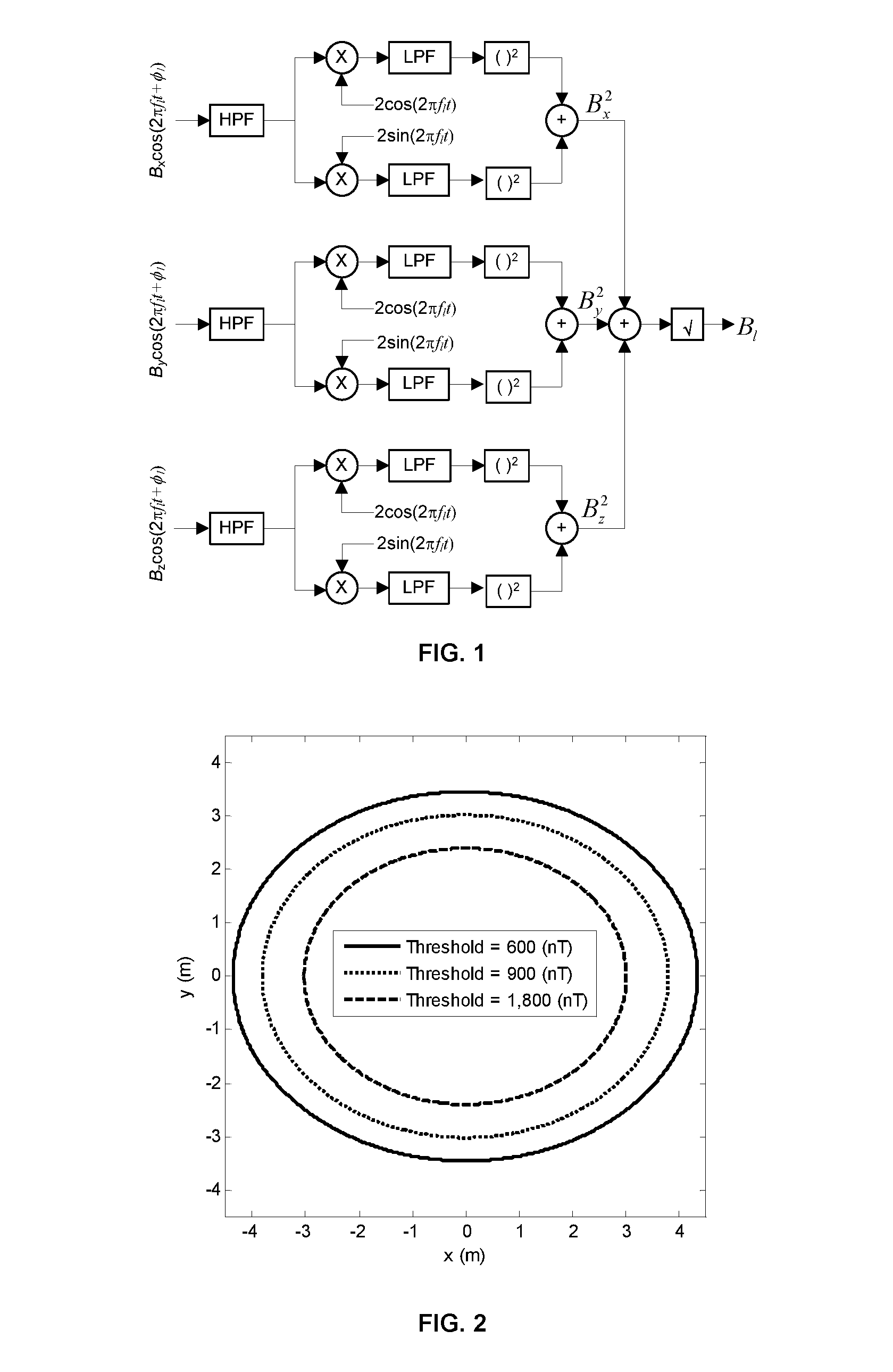
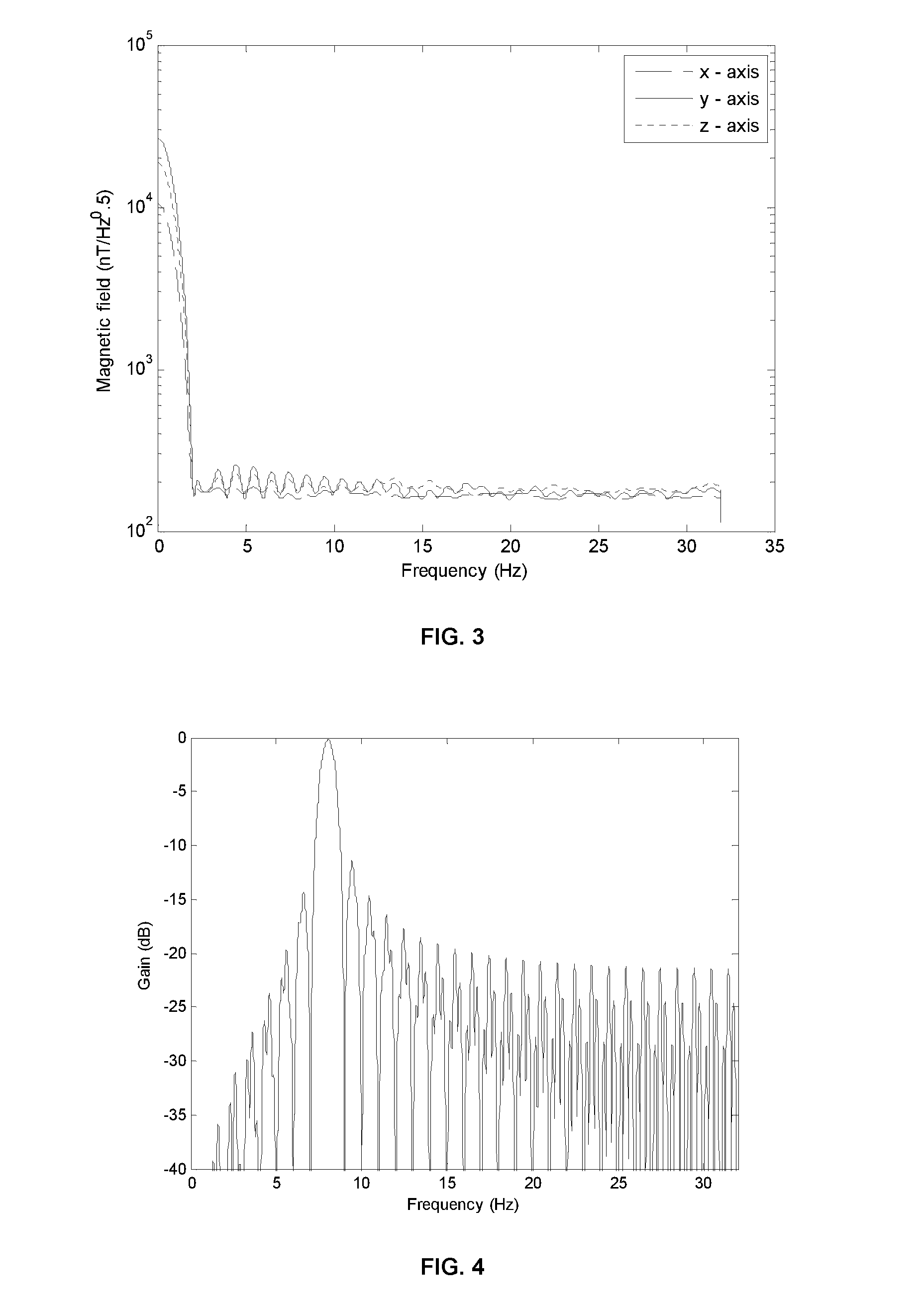
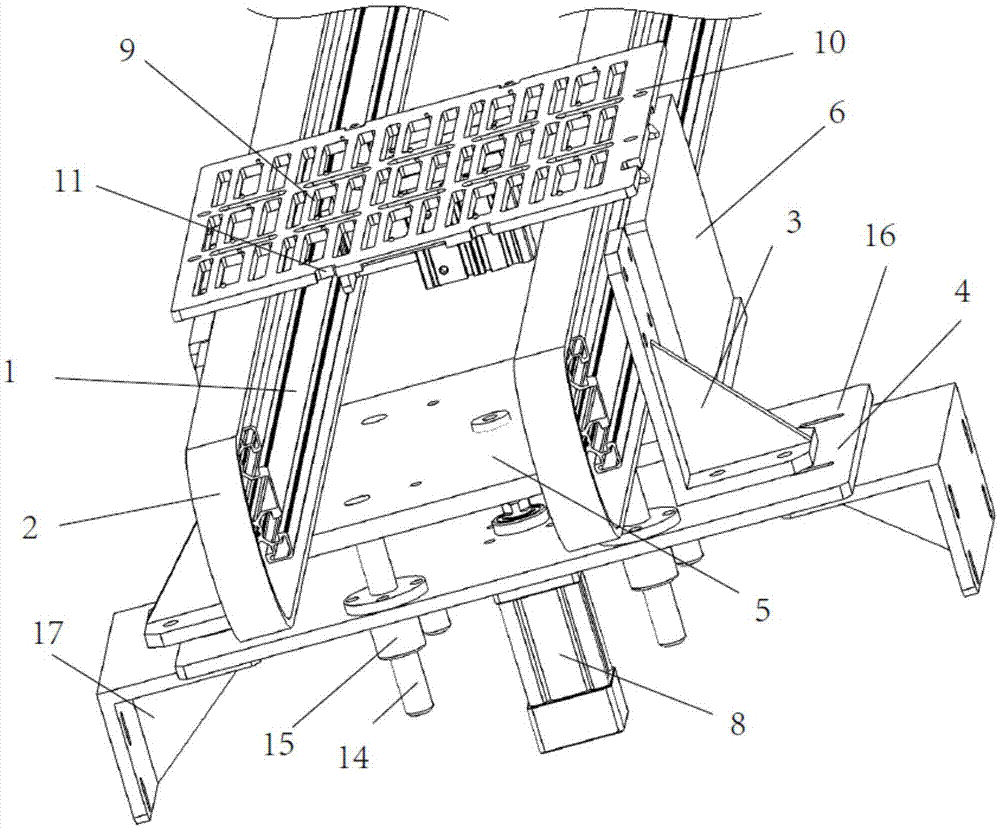
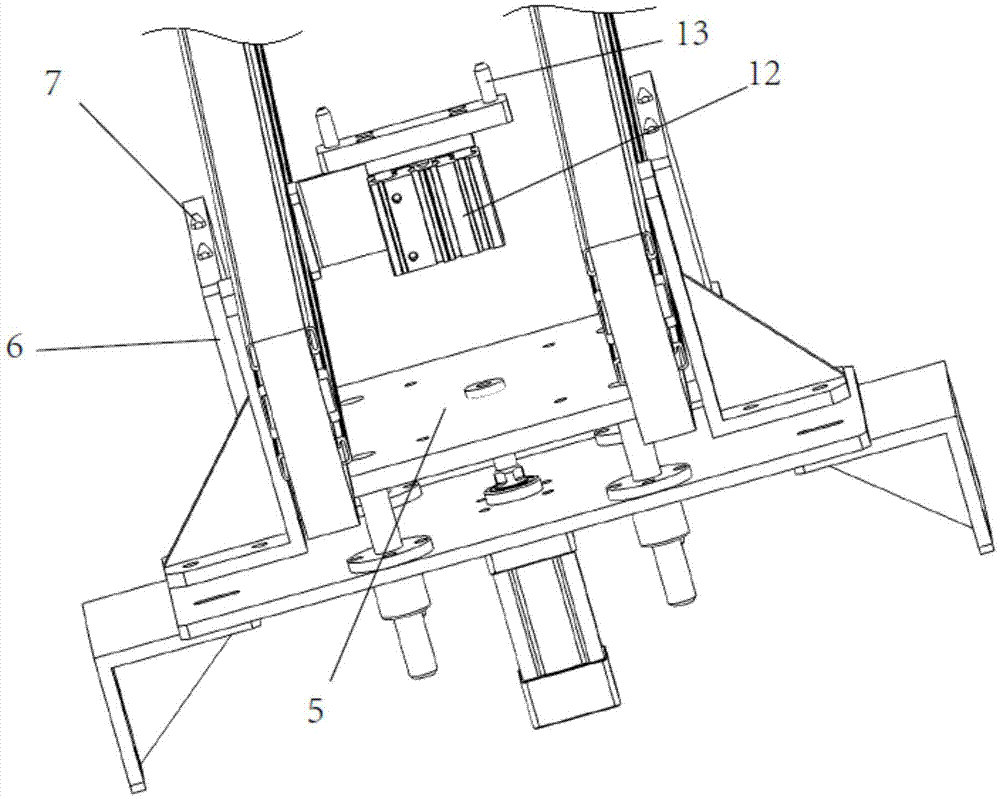
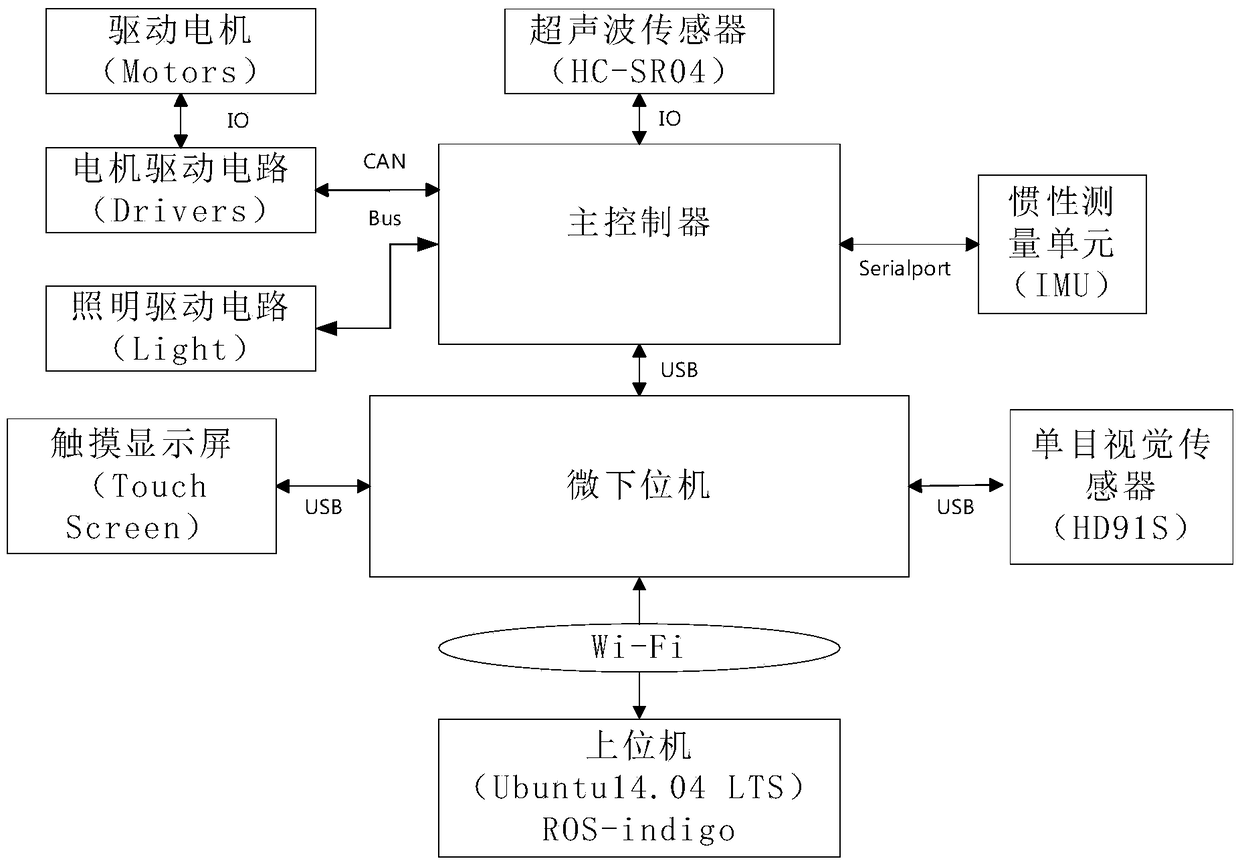
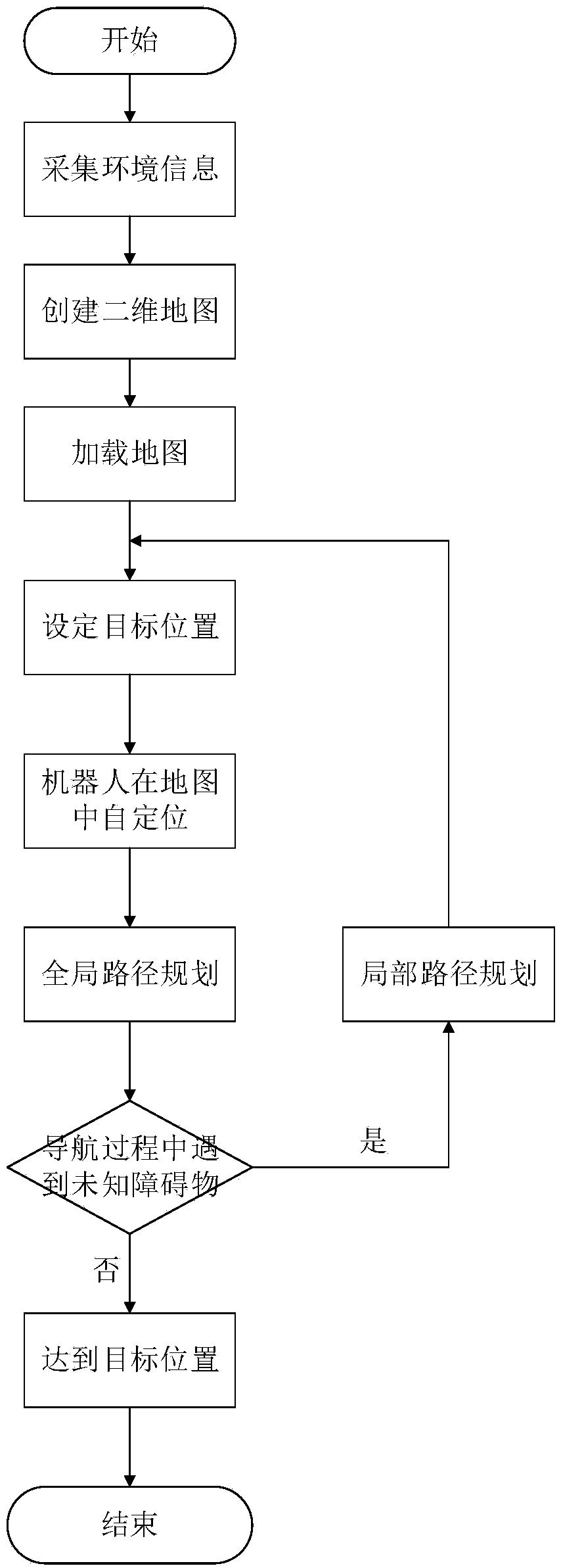
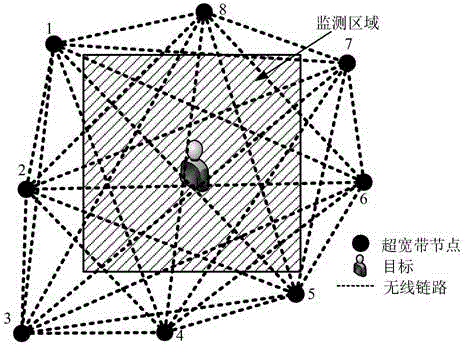
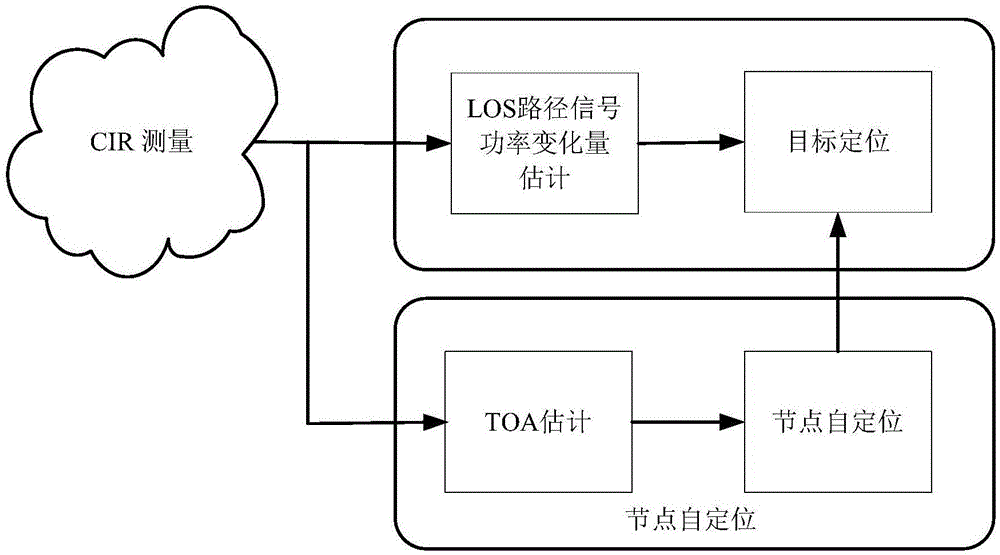
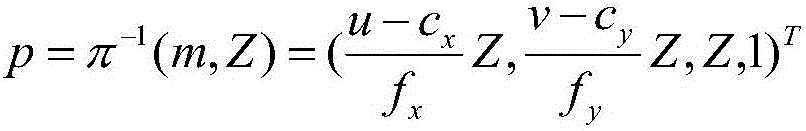Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Self localization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
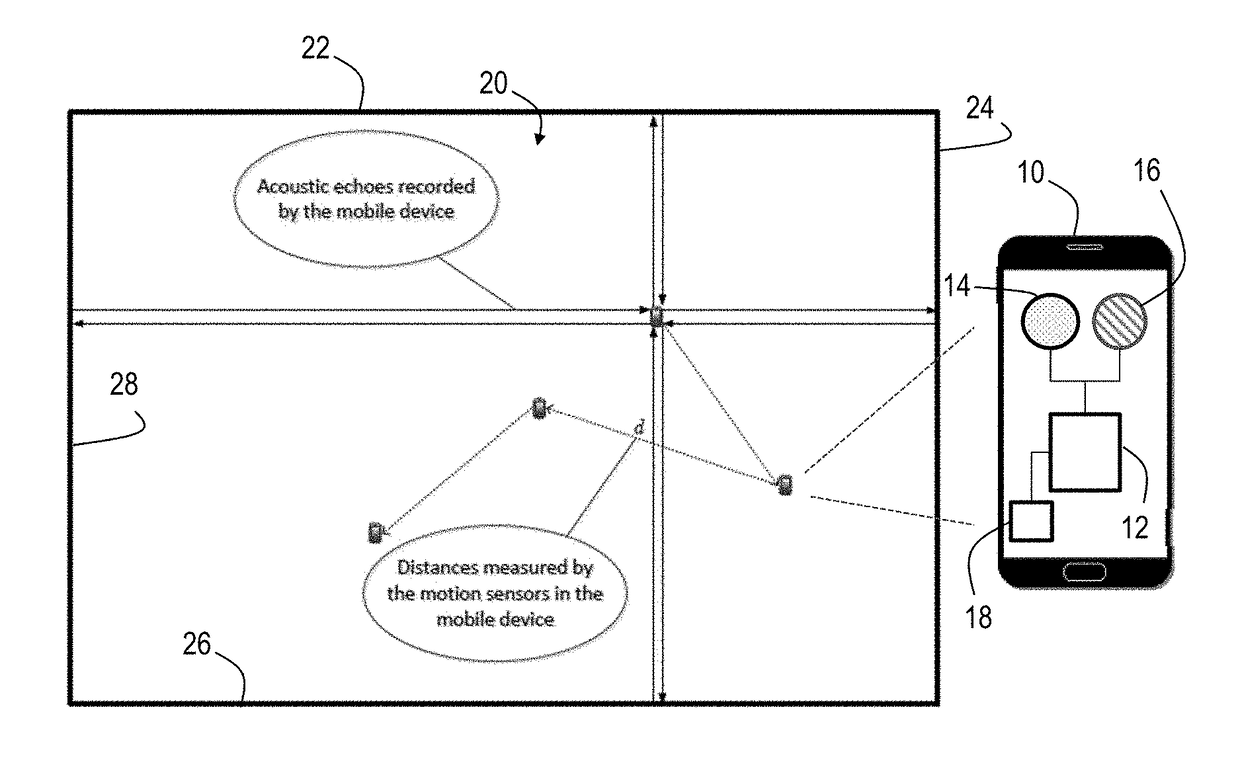
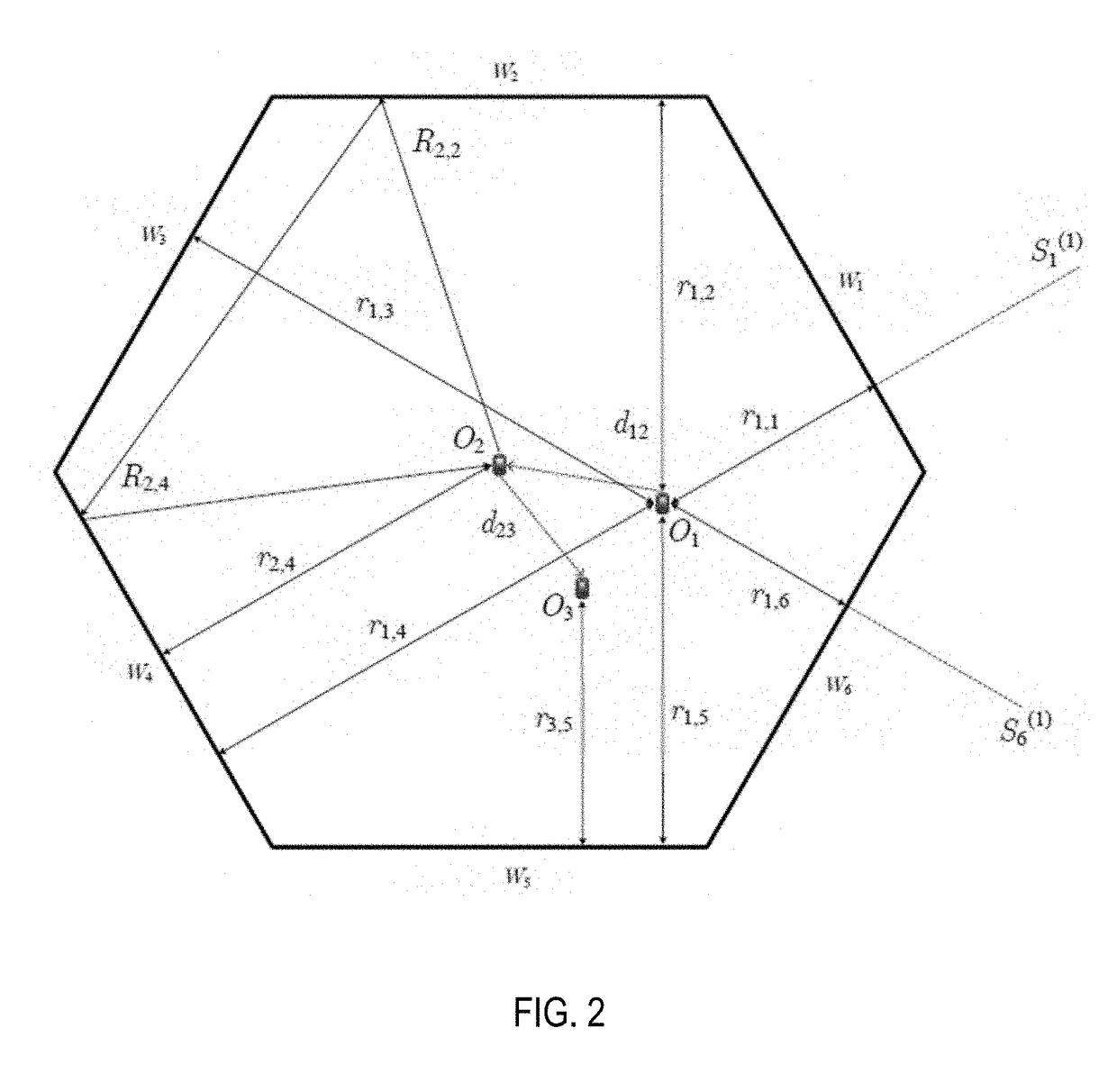
Motion sensor assisted room shape reconstruction and self-localization using first-order acoustic echoes
ActiveUS20170370710A1Improve performanceUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansAcoustic wave reradiationPractical algorithmContinuous measurement
Simultaneous 2-D room shape reconstruction and self-localization is accomplished using no pre-established infrastructure. A mobile device with co-located microphone and loudspeaker is used to collect echoes reflected by the walls. The system uniquely recovers arbitrary 2-D convex room shape as well as the position of mobile device 10 by collecting and processing distances between three consecutive measurement points as well as acoustic echoes from the device. A practical algorithm for room shape reconstruction and self-localization in the presence of noise and higher order echoes is proposed. Experimental results are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
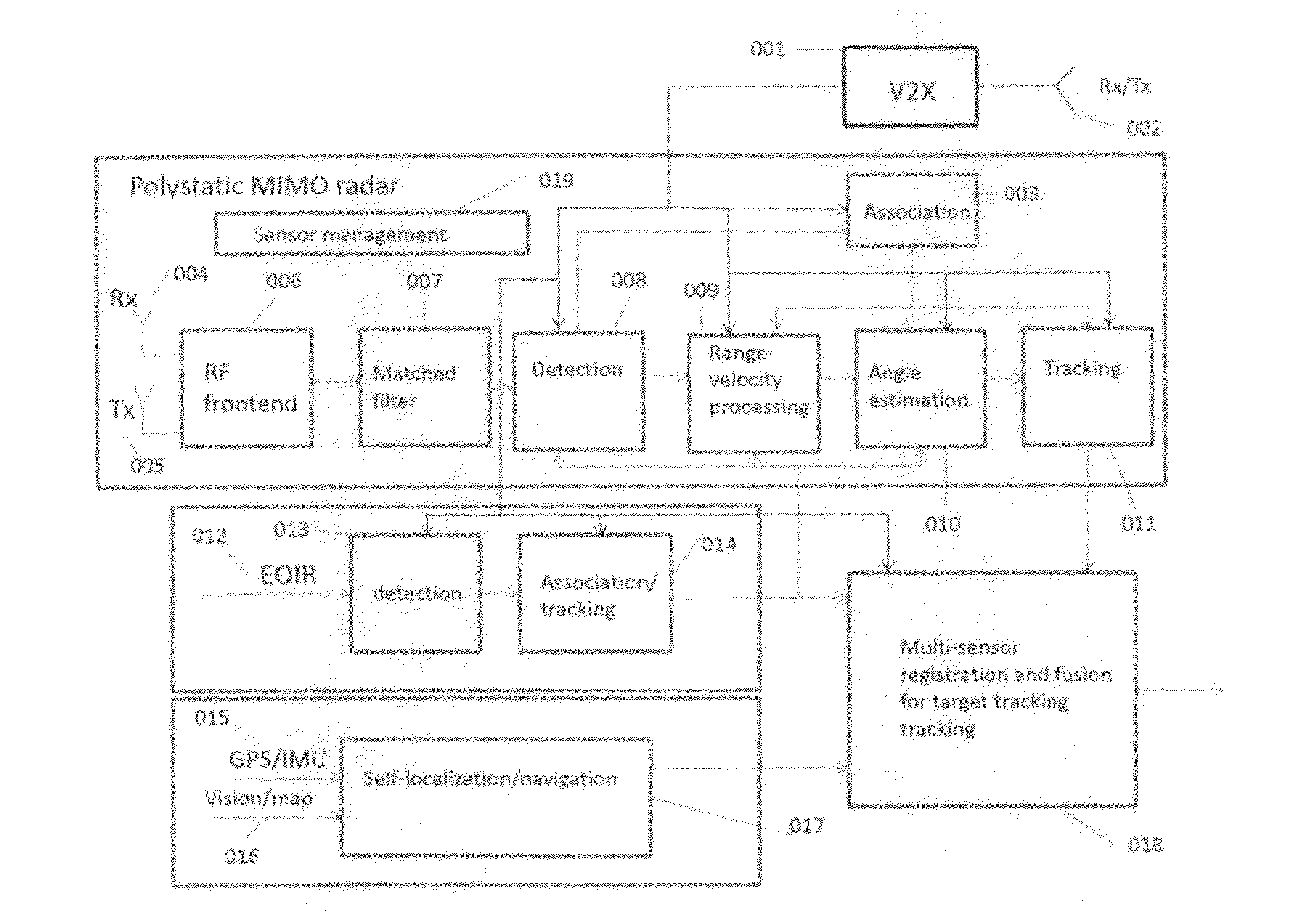
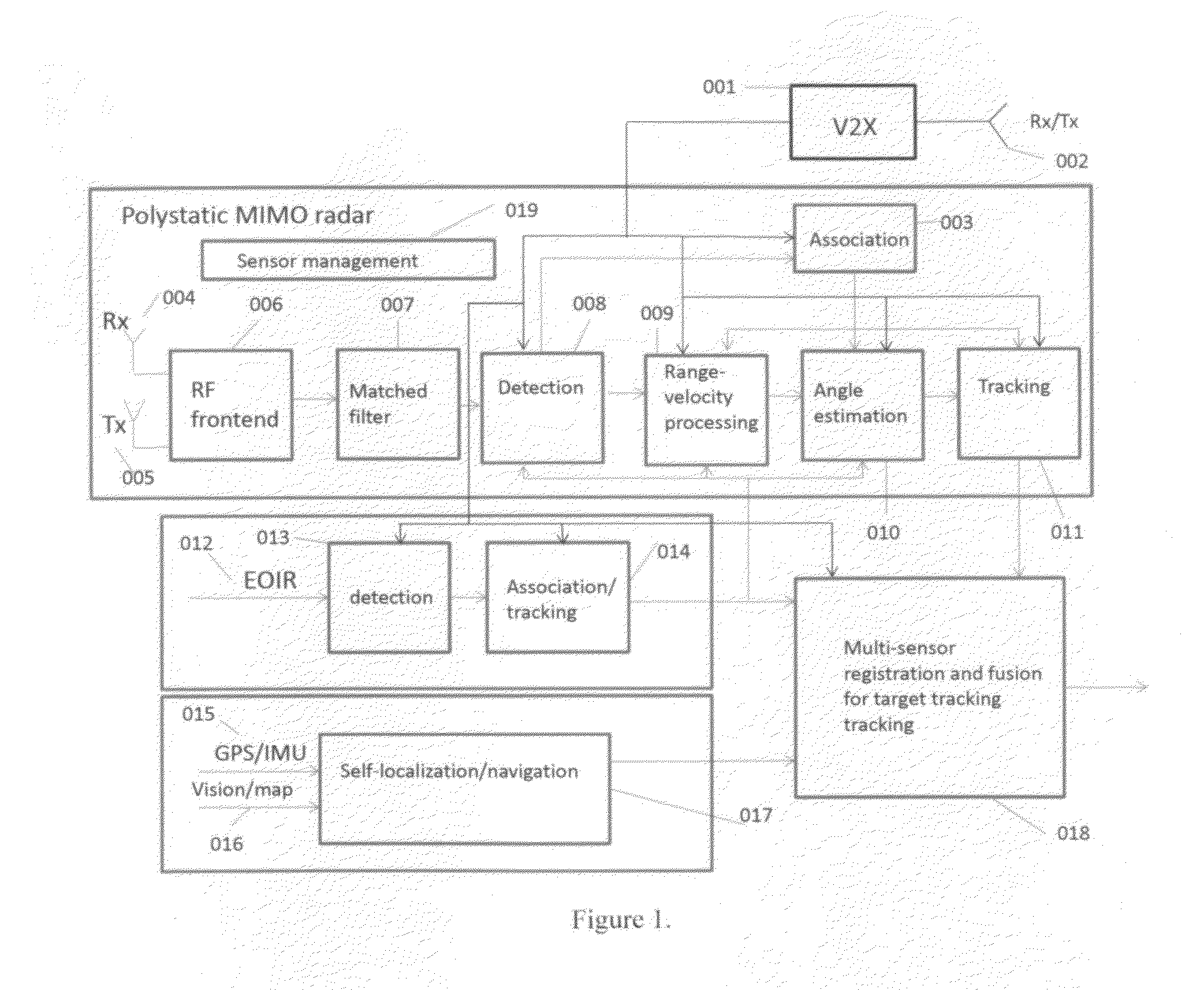
Deep Fusion of Polystatic MIMO Radars with The Internet of Vehicles for Interference-free Environmental Perception
InactiveUS20160223643A1Improve performanceSimple signal processingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputData center
This invention is related to a deep multi-sensor fusion system for inter-radar interference-free environmental perception comprising of (1) polystatic Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) radars such as radio frequency radar and laser radar; (2) vehicle self-localization and navigation; (3) the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) including Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication (V2V), Vehicle-to-Infrastructure communication (V2I), other communication systems, data center / cloud; (4) passive sensors such as EOIR, and (5) deep multi-sensor fusion algorithms. The self-localization sensors and V2X formulate cooperative sensors. The polystatic MIMO radar on each vehicle utilizes both its own transmitted radar signals and ones from other vehicles to detect obstacles. The transmitted radar signals from other vehicles are not considered as interference or uselessness as conventional radars, but considered as useful signals to formulate a polystatic MIMO radar which can overcome the interference problem and improve the radar performance. This invention can be applied to all kinds of vehicles and robotics.
Owner:LI WENHUA +1
Device and method for composition based on small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN103941750AAchieve positioningImplement navigationPosition/course control in three dimensionsRobot environmentRadar
The invention relates to a device and method for composition based on a small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle and belongs to the technical field of mobile robot positioning and navigation. The small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle can rapidly enter a complex environment which a mobile robot cannot enter, carried laser radar is utilized to construct a two-dimensional map in real time according to an SLAM method, self localization and navigation of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be achieved by combining an IMU device and the like, and efficient exploration of a true complex area is achieved; the height of the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle can be conveniently adjusted to obtain two-dimensional maps on horizontal planes of different heights; the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is rapid in movement speed and more flexible, movement and mapping of the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle are not subject to disturbance of obstacles on the ground, the range limitation of a detecting robot is broken through, the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is extremely high in practical value, and accurate and rapid map construction can be achieved; compared with robot environment composition, the rotor wing robot can perform environment scouting more rapidly and more flexibly, and three-dimensional spatial images can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
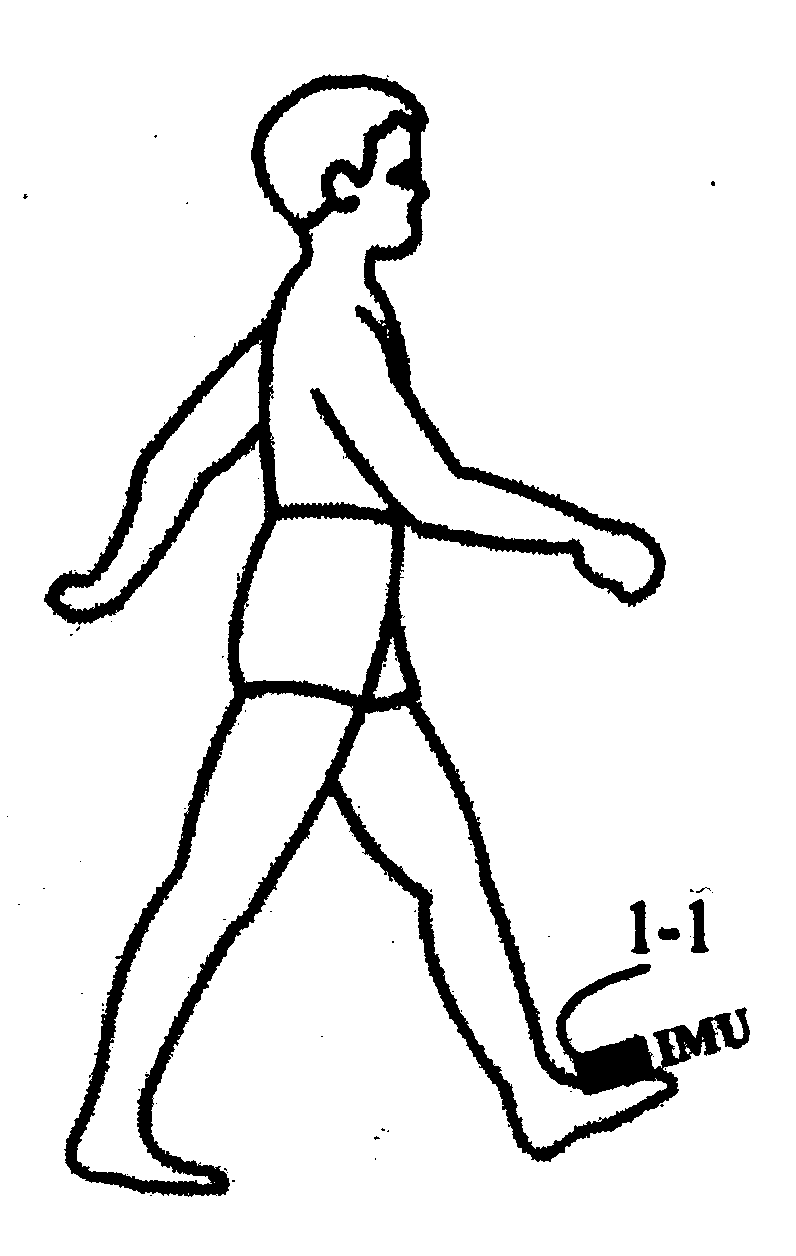
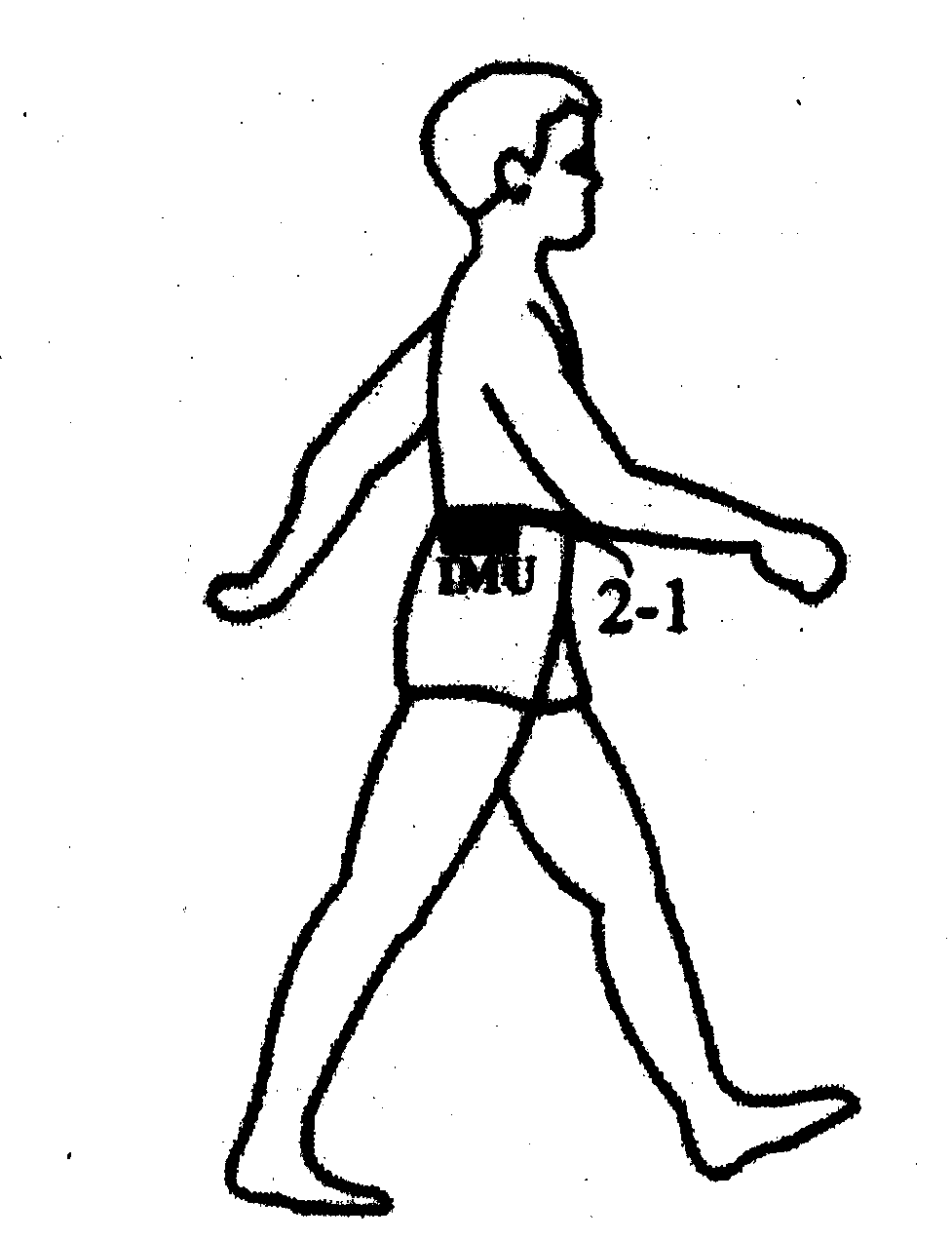
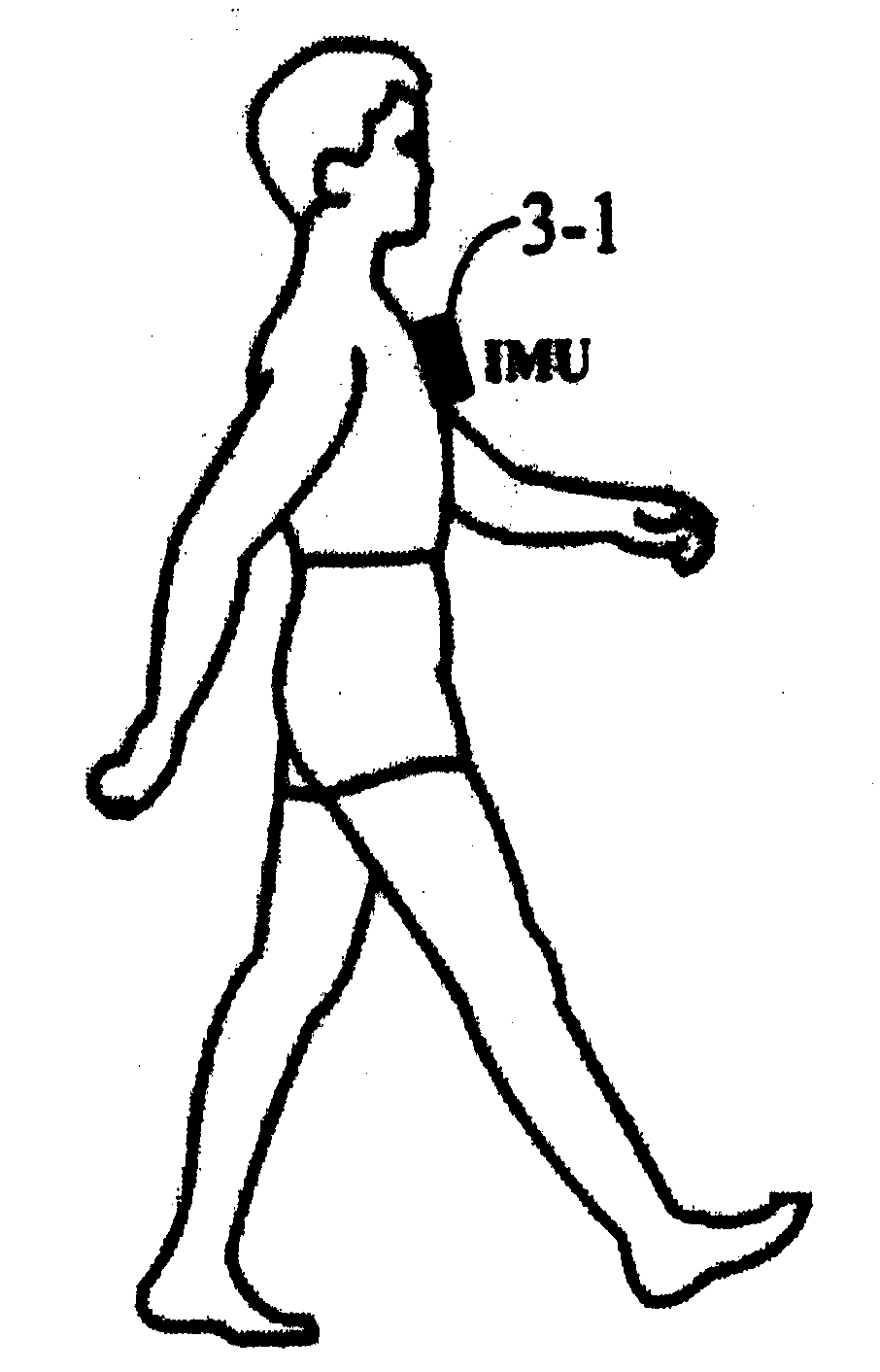
Wearable human body gait detection self-localization method
ActiveCN103968827ASuitable for precise positioningImprove reliabilityNavigation instrumentsHuman bodyGait
The invention discloses a wearable human body gait detection self-localization method which comprises the following steps: (1) aiming at the motion of a human body, establishing a state transition model, and calculating a position, a speed and a posture of a strapdown inertial navigation system; (2) utilizing constraint conditions of human body behavior detection to capture and extract human body static gait features; (3) performing attitude error integration according to zero-speed, zero angular speed and posture correction; (4) utilizing an intelligent filter to perform error estimation; (5) utilizing evaluated error to correct the posture and position of the human body motion. According to the invention, in terms of indoor positioning, powerful support is provided for convenient level and accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV +1
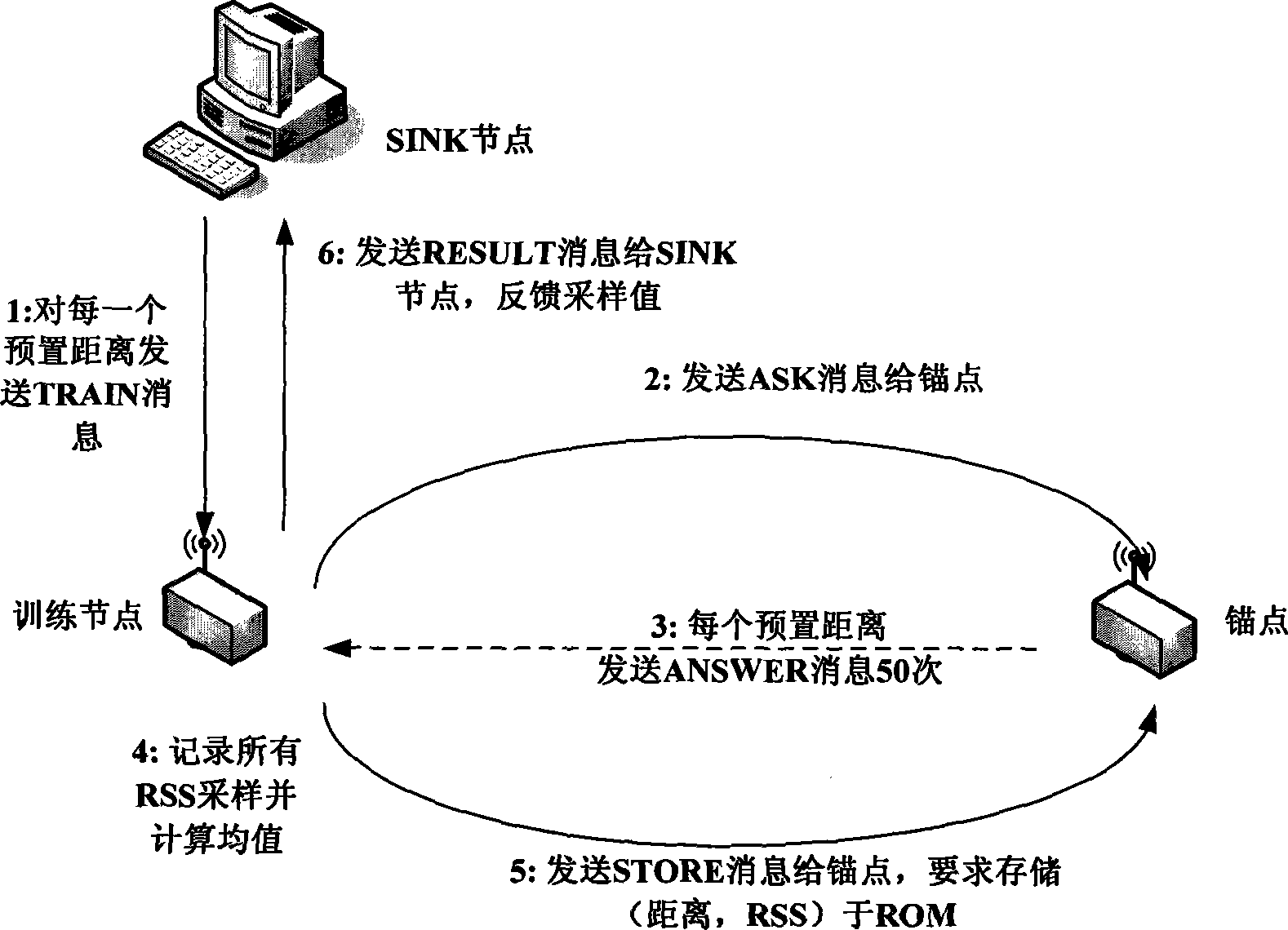
Node indoor locating method based on wireless signal strength in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101247650AReduce communication consumptionSmall amount of calculationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless mesh networkAnchor point
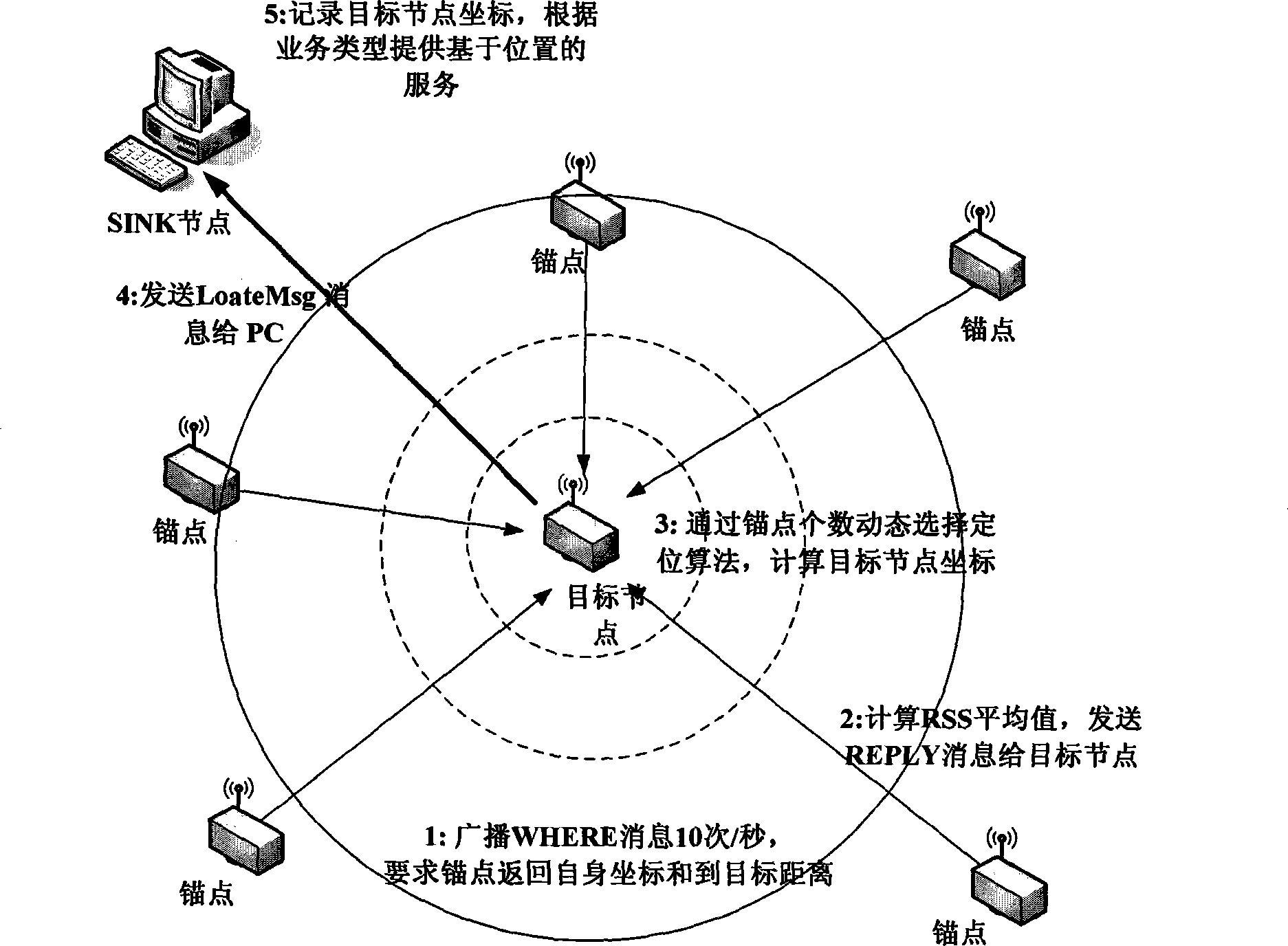
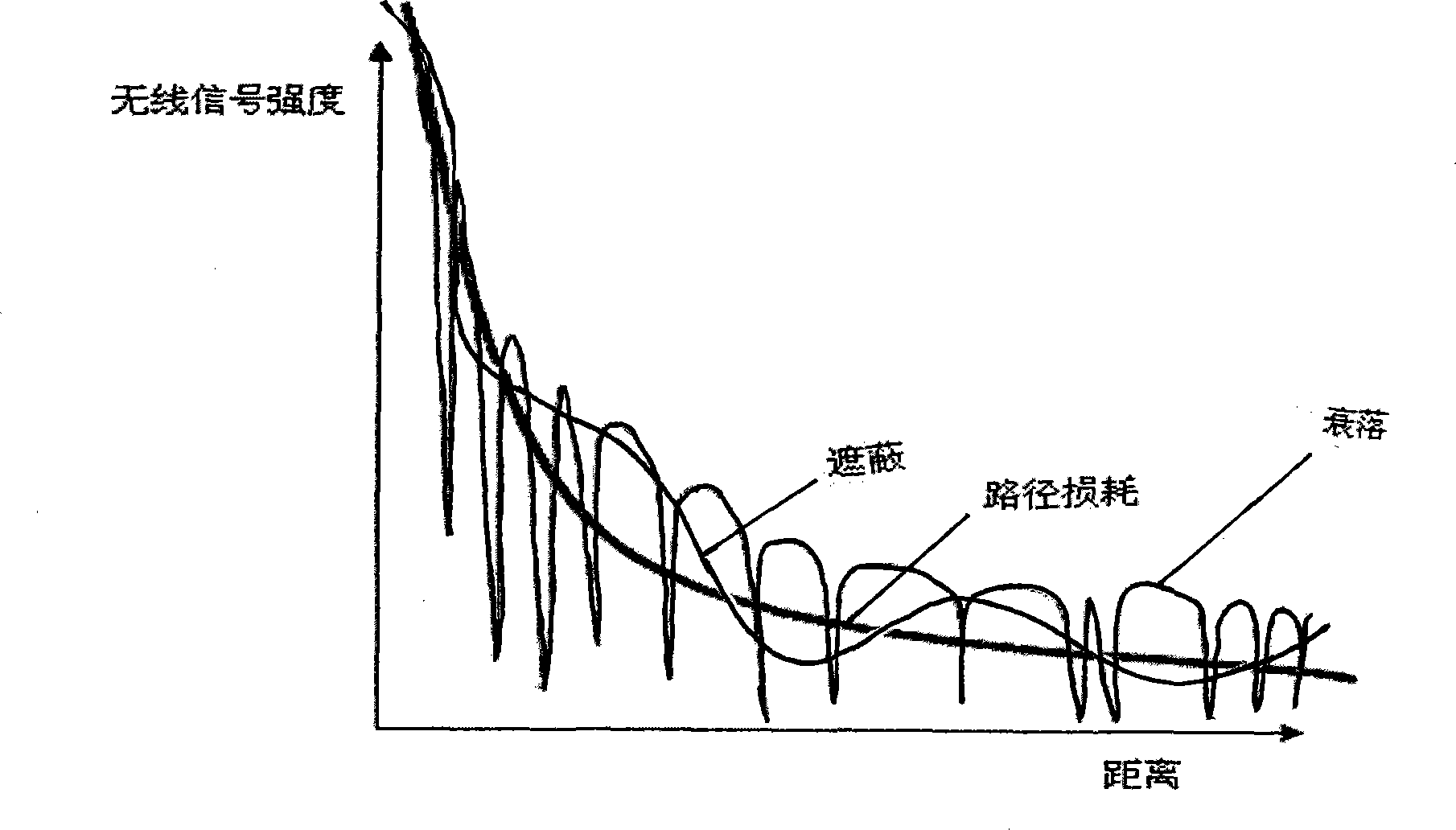
The present invention belongs to node self-localization field in large-scale wireless sensor network, and discloses a node indoor localization method based on wireless signal intensity, which main includes: getting relationship curve of signal intensity and distance, and putting forward concept of effective wireless signal intensity (Effective RSS, ERSS); obtaining coordinates of target node by selecting localization arithmetic (ERSS filter + maximum likelihood estimation, triangle localization, approximate location estimation) according with anchor point amount through distance between anchor point and target by training RSS curve; providing alerting service by using physics coordinate, providing navigation service according with route arithmetic and address chain by using sign coordinate (for example in hall). Precisely localization of indoor target can be realized in condition of low-cost, simple initial configuration, and a plurality of services based on location can also be provided.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
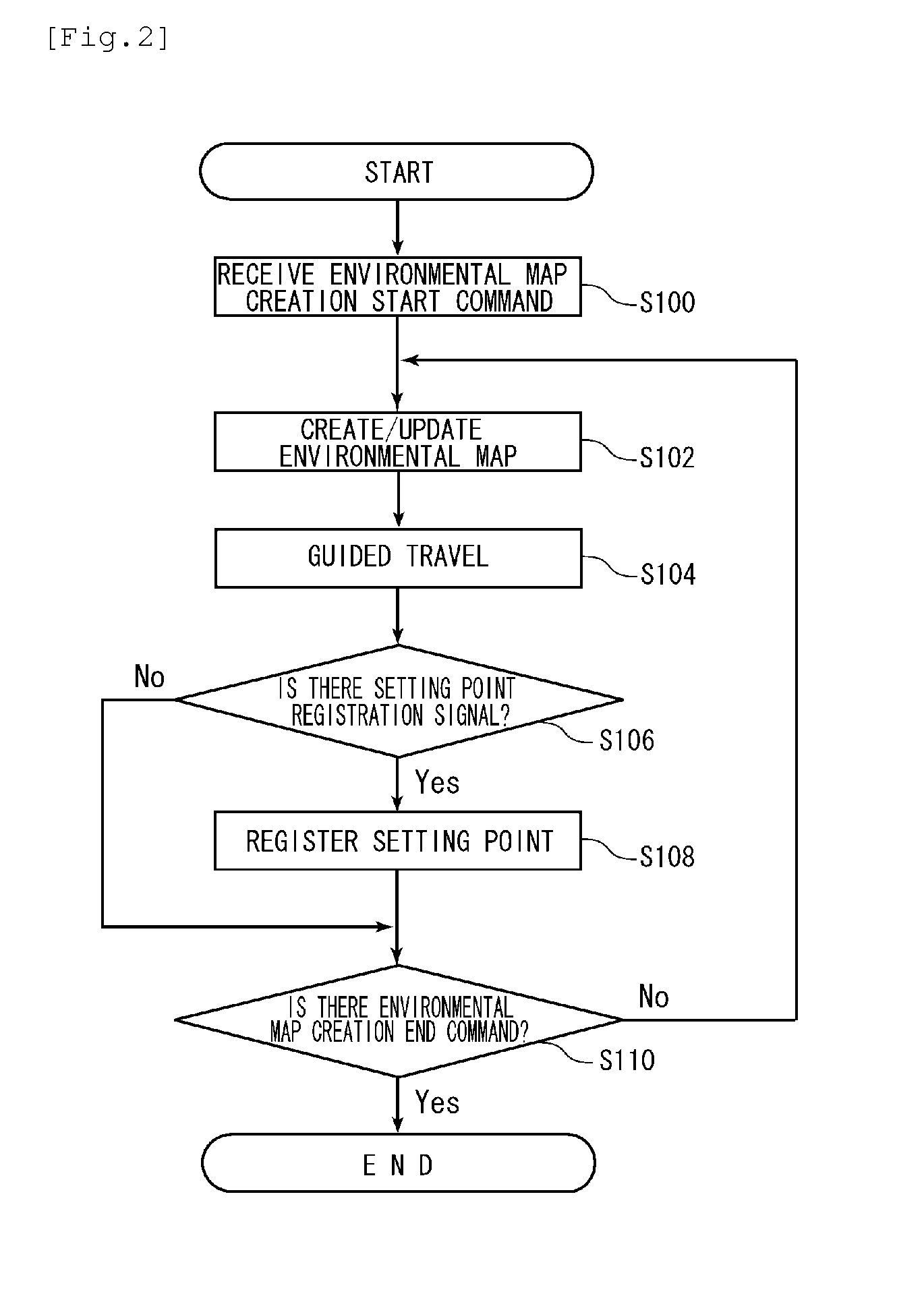
Autonomous mobile device
ActiveUS20110178669A1Accurate autonomous travelReduce the burden onAutonomous decision making processPosition/course control in two dimensionsJoystickElectronic controller
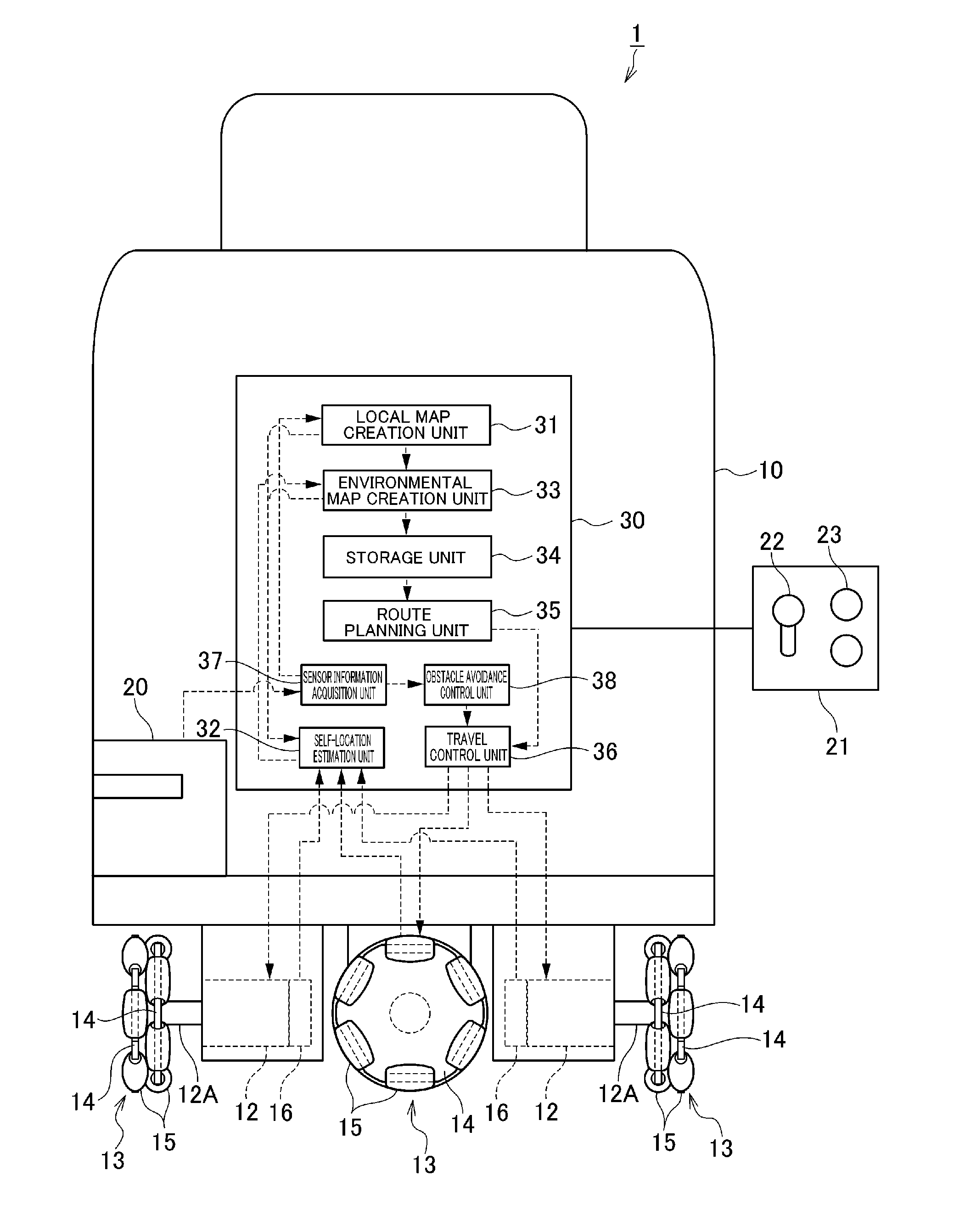
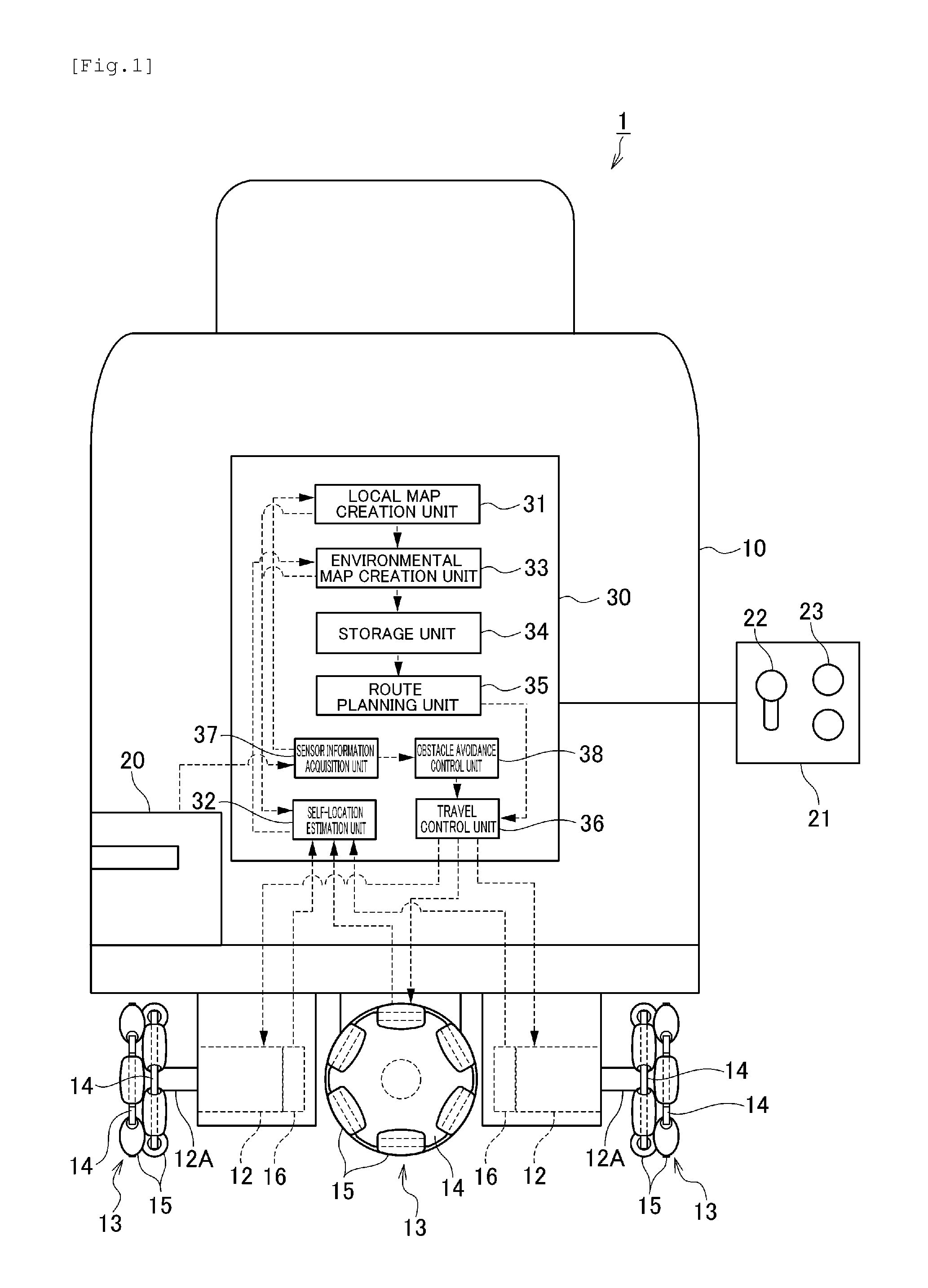
An electronic controller defining an autonomous mobile device a self-location estimation unit to estimate a self-location based on a local map that is created according to distance / angle information relative to an object in the vicinity and the travel distance of an omni wheel, an environmental map creation unit to create an environmental map of a mobile area based on the self-location and the local map during the guided travel with using a joystick, a registration switch to register the self-location of the autonomous mobile device as the position coordinate of the setting point when the autonomous mobile device reaches a predetermined setting point during the guided travel, a storage unit to store the environmental map and the setting point, a route planning unit to plan the travel route by using the setting point on the environmental map stored in the storage unit, and a travel control unit to control the autonomous mobile device to autonomously travel along the travel route.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
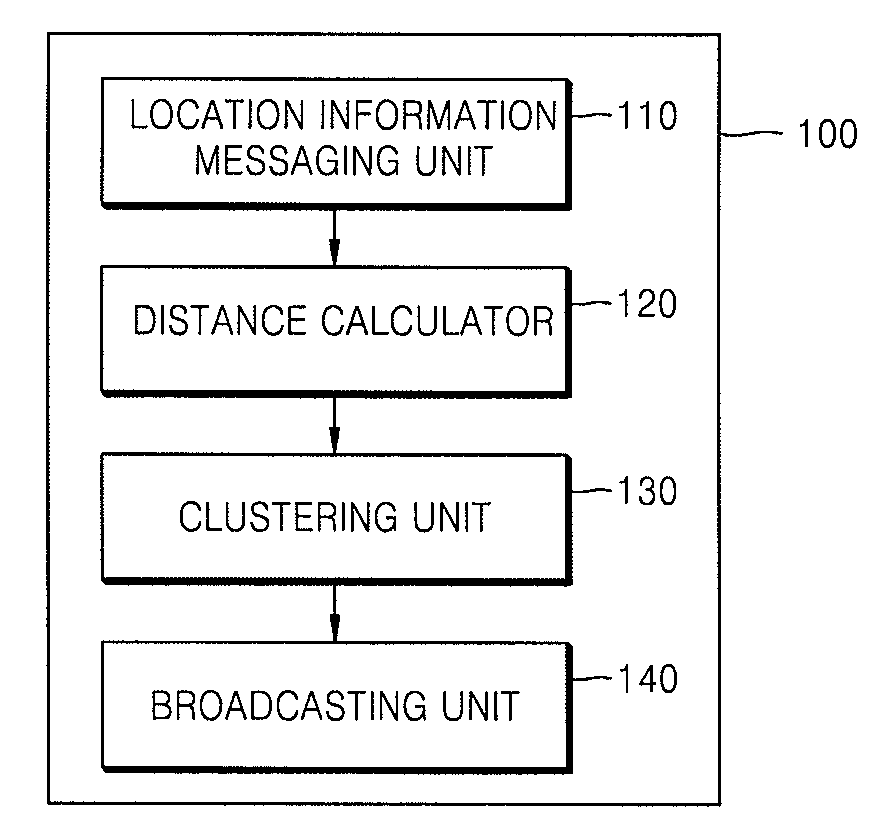
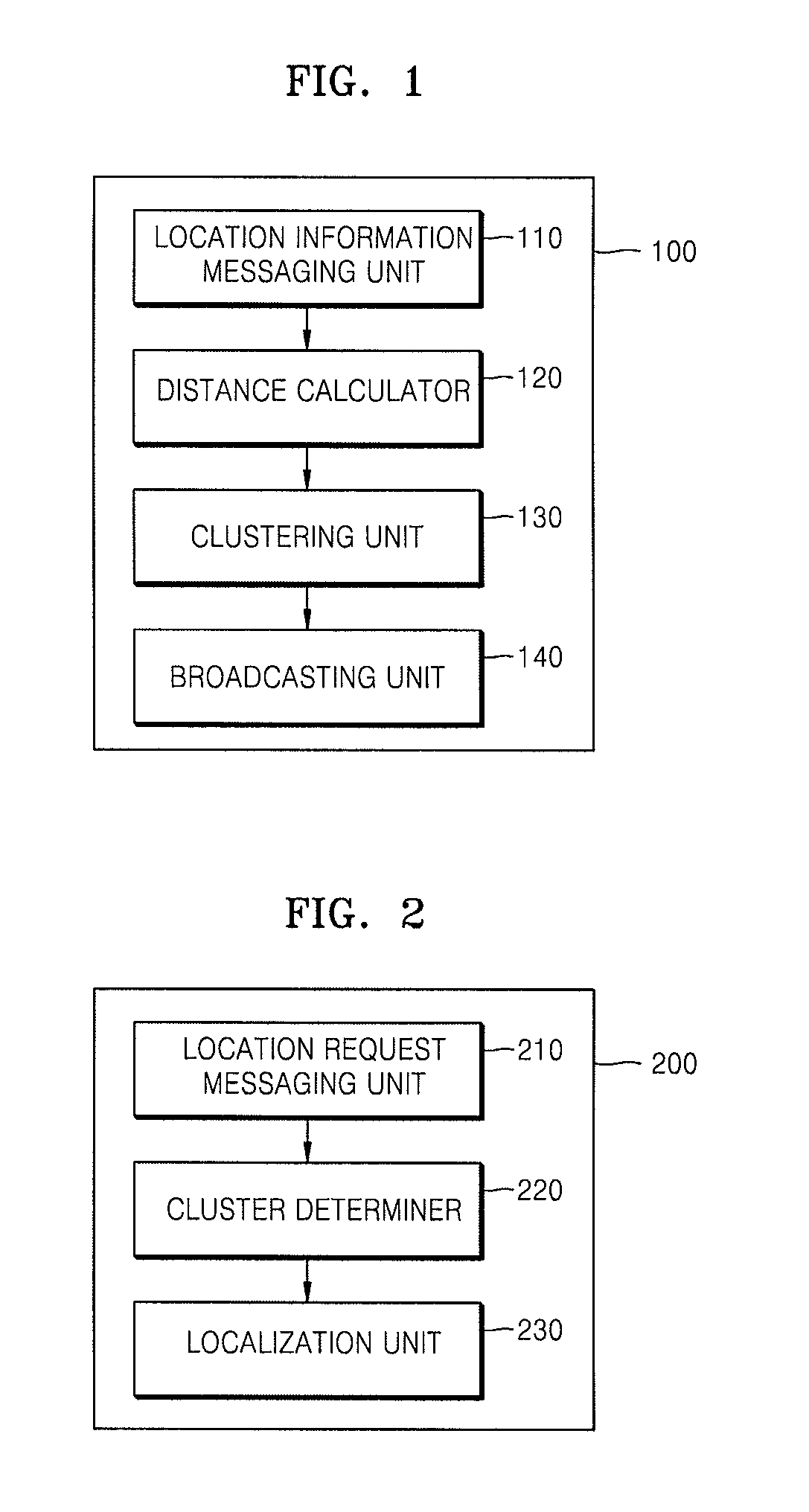
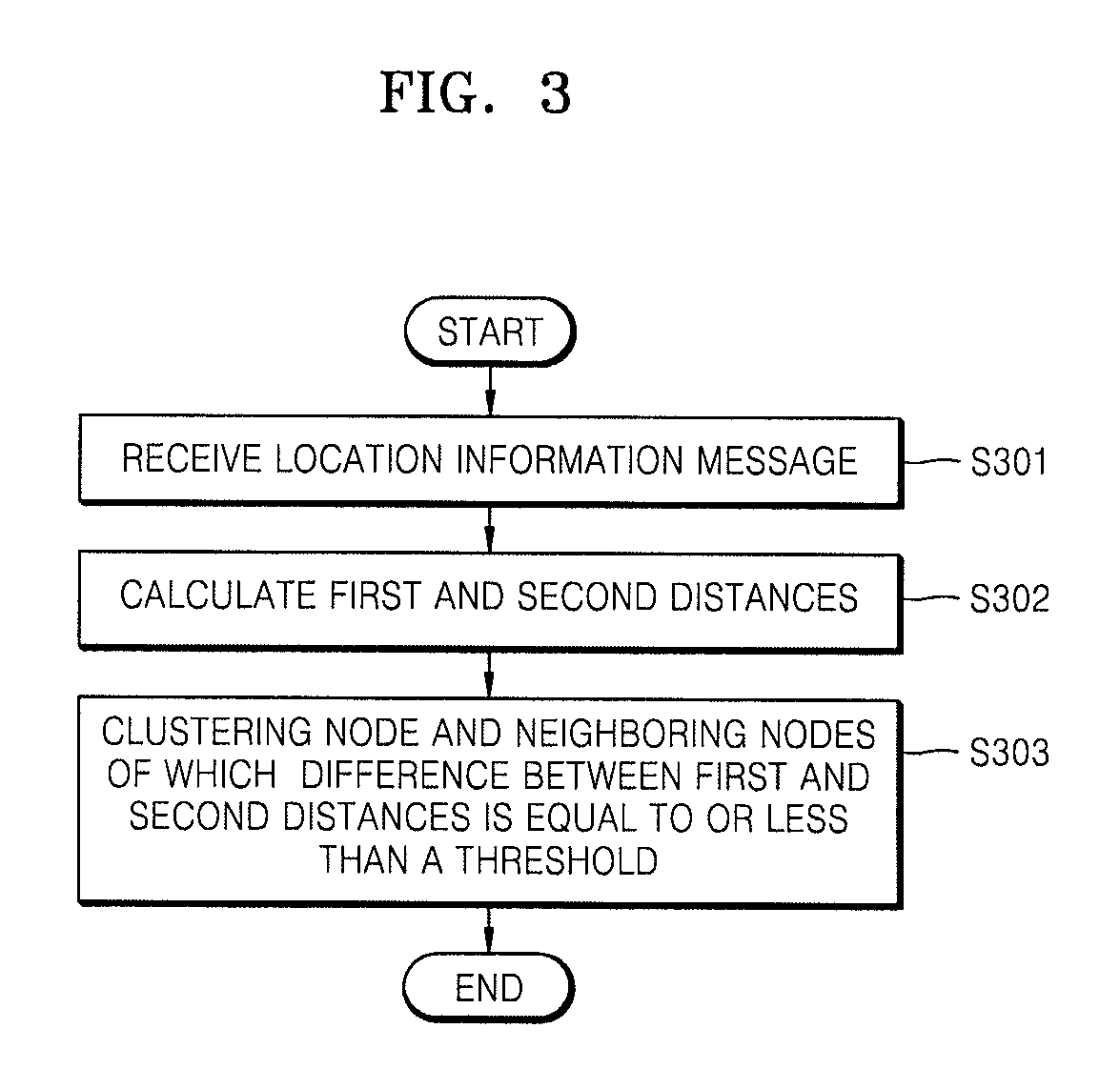
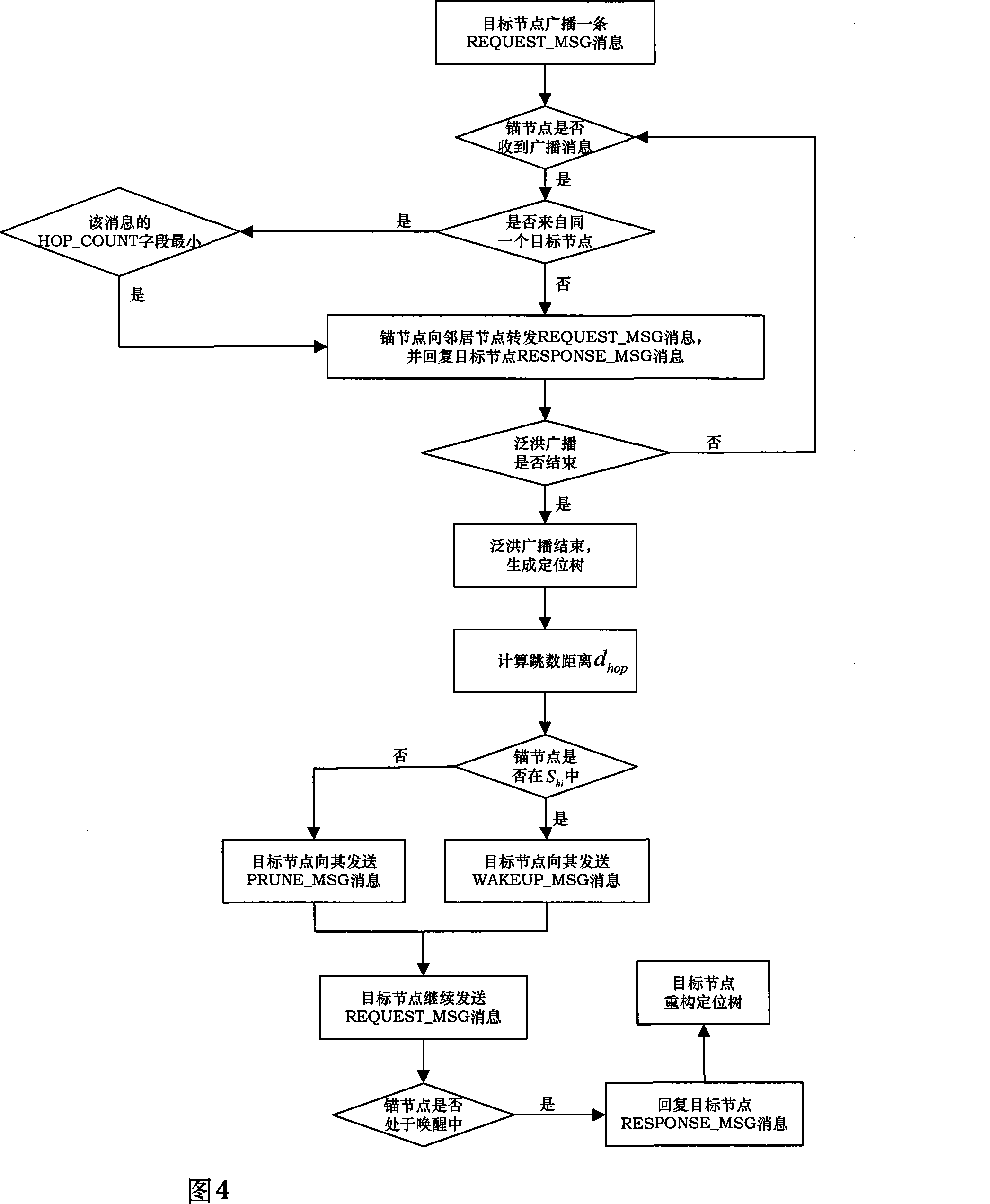
Node for self localization, clustering method using the same, and localization method
InactiveUS20080069008A1Precise positioningAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesComputer scienceCalculator
A node for self localization, a clustering method using the same, and a localization method are provided. The node, which is located in a specific space so as to constitute a sensor network, includes a location information messaging unit which receives one or more location information messages including information on spatial locations of one or more neighboring nodes in the sensor network from the neighboring nodes in the sensor network; a distance calculator which calculates a first distance to the neighboring node on the basis of the location information included in the received location information messages and calculates a second distance to one or more neighboring nodes on the basis of the received time or intensity of the message on the location information; and a clustering unit which forms clusters of the node and a plurality of neighboring nodes in which the difference between the first and second distances is less than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
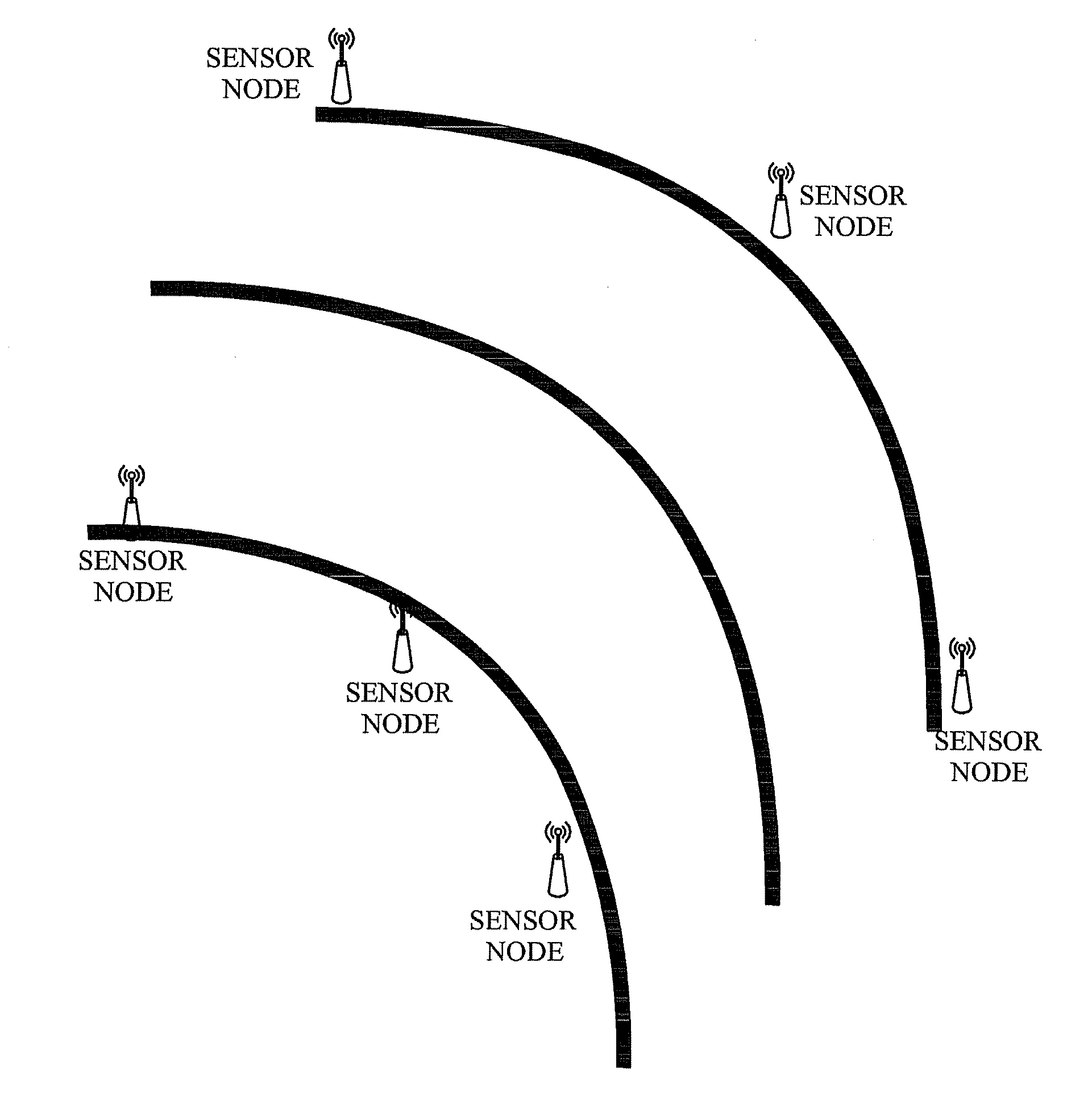
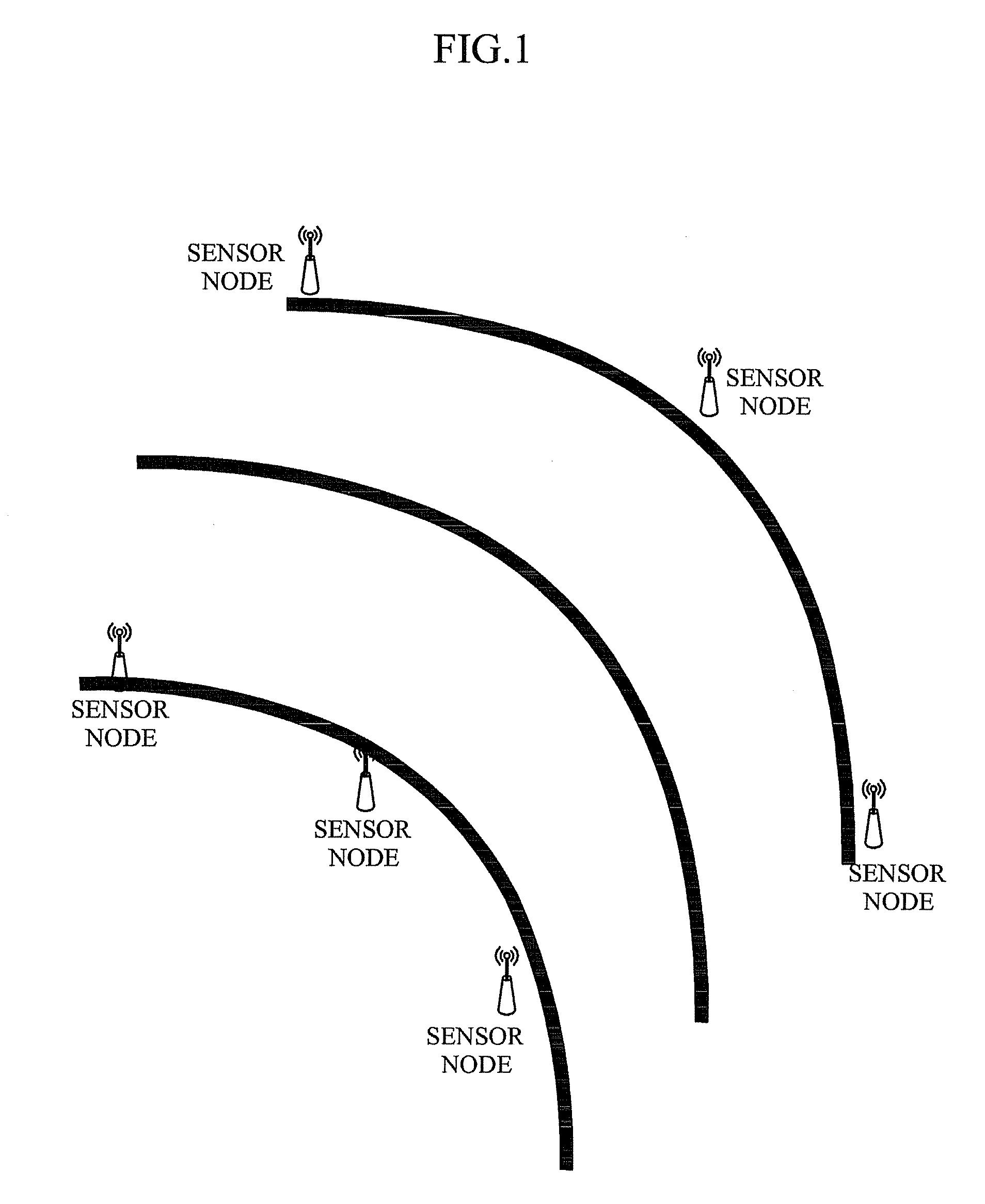
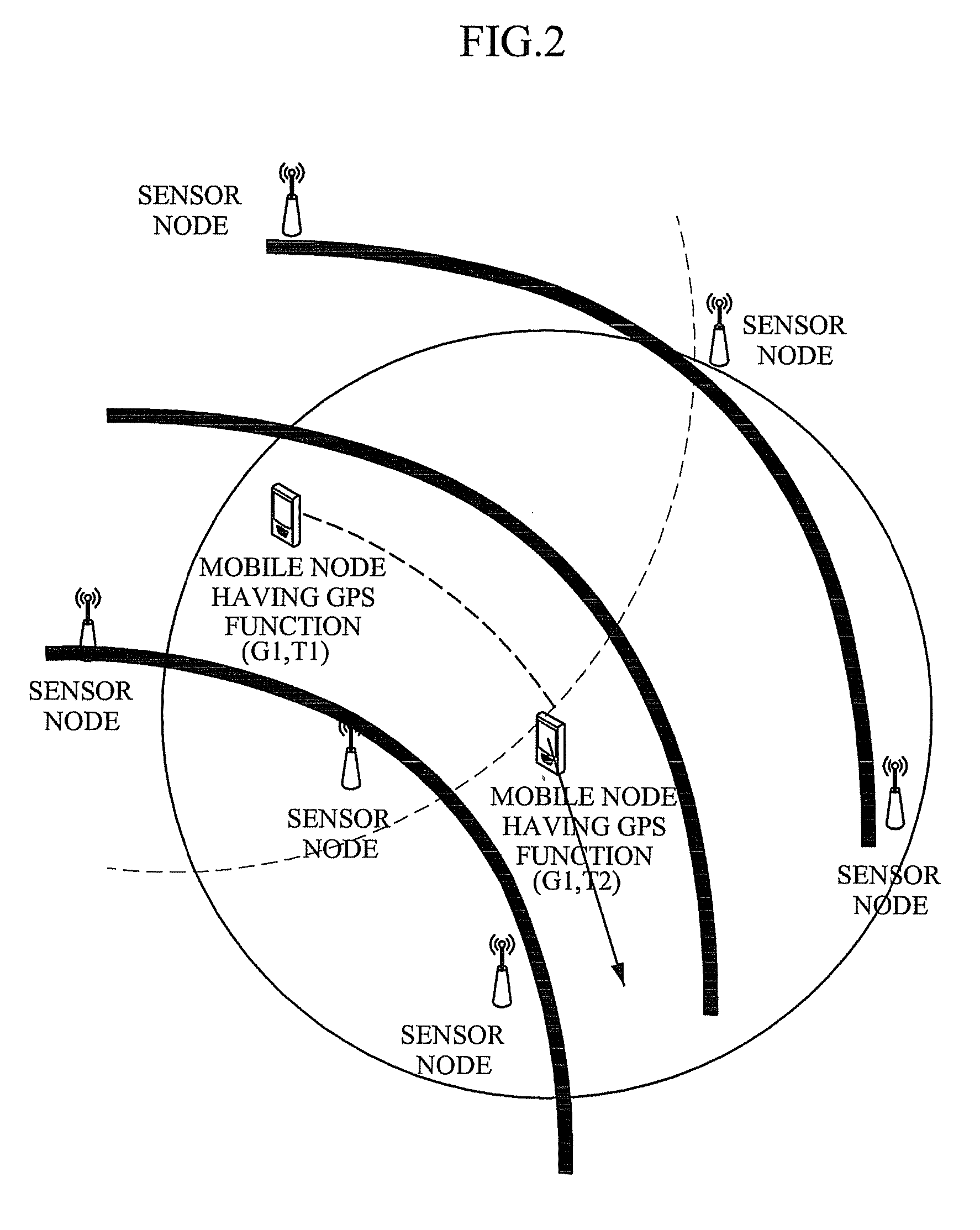
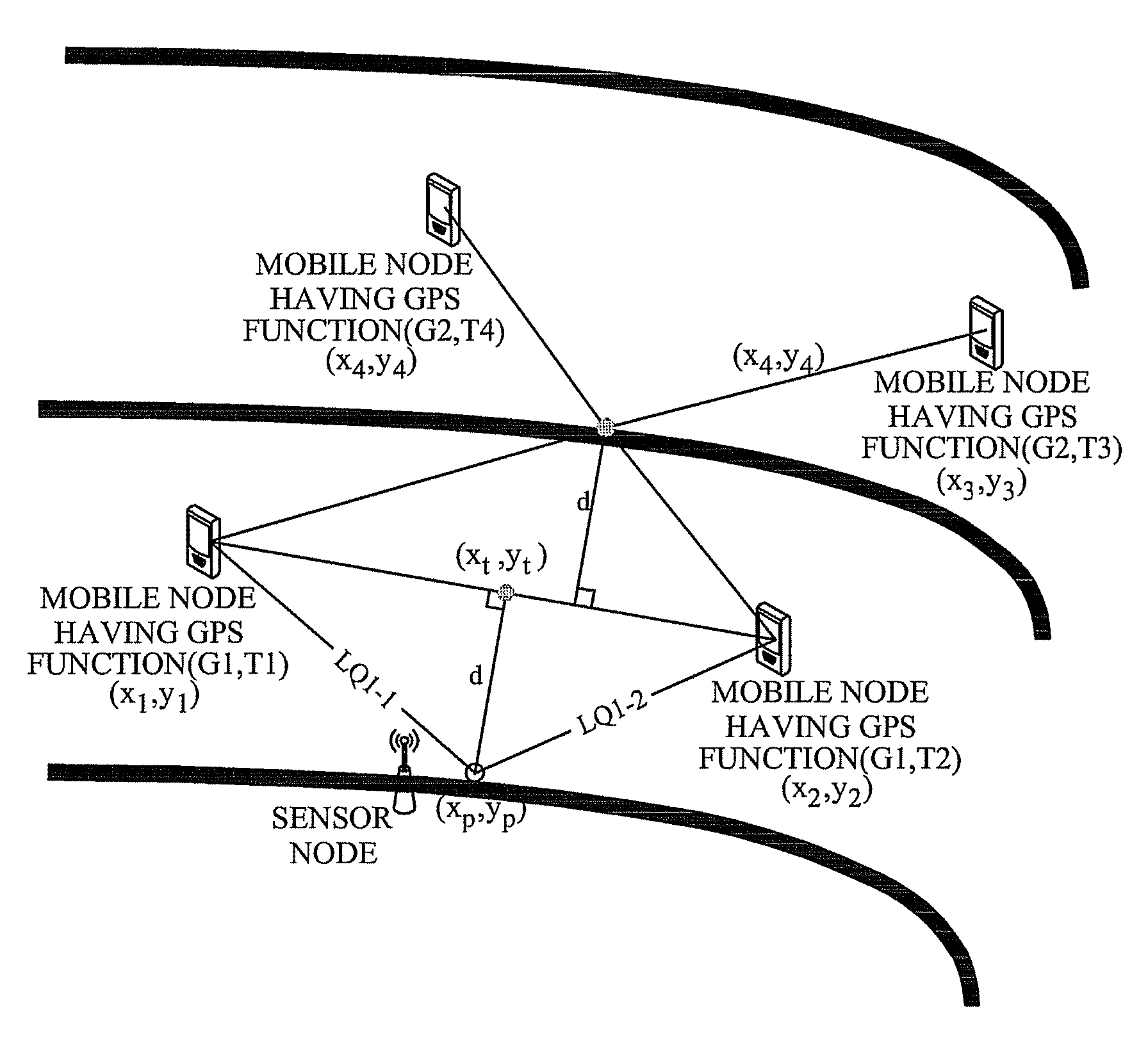
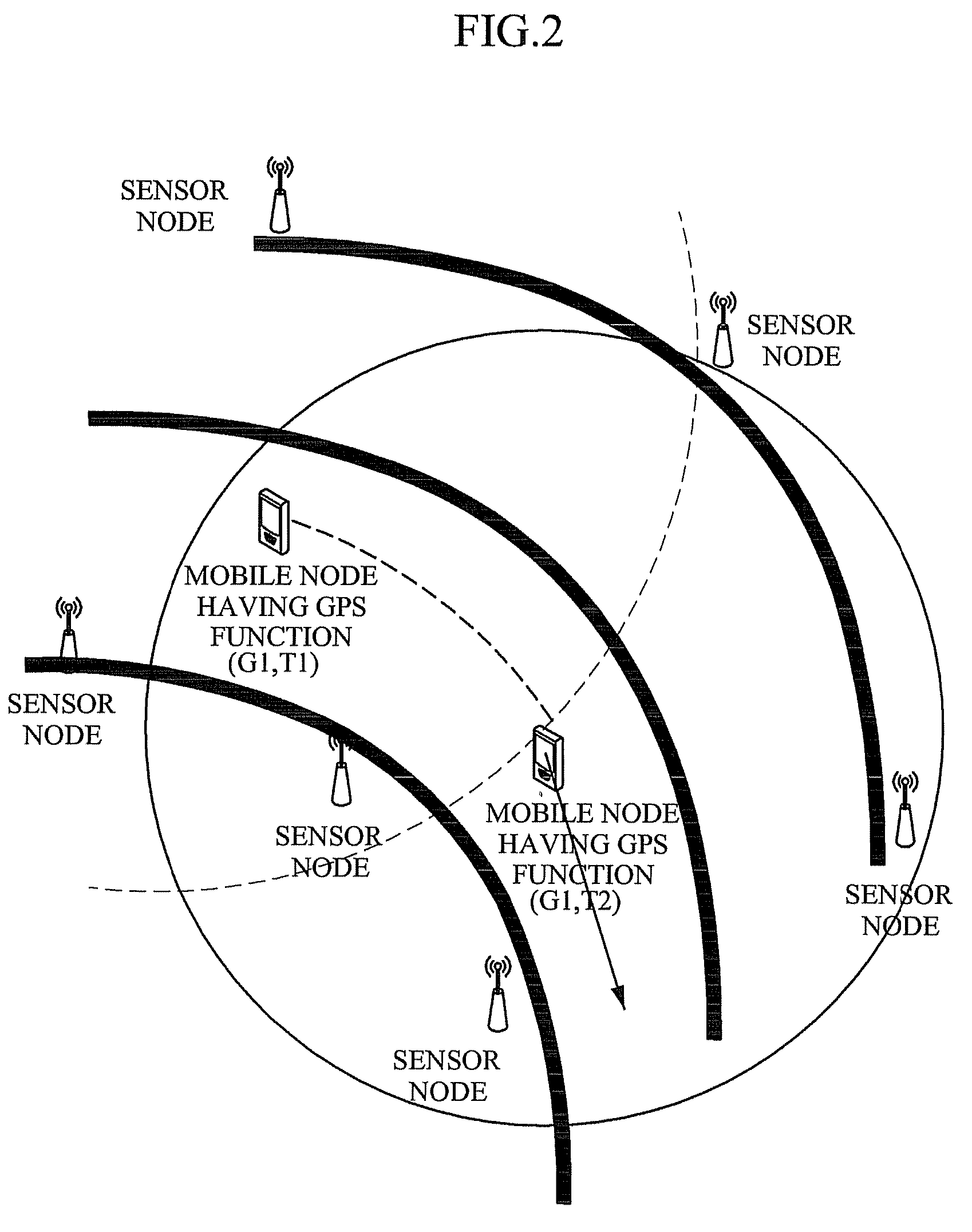
Sensor node having self localization function and self localization method thereof
InactiveUS20100150070A1Low additional costReduce power consumptionPosition fixationWireless commuication servicesTransceiverAudio power amplifier
Disclosed are a sensor node having a self localization function and a self localization method of the sensor node. The sensor node calculates a location thereof by receiving location information measured at each of two mobile nodes at different times and using four location information of the received location information. Additional cost and power consumption required for installing additional equipment such as an anchor node, a ultrasonic transceiver and a signal amplifier are reduced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
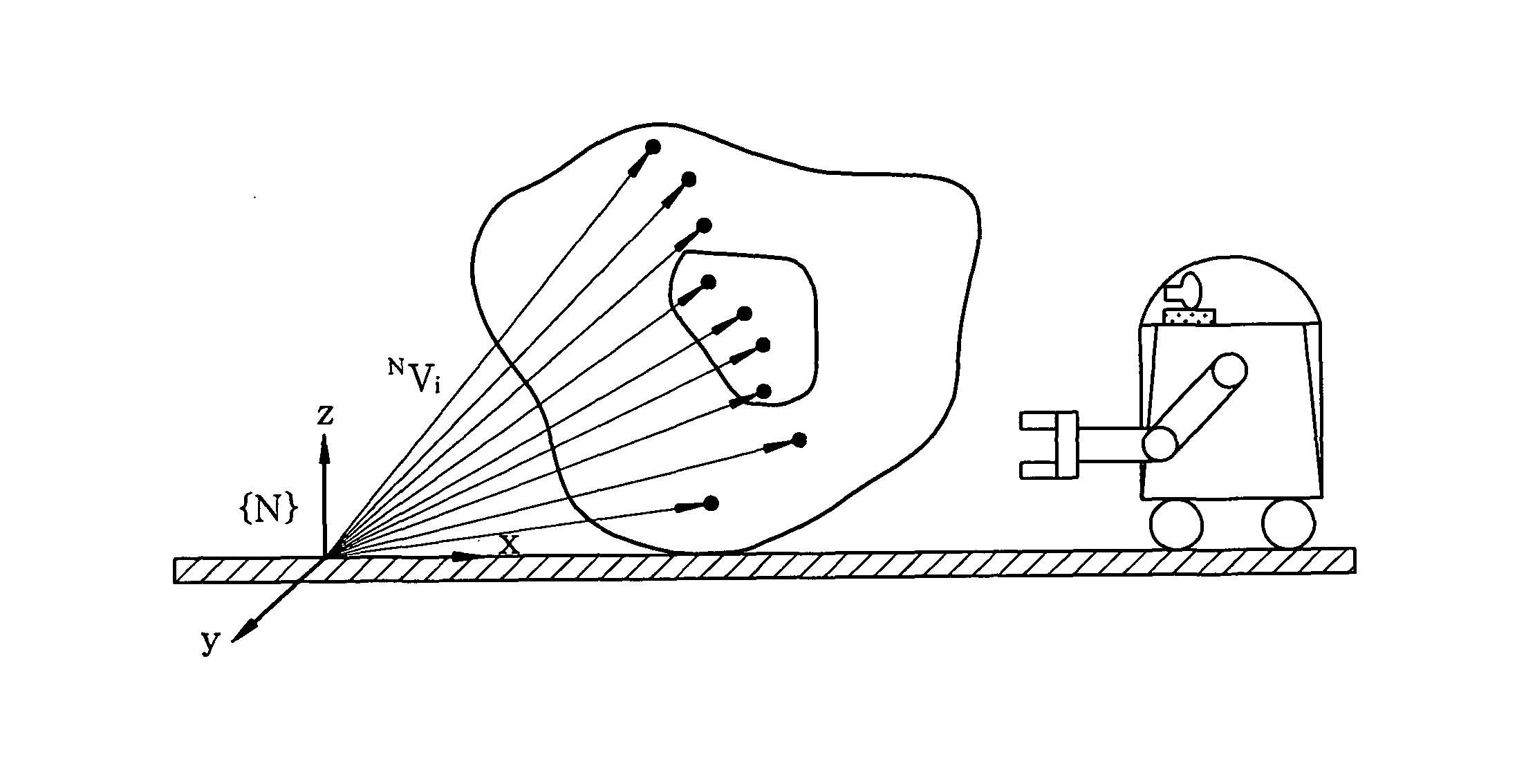
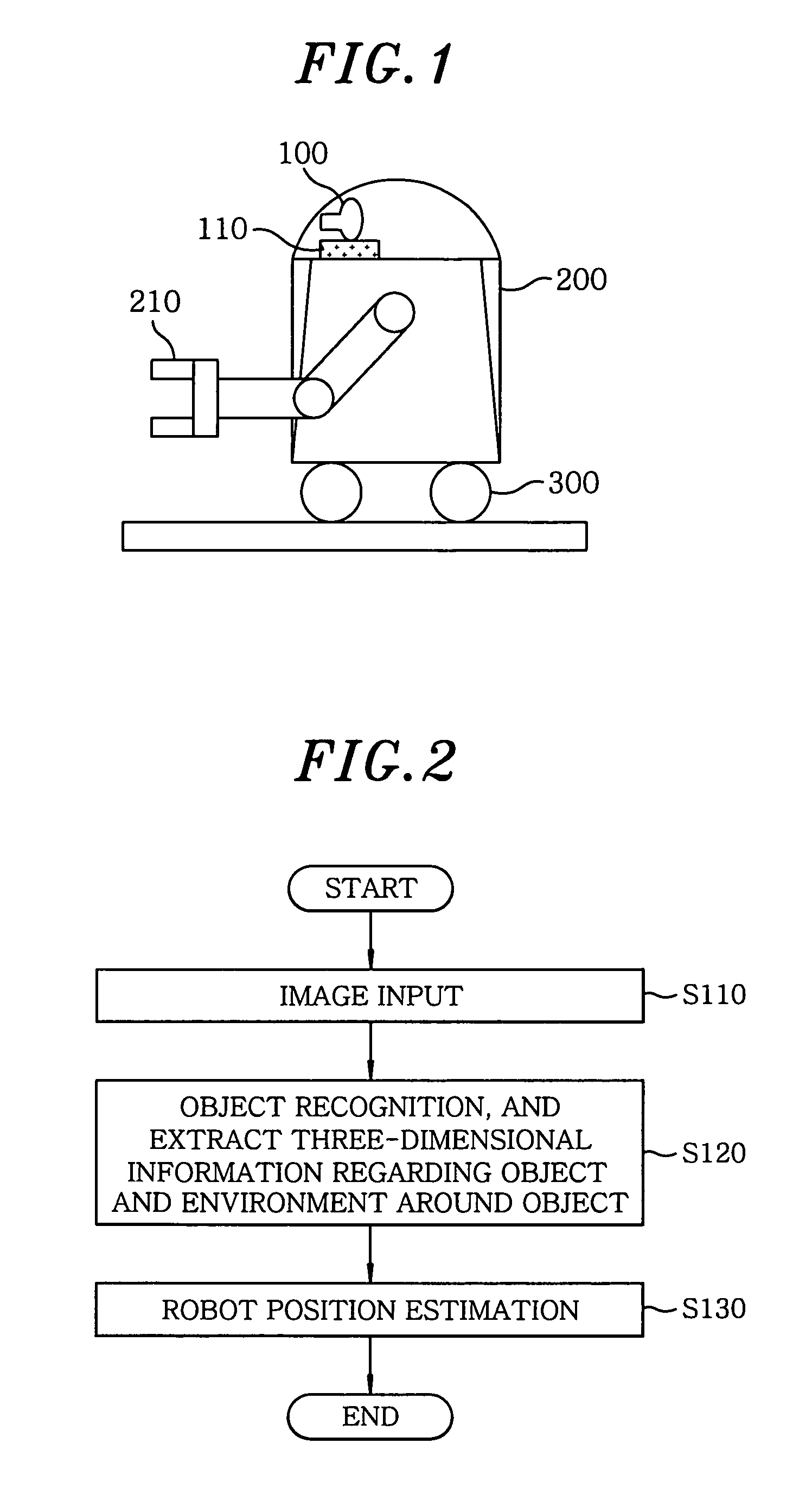
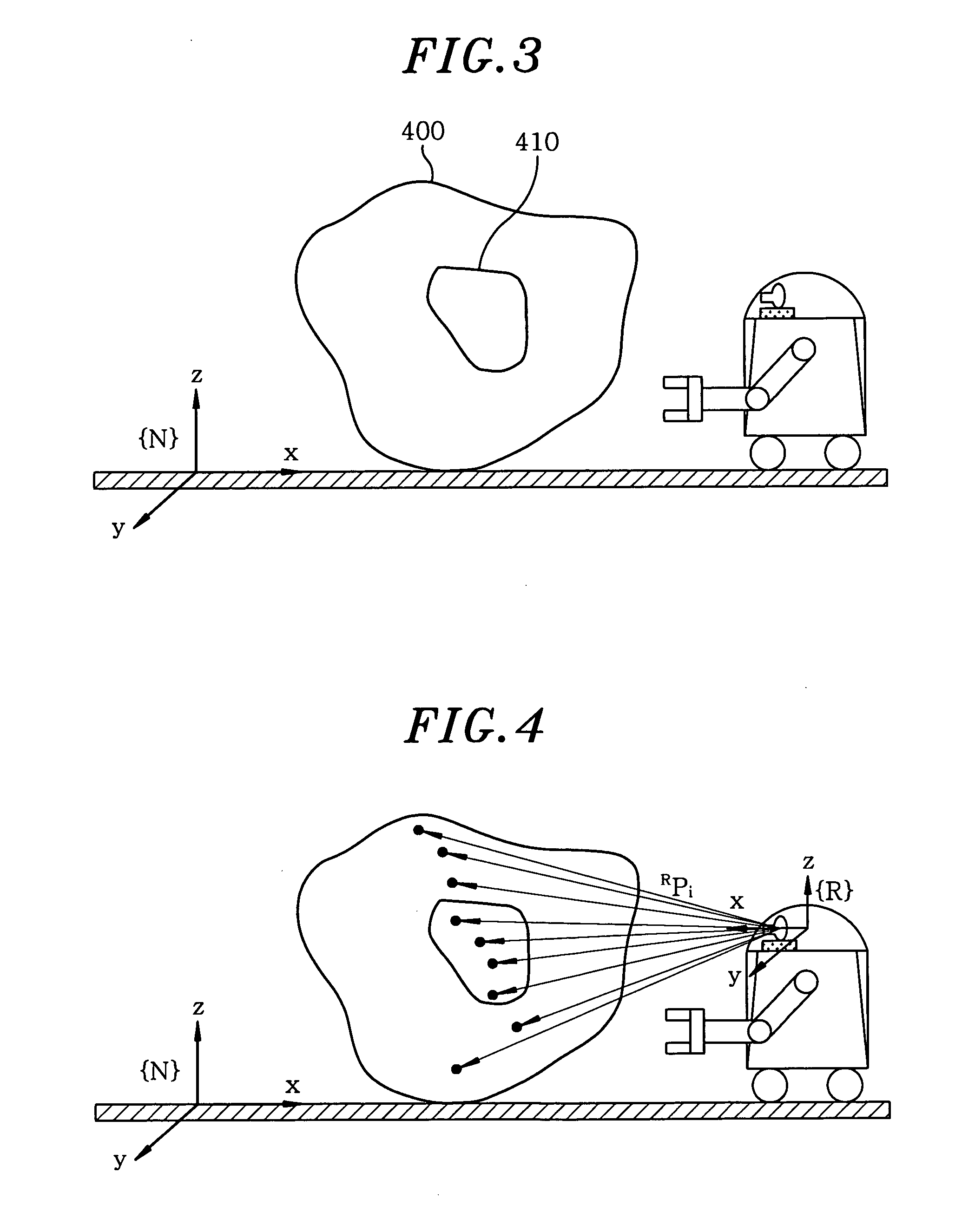
Method for self-localization of robot based on object recognition and environment information around recognized object
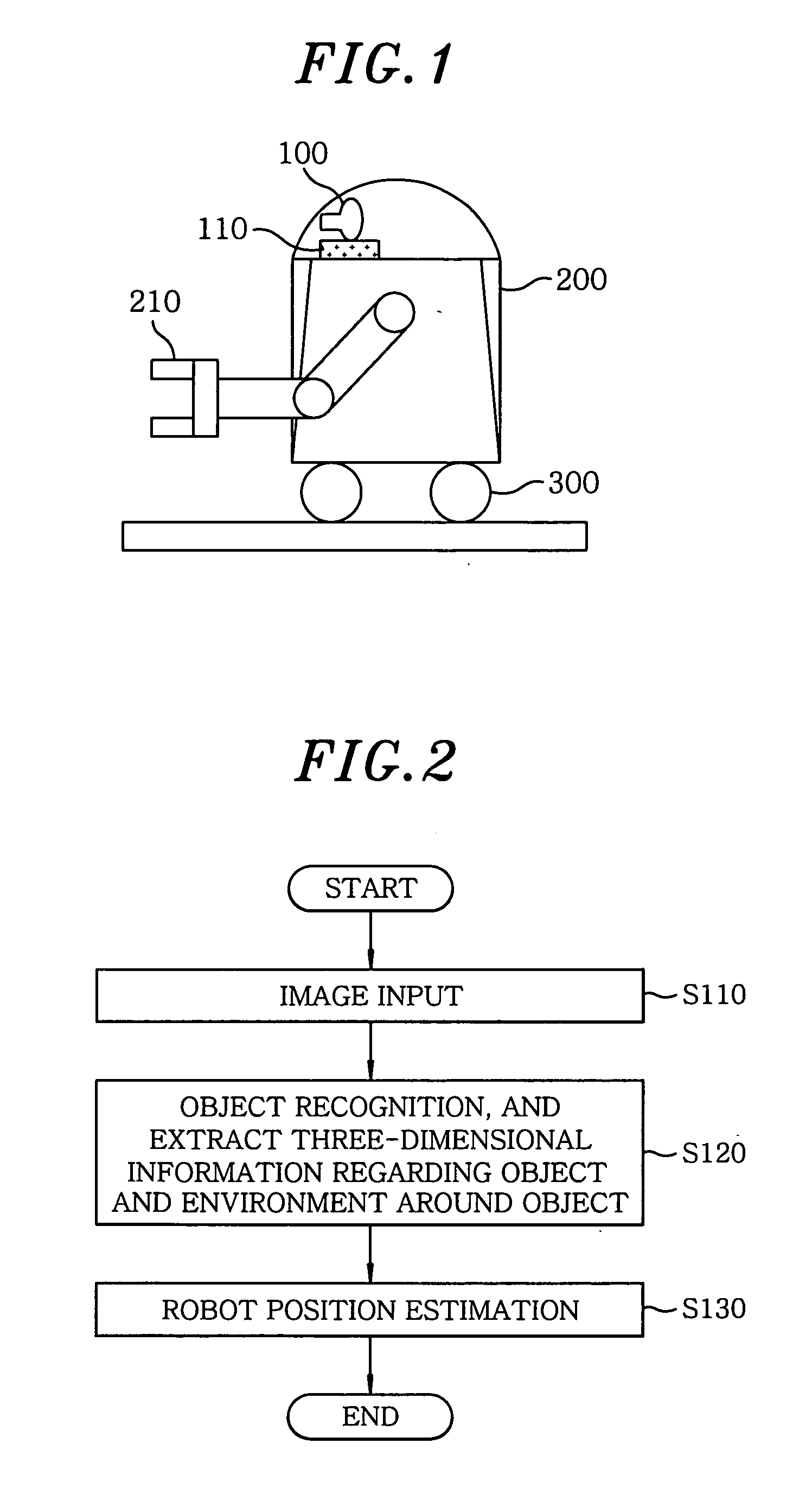
ActiveUS20090210092A1Accurate position estimationPrecise positioningProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPattern recognitionObject based
A method for self-localization of a robot, the robot including a camera unit, a database storing a map around a robot traveling path, and a position arithmetic unit estimating the position of the robot, includes: acquiring an image around the robot, in the camera unit. Further, the method includes recognizing, in the position arithmetic unit, an individual object in the image acquired by the camera unit, to generate position values on a camera coordinate system of local feature points of the individual objects and local feature points of a surrounding environment including the individual objects; and estimating, in the position arithmetic unit, the position of the robot on the basis of the map and the position values on the camera coordinate system of local feature points of the individual objects and local feature points of a surrounding environment including the individual objects.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
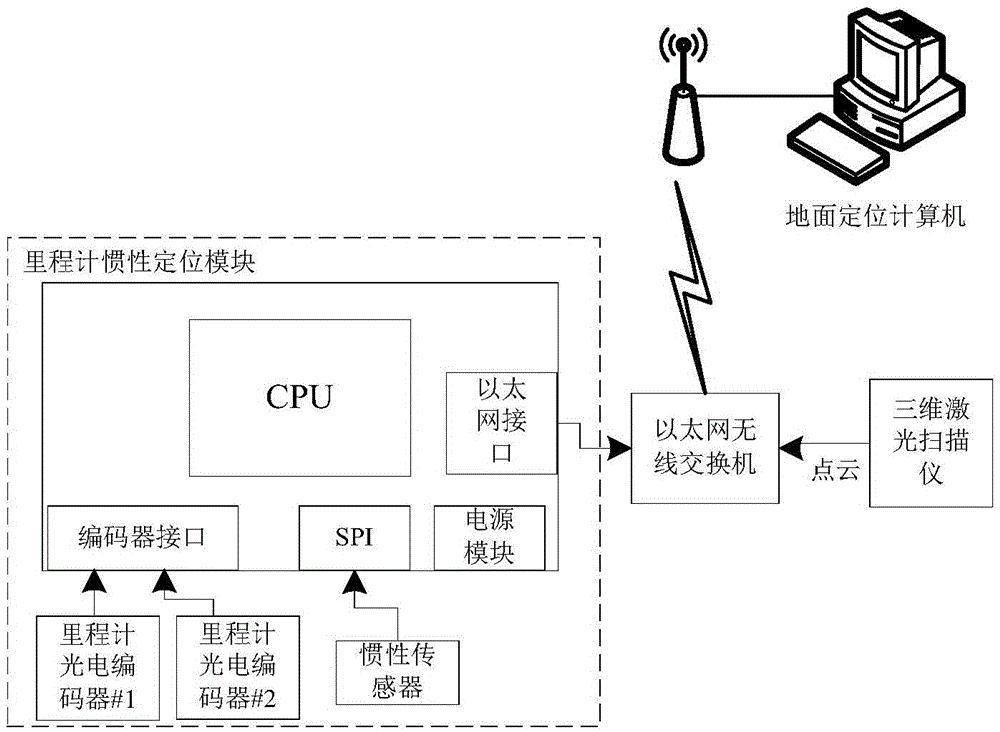
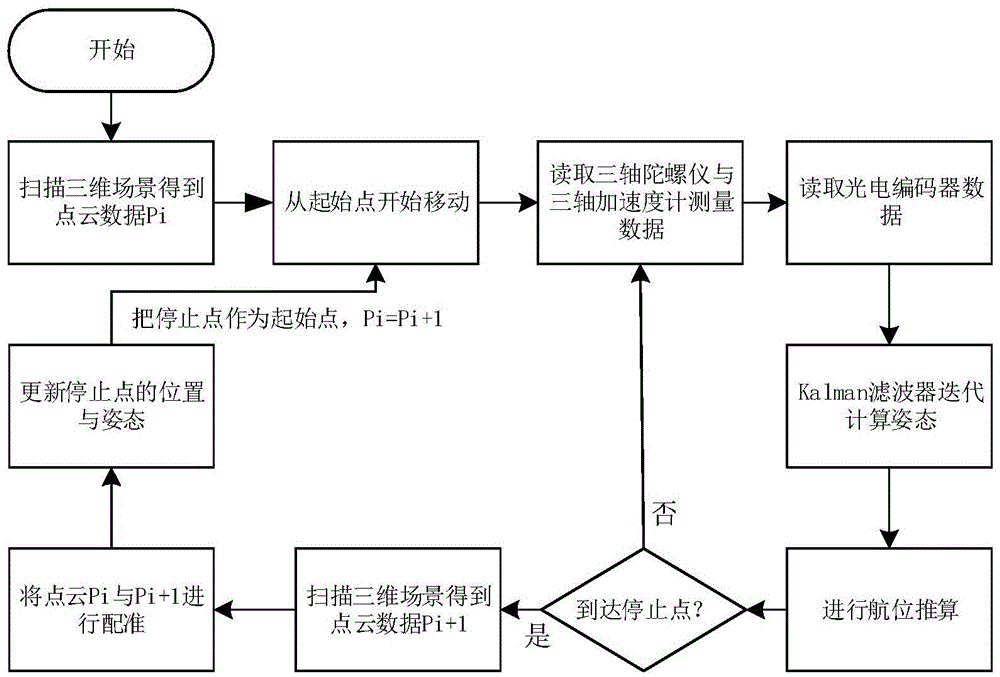
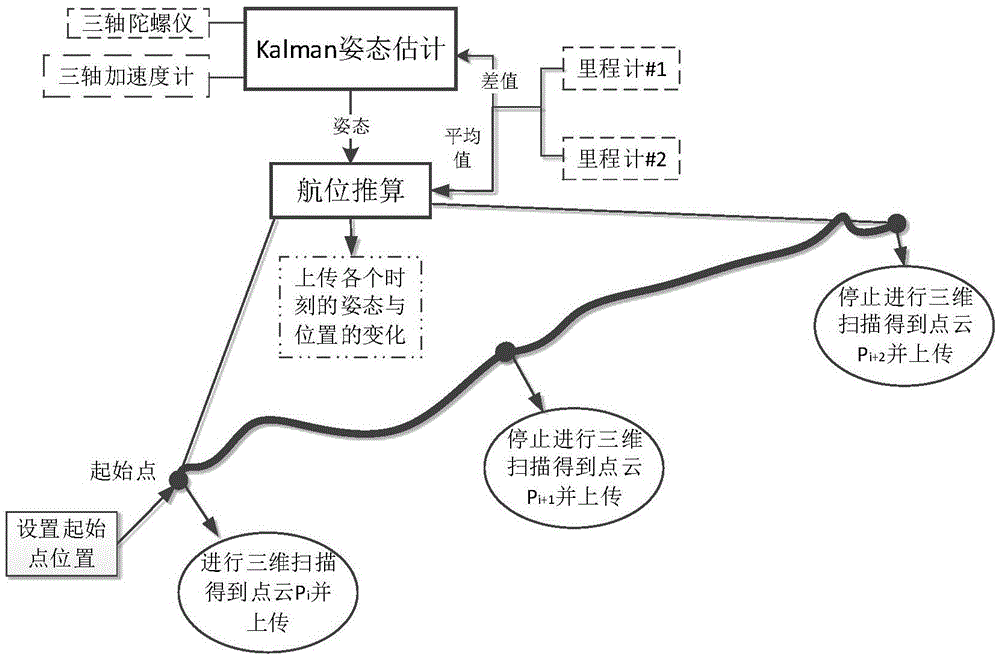
Self-localization method and system for mobile device in underground coal mine
InactiveCN105547288AReduce measurement errorHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLocalization systemPoint cloud
The invention discloses a self-localization method for a mobile device in an underground coal mine. The method comprises: performing scanning at a start point through a three-dimensional laser scanner to obtain three-dimensional point cloud data P; making the mobile device start moving, and performing dead reckoning through integration of data measured by an inertial transducer and a mileometer transducer to obtain a real-time position of the device; making the mobile device stop moving at a point not far from the start point, and performing scanning at the stop point to obtain three-dimensional point cloud data P<i+1>; registering P and P<i+1> to obtain displacement and attitude variation between the two points, and updating the position of the stop point; and taking the stop point as a new start point, and repeating the above steps to complete a whole real-time localization process. Accordingly, the invention further provides a localization system corresponding to the method. The system has low environment requirements; high-precision localization can be realized in a severe environment in an underground coal mine; and a three-dimensional visualization module of the whole environment is established.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
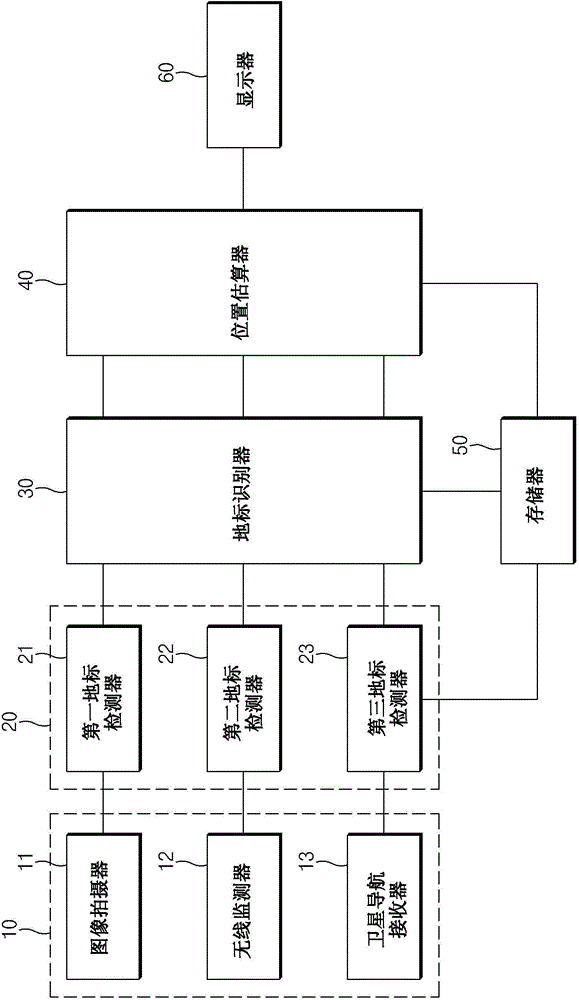
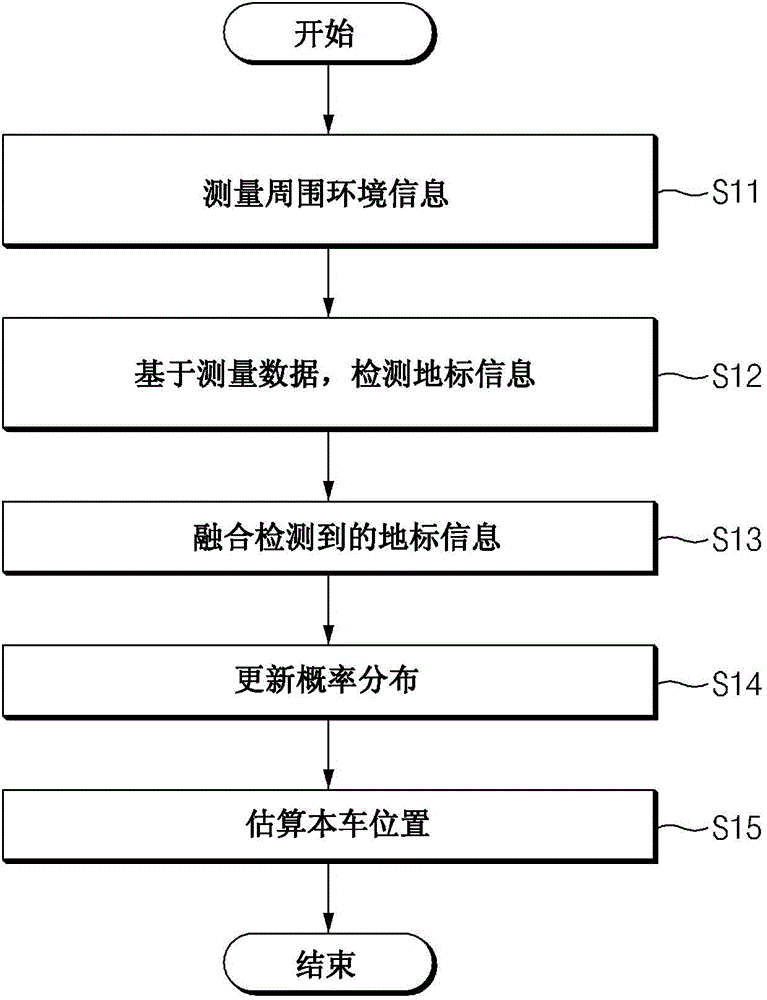
Apparatus for a self localization of a vehicle
InactiveCN105277190AInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlPattern recognitionLandmark
The invention relates to an apparatus for a self localization of a vehicle. The apparatus includes a sensor unit, a landmark detector, a landmark recognizer, and a location estimator. The sensor includes at least two sensors and is configured to measure information on environment around the vehicle using each of the at least two sensors. The landmark detector is configured to detect landmark information based on data measured by each sensor. The landmark recognizer is configured to selectively combine landmark information detected based on data measurement of at least one of the at least two sensors to recognize a landmark and reflect fused landmark information to update a probability distribution. The location estimator is configured to use the probability distribution updated by the landmark recognizer to estimate a self location of the vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Landmark, apparatus, and method for effectively determining position of autonomous vehicles
ActiveUS7333631B2Efficiently determinedImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation analysisLocation Equipment
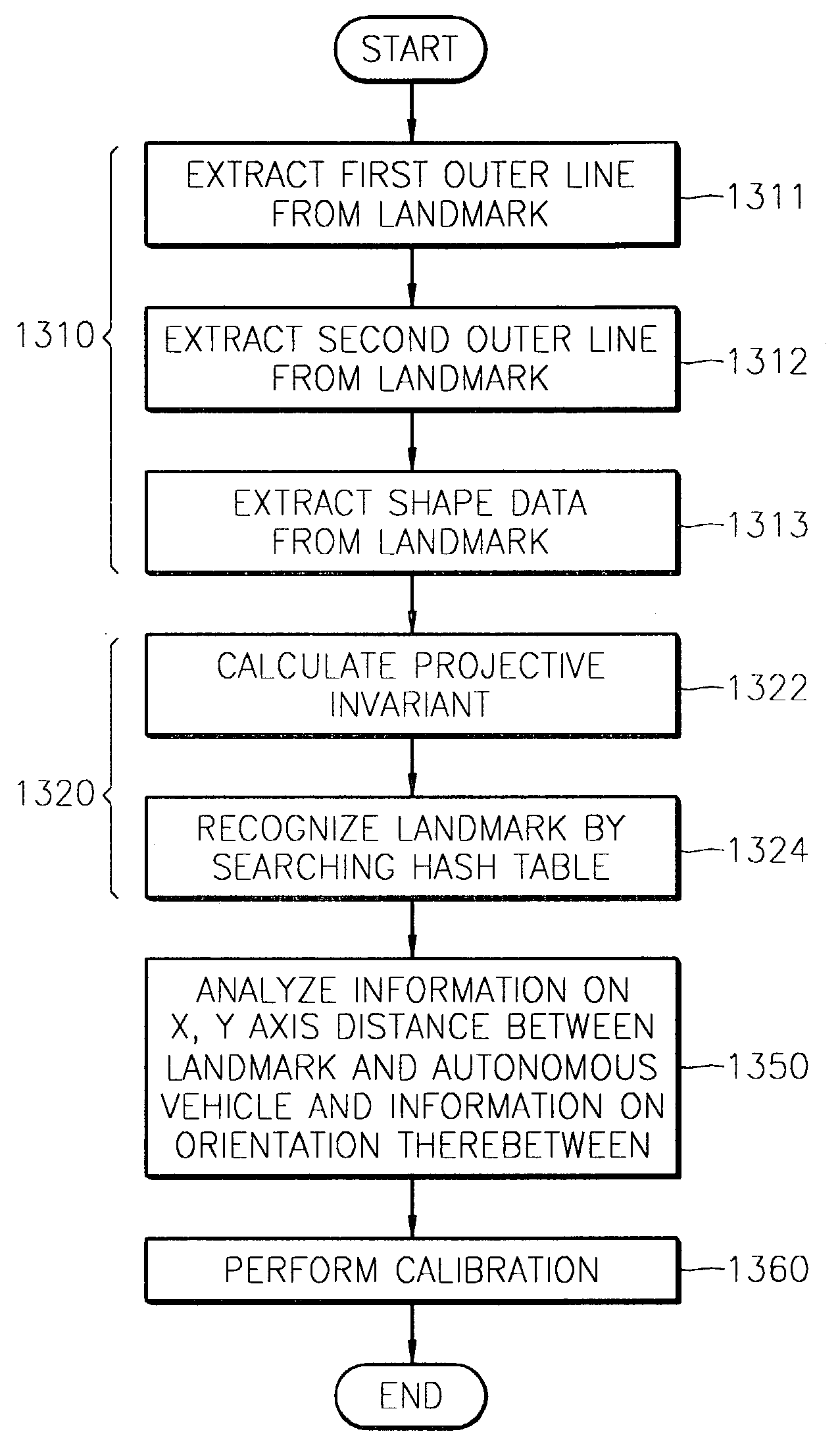
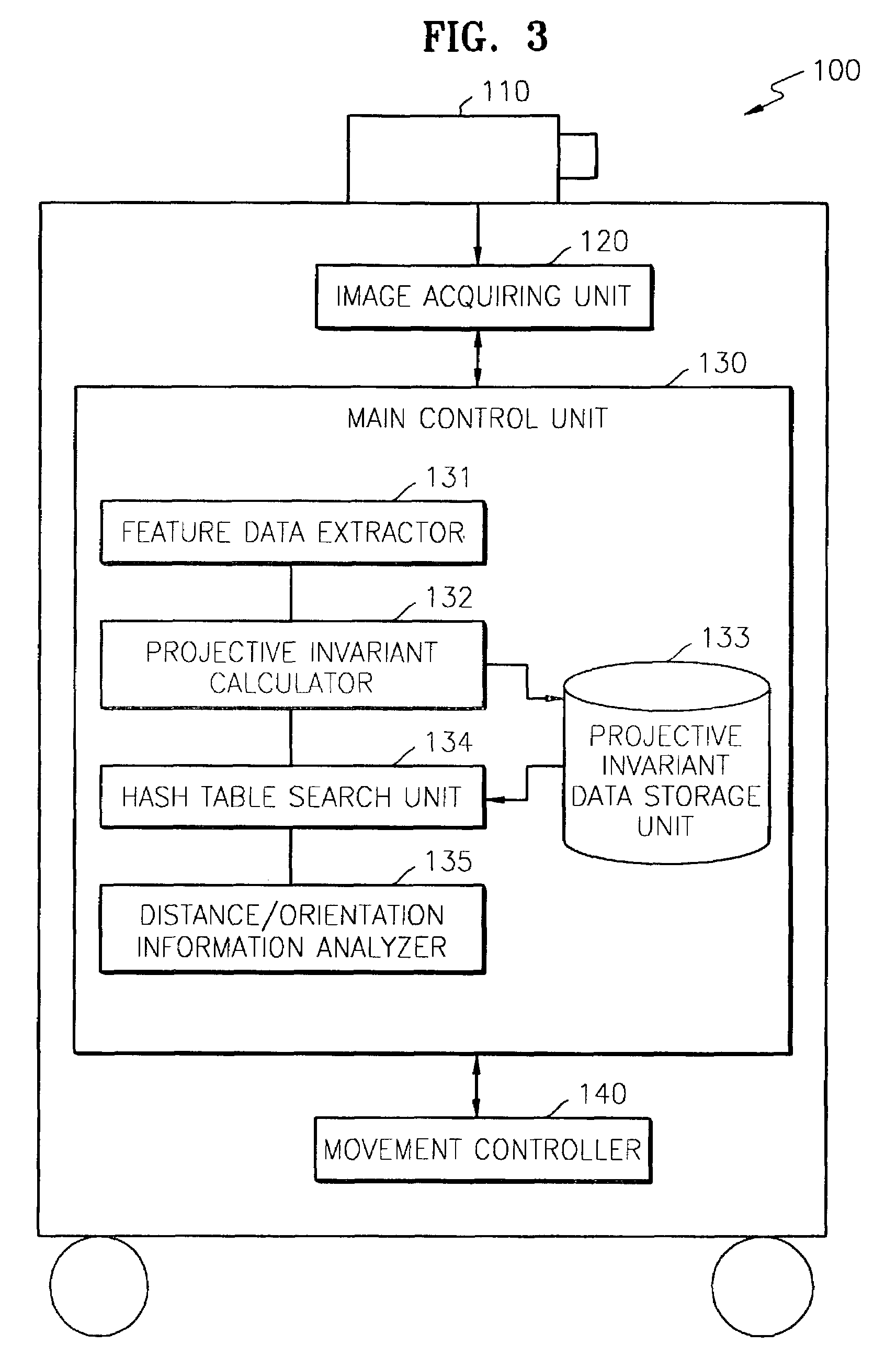
A landmark used to effectively determine the location of an autonomous vehicle, and a self-localization apparatus and method using the landmark are provided. In the self-localization method, first, first and second outer line information and shape information are extracted from a landmark image received from a camera. Next, a projective invariant is calculated from the shape information and stored in a hash table. Thereafter, the calculated projective invariant is compared with reference projective invariants for a plurality of landmarks stored in a predetermined data storage area in the form of a hash table, thereby determining which landmark corresponds to the landmark image. Then, information on the distance and orientation of the determined landmark with respect to the autonomous vehicle is analyzed in response to the first and second outer line information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Moving robot's vision navigation method based on image representation feature
InactiveCN1569558ASolve hardware problemsLong detection distanceNavigational aid arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVision basedNavigation system
The invention is a vision navigating method for mobile robot based on image representation character. It includes steps: the mobile robot detects the natural marked object automatically; matches the current image with the image and scene in sample bank, in order to determinate the current position. The method solves the hardware problem caused by former navigation system with sensor, which can be applied to non-field environment where the traditional navigation mode is difficult to be adaptive, and carries on the self localization of mobile robot. The navigation method combines the scene mark detection and scene image representation analysis.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sensor node having self localization function and self localization method thereof
InactiveUS8462697B2Low costReduce power consumptionPosition fixationWireless commuication servicesTransceiverAudio power amplifier
Disclosed are a sensor node having a self localization function and a self localization method of the sensor node. The sensor node calculates a location thereof by receiving location information measured at each of two mobile nodes at different times and using four location information of the received location information. Additional cost and power consumption required for installing additional equipment such as an anchor node, a ultrasonic transceiver and a signal amplifier are reduced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
RGB-D visual odometry taking ground constraint into consideration in indoor environment
InactiveCN106556412AImprove estimation accuracyIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisColor imagePoint cloud
The invention belongs to the field self-localization of a mobile robot, and particularly relates to RGB-D visual odometry taking ground constraint into consideration in an indoor environment. The method comprises: (1) in an indoor environment, collecting color image information and depth image information in the environment during a motion process of an RGB-D camera loaded on a mobile platform and marking adjacent frame images as Is and It; (2) performing solution through a reverse projection function [pi]-1 according to the depth image information to obtain three dimensional point cloud data Vs and Vt of the environment; and (3) extracting and matching ORB characteristics including extracting and matching characteristic points of RGB-D images through an ORB algorithm. Image pre-treatment including characteristic extraction and matching is completed through an ORB algorithm. Compared with SIFT and SURF algorithms, the ORB algorithm is accelerated by one order of magnitude. The point cloud ground is obtained through use of depth image detection and point set alignment is improved through use of ground information, thereby improving the estimation precision of motion transformation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Device and method for controlling self-localization, butting and charging of high-voltage line inspection robot
InactiveCN103825338AControl running speedImprove the efficiency of autonomous charging and dockingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerProximity sensorHigh pressure
The invention discloses a device and a method for controlling self-localization, butting and charging of a high-voltage line inspection robot. According to the device and the method, the specific position of the robot in a high-voltage power transmission line is located through a GPS-GIC (Global Position System-Geographic Information System) technology according to a self line structure of the high-voltage power transmission line and a self obstacle crossing function of the robot, and a moving speed of the robot in the high-voltage power transmission line is controlled by combining an ultrasonic wave sensor and a hall proximity sensor, so that the efficiency of an automatic butting process is improved; joints of the robot are controlled by using a speed mode, a moment mode and a position mode, so that the charging and butting process is accurately controlled; finally, the charging and butting process is accurately adjusted according to signal feedback of a strain gage of a charging plug and the hall proximity sensor, so that the tangential internal stress between the charging plug and a charging socket is reduced and the safe and reliable processing of the charging process is ensured.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
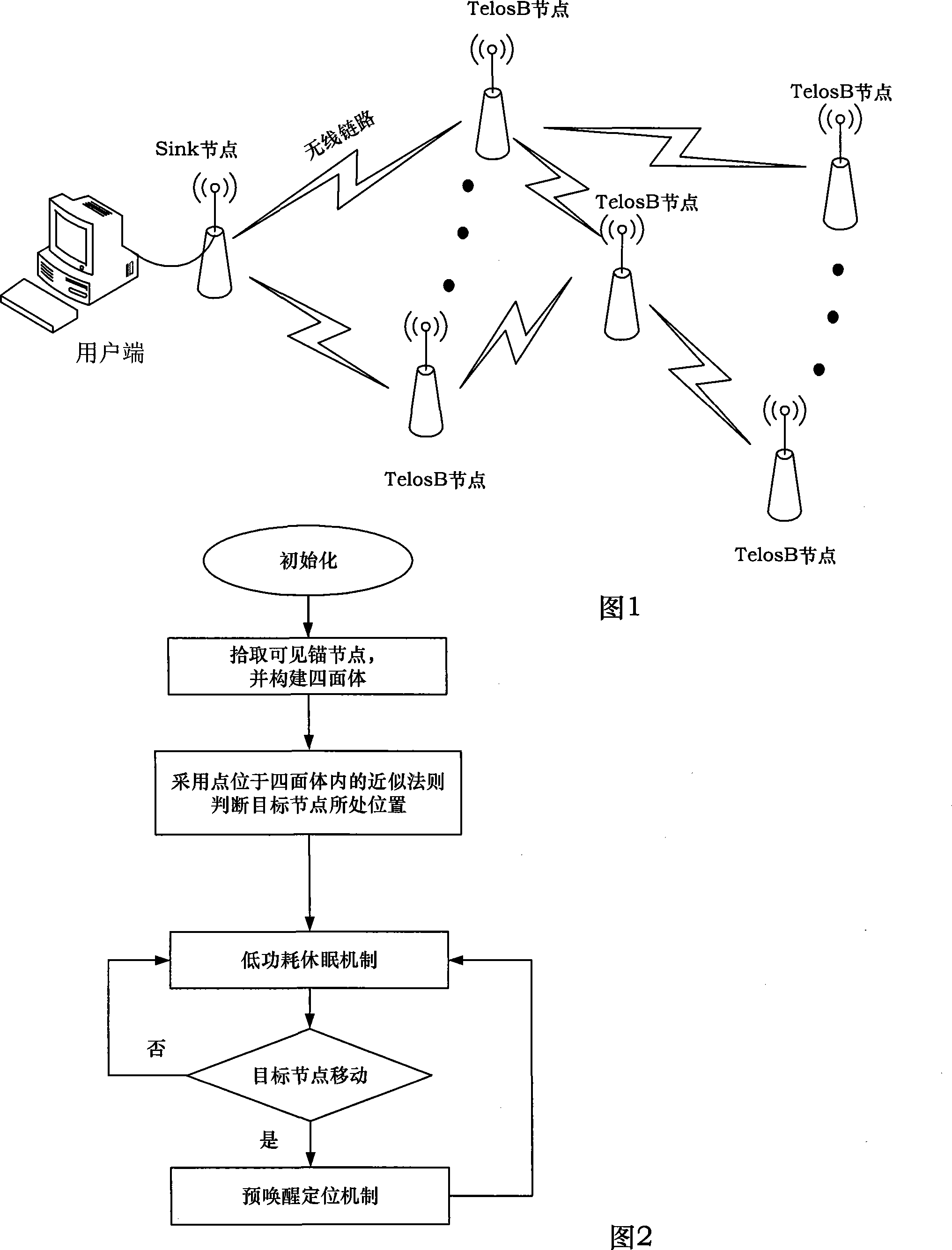
Wireless sensor network positioning system facing to three dimensional space
InactiveCN101241177AExtend your lifeEnsure h-hop connectivityPosition fixationWireless mesh networkThe Internet
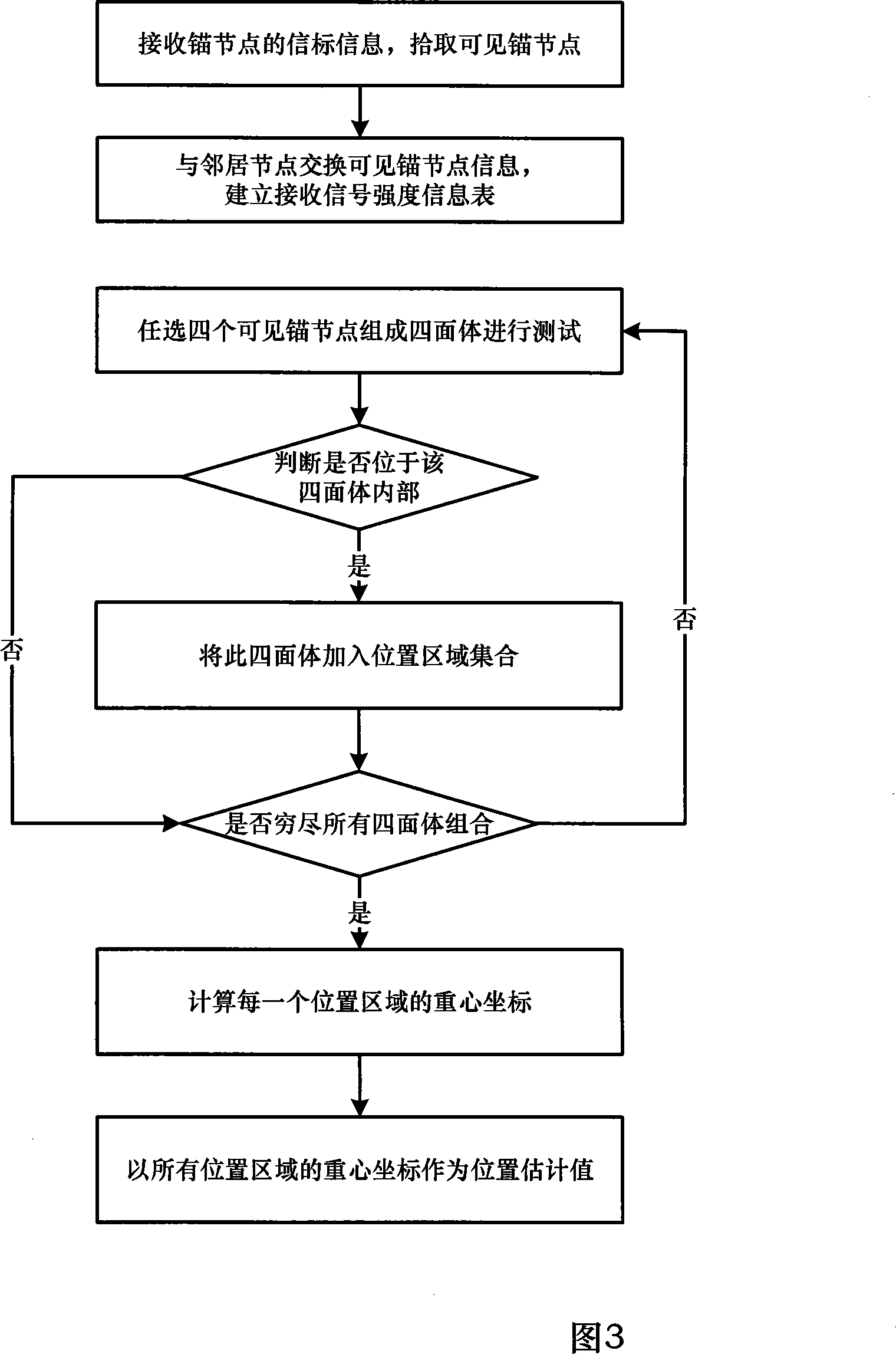
The present invention discloses a system for locating wireless sensor network based on 3D space, which comprises of multiple TelosB sensor nodes, Sink nodes and user end. Wherein, each TelosB node, and each TelosB node to each Sink node are communicated by wireless type, Sink nodes and user end can communicate by Internet or USB interface. In the 3D self-localization of random target nodes Mb in wireless sensor network, location region P is screened by judging whether the random target point Mb is located in the tetrahedron formed of random four visual anchor nodes, and barycenter set of all location region P are calculated and the average coordinate value of all elements in barycenter set G is looked as coordinate location of target nodes Mb in wireless sensor network. The all orientation resolution of 3D self-localization of present invention is processed on single sensor node, so the method of present invention is a distributing orientation method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
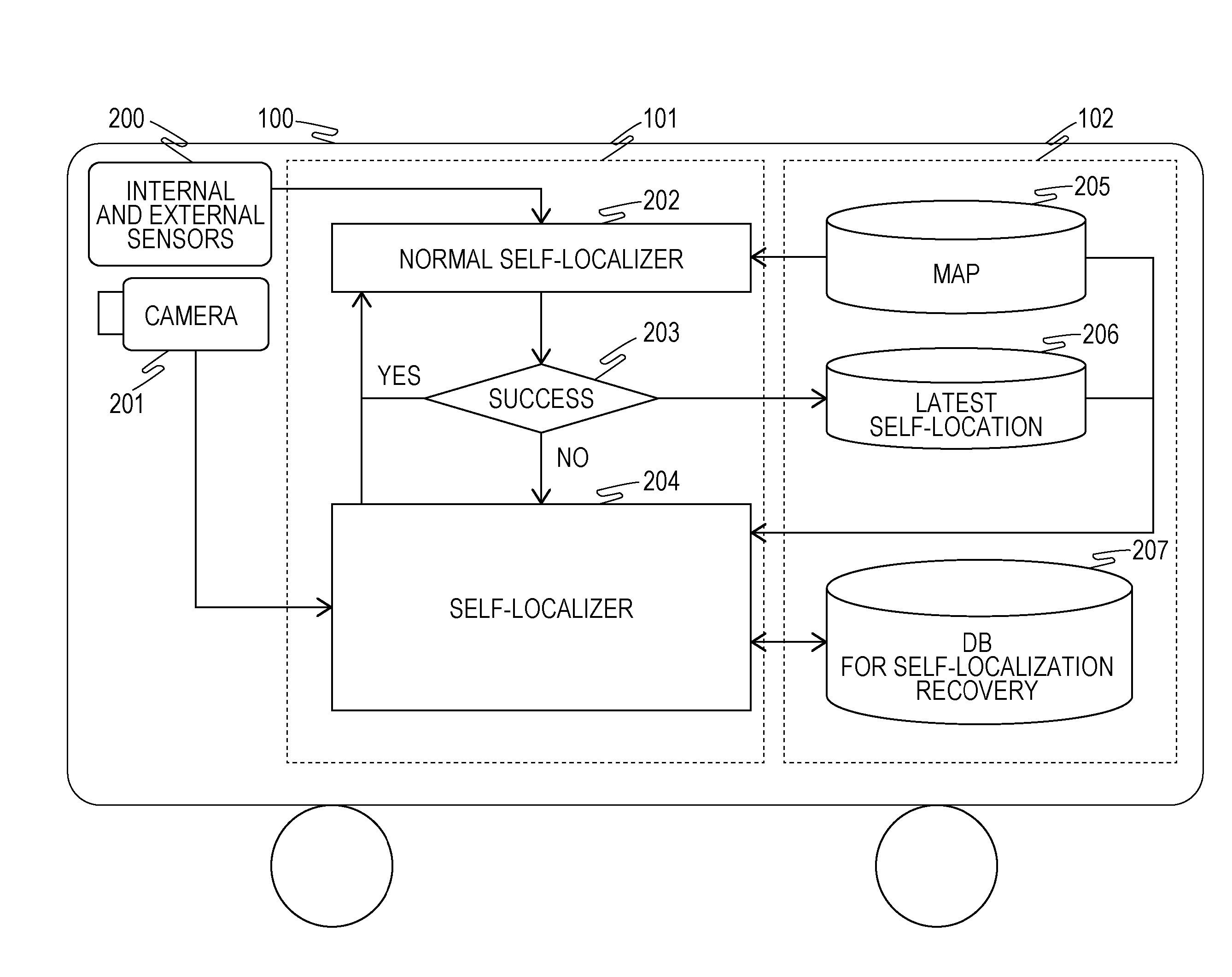
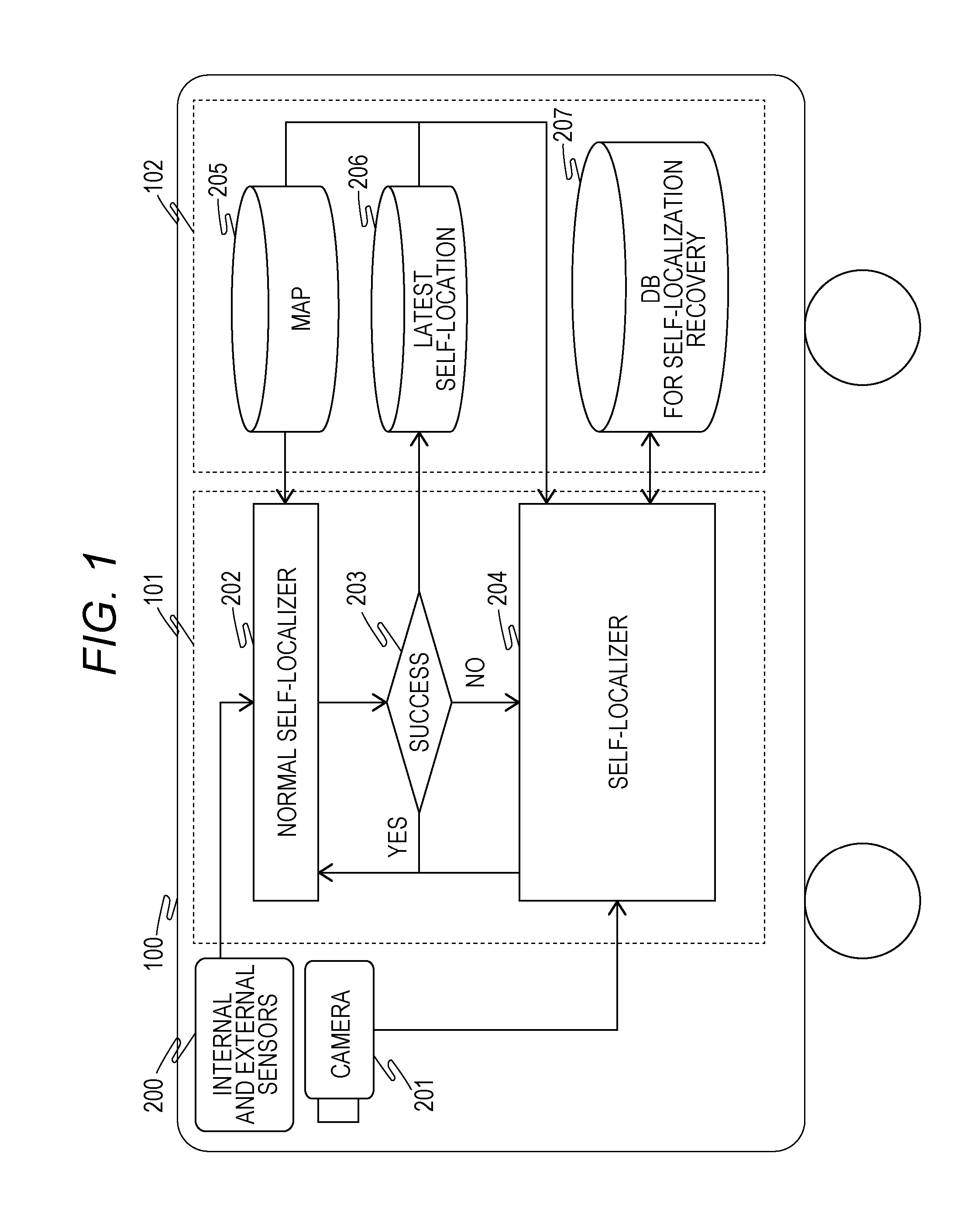
Self-Localization Device and Movable Body
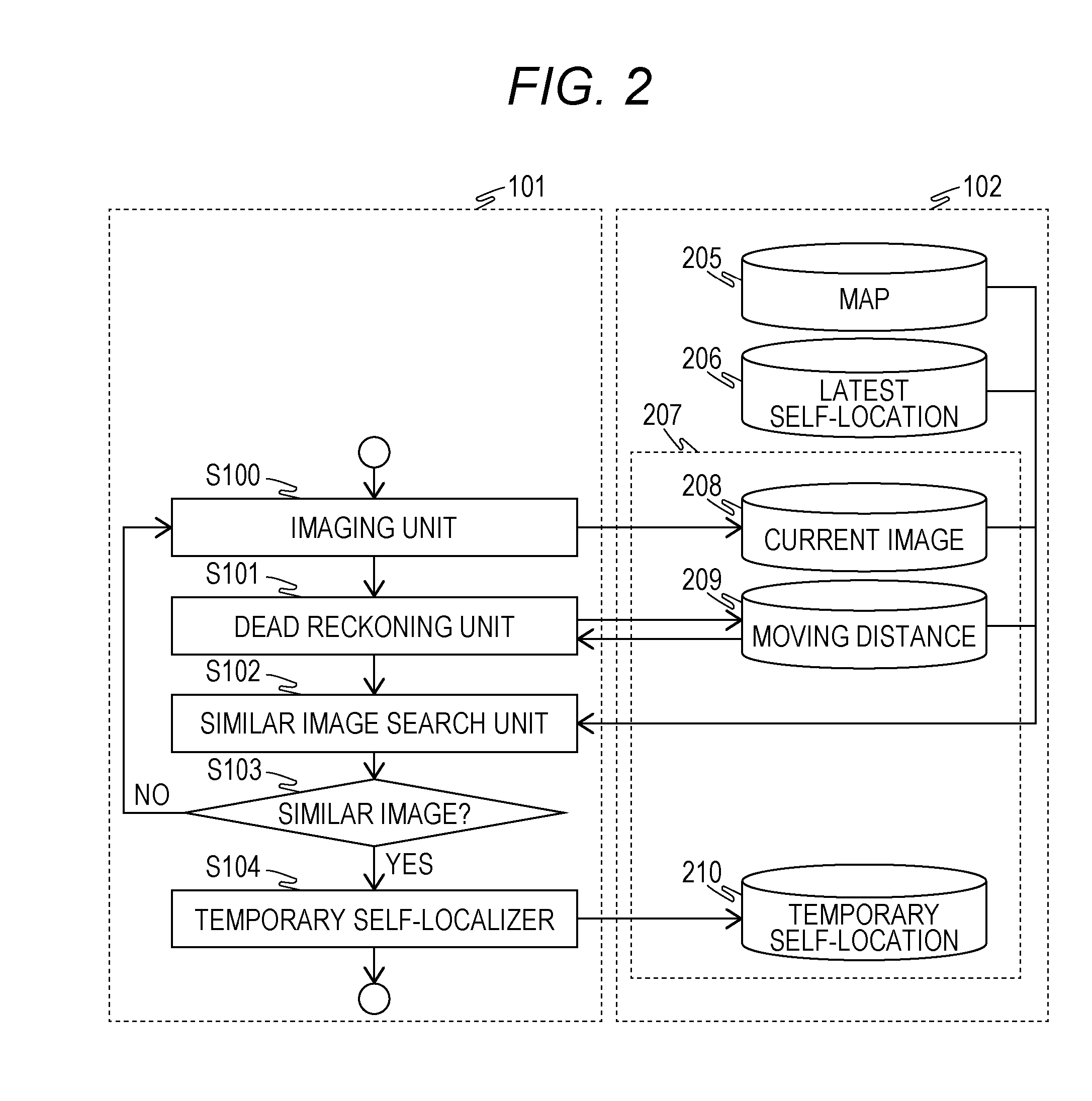
ActiveUS20160253806A1Increase blockingImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageImage capture
A self-localization device including a storage unit that associates and stores a plurality of reference images and imaging positions of the plurality of respective reference images and an operation unit that periodically estimates a self-location of a movable body based on information obtained from a sensor included in the movable body, wherein the operation unit determines, when estimation of the self-location fails, a moving distance from a latest self-location obtained from successful estimation of the self-location before the estimation fails using the information from the sensor and extracts a plurality of the reference images belonging to a range of the moving distance from the latest self-location and searches the plurality of extracted reference images for images similar to a current image captured by an imaging device included in the movable body to estimate the self-location of the movable body.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for achieving self-localization and map building of mobile robot
ActiveCN107741745APrevent deviationThe effect is accurateNavigational calculation instrumentsAttitude controlComputer graphics (images)Dependability
The invention relates to the technical field of robot navigation, and aims to provide a method for achieving self-localization and map building of a mobile robot. An algorithm of simultaneous localization and map building of the robot is provided, the motion trail of the robot is divided into a pose and position estimation mode fusing straight lines with arcs in a complex environment, and on the basis that the pose and position of the robot are obtained, an environment characteristic processing method is invented to update map features, so that a more precise pose and position of the robot anda more precise environmental map are obtained. The method has high adaptability and reliability in the complex environment. It can be ensured that the pose and position error of the robot is kept within a very small and stable range during long-time motion; on the basis that the precise pose and position of the robot are determined, the surrounding environment characteristics are obtained, the environmental map is obtained, and then self-localization and navigation are achieved based on the environmental map. By means of the method, the possibility that the whole map has deviations due to therobot errors is avoided, and the method has high adaptability in various complex environments.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
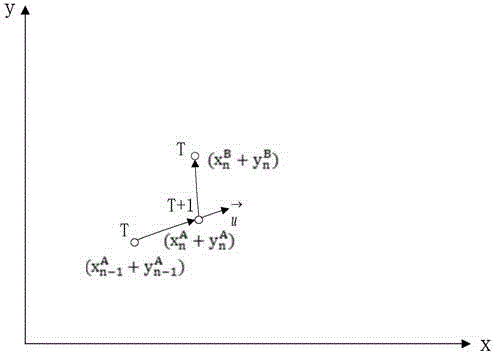
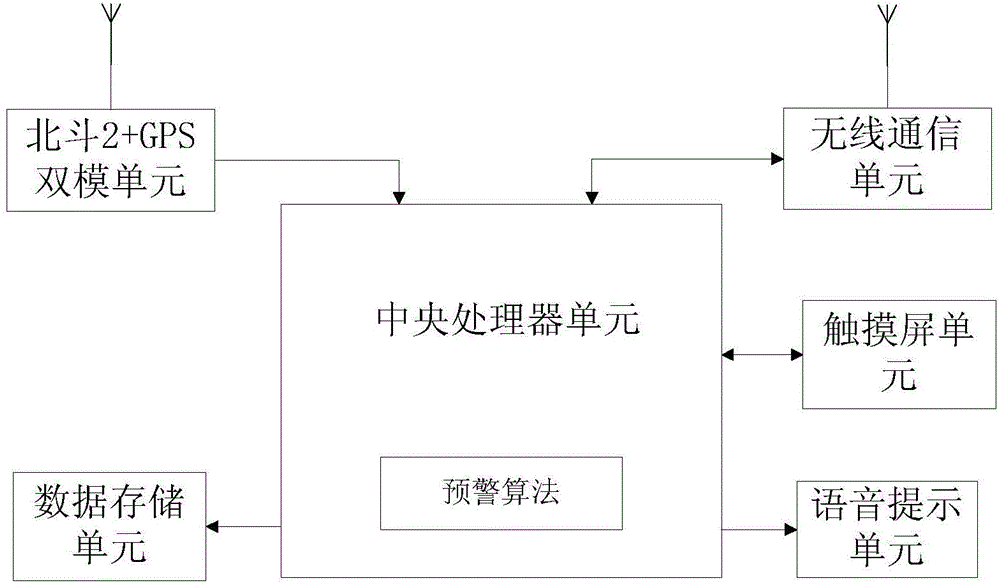
Vehicle collision-proof network early-warning method and device and confirmatory experiment platform
InactiveCN104554105AReduce mistakesReduce volumeVehicle headlampsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention relates to a vehicle collision-proof network early-warning method. The vehicle collision-proof network early-warning method comprises the following steps of measuring vehicle speed, acceleration and position information and storing the information; receiving location information of surrounding vehicles by a wireless mode and transmitting self-localization information outwards; displaying relative positions of the current vehicle and the surrounding vehicles on a display device of a current vehicle; calculating a distance between the current vehicle and each surrounding vehicle and judging whether the current vehicle has a collision danger by combining the speeds and the accelerations of the current vehicle and the surrounding vehicles; if collision danger exists, giving an alarm to a driver of the current vehicle in a voice manner. In the meantime, the invention provides an early warning algorithm of a vehicle under four circumstances, vehicle rear-end early-warning, overtaking early-warning, blind point early-warning and crossroad early-warning and provides a corresponding collision-proof network early-warning device and a confirmatory experiment platform.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
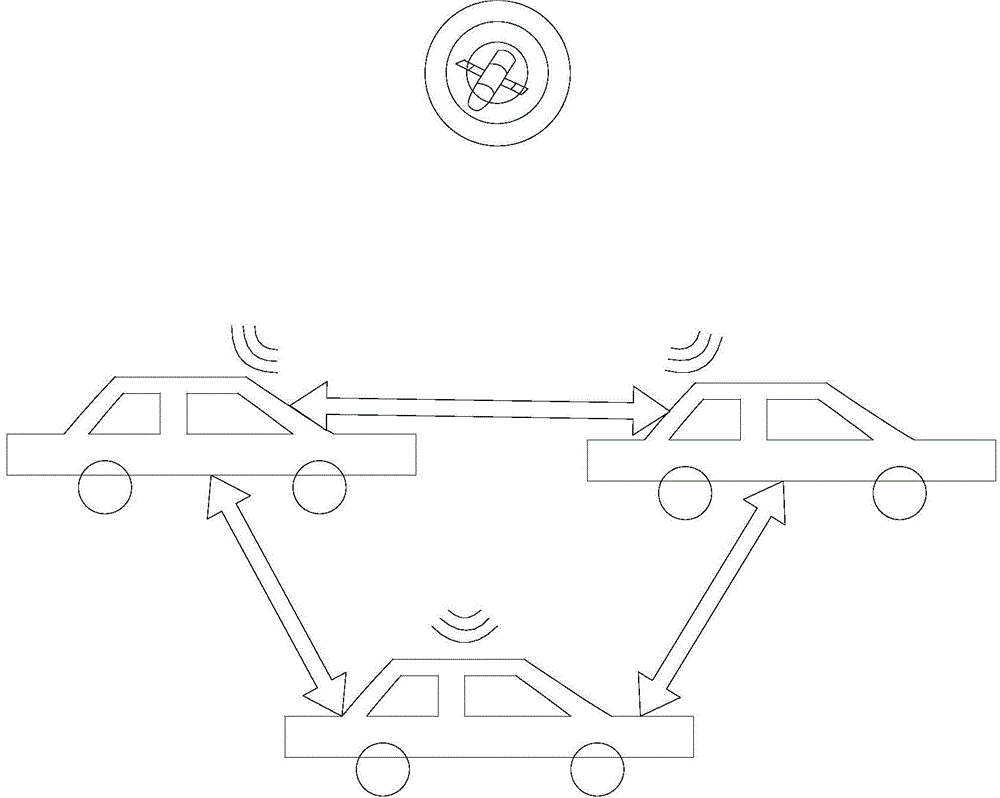
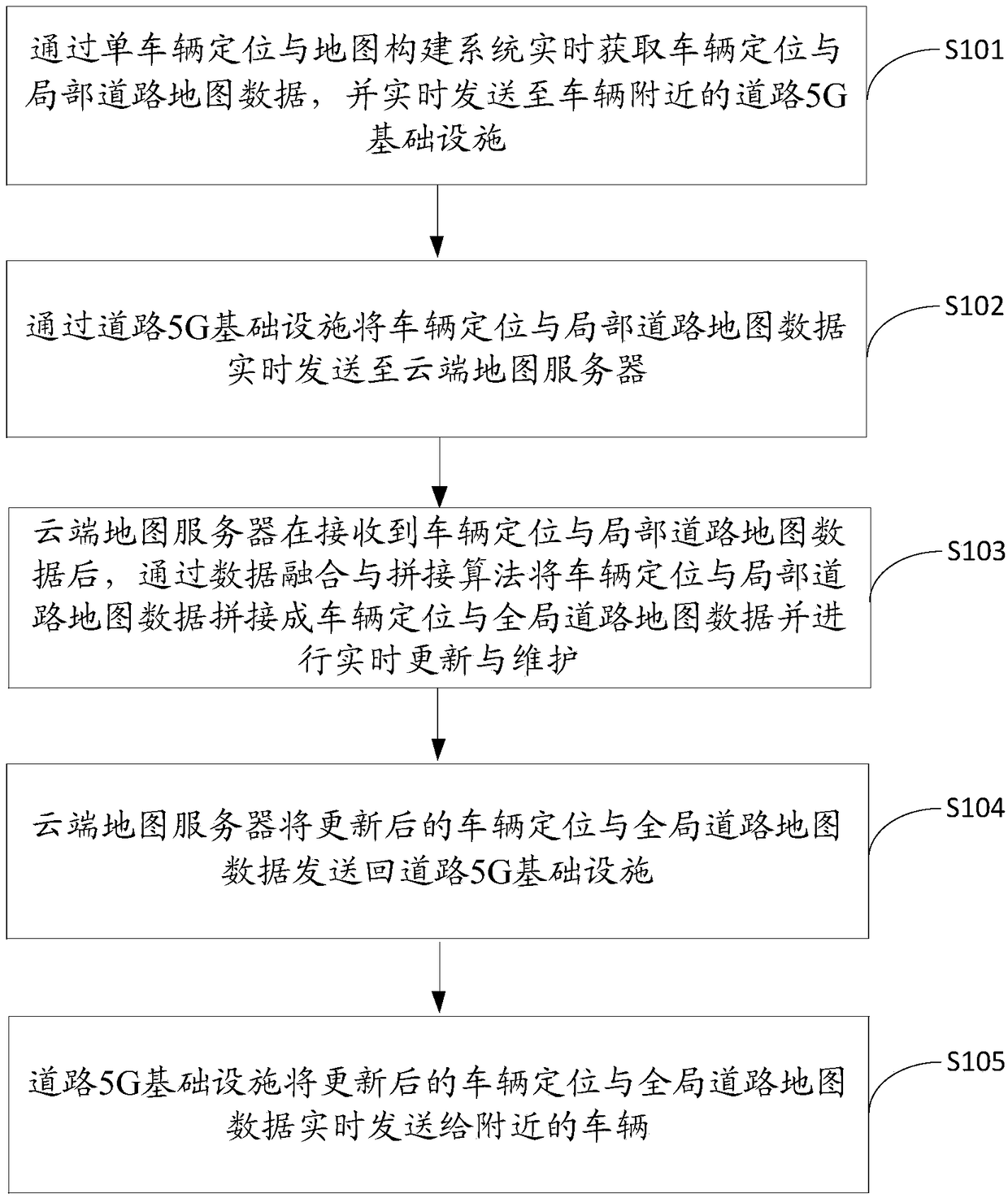
Multi-vehicle cooperative location and map building method, device and equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN109084785AReduce hardware costsImprove build efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationSingle vehicleCo operative
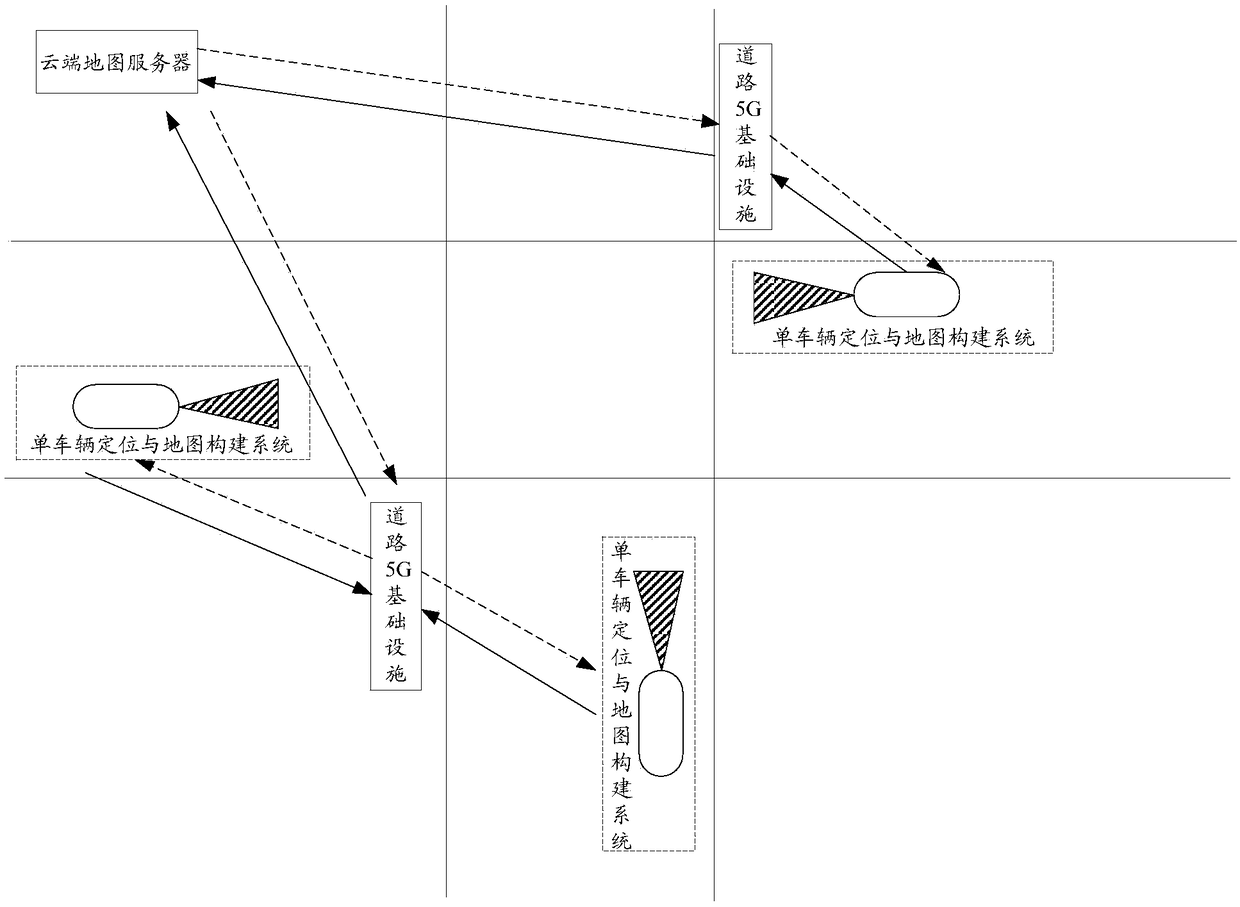
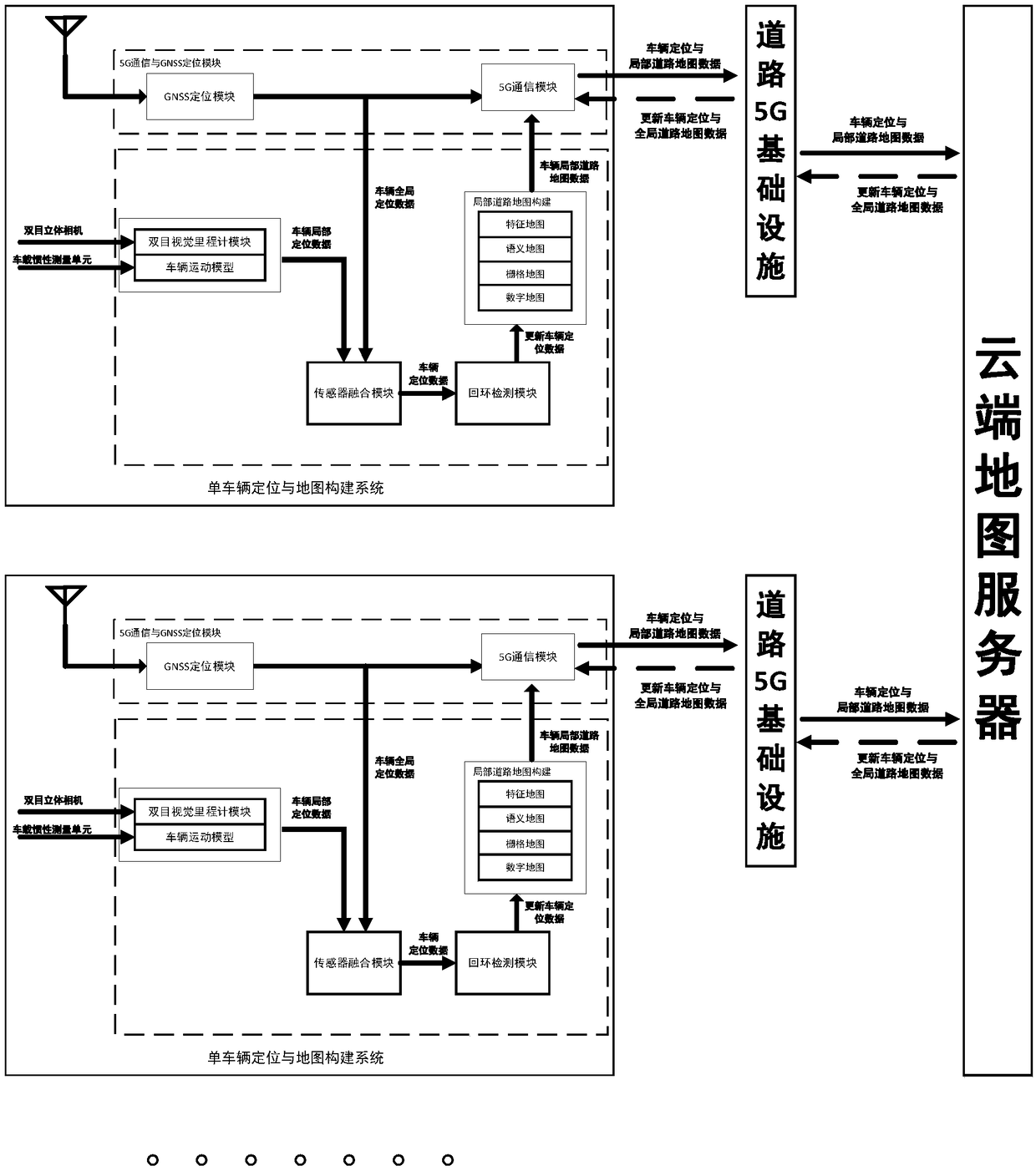
This application discloses a multi-vehicle cooperative location and map building method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The multi-vehicle cooperative location and map building method comprises the steps that a single-vehicle location and map building system obtains vehicle location and local road map data in real time and sends the data to a road 5G infrastructure near a vehicle; the road 5G infrastructure sends the vehicle location and local road map data to a cloud map server in real time; after the cloud map server splices the local road map data into global road map data through a data fusion and splicing algorithm, the global road map data are updated and maintained in real time and sent back to the road 5G infrastructure; and the road 5G infrastructure sends the updated vehicle location and global road map data to nearby vehicles in real time. When self-localization of a single vehicle is realized, cooperative location and map building with other surrounding vehiclesis carried out, constant updating of a local map is realized, a global map is maintained regularly, and the multi-vehicle cooperative location and map building method is more accurate, more efficientand more robust; and meanwhile, the cost is low, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
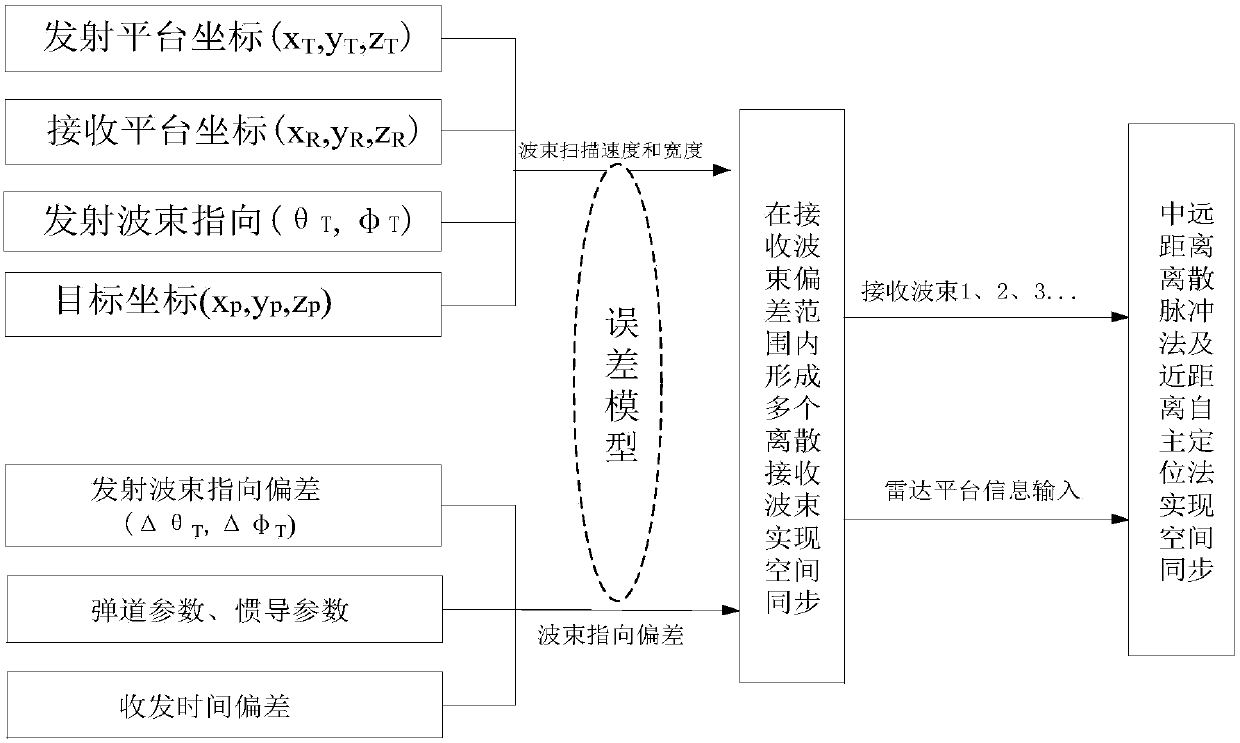
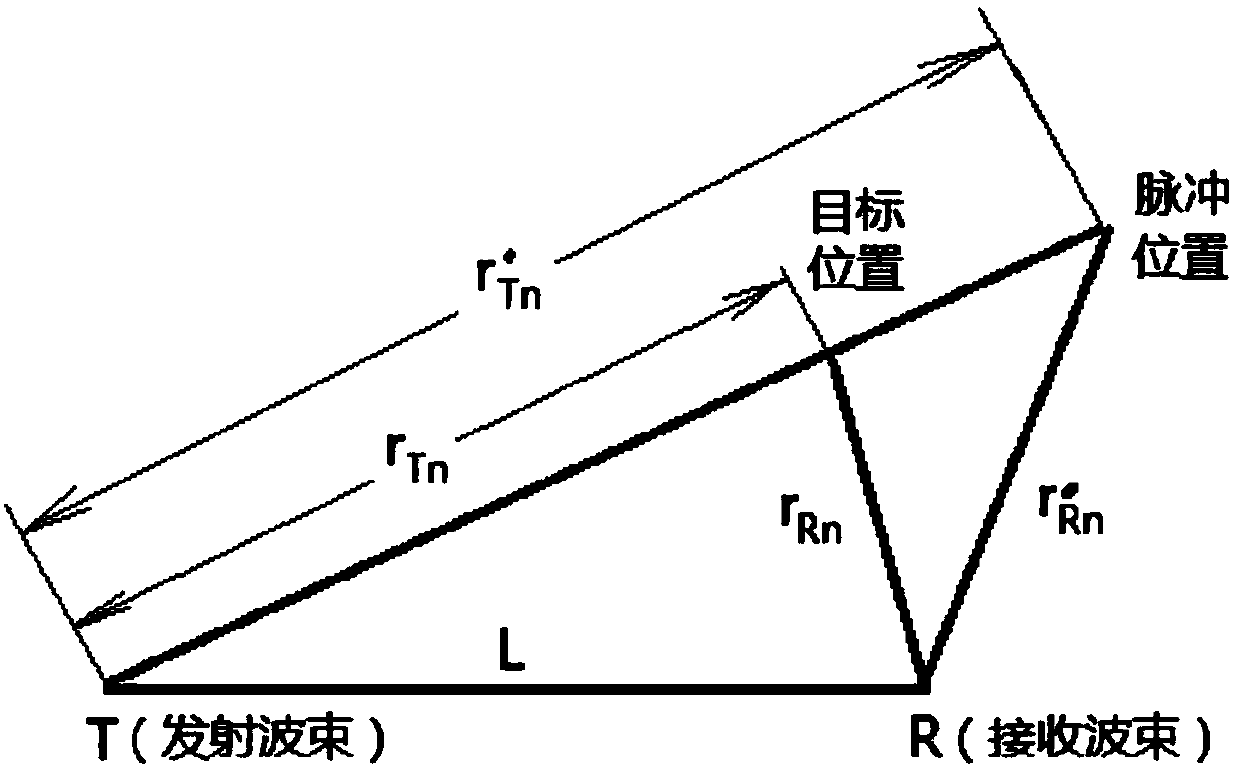
Distributed multi-static radar transmit-receive wave beam synchronization and wave beam control high-precision method
InactiveCN107064880ACatch up withImproving Pulse Tracking AccuracyWave based measurement systemsSelf localizationClassical mechanics
The present invention provides a distributed multi-static radar transmit-receive wave beam synchronization and wave beam control high-precision method. The method is based on the discrete pulse chasing method and the self-localization method to control the transmit-receive wave beam space synchronization error to realize high-precision transmit-receive wave beam synchronization and wave beam control. When a receiving platform is far away from a target and the distance between the receiving platform and the target is larger than 10km, the transmit-receive wave beam employs the pulse chasing method to realize space synchronization. When the distance between the receiving platform and the target is smaller than 10km, the synchronization performance of the pulse chasing method is sharply deteriorated. The self-localization method is employed to improve the space synchronization performance when the distance is small, namely the target position coordinates and the actual position of the receiving platform are employed to determine the orientation and the pitching direction of the receiving wave beams. Besides, pointing errors of the receiving wave beams and the emission wave beams are controlled in a certain range to actually realize the space synchronization of transmit-receive wave beams.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
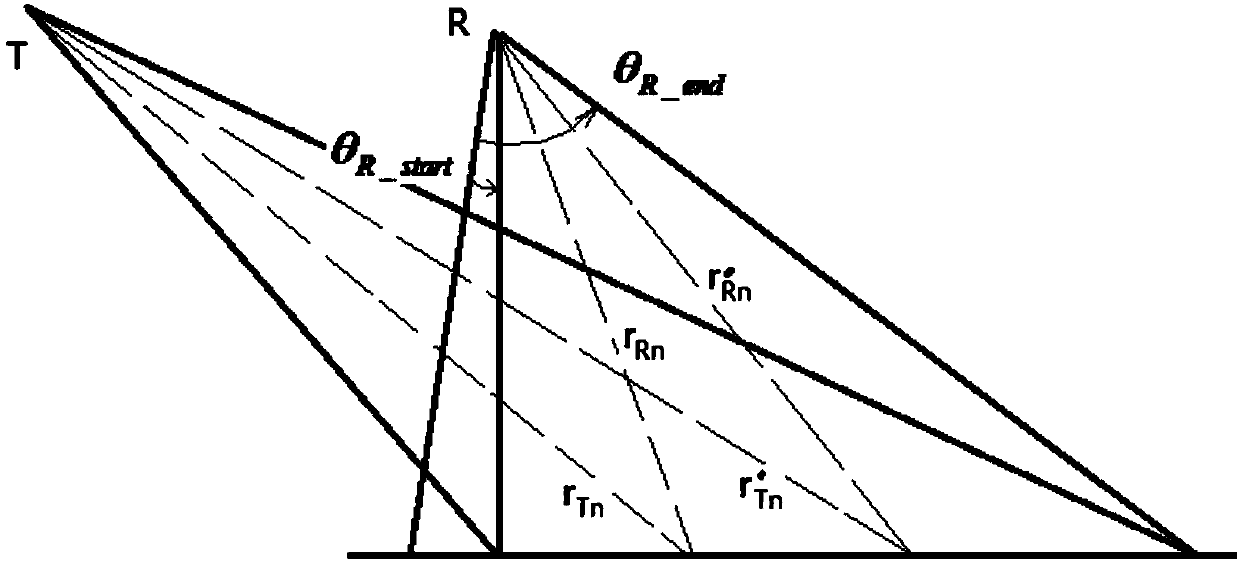
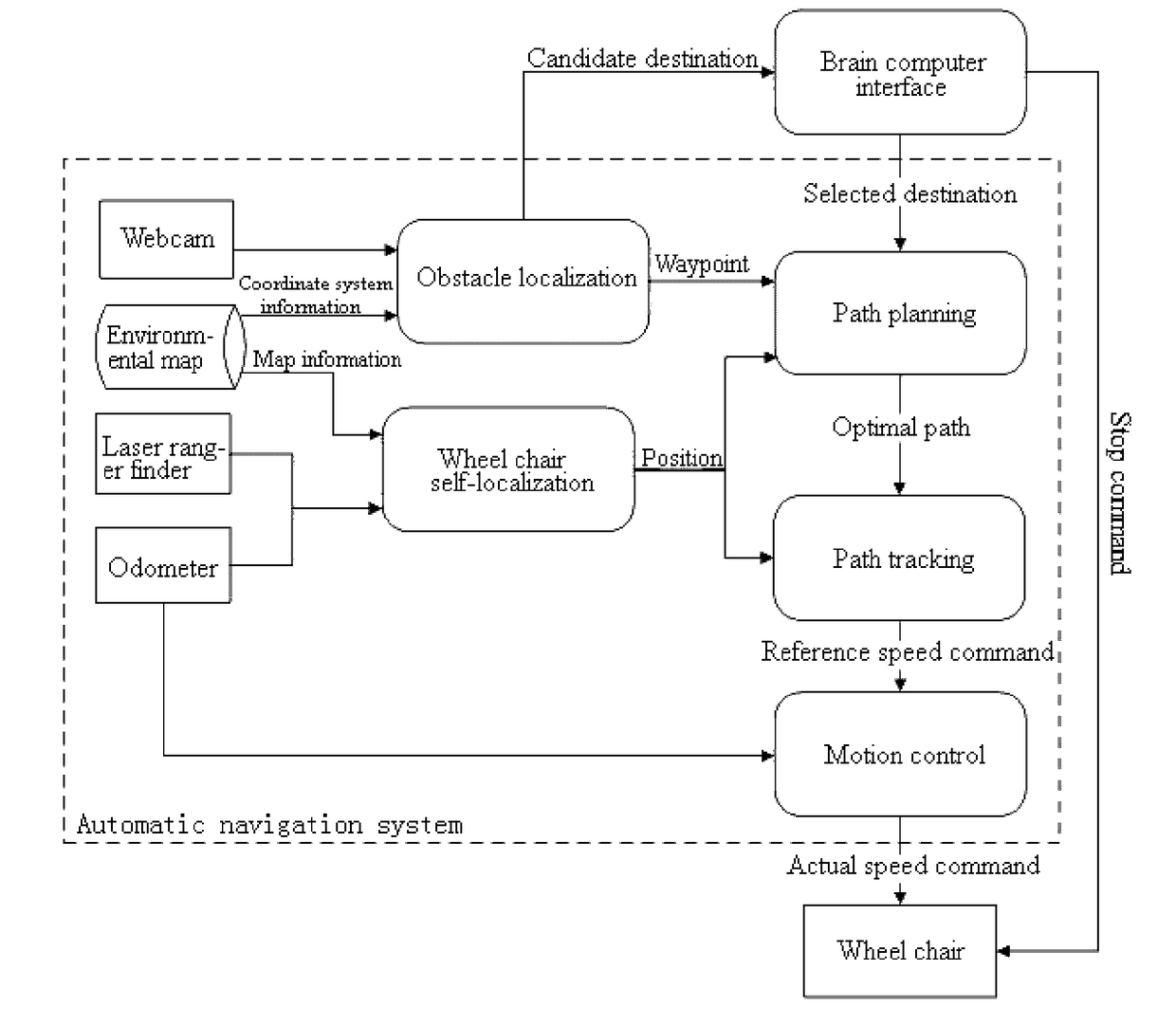
Intelligent wheel chair control method based on brain computer interface and automatic driving technology
InactiveUS20170095383A1Reduce mental burdenInput/output for user-computer interactionEnsemble learningBrain computer interfacingAngular velocity
Disclosed is an intelligent wheel chair control method based on a brain computer interface and an automatic driving technology. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring current pictures by webcams to perform obstacle localization; generating candidate destinations and waypoints for path planning according to the current obstacle information; performing self-localization of the wheel chair; selecting a destination by a user through the brain computer interface (BCI); planning an optimal path according to the current position of the wheel chair as a starting point and the destination selected by the user as an end point in combination with the waypoints; calculating a position error between the current position of the wheel chair and the optimal path as the feedback of aPID path tracking algorithm; and calculating a reference angular velocity and linear velocity by means of the PID path tracking algorithm and transmitting them to a PID motion controller, converting odometry data from encoders into current angular and linear velocities as a feedback of the PID motion controller, and controlling the driving of the wheel chair in real time to the destination. The intelligent wheel chair control method greatly relieves the mental burden of a user, can adapt to changes in the environment, and improves the self-care ability of patients with severe paralysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic Beacon Self-Localization Using Mobile Device Magnetometers
ActiveUS20160245638A1Easy to implementPromote resultsNavigation instrumentsPoint coordinate measurementsPosition dependentData memory
A computer-implemented method for determining position of a mobile device using magnetic beacons including detecting, by a sensor in the mobile device, a magnetic signal having a unique signature associated with a given magnetic beacon; storing location and an associated signature for each of a plurality of magnetic beacons in a data store of the mobile device, where each of the magnetic beacons is assigned a different signature; extracting the unique signature from the magnetic signal; comparing the extracted signature to each of the signatures stored in the data store; identifying a given magnetic beacon from the plurality of magnetic beacons, where signature for the given beacon matches the extracted signature; and retrieving the location for the given magnetic beacon for the data store and correlating location of the mobile device with the location of the given magnetic beacon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Stable type self-localization conveying line
ActiveCN105438714APrecise positioningAvoid instabilityConveyorsConveyor partsSalient pointAutomation
The invention discloses a stable type self-localization conveying line. The conveying line comprises two belt supports which are arranged in parallel. The belt supports are sleeved with a conveying belt, and the side portions of the belt supports are connected with a bottom plate through a connecting plate; a lifting seat is arranged above the middle of the bottom plate, and side locating plates are arranged on the two sides of the lifting seat and are parallel to the belt supports; locating salient points are arranged on the tops of the side locating plates, and the bottom of the lifting seat is connected with an air cylinder; the air cylinder is fixed to the bottom plate, and a carrier is further arranged on the belt; locating holes are formed in the two sides, located on the two sides of the belt supports, of the carrier, and stop grooves are formed in the other two side edges; and a second air cylinder is further arranged between the two belt supports, and a jacking stop rod is arranged on the top of the second air cylinder. By means of the stable type self-localization conveying line, products can be stably conveyed, the precise locating function is achieved, and the conveying line can be matched with a machine for achieving automation production.
Owner:福耐姆智能传输系统(苏州)有限公司
Method for self-localization of robot based on object recognition and environment information around recognized object
ActiveUS8024072B2Precise positioningProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPattern recognitionObject based
A method for self-localization of a robot, the robot including a camera unit, a database storing a map around a robot traveling path, and a position arithmetic unit estimating the position of the robot, includes: acquiring an image around the robot, in the camera unit. Further, the method includes recognizing, in the position arithmetic unit, an individual object in the image acquired by the camera unit, to generate position values on a camera coordinate system of local feature points of the individual objects and local feature points of a surrounding environment including the individual objects; and estimating, in the position arithmetic unit, the position of the robot on the basis of the map and the position values on the camera coordinate system of local feature points of the individual objects and local feature points of a surrounding environment including the individual objects.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Wheelchair robot and indoor autonomous navigation method thereof
PendingCN108897328ARealize autonomous navigationImprove work efficiencyWheelchairs/patient conveyancePosition/course control in two dimensionsPoint cloudWheelchair
The invention discloses a wheelchair robot and an indoor autonomous navigation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: sensing the environmental information through a monocular vision sensor, and constructing a three-dimensional point cloud map for the obtained environmental features by use of a vision SLAM algorithm; performing storage, perfection and rasterization treatment onthe formed point cloud map; loading the treated raster map, and performing self-localization of a moving wheelchair robot by the Monte-Carlo algorithm; finally, while performing continuous localization, finishing global path planning and local dynamic path planning by the wheelchair robot in the navigation process by combining the ant colony algorithm and the dynamic raster algorithm. The method disclosed by the invention can realize autonomous navigation of a wheelchair.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Ultra-wideband node network-based device-free localization method
ActiveCN105960017ARealize self-positioningGood multipath resolutionReceivers monitoringPosition fixationDevice free localizationUltra-wideband
The present invention discloses an ultra-wideband node network-based device-free localization method, belonging to the field of wireless localization technologies in a wireless network. According to the method, an ultra-wideband signal is sent by using a node so as to realize device-free localization (DFL), a channel pulse response in a line of sight (LOS) is detected, and localization is performed by using change of an LOS path signal power. In addition, the ultra-wideband node has a precise distance measurement capability, and can achieve precise node self-localization. Node self-localization is achieved by using distance measurement provided by the ultra-wideband node according to a cooperation localization method, shadow fading caused by shielding by a target is obvious, and an imaging effect is further improved, so that the method is more applicable to an environment with low LOS power, can improve localization precision in a more complex environment, and greatly reduces manpower and time cost for node deployment.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wireless sensor network target locating method and locating system without need of node self-localization
InactiveCN103200675AHigh positioning accuracyReduce the difficulty of implementationPosition fixationTransmission monitoringBroadcast packetWireless sensor networking
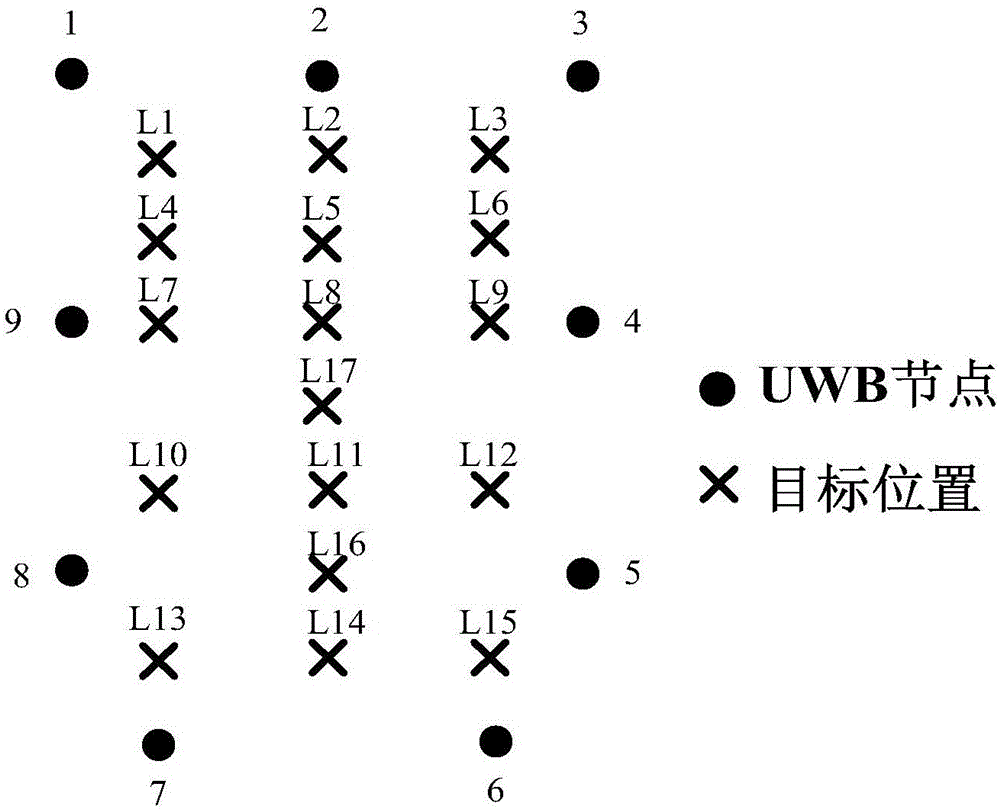
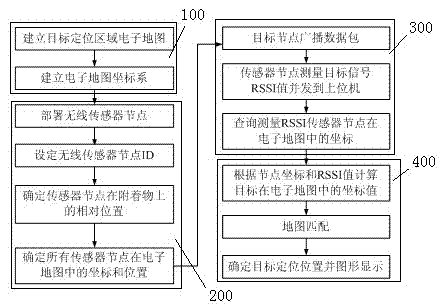
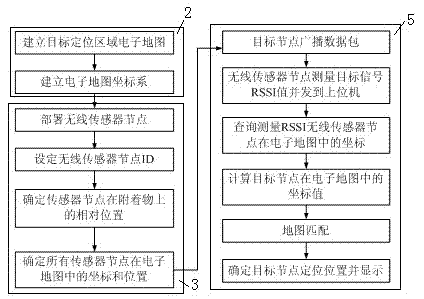
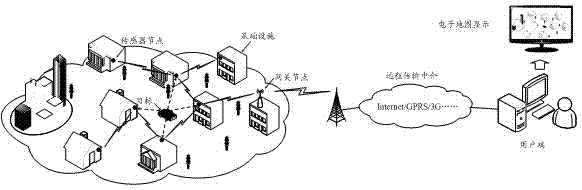
The invention relates to a wireless sensor network target locating method and a locating system without the need of node self-localization. The locating method includes a first step of establishing an electronic map in a target locating area, and establishing an electronic map coordinate system, a second step of setting a plurality of wireless sensor nodes, and confirming the coordinate values and positions of the wireless sensor nodes in the electronic map, a third step of enabling the wireless sensor nodes to measure RSSI values of target nodes in a target node broadcast data package, a fourth step of obtaining coordinates of the target nodes in the electronic map according to the coordinate values of the wireless sensor nodes used for measuring the RSSI values of the target nodes in the electronic map and the obtained RSSI values of the target nodes, and obtaining the locating positions of the target nodes in the electronic map according to the coordinates of the target nodes. By means of the electronic map, the wireless sensor network target locating method and the locating system without the need of the node self-localization achieve target locating under the condition of not carrying out node self-localization, improve locating precision, reduces implementing difficulty, and enlarge the locating application scope.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
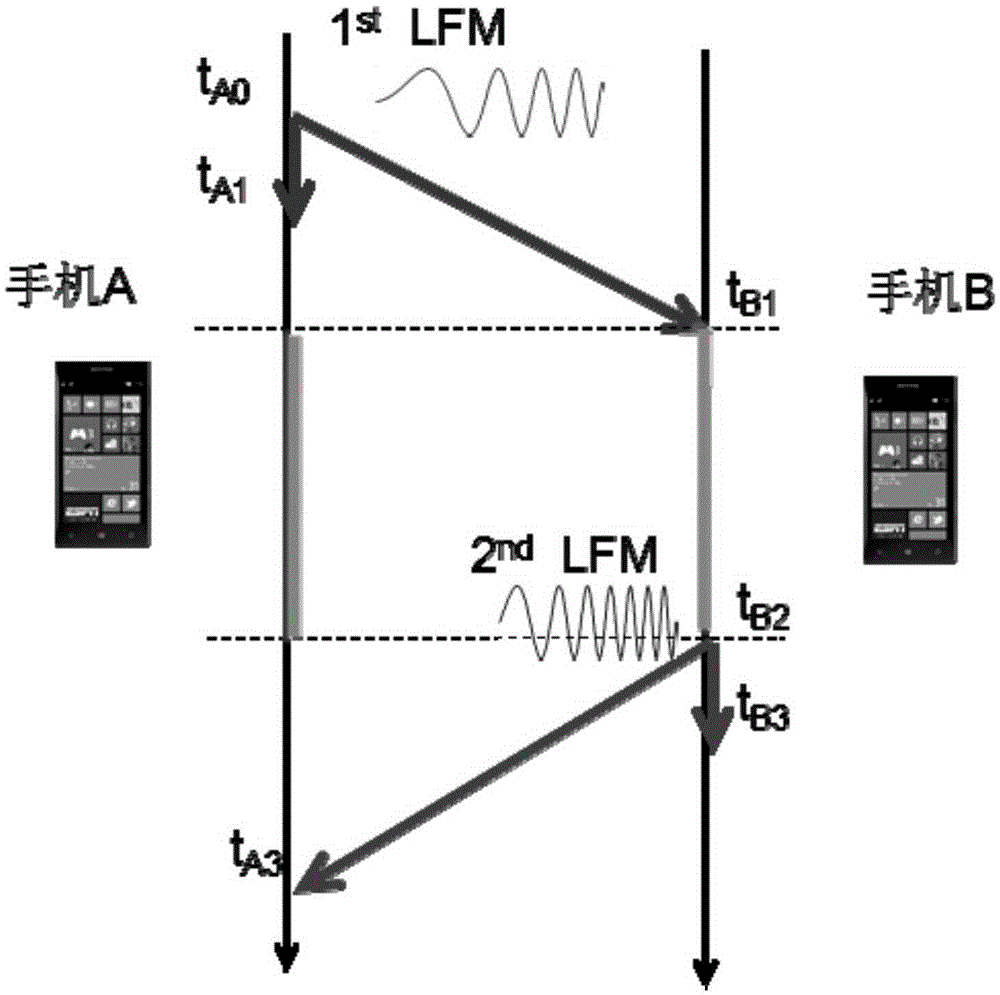
Self-localization method of sensor network node based on smartphone
ActiveCN105323772AHigh positioning accuracyLow costNetwork topologiesNetwork planningTime–frequency analysisFrequency modulation
The invention discloses a self-localization method of a sensor network node based on a smartphone. The method uses a general smartphone to replace a custom hardware module to be used as a network node, a plurality of mobile phone nodes orderly transmit linear frequency modulation (LFM) sound signals of 2k-6kHz by means of a loudspeaker and a microphone, and meanwhile, different mobile phone nodes sample the linear frequency modulation sound signals at a fixed frequency (44.1 kHz). Detection is performed on a sampling waveform by means of a generalized correlation method, and in view of a multipath effect, the self-localization method of the sensor network node based on the smartphone provided by the invention adopts a method of combining a threshold value method and time-frequency analysis to effectively inhibit the multipath effect, so that the arrival time of the linear frequency modulation sound signals can be obtained, then distance information between different nodes can be obtained, and finally, the unknown nodes can be located by adopting a multidimensional scaling (MDS) algorithm. The method of the invention does not need clock synchronization between the mobile phone nodes, and since the frequency is fixed, the arrival time of the sound signals can be accurately estimated through a sampling number; besides, the location accuracy is high, the cost is low, the networking is convenient and the prospect is wide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com