Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2885results about "Power current collectors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
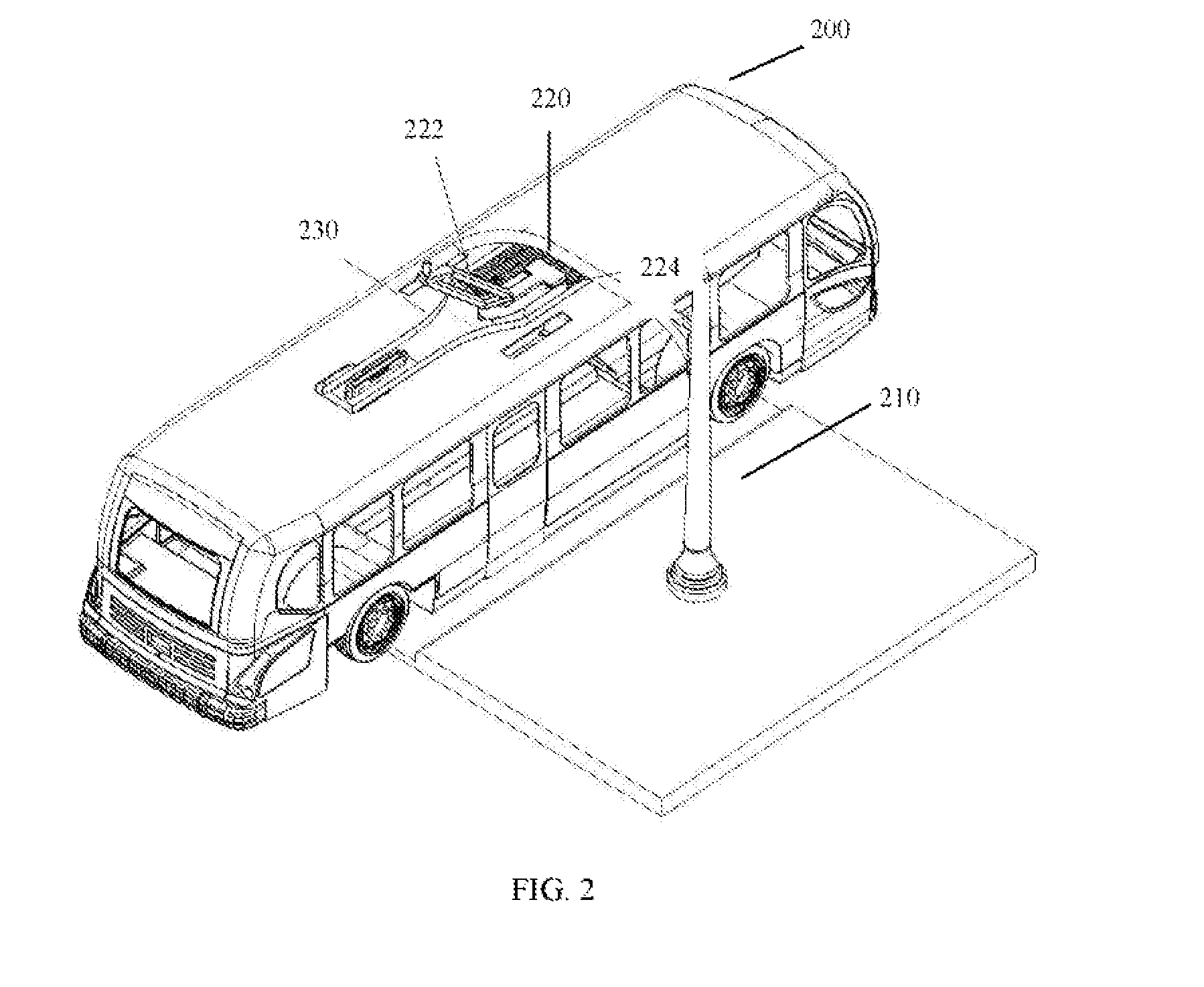
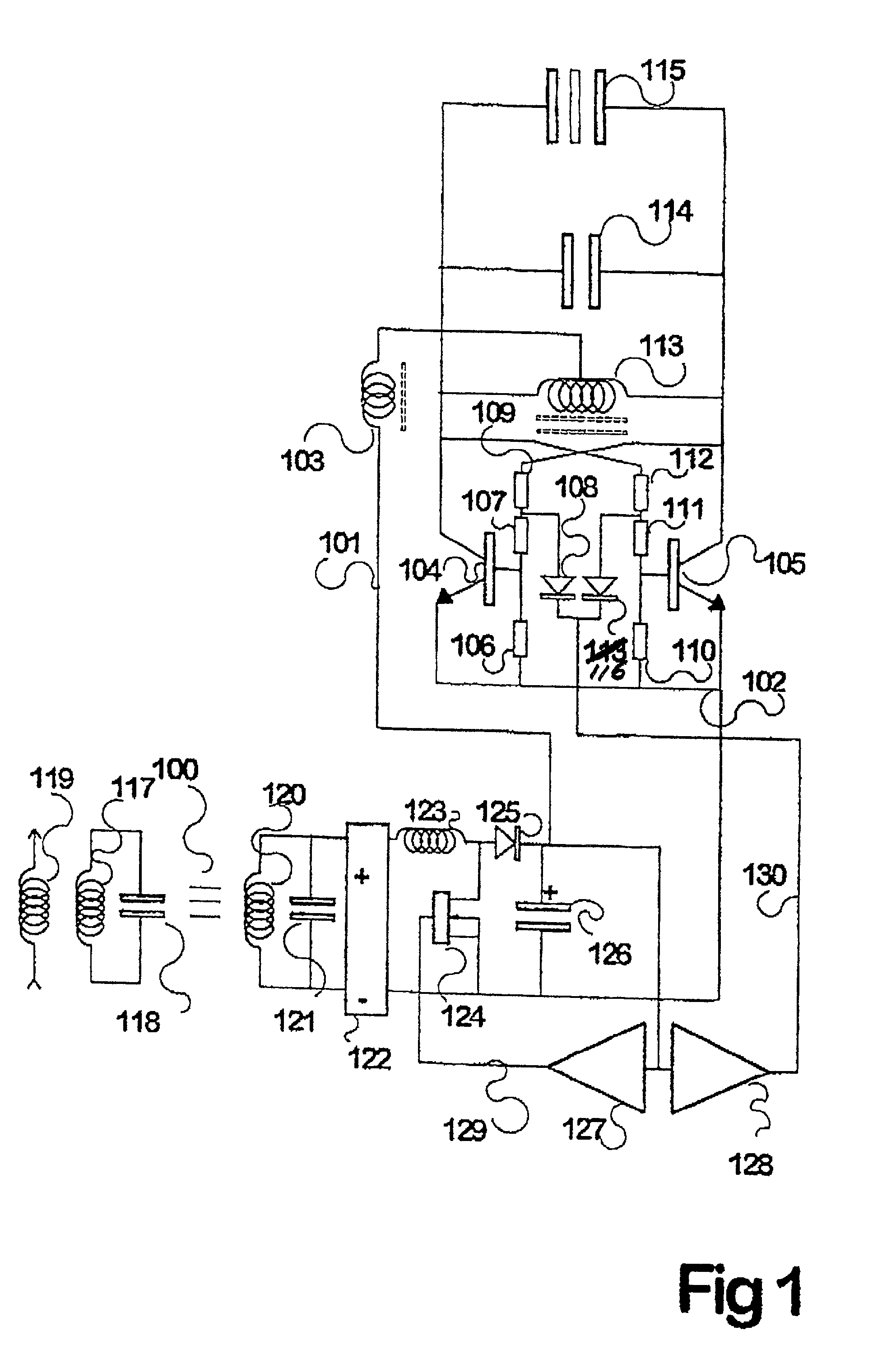
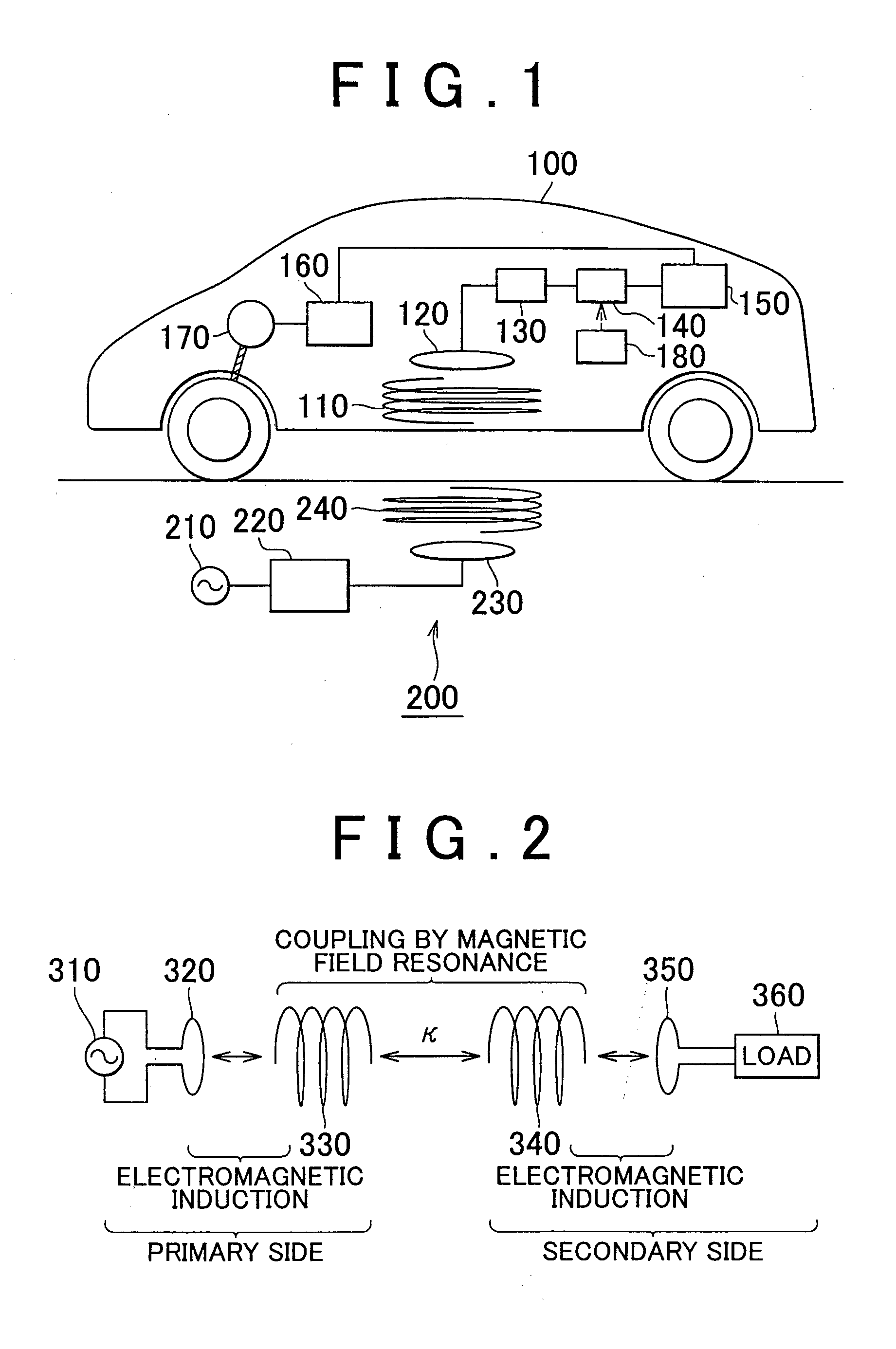
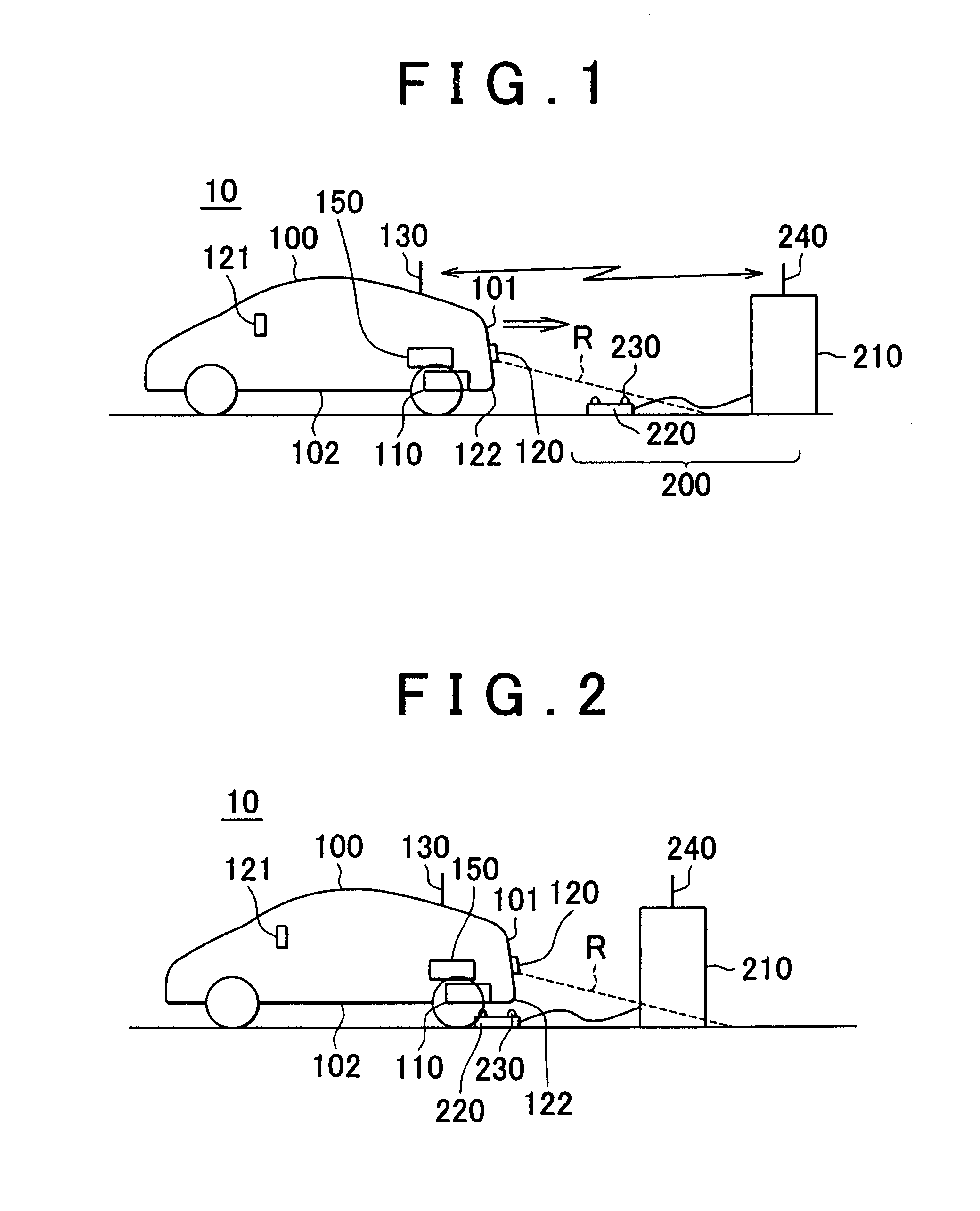
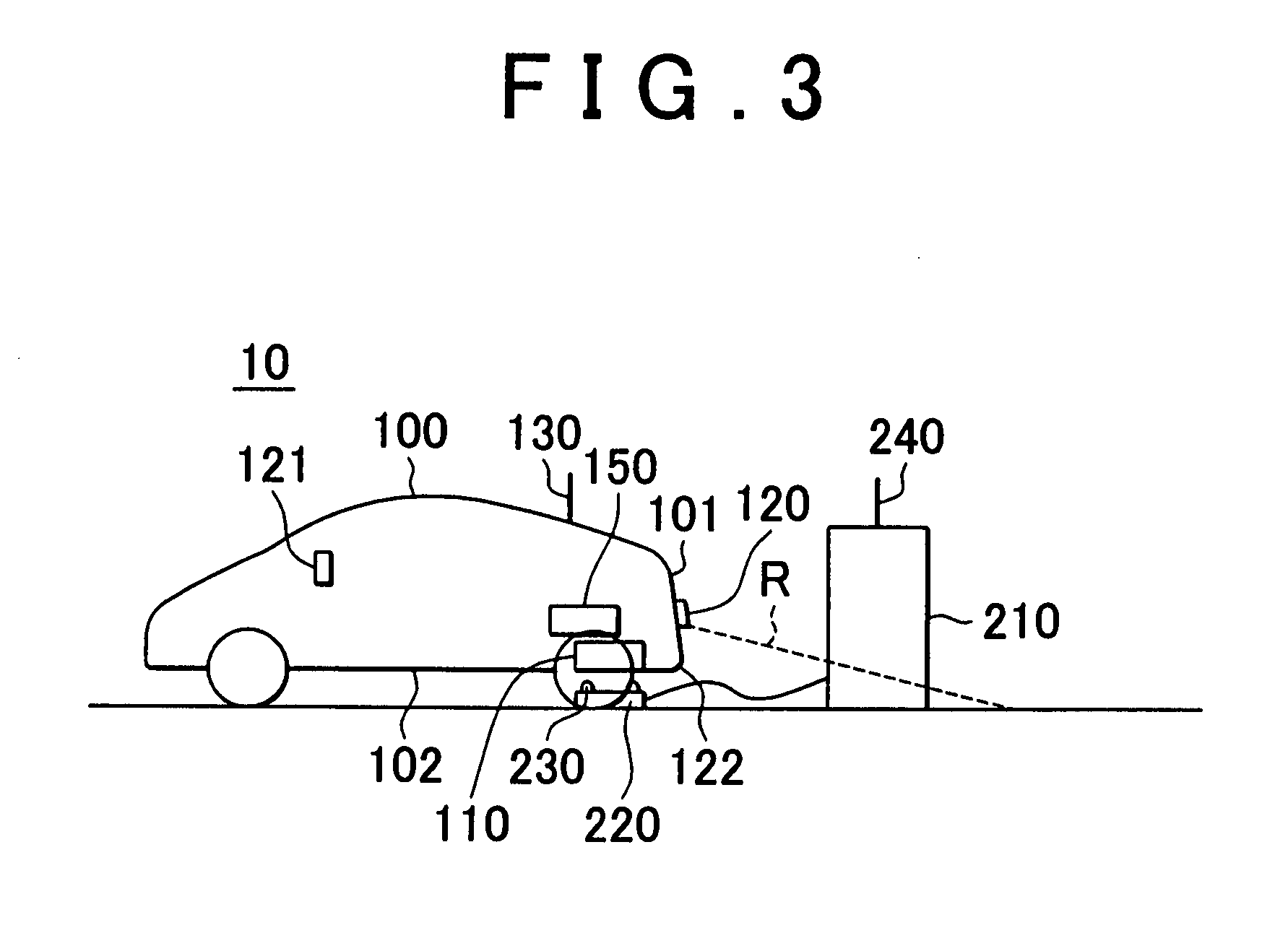
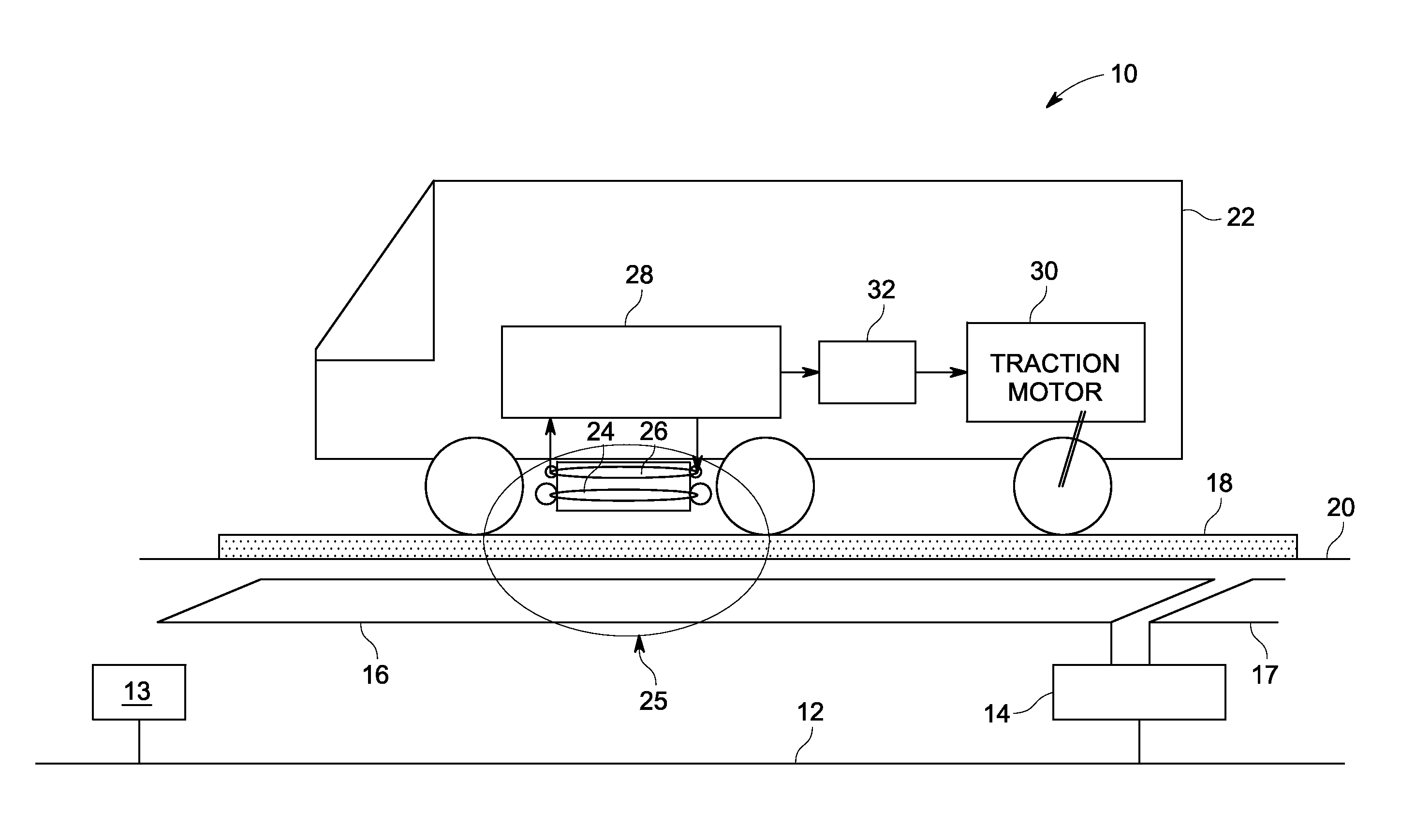
Wireless Charging System for Vehicles
ActiveUS20090045773A1Eliminate needBatteries circuit arrangementsIn situ pavingsElectric power transmissionTransmitted power
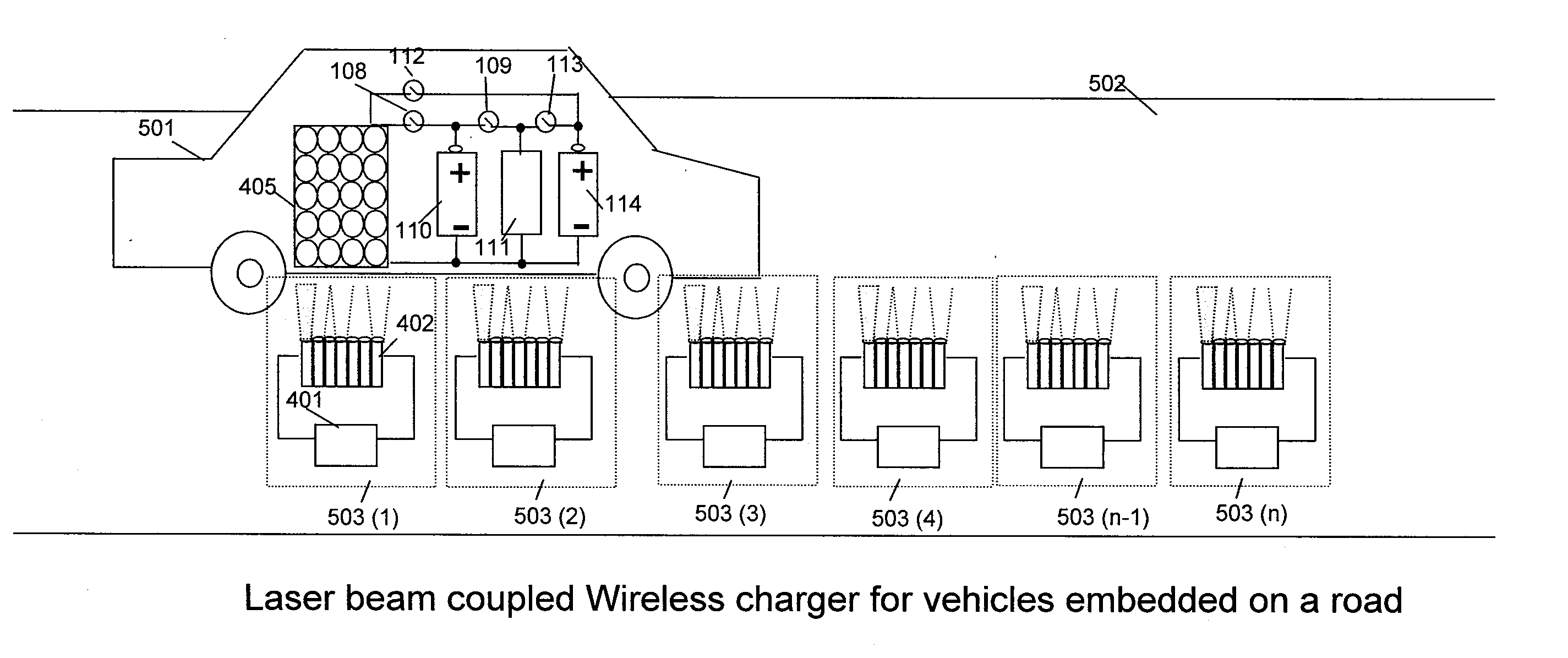
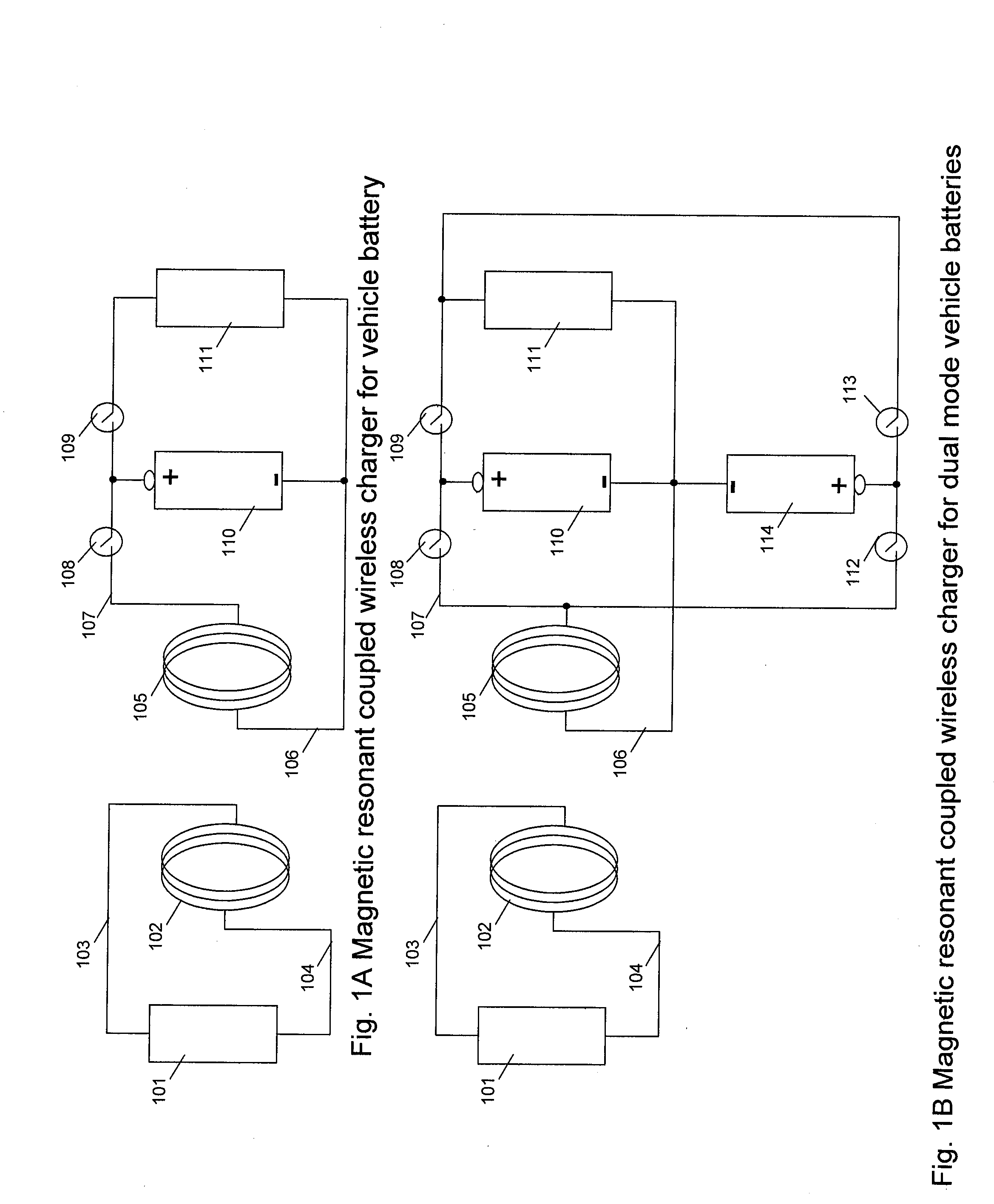
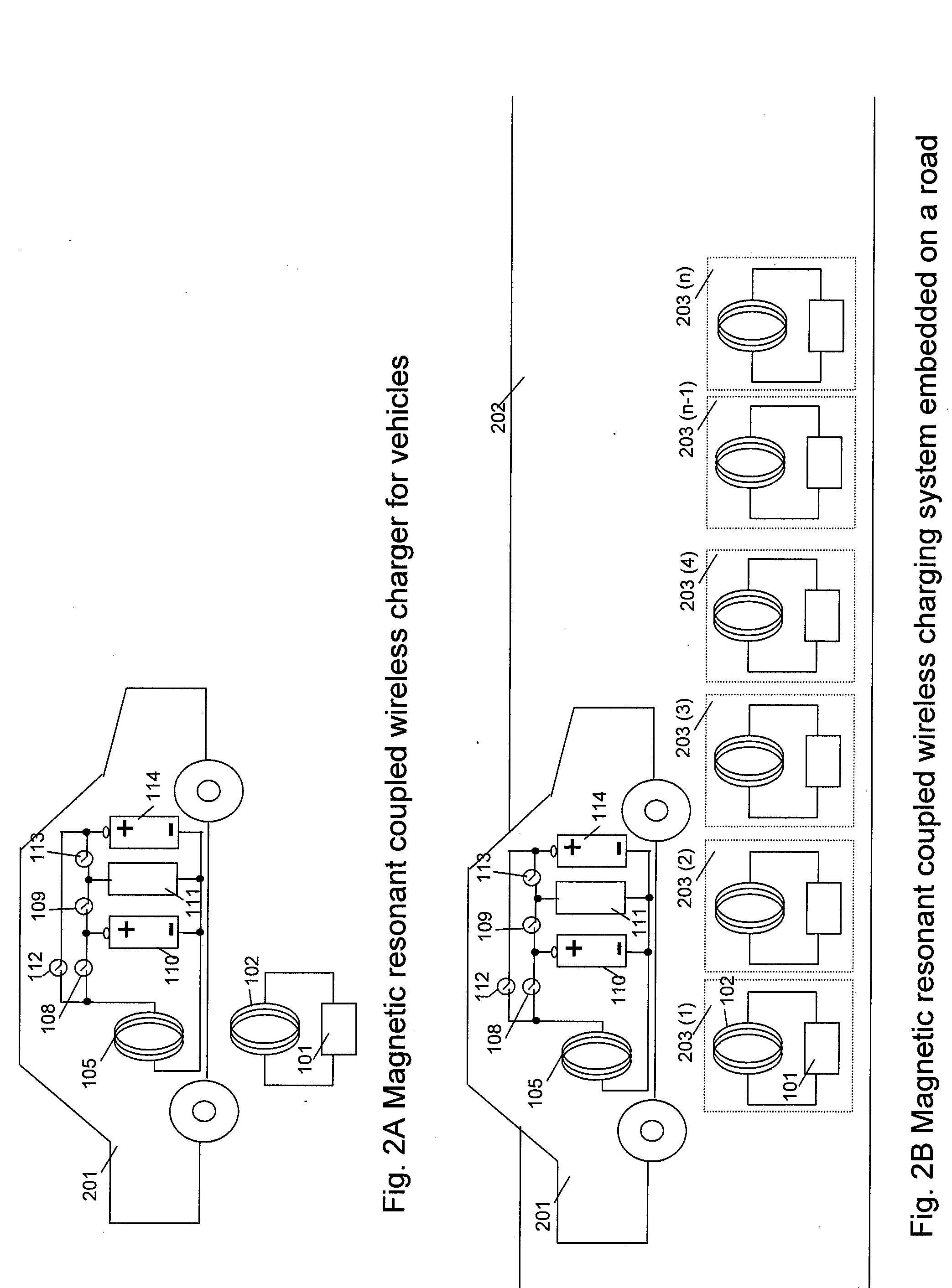
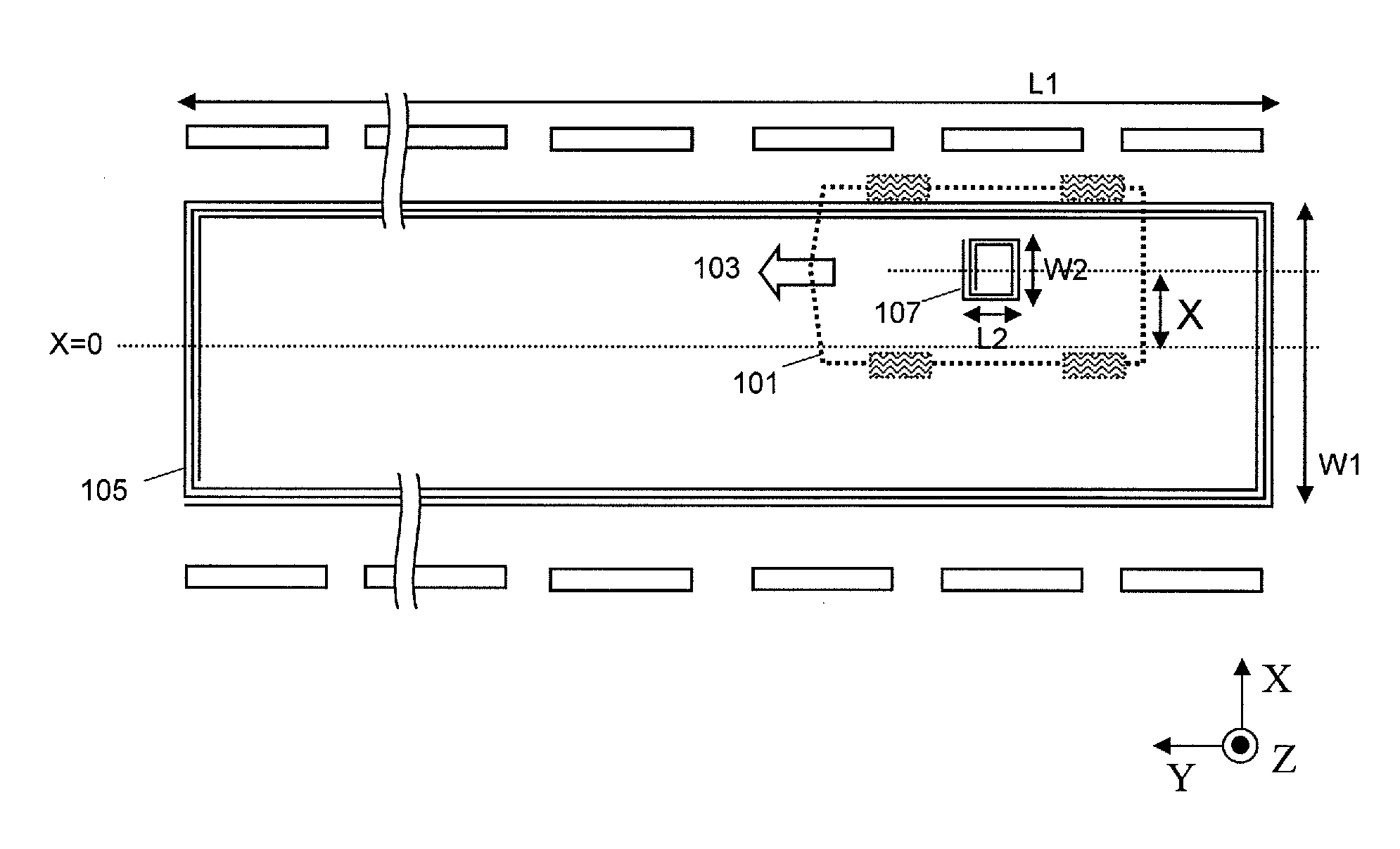
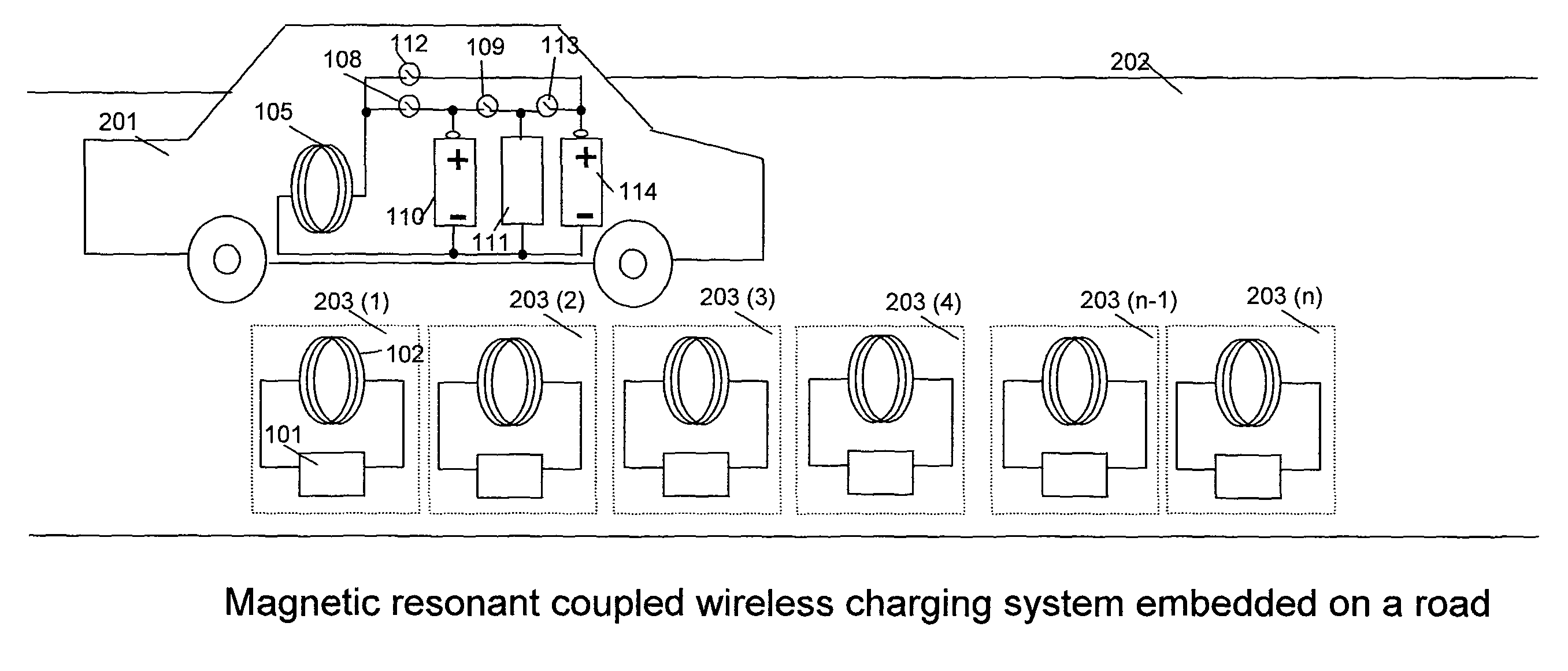
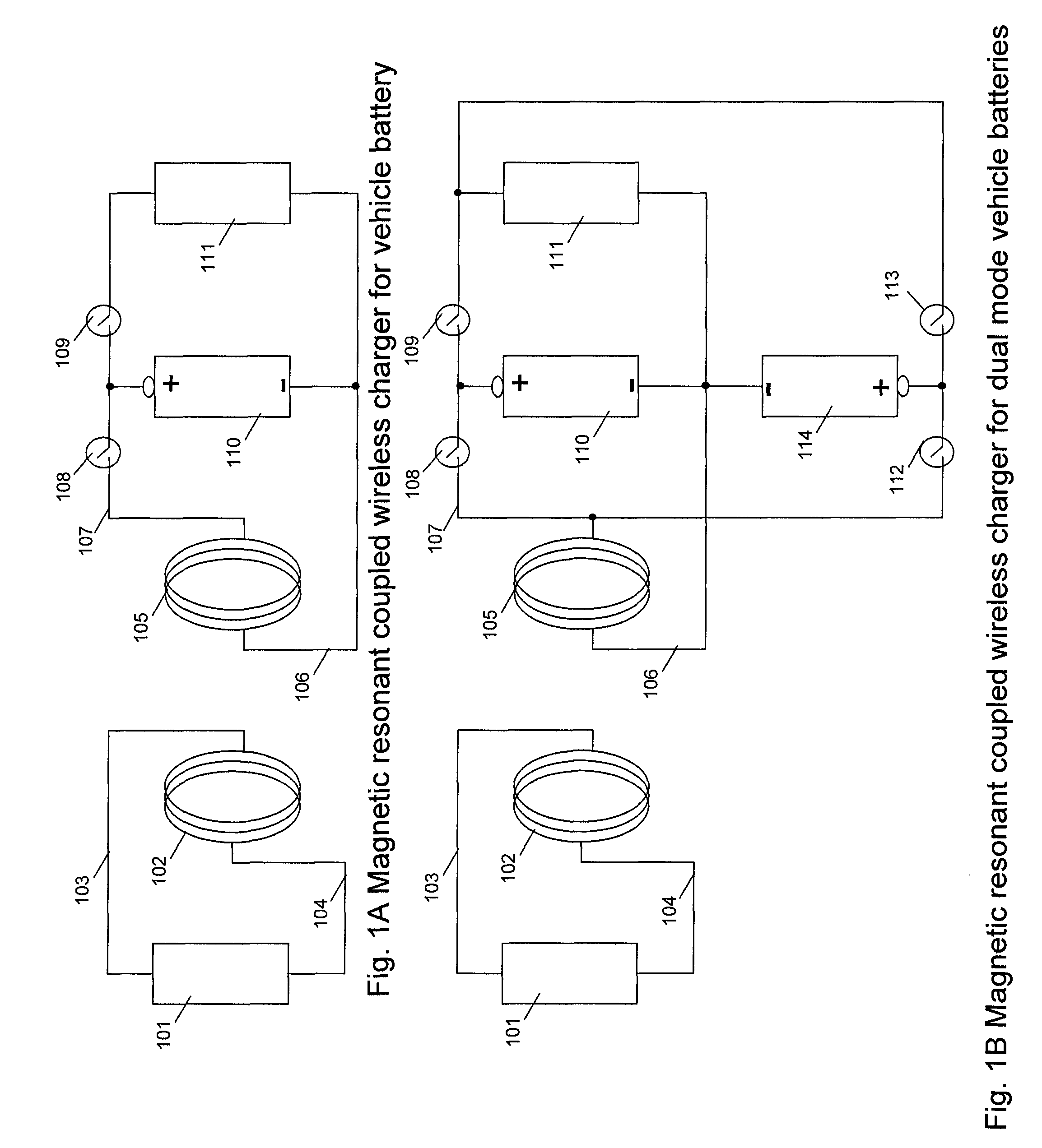
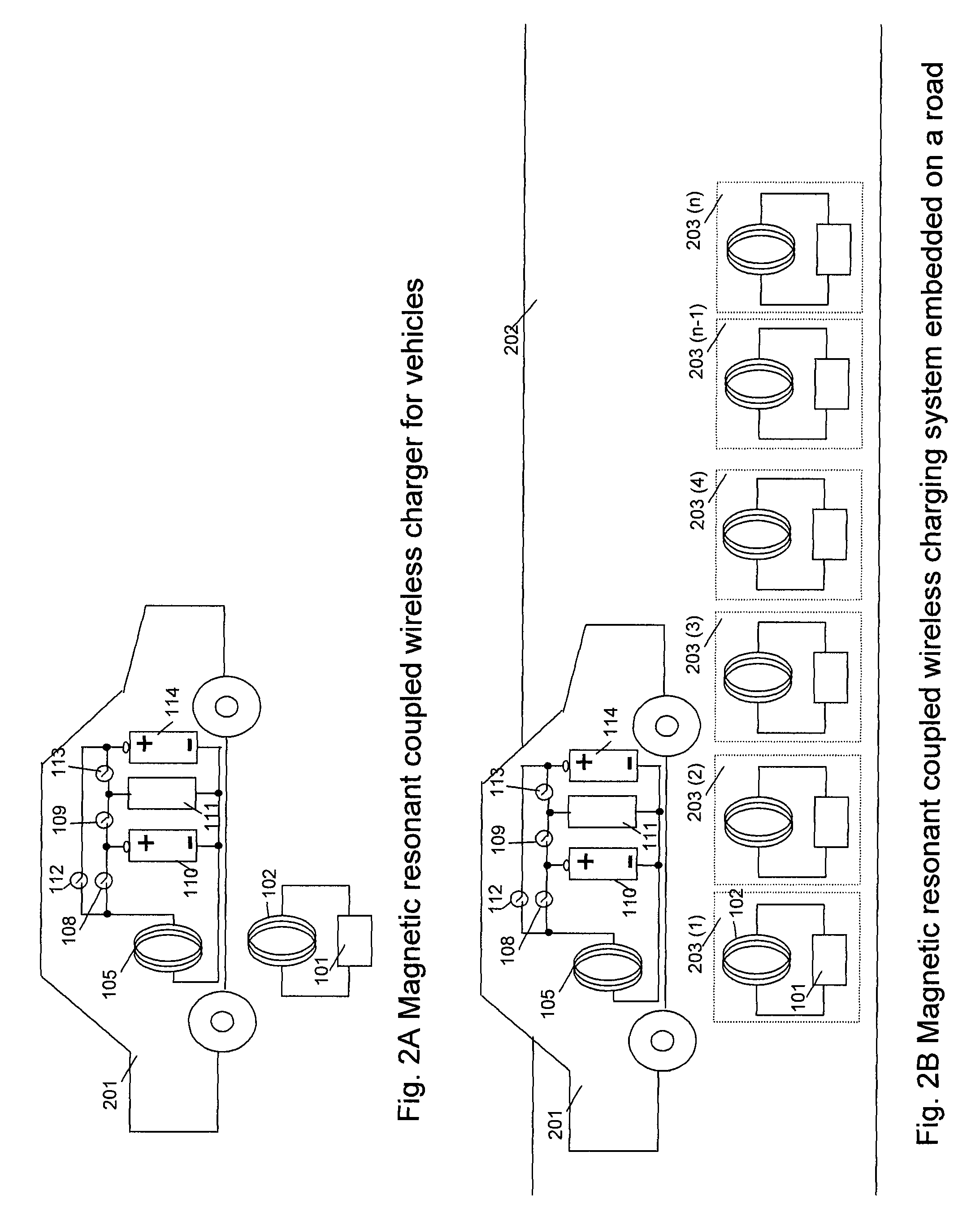
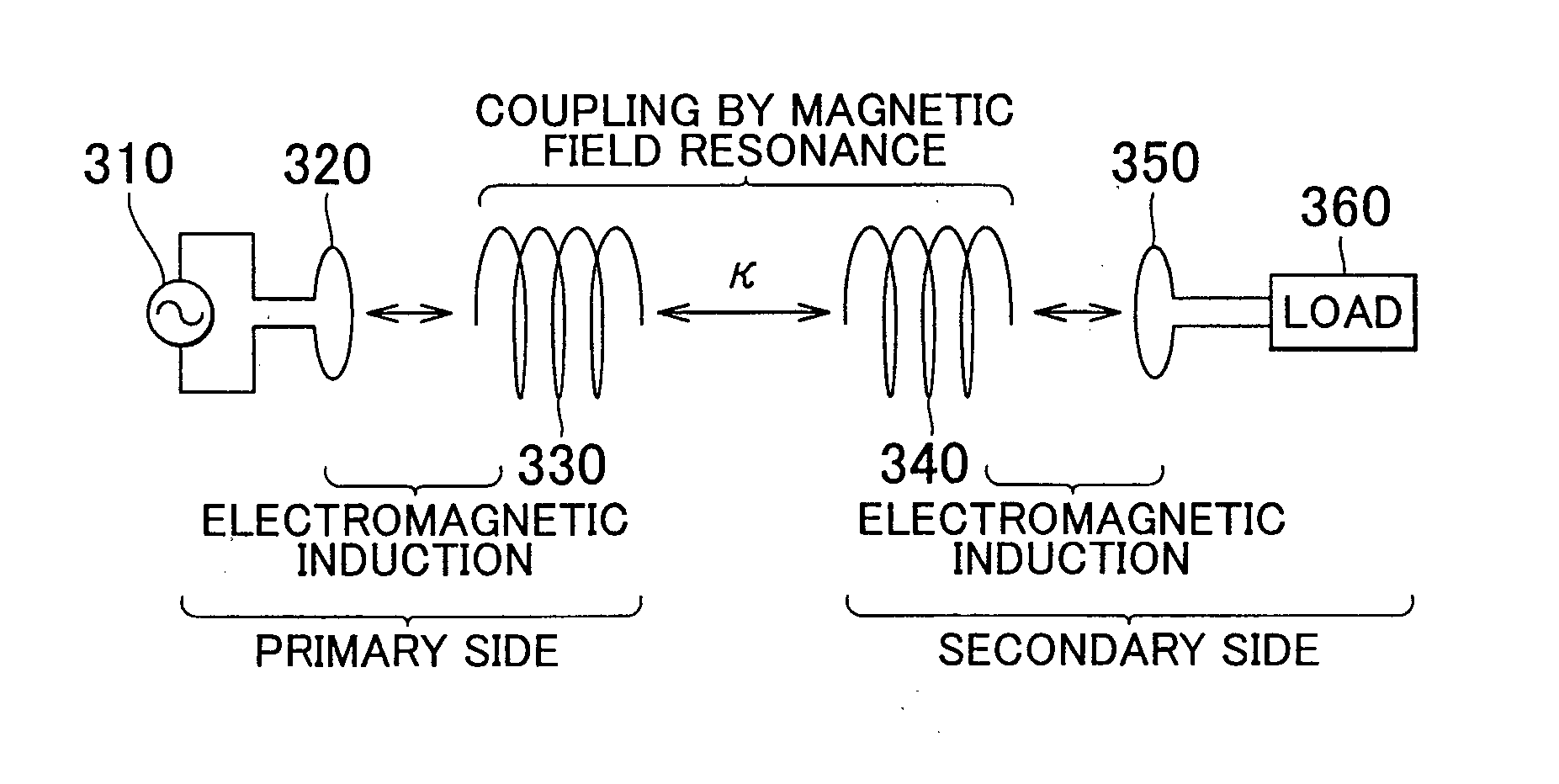
A system of energy storage and charging usable in vehicles and other applications that eliminate the battery capacity and automotive range issues is described. In our invention, vehicles are equipped with charging mechanisms to charge and recharge onboard batteries using wireless electricity and power transmission using magnetic resonant coupling between tuned electromagnetic circuits. The batteries may be charged using wireless charging systems installed along the roads while the vehicle is in use on the road. Charging system may optionally utilize infrared laser beam radiation to transmit power for charging the batteries on board a vehicle while it is in use as well. The onboard vehicle batteries may also be charged when the vehicle is not being driven either by plugging in the vehicle into wall electricity using wired power connection or may be wirelessly charged using the magnetic resonant coupling. By locating the charging circuits on roads, a continuous operation of electric-only mode of hybrid vehicles or pure electric-only vehicles can be accomplished and fully eliminate the need for gasoline usage
Owner:PANDYA RAVI A +1
Electric power supply system for vehicle
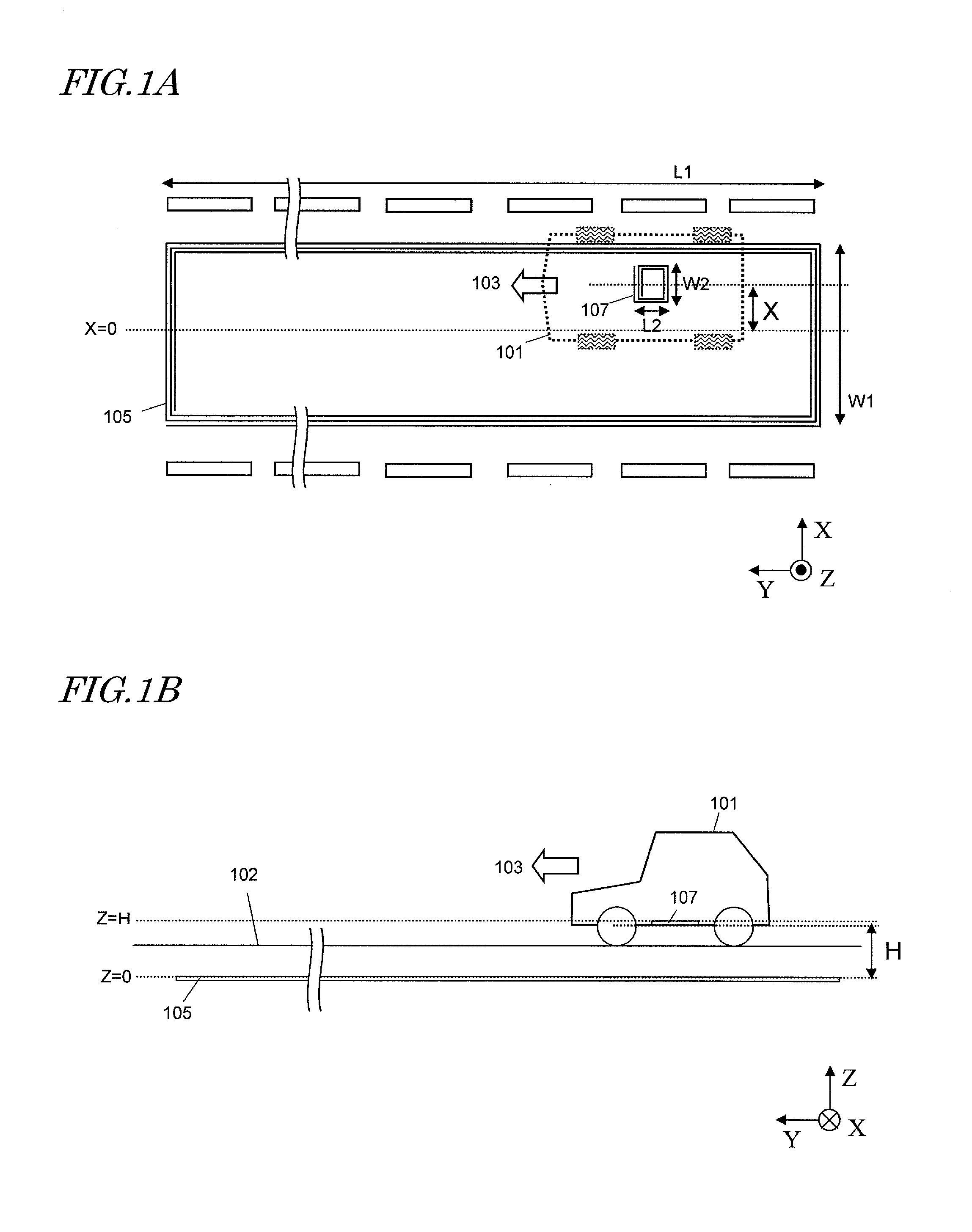
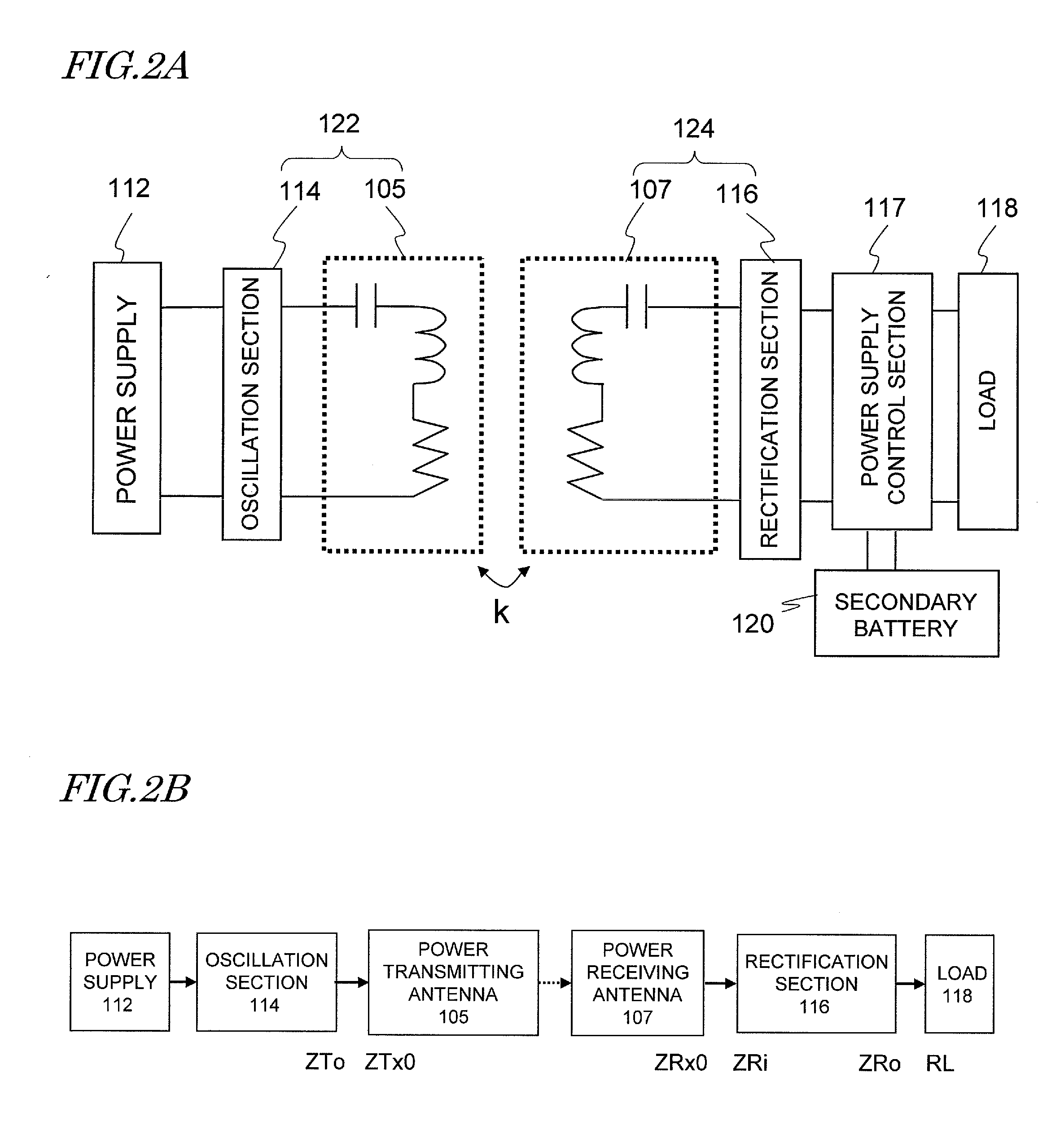
ActiveUS20110114401A1Improve stabilitySimply circuit configurationCharging stationsElectromagnetic wave systemElectricityCoupling
To stabilize the transmission characteristic of an electric power supply system for vehicle even when the vehicle being charged and powered by it shifts horizontally, a power transmitting antenna, which is arranged on the ground, and a power receiving antenna, which is arranged at the bottom of the vehicle, set up resonances at substantially the same resonant frequency and produce magnetic coupling between them. When the power receiving antenna enters the zone in which the power transmitting antenna is located, power is transmitted to the vehicle. By setting H, which is the distance between the power transmitting and receiving antennas that face each other, so that H satisfies 0.11×W1≦H≦0.26×W1 with respect to the width W1 of the power transmitting antenna, the transmission characteristic can be stabilized.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wireless power transfer system and wireless power transfer method
InactiveUS20130234530A1Improve efficiencyIncrease possible power transfer areaRail devicesElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionCapacitance
A wireless power transfer system includes a power transmitter including a power transmission resonator composed of a power transmission coil and a resonant capacitance; and a power receiver including a power receiving resonator composed of a power receiving coil and a resonant capacitance. The system further includes a power transmission auxiliary device including an auxiliary resonator composed of an auxiliary coil and a resonant capacitance. The power transmission auxiliary device and the power transmission device oppose each other, forming a power receiving space for placing the power receiving coil between the power transmission coil and the auxiliary coil, and power transfer is performed in the power receiving space while involving a movement of the power receiving coil including at least one of a displacement and a rotation. The power transfer can be performed with stable efficiency in spite of the movement of the power receiver.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Control of inductive power transfer pickups
InactiveUS6483202B1Reliable fail-safe control featureDecrease in saturation capacityRail devicesElectromagnetic wave systemDc currentEngineering
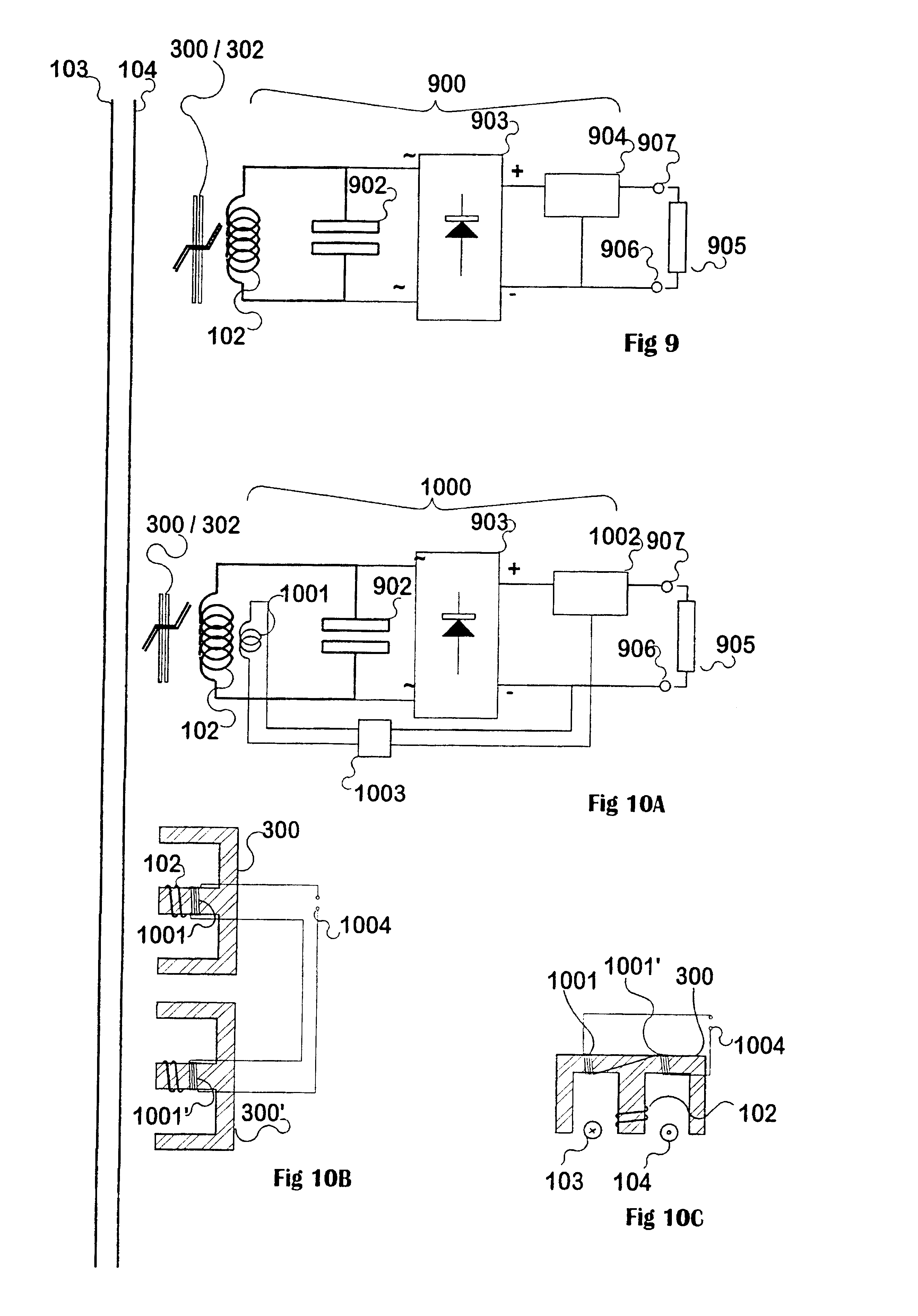
Secondary resonant pickup coils (102) used in loosely coupled inductive power transfer systems, with resonating capacitors (902) have high Q and could support large circulating currents which may destroy components. A current limit or "safety valve" uses an inductor designed to enter saturation at predetermined resonating currents somewhat above normal working levels. Saturation is immediate and passive. The constant-current characteristic of a loosely coupled, controlled pickup means that if the saturable section is shared by coupling flux and by leakage flux, then on saturation the current source is terminated in the saturated inductor, and little detuning from resonance occurs. Alternatively an external saturable inductor (1101, 1102) may be introduced within the resonant circuit (102 and 902), to detune the circuit away from the system frequency. Alternatively DC current may be passed through a winding to increase saturation of a saturable part of a core. As a result, a fail-safe pickup offering a voltage-limited constant-current output is provided.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
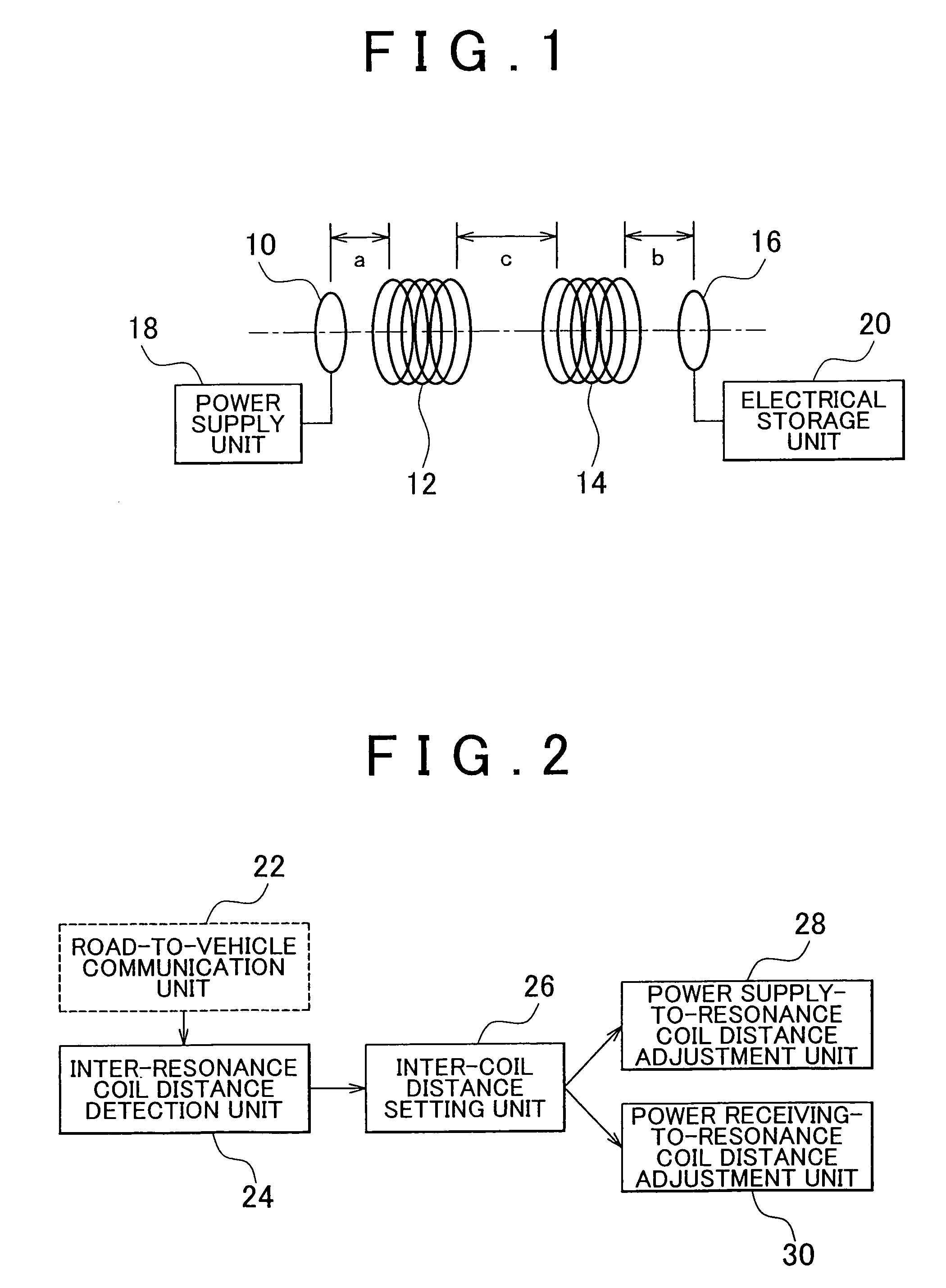
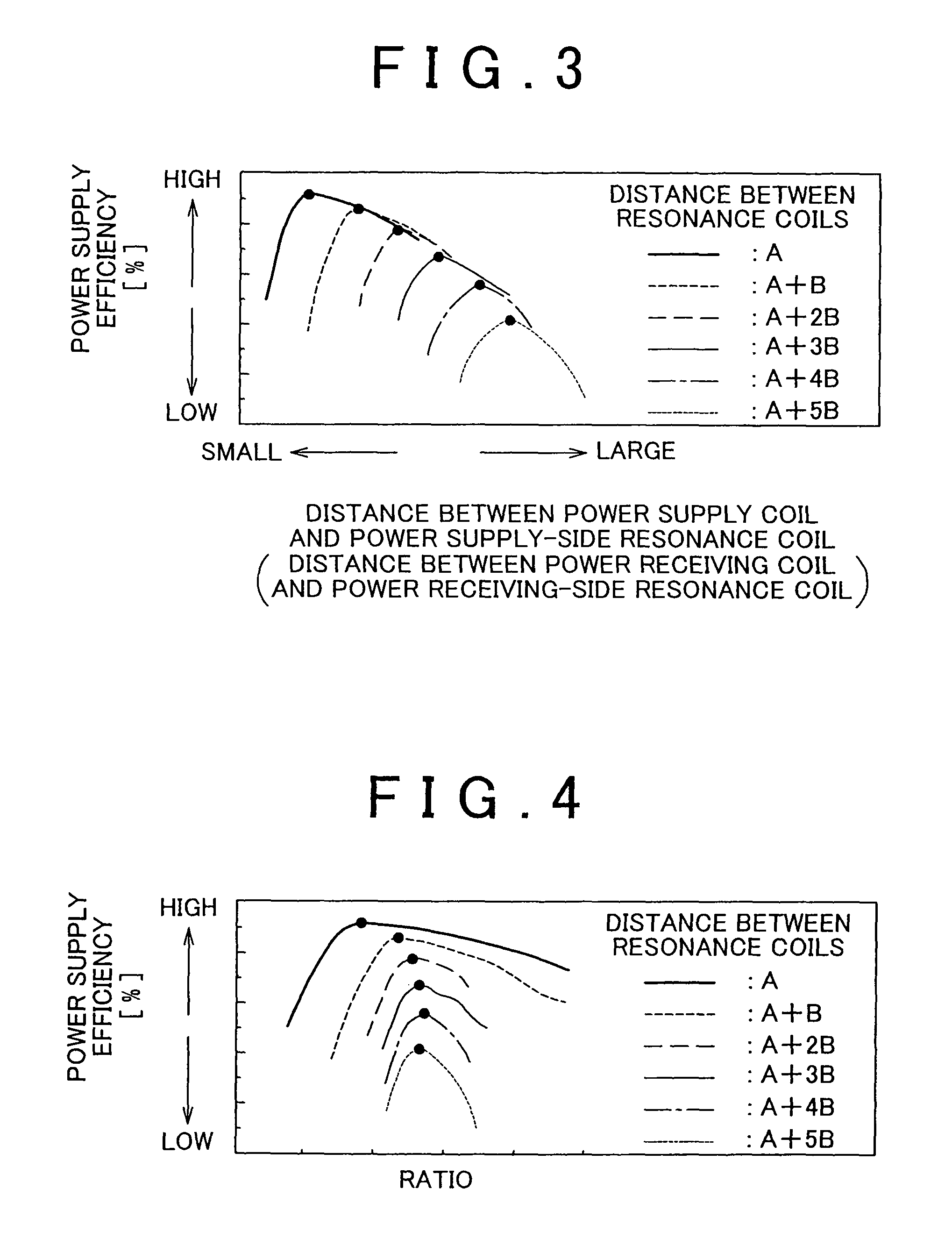
Power supply system and method of controlling power supply system
ActiveUS20100123452A1Maximize total power supply efficiencyMaintain and improve power supply efficiencyCircuit monitoring/indicationCharging stationsElectricityControl power
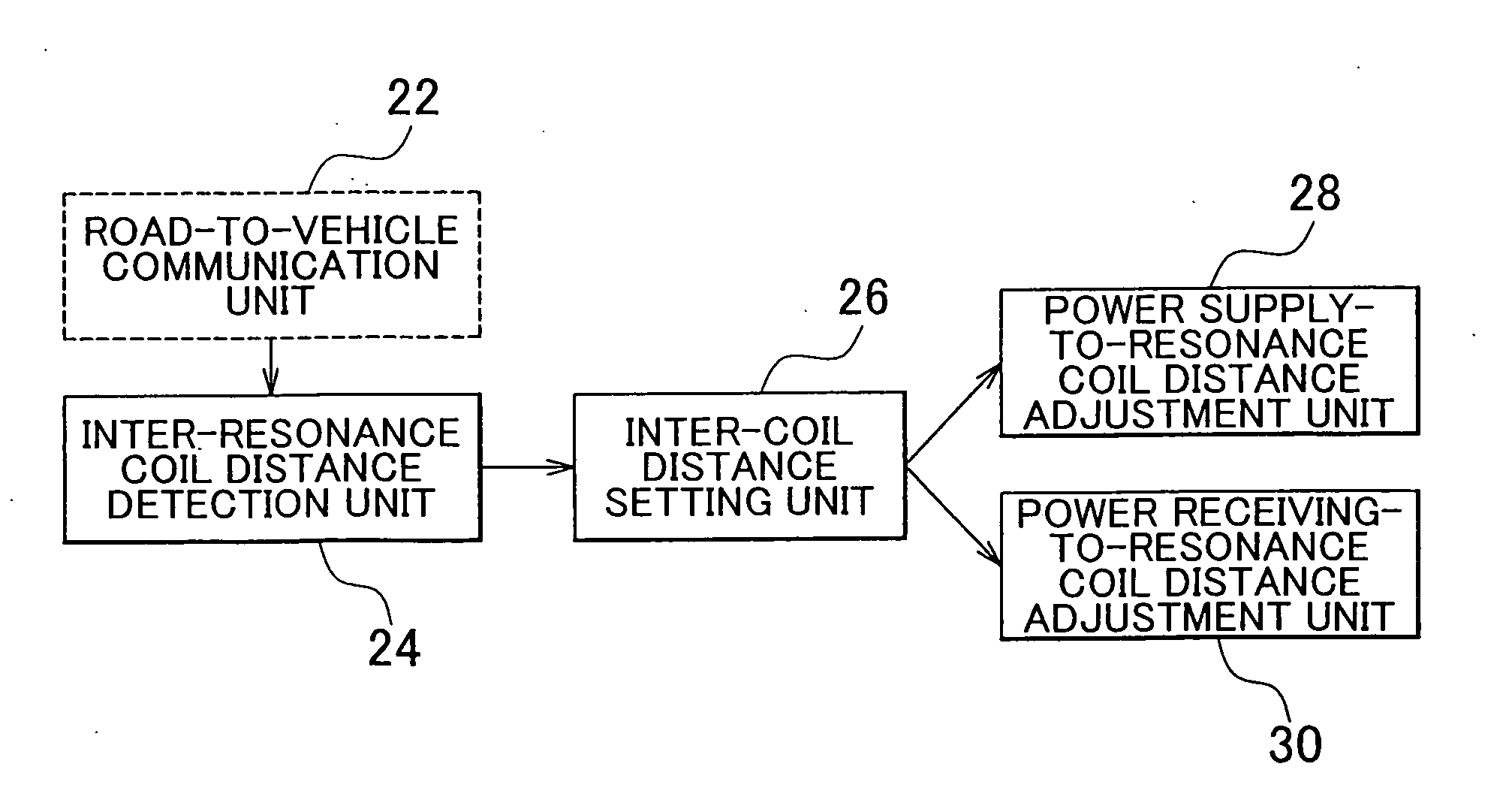
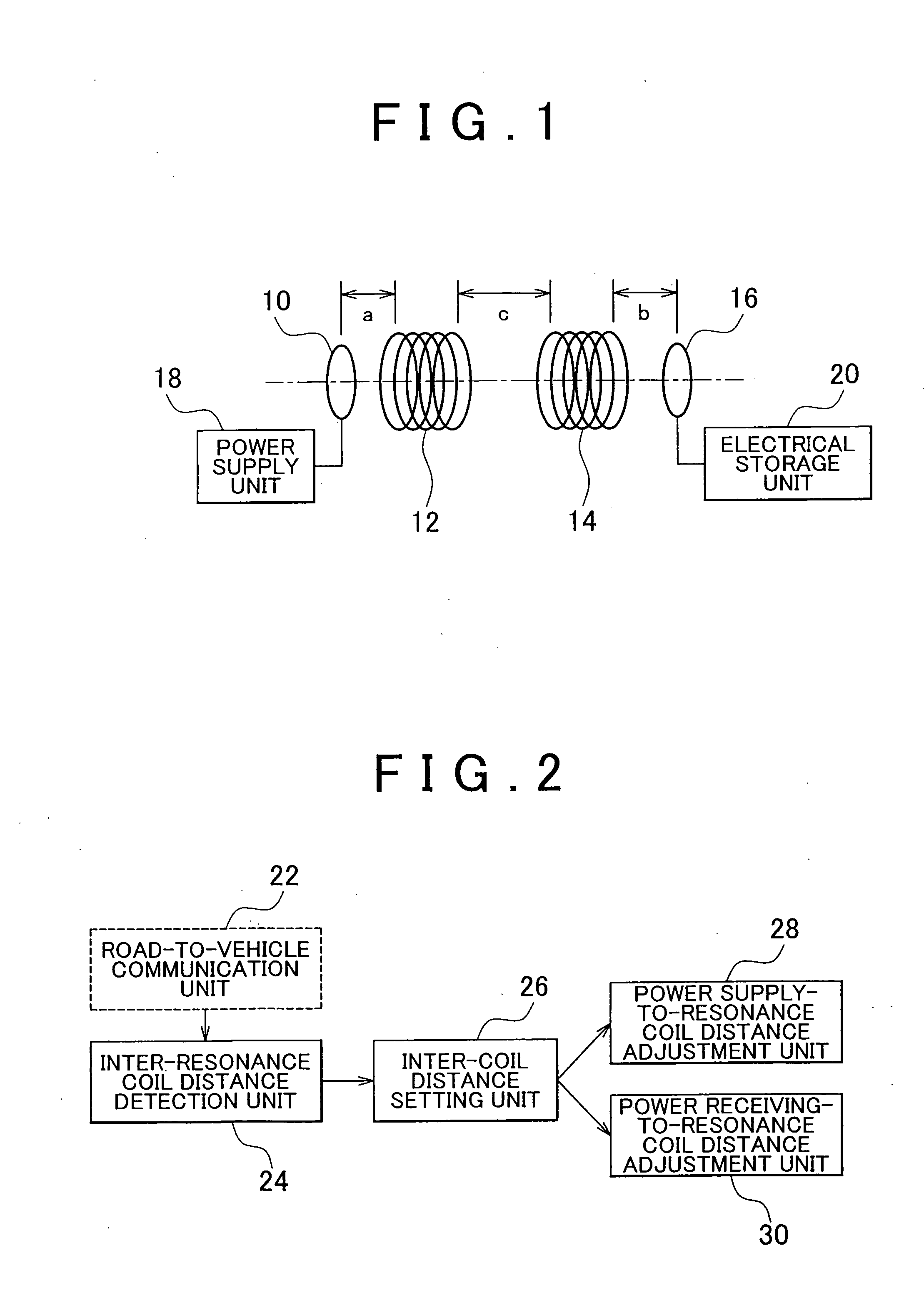
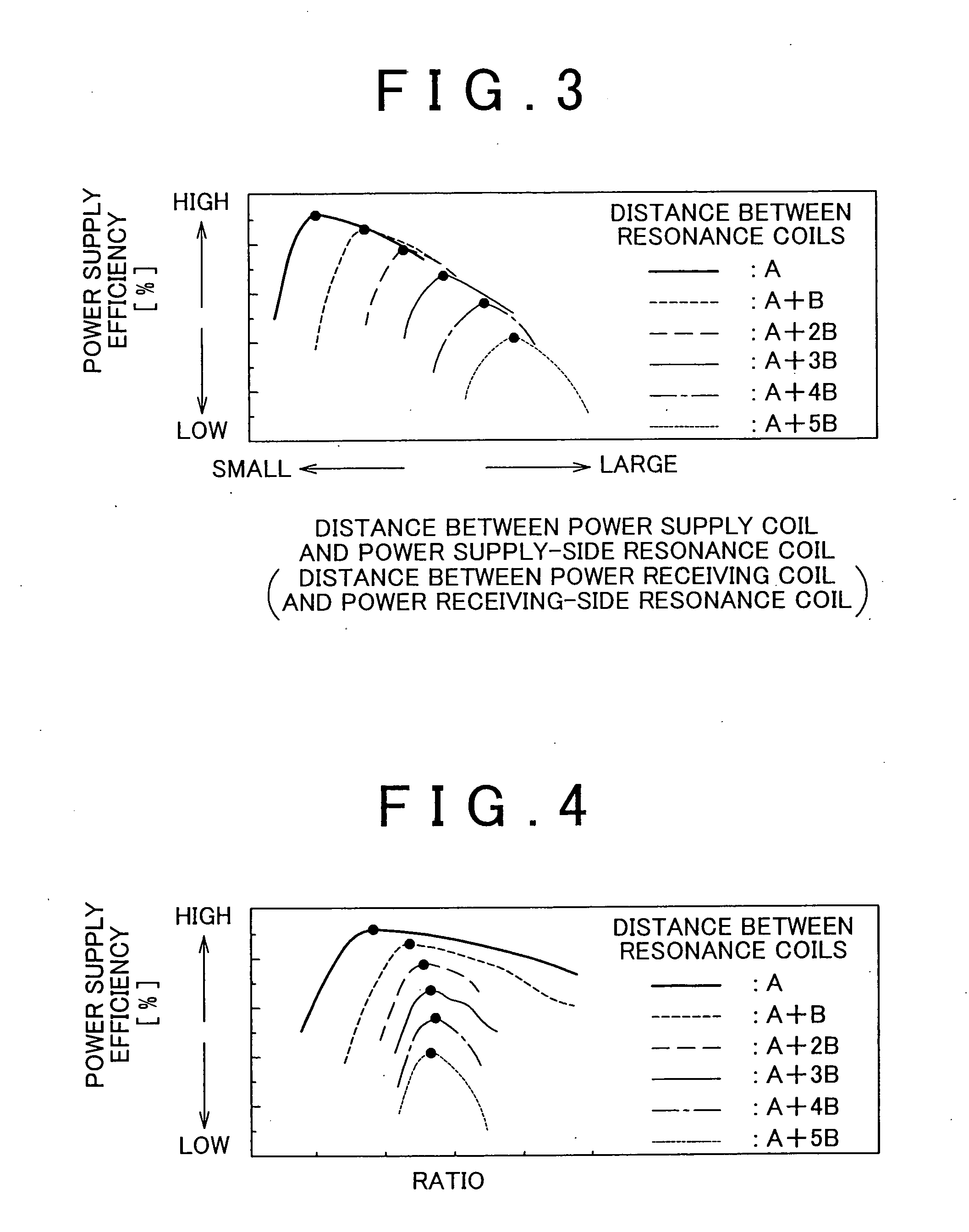
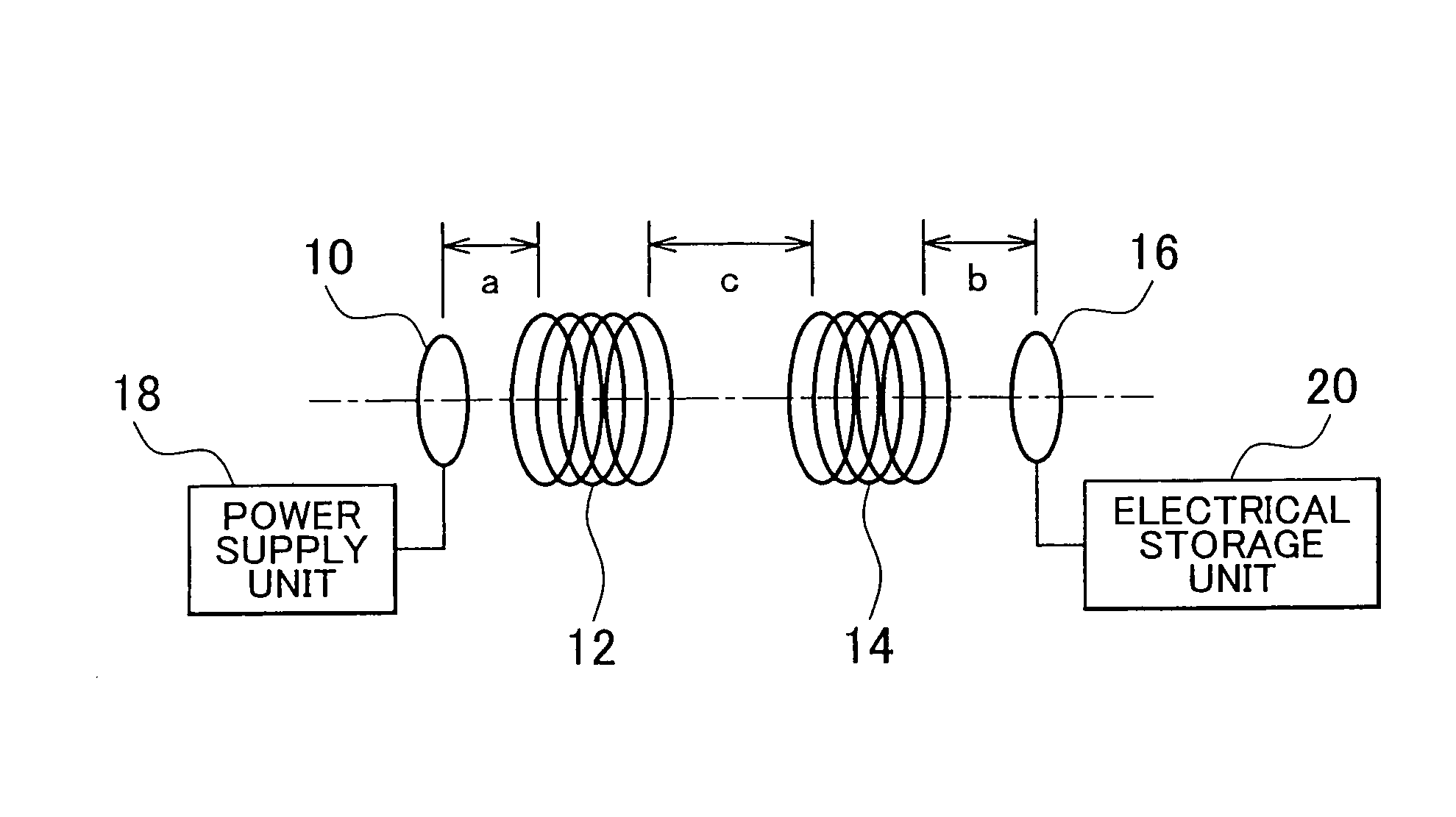
A power supply system that includes: a power supply coil and a power supply-side resonance coil that are provided at a facility; a power receiving coil and a power receiving-side resonance coil that are provided for a mobile unit; a power supply-side detection unit that detects a position of the power supply-side resonance coil; a power receiving-side detection unit that detects a position of the power receiving-side resonance coil; and an adjustment unit that adjusts a relative position of the power supply coil with respect to the power supply-side resonance coil and a relative position of the power receiving coil with respect to the power receiving-side resonance coil on the basis of the position of the power supply-side resonance coil and the position of the power receiving-side resonance coil.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Power supply system and method of controlling power supply system
ActiveUS8178995B2Improve efficiencyEasy maintenanceCircuit monitoring/indicationCharging stationsElectricityControl power
A power supply system that includes: a power supply coil and a power supply-side resonance coil that are provided at a facility; a power receiving coil and a power receiving-side resonance coil that are provided for a mobile unit; a power supply-side detection unit that detects a position of the power supply-side resonance coil; a power receiving-side detection unit that detects a position of the power receiving-side resonance coil; and an adjustment unit that adjusts a relative position of the power supply coil with respect to the power supply-side resonance coil and a relative position of the power receiving coil with respect to the power receiving-side resonance coil on the basis of the position of the power supply-side resonance coil and the position of the power receiving-side resonance coil.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
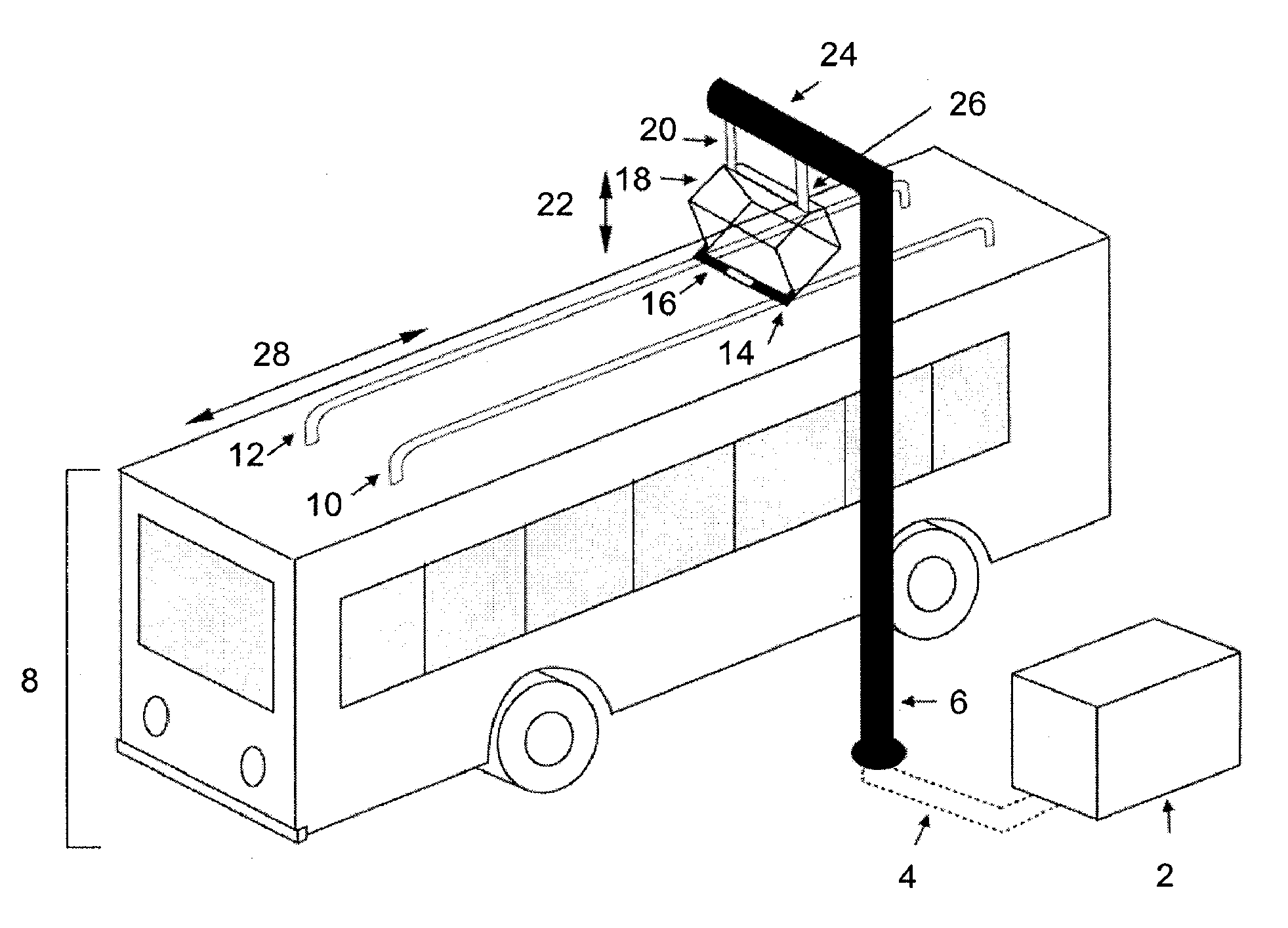
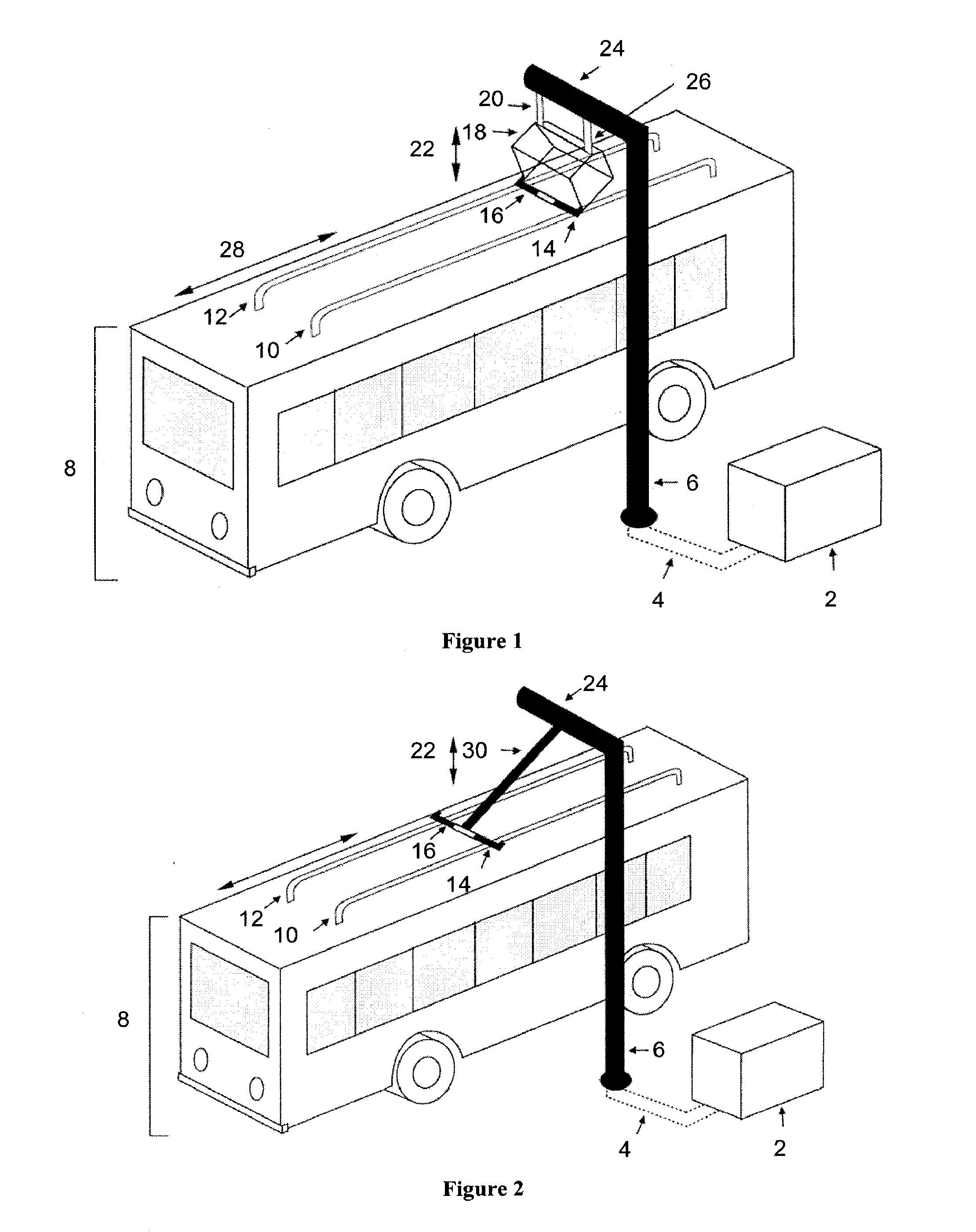
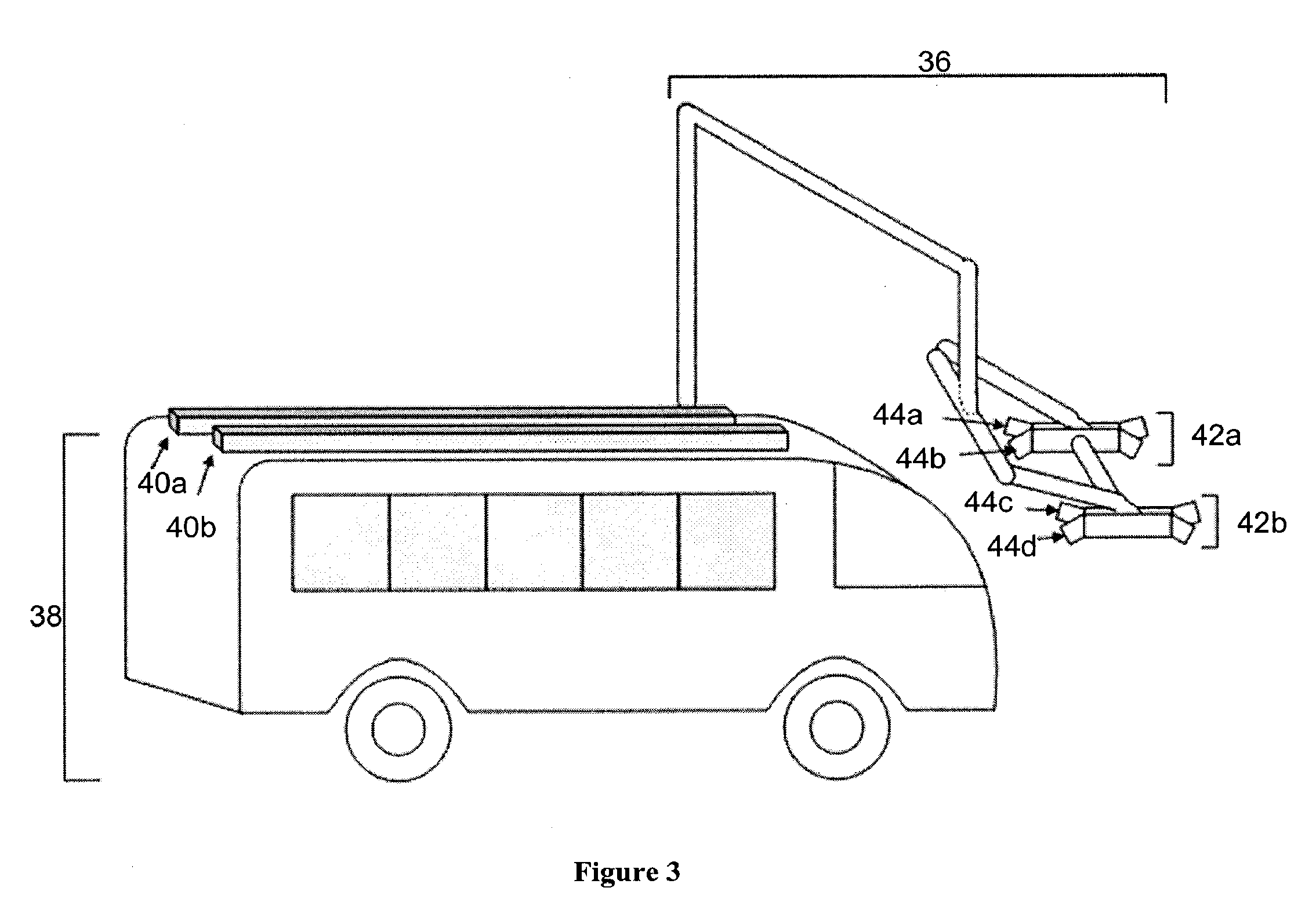
Systems and methods for automatic connection and charging of an electric vehicle at a charging station
ActiveUS20130193918A1Reducing duty cycleResistance changeCircuit monitoring/indicationMobile unit charging stationsEngineeringBattery electric vehicle
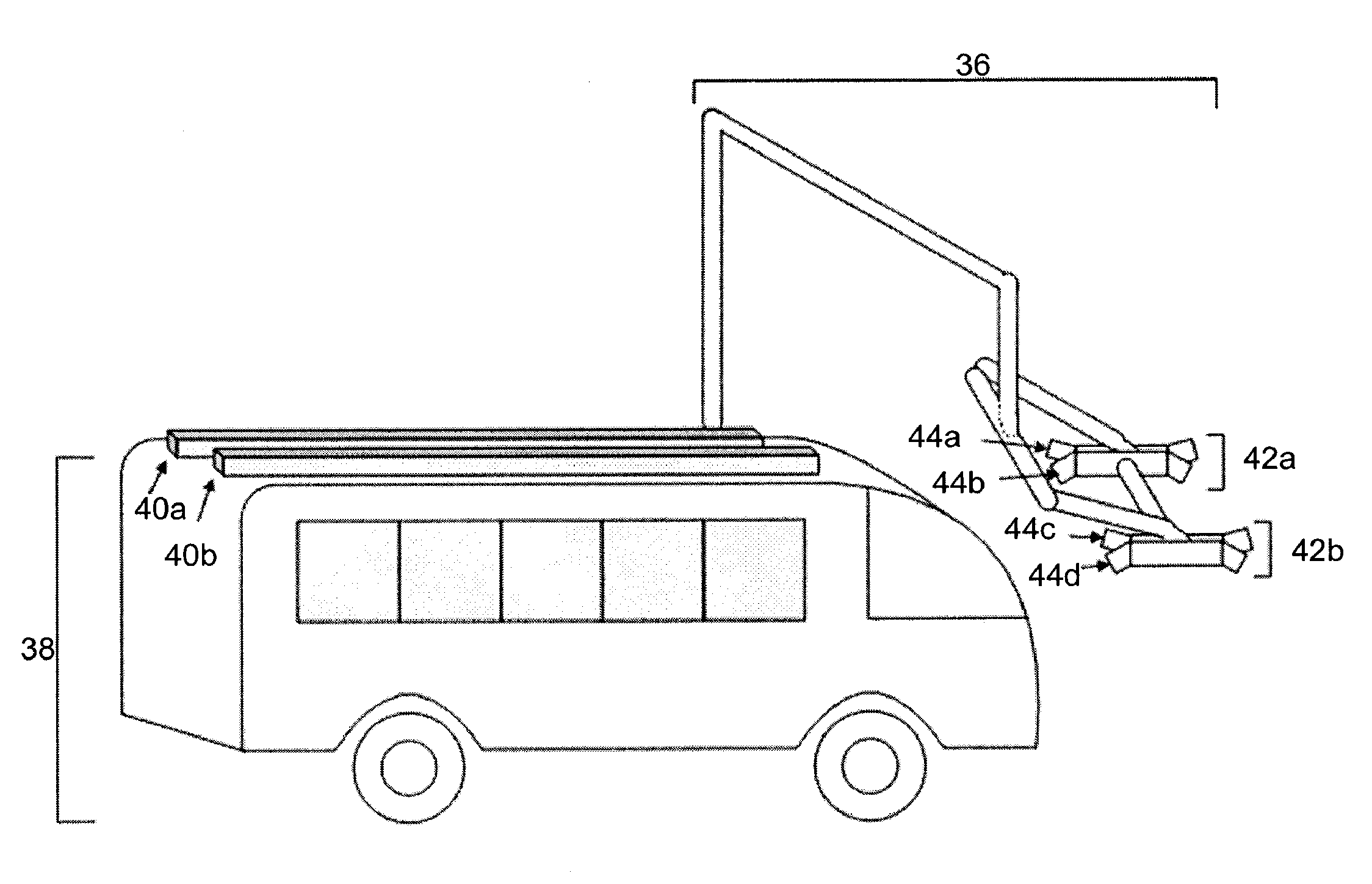
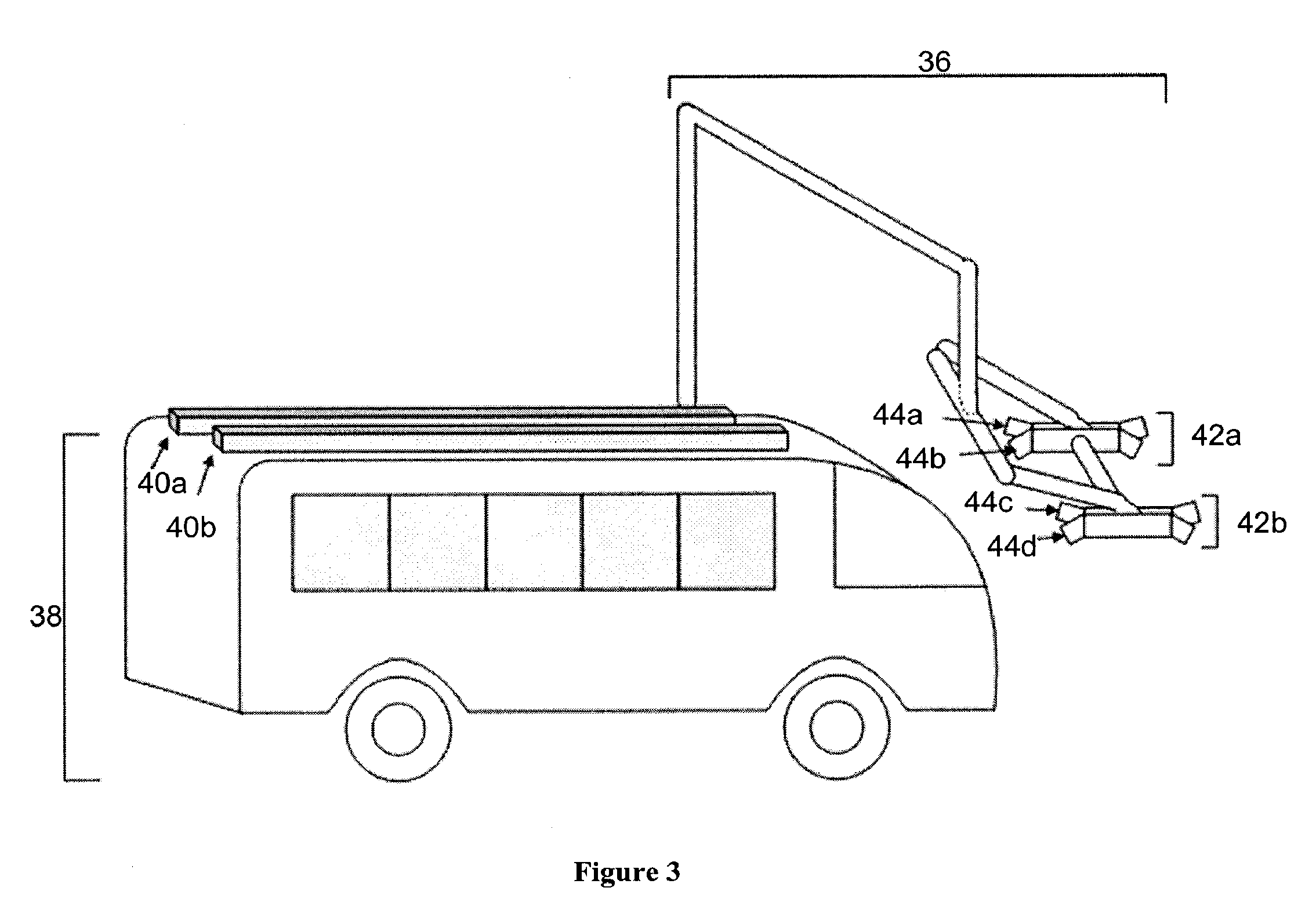
The invention provides systems and methods for connecting an electric or hybrid electric vehicle to a charging station. Automated charging and docking processes may be provided. In some embodiments, a vehicle arrival and position may be detected. The vehicle may be charged with a charging arm and some automated vehicle positioning may occur. The vehicle may be charged and released. Fault detection may occur.
Owner:PROTERRA OPERATING CO INC
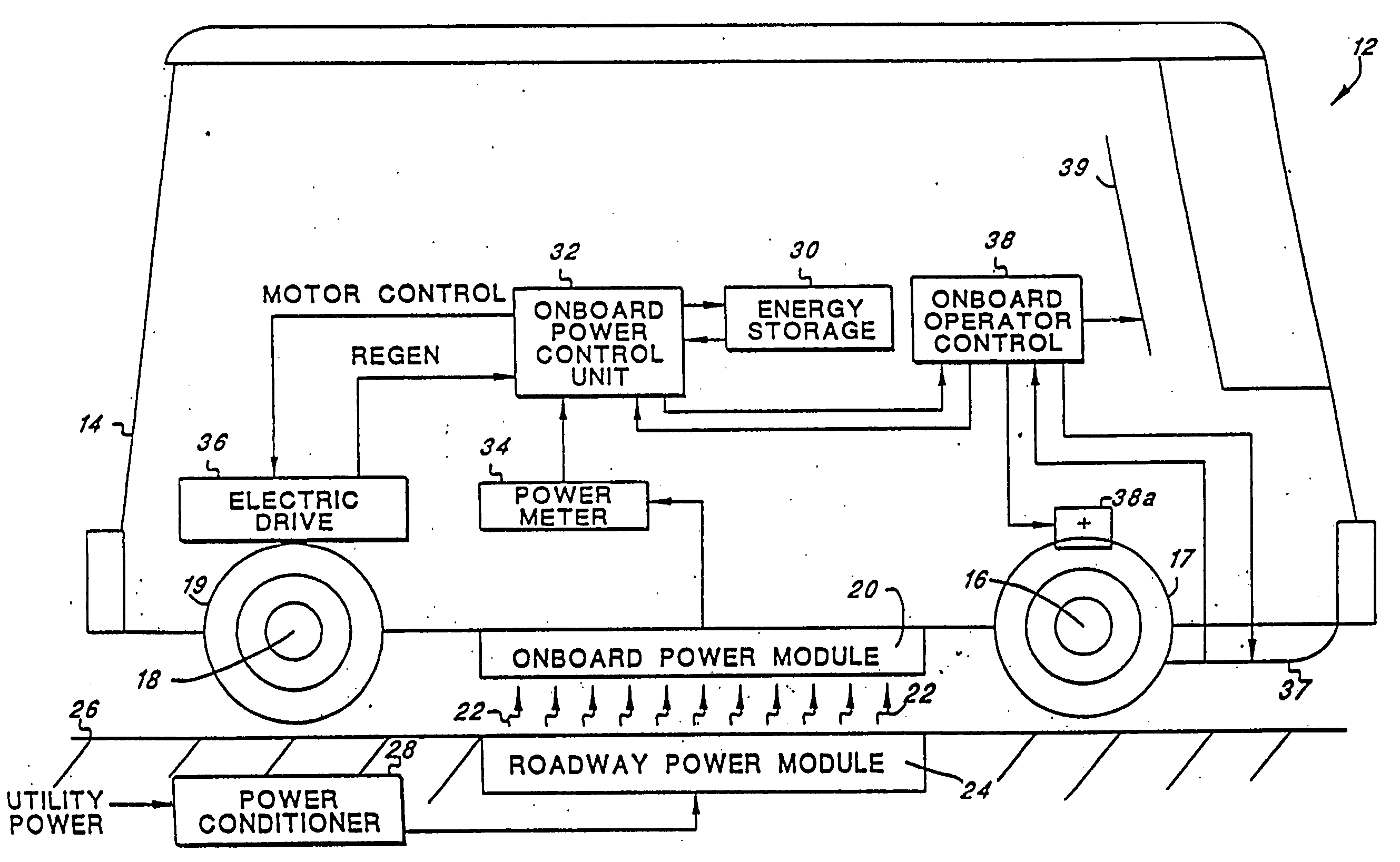
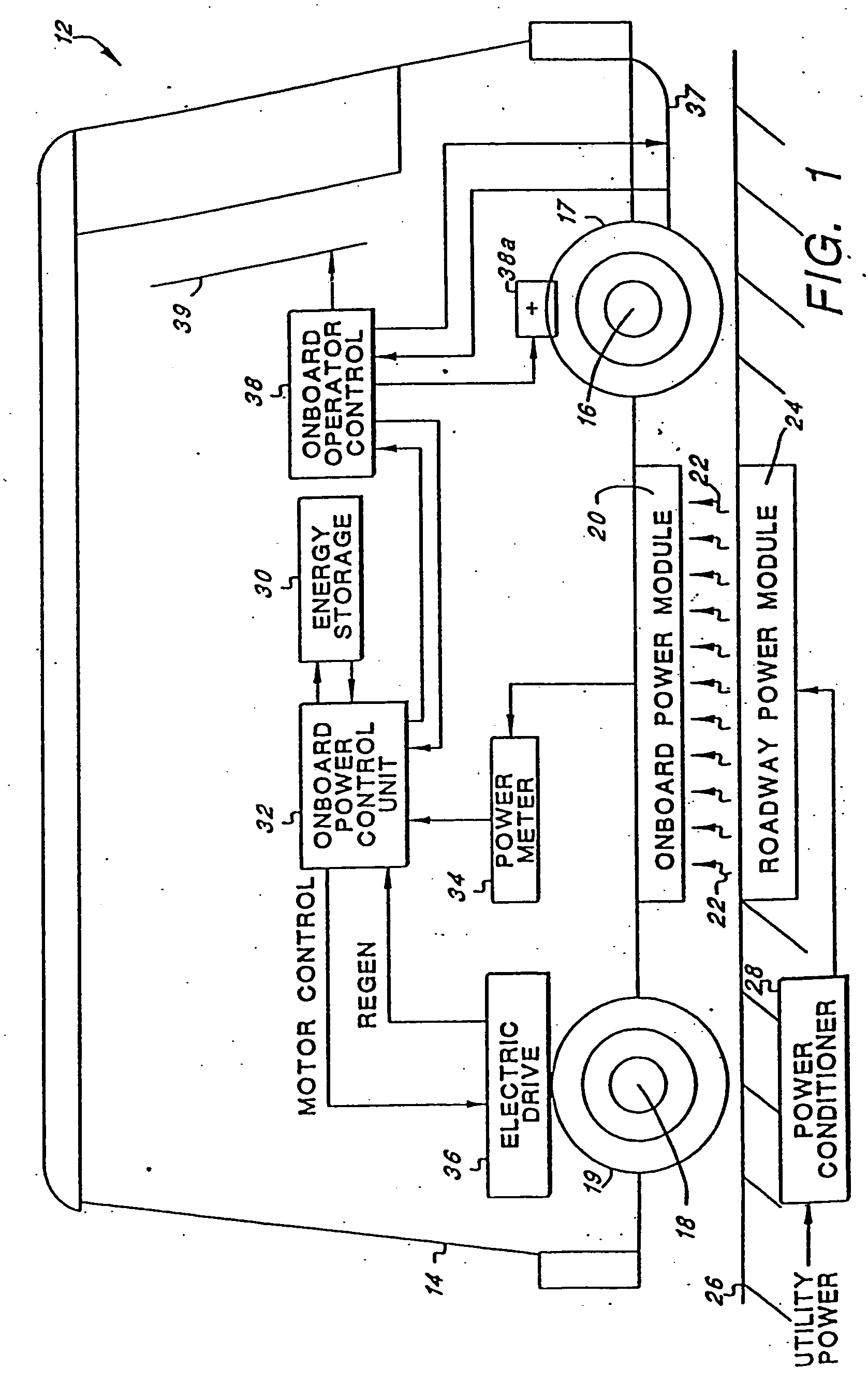
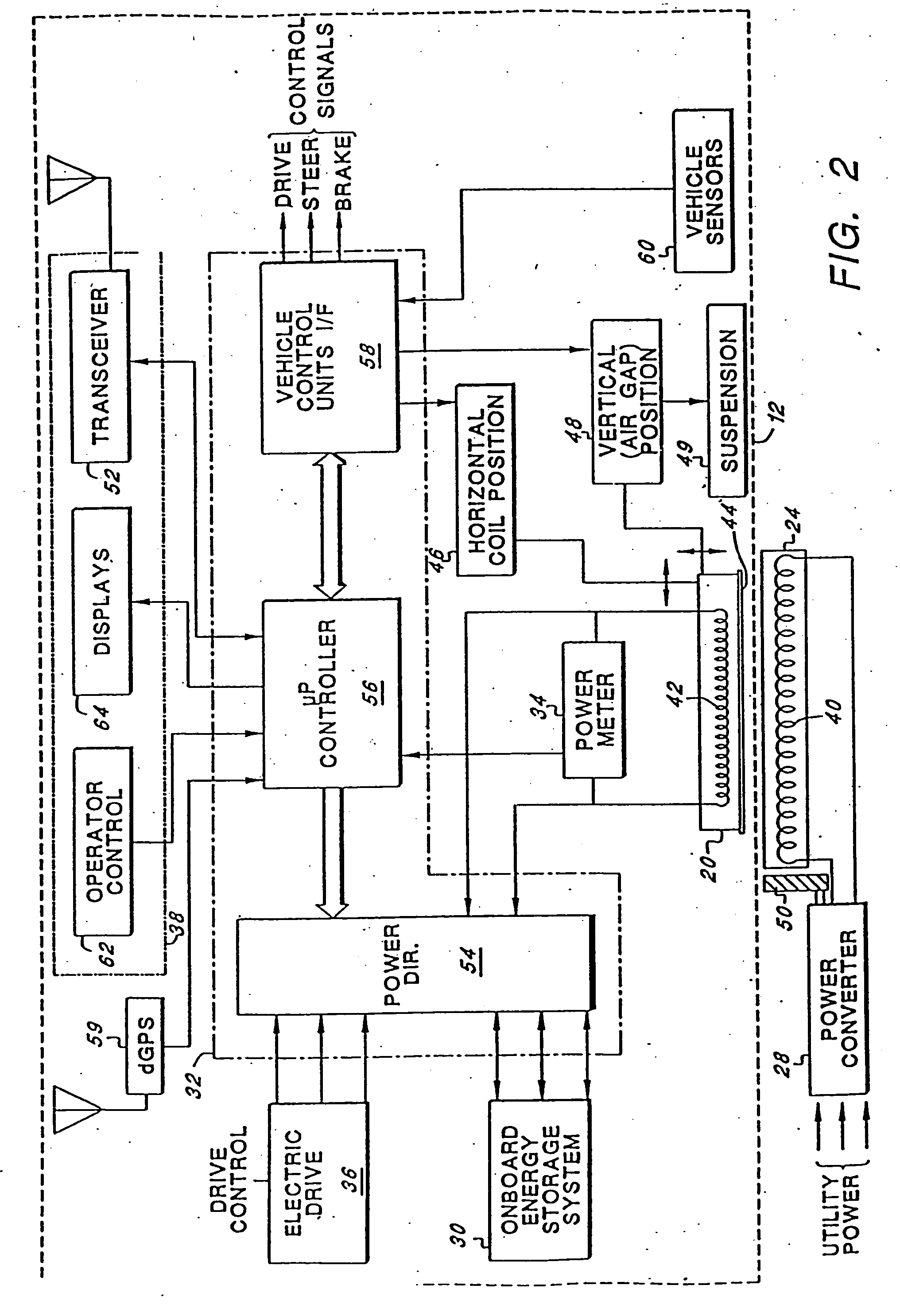
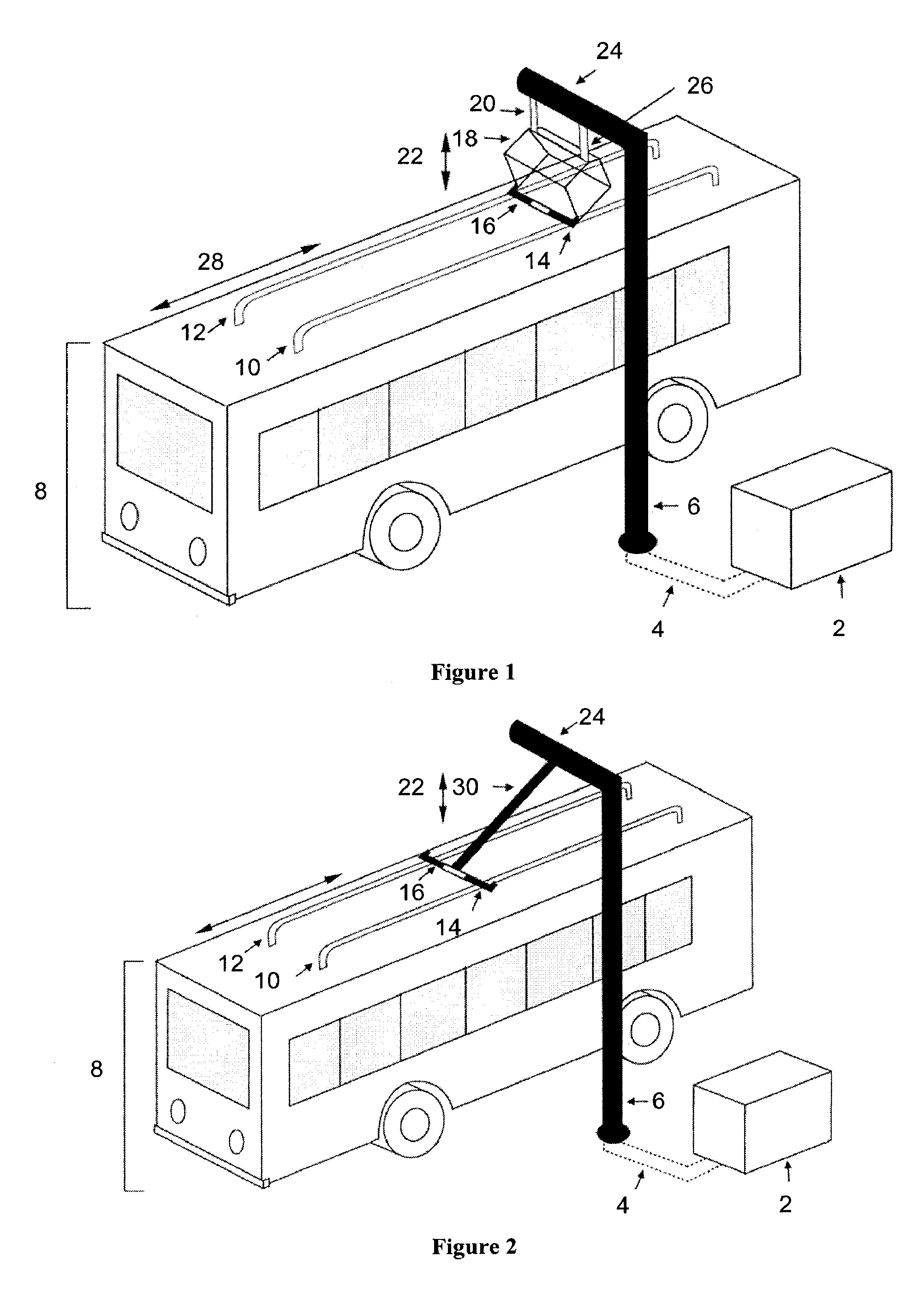
Roadway-powered electric vehicle system having automatic guidance and demand-based dispatch features
A roadway-powered electric vehicle (RPEV) system includes: (1) an all-electric vehicle; and (2) a roadway network over which the vehicle travels. The all-electric vehicle has one or more onboard energy storage elements or devices that can be rapidly charged or energized with energy obtained from an electrical current, such as a network of electromechanical batteries. The electric vehicle further includes an on-board controller that extracts energy from the energy storage elements, as needed, and converts such extracted energy to electrical power used to propel the electric vehicle. The energy storage elements may be charged while the vehicle is in operation. The charging occurs through a network of power coupling elements, e.g., coils, embedded in the roadway. The RPEV system also includes: (1) an onboard power meter; (2) a wide bandwidth communications channel to allow information signals to be sent to, and received from, the RPEV while it is in use; (3) automated garaging that couples power to the RPEV for both replenishing the onboard energy source and to bring the interior climate of the vehicle to a comfortable level before the driver and / or passengers get in; (4) electronic coupling between “master” and “salve” RPEV's in order to increase passenger capacity and electronic actuators for quick-response control of the “slave” RPEV; (5) inductive heating coils at passenger loading / unloading zones in order to increase passenger safety; (6) an ergonomically designed passenger compartment; (7) a locating system for determining the precise location of the RPEV; and (8) a scheduling and dispatch computer for controlling the scheduling of RPEV's around a route and dispatch of RPEV's based on demand.
Owner:ROSS HOWARD R
Power supply for an electroluminescent display
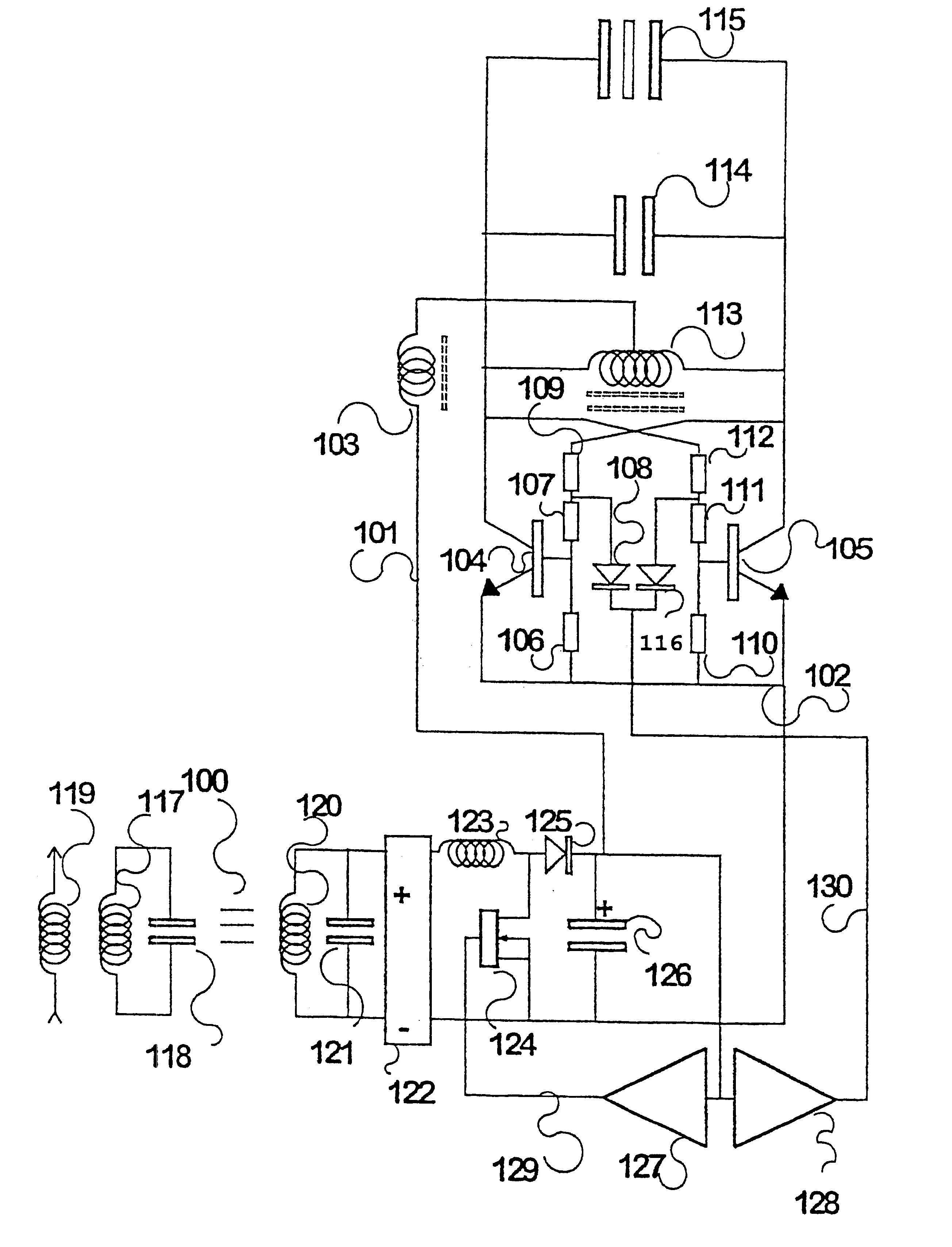
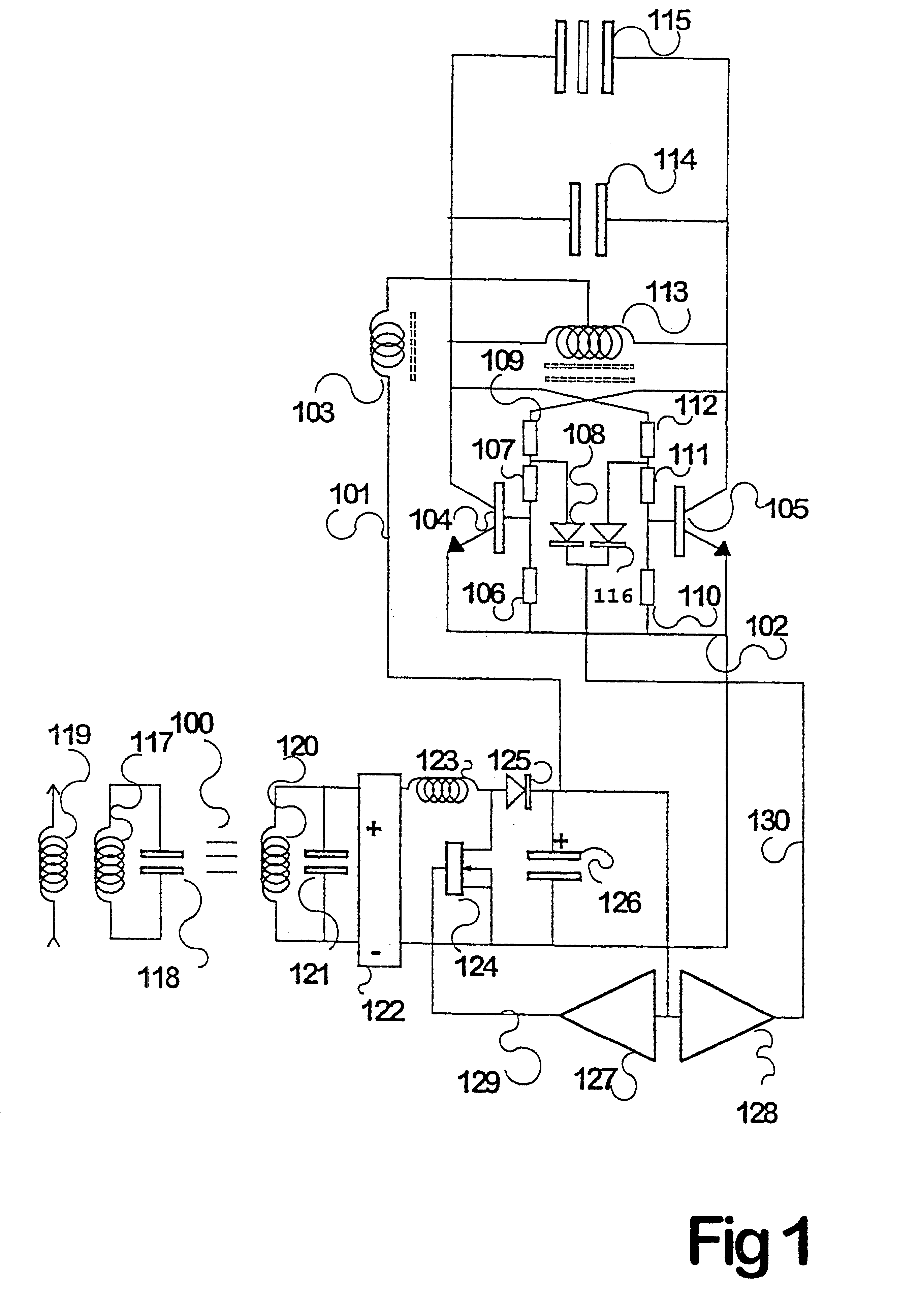
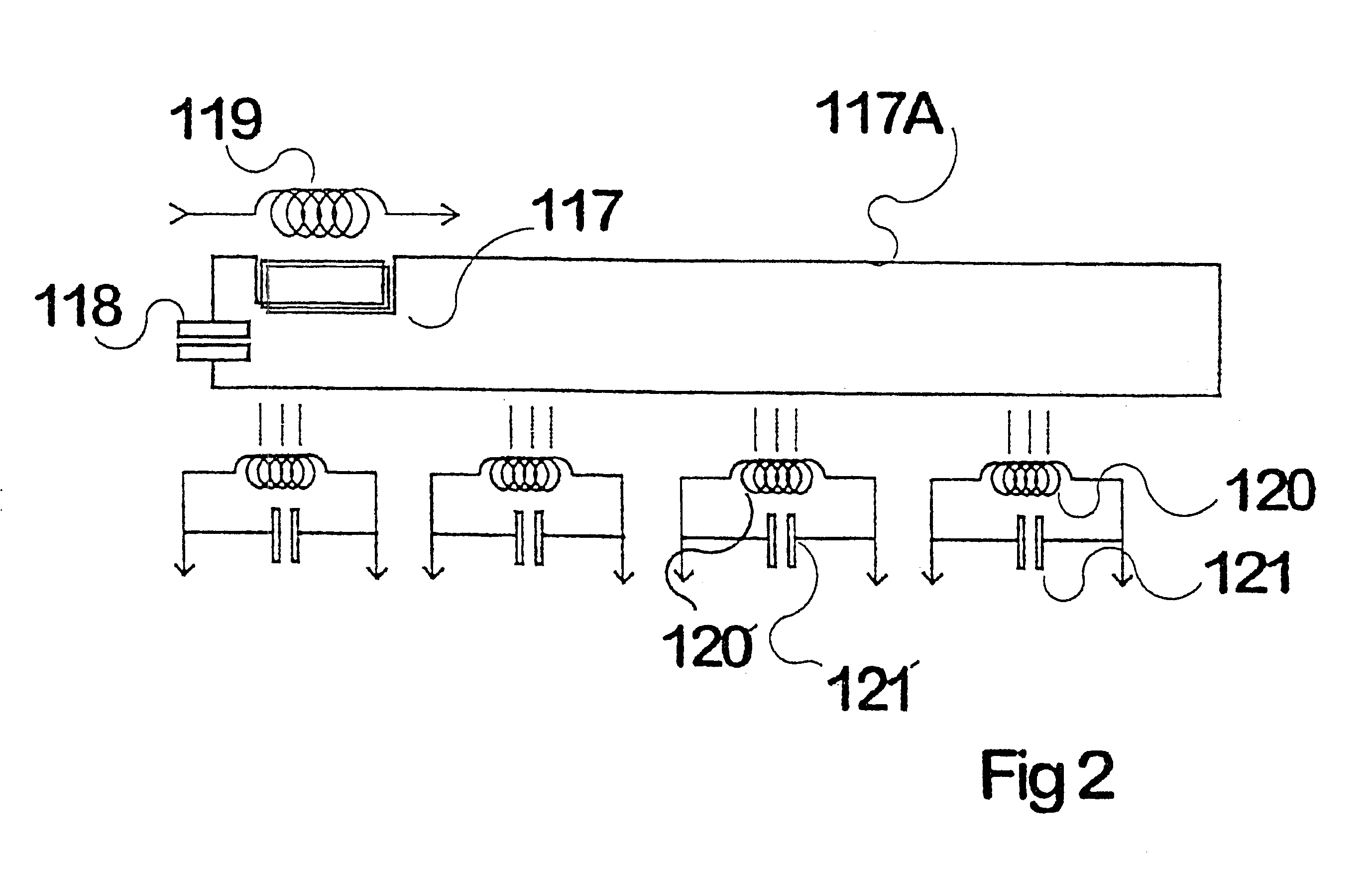
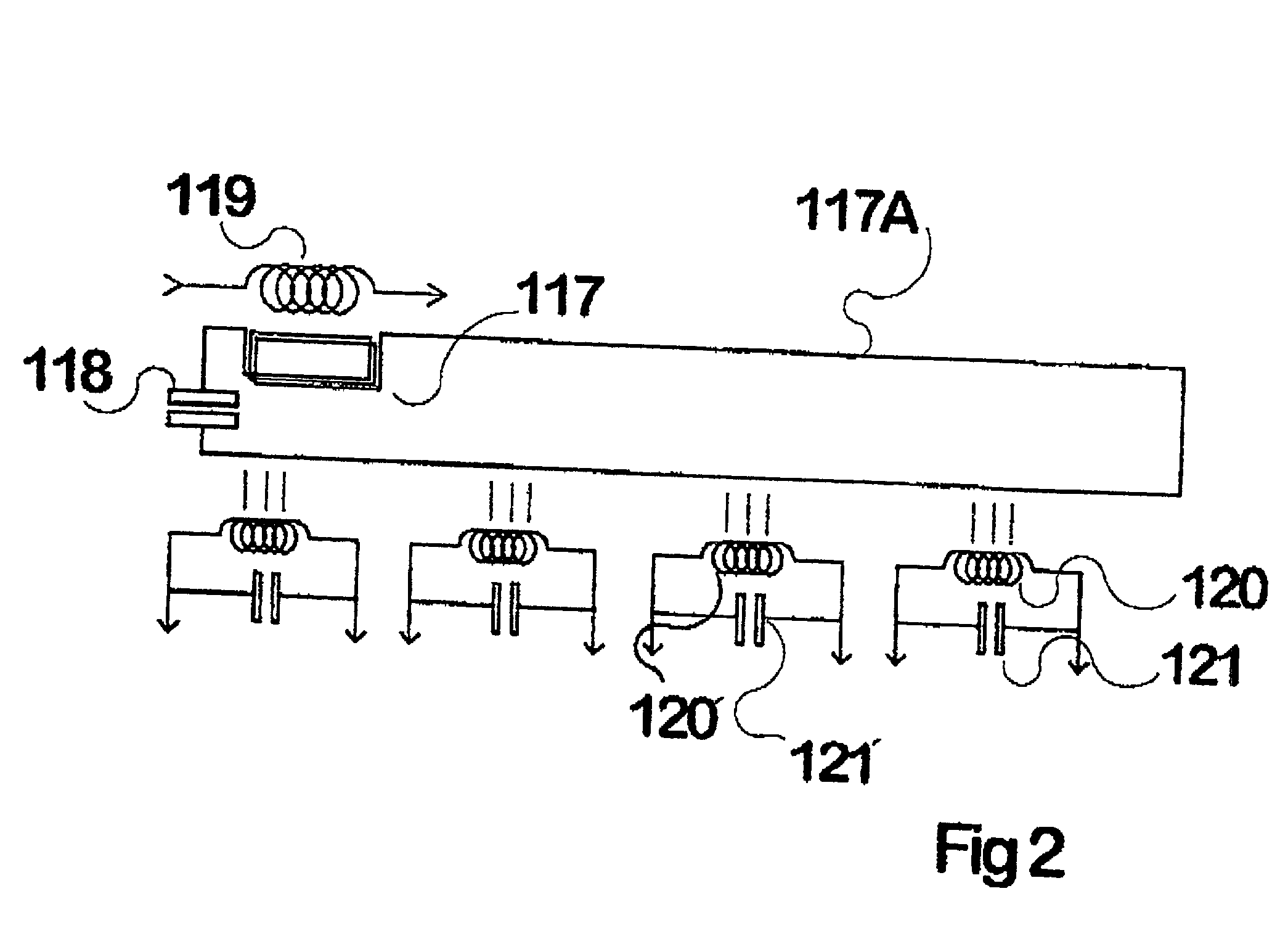
InactiveUS6317338B1Raise transfer toIncrease powerRail devicesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical conductor
Inductive power transfer across an extended gap (100) from a primary conductor (119) is provided by means of a resonant intermediate loop comprised of capacitor (118) with inductor (117) carrying a larger resonating current, that can in turn generate an inductive field to be collected by a pickup coil (120). This process and device find application in an electroluminescent advertising panel.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
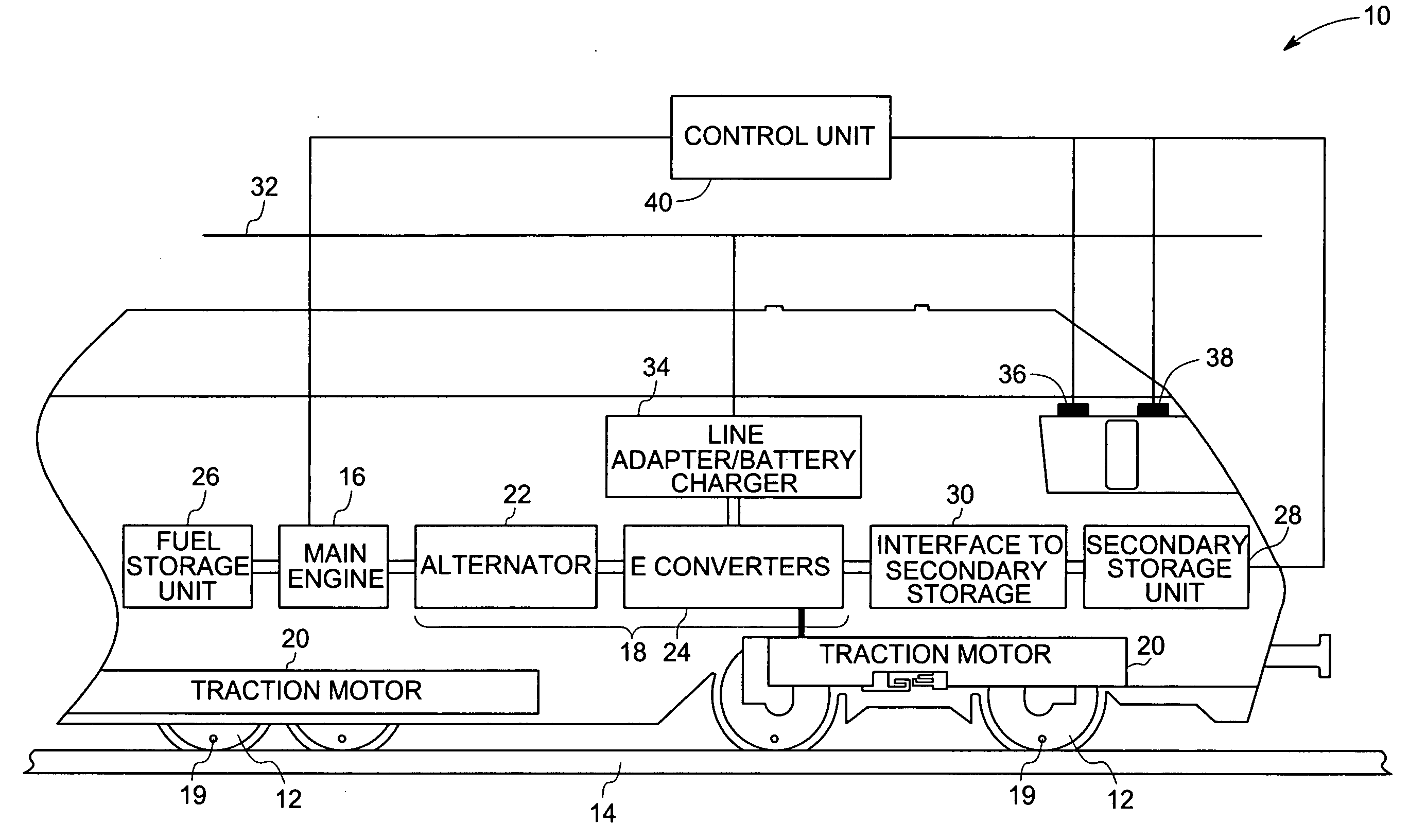
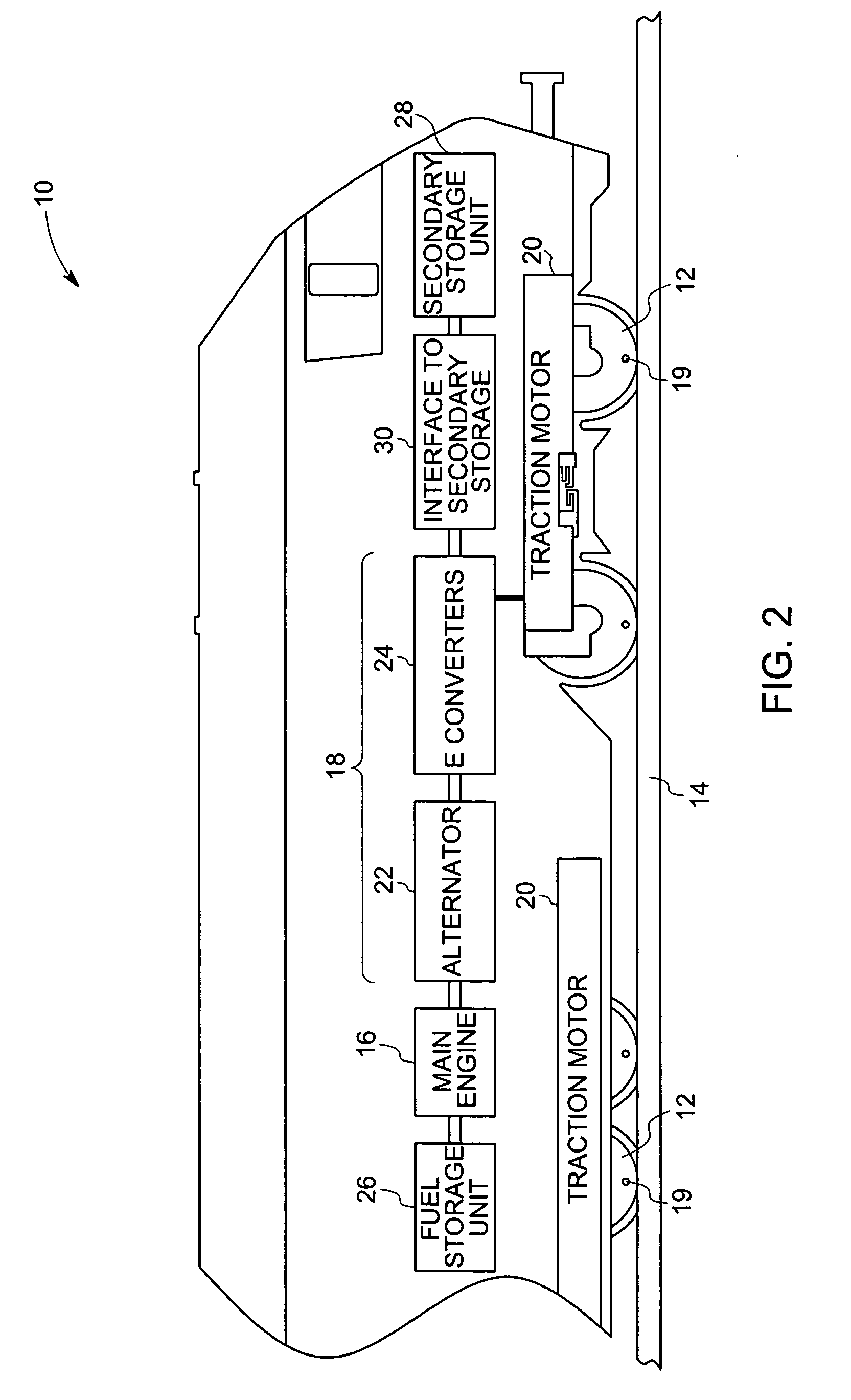
Hybrid locomotive and method of operating the same
A hybrid locomotive includes at least one traction motor coupled to at least one of a plurality of axles and configured to drive at least one axle. A power converter is coupled to a main engine and to at least one traction motor and configured to supply electrical energy to the at least one traction motor and a secondary energy storage unit. A fuel storage unit is coupled to the main engine and configured to supply a gaseous fuel to the main engine. The main engine is adapted to burn gaseous fuel for reduced emissions, while maintaining excellent power output characteristics, that may be supplemented by secondary power sources.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
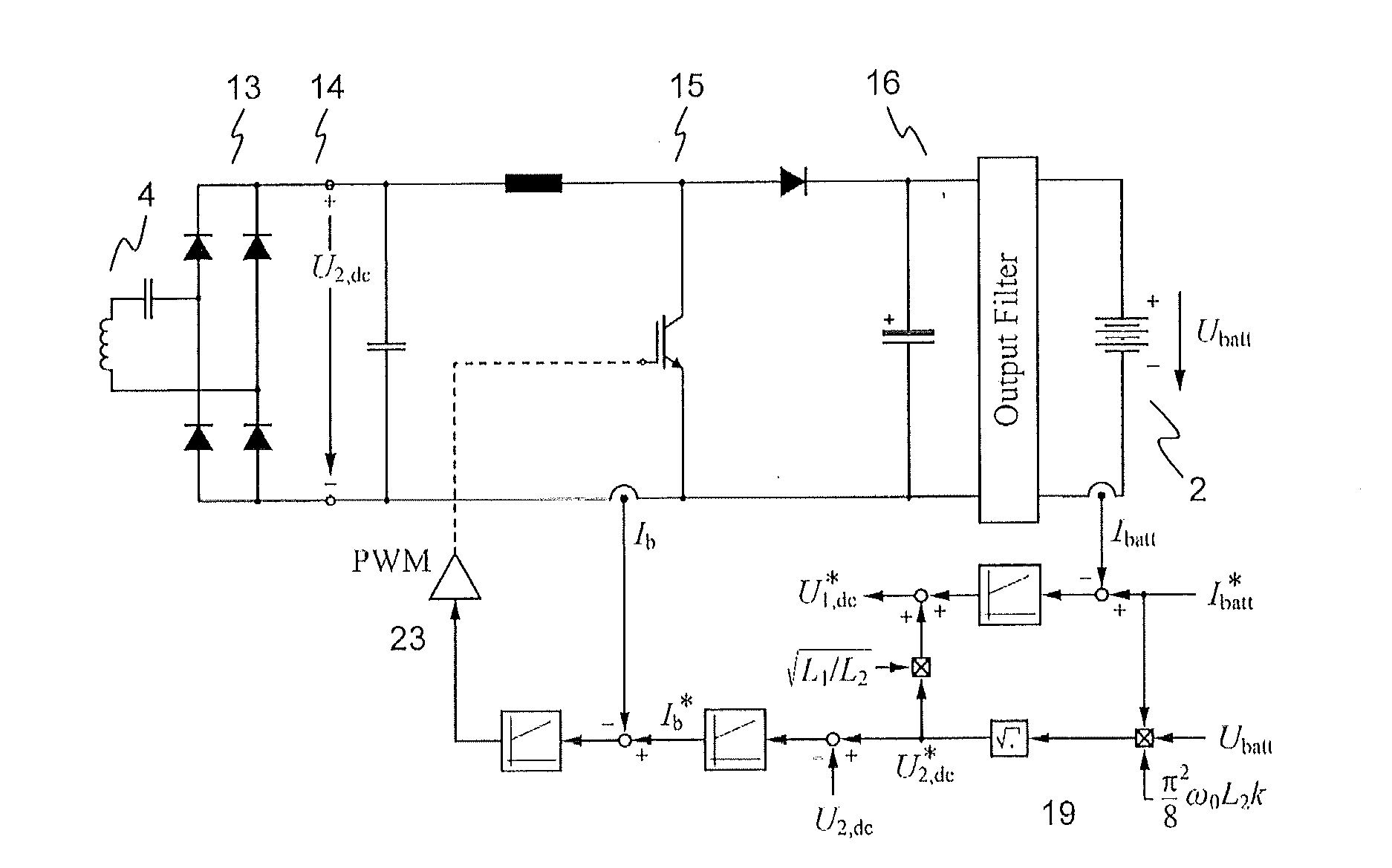
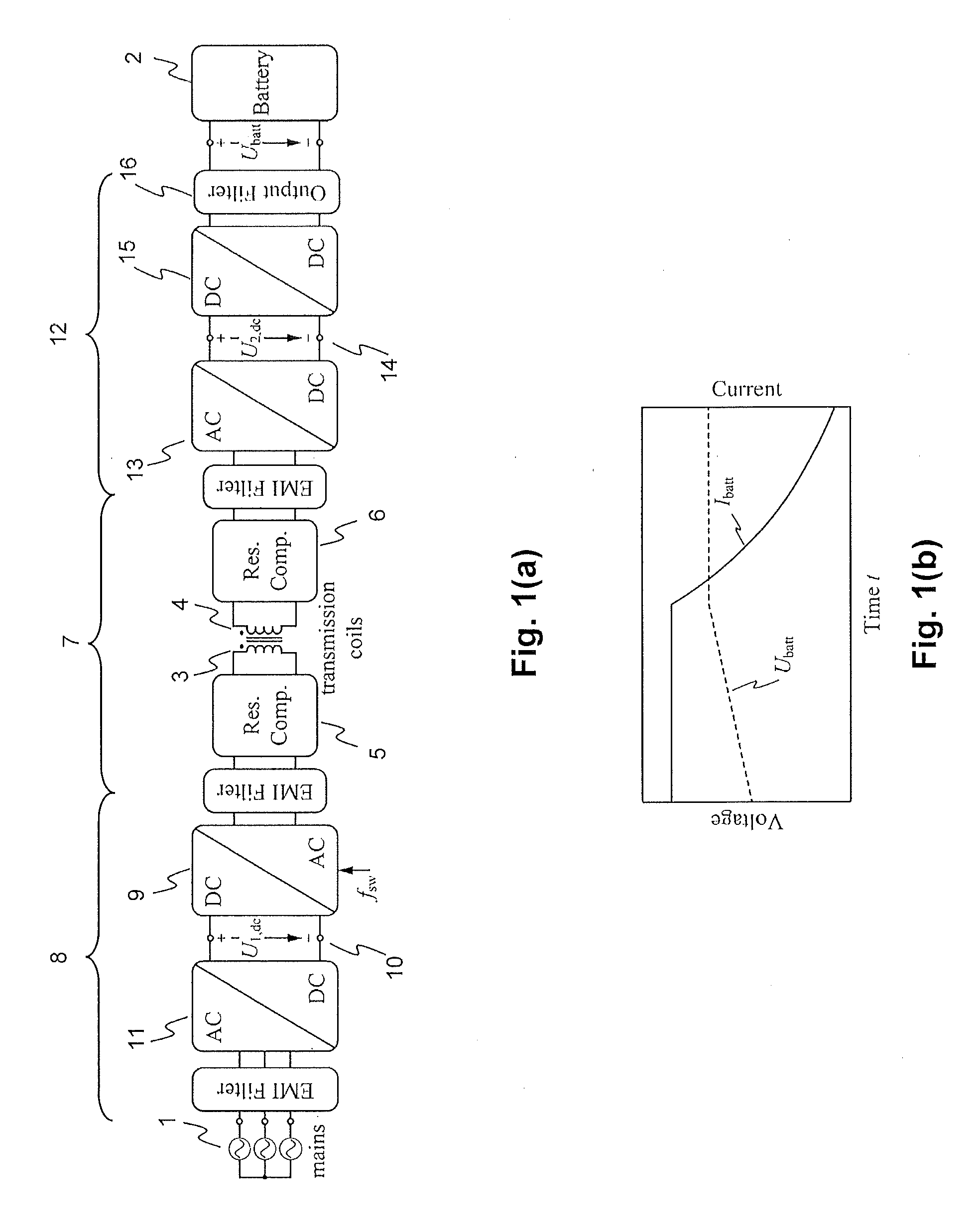
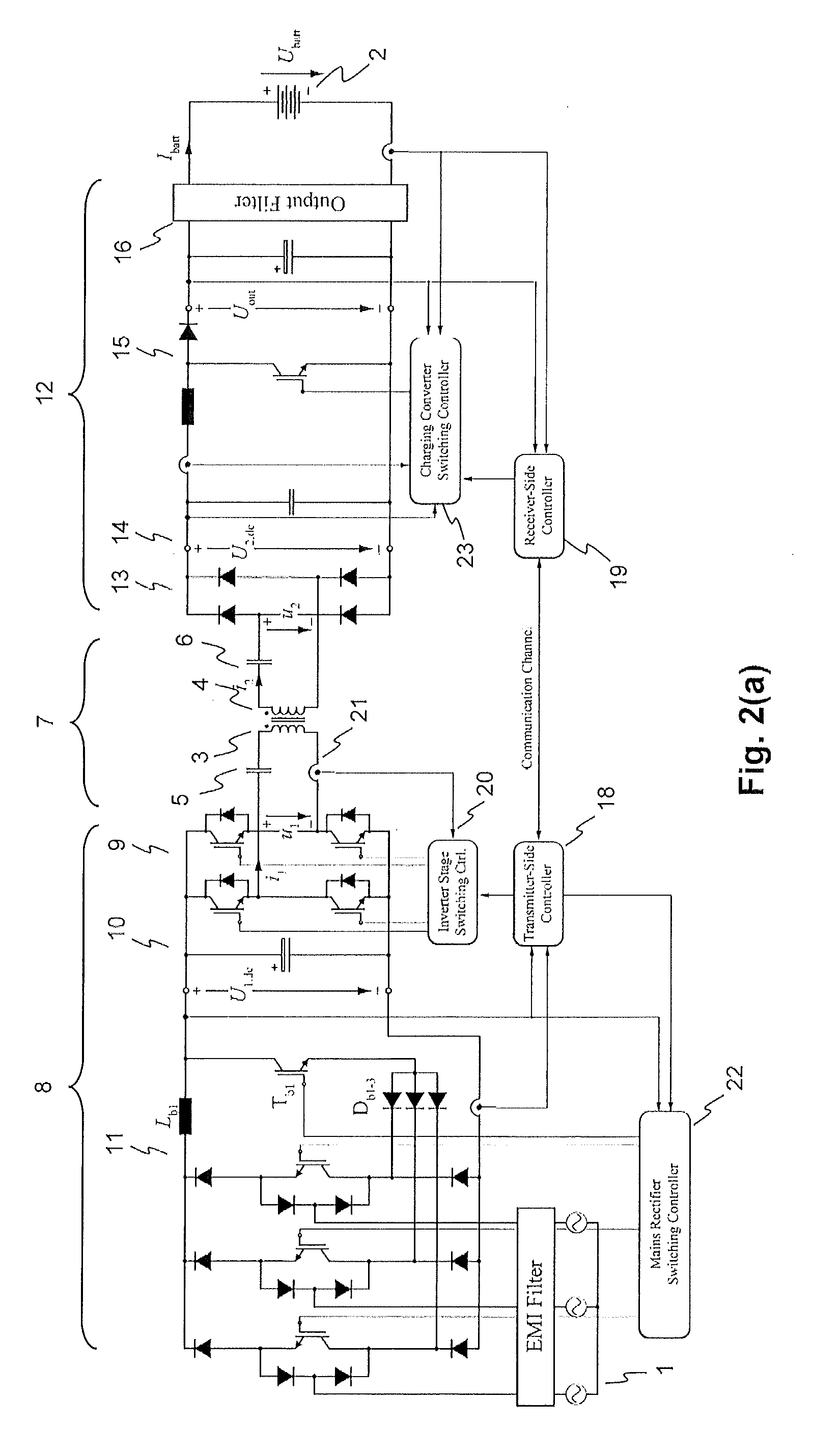
Inductive power transfer system and method for operating an inductive power transfer system
InactiveUS20150280455A1Minimize switching lossesBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsTransmitter coilEngineering
An exemplary inductive power transfer system having a transmitter coil and a receiver coil. A transmitter-side power converter having a mains rectifier stage powering a transmitter-side dc-bus and controlling a transmitter-side dc-bus voltage U1,dc. A transmitter-side inverter stage with a switching frequency fsw supplies the transmitter coil with an alternating current. A receiver-side power converter having a receiver-side rectifier stage that rectifies a voltage induced in the receiver coil and powering a receiver-side dc-bus and a receiver-side charging converter controlling a receiver-side dc-bus voltage U2,dc. Power controllers that determine from a power transfer efficiency of the power transfer, reference values U1,dc*, U2,dc* for the transmitter and receiver side dc-bus voltages. An inverter stage switching controller controls the switching frequency fsw to reduce losses in the transmitter-side inverter stage.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
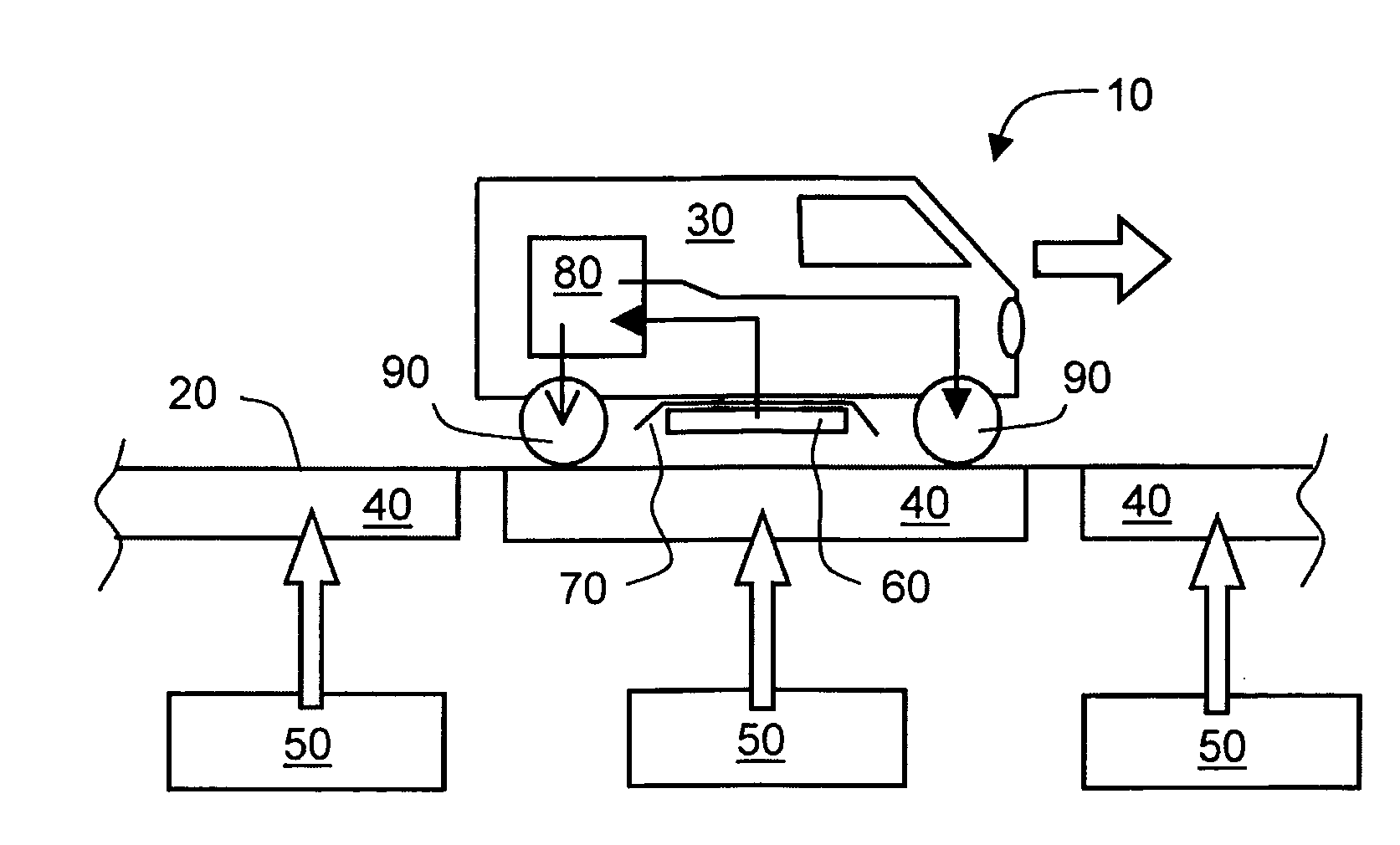
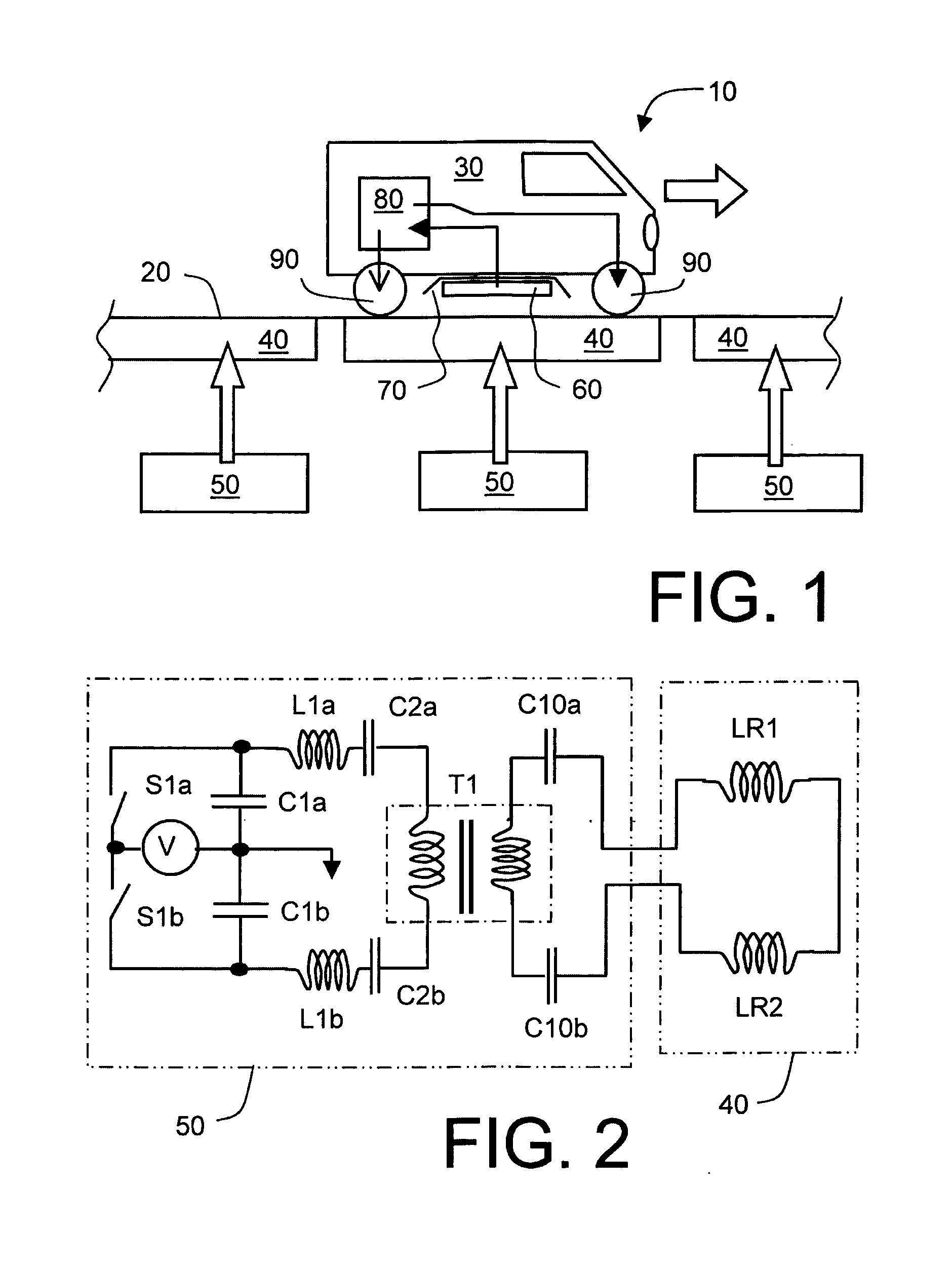
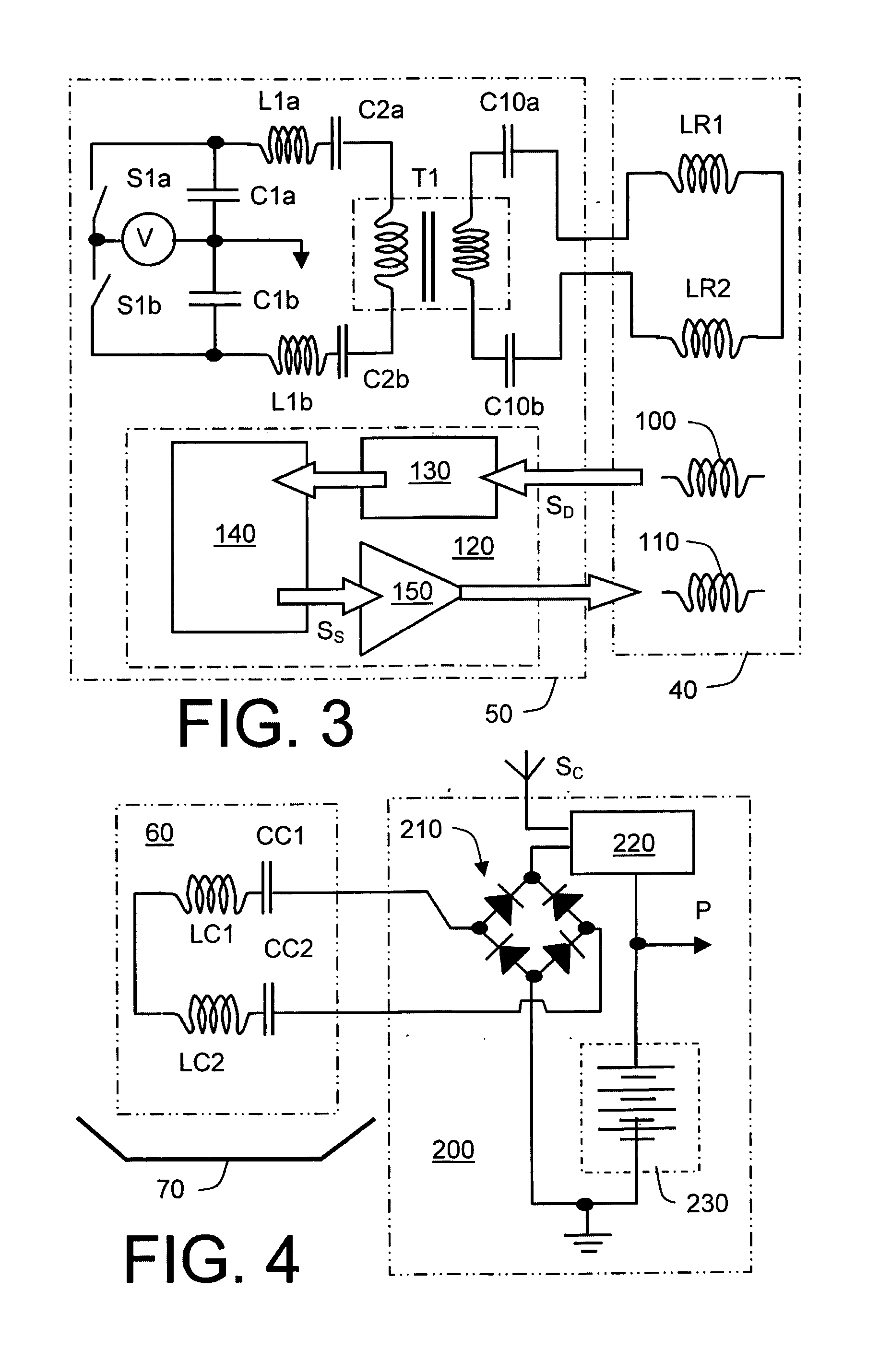
Inductive power coupling systems for roadways
InactiveUS20150246614A1Less-expensive to implementSimpler to implementRail devicesShielding materialsFundamental frequencyEngineering
An inductive power transfer system (10) for roadways includes at least one drive unit arrangement (50) coupled to at least one drive coil arrangement (40) disposed along a roadway (20) for generating a magnetic field extending upwardly from the roadway (20), and at least one vehicle (30) including a corresponding pickup coil arrangement (60) coupled to a power conditioning circuit arrangement (80, 200) for receiving the extending magnetic field for providing power to operate the at least one vehicle (30). The at least one drive unit arrangement (50) is operable to excite, for example at resonance, the at least one drive coil arrangement (40) at a fundamental frequency (f0) of at least 30 kHz, preferably at least 50 kHz, more preferably at least 100 kHz, and most preferably at least 140 kHz. The at least one drive coil arrangement (40) is implemented to be substantially devoid of ferromagnetic components for providing a path for the extending magnetic field. Optionally, the at least one drive unit arrangement (50) is operable to employ a balanced class-E amplifier arrangement for exciting the at least one drive coil arrangement (40) at the fundamental frequency (f0). Optionally, the at least one drive unit arrangement (50) is operable to employ one or more Silicon Carbide semiconductor devices for switching the currents provided to the corresponding at least one drive coil arrangement (40). Optionally, there is further included a passive and / or active suppression arrangement (100, 110, 120, 130, 140) for suppressing harmonic magnetic field components generated by the system (10) at multiples of the fundamental frequency (f0) when in operation.
Owner:DAMES ANDREW NICHOLAS +2
Charging stations for electric vehicles
ActiveUS20100039067A1Lower impedanceGood electrical contactHybrid vehiclesRail devicesHybrid vehicleCharging station
The invention relates to systems and methods for charging a vehicle. A vehicle and charging station can be designed such that an electric or hybrid vehicle can operate in a fashion similar to a conventional vehicle by being opportunity charged throughout a known route.
Owner:PROTERRA OPERATING CO INC
Inductive power distribution system
InactiveUS20010012208A1Spatial width can be increasedEffective distanceRail devicesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical conductor
Inductive power transfer across an extended gap (100) from a primary conductor (119) is provided by means of a resonant intermediate loop comprised of capacitor (118) with inductor (117) carrying a larger resonating current, that can in turn generate an inductive field to be collected by a pickup coil (120). This process and device find application in an electroluminescent advertising panel.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Moving Object, Wireless Power Feeding System, and Wireless Power Feeding Method
ActiveUS20110193520A1Reduced strengthIncrease powerEnergy efficient ICTRail devicesObject structureRadio wave
An object is to provide a moving object structure capable of reducing power loss caused when power is supplied from a power feeding device to a moving object by wireless communication. Another object is to provide a moving object structure capable of reducing the strength of a radio wave radiated to the surroundings. Before power is supplied to a moving object, a radio wave for alignment of antennas is output from a power feeding device. That is, radio waves are output from a power feeding device in two stages. In a first stage, a radio wave is output to align positions of antennas of the power feeding device and the moving object. In a second stage, a radio wave is output to supply power from the power feeding device to the moving object.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Wireless charging system for vehicles
ActiveUS8030888B2Eliminate needBatteries circuit arrangementsIn situ pavingsElectric power transmissionOn board
A system of energy storage and charging usable in vehicles and other applications that eliminate the battery capacity and automotive range issues is described. In our invention, vehicles are equipped with charging mechanisms to charge and recharge onboard batteries using wireless electricity and power transmission using magnetic resonant coupling between tuned electromagnetic circuits. The batteries may be charged using wireless charging systems installed along the roads while the vehicle is in use on the road. Charging system may optionally utilize infrared laser beam radiation to transmit power for charging the batteries on board a vehicle while it is in use as well. The onboard vehicle batteries may also be charged when the vehicle is not being driven either by plugging in the vehicle into wall electricity using wired power connection or may be wirelessly charged using the magnetic resonant coupling. By locating the charging circuits on roads, a continuous operation of electric-only mode of hybrid vehicles or pure electric-only vehicles can be accomplished and fully eliminate the need for gasoline usage.
Owner:PANDYA RAVI A +1
Coil unit, non-contact power transmission device, non-contact power reception device, non-contact power supply system, and vehicle
InactiveUS20130038281A1Reduce leakage electromagnetic fieldReduce leakageRail devicesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerPrimary resonance
A coil unit performs at least one of transmission and reception of electric power using electromagnetic resonance between the coil unit and a primary resonance coil disposed to face the coil unit. The coil unit includes a secondary resonance coil that includes a plurality of coils, and that electromagnetically resonates with the primary resonance coil. A first coil among the plurality of coils is disposed in a manner such that a magnetic field generated by the first coil has a phase opposite to a phase of a magnetic field generated by at least one coil other than the first coil among the plurality of coils, with respect to a plane that faces the primary resonance coil.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Vehicle
A vehicle includes a power receiving portion that contactlessly receives electric power from a power transmitting portion provided outside the vehicle and includes a shield member that is arranged around the power receiving portion in the same plane as a plane in which the power receiving portion is arranged, wherein the shield member includes a first shield region having a high shielding function and a second shield region having a shielding function lower than that of the first shield region at a position around the power receiving portion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
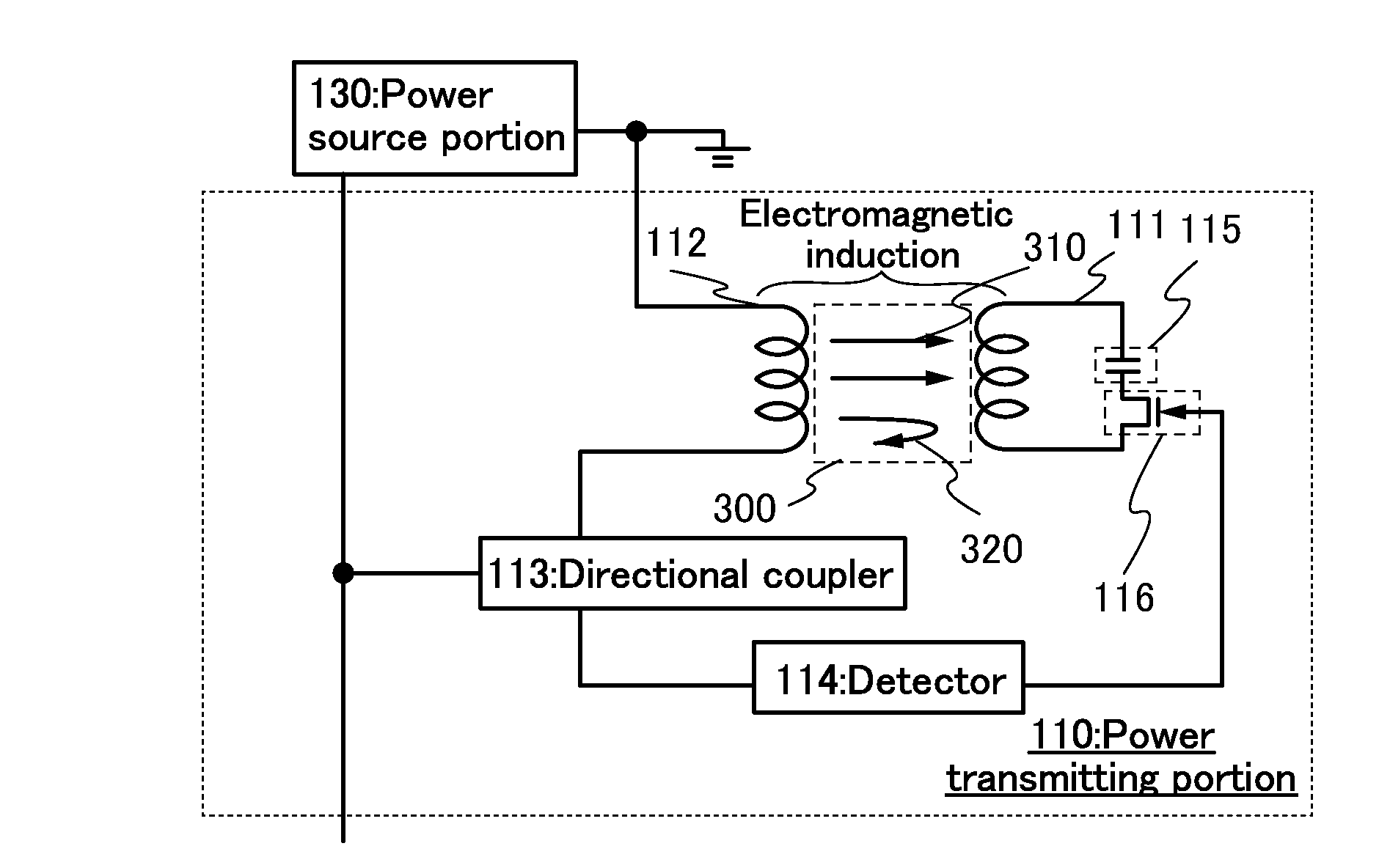
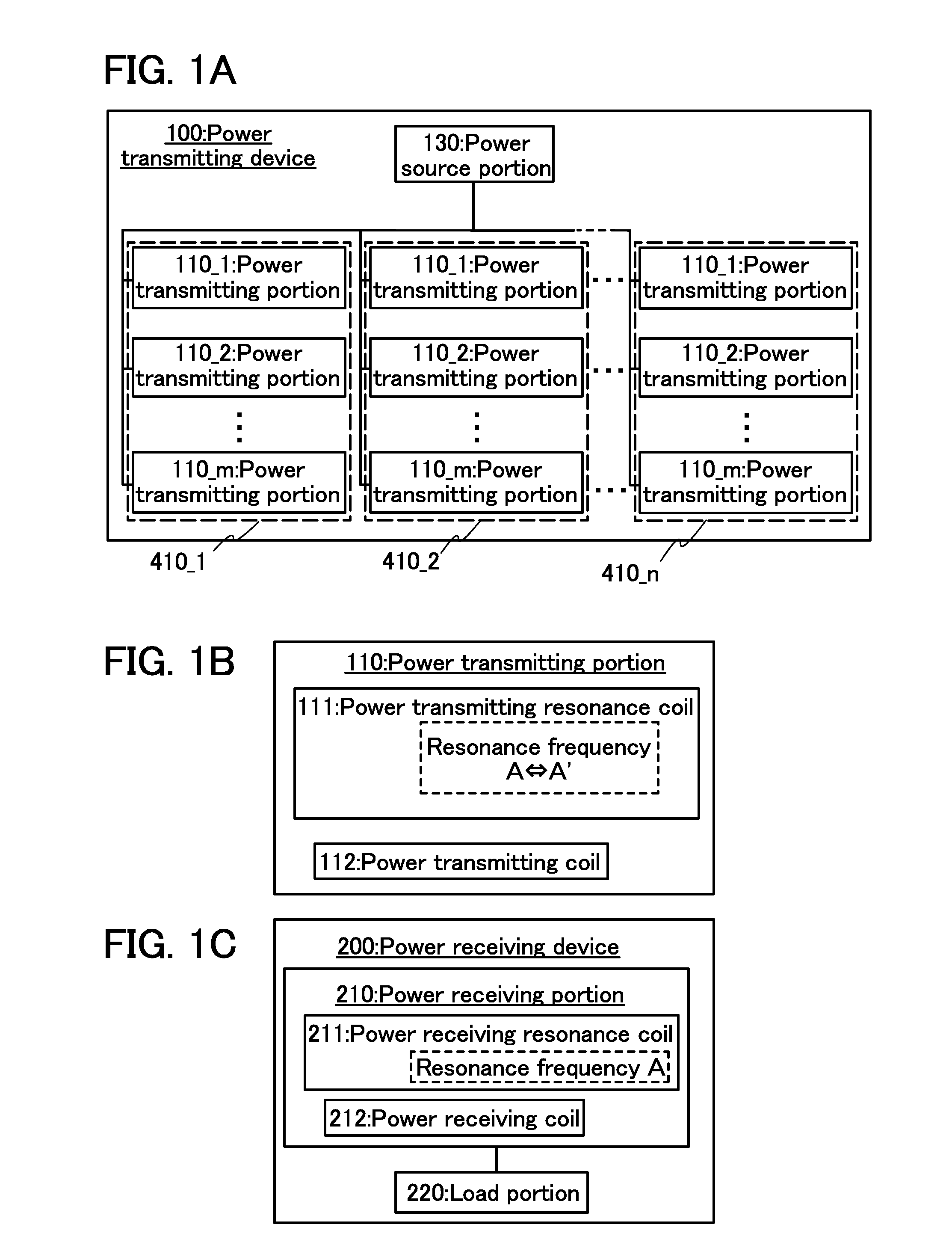
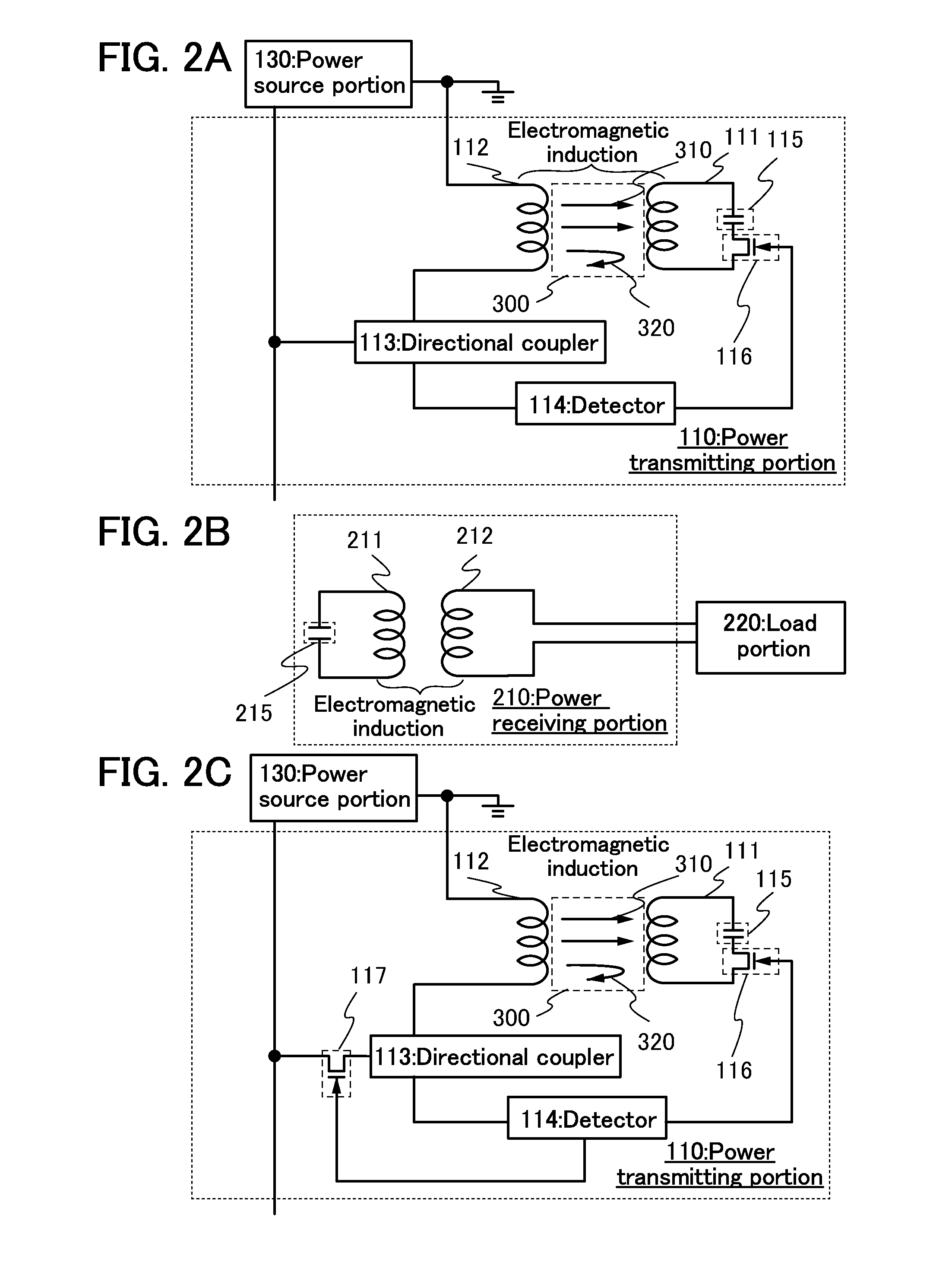
Power feeding system and power feeding method
ActiveUS20130285464A1Reduce total powerNear-field transmissionRail devicesElectric power transmissionResonance
To provide a power feeding system and the like with which charging can be performed without a decrease in the power supply efficiency. To provide a power feeding system and the like with which can offer a power feeding service which is efficient to both a power feeding user and a power feeding provider. The power transmission state in each of power transmitting portions is monitored, the power transmitting portion having the highest power transmission efficiency is selected based on positional advantage, and the power transmitting resonance coil included in the selected power transmitting portion is kept at a first resonance frequency, whereby power transmission continues. The resonance frequency of the power transmitting resonance coil included in the non-selected power transmitting portion (the number of the non-selected power transmitting portions may be plural) is set to a second resonance frequency, whereby power transmission is stopped.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Charging stations for electric vehicles
The invention relates to systems and methods for charging a vehicle. A vehicle and charging station can be designed such that an electric or hybrid vehicle can operate in a fashion similar to a conventional vehicle by being opportunity charged throughout a known route.
Owner:PROTERRA OPERATING CO INC
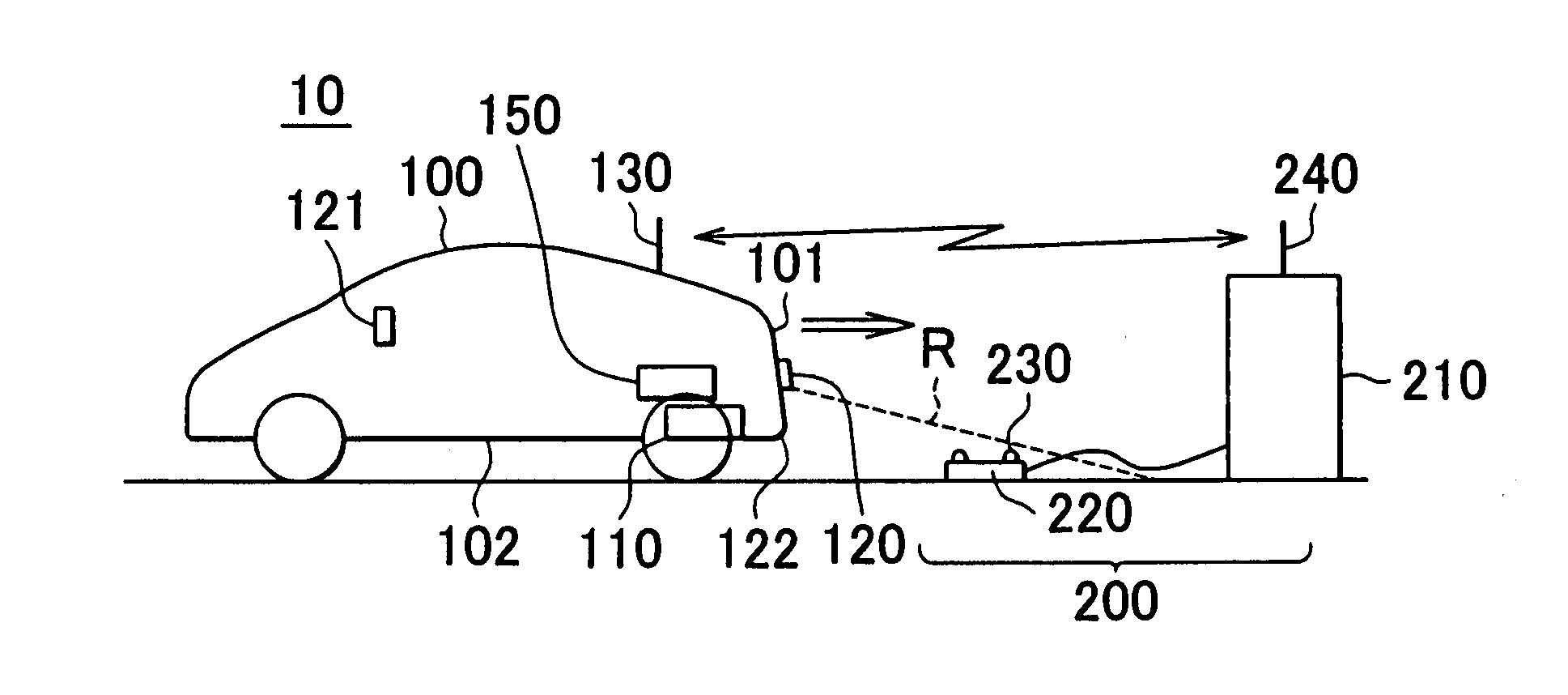
Inductively charged vehicle with automatic positioning
ActiveUS20130037365A1Easy alignmentRail devicesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionResonance
An electric vehicle receives electric power, in a non-contact manner, from an electric power transmitting coil provided externally to the vehicle. The electric vehicle includes an electric power receiving unit that is disposed at a bottom of the vehicle and receives electric power from the electric power transmitting unit via electromagnetic field resonance; a camera that captures an image of the outside; and a display unit that displays an outside view from the vehicle that is captured by the camera. The electric power receiving unit is disposed at a position that is offset toward a peripheral face, on which the camera is disposed, with respect to the center of the bottom in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
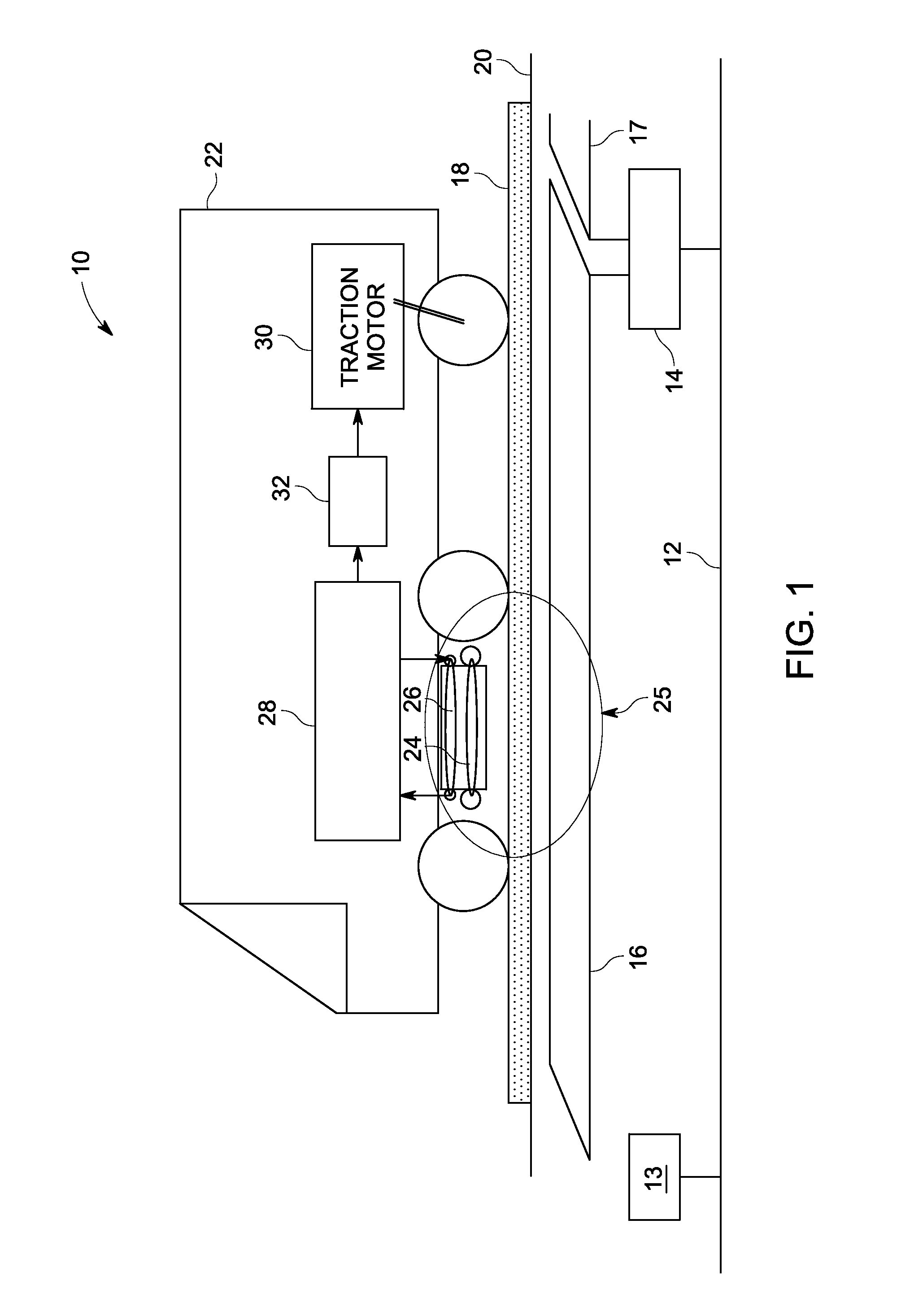
Power transfer system and method
A contactless power transfer system for a mobile asset is presented. The system includes a primary loop disposed adjacent to a location that is coupled to a power source. A secondary receiving coil is disposed on the mobile asset and coupled to a traction motor for receiving power from the primary loop. The power transfer system further includes a field-focusing element that can focus a magnetic field from the primary loop onto the secondary receiving coil, the field-focusing element having a non-linear current distribution.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Multiple layer solar energy harvesting composition and method, solar energy harvesting buckyball, inductive coupling device; vehicle chassis; atmospheric intake hydrogen motor; electrical energy generating tire; and mechanical energy harvesting device
Provided is a multiple layer composition and method for deposition of a solar energy harvesting strip onto a driving surface that will allow electric cars to charge by an inductive coupling. The multiple layer composition includes at least one magnetic material for generating a magnetic field, wherein at least one of the multiple layers comprises the magnetic material. Further, the a multiple layer composition includes at least one solar energy harvesting material for converting at least one of thermal and photonic energy into electrical energy, wherein at least one of the multiple layers comprises the at least one solar energy harvesting material and wherein the at least one solar energy harvesting material is located within a magnetic field generated by the at least one magnetic material. An alternative multiple layer composition includes a thermal energy harvesting material for converting thermal energy into electrical energy, wherein at least one layer comprises the thermal energy harvesting material, and a photonic energy harvesting material for converting photonic energy into electrical energy, wherein at least one layer comprises the thermal energy harvesting material. Additionally provided is a solar energy harvesting buckyball, inductive coupling device, vehicle chassis for storing electrical energy, atmospheric intake hydrogen motor, electrical energy generating tire and mechanical energy harvesting device.
Owner:SOLARBUILDER LLC
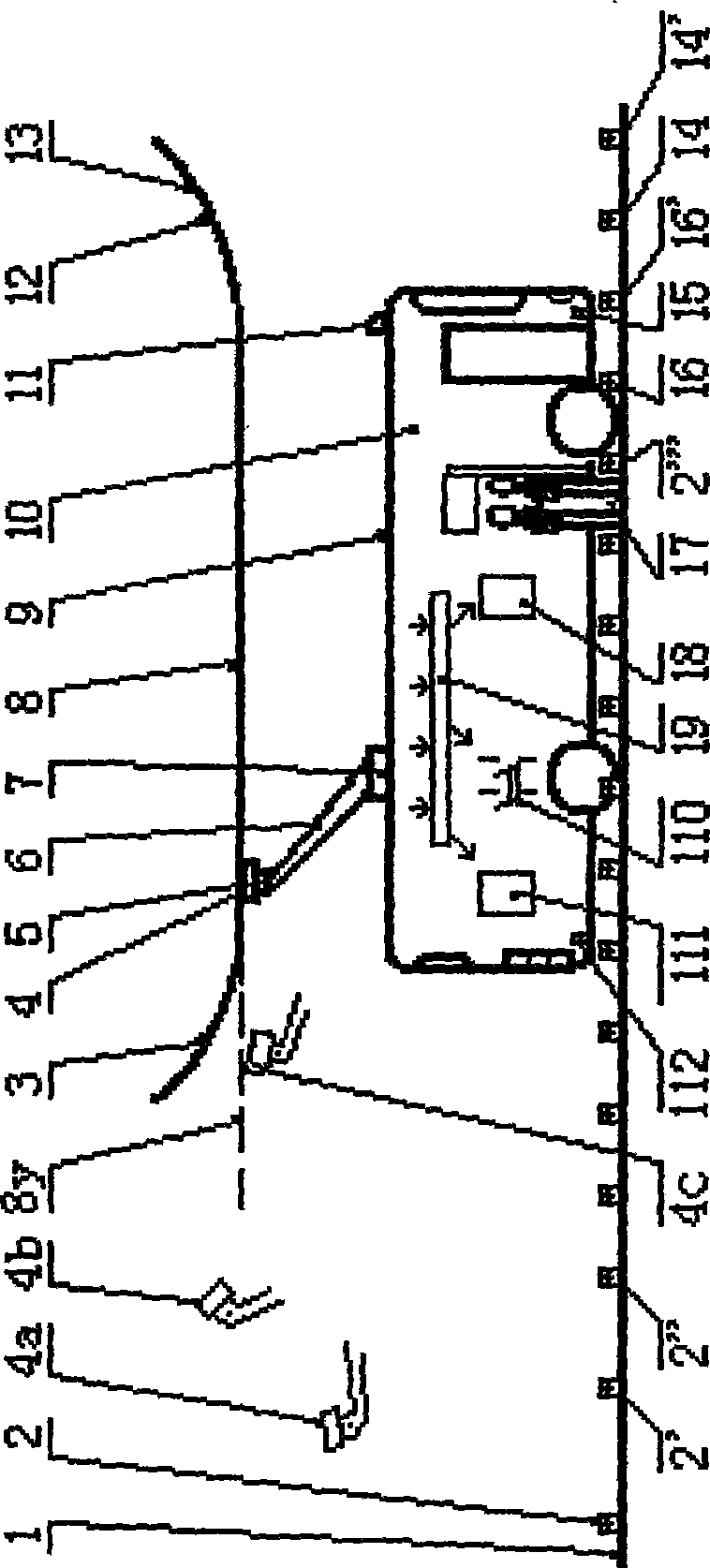
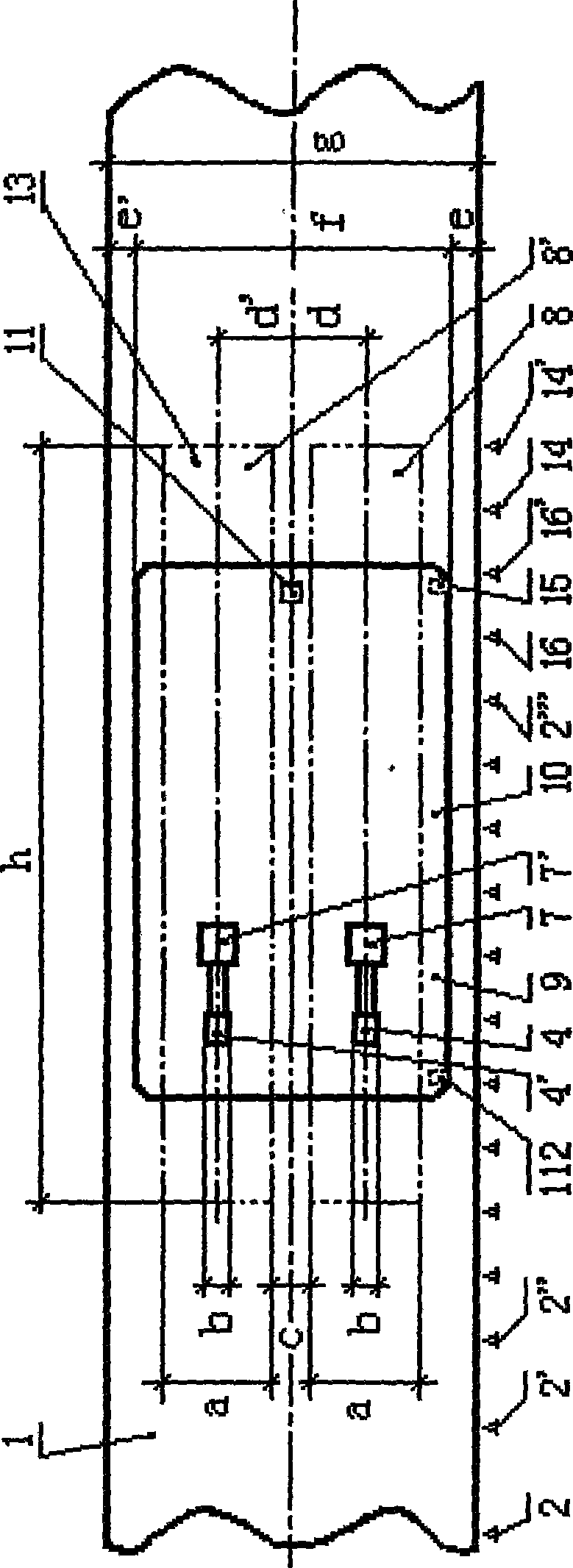
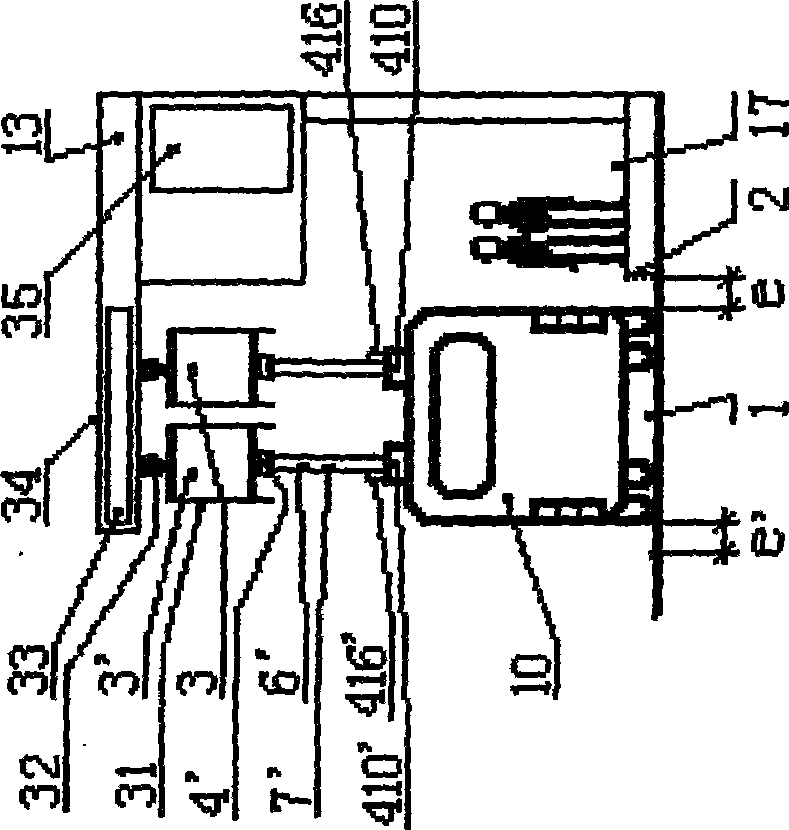
Pantograph type current collector of electric automobile and automatic rapid charging station
InactiveCN101531141AEasy to introduceGuaranteed contactCharging stationsElectric vehicle charging technologyElectricityGas cylinder
The invention provides a pantograph type current collector of electric automobile and an automatic rapid charging station. Two pantograph type current collectors are parallel installed on the electric automobile top which has a single main shaft driven by gas cylinder or hydraulic pressure cylinder, and can act local arc movement, a gimbal is installed on the current collector end, a current slide block is fixed on the gimbal; an output end of the electric automobile charging station is two parallel contact plates on the automobile road upper part, two ends of the contact plate has introduce arc and educe arc; the electric automobile runs over the automobile charging station with standard speed along the road under control by relative sensing, detecting and controller which can complete whole process of collecting bow, charging, de-charging and depressing bow automatically.
Owner:田耕
Contactless power transfer system for movable object
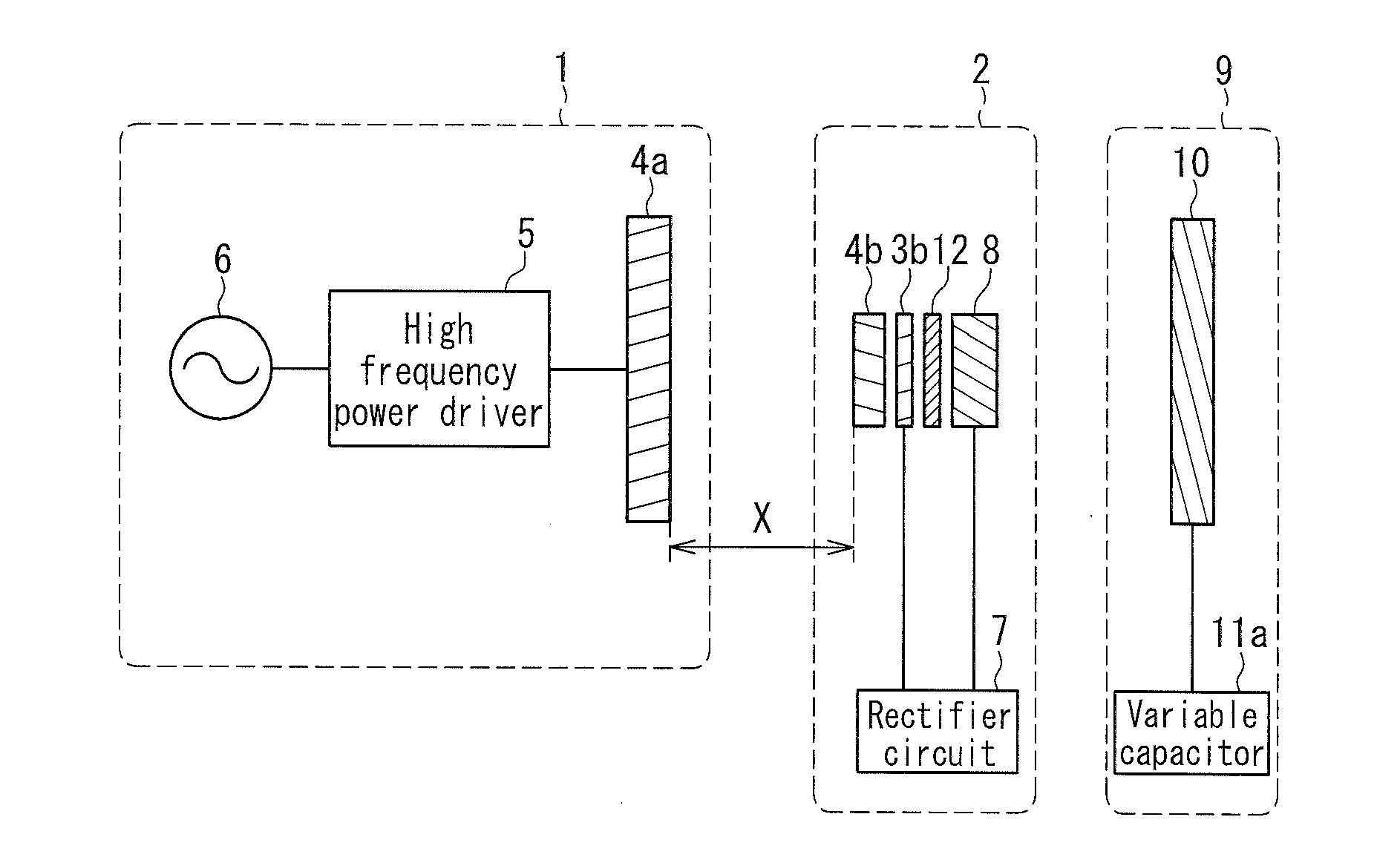
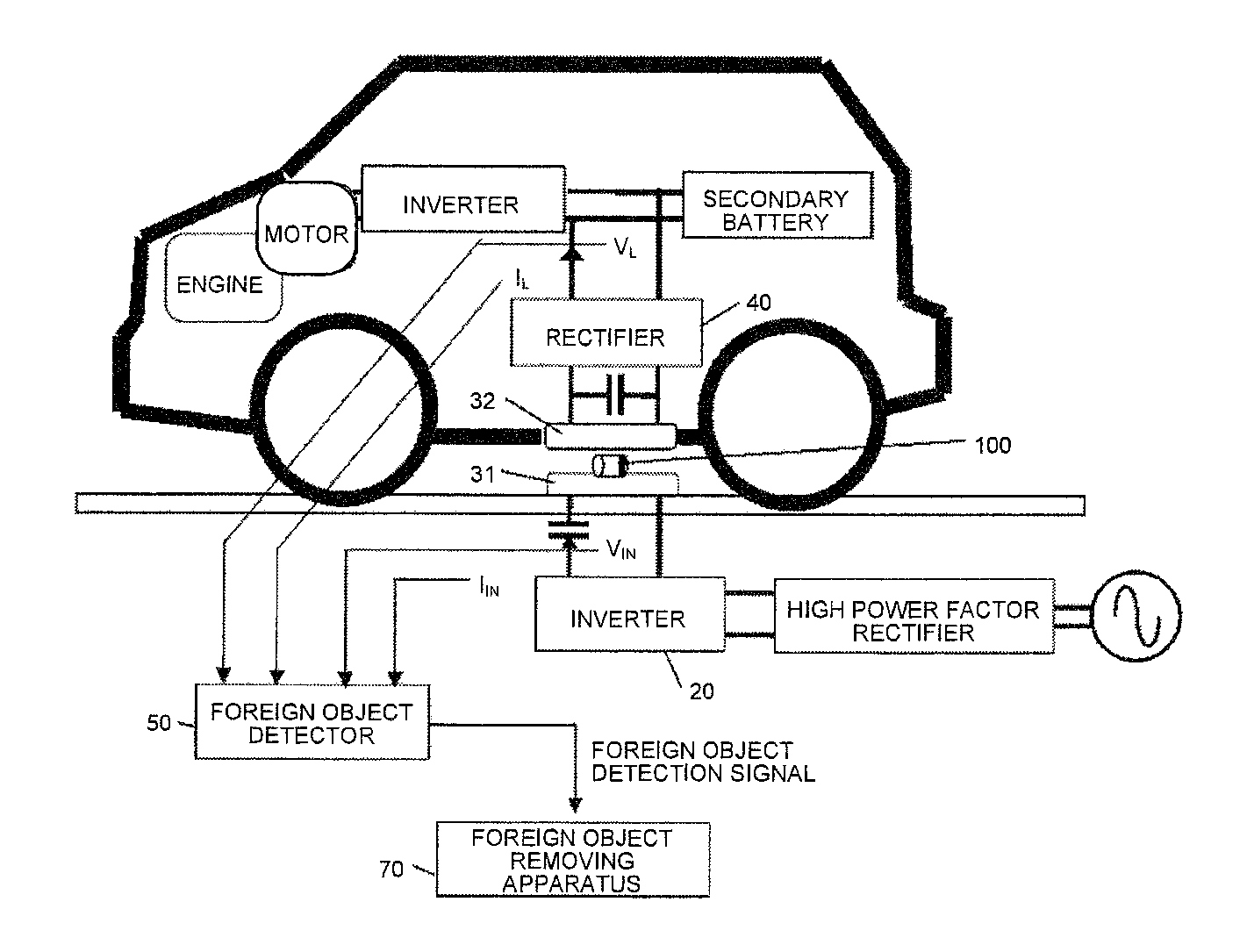
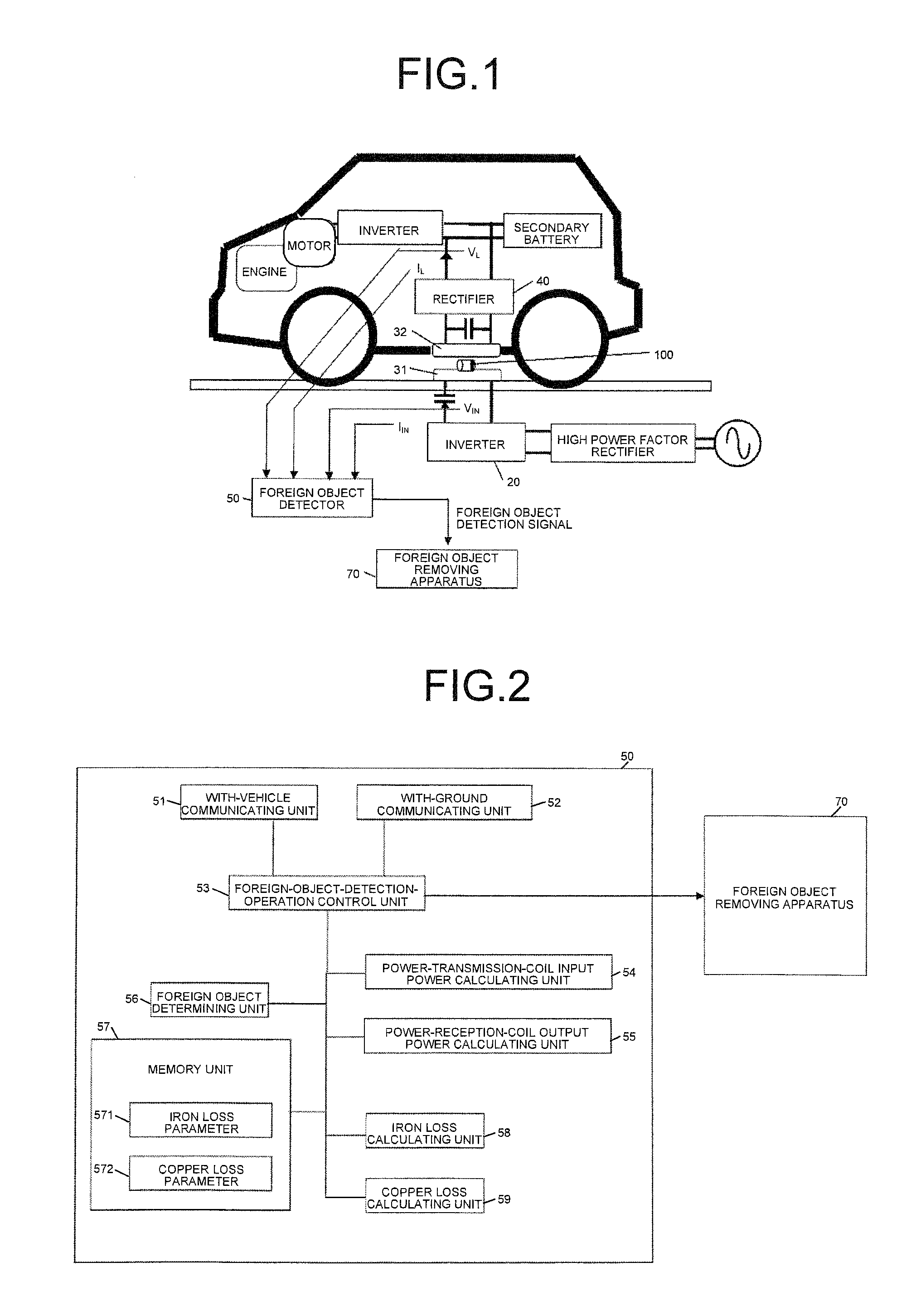
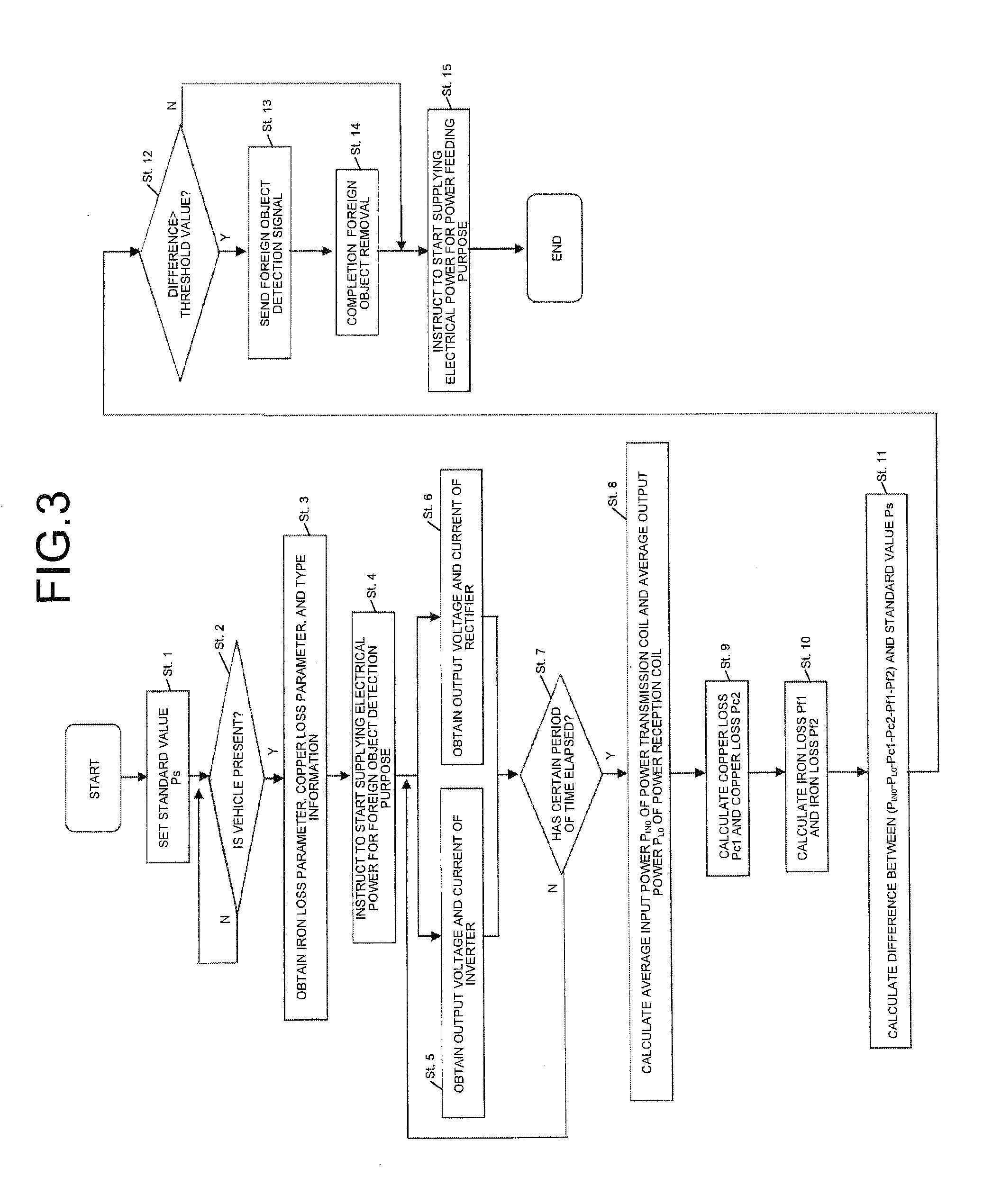
InactiveUS20140239735A1High precisionWithout delayRail devicesElectromagnetic wave systemForeign objectTransfer system
In an example of a system, power is transferred from a transmission coil to a reception coil by electromagnetic induction. A detecting unit calculates a difference between a standard value and a measured value, detects presence of a metallic foreign object on the transmission coil based on the difference, and outputs a signal when the metallic foreign object is detected. The standard value is obtained by supplying electrical power to the transmission coil when a metallic foreign object is absent on the transmission coil. The measured value is obtained by supplying electrical power to the transmission coil. If PIN0 represents input power of the transmission coil, PL0 represents output power of the reception coil, Pc1 represents copper loss of the transmission coil, and Pc2, represents copper loss of the reception coil, the detecting unit uses a value expressed by (PIN0-PL0-Pc1-Pc2) as the standard value and the measured value.
Owner:TECHNOVA
Preparation process of carbon base sliding block material for track vehicle
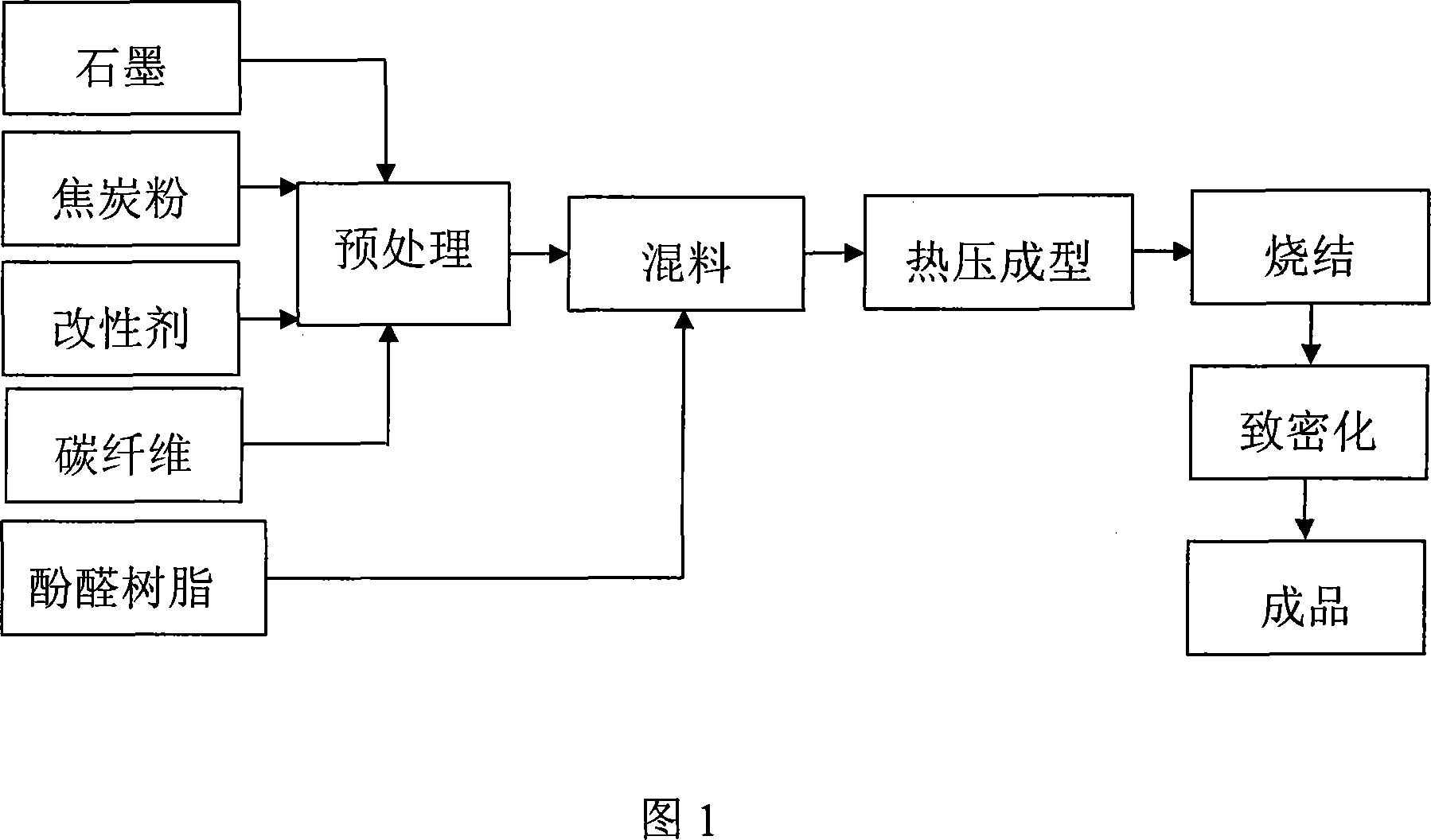
InactiveCN101165819AImprove conductivityImprove friction and wear propertiesNon-metal conductorsNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialFiberCarbon fibers
The preparation method comprises: 1) raw material processing: placing graphite, coke blacking, chopped carbon fiber and modifier at the drying cabinet to remove moisture from them; the drying temperature is 100 deg. C, and the drying time is 2-4 hours; 2) blending: evenly blending the graphite, coke blacking and chopped carbon fiber; adding the copper powder, copper fiber and modifier; in the last, adding phenolic resin to make mould material; 3) hot compacting and forming: placing the mould materials into die; heating and pressing it to make solidification forming; the press is 50-100MP, and the temperature is 160-170 deg. C; keeping 0.5-1 hours in room temperature; 4) sintering: making the sintering form the sample; the temperature is 800-900 deg. C, and the time length is 2-4 hours; 5) densification processing: after chemical vapor deposition or bituminizing, making the carbonizing treatment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Moving Object, Wireless Power Feeding System, and Wireless Power Feeding Method
InactiveUS20110199028A1Reduce power lossReduce intensityEnergy efficient ICTRail devicesObject structureEngineering
An object is to provide a moving object structure capable of reducing power loss caused when power is supplied from a power feeding device to a moving object by wireless communication. Another object is to provide a moving object structure capable of reducing the intensity of radio waves radiated to the surroundings. A moving object having a plurality of antennas receives radio waves transmitted from a power feeding device. At least one of the plurality of antennas is installed apart from the other antenna(s) of the moving object. Then, the radio waves transmitted from the power feeding device are received by all the plurality of antennas and converted into electric energy. Alternatively, the radio waves transmitted from the power feeding device are received by one or more selected from the plurality of antennas and converted into electric energy.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electric locomotive pantograph copper-soaking carbon contact strip producing method
ActiveCN104774012AImprove conductivityHigh mechanical strengthPower current collectorsShock resistanceNitrogen gas
The invention discloses an electric locomotive pantograph copper-impregnated carbon contact strip producing method. The method comprises the steps that 1, pitch coke powder, graphite powder, siliconized graphite powder and high temperature pitch are mixed according to the proportion to be ground into powder; the mixed powder is prepressed into a stage stock column, and then the stage stock column is solidified and squeezed to be molded and roasted, so that a composite carbon contact strip is obtained; 2, the composite carbon contact strip is cleaned and dried, then is cooled and placed into a graphite crucible, and is placed in an electric furnace at temperature of 1300-1400 DEG C to be preheated; copper liquid is poured into the crucible to soak the composite carbon contact strip, then the crucible is placed in an oil press cover, nitrogen is led in, heat preservation is kept for 3-5 min under the specific intensity of pressure, and finally cooling is carried after pressure releasing. According to the electric locomotive pantograph copper-impregnated carbon contact strip producing method, the electroconductibility of the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is improved, the electrical resistivity is lowered, the mechanical strength of the carbon contact strip and copper impregnated angle can be increased, then the carbon contact strip abrasive resistance and self-lubrication are improved, the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is more resistant to abrasion, main line damage and block dropping are avoided, the shock resistance is high, and the service life of the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is prolonged.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Non-contact type power feeder system for mobile object
Provided is a noncontact type power feeder system for feeding an electric power to a mobile object, which enables a quick charge and transmission of a high electric power and in which a power feeder and a power receiver can be readily manufactured at low cost, comprising a power feeder arranged along a running road surface for the mobile object 1, and a power receiver mounted to the mobile object, the power feeder and the power receiver being opposed fact-to-face to each other for feeding an electric power, wherein the power feeder is secured on the running road surface for the mobile object, or aerially above the running road surface while the power receiver is mounted at a position where the power receiver is opposed face-to-face to the power feeder with a predetermined gap therebetween when the mobile object is stopped at a position where the power feeder is set up, and each of the power feeder and the power receiver is composed of a planer core having long sides extended in the travel direction of the mobile object while the power feeder is fed thereto with an electric power through a power feed line laid underground or aerially.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENG LTD
Widely deployable charging system for vehicles
Owner:GREEN DOT TRANSPORTATION INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com