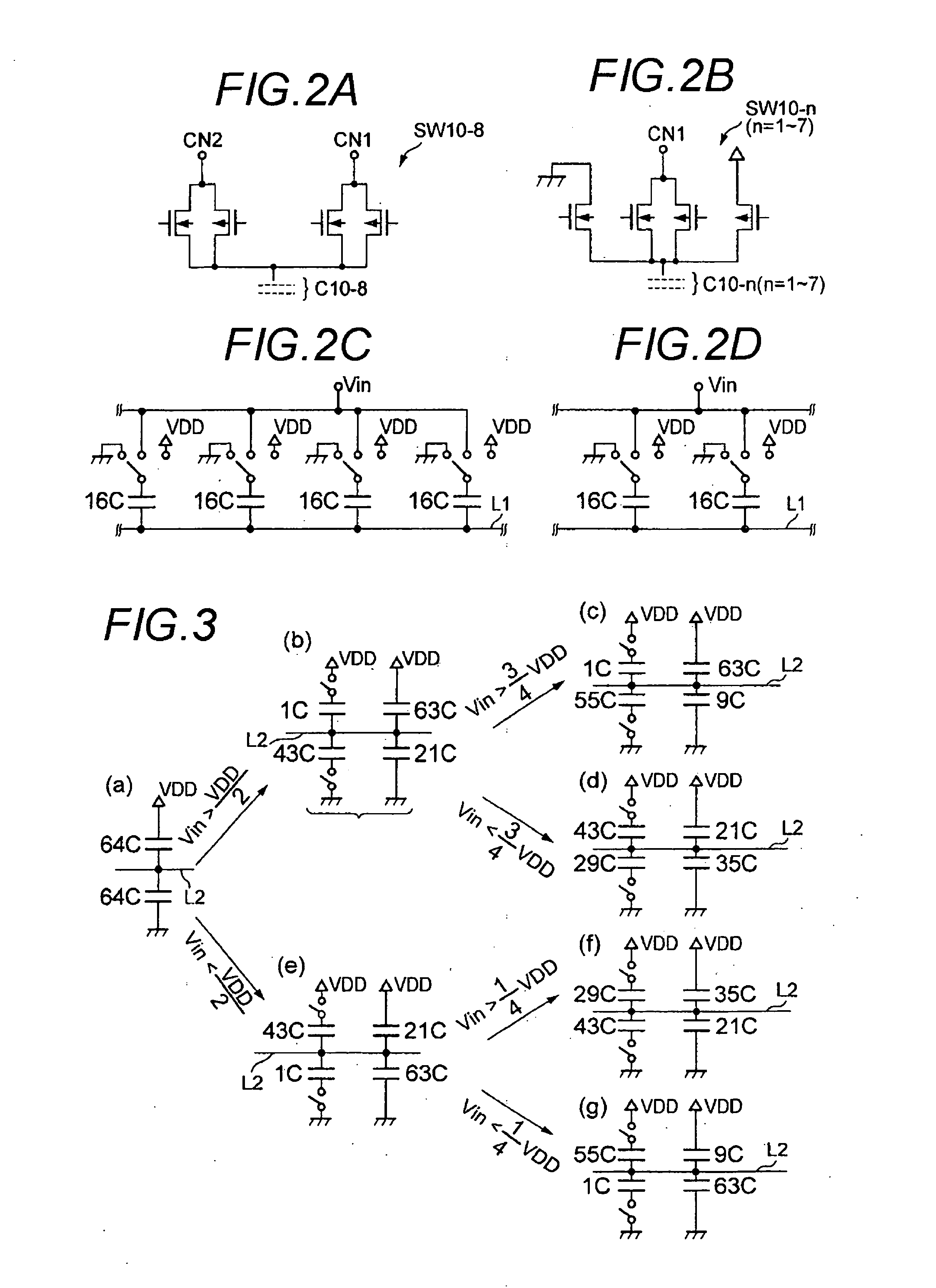
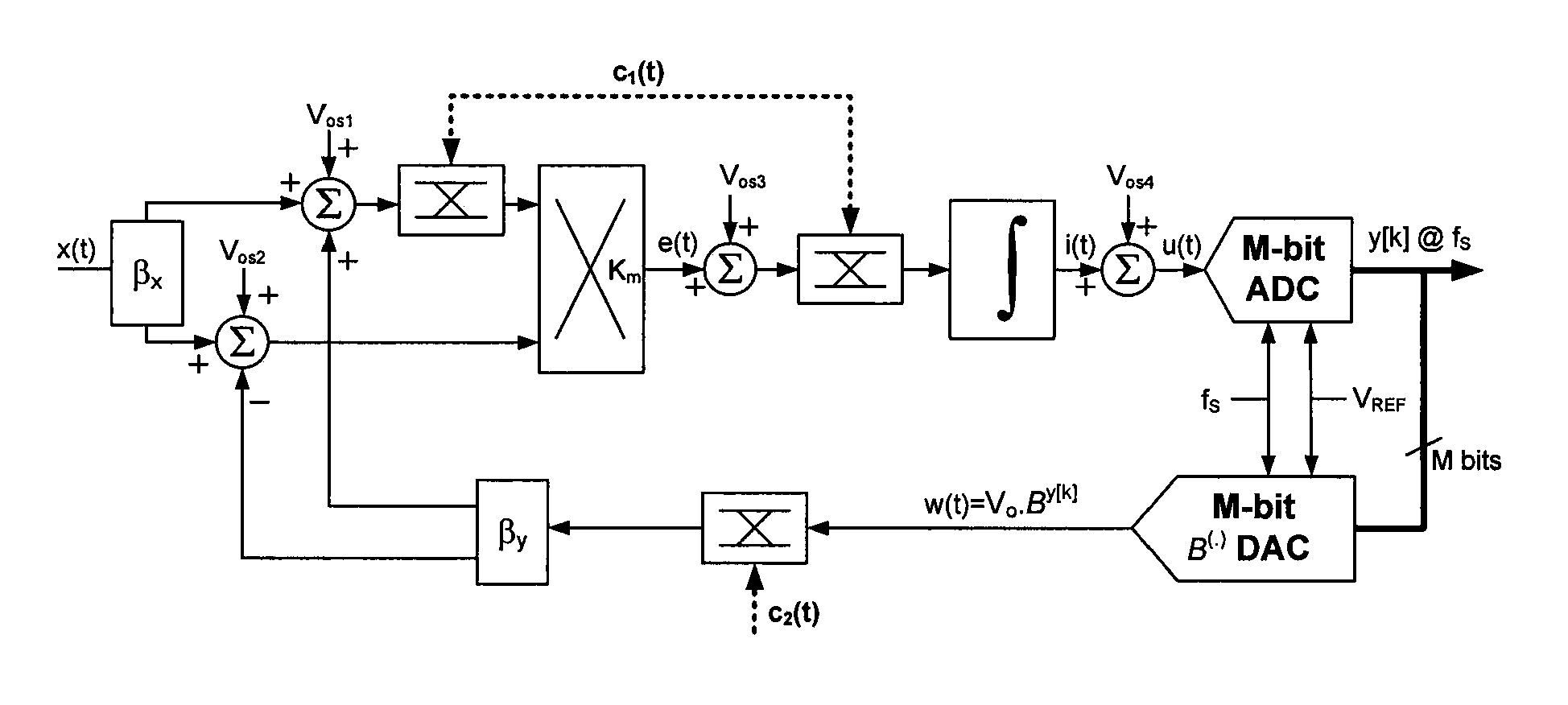
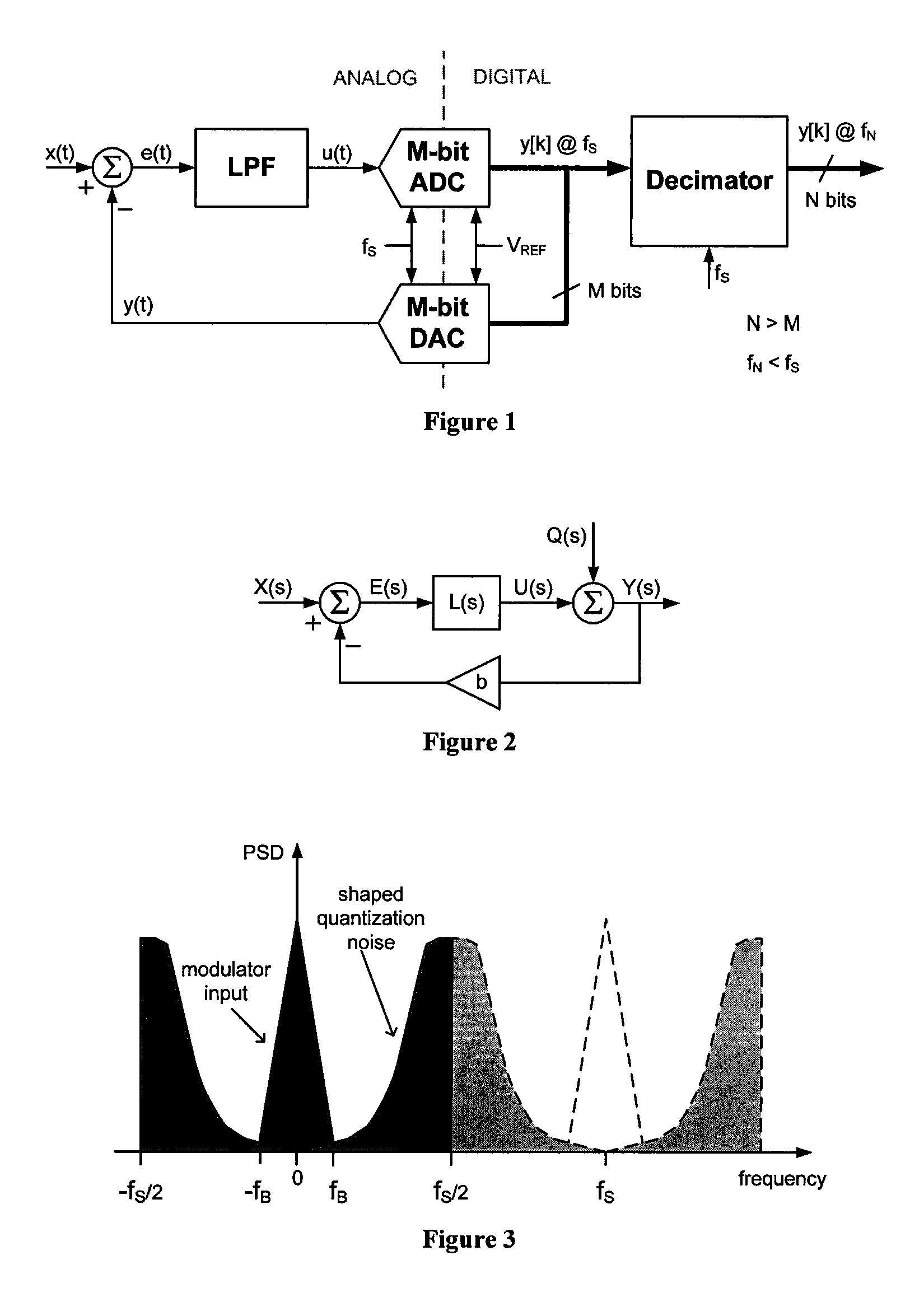
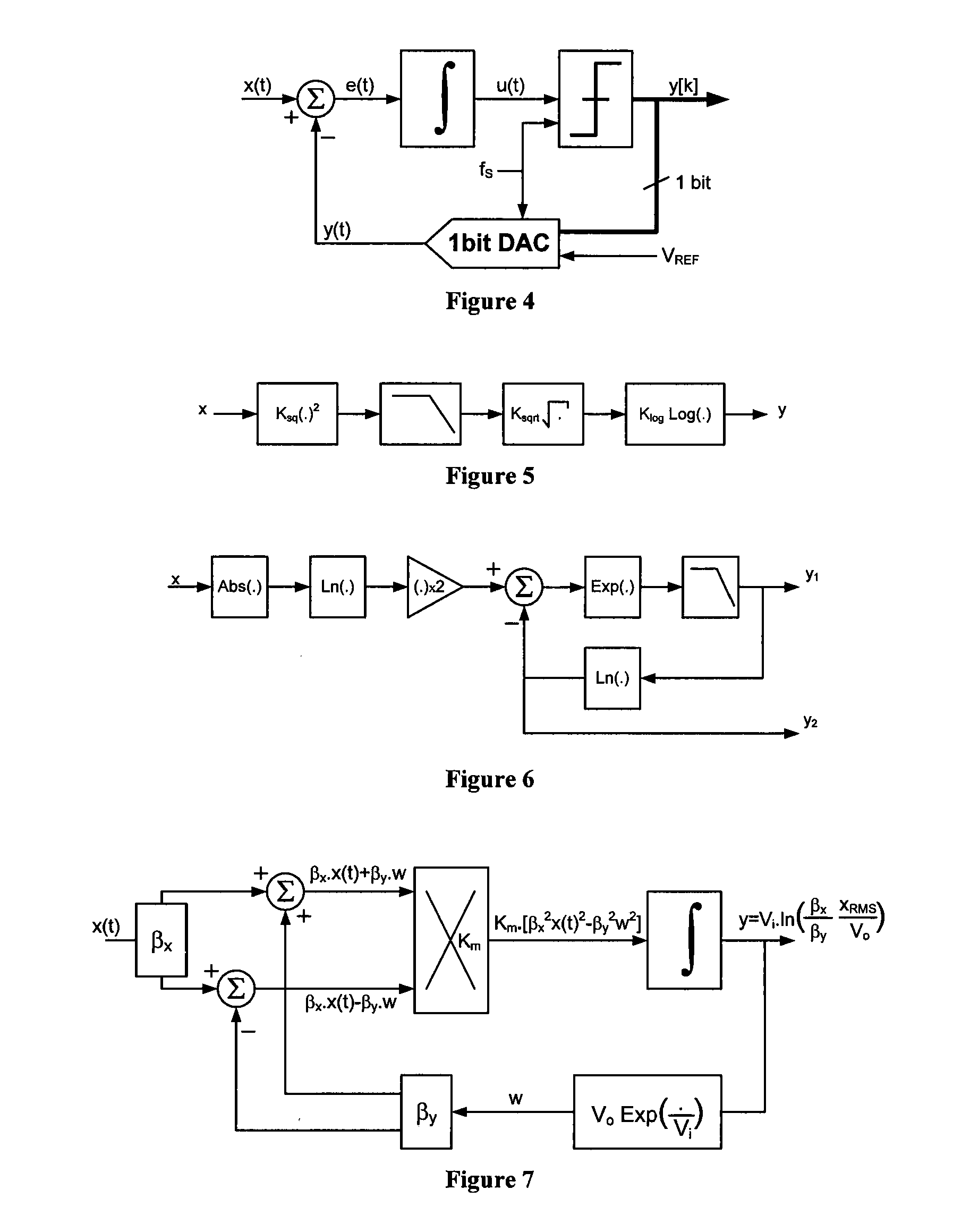
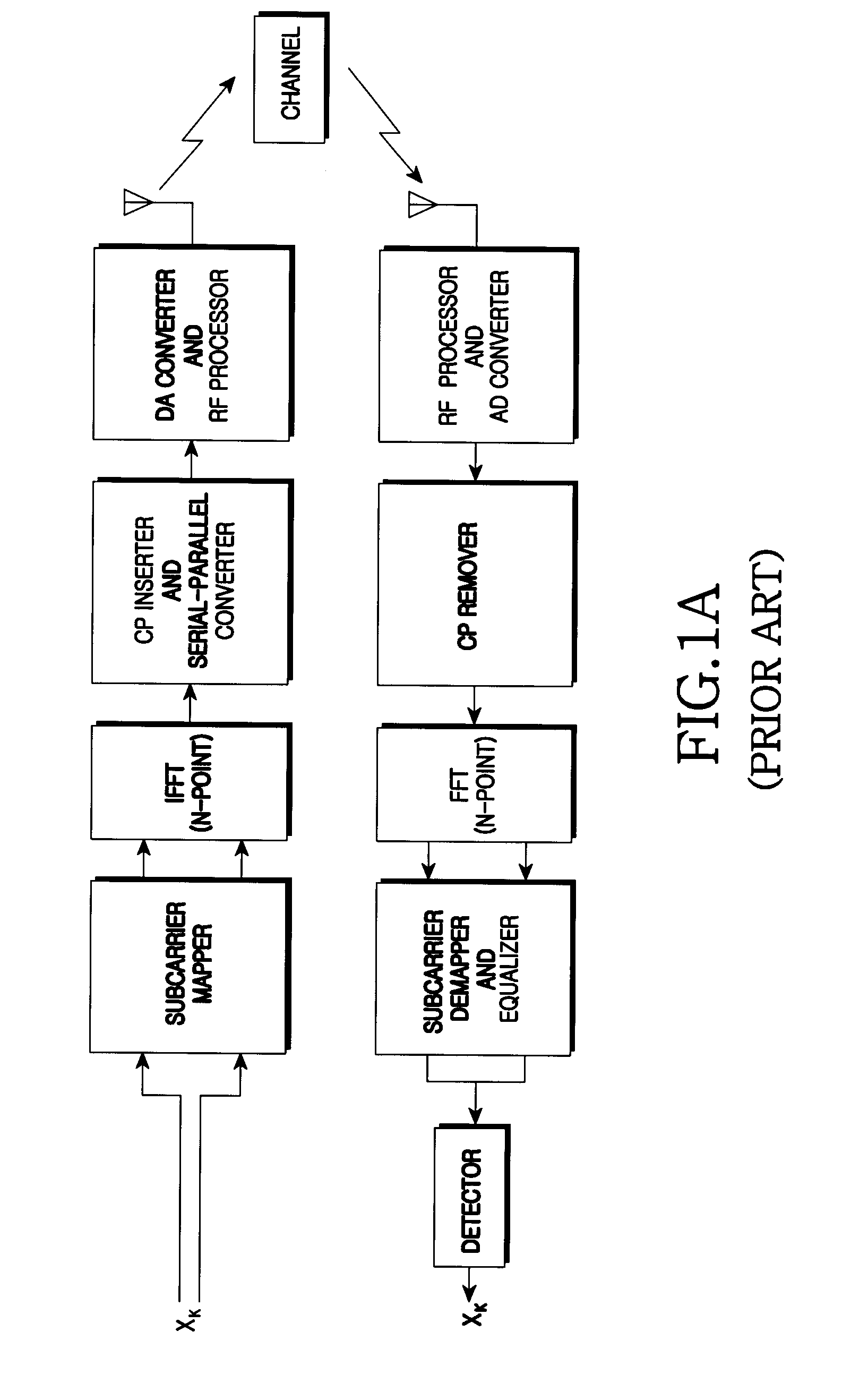
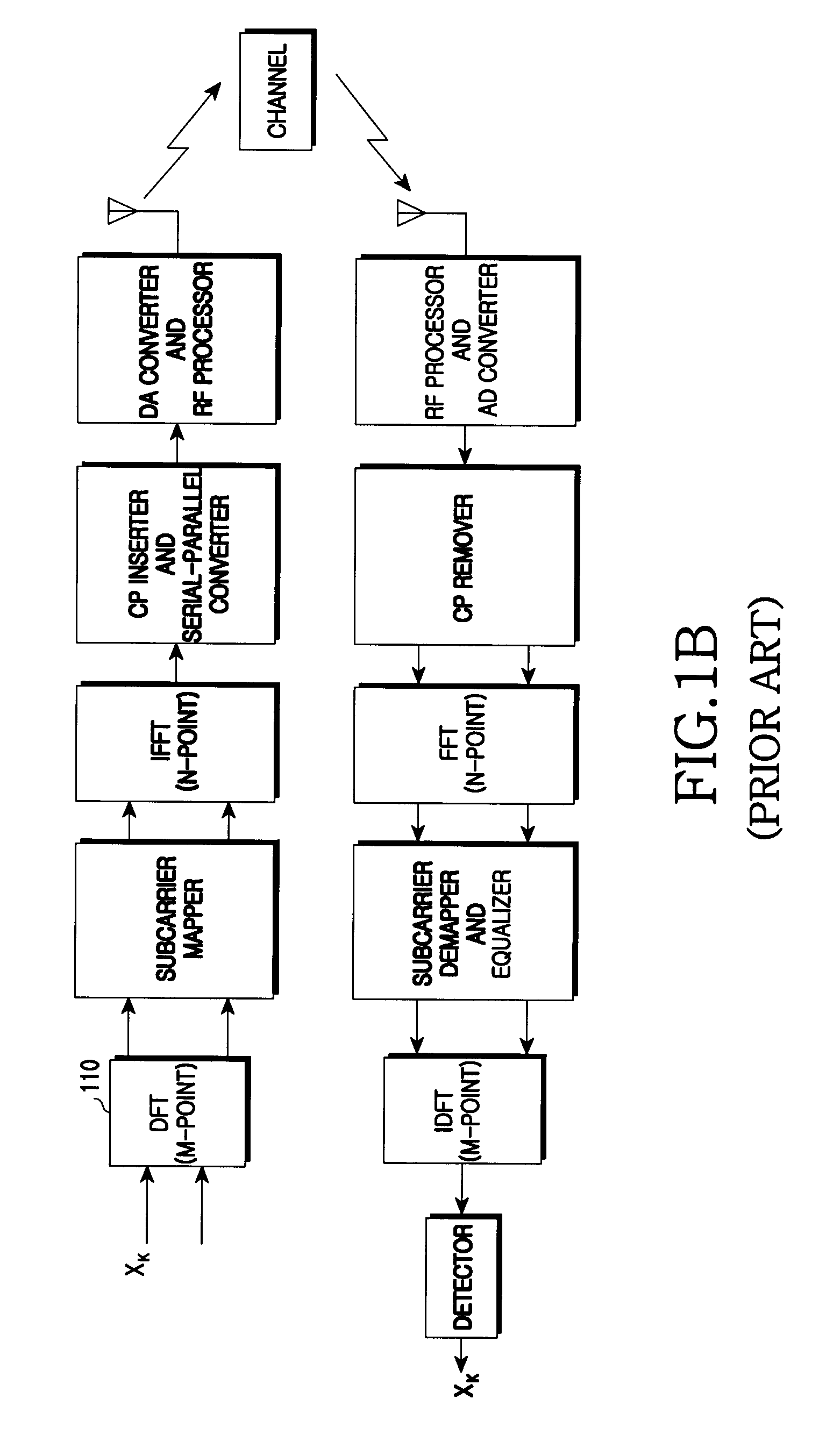
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72results about "Reversible analogue/digital convertors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
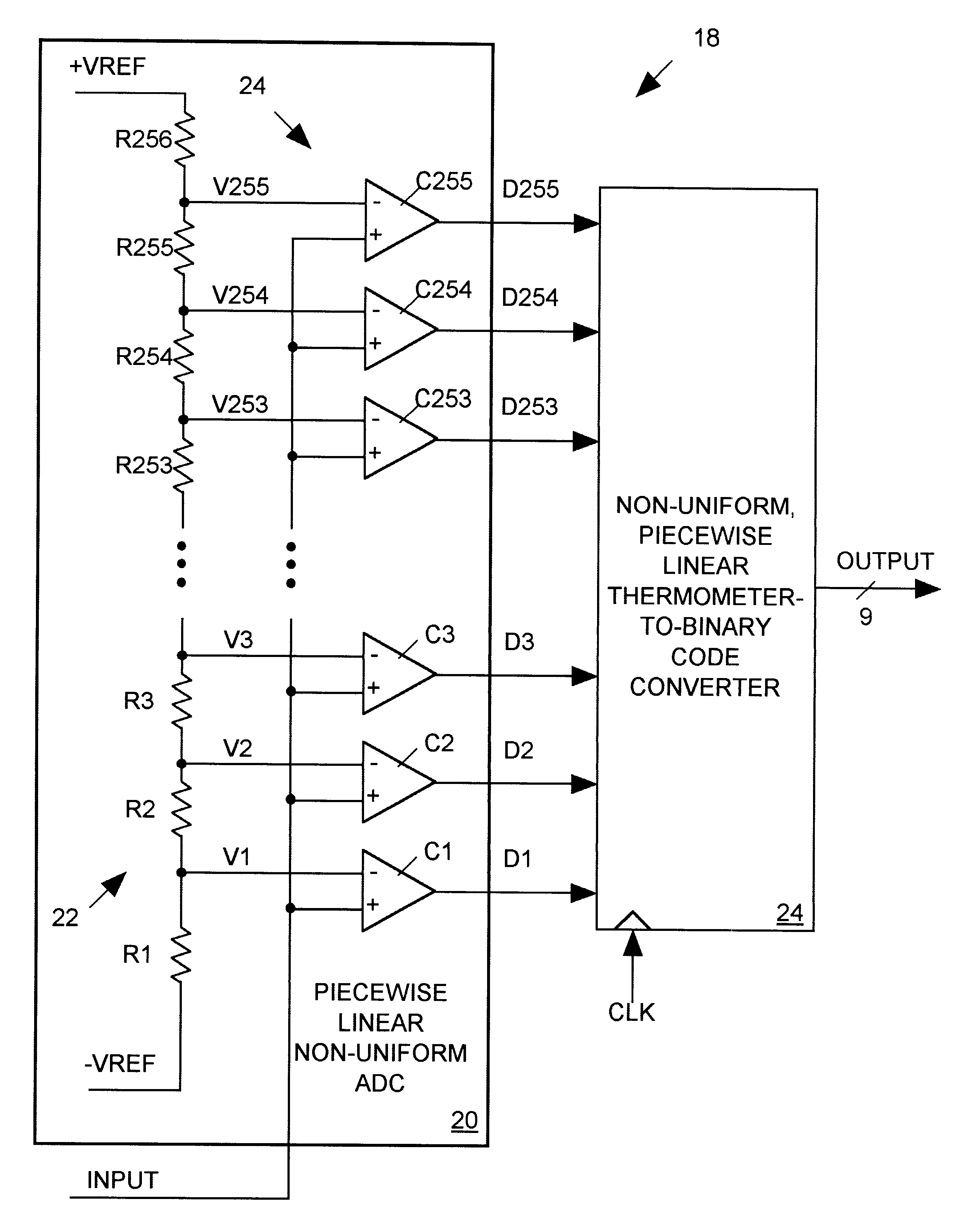
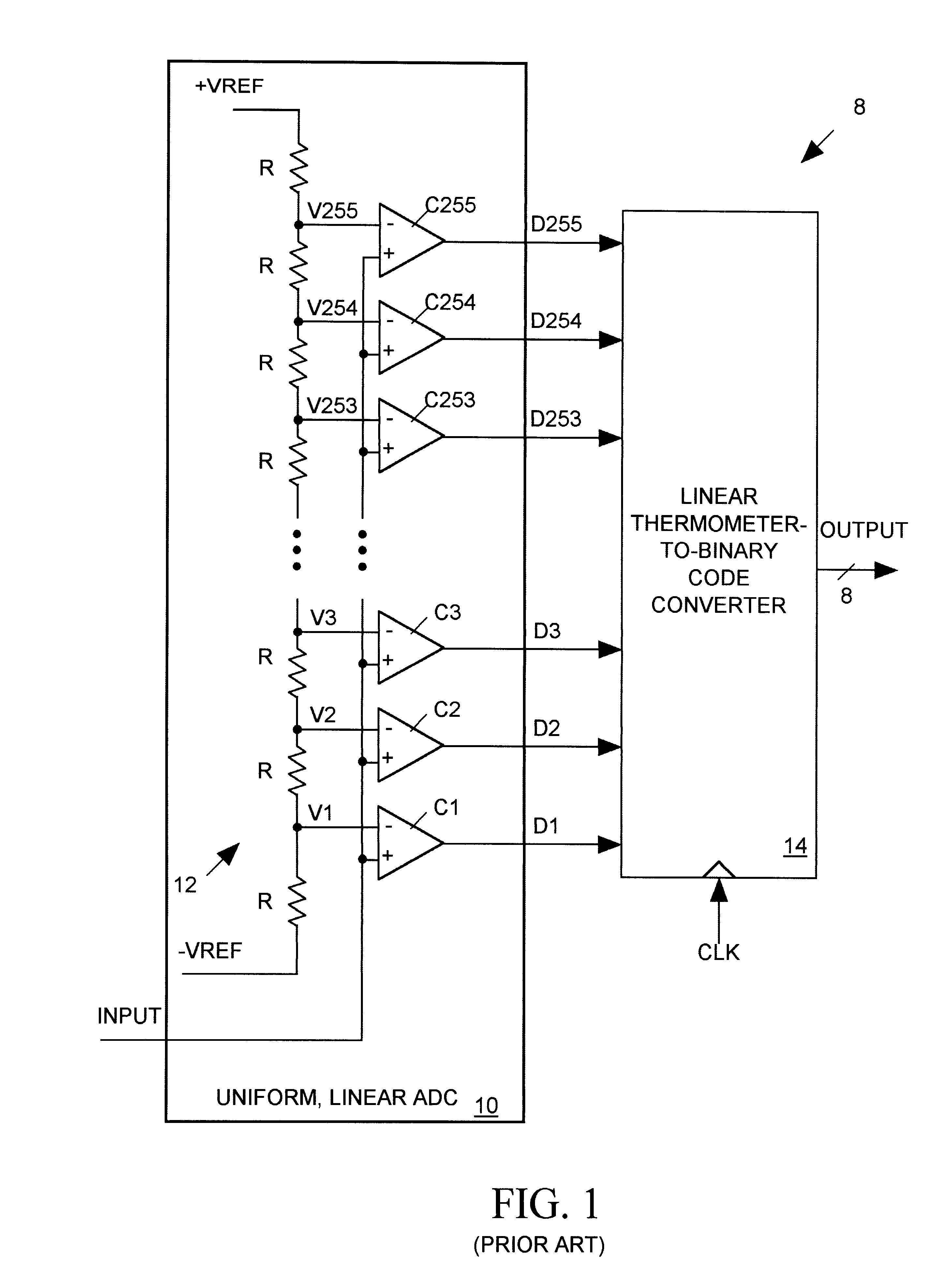
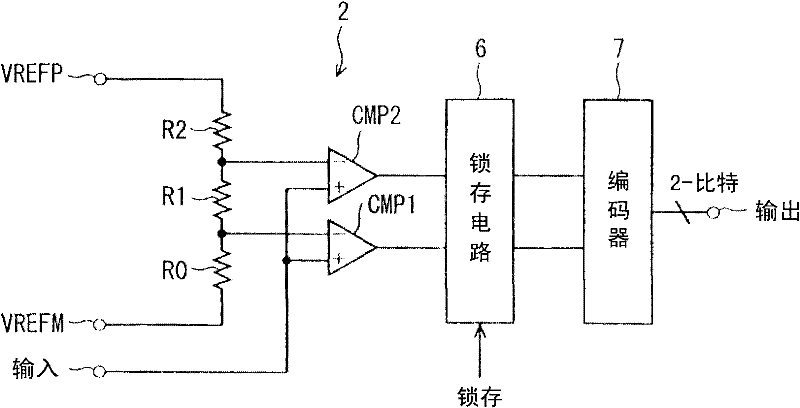
Piecewise-linear, non-uniform ADC
InactiveUS6498577B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersImage resolutionEngineering
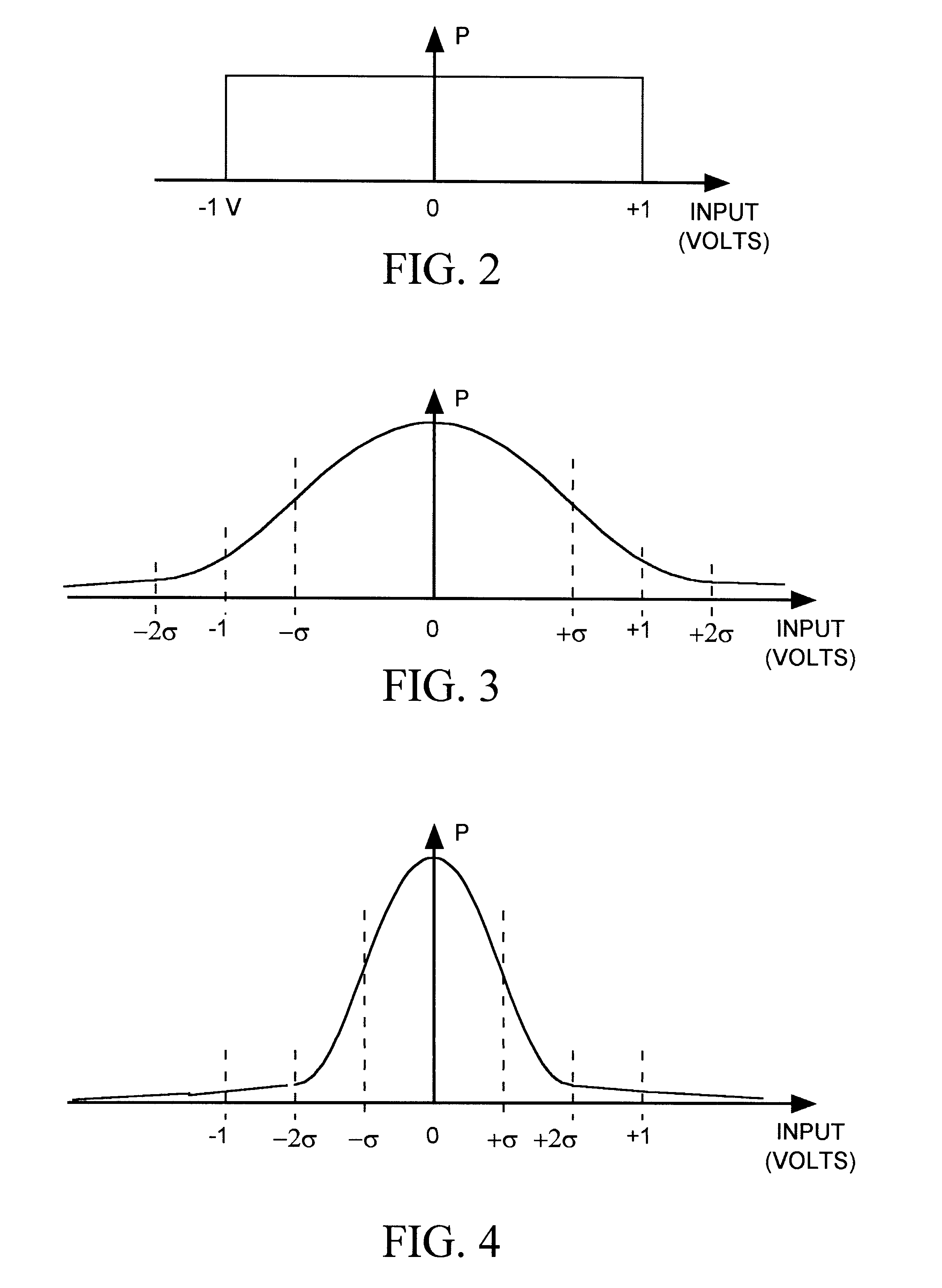
A non-uniform analog-to-digital converter (ADC) produces digital output data representing the magnitude of an analog input signal having a non-uniform magnitude probability distribution. The digital output data represents the analog input signal with relatively high resolution for the input signal's more frequently occurring magnitudes and with relatively lower resolution for the input signals less frequently occurring magnitudes.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
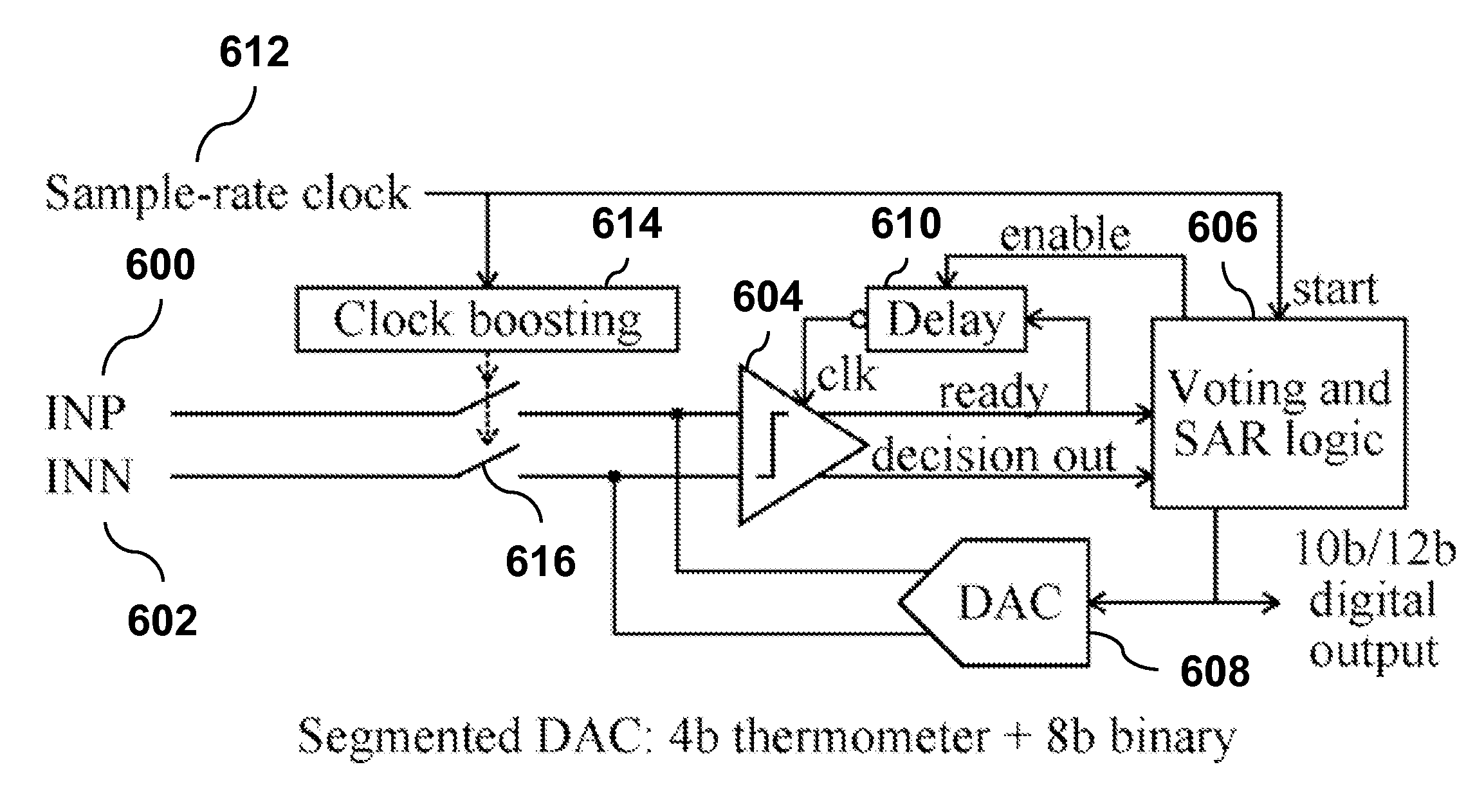
Data-driven noise reduction technique for analog to digital converters
InactiveUS8896476B2Improved accuracy and power-efficiencyInhibition is effectiveElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterA d converter
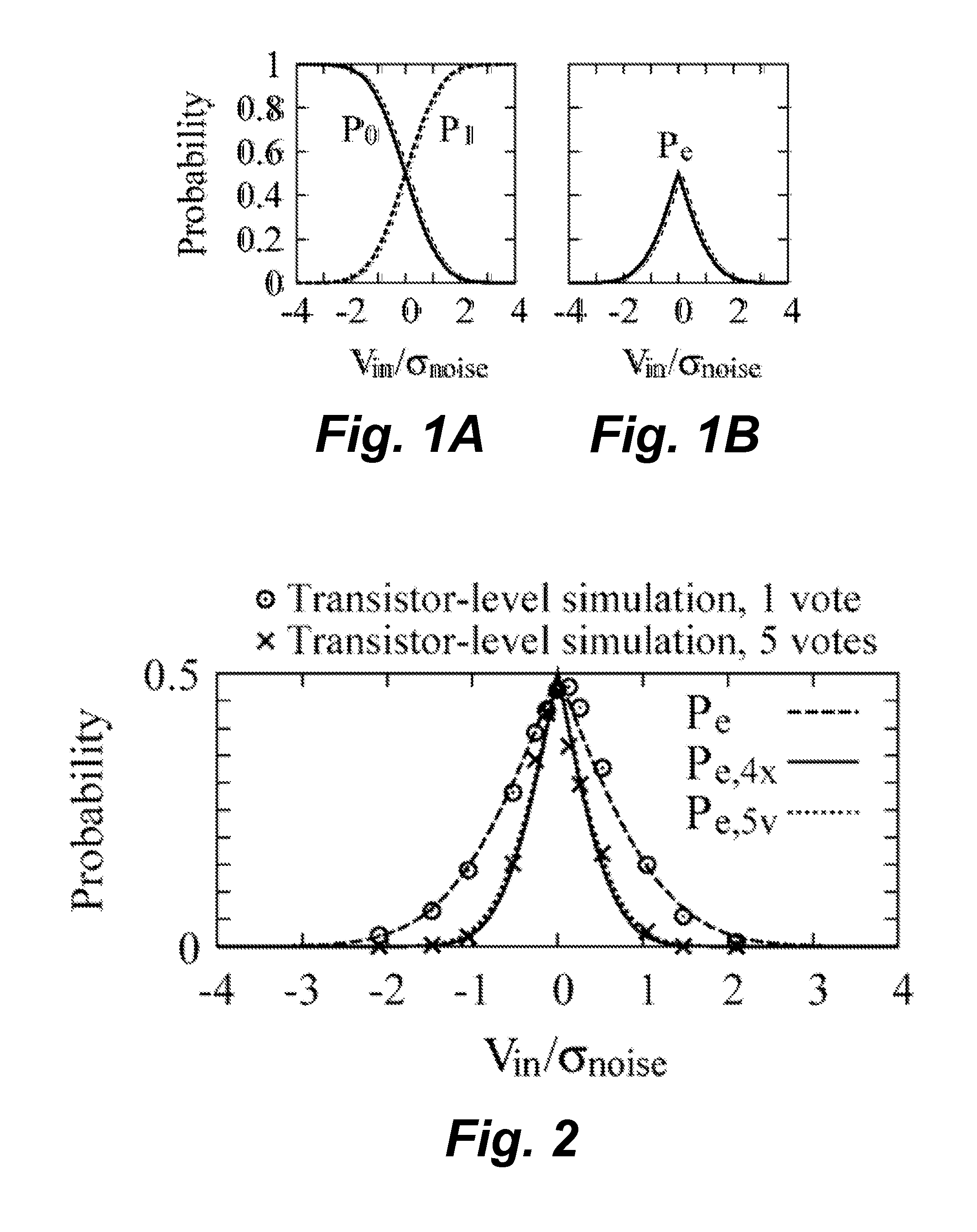
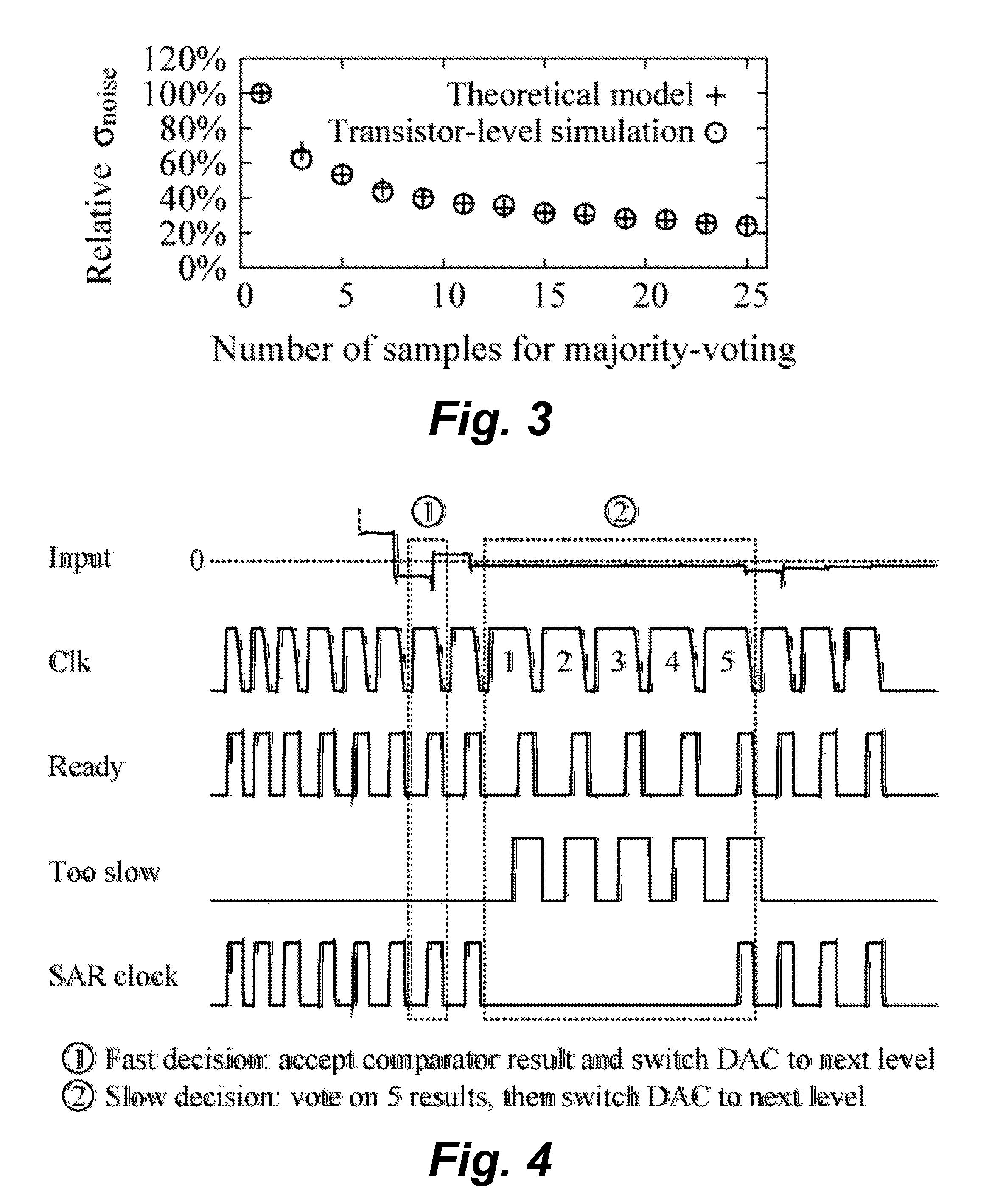
A successive operation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) circuit includes a bit reliability circuit that detects a delay time of the voltage comparator and, if the detected delay time is greater than a delay threshold time τMV, outputs a bit reliability decision signal; a digital noise reduction circuit that is selectively activated if the bit reliability decision signal indicates the detected delay time is greater than the delay threshold time τMV and produces a noise-reduced decision output that supersedes the decision output of the voltage comparator. In a preferred embodiment, the digital noise reduction circuit uses a multiple voting logic to produce a majority vote value as the noise-reduced decision output.
Owner:TECH UNIV EINDHOVEN
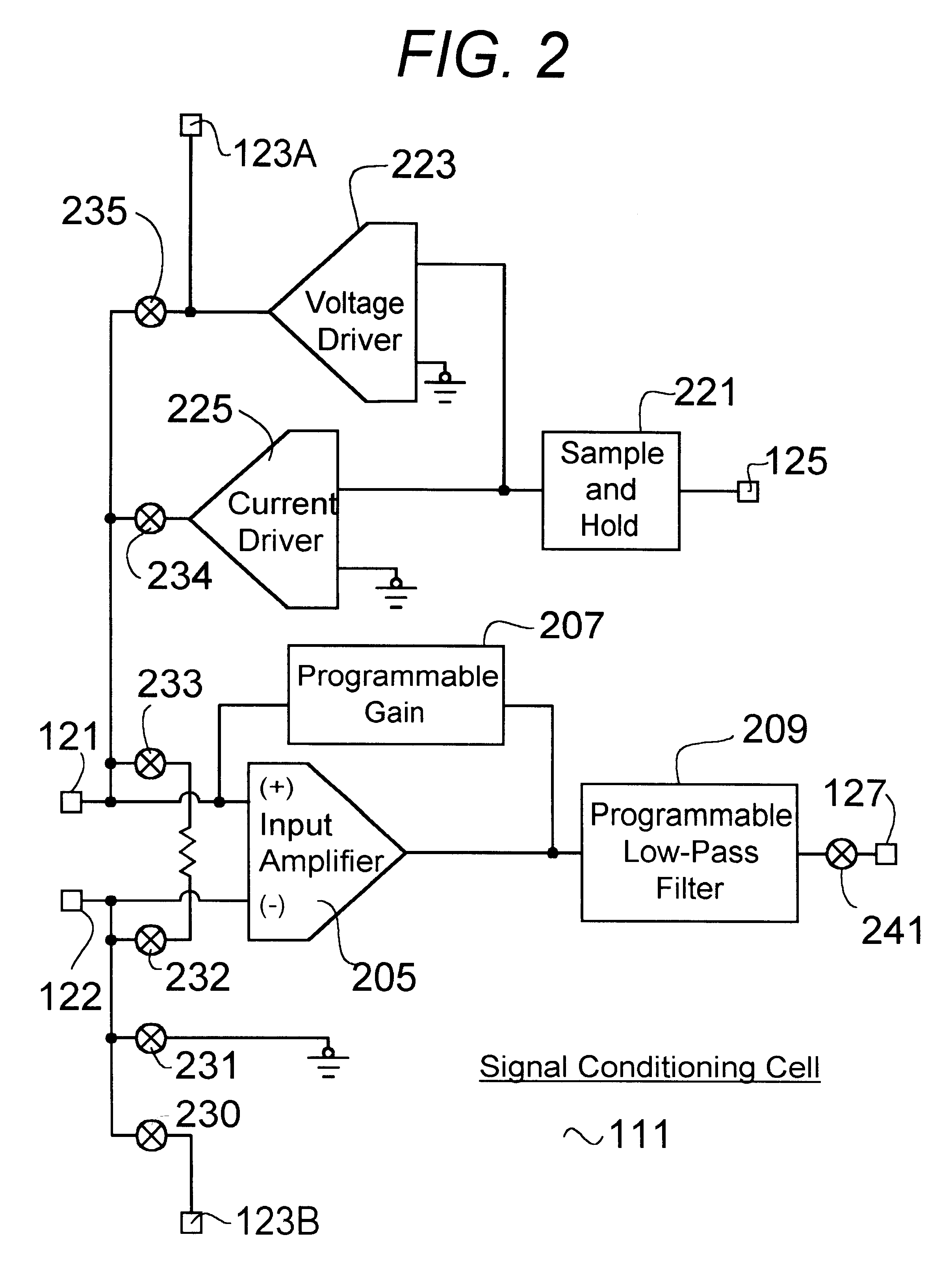
Integrated circuit for conditioning and conversion of bi-directional discrete and analog signals
InactiveUS6448914B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersSignal conditioningAnalog signal
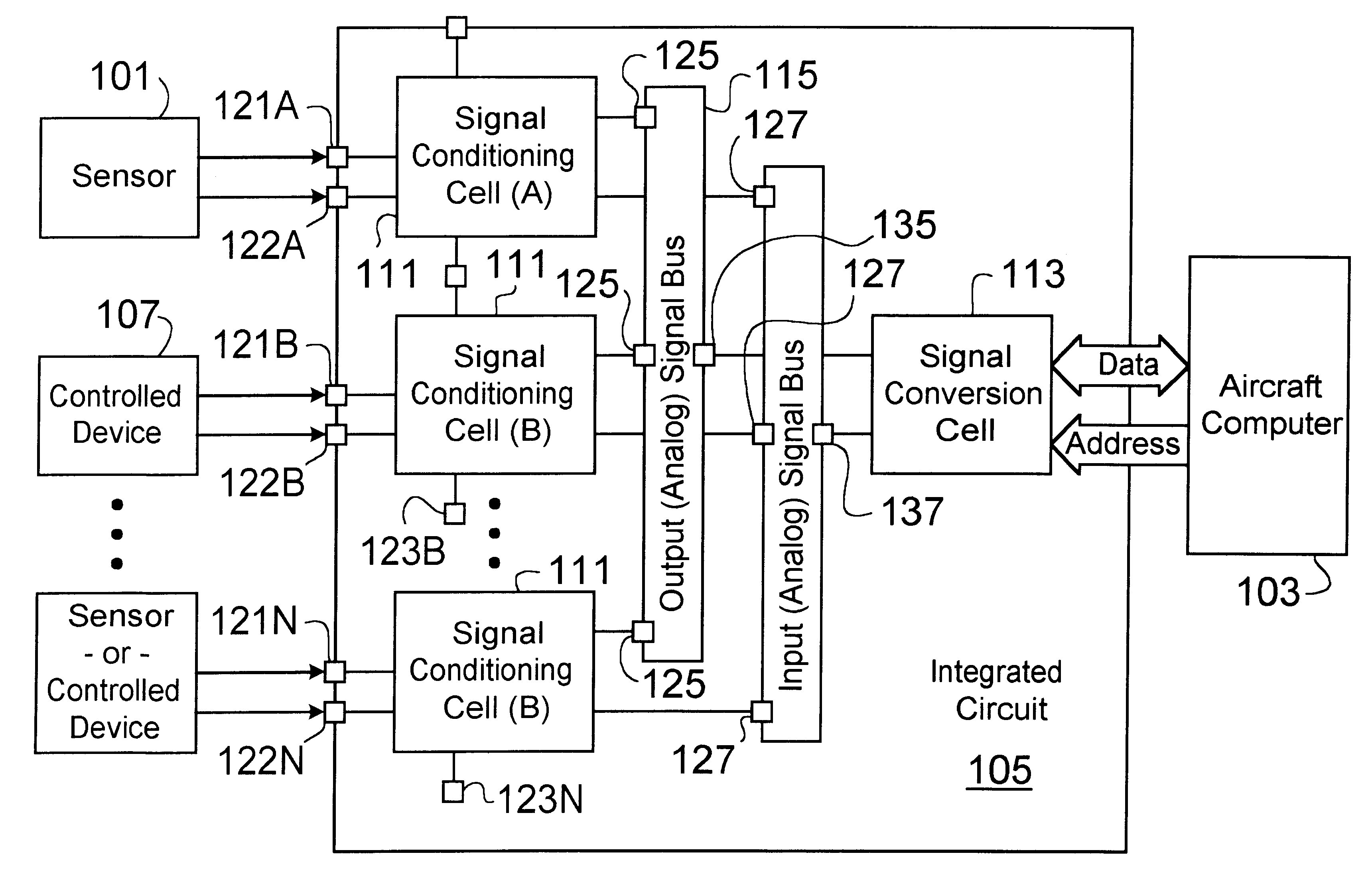
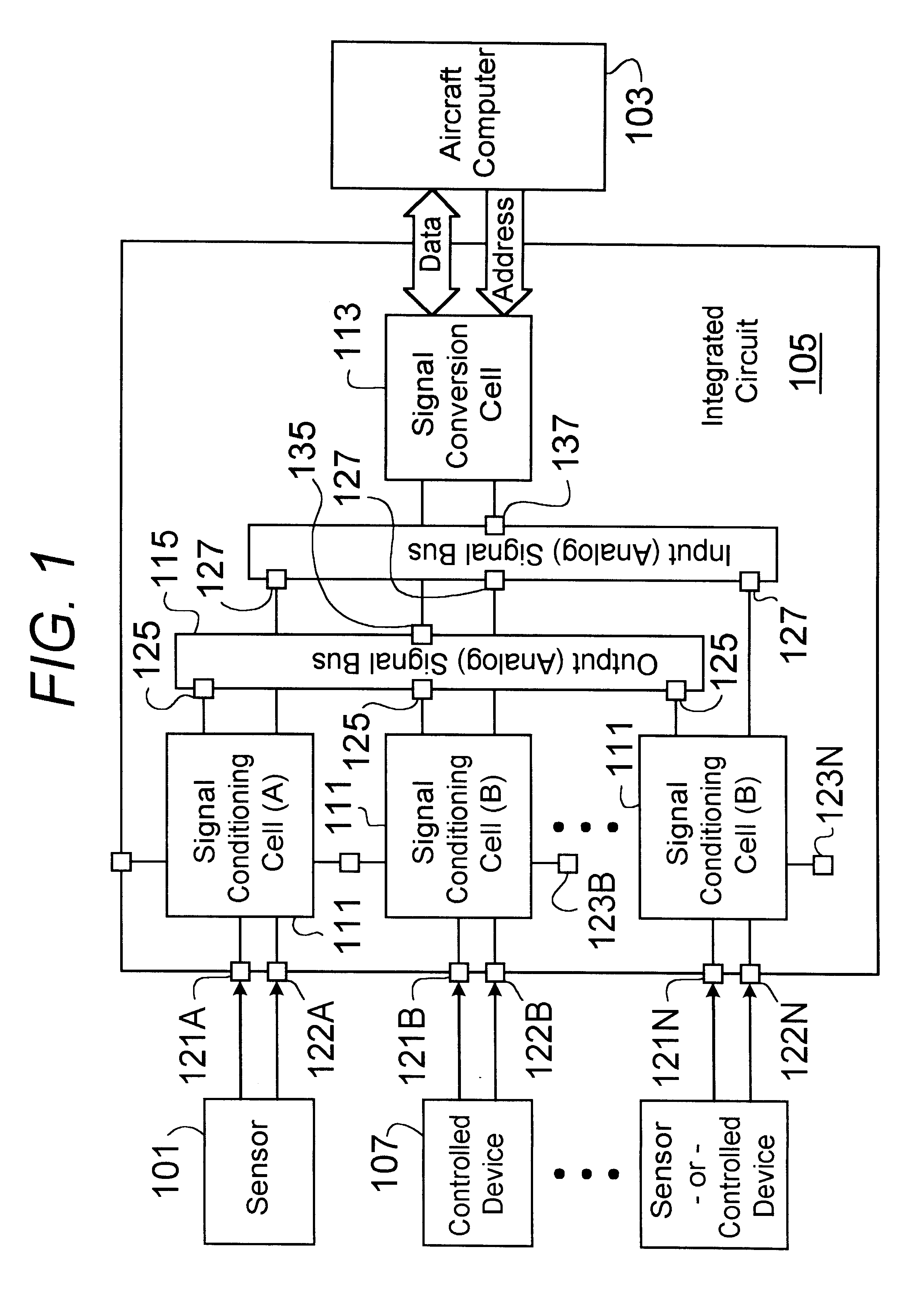
An integrated circuit chip for interfacing a digital computer to sensors and controlled devices can be configured to accept and provide a variety of analog and discrete input and output signals. The circuit includes a plurality of signal conditioning cells, a plurality of signal conversion cells, and input and output signal multiplexors.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
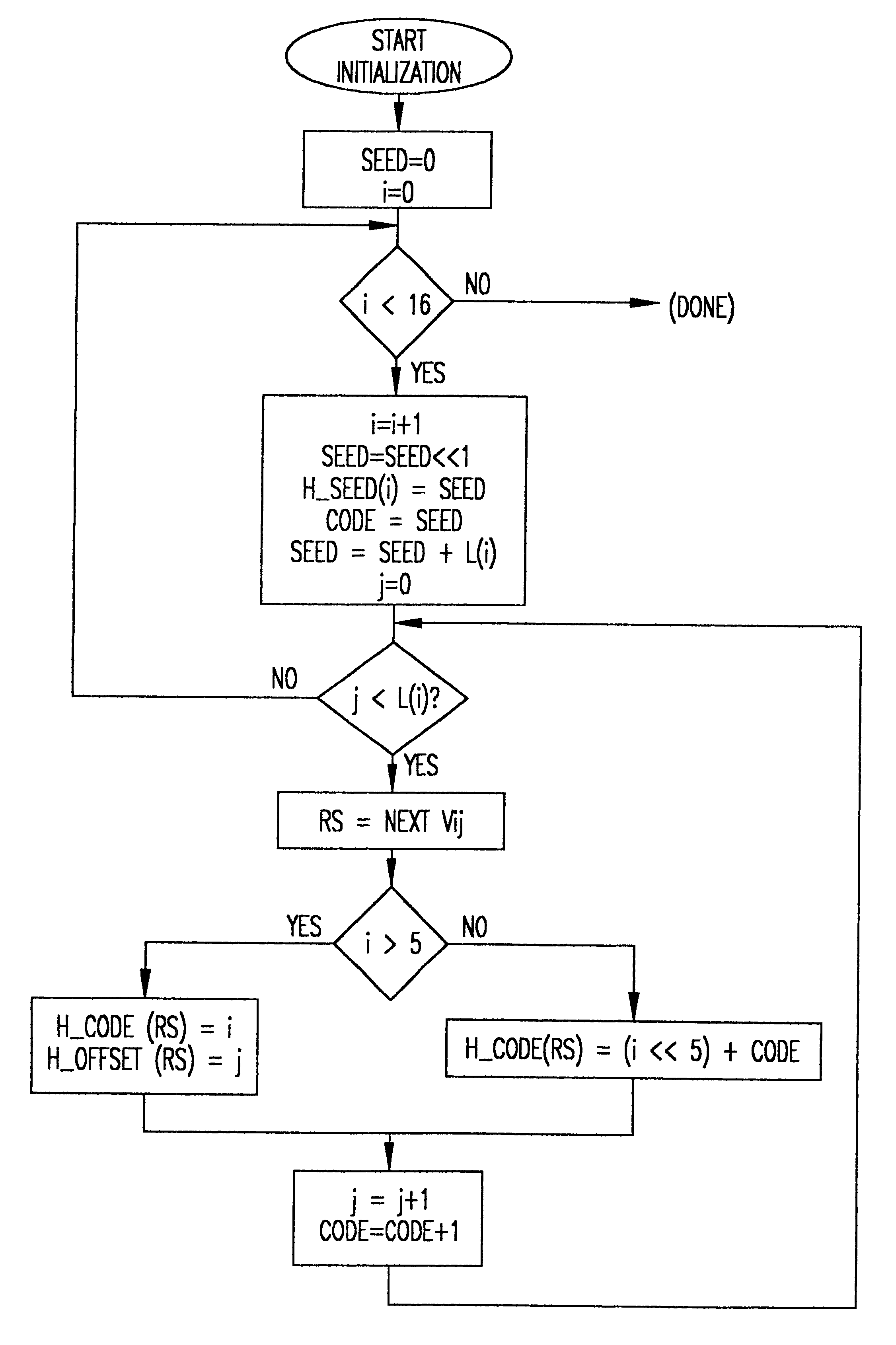
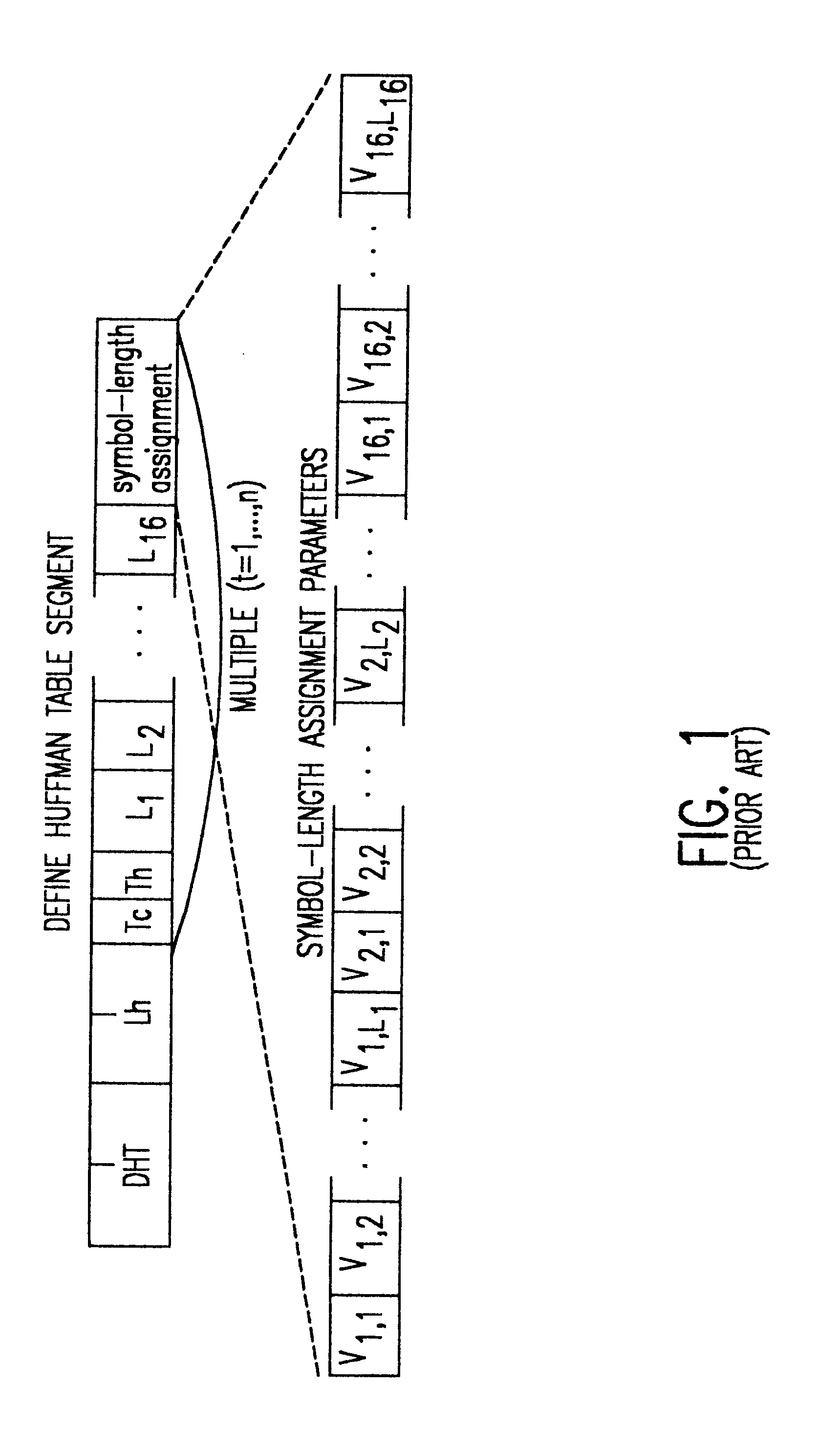
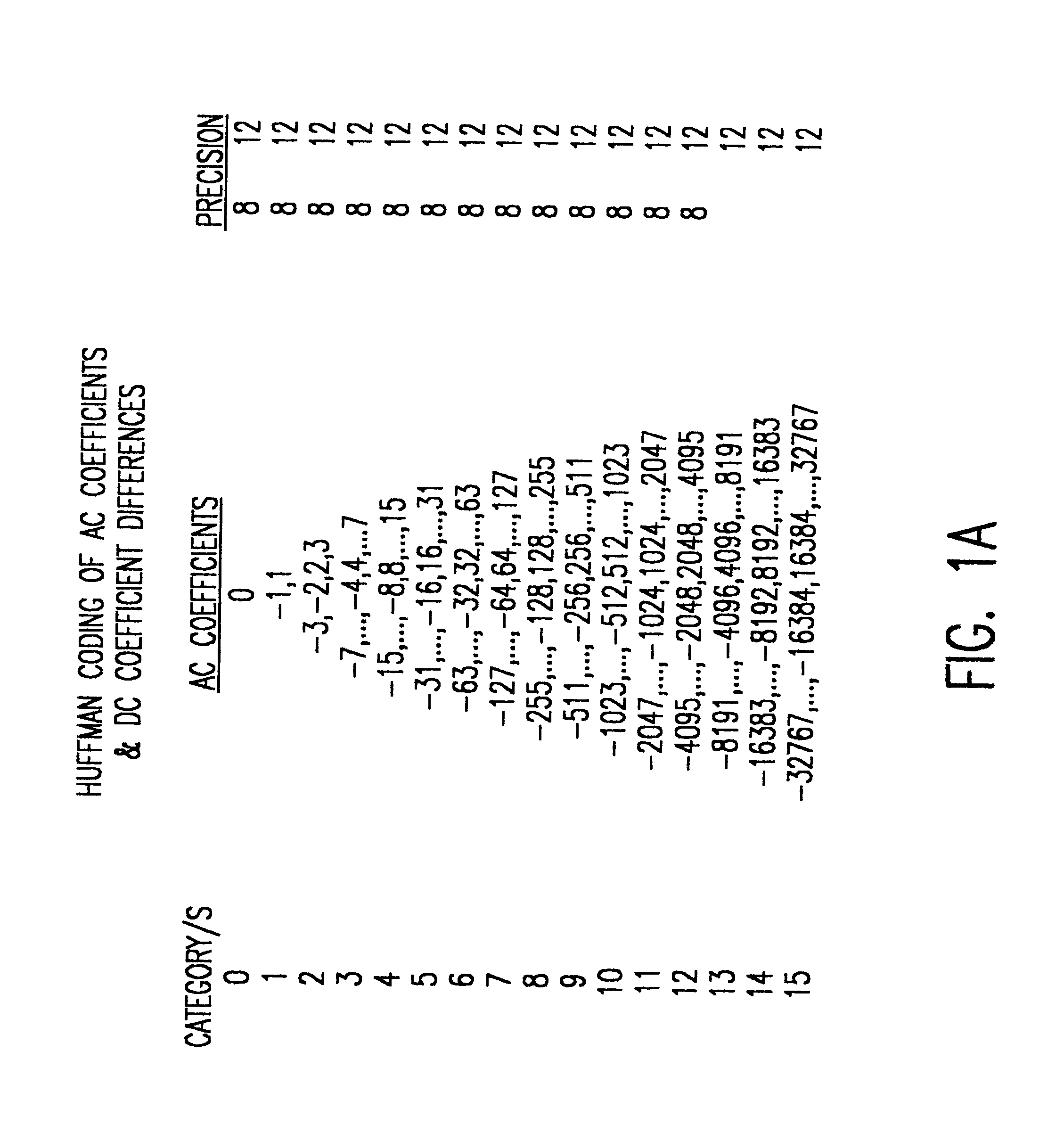
Fast JPEG huffman encoding and decoding
InactiveUS6373412B1Electric signal transmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamJPEG
Huffman encoding, particularly from a packed data format, is simplified by using two different table formats depending on code length. Huffman tables are also reduced in size thereby. Decoding is performed in reduced time by testing for the length of valid Huffman codes in a compressed data stream and using an offset corresponding to a test criterion yielding a particular test result to provide a direct index into Huffman table symbol values while greatly reducing the size of look-up tables used for such a purpose.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low-current sample rate converter
InactiveUS6347123B1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital technique networkCurrent sampleTransceiver
A low power sample rate converter adapted for use with a telecommunications system transceiver. The sample rate converter includes a first circuit that provides an input signal characterized by a first sample rate and a delayed version of the input signal. A second circuit periodically multiplies, at a second sample rate, samples in the input signal by a first predetermined coefficient in accordance with a predetermined transfer function and provides a first signal in response thereto. A third circuit periodically multiplies, at the second sample rate, samples in the delayed version of the input signal by a second predetermined coefficient in accordance with the predetermined transfer function and provides a second signal in response thereto. A fourth circuit combines the first signal and second signal providing a rate-converted version of the input signal as an output signal in response thereto. In a specific embodiment, the delayed version of the input signal is delayed by one sample with respect to the input signal. The sample rate converter further includes a counter that is clocked by a first periodic signal. The first periodic signal has a frequency related to the first sample rate by a predetermined fraction. The counter is cleared by a second periodic signal having a second frequency equivalent to the first sample rate. The counter produces a counter output at the first frequency. In the preferred embodiment, the predetermined fraction is ⅓ and the first predetermined coefficient is equivalent to the sum of 1 and the counter output. The second predetermined coefficient is equivalent to the difference of 2 and the counter output. The fourth circuit includes an adder for adding the first signal and the second signal and providing the output signal in response thereto. The predetermined transfer function is represented by the following coefficient sequence: [1 2 3 2 1].
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
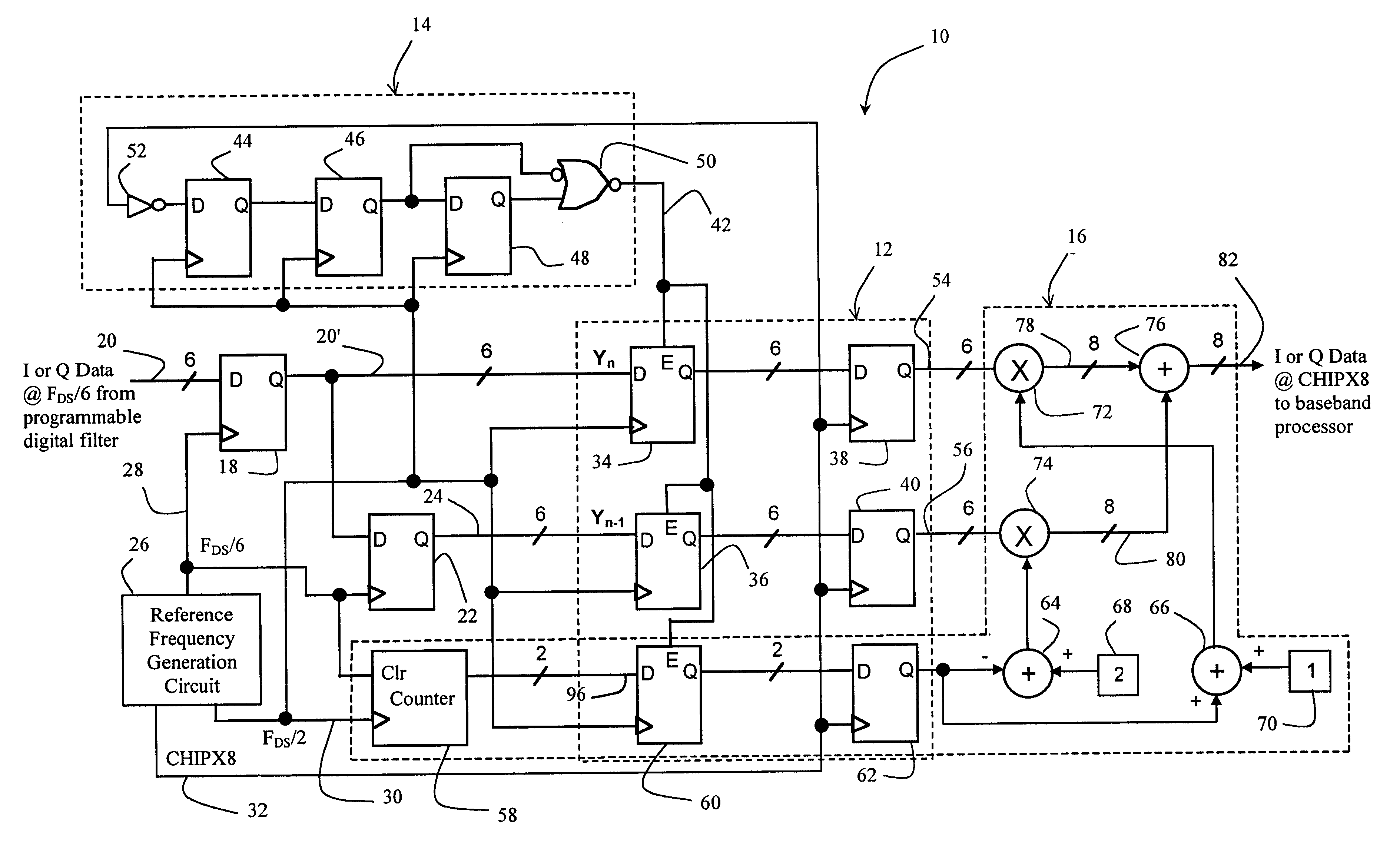
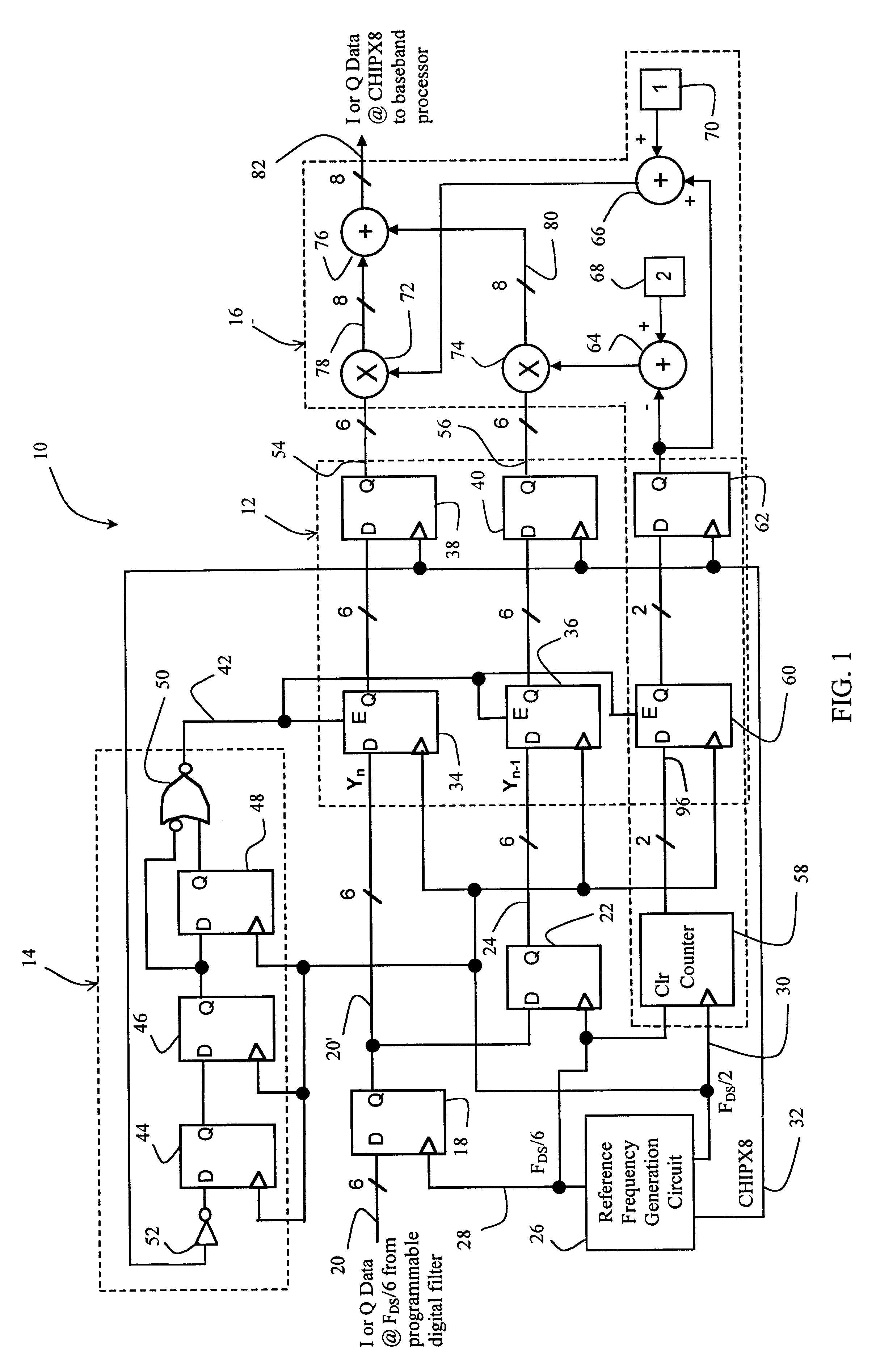
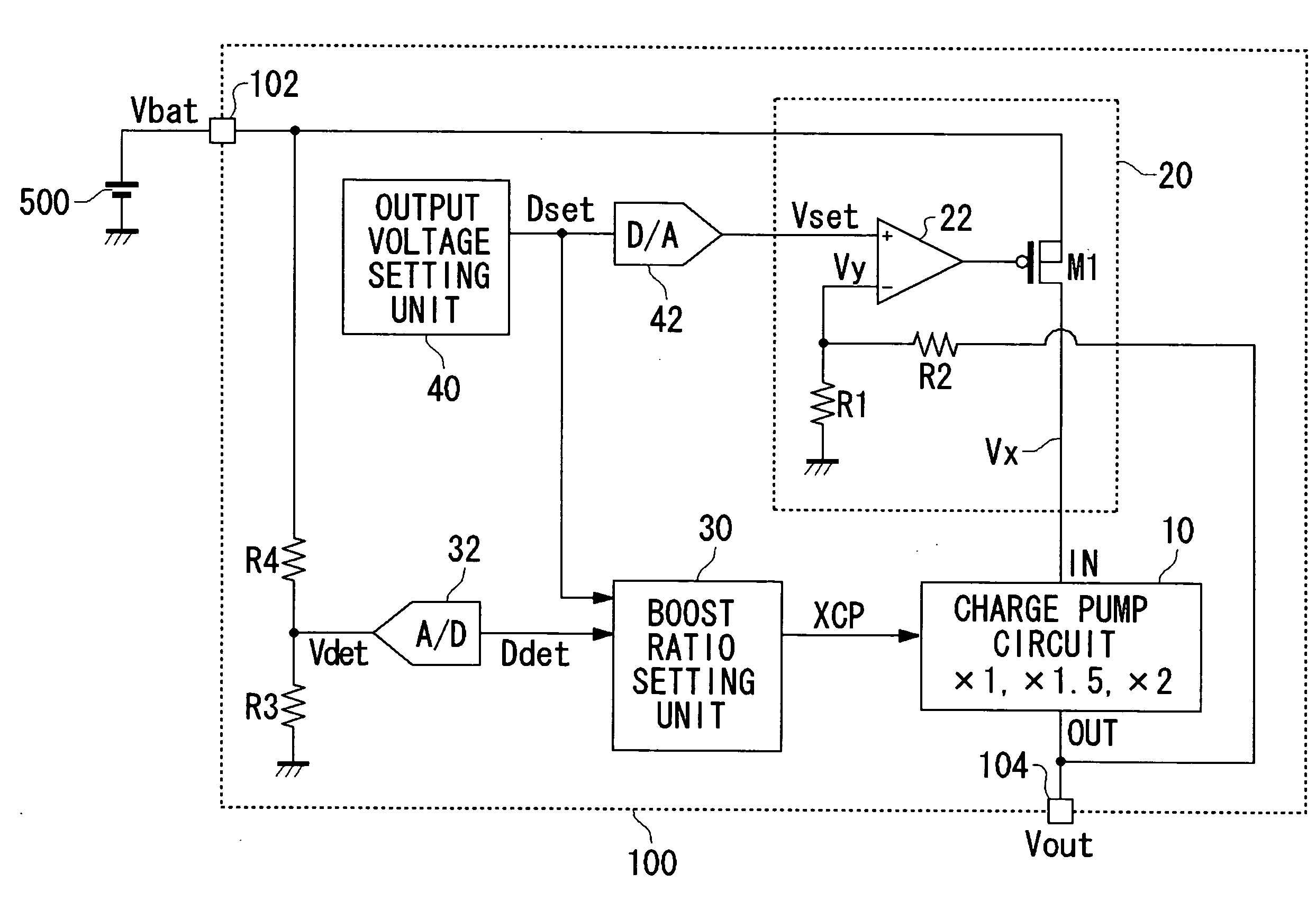
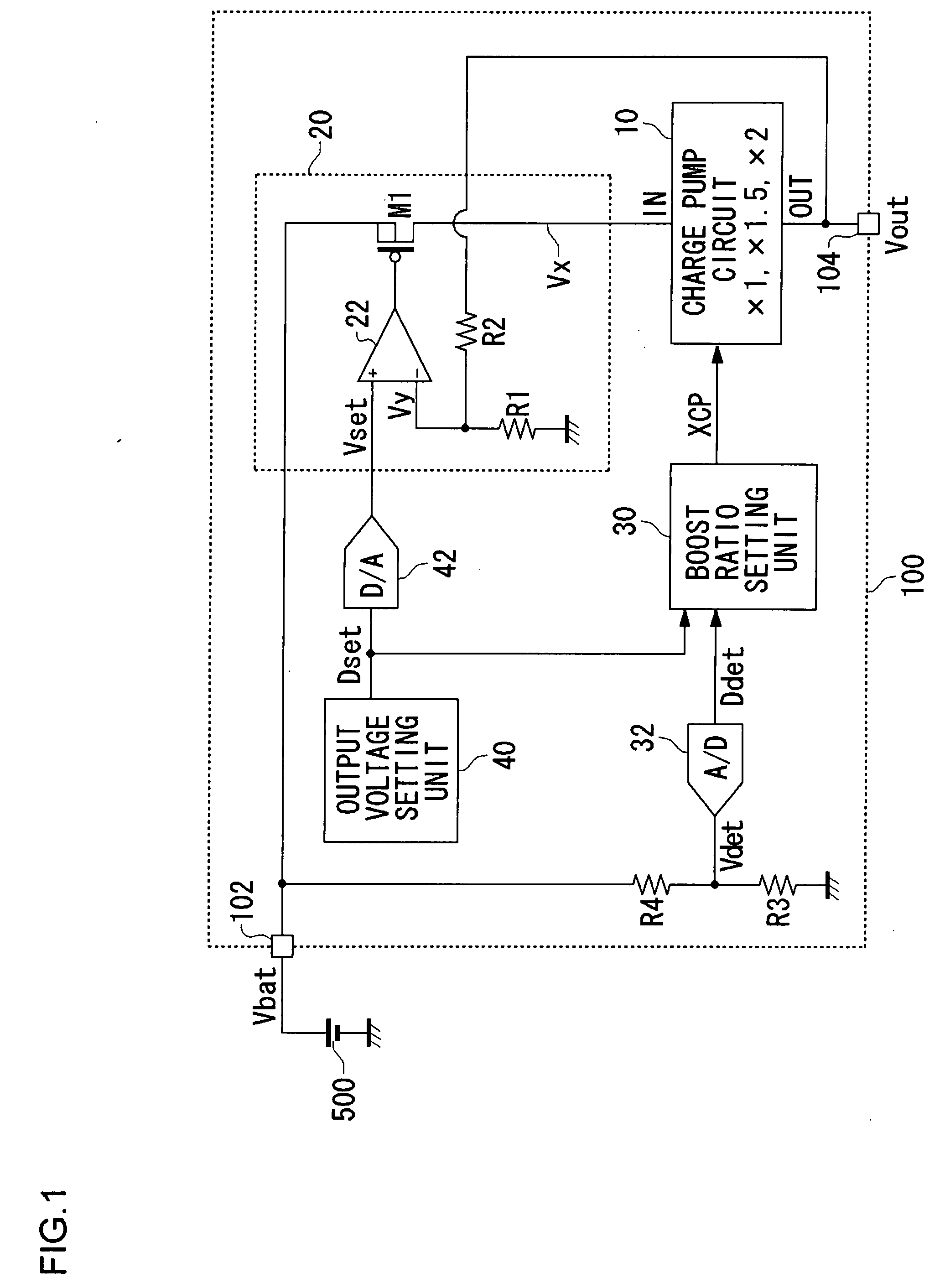
Power Supply Device, Electronic Device, and A/D Converter Used for Them
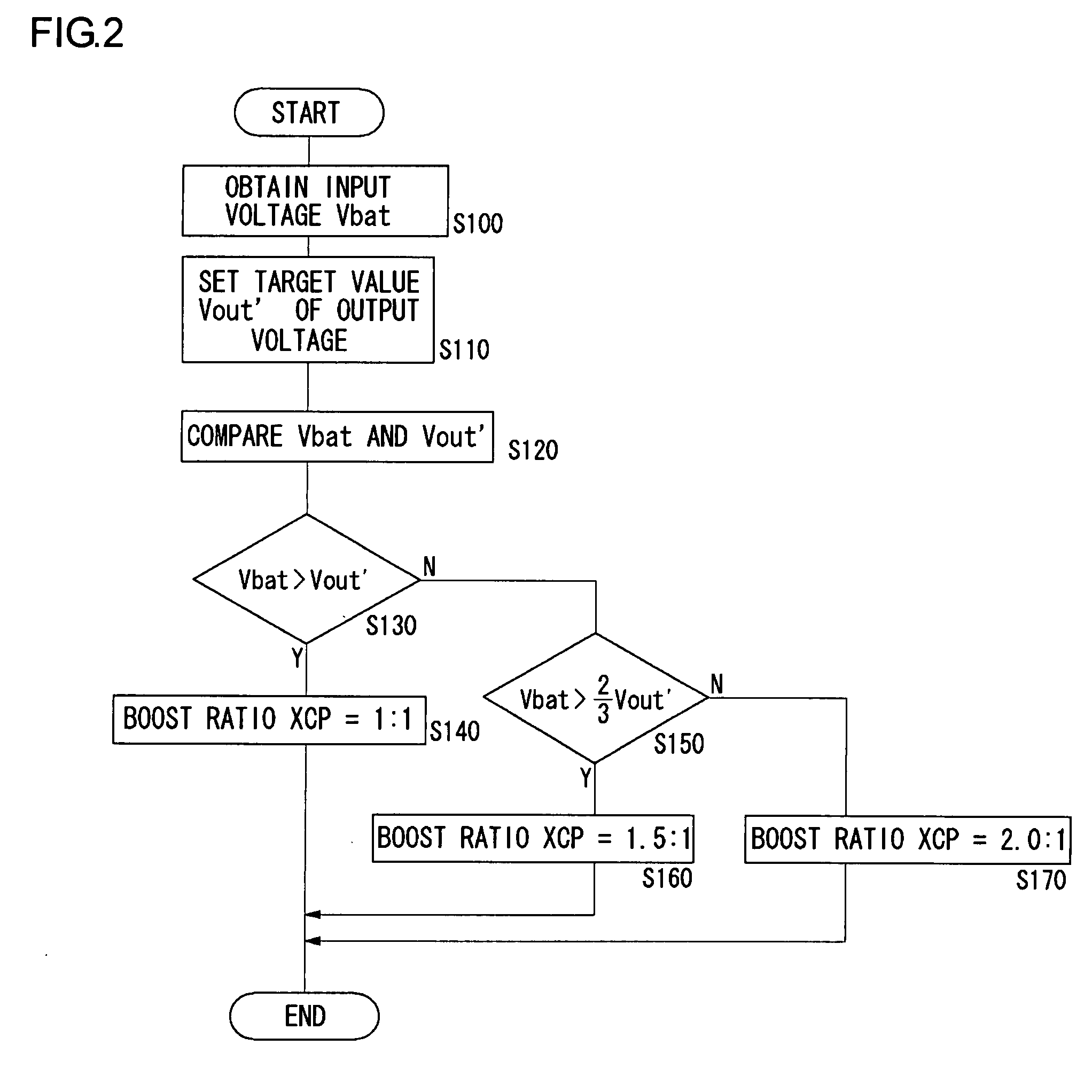
InactiveUS20090085538A1Appropriate settingImprove accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsElectroluminescent light sourcesVoltage regulationEngineering
In the power supply apparatus which performs voltage conversion of an input voltage (Vbat), with a predetermined set voltage as a target value, and outputs the converted voltage, a boost ratio setting unit sets a boost ratio (XCP) of the charge pump circuit based on the input voltage (Vbat) and a predetermined set voltage. A voltage adjustment unit is a regulator circuit, and adjusts voltage (Vx) so that output voltage (Vout) of the charge pump circuit approaches the set voltage. An output voltage setting unit generates a predetermined set voltage as a digital value (Dset). An A / D converter performs analog-digital conversion of the input voltage (Vbat). The boost ratio setting unit sets the boost ratio based on a result of comparing an input voltage (Ddet) that has undergone analog-digital conversion, and the set voltage (Dset).
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
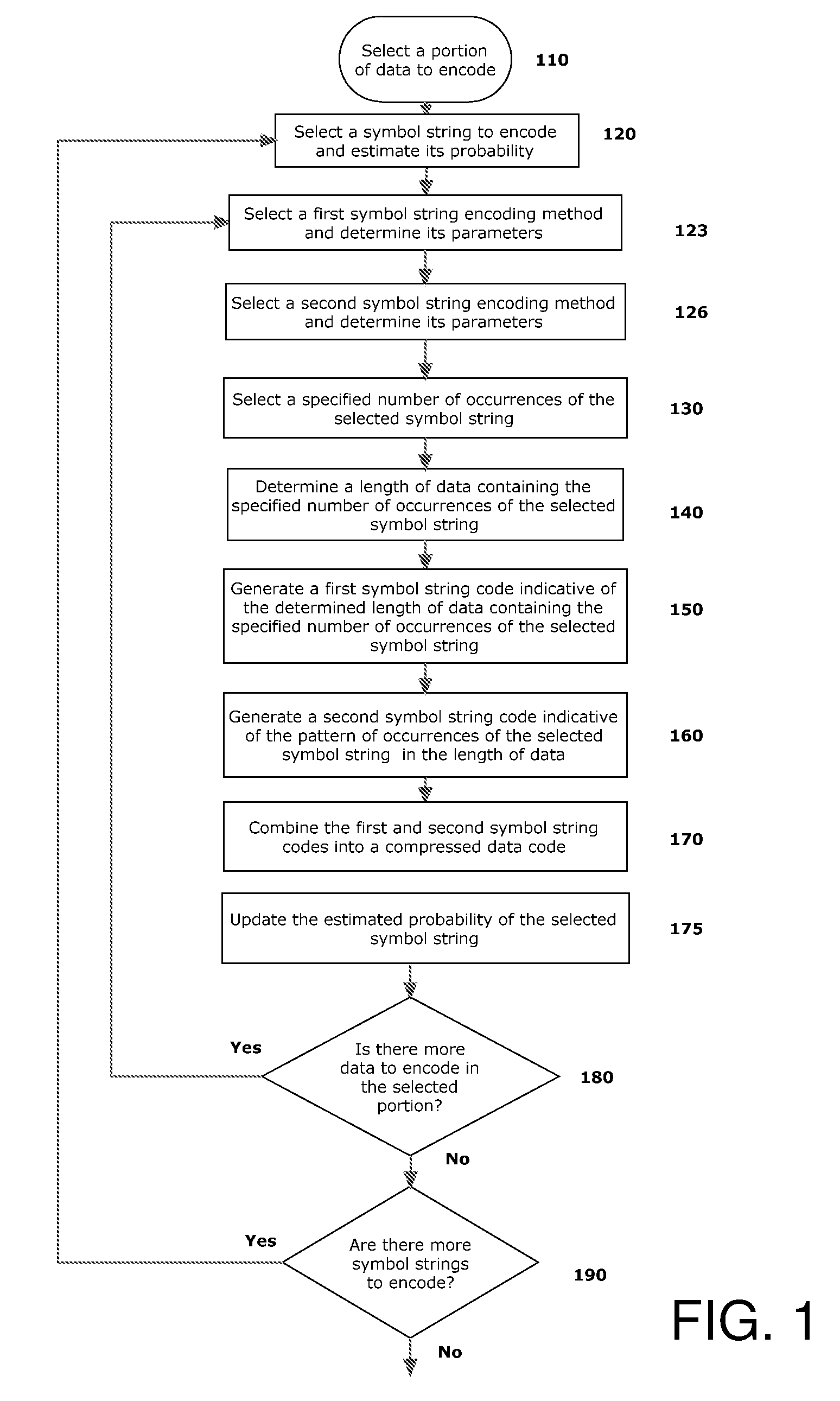
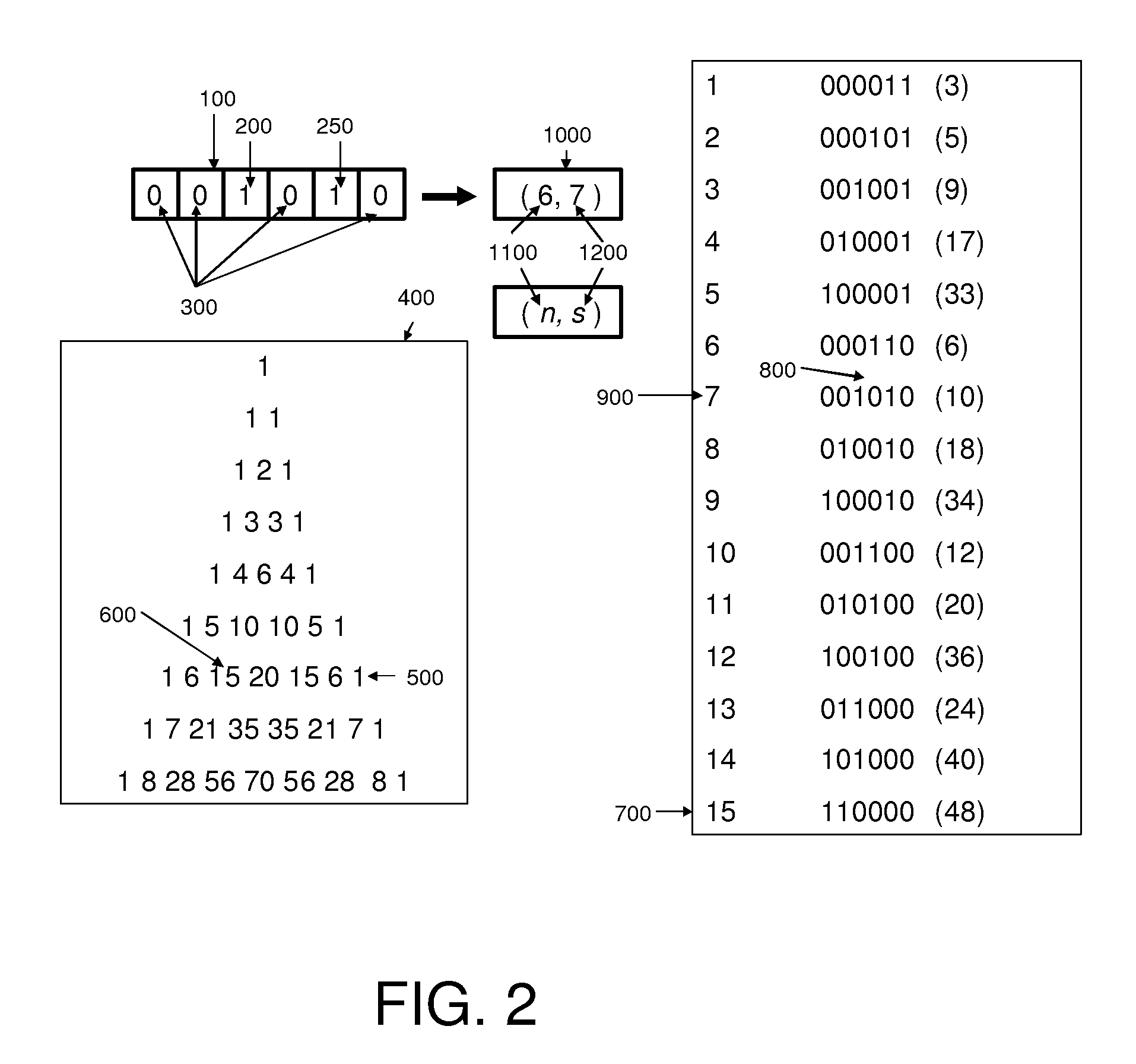
Adaptive combinatorial coding/decoding with specified occurrences for electrical computers and digital data processing systems
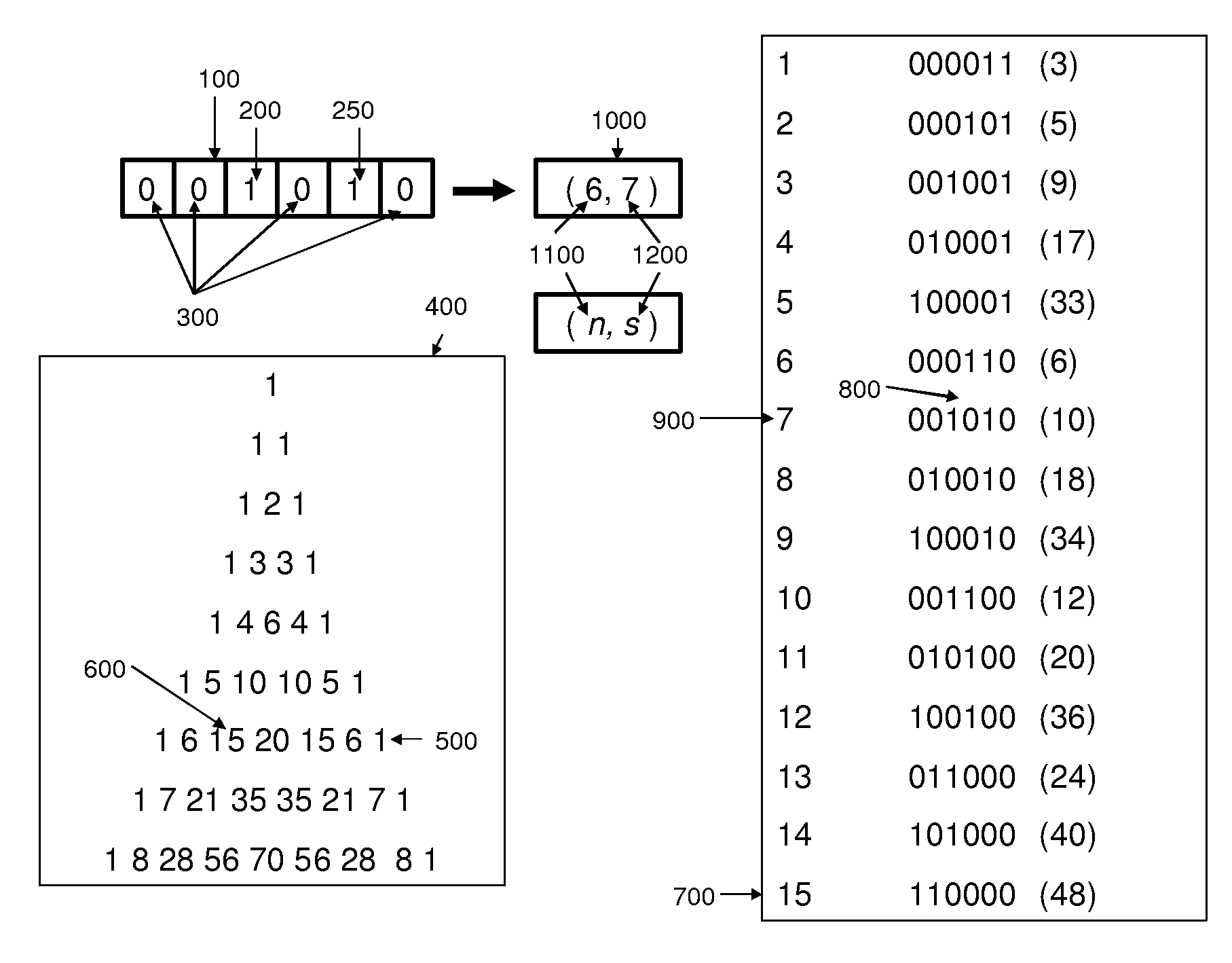
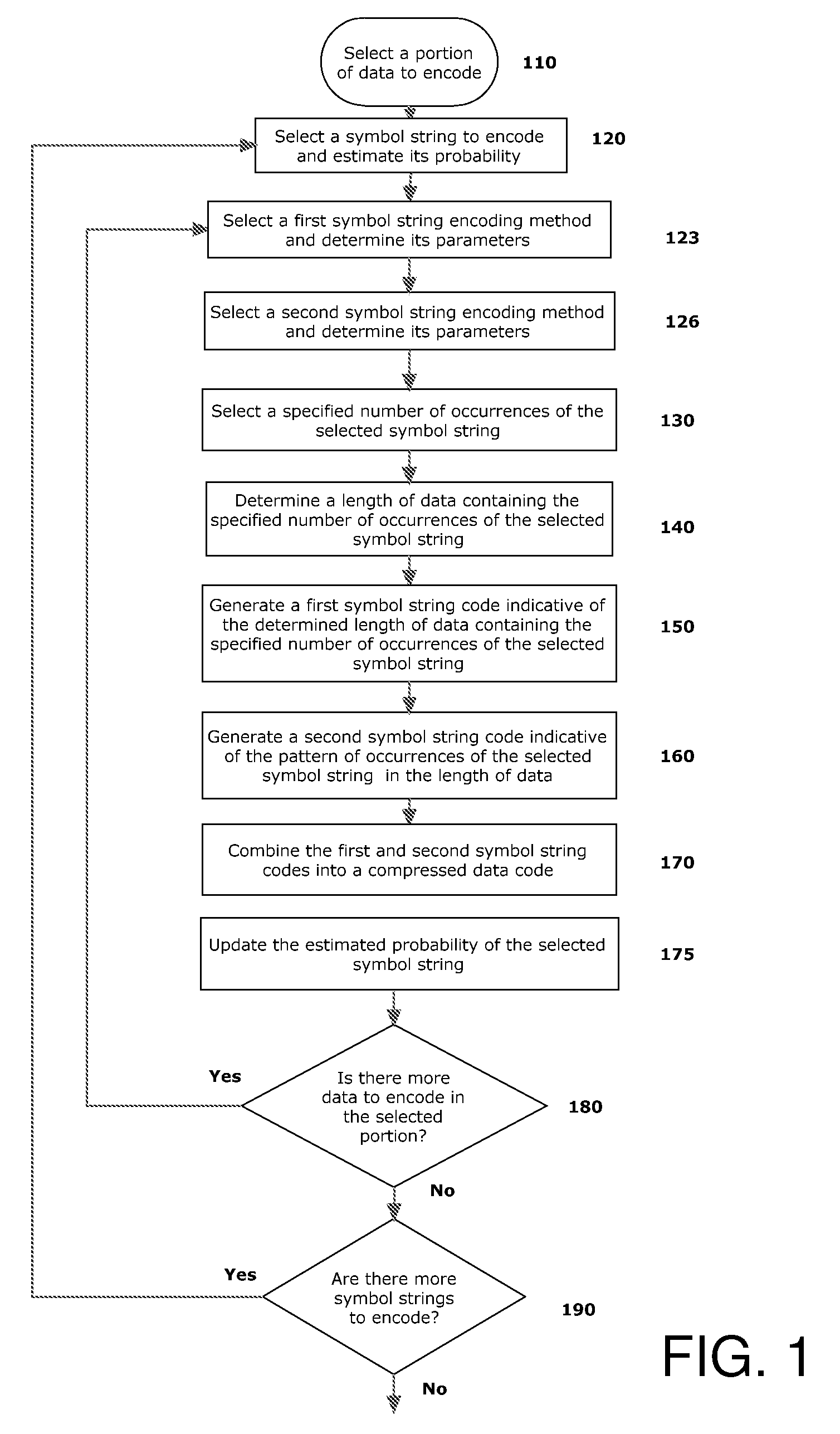
InactiveUS20100085224A1Electric signal transmission systemsReversible analogue/digital convertorsData processing systemDigital signal processing
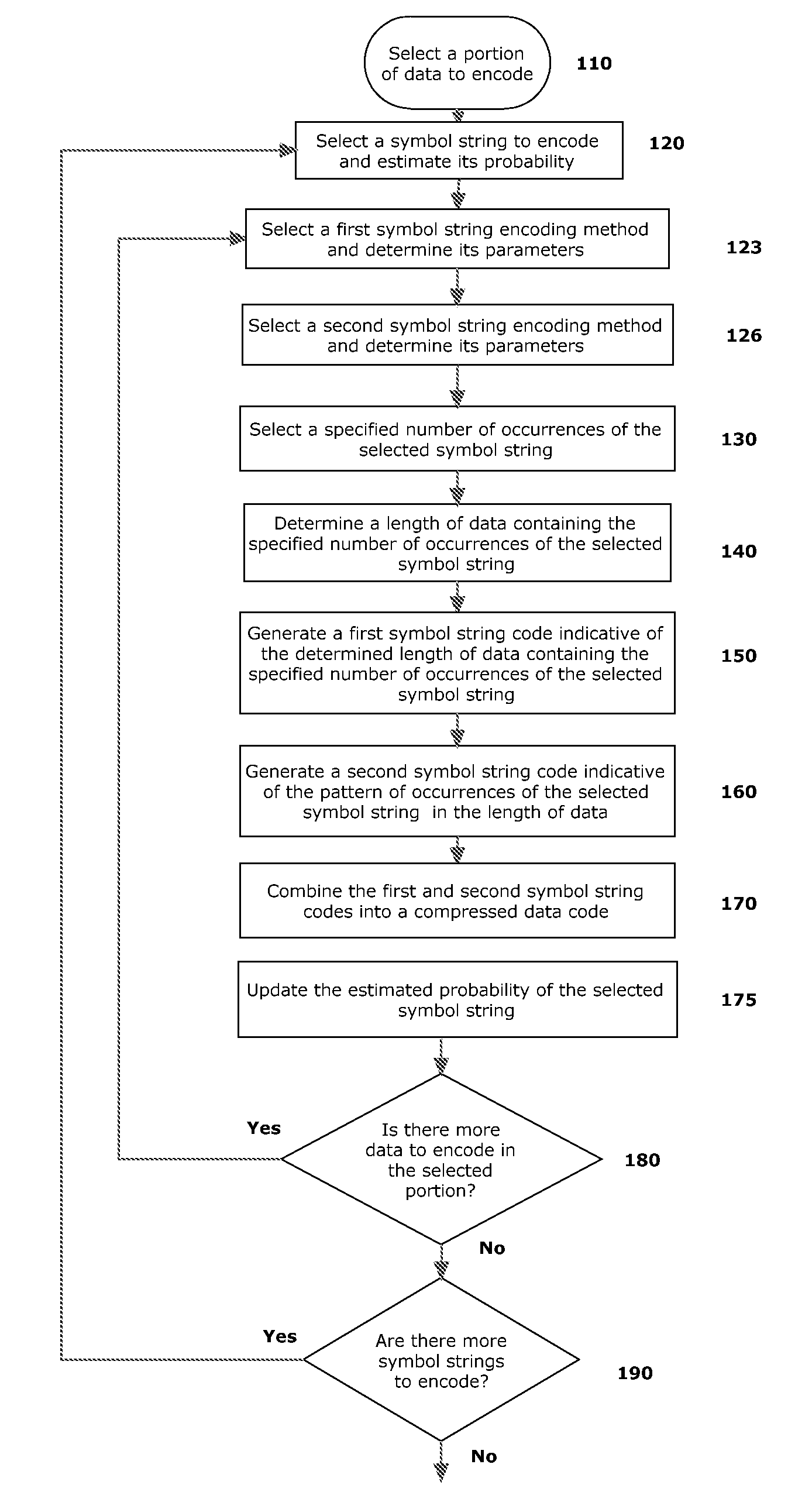
Embodiments described herein may include example embodiments of a method, article and apparatus for compressing data utilizing a combinatorial encoder with specified occurrences which may be used for communicating between two or more components connected to an interconnection medium (e.g., a bus) within a single computer or digital data processing system, and / or for communication between computing platforms via a network or other interconnection medium.
Owner:TECH VALUE GRP LLC
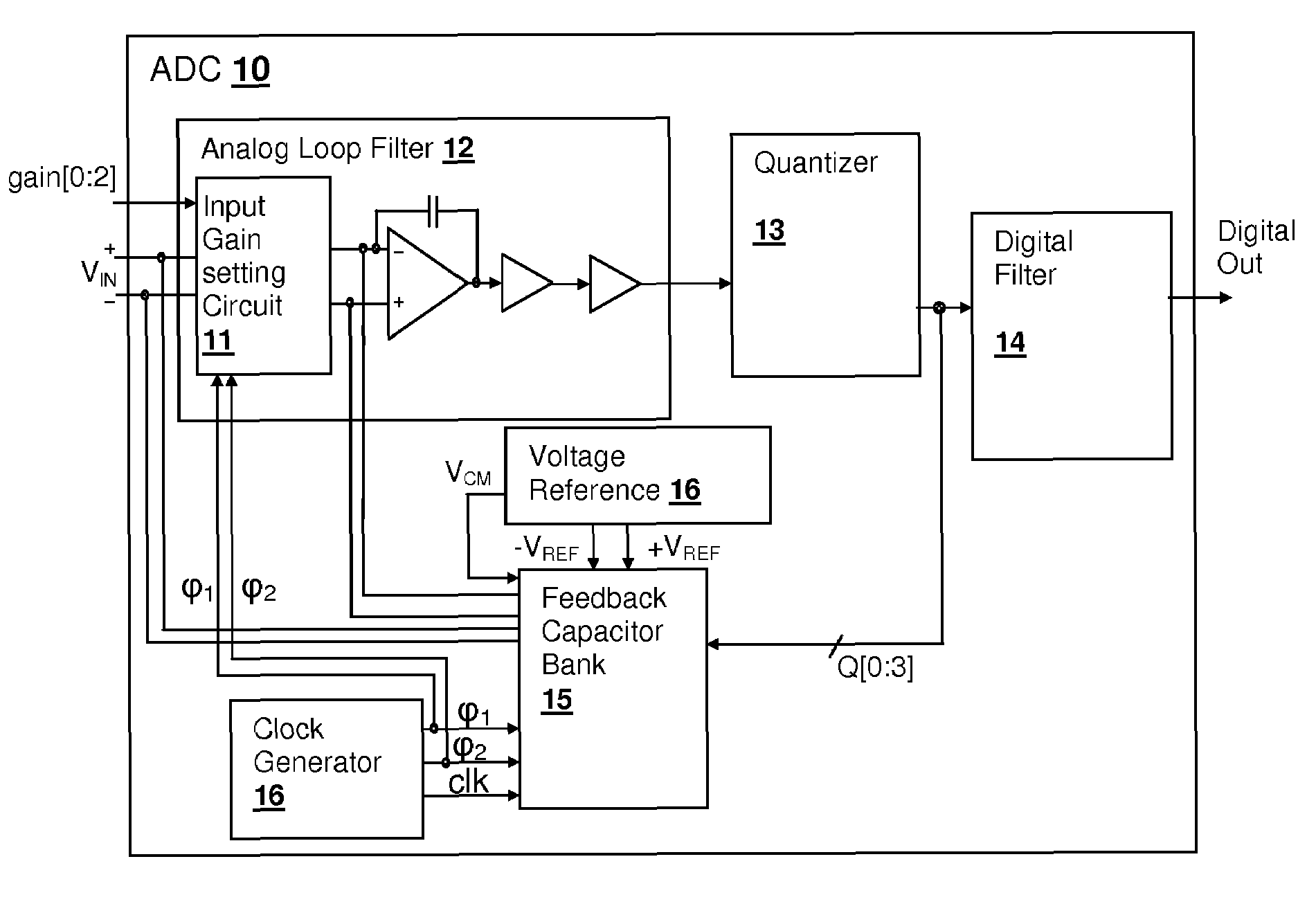
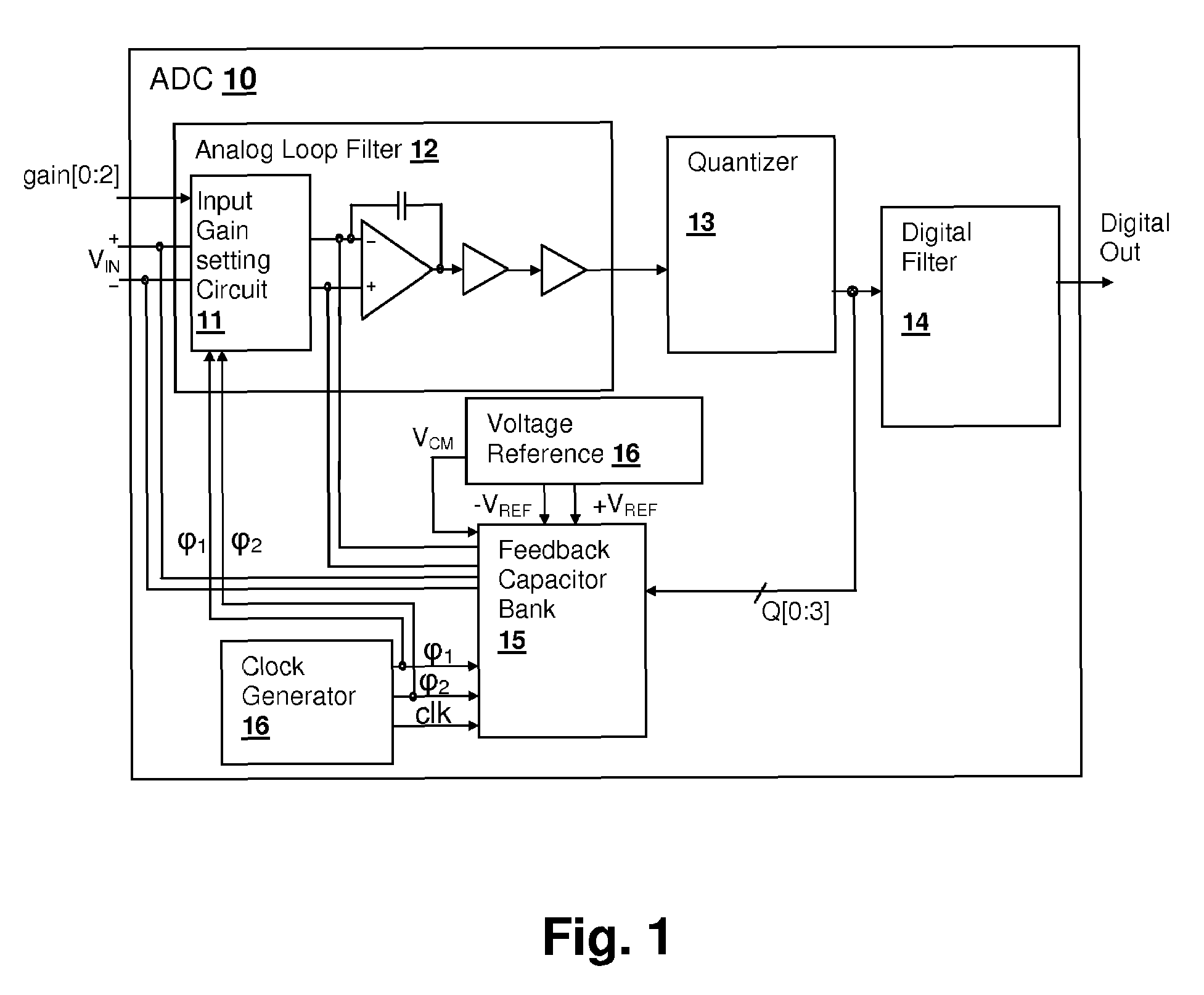
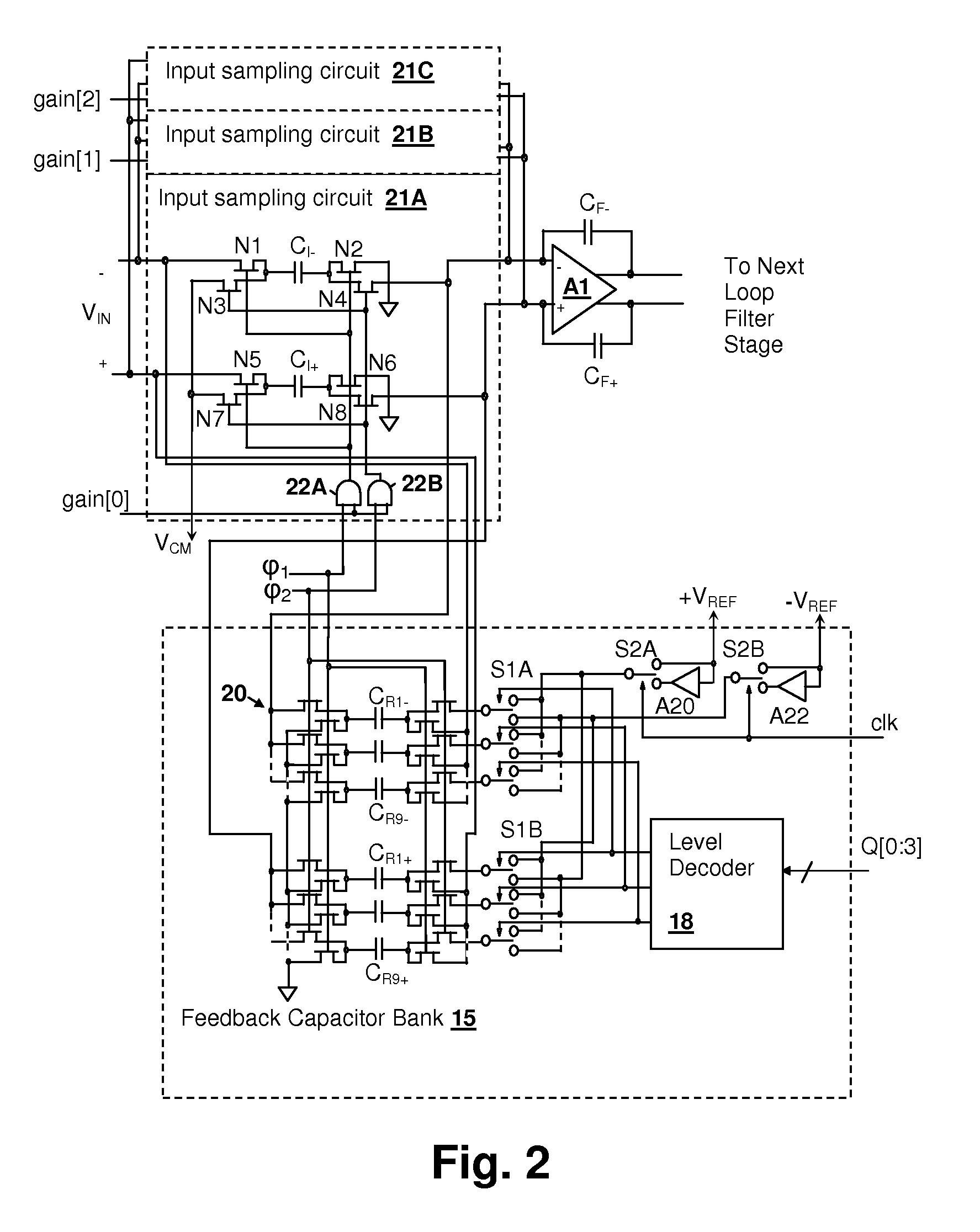
Discrete-time programmable-gain analog-to-digital converter (ADC) input circuit with multi-phase reference application
ActiveUS7489263B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital down converterIntegrator
A discrete-time programmable-gain analog-to-digital converter (ADC) input circuit with multi-phase reference application, provides a high input impedance level substantially independent of input capacitor size and input signal gain setting. An input voltage is sampled at the common mode voltage of the input, using one or more reference capacitor(s) that has been charged in a previous clock phase to the reference feedback voltage. The sampled input voltage is then applied in series with a quantizer-controlled reference voltage to the input of an integrator in a second clock phase. The summing mode of the integrator is maintained at the reference common-mode voltage. Since the charge pulled from the input voltage source is substantially determined only by the quantization error and input noise voltage, the circuit has a high signal input impedance. Since the input voltage source is sampled with respect to its common-mode voltage, the common-mode input impedance is also high.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
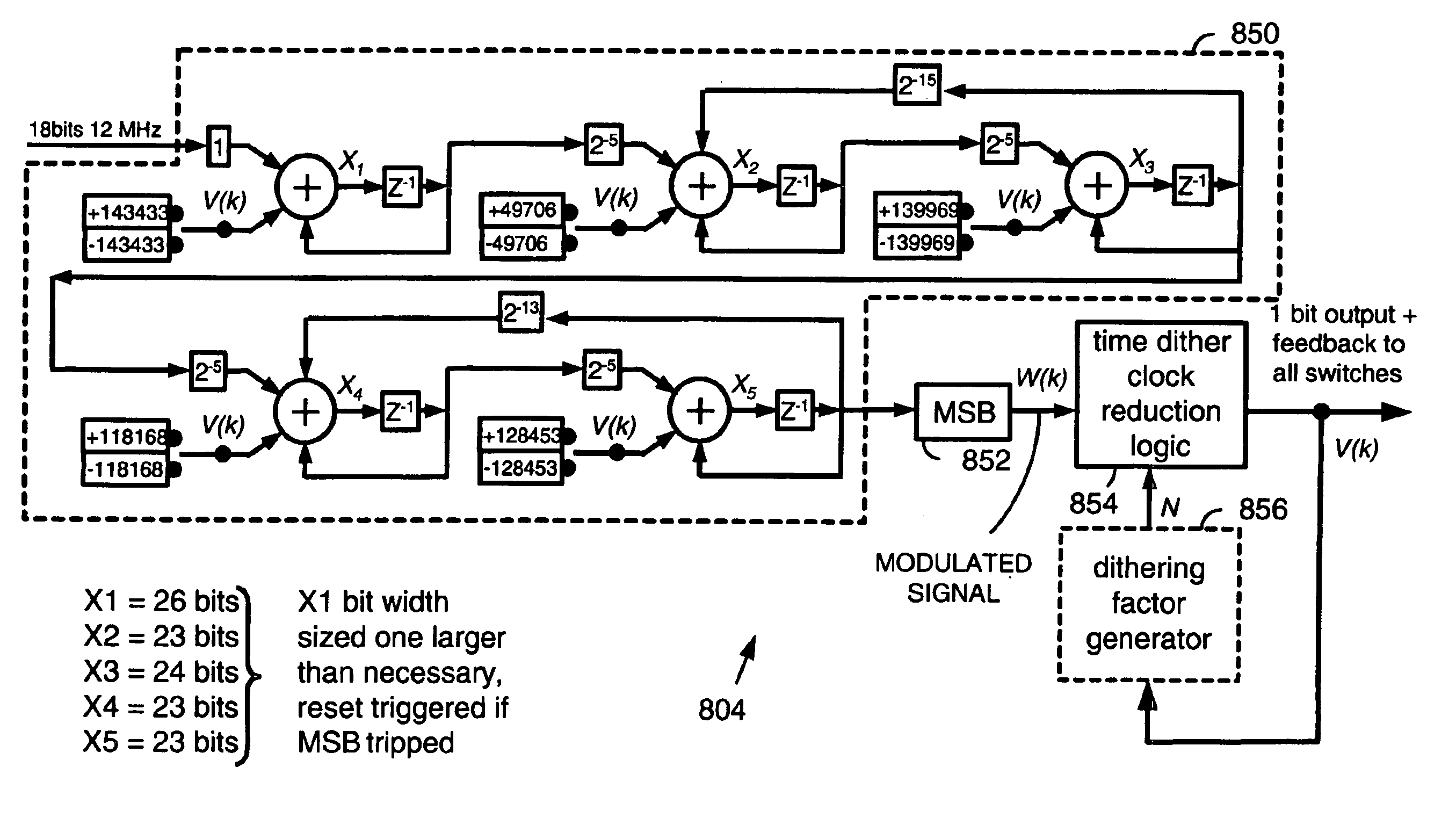
Analog to digital converter that services voice communications
InactiveUS6917318B2Easy to trackLess output noiseElectric signal transmission systemsNetwork topologiesDigital dataDigital down converter
An Analog-to-Digital-Converter (ADC) converts an analog signal to digital data. The ADC includes a modulator, a decimation filter, and a time dither clock reduction circuit. The modulator receives the analog signal and a feedback signal and, based there upon, produces a modulated signal at a modulator clock rate. The decimation filter couples to the modulator, receives the modulated signal, and decimates and filters the modulated signal to produce the digital data. The time dither clock reduction circuit receives the modulated signal and provides the feedback signal to the modulator. The time dither clock reduction circuit applies both clock reduction and time dithering to the modulated signal to produce the feedback signal. At each modulator clock cycle, the time dithering clock reduction circuit considers modulated signals for a dithering factor, N, previous modulator clock cycles and a modulated signal for a current modulator clock cycle. If at least one constraint is satisfied for the N previous modulator clock cycles, the time dithering clock reduction circuit is allowed to transition the feedback signal with the modulated signal. If not, the time dithering clock reduction circuit holds the prior value of the feedback signal. After a transition, a new dithering factor may be determined. The ADC may be contained in a wireless local area network (WLAN) transceiving integrated circuit that services voice communications in a WLAN with at least one other WLAN device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Successive aproximation A/D Converter
InactiveUS20110133963A1Simple configurationControl is complicatedElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitancePotential difference
A successive approximation A / D converter, includes a reference voltage generation circuit, a sample / hold circuit, a D / A converter circuit, a comparator, and a control circuit. A potential difference between the comparison target voltage generated by the D / A converter circuit and the internal analog voltage is applied to one input terminal of the comparator through a first signal line, and the reference voltage generation circuit is connected to the other input terminal of the comparator through a second signal line and a switch. Capacitive elements are disposed between the high potential power supply and the second signal line, and between the second signal line and the low potential power supply, respectively. The control circuit turns ON the switch to charge the first and second capacitive elements during a period when the sample / hold circuit samples and holds the internal analog voltage and turns OFF the switch in response to end of the period.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Sigma-delta difference-of-squares log-rms to DC converter with forward path multiplier and chopper stabilization
ActiveUS20120146819A1Reduce sensitivityExtension of useful input-referred dynamic rangeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionLoop filterFrequency compensation
A sigma-delta (ΣΔ) difference-of-squares LOG-RMS to digital converter for true RMS detection by merging a ΣΔ modulator with an analog LOG-RMS to DC converter based on a difference-of-squares. Chopper-stabilization, implemented through commutators running at two different frequencies, can be employed to reduce sensitivity to DC offsets and low-frequency errors, resulting in an extension of the useful input-referred dynamic range. High-order ΣΔ LOG-RMS converters can be implemented with a loop filter containing multiple integrators and feedforward and / or feedback paths for frequency compensation. The resulting implementations are ΣΔ difference-of-squares LOG-RMS to DC converters with a natural digital output and a logarithmically compressed dynamic range.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
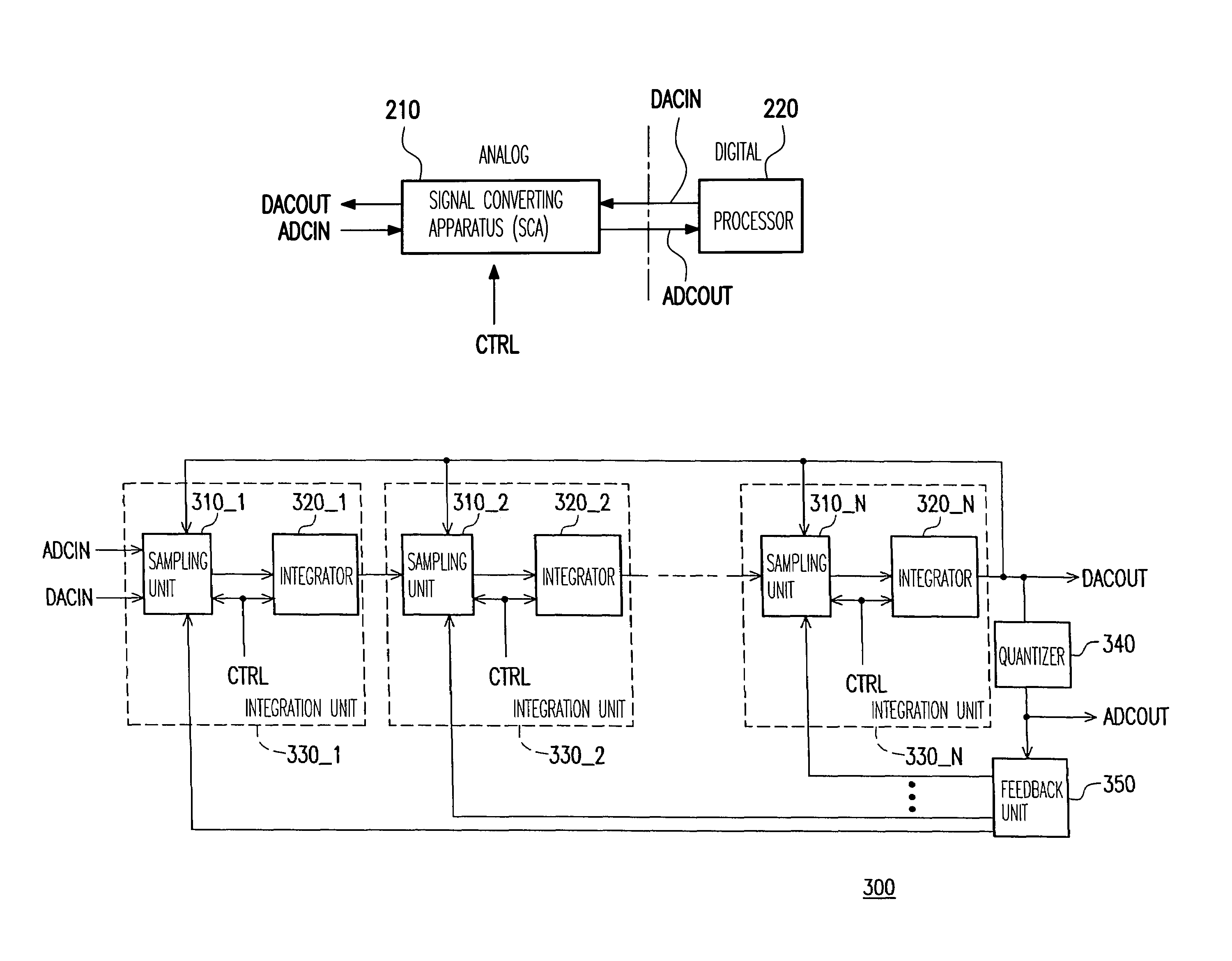
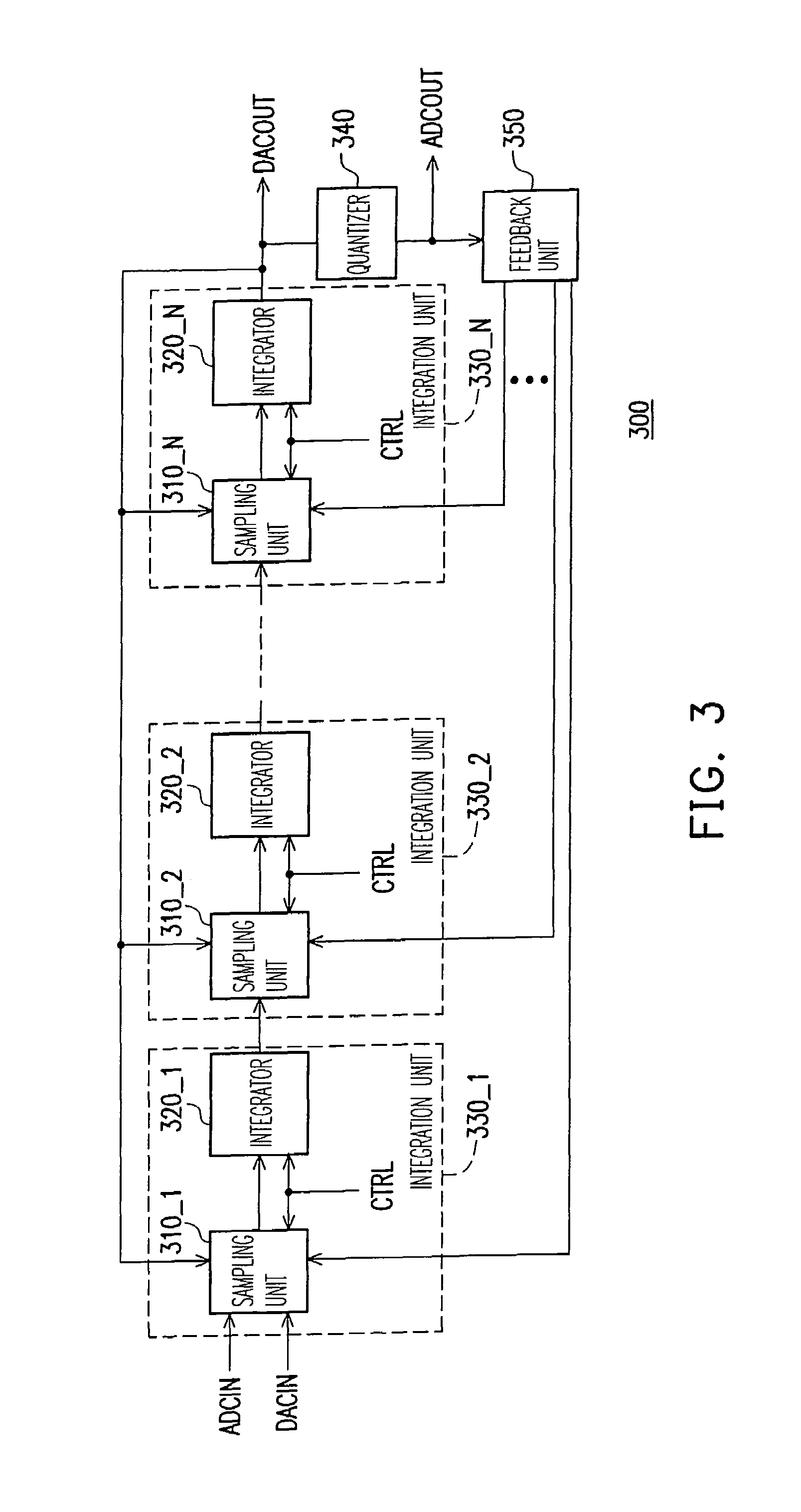
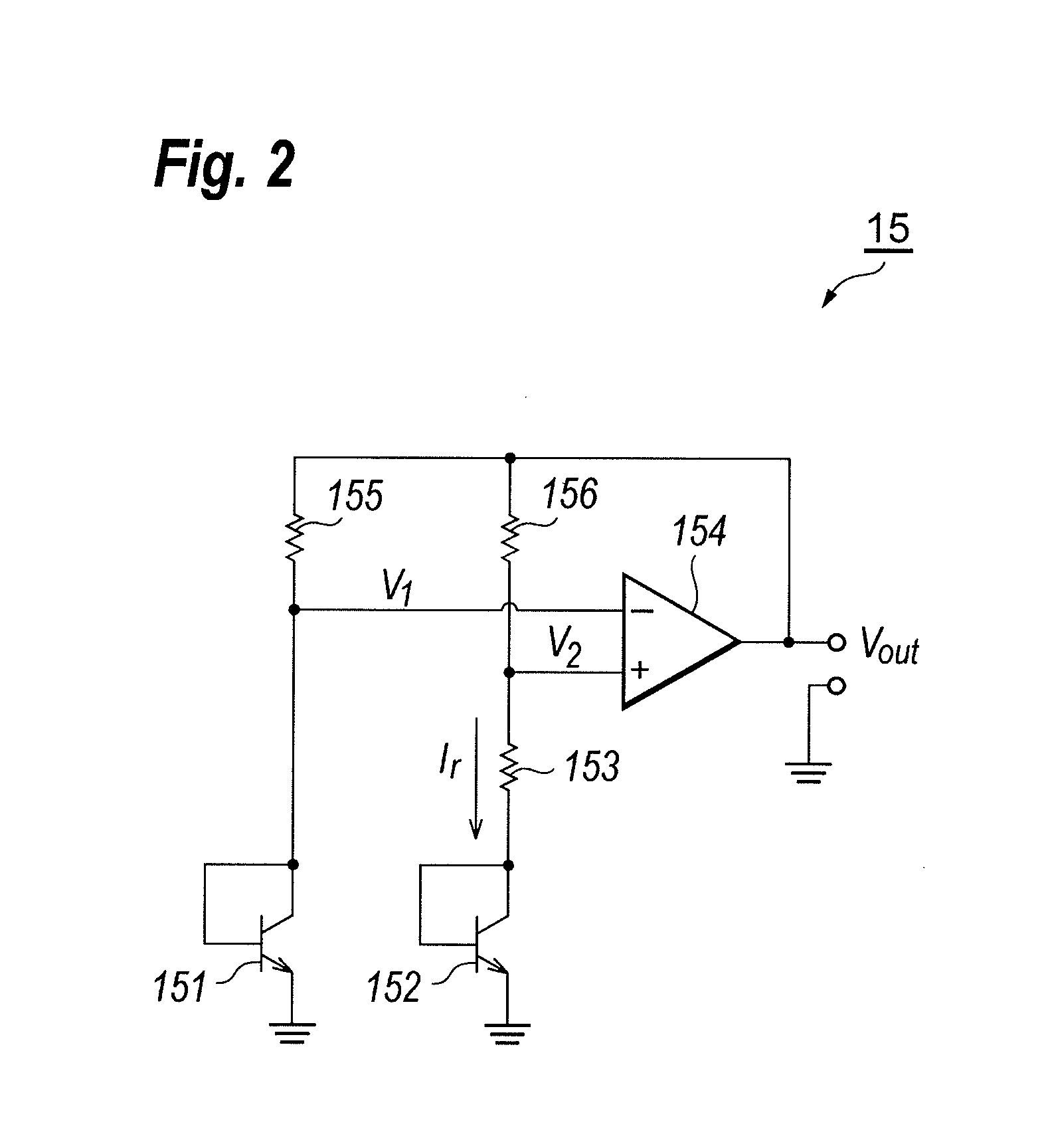
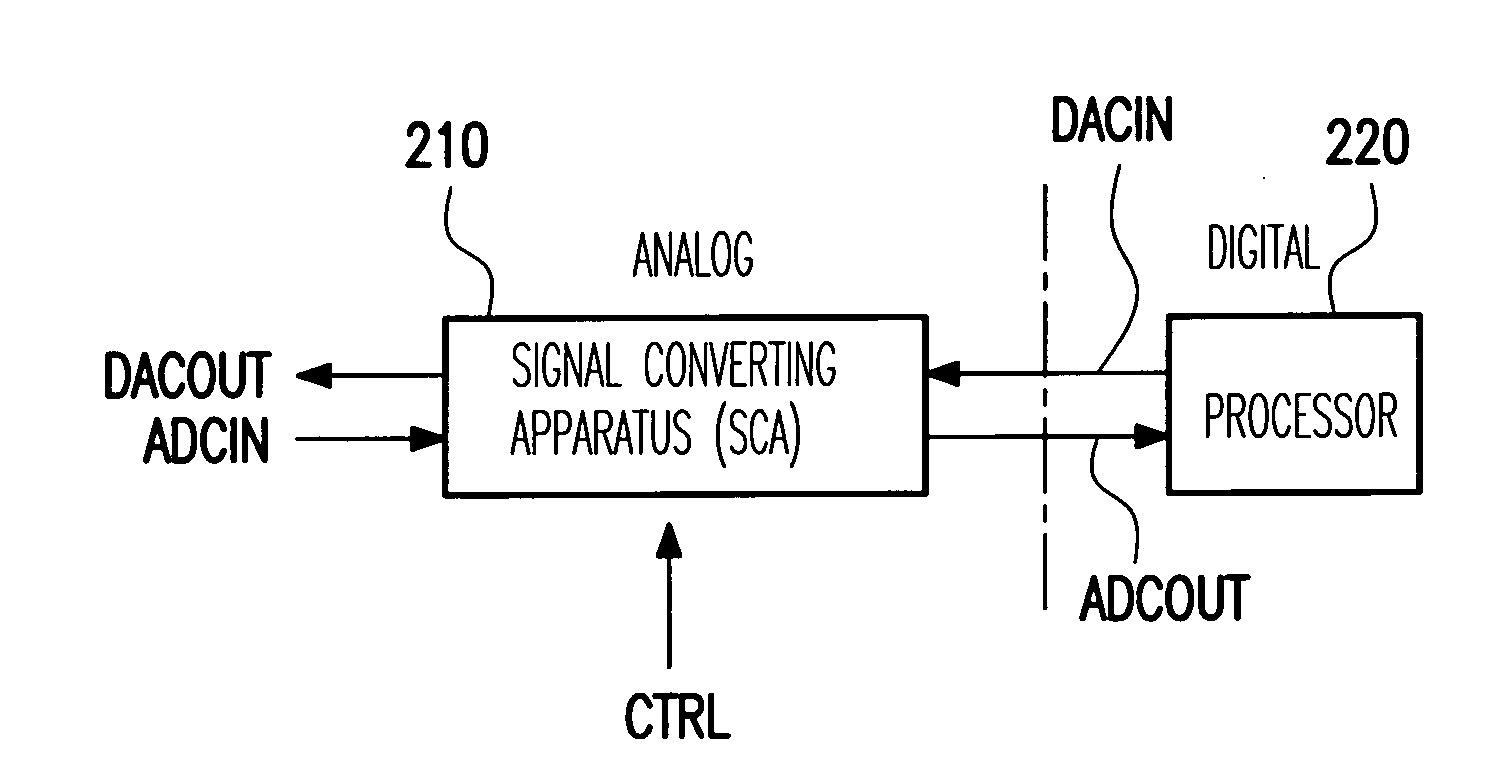
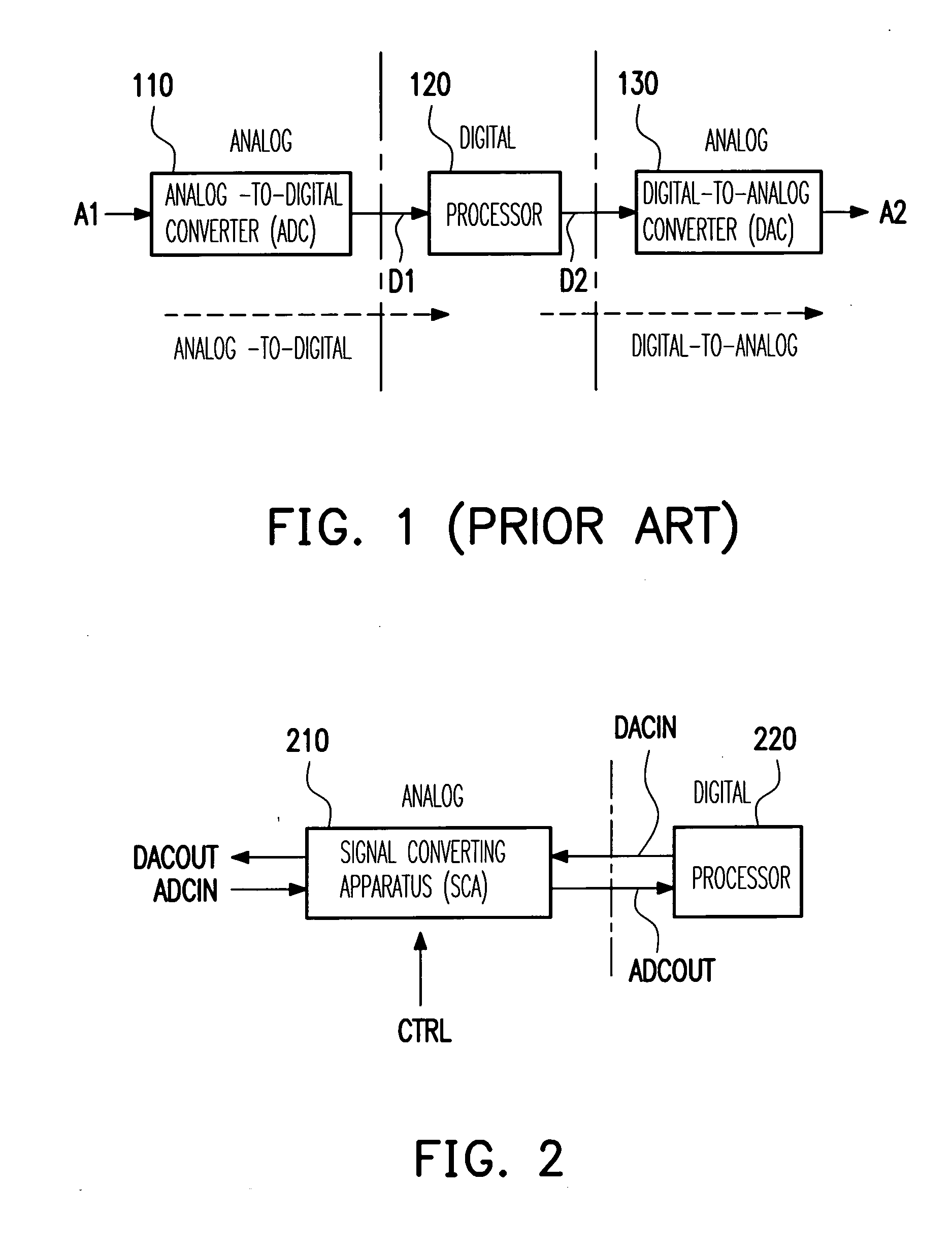
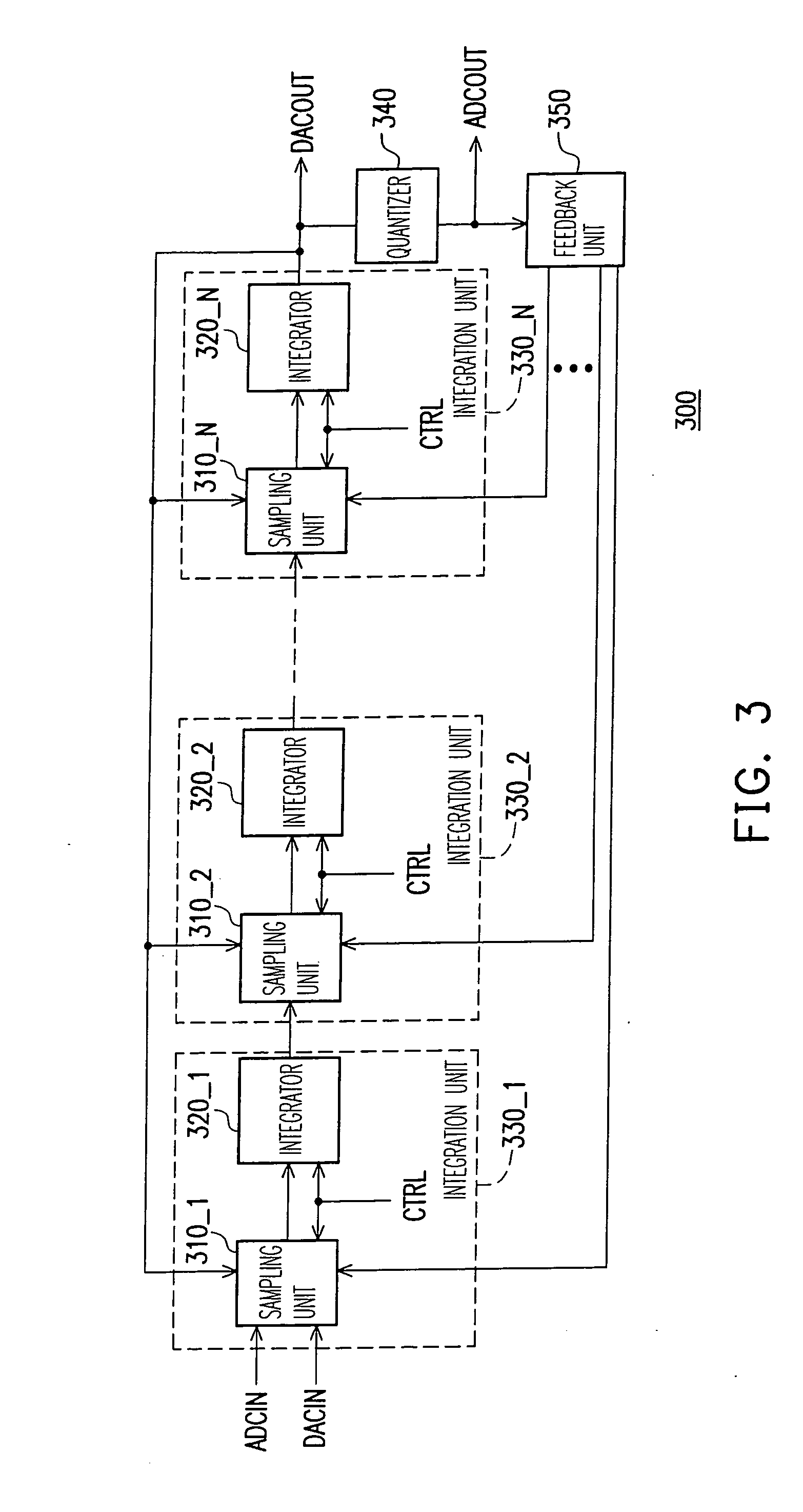
Signal converting apparatus for integrating analog-to-digital converter and digital-to-analog converter and integration unit
InactiveUS7138932B1Low production costReduce areaElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital down converterAudio power amplifier
A signal converting apparatus for integrating an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and an integration unit thereof are provided. The present invention integrates ADC and DAC, that do not operate simultaneously, into a signal converting apparatus (SCA), wherein a control signal decides whether an analog-to-digital mode or a digital-to-analog mode is selected. By sharing the operational amplifiers and other components in the SCA, the chip area and the cost are significantly reduced. In addition, in the integration unit, by switching a plurality of capacitor sets with various capacitances, the capacitance coefficients required for switching ADC and DAC are obtained.
Owner:ITE TECH INC
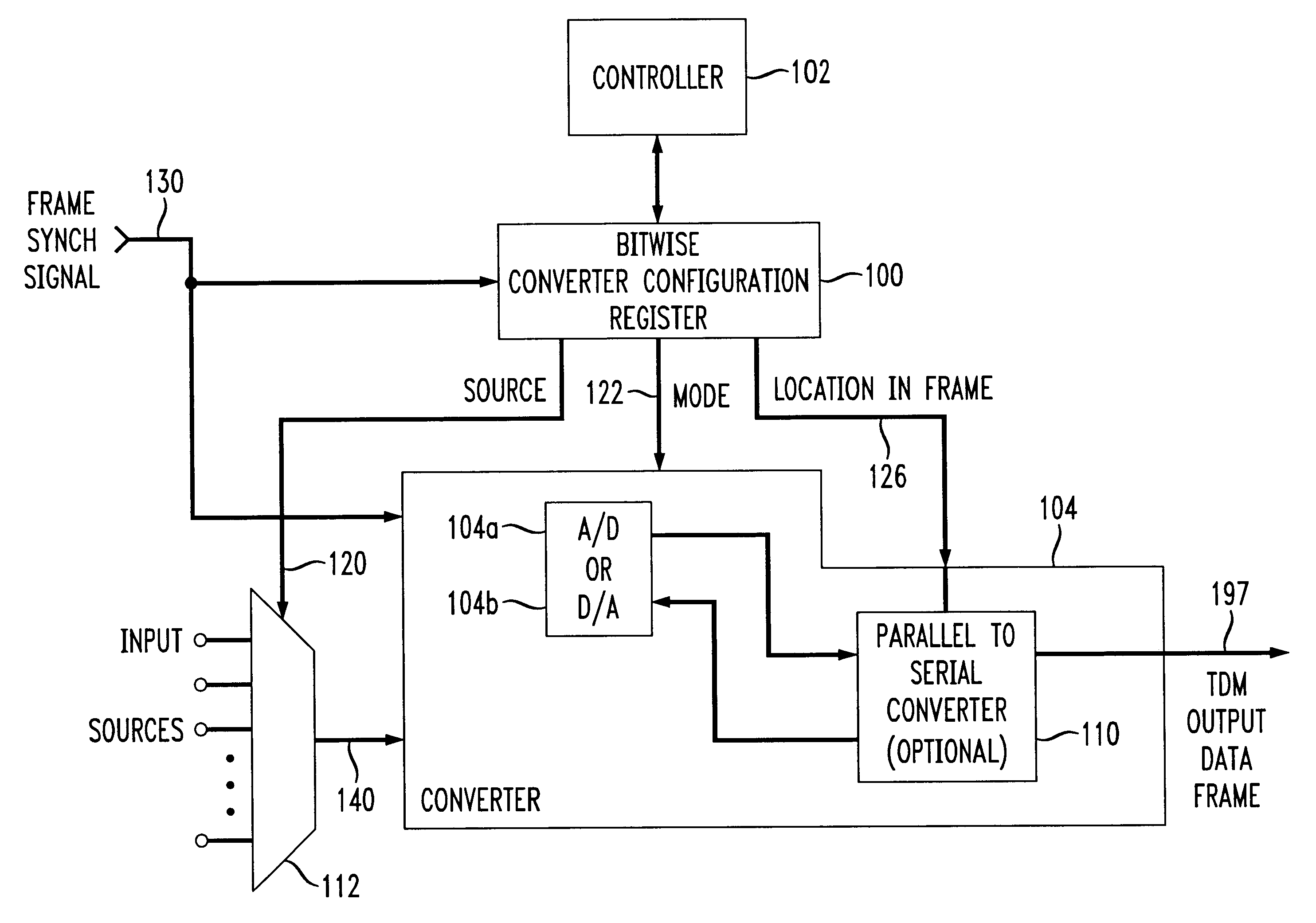
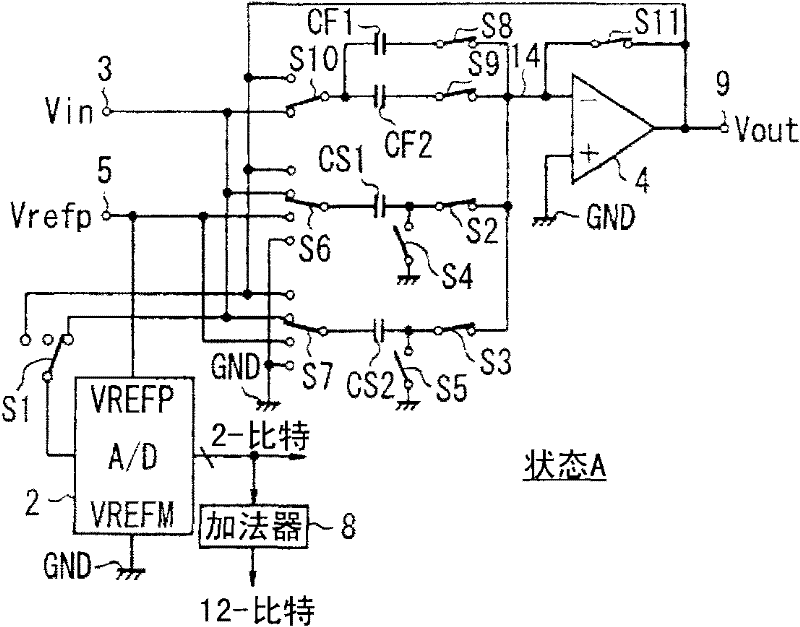
Configurable data converter
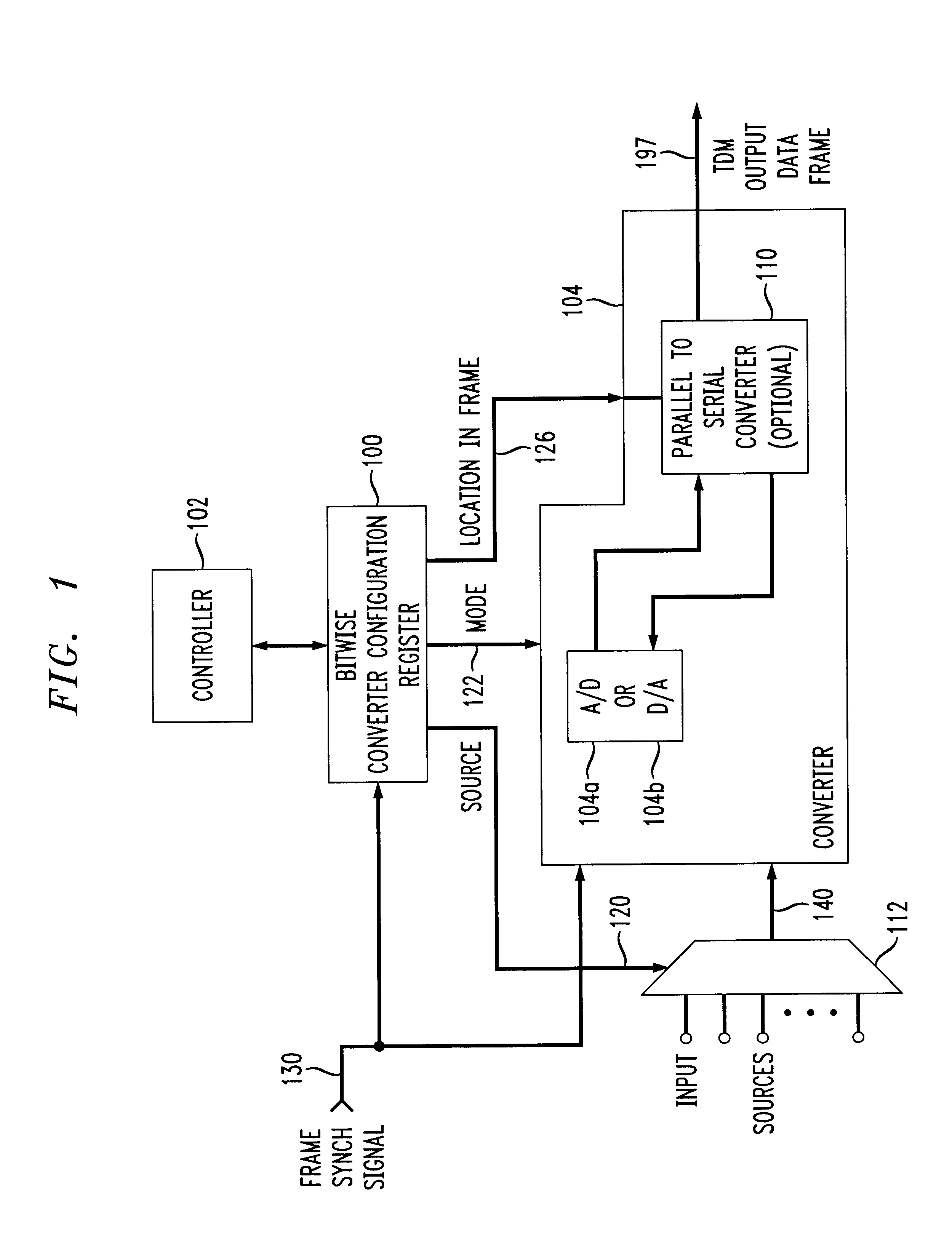
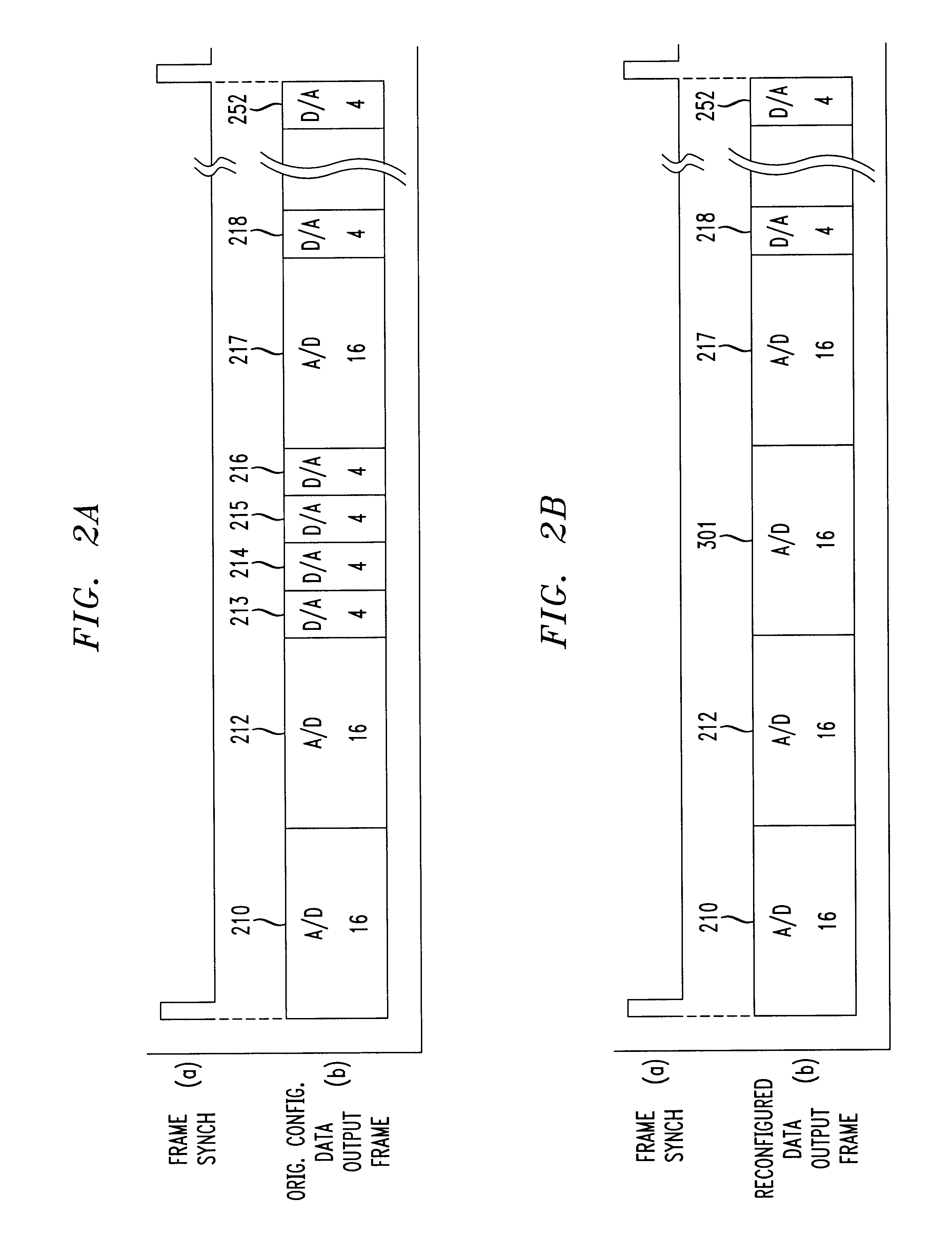
InactiveUS6255972B1Electric signal transmission systemsReversible analogue/digital convertorsData transformationProcessor register
A / D converter or as a D / A converter forms a data converter embedded in a digital circuit for reconfigurable use. Conversion parameters of the data converter are controlled on a bitwise basis from a bitwise converter configuration register. For instance, output locations (i.e., time slots) of the data converter are determined by a bitwise converter configuration register, as is the selection of a D / A conversion mode or A / D conversion mode of the data converter for that particular output location, and / or the output sample length are controlled by appropriate signals from the bitwise converter configuration register. The bitwise converter configuration register also preferably configures the input source to the data converter and / or to an interface, e.g., to a parallel-to-serial, serial-to-serial, or parallel-to-parallel interface device, on a bitwise basis, to provide flexibility both in the source of the channels as well as the output location of particular channels in the data frame.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Arithmetic code decoding method and apparatus
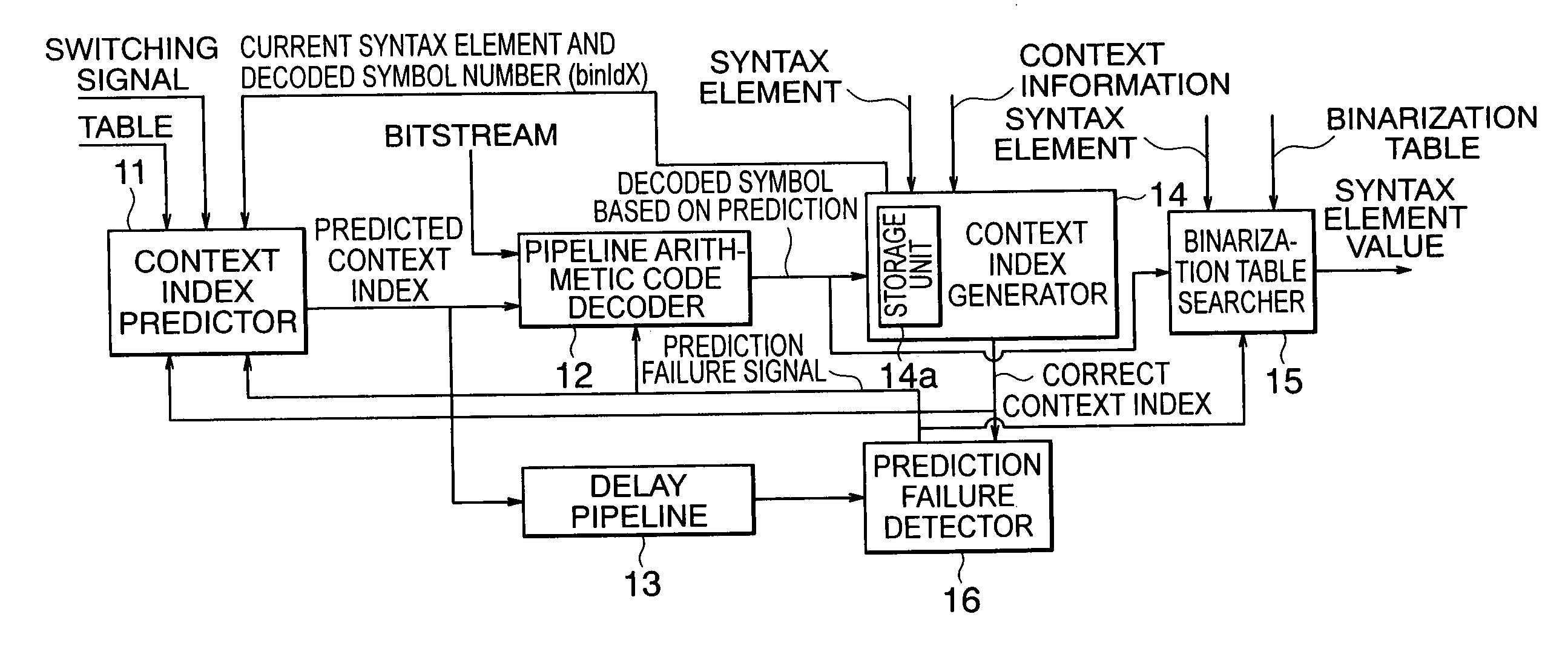
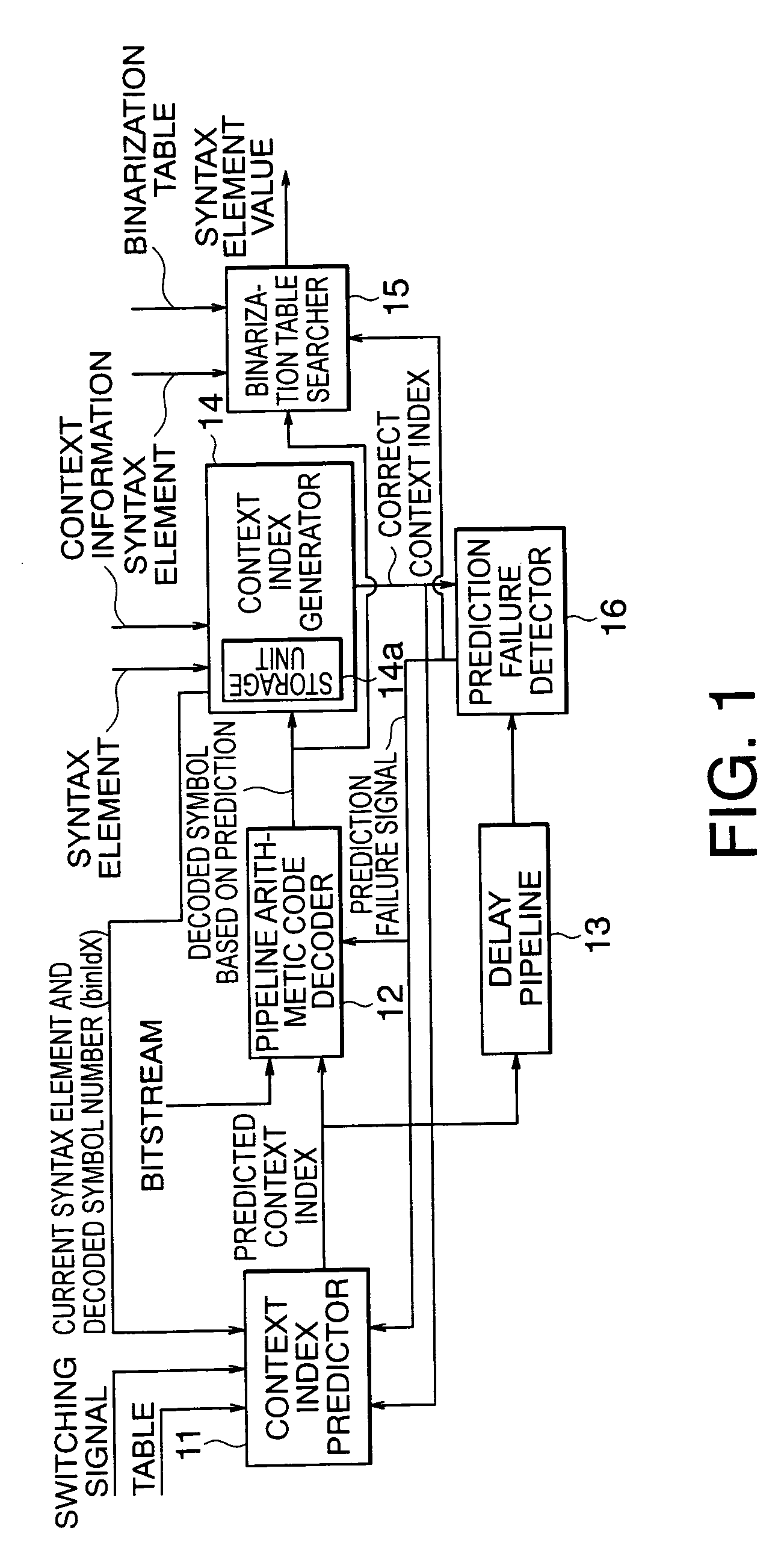
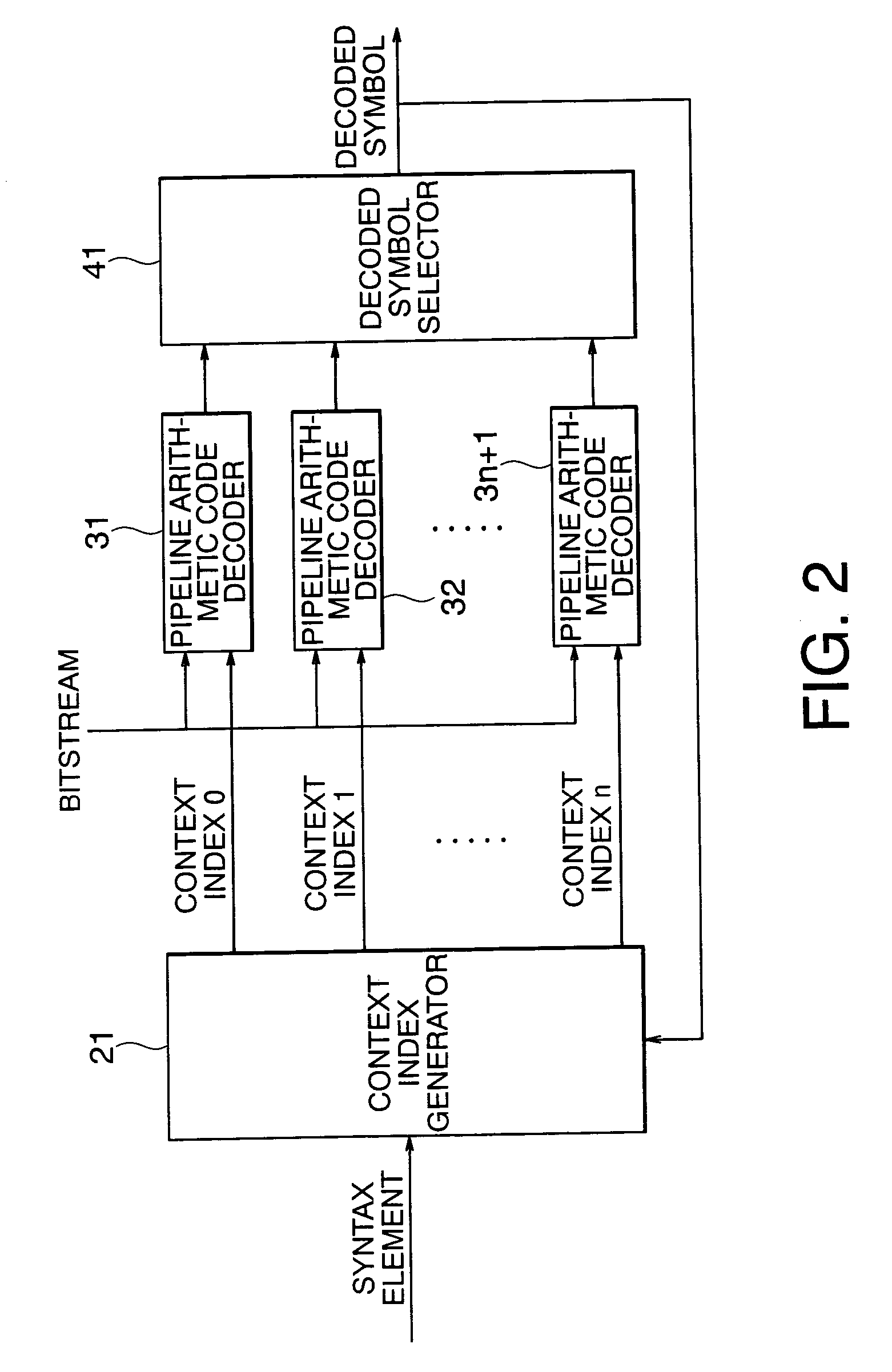
InactiveUS20060022848A1Output valueElectric signal transmission systemsReversible analogue/digital convertorsTheoretical computer scienceCoding decoding
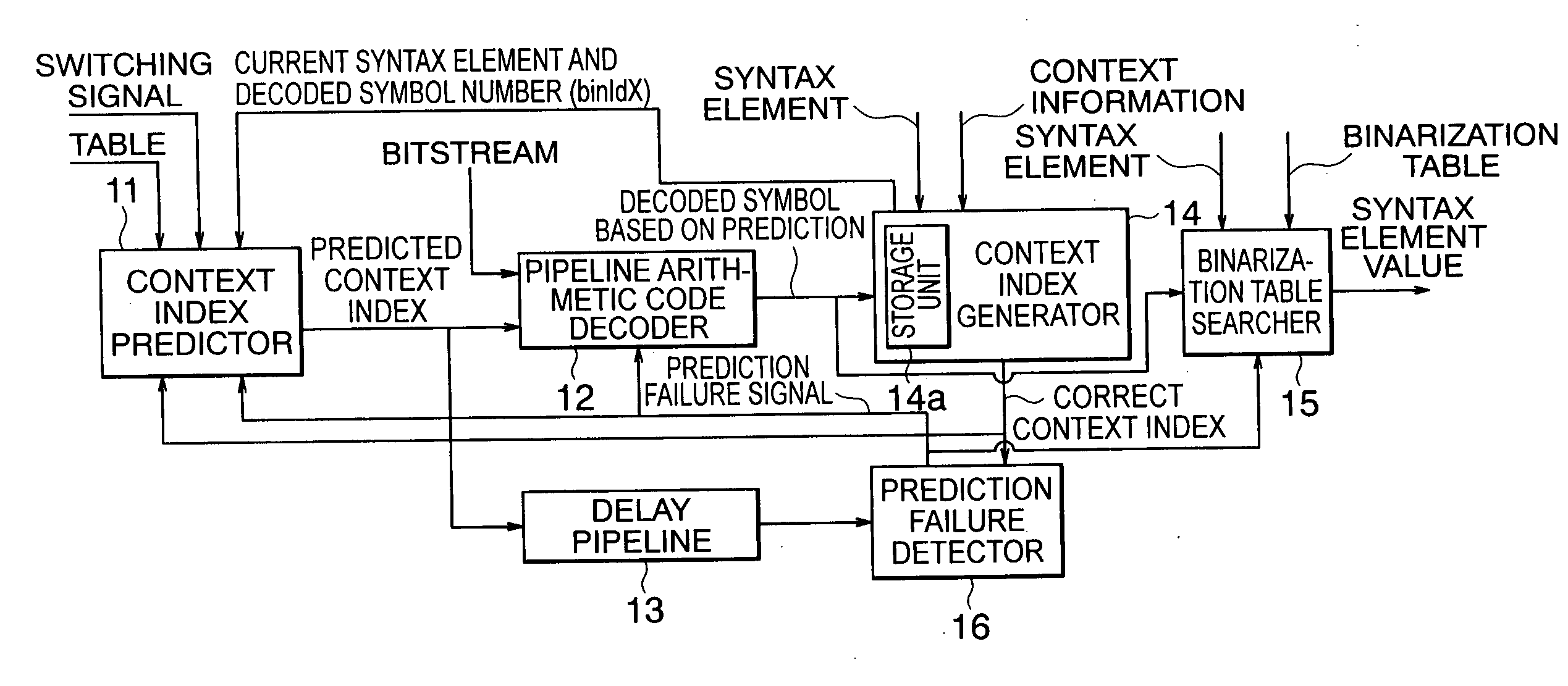
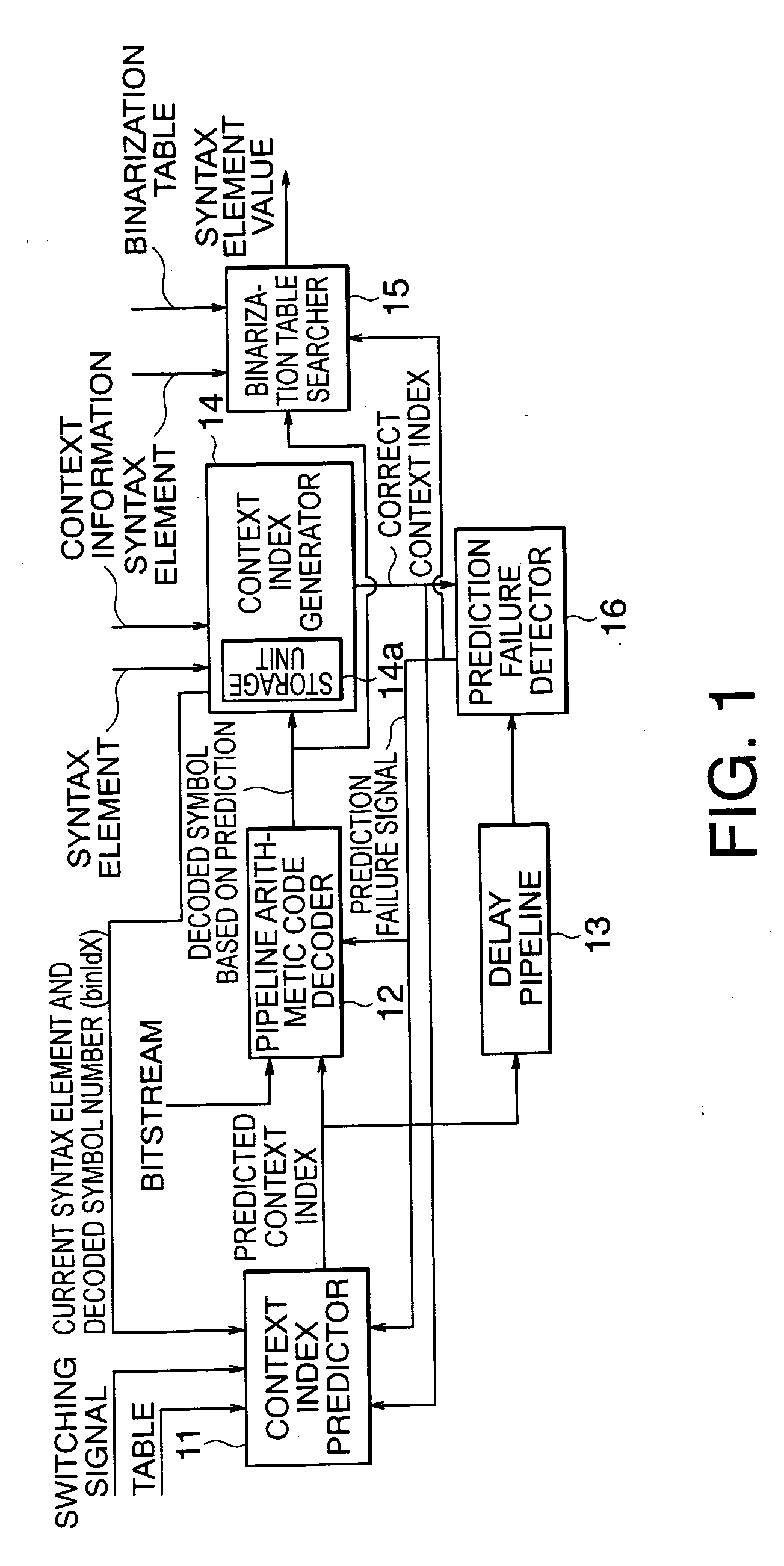
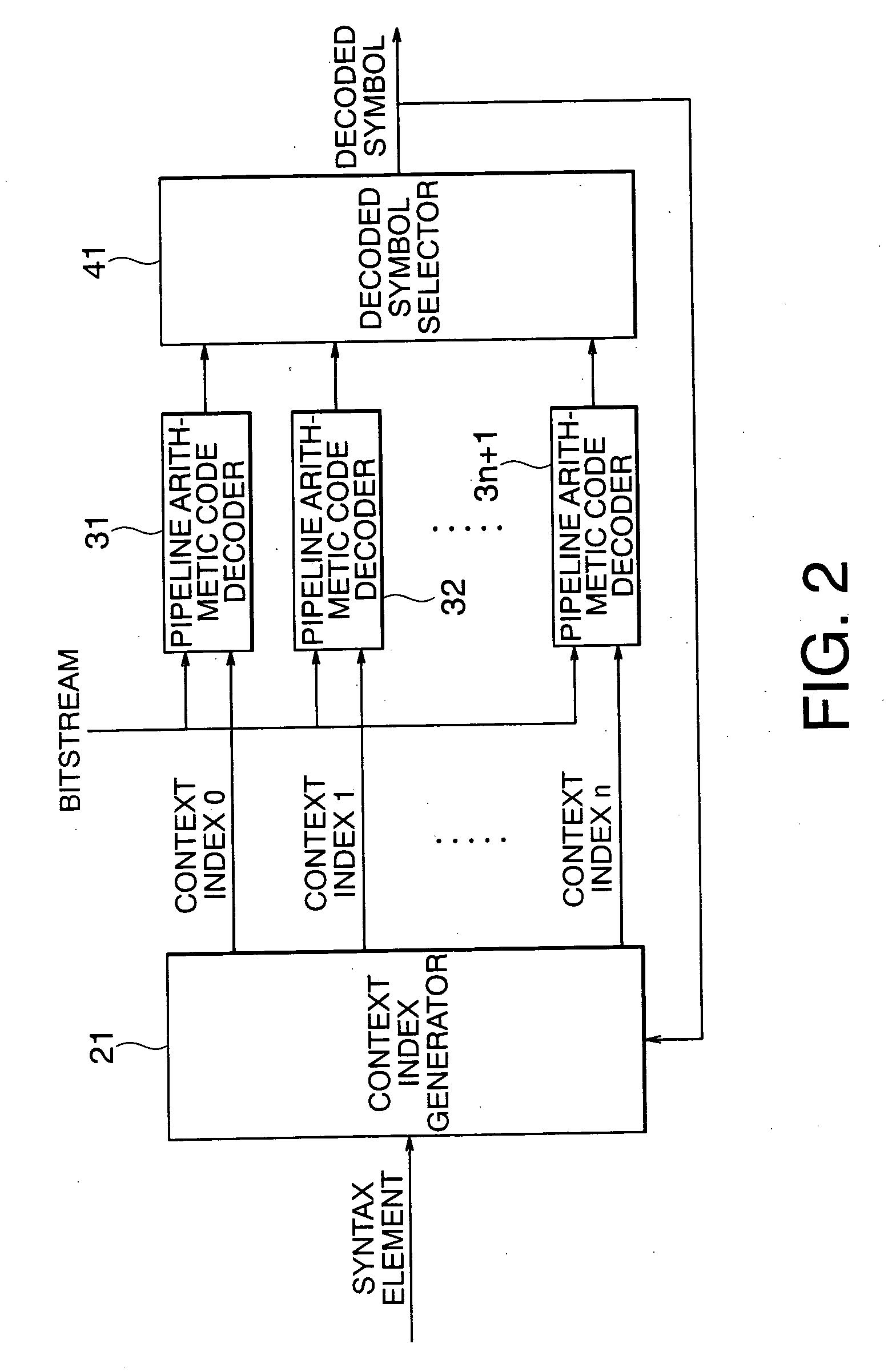
According to the present invention, there is provided a arithmetic code decoding apparatus for generating a decoded symbol by decoding an input bitstream generated by encoding information, and outputting a value of a syntax element corresponding to the decoded symbol, comprising: a context index predictor which receives the syntax element indicating a type of the information included in the bitstream, predicts a context index required to decode the bitstream, and outputs the predicted context index; a pipeline arithmetic code decoder which has a plurality of stages of pipelines, receives the predicted context index and the bitstream, executes a decoding process of the bitstream using the predicted context index, and generates and outputs a decoded symbol based on prediction; a context index generator which includes a storage unit that receives and holds previous decoded symbols output before a decoded symbol at the present timing of the decoded symbols output from said pipeline arithmetic code decoder, receives the previous decoded symbols, the syntax element, and context information of the bitstream, and generates a correct context index required for decoding at the present timing; a binarization table searcher which receives the syntax element, externally acquires a predetermined binarization table corresponding to a type of the syntax element, receives the decoded symbol at the present timing output from said pipeline arithmetic code decoder, searches the binarization table using the decoded symbol for a value of the syntax element, and outputs the value of the syntax element; and a prediction failure detector which receives the correct context index output from said context index generator and the predicted context index output from said context index predictor, compares the two context indices, and outputs a prediction failure signal when the two context indices do not match, wherein when the prediction failure signal is output, said pipeline arithmetic code decoder flashes the decoding process executed using the predicted context index, re-executes a decoding process using the correct context index, and outputs a correct decoded symbol.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for reducing digital to analog conversion (DAC) bits in frequency division multiple access (FDMA) system
InactiveUS20090154442A1Reduce in quantityReduce consumptionResonant long antennasAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
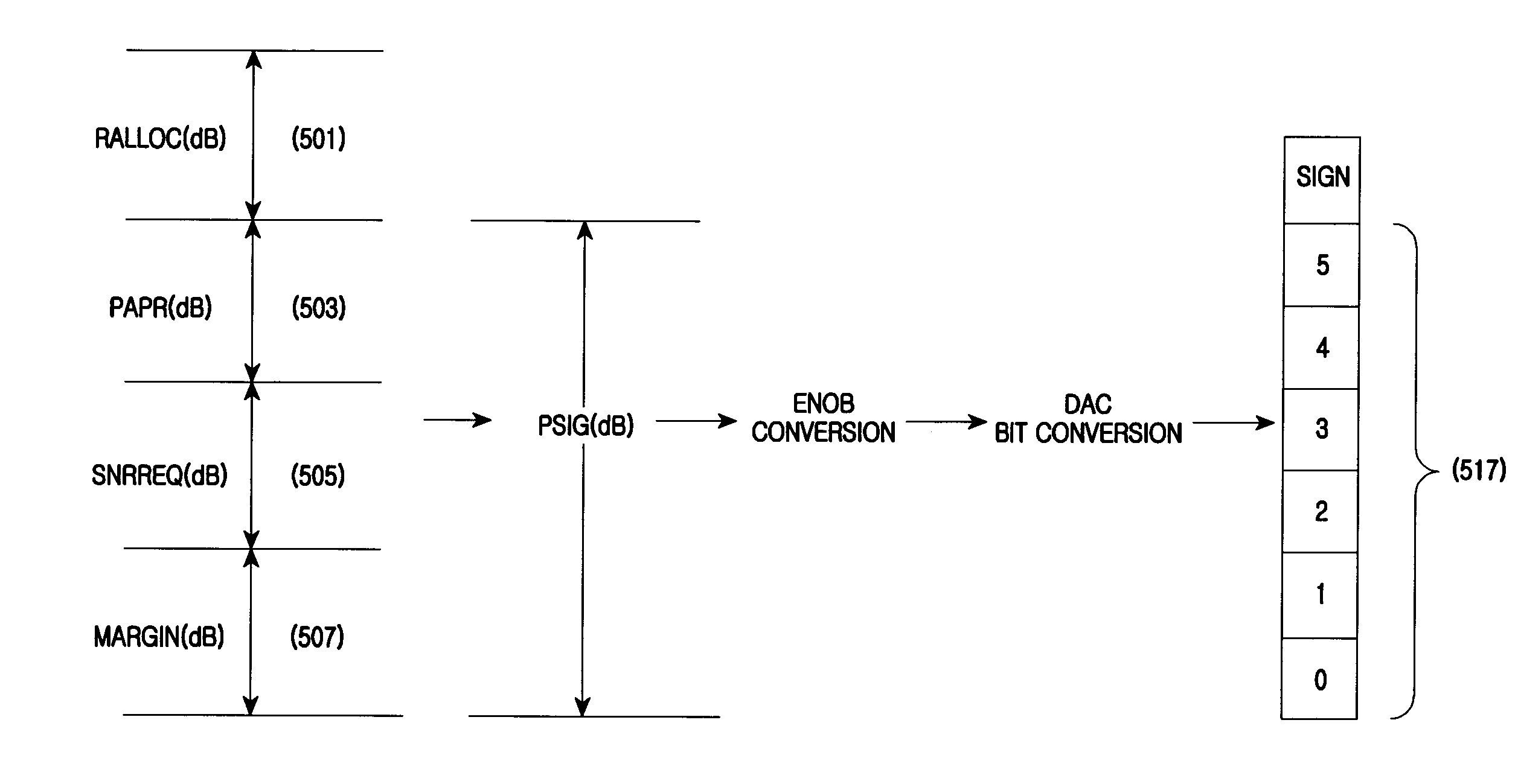
A method and an apparatus for reducing Digital-to-Analog Conversion (DAC) bits at a transmitter of a Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) system reduces a number of the bits for conversion so as to save power and reduce the cost of operation. The method can include generating a digital signal gain control value and an analog signal gain control value using subcarrier allocation information, a required Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR), and a Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR); controlling a gain of a signal input to a digital-to-analog converter using the digital signal gain control value; converting a digital signal of the controlled gain to an analog signal using the digital-to-analog converter; and restoring an original signal by controlling a gain of a signal output from the digital-to-analog converter using the analog signal gain control value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
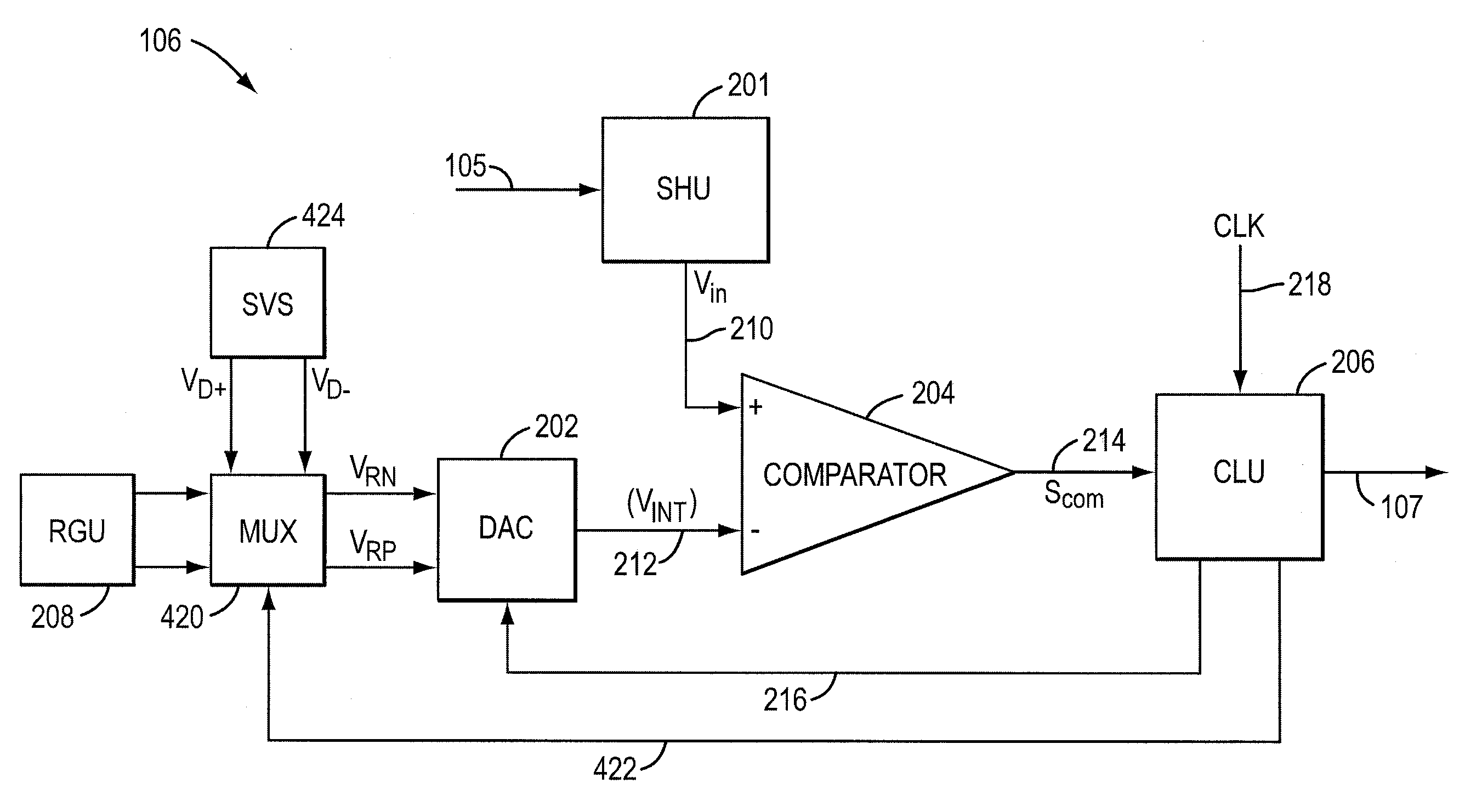
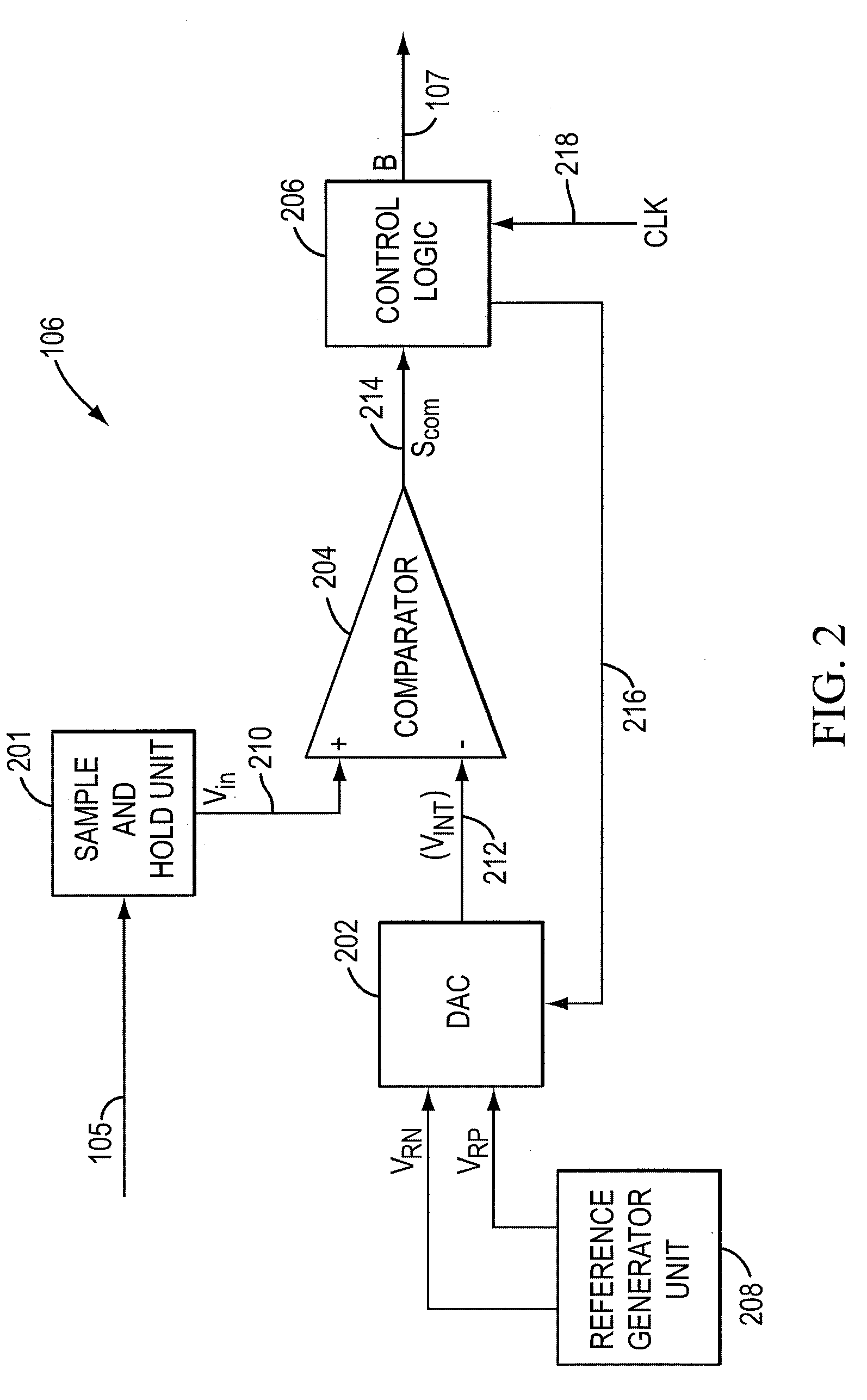
Method and apparatus to improve reference voltage accuracy
InactiveUS20100309035A1Electric signal transmission systemsReversible analogue/digital convertorsVoltage reference
A method and apparatus for converting an analog input voltage signal to a discrete signal, the method including generating at least one reference voltage and at least one secondary voltage. The method further including selecting at least one voltage between the at least one reference voltage and the at least one secondary voltage and generating at least one intermediate voltage based on the at least one voltage and at least one digital code. The at least one intermediate voltage and the analog input voltage further being used to generate at least one comparison signal and the discrete signal being generated based on the at least one comparison signal and the at least one digital code.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
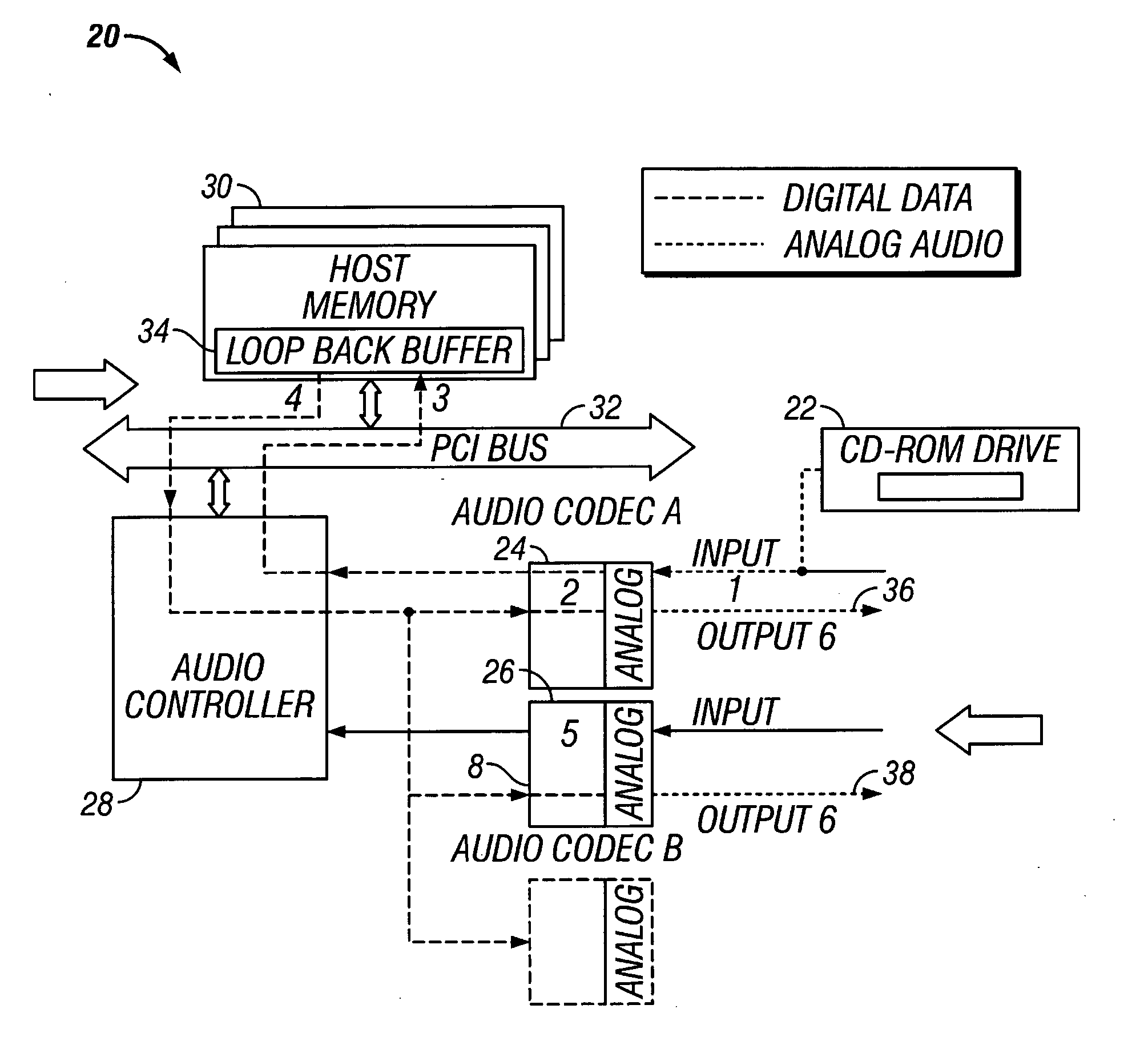
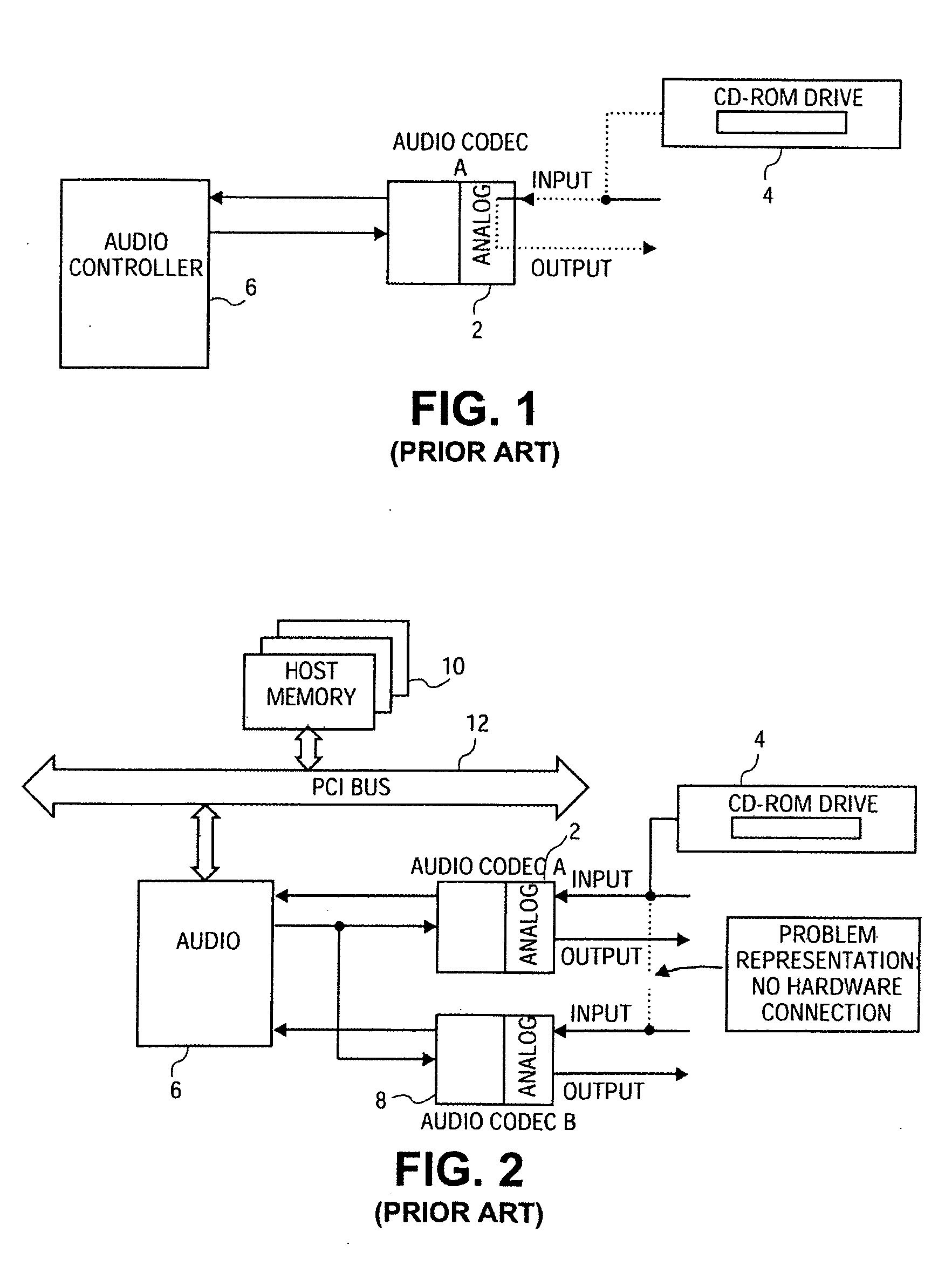
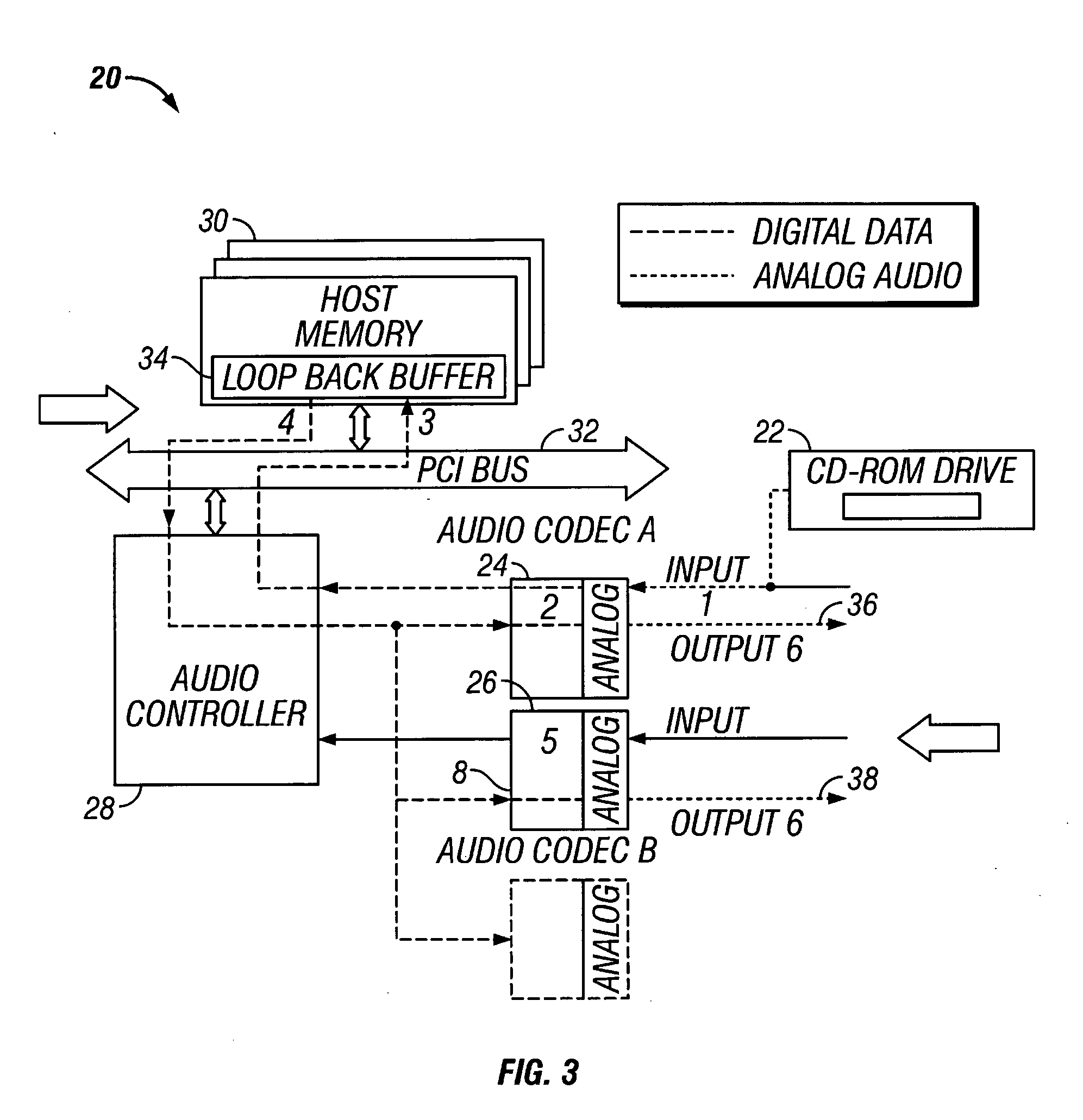
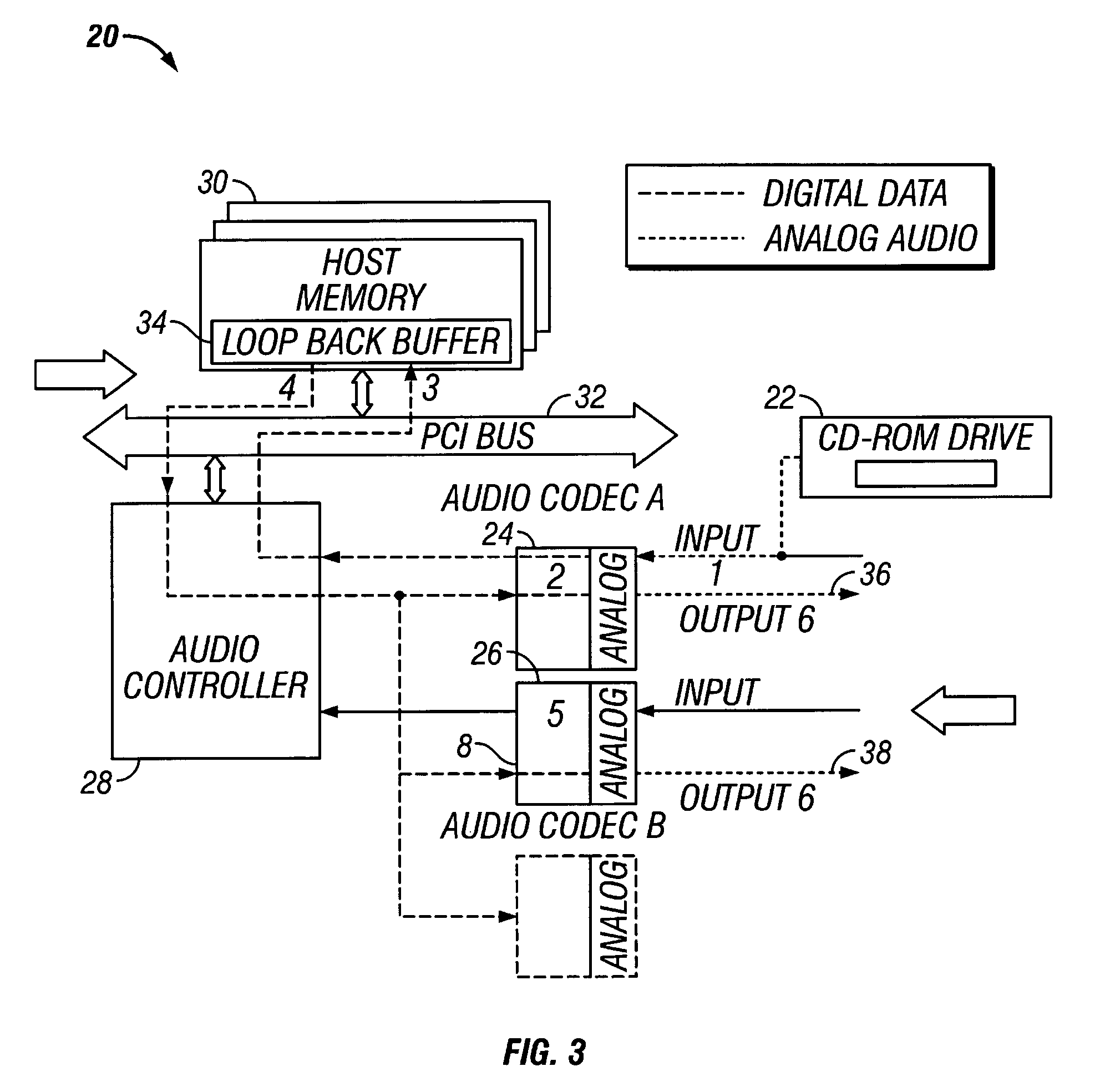
Method and apparatus for playing analog audio to multiple codec outputs
InactiveUS20060010267A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDocking stationRecord status
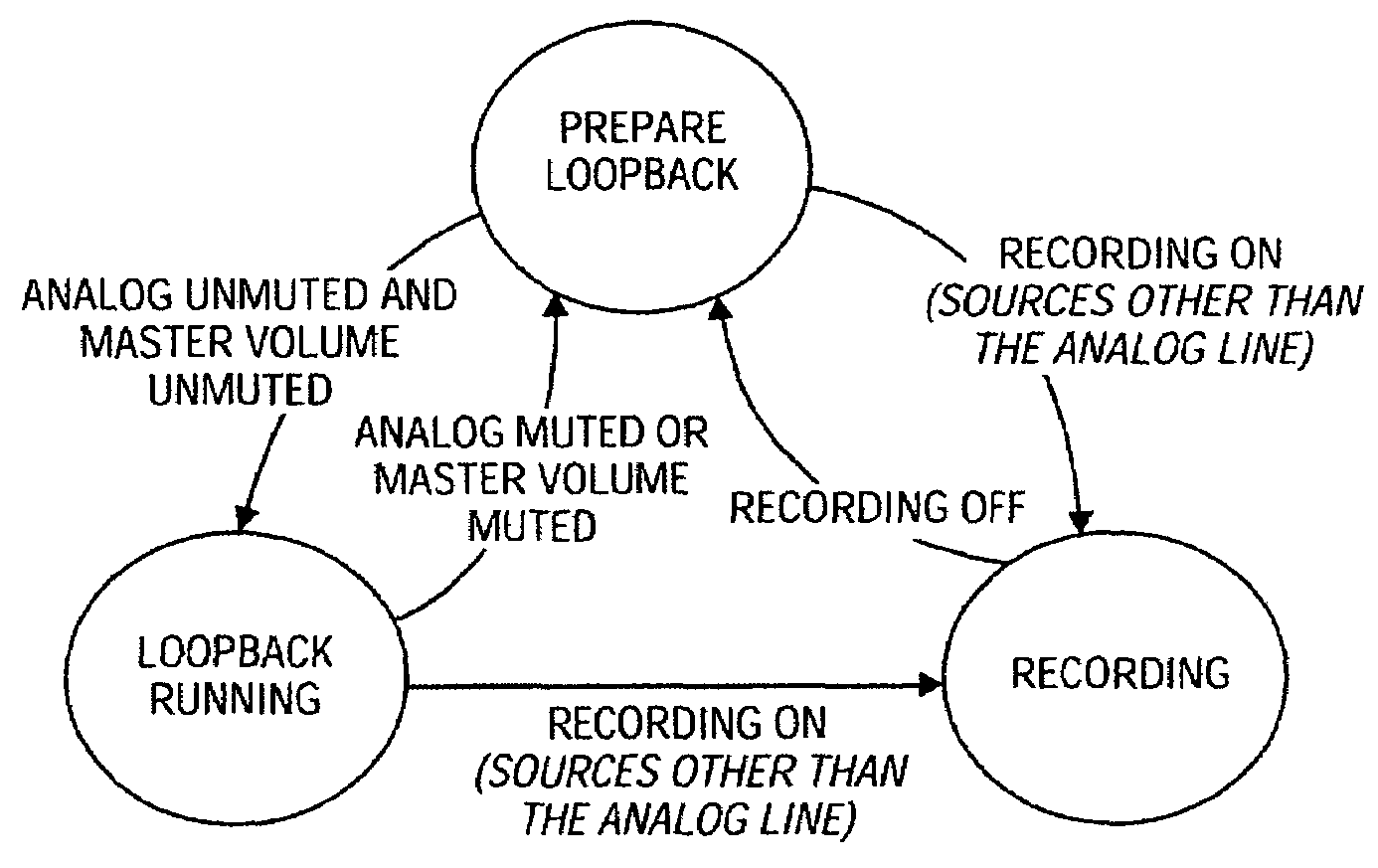
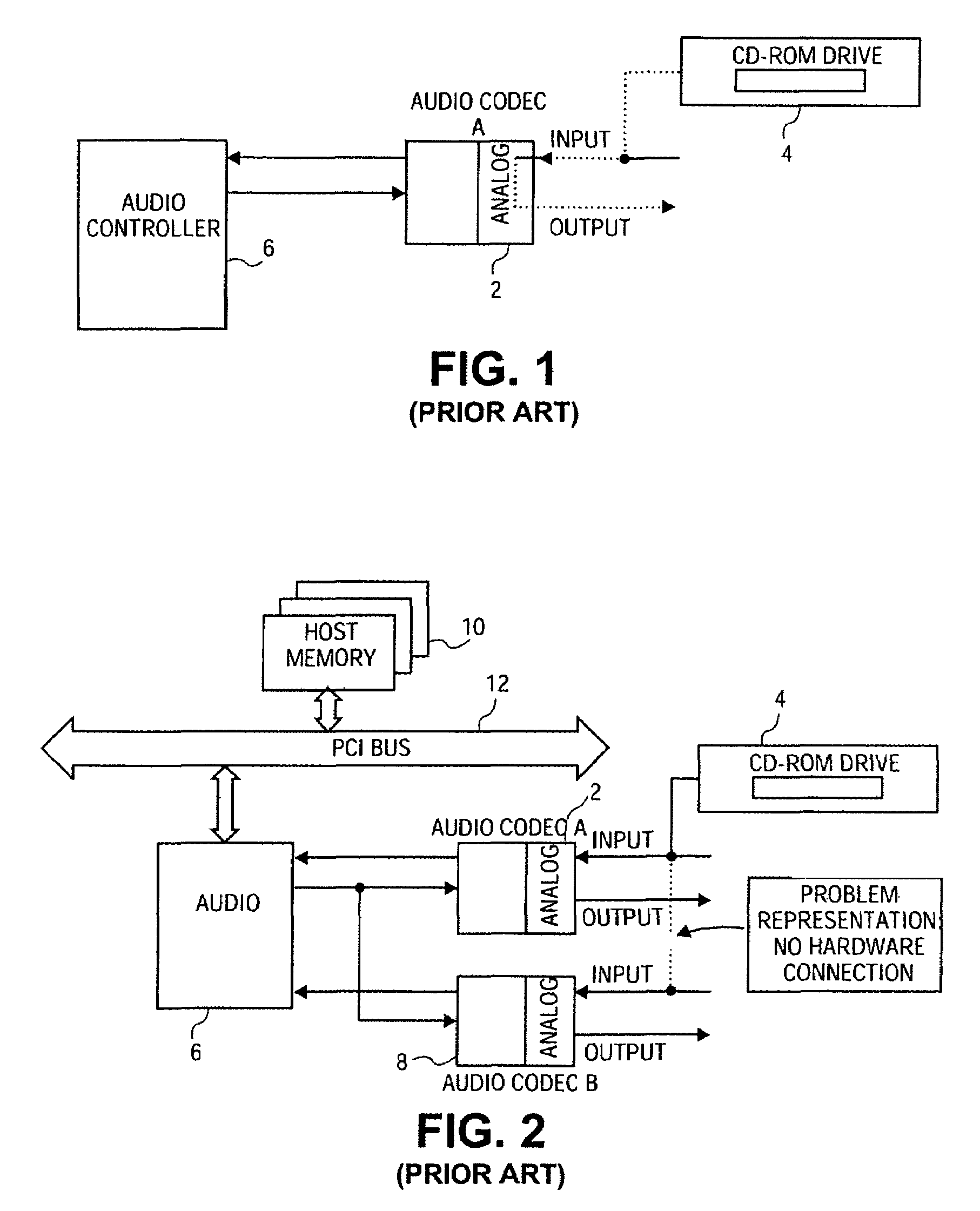
A method and apparatus for playing analog audio in an electronic audio system having multiple audio codecs, only one of which has a direct hardware connection to the analog audio source (e.g., a CD-ROM drive). First analog audio data is received from the analog audio source at a first audio codec, and is converted to digital audio data using the first audio codec. The digital audio data is stored in a memory device, and read back from the memory device, and transferred to a second audio codec. The digital audio data is then converted to second analog audio data using the second audio codec, and output from the second audio codec. An audio controller may be used to store the digital audio data in a loopback buffer within the memory device, and to read the digital audio data from the loopback buffer. The audio controller can also mix the digital audio data with other digital audio data from the memory device. The method can be applied to a system having more than two codecs, i.e., the digital audio data may additionally be transferred to a third audio codec where the digital audio data is converted to third analog audio data, and the third analog audio data is output from the third audio codec. In a particularly advantageous implementation, the first audio codec is part of a portable computing system (e.g., notebook computer), and the second codec is integrated into a docking station which is adapted to operably receive the portable computing system. The audio controller may further be programmed to operate in at least three different states including a prepare loopback state, a loopback running state, and a recording state.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
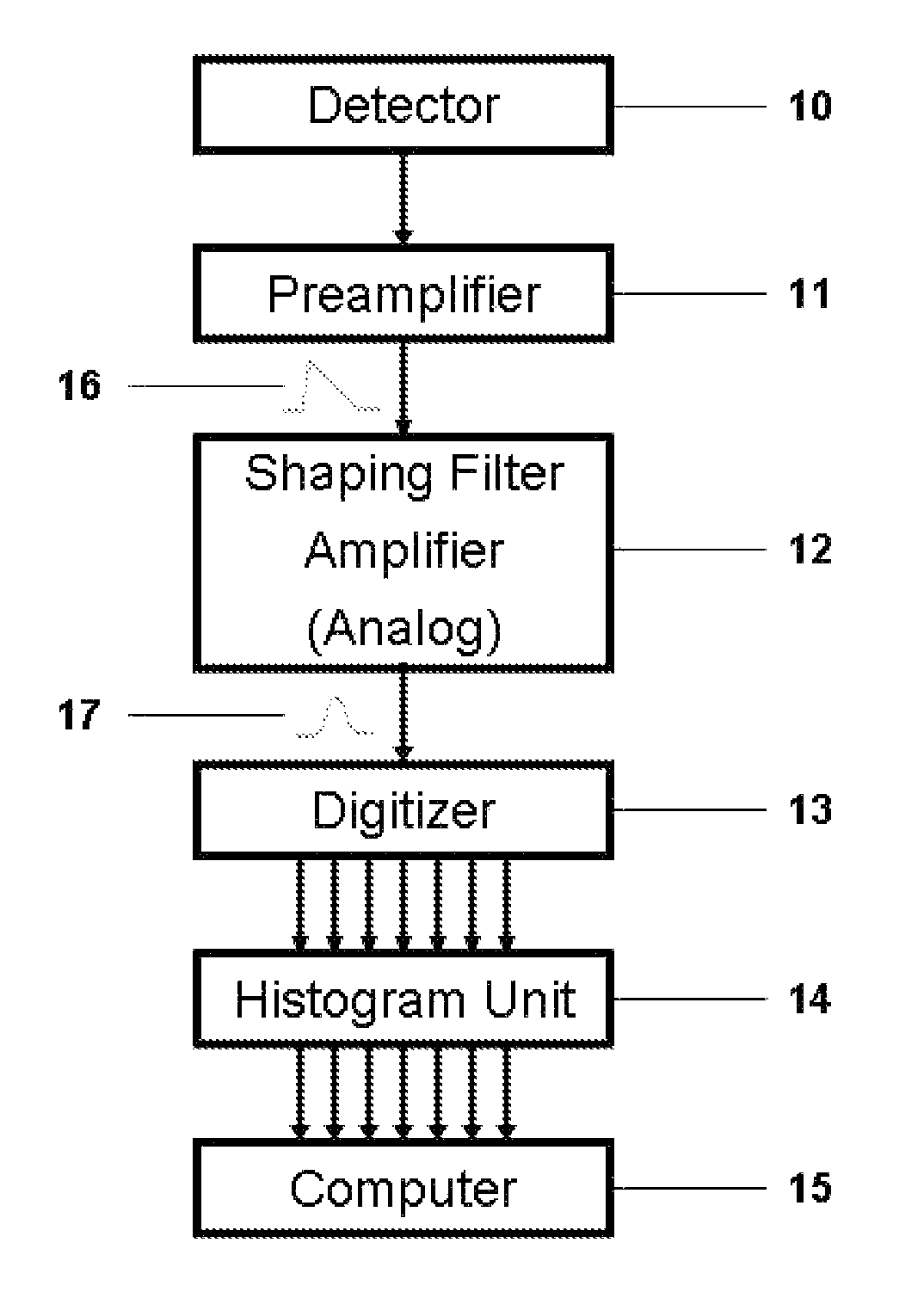
Analog interface for digital instrumentation
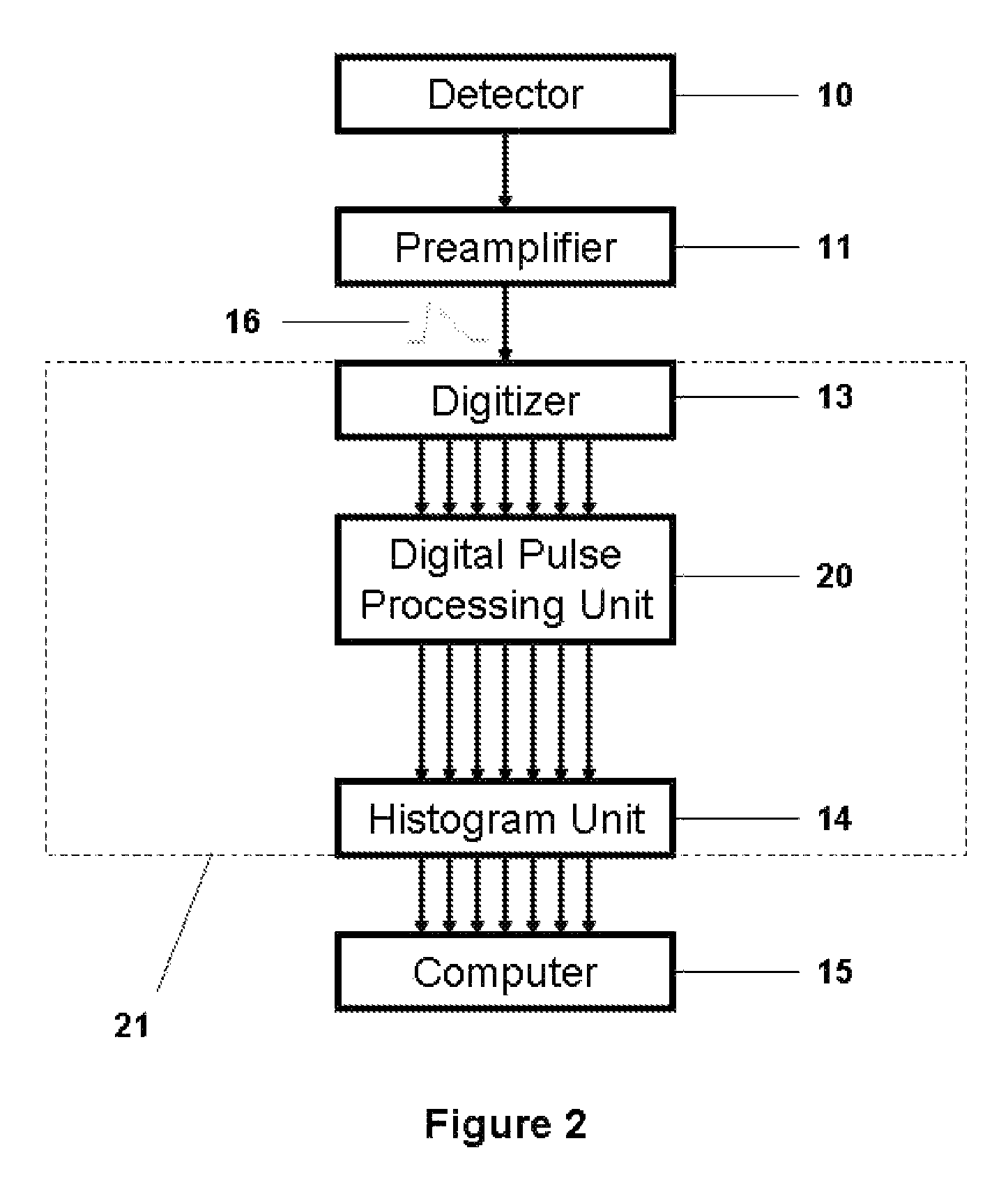
InactiveUS7498964B1Electric signal transmission systemsParticle separator tubesDigital signal processingComputer compatibility
Nuclear spectroscopy systems have improved over the course of time especially with the advent of digital pulse processing. One disadvantage of digital processing, however, is that it has eliminated the older, universally compatible interface standard of analog signals. Digital component interfaces are often defined by computer software, protected by copyright and unique to a single manufacturer. Consequently, all components of an entire spectroscopy system must be from a single manufacturer. This not only dictates system wide component replacement, but also impedes optimization that would otherwise occur were component compatibility the rule rather than the exception. The present innovation describes a method and apparatus to relieve the present incompatibility between digital components of a nuclear spectroscopy system that are supplied by more than one manufacturer.
Owner:BEYERLE ALBERT G
Pipeline arithmetic code decoding method and apparatus using context index predictor
InactiveUS7088272B2Electric signal transmission systemsReversible analogue/digital convertorsCoding decodingSyntax
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Gain preset method of collecting double-channel analog-digital joint mode variable gain data
InactiveCN101895267AImprove dynamic rangeTaking into account the sampling accuracyGain controlReversible analogue/digital convertorsAudio power amplifierData acquisition
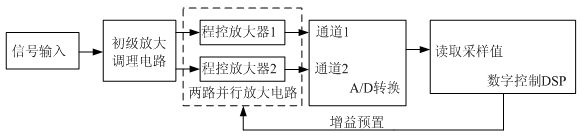
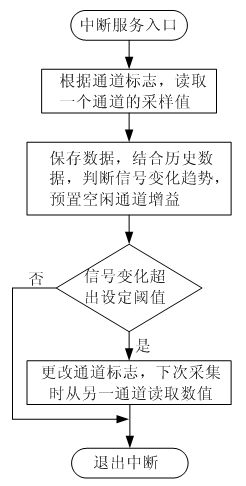
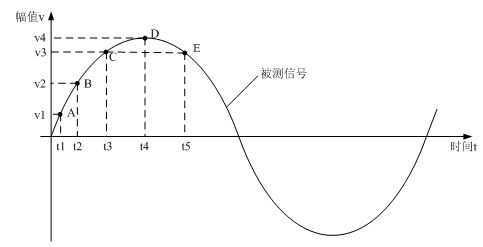
The invention relates to a gain preset method of collecting double-channel analog-digital joint mode variable gain data. The method comprises the following steps: measured signal is amplified and conditioned preliminarily by a primary amplification conditioning circuit and then is sent to two parallel programmable amplifiers to amplify and send to the corresponding channels of A / D converters, a digital control module reads and stores the A / D conversion value of one channel, and a digital signal processor (DSP) compares the collected data with the history data, predicts the change trend of signal and presets the gain of the other idle programmable amplifier so that when the change of signal exceeds a preset threshold, the sampling value of the other channel with the preset gain is adopted.Therefore, the defect that the circuit establishment time required by gain is changed temporarily in the traditional collection method, thus effective information can not lose, the measured signal can be in the optimum measuring range and then the data collection requirements of high speed and high accuracy can be satisfied.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Interface adaptation method and circuit used for airborne collision avoidance system
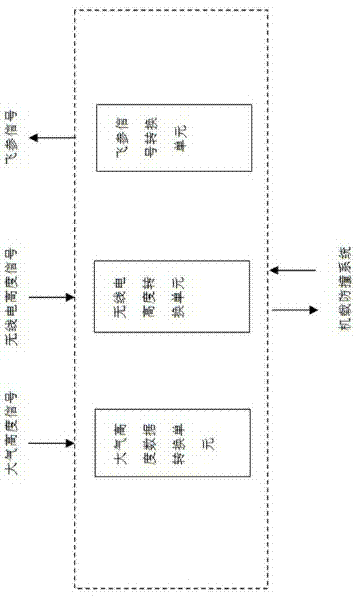
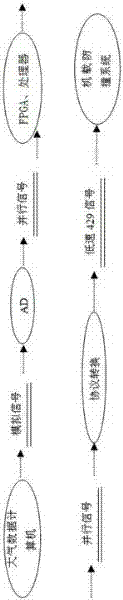
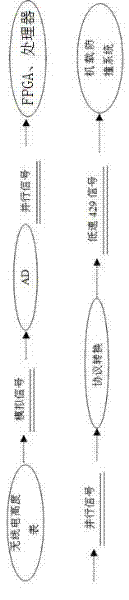
ActiveCN102436765AFix compatibility issuesReversible analogue/digital convertorsAircraft traffic controlCode moduleAtmospheric air
The invention discloses an interface adaptation method and a circuit used for an airborne collision avoidance system, relates to an air collision avoidance technology, and aims to provide a data conversion method and a circuit based on an aerialcarrier platform. The technical note of the circuit provided by the invention is as follows: the circuit comprises an atmosphere height acquiring and coding module, a radio altitude acquiring and coding module, and a fly parameter data conversion module, wherein the atmosphere height acquiring and coding module is used for acquiring current atmosphere height value, and the atmosphere height value is changed into an ARINC 429 data format so as to be finally output to the airborne collision avoidance system; the radio altitude acquiring and coding module is used for acquiring current radio altitude value, and the radio altitude value is changed into the ARINC429 data format so as to be finally output to the airborne collision avoidance system; and the fly parameter data conversion module is used for collecting alarm information generated by the airborne collision avoidance system, the alarm information is subjected to digital-analog conversion so as to be finally output to an airplane reference record instrument. By using the method and the circuit provided by the invention, a compatible problem of the existing airplane and digital airborne collision avoidance system following a Russian-made protocol can be solved.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
Method and apparatus for playing analog audio to multiple codec outputs
InactiveUS7188196B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio frequencyComputer science
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
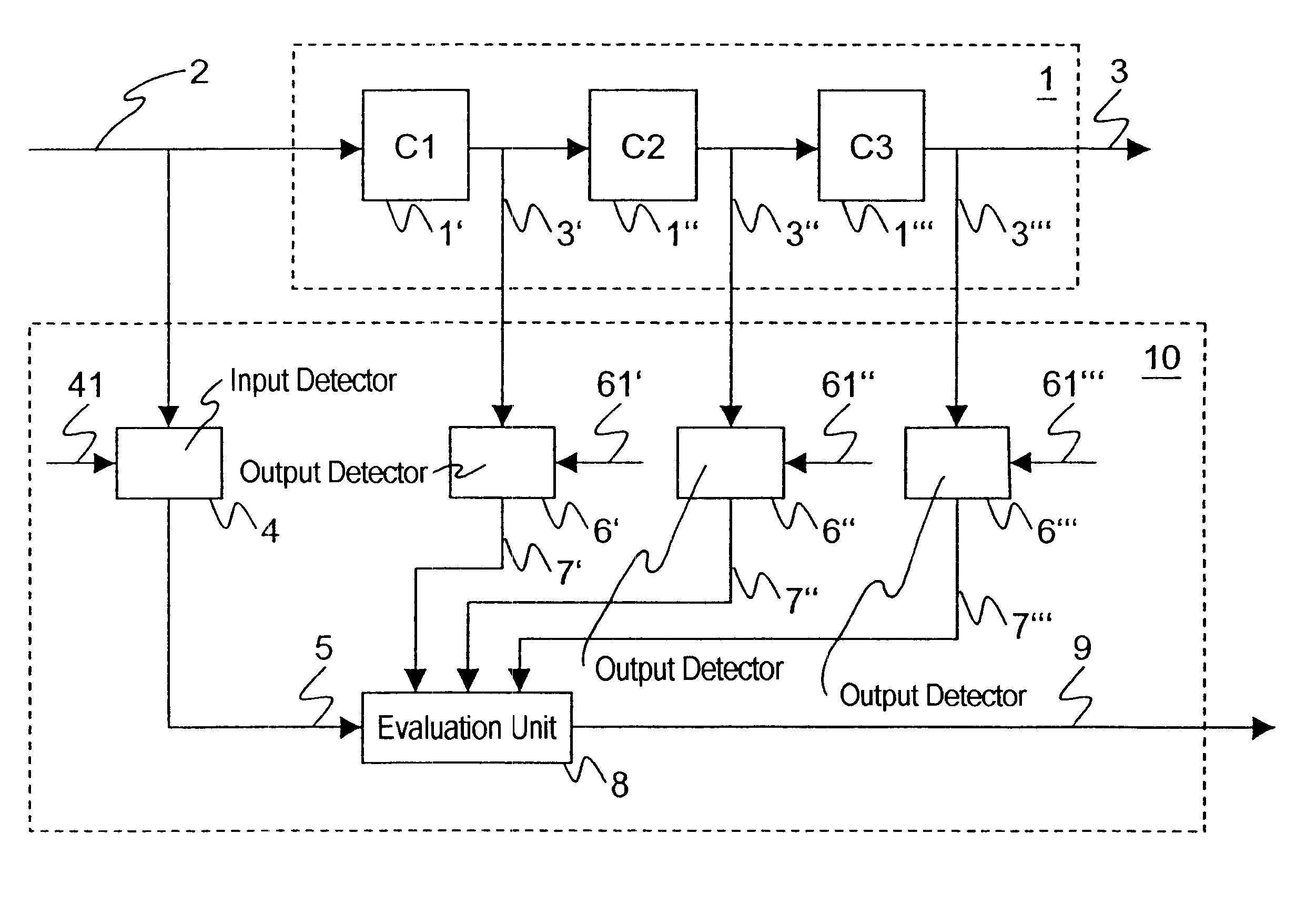
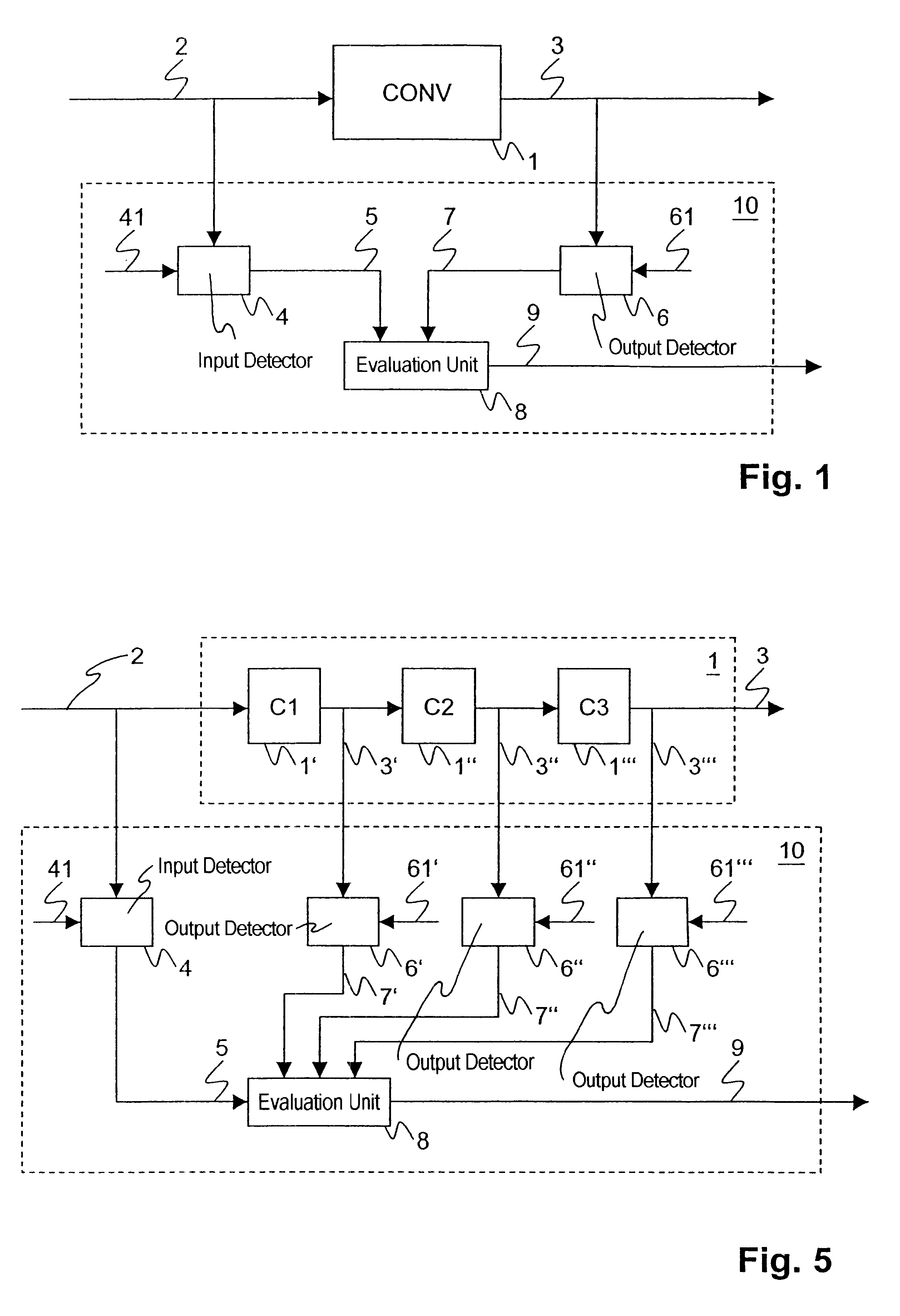
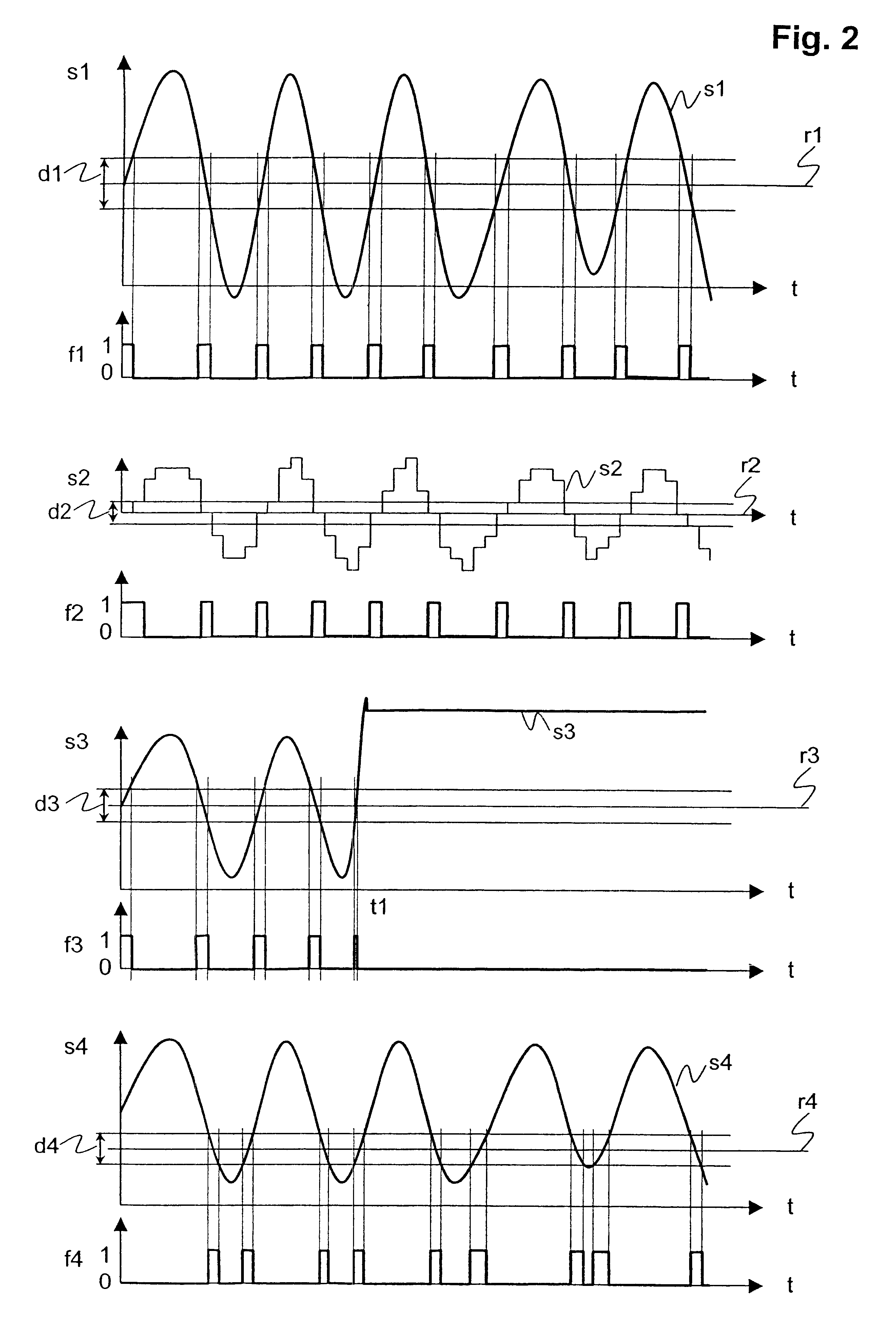
Operational monitoring for a converter
InactiveUS6577987B1Easy to produceElectric signal transmission systemsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringSwitchgear
Monitoring a converter (1) includes detecting whether a value of an input variable (2) for the converter (1) assumes a first prescribed input reference value (41) and checking whether an output variable (3) from the converter (1) likewise assumes a corresponding, second prescribed output reference value (61). This means that the operation of the converter is tested only at occasional instants, specifically only using individual, prescribed values. The fact that only prescribed values (41, 61) are compared with instantaneous values of the input and output variables (2, 3) means that the invention can be implemented using very simple means. The method is particularly suitable for monitoring the operation of a converter (1) in a control or protective device for an electrical switchgear assembly. In this context, when a malfunction in the converter (1) is detected, all protective functions which are dependent on the converter (1) are preferably turned off.
Owner:LIBERTY PATENTS LLC +1
Determination of environmental effects on electrical load devices
ActiveUS10433046B2Ear treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationEnvironmental noiseEnvironmental effect
Owner:ESS TECHNOLOGY
a/d converter and signal processing unit
InactiveCN102291137AWith D/A conversion functionChange resolutionReversible analogue/digital convertorsBuck converterĆuk converter
An A / D converter device is provided, which has a D / A conversion function and changes a resolution of A / D conversion and D / A conversion. The A / D converter device is configured to selectively execute an A / D conversion operation and a D / A conversion operation, by the operation of a control circuit controlling switching of switches according to an ADC / DAC function switching signal supplied from an external side. The A / D conversion operation performs A / D conversion of an input signal voltage inputted via a signal input terminal from an external side and outputs an A / D conversion value of 12 bits. The D / A conversion operation outputs, via a signal output terminal, an analog voltage produced by performing D / A conversion of a digital value supplied from the external side.
Owner:DENSO CORP
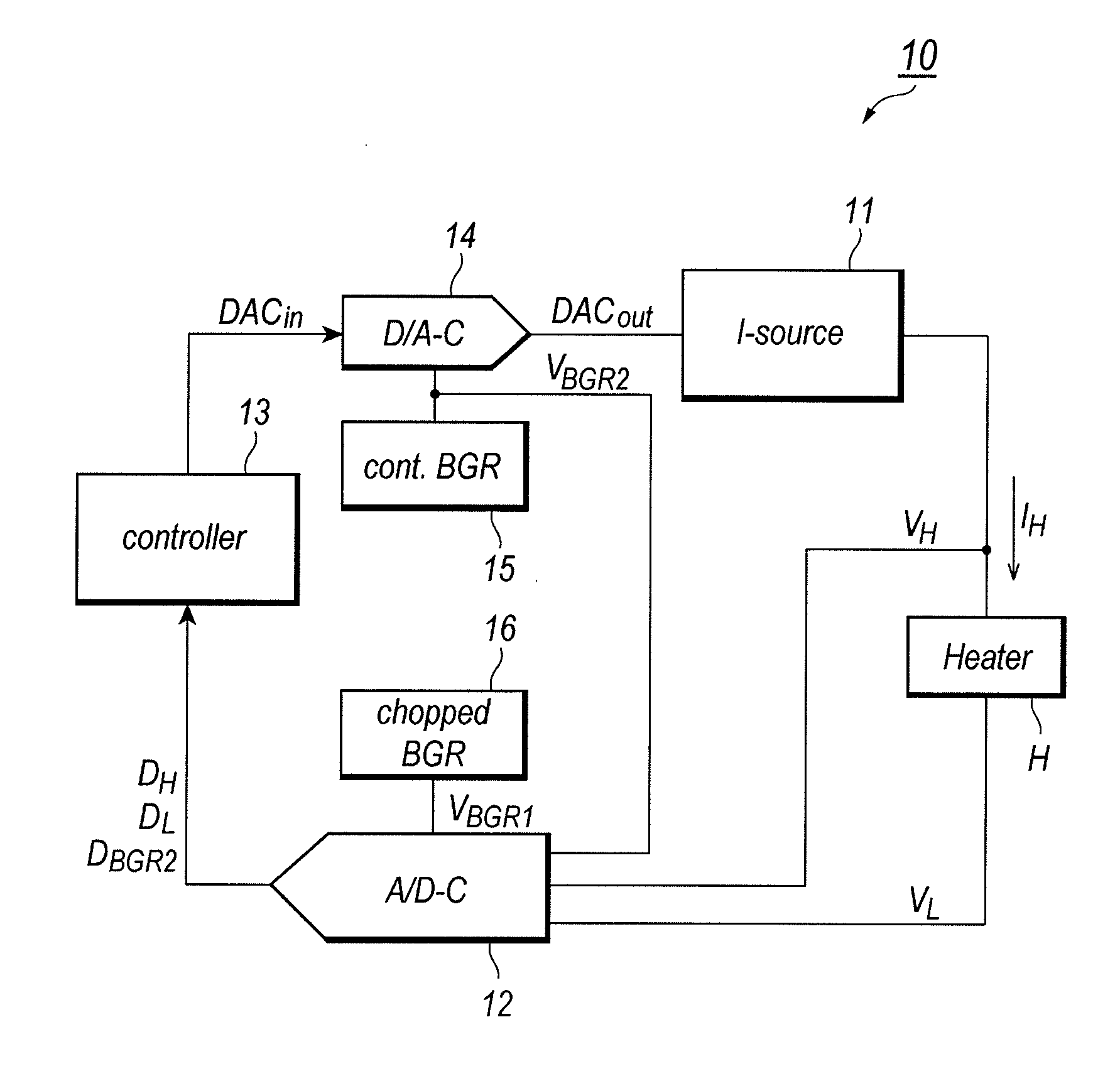
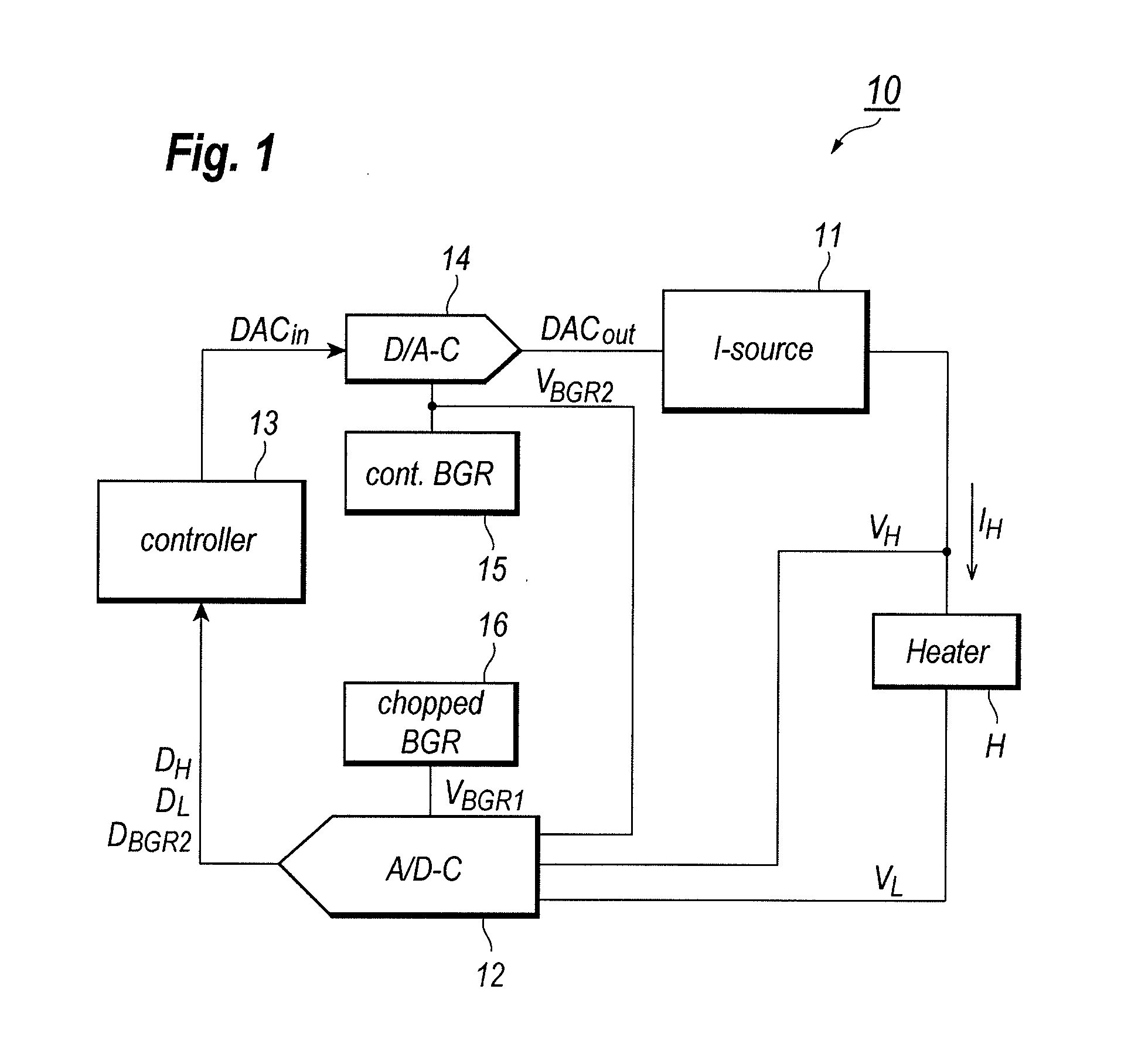
Controller to control electrical power of load in constant
ActiveUS20110254715A1Accurate compensationElectric signal transmission systemsResistance/reactance/impedencePower modeVoltage drop
A heater controller for controlling a heater precisely in the equi-power mode is disclosed. The controller includes a current source, a voltage monitor to detect a voltage drop caused in the heater, and a controller. The voltage drop may be converted to the digital form as refereeing to the first reference, while, the heater current is converted from the digital form as referring to the second reference. The second reference shows substantial temperature dependence, while, the first reference has lesser temperature dependence. The control corrects the temperature dependence of the second reference as referring to the first reference.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Signal converting apparatus for integrating analog-to-digital converter and digital-to-analog converter and integration unit
InactiveUS20060261993A1Reduce areaLow costElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital down converterDigital analog converter
A signal converting apparatus for integrating an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and an integration unit thereof are provided. The present invention integrates ADC and DAC, that do not operate simultaneously, into a signal converting apparatus (SCA), wherein a control signal decides whether an analog-to-digital mode or a digital-to-analog mode is selected. By sharing the operational amplifiers and other components in the SCA, the chip area and the cost are significantly reduced. In addition, in the integration unit, by switching a plurality of capacitor sets with various capacitances, the capacitance coefficients required for switching ADC and DAC are obtained.
Owner:ITE TECH INC
Transceiver and method for converting signals of the transceiver thereof
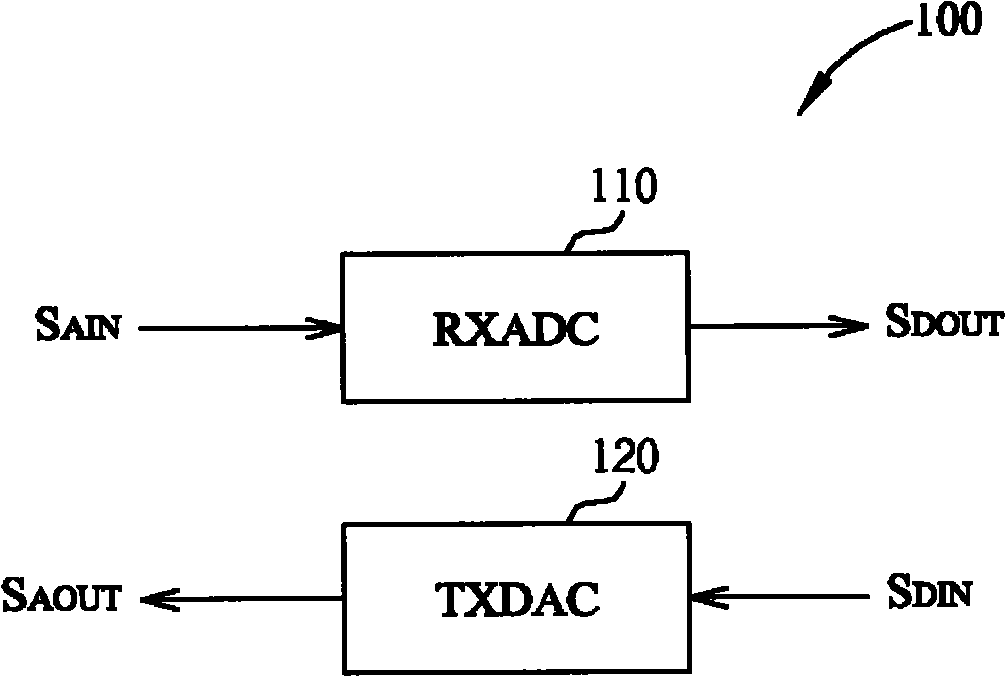
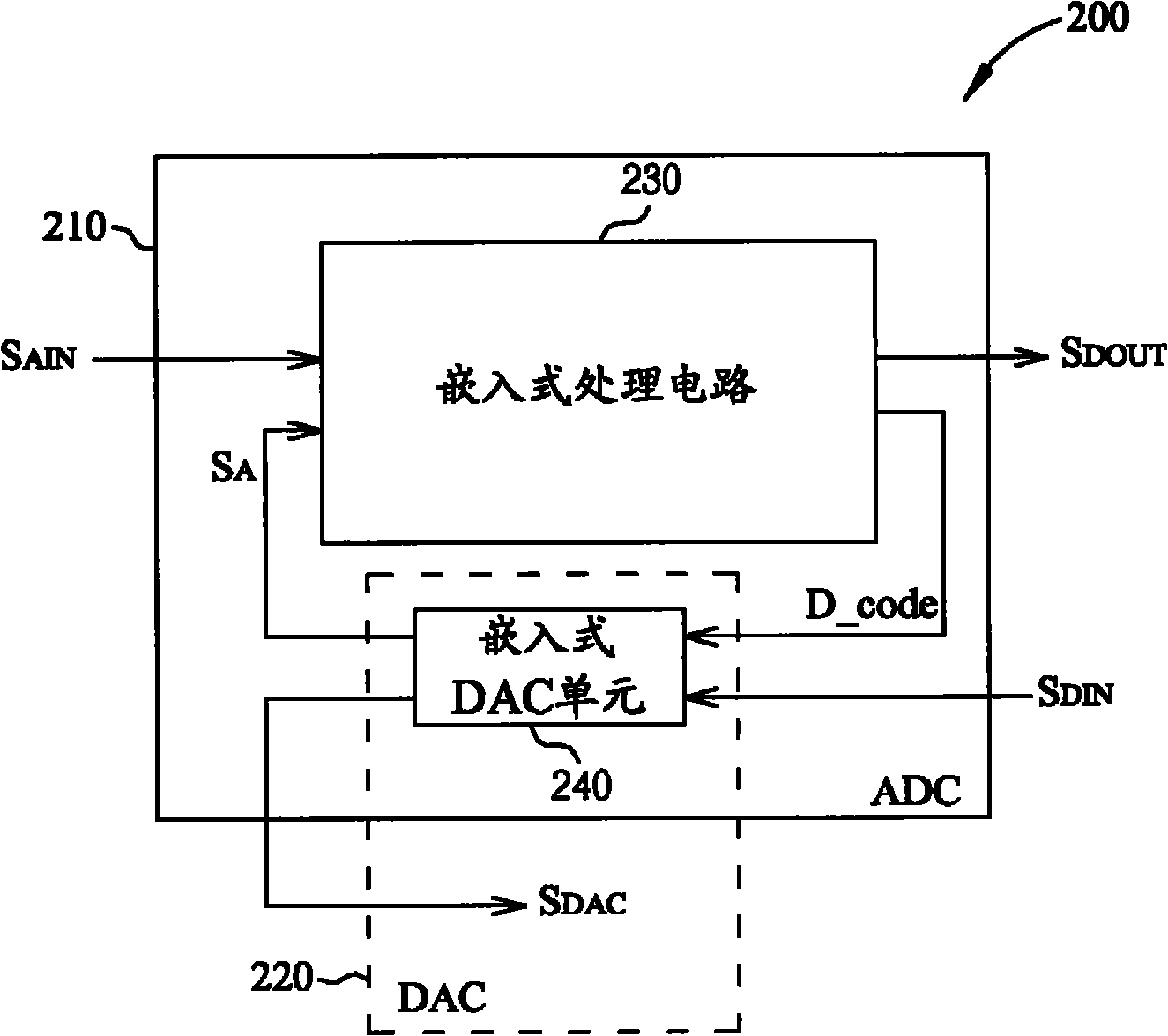
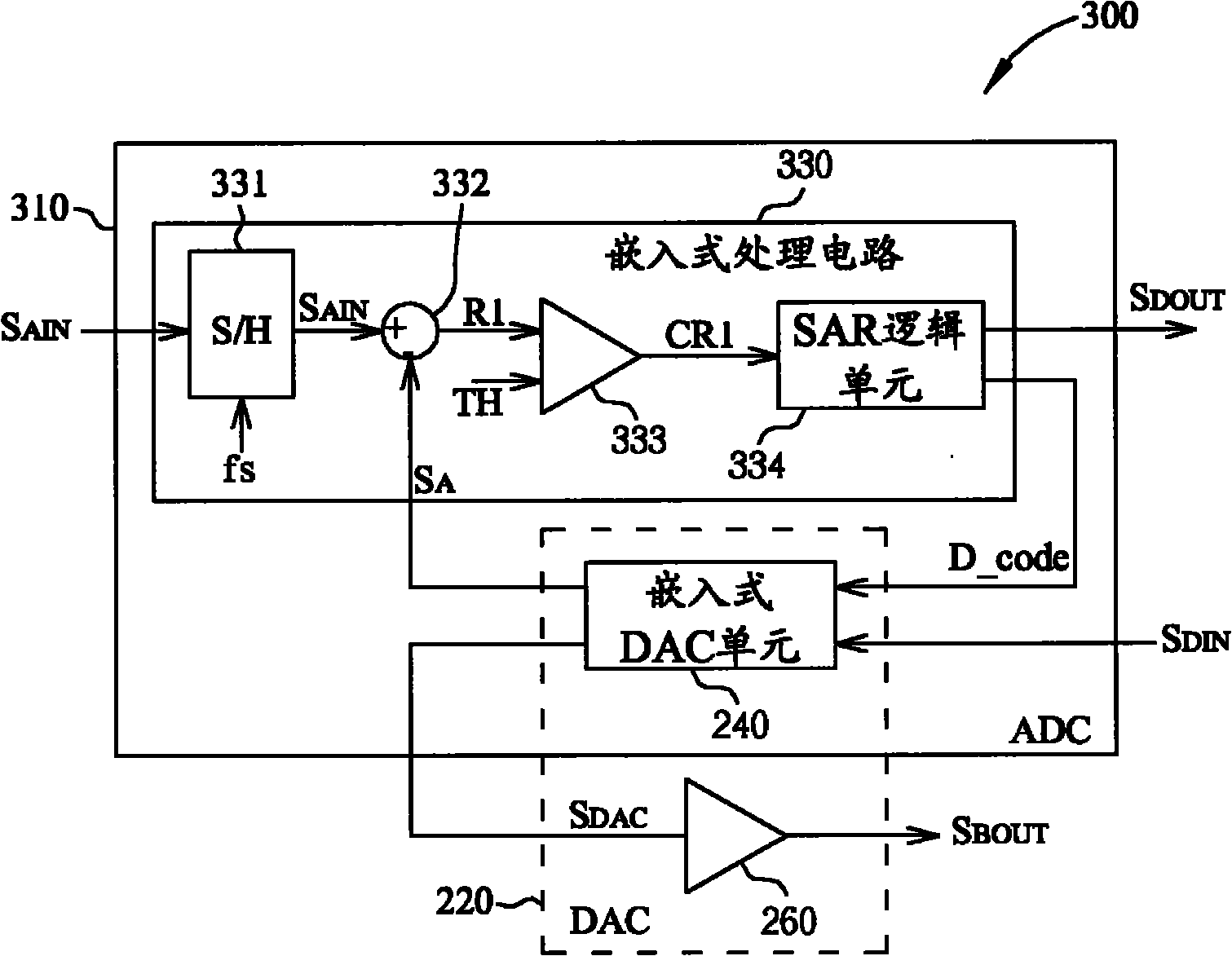
The invention provides a transceiver and a method for converting signals of the transceiver thereof, wherein the transceiver includes an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for converting an analog input signal into a digital output signal during a first operational phase of the transceiver, and converting the digital output signal into the analog input signal during a second operational phase of the transceiver. The ADC includes: an embedded processing circuit and an embedded digital-to-analog converting (DAC) unit, wherein the embedded processing circuit is arranged to generate a digital code and digital output signals according to the analog input signal and an analog signal in the first operational phase of the transceiver; the DAC unit is coupled to the embedded processing circuit, the embedded DAC unit is arranged to convert the digital code into the analog signal during the first operational phase, and is arranged to convert a digital input signal into an analog output signal during a second operational phase of the transceiver. One of the advantages of the invention is saving the layout area and decreasing the hardware manufacturing cost under the premise of realizing the transceiving function.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Adaptive combinatorial coding/decoding with specified occurrences for electrical computers and digital data processing systems
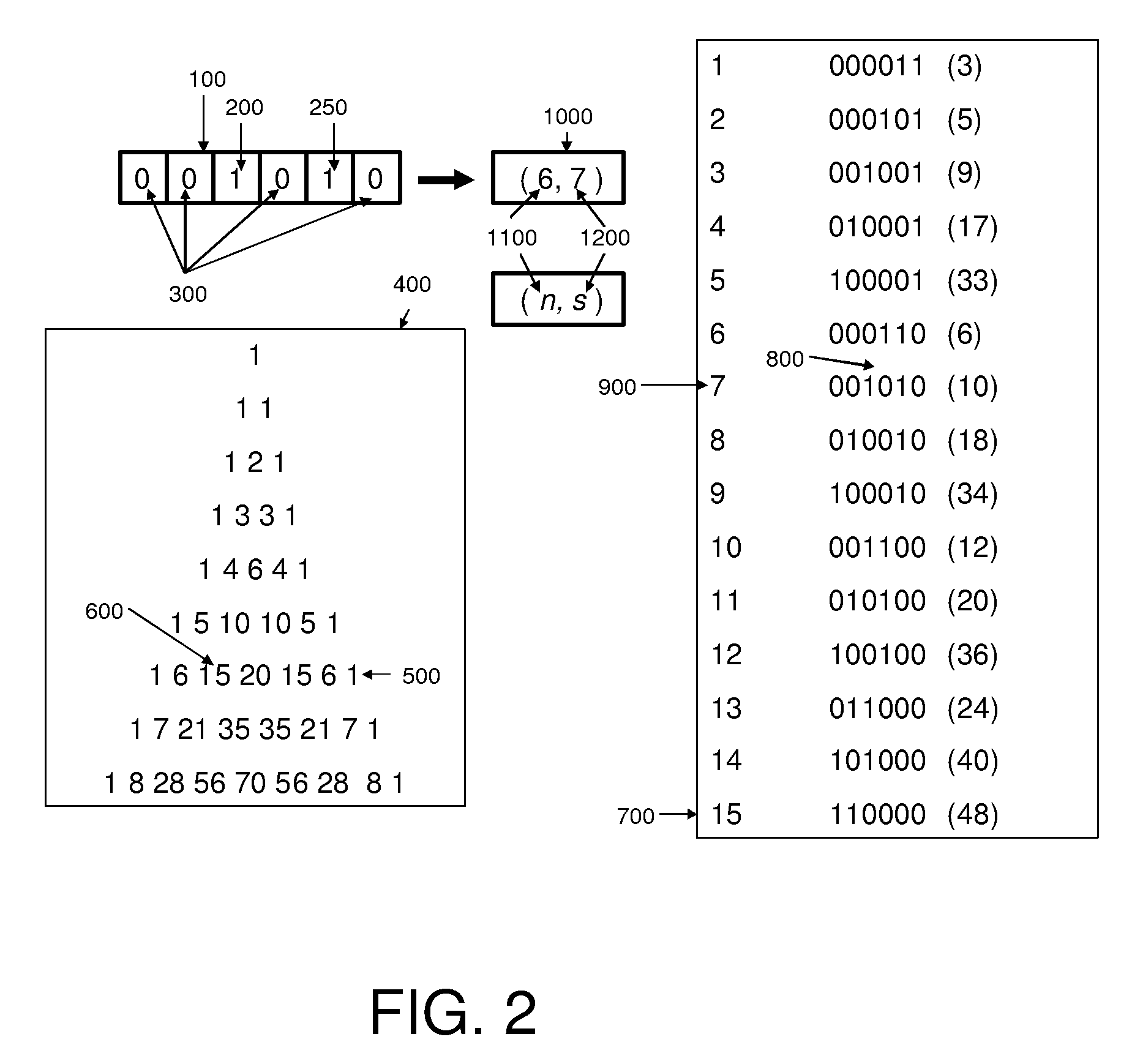
InactiveUS7791513B2Electric signal transmission systemsReversible analogue/digital convertorsDigital signal processingData processing system
Embodiments described herein may include example embodiments of a method, article and apparatus for compressing data utilizing a combinatorial encoder with specified occurrences which may be used for communicating between two or more components connected to an interconnection medium (e.g., a bus) within a single computer or digital data processing system, and / or for communication between computing platforms via a network or other interconnection medium.
Owner:TECH VALUE GRP LLC
Data converter system capable of avoiding interleave images and distortion products
ActiveCN102801418AAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingReversible analogue/digital convertorsEngineeringDistortion
The invention relates to a data converter system capable of avoiding interleave images and distortion products. The data converter system supplies an output signal with low stray single frequency by making a converted input signal 'step over' or 'get rid of' the stray single frequency by limiting the input signal in an appointed frequency band and performing over-sampling; the stray single frequency can be filtered out; and therefore, compared with the conventional data converter, the data converter system can supply a much more cleaned output signal without a stray dynamic range. For example, according to the embodiment, the interleave data converter system converts the input signal which is limited in a second Nyquist region interleaved into a data converter into an interleave signal, so that a filter with a passband for transmitting a converted input frequency and a stop band for attenuating the stray single frequency is used for filtering the interleave signal; and the obtained output signal is provided with the bandwidth which is the same as that of the output signal obtained by the single data converter, but the obtained output signal is not influenced by the interleave images or some distortion products.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Popular searches
Digital-analogue convertors Physical parameters compensation/prevention Input/output processes for data processing Image coding Television systems Digital video signal modification Frequency-modulated carrier systems Amplitude demodulation Digital filters Apparatus without intermediate ac conversion
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com