Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1048results about "Fluorescent layers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
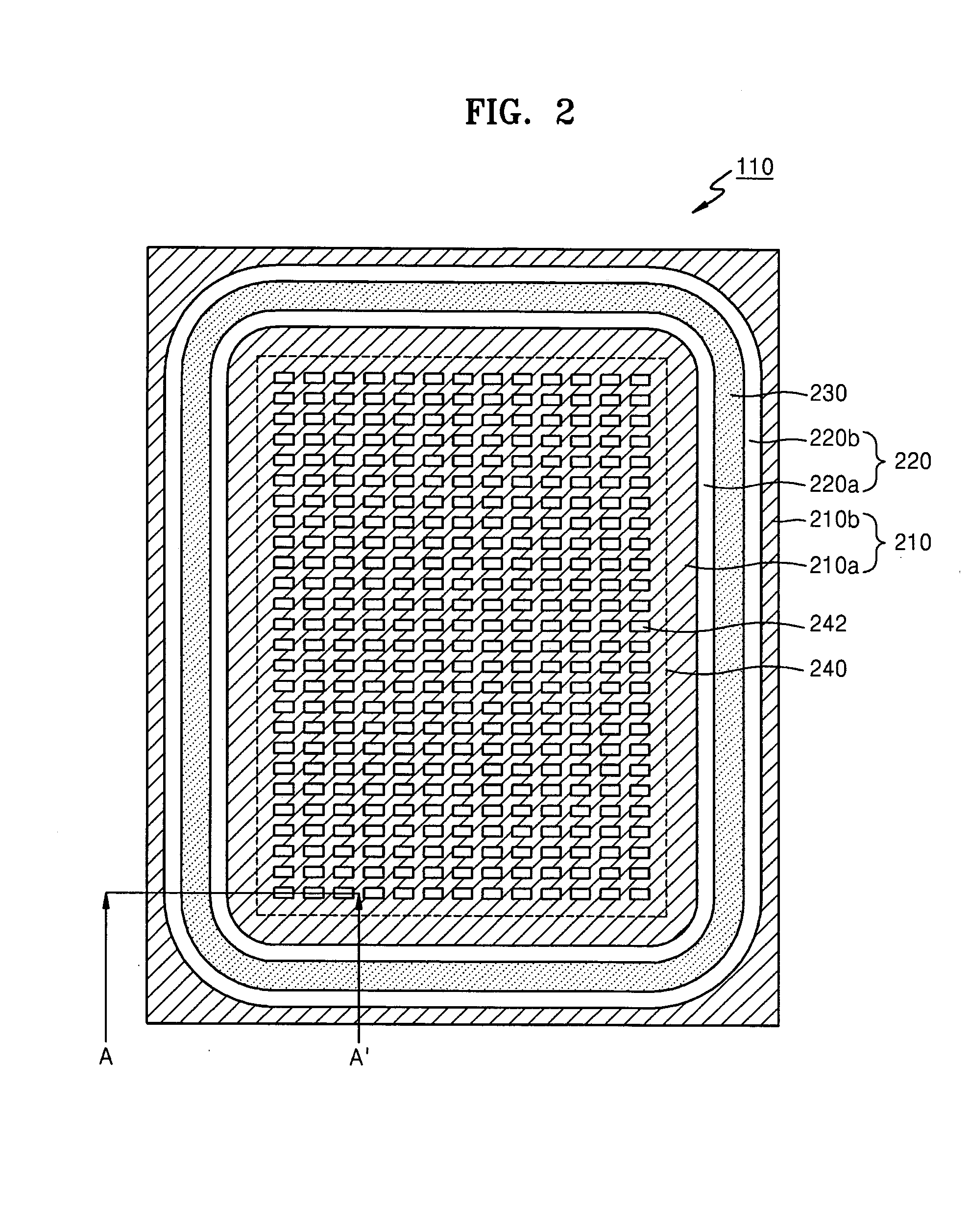
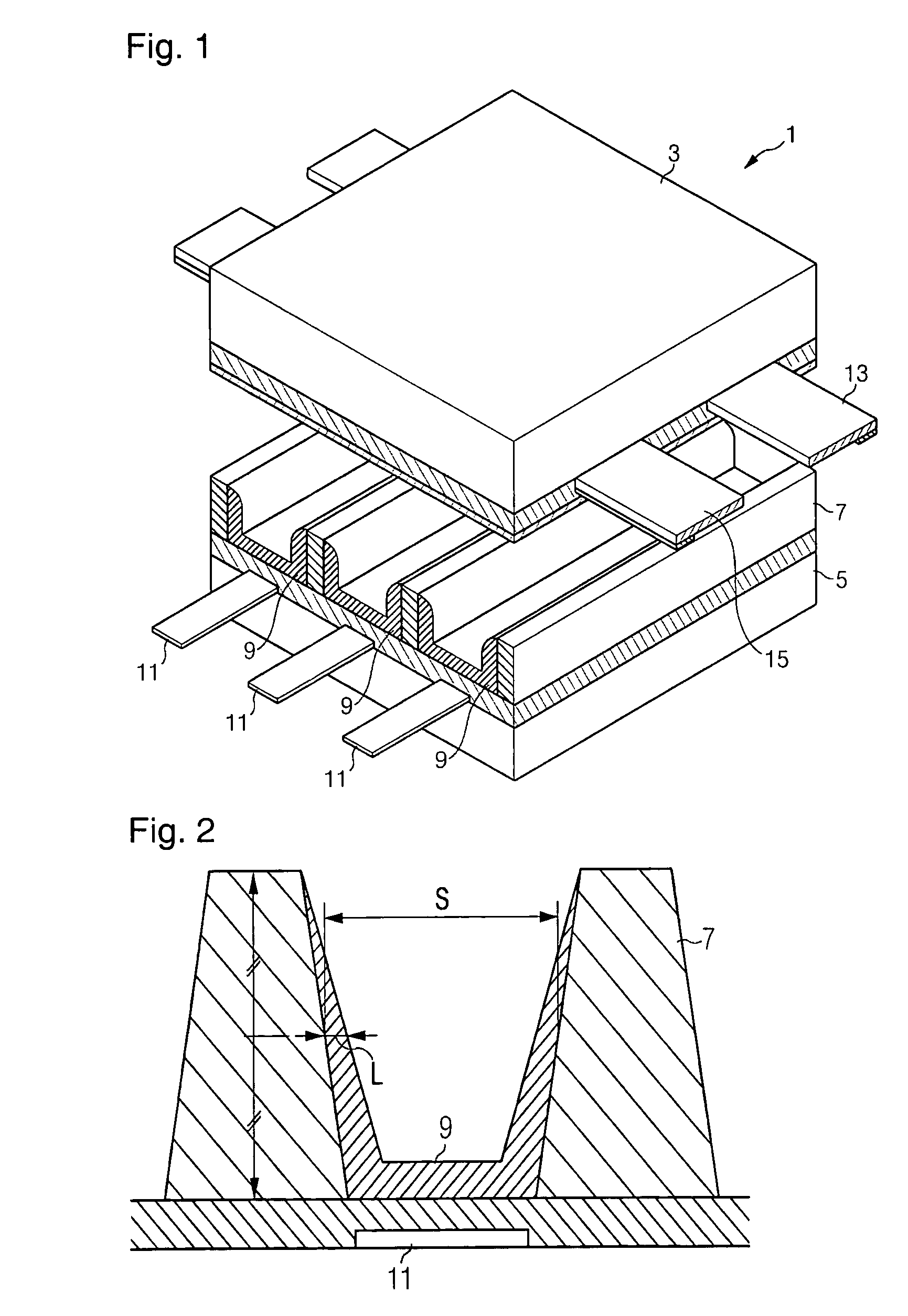
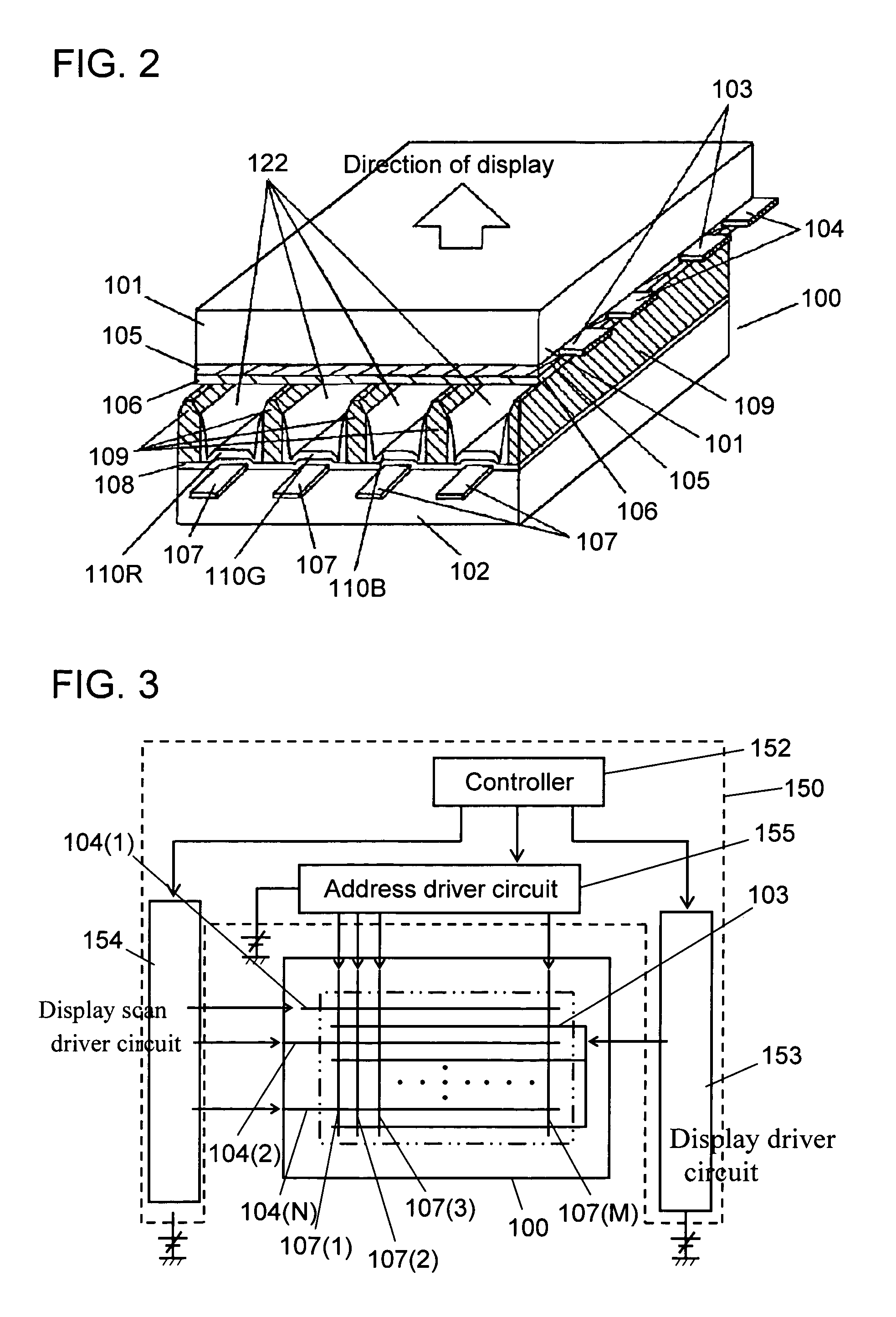
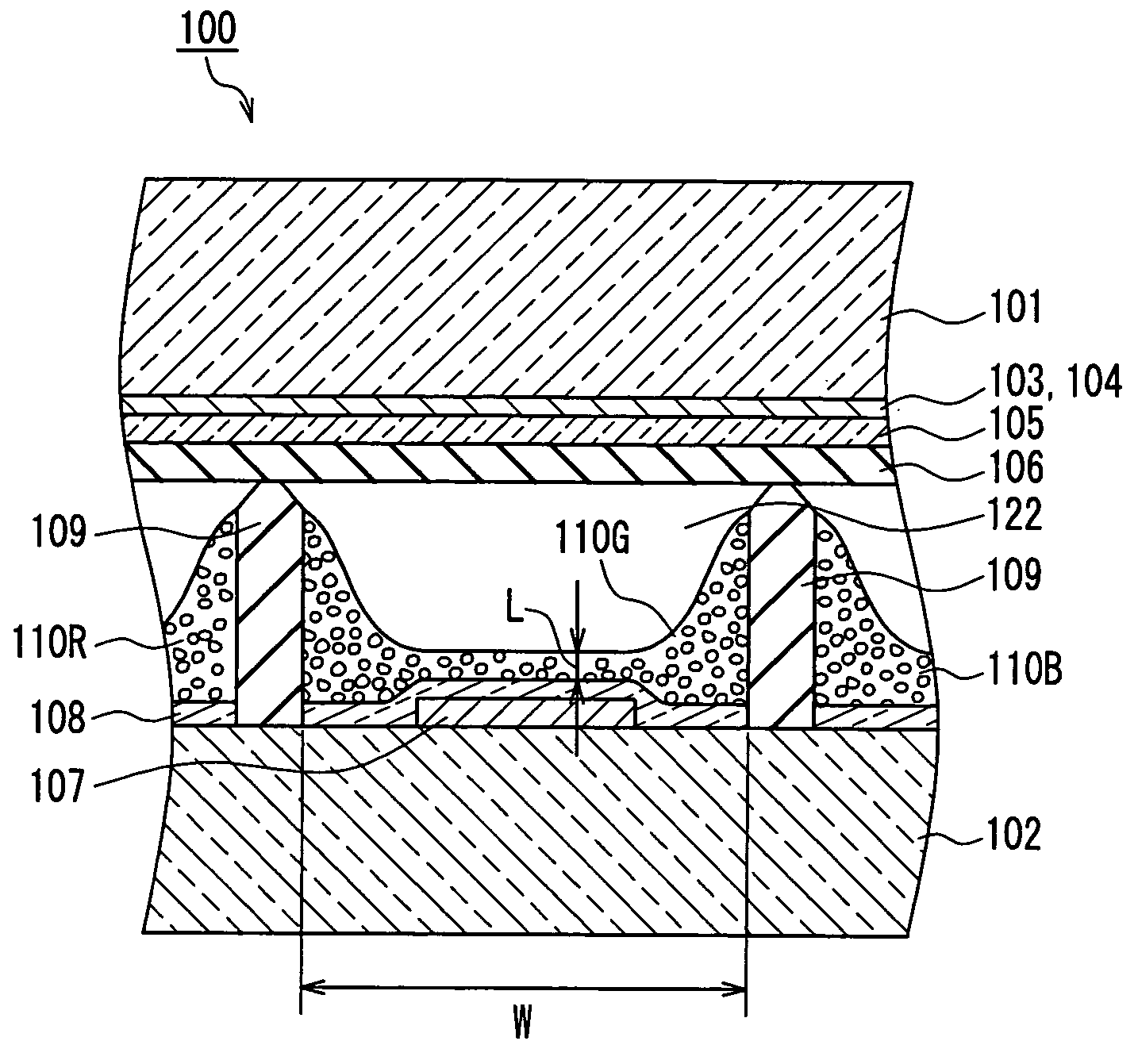
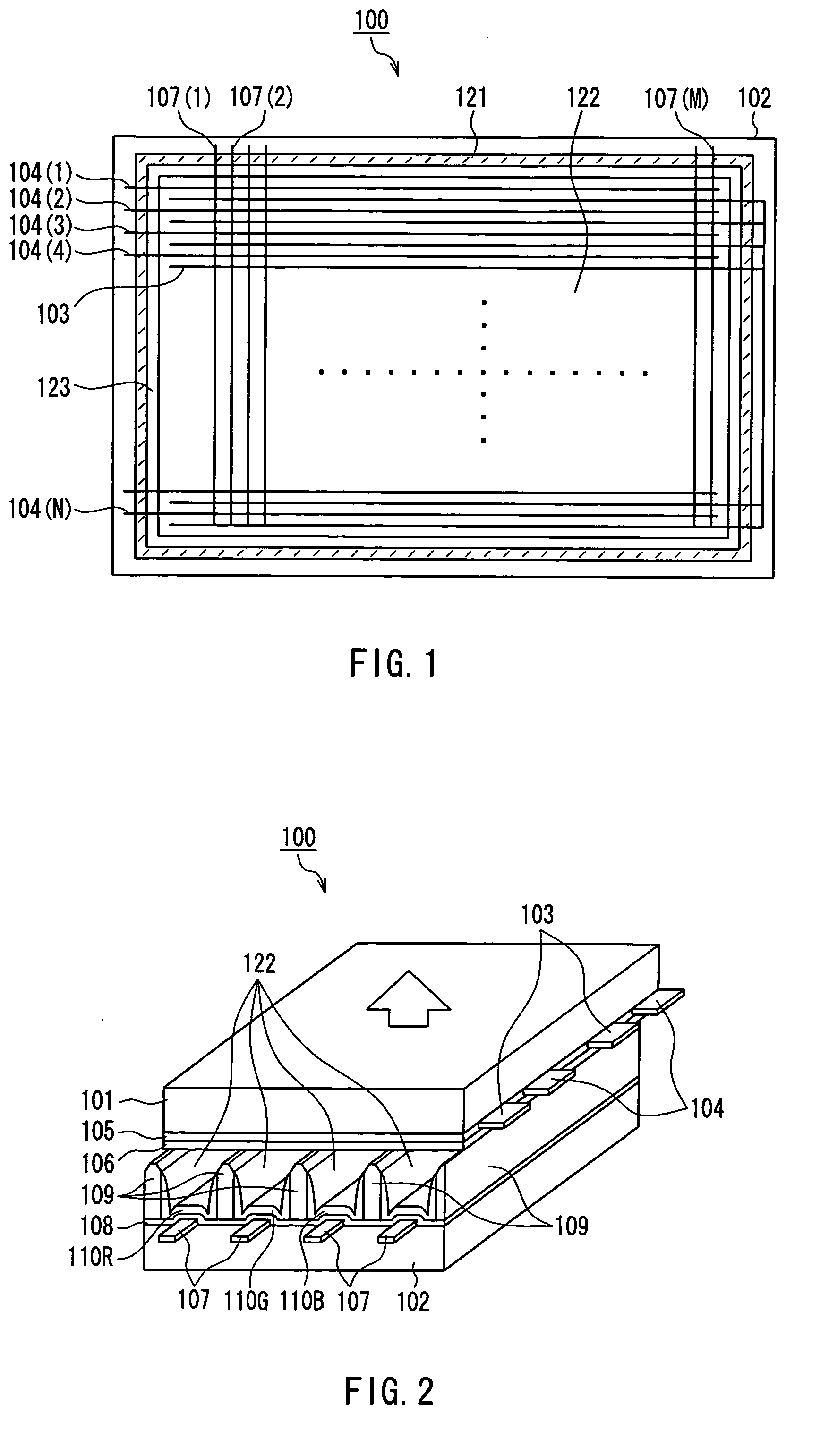
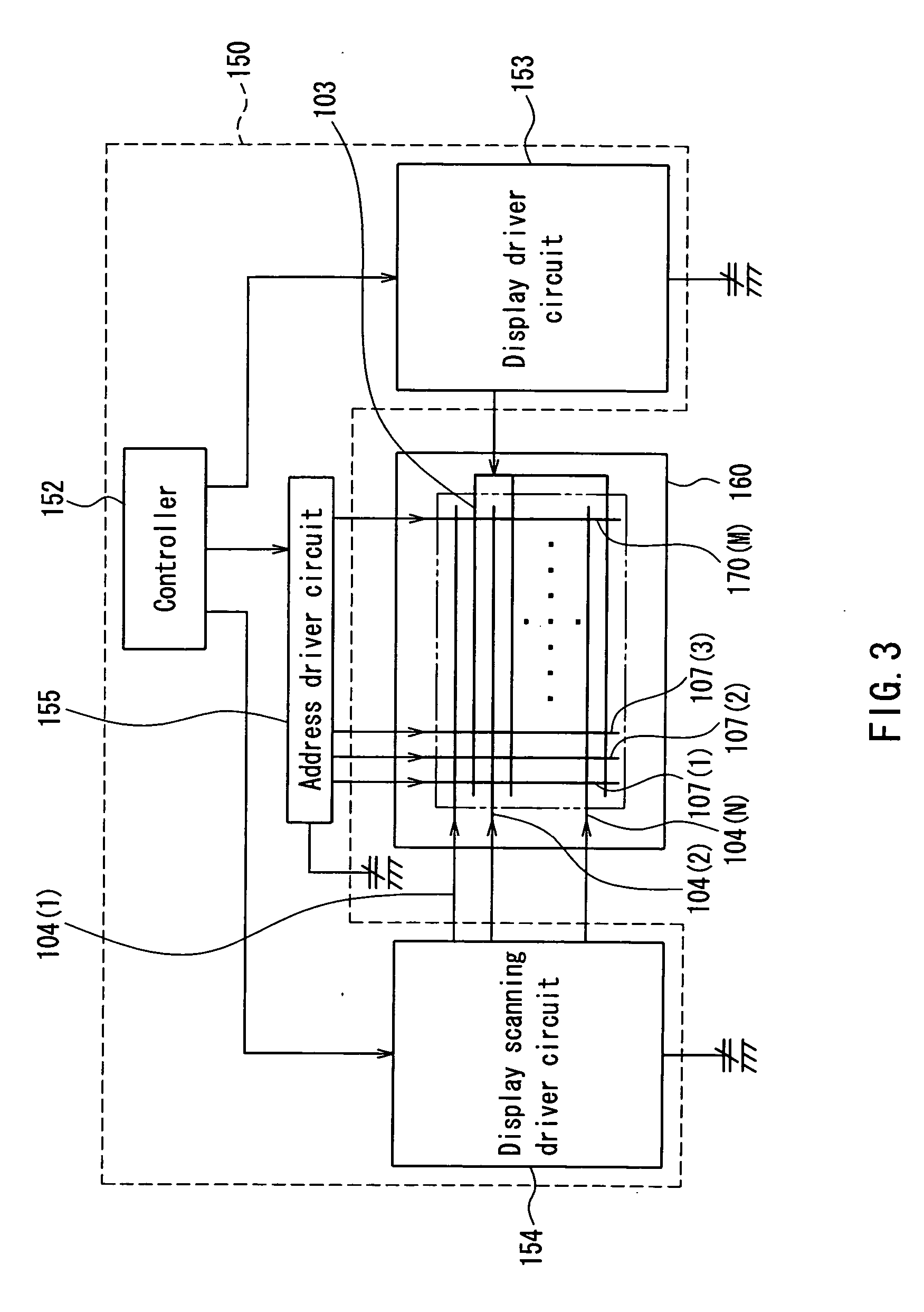
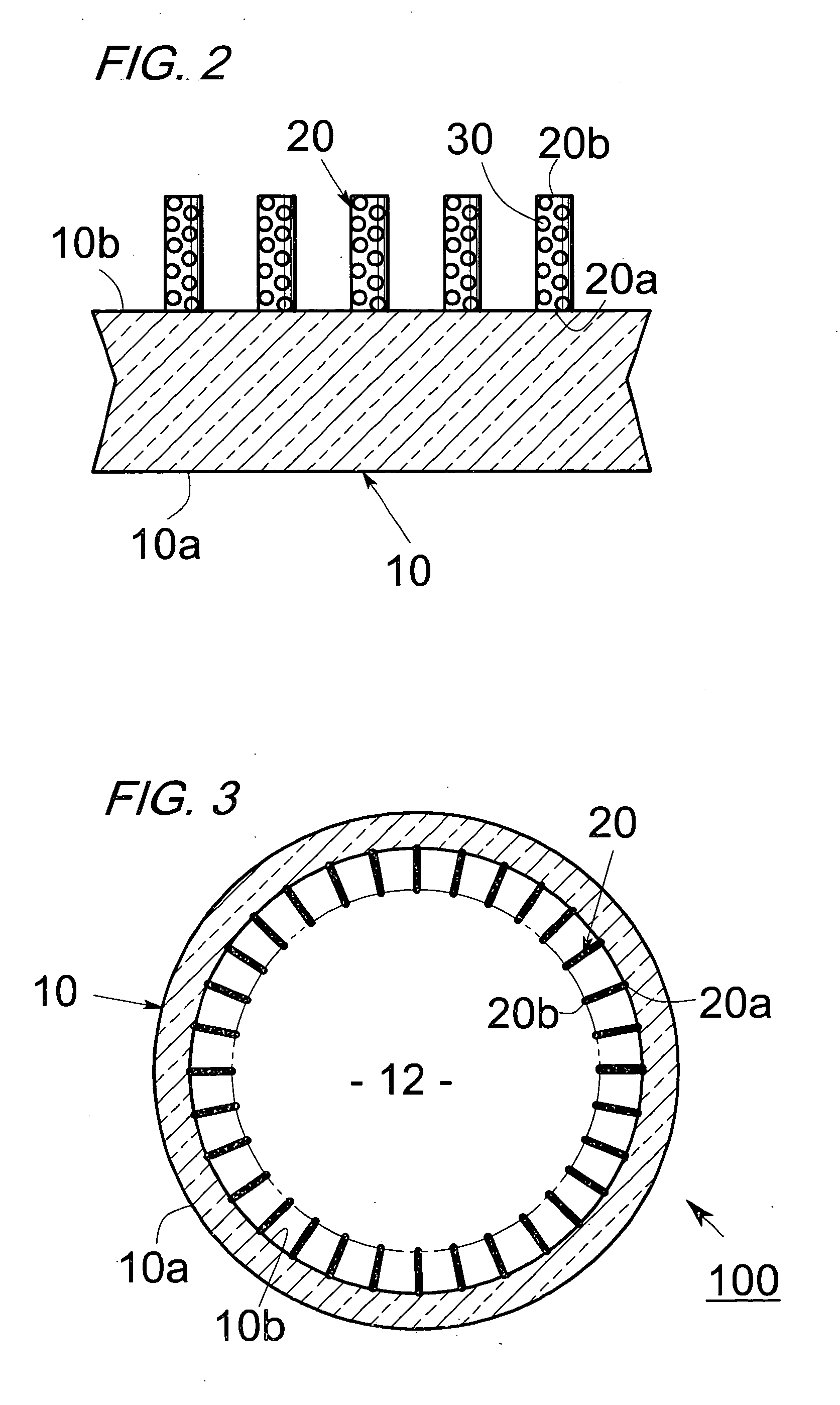
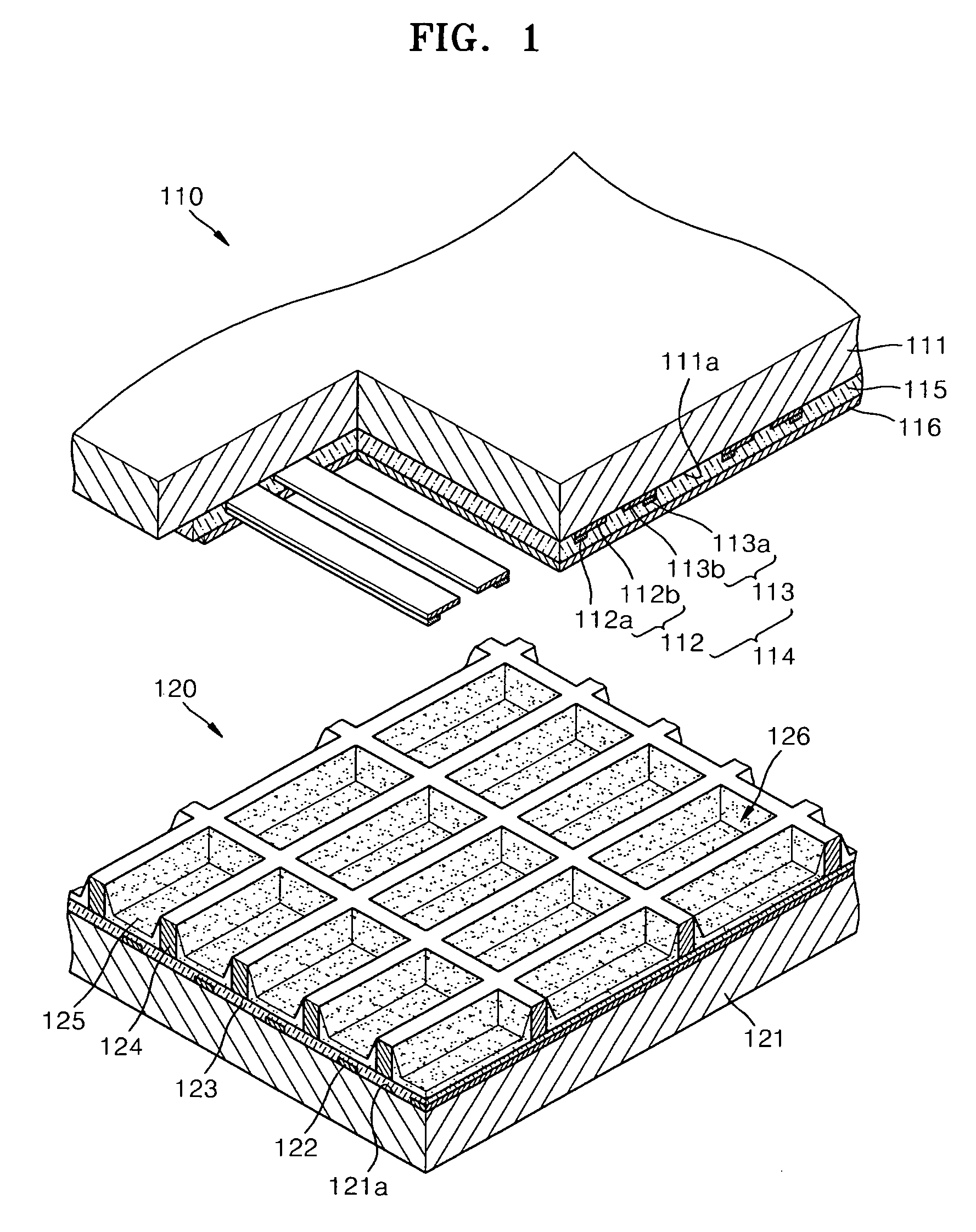
Flat display panel, mother substrate for flat display panel, and method of manufacturing the flat display panel
ActiveUS20120099061A1Solid-state devicesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureBlack matrixElectrical and Electronics engineering
A flat display panel includes a first substrate and a second substrate, and the first and second substrates are sealed via a sealing member therebetween. The second substrate includes a display region and a non-display region. The display region and the non-display region include black matrix patterns, and the black matrix patterns have at least one opening in a sealing region of the second substrate. The sealing member is arranged in the sealing region
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20050264161A1Effective lightingIncrease brightnessSustain/scan electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensDisplay deviceUltraviolet lights
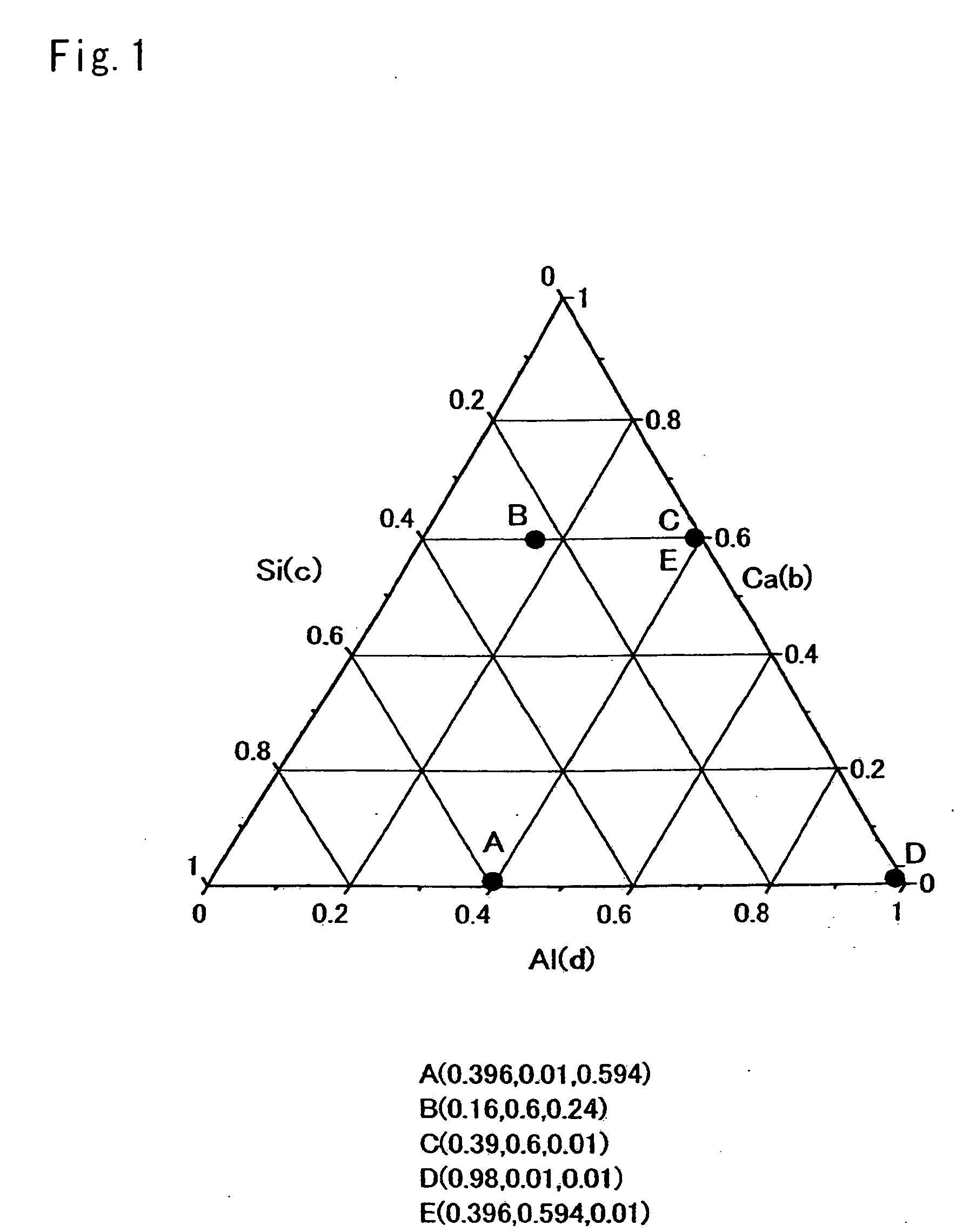
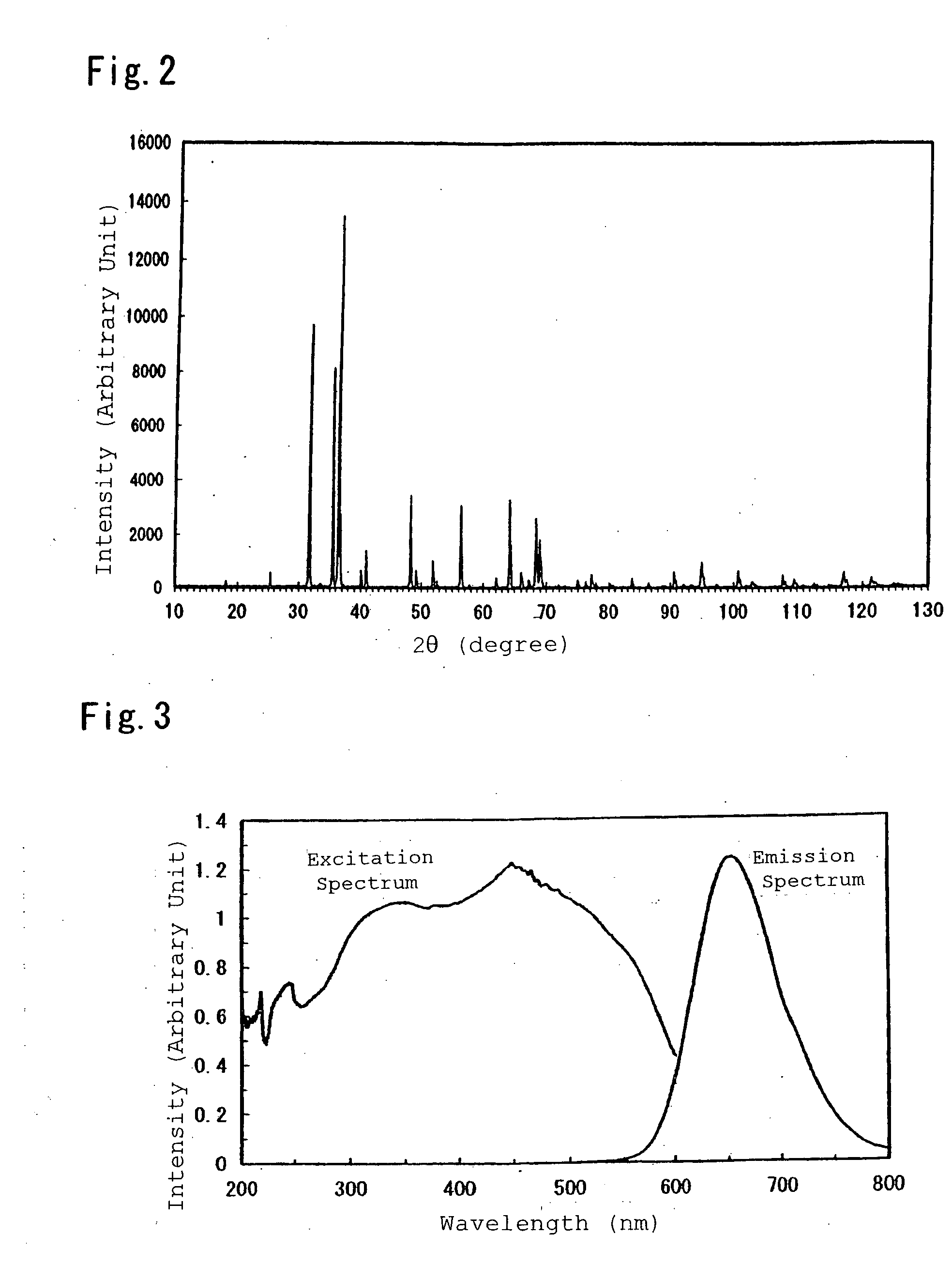
A blue-emitting phosphor is optimized by controlling mole fractions typically of Mg and Si in Sr3-eMgbSi2cO8d:Eue or by further including an optimal amount of at least one additional component such as Ba or Ca. The resulting phosphor exhibits a higher brightness and a higher color purity upon excitation by ultraviolet light emitted as a result of discharge of xenon gas. The optimized phosphor is incorporated into light emitting devices such as lamps and PDPs, and further into display devices.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Plasma display panel with defined phosphor layer thicknesses
InactiveUS7164231B2Increase brightnessGood colorDischarge tube luminescnet screensGas discharge electrodesPhosphorOptoelectronics
A plasma display panel includes a red phosphor layer, a green phosphor layer, and a blue phosphor layer. The thickness of the phosphor layer is satisfied by the following condition: when D is (S−2L) / S, D≧0.64, S being a distance between barrier ribs at half the height of the barrier ribs, and L being a side thickness of the phosphor layer coated on the barrier ribs at half the height thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
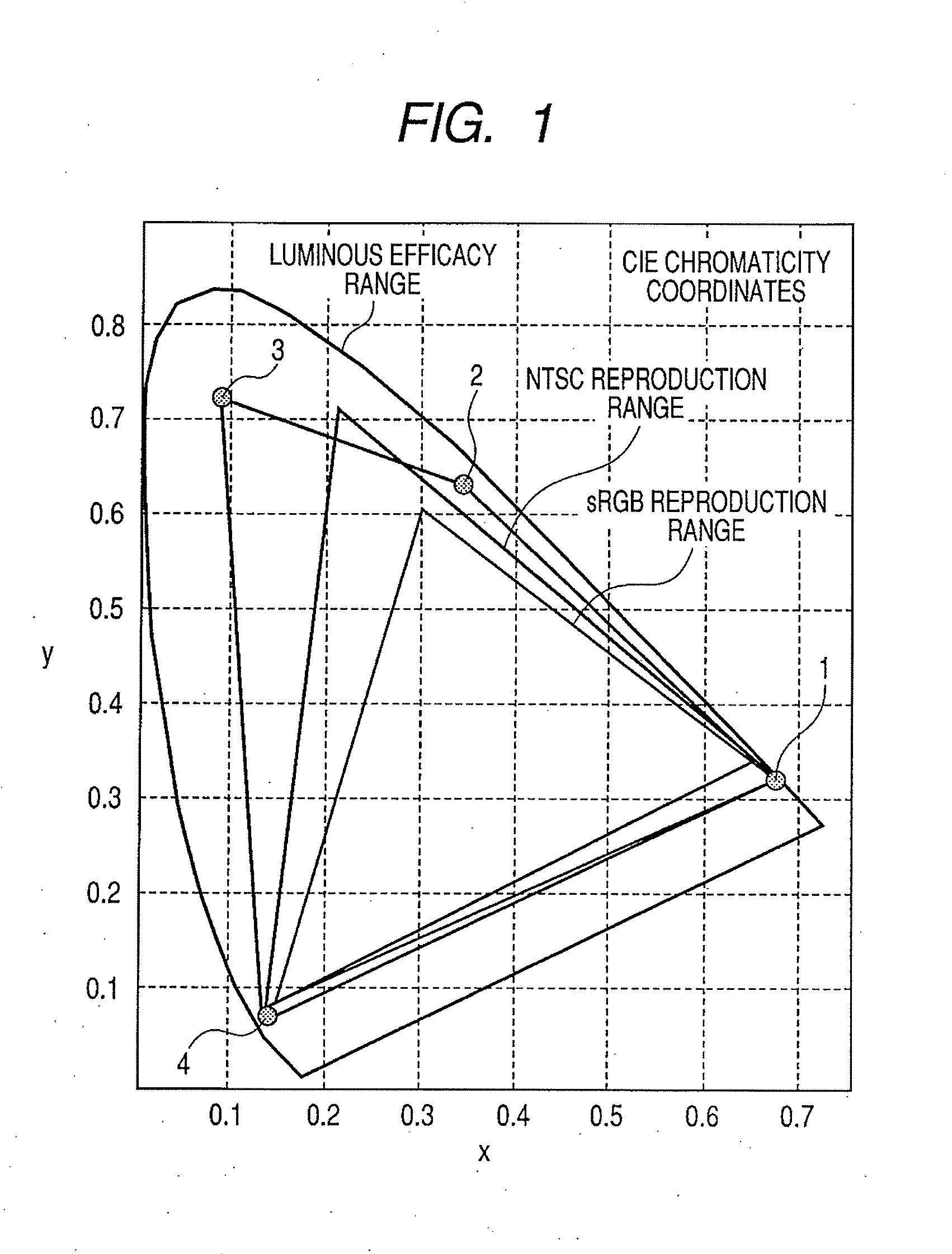
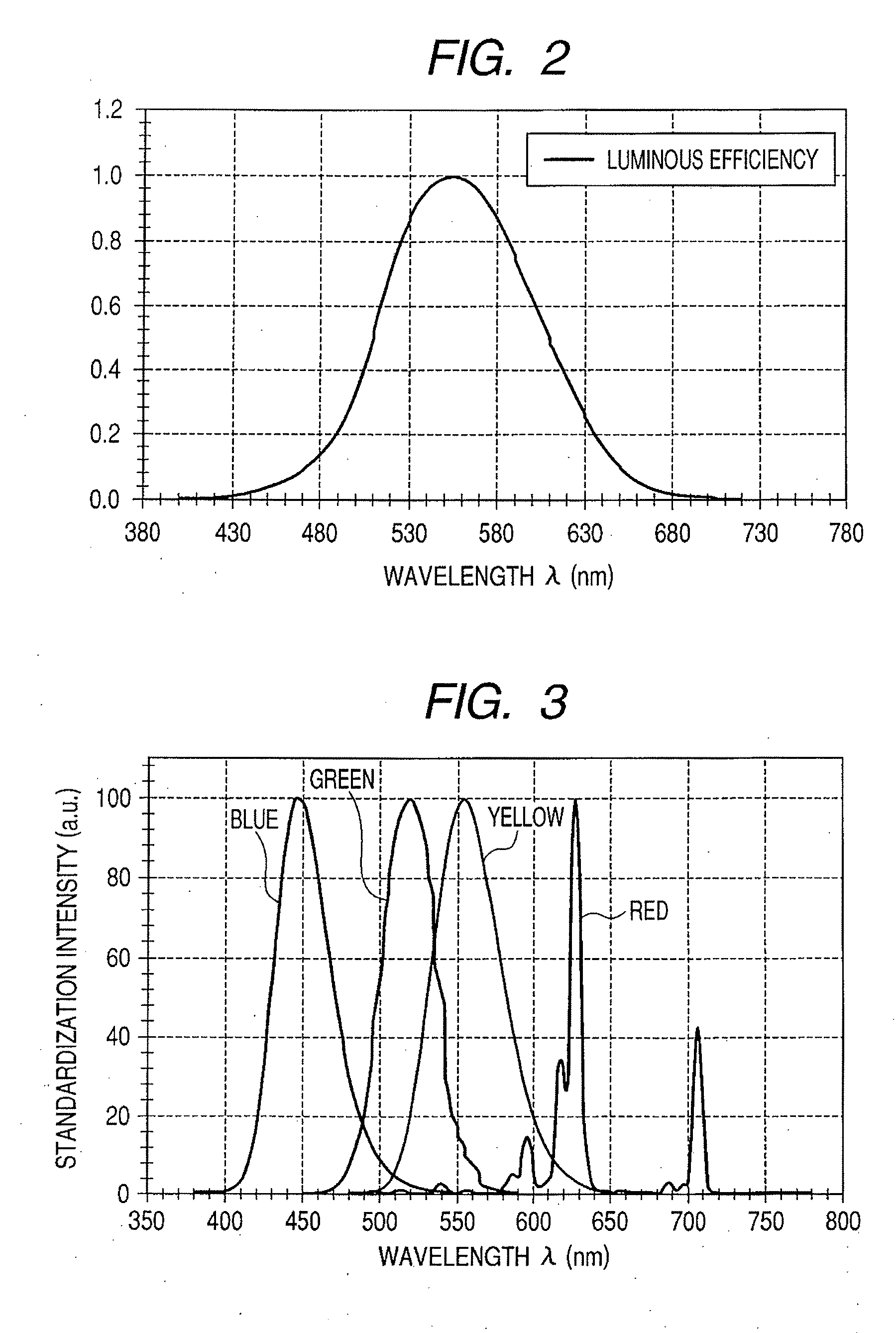
Multiprimary color display
InactiveUS20070268205A1Wide color reproduction rangeIncrease brightnessGas discharge electrodesStatic indicating devicesColor imageDisplay device
A display displays a color image by using a light source of at least four or more primary colors, and at least one color of the light source is yellow. Thus, it is possible to provide a flat panel display that can acquire a wider color reproduction range without sacrificing luminance.
Owner:CANON KK
Plasma display panel
InactiveUS7239085B2Suppress brightness changesReduce brightnessAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesFluorescencePhosphor
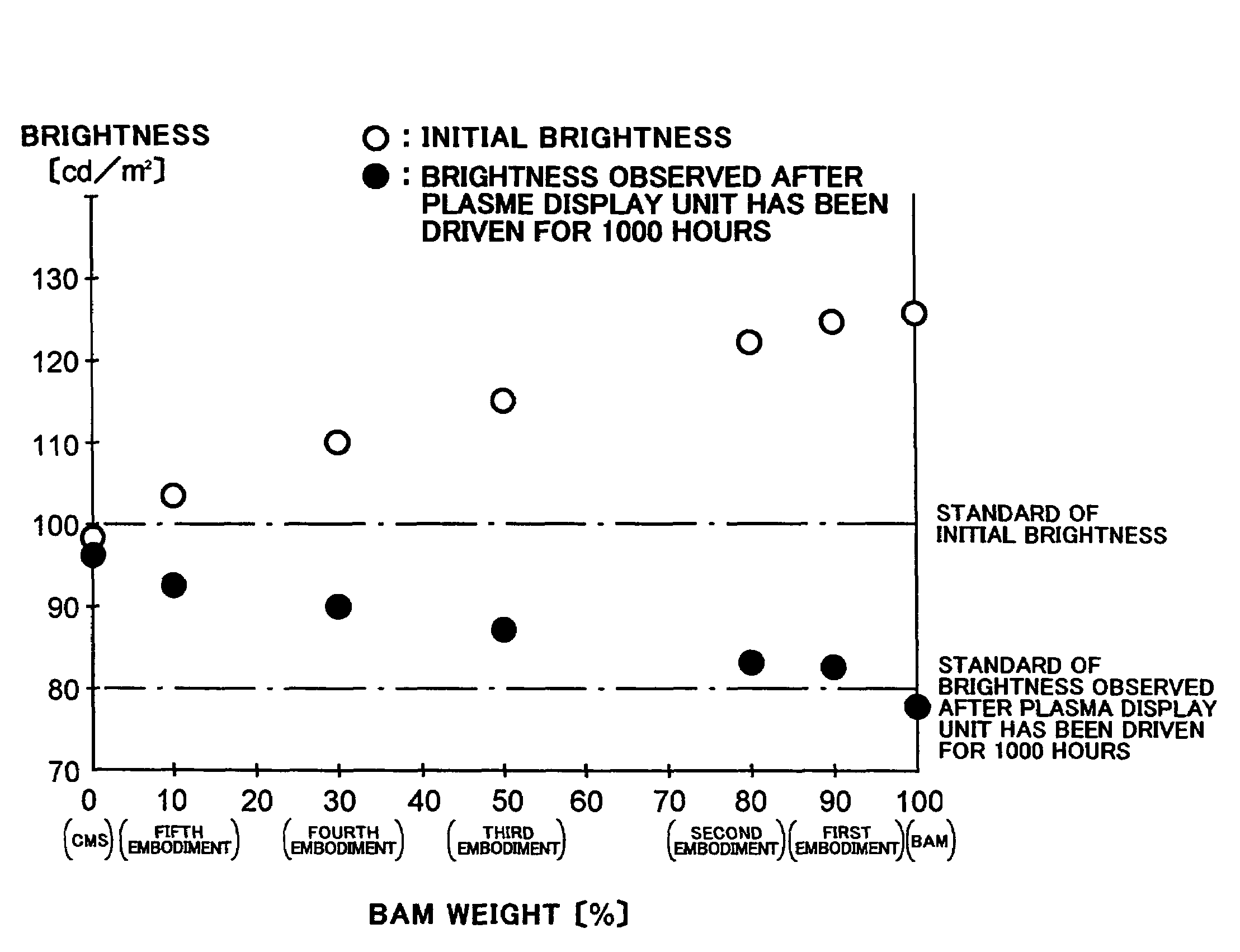
A plasma display panel includes a first substrate, and a second substrate facing the first substrate. The first substrate includes a transparent substrate, a scanning electrode and a common electrode both formed on the transparent substrate, and a dielectric layer covering the transparent substrate, the scanning electrode and the common electrode therewith. The second substrate includes an electrically insulating substrate, data electrodes formed on the electrically insulating substrate, partition walls formed on the electrically insulating substrate, and a phosphor layer covering the electrically insulating substrate and the data electrodes therewith between adjacent partition walls. The phosphor layer includes a blue-phosphor layer composed of phosphor which emits a blue light. The blue-phosphor layer is composed of a mixture of two or more phosphors each of which emits a blue light and has an initial brightness and variation of brightness with the lapse of time both different from one another.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Plasma display unit, phosphor and process for producing phosphor
InactiveUS7208102B2Inhibition of adsorptionDecrease in luminanceAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesPhosphorFluorescence
A plasma display device exhibits suppressed luminance degradation of a phosphor, a suppressed change in chromaticity and improved discharge characteristics as a result of suppression of adsorption of water or hydrocarbon-containing gas on a surface of a blue phosphor. A blue phosphor layer used in the plasma display device is formed of a compound expressed by Ba1−XMgAl10O17:EuX or Ba1−x−ySryMgAl10O17:EuX and includes at least one element that is selected from Nb, Ta, Pr, P, As, Sb, Bi and Tm which substitutes for a part of its Al or Mg element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
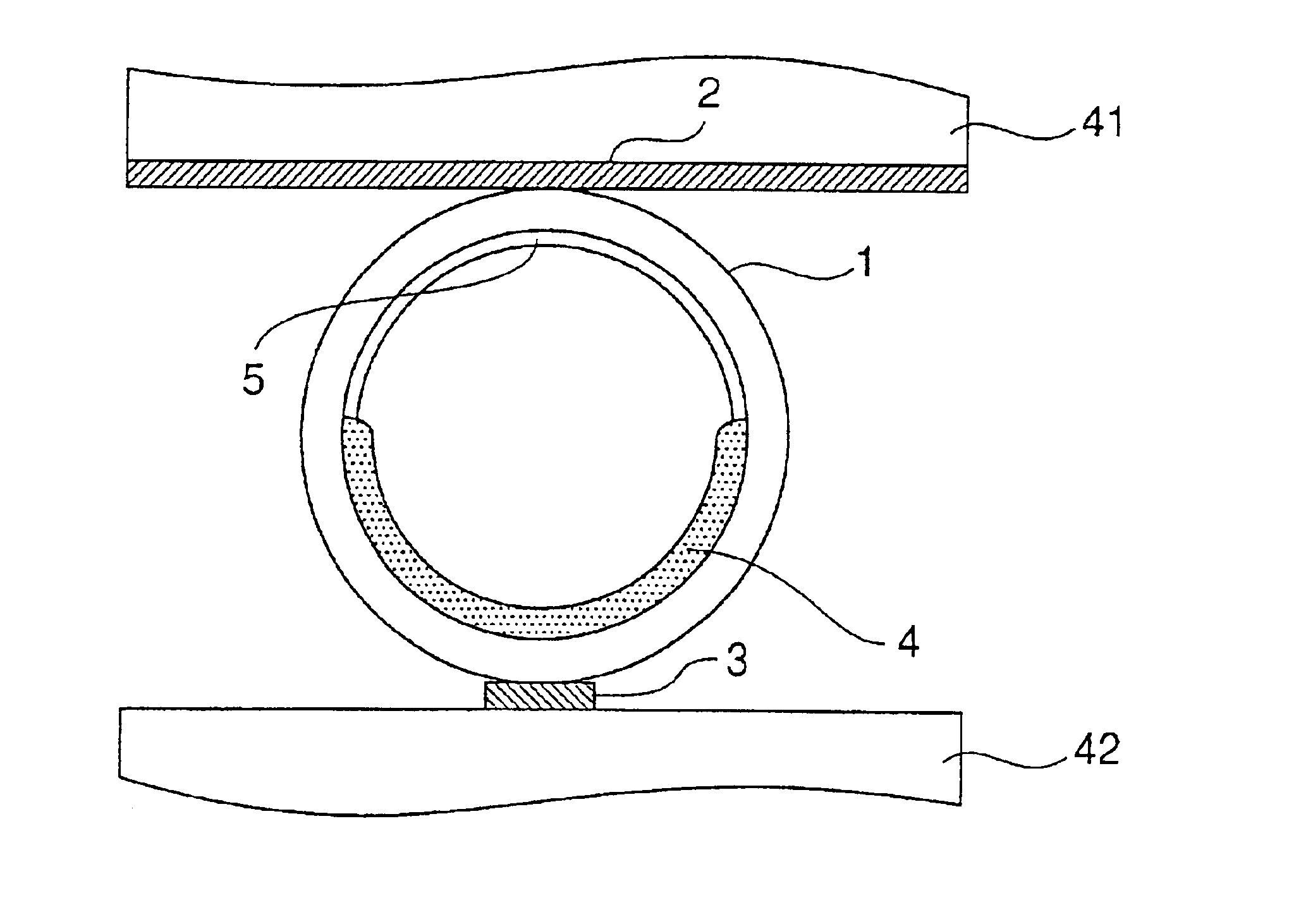
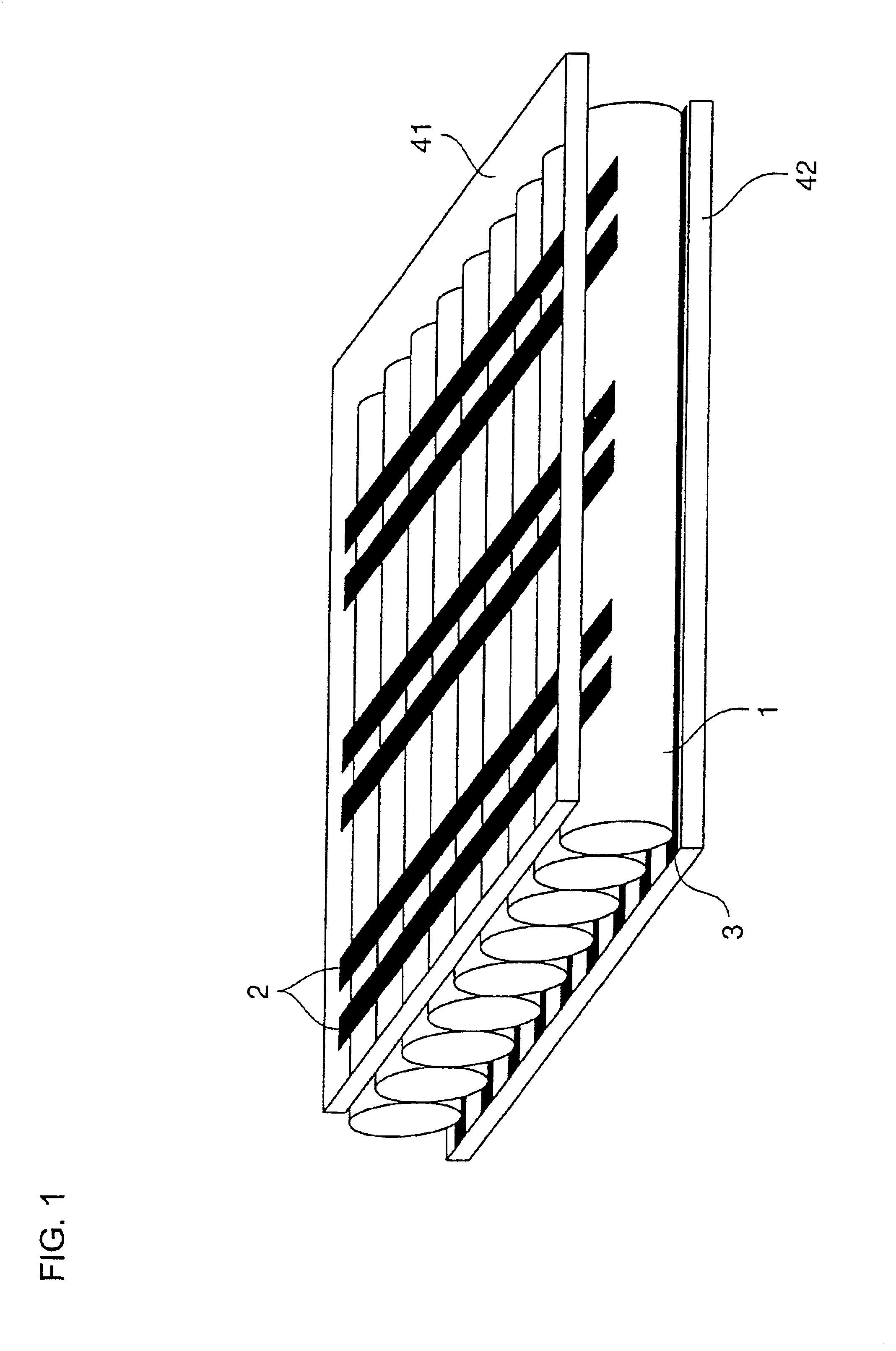
Display device employing gas discharge tubes arranged in parallel between front and rear substrates to comprise a display screen, each tube having a light emitting section as part of the display screen and a cleaning section connected to the light emitting section but displaced from the display screen
InactiveUS7049748B2Deterioration of discharge characteristic is preventedInhibit deteriorationAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesFluorescencePhosphor
A gas discharge tube has a phosphor layer formed and a discharge gas enclosed within an elongated tube which is to serve as the gas discharge tube. The gas discharge tube includes a light-emitting section and a cleaning section for cleaning the discharge gas. The cleaning section is connected to the light-emitting section.
Owner:SHINODA PLASMA
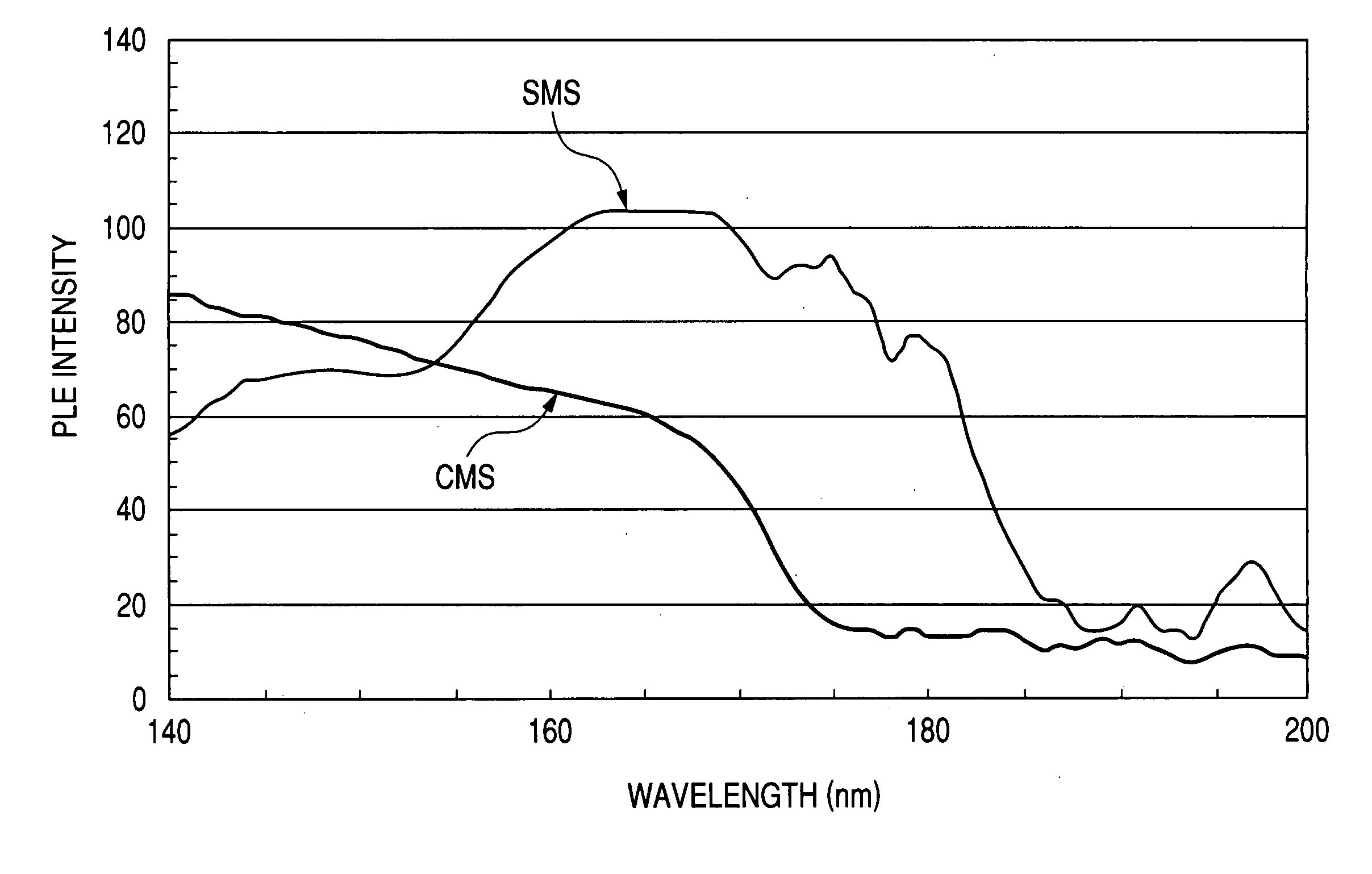
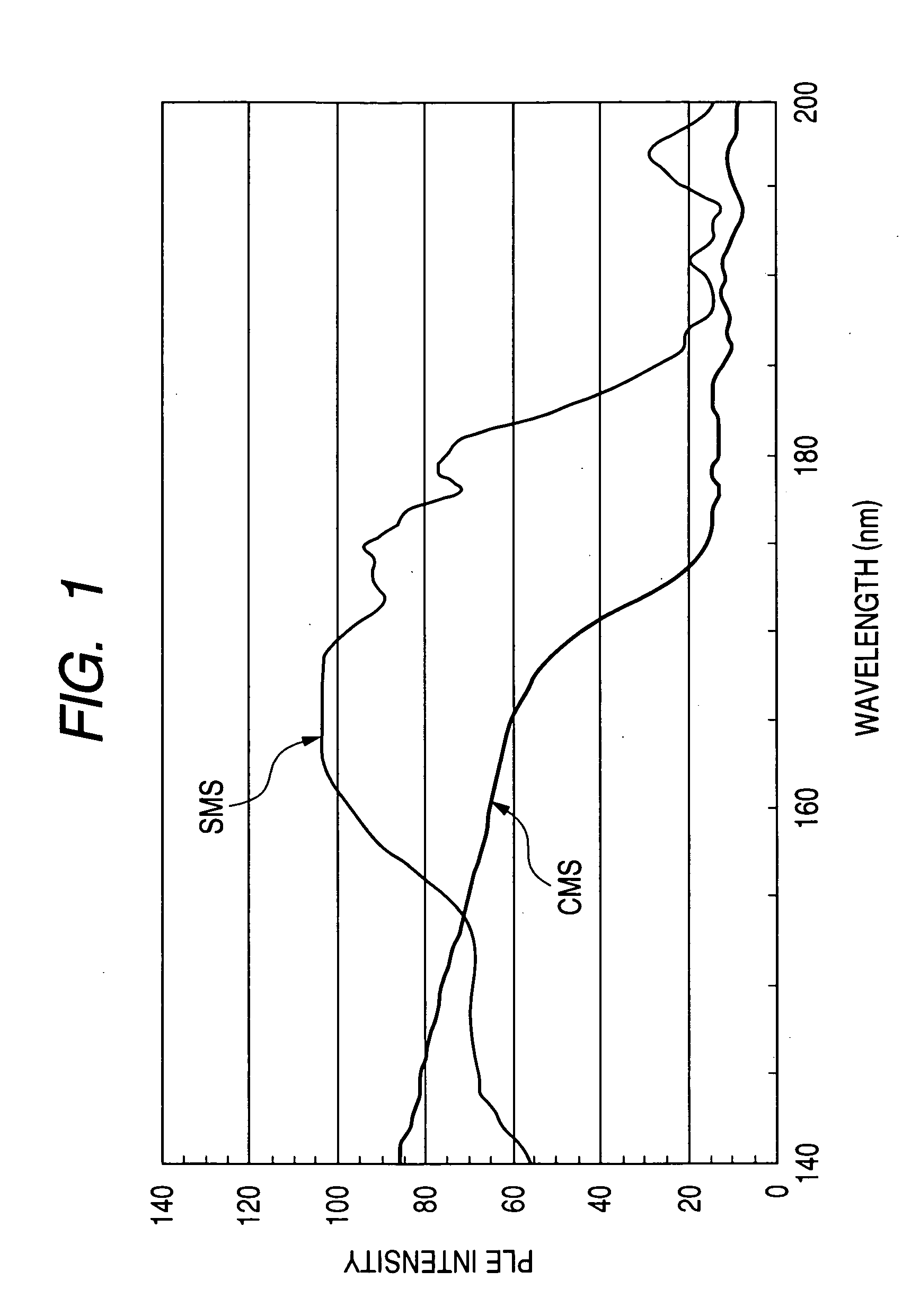
Oxynitride phosphor and light-emitting instrument
InactiveUS20070018567A1Increase brightnessReduced in material deterioration and luminance dropAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesRare-earth elementPhosphor
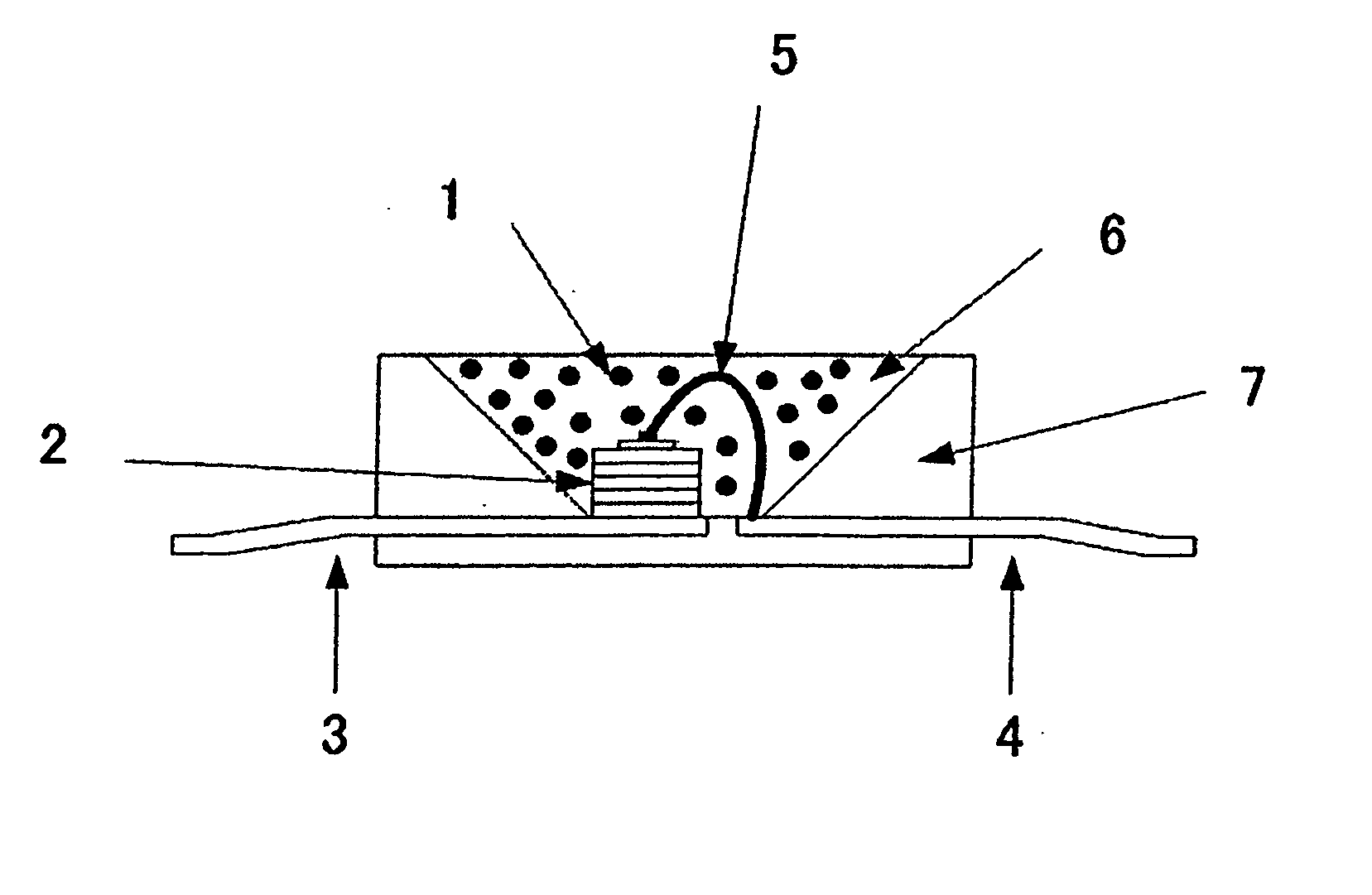
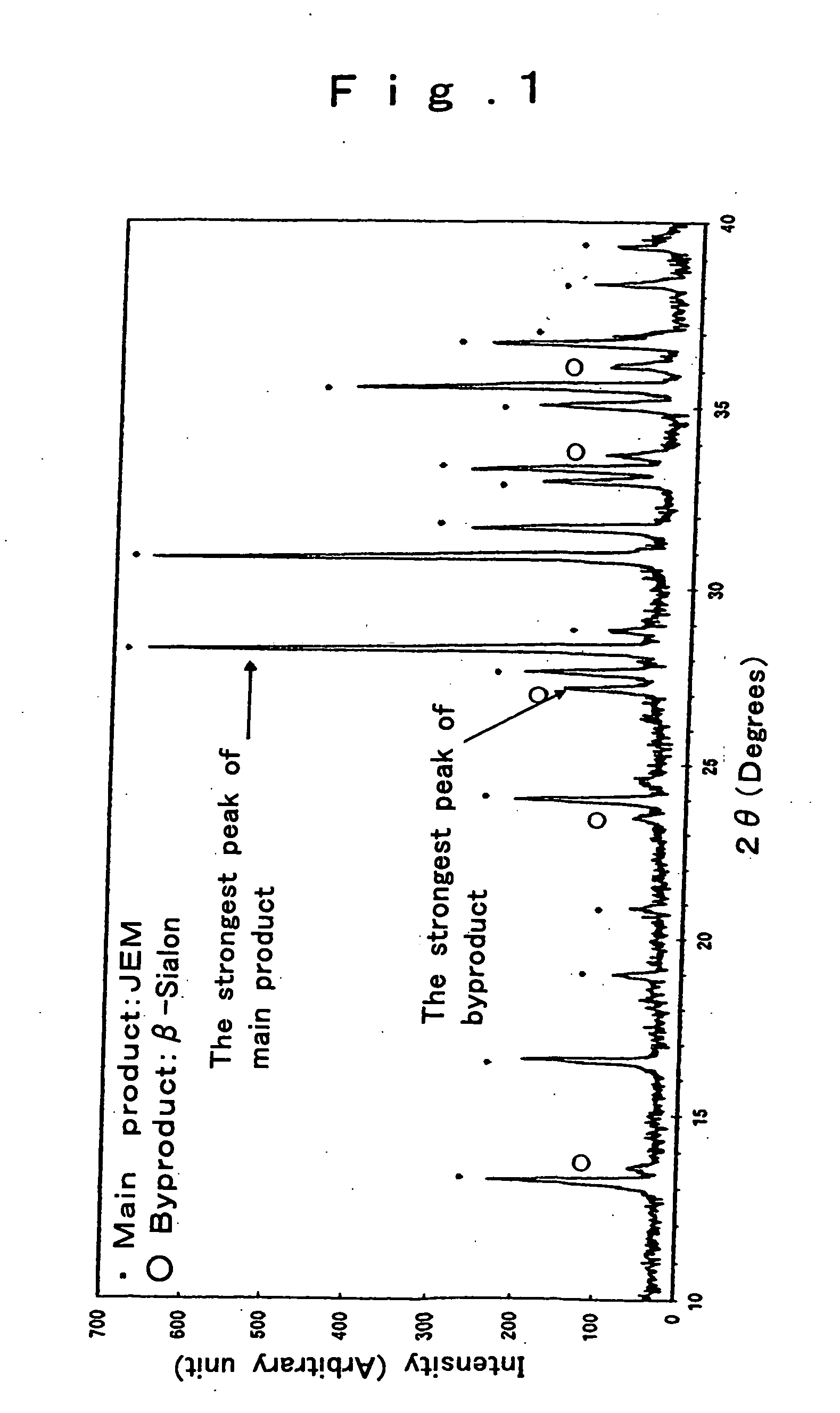
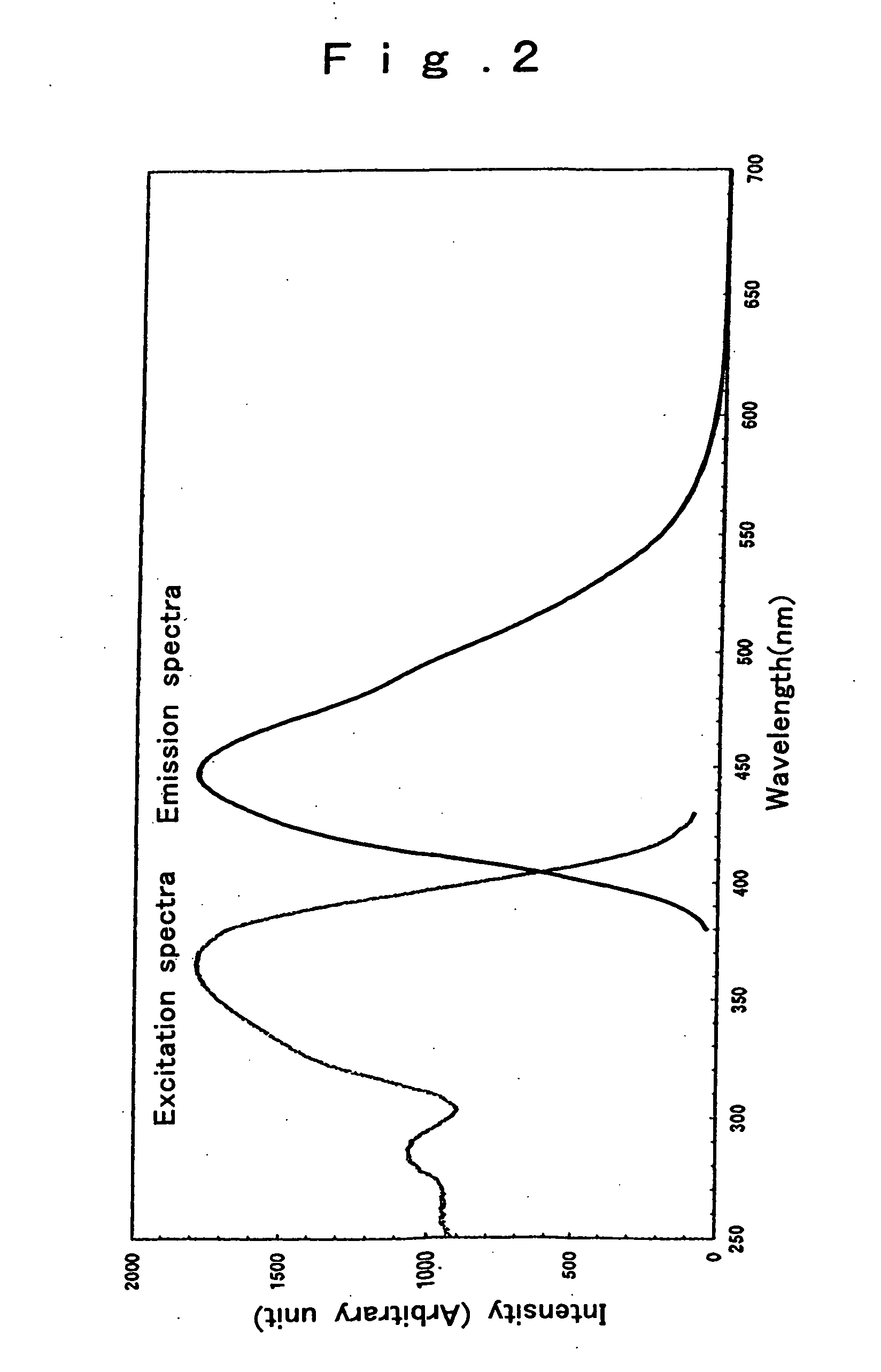
The invention has for its object the provision of an oxynitride fluorescent material has higher emission luminance than conventional rare earth element-activated sialon fluorescent materials. To this end, an oxynitride fluorescent material is designed in such a way as to contain as the primary constituent a JEM phase represented by a general formula MA1(Si6−zAlz)N10−zOz wherein M is one or two or more elements selected from the group consisting of La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu. For instance, this fluorescent material has a fluorescent spectrum maximum emission wavelength of 420 nm to 500 nm inclusive and an excitation spectrum maximum emission excitation wavelength of 250 nm to 400 nm inclusive.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
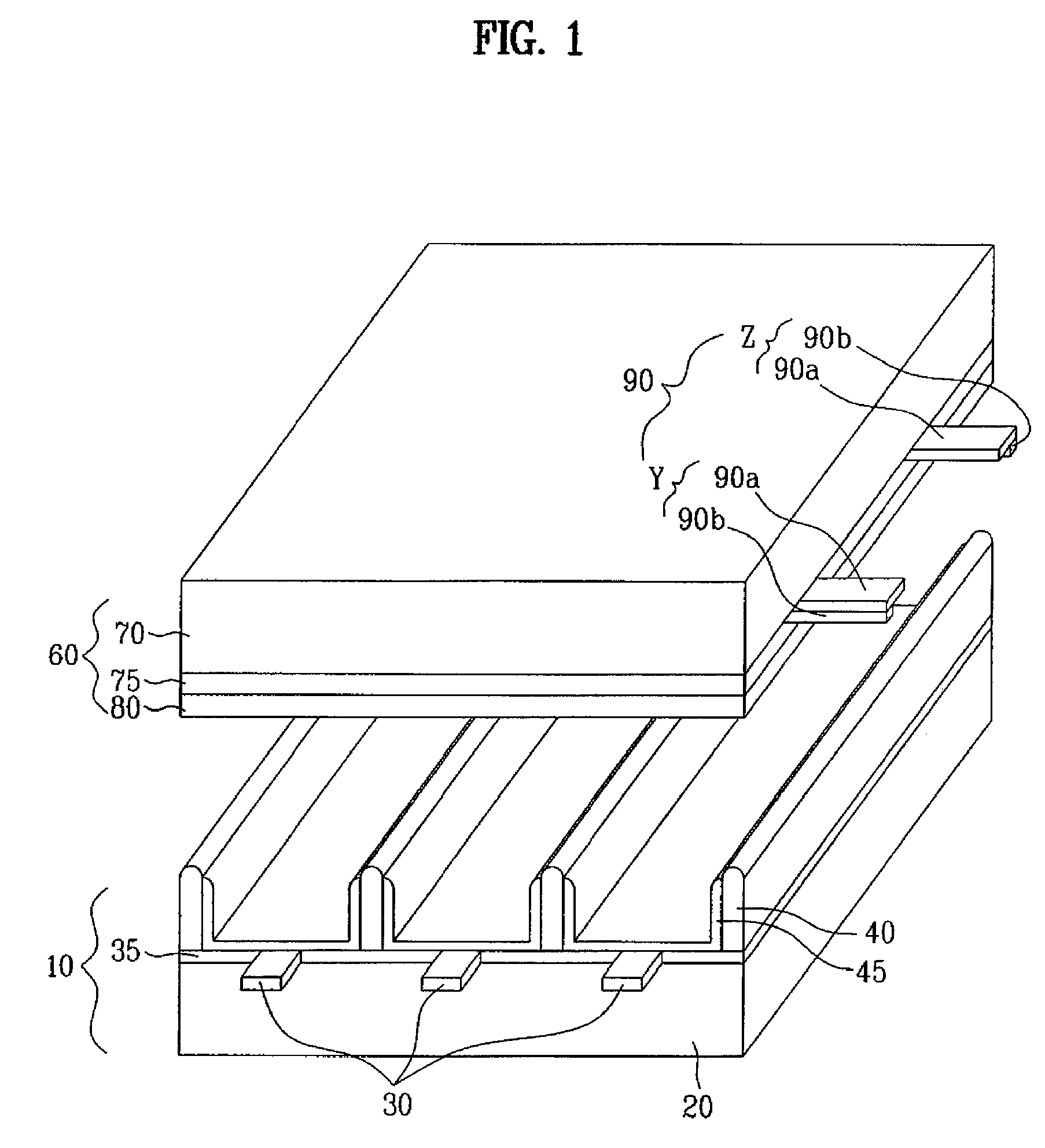
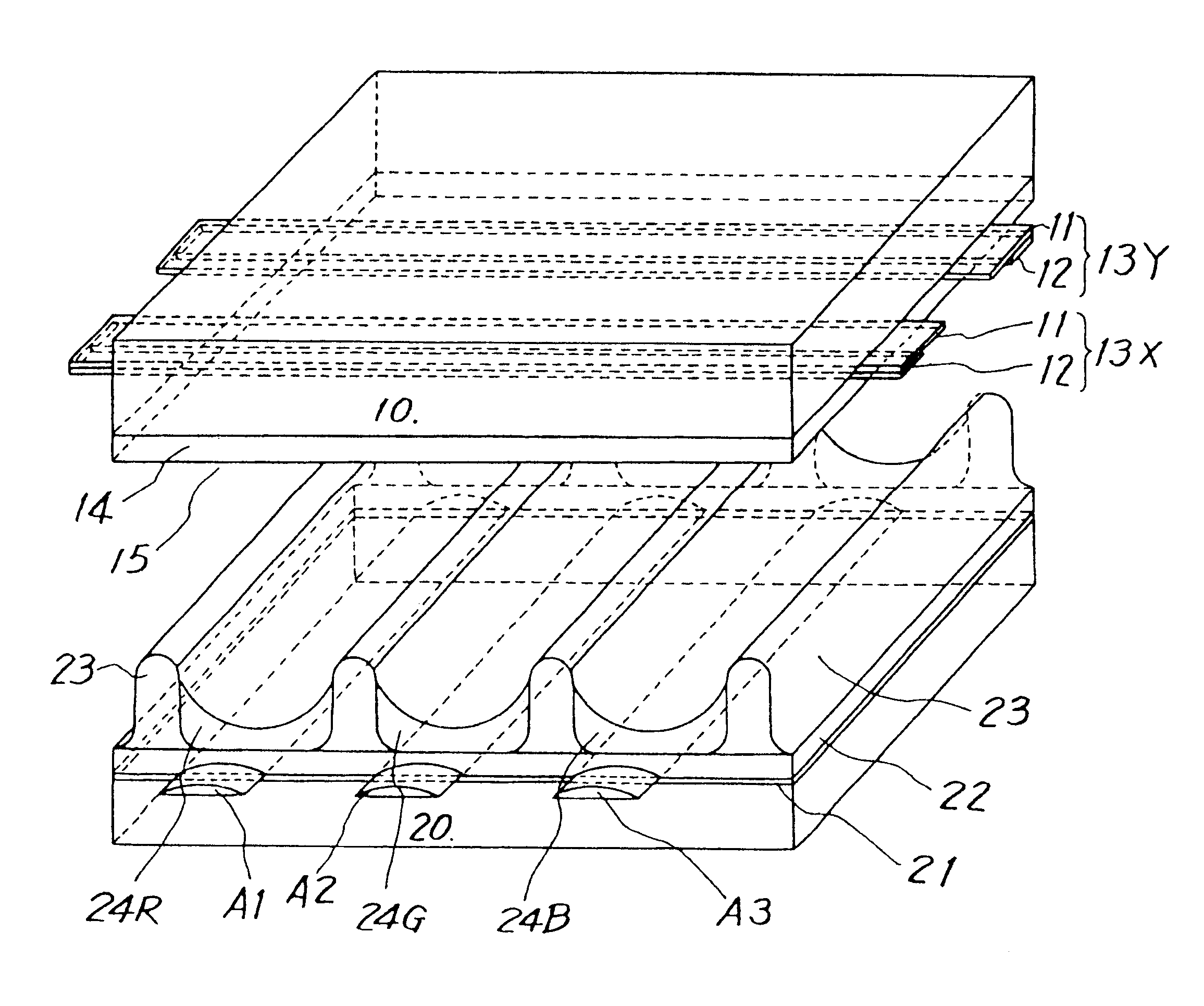
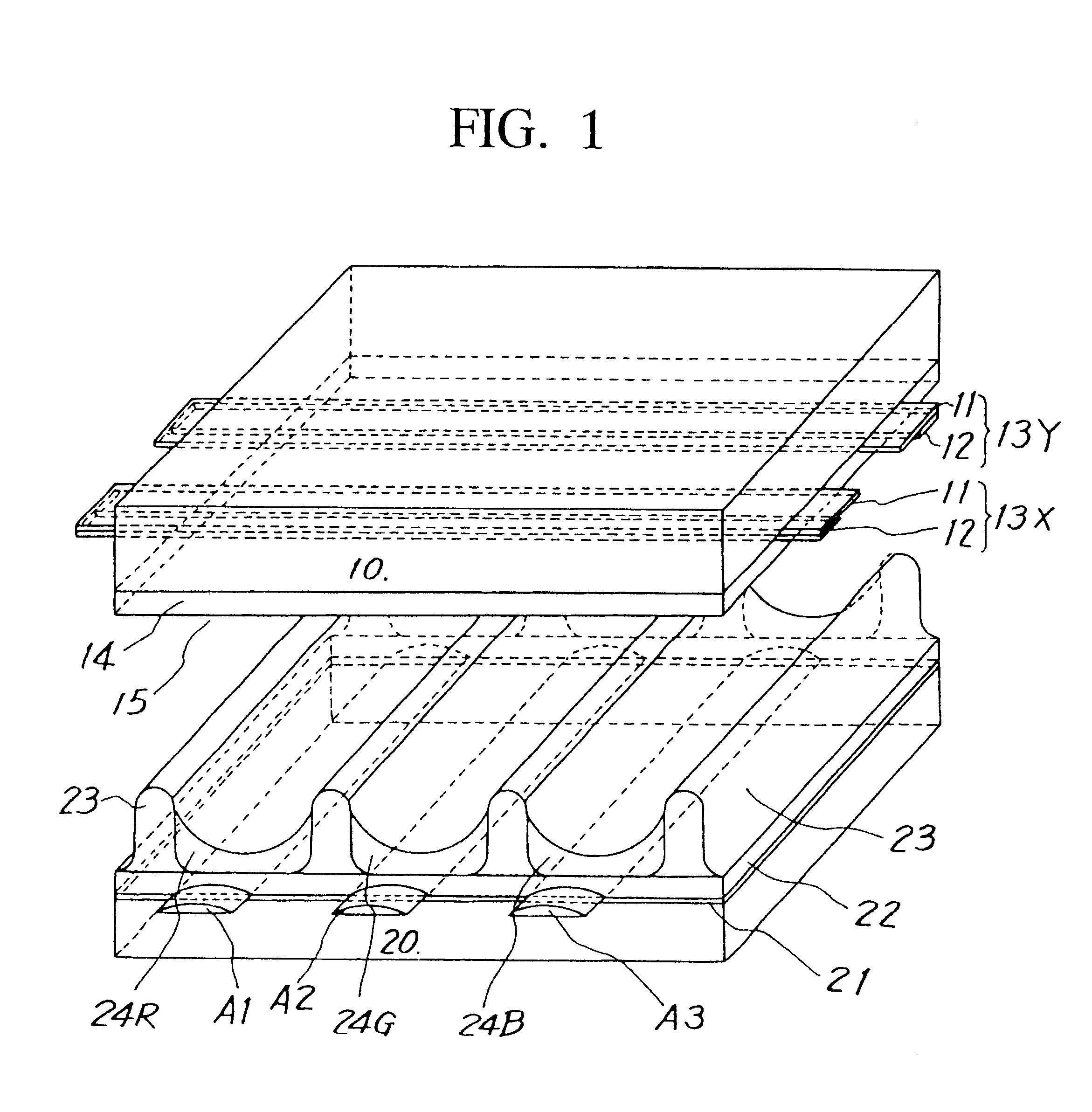
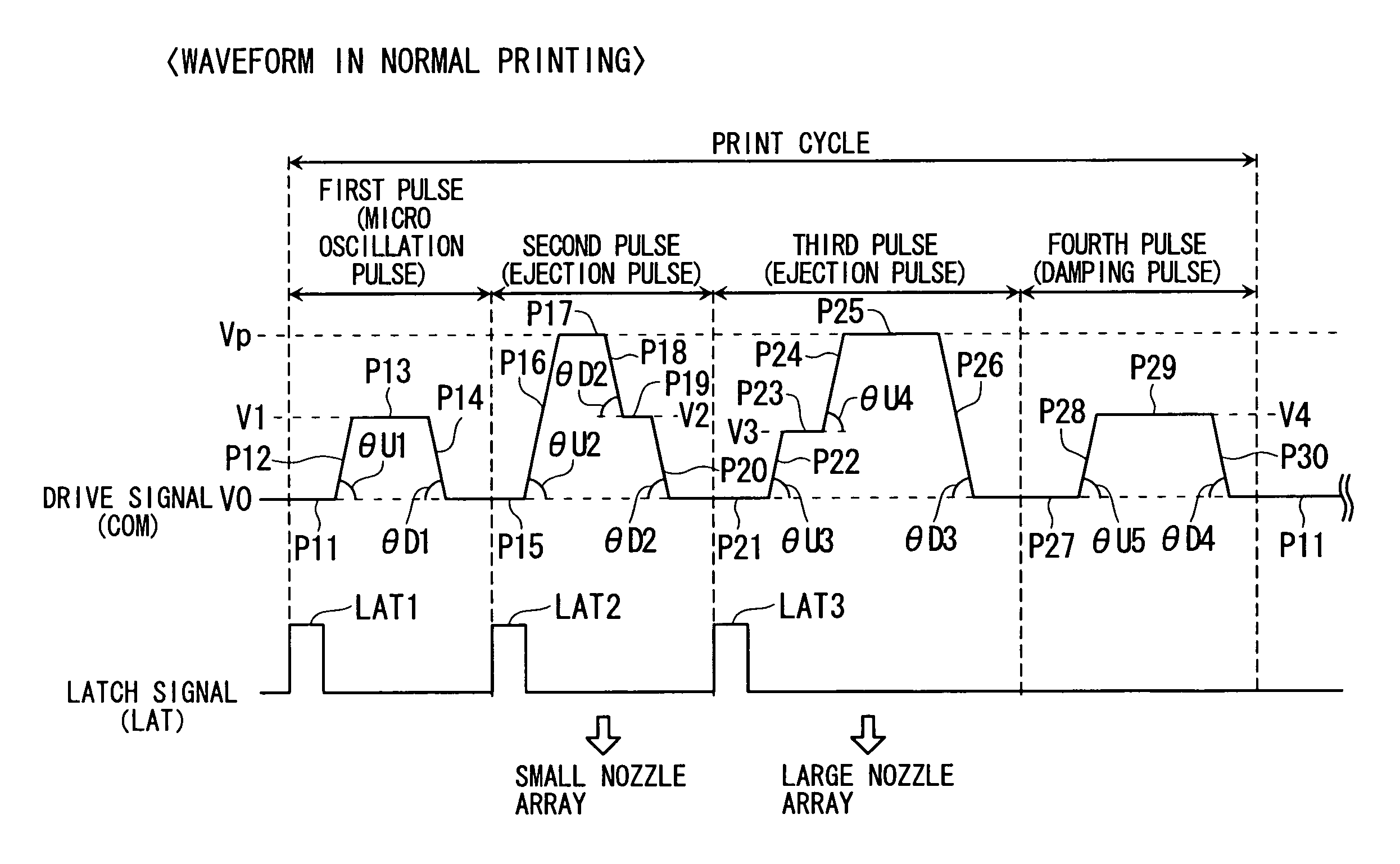
Method of controlling drive of function liquid droplet ejection head; function liquid droplet ejection apparatus; electro-optic device; method of manufacturing LCD device, organic EL device, electron emission device, PDP device, electrophoretic display device, color filter, organic EL; method of forming spacer, metallic wiring, lens, resist, and light diffusion body
ActiveUS7258408B2Easy to controlReduce throughputLiquid surface applicatorsInking apparatusDisplay deviceEngineering
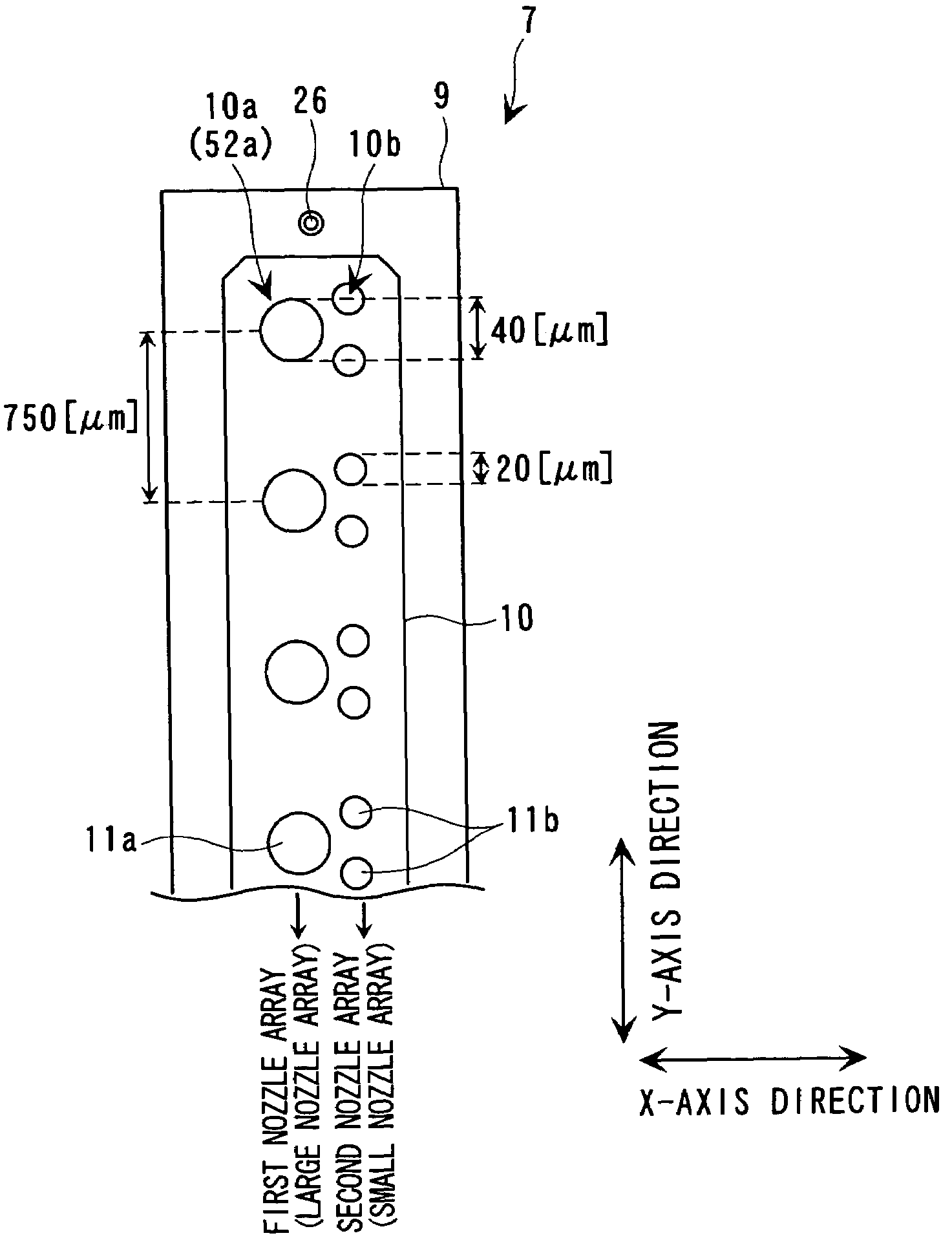
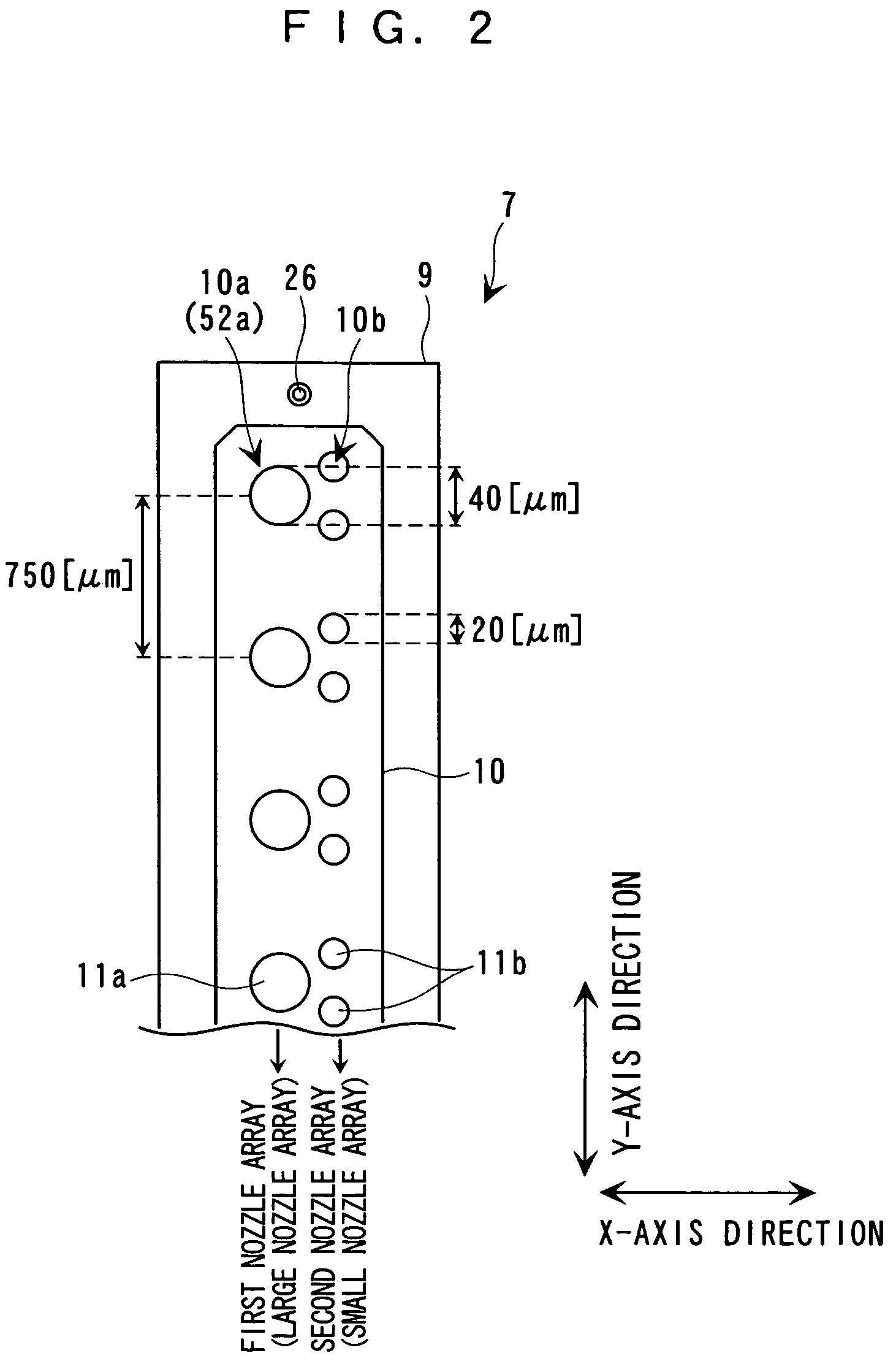
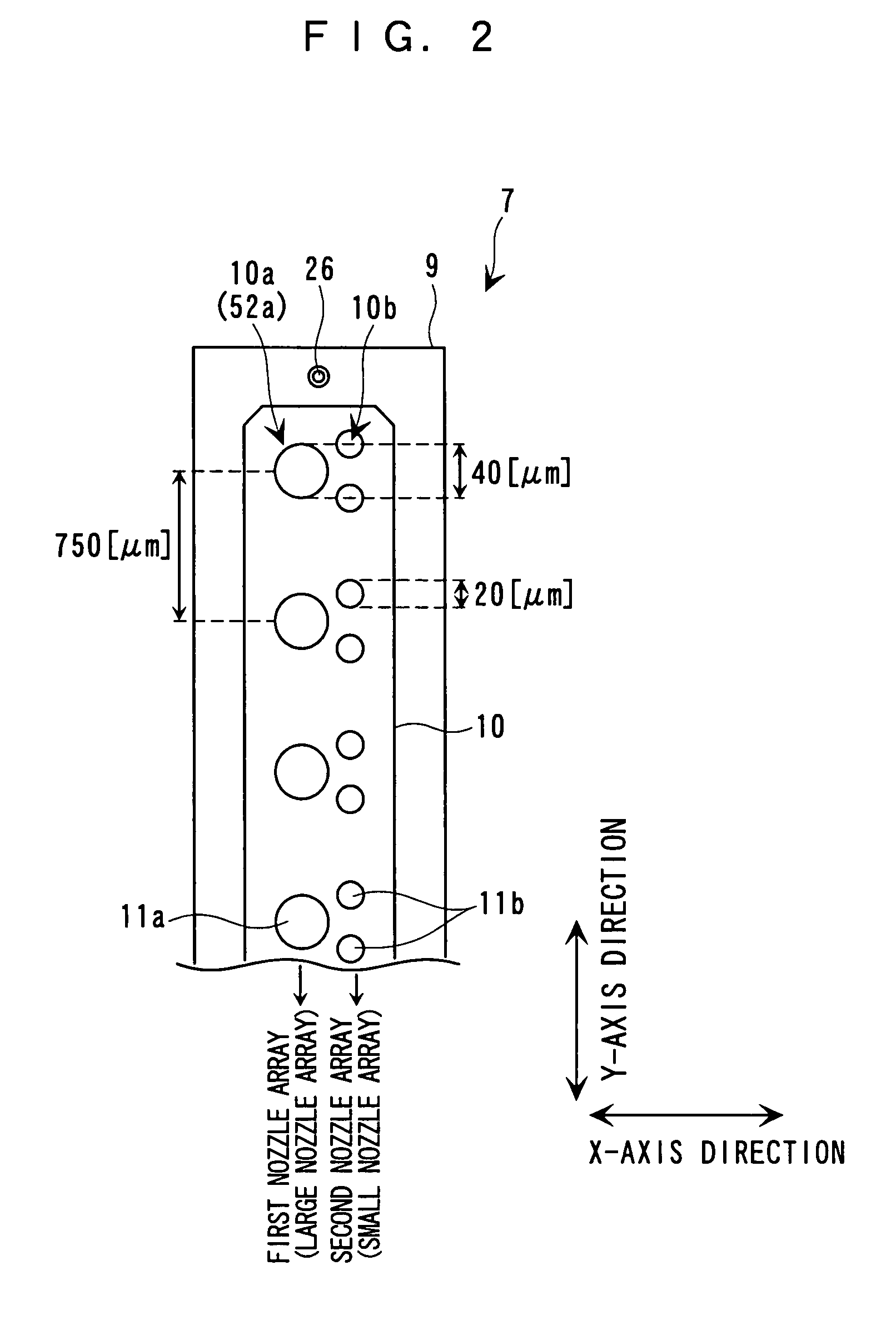
In a method of controlling drive of a function liquid droplet ejection head in which a plurality of nozzle arrays are arranged, the nozzle arrays have function liquid droplet ejection amounts which are different from each other per unit nozzle. The drive of the plurality of nozzle arrays is controlled by using a single drive signal having a plurality of ejection pulses corresponding to the plurality of nozzle arrays in one print cycle. Thus, even if a plurality of nozzle arrays having function liquid droplet ejection amounts which are different from each other per unit nozzle are disposed in one function liquid droplet ejection head, easy drive control is possible without lowering printing throughput.
Owner:KATEEVA
Glass composition for covering electrodes and glass paste containing the same
InactiveUS20060276322A1Improve reliabilityImprove pressure resistanceSustain/scan electrodesGas discharge fillingPolymer chemistryElectrode
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
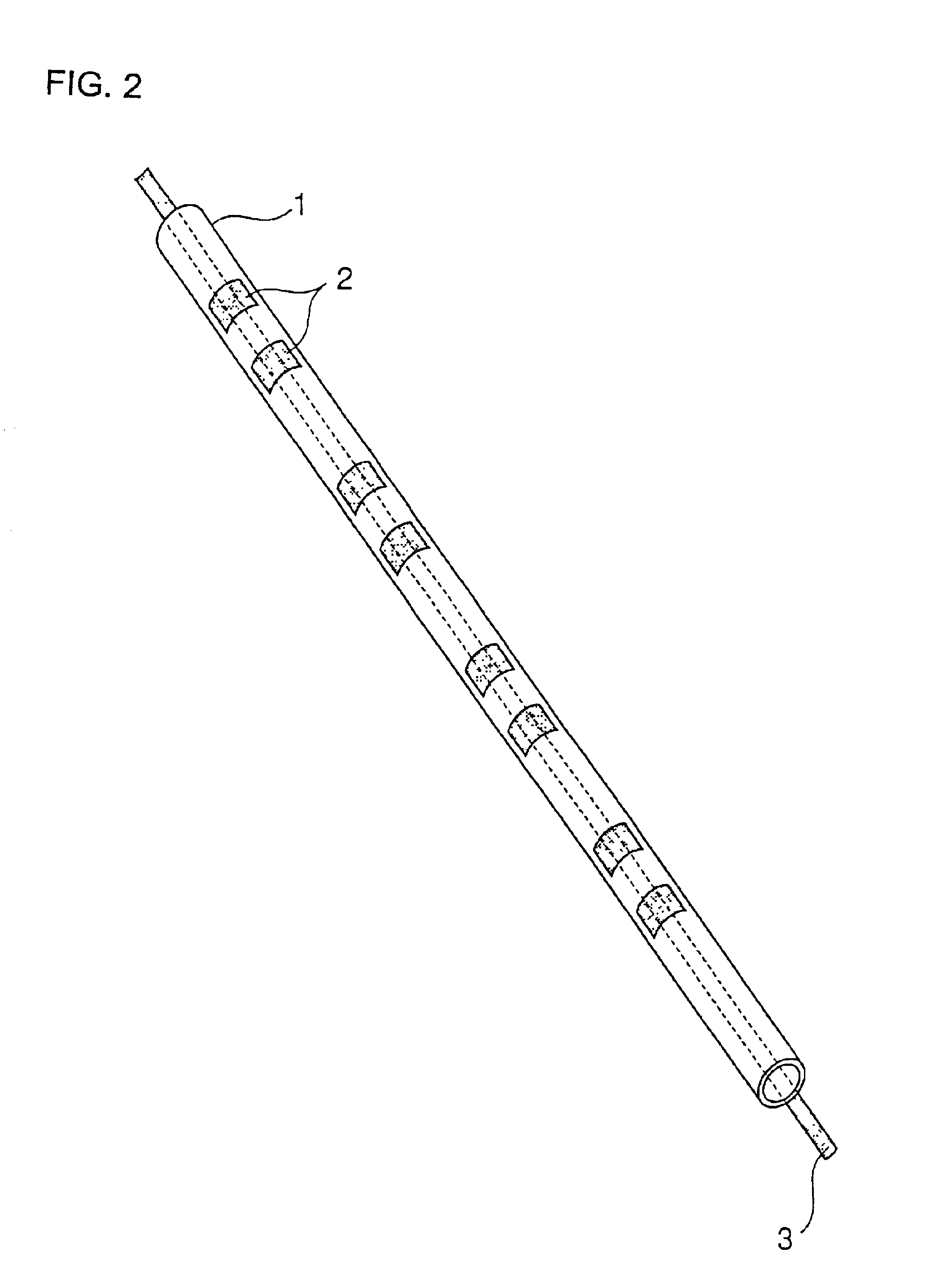
Method for forming phosphor layer of gas discharge tube and method for fabricating phosphor layer supporting member
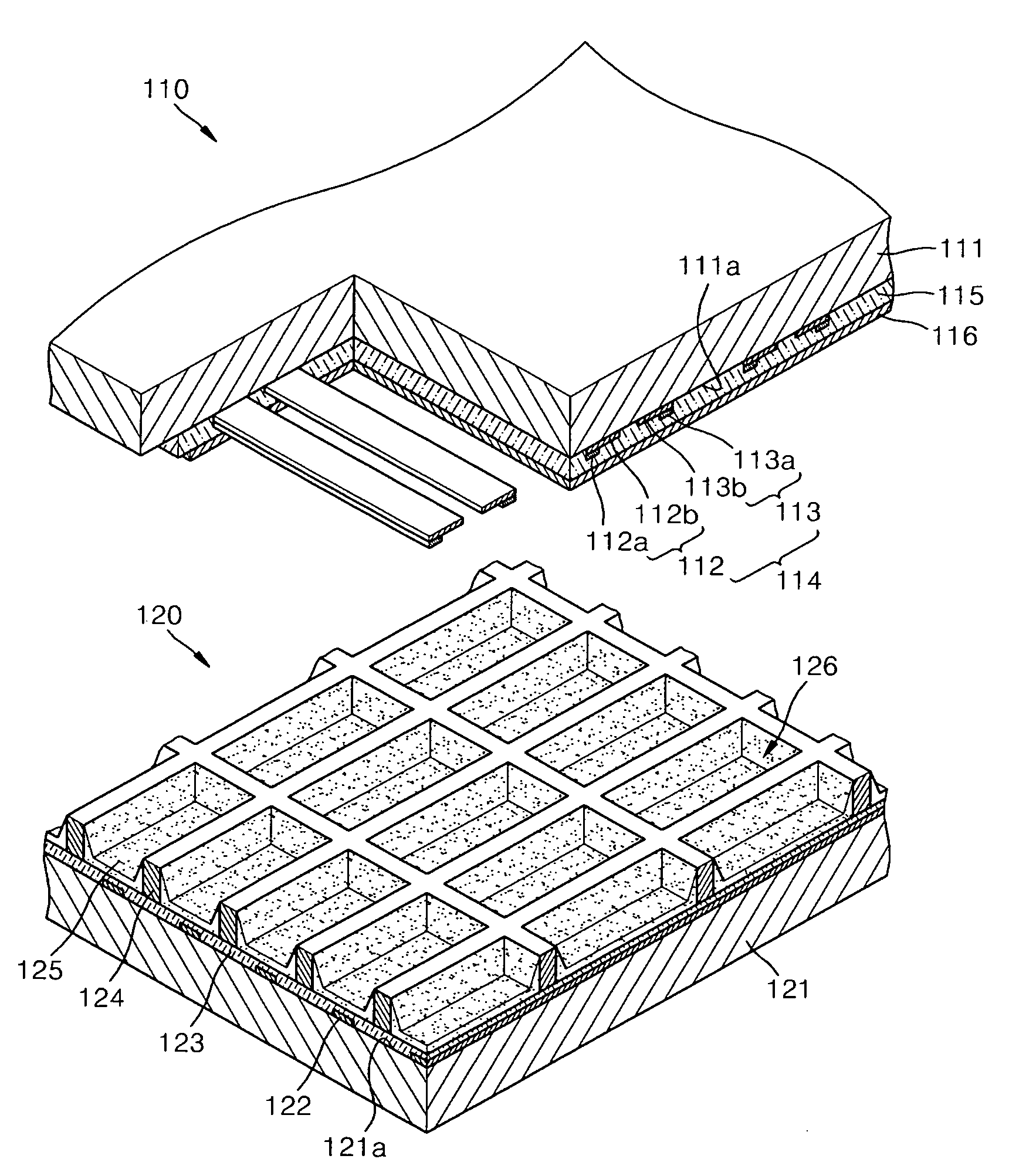
InactiveUS6969292B2Well formedHigh yieldAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesFluorescencePhosphor
A phosphor layer is formed efficiently in a gas discharge tube by drawing a mother material to fabricate a supporting member which is insertable in a small glass tube used for a gas discharge tube, forming a phosphor layer on the supporting member, and inserting and placing the supporting member in the small glass tube.
Owner:SHINODA PLASMA
Method of forming phosphor layer of gas discharge tube
InactiveUS6857923B2Quality improvementExtended service lifeAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesFluorescencePhosphor
A method of forming a phosphor layer of a gas discharge tube provided with the phosphor layer on an internal surface of an elongated tubular vessel forming a discharge space. The method includes the steps of introducing a slurry of phosphor powder and a binding resin dispersed in a medium into the tubular vessel, holding the tubular vessel sideways to deposit the phosphor powder and the binding resin in the tubular vessel, and removing the medium from the tubular vessel, thereby forming a phosphor layer on one side of the internal surface of the tubular vessel.
Owner:SHINODA PLASMA
Phosphor and Light Emitting Instrument
ActiveUS20080303409A1Without luminance deteriorationLong wavelengthSustain/scan electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhosphorRare earth
The present invention aims at providing a chemically stabilized inorganic phosphor which emits orange light or red light at wavelengths longer than the conventional rare-earth activated sialon phosphor and which has a higher luminance.The solving means resides in an inorganic phosphor design represented by a composition formula MaAbDcEdNeOfXg and containing: an M element (M is one kind or two or more kinds of element(s) selected from Mn, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, and Lu); a divalent A element (A is one kind or two or more kinds of element(s) selected from Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba); a trivalent E element (E is one kind or two or more kinds of element(s) selected from B, Al, Ga, and In); a tetravalent D element (D is one kind or two or more kinds of element(s) selected from Si, Ge, and Sn); nitrogen; oxygen (including an oxygen absent condition); and another X element (including an X absent condition); wherein the parameters a, b, c, d, e, f, and g included in the equation are adjusted to and set at particular regions to provide an inorganic phosphor which emits orange light at wavelengths of 570 nm or longer or red light at wavelengths of 600 nm or longer with excellent color rendering property.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Method for producing substrate assembly for plasma display panel, and plasma display panel
InactiveUS20080049382A1Form evenlyAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesRough surfaceOptoelectronics
A method for producing a substrate assembly for a plasma display panel includes the steps of applying a suspension to a dielectric layer covering display electrodes formed on a substrate, the suspension containing a dispersion medium and a large number of magnesium oxide crystals dispersed in the dispersion medium, and thereafter evaporating the dispersion medium to form a layer of the magnesium oxide crystals on the dielectric layer, wherein the dielectric layer has a rugged surface structure having uniformly-dispersed projections and depressions, the rugged surface structure being capable of trapping the magnesium oxide crystals.
Owner:FUJITSU HITACHI PLASMA DISPLAY LTD
Luminescence crystal particle, luminescence crystal particle composition, display panel and flat-panel display
InactiveUS20010024084A1Uniform electron-emitting propertyImprove adhesionDischarge tube luminescnet screensGas discharge electrodesDisplay deviceVolumetric Mass Density
A luminescence crystal particle which emits light upon irradiation with an energy beam and which has a crystal defect density of 5x107 defects / cm2 or less in a region located from the surface of the luminescence crystal particle to a portion as deep as the energy beam reaches.
Owner:SONY CORP
Phosphor and plasma display device
InactiveUS20050062417A1Excellent initial characteristicDeterioration in brightnessSustain/scan electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensAluminateAlkaline earth metal
Phosphor and a plasma display device are provided whose deterioration in brightness of phosphors and a degree of change in chromaticity are alleviated and whose discharge characteristics are improved and that has excellent initial characteristics. Phosphor of the present invention is an alkaline-earth metal aluminate phosphor containing an element M (where M denotes at least one type of element selected from the group consisting of Nb, Ta, W and B). In this phosphor, a concentration of M in the vicinity of a surface of the phosphor particles is higher than the average concentration of M in the phosphor particles as a whole. A plasma display device according to the present invention includes a plasma display panel in which a plurality of discharge cells in one color or in a plurality of colors are arranged and phosphor layers are arranged so as to correspond to the discharge cells in colors and in which light is emitted by exciting the phosphor layers with ultraviolet rays. The phosphor layers include blue phosphor, where the afore-mentioned phosphor is used as the blue phosphor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
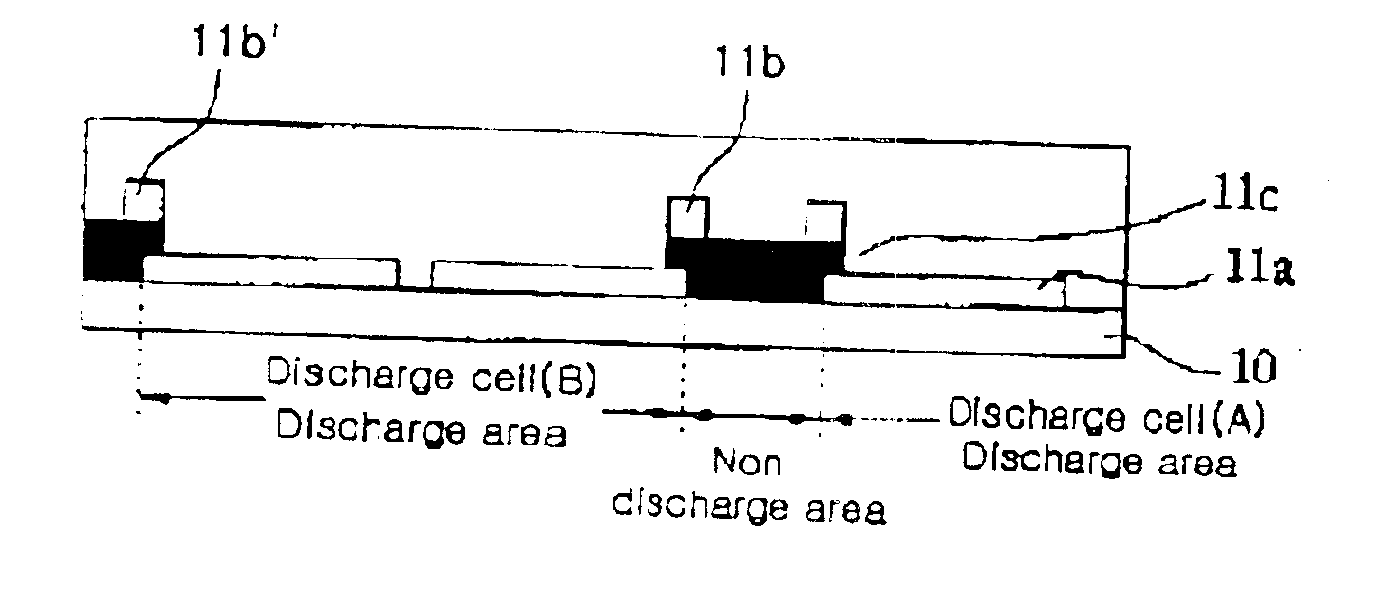
Plasma display panel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6838828B2Simple manufacturing processIncrease brightnessTube/lamp screens manufactureAddress electrodesEngineeringBrightness perception
The present invention relates to plasma display panel and manufacturing method thereof to simplify the manufacturing steps and reduce cost of production. In the present invention, a black layer formed between a transparent electrode and a bus electrode is formed together with a black matrix at the same time. In this case, the black layer is formed together with the black matrix in one. Cheap nonconductive oxide is used as a black powder of a black layer. Specifically, in case the black layer and the black matrix are formed in one, the bus electrode is shifted to a non-discharge area to improve the brightness of the plasma display panel.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Luminescence crystal particle, luminescence crystal particle composition, display panel and flat-panel display
InactiveUS6819041B2Improve adhesionImprove propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensGas discharge electrodesDisplay deviceVolumetric Mass Density
Owner:SONY CORP
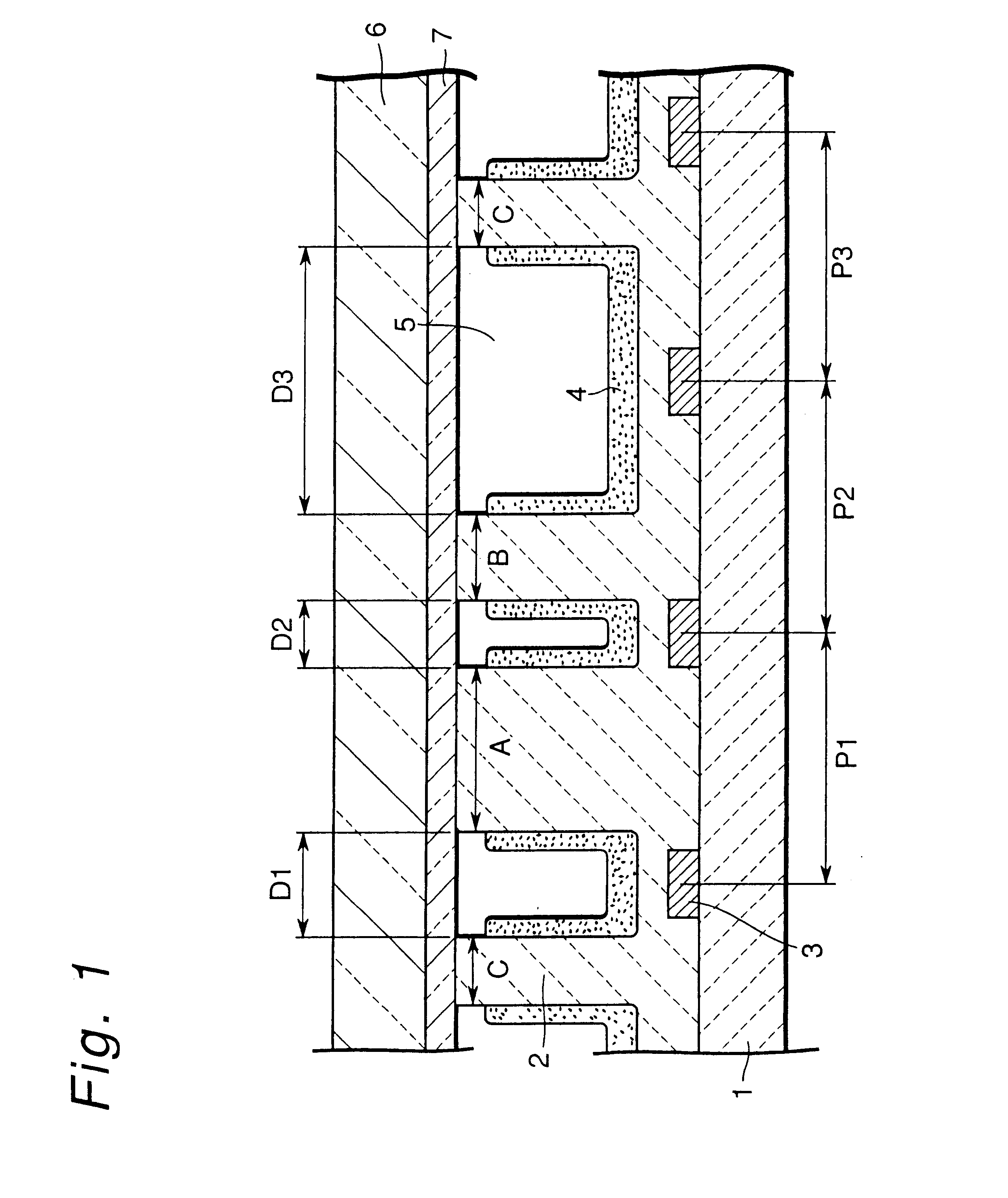
Plasma display panel
InactiveUS20050001551A1Maximize discharge efficiencyImprove efficiencyAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesPhosphorPlasma display
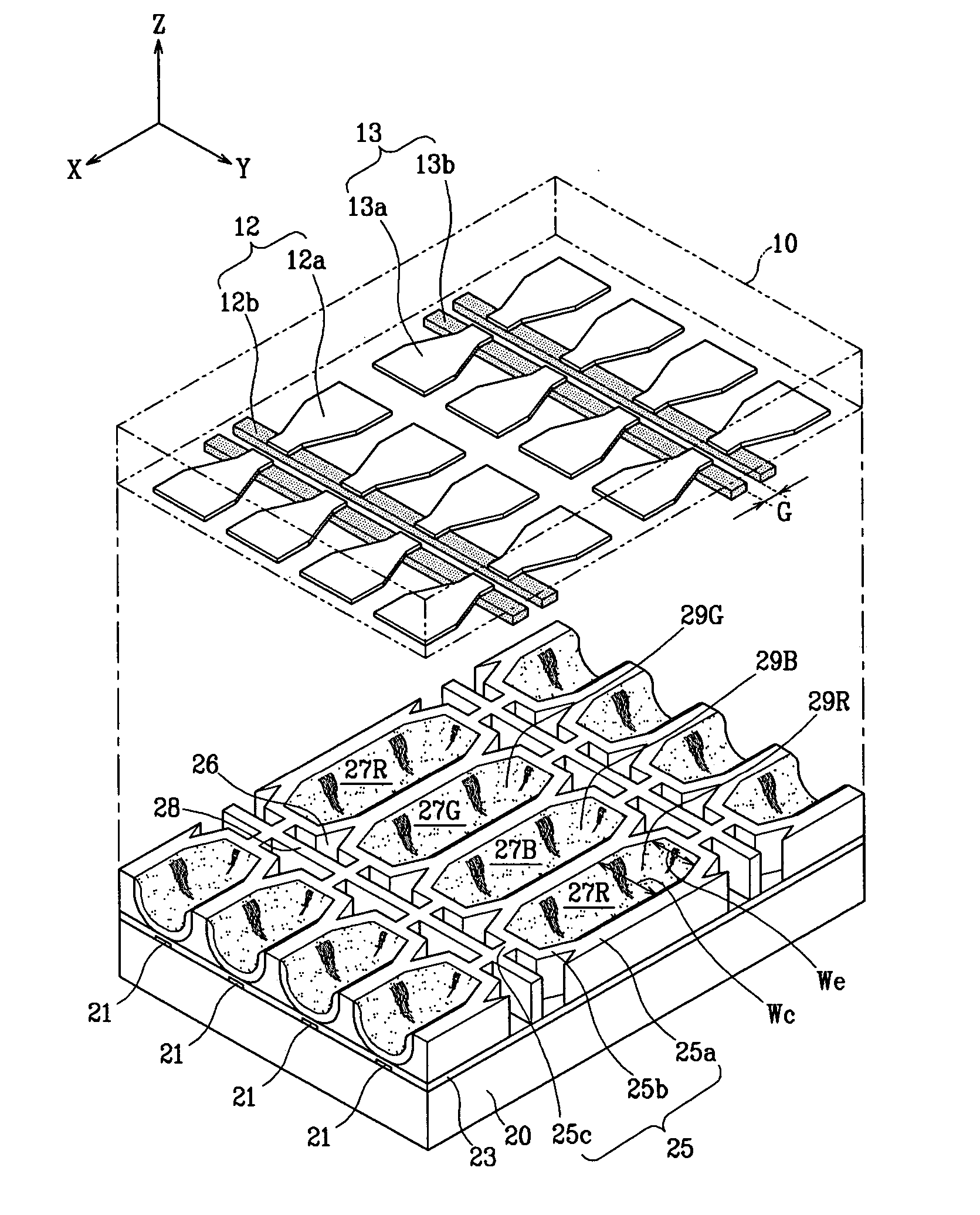
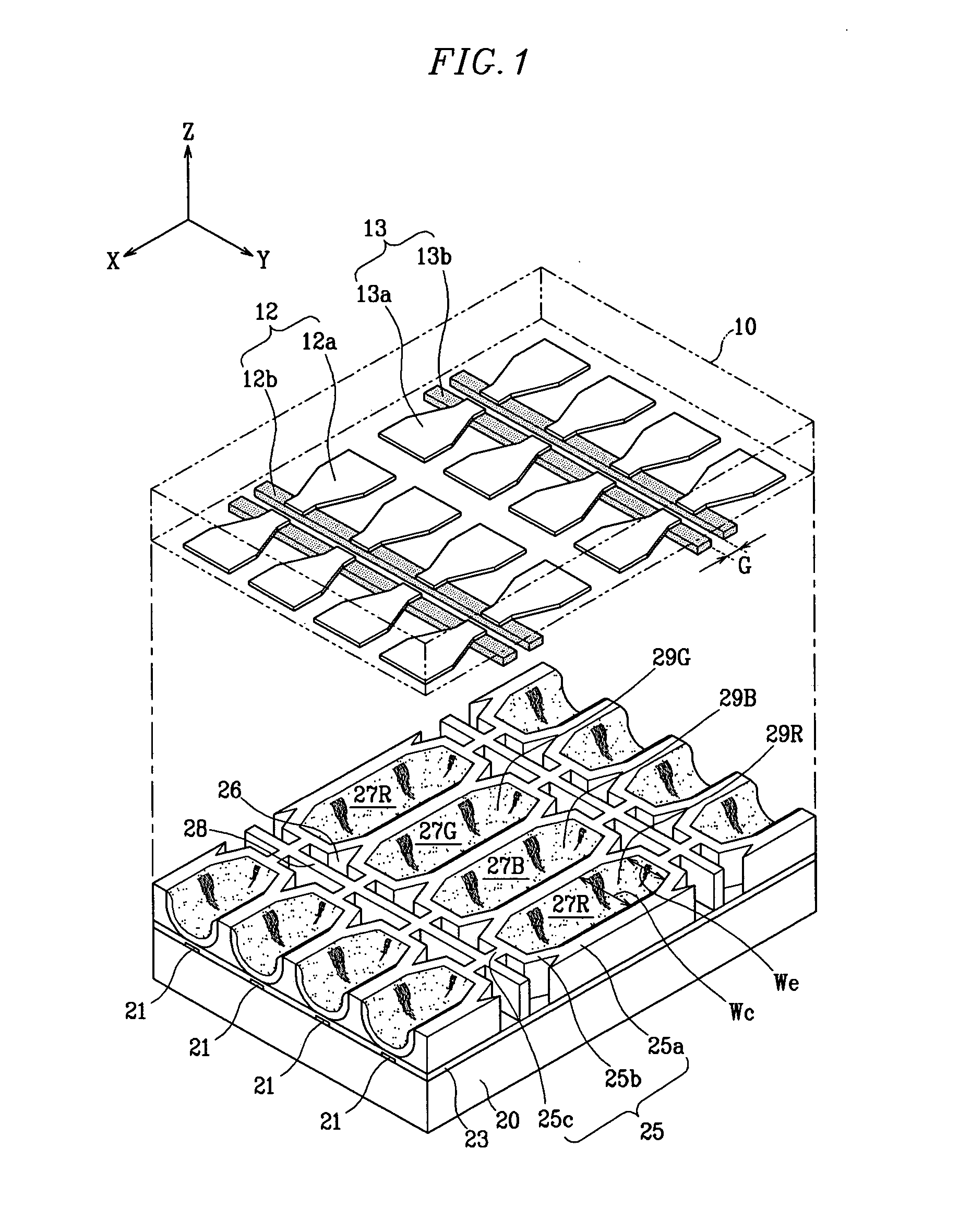
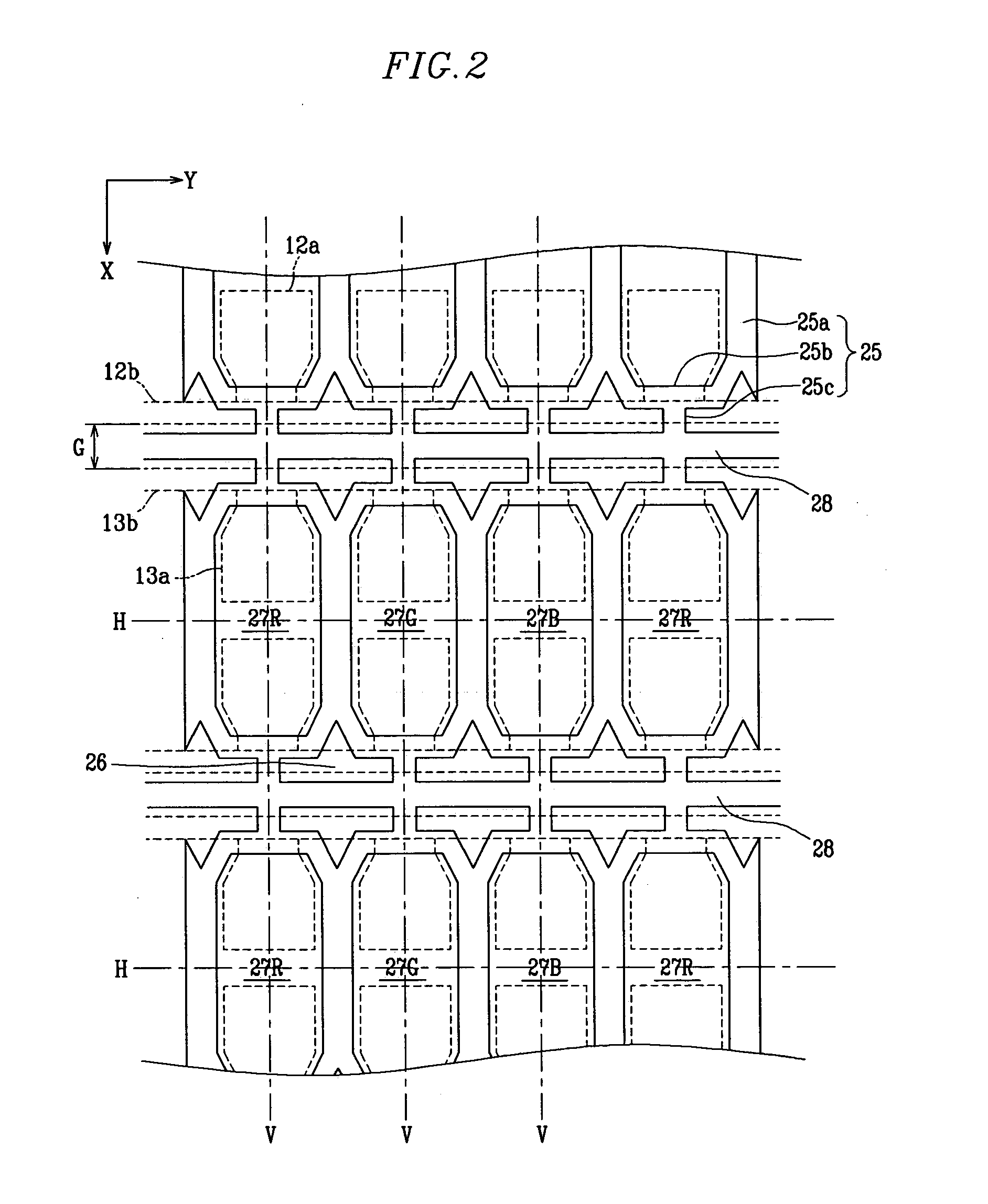
A plasma display panel. A first substrate and a second substrate are provided opposing one another with a predetermined gap therebetween. Address electrodes are formed on the second substrate. Barrier ribs are mounted between the first substrate and the second substrate, the barrier ribs defining a plurality of discharge cells and a plurality of non-discharge regions. Phosphor layers are formed within each of the discharge cells. Discharge sustain electrodes are formed on the first substrate. The non-discharge regions are formed in areas encompassed by discharge cell abscissas that pass through centers of adjacent discharge cells and discharge cell ordinates that pass through centers of adjacent discharge cells, the non-discharge regions having a width that is at least as large as a width of an end of barrier ribs. Also, a transverse barrier rib is formed extending between each pair of adjacent rows of discharge cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
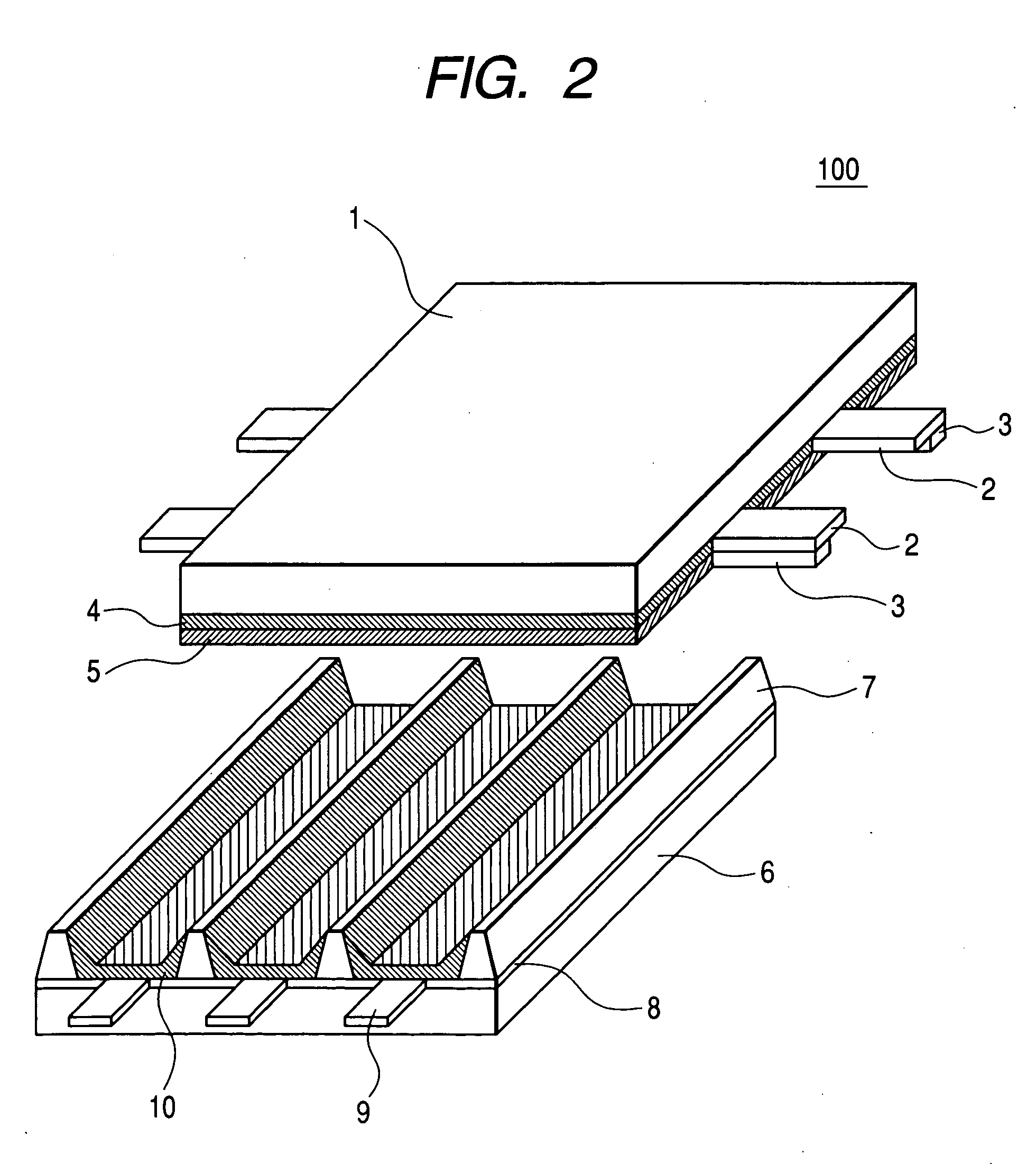
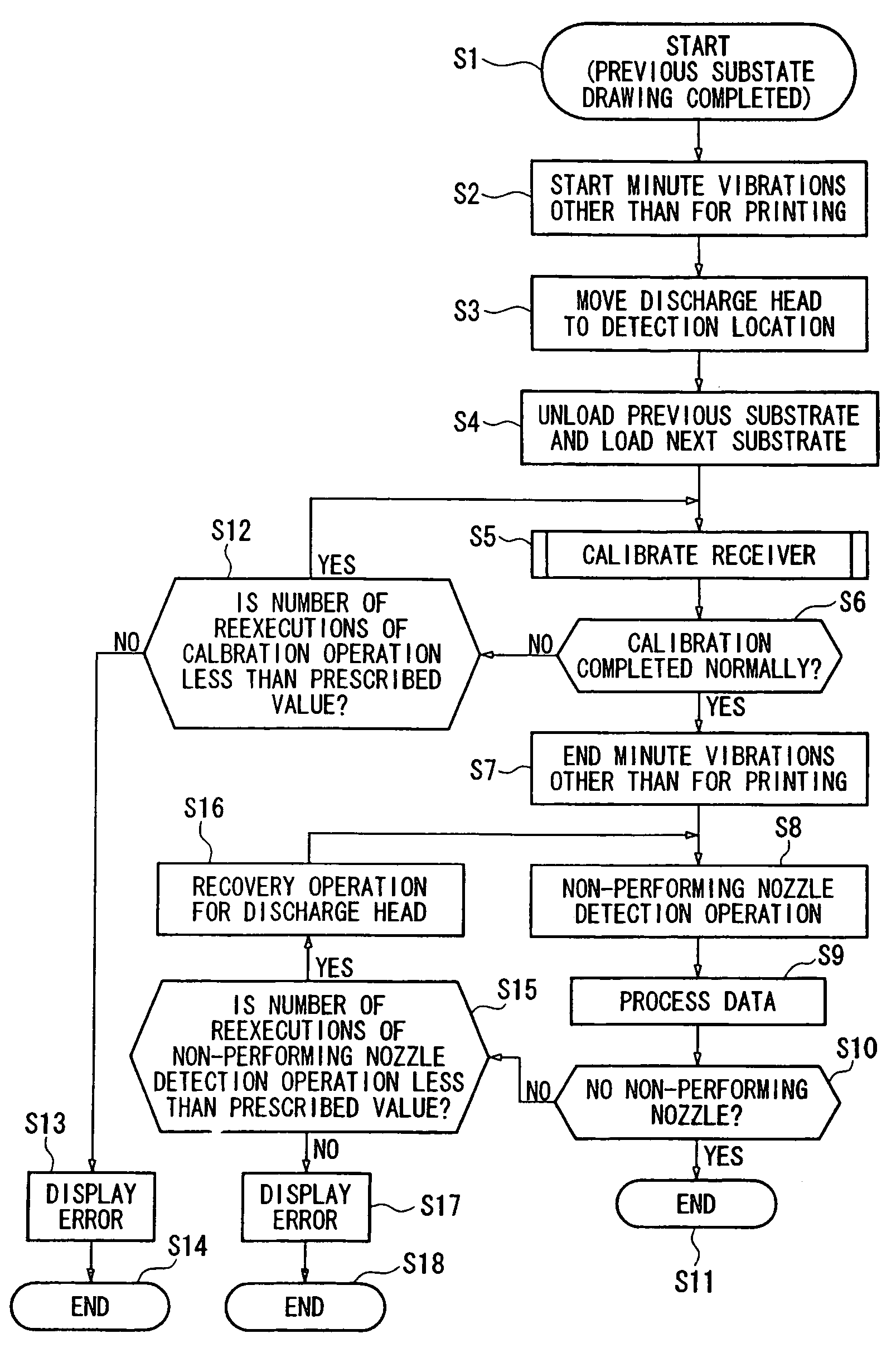
Device manufacturing apparatus, device manufacturing method, and electronic equipment
InactiveUS7461912B2Improve efficiencyLow costAddress electrodesLiquid surface applicatorsManufactured apparatusEngineering
A device manufacturing apparatus includes a discharge head discharging a droplet containing a functional material, a stage supporting a substrate on which the droplet is discharged, and which is capable of moving relative to the discharge head, a carrier carrying the substrate, a detector detecting a discharge condition of the droplet which is discharged from a discharge nozzle formed in the discharge head, and a controller executing a detection operation by the discharge device during a carrying operation of the substrate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Discharge fluorescen apparatus including fluorescent fibers
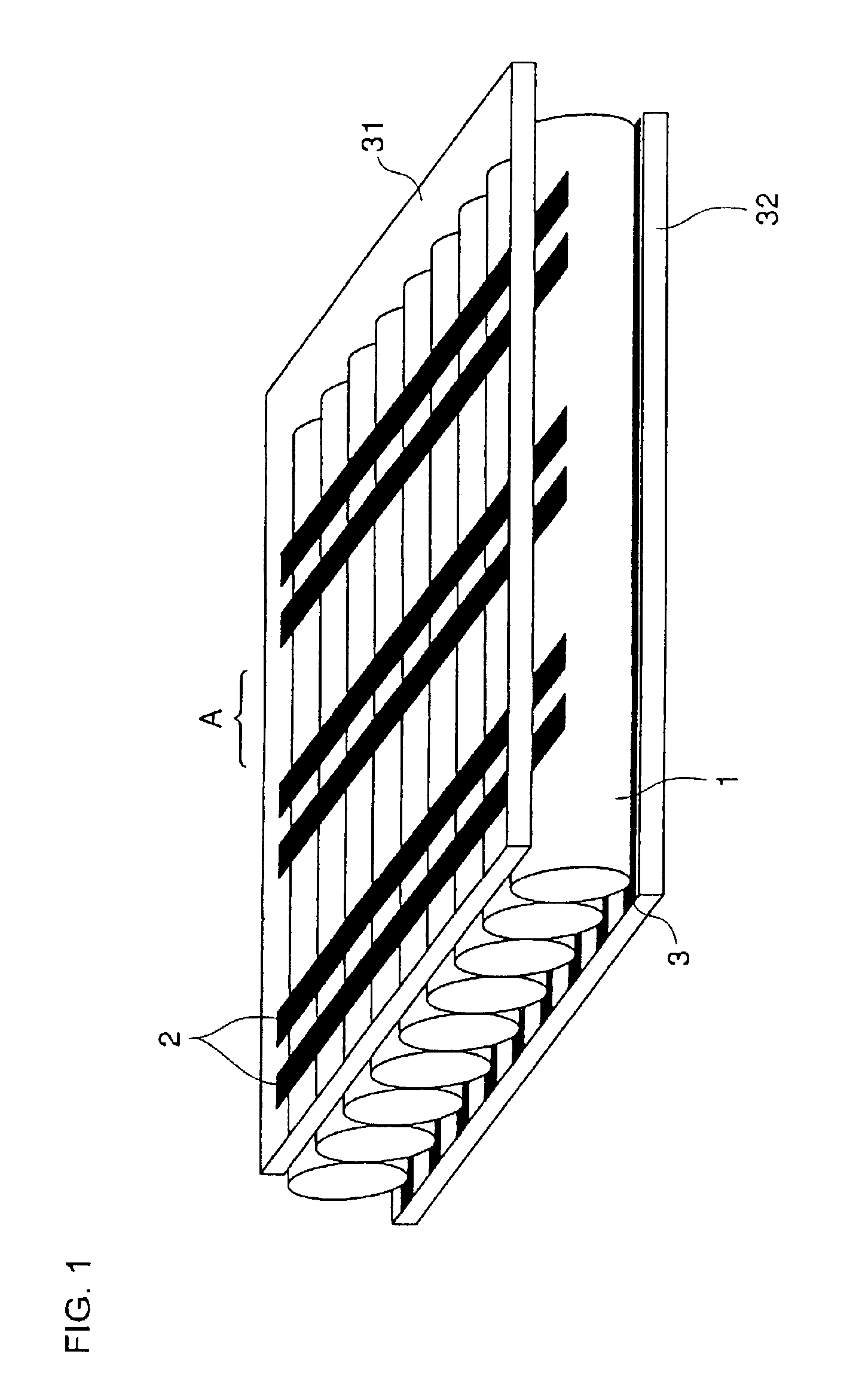
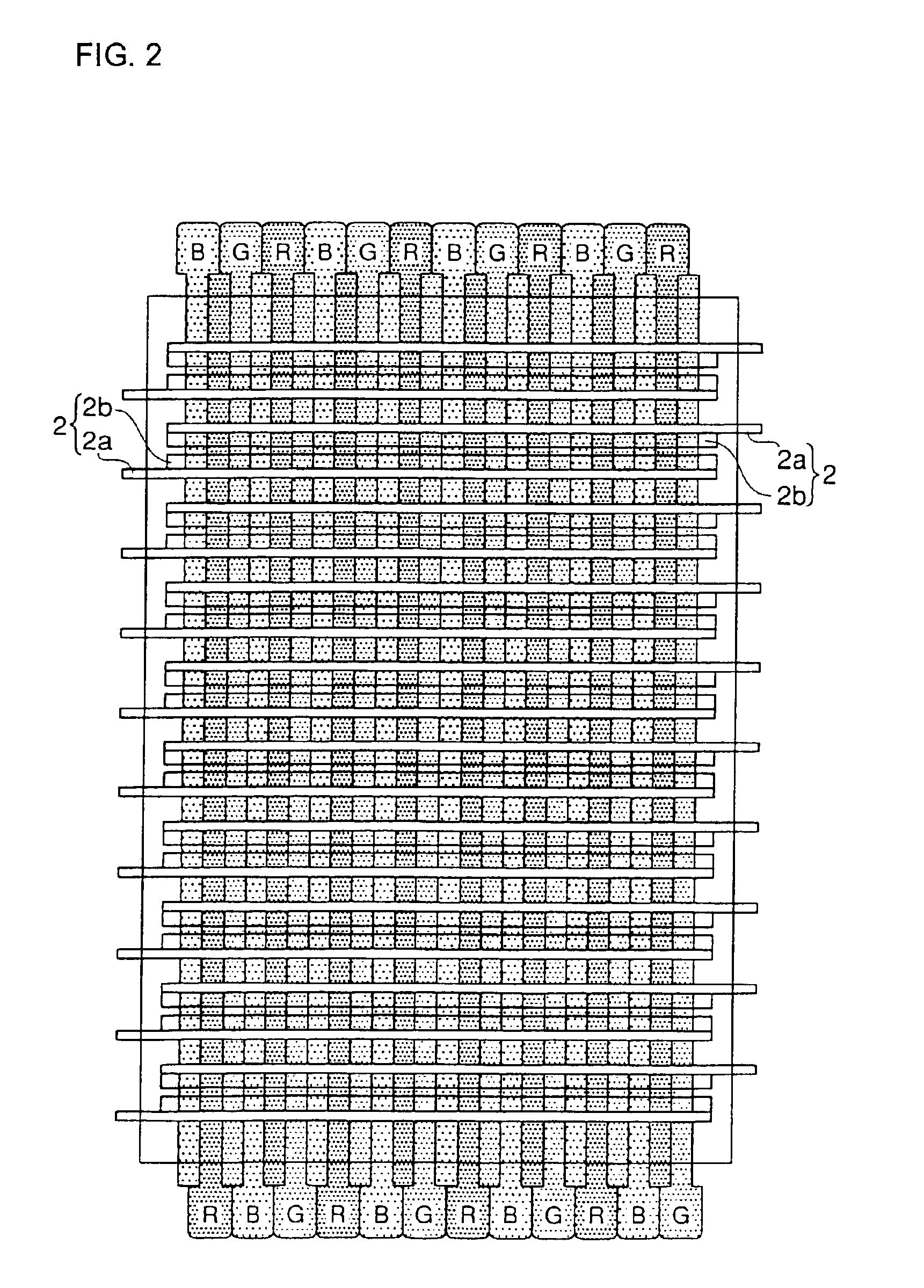
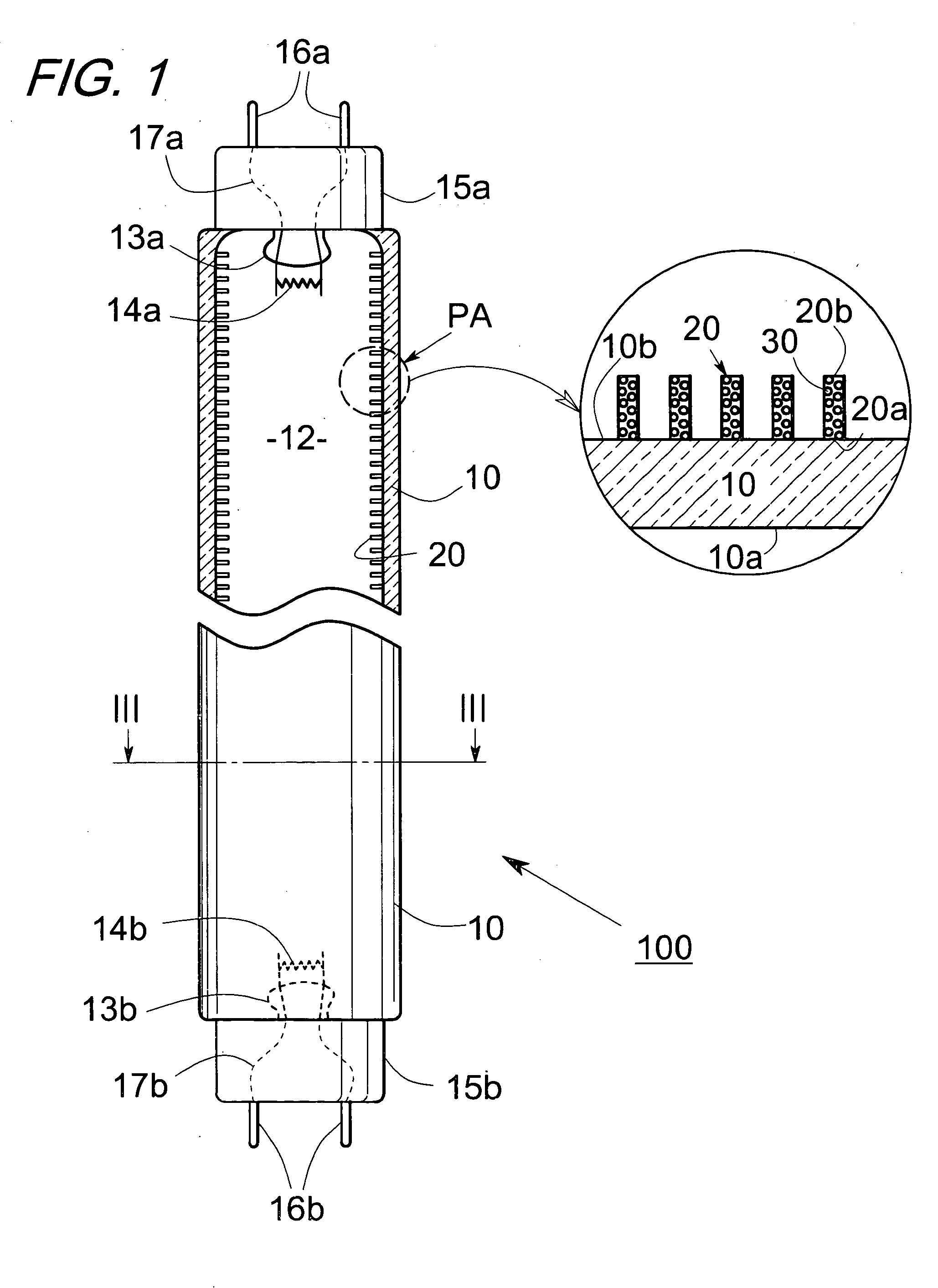
InactiveUS20060113885A1Avoid high brightnessLow luminanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsFiberPhosphor
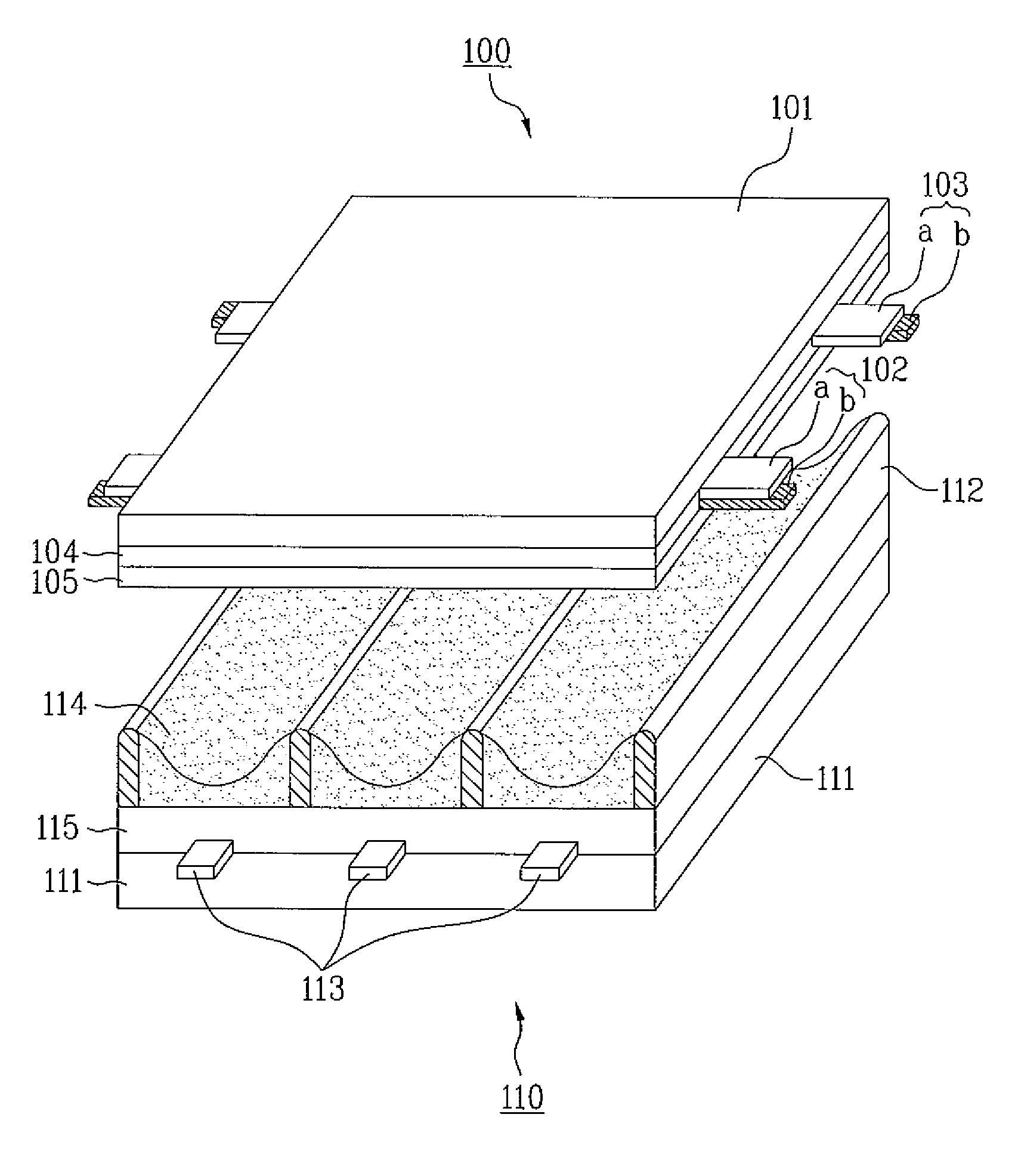
A discharge fluorescent apparatus is composed of an air-tight envelope having a discharge-space containing a dischargeable gas therein and plural fluorescent fibers having a phosphor, preferably fluorescent optical fibers, positioned in / on the envelope. Further, at least one protrusion or barrier wall preferably having the phosphor may be positioned in / on the envelope. The fluorescent fibers are positioned on the envelope and / or on the protrusion or barrier wall. The fluorescent fibers emit visible light when excited by ultraviolet rays generated from the gas. The fluorescent optical fibers each may be composed of a light-conductive core or the core and a clad, in which the core and / or the clad contain the phosphor or plural phosphor particles therein. The fluorescent fibers may be positioned on the envelope and / or on the protrusion or barrier wall by an electrostatic process. The discharge fluorescent apparatus may apply to a tubular fluorescent lamp, a flat fluorescent lamp and a plasma display panel. Therefore, the discharge fluorescent apparatus exhibits a remarkably enhanced luminance, because it has a massive surface area in / on the fluorescent fibers, the protrusion and / or the barrier wall that may contain the phosphor.
Owner:IIMURA KEIJI
Plasma display panel and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20070096653A1Lower firing voltageIncrease contrastAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesEngineeringDielectric layer
Disclosed is a plasma display panel with improved discharge characteristics. The plasma display panel comprises an upper panel and a lower panel integrally joined to the upper panel through barrier ribs wherein the upper panel includes a dielectric layer, a first protective film formed on one surface of the dielectric layer and composed of magnesium oxide, and a second protective film formed on the first protective film and composed of crystalline magnesium oxide.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
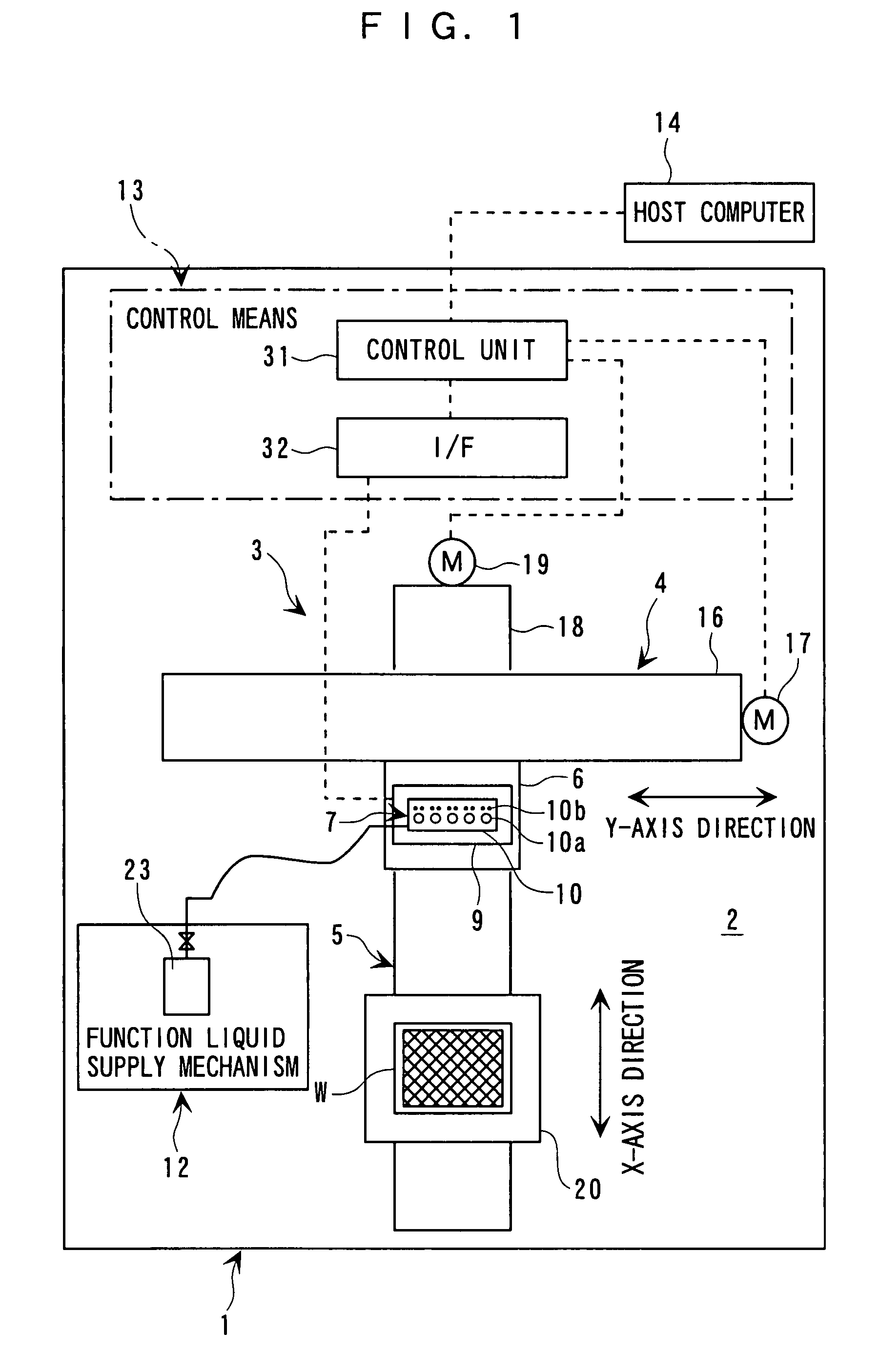
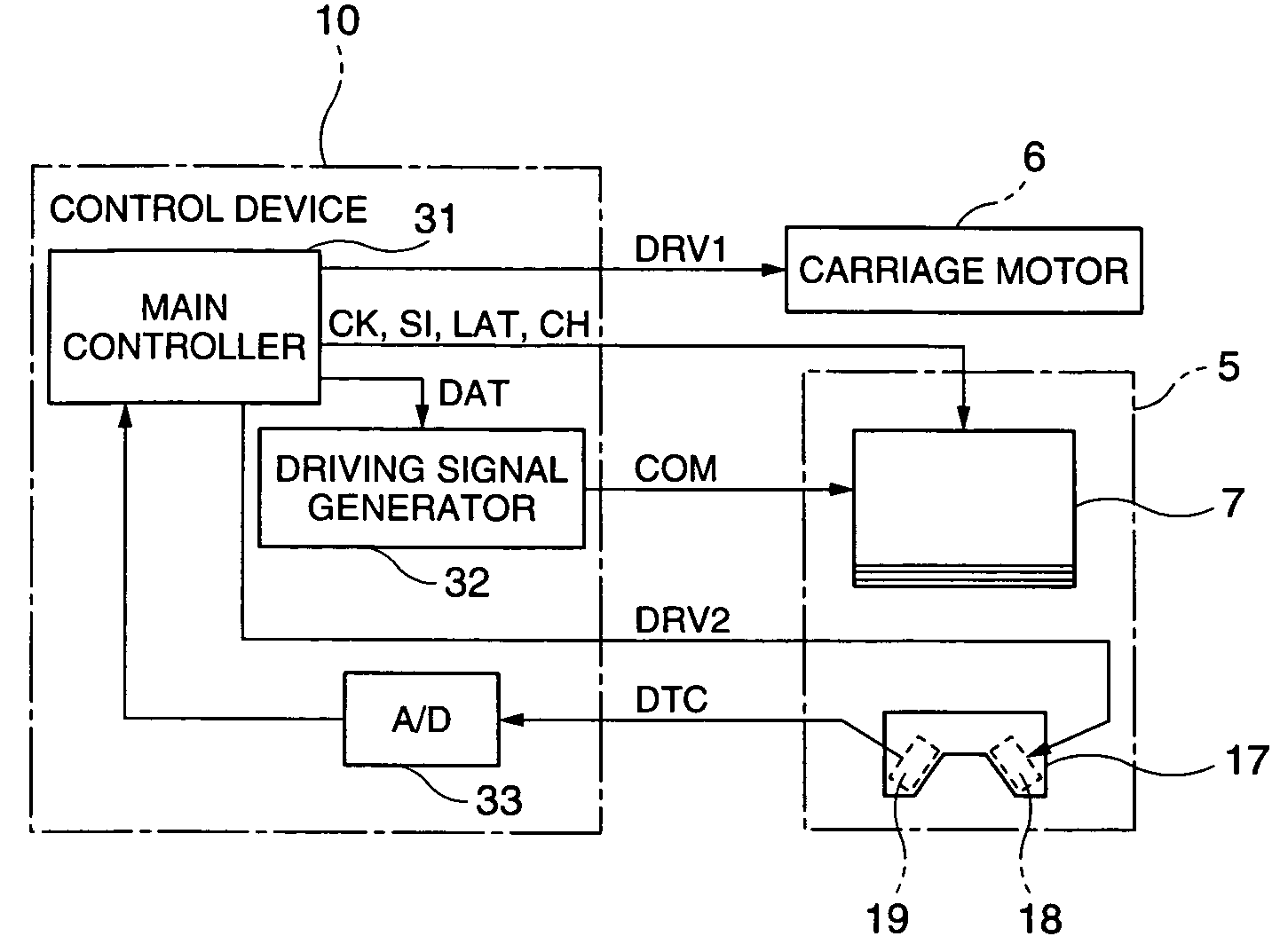
Display manufacturing apparatus and display manufacturing method
ActiveUS20040051817A1Simple configurationImprove precision controlAddress electrodesLiquid surface applicatorsManufactured apparatusDisplay device
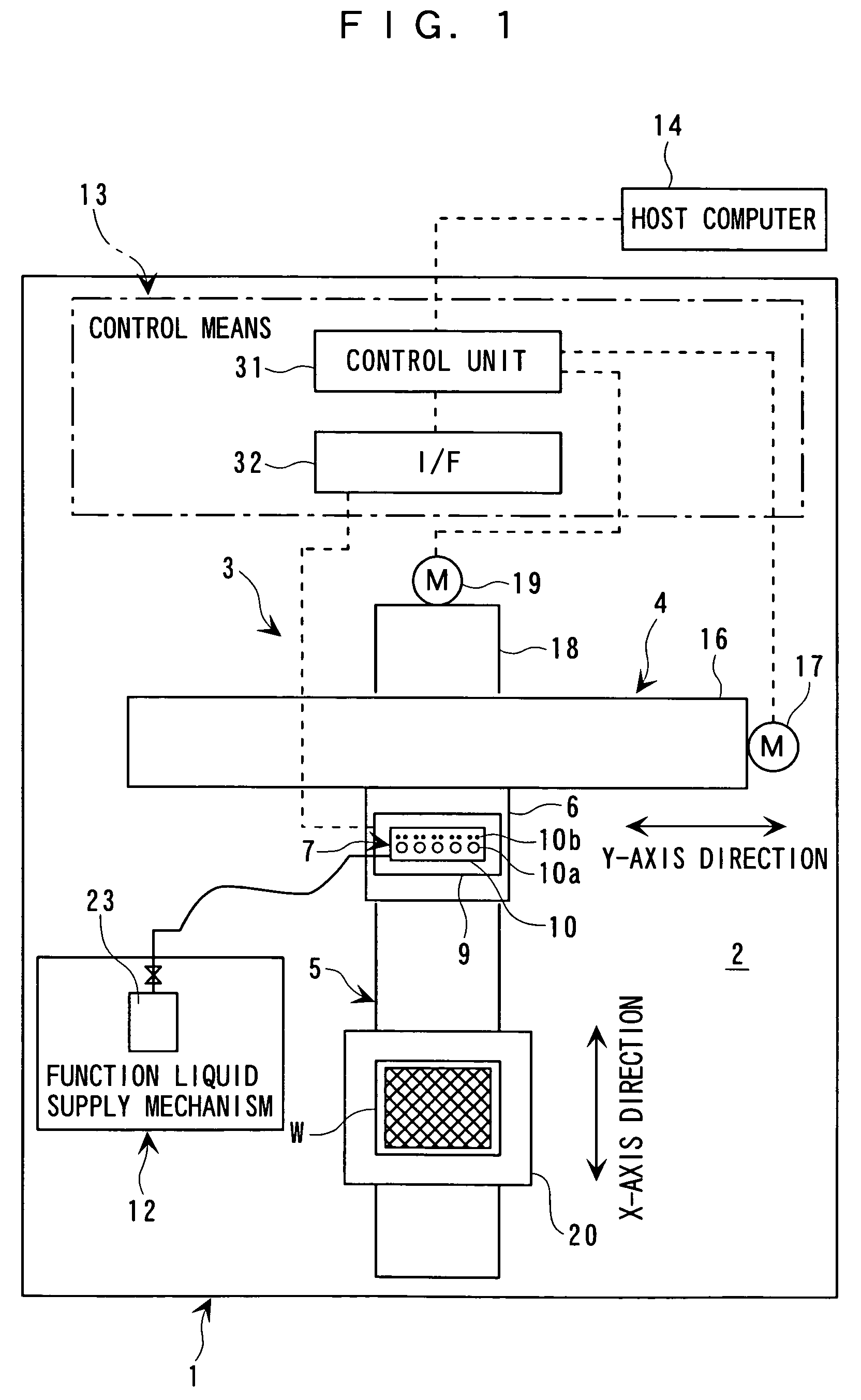
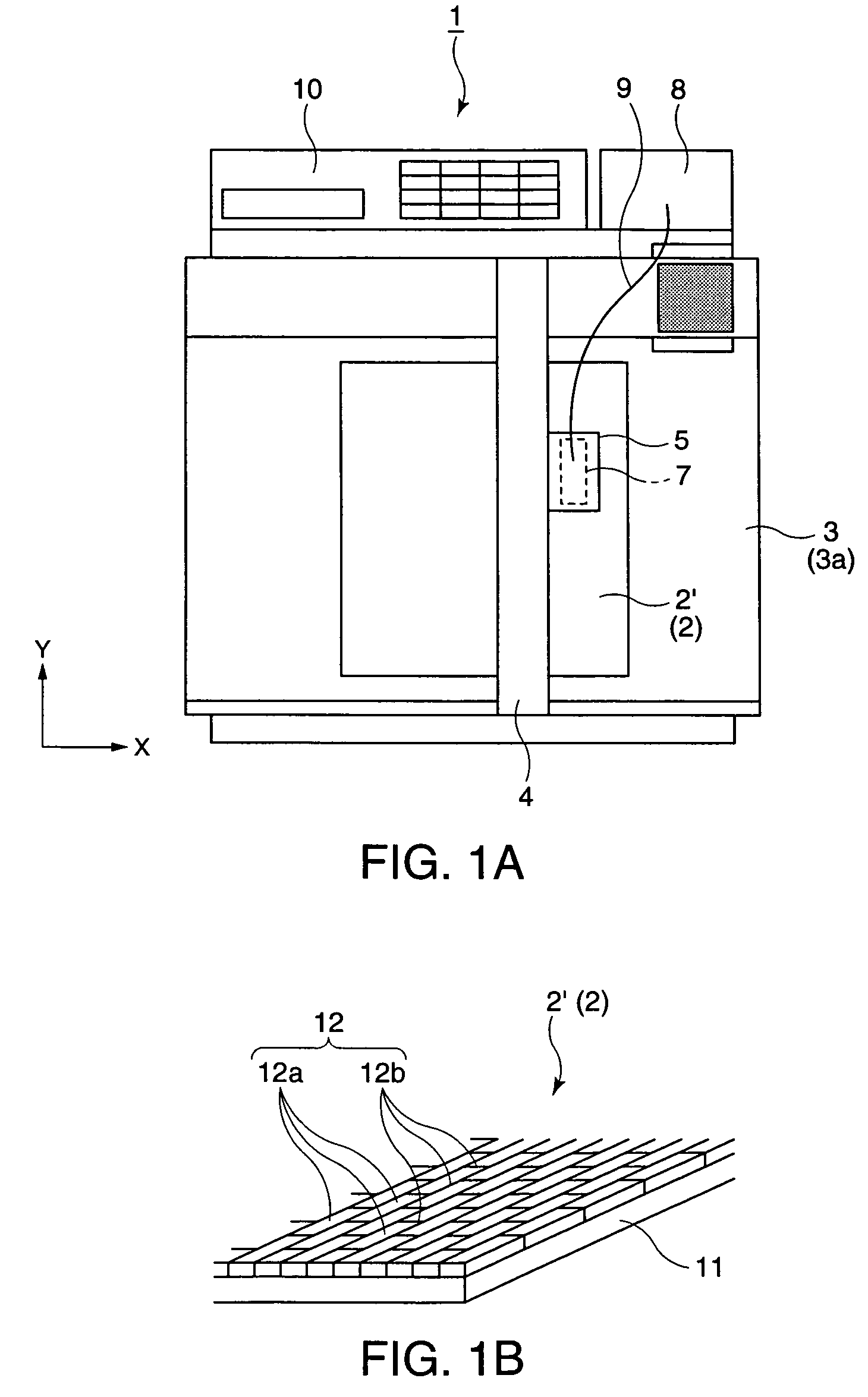
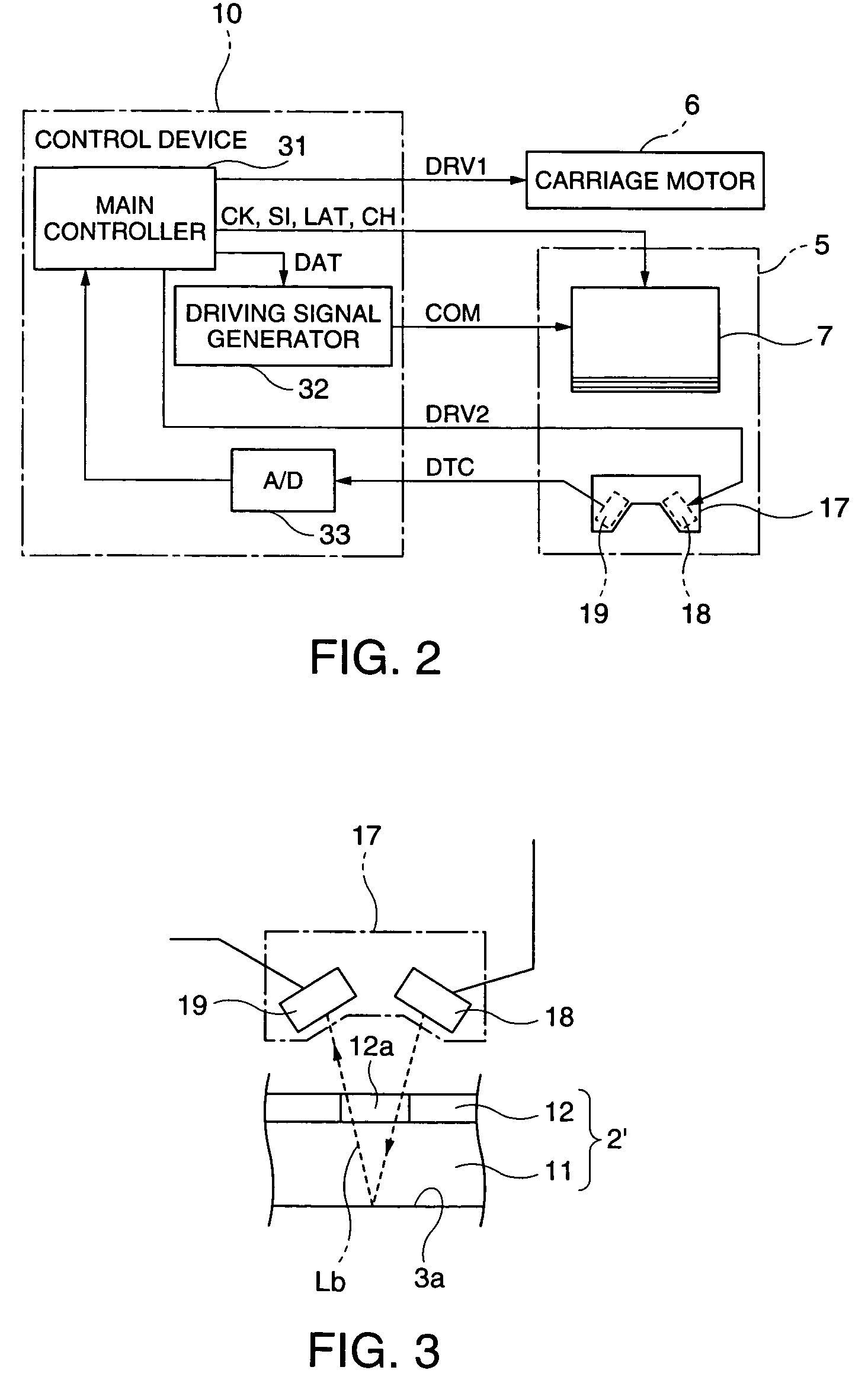
A carriage 5 is provided with an injection head 7 to discharge an amount of liquid drops according to the supplied driving pulses and a liquid material sensor 17 to detect the ink amount hit at a filter substrate at each pixel region. A main controller 31 determines a waveform of the driving pulses capable of discharging the short amount of liquid drops according to a level of a detection signal from the liquid material sensor 17 and outputs the determined information on the waveform of the driving pulses to driving signal generator 32. The driving signal generator 32 generates driving pulses according to the received information on the waveform and outputs it to the injection head 7. The injection head 7 adjusts an ink amount at the corresponding pixel region to the target amount of liquid material by injecting the short amount of liquid drops to the corresponding pixel region.
Owner:KATEEVA
Method of making plasma display panel with dielectric layer suppressing reduced electrode conductivity
InactiveUS6296539B1Drop in conductivitySuppresses resistance riseAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesIndiumIndium tin oxide
The present invention relates to a plasma display panel comprising transparent electrodes and a dielectric layer covering said transparent electrodes on at least one substrate of a pair of substrates facing each other with a discharge space therebetween, the main constituent of the transparent electrodes is included in the dielectric layer. Further, the main constituent of the transparent electrode is indium oxide and indium oxide is included in the dielectric layer. By including the main constituent of the transparent electrodes in the dielectric layer, it is believed that the drop in conductivity caused by diffusion of the dielectric substance in the transparent electrodes during high-temperature processing is prevented.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Method of controlling drive of function liquid droplet ejection head; function liquid droplet ejection apparatus; electro-optic device; method of manufacturing LCD device, organic EL device, electron emission device, PDP device, electrophoretic display device, color filter, organic EL; method of forming spacer, metallic wiring, lens, resist, and light diffusion body
ActiveUS7850267B2Easy to controlReduce throughputInking apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsDisplay deviceElectron
In a method of controlling drive of a function liquid droplet ejection head in which a plurality of nozzle arrays are arranged, the nozzle arrays have function liquid droplet ejection amounts which are different from each other per unit nozzle. The drive of the plurality of nozzle arrays is controlled by using a single drive signal having a plurality of ejection pulses corresponding to the plurality of nozzle arrays in one print cycle. Thus, even if a plurality of nozzle arrays having function liquid droplet ejection amounts which are different from each other per unit nozzle are disposed in one function liquid droplet ejection head, easy drive control is possible without lowering printing throughput.
Owner:KATEEVA
Plasma display panel and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20070152593A1Improved secondary electron emission characteristicReduce ignition voltageAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesEngineeringSecondary electrons
A plasma display panel with low firing voltage is disclosed. The plasma display panel includes an upper panel and a lower panel facing each other through barrier ribs wherein the upper panel includes a first protective film composed of magnesium oxide and a second protective film formed on the first protective film and composed of a secondary electron-emitting material.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
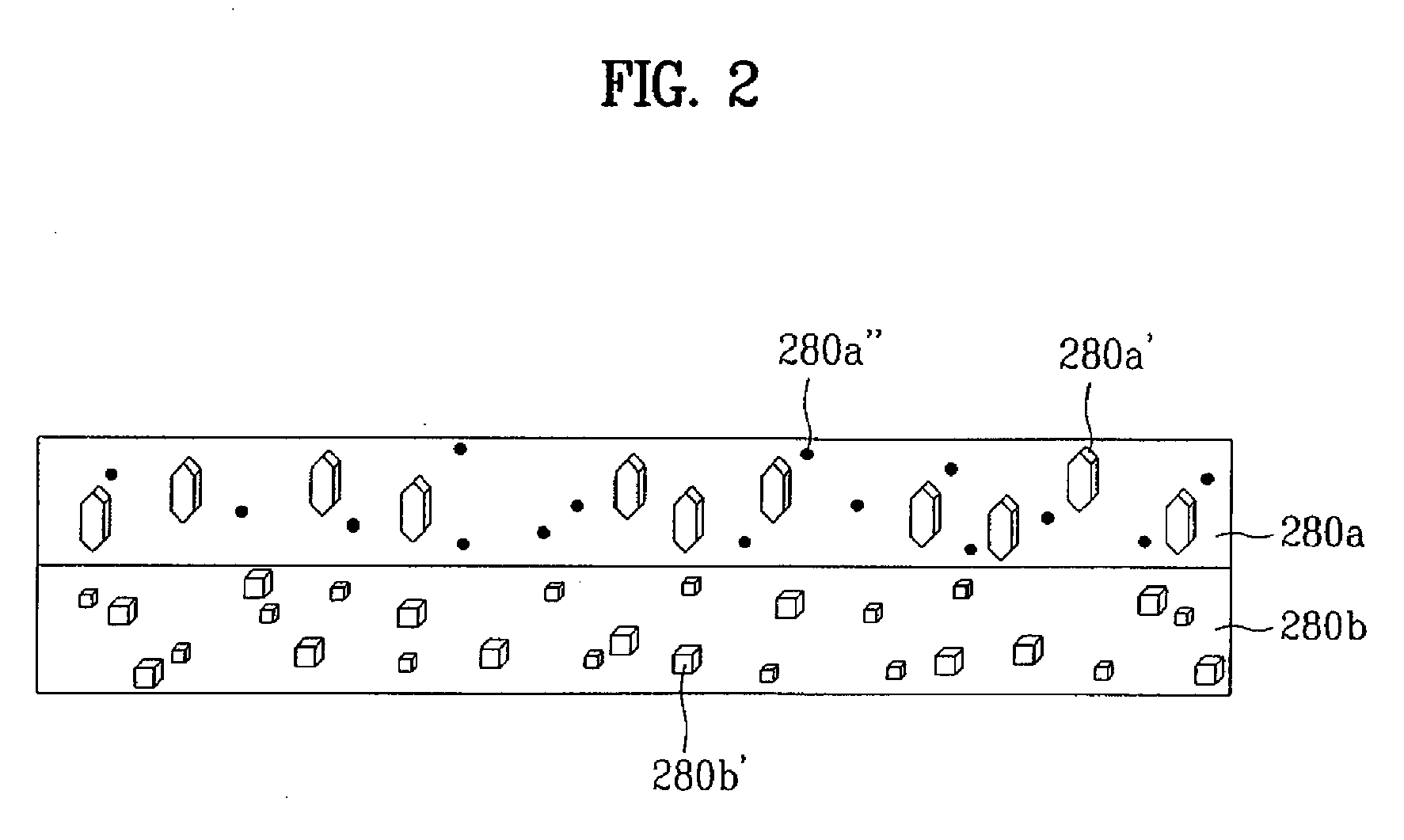
Phosphor for a plasma display device coated with a continuous thin protective layer and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20020039665A1Conductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialOrganic solventPhosphor
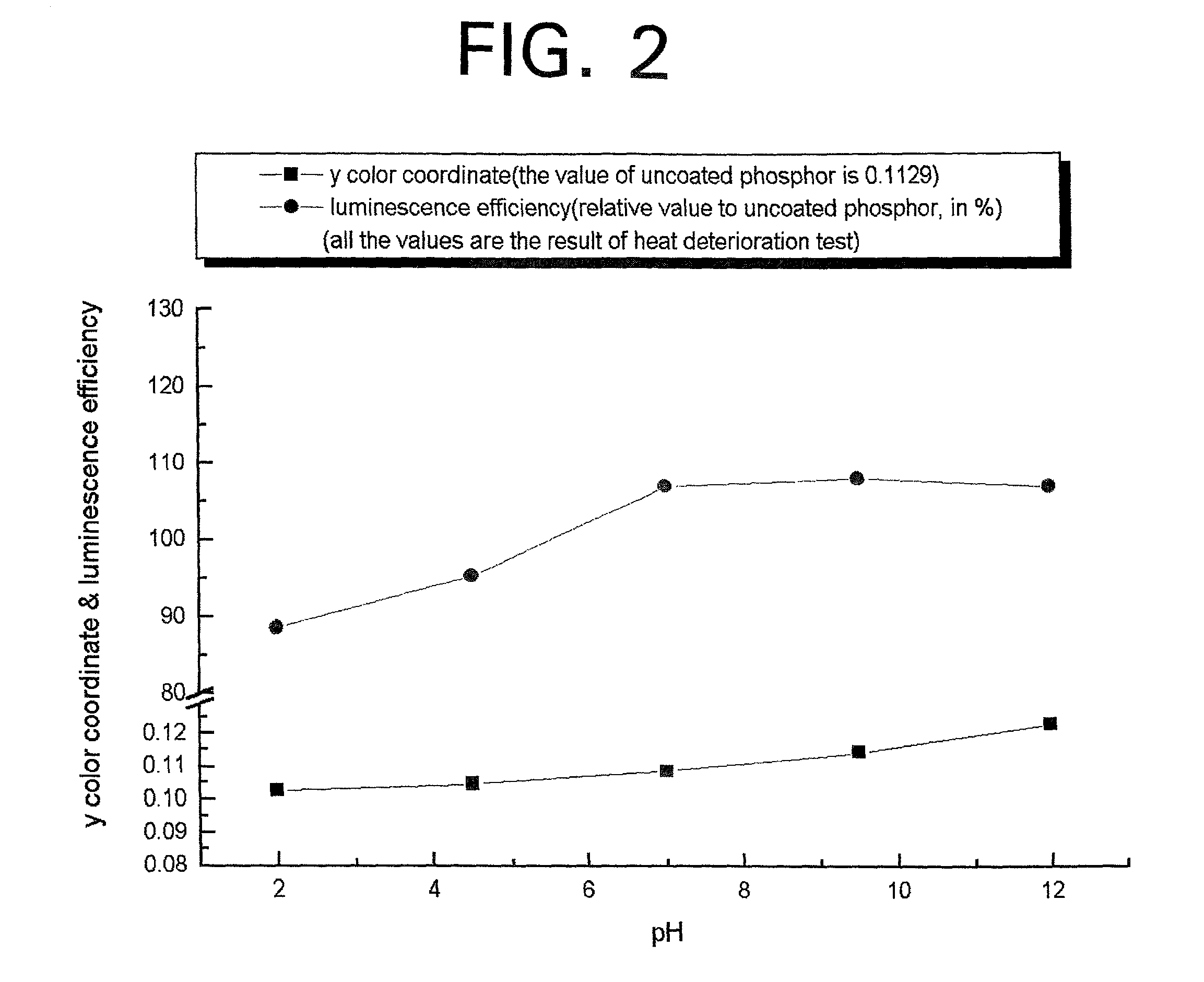
Phosphor coated with wide bandgap metal oxide which can be used for a plasma display panel (PDP) has a surface that is coated with a continuous, thin film of wide bandgap metal oxide. In preparing the phosphor coated with wide bandgap metal oxide, a pH of the wide bandgap metal oxide precursor solution containing an organic solvent and water is adjusted to 0.1-10 and heated under a reflux, thereby obtaining a metal hydroxide gel. The wide bandgap metal hydroxide gel is made to contact a phosphor for a PDP, thereby obtaining the gel-coated phosphor. The gel-coated phosphor is then dried and sintered.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
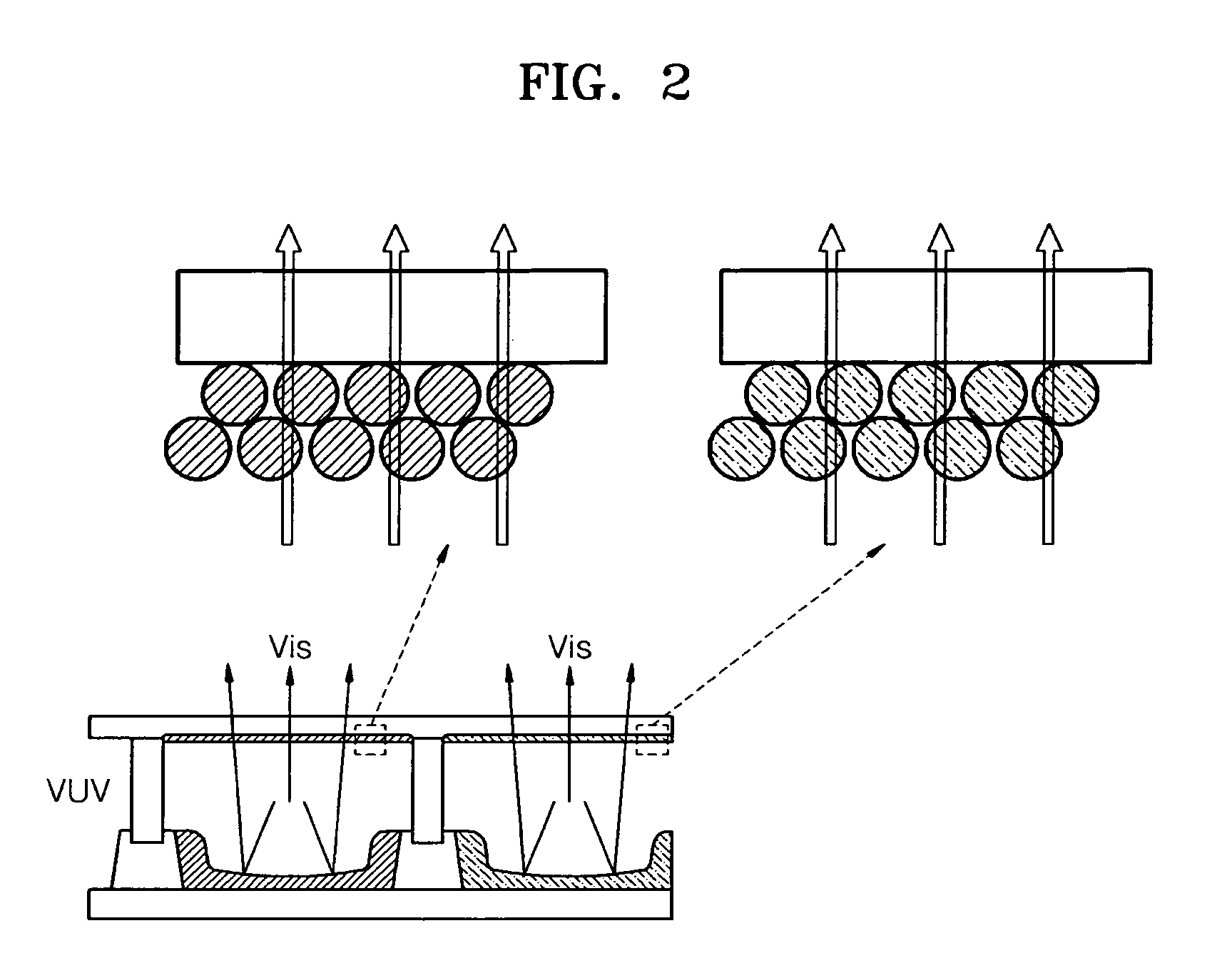
Metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer, applications thereof, and method of preparing a metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer
InactiveUS20090009059A1Excellent phosphor layer propertyMaintain good propertiesNanostructure manufactureDischarge tube luminescnet screensFluorescenceUltraviolet
A metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer, in which the metallic compound is metallic oxide or metallic sulfide. The metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer is prepared in consideration of physical, mechanical, and chemical stabilities. The metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer has an excellent light scattering effect and high durability against damage from ion-bombardment. In addition, the charging effect caused by V-UV vacuum-ultraviolet ray can be considerably reduced. Thus, the metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer is very suitable for various display devices having high efficiency and high resolution. Accordingly, a display device using the metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer shows high performance and long lifetime. The method of forming the metallic compound hybridized nanophosphor layer is a low temperature layer forming process through which a thin film-type layer can be formed at low temperature. Therefore, a phosphor layer having physical, mechanical, and chemical stabilities can be formed at low cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
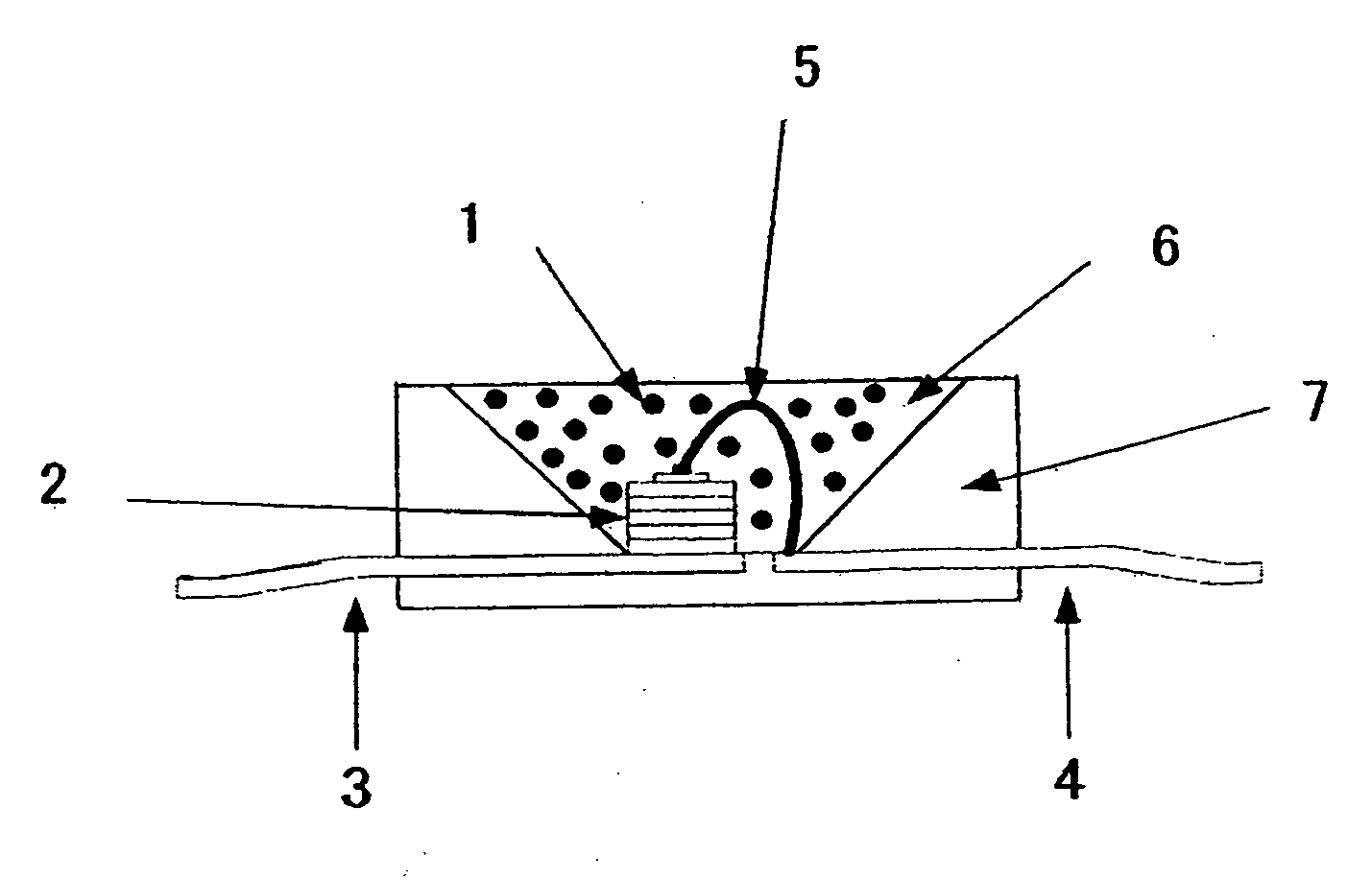
Plasma display device
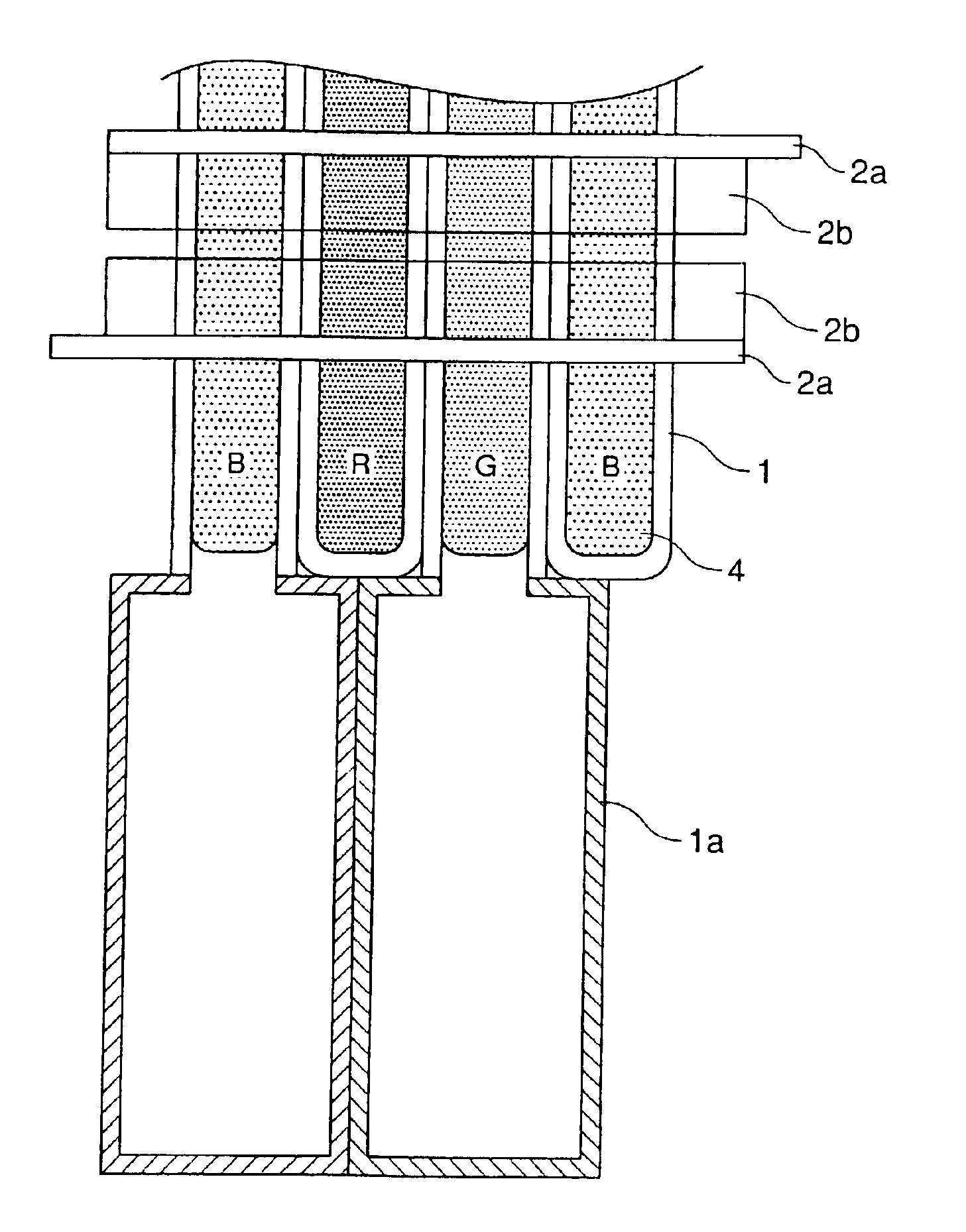
InactiveUS6498430B1Equal levels of luminance with different colorsAvoid excessive deviationVacuum tubesAddress electrodesFluorescenceImaging quality
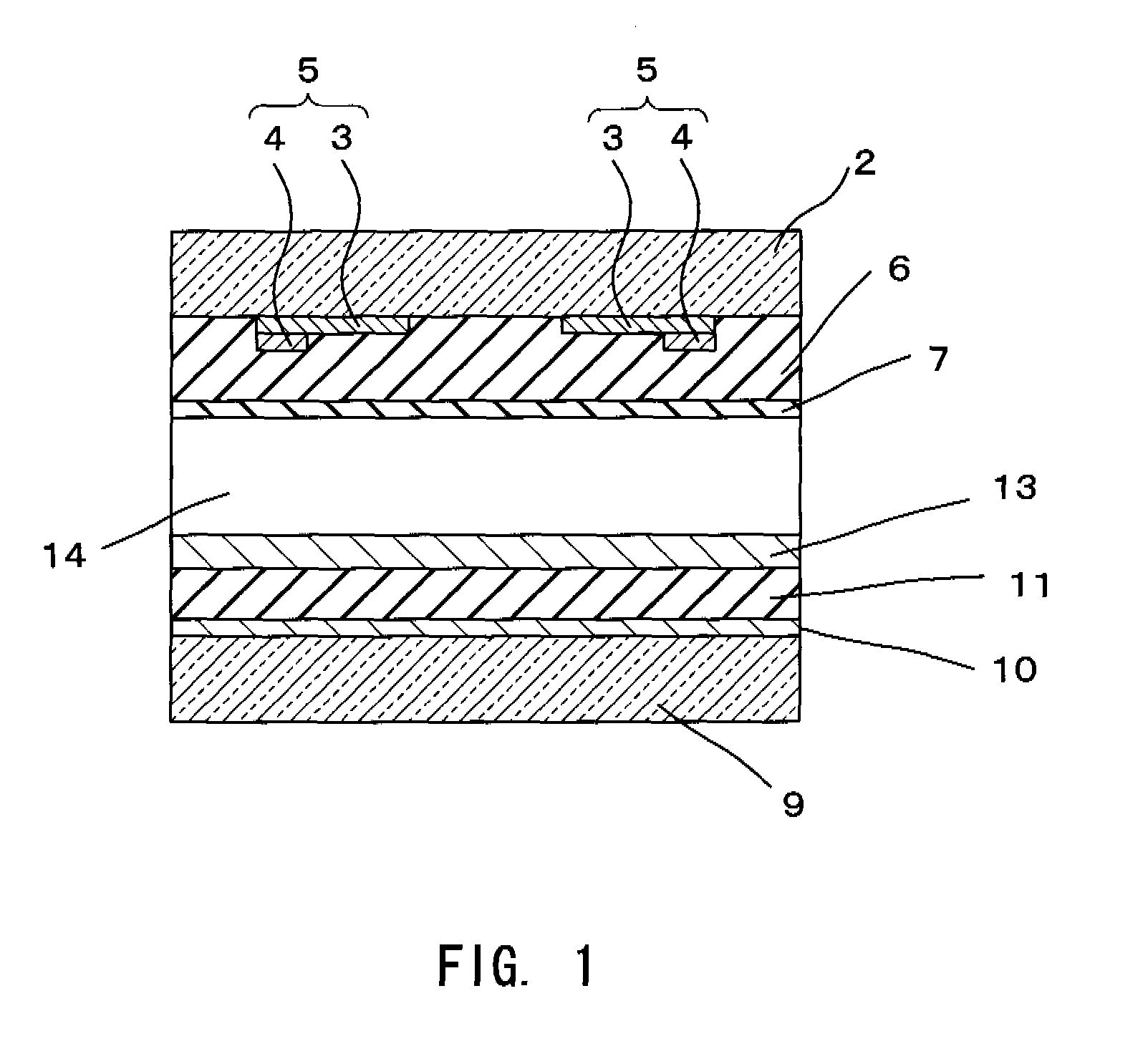
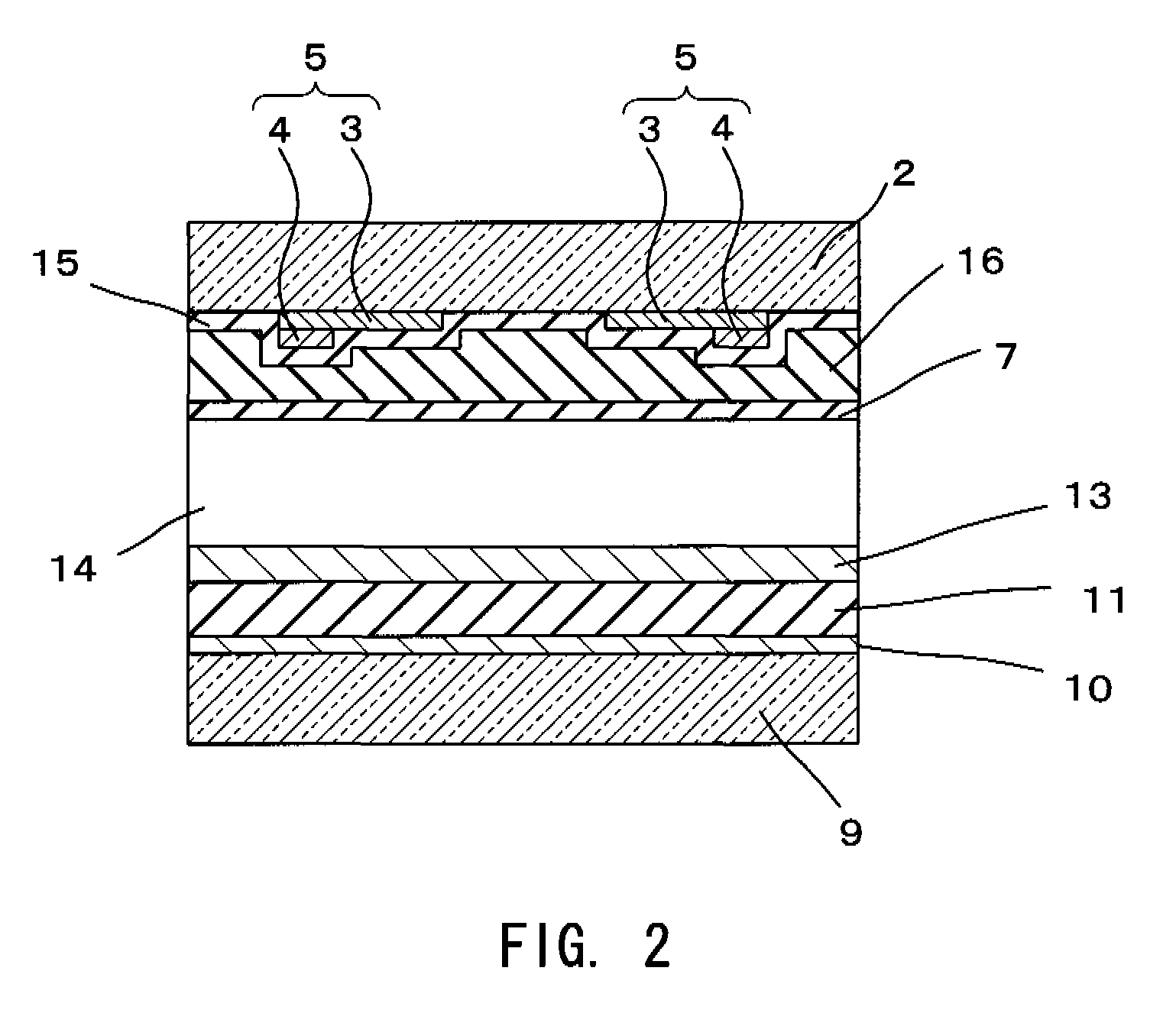
In a plasma display device comprising a pair of opposing insulating substrates and a plurality of light emitting cells 5 formed from partition walls which divide the space between the insulating substrates while a plurality of electrodes are formed in the light emitting cells 5 and the inner space is filled with a discharge gas and plasma being generated by applying a voltage selectively between the electrodes so that the fluorescent substances 4 formed on the inner walls of the light emitting cells emit light as light emitting elements, wherein sizes of the light emitting cells 5 of different colors are made different according to the luminance of the fluorescent substance of the corresponding color. That is, cells which emit light of a color of luminance lower than the other cells are made with larger opening to obtain equally high luminance for all the three primary colors, thereby mitigating the deviation in the luminance among the fluorescent substances and achieving full-color display of high image quality with high color purity.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Display manufacturing apparatus and display manufacturing method
ActiveUS7223309B2Simple configurationImprove precision controlAddress electrodesInking apparatusDisplay deviceManufactured apparatus
A carriage 5 is provided with an injection head 7 to discharge an amount of liquid drops according to the supplied driving pulses and a liquid material sensor 17 to detect the ink amount hit at a filter substrate at each pixel region. A main controller 31 determines a waveform of the driving pulses capable of discharging the short amount of liquid drops according to a level of a detection signal from the liquid material sensor 17 and outputs the determined information on the waveform of the driving pulses to driving signal generator 32. The driving signal generator 32 generates driving pulses according to the received information on the waveform and outputs it to the injection head 7. The injection head 7 adjusts an ink amount at the corresponding pixel region to the target amount of liquid material by injecting the short amount of liquid drops to the corresponding pixel region.
Owner:KATEEVA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com