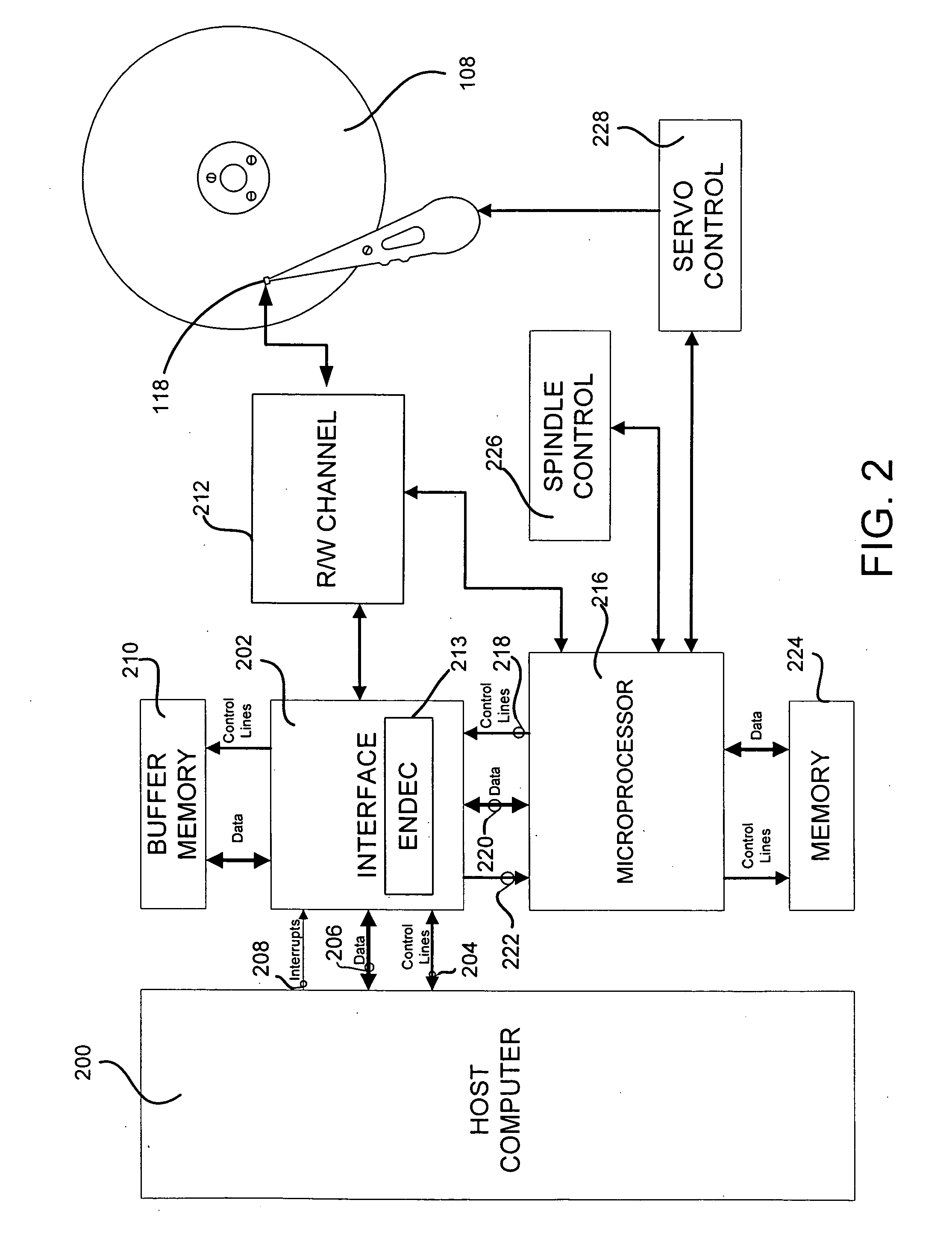
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127 results about "Run-length limited" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
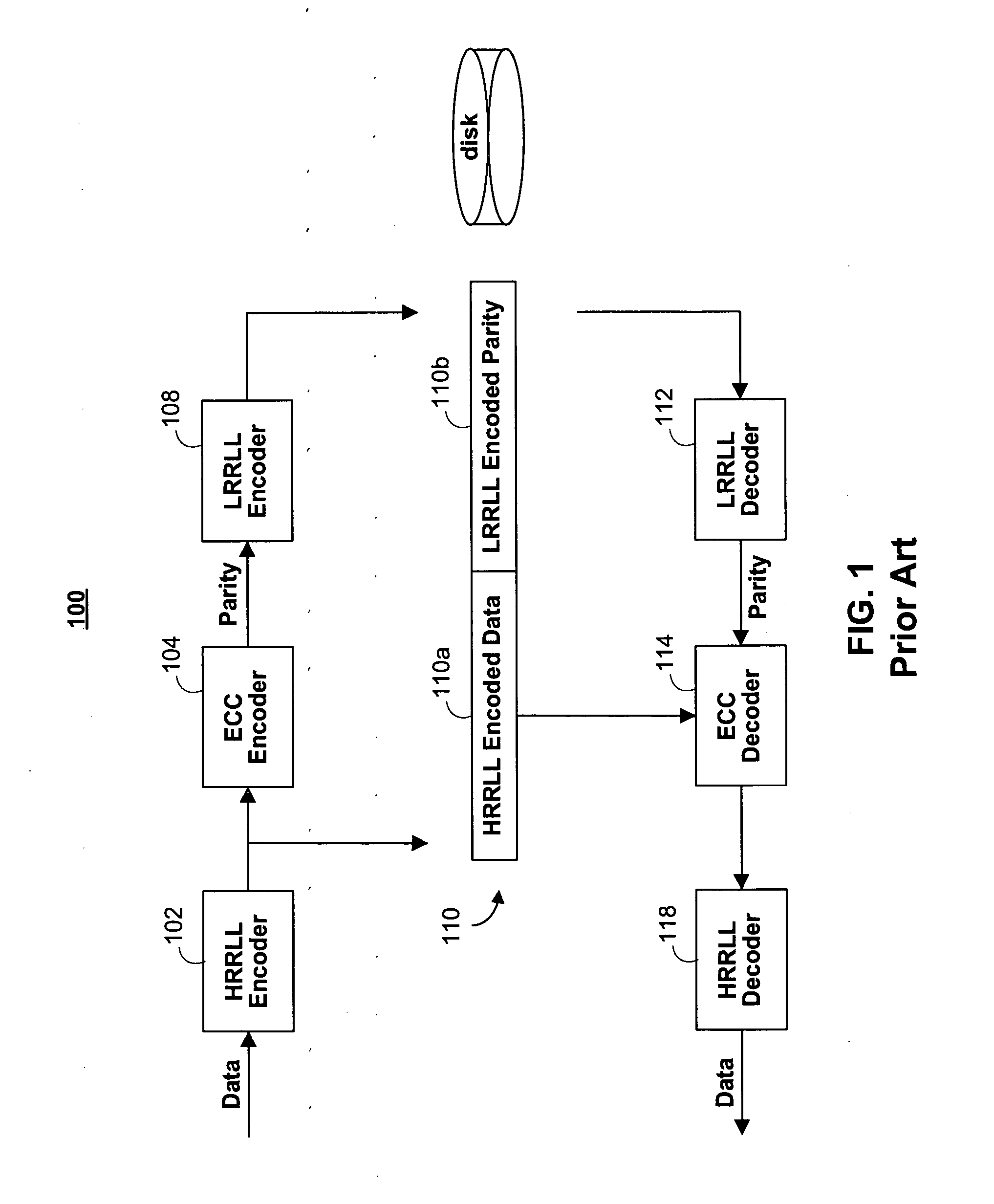
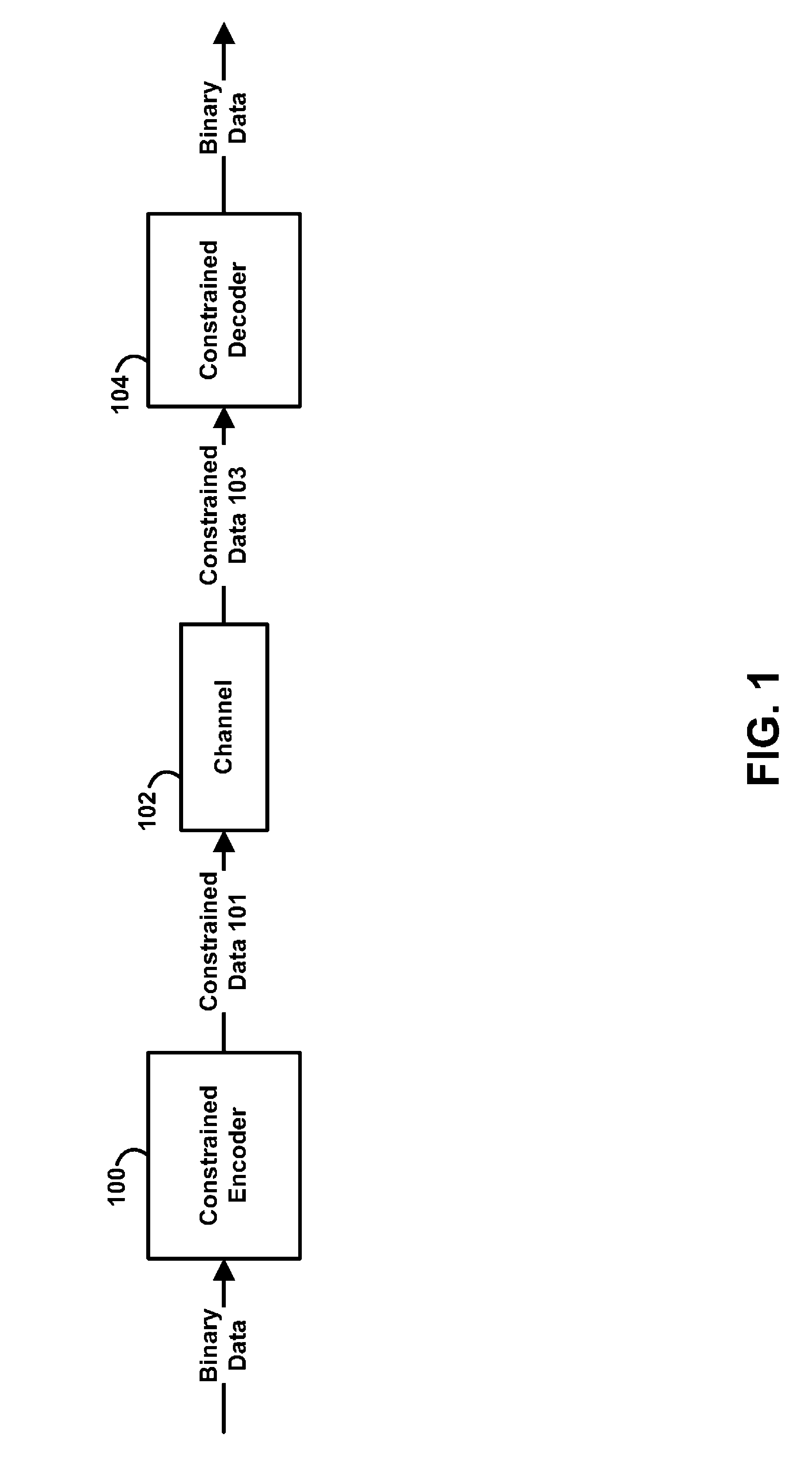
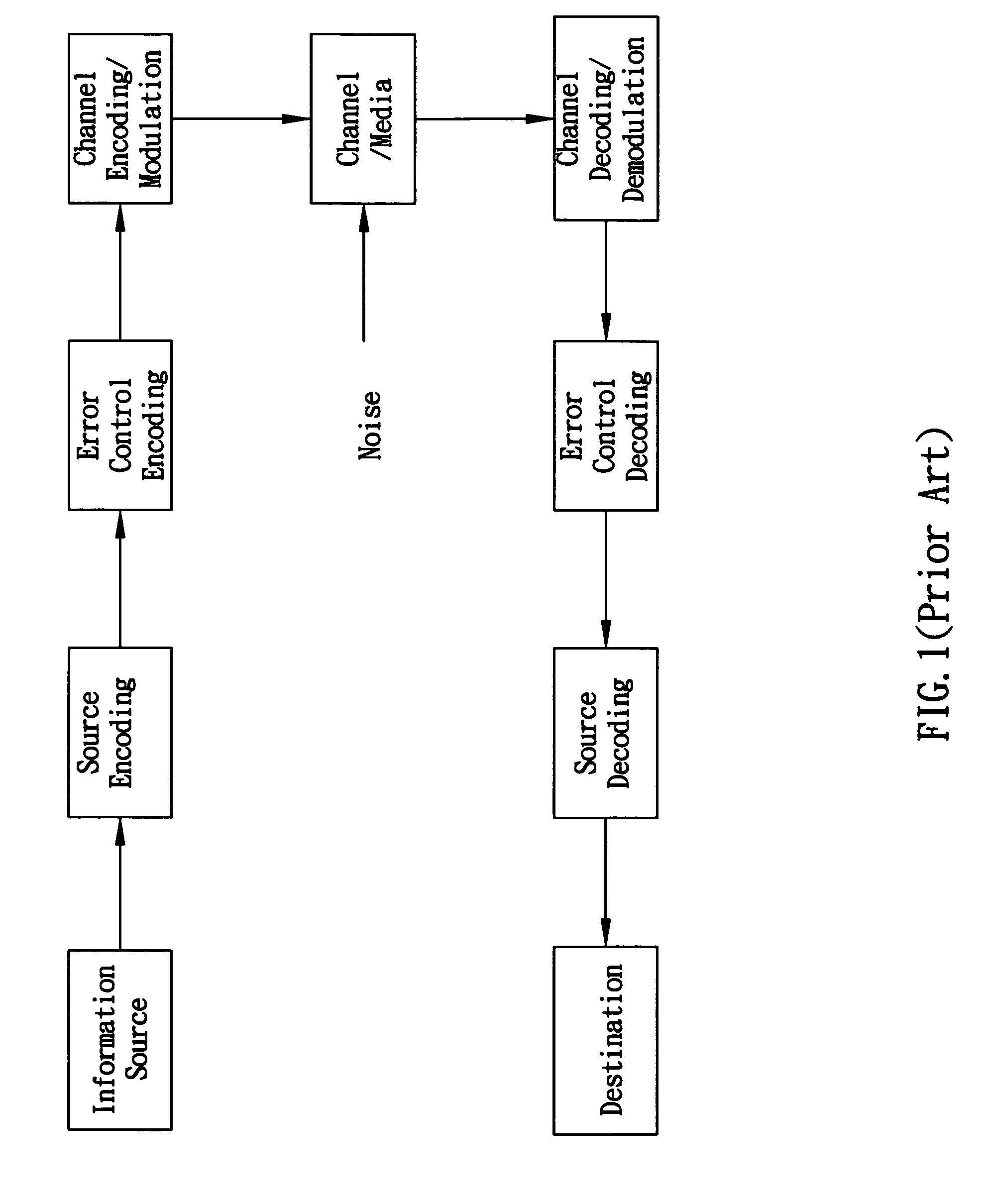
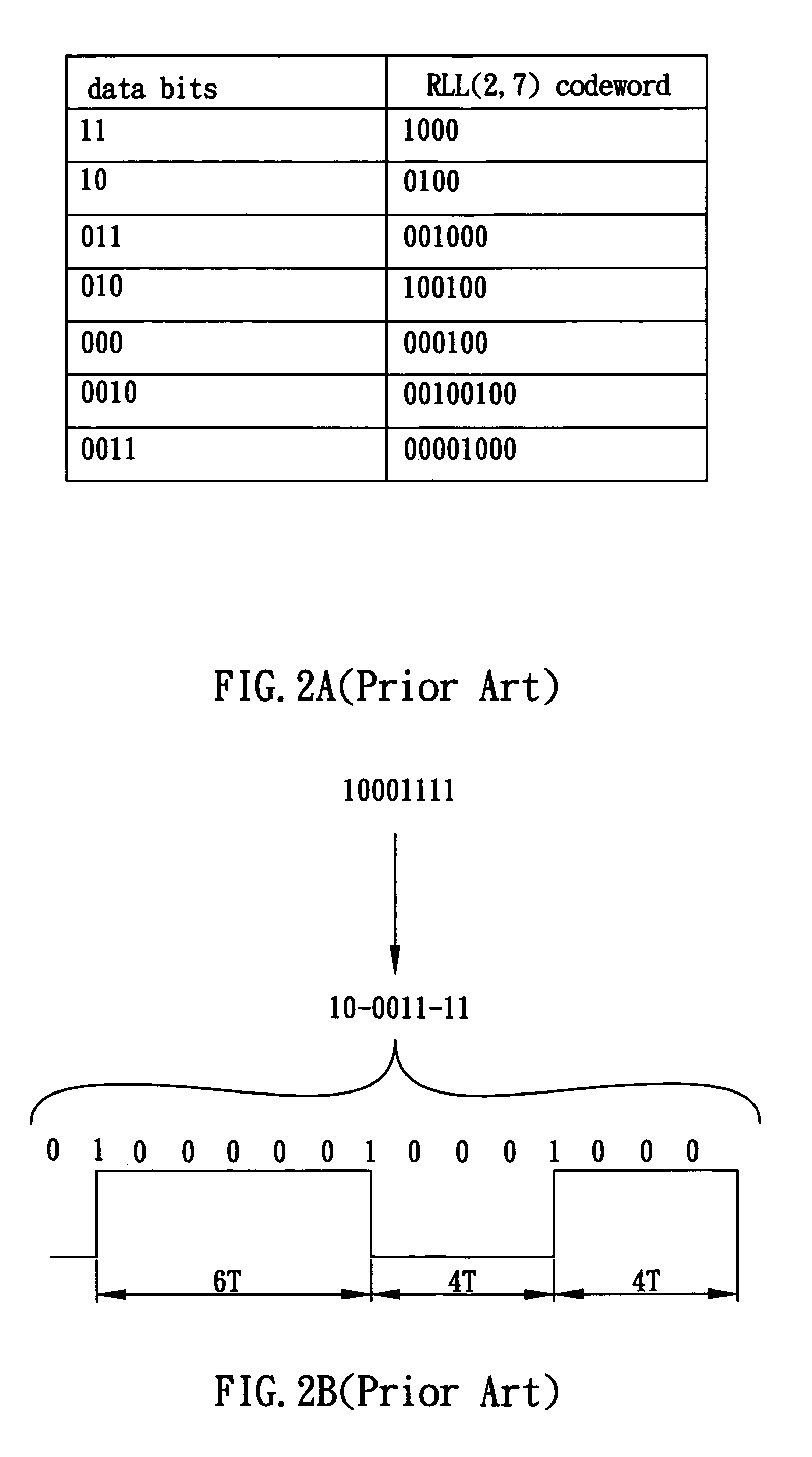
Run-length limited or RLL coding is a line coding technique that is used to send arbitrary data over a communications channel with bandwidth limits. RLL codes are defined by four main parameters: m, n, d, k. The first two, m/n, refer to the rate of the code, while the remaining two specify the minimal d and maximal k number of zeroes between consecutive ones. This is used in both telecommunication and storage systems that move a medium past a fixed recording head.
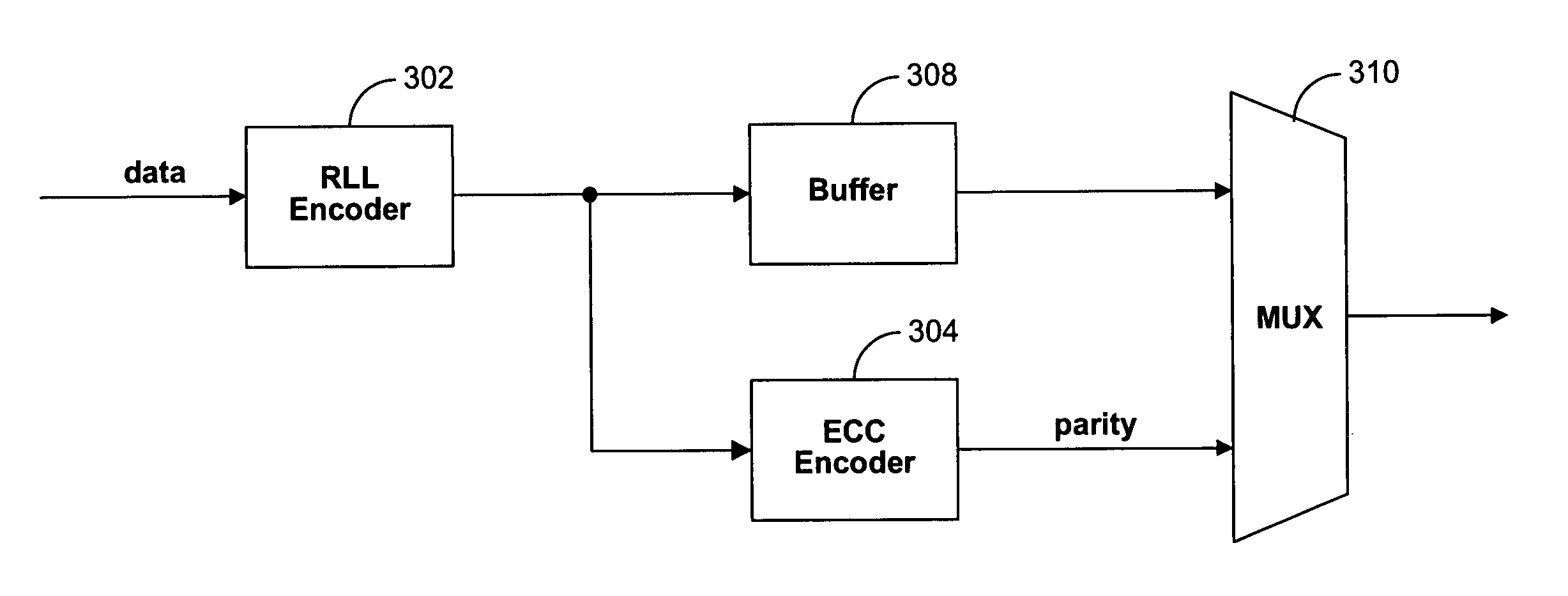
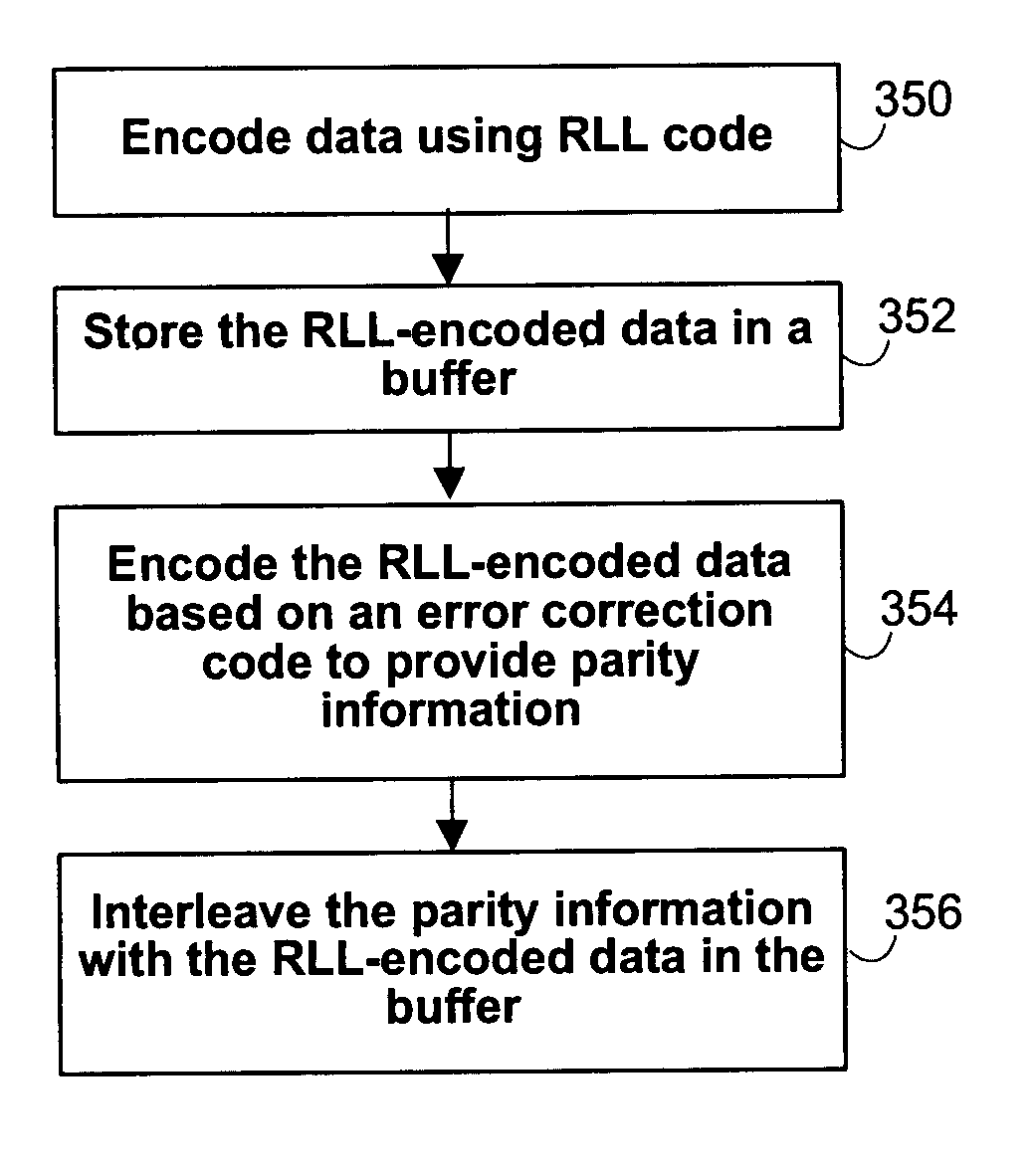
Systems and methods for achieving higher coding rate using parity interleaving
ActiveUS20070226582A1Record information storageIndividual digits conversionComputer scienceCorrection code
The disclosed technology provides systems and methods for encoding data based on a run-length-limited code and an error correction code to provide codewords. The codewords include RLL-encoded data that are produced based on the RLL code, and parity information that are produced based on the error correction code. The parity information is interleaved among the RLL-encoded data. In one embodiment, the codeword is produced by separately producing the RLL-encoded data and the parity information, and interleaving the parity information among the RLL-encoded data. In one embodiment, the codeword is produced by producing the RLL-encoded data, and using erasure decoding to compute the parity information.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
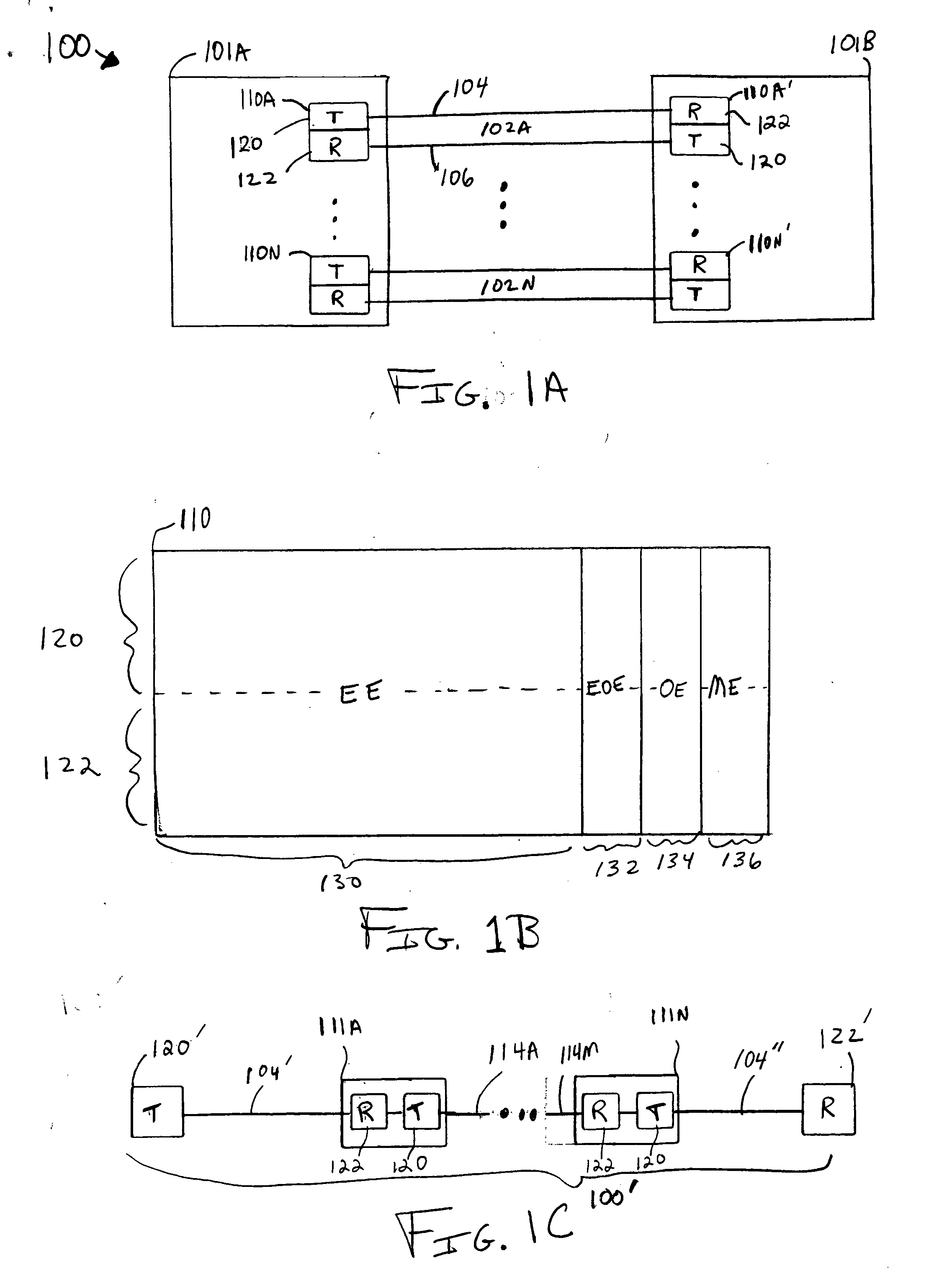
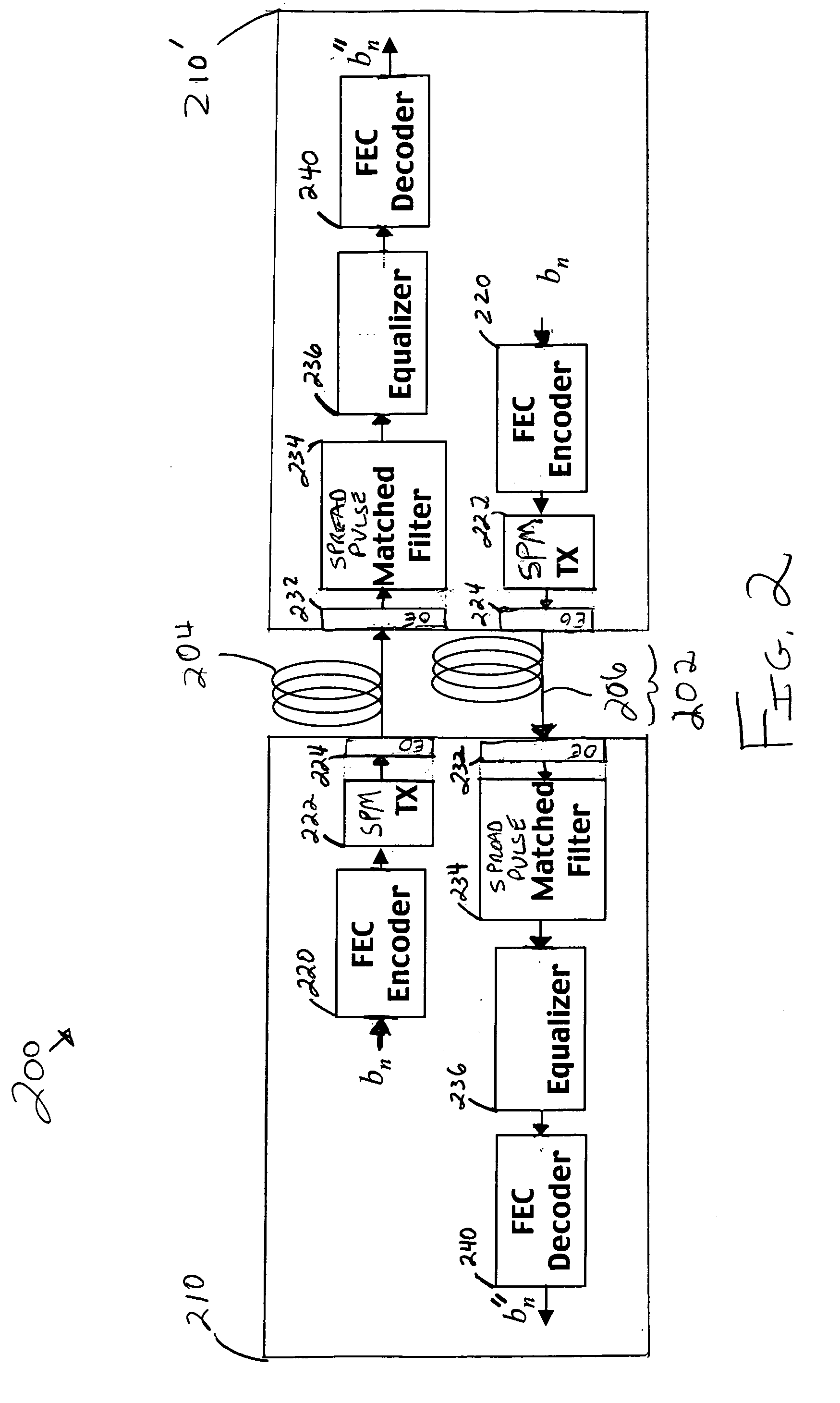
Methods of spread-pulse modulation and nonlinear time domain equalization for fiber optic communication channels
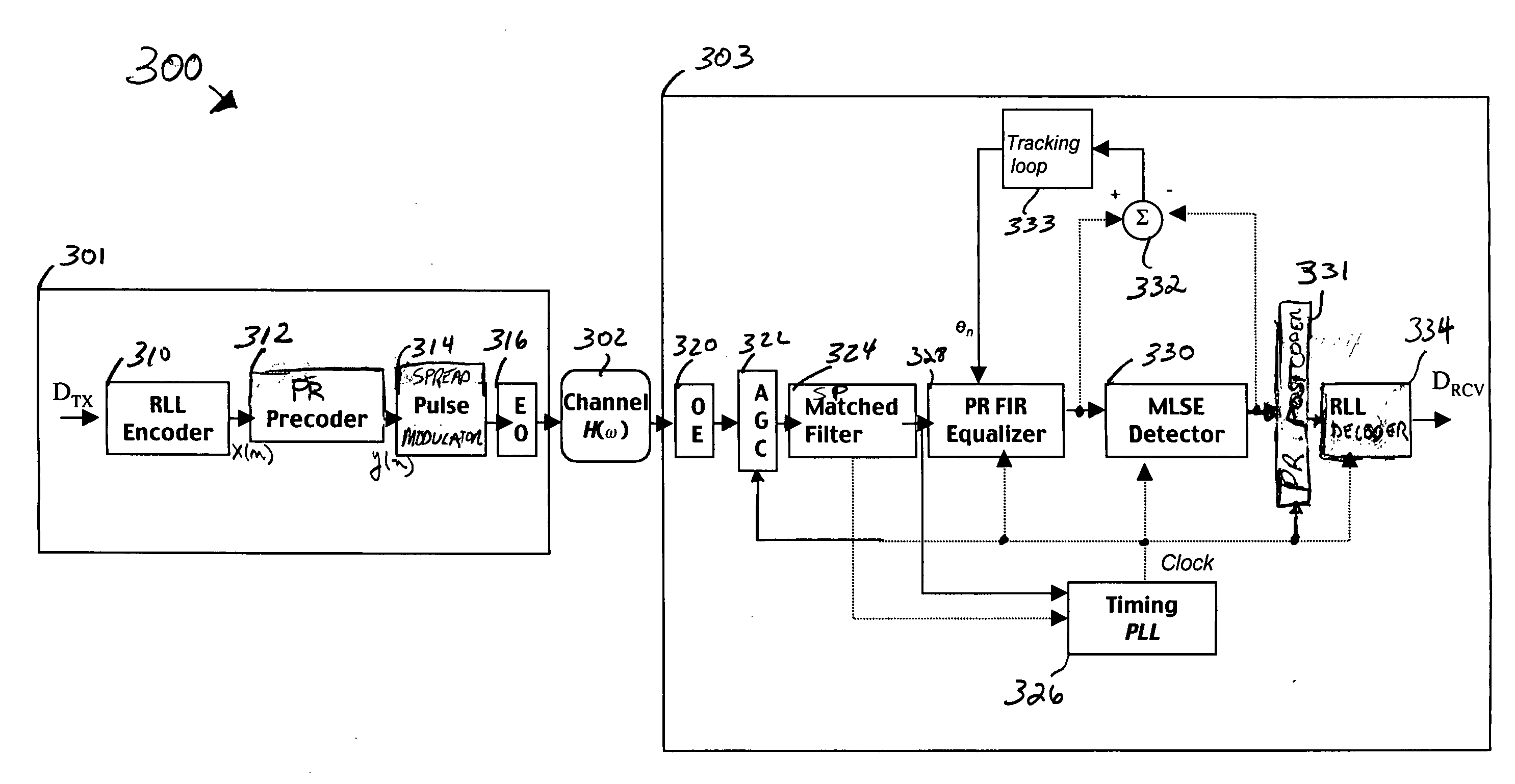
Methods, apparatus, and systems for an optical communication channel. A data signal is preconditioned prior to transmission over a fiber optic cable to minimize signal distortion and transmitted over a fiber optic cable. Preconditioning may include none, one or more, or all of the following: encoding the data signal using a run length limited code, correlating bits of the data signal, and spreading out the pulses in the time-domain in the data signal. The pulse spreading function can be implemented either in the electrical domain prior to the electrical-to-optical conversion; in the optical domain during and / or after the electrical-to-optical conversion; or a combination of both. During reception, the data signal and clock are recovered. Recovery may include maintaining an amplitude in an electrical signal, filtering the electrical signal, shaping the electrical signal, and removing distortions and intersymbol interference (ISI) from the received electrical signal.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
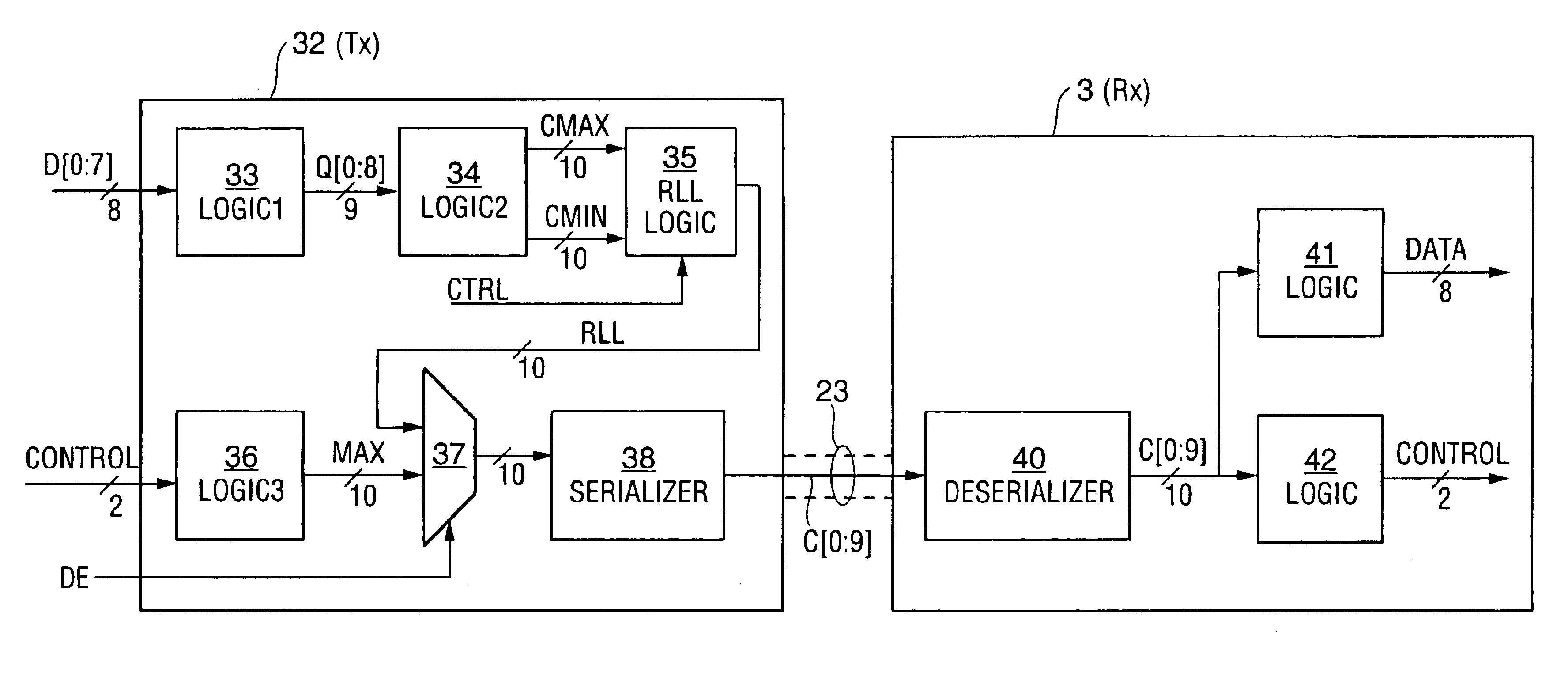
Method and apparatus for run length limited TMDS-like encoding of data
ActiveUS6897793B1Long run lengthReduce in quantityIndividual digits conversionComputer hardwareEncoding algorithm
A serial data transmission system in which a transmitter encodes data in accordance with a TMDS-like encoding algorithm and transmits the TMDS-like encoded data over a serial link to a receiver. The encoded data are transmitted as a run length limited (“RLL”) code word sequence, including transition-minimized code words. In some embodiments, the RLL code word sequence includes only Min words, including both DC balancing Min words and DC unbalancing Min words. In other embodiments, the RLL code word sequence includes both transition-maximized code words and transition-minimized code words. Other aspects of the invention are circuitry and methods for TMDS-like encoding of data for transmission as an RLL code word sequence.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Reverse error correction coding with run length limited constraint
ActiveUS7174485B2Error detection/correctionOther error detection/correction/protectionComputer hardwareForward error correction
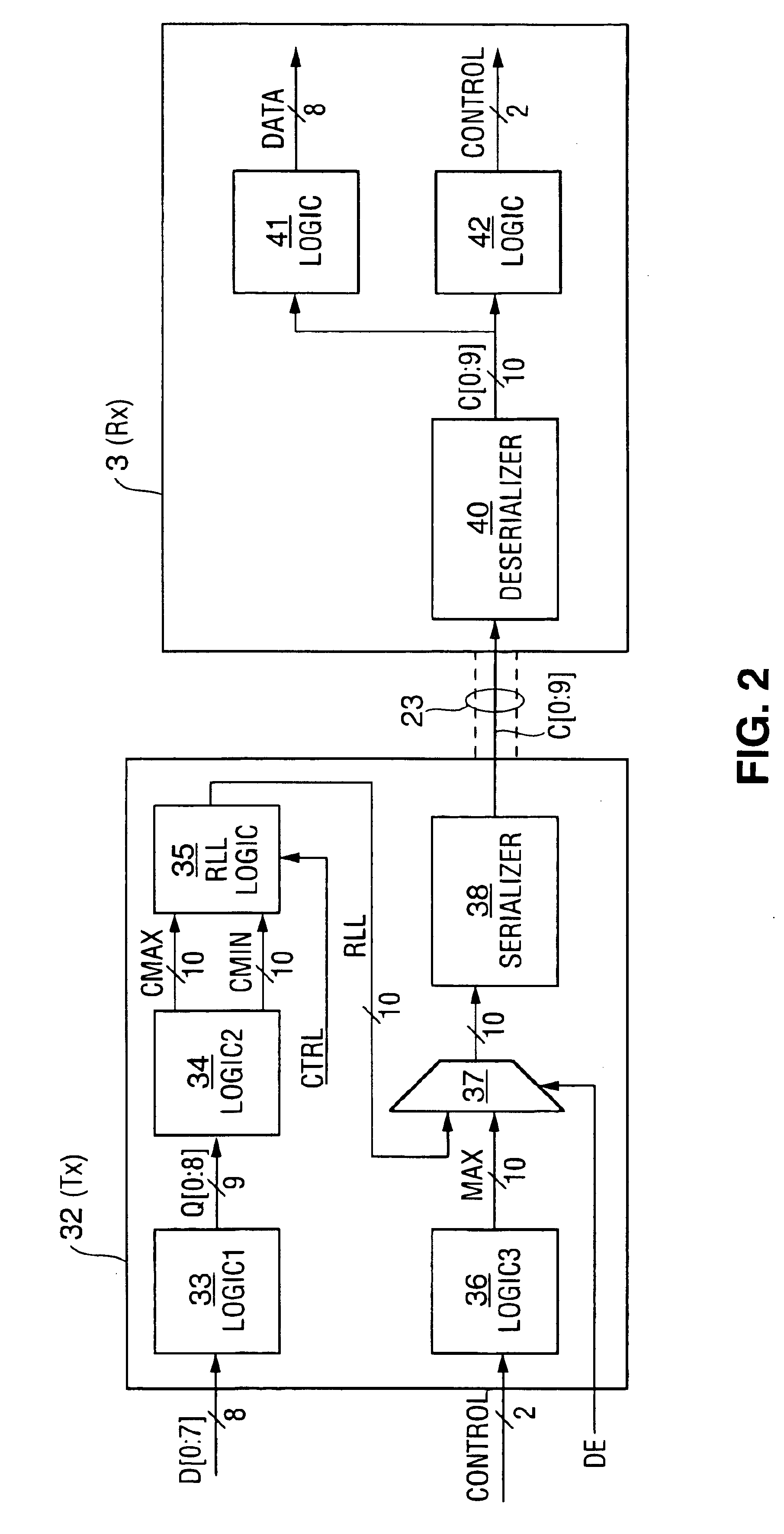
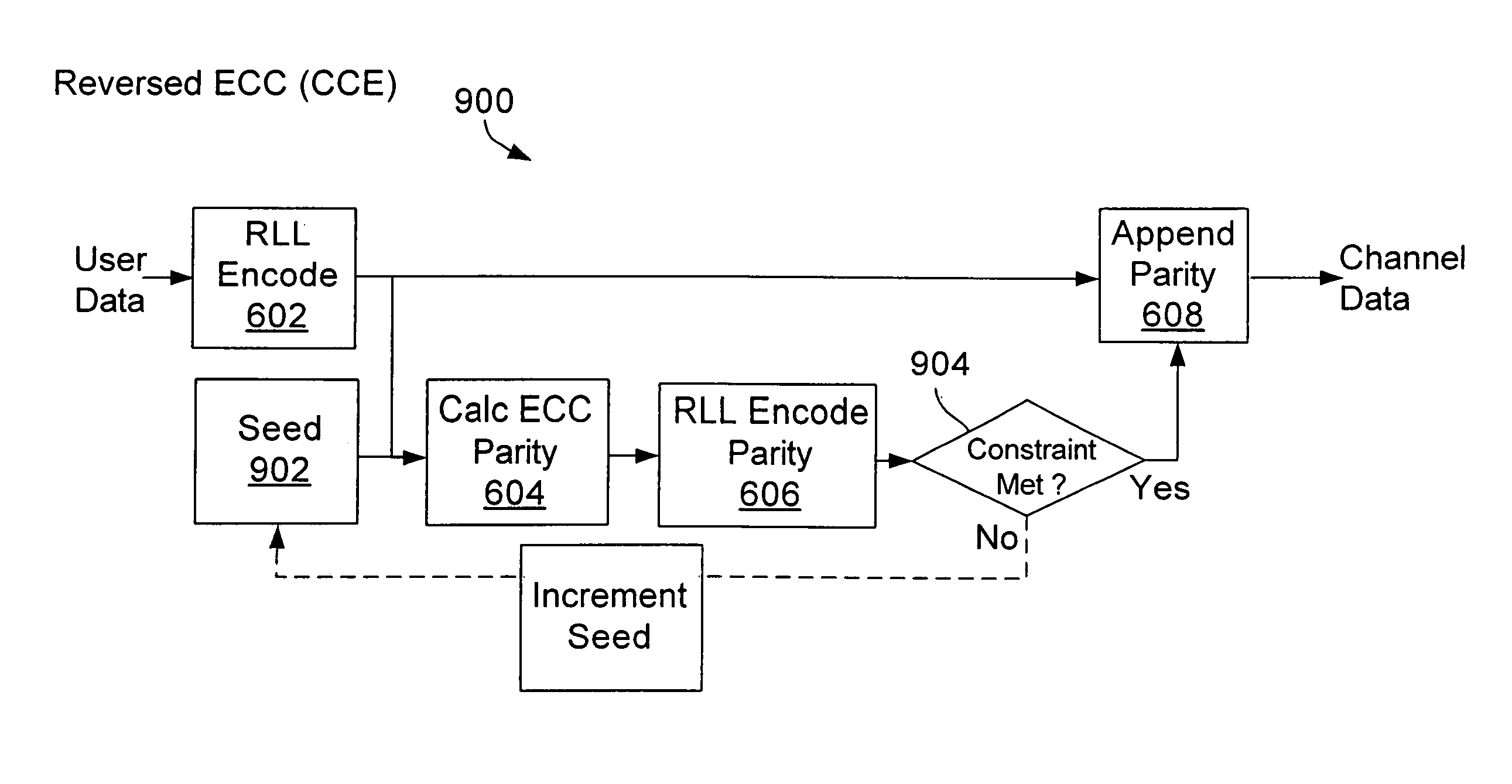
A method and apparatus for communicating data is provided. The data is encoded in accordance with a run length limited (RLL) code. A seed is appended to the RLL encoded data. The seed can be used to alter the error correction code (ECC) parity to meet an RLL constraint.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Optical disk, optical disk device, and method of reproducing information on optical disk
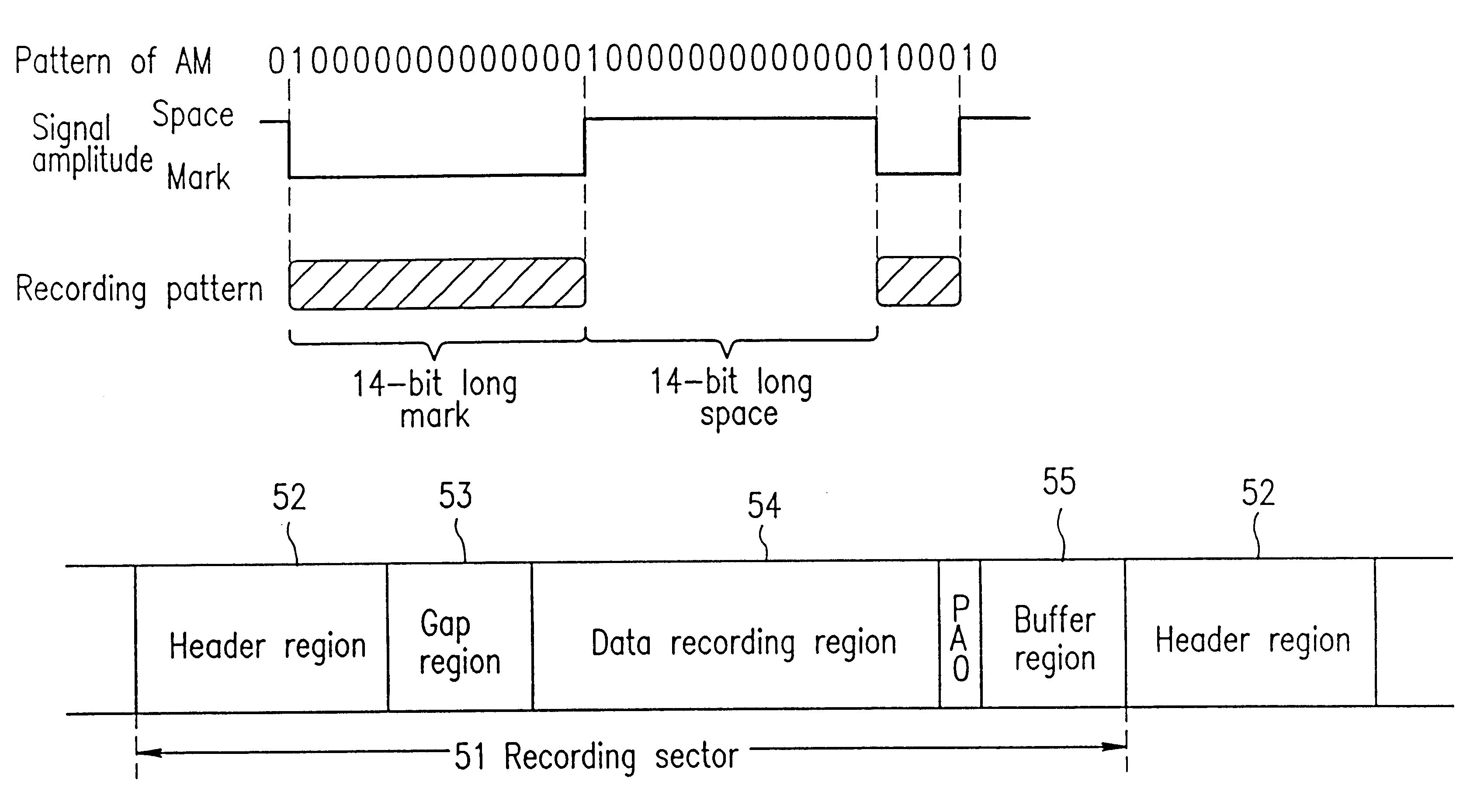
The present invention is aimed at providing an optical disk, an optical disk device, and an optical disk reproduction method, for allowing for stable and efficient reading of address information. The optical disk includes a plurality of tracks each divided into a plurality of recording sectors. Each of the recording sectors includes a header region. The header region includes address information for identifying the position of the corresponding recording sector and address synchronous information for identifying the recording position of the address information for bit synchronization. The address information has been modulated using a run length limit code of a maximum inversion interval of Tmax bits (Tmax is a natural number), and the address synchronous information includes two patterns of which inversion interval is (Tmax+3) bits or more, so that the reproduced signal of the address synchronous information is distinguished from the reproduced signal of other information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rate 32/33 (D=0, K=6) run length limited modulation code having optimized error propagation
InactiveUS6184806B1High bit rateSimplified and reliable encodingModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageDigital dataMagnetic media
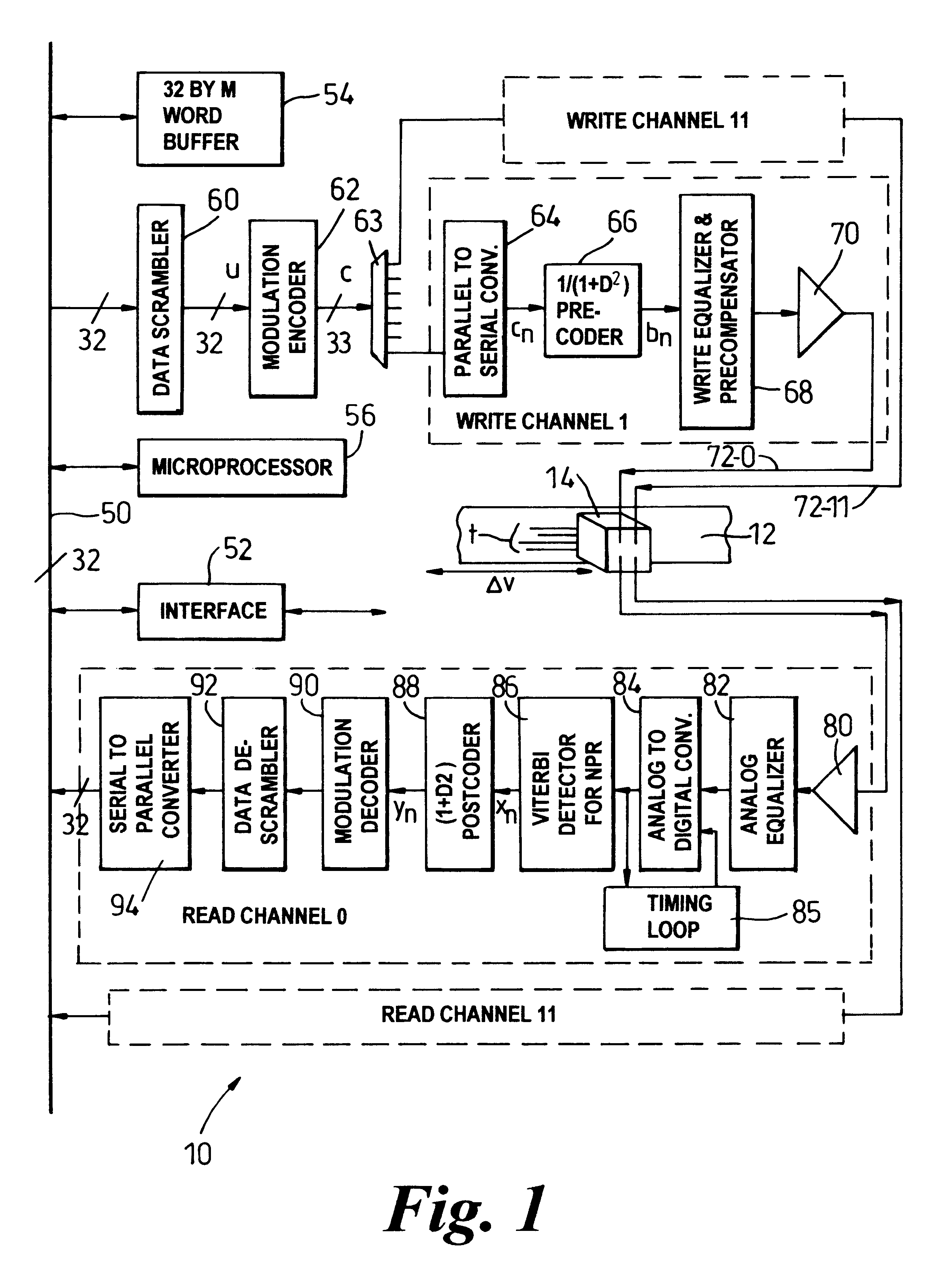
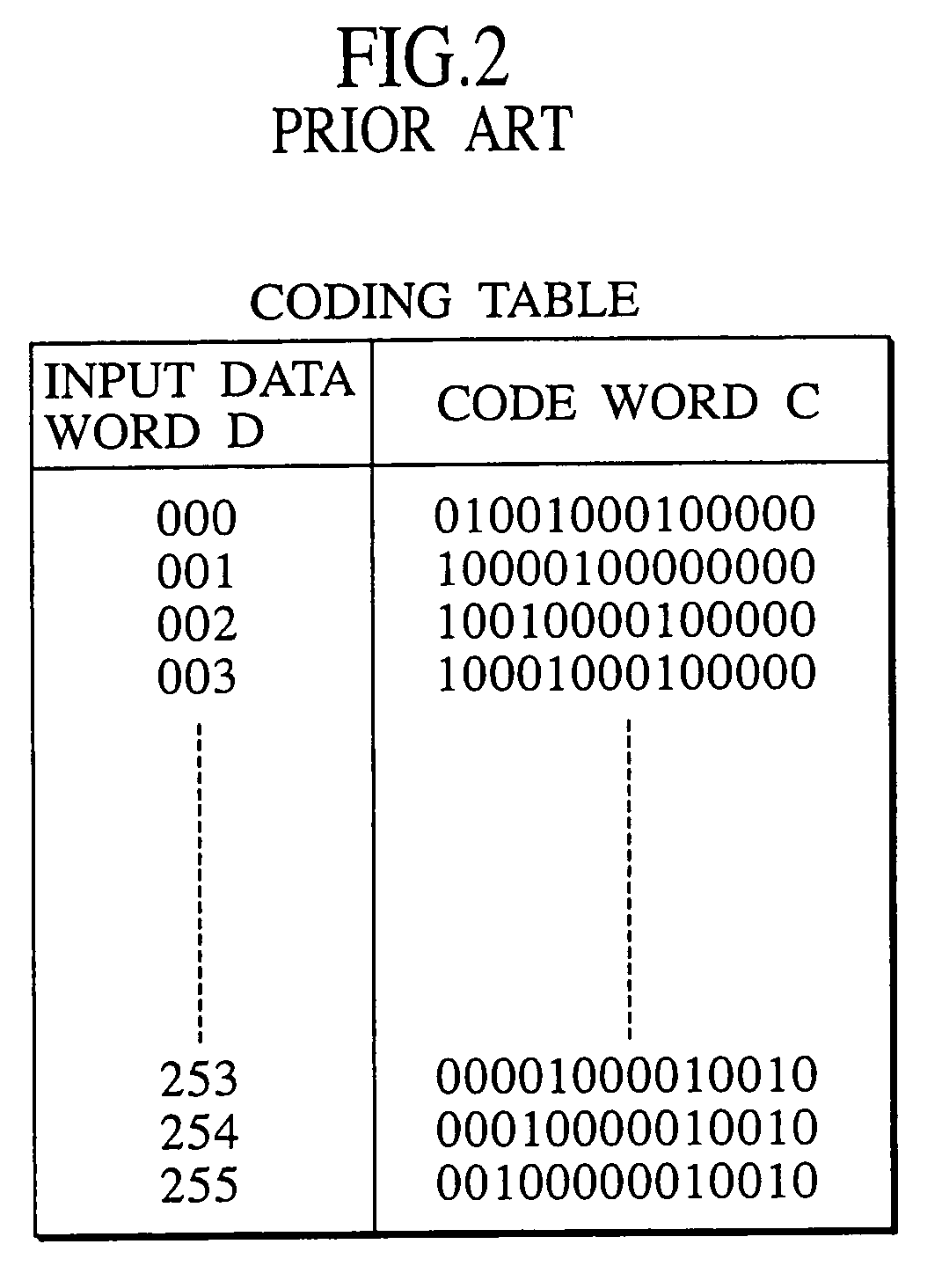
A method and apparatus for encoding a sequence of 32 bit digital data words into a sequence of 33 bit code words in consonance with predetermined minimum zero run length (d) and predetermined maximum zero run length (k) for recording upon a magnetic medium within a magnetic recording channel is disclosed. The method comprises steps of dividing each data word into eight data nibbles, determining whether any data nibble contains all zeros. If no code violation, mapping the eight data nibbles to seven code nibbles and to four bits of a five bit code sub-word and setting a fifth control bit to one. If one or more code violations are present, embedding code violation locations within at least the five bit code sub-word and other code nibbles if necessary and remapping data nibbles ordinarily directed to the code sub-word and nibble locations to code locations otherwise containing the data nibbles determined to be code violations.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Recording apparatus, reproducing apparatus and recording medium
ActiveUS20060123328A1Reduce the numberDrop in encoding rateError detection/correctionCode conversionComputer scienceSignal transition
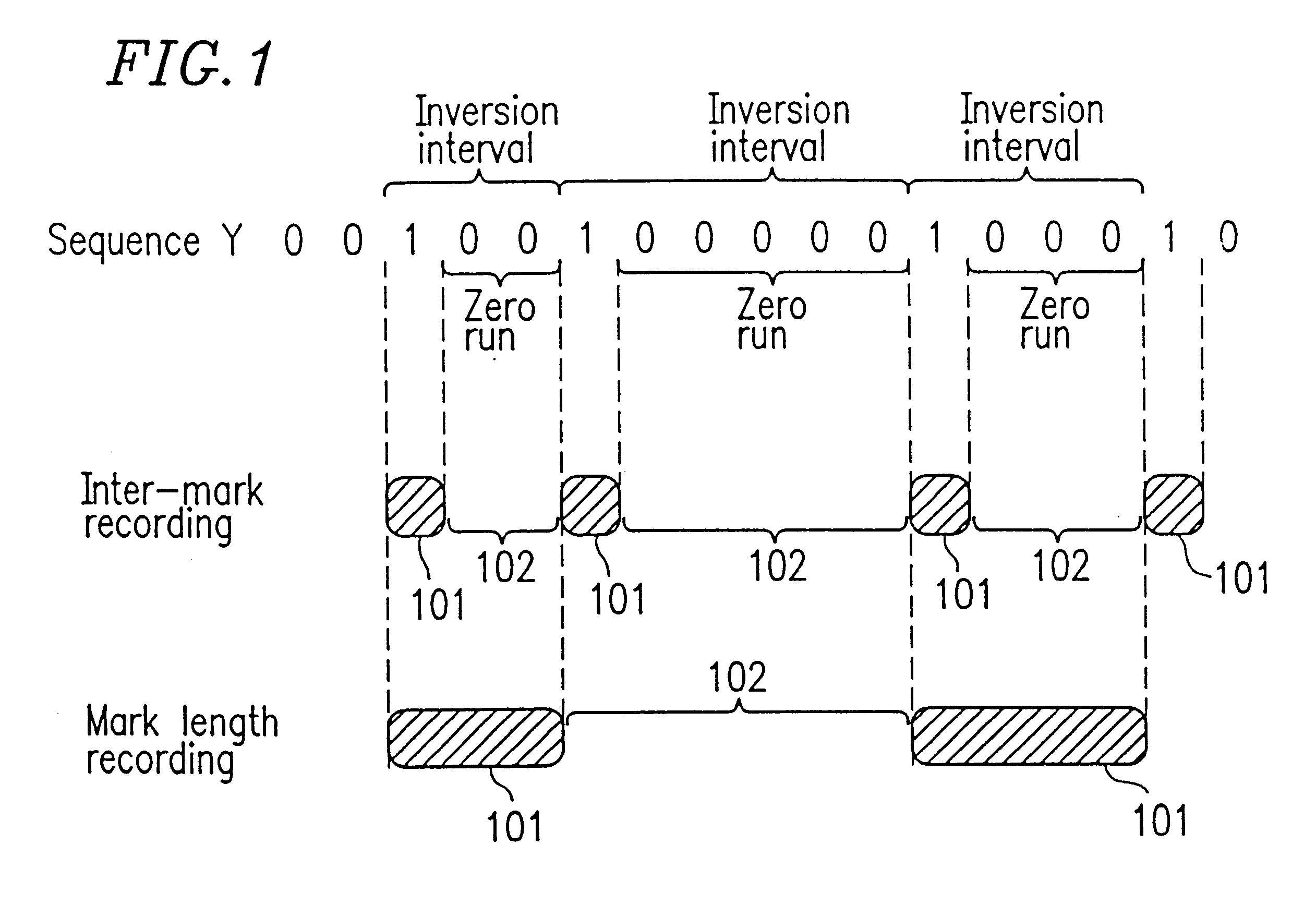
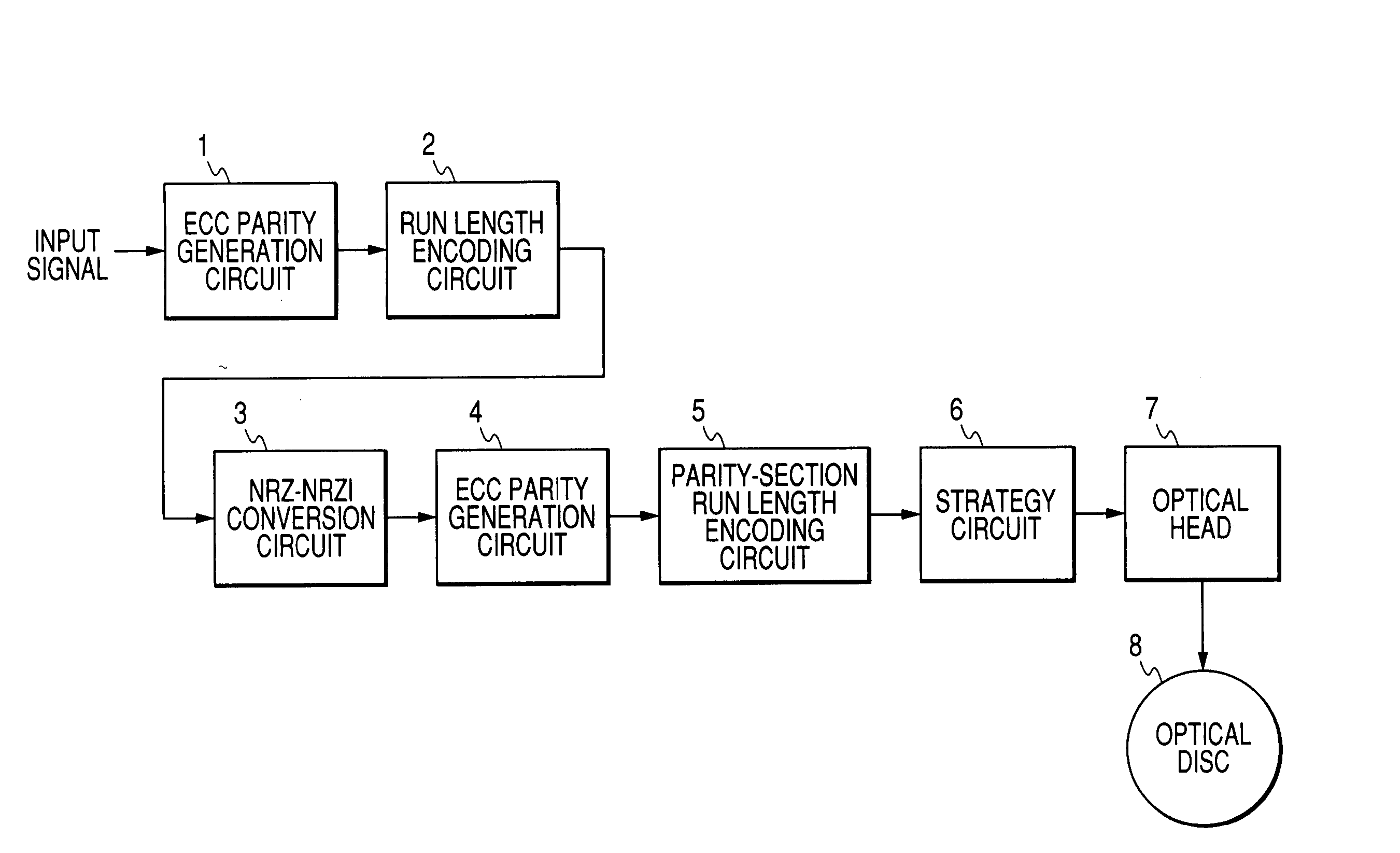
A first run length encoder implements run length modulation of a first information signal to generate a second information signal of a run-length-limited code while subjecting the second information signal to DSV control and adding a sync signal to the second information signal to get a third information signal. A converter changes the third information signal into an NRZI signal including information code words. A parity generator produces original parity signals in response to the information code words in the NRZI signal, and combines the information code words and the original parity signals to form a first parity-added signal. A second run length encoder implements run length modulation of only the original parity signals in the first parity-added signal to convert the first parity-added signal into a second parity-added signal while subjecting the second parity-added signal to DSV control. The second parity-added signal is recorded on a recording medium.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Systems and methods for constructing high-rate constrained codes
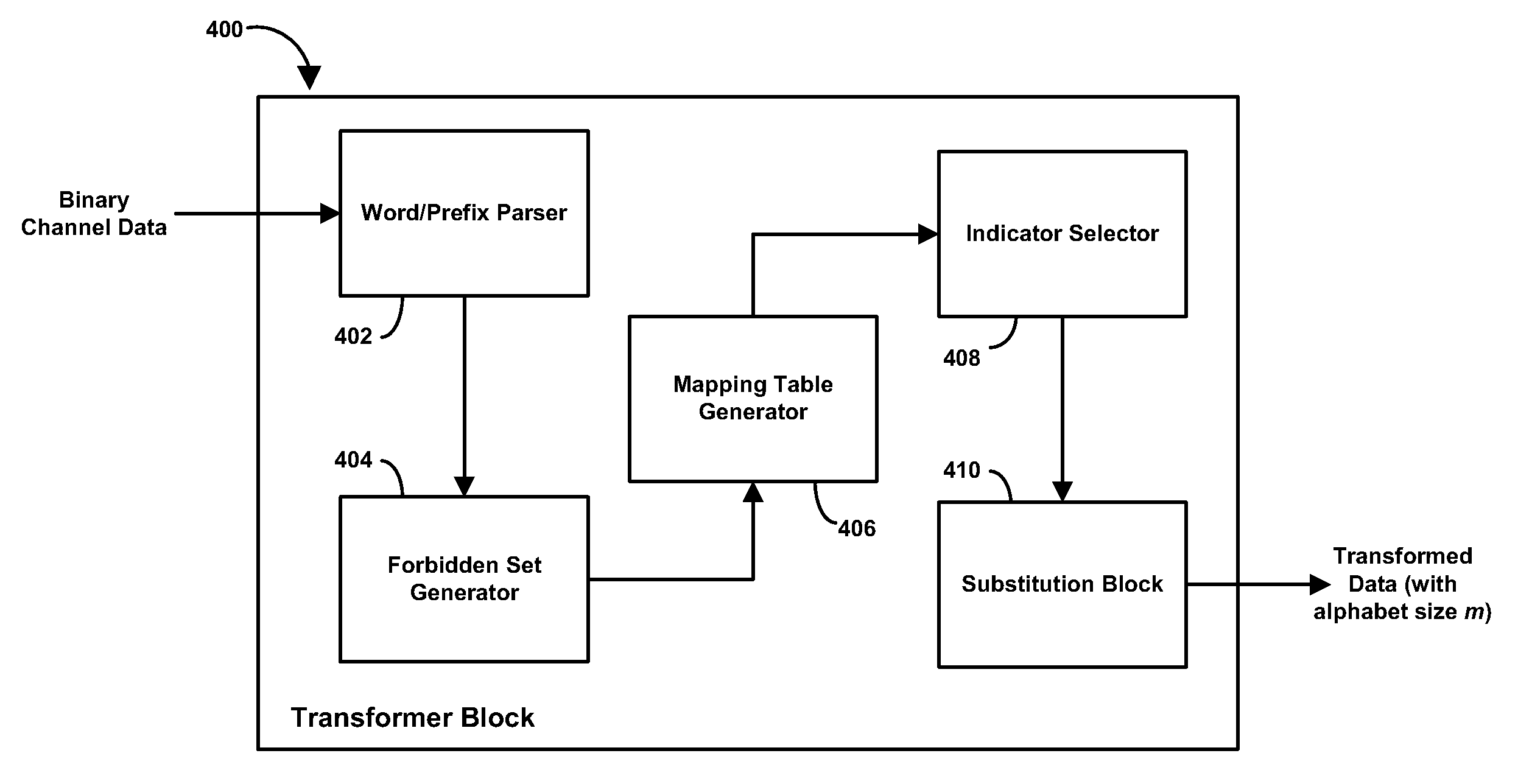
A high-rate constrained code is provided to encode / decode channel data. A transformer translates binary channel data into an arbitrary alphabet size. The transformer selects an indicator word and makes forbidden prefix substitutions in the data to be transformed. A finite-state encoder imposes some user-defined constraint on the transformed data before the data is transferred to the channel. The high-rate constrained coding technique may be used to produce high-rate DC-limited and run-length-limited codes. The high-rate code can be used in tandem with error-correcting codes.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Reverse error correction coding with run length limited constraint
ActiveUS20050138522A1Error detection/correctionIndividual digits conversionComputer hardwareCorrection code
A method and apparatus for communicating data is provided. The data is encoded in accordance with a run length limited (RLL) code. A seed is appended to the RLL encoded data. The seed can be used to alter the error correction code (ECC) parity to meet an RLL constraint.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Data recording medium, data recording method, and apparatus
InactiveUS7030788B2Reduce the valueLimiting conditionTelevision system detailsInformation arrangementMultiplexingMultiplexer
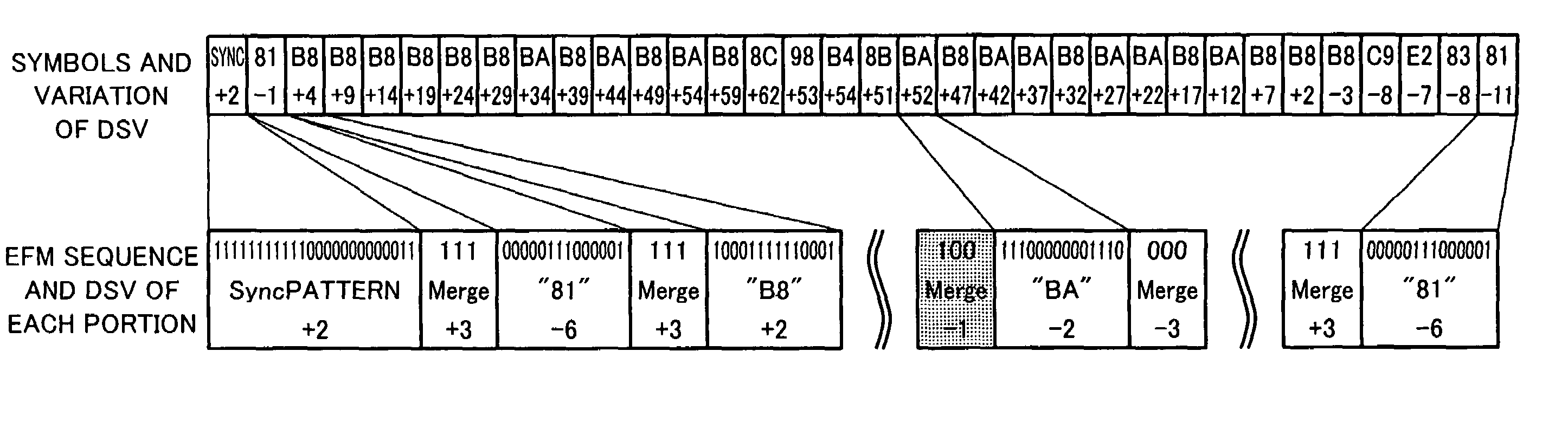
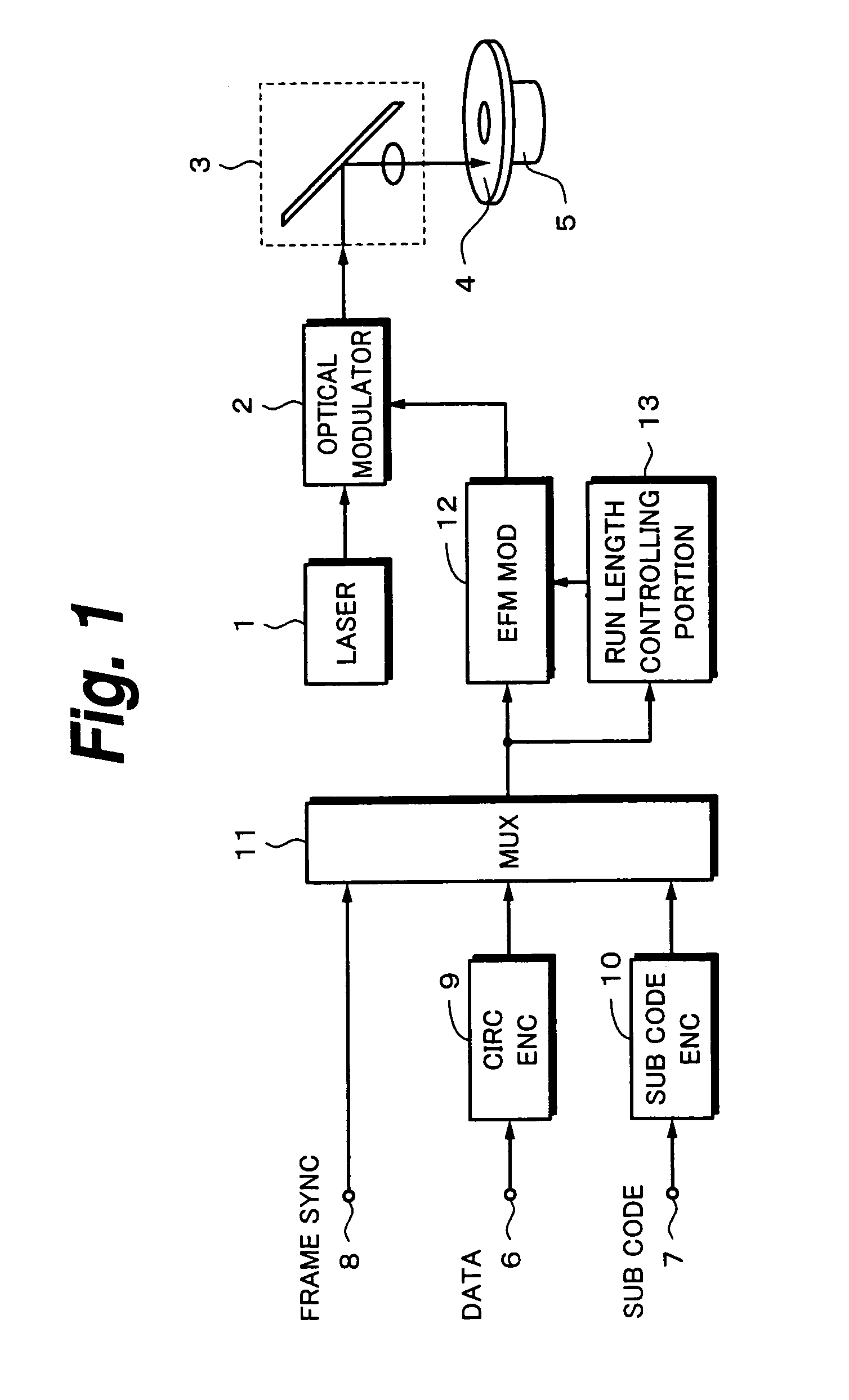
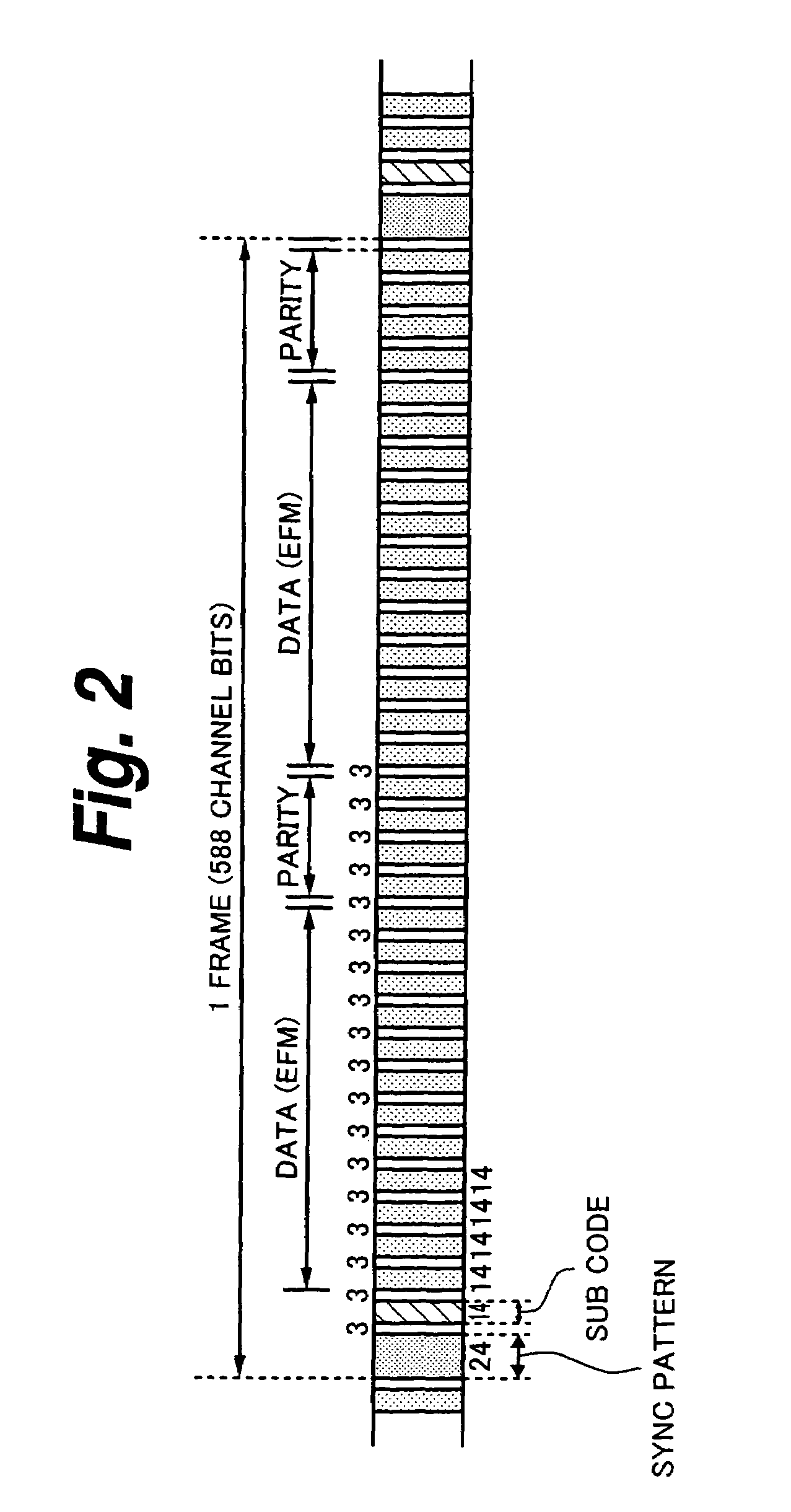
Output data of a multiplexer 11 is EFM-modulated by an EFM modulator 12. In the EFM modulation, merging bits that satisfy run length limit conditions Tmin=3 and Tmax=11 are selected. Among them, merging bits that converge DSV are selected. A run length controlling portion 13 detects a particular data pattern that causes DSV to increase as large as a data read error takes place and controls the EFM modulator 12 so that the run length limit conditions of the EFM are loosened. As a result, an increase of DSV is suppressed. Data is reproduced from a data recording medium on which the data has been recorded in such a manner and the reproduced data is decoded. The decoded data is re-encoded so as to record it to another recoding medium. When the data pattern is re-encoded, DSV increases. As a result, data cannot be correctly reproduced from the other recording medium. Consequently, a copying operation can be prevented.
Owner:SONY DISC & DIGITAL SOLUTIONS INC
Process for learning the limits of travel of a roller blind actuator
InactiveUS6867565B2Reduce decreaseDC motor speed/torque controlDoor/window protective devicesEngineeringActuator
Owner:SOMFY ACTIVITES SA
Systems and methods for constructing high-rate constrained codes
A high-rate constrained code is provided to encode / decode channel data. A transformer translates binary channel data into an arbitrary alphabet size. The transformer selects an indicator word and makes forbidden prefix substitutions in the data to be transformed. A finite-state encoder imposes some user-defined constraint on the transformed data before the data is transferred to the channel. The high-rate constrained coding technique may be used to produce high-rate DC-limited and run-length-limited codes. The high-rate code can be used in tandem with error-correcting codes.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Systems and methods for achieving higher coding rate using parity interleaving
ActiveUS7962827B2Record information storageIndividual digits conversionComputer scienceCorrection code
The disclosed technology provides systems and methods for encoding data based on a run-length-limited code and an error correction code to provide codewords. The codewords include RLL-encoded data that are produced based on the RLL code, and parity information that are produced based on the error correction code. The parity information is interleaved among the RLL-encoded data. In one embodiment, the codeword is produced by separately producing the RLL-encoded data and the parity information, and interleaving the parity information among the RLL-encoded data. In one embodiment, the codeword is produced by producing the RLL-encoded data, and using erasure decoding to compute the parity information.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method and data structure for compressing file-reference information
InactiveUS6886161B1Quick decompressionMinimizing delay of responseSoftware maintainance/managementProgram loading/initiatingSource code fileBitmap
Compression of local data uses various methods to encode location data (e.g. line numbers and, optionally, column numbers) representing references to a source code information symbol in a source code file. Run length encoding and other run encoding methods are used. A preferred run encoding method encodes a run-encoded bitmap comprising a set of runs, in which each run has a first run field that provides a starting line for the run, and a second run field that encodes as a bitmap the remaining lines in the run in which the reference appears. A run length field may be used to indicate the length of the second run field. Another run field may be used to encode the length of the first run field, to permit further compression.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Digital information reproduction method
InactiveUS20090106627A1Reduce Signal ErrorImprove reliabilityModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageComputer hardwareSignal quality
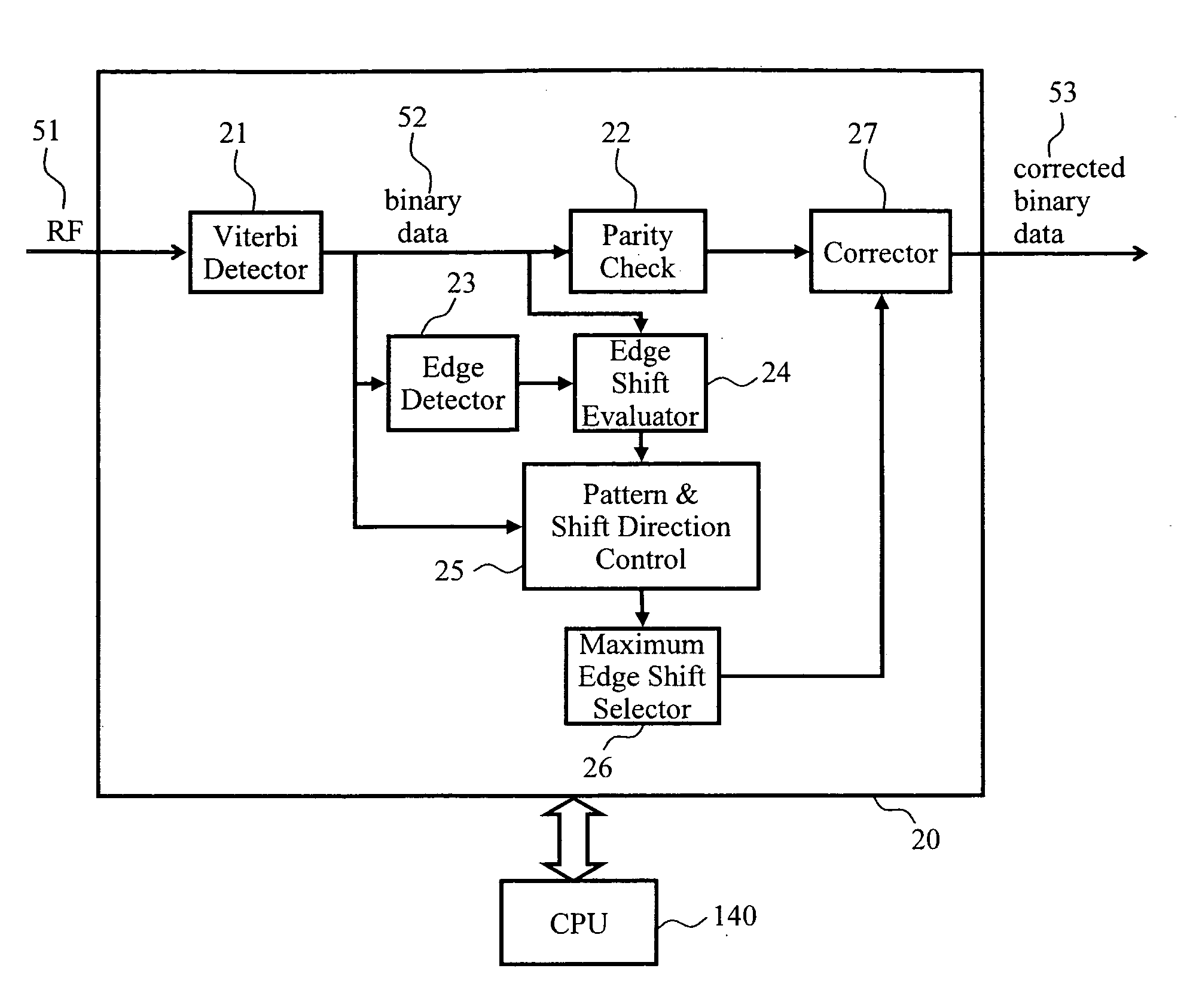
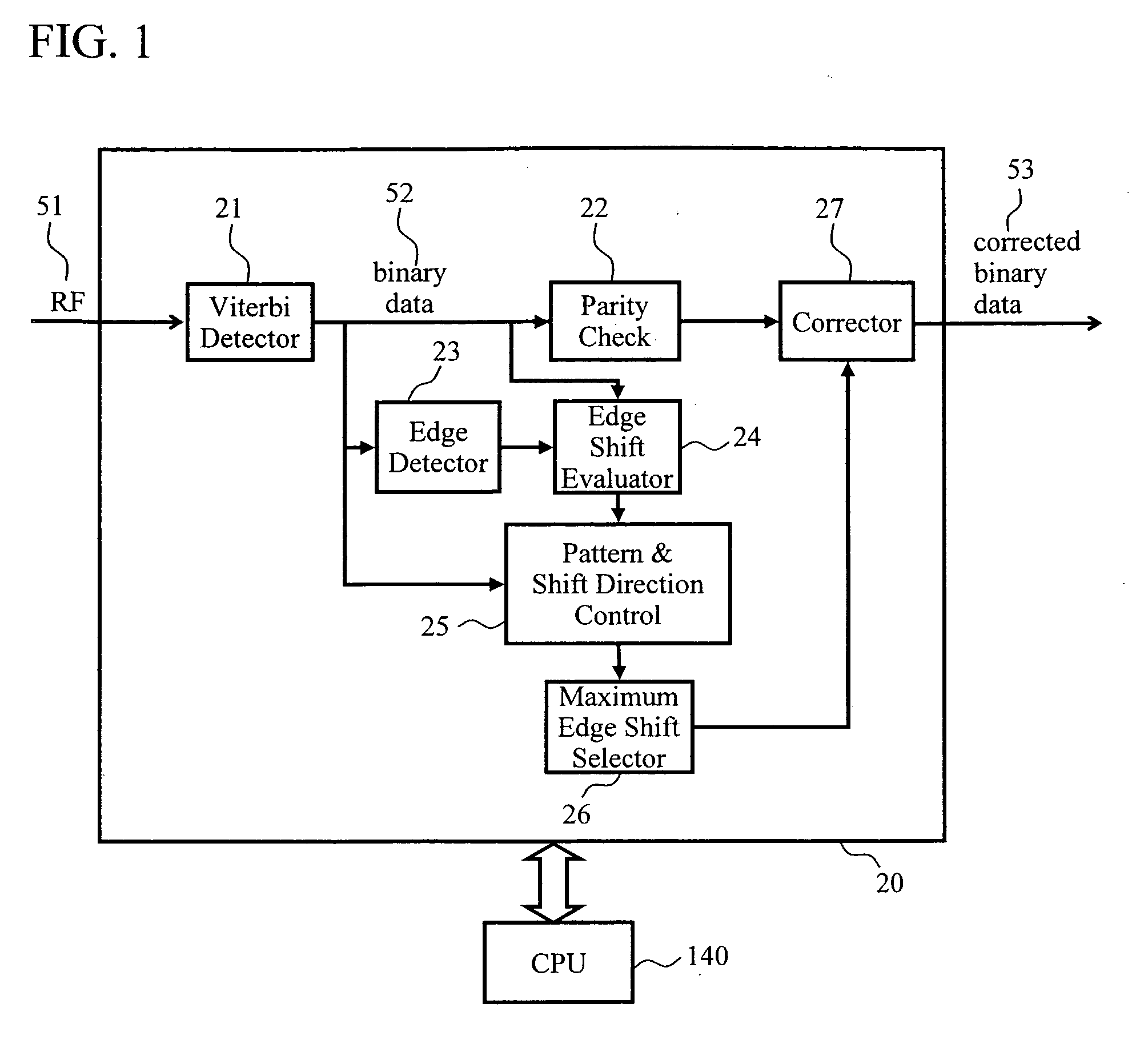
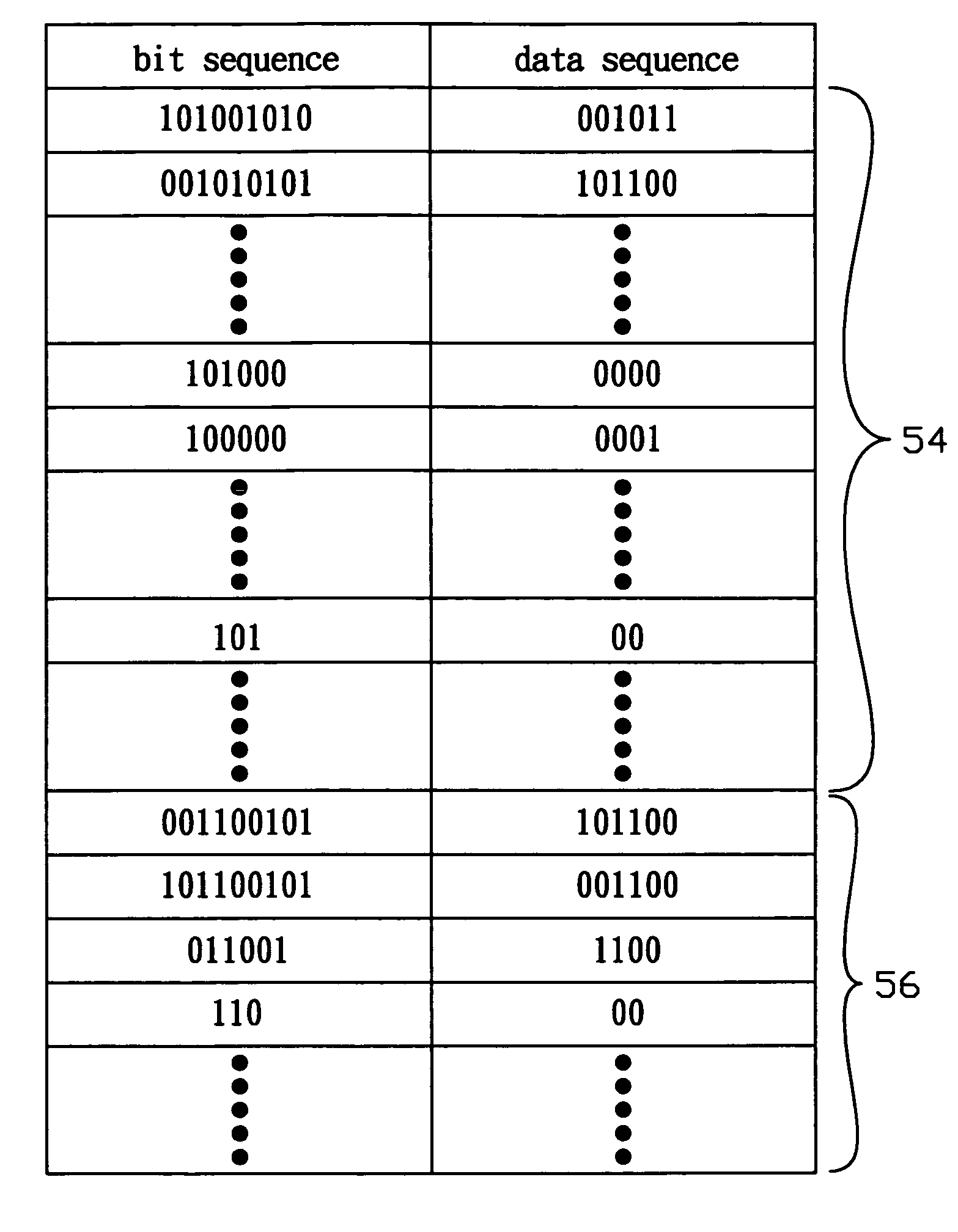
An optical disc using super-resolution effects that achieves higher-density recording exceeding the optical resolution suffers from the signal-quality degradation caused by the normal resolution component included in the reproduction signal. To address this problem, a data reproduction method is provided. In the method, characteristic error patterns are identified and parity check codes in conformity with run-length limited coding are used to carry out efficient and reliable error correction. Error patterns caused by the normal resolution crosstalk are localized in the leading edges of a mark following a long space and in the trailing edges of a long mark. Whether an error exists in the data is determined by use of the parity check codes. When an error occurs, a pattern in which an error is most likely to occur is selected from the above-mentioned patterns by taking account of the edge shift direction, and then the error therein is corrected.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Data modulation method, modulator, recording method, and recording apparatus
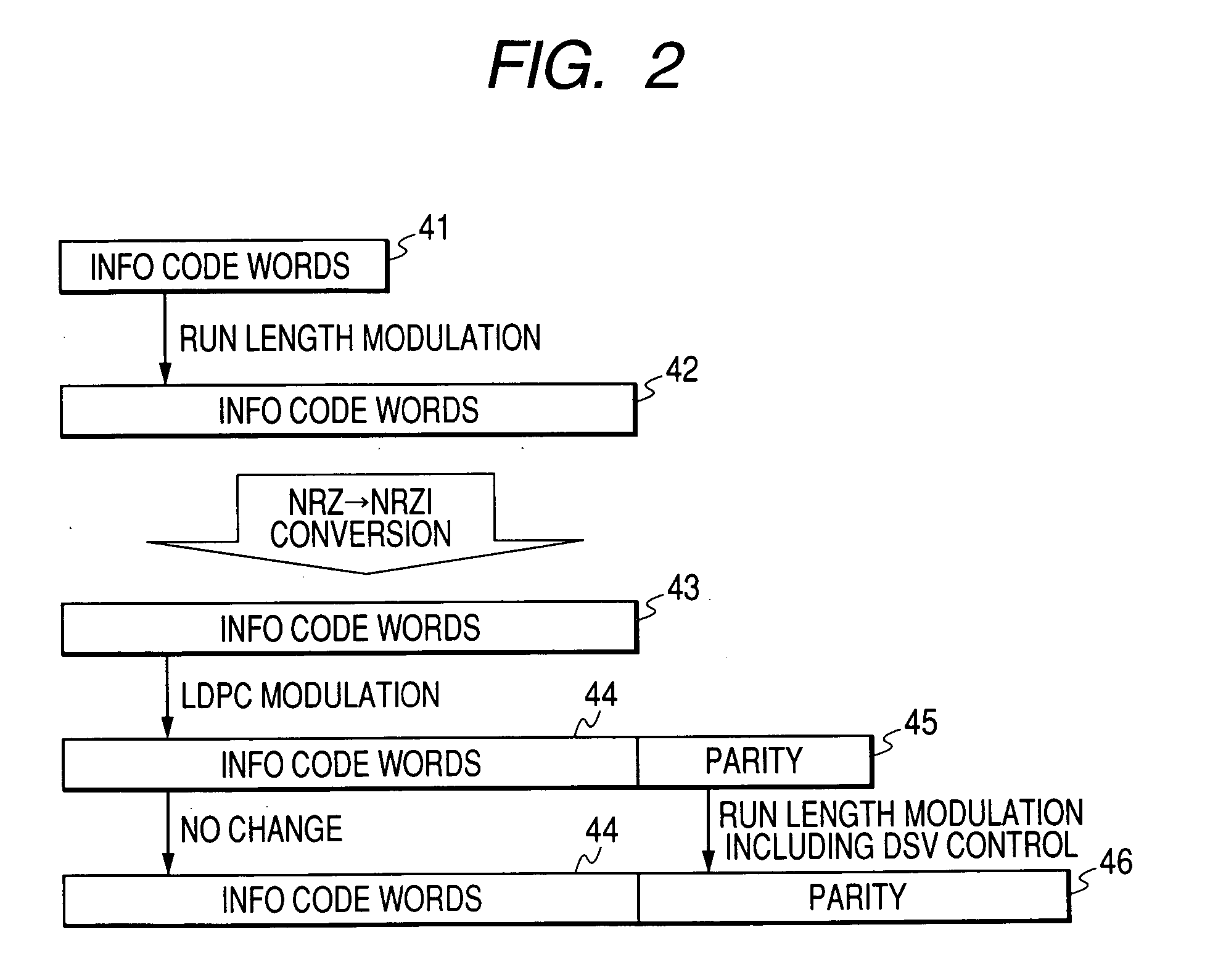
InactiveUS20110055665A1Easy to changeAvoid mistransmissionCode conversionRecord information storageParity-check matrixData error
A data modulation method and a data error correction method are provided. The data modulation method includes generating a channel sequence for an input sequence, determining whether or not the channel sequence violates a Run Length Limit (RLL) constraint, and performing, when the channel sequence violates the RLL constraint, bit flip at a position prior to a position at which the RLL constraint is violated among positions of bits included in the channel sequence. The data error correction method includes detecting an error bit of received data using a parity check matrix, determining whether or not the error bit is an error caused by bit flip, and correcting the error bit when the error bit is an error caused by bit flip for applying an RLL constraint.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Error correction for RLL channel bits in demodulation rules
InactiveUS7307556B2Accurate sortingCorrection errorElectric signal transmission systemsRecord information storageForward error correctionComputer science
RLL (Run Length Limited) code is a well-known channel coding technique, which has no error correction ability itself. The present invention discloses a decoding method, which corrects the channel bit errors via a modified demodulation table with added demodulation rules without increasing any modification circuit, to reduce channel bit errors of RLL code sequences and improve the decoding accuracy of error correction table.
Owner:LITE ON IT
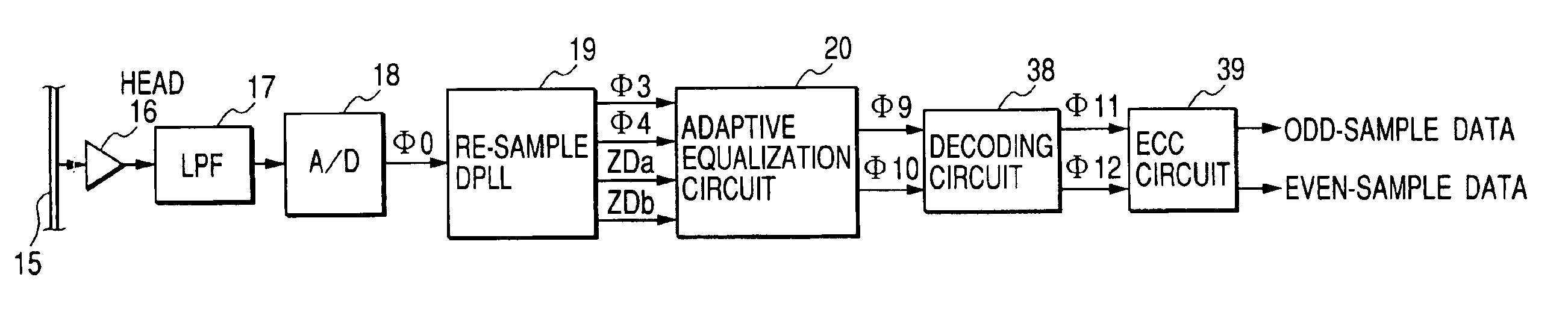
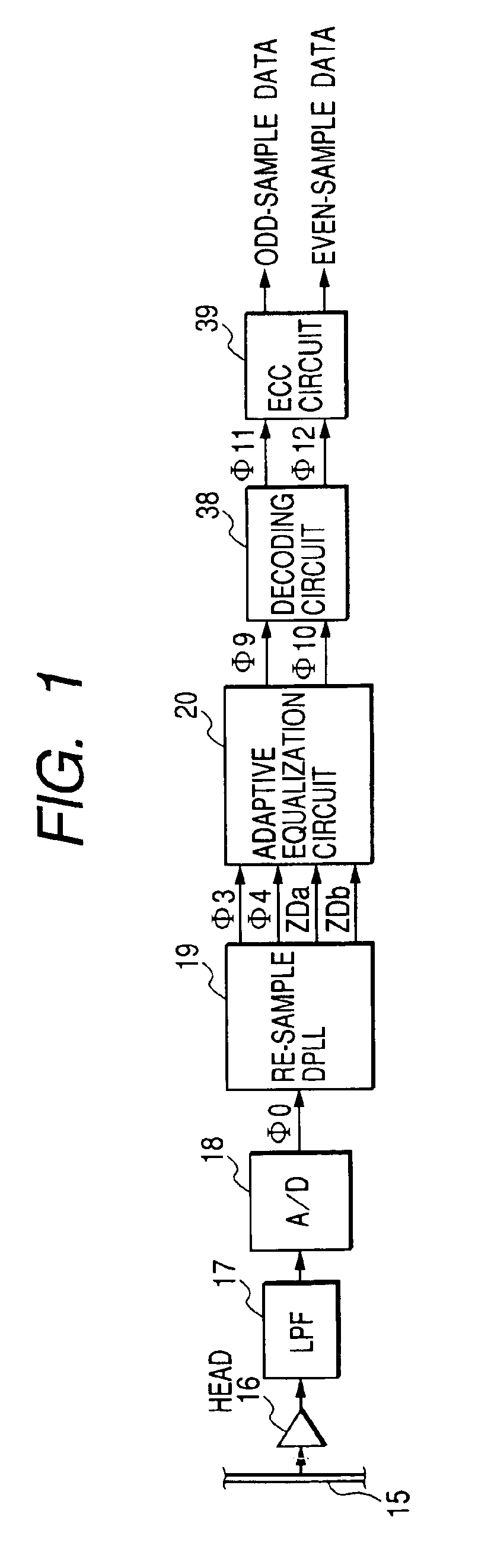
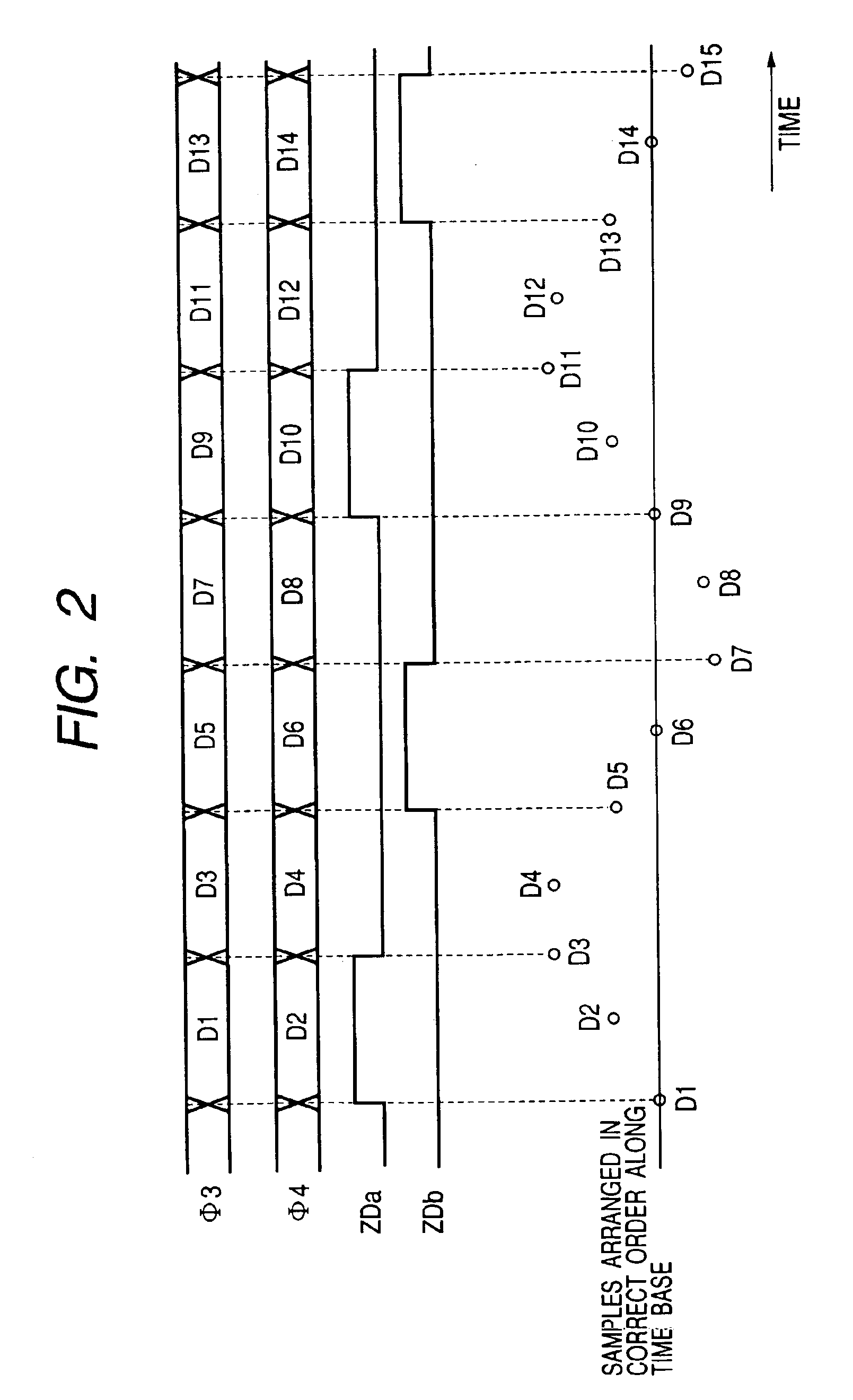
Reproducing apparatus
A signal of a run-length-limited code is reproduced from a recording medium. The reproduced signal is sampled to generate a sampling-resultant signal. An odd-sample signal and an even-sample signal are generated in response to the sampling-resultant signal. A first transversal filter subjects the odd-sample signal to first partial-response waveform equalization to generate an equalization-resultant odd-sample signal. The first partial-response waveform equalization depends on first tap coefficients. The first tap coefficients are controlled on a feedback basis to minimize an error of the equalization-resultant odd-sample signal. A second transversal filter subjects the even-sample signal to second partial-response waveform equalization to generate an equalization-resultant even-sample signal. The second partial-response waveform equalization depends on second tap coefficients. The second tap coefficients are controlled on a feedback basis to minimize an error of the equalization-resultant even-sample signal. The equalization-resultant odd-sample signal is decoded. The equalization-resultant even-sample signal is decoded.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Modulation apparatus/method, demodulation apparatus/method and program presenting medium
InactiveUS7158060B2Reduce the numberGrowth inhibitionDigital variable displayDigital data processing detailsVariable-length codeTheoretical computer science
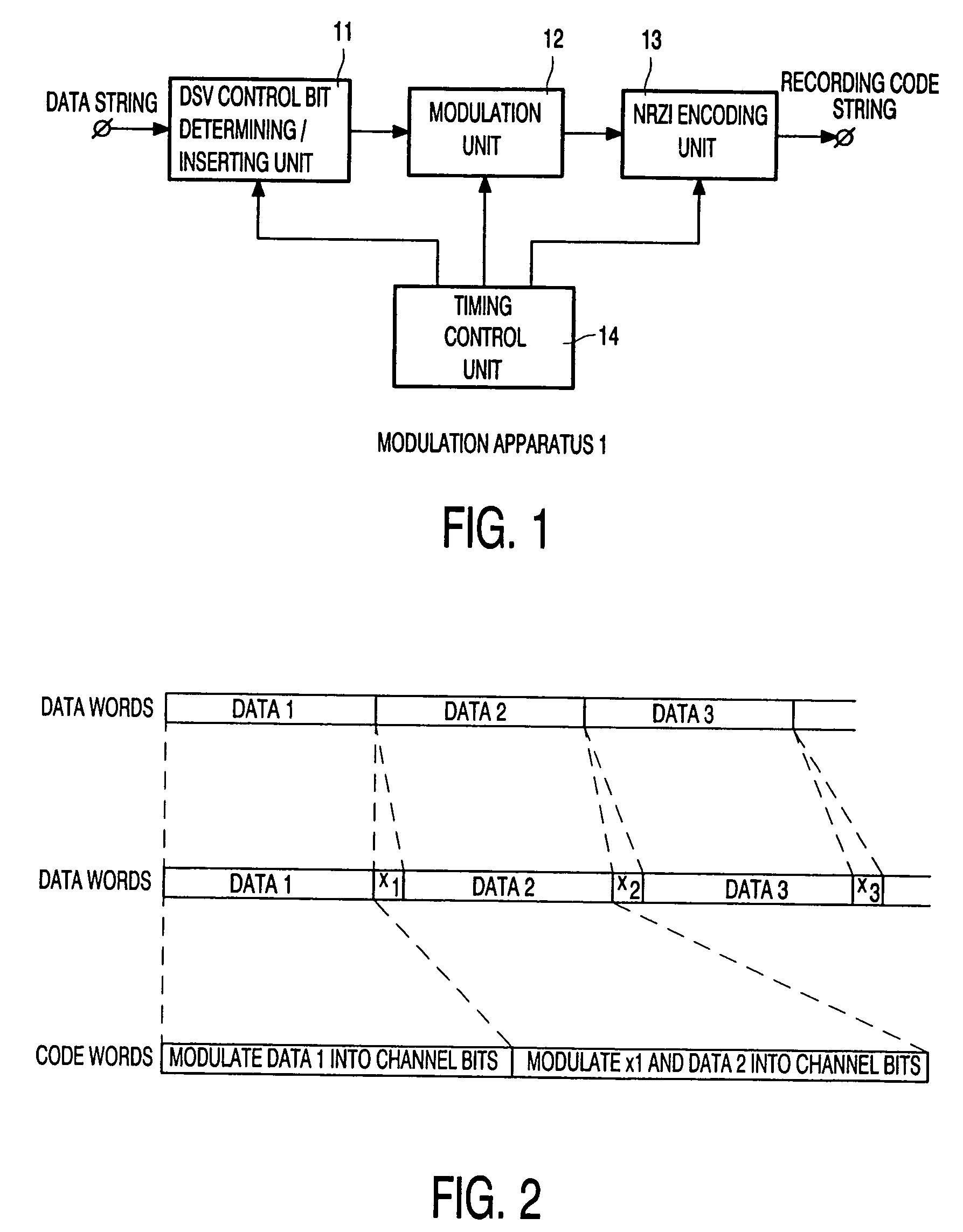
How to record and play back data at a high line density. A DSV control bit determining / inserting unit 11 inserts DSV control bits for execution of DSV control into an input data string and outputs the data string including the DSV control bits to a modulation unit 12. The modulation unit 12 converts the data string with a basic data length of 2 bits into variable length code with a basic code length of 3 bits in accordance with a conversion table and outputs the code resulting from the conversion to a NRZI encoding unit 13. The conversion table used by the modulation unit 12 includes substitution codes for limiting the number of consecutive appearances of a minimum run to a predetermined value and substitution codes for keeping a run length limit. In addition, the conversion table enforces a conversion rule, according to which the remainder of division of the “1” count of an element in a data string by 2 having a value of 0 or 1 shall always be equal to the remainder of division of the “1” count of an element in the code resulting from conversion of the data string by 2.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding modulation code
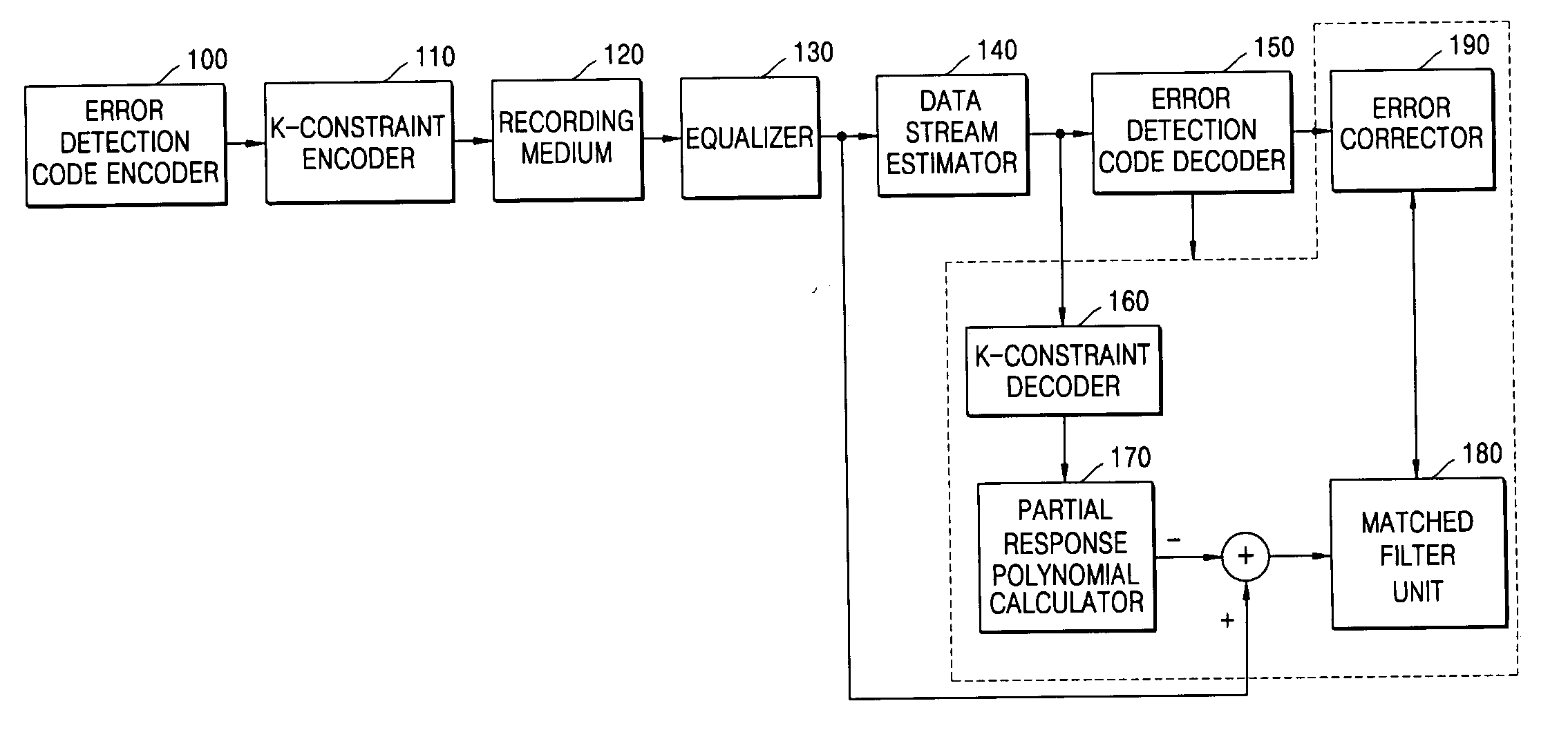
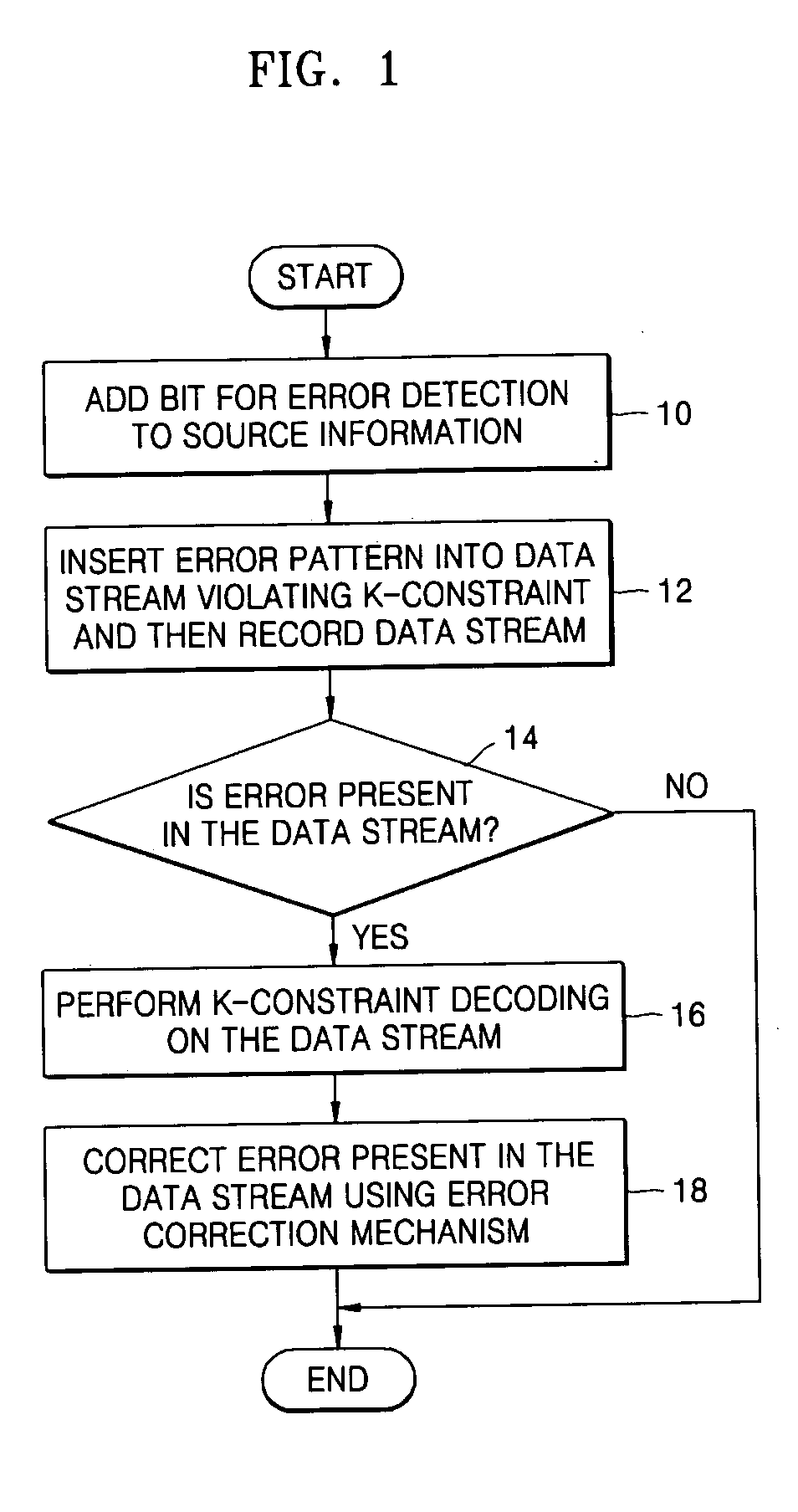
InactiveUS20060164263A1Code rate lossError preventionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareData stream
A method and an apparatus for encoding and decoding a modulation code are provided. The method includes: adding an error detection bit(s) to source information; performing k-constraint coding by inserting an error pattern that can be detected using an error detection code into a data stream that violates a k-constraint for a run length limited (RLL) code in a data stream comprising the error detection bit(s) and the source information, and recording the data stream after being k-constraint coded onto a recording medium; and reading the data stream recorded onto the recording medium and determining whether an error is present in the data stream.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Modulation - forward error correction (MFEC) codes and methods of constructing and utilizing the same
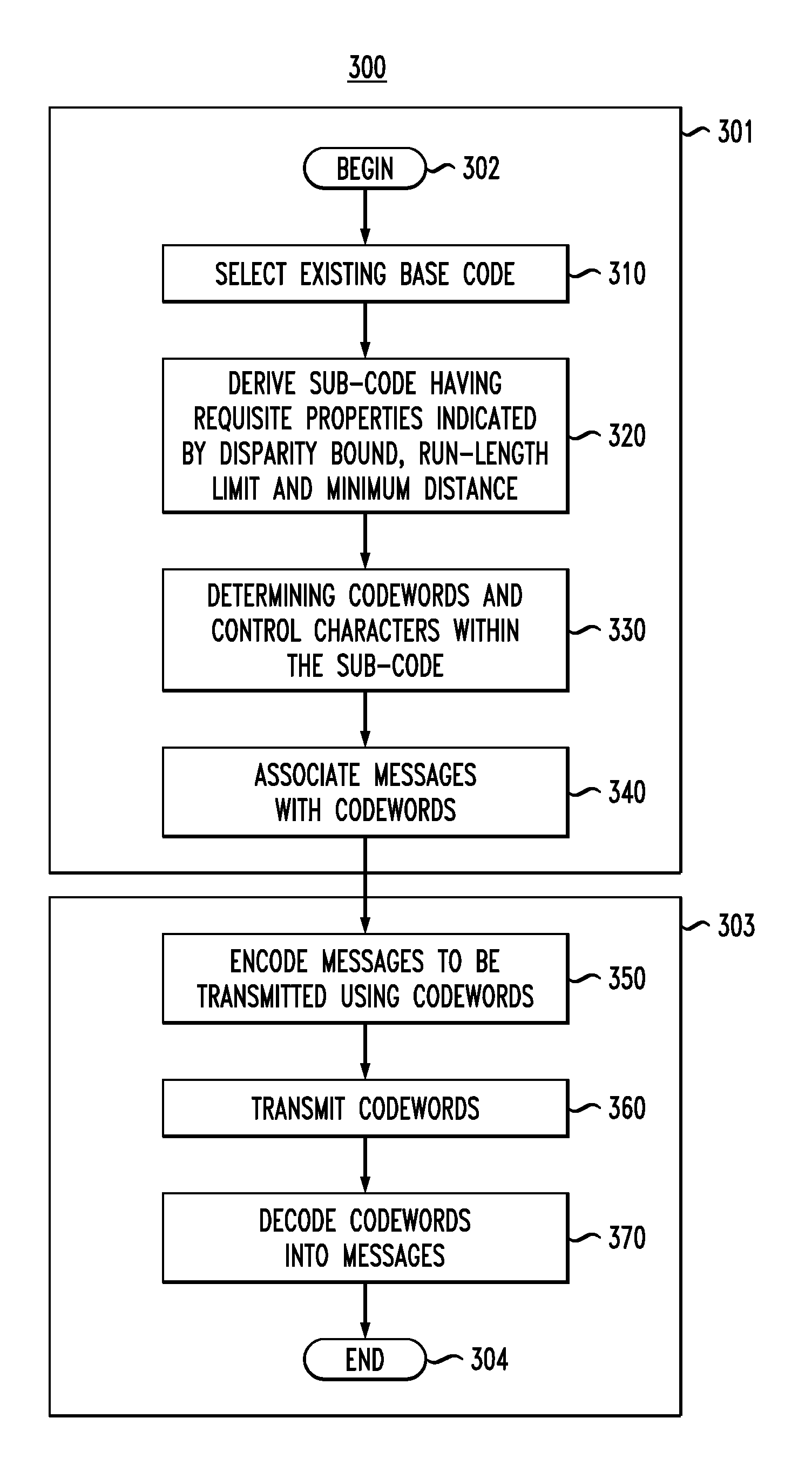
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to binary block transmission codes for high-speed network transmissions. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention relate to bounded-disparity run-length-limited forward error correction codes and methods of constructing and utilizing same. In one embodiment, a method for generating binary block bounded-disparity run-length-limited forward error correction transmission codes comprises selecting an existing base code, deriving a sub-code from the existing base code, having properties indicated by disparity bound, run-length limit and minimum distance, ascertaining a plurality of codewords and control characters from within the sub-code, encoding Messages to be transmitted with at least one codeword from the plurality of codewords, transmitting codewords from a transmitter to a receiver, and decoding the codewords into Messages.
Owner:ZEPHYR PHOTONICS
Two-dimensional run length constrained codec with protected words and its usage method
InactiveCN102298953ASimple structureRealize decodingElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsIndividual digits conversionData streamData recording
The invention provides a codec with a protection word and a limited and restrained two dimension run length and an application method thereof. The codec comprises: an encoder and a decoder. The encoder comprises: a data buffer and packet module, a two dimension code word generation module, a two dimension word unit page structure module, a two-dimension code-word write-in array module and a protection word filling module. The above five modules are successively connected and are output to a two dimension data recording apparatus through the protection word filling module. The decoder comprises: a two dimension data buffer module, the two dimension word unit page structure module, a one-dimensional data word decoding module and a one-dimensional data flow assembly module. The above five modules are successively connected and are output through the one-dimensional data flow assembly module. By using the encoding and decoding method and the apparatus of the invention, two dimension (1, 3) RLL technology problem that the two dimension data array formed by 0 and 1 satisfies a (1, 3) RLL constraint in two directions can be solved.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Modulation-forward error correction (MFEC) codes and methods of constructing and utilizing the same
ActiveUS8904258B2Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareParallax
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to binary block transmission codes for high-speed network transmissions. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention relate to bounded-disparity run-length-limited forward error correction codes and methods of constructing and utilizing same. In one embodiment, a method for generating binary block bounded-disparity run-length-limited forward error correction transmission codes comprises selecting an existing base code, deriving a sub-code from the existing base code, having properties indicated by disparity bound, run-length limit and minimum distance, ascertaining a plurality of codewords and control characters from within the sub-code, encoding Messages to be transmitted with at least one codeword from the plurality of codewords, transmitting codewords from a transmitter to a receiver, and decoding the codewords into Messages.
Owner:ZEPHYR PHOTONICS
Modulation device, modulation method and recording medium
InactiveUS20040062168A1Television system detailsRecord information storageAlgorithmAlternating current
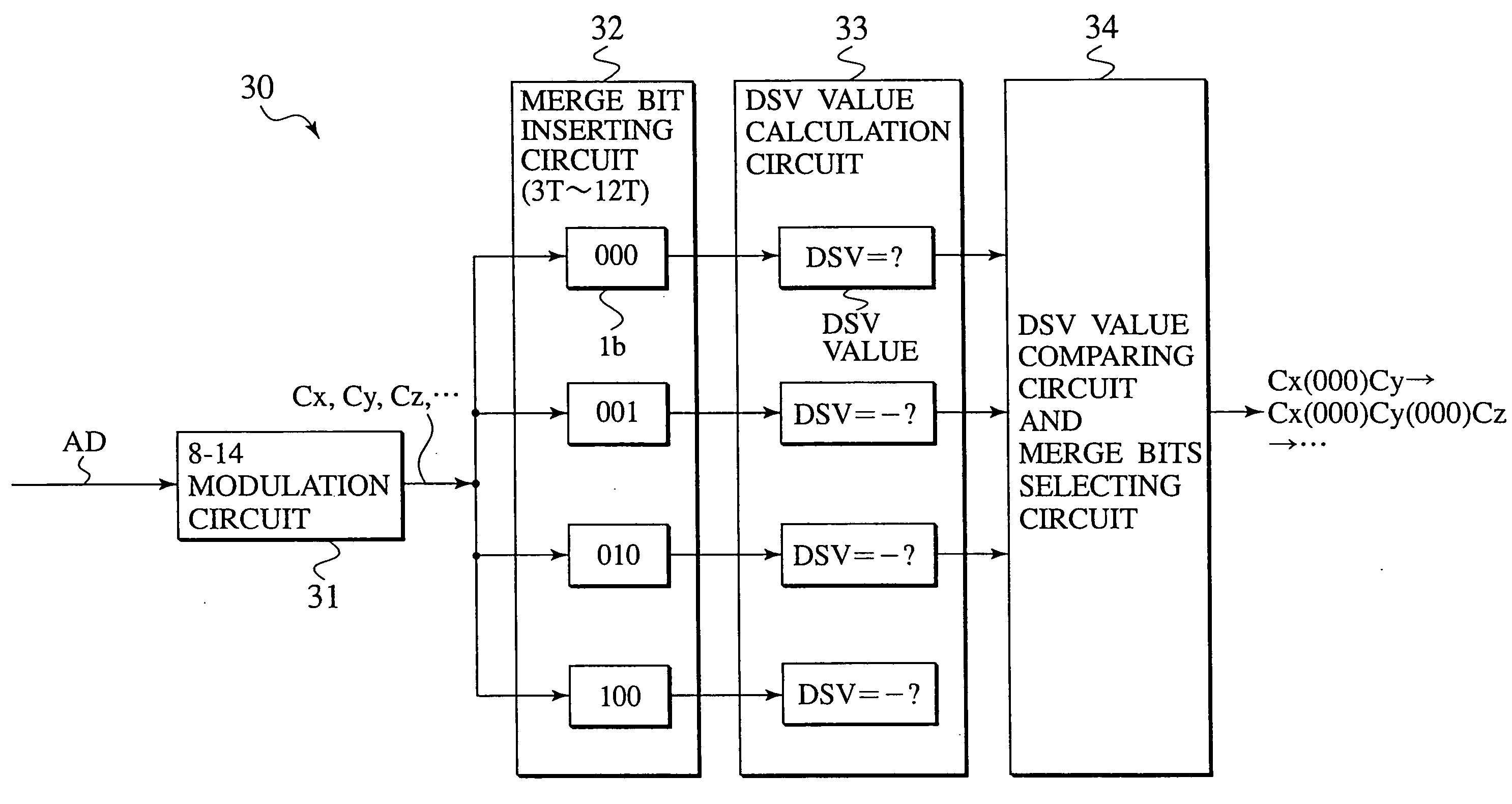
When a code word sequence is generated by converting input data words of p bits into code words of q bits and concatenating adjacent ones of the code words with a merge bit sequence of r bits in order to obtain the best DSV value, according to one aspect, the adjacent code words are concatenated with the merge bit sequence of r bits which is selected, free from the restriction of the minimum run-length of (d+1)T and the maximum run-length of (k+1)T based on the run-length limiting rule RLL(d, k) but permitting the minimum run-length of (d+1)T and the maximum run-length of (k+2)T. According to another aspect, a merge bit sequence to be inserted after a current code word is selected by prefetching the current code word, a next code word, and a further next code word, temporarily concatenating these code words with merge bit sequences of r bits respectively to prepare code word sequence candidates free from the predetermined run-length limiting rule, calculating the DSV values of the code word sequence candidates, selecting one of the code word sequence candidates having a DSV value whose absolute value is closest to zero, and selecting the merge bit sequence between the current code word and the next code word of the selected merge bit sequence candidate. According to a further aspect, the input data words are encoded by a p-q modulation scheme after introducing for a predetermined period, as an input data word, specific data comprising alternating current signals or direct current signals which would cause a modulation device that prefetches only the next code word to output a code word sequence which includes particular frequency components.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Method of storing rll encoded information to an optical disc with control of the frequency of the information with respect to the cut-off frequency of the optical system
InactiveUS20070030786A1Improve efficiencyControl moreTelevision system detailsRecord information storageOptical disk storageLength wave
A method of storing / retrieving information to / from an optical disc by means of an optical system with a cut-off frequency νcut-off, above which frequencies cannot be detected, is disclosed. The invention relates to Run Length Limited encoded information. According to the invention, some frequencies of the encoded information can be higher than cut-off frequency of the optical system, such that the equation 4*(d+1)*Lcd*NA / λlaser<1 is satisfied, where d+1 is the minimum run length of the coding, Lcd is the length of a channel bit, NA is the numerical aperture and λlaser is the wavelength of the optical system. Hereby, the capacity of the optical disc is increased, while the prevailing coding technique is used. Moreover, the invention relates to a disc for storing of data, a drive capable of storing data and an apparatus for manufacturing optical discs.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
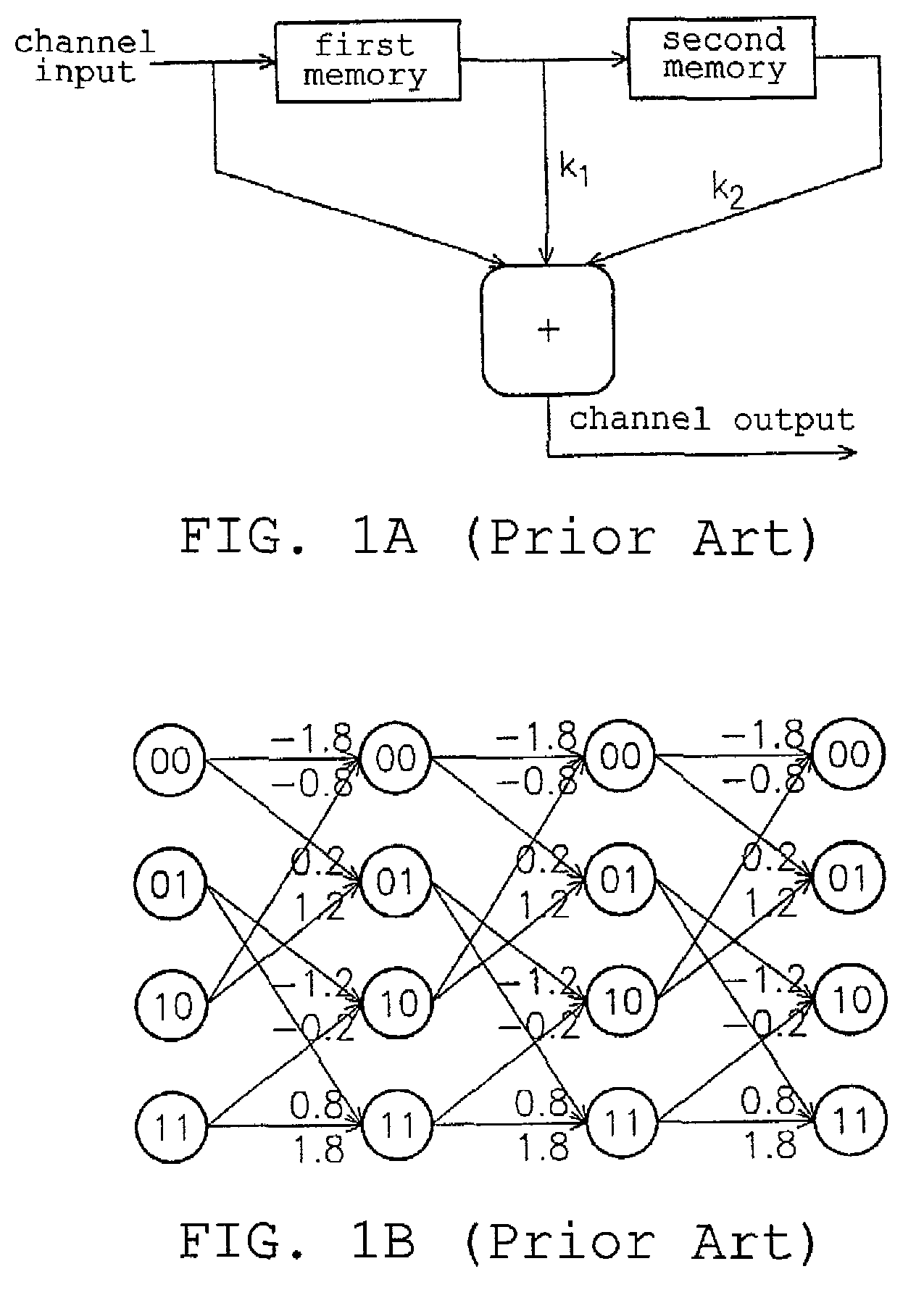
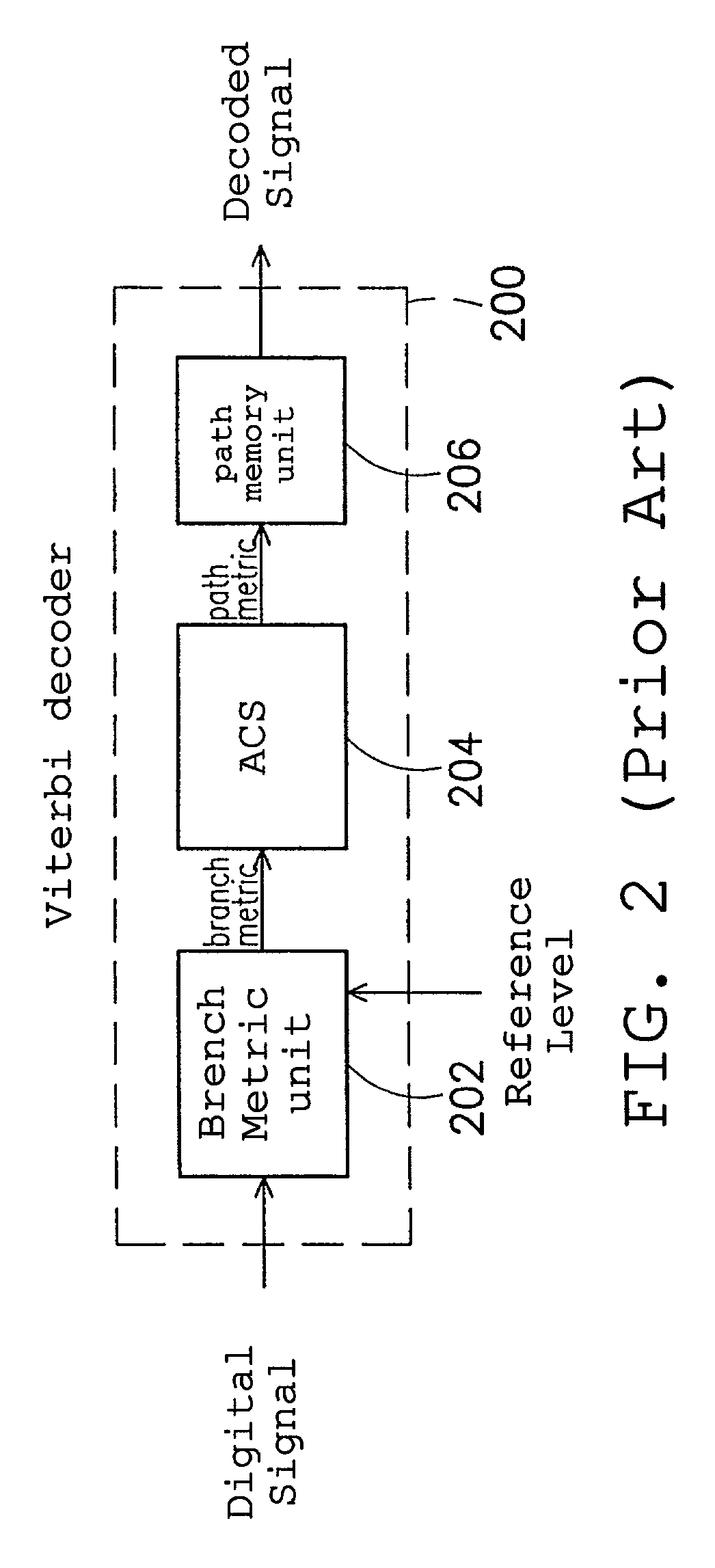
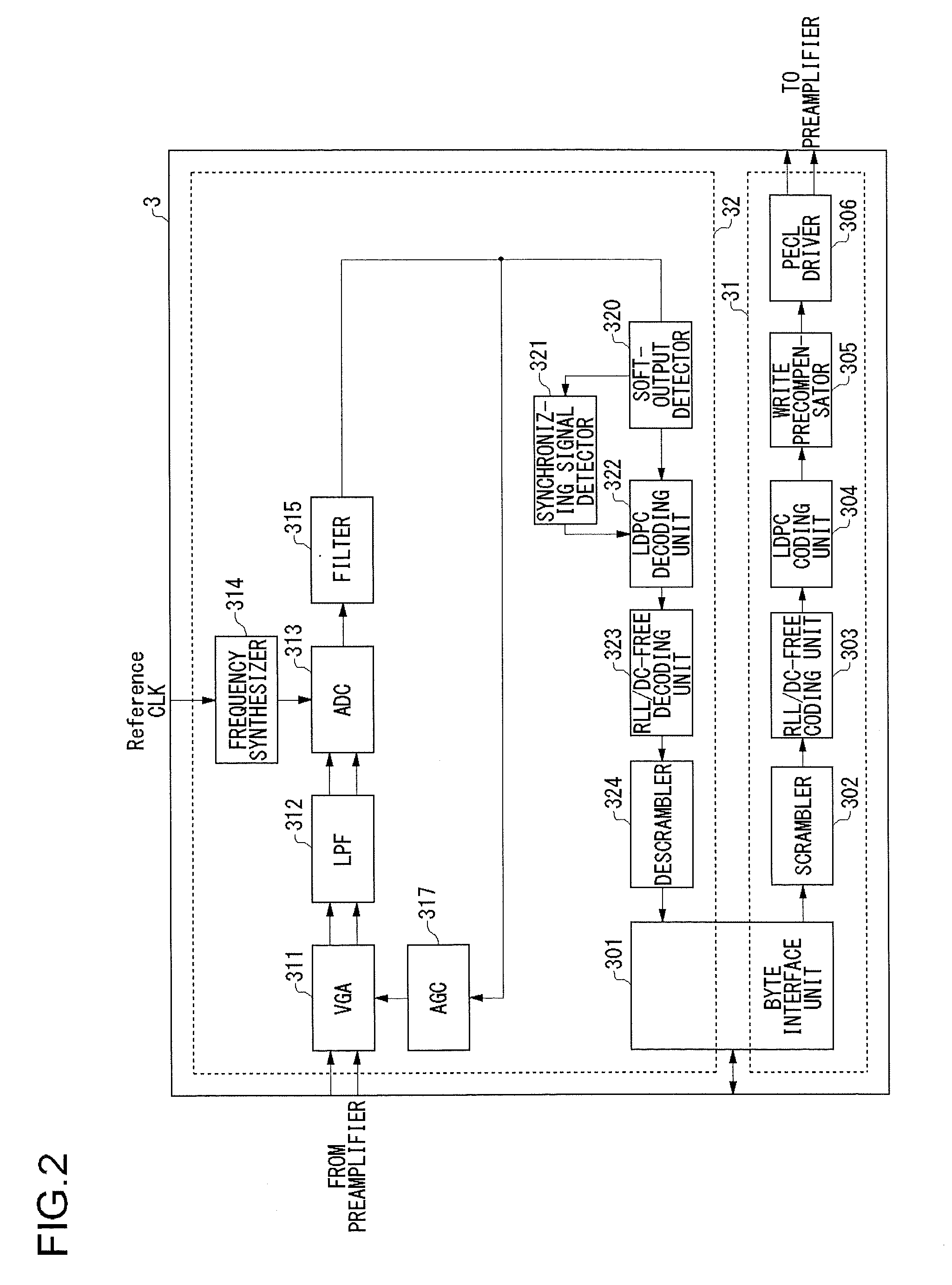
Decoding circuit and method of Viterbi decoder
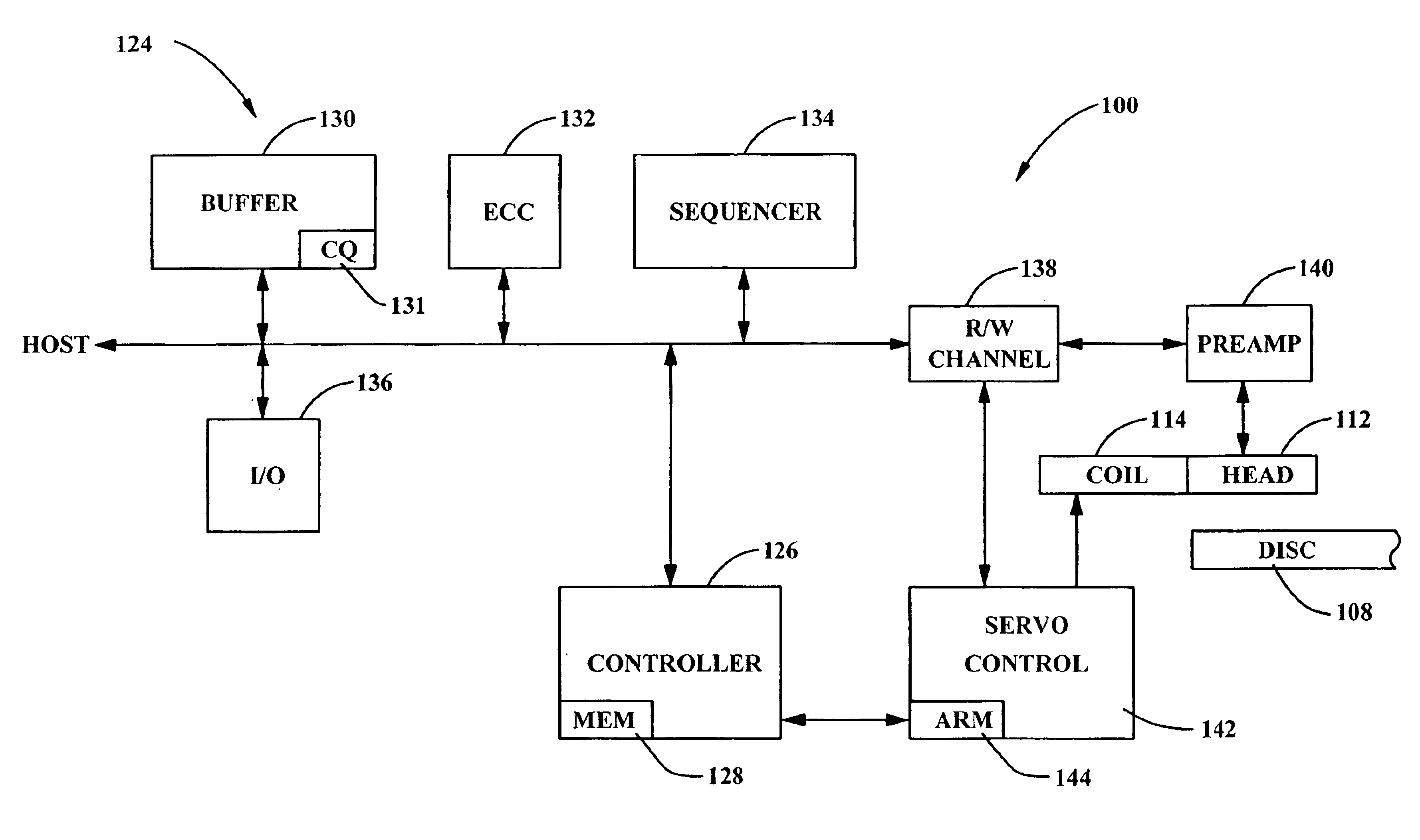
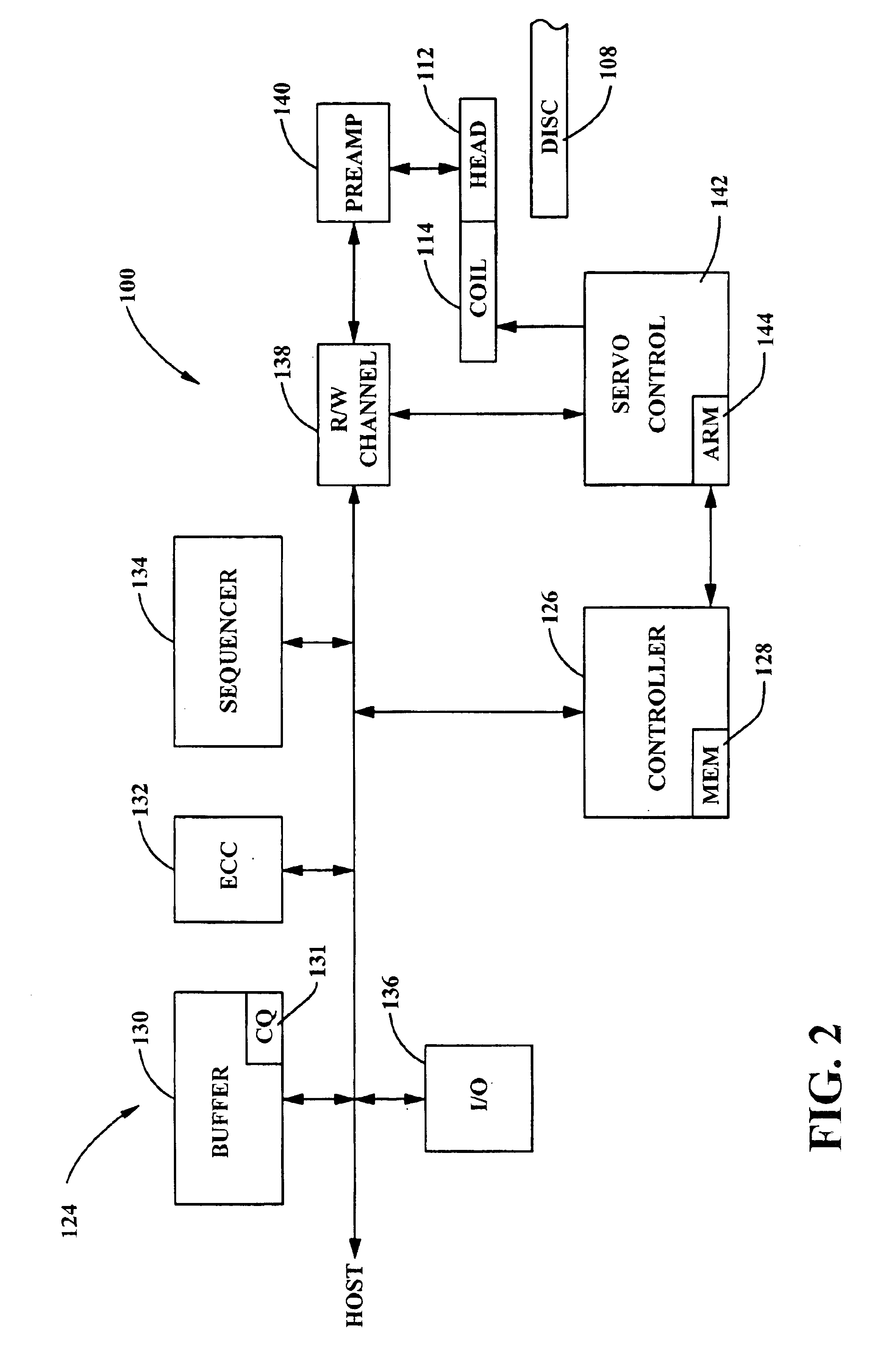
ActiveUS6999532B2Increase speedEfficient solutionModification of read/write signalsData representation error detection/correctionProcessor registerRun-length limited
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Coding apparatus, decoding apparatus, amplitude adjustment apparatus, recorded information reader, signal processing apparatus and storage system
InactiveUS20090045989A1Simple circuit configurationReduce circuit sizeModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageComputer hardwareGeneral purpose
A general purpose of the present invention is to improve a DC-free property with a further reduced circuit scale while satisfying a run-length limit. An RLL / DC-free coding unit coding includes a first RLL coding unit, a first signal processing unit, a second RLL coding unit, and a DC component removal coding unit. The first RLL coding unit generates a first coded sequence by subjecting a digital signal sequence outputted from a scrambler to run-length limited coding. The first signal processing unit performs a predetermined signal processing on the digital signal sequence without changing the number of a plurality of bits contained in the digital signal sequence outputted from the scrambler 302. The second RLL coding unit generates a second coded sequence by subjecting the digital signal sequence, which is outputted from the first signal processing unit and on which the predetermined signal processing has been performed by the signal processing unit, to run-length limited coding.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Modulation device, modulation method and recording medium
InactiveUS7212483B2Prevent copyingTelevision system detailsRecord information storageAlgorithmAlternating current
When a code word sequence is generated by converting input data words of p bits into code words of q bits and concatenating adjacent ones of the code words with a merge bit sequence of r bits in order to obtain the best DSV value, according to one aspect, the adjacent code words are concatenated with the merge bit sequence of r bits which is selected, free from the restriction of the minimum run-length of (d+1)T and the maximum run-length of (k+1)T based on the run-length limiting rule RLL(d, k) but permitting the minimum run-length of (d+1)T and the maximum run-length of (k+2)T. According to another aspect, a merge bit sequence to be inserted after a current code word is selected by prefetching the current code word, a next code word, and a further next code word, temporarily concatenating these code words with merge bit sequences of r bits respectively to prepare code word sequence candidates free from the predetermined run-length limiting rule, calculating the DSV values of the code word sequence candidates, selecting one of the code word sequence candidates having a DSV value whose absolute value is closest to zero, and selecting the merge bit sequence between the current code word and the next code word of the selected merge bit sequence candidate. According to a further aspect, the input data words are encoded by a p-q modulation scheme after introducing for a predetermined period, as an input data word, specific data comprising alternating current signals or direct current signals which would cause a modulation device that prefetches only the next code word to output a code word sequence which includes particular frequency components.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
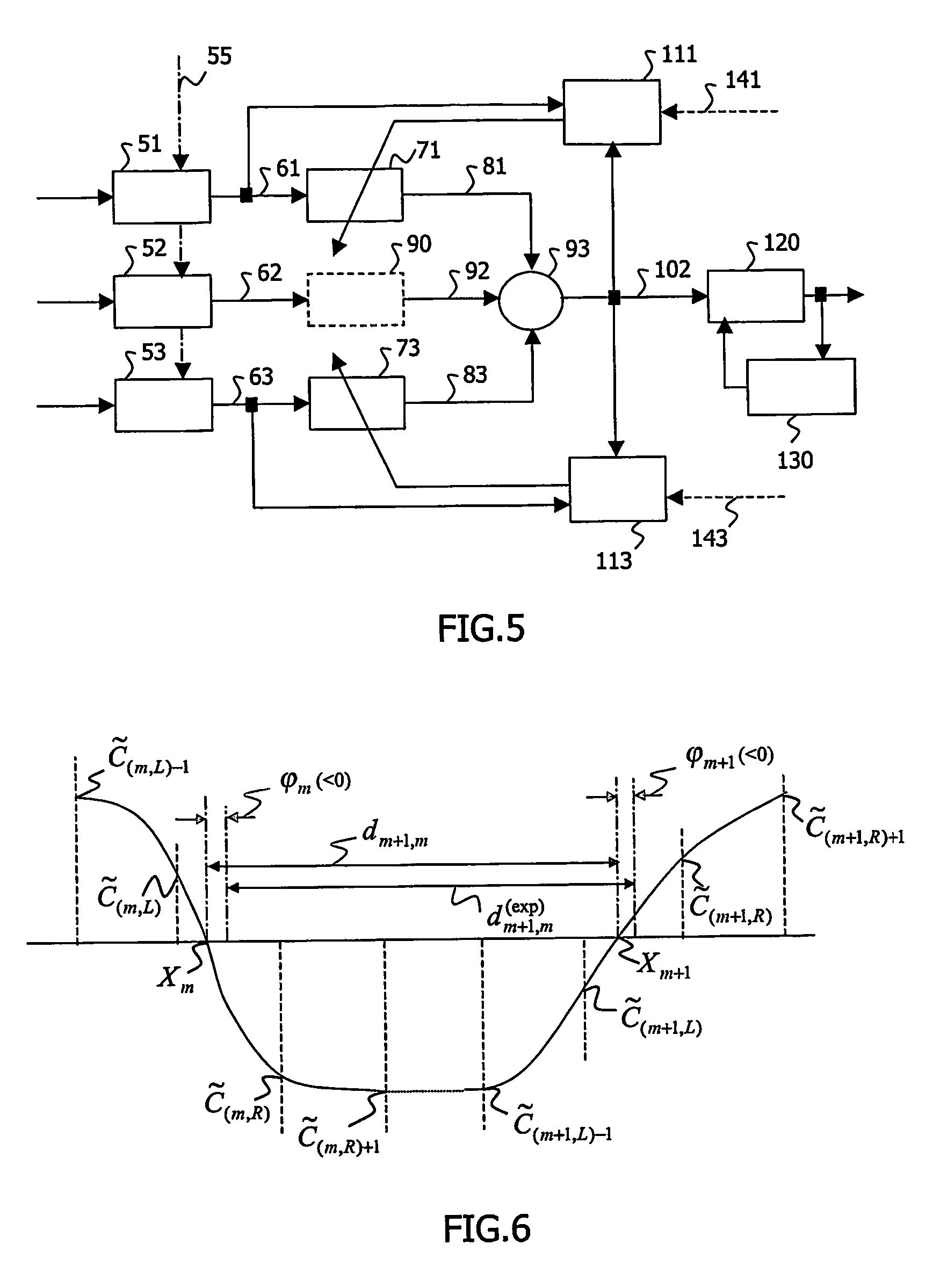
Cross-talk cancellation scheme for rll-based storage systems
InactiveUS20060181975A1Resolution problemMinimize mismatchPower managementTransmission control/equalisingVolumetric Mass DensityHardware implementations
The invention relates to Run length Limited-codes storage systems. In modern storage systems, the inter-track spacing is chosen to be relatively small to allow for high storage densities. As a result, when reading a target track, data written on side tracks may appear in the recovered signal. This inter-track interference is called cross-talk. The invention proposes a cross-talk cancellation scheme based on the minimization of the mismatch between the actual (dm+1m) and the expected (exp) run length between two transitions (xm, xm+1) of the (dm+1,m) signal. The proposed solution significantly improves the ramp-up properties of the receiver and allows more efficient hardware implementation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High rate run length limited code
InactiveUS6839004B2Increase valueRecord information storageImage codingHigh rateCommunications system
Methods of encoding and decoding, as well as an encoding system and a digital communications system are provided for encoding data words into code words and decoding code words into data words. The data words are encoded according to a run-length-limited (RLL) code of “k” constraint, the encoding producing u-bit non-zero code words. The “k” constraint can be increased to a higher value by extending the u-bit non-zero code words to generate q-bit non-zero code words.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com