Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
532results about "Groove/land recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
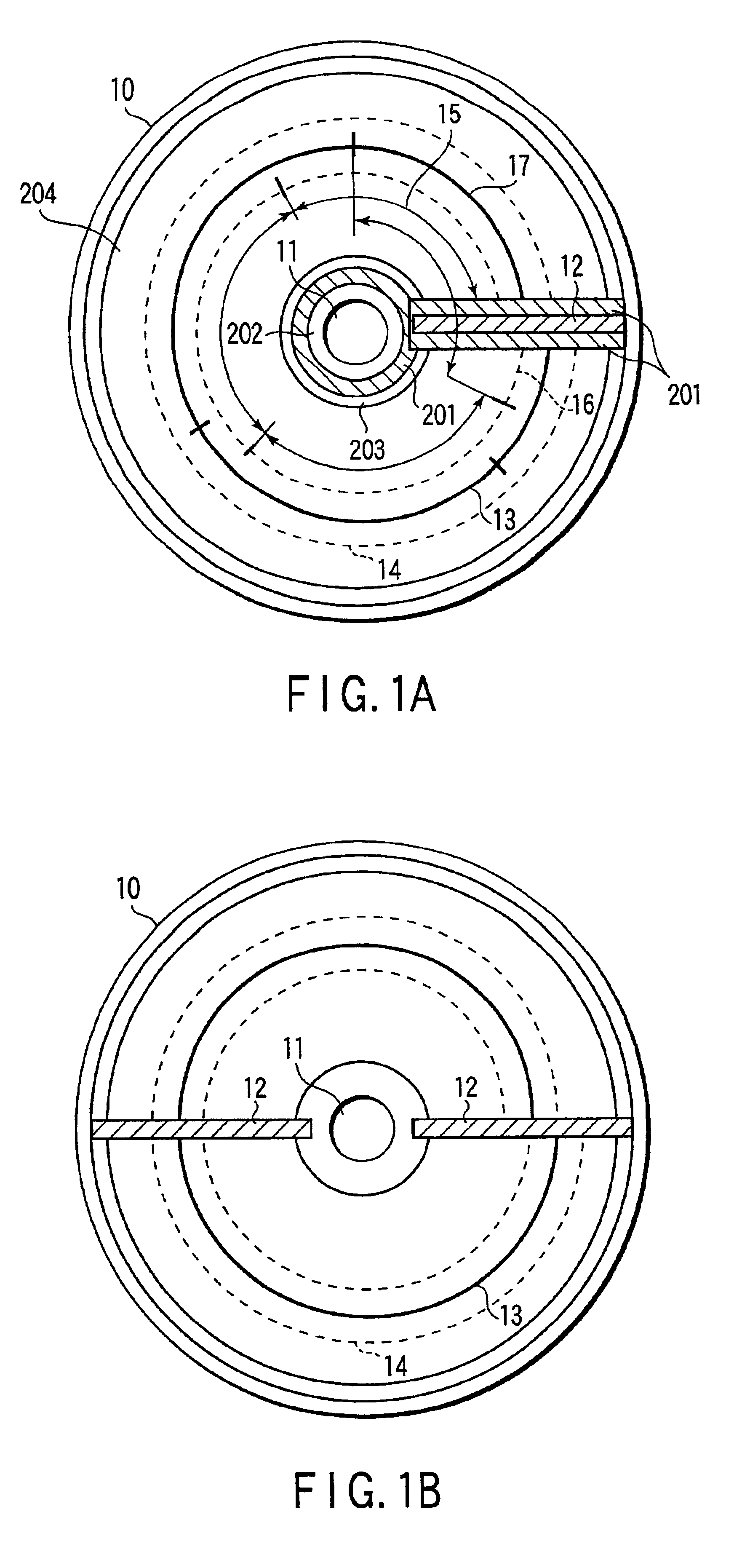
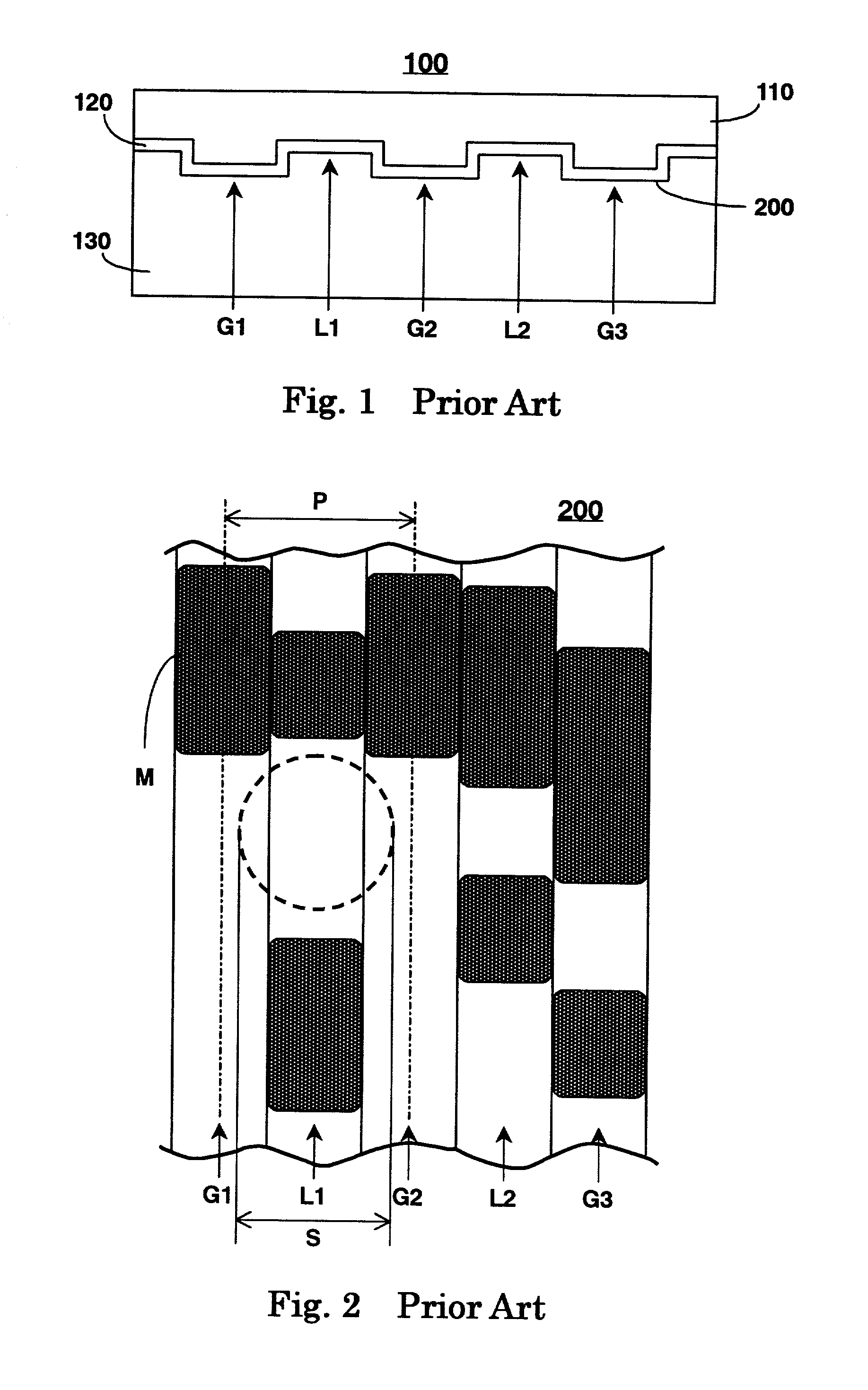
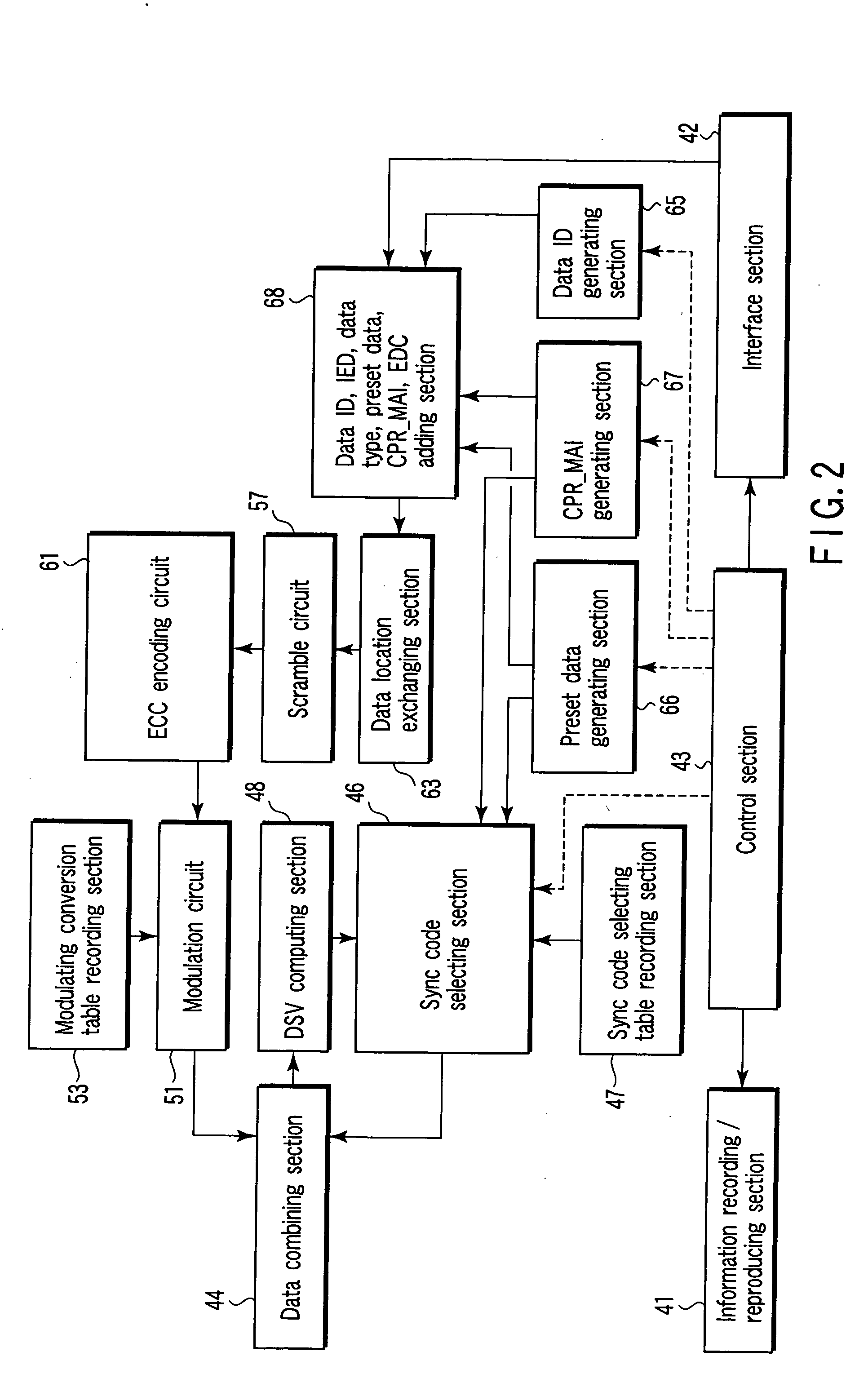
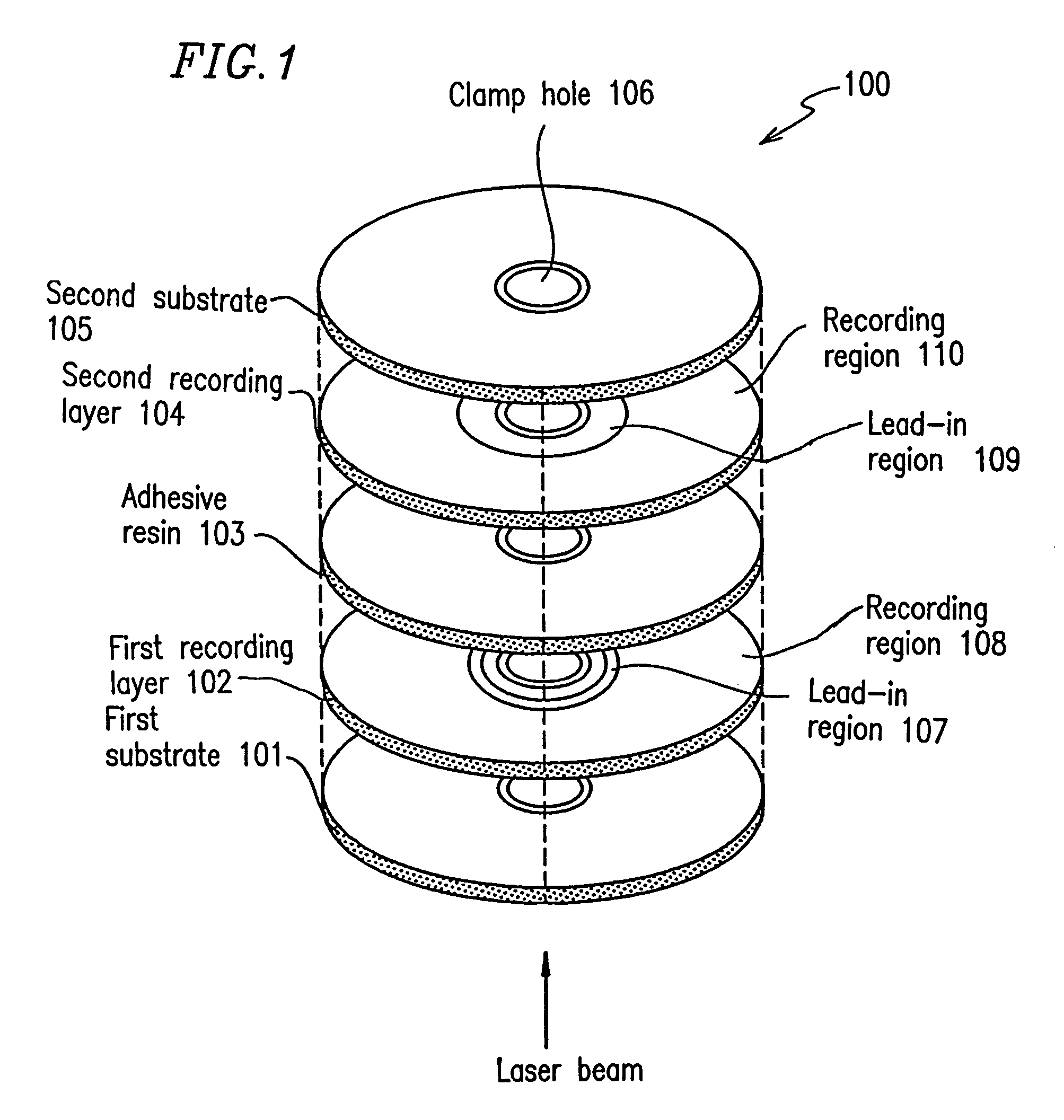
Information recording medium which indicates information according to the wobbling of a track and information recording and reproducing apparatus
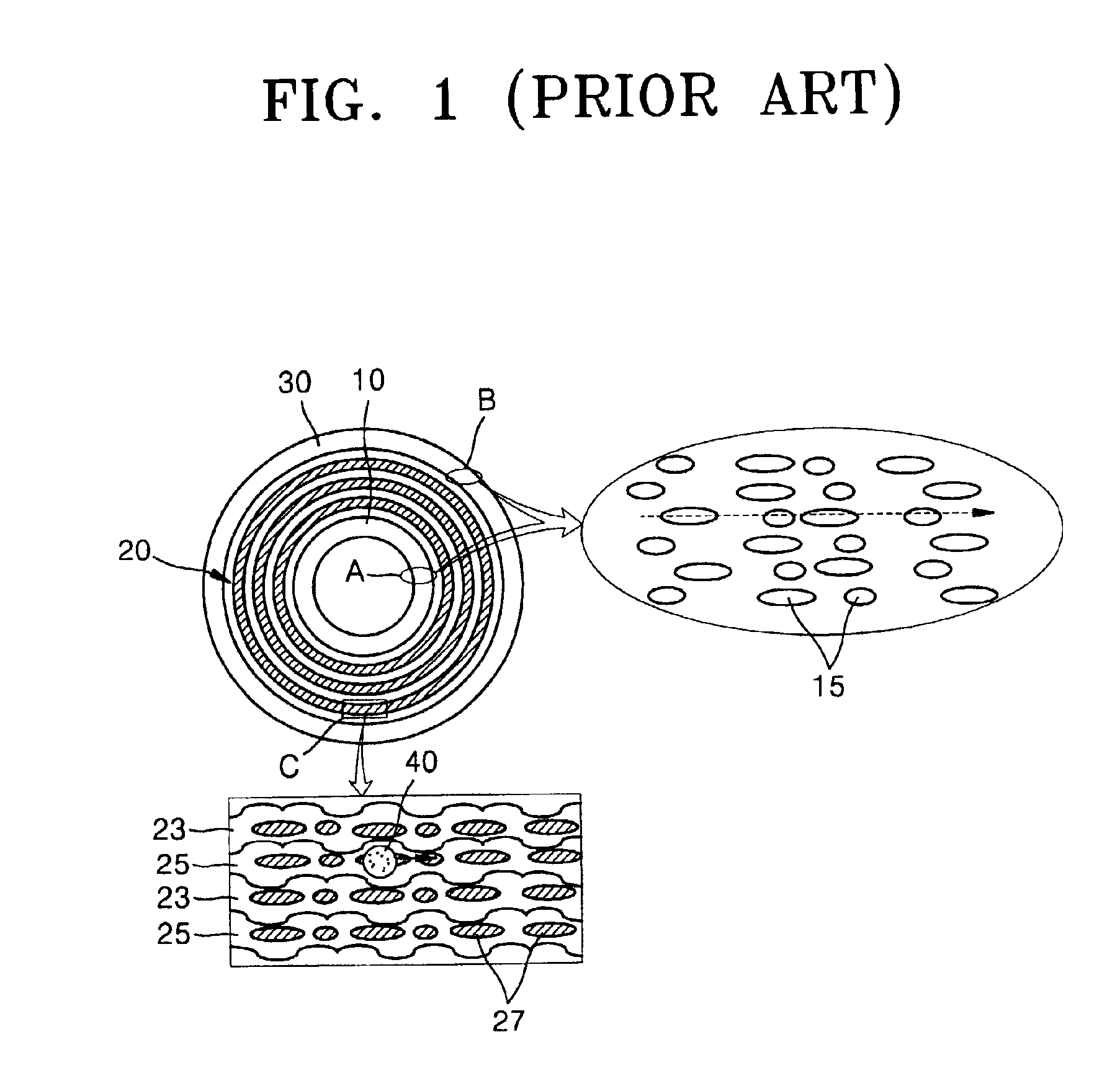
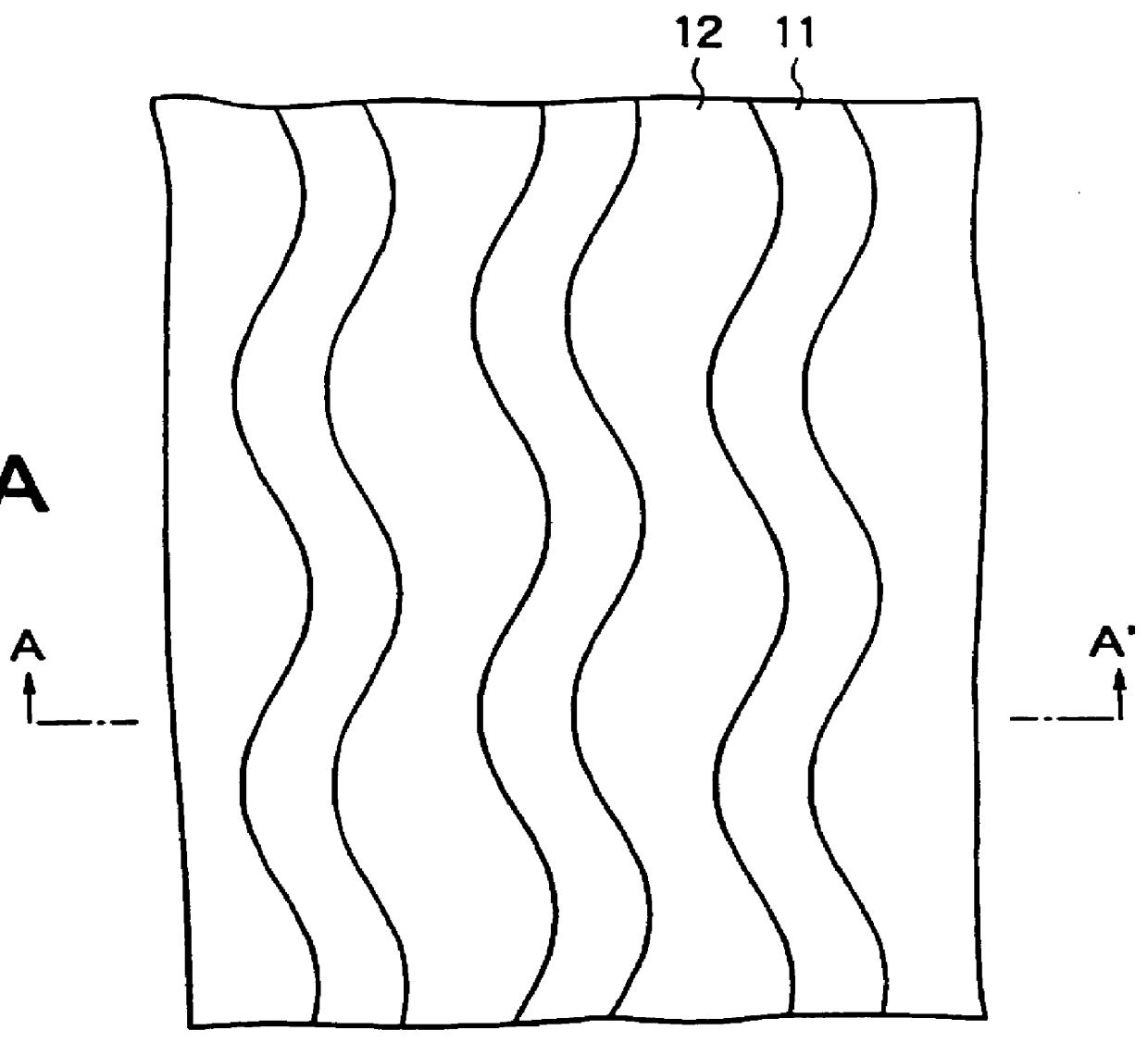
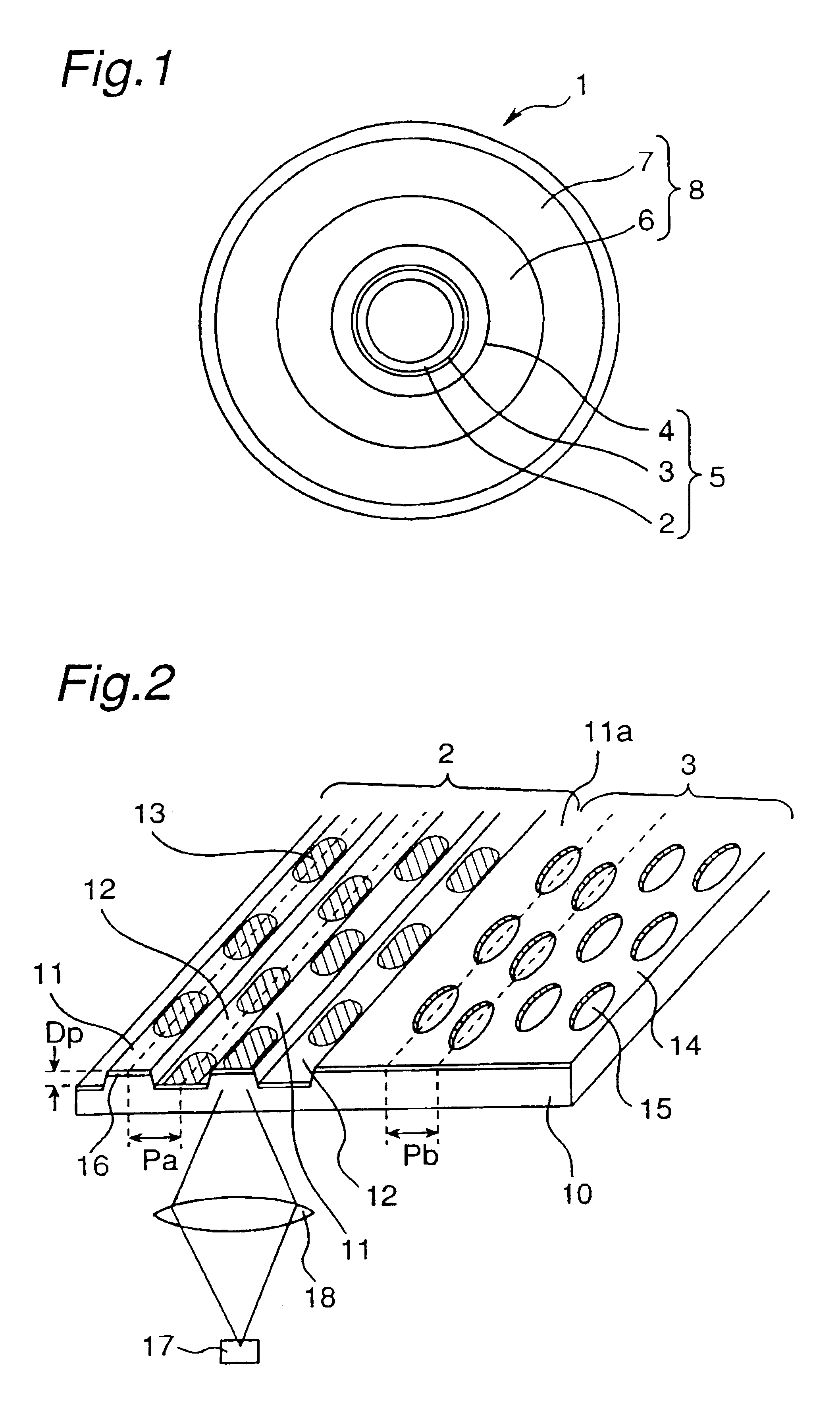
An optical disk comprising a substrate 4, and a plurality of tracks 269 to 273 formed on the substrate 4, wherein the plurality of tracks 269 to 273 include groove tracks 270, 272 consisting of a plurality of grooves mutually space apart by a fixed space, and land tracks 269, 271, 273 consisting of areas between the groove tracks, wherein the borders 14, 15 between the groove tracks and the land tracks represent information using the waveforms from their wobbling patterns, wherein the period of the wobbling waveforms of the borders 14, 15 are constant on each border, but the wobbling waveforms of the opposite portions of the borders across the track are shifted in phase by a predetermined phase difference.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for recording information on information recording medium
InactiveUS6999398B2Reduce decreaseHigh track densityRecord information storageLight beam reproducingComputer hardwareMagneto optical
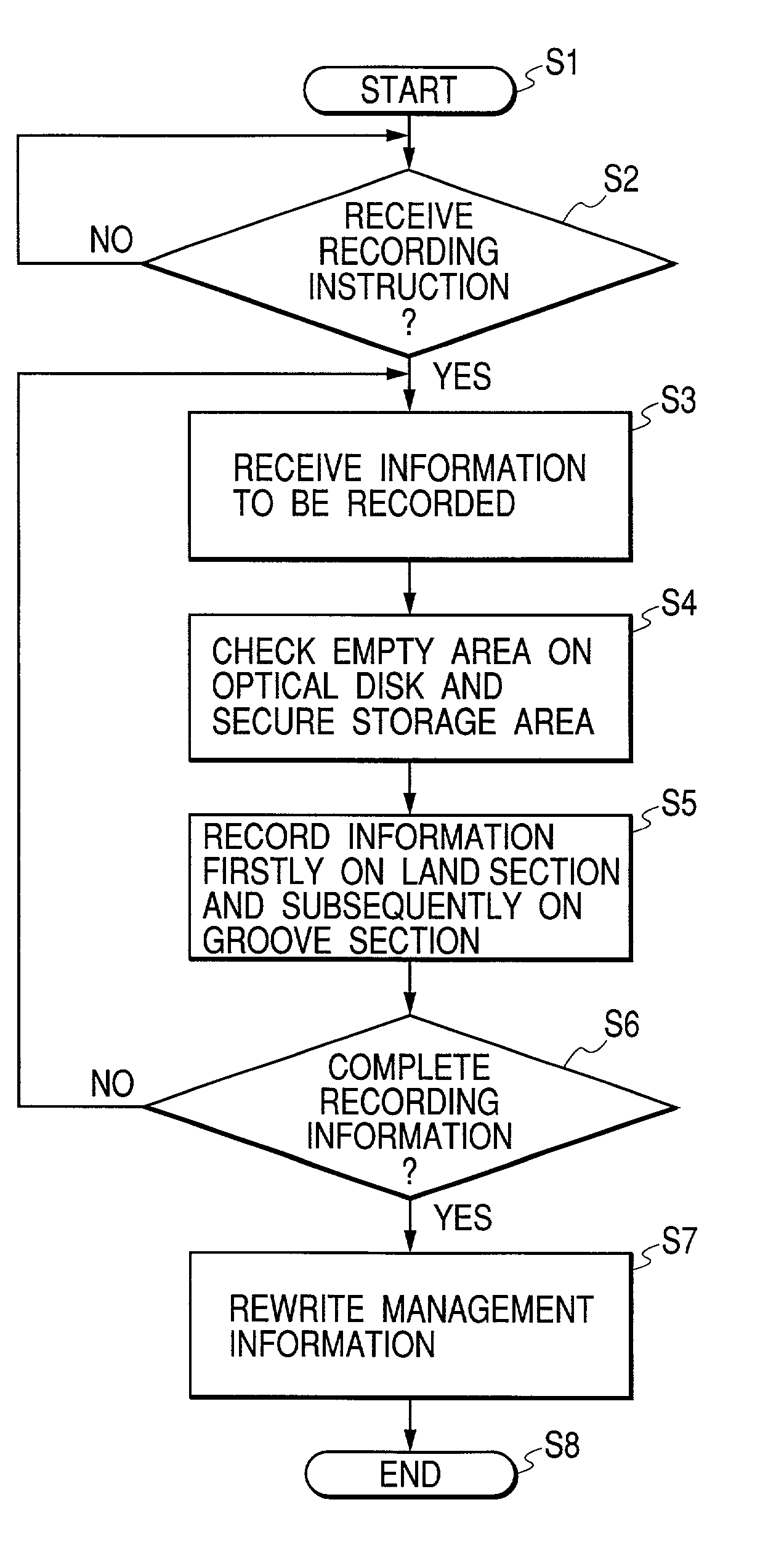
Information is recorded on an information recording medium such as a magneto-optical recording medium, having two recording tracks arranged alternately, typically in a double spiral manner. The two recording tracks have different recording characteristics and information is firstly recorded on the recording track less liable to cross write, typically on a land section, and subsequently on the recording track more liable to cross write, typically on a groove section.
Owner:CANON KK
Recording medium, recording device, reproduction device, recording method and reproduction method
InactiveUS20050207262A1Easy to masterImprove efficiencyRecord information storageOptical erasing systemsUsabilityDatabase
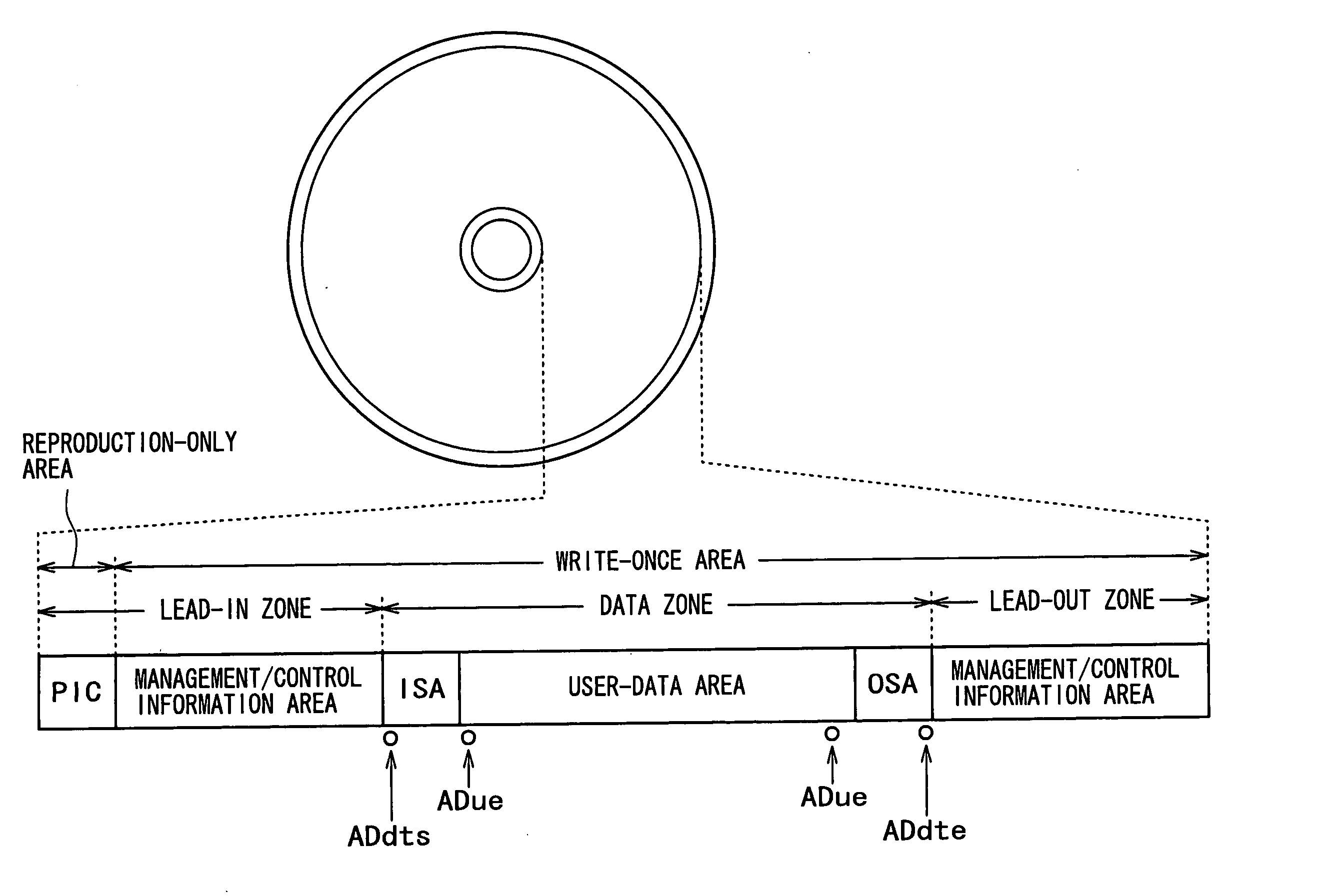
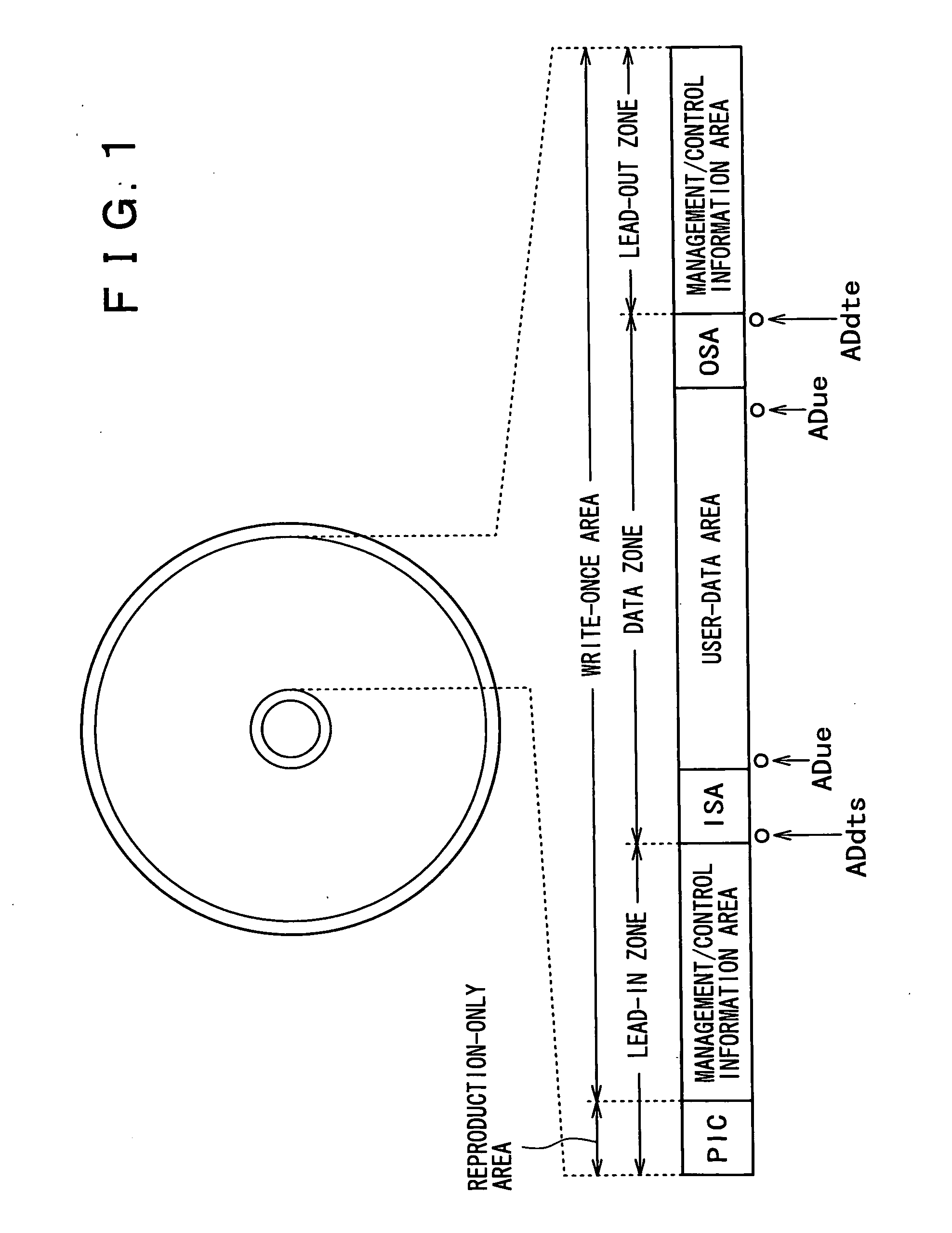
In order to enhance the usability of a write-once recording medium, the recording medium is provided with an ordinary recording / reproduction area, an alternate area, a first alternate-address management information area and a second alternate-address management information area. In addition, written / unwritten state indication information is recorded in a predetermined area. The second alternate-address management information area is an area allowing alternate-address management information recorded therein to be renewed by adding alternate-address management information to the area. Alternate-address management information recorded in the second alternate-address management information area includes information recorded in a first information format and information recorded in a second information format. The first information format shows an alternate source address and an alternate destination address for each data unit. On the other hand, the second information format shows an alternate source address and an alternate destination address for a group of a plurality of physically continuous data units. The second information format is used as a format for effectively carrying out an alternate-address process on such a group of data units. All alternate-address management information is recorded in the first alternate-address management information area in the first information format.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information recording mediums, supporter used in the mediums, manufacture methods of the supporter, manufacturing apparatus of the supporter and stampers for producing the mediums
InactiveUS6254966B1Magnetic materials for record carriersLayered productsHigh densityManufactured apparatus
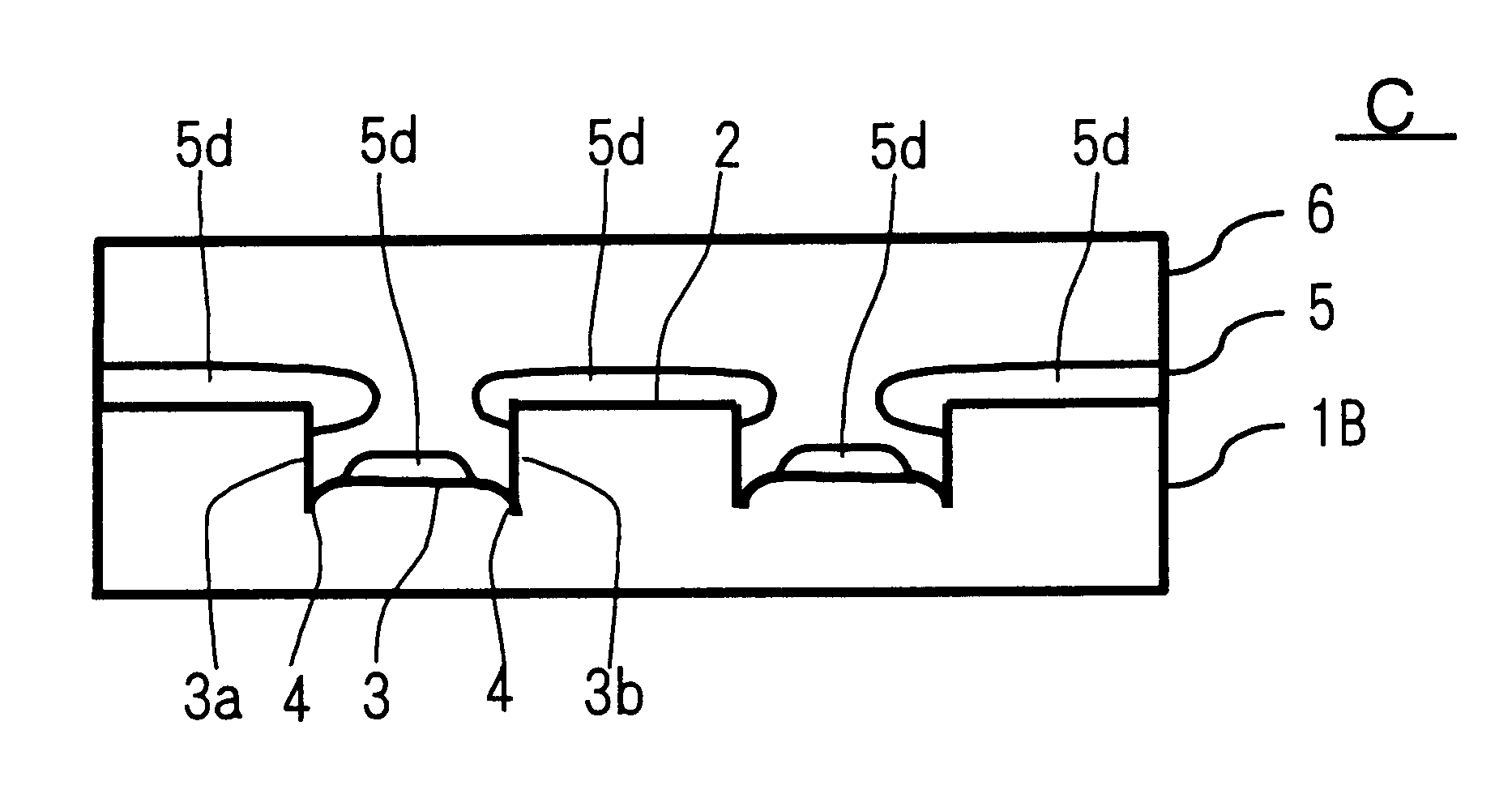
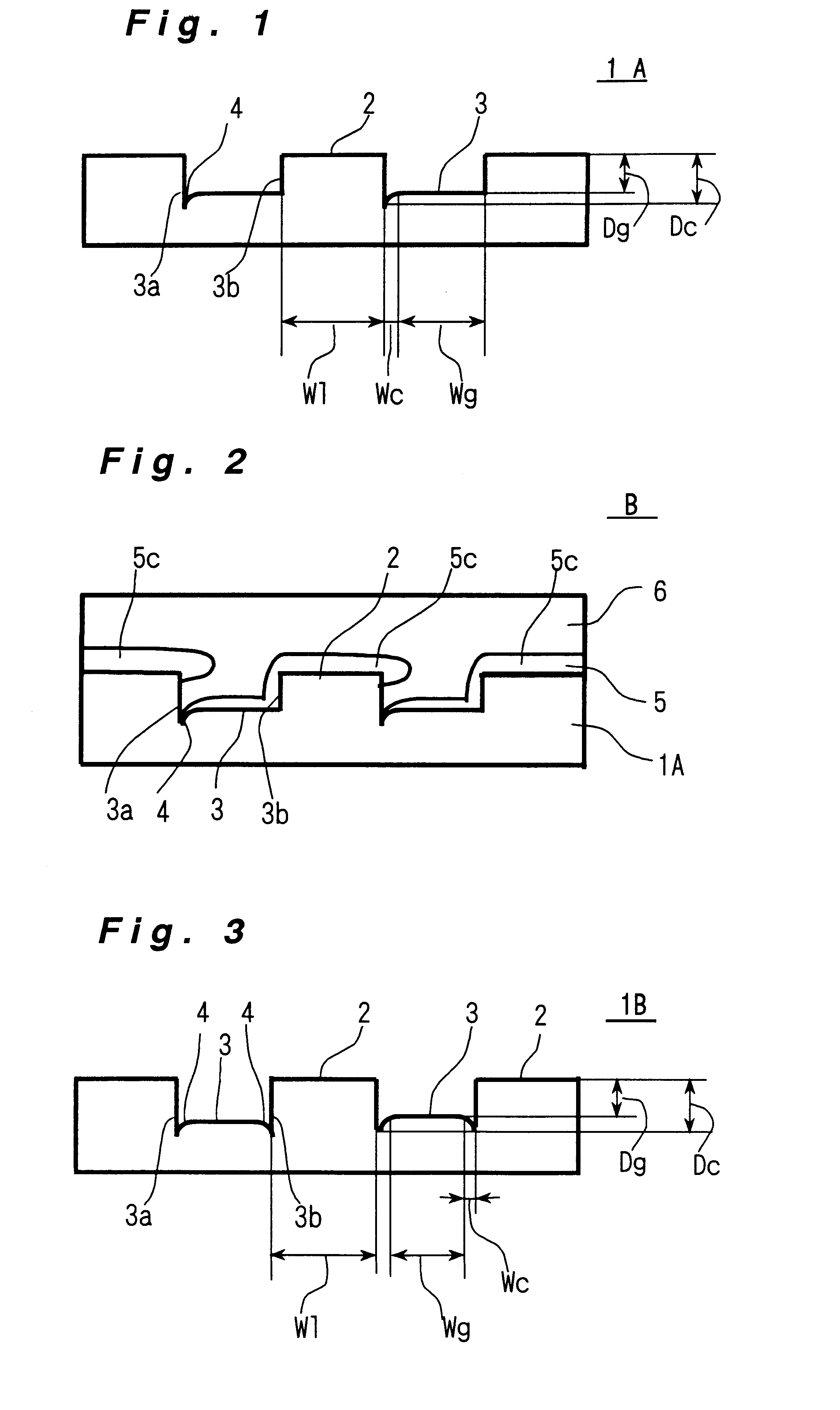
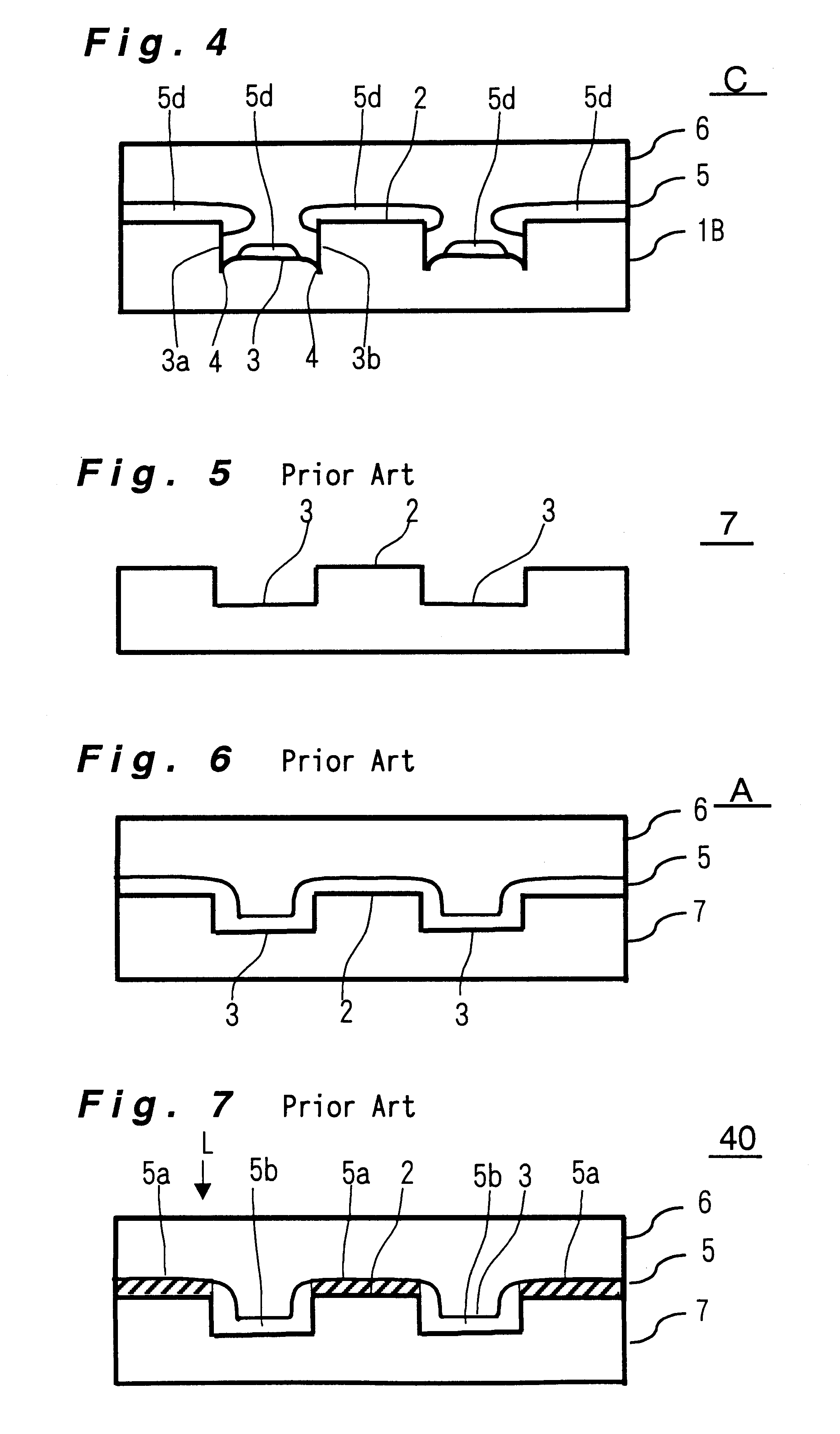
An information recording medium and a supporter used for the information recording medium capable of recording a land / groove recording by using a high density recording technique such as a super-resolution, resulting in a high density recording. An information recording medium B has a supporter 1A, on which a recording layer 5 is formed. On the supporter 1A, lands 2 and groove 3 are alternately formed as a minute track pattern. A crevice 4 having a depth Dc larger than a depth Dg of the respective grooves 3 is formed in the respective grooves 3 at one end of the respective grooves 3 in a width direction of the respective grooves.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
In a phase-change recording medium, a recording medium is provided with a barrier layer including Ge-N, Ge-N-O between a recording layer and a dielectric protective layer in order to prevent a chemical reaction and an atom diffusion between the recording layer and the dielectric protective layer. A barrier material can be also applied to the protective layer itself. Thereby, it is possible to considerably suppress a reduction of a reflectivity and a reduction of a signal amplitude due to the repeat of recording and erasing, such reductions being observed in a conventional phase-change optical information recording medium, and thereby the number of overwriting times can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical disc having uniform structure
InactiveUS7065015B2Increase productionReduce manufacturing costFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
An optical disc is manufactured under a uniform condition by forming grooves and lands on the entire surface of the disc. The optical disc is configured to obtain a reliable reproduction signal, and the grooves and lands are formed on a lead-in area, a user data area and a lead-out area of the optical disc. Since the same manufacturing condition can be adopted in mastering discs, the yield can be enhanced and the manufacturing cost can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical phase-change disc
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Method of recording or reproducing data on or from high density multi-layer recording medium using variable light intensity
InactiveUS7009927B2Diminishing of dataDiminishing of surfaceOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageHigh densityData recording
A high-density optical recording medium and method of recording data on the optical recording medium. The optical recording medium includes a plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces having reflectances for light passing through a pit area, a land / groove area, and a land / groove area on which data are recorded, of a data recording / reproducing surface included between a light source for emitting light and a recording / reproducing surface selected from the plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces, the reflectances satisfy the expressions r1≧r2≧r3 and {(r1−r3) / r3}≦0.2, where r1, r2 and r3 are the reflectances of the pit area, the land / groove area and the land groove area on which data are recorded, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information recording medium with index header
InactiveUS6850469B2Accurately record informationAccurately reproduce informationTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersRecording layerMechanical engineering
An information recording medium has a plurality of stacked recording layers. Each recording layer has a spiral track which defines a plurality of rounds, and at least one index header aligned in the radial direction of the disk to partially intercept the spiral track. The index header has address data of each round of the spiral track, which is formed by embossed pits, and some or all of the index headers of the first and second recording layers are laid out to overlap each other when viewed from the predetermined surface.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical phase-change disc having a grooved substrate, with the groove having specific wobbled and non-wobbled regions
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
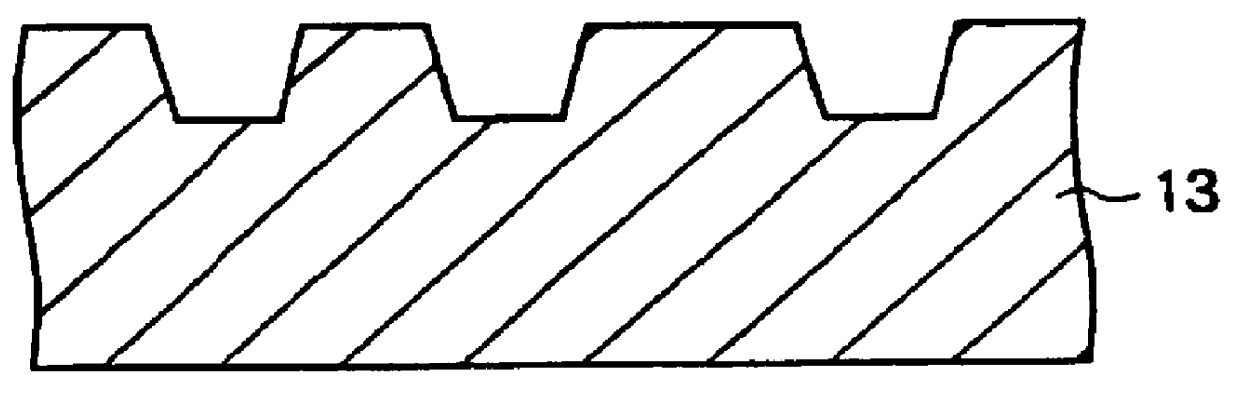
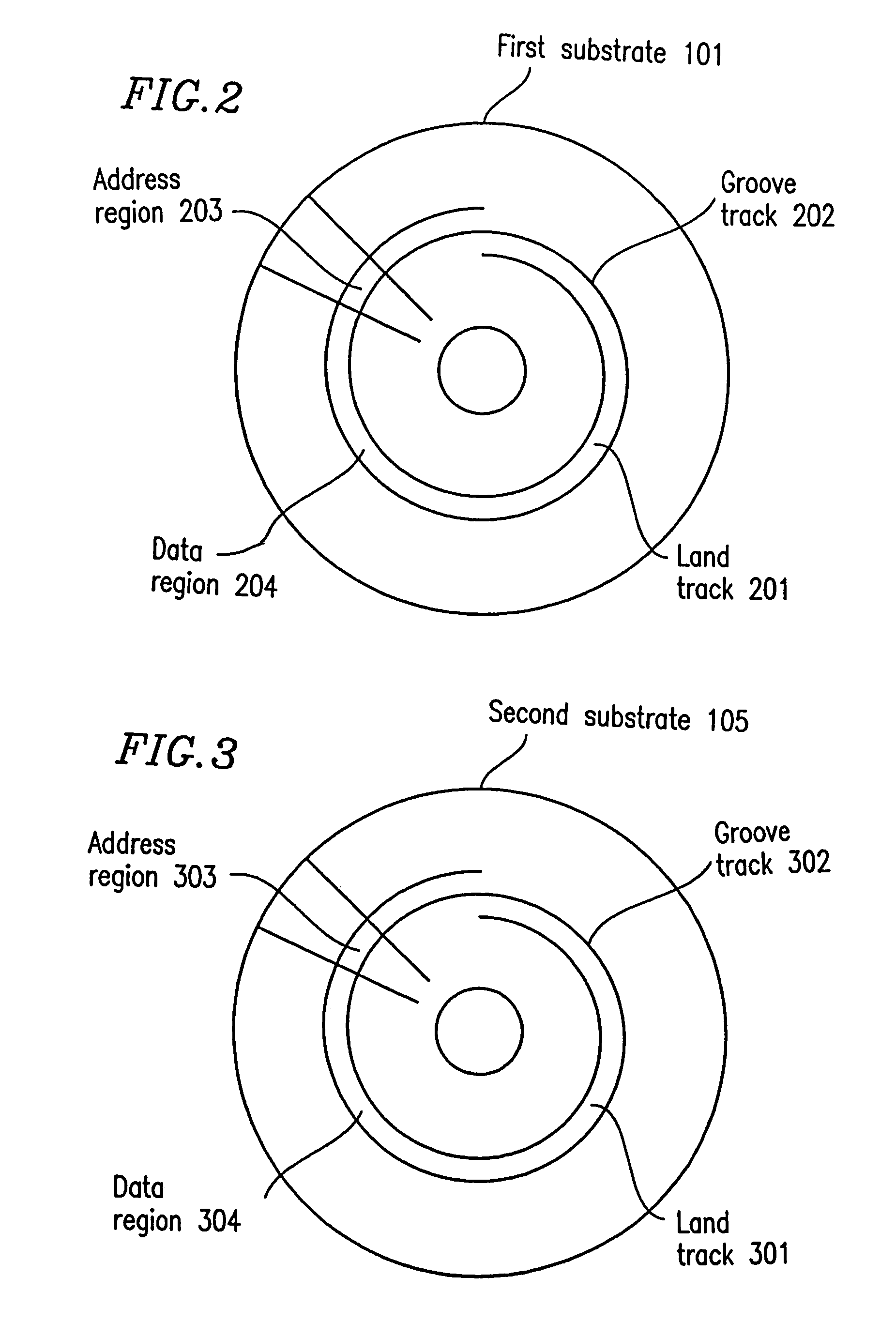
Optical recording medium having groove and land tracks, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6535477B1Quality improvementEasy to provideMechanical record carriersRecord information storageEngineeringOptical recording
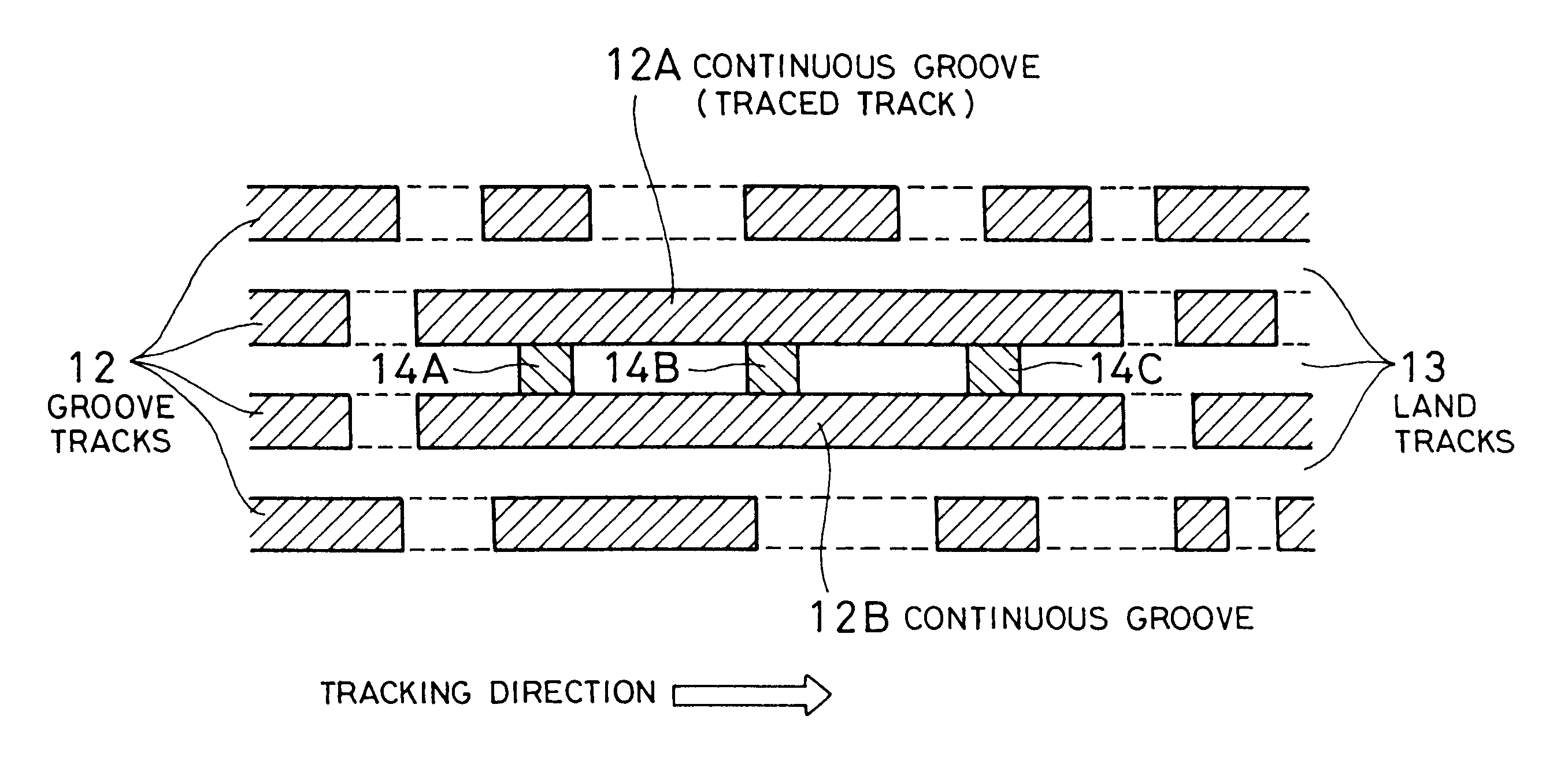
At least a portion of groove tracks in a information-data recording region of an optical recording medium comprises a plurality of groove portions separated by groove-absent portions in a rotational direction of the optical recording medium, each of the mark portions or each of the space portions includes one of the groove-absent portions. At least one of two groove tracks adjacent to prepit train, which is formed in land tracks, has a continuous groove portion or a groove-absent portion extending at least from a leading end to a trailing end of at least one prepit included in the prepit train in a rotational direction of the optical recording medium. The frequency band for separation of the groove tracks includes at least a portion of a frequency band of a modulated recording signal for recording information data on the optical recording medium.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Information recording medium
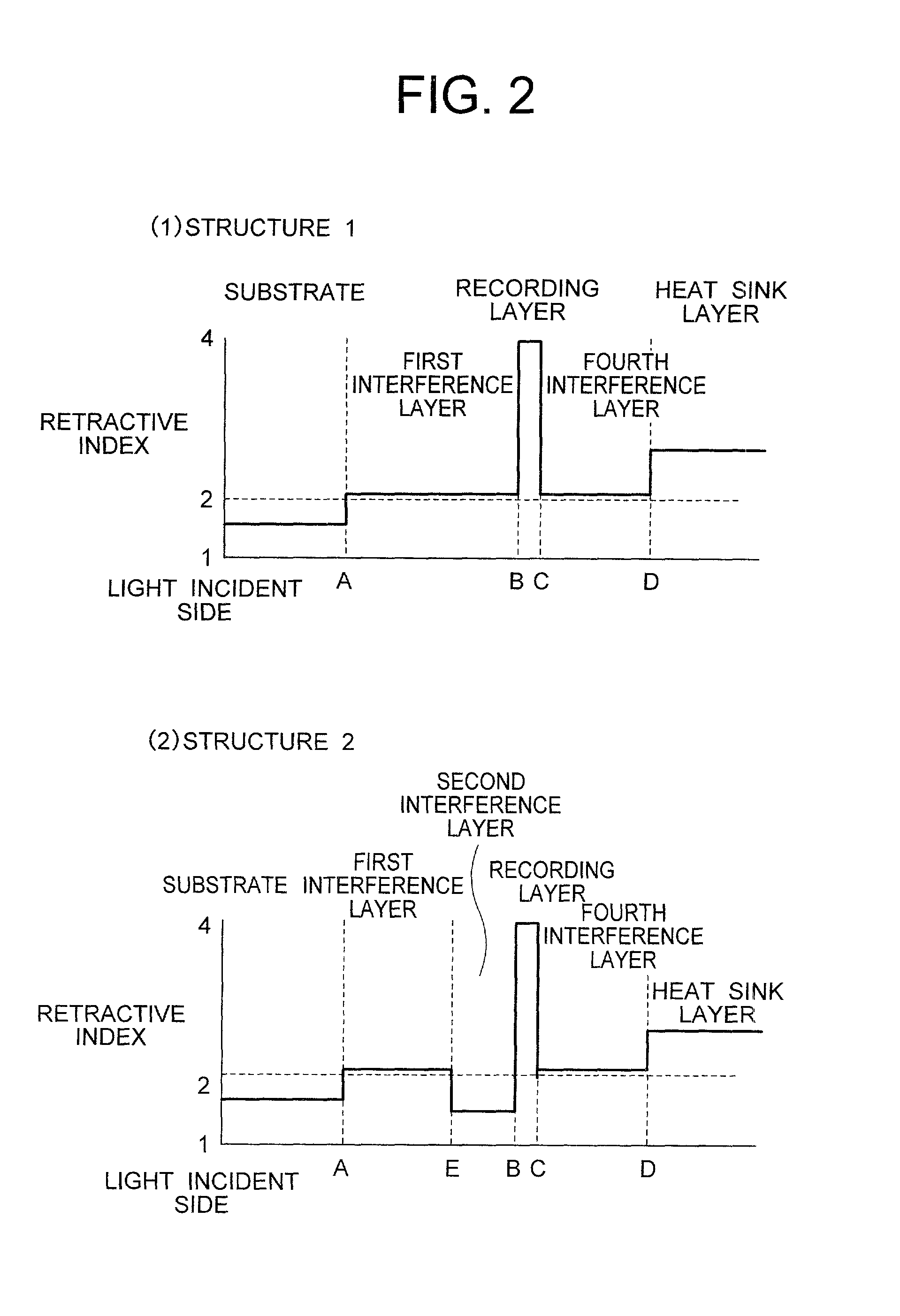
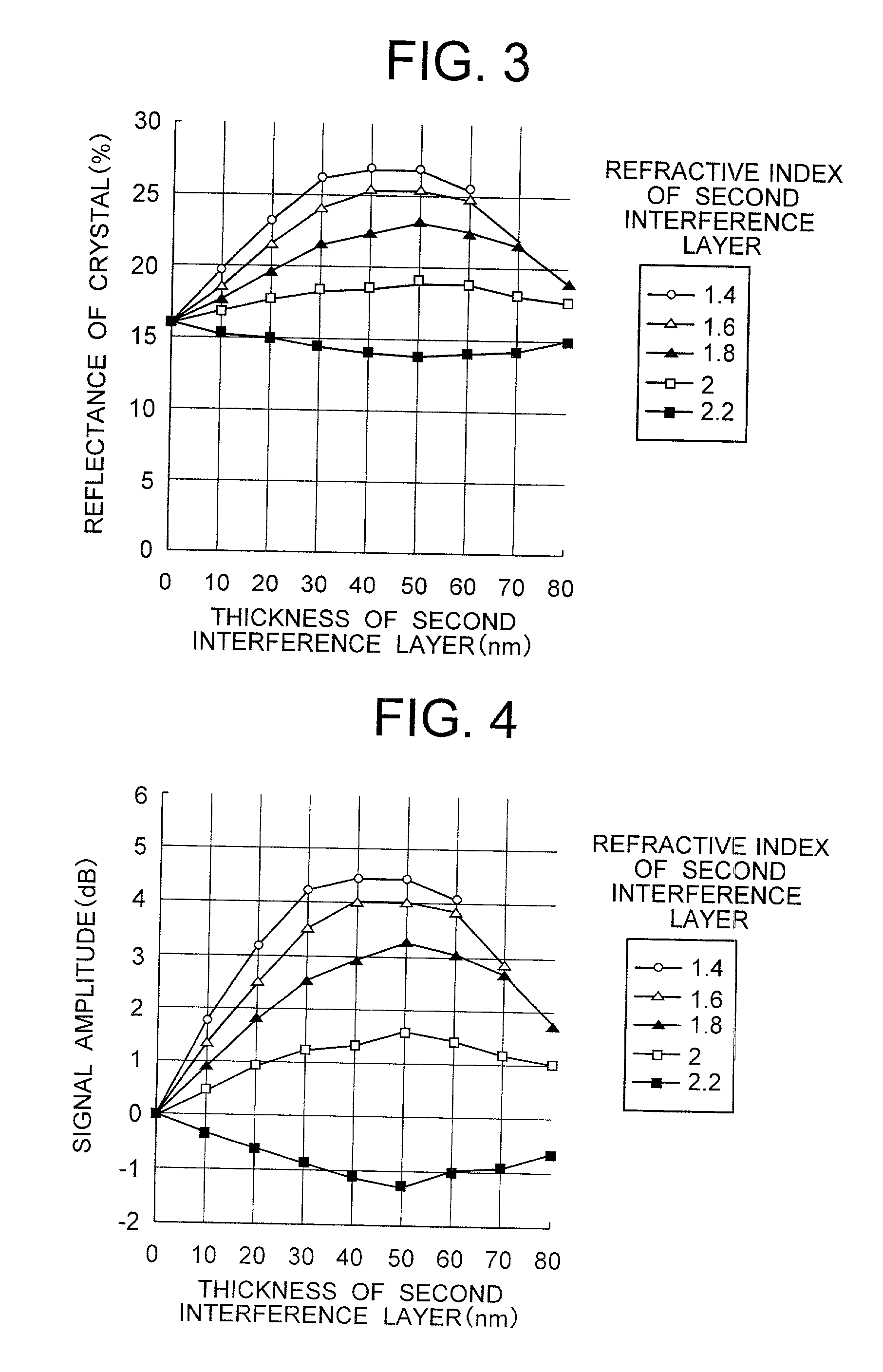
InactiveUS20010016242A1Reflectance can be improvedPrevent peelingRadiation applicationsLayered productsHigh densityRefractive index
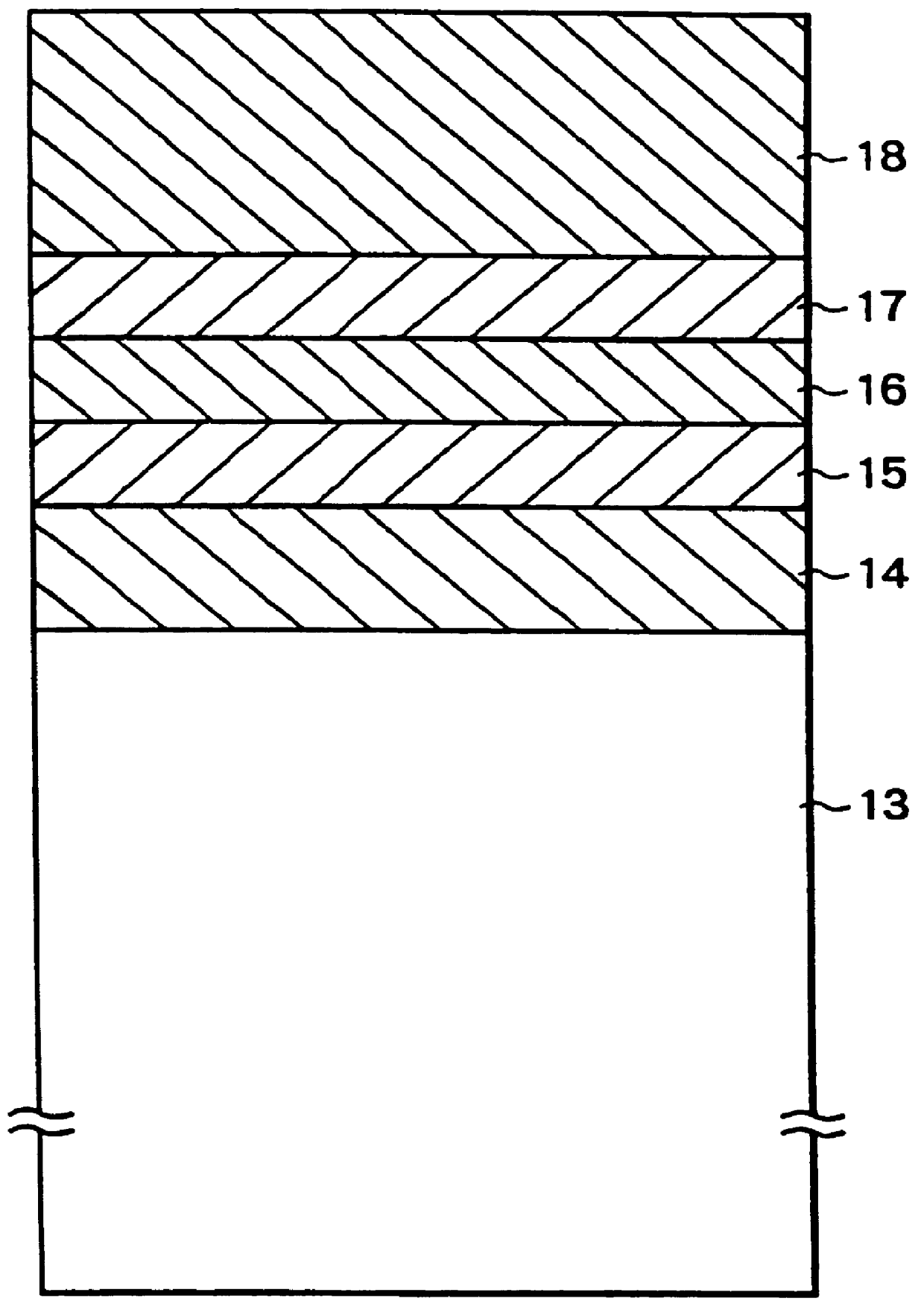
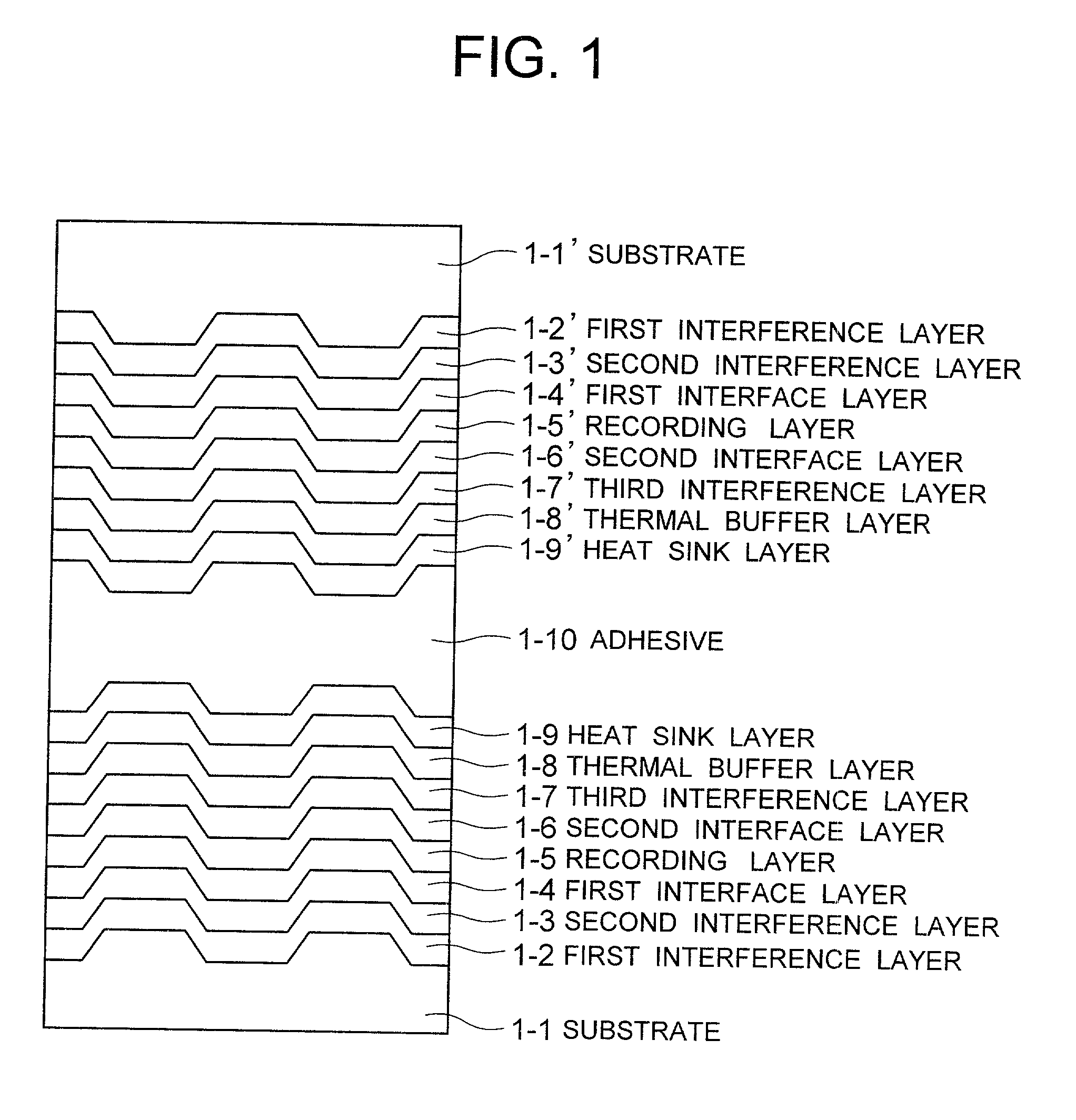
A high-density information recording medium free from lowering the reflectance by over-write of a large number of times and exfoliation defect in a structure for suppressing cross-erase. This medium includes, over a substrate having a groove shape, a recording layer, and three-layered thin films of a first interference layer, a second interference layer and an interface layer having mutually different compositions and disposed on a laser beam incidence side of the recording layer in order named from the laser beam incidence side. The first interference layer has a smaller refractive index and a larger thermal conductivity than the second interference layer, the interface layer is interposed between the second interference layer and the recording layer, and a distance between the first interference layer and the recording layer is greater than at least a groove depth.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
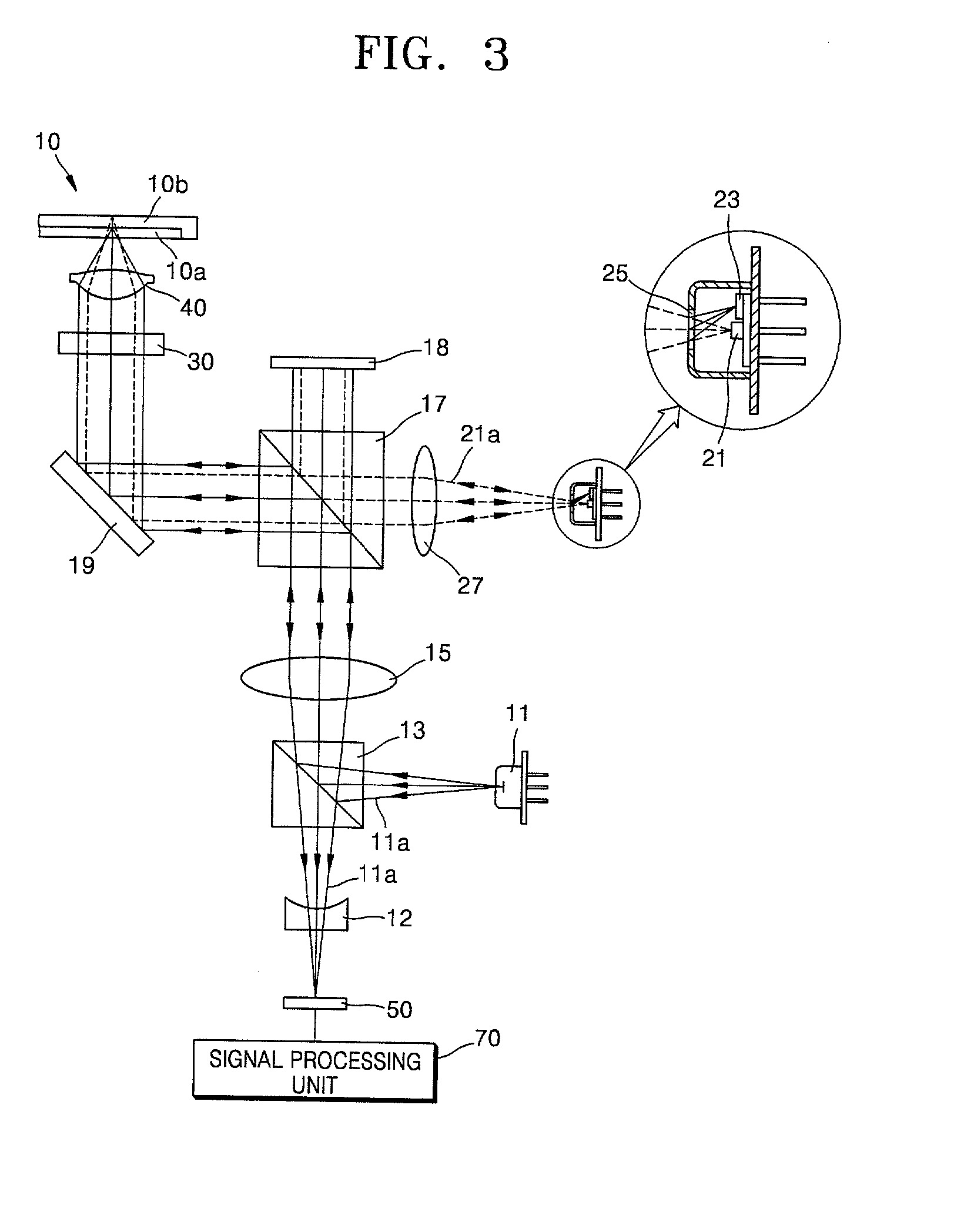
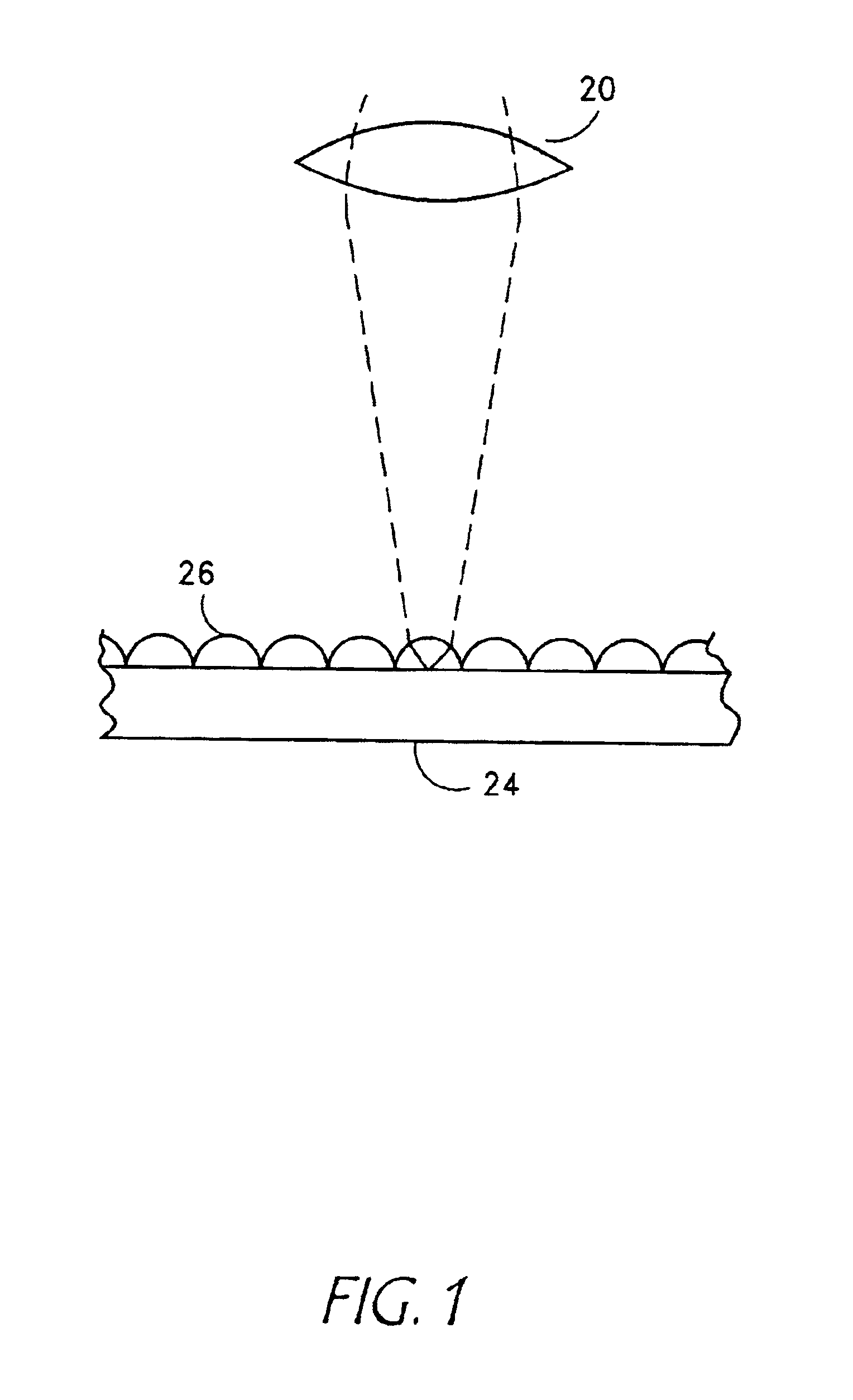
Optical pickup apparatus and optimal light spot focusing method
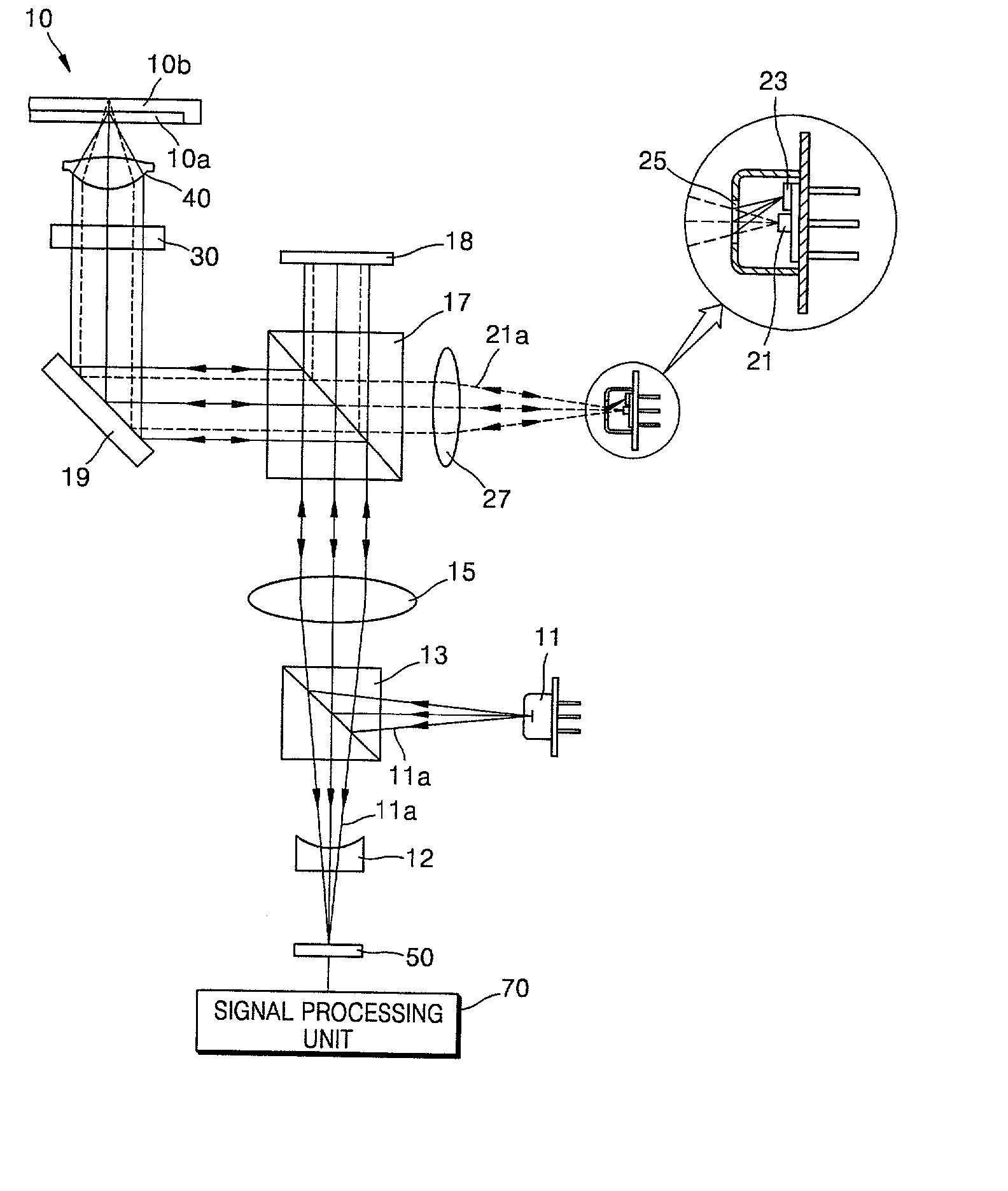
InactiveUS20020159378A1Minimized in sizeOptical beam sourcesOptical detectorsOptical pickupPhotodetector
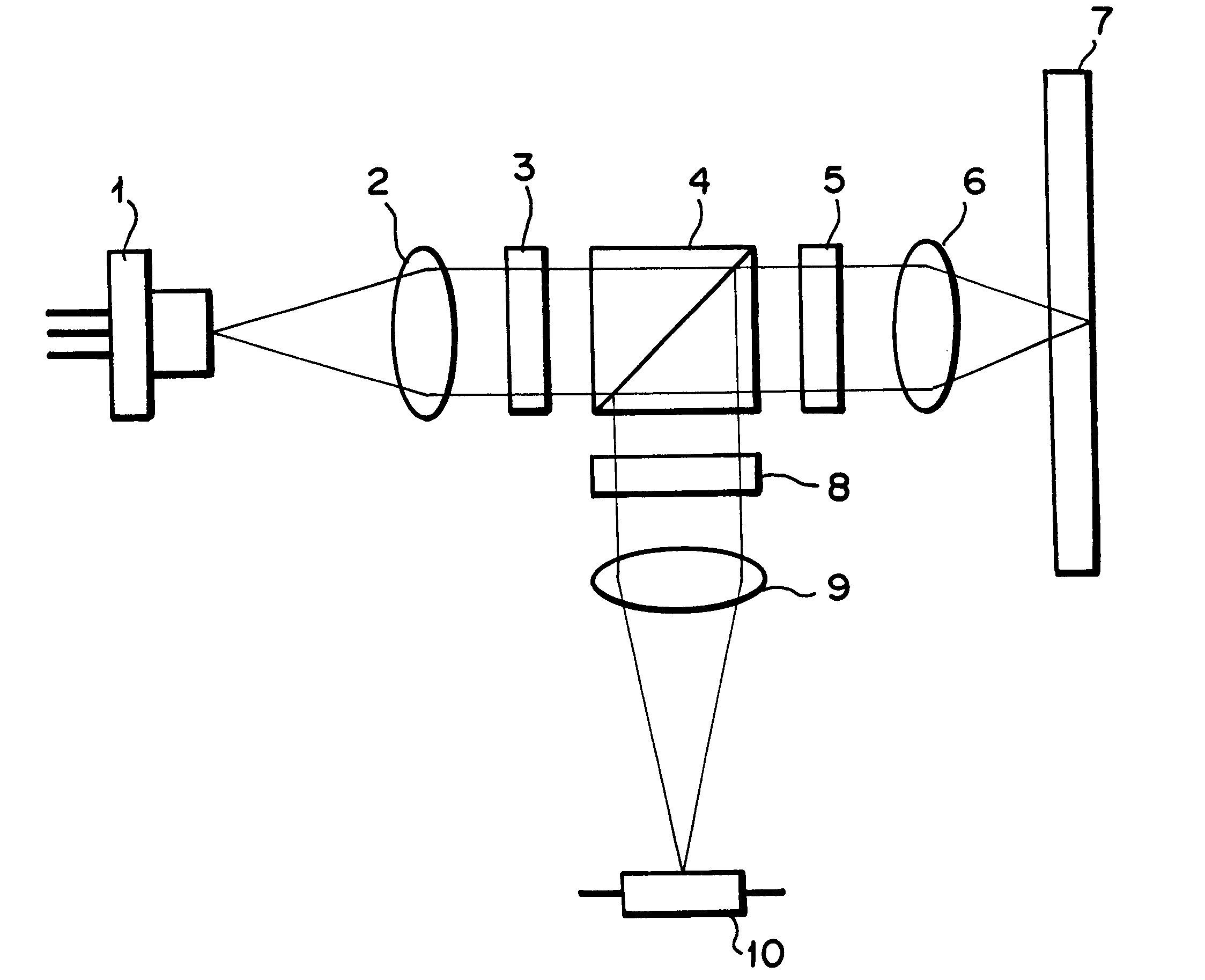
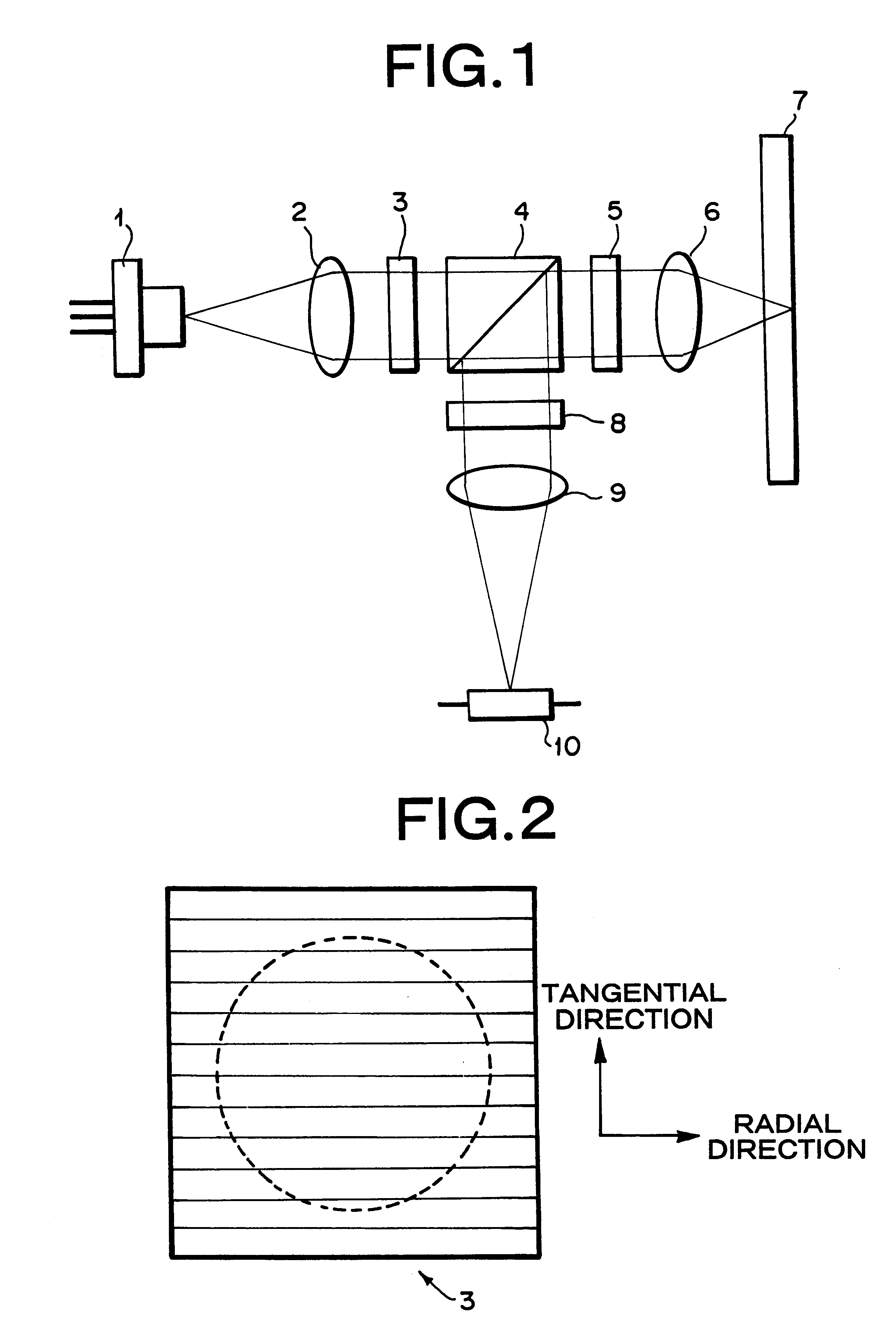
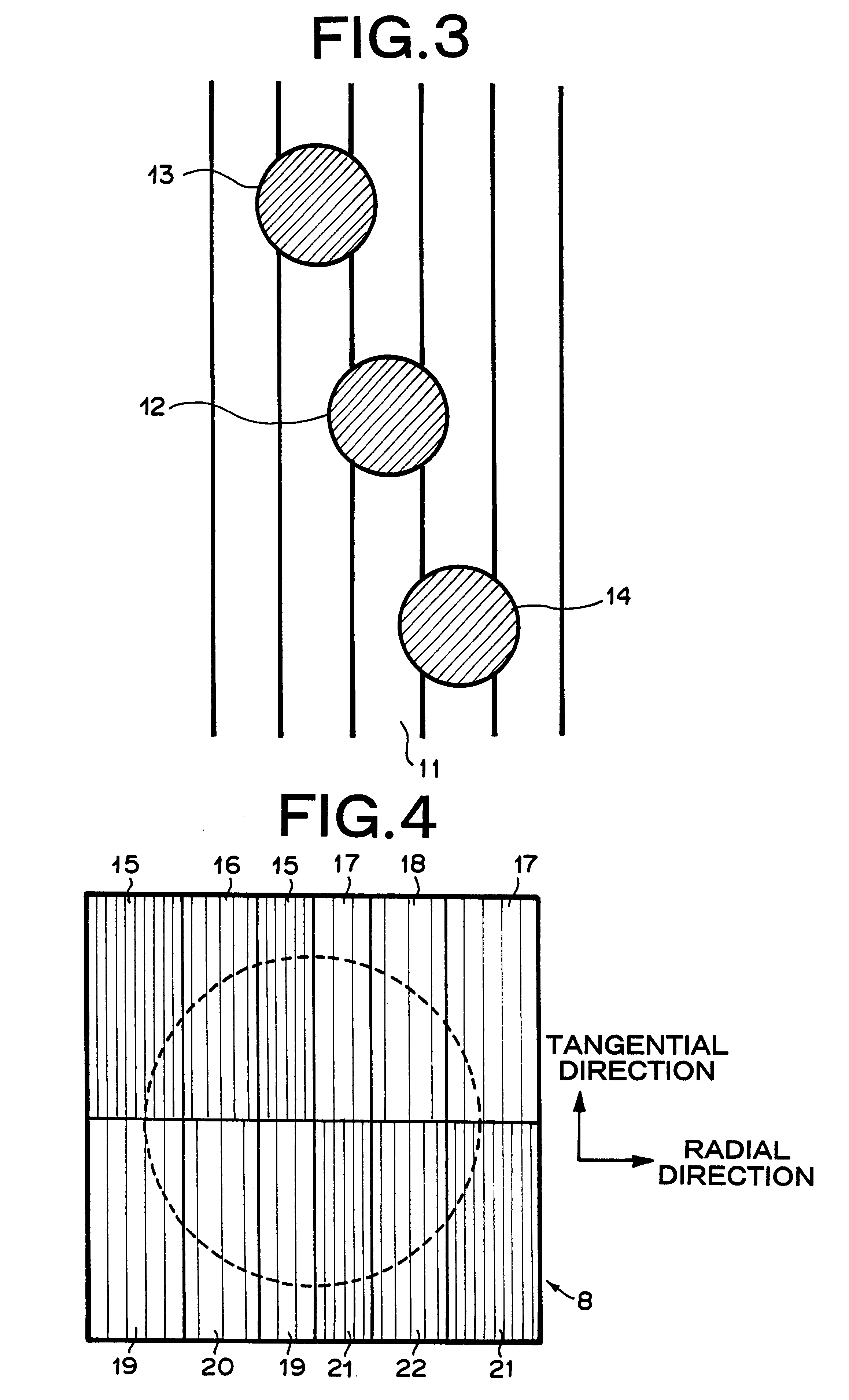
An optical pickup apparatus includes a first light source to emit a first light beam having a predetermined wavelength, a first optical path changer to change a proceeding path of the first light beam, an objective lens to focus the first light beam on a recording medium, a diffraction member to divide the first light beam reflected by the recording medium into five light regions, the diffraction member having a first diffraction region having a wide width in a direction corresponding to a tangential direction of the recording medium and second through fifth diffraction regions sequentially arranged around the outside of the first diffraction region in a direction corresponding to a radial direction of the recording medium, and a first photodetector having first through fifth light receiving portions to receive the first light beam reflected by the recording medium.
Owner:TS OPTICS CORP
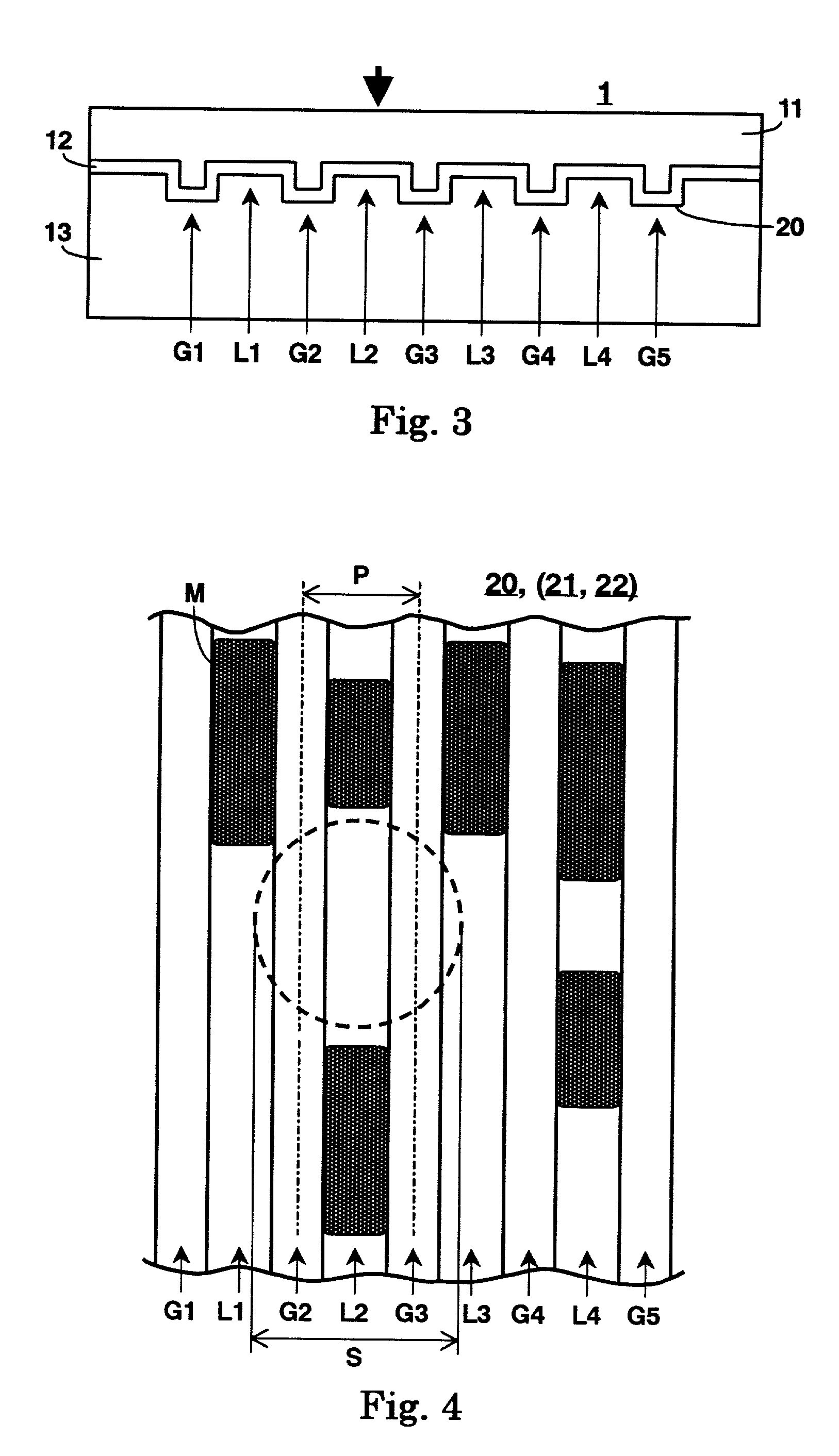
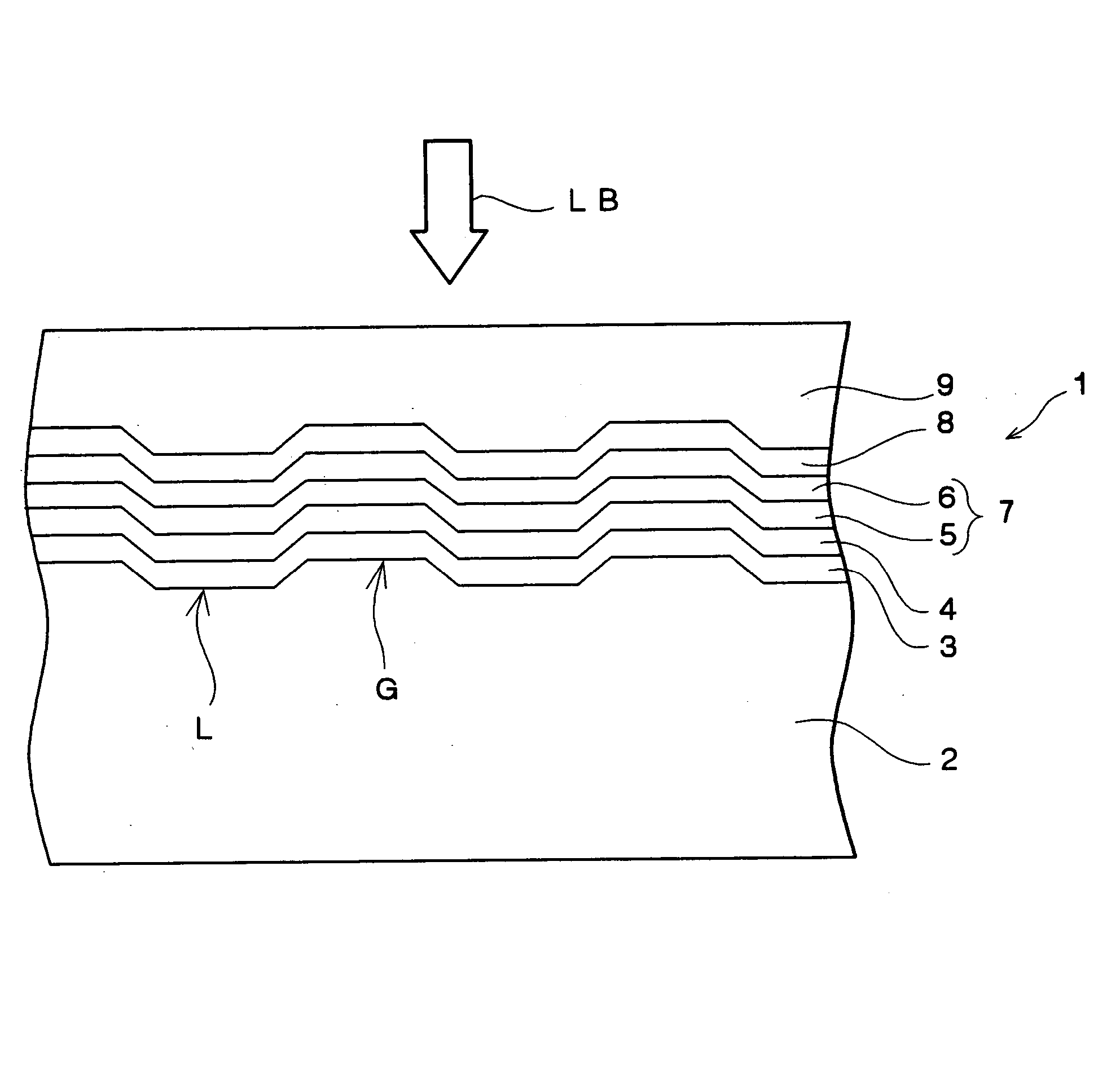
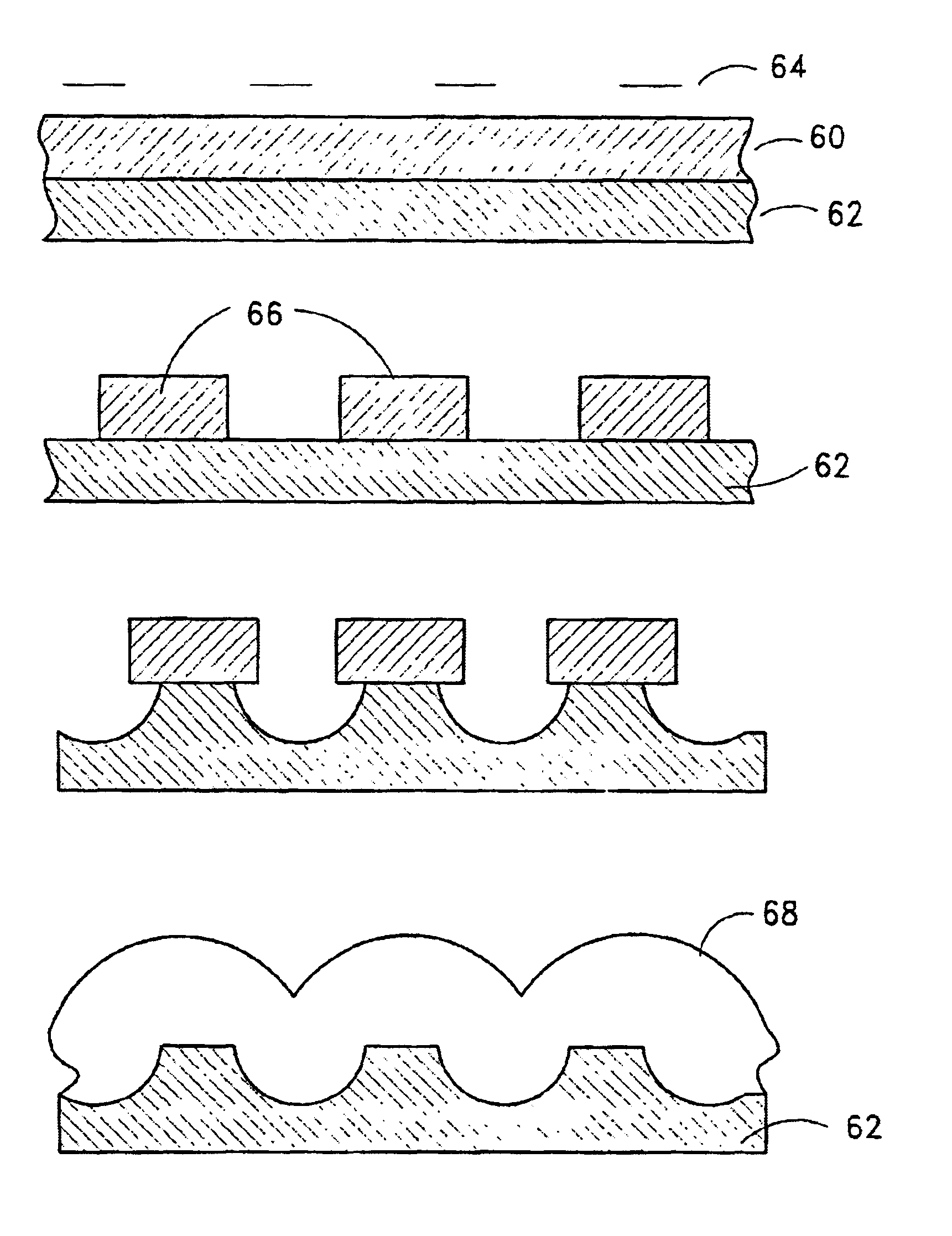
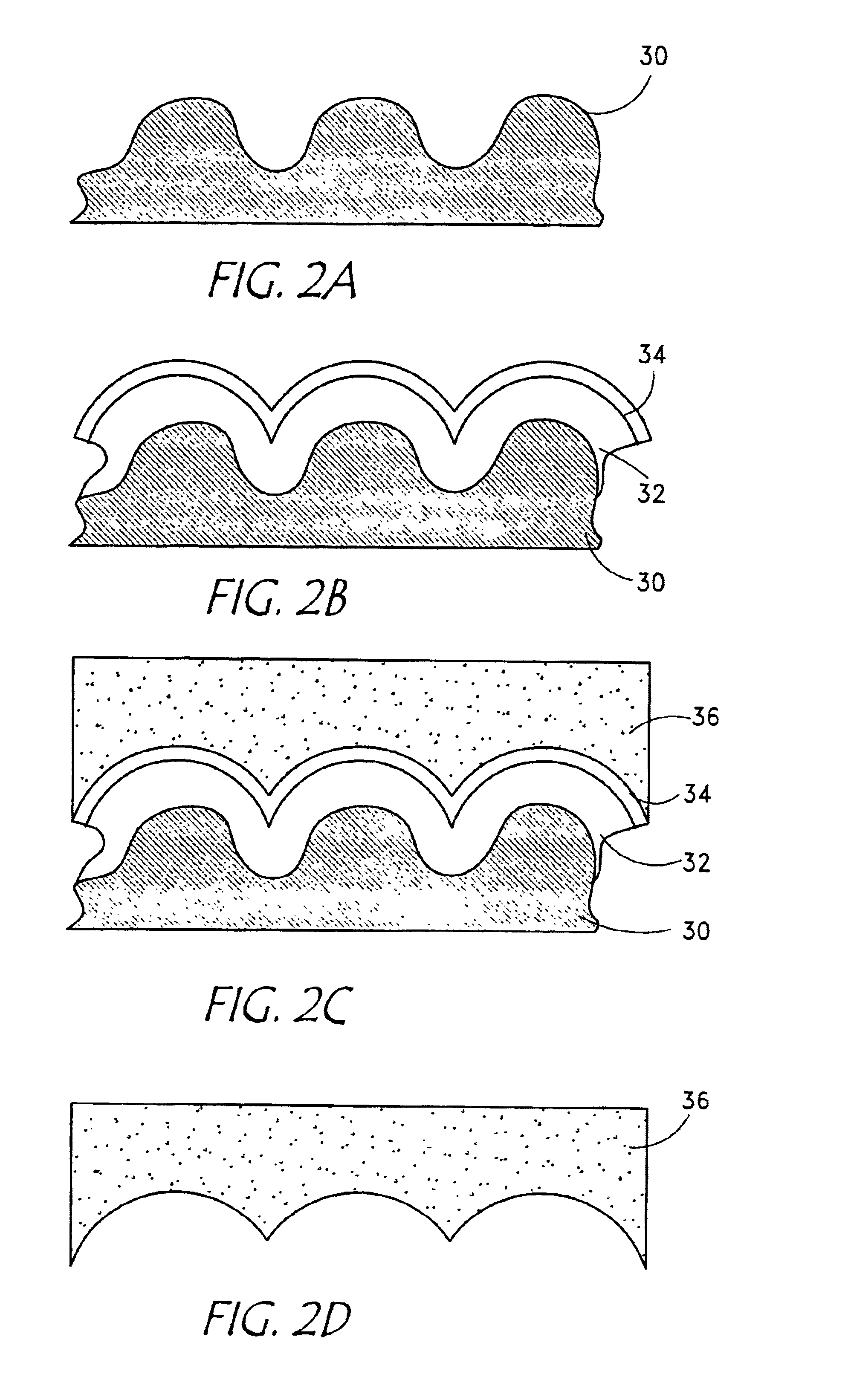
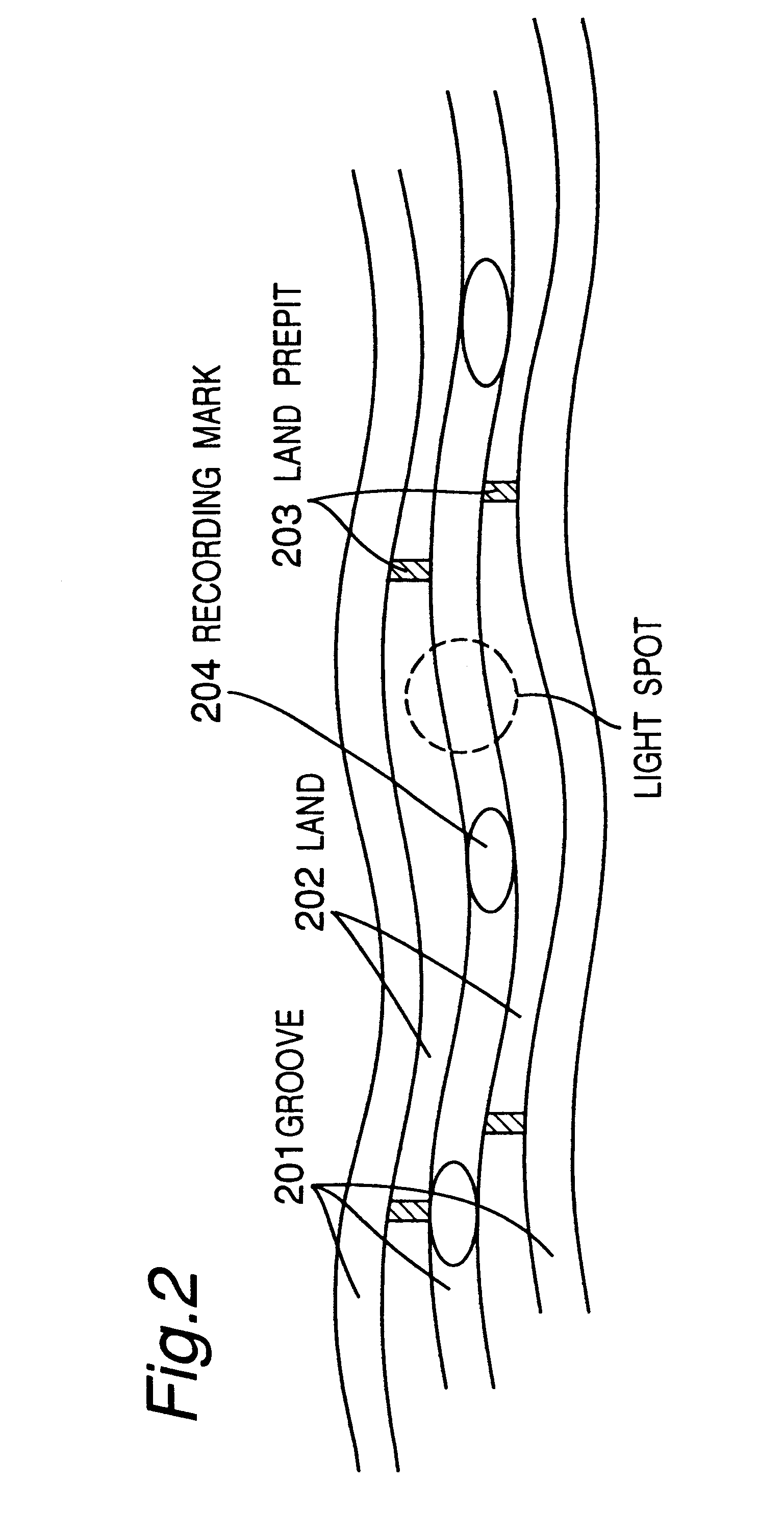
Recording medium having a substrate containing microscopic pattern of parallel groove and land sections and recording/reproducing equipment therefor
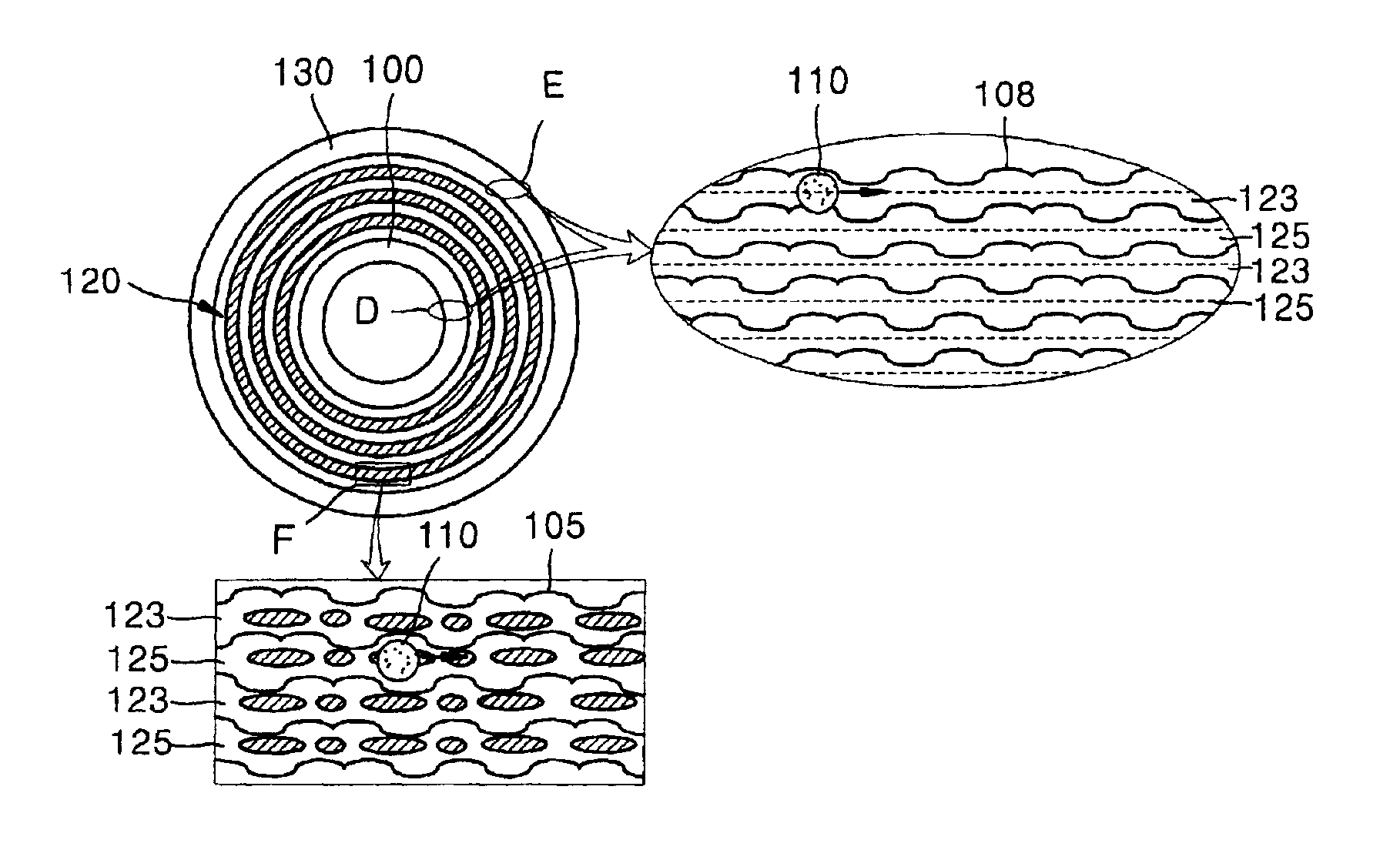
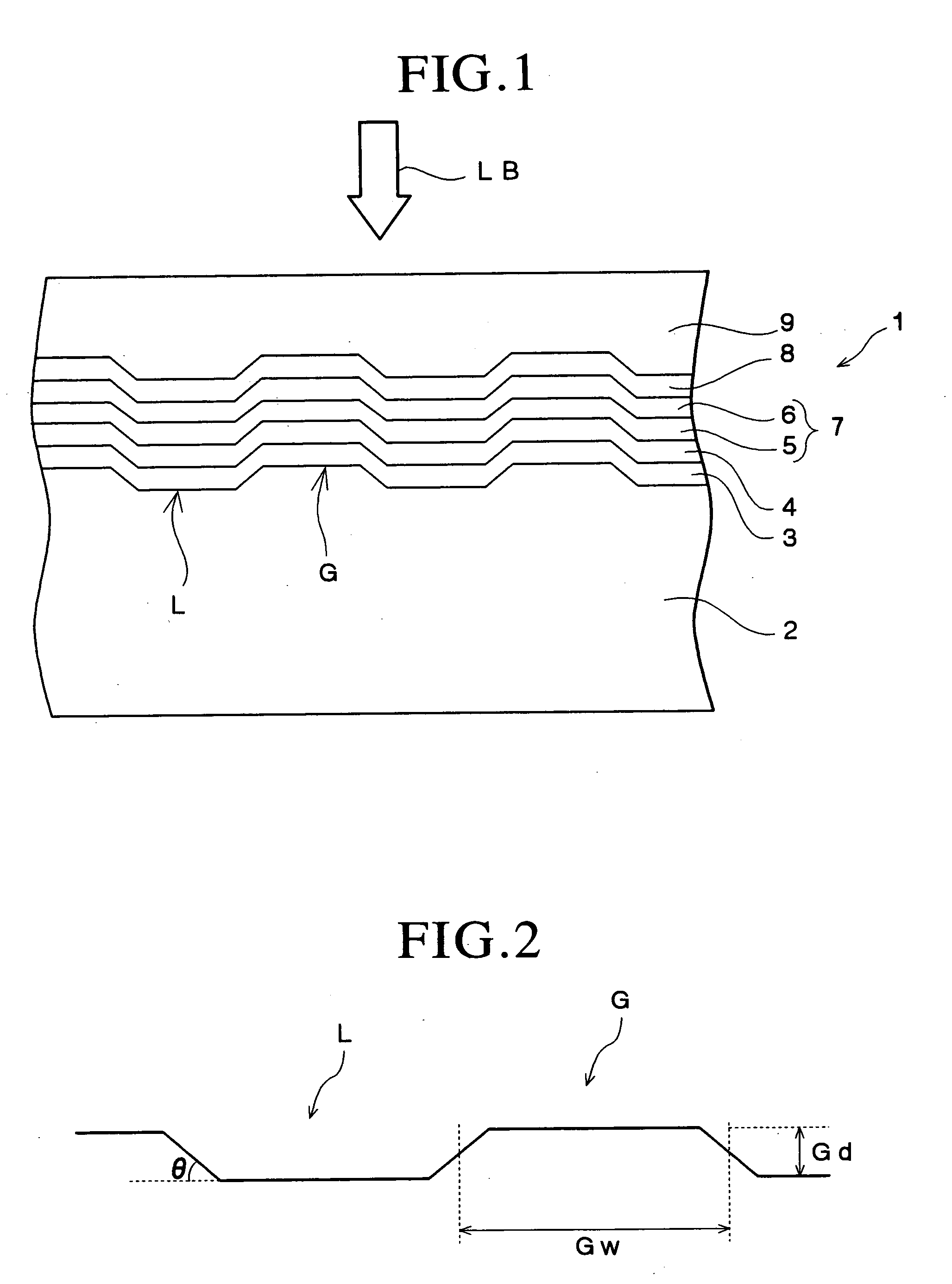
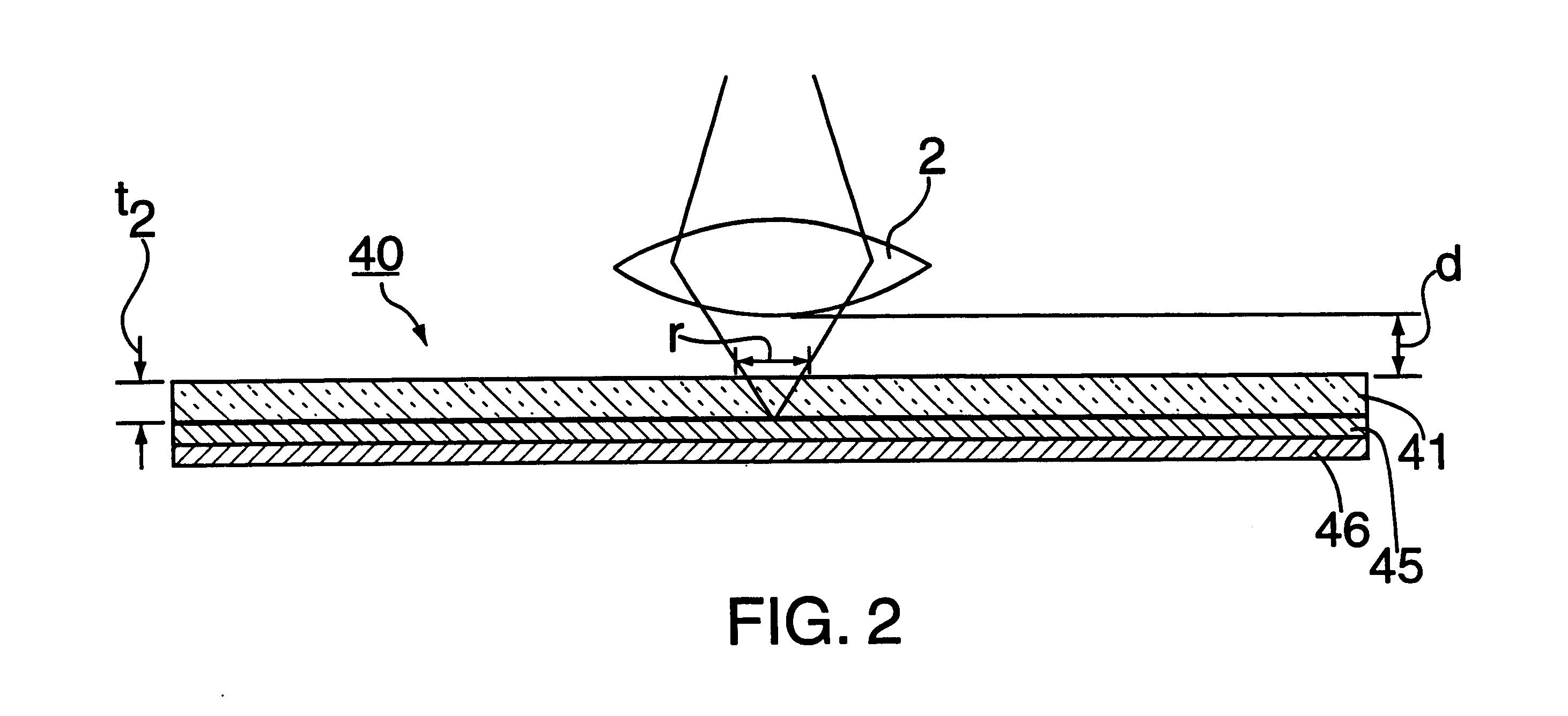
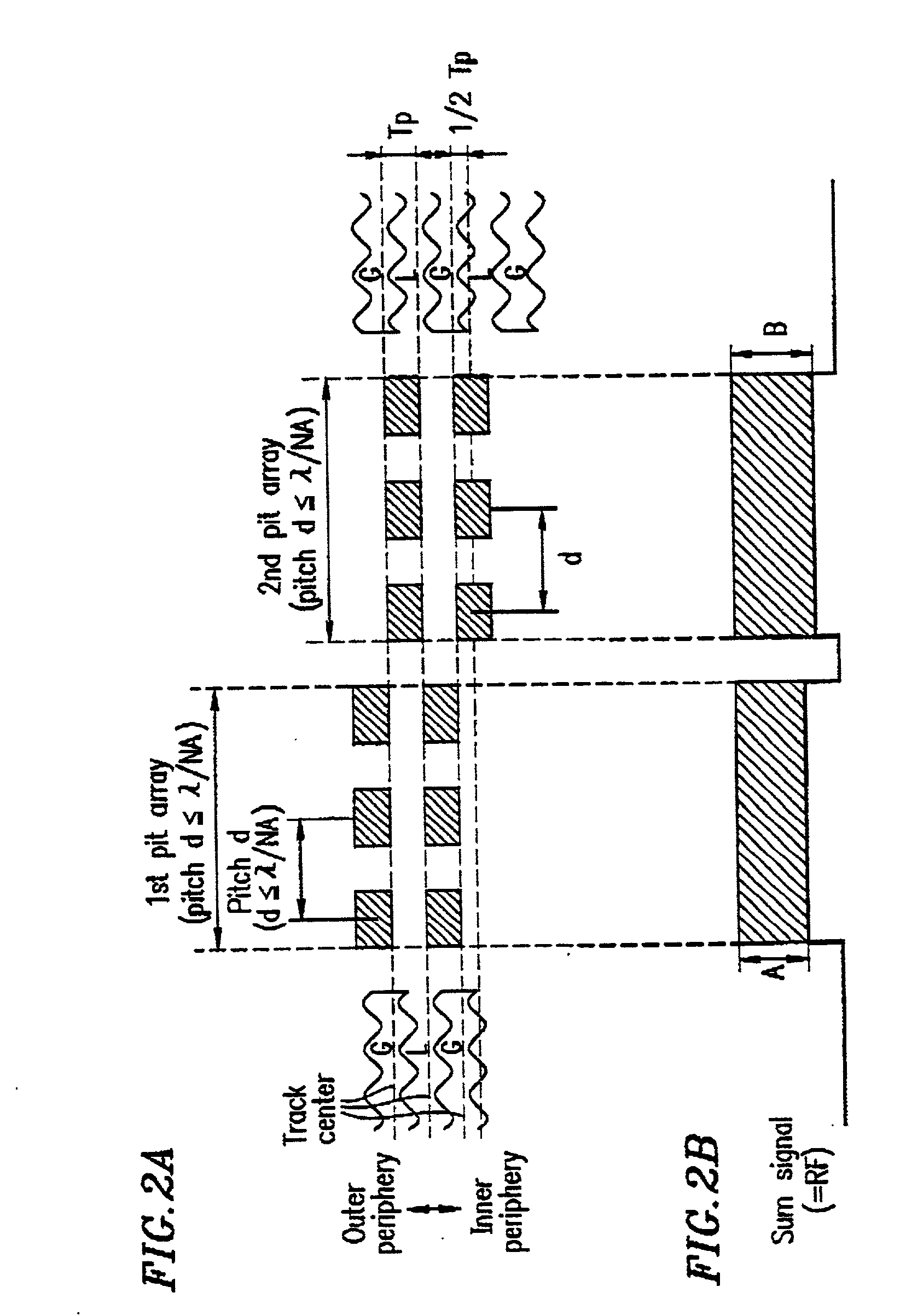
An information recording medium 1 at least comprises a substrate 13 having a microscopic pattern 20, which is constituted by a shape of continuous substance of approximately parallel grooves formed with a groove section G and a land section L alternately, a recording layer 12 formed on the microscopic pattern 20 and a light transmission layer 11 formed on the recording layer. The microscopic pattern 20 is formed so as to satisfy a relation of P<λ / NA and a thickness of the light transmission layer 11 is within a range of 0.07 to 0.12 mm, wherein P is a pitch of the groove section G or the land section L, λ is a wavelength of reproducing light beam and NA is a numerical aperture of an objective lens. Further, there provided an information recording medium, which is improved in cross erase and recorded in high density, and a reproducing apparatus and a recording apparatus for the information recording medium.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
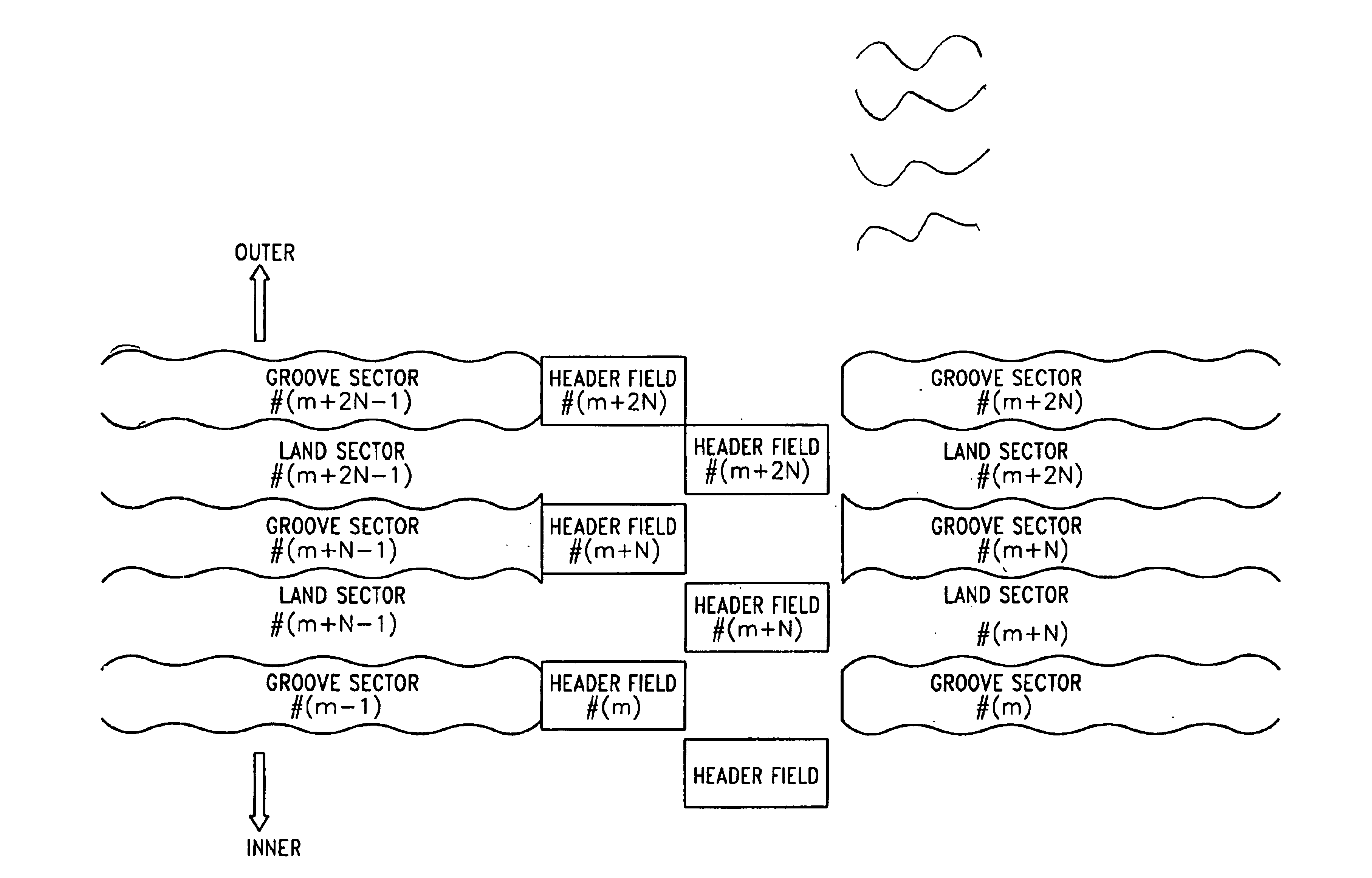
Method and apparatus for improved seek performance and stability in a header-included land/groove optical disc
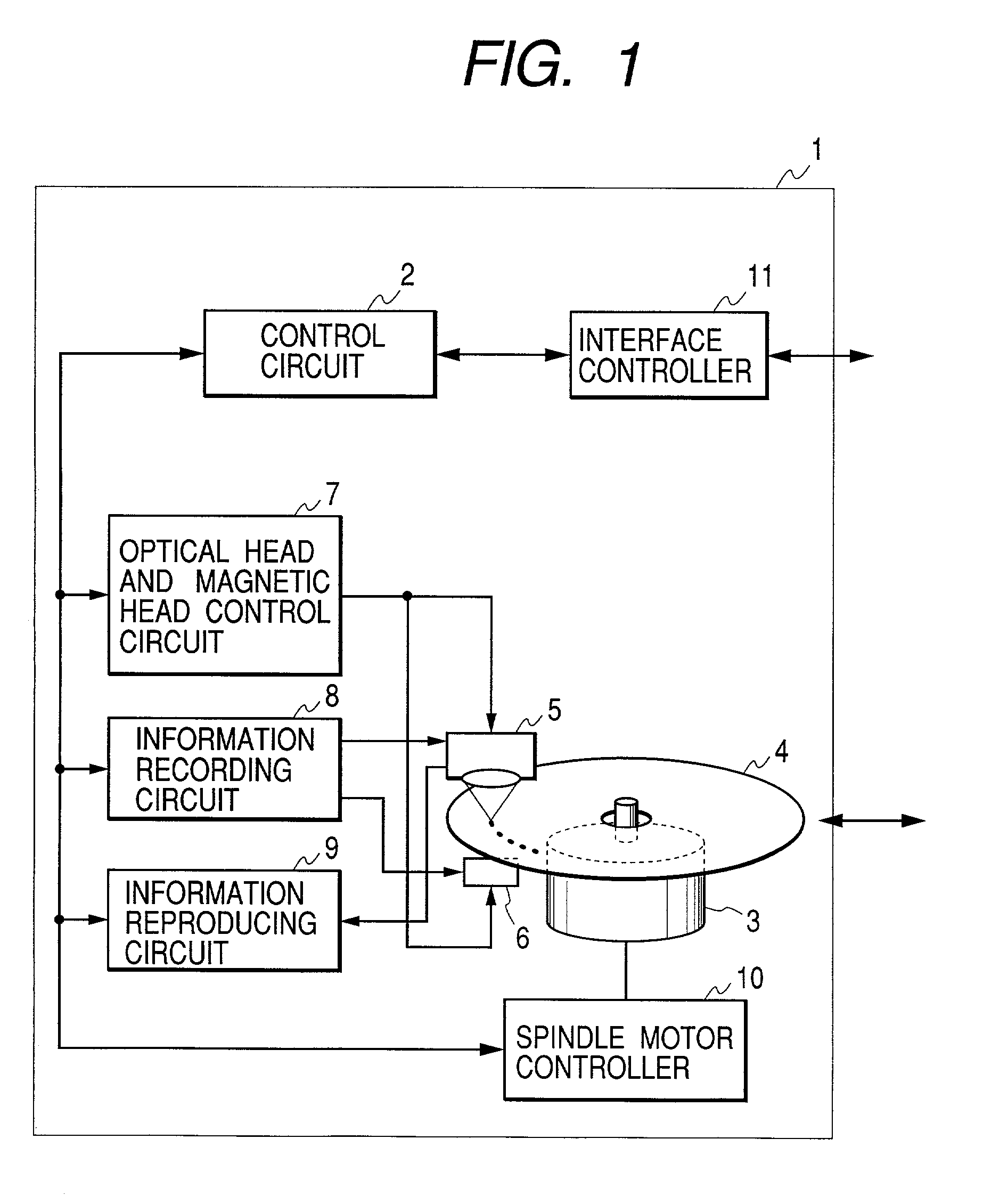
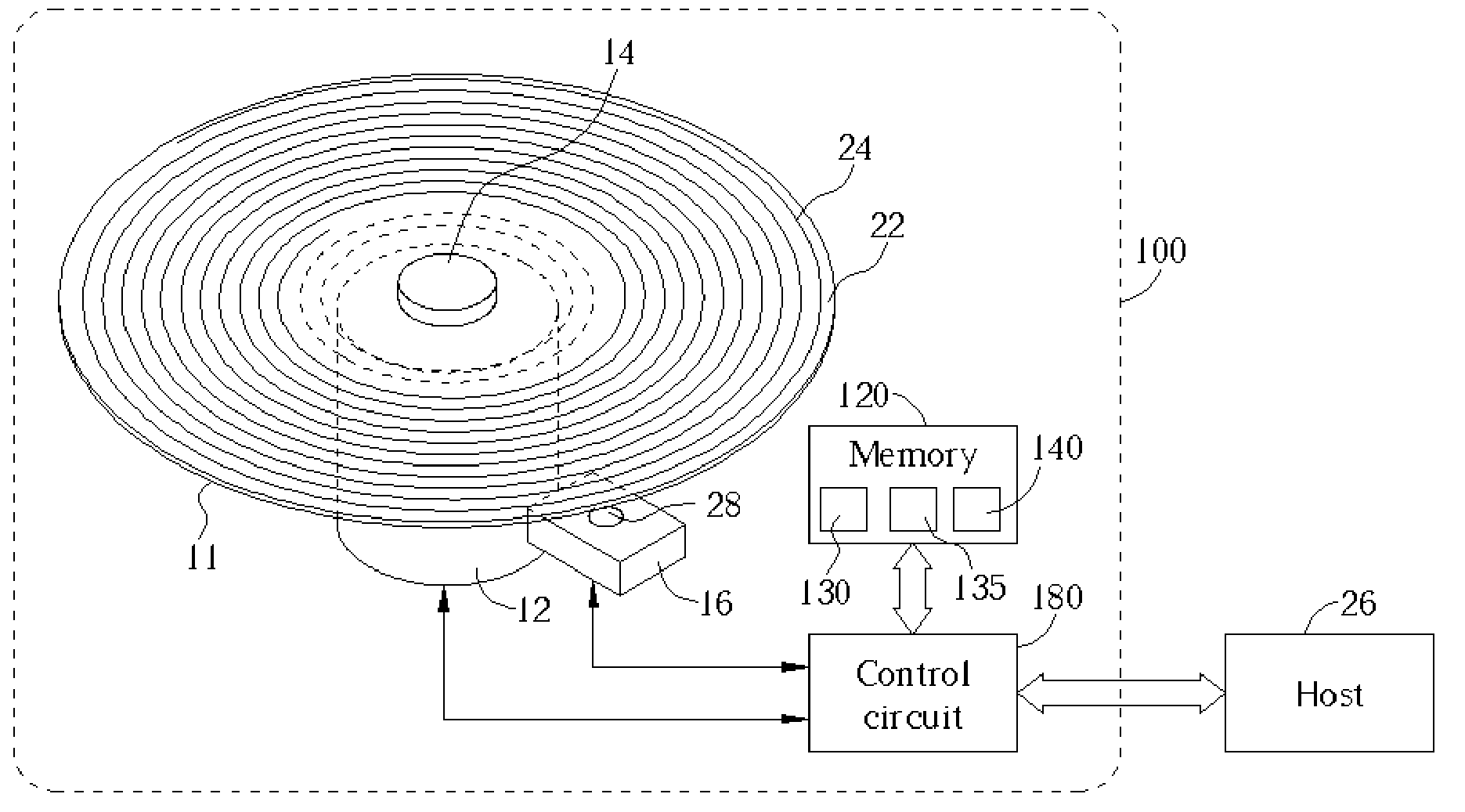
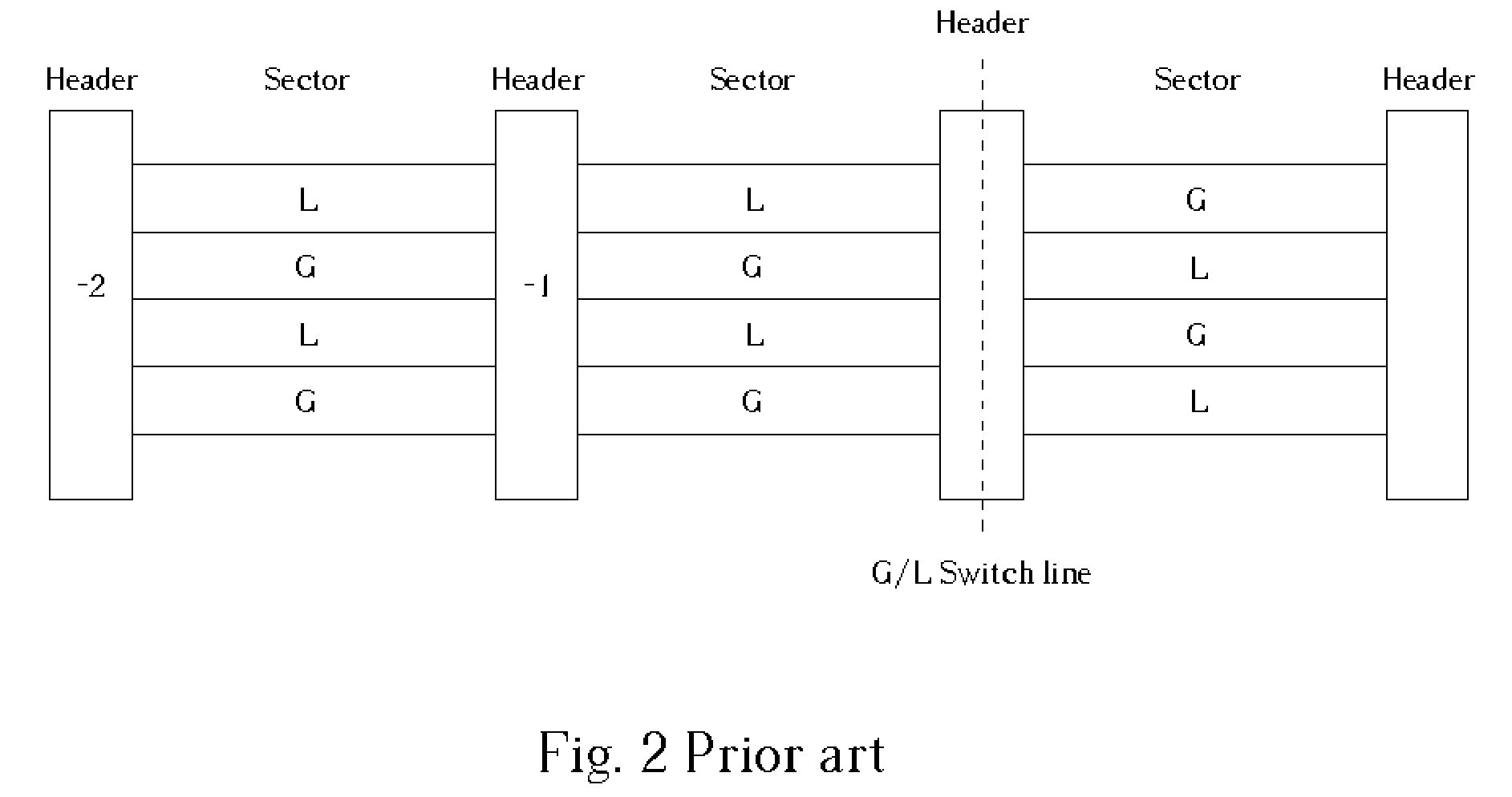
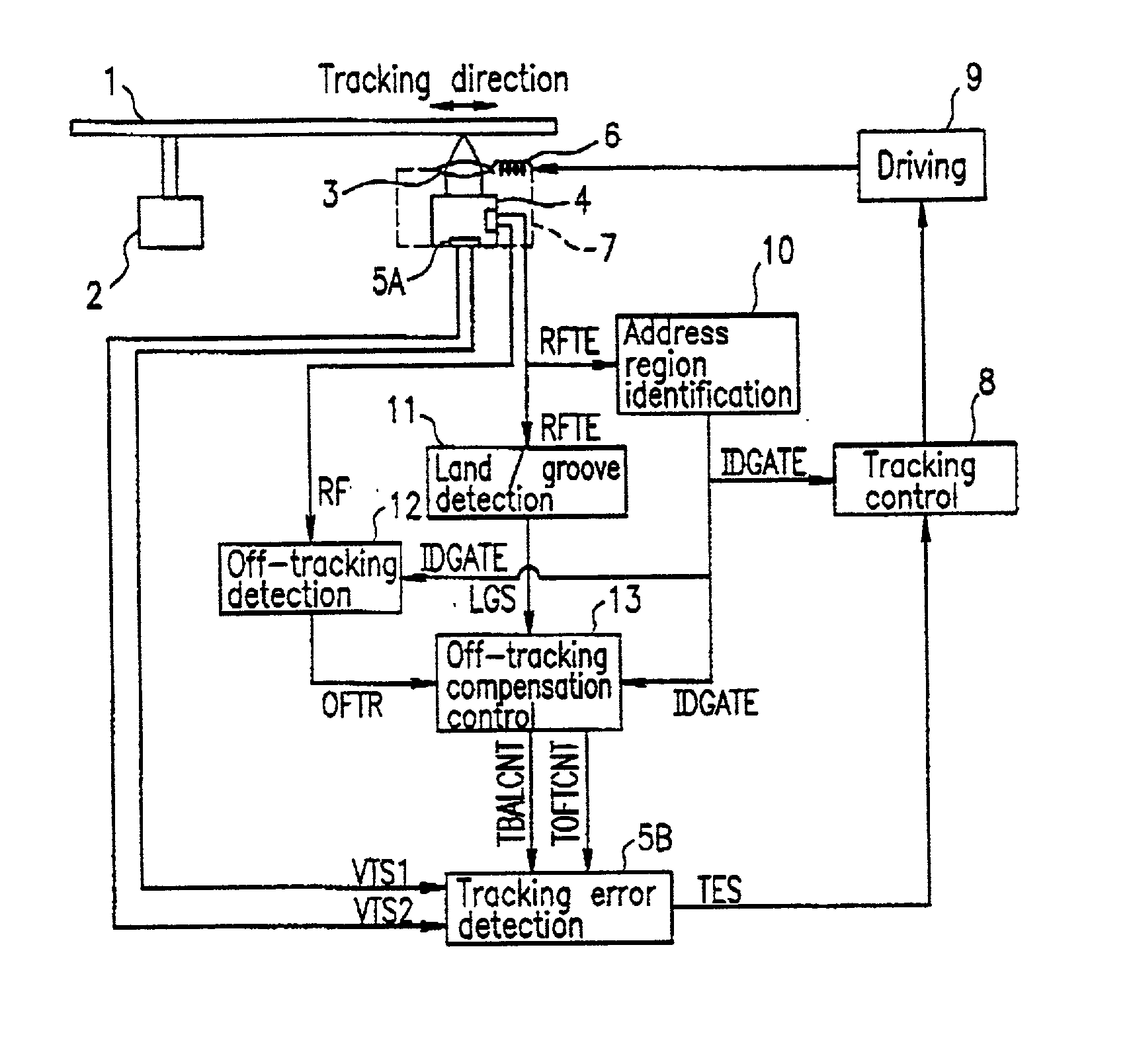
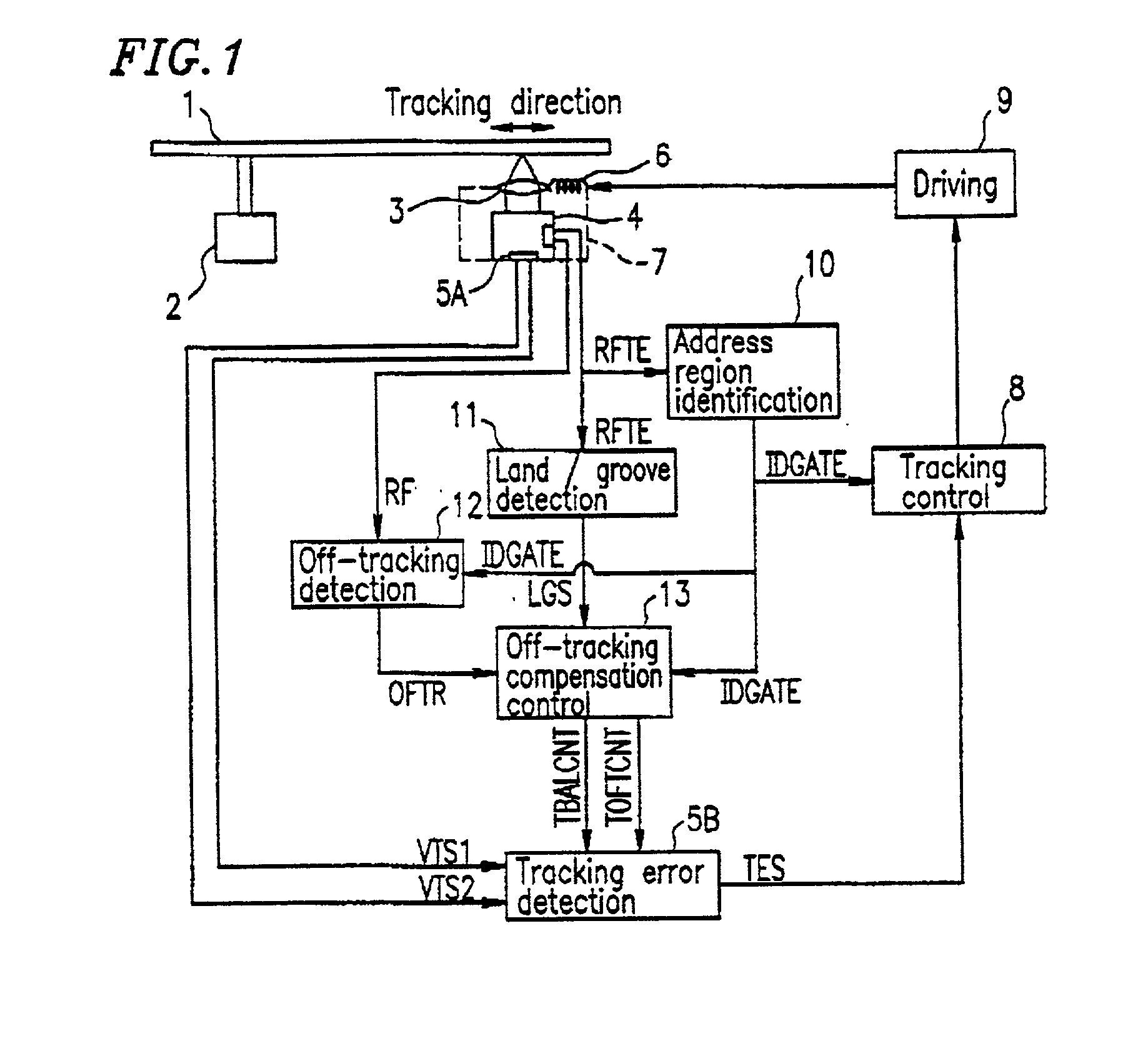
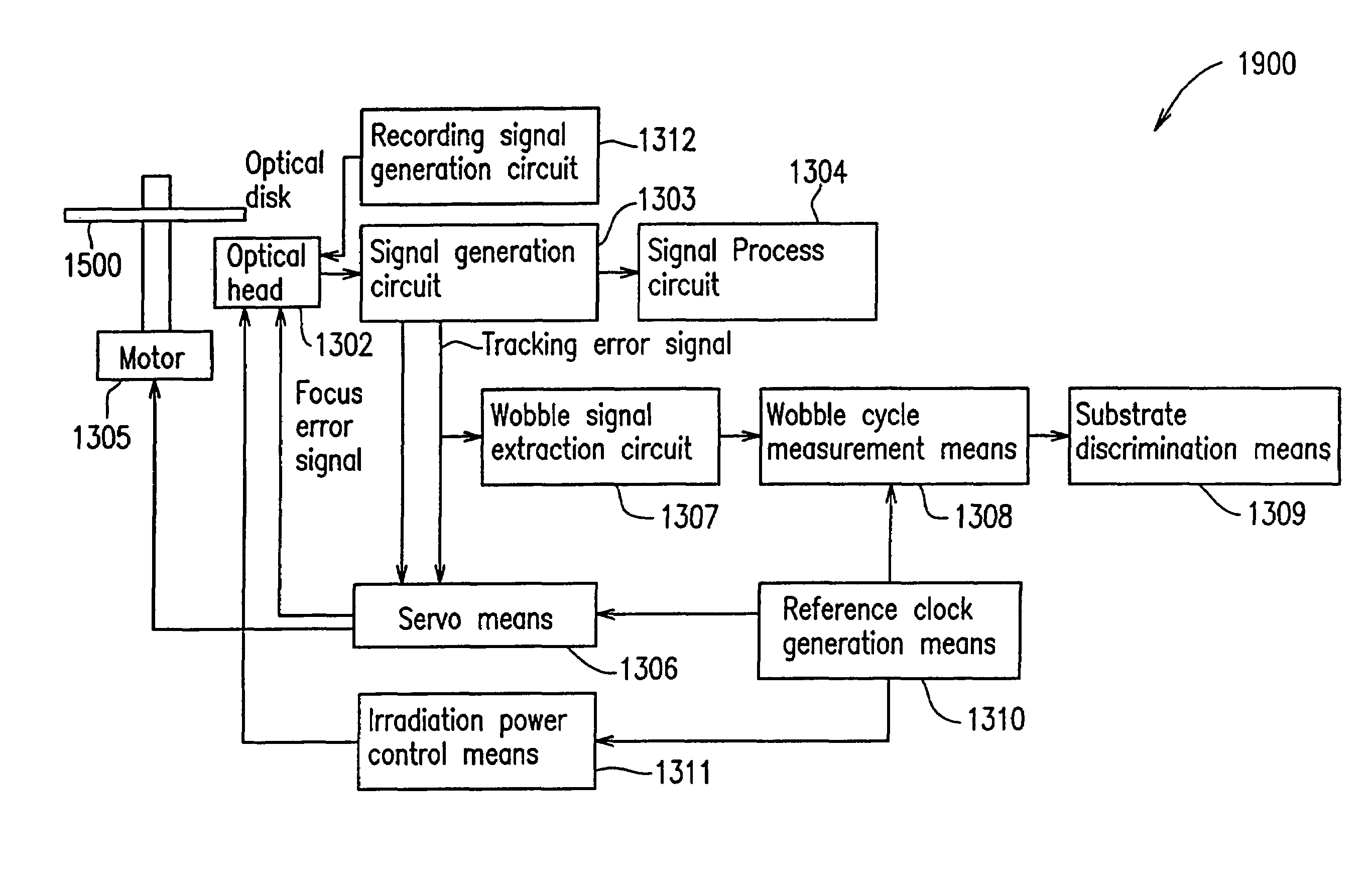
InactiveUS20050157603A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityRecord information storageGroove/land recordingEngineeringControl circuit
An optical disc drive utilized for transferring data to and / or from a header-included land / groove optical disc includes a motor, a spindle, a focusing lens, a laser, a pickup head, a memory, and a control circuit. A header position signal is utilized as a mask to eliminate false track readings produced by passing headers in a track count signal, improving track count and allowing more precise control over the accelerative and braking radial forces applied to the pickup head during a jump. Additionally, the memory includes computer code to delay initiating and / or ending a jump when passing headers may interfere with normal seek operations and may prevent some jumps in the immediate vicinity of an upcoming G / L Switch Line.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Optical recording disk
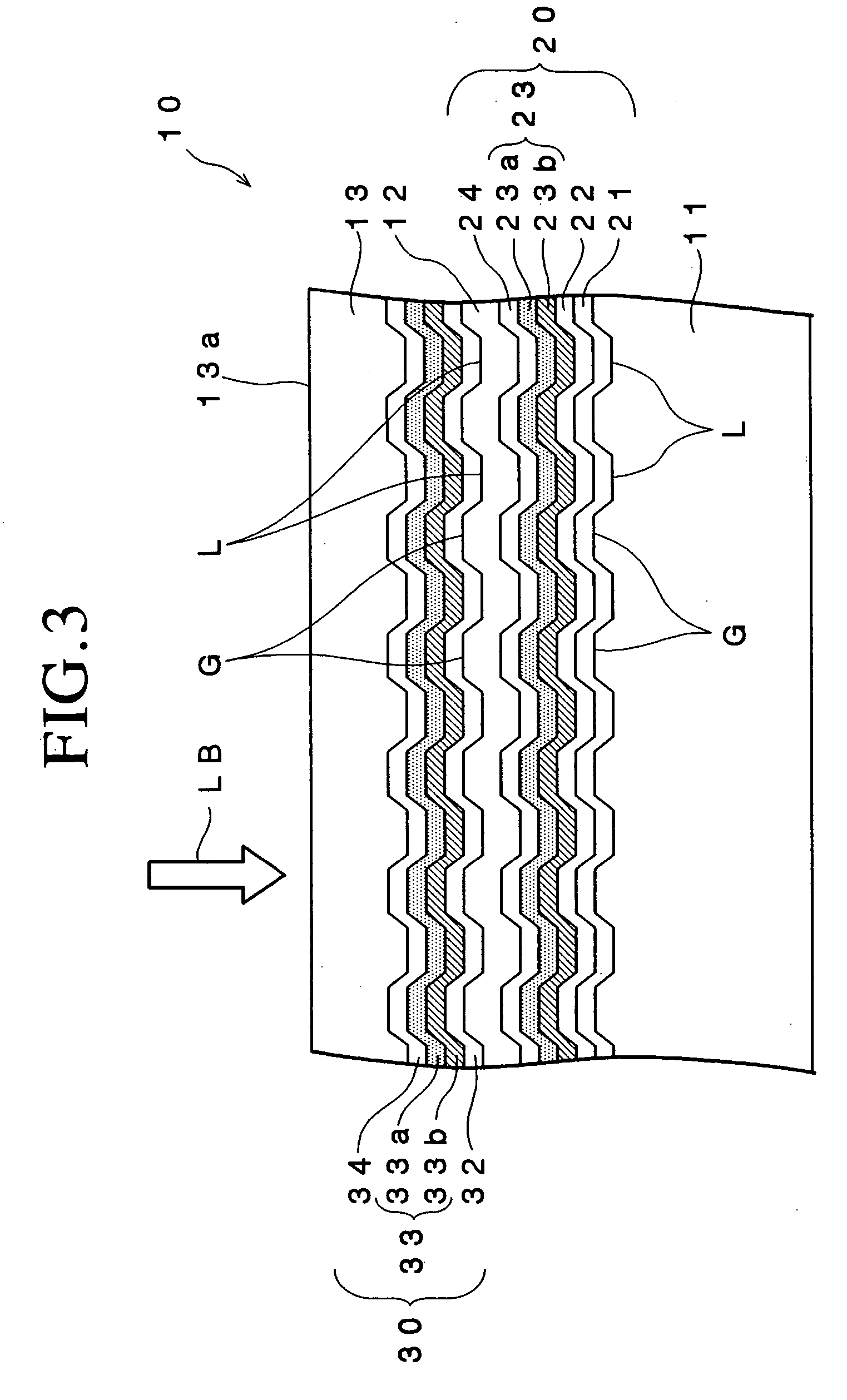
InactiveUS20040202097A1Maintain standardMechanical record carriersRecord information storagePush pullOptical recording
An optical recording disk includes a support substrate, grooves and lands alternately formed on one major surface of the support substrate, an optical functioning layer formed on the one major surface of the support substrate on which the grooves and the lands are formed and including a recording layer and a light transmission layer formed on the optical functioning layer, the grooves and the lands being formed so that the depth Gd of each of the grooves is equal to or larger than 15 nm and equal to or smaller than 25 nm and the half width Gw is equal to or larger than 150 nm and is equal to or smaller than 230 nm, and the recording layer including a first recording film containing Si as a primary component and a second recording film containing Cu as a primary component. According to the thus constituted optical recording disk, it is possible to suppress jitter of a signal obtained by reading data within a predetermined range, thereby suppressing reading errors, and it is possible to maintain the level of a push-pull signal equal to or higher than a predetermined value, thereby enabling tracking control in a desired manner.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical disk, optical disk device, and method of reproducing information on optical disk
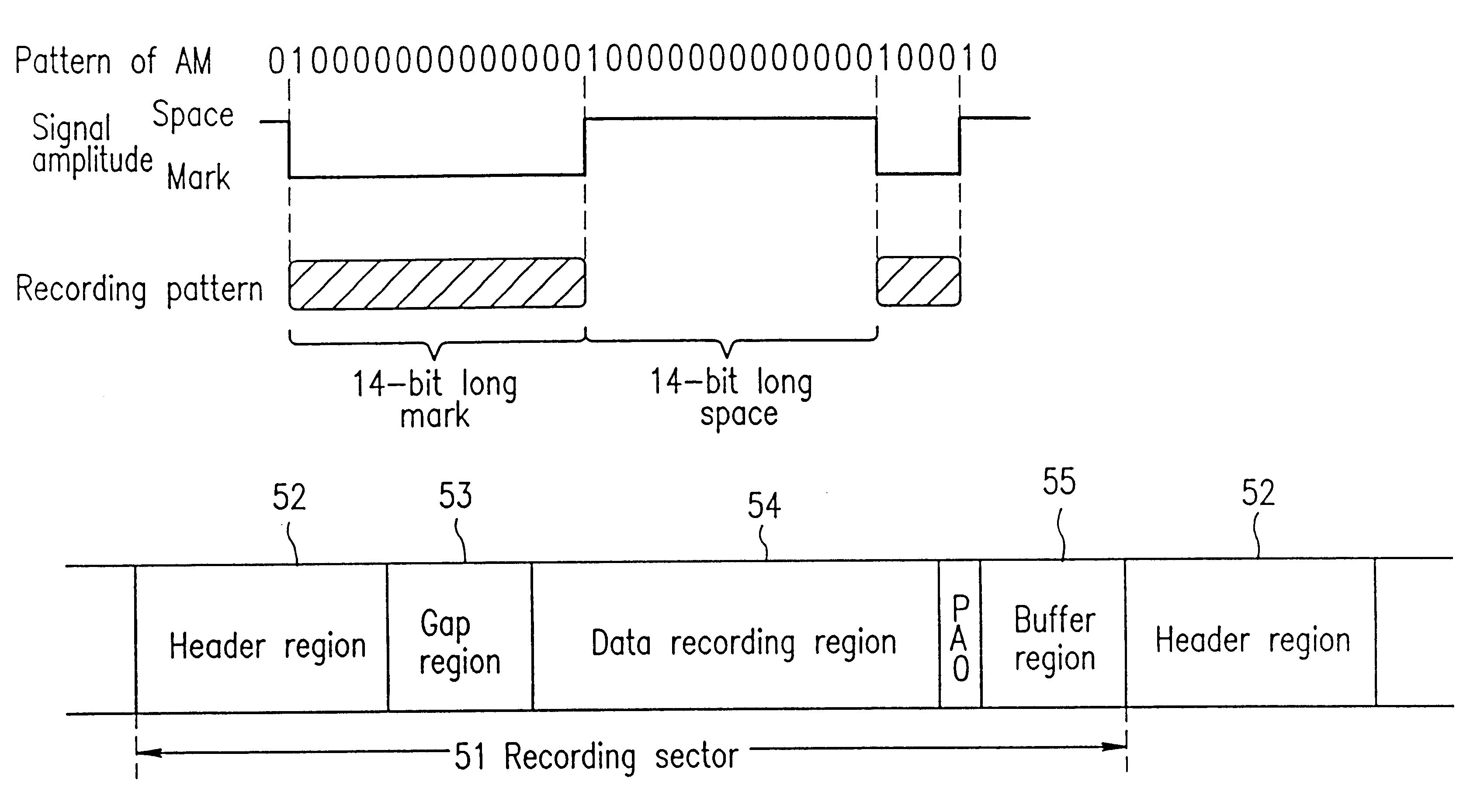
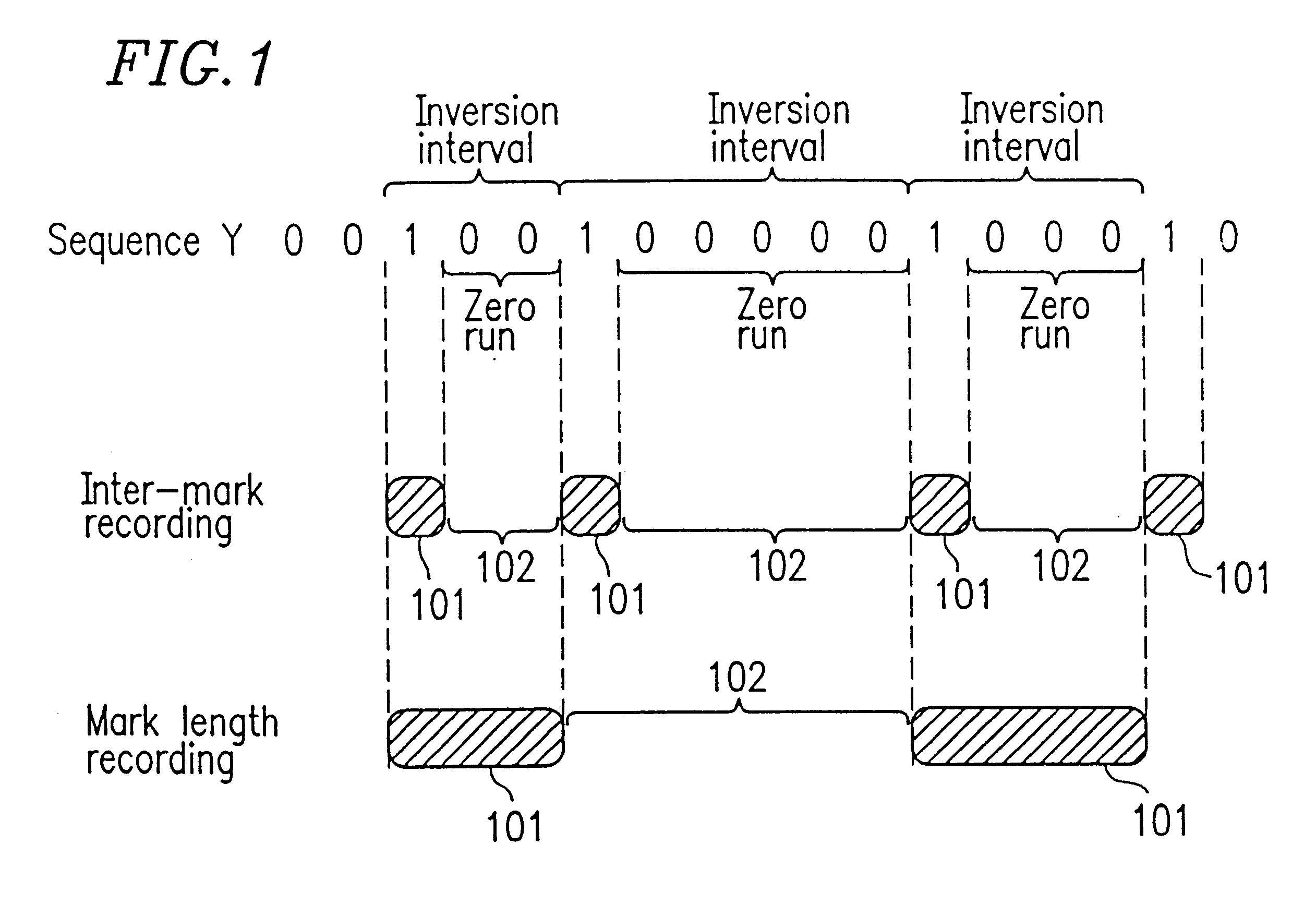
The present invention is aimed at providing an optical disk, an optical disk device, and an optical disk reproduction method, for allowing for stable and efficient reading of address information. The optical disk includes a plurality of tracks each divided into a plurality of recording sectors. Each of the recording sectors includes a header region. The header region includes address information for identifying the position of the corresponding recording sector and address synchronous information for identifying the recording position of the address information for bit synchronization. The address information has been modulated using a run length limit code of a maximum inversion interval of Tmax bits (Tmax is a natural number), and the address synchronous information includes two patterns of which inversion interval is (Tmax+3) bits or more, so that the reproduced signal of the address synchronous information is distinguished from the reproduced signal of other information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical disk having a protective layer specified thickness relative to the NA of an objective lens and the wavelength of light source
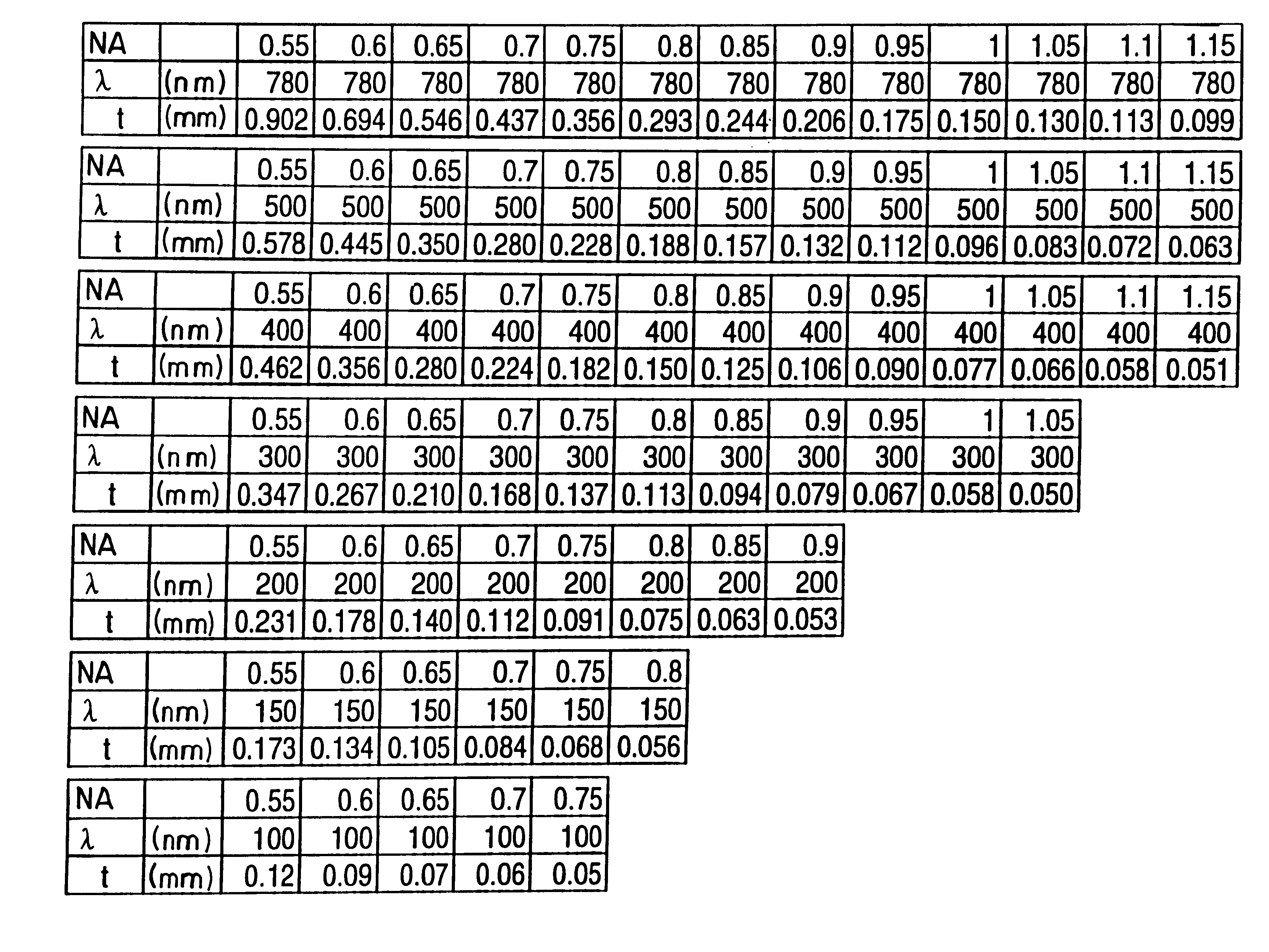
InactiveUS6262948B1Higher-capacity recording and reproductionEasy to trackRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansLight beamLength wave
An optical disc system uses an optical disc with a light-transmitting cover and an objective lens for bundling or focusing a light beam on a recording layer of the optical disc in order to perform recording and / or reproducing of information. The thickness of the light-transmitting cover falls within the range of 0.05 mm to 0.6 mm, the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens is set to fall within the range of 0.55 to 1.10, and the wavelength of the light beam is selected to be between 100 nm to 780 nm.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information recording medium and information recording/ reproducing device and method
InactiveUS20050122890A1Increase recording capacityIncrease capacityRecord information storageDigital recordingEngineeringRecording media
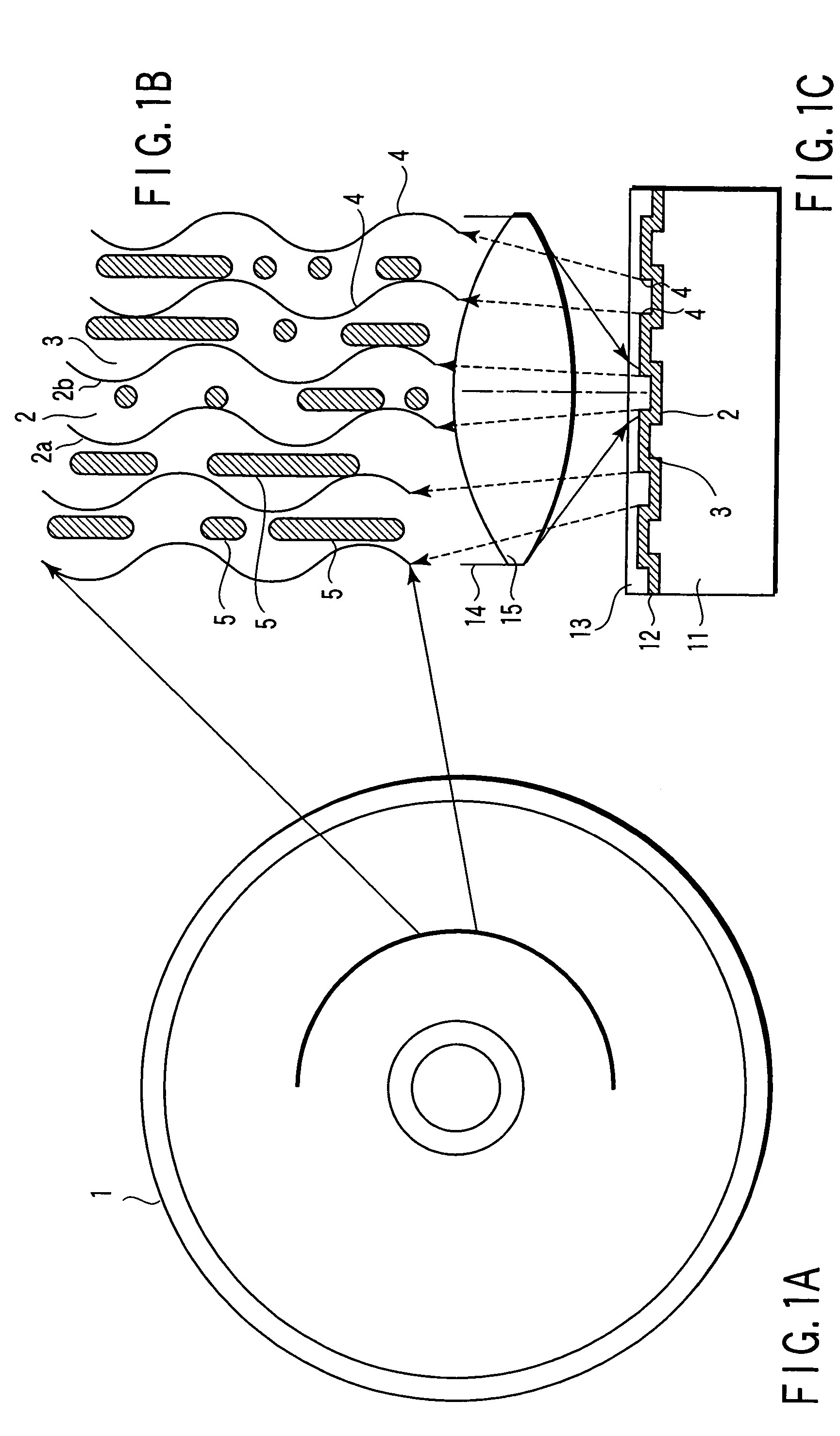
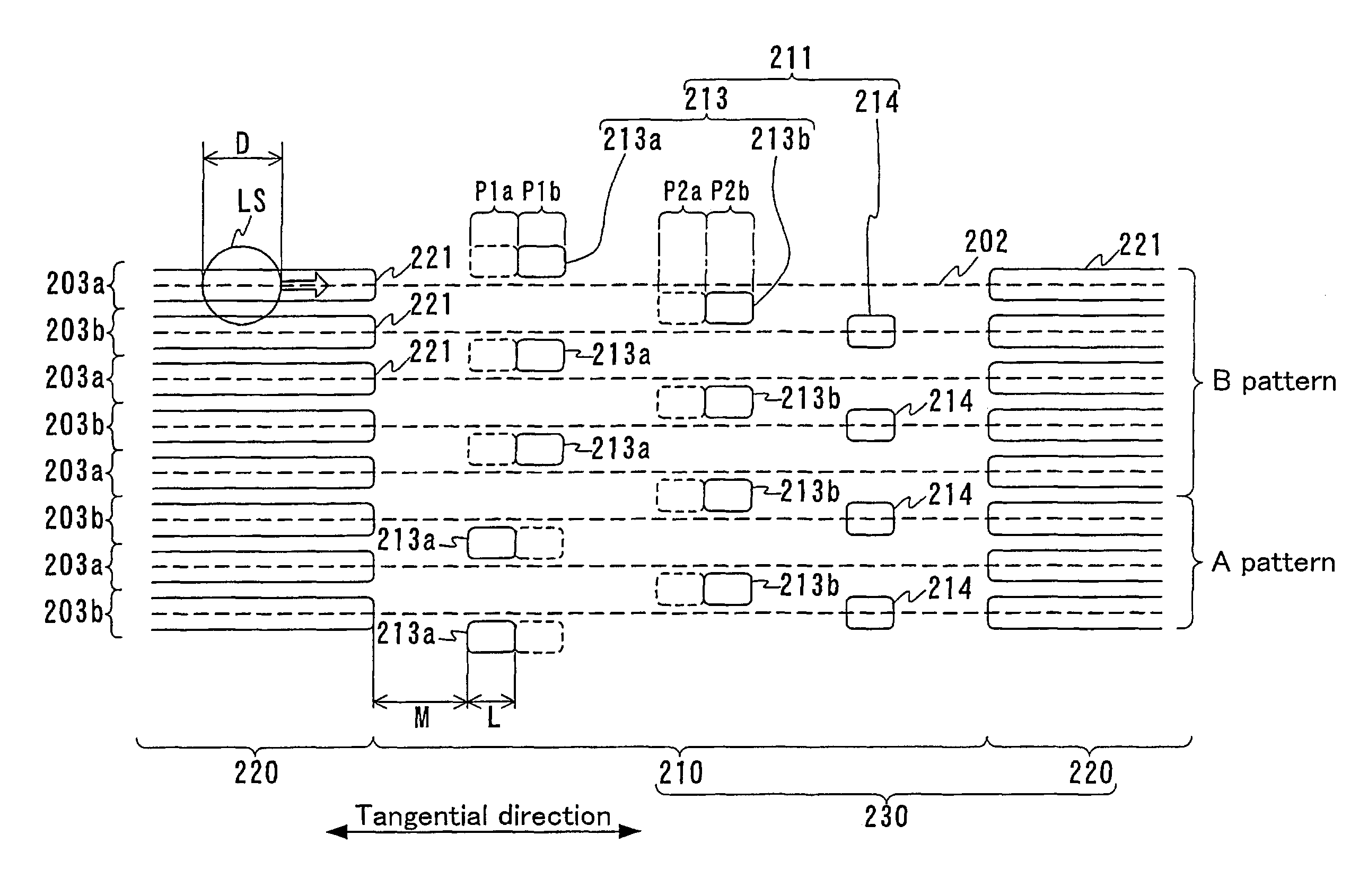
An information storage medium (1) has tracks in which information is recorded. The tracks are formed as a groove section (2) and a land section (3). The groove section (2) has a synchronous structure in which wobbles (2a) and (2b) formed on both walls of the groove section (2) are not displaced from each other in the circumferential direction of the medium, and the land section (3) has an asynchronous structure in which wobbles formed on both sides of the land section (3) are displaced from each other. A good signal is reproduced from each of the groove and land sections.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of fabricating sub-micron hemispherical and hemicylidrical structures from non-spherically shaped templates
InactiveUS6969472B2Mechanical working/deformationDecorative surface effectsCrystallographyMicro structure
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Method of recording and reproducing an optical recording medium
InactiveUS6963520B1Combination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsMaximum levelHigh density
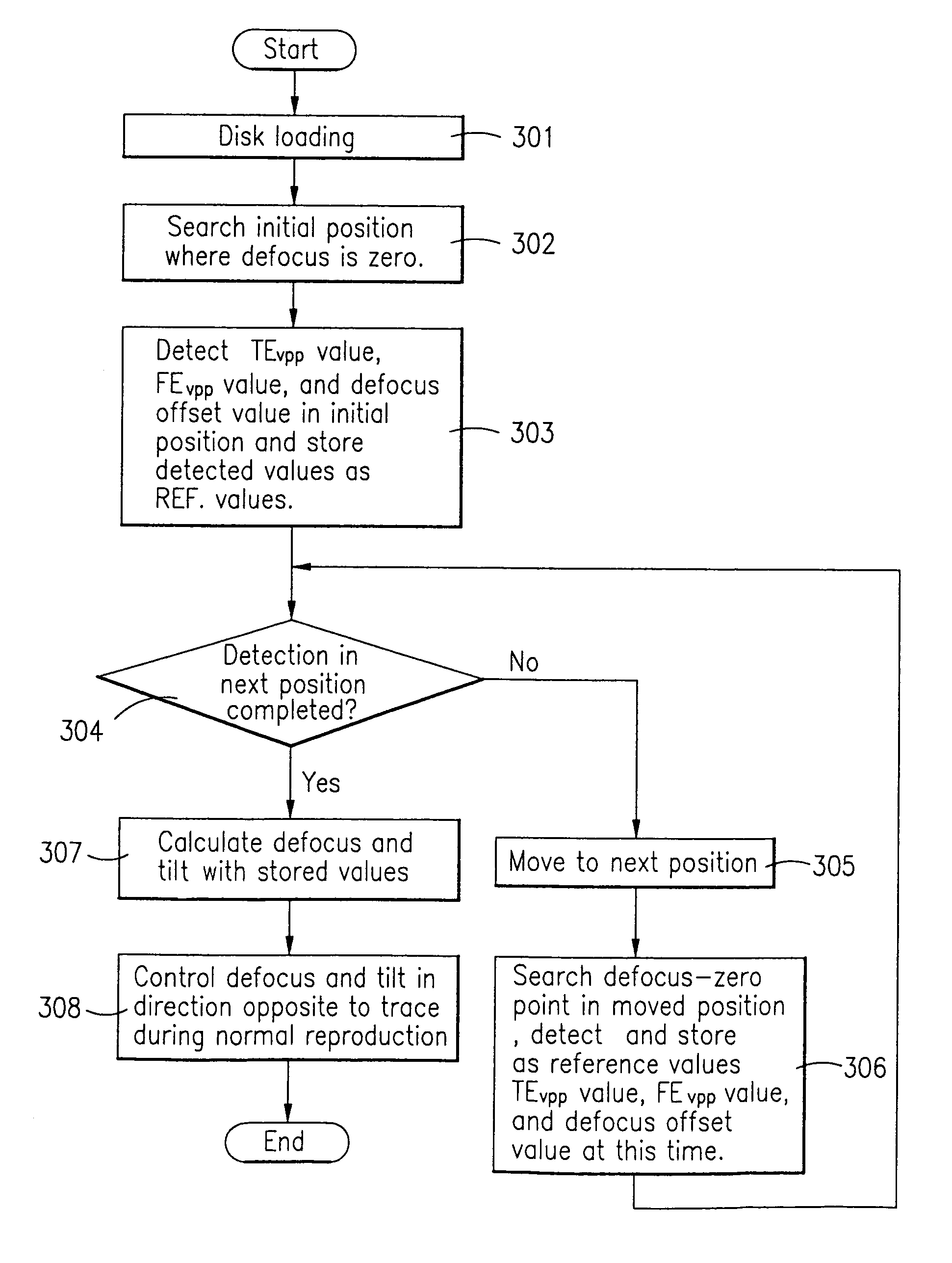
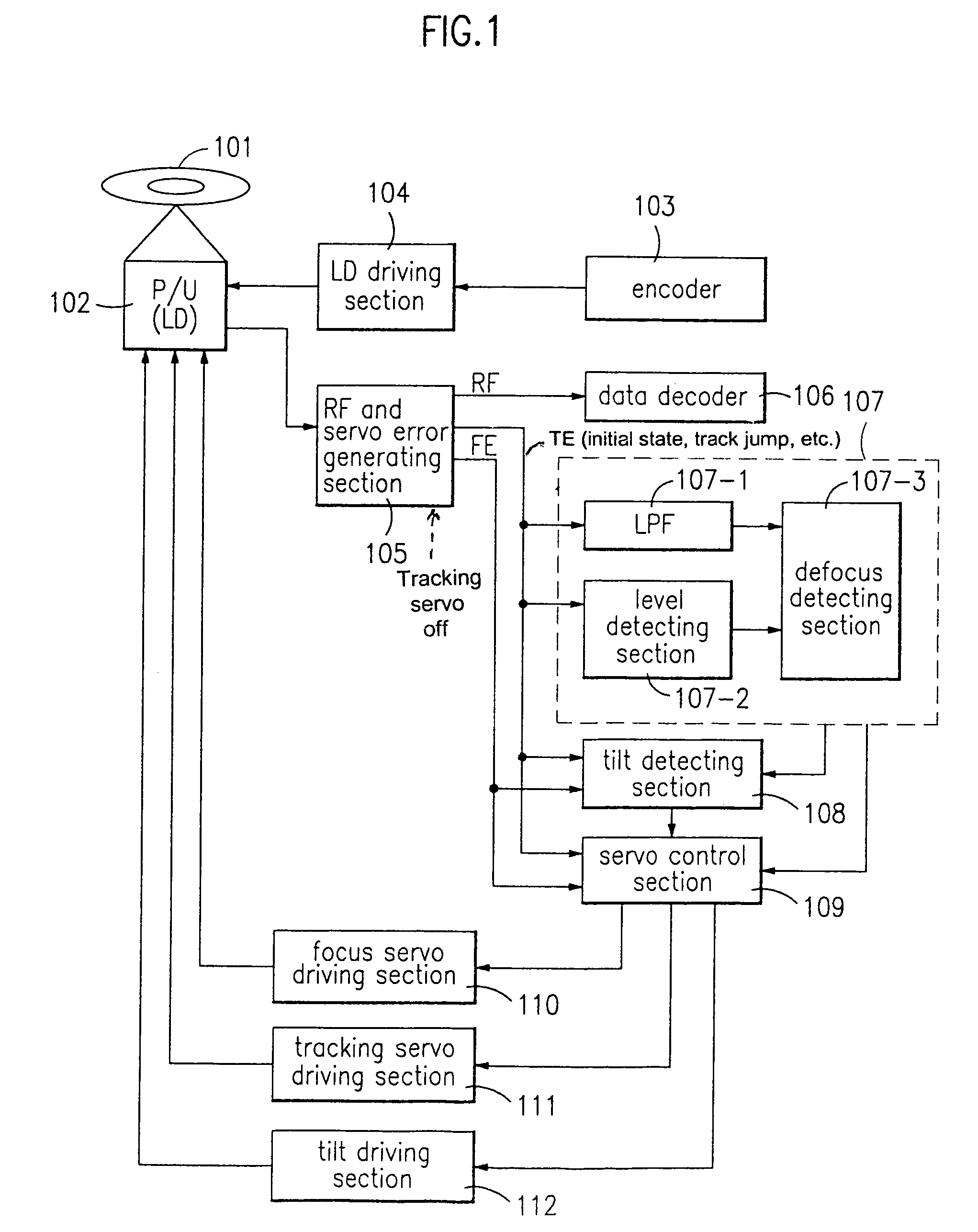
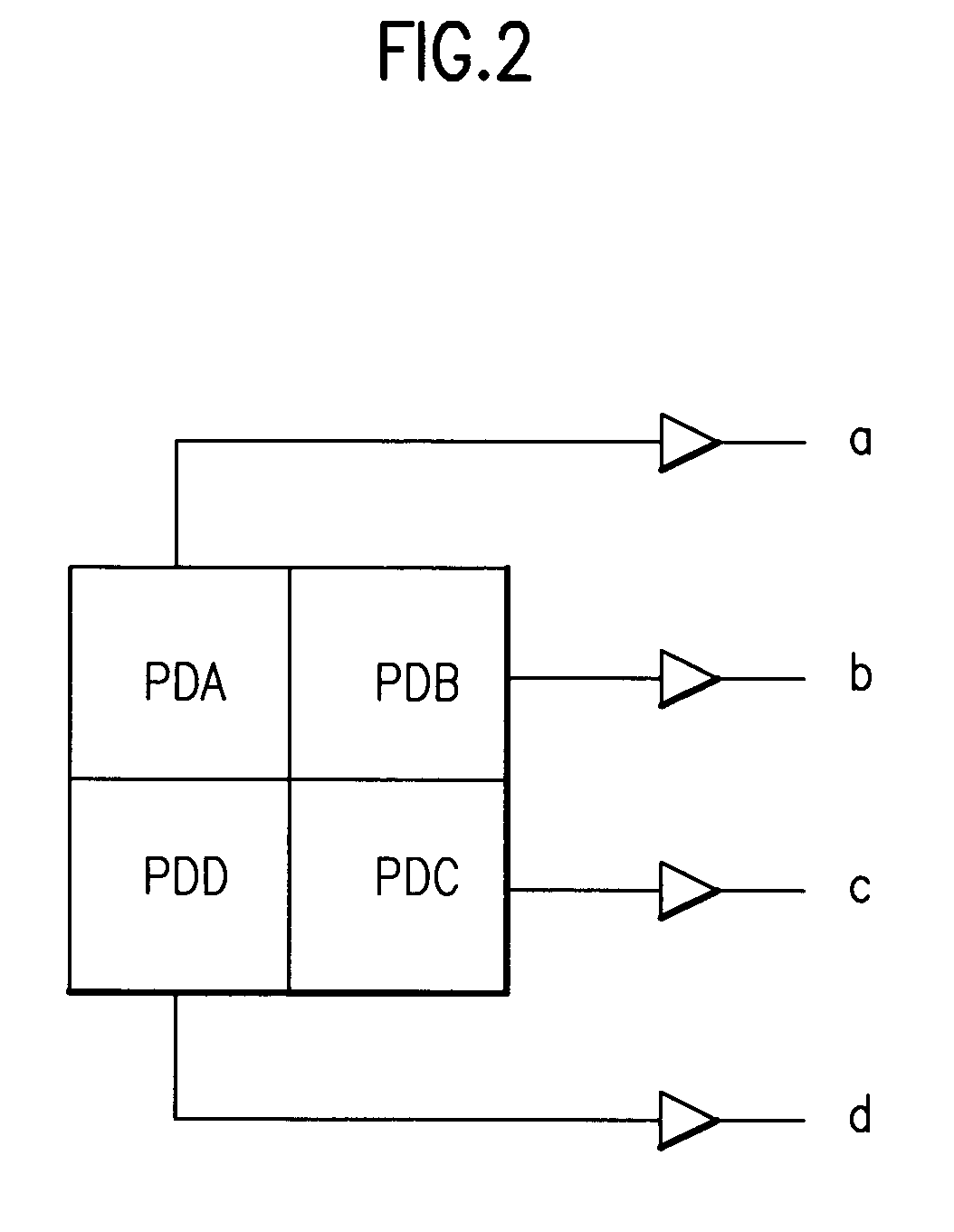
A method of recording and reproducing an optical recording medium which detects a defocus and a tilt of the optical recording medium and compensates the detected defocus and tilt in a high-density optical recording medium. In a free running state in which only a focus servo is turned on, the amount of defocus offset that corresponds to a maximum level of a tracking error signal is detected in a plurality of positions on inner and outer peripheries of a disc, and a tilt-zero in the respective position is detected and stored, so that a tilt servo and a focus servo are performed with the value stored in the corresponding position during an actual recording / reproduction. The method can prevent the deterioration of quality of data due the defocus during recording / reproduction, enabling real time recording by quickly stabilizing the focus servo, and stable operation of the system. Also, the method can follow corresponding tracks with a rapid stabilization of servo during a search or seek, and detect and compensate for the tilt stably and accurately in the high-density optical disc. The method can also prevent the deterioration of quality of data and a detrack due to the tilt during recording / reproduction, and thus achieve stable operation of the system.
Owner:DIGITAL CACHE LLC
Optical disc with a rewritable area and a read-only area
InactiveUS6396798B1Avoid crossingRecord information storageGroove/land recordingLeading edgePhysical address
An optical disc having both rewritable area and read-only area is disclosed. The rewritable area has a single spiral pattern of start track land at a leading edge, and a single spiral pattern of end track land at a trailing edge, whereby portions of the physical address area PID deviated approximately Pa / 2 from the track of the rewritable area are being intruded into the start track land and the end track land.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Allocating real time data on a disc like recording medium
InactiveUS20010016114A1More constraintConsume moreTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersTime informationComputer hardware
Method of recording a series of ordered real-time information signals, such as audio / video information, on a disc like recording medium, such as an optically readable disc. The method comprises recording of contiguous sequences of detectable marks, each sequence representing a successive series of information signals of an A / V program, in a distributed manner across the recordable area of the disc like recording medium. Between the recorded sequences, preferably free space remains available for recording contiguous sequences of information signals of another A / V program in a same distributed manner. In an embodiment, a logical address space is divided in successive allocation areas, each allocation area used for subsequently recording a specific sequence of an A / V program.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
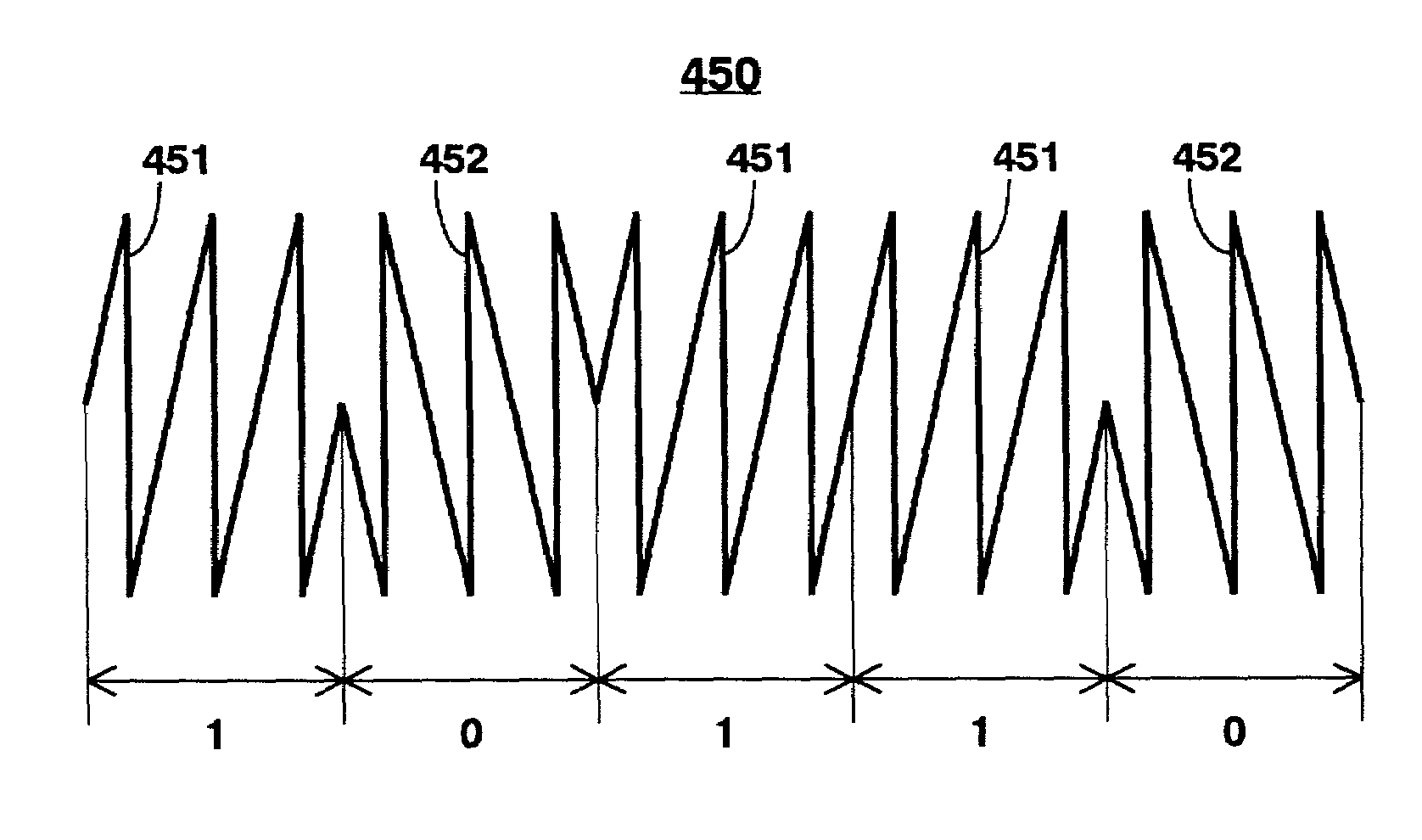
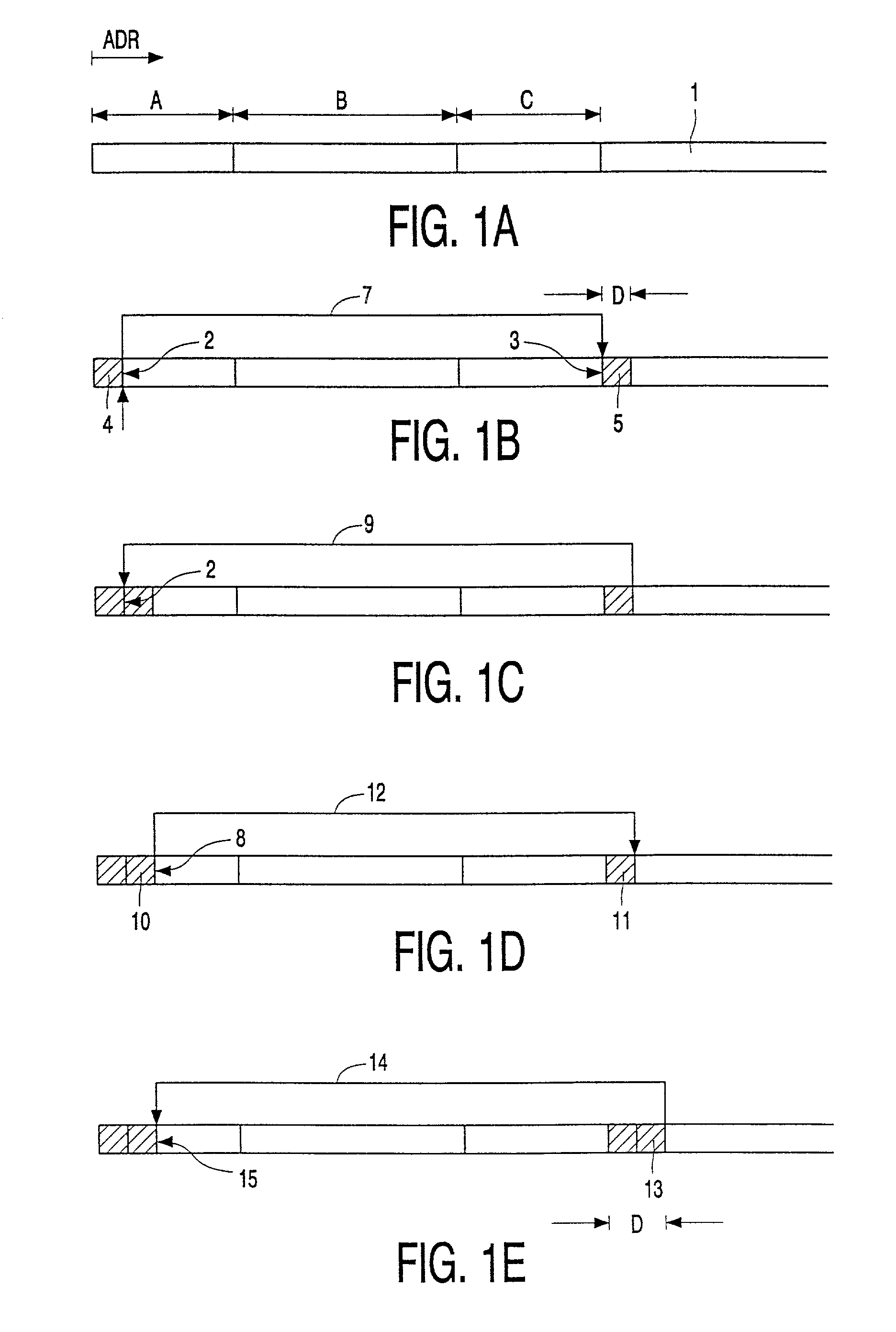
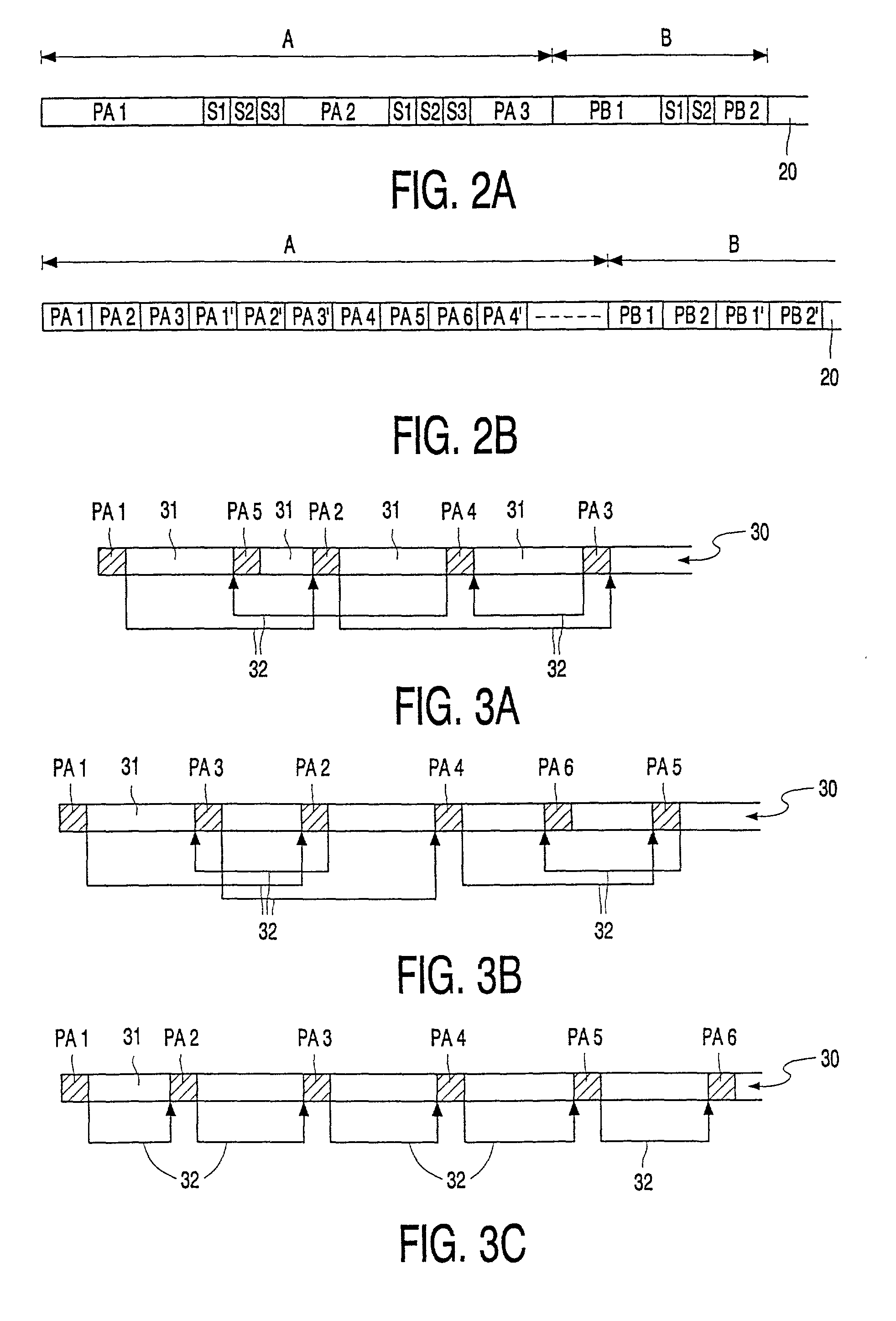
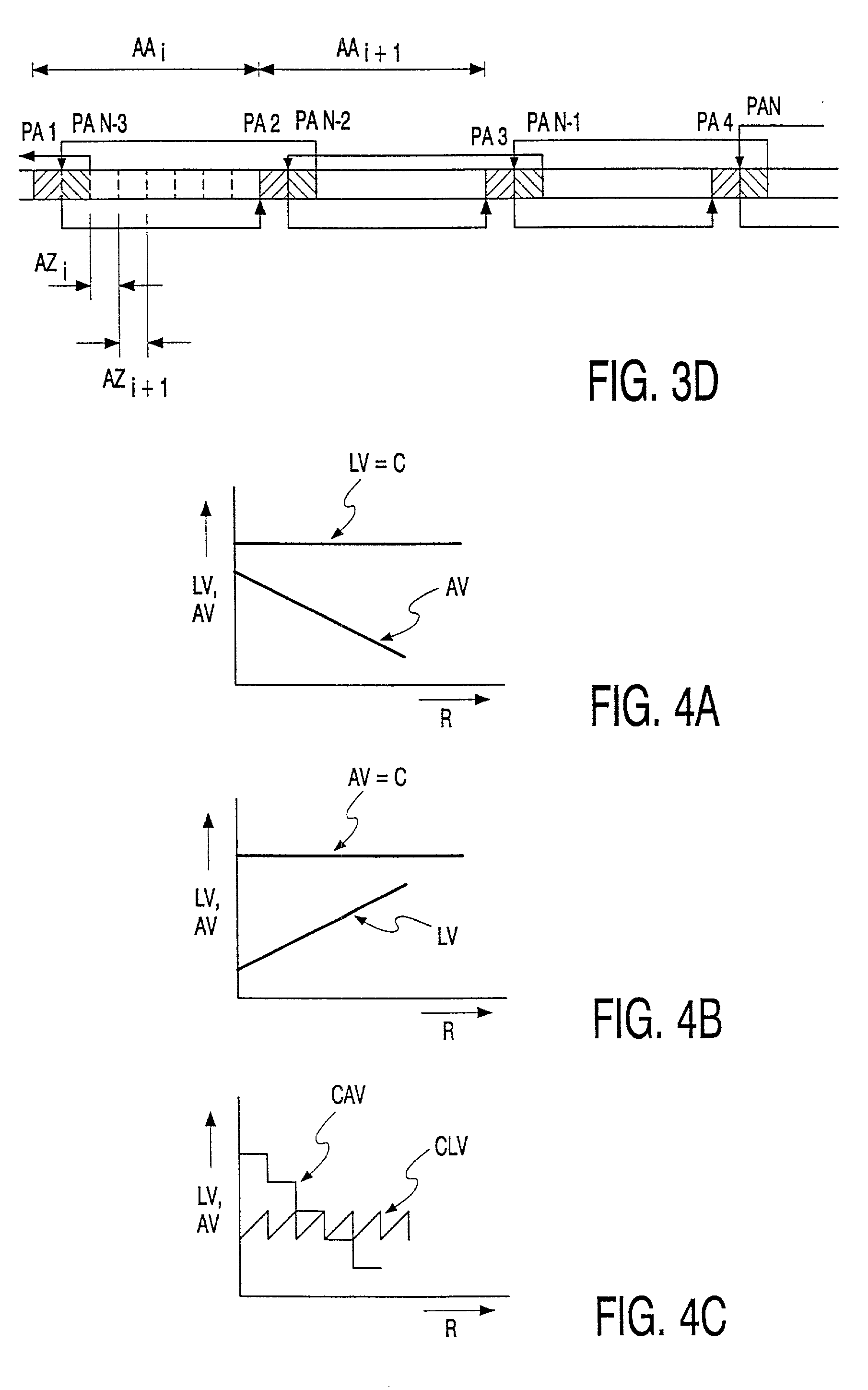
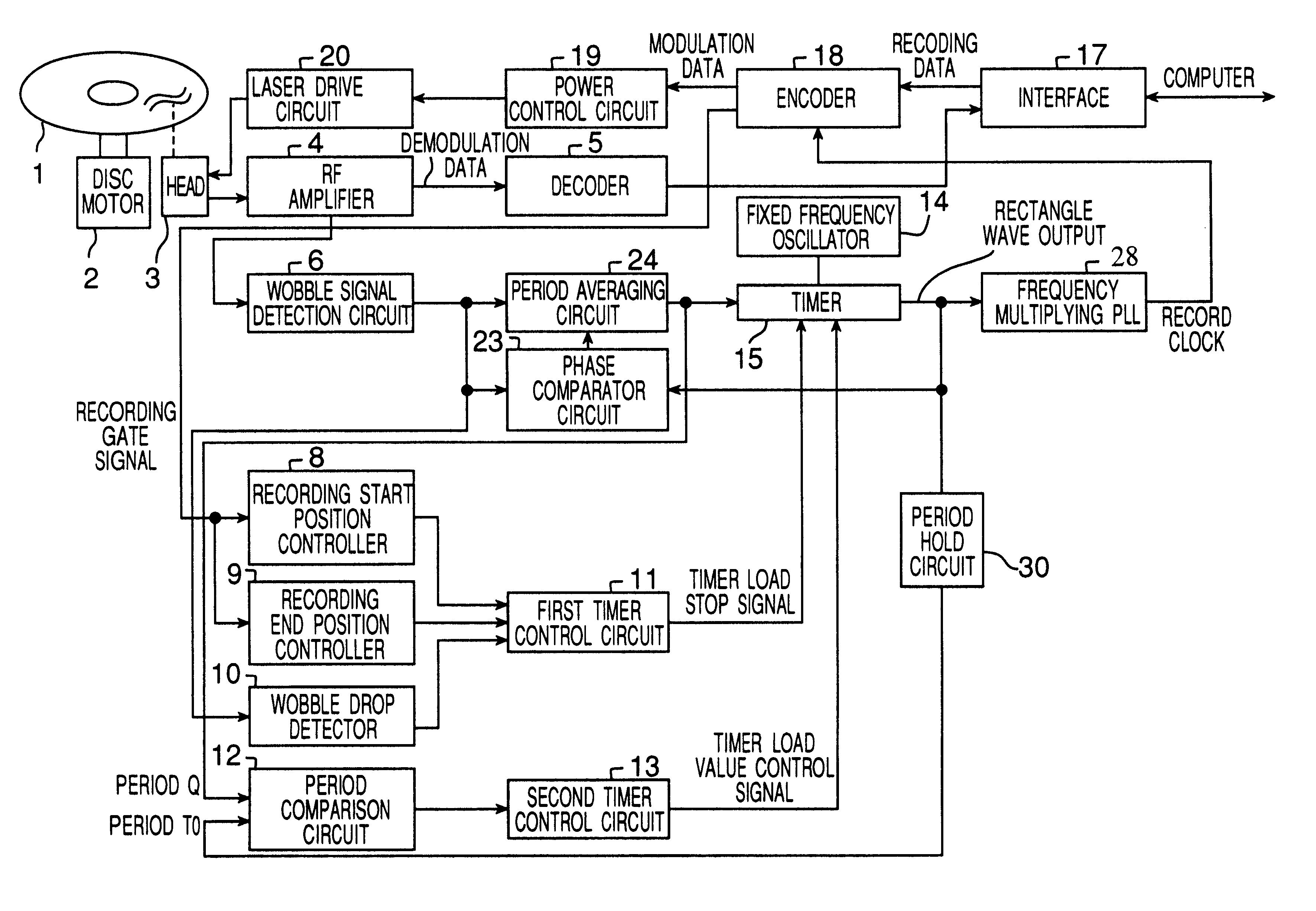
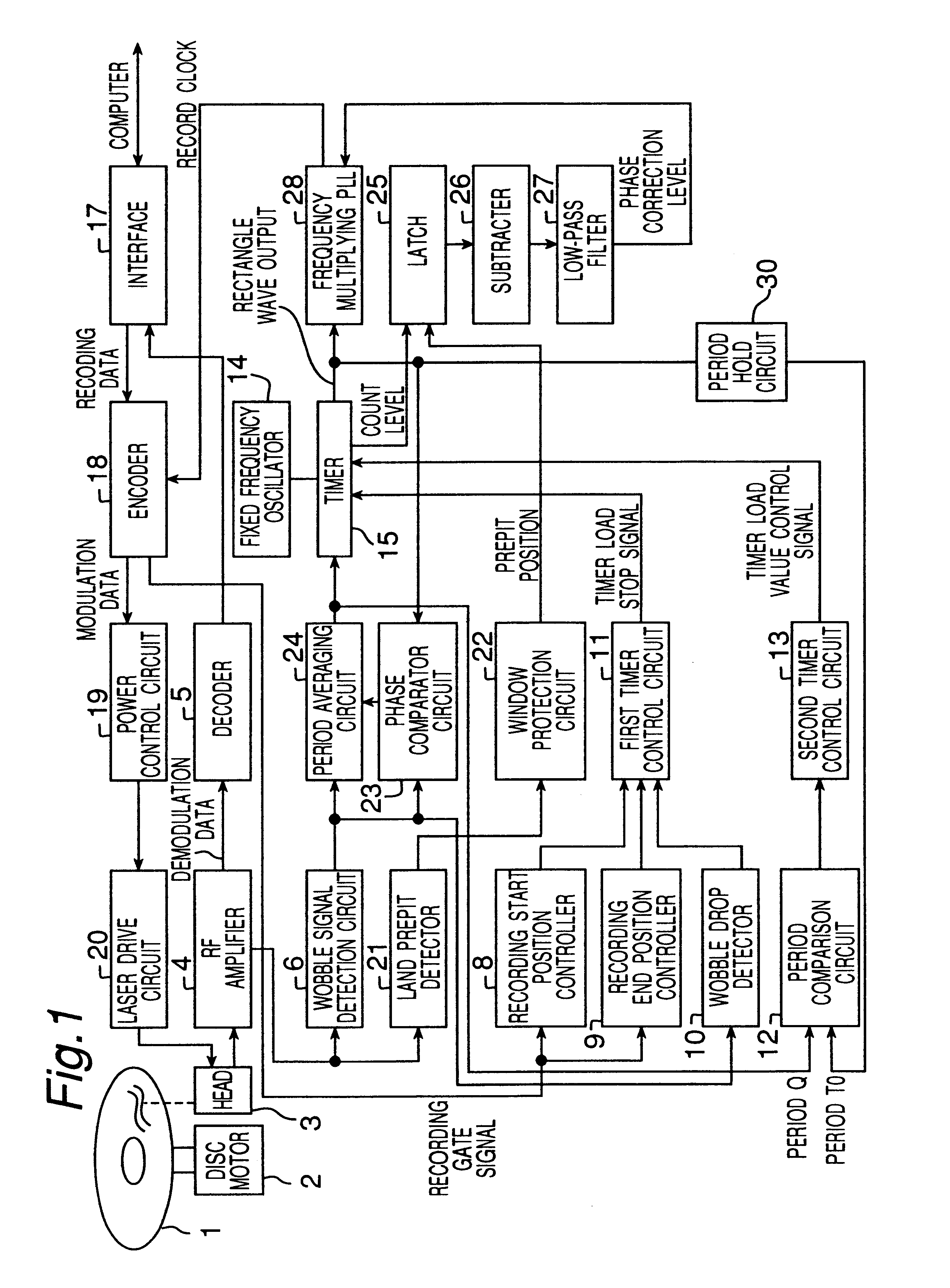
Recording clock generating device and method thereof
InactiveUS6856586B2Prevent movementEfficient use ofFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storagePower modulationPhase difference
Crosstalk between tracks, land prepit leakage, and effects of recording power modulation can cause the wobble signal period to change irregularly, thereby producing jitter in the recording clock which is derived by frequency multiplying the wobble signal. This problem is resolved by a recording clock generating circuit having an arrangement to average the wobble signal period, a timer for generating a rectangular wave with substantially the same period as the average period, and a frequency multiplying PLL for multiplying the timer output. The period averaging arrangement in particular determines the approximate average period at every wobble period and reflects the phase difference between the wobble signal and the timer in the timer setting so as to improve recording clock stability.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN +1
Recording medium having wobbled groove tracks out of phase with wobbled land tracks, servo controlling apparatus using wobble signal and method thereof
InactiveUS6847594B1Restrict movementFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageControl theoryRecording media
A recording medium having wobbled groove tracks out of phase with wobbled land tracks, a servo controlling apparatus using a wobble signal and a method thereof. The recording medium has land tracks and groove tracks, wherein both the land tracks and the groove tracks are wobbled, and wherein the wobbles of either individual groove tracks or individual land tracks are out of phase and the wobbles of the other type of individual tracks are in phase. Thus, it is possible to reliably address whether a groove (or land) track which is currently tracked by the pickup unit is a groove track or a land track, thereby ensuring addressing, and servo control can be effectively performed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information recording medium
InactiveUS6709801B2Reflectance can be improvedPrevent peelingRadiation applicationsLayered productsHigh densityRefractive index
A high-density information recording medium free from lowering the reflectance by over-write of a large number of times and exfoliation defect in a structure for suppressing cross-erase. This medium includes, over a substrate having a groove shape, a recording layer, and three-layered thin films of a first interference layer, a second interference layer and an interface layer having mutually different compositions and disposed on a laser beam incidence side of the recording layer in order named from the laser beam incidence side. The first interference layer has a smaller refractive index and a larger thermal conductivity than the second interference layer, the interface layer is interposed between the second interference layer and the recording layer, and a distance between the first interference layer and the recording layer is greater than at least a groove depth.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Optical recording medium with prepit regions and recording/reproducing method thereof
InactiveUS6965545B2Improve recording densityShortening the wobble pitsRecord information storageDigital storageLight beamRecording layer
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical head and optical information recording and playback apparatus
An object of the present invention is to provide an optical head apparatus which are capable of detecting correctly a radial tilt of an optical recording medium, without allowing offsets in radial tilt signals, even when an objective lens is shifted in a radial direction. A beam emitted from a semiconductor laser is divided into 0th order main beam and ±1st order sub beams. The three beams are shifted in the radial direction of the disc. The three beams reflected from the disc are diffracted by a holographic element, and are received by a photo detector. With respect to the main beam and the sub beams, a radial tilt of the disc is detected on the basis of a difference between intensities of the main and sub beams diffracted from a plurality of regions of the holographic element.
Owner:NEC CORP
An optical disk and optical disk apparatus with tracks and grooves
InactiveUS20020126591A1Accurate trackingRecord information storageUsing detectable carrier informationLight beamEngineering
An optical disk includes tracks and grooves, the grooves being formed with a pitch equal to or greater than about .lambda. / NA. A first array of pits is provided at a position which is shifted by a predetermined amount with respect to each track in one of two directions substantially perpendicular to the tracks, the first array of pits being formed with a predetermined pitch, where the predetermined pitch is a function of a pitch of the grooves taking a value within a range from about 0 to about .lambda. / NA. A second array of pits is provided at a position which is shifted by a predetermined amount with respect to the track in the other one of the two directions substantially perpendicular to the tracks, the second array of pits being formed with a predetermined pitch, where the predetermined pitch is a function of the pitch of the grooves taking a value within the range from about 0 to about .lambda. / NA. .lambda. is a wavelength of a light beam which is radiated on the optical disk, and NA to a numerical aperture of a lens.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Recording medium, method and apparatus for recording, and method and apparatus for reproducing
In a recording medium which is circular and has first and second recording layers, the first and second recording layers each include one or more first tracks extending concentrically or spirally and one or more second tracks extending concentrically or spirally, each of the one or more first tracks and the one or more second tracks includes a plurality of first sectors and a plurality of second sectors, each of the plurality of first sectors includes first and second regions, each of the plurality of second sectors includes third and fourth regions, first and second grooves are formed in each of the second and fourth regions, the first and second grooves extending concentrically or spirally and oscillating sinusoidally, oscillation of the first groove has a first oscillation characteristic at a first prescribed position in the second region, oscillation of the second groove has a second oscillation characteristic at a second prescribed position in the fourth region, and the first and second oscillation characteristics are different from each other.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com