Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
418results about "Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic device testing/calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
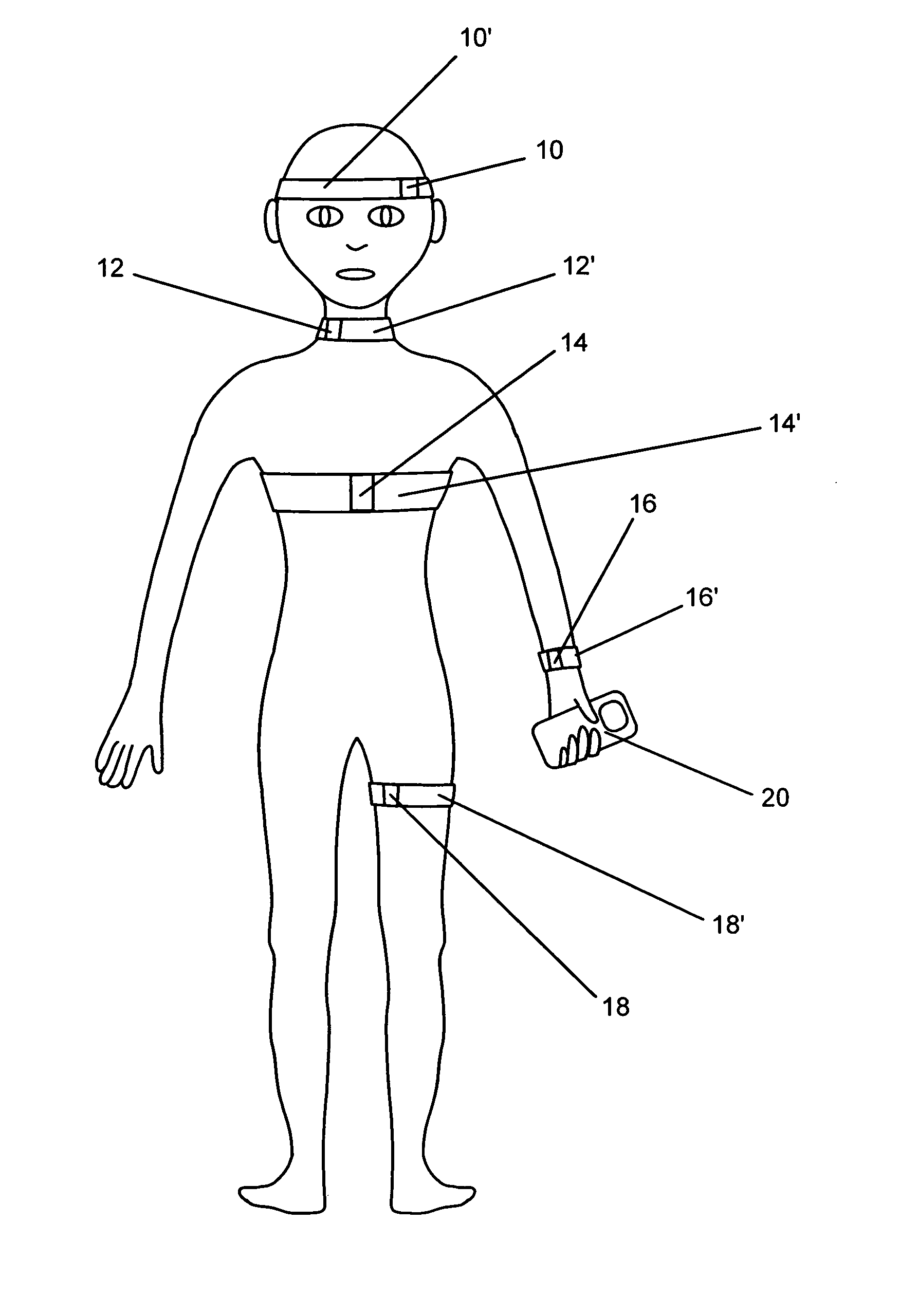
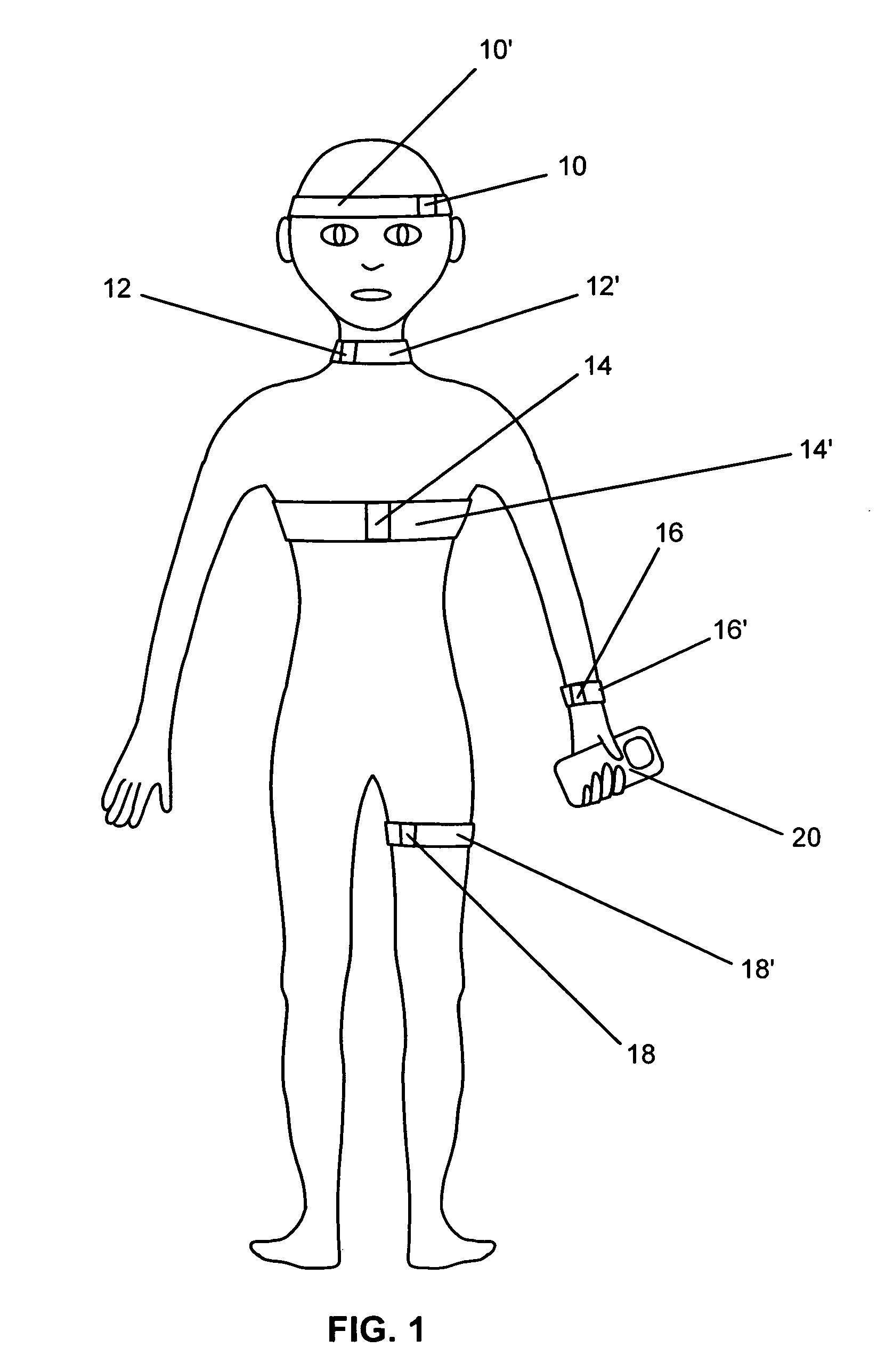
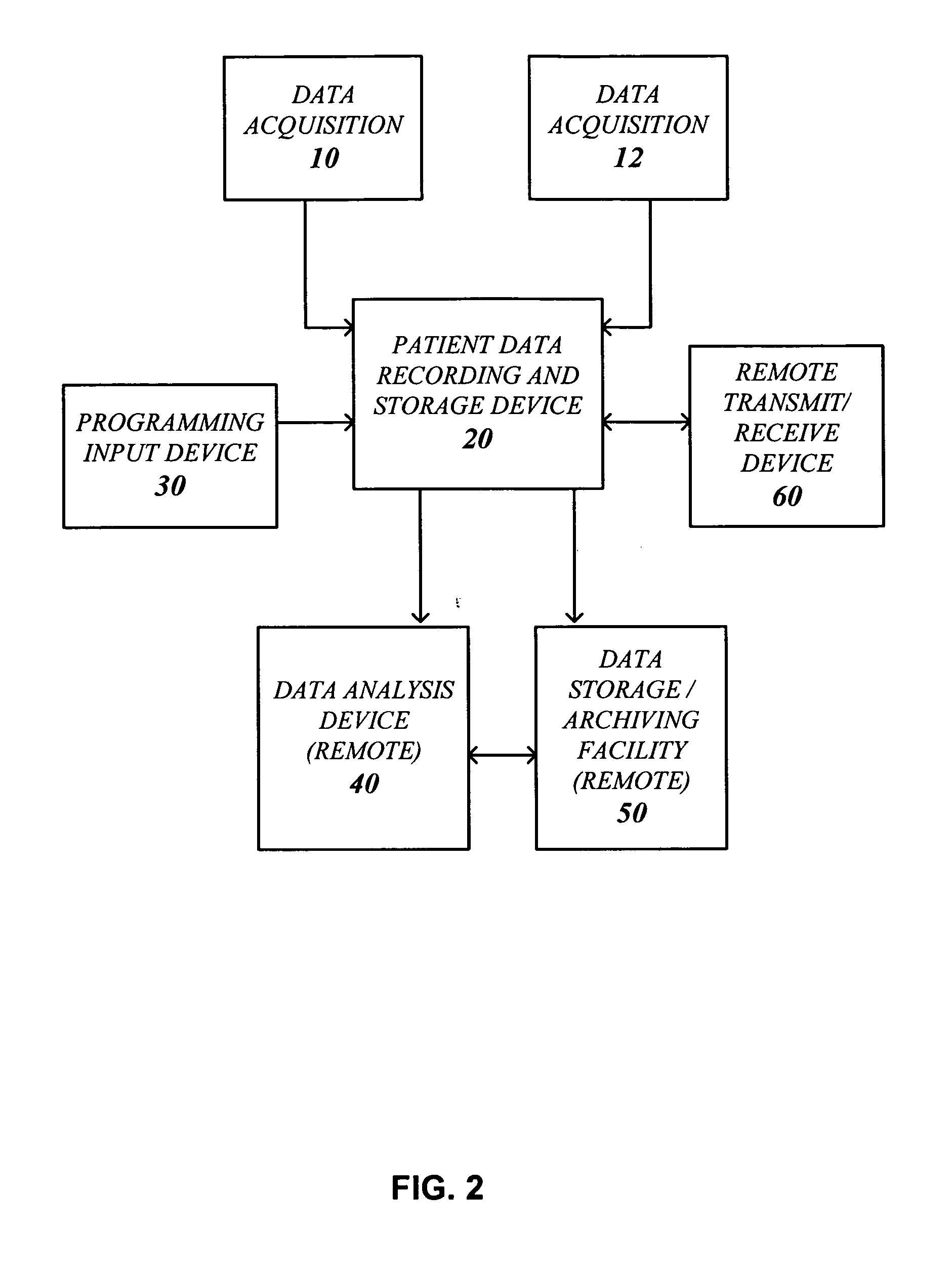
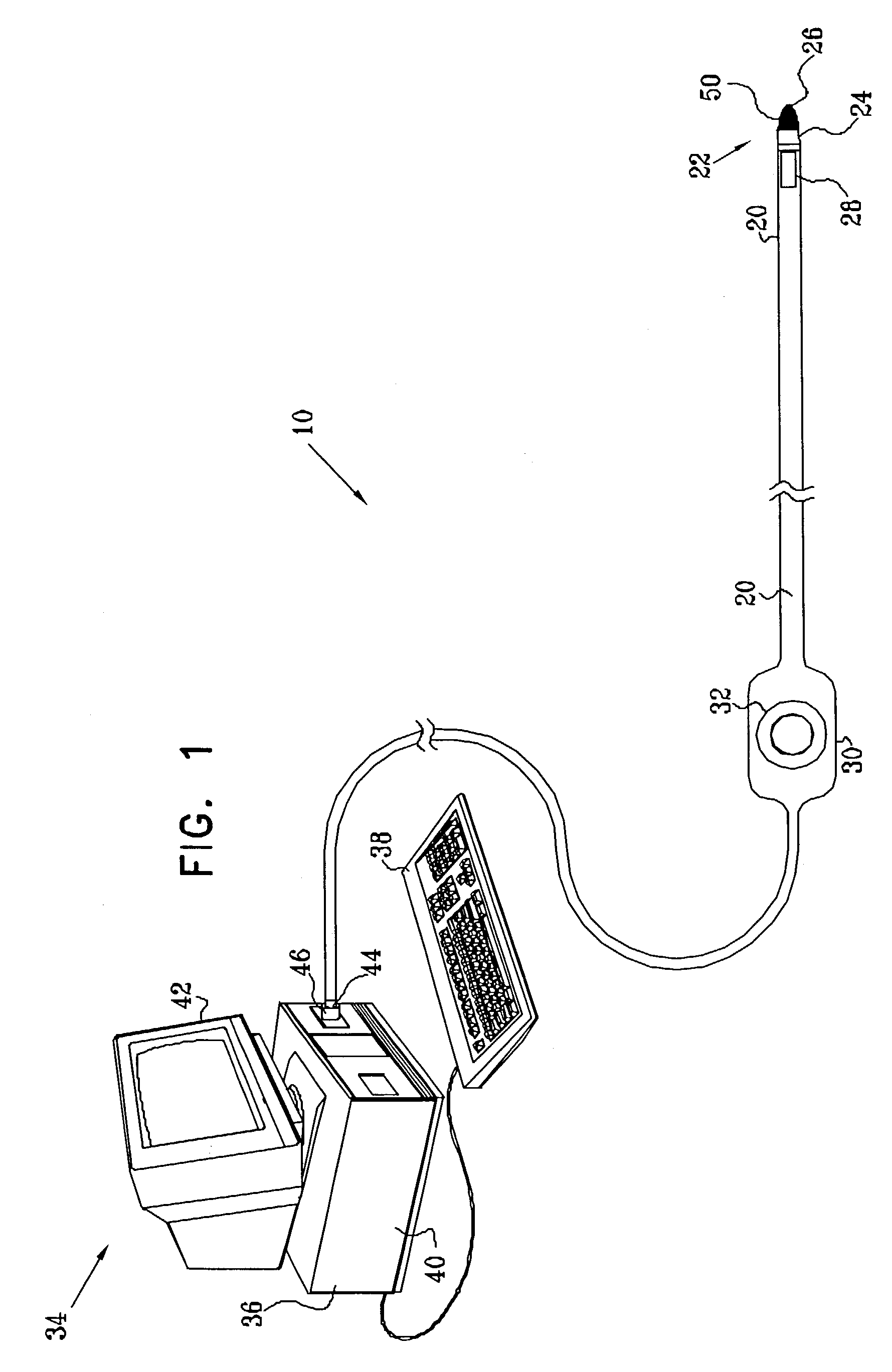
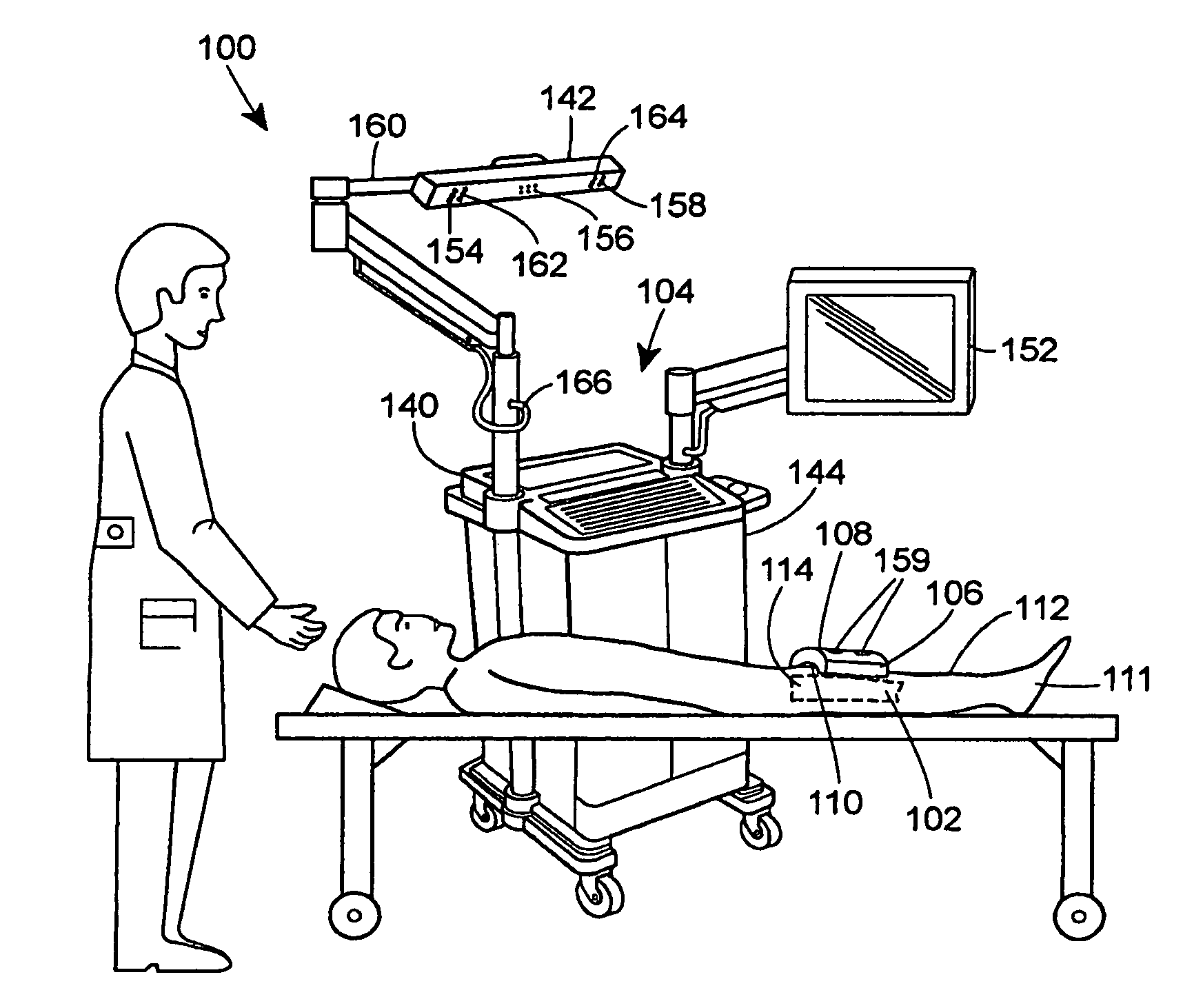
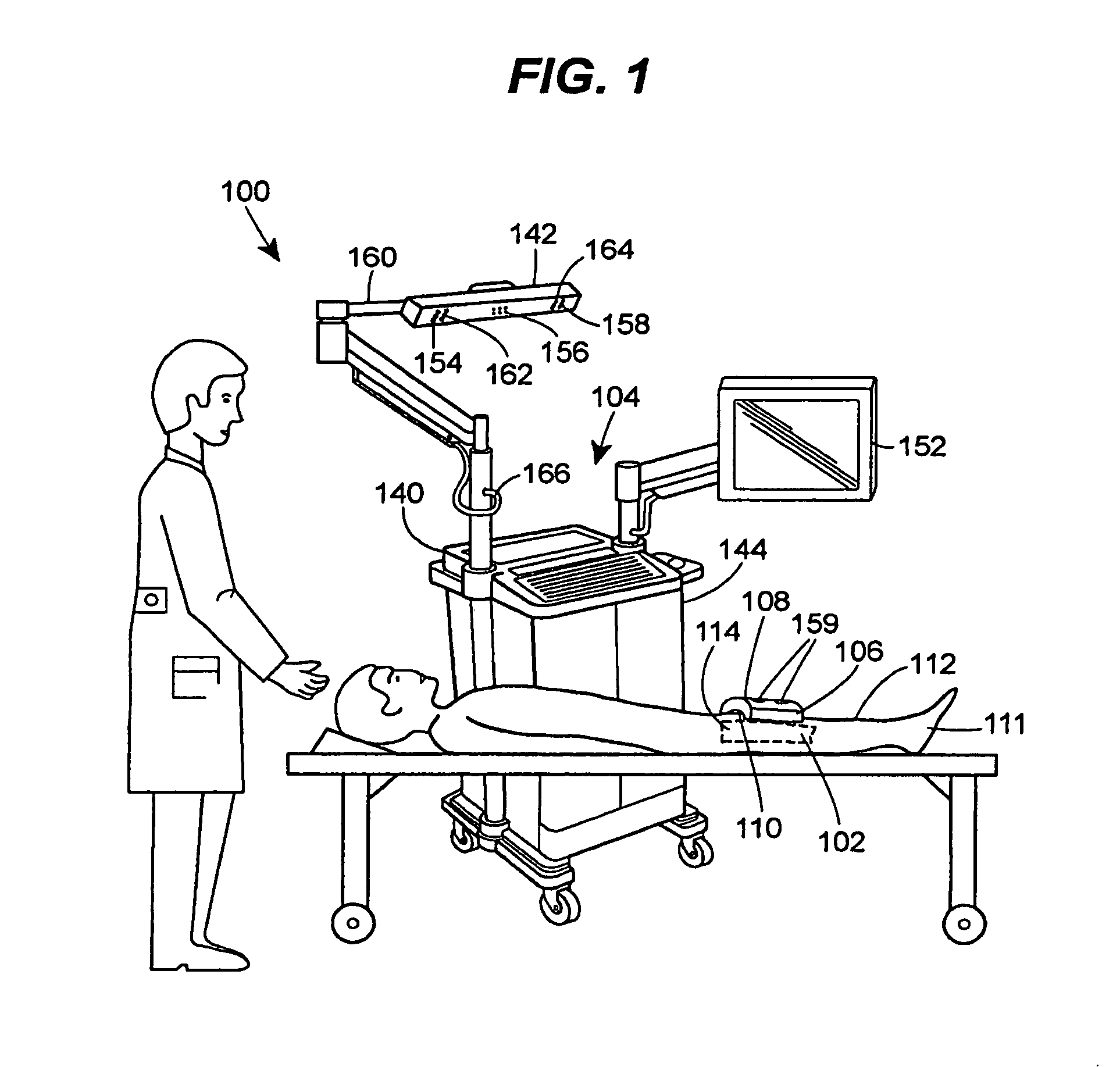
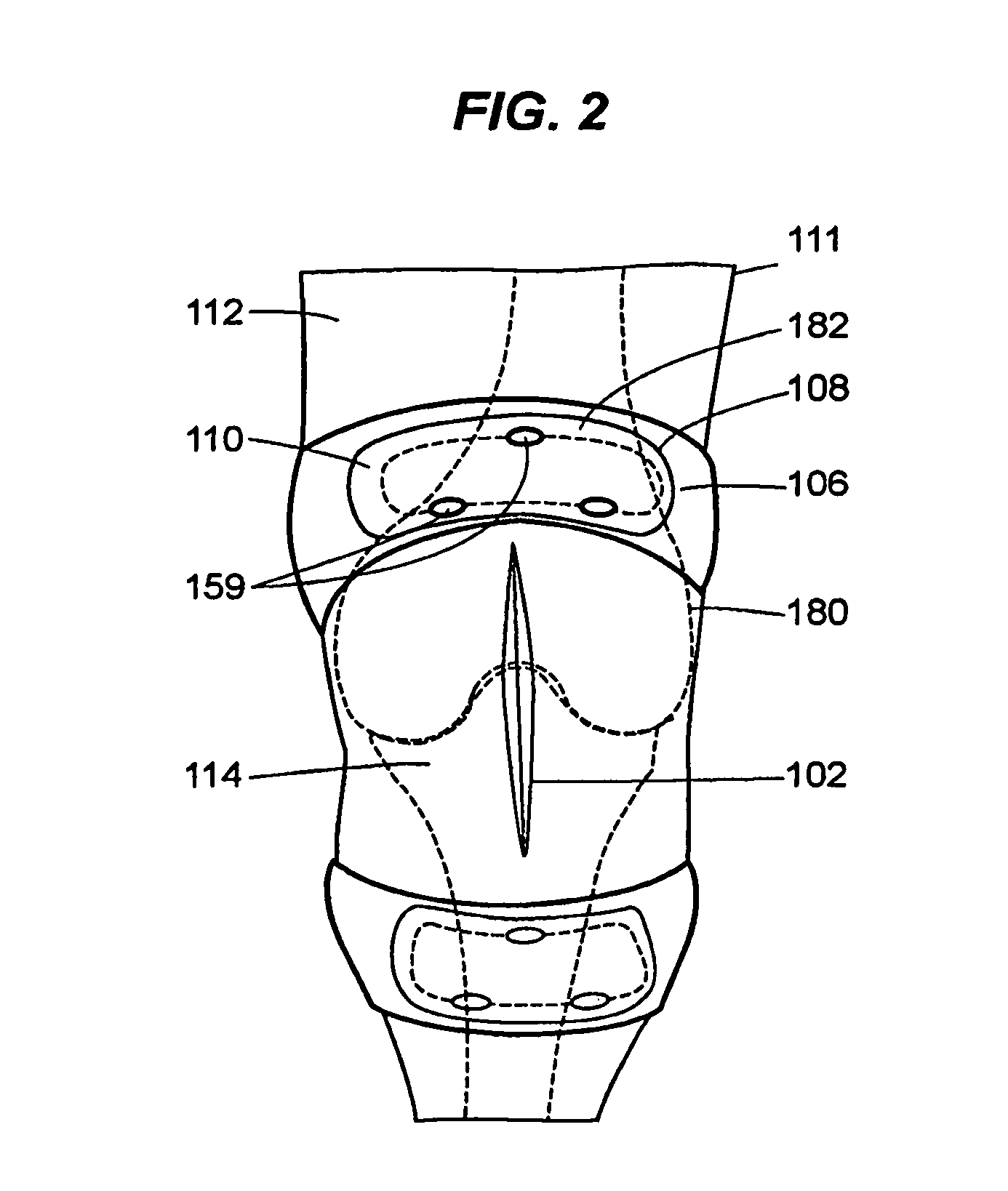
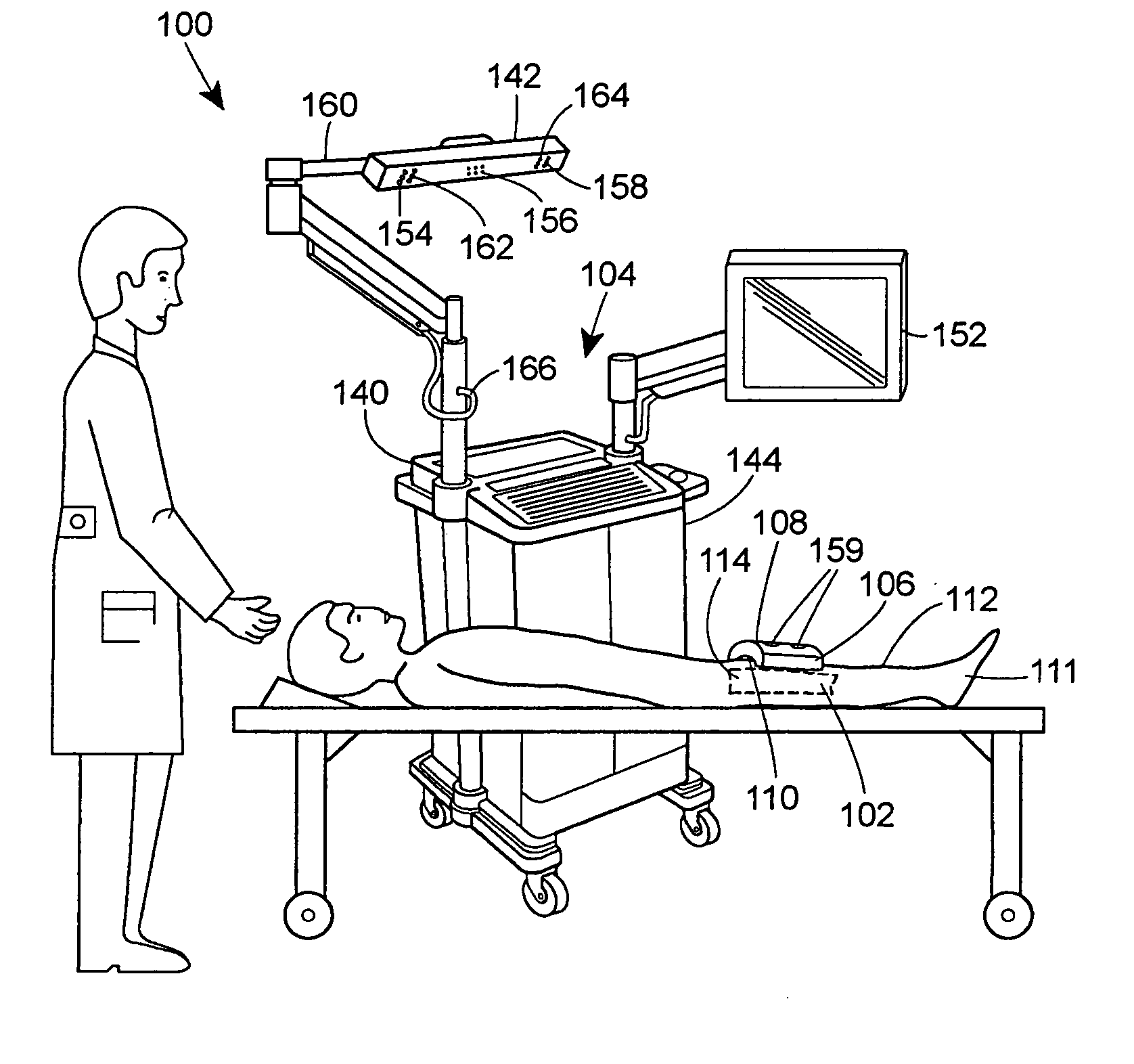
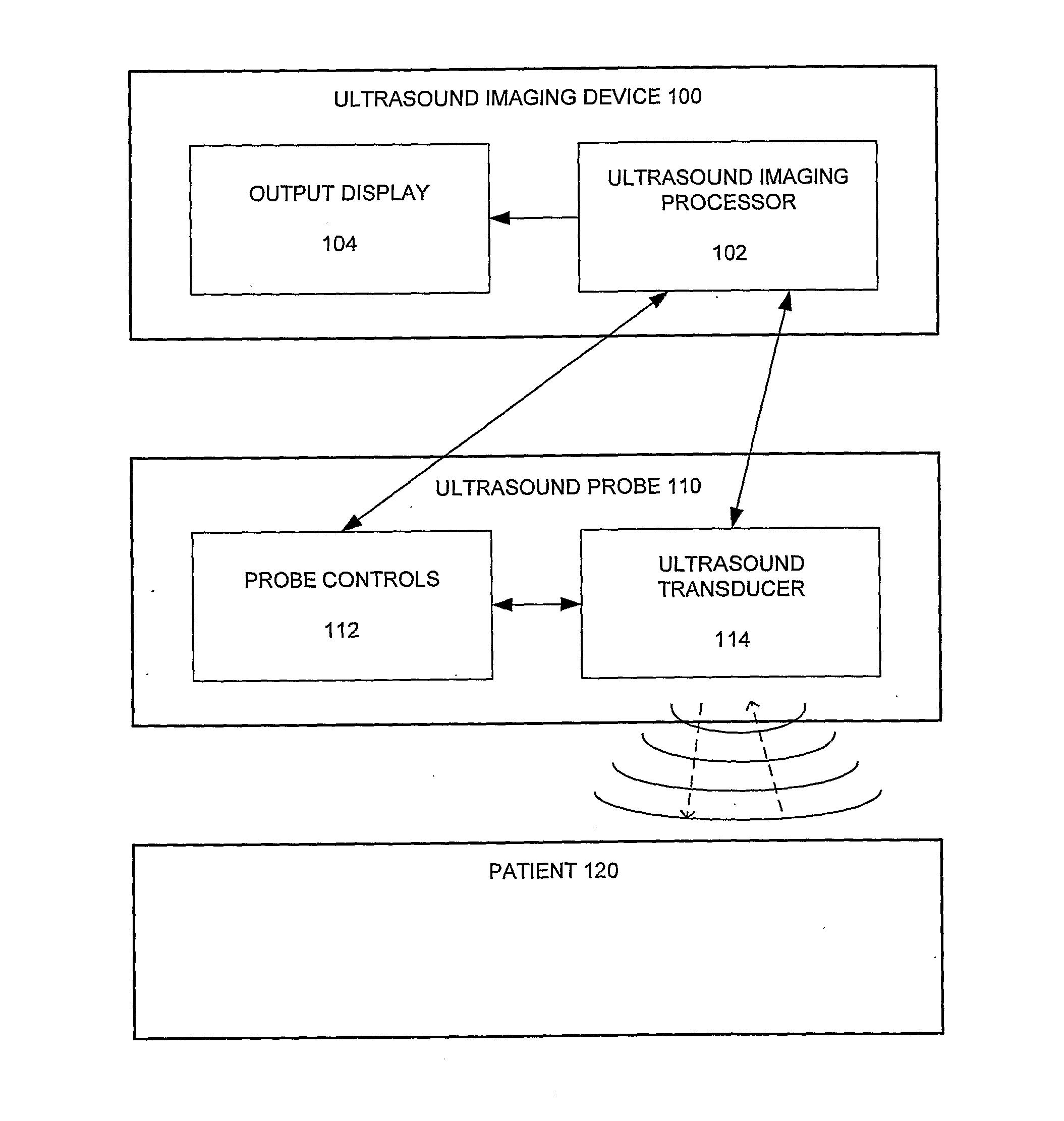
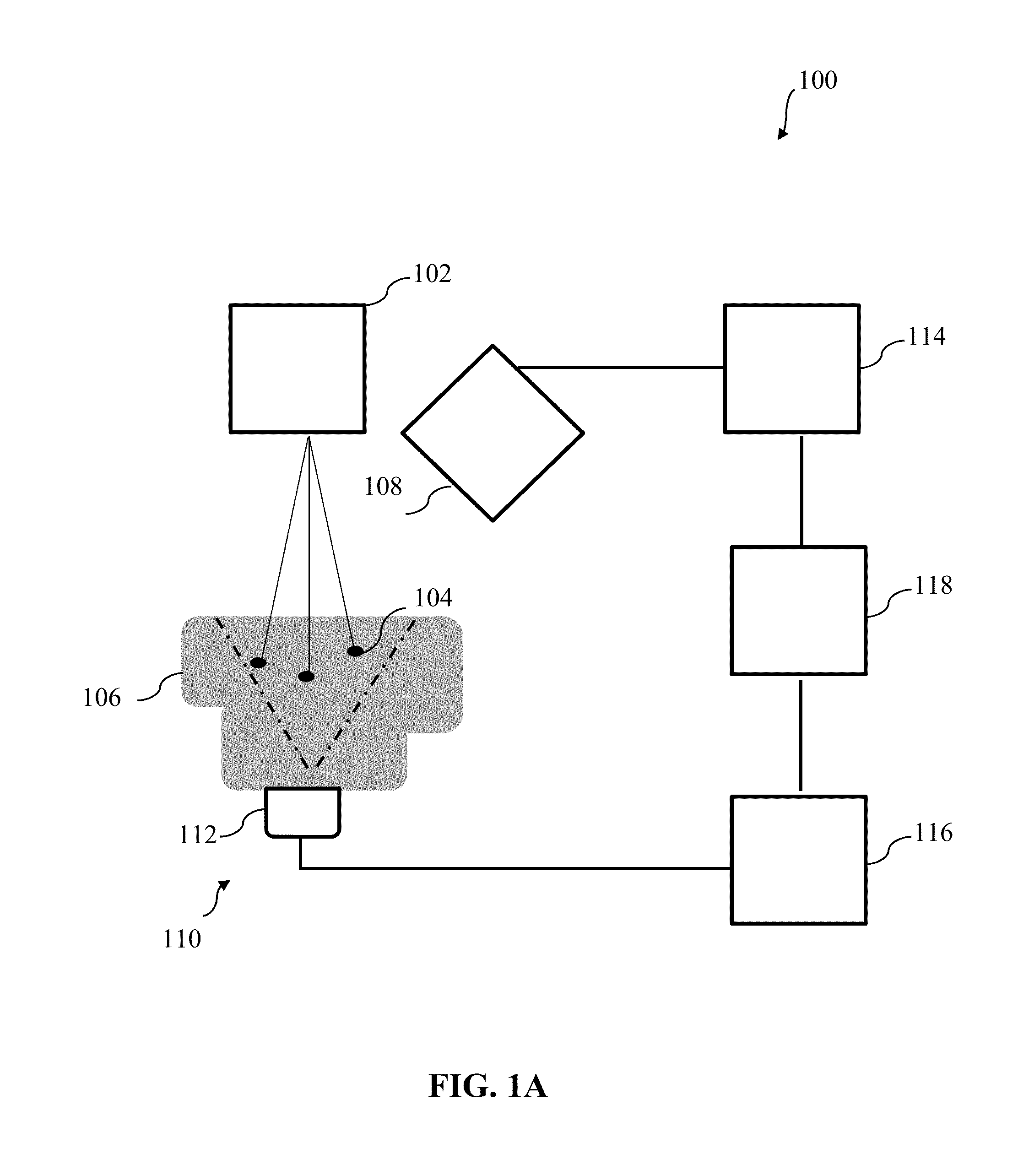
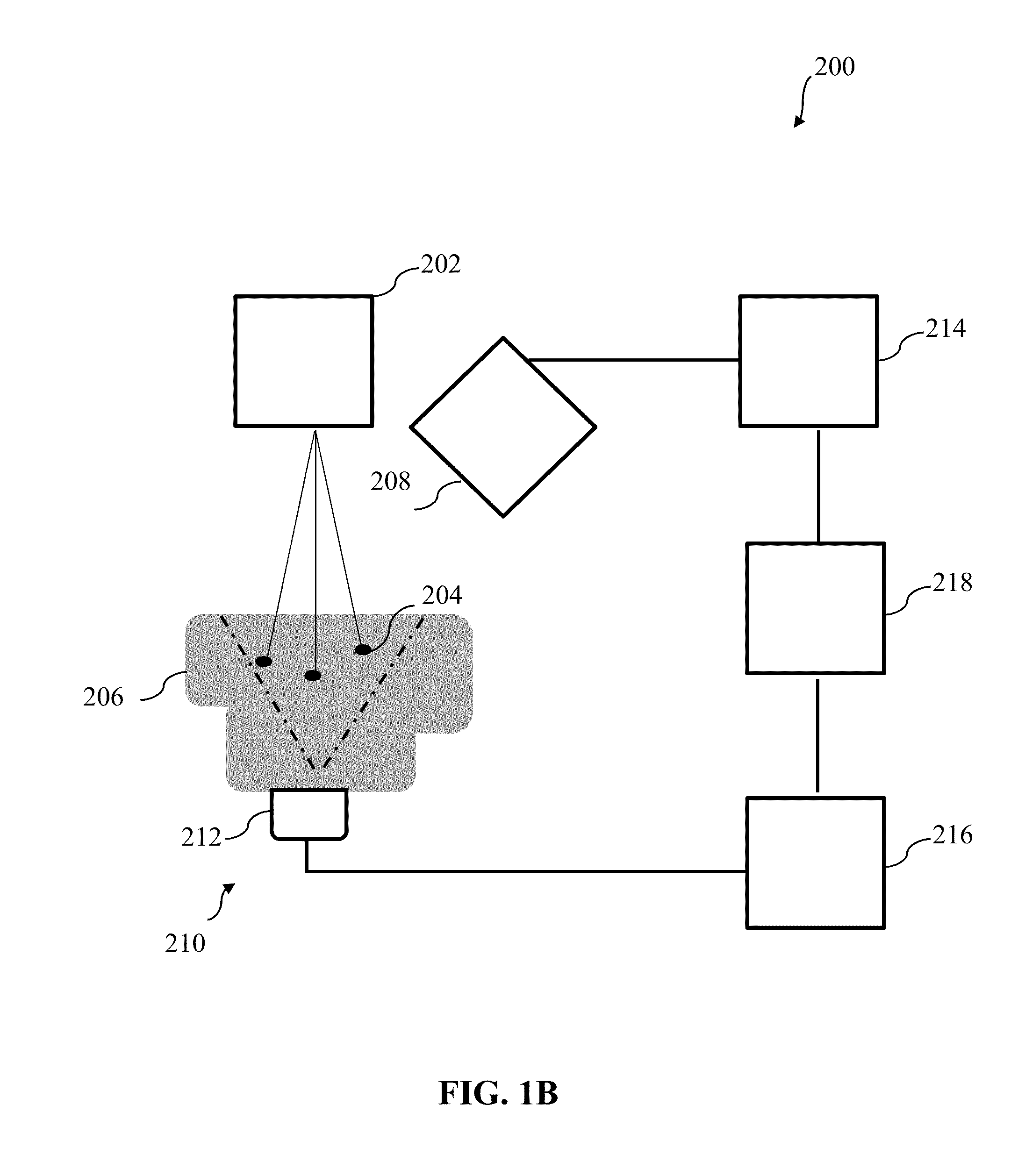
Systems and methods for non-invasive detection and monitoring of cardiac and blood parameters
InactiveUS20060100530A1Easy to detectEffective assessmentBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterData acquisitionNon invasive
Methods and systems for long term monitoring of one or more physiological parameters such as respiration, heart rate, body temperature, electrical heart activity, blood oxygenation, blood flow velocity, blood pressure, intracranial pressure, the presence of emboli in the blood stream and electrical brain activity are provided. Data is acquired non-invasively using ambulatory data acquisition techniques.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
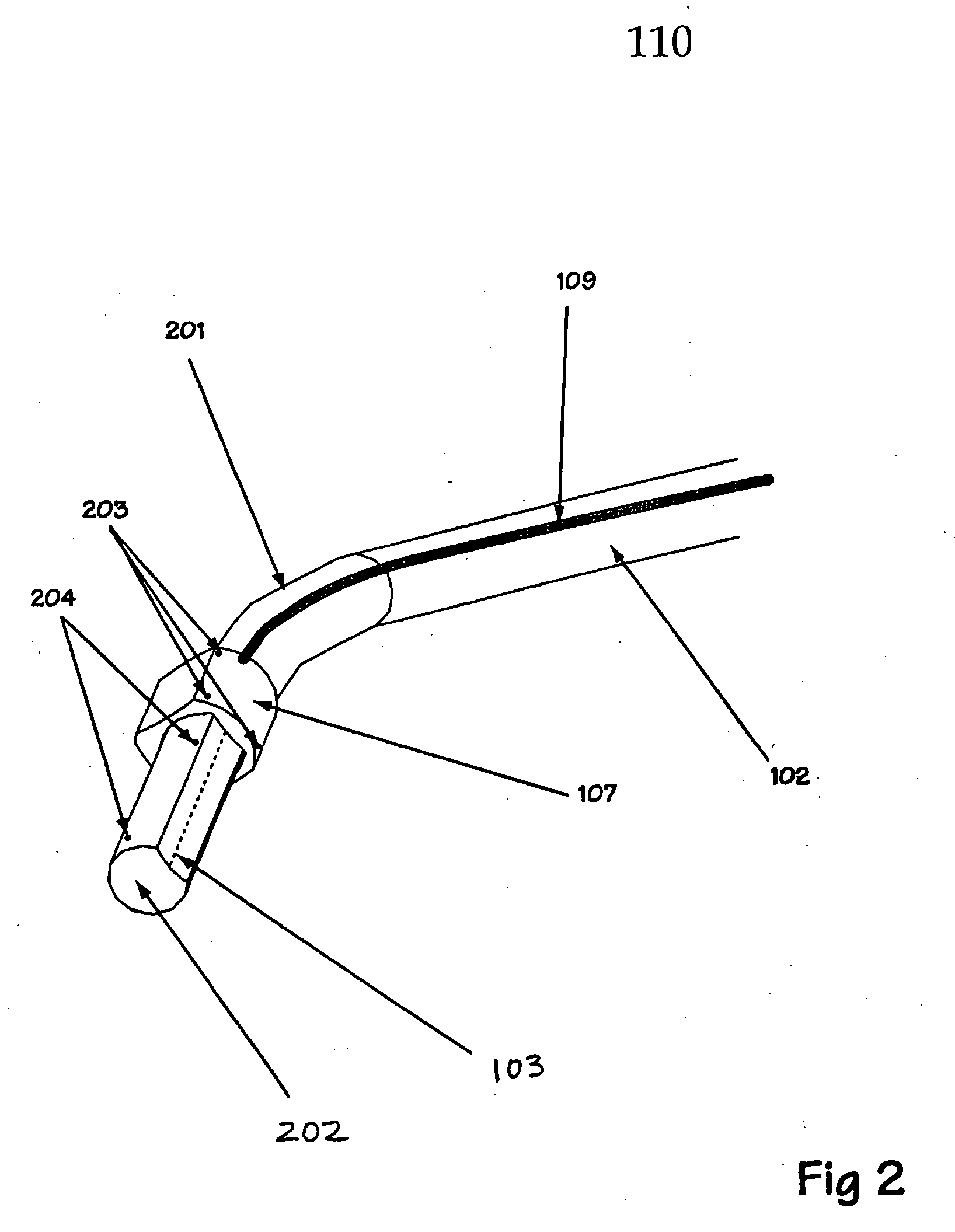
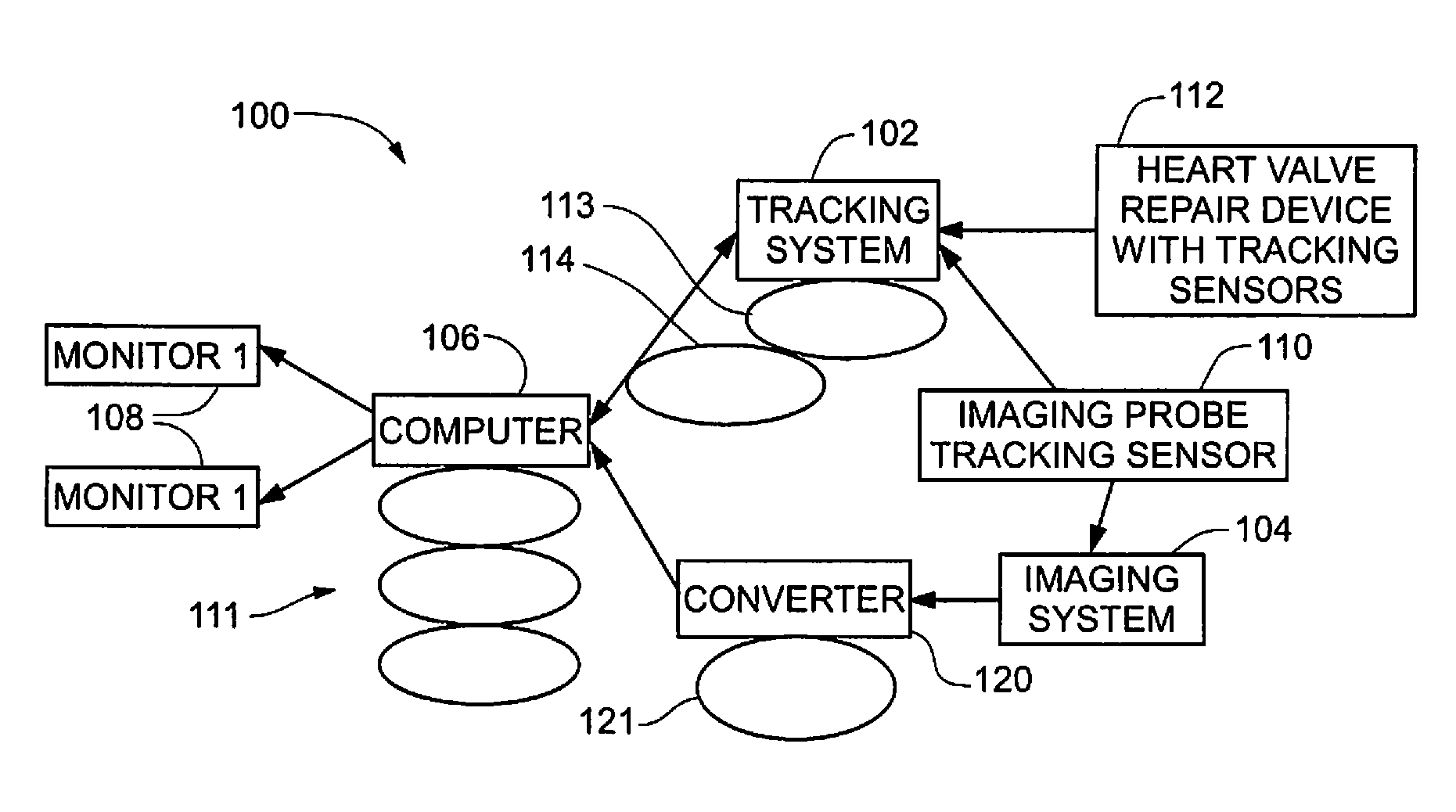
Ultrasound system with stereo image guidance or tracking
ActiveUS20150148664A1Prevent movementOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsDisplay deviceStereo image
An image-guided ultrasound system may include an ultrasound probe, a display configured to communicate with the ultrasound probe to receive ultrasound signals to display images from the ultrasound probe, and an imaging device that may be attached to or integral with the ultrasound probe and configured to communicate with the display to display information derived from images from the imaging device. The imaging device may include a stabilization assembly, an imaging device assembly physically coupled to the stabilization assembly, a plurality of light-sensitive devices physically coupled to the stabilization assembly, and a memory unit physically coupled to the imaging device assembly, the memory unit configured to store calibration or usage information for the image-guided ultrasound system.
Owner:CLEAR GUIDE MEDICAL
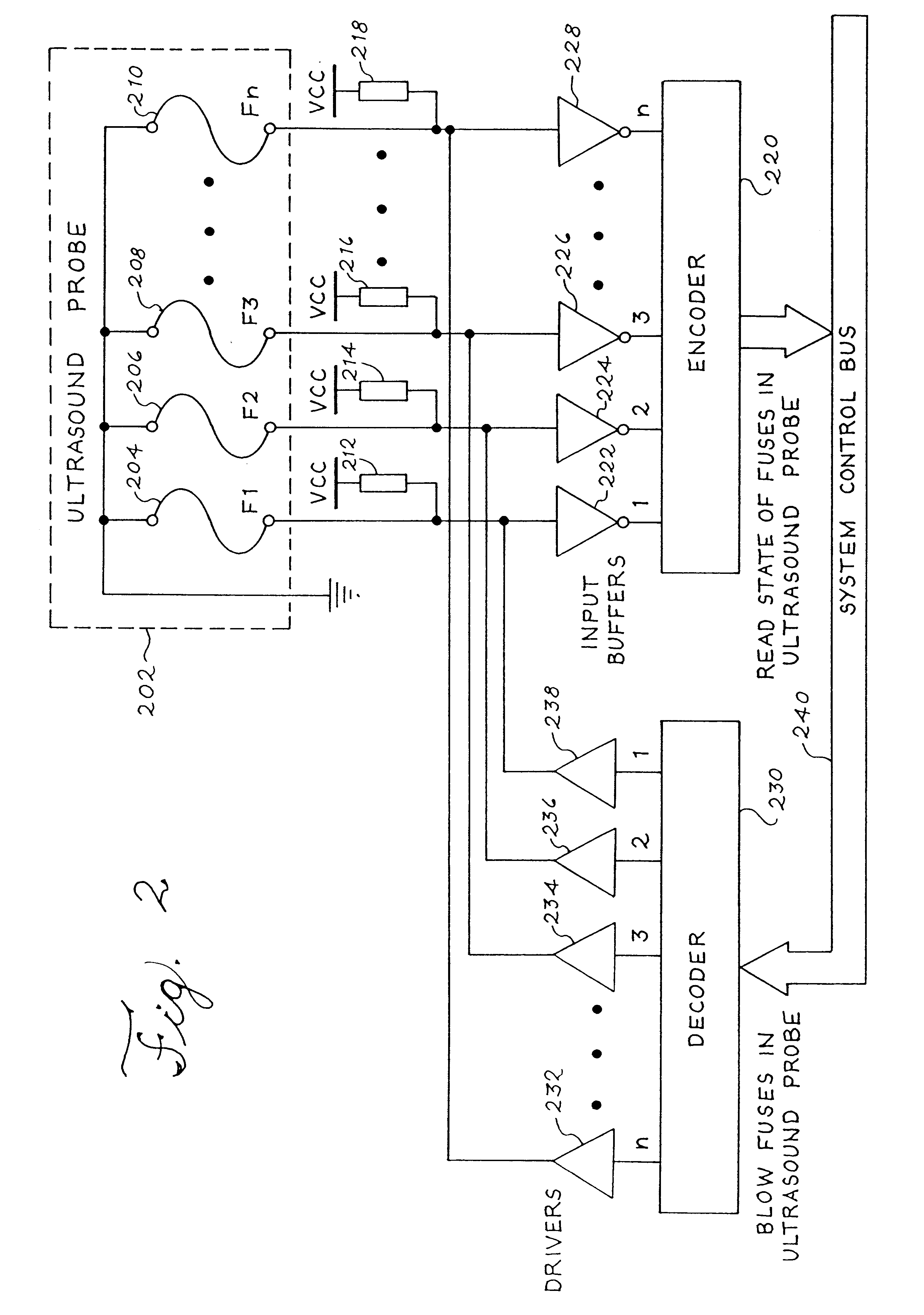
Apparatus and method to limit the life span of a diagnostic medical ultrasound probe
An ultrasound probe for diagnostic medical ultrasound imaging, including an ultrasound transducer and a circuit having a plurality of states to limit the use of the ultrasound probe. Ultrasound probe use can be limited based on a unique identification number (e.g., selected by means of electrically programmable fuses) assigned to each ultrasound probe. Alternatively, the ultrasound system software monitors and updates the number of times that the ultrasound probe has been used. Another aspect of the invention is directed to an ultrasound system, including an ultrasound probe with multiple states, a circuit to program and to receive state data from the ultrasound probe and interpret the state data, and a cable to communicate state data between the ultrasound probe and the processor. Another aspect of the invention is directed to a method for using a limited use ultrasound probe, including the steps of determining the state of a circuit in the limited use ultrasound probe and determining if the ultrasound probe can be used.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
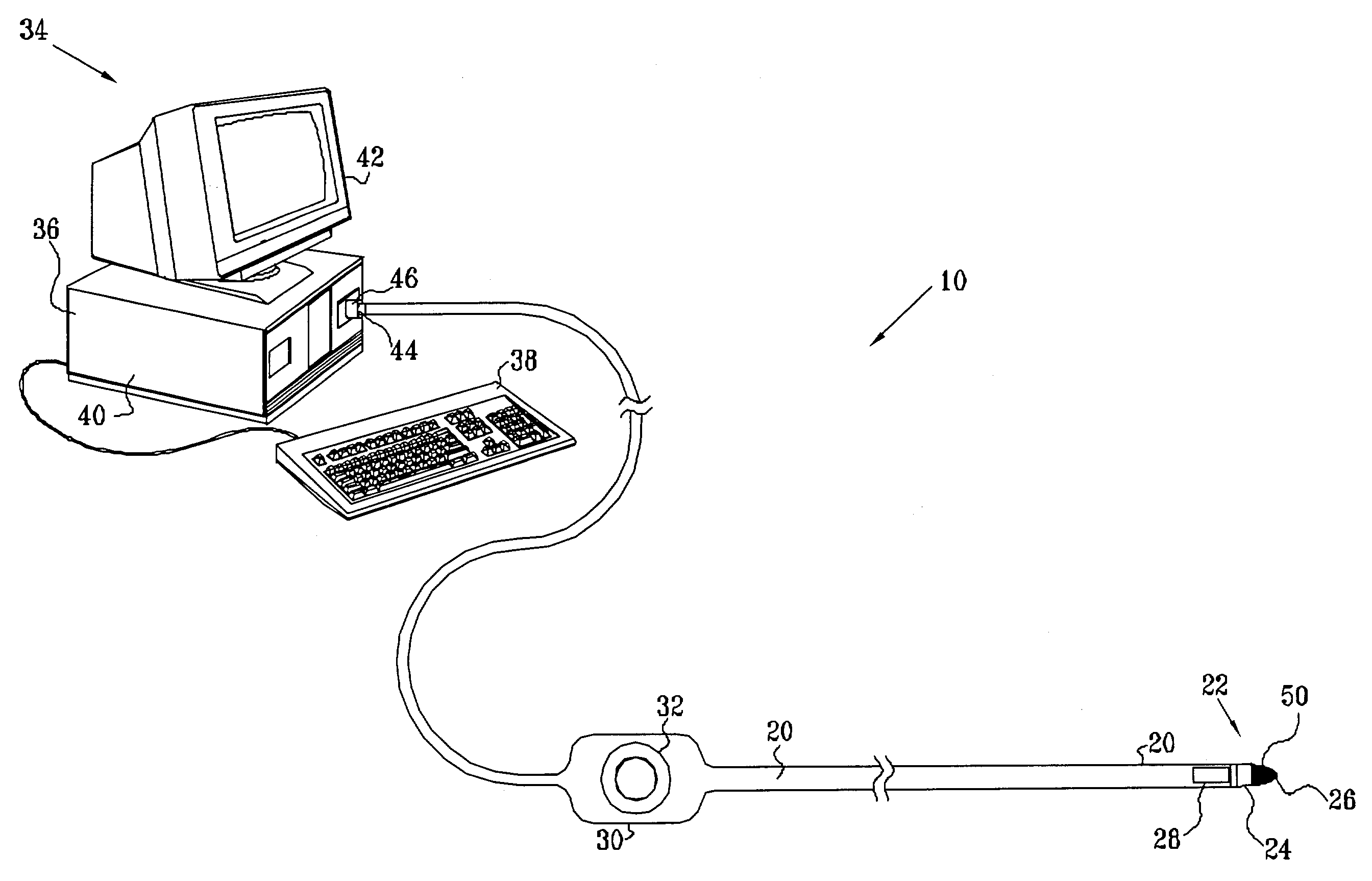
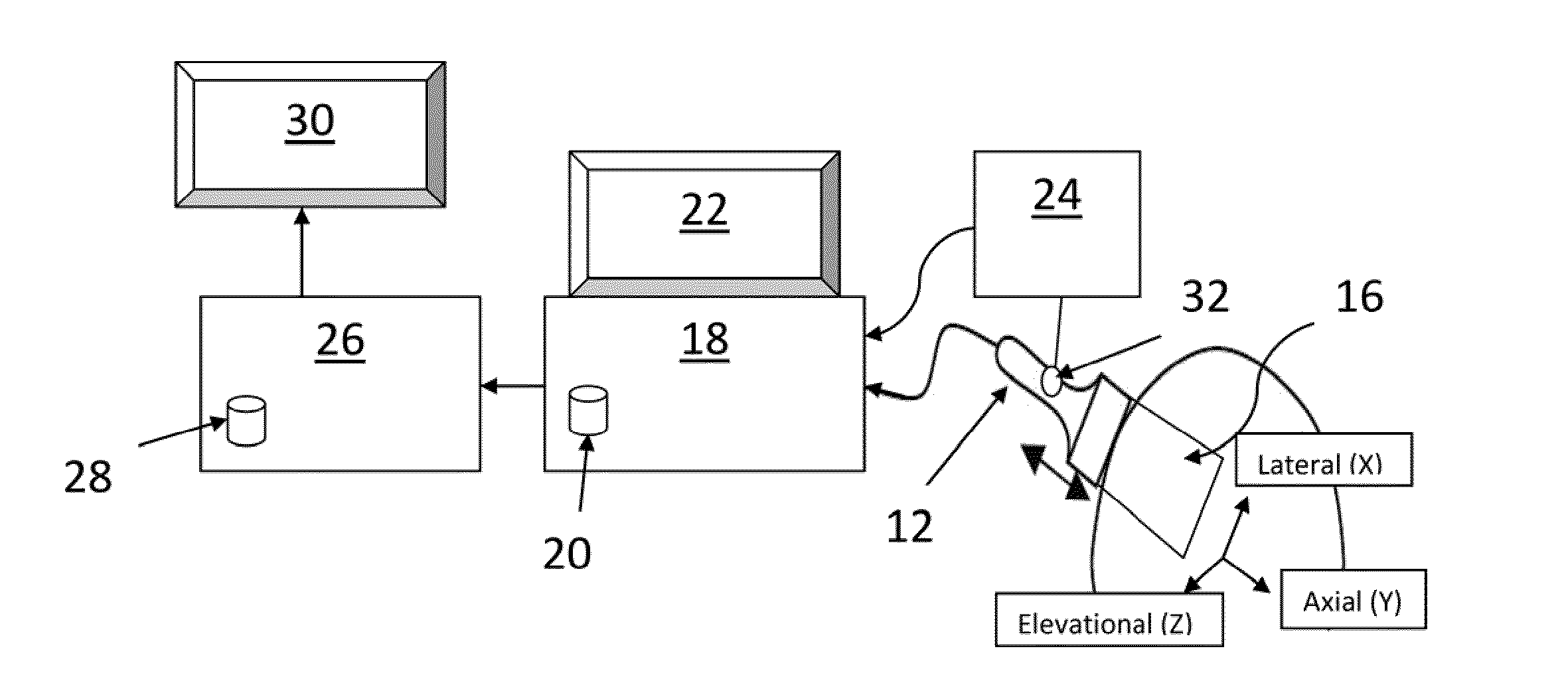
Method and apparatus for calibration, tracking and volume construction data for use in image-guided procedures
An apparatus that collects and processes physical space data while performing an image-guided procedure on an anatomical area of interest includes a calibration probe that collects physical space data by probing a plurality of physical points, a tracked ultrasonic probe, a tracking device that tracks the ultrasonic probe in space and an image data processor. The physical space data provides three-dimensional coordinates for each of the physical points. The image data processor includes a computer-readable medium holding computer-executable instructions. The executable instructions include determining registrations used to indicate position in both image space and physical space based on the physical space data collected by the calibration probe; using the registrations to map into image space, image data describing the physical space of the tracked ultrasonic probe used to perform the image-guided procedure and the anatomical area of interest; and constructing a three-dimensional volume based on the ultrasonic image data on a periodic basis.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
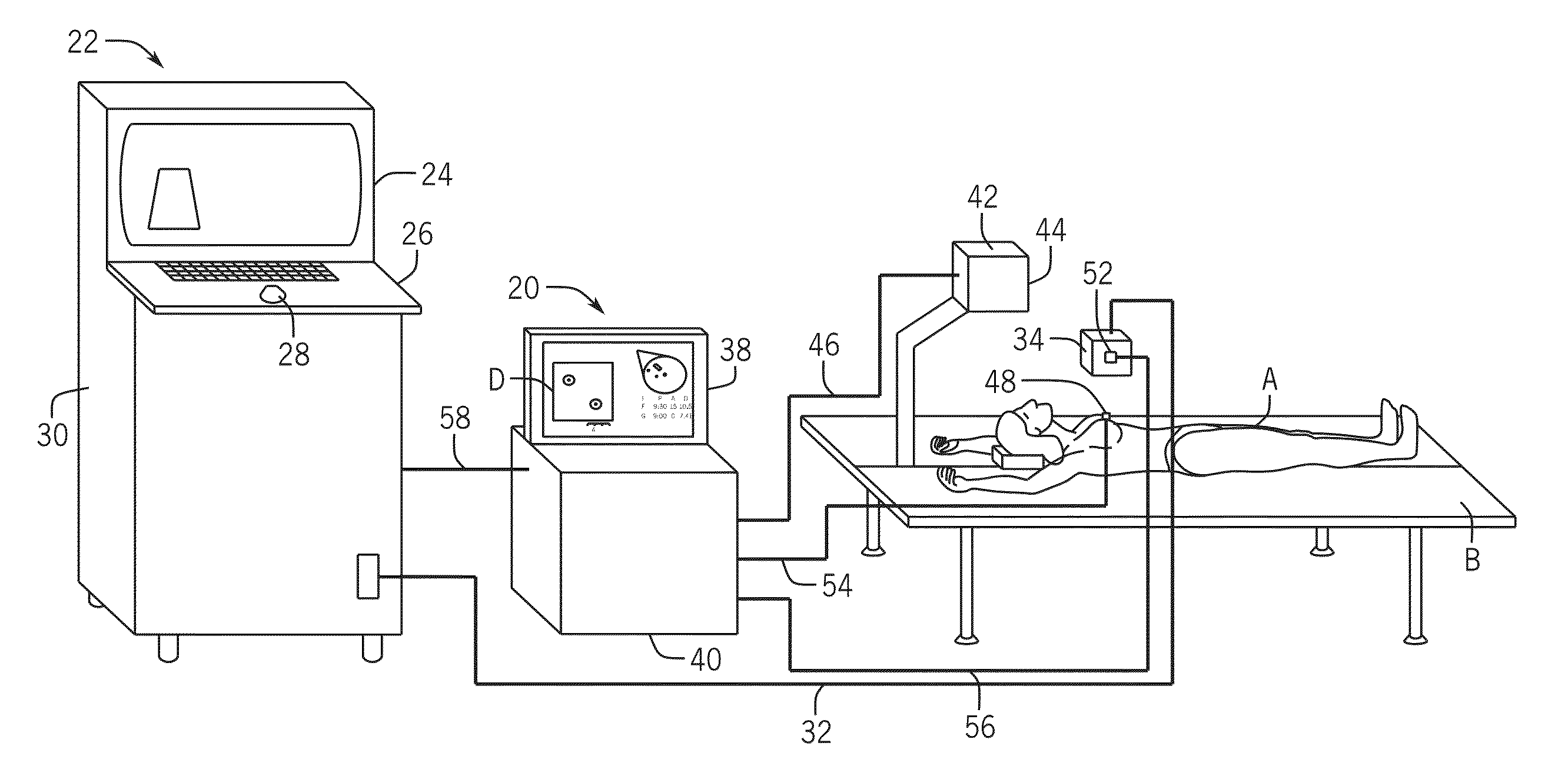
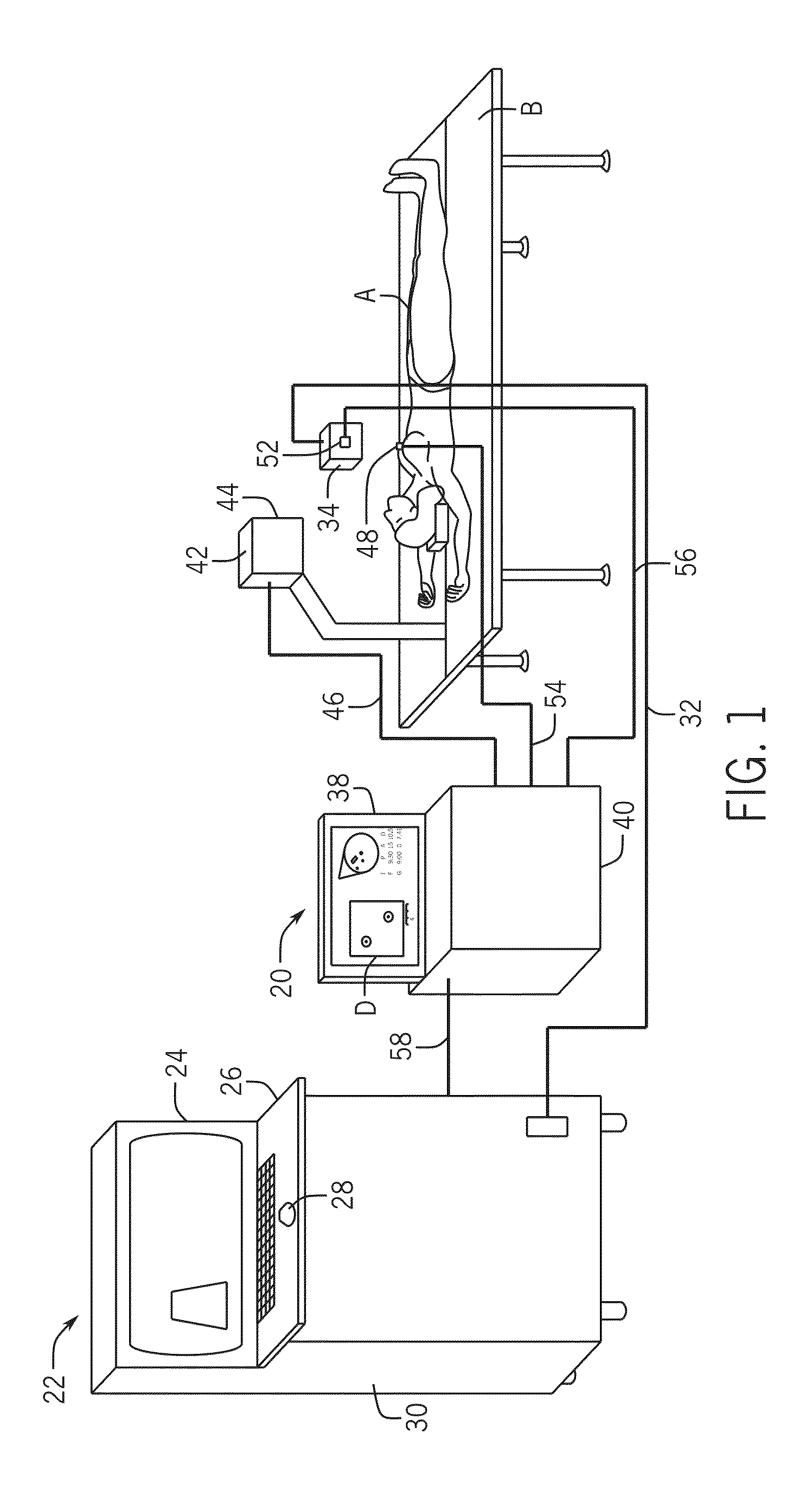
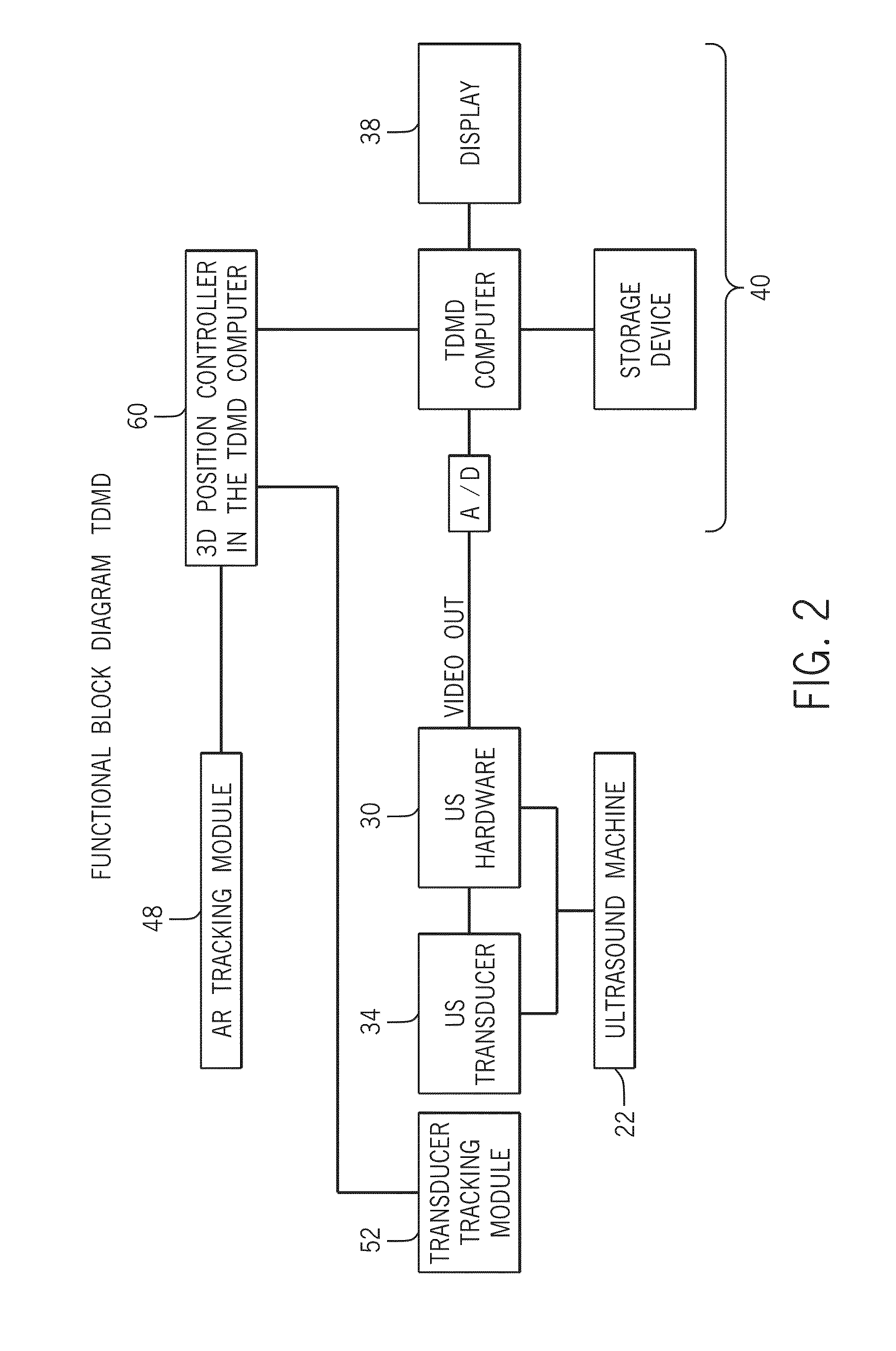
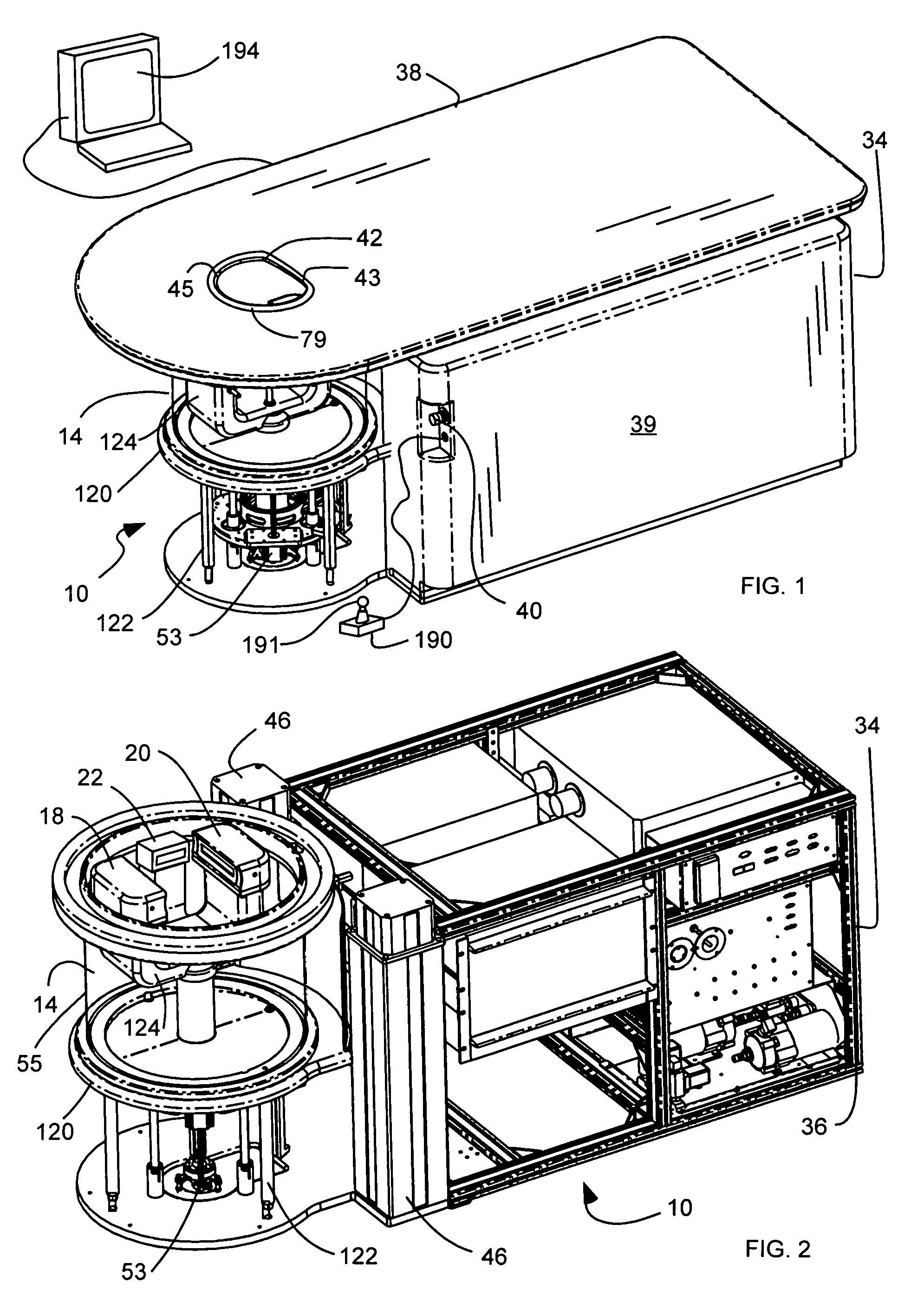
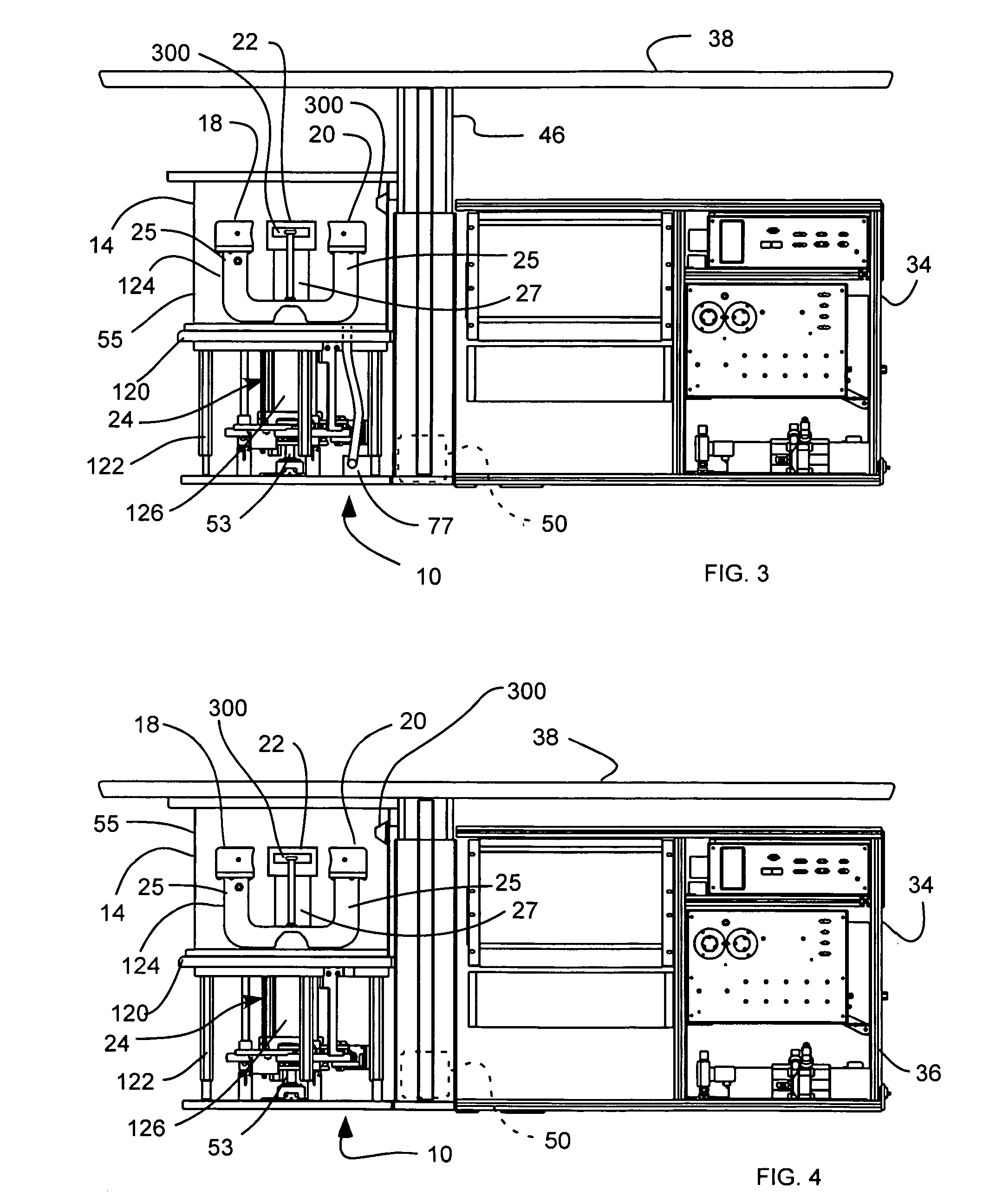
Three Dimensional Mapping Display System for Diagnostic Ultrasound Machines
ActiveUS20150051489A1Shorten the timeTime-consuming to eliminateOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImaging interpretation
An automated three dimensional mapping and display system for a diagnostic ultrasound system is presented. According to the invention, ultrasound probe position registration is automated, the position of each pixel in the ultrasound image in reference to selected anatomical references is calculated, and specified information is stored on command. The system, during real time ultrasound scanning, enables the ultrasound probe position and orientation to be continuously displayed over a body or body part diagram, thereby facilitating scanning and images interpretation of stored information. The system can then record single or multiple ultrasound free hand two-dimensional (also “2D”) frames in a video sequence (clip) or cine loop wherein multiple 2D frames of one or more video sequences corresponding to a scanned volume can be reconstructed in three-dimensional (also “3D”) volume images corresponding to the scanned region, using known 3D reconstruction algorithms. In later examinations, the exact location and position of the transducer can be recreated along three dimensional or two dimensional axis points enabling known targets to be viewed from an exact, known position.
Owner:METRITRACK
Ultrasound catheter calibration system
ActiveUS7090639B2Improve accuracyConvenient electronic storageMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurgical navigation systemsUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Apparatus is provided for calibrating a probe having a position sensor and an ultrasonic transducer. The apparatus includes a test fixture, which includes an ultrasonic target disposed therein at a known position. A computer is adapted to receive a position signal generated by the position sensor while the transducer is in alignment with the ultrasonic target, determine an orientation of the probe in a frame of reference of the test fixture, and determine calibration data for the probe responsive to the orientation of the probe.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Concave Ultrasound Transducers and 3D Arrays
ActiveUS20120095343A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationUltrasound imagingSonification
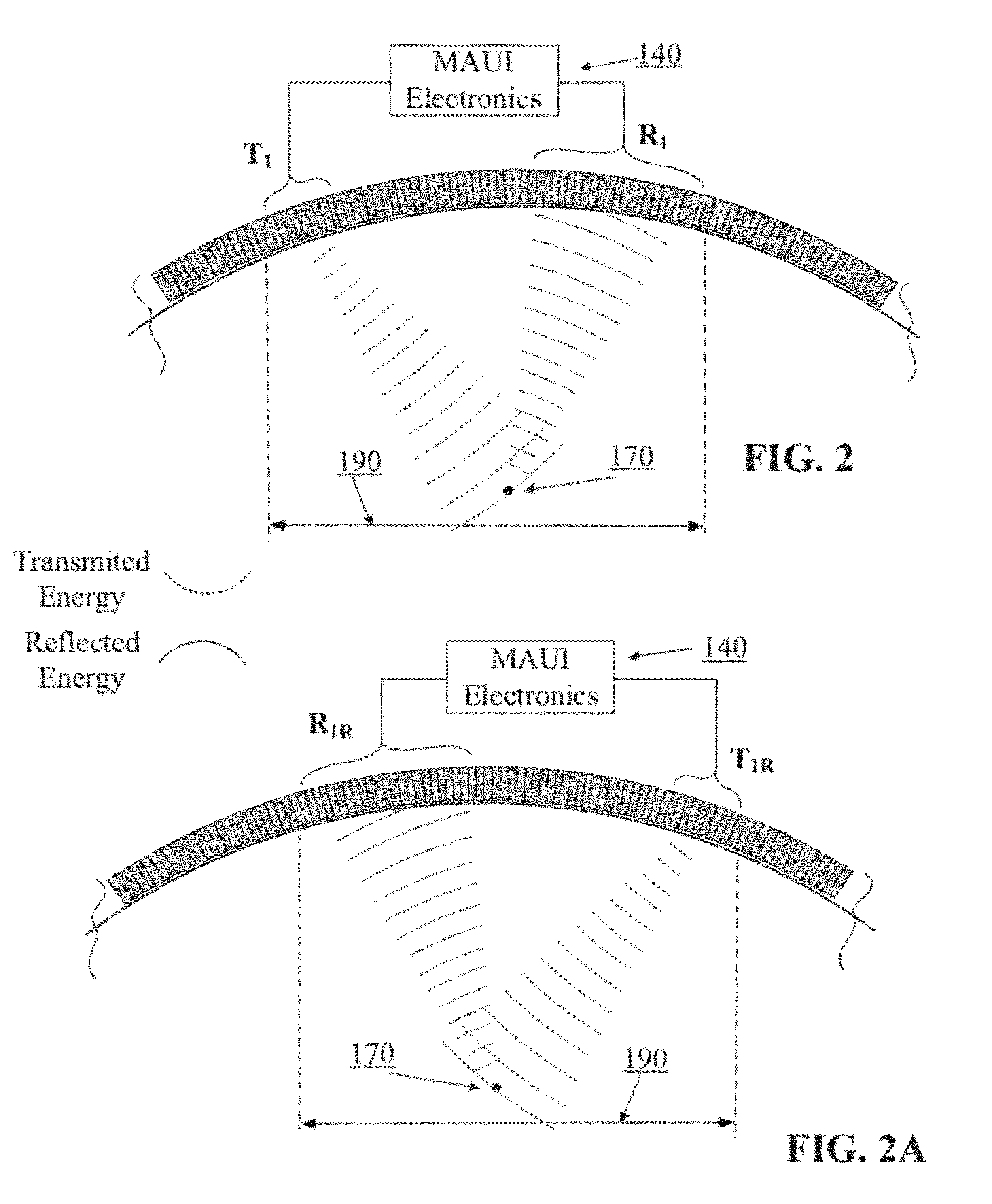
A Multiple Aperture Ultrasound Imaging (MAUI) probe or transducer is uniquely capable of simultaneous imaging of a region of interest from separate apertures of ultrasound arrays. Some embodiments provide systems and methods for designing, building and using ultrasound probes having continuous arrays of ultrasound transducers which may have a substantially continuous concave curved shape in two or three dimensions (i.e. concave relative to an object to be imaged). Other embodiments herein provide systems and methods for designing, building and using ultrasound imaging probes having other unique configurations, such as adjustable probes and probes with variable configurations.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Catheter comprising capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers with an adjustable focus
ActiveUS20140005521A1Wide angleEliminate needChiropractic devicesEye exercisersCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
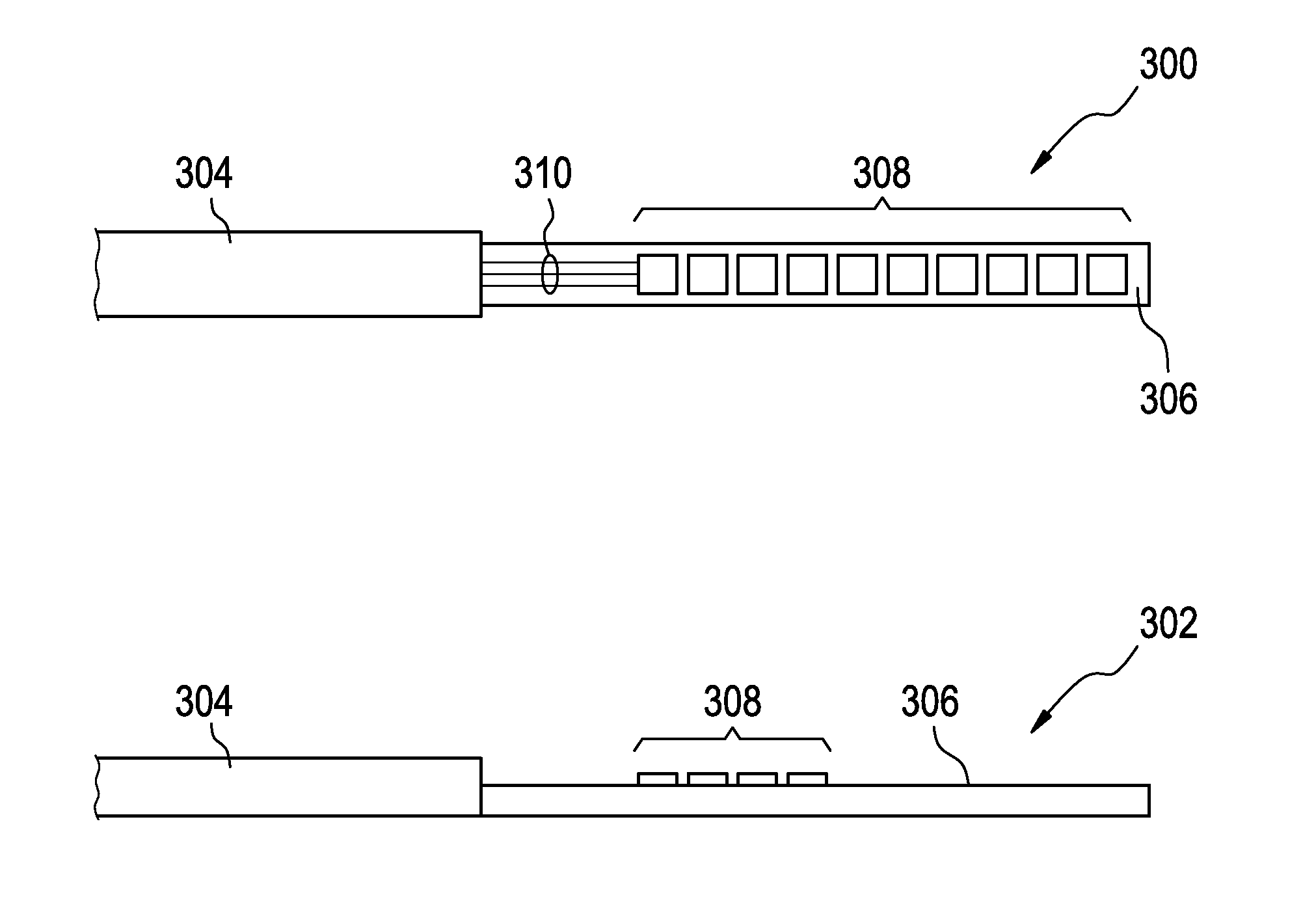
A catheter (700, 800, 1206) comprising: a shaft with distal (808, 906, 1004, 208) and proximal ends (1006),wherein the distal end comprises at least one array of capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers (308, 402, 404, 500, 512, 600, 604,802, 008) with an adjustable focus for controllably heating a target zone (806, 1014, 1210); and a connector (1012) at the proximal end for supplying the at least one array of capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers with electrical power and for controlling the adjustable focus.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System, device, and method for determining a position of an object
ActiveUS7657298B2Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersAnatomical structuresComputerized system
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
System, device, and method for determining a position of an object
ActiveUS20050203383A1Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersAnatomical structuresNavigation system
A system is disclosed for determining a position and a change in the position of an anatomical structure. The system utilizes a surgical navigation system and a substrate that is capable of being removably mounted to an outer surface of a patient's body. The substrate includes a sensor that is tracked by the surgical navigation system and a positional device that determines the position of an anatomical structure relative to the sensor. The concatenation of the position of the sensor and the relative position of the anatomical structure allows a global position of the anatomical structure to be determined by a computer system and displayed to the user.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
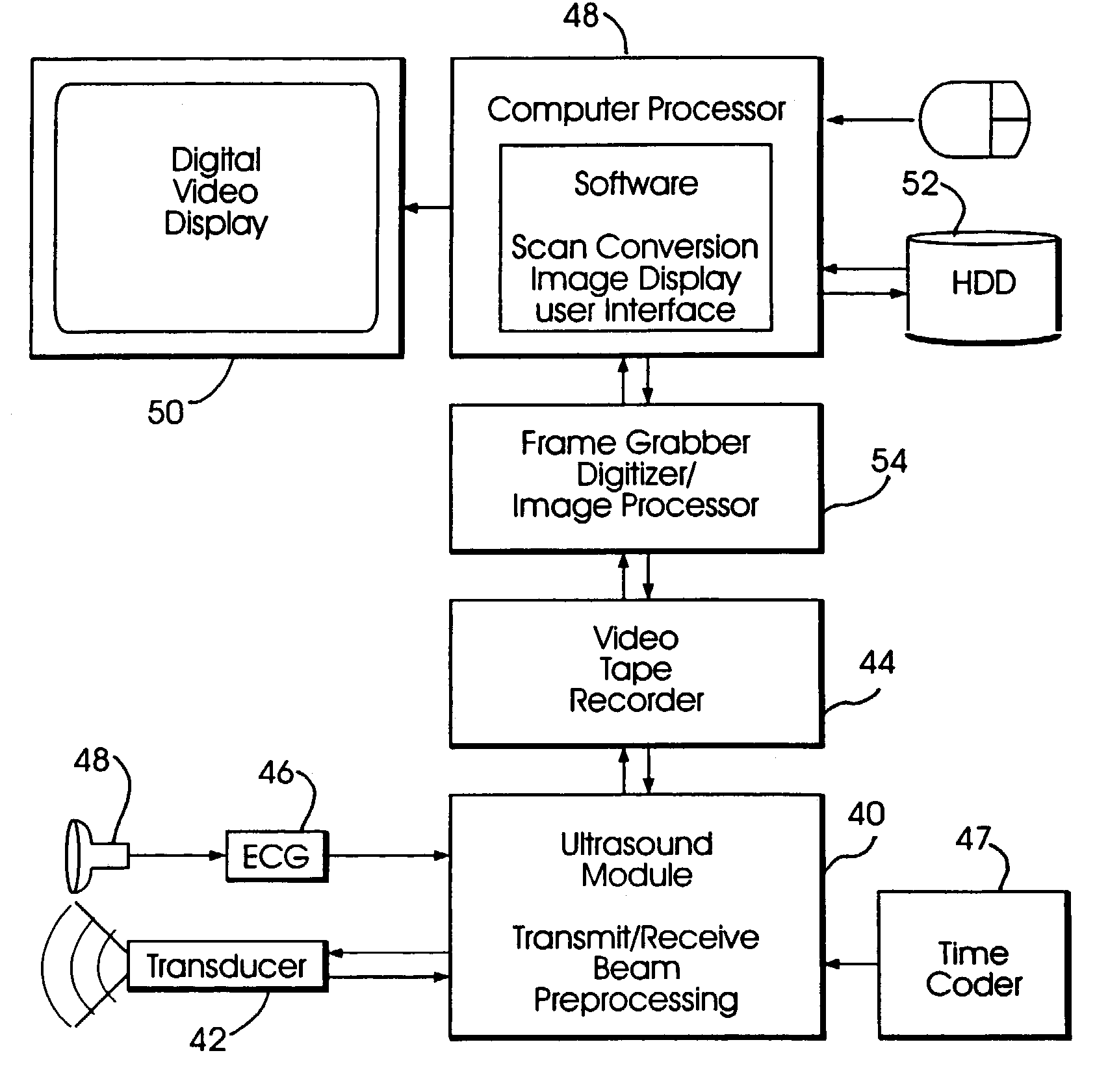
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS20040116812A1ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time "live" ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Systems, methods and apparatus for dual mammography image detection
InactiveUS20060074287A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImaging quality
Systems and methods are provided by which a mammography imaging system offers X-ray and ultrasound imaging that allows sharing of common hardware such as the computer and display. Small regions of interest are imaged with X-ray at higher image quality by using a second sensor with higher DQE than the full-field sensor can obtain. In some embodiments a specialized chamber is provided for securing the anatomy to a fixed location, ultrasound image data is collected along with ultrasound probe location and orientation data from sensors on a handheld probe from which data images can be viewed directly, or used to reconstruct tomographic images of any desired cross-section, or used for various “3-D” image visualization methods. An imaging schedule defined by location and orientation of an ultrasound probe is used to generate a three-dimensional ultrasound image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Medical training method and apparatus
ActiveUS20110170752A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresMedical imaging
There is disclosed a method of simulating the output of a medical imaging device, the medical imaging device being operable to image an anatomical structure, and the method including: accessing model data representing a model of the anatomical structure; accessing selection data representing a selected region of the anatomical structure to be imaged; and processing the selection data and the model data to generate output data representing a simulation of the output of the medical imaging device when imaging the selected region.
Owner:INVENTIVE MEDICAL
Breast scanning system
ActiveUS20080319318A1Easy diagnosisReduce unnecessary biopsiesInfrasonic diagnosticsTomographyRadiologyTransducer
Owner:TECHNISCAN +1
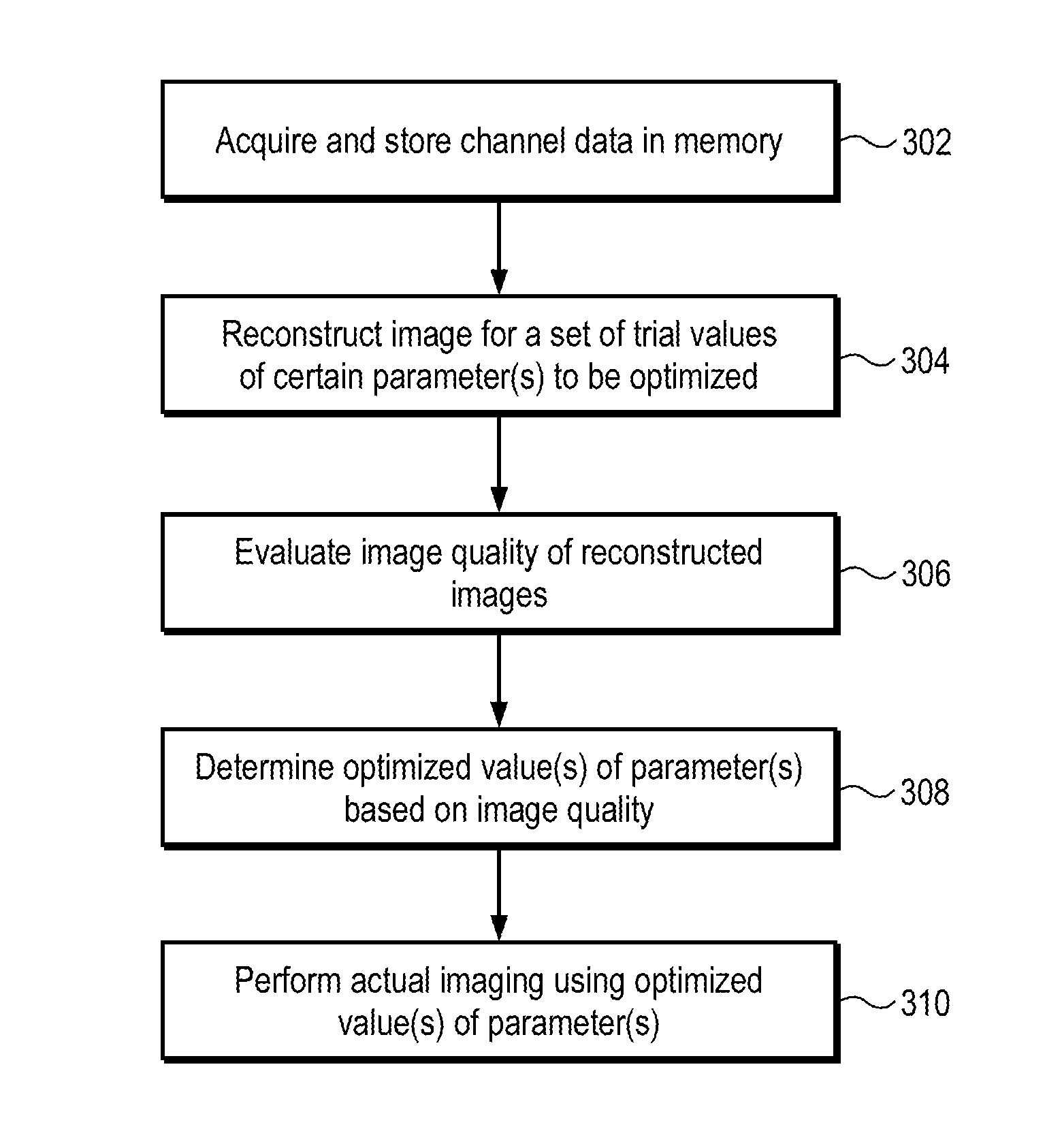
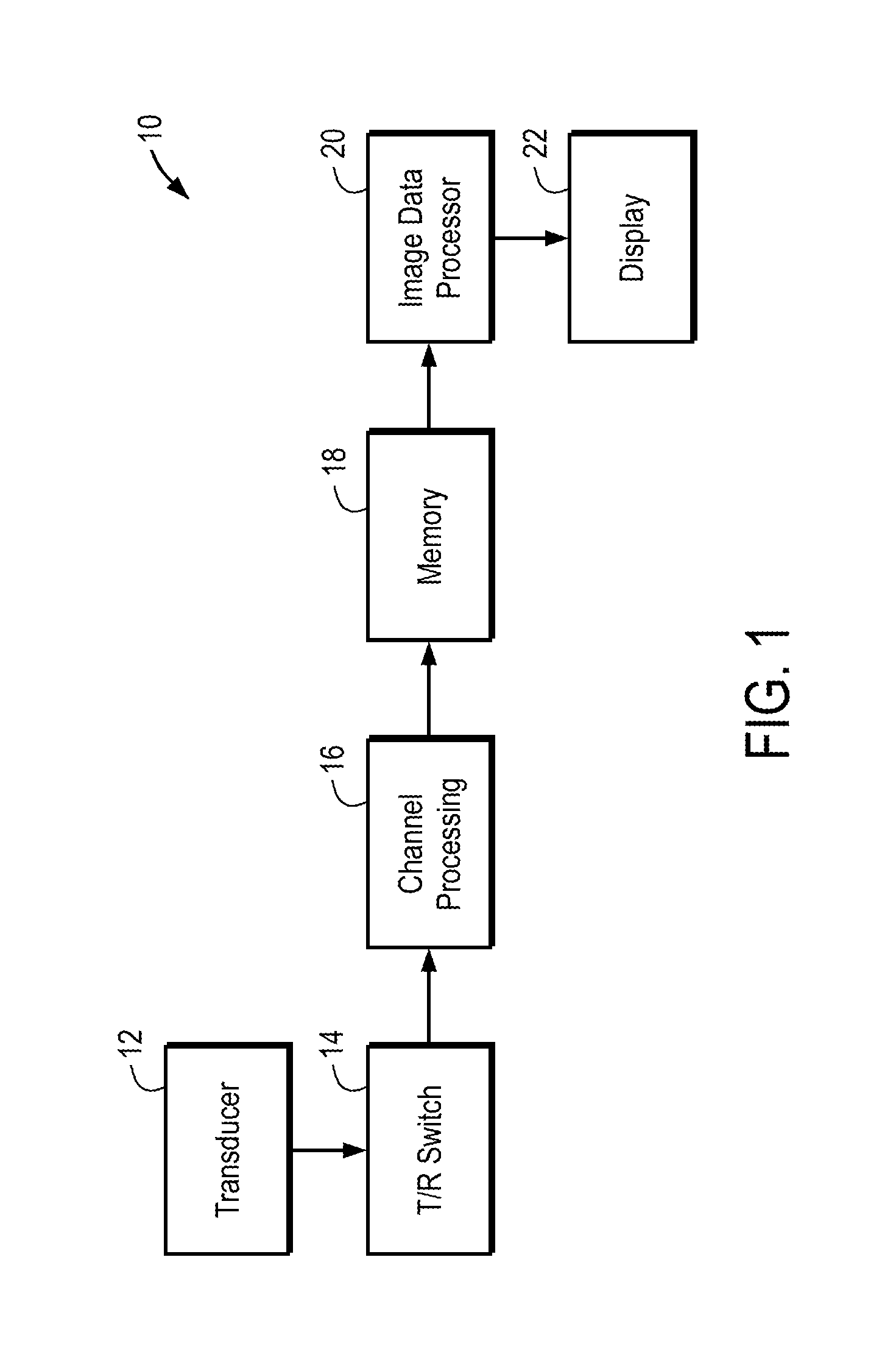
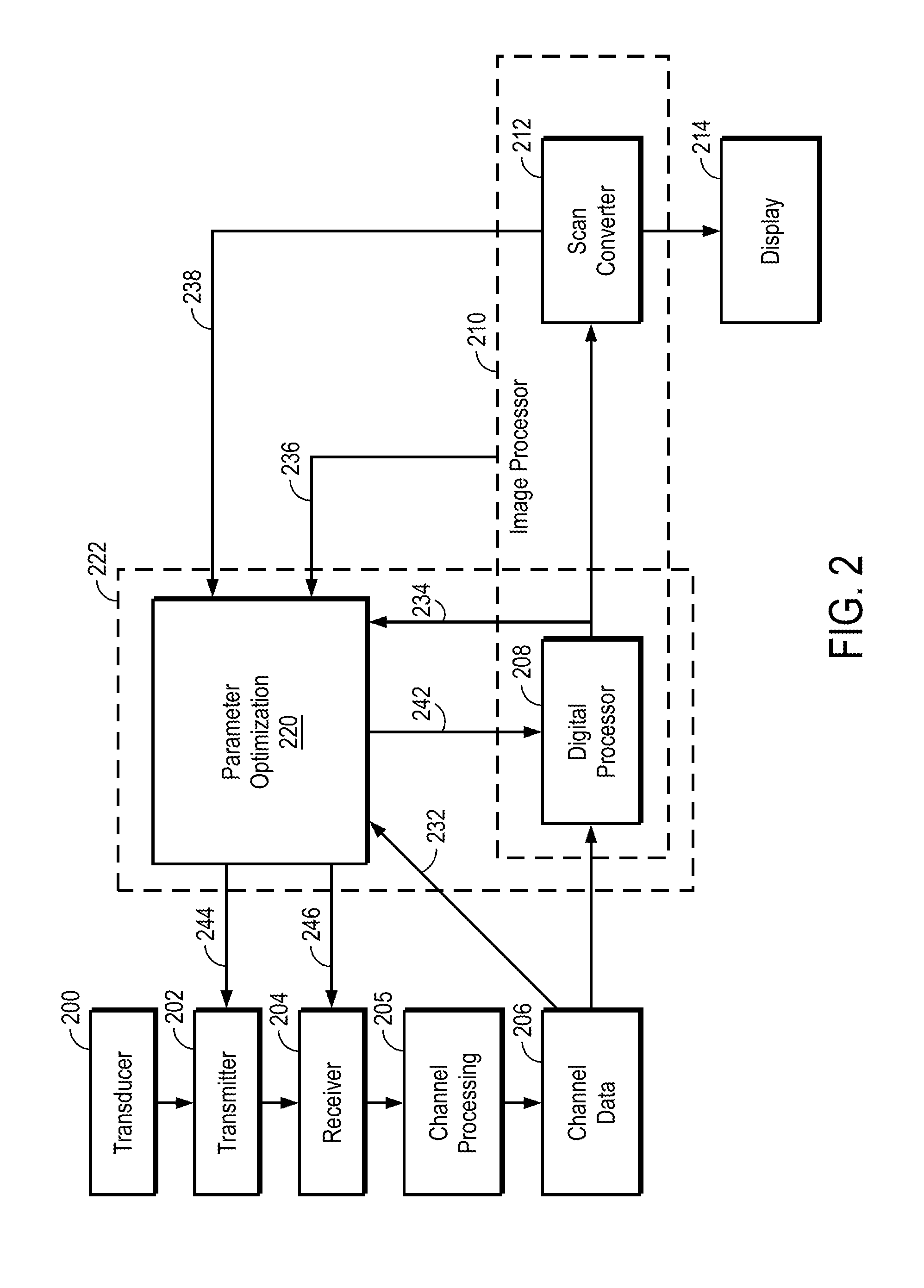
Aberration correction using channel data in ultrasound imaging system
Embodiments of the present invention provide an ultrasound scanner equipped with an image data processing unit that can perform adaptive parameter optimization during image formation and processing. In one embodiment, an ultrasound system comprises a channel data memory to store channel data obtained by digitizing ultrasound image data produced by an image scan; an image data processor configured to process the stored channel data in the memory to reconstruct an ultrasound image for each of a plurality of trial values of at least one parameter to be optimized; and a parameter optimization unit configured to evaluate an image quality of the reconstructed ultrasound image for each trial value of the at least one parameter, and to determine the optimized value of the at least one parameter based on the evaluated image quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
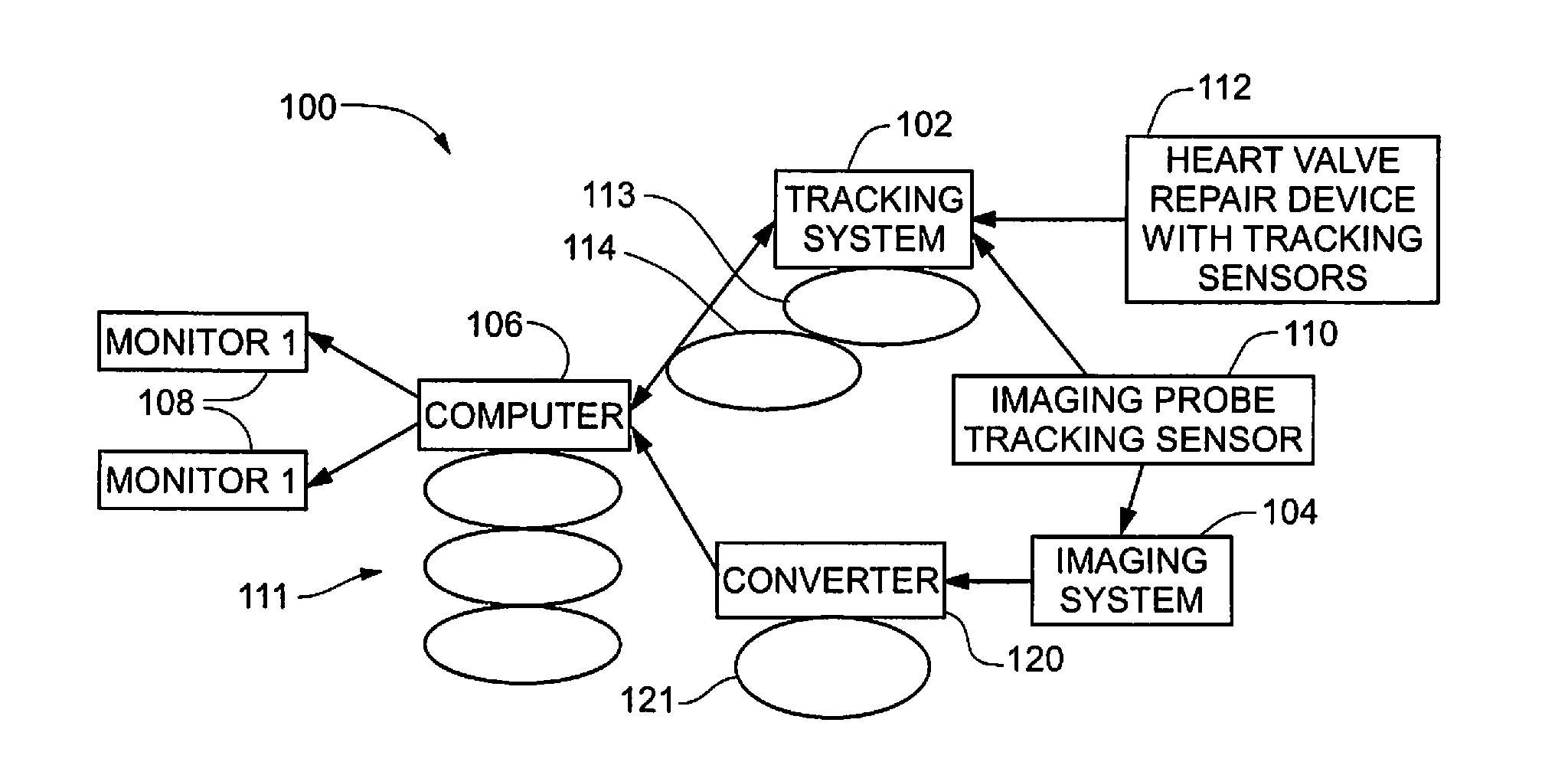
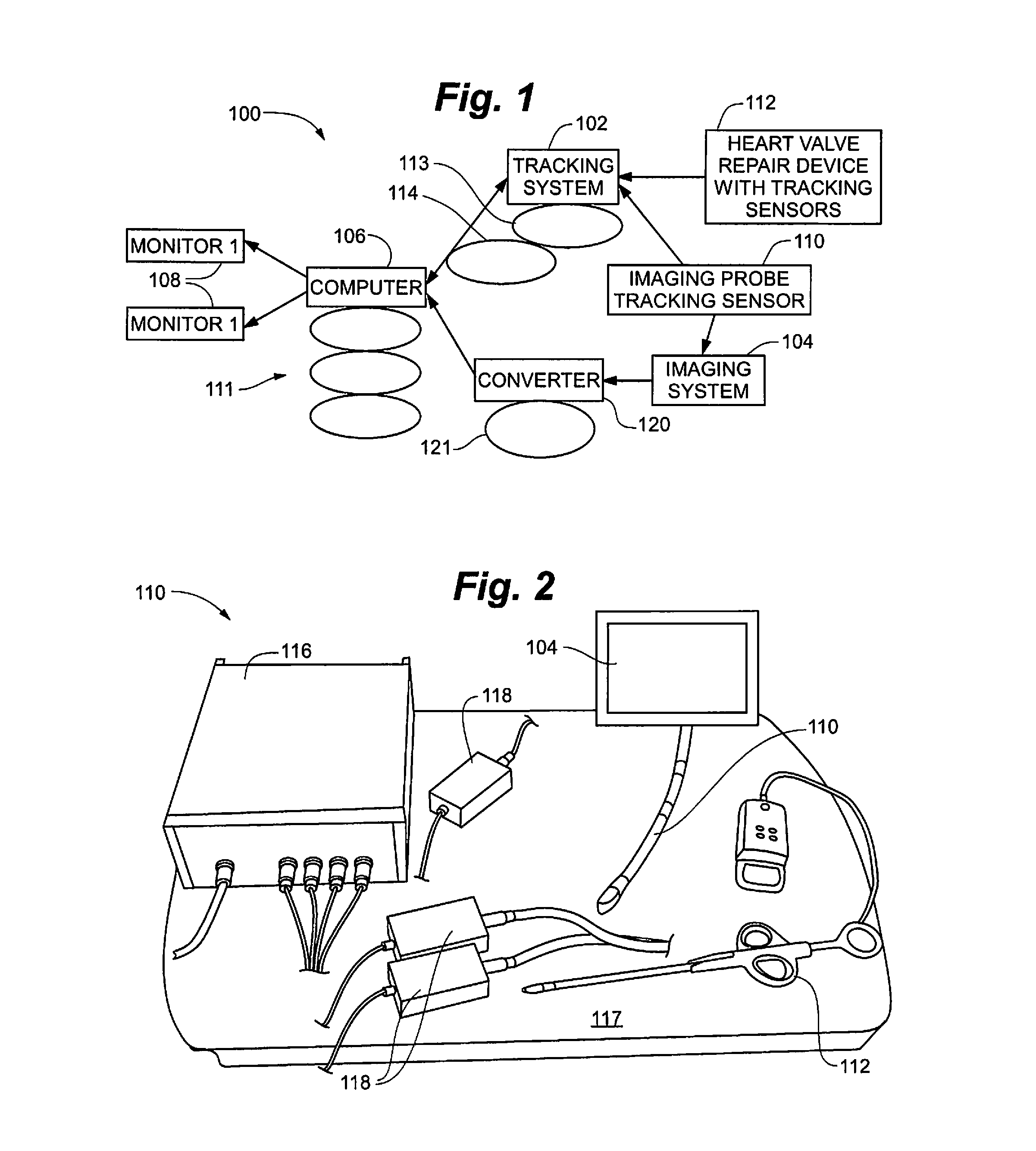
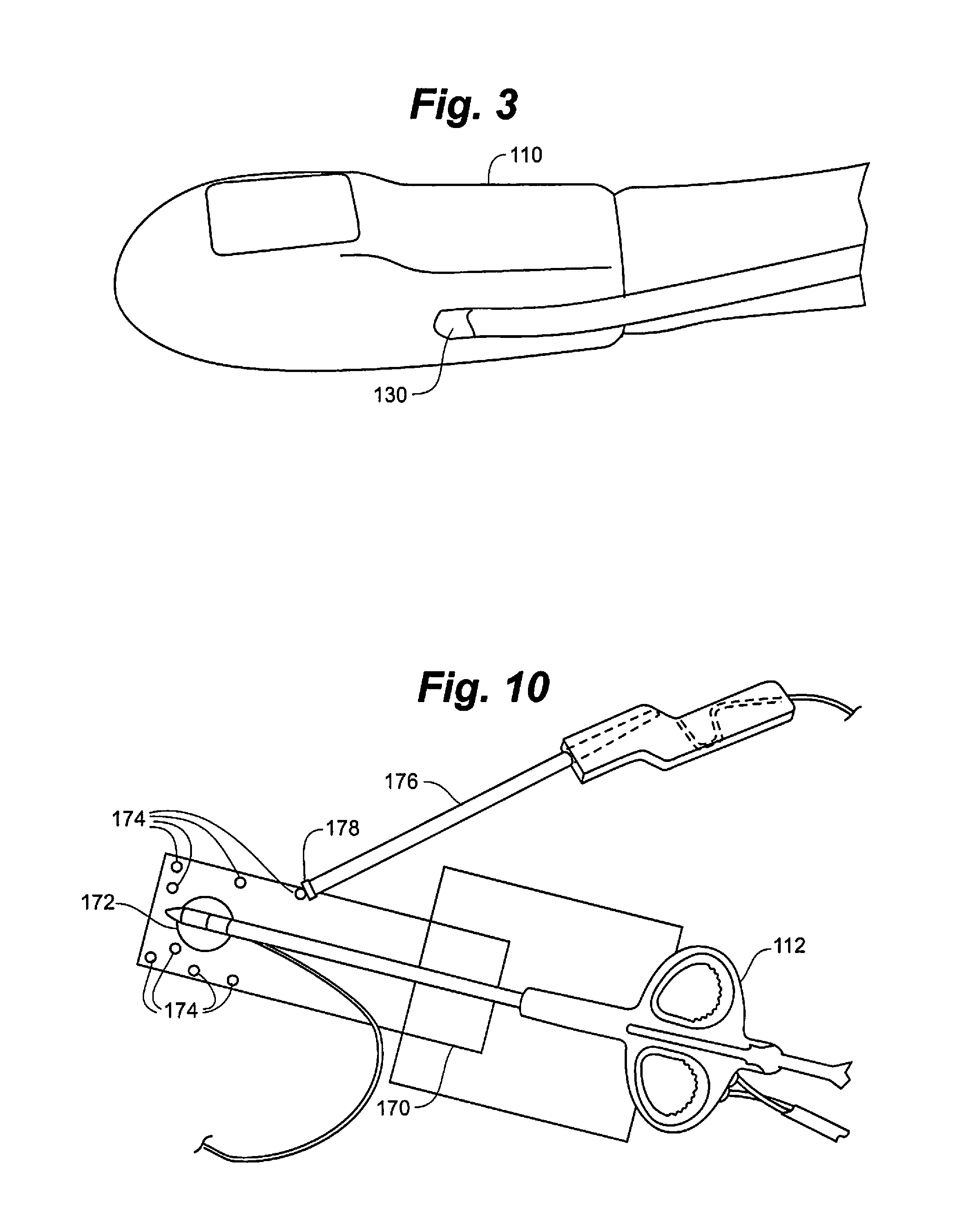
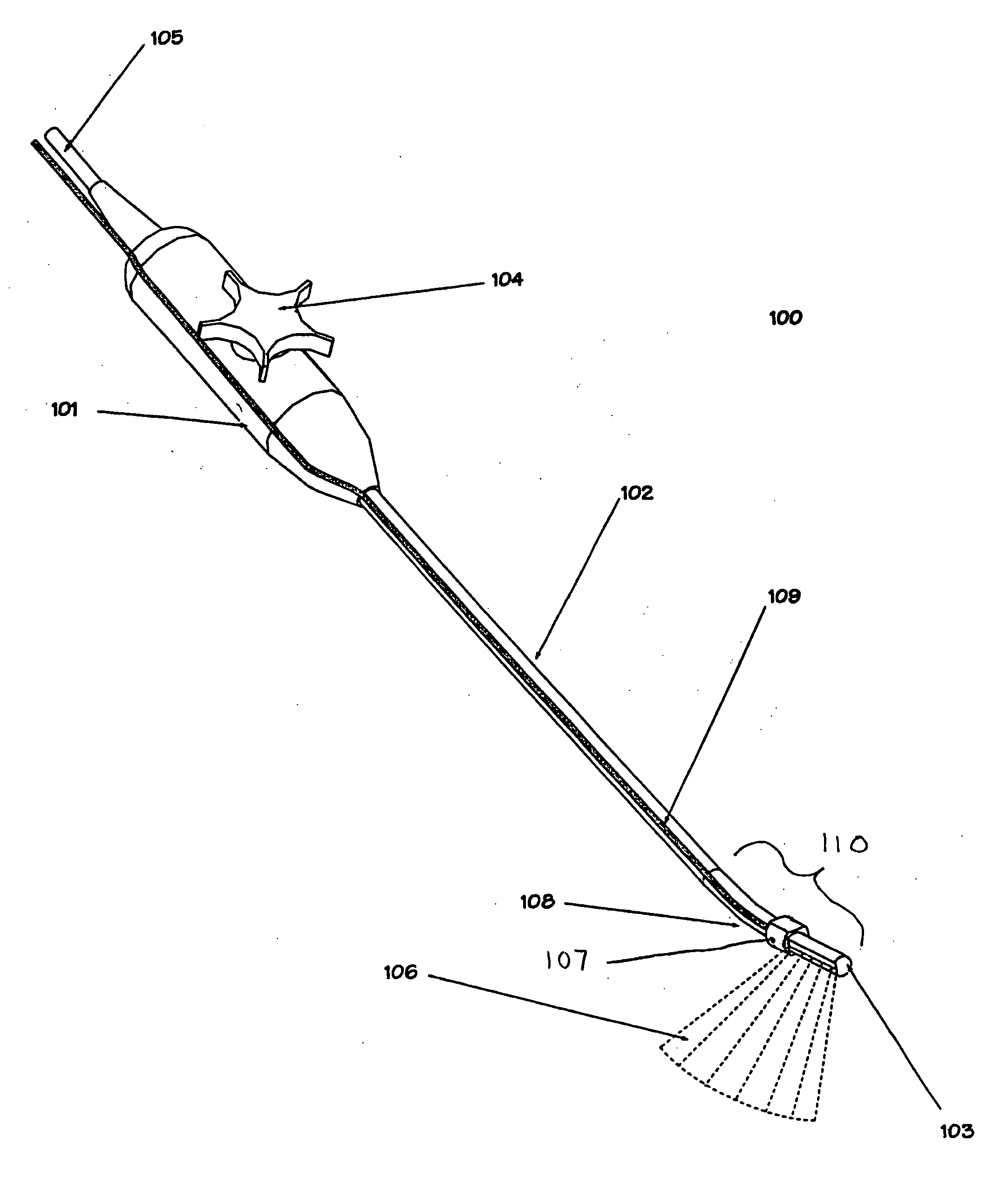
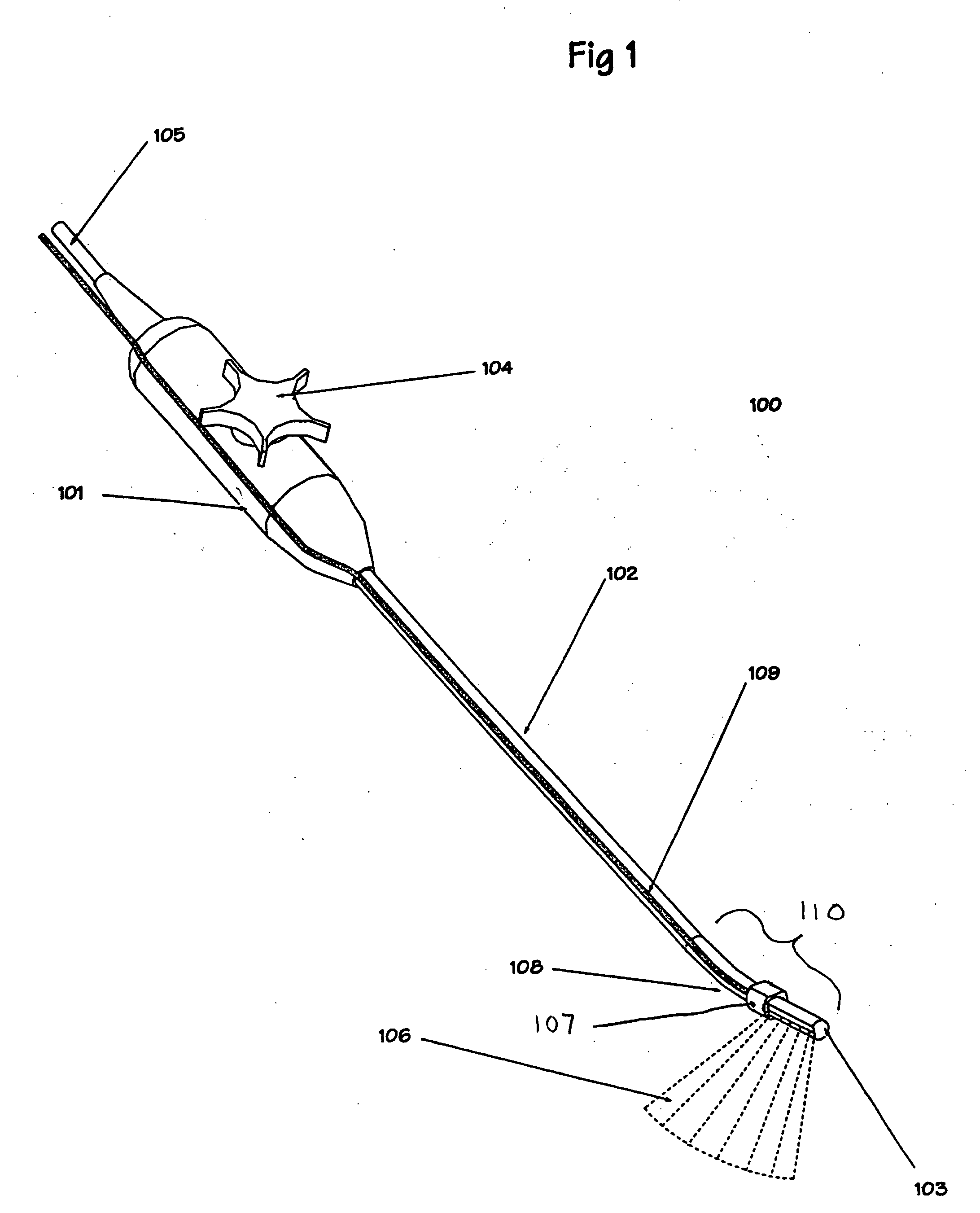
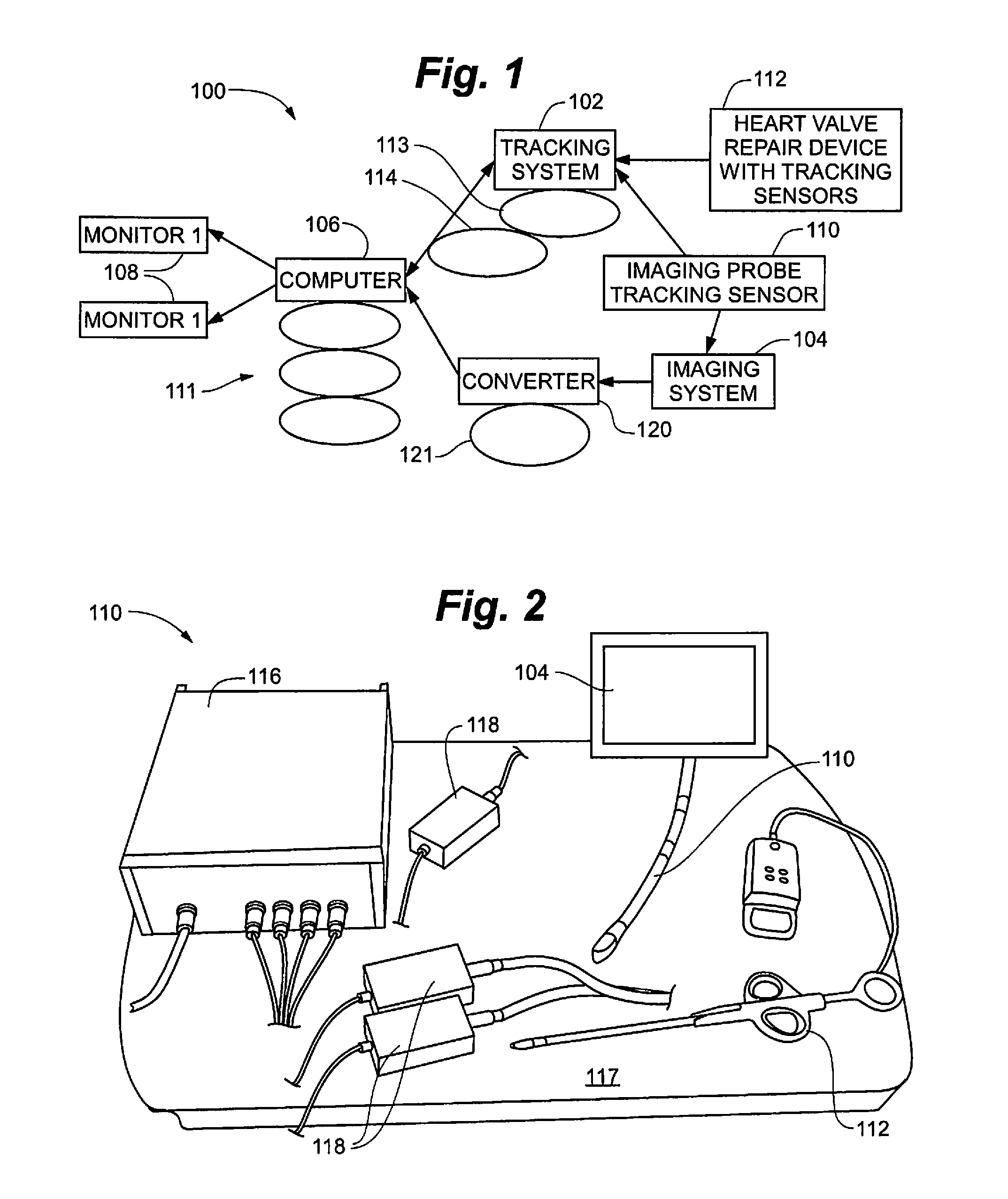
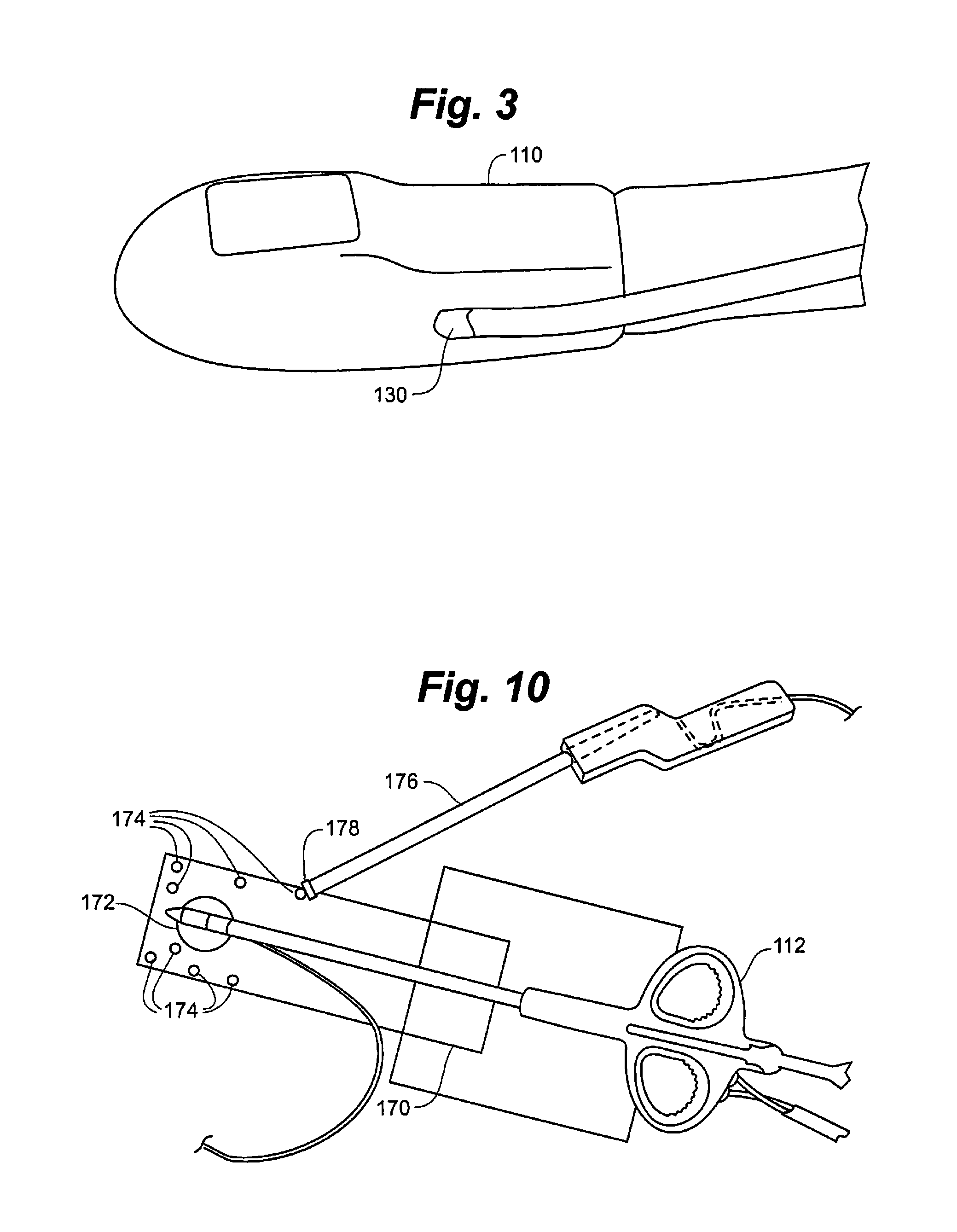
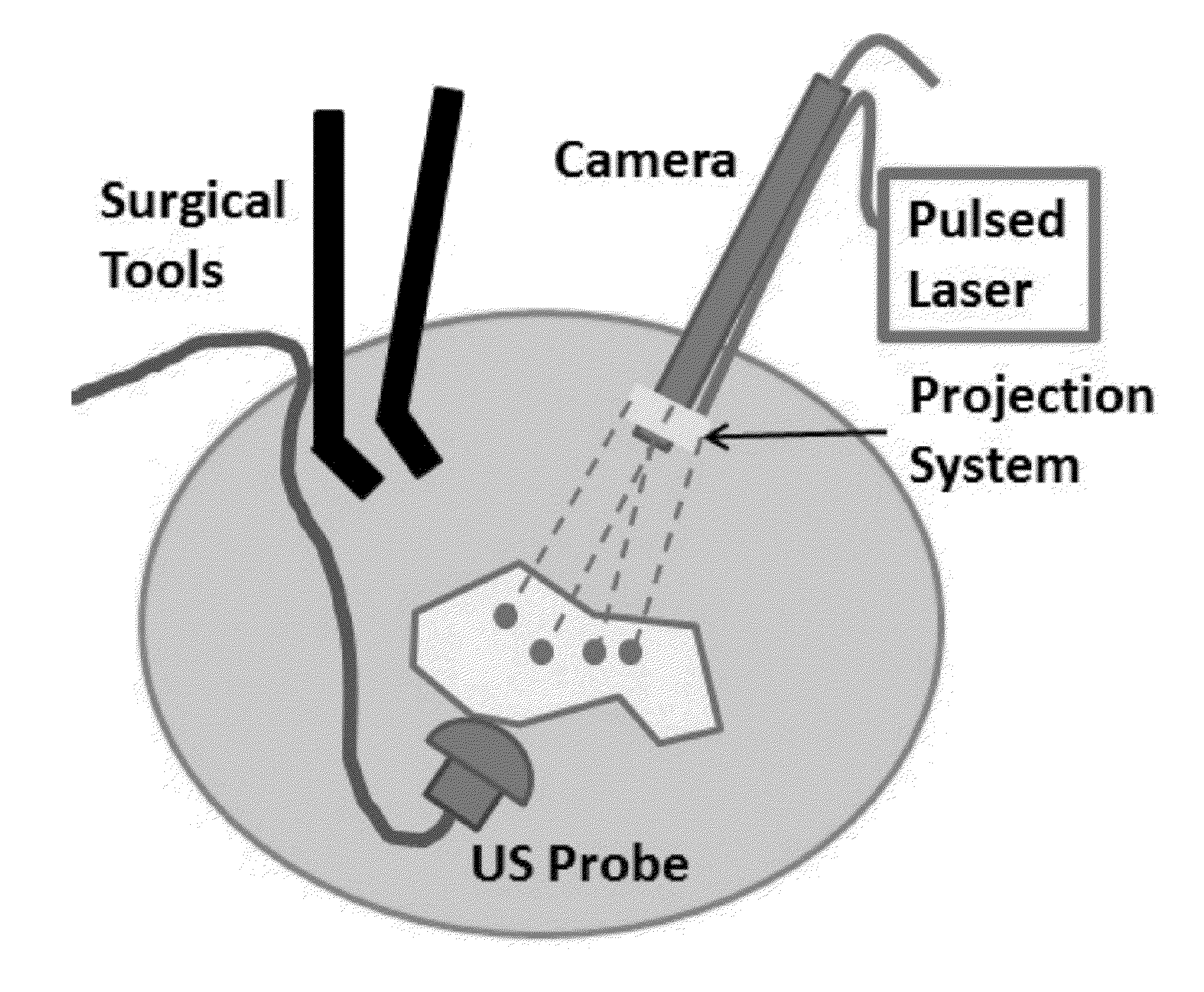
Surgical navigation for repair of heart valve leaflets
ActiveUS20130150710A1Improve overall navigation processHigh areaSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCardiac echoMedicine
To improve the overall navigation process for minimally invasive repair of heart valve leaflets, an augmented reality technique capable of providing a robust three-dimensional context for transesophogeal echocardiography data has been developed. In the context of various embodiment of the invention, augmented reality essentially refers to a system in which the primary environment is virtual but the environment is augmented by real elements. In this real-time environment, the surgeon can easily and intuitively identify the tool, surgical targets, and high risk areas, and view tool trajectories and orientations.
Owner:NEOCHORD
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
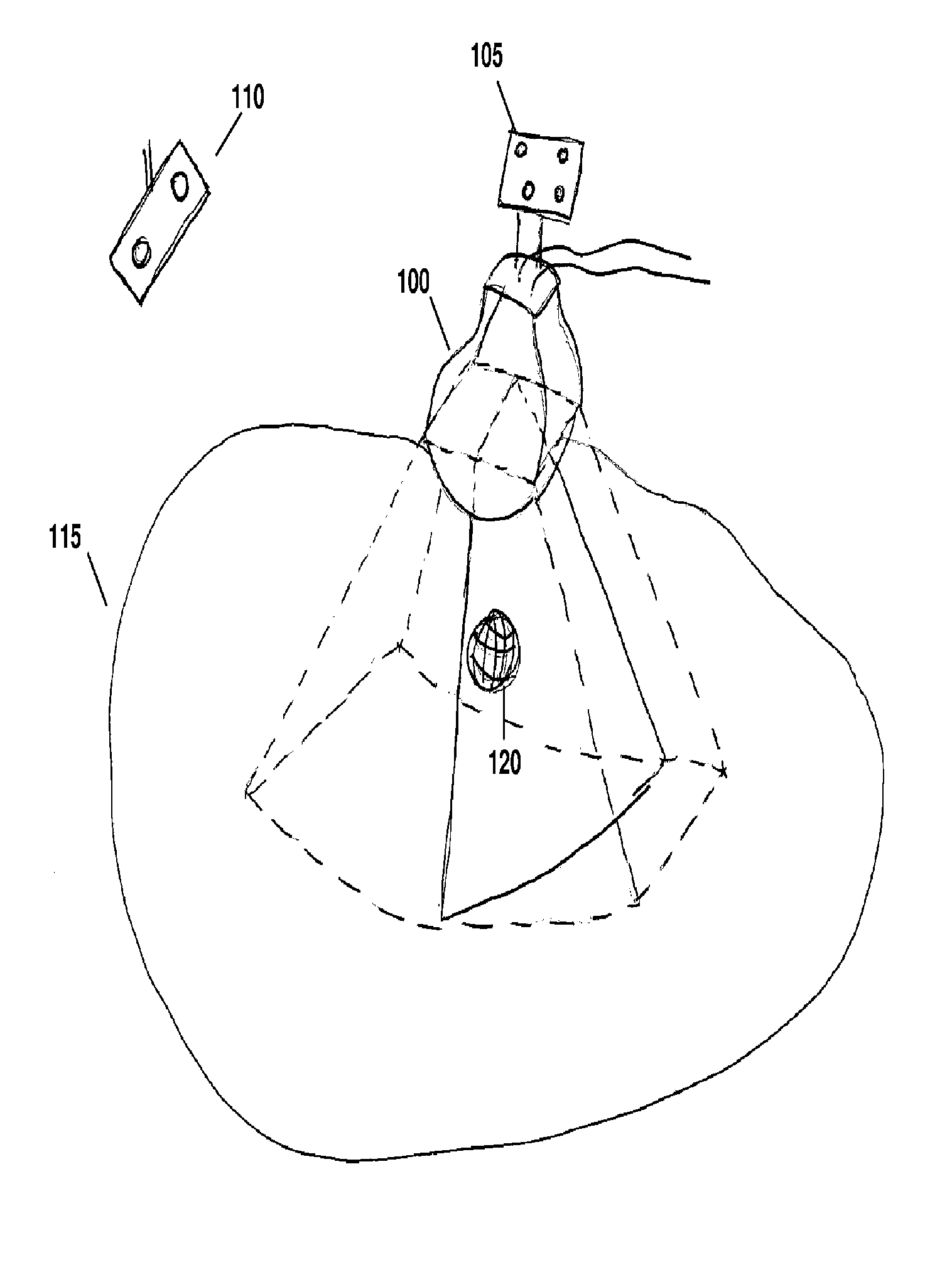
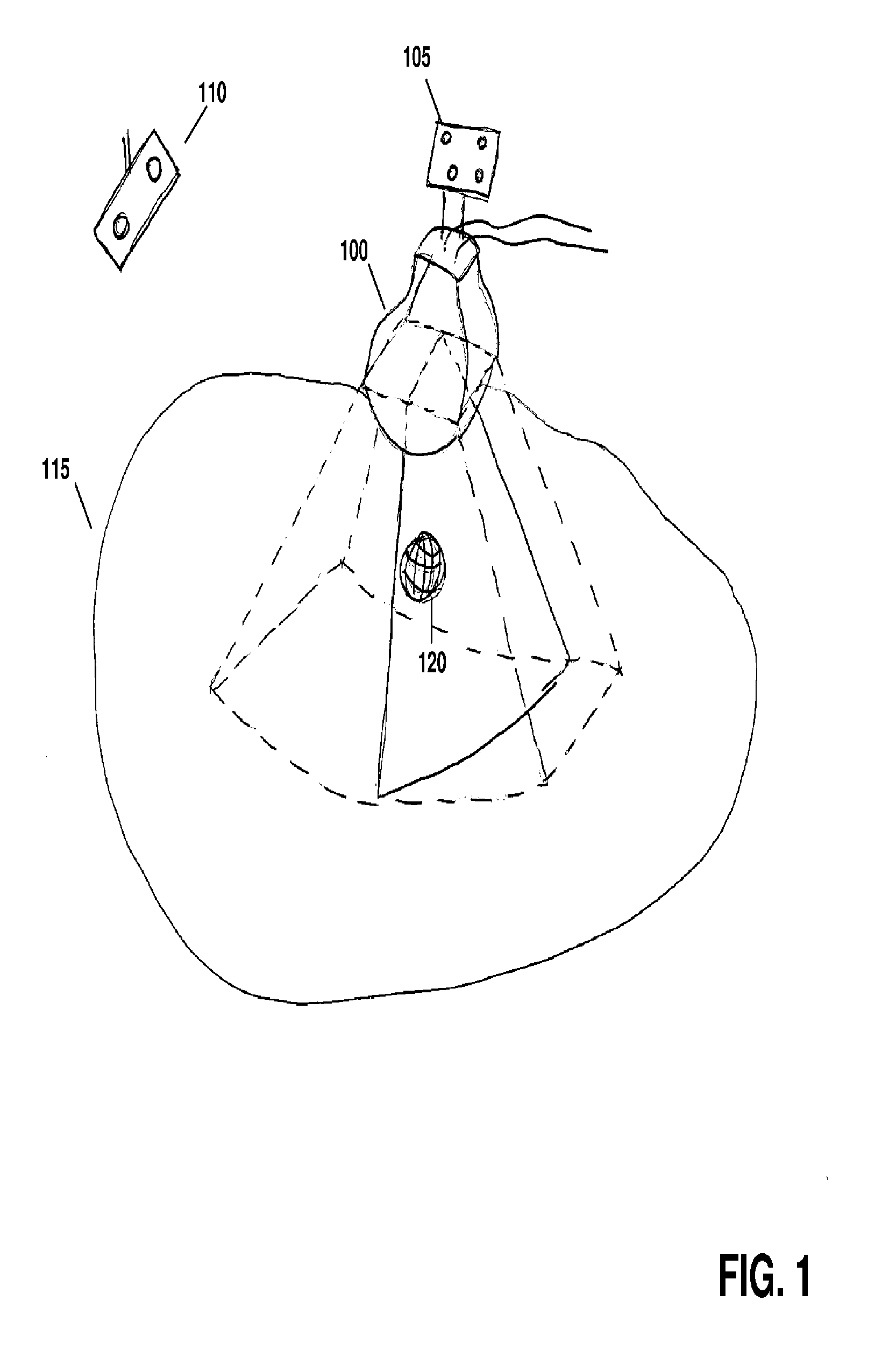
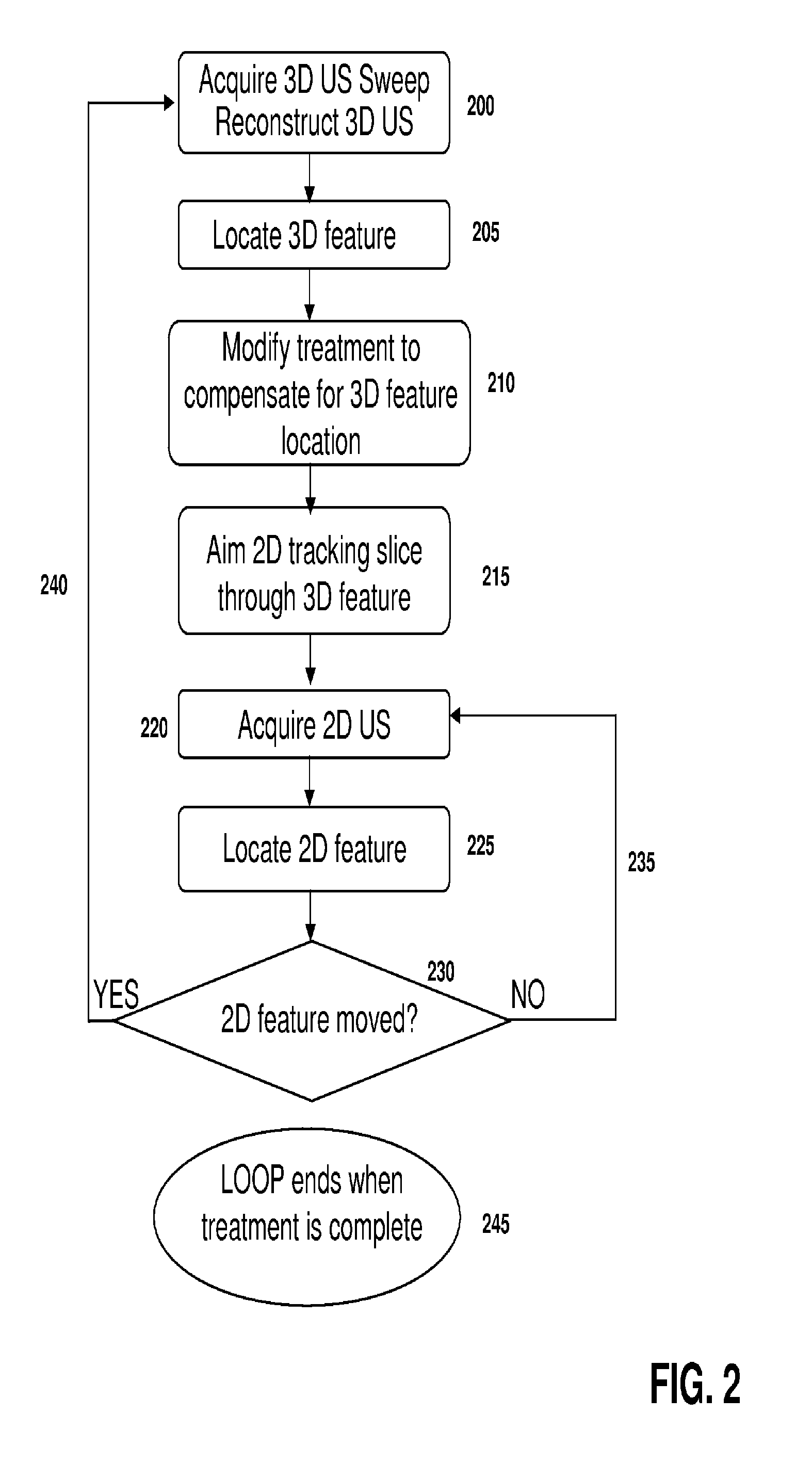
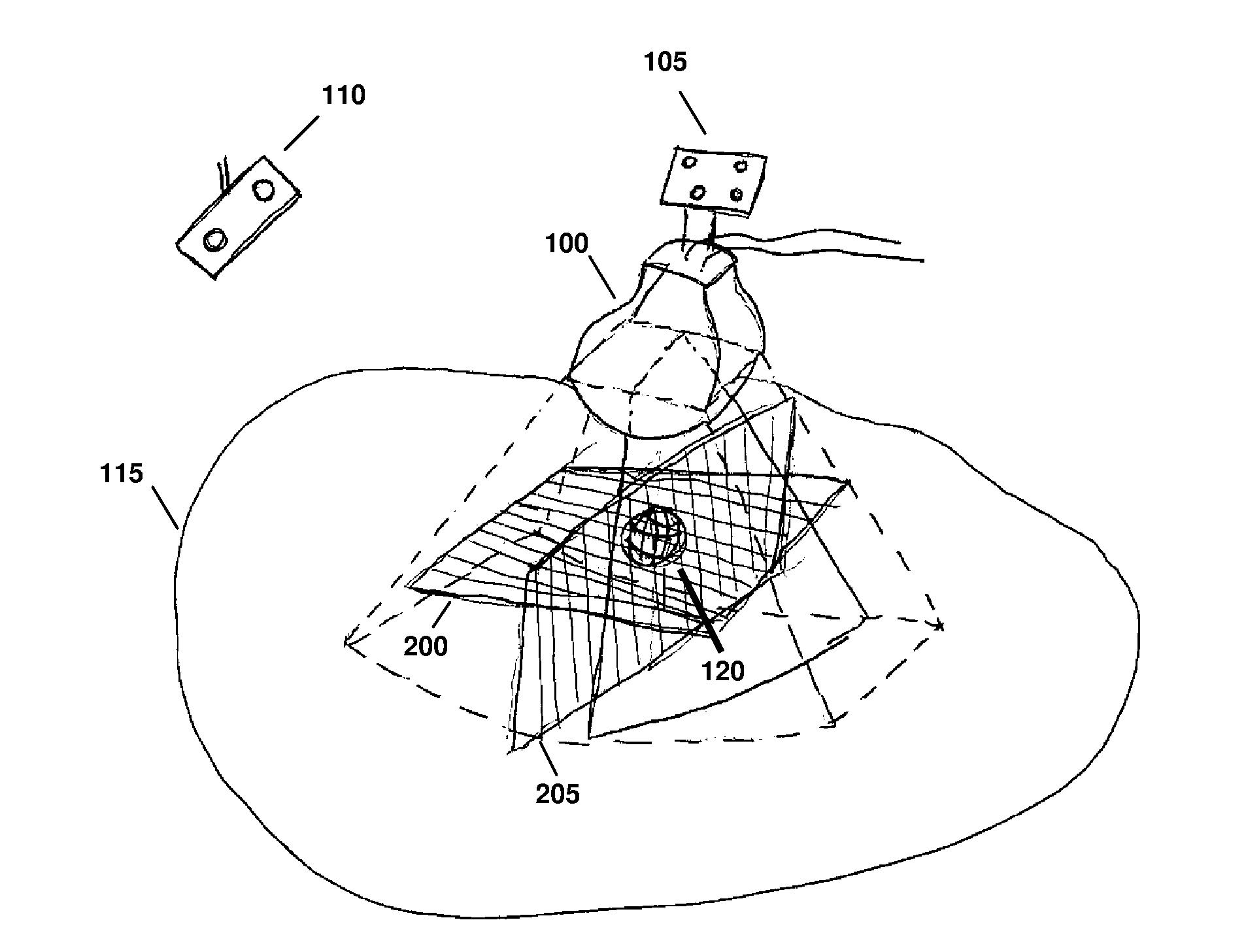
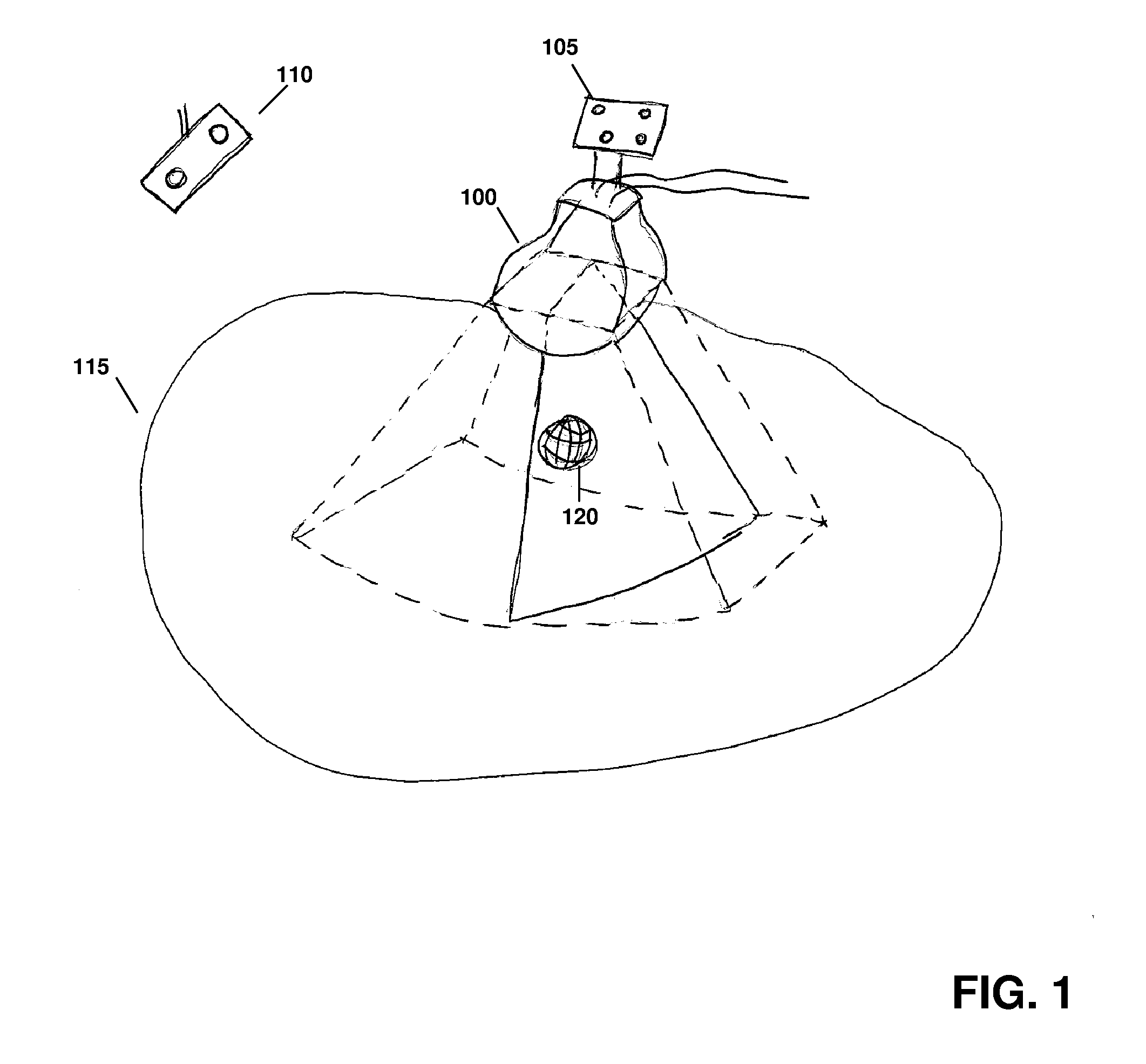
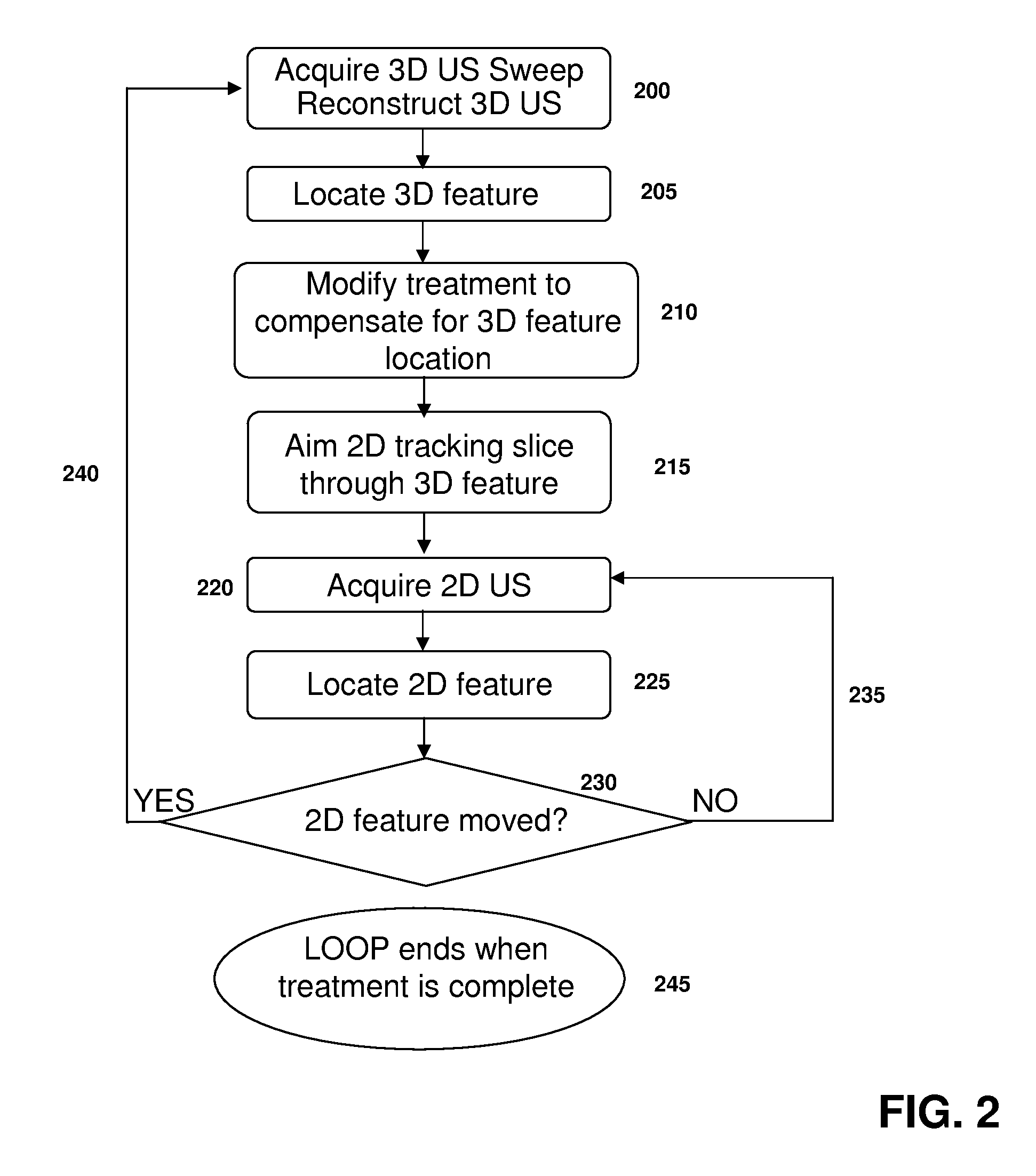
ActiveUS20120071758A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
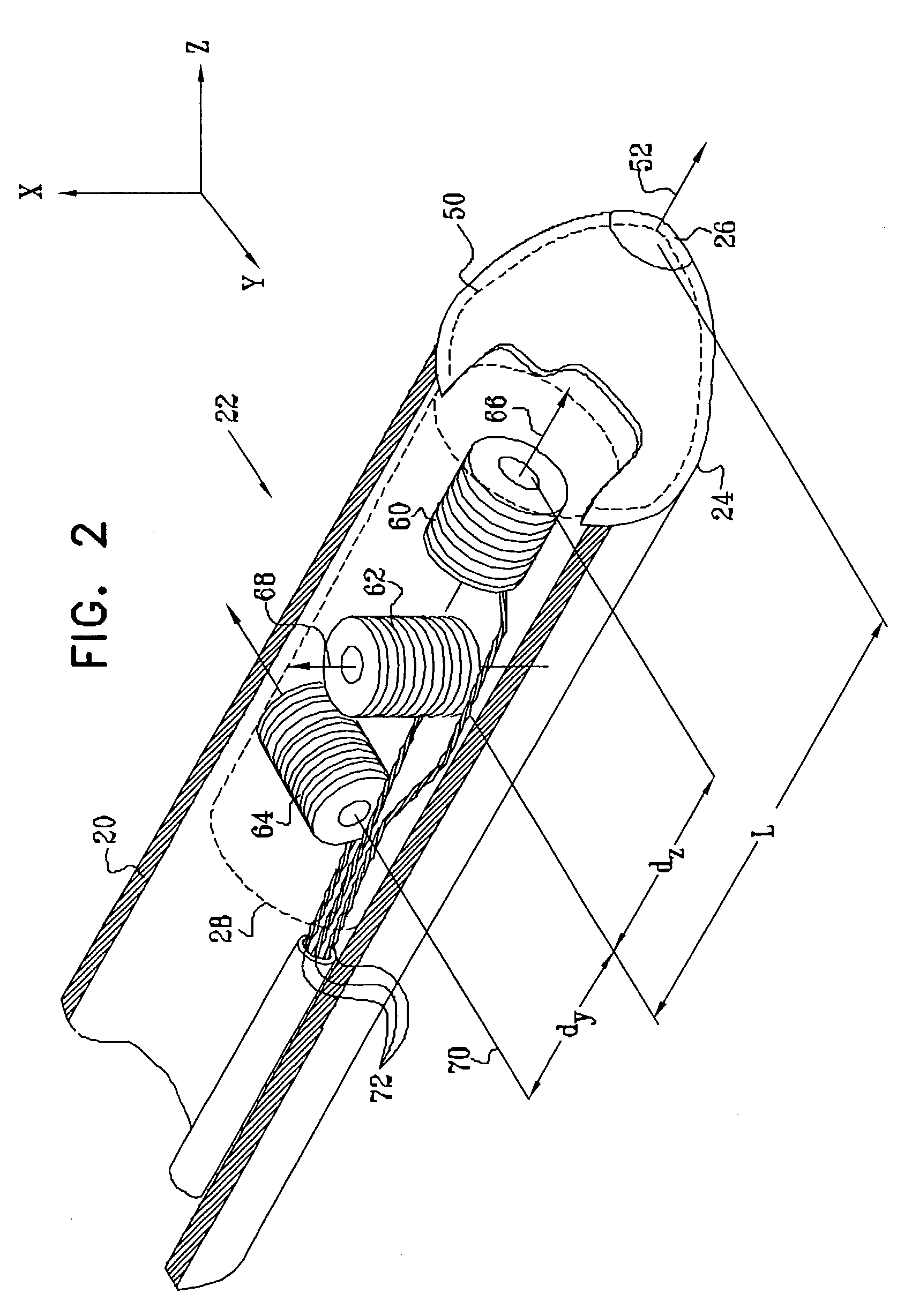
Mapping Movement of a Movable Transducer
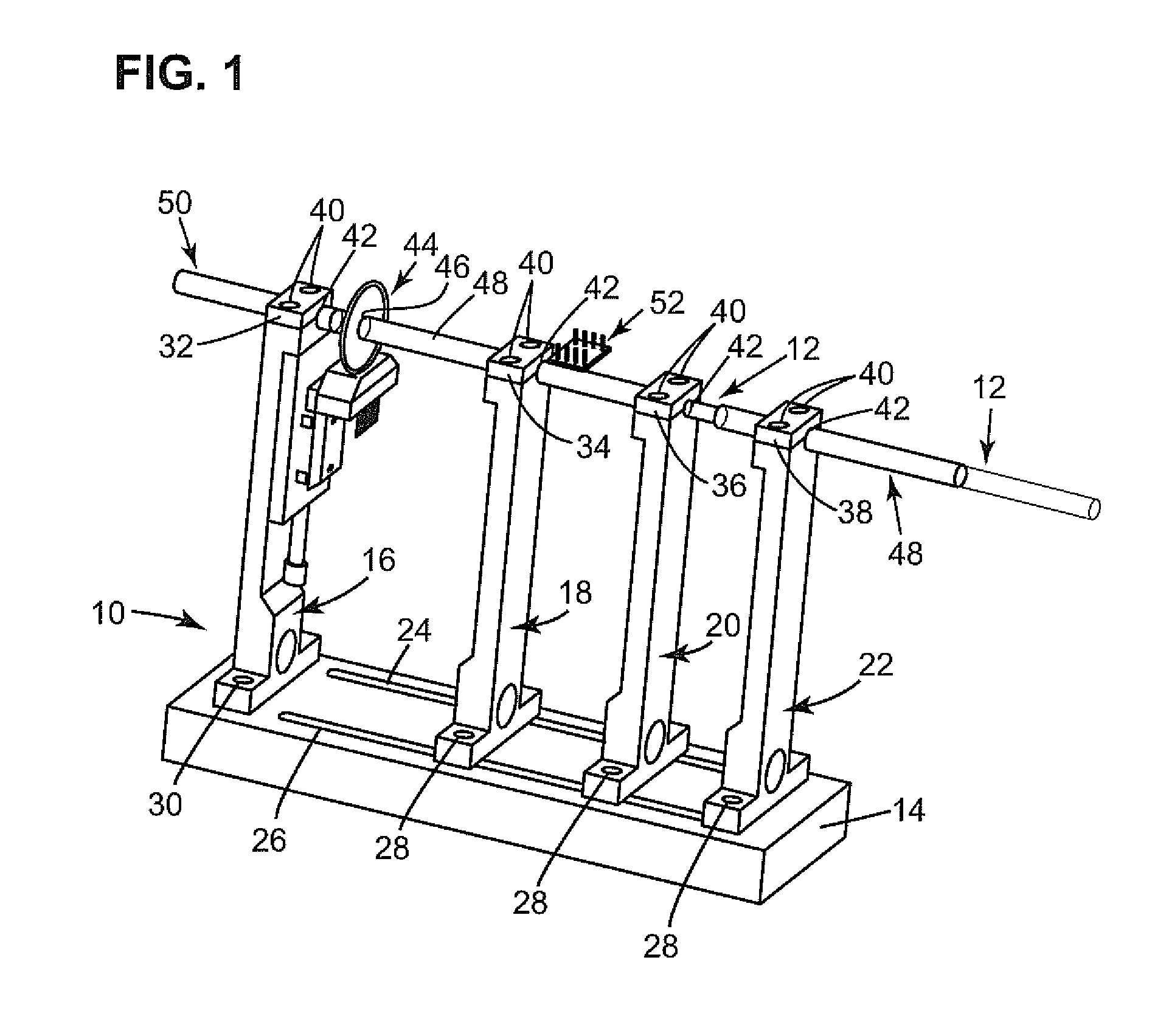
A catheter probe includes a transducer configured for at least one cycle of movement within the probe and a sensor that is at least partially supported within the probe for identifying a position of the transducer during the at least one cycle of movement. A method of mapping movement and a test fixture are also presented.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
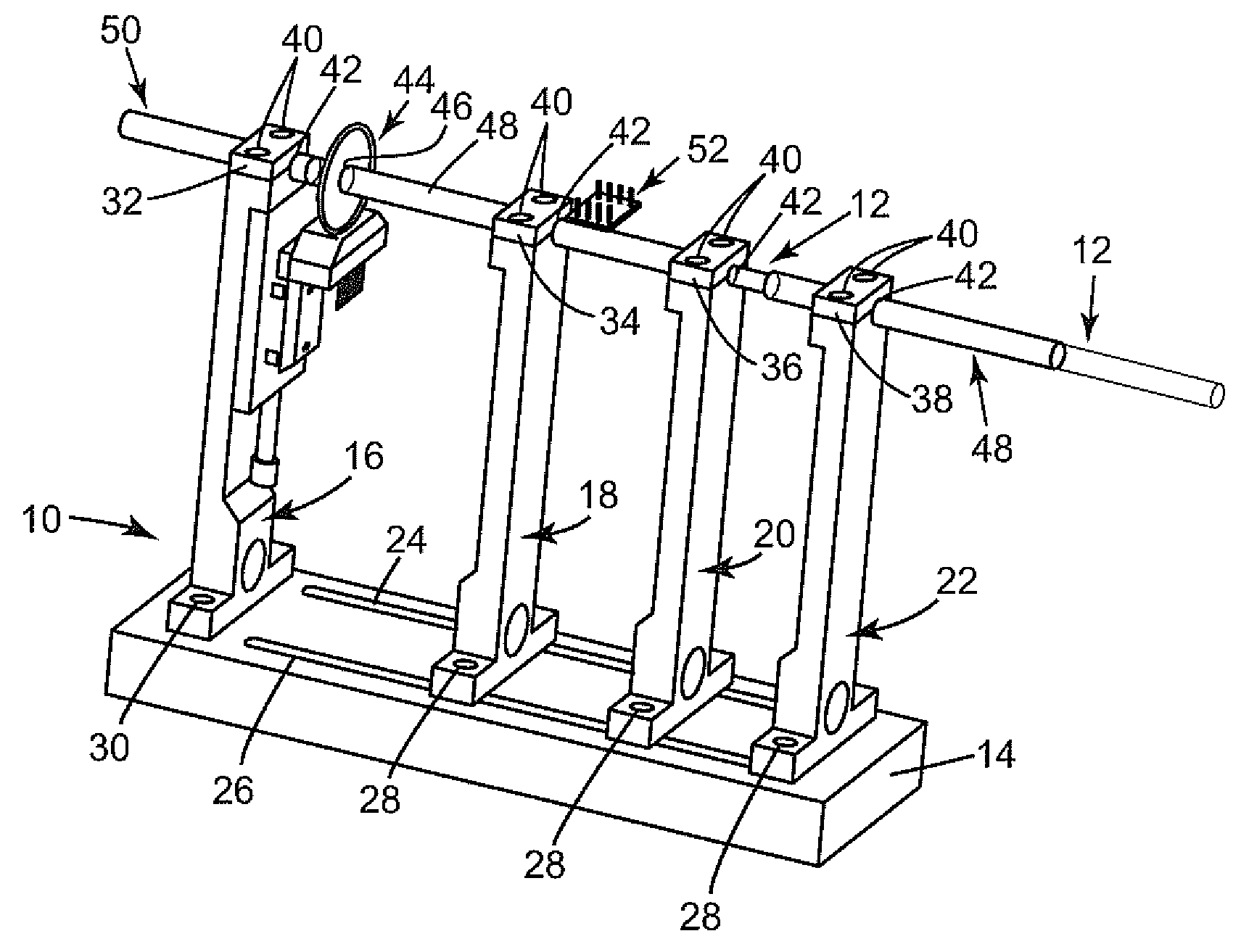
Device and method for a trackable ultrasound
ActiveUS20070167787A1Prevent movementReliable replacementCatheterInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound deviceEngineering
The invention provides a method for adjusting the calibration of a tracked ultrasound device using the measured difference between two sets of fiducial markings in two relative positions of a tracker and an scan head of the device. The invention also provides a trackable ultrasound device that enables repeatable attachment of a tracker to a scan head, thus preserving an initial calibration between the tracker and the scan head. Furthermore, the invention provides a calibration jig that can be used to repeatably attach a tracker to an ultrasound scan head or to measure the difference between two relative positions of a tracker and a scan head.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS7074187B2ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
InactiveUS20110172526A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Methods and apparatus for ultrasound strain imaging
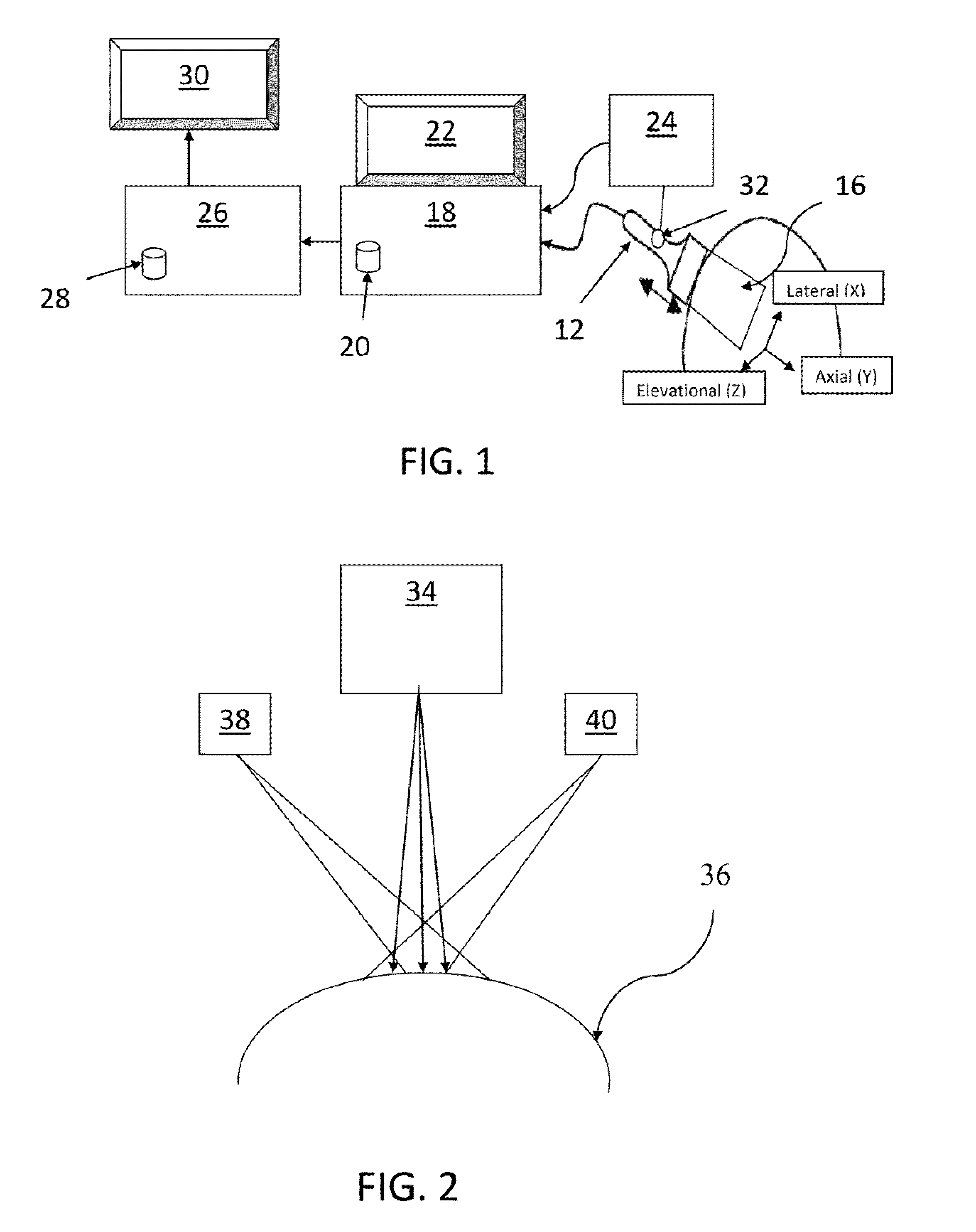
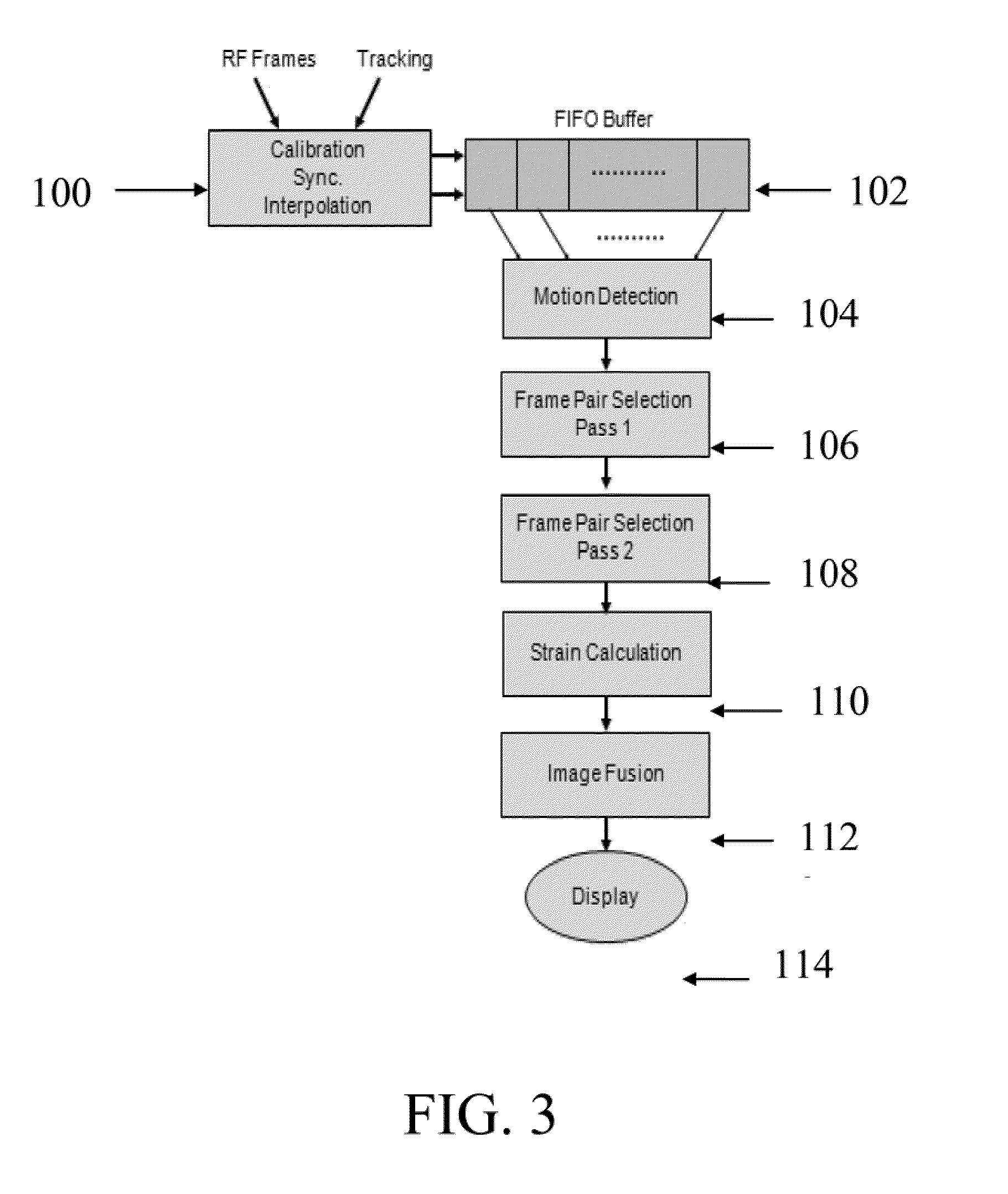
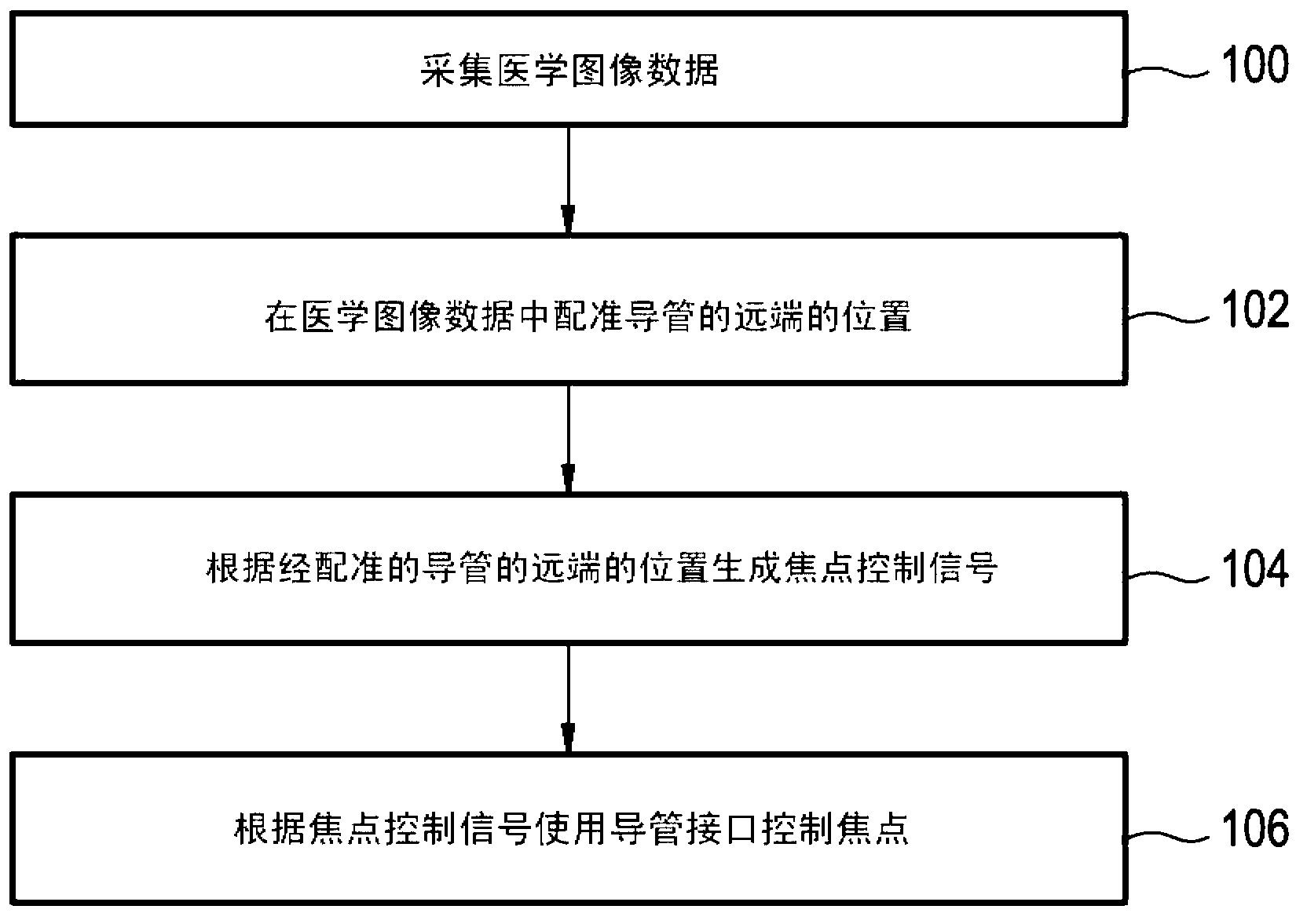
ActiveUS20110237945A1Minimize cost functionMedical automated diagnosisInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingAccelerometer
A system and method for improved ultrasound strain imaging includes using data from a tracking system to enhance the quality of ultrasound strain image and to reduce the dependency of image quality of the user's expertise. The tracking information is synchronized with the RF frames and interpolated to find the transformation corresponding to each frame. The RF frames with their transformations are incorporated into calculation of ultrasound strain images. The tracking system may be an optical tracker, electromagnetic tracker, accelerometer, or a structured light system. The structured light system may also be used for probe calibration, by calibrating the surface of the probe pre-operatively. In addition, a relative Young's Modulus may be calculated using tracking information that is independent from the distribution of input force.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Catheter comprising capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers with an adjustable focus
InactiveCN103221093ACatheterSurgical instrument detailsCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
A catheter (700, 800, 1206) comprising: a shaft with distal (808, 906, 1004, 208) and proximal ends (1006),wherein the distal end comprises at least one array of capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers (308, 402, 404, 500, 512, 600, 604, 802, 008) with an adjustable focus for controllably heating a target zone (806, 1014, 1210); and a connector(1012) at the proximal end for supplying the at least one array of capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers with electrical power and for controlling the adjustable focus.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Ultrasound probe with integrated electronics
InactiveUS20140051984A1Simplifies cable requirementDifficult to upgradeVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCatheterVisual BasicSonification
A hand-held ultrasound system includes integrated electronics within an ergonomic housing. The electronics includes control circuitry, beamforming and circuitry transducer drive circuitry. The electronics communicate with a host computer using an industry standard high speed serial bus. The ultrasonic imaging system is operable on a standard, commercially available, user computing device without specific hardware modifications, and is adapted to interface with an external application without modification to the ultrasonic imaging system to allow a user to gather ultrasonic data on a standard user computing device such as a PC, and employ the data so gathered via an independent external application without requiring a custom system, expensive hardware modifications, or system rebuilds. An integrated interface program allows such ultrasonic data to be invoked by a variety of such external applications having access to the integrated interface program via a standard, predetermined platform such as visual basic or c++.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
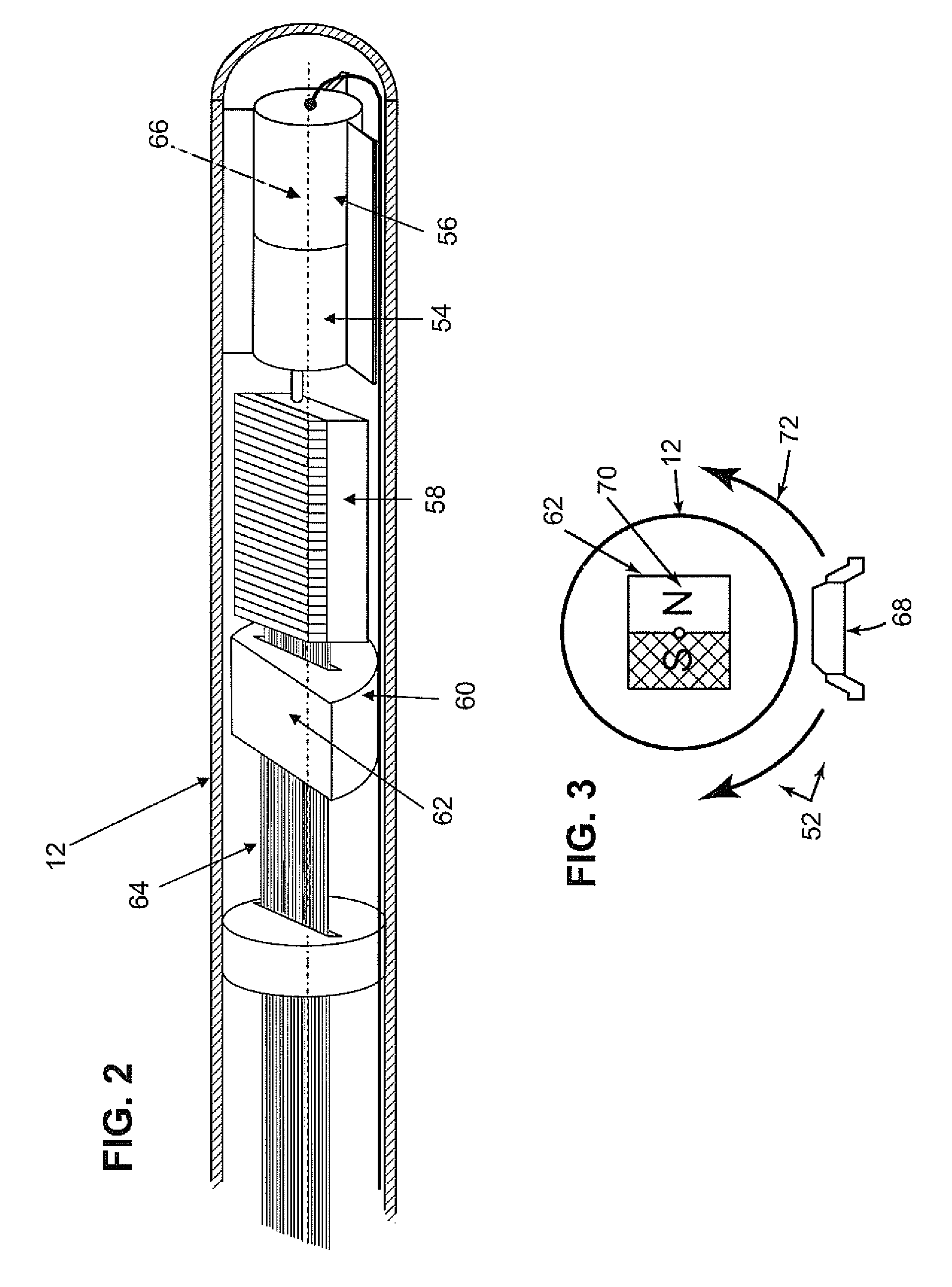
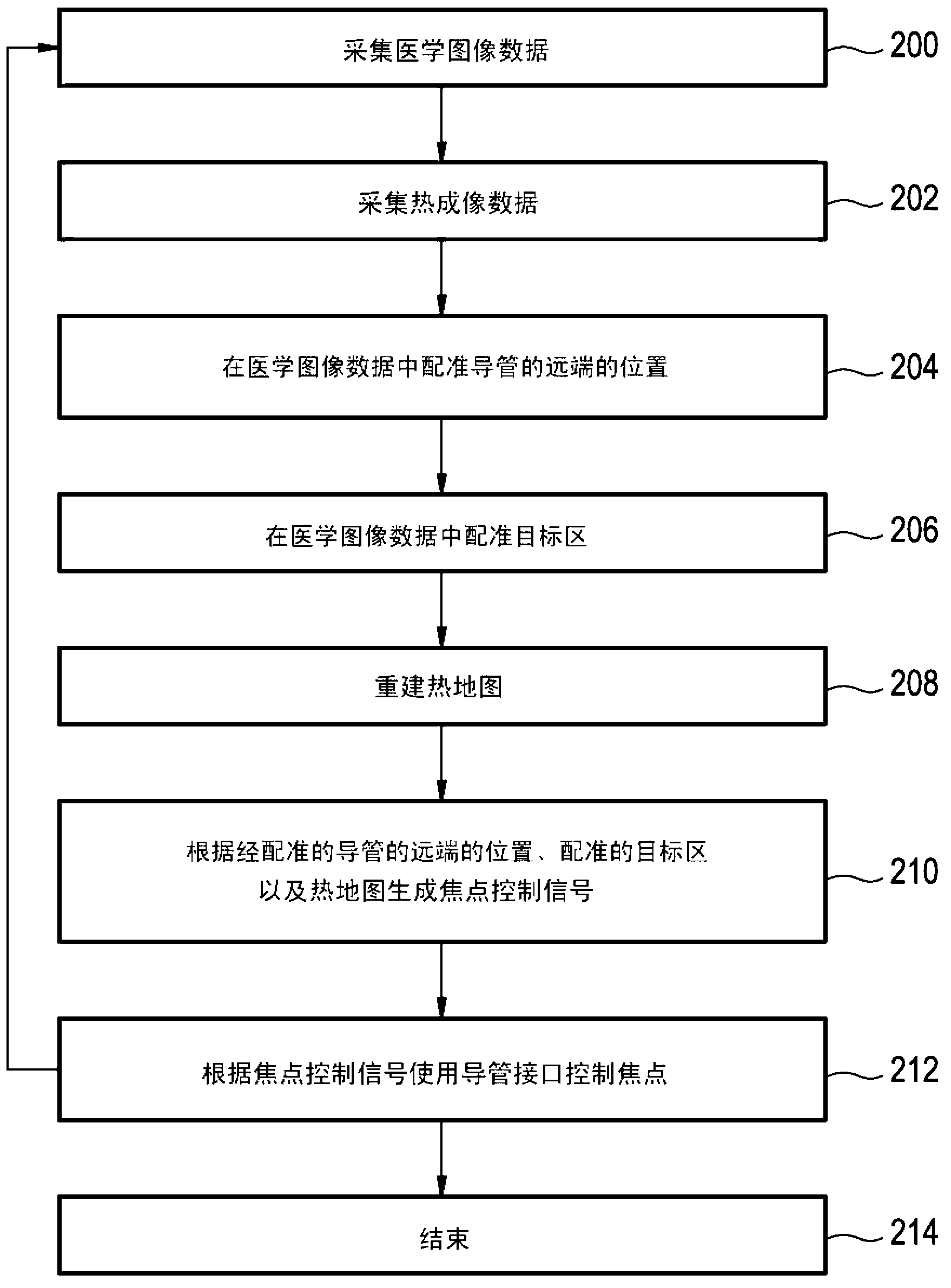
Determining intracranial pressure non-invasively by acoustic transducer
A plurality of acoustic source and / or detector elements are employed in a scanning mode to acoustically illuminate and acquire acoustic data from numerous sites within a larger target area. Based on the acoustic data collected in the scanning mode, a localised site within the target area is selected as the target site for focused acoustic illumination and / or probing. Elements of the acoustic source / detector array are focused on the selected target site in an automated fashion. Thereafter, the target area is periodically scanned and the acoustic focus repositioned, as required, to maintain the focus of the acoustic source at the desired target site.
Owner:菲西奥松尼克斯公司 +1
Surgical navigation for repair of heart valve leaflets
To improve the overall navigation process for minimally invasive repair of heart valve leaflets, an augmented reality technique capable of providing a robust three-dimensional context for transesophogeal echocardiography data has been developed. In the context of various embodiment of the invention, augmented reality essentially refers to a system in which the primary environment is virtual but the environment is augmented by real elements. In this real-time environment, the surgeon can easily and intuitively identify the tool, surgical targets, and high risk areas, and view tool trajectories and orientations.
Owner:NEOCHORD
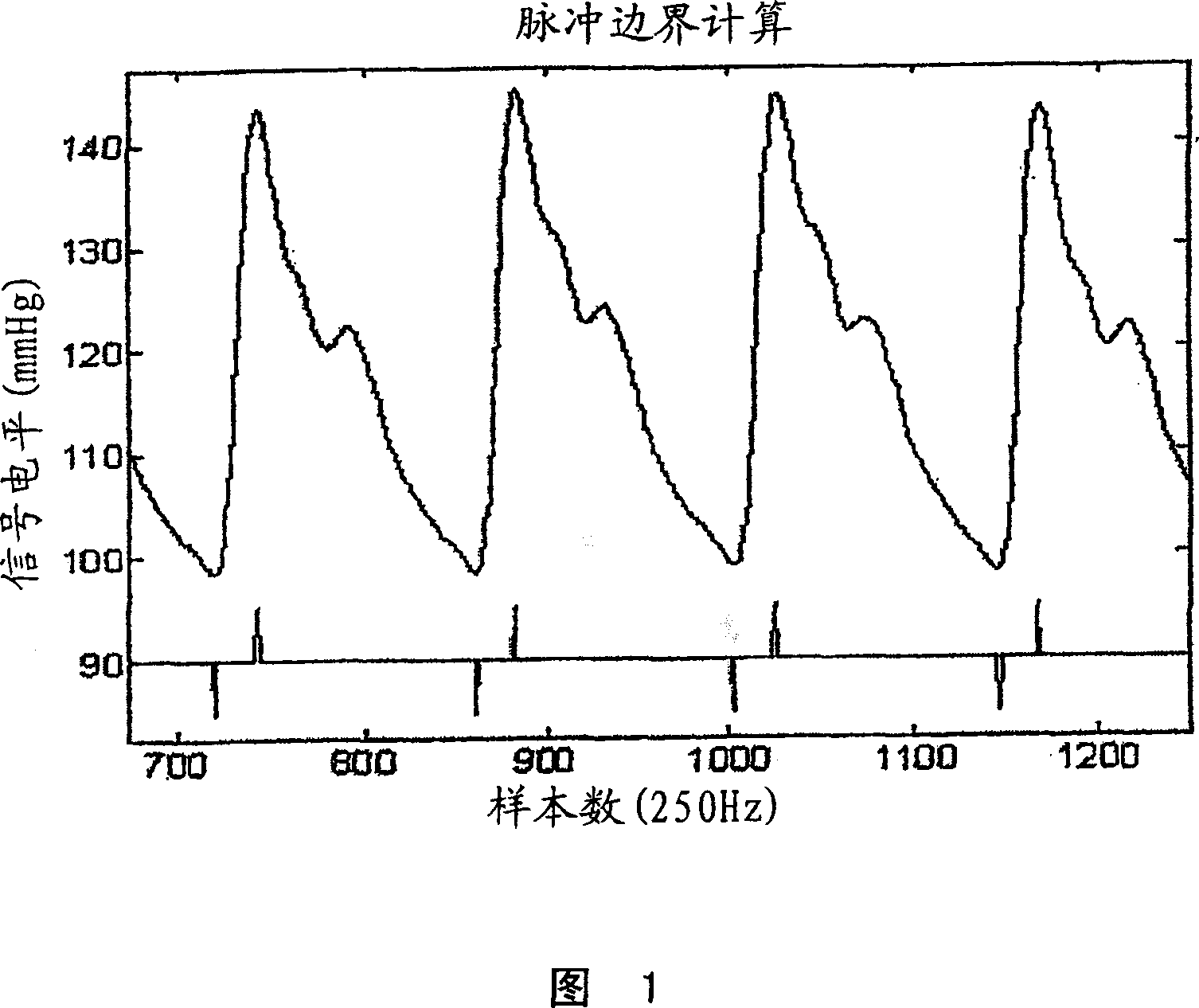
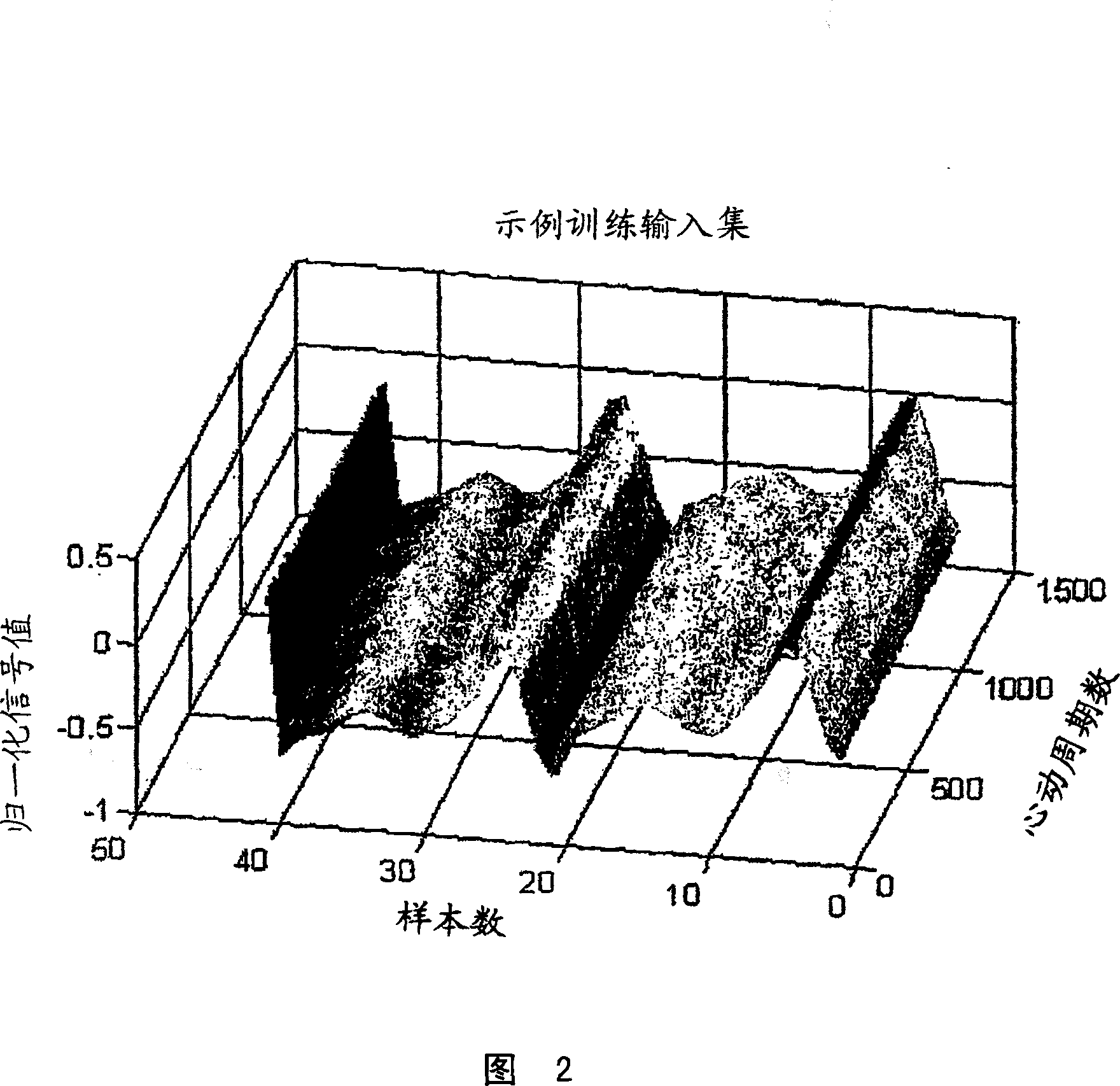
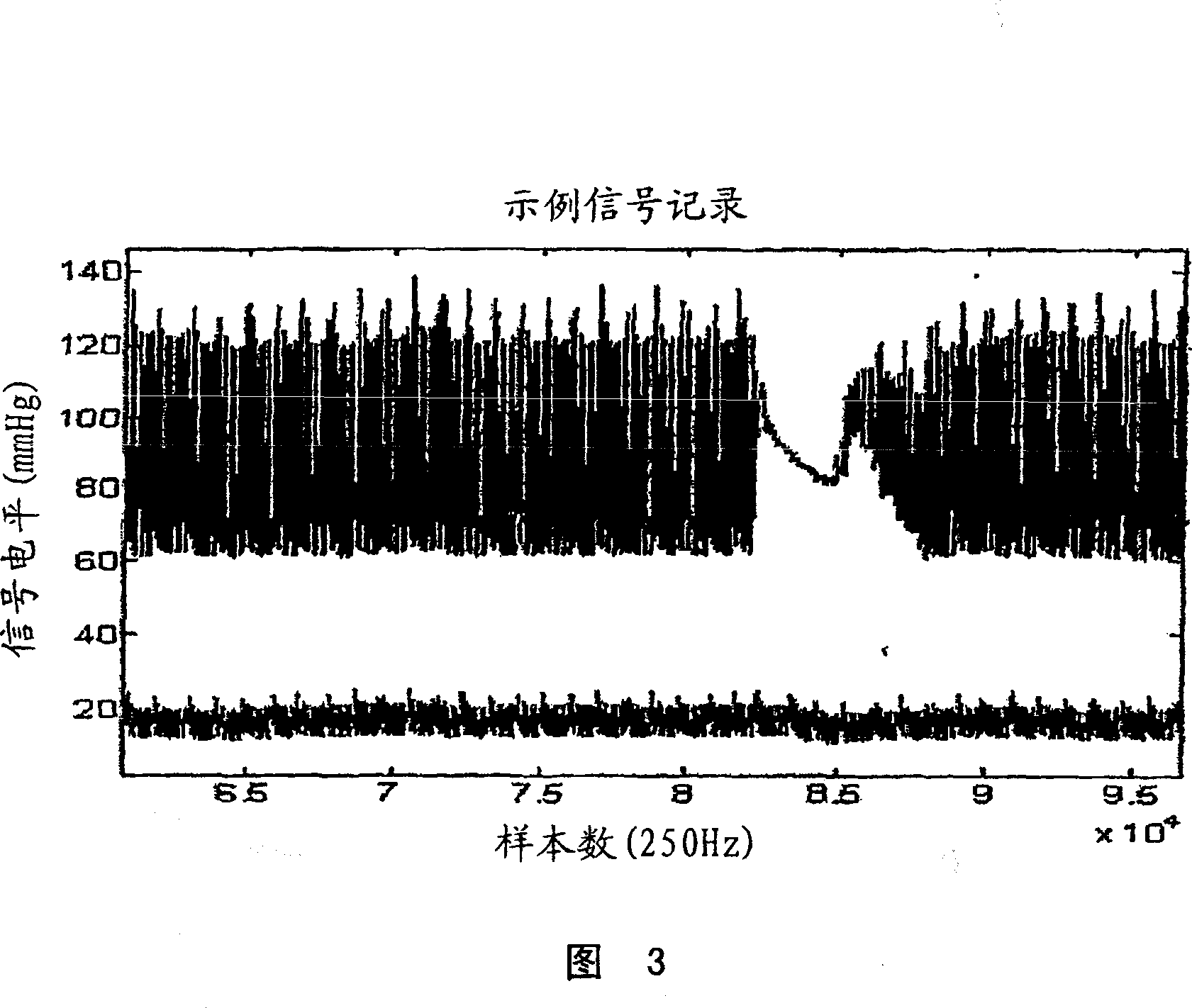
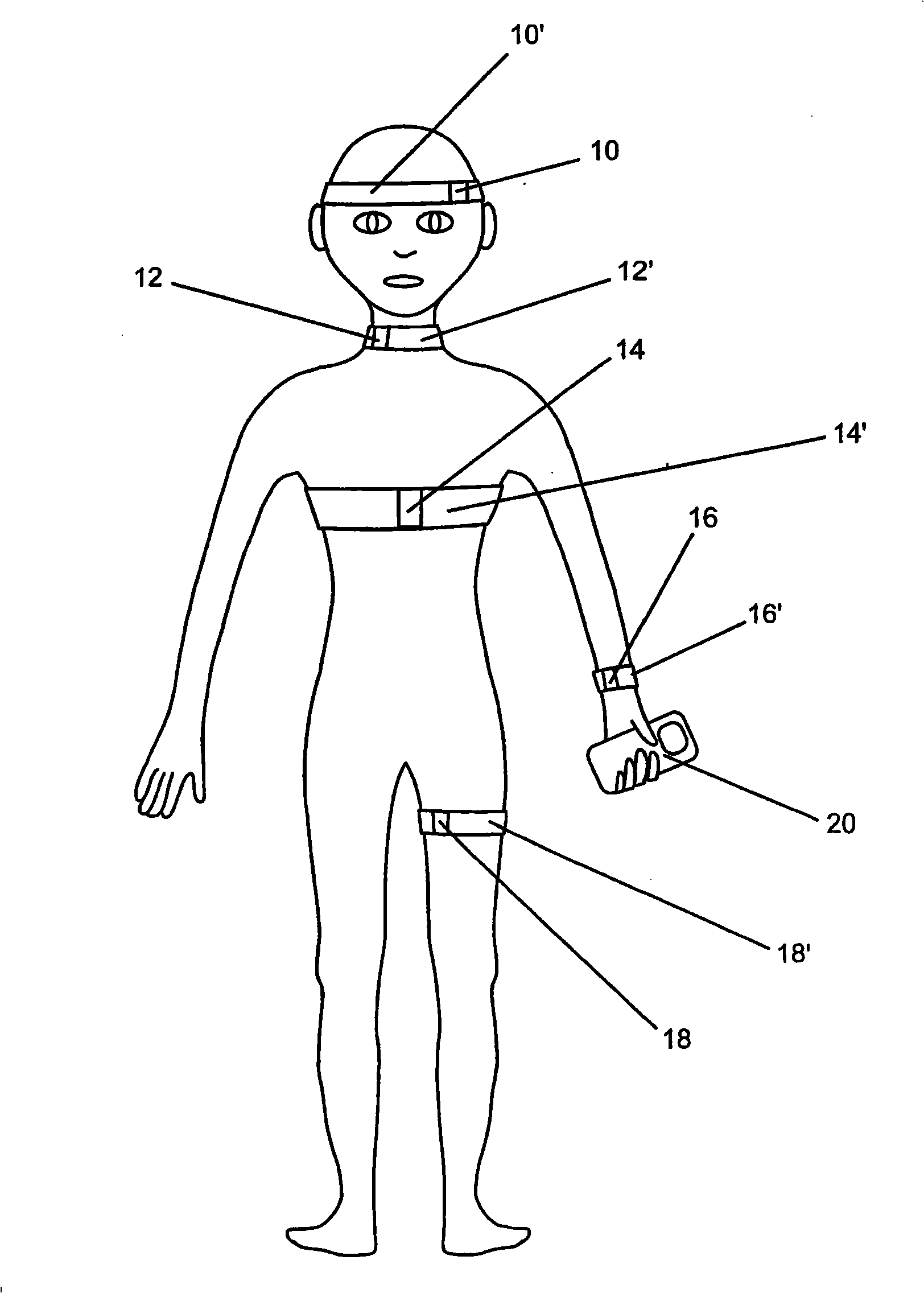
Systems and methods for non-invasive detection and monitoring of cardiac and blood parameters
Methods and systems for long term monitoring of one or more physiological parameters such as respiration, heart rate, body temperature, electrical heart activity, blood oxygenation, blood flow velocity, blood pressure, intracranial pressure, the presence of emboli in the blood stream and electrical brain activity are provided. Data is acquired non-invasively using ambulatory data acquisition techniques.
Owner:菲西奥松尼克斯公司 +1
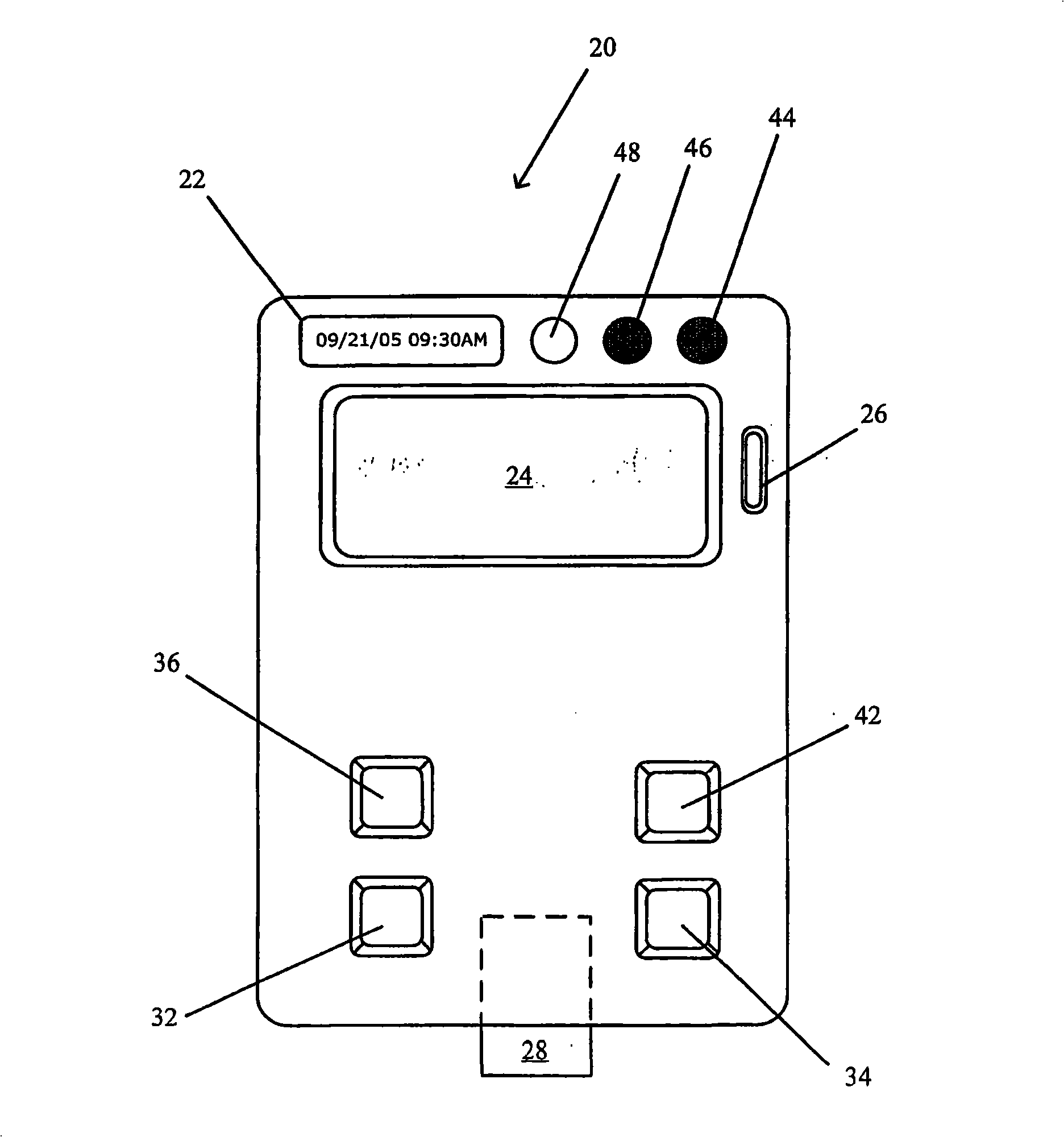
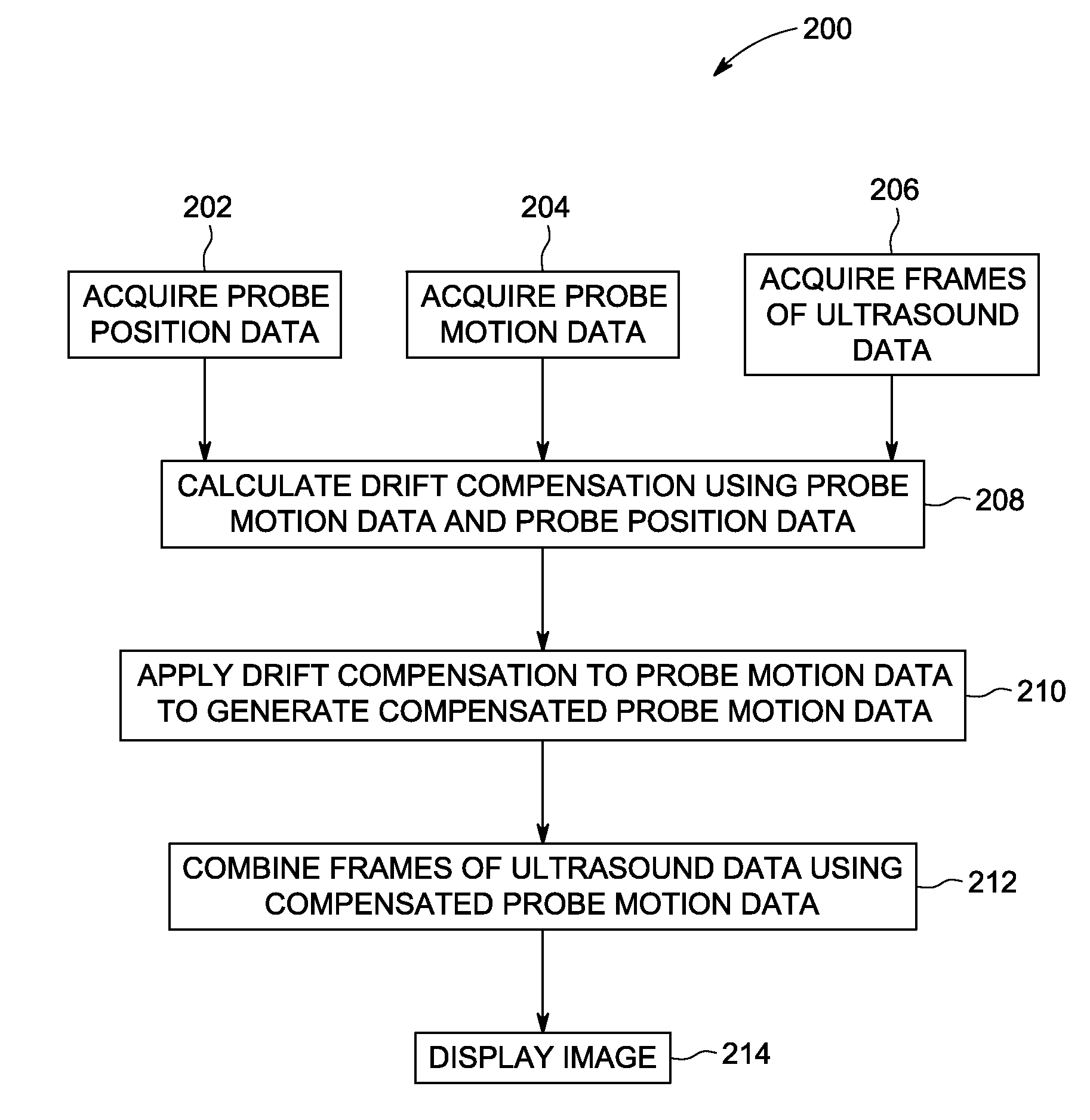
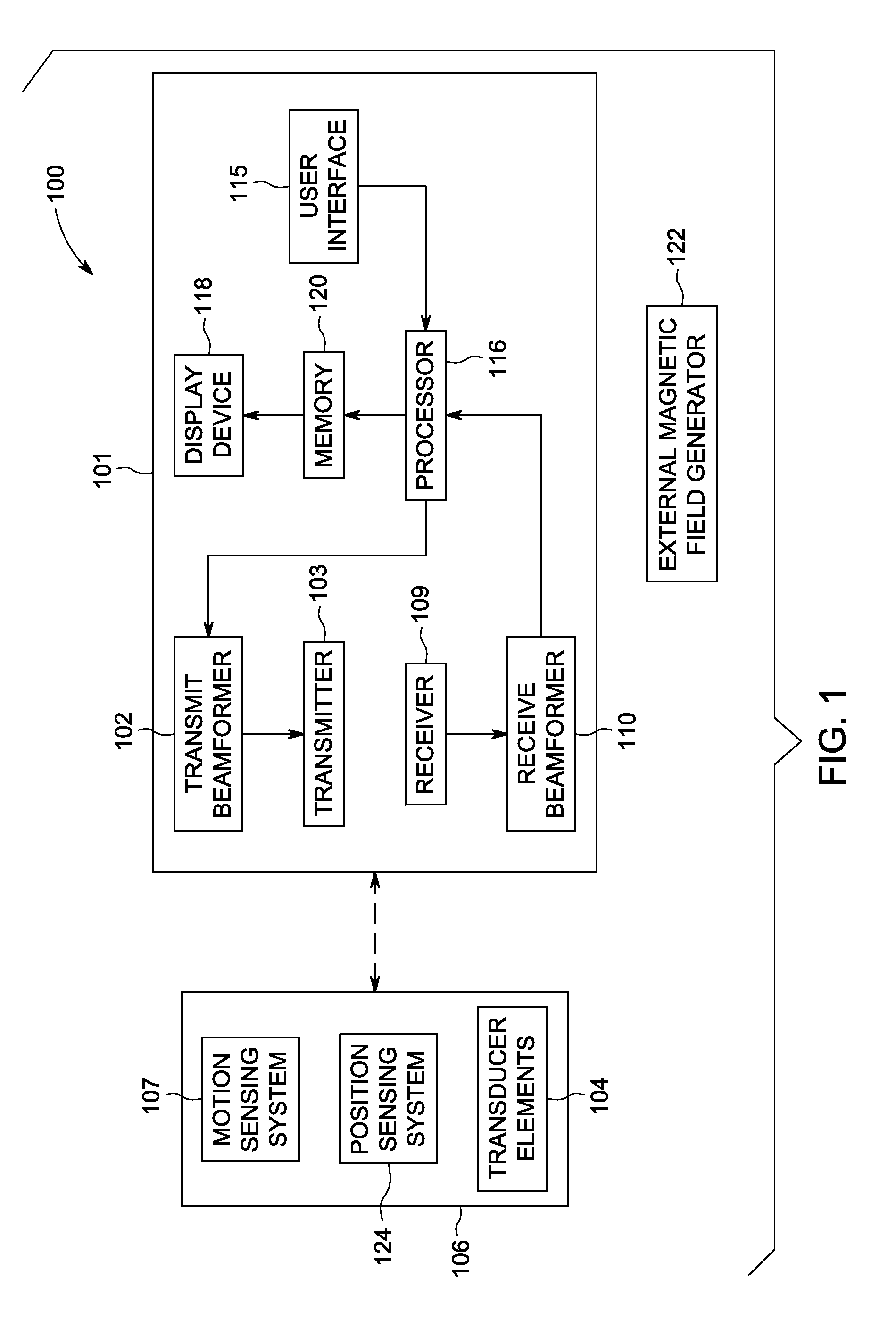
Ultrasound imaging system and method for drift compensation
An ultrasound imaging system and method includes acquiring motion data from a motion sensing system on a probe while acquiring ultrasound data with the probe. The system and method includes acquiring probe motion data with a motion sensing system, acquiring probe position data with a position sensing system and calculating a drift compensation using the probe motion data and the probe position data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
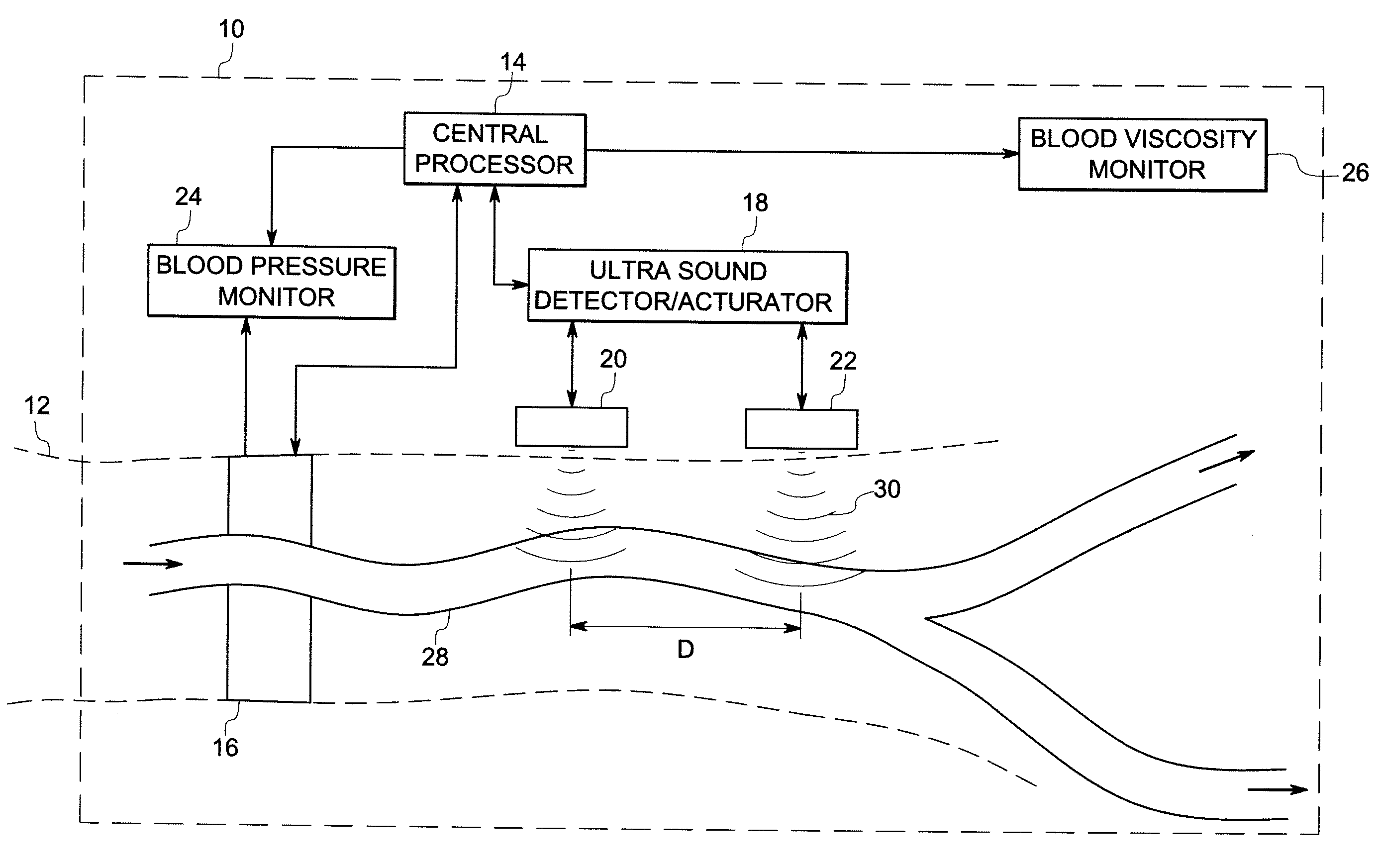
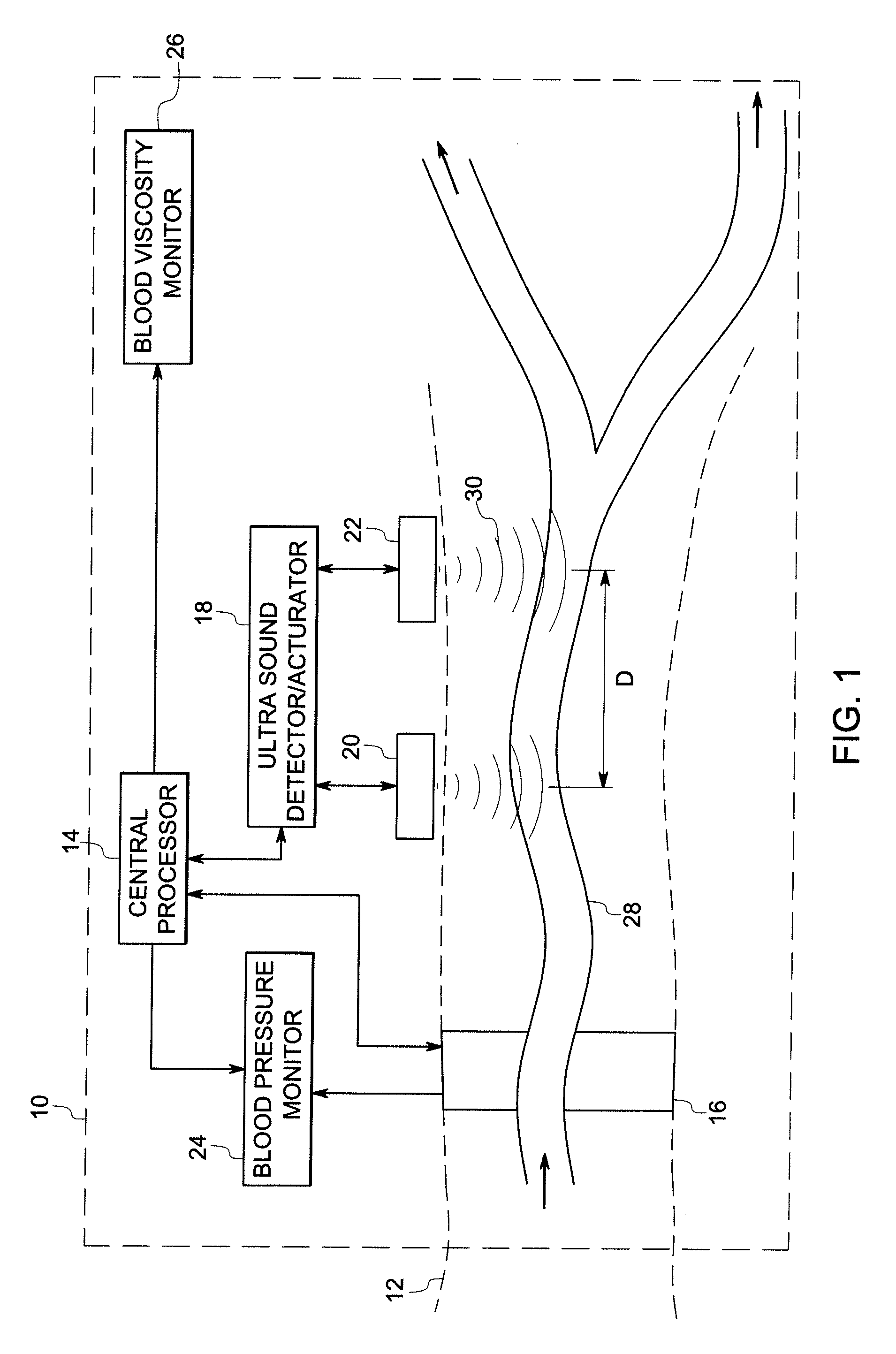
System and method for measuring blood viscosity
ActiveUS20070123779A1Accurate and non-invasive blood viscosity measurementBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationBlood flowBiomedical engineering
A technique is provided for computing or monitoring blood viscosity. The technique includes measuring a cross sectional area of a arterial segment and a volumetric flow rate of blood flowing through the arterial segment at two or more locations, estimating a compliance transfer function from blood measurements to scale the arterial cross sectional area into a pressure waveform, deriving a transmission line model of the arterial segment based on the cross sectional area, as scaled by the compliance transfer function, of the arterial segment at the two or more locations and the volumetric flow rate of blood at the two or more locations. The technique also includes computing the blood viscosity based on the transmission line model.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Photoacoustic tracking and registration in interventional ultrasound
ActiveUS20160228090A1Diagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound pulse
According to some embodiments of the invention, an ultrasound imaging system having real-time tracking and image registration includes a fiducial-marker system comprising an ultrasound transmitter structured to provide a localized ultrasound pulse at an optically observable localized spot on a body of interest. The system further includes an optical imaging system, a two-dimensional ultrasound imaging system, an optical image processing system, and an ultrasound image processing system The ultrasound imaging system further includes a registration system configured to communicate with the optical image processing system and the ultrasound image processing system to receive information, the registration system being further configured to determine a coordinate transformation that registers the optical image with the two-dimensional ultrasound image based at least partially on information concerning the spatial locations determined for the combined ultrasound and optical fiducial marker observed in the optical image and in the two-dimensional ultrasound image.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Popular searches
Respiratory organ evaluation Sensors Sonic diagnostics Blood characterising devices Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic device testing/calibration Blood pressure measurement devices Telemetric patient monitoring Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic data transmission Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniques Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic image/data processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com