Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Septal formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
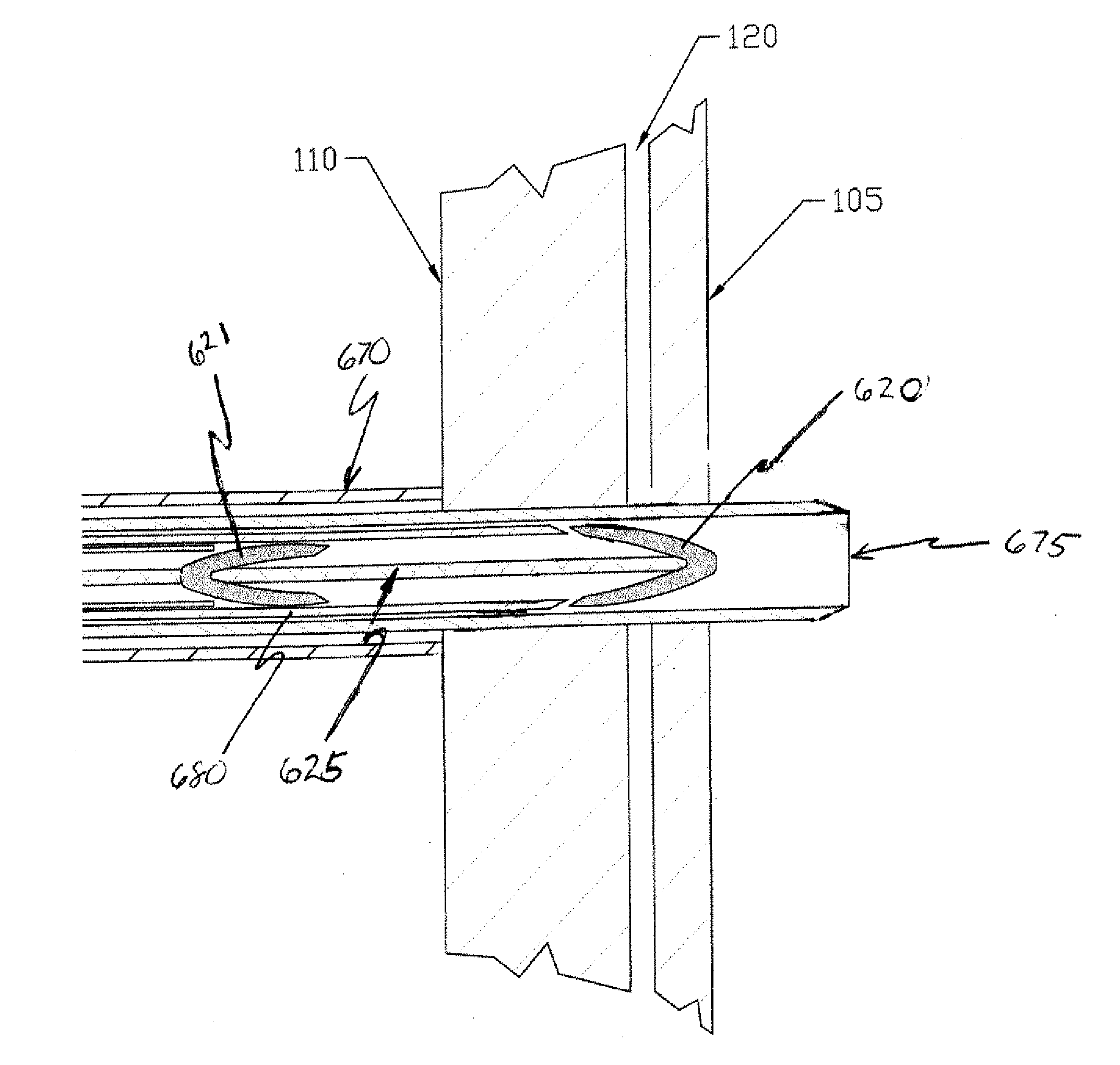
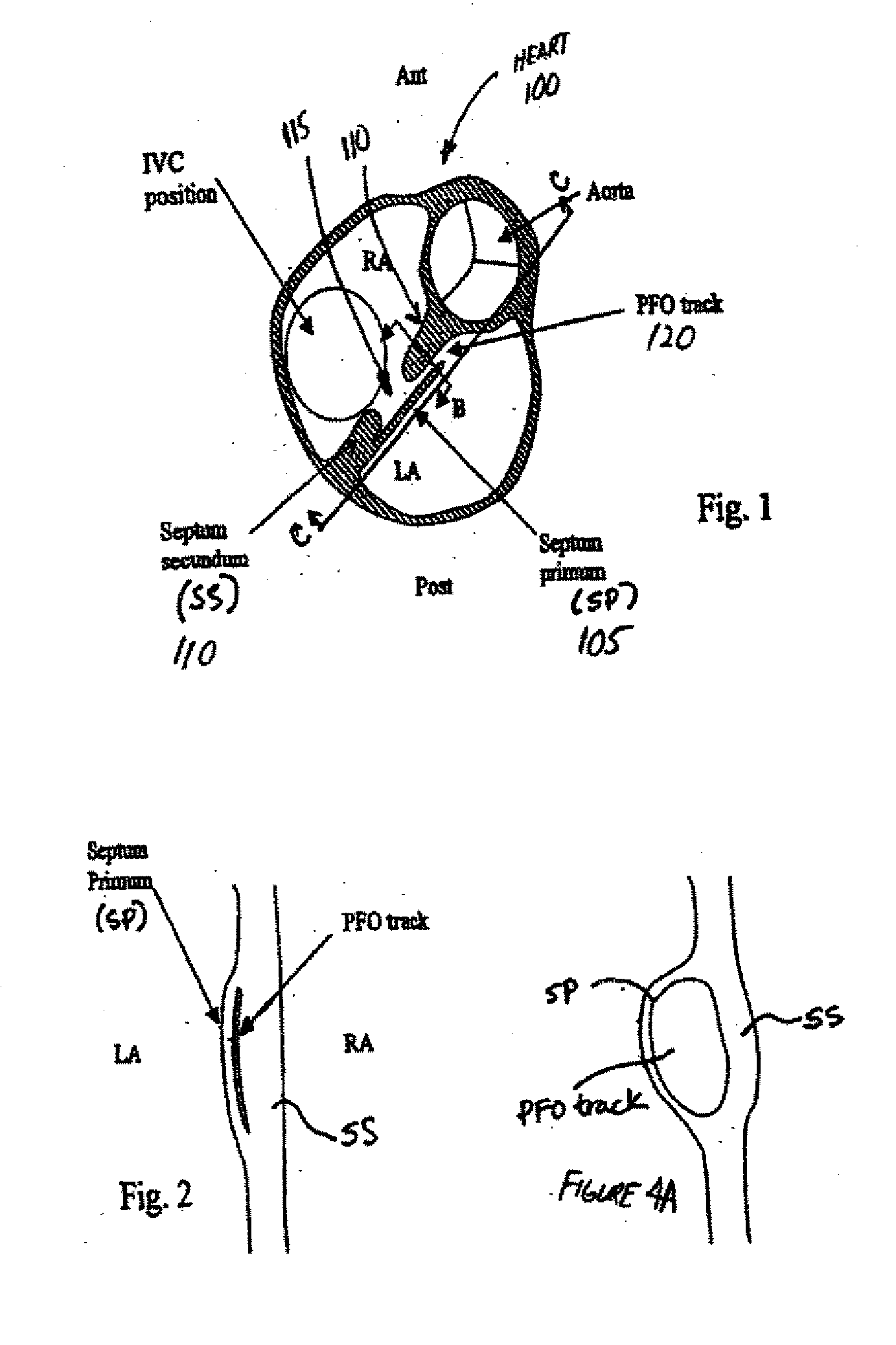
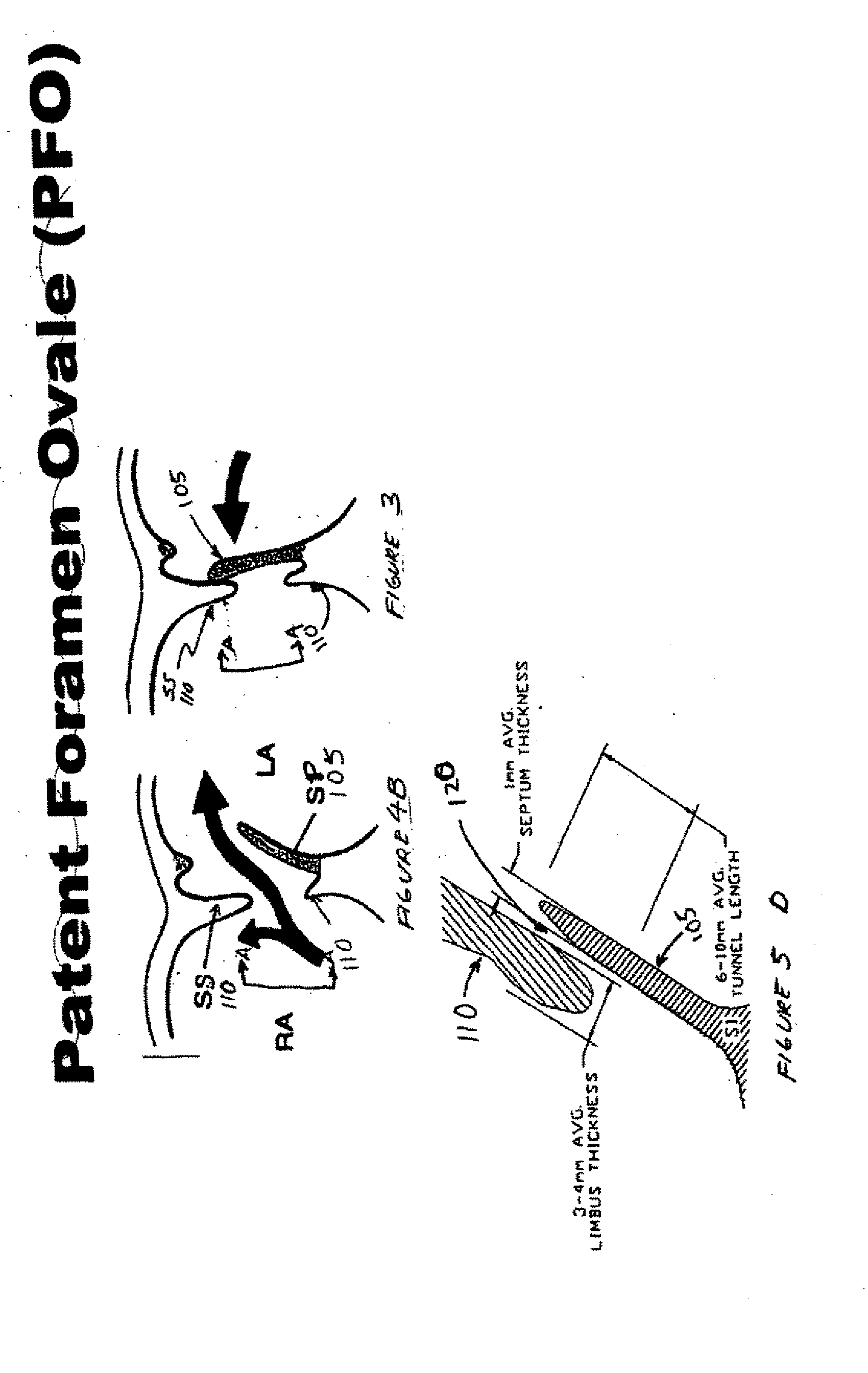
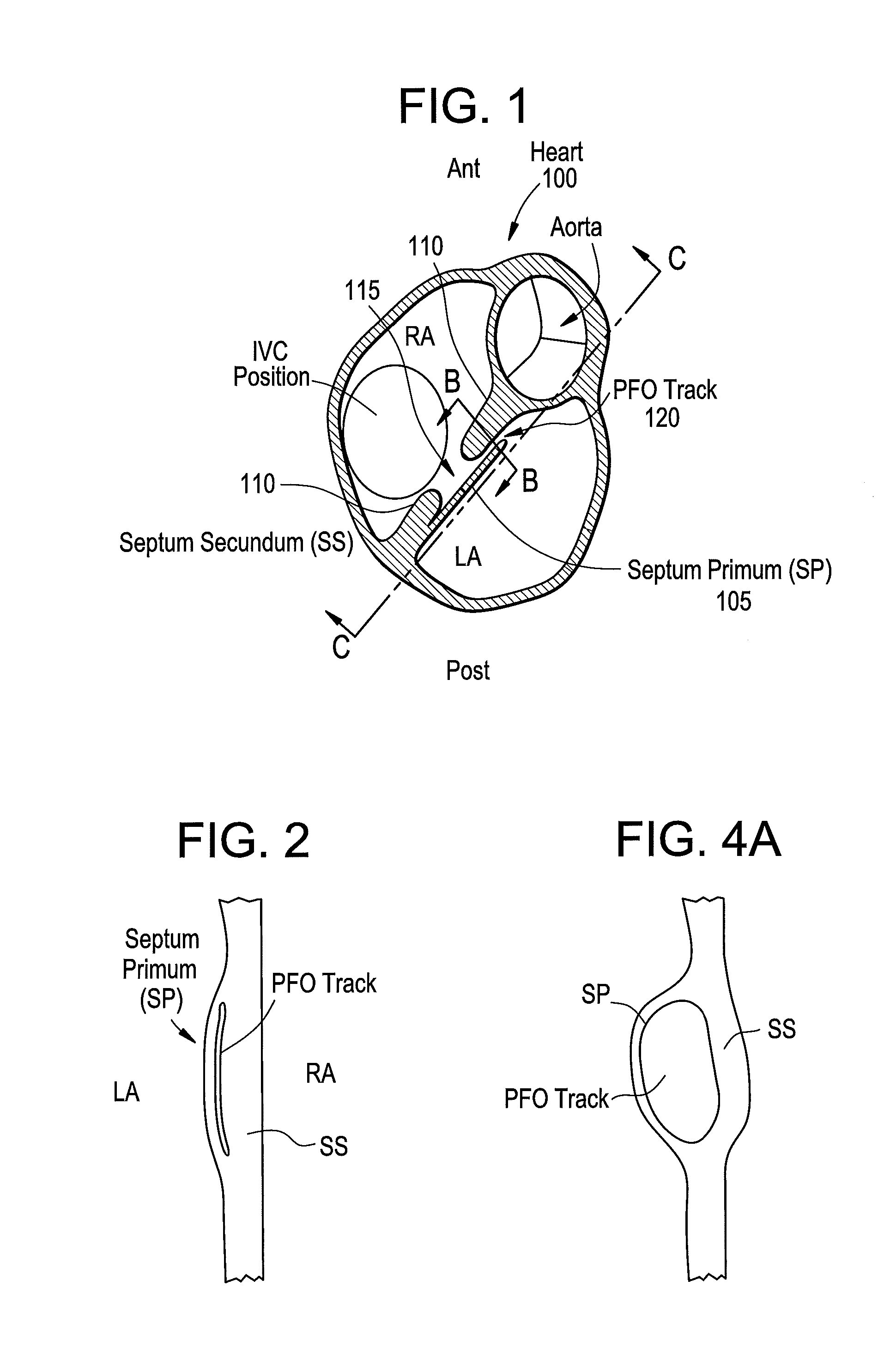
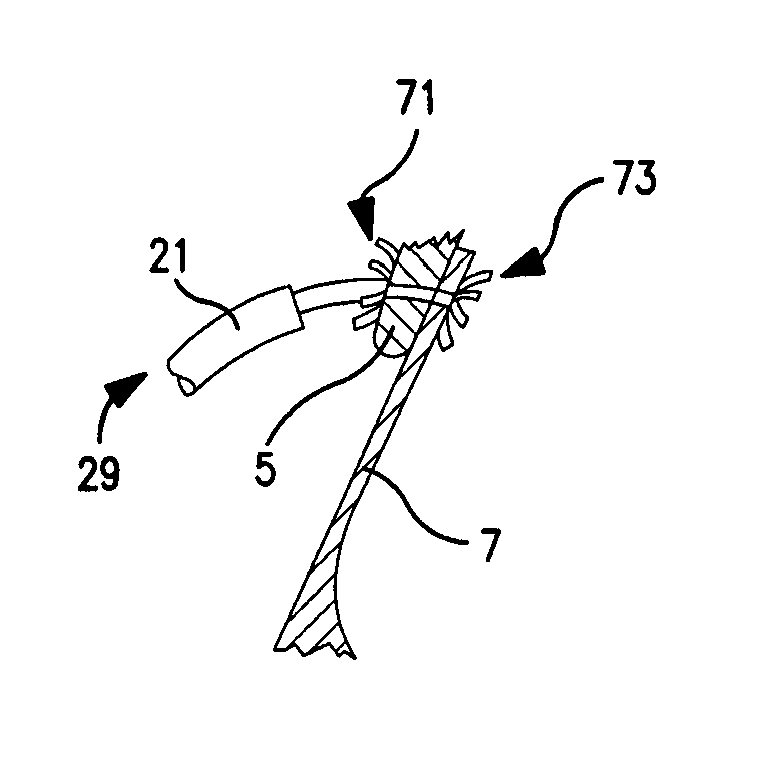
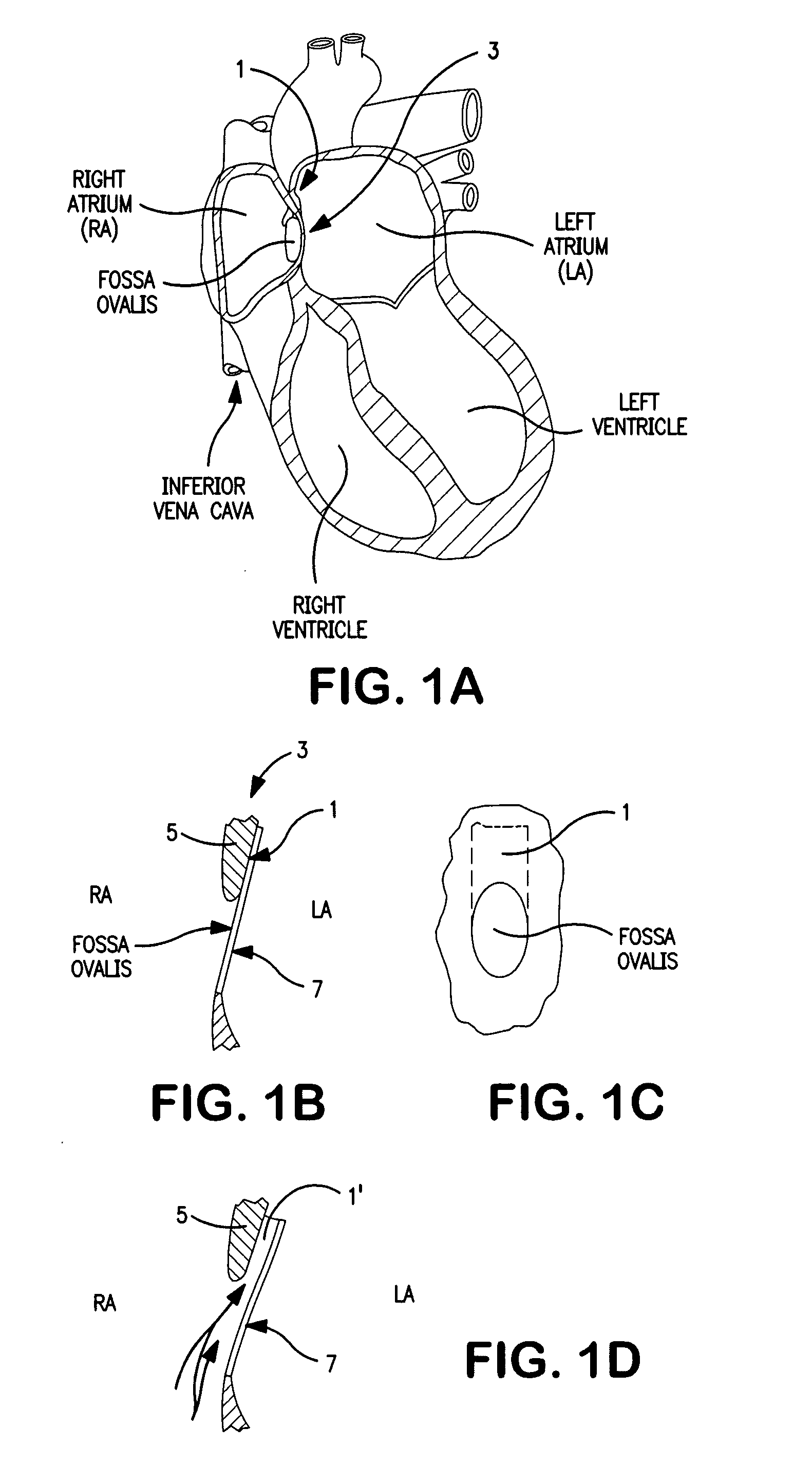
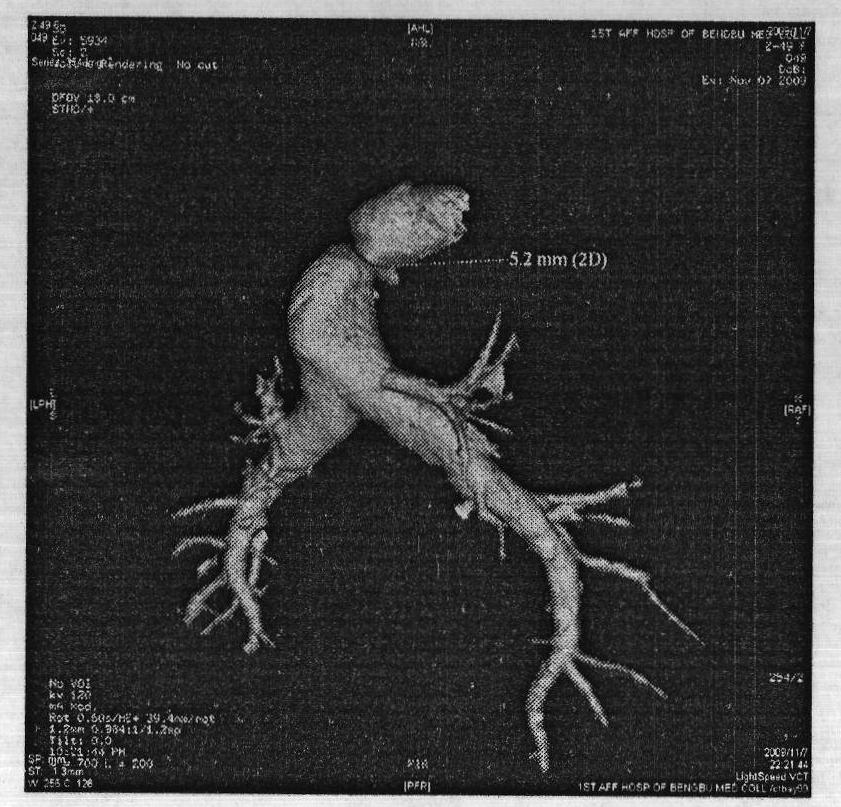
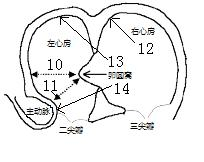
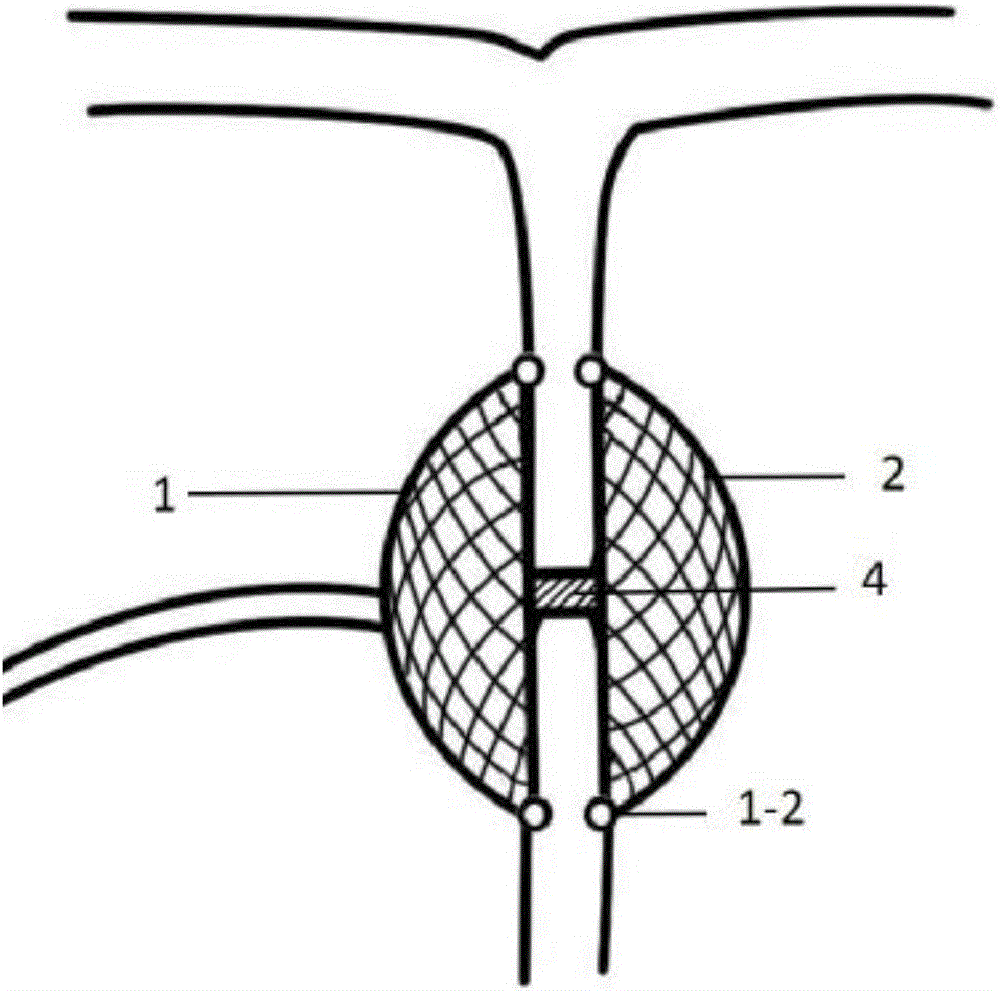
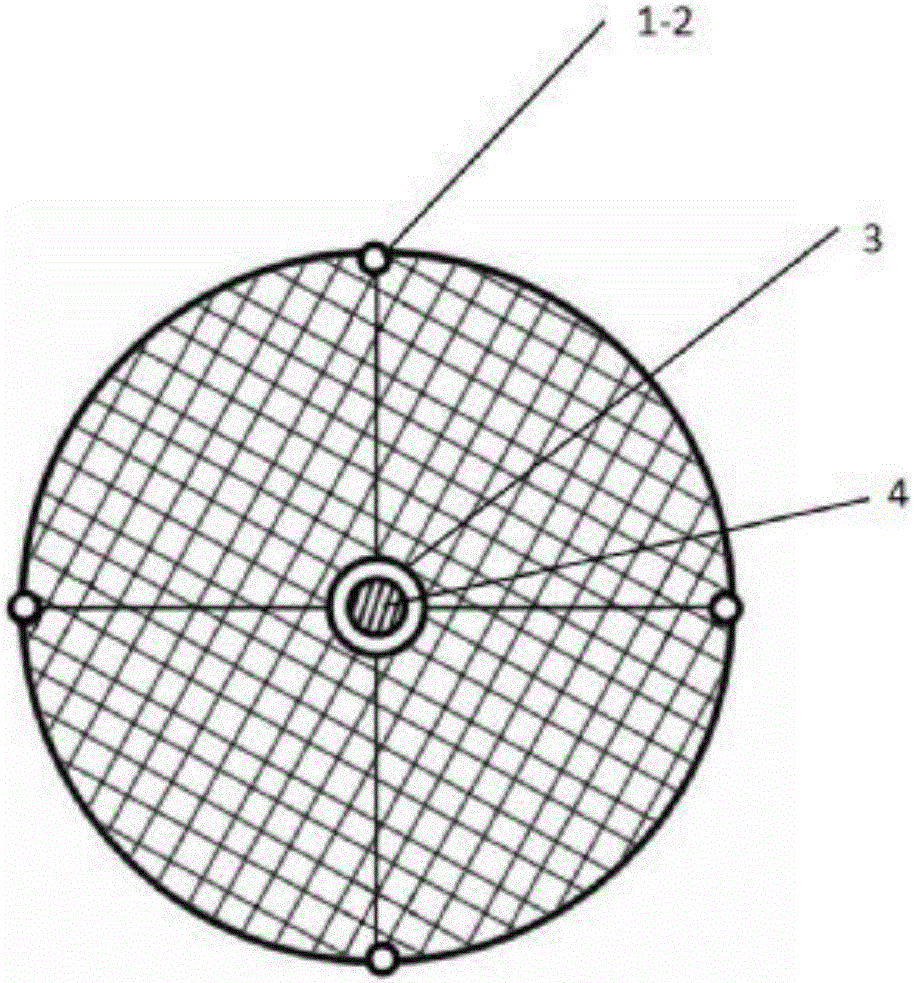
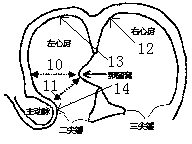
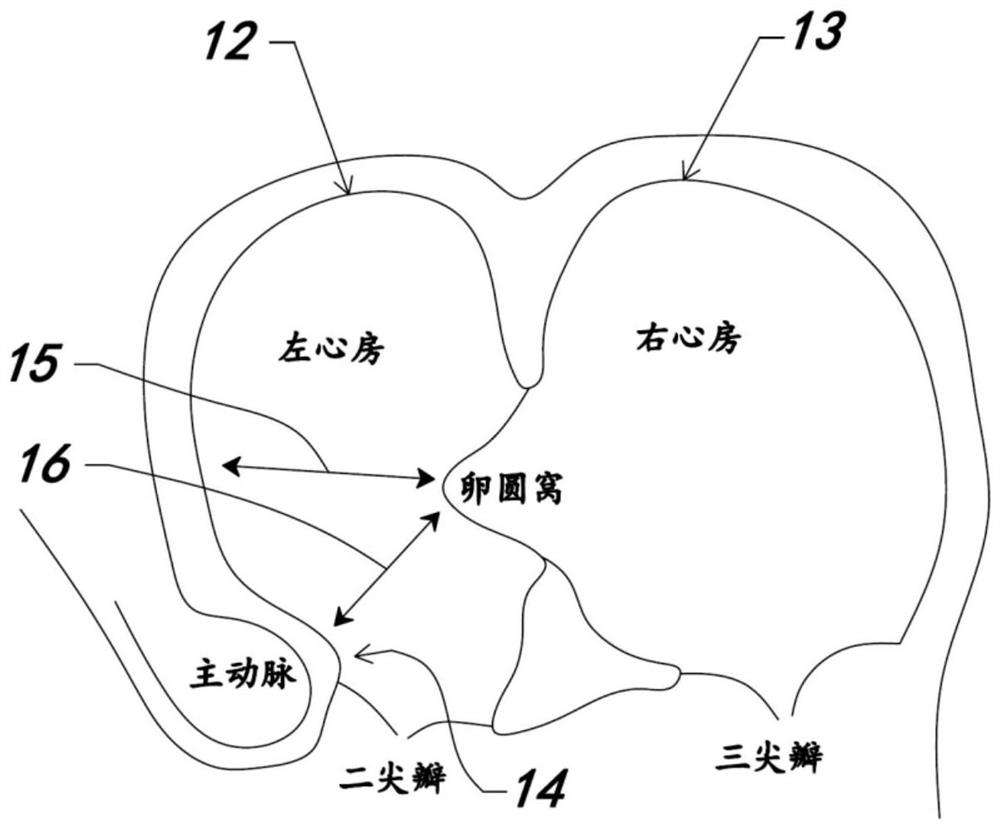
The interatrial septum forms during the first and second months of fetal development. Formation of the septum occurs in several stages. The first is the development of the septum primum, a crescent-shaped piece of tissue forming the initial divider between the right and left atria.
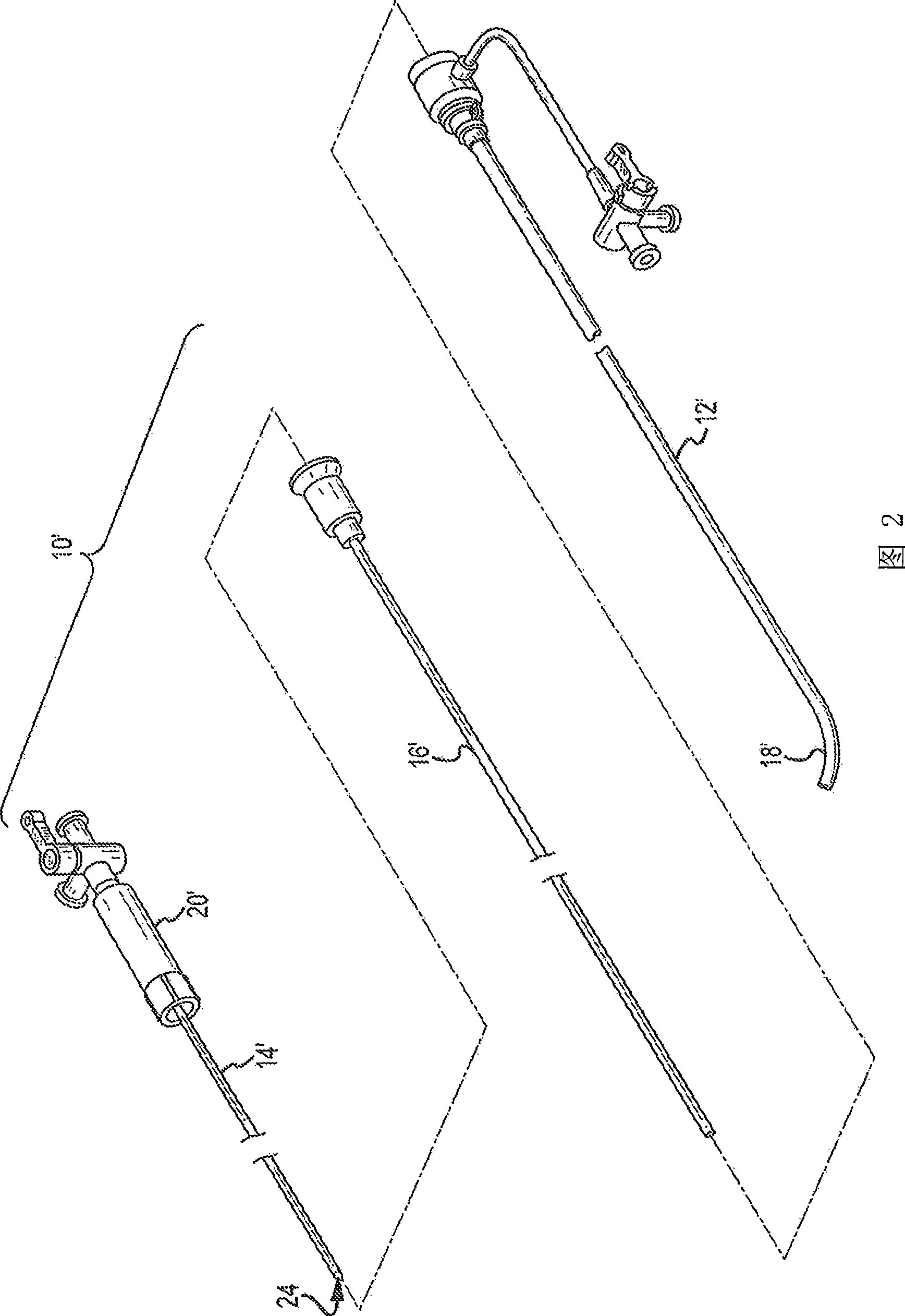
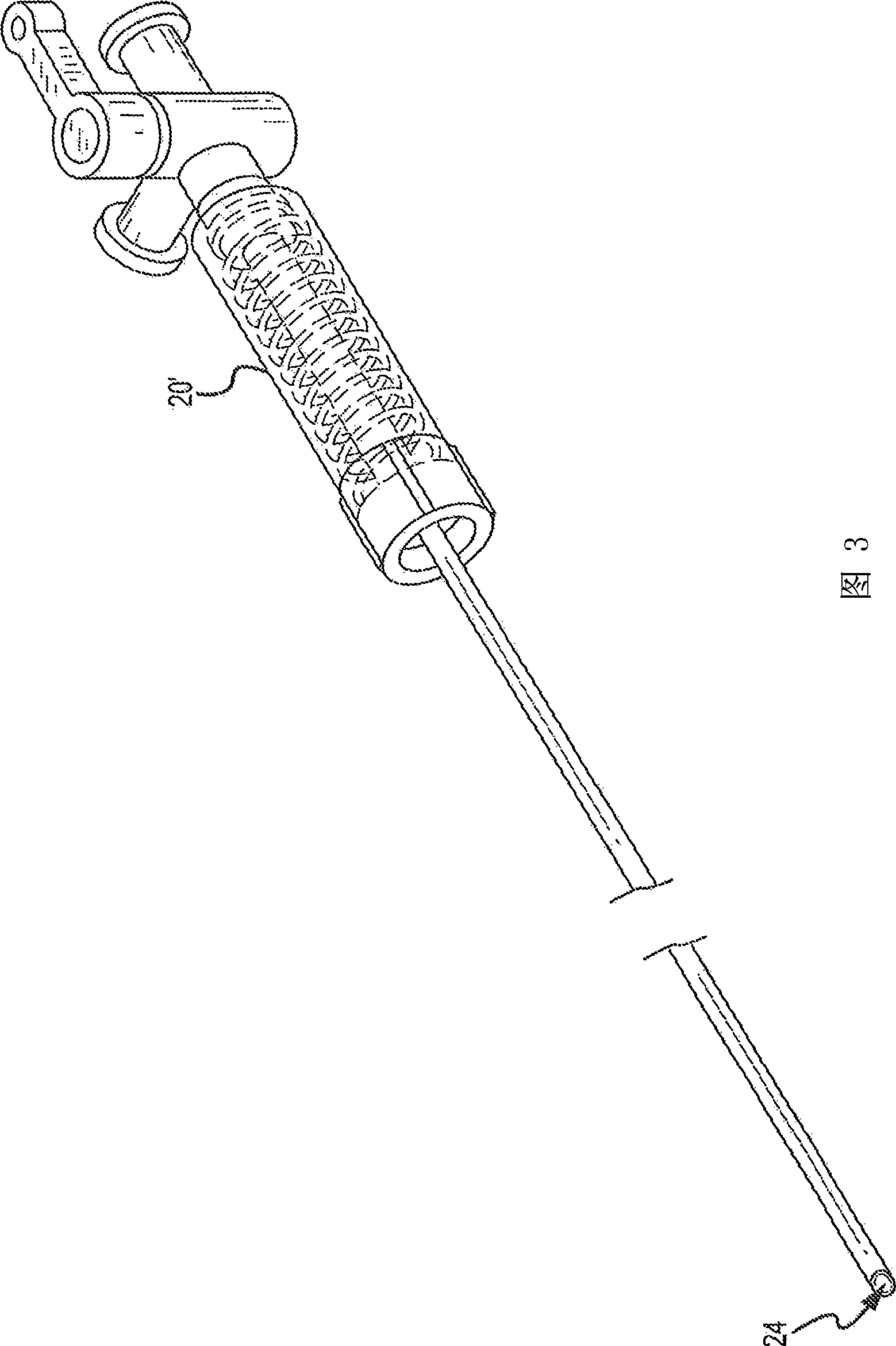
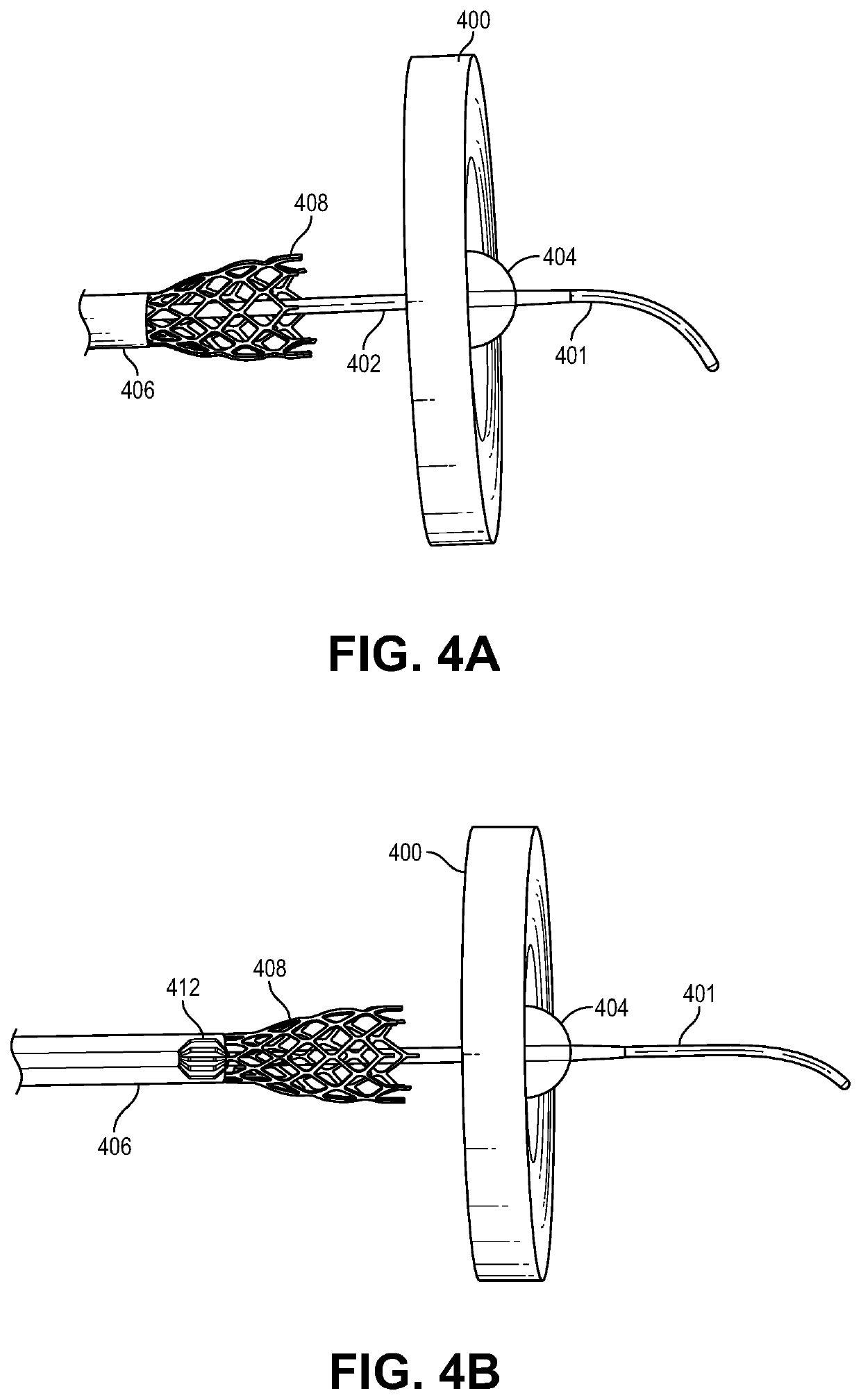
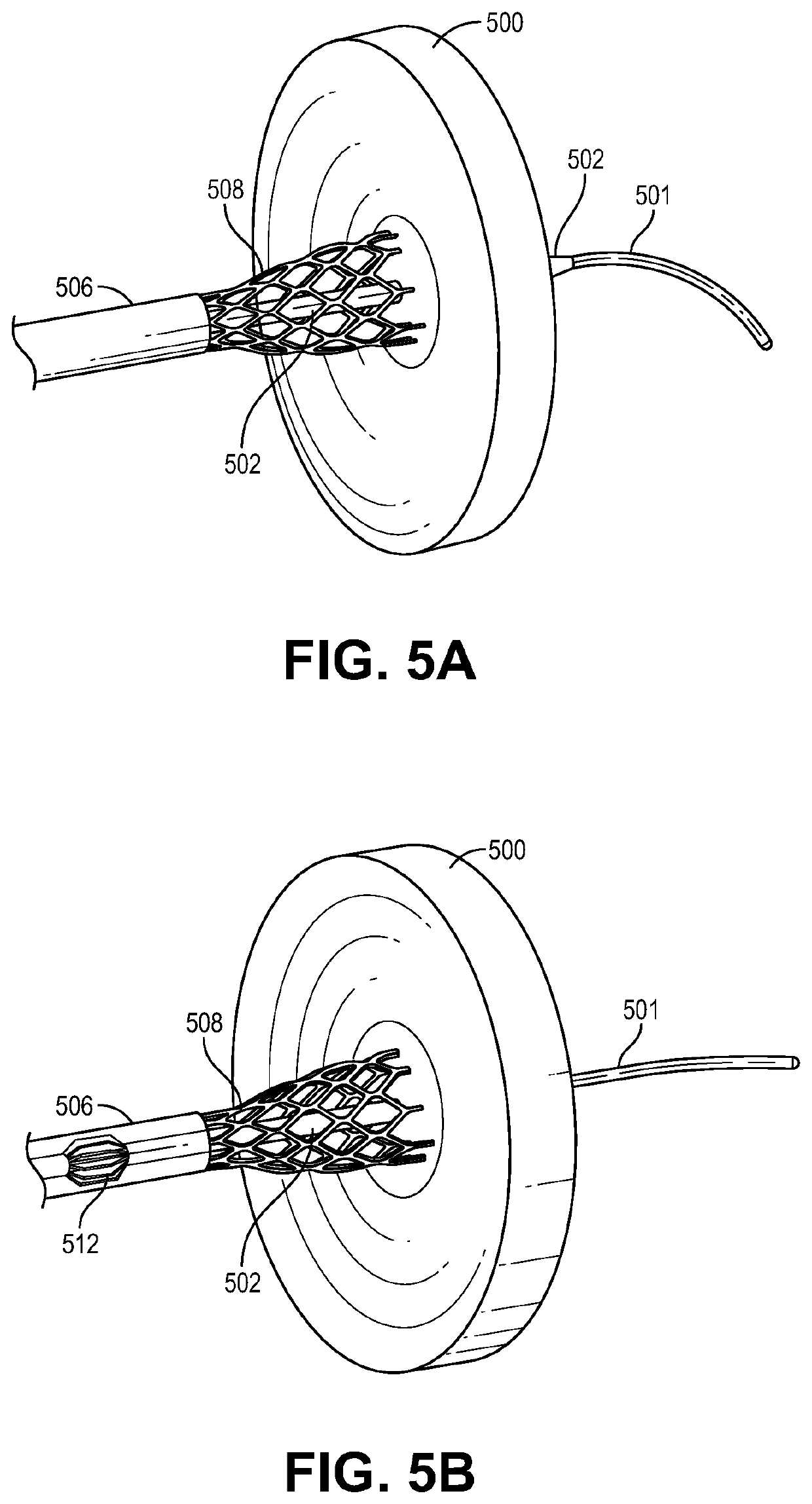
Patent foramen ovale closure method
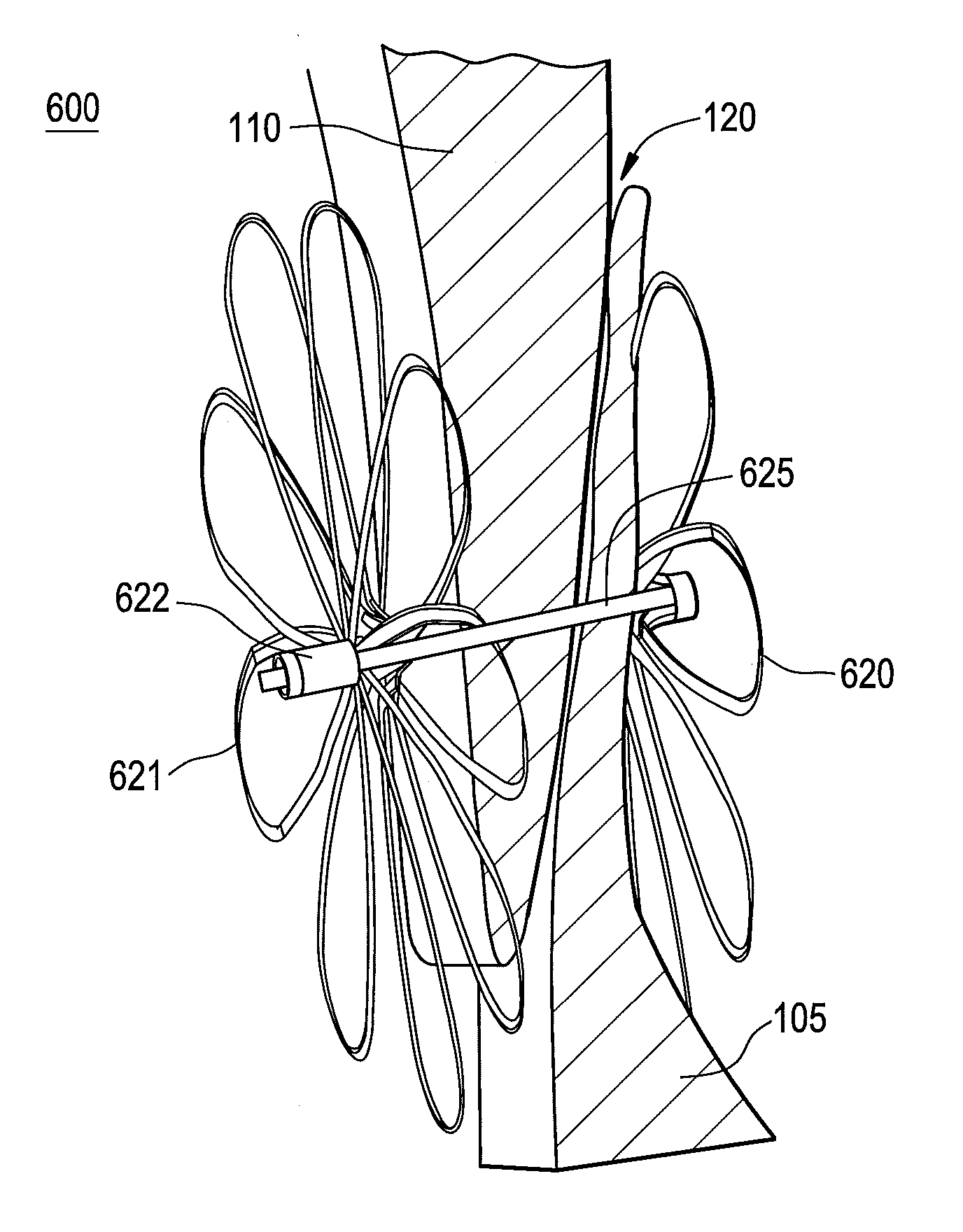
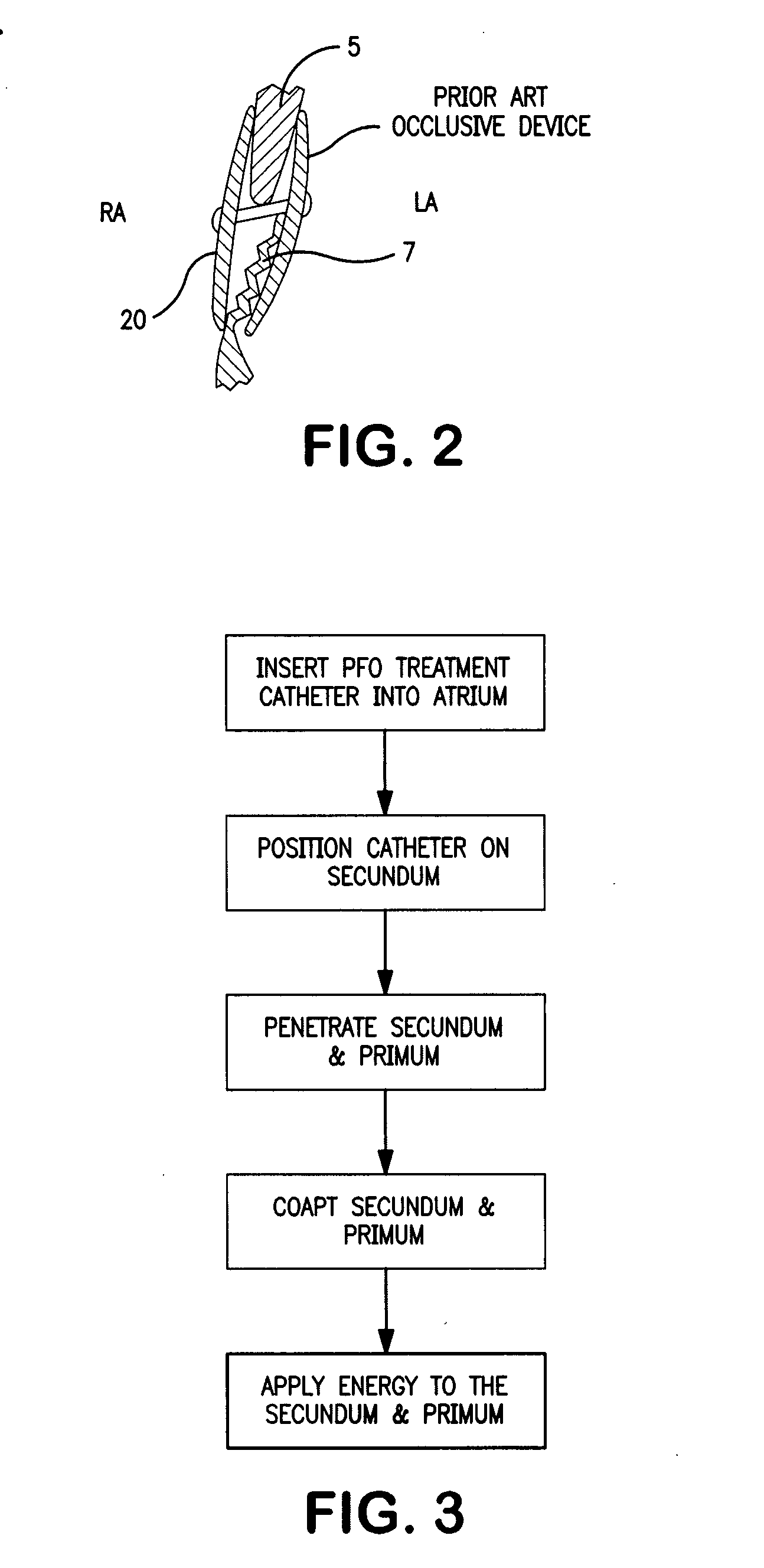
The present invention relates to devices for closing a passageway in a body, for example a patent foramen ovale (PFO) in a heart, and related methods of using such closure devices for closing the passageway. The method includes introducing a mechanical closure device into an atrium of the heart and transeptally deploying the closure device across the interatrial septum to provide proximation of the septum secundum and septum primum.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Patent foramen ovale closure method
Owner:CORDIS CORP
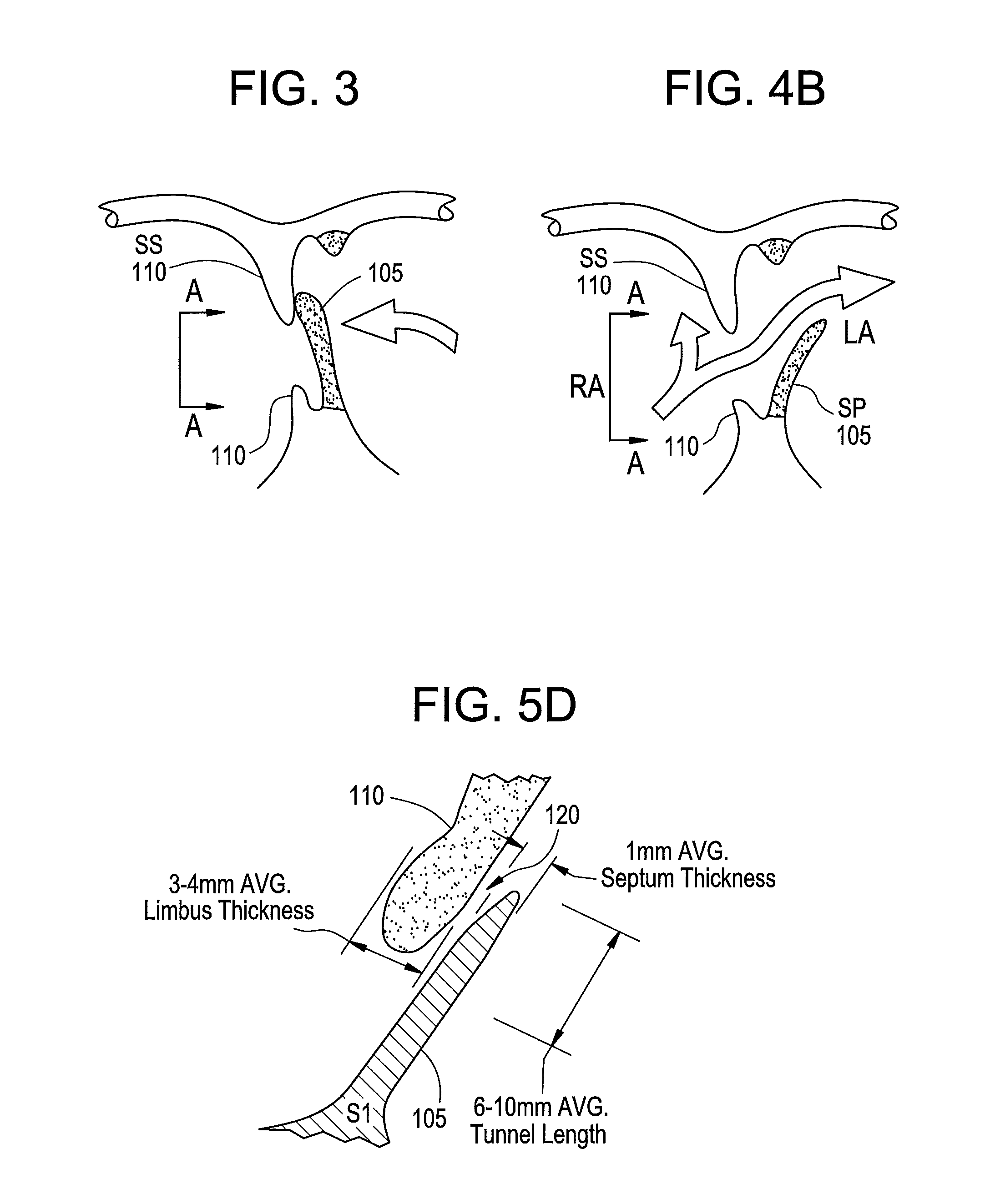
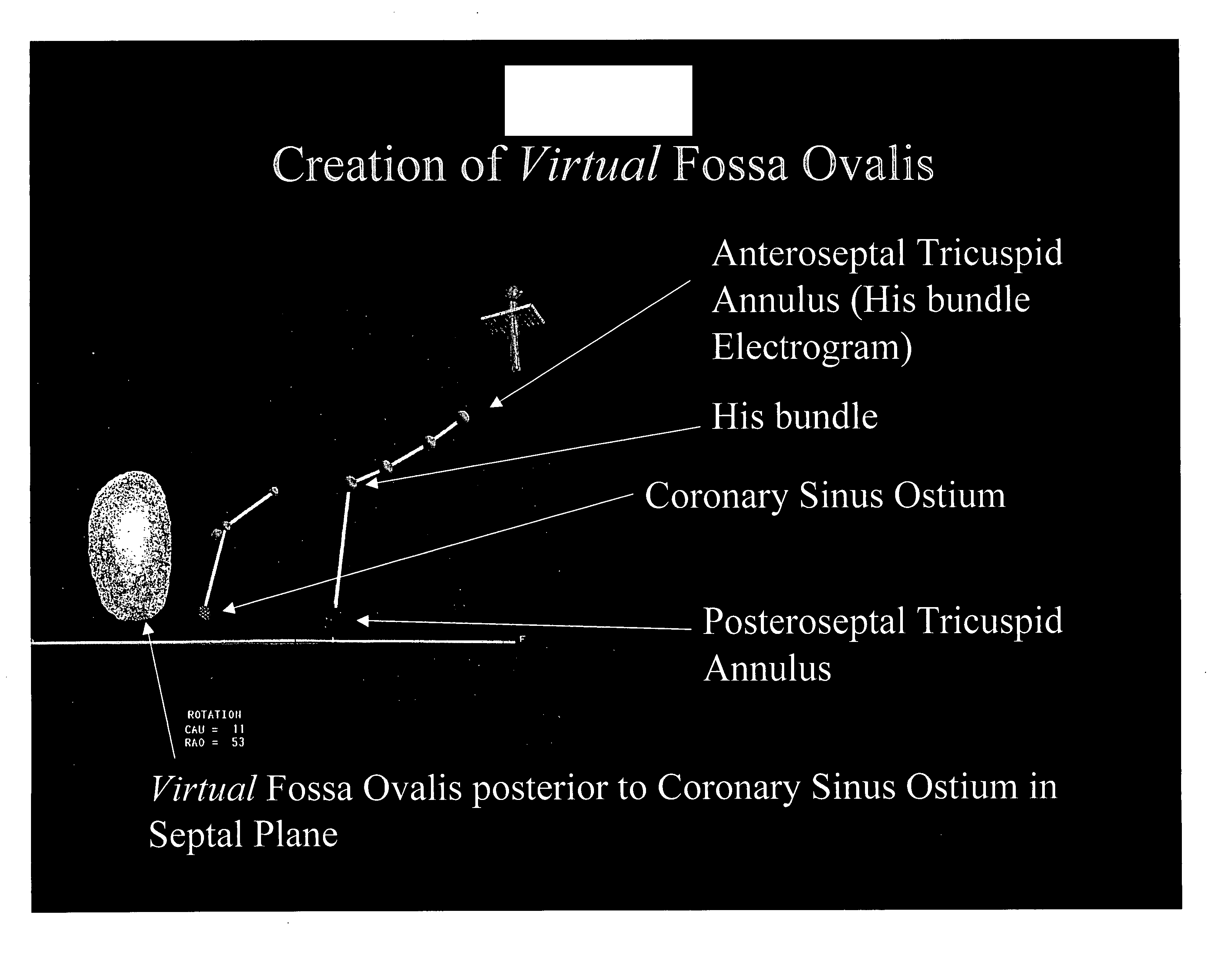
Method and apparatus for locating the fossa ovalis, creating a virtual fossa ovalis and performing transseptal puncture
ActiveUS20060276710A1Easy to identifyElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCoronary sinus ostiumInteratrial septum
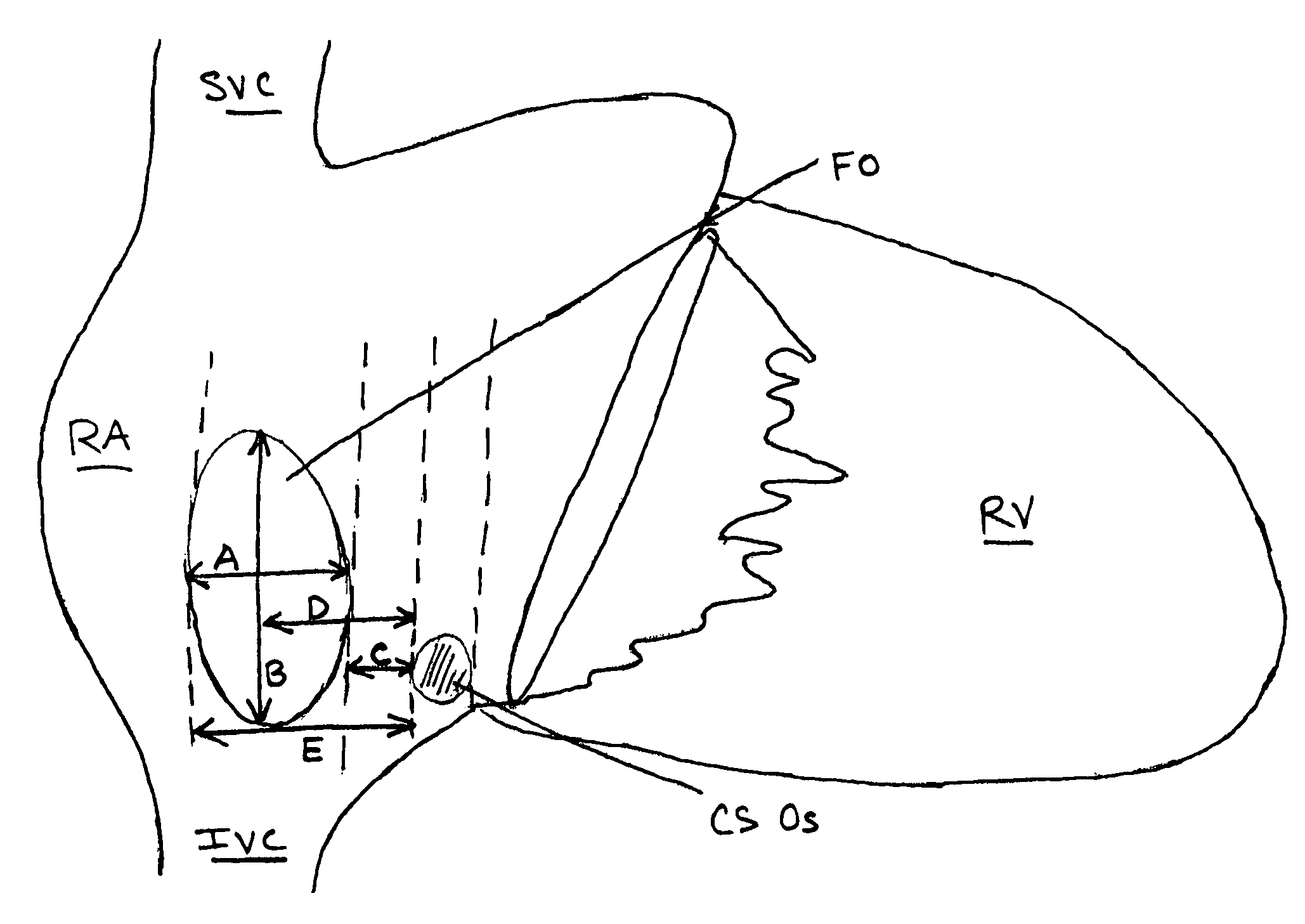
A method of locating the fossa ovalis in a patient by locating the His bundle, plane of the interatrial septum, and coronary sinus ostium in a patient, and thereafter locating the fossa ovalis on the basis of one or more predetermined distances between the fossa ovalis and the His bundle and the coronary sinus ostium. An apparatus for locating the fossa ovalis and performing a transseptal puncture is also provided.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method and apparatus for detecting and achieving closure of patent foramen ovale
A method for detecting and closing the patent foramen ovale including the steps of locating a His bundle, plane of the interatrial septum, and coronary sinus ostium in a patient; identifying a fossa ovalis on the basis of one or more predetermined distances between the fossa ovalis and the His bundle, the plane of the interatrial septum, and the coronary sinus ostium; locating a patent foramen ovale by probing the junction between the fossa ovalis and a limbus of the fossa ovalis; and causing injury to the surfaces of at least one of a septum primum and a septum secundum within the patent foramen ovale. Another method includes the steps of locating a tunnel of a patent foramen ovale by probing the junction between a fossa ovalis and a limbus of the fossa ovalis and causing injury to the surfaces of at least one of a septum primum and a septum secundum within the tunnel of the patent foramen ovale by applying energy to at least one of the septum primum and the septum secundum. Apparatuses to perform these methods are also provided.
Owner:KRISHNAN SUBRAMANIAM C
Transseptal closure of a patent foramen ovale and other cardiac defects
InactiveUS20070203479A1Easily identifying and positioning and penetratingSurgical instruments for heatingCardiac defectsTherapeutic treatment
The present invention provides for therapeutic treatment methods, devices, and systems for the partial or complete closure or occlusion of a patent foramen ovale (“PFO”). In particular, various methods, devices, and systems for joining or welding tissues, in order to therapeutically close a PFO are described. In yet another aspect of the invention, various methods, devices, and systems for the penetration of the interatrial septum enabling left atrial access are also provided.
Owner:COAPTUS MEDICAL CORP
Method and apparatus for locating the fossa ovalis, creating a virtual fossa ovalis and performing transseptal puncture
ActiveUS7815577B2Easy to identifyElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCoronary sinus ostiumInteratrial septum
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
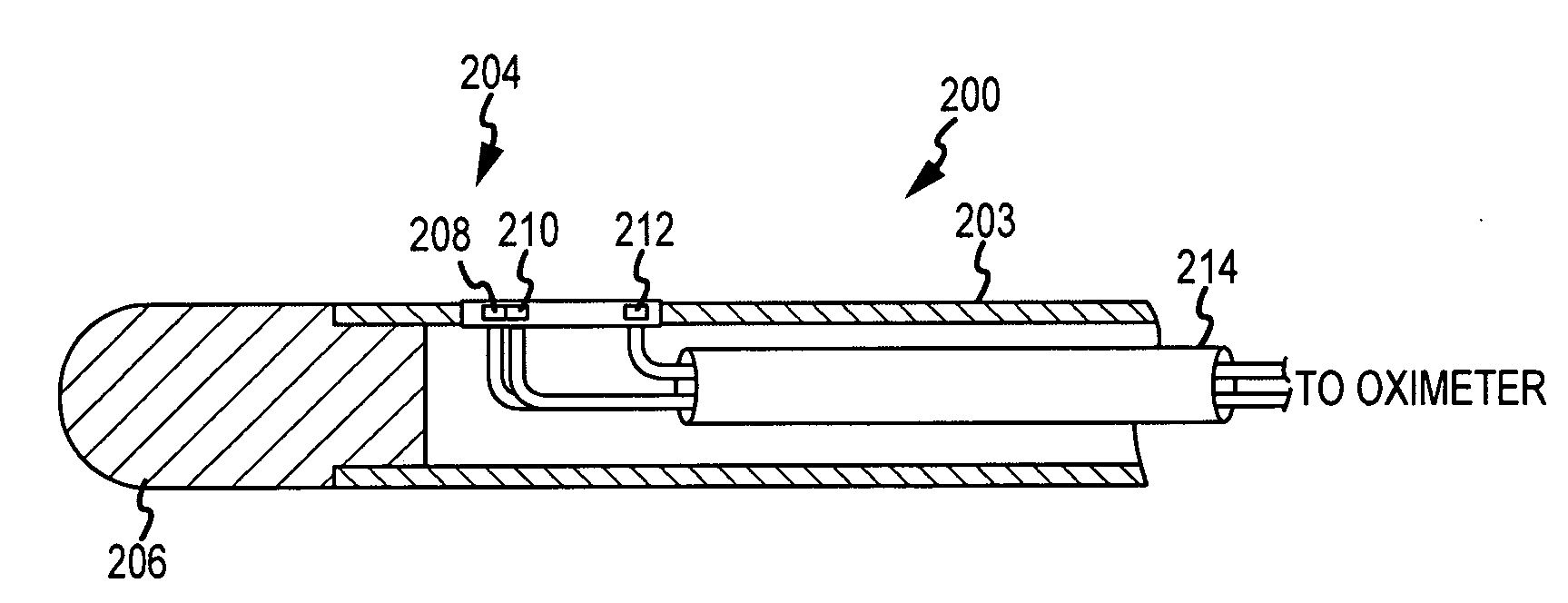
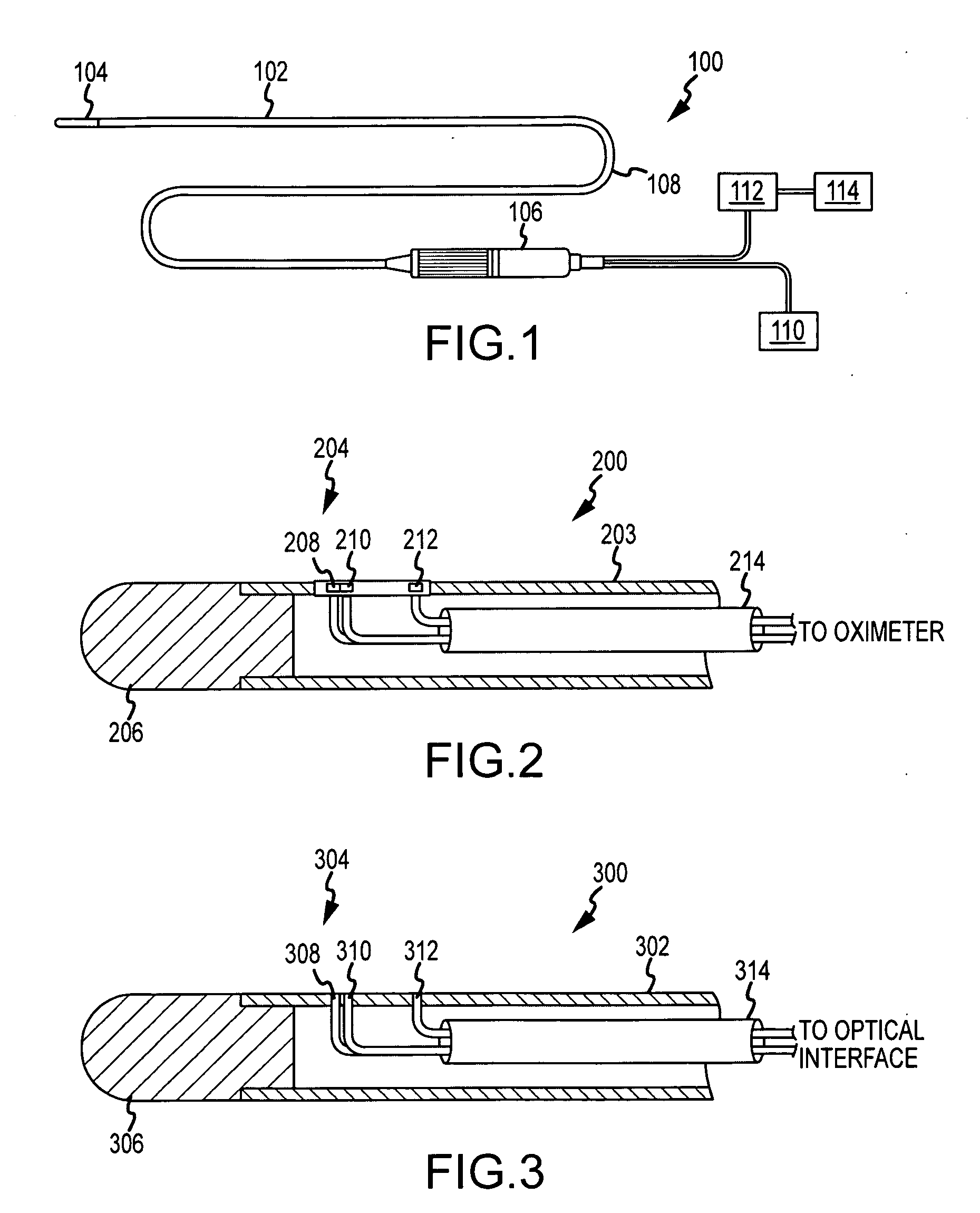
Cardiac ablation catheter with oxygen saturation sensor
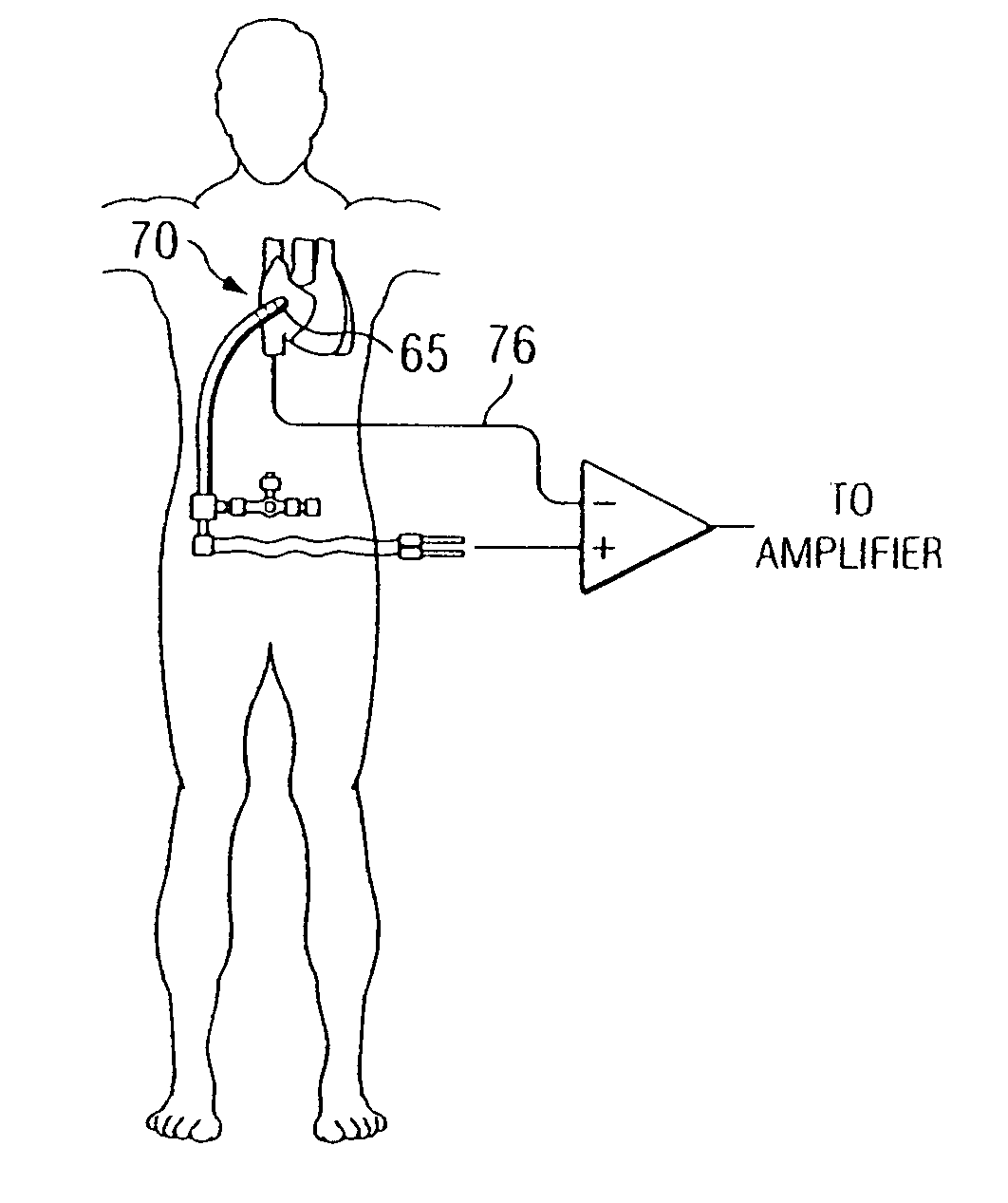
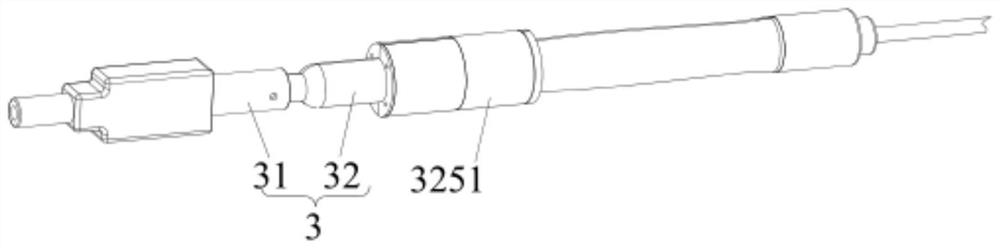
Positioning of the distal end of a catheter at a desired location, for example, in the desired atrium of a patient's heart, can be determined or verified through measurement of blood gas values proximate to the distal end. In one embodiment, an oximeter is used to monitor oxygen saturation, for example, to distinguish between de-oxygenated venous blood and well-oxygenated arterial blood. Optical signals may be transmitted to the distal end of the catheter and received therefrom via optical fibers. Specifically, a catheter (300) has a number of optical fiber ends (308, 310 and 312) disposed at a distal end (304) thereof. A first fiber end (310) transmits the red and infrared optical signals. Fiber ends (308 and 312) are used for detecting reflected optical signals. The optical signals are then processed by a detector and an oximeter instrument to provide oxygen saturation readings that can indicate the position of the distal end of the catheter within the patient's heart or successful penetration of the interatrial septum.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
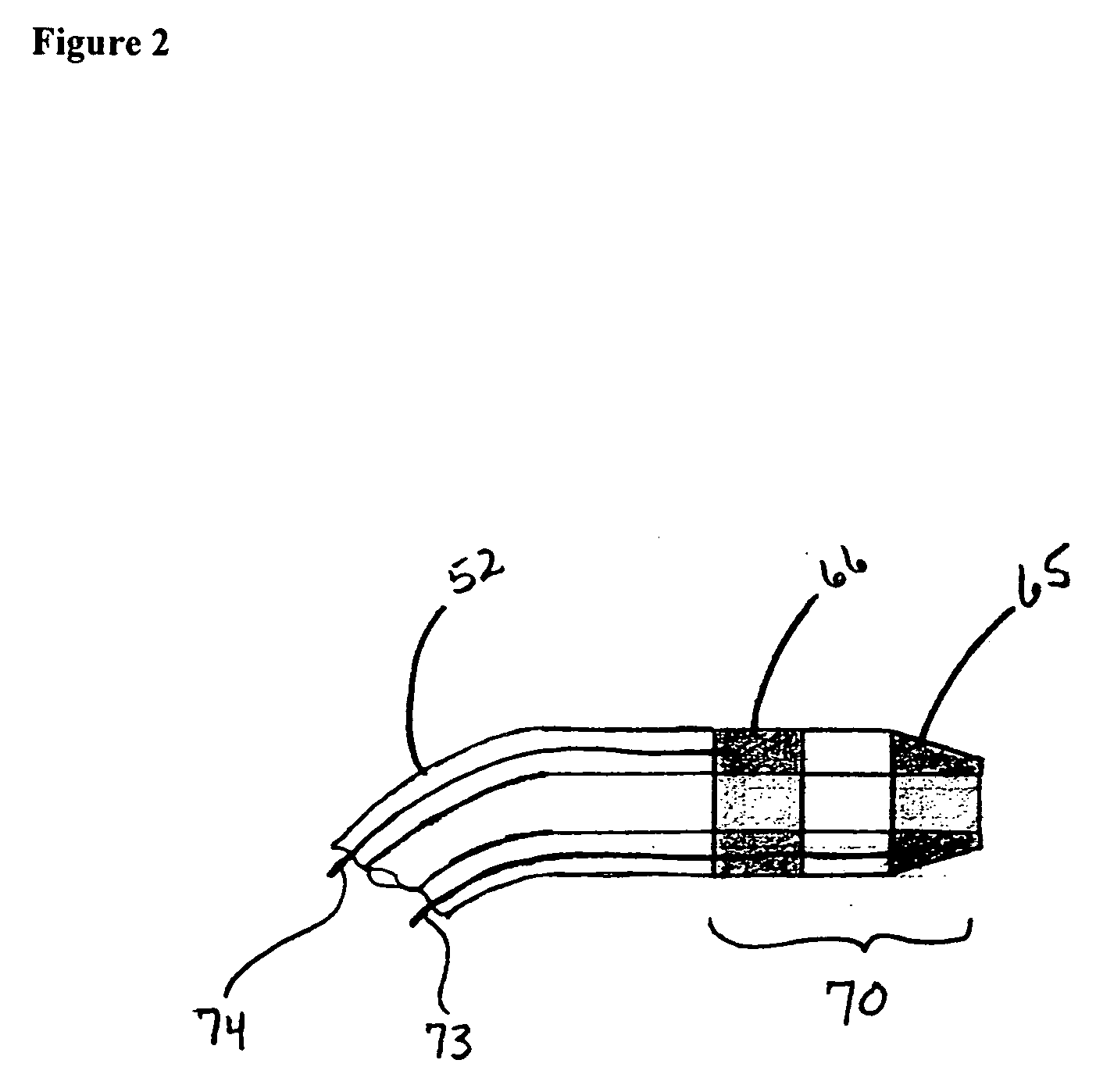
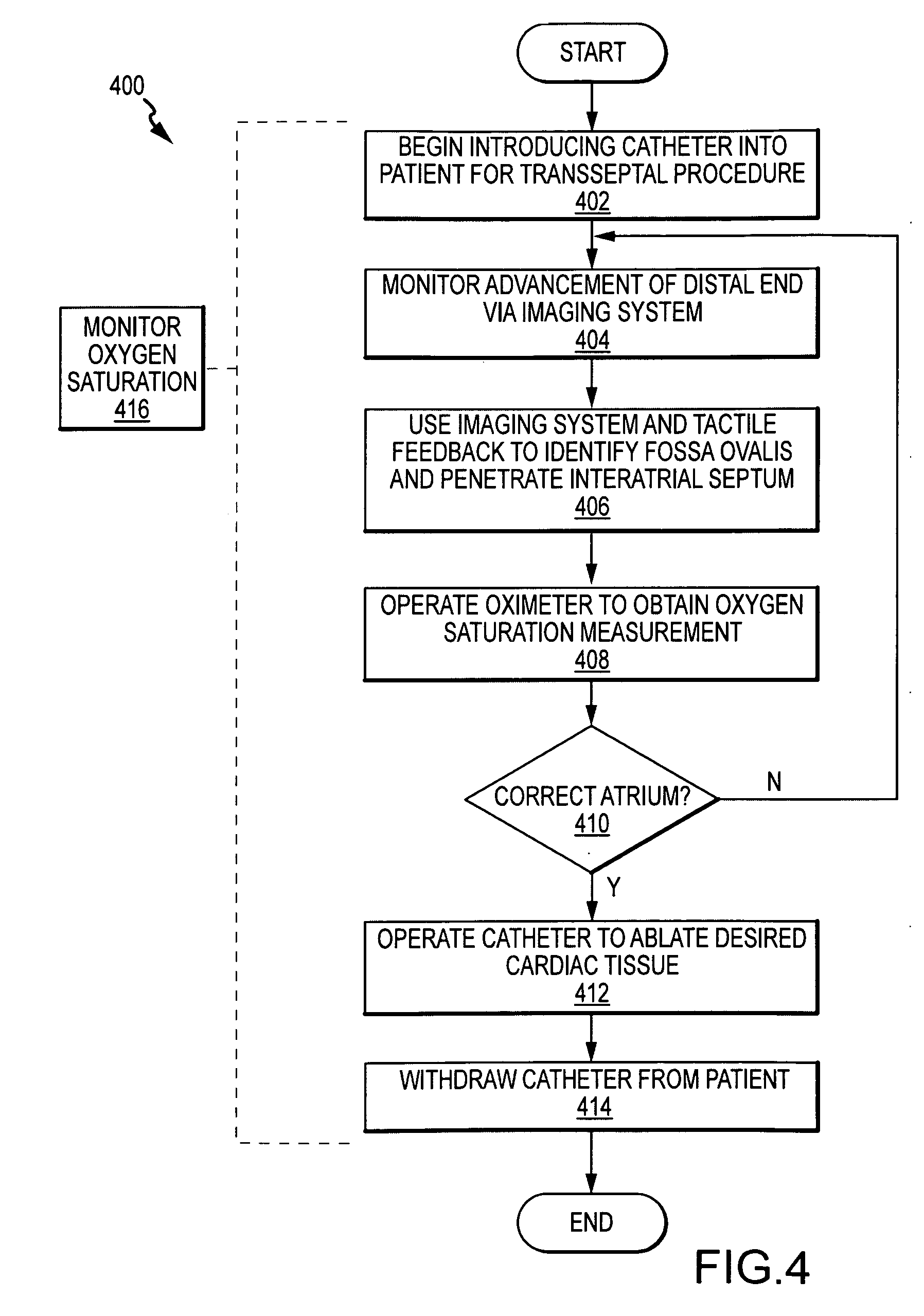
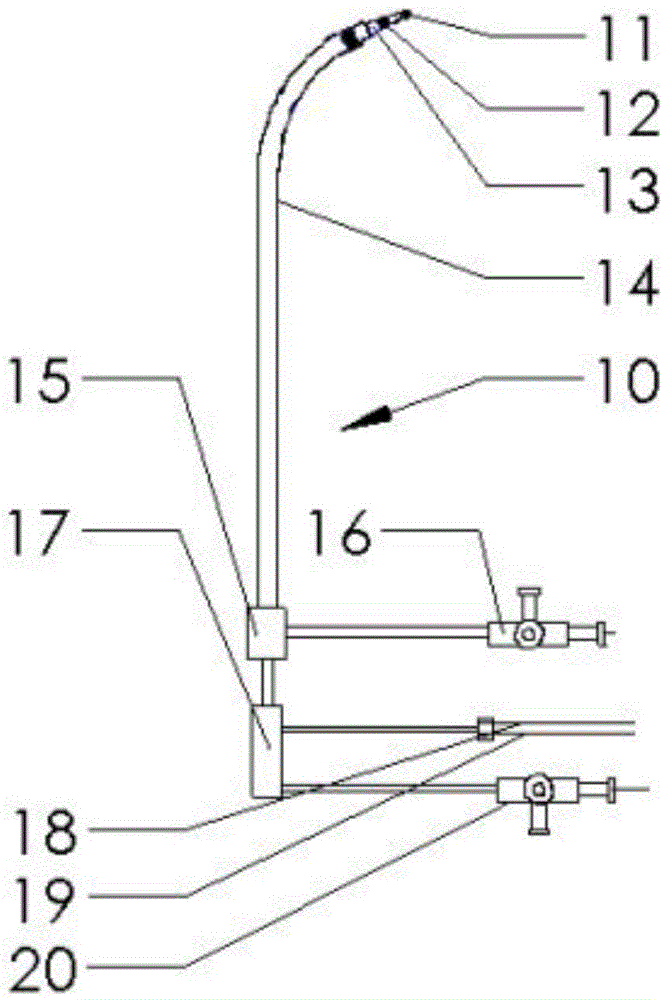
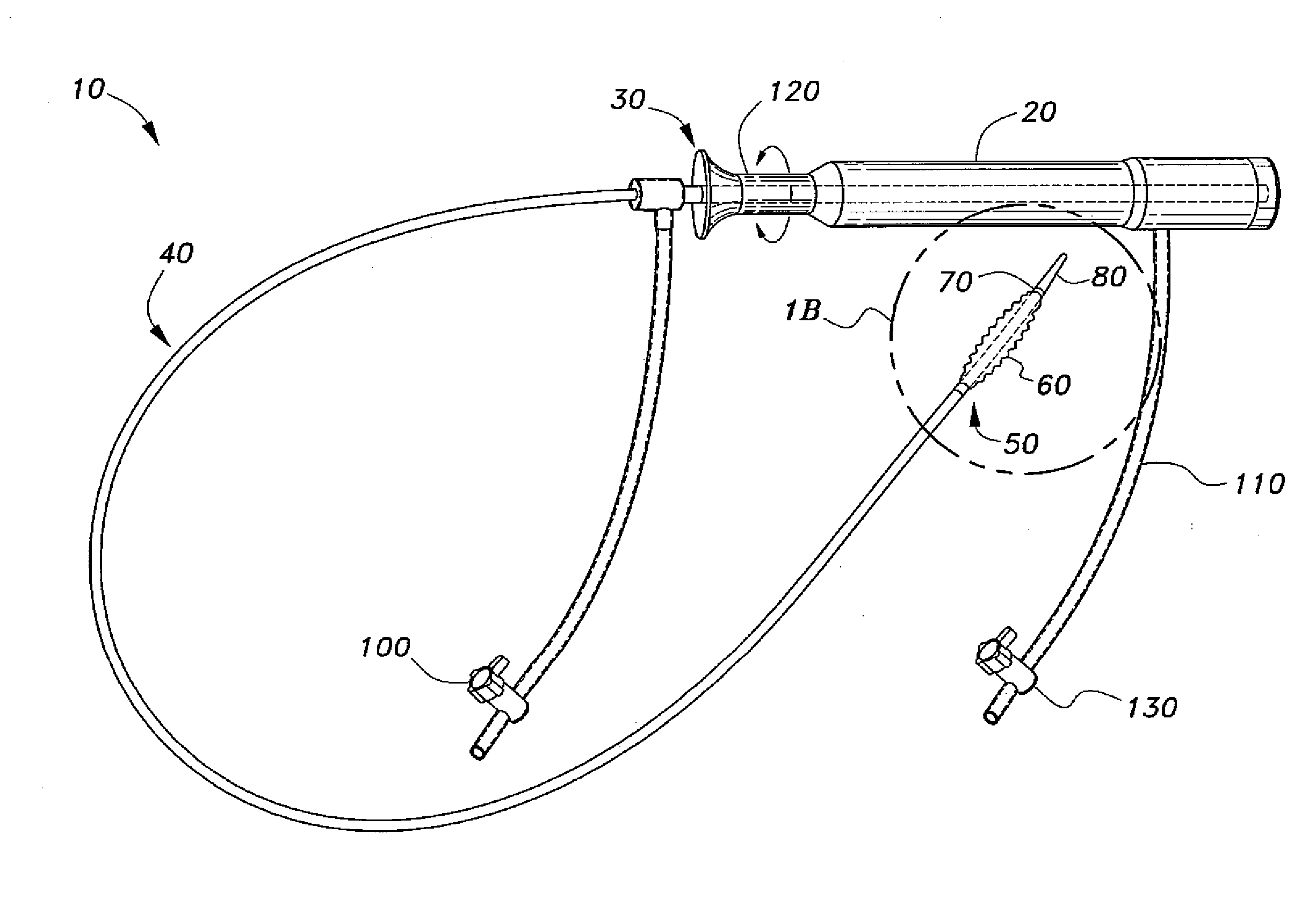
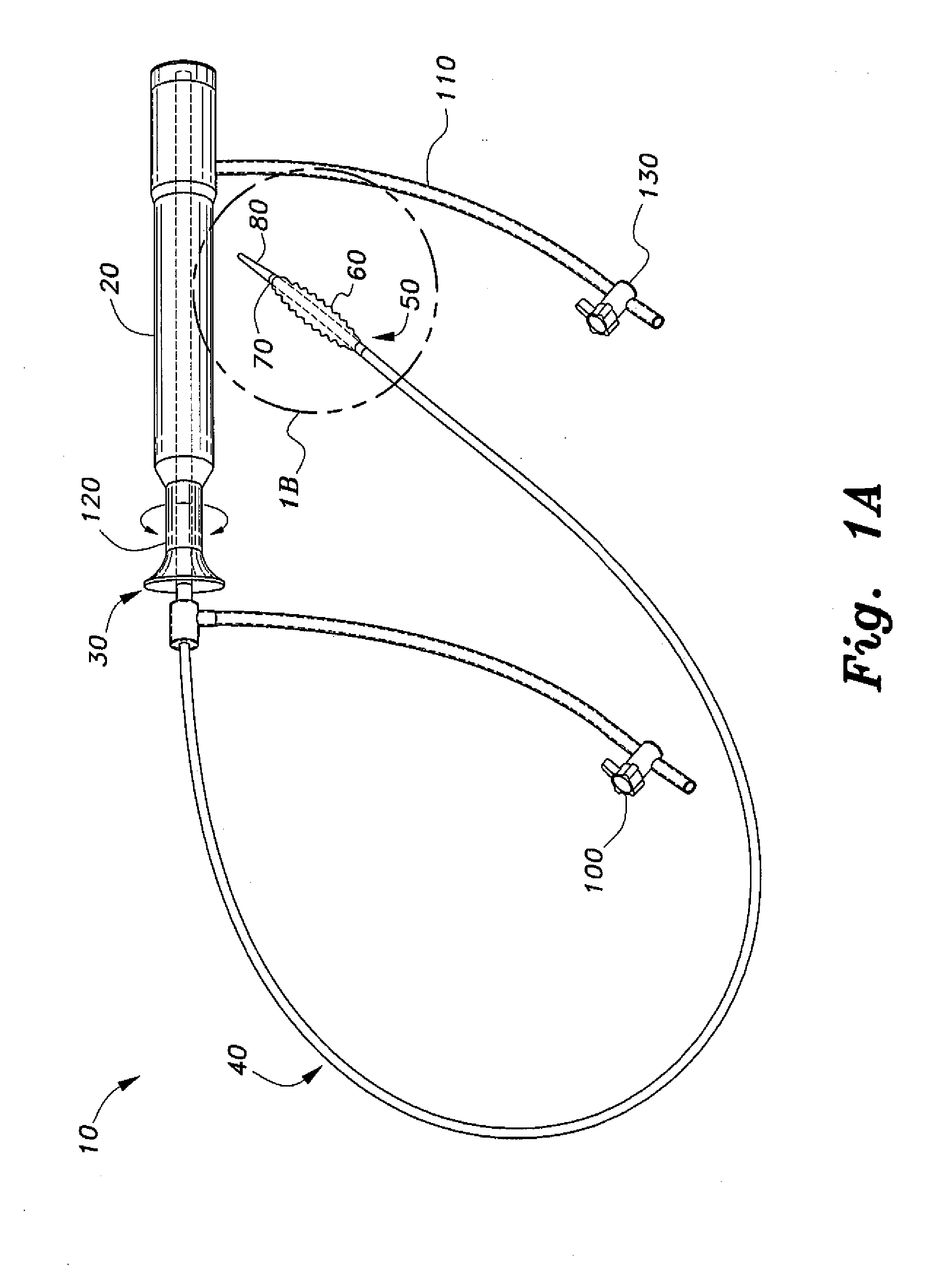
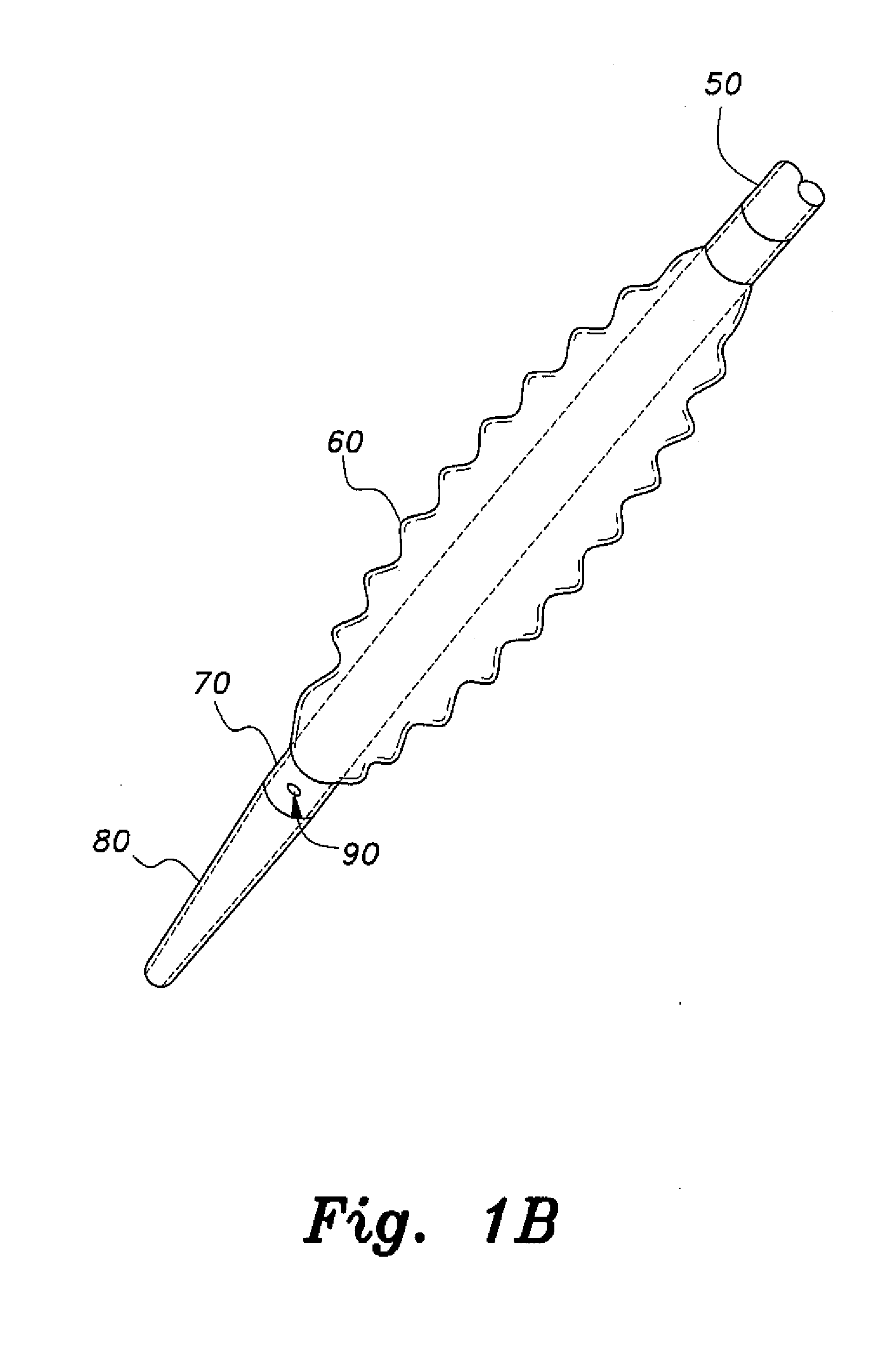
Transseptal needle assemblies and methods
The instant invention relates to transseptal access systems and methods for accessing the left atrium (52) from the right atrium (48) by crossing the interatrial septum (50). In particular, the instant invention is directed toward medical devices used with catheter assemblies in cardiology procedures that require transseptal puncture(s). The puncture assemblies (e.g., 10) have a moveable puncture device (e.g., 14) within a dilator (e.g., 16). The puncture device is biased in a retracted position. The position of the puncture assembly is precisely locatable. The puncture assembly is preferably flexible along the majority of the length of its and, therefore, can be used with any catheter assembly of any predetermined shape. The puncture device is adjustable from a position within the dilator to a position extending beyond the end of the dilator when necessary for use in transseptal procedures.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for the catheterization of the coronary arteries and catheter for the implementation thereof
InactiveUS20150273136A1Improve processing efficiencySecurity upgradeMedical devicesCatheterAscending aortaCoronary arteries
What is proposed is a method for the catheterization of the coronary arteries in which a catheter is introduced via the venous system into the right atrium, then passed through the interatrial septum and introduced into the left atrium, followed by the left ventricle, and into the ascending aorta to the opening of the coronary arteries, and also a catheter for the implementation of this method.
Owner:OSIEV ALEKSANDR GRIGORIEVITCH
Interatrial septum puncturing assembly and interatrial septum puncturing method
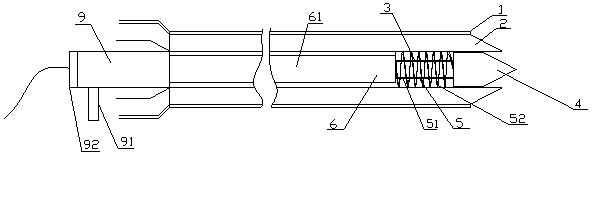
The invention provides an interatrial septum puncturing assembly and an interatrial septum puncturing method. The interatrial septum puncturing assembly comprises a catheter sheath and an expansion tube, the expansion tube is arranged in the catheter sheath in an attaching and penetrating mode, and one end of the expansion tube is fixedly provided with multiple electrodes. According to the interatrial septum puncturing assembly and the interatrial septum puncturing method, due to the fact that one end of the expansion tube is fixedly provided with the electrodes, ablation puncturing can be performed, a tent shape cannot be formed in an ejecting mode when the expansion tube passes through the fossa ovalis myocardium, and safe and rapid puncturing is achieved; meanwhile, use of a puncture needle is omitted, therefore, the surgical operation steps are simplified, and not only is the operation time saved, but also the cost of the puncture needle is saved; in addition, the electrodes can be attached to the inner wall of a heart chamber to extract electrical signals in the heart chamber, the position of the fossa ovalis is accurately determined through the electrical signals, and the puncturing safety is improved.
Owner:吕斐
Apparatus for closure of atrial septal defects
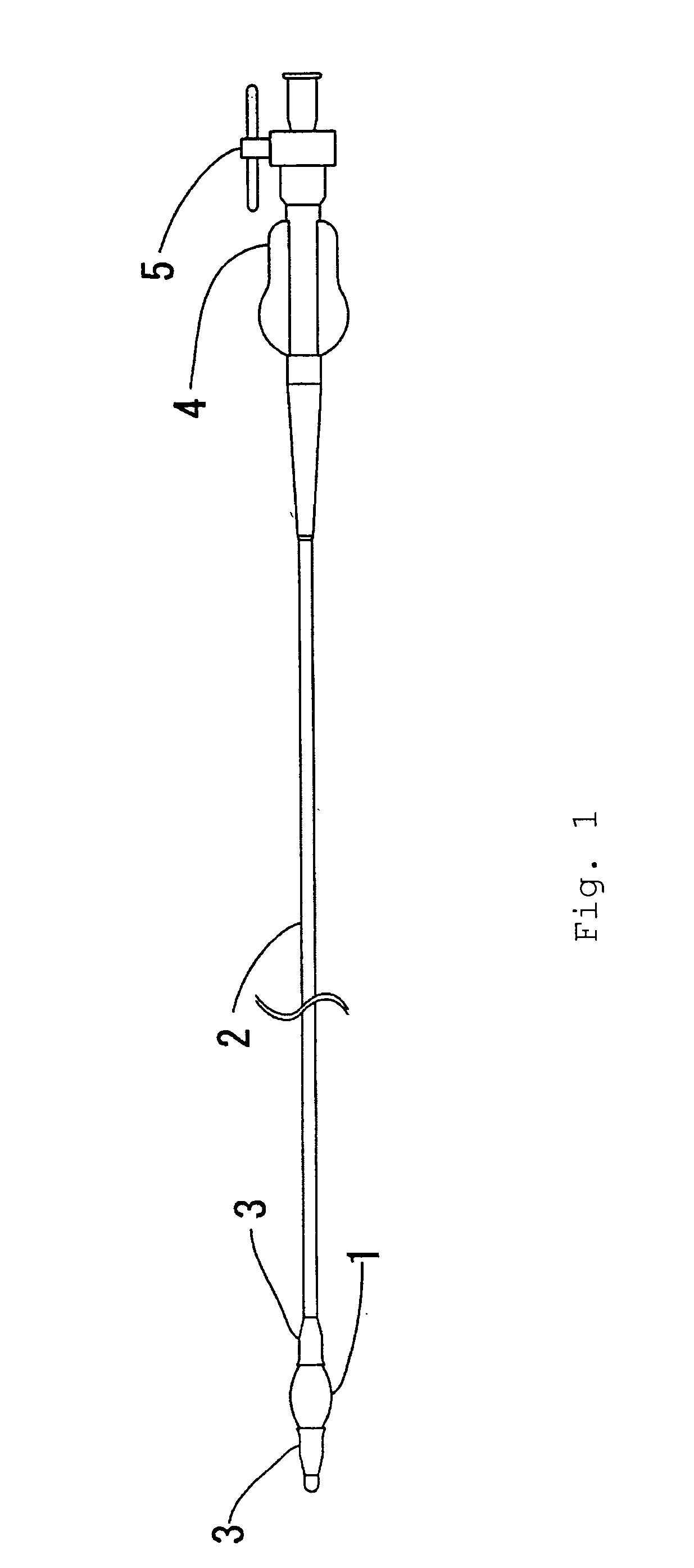
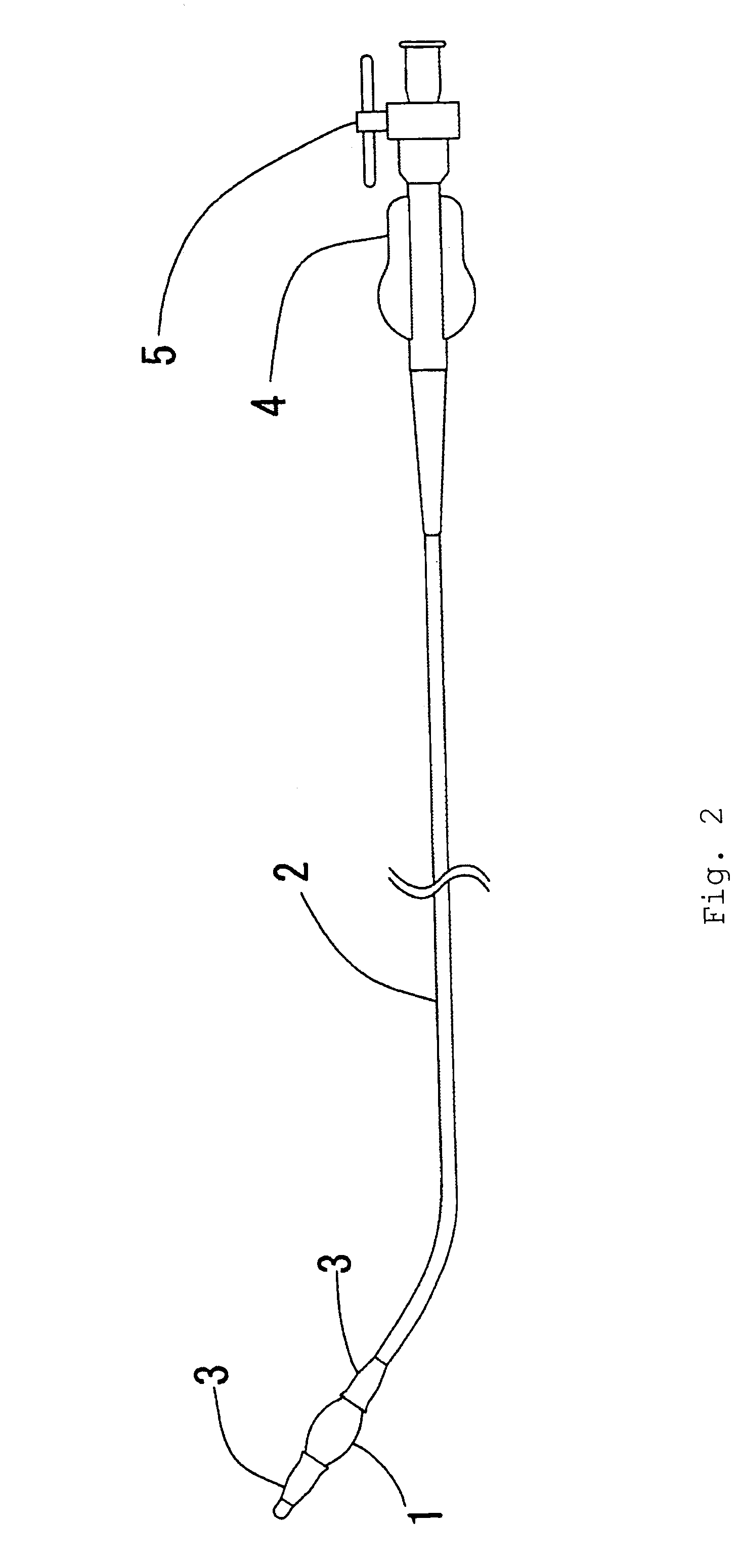
The apparatus for closure of atrial septal defects includes a sheath having a proximal portion and a distal portion, the sheath defining a lumen extending therethrough, a handle positioned in communicating relation with the proximal portion of the sheath, and a balloon positioned in communicating relation the distal portion of the sheath. The distal portion of the sheath can include a soft tip having at least one hole defined therein. The handle can have a bidirectional control configured for controlling or deflecting the direction of the distal portion of the sheath by at least 90 degrees to aid in positioning and aligning the balloon, as well as an occlusion device into the ASD. The balloon, such as a sizing balloon, can measure the size of the ASD within the interatrial septum of a heart of a patient.
Owner:AL QBANDI MUSTAFA H ABDULLAH DR
Method and apparatus for locating the fossa ovalis and performing transseptal puncture
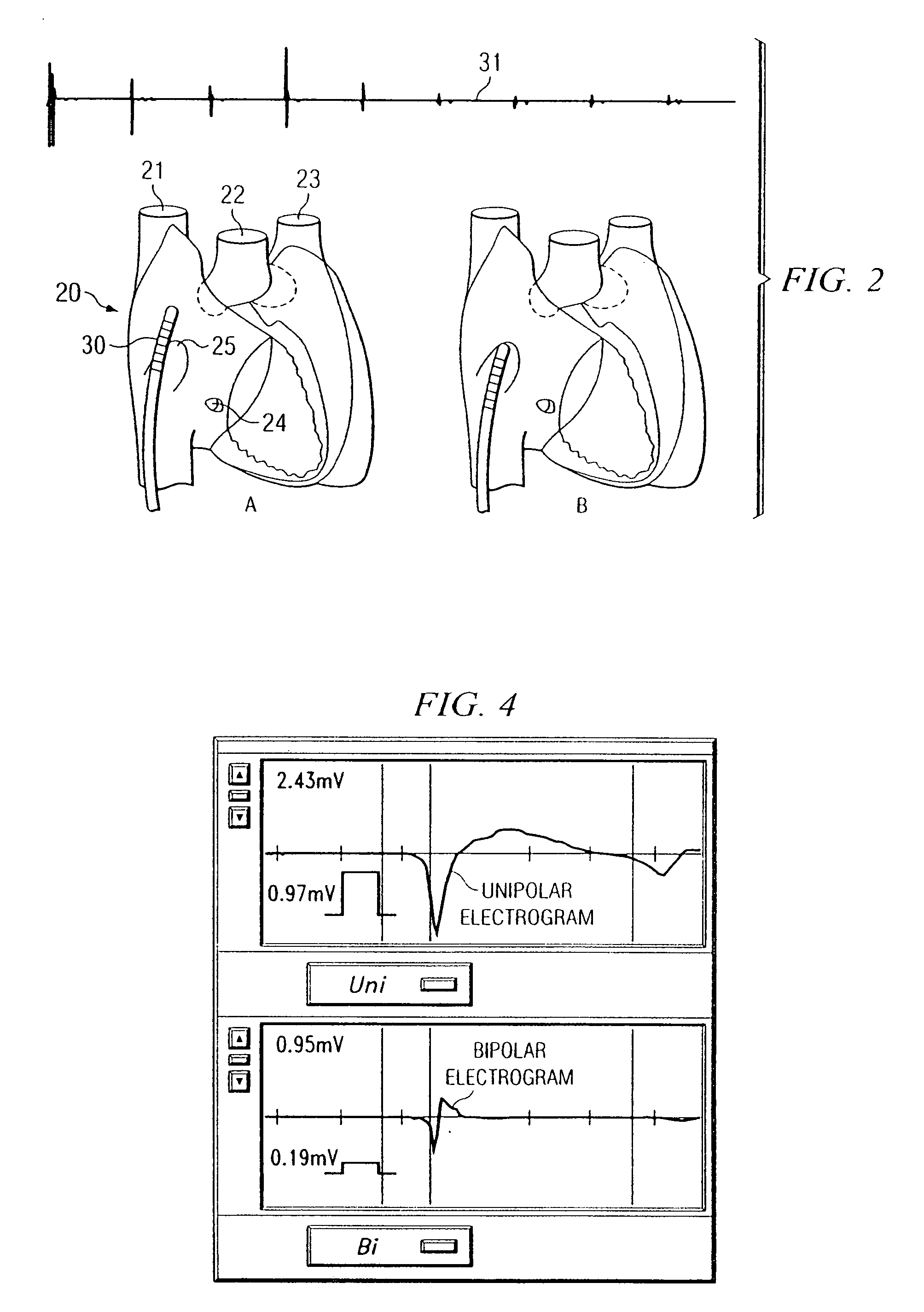
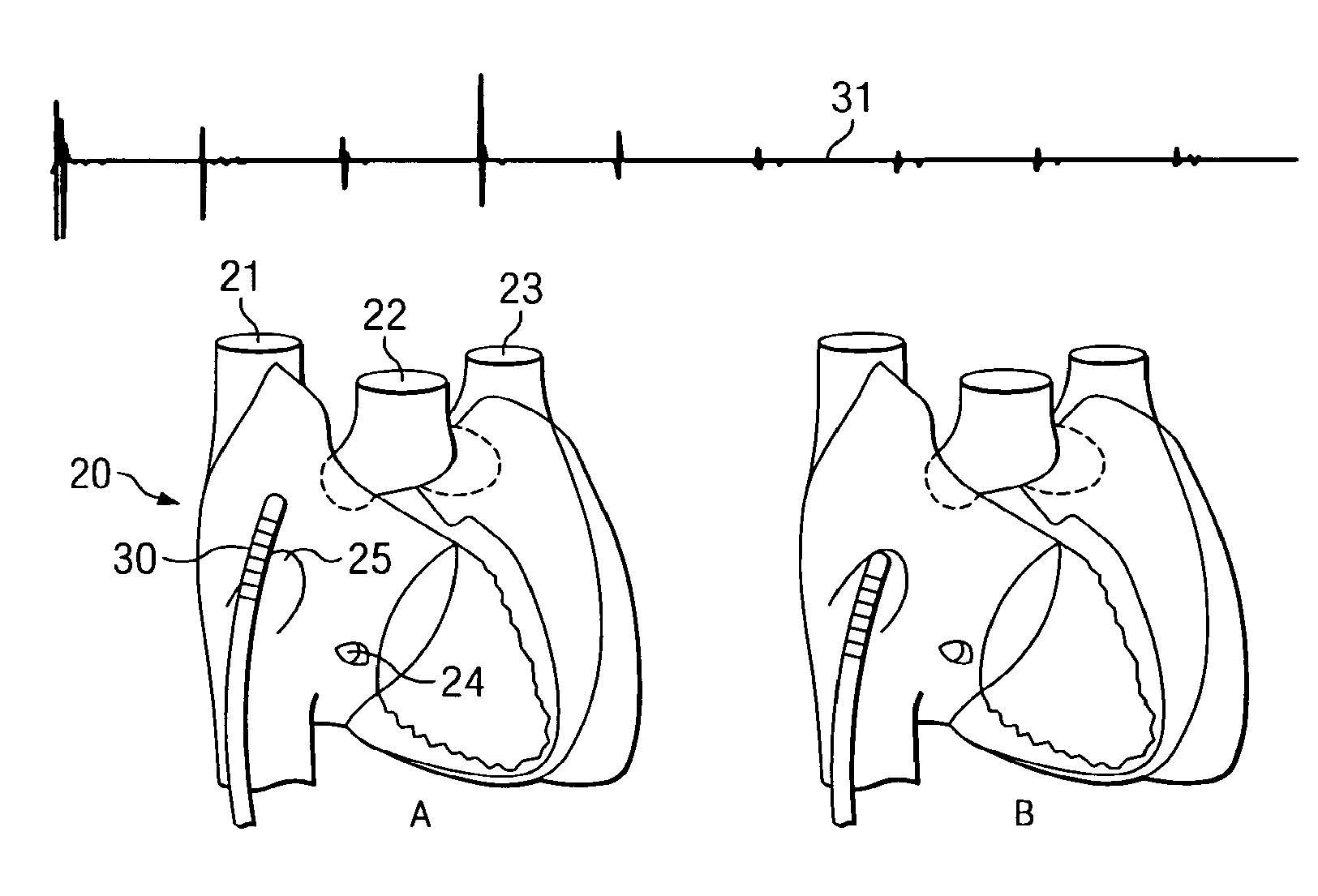
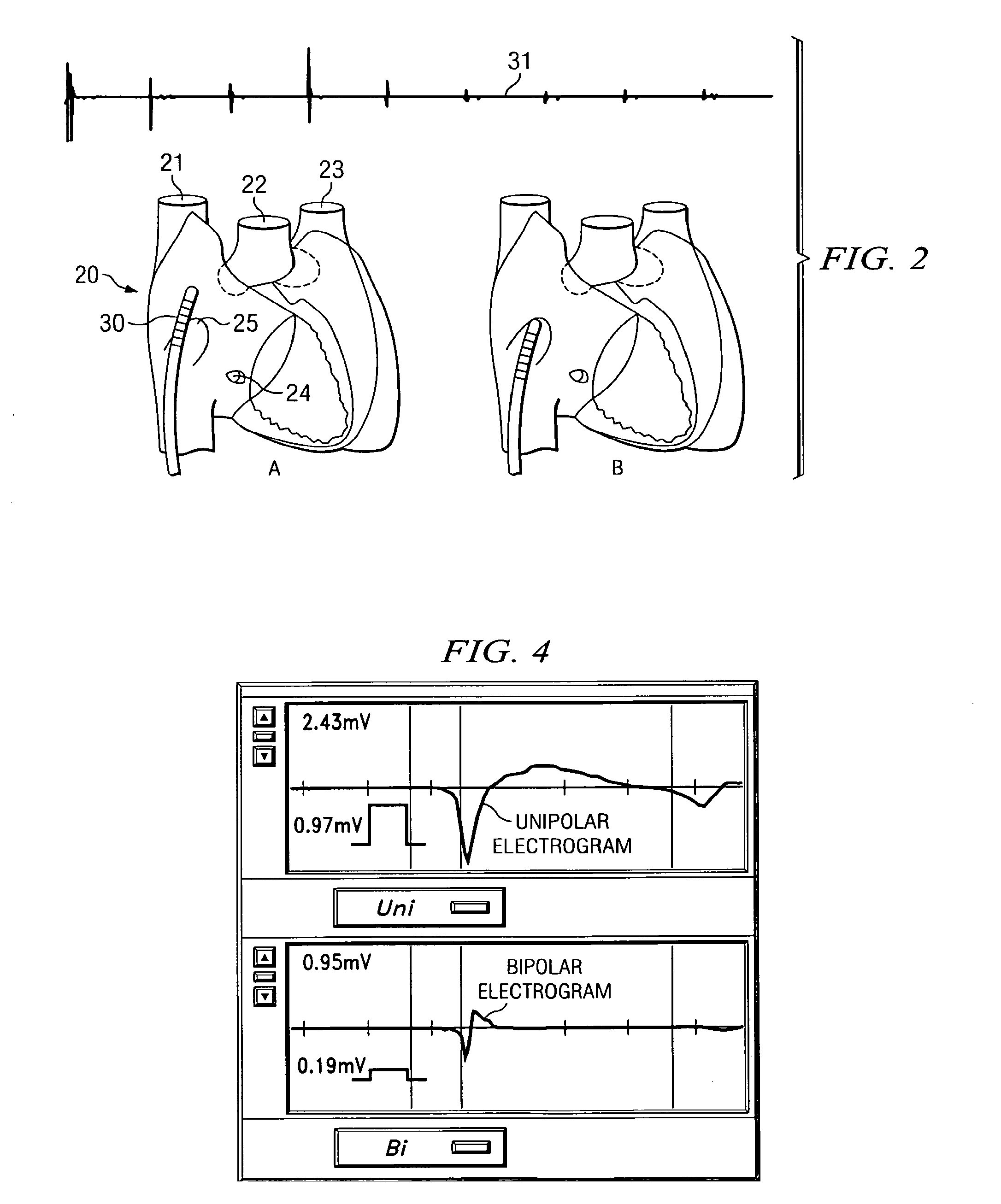
A method of identifying the fossa ovalis in a patient by positioning one or more electrodes against the tissue of the interatrial septum of the patient and acquiring unipolar and / or bipolar electrograms of the tissue of the interatrial septum while moving the electrodes to a plurality of positions against the tissue of the interatrial septum. The fossa ovalis is identified on the basis of unipolar voltage reduction, signal fractionation, broadened signal, reduced signal slew rate, reduced local myocardial impedance, increased phase angle and / or increased pacing threshold. An apparatus for identify the fossa ovalis is also provided.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Transcatheter device for interatrial anastomosis
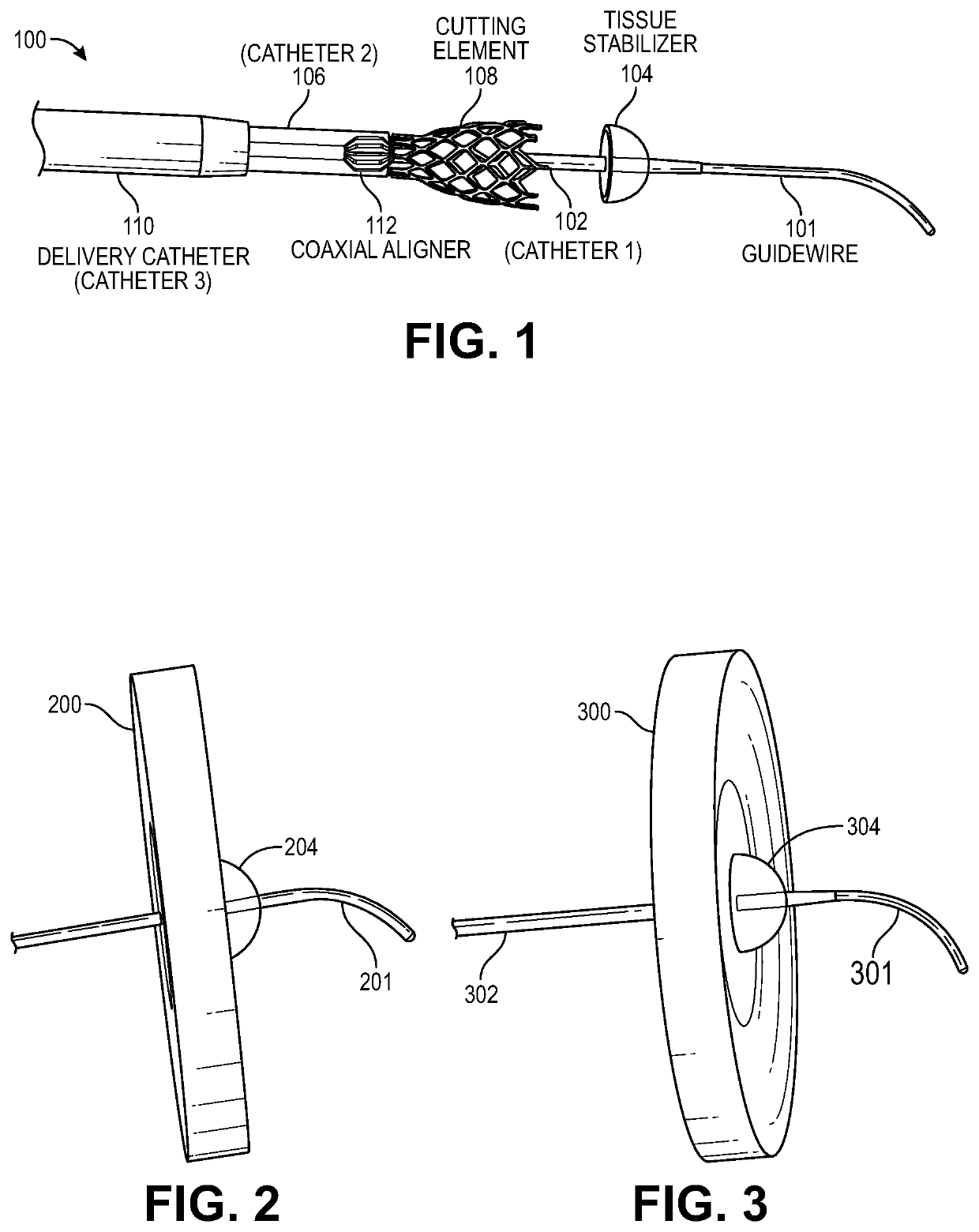
PendingUS20190374254A1Small sizeGuide needlesIncision instrumentsLeft atrial pressureAppliance component
The present disclosure relates to a device assembly and a method for treating heart failure by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left atrium of a heart of a mammal. Disclosed herein is a transcatheter interatrial septum excision device assembly configured to create a sized interatrial aperture between the right and left atria of a heart for the relief of elevated left atrial pressure. The device assembly comprises a delivery catheter, a tissue stabilizer attached to a first catheter having a central lumen and a penetrating tip that permits passage of a guidewire, and a cutter attached to a second catheter having a central lumen that permits passage of the first catheter. Alternative configurations comprise a (third) catheter having a central lumen that permits passage of the aforementioned components to and from the right atrium, a tissue retention mechanism and an optional coaxial alignment mechanism.
Owner:TEXAS MEDICAL CENT
Medical device and fixing mechanism of medical equipment
The invention provides a medical device and a fixing mechanism of medical equipment. The medical equipment can be conveniently located at a target position in the body through the fixing mechanism toachieve corresponding implantation or interventional treatment of the medical equipment, and accordingly, the medical effect is improved. The medical equipment can be a lead-free pacemaker, and physiological pace-making on the heart by the pacemaker is conveniently realized. The fixing mechanism comprises a base and fixing member, the extension direction of the base is parallel to that of a presetobject, and the fixing member is arranged on the outer wall of the base and extends around the base; one end of the fixing member is connected with the outer wall of the base, and a gap is formed between the other end of the fixing member and the outer wall of the base. During actual use, the base is stressed to rotate along the extension direction of the fixing member, and drives the fixing member to rotate together; during rotation, the fixing member is directly inserted into a tissue or a blood vessel wall parallel to the base, so that the medical equipment can be fixed into the atrium, the ventricle, the precava or other blood vessels, or fixed onto the interventricular septum or the interatrial septum.
Owner:MICROPORT SORIN CRM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Puncture needle component
ActiveCN105342671AReduce operational technical difficultyNo risk of injury or even perforationSurgical needlesTrocarDilatorSurgical site
The invention relates to a puncture needle component which comprises a puncture needle, a navigation guide wire, a sheathing tube with a dilator and a three-dimensional positioning and orienting device. The navigation guide wire is arranged inside the puncture needle to form an integrated guide-wire-shaped solid core puncture needle which is connected with the sheathing tube and the three-dimensional positioning and orienting device. The puncture needle component can be used for completing interventricular septum puncture and interatrial septum puncture through a venipuncture approach, the problems of the prior art can be solved effectively, unlimited selecting of surrounding blood vessel approaches of a pre-operation position can be realized, spatial position selecting of a puncture target can be limited effectively while moving direction of a needle tip of the puncture needle can be positioned accurately and objectively, and two steps of puncture spacing of the puncture needle and building of a guide wire rail can be completed in one step; the puncture needle component is safe, simple and convenient to operate, operating technical difficulty is lowered substantially, operating technical error risk is avoided completely, and risks such as perforation of free ventricular wall and cardiac tamponade are avoided fully.
Owner:祝金明
Balloon catheter
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Method for constructing congenital heart disease with diminutive pulmonary blood animal model
The invention discloses a method for constructing a congenital heart disease with diminutive pulmonary blood animal model, which is characterized in that: a surgical knife enters a fourth intercostal of right chest lateral incision, and a pericardium is opened and suspended; an interatrial septum is directly expanded by a puncture needle and a balloon dilator from the right chest lateral under ultrasound guidance to form an atrial septal defect with the diameter of 1.0cm; a main pulmonary artery is sleeved by an artificial blood vessel sheet to monitor peripheral arterial blood pressure and differential pressure of a girdle place, and then the differential pressure is decreased gradually; and when the differential pressure of the girdle place of mild-moderate pulmonary stenosis is 20 to 30mmHg, or the differential pressure of the girdle place of severe pulmonary stenosis is more than or equal to 30mmHg, and the arterial blood pressure is kept stable, a girdle belt is fixed so as to form the congenital heart disease with diminutive pulmonary blood animal model. The method has the advantages of exactness, feasibility, simple and reliable operation method, convenient operation and a few complications; and the constructed animal model is more ideal and better adapts to changes of clinical pathophysiology of the disease.
Owner:蚌埠医学院附属医院
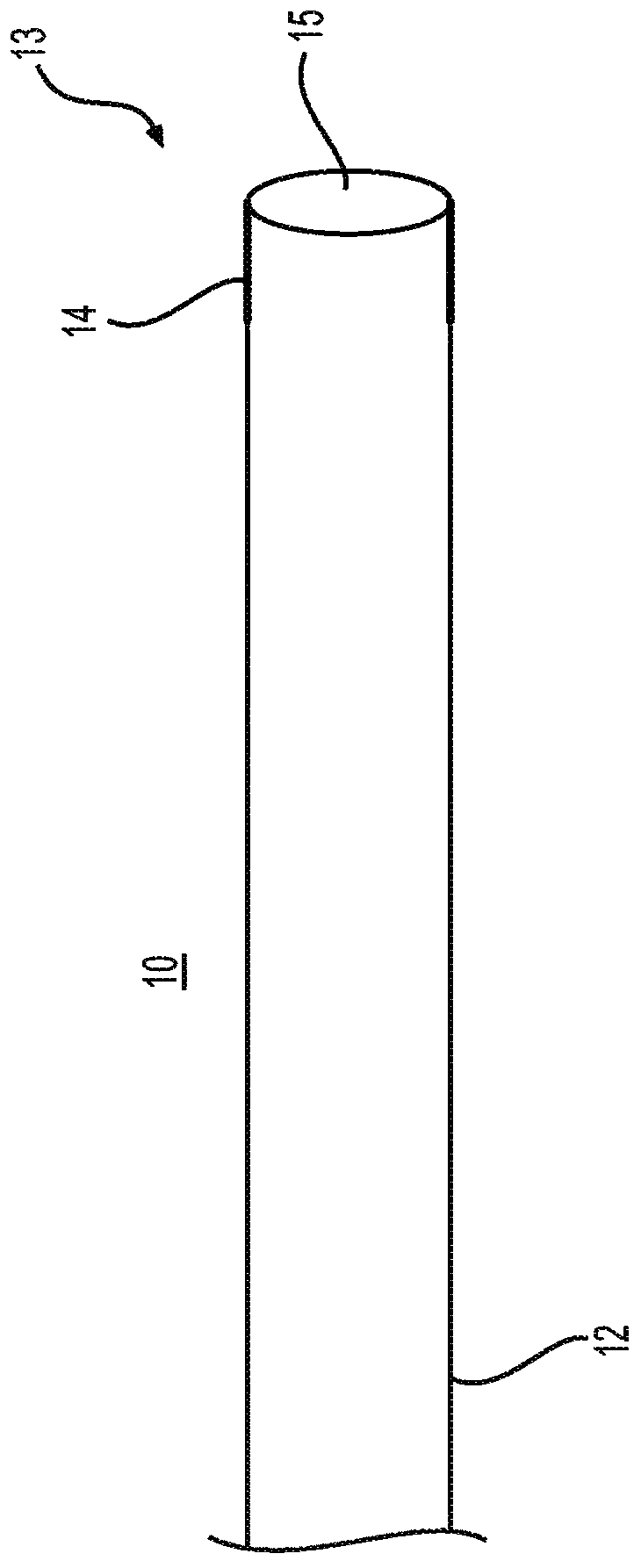
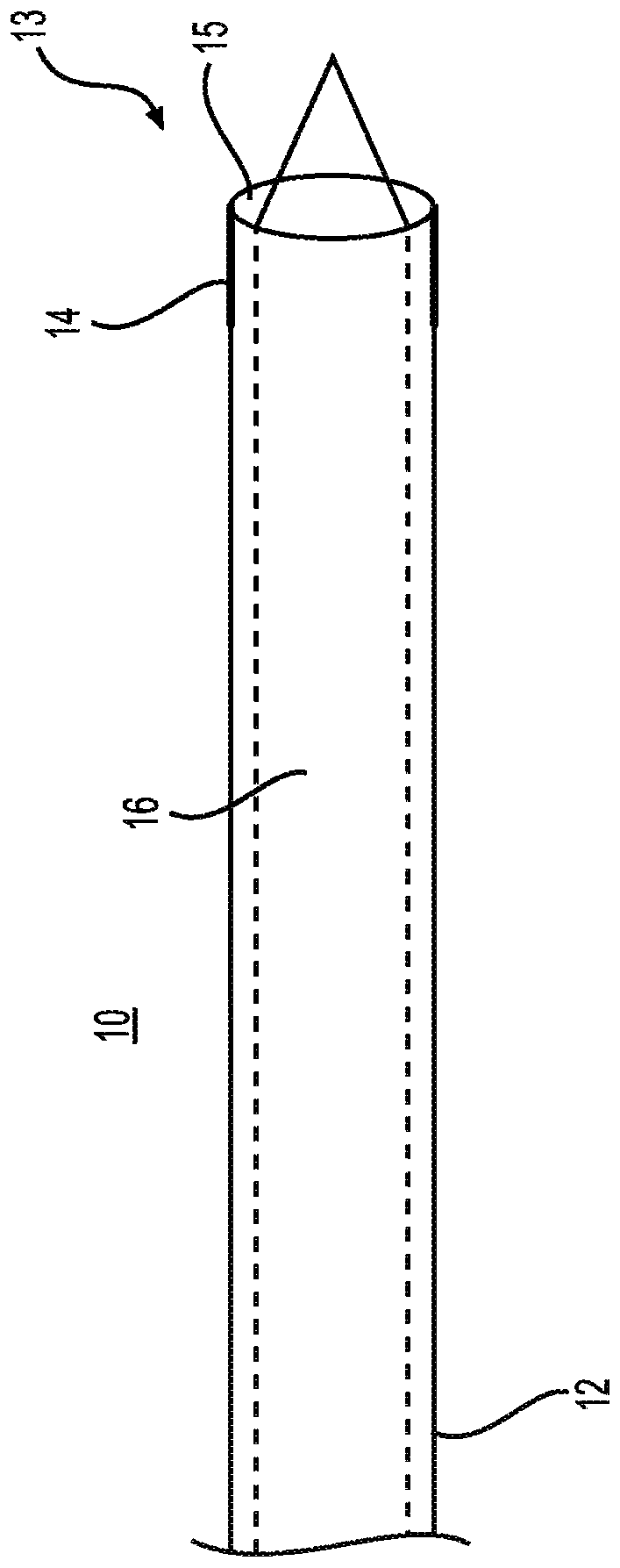
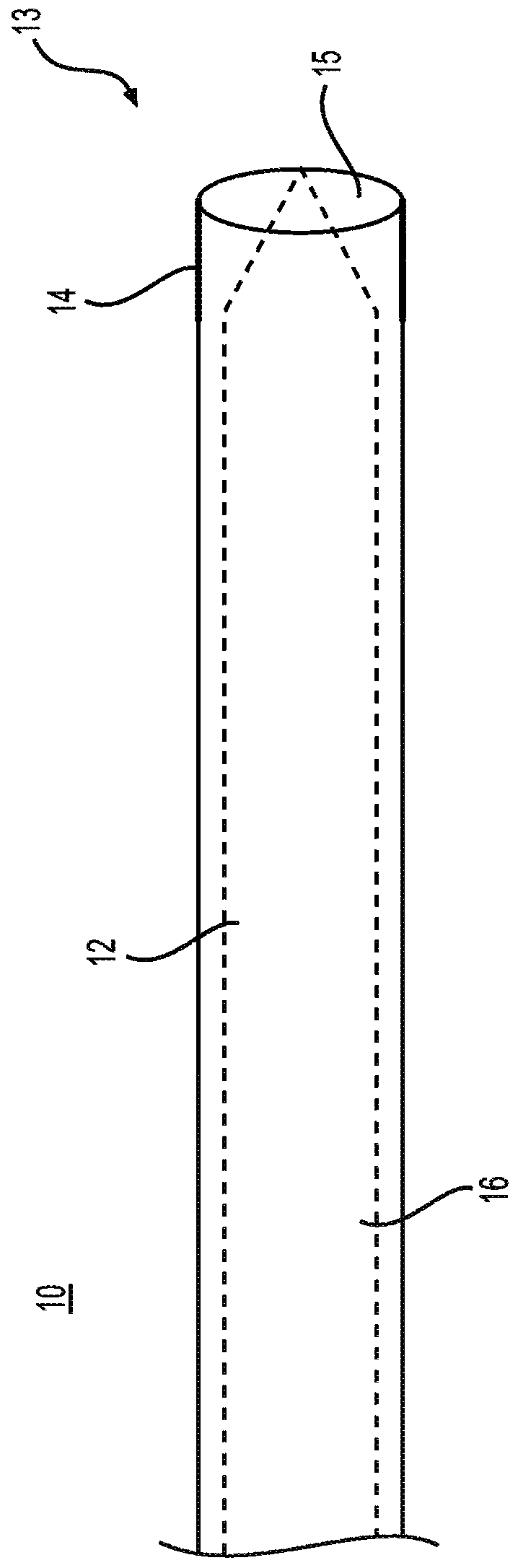
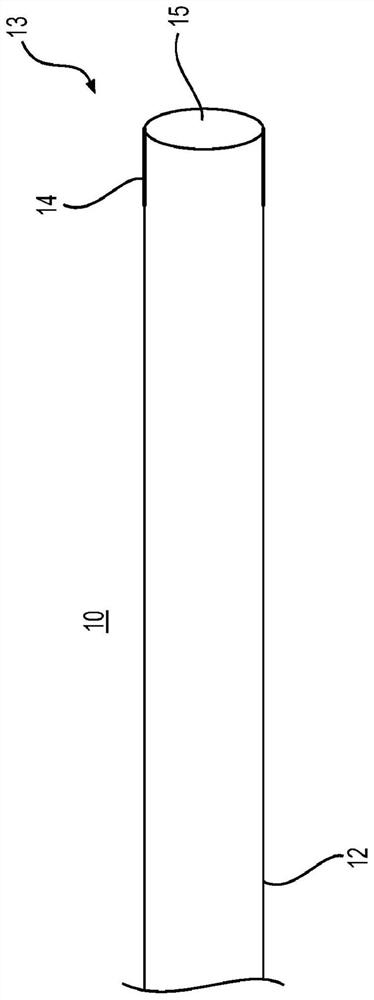
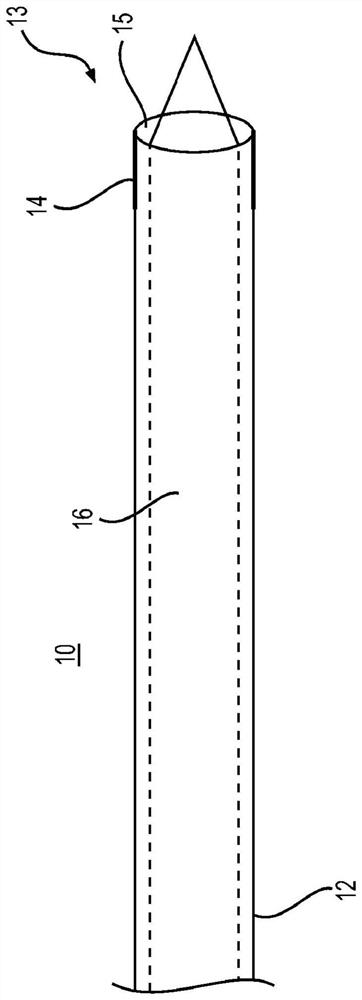
Directional balloon transseptal insertion device for medical procedures
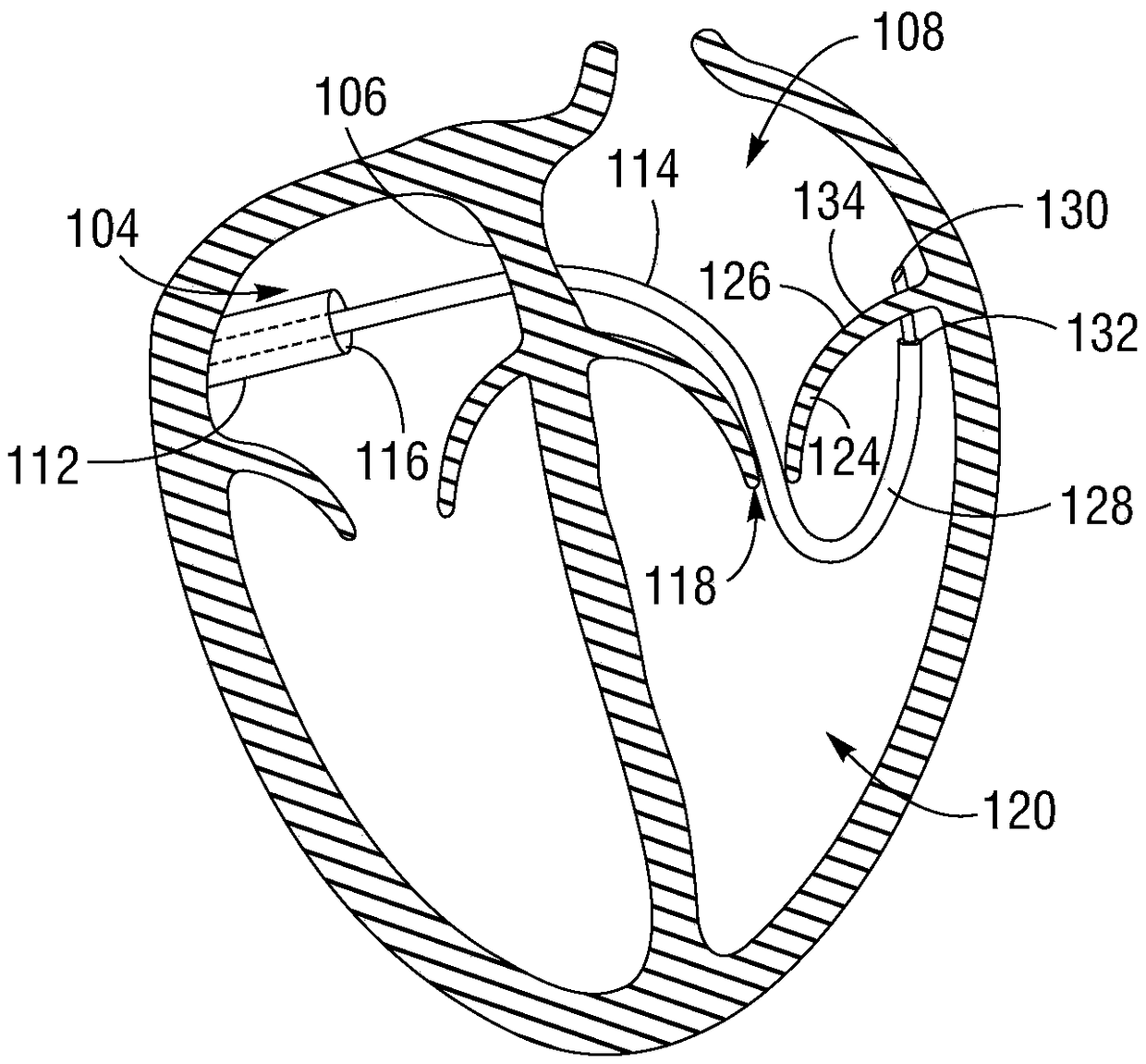
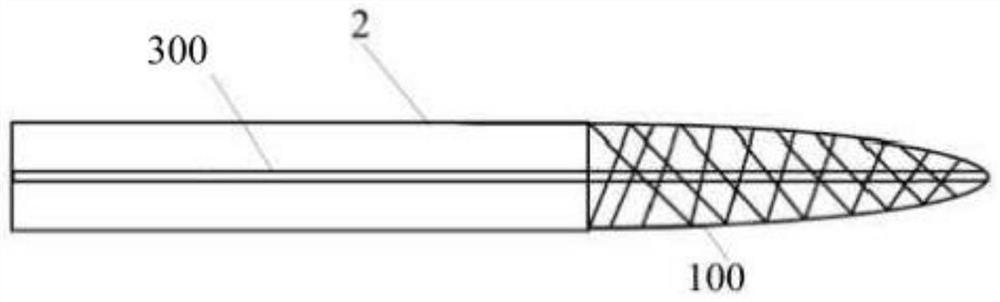
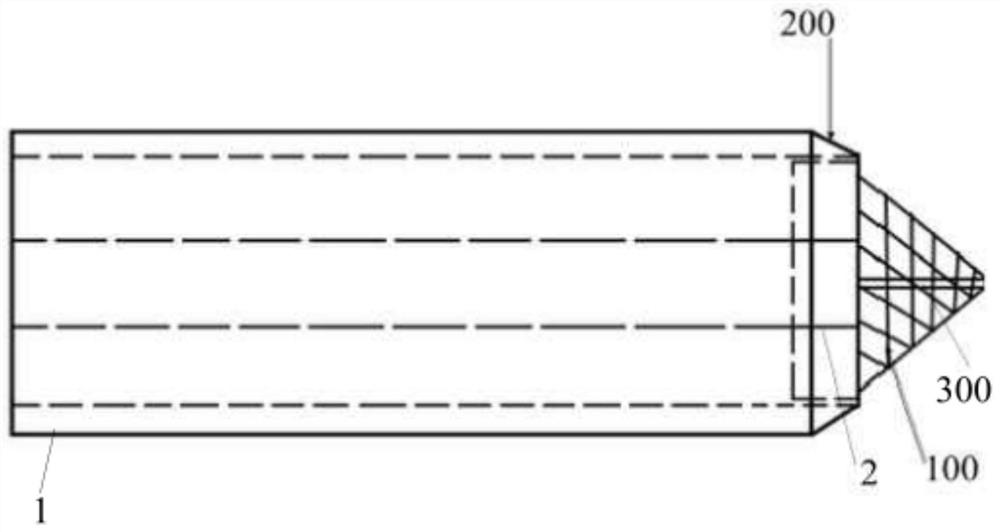
A transseptal insertion device suitable for facilitating precise and safe transseptal puncture of a cardiac interatrial septum (100) includes a sheath (12) that defines a lumen and has a distal end that is closest to the cardiac interatrial septum of a patient and a proximal end that is external to the patent, a balloon (14) that is connected to the distal end of the sheath (12) in which the balloon (14), when inflated, overhangs and extends past the distal end of the sheath, preventing accidental puncturing of the cardiac interatrial septum (100) and stabilizing the transseptal insertion device against fossa ovalis of the cardiac interatrial septum (100), and a dilator (16) that is positioned within the at least one lumen. The dilator (16) has a distal end and is designed to and is capable of precisely puncturing the cardiac interatrial septum without the use of a needle or other sharp instrument. The balloon (14) includes one or more ultrasound transceivers (26).
Owner:EAST END MEDICAL LLC
Interatrial septum puncture tool
ActiveCN102370513AAvoid damageAvoid puncturing the inner wall of the left atriumSurgical needlesTrocarDilatorNeck parts
The invention relates to an interatrial septum puncture tool, which comprises an epitheca, an expander and a puncture needle, wherein the expander is pasted and arranged in the epitheca in a penetrating way, and the puncture needle is arranged in the expander in a penetrating way. The interatrial septum puncture tool is characterized in that the puncture needle comprises a head part, a neck part and a body part in sequential connection, the head part is a puncture needle head, the neck part is a tight spiral fine steel wire with at least one micro fine steel wire penetrating at the inner side, and the body part is a long soft steel wire. The tool has the advantages that the design is reasonable, and in addition, the condition of left atrium inner wall puncture injury by the needle head caused by puncture positioning inaccuracy or excessive puncture acting force can be avoided.
Owner:苏州市弋翔众惠医疗科技有限公司
Wireless atrial pacing device implanted through catheter
InactiveCN106178262APacing achievedPhysiological pacingInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsDevice implantMedicine
The invention discloses a wireless atrial pacing device implanted through a catheter. The device comprises a waist part provided with a left disk, a right disk and two disks on the two sides, wherein the disks are in bowl shapes, the waist part is cylindrical, the diameter of each disk is larger than that of the waist part, and a wireless pacemaker host is implanted in the waist part; the left disk, the right disk and the cylindrical support waist part are braided and connected into a whole through nitinol. Through the device, physiological atrial pacing on the basis of the wireless technology is realized, the disks enable the pacemaker to be fixed to the interatrial septum of the atrium more firmly, and an electrode is more closely attached to the interatrial septum tissue; the net-shaped cylindrical support waist part is formed by braiding nitinol wires, the two sides of the support are provided with the left disk and the right disk, the wireless pacemaker host is implanted in the cylindrical support waist part, and containing space and supporting are provided for the pacemaker host; the electrode at the head end of the wireless pacemaker host stretches towards the two side disks, the tail end of the electrode is connected with four metal electrodes located on the inner sides of the disks, and the electrode is in contact with the interatrial septum tissue, so that atrial pacing is realized.
Owner:李攀 +1
Directional balloon transseptal insertion device for medical procedures
A transseptal insertion device includes a sheath that defines a lumen and has a distal end that is closest to the cardiac interatrial septum of a patient, at least one balloon connected to the distal end of the sheath, in which the at least one balloon, when inflated, overhangs and extends past the distal end of the sheath, preventing accidental puncturing of the cardiac interatrial septum and stabilizing the transseptal insertion device against fossa ovalis of the cardiac interatrial septum, and a dilator positioned within the lumen. The dilator has a distal end and is capable of precisely puncturing the cardiac interatrial septum without the use of a needle or other sharp instrument. The at least one balloon is connected to at least one hypotube through which the at least one balloon is inflated or deflated by gas or fluid flowing through the at least one hypotube.
Owner:EAST END MEDICAL LLC
Device for left auricle ligation and using method of device
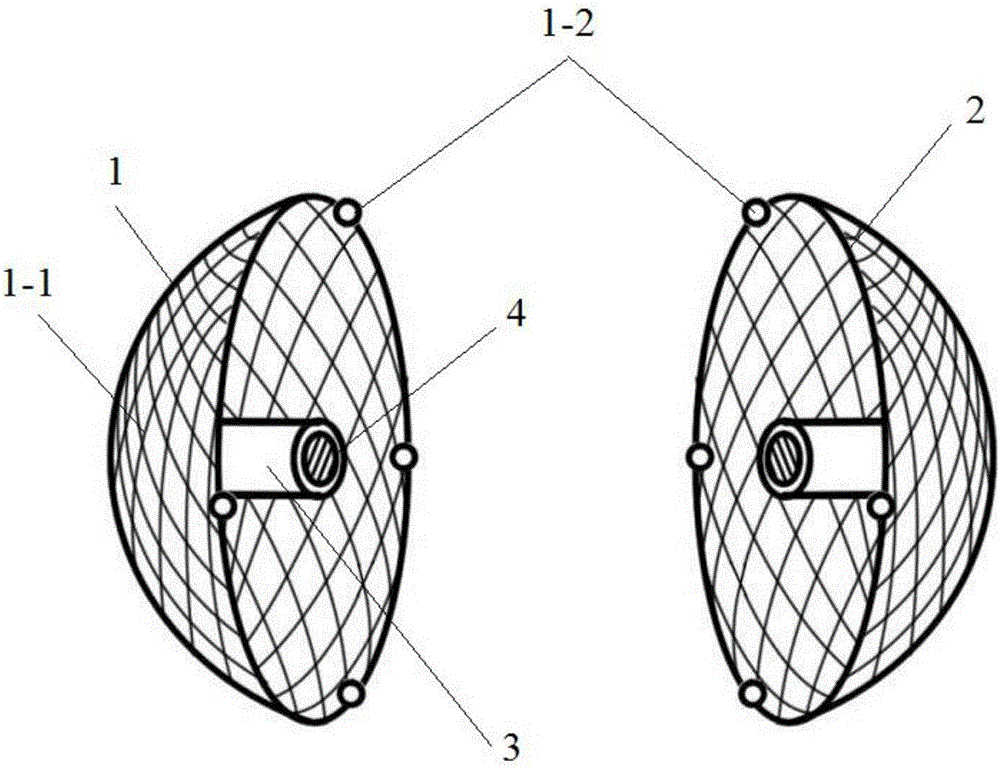
The invention discloses a device for a left auricle ligation. The device comprises an epitheca tube, an endotheca tube, guide wires, a spiral device, a knotting and sewing device and a cutting device. The epitheca tube reaches a left auricle through a vein blood vessel. The endotheca tube is used for interatrial septum puncturing and positioning the guide wires in the left auricle. The guide wires are used for being introduced into a minimally invasive surgery device. The spiral device is used for being connected with the tip of the left auricle. The knotting and sewing device is used for knotting and sewing the tip of the left auricle. The cutting device is used for cutting the knotted part of the tip of the left auricle. The caliber of the epitheca tube is larger than that of the endotheca tube. The device has the benefits that the part, prone to cause thrombus, in the left auricle is cut, so that the hidden danger of stroke is eliminated thoroughly; the guide wires are arranged in the endotheca tube to reduce the danger that the tip of the left auricle is mistakenly punctured by the epitheca tube; the whole operation is conducted in a vein blood vessel, and a thoracotomy is not needed, so that the invasive surgery is reduced, and the postoperative recovery time is shortened; and since the left auricle is cut, the problem of related complications caused by left atrial appendage occluder at present is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Methods and Apparatus for Locating the Fossa Ovalis and Performing Transseptal Puncture
A method of identifying the fossa ovalis in a patient by positioning one or more electrodes against the tissue of the interatrial septum of the patient and acquiring unipolar and / or bipolar electrograms of the tissue of the interatrial septum while moving the electrodes to a plurality of positions against the tissue of the interatrial septum. The fossa ovalis is identified on the basis of unipolar voltage reduction, signal fractionation, broadened signal, reduced signal slew rate, reduced local myocardial impedance, increased phase angle and / or increased pacing threshold. An apparatus for identifying the fossa ovalis is also provided.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Posterior mitral valve leaflet approximation
The present disclosure provides embodiments of an assembly that can be used in a method for improving coaptation of the anterior and posterior mitral valve leaflets by applying a remodeling force to the posterior leaflet. In particular embodiments, the assembly includes an elongate delivery catheter having at least one lumen and an elongate flexible tension member having first and second ends. Thetension member is deployable from the delivery catheter. The assembly further includes a closure member configured to be implanted in the interatrial septum of a patient' s heart, and a deployable fastener configured to be secured on the tension member adjacent to the closure member. Once secured to the heart, tension can be applied to the tension member in a direction superiorly and anteriorly toward the interatrial septum, providing a remodeling force pulling the posterior leaflet superiorly and anteriorly to improve coaptation with the anterior leaflet.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Three-dimensional interatrial septum puncture assembly
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional interatrial septum puncture assembly. The three-dimensional interatrial septum puncture assembly comprises an interatrial septum puncture needle anda dilator, the dilator comprises an dilator tube body, the dilator tube body comprises a central cavity, a far end and a near end, the far end of the dilator tube body is provided with a small hole,a contact assembly is arranged in the small hole, and the contact assembly comprises an elastic element; and the near end of the dilator tube body is connected with a luer connector. The three-dimensional interatrial septum puncture assembly enables a position of a needle tip of the interatrial septum puncture needle to be displayed in a three-dimensional system in real time, and reduces or eliminates risks of damages on superior vena cava and endocardial tissues caused by the needle tip.
Owner:蔡衡
Interatrial septum puncture tool
ActiveCN102370513BAvoid damageAvoid puncturing the inner wall of the left atriumSurgical needlesTrocarDilatorNeck parts
The invention relates to an interatrial septum puncture tool, which comprises an epitheca, an expander and a puncture needle, wherein the expander is pasted and arranged in the epitheca in a penetrating way, and the puncture needle is arranged in the expander in a penetrating way. The interatrial septum puncture tool is characterized in that the puncture needle comprises a head part, a neck part and a body part in sequential connection, the head part is a puncture needle head, the neck part is a tight spiral fine steel wire with at least one micro fine steel wire penetrating at the inner side, and the body part is a long soft steel wire. The tool has the advantages that the design is reasonable, and in addition, the condition of left atrium inner wall puncture injury by the needle head caused by puncture positioning inaccuracy or excessive puncture acting force can be avoided.
Owner:苏州市弋翔众惠医疗科技有限公司
Atrial septal stoma device
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly discloses an atrial septal stoma device which comprises a first sheath tube, and the far end of the first sheath tube is connected with a supporting piece; the second sheathing canal sleeves the first sheathing canal, and the far end of the second sheathing canal is connected with a cutting assembly; the handle assembly is connected with the near ends of the first sheathing canal and the second sheathing canal and used for controlling axial movement of the first sheathing canal relative to the second sheathing canal so as to drive the supporting piece to be away from or close to the cutting assembly. According to the arrangement, the supporting piece can penetrate through the pre-opening hole in the atrial septum before the atrial septum tissue is cut, and the supporting piece in the contraction state and the cutting assembly can clamp the atrial septum tissue needing to be cut through movement of the first sheath tube; and the supporting piece is controlled to pull the cut tissue into the inner cavity of the cutting assembly and block the far-end opening of the cutting assembly. The situation that when the cutting assembly retreats out of the body from the interatrial septum, cut tissue is scattered into the body and embolism is formed is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENQI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Puncture assembly suitable for atrial septum
The invention provides a puncture assembly suitable for atrial septum, and the assembly comprises an outer sheath, a dilator and a puncture needle; the dilator is sleeved in the outer sheath, the puncture needle is sleeved in the dilator, the head end of the puncture needle is a puncture head with a variable state, the puncture head is in a closed cone shape when the puncture head is located in the dilator, the puncture head is separated from the dilator after puncturing the interatrial septum, and the puncture head is in an open blunt end shape. The puncture head part of the puncture needle extends out of the dilator, at the moment, the puncture head is in a closed (closed) state, and then the whole puncture head is conical, so that puncture is facilitated; when the puncture head punctures the interatrial septum, the puncture head is separated from the dilator, and at the moment, the fork part can be opened and is in a blunt end shape due to the loss of the constraint of the check block, so the puncture state can be changed immediately; the puncture head is not enough to puncture the atrium wall, tissues such as the heart cannot be punctured, and the inner wall of the left atrium is prevented from being damaged.
Owner:蚌埠冠硕医疗科技有限公司
Cardiac interatrial septum shunt system
PendingCN112754651AAvoid cloggingRegular shapeSurgical instruments for heatingInteratrial septumRat heart
The invention provides a cardiac interatrial septum shunt system. The cardiac interatrial septum shunt system comprises a stomy member for forming a stoma in an interatrial septum. The cardiac interatrial septum shunt system further comprises an extending member arranged in an inner side space of the stomy member, wherein the extending member can be filled with fluid, and the stomy member comprises a conductive part for ablating tissue around the stoma. The extending member is used for changing a diameter size of the stomy member through volume of the filled fluid, so as to adjust the size of the stoma to be appropriate; and the conductive part is in contact with interatrial septum tissue nearby the stoma and is used for receiving a radio-frequency power supply so as to ablate the tissue of the interatrial septum at the stoma, thus, the interatrial septum tissue nearby the stoma can be deactivated, the condition that the stoma is blocked up due to crawling of repair endothelia of the tissue is prevented, and a stomy form can be fixed after stomy by an interatrial septum stomy system.
Owner:HANGZHOU NOYA MEDTECH CO LTD
Atrial septum blood flow channel creating device
The embodiment of the invention provides an atrial septum blood flow channel creating device. The device comprises a clamping mechanism used for clamping and positioning the atrial septum from the two ends of the atrial septum; the cutting pipe can axially move relative to the clamping mechanism and is used for cutting off part of the interatrial septum from the interatrial septum clamped by the clamping mechanism, so that a blood flow channel is formed in the interatrial septum. Therefore, the blood flow of the interatrial septum can be kept smooth for a long time and an implant does not need to be arranged on the interatrial septum.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENDFO MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com