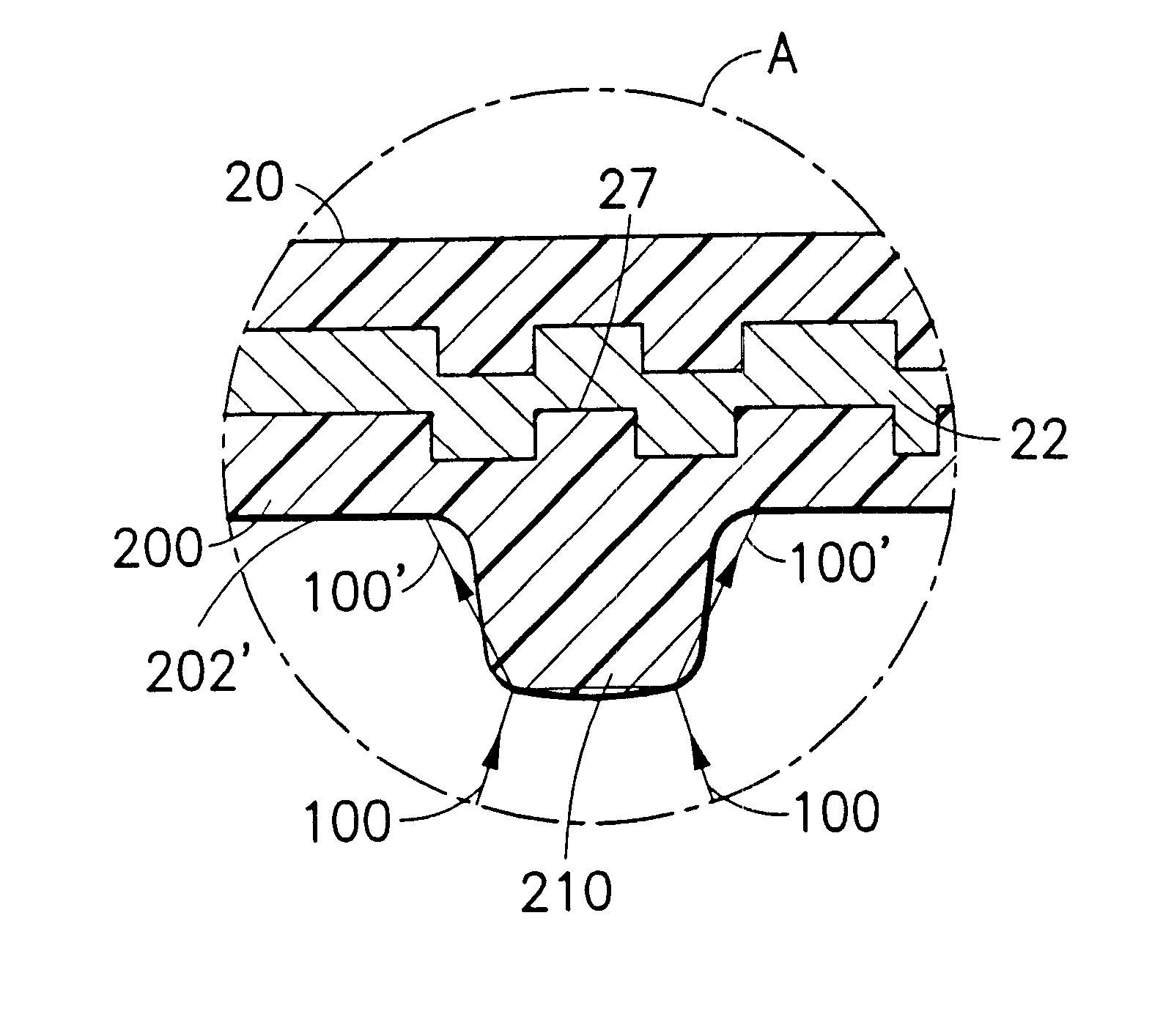
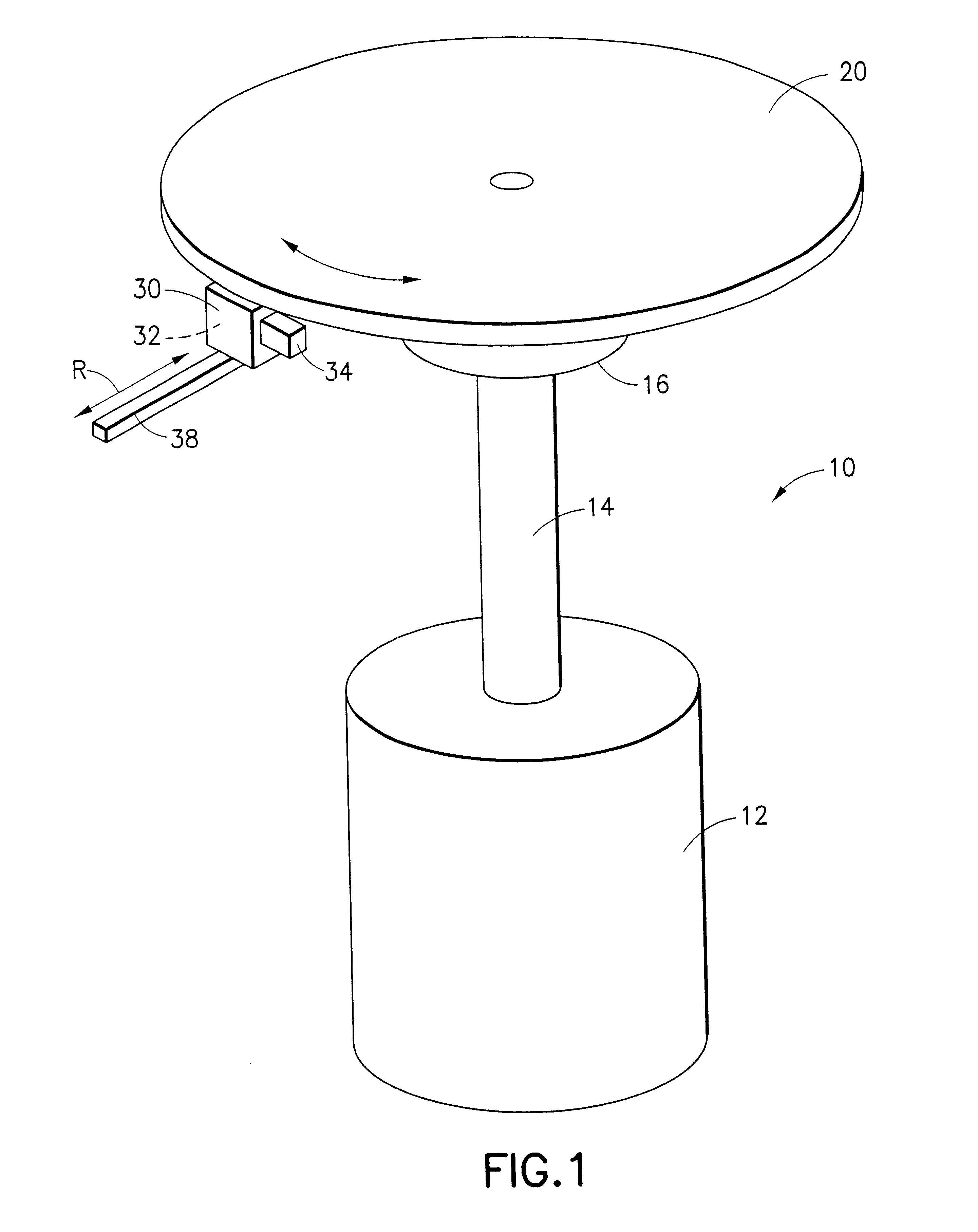
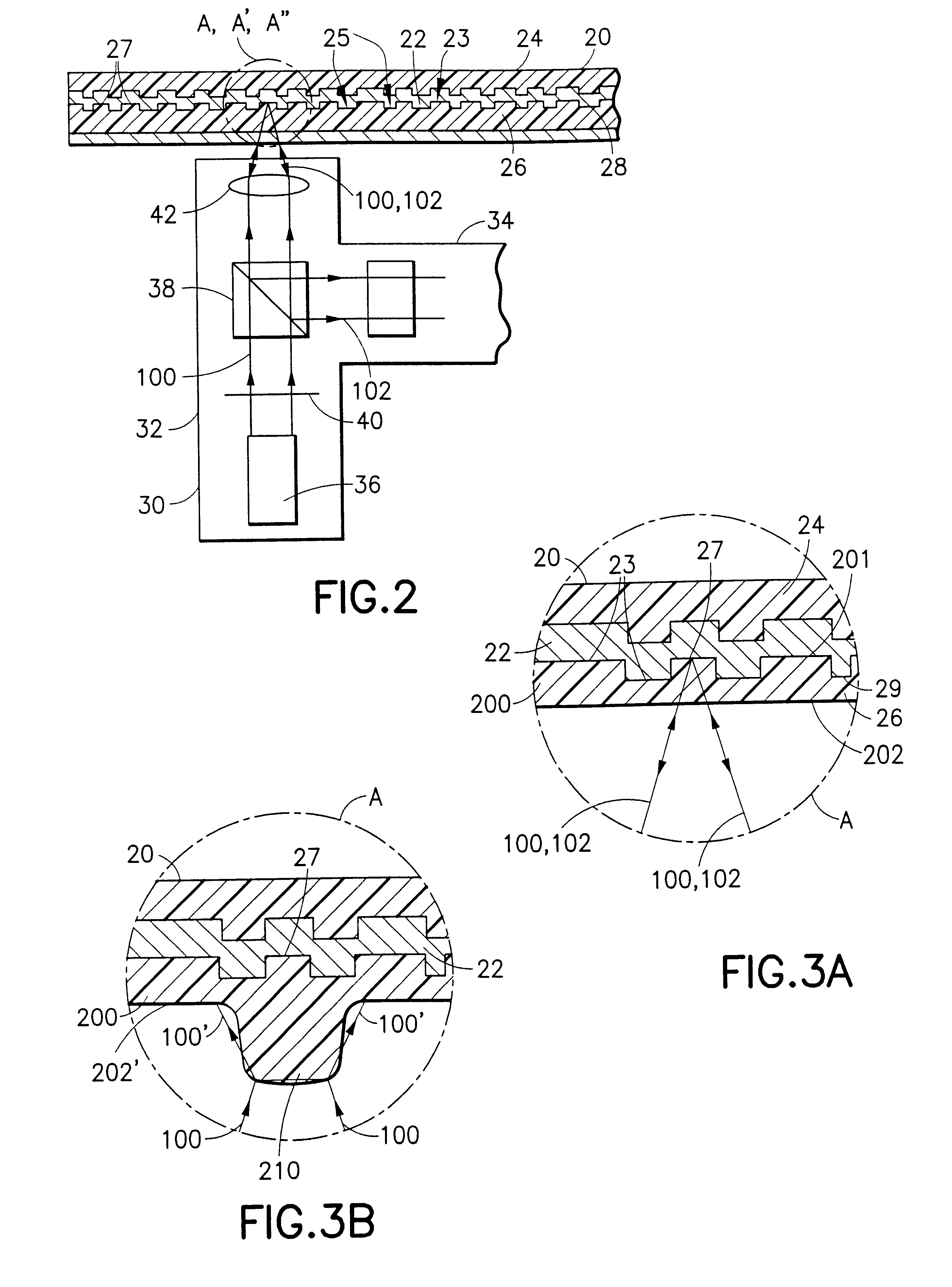
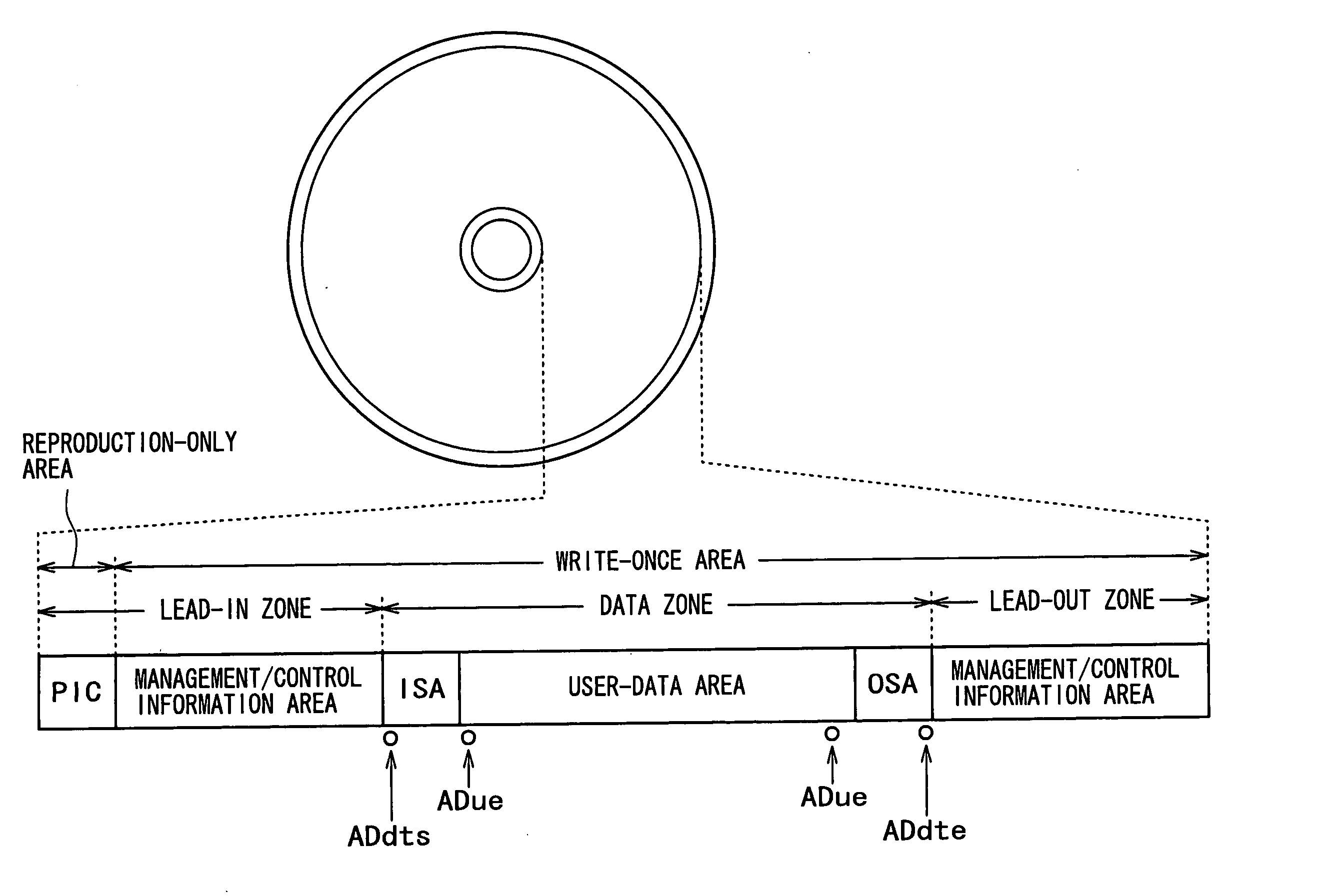
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
219results about "Optical erasing systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
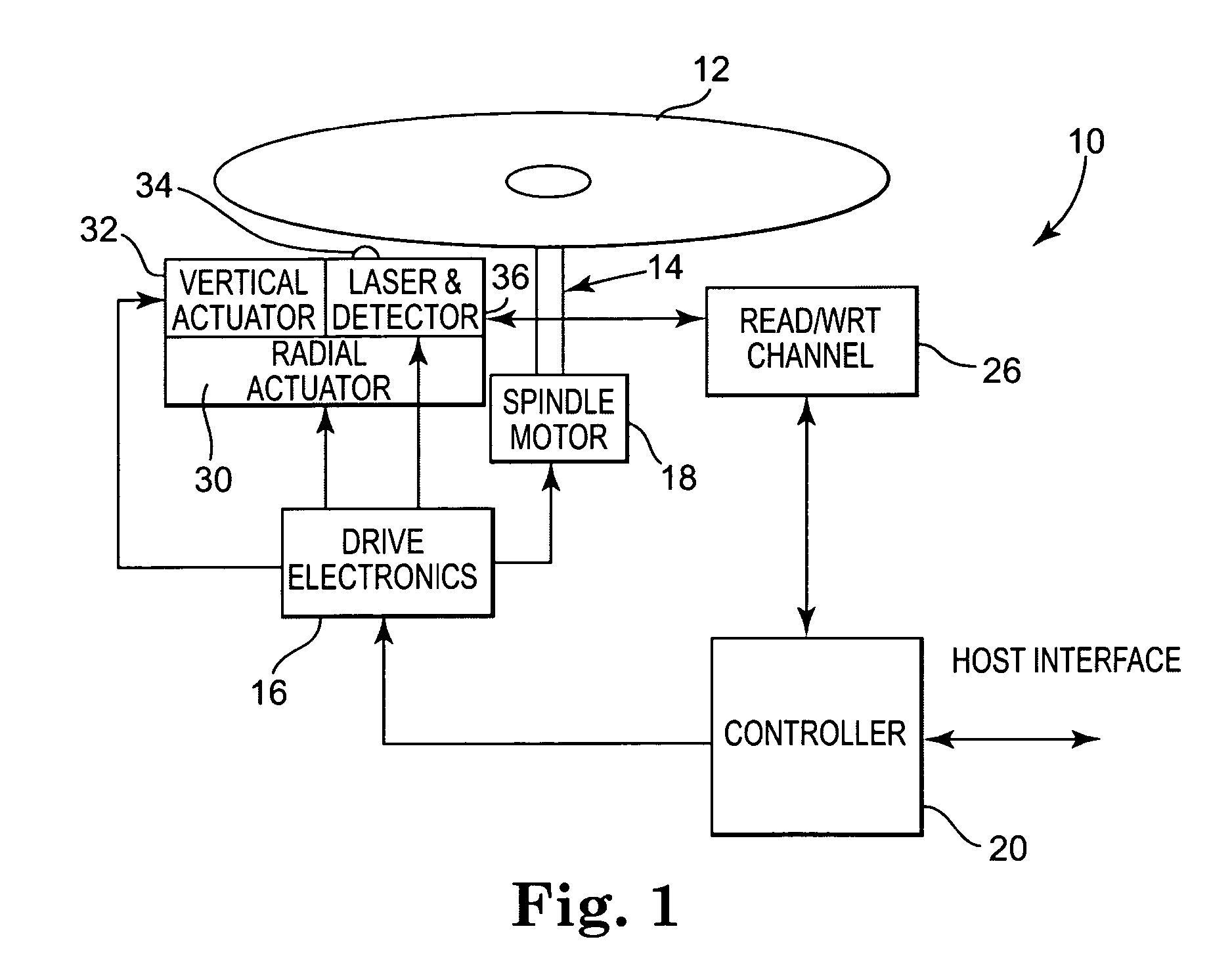
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
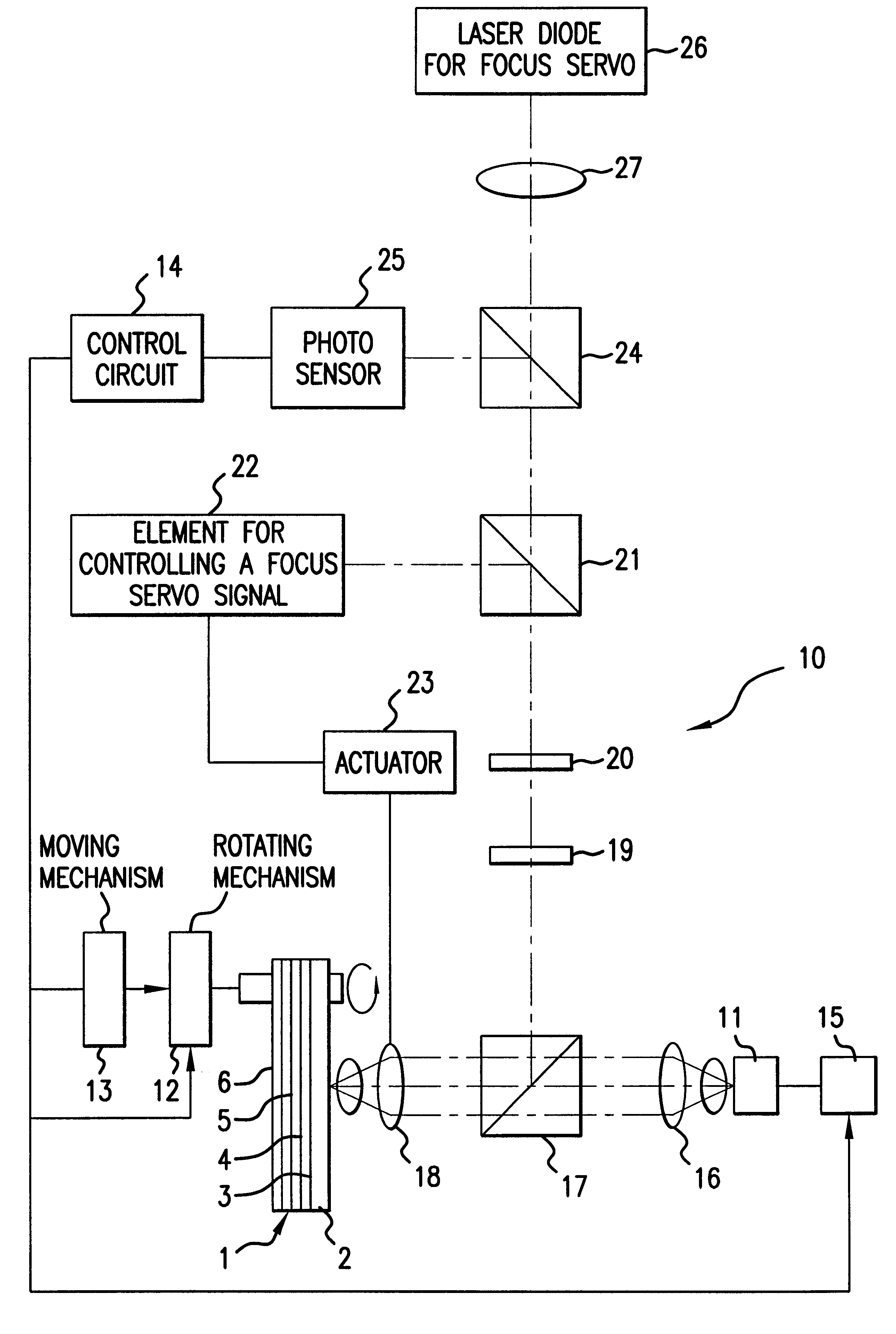
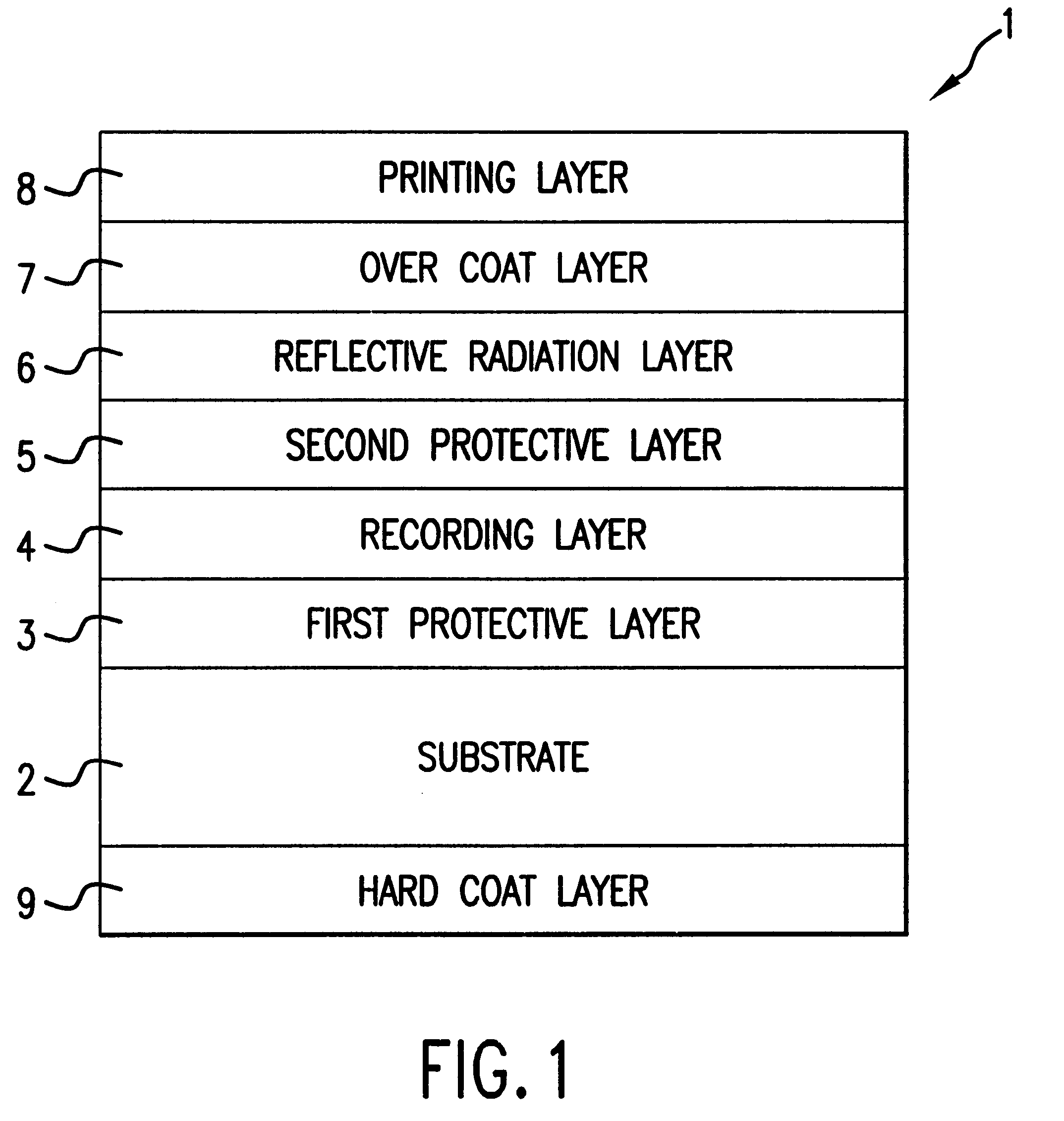
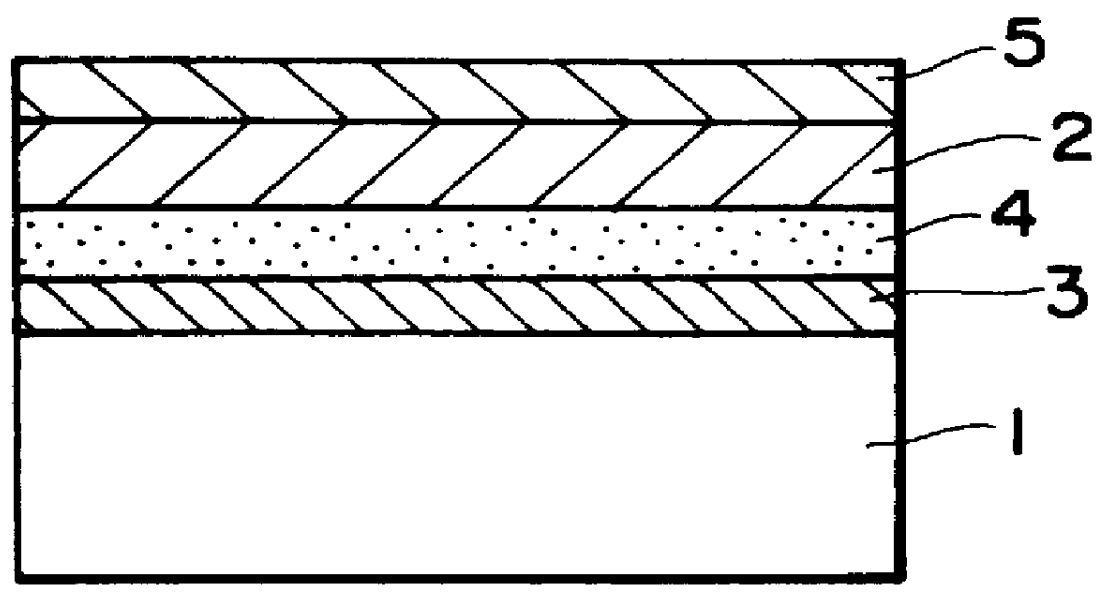
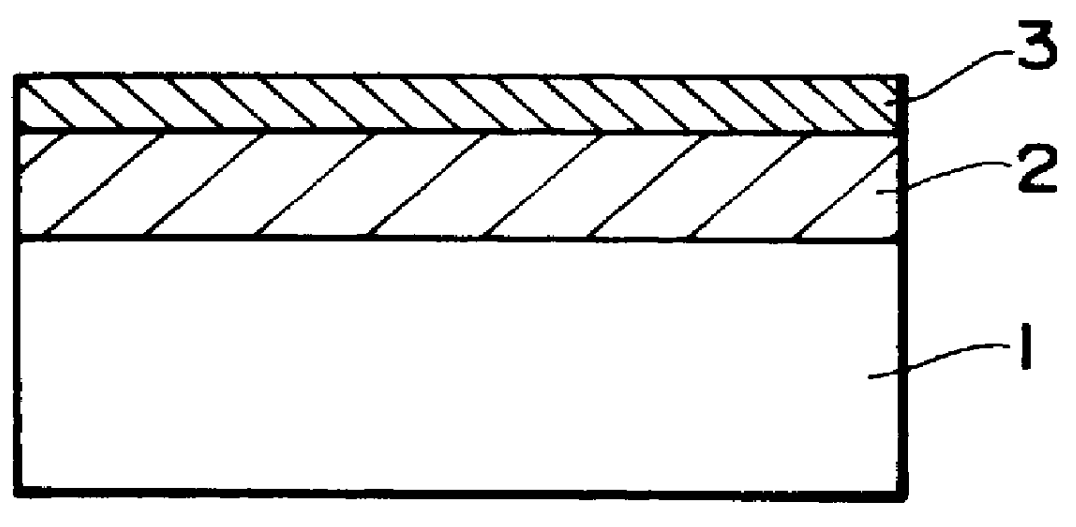
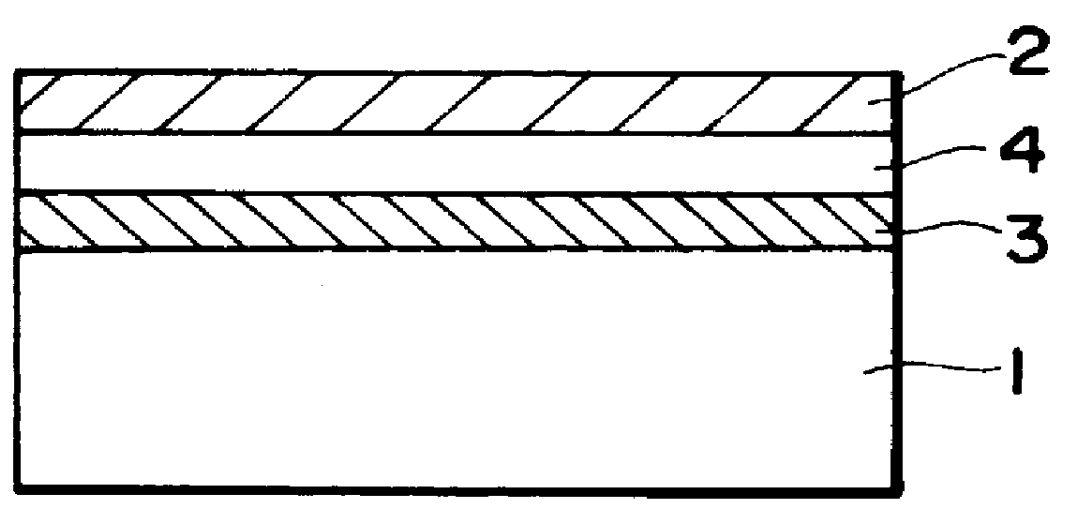
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
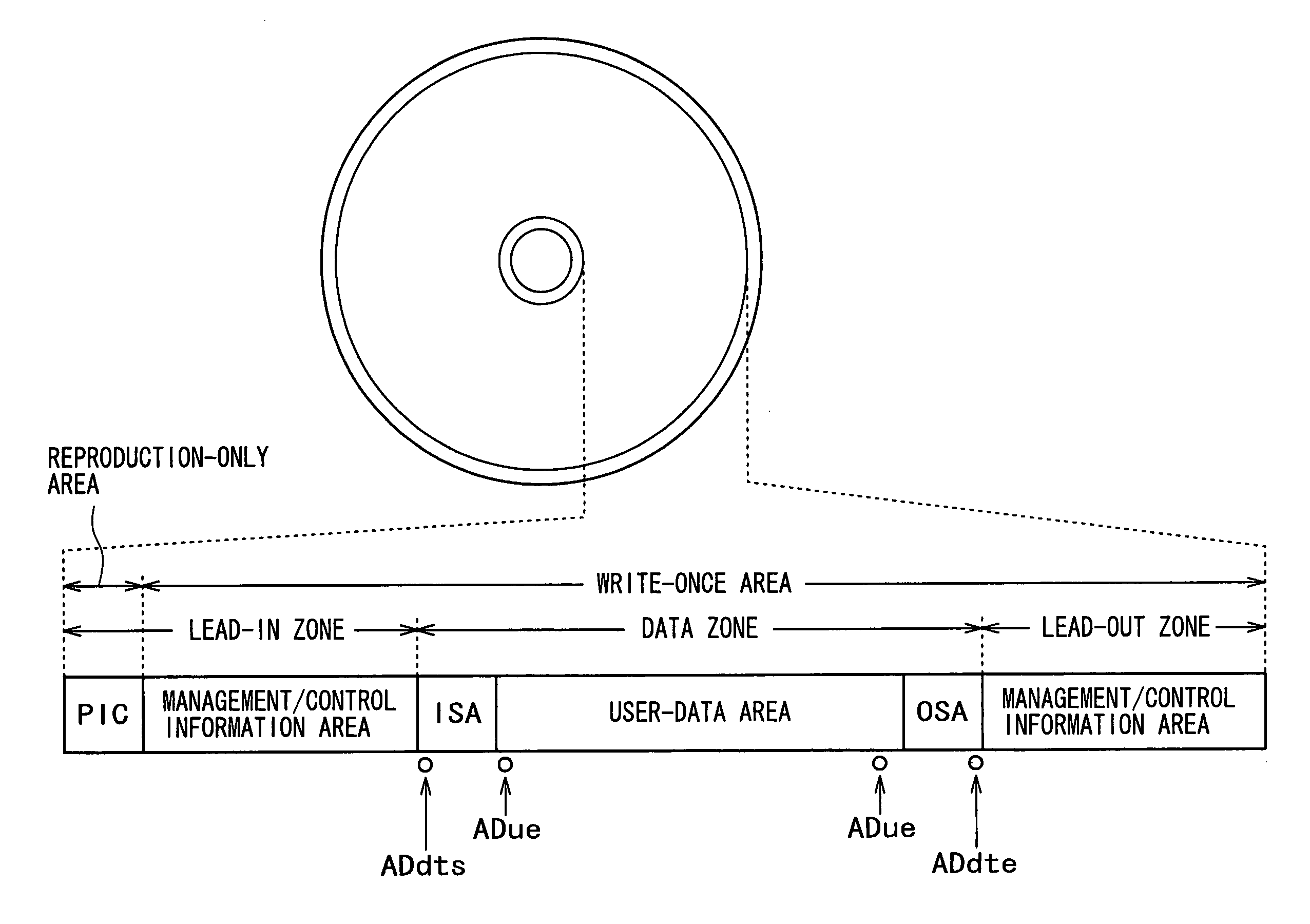
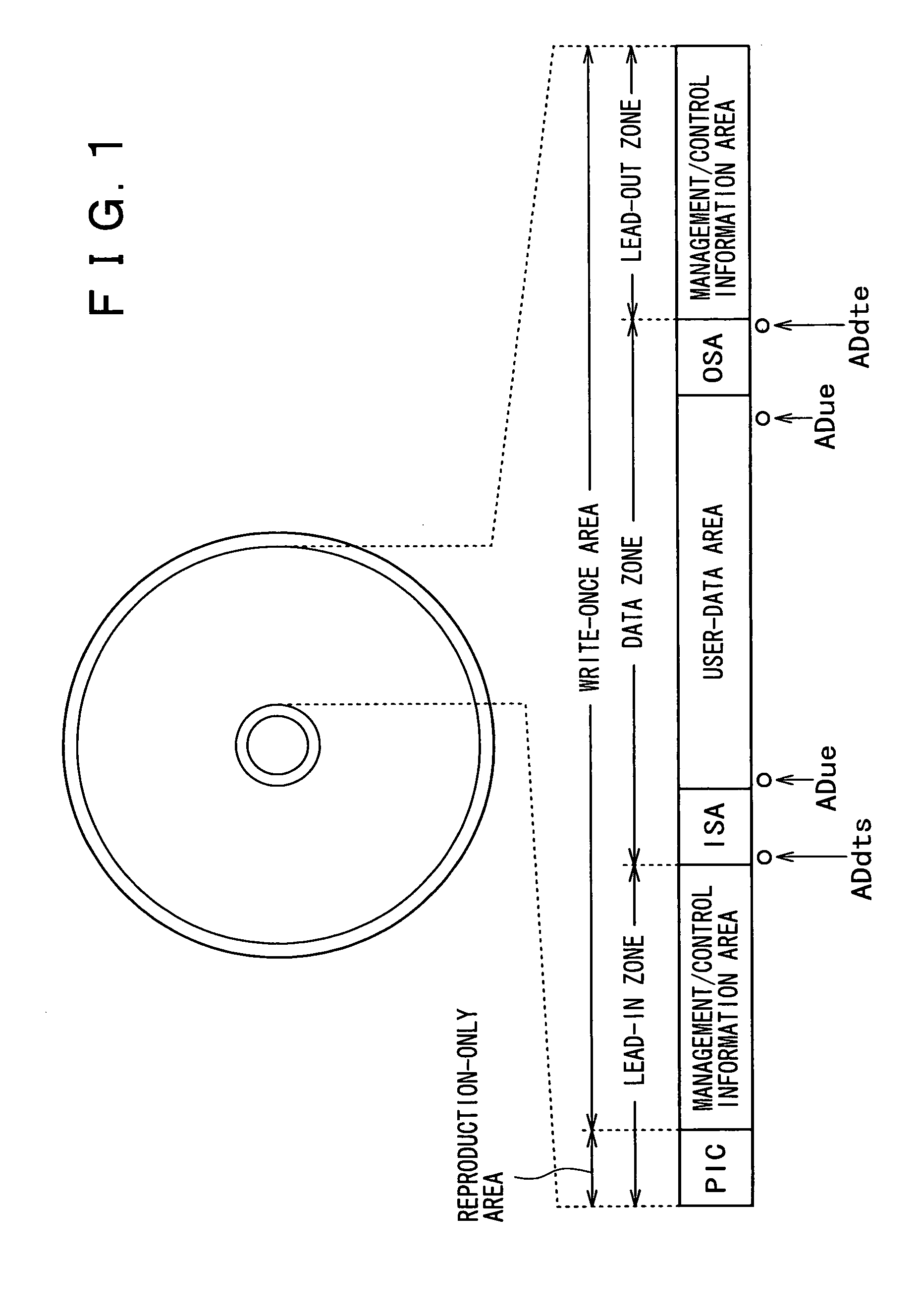
Recording medium, recording device, reproduction device, recording method and reproduction method
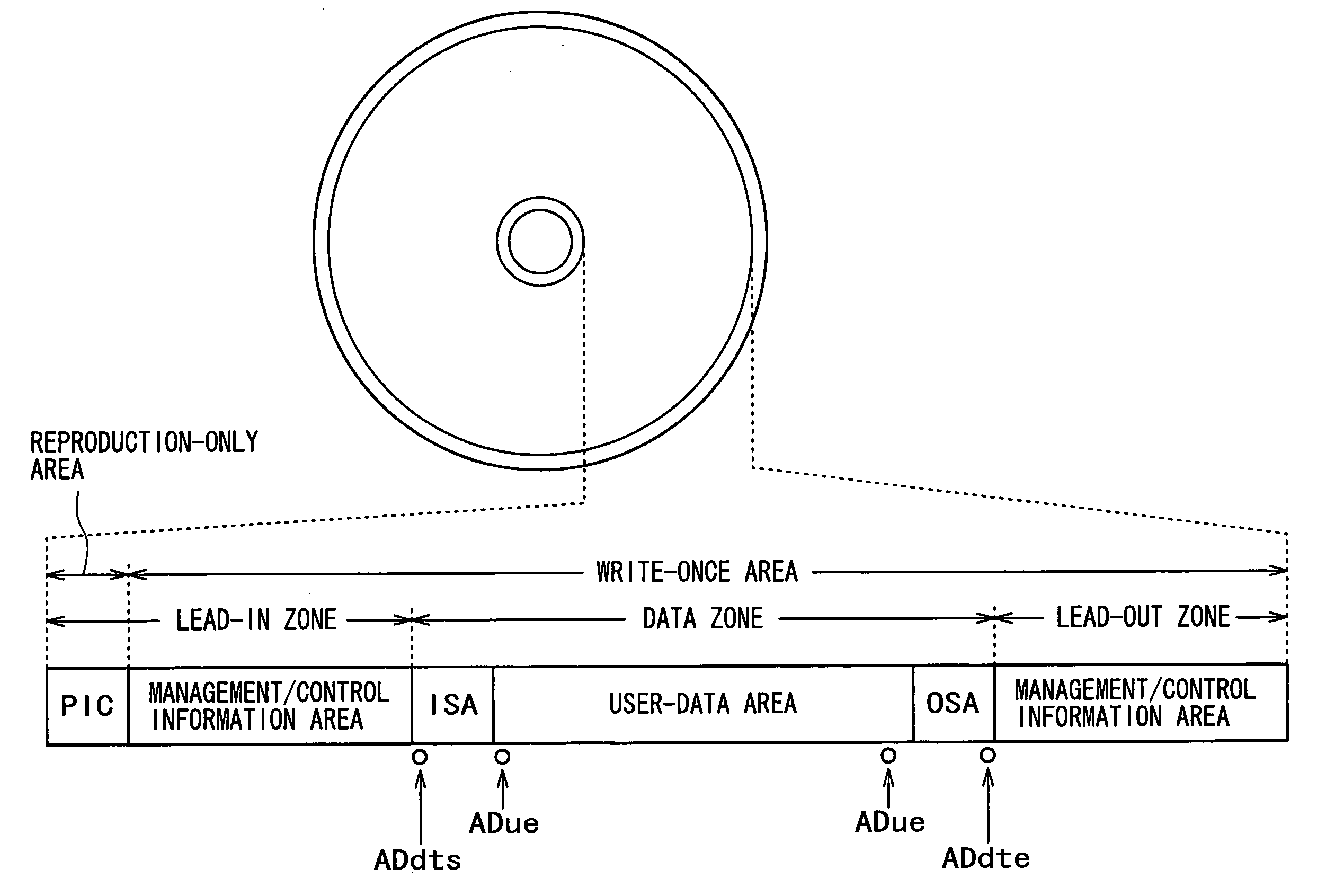
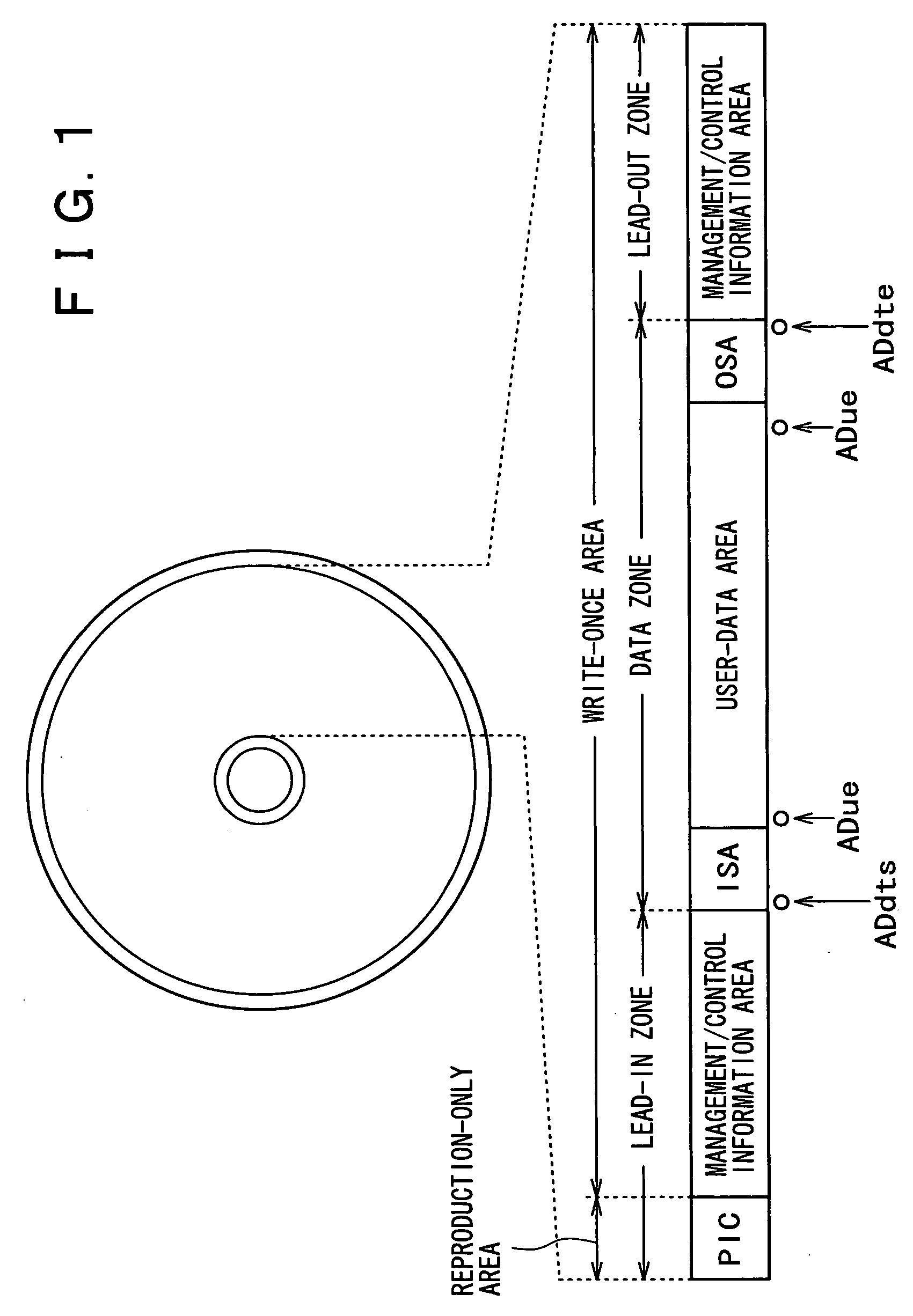
InactiveUS20050207262A1Easy to masterImprove efficiencyRecord information storageOptical erasing systemsUsabilityDatabase
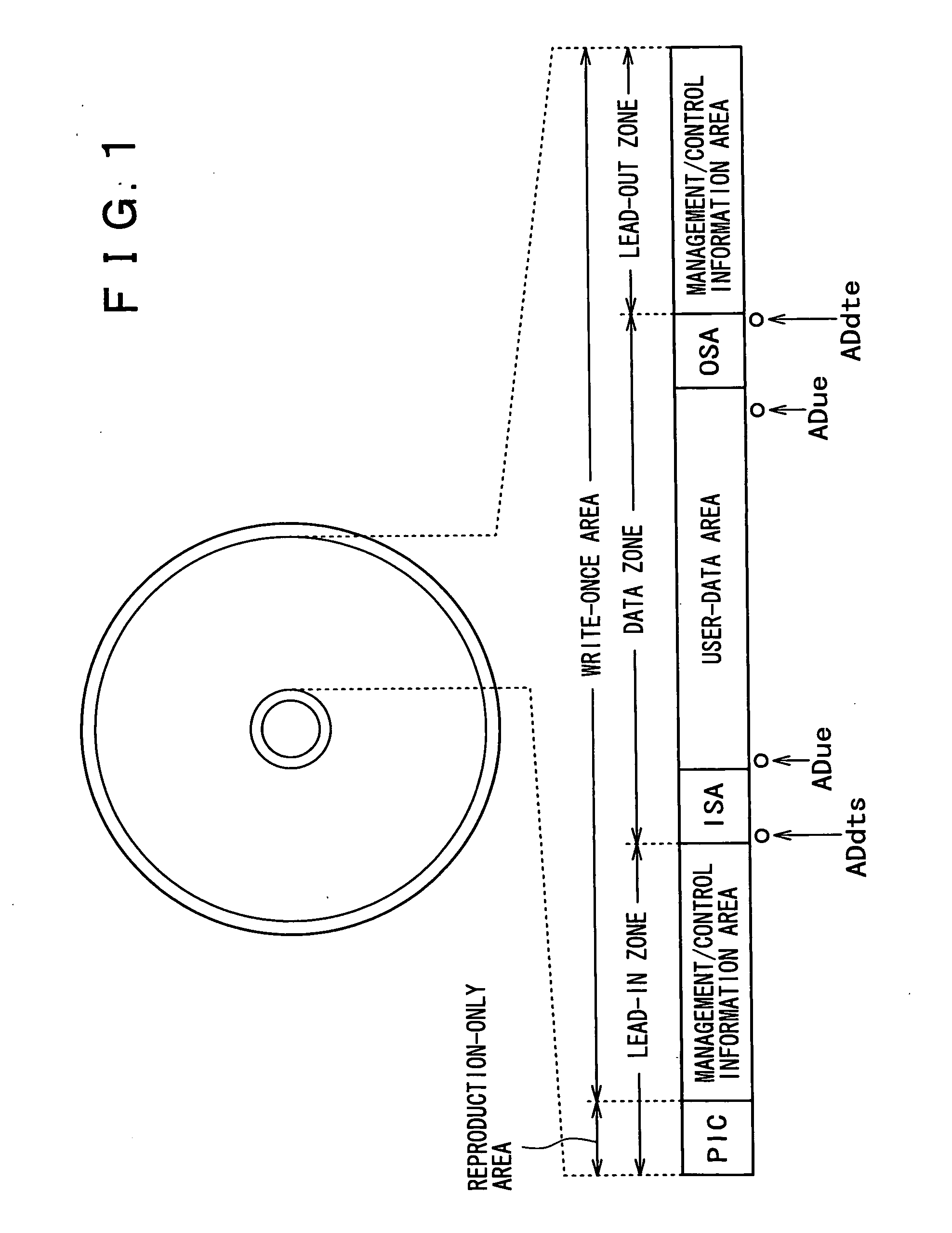
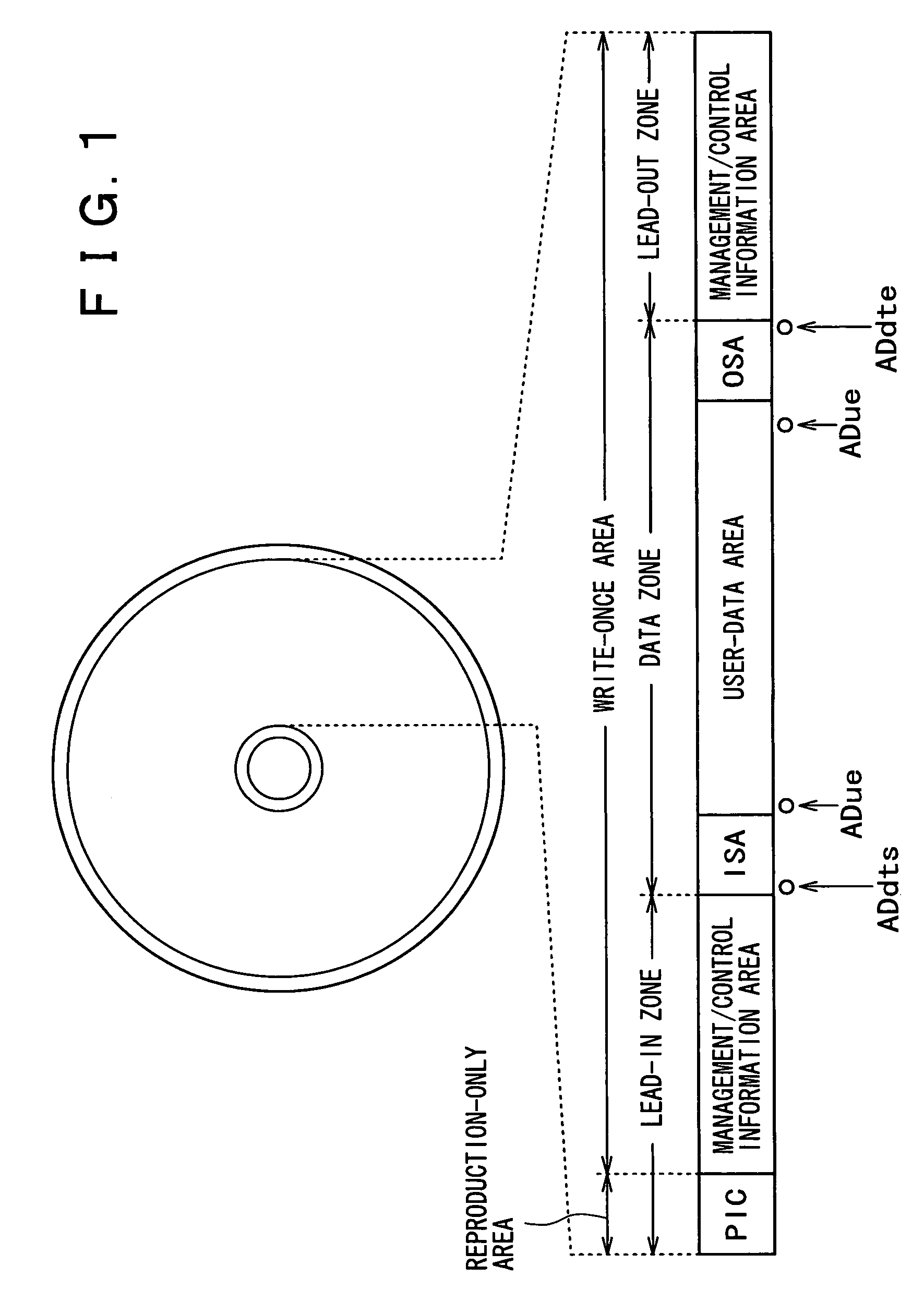
In order to enhance the usability of a write-once recording medium, the recording medium is provided with an ordinary recording / reproduction area, an alternate area, a first alternate-address management information area and a second alternate-address management information area. In addition, written / unwritten state indication information is recorded in a predetermined area. The second alternate-address management information area is an area allowing alternate-address management information recorded therein to be renewed by adding alternate-address management information to the area. Alternate-address management information recorded in the second alternate-address management information area includes information recorded in a first information format and information recorded in a second information format. The first information format shows an alternate source address and an alternate destination address for each data unit. On the other hand, the second information format shows an alternate source address and an alternate destination address for a group of a plurality of physically continuous data units. The second information format is used as a format for effectively carrying out an alternate-address process on such a group of data units. All alternate-address management information is recorded in the first alternate-address management information area in the first information format.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recording medium, recording device, reproduction device, recording method and reproduciton method
InactiveUS20050169132A1Improve usabilityDisc-shaped record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareUsability
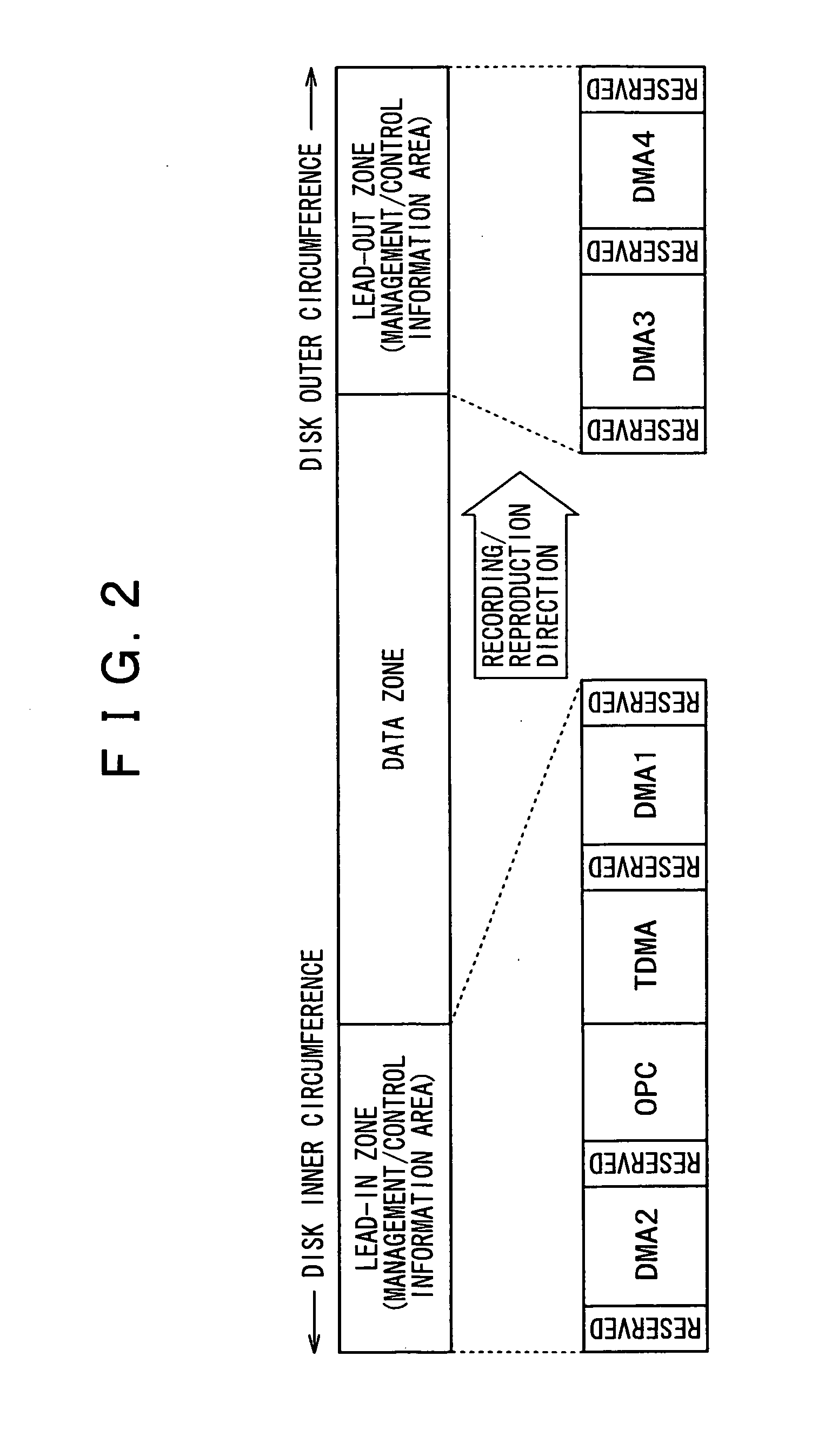
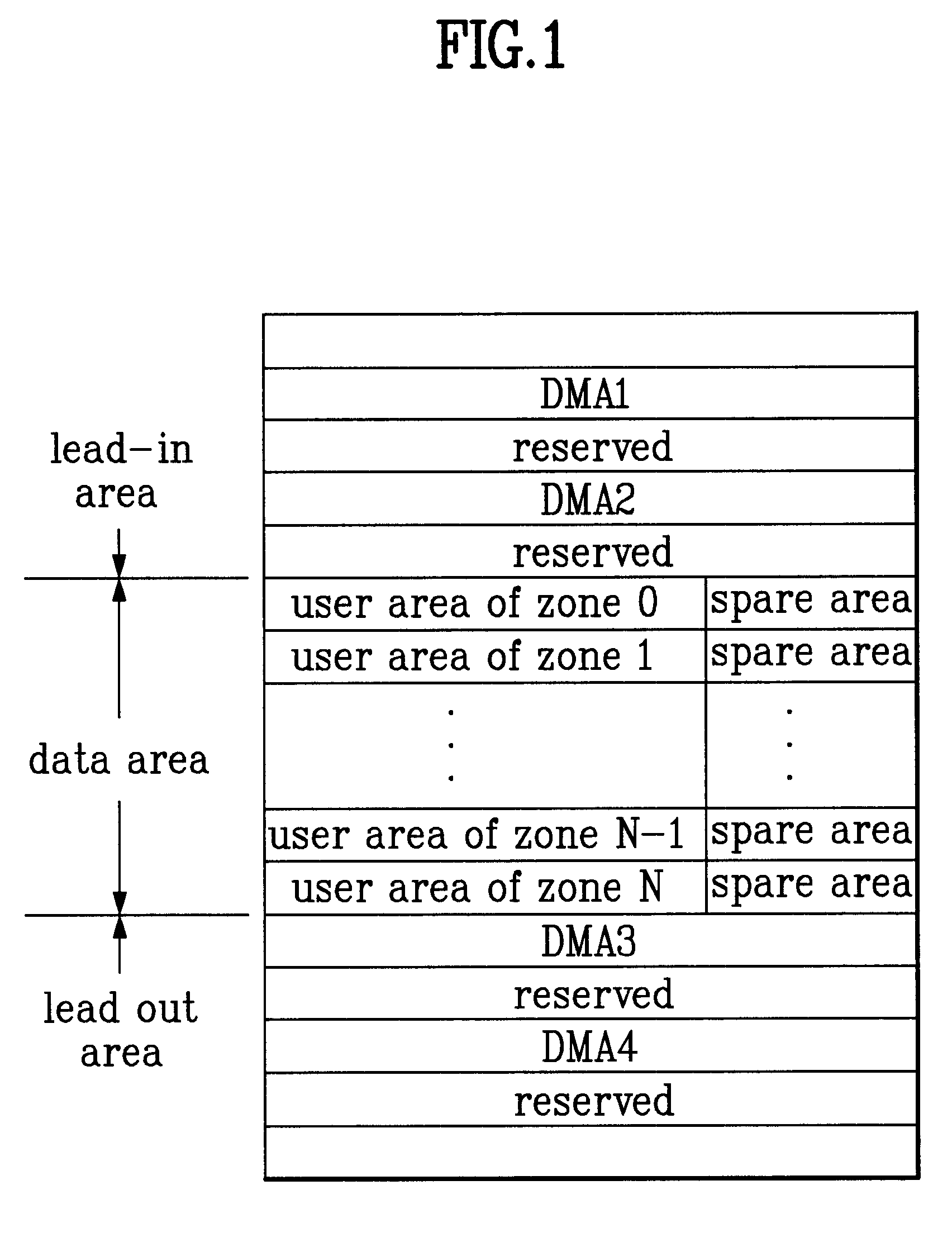
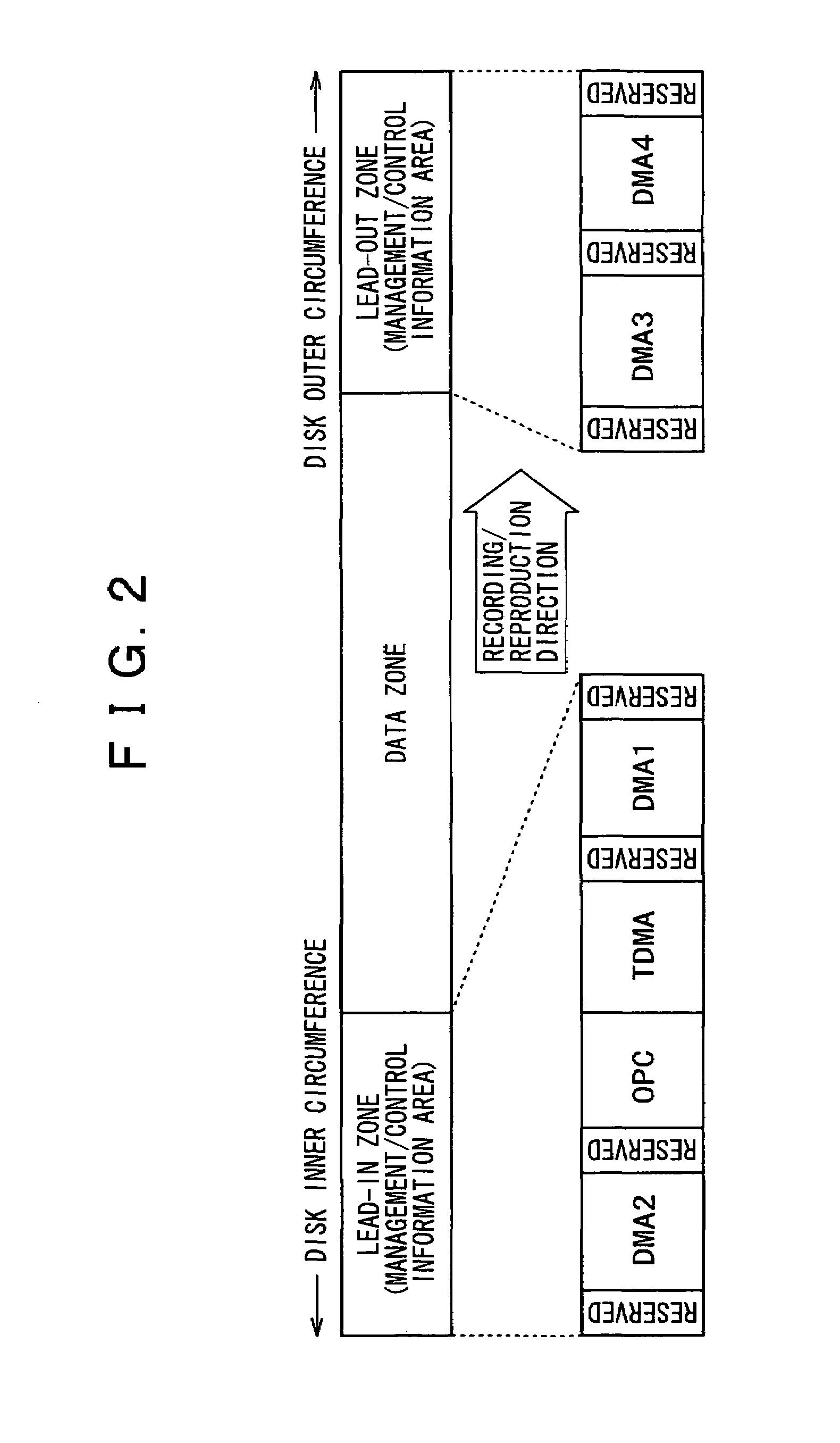
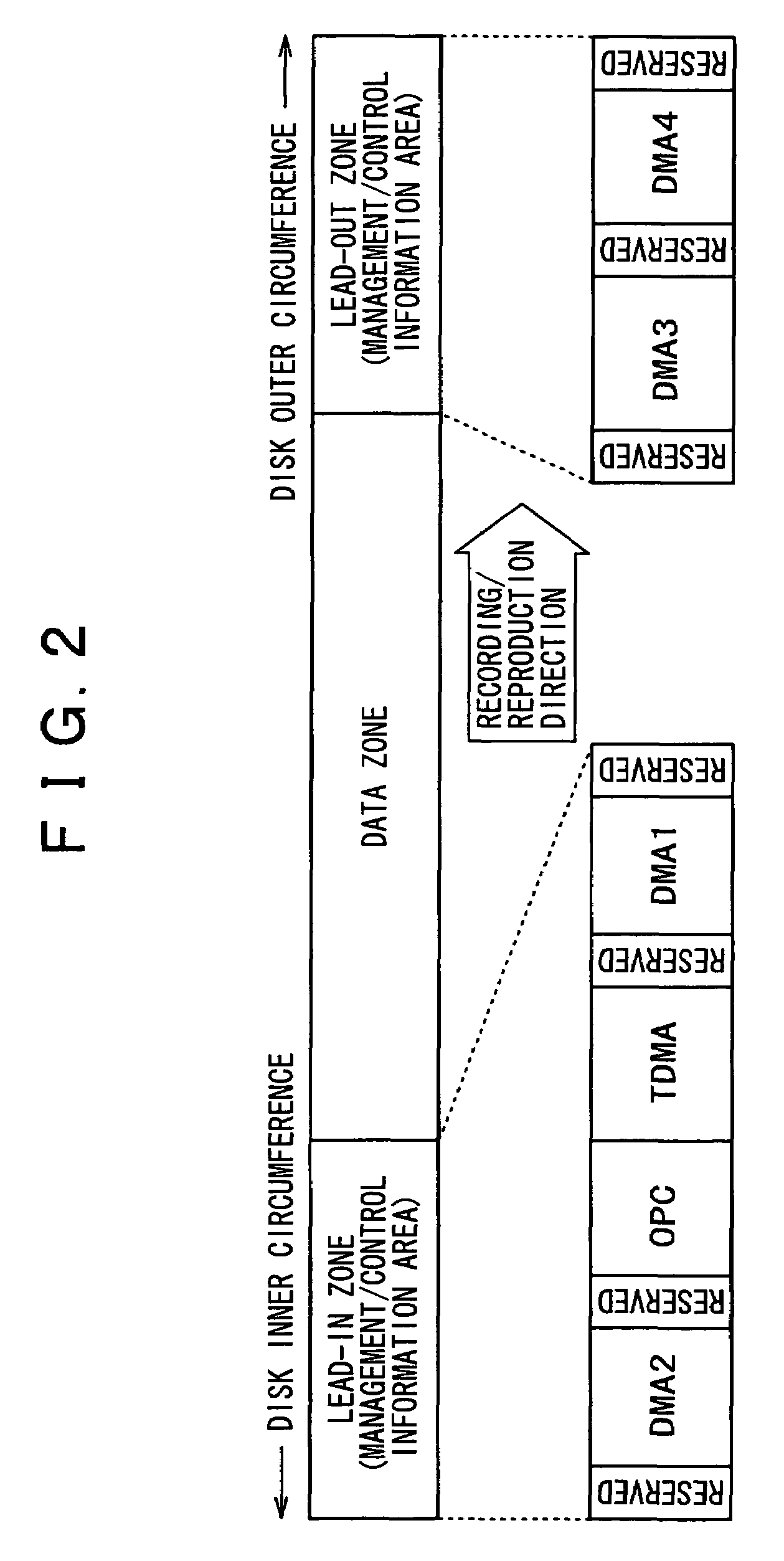
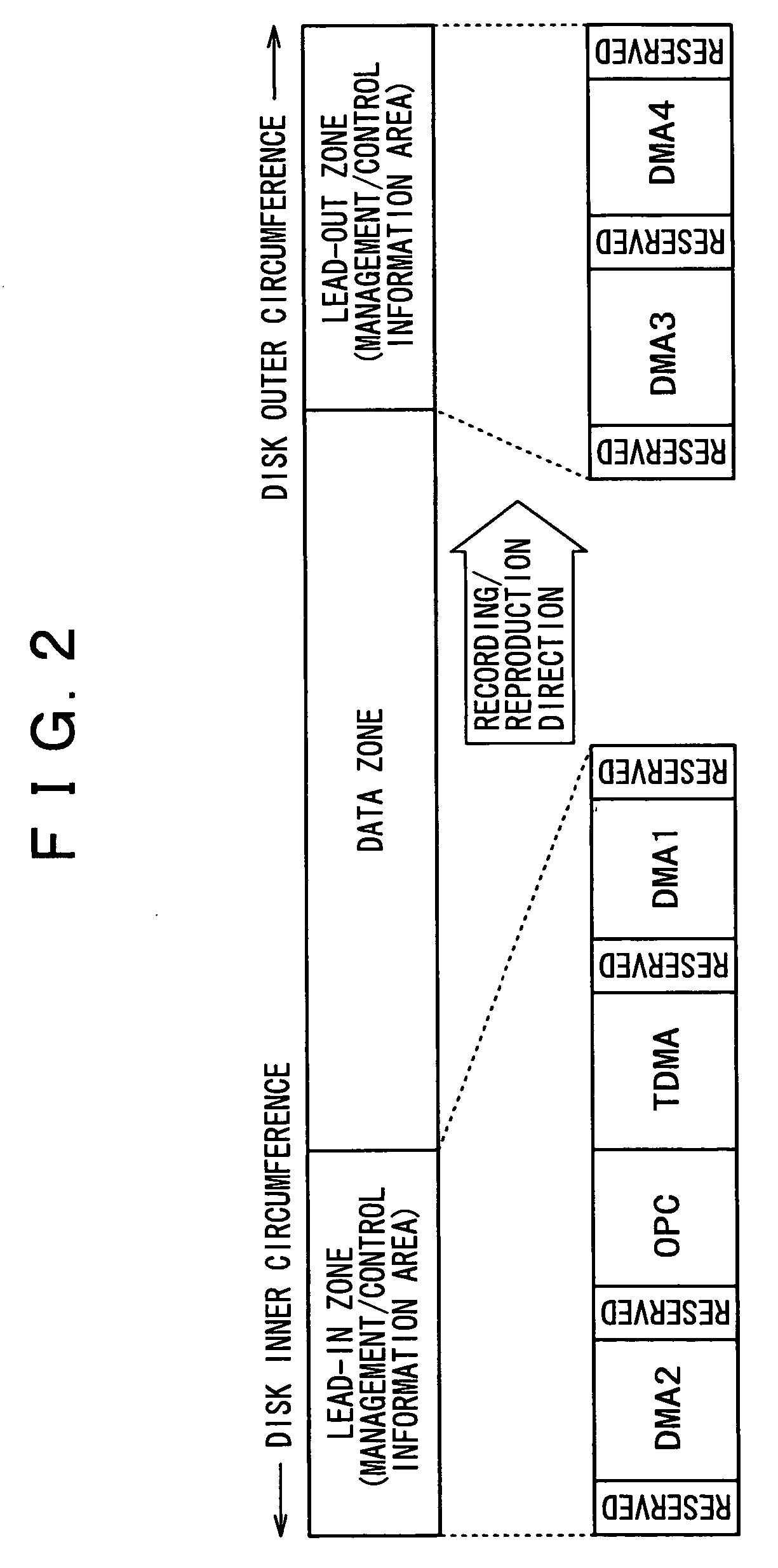
The present invention allows the usability of a write-once recording medium to be enhanced. The write-once recording medium is provided with an ordinary recording / reproduction area, an alternate area, a first alternate-address management information area (DMA) and a second alternate-address management information area (TDMA). In addition, written / unwritten state indication information (a space bitmap) is also recorded. The second alternate-address management information area is an area allowing alternate-address management information recorded therein to be renewed by adding alternate-address management information thereto. In addition, the written / unwritten state indication information indicates whether or not data has been recorded in each data unit (cluster) on the recording medium. Thus, it is possible to correctly execute management of defects and properly implement renewal of data in the write-once recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
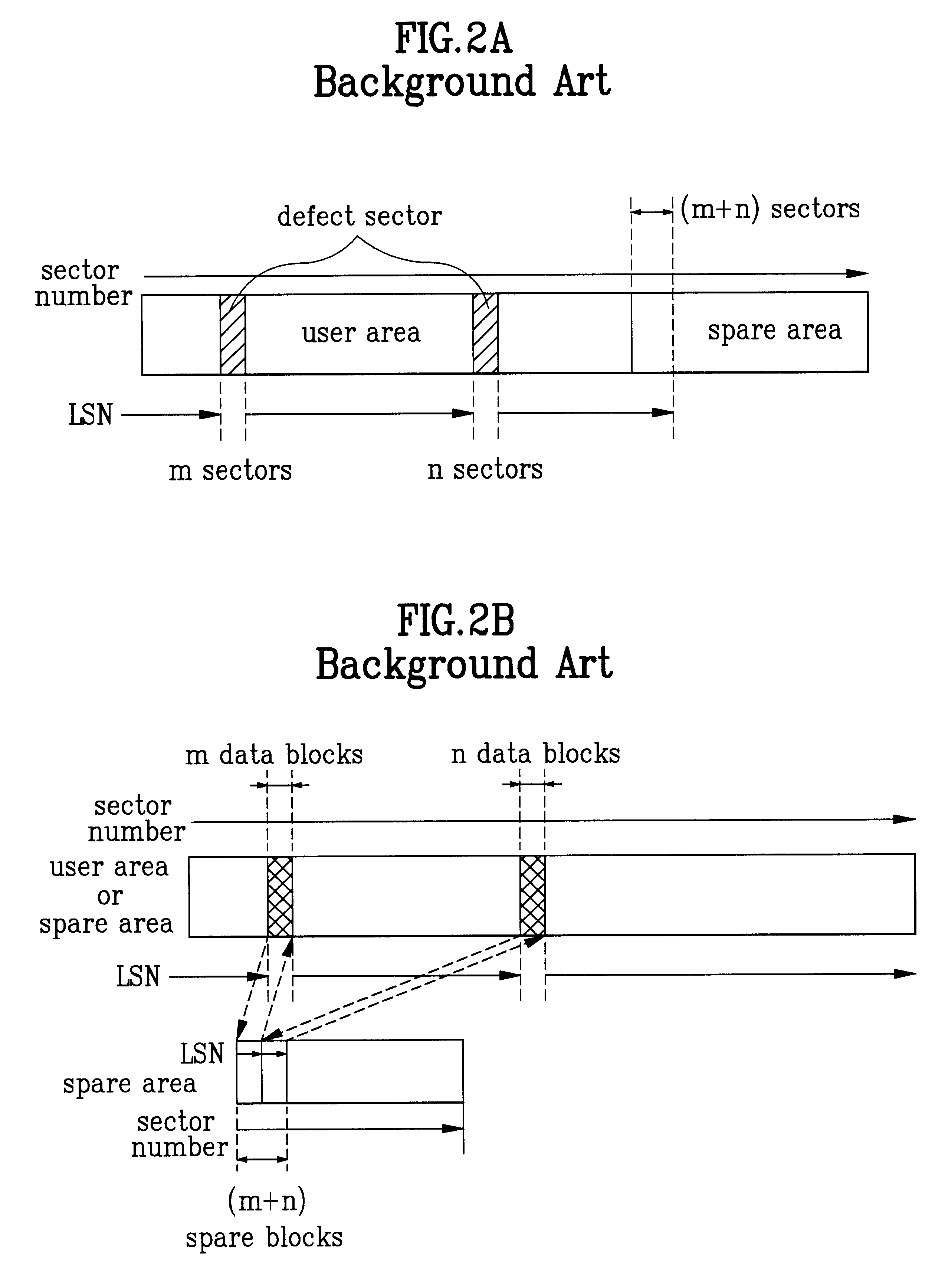
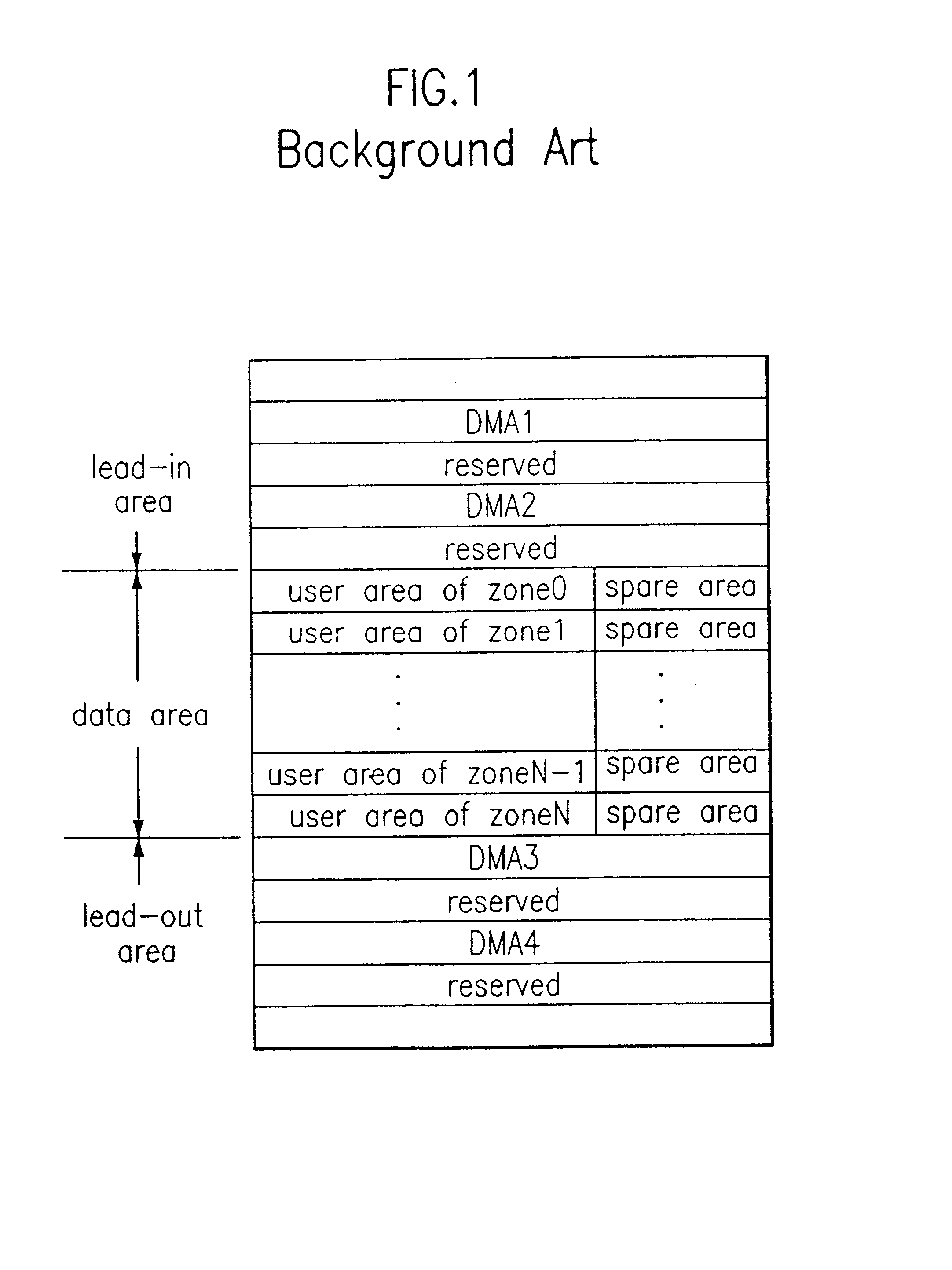
Optical recording medium and method of assigning its spare area
InactiveUS6477126B1Television system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer hardwareOptical recording
A rewritable optical recording medium and a method of assigning a spare area in the rewritable optical recording medium is disclosed. In the present invention, a primary spare area of optical discs, which have the same disc size and track pitch but different initial user sizes, are assigned to have a same size, thereby improving the compatibility the discs.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS20020076647A1Increase scatteringReduce the ratioPhotography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationSinglet oxygen
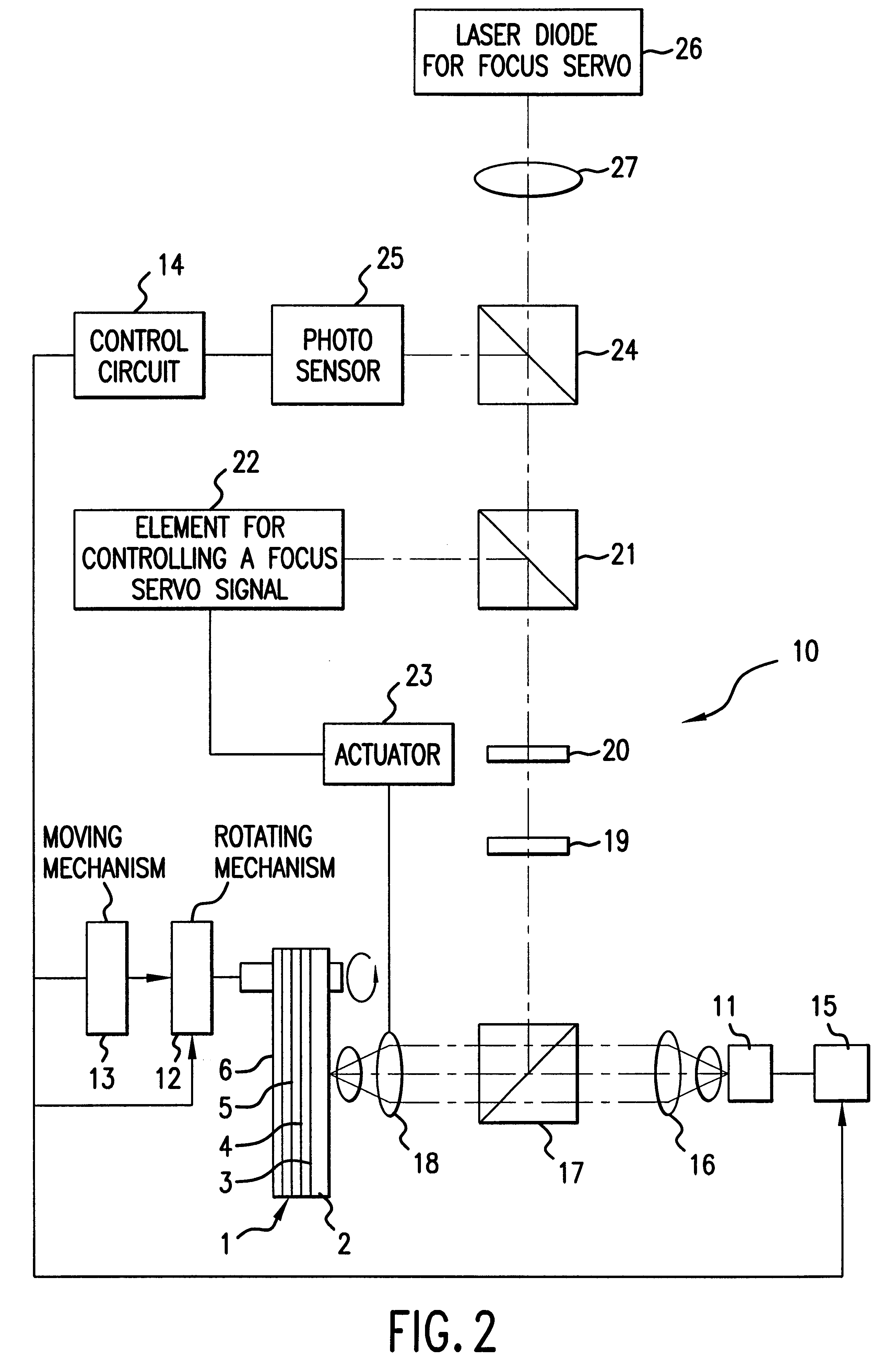
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
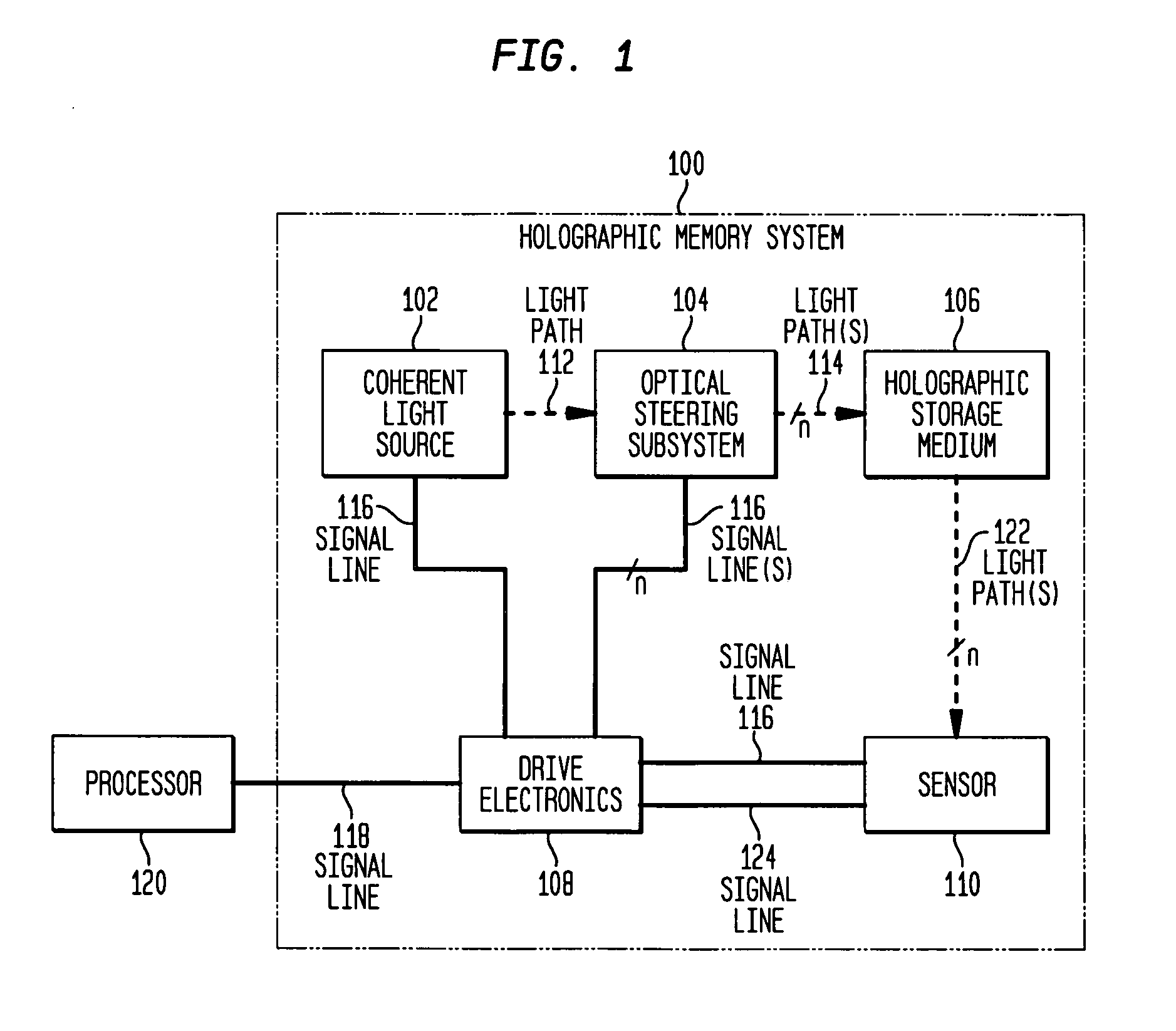
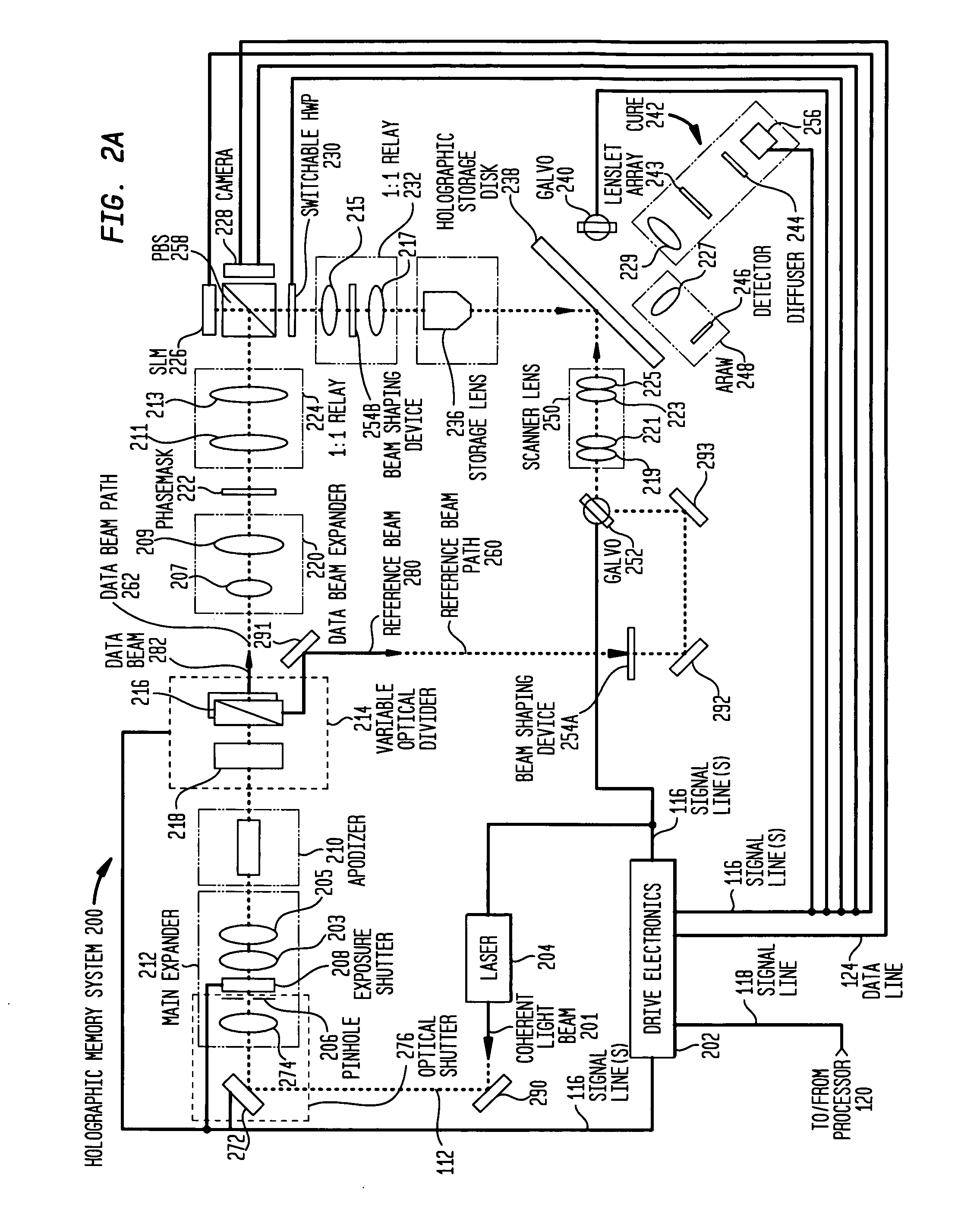
Erasing holographic media
InactiveUS20060280096A1Reduce coherenceIncreased ability to stably record holographic dataRecord information storageOptical erasing systemsHolographic storageLight beam
The present invention relates to embodiments of a process for subjecting a holographic storage medium to illuminative treatment to: (1) enhance or optimize recording of holographic data; (2) enhance or optimize reading of recorded holographic data; and / or (3) erase recorded holographic data. The present invention also relates to embodiments of a system comprising: (a) an illuminative treatment beam; (b) means for reducing the coherence of the beam and (c) means for transmitting the reduced coherence beam to cause illuminative treatment of: (1) an unrecorded portion of a holographic storage medium to provide pre-cured portions having increased ability to stably record holographic data; (2) a recorded portion of a holographic storage medium to provide a post-cured portion having reduced residual sensitivity; and / or (3) a recorded portion of a holographic storage medium having holographic data to provide an erased portion wherein at least some of the recorded holographic data is erased.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
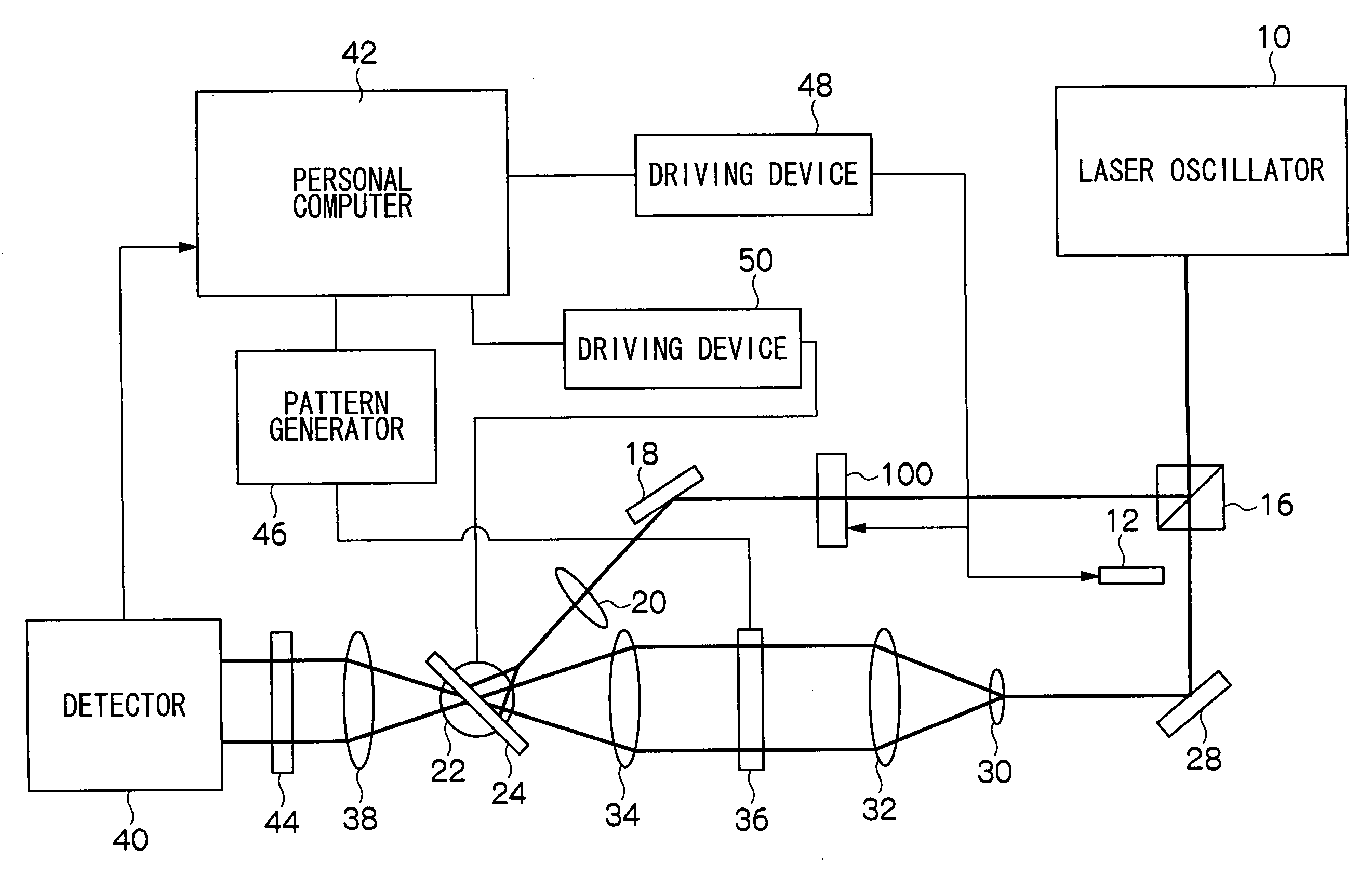
Hologram erasing method and hologram erasing apparatus
InactiveUS20050013231A1Record information storageOptical beam guiding meansOriginal dataMethod selection
The present invention discloses a hologram erasing method, in which a predetermined hologram is erased by irradiating a predetermined region of a hologram recording medium in which the hologram to be erased is recorded with a reference light beam and a signal light beam holding a random data pattern at the same time. In this method, the signal light beam and the reference light beam interfere with each other in the medium, and a Fourier transform hologram recorded in the region where the interference occurs is destroyed and erased by interference light beam. That is, a data page for erasing including a random pattern is overwritten to erase an original data page. According to the present invention, the hologram recorded in the optical recording medium can be selectively and completely erased in a simple method.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Method and apparatus for initializing optical recording media
InactiveUS6373802B1Prevent poor initializing conditionUniform crystallizationCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsPhase changeOptical recording
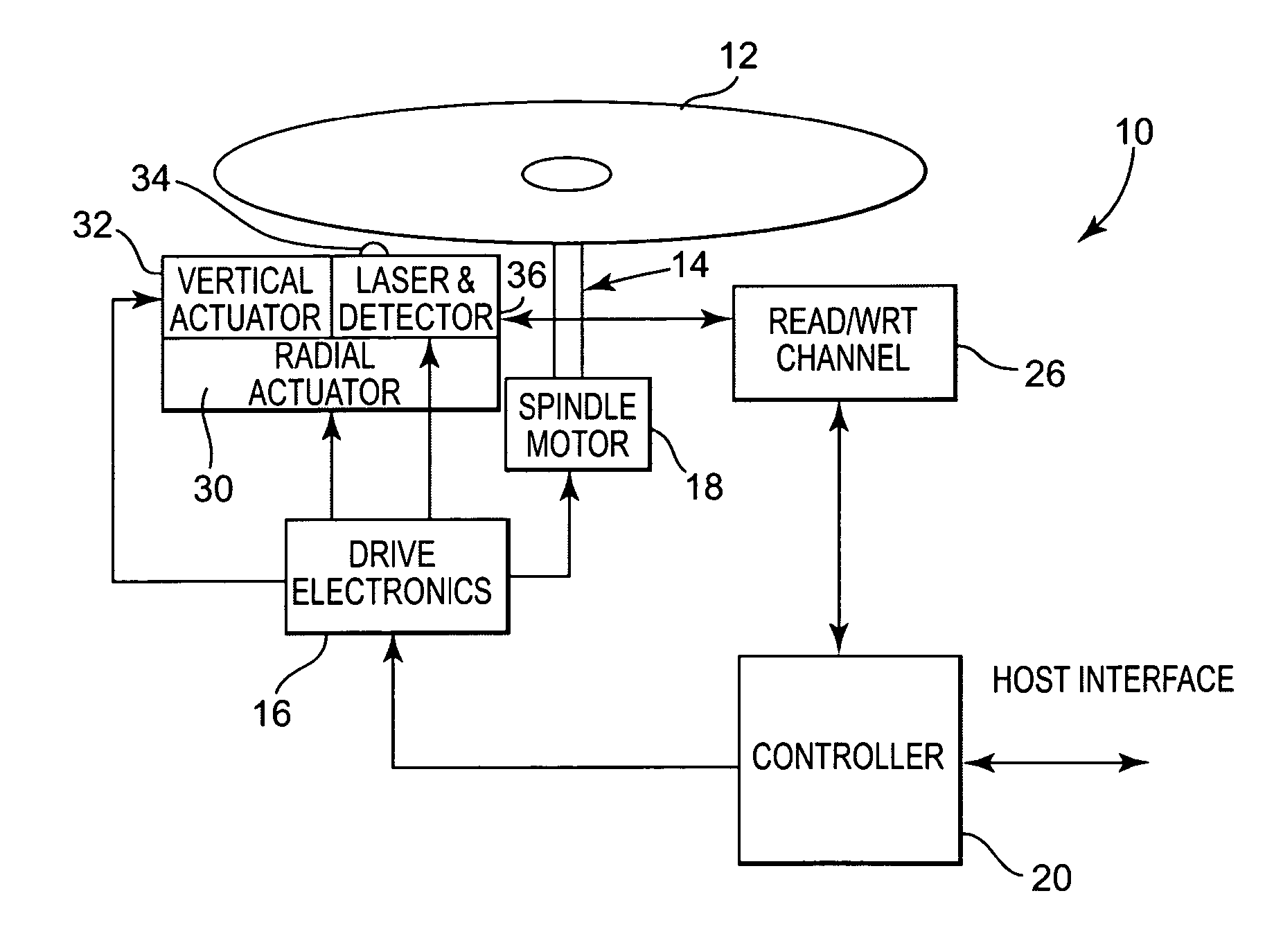
A method and apparatus for initializing optical recording media is provided that detects the intensity of a reflective light off of an optical recording media and analyzes the initializing condition based on the detected intensity during an initializing process. The light is radiated on a rotating phase-change optical recording medium. The light may be moved in a radial direction of the optical recording medium. The detected intensity of the reflected light may be used to identify crystallized portions and amorphous portions of the optical media. The initialization process can be adaptively controlled to ensure proper initialization. If desired, re-initialization can be limited to those areas detected to be outside of the predetermined parameters.
Owner:RICOH KK
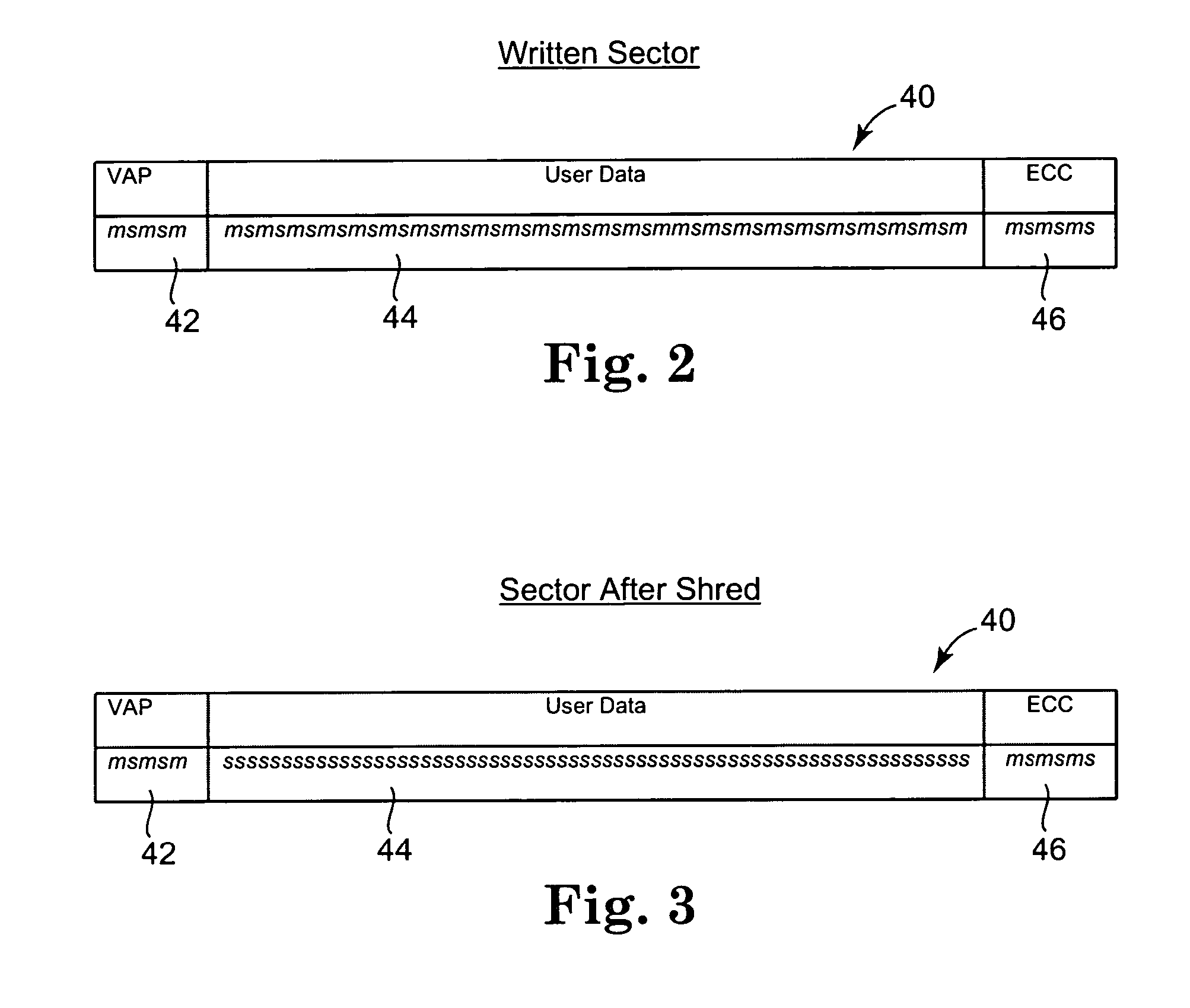
Optical disk shred operation with detection
InactiveUS20070047395A1Easy to identifyCarry-out quicklyMultilayered discsRecording verificationConfusionData store
Data protection and security is provided by incorporating a data shredding operation which renders data previously stored on storage media unrecoverable. In the shredding operation of the present invention, certain overhead portions of a data storage sector remain unchanged, while the data area is overwritten with a predetermined pattern. By maintaining the overhead portions of the sectors (addressing, verify and protect, error correction codes, etc.) the sectors can be easily identified as being previously shredded, thus not providing a source of possible confusion to the data storage device. Further, the data becomes unrecoverable as it has been overwritten by the predetermined pattern, which thus eliminates all previously existing transitions which contained the encoded data.
Owner:PLASMON LMS
Recording medium, recording device, reproduction device, recording method and reproduction method
InactiveUS7203153B2Improve usabilityDisc-shaped record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareUsability
The present invention allows the usability of a write-once recording medium to be enhanced. The write-once recording medium is provided with an ordinary recording / reproduction area, an alternate area, a first alternate-address management information area (DMA) and a second alternate-address management information area (TDMA). In addition, written / unwritten state indication information (a space bitmap) is also recorded. The second alternate-address management information area is an area allowing alternate-address management information recorded therein to be renewed by adding alternate-address management information thereto. In addition, the written / unwritten state indication information indicates whether or not data has been recorded in each data unit (cluster) on the recording medium. Thus, it is possible to correctly execute management of defects and properly implement renewal of data in the write-once recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical information recording medium and method for manufacturing the medium
InactiveCN1627401AIncrease productionAvoid stopRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageInformation layerComputer science
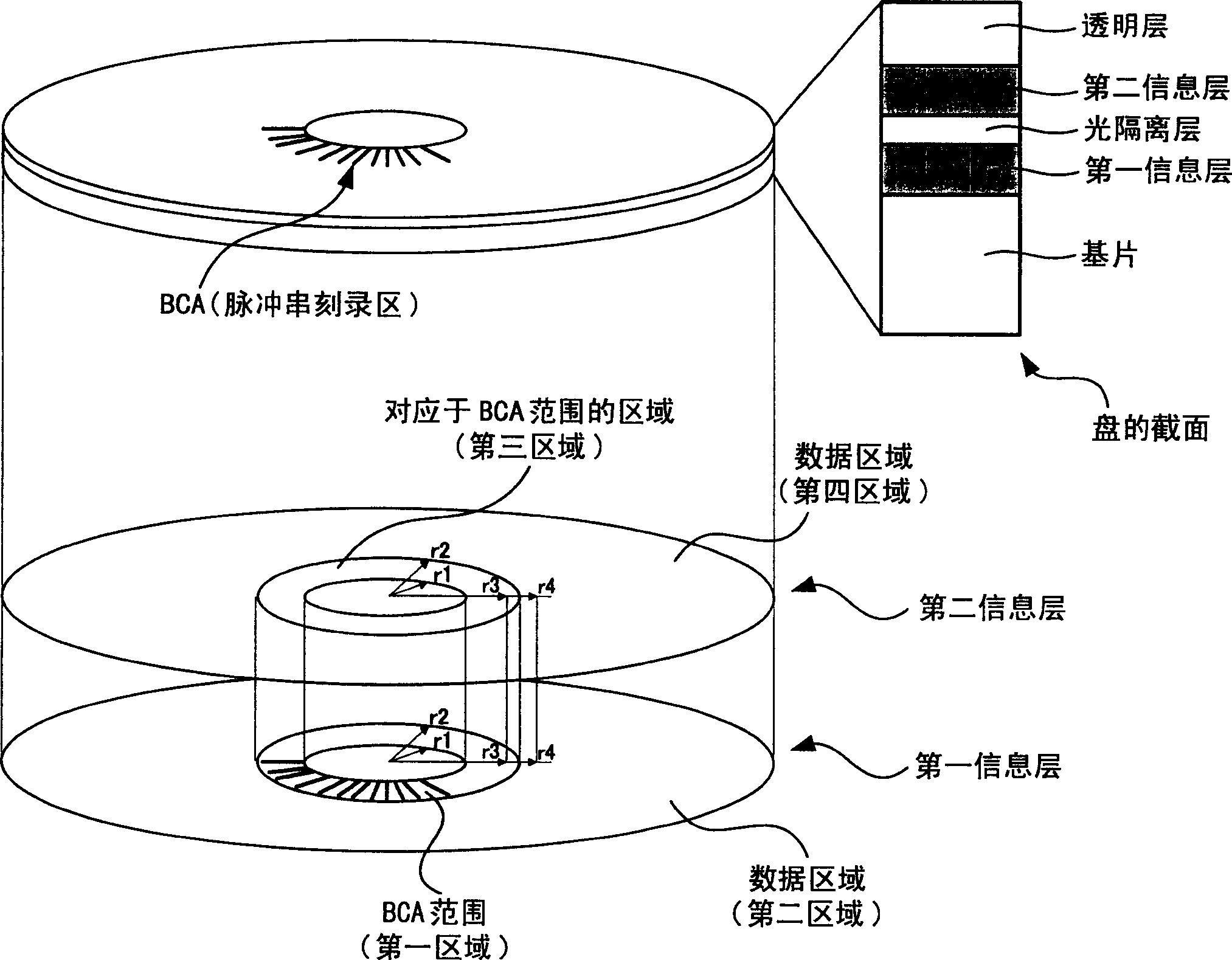
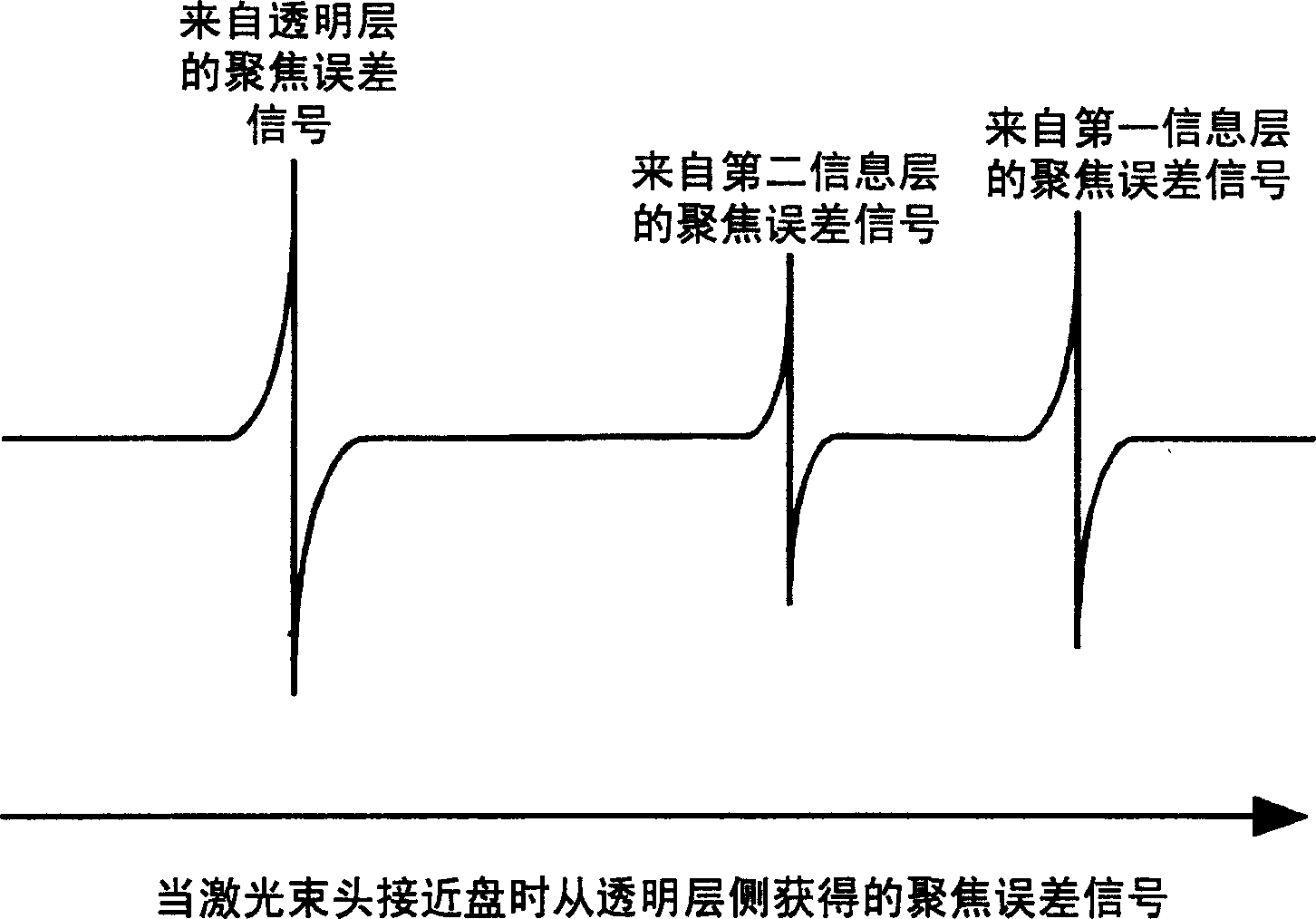
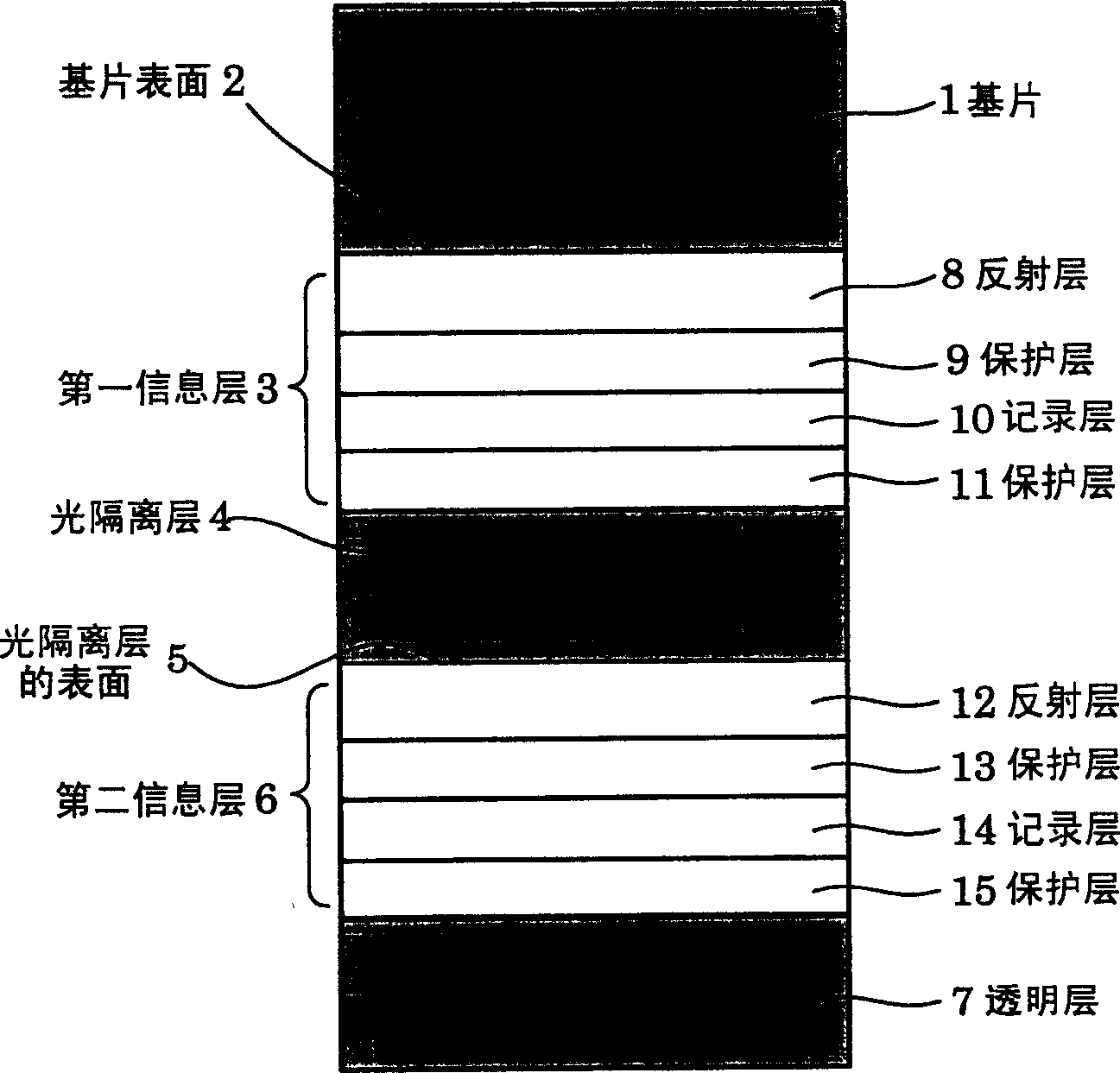
The present invention provides a method of properly performing initialization of an optical information recording medium in which the stop of the initialization process is avoided, thereby improving the yield of manufacturing the optical information recording medium. In initializing the information layer with a burst recording area (hereinafter referred to as "BCA"), the laser power, linear velocity and laser light used for the information layer are changed between the BCA range and the data area of the area for recording and reproducing information. At least one initialization condition in the focus of the bundle. In initializing the information layer without BCA, at least one initialization condition including laser power, linear velocity, and laser beam focus and feeding pitch for the information layer is changed between an area corresponding to the BCA and an area corresponding to the data area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
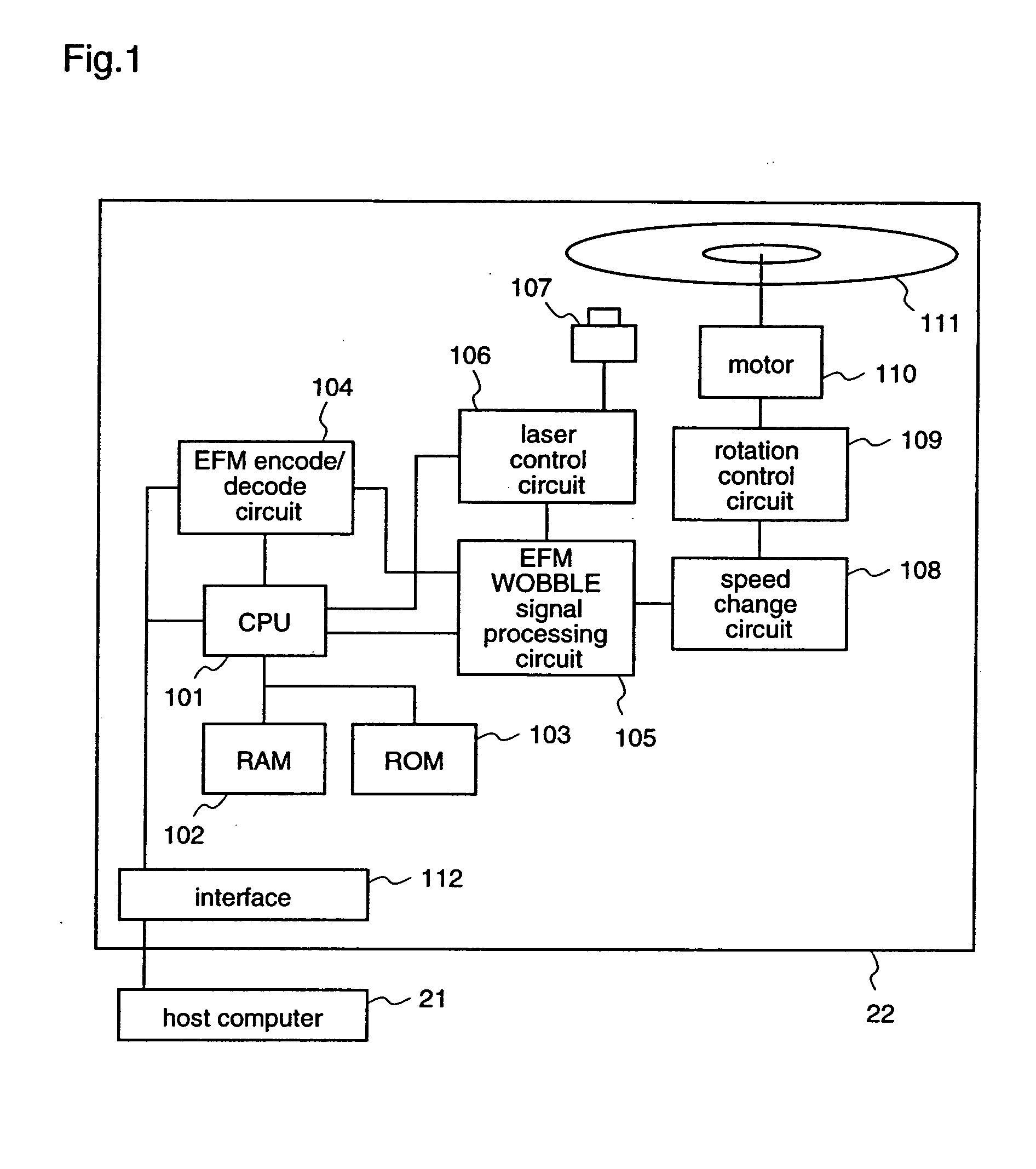
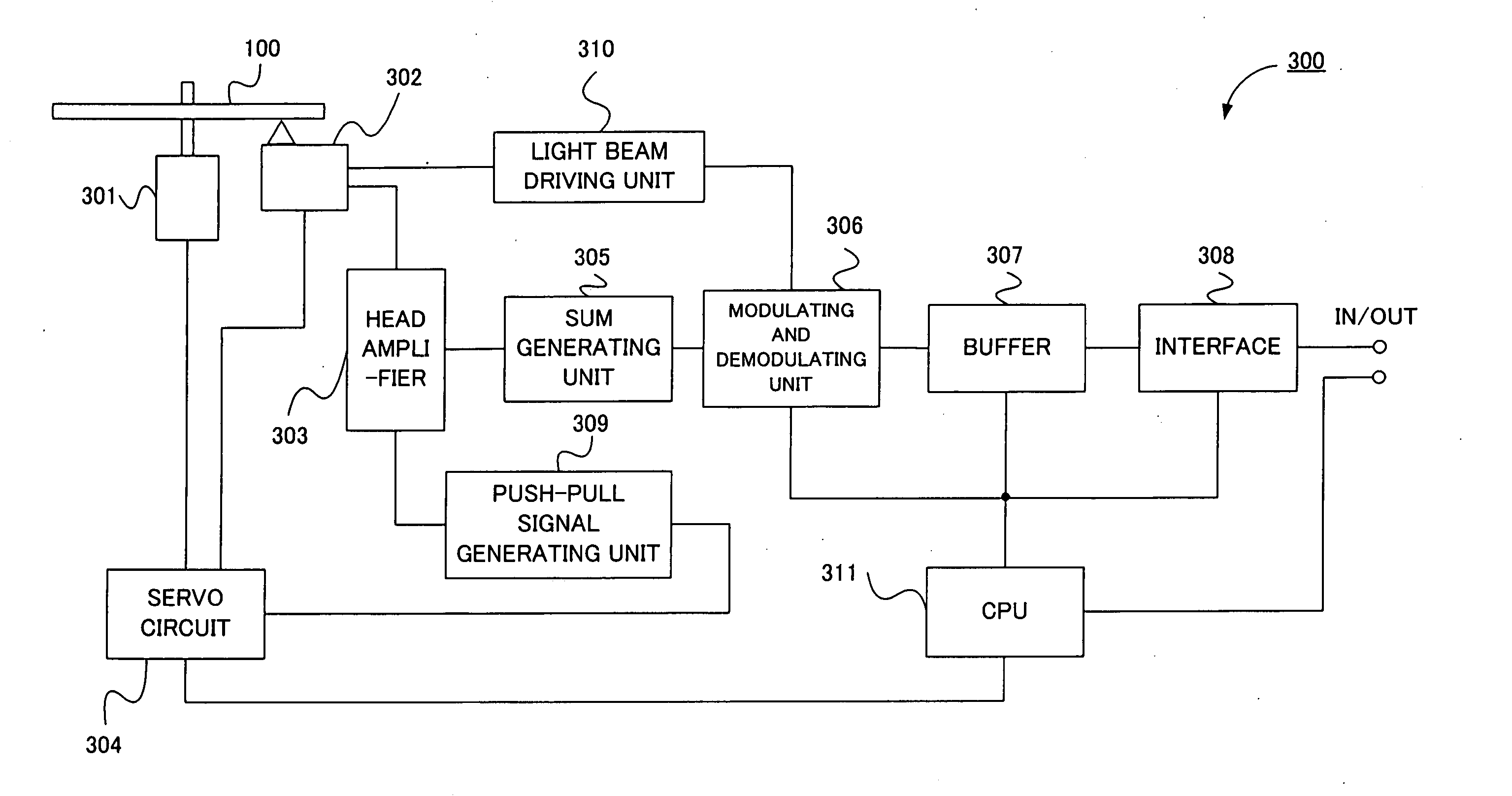
Information recording apparatus
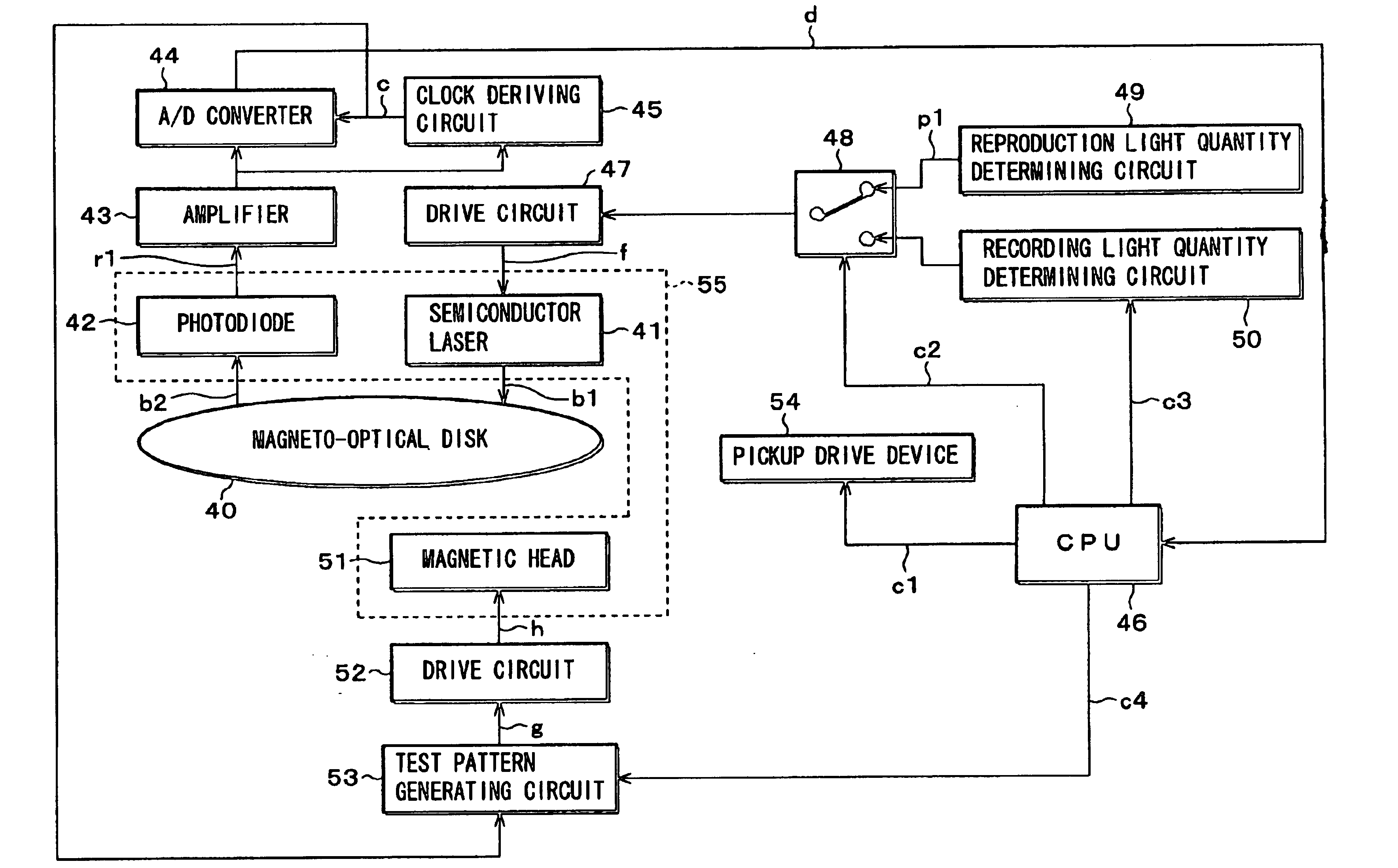
InactiveUS6678220B1Variation of the mark shapeReduce variationOptical beam sourcesRecord information storagePosition controlIrradiation
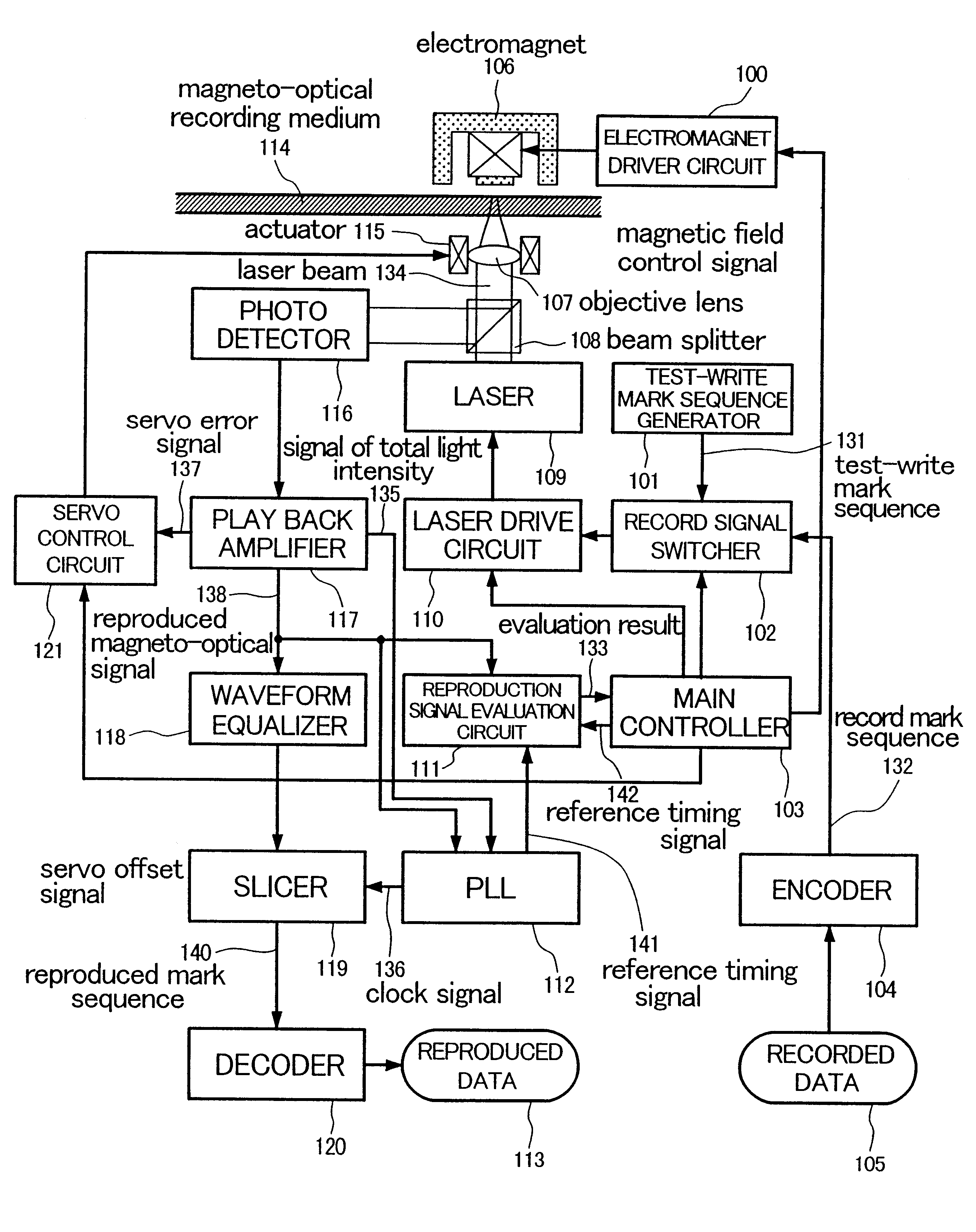
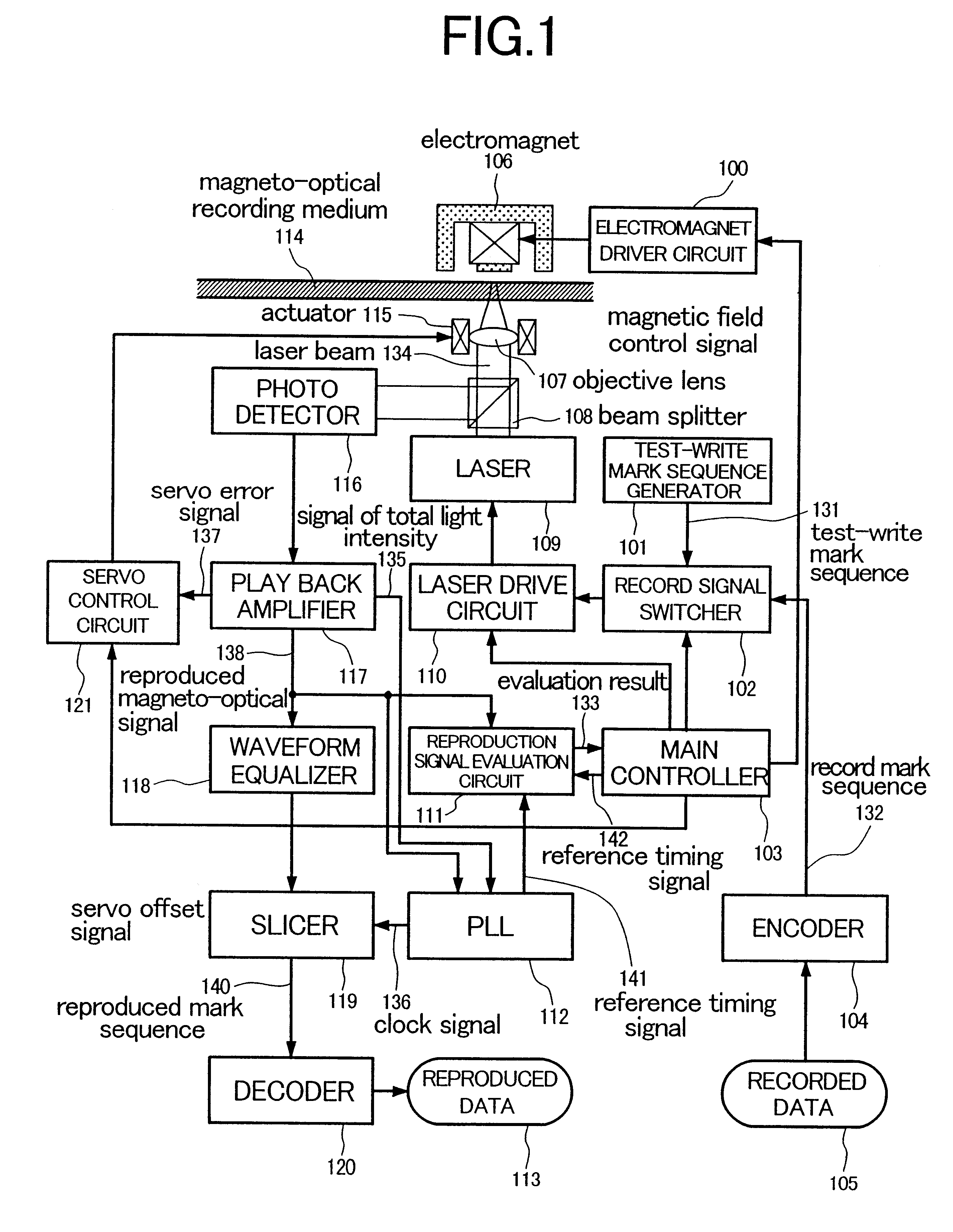
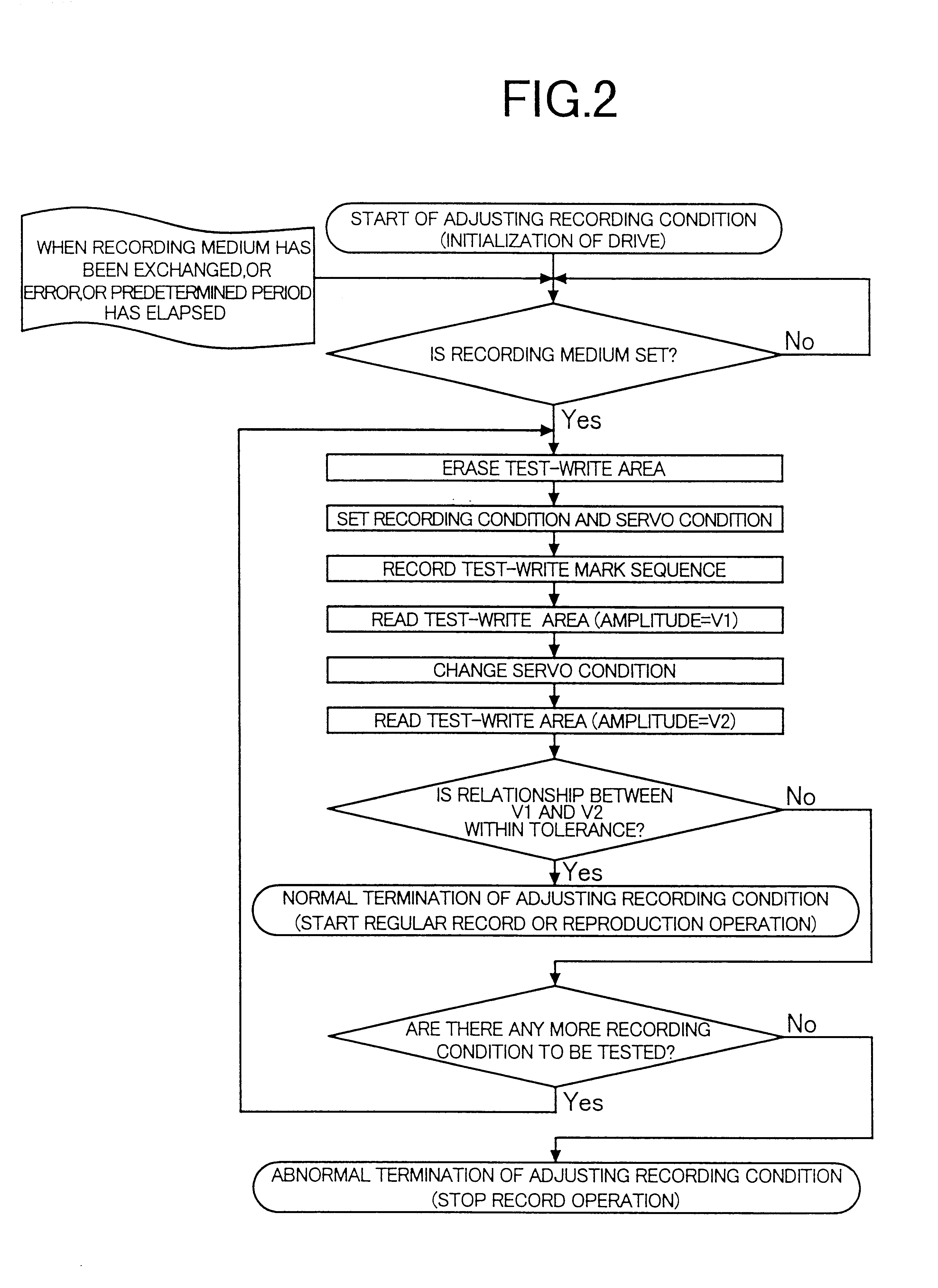
An information recording apparatus includes an energy generation device for generating recording energy; a position control device for controlling a position of irradiation on the recording medium with an output of the energy generation device; a drive device for driving the energy generation device; a switching device for switching information based on user data and test information to supply the two kinds of information selectively to the drive device; a reading device for reading the marks recorded on the recording medium; an evaluation device for evaluating a reproduced signal obtained by the reading device; and a recording condition control device for controlling a recording condition on the basis of an evaluation result obtained by the evaluation device, wherein, when the marks used for recording the test information are to be reproduced, controlling operation of the position control device is changed to be different from that used for recording the test information.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
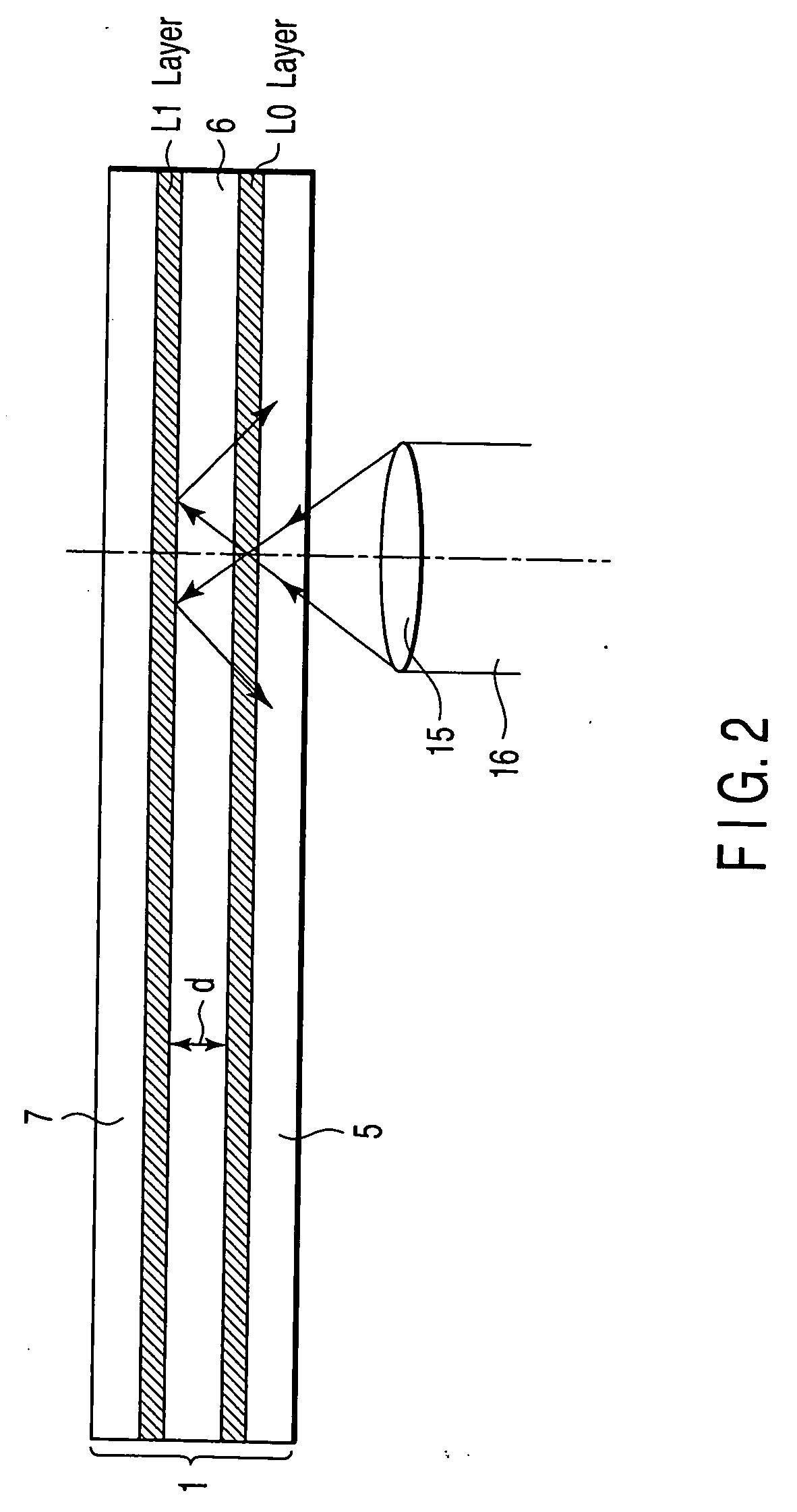
Information recording medium, method of recording information thereto, and information recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20050058034A1Filamentary/web record carriersMechanical record carriersComputer hardwareRecording layer
The present invention provides an information recording medium and an information recording method that can stably record and reproduce information to or from an information recording medium capable of recording and reproducing information to and from two recording layers from one side thereof and can eliminate an effect of a crosstalk. In the invention, premarks (different from initialization) are formed to each of first and second recording layers of an information recording medium simultaneously with the initialization of the respective recording layers using an elliptical laser spot. With this operation, information can be stably reproduced from an information recording medium having at least two recording layers.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Recording medium, recording apparatus, and reading apparatus
InactiveUS6917572B2Easily and precisely determineOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageComputer scienceRecording media
Owner:SONY CORP
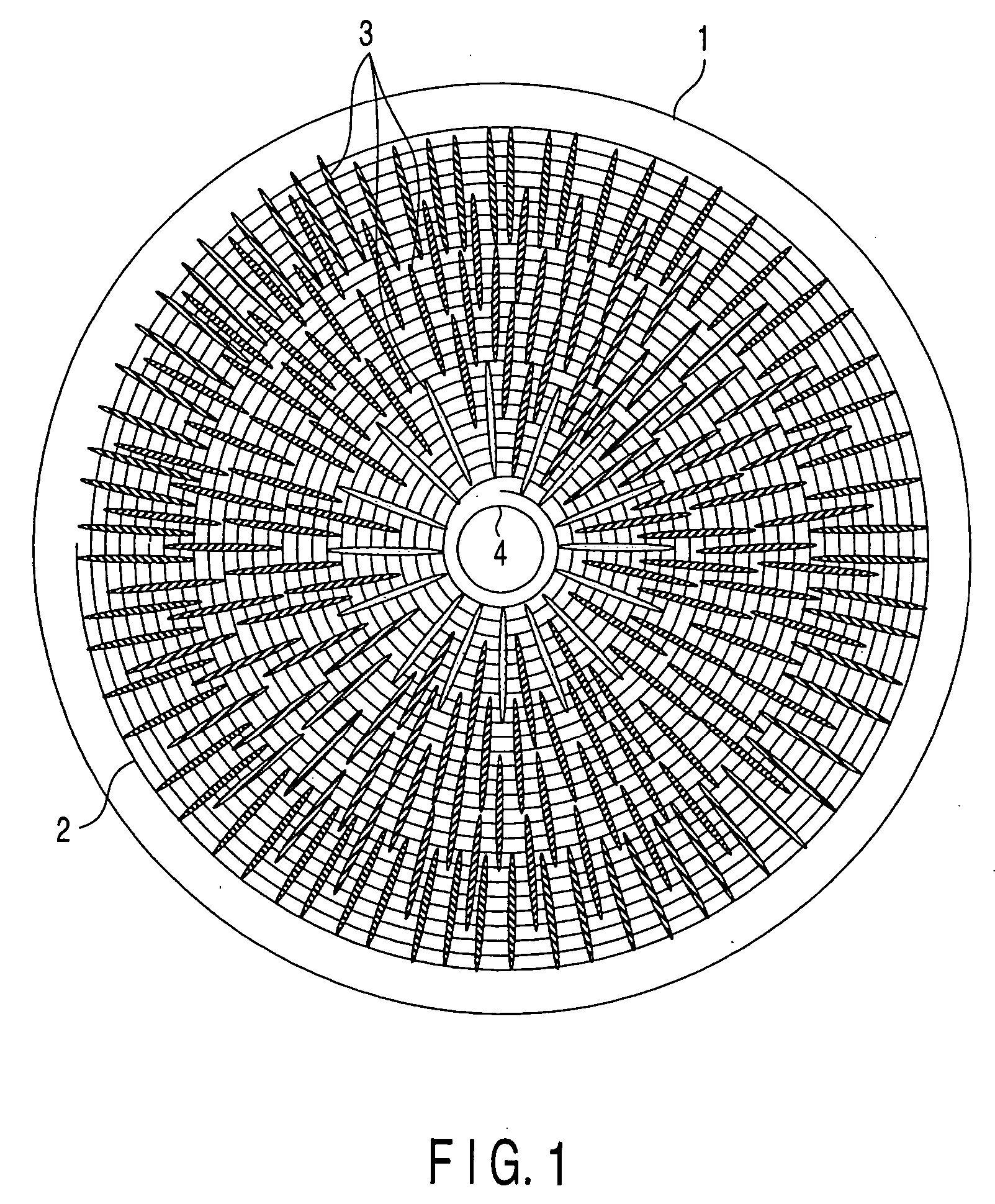
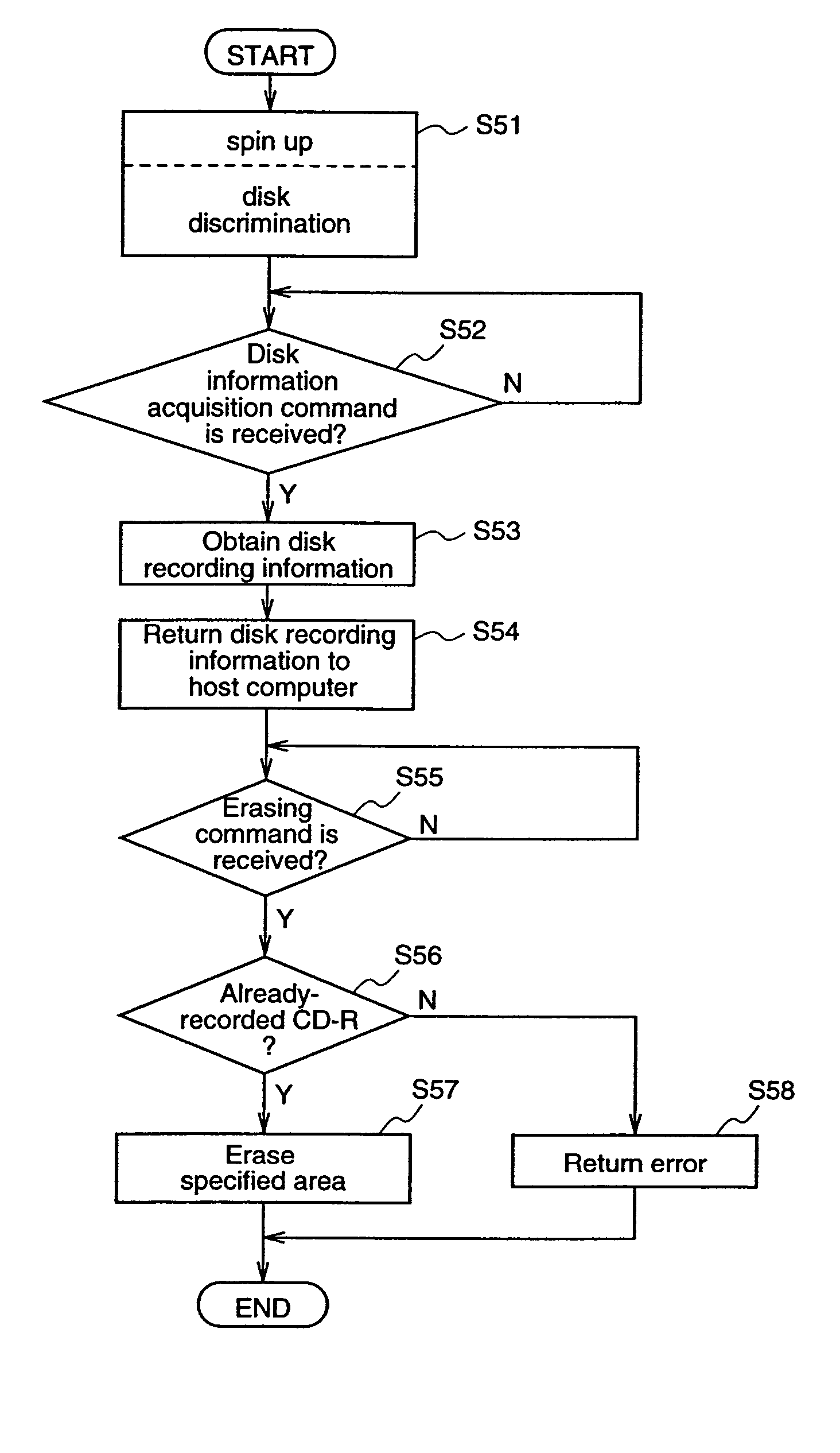
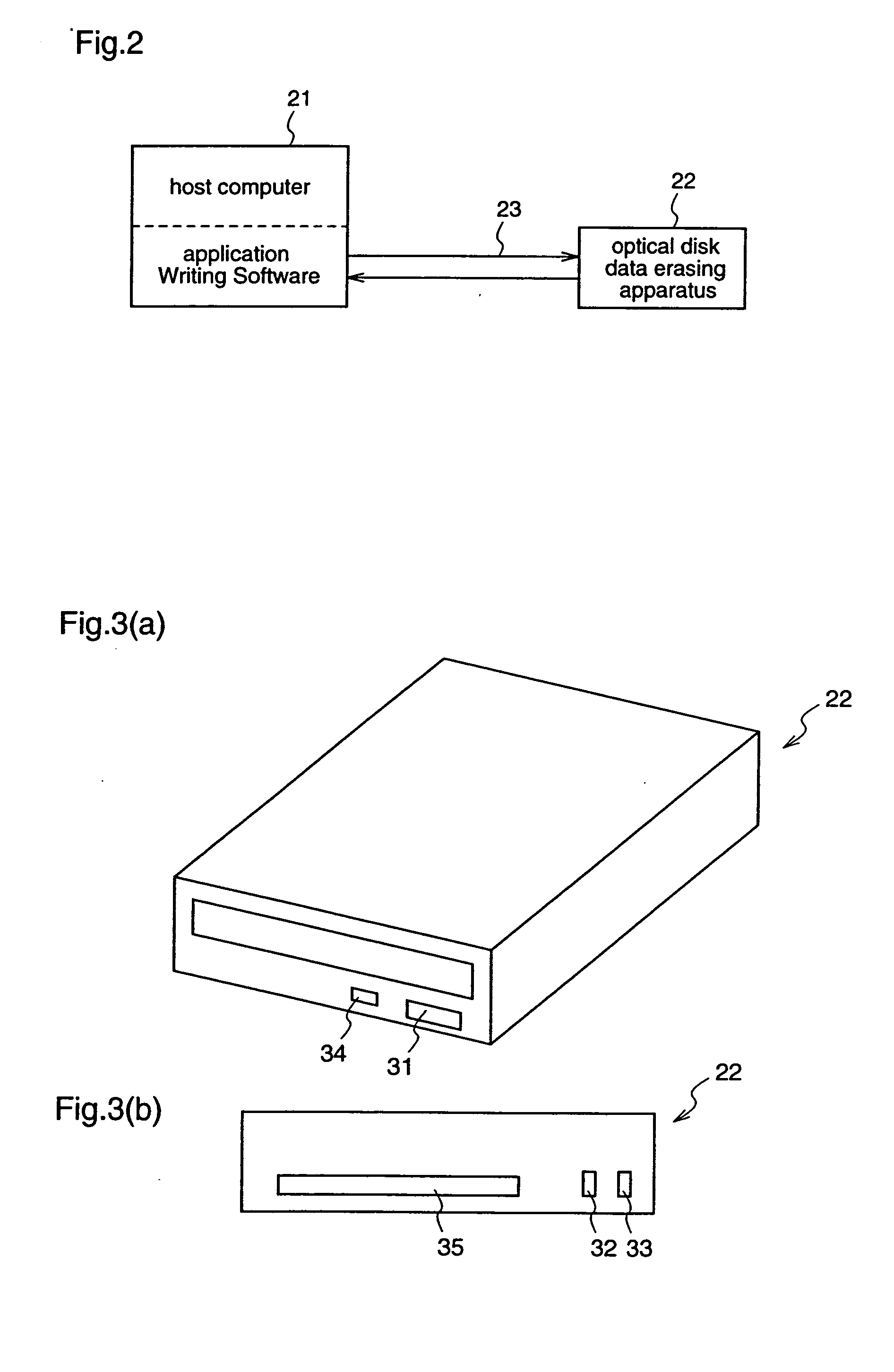
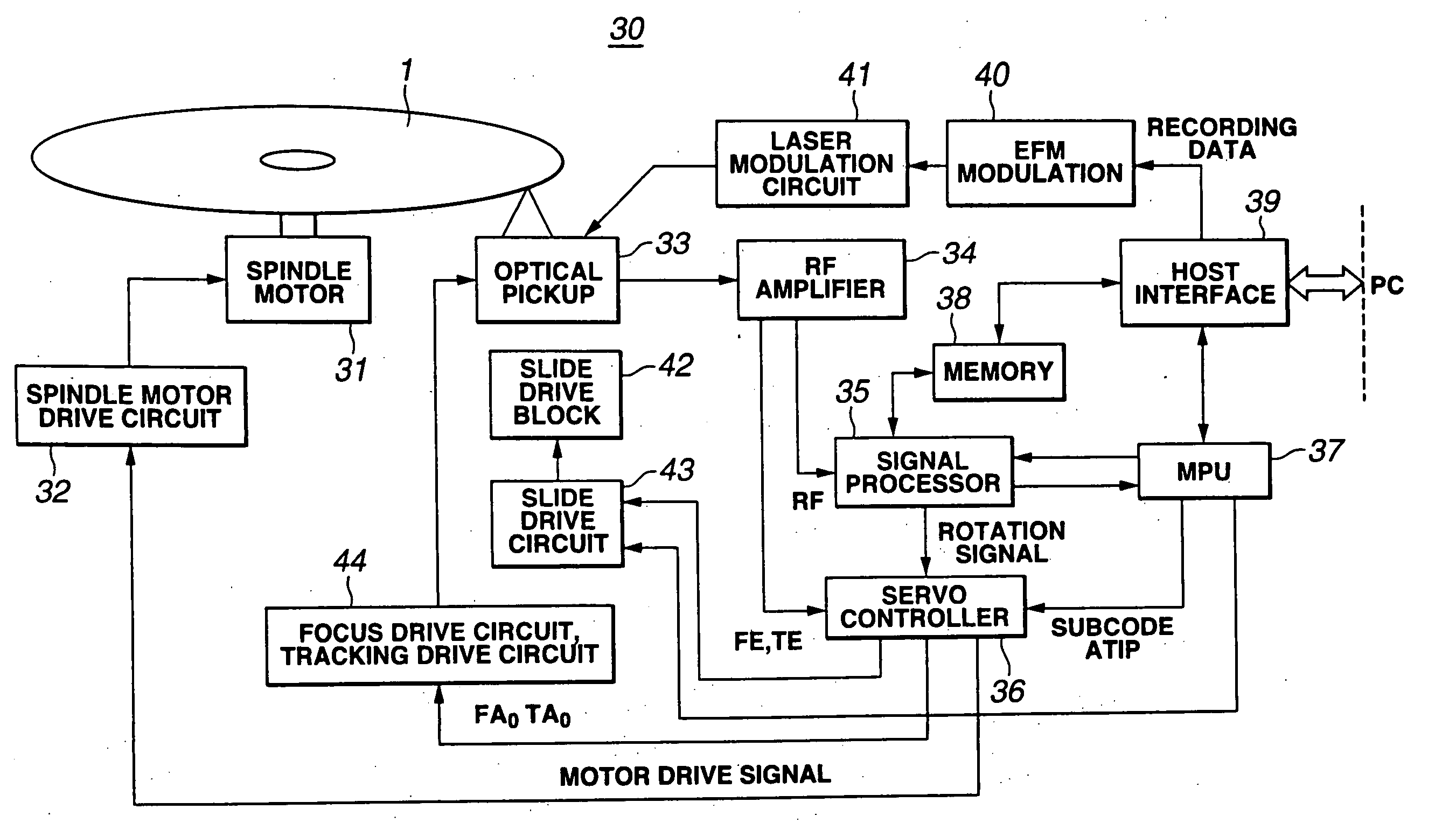
Optical disk data erasing apparatus and optical disk data erasing method
InactiveUS20050094522A1Easily realizedLow costCombination recordingReconditioning/cleaning record carriersComputer scienceLaser beams
In an optical disk data erasing apparatus, it is judged whether a loaded optical disk is a write-once optical disk or not, and when the optical disk is a write-once optical disk, disk recording information of the optical disk is obtained according to an instruction from a host computer, and overwriting of the optical disk is performed by irradiating the optical disk with a laser beam having a recording power equal to or higher than that at recording, thereby erasing data recorded on the optical disk. Therefore, the optical disk data erasing apparatus can completely erase the data recorded on the optical disk, easily and inexpensively, without having to use a special apparatus, and without generating substances detrimental to environment.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
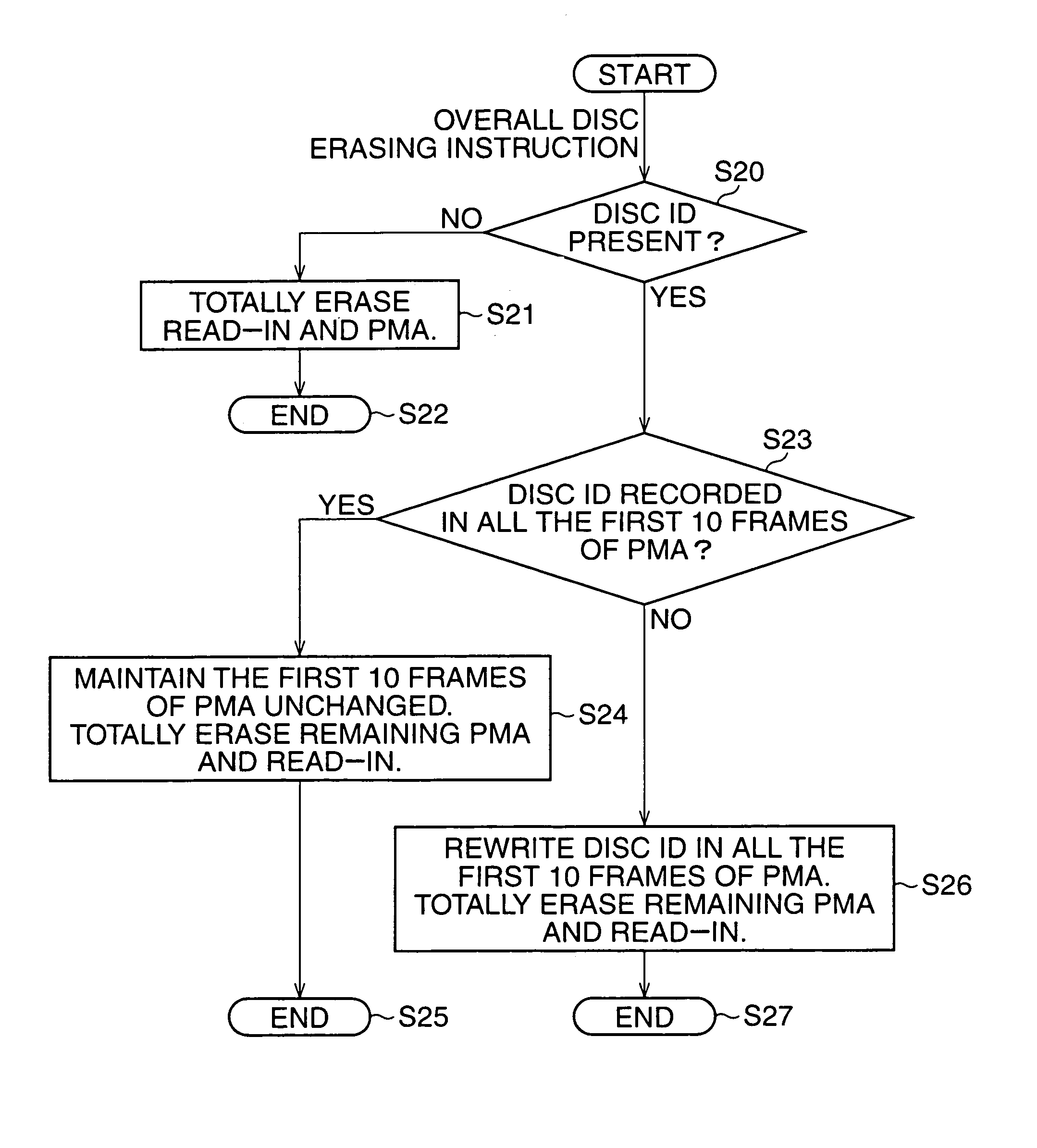
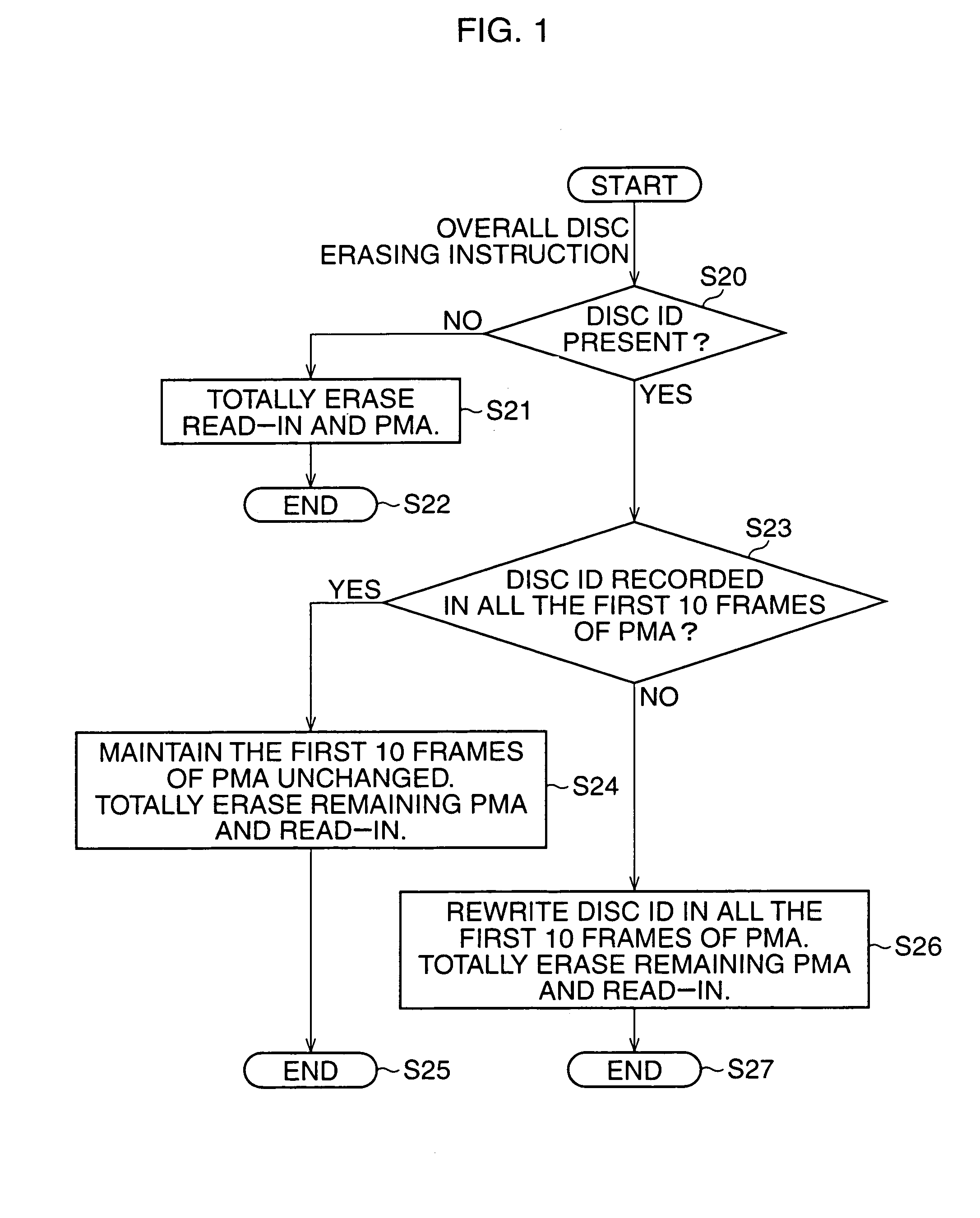
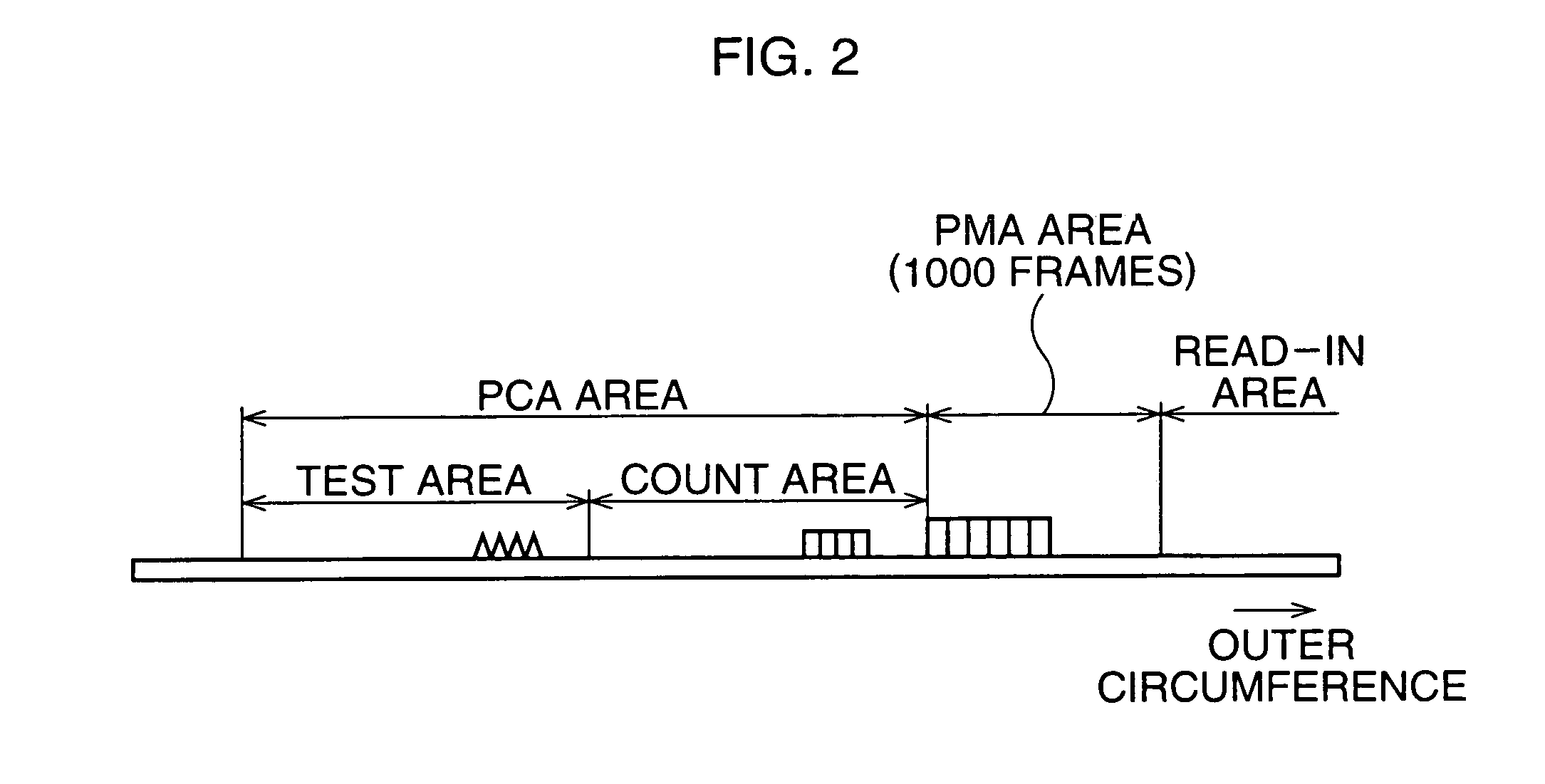
Method of logically erasing contents of a CD-RW disc while preserving disc ID
A method is designed to logically erase contents of a CD-RW disc in response to an erase command. The CD-RW disc is optically rewriteable, and has a program area and a PMA area. The program area is recorded with the contents in the form of tracks. The PMA area is recorded with at least two kinds of frames, one kind of frames containing identification information for identifying the CD-RW disc and the other kind of frames containing track information for indicating the tracks of the contents recorded in the program area. The method is carried out by the steps of accessing to the PMA area in response to the erase command, deleting all of frames which contain the track information from the PMA area, thereby logically erasing all of the contents from the program area, and reserving frames which contain the identification information in the PMA area, so that the CD-RW disc can be identified at rewriting thereof even after all of the contents are logically erased from the program area of the CD-RW disc. Specifically, the step of reserving reserves frames containing the identification information at a leading section of the PMA area. Practically, the PMA area is divided into sections by every ten number of frames, and the step of reserving reserves a ten number of frames containing the identification information into a predetermined section of the PMA area so as to fill the predetermined section.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Recording medium, recording device, reproduction device, recording method and reproduction method
InactiveUS7203139B2Improve usabilityTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareUsability
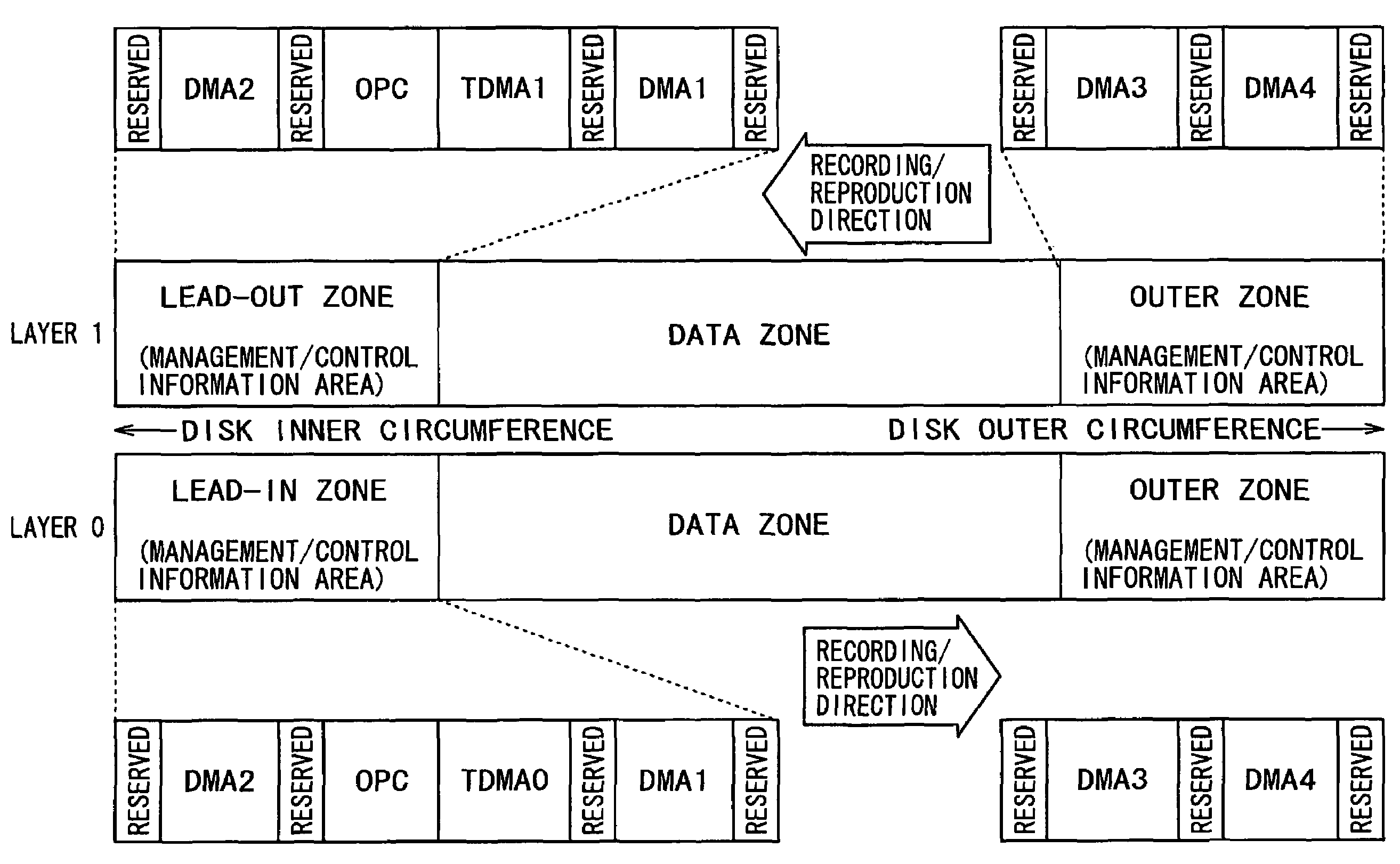
The present invention enhances the usability of a write-once recording medium having a plurality of recording layers. The write-once recording medium has a plurality of recording layers each including a regular recording reproduction area, an alternate area, a first alternate-address management information area and a second alternate-address management information area (a TDMA). In addition, written unwritten state indication information (a space bitmap) is recorded therein. Typically, the written unwritten state indication information is recorded in the second alternate-address management information area. By additionally recording alternate-address management information related to an alternate-address process in the second alternate-address management information area, the second alternate-address management information area can be used as an area for implementing renewal of the alternate-address management information. In addition, for every data unit (each cluster) on each of the recording layers on the write-once recording medium, written unwritten state indication information is used as information indicating whether or not data has been written into the data unit. On top of that, the second alternate-address management information areas (TDMAs), which are each provided on one of recording layers, are used sequentially one after another each as an area for updating alternate-address management information and written unwritten state indication information.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recording medium destruction apparatus, recording medium destruction system, electronic equipment supervising apparatus, and computer program
InactiveUS20070147776A1Managing dataTelevision system detailsReconditioning/cleaning record carriersComputer hardwareComputer program
Owner:ORIENT INSTR COMP CO LTD
Recording medium, recording device, reproduction device, recording method and reproduction method
InactiveUS20050219979A1Improve usabilityTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareUsability
The present invention enhances the usability of a write-once recording medium having a plurality of recording layers. The write-once recording medium has a plurality of recording layers each including a regular recording reproduction area, an alternate area, a first alternate-address management information area and a second alternate-address management information area (a TDMA). In addition, written unwritten state indication information (a space bitmap) is recorded therein. Typically, the written unwritten state indication information is recorded in the second alternate-address management information area. By additionally recording alternate-address management information related to an alternate-address process in the second alternate-address management information area, the second alternate-address management information area can be used as an area for implementing renewal of the alternate-address management information. In addition, for every data unit (each cluster) on each of the recording layers on the write-once recording medium, written unwritten state indication information is used as information indicating whether or not data has been written into the data unit. On top of that, the second alternate-address management information areas (TDMAs), which are each provided on one of recording layers, are used sequentially one after another each as an area for updating alternate-address management information and written unwritten state indication information.
Owner:SONY CORP
Data recording control apparatus
InactiveUS20070112862A1Raise priorityDigital data processing detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsData recordingData science
Owner:SONY CORP
Data recording apparatus, data recording method, and optical recording medium including pseudo-erasing features
InactiveUS20050152242A1Accurate detectionAccurate recordRecord information storageOptical erasing systemsFeature dataData recording
Data is recorded on packet basis to a track of an optical recording medium and the data is pseudo-erased by erasing contents information of the track having the data. Information indicating the end position of the packet containing the data is recorded on the optical recording medium and a new data is recorded to the track where the data has been pseudo-erased in accordance with the information indicating the end position of the packet.
Owner:SONY CORP
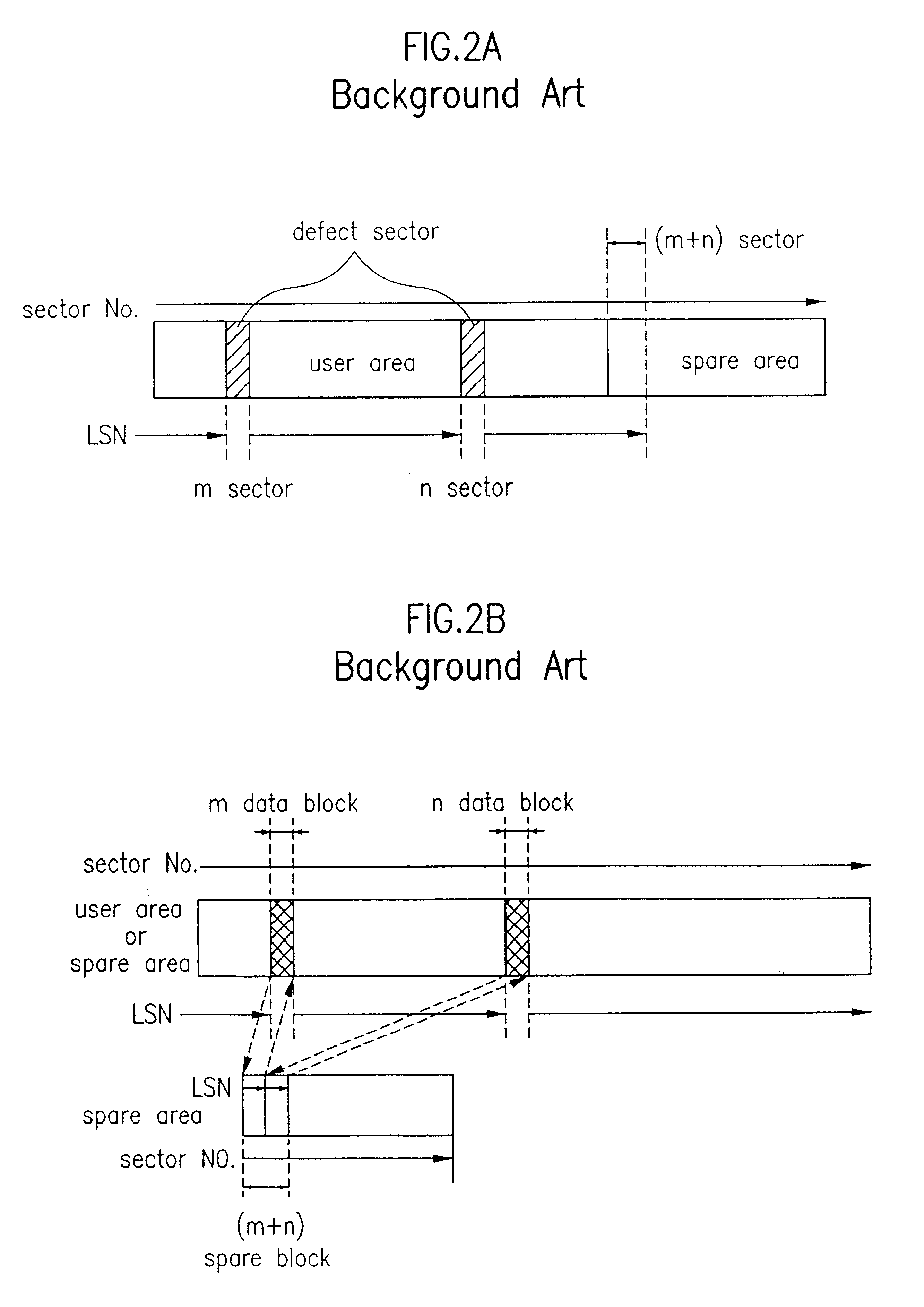
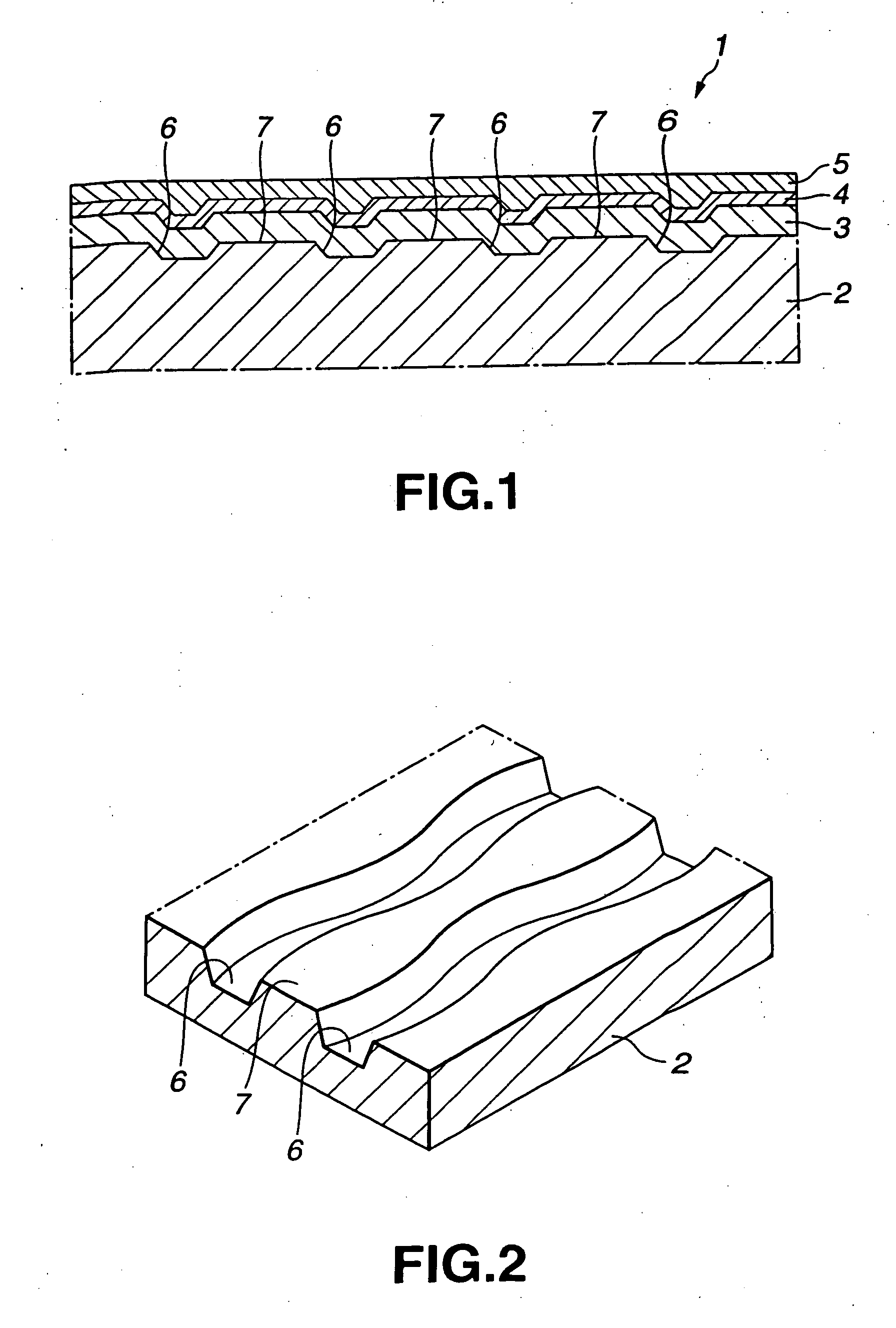
Spare area management method of optical recording medium
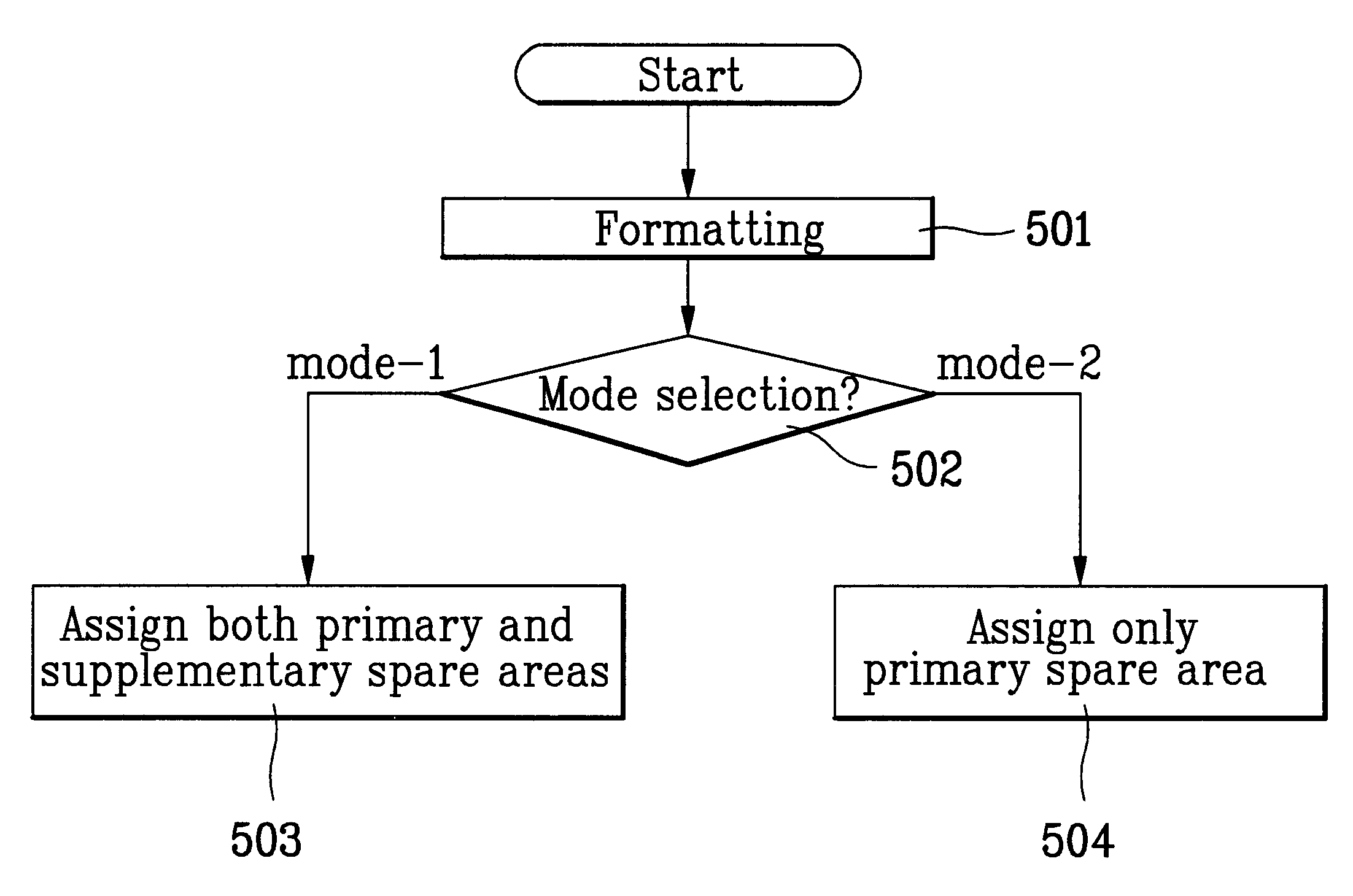
InactiveUS6671775B2Disc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageComputer hardwareOptical recording
A recording medium and a spare area management method for an optical recording medium are provided. The spare area management method utilizes an identification information to indicate whether a primary spare area is full or a supplementary spare area has been assigned or extended, as necessary. The spare area management method improves the performance of the driver by replacing a defective block with a spare block nearer to the defective block.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
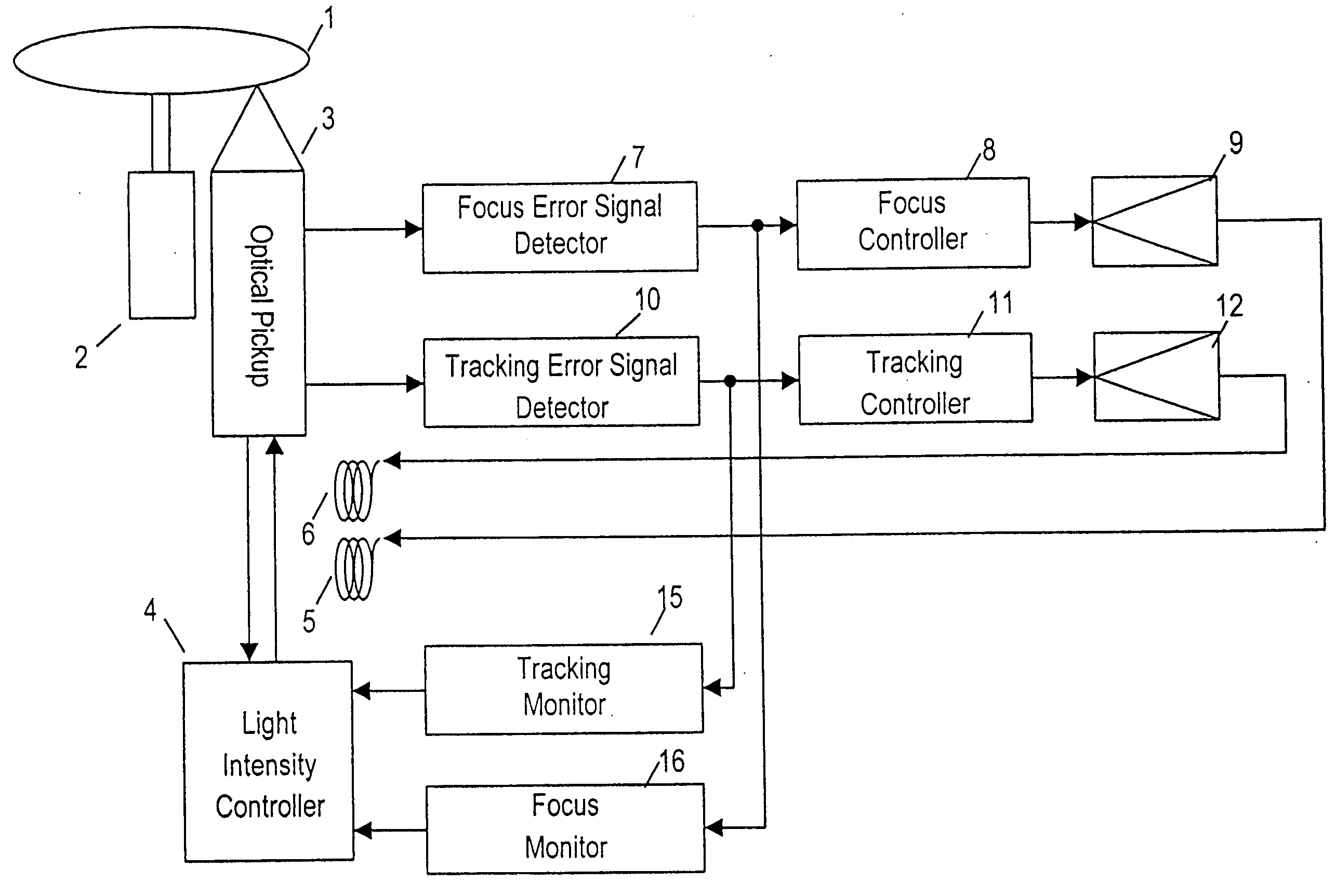
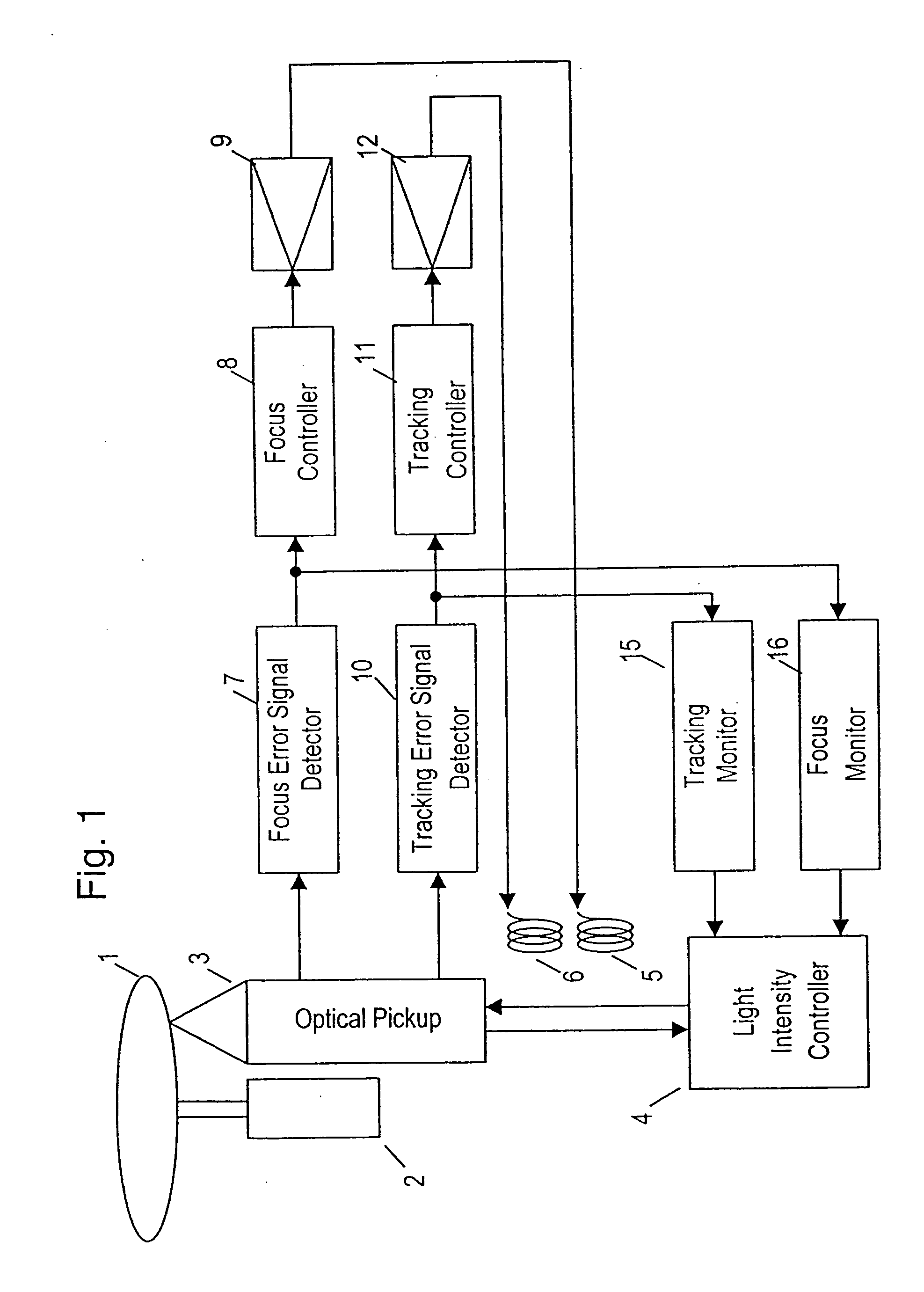
Optical disk device
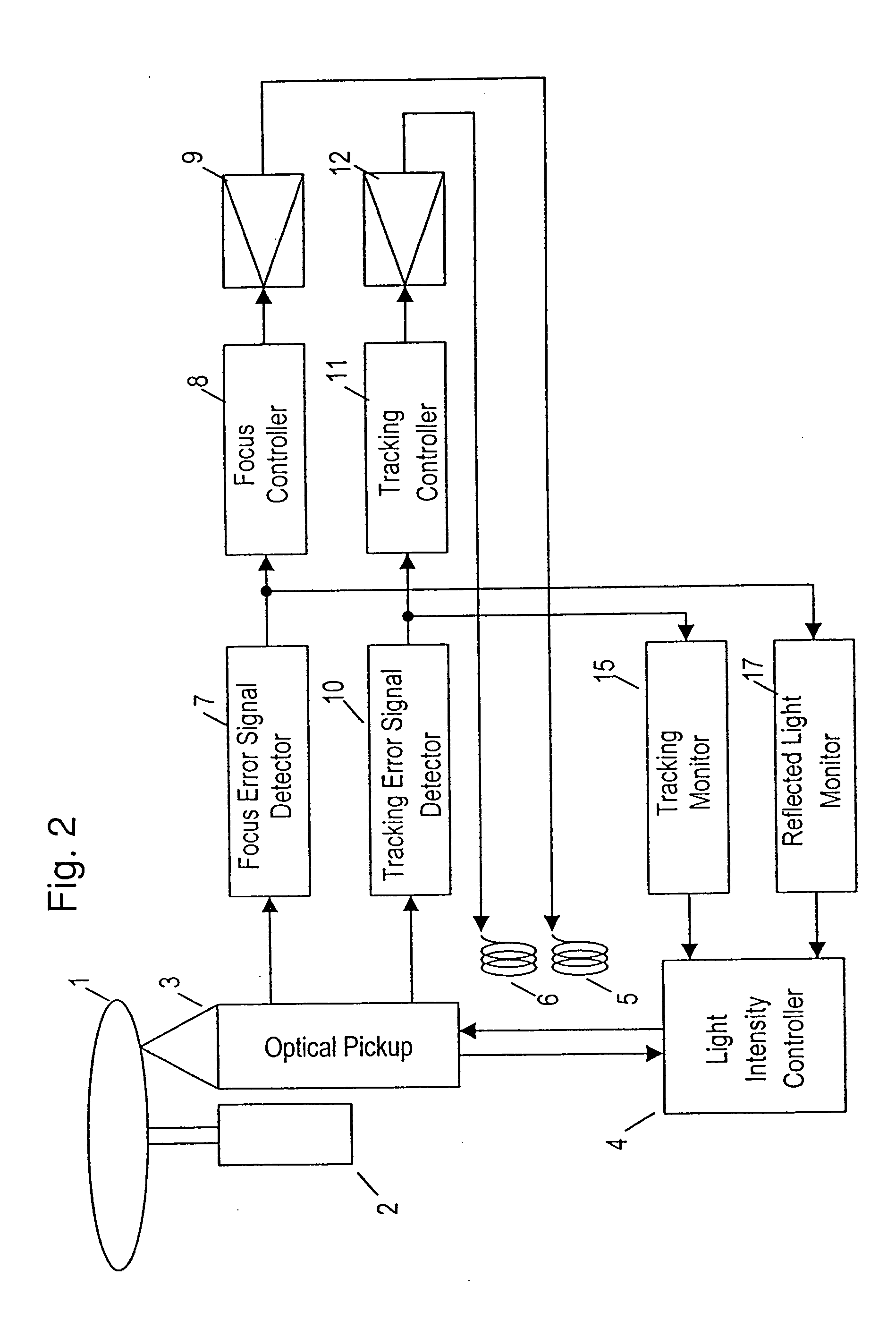
InactiveUS20050030846A1Error signalReduce intensityOptical discsOptical beam sourcesComputer hardwareLight beam
An optical disk device is capable of preventing a signal from being incorrectly recorded or erased on another data plane different from a data plane in a recording operation on a disk having plural layers of data plane. A focus monitor monitors an increase of a focus error signal. A reflected light quantity monitor may monitor a drop of reflected light quantity. A move from a layer of a data plane during recording may be detected. Depending on these results, a light intensity controller reduces an intensity of a light beam to a reproducing level. The light intensity controller once reduces the intensity to a reproducing level when recording signals in plural layers of data plane. After moving to the layer followed by the focus of the light beam, the intensity of the light beam is raised again to the recording level.
Owner:KONO KAZUHIKO
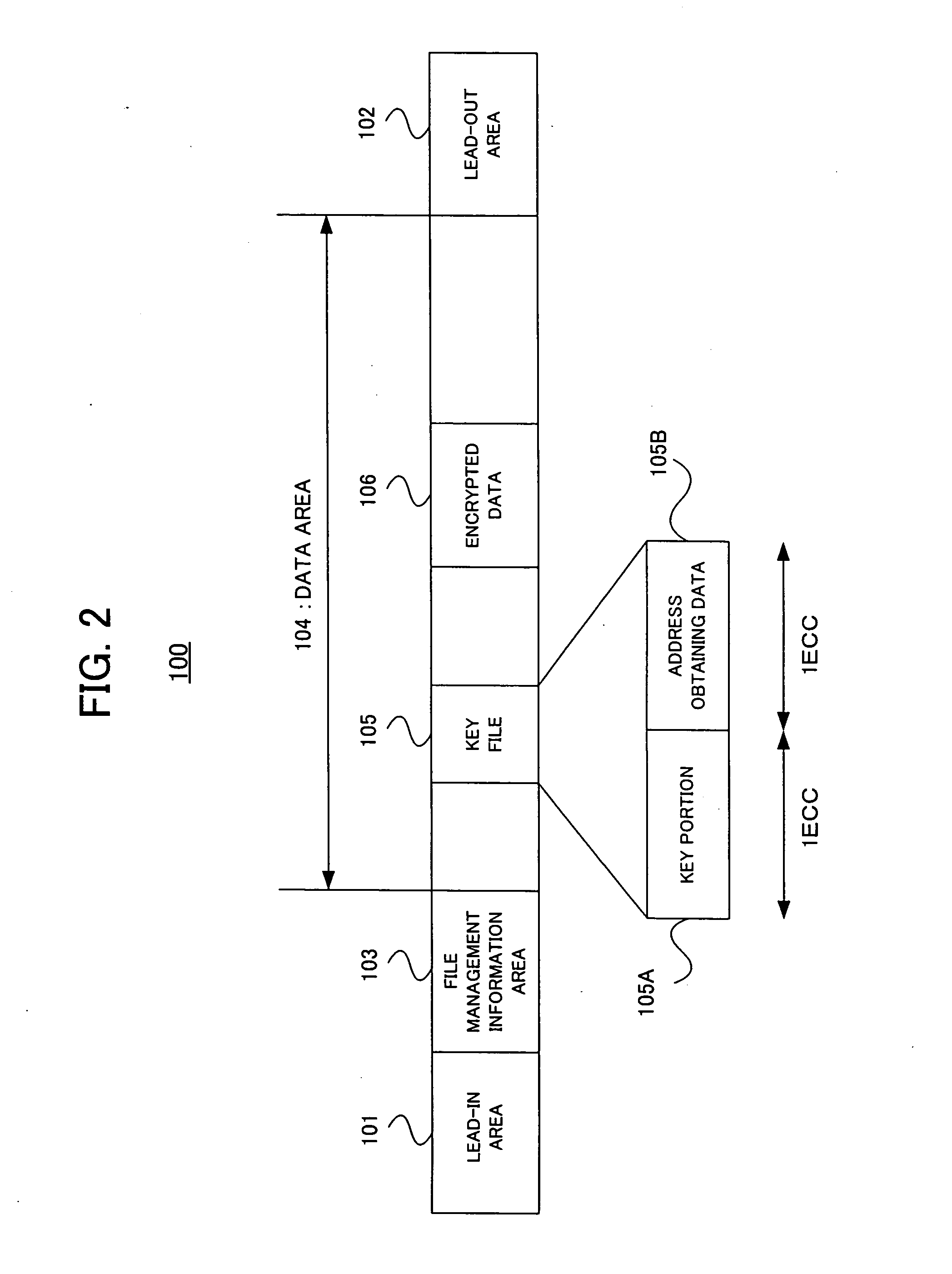
Information recording and reproducing apparatus, and information recording and erasing method
InactiveUS7372789B2Short timeTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer hardwareRecovery record
When data is recorded on an optical disc capable of recording information only once, such as a DVD-R and the like, encrypted data obtained by encrypting the recording data and a key for decrypting the encrypted data are generated, and they are recorded in different areas on the recording medium. When the data recorded by the recording method is erased, only a key portion in a file including the key for decrypting the encrypted data is physically made a defect, or is registered as the defect by a defect management system. Thereby, since the key portion becomes unreadable, it becomes impossible that the recording data is restored by decrypting the encrypted data. Therefore, the recording data can be substantially completely erased.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Optical recording method and optical recording device
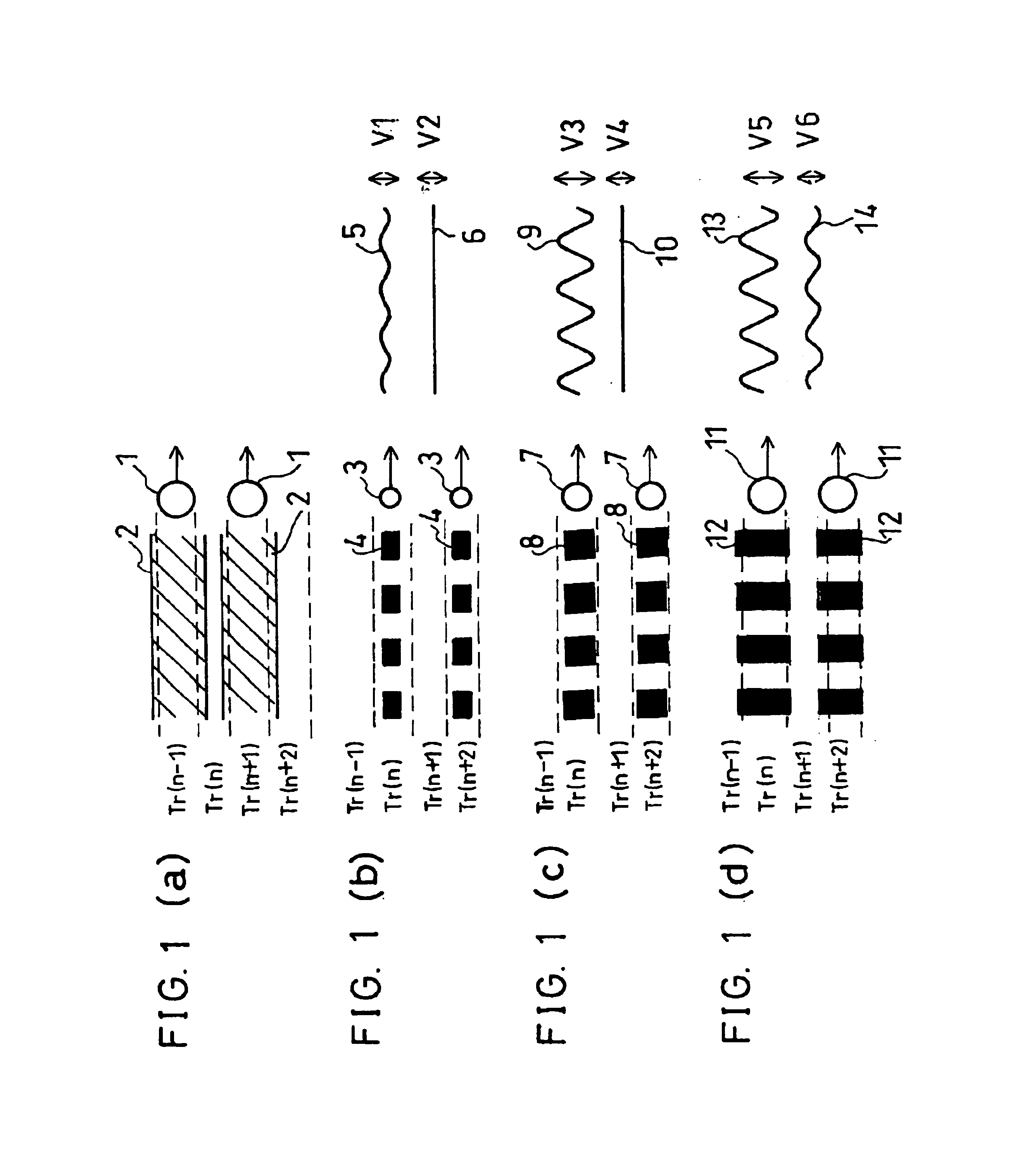
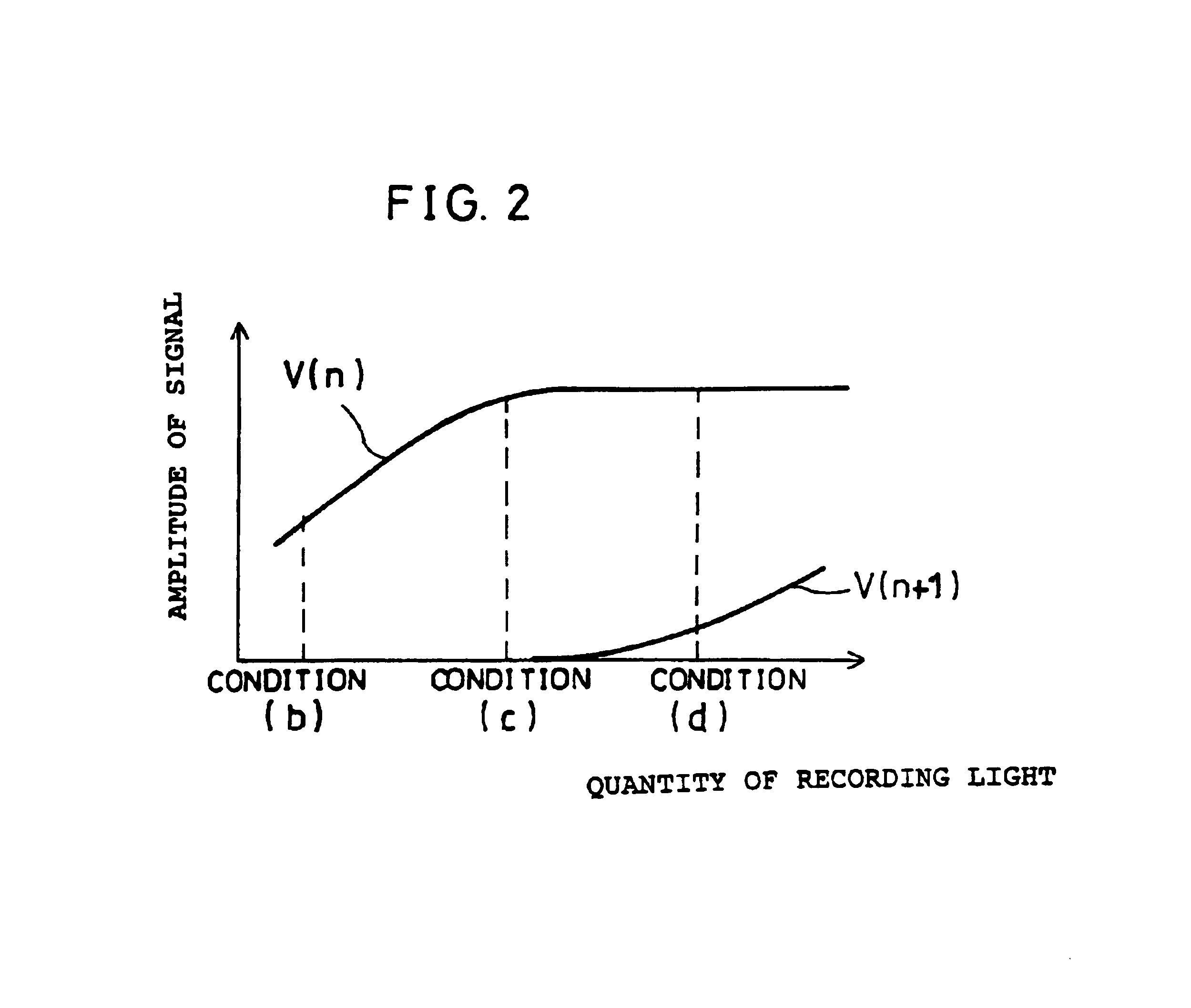
InactiveUS6876611B1Improve the level ofIncrease widthCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersLight beamEngineering
A reverse pattern is formed in a track adjacent to a specified track on an optical recording medium with a predetermined light beam capable of writing large recording marks. Thereafter, a normal pattern is formed in an area, of an adjacent track, which is adjacent to the reverse pattern in the specified track with recording light beams of various strengths, the adjacent track being adjacent to the specified track. The specified track is read to detect a plurality of re-out signals according to individual light beam conditions. The adjacent track is read to detect a plurality of read-out signals according to individual light beam conditions. An optimum recording condition is determined for the specified track from the plurality of light beam condition and the read-out signals from the specified track and the adjacent track, and information is recorded in the specified track according to the optimum recording condition. Thus, even when there exists a difference in recording sensitivity between adjacent tracks, since the width of the recording marks can be controlled to be optimum, cross-talk between tracks during signal reproduction and cross-erase during signal recording are restrained to minimum levels, and recording density is improved.
Owner:SHARP KK
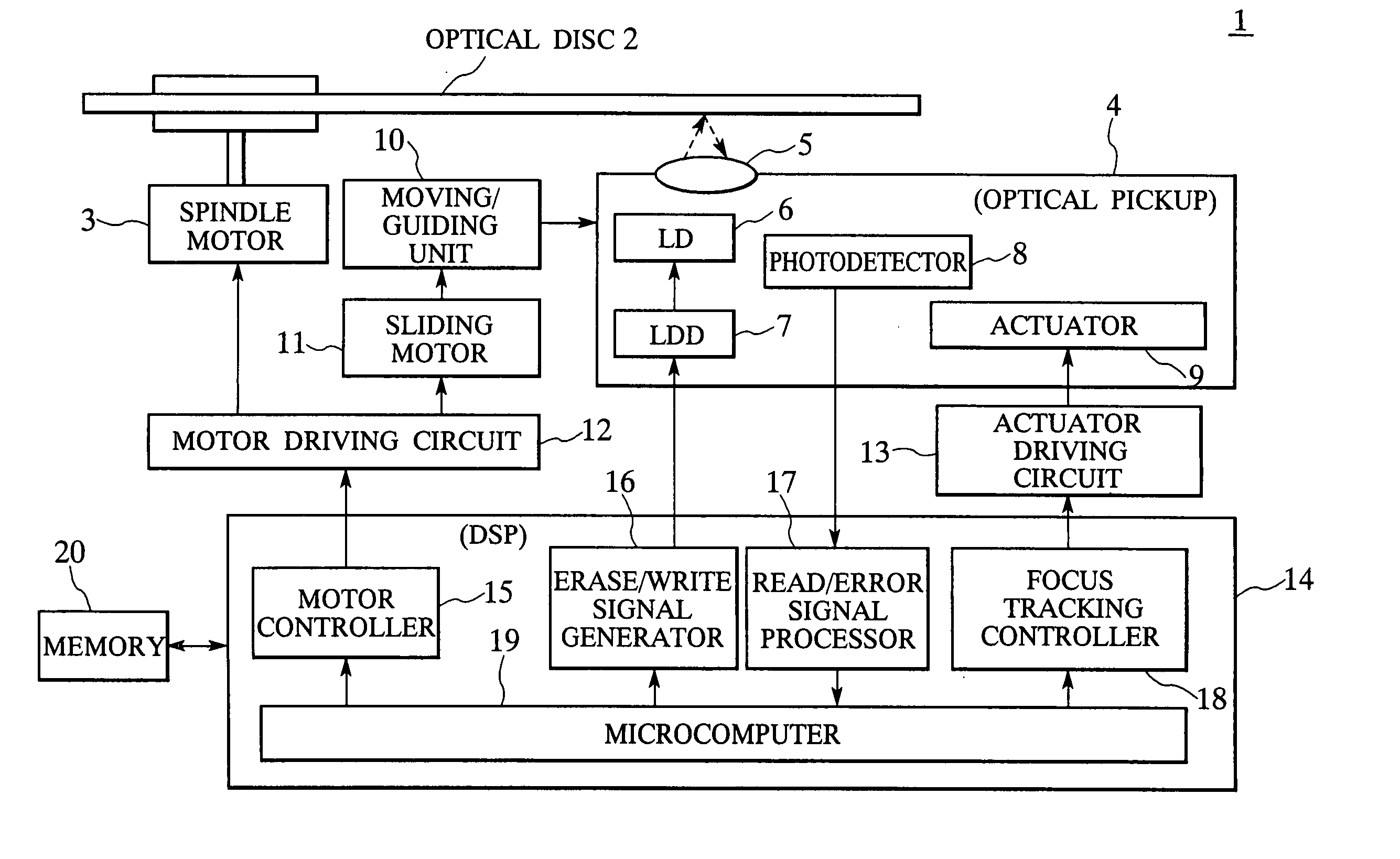
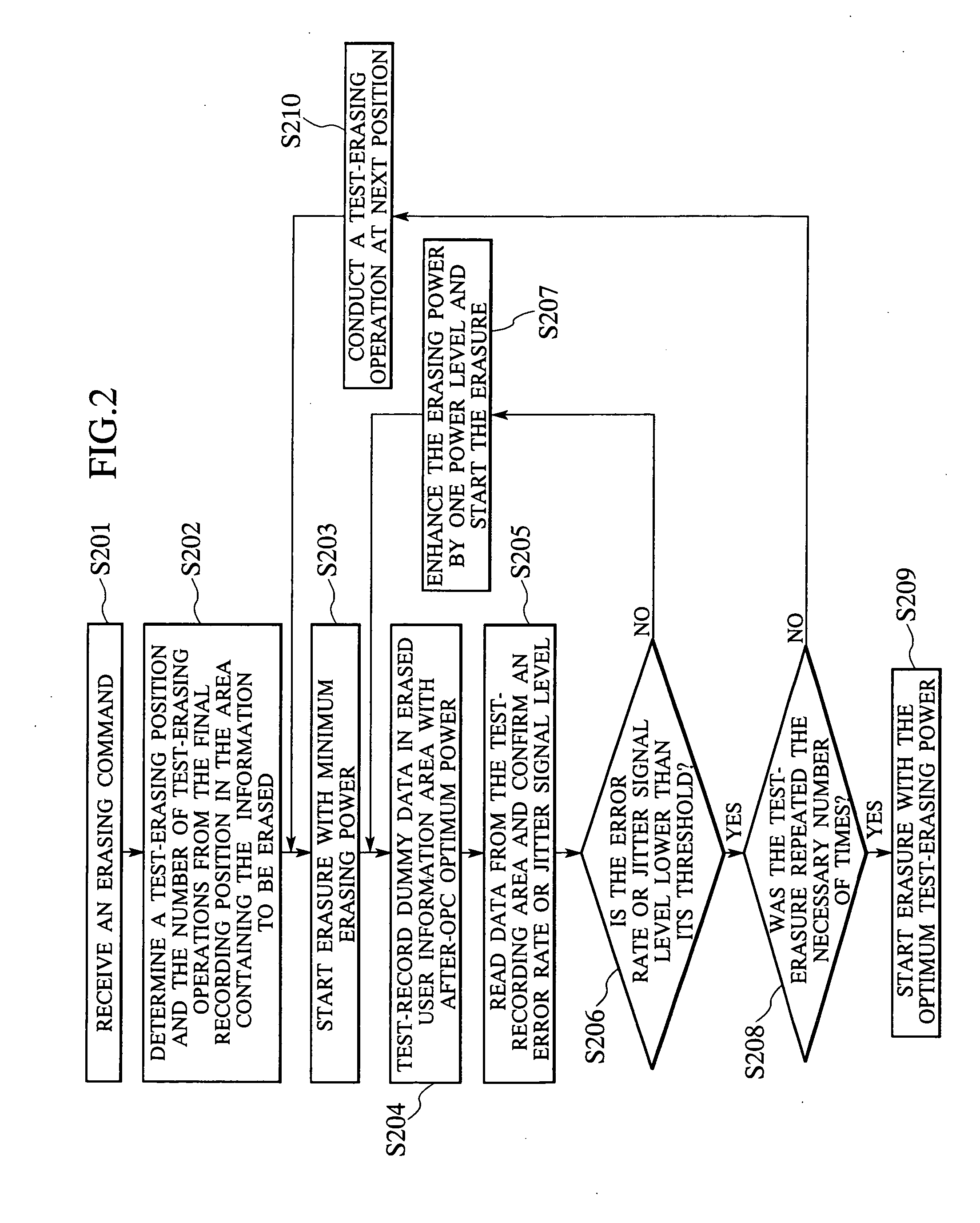
Optical disc apparatus and method of erasing information recorded thereon
InactiveUS20060203693A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareLaser light
In an optical disc apparatus, before the information already existing on an optical disc is erased, the information recorded in a user data area of the optical disc is test-erased with laser light of previously set erasing power first, then after test recording of information in the user date area and evaluation of the test-recorded information in terms of recording quality, erasing power for actually erasing desired information is set in accordance with evaluation results.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE
Data recording apparatus, data recording method, and optical recording medium including pseudo-erasing features
InactiveUS20050152243A1Accurate detectionAccurate recordRecord information storageOptical erasing systemsFeature dataData recording
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for dealing with data recording media and device for carrying out said method, and method for disposing of electronic devices and device for carrying out said method
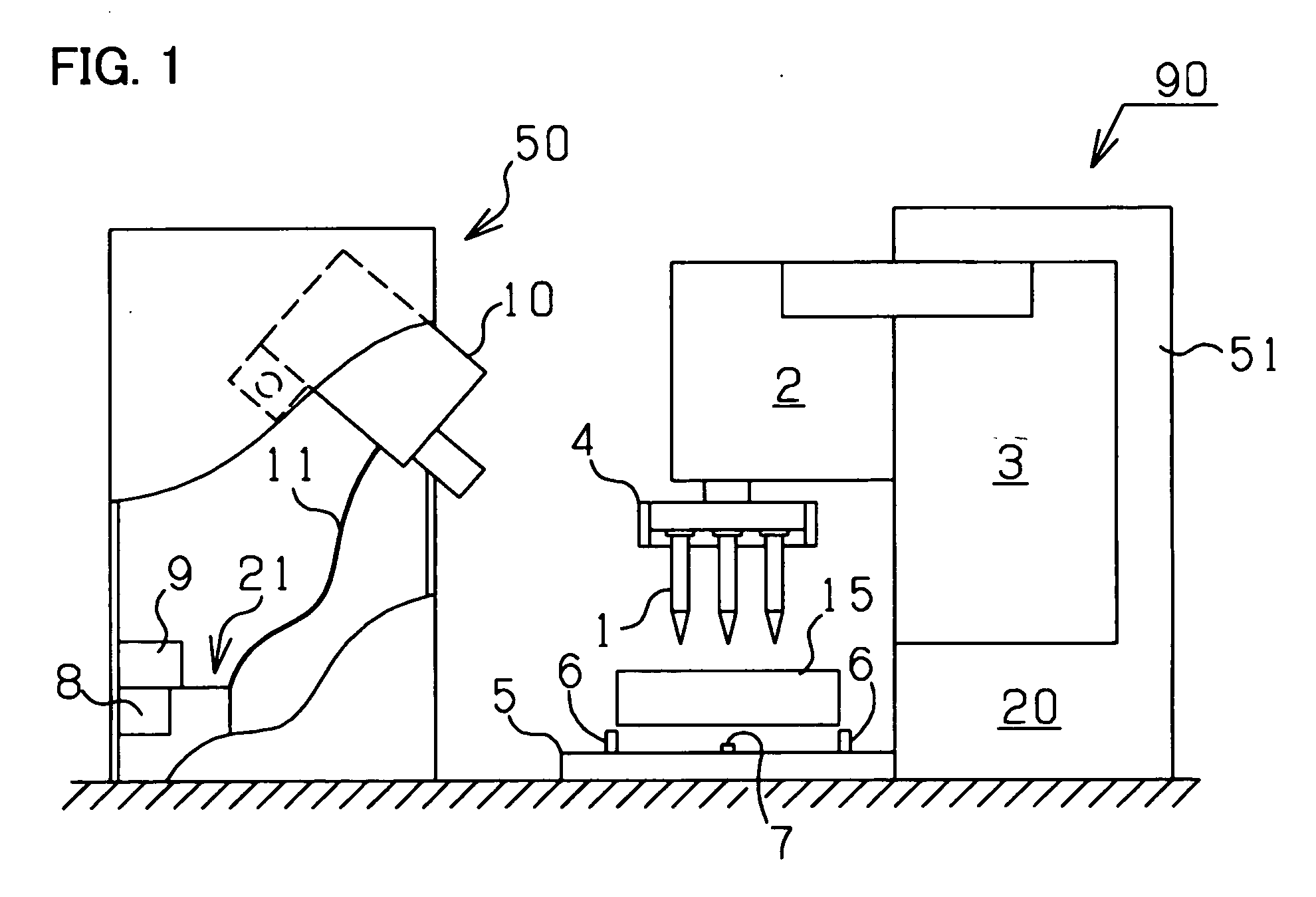
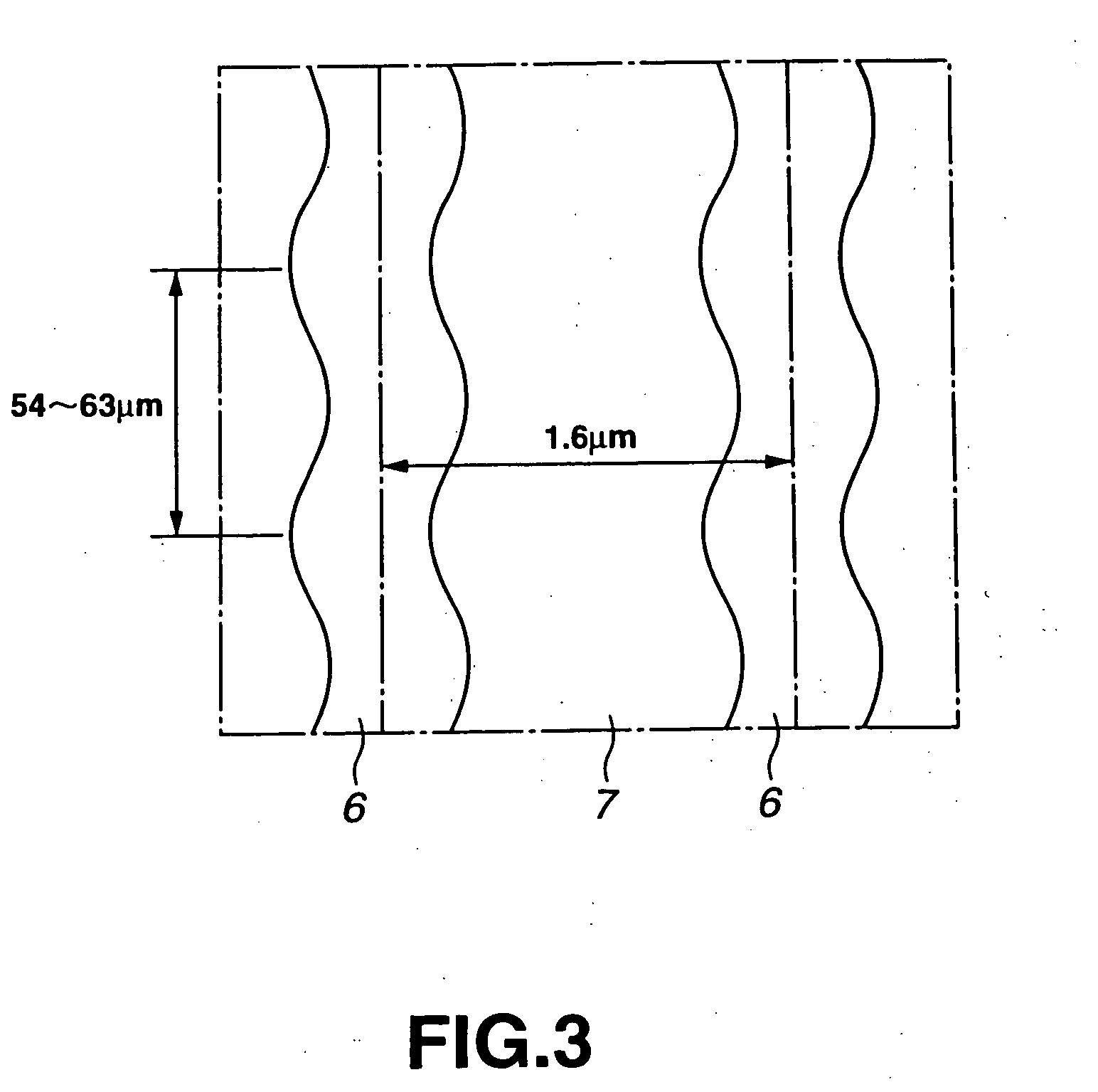
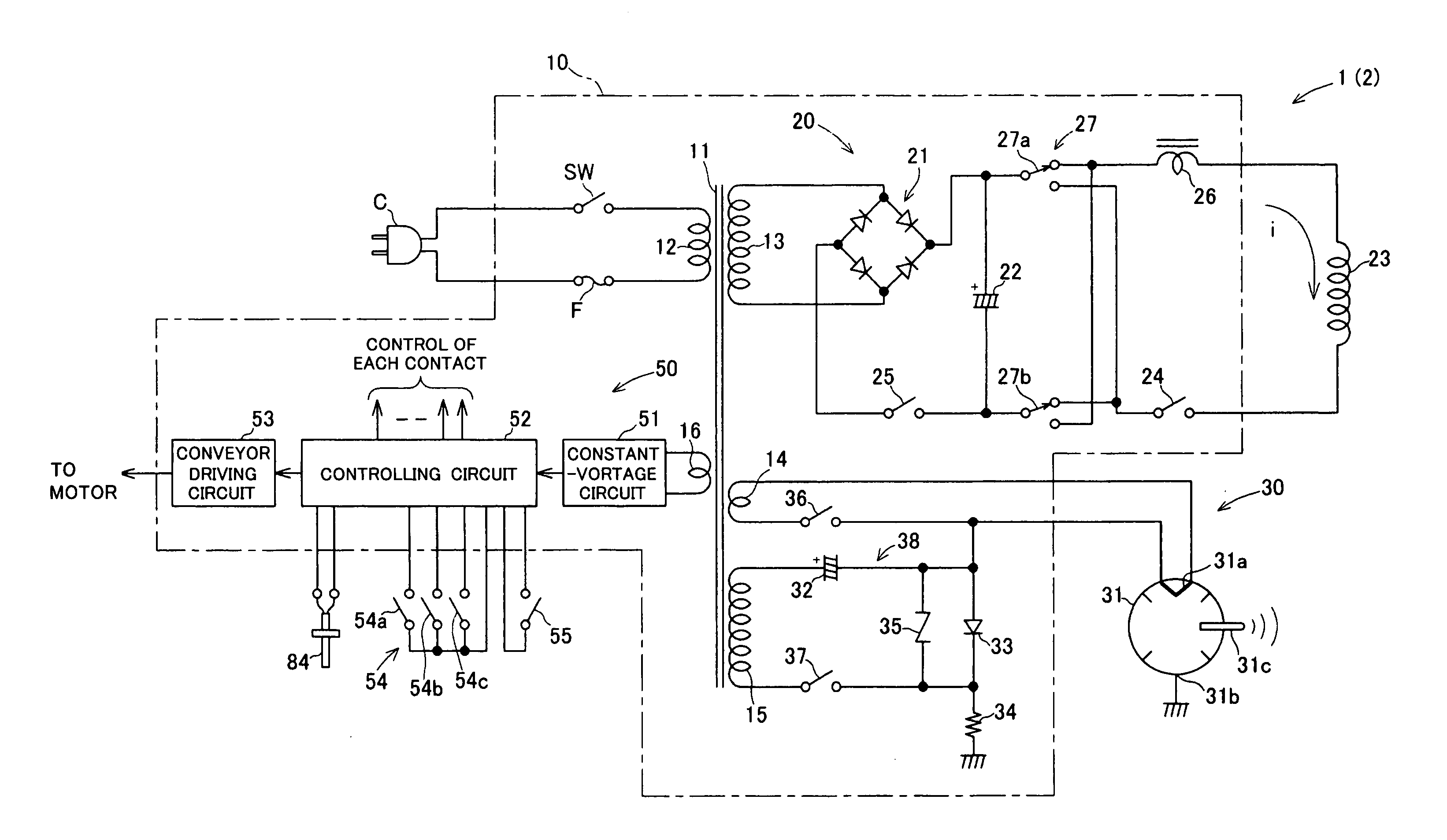
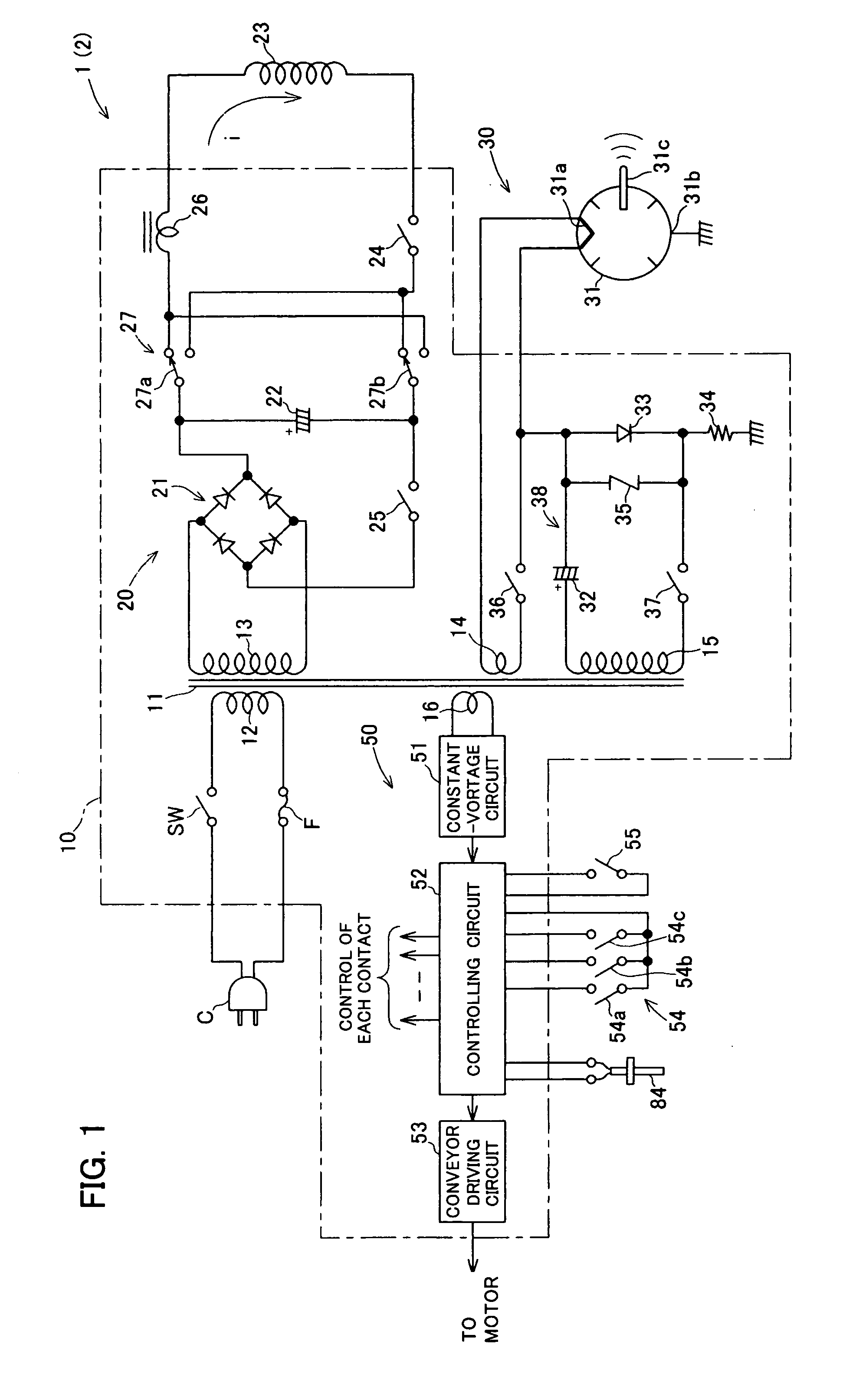
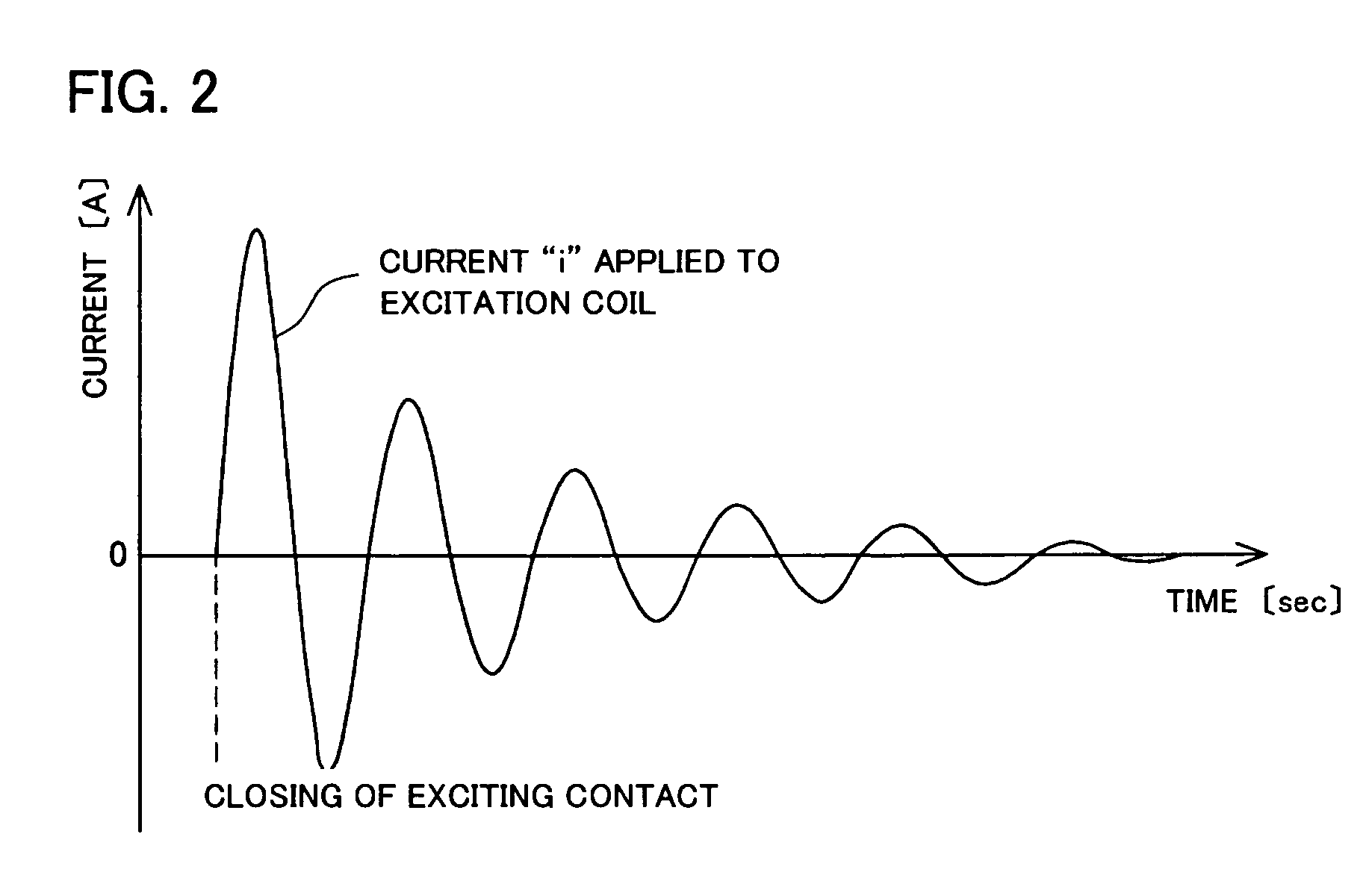
InactiveUS20070076326A1Efficiently eraseEfficiently destroyCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsOptical recordingData recording
There is provided with a method for dealing with data recording media adapted to readily erase magnetic data recorded in magnetic recording media or destroy data recorded in optical recording media and a device for carrying out said method. Further, there is provided with a method for disposing of electronic device for destroying electronic devices and a device for carrying out said method. A device for dealing with data recording media including an excitation coil for generating a magnetic field having a predetermined strength, a magnetron for radiating an electromagnetic wave having a predetermined frequency at a predetermined strength, and a receptacle adapted to accommodate a magnetic recording medium or an optical recording medium, wherein the receptacle is made of a non-magnetic material capable of shielding the electromagnetic wave, wherein the receptacle has an outer periphery around which the excitation coil is wound so as to induce a magnetic field within the receptacle, and wherein the receptacle has a wall provided with the magnetron, so that the electromagnetic wave is radiated toward inside of the receptacle.
Owner:ORIENT INSTR COMP CO LTD
Optically anisotropic recording medium and method of recording and erasing information using the same
InactiveUS6090508AHigh densityIncrease speedLiquid crystal compositionsPhotography auxillary processesRecording layerRecording media
An optically anisotropic recording medium and a method of recording and erasing method using the recording medium are disclosed, which comprises the steps of applying heat or light to the recording medium which comprises a recording layer made of optically anisotropic organic thin-film-shaped crystals to raise the temperature of an organic material or which comprises the optically anisotropic organic thin-film-shaped crystals to a recording temperature at which the crystals are fused, performing partial changing of the crystalline state of the crystals by rapidly cooling the recording layer, thereby recording information in the recording layer; and heating the recording layer to an erasing temperature which is lower than the recording temperature, at which the crystals are not fused, but the molecules thereof can be thermally moved.
Owner:RICOH KK
Information recording and reproducing apparatus, and information recording and erasing method
InactiveUS20050013217A1Short timeTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer hardwareRecovery record
When data is recorded on an optical disc capable of recording information only once, such as a DVD-R and the like, encrypted data obtained by encrypting the recording data and a key for decrypting the encrypted data are generated, and they are recorded in different areas on the recording medium. When the data recorded by the recording method is erased, only a key portion in a file including the key for decrypting the encrypted data is physically made a defect, or is registered as the defect by a defect management system. Thereby, since the key portion becomes unreadable, it becomes impossible that the recording data is restored by decrypting the encrypted data. Therefore, the recording data can be substantially completely erased.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com