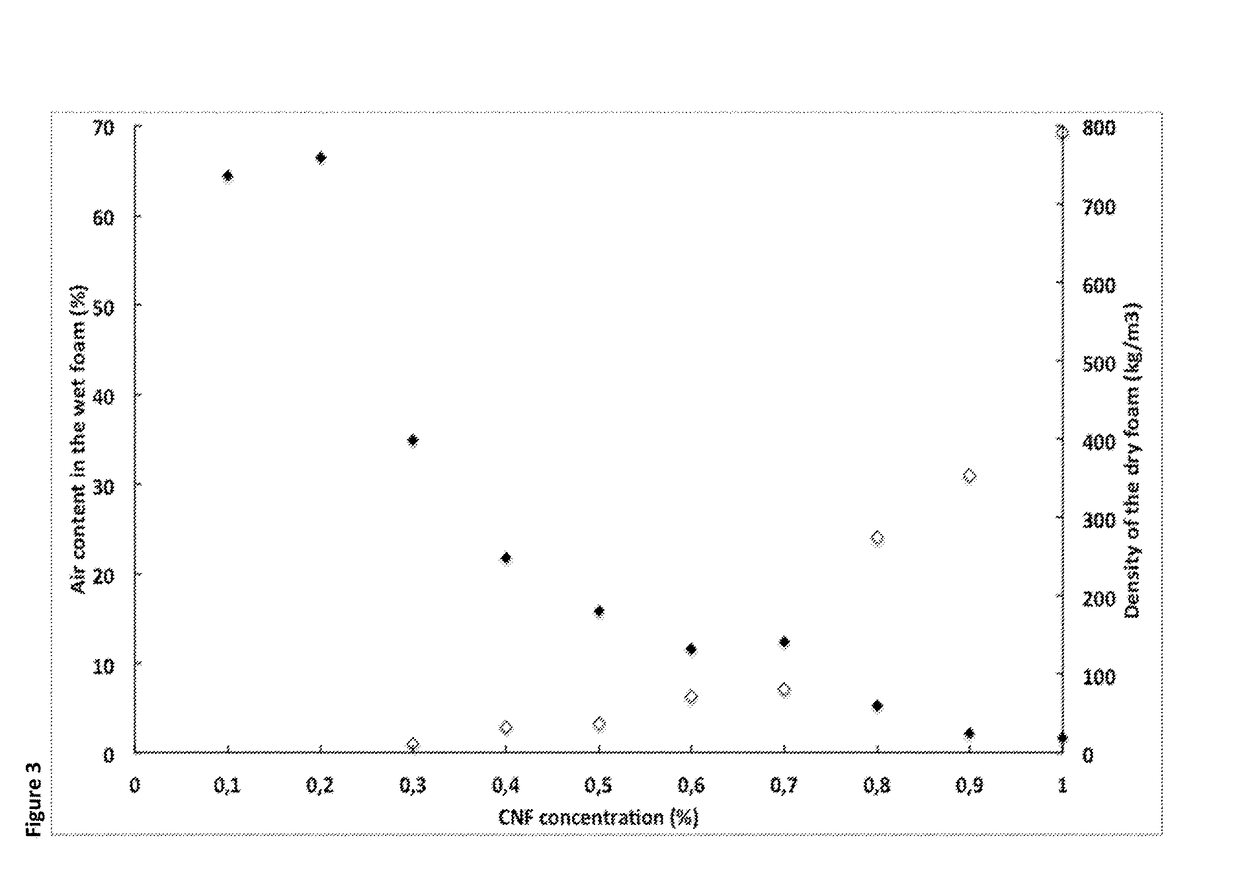
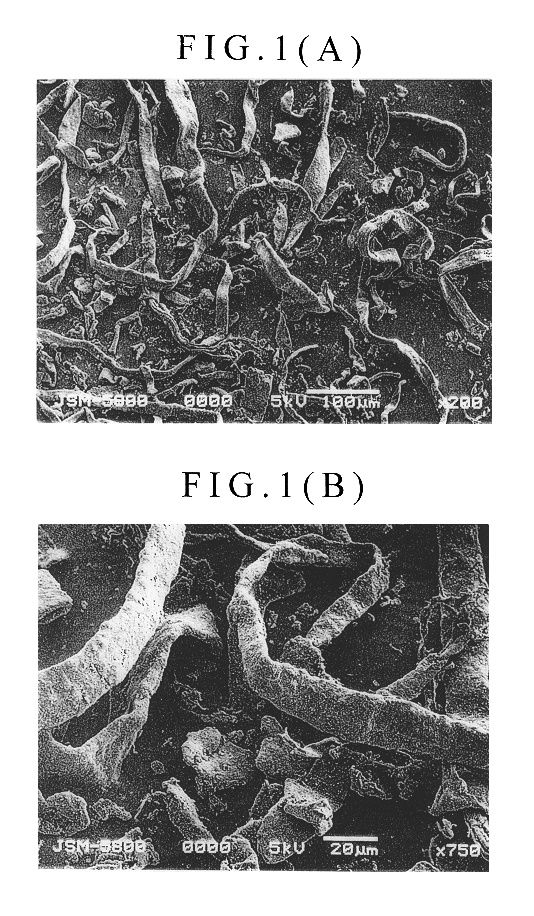
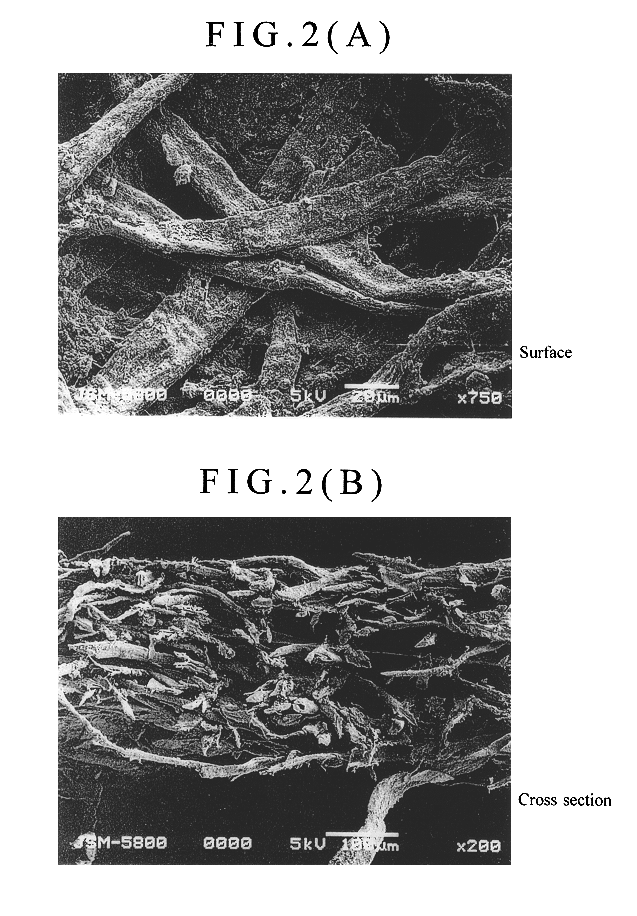
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
98results about "Foam addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
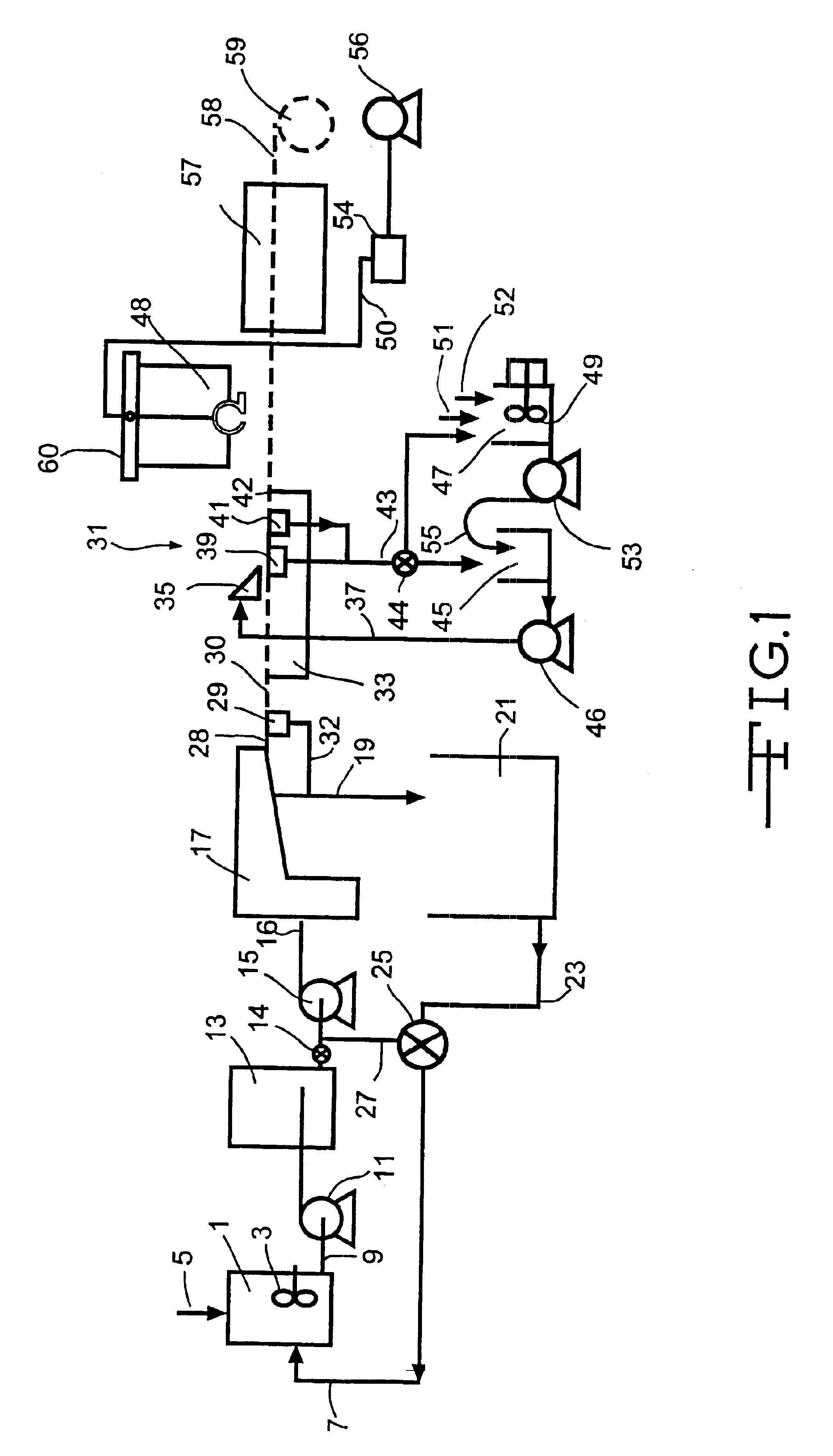
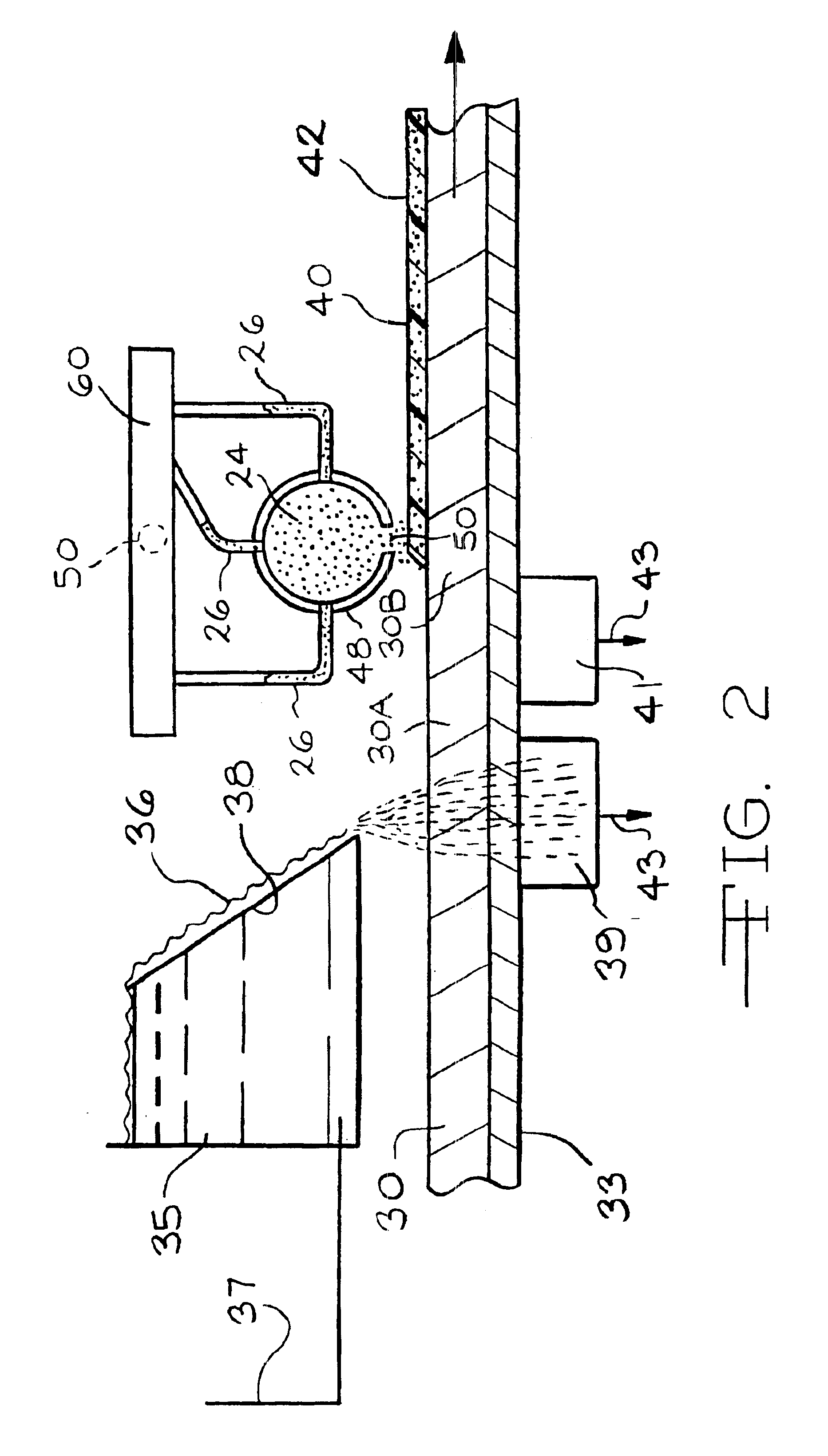
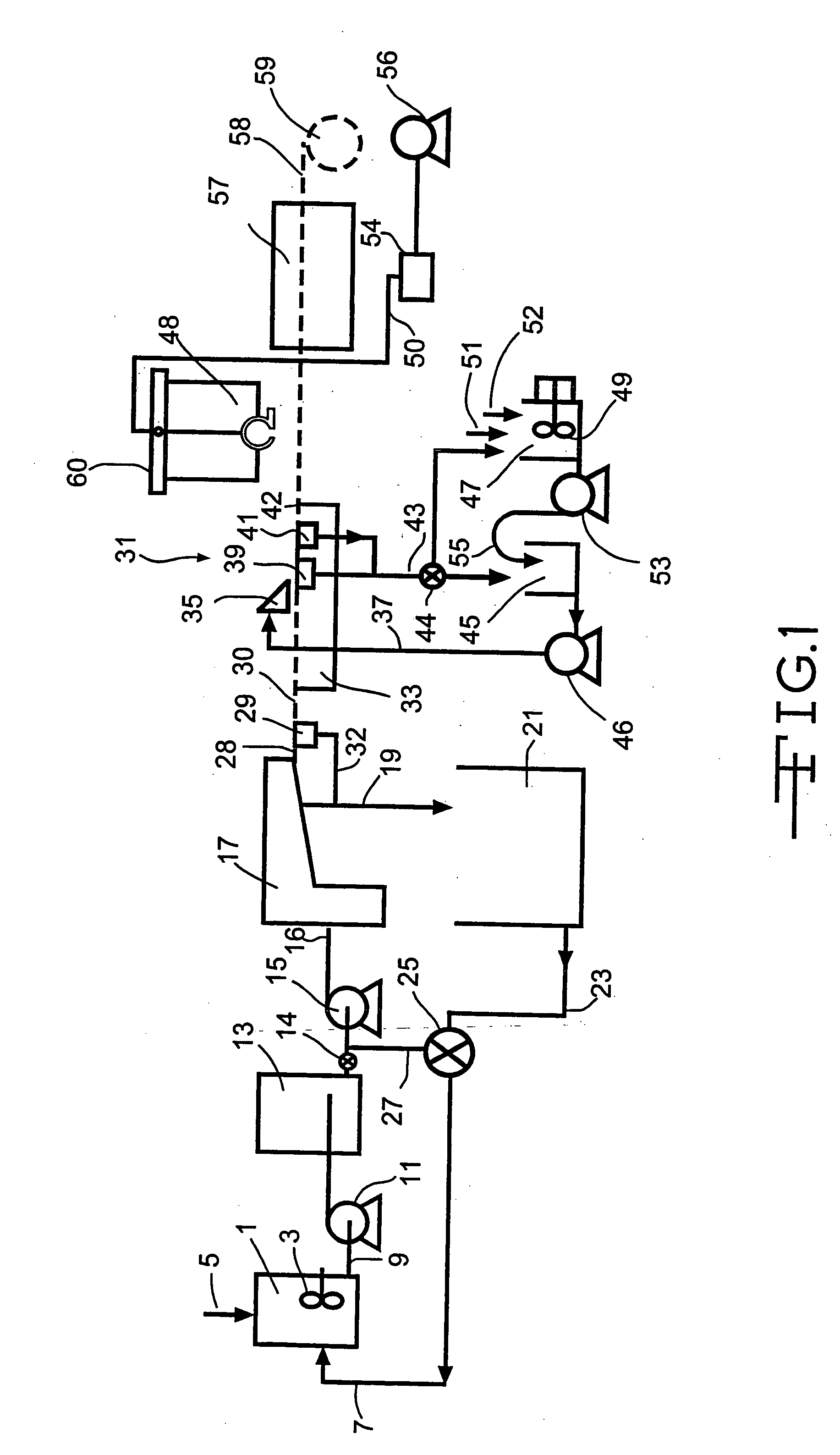
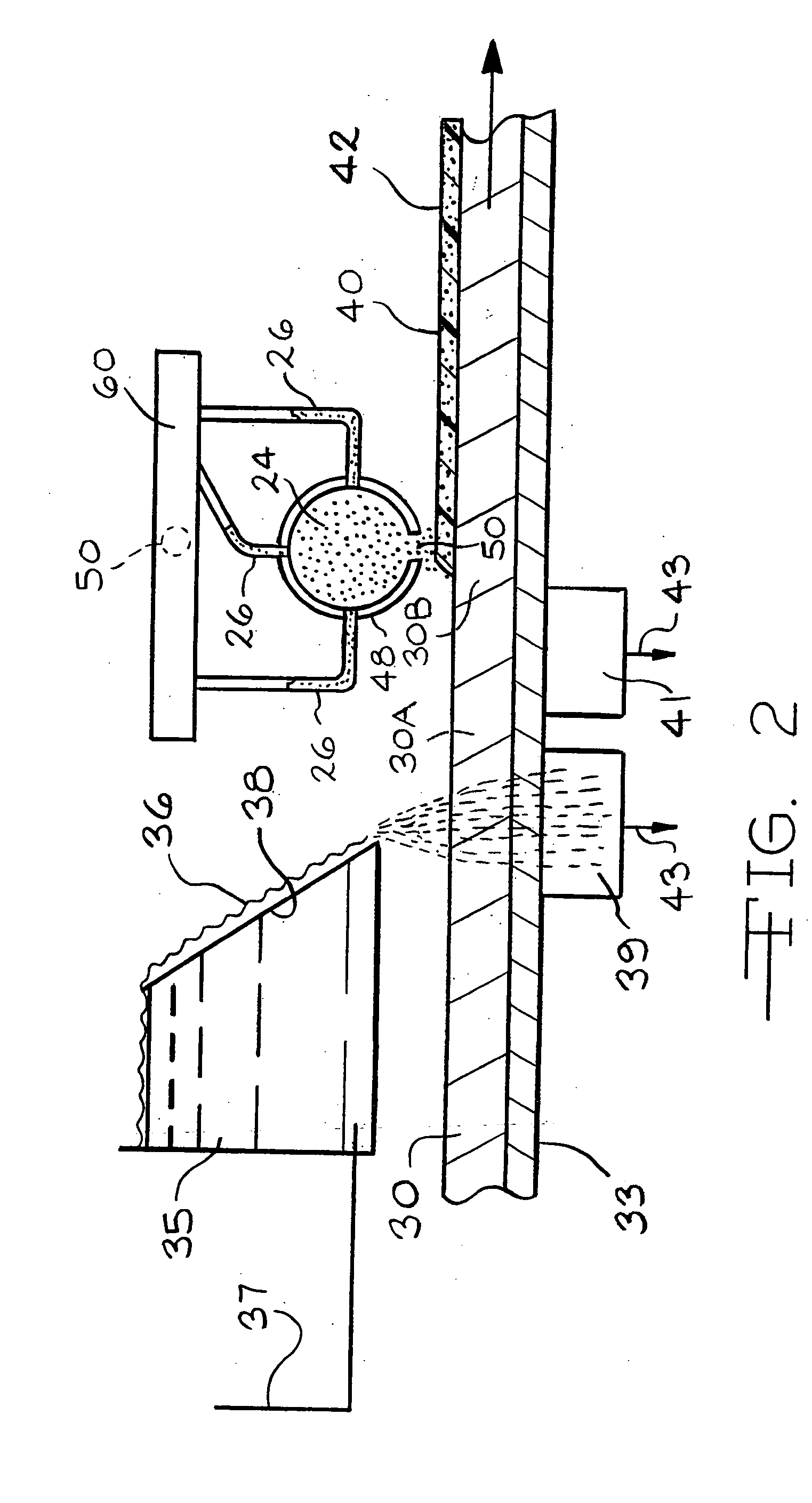
Flushable wipe and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20150330029A1Without losing its functional strength propertiesNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationEngineeringLength weight
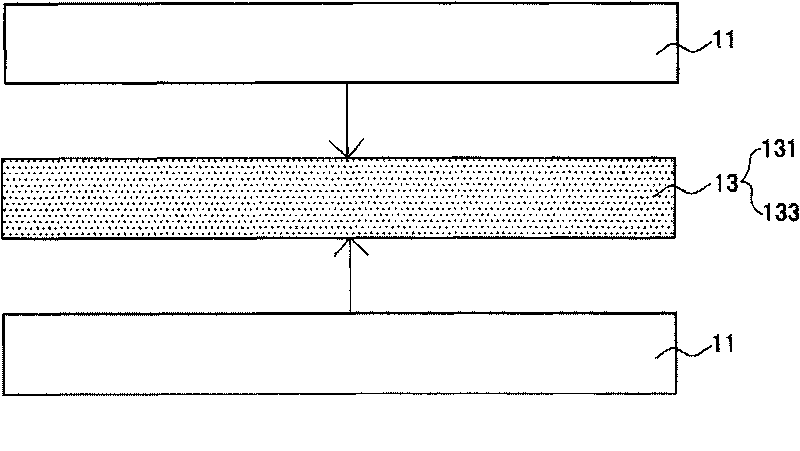
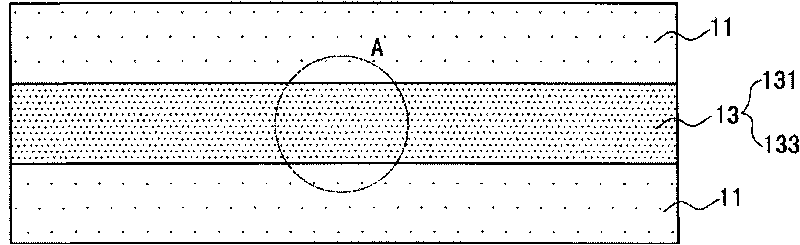
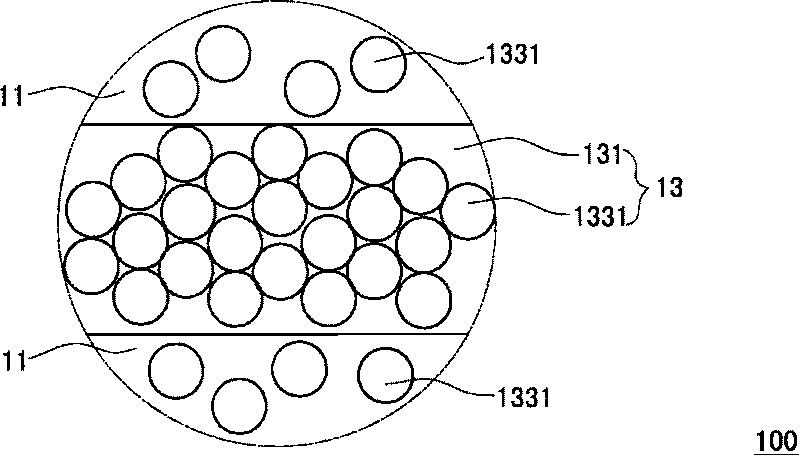
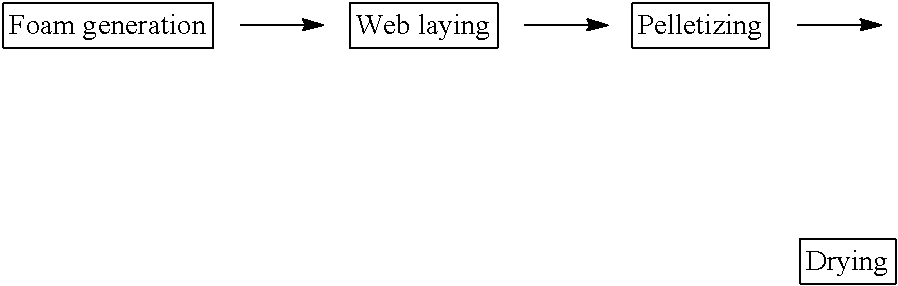
A multi-ply flushable wipe includes a ply having first and second exterior layers and a middle layer disposed therebetween. Each of the exterior layers includes at least 50% by weight natural fibers. When foam-formed, the middle layer includes at least 25% by weight natural fibers. In embodiments, the middle layer may include at least 75% by weight natural fibers. The middle layer also includes synthetic fibers that have a length within the range of 1 mm and 20 mm. The wipe may have a length weight weighted average fiber length of less than 4 mm and a wet CD strength of greater than 20 N / m. Each ply of the wipe may be formed by wetlaying the first and second exterior layers and a foam formed middle layer to form a web, imprinting the web with a structured fabric, and drying the web. The plies are then attached using a binder.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY TISSUE
Cosmetic compositions containing water-soluble polymer complexes
A composition for treating a keratin based substrate that includes a cosmetically acceptable medium containing a water-soluble interjacent complex. The water-soluble interjacent complex includes a first water-soluble polymer and a second water-soluble polymer formed by polymerizing one or more water-soluble monomers in the presence of the first water-soluble polymer. The water-soluble interjacent complex is characterized in that it forms a solution in water that is free of insoluble polymer particles. The water-soluble interjacent complex is used in a method of treating a keratin based substrate, whereby a cosmetically acceptable medium is applied to the substrate and contains from 0.1-20% by weight of the water-soluble interjacent complex.
Owner:SOLVAY USA
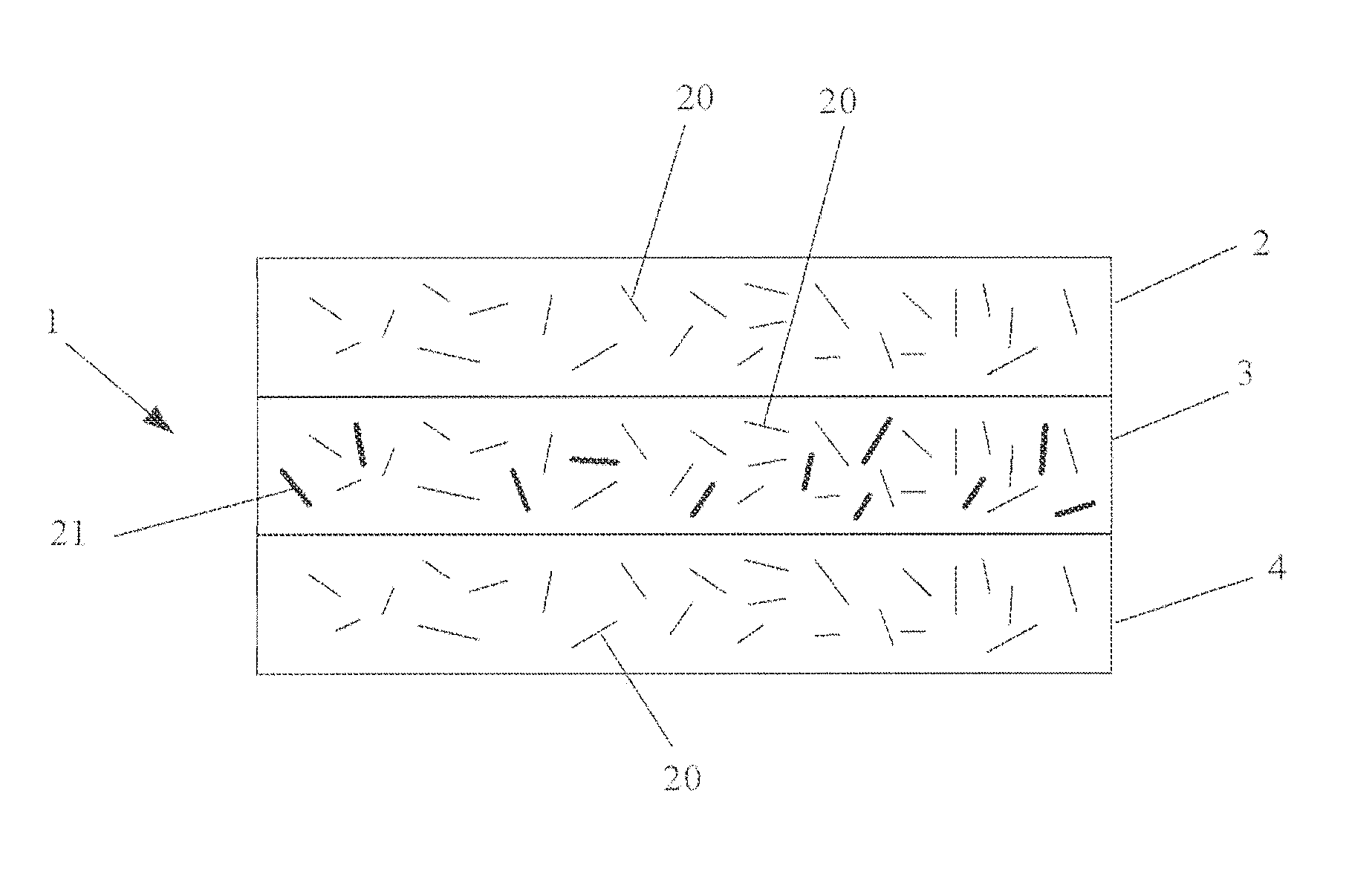
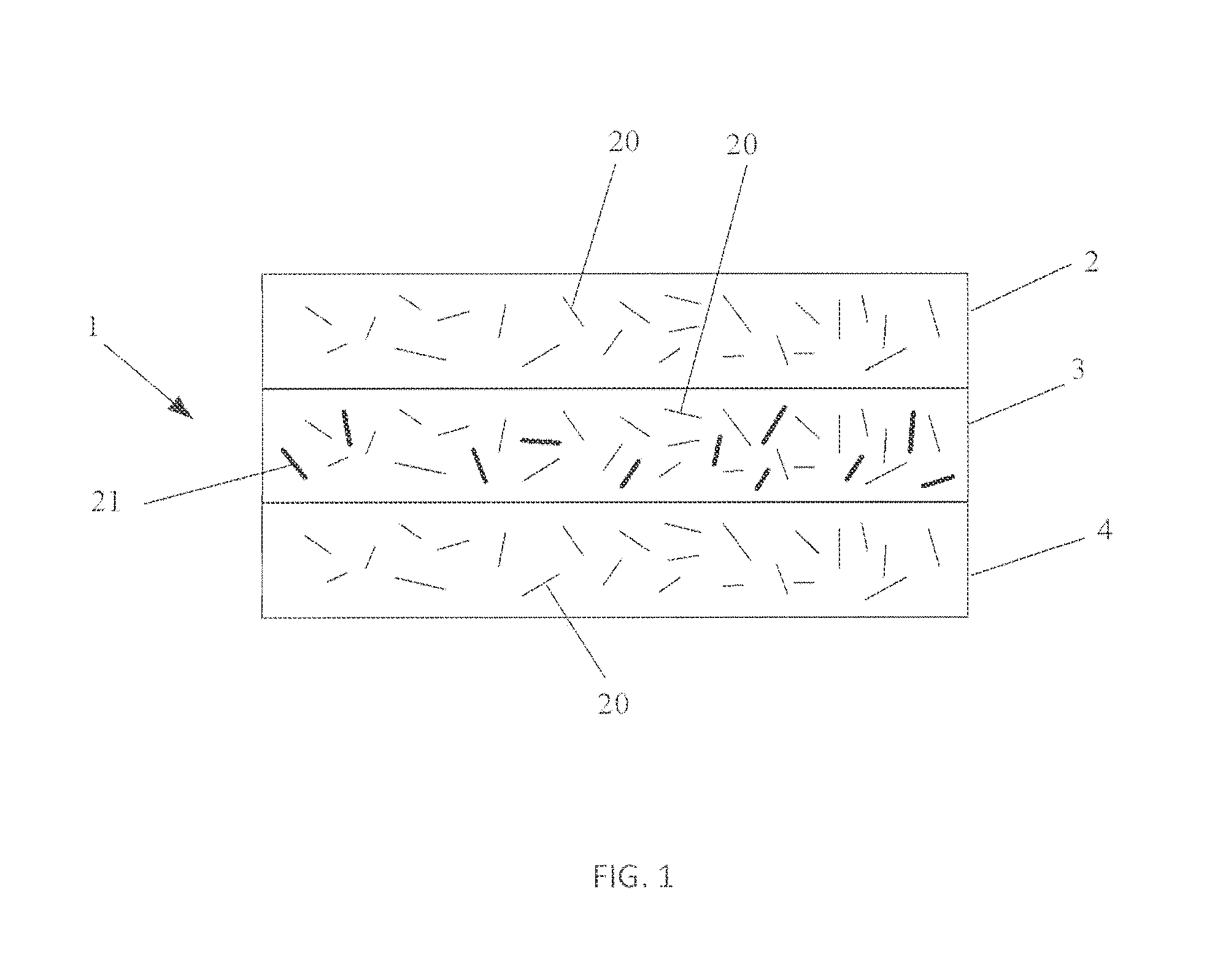
Fibrous web of paper or board and method of making the same
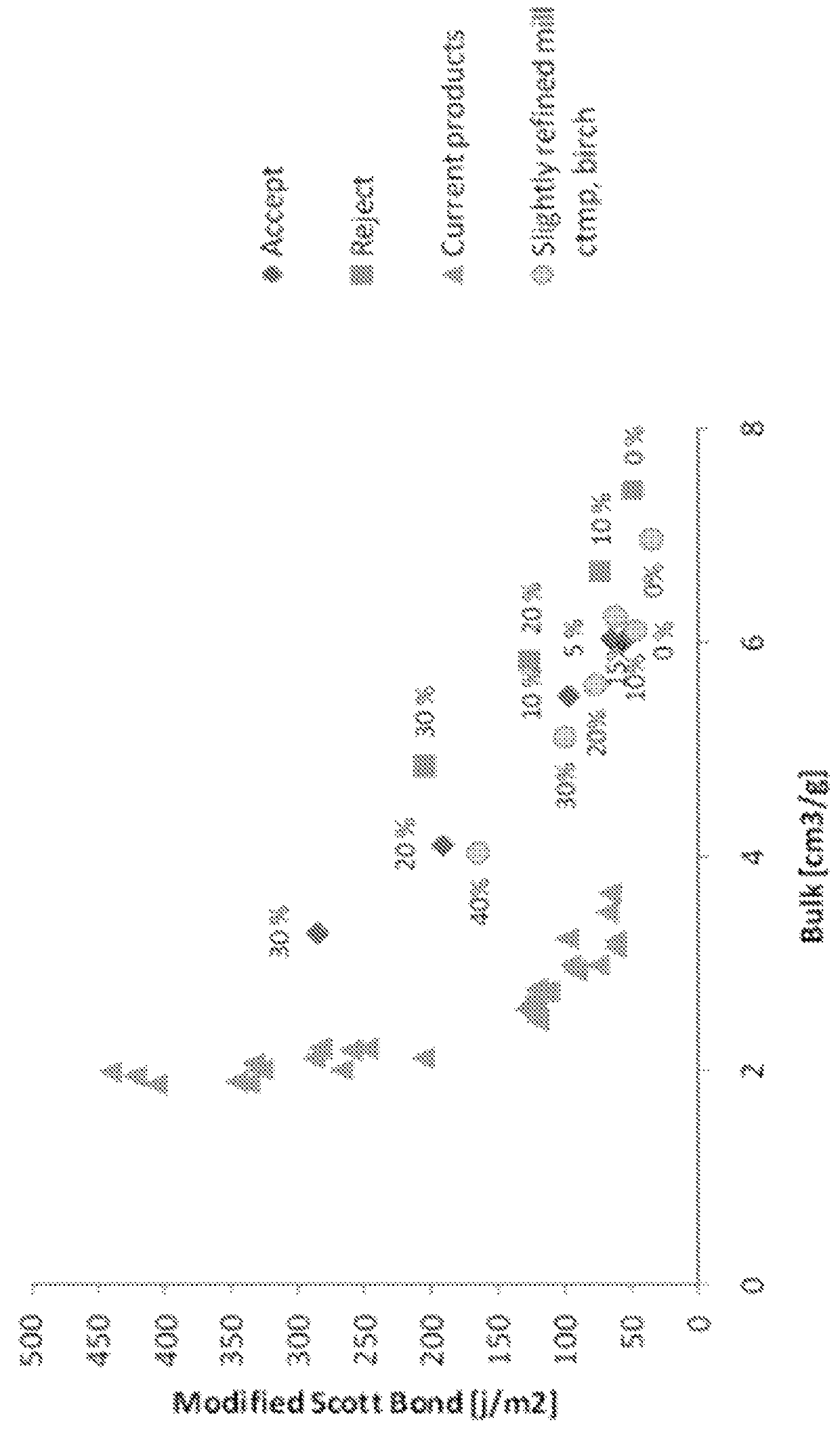
The invention relates to a fibrous web product such as paper, and a method for the preparation of such fibrous web. According to the method microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) together with a pulp of a greater fibre length, such as chemithermomechanical pulp (CTMP), are mixed with a foam of water and a sur-factant, the foam is supplied to a forming fabric of a paper or board machine, dewatered by suction of air through the forming fabric, and dried to the final web product. The method brings a high bulk in combination with a high Scott bond value, to provide improved wet and dry tensile strength for the paper and board products.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Method of making foam coated mat online and coated mat product
InactiveUS20050142348A1High strengthIncreased durabilityPaper coatingSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperFiberGlass fiber
A new foam coated nonwoven fibrous mat having properties particularly suited for a facer on gypsum wallboard, laminates made therefrom and the method of making the mat is disclosed. The mat preferably contains a major portion of glass fibers and a minor portion of a resinous binder. The foam coating is permeable and reduces fiber dust and abrasion experienced in the past with relatively coarse, relatively inexpensive glass fibers in the mat. Contrary to previous methods, the foam coated fibrous mat is made in-line on a wet mat forming production line by applying a wet foam binder onto a wet, fibrous web followed by drying and curing in-line.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE INT INC
Foam assisted application of strength additives to paper products
A foaming formulation is provided herein. The foaming formulation includes at least one foaming agent in an amount of from about 0.001% to about 10% by weight based on a total weight of the foaming solution. The foaming formulation further includes a synthetic strength additive having a cationic functional group in an amount from about 0.01% to about 50% by weight based on a total weight of the foaming solution. The foaming formulation further includes water.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Low density paperboard articles
InactiveUS20050133183A1Improve thermal conductivityHigh densityDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusCardboardLow-density polyethylene
The invention provides a low density paperboard material and associated method for use in producing an insulated container, and is especially well-suited for making cups. The paperboard material comprises a paperboard web including wood fibers and expanded microspheres, and has a relatively low density ranging from about 6 to about 10 lb / 3MSF / mil, a relatively high caliper ranging from about 24 to about 35 mil, and an internal bond strength of at least about 80×10−3 ft−lbf., preferably at least 100×10−3 lft−lbf. For applications such as cups the material is also coated on one or both sides with a barrier coating, preferably low density polyethylene, to limit liquid penetration into the web. The low density paperboard material of the invention is convertible for manufacture of containers, particularly cups, and exhibits insulative properties comparable to higher cost materials conventionally used to make cups. Also, the surface of the low density board may have a Sheffield smoothness of 300 SU or greater compared with the surface smoothness of 160 to 200 SU for conventional cupstock, the latter having been thought necessary for adequate print quality. However, it has been found that the low density board exhibits good printability on flexo printing machines despite its relatively rough surface, which is surprising and bonus effect realized along with the insulative and other properties of the board.
Owner:MOHAN KOSARAJU KRISHNA +3
Method of making foam coated mat online
InactiveUS6875308B2Large fiber diameterNon abrasiveNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberGlass fiber
A new foam coated nonwoven fibrous mat having properties particularly suited for a facer on gypsum wallboard, laminates made therefrom and the method of making the mat is disclosed. The mat preferably contains a major portion of glass fibers and a minor portion of a resinous binder. The foam coating is permeable and reduces fiber dust and abrasion experienced in the past with relatively coarse, relatively inexpensive glass fibers in the mat. Contrary to previous methods, the foam coated fibrous mat is made in-line on a wet mat forming production line by applying a wet foam binder onto a wet, fibrous web followed by drying and curing in-line.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE INT INC
Hydrophobically sized fibrous web and a method for the preparation of a sized web layer
ActiveUS20150096700A1Suppress hydrophilic functionality of surfactantSpecial paperWater-repelling agents additionFiberCellulose
A hydrophobically sized fibrous web layer, preparation of a fibrous web or a fibre-based coating, a multiplayer board product having at least a middle layer formed of said fibrous web, as well as use of a heat-sensitive surfactant for said methods and products, whereby microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) and hydrophobic size are brought to a foam with water and the heat-sensitive surfactant, the foam is supplied to a forming fabric of a paper or board machine, dewatered by suction of air through the forming fabric, and dried to a web product. Alternatively the foam may be supplied onto a premade fibrous web and dried to form a coating layer. The hydrophilic functionality of the surfactant contained in the web may be destroyed by heating. Pulp of a greater fibre length, such as CTMP, may be included, to provide improved wet and dry tensile strength for the paper and board products.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Method of making coated mat online and coated mat products
InactiveUS20050136241A1High strengthIncreased durabilityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberGlass fiber
New coated nonwoven fibrous mats having properties particularly suited for a facer on gypsum wallboard and other substrates and in laminates of various types, and the method of making the coated mat is disclosed. The mat preferably contains a major portion of glass fibers and a minor portion of a resinous binder. The coating is preferably permeable and reduces fiber dust and abrasion experienced in the past with relatively coarse, relatively inexpensive glass fibers in the mat. Contrary to previous coating methods, the coated fibrous mat is made in-line on a wet mat forming production line by applying a wet foam binder onto a wet, fibrous web followed by drying and curing in-line.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Emulated wood with pores and fibers and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20150376840A1Reduce surface polarityImprove compatibilityNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaper after-treatmentPolymer scienceFoaming agent
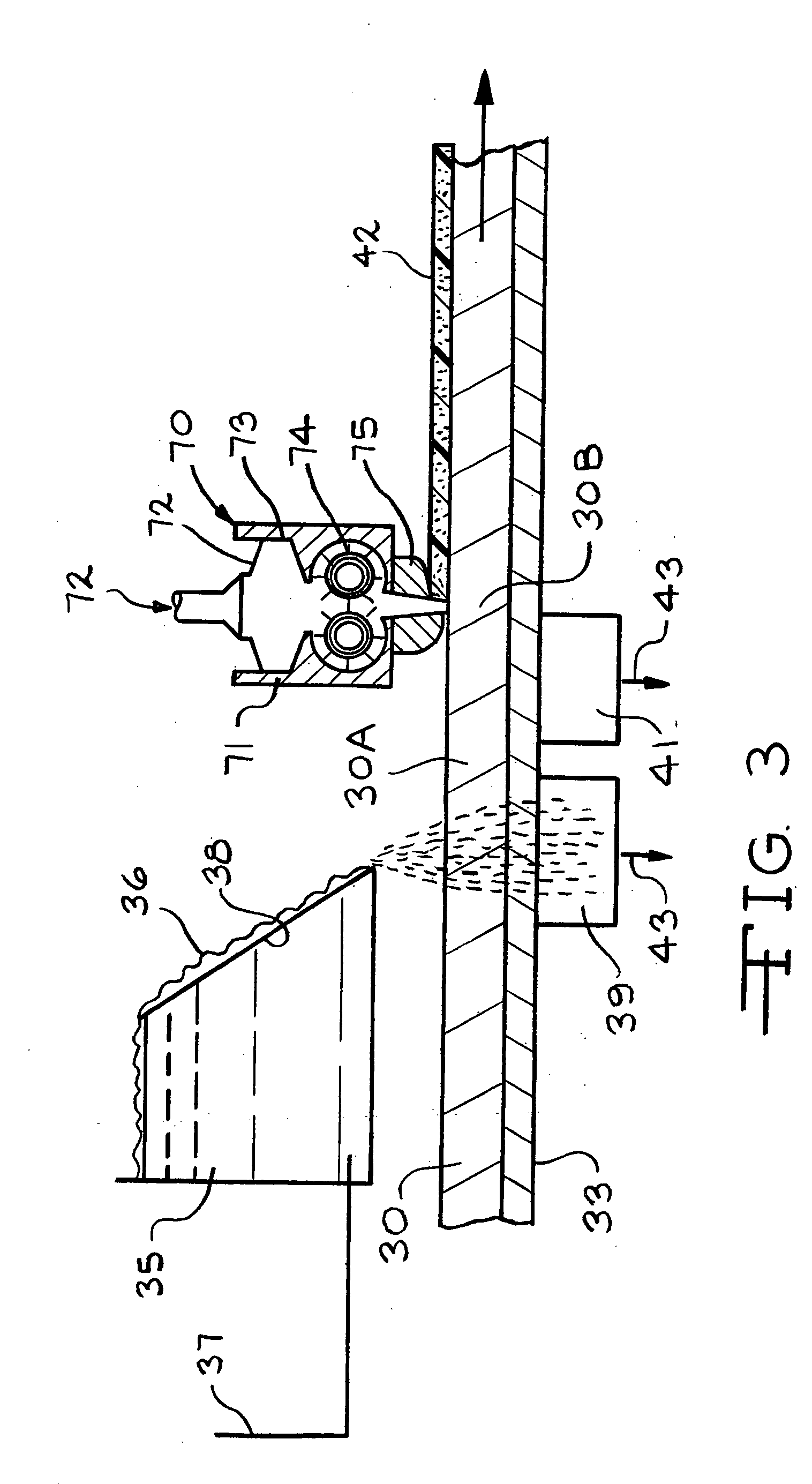
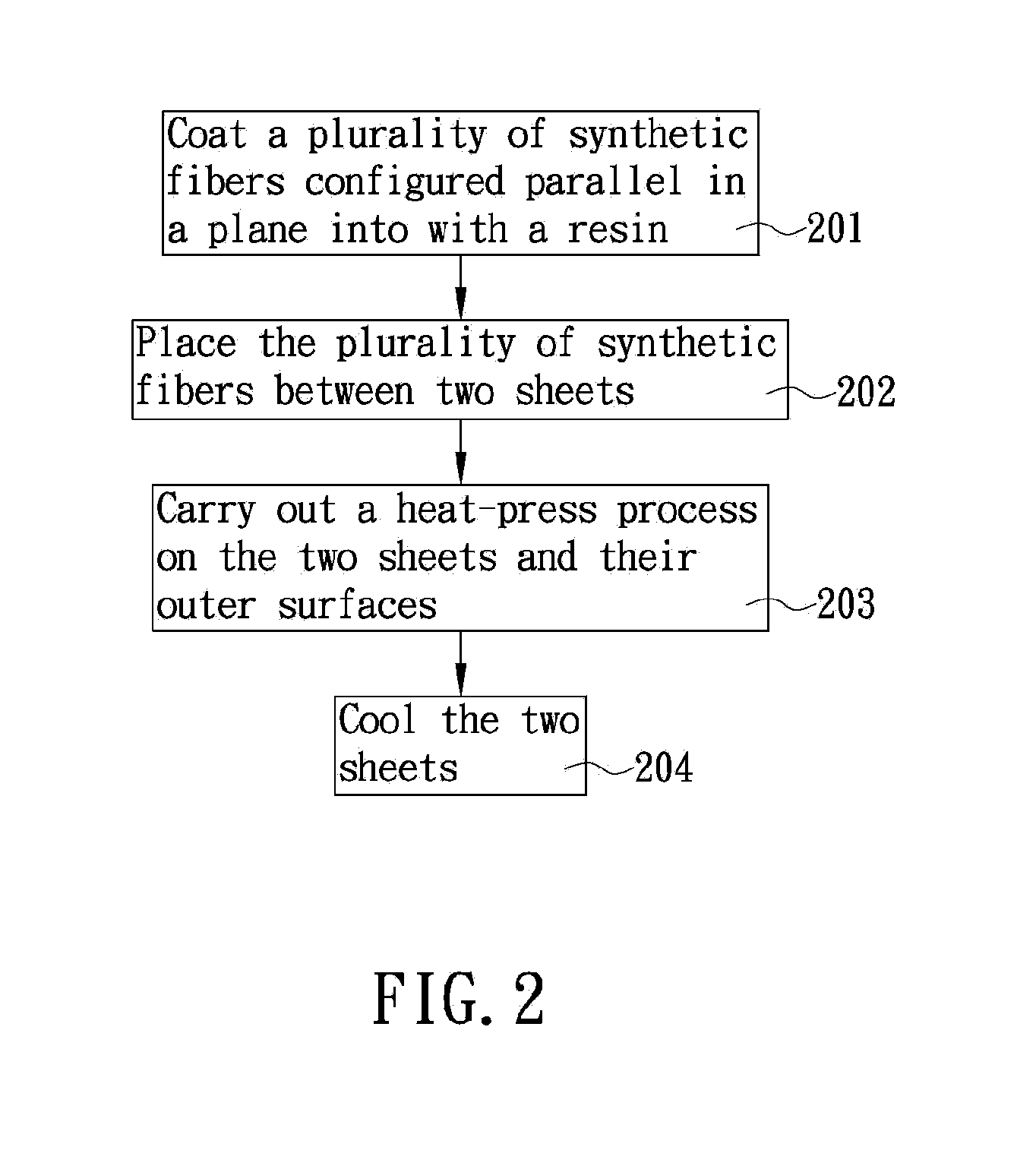
A method for fabricating emulated wood with pores and fibers, comprising: immersing a plurality of synthetic fibers configured parallel in a plane into a resin so that the resin is coated on the surfaces of the plurality of synthetic fibers and in the gaps between the plurality of synthetic fibers; placing the plurality of synthetic fibers between two sheets, wherein the two sheets are planar sheets made from a uniform composition comprising a thermoplastic elastomer, a foaming agent, and a crosslinking agent; carrying out a heat-press process on the two sheets so that the foaming agent undergoes microcellular foaming and forms dense closed pores in the two sheets, and so that the composition on inner surfaces of the two sheets expands towards the plurality of synthetic fibers and penetrates through the gaps between the plurality of synthetic fibers; and cooling the two sheets to yield an emulated wood board.
Owner:MICROCELL COMPOSITE CO LTD
Use of water-soluble polymer complexes in aqueous systems
InactiveUS20050183837A1High viscosityCosmetic preparationsNatural cellulose pulp/paperSludgeFlow curve
A water-soluble interjacent complex that includes a first water-soluble polymer and one or more water-soluble monomers polymerized to form a second water-soluble polymer in the presence of the first water-soluble polymer. The water-soluble interjacent complex forms a solution in water that is free of insoluble polymer particles. The interjacent complexes may be used to treat a waste sludge by adding an effective amount thereof to the waste sludge. The interjacent complexes may also be used in making paper by adding an effective amount thereof to a pulp or a forming sheet at a suitable location on a paper making machine. The interjacent complexes may further be used as a rheology modifier in aqueous systems by adding an effective amount thereof to an aqueous medium to effect a desired viscosity, rheology, or flow curve property.
Owner:SOLVAY USA
Moldable fibrous product and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20150284911A1High elongationSpecial paperPaper after-treatmentCarbohydrate derivativeFiber
A moldable fibrous product, includes foam-formed fibrous material selected from fibrous webs, paper webs, board webs, or sheets cut from any of the webs, at least one polymer selected from carbohydrate derivatives, polylactic acid, polyurethane and polyolefins impregnated in the web, and from 0.001 to 0.1% by weight of at least one foaming agent.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Fibrous web of paper or board and method of making the same
ActiveCN104302834AIncrease bulkImprove internal strength propertiesSpecial paperTransportation and packagingCardboardCellulose
The invention relates to a fibrous web product such as paper, and a method for the preparation of such fibrous web. According to the method microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) together with a pulp of a greater fibre length, such as chemithermomechanical pulp (CTMP), are mixed with a foam of water and a sur- factant, the foam is supplied to a forming fabric of a paper or board machine, dewatered by suction of air through the forming fabric, and dried to the final web product. The method brings a high bulk in combination with a high Scott bond value, to provide improved wet and dry tensile strength for the paper and board products.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Making foam coated mats on-line
InactiveUS7285183B2High strengthIncreased durabilityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberProduction line
A new foam coated nonwoven fibrous mat having properties particularly suited for a facer on gypsum wallboard, laminates made therefrom and the method of making the mat is disclosed. The mat preferably contains a major portion of glass fibers and a minor portion of a resinous binder. The foam coating is permeable and reduces fiber dust and abrasion experienced in the past with relatively coarse, relatively inexpensive glass fibers in the mat. Contrary to previous methods, the foam coated fibrous mat is made in-line on a wet mat forming production line by applying a wet foam binder onto a wet, fibrous web followed by drying and curing in-line.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Method of forming a fibrous product
ActiveUS20160221233A1Simple and inexpensive and environmentally soundImprove bindingNatural cellulose pulp/paperSurfactants additionShell moldingNatural fiber
The present invention relates to a method of forming a moulded fibrous product, comprising the steps of foaming an aqueous suspension of natural fibres, optionally in combination with synthetic fibres, to provide a first fibrous foam, a surfactant may be added to aid the foaming, feeding the fibrous foam into a mould, mechanically withdrawing a part of the water contained in the foam to produce a solidified, moist fibrous composition, and evaporating water from the solidified, moist fibrous composition to produce a dry fibrous product.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Hydrophobically sized fibrous web and a method for the preparation of a sized web layer
ActiveCN104285006AInhibition of hydrophilic functionalitySolve the problem of damaging hydrophobic sizingSpecial paperWater-repelling agents additionCelluloseFiber
The invention relates to a hydrophobically sized fibrous web layer, methods for the preparation of a fibrous web or a fibre-based coating, a multilayer board product having at least a middle layer formed of said fibrous web, as well as use of a heat-sensitive surfactant for said methods and products. According to the method microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) and hydrophobic size are brought to a foam with water and the heat- sensitive surfactant, the foam is supplied to a forming fabric of a paper or board machine, dewatered by suction of air through the forming fabric, and dried to a web product. Alternatively the foam may be supplied onto a premade fibrous web and dried to form a coating layer. To prevent gradual degradation of the hydrophobic sizing the hydrophilic functionality of the surfactant contained in the web is finally destroyed by heating. The method uses e.g. AKD-based surfactants with a hydrophilic moiety which is decomposed by heat. If pulp of a greater fibre length, such as CTMP, is also included, a high bulk in combination with a high Scott bond value is achieved, to provide improved wet and dry tensile strength for the paper and board products.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Method of producing ultra-low density fiber composite materials
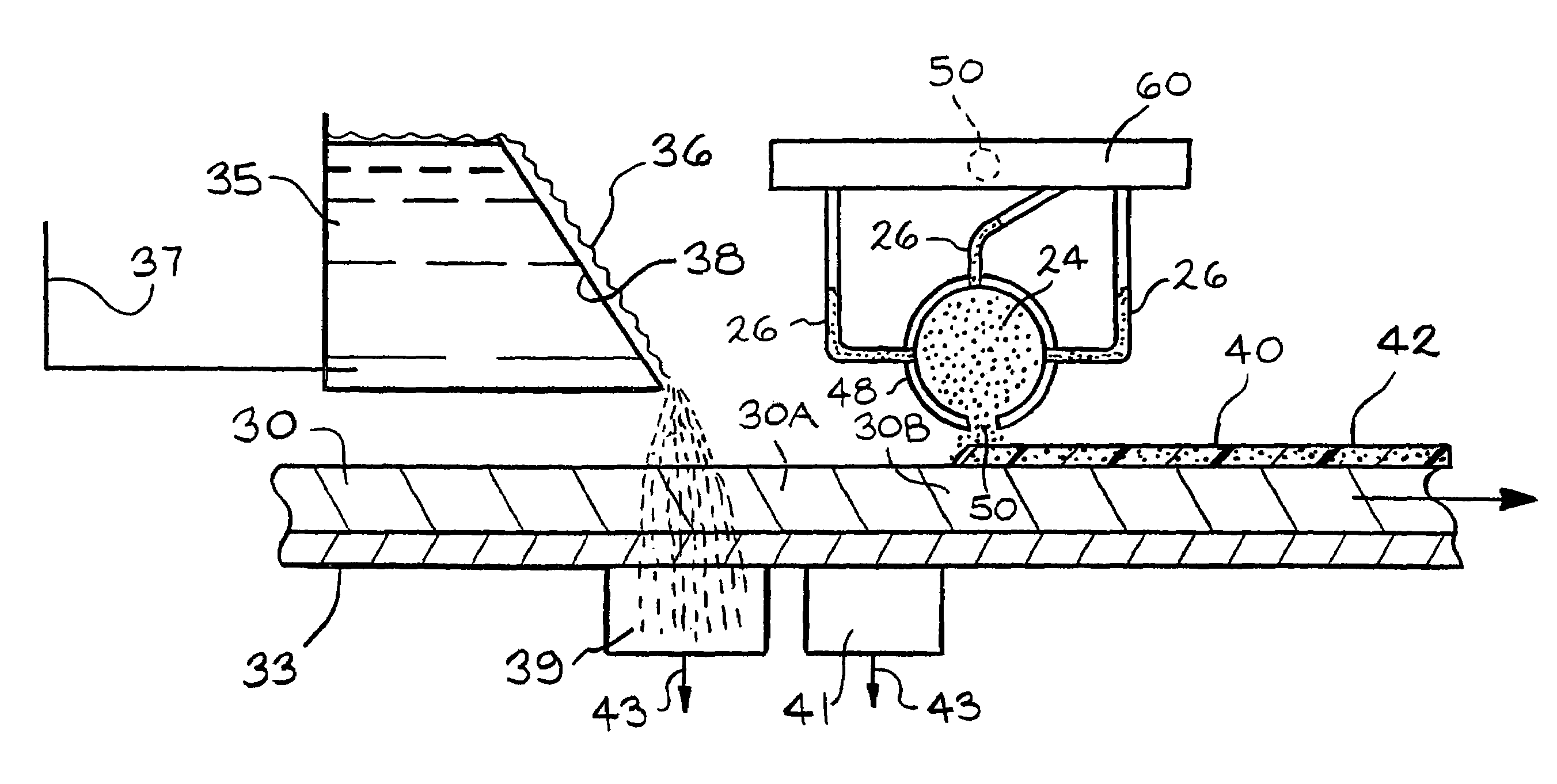
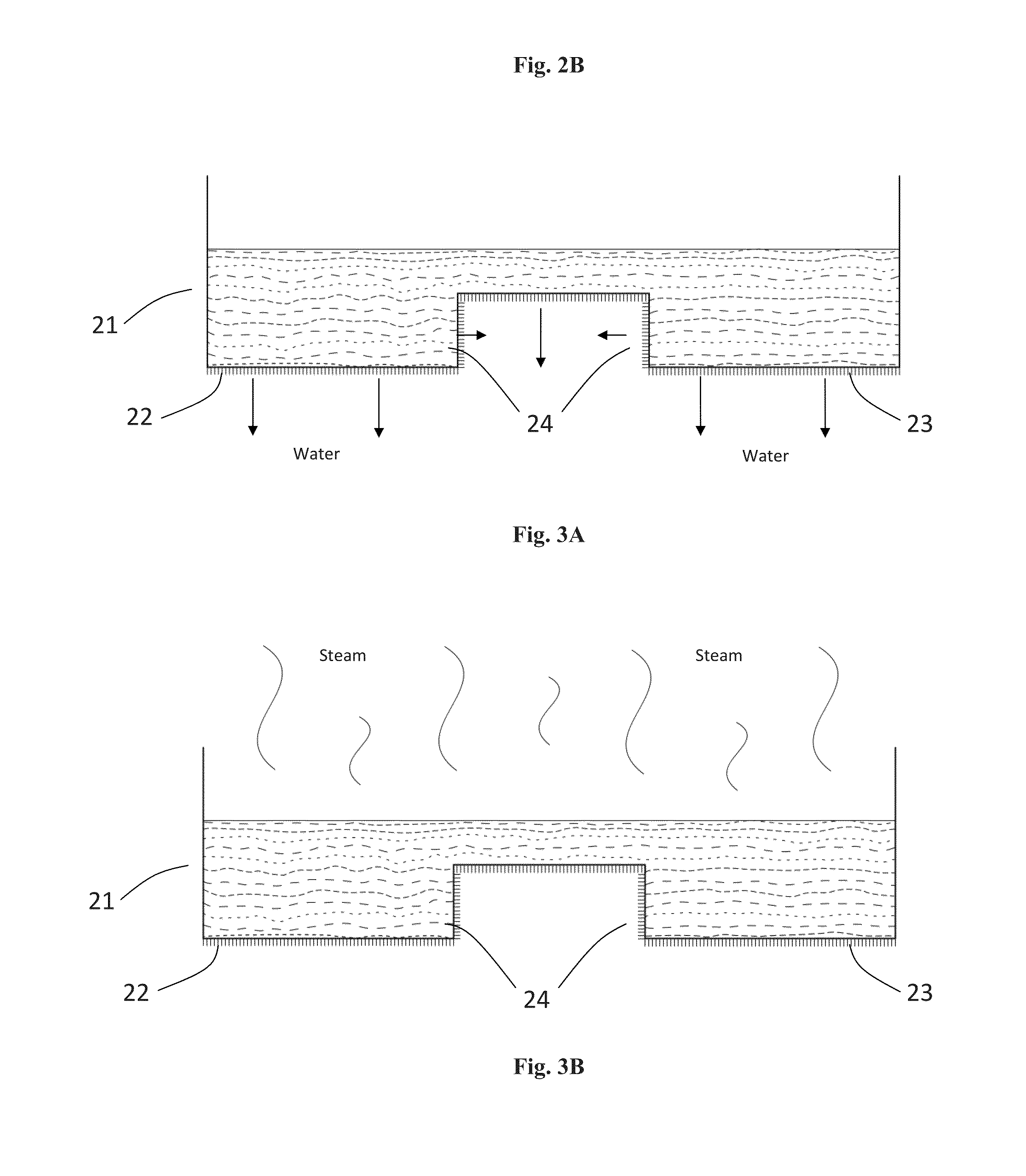
InactiveUS20160289453A1Reduce moistureReduce moisture contentPaper-making machinesFoam additionFiberAir filter
A method of producing ultra-low density fiber composite (ULDC) foam materials using natural fibers with gas injection through liquid foaming is disclosed, wherein in a particular embodiment includes also cellulose filaments. The method includes a continuous overflow foaming process and a novel apparatus to produce the ULDC materials. The disclosed ULDC composite foam produced includes moisture, mold, decay and fire resistant properties which can be used for building thermal and acoustic insulations, protection packaging, air filter products, hygiene products. The apparatus comprise a vessel, counter rotating dual impellor, a plurality of baffles and gas injection that produce.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Cnf cellular solid material with anionic surfactants
ActiveUS20170313838A1High porosityImprove mechanical propertiesFlexible coversWrappersCelluloseNanofiber
Owner:CELLUTECH
Thermoplastic fibrous materials and a method of producing the same
The invention relates to a method for the manufacture of thermoplastic fibrous materials comprising forming at least one foamed liquid comprising water and at least one foaming agent, forming a dispersion by dispersing fibers including long fibers in said at least one foamed liquid comprising water and at least one foaming agent, mixing the dispersion with a foamable liquid or dispersion comprising at least one thermoplastic polymer, forming at least one foamed dispersion, and conveying the foamed dispersion or dispersions to a foraminous support and draining liquid trough the foraminous support to form a web or a sheet, to obtain the thermoplastic fibrous material. The invention also relates to materials and products obtainable by the method, and uses related thereto.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Fibrous web of paper or board and method of making the same
The invention relates to a fibrous web product such as paper, and a method for the preparation of such fibrous web. According to the method microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) together with a pulp of a greater fiber length, such as chemithermomechanical pulp (CTMP), are mixed with a foam of water and a sur-factant, the foam is supplied to a forming fabric of a paper or board machine, dewatered by suction of air through the forming fabric, and dried to the final web product. The method brings a high bulk in combination with a high Scott bond value, to provide improved wet and dry tensile strength for the paper and board products.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Hydrophobically sized fibrous web and a method for the preparation of a sized web layer
ActiveUS9663901B2Suppress hydrophilic functionality of surfactantSpecial paperWater-repelling agents additionFiberCellulose
A hydrophobically sized fibrous web layer, preparation of a fibrous web or a fiber-based coating, a multilayer board product having at least a middle layer formed of said fibrous web, as well as use of a heat-sensitive surfactant for said methods and products, whereby microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) and hydrophobic size are brought to a foam with water and the heat-sensitive surfactant, the foam is supplied to a forming fabric of a paper or board machine, dewatered by suction of air through the forming fabric, and dried to a web product. Alternatively the foam may be supplied onto a premade fibrous web and dried to form a coating layer. The hydrophilic functionality of the surfactant contained in the web may be destroyed by heating. Pulp of a greater fiber length, such as CTMP, may be included, to provide improved wet and dry tensile strength for the paper and board products.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Thermoplastic fibrous materials and method of producing the same
The invention relates to a method for the manufacture of thermoplastic fibrous materials, comprising forming at least one foamed liquid comprising water and at least one foaming agent, forming a dispersion by dispersing fibers including long fibers in said at least one foamed liquid comprising water and at least one foaming agent, mixing the dispersion with a foamable liquid or dispersion comprising at least one thermoplastic polymer, forming at least one foamed dispersion, and conveying the foamed dispersion or dispersions to a foraminous support and draining liquid trough the foraminous support to form a web or a sheet, to obtain the thermoplastic fibrous material. The invention also relates to materials and products obtainable by the method, and uses related thereto.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Method for preparing a coffee polyol and compositions and materials containing the same
InactiveUS20150051306A1Pigmenting treatmentMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentPolyurethane dispersionPolyol
A method for preparing a coffee polyol includes: (a) extracting coffee oil from coffee grounds; (b) modifying the coffee oil to obtain an epoxidized coffee oil; and (c) reacting an alcohol with the epoxidized coffee oil to obtain a coffee polyol. A polyurethane dispersive solution is prepared from a prepolymer composition that includes: a coffee polyol prepared from the abovementioned method; an isocyanate; and a solvent. A foam-based material is made from a foaming composition that includes a coffee polyol prepared from the abovementioned method. A polyurethane material is made from a polyurethane composition that includes a coffee polyol prepared from the abovementioned method.
Owner:MAGICTEX APPAREL CORP
Method for applying softening compositions to a tissue product
InactiveUS6977026B2Natural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationAmino functionalizedChemistry
A method for applying a softening composition to a paper web of a tissue product is provided. The softening composition is applied primarily to the elevated regions of the tissue product. The application of the softening composition in this manner allows for the use of hydrophobic softeners, such as amino-functionalized polysiloxanes, in an amount of from about 0.05% to about 5% by weight of the tissue product while maintaining a Wet Out Time of less than about 10 seconds.
Method of forming a fibrous product
ActiveUS10259151B2Simple and inexpensive and environmentally soundImprove bindingNatural cellulose pulp/paperSurfactants additionNatural fiberSURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Photocatalytic pulp composition
There is provided a photocatalytic pulp composition characterized in that 40 to 95 wt % of a pulp and / or a paper having the water content of 3 wt % or less, the average fiber diameter of 5 to 300 mum and the average fiber length of 0.7 to 70 mm is blended with 5 to 60 wt % of titanium oxide. A photocatalytic pulp composition is provided in which 25 to 100 wt % of a thermoplastic resin is blended relative to the total weight of titanium oxide with a pulp and / or a paper blended at the above ratio.
Owner:EIN KOHSAH CO LTD
Dissolved air de-bonding of a tissue sheet
ActiveUS20170335521A1Increase the slopePaper/cardboardPhysical paper treatmentCalipersBiomedical engineering
Tissue papers and methods of making are disclosed herein. In one aspect, a tissue paper is substantially free of a chemical debonder and has a geometric mean tensile (GMT) in a range between about 500 and about 5,000 g / 3 inches (g / 3 in.) and a caliper in a range between about 50 and about 350 mils / 8 sheets.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Process and apparatus for making a sheet of aramid fibers using a foamed medium
InactiveUS20060011315A1Improve integrityEfficient and effectiveNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPolymer scienceAramid
The present invention relates to a method for forming a non-woven fibrous web comprised of aramid fibers and aramid fibrid which comprises forming a foam furnish by agitating the fibers and fibrid in a foamed medium, and passing the foam furnish onto a screen and defoaming the furnish. In effectively agitating the aramid fibers in the foamed medium, the agitating means is mounted for displacement within the foamed medium and includes a convex leading surface facing in the direction of displacement. The leading surface includes upper and lower portions converging in the direction of displacement to form a generally convex leading surface and driving means for displacing the agitating means in the direction of displacement for dispersing and mutually separating the aramid fibers within the foamed medium.
Owner:FIBERMARK NORTH AMERICA
Antibacterial paper and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101718057AProduce antibacterial effectAnti-slip effectPaper/cardboardFoam additionPulp and paper industryAntibacterial agent
The invention relates to antibacterial paper and a manufacturing method thereof, the antibacterial paper comprises: a plurality of paper layers, a first composite layer arranged between the paper layers, and the manufacturing method thereof comprises the steps of: providing a plurality of paper layers, stirring and mixing a first adhesion agent with an antibacterial agent in a fixed amount to form a first composite layer, and coating the first composite layer between the paper layers so that two paper layers, upper and lower, are bonded and fixed with each other via the adhesion agent and antibacterial particles in the antibacterial agent are diffused into the paper layers from the first composite layer, stirring and mixing a second adhesion agent with a foaming particle or heating and foaming the foaming particle in advance and then adding the foaming particle into the second adhesion agent to form a second composite layer, coating the second composite layer on one of the surfaces of the antibacterial paper, afterwards, implementing the procedure of heating or not according to the requirement of process; therefore, a paper article with the antibacterial function and slippery-stopping effect can be manufactured.
Owner:CHAN LI MACHINERY
Production of high performance thermoplastic composites
The present invention concerns a process for producing a thermoformable porous web using a mixture of cellulosic fibres and one or more thermoplastic materials, particularly by foam forming said mixture into a composite foam, and applying the foam into one or more layers on a support to obtain a porous pre-form web. The thus produced porous composite web can be further processed by compression moulding to give a rigid high-strength composite structure, which is suitable for use in producing, e.g. panels or plates, packages or hygiene products, insulators or filters, or printed intelligence, electronics or microcellulose products.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com