Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
153results about How to "Adjustable level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
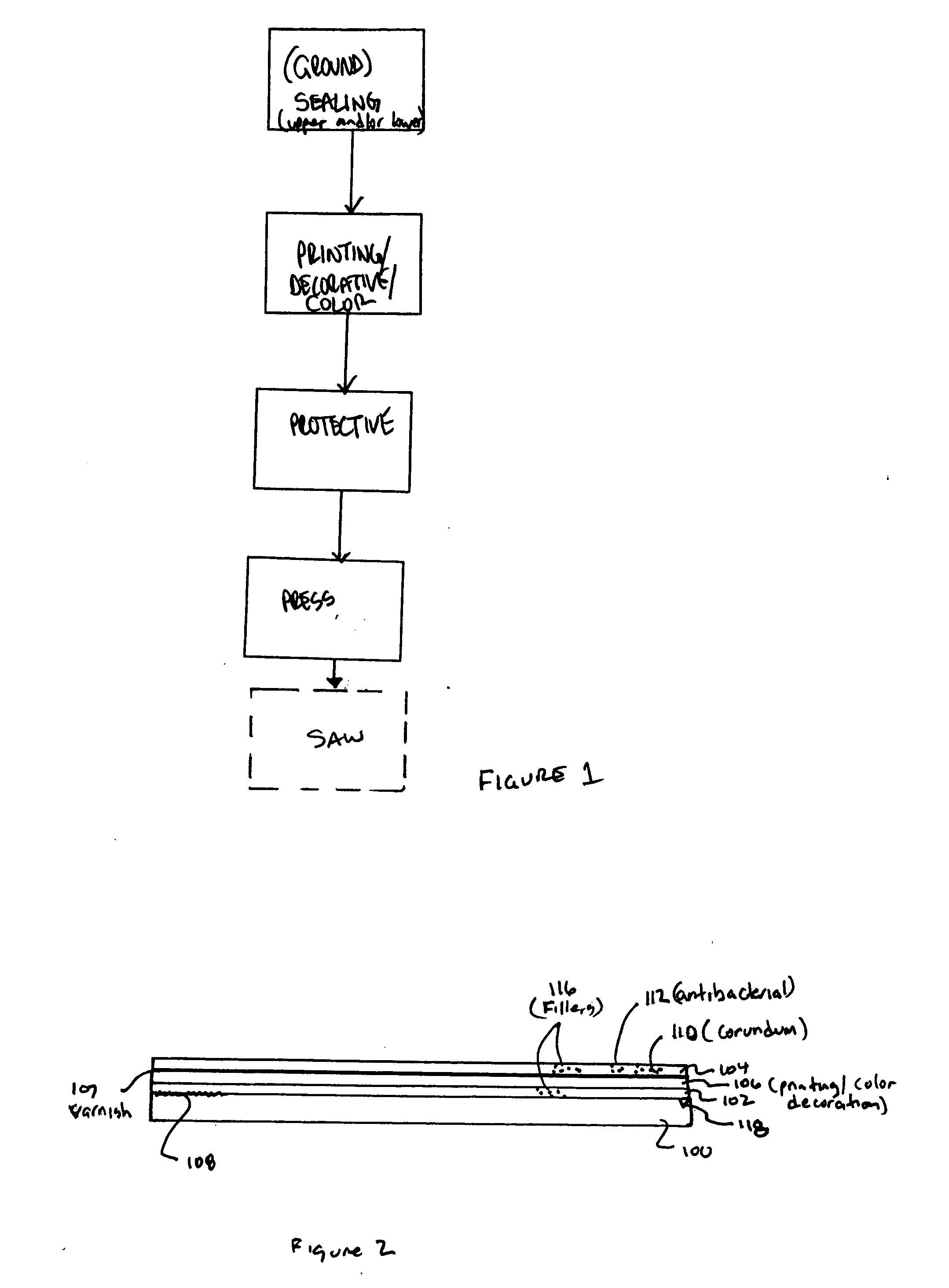
Process for finishing a wooden board and wooden board produced by the process
ActiveUS20040191547A1Avoid absorptionAdjustable levelFibreboardSynthetic resin layered productsMelamine resinEngineering
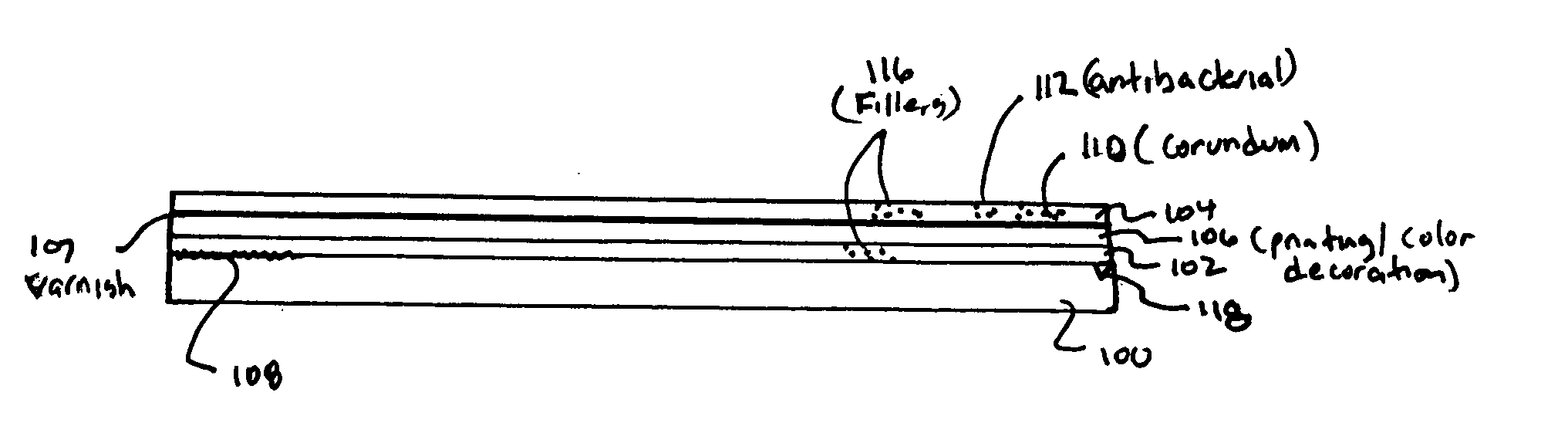
A process for finishing a wood or wooden board, in particular an MDF or HDF board, with an upper side and an underside. The process includes applying a sealing layer of melamine resin to the upper side of the board and printing a decoration onto the sealing layer. A protective layer is applied of melamine resin to the decoration and the board is pressed under the action of temperature until the protective layer and the sealing layer melt and bond to each other with the inclusion of the decoration printed on.
Owner:FLOORING TECH
Adaptive rate shifting for delivery of video services to service groups
ActiveUS20110255555A1Adjustable levelPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningQuality of serviceSelf adaptive
A video stream is provided to a set top box of a viewer to fulfill the viewer's request for a video on-demand service. The video stream is encoded at one of a plurality of encoding rates selected by a Service Quality Manager based on parameters defined for a service group, which in various embodiments may comprise the viewer, or the viewer along with other customers serviced by a single QAM. The parameters used for determining the encoding rate may involve currently allocated bandwidth, the viewer's service parameters, other customer's service parameters, and historical data regarding encoding rate selection data. The encoding rate used to encode a stream may be modified during streaming in response to other service requests. The encoding rate may be shifted based on anticipated service requests from other members in the service group.
Owner:ERICSSON TELEVISION
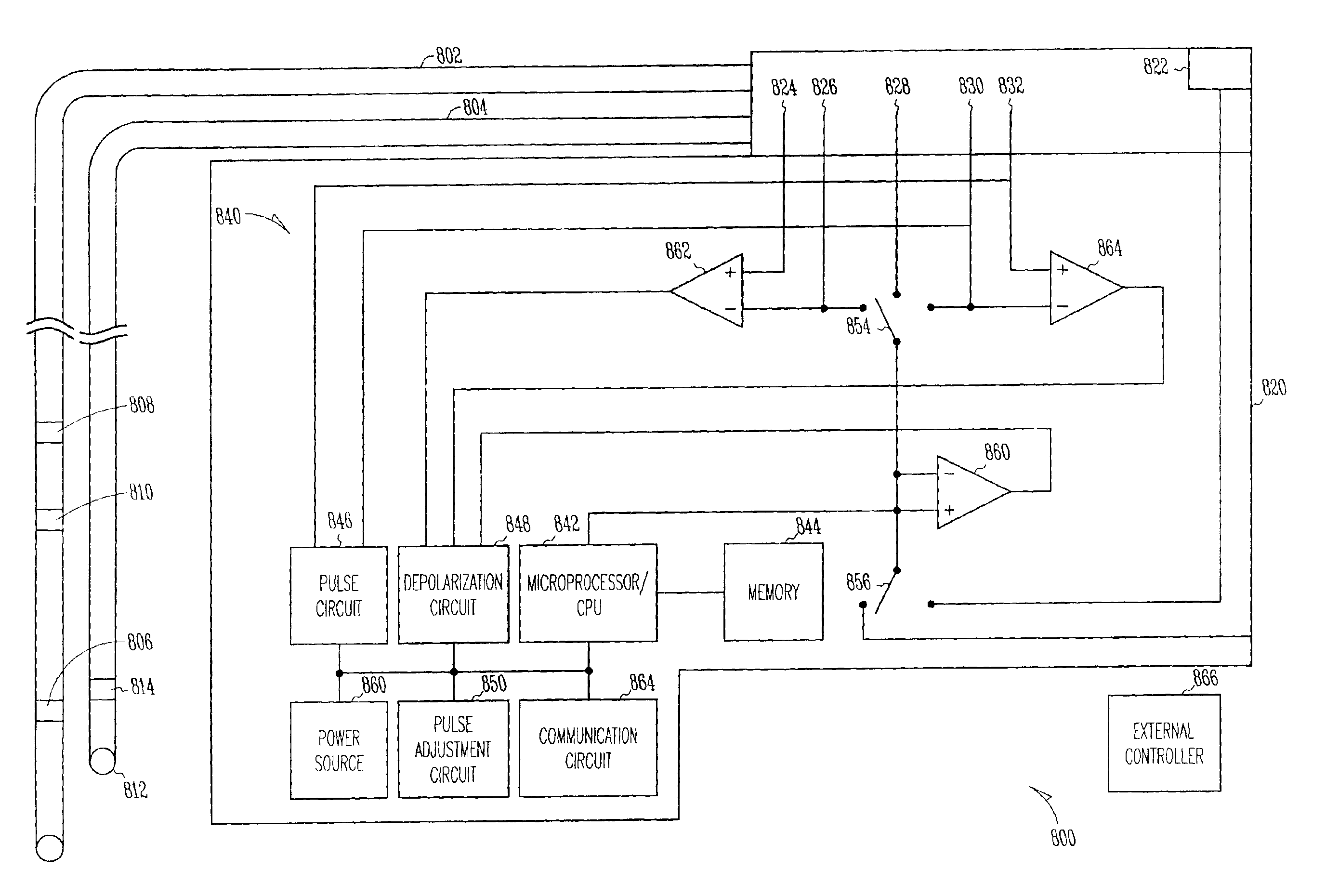
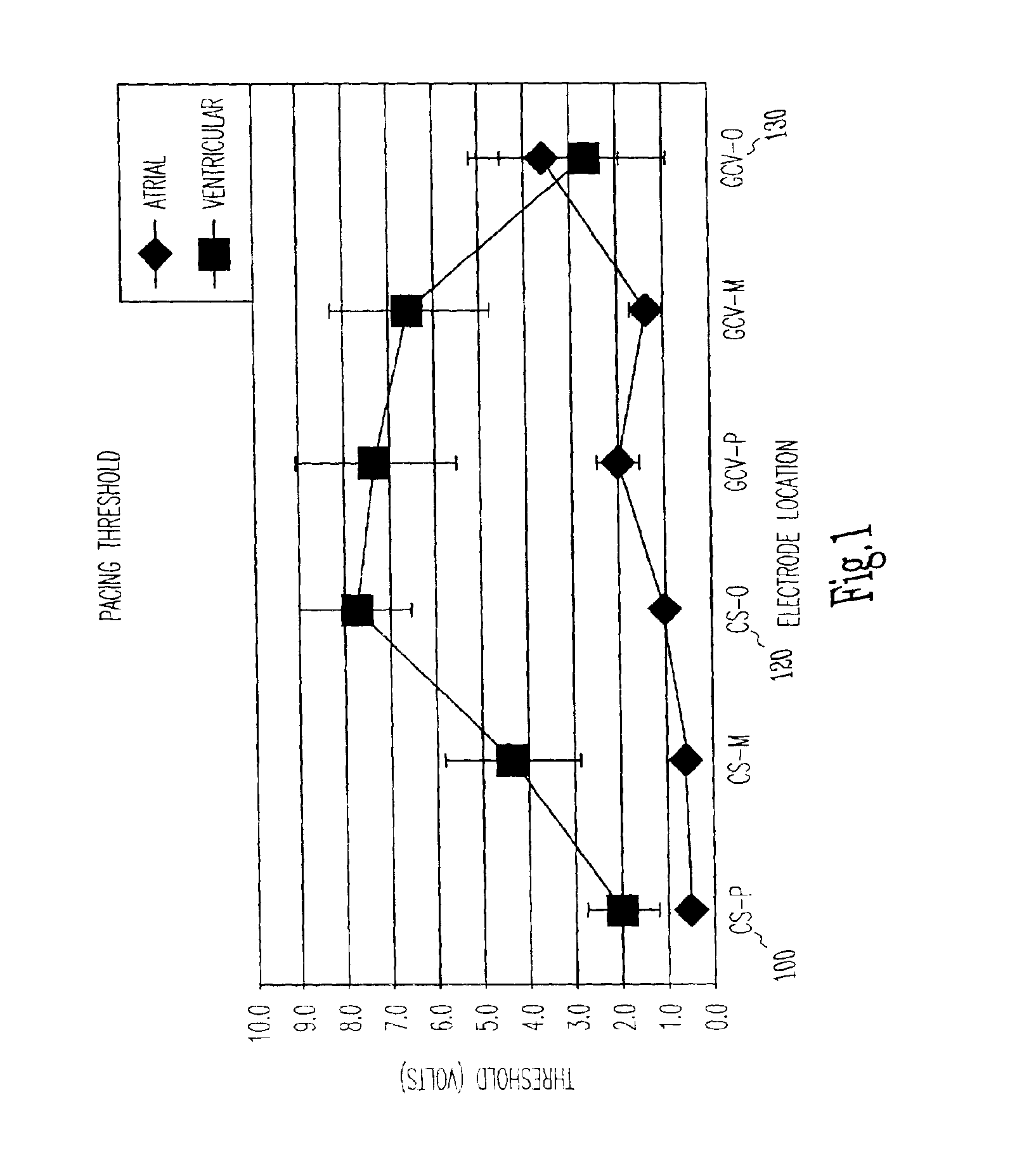
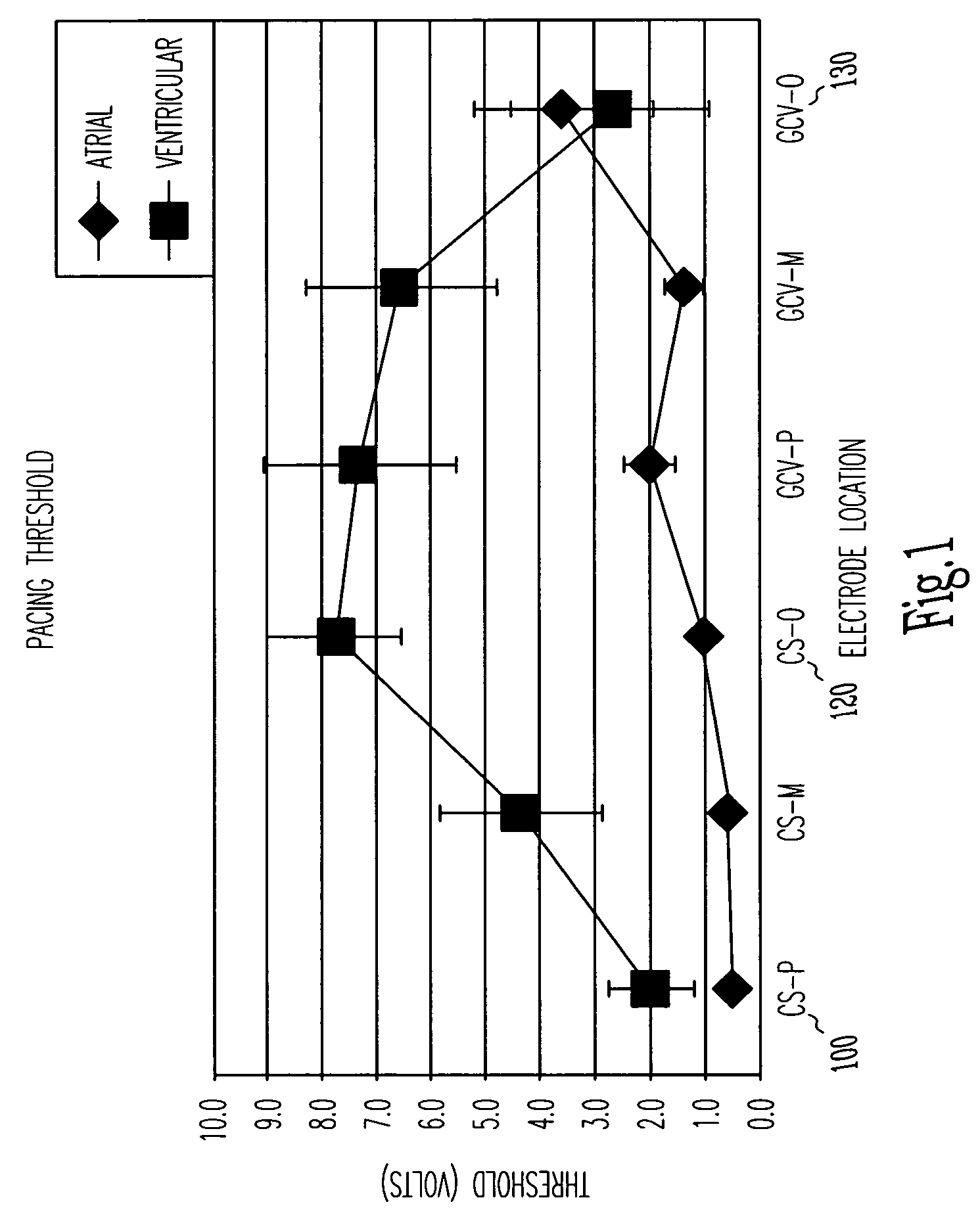
Cardiac rhythm management system and method
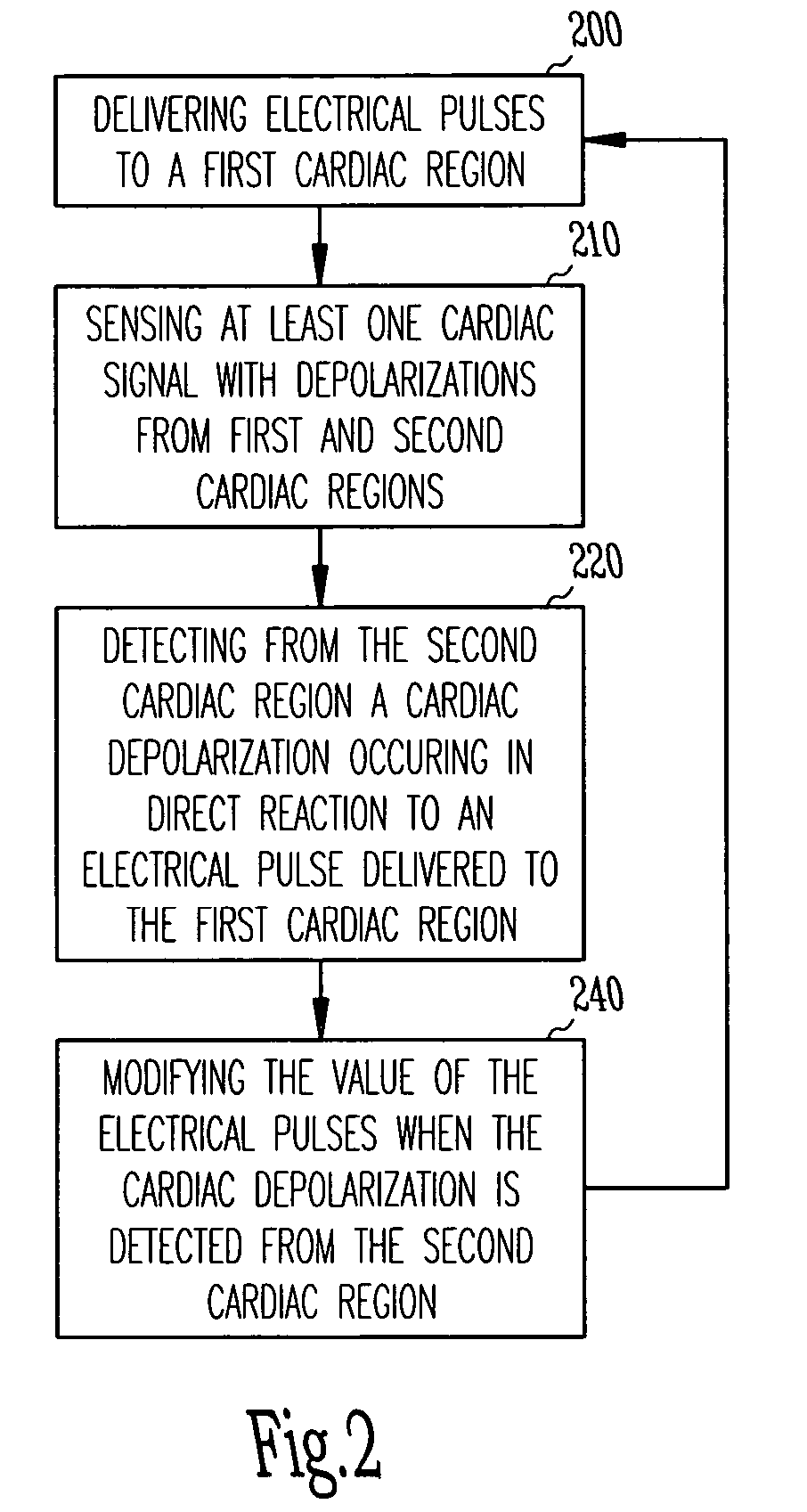
A system and method for cardiac rhythm management, which includes an electrode system having at least one electrode and control circuitry coupled to the electrode system from which a first cardiac signal is sensed. The control circuitry includes a pulse circuit to produce electrical pulses at a first value to be delivered to the electrode system in a first cardiac region. At least one cardiac signal is sensed from a second cardiac region, where the cardiac signal includes indications of cardiac depolarizations from the second cardiac region which occurs in direct reaction to the electrical pulses delivered to the first cardiac region. The first value of the electrical pulses are then modified by a pulse adjustment circuit when a cardiac depolarization which occurs in direct reaction to the electrical pulse delivered to the first cardiac region is detected from the second cardiac region.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and Method for Controlling Output of a Battery Pack
ActiveUS20120074904A1Reduce the possibilityReduce in drive operationElectrical testingSecondary cells charging/dischargingEngineeringBattery pack
Systems and methods for controlling the output of a battery pack are disclosed. In one example, a battery pack contactor is opened in response to battery pack current. The system and method may reduce battery pack degradation and increase system flexibility.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
Abrasion resistant coating composition
The invention provides a coating composition for an optical element, such as an ophthalmic lens. The coating composition includes a relatively rigid multifunctional monomer and a relatively flexible difunctional monomer. The rigid multifunctional monomer and the flexible difunctional monomer are capable of co-reacting to form an abrasion resistant coating on the optical element. The invention also provides a method of forming an abrasion resistant coating on an optical element, such as an ophthalmic lens. The method includes the steps of coating the optical element with a relatively rigid multifunctional monomer and a relatively flexible difunctional monomer, and polymerising the coating to form an abrasion resistant coating on the optical element.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
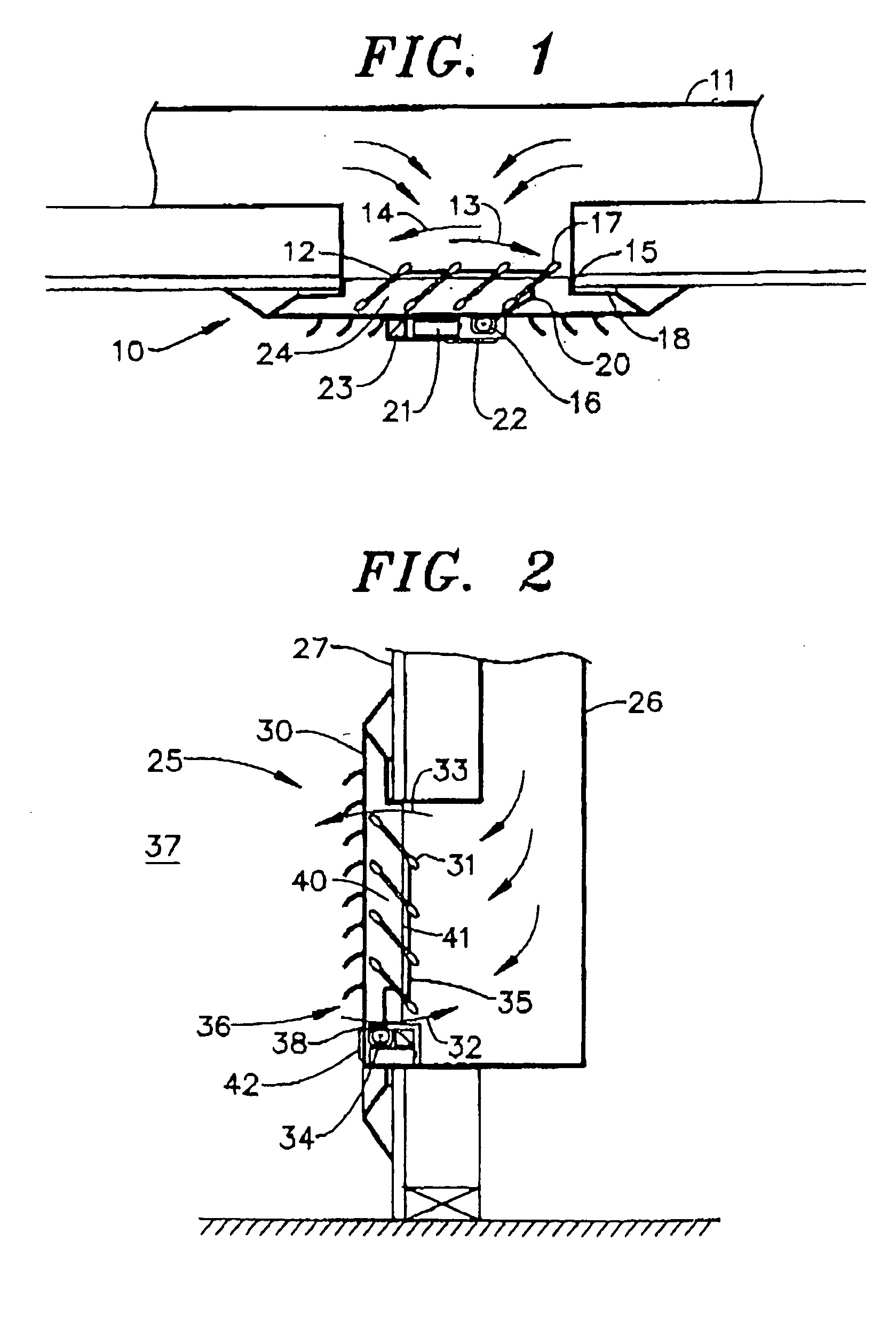
Electromagnetic frequency-controlled zoning and dampering system
InactiveUS20070119961A1Save energyHigh trafficMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsWireless controlRemote control
A portable remote wireless control for establishing different temperatures in separate portions of a building. The remote control not only regulates hot and cold airflow through rotatable damper vanes in one or more diffusers, but it also recharges the batteries that power the wireless receiver, servomotor and servomotor controls that selectively rotate the damper vanes. Damper vane rotation regulates air flow from the diffuser to control the temperature in the portion of the building. The damper vanes, moreover, are of a light plastic with a marginal band of a foam material to enable the vanes to rotate silently and freely also to form a seal that eliminates a great deal of air seepage past the individual vanes.
Owner:ENERGY PLUS TECH
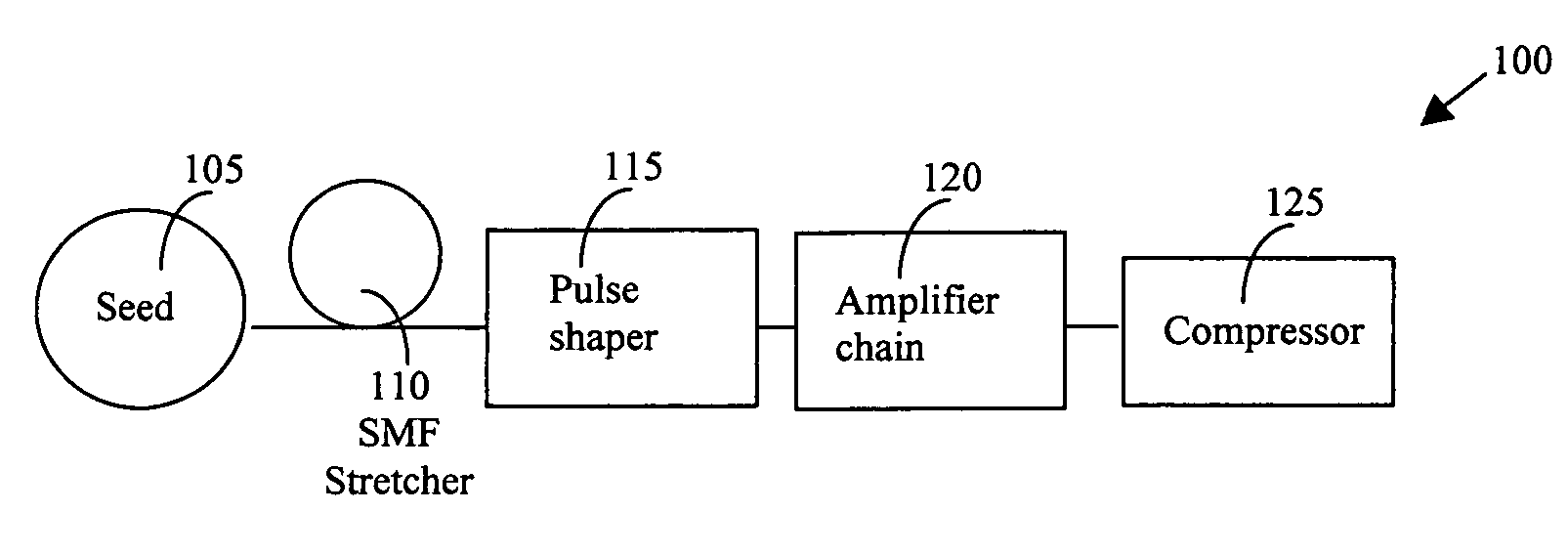
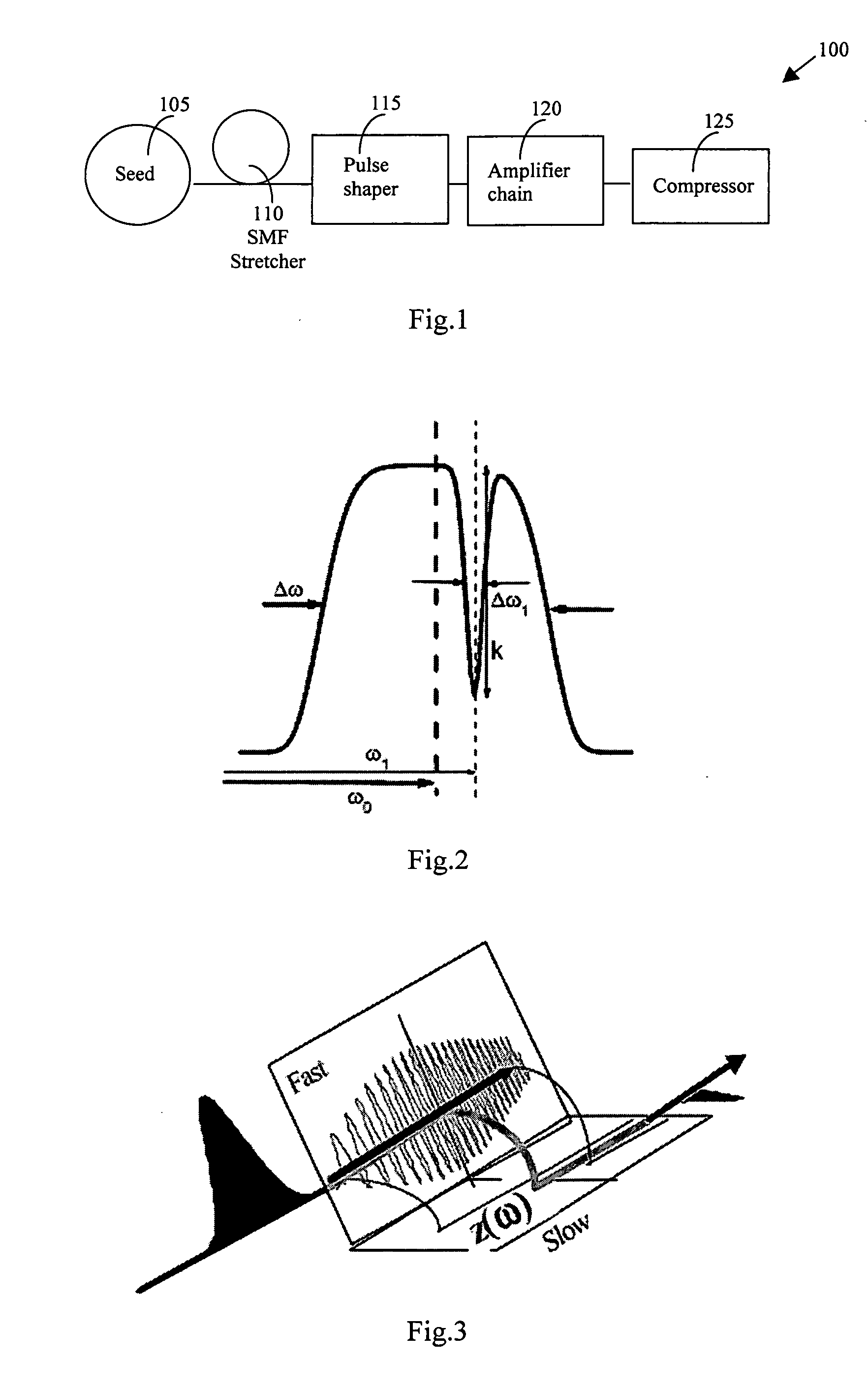
Dynamic amplitude and spectral shaper in fiber laser amplification system
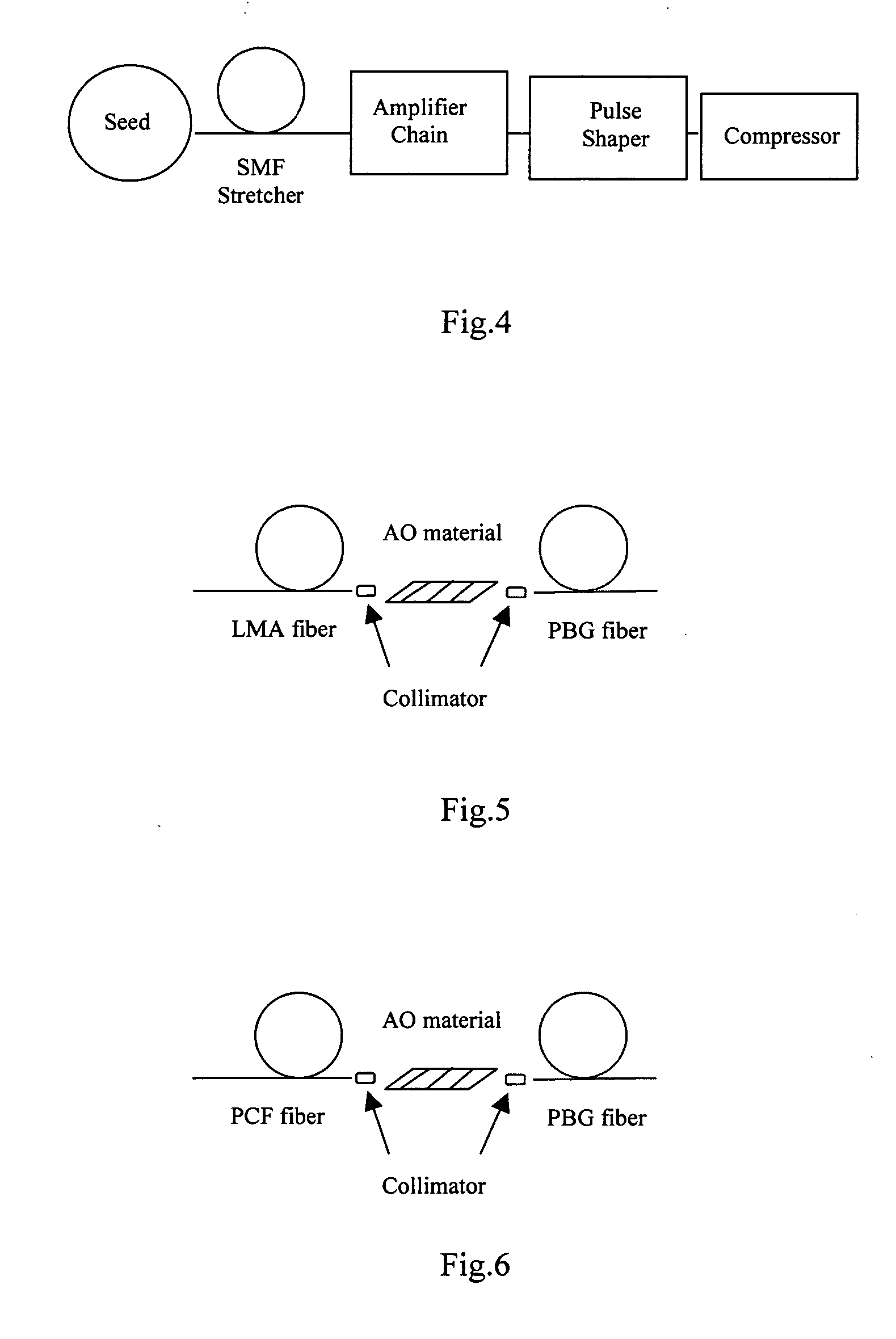
InactiveUS20070047965A1Short pulse durationAdjustable levelLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionPulse shaperPulse shaping
A method for overcoming the drawback in a fiber CPA laser system that includes a process of generating a large negative TOD by implementing an AODS in a pulse shaper as a dispersive component. The AODS is implemented to arbitrarily modulate both the spectrum shape and phase to control with controllable amplitude to generate different orders of dispersions including a large negative TOD for compensating the positive TOD generated by the pulse stretching and amplification processes. The AODS, implemented as a dispersive component, can be an active and controllable dispersive component to generate adjustable levels of dispersions for flexibly compensating any order of dispersions generated in the amplifier chain including the nonlinear phase shift. The AODS implemented as a dispersive component can be an active and programmable dispersive component to interactively generate adjustable levels of dispersions in response to output laser amplitude and pulse shape measurements for flexibly compensating any order of dispersions generated in the amplifier chain including the nonlinear phase shift to achieve the shortest pulse duration.
Owner:POLARONYX
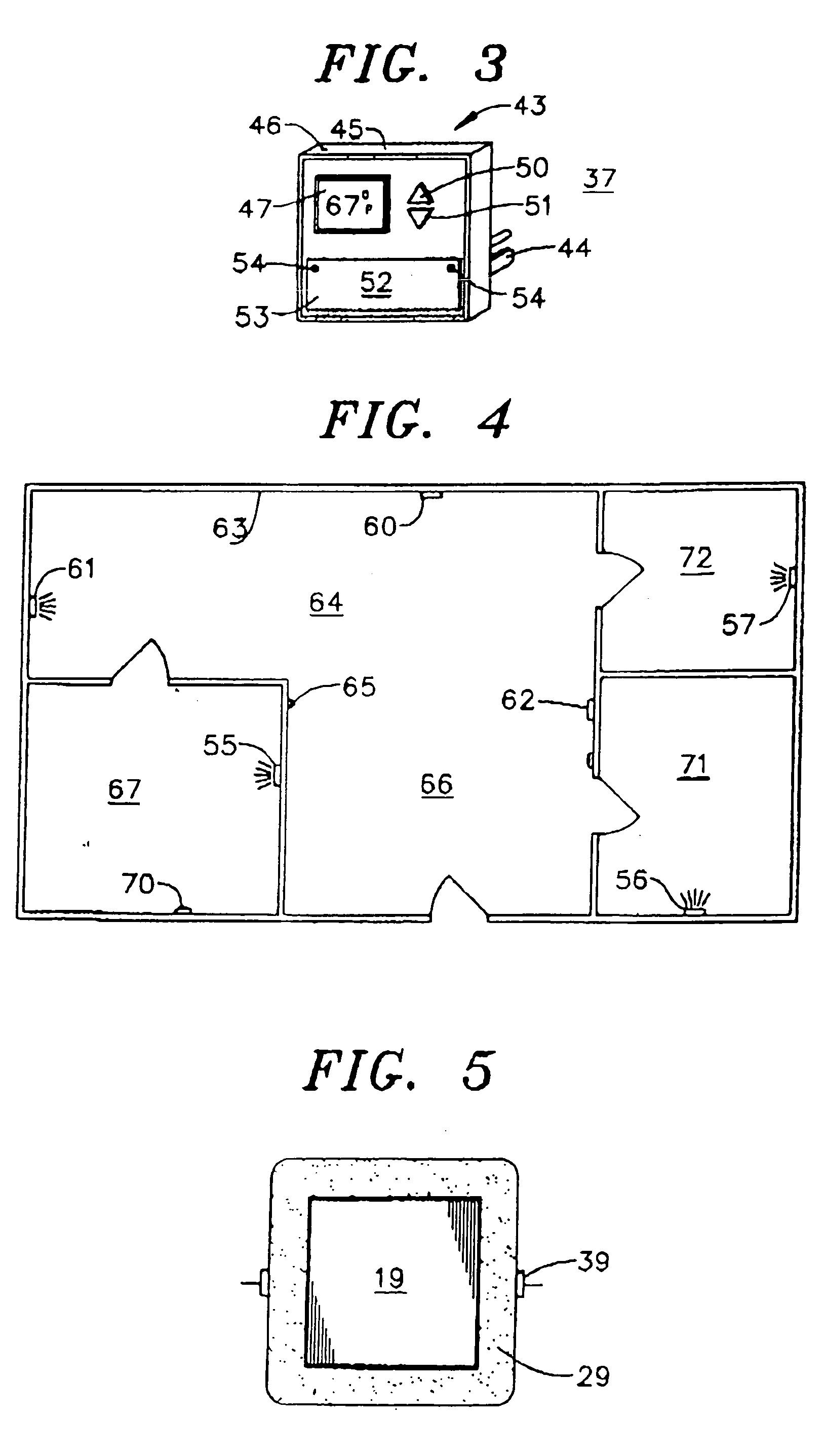
Brightness adjustment method and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060082677A1Adjust the brightness level of the imageAdjustable levelImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingBrightness perception
An adjustment amount of a brightness level is determined for each pixel of an image based on the value of each pixel of a luminance distribution image which represents the distribution of luminance of the image. A portion contributing to adjustment of brightness and a portion contributing to adjustment of saturation are determined for each pixel of the image so that the sum thereof is equal to the adjustment amount of the brightness level. Then, an adjustment value of saturation, which is obtained by weighting the value of each pixel in the image based on the portion contributing to saturation, and an adjustment value of brightness, which is obtained by weighting the value of each pixel in the luminance distribution image, which corresponds to each pixel of the image, based on the portion contributing to brightness are added to the value of each pixel of the image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Optical termination apparatus and optical transmission system
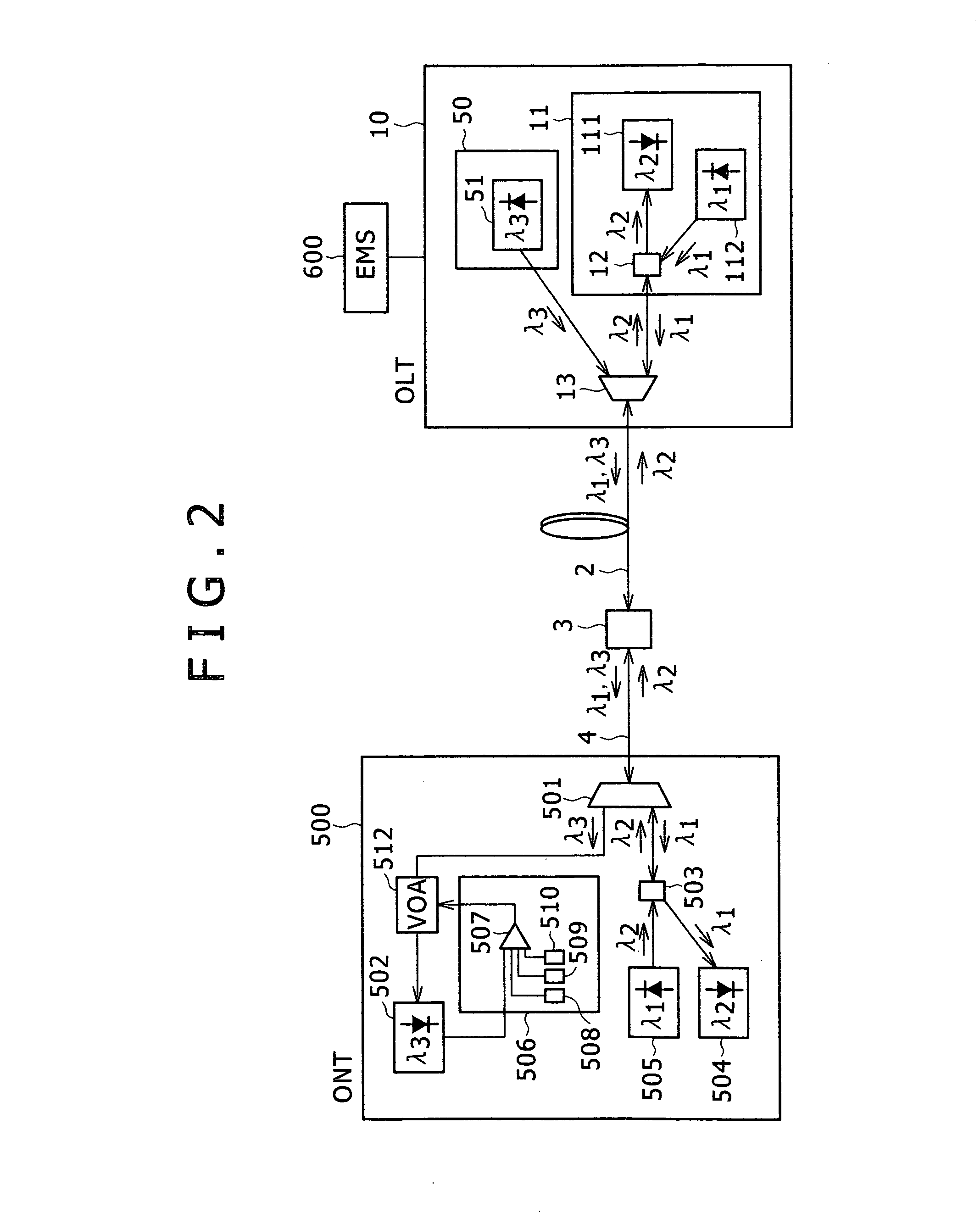
InactiveUS20070065089A1Adjustable levelWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationElement management system
A Triple-Player PON system is configured to have an optical line terminal (OLT) and an element management system (EMS), which are placed in a central office, an optical network terminal (ONT) placed in a subscriber's house, an optical splitter, a trunk line optical fiber, and a termination optical fiber. A variable optical attenuator is provided before a video optical receiver of the ONT, thereby to control the optical attenuation of the variable optical attenuator by a controller so that an input into the video optical receiver becomes an appropriate power.
Owner:HITACHI COMM TECH
Electrohydraulic valve servomechanism with adaptive resistance estimator
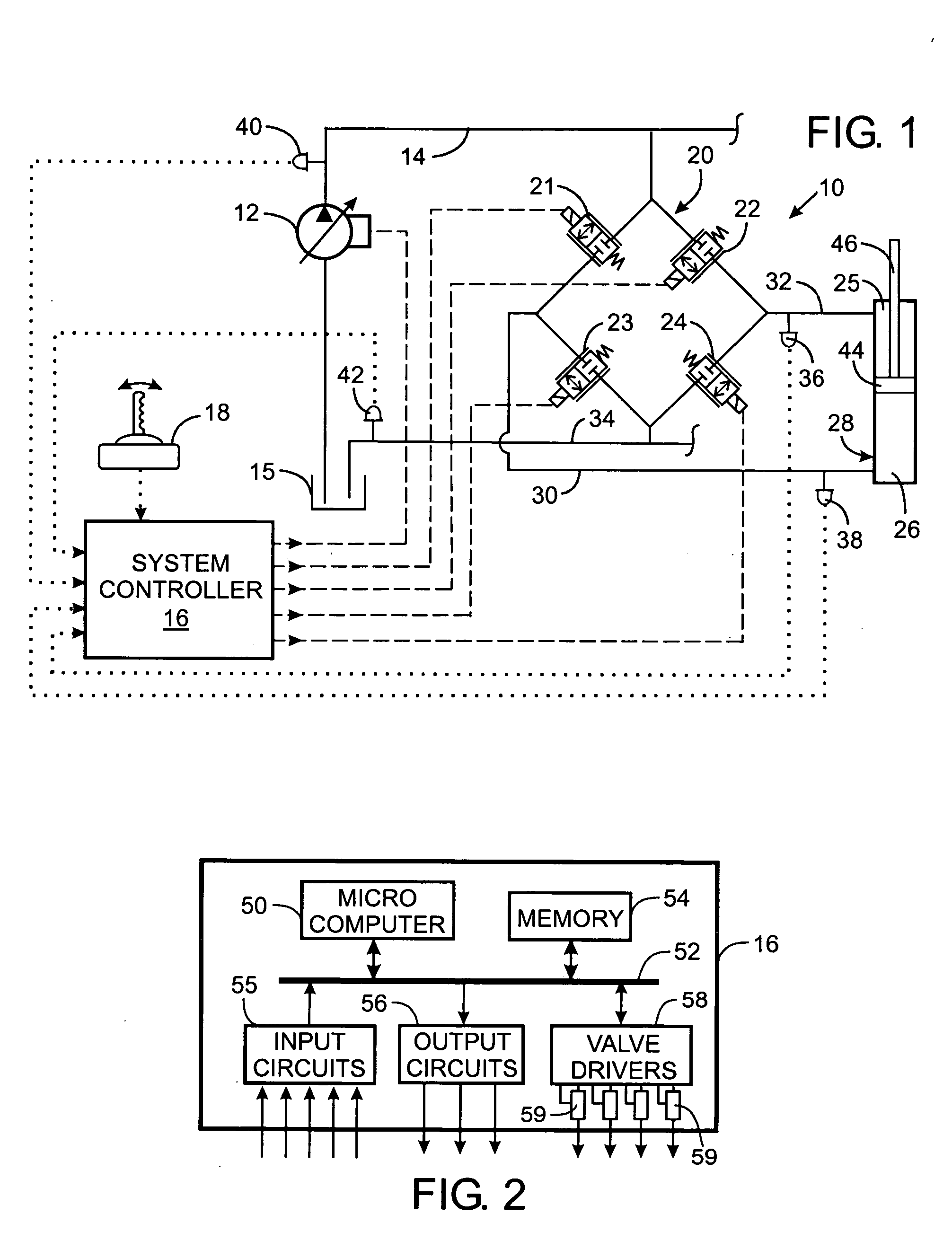
InactiveUS20050211936A1Adjustable levelFluid-pressure actuator testingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical resistance and conductancePwm signals
A servomechanism includes a controller which dynamically estimates the resistance of the solenoid coil in an electrohydraulic valve as part of determining a level of electric voltage to apply to open the valve. The servomechanism receives a current setpoint designating a desired electric current level and senses the actual level of current flowing through the coil. A proportional term is derived from the current setpoint and the actual level of current. Creation of a derivative term is based on the difference between the current setpoint and the actual level of current. A feedforward term is produced by estimating the resistance of the electrohydraulic valve and limiting the feedforward term to a predefined range of acceptable values. The proportional term, derivative term, and the feedforward term are summed to define a desired voltage level, and a PWM signal for driving the electrohydraulic valve is generated based on the desired voltage level.
Owner:HUSCO INT INC
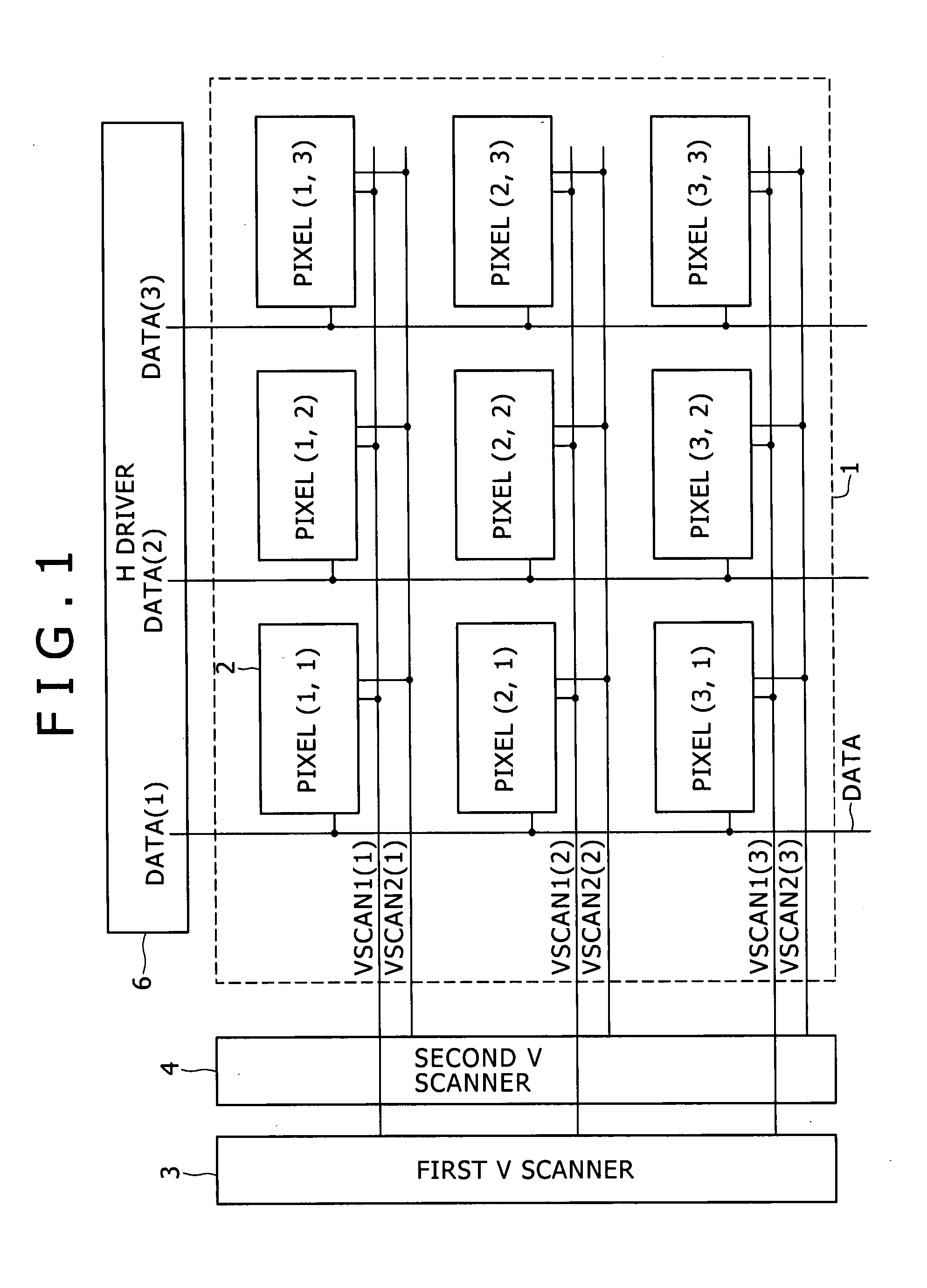
Image display apparatus
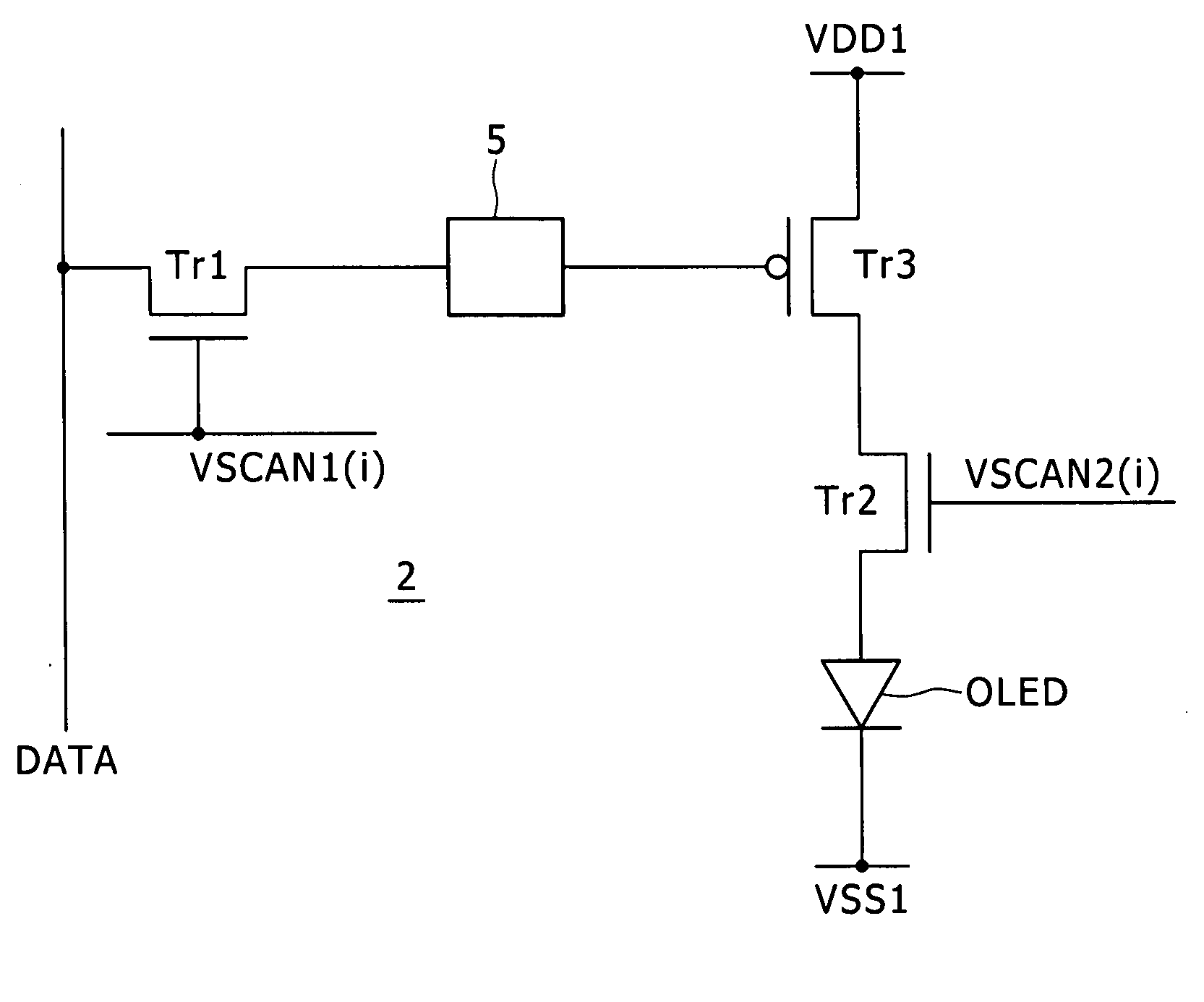
ActiveUS20080079670A1Luminance level be adjustAdjustment width be reduceElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesSynchronismEngineering
Disclosed herein is an image display apparatus, including: a plurality of scanning lines extending along rows and configured to successively supply a control signal in synchronism with a horizontal period in order to perform line-sequential scanning over one field; a plurality of signal lines extending along columns and configured to supply an image signal in accordance with the line-sequential scanning; and a plurality of pixel circuits disposed at locations at which the scanning lines and the signal lines intersect with each other and configured to form a screen.
Owner:JOLED INC
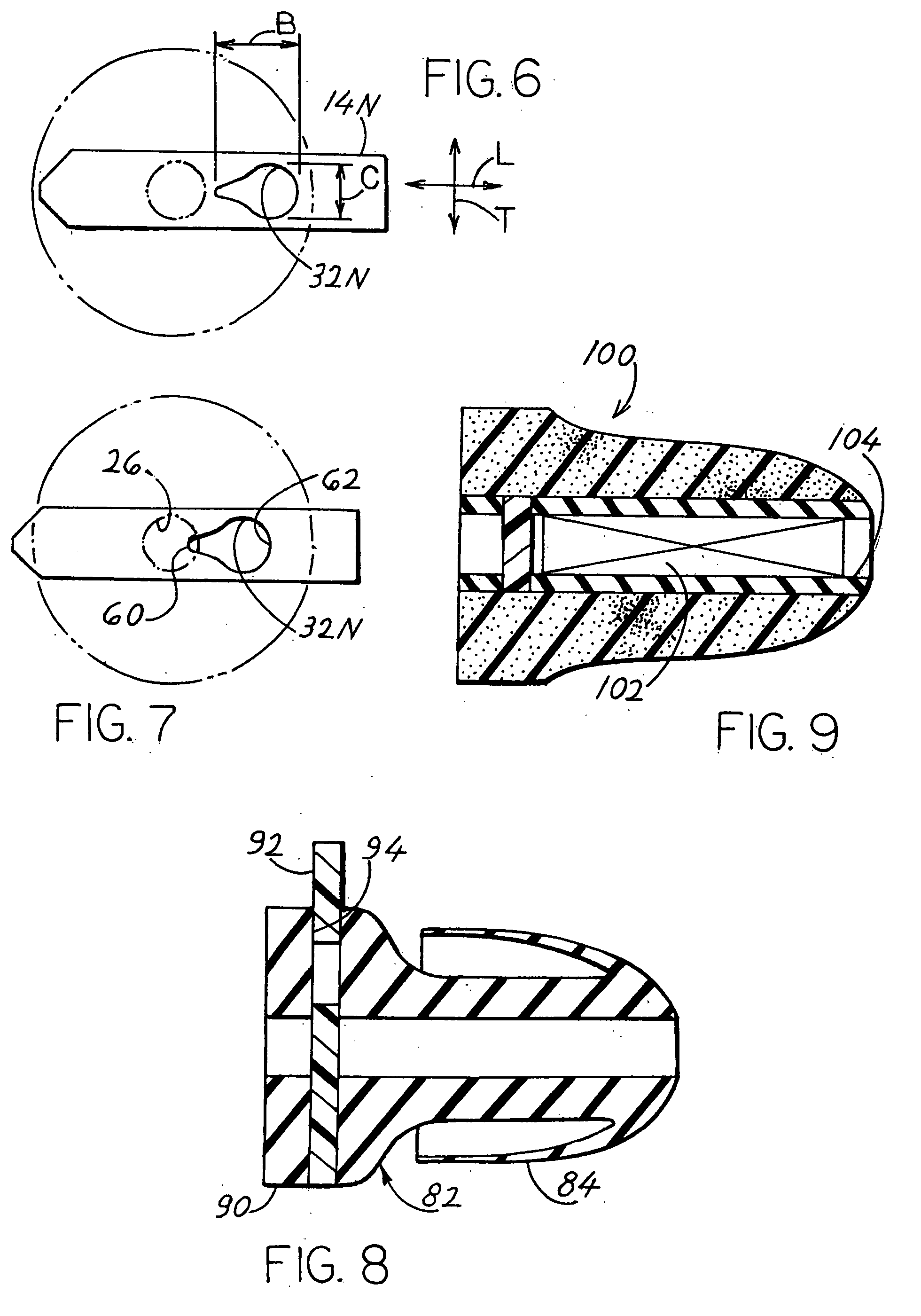
Lateral sliding adjustable earplug
An earplug has an earplug body (12) with a front sealing portion (20) that seals to a person's ear canal, a body rear portion (22) that lies out of the ear canal, and a passage (26) that extends along the body axis and that allows environmental sound to flow into the ear canal when the passage is not blocked. The body rear portion has a lateral slot (30), and the earplug includes a blocking element (14) that is laterally (L) slidable along the slot. The blocking element can slide between a first position (14A) wherein a hole (32) in the element is not aligned with the passage to prevent sound from reaching the ear canal, and a second position (14B) wherein the hole is aligned with the passage to allow sound to reach the passage.
Owner:SPERIAN HEARING PROTECTION
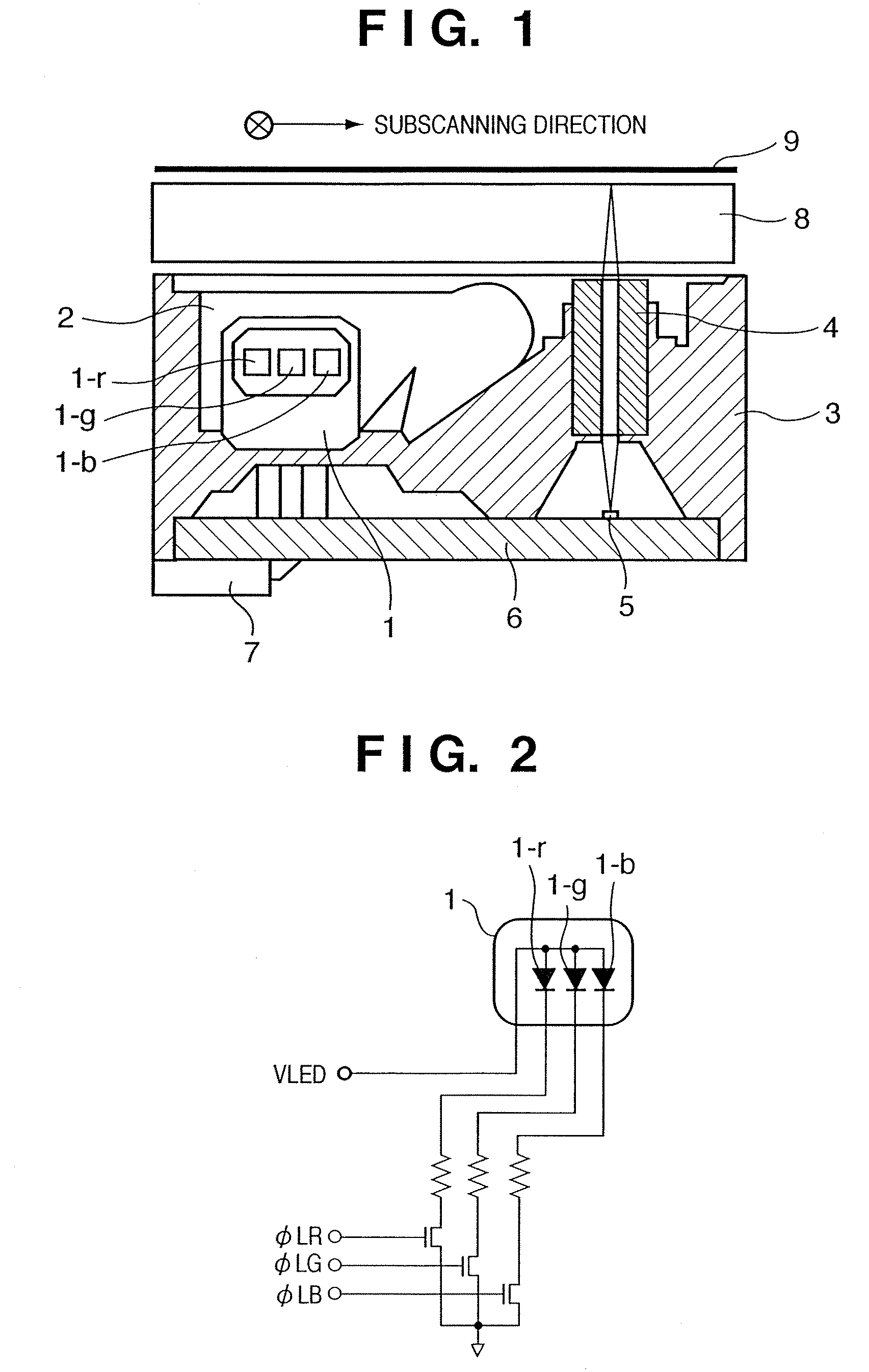
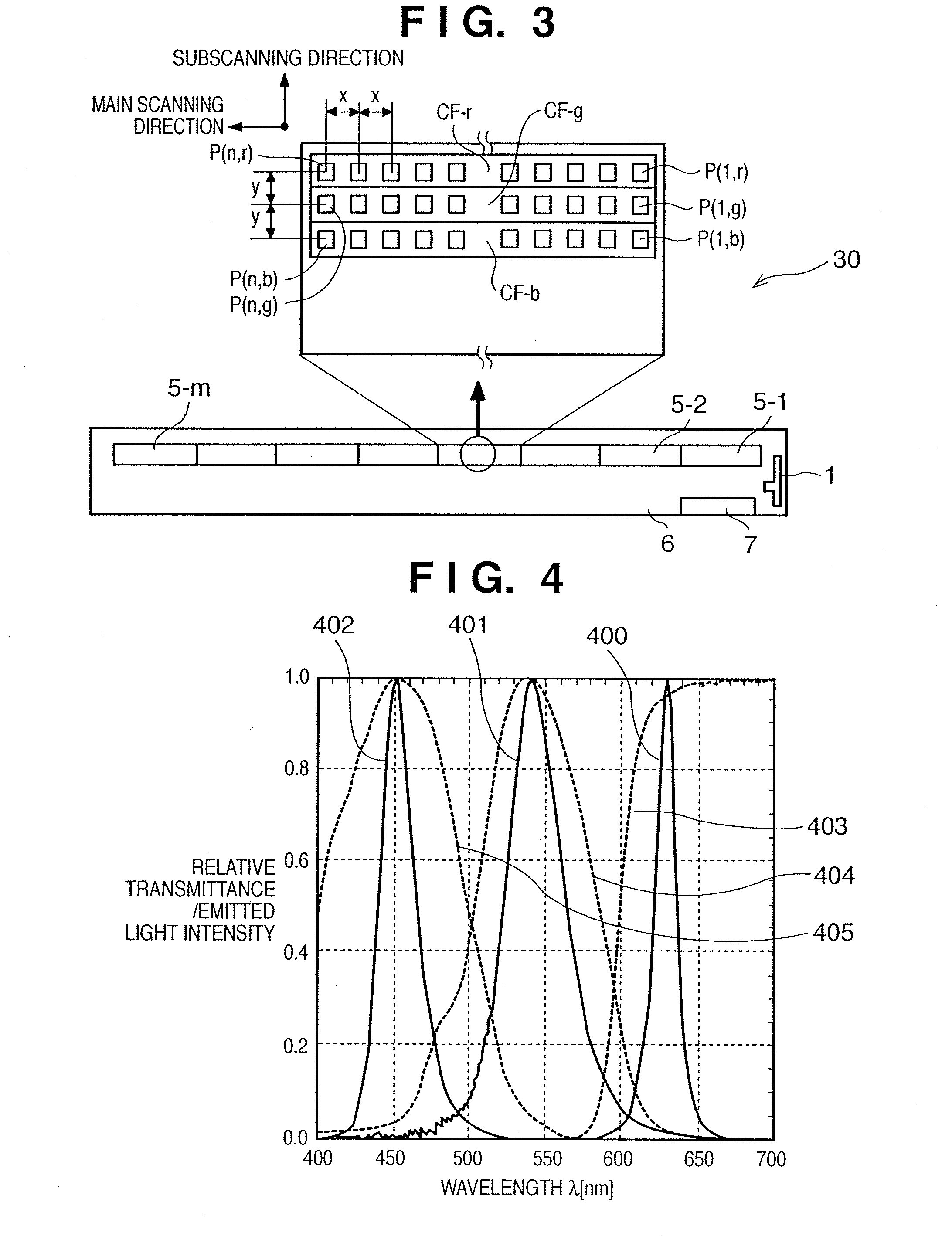
Color image sensor unit and image reading apparatus using the sensor unit and control method therefor
ActiveUS7449666B2Adjustable levelPreventing color misalignmentPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometrySensor arrayColor image
A color image sensor which uses a sensor array that has, as a lighting light source, 3-color light emitting elements capable of independently controlling light emitting timings respectively and at least three pixel arrays respectively constituted by a plurality of pixels, respective pixel arrays being comprising color filters having different transmitting wavelength regions from each other, and which independently controls the lighting start and lighting period of each light emitting element, whereby it is possible to prevent color misalignment in an output image signal and regulate the image signal level of each color component.
Owner:CANON COMPONENTS INC
Receiver based decision feedback equalization circuitry and techniques
ActiveUS20050025228A1Adjustable levelMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsData sliceSelf adaptive
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a technique of, and circuitry and system for enhancing the performance of data communication systems using receiver based decision feedback equalization circuitry. In one embodiment, the equalization circuitry and technique employs a plurality of data slicers (for example, two) to receive an analog input and output a binary value based on the reference or slicer level. The output of the data slicers is provided to logic circuitry to determine whether the analog input was a binary high or binary low. In those instances where the data slicers “agree” and both indicate either a high or a low, the logic circuitry outputs the corresponding binary value. In those instances where the data slicer do not “agree”—that is, where one data slicer indicates the input to be a binary or logic high value and the other data slicer indicates the input to be a binary or logic low value, in one embodiment, the logic circuitry outputs the complement of the previous binary value. In another embodiment, the logic circuitry selects the output from the slicer that changed its output from the previous binary value. In yet another embodiment where the slicers do not “agree”, the logic circuitry selects the decision of the data slicer with higher slicer value if the previous binary value was “high”, or selects the decision of the data slicer with the lower slicer value if the previous binary value was “low”. The data slicers employ slicer levels that may be fixed, pre-programmed, predetermined, preset, changed, modified, optimized, enhanced and / or programmed or re-programmed (for example, adaptively) before or during operation of the decision feedback equalization circuitry.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System And Method For Controlling Output Of A Battery Pack
ActiveUS20120098543A1Reduce the possibilityImprove drivabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingElectrical batteryBattery pack
Systems and methods for communicating a state of a battery to a vehicle controller are disclosed. In one example, a battery pack outputs a signal indicative of an amount of capability the battery pack has to source or sink current at present operating conditions. The system and method may improve vehicle drivability and reduce battery pack degradation.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
Device for extracting, storing and/or processing blood or other substances of human or animal origin, and for applying blood compounds or other biological compounds
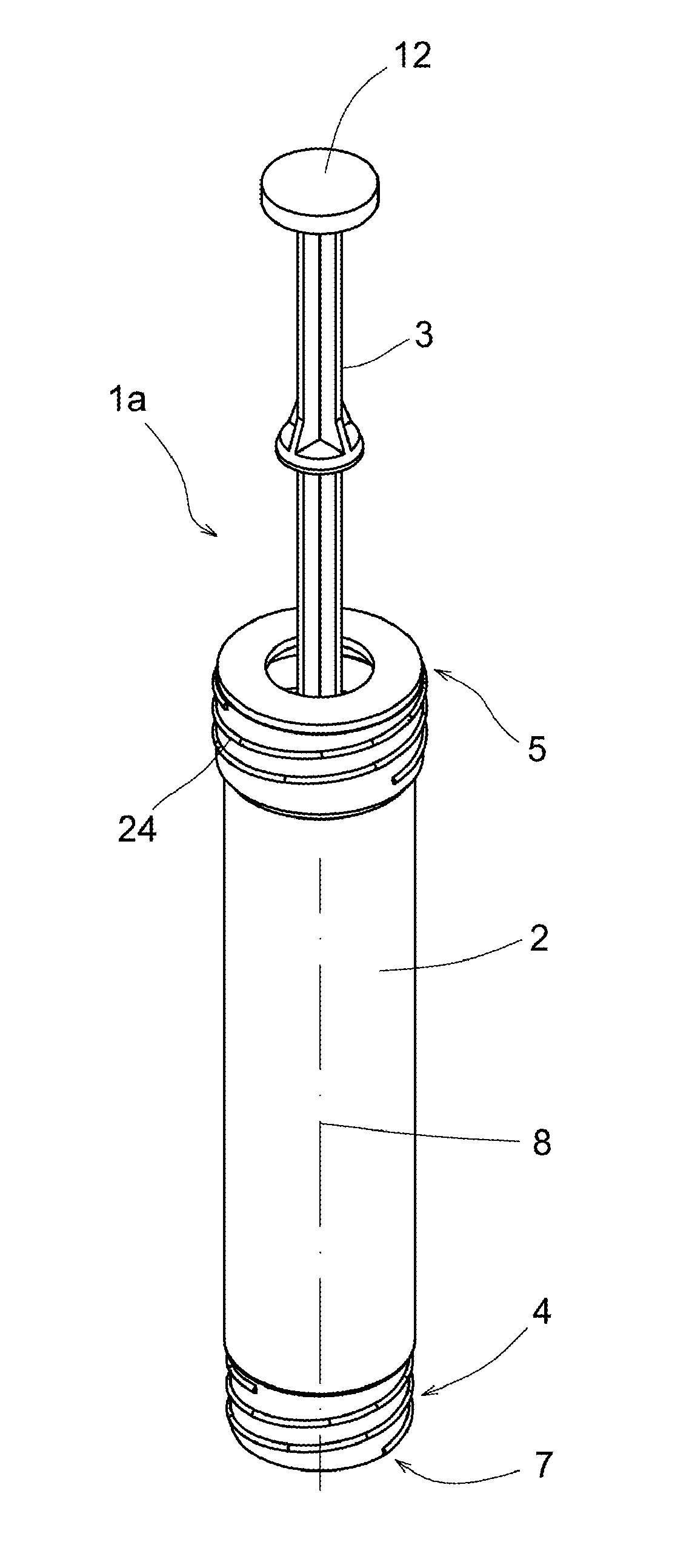
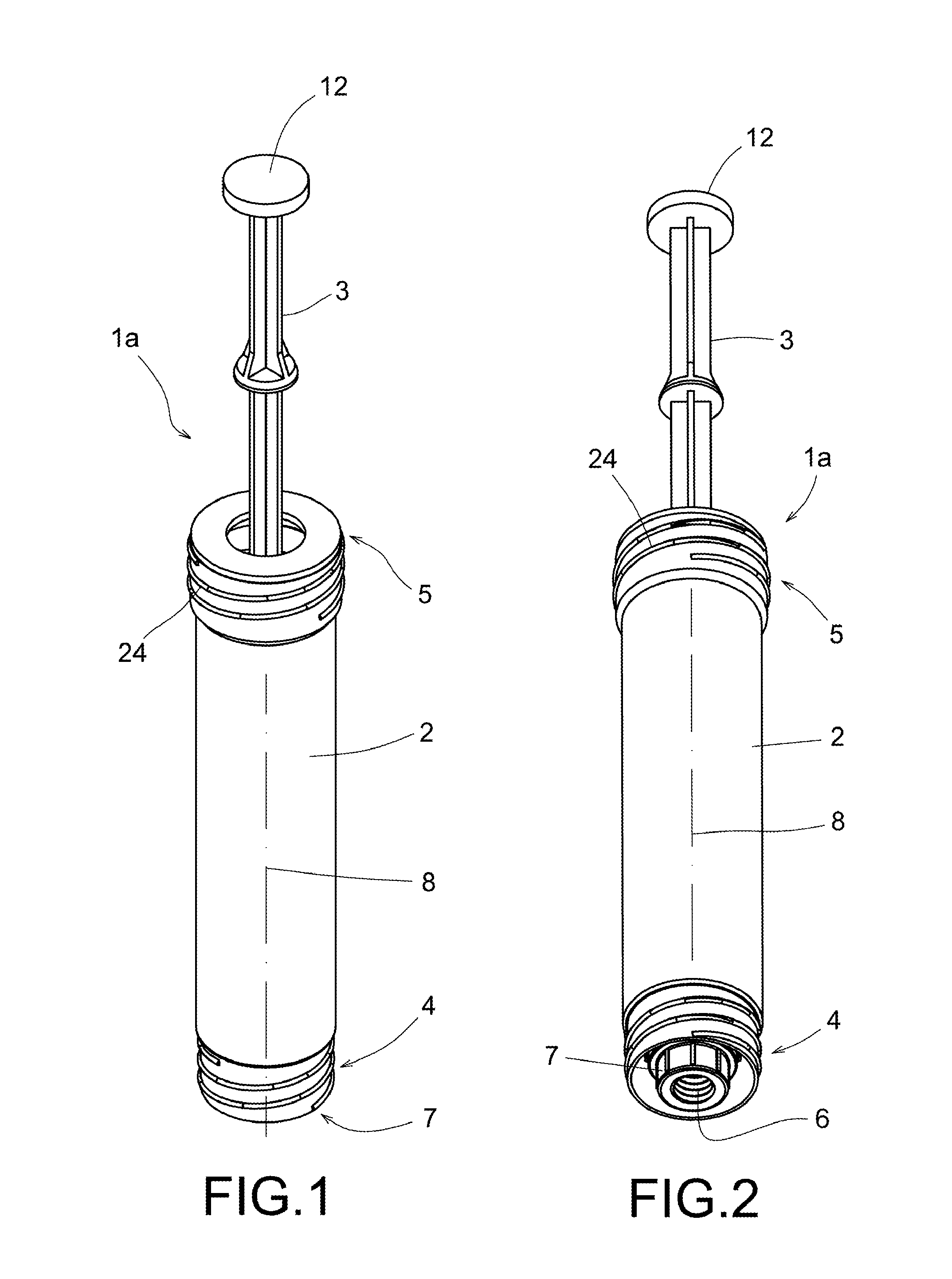
ActiveUS20140010740A1Performs betterAdjustable levelInfusion syringesPharmaceutical containersBiomedical engineeringPiston
Device (1a, 1b, 1c, 1d; 40) for extracting, storing and / or processing blood or other substances of human or animal origin, and for applying blood compounds or other biological compounds, which comprises a body (2; 41) inside which a piston (3; 42) is capable of moving longitudinally and is separable at least in part, where the body (2; 41) is provided with an internal space (9; 51) that may be connected to the outside by means of a conduit (6; 50) at a first end (4; 48) of the body (2; 41), where the body (2; 41) and the piston (3; 43) may be blocked longitudinally in at least one position to allow the creation of different degrees of vacuum. The device has multiple uses and is extremely versatile.
Owner:BIOTECHNOLOGY INST I MAS D SL
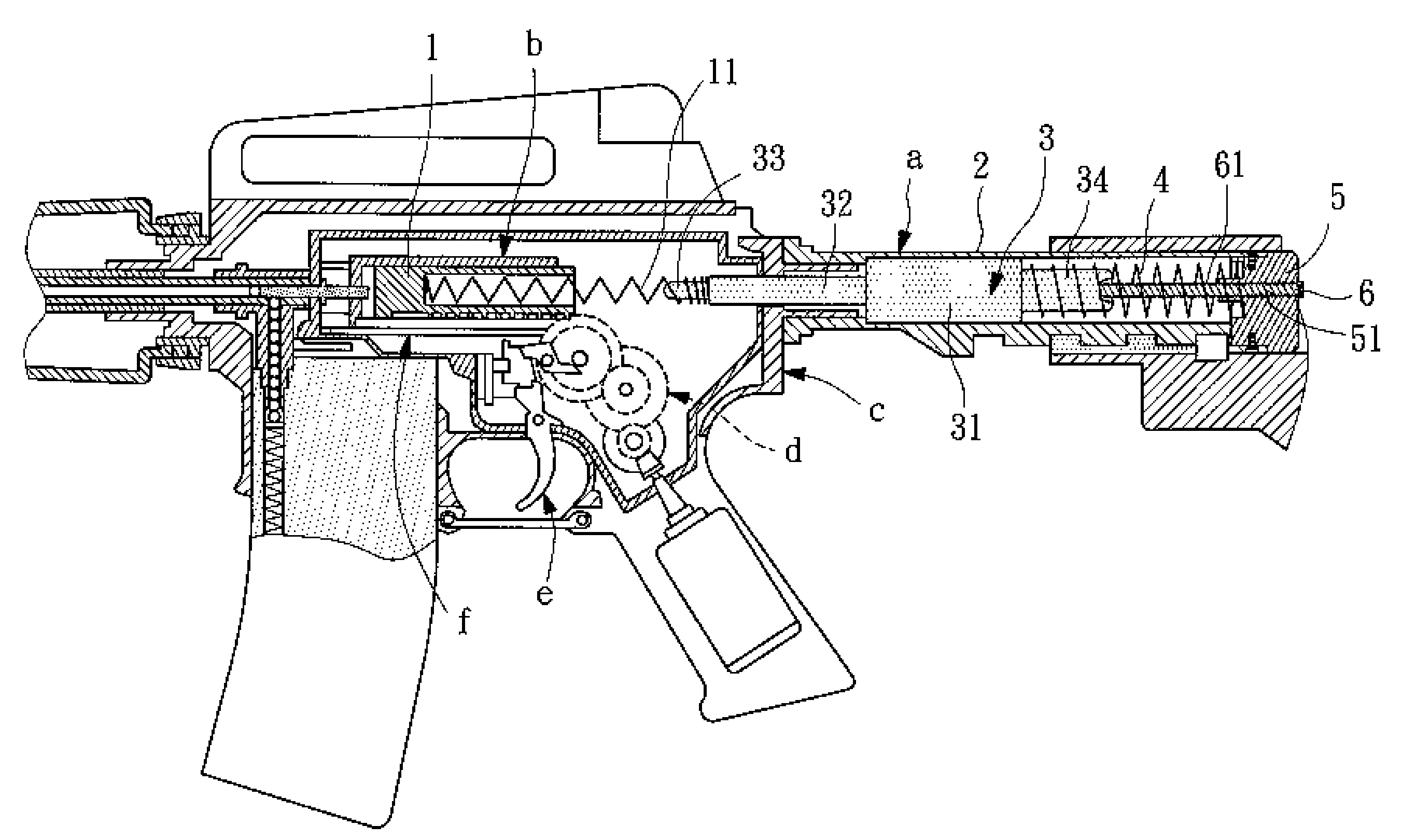
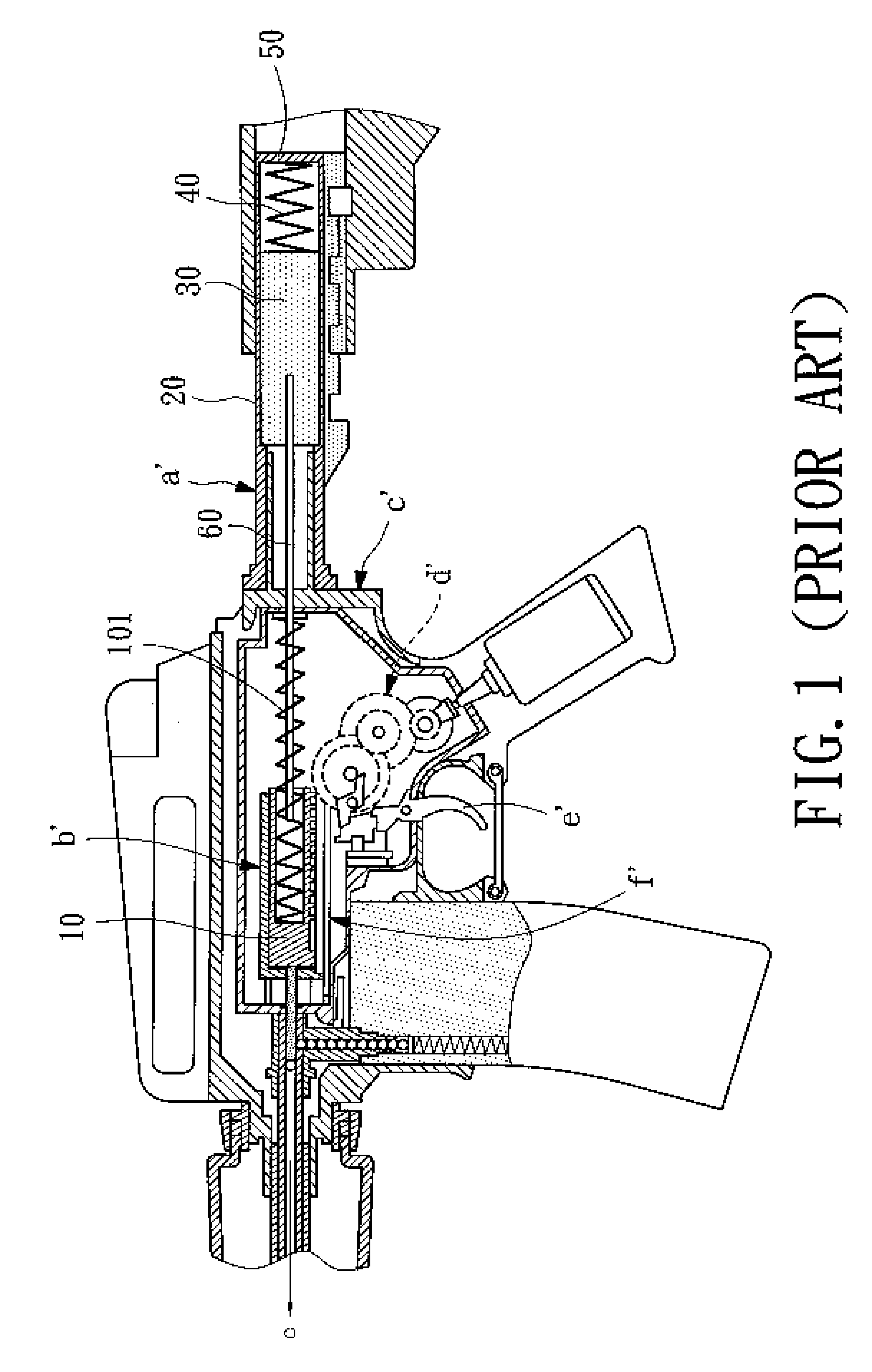
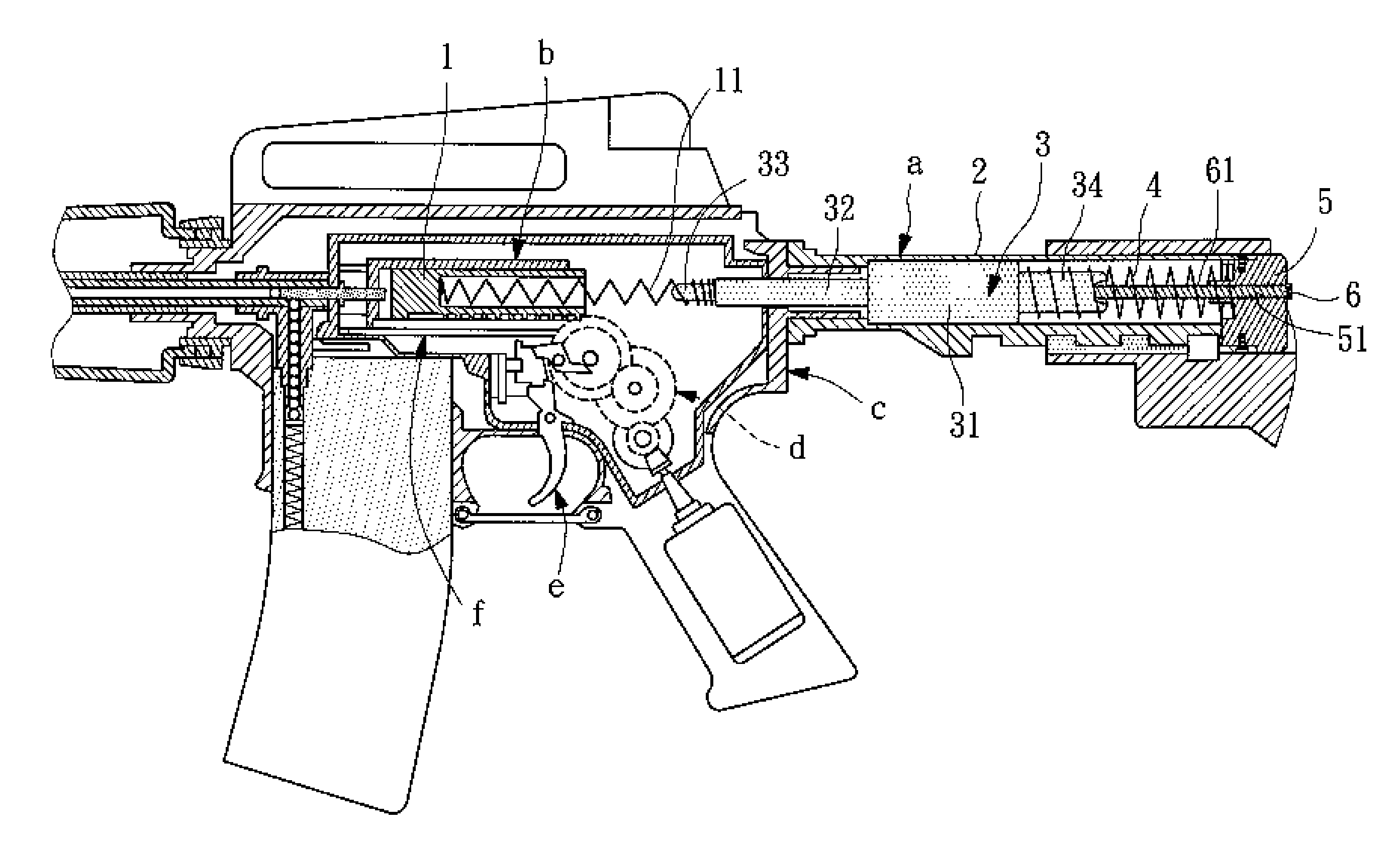
Toy rifle backlash vibration structure
A toy rifle (air soft rifle, BB-rifle) backlash vibration structure is disclosed formed of a receiver extension, a weight, a reaction spring and a buttcap spacer The weight has a front extension inserted through the frame of the toy riffle and connected to the rear end of the piston spring at the rear side of the piston so that the component parts of the backlash vibration structure doe not touch the piston during movement of the piston. The buttcap spacer is detachably fastened to the rear side of the receiver extension and mounted with an adjustment screw rod that is rotatable relative to the buttcap spacer to adjust the level of the backlash vibration from zero to the maximum.
Owner:HU SHIH CHE
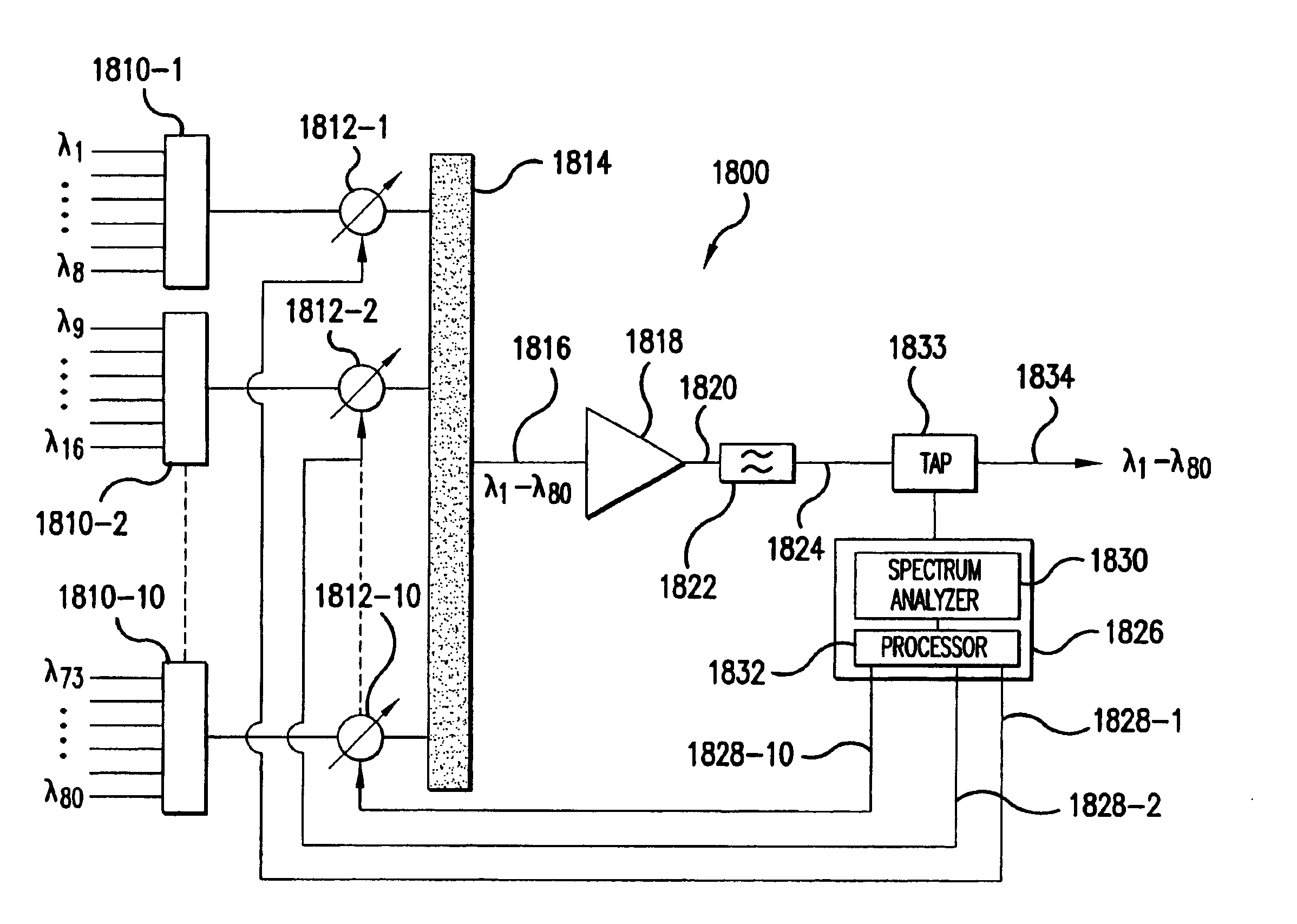
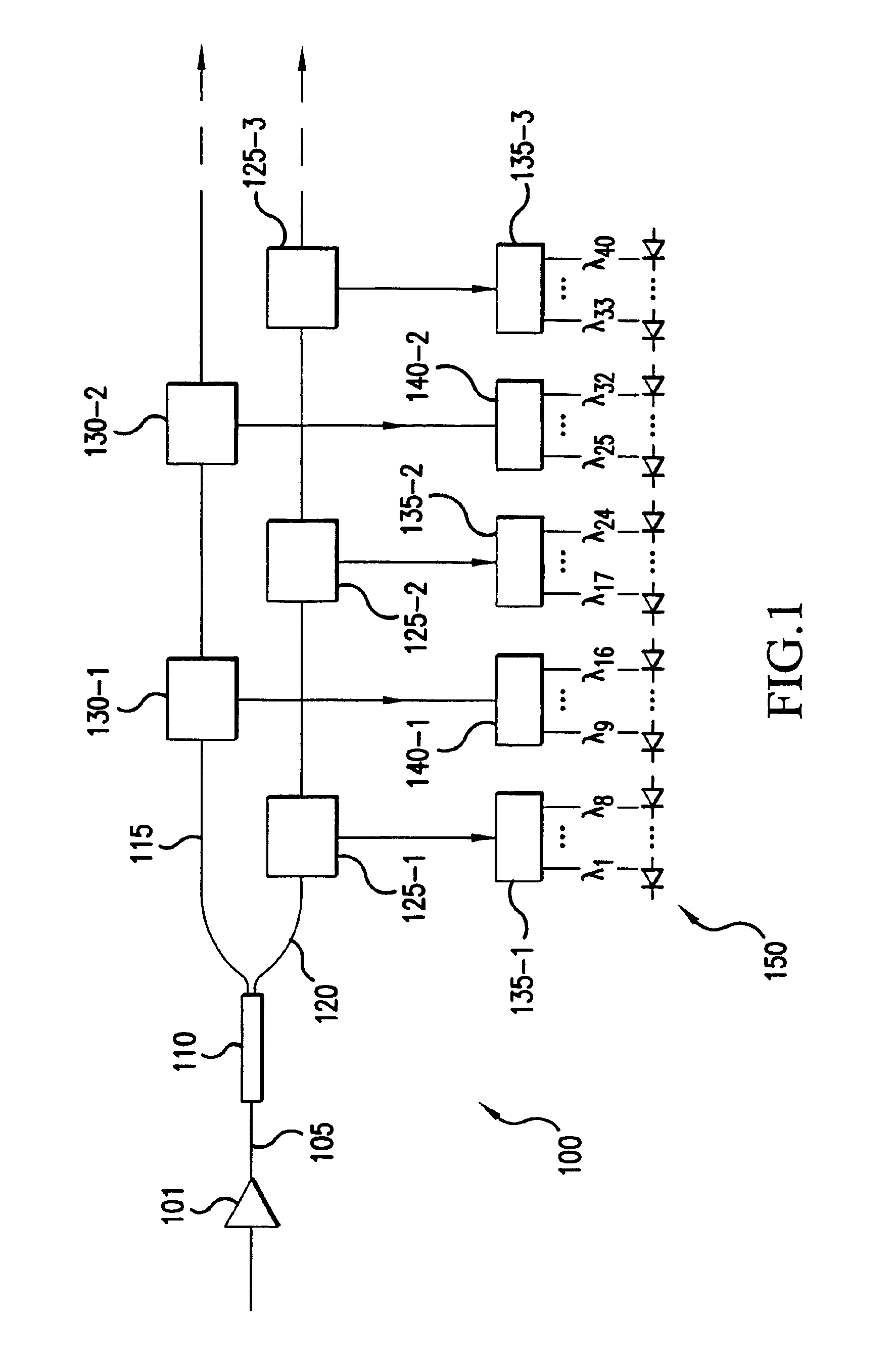
Optical device including dynamic channel equalization
InactiveUS6931196B2Adjustable levelLaser detailsCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationDynamic channel
An optical device including dynamic channel equalization is provided. In an exemplary multiplexer or line amplifier configuration the device includes a plurality of separate optical paths, each of which receiving a separate group of optical signals. Each group of optical signals is provided to an associated variable optical attenuator. Separate inputs of an optical combiner are each coupled to an output of an associated one of the variable optical attenuators. The optical combiner has an output providing the separate groups of optical signals in an aggregated form on an aggregate optical signal path. An optical performance monitor is coupled to the aggregate optical signal path, and is configured to detect an optical signal to noise ratio of each of the separate groups. The monitor supplied a feedback signal to corresponding ones of the variable optical attenuators for adjusting a respective attenuation associated with each of the attenuators in dependence of the detected optical signal to noise ratios. The device may also be provided in a demultiplexer configuration.
Owner:CIENA
Color image sensor unit and image reading apparatus using the sensor unit and control method therefor
ActiveUS20070145233A1Adjustable levelPreventing color misalignmentPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryColor imageSensor array
A color image sensor which uses a sensor array that has, as a lighting light source, 3-color light emitting elements capable of independently controlling light emitting timings respectively and at least three pixel arrays respectively constituted by a plurality of pixels, respective pixel arrays being comprising color filters having different transmitting wavelength regions from each other, and which independently controls the lighting start and lighting period of each light emitting element, whereby it is possible to prevent color misalignment in an output image signal and regulate the image signal level of each color component.
Owner:CANON COMPONENTS INC
Apparatus for metering, mixing, and spraying component liquids
InactiveUS20010023900A1Minimize likelihoodLevel of concentration be adjustTobacco devicesFire rescueFree flowEngineering
An apparatus for metering, mixing, and spraying liquids is provided. The apparatus includes a first storage chamber and a second storage chamber connected to one another via channels that permit the free flow of air between the first storage chamber and the second storage chamber so that the pressure in each of the chambers is equal. The channels are fitted with liquid flow limiting members for preventing the flow of liquid from the first storage chamber to the second storage chamber and from the second storage chamber to the first storage chamber. Liquid delivery tubes associated with each storage chamber permit liquid from the storage chamber to flow into a mixing chamber. In the mixing chamber, the two liquids combine to form a solution. The concentration of that solution is variably adjustable by means of a flow restriction member associated with the first storage chamber. There is a storage area for receiving the liquids in the storage chambers if the device is tipped onto its side or while moving the device through various angles during its operation.
Owner:ENVIROX
Radiotherapeutic bed apparatus
InactiveUS7181792B2High positioning accuracyEnsure correct executionOperating tablesPatient positioning for diagnosticsUniversal jointTherapeutic bed
A therapeutic bed is arranged so that its inclination is adjusted by a bed inclination adjusting device provided to a rotation drive device disposed in a Y-direction moving device. The bed inclination adjusting device supports the therapeutic bed at three points by its three inclination adjusters. Each of the inclination adjusters converts the rotation of a motor into the rectilinear motion of a slider, and varies the level of a universal joint provided to the therapeutic bed by a support rod rotatably attached to the slider. This allows the inclination angle of the therapeutic bed to be varied. The provision of the bed inclination adjusting device reduces the number of drive devices for positioning the therapeutic bed, thereby decreasing the cumulative value of errors in all drive devices.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Guided endotracheal intubation system
ActiveUS20160227991A1Simple low-cost manufactureEfficient discriminationTracheal tubesBronchoscopesThroatIlluminance
A guided tracheal intubation system using an autonomous modulated light source, outputting modulated illumination at a constant level, and externally applied to the subject's larynx region. An optical imaging system receives a video stream from within the subject's throat, including modulated illumination from the subject's trachea. A display control system performs signal processing on the modulated content of the images, and outputs frames of those images in which the intensity level of illumination from the trachea can be controlled without any need to change the illumination output from the modulated light source. The light source has no connection with the rest of the system, and need contain no more than a battery, a power supply circuit and a light source. It can therefore be of low cost and can be made disposable, such as in the form of an adhesive patch applied to the subject's neck.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Steel for machine structural use
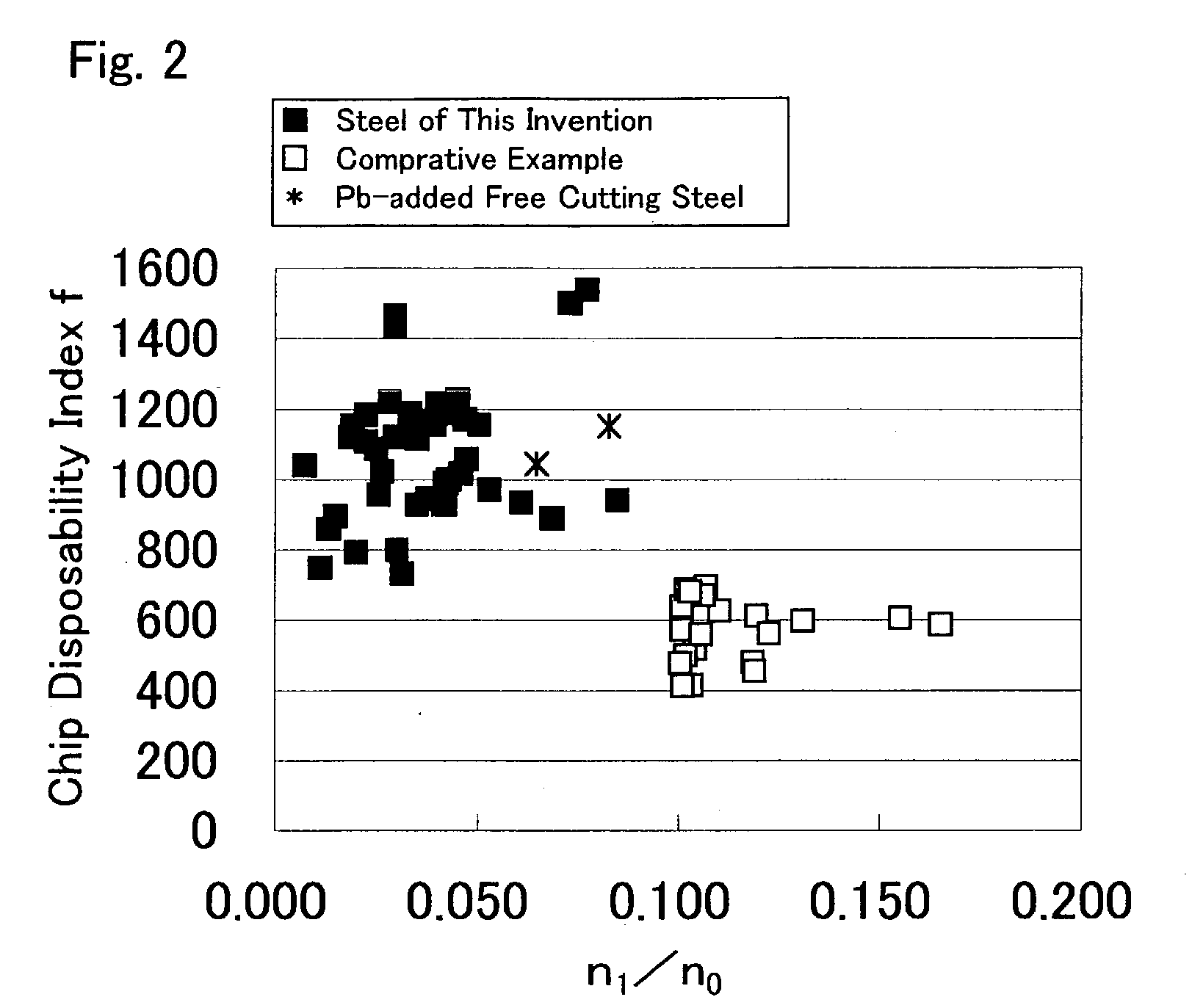
The invention provides a steel for machine structural use, which is excellent in machinability, comprising, in percent by mass, C: 0.1-0.6%, Si: 0.01-2.0%, Mn: 0.2-2.0%, S: 0.005-0.2%, Al: not more than 0.009%, Ti: not less than 0.001% but less than 0.04%, Ca: 0.0001-0.01%, O (oxygen): 0.001-0.01%, and N: not more than 0.02% and satisfying the following relations (1) to (3):n0 / S (%)>=2500 (1)n1 / n0<=0.1 (2)n2>=10 (3)where n0: total number of sulfide inclusions not smaller than 1 mum per mm2 of a cross section parallel to the direction of rolling (number / mm2); n1: number of MnS inclusions having not smaller than 1 mum and containing not less than 1.0% of Ca per mm2 of a cross section parallel to the direction of rolling (number / mm2); n2: number, per mm2 of a cross section parallel to the direction of rolling, of oxide inclusions having a specific composition comprising CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2 and having a diameter of not less than 1 mum (number / mm2).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
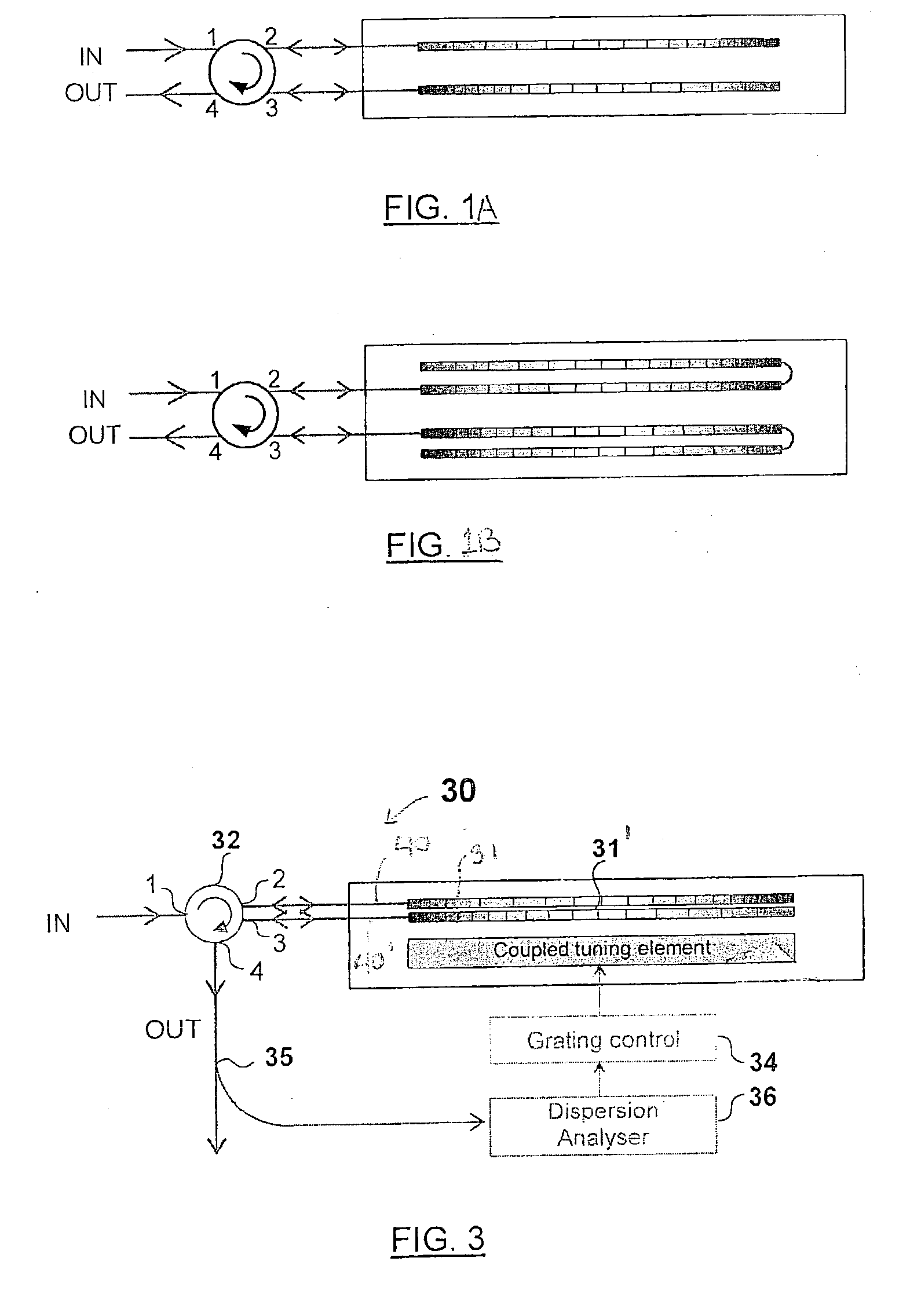
Tunable chromatic dispersion compensator
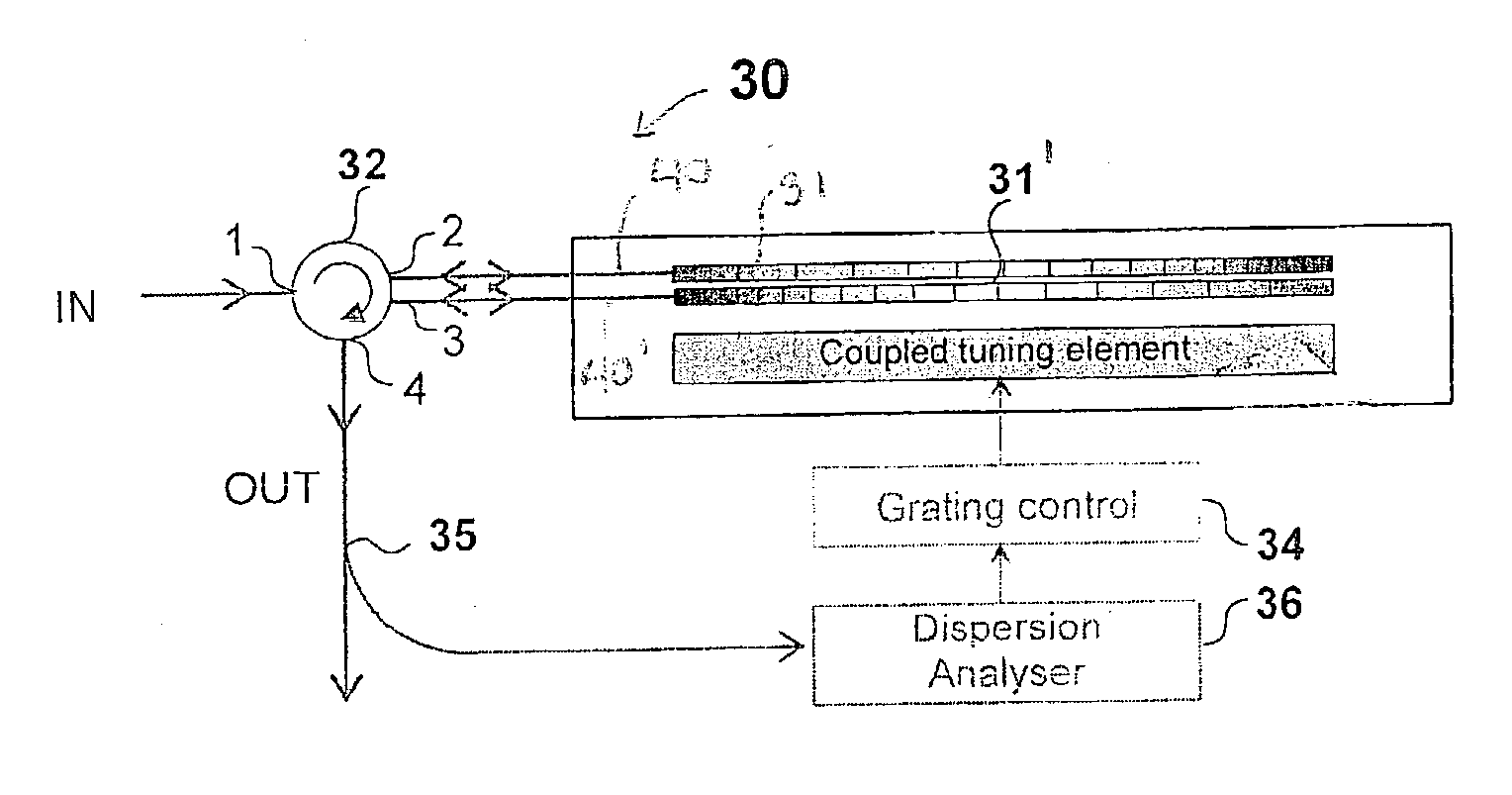
ActiveUS20040017972A1Good optical performanceIncrease rangeWeb data indexingWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringTemperature gradient
A tunable dispersion compensator for the compensation of the chromatic dispersion experienced by a single-channel or multi-channel light signal. The compensator includes a plurality of optical structures such as chirped Bragg gratings or combinations thereof, each having a characteristic dispersion profile. An optical coupling arrangement successively propagates the light signal in each of these structures, so that it accumulates the dispersion compensation effect of each. A tuning device jointly tunes the dispersion profile of each optical structure by applying a same tuning force thereto, preferably a temperature gradient.
Owner:TERAXION
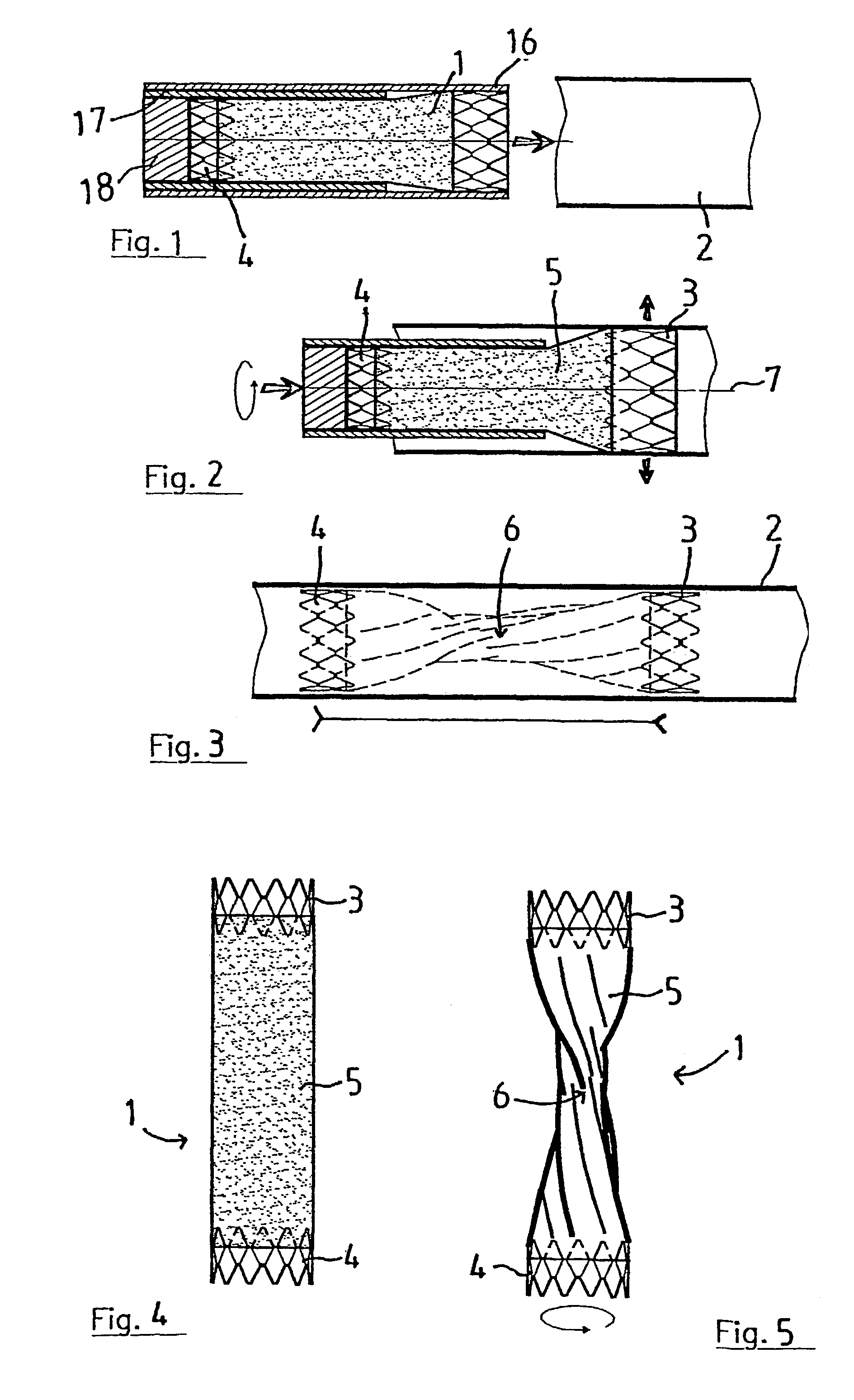
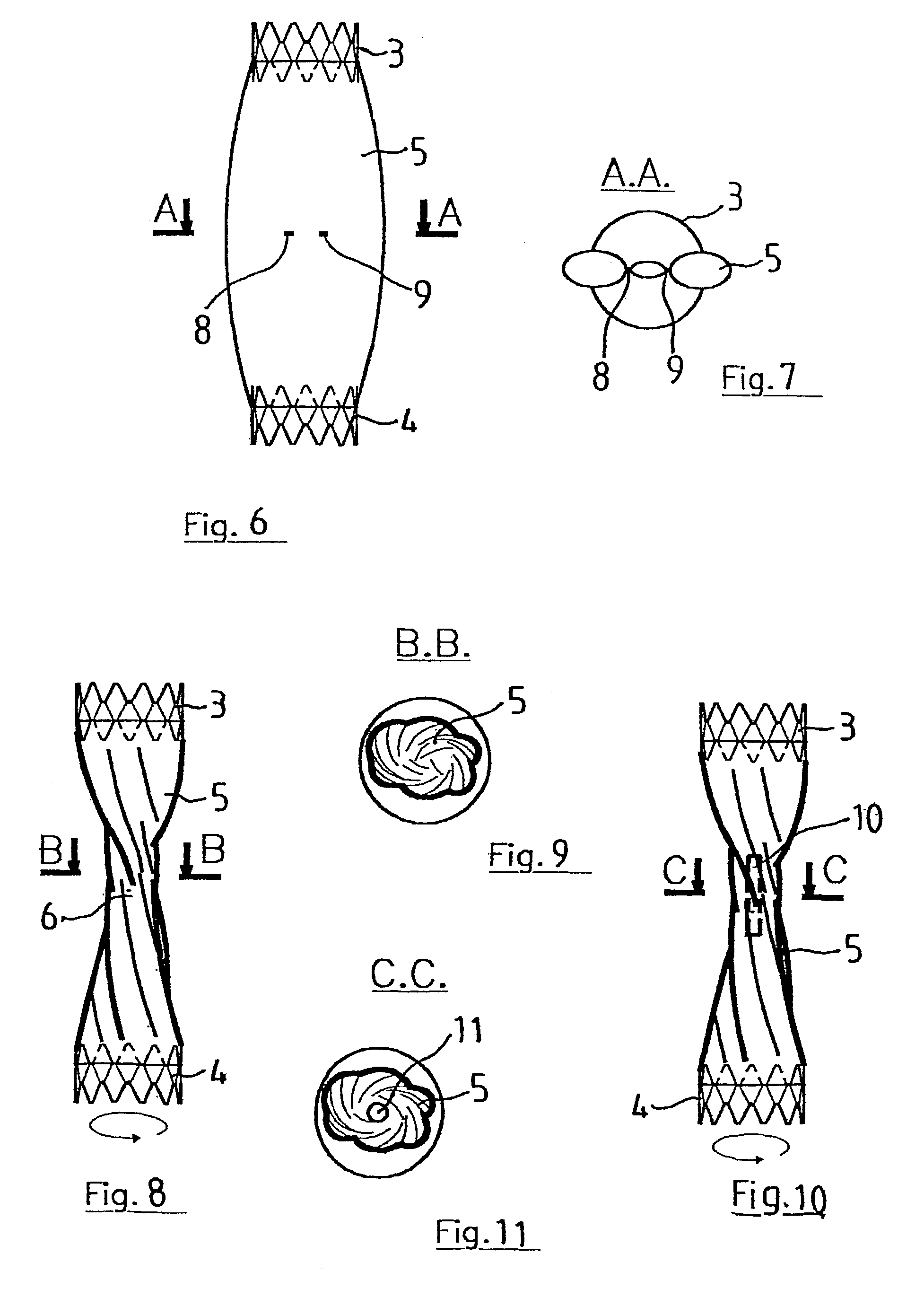
Vascular occlusion device, apparatus and method for using same
InactiveUS7316695B2Adjust level of achievedAdjustable levelDilatorsOcculdersEngineeringBiomedical engineering
The invention concerns a vascular occlusion device. The invention is characterized in that it comprises two expandable members (3, 4) enabling it to be fixed by pressure on two portions of the vessel; it further comprises an intermediate part (5) deformable in twisting to an adjustable degree depending on the relative position of the two expandable members (3, 4); thereby producing a maximum constricted region (6) defining the extent of occlusion. The invention also concerns a apparatus for setting and a method for using such a device.
Owner:MIALHE CLAUDE
Cardiac rhythm management system and method
A system and method for cardiac rhythm management, which includes an electrode system having at least one electrode and control circuitry coupled to the electrode system from which a first cardiac signal is sensed. The control circuitry includes a pulse circuit to produce electrical pulses at a first value to be delivered to the electrode system in a first cardiac region. At least one cardiac signal is sensed from a second cardiac region, where the cardiac signal includes indications of cardiac depolarizations from the second cardiac region which occurs in direct reaction to the electrical pulses delivered to the first cardiac region. The first value of the electrical pulses are then modified by a pulse adjustment circuit when a cardiac depolarization which occurs in direct reaction to the electrical pulse delivered to the first cardiac region is detected from the second cardiac region.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System for assembling substrates to bonding zones provided with cavities
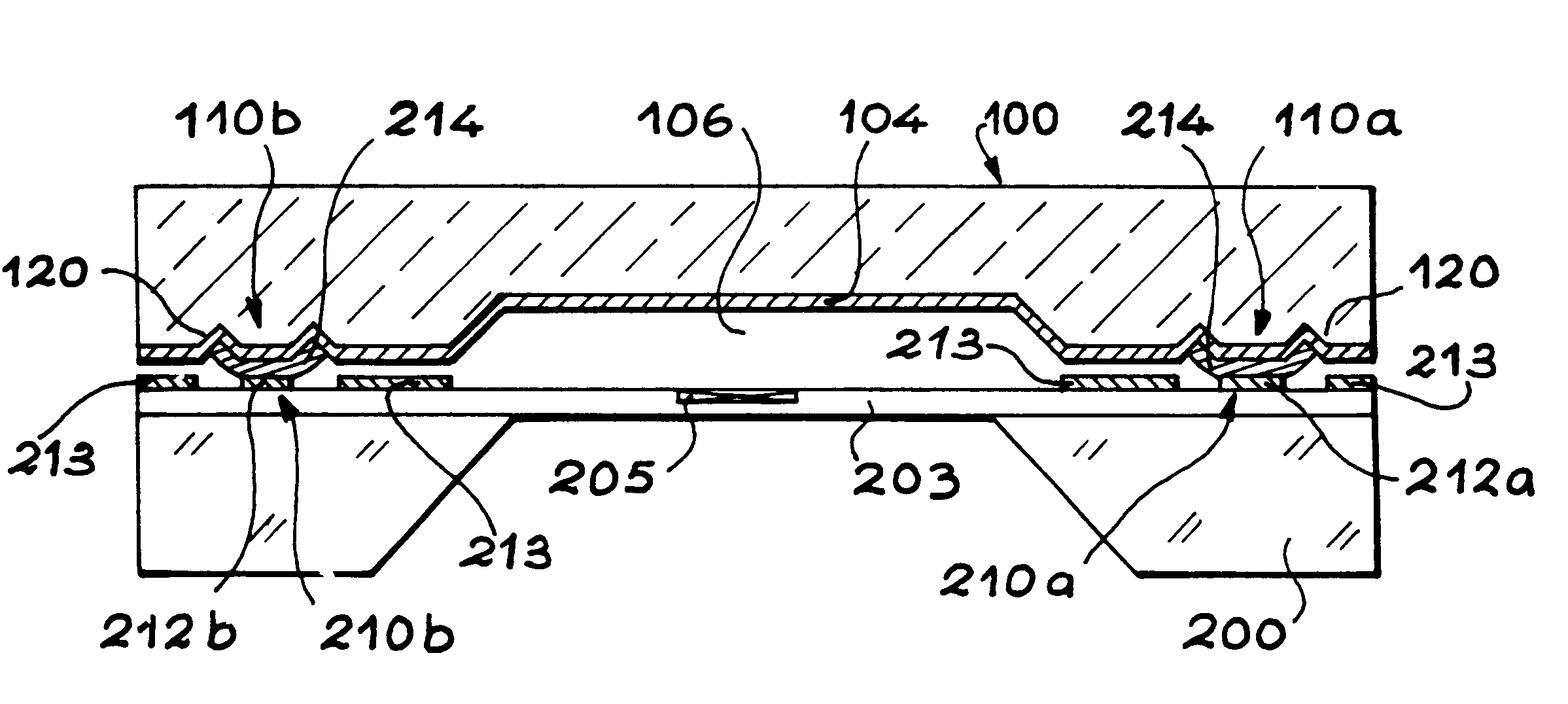
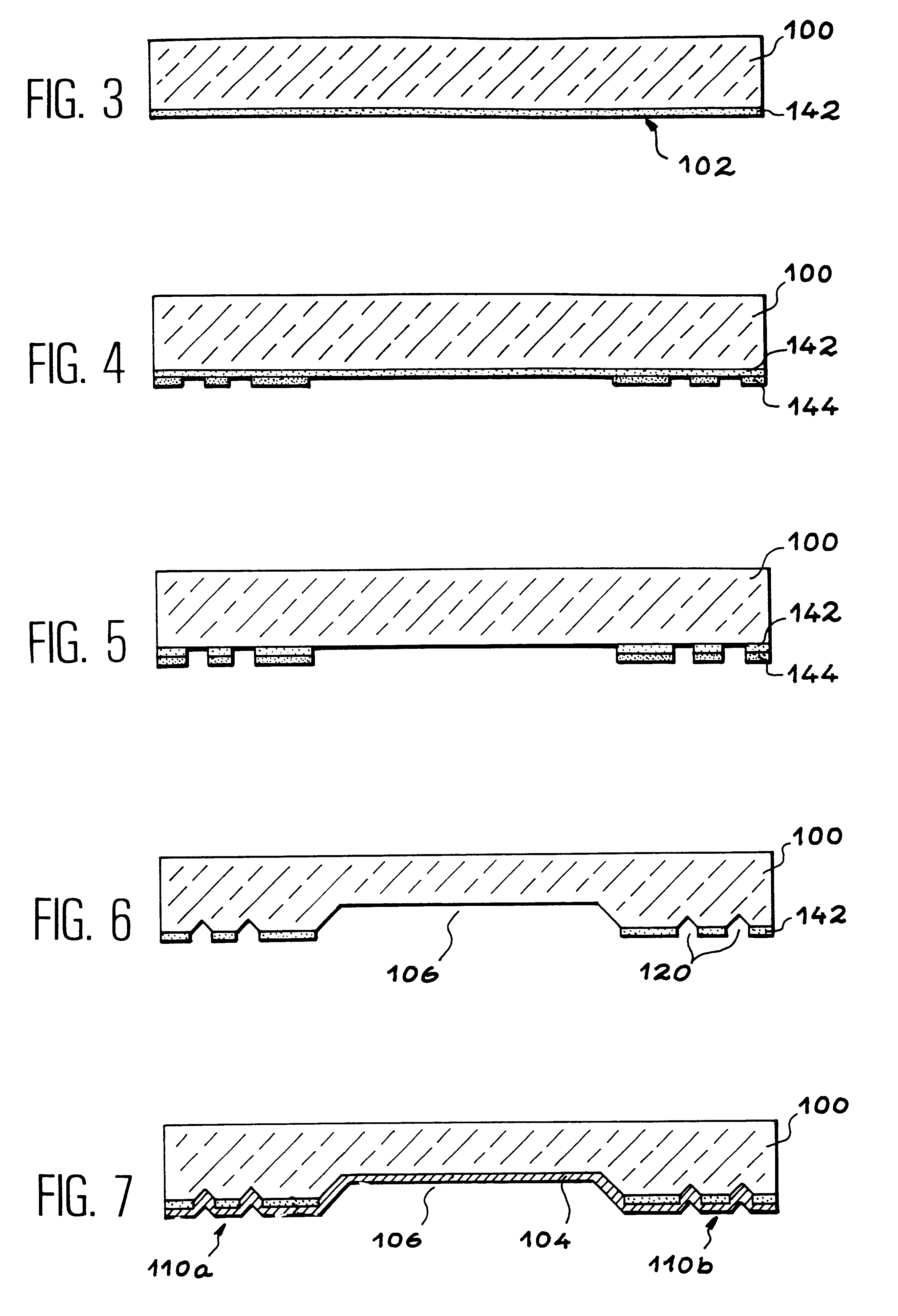
InactiveUS6531232B1Inexpensive to produceCheap implementationDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention relates to a system comprising a first substrate (100) with at least one bonding area (110a, 110b), liable to be assembled with a second substrate (200), the bonding area (110a, 110b) comprising an area made of a material (104) that can be wetted with a meltable material. According to the invention, the bonding area (110a, 110b) comprises at least one cavity (120) to receive meltable material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Toy rifle backlash vibration structure
A toy rifle (air soft rifle, BB-rifle) backlash vibration structure is disclosed formed of a receiver extension, a weight, a reaction spring and a buttcap spacer. The weight has a front extension inserted through the frame of the toy riffle and connected to the rear end of the piston spring at the rear side of the piston so that the component parts of the backlash vibration structure does not touch the piston during movement of the piston. The buttcap spacer is detachably fastened to the rear side of the receiver extension and mounted with an adjustment screw rod that is rotatable relative to the buttcap spacer to adjust the level of the backlash vibration from zero to the maximum.
Owner:HU SHIH CHE
A galvanically isolated resonant power converter assembly
InactiveUS20180175741A1Level adjustmentSave board spaceEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPower inverterResonant power converters
The present invention relates in a first aspect to a galvanically isolated power converter assembly comprising a first set of electrically interconnected resonant power inverters configured for generating respective output voltages and output currents. The galvanically isolated power converter assembly further a first positive summing node and a first negative summing node configured to combining the output voltages and output currents of the first set of resonant power inverters and a first common load circuit comprising a positive load input and a negative load input. A galvanic isolation barrier comprises first and second common isolation capacitors electrically insulating the common load circuit. Each of the first and second common isolation capacitors possesses an official safety rating.
Owner:NPC TECH APS
Method and system for assisting individual ambulation
InactiveUS7510214B1Adjustable levelAdjustable of lateral stabilityRiding toy animalsStiltsUpper limbEngineering
An ambulatory assistance device is provided, having a base that supports an individual in a generally upright position. A forward support frame is provided for engagement between the individual's upper extremities and the operating surface. Forward ambulation may be achieved by shifting the individual's mass toward one side of the device and then pulling on the support frame to pivot the opposite side of the device in a generally forward direction. Repeating the process in a mirror fashion moves the other side of the individual and the device in a generally forward direction. Optional platforms and foot restraints are provided for positioning and securing the individual on the base. Various base configurations are provided to adjust the performance of the device according to conditions.
Owner:OXFORD STUART G
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com