Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5272results about "Wind motor monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
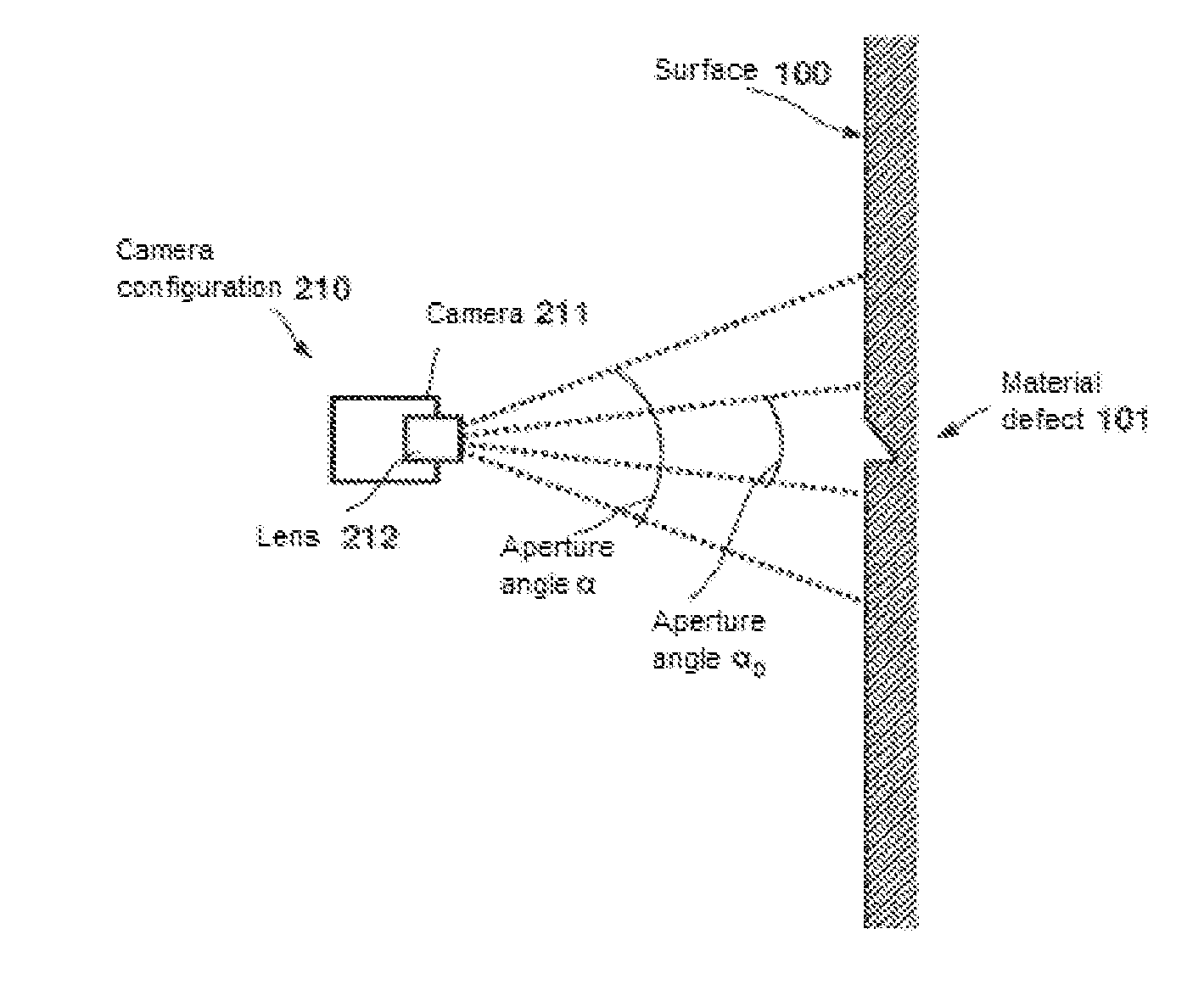
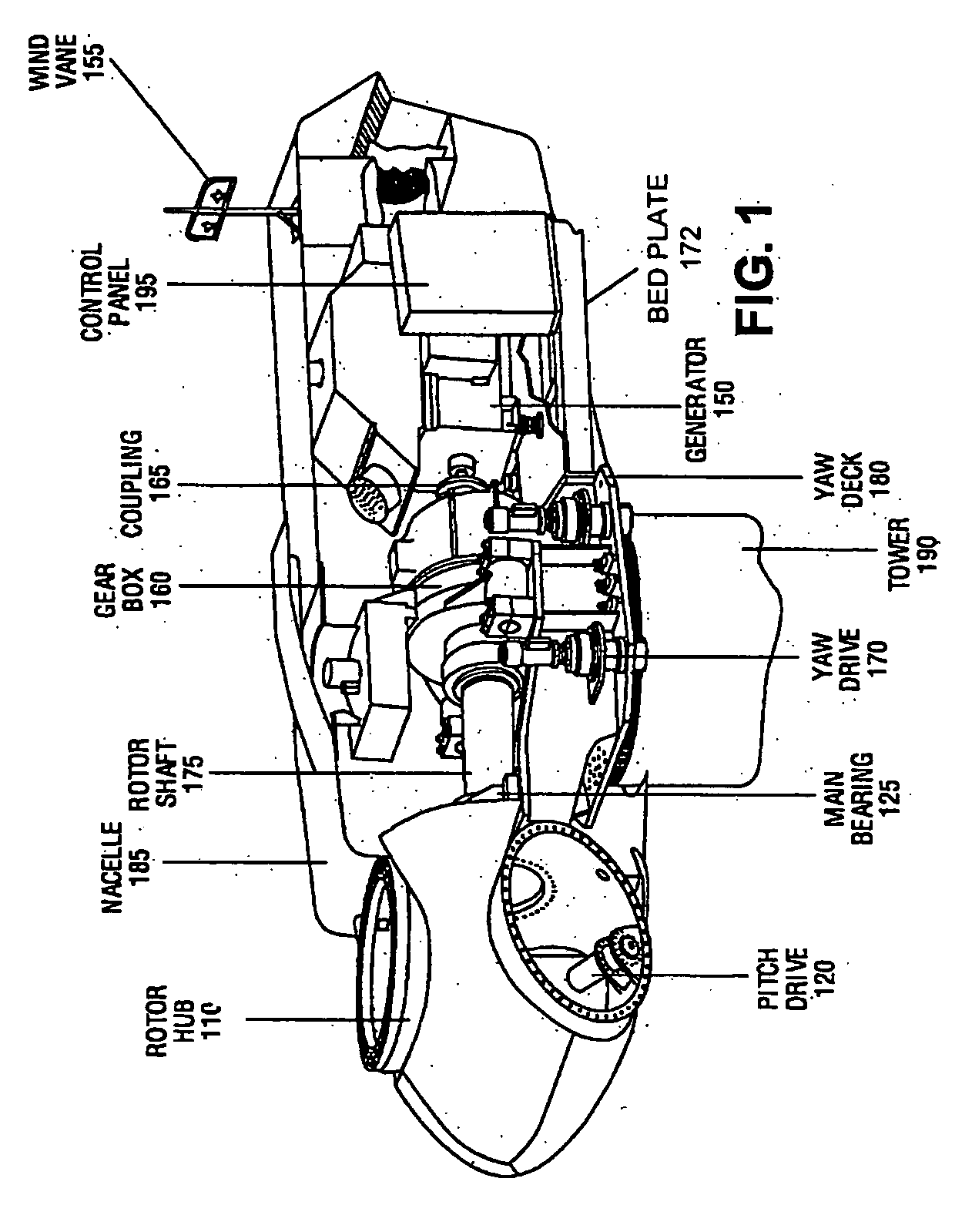
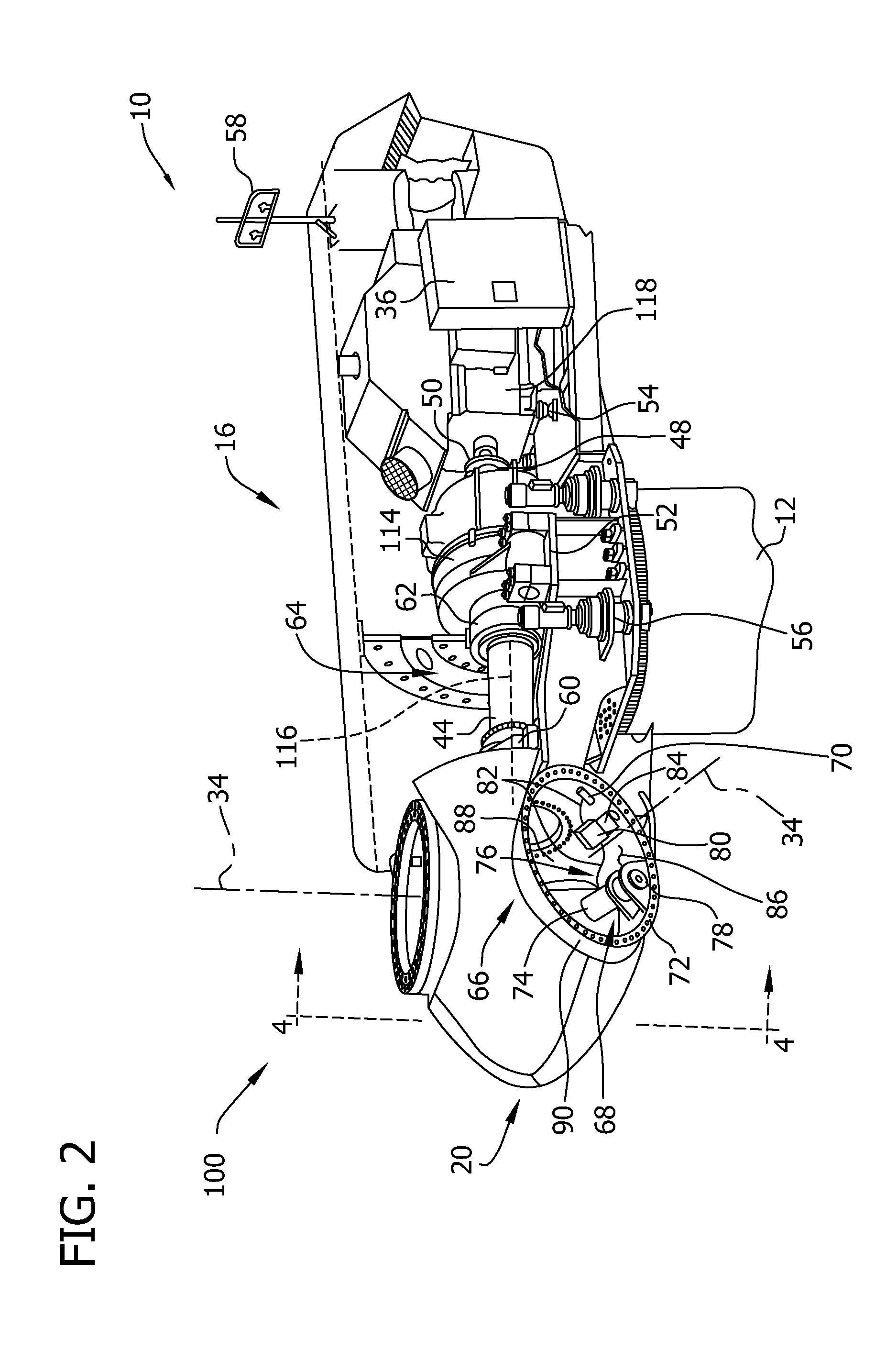
Method and System for Inspecting a Surface Area for Material Defects
ActiveUS20140168420A1Reduce associated effortReduce security risksPicture taking arrangementsColor television detailsMaterial defectEngineering
A camera assembly arranged on an unmanned and autonomously navigating aerial vehicle is employed to inspect a surface area of for material defects. The vehicle is automatically flown to the surface area from a launch site, wherein it can fly around obstacles using automatic obstacle detection and avoidance methods. A relative position of the aerial vehicle with respect to the surface area with the aid of a position sensor is continuously measured and a sequence of images of the surface area is recorded. Between the individual images, the aerial vehicle is moved along a flight path overlapping image details of the surface area. The images of the sequence are composed into an overall image of the surface area to allow for the surface area to be inspected for defects and the location of defects to be ascertained on the basis of the overall image.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
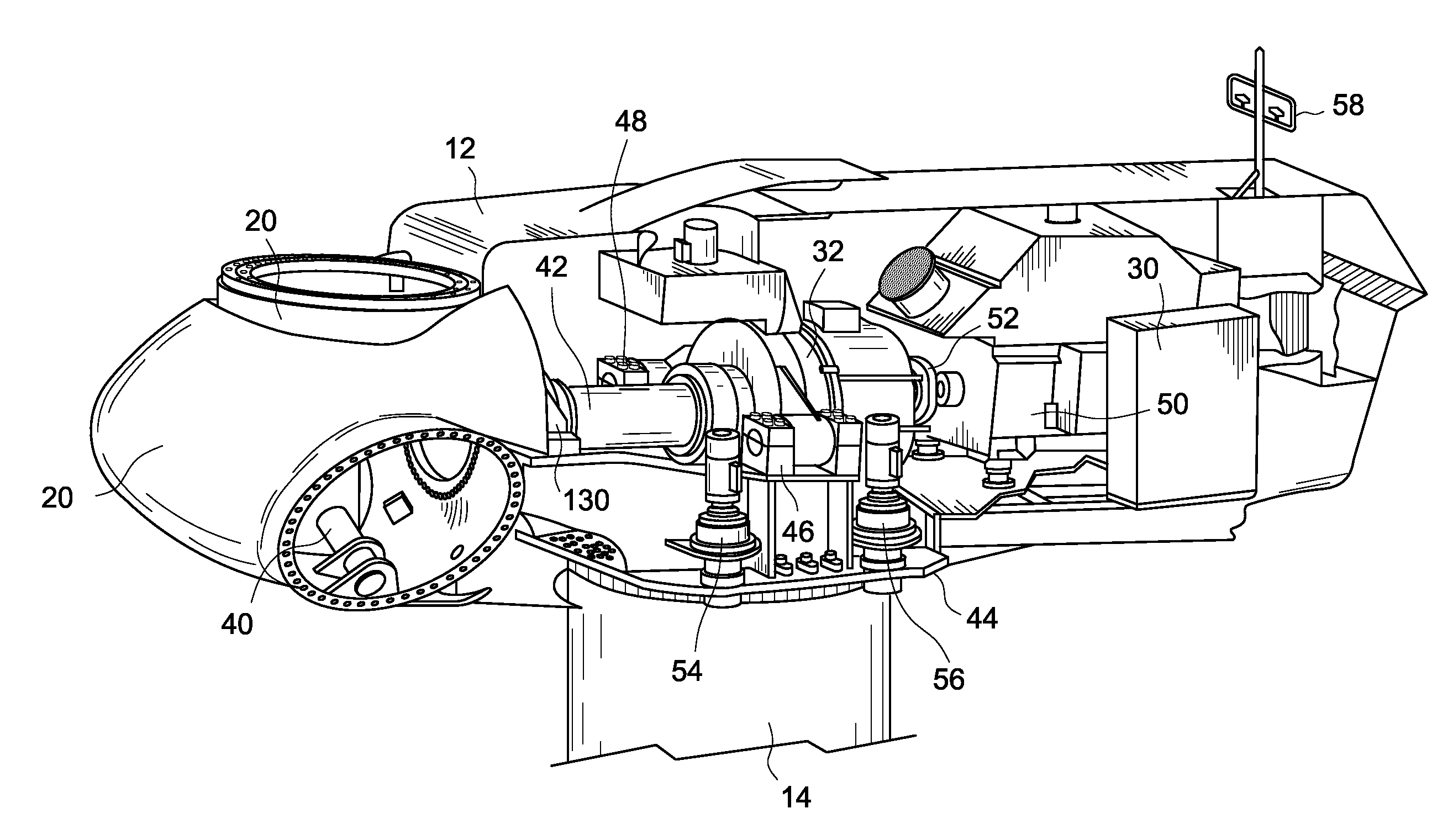
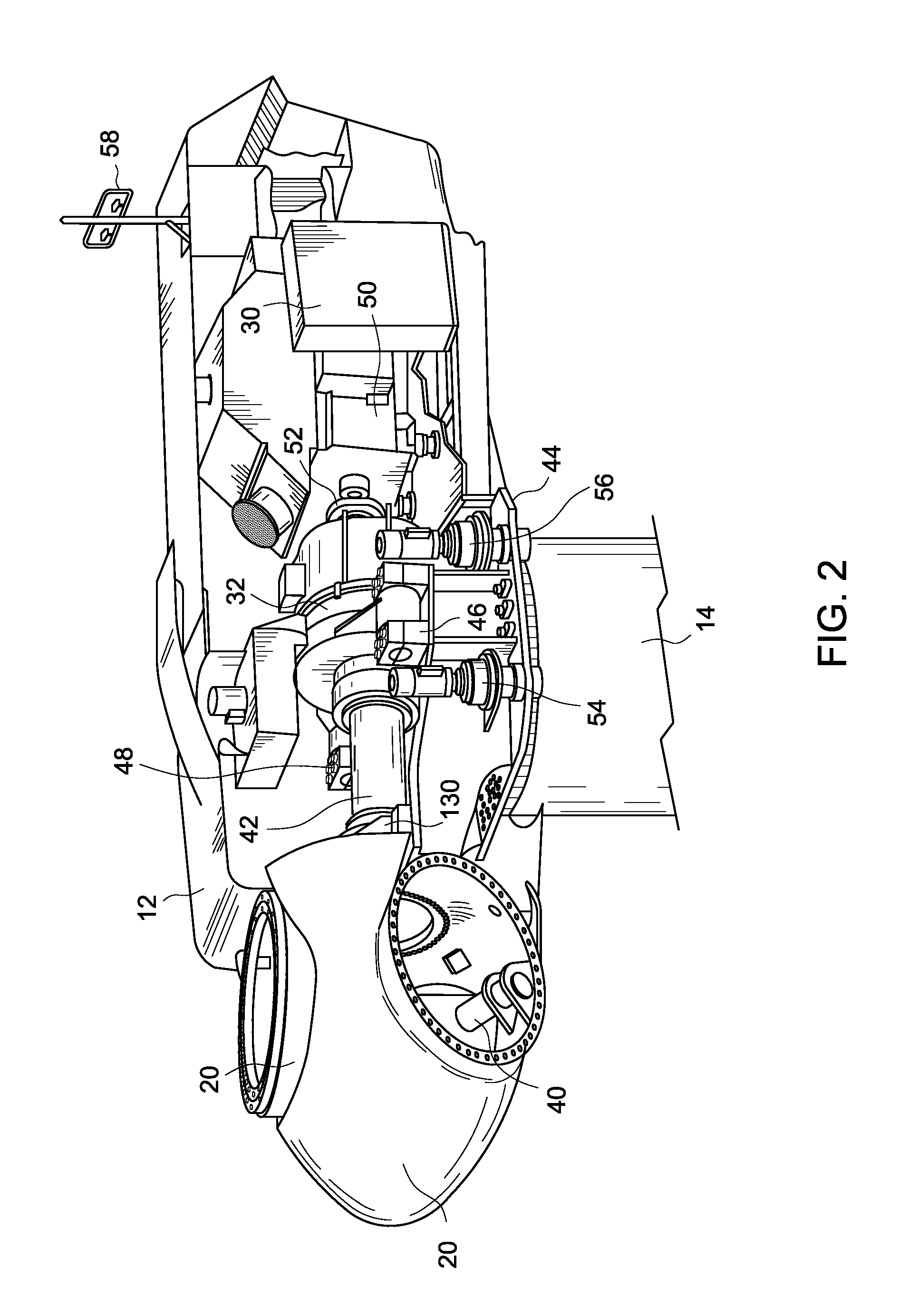
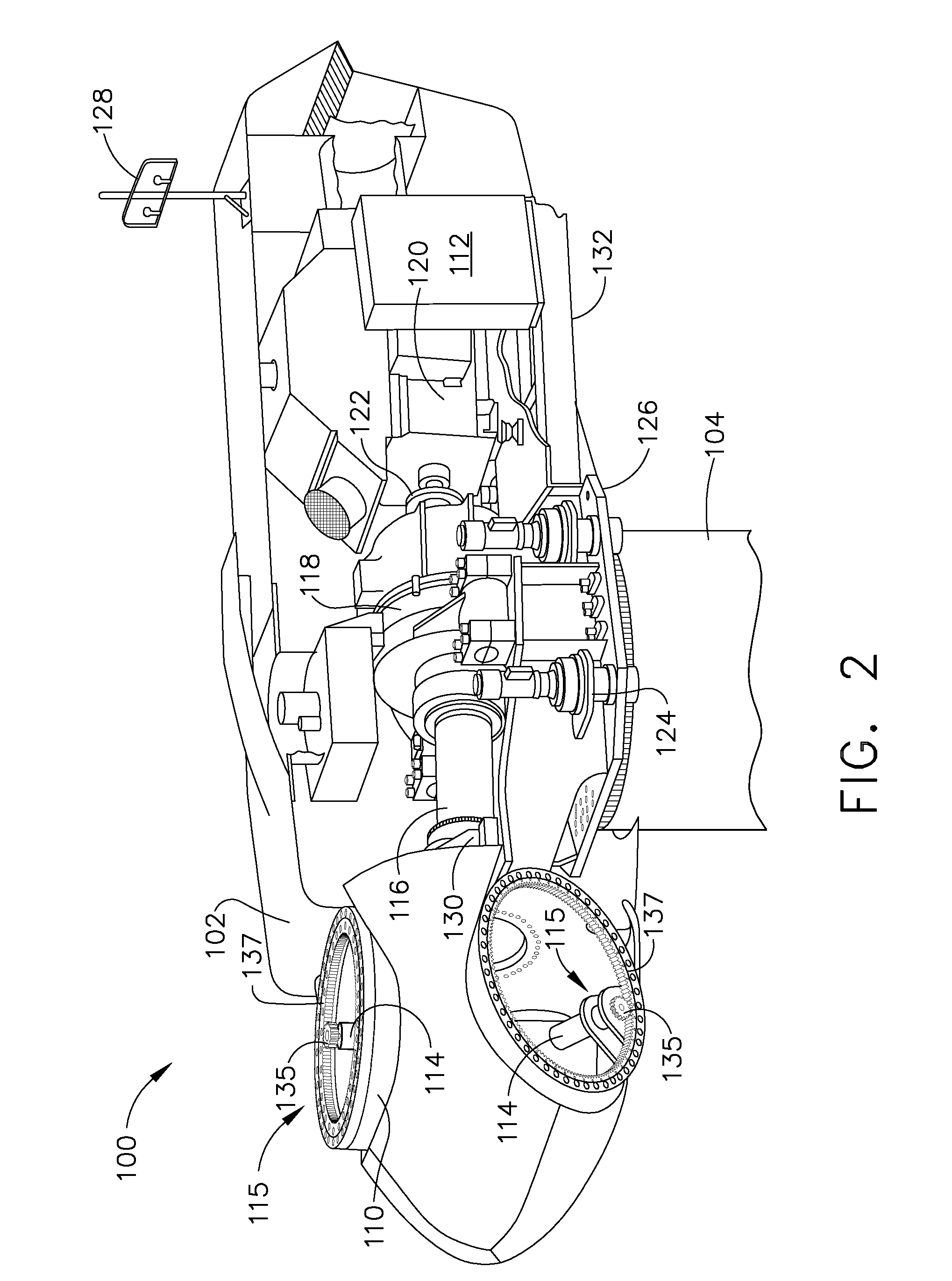
System and method for monitoring wind turbine gearbox health and performance
A system and method are provided to monitor the health and performance of a wind turbine gearbox. A plurality of sensors coupled to the wind turbine gearbox provide input to a controller. The controller generates output information that includes performance and health information of the wind turbine gearbox based on the input received from each of the sensors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
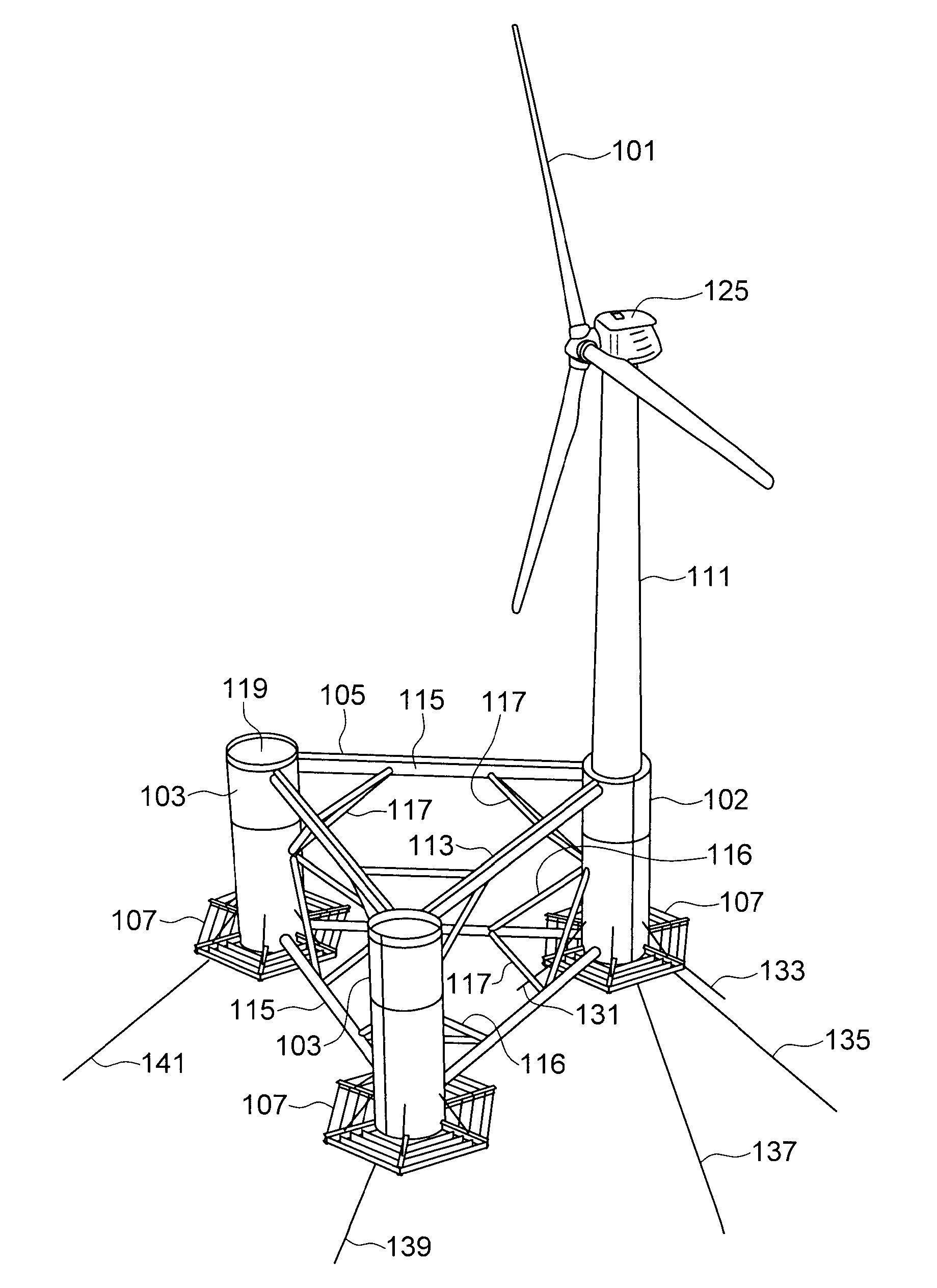
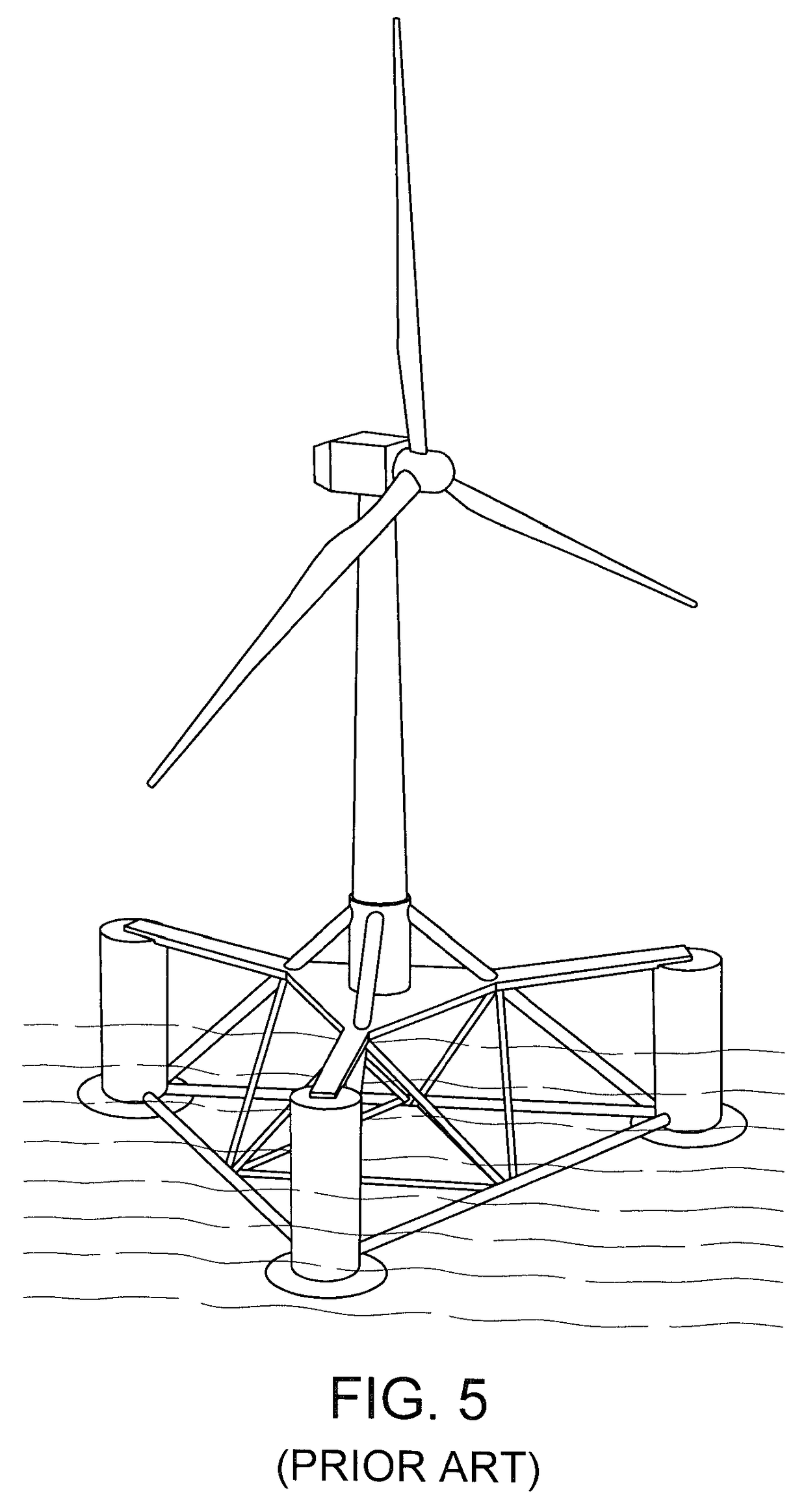
Column-stabilized offshore platform with water-entrapment plates and asymmetric mooring system for support of offshore wind turbines
ActiveUS20110037264A1Improve performanceEasy to produceWind motor controlWind motor assemblyNacelleMooring system
A floating wind turbine platform includes a floatation frame (105) that includes three columns (102, 103) that are coupled to each other with horizontal main beams (115). A wind turbine tower (111) is mounted above a tower support column (102) to simplify the system construction and improve the structural strength. The turbine blades (101) are coupled to a nacelle (125) that rotates on top of the tower (111). The turbine's gearbox generator and other electrical gear can be mounted either traditionally in the nacelle, or lower in the tower (111) or in the top of the tower-supporting column (102). The floatation frame (105) includes a water ballasting system that pumps water between the columns (102, 103) to keep the tower (111) in a 10 vertical alignment regardless of the wind speed. Water-entrapment plates (107) are mounted to the bottoms of the columns (102, 103) to minimize the rotational movement of the floatation frame (105) due to waves.
Owner:PRINCIPLE POWER
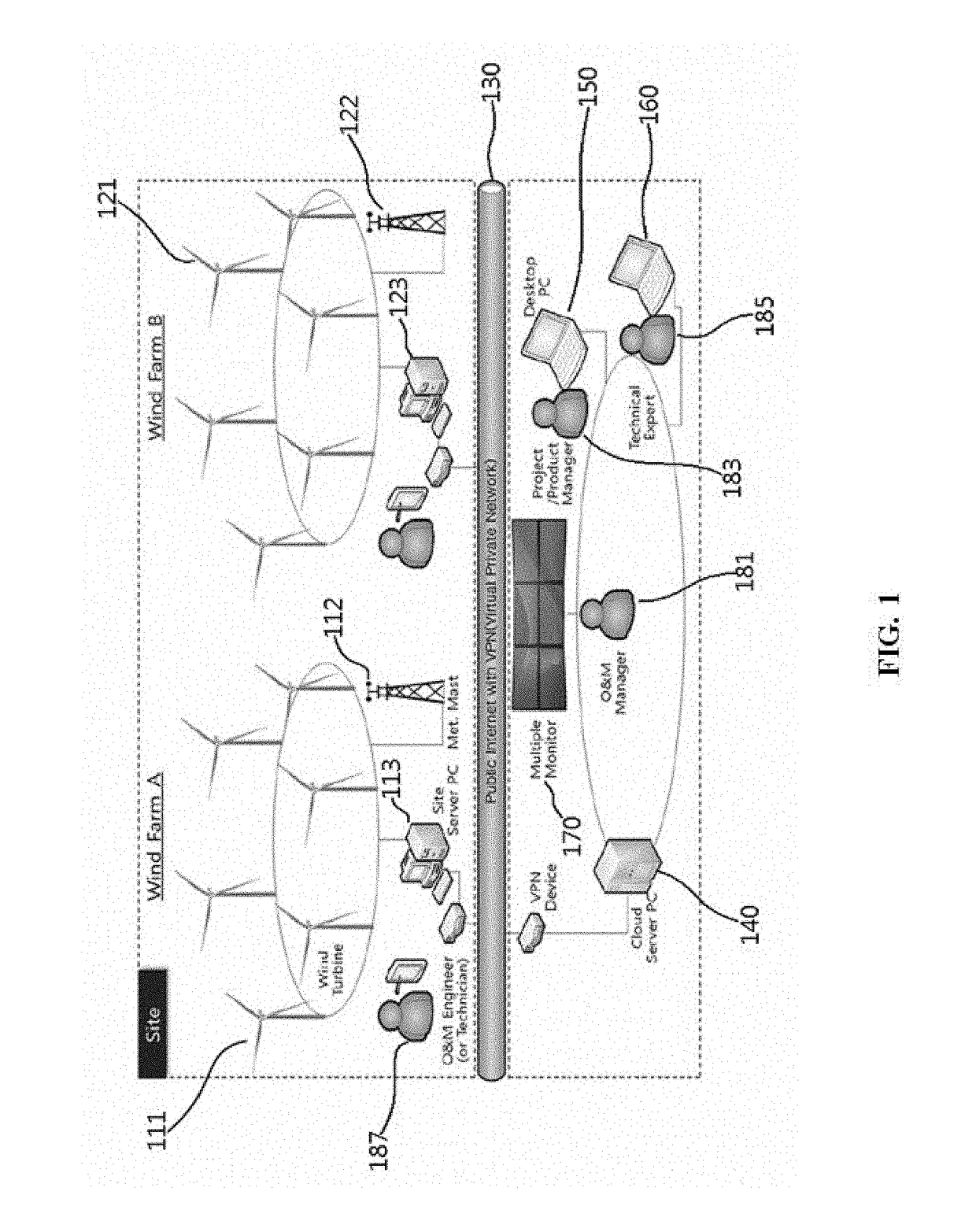
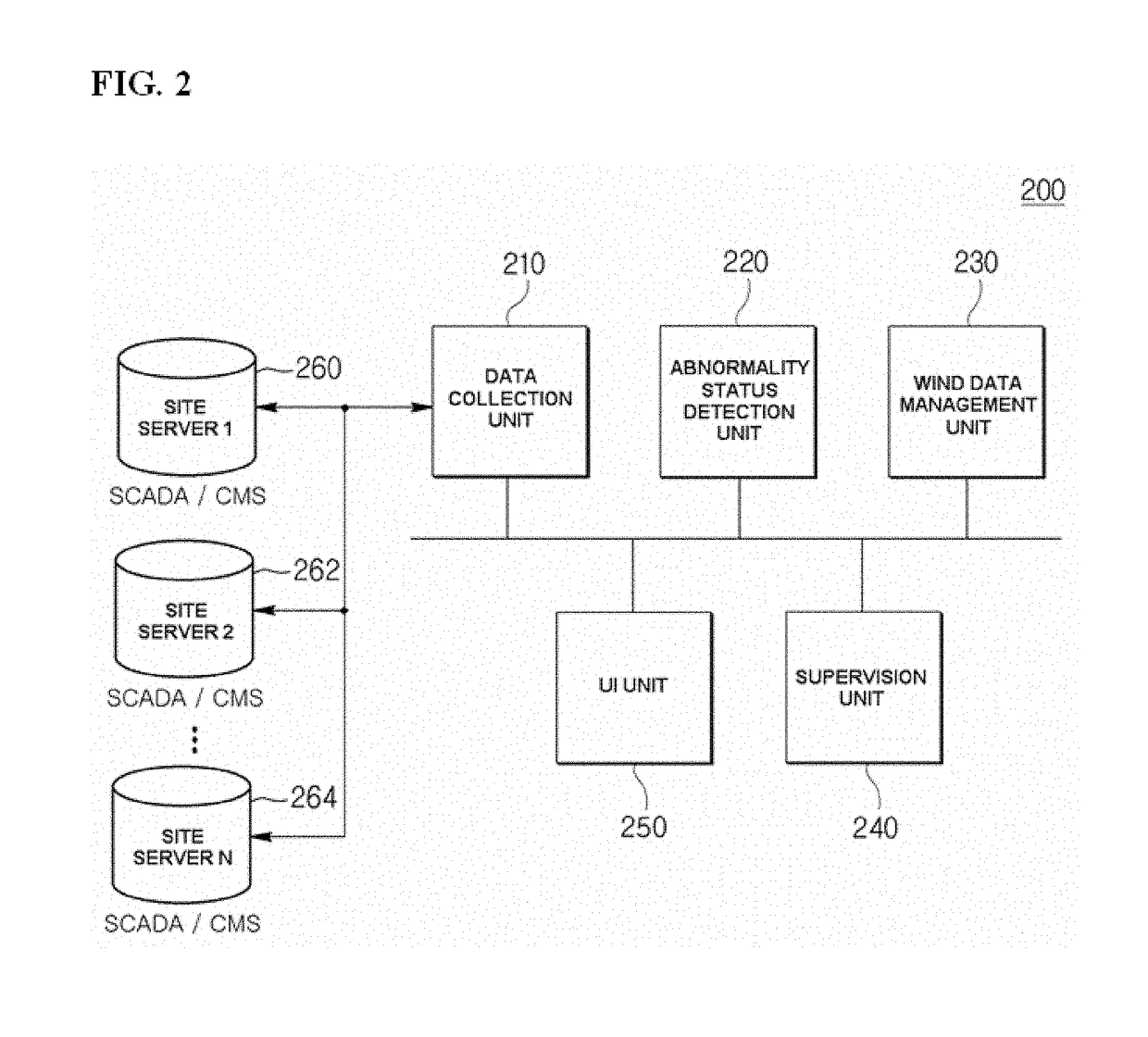
Wind farm supervision monitoring system
ActiveUS20170352010A1Minimize impactEarly detectionWind motor controlElectric testing/monitoringManagement unitMonitoring system
A wind farm supervision monitoring system includes: a data collection unit configured to collect data about a status monitoring of each wind turbine from at least one site server; an abnormality status detection unit configured to detect an abnormality status of each wind turbine based on the collected data about the status monitoring and issue an alarm; a wind data management unit configured to early detect a fault of each wind turbine and or monitor performance of each wind turbine based on the data about the status monitoring or the data about the abnormality status; and a supervision unit configured to manage a turbine operation status and operation and maintenance of each wind turbine and provide information for establishing an operation and maintenance plan for the detected abnormality status of the wind turbine.
Owner:DOOSAN HEAVY IND & CONSTR CO LTD
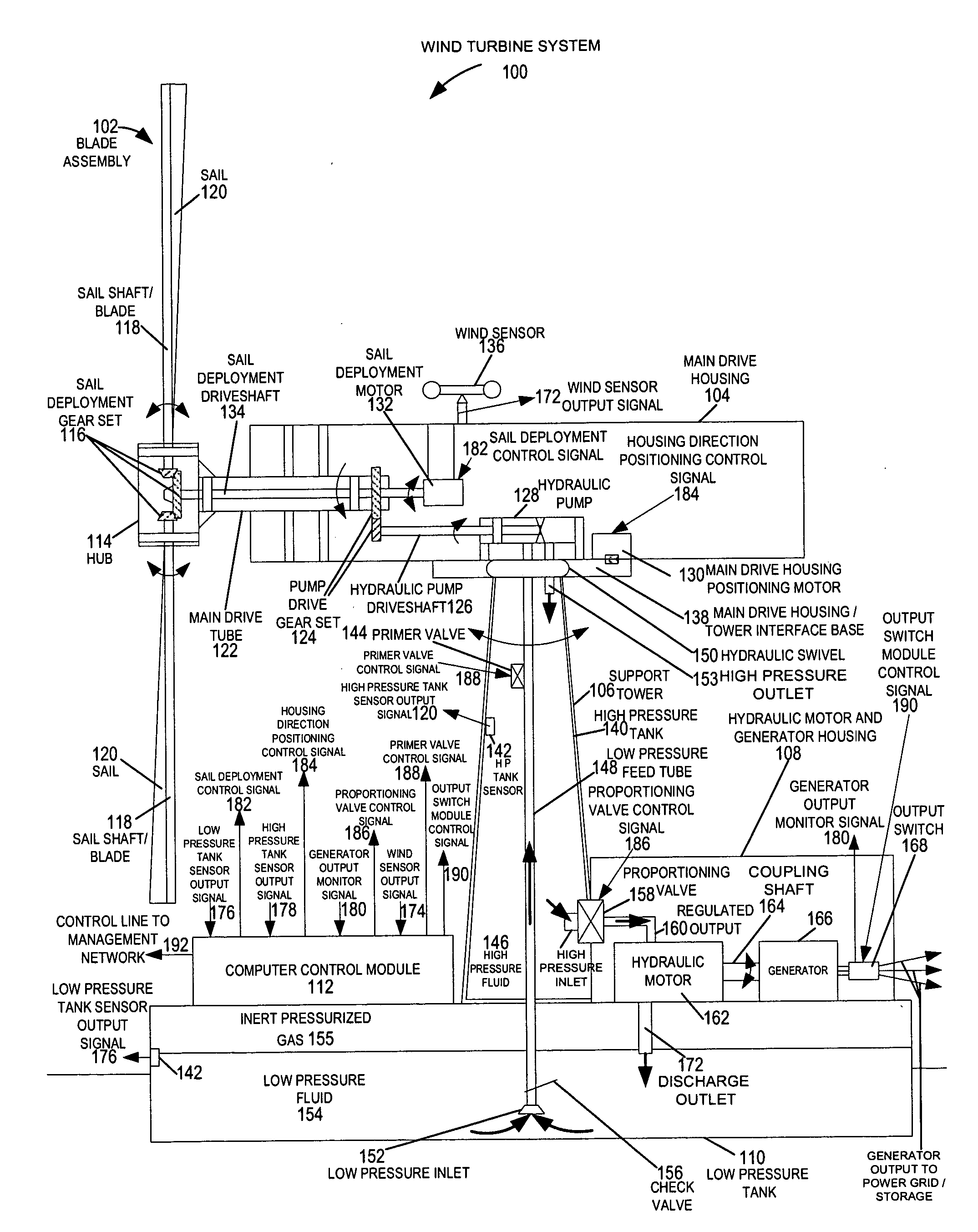
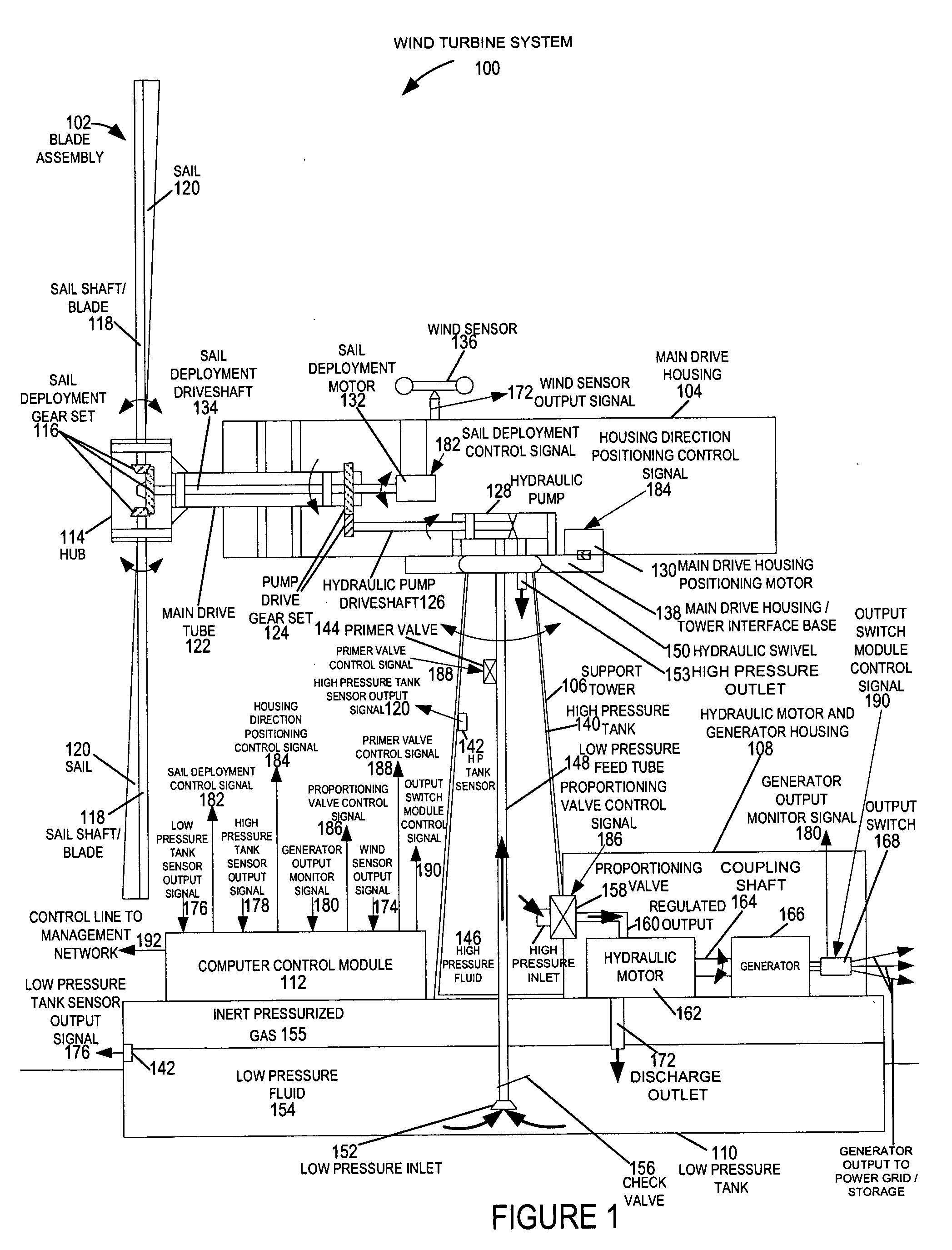
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS20070024058A1Eliminate needReduced pressure levelWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
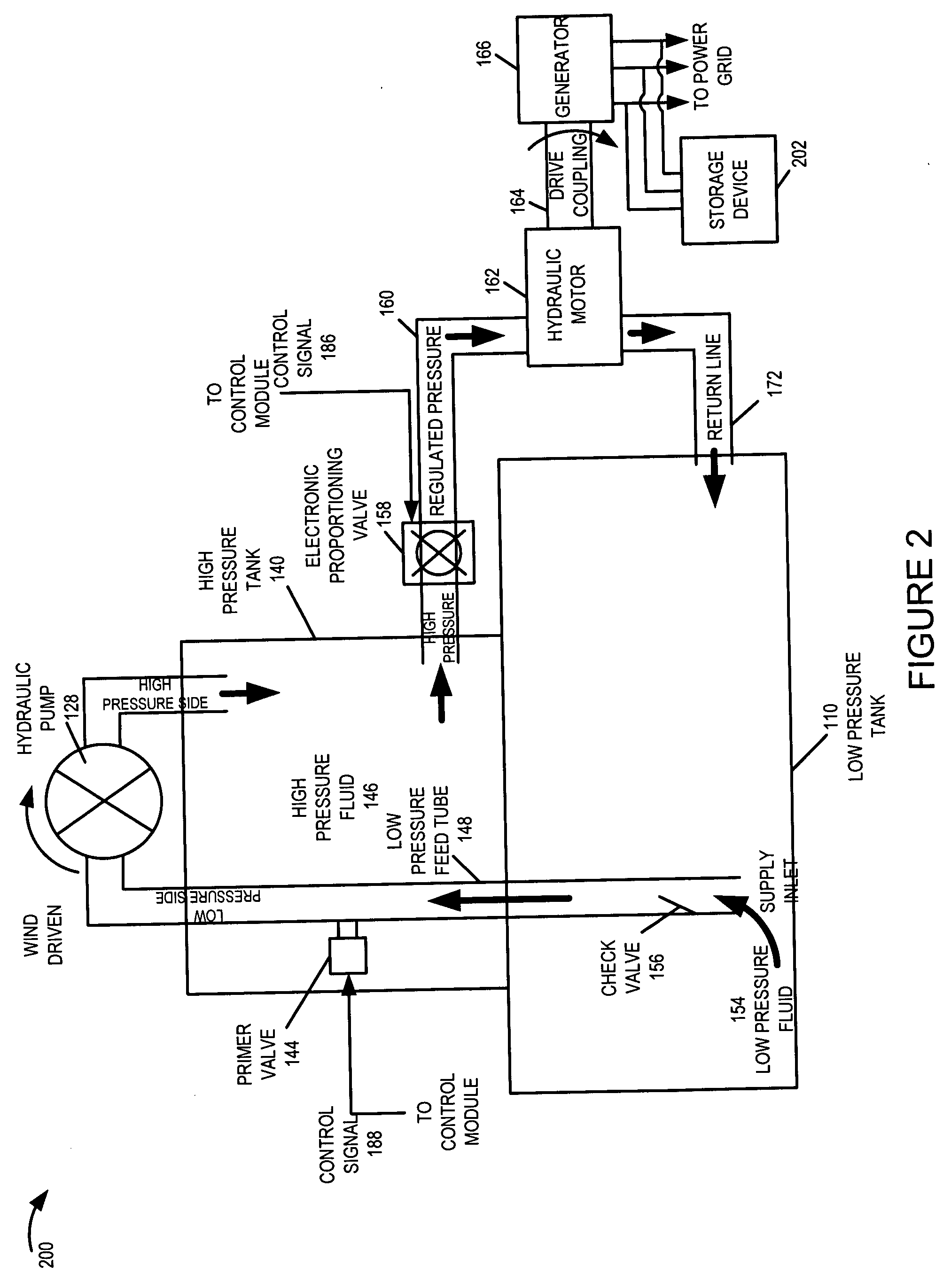
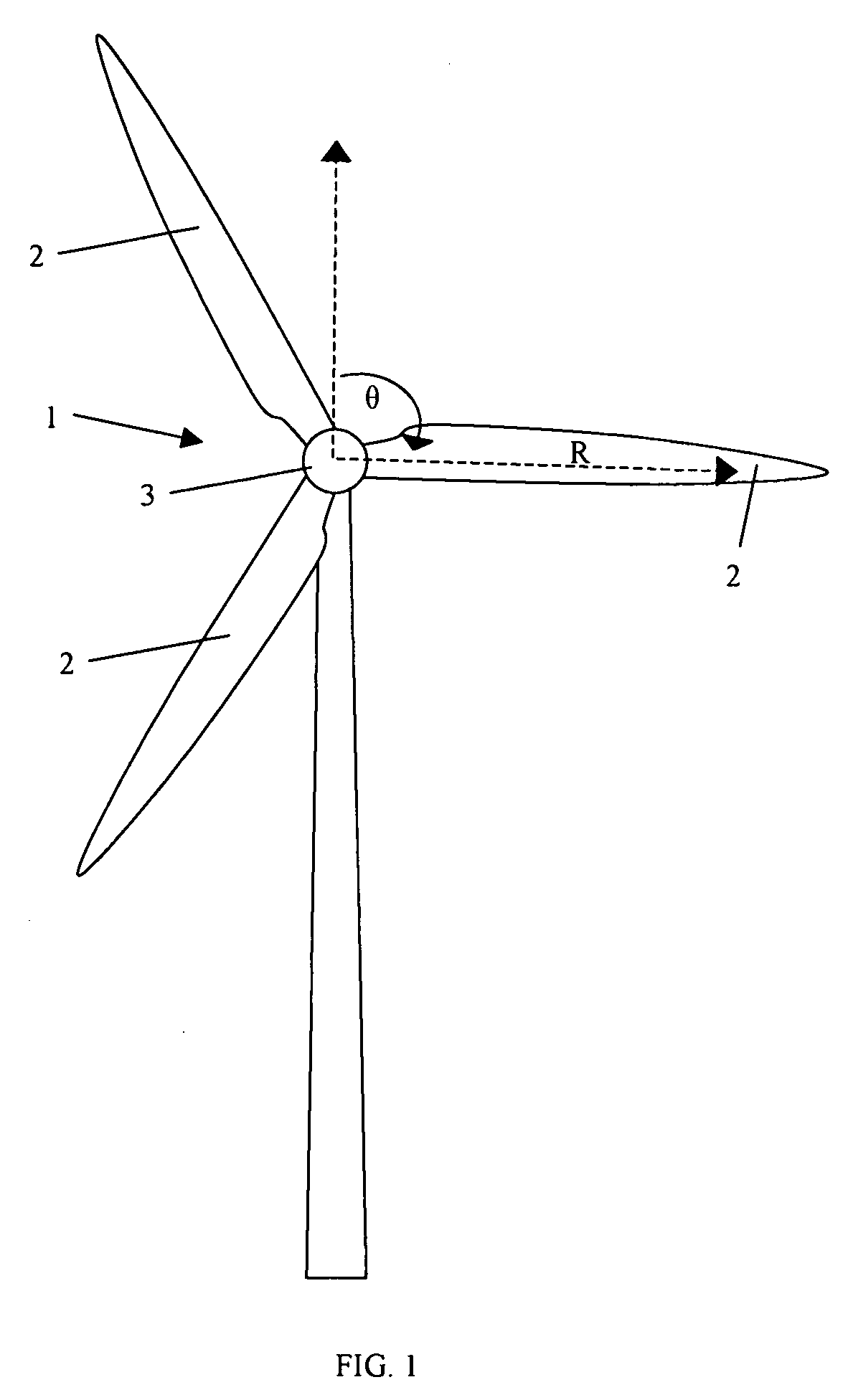
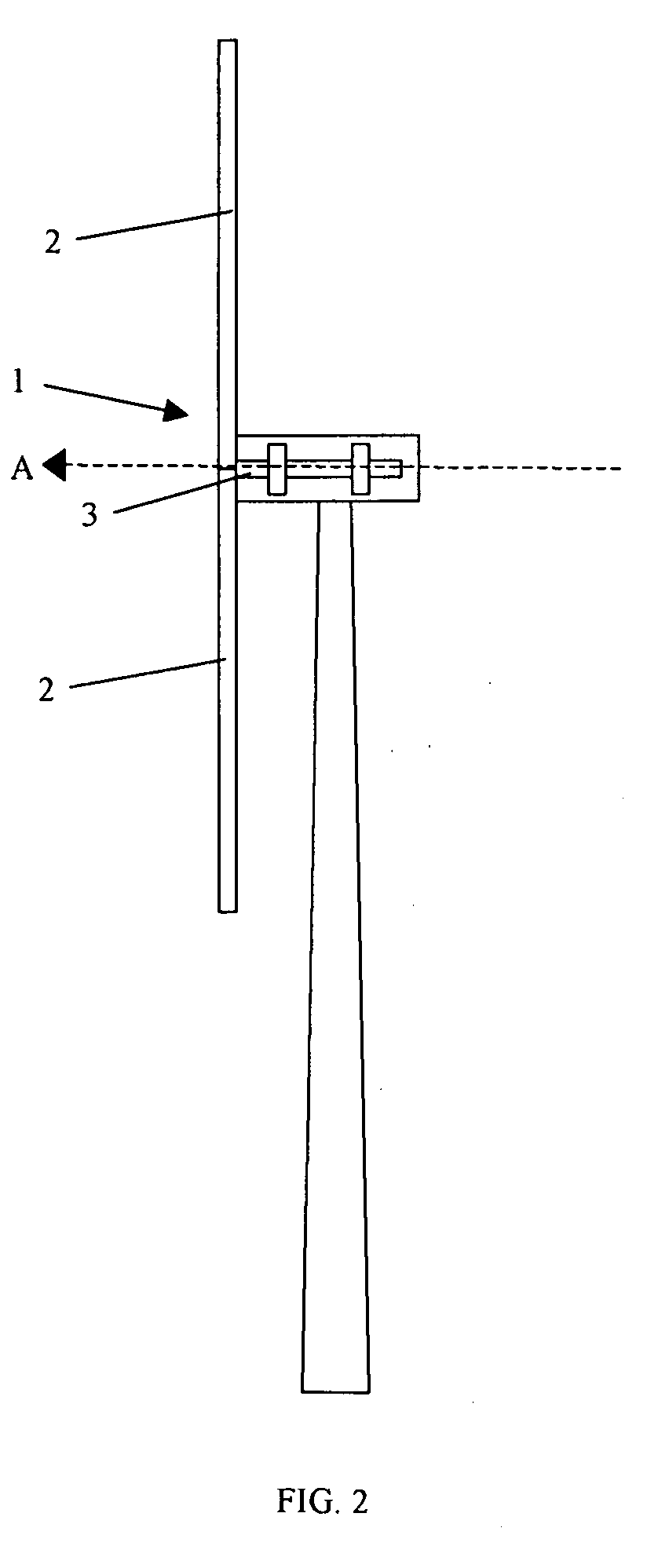
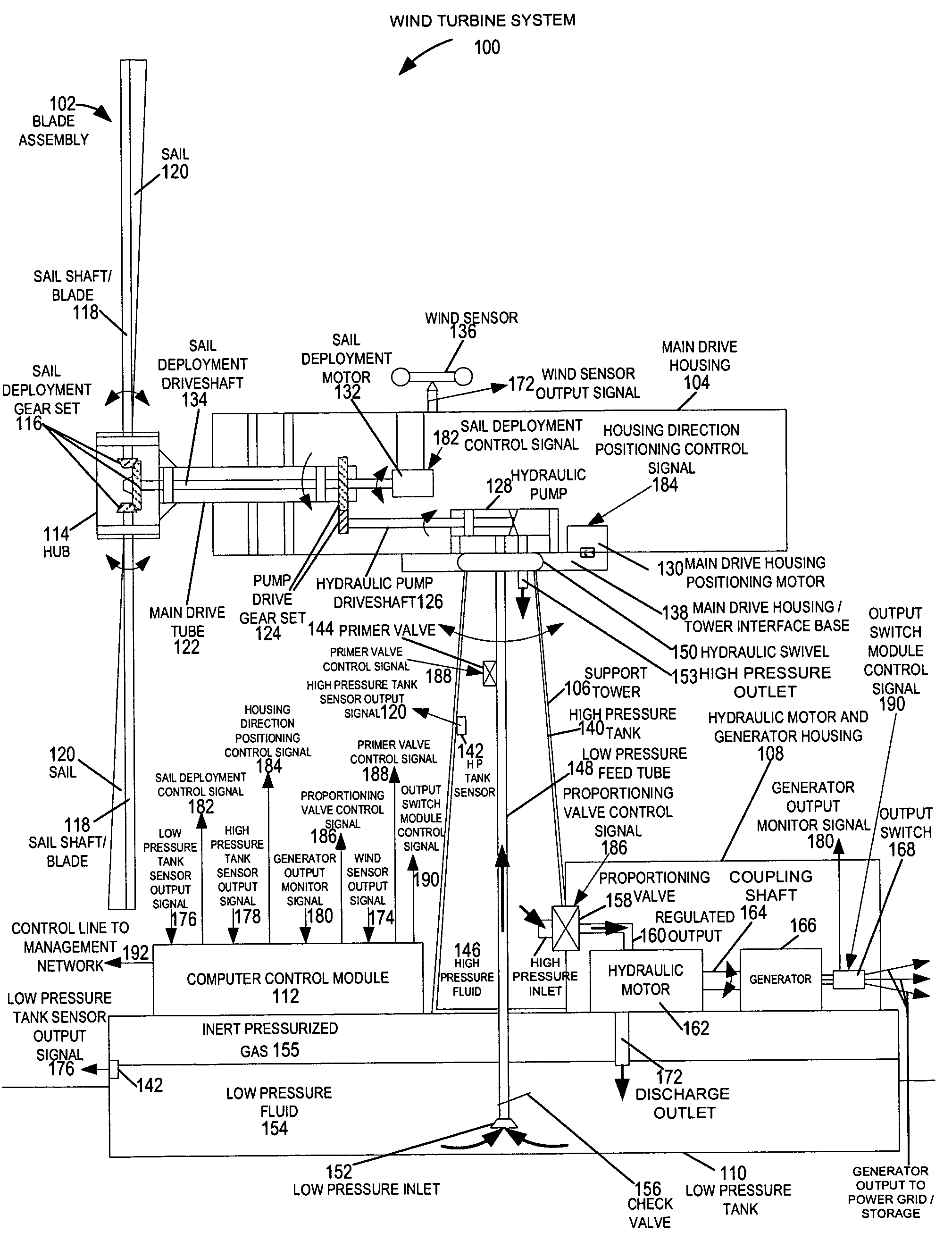
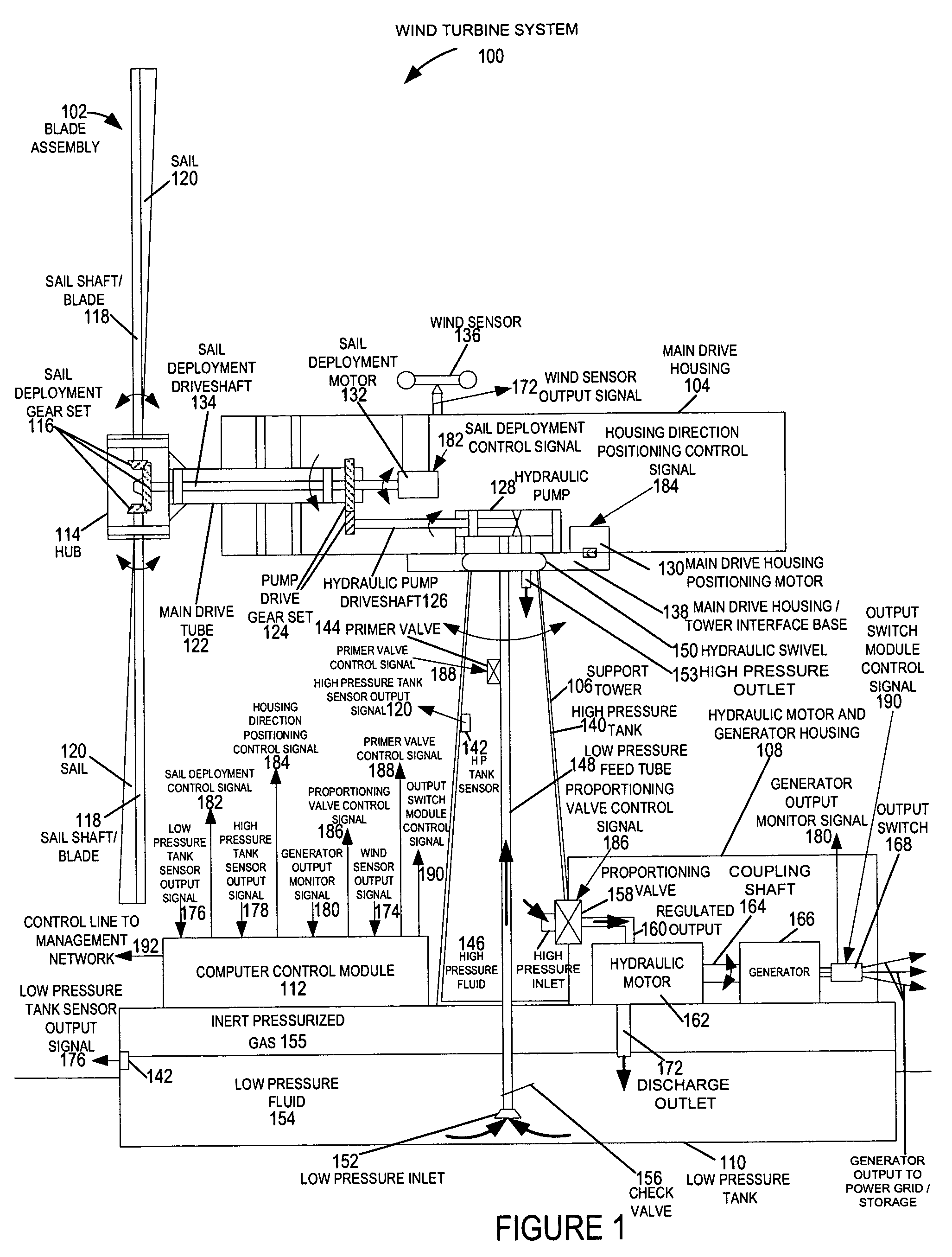
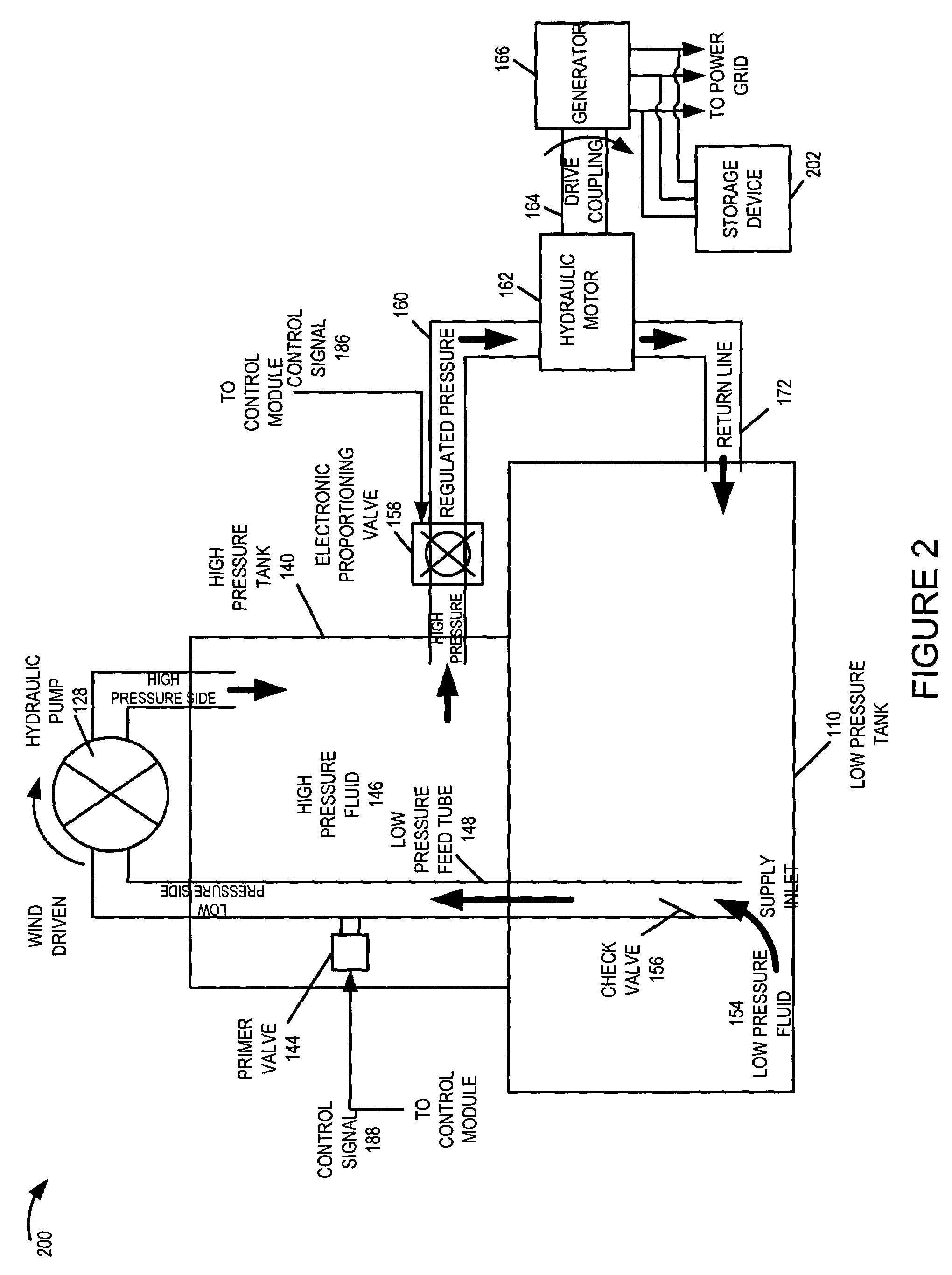
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Method and system for wind turbine inspection
A method and system for inspecting a wind turbine is provided. The method includes providing at least one remotely operated aerial platform (ROAP), providing at least one non-destructive evaluation (NDE) device attached to the ROAP, and providing at least one distance measuring system attached to the ROAP. The distance measuring system is used for determining the distance between the ROAP and at least a portion of the wind turbine. The method also includes positioning the ROAP so that the at least one non-destructive evaluation device captures data used for inspecting the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
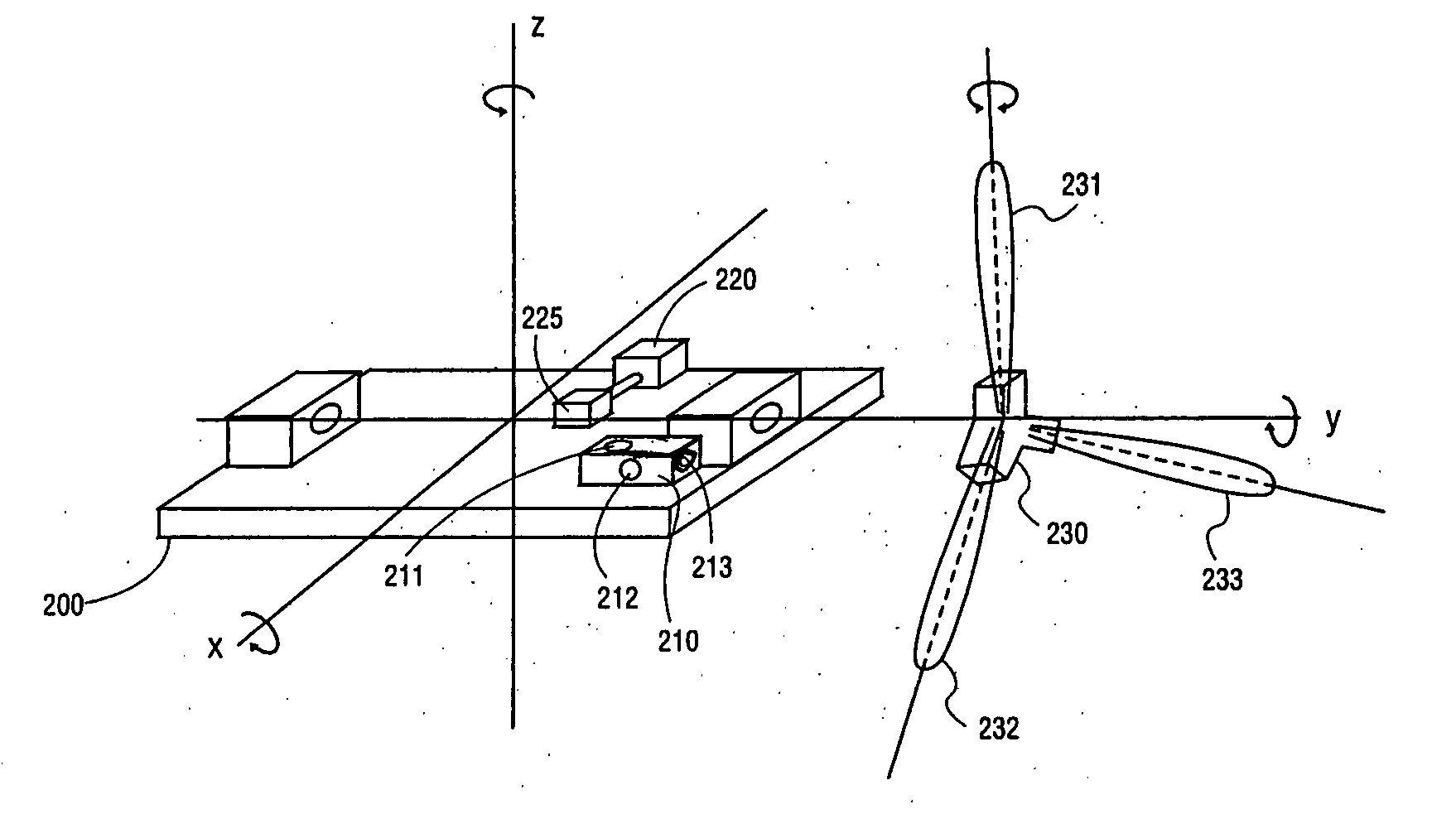
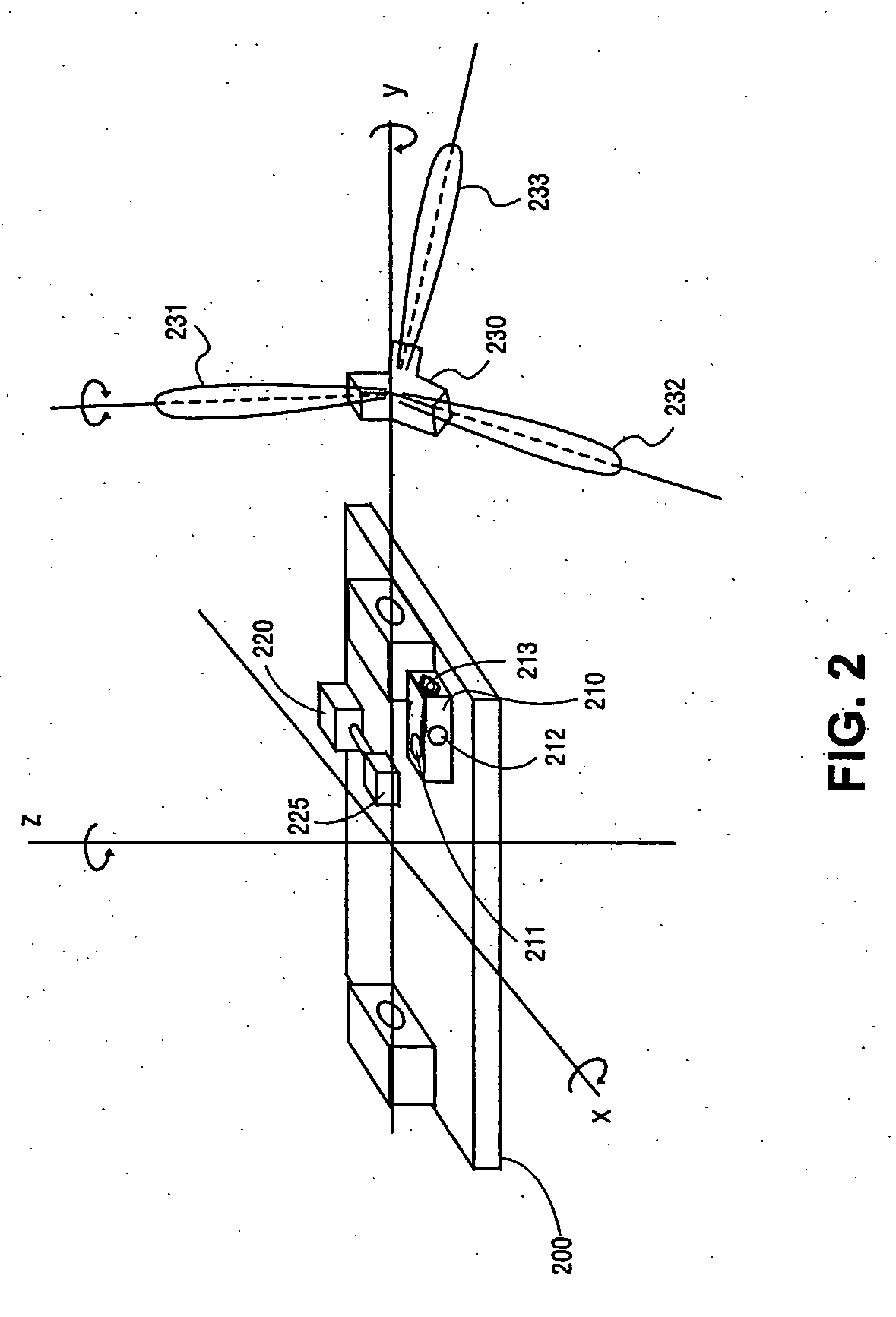
Methods and apparatuses for wind turbine fatigue load measurement and assessment
Techniques and apparatuses for wind turbine component fatigue load measurement and assessment are disclosed. In one embodiment the component is a tower, fore-aft and side-to-side signals from a two-axis accelerometer attached to a bedplate of a wind turbine are used to measure tower fatigue loads. A yaw axis azimuth position signal can also be used for tower fatigue load measurement and assessment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for operating a wind turbine
A method for operating a wind turbine having at least one blade includes determining an ambient air operating envelope and controlling a power output of the wind turbine at least partially based on the determined ambient air operating envelope. Determining an ambient air operating envelope includes measuring at least one of an ambient air temperature, an ambient air pressure, an ambient air humidity, and wind turbine power output. The method also includes comparing at least one of a measured ambient air temperature, a measured ambient air humidity and a measured ambient air pressure to predetermined ambient air temperature, pressure and humidity values. The method further includes referencing the predetermined ambient air temperature, pressure and humidity values to at least one operational parameter of the wind turbine. The method also includes determining if an existing wind turbine power output is within a range associated with the determined ambient air operating envelope.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
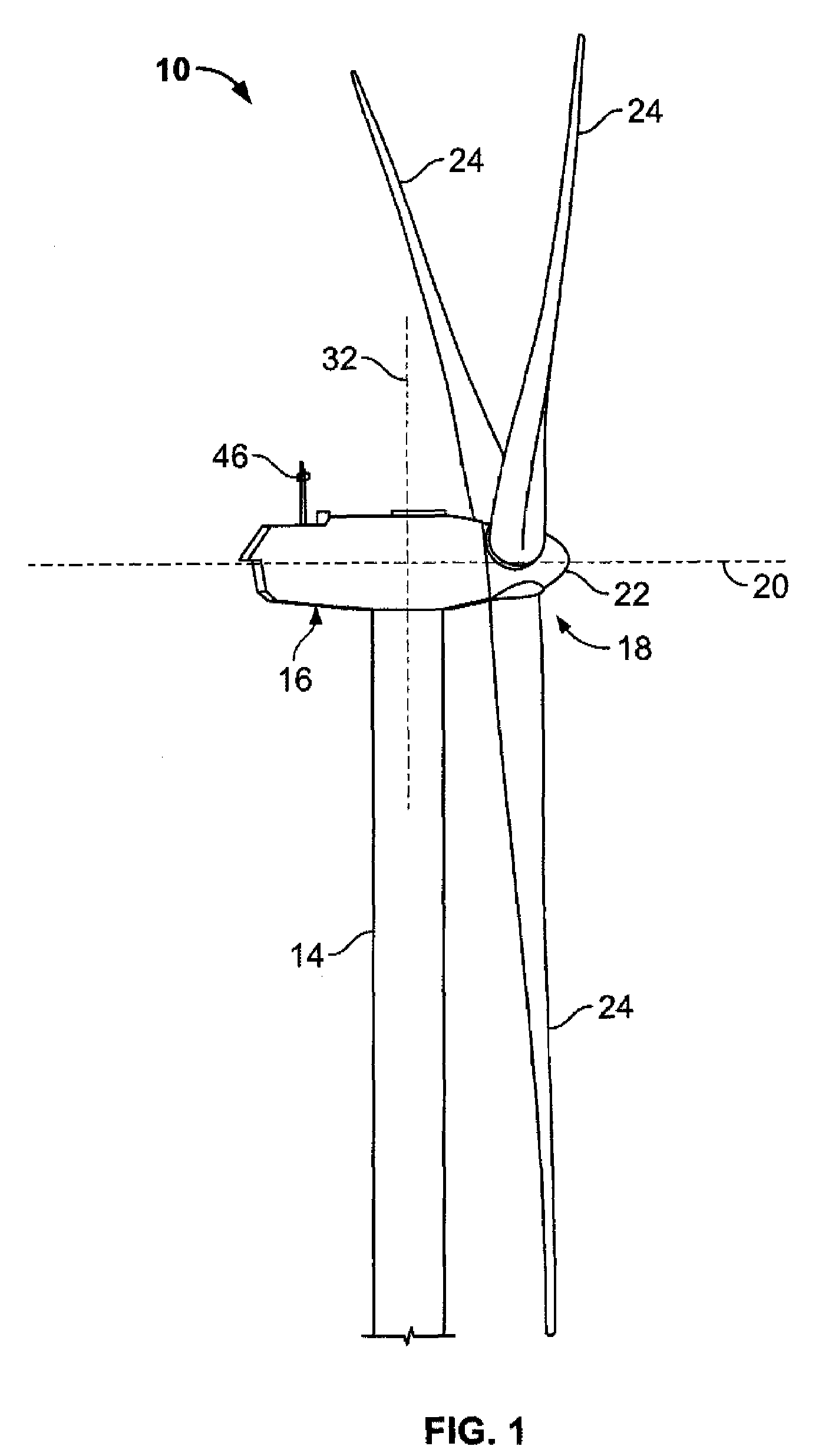
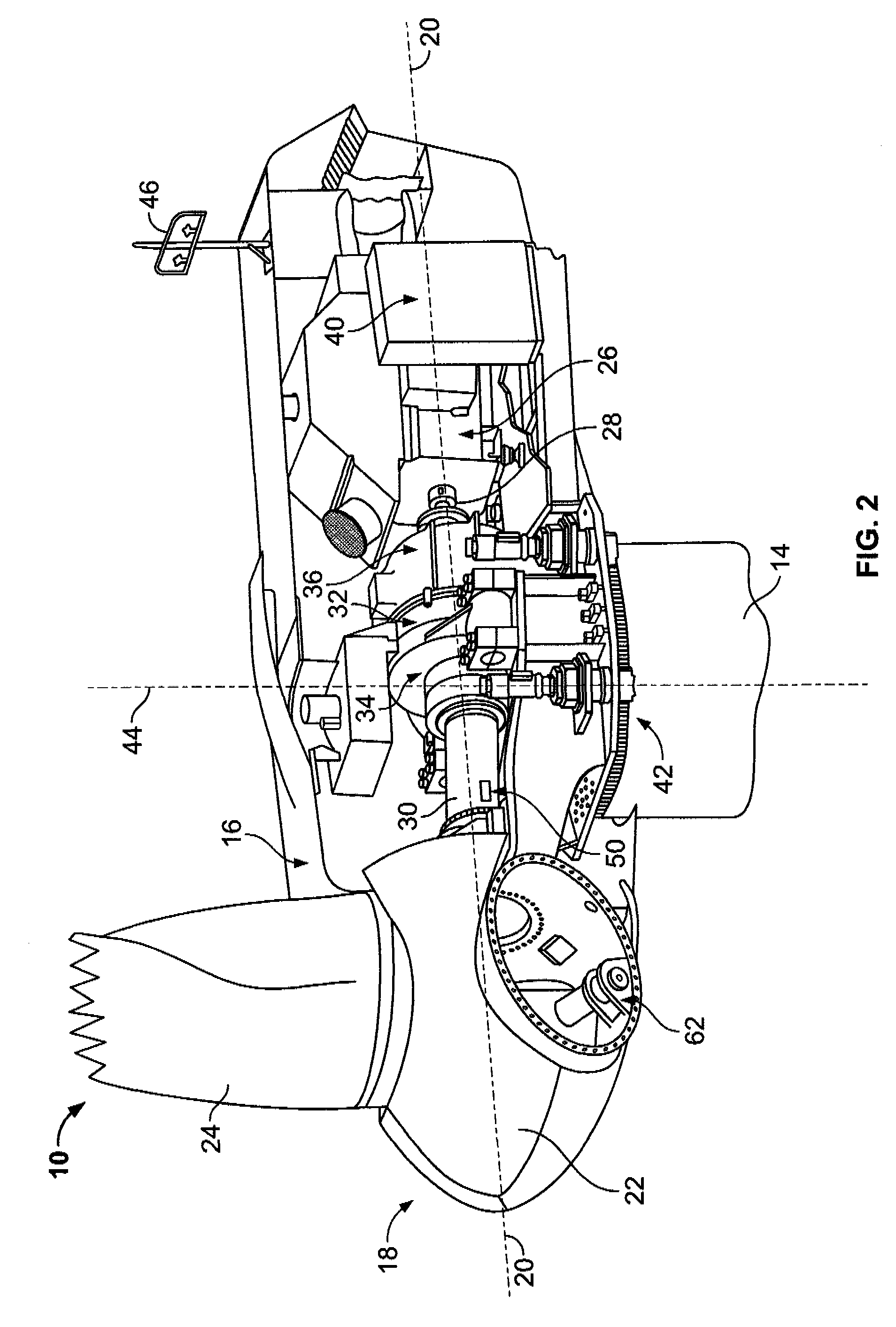
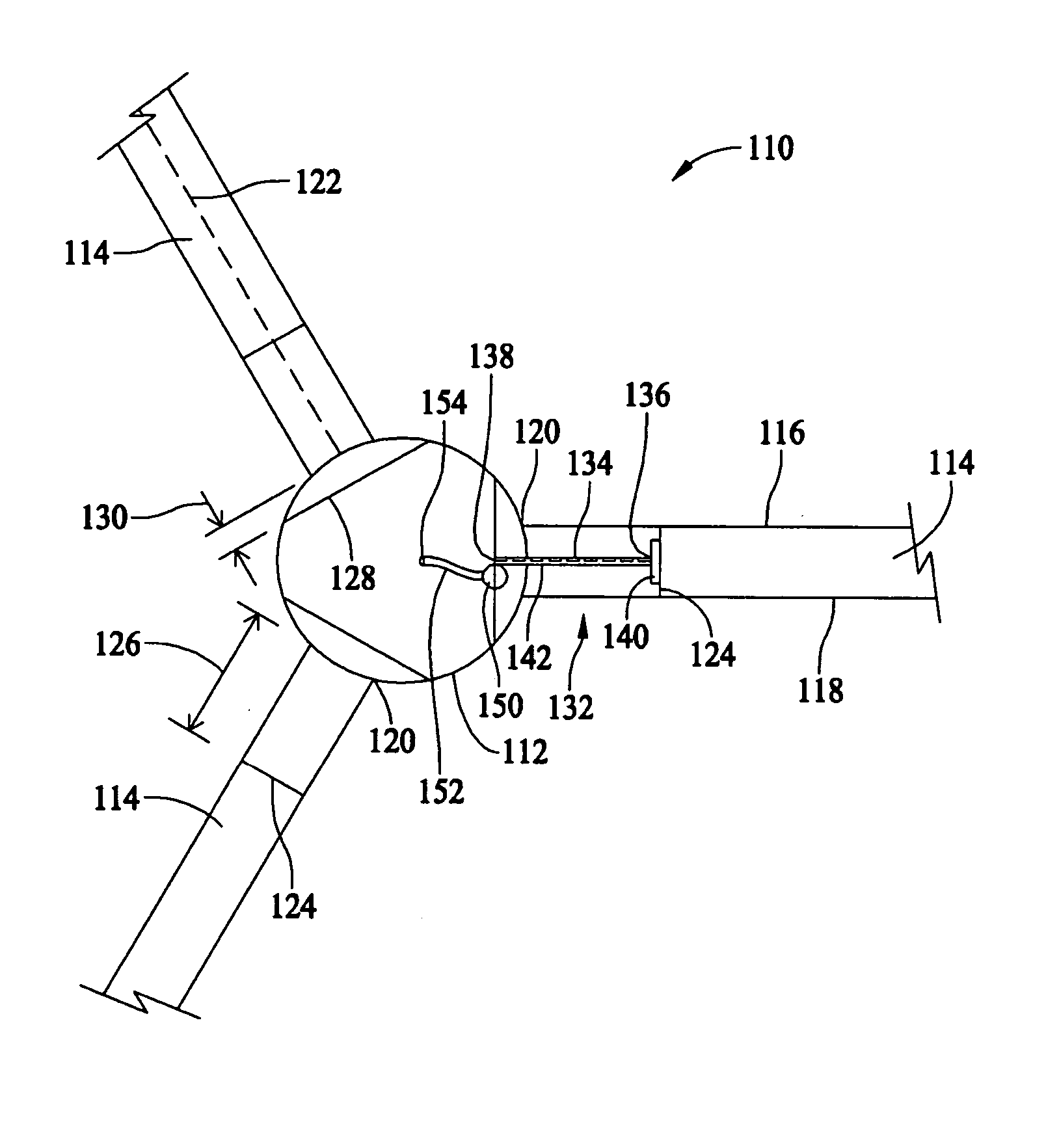
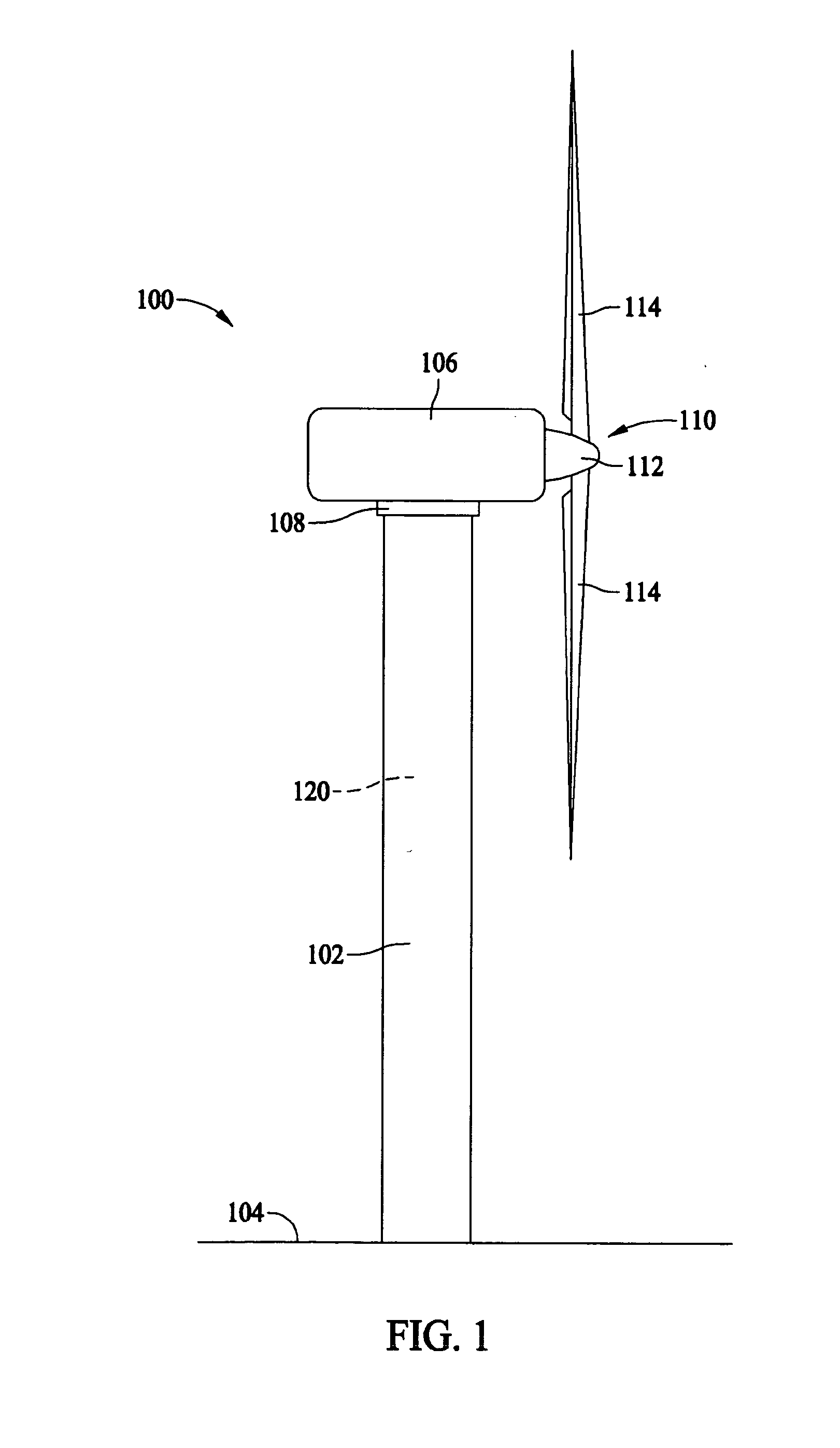
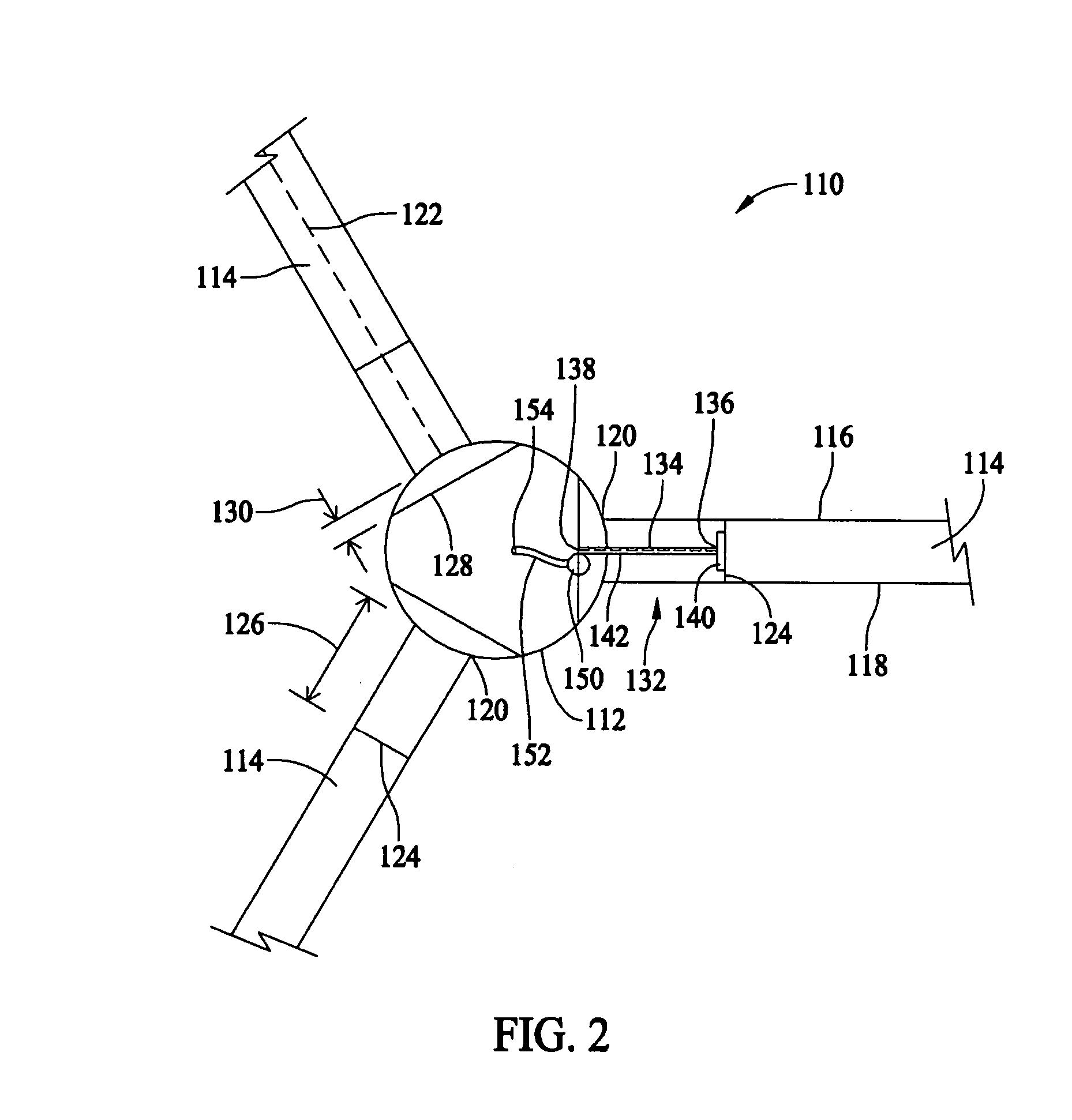
Methods and apparatus for measuring wind turbine blade deflection
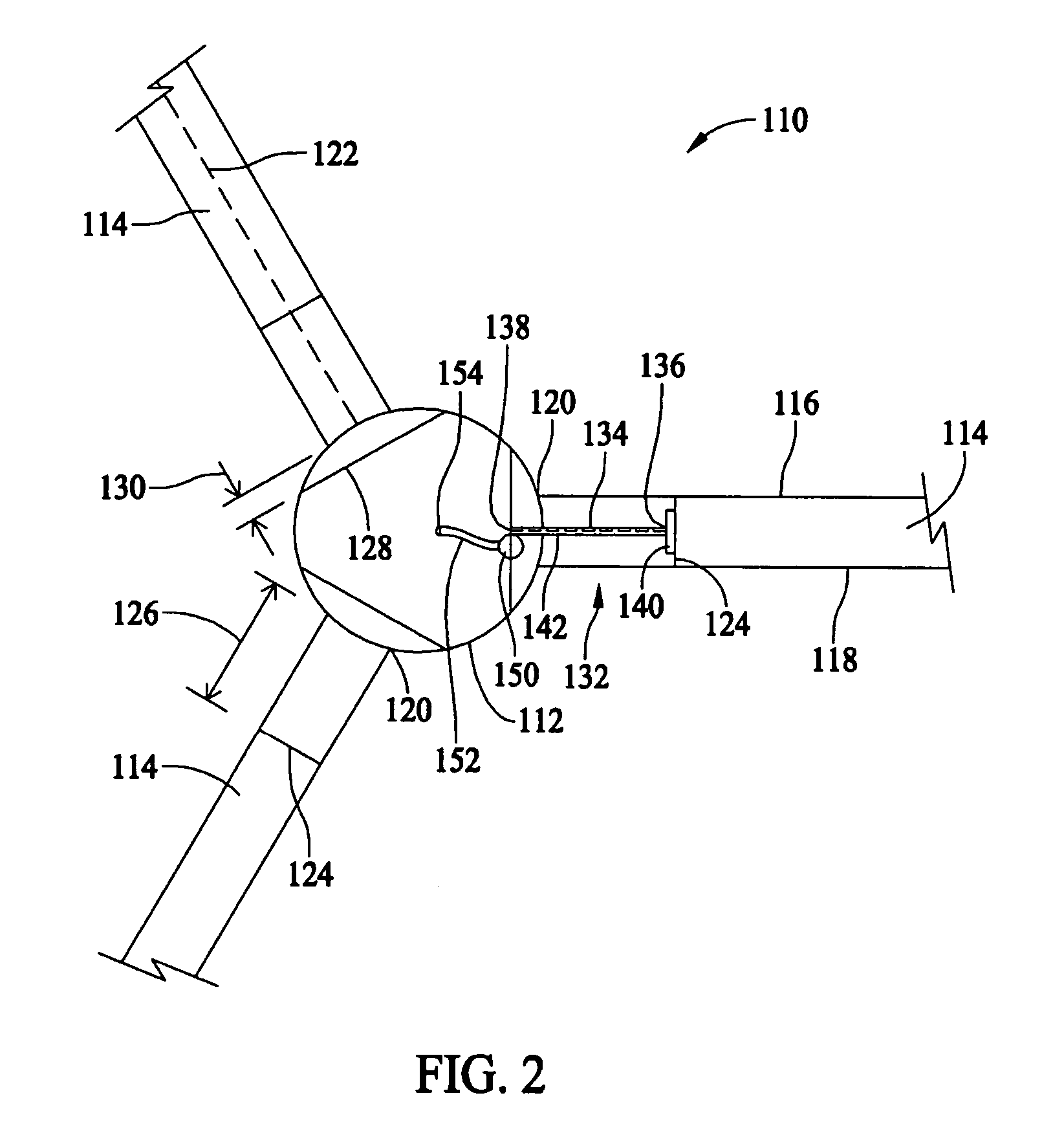
A method for determining rotor blade deflection, wherein a rotor blade is coupled to a hub, includes coupling a first end of a beam to the rotor blade, positioning a second end of the beam adjacent the hub, measuring the deflection of the beam using at least one sensor, and determining the deflection of the blade based on the deflection of the beam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Forecasting output power of wind turbine in wind farm
A method and apparatus for forecasting output power of wind turbine in a wind farm. The present invention provides a method for forecasting output power of a wind turbine in a wind farm, including: generating a corrected data set based on environmental data collected from at least one sensor in the wind farm; correcting a weather forecasting model by using the corrected data set; obtaining a forecast value of wind information at the wind turbine based on the corrected weather forecasting model; and forecasting the output power of the wind turbine based on the forecast value and a power forecasting model.
Owner:UTOPUS INSIGHTS INC
Wind turbine monitoring
InactiveUS20090246019A1Efficiency of wind turbineMeasure directlyPropellersTesting/calibration apparatusTurbine bladeEngineering
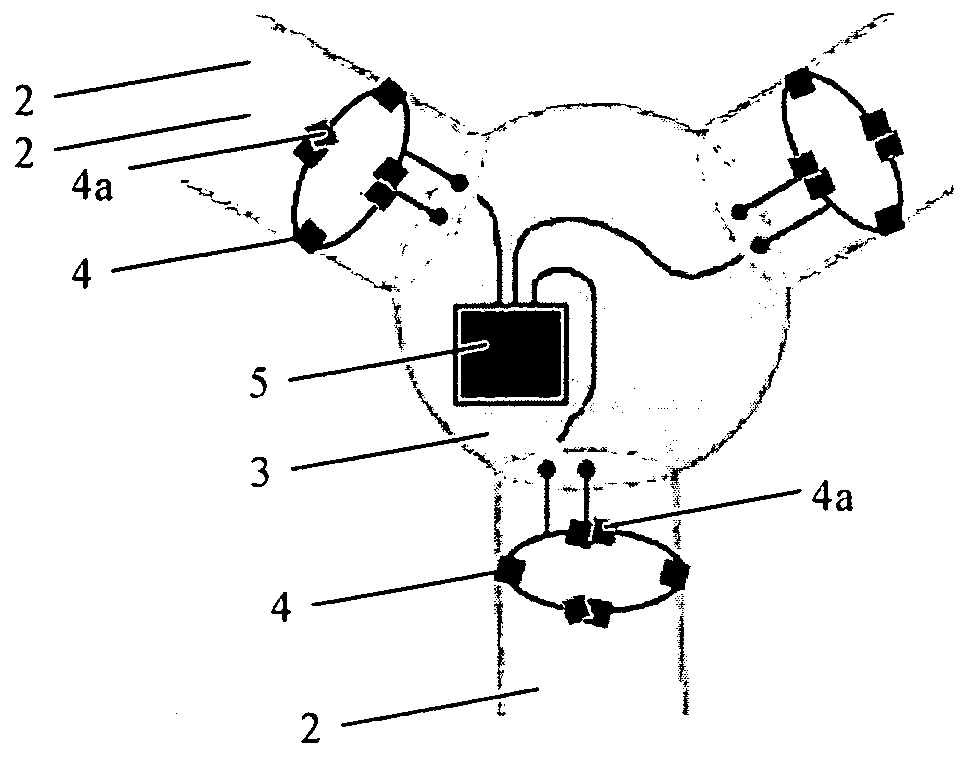
A method of detecting the formation of ice on the blades of a wind turbine 1. The wind turbine has at least one turbine blade 2 mounted to a rotor and provided with at least a first strain sensor 4 for measuring mechanical strain of the turbine blade. The method comprises detecting changes in an output signal of the strain sensor 4 due to changes in the mass of the turbine blade 2 caused by the formation of ice on the turbine blade.
Owner:INSENSYS
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS7183664B2Eliminate needReduce pressureWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Condition monitoring of windturbines
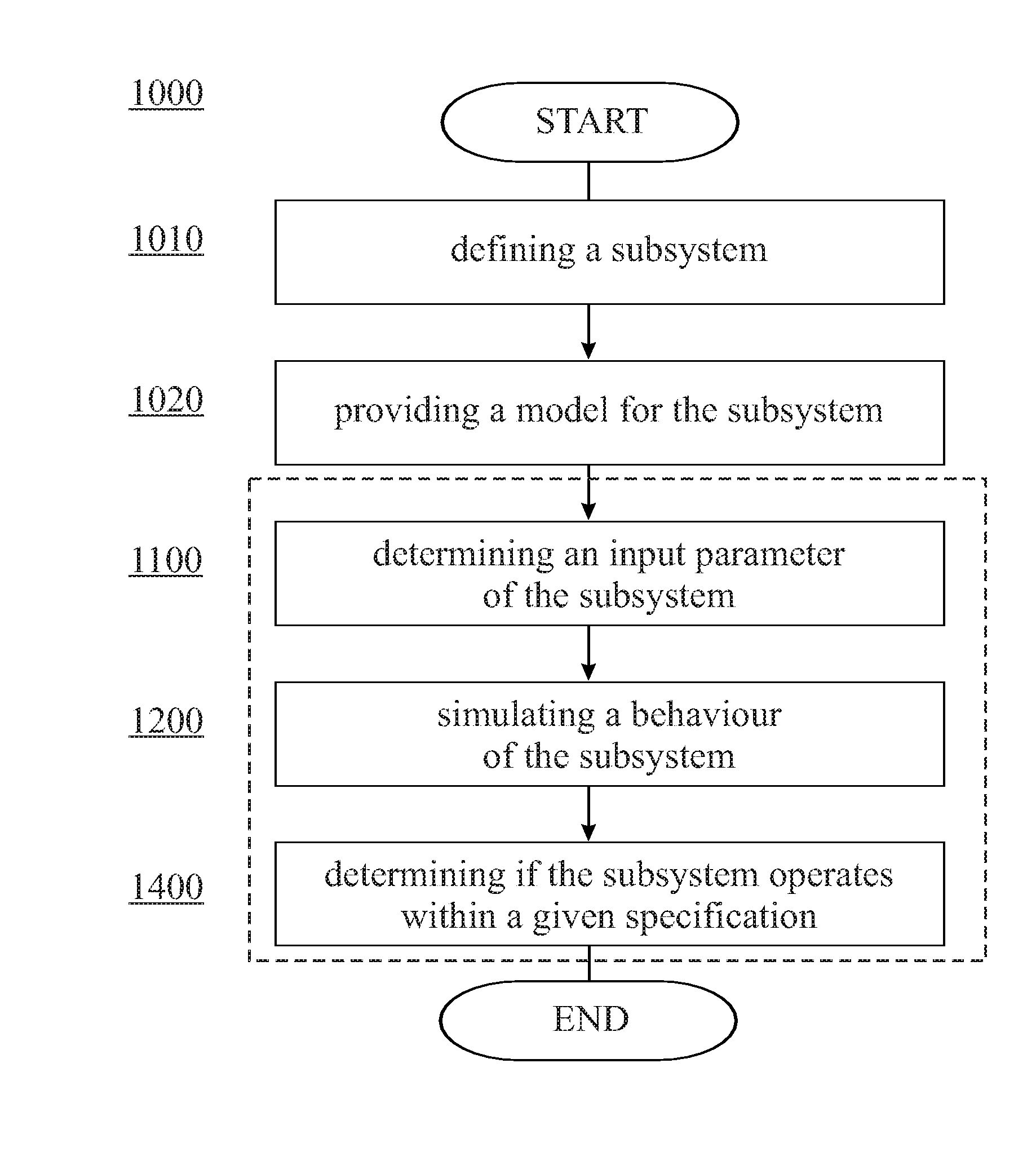
A method for monitoring a wind turbine is provided. The method includes defining at least one subsystem of the wind turbine and providing a simulation model for the at least one subsystem. During normal operation of the wind turbine at least an input parameter of the at least one subsystem is determined A behavior of the at least one subsystem is simulated using the at least one input parameter as an input of the simulation model. Based on the simulated behavior, it is determined, if the at least one subsystem operates within a given specification.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
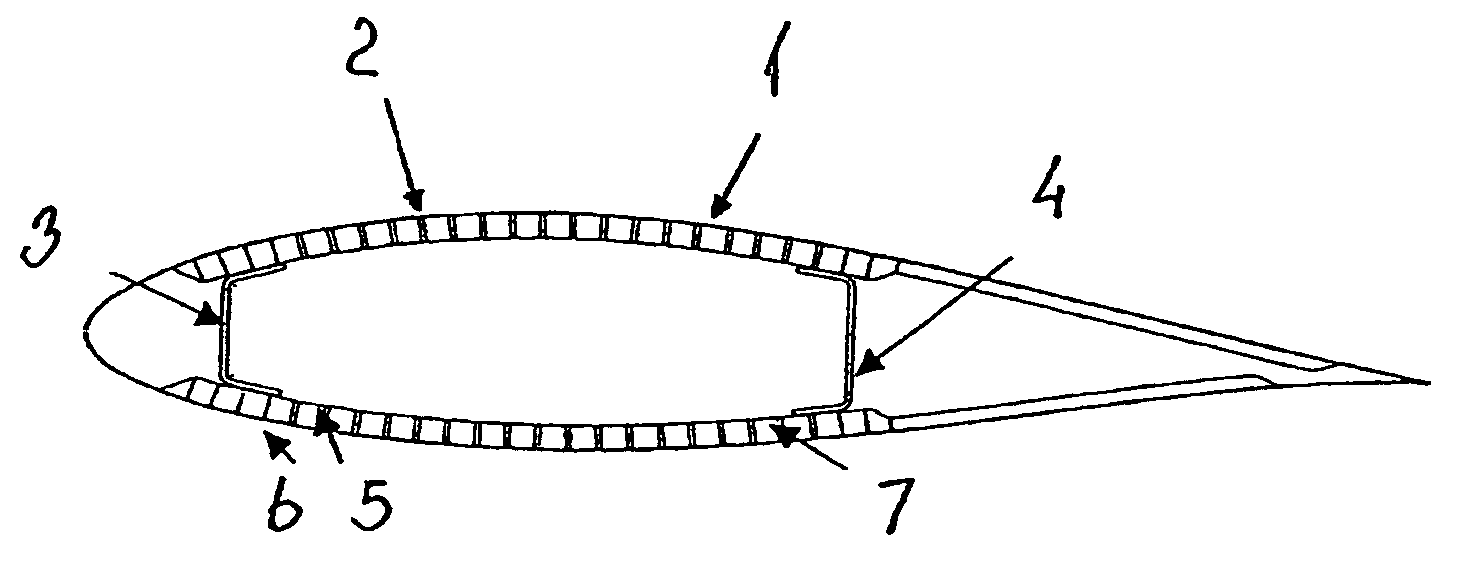
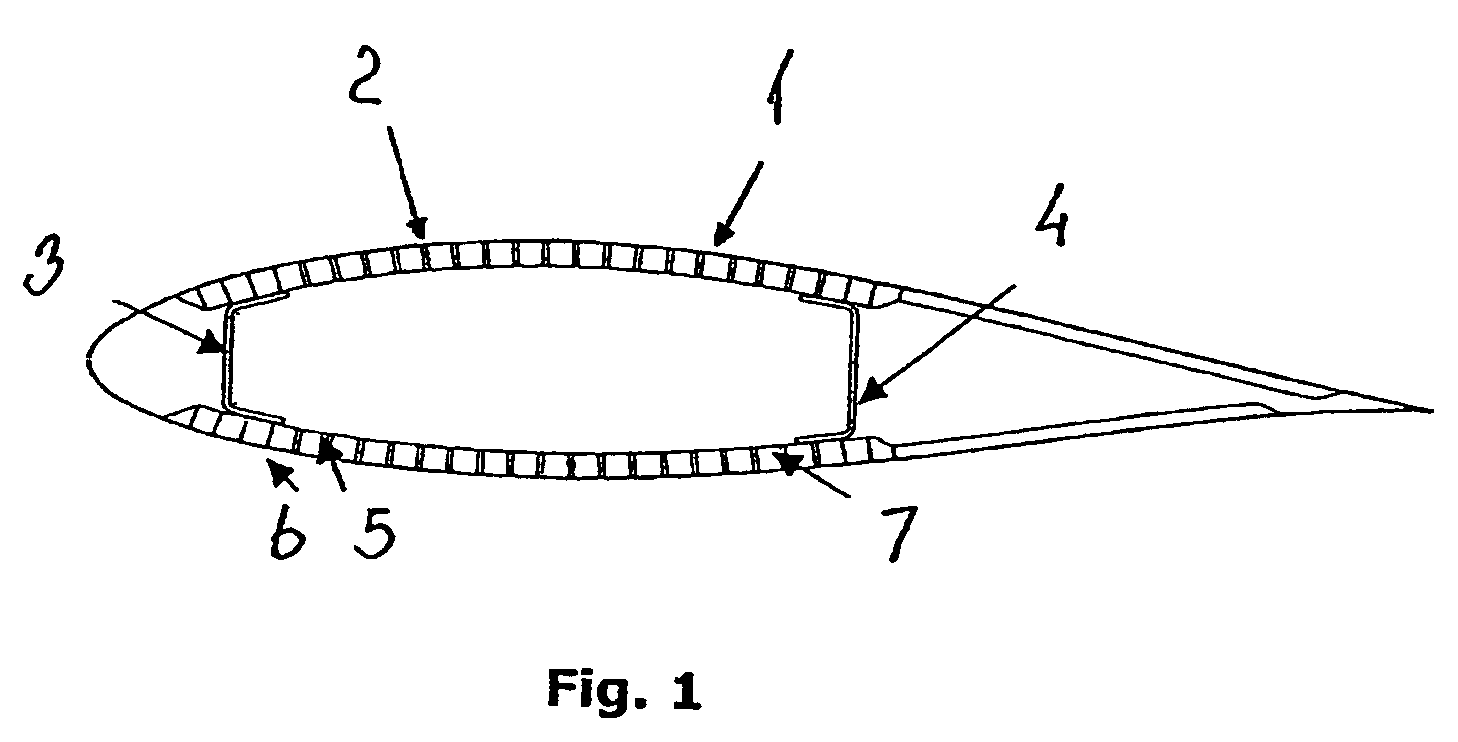
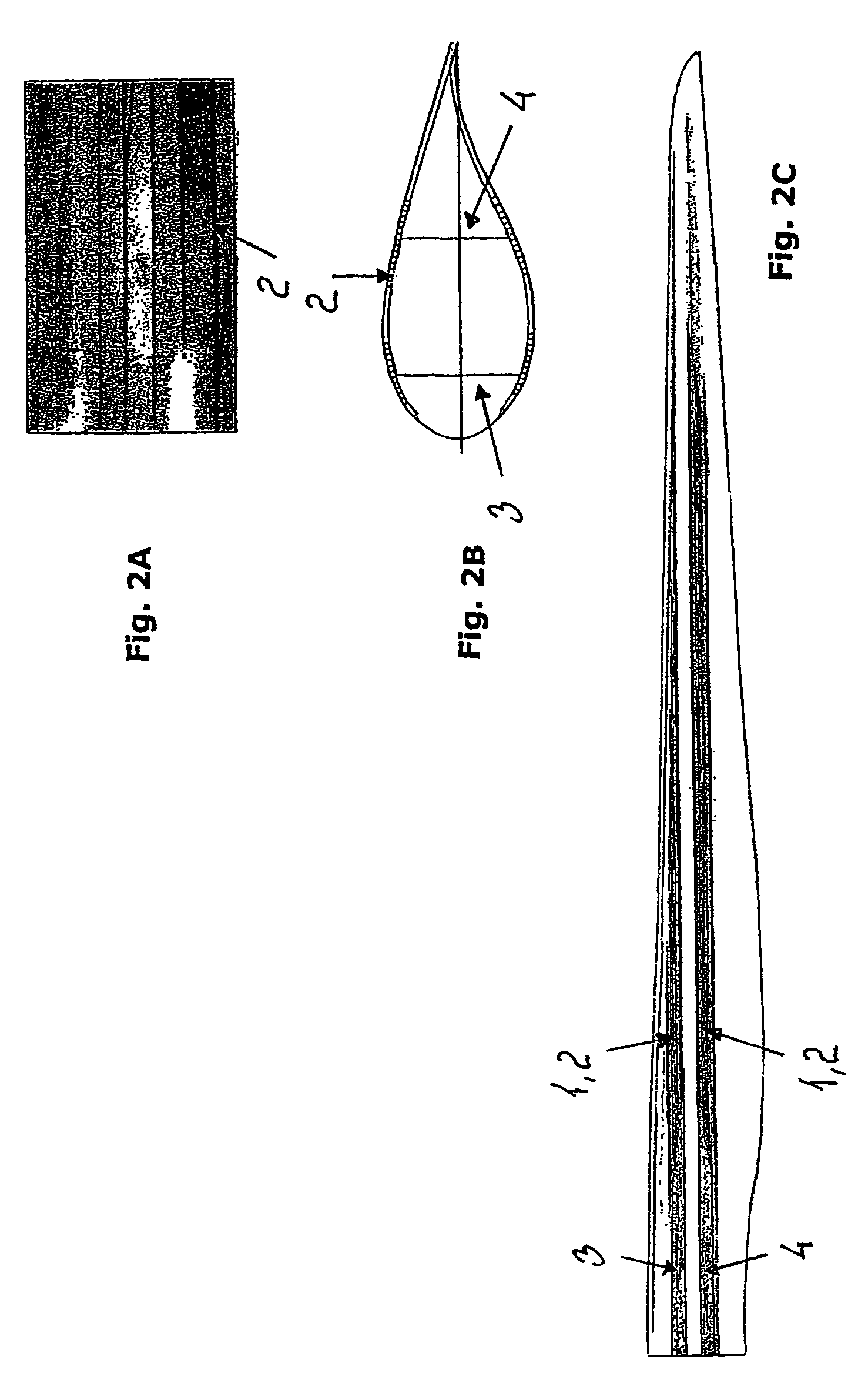
Wind turbine blade
InactiveUS7198471B2Save materialSave weightFinal product manufactureBlade accessoriesCarbon fibersTurbine blade
The invention relates to a wind turbine blade comprising a number of pre-fabricated strips arranged in a sequence along the outer periphery. The strips consist of a fibrous composite material, preferably carbon fibres, and consist of a wooden material, preferably plywood or wooden fibres held in a cured resin. The advantage is that it is possible to manufacture blades for wind turbines which are very stiff and generally have a high strength, but which nevertheless are easy to manufacture and also is much cheaper to manufacture compared to conventional manufacturing techniques. The invention also relates to methods for manufacturing prefabricated strips and for manufacturing wind turbine blades.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method and apparatus to determine the wind speed and direction experienced by a wind turbine
ActiveUS20070086893A1Low costSimple and robust and low cost apparatusPropellersWind motor controlNacelleEngineering
An apparatus and a method used to determine the speed and direction of the wind experienced by a wind turbine are provided. The apparatus comprises at least one sensor fixed to the rotor of the wind turbine, an angular sensor to measure the angular position of the rotor of the wind turbine, and a circuit which converts the relationship between the output of the at least one sensor and the output of the angular sensor into the speed and direction of the wind experienced by the wind turbine. According to the invention, the sensing apparatus can measure the wind speed and direction in three dimensions. In addition, mounting the sensors directly to the rotor of the wind turbine results in a very simple and robust installation. Mounting the sensors directly to the rotor also eliminates the turbulence from the rotor and the nacelle of the wind turbine from affecting the sensors.
Owner:ROMO WIND AG
Column-stabilized offshore platform with water-entrapment plates and asymmetric mooring system for support of offshore wind turbines
ActiveUS8471396B2Improve performanceEasy to produceWind motor controlWind motor assemblyNacelleMooring system
A floating wind turbine platform includes a floatation frame that includes at least three columns that are coupled to each other with horizontal main beams. A wind turbine tower is mounted above a tower support column to simplify the system construction and improve the structural strength. The turbine blades are coupled to a nacelle that rotates on top of the tower. The turbine's gearbox generator and other electrical gear can be mounted either traditionally in the nacelle, or lower in the tower or in the top of the tower-supporting column. The floatation frame includes a water ballasting system that pumps water between the columns to keep the tower in a vertical alignment regardless of the wind speed. Water-entrapment plates are mounted to the bottoms of the columns to minimize the rotational movement of the floatation frame due to waves.
Owner:PRINCIPLE POWER
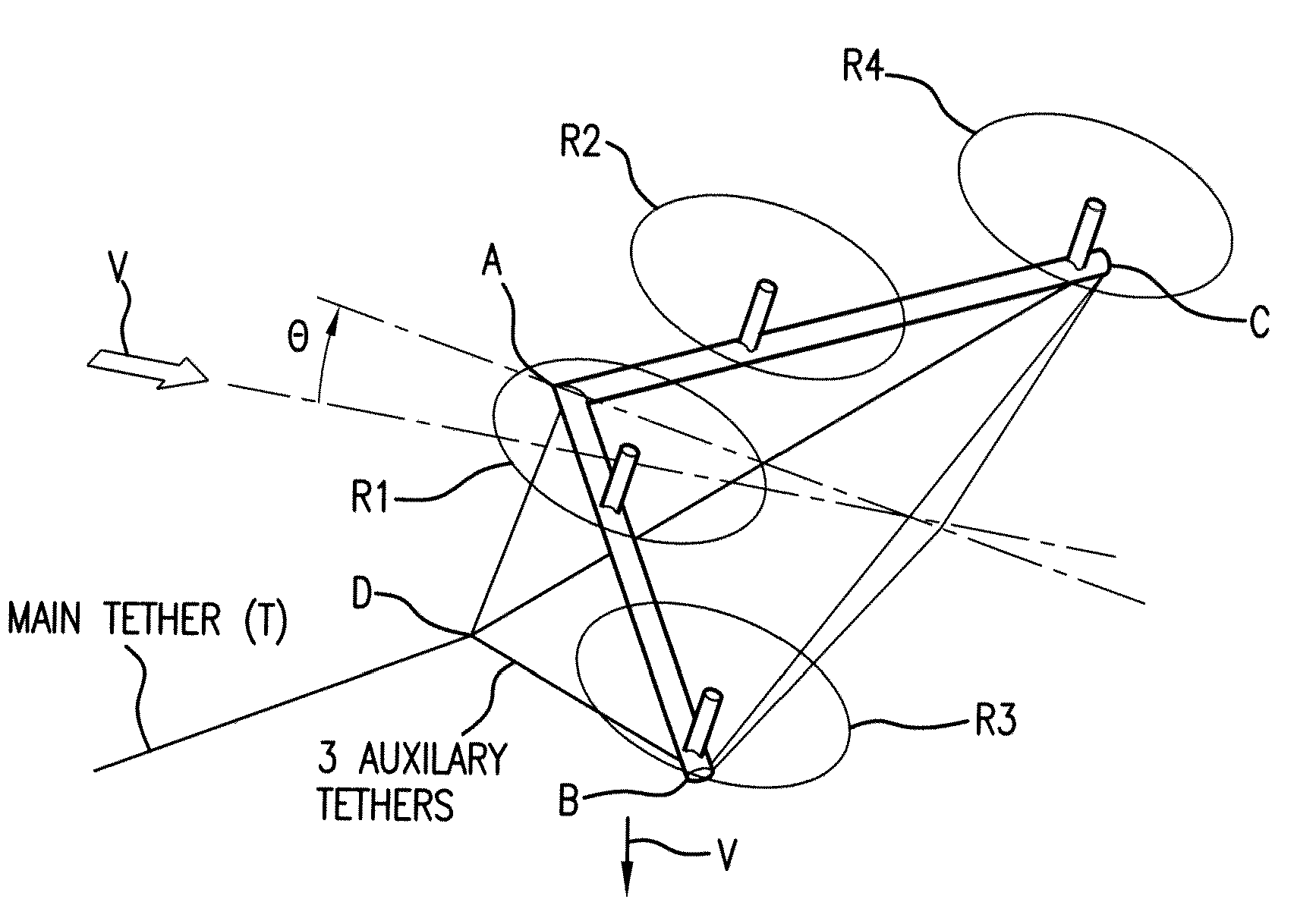
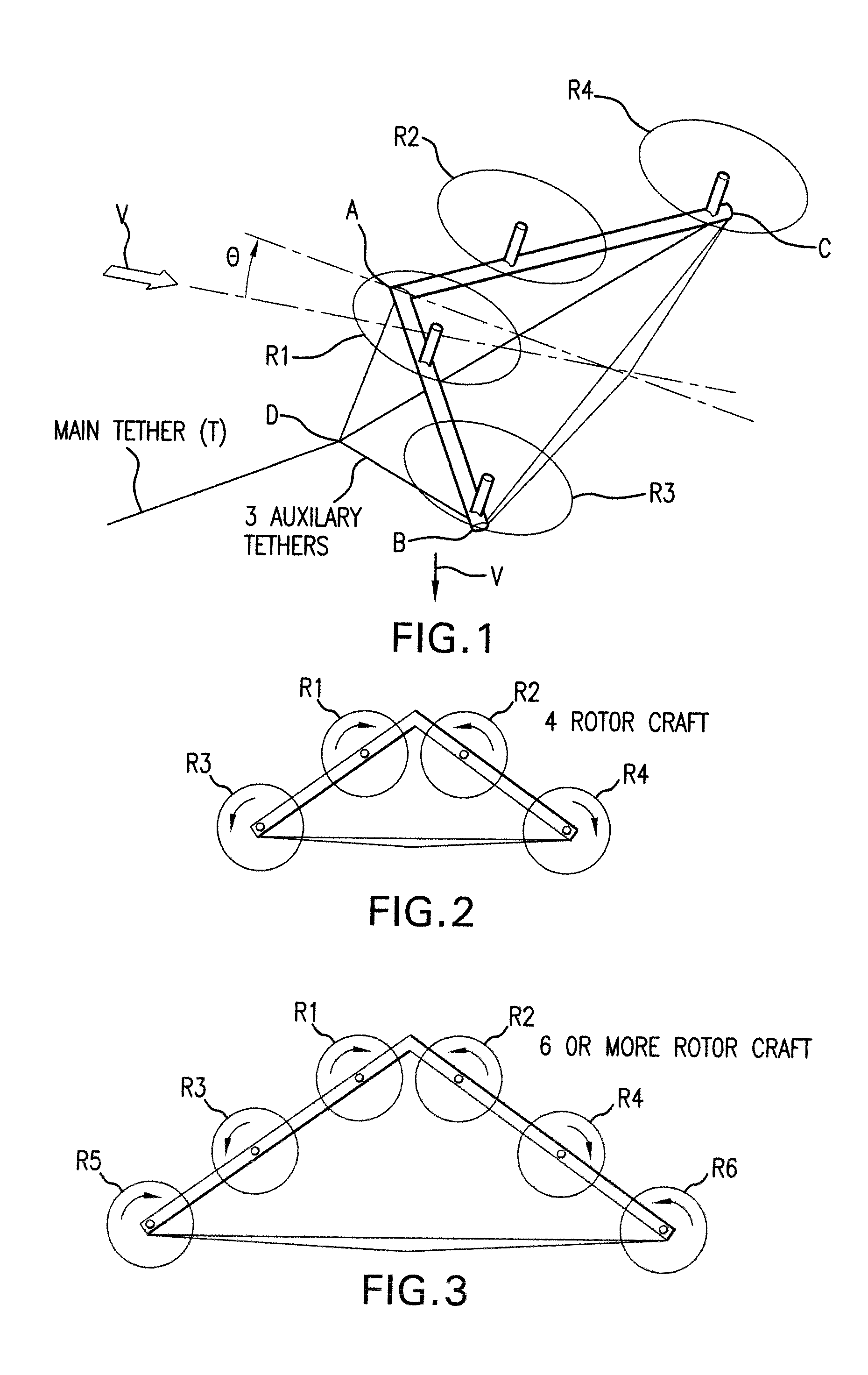
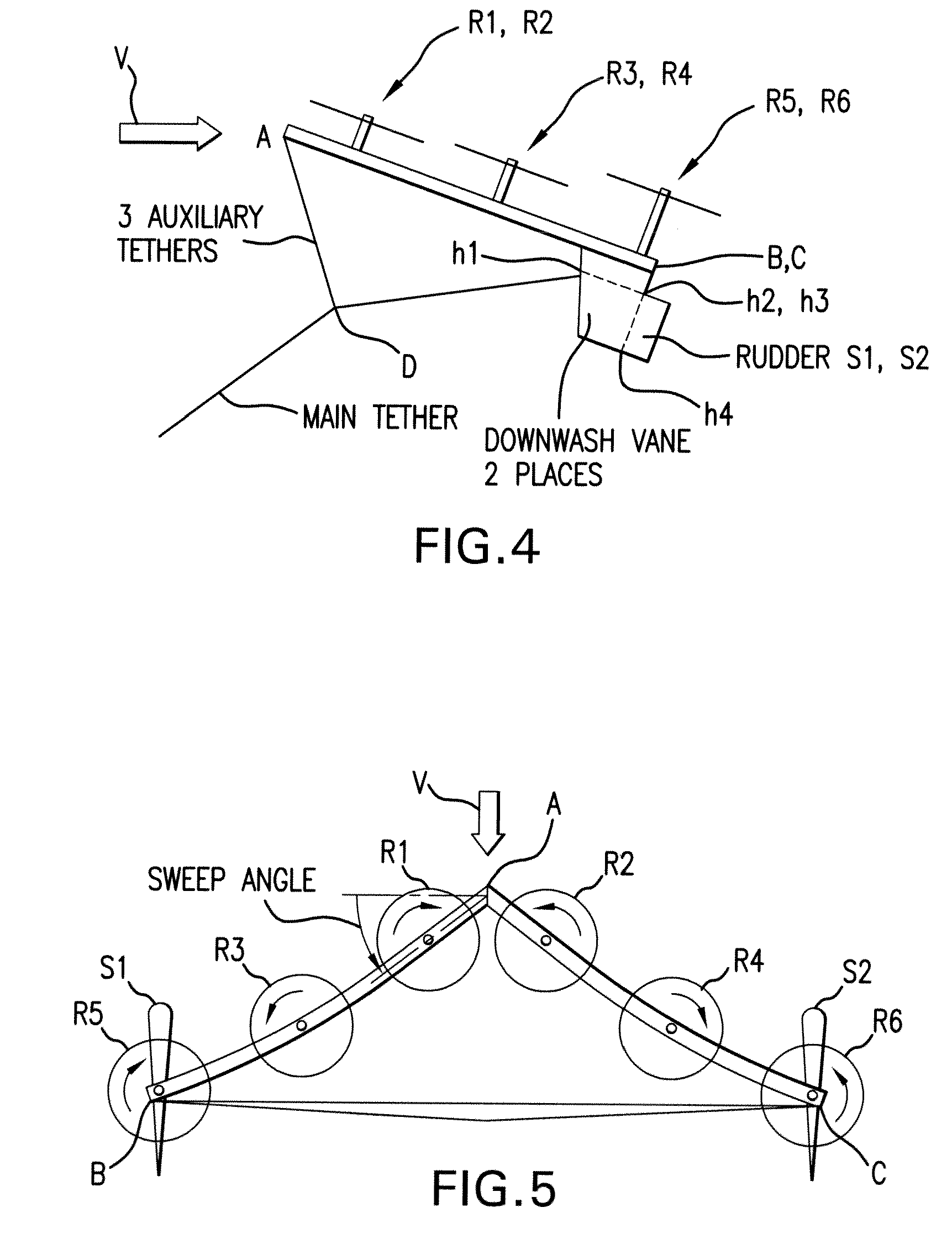
Tethered airborne wind-driven power generator
InactiveUS20110057453A1Reduce stressImprove power production efficiencyWind energy with electric storageMachines/enginesWind drivenInstability
A tethered airborne wind-driven power generation device providing, in various embodiments, a main tether and plurality of auxiliary tethers, feedback controls for continuously adjusting pitch, roll and yaw, and a Vee-shaped configuration for disposing rotors along the frame of the device. The auxiliary tethers avoid slack and resultant transient instability, and the Vee-shaped rotor disposition takes advantage of upwash or any other aerodynamic benefit from the rotors adjacent to it, to improve efficiency.
Owner:ROBERTS BRYAN WILLIAM
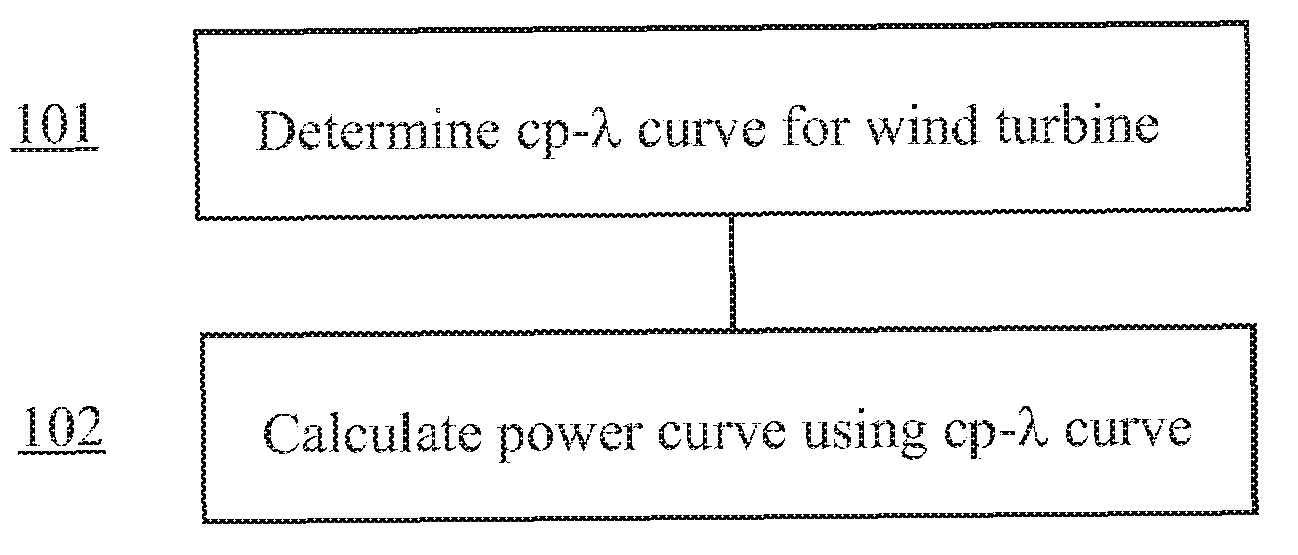
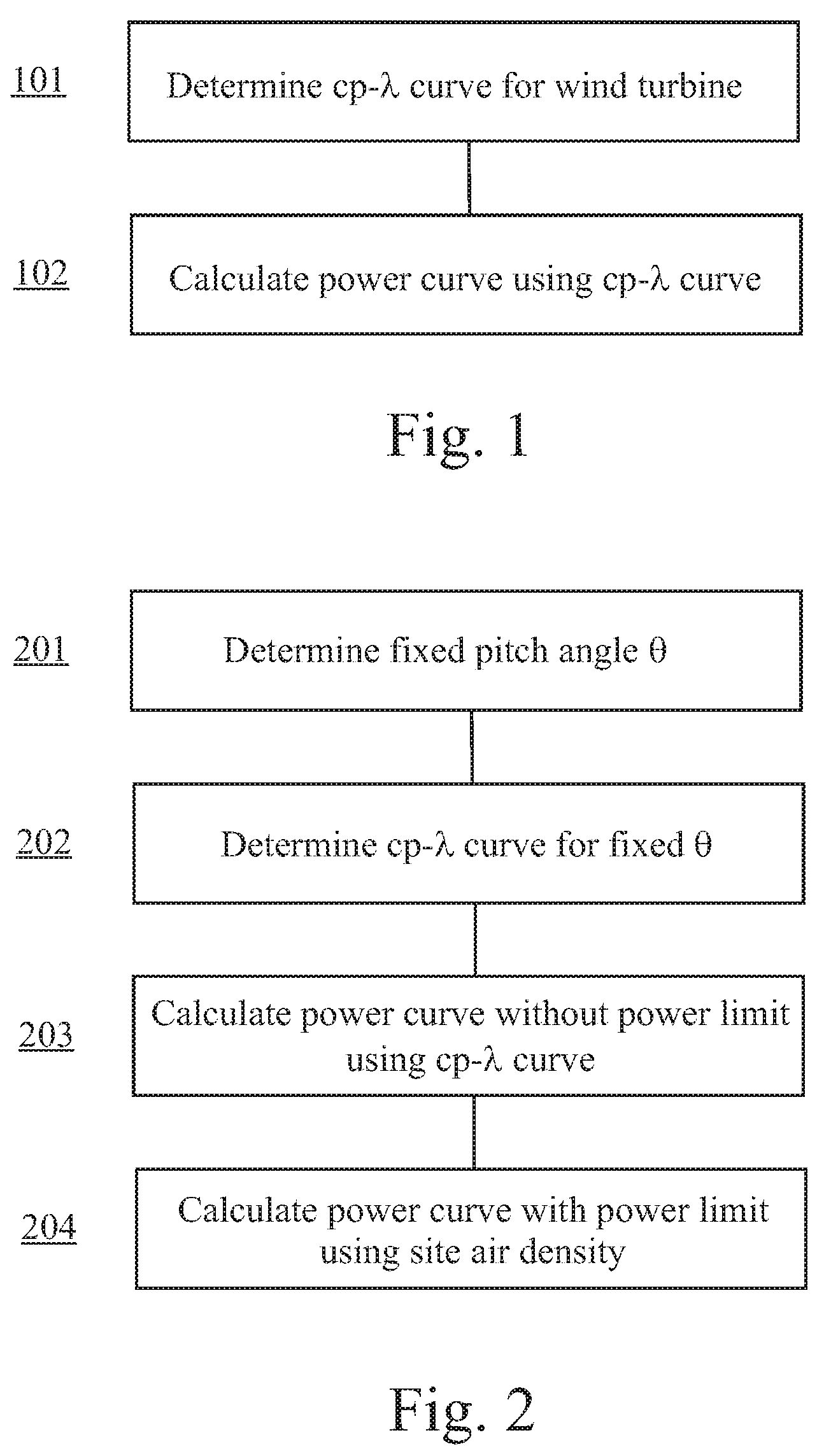
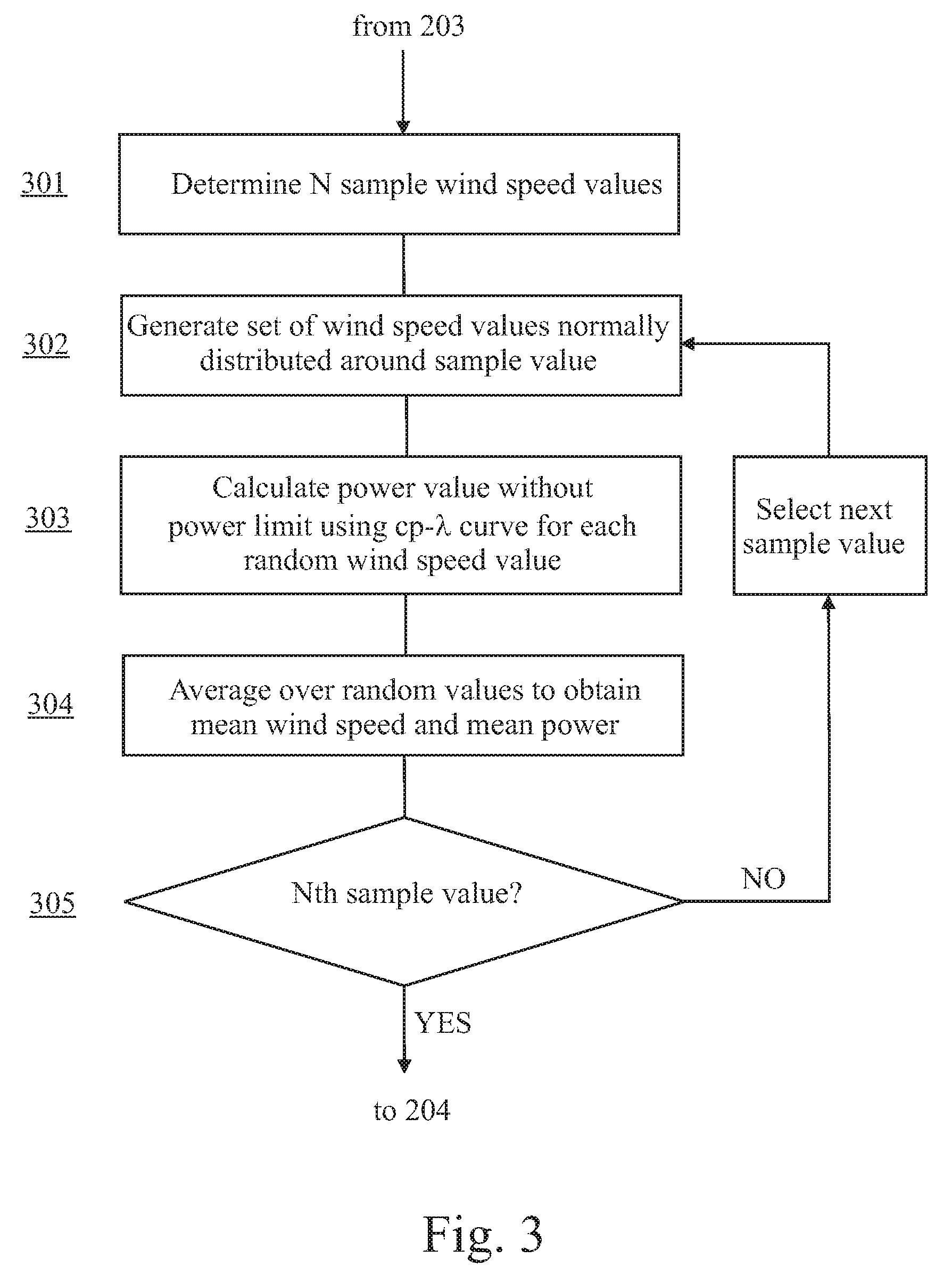
Method for predicting a power curve for a wind turbine
ActiveUS7420289B2Easy to controlQuality improvementRotational speed controlLevel controlEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A method for calculating a high-altitude power curve for a wind turbine is provided, the method including the steps of determining a cp-λ curve for a predetermined blade pitch angle of said wind turbine; calculating a first power curve without power limit based on the cp-λ curve; and calculating the high-altitude power curve with power limit from said first power curve, thereby using a site air density.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
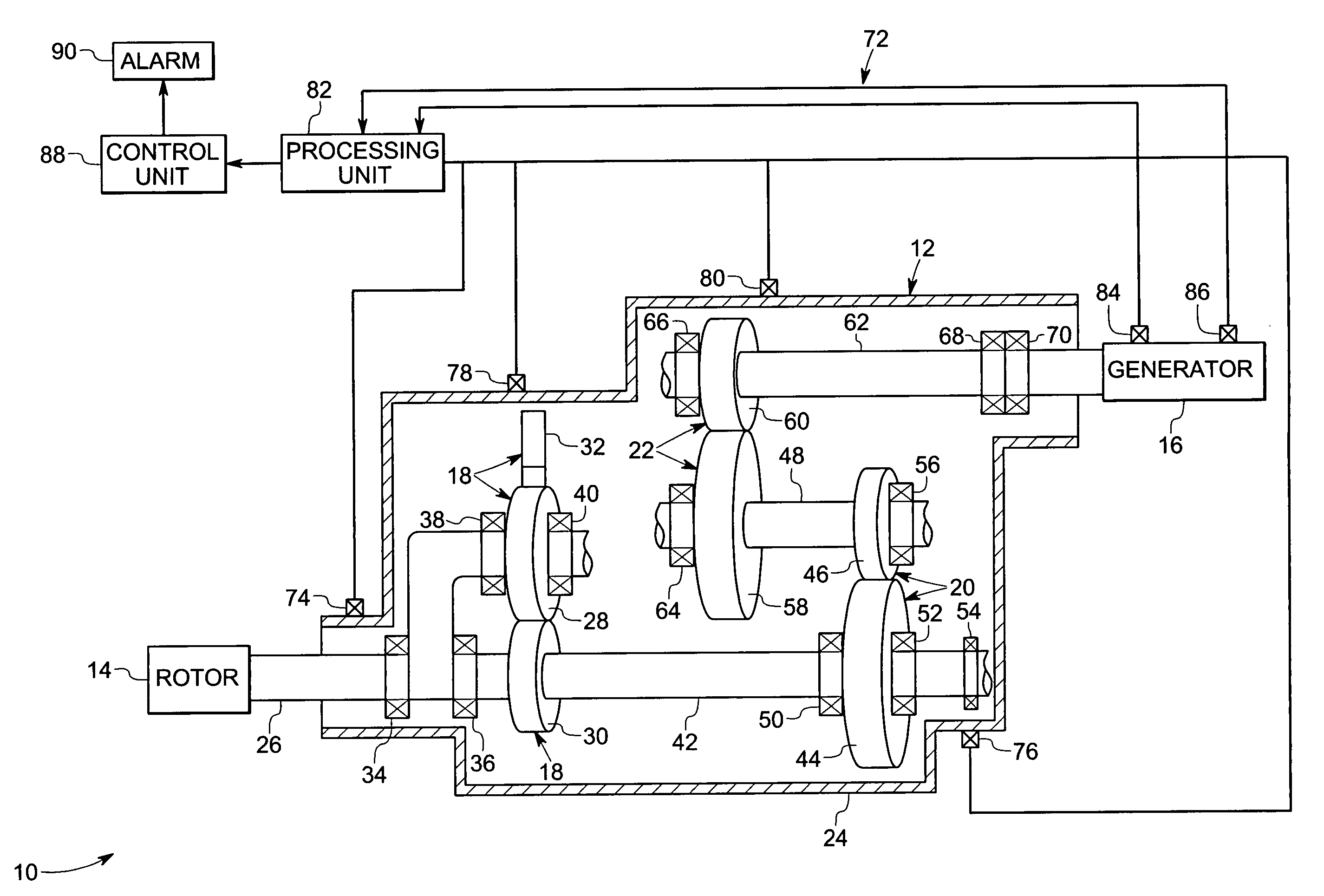
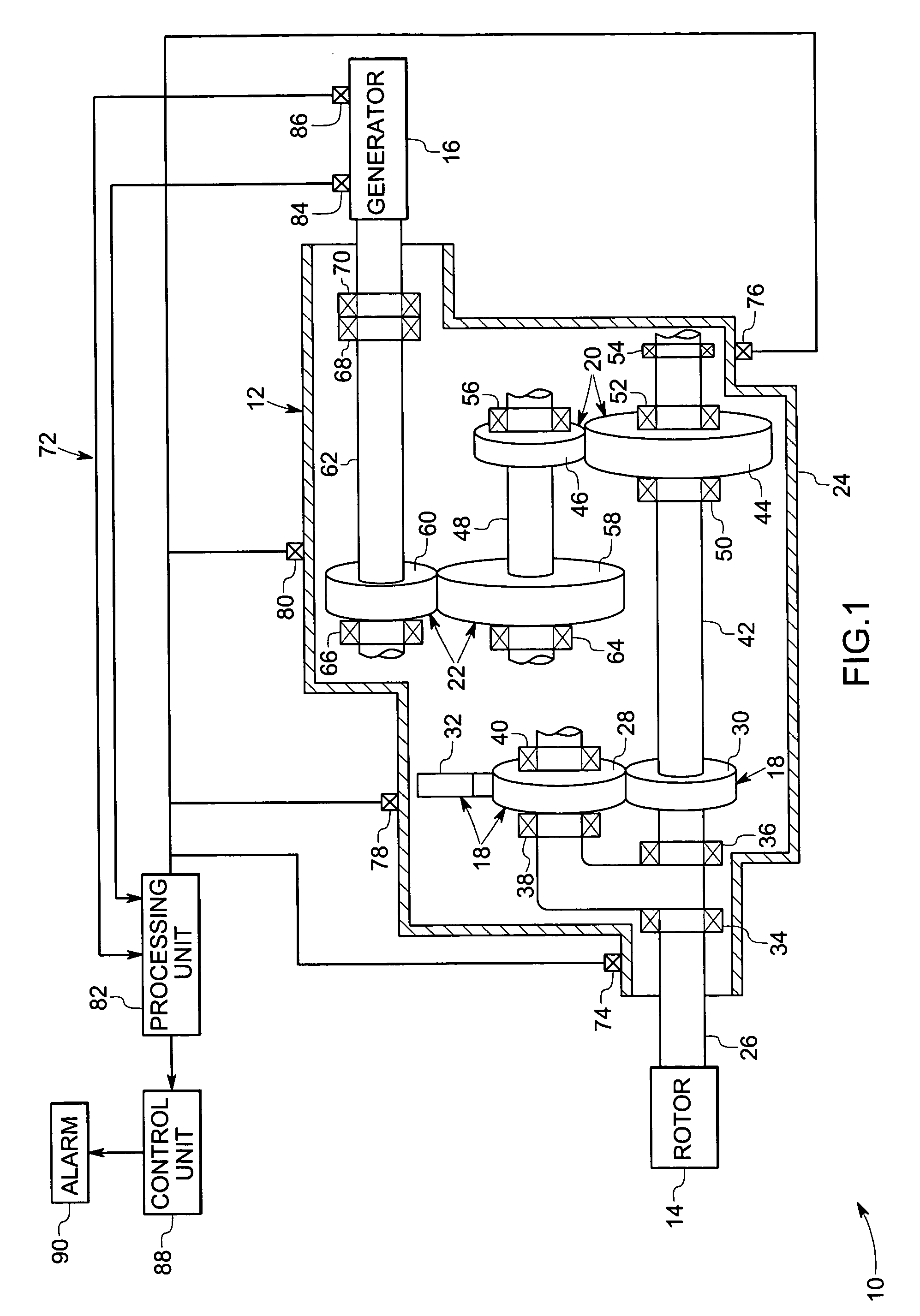
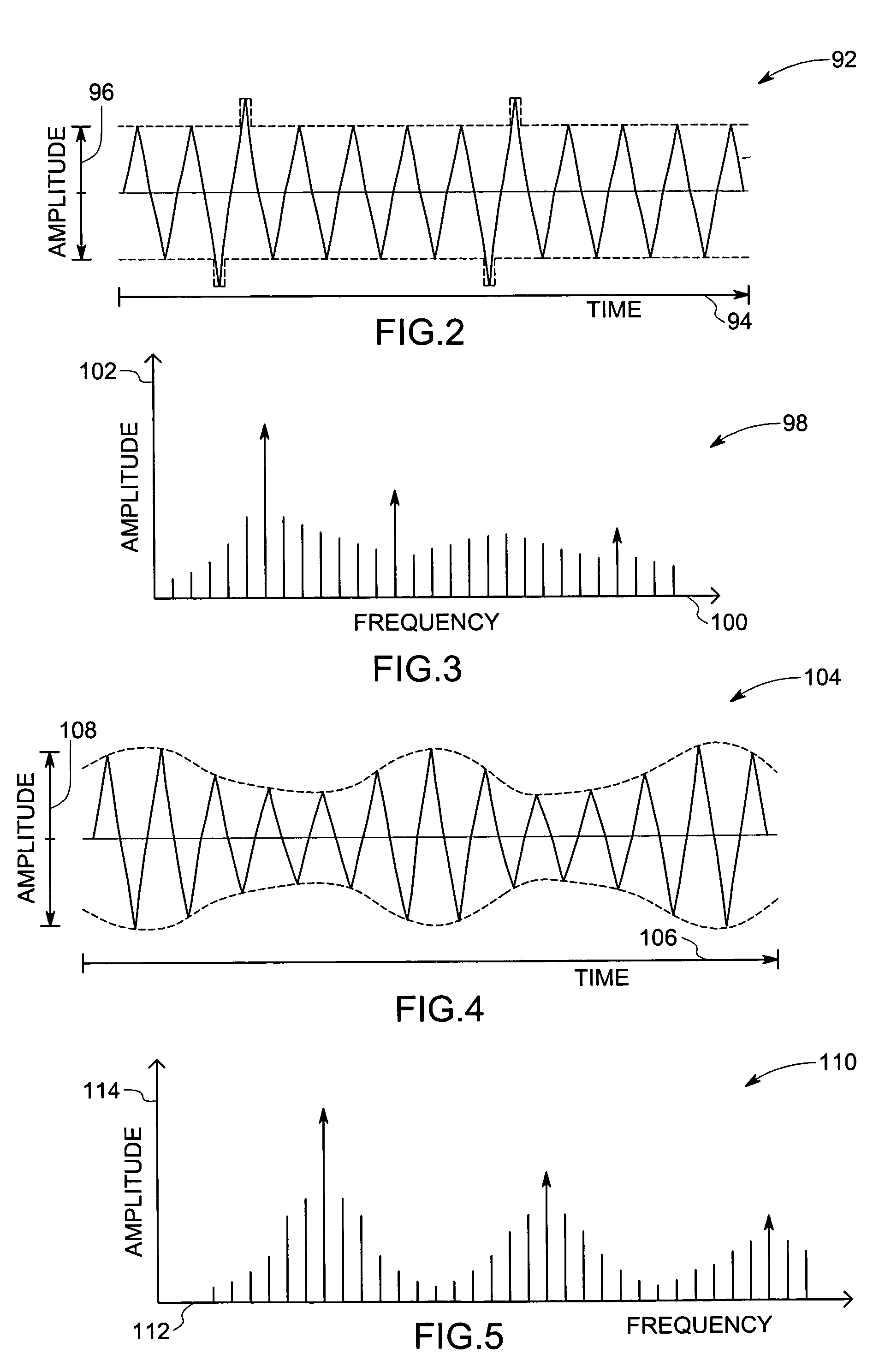
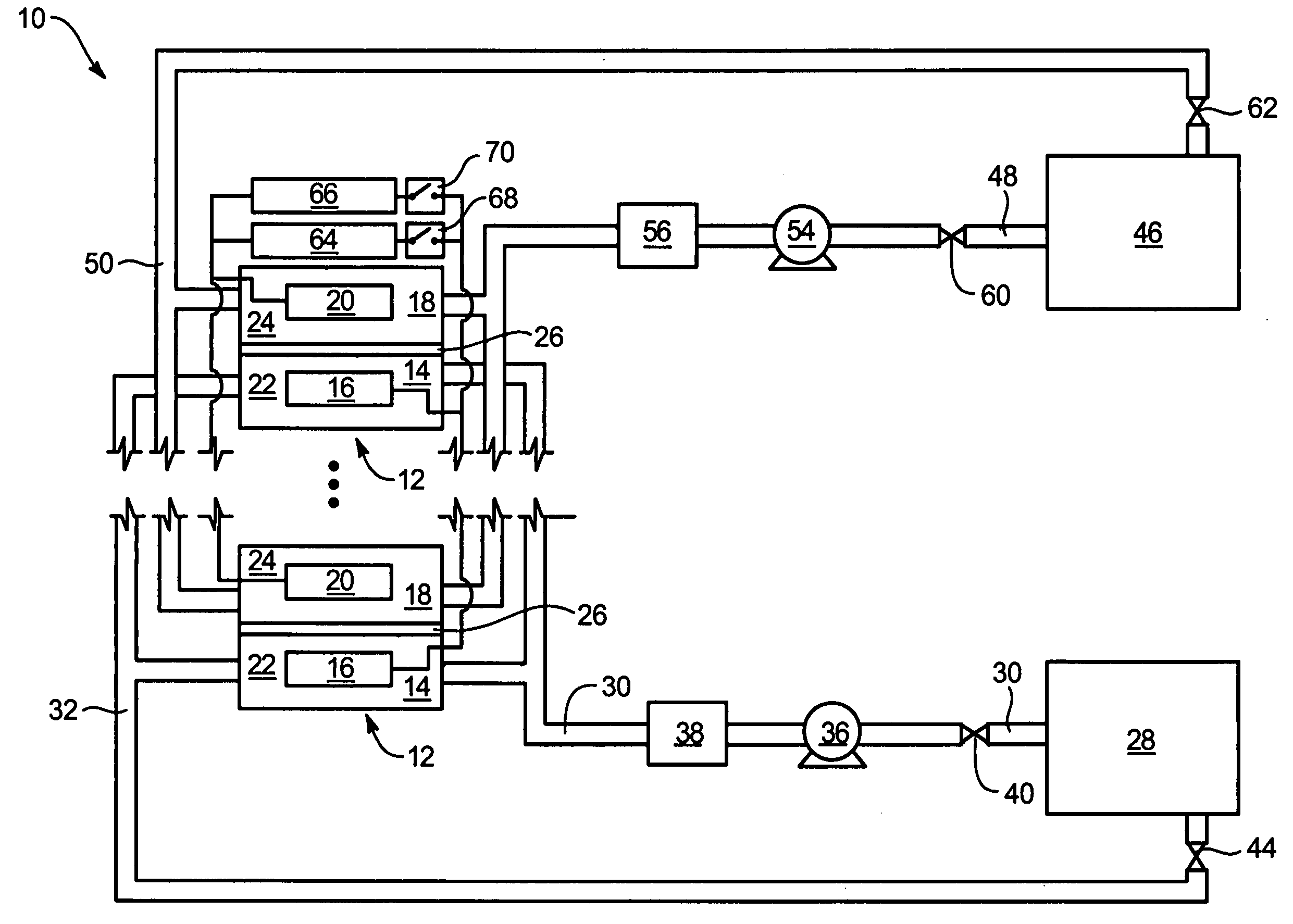
System and method for monitoring the condition of a drive train
ActiveUS20050284225A1Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingEngineeringCondition monitoring
A gearbox condition monitoring system comprises at least one vibration sensor located on a gearbox casing. A processing unit is coupled to the vibration sensor and is configured to receive signals representative of the detected vibrations from the vibration sensor. The processing unit may be operable to process the signals representative of detected vibrations of gears and bearings and to compute at least one dynamic energy index or location of fault.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Power control interface between a wind farm and a power transmission system
ActiveUS6858953B2Isolates power fluctuationInhibit injectionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngine fuctionsElectric power transmissionEngineering
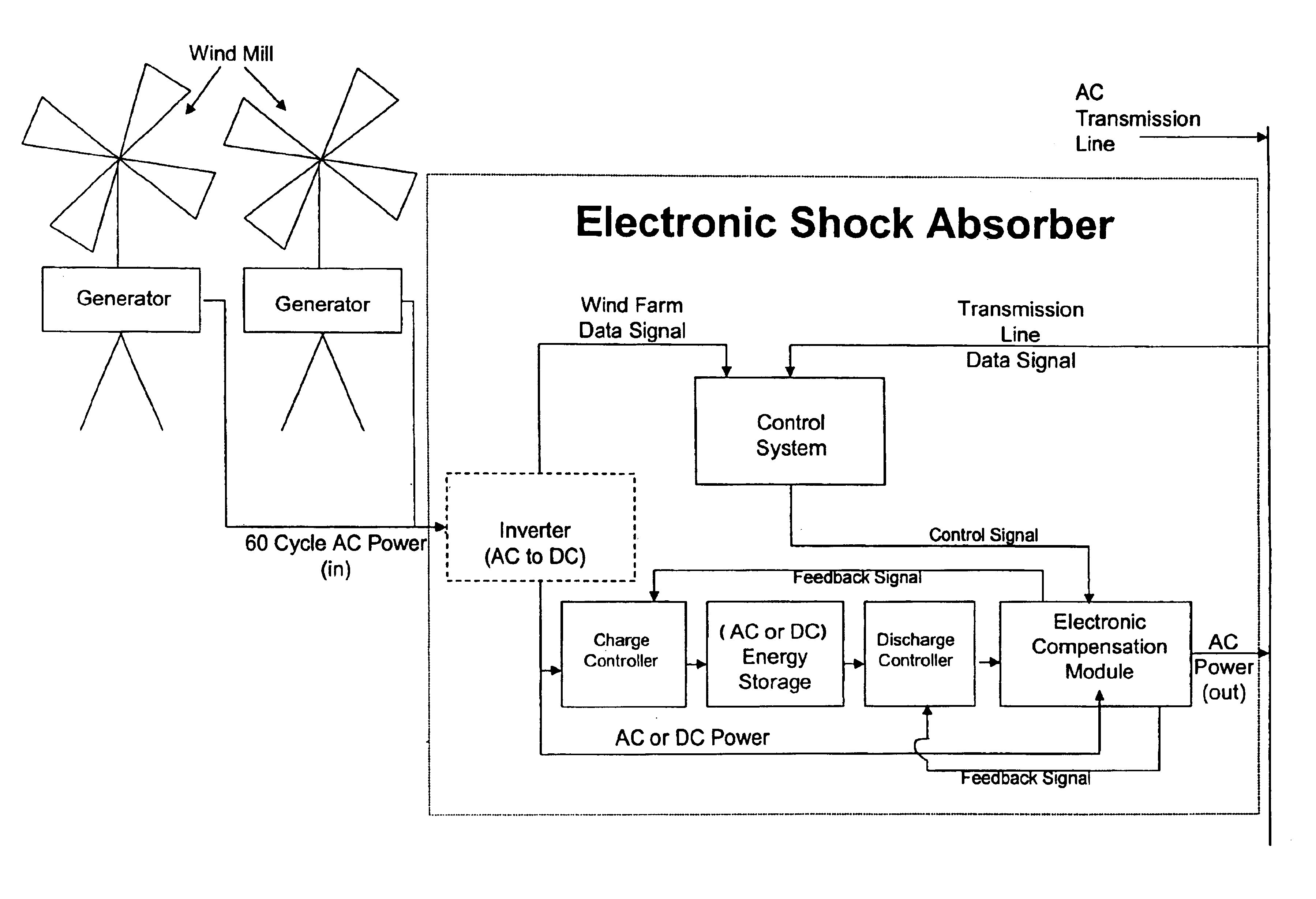
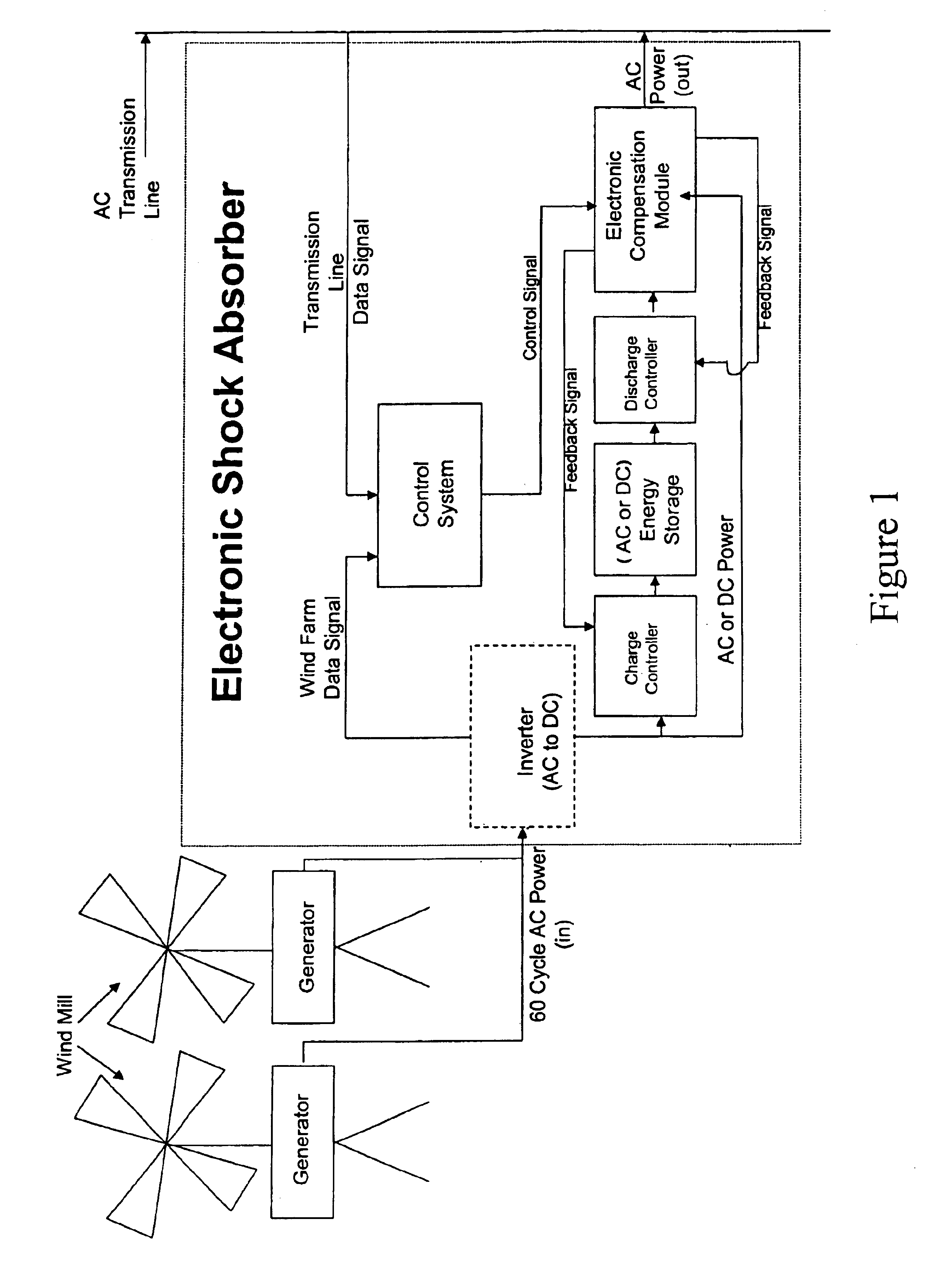
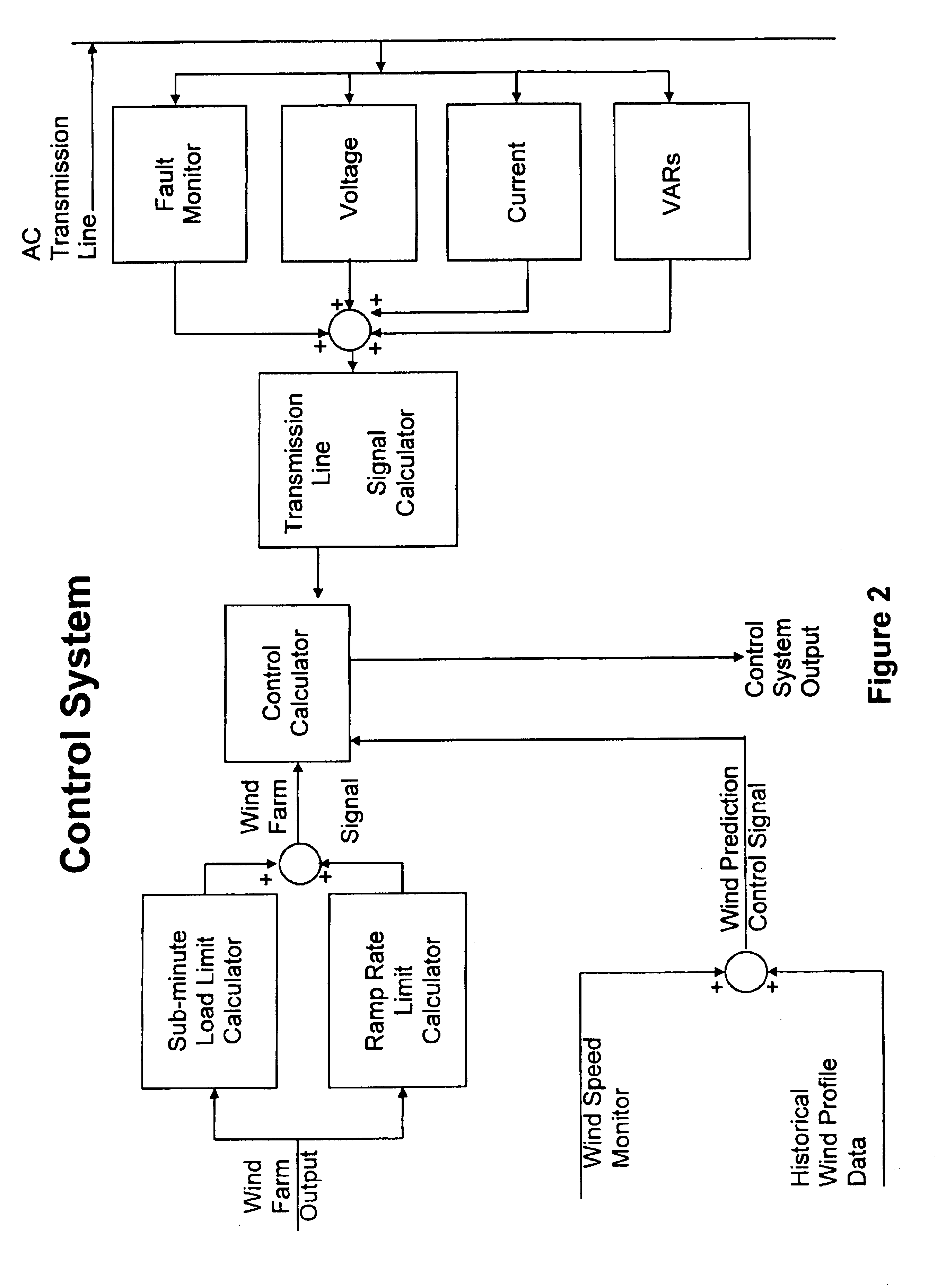
A power control interface between an unstable power source such as a wind farm and a power transmission line employs an electrical energy storage, control system, and electronic compensation module which act together like an “electronic shock absorber” for storing excess power during periods of increased power generation and releasing stored energy during periods of decreased power generation due to wind fluctuations. The control system is provided with a “look ahead” capability for predicting power output (wind speed conditions) and maintaining energy storage or release over a “narrow-band” range despite short duration fluctuations. The control system uses data derived from monitoring the wind farm power output and the power transmission line, and employs system-modeling algorithms to predict narrow-band wind speed conditions. The power control interface can also use its energy storage capacity to provide voltage support at the point of injection into the power transmission system, as well as fault clearance capability for “riding out” transient fault conditions occurring on the power transmission line.
Owner:HAWAIIAN ELECTRIC
Vanadium redox battery energy storage and power generation system incorporating and optimizing diesel engine generators
ActiveUS20050156431A1Batteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlVanadium redox batteryElectrical battery
A power generation system includes a vanadium redox battery that interfaces with a control system to optimize performance and efficiency. The power generation system may include one or more wind turbine generators and one or more diesel fuel generators. The control system manages the vanadium redox battery's absorption and power generation to control system stability and system frequency. The control system further manages the operation of the wind turbine generators and diesel fuel generators to control system stability and voltage.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
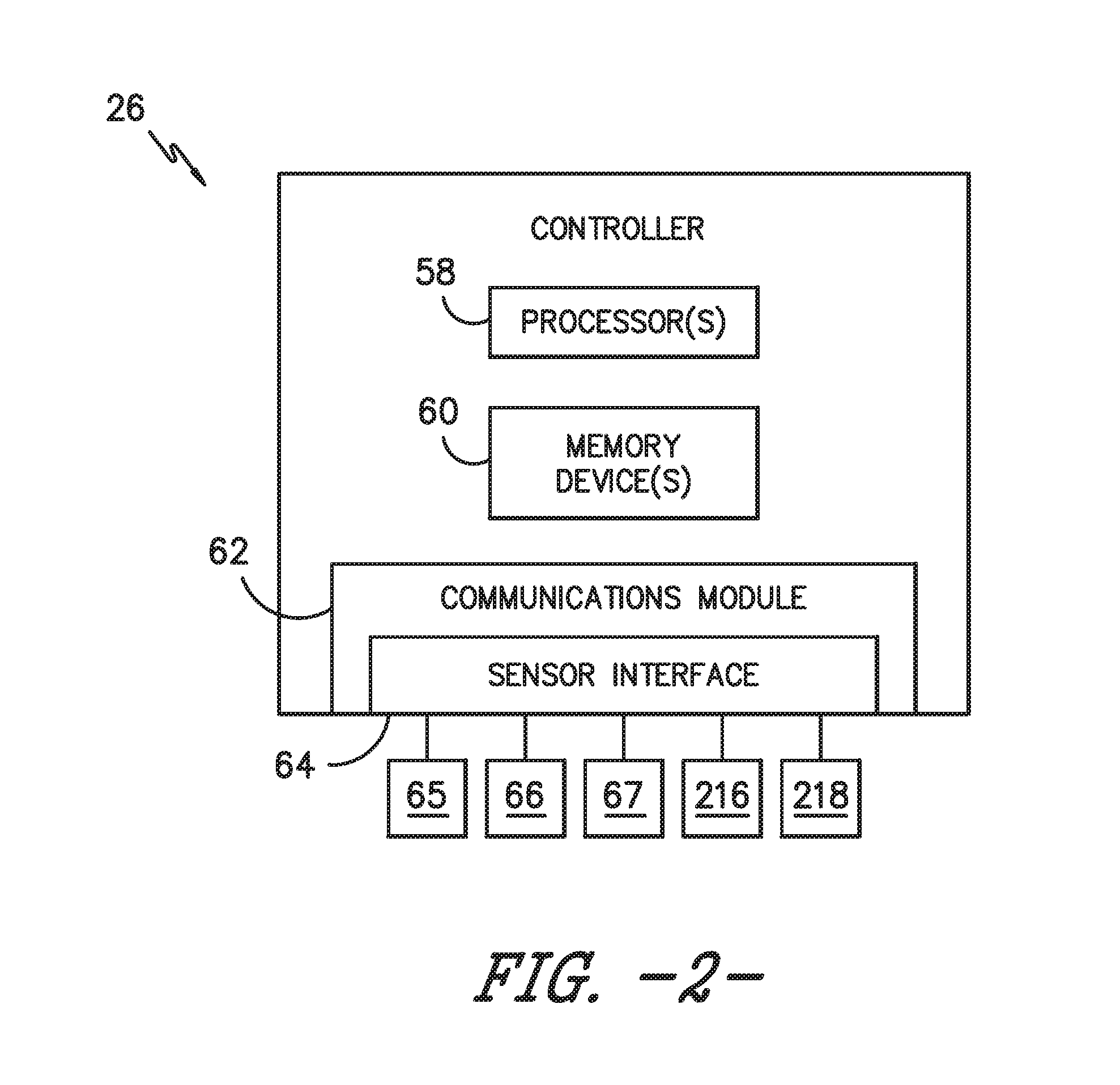
Independent sensing system for wind turbines
InactiveUS20090232635A1Preventing and eliminating propagationPermit flexibilityPropellersWind motor controlTurbineWind force
A wireless sensing device for use in a wind turbine having a sensor capable of measuring one or more parameters for wind turbine operation. The sensing device also include a transmission device capable of wirelessly transmitting one or more signals corresponding to the one or more measured parameters to a controller. An independent power source is included to power the transmission device and the sensor. A method for system for operating and monitoring wind turbine operation are also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
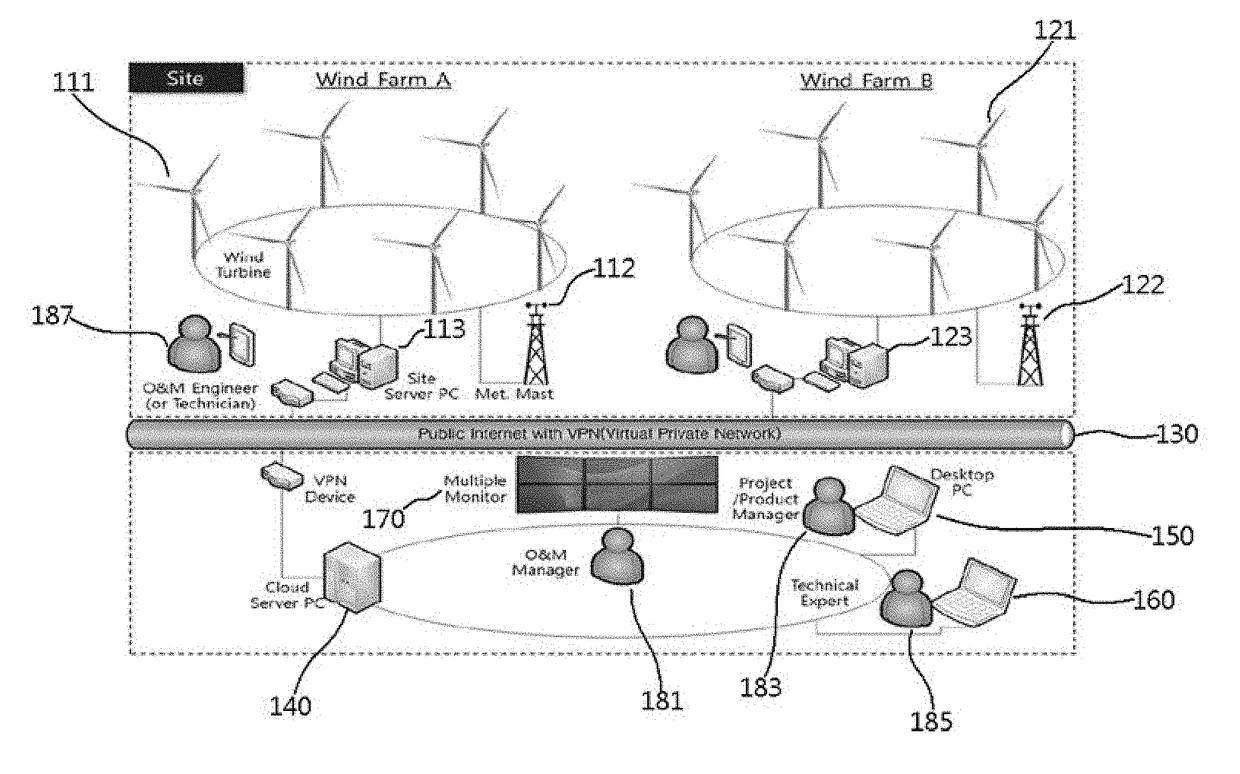
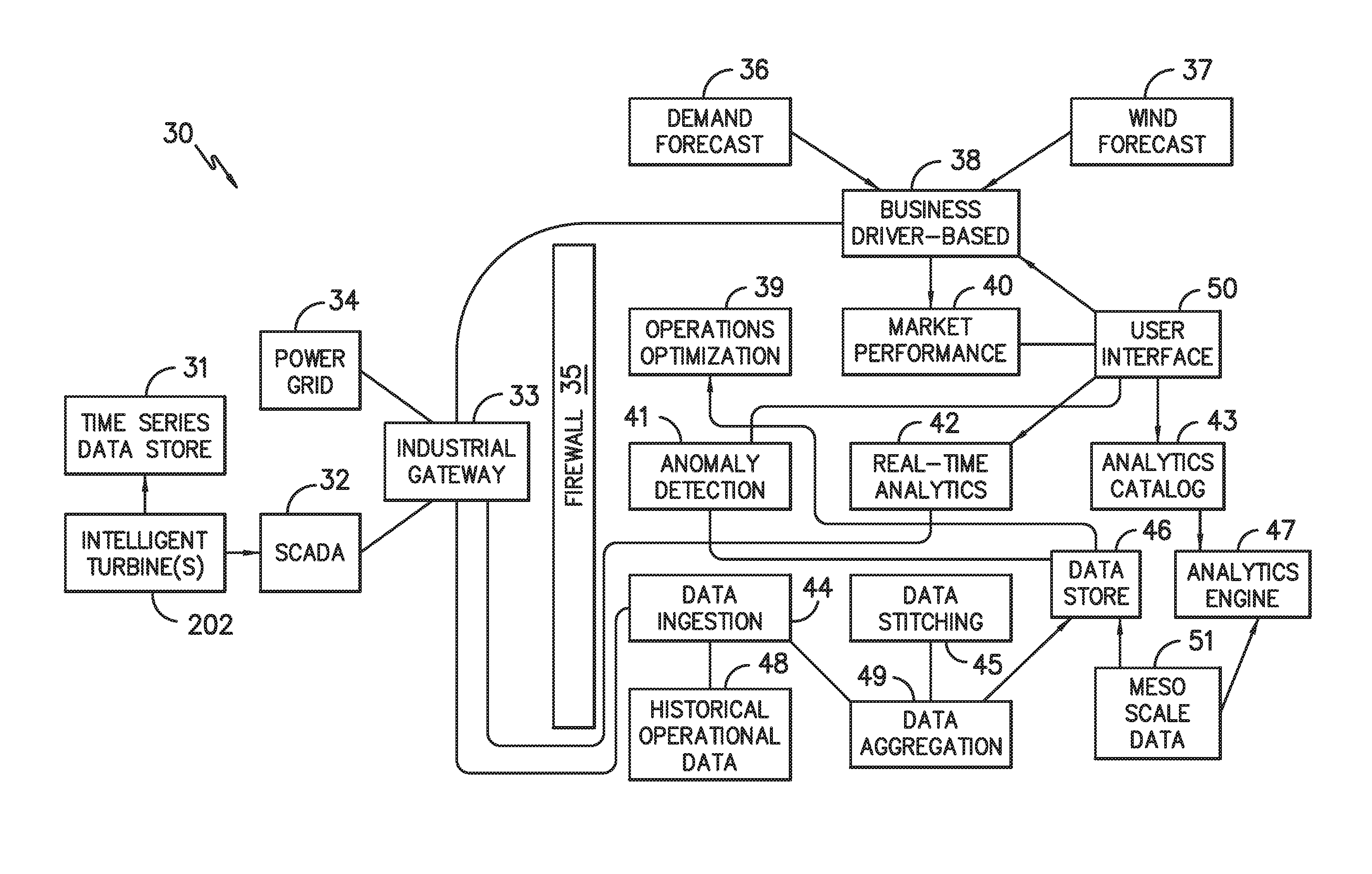
Digital Twin Interface for Operating Wind Farms
ActiveUS20160333854A1Improve performanceEngine manufactureWind motor controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
The present disclosure is directed to a digital twin interface for managing a wind farm having a plurality of wind turbines. The digital twin interface includes a graphical user interface (GUI) displaying a digital equivalent of the wind farm. For example, the digital equivalent of the wind farm includes environmental information and a digital representation of each of the wind turbines arranged in the wind farm. The interface also includes a control icon arranged with each of the digital representations of the wind turbines. In certain embodiments, the control icons of each wind turbine may correspond to a control dial. More specifically, the control icon of each digital representation of the wind turbines includes information regarding current and optimum operating conditions of the digital wind turbine. The interface also includes one or more control features configured to optimize performance of the wind farm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
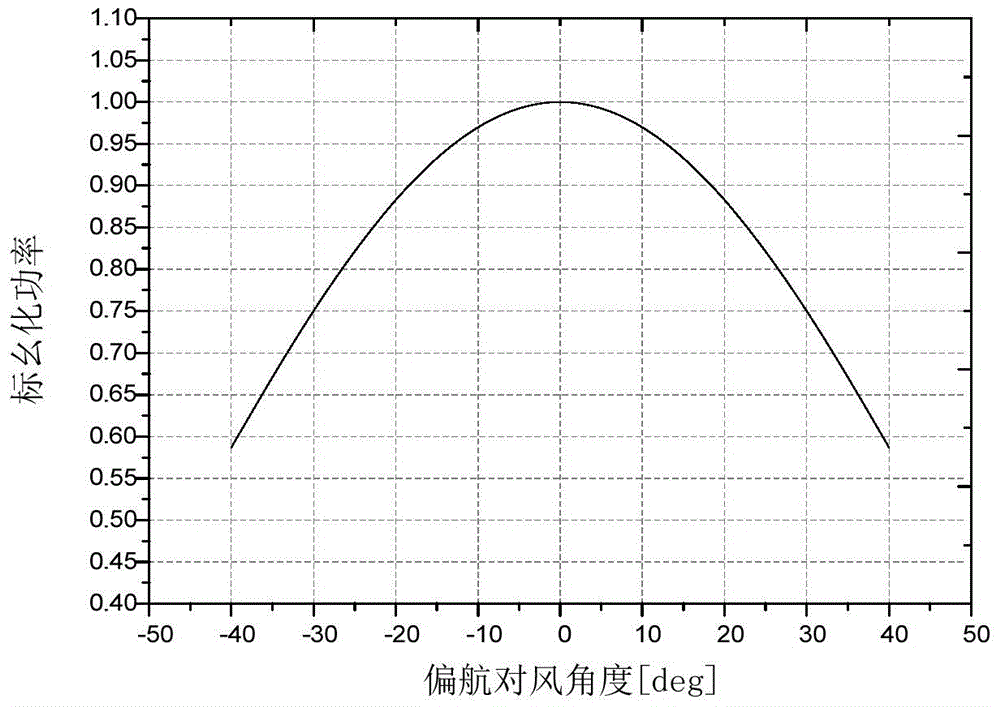
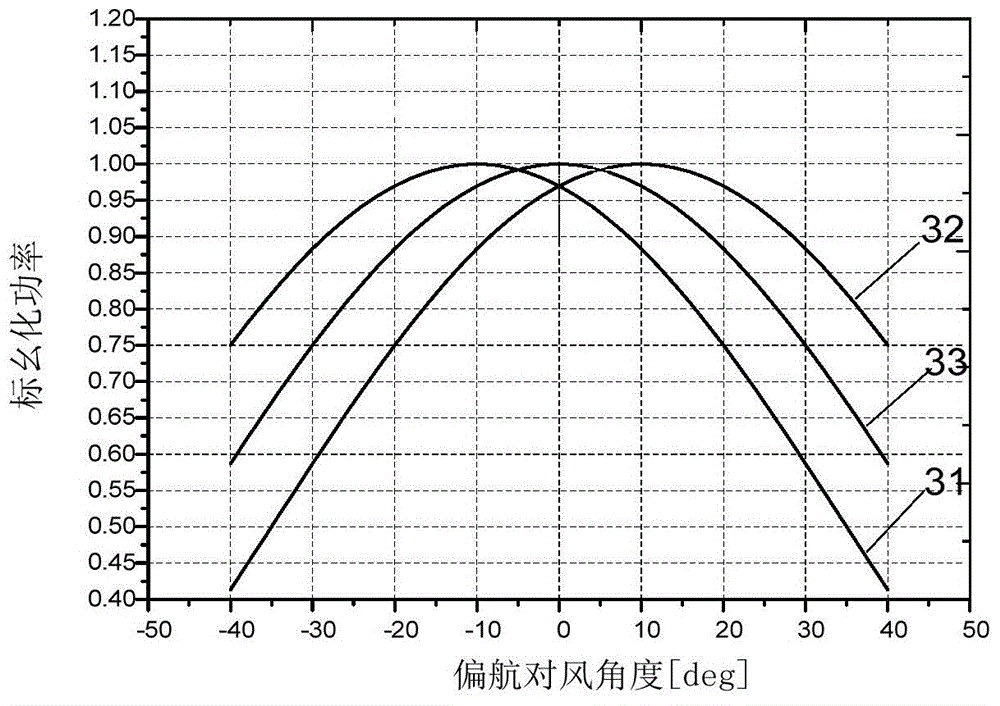
Method, device and system for controlling wind alignment correction of wind turbine generator systems
ActiveCN104481804ACorrective Control RealizationImprove correction efficiencyMeasurement devicesWind motor controlEngineeringTurbine
An embodiment of the invention provides a method, a device and a system for controlling wind alignment correction of wind turbine generator systems. The method includes acquiring environmental wind speed values, yawing wind alignment angle measured values and generated power values of the wind turbine generator systems in real time; dividing the various acquired environmental wind speed values into a plurality of wind speed sections according to the magnitude of the environmental wind speed values and extracting the various yawing wind alignment angle measured values and the generated power values in at least one wind speed section; determining the maximum values of the extracted generated power values in the various wind speed sections; computing wind alignment correction deviation of the wind turbine generator systems according to the yawing wind alignment angle measured values corresponding to the maximum values of the extracted generated power values in the various wind speed sections; correcting follow-up acquired yawing wind alignment angle measured values by the aid of the wind alignment correction deviation. According to the technical scheme, the method, the device and the system have the advantages that wind alignment correction control operation can be implemented on the wind turbine generator systems, and the correction efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
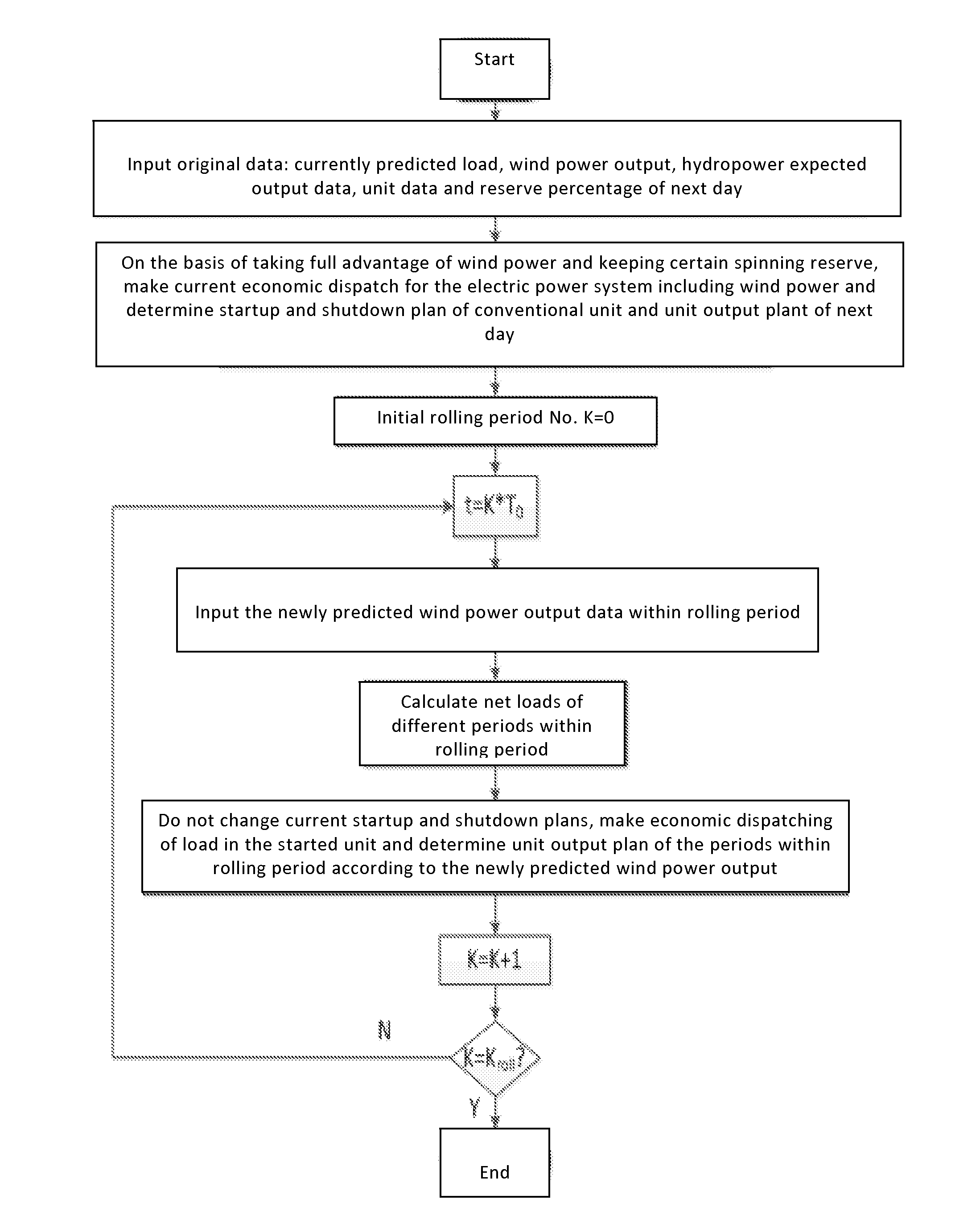
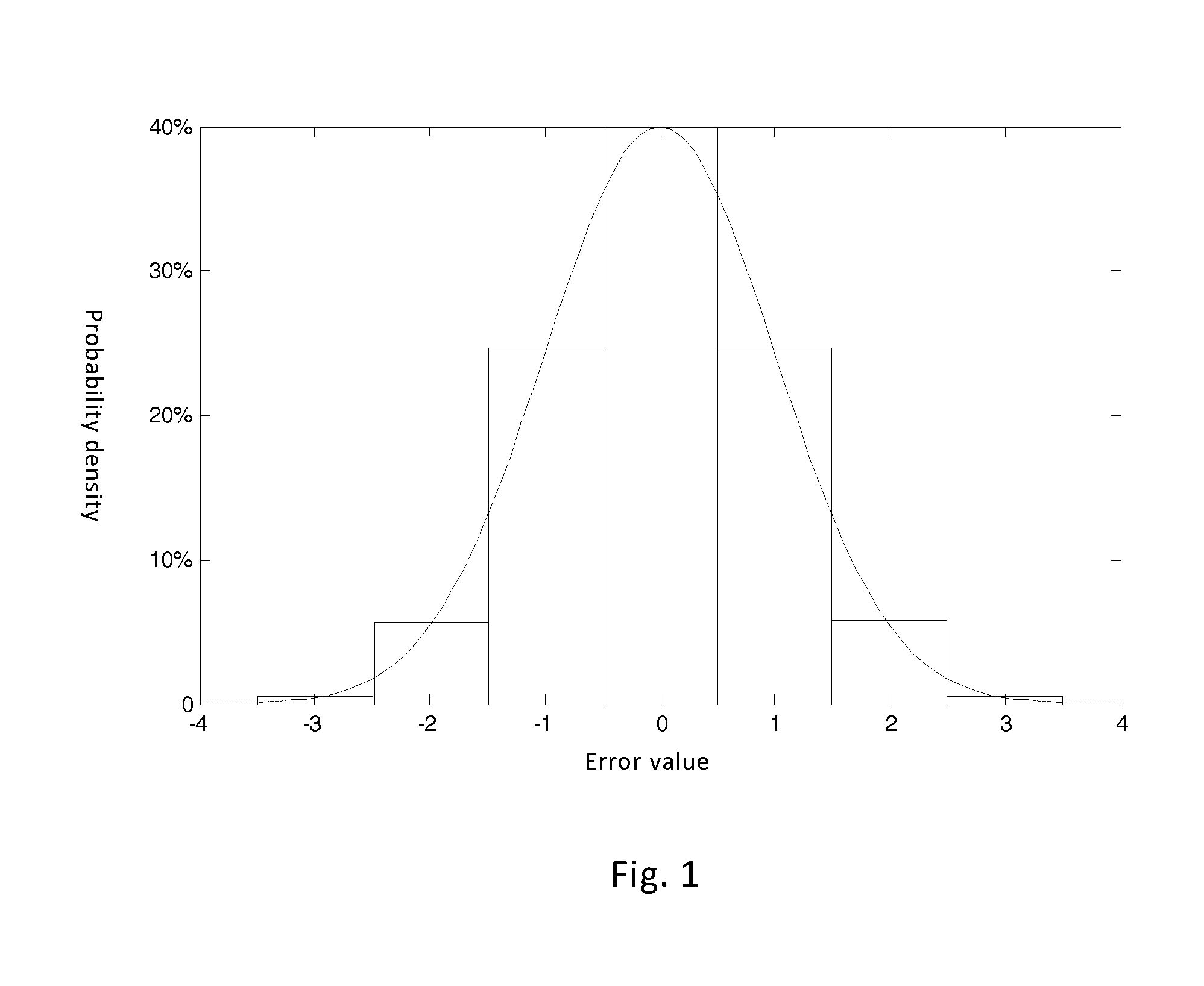
Short-term operation optimization method of electric power system including large-scale wind power
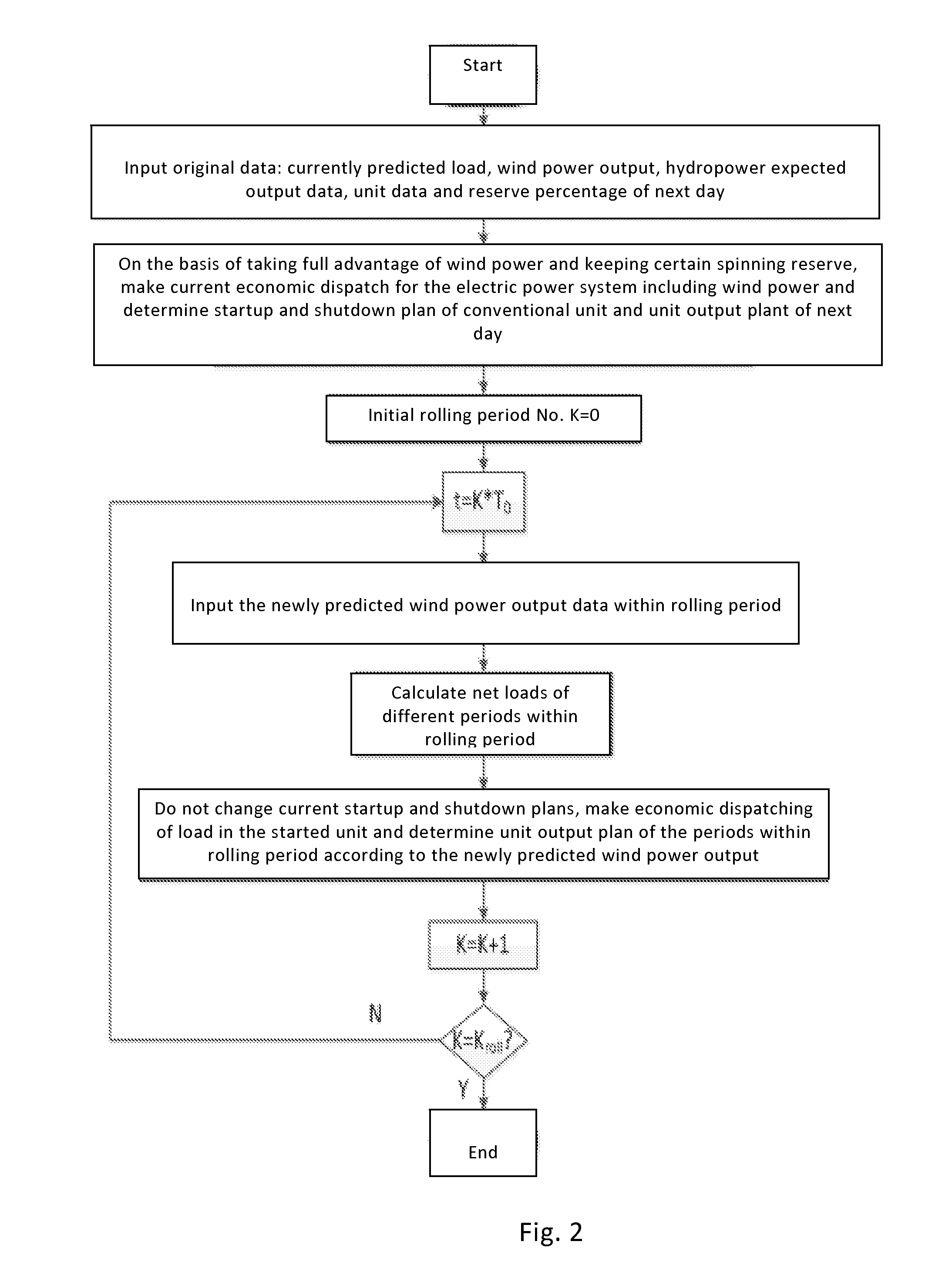
InactiveUS20160169202A1Adjust correlationWind motor controlEngine fuctionsElectricityLoad forecasting
The present invention discloses a short-term operation optimization method for a power system including large-scale wind power, comprising modeling the randomness of wind power output, modeling the randomness of the load of electric power system and modeling net load of electric power system. Net load refers that for probability distribution of net load that is too discretized, probability distribution curve of net load is divided into N intervals, the probabilities for each interval are obtained and probability distribution curve of net load is obtained through calculating and weighing each interval. Through calculating randomness of power wind output and standard deviation of load prediction error of the electric power system, net load prediction error of the electric power system is obtained and reasonable coordination is made on the electric power system according to prediction error and prediction amount to better regulate the correlations between randomness, volatility, regionalism, double-circuit peak shaving and load of wind power generation, so as to realize optimization operation of the electric power system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
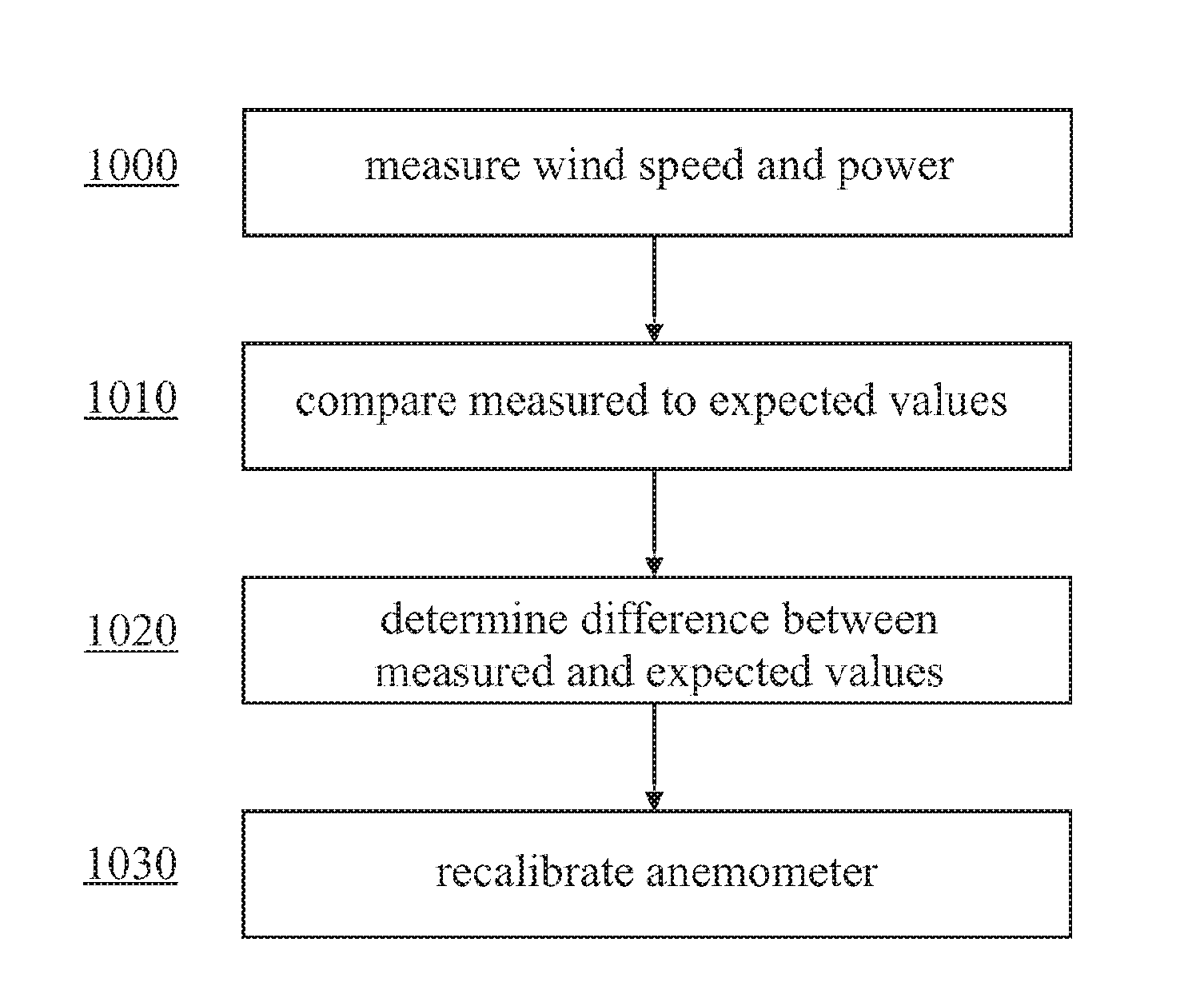
Anemometer calibration method and wind turbine
A method for re-calibrating an anemometer of a wind turbine is provided, the method comprising the steps of obtaining pairs of measured values of wind speed and a wind-speed dependent turbine variable; comparing said measured value pairs to pairs of wind speed and the turbine variable obtained from an expected turbine variable curve of the wind turbine to determine a difference between a measured wind speed value and an expected wind speed value for a given turbine variable value; and adjusting a calibration function of said anemometer on the basis of said determined difference.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
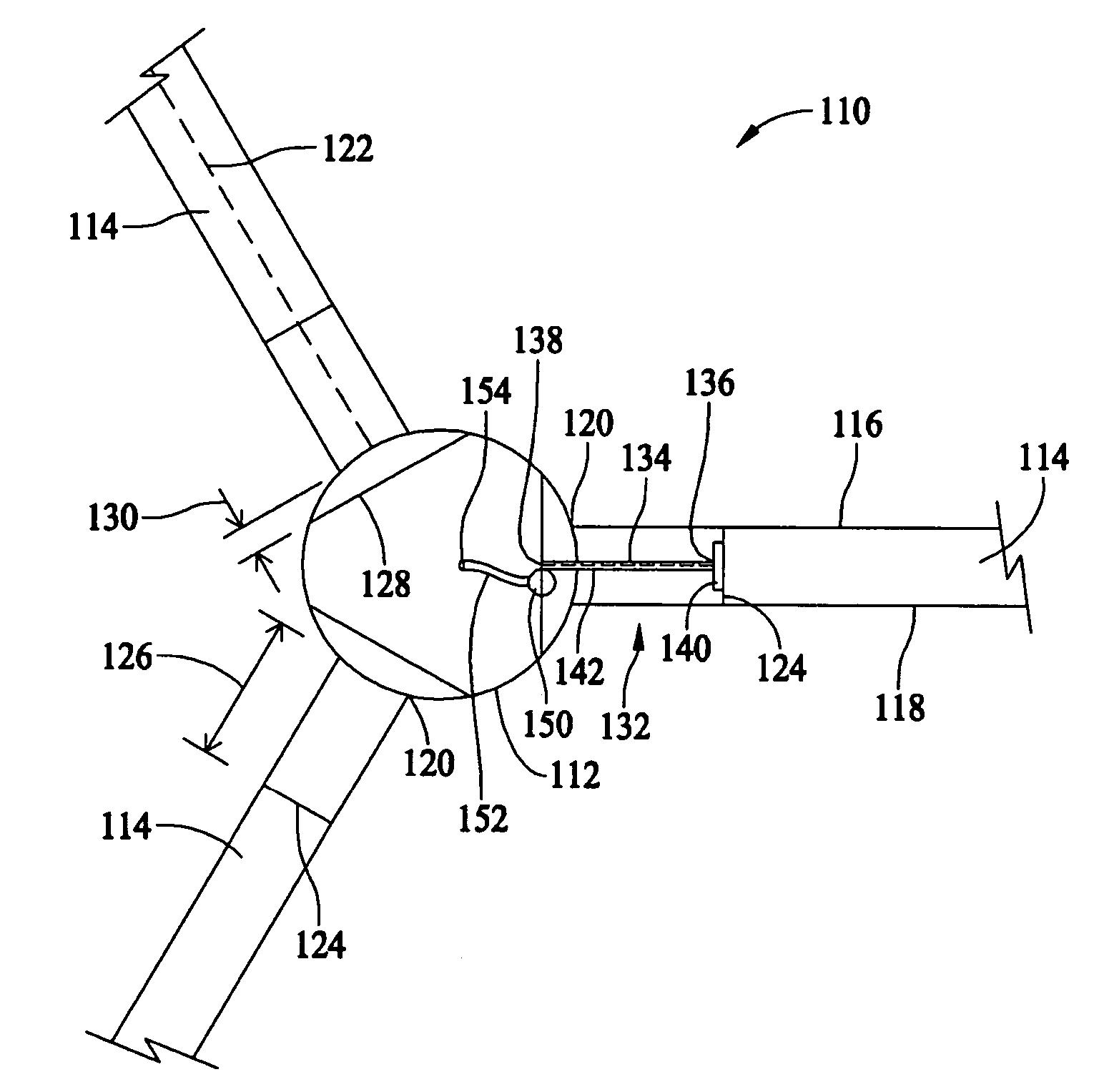
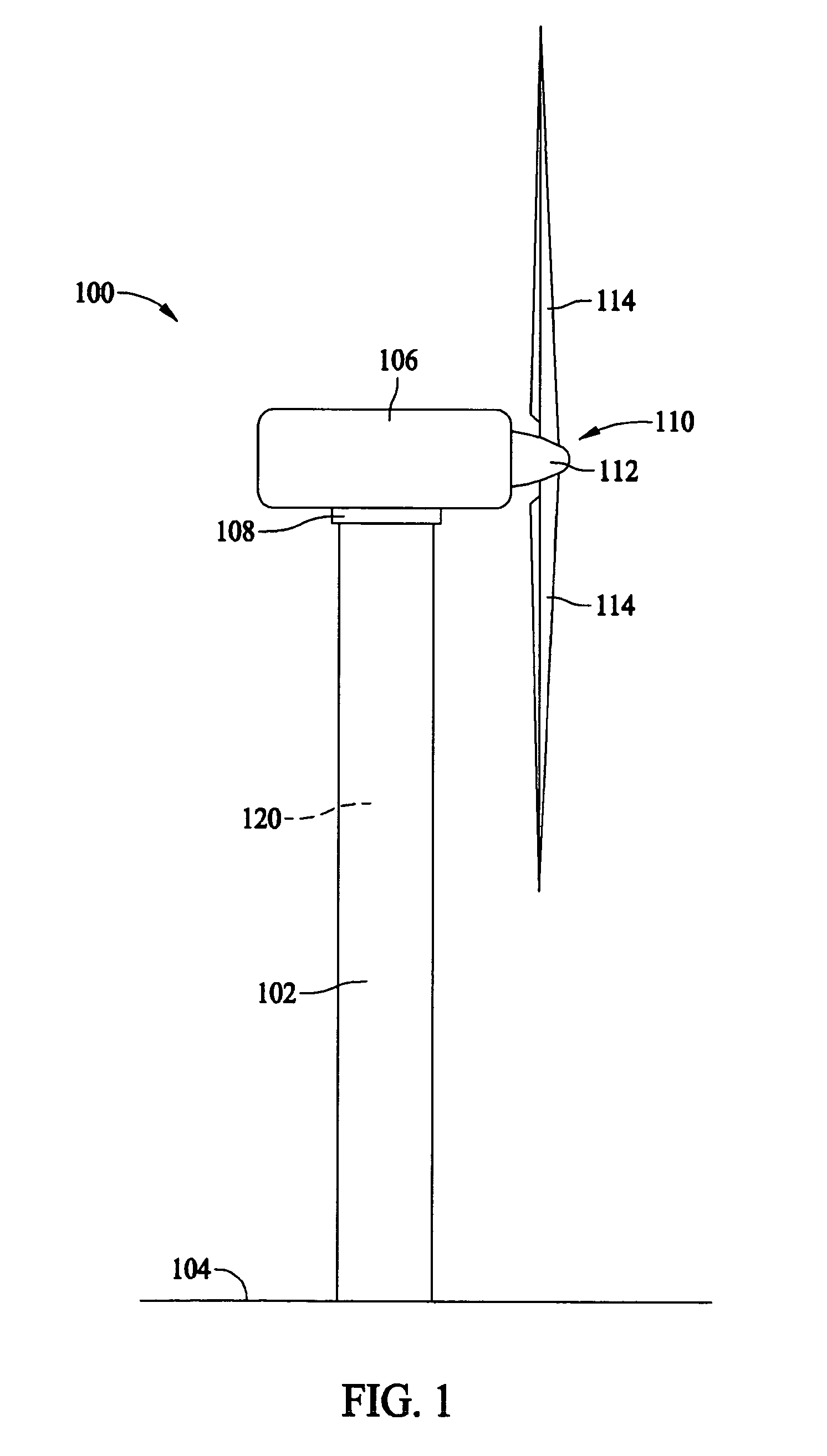
System and method for monitoring and controlling wind turbine blade deflection
A system is disclosed for monitoring and controlling the deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a passive position detecting apparatus and a controller. The passive position detecting apparatus may be configured to acquire and transmit data relating directly to a position of at least one of the turbine blades. The controller may be configured to receive the data from the passive position detecting apparatus and compare such data to a known position reference to determine turbine blade deflection.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
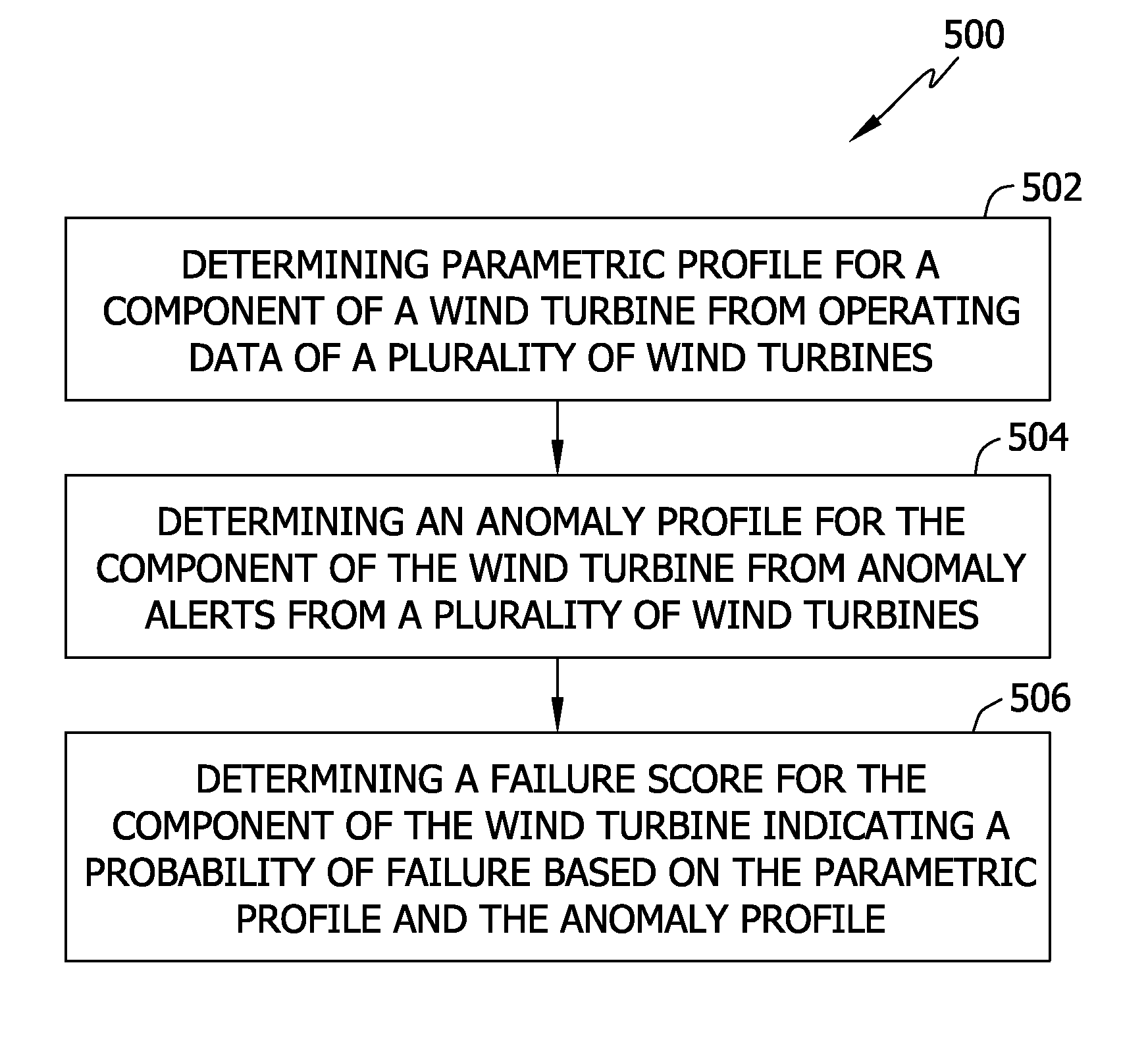
System and method for predicting wind turbine component failures
Methods and systems for use in predicting wind turbine failures are provided. One example method includes determining a parametric profile for a component of a wind turbine from operating data of a plurality of wind turbines, determining an anomaly profile for the component of the wind turbine from anomaly alerts from a plurality of wind turbines, and determining a probability of failure for the component of the wind turbine based on the parametric profile and the anomaly profile. The parametric profile defines at least one parametric event associated with the component prior to failure of the component, and the anomaly profile defines at least one anomaly associated with the component prior to failure of the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
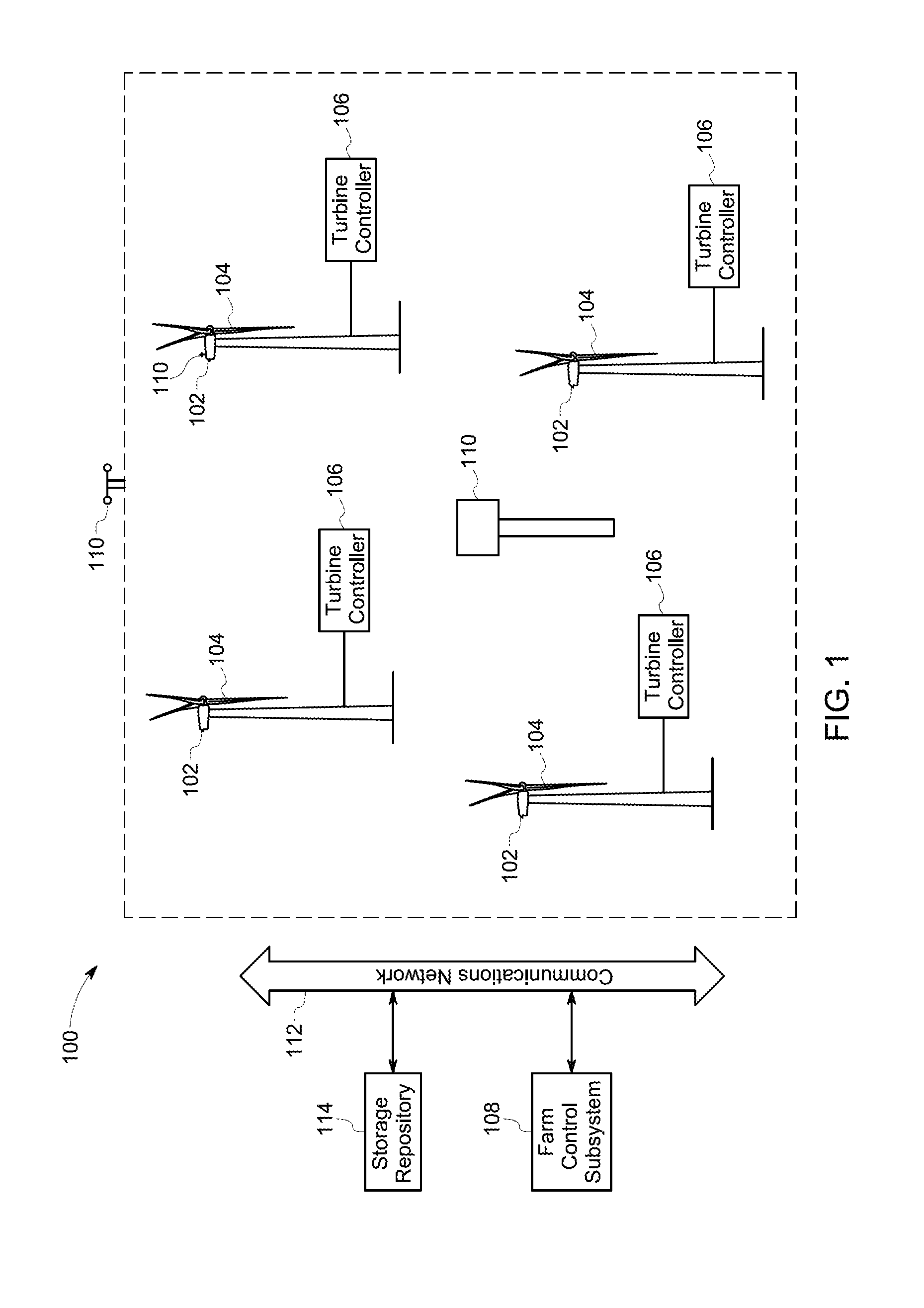
Systems and methods for optimizing operation of a wind farm
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
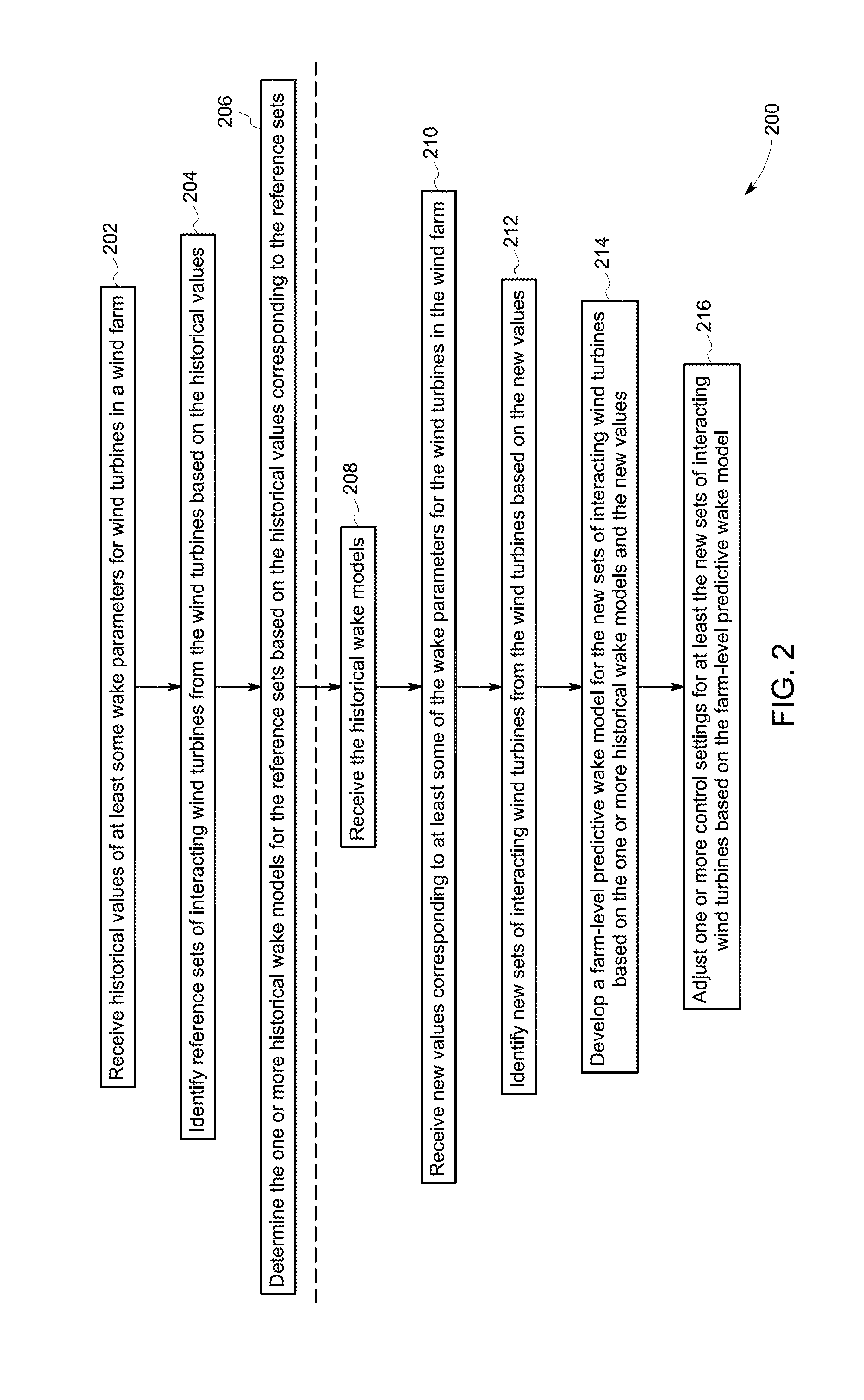
Methods and apparatus for measuring wind turbine blade deflection
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Popular searches
Material flaws investigation Optically investigating flaws/contamination Closed circuit television systems Wind motor monitoring Wind energy generation Vehicle position/course/altitude control Renewable energy source integration Elasticity measurement Wind motor combinations Mechanical power transmission
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com