Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48results about "Reproducing by electric probe means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
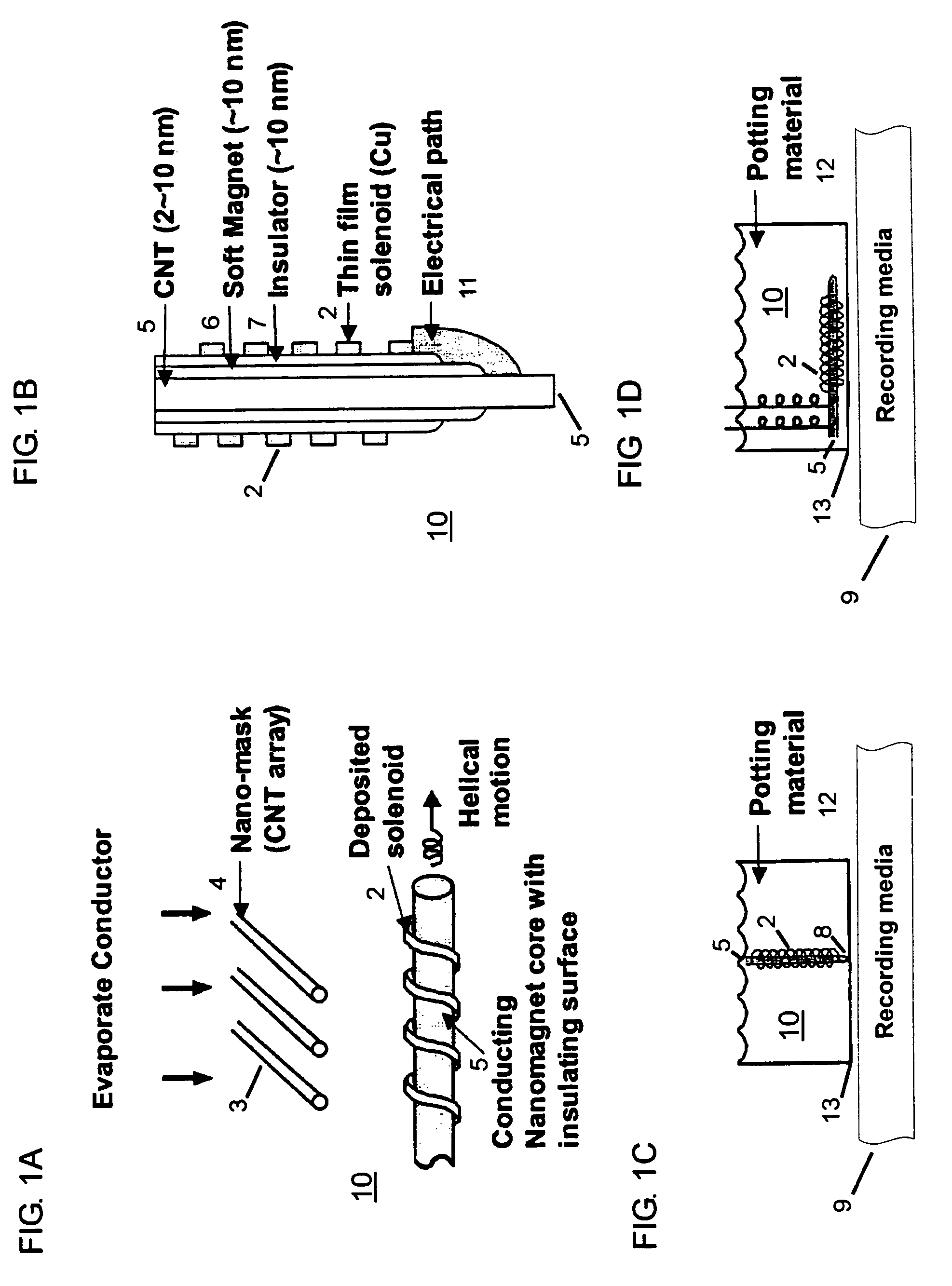
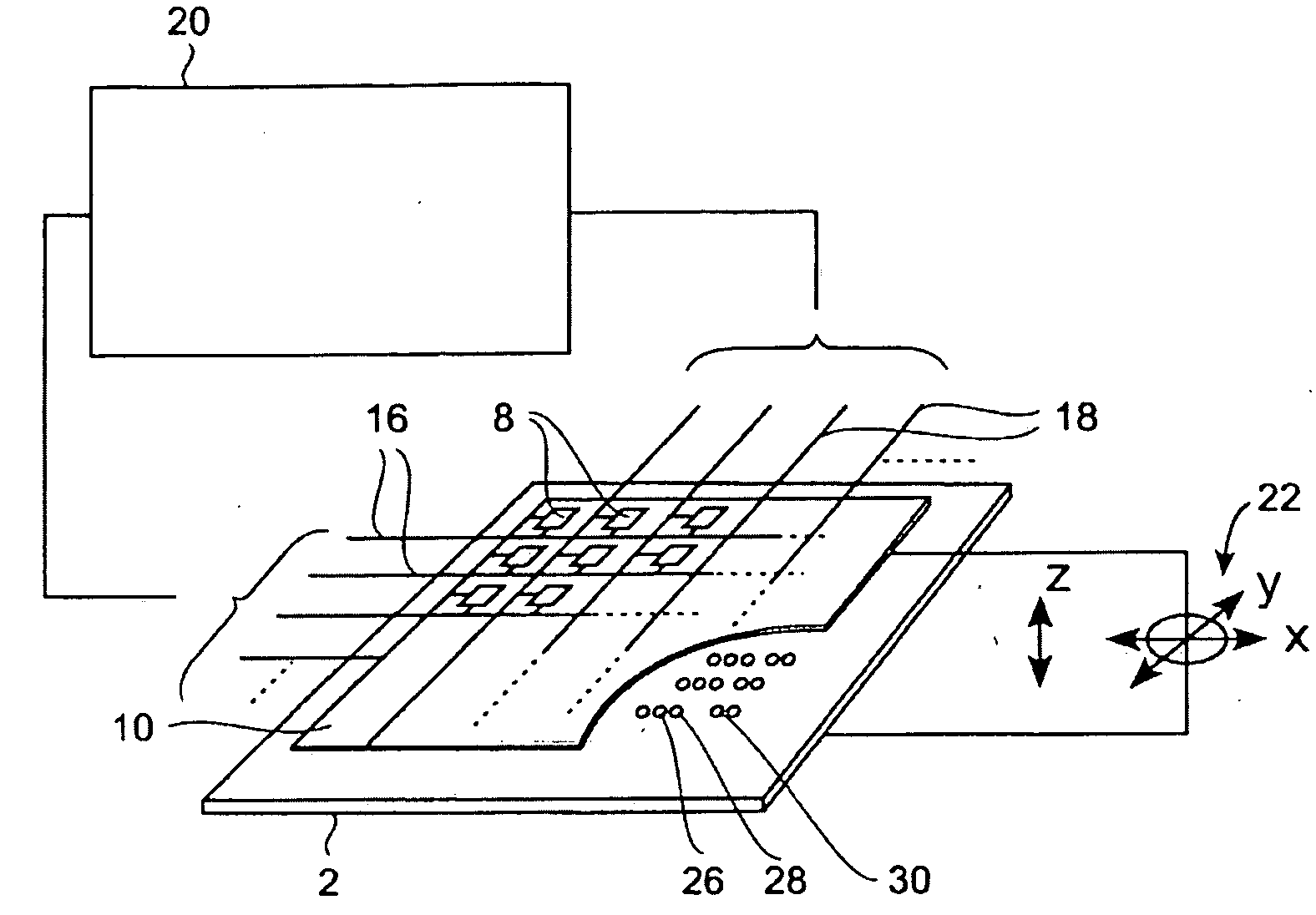
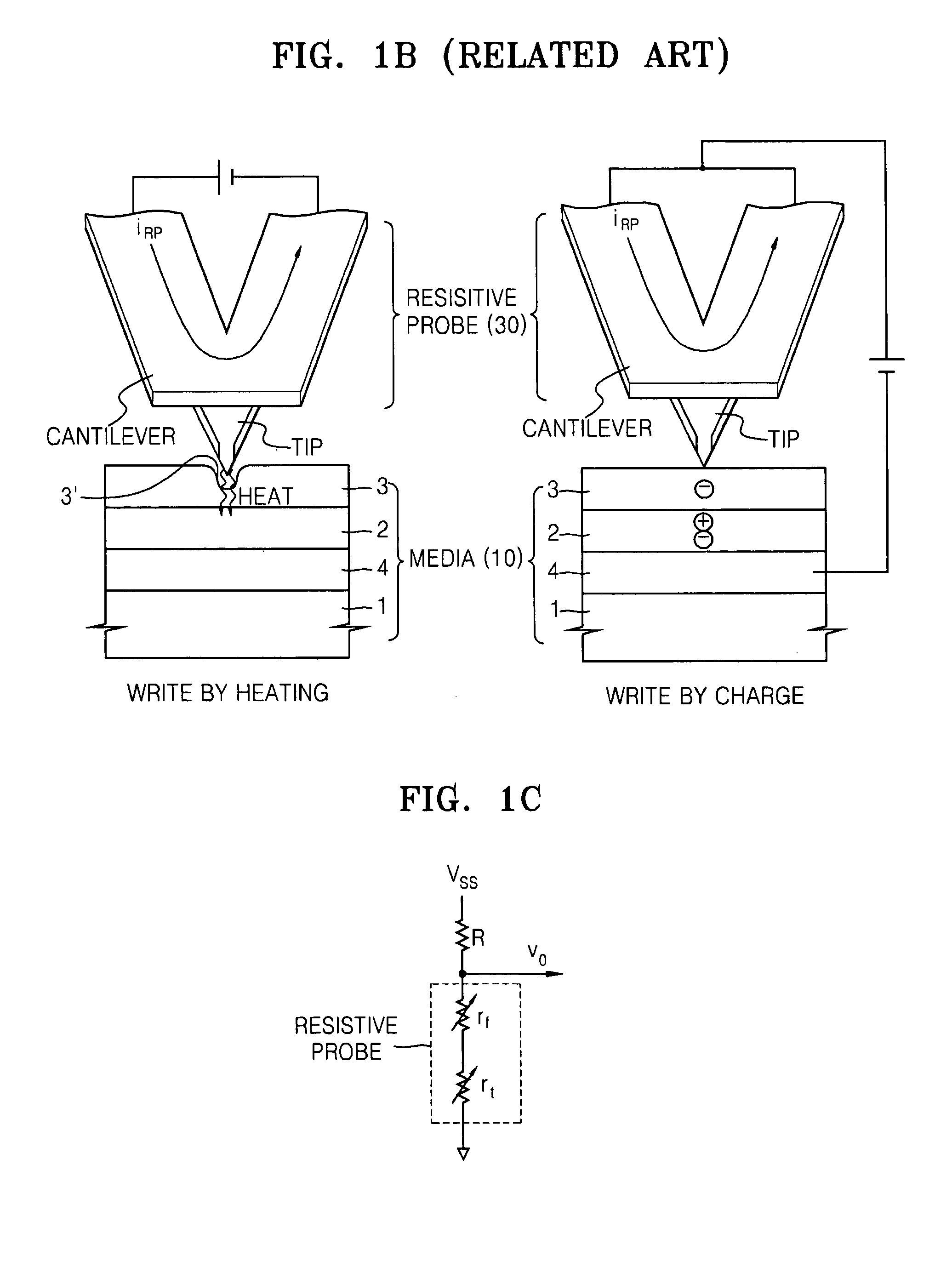
High density data storage medium
InactiveUS20050050258A1Toughening of surfaceImprove wearing rateNanoinformaticsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAtomic force microscopyCross-link
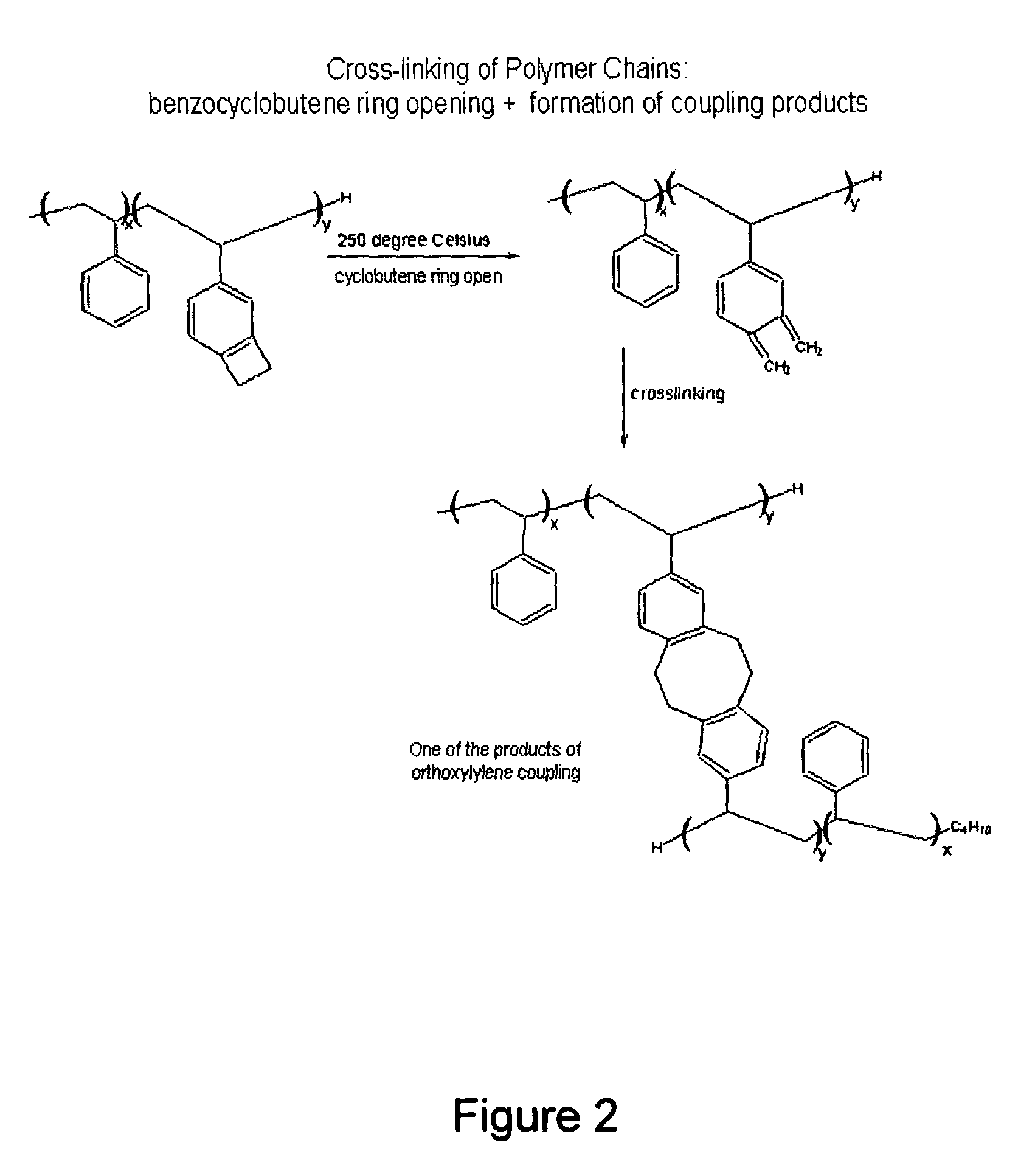
An approach is presented for designing the polymeric recording layer for nanometer scale thermomechanical storage devices. Cross linked polymers are used as the recording layers in atomic force microscopy data storage devices, giving significantly improved performance when compared to the previously reported linear polymers. This results in superior wear resistance and enhanced erasing, critical features for the long-term multiple read-write cycles of such thermomechanical storage devices. In addition, this ability to introduce a predetermined extent of cross linking allows fine tuning of the thermal and force parameters in the R / W / E (read-write-erase) cycles.
Owner:IBM CORP
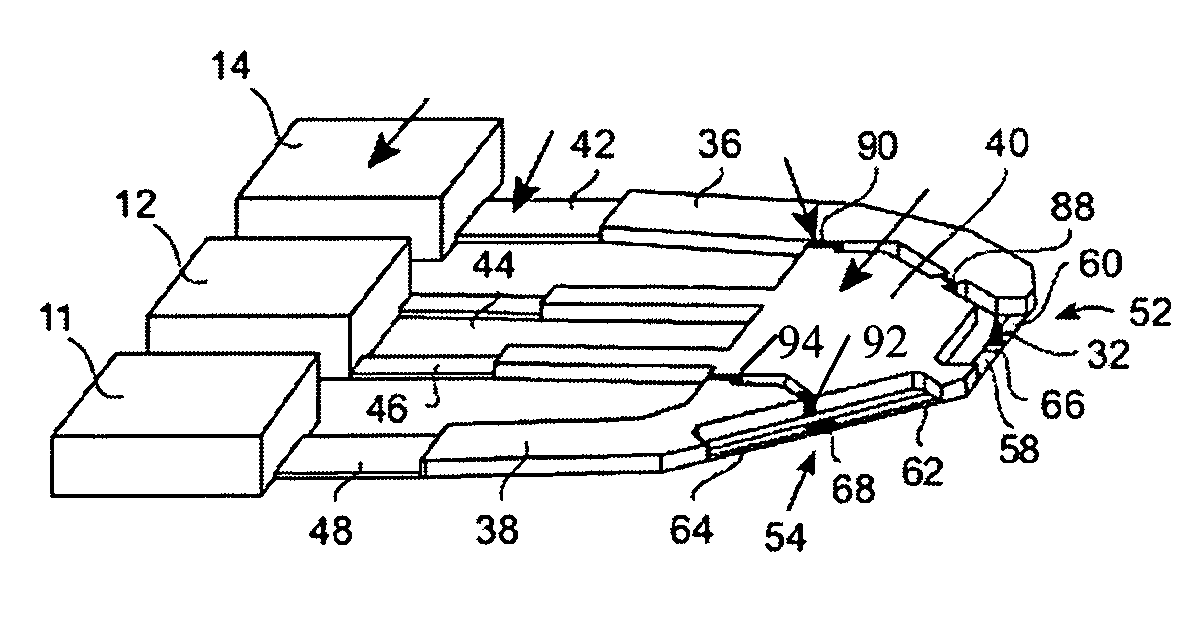
Recording/reproducing head, method of producing the same, and recording apparatus and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20050122886A1Easily and efficiently producedRecord data with stabilityElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingComputer hardwareHead parts
A recording / reproducing head for performing at least one of a record operation of recording information onto a dielectric recording medium and a reproduction operation of reproducing the information from the dielectric recording medium, the recording / reproducing head provided with: a support member which extends in a longitudinal direction of the recording / reproducing head; and a projection portion which is mounted on the support member such that a tip of the projection portion faces the dielectric recording medium, the projection portion having a ridge-line on the tip, the projection portion being capable of contacting the dielectric recording medium at one point on the ridge-line.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Record condition extraction system and method of dielectric recording medium, and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS6912193B2High-density and stable microdomainHigh-density and stableNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingMeasurement deviceOutput device
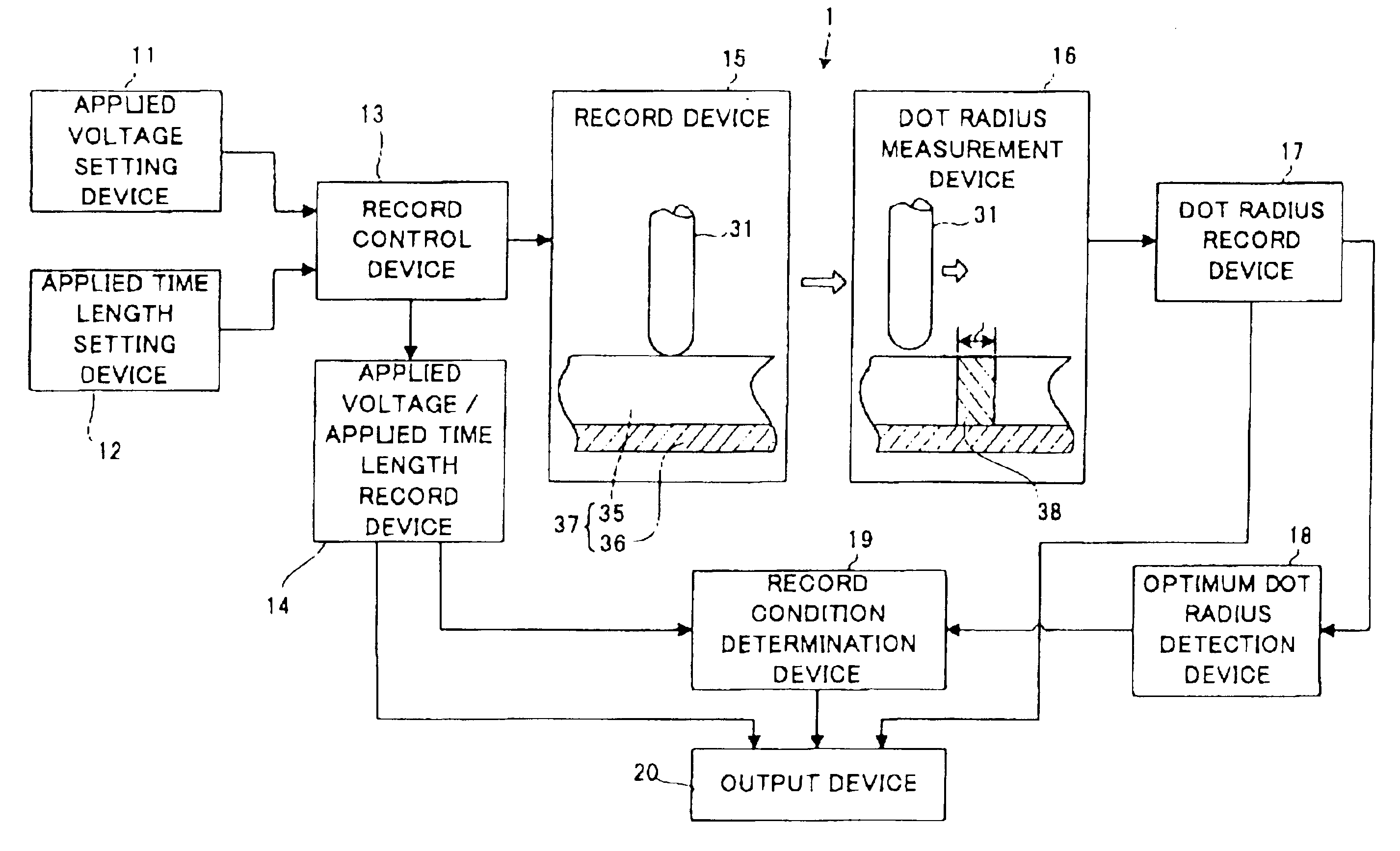
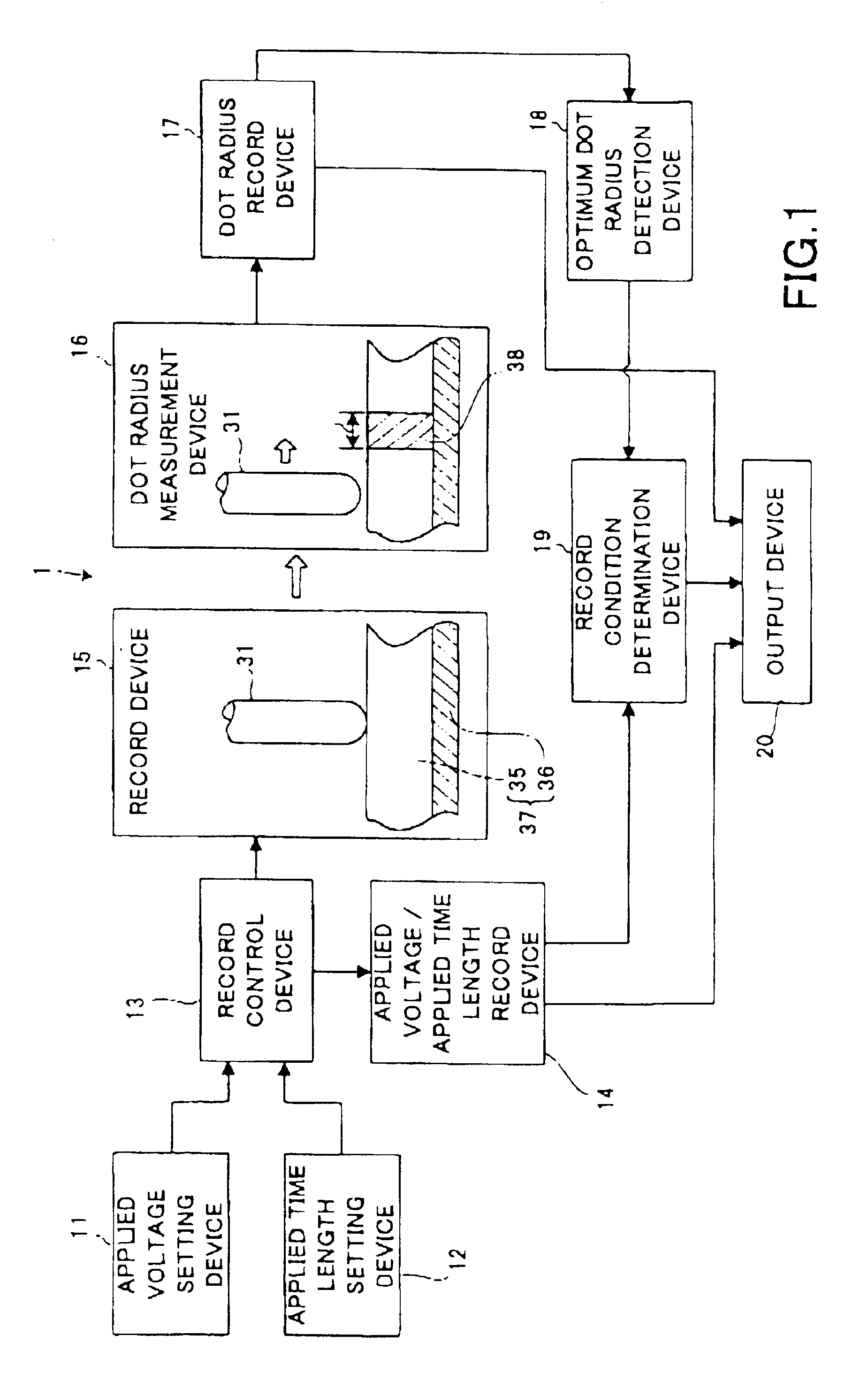
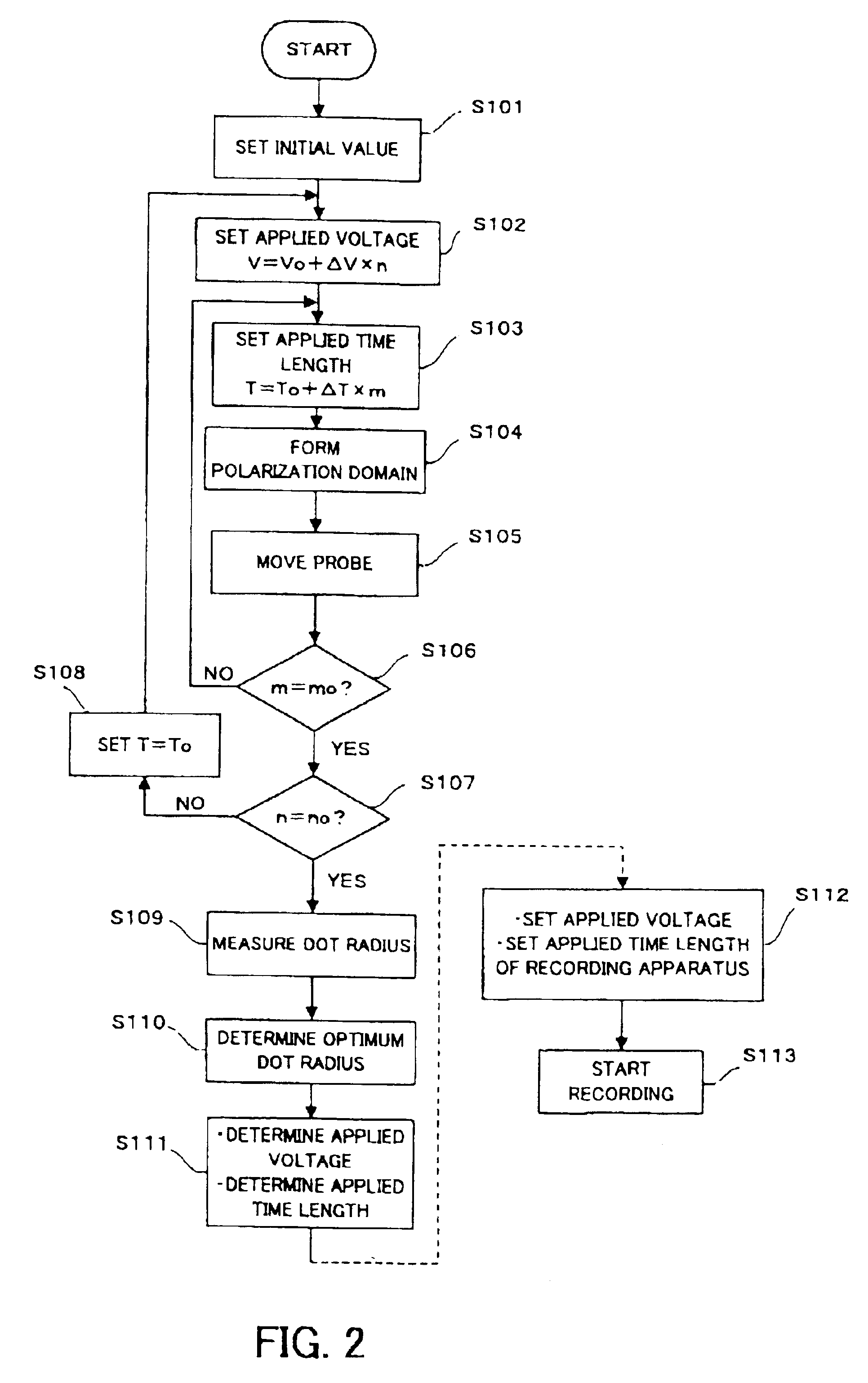
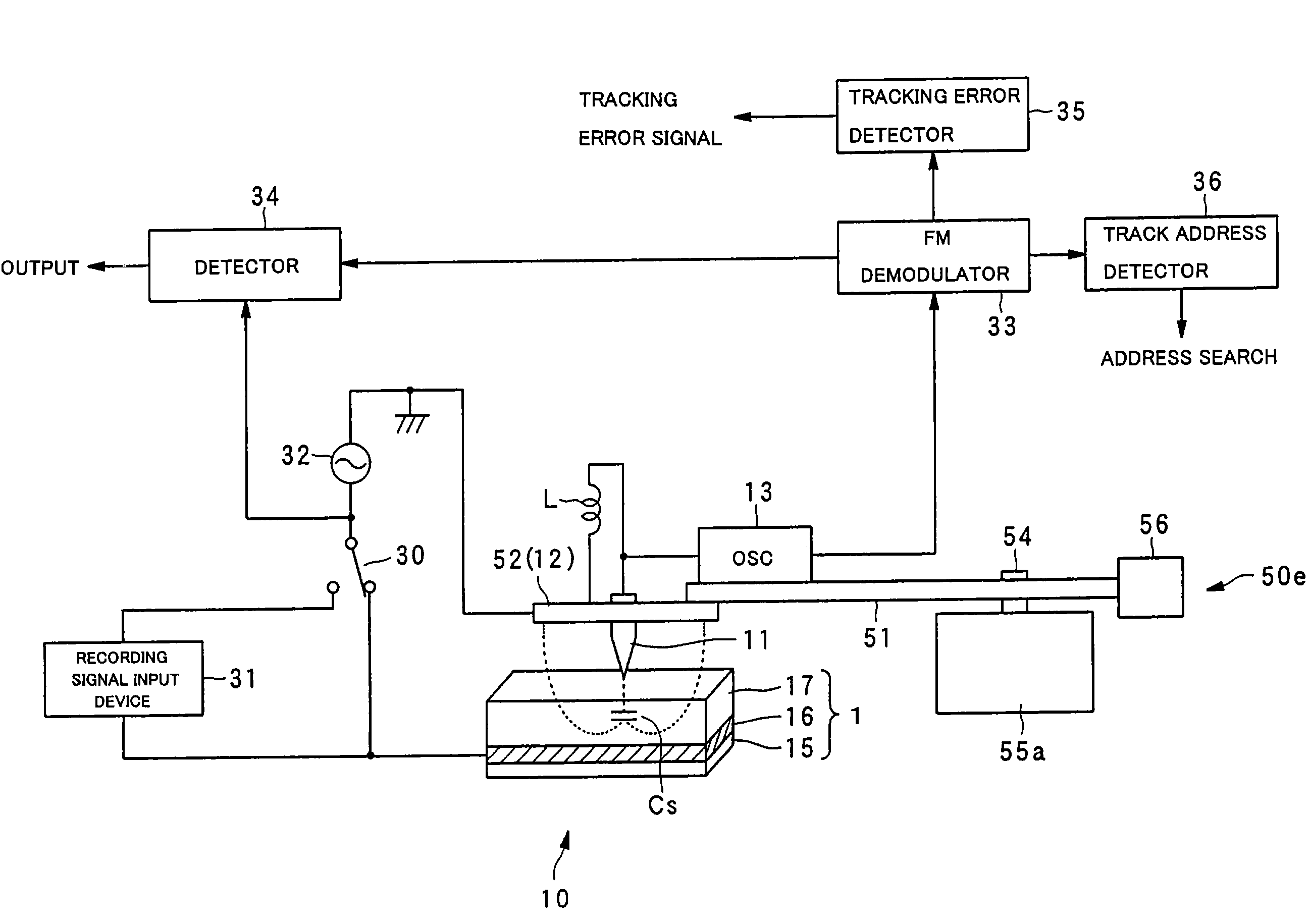
The record condition extraction system (1) of a dielectric recording medium is intended to obtain an applied voltage and an applied time length to be recorded when recording information in the dielectric recording medium. The record condition extraction system (1) is provided with: an applied voltage setting device (11); an applied time length setting device (12); a record control device (13); an applied voltage / applied time length record device (14); a record device (15); a dot radius measurement device (16); a dot radius record device (17); an optimum dot radius detection device (18); a record condition determination device (19); and an output device (20). The applied voltage setting device (11) and the applied time length setting device (12) set a voltage and a time applied to a probe (31) of the record device (15), respectively. The dot radius of a polarization domain 38, which is recorded at the record device (15), is measured at the dot radius measurement device (16), and the optimum polarization domain (38) is obtained at the optimum dot radius detection device (18). The applied voltage and the applied time length which have formed the polarization domain (38) are extracted as an optimum record condition.
Owner:YASUO CHO +1
Apparatus for recording information in and/or reproducing information from a ferroelectric recording medium
InactiveUS7149180B2Increase ratingsImprove signal-to-noise ratioVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsPhysicsInternal zone
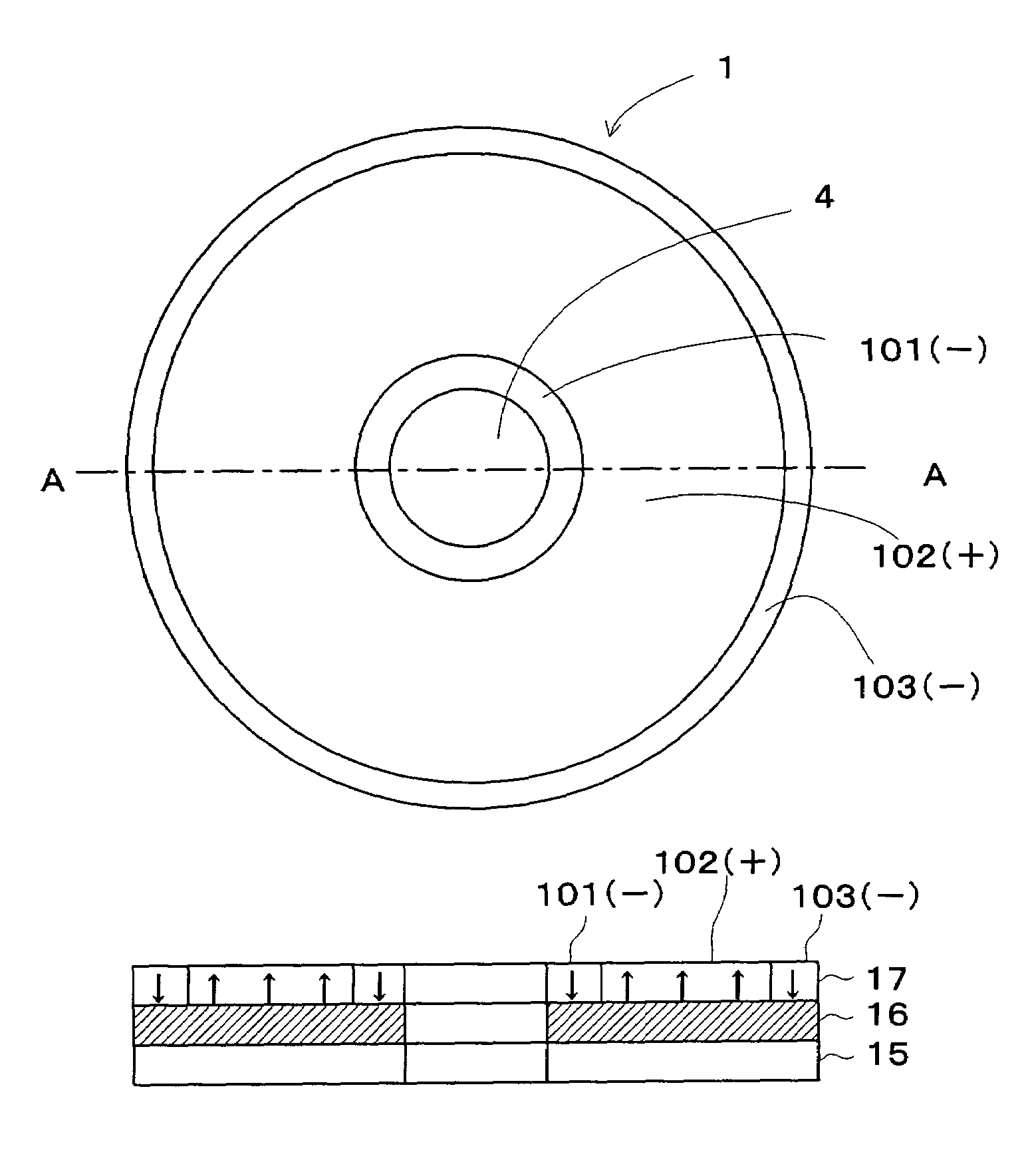
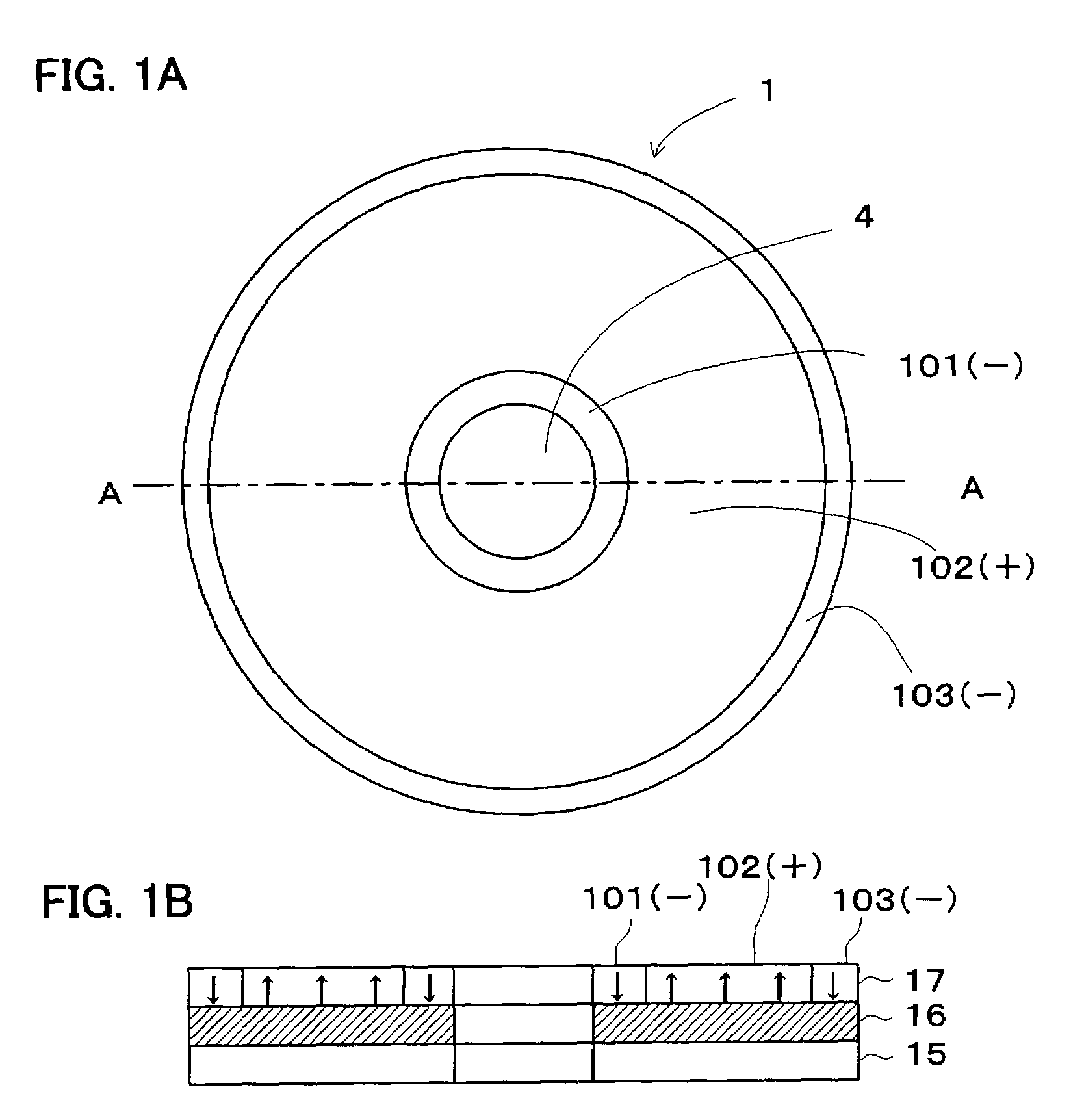
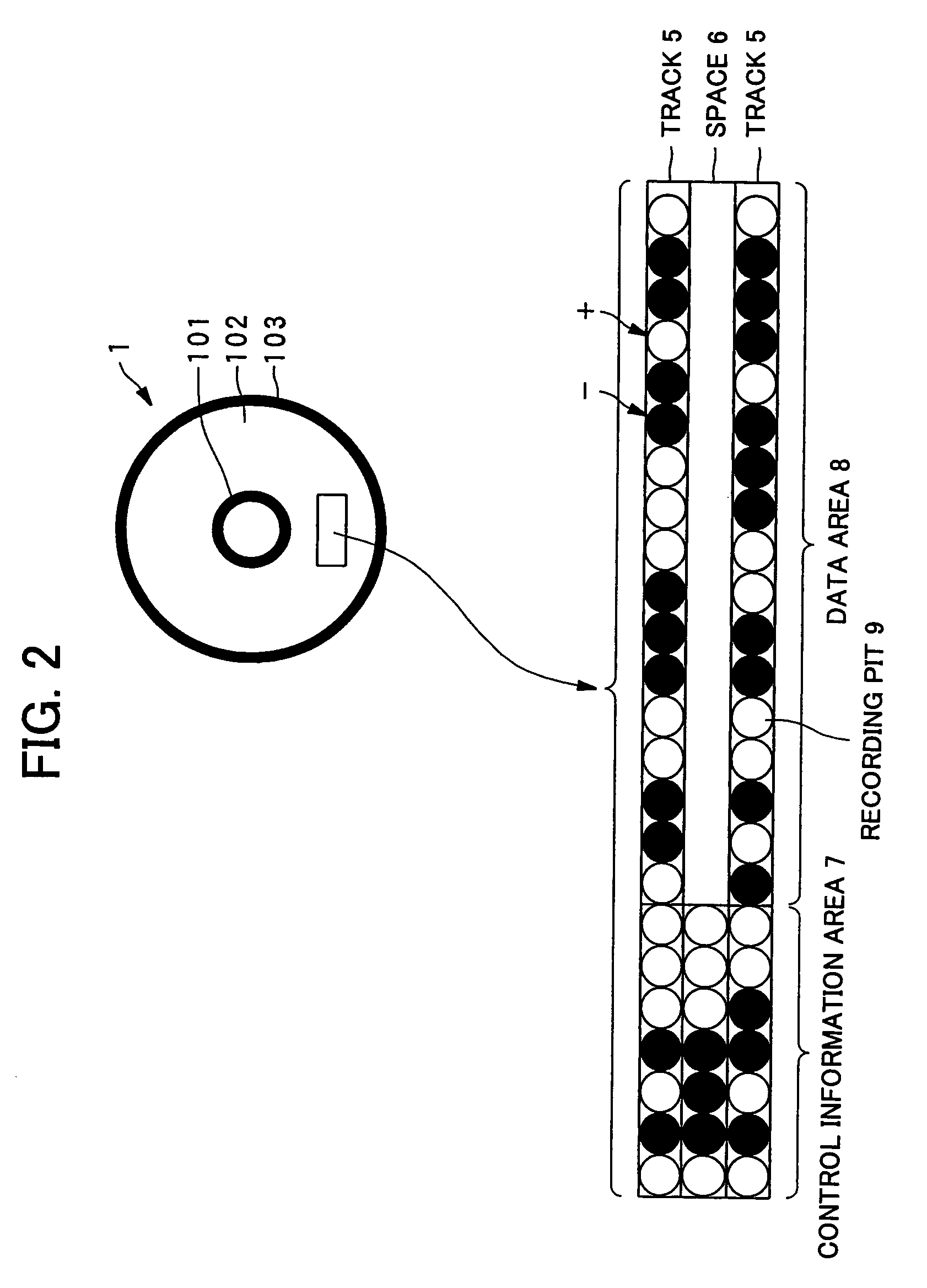
A dielectric recording medium in a disc form is provided with: a center hole; an inner area; a recording area; and an outer area, arranged concentrically from the inside in this order. The inner area, the recording area, and the outer area contain a uniform and flat dielectric material and are polarized with the polarization direction of the recording area opposite to that of the inner area and the outer area in their initial condition. The recording area in which data is recorded has tracks and spaces, each of which is between two of the tracks, and is provided with areas in which control information about the recording / reproducing is recorded, in the track and the space.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Pickup device
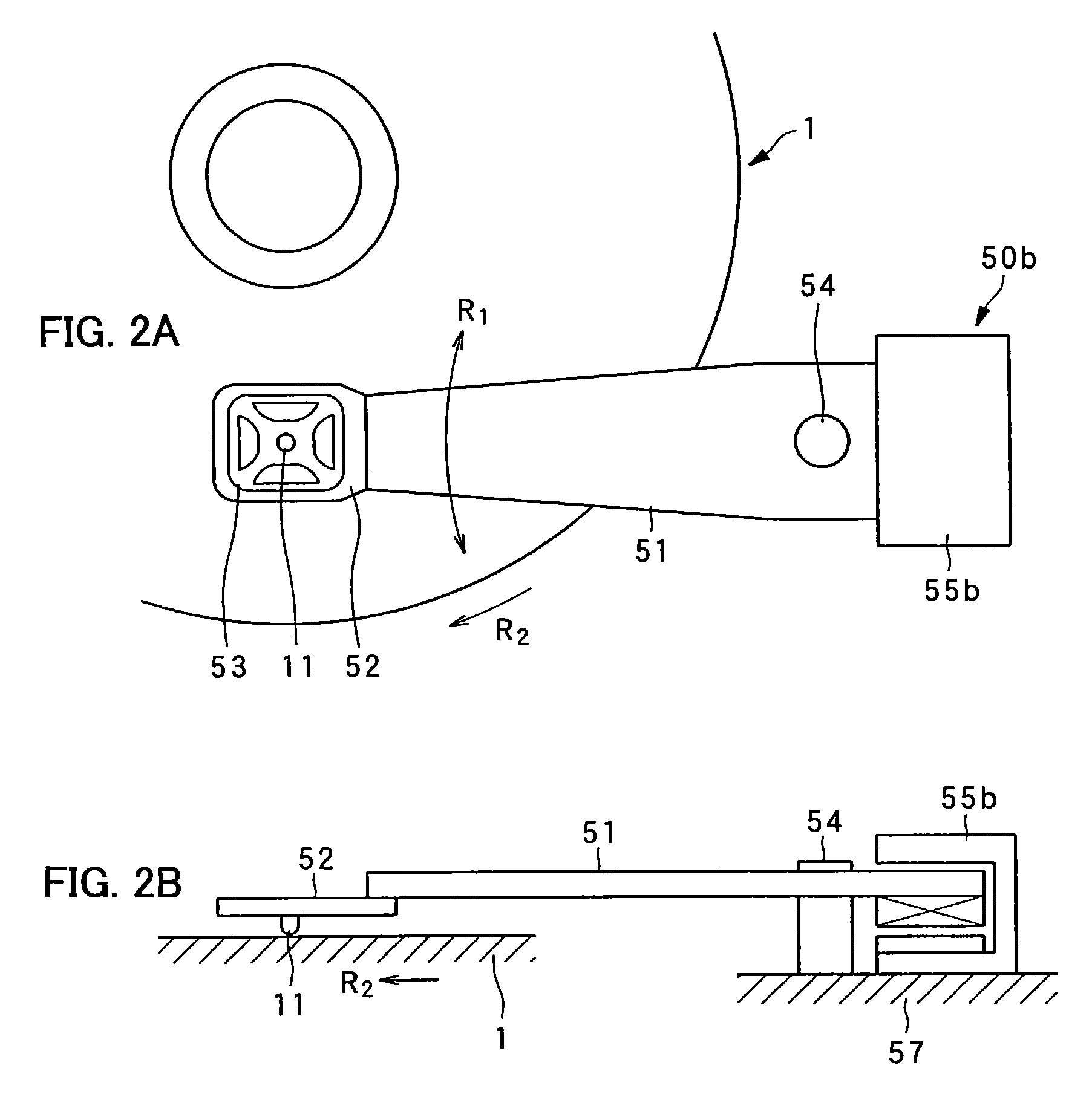
InactiveUS7221639B2Simple structureEasy to produceVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringGimbal
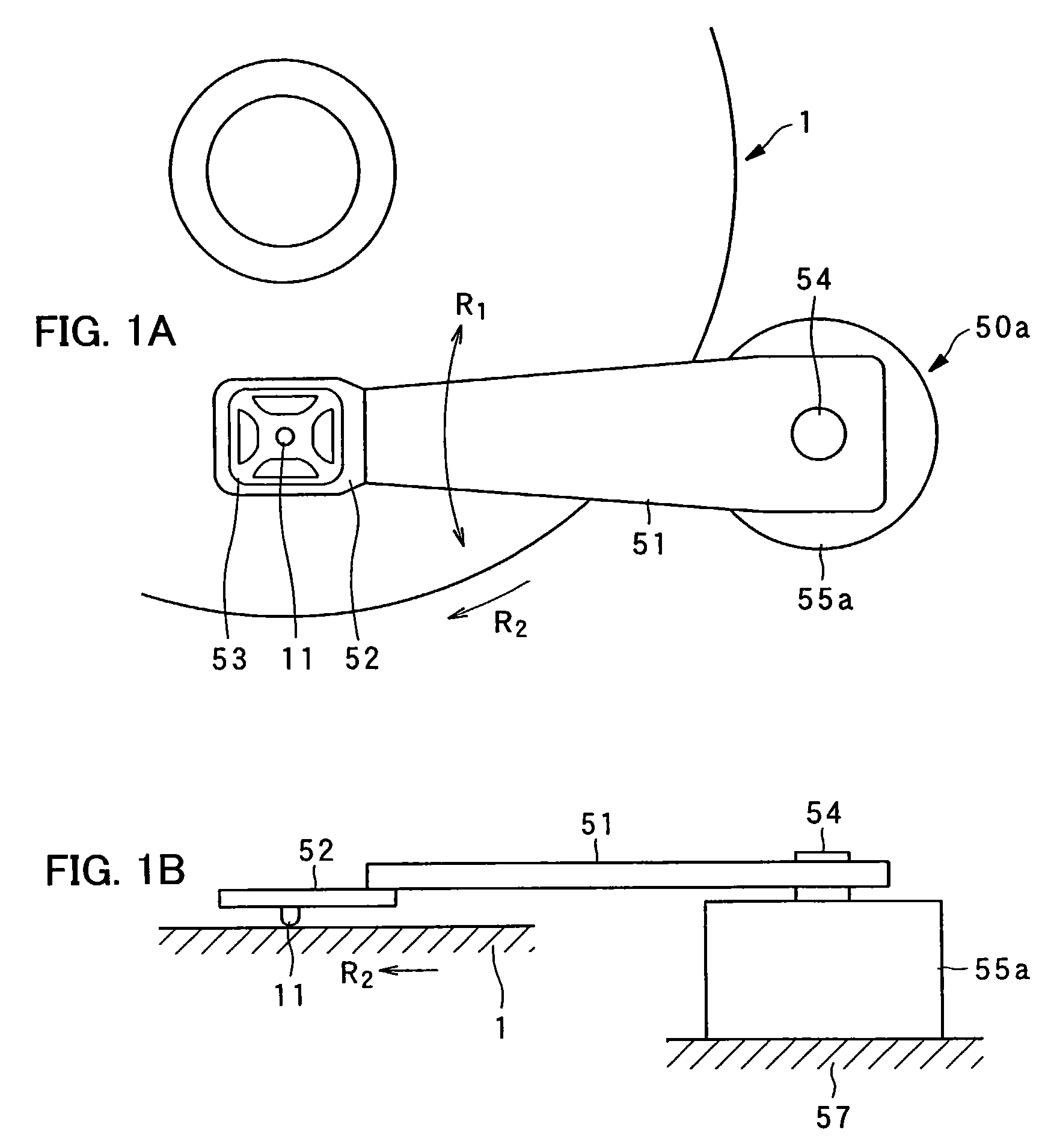
An example pickup device is provided with: an arm; a gimbal holding device disposed on one end portion of the arm; a gimbal held by the gimbal holding device with a probe set in its center portion; and a motor of rotational type for rotating the arm around a rotating shaft. The probe, which is disposed on one end of the arm, is rotated in the radial direction of a dielectric recording medium by the rotation of the motor, causing accurate and quick tracking control and track access control.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Method for positioning a scanning probe on a target track of a multi-track storage medium, storage device, scanning device, and storage medium
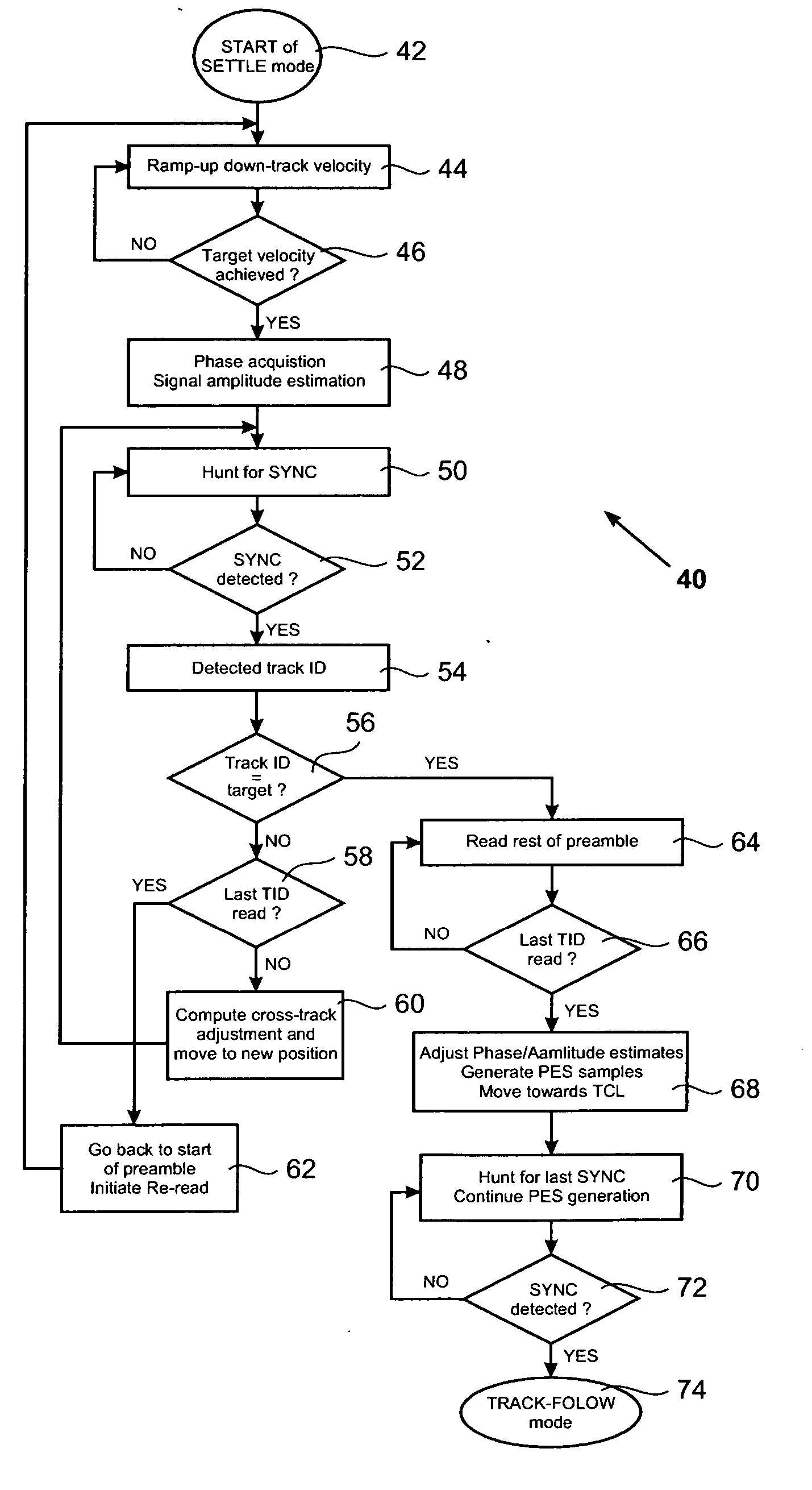
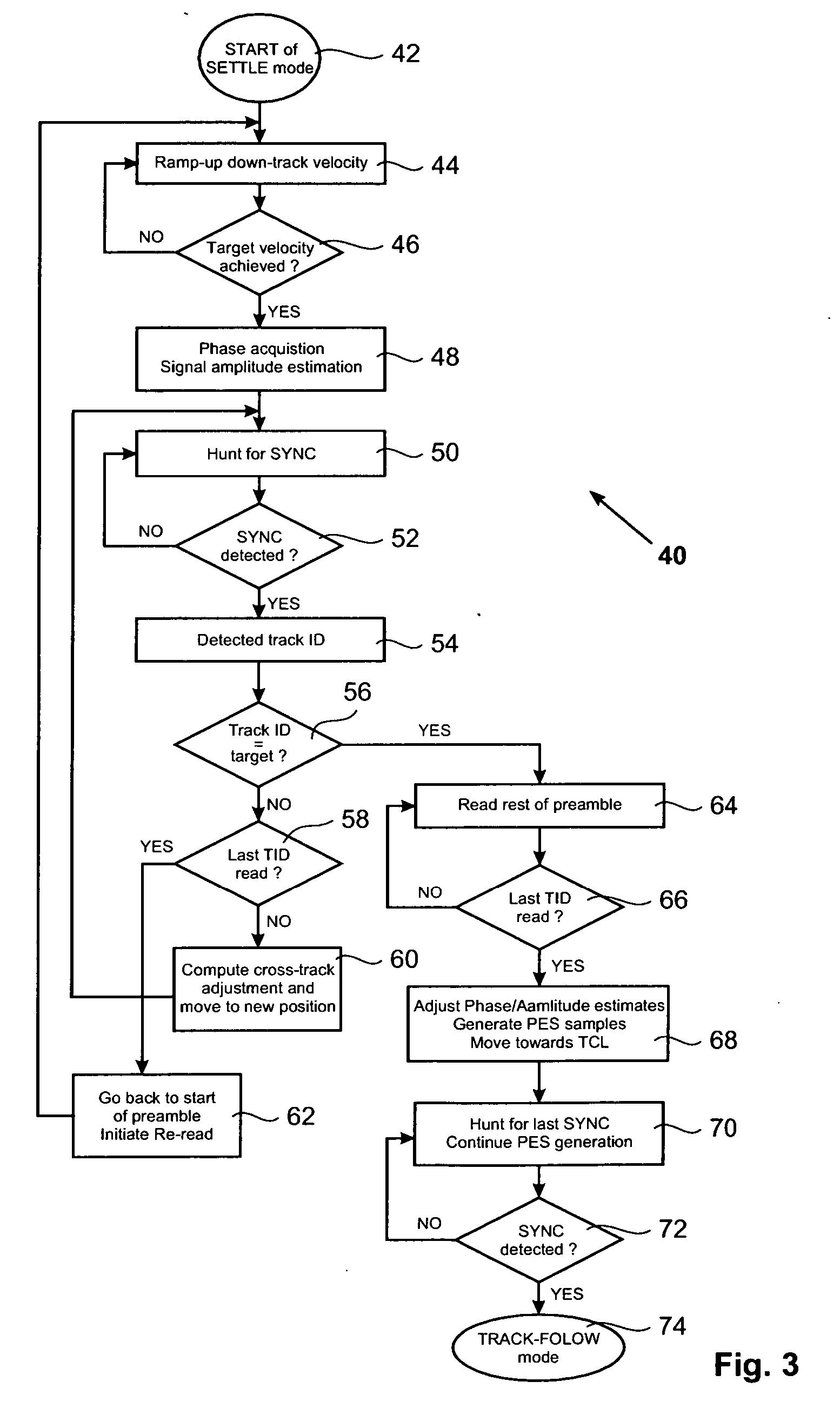
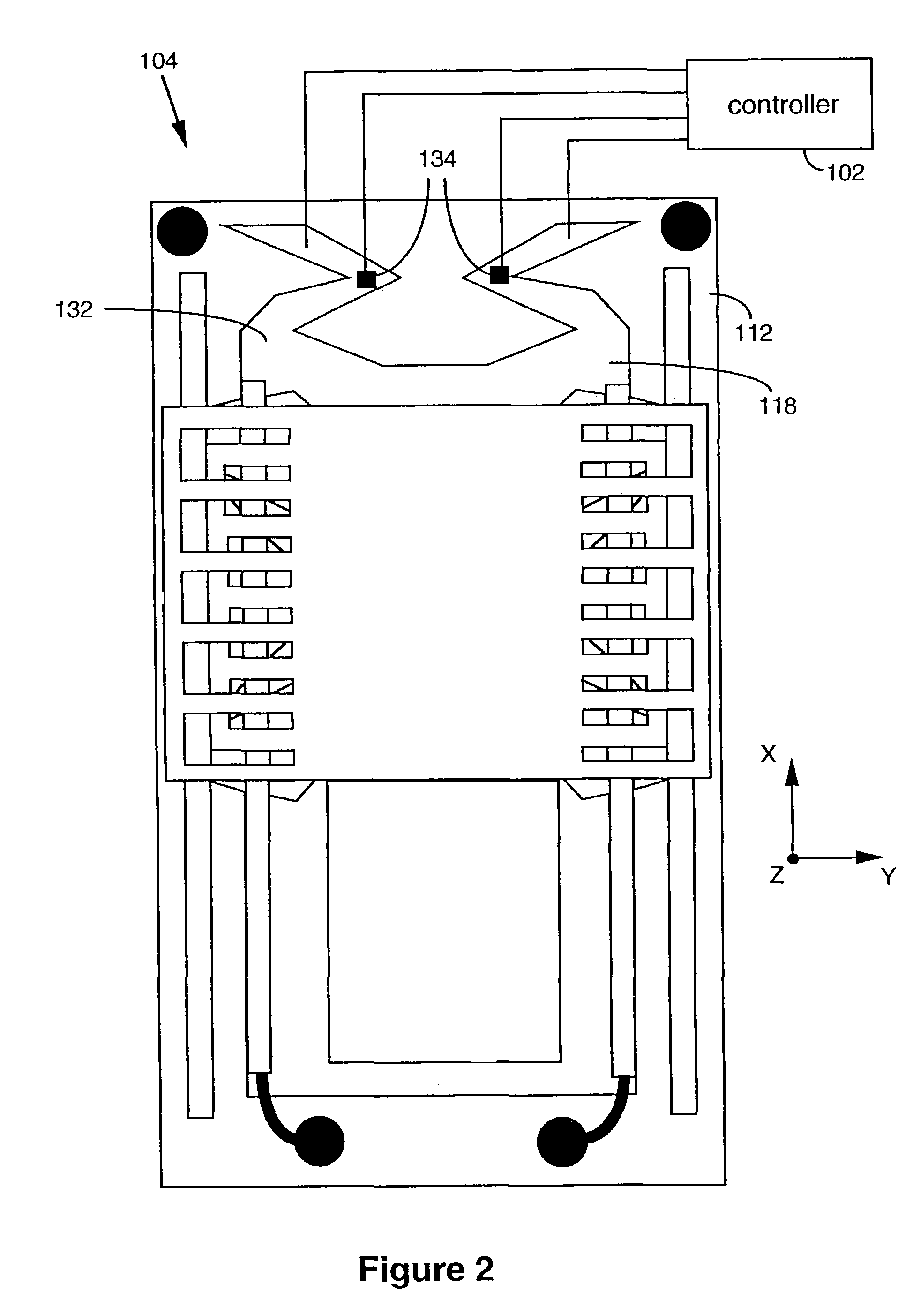
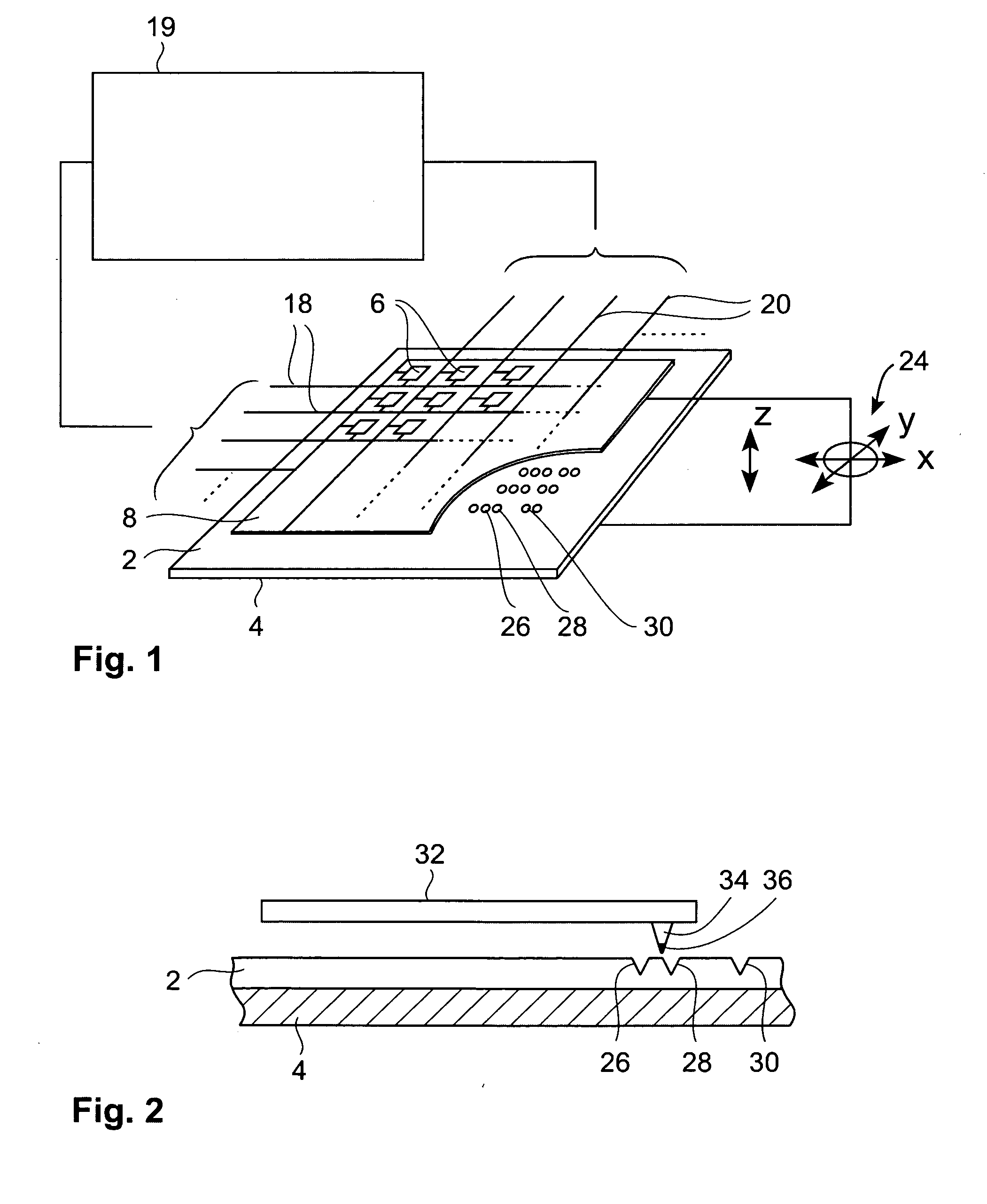
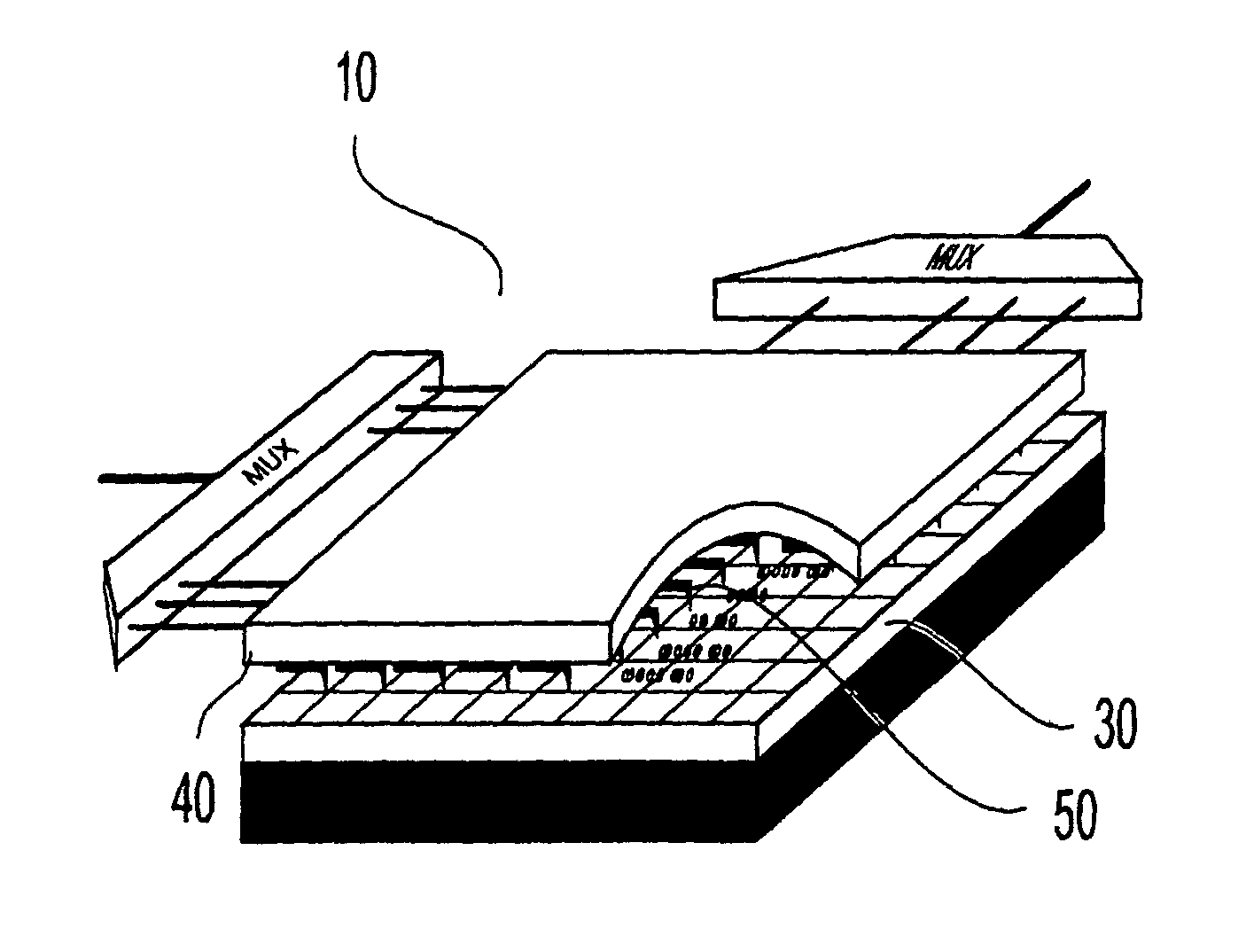
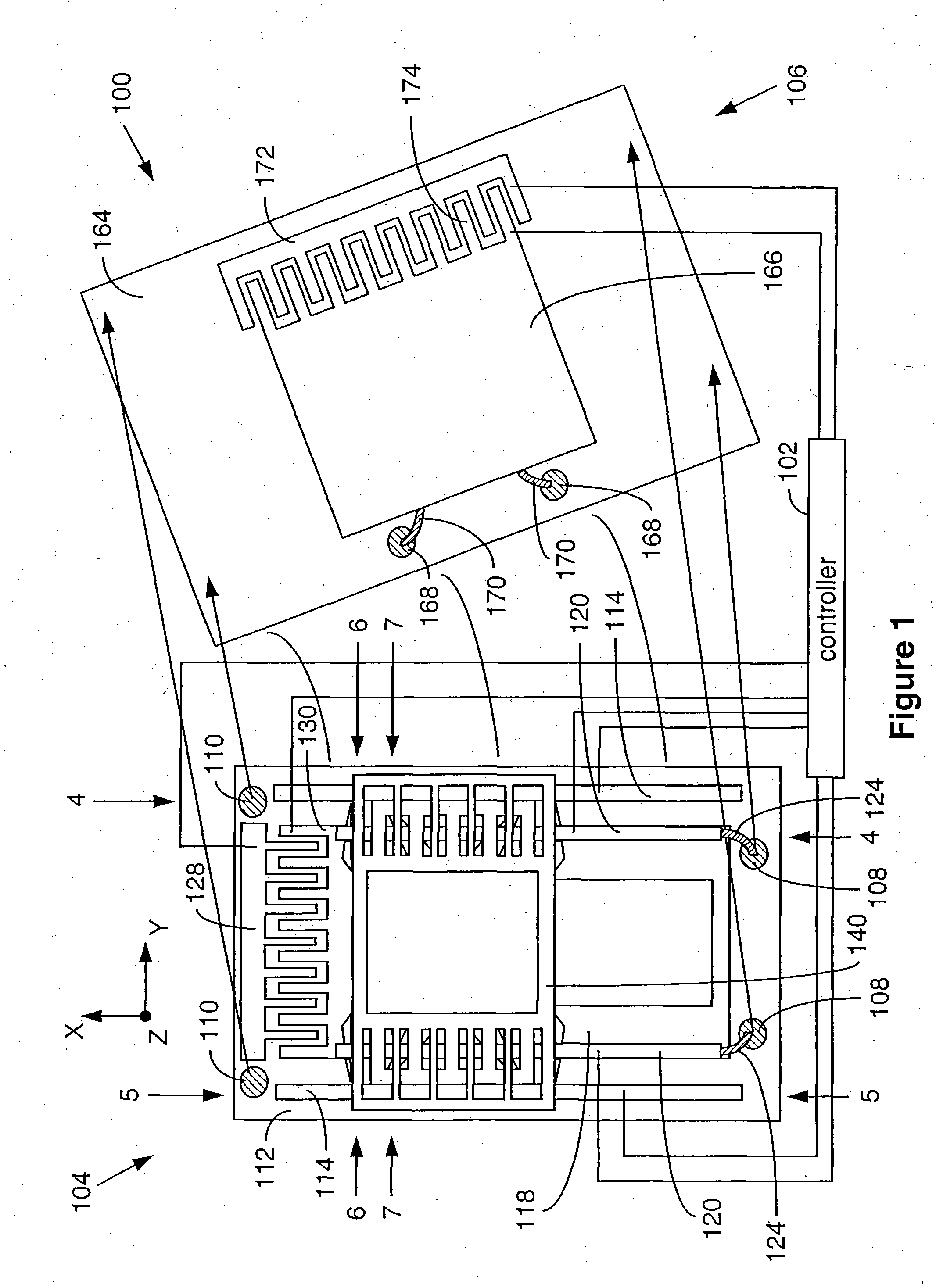
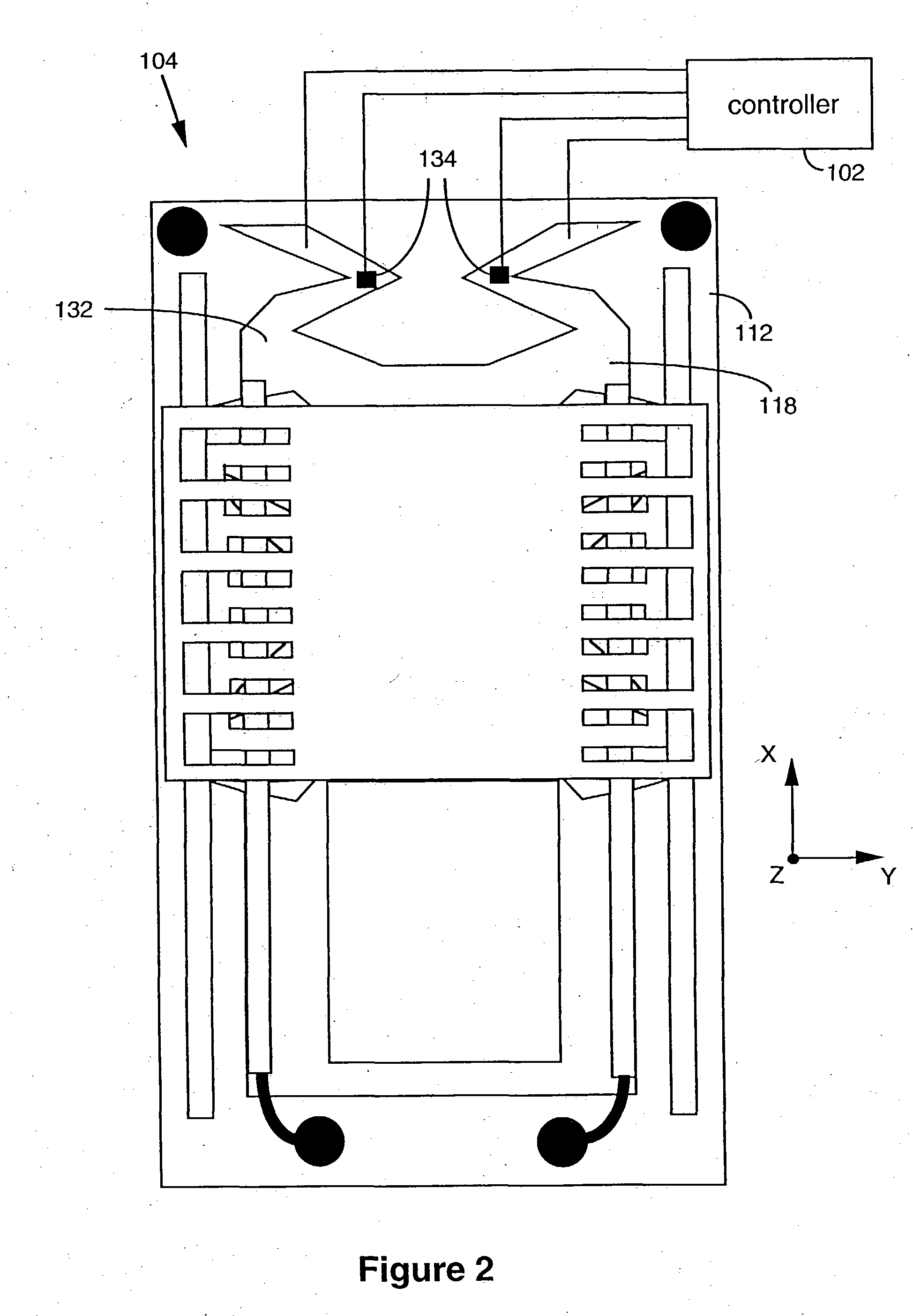
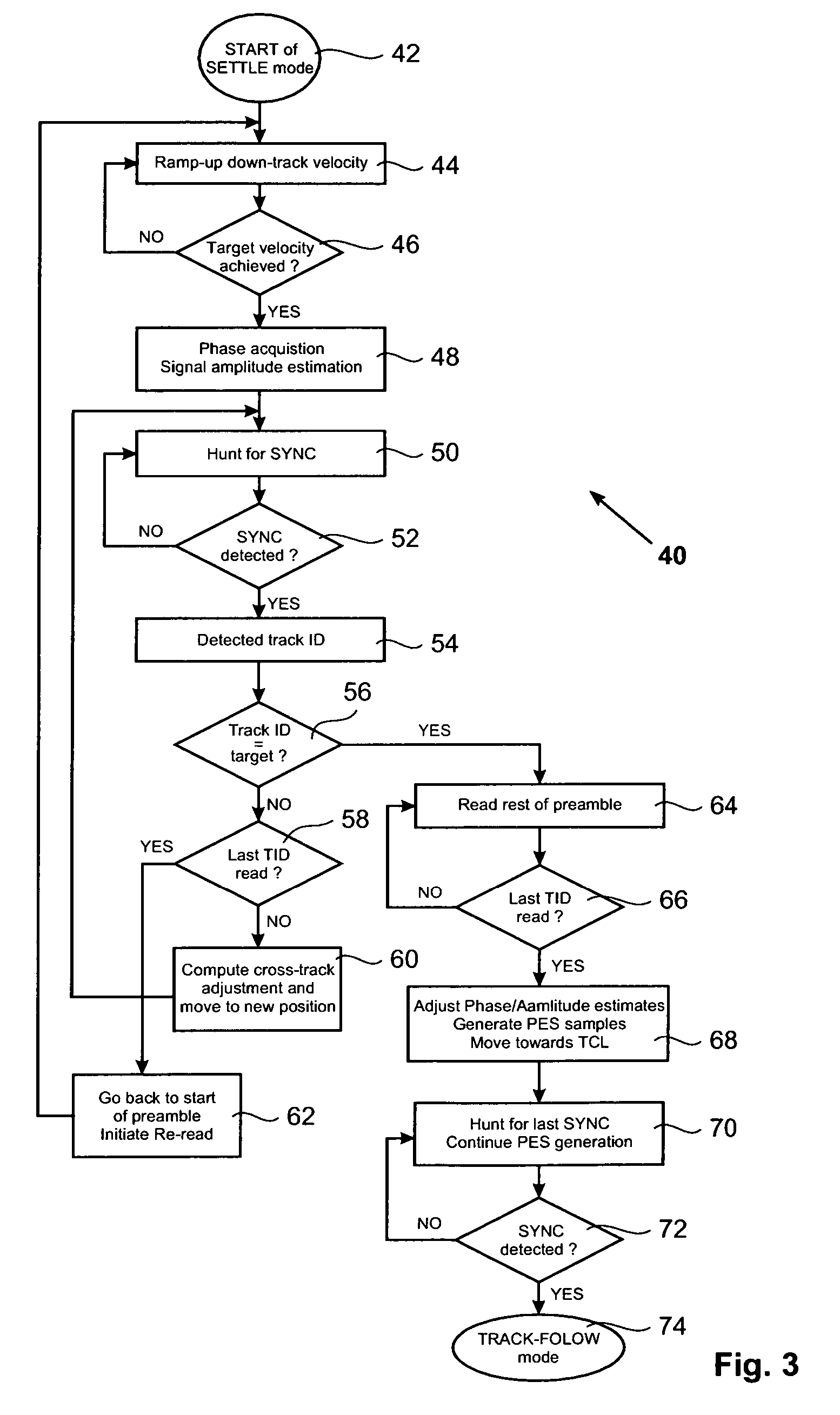
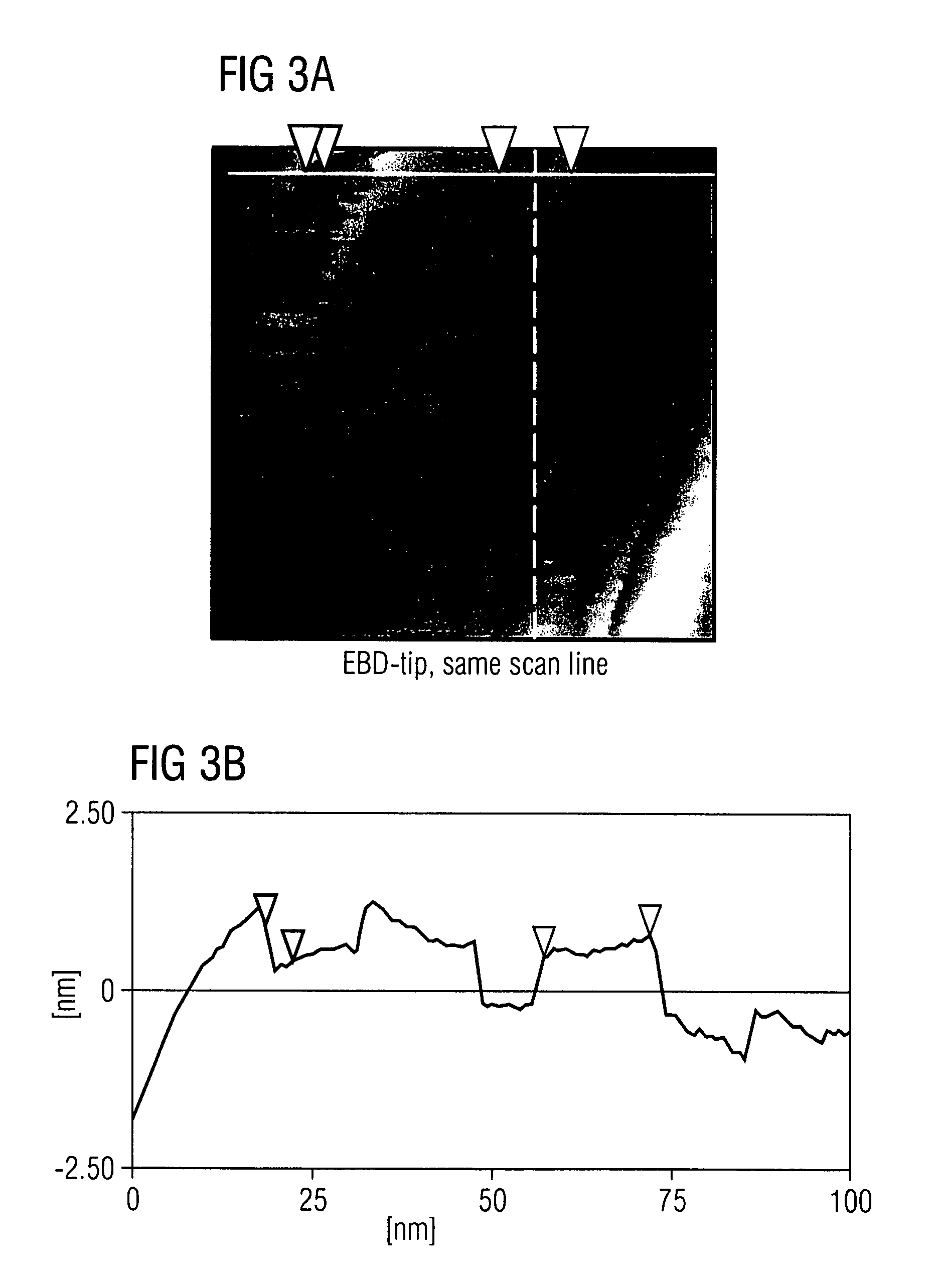
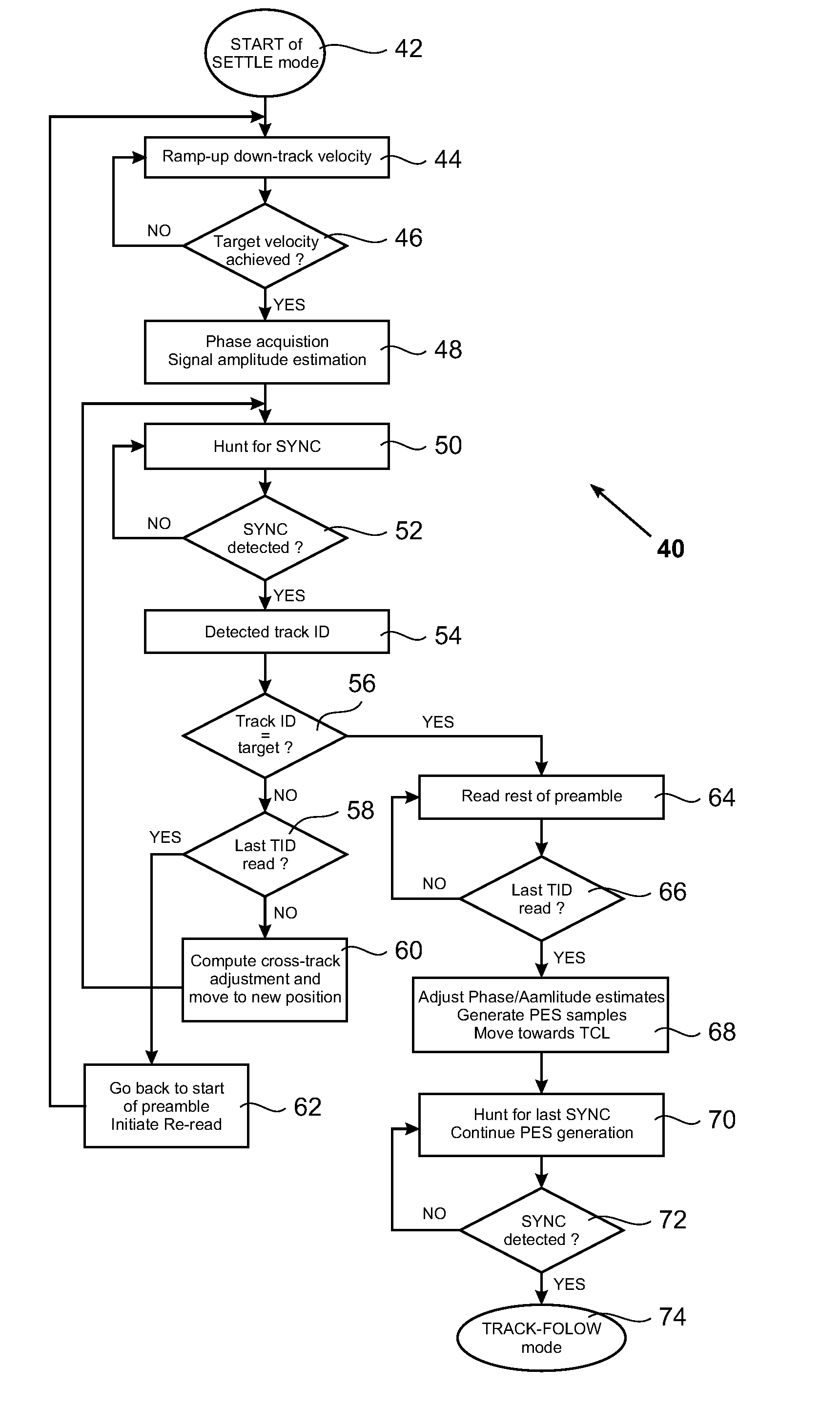
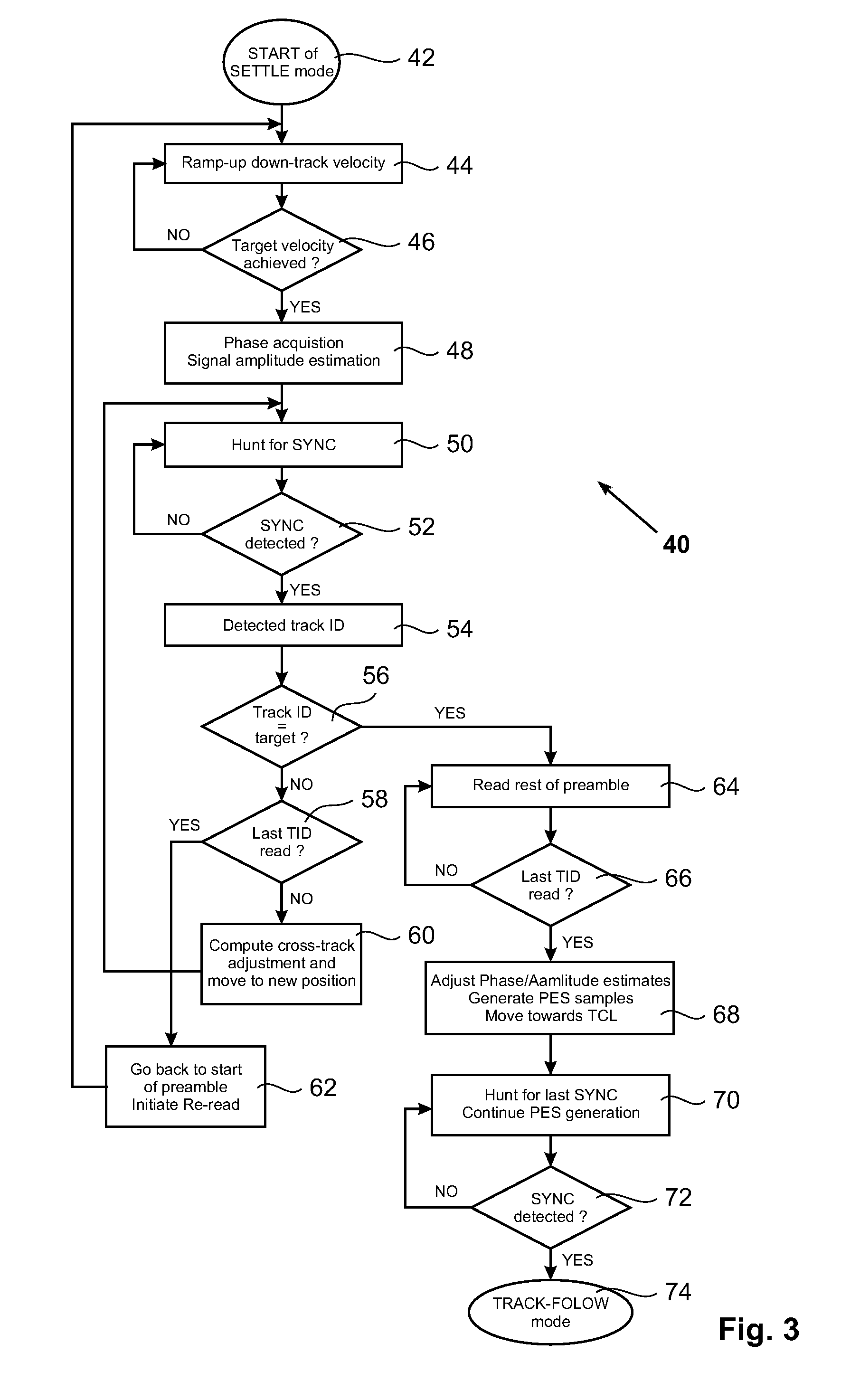
A method for settling on a target track of a servo system in a storage device (110) comprising a scanning probe (e.g., a scanning probe array system (124)) is disclosed, as well as a corresponding storage device (110). A data format is employed for the data stored in servo fields (18), consisting mainly of a preamble for assisting the settle process.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Apparatus for recording and reproducing high-density information using multi-functional probe
InactiveUS20020080709A1Shorten the timeImprove data transfer rateNanoinformaticsPhotometryComing outHigh density
In the apparatus for recording and reproducing high-density information using a multi-functional probe, media is locally heated not only by near-field optics come out of an aperture and but also by current induced from an end of an conducting cantilever, to record information and thereby increase a recording speed. The apparatus and method for recording and reproducing the high-density information using the multi-functional probe includes a conducting cantilever, in which a cantilever stage and a near-field optical aperture probe are formed in one body, the media is locally heated not only by the near-field optics from a near-field optical aperture probe but also by the current induced from the probe to the media or induced from the probe itself, and then the information is recorded; and an optical detector for reproducing the recorded information with a reflectivity of light come out of the near-field optical aperture probe or a transmission onto the media.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Nanoscale digital data storage device
InactiveUS20050018587A1Improve energy efficiencyMechanical recordingNanoinformaticsDigital dataWrite bit
A nanoscale digital data storage device is provided. In the nanoscale digital data storage device, a storage medium has a polymer layer deposited on a substrate, for writing and reading digital data on and from. A cantilever chip has a plurality of cantilevers arranged therein. Each cantilever is fixed to another substrate at one end and has a tip formed at its free end, for emitting heat according to an applied current. The tips in the cantilever chip are in contact with the storage medium at predetermined bit positions during data writing, and the cantilever chip applies a relatively low current to a tip when the tip writes bit 1 and a relatively high current to the tip when the tip writes bit 0.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data storage device
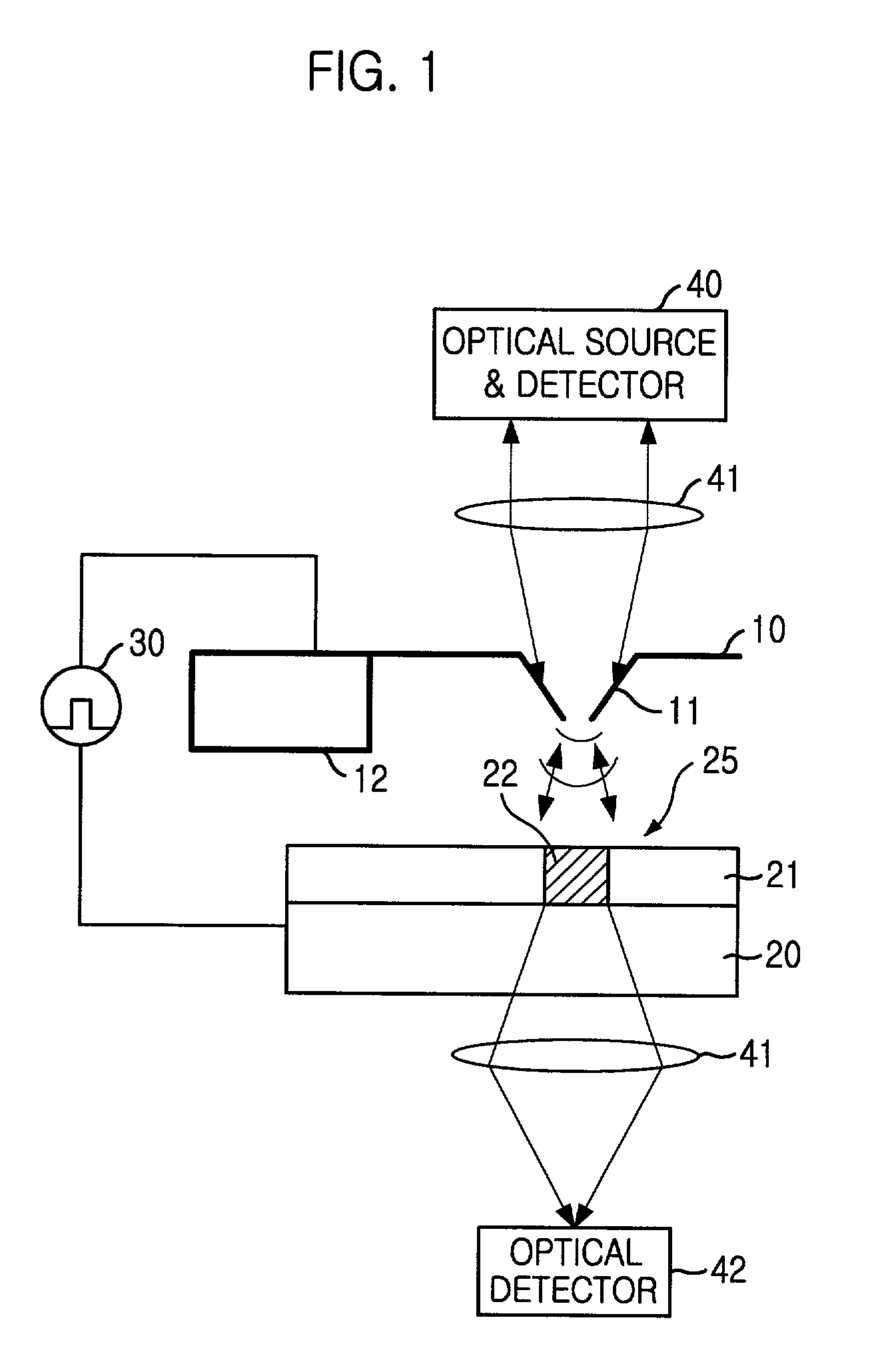
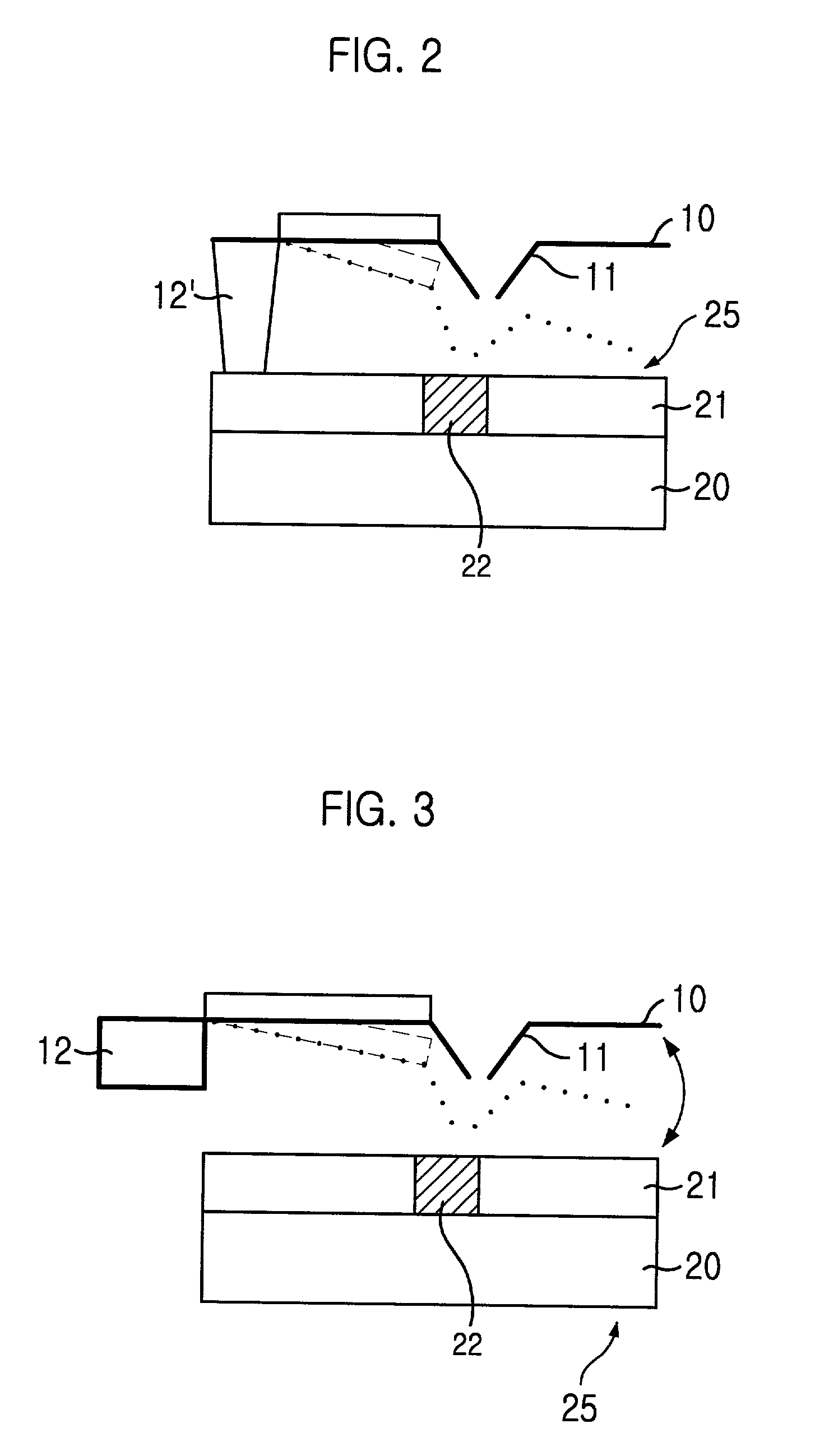
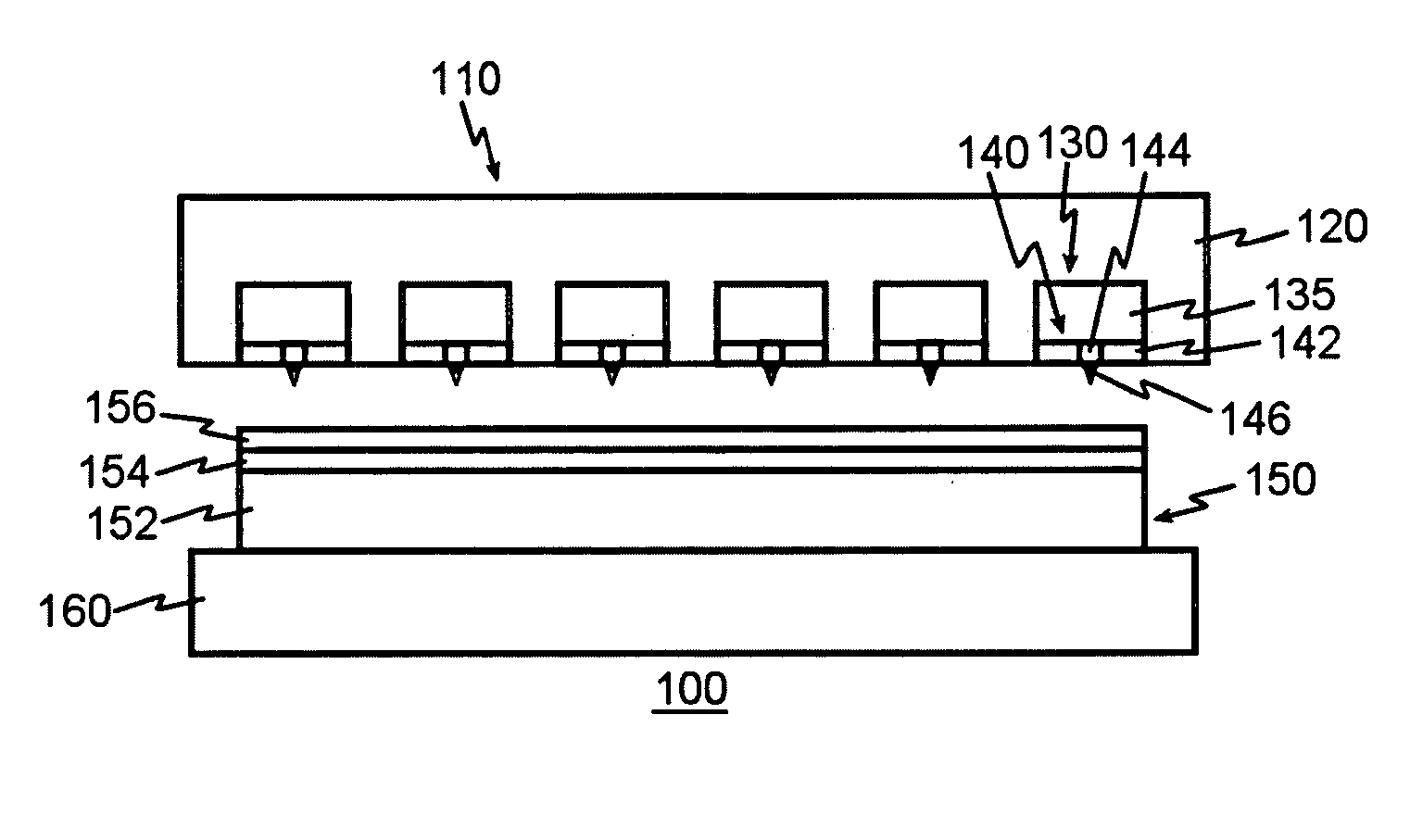
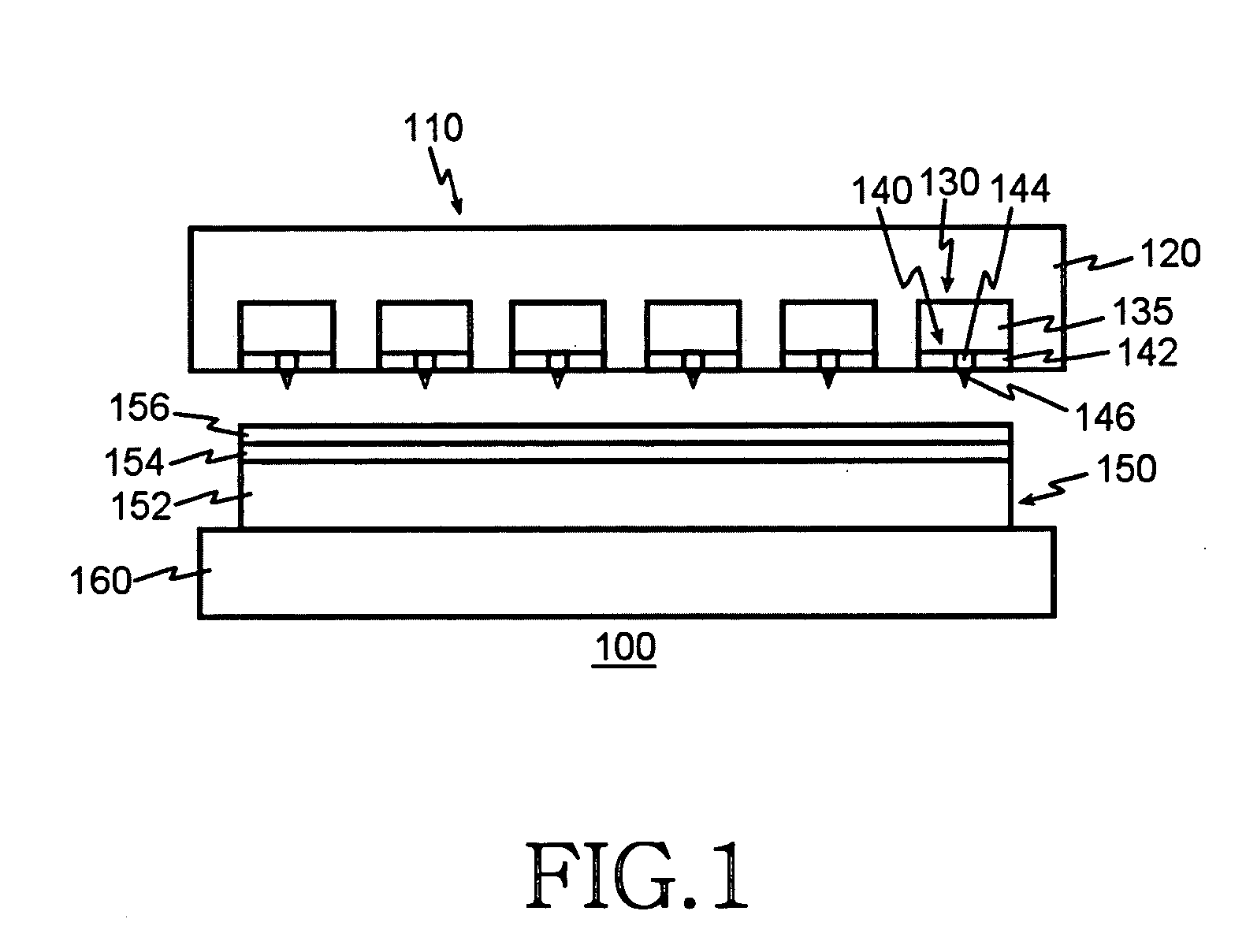
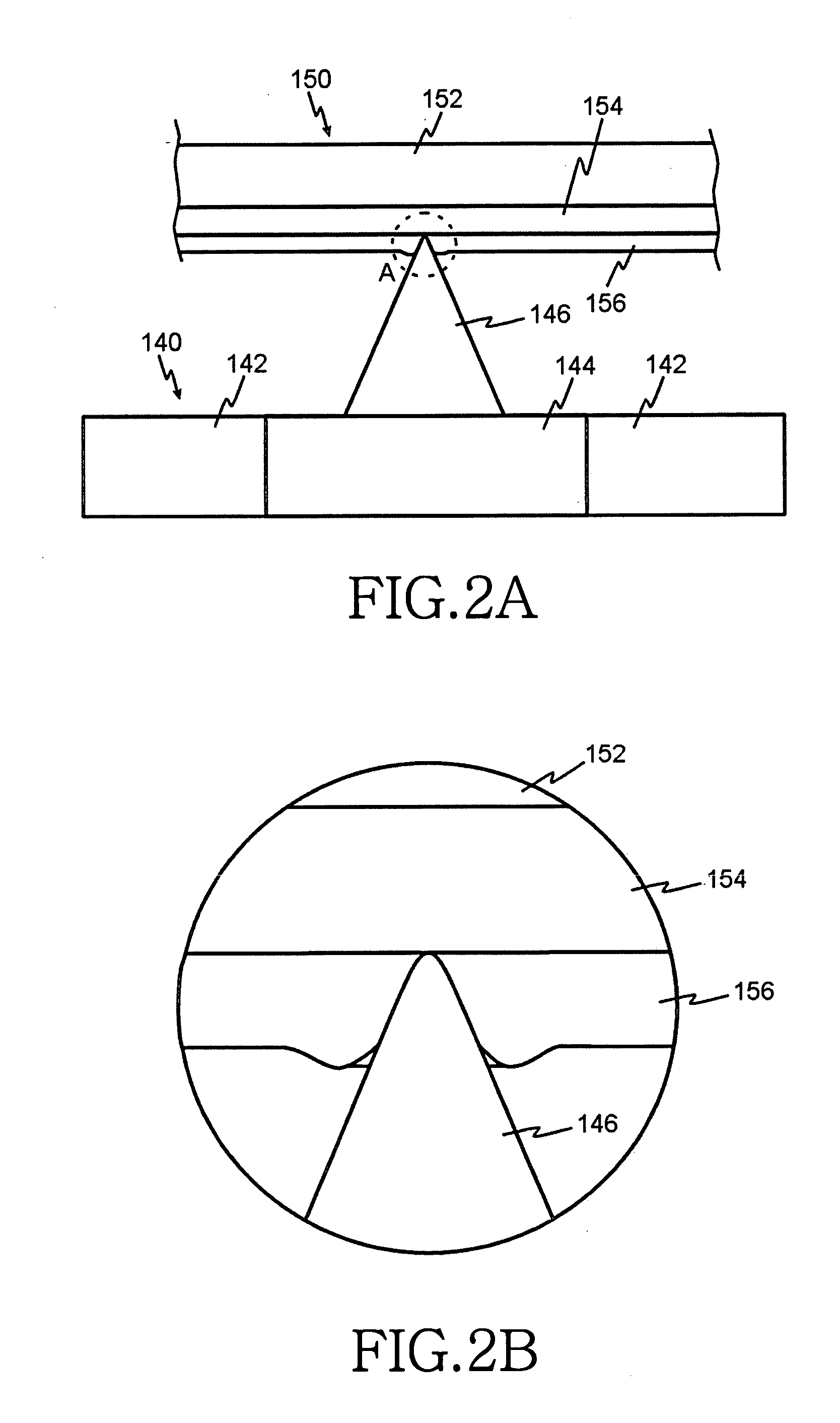
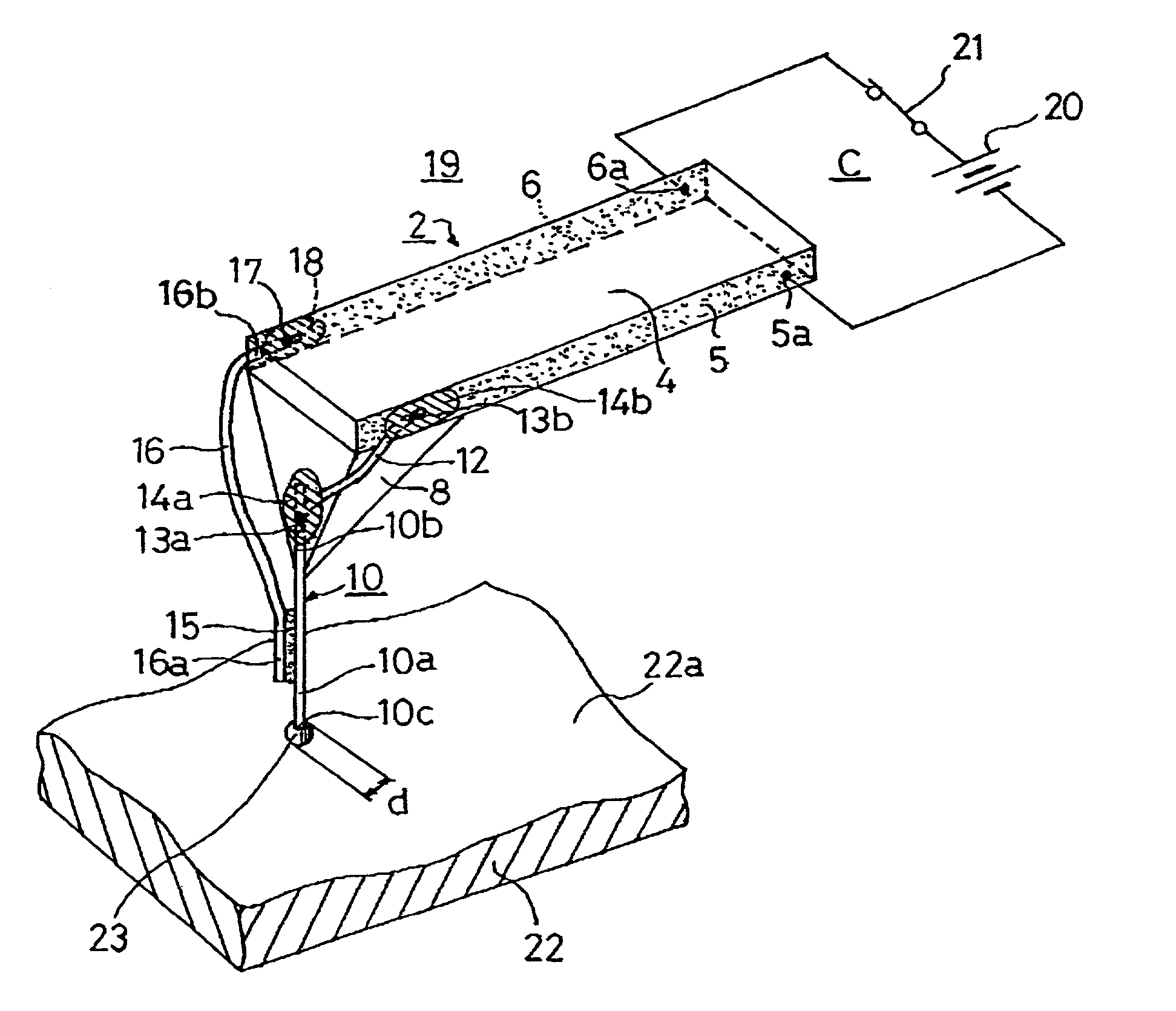
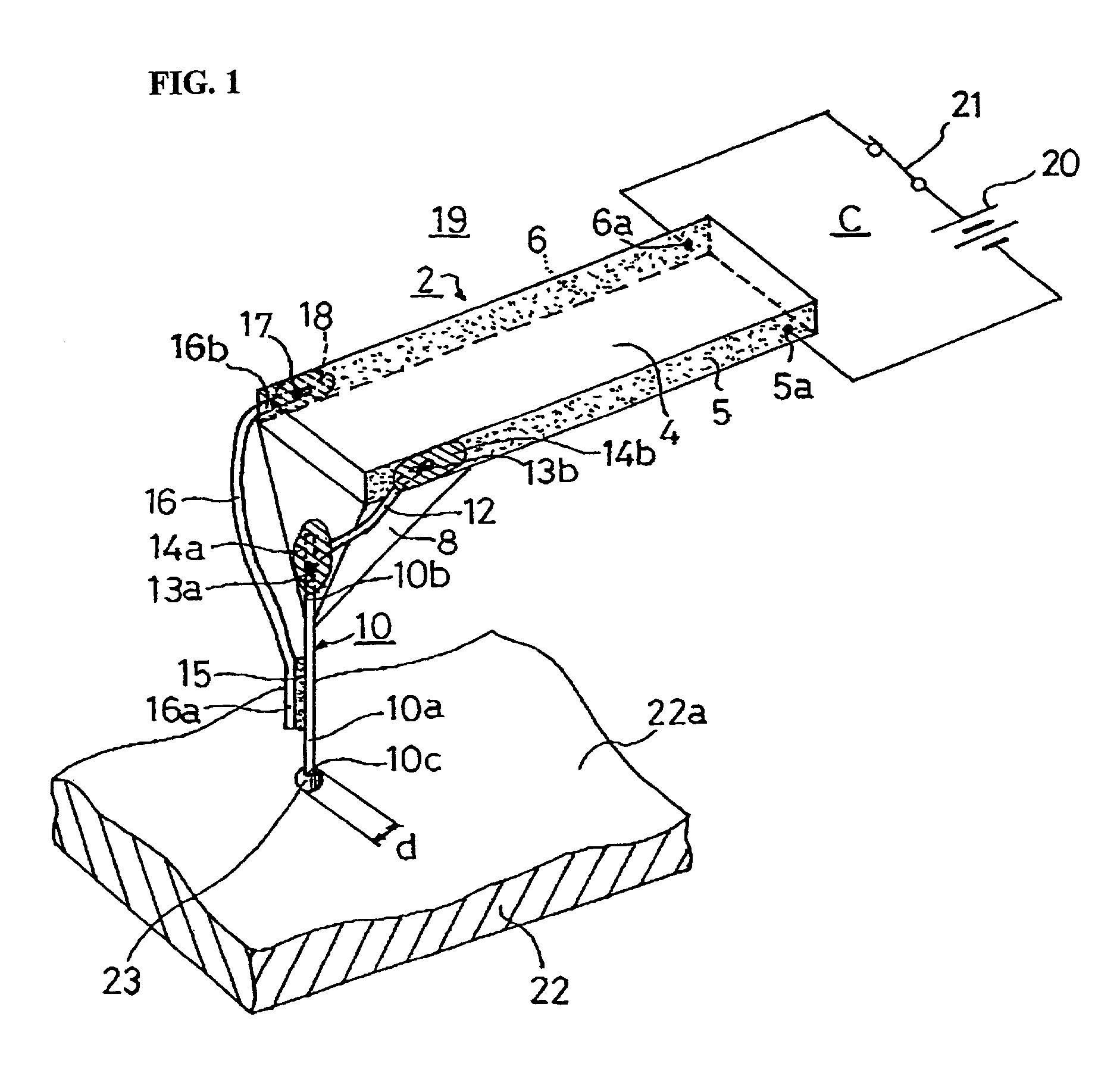
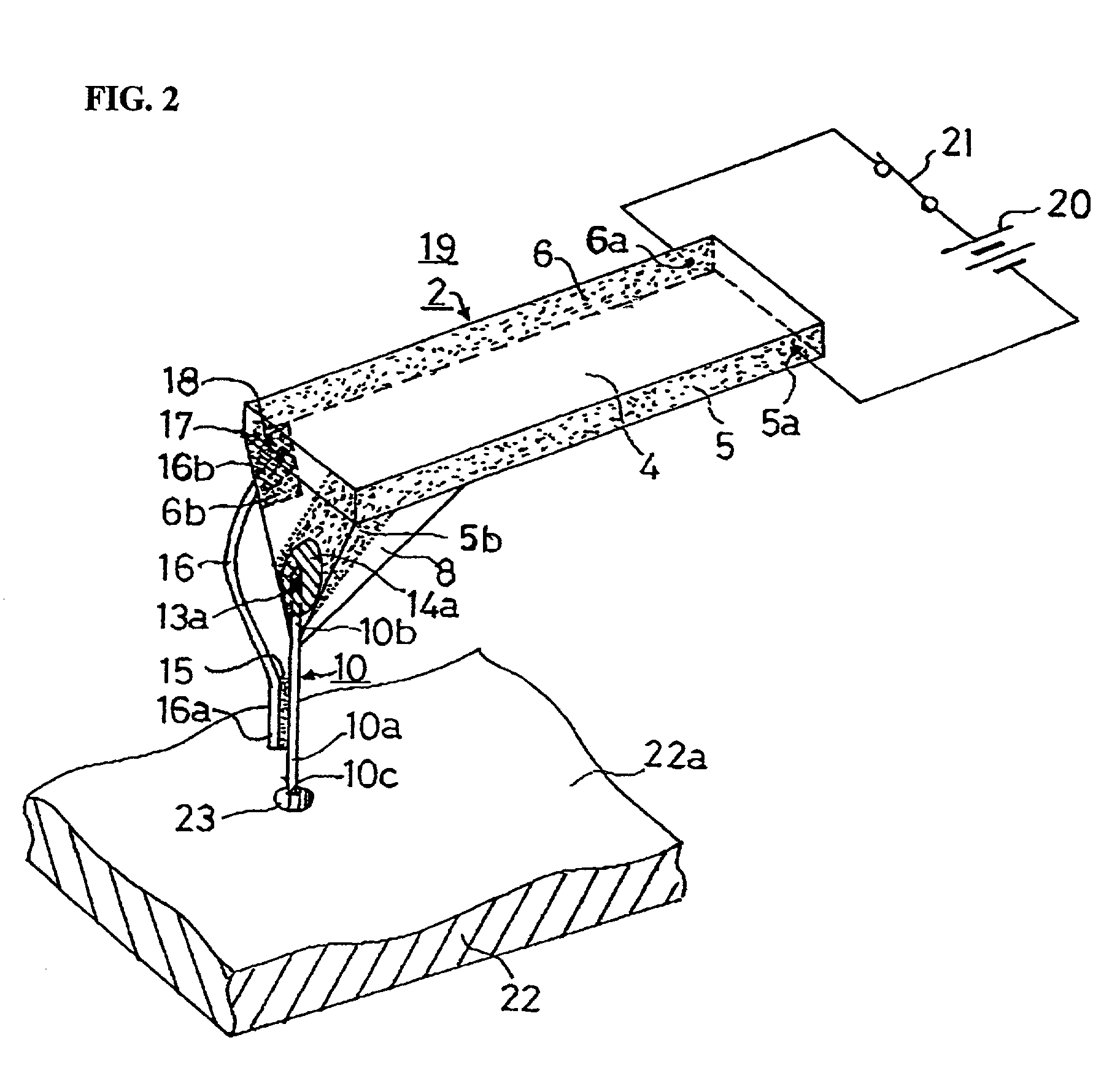
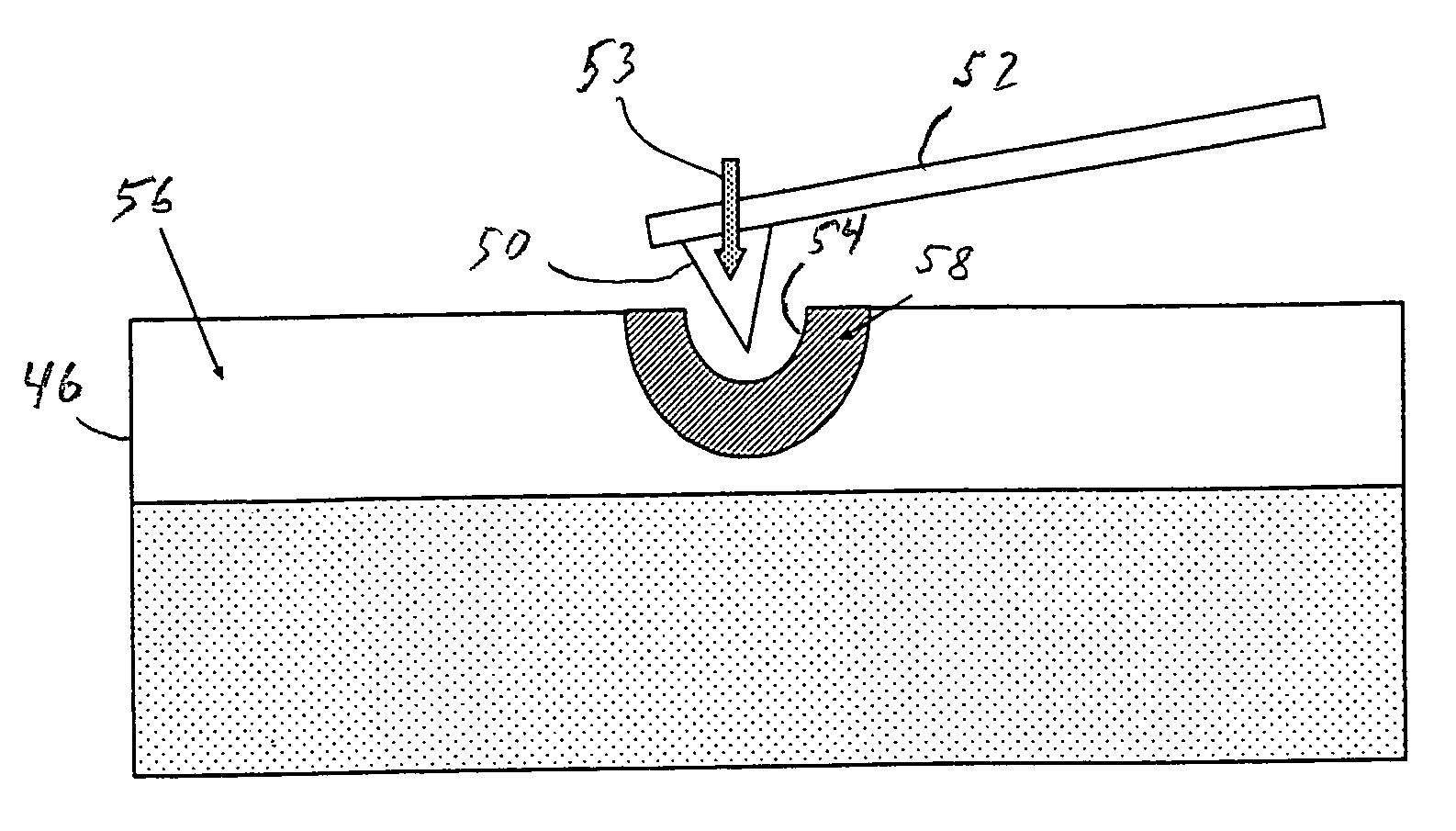
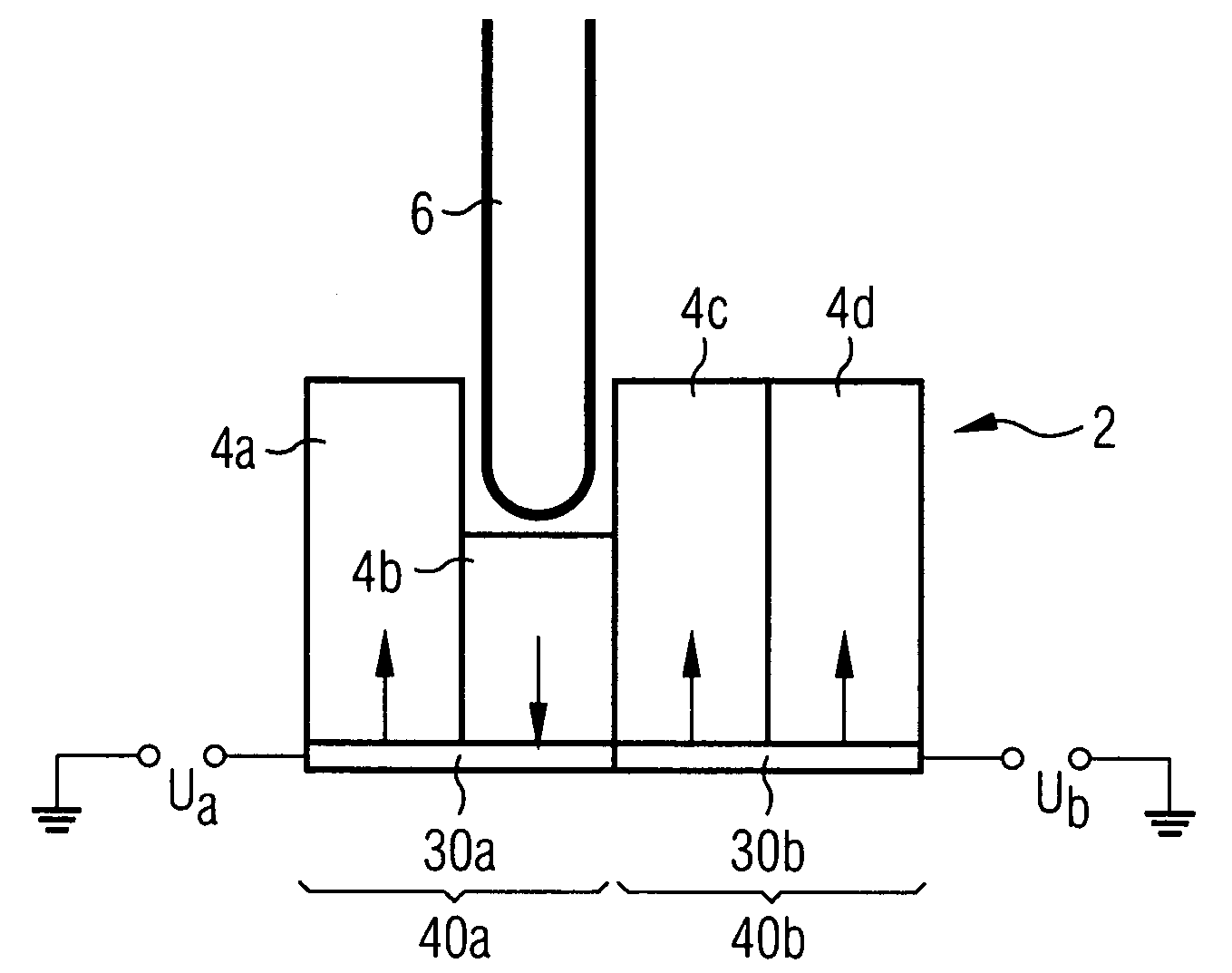
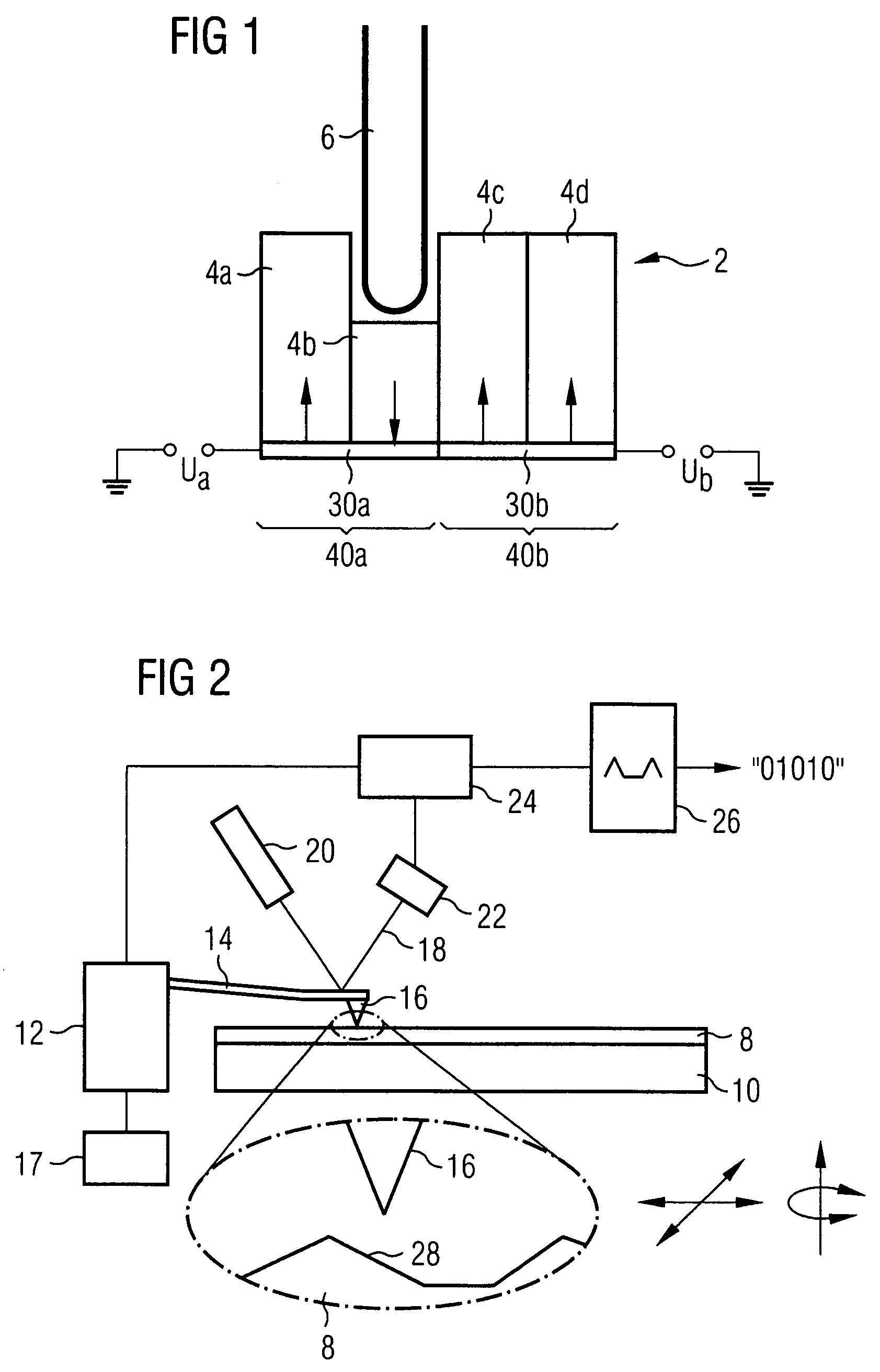
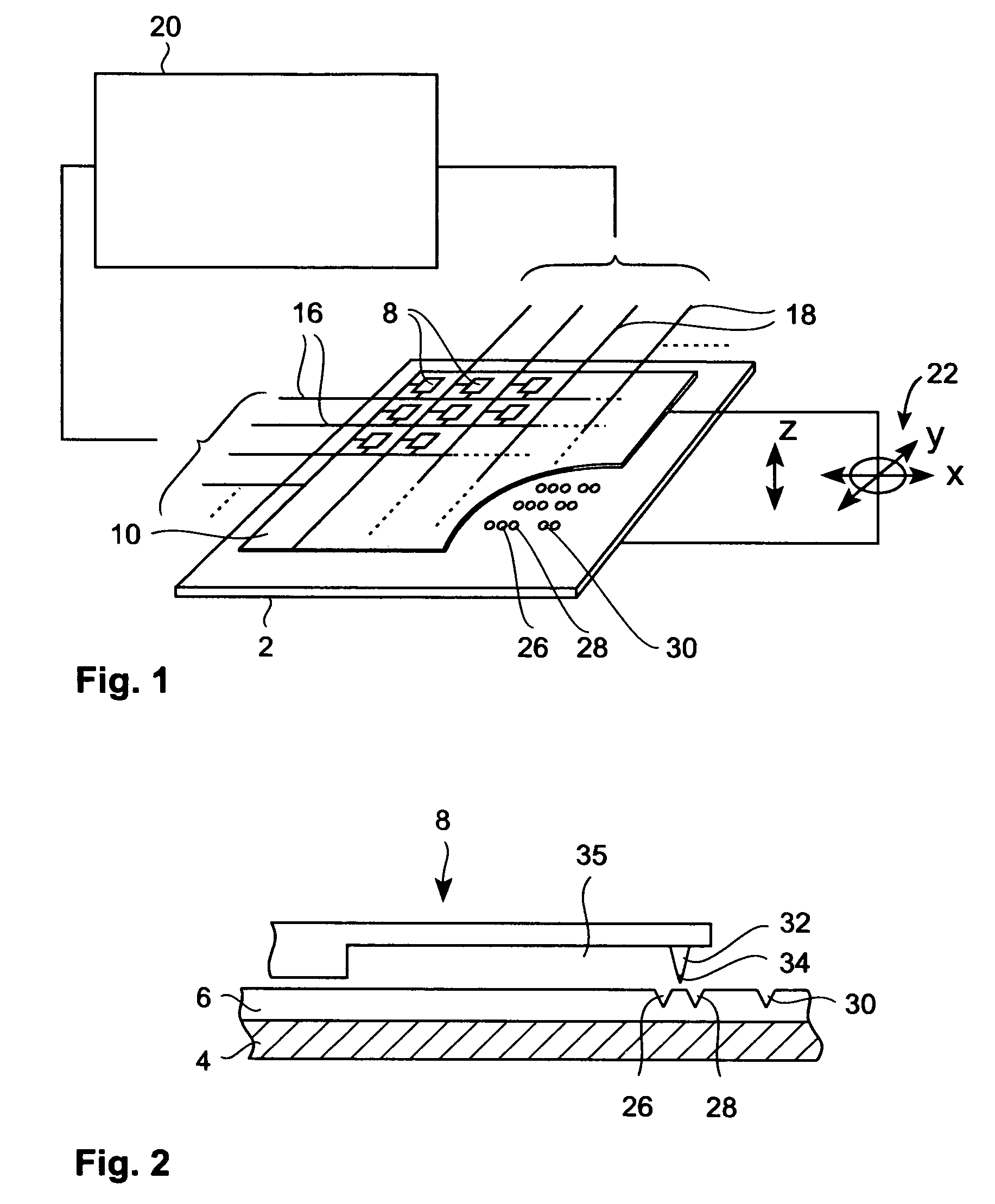
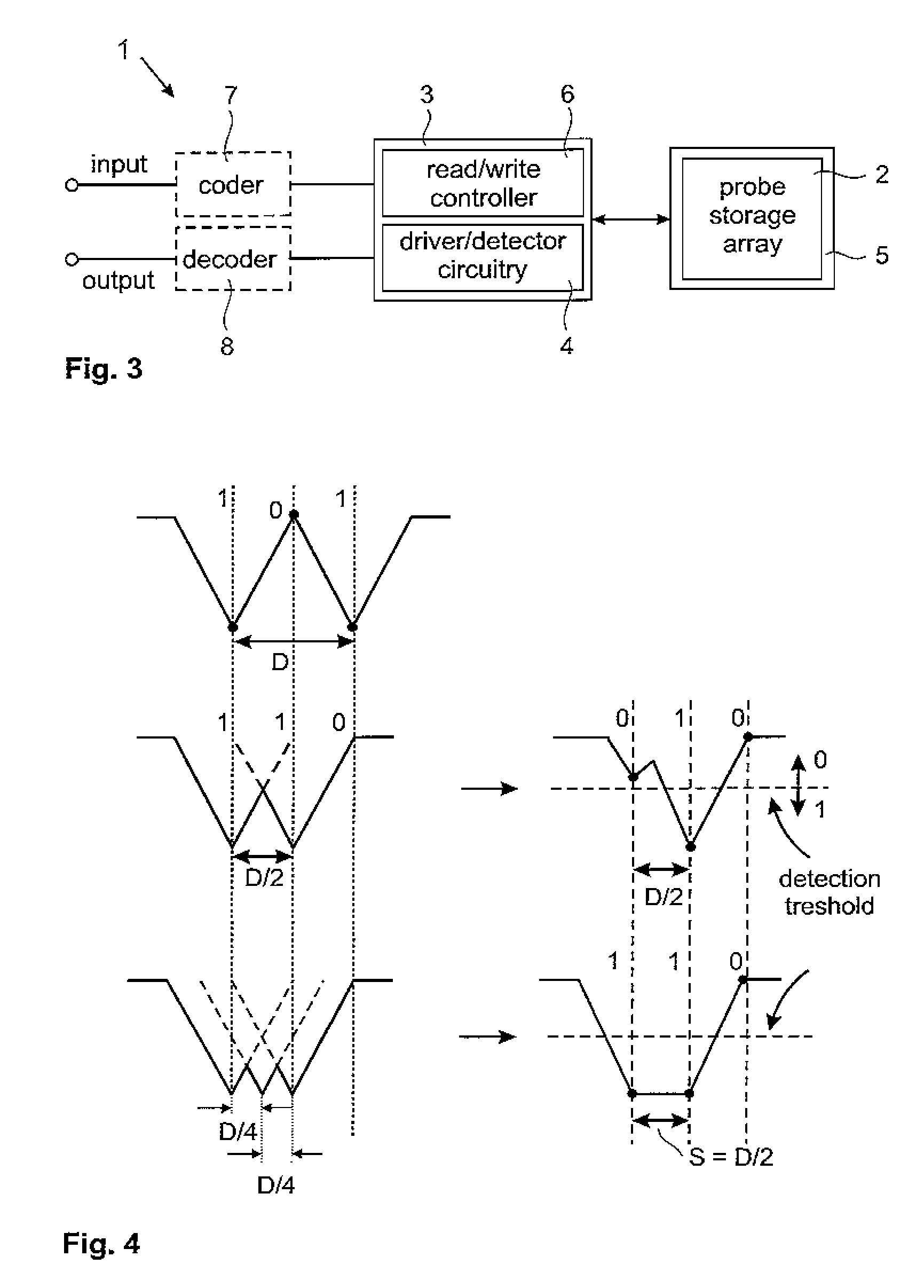
InactiveUS20060187803A1Reduce wearEasy to correctNanoinformaticsReproducing by electric probe meansCapacitanceMedia design
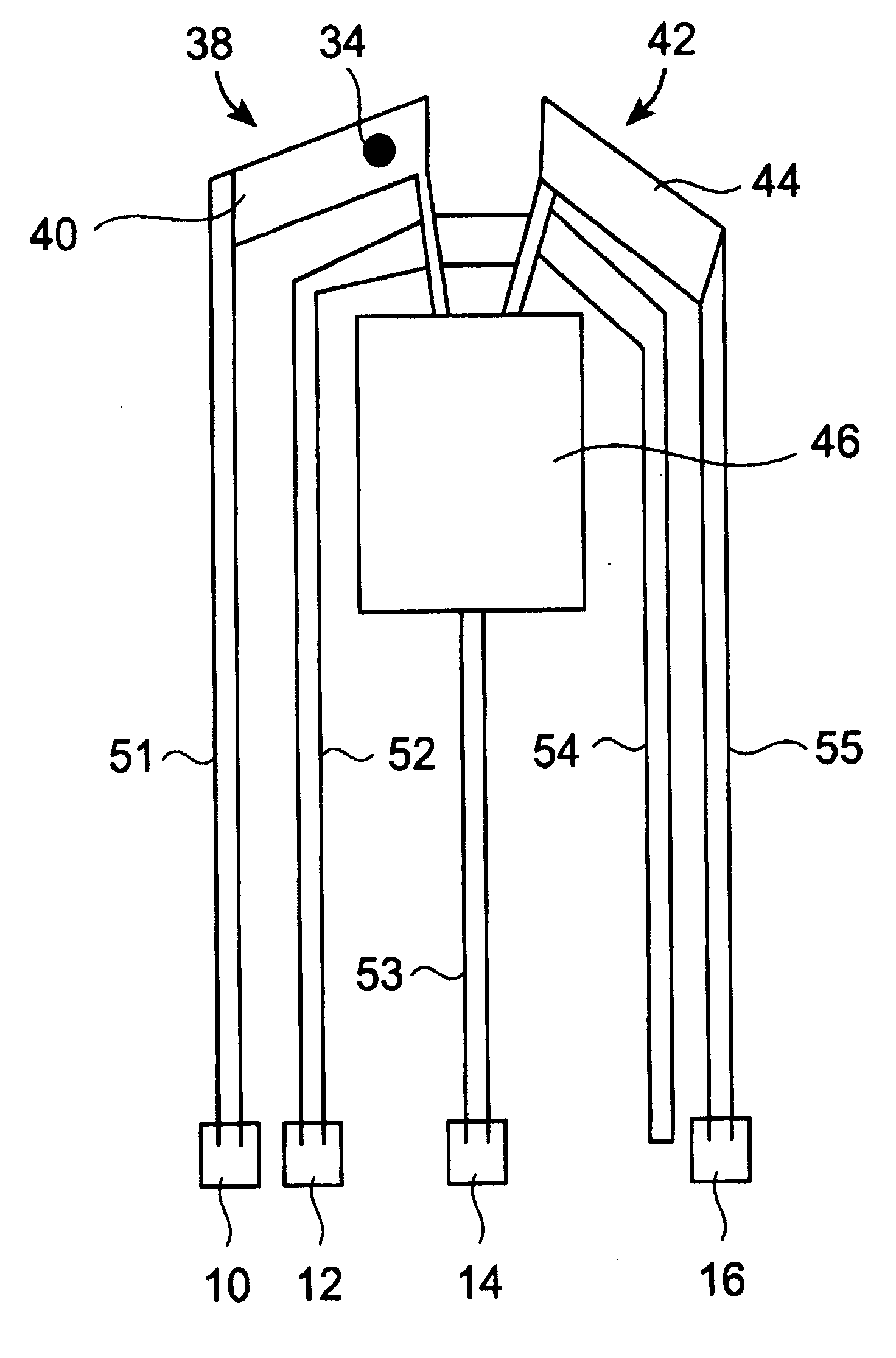
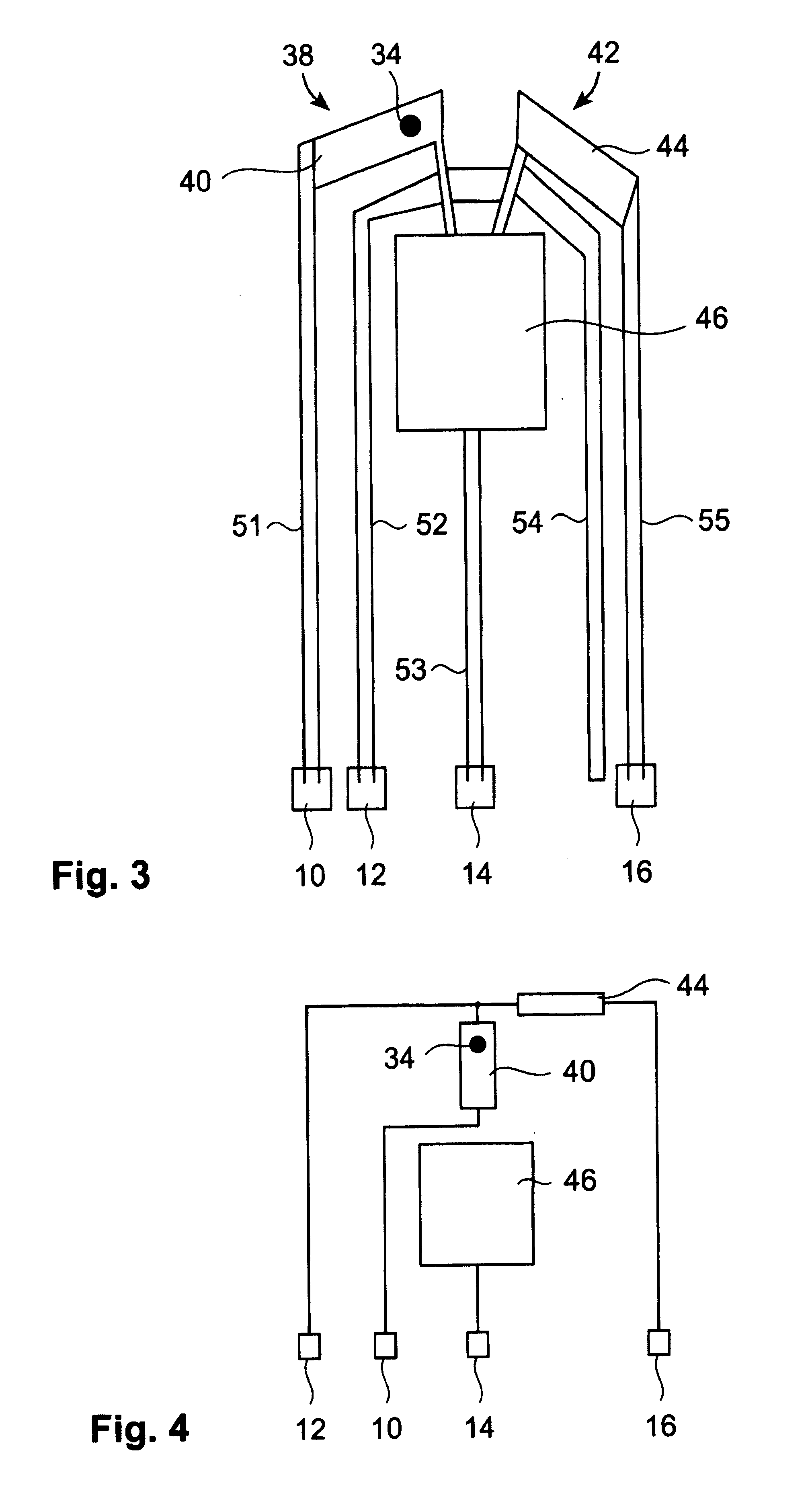
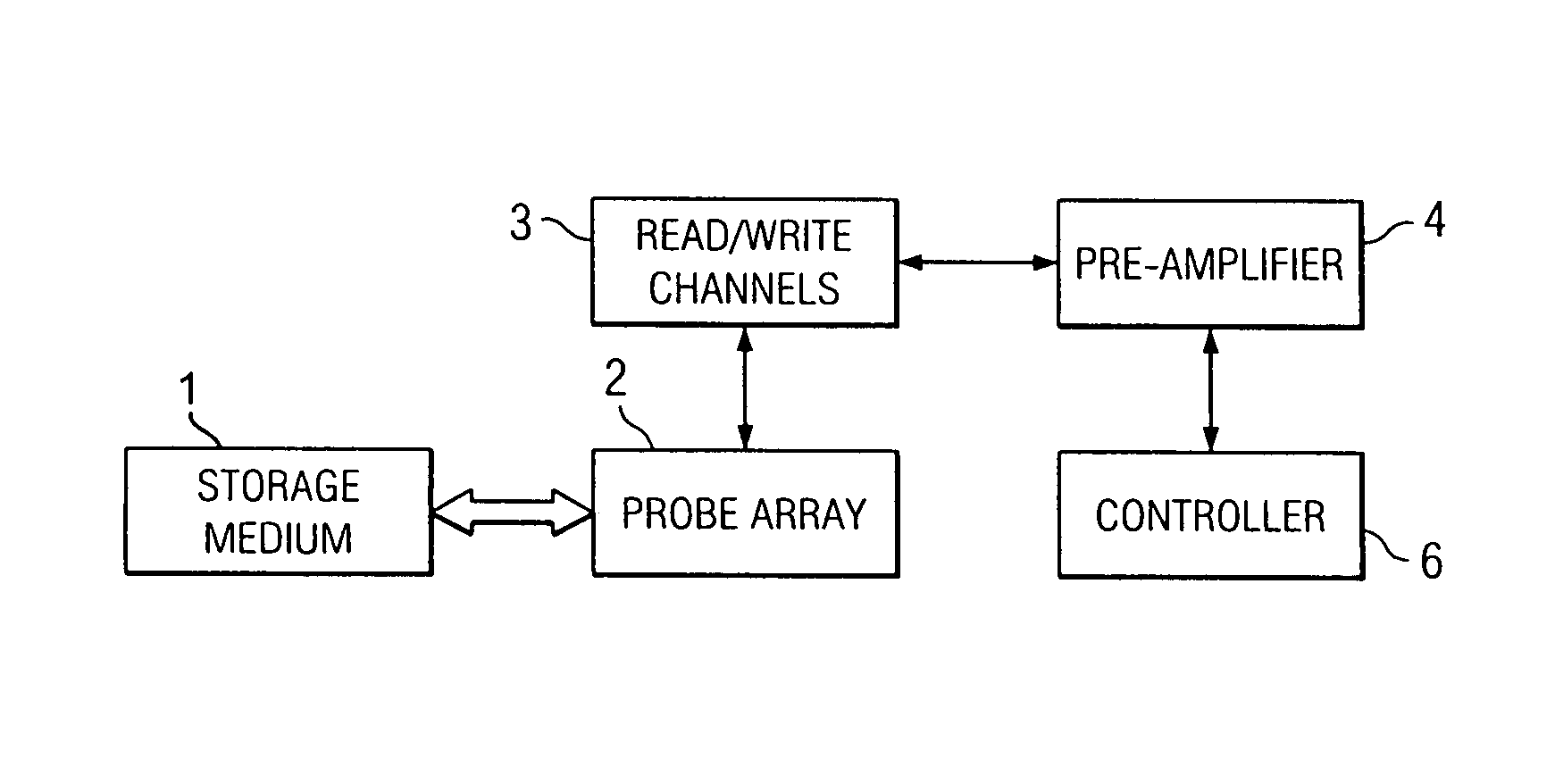
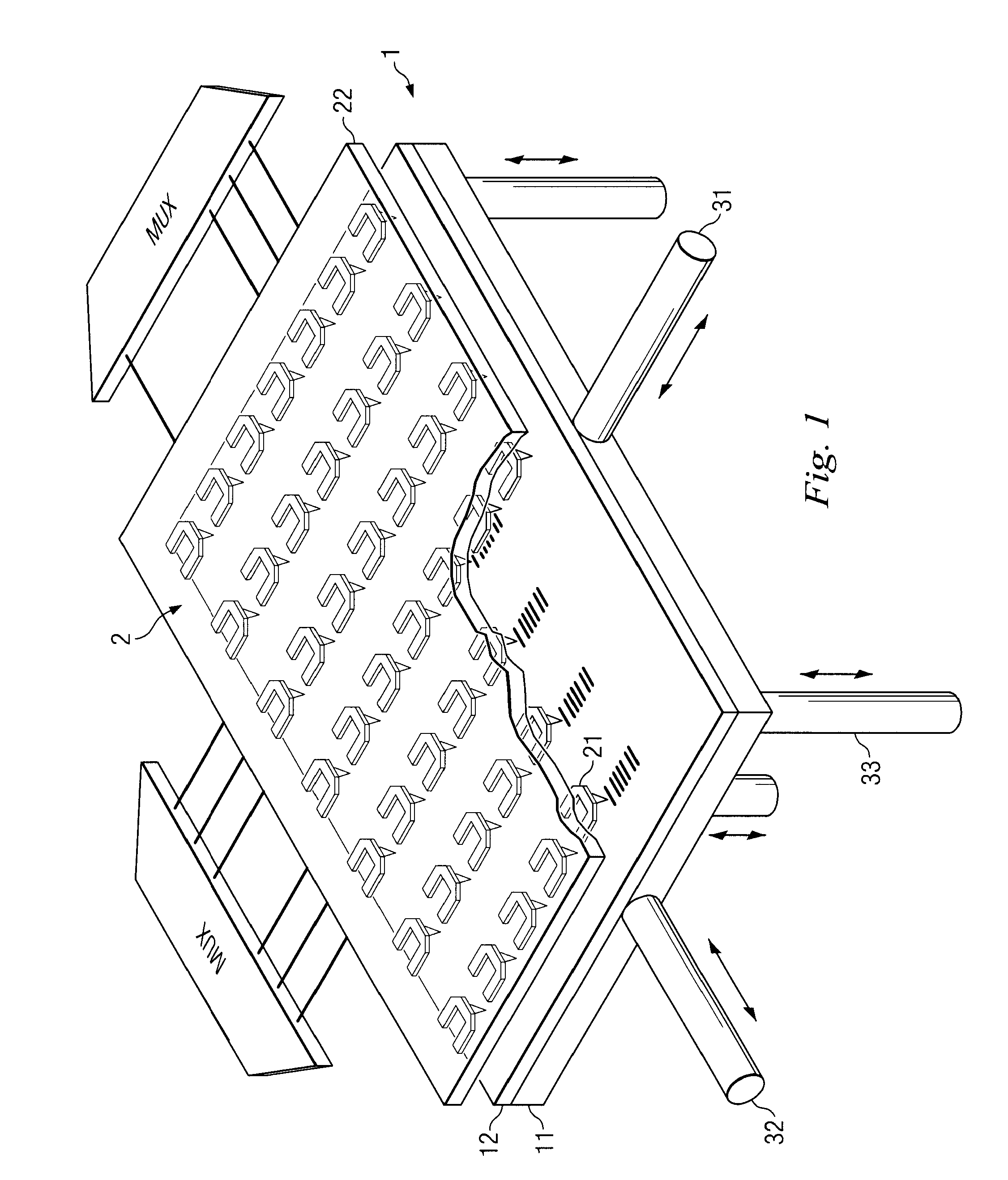
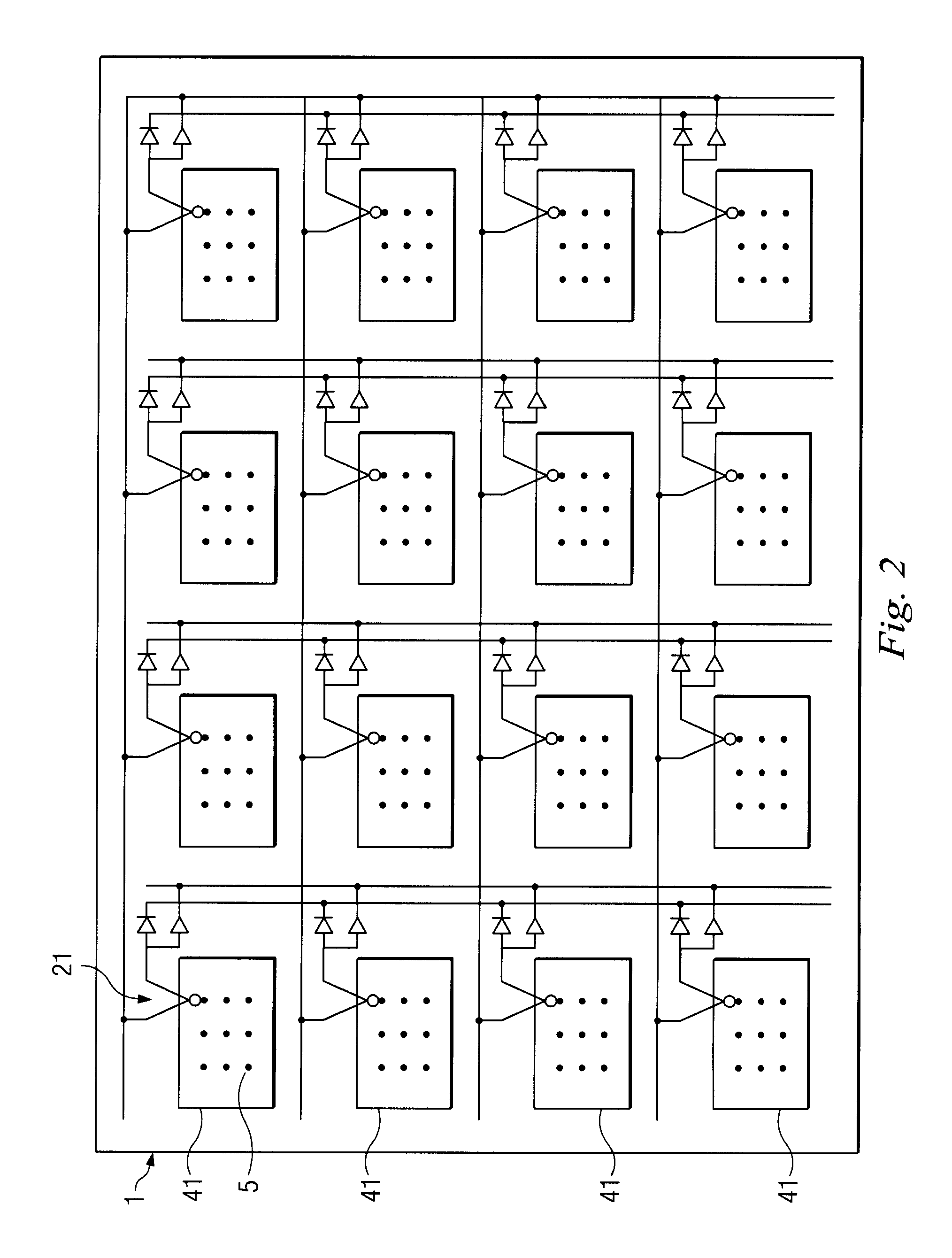
A storage device including a storage medium for storing data in the form of topographic or magnetic marks. At least one probe is mounted on a common frame, the common frame and the storage medium designed for moving relative to each other for creating or detecting said marks. Each probe includes a tip facing the storage medium, a read sensing element, a write element and a capacitive platform, that forms a first electrode and is designed for a voltage potential applied to it independent from a control signal for said read sensing element and for said voltage potential applied to said capacitive platform being independent from a control signal for said write heating element. It further comprises a second electrode arranged in a fixed position relative to the storage medium forming a first capacitor together wherein said first electrode and a medium between the first and second electrode.
Owner:IBM CORP
High density data storage medium
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Heat emitting probe and heat emitting probe apparatus
InactiveUS7073937B2Improve recording densityReduce the overall diameterMaterial thermal conductivityRecording by optical meansControl circuitNanotube
A heat emitting probe including a conductive nanotube probe needle with its base end fastened to a holder and its tip end protruded, a heat emitting body formed on the probe needle, a conductive nanotube lead wire fastened to the heat emitting body, and an electric current supply that causes an electric current to pass through the conductive nanotube lead wire and both ends of the probe needle. The tip end of the probe needle is thus heated by an electric current flowing through the heat emitting body. A heat emitting probe apparatus includes the above-described heat emitting probe, a scanning mechanism that allows the heat emitting probe to scan over a thermal recording medium, and a control circuit that causes the tip end of the probe needle to emit heat, thus recording extremely small hole patterns in the surface of a thermal recording medium.
Owner:NAKAYAMA YOSHIKAZU +1
Magnetic data storage system
InactiveUS7586828B1Large storage densityMechanical recordingNanoinformaticsMagnetic transitionsFerromagnetism
A magnetic data storage system having a scanning tip array based system and a shape memory thin film-based data storage medium. Prior to storing data, the medium is in its non-ferromagnetic austenitic phase. Indentation stress locally induces martensitic transformation of the medium, which in turn generates a locally ferromagnetized surface. By measuring the magnetic force interaction between the tip and the medium surface, inscribed magnetic information can be read. The shape memory thin film enables the stress-induced local magnetic transition to provide a fast data storage system with high data storage density.
Owner:TINI ALLOY
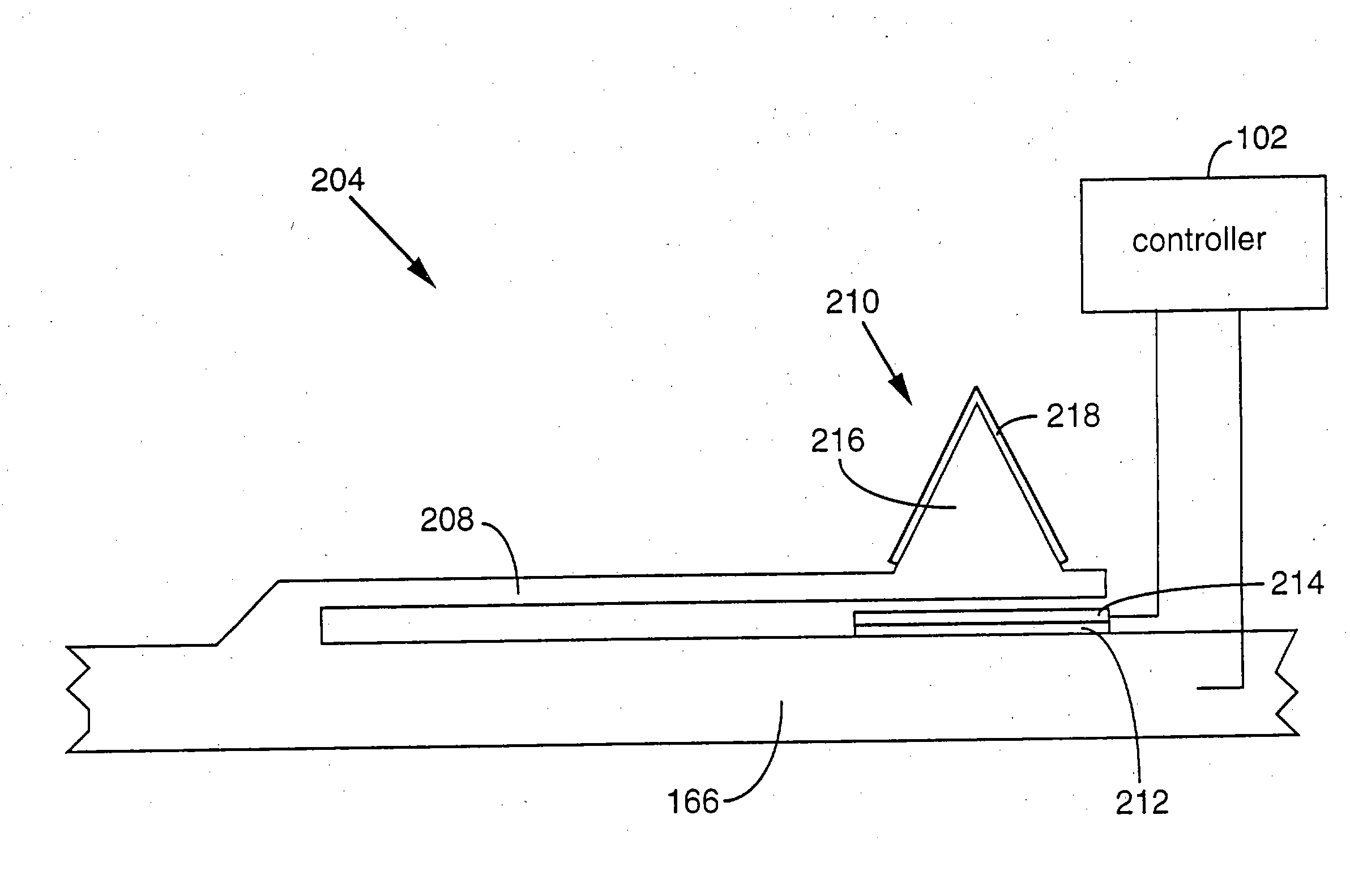
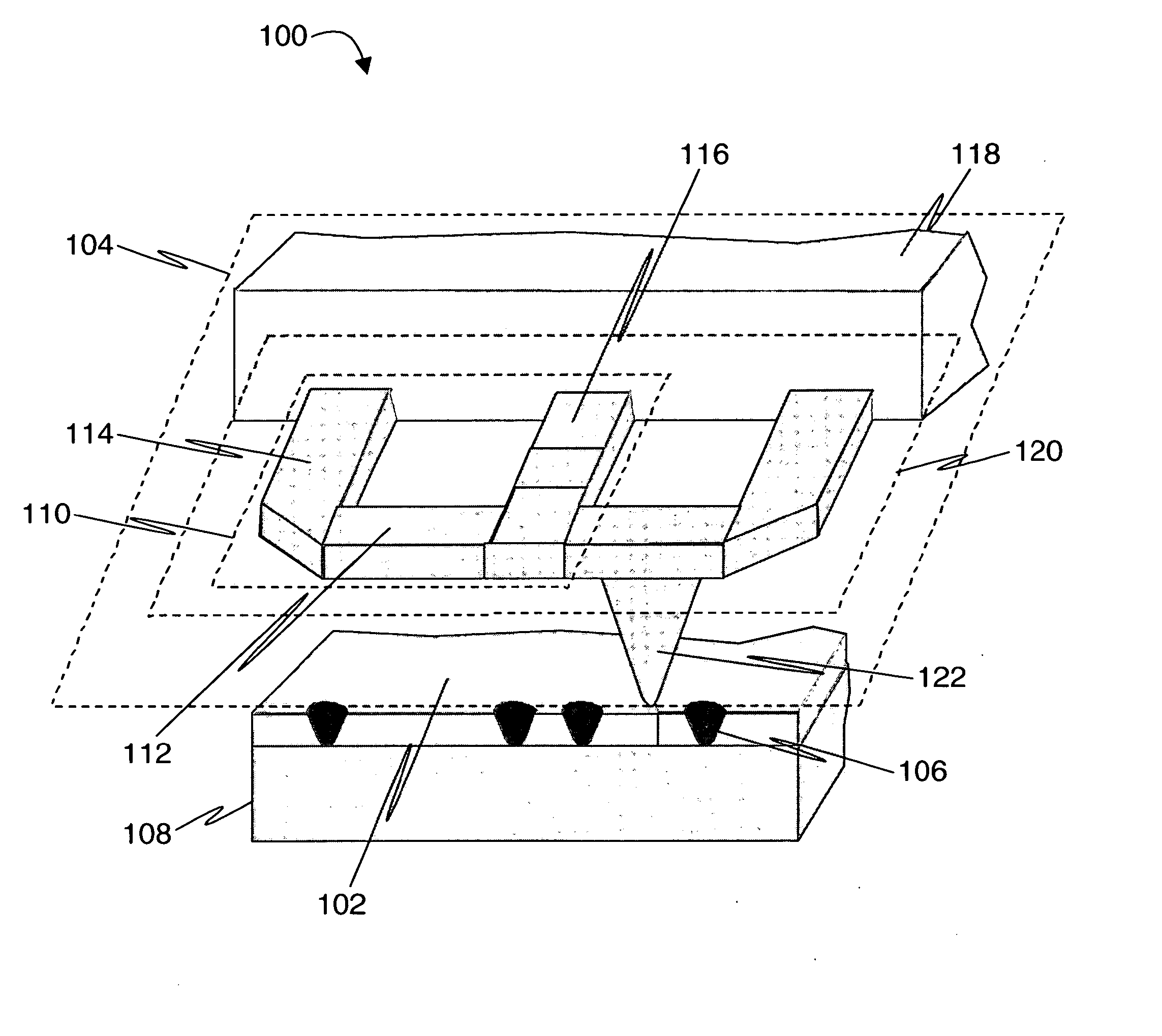
Probe for scanning over a substrate and a data storage device
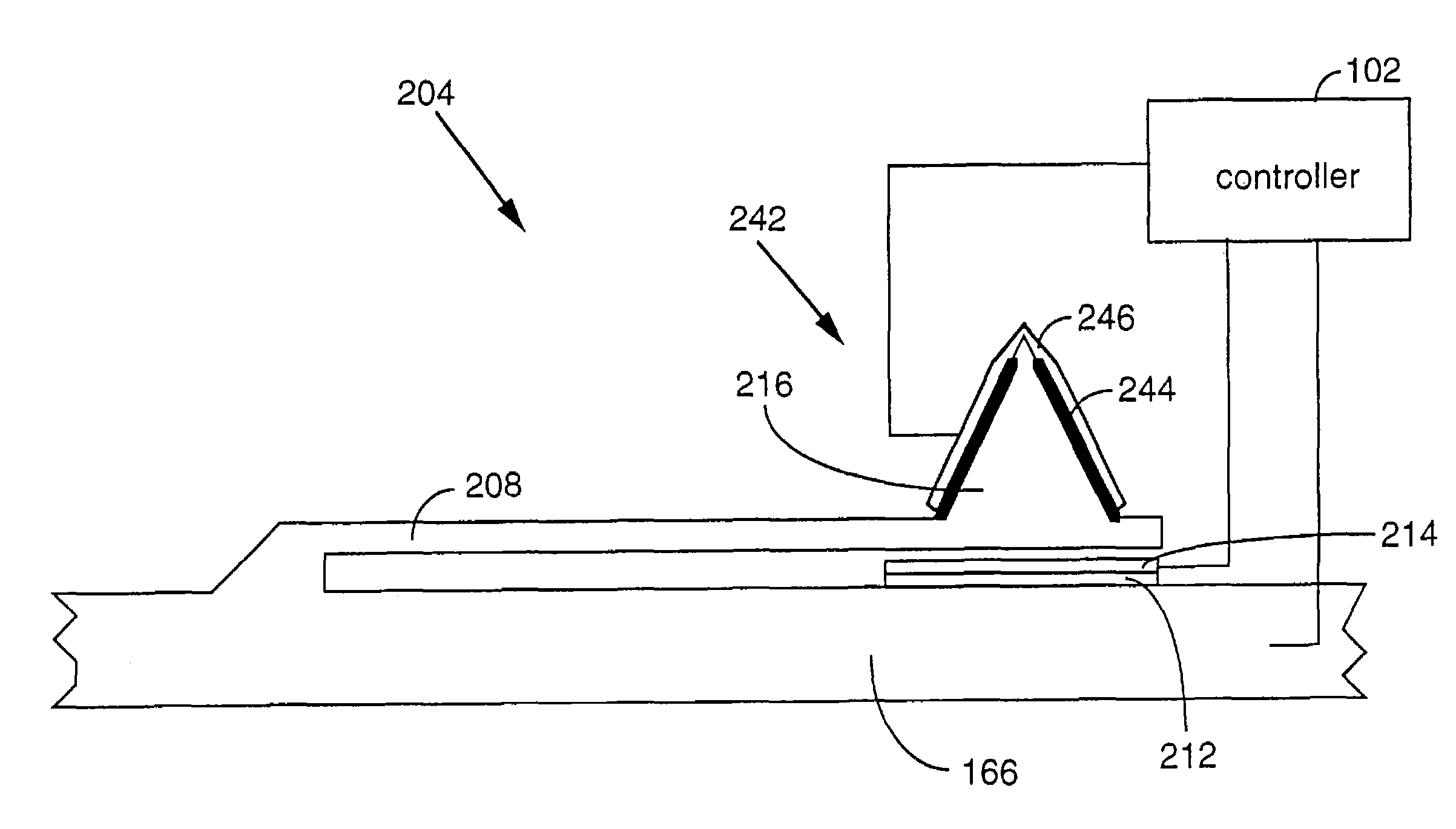
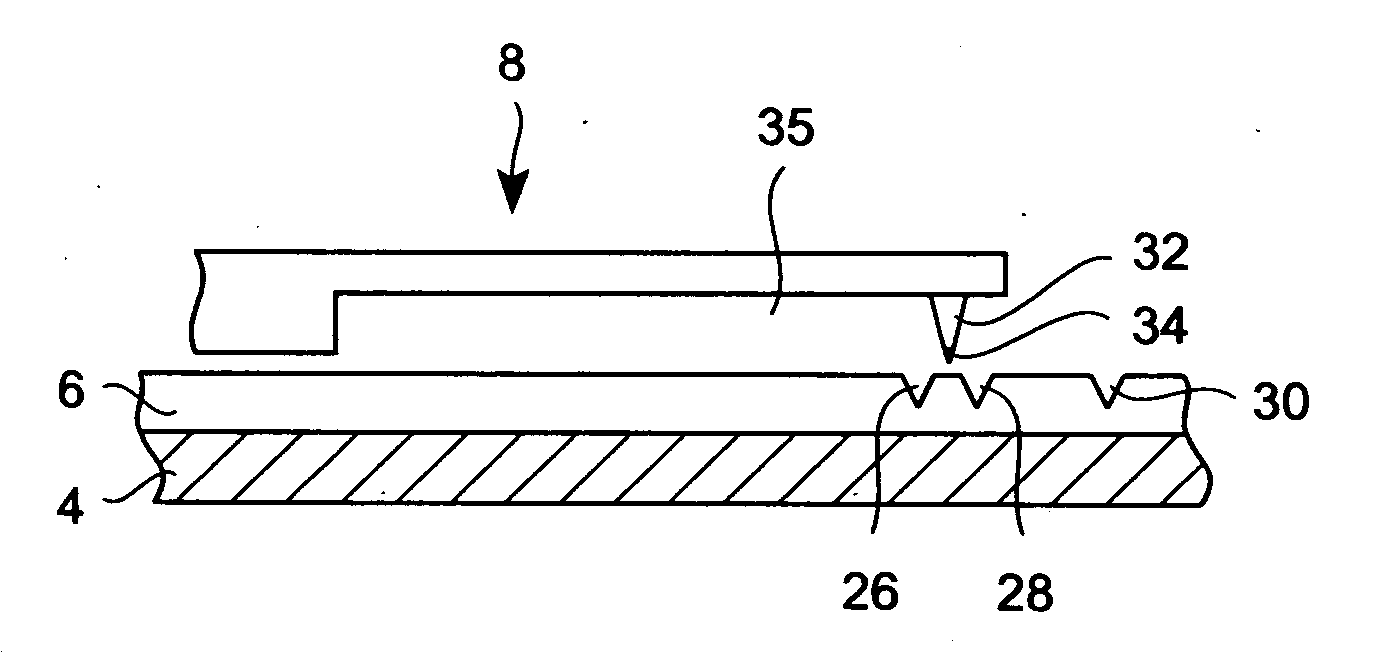
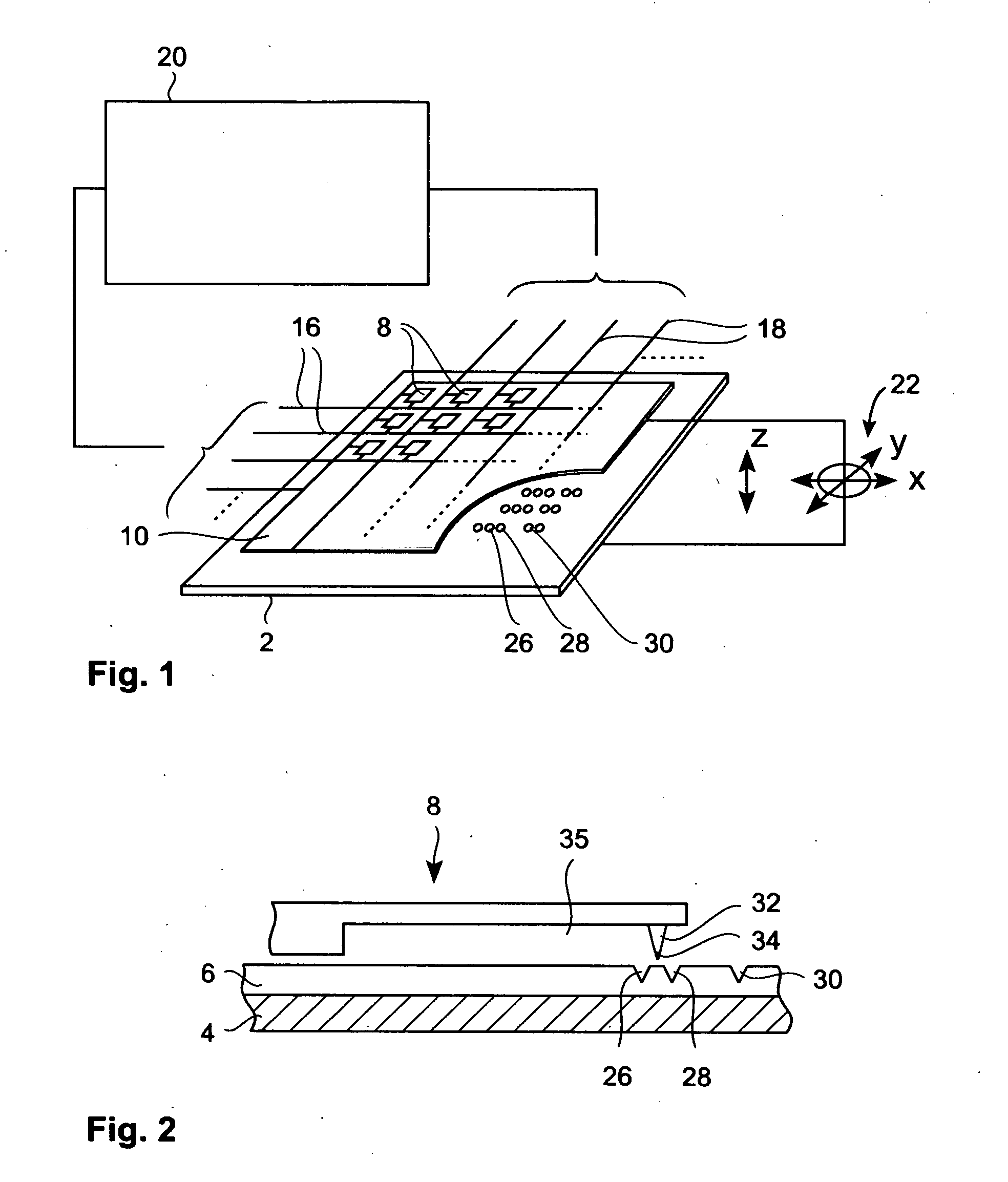
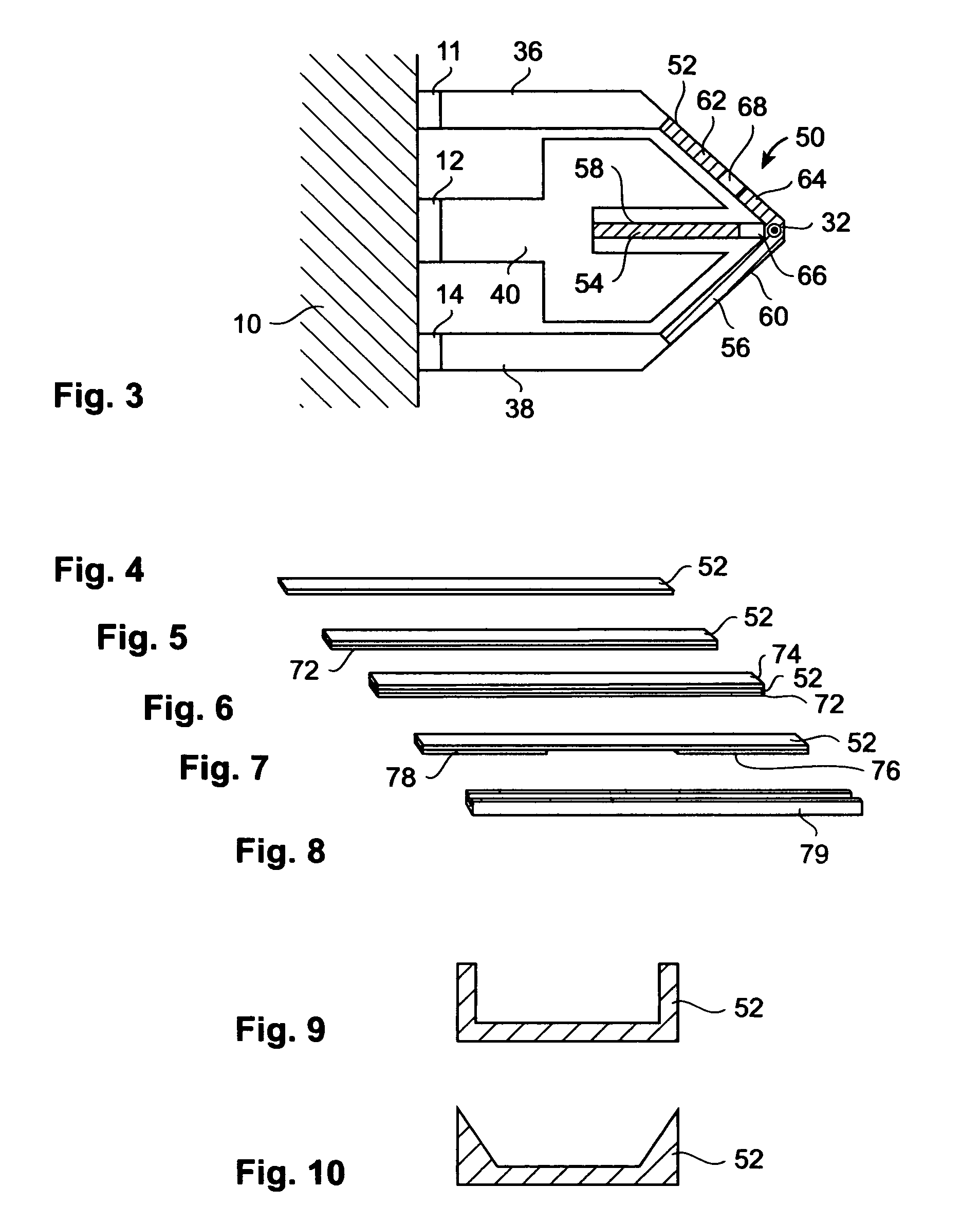
InactiveUS20080013437A1Guaranteed uptimeReduce the total massNanoinformaticsMechanical recordingElectricityDirect coupling
A data storage device comprises a storage medium for storing data in the form of marks and at least one probe for scanning the storage medium. The storage medium may be comprised in a substrate. The probe comprises a cantilever that comprises terminals serving as electrical contacts an being during operation of the probe mechanically fixed to a probe-holding structure, which may be a common frame of the data storage device. A probe further comprises a supporting structure, to which the terminals are mechanically directly coupled or coupled via hinges and which extends away from the terminals. A tip with a nanoscale apex is provided. A beam structure comprises a heating resistor and is attached at ends to the supporting structure. The beam structure is thinned at least in a direction parallel to an axis of the tip compared to an area of the supporting structure abutting the beam structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for patterning nanoscale patterns of molecules on material surfaces
Probe-based methods for patterning a surface of a material are described. In particular, high resolution patterning of molecules on a surface of a material, such as nano-scale patterns with feature sizes of less than 30 nanometers, are described. In one aspect, a method for patterning a surface of a material includes providing a material having a polymer film. A heated, nano-scale dimensioned probe is then used to desorb molecules upon interacting with the film. The film includes a network of molecules (such as molecular glasses) which are cross-linked via intermolecular (noncovalent) bonds, such as hydrogen bonds.
Owner:IBM CORP
Storage device and method
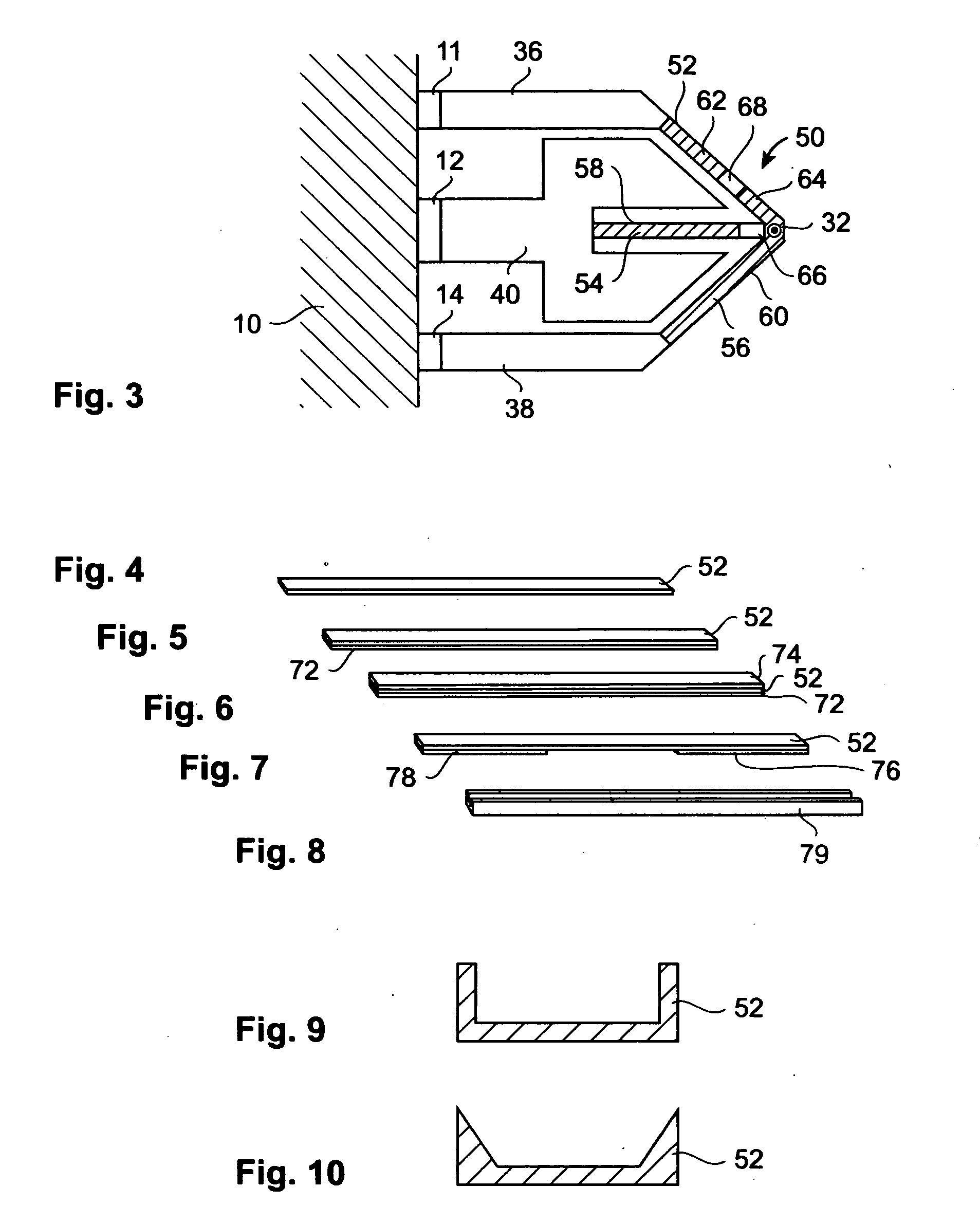
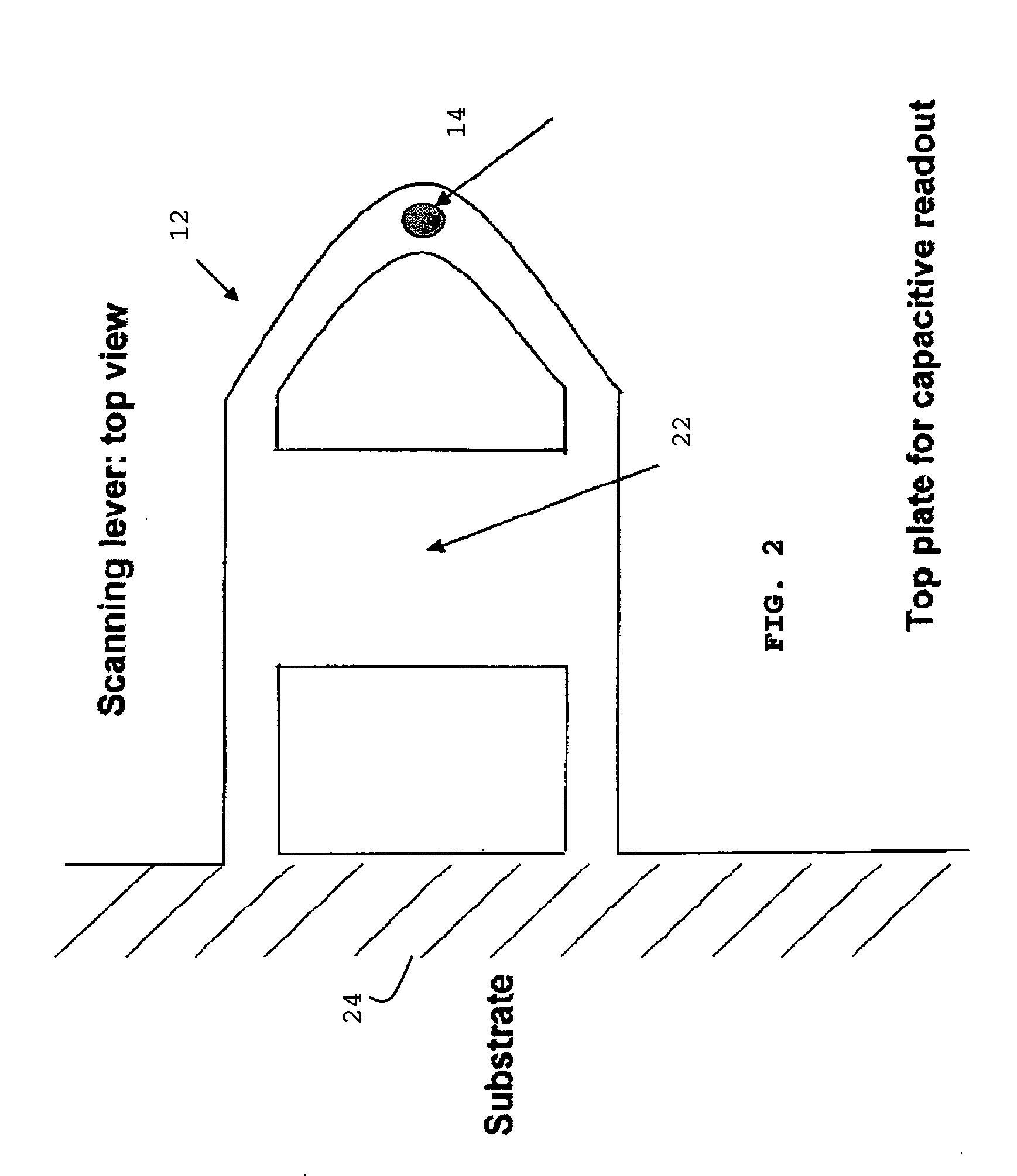
A storage device is provided, comprising of a storage surface having perturbations representative of information stored in the storage device; a lever having at least one tip facing the storage surface and movable substantially parallel thereto; and a variable capacitor having a first plate and a second plate, the first plate being integral to the storage surface and the second plate being integral to the lever, wherein movement of the lever relative to the surface produces variation in the capacitance of the variable capacitor in response to the tip scanning across the perturbations of the surface.
Owner:IBM CORP
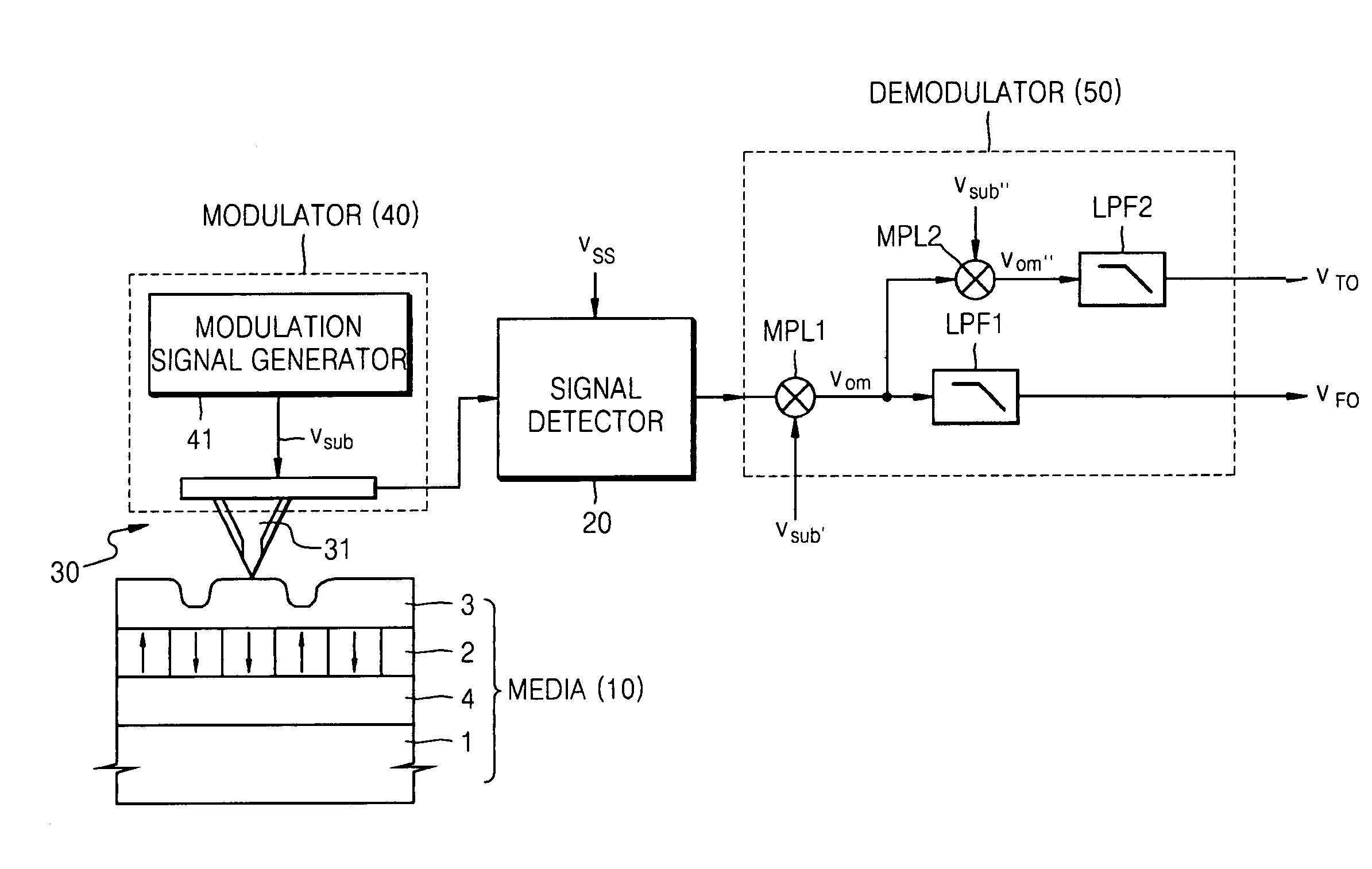
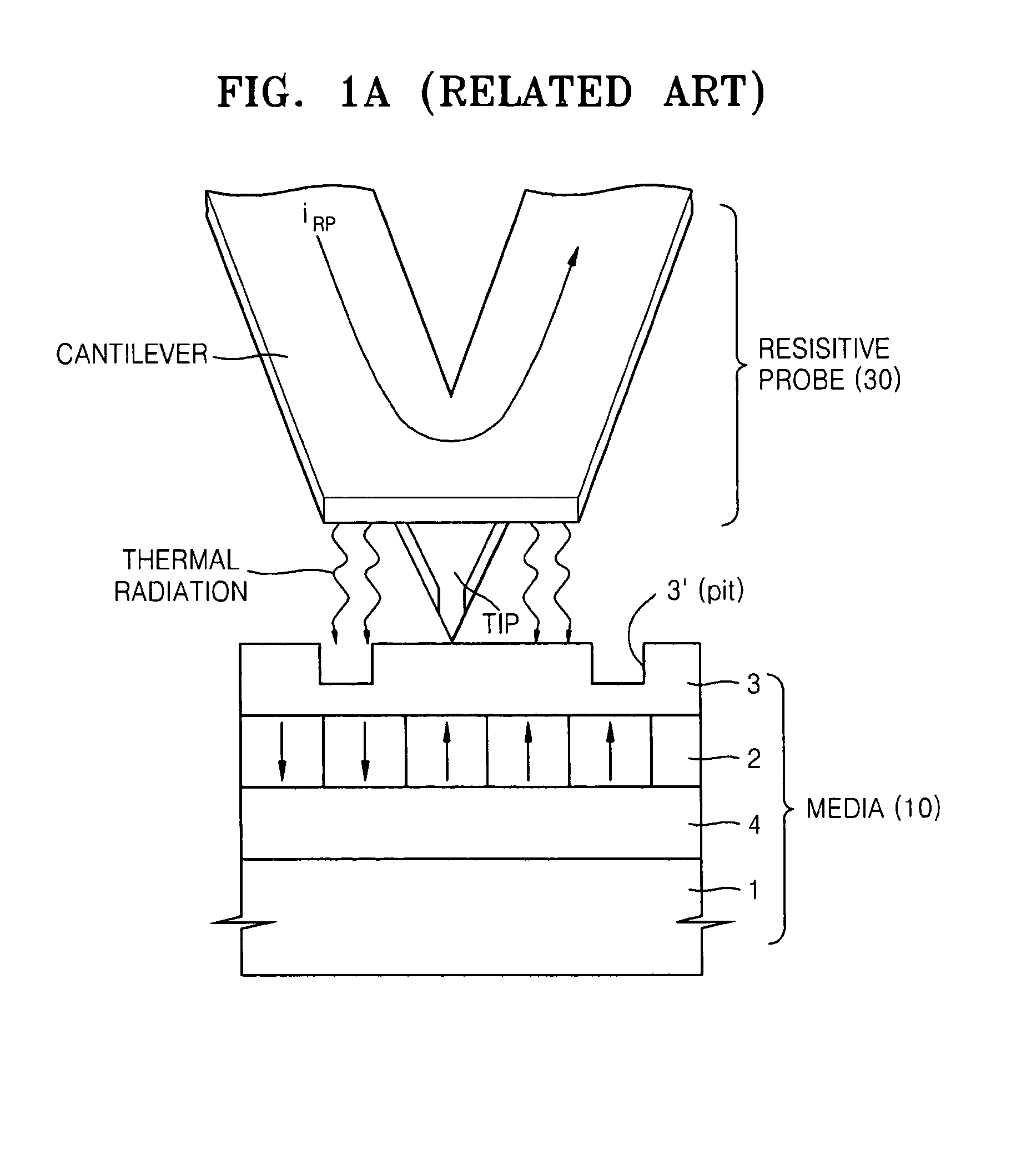
Information media and method and apparatus for writing and reproducing information using the same
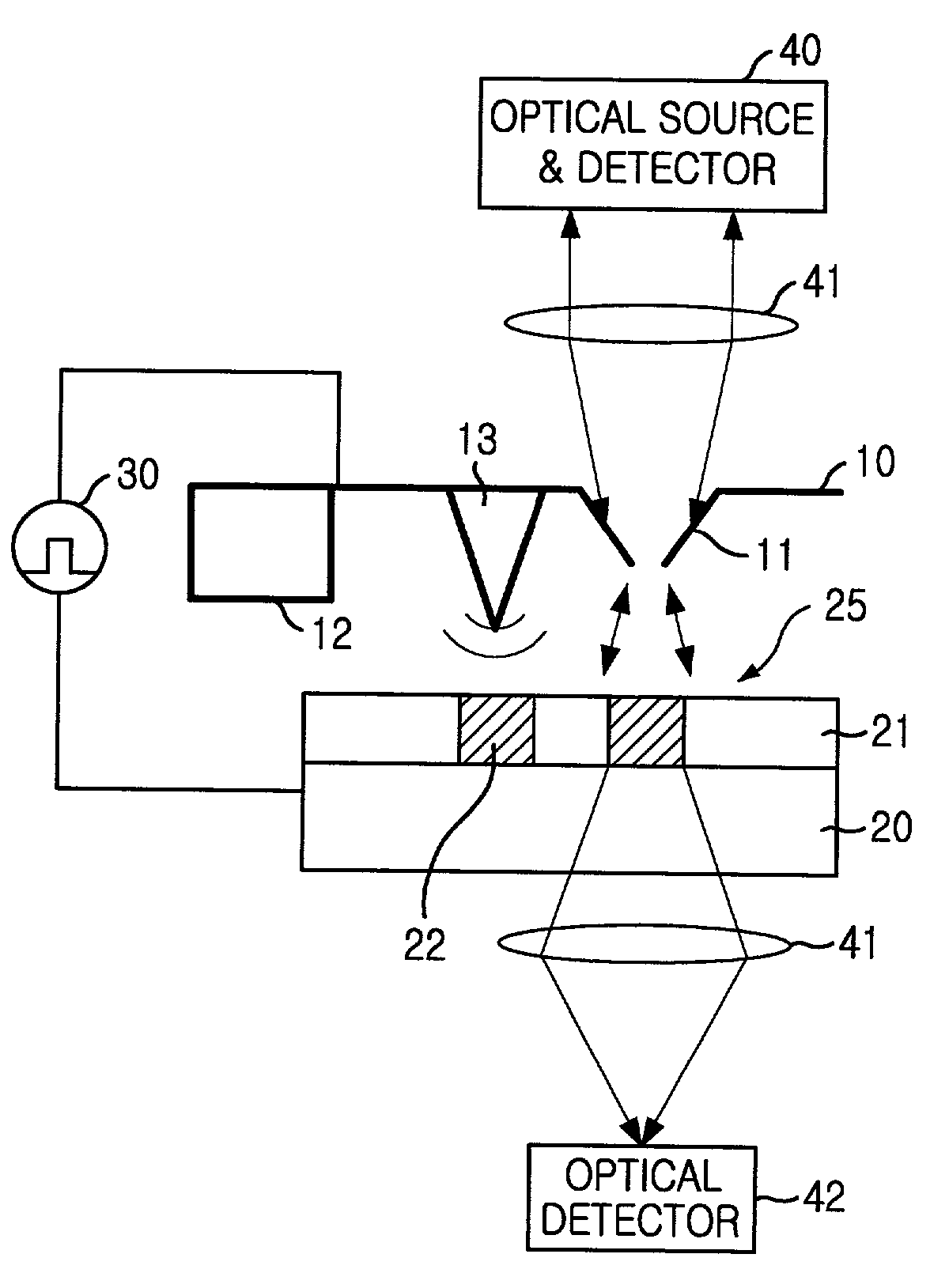
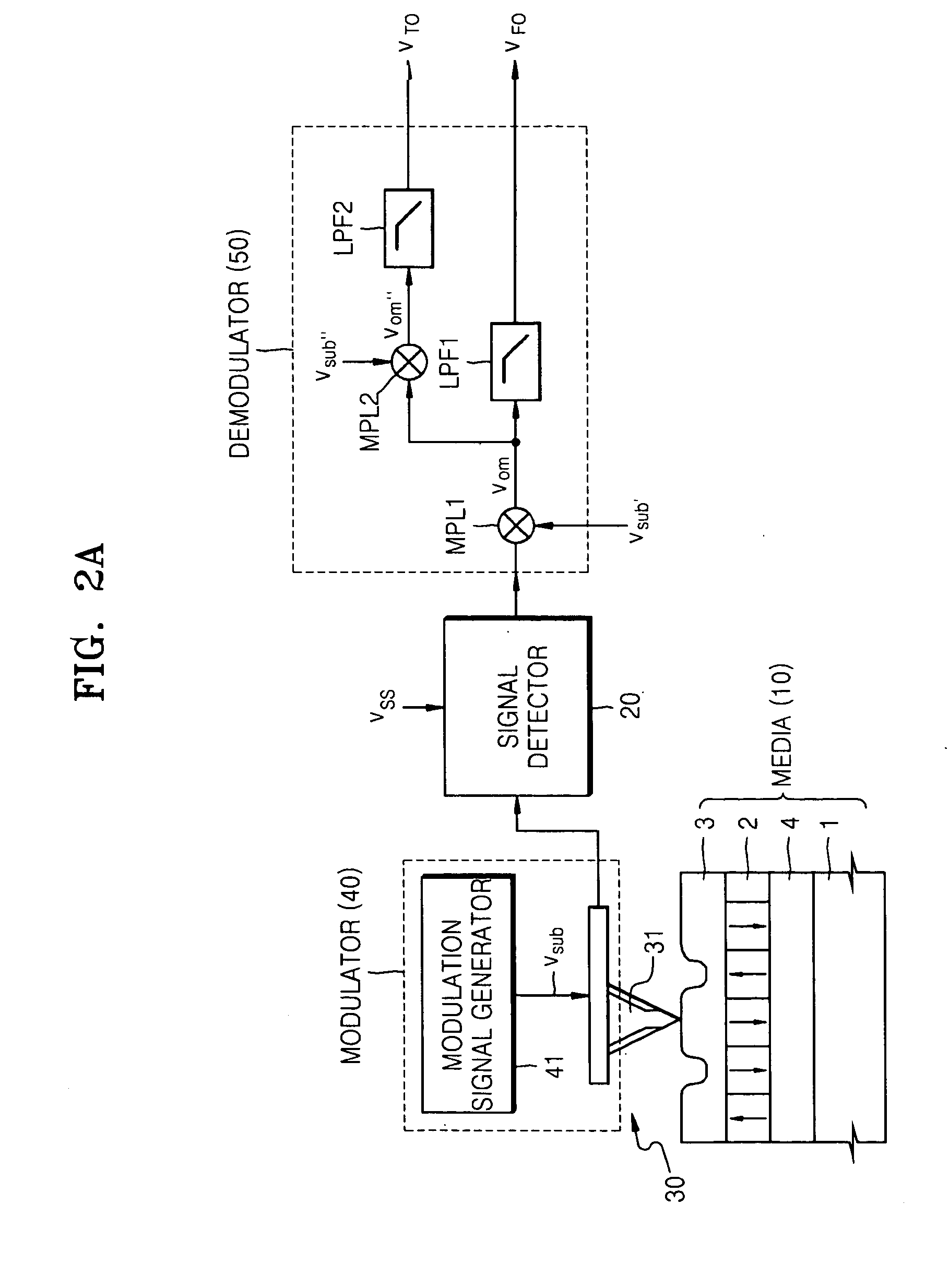
Provided are a method and an apparatus for reproducing information using a semiconductor probe. The apparatus includes a storage media including a ferroelectric recording layer which stores information by arranging a polarization direction of polarization domains of the ferroelectric recording layer and a physical recording layer disposed on the ferroelectric recording layer and whereupon information is written by forming pits in the physical recording layer, a semiconductor probe generating a composite signal including an electric field signal generated by an electric field variation of the ferroelectric recording layer of the storage media and a thermal signal generated by a temperature variation generated due to a variation in a shape of the physical recording layer, a signal detector detecting the composite signal from the semiconductor probe, and a demodulator demodulating the composite signal from the signal detector and extracting the electric field signal and the thermal signal from the composite signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for storing and reading information in a ferroelectric material
InactiveUS7262984B2Tapping mode is particularly favorableImprove accuracyProjector focusing arrangementNanoinformaticsTopographyMaterials science
To store information in a ferroelectric material, a sample probe is used to bring about mechanical action on individual domains and thereby to cause a reversal of polarization in the individual domains, with electrodes situated below the ferroelectric material being able to have a bias applied to them to stabilize the change / reversal of polarization. The reversal of polarization causes an alteration in the surface topography of the ferroelectric material, and this alteration can be used to read the information. The stored information is therefore obtained by ascertaining the surface topography of the ferroelectric material. The information is written and read using an AFM tip, with the tip being able to be operated in contact or tapping mode for the purpose of writing, and additionally in noncontact mode for the purpose of reading.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
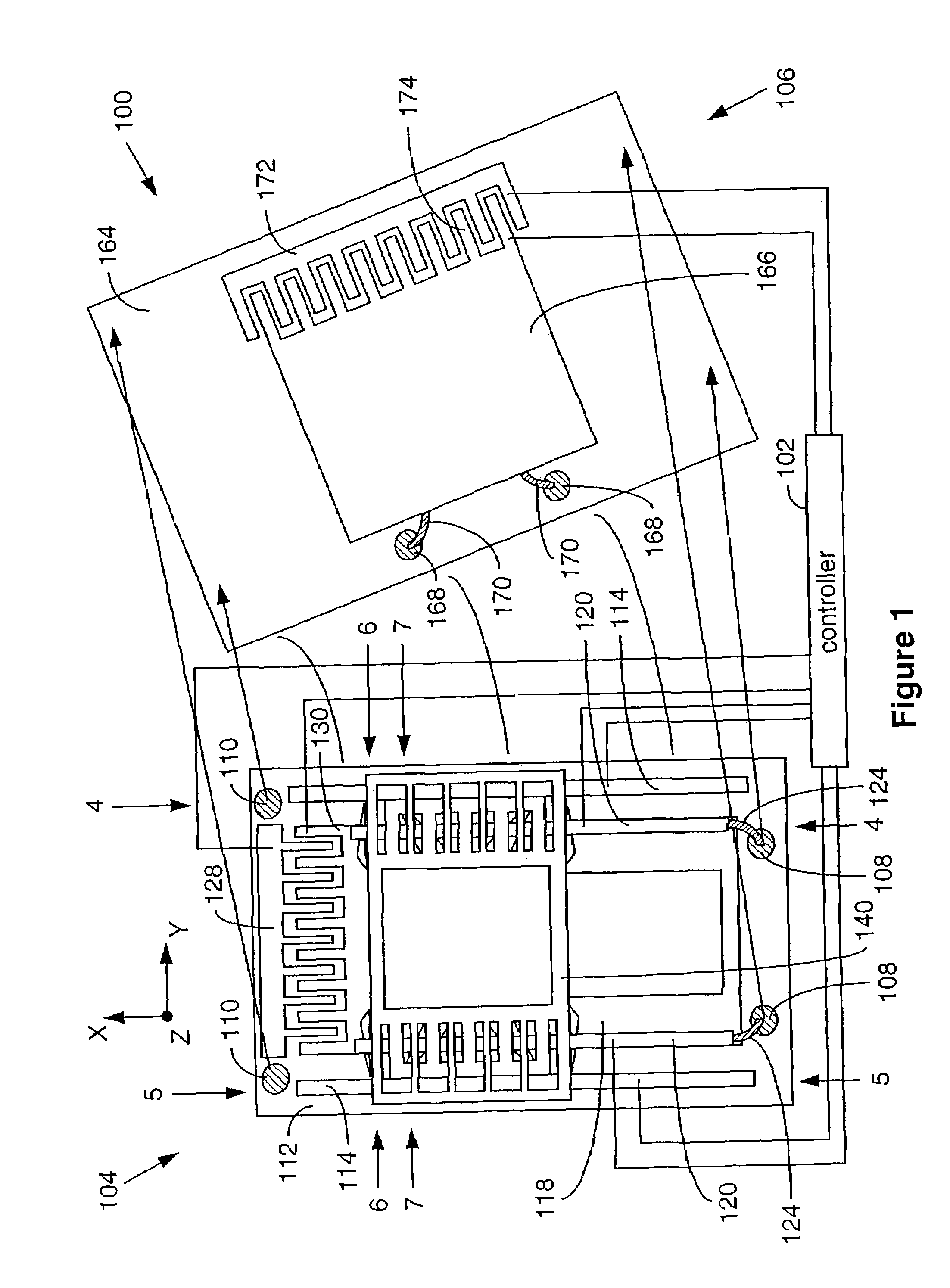
Nanometer scale data storage device and associated positioning system
A data storage system that includes a positioning system for positioning the write / read mechanism and the storage medium of the data storage device with respect to each other in first and second predefined directions. The positioning system comprises a positioning apparatus comprising microfabricated first and second positioning assemblies. The positioning system further comprises a controller to position a positionable support structure of the first positioning assembly in a first predefined direction within a range of positioning that is larger, than the range of movement of a moveable support structure of the first positioning assembly by controlling (A) a stationary support structure clamp in clamping and unclamping the positionable structure to and from the support structure, (B) a moveable structure clamp in clamping and unclamping the positionable support structure to and from the moveable support structure, and (C) the movement of the moveable support structure. In one embodiment, one of the write / read mechanism and the storage medium is carried by the positionable support structure so that it is positioned with the first positioning assembly. The other one of the write / read mechanism and the storage medium is positioned with the second positioning assembly. In another embodiment, the positionable support structure carries the second positioning assembly and one of the write / read mechanism and the storage medium is positioned with the second positioning assembly while the other is held stationary. In several embodiments, the read / write mechanism is used:to mechanically write data to and electrically read data from the storage medium. In still another embodiment, the read / write mechanism is used to optically write data to and electrically read data from the storage medium. In yet another embodiment, the read / write mechanism is acoustically aided in electrically writing data to and reading data from the storage medium.
Owner:TERRASPAN
Method for positioning a scanning probe on a target track of a multi-track storage medium, storage device, scanning device, and storage medium
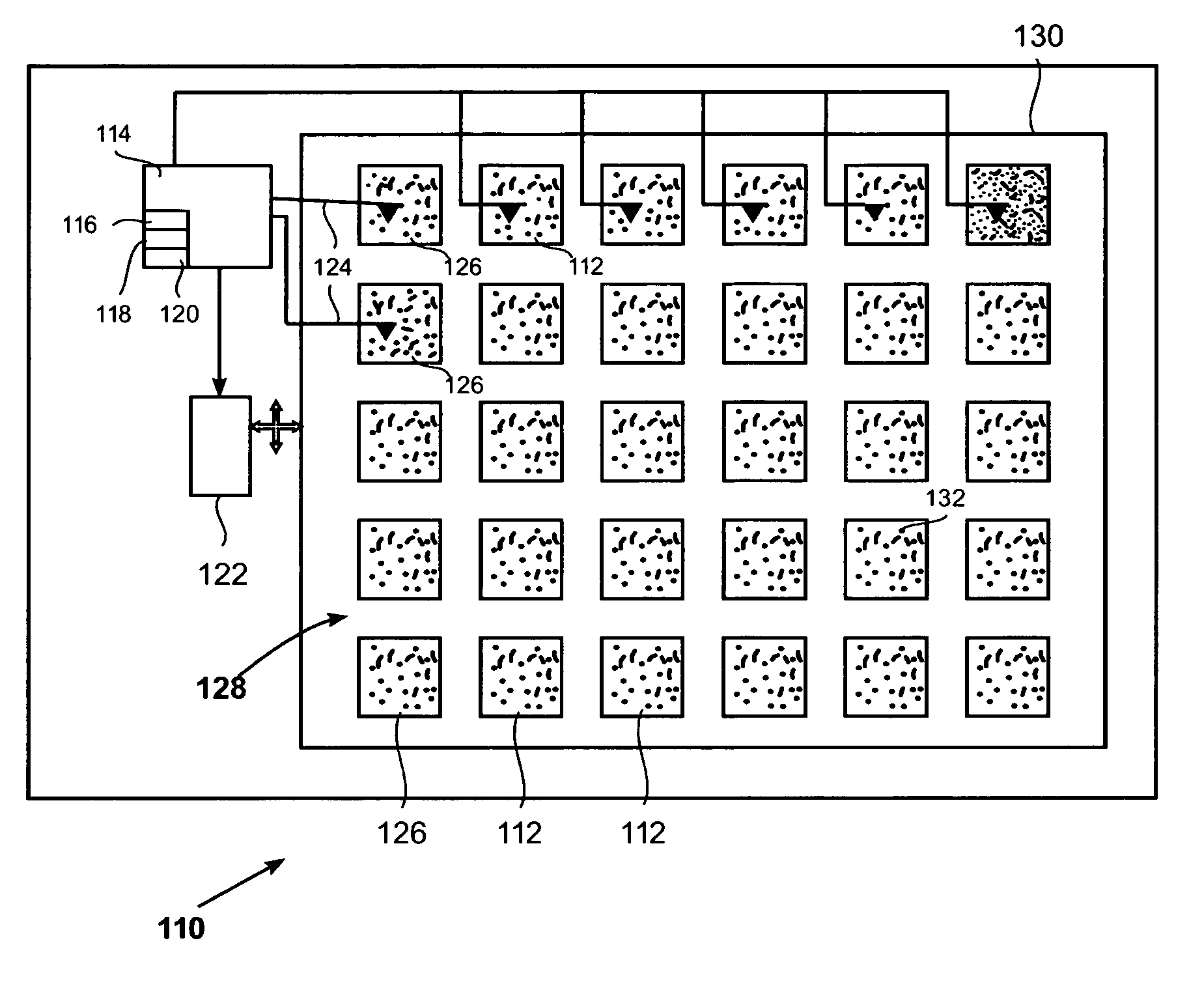
A method for settling on a target track of a servo system in a storage device (110) comprising a scanning probe (e.g., a scanning probe array system (124)) is disclosed, as well as a corresponding storage device (110). A data format is employed for the data stored in servo fields (18), consisting mainly of a preamble for assisting the settle process.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
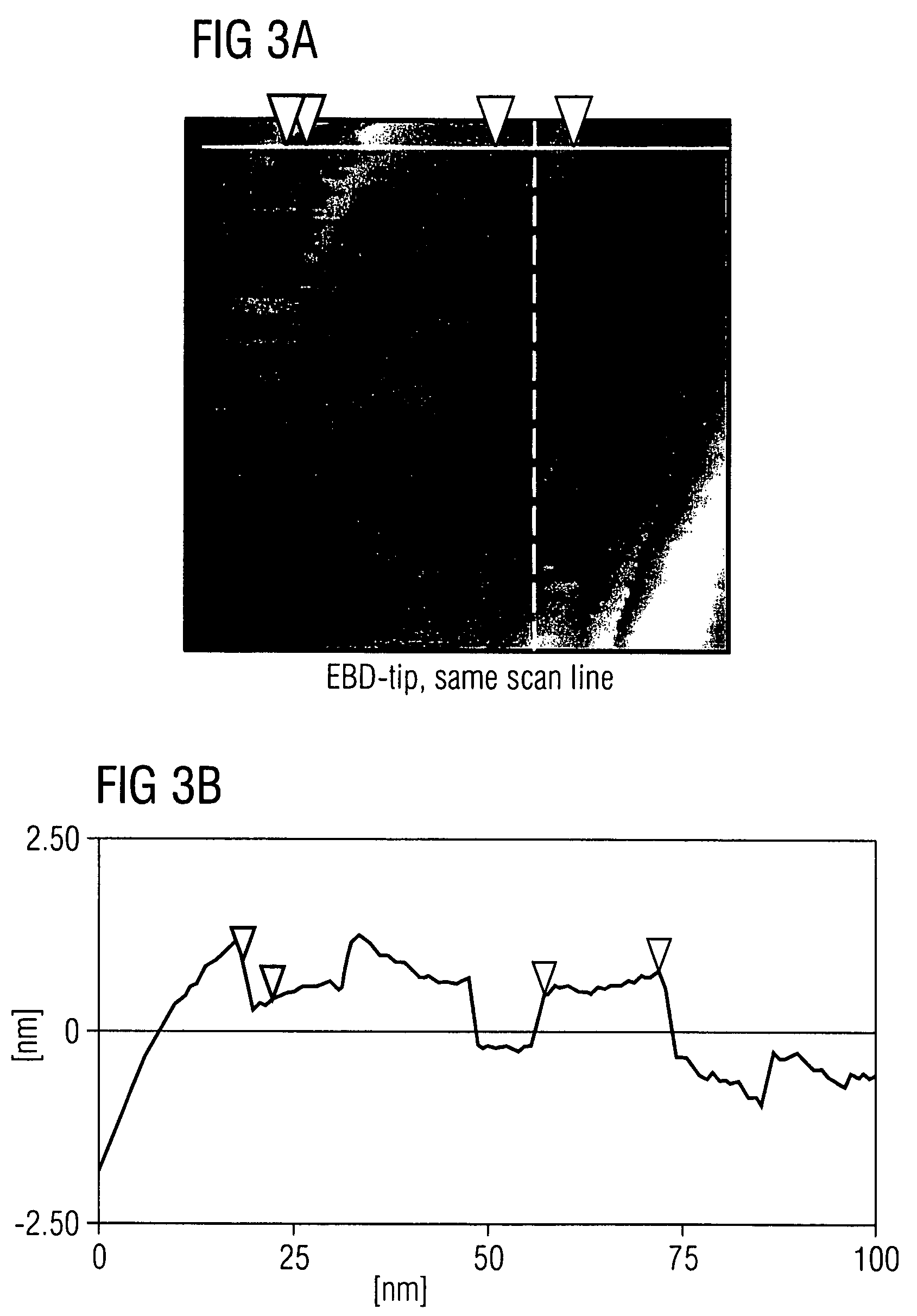
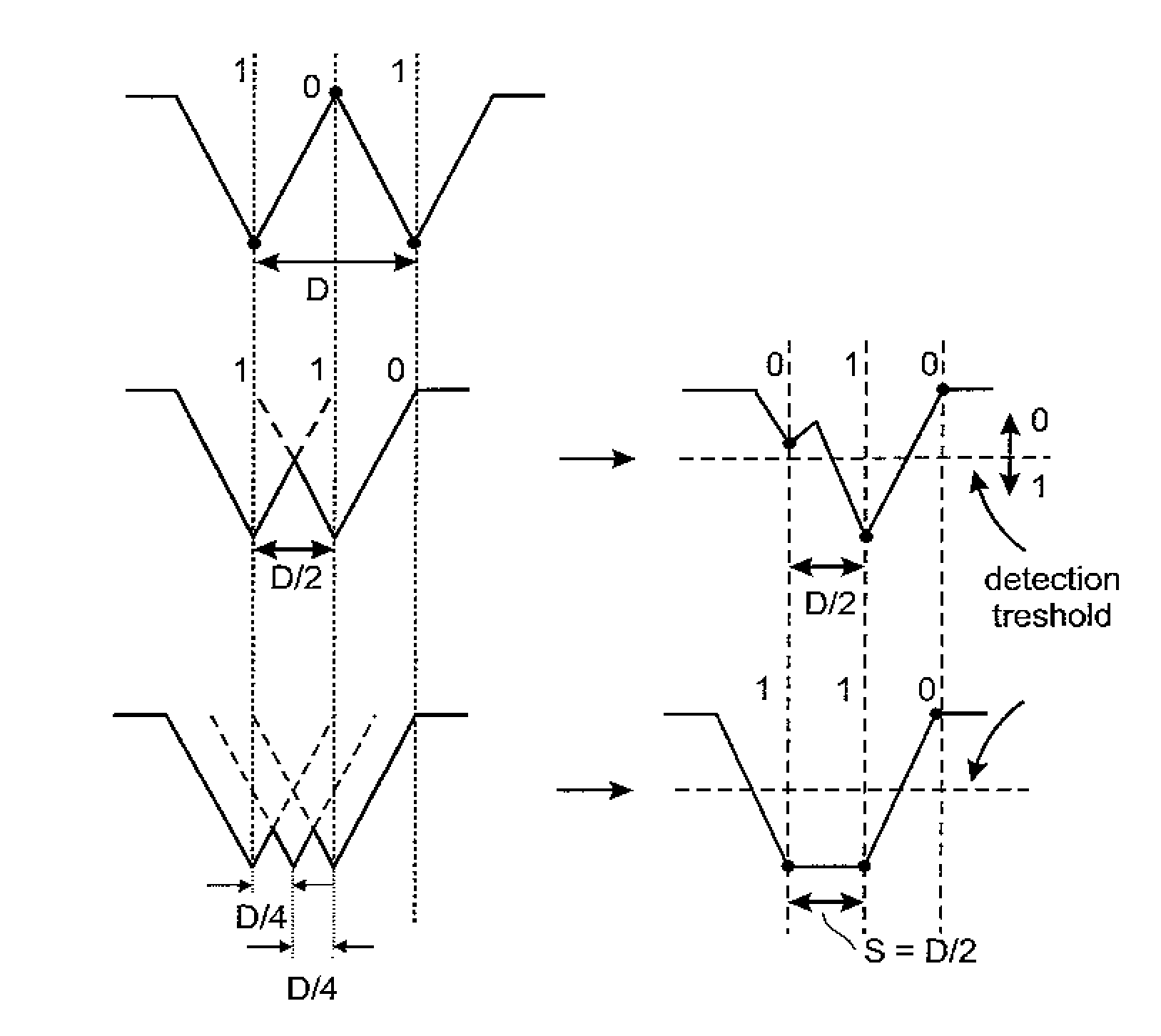
Method for determining wear of a data storage medium and data storage device
InactiveUS7852582B2NanoinformaticsReproducing by electric probe meansDetection thresholdOperating system
Owner:RPX CORP
Read head for ultra-high-density information storage media and method for making the same
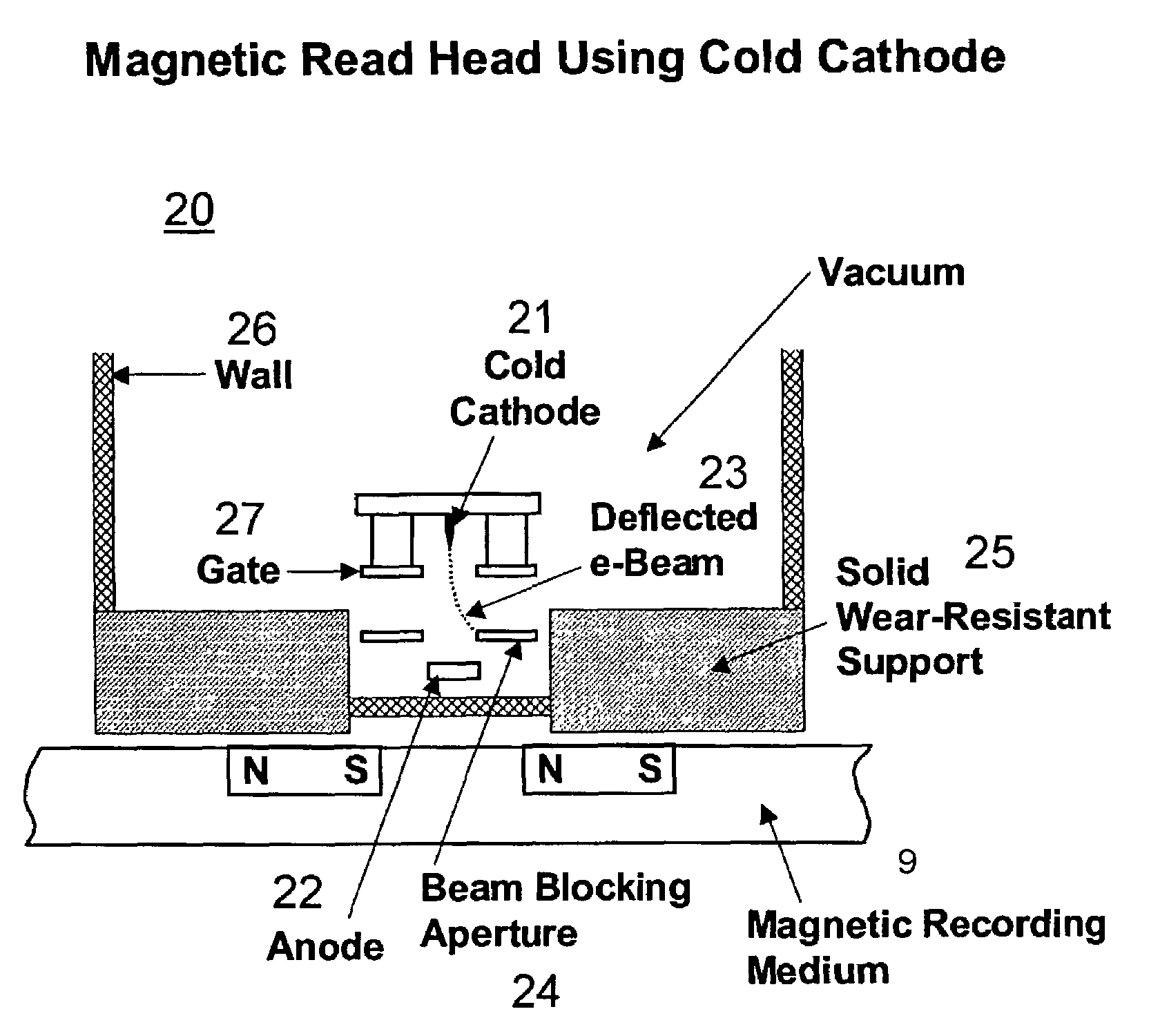
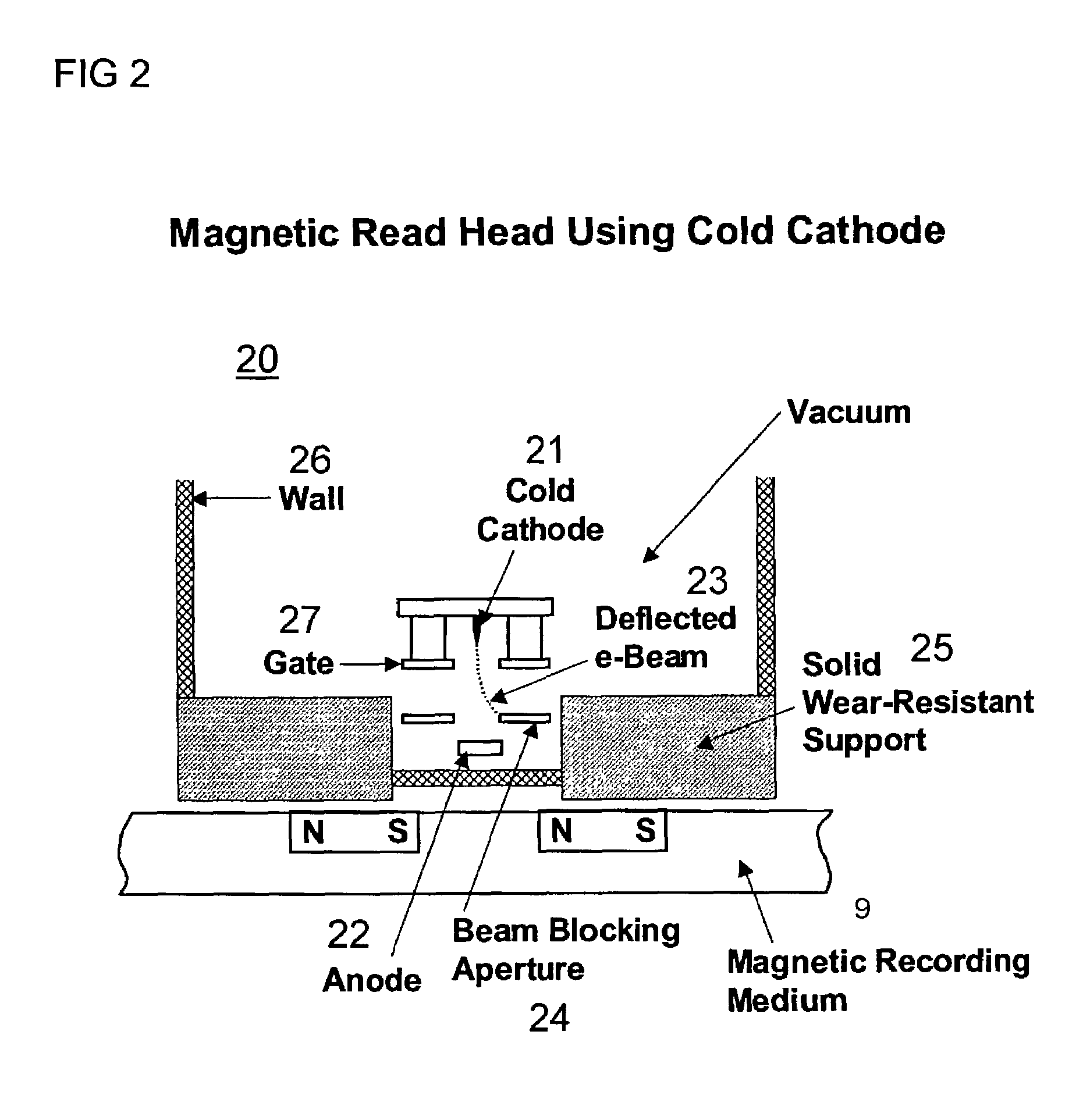
InactiveUS7068582B2High densityConstruction of head windingsElectron beam carrier recordingHigh densityMagnetic media
A micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) device is presented that can read very high density magnetic media and very high density CD ROMs. Both the magnetic and optical read heads comprise one or more cold cathode MEMS e-beam cells. The e-beams are deflected according to the data bit being interrogated and the state of that bit is determined by a detector. Large arrays of such cells can simultaneously read large areas of the memory media. Arrays of such MEMs detectors can comprise a plurality of “steerable” e-beam emitters that can be directed to interrogate specific data sites on the magnetic media. Thus, in some cases, the media can remain stationary. Densities of 200 gigabits per square inch or more and read speeds greater than 1000 times faster can be achieved.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
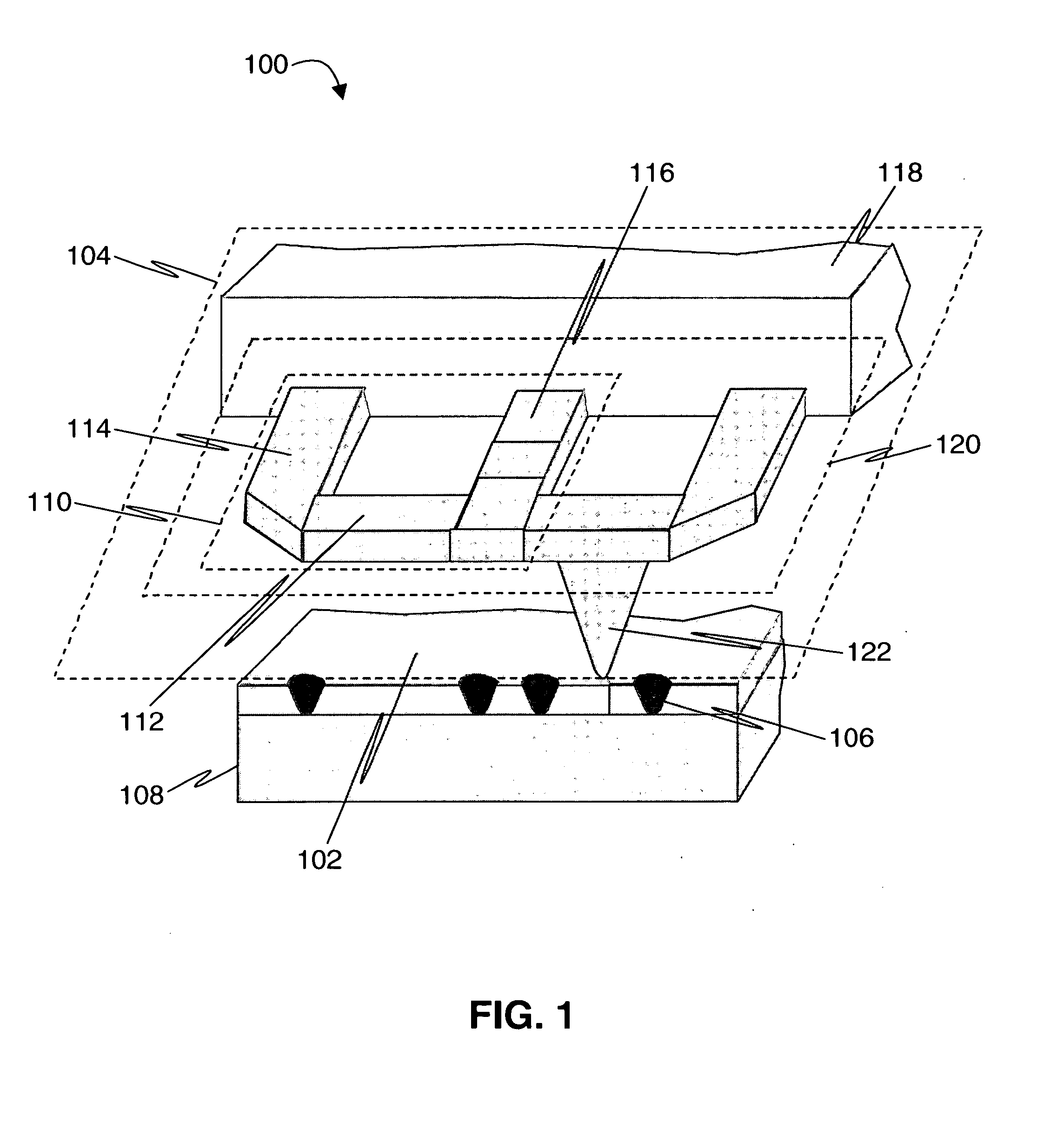
Probe for scanning over a substrate and a data storage device
InactiveUS7482826B2Guaranteed uptimeReduce heatElectrical measurement instrument detailsNanoinformaticsElectricityDirect coupling
A data storage device comprises a storage medium for storing data in the form of marks and at least one probe for scanning the storage medium. The storage medium may be comprised in a substrate. The probe comprises a cantilever that comprises terminals serving as electrical contacts an being during operation of the probe mechanically fixed to a probe-holding structure, which may be a common frame of the data storage device. A probe further comprises a supporting structure, to which the terminals are mechanically directly coupled or coupled via hinges and which extends away from the terminals. A tip with a nanoscale apex is provided. A beam structure comprises a heating resistor and is attached at ends to the supporting structure. The beam structure is thinned at least in a direction parallel to an axis of the tip compared to an area of the supporting structure abutting the beam structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and apparatus for storing and reading information in a ferroelectric material
InactiveUS20050195631A1Tapping mode is particularly favorableImprove accuracyProjector focusing arrangementNanoinformaticsTopographyMaterials science
To store information in a ferroelectric material, a sample probe is used to bring about mechanical action on individual domains and thereby to cause a reversal of polarization in the individual domains, with electrodes situated below the ferroelectric material being able to have a bias applied to them to stabilize the change / reversal of polarization. The reversal of polarization causes an alteration in the surface topography of the ferroelectric material, and this alteration can be used to read the information. The stored information is therefore obtained by ascertaining the surface topography of the ferroelectric material. The information is written and read using an AFM tip, with the tip being able to be operated in contact or tapping mode for the purpose of writing, and additionally in noncontact mode for the purpose of reading.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
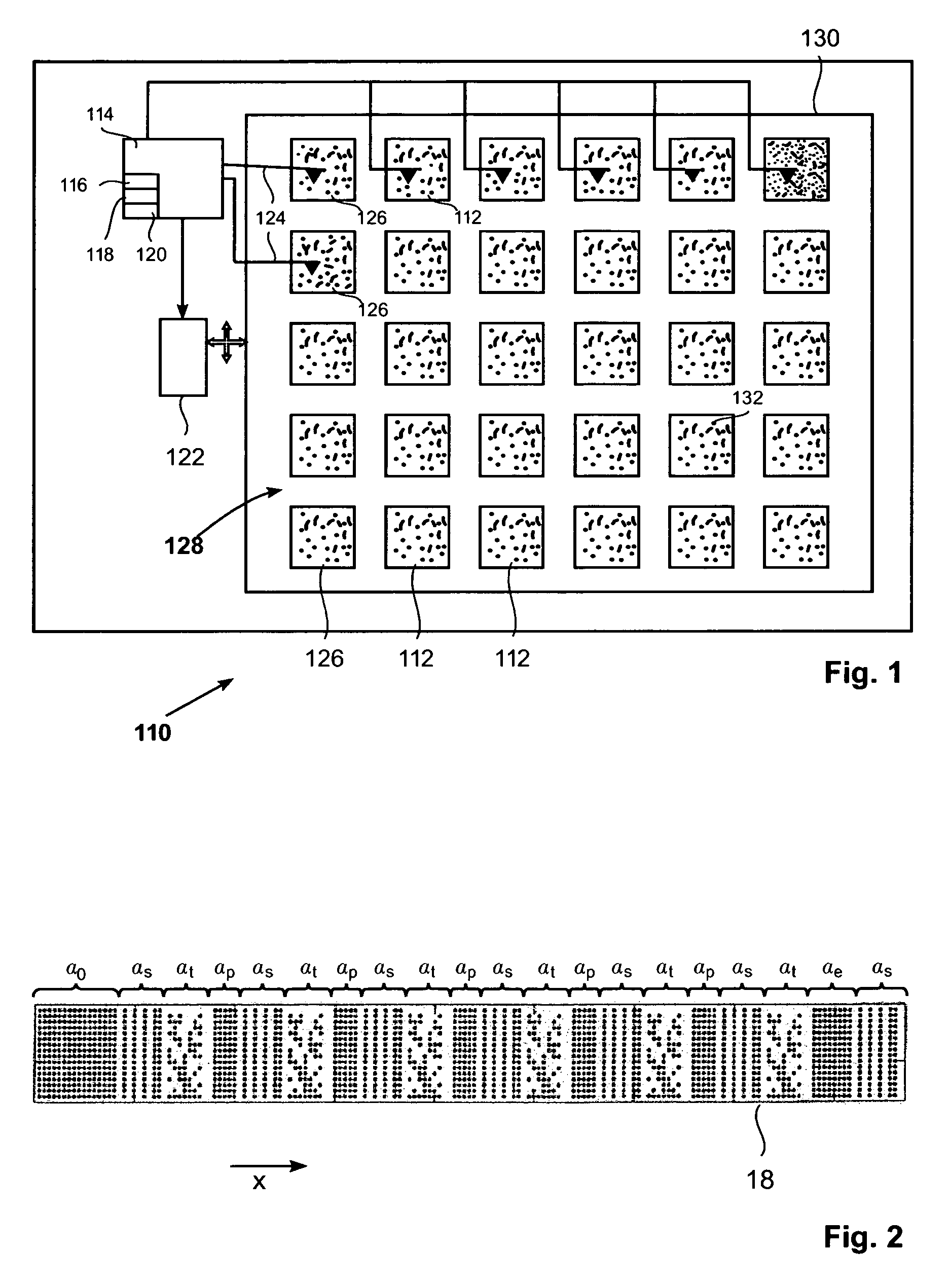
Method for Positioning a Scanning Probe on a Target Track of a Multi-Track Storage Medium, Storage Device, Scanning Device, and Storage Medium
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Probe for scanning over a substrate and data storage device
InactiveUS20090003188A1Guaranteed uptimeReduce the total massElectrical measurement instrument detailsNanoinformaticsElectricityDirect coupling
A data storage device comprises a storage medium for storing data in the form of marks and at least one probe for scanning the storage medium. The storage medium may be comprised in a substrate. The probe comprises a cantilever that comprises terminals serving as electrical contacts an being during operation of the probe mechanically fixed to a probe-holding structure, which may be a common frame of the data storage device. A probe further comprises a supporting structure, to which the terminals are mechanically directly coupled or coupled via hinges and which extends away from the terminals. A tip with a nanoscale apex is provided. A beam structure comprises a heating resistor and is attached at ends to the supporting structure. The beam structure is thinned at least in a direction parallel to an axis of the tip compared to an area of the supporting structure abutting the beam structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
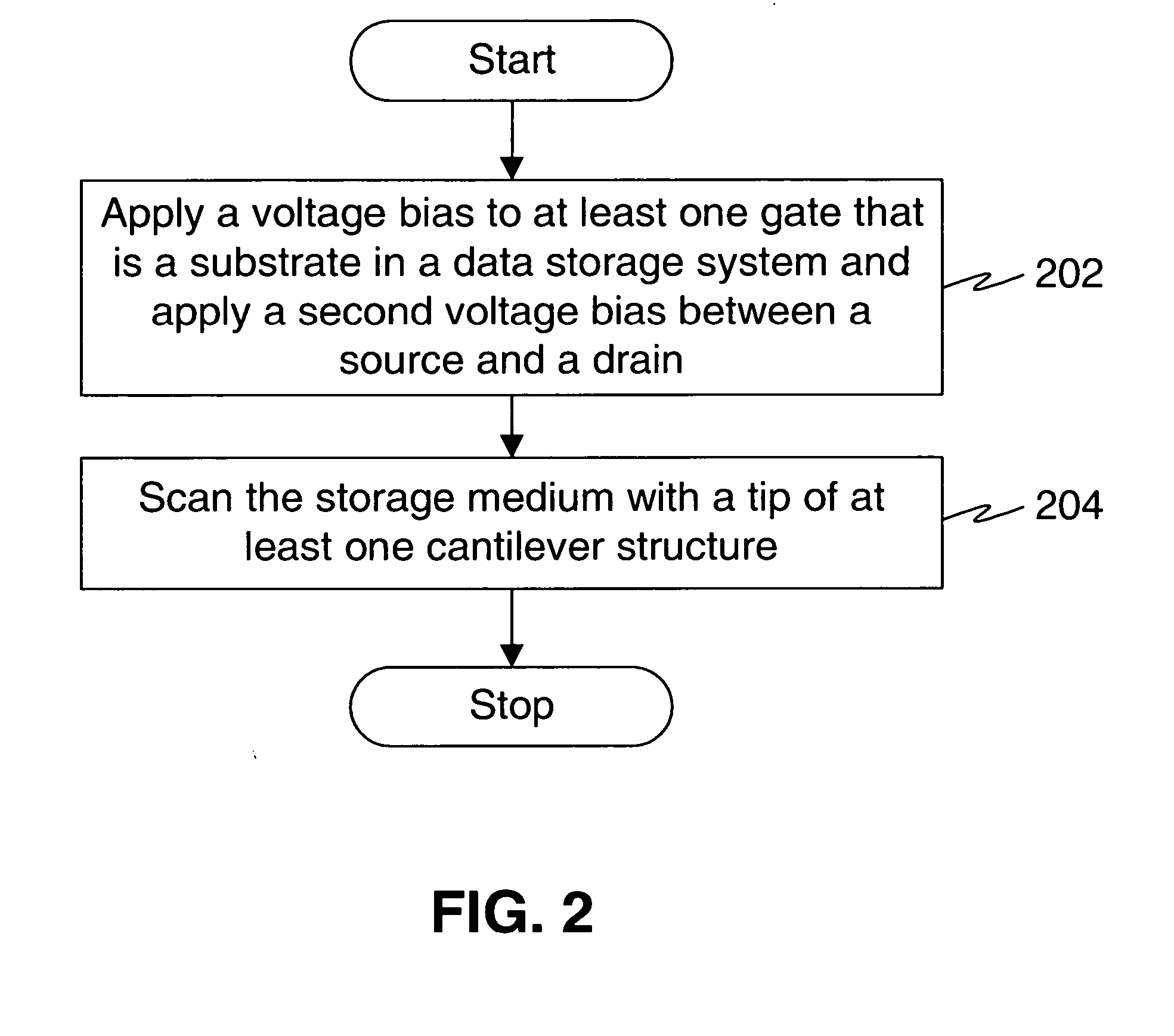
Systems and methods for storing and reading data in a data storage system
InactiveUS20070242594A1High data speedIncrease speedMechanical recordingNanoinformaticsComputer hardwareTransducer
Systems and methods for storing and reading data in a data storage system are provided. The data storage system includes a storage medium for storing data. The storage medium stores data as a plurality of topographical features. Further, the data storage system includes one or more transducer. One or more transducer writes data on the storage medium. Additionally, the data storage medium includes one or more gates. A first voltage bias is applied to one or more gates. The data storage system further includes, one or more read heads. One or more read heads include one or more Floating Gate Transistors (FGTs). The first voltage bias creates an electric field between one or more FGTs and one or more gates. A change in the electric field is detected by one or more FGTs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Recording in probe-based data storage devices
InactiveUS7876662B2Reduce impactImprove storage densityNanoinformaticsReproducing by electric probe meansHigh densityVia device
Methods and apparatus are provided for recording / reproduction of data in a probe-based data storage device (1) in which application of a write signal causes formation of an indentation in a storage surface (5) by a probe of the device (1). Instead of storing information in the presence or absence of indentations on the storage surface as is conventionally done in such devices, information is stored in the form of grooves of variable length separated by lands of variable length. More particularly, a sequence of n>1 successive bits of a first value (typically “1's”) in a recording signal is recorded by applying a series of write signals at respective probe-positions on the storage surface (5). These probe-positions are spaced at w≦M, where M is the indentation merging distance, so that the resulting indentations merge to form a groove in the storage surface (5) spanning n readback sample positions. The readback signal corresponding to the recording signal is sampled at timings corresponding to the readback sample positions to recover the original bit sequence. High density recording is provided because the readback sample position spacing s here satisfies s<D, where D is the indentation interference threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
Information media and method and apparatus for writing and reproducing information using the same
Provided are a method and an apparatus for reproducing information using a semiconductor probe. The apparatus includes a storage media including a ferroelectric recording layer which stores information by arranging a polarization direction of polarization domains of the ferroelectric recording layer and a physical recording layer disposed on the ferroelectric recording layer and whereupon information is written by forming pits in the physical recording layer, a semiconductor probe generating a composite signal including an electric field signal generated by an electric field variation of the ferroelectric recording layer of the storage media and a thermal signal generated by a temperature variation generated due to a variation in a shape of the physical recording layer, a signal detector detecting the composite signal from the semiconductor probe, and a demodulator demodulating the composite signal from the signal detector and extracting the electric field signal and the thermal signal from the composite signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for Determining Wear of a Data Storage Medium and Data Storage Device
InactiveUS20090128942A1Reduce wearNanoinformaticsReproducing by electric probe meansDetection thresholdOperating system
The invention relates to a method of determining wear of a data storage medium actively by performing a read operation on the data storage medium and detecting a read signal, comparing the read signal to at least one wear threshold; and determining a wear level of an area of the data storage medium based on the comparison. The wear threshold is lower than a detection threshold, wherein the detection of the read signal above the detection threshold indicates the presence of stored data.
Owner:RPX CORP
Popular searches
Record information storage Digital storage Other recording methods Recording by electric charge/resistance/capacitance Microscopic probe carrier recording Optical recording/reproducing Carrier monitoring Functional testing of recording heads Digital signal error detection/correction Scanning probe microscopy
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com