Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
584results about "Swabs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
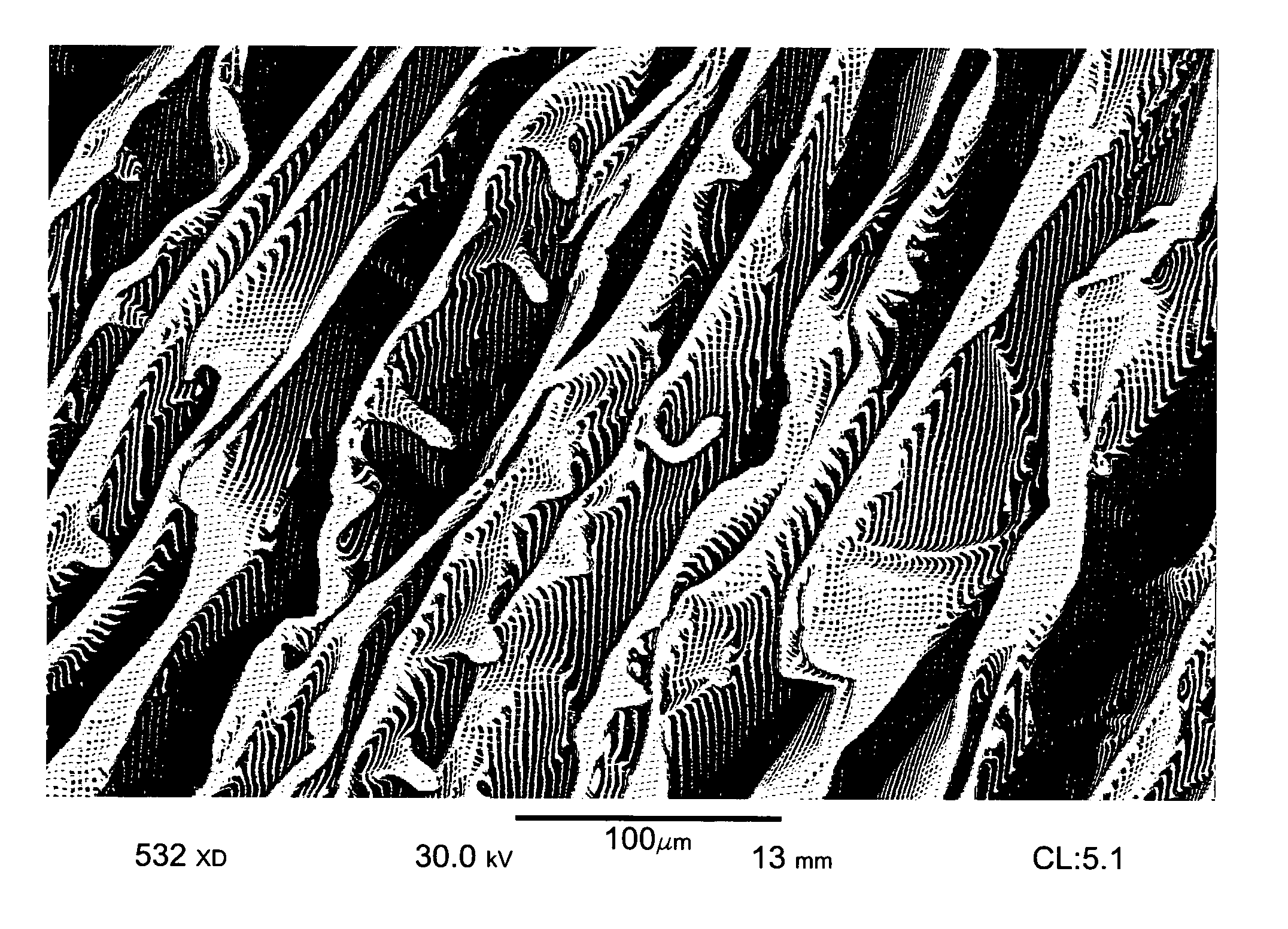
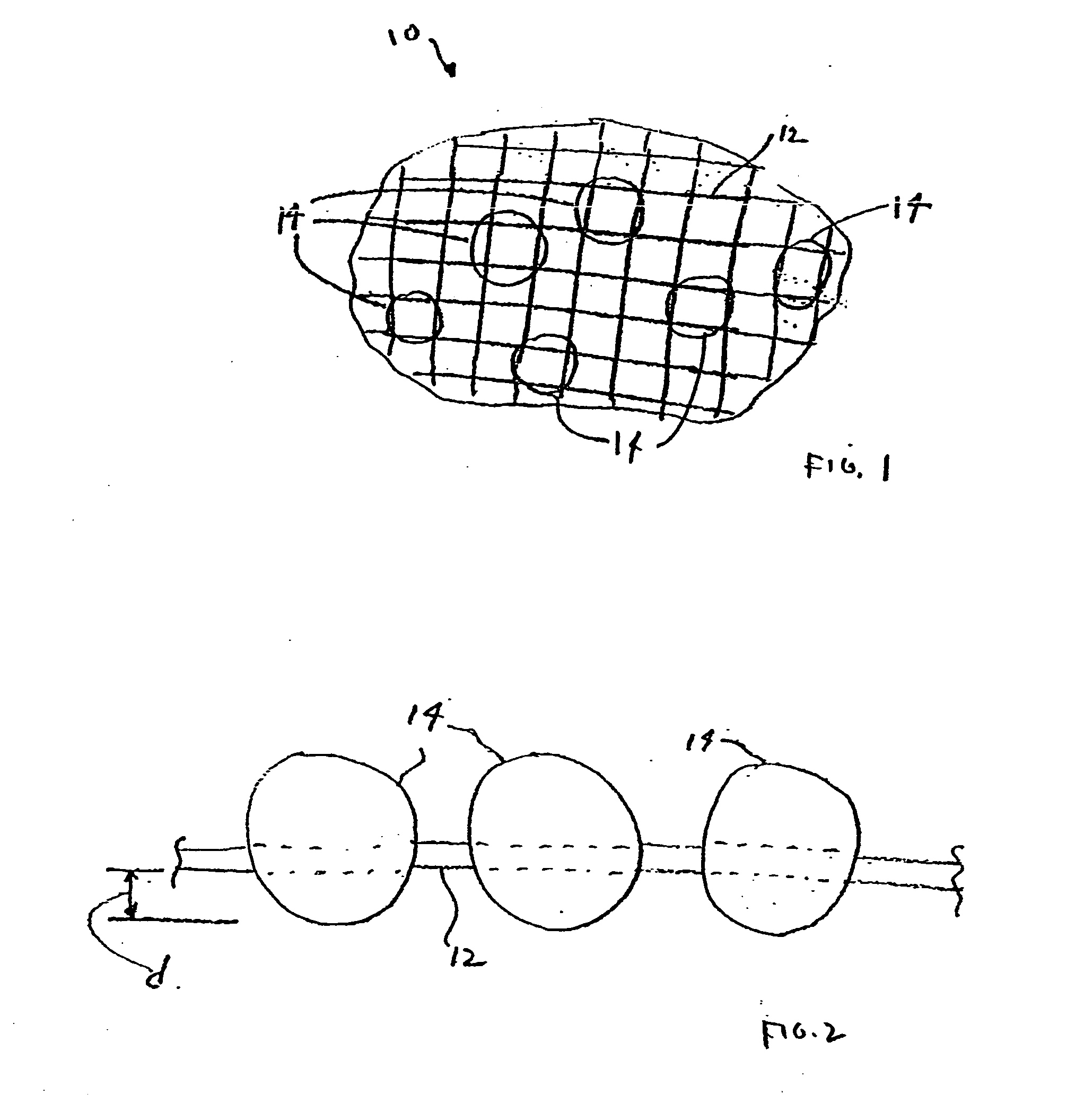
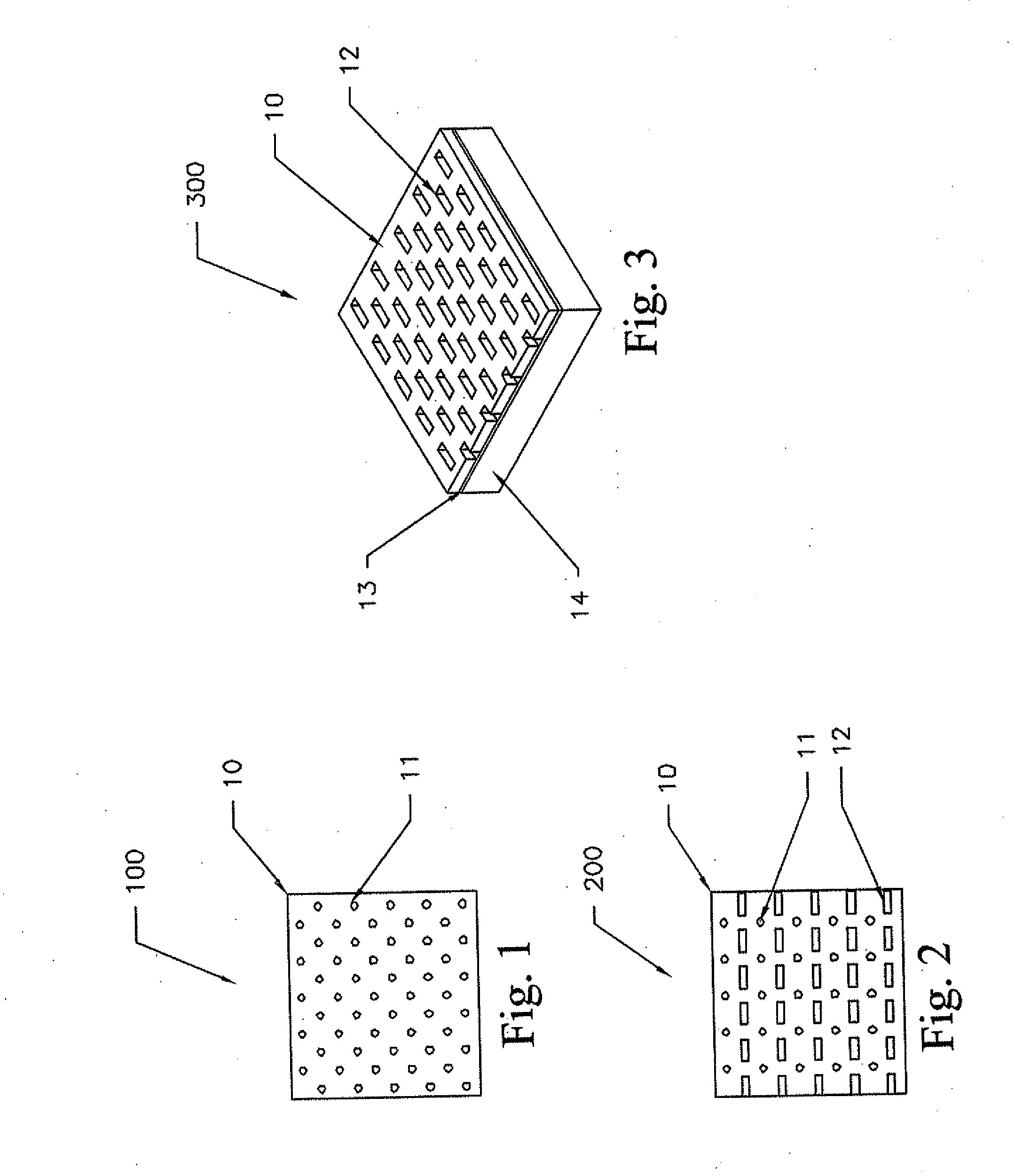
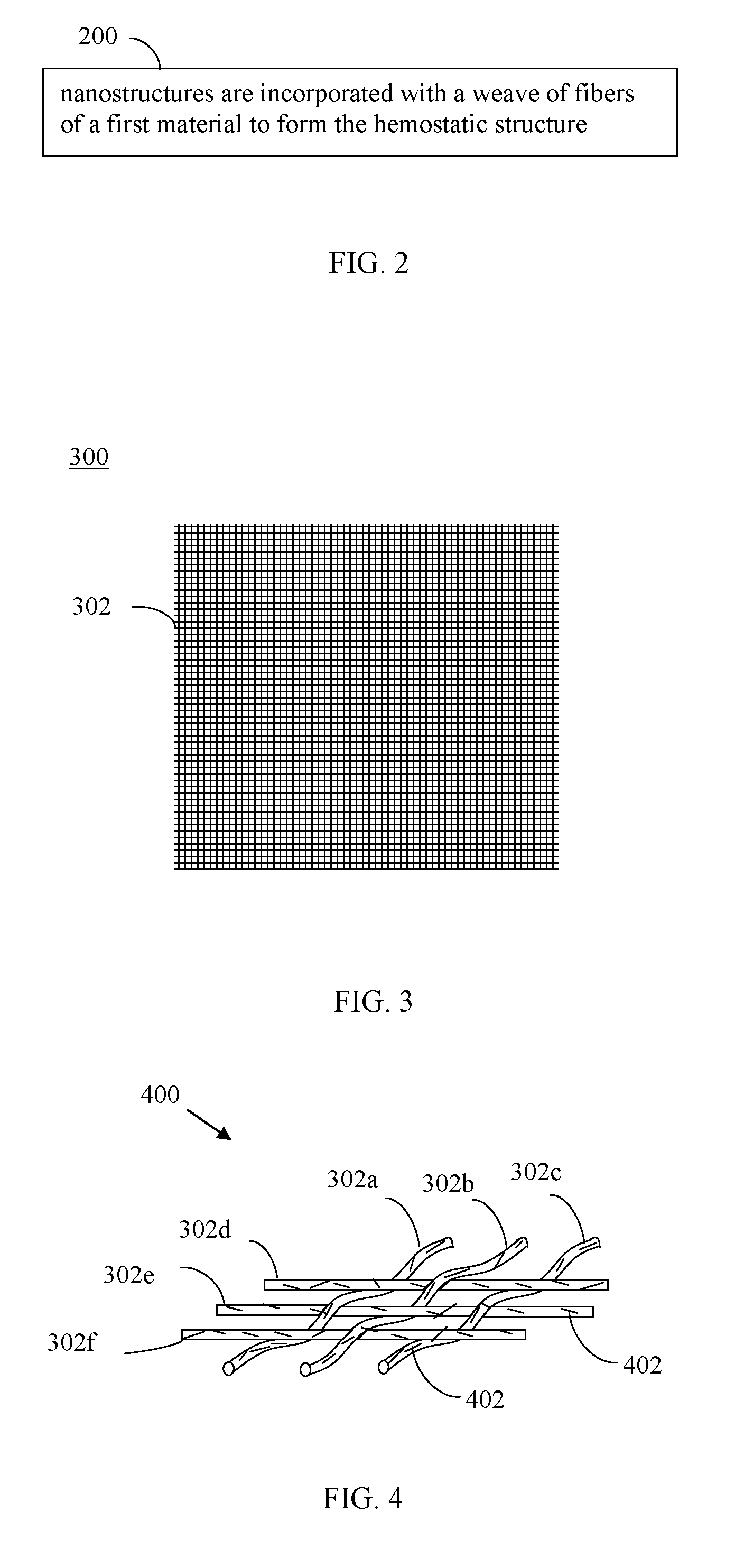
Nanostructure-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic structures
InactiveUS8319002B2Enhancing overall rate and strengthInduce platelet binding and efficient hemostasisBiocideSurgical adhesivesPlateletNanofiber
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for nanomaterial-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic medical devices are provided. Hemostatic materials and structures are provided that induce platelet binding, including platelet binding and the coagulation of blood at a wound / opening caused by trauma, a surgical procedure, ulceration, or other cause. Example embodiments include platelet binding devices, hemostatic bandages, hemostatic plugs, and hemostatic formulations. The hemostatic materials and structures may incorporate nanostructures and / or further hemostatic elements such as polymers, silicon nanofibers, silicon dioxide nanofibers, and / or glass beads into a highly absorbent, gelling scaffold. The hemostatic materials and structures may be resorbable.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Wound dressing and method for controlling severe, life-threatening bleeding
ActiveUS7371403B2Stanching flowProhibiting flow of bloodBiocideSuspensory bandagesHydrophilic polymersWound dressing
This invention is directed to advanced hemorrhage control wound dressings, and methods of using and producing same. The subject wound dressing is constructed from a non-mammalian material for control of severe bleeding. The wound dressing for controlling severe bleeding is formed of a biomaterial comprising chitosan, a hydrophilic polymer, a polyacrylic polymer or a combination thereof. The kind of severe, life-threatening bleeding contemplated by this invention is typically of the type not capable of being stanched when a conventional gauze wound dressing is applied with conventional pressure to the subject wound. The wound dressing being capable of substantially stanching the flow of the severe life-threatening bleeding from the wound by adhering to the wound site, to seal the wound, to accelerate blood clot formation at the wound site, to reinforce clot formation at the wound site and prevent bleed out from the wound site, and to substantially prohibit the flow of blood out of the wound site.
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGONDBA ST VINCENTMEDICAL CENT
Wound packing material for use with suction
InactiveUS20050209574A1Overcome deficienciesWound drainsMedical applicatorsPack materialWound packing material
A wound packing for use with suction is provided. The wound packing comprises a plurality of nonabsorbent synthetic polymeric fibers coupled together to form a nonabsorbent material suitable for placement in the wound of a mammal. A method for treating the wound in a mammal using the disclosed wound packing is also provided.
Owner:BOEHRINGER TECH
Apparatus and methods for preventing or treating failure of hemodialysis vascular access and other vascular grafts
InactiveUS6726923B2Reduce calcificationInhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferationBiocideOrganic chemistryVascular graftBlood vessel
Owner:VASCULAR THERAPIES INC
Diagnostic Test Devices
InactiveUS20070244368A1Increase rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiagnostic testProximate
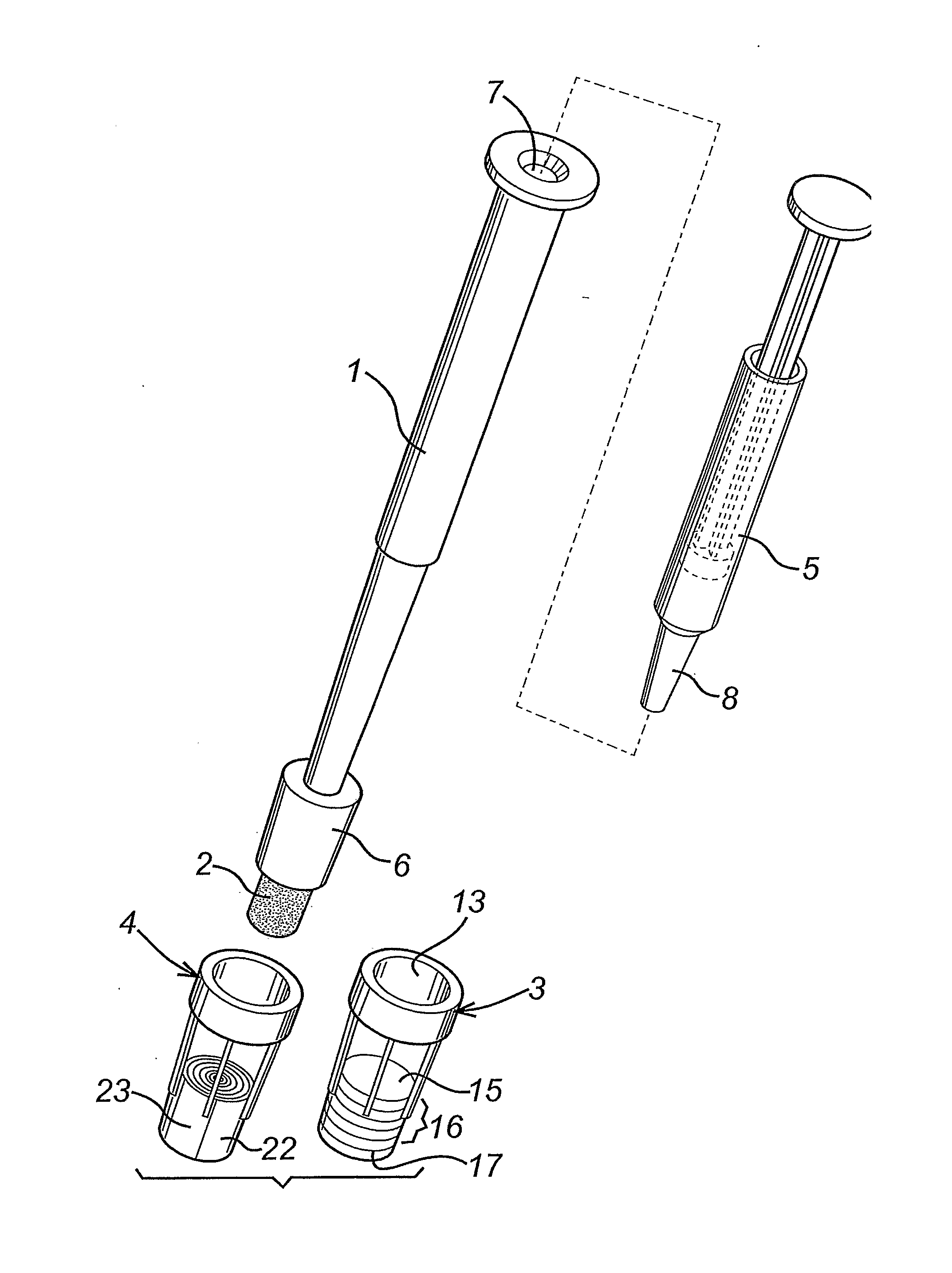
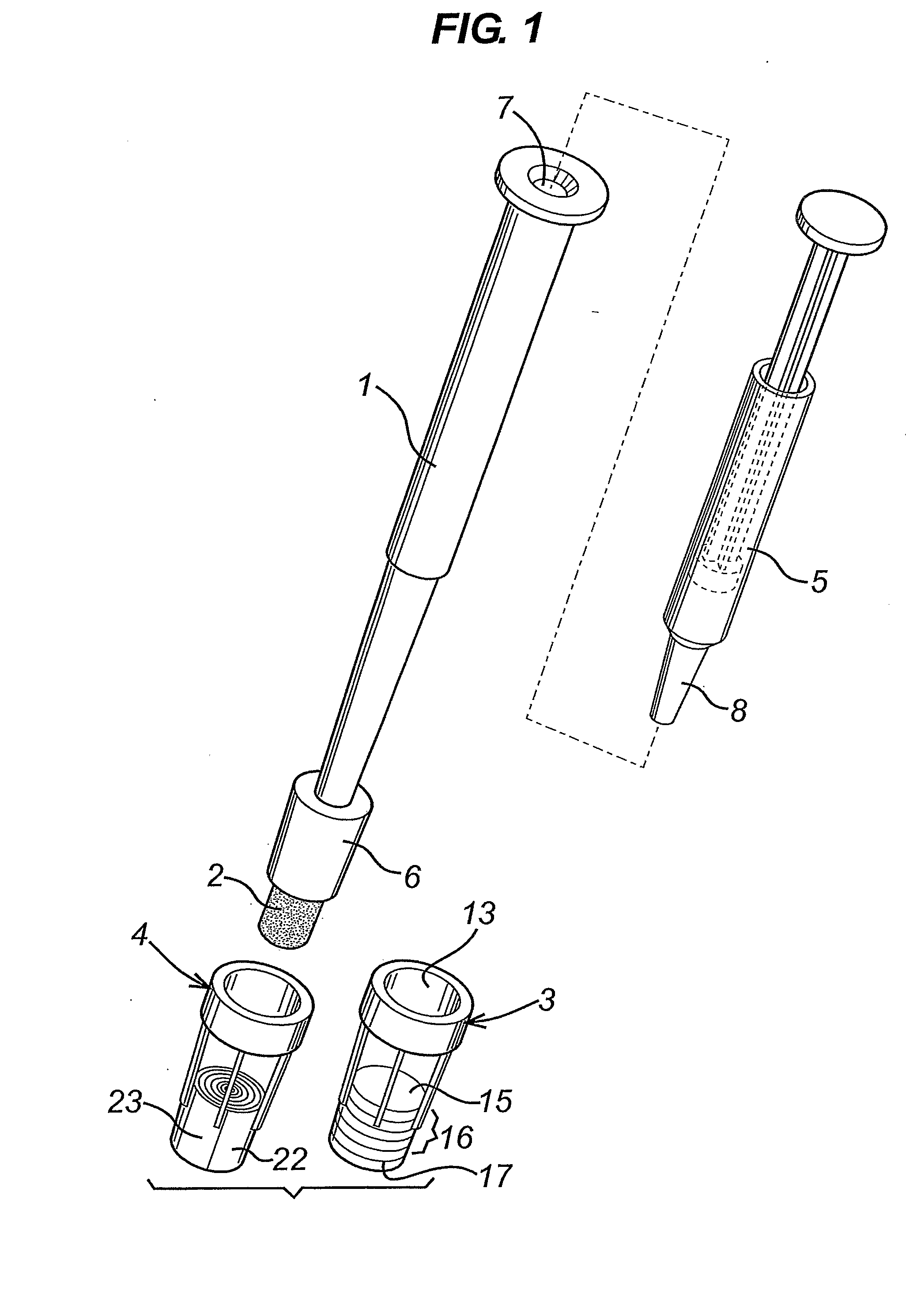
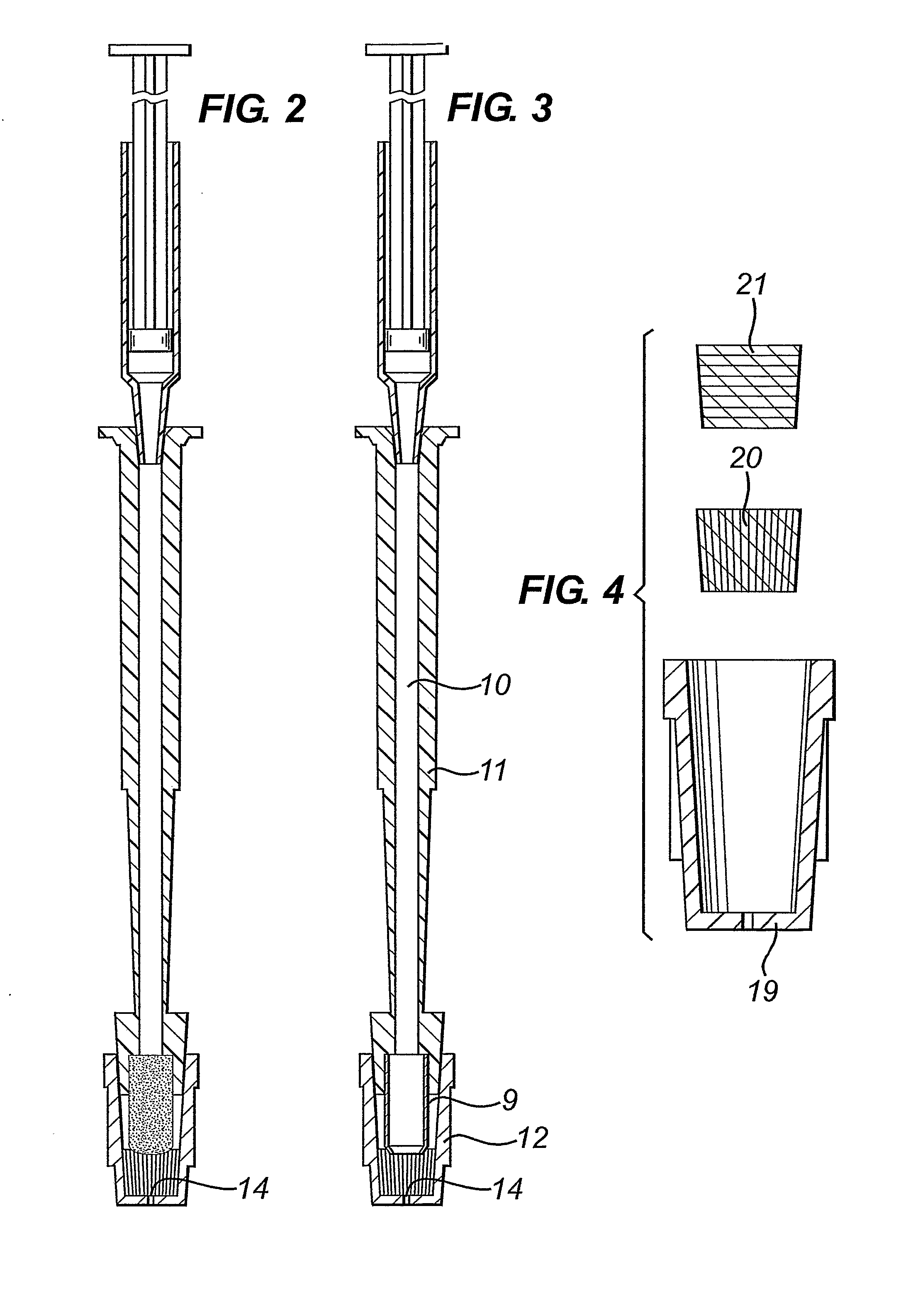
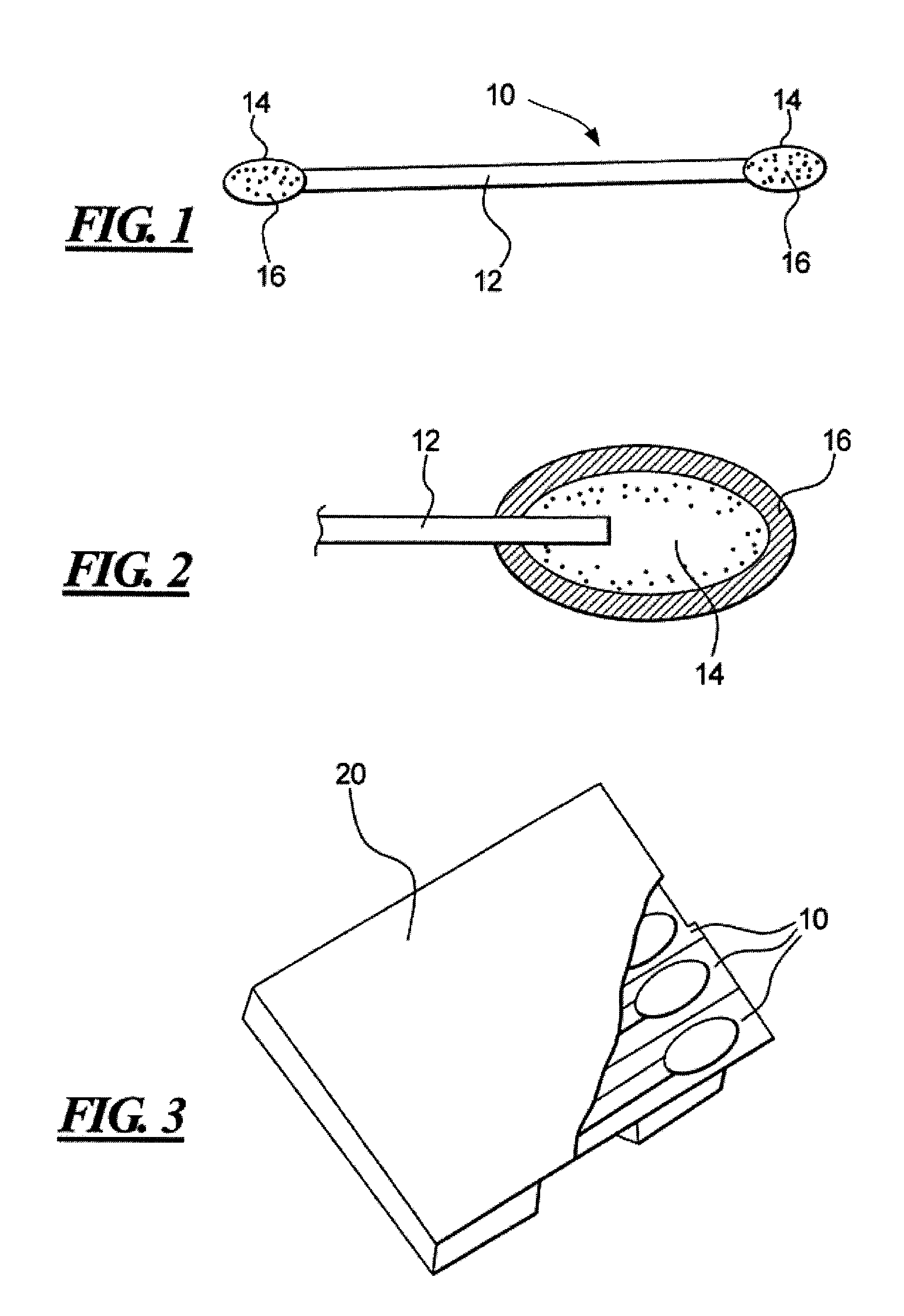
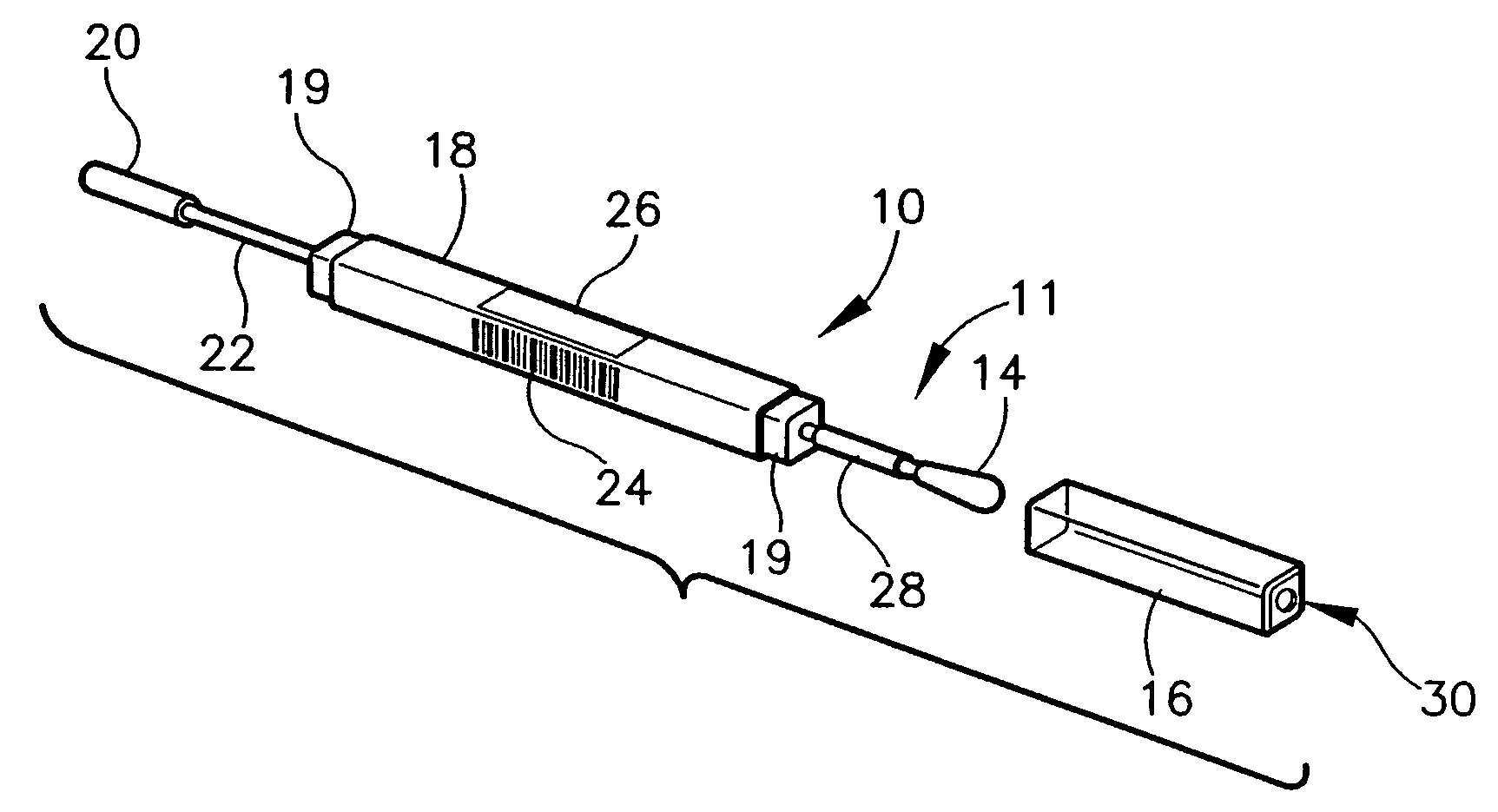
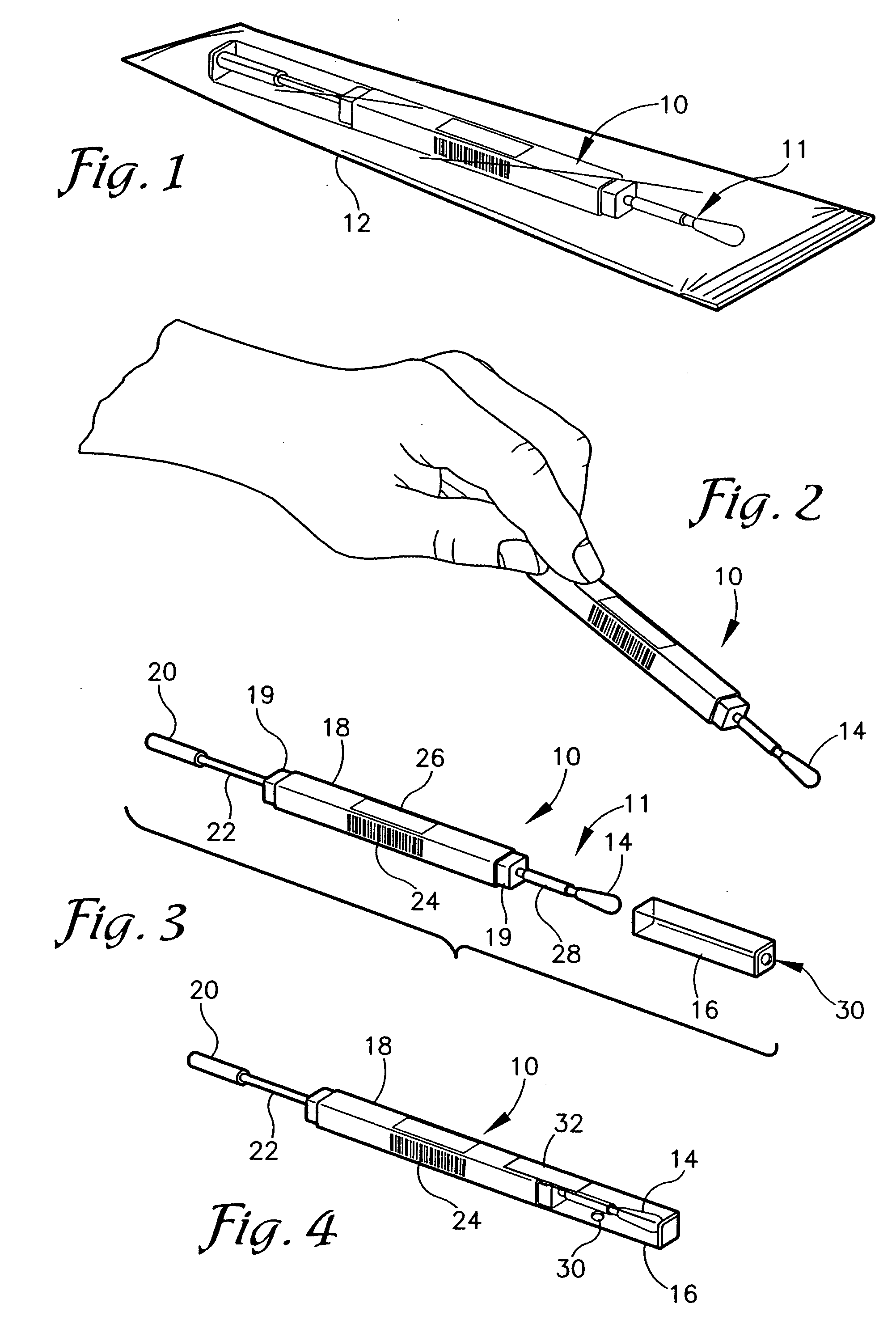
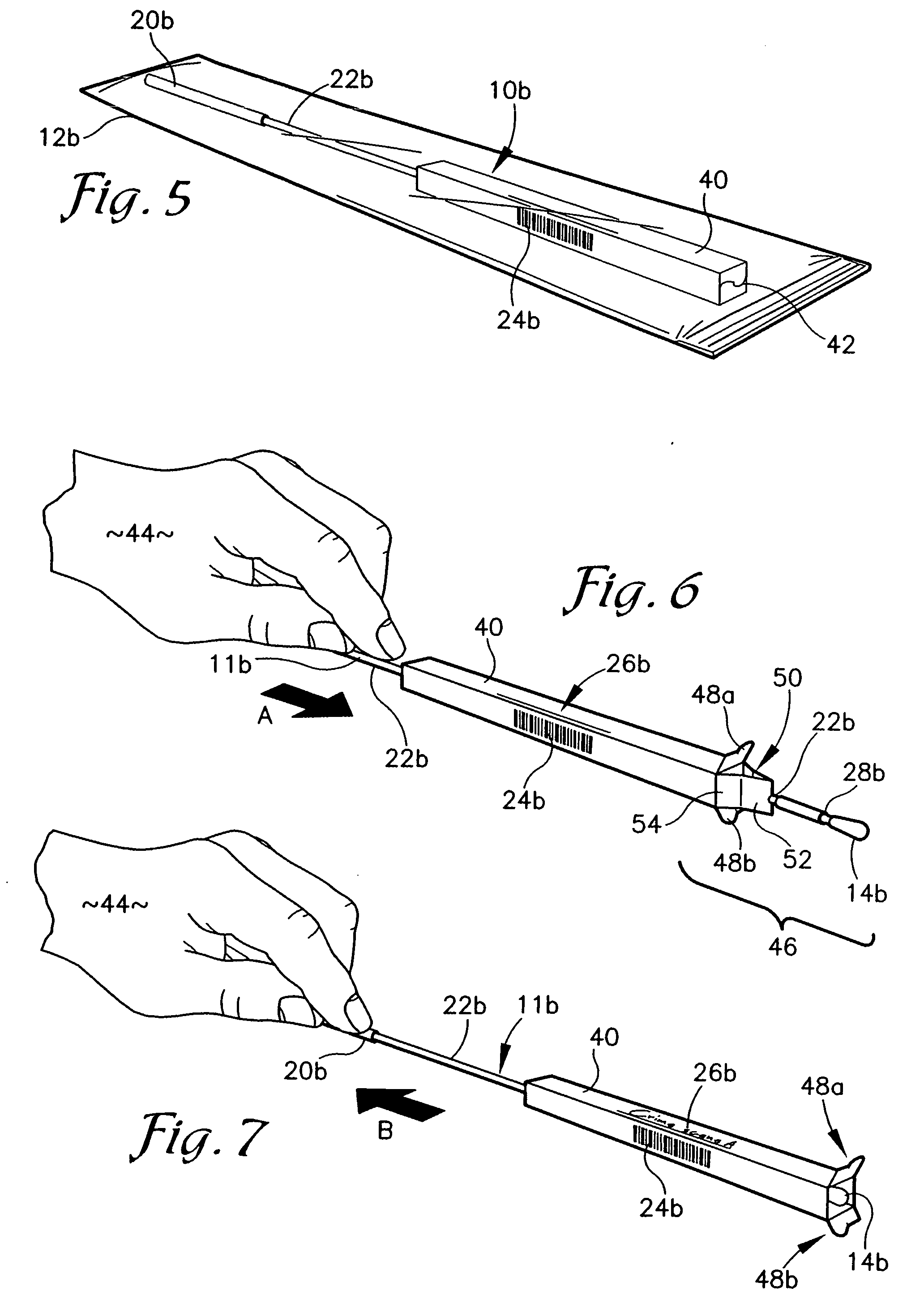
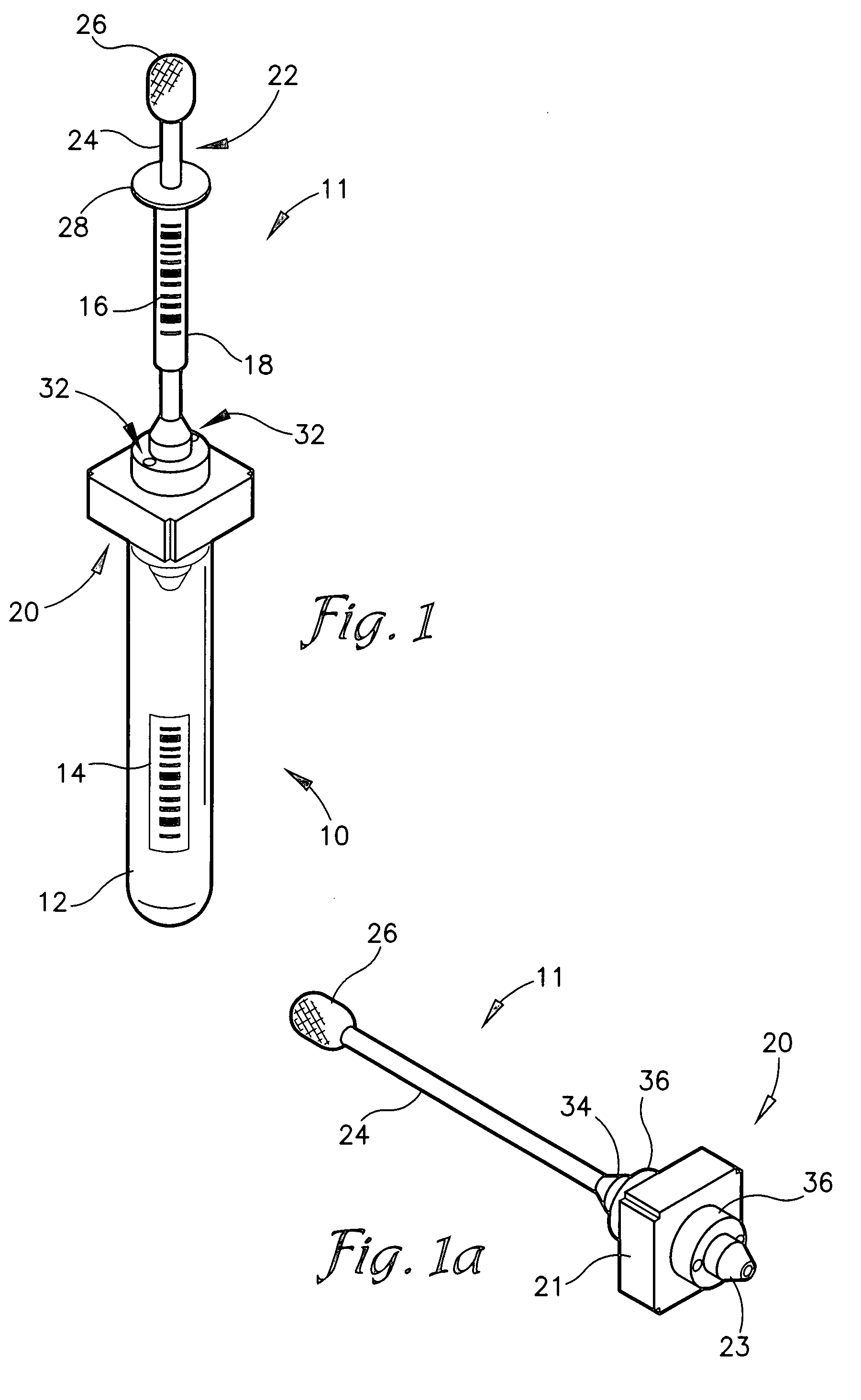
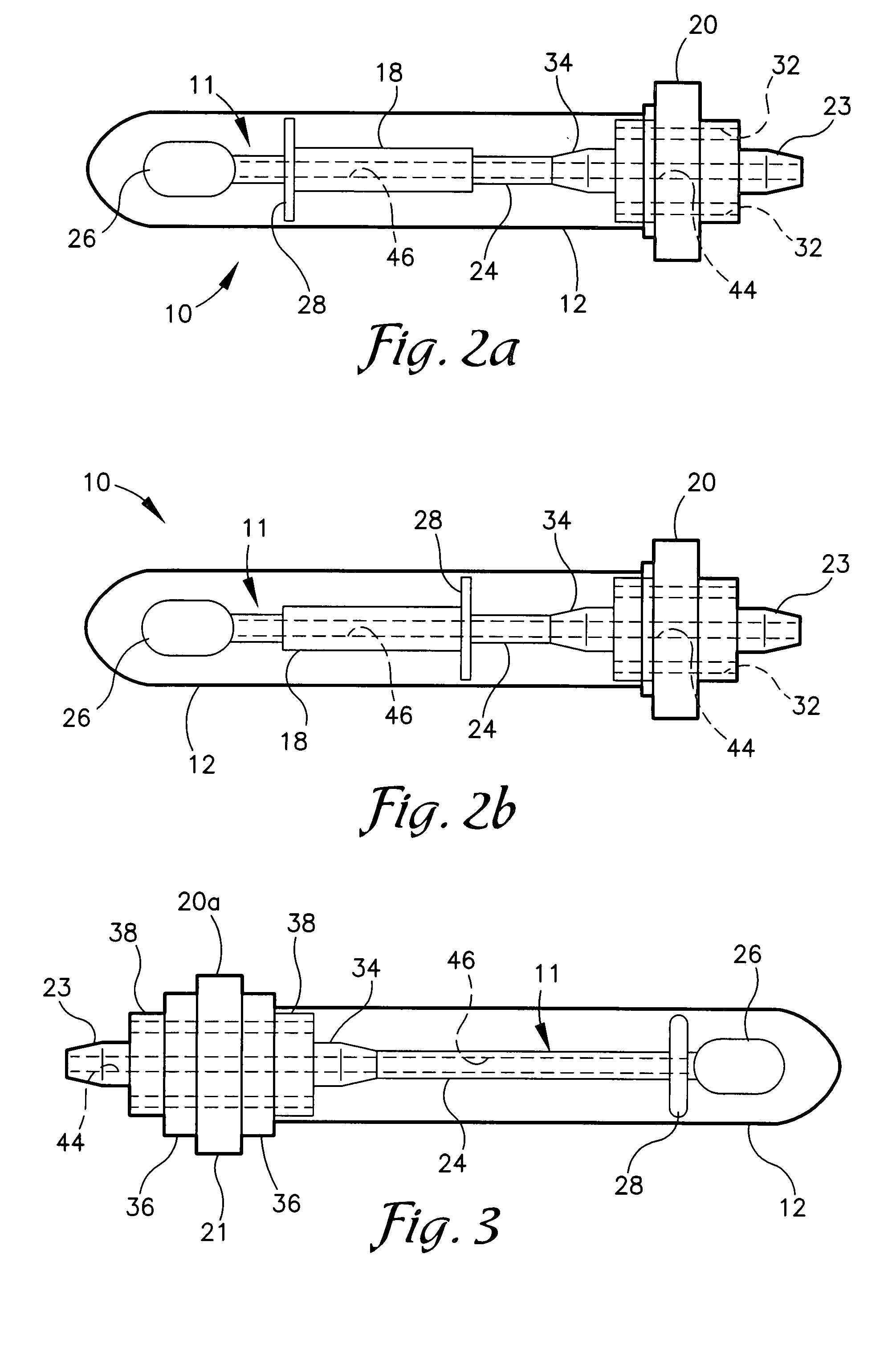
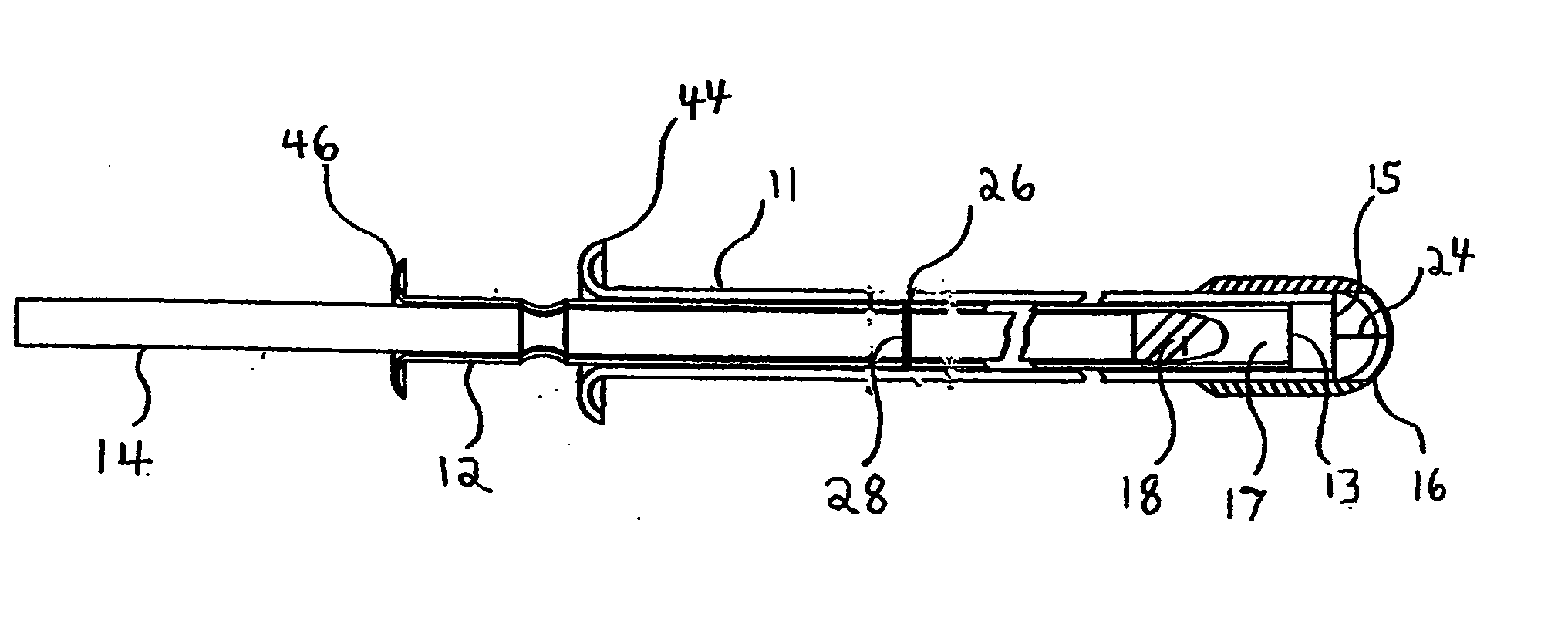
A diagnostic test apparatus comprising: a shaft having a first end and a second end; a swab or a biopsy punch mounted on the first end of a shaft; and a cap for fitting over the first end of the shaft, said cap containing at least one diagnostic test reagent; wherein the shaft comprises at least one cap engagement element located proximate to the first end, said element extending radially outwardly of the swab or the biopsy punch for engagement with the cap to retain the cap on the shaft. Also provided are diagnostic caps for use in the test apparatus having a small internal volume and at least one diagnostic test reagent located in or on an absorbent plug inside the cap. Also provided are diagnostic caps for use in the test apparatus having a housing extending from a sample receiving port, said housing defining a lateral flow path for the sample. Also provided is a test system comprising a swab shaft, a biopsy punch shaft and a diagnostic cap in accordance with the invention, wherein the cap can be used interchangeably between the two different shafts.
Owner:WOUNDCHEK LAB US
Wound packing material for use with suction
A wound packing for use with suction is provided. The wound packing comprises a plurality of nonabsorbent synthetic polymeric fibers coupled together to form a nonabsorbent material suitable for placement in the wound of a mammal. A method for treating the wound in a mammal using the disclosed wound packing is also provided.
Owner:BOEHRINGER TECH
Wound drainage dressing
ActiveUS20100262091A1Easy constructionEasy to transportSurgical needlesPlastersSecretionBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a wound drainage covering for covering, by means of low pressure, a wound that is to be treated. The covering comprises at least two layers that are superimposed. A first layer that is applied on the side of the wound is made of a functional textile material and second layer that is arranged thereon is dimensionally stable and permeable to liquid. The wound drainage covering has a simple design and due to the functional first layer, is effective and ensures, due to the dimensionally stable second layer, an optimal removal of wound secretion.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
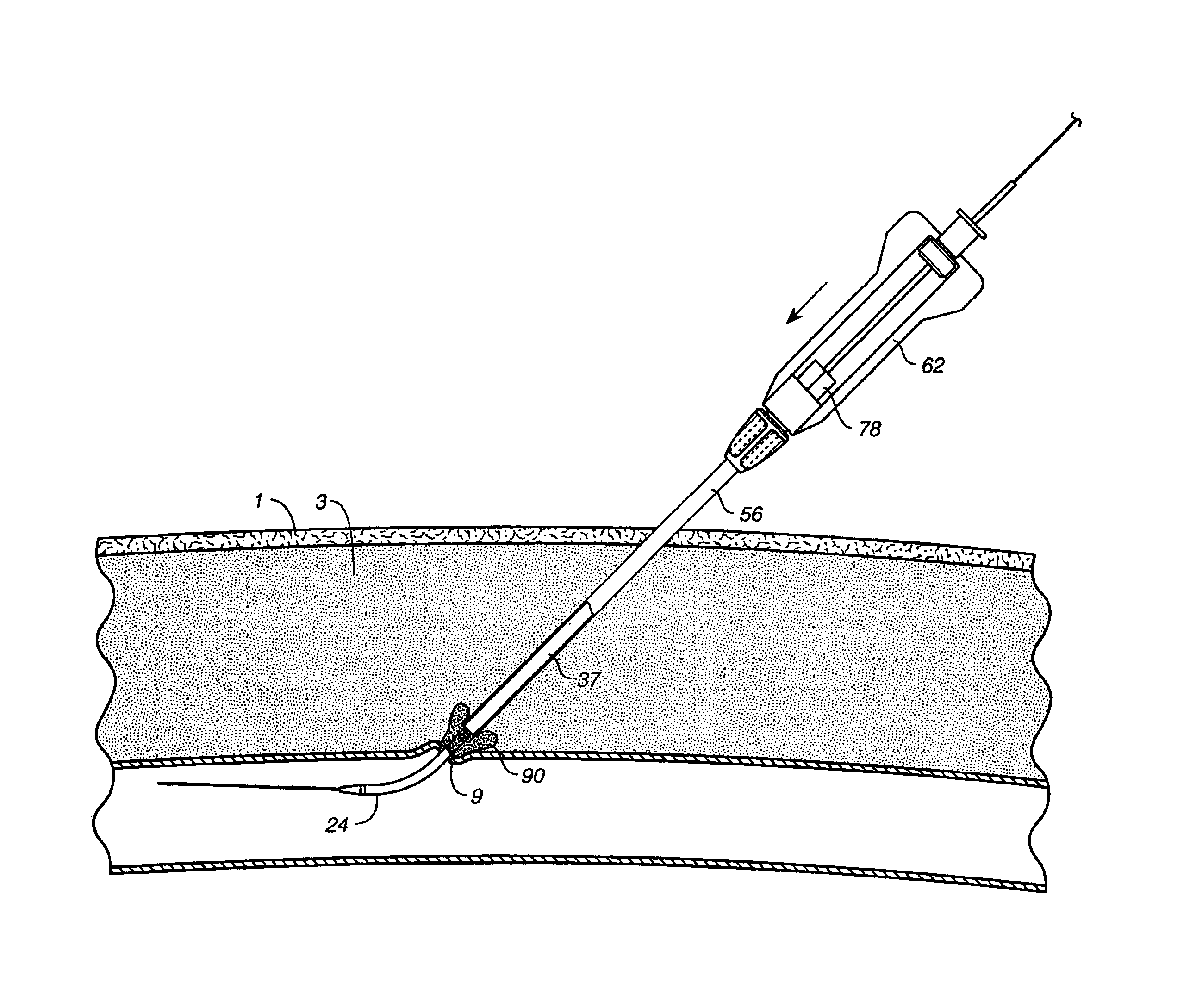
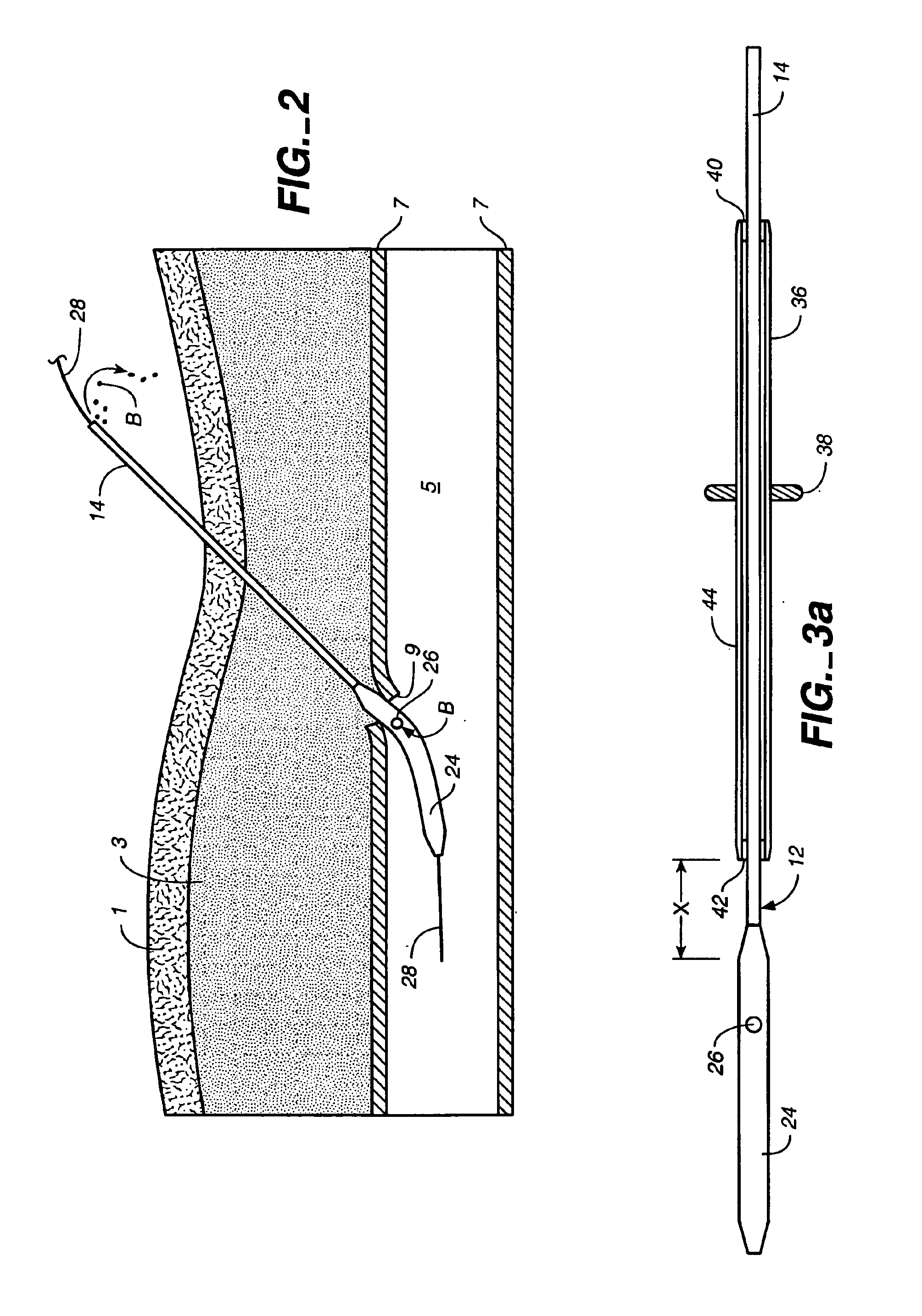
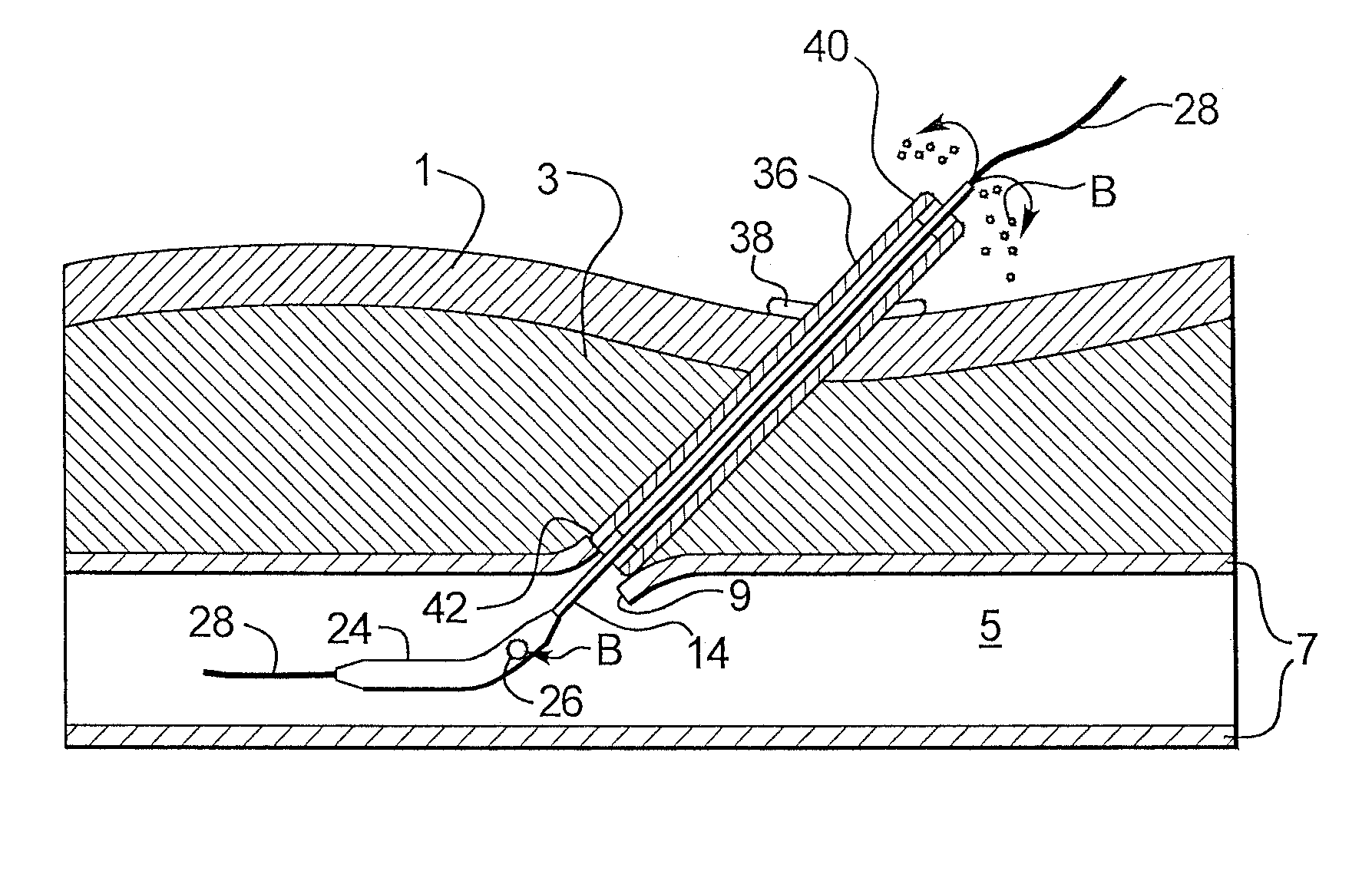
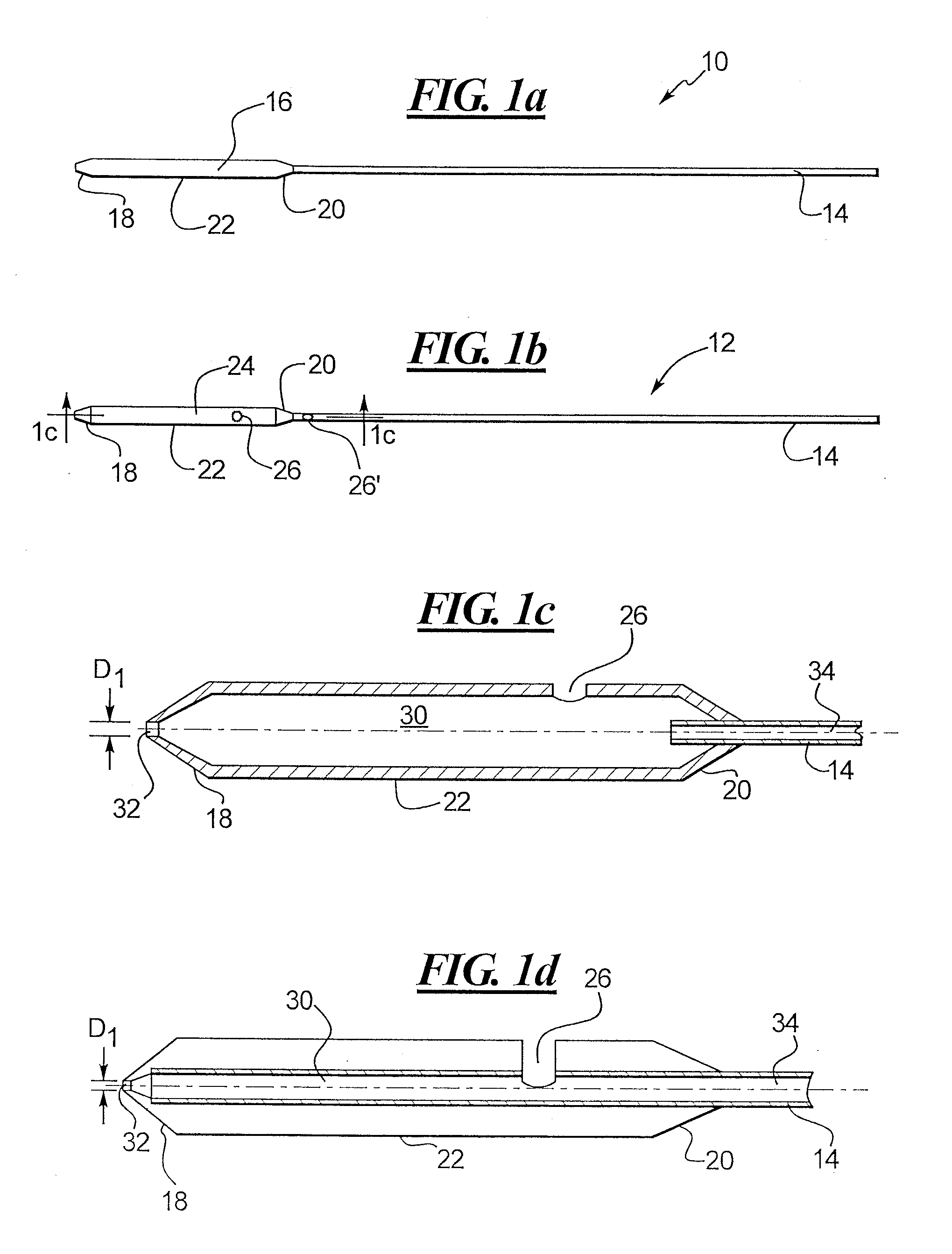
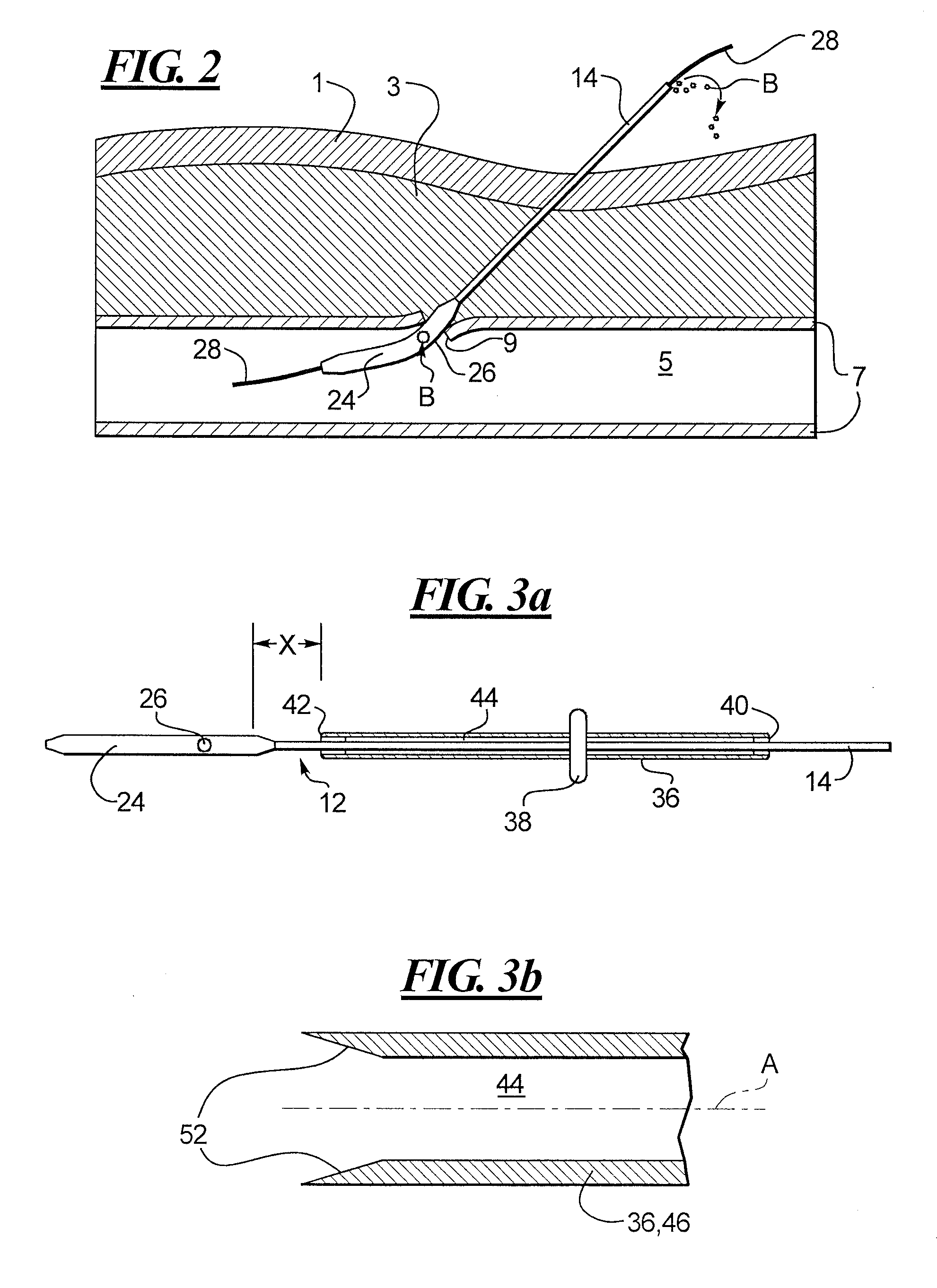
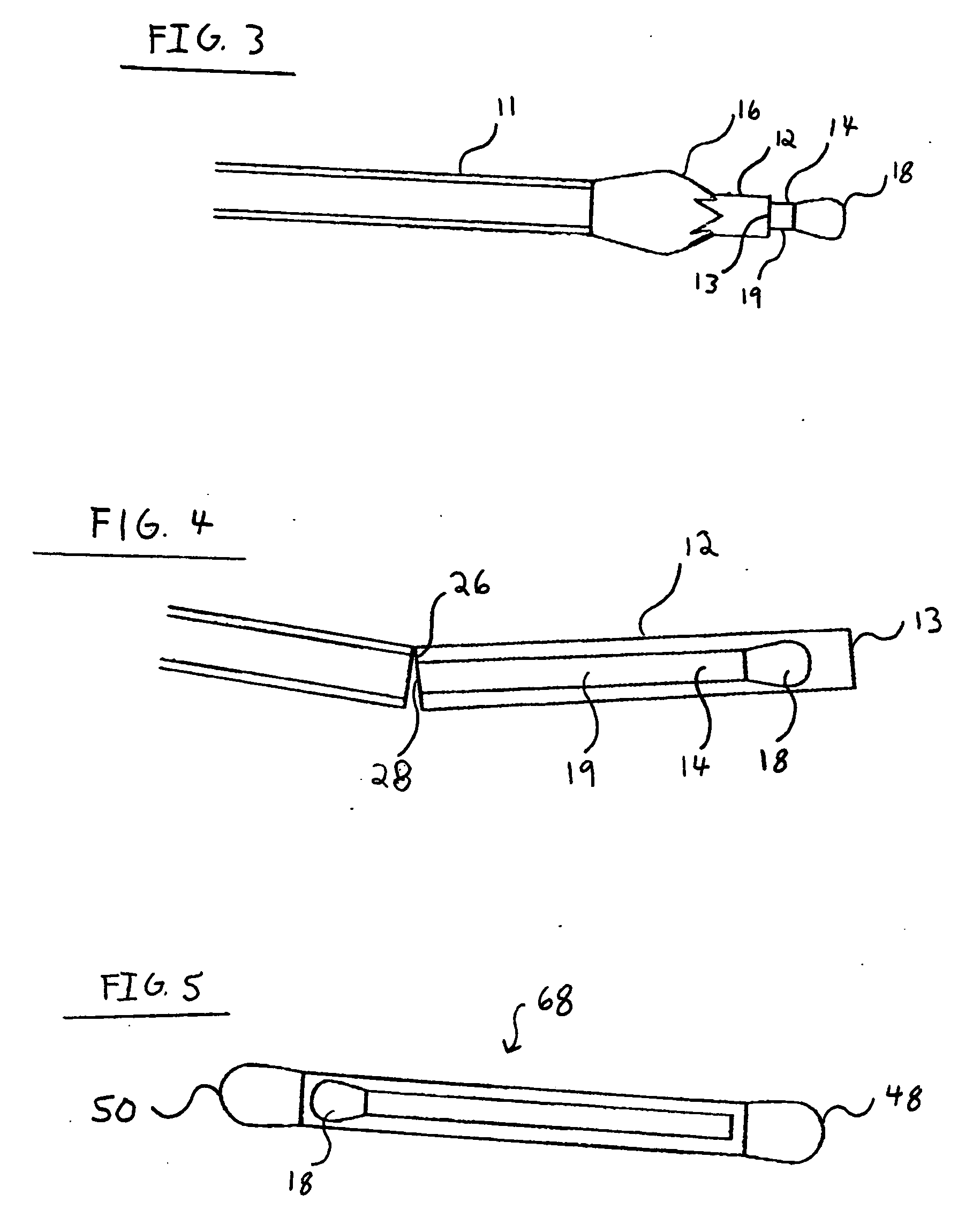
Depth and puncture control for blood vessel hemostasis system
A depth and puncture control system for a blood vessel hemostasis system includes a blood vessel puncture control tip which, when positioned in the lumen of a blood vessel, can inhibit the flow of blood out of the puncture site. When used together with a pledget delivery cannula and a pledget pusher, the control tip and the delivery catheter can both inhibit blood loss out the puncture site and inhibit the introduction of pledget material and tissue fragments into the blood vessel. The system also includes a handle which releasably connects together the control tip, pusher, and delivery cannula to permit limited longitudinal motion between the control tip and the delivery cannula, and between the pusher and the delivery cannula.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
Hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
InactiveUS20070276308A1Minimize injuryEliminate feverNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersMedicineHemostatic Agent
A hemostatic agent comprises diatomaceous earth in particle form. Devices for promoting hemostasis comprise diatomaceous earth in particle form and a receptacle for retaining the particles therein. The receptacle is defined by a mesh having openings therein. A hemostatic sponge comprises a substrate, diatomaceous earth disposed on the substrate, and a release agent disposed on the substrate. A hemostatic sponge may also comprise a film into which diatomaceous earth is incorporated, or it may comprise a substrate, diatomaceous earth disposed on the substrate, and a film disposed over the diatomaceous earth. A hemostatic sponge may also comprise a first substrate, diatomaceous earth disposed on the first substrate, and a second substrate disposed on the diatomaceous earth. When treating a bleeding wound using any of the foregoing devices, application of the device causes the diatomaceous earth to come into contact with blood to cause a clotting effect.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Methods for treating wound tissue and forming a supplemented fibrin matrix
InactiveUS7196054B1Low antigenicityDecreasing thrombogenicityOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesTissue sealantVascular dilatation
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Hemostatic sponge
ActiveUS20100318048A1Good hemostasisImprove abilitiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBaby linensWound healingMaterials science
The present invention provides a hemostatic porous sponge comprising a matrix of a fibrous biomaterial and particles of a fluid absorbing, particulate material adhered to said matrix material, a method of producing these sponges and their use for wound healing.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
Surgical packing devices
InactiveUS20110028934A1Avoid lossImproved haemostatic packing devicesPlastersTourniquetsTrauma surgeryInjury mouth
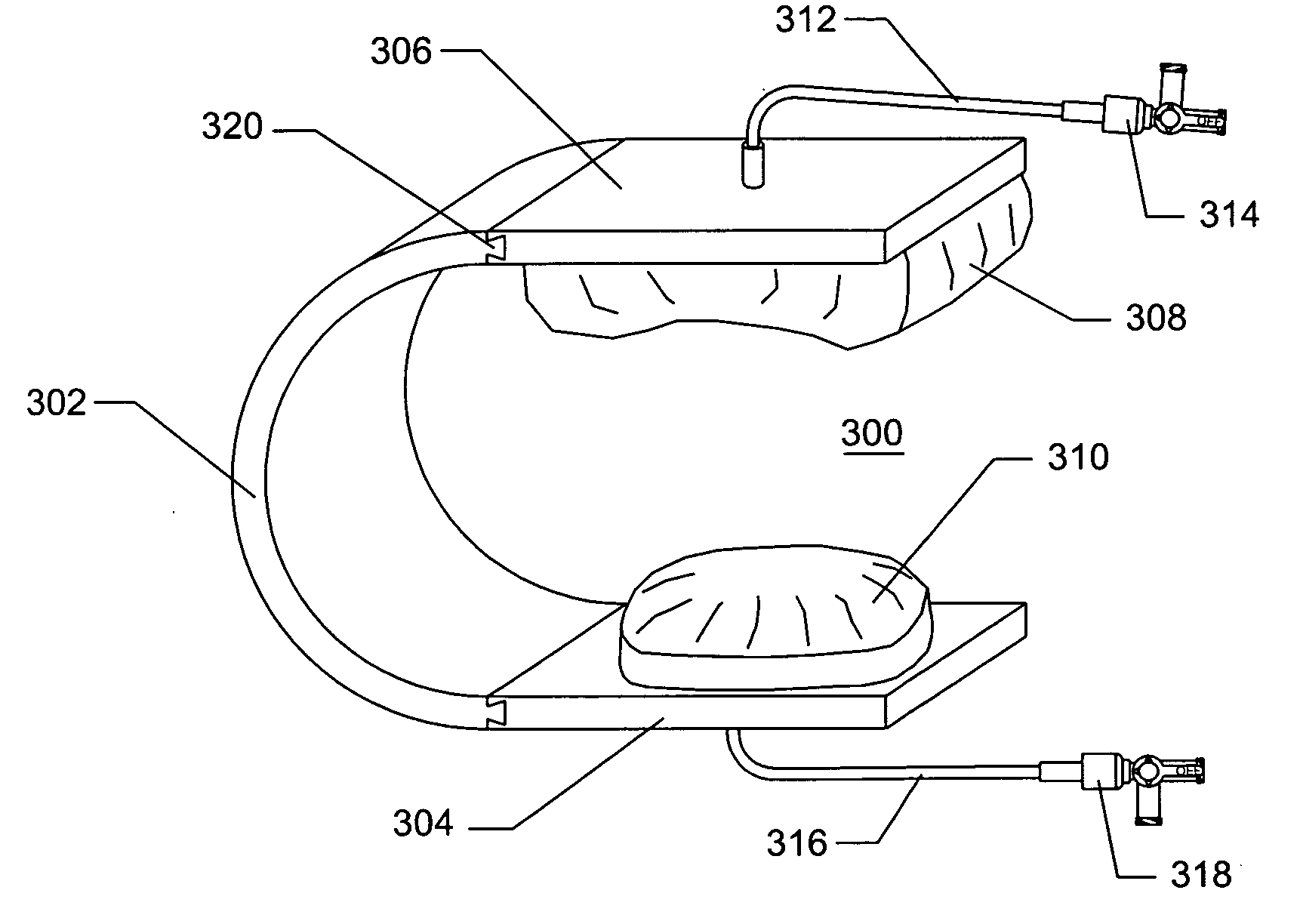
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the body in regions such as the shoulder, pelvis, neck, or groin, where standard bandages are difficult to apply and where large blood vessels exist which can hemorrhage severely. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize packing pillows that are held in place by rigid structures that can cause the packing pillows to be brought into the wounds and be held in place while the packing pillows are inflated to fill the wounds, prevent bleeding, and tamponade hemorrhaging large blood vessels exposed therein.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
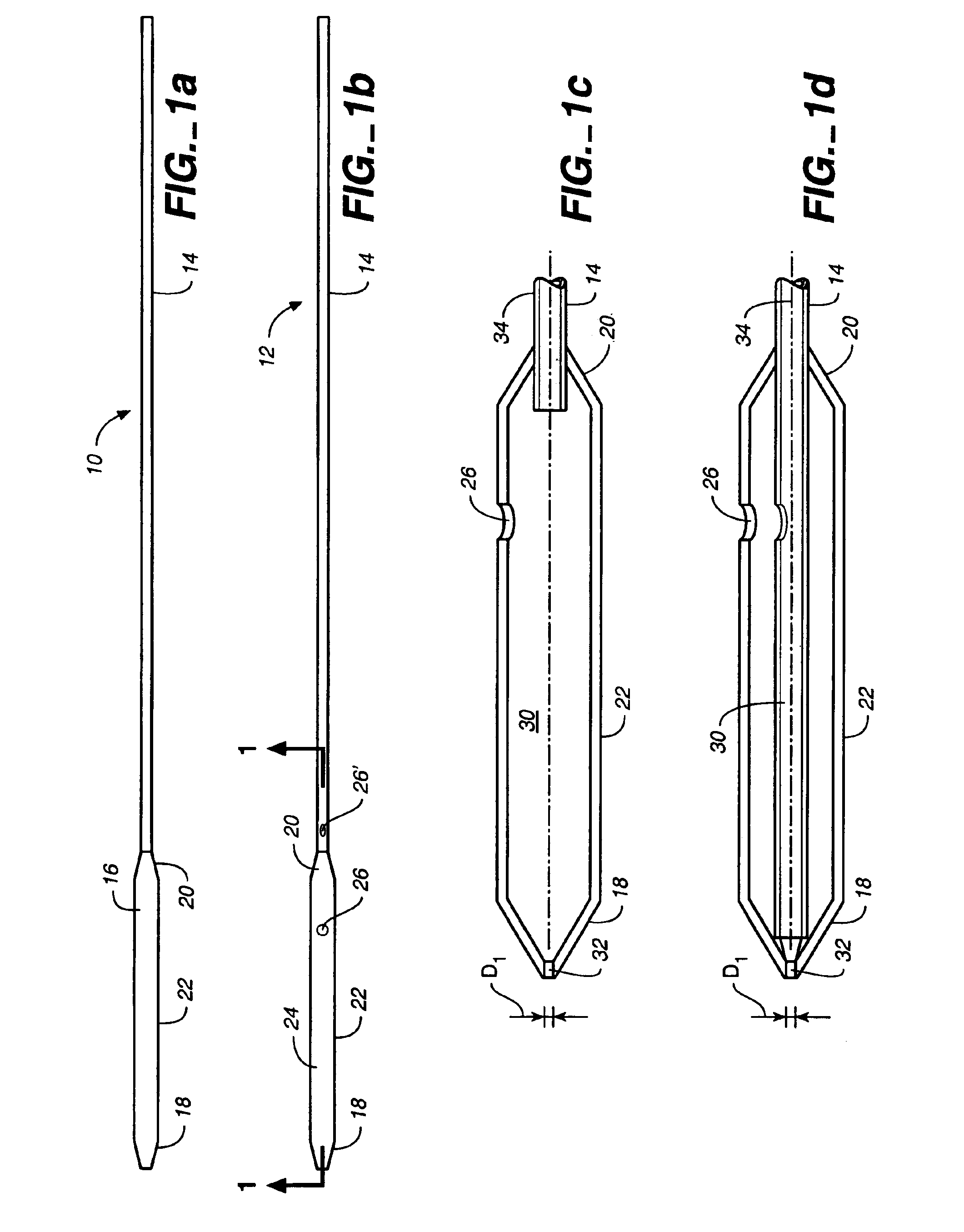
Gelatine-based materials as swabs
InactiveUS20060115805A1High recovery levelHigh recovery rateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSporeMicroorganism
A swab comprising gelatine or collagen has been found to have a remarkably high recovery of microorganisms. Furthermore, the samples, such as microorganisms, spores, nucleotides and other biologically or biochemically relevant compounds can be fully recovered from the collagen- or gelatine-comprising swab. The invention thus provides a method and swab which has a high recovery of a target from a sample and furthermore a second high recovery when transferring from the swab to a medium for analysis.
Owner:FERROSAN MEDICAL DEVICES
Bioactive wide-weave mesh
InactiveUS20090204129A1Good curative effectSuture equipmentsNon-adhesive dressingsVaginal ProlapsesTreatment efficacy
A wide-weave mesh is disclosed which is coated with a bioactive material to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of the mesh. The mesh may be used for the treatment of hernias, vaginal prolapses and other similar injuries.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical device
InactiveUS20080125687A1Reduce microbial bio-burdenRestoring the transepithelial skin potentialPlastersAdhesive dressingsWound dressingSurgical incision
A medical device for example a wound dressing having antibacterial and optionally, antifungal properties, are provided together with methods for making the device. An exemplary dressing includes a layer of silver-containing fabric, (optionally) a layer of absorbent material, and (optionally) a layer of flexible air-permeable and / or water-impermeable material. The dressing can be used for prophylactic and therapeutic care and treatment of skin infections and surface wounds (including surgical incisions), as a packing material, and as a swab for surface cleaning.
Owner:ARGENTUM MEDICAL
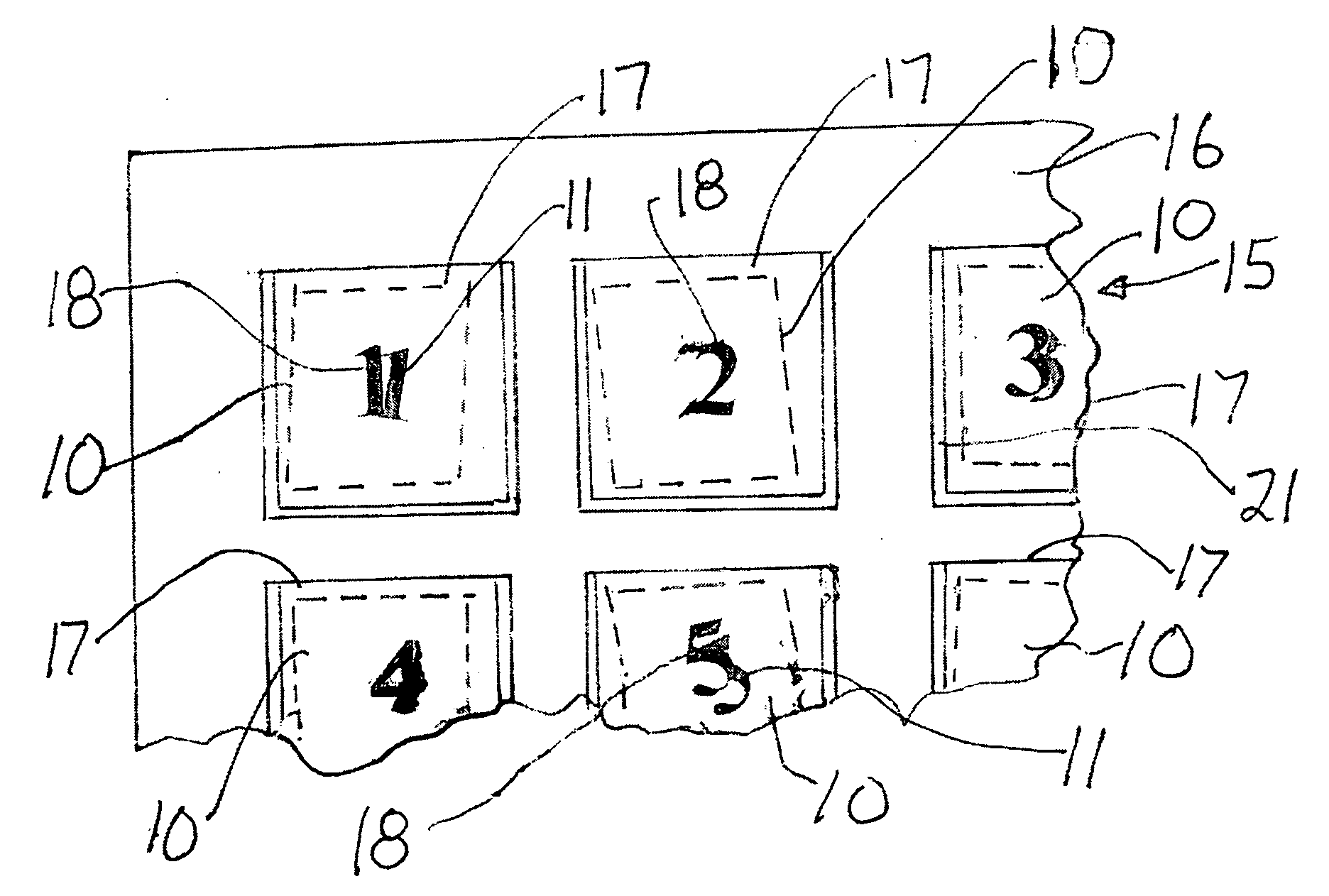
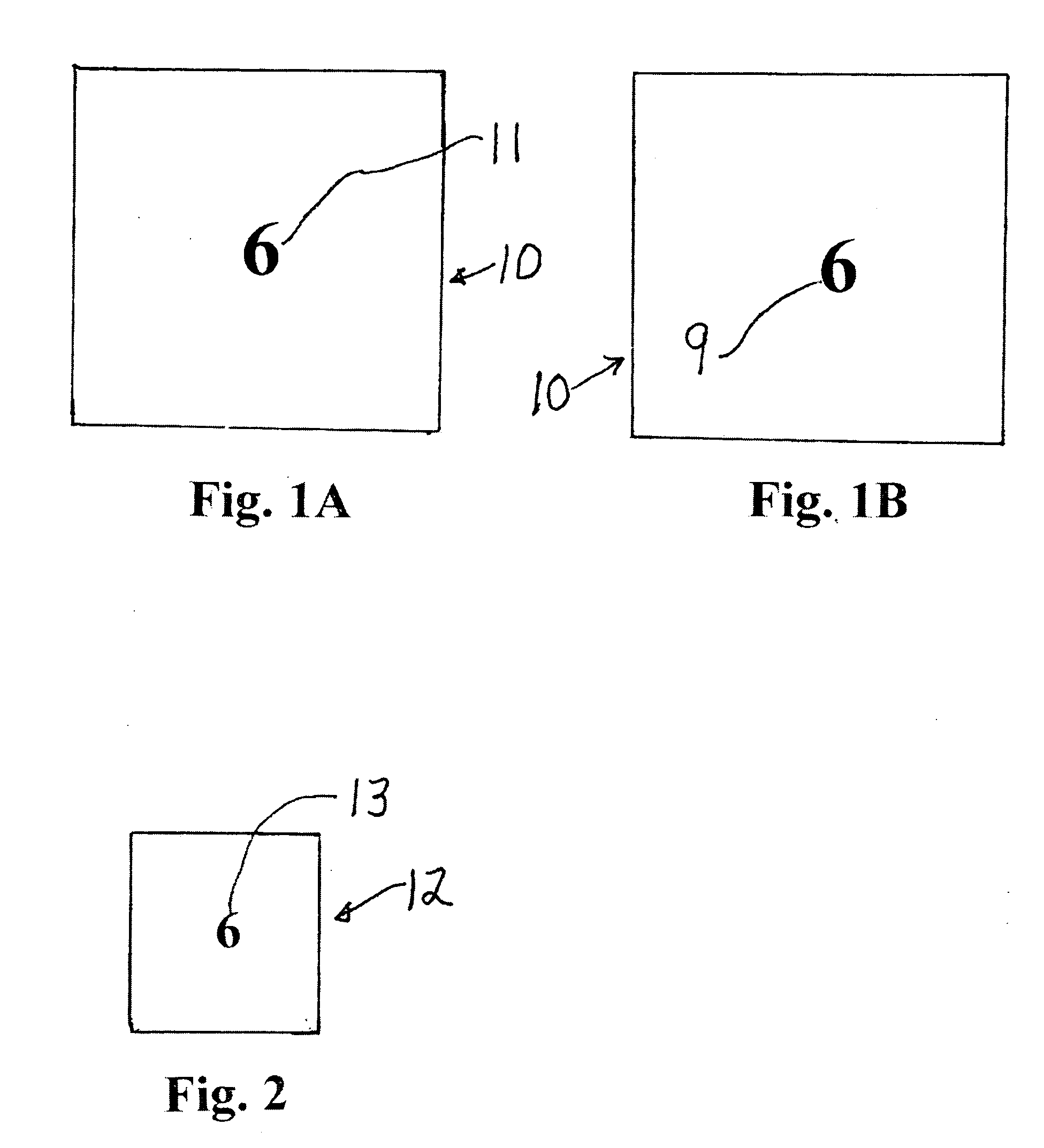
Surgical pad accounting system and method
InactiveUS20080030303A1Improve securityElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsMedicineVisual inspection
In a surgical procedure absorbent pads, such as sterile gauze lap pads and sponges are used to absorb blood and other fluids. It is vital that none of the pads be left in the patient after the operation.To account for each pad and be certain none are left in the patient, each pad is marked with unique human readable alphanumeric character, for example each pad in its face is printed with one number from the numbers 1,2,3 . . . 10 or more.Similarly a container has pockets, each pocket being sealed on its top and two sides and with its top open. The surface of each pocket is marked with a alphanumeric human readable character, matching the characters on the pads. During ,or after the operation, each used pad is placed in its matching pocket i.e. pad “6” is placed in pocket “6”. A visual inspection reveals if any used pad is not in its matching packet which may indicate the pad has been incorrectly retained within the patient's body.
Owner:KOBREN MYLES +1
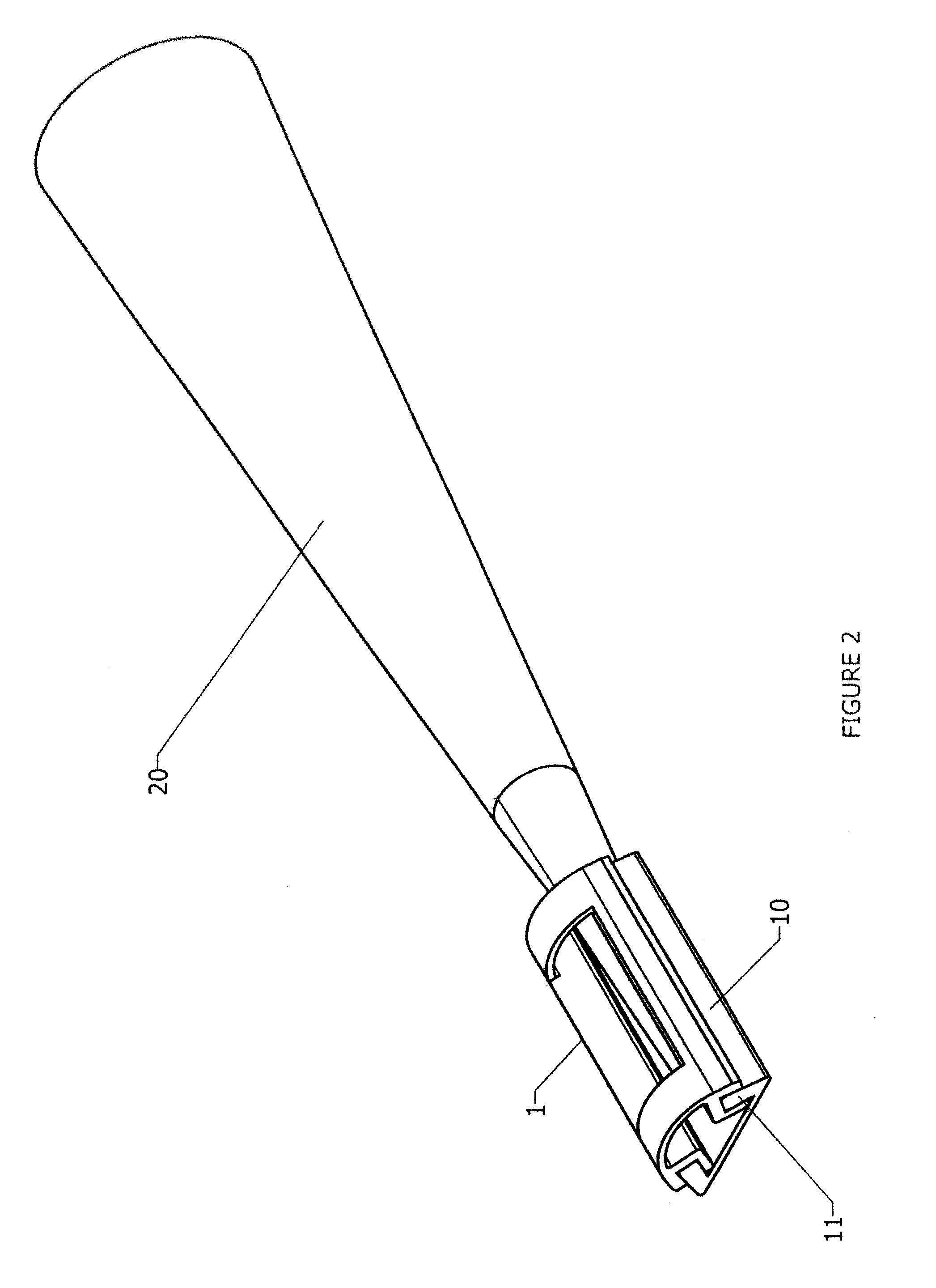
Ear cleaning system and method
A device for cleaning the ear canal of cerumen or contaminants includes a handle, a material expandable upon exposure to a fluid, and a limiter connected to the handle operative to prevent insertion of the expandable material into the ear to a depth which could contact the ear drum. Fluid is passed through the handle and through apertures to the ear canal, and or to the expandable material, whereby the ear canal and expandable material are moistened. The expandable material expands to contact the ear canal walls and cerumen, whereby the cerumen may be extracted by withdrawing the handle and connected expandable material from the ear. The fluid may be an alcohol solution, which loosens cerumen, reduces the potential for infection, and promotes drying of the ear canal.
Owner:SILVERSTEIN HERBERT
Depth and puncture control for system for hemostasis of blood vessel
A depth and puncture control system for a blood vessel hemostasis system includes a blood vessel puncture control tip which, when positioned in the lumen of a blood vessel, can inhibit the flow of blood out of the puncture site. When used together with a pledget delivery cannula and a pledget pusher, the control tip and the delivery catheter can both inhibit blood loss out the puncture site and inhibit the introduction of pledget material and tissue fragments into the blood vessel. The system also includes a handle which releasably connects together the control tip, pusher, and delivery cannula to permit limited longitudinal motion between the control tip and the delivery cannula, and between the pusher and the delivery cannula.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
Prepared medication applicator including a swab and a pharmacological active agent
A disposable swab tipped medication applicator containing one or more pharmacologically active agents in an anhydrous crystalline or powdered form at the swab. A method for use of the swab tipped applicator provides for delivery the pharmacological agent(s) to an area of the skin, such as the external auditory canal, preferably after showering or bathing, so that the dry agent is dampened so as to treat conditions of the skin. A package of the prepared applicators is provided in one embodiment, while in another embodiment applicators having two different medicaments are provided in a single package for treatment of a condition.
Owner:VAN ACKER TED GERARD
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Containerized sample collection apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070299364A1Keep dryReduce stressSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEngineeringSample collection
A containerized low pressure sample collection apparatus includes an elongated tubular shaft with a vacuum connection at one end and a swab at an opposite end. The shaft extends through a housing which can be used as a handle. The housing is adapted to receive a cap at either end, at one end for storage and at the other to cover and protect the swab with a collected sample. A second slide-out of the apparatus embodiment includes a swab structure including a tubular shaft, a swab, and a centering structure which can be slid out of and back into a housing which can also be used as a handle to manipulate the apparatus to collect a sample. Both embodiments can be connected to a vacuum unit to draw air through the swab to collect certain kinds of samples.
Owner:BODE TECH GROUP
Attachment of electronic tags to surgical sponges and implements
InactiveUS20050049564A1Avoid injuryEasy accessSurgeryDiagnostic markersEngineeringSurgical department
Externally detectable electronic article surveillance markers are attached to surgical implements, such as sponges and surgical instruments, appointed for use in a surgical wound. The attachment mechanism facilitates detection by an external interrogating field before the wound has been closed and the patient has left the operating table. The markers are responsive to the imposition of an interrogating field produced by an electronic article surveillance system. Use of the attachment mechanism and markers assure that the surgical implements are reliably detected and removed before completion of the surgical procedure. This technique eliminates the not infrequent mishap in which an implement is undiscovered at the time of surgery and remains indefinitely within the surgical cavity, often entailing dire consequences to the patient.
Owner:FABIAN CARL E
Biological sample collection device
InactiveUS20070249961A1Raise transfer toAvoid pollutionSamplingSurgical furnitureBiotechnologyMedicine
A swab device for collecting a biological sample from an individual is disclosed, the swab device comprising a head having a swab material for trapping a biological sample thereon and a body comprising means for moving the head relative to the body. Also disclosed is method of obtaining a biological sample from an individual which method comprises contacting at least a portion of the head of a swab device with a surface of the individual, the head of the swab device being moved relative to the body of the swab device whilst the head of the device is in contact with the surface.
Owner:BIZPAC (AUSTRALIA) PTY LTD
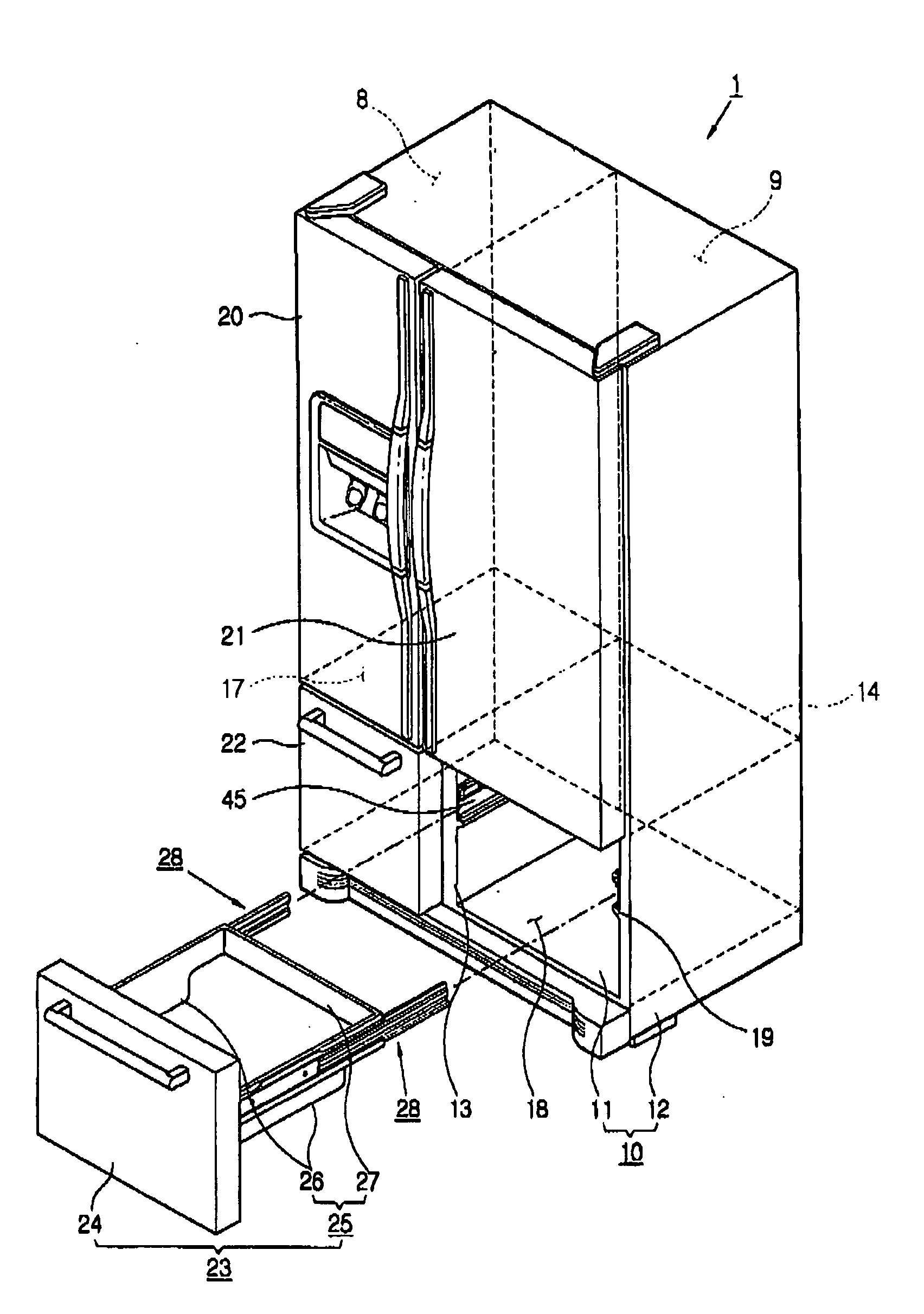
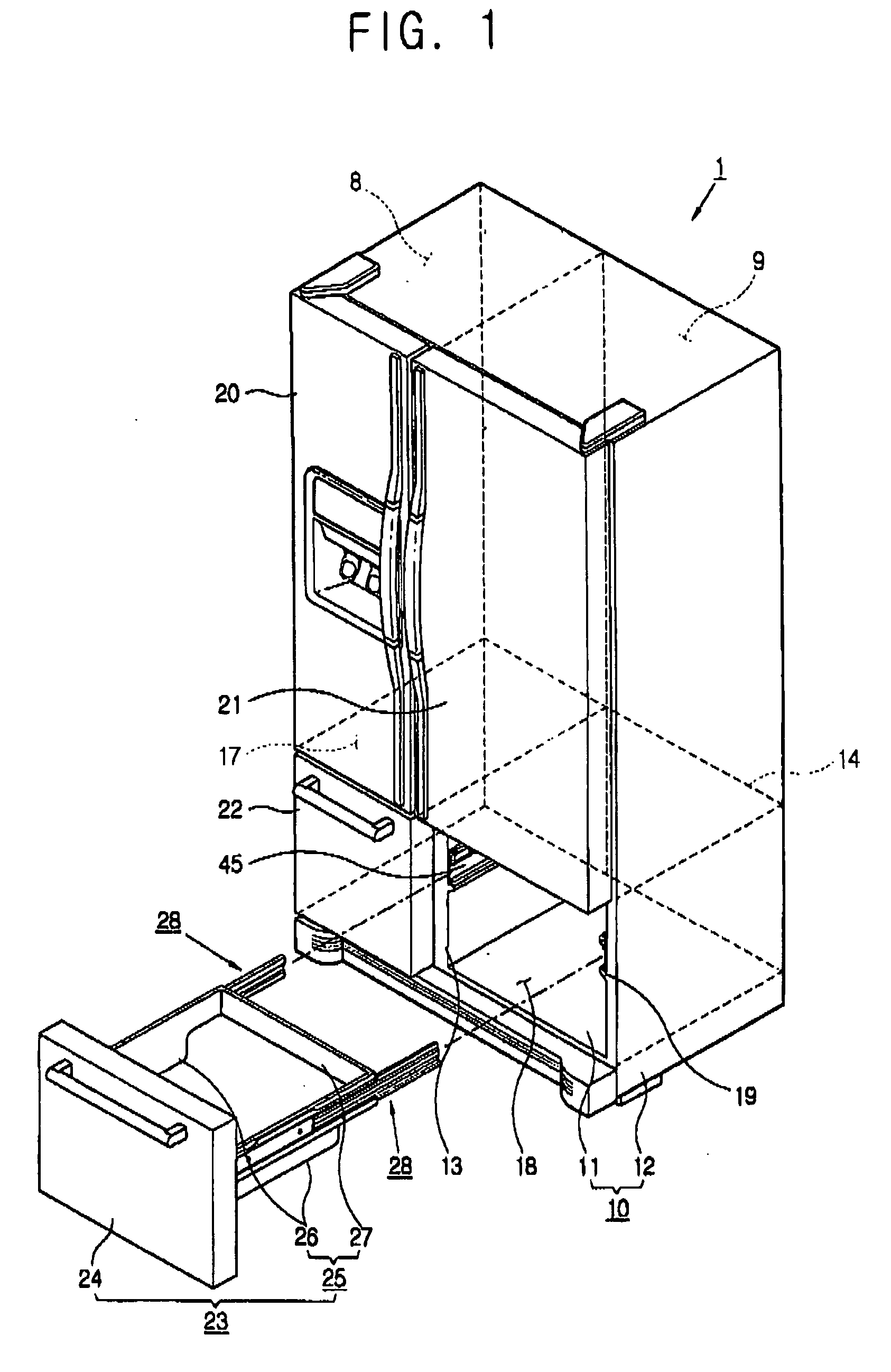
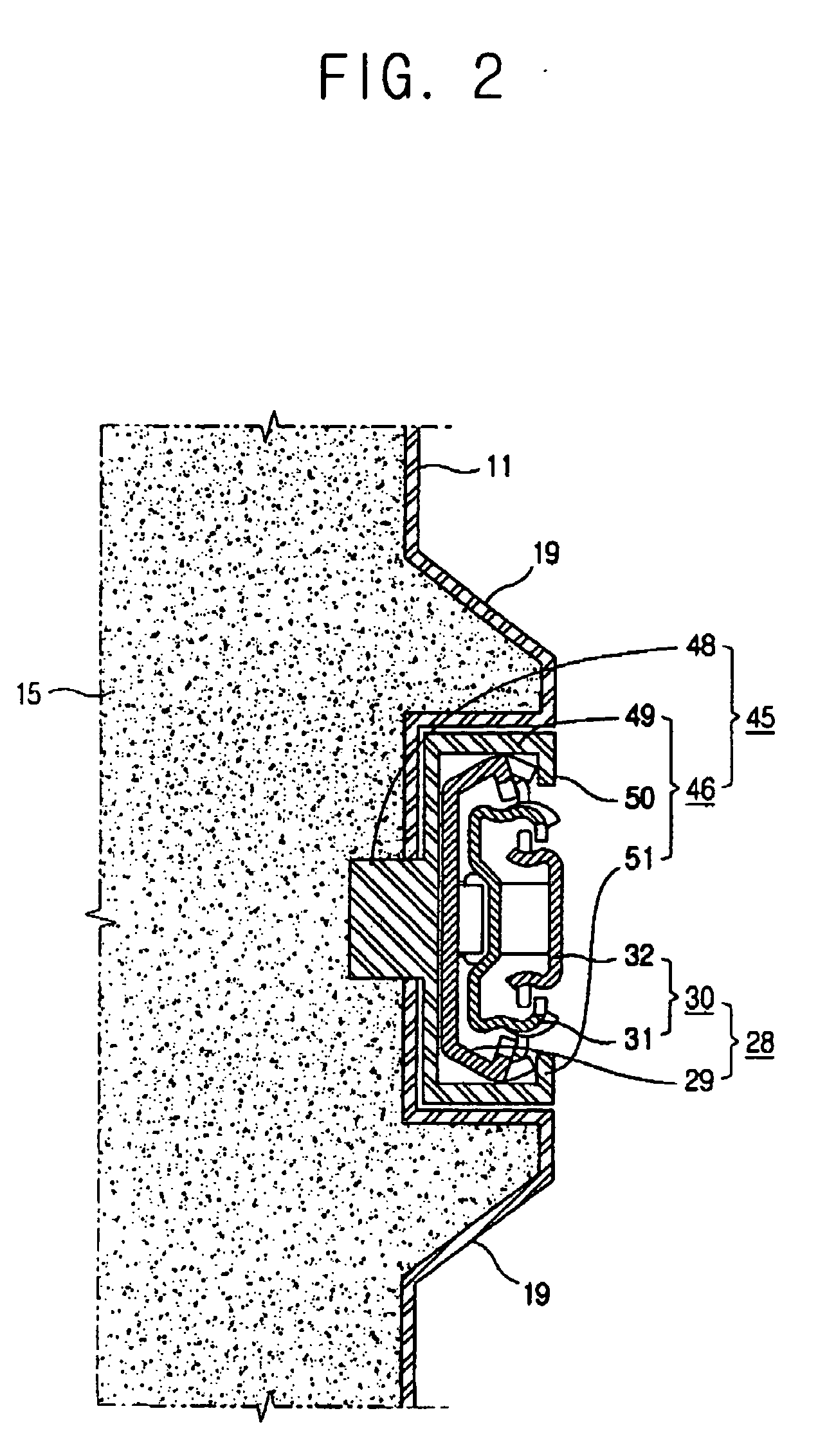
Refrigerator
InactiveUS20060152119A1Easy to installLighting and heating apparatusSwabsRefrigerated temperatureMechanical engineering
A refrigerator includes a main body cabinet having an inner casing formed with a storage chamber and an outer casing defining an external appearance of the inner casing. A door assembly is mounted on the main body cabinet, for opening and closing the storage chamber, and a rail assembly is provided between the main body cabinet and the door assembly, for moving the door assembly slidably relative to the main body cabinet. A support part is formed on the inner casing of the main body cabinet, for supporting the rail assembly. The rail assembly includes a guide rail coupled to the support part, and a slide rail coupled with the guide rail and the door assembly, being slidably moved relative to the guide rail. A connection part is provided on the support part, for maintaining or releasing a connection of the guide rail of the rail assembly with the support part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hemostatic compositions, devices, and methods
Compositions that include a clay such as kaolin dispersed in a liquid such as water may be useful for promoting the clotting of blood. The compositions may be in a liquid, gel, paste, foam, or another form. Uses may include treating a traumatic injury such as in injury caused by a bullet, an explosive, a blade etc., or an injury caused during a medical procedure such as surgery.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Low pressure sample collection apparatus
InactiveUS20070255175A1Easy sample collectionPromote drying of a sampleSurgical furnitureSamplingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A low pressure sample collection apparatus includes a double-ended cap member having similarly sized plug members extending from opposite sides, a vacuum connection nipple on one side and a shaft connection portion one the opposite, a passage extending through the cap from the nipple to the shaft connection portion, a tubular shaft connected to the shaft connection portion and having a sample collection swab member secured to an outer end thereof, and a container member having one end closed and an opposite end open. The cap member is reversibly plugged into the container either to use the container as a handle or to position the swab within the container for protection. A vacuum source may be connected to the assembly to draw air through the swab. The shaft may have a barrel telescoped thereon for separation of the swab from the shaft without contacting the swab.
Owner:BODE TECH GROUP
Culture swab with protective cap and safety pin
InactiveUS20050288606A1Reduce chancePrevents premature deploymentAnimal reproductionSurgical needlesEngineeringAnimal husbandry
A veterinary instrument for use in animal husbandry that includes an inner member with a swab or similar element attached at one end, located inside a second inner member meant to protect the innermost member and attached swab, and an outermost member that surrounds both inner members and has a closed mold manufactured protective cap on one end. The instrument has one or two safety pins which ensure that the instrument cannot be used until they are removed.
Owner:CONTINENTAL PLASTICS
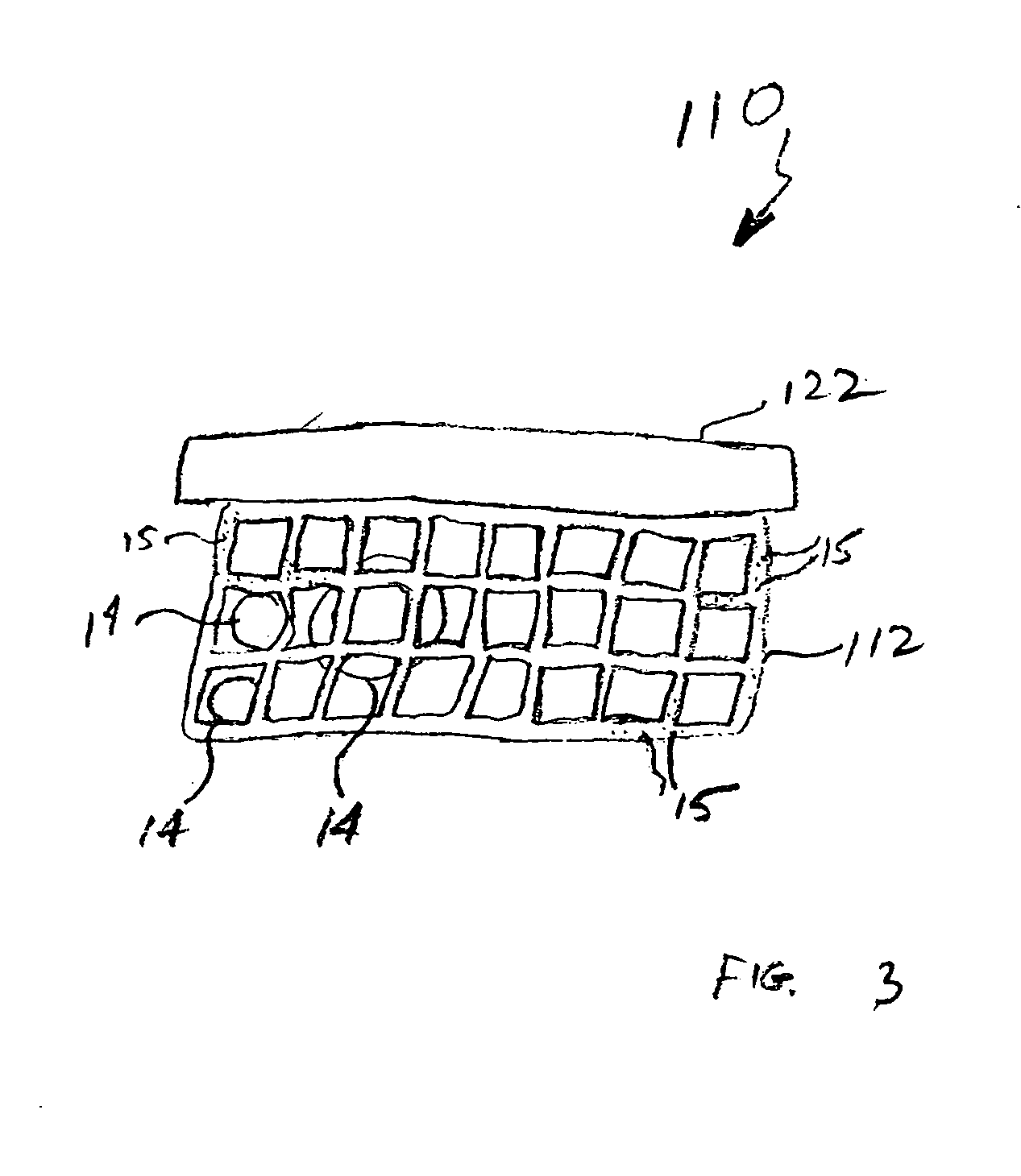
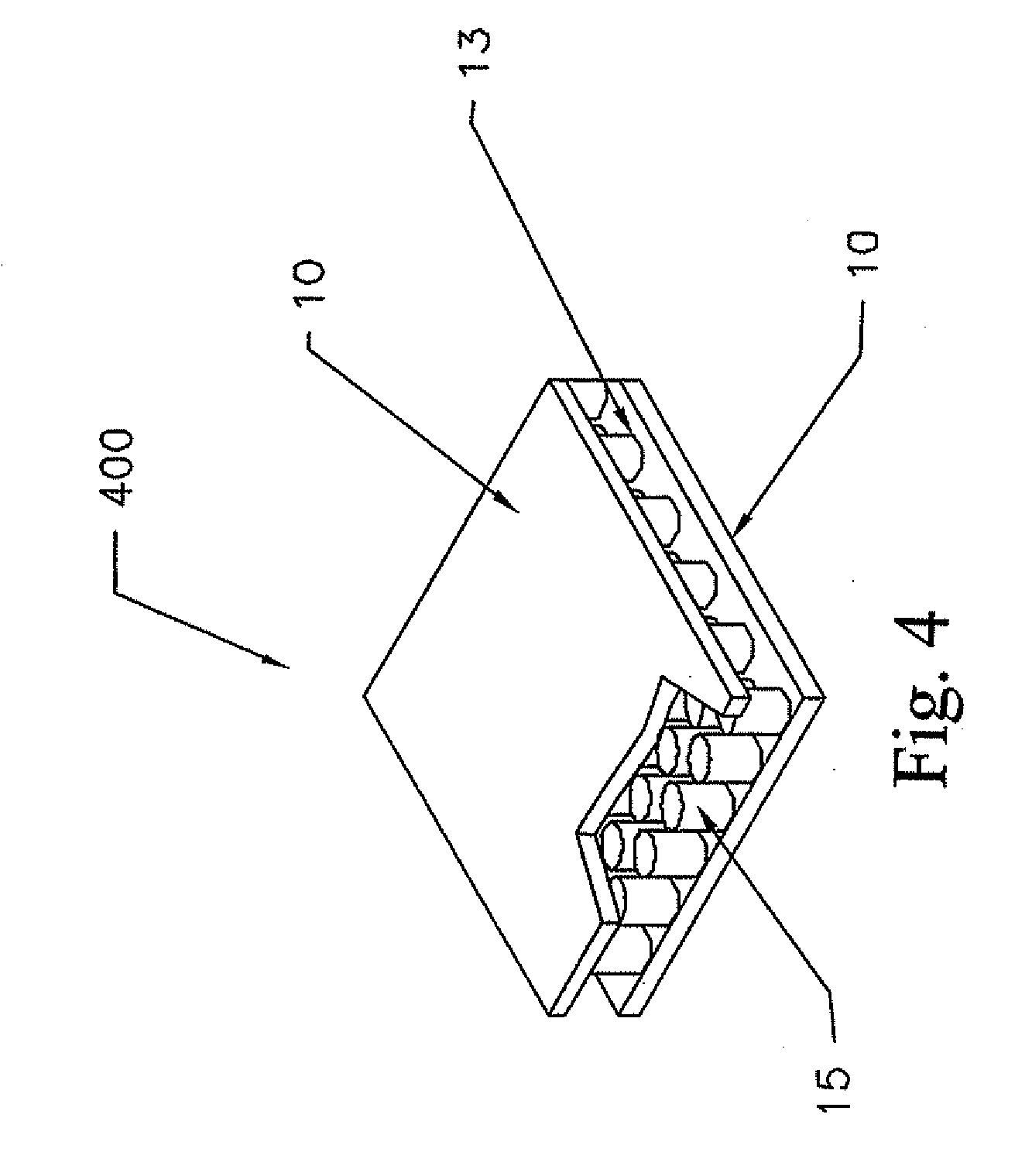
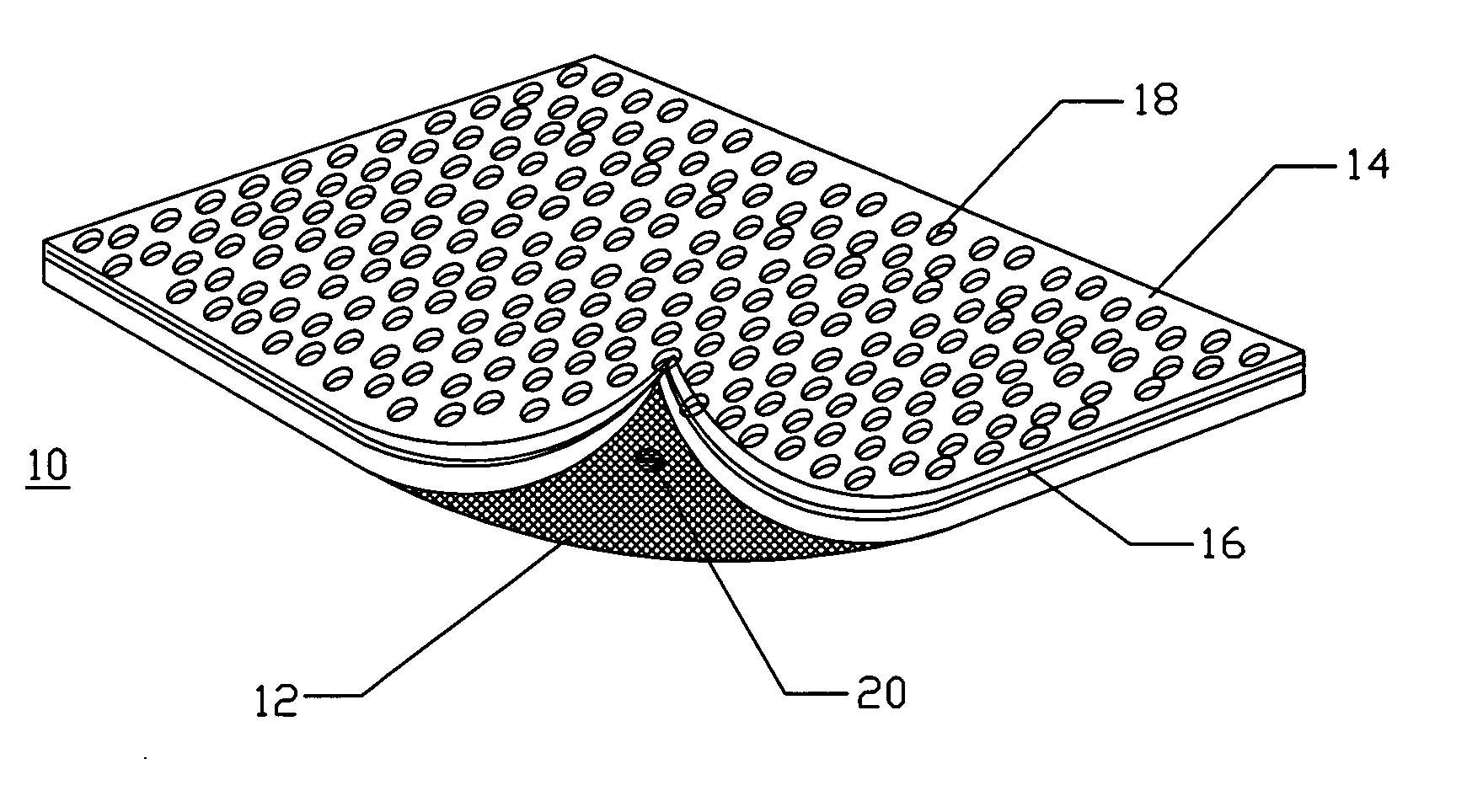
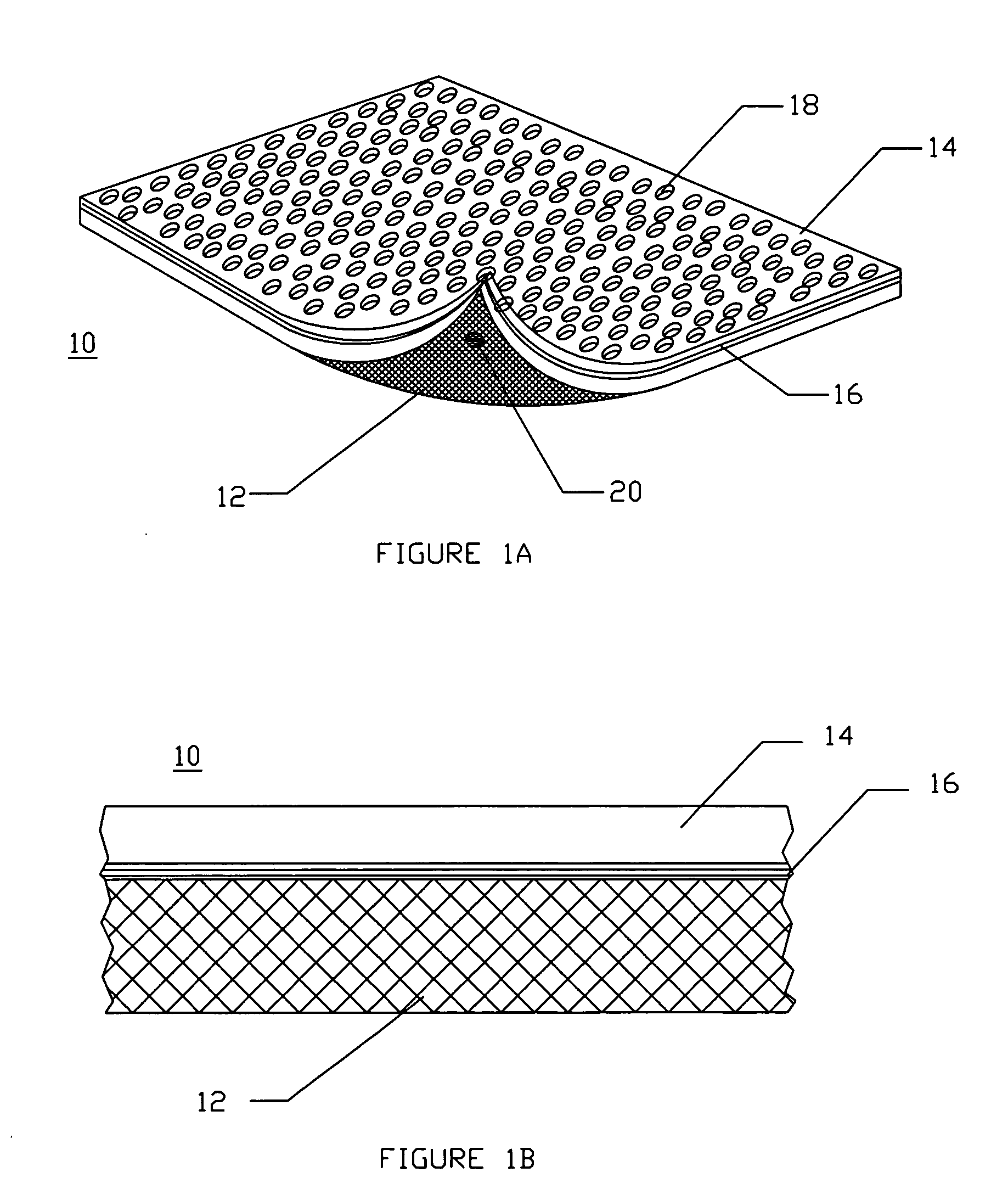
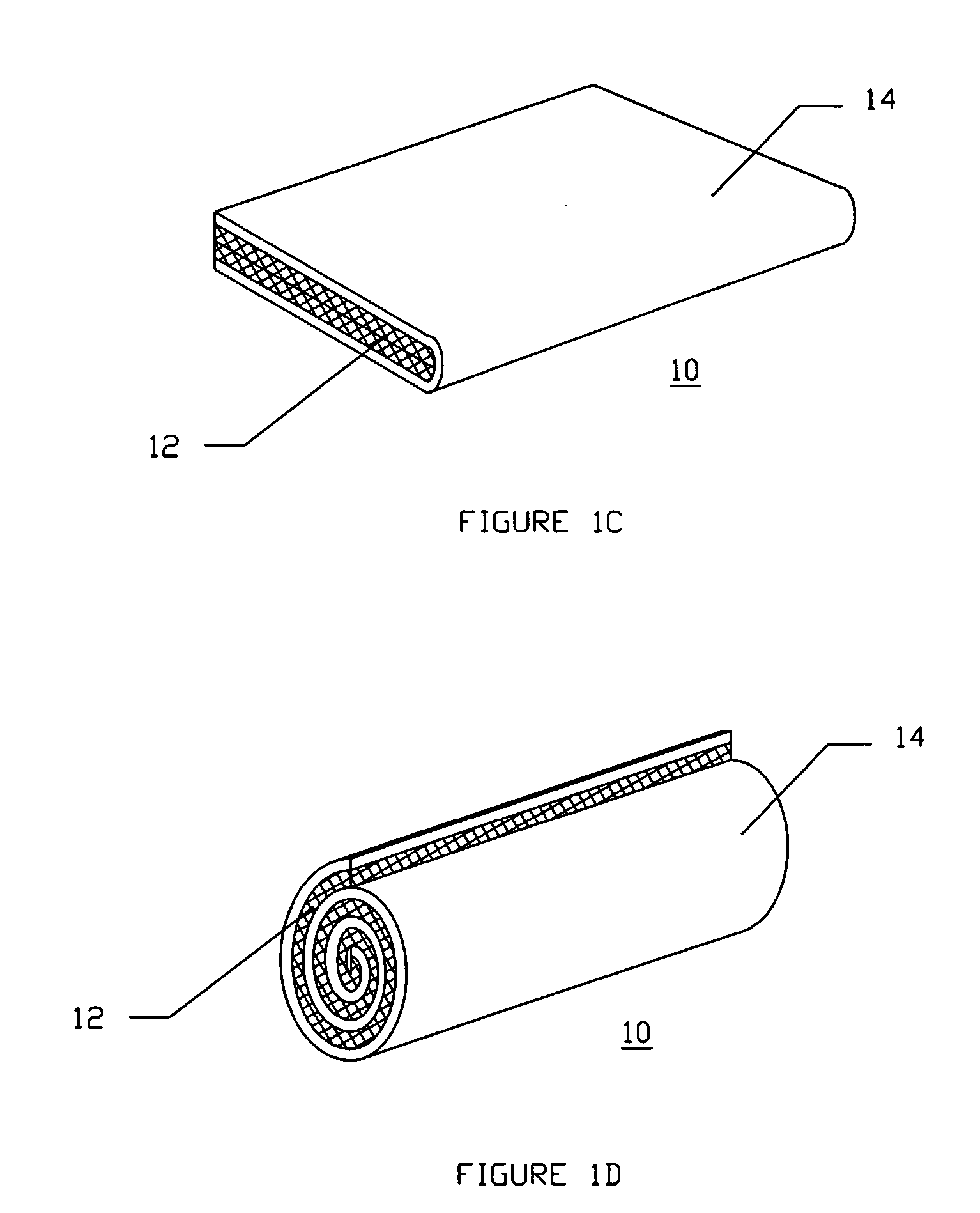
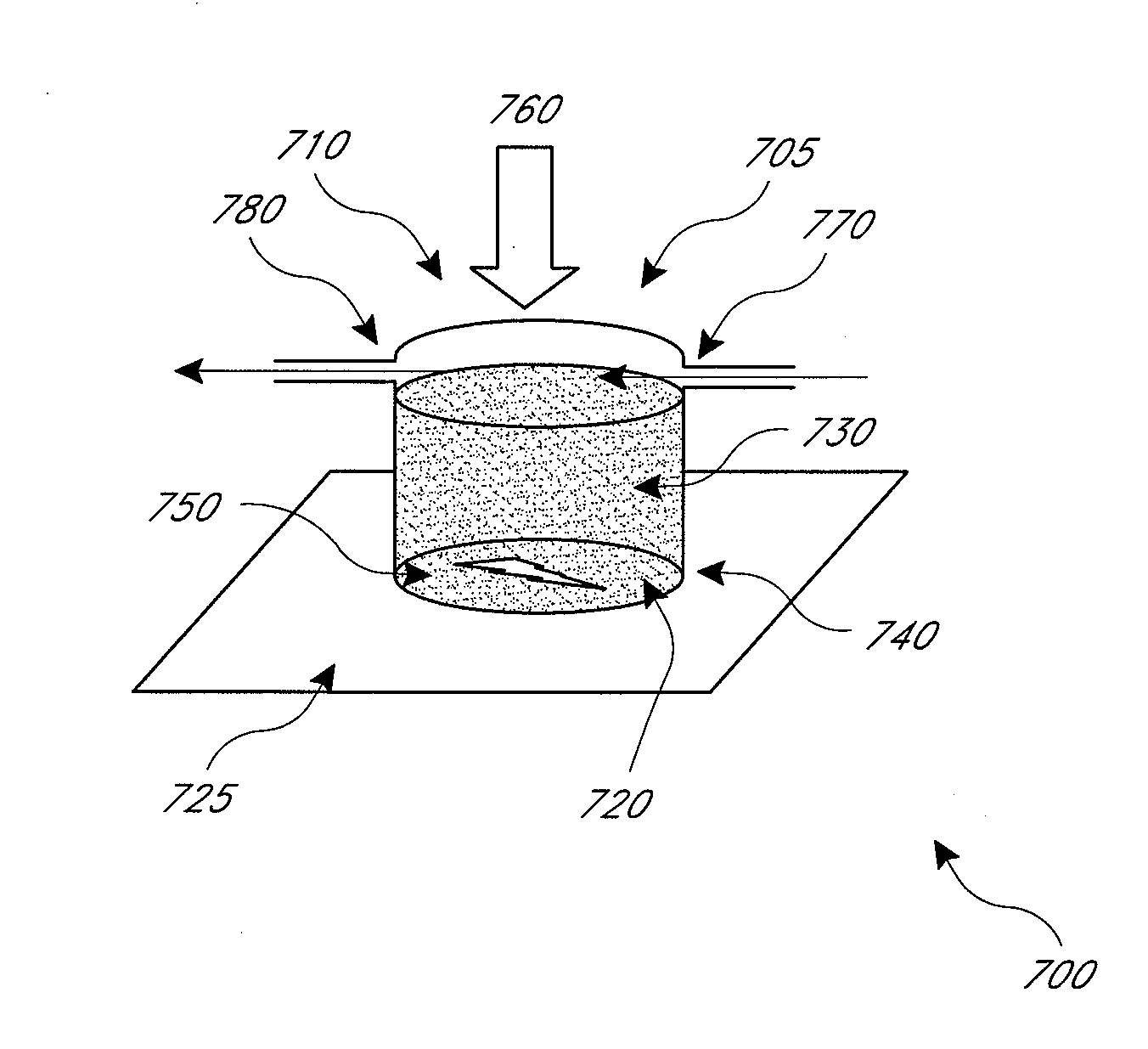
Resorbable nanoenhanced hemostatic structures and bandage materials
InactiveUS20090192429A1Increasing resorption rateInduce coagulation of bloodNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersMedicineNanostructure
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Wound dressing and method for controlling severe, life-threatening bleeding
InactiveUS20080213344A1Stanching flowProhibiting flow of bloodBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWound dressingHydrophilic polymers
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com