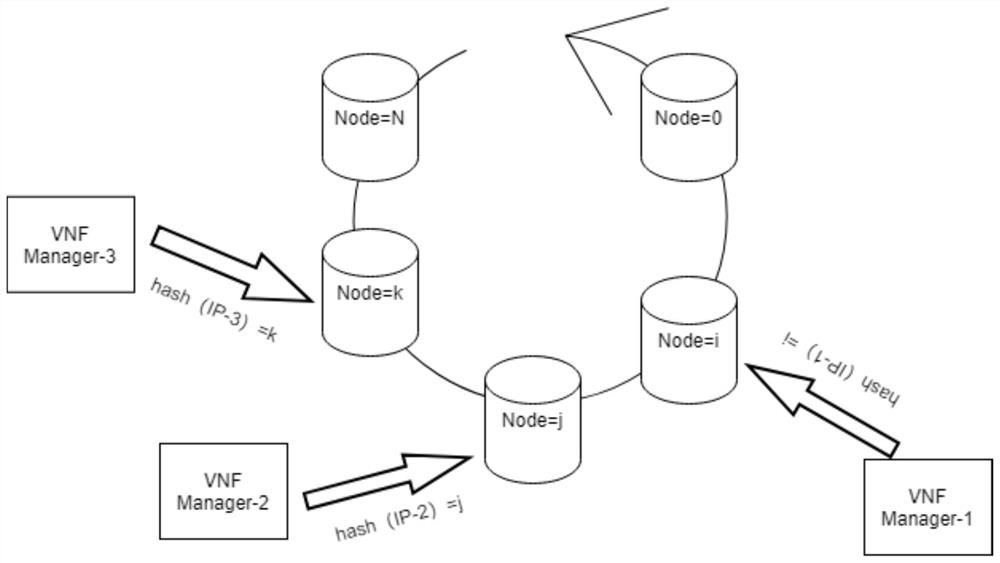
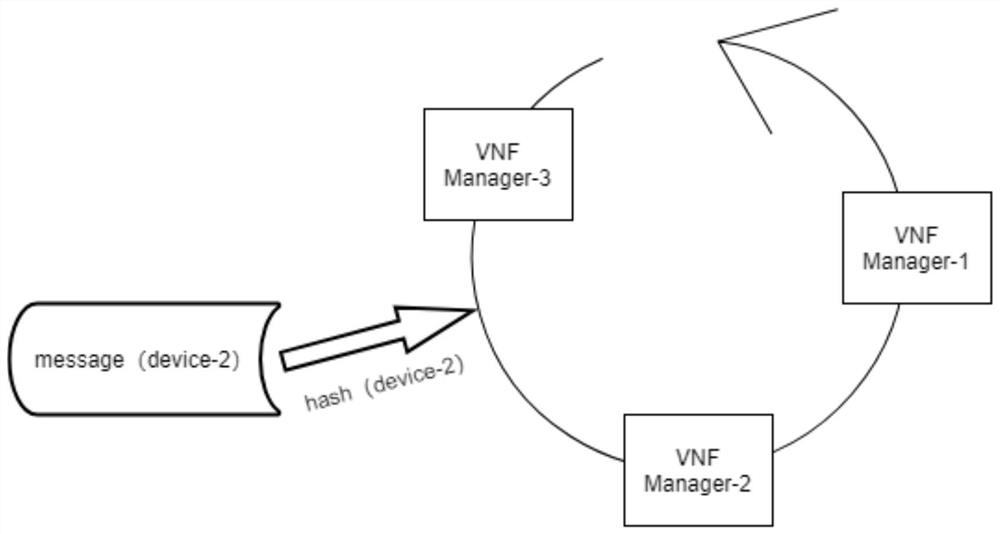
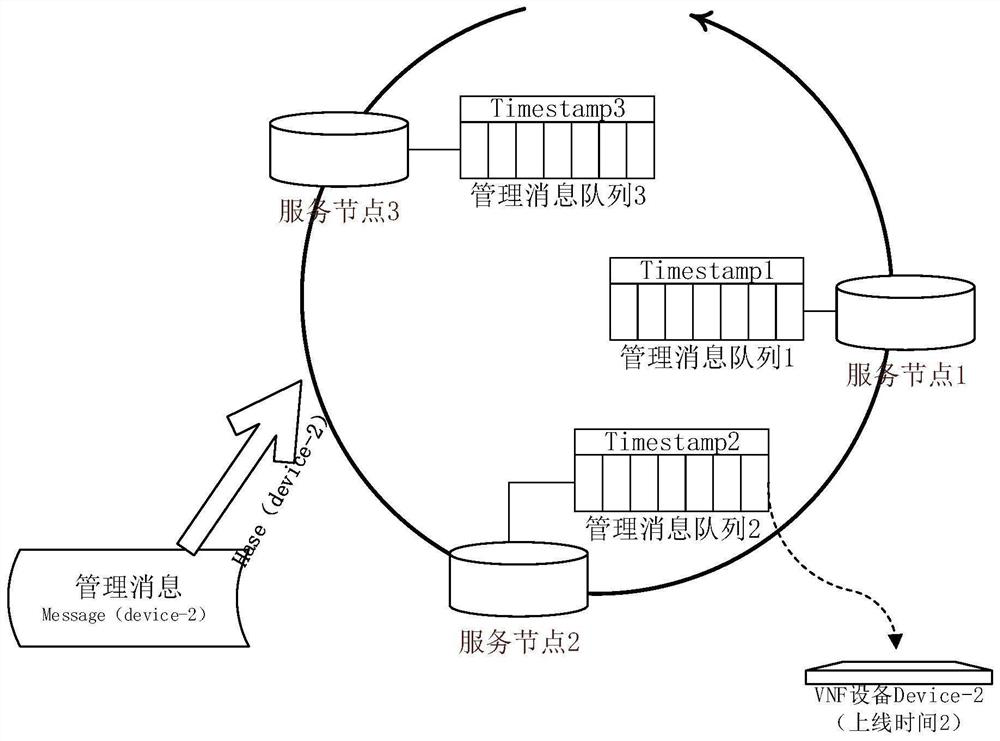
Virtual network function management message distribution method, device and equipment
ActiveCN113542013AAvoid reallocationAvoid the situationData switching networksMessage queueVirtualization
The invention provides a virtual network function management message distribution method, device and equipment, and is used for solving the technical problem of consistent distribution of VNF management messages. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the method comprises the steps: mapping a service node in a cluster to a directed hash addressing ring; when a management message is issued, positioning an affiliated service node based on an equipment identifier of the VNF equipment, and determining the affiliated service node of the VNF equipment by taking the use time of the service node and the online time of the VNF equipment as time constraint conditions; further determining a message queue for issuing the management message. Through the technical scheme of the invention, the situation that the stock VNF management message needs to be redistributed and migrated after a new VNF manager service node is added each time can be avoided, and meanwhile, the orderliness of each VNF message is ensured.
Owner:NEW H3C BIG DATA TECH CO LTD
Portioning and storing foods
A mass of divisible food in a sealed bag is placed between a first part of a frame having a plurality of walls depending from a common plane and forming a plurality of cavities and a second part of the frame having cavities that correspond with and confront the cavities of the first part. The second part is forced toward the first part to pressurize the divisible food in the bag and force the bag to occupy the cavities. Then, the frame, bag and contents are placed in a freezer.
Owner:KALB JOHN R
Garment for preventing redistribution hypothermia
ActiveUS10893709B2Reduce heat lossIncrease core temperatureChemical protectionHeat protectionMedicineThermal reflex
A thermal therapy garment that covers at least the lower extremities of a patient. The garment has an air impermeable outer layer and an air permeable inner layer. An inflatable air chamber is defined between the inner and outer layers. An inlet port connects to the chamber to allow inflation with conditioned air, which is exhausted through the inner layer over a selected region of the patient's lower body. A gown has a length sufficient to overlap a waist portion of the garment, The gown has an opening that coincides with the inlet port, thereby allowing a hose to pass through the gown and connect to the inlet port. In one embodiment, the gown has sleeves and / or a posterior portion that are heat reflective whereby the extremities are warmed to minimize the core to peripheral temperature gradient.
Owner:THE SURGICAL INT
Channel allocation method of air-ground data link in UAV one-station multi-machine system
ActiveCN110022545BEnhanced resource reuse capabilityImprove resource utilizationParticular environment based servicesVehicle infrastructure communicationMultiplexingHyperlink
A method for allocating air-to-ground data link channels of a one-station multi-machine system for unmanned aerial vehicles disclosed by the present invention aims to provide a method for allocating link channels that can reduce computational complexity and improve the degree of reuse of channel resources. The present invention is realized through the following technical solutions: the ground control station obtains the position information of the UAV platform, counts the number of air-ground data links, calculates the angles between all air-ground data links, and arranges all the angle values in descending order ; Then, starting from the air-ground data link corresponding to the maximum included angle, a "hyperlink" is constructed according to the relationship between the included angle between the links and the "multiplexing threshold", and the number of air-ground data links contained in the hyperlink As the weight of the hyperlink; the ground control station iteratively performs the above hyperlink merging process until there is no hyperlink that can be further combined, and distributes the channel resources to each hyperlink on average; after the allocation process is completed, the channel allocation Results are sent to the UAV platform via an uplink ground-to-air link.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Data processing system, method and device
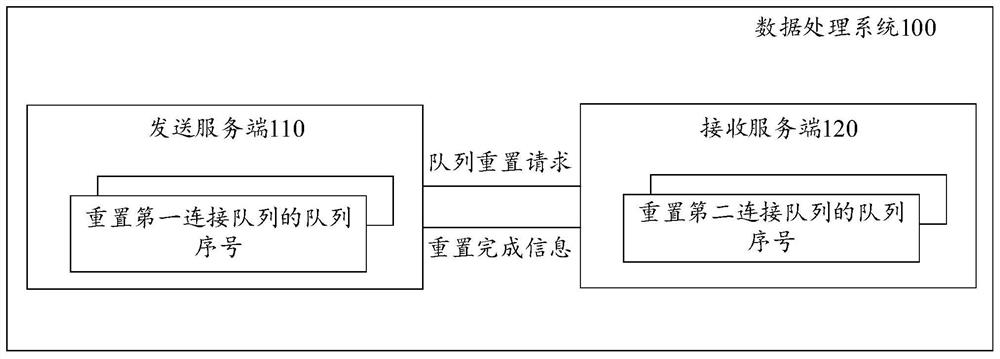
PendingCN113301103AAvoid disconnectionAvoid ineffectiveData switching networksEngineeringServer-side
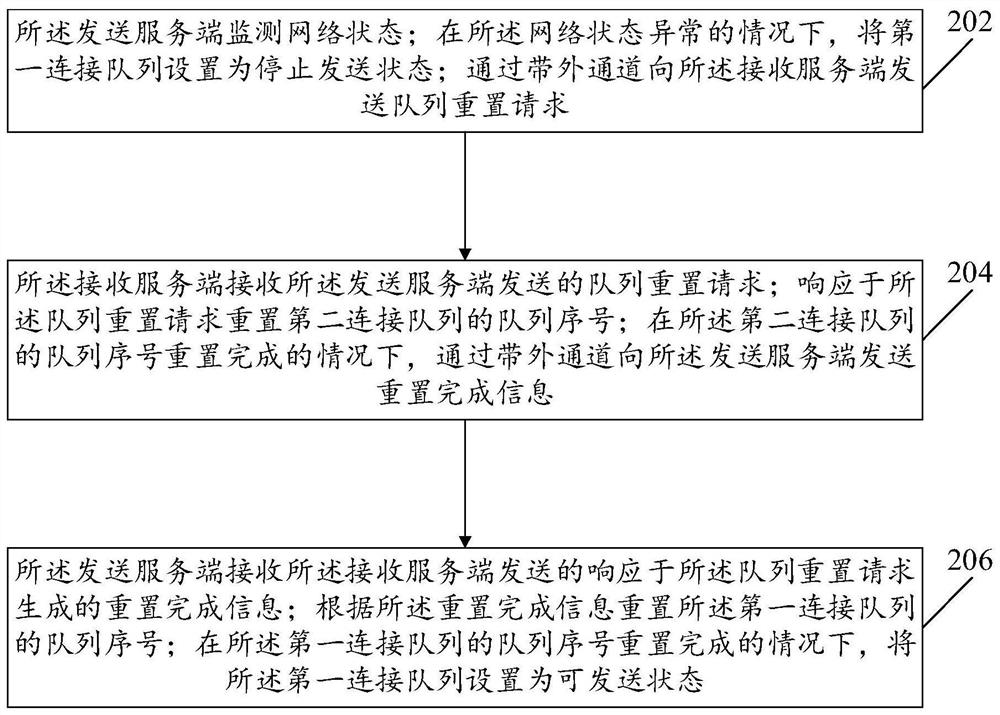
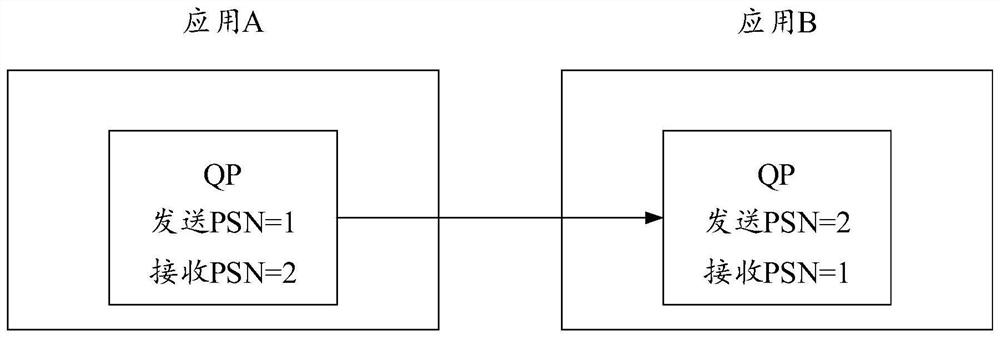
The invention provides a data processing system, method and device, and the system comprises a sending server which is configured to monitor a network state; under the condition that the network state is abnormal, a first connection queue is set to be in a sending stopping state; a queue reset request is sent to the receiving server through an out-of-band channel; the receiving server side is configured to receive the queue reset request sent by the sending server side; in response to the queue reset request, a queue serial number of a second connection queue is reset; under the condition that the queue serial number of the second connection queue is reset, reset completion information is sent to the sending server through the out-of-band channel; the sending server is further configured to receive reset completion information; the queue serial number of the first connection queue is reset according to the reset completion information; and under the condition that the queue serial number of the first connection queue is reset, the first connection queue is set to be in a sendable state.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
A method for automatically assigning addresses to identical nodes on a communication bus
ActiveCN107835266BAvoid reallocationReduce manual operationsData switching networksComputer networkEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for automatically allocating addresses for the same node on a communication bus, comprising: step S1, setting a global variable address allocation flag, initializing the address allocation flag as address unallocated, judging whether the address allocation flag of this node is unallocated, if not, Execute step S2, yes, execute step S3; step S2, judge whether the address of this node conflicts with the stored address, yes, execute step S3, no, execute step S5; step S3, assign the initial address to the node as the minimum address on the bus No. "1"; step S4, judge whether the address of this node conflicts with the stored address, if no, execute step S5, if yes, increase the address of this node by 1, and execute step S4 again; step S5, change the address assignment flag to address assigned , and remain unchanged. The present invention avoids address redistribution when the CAN bus is changed due to node movement, automatically rearranges repeated addresses in time, and avoids bus data errors caused by address repetition.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
A method and system for allocating and persisting IDs
The invention discloses an ID identification allocation and persistence method, which relates to the technical field of routers, including calling a registration function to register an IDAP library, assigning a module index of an IDAP library to each business module of the router, and setting ID allocation rules and KEYs. Value type and KEY value comparison function; when each business module needs to assign an ID to the specified KEY value, assign an ID to the specified KEY value according to the ID allocation rules; when the module is restarted or switched and restored, the backup IDAP library file is read and loaded. All KEY values and ID mapping relationship table items in the IDAP library file, read the KEY value and ID value in the table item and store them in the cache, and set the aging mark, and restore the mapping relationship between the Key and the ID by the method of the present invention . At the same time, the aging marks are removed from the table entries hit during the recovery process of the service module, and the table items still with the aging marks are aged after the service module is restored. The invention also discloses an ID mark allocation and persistence system.
Owner:武汉光网信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com