Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
302 results about "Robot leg" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
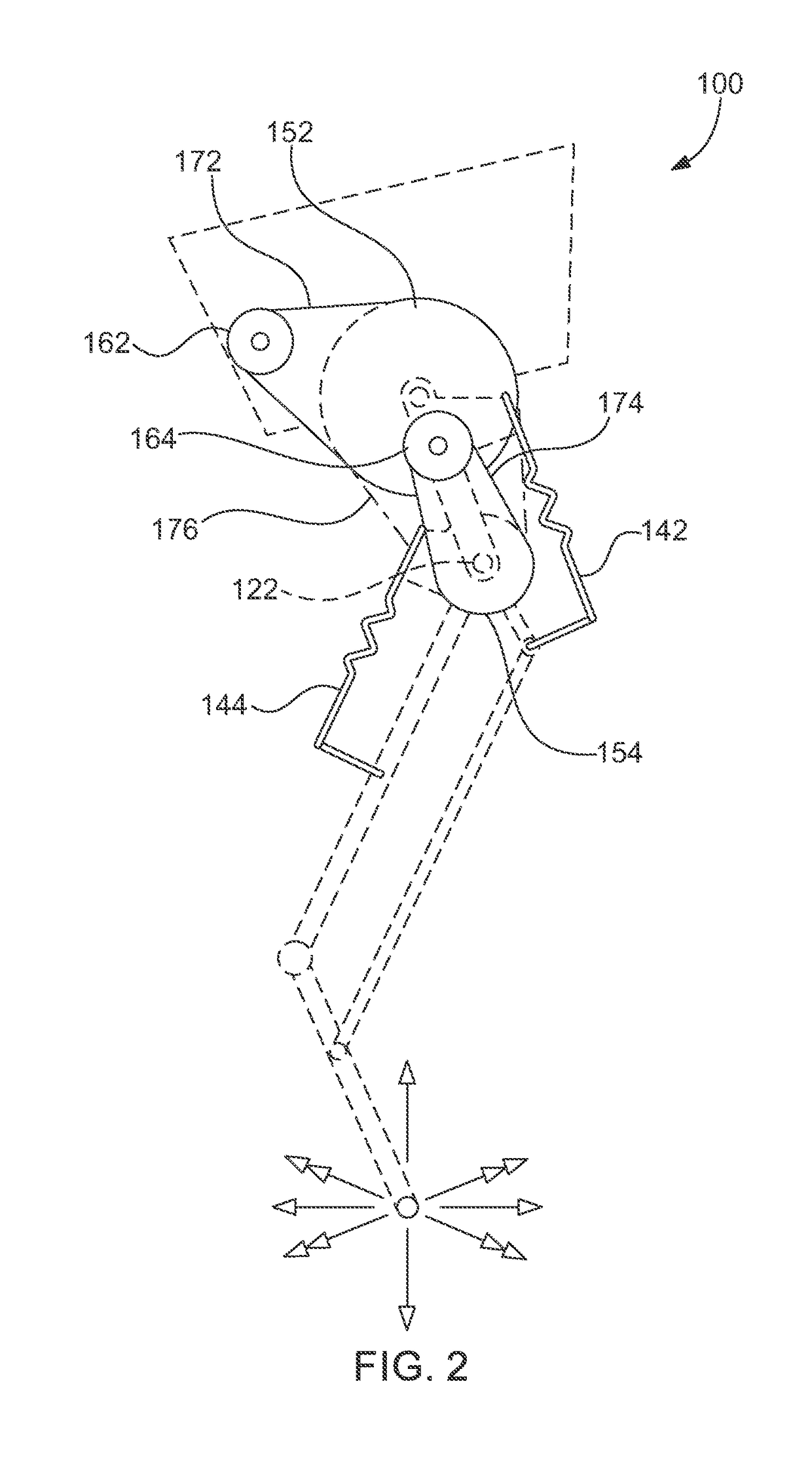
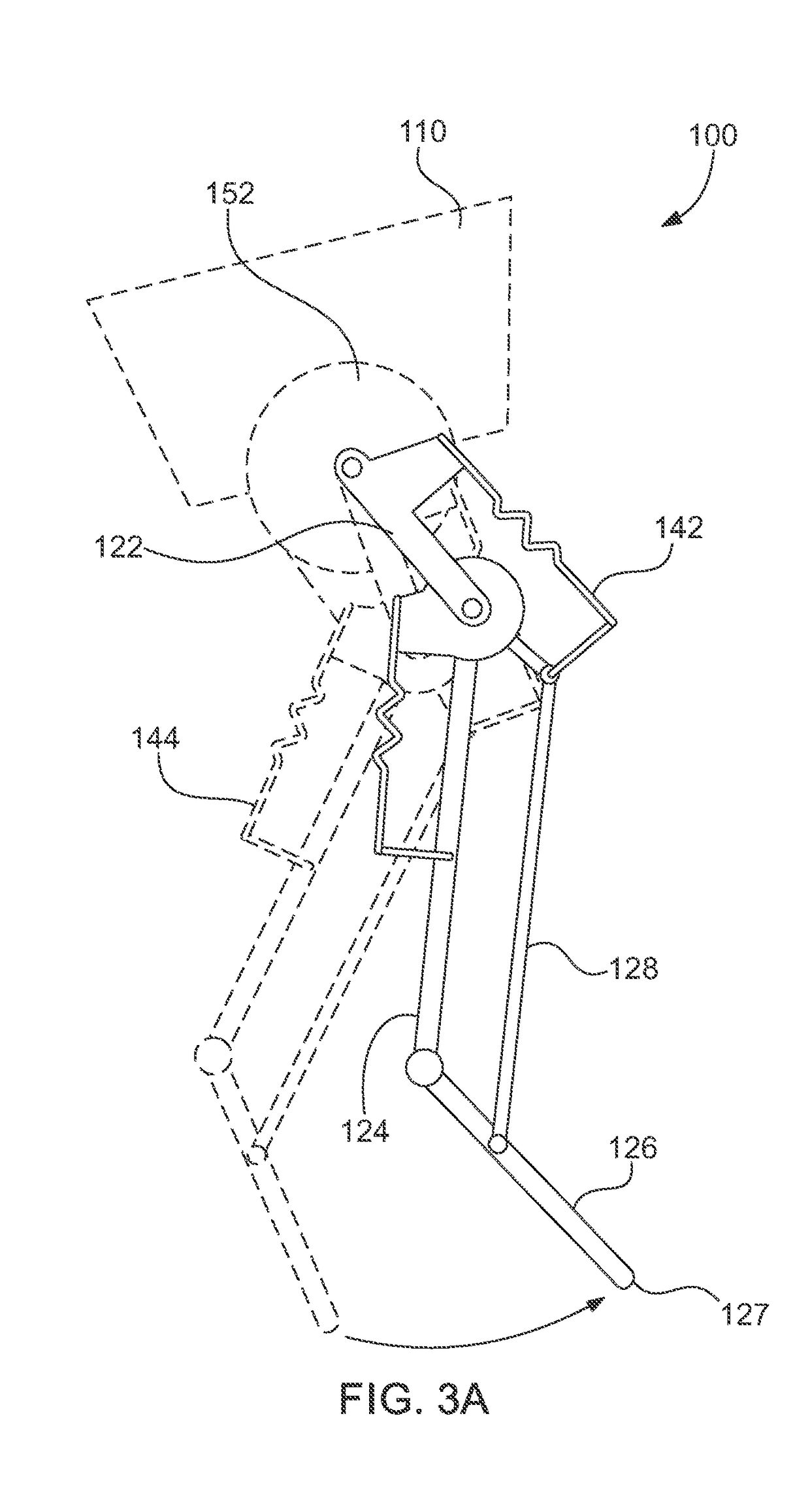
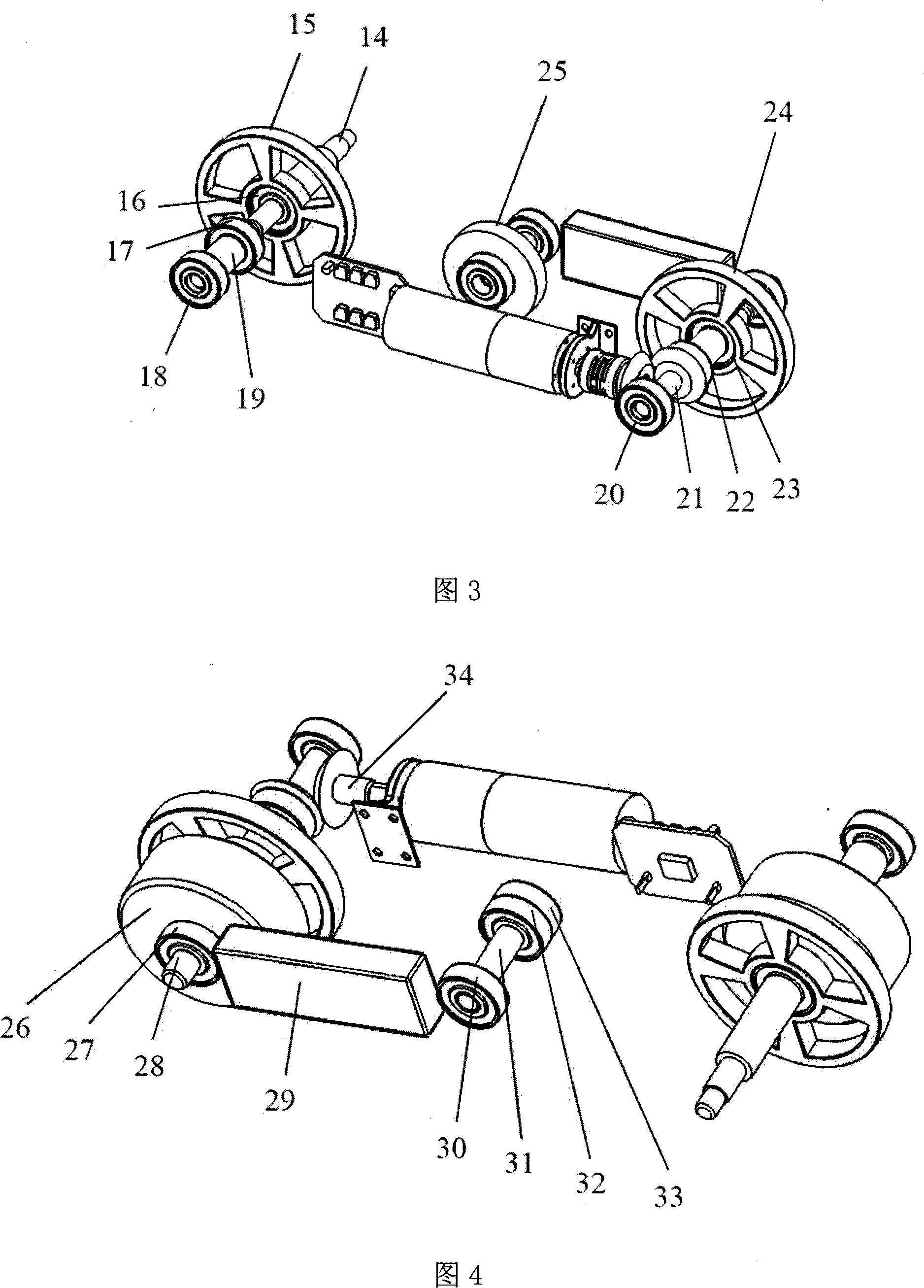
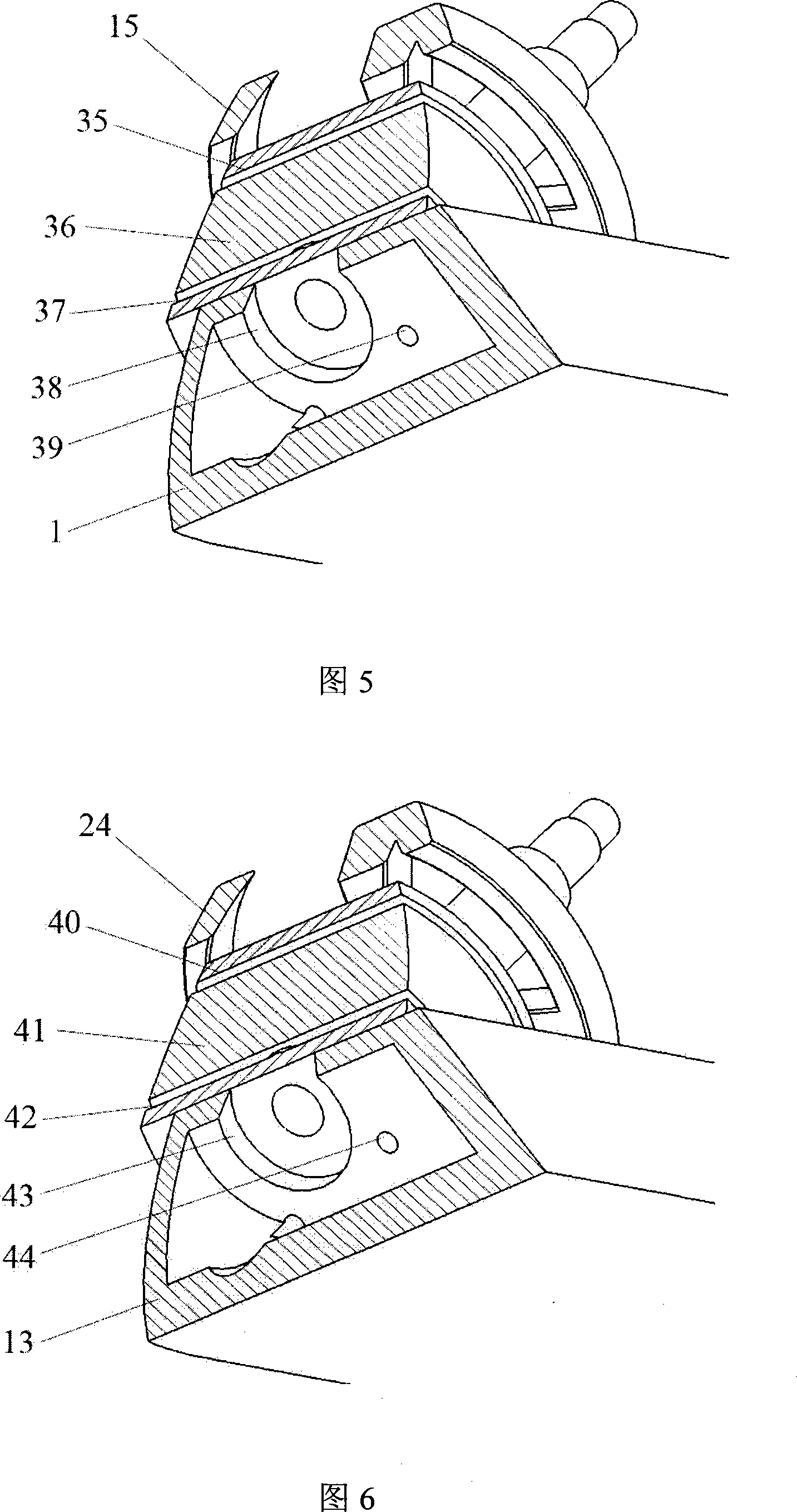
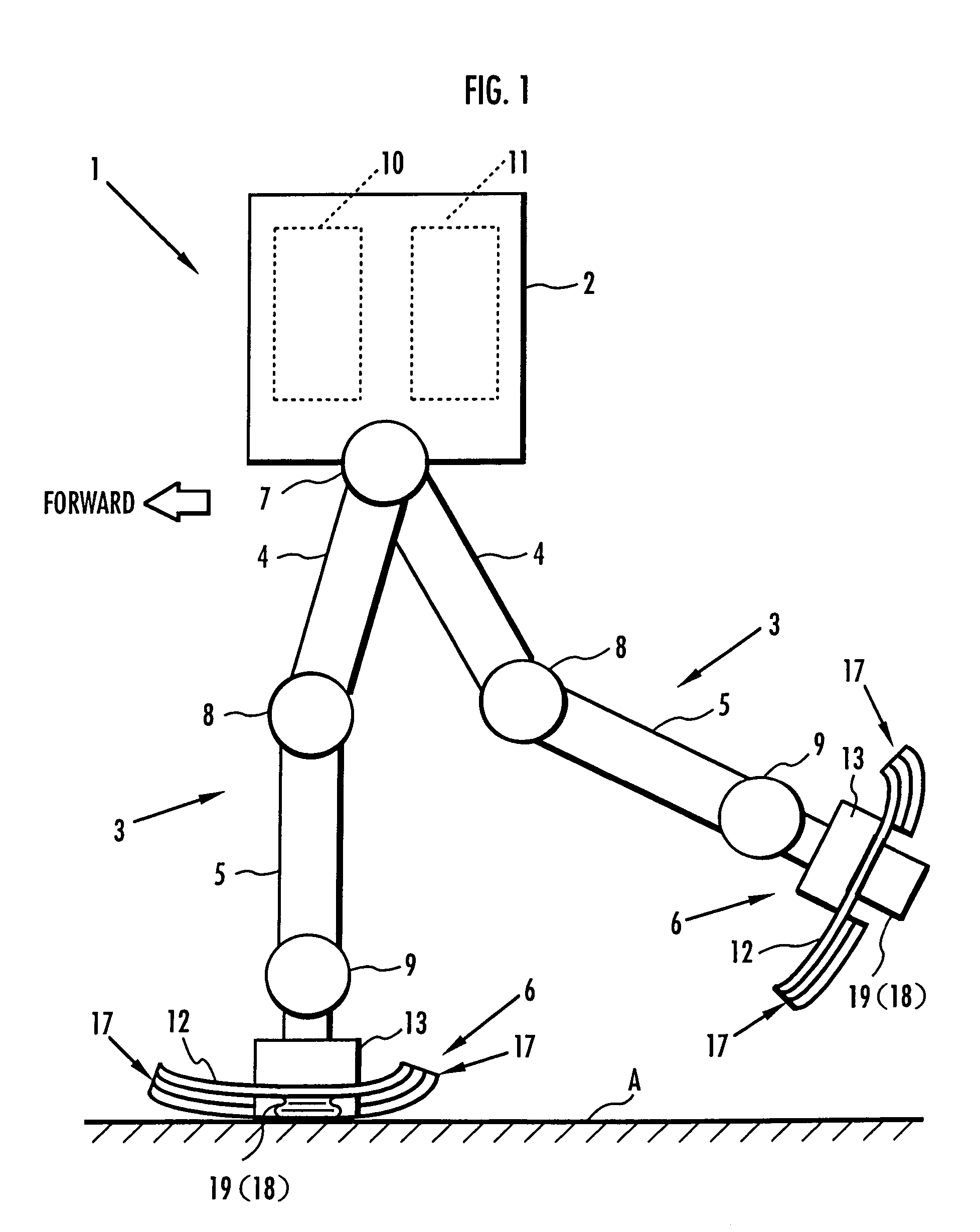
A robot leg (or robotic leg) is a mechanical leg that performs the same functions that a human leg can. The robotic leg is typically programmed to execute similar functions as a human leg. A robotic leg is similar to a prosthetic leg. However, a robotic leg can be controlled electrically or mechanically. To have the robotic leg emulate human leg behaviors, surgeons must redirect the nerves that previously controlled some of the person’s lower-leg muscles to cause the thigh muscles to contract. Sensors embedded in the robotic leg measure the electrical pulses created by both a re-innervated muscle contraction, and the existing thigh muscle.
Neuromuscular Model-Based Sensing And Control Paradigm For A Robotic Leg
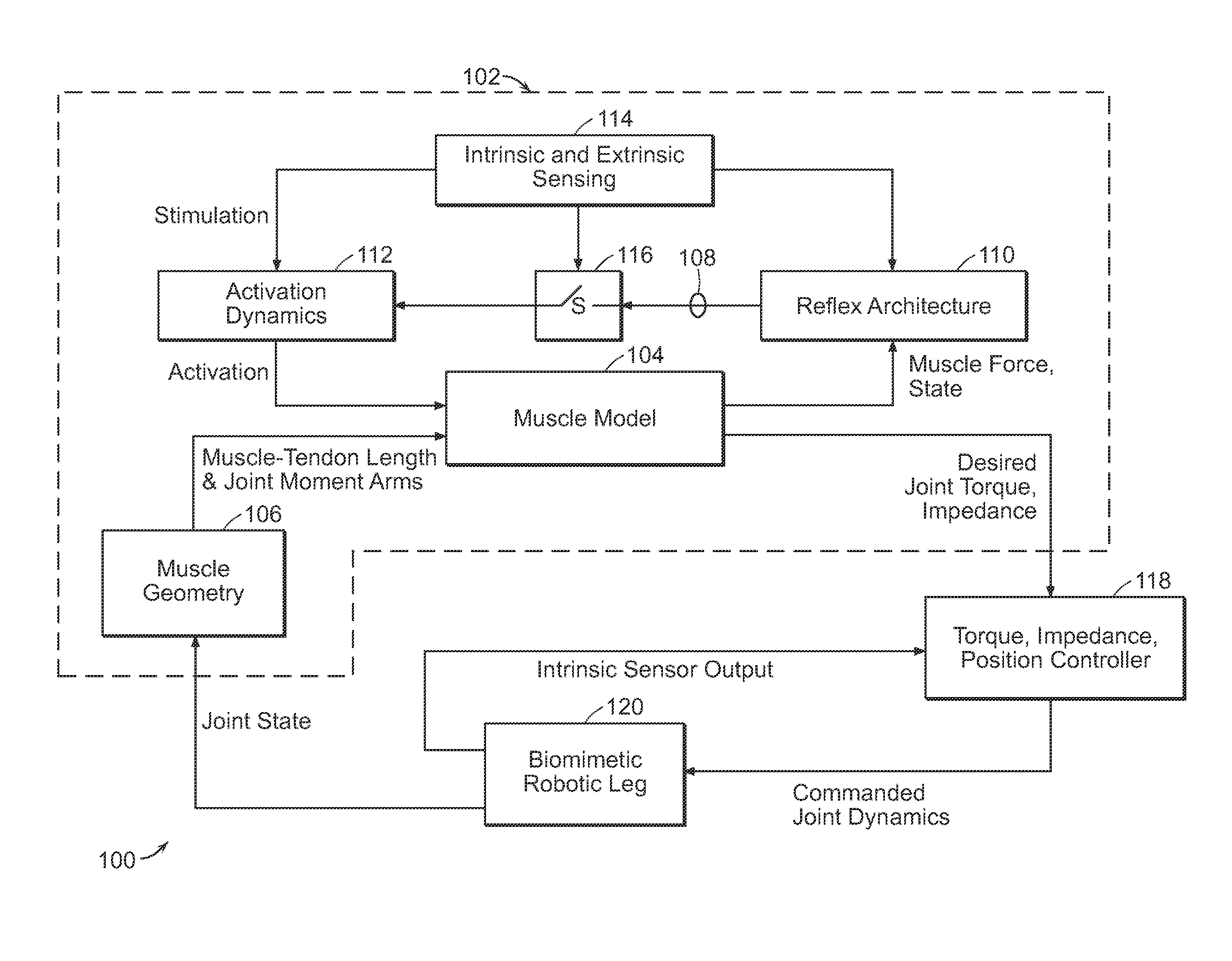
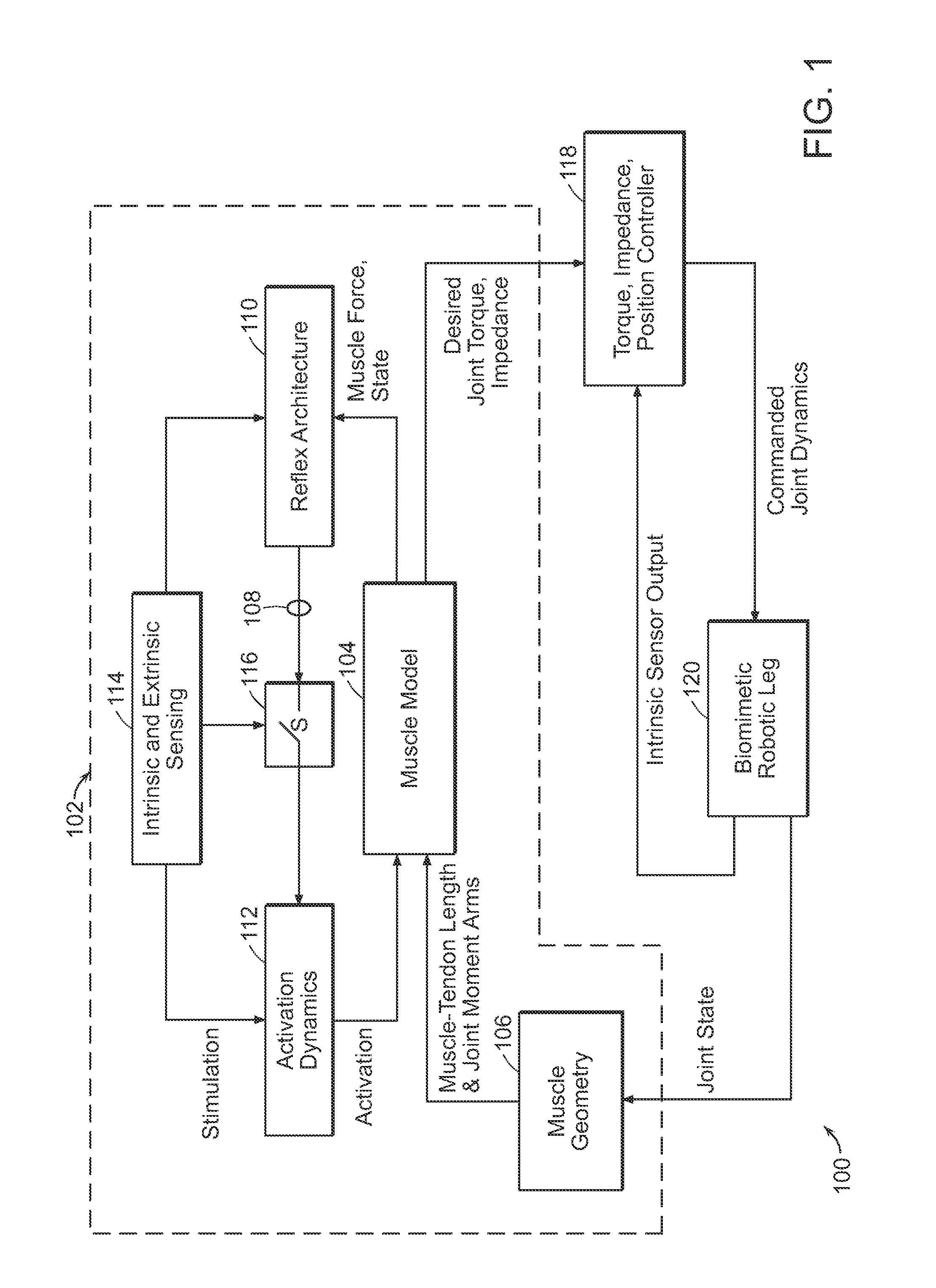
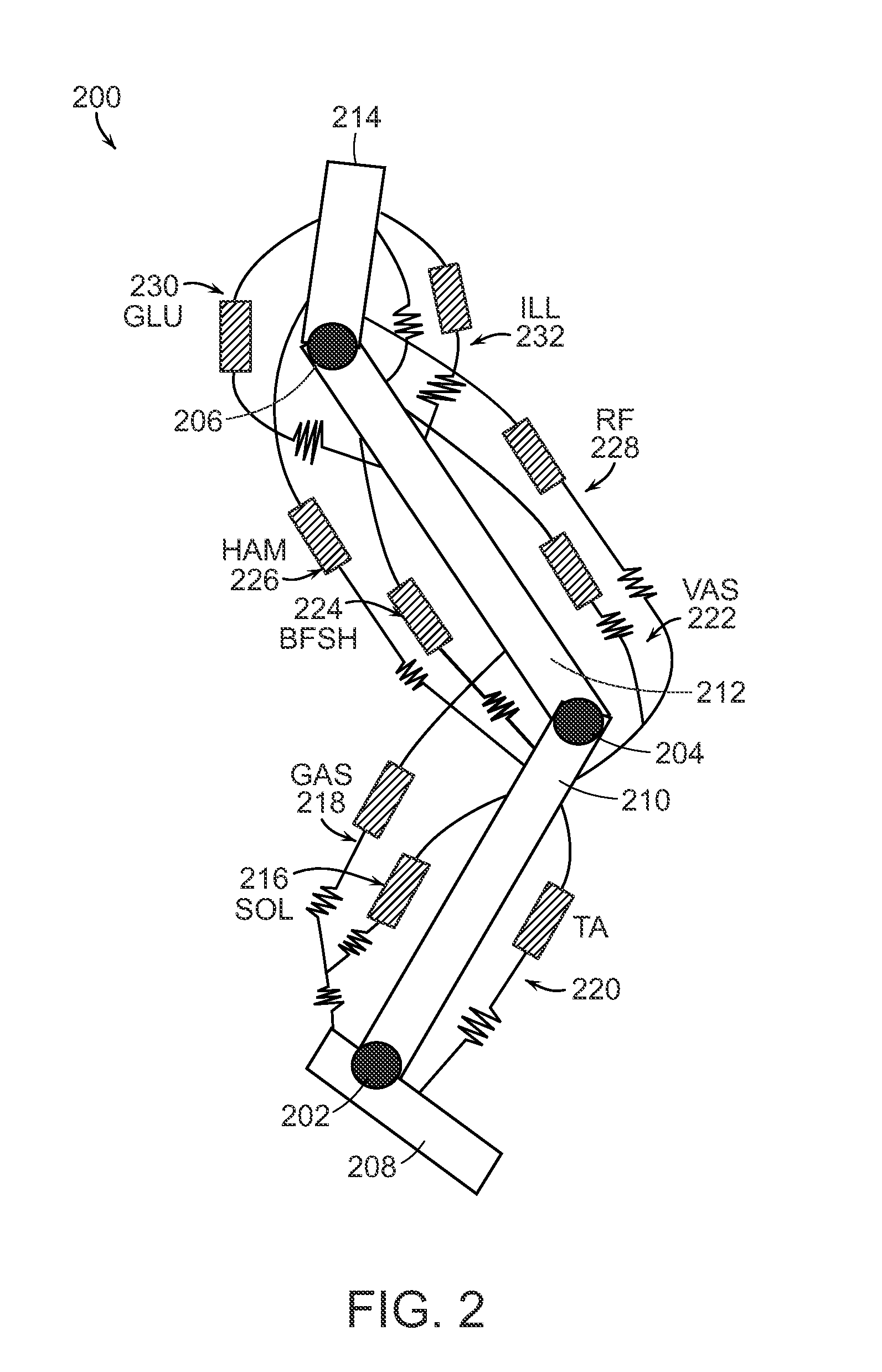
A neuromuscular model-based controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a neuromuscular model having a muscle model, muscle geometry and reflex feedback loop to determine at least one torque or impedance command to be sent to the robotic limb. One or more parameters that determine relation between feedback data and activation of the muscle model are adjusted consequent to sensory data from at least one of an intrinsic sensor and an extrinsic sensor. A controller in communication with the neuromuscular model is configured to receive the at least one torque or impedance command and controls at least one of position, torque and impedance of the robotic limb joint.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Gait creation device of leg-type mobile robot
A provisional desired motion trajectory of an object is determined based on a moving plan of the object. Then, it is determined whether a robot leg motion can satisfy a necessary requirement. The requirement is related to a position / posture relationship between the object and the robot, and a determination of whether the requirement can be satisfied is made at a future, predetermined step. A restrictive condition related to robot leg motion is satisfied at each step up to the predetermined number of steps. If the requirement is satisfied, then a desired gait is generated on the basis of the provisional desired motion trajectory. Otherwise, a desired gait is generated on the basis of a desired motion trajectory of the object according to a corrected moving plan.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
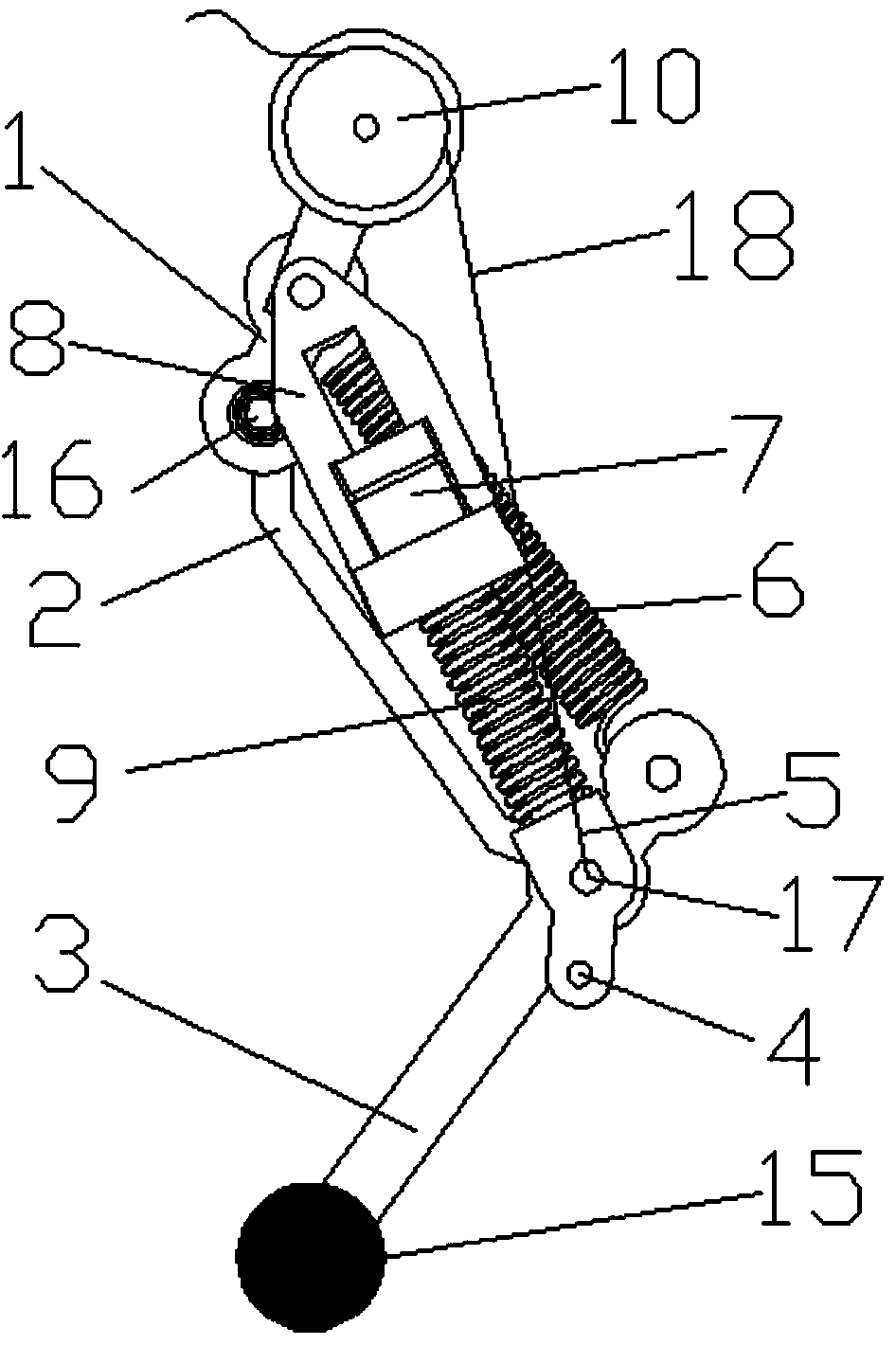
Leg joint assist device for leg type movable robot
InactiveUS6962220B2Free vibration can be preventedStable control can be smoothlyJointsGas and liquid based dampersRelative displacementLeg type
An assist device that applies an auxiliary driving force to a joint in parallel with a driving force of a joint actuator between a thigh portion and a crus portion, which are a pair of link members of a leg. The assist device generates the auxiliary driving force by use of spring device, such as a solid spring or an air spring. A member supporting a rod member connected to the spring device is provided with a device for transmitting a bending and stretching motion of the leg at the joint (a relative displacement motion between the thigh portion and the crus portion) to the spring device to generate an elastic force of the spring device, and for discontinuing the transmission of the bending and stretching motion to the spring device. This transmitting device is controlled in accordance with a gait of a robot. Thus, a burden on the joint actuator is reduced where necessary and favorable utilization efficiency of energy can be stably ensured.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Robot and robot leg mechanism
ActiveUS20050275367A1Compact processLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringFuselage
Owner:BOSTON DYNAMICS INC
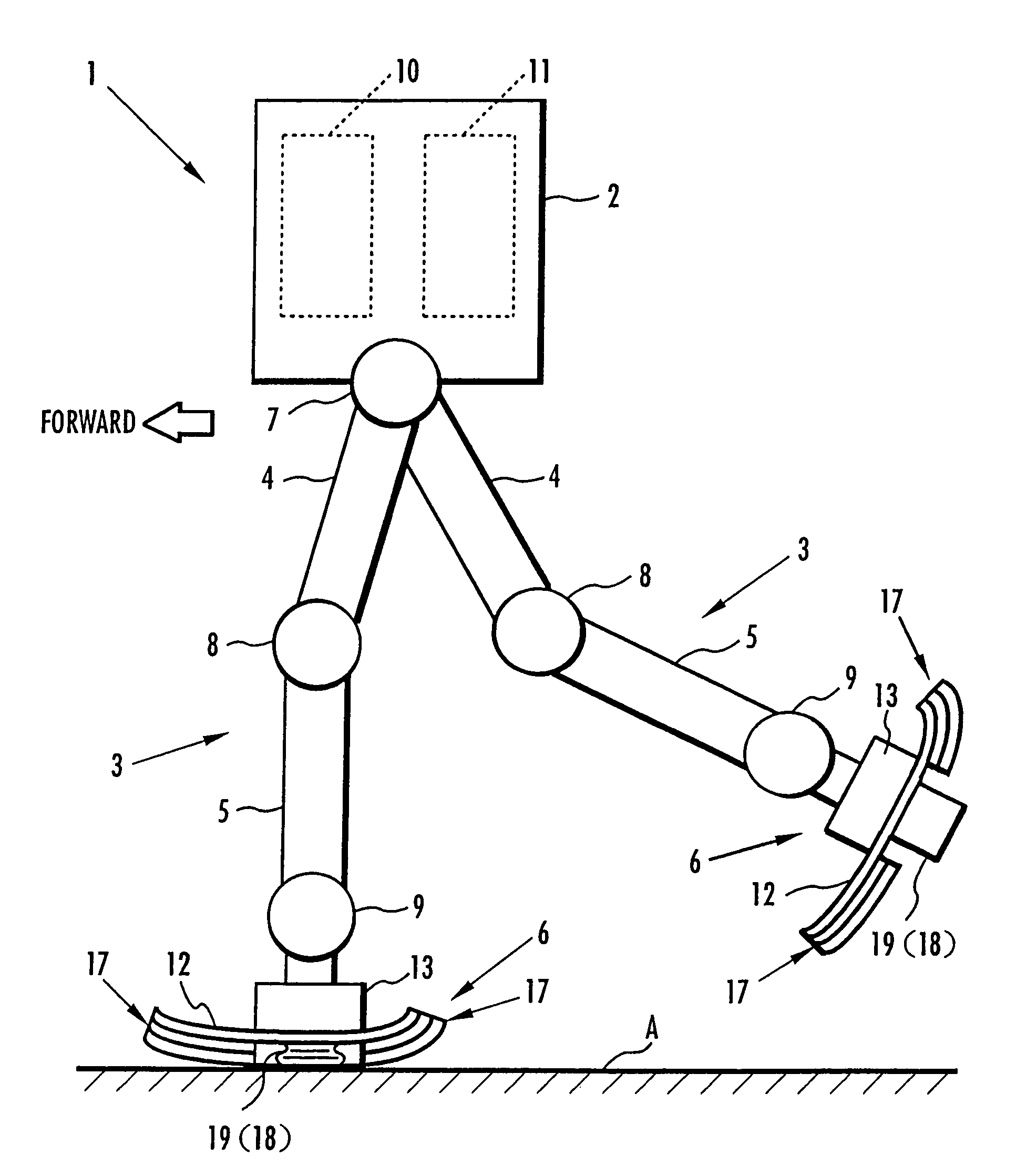
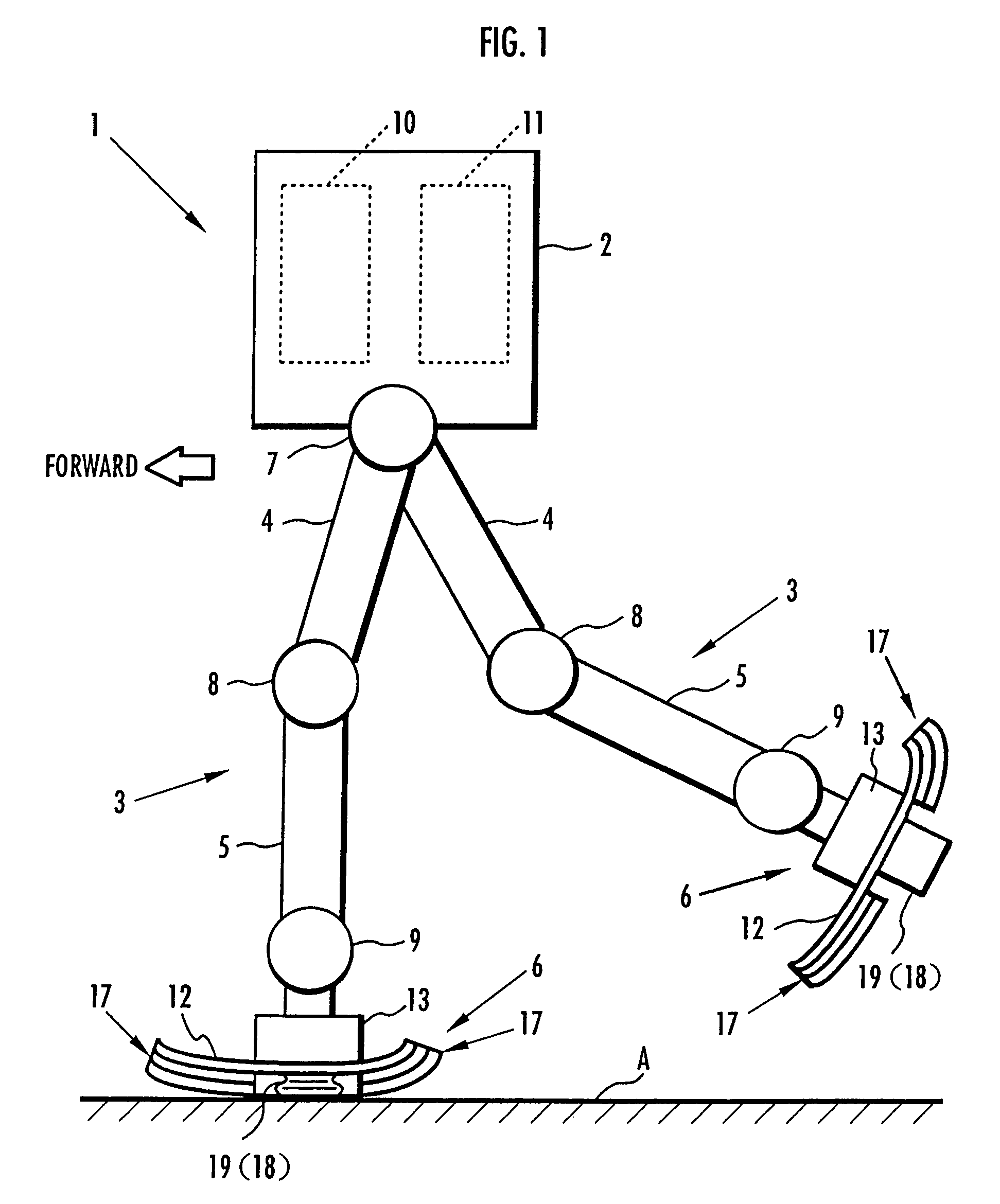
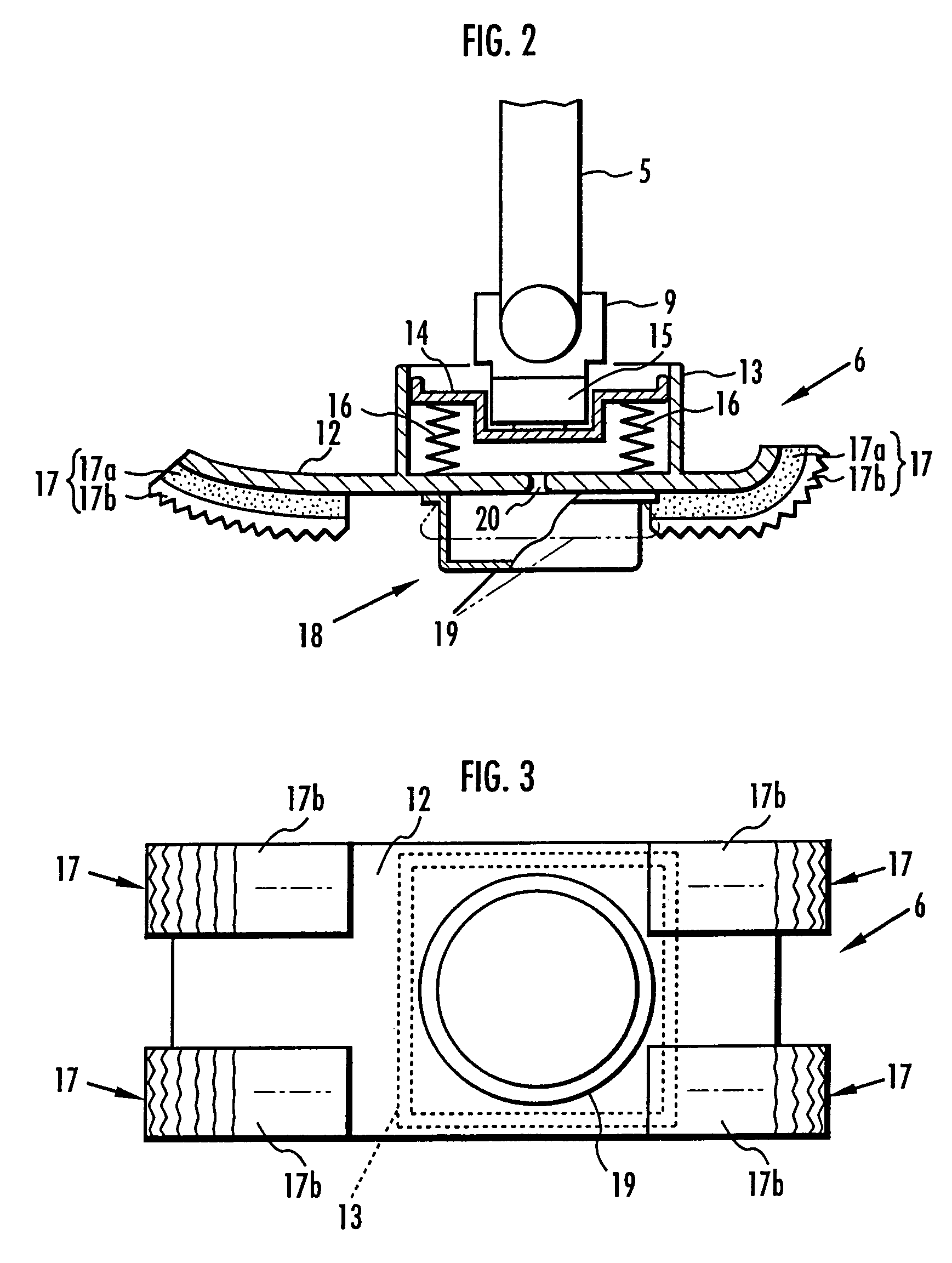
Device for absorbing floor-landing shock for legged mobile robot
InactiveUS20050077856A1Improve stabilityReduce shock loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpringsSolenoid valvePostural stability
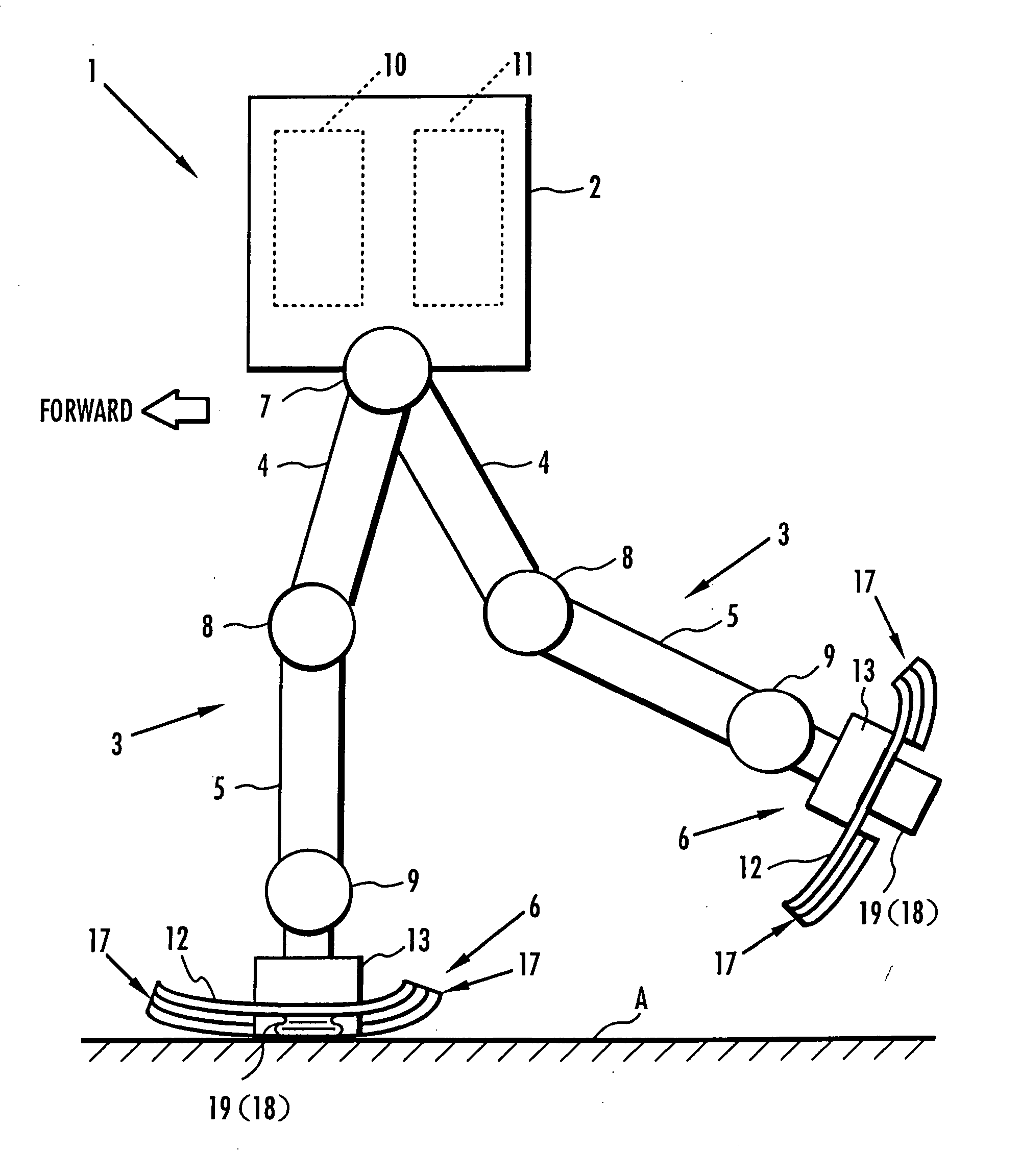
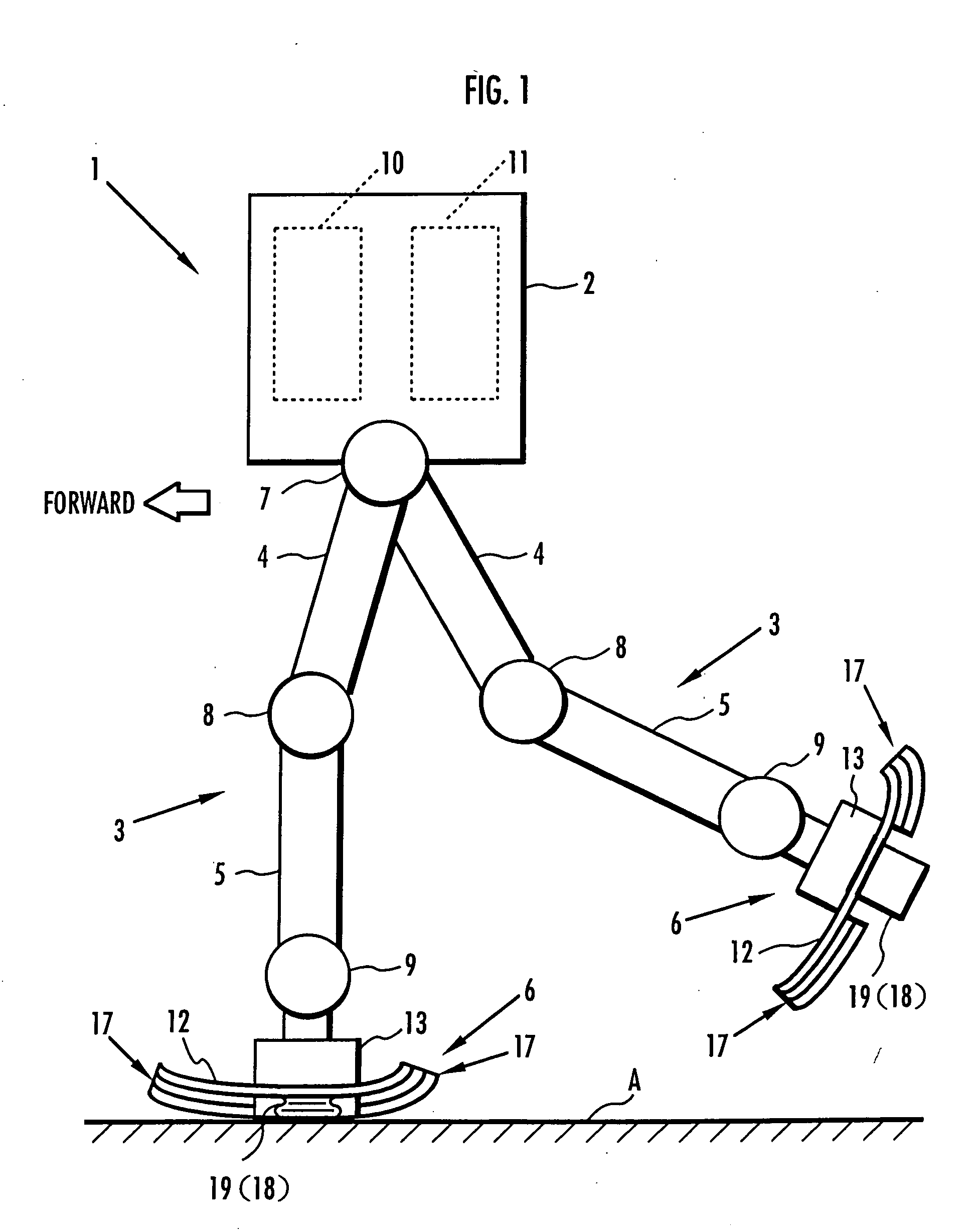
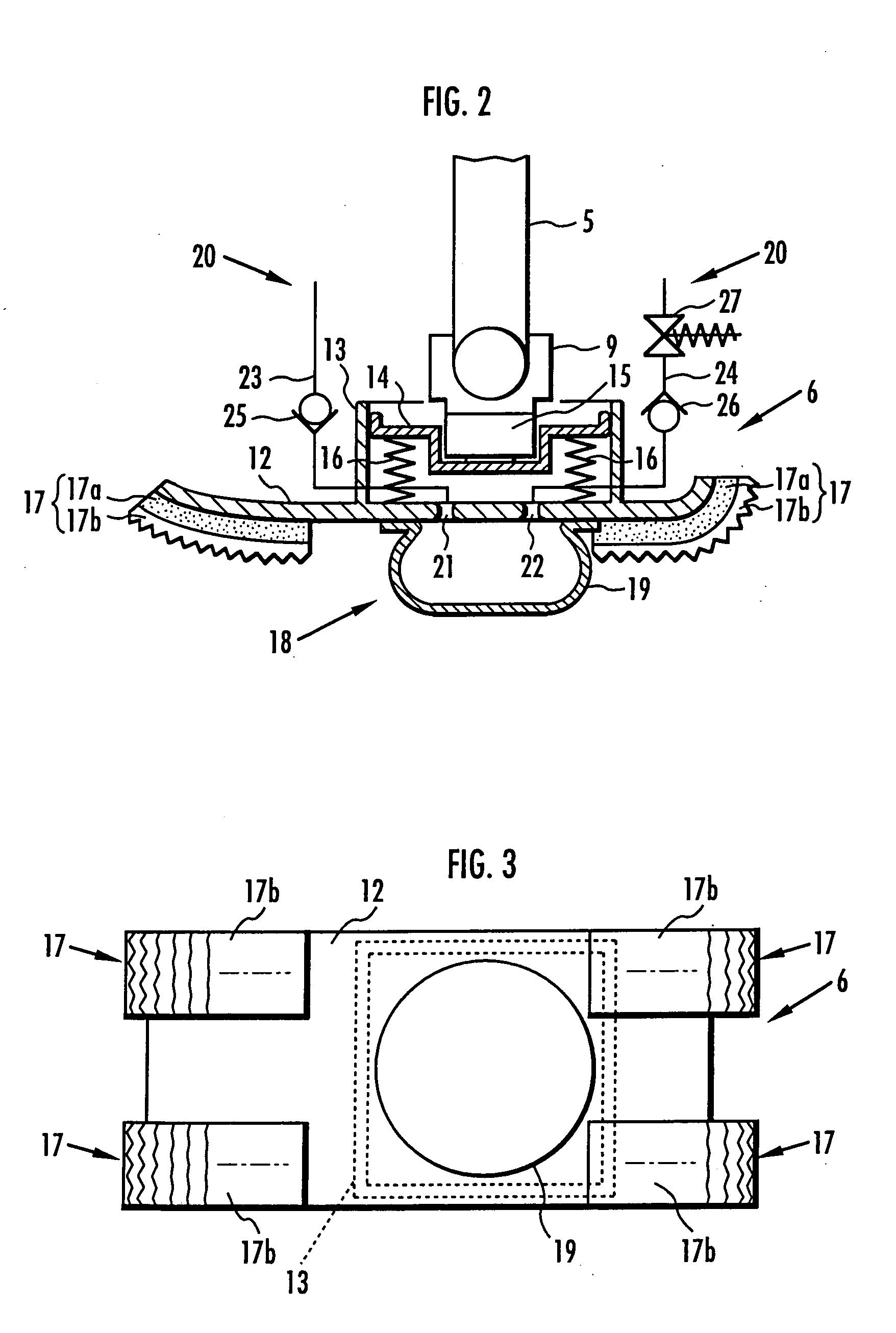
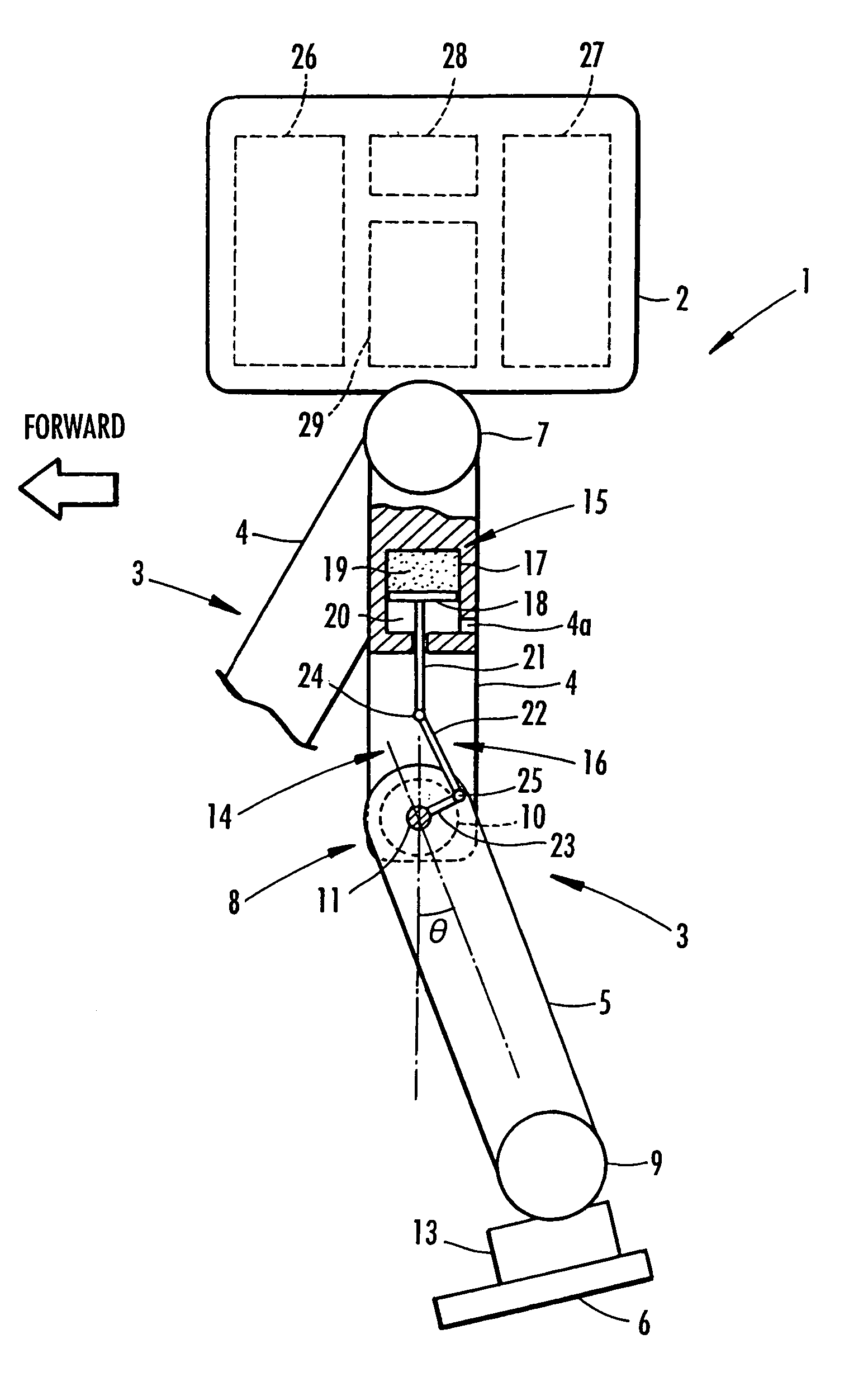
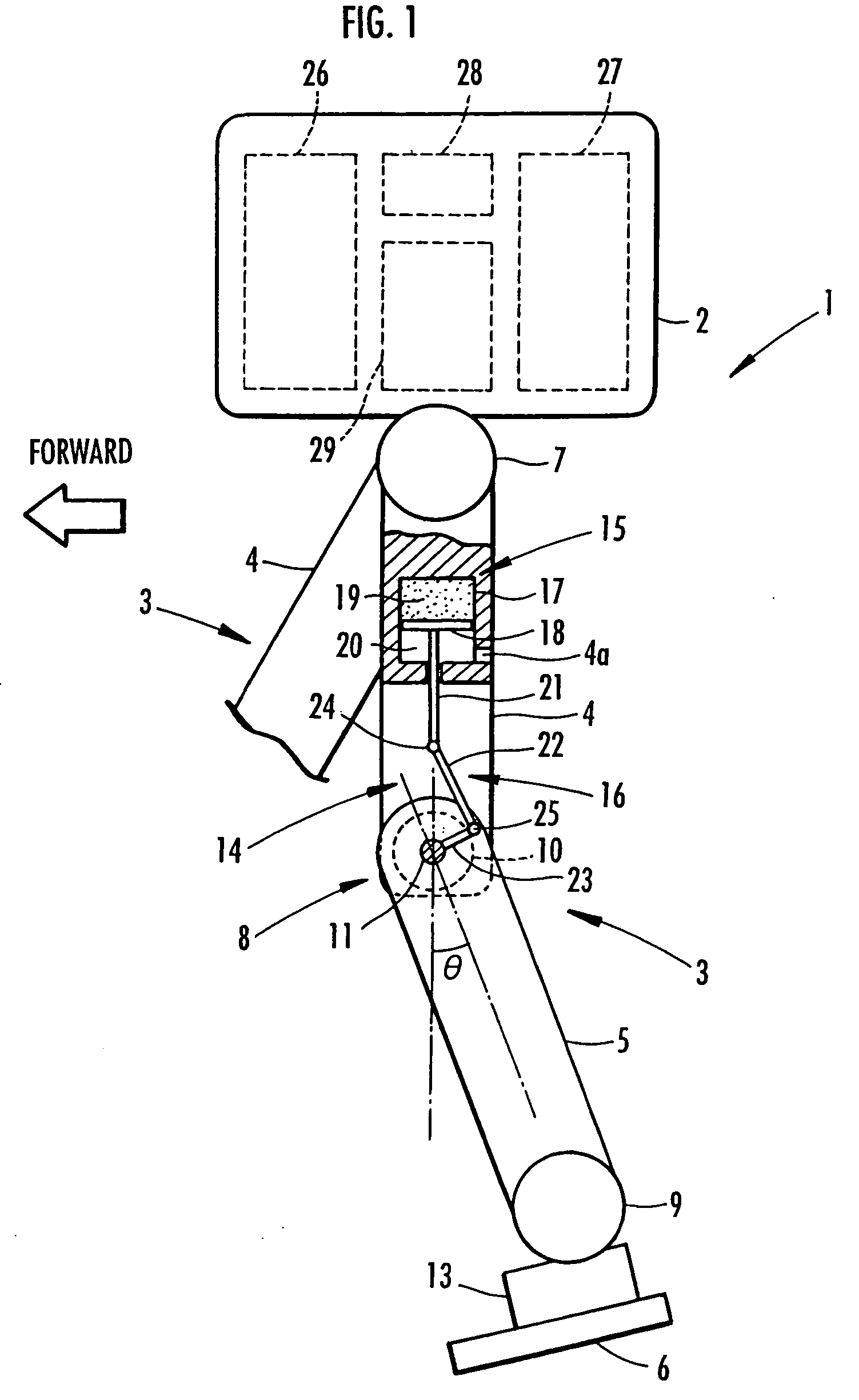
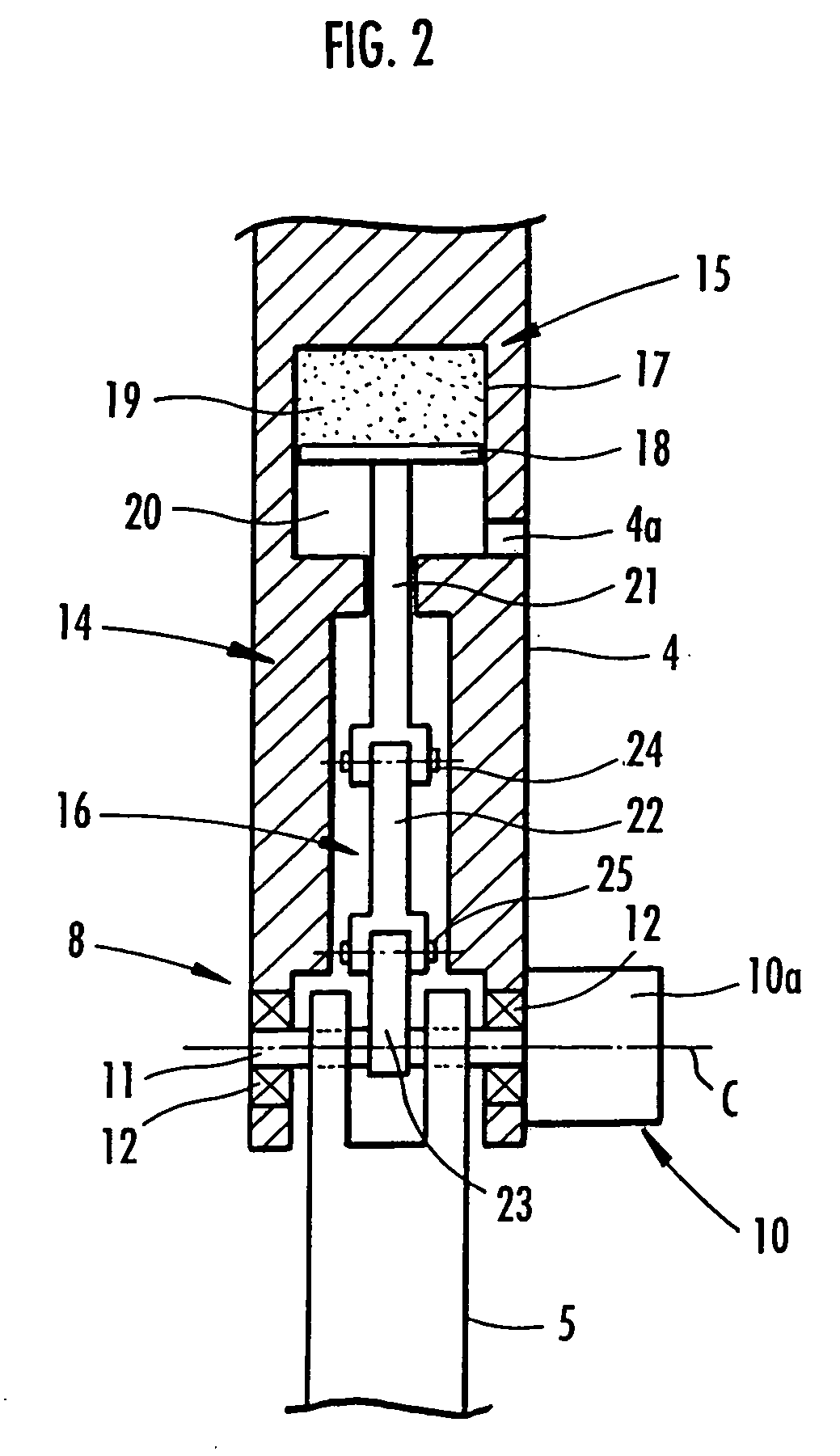
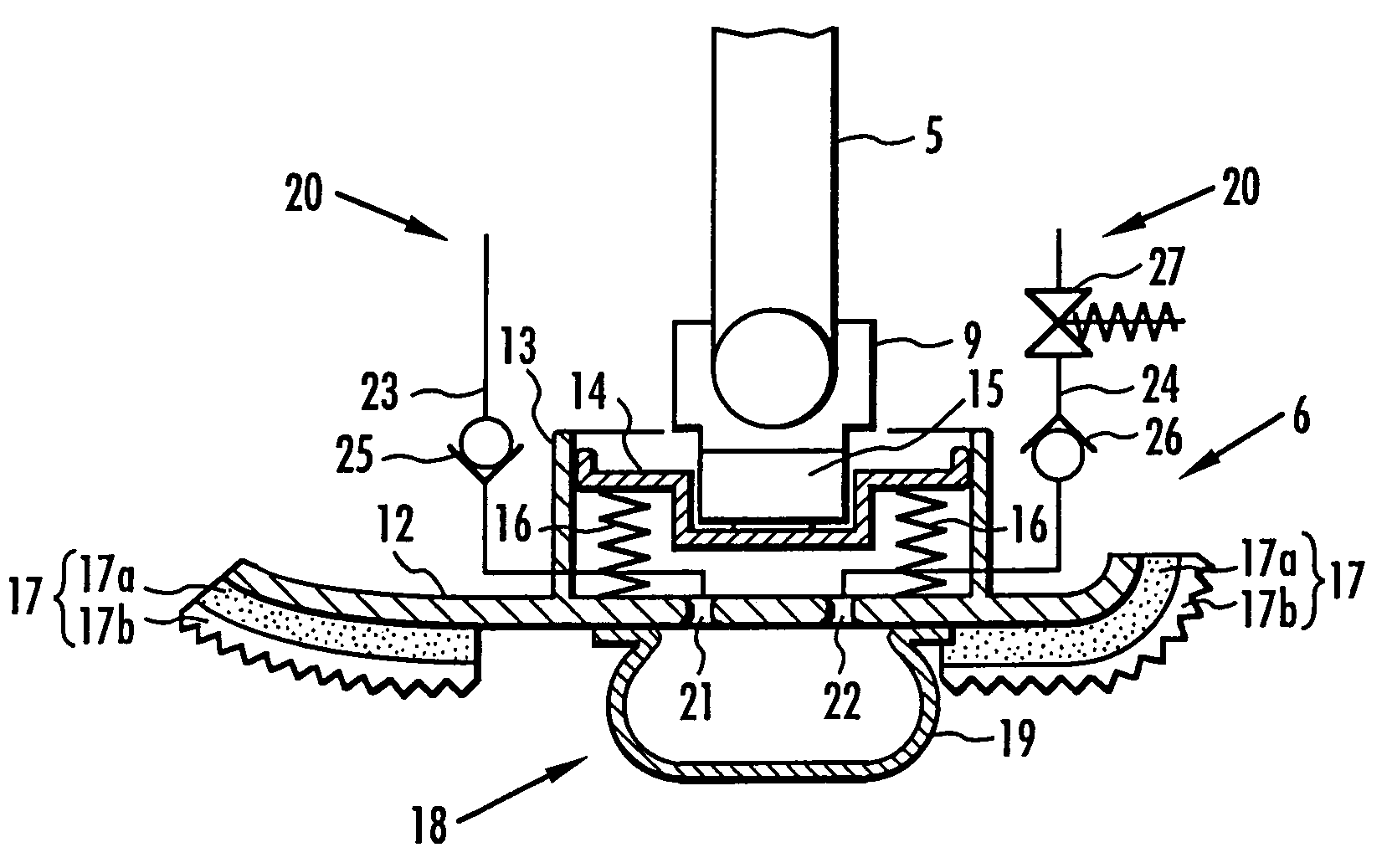
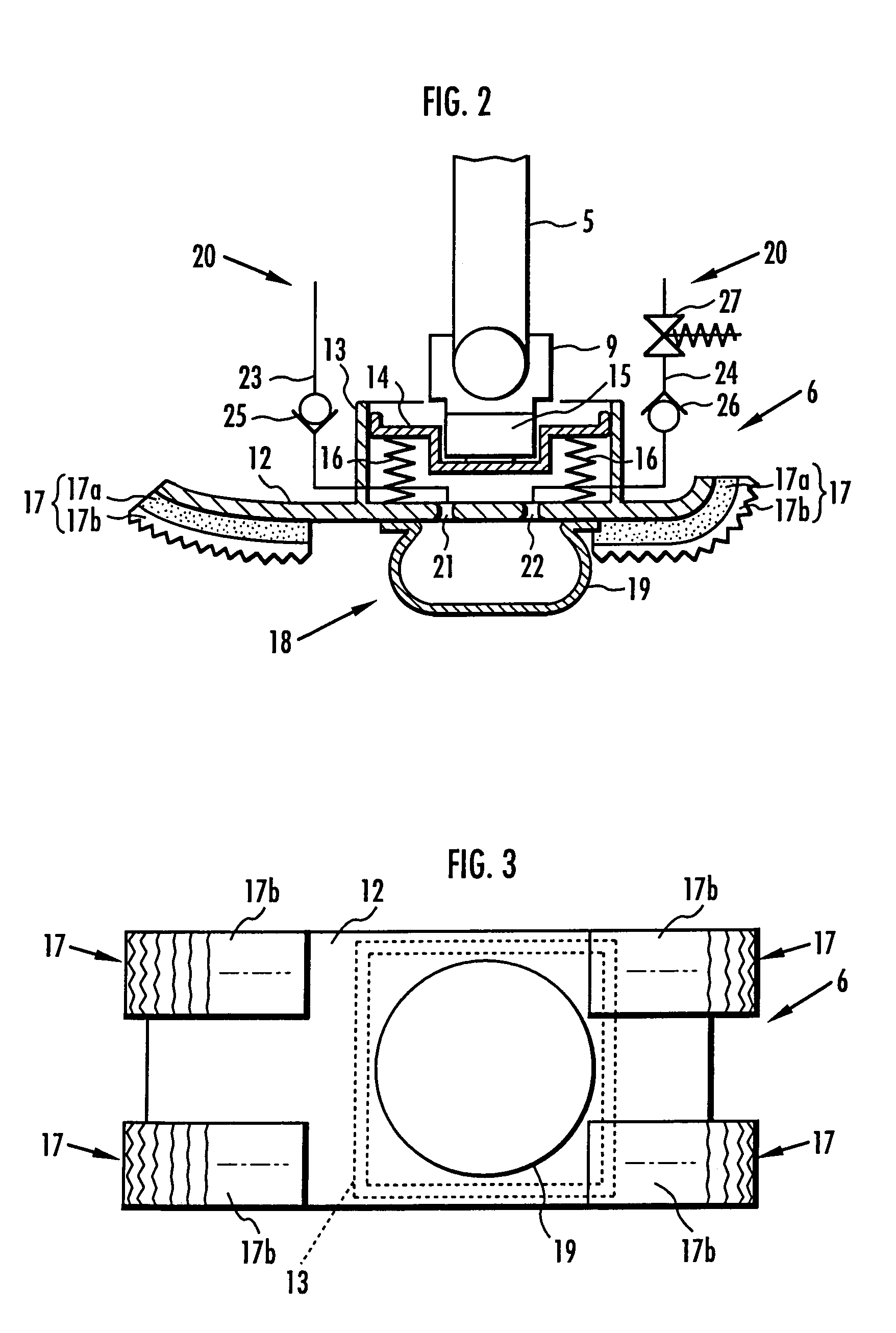
A landing shock absorbing device 18 provided in a foot mechanism 6 of a leg of a robot comprises an inflatable and compressible bag-like member 19 (a variable capacity element) on a bottom face side of the foot mechanism 6. The bag-like member 19 is constructed of an elastic material such as rubber. Air in the atmosphere can flow into and out of the bag-like member 19 by inflow / outflow means 20 provided with a solenoid valve 27 and the like. In a landing state of the foot mechanism 6 and in a state immediately after the foot mechanism shifts from the landing state to a lifting state, the solenoid valve 27 is closed to maintain the bag-like member 19 in a compressed state. Furthermore, during the bag-like member 19 in the inflating state during the lifting state of the foot mechanism 6, by controlling timing when the solenoid valve 27 is switched from a valve opening state to a valve closing state, a height of the bag-like member 19 in a compression direction is controlled to be a height suitable for a gait type of the robot. Thereby, posture stability of the robot can be secured easily while reducing a impact load in the landing motion of the leg of the legged mobile robot, and further, a lightweight configuration can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Robot and robot leg mechanism
ActiveUS7734375B2Compact processLow costControl mechanismProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringFuselage
Owner:BOSTON DYNAMICS INC
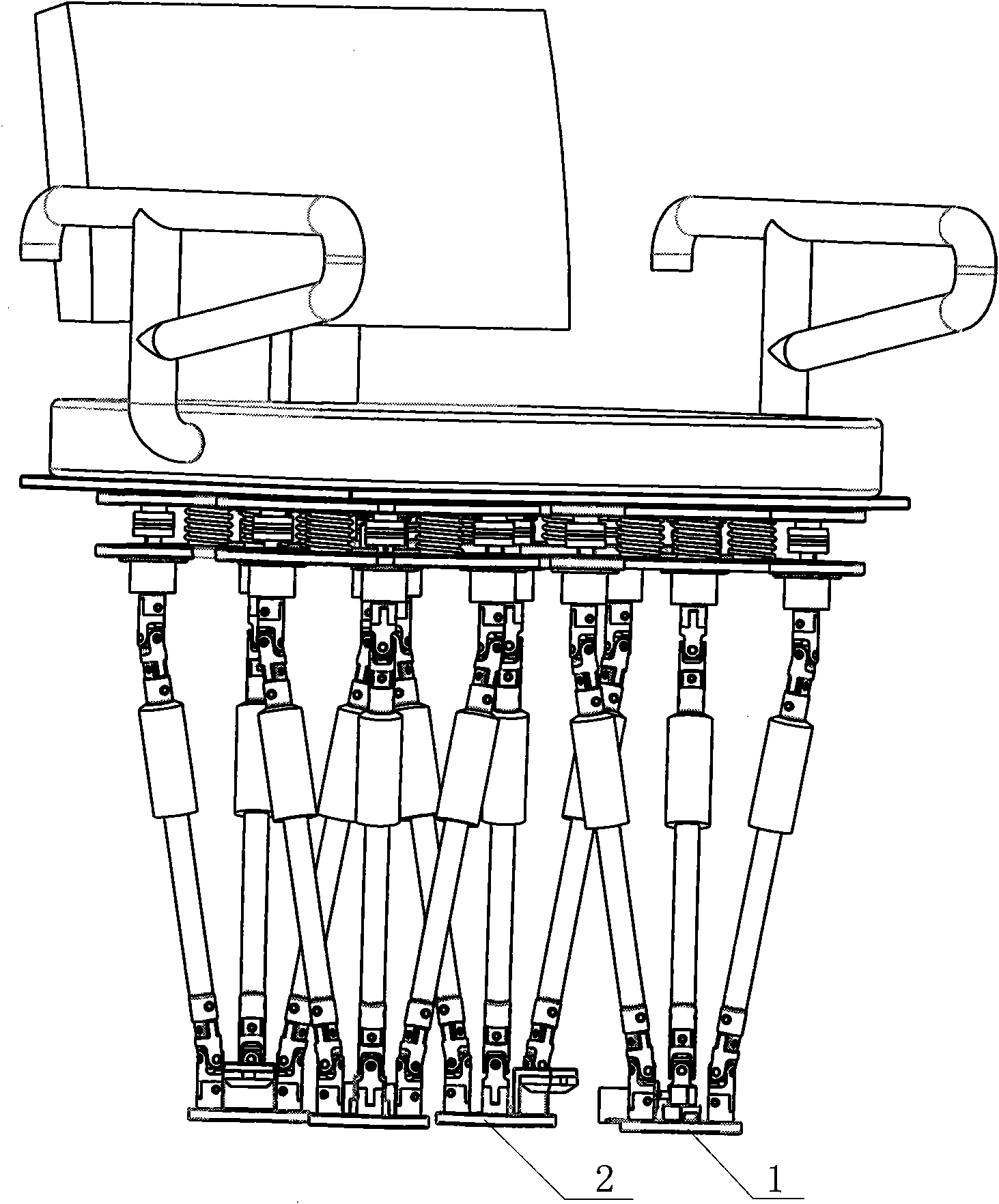
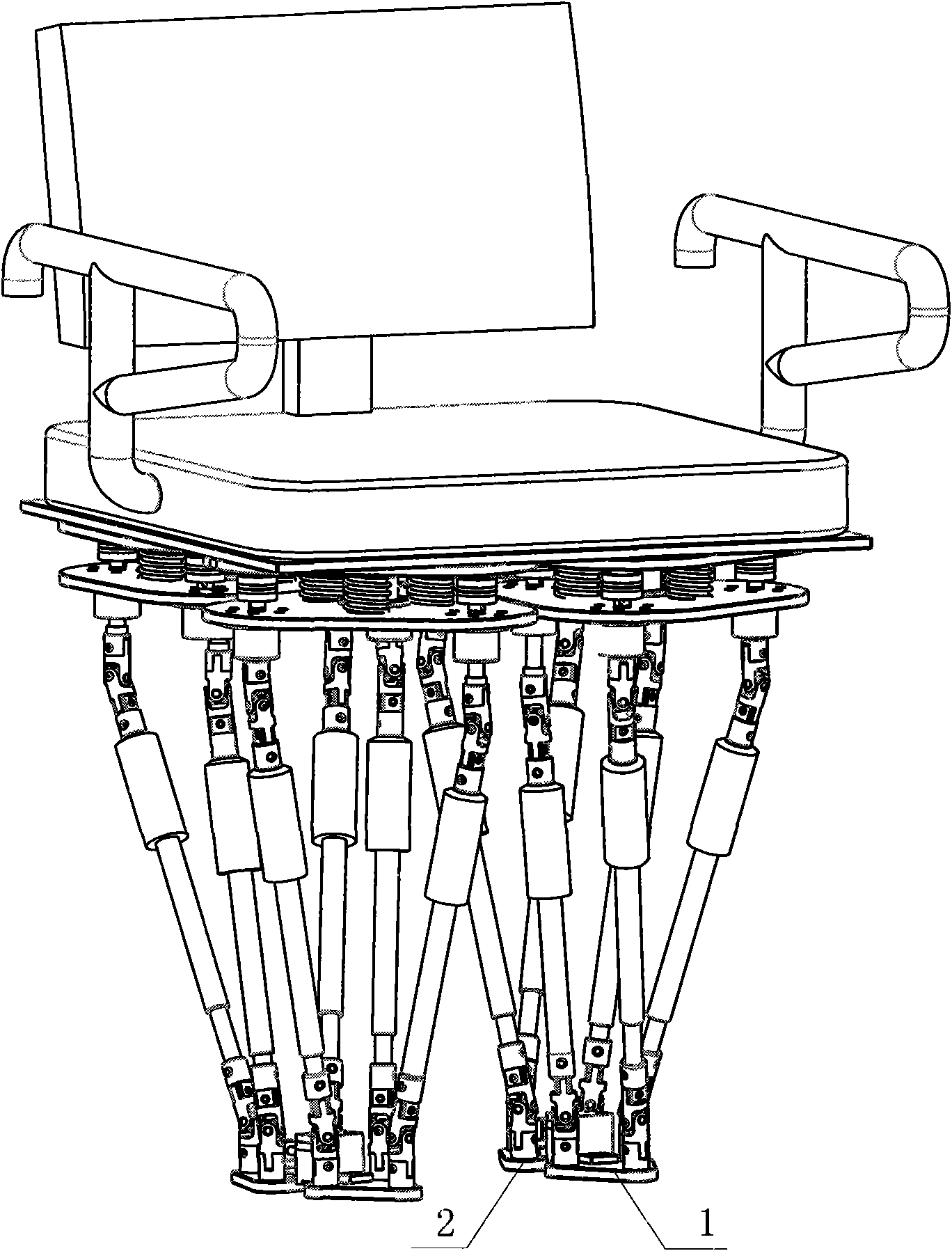
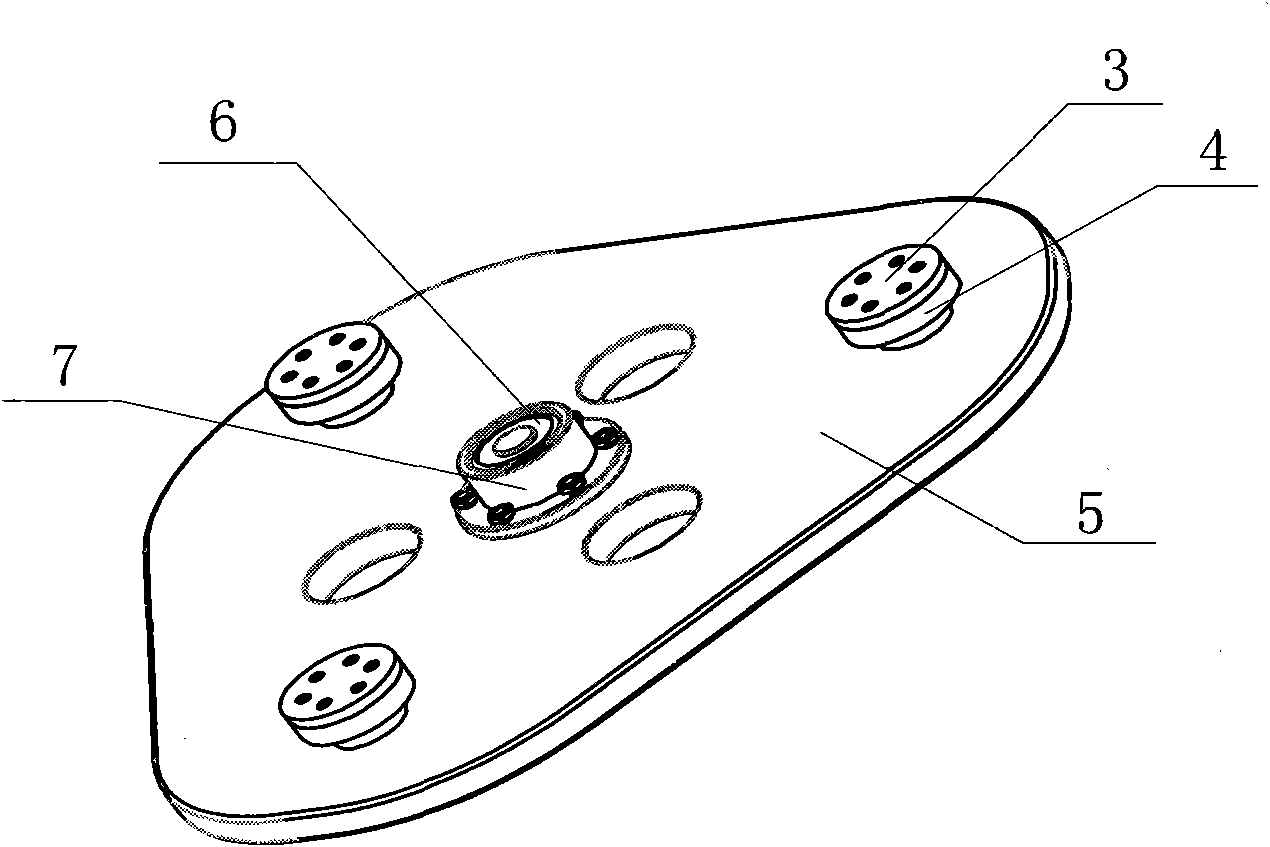
Sitting horizontal type individual lower limb rehabilitation training robot
ActiveCN102743270AEasy seatingFlexible implementation of passive trainingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesHuman–machine interfaceDrive motor
The invention discloses a sitting horizontal type individual lower limb rehabilitation training robot. The robot comprises a leg part mechanism, a middle seat mechanism and a man-machine interface. The leg part mechanism comprises an electric control box, a leg part mechanism substrate, a leg part mechanism machinery arm and handrails; the middle seat mechanism comprises a seat, a seat lifting mechanism, a seat push mechanism and a seat angle adjusting mechanism. A thigh and a crus of the leg mechanism machinery arm of the robot are adjustable in length, the seat is adjustable in both width and height; the functions are helpful to meet the demand of a patient with different figures and provide a proper training guest for the patient. Every joint of the leg part mechanism is configured with a driving motor, a pull pressure sensor and a position sensor for providing multiple training tracks to the patient and also providing hardware support to a plurality training methods including passive training, active training and assistant training. In the process of training, the pull pressure sensor of every joint of the leg part mechanism can provide a joint force monitor in order to avoid the unexpected cases.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Control device for legged mobile body
InactiveUS20110098857A1Avoid lengthProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMotion parameterEngineering
A desired motion determiner of a control unit of a legged mobile robot determines a leg motion parameter specifying the motion trajectory of a distal end of a leg of the robot on the basis of the information on a floor geometry of an environment in which the robot travels and a requirement related to a travel route of the robot, thereby sequentially determining the desired motion of the robot. A floor geometry information output unit which outputs floor geometry information to the desired motion determiner outputs floor geometry information in which a rising surface of a stepped portion of a predetermined type, the contact thereof with a leg of the robot should be avoided, has been shaped into a surface having a gentler slope than an actual rising surface. The desired motion determiner determines the leg motion parameter such that the leg will not come in contact with the stepped portion having the shaped rising surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Reversible and amphibious multi-legged robot with variable postures
InactiveCN101570220AWith posture adjustment functionHigh inertiaSelf-moving toy figuresMechanical energy handlingTime changesClosed loop
The invention provides a reversible and amphibious multi-legged robot with variable postures. The robot comprises three parts, i.e. a body bracket, a one-way input and vertical output module and a leg mechanism, wherein the one-way input and vertical output module is installed on the body bracket, and the leg mechanism is installed on the one-way input and vertical output module. The reversible and amphibious multi-legged robot with variable postures of the invention is formed by the parallel connection of a plurality of walking legs, and by controlling a posture adjustment motor, the real-time change of the standing and moving postures of the robot can be realized, thereby improving the capability of adapting to the complex amphibian environment; and each walking leg is formed by the serial connection of the one-way input and vertical output module and the leg mechanism. A tridimensional force sensor is installed at the leg end and is used for feeding back the stress of the leg end during movement, so as to realize the closed loop control of the stress of each leg of the robot.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Four-foot bio-robot leg
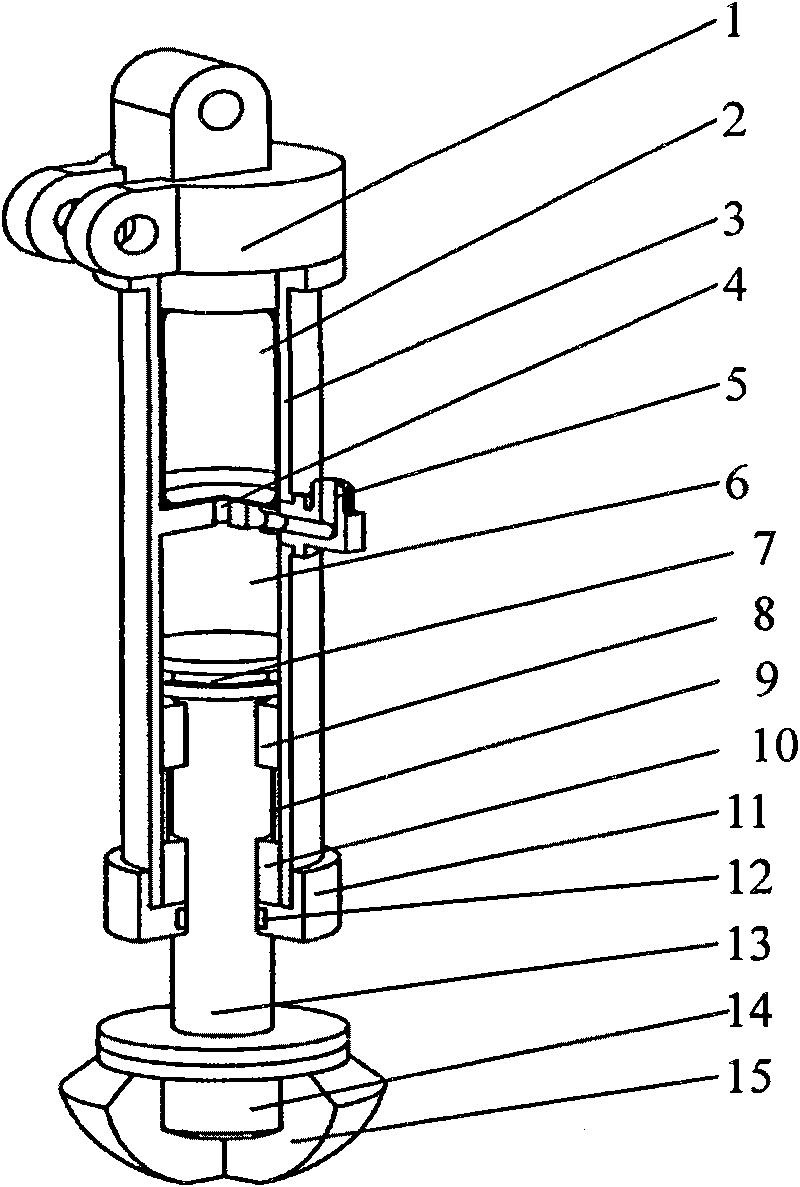
The invention discloses a four-foot bio-robot leg which is used for solving the technical problem of a single movement structure, caused by a rigid structure, of an existing robot leg. According to the technical scheme, the four-foot bio-robot leg is composed of an articular disc, an articular disc hydraulic cylinder shaft rigid and soft regulating mechanism, rigid structures such as a machine body support, a thigh support, a crus connecting rod, a crus connecting plate, an articular disc limiting block, a crus supporting base, a crus sleeve and soft structures such as a sole. A power drive device is driven in a hydraulic mode. Due to the fact that a soft link spring is arranged based on the rigid structure to buffer and absorb vibration, and the cooperation of the articular disc and the articular disc limiting block imitates the human body knee-joint tissue, the crus can move flexibly, go upstairs, jump and do other movements.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
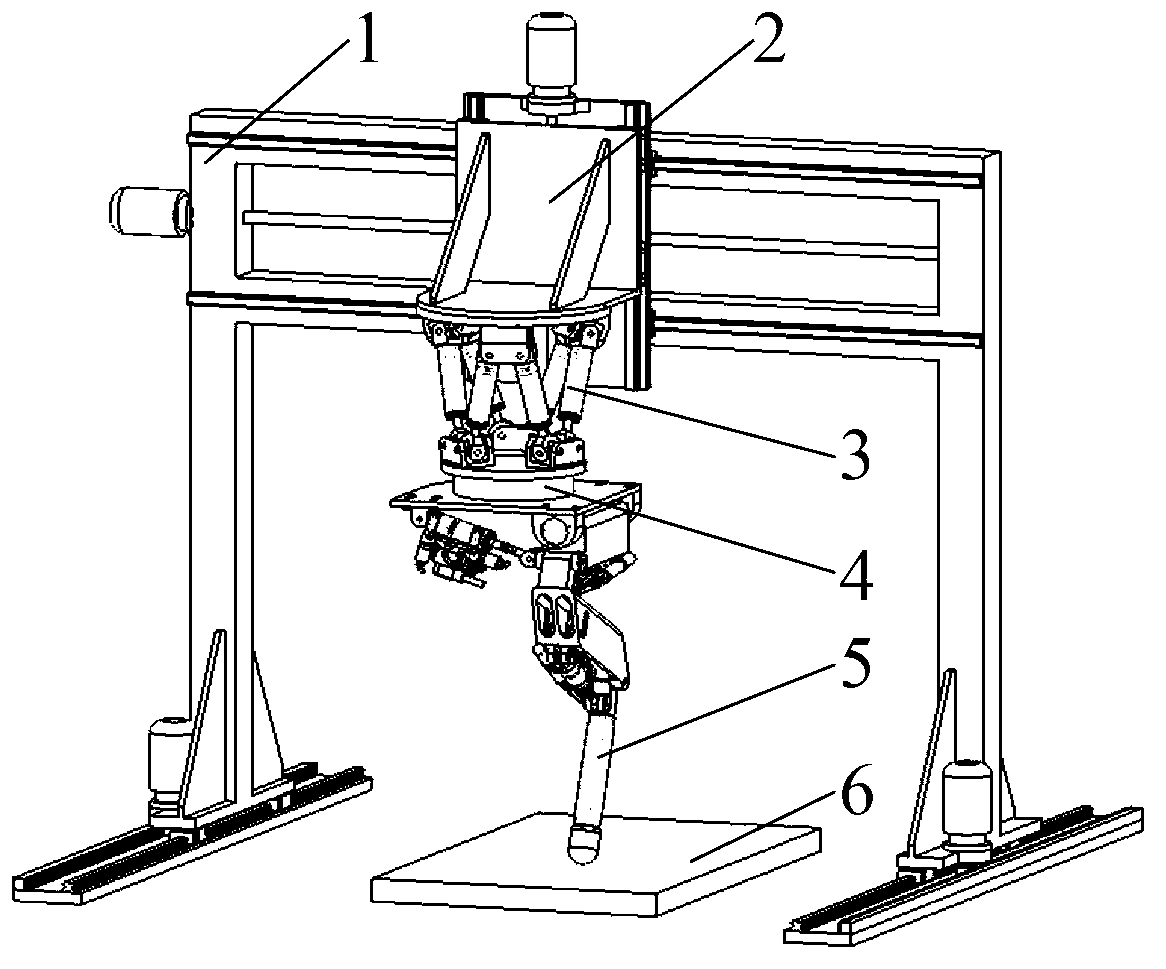
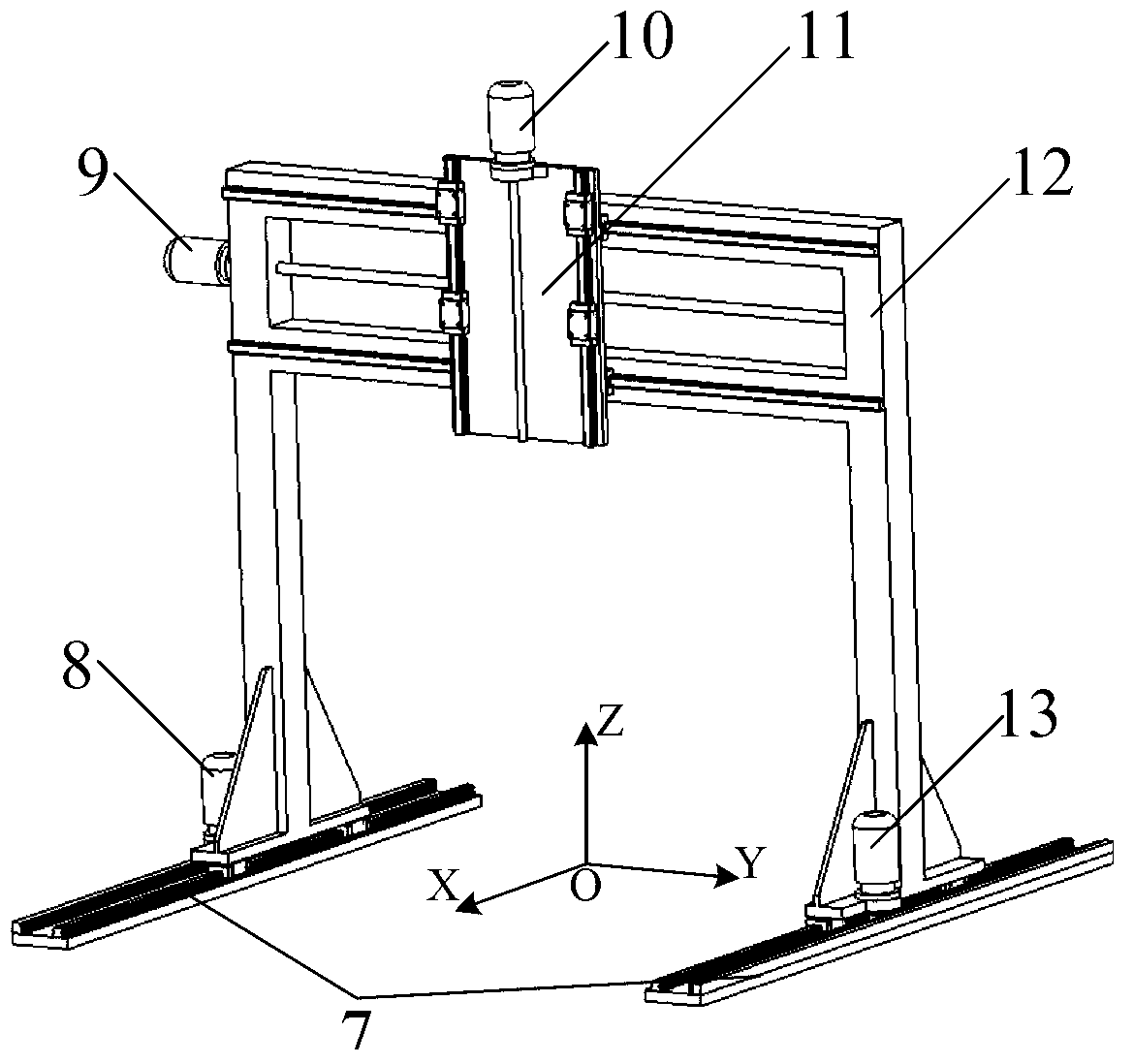
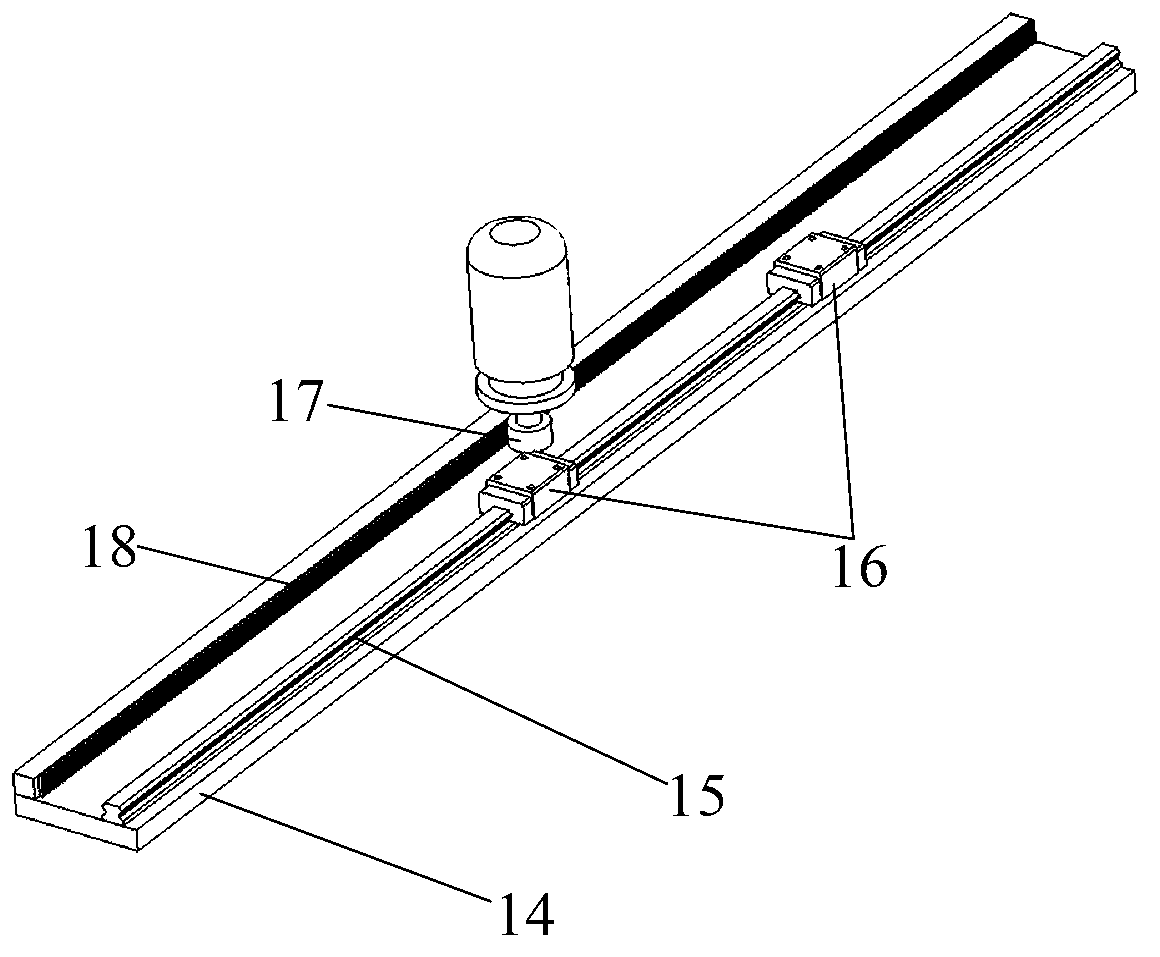
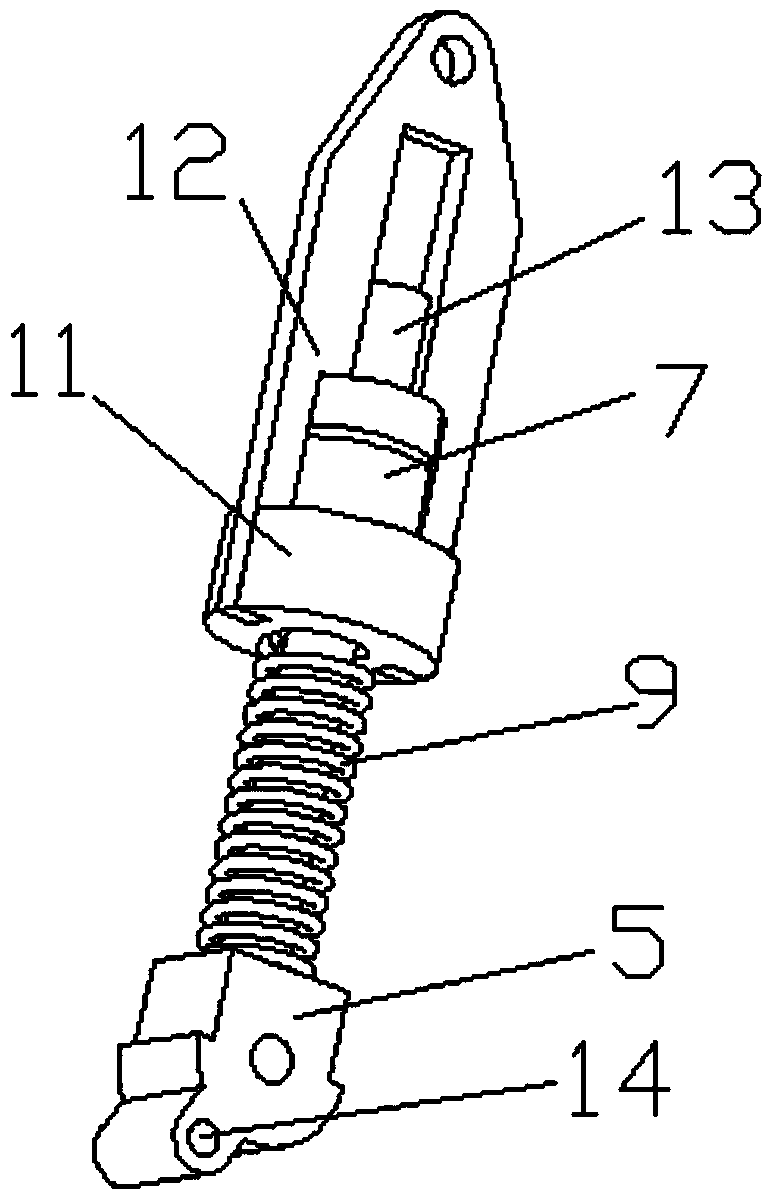
Robot single-leg assembly control development performance test platform and method
The invention discloses a robot single-leg assembly control development performance test platform and method. The platform comprises a gantry three-coordinate mechanical arm assembly, a robot leg connection bracket, a Stewart platform, a six-dimensional force sensor, a robot single-leg assembly and a five-dimensional force measurement platform, wherein a servo controller and a displacement sensor are integrated in the Stewart platform; the Stewart platform is invertedly arranged on a base of the robot leg bracket; the five-dimensional force measurement platform is arranged at the center of the ground below the robot single-leg assembly; and the robot leg connection bracket is fixed on a Z-axis-direction mobile supporting frame assembly of the gantry three-coordinate mechanical arm assembly. The test platform is suitable for single-leg movement and quick gait control during bionic gait generation of a four-foot or multi-foot hydraulic driving robot as well as development and research on multiple control strategies for robot load distribution, control force distribution, single-leg force feedback control and 'discrete gait and continuous force control' attitude stabilization control.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Quadruped robot leg with elastic four-rod mechanism
The invention provides a quadruped robot leg with an elastic four-rod mechanism. The quadruped robot leg comprises a thigh, a shank, a foot, a tension spring and a reeling wheel, wherein one end of the thigh is connected with an output shaft of a power source to form a hip joint; the reeling wheel and the end of the thigh are connected by a transmission pair and the axis of the reeling wheel is coaxial to the output shaft of the power source; the other end of the thigh is connected with one end of the shank by a transmission pair to form a knee joint, and the other end of the shank is connected with a quarter part of the foot by a transmission pair to form an ankle joint; one end of the tension spring is connected with the middle part of the thigh by a transmission pair and the other end of tension spring is connected with the end of one foot by a transmission pair; one end of a steel wire rope is fixedly arranged on the ankle joint and the steel wire ripe spans across the reeling wheel to be connected with the power source. According to the quadruped robot leg, a driven degree of freedom is adopted and the loss of energy is reduced; the driven degree of freedom is realized by a four-connection-rod mechanism; a spring is arranged on one side of the four-connection-rod mechanism so that the four-connection-rod mechanism can be freely retracted in a certain range and the free movement of the foot of the leg is realized.
Owner:哈尔滨斑之斓海洋科技有限公司
Device for absorbing floor-landing shock for legged mobile robot
InactiveUS7228923B2Increase pressureReduce relative motionSpringsSelf-moving toy figuresGround contactEngineering
A landing shock absorbing device 18 disposed in a foot mechanism 6 of a leg of a robot, wherein an inflatable bag-like member 19 (a variable capacity element) is provided at a ground-contacting face side of the foot mechanism 6. The bag-like member 19 is constructed of an elastic material such as rubber and has a restoring force. An interior portion of the bag-like member 19 is communicated with the atmosphere side through a flow passage 20. During a landing motion of the leg, the bag-like member 19 makes contact with the ground to be compressed, and the air in the interior portion thereof flows out into the atmosphere through the flow passage 20, so that its outflow resistance is generated. Accordingly, a landing shock is reduced. In a lifting state of the leg, the restoring force of the bag-like member 19 allows the bag-like member 19 to be inflated while the air flows into the interior portion thereof. An impact load during the landing of the leg of the legged mobile robot may smoothly be reduced in a light-weight configuration.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
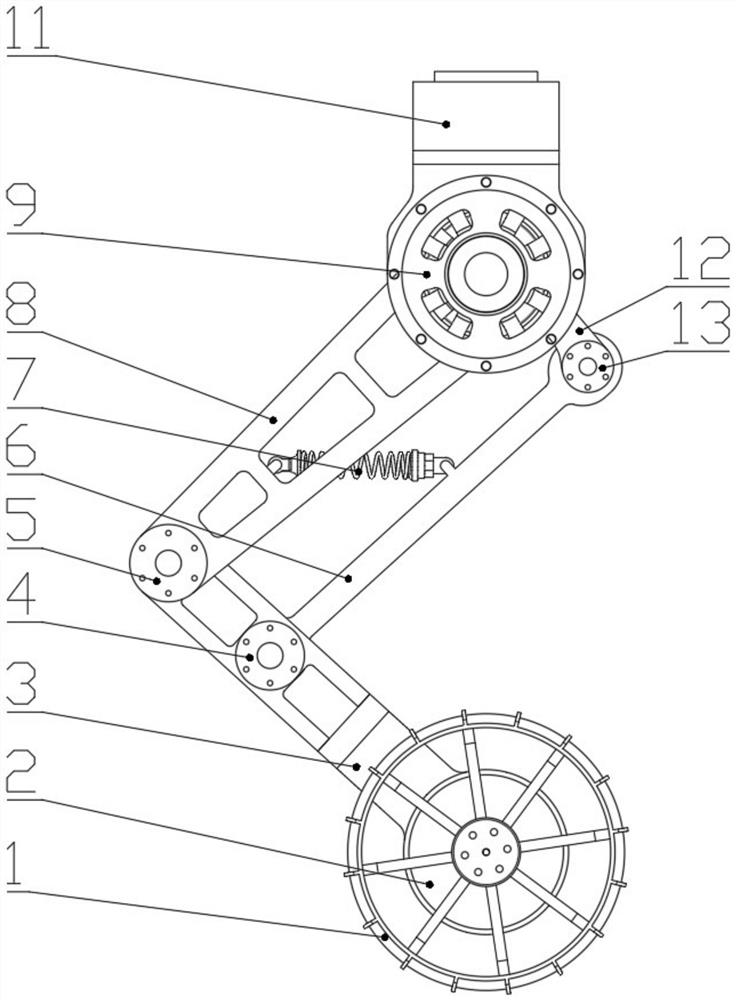
Leg mechanism for four-legged robots
The invention relates to a leg mechanism for four-legged robots, the leg mechanism comprises a drive motor, a femur mechanism, a knee-joint hinge, a tibia mechanism, a naked joint hinge and a metatarsus mechanism, wherein the femur mechanism is hinged with the tibia mechanism by the knee-joint hinge; the drive motor is fixed on the femur mechanism, and an output shaft of the drive motor drives the tibia mechanism to rotate by a bevel gear transmission mechanism in the knee-joint hinge; the tibia mechanism is hinged with the metatarsus mechanism by the naked joint hinge; and the drive motor drives the metatarsus mechanism to rotate by the bevel gear transmission mechanism in the knee-joint hinge and a bevel gear transmission mechanism in the naked joint hinge. In the invention, the number of joints of a leg structure is increased under the condition of not increasing the degree of freedom, so that the leg movement of the robot is more flexible, and the leg mechanism has the advantage of better movement performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Humanoid robot foot section impact absorption mechanism
ActiveCN101402380AFlexible and continuously adjustableFlexible and easy to changeSelf-moving toy figuresVehiclesLeading edgeEngineering
The invention discloses a food shock absorbing mechanism for an anthropomorphic robot, which comprises soles, wherein damping columns are arranged on the soles; upper surfaces of the damping columns are provided with upper pressure plates; force transducers and upper cover plates are arranged on the upper pressure plates; the upper cover plates are connected with the soles through four upper cover plate mounting holes; four groups of adjusting washers are arranged between the upper cover plates and the soles; the force transducers are connected with legs of the robot; the number of the damping columns is four, and the four damping columns are connected with the soles through the four damping column mounting holes which are positioned on the soles; front ends of the soles are provided with front sole bevels, and rear ends of the soles are provided with rear sole bevels; and non-skid mats are arranged below the soles. The invention designs the more compact and more effective shock absorbing mechanism, realizes continuous flexible adjustment of the shock absorbing mechanism, and can make the anthropomorphic robot easier to meet different operation requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Biped walking robot
The invention discloses a biped walking robot. The biped walking robot comprises a robot waist part and a robot leg part, wherein a power supply and a control unit are placed on a waist bracket of the robot waist part, the robot leg part comprises a left leg and a right leg, and both the left leg and the right leg are connected with the robot waist part. The biped walking robot comprises the robot waist part and the robot leg part, wherein the robot waist part is connected with the robot leg part, the control unit and the power supply are stored at the robot waist part, and the leg part is driven through servomotors so as to drive the robot to move. Each leg of the biped walking robot is provided with a freedom hip joint, a freedom knee joint and a freedom ankle joint, so that a plurality of driven advancing manners, such as walking, climbing and turning, can be realized under complicated road conditions, such as inclined ramps and steps.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Reconfigurable device for walking robot with four/two parallel legs
The invention provides a reconfigurable device for a walking robot with four / two parallel legs, belonging to the technical field of robots. The leg mechanism of the robot is structurally designed in a modularization way, and the legs are of a same structure. When four-leg walking is carried out, the leg mechanism is a 3-UPU, and when two-leg walking is carried out, the leg mechanism is a 3-SPU (Synergistic Processing Unit), wherein the conversion between the two leg mechanisms is realized through a rotation-pair retaining device, and the conversion between four legs and two legs is realized through a merging device. The rotation-pair retaining device comprises an electromagnet, an electromagnetic chuck base, friction plates, a friction plate carrier, a support column, a spring and a rotation-pair retaining plate, a rotation pair in a pair S is controlled to be locked and unlocked through the lamination and the separation of the friction plates, and the lamination and the separation of the friction plates are controlled by the sucker type electromagnet. The merging device comprises an electromagnetic chuck, a guiding device, a push-pull type electromagnet and a locking clamp, and the merging device is locked by controlling the positions of two legs to be merged, merging the soles through the electromagnetic chuck and the guiding device, and driving the locking clamp to act by the push-pull type electromagnet.
Owner:秦皇岛燕盛智能科技有限公司
Wheel-legged robot leg structure and mobile robot
The invention provides a wheel-legged robot leg structure which comprises wheels, a shank connecting rod, a buffer energy storage spring, a thigh connecting rod, a shank driving motor, a thigh drivingmotor and a first shank transmission connecting rod. The thigh driving motor and the shank driving motor can rotate independently and drive the thigh connecting rod and the first shank transmission connecting rod to rotate respectively; and when the wheel impacts the ground, an included angle between the shank connecting rod and the thigh connecting rod is reduced, and the buffer energy storage spring can reduce an impact load transmitted to the thigh driving motor and the shank driving motor. By the adoption of the buffer energy storage spring in a parallel connection mode, impact on the motors when a foot end makes contact with the ground is reduced, energy can be stored, a peak torque of the driving motor is effectively reduced, the number of the motors needed by the adopted leg configuration is small, a working space is large, and the structure can walk in a complex terrain environment; and the structure has advantages of light weight and a small moment of inertia.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hydraulic-drive lower-limb mechanism with load bearing capability of biped robot
The invention discloses a hydraulic-drive lower-limb mechanism with load bearing capability of a biped robot, which comprises two robot legs. The upper portion of each robot leg is connected with a robot steering mechanism, the robot steering mechanisms are arranged on the body of a robot, the lower portion of the each robot leg is connected with a robot foot, and each robot leg, each robot steering mechanism and each robot foot are driven hydraulically. A driving rotation freedom-degree rotation pair I utilizing the normal direction of the body of the robot as the axis, a lateral driving freedom-degree rotation pair II and a lateral driven freedom-degree rotation pair VI are arranged on one robot leg, one robot steering mechanism and one robot foot, and three front driving freedom degrees include the rotation pair II, the rotation pair IV and a rotation pair V. The hydraulic-drive lower-limb mechanism is simple in structure, capable of steering, easy to maintain and high in dynamic response capability and has obstacle detouring performance and the load bearing capability.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Quadruped robot control method and control device on the basis of sine opposite angle gait and quick table look-up method
ActiveCN107045552AWide application valueExtensive research significanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDatabase queryingNonlinear systems of equationsPeriod stopping
The invention relates to a quadruped robot control method and control device on the basis of a sine opposite angle gait and a quick table look-up method. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) combining with the opposite angle gait to analyze the leg structure of a quadruped robot, establishing the leg movement mathematical model of the quadruped robot, and adopting a novel sine gait; (2) solving a nonlinear equation set to obtain the control rate of each joint of four limbs, establishing a database which specially faces robot movement control, obtaining an accurate joint opening and closing angle through the quick table look-up method, and quickly and accurately realizing foot end trajectory control; and (3) designing a foot end trajectory control unit and a steering control unit so as to bring convenience to the access of other control systems. On an aspect of trafficability characteristics, the novel sine gait is designed and adopted, and therefore, and the robot owns high trafficability when the robot faces a complex terrain. On the aspect of operation stability, when a step taking period stops, the horizontal speed of a swing phase is zero, and therefore, the method is high in stability. The table look-up method is adopted to quickly, accurately and stably carry out the foot end trajectory control.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Leg joint assist device for legged movable robot
InactiveUS7143850B2Simple configurationIncrease the burdenMechanical apparatusManipulatorGas springEngineering
An assist device is provided with a spring device that generates an auxiliary driving force, by an elastic energy, acting on a joint of a leg. The spring device includes a gas spring having a cylinder and a piston. Bending / stretching motion between link members and at the joint is transmitted to the spring device through a motion transmission device that includes a link arm. The spring device is provided so that the auxiliary driving force increases as a knee bending angle θ increases until the knee bending angle θ reaches a predetermined angle, and so that, once the knee bending angle θ exceeds the predetermined angle, the auxiliary driving force becomes smaller than or equal to the driving force obtaining at the predetermined angle, effectively reducing a burden on an actuator of the legged mobile robot joint.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
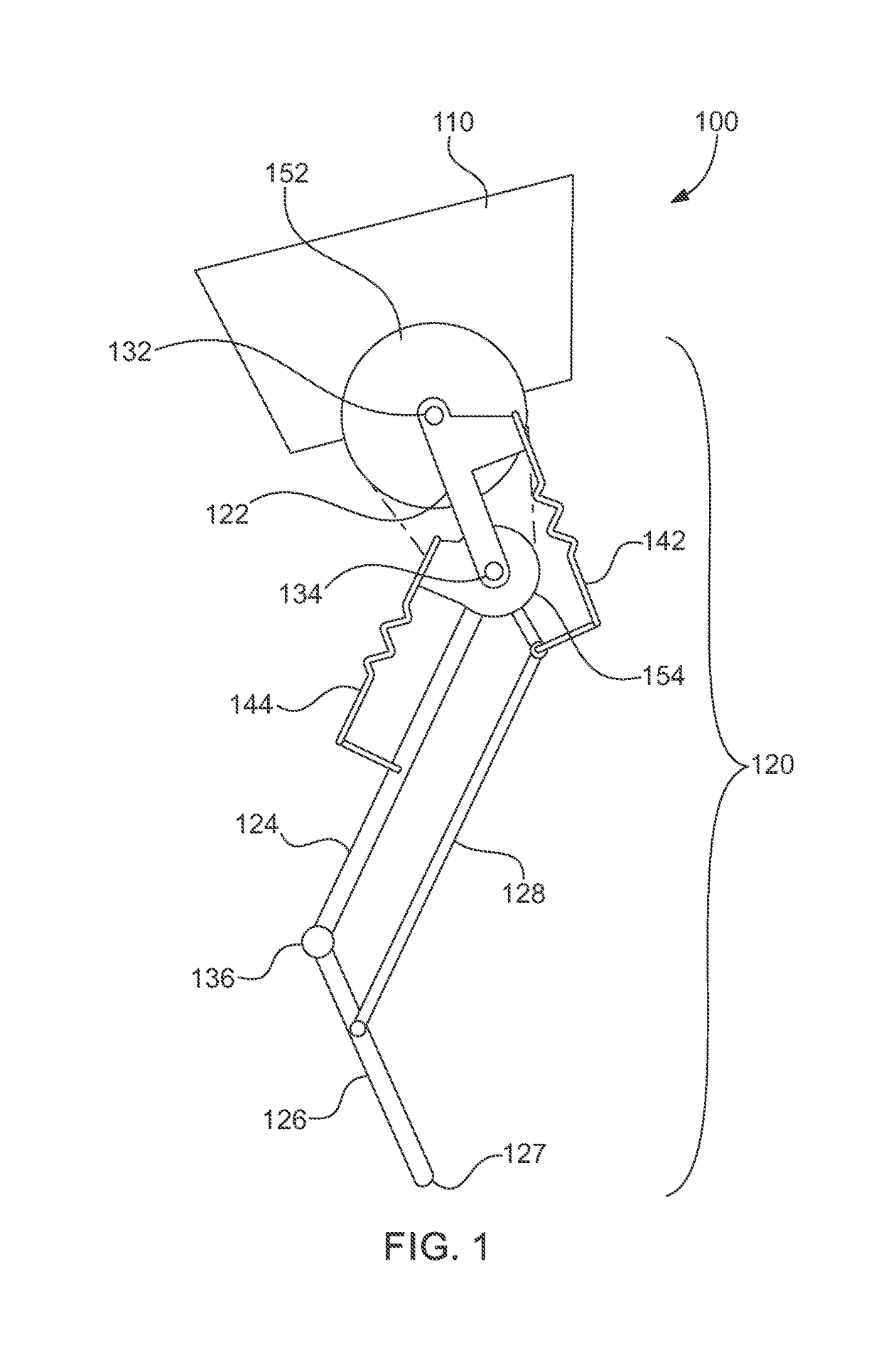
Leg configuration for spring-mass legged locomotion
ActiveUS10189519B2Relatively large bandwidthHigh force controlRobotVehiclesPassive dynamicsEngineering
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
Method of controlling biped walking robot
InactiveUS20050029979A1Accurate balanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlReference vectorEngineering
A method of controlling a biped walking robot to balance the robot based on a sensed ground reaction force. In the method, X and Y coordinates are assigned to positions of sensors attached to a sole of a leg of the robot and a corresponding Z coordinate is assigned for at least three of the sensors based on the sensed ground reaction force sensed by at the sensors, respectively. A ground reaction force plane is specified based on the sensed ground reaction force and a normal vector perpendicular to the ground reaction force plane is calculated. A roll angle about an X-axis and a pitch angle about a Y-axis are calculated and an actuator is driven in correspondence to the roll angle and the pitch angle to move a part of the robot to align the normal vector with a reference vector of the gravity direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Household teaching-assistant robot system for children
The invention discloses a household teaching-assistant robot system for children. The system comprises a robot head, a robot body, robot arms, robot legs, a moving plate and a display desk, wherein the robot head and the robot body are mounted in a matched manner by the aid of a connecting piece, the two robot arms are symmetrically arranged on two sides of the robot body, the two robot legs are symmetrically arranged at the bottom of the robot body, and the moving plate is fixedly arranged at bottoms of the robot legs. The system is intelligently controlled and is lively and interesting.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINYIJIA SCI & TECH
Dual-purpose robot leg with wheel and foot
InactiveCN101224765AGuaranteed movement speedEnsure Terrain AdaptabilityVehiclesControl devicesAgricultural engineeringDual purpose
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots and more particularly relates to a robot leg which uses both a wheel and a foot. A first clutch of the robot leg is connected with a first shaft and a second shaft, a first bearing inner race is connected with the first shaft, a first bearing outer race is connected with a first large wheel hub, a second bearing inner race and a third bearing inner race are connected with the second shaft, a second bearing outer race and a third bearing outer race are connected with a long connecting rod, and simultaneously a first driven sheet of the first clutch is connected with the first large wheel hub and a second driven sheet of the first clutch is connected with the long connecting rod. A second clutch is connected with a third shaft and a fourth shaft, a sixth bearing inner race is connected with the third shaft, a sixth bearing outer race is connected with a second large wheel hub, a seventh bearing inner race is connected with the fourth shaft, a seventh bearing outer race is connected with a short connecting rod, and simultaneously a first driven sheet of the second clutch is connected with the second large wheel hub and a second driven sheet of the second clutch is connected with the short connecting rod. The robot leg has compact structure, flexible movement, strong ground adaptability and quick movement speed, and is favorable for reducing energy consumption due to changing movement postures according to special landforms.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
A twelve-legged robot and its motion method
The invention relates to a robot with twelve feet, and the robot provided by the invention comprises a main body, a main servo motor, moving servo motors, rotating servo motors, moving mechanisms, leg structures and foot components, wherein the main servo motor is arranged in the main body; separating plates are used for dividing the main body into six areas; rotating position sensors are arranged on the separating plates; the moving mechanisms are fixed in all the areas of the main body by virtue of fastening components; two servo motors which are used for controlling the leg structures of the robot to move up and down and two servo motors which are used for controlling the leg structures of the robot to rotate are arranged in support plates of the moving mechanisms; each of the servo motors used for controlling the leg structures of the robot to move up and down is provided with one leg structure; and the foot components are mounted at the bottoms of the leg structures. The robot with twelve feet, which is composed of six legs, provided by the invention is designed for realizing wide-angle steering by stopping the travelling moving mechanism and starting the to-be-rotated movingmechanism when a steering angle is wider.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
Wheel-foot hybrid robot leg and wheel-foot hybrid robot
The invention provides a wheel-foot hybrid robot leg and a wheel-foot hybrid robot. In the robot leg, a first driving wheel and a second driving wheel are arranged in parallel and are both rotationally mounted at the hip joint of the leg through hip joint rotating shafts; the first driven wheel and the second driven wheel are arranged in parallel and are rotationally mounted at knee joints of legsthrough knee joint rotating shafts; the output power of the driving unit sequentially passes through the first driving wheel and the first driven wheel to reach shanks to form a first power transmission line, so that the robot moves in a foot type state, or the output power of the driving unit sequentially passes through the second driving wheel and the second driven wheel to reach the roller toform a second transmission line, so that the robot moves in a wheel type state; the power switching unit can enable the output power of the driving unit to be switched between the first power transmission line and the second power transmission line so as to enable the wheel-foot hybrid robot to be switched between foot type state motion and wheel type state motion.
Owner:THE 21TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
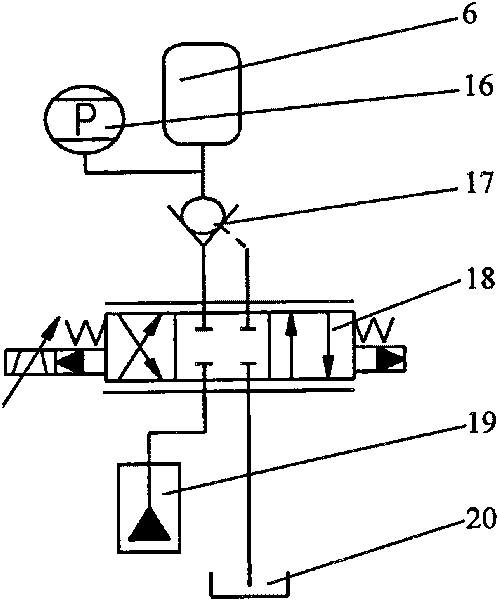
Gasbag robot leg buffer mechanism with adjustable rigidity
The invention discloses a gasbag robot leg buffer mechanism with adjustable rigidity, which comprises a connecting block, a gasbag, an outer barrel of a leg, a telescopic link and a force sensor. The connecting block is arranged at an upper end of the outer barrel of the leg, the telescopic link is arranged in the outer barrel of the leg, the lower part of the telescopic link extends out of the outer barrel of the leg. An oil chamber is formed between a piston part at the upper end of the telescopic link and the inner top of the outer barrel of the leg. The oil chamber is divided into an upper part and a lower part by a partition plate, wherein the gasbag is arranged on the upper part of the oil chamber, and hydraulic oil is stored in the lower part of the oil chamber and is connected with an external pressure regulation loop. A damping hole is formed on the partition plate, and the force sensor which is used for measuring magnitude and direction of contact force between foot and ground is arranged at the lower end of the telescopic link. The gasbag robot leg buffer mechanism with adjustable rigidity can regulate rigidity of an air spring on line according to the ground rigidity information detected by a sensing unit, reduce the impact of the round to the robot and improve the stability of dynamic walk of the robot. Then the robot walks in the most stable state.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
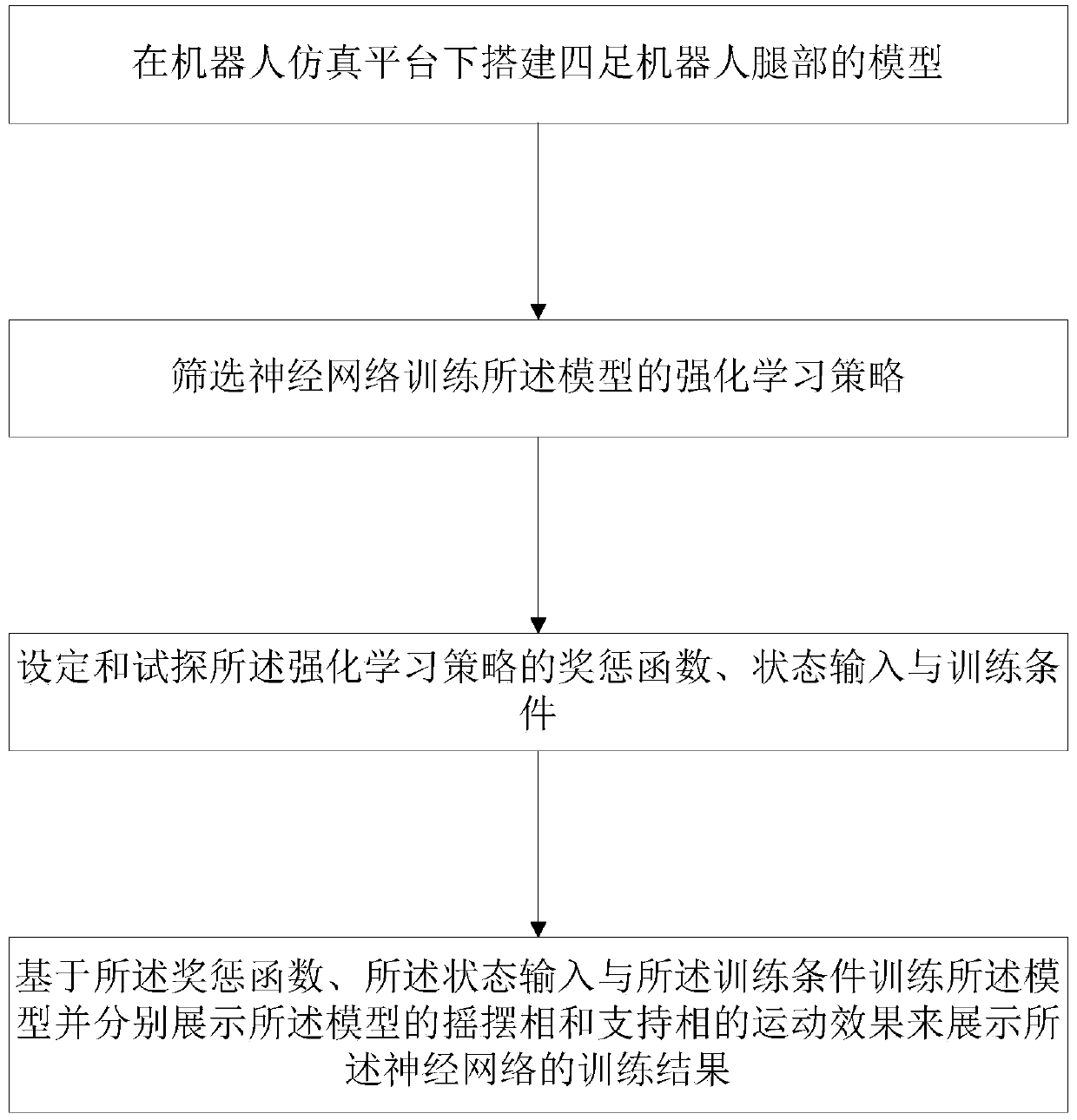
Gait planning method for leg movement of four-legged robot
The invention provides a gait planning method for leg movement of a four-legged robot. The gait planning method comprises the following steps that S1, models of legs of the four-legged robot are constructed under a robot simulation platform; S2, enhanced learning strategies for training the models by a neural network are screened; S3, reward and punishment functions, state input and training conditions of the enhanced learning strategies are set and sounded out; and S4, the models are trained on the basis of the reward and punishment functions, state input and the training conditions, and themotion effects of swing phases and supporting phases of the models are displayed respectively to display training results of the neural network. By adopting an enhanced learning algorithm and utilizing a heuristic learning training scheme, leg kinematics is planned, and the robot can be made to adaptively adjust gaits under the algorithm network.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Device for absorbing floor-landing shock for legged mobile robot
InactiveUS6967456B2Reduce the amount requiredProcess stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpringsSolenoid valveAtmospheric air
A landing shock absorbing device 18 provided in a foot mechanism 6 of a leg of a robot comprises an inflatable and compressible bag-like member 19 (a variable capacity element) on a bottom face side of the foot mechanism 6. The bag-like member 19 is constructed of an elastic material such as rubber. Air in the atmosphere can flow into and out of the bag-like member 19 by inflow / outflow means 20 provided with a solenoid valve 27 and the like. In a landing state of the foot mechanism 6 and in a state immediately after the foot mechanism shifts from the landing state to a lifting state, the solenoid valve 27 is closed to maintain the bag-like member 19 in a compressed state. Furthermore, during the bag-like member 19 in the inflating state during the lifting state of the foot mechanism 6, by controlling timing when the solenoid valve 27 is switched from a valve opening state to a valve closing state, a height of the bag-like member 19 in a compression direction is controlled to be a height suitable for a gait type of the robot. Thereby, posture stability of the robot can be secured easily while reducing a impact load in the landing motion of the leg of the legged mobile robot, and further, a lightweight configuration can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com