Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
317 results about "Ground reaction force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
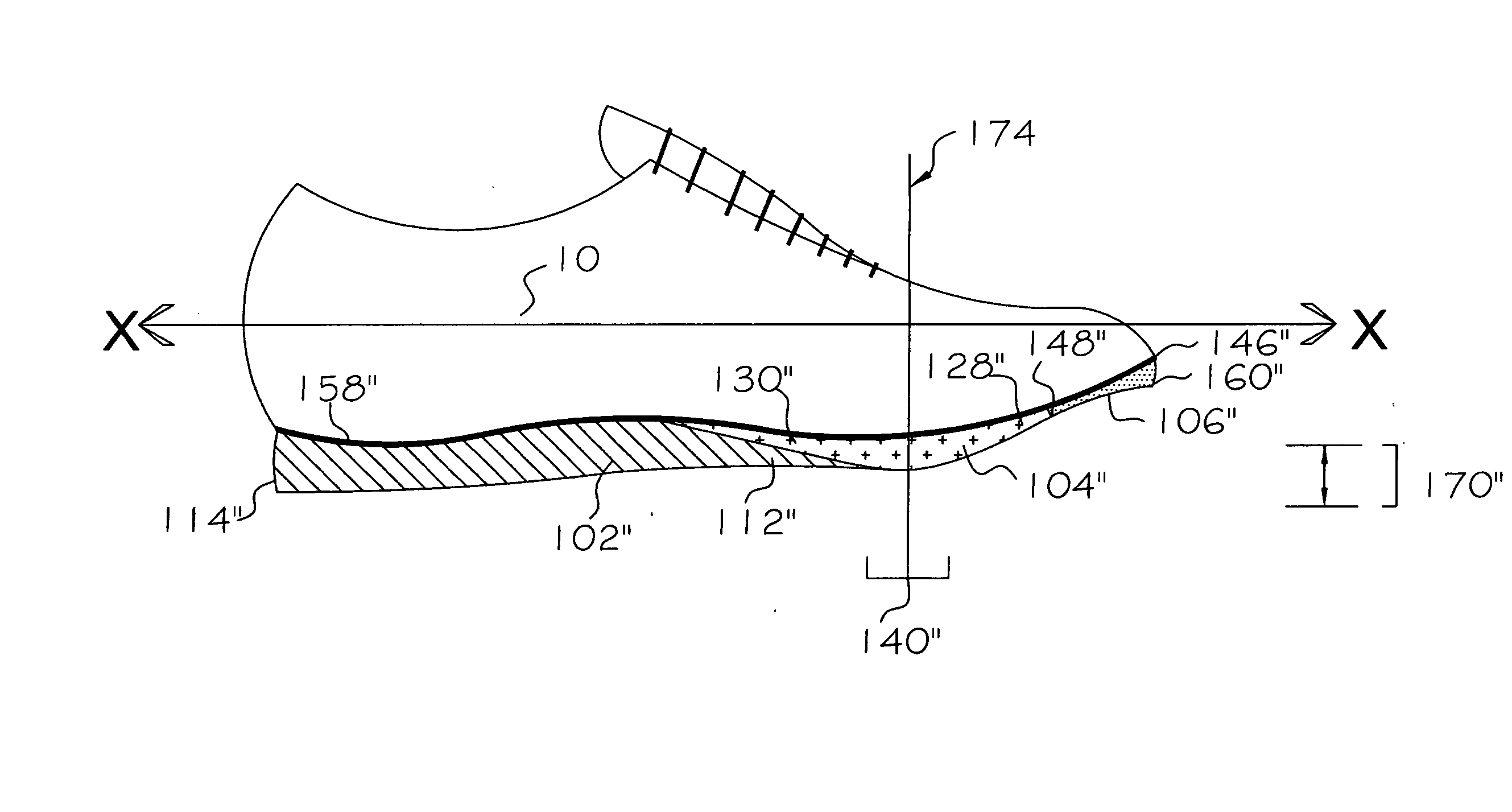
In physics, and in particular in biomechanics, the ground reaction force (GRF) is the force exerted by the ground on a body in contact with it. For example, a person standing motionless on the ground exerts a contact force on it (equal to the person's weight) and at the same time an equal and opposite ground reaction force is exerted by the ground on the person.
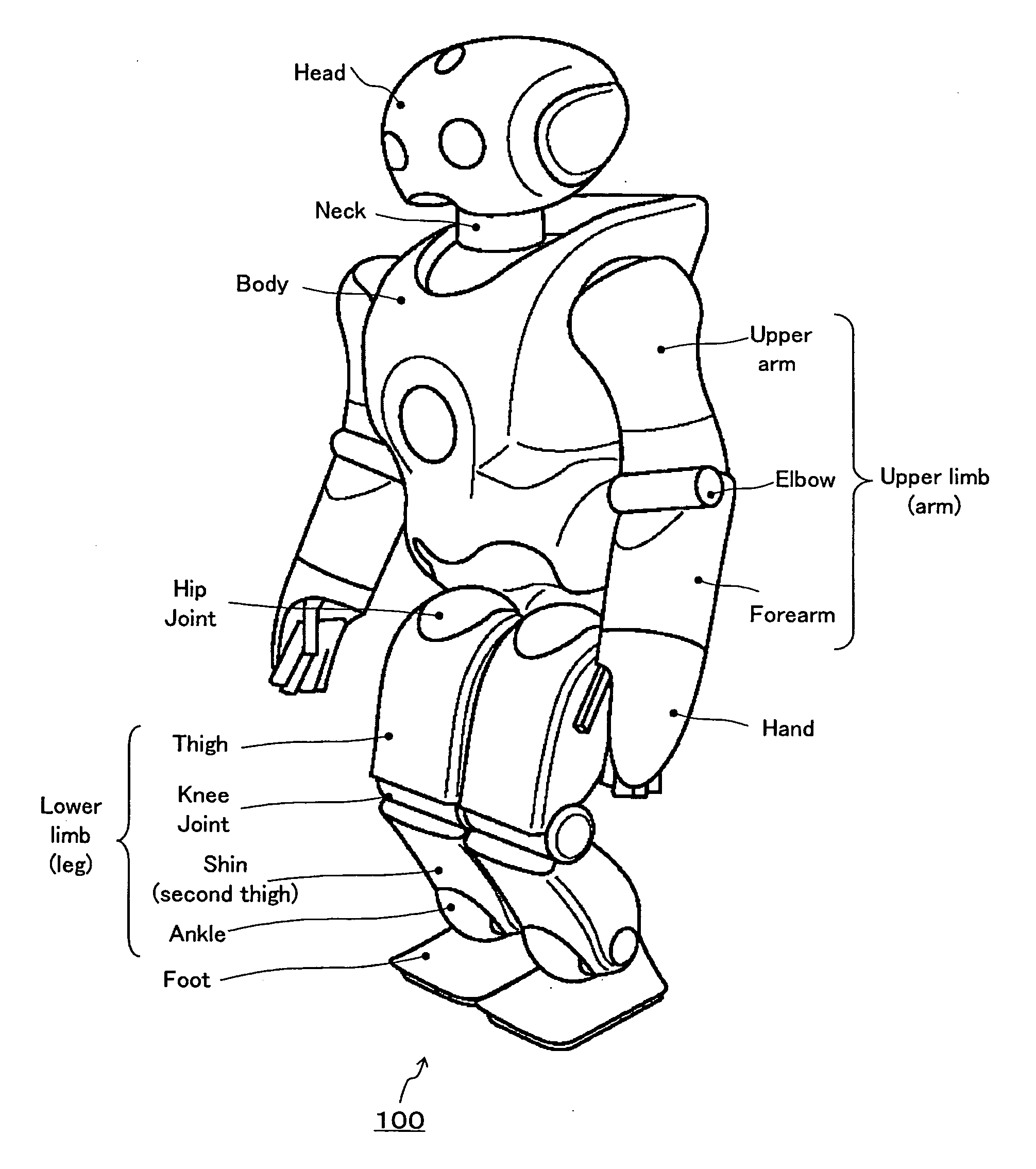
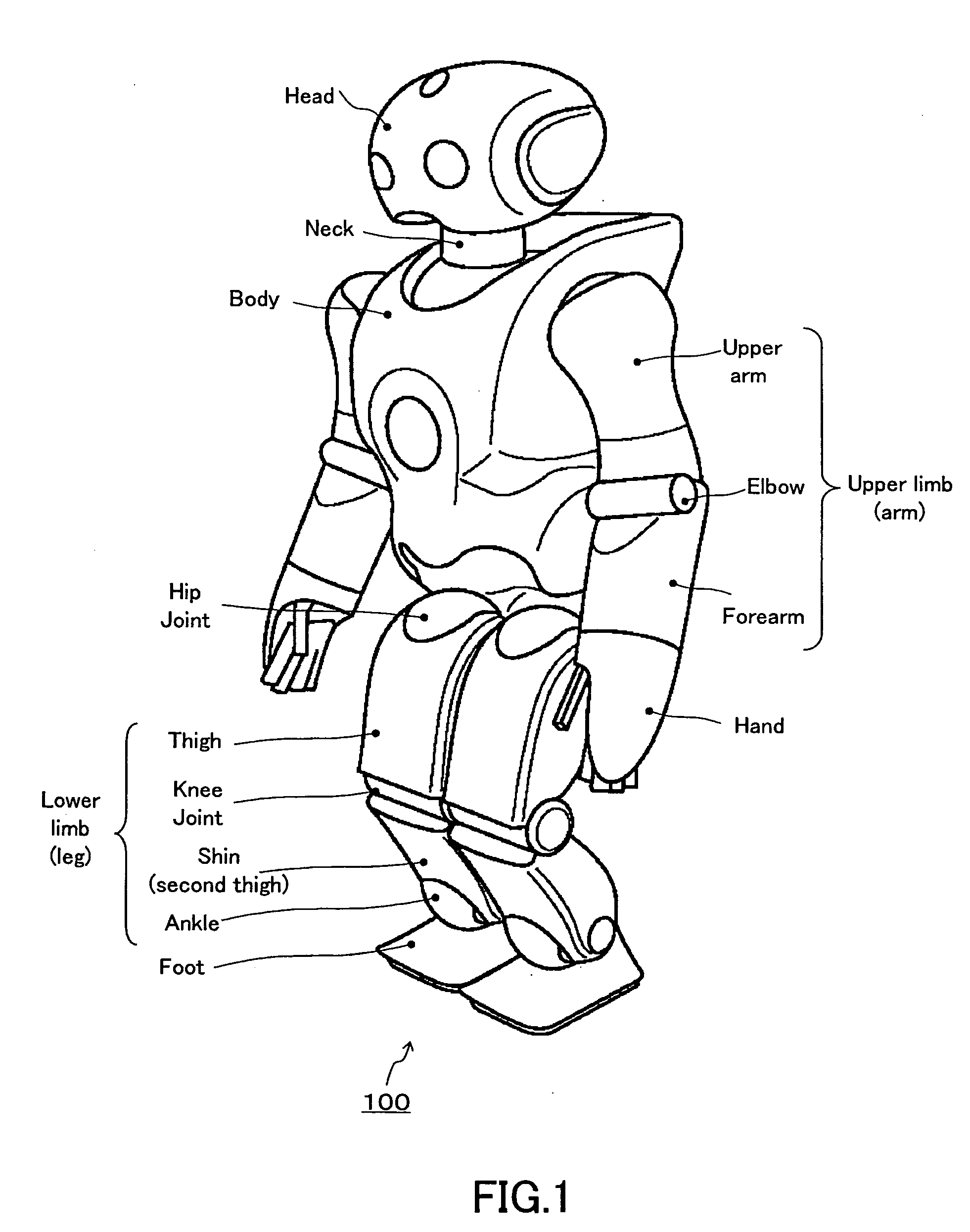
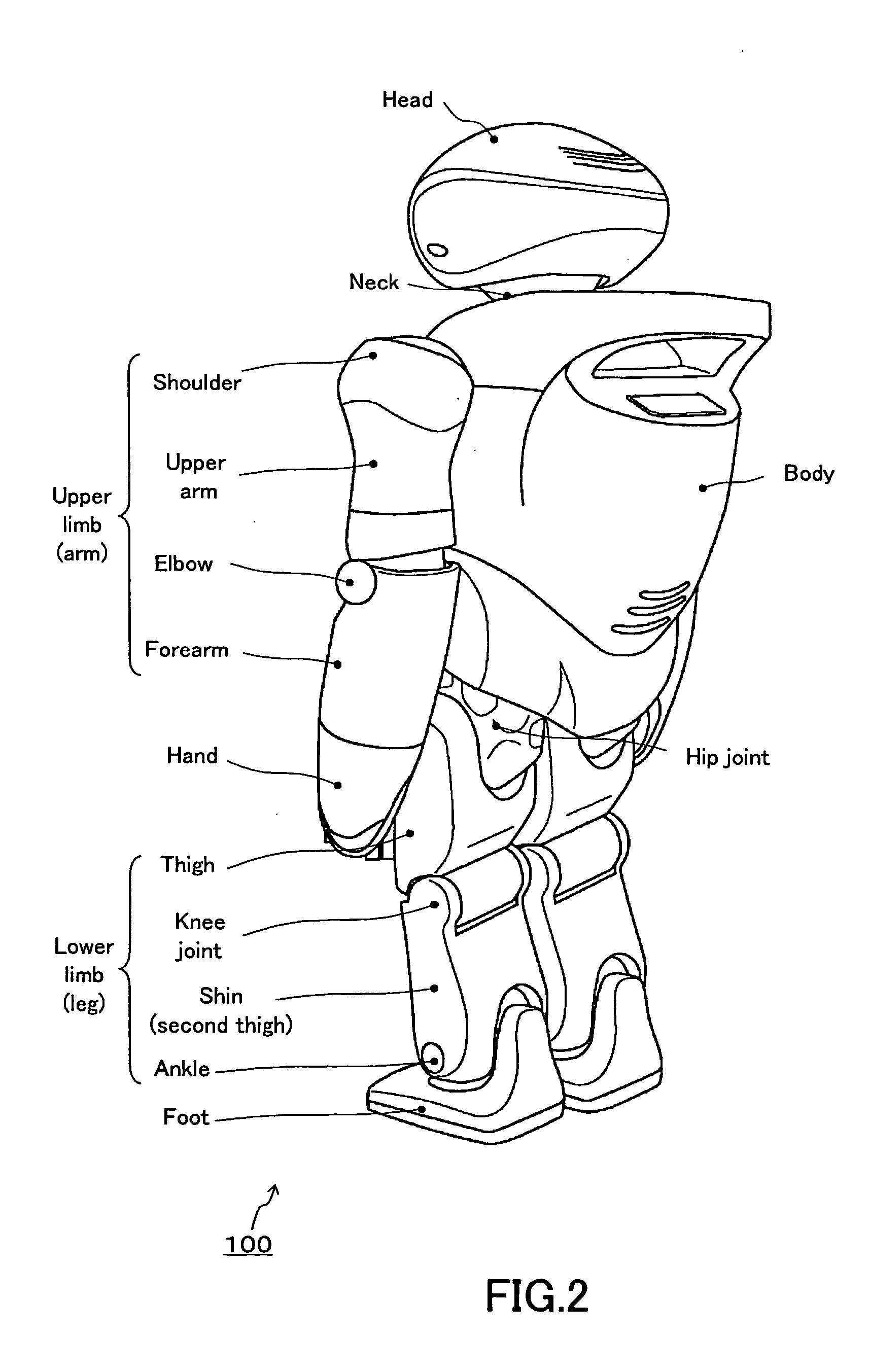
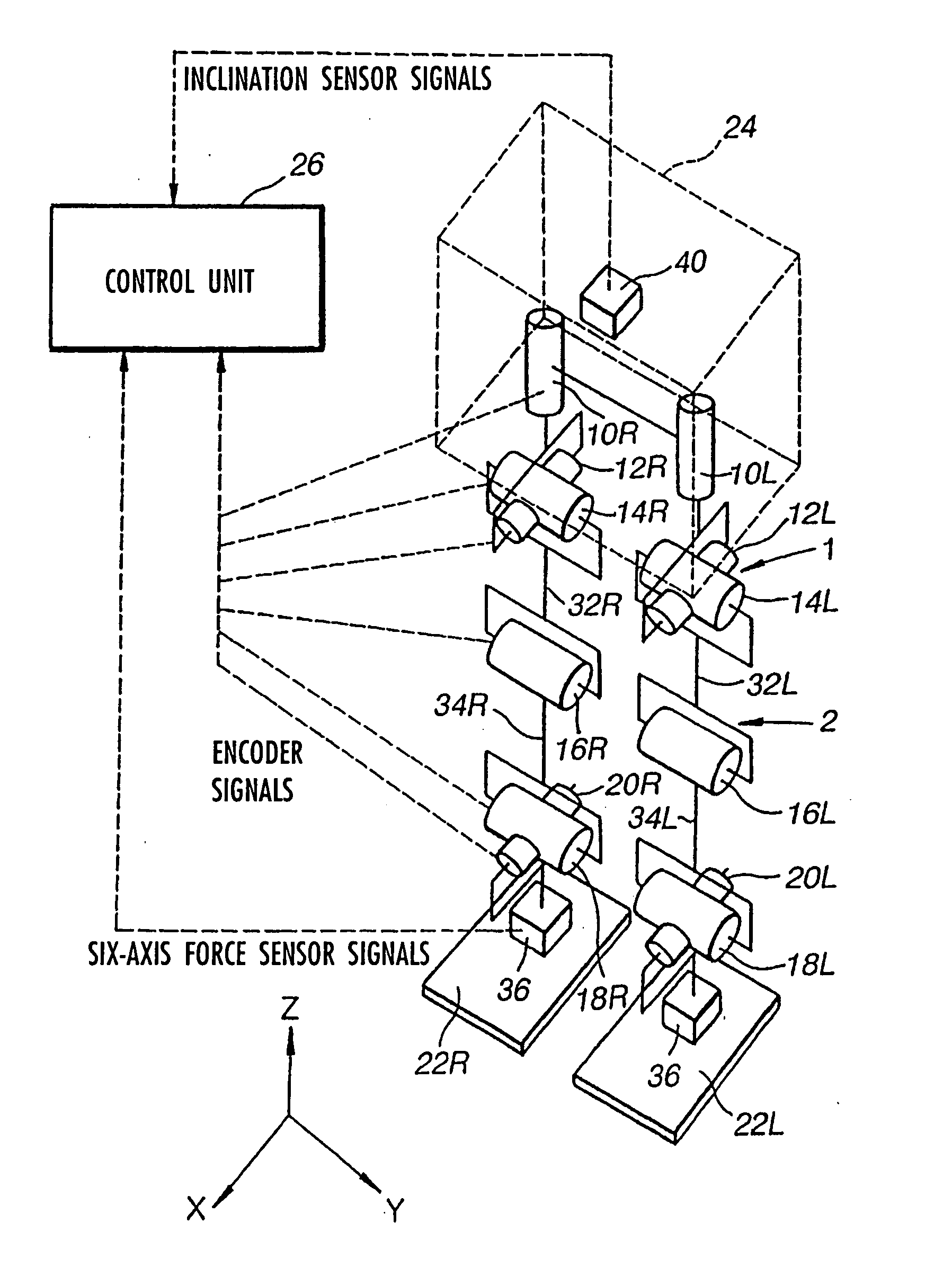
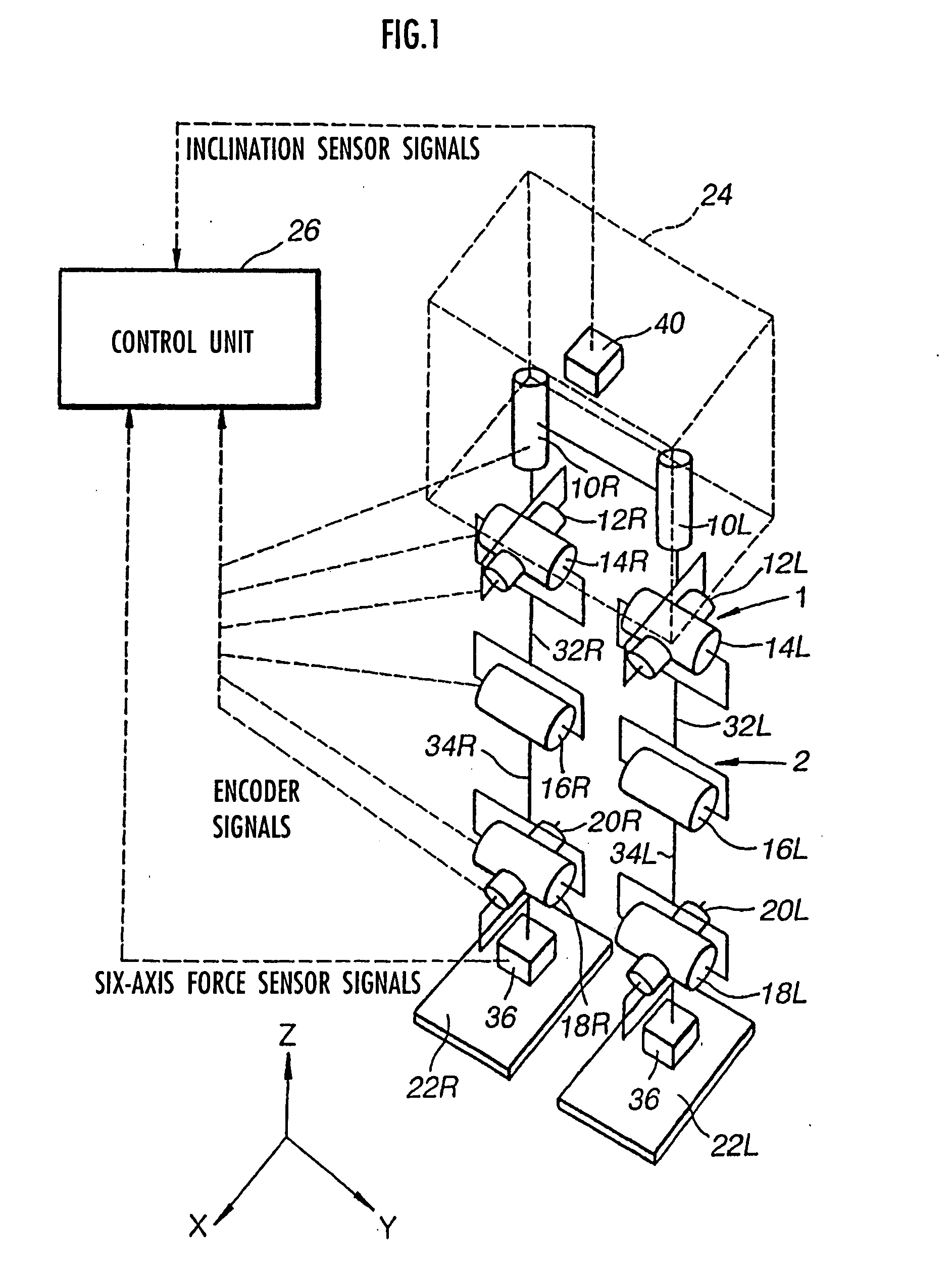
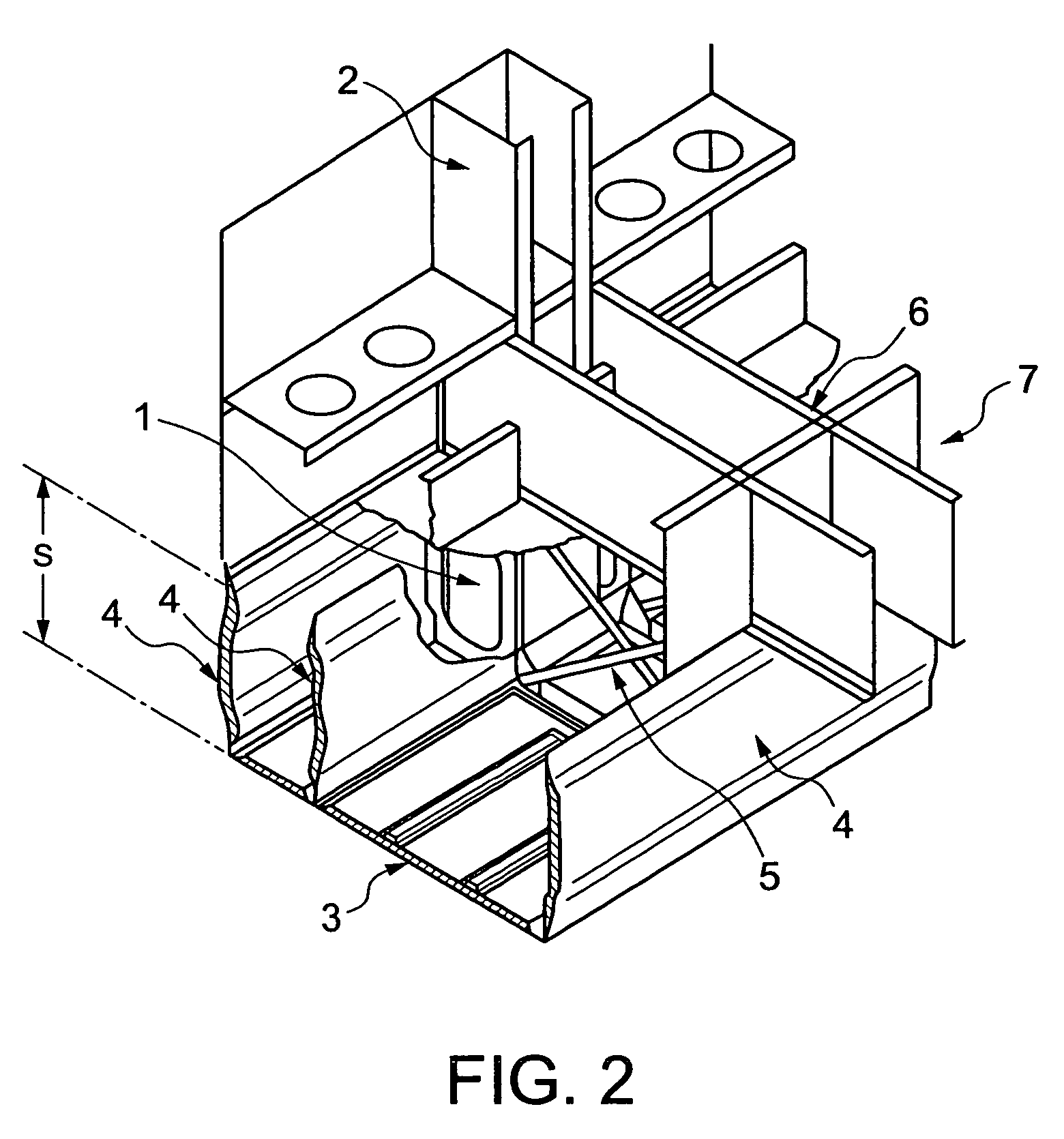
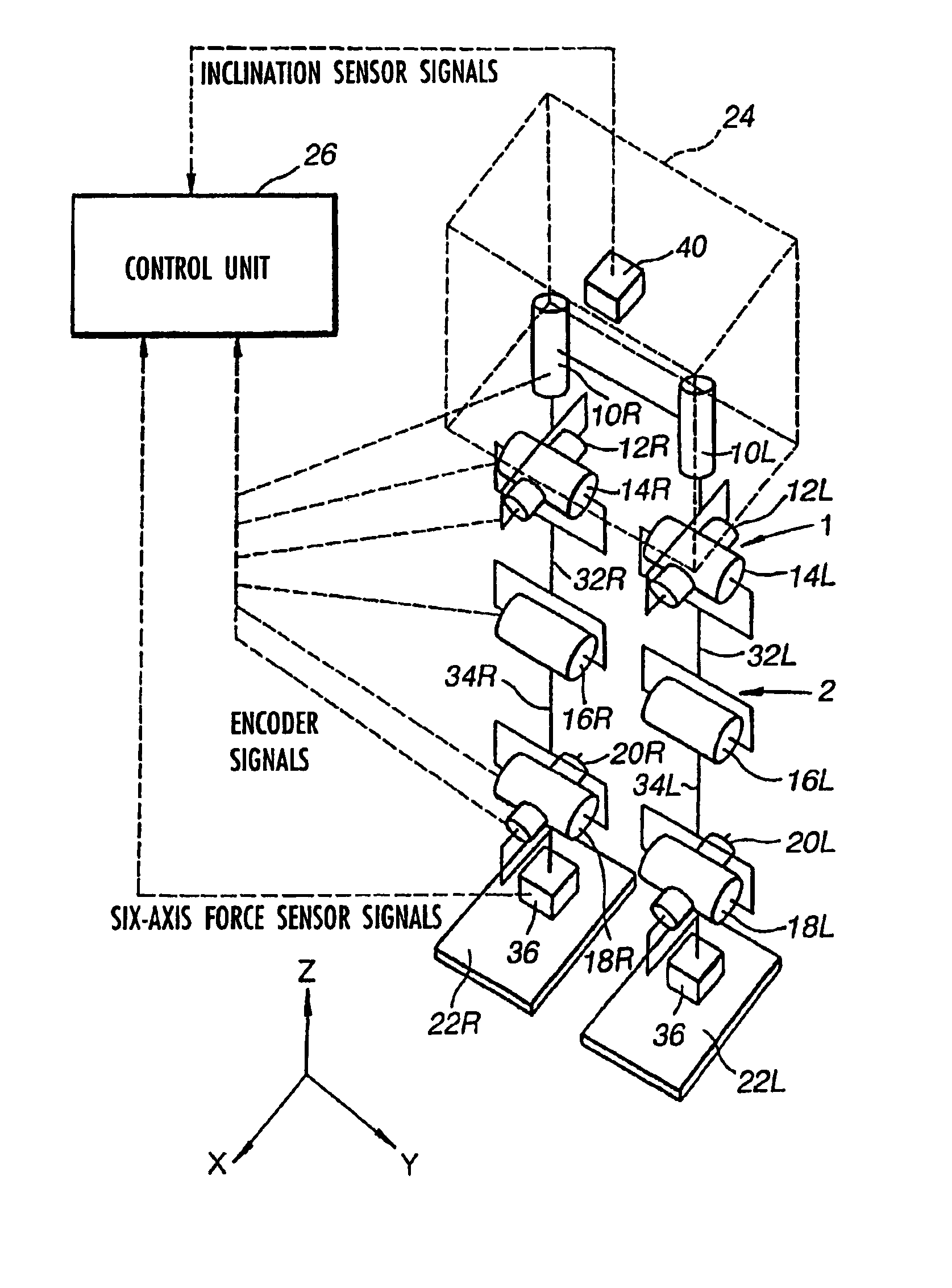
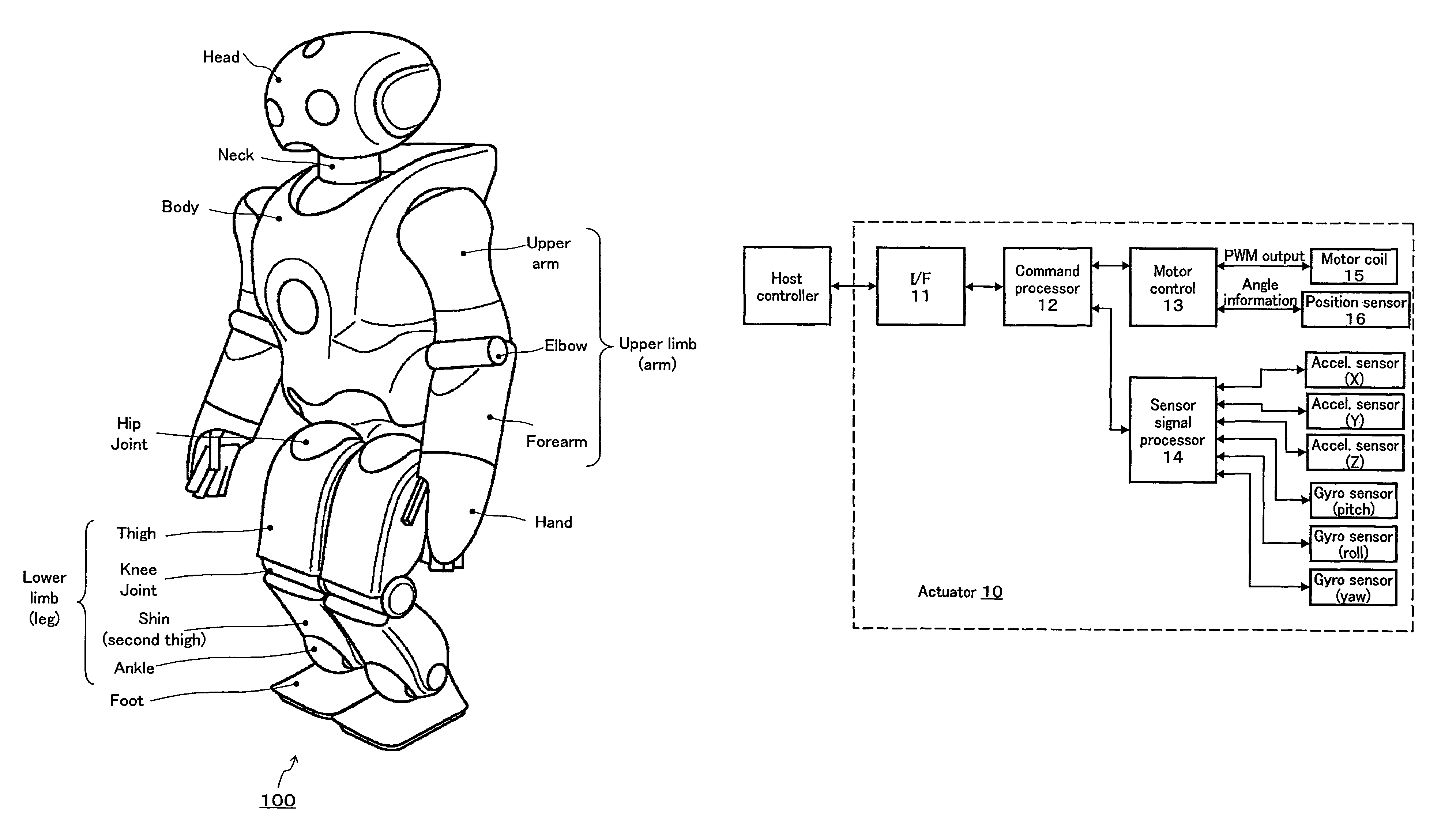
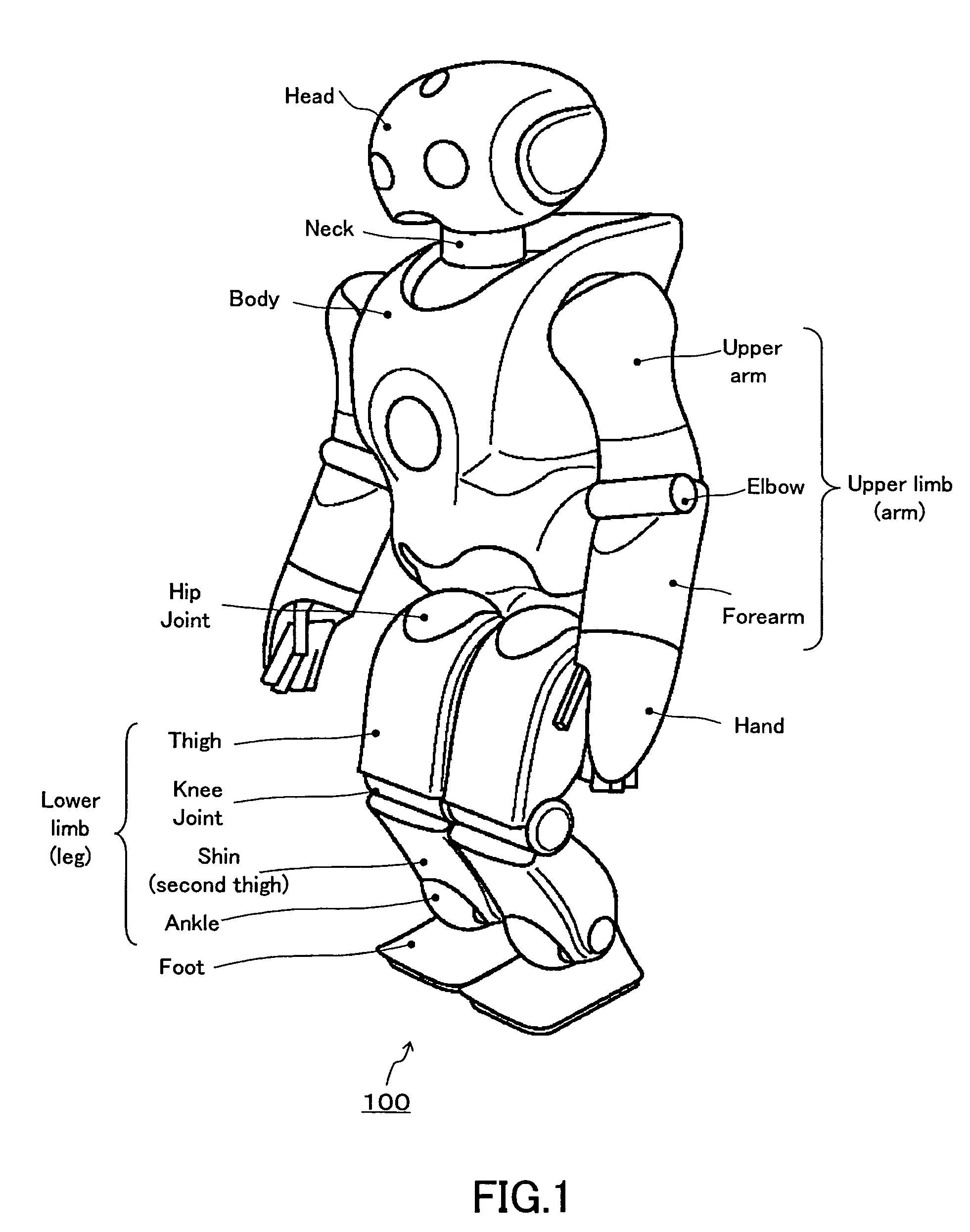
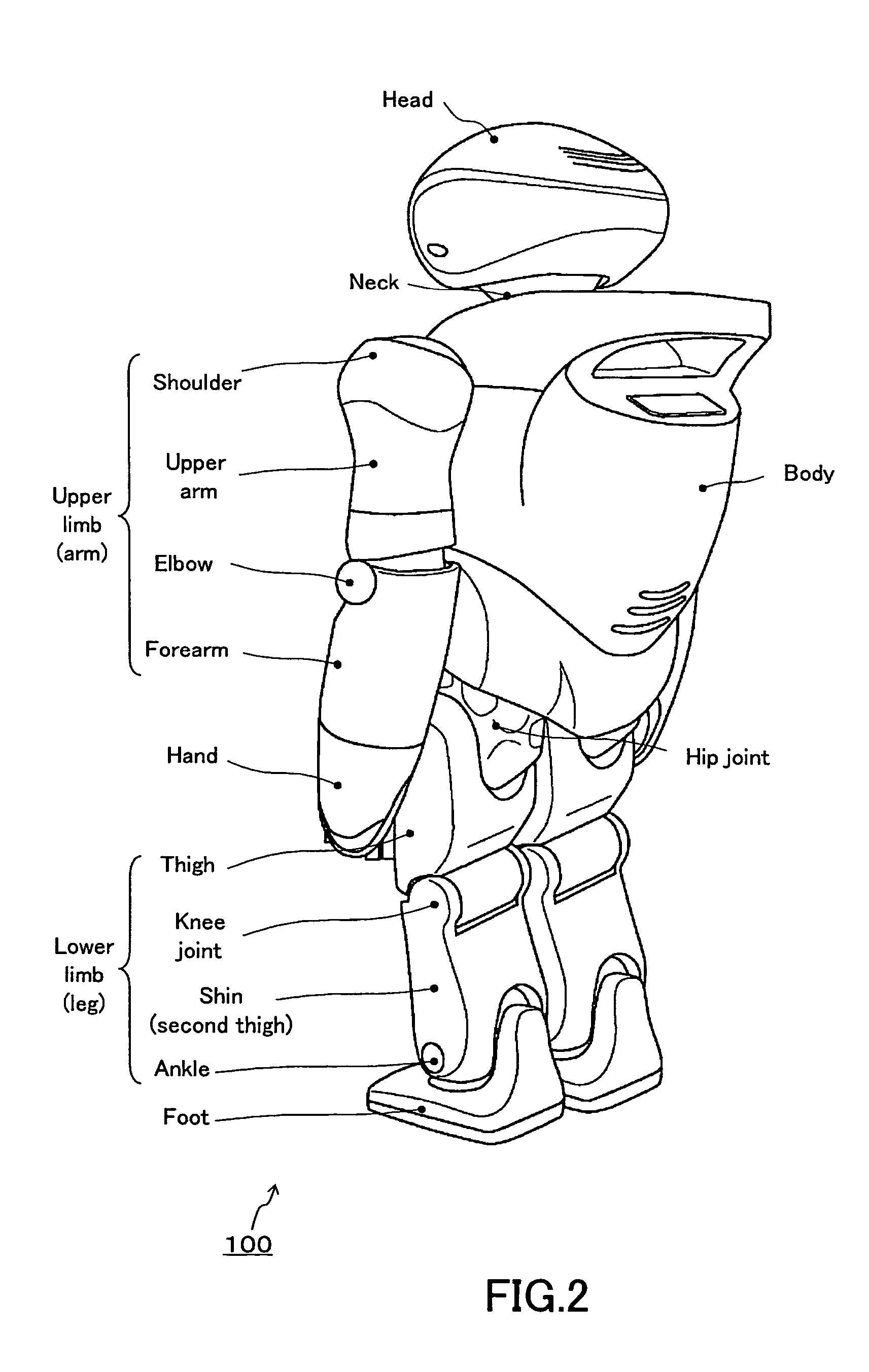
Robot device , legged locomotion robot operation control device and operation control method, legged locomotion robot sensor system, and locomotion device
ActiveUS20050240307A1Improve accuracyStrict controlComputer controlSimulator controlObject pointControl theory
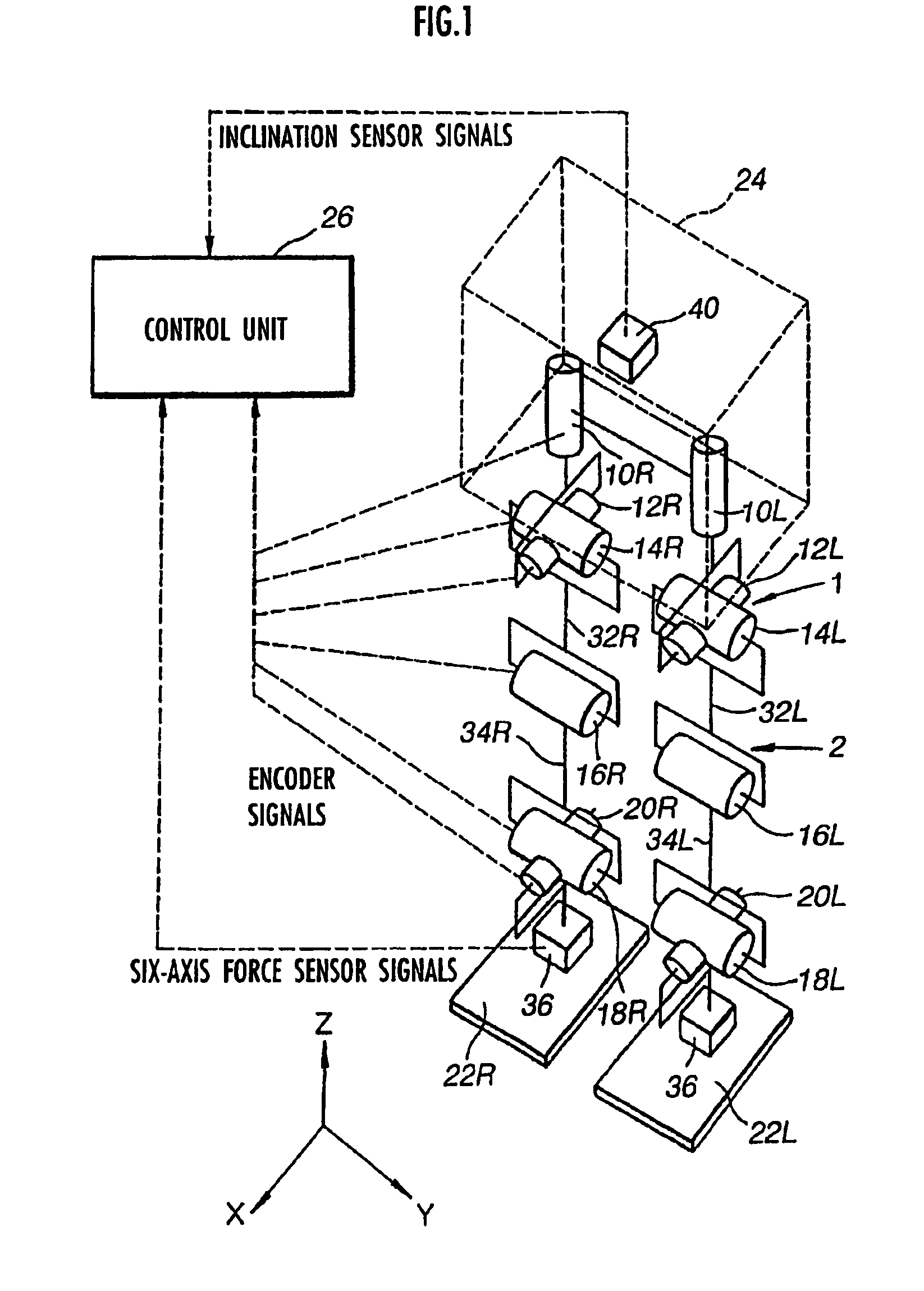
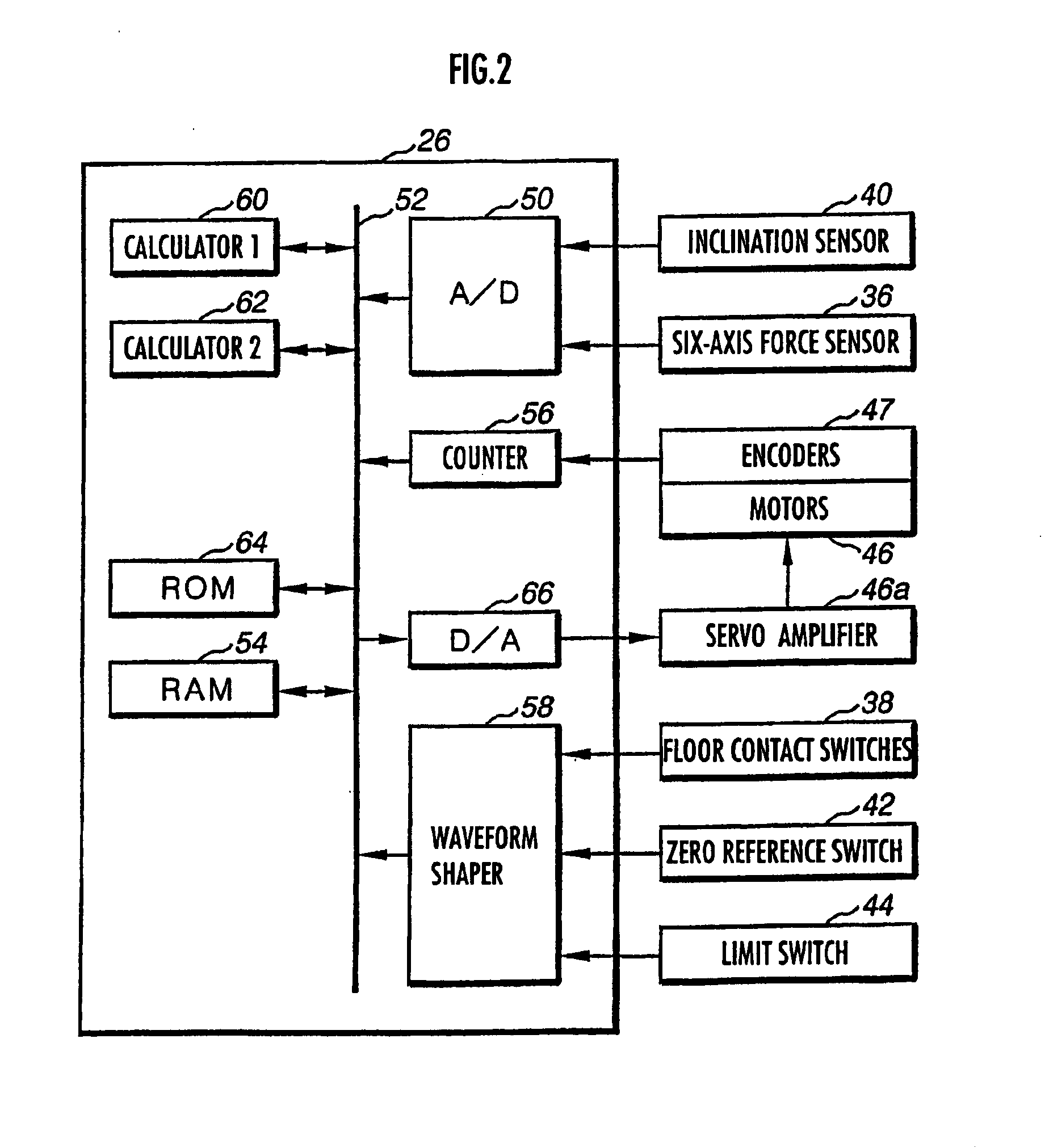
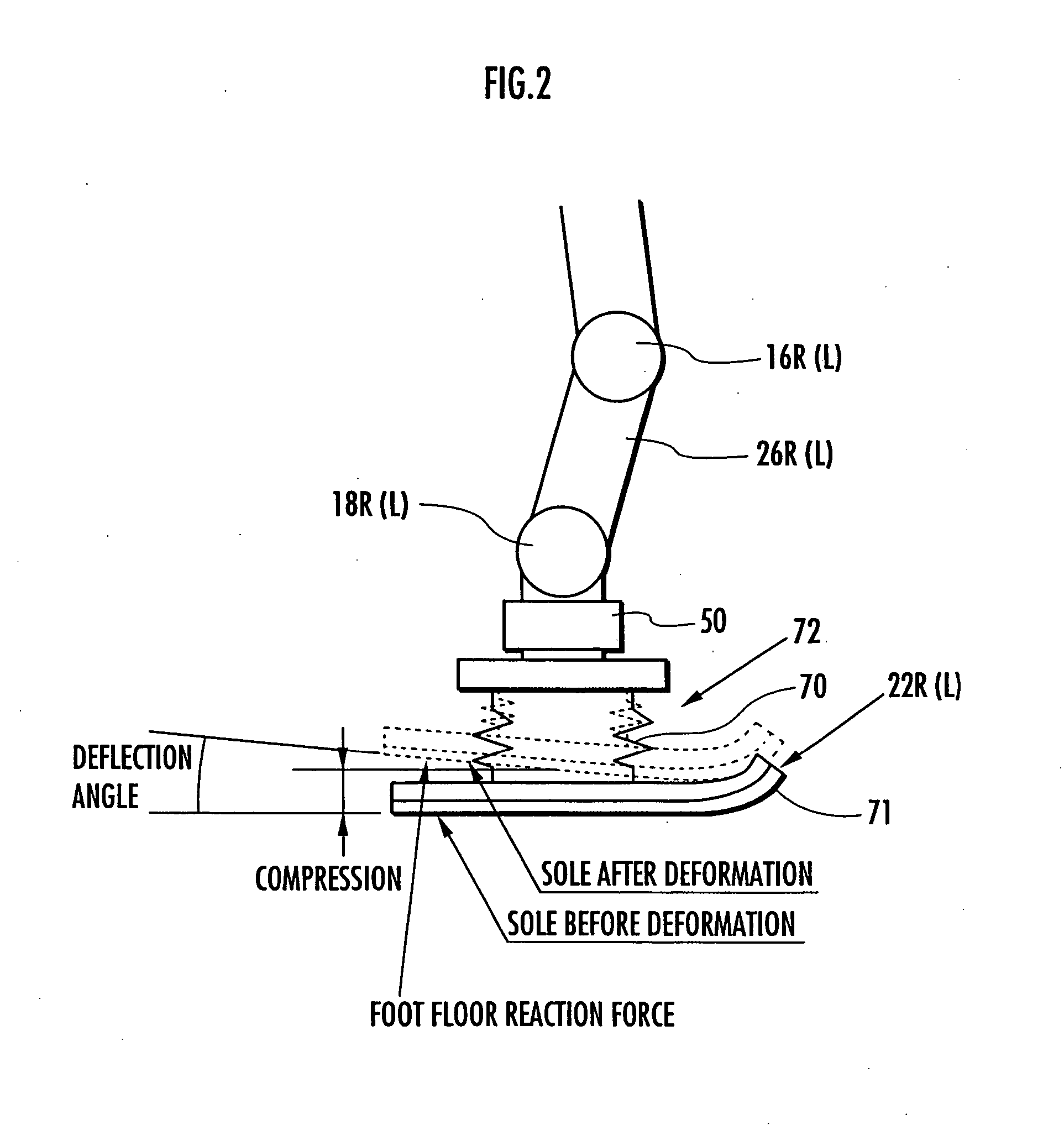
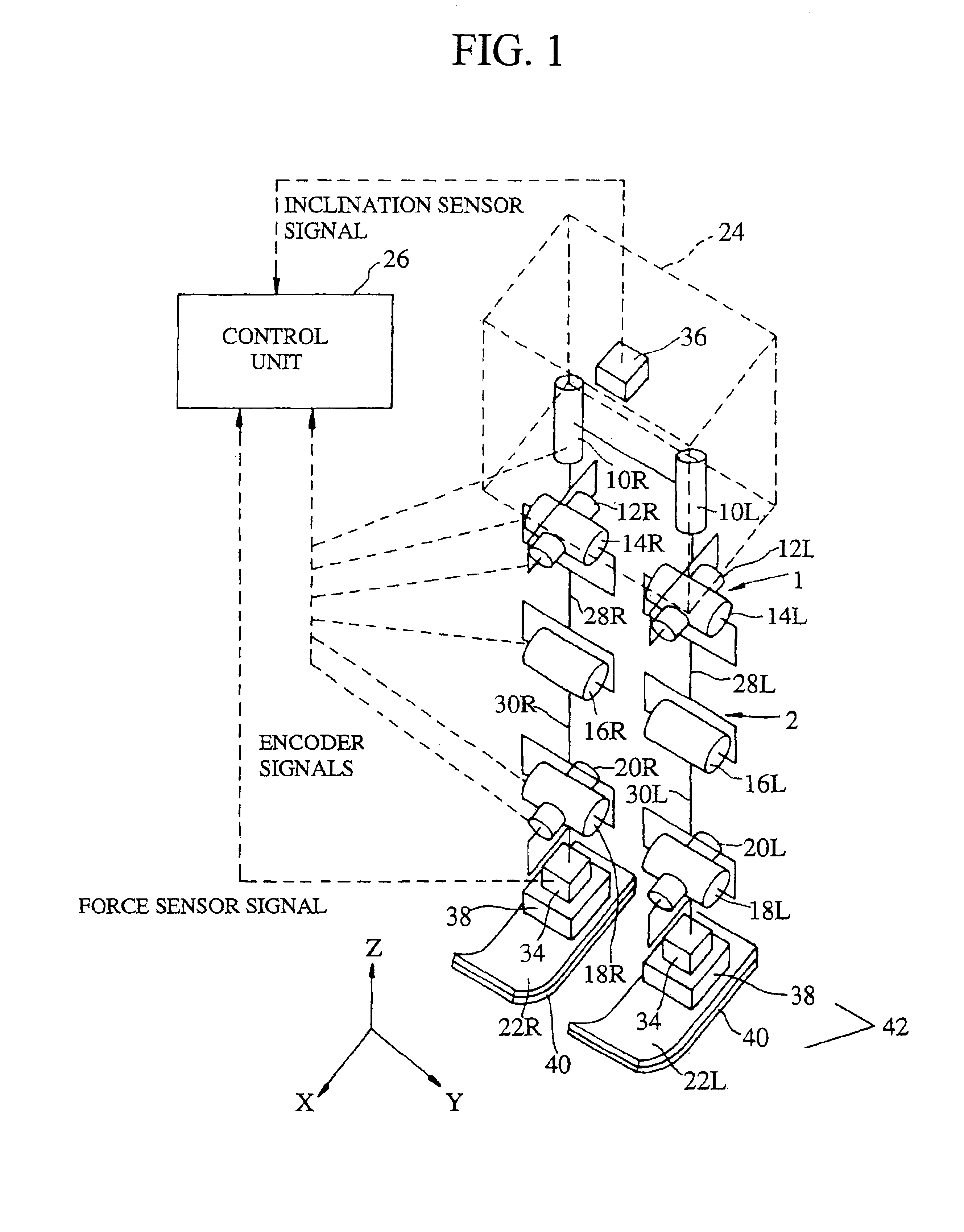
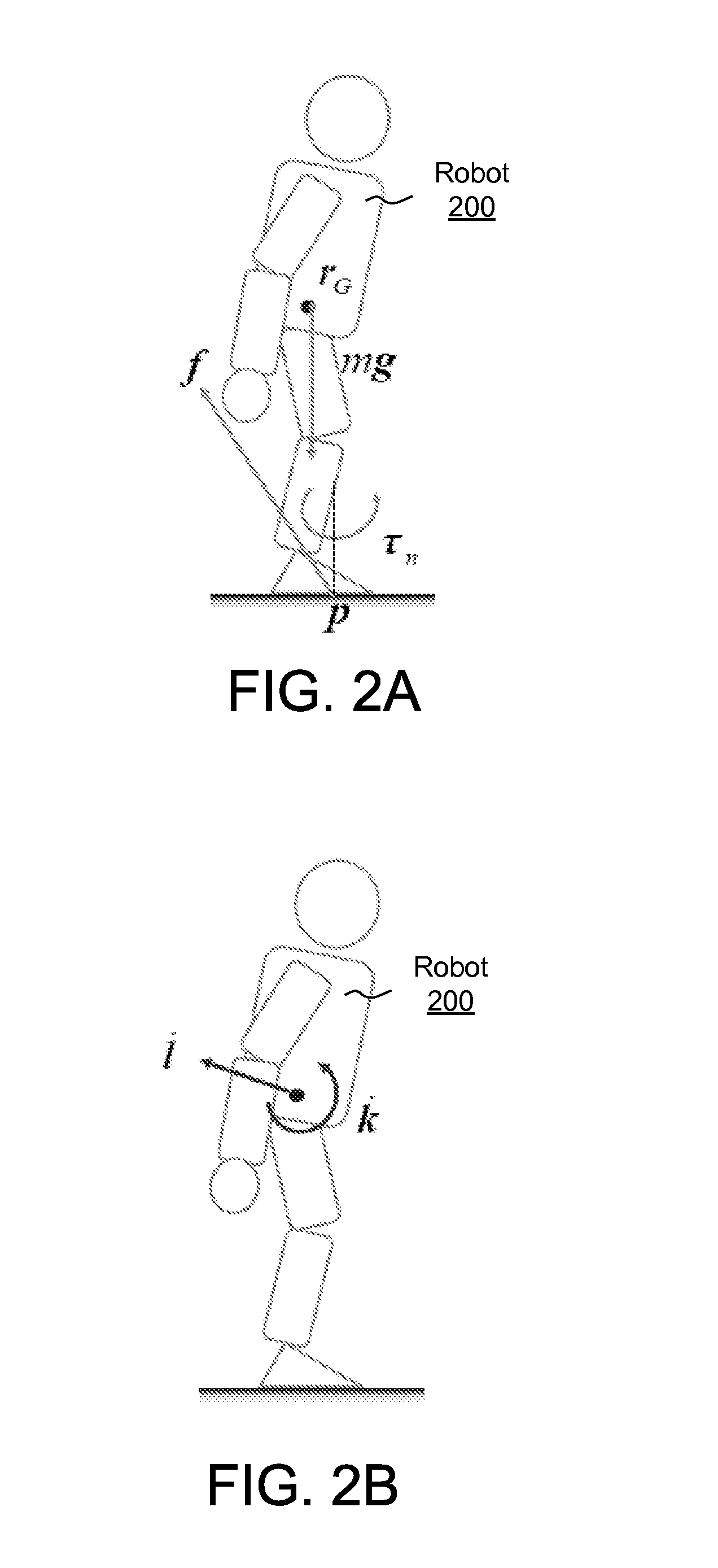
The lumbar part of a robot as a controlled-object point where the mass is moved to the largest extent is set as the origin of a local coordinate, an acceleration sensor is disposed at the controlled-object point to directly measure the attitude and acceleration at that position to control the robot to take a stable posture on the basis of a ZMP. Further, at each foot which touches the walking surface, there are provided a floor reaction force sensor and acceleration sensor to directly measure a ZMP and force, and a ZMP equation is formulated directly at the foot nearest to a ZMP position. Thus there can be implemented a stricter and quick control of the robot for a stable posture.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Ground opening device
InactiveUS20070272134A1Adjustable loadImprove variationPlantingAdjusting devicesEngineeringForce sensor
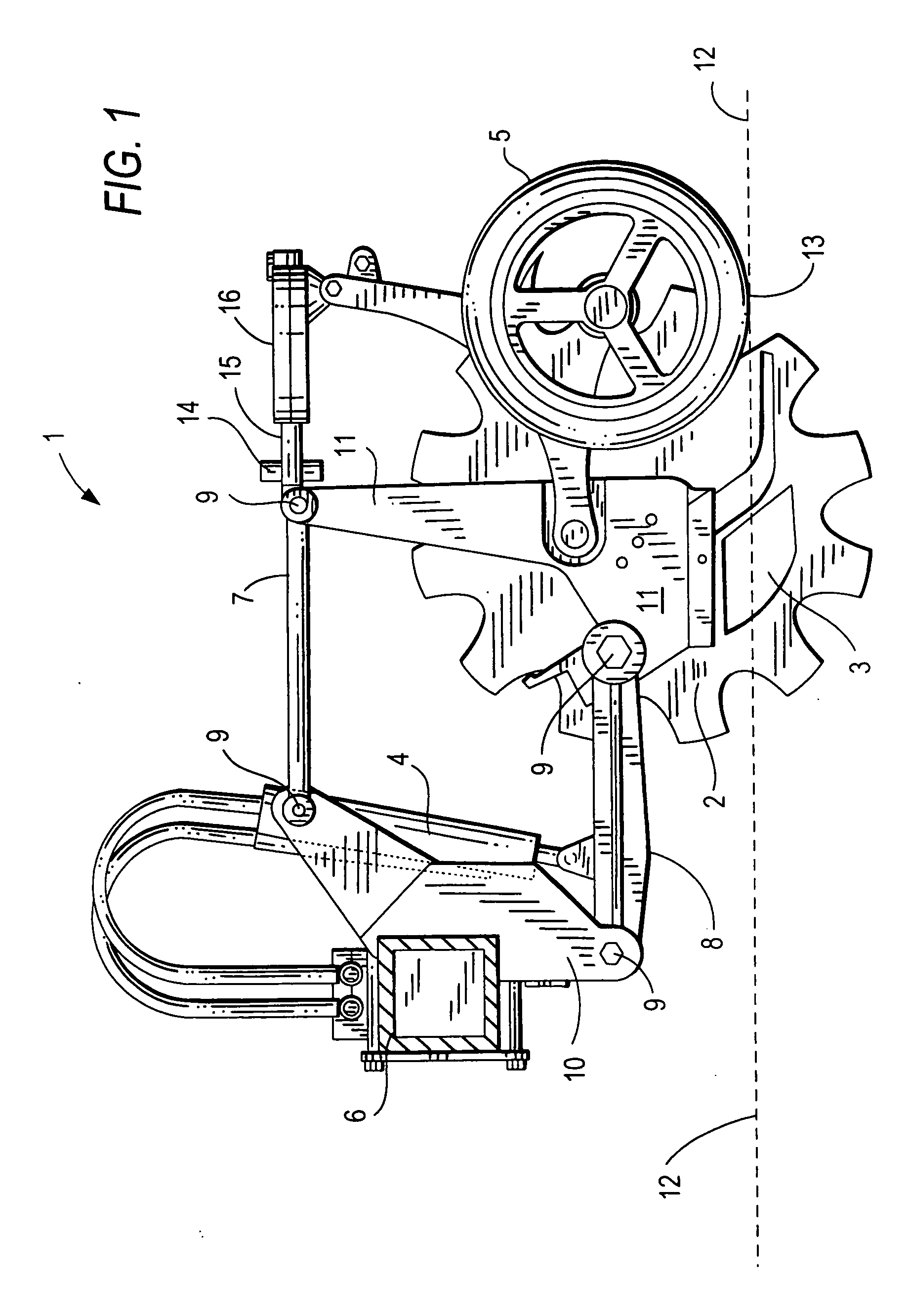
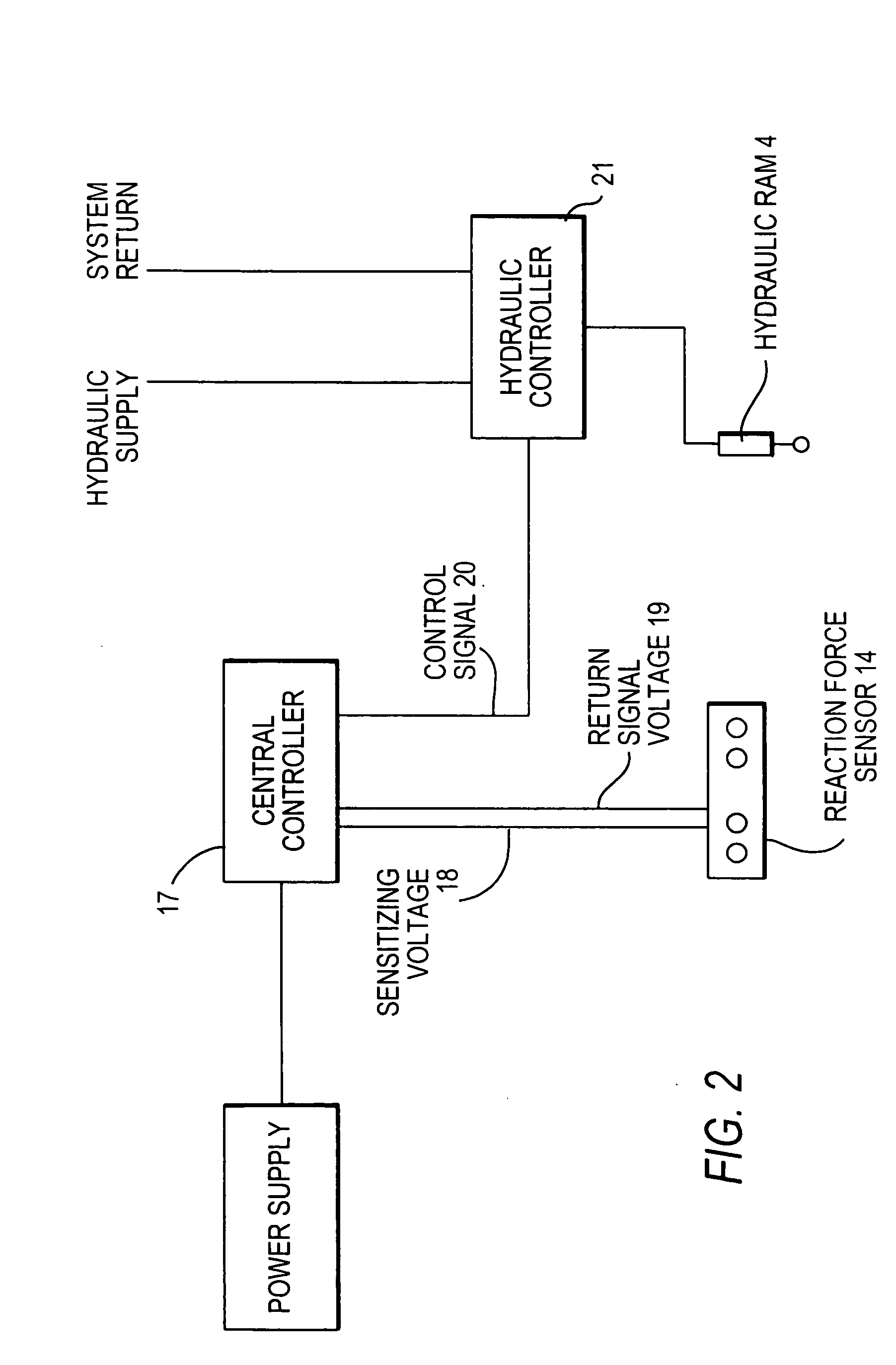
A ground opening device includes a ground-penetrating element configured to penetrate a ground surface, a down drive element configured to apply a downward force to the ground-penetrating element, a reaction force sensor configured to sense a ground reaction force in response to the action of the ground-penetrating element, and a controller configured to adjust the downward force on the ground-penetrating element in response to the sensed ground reaction force.
Owner:BAKER
Active control of an ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS7650204B2Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationGravitational forceOrthotic device
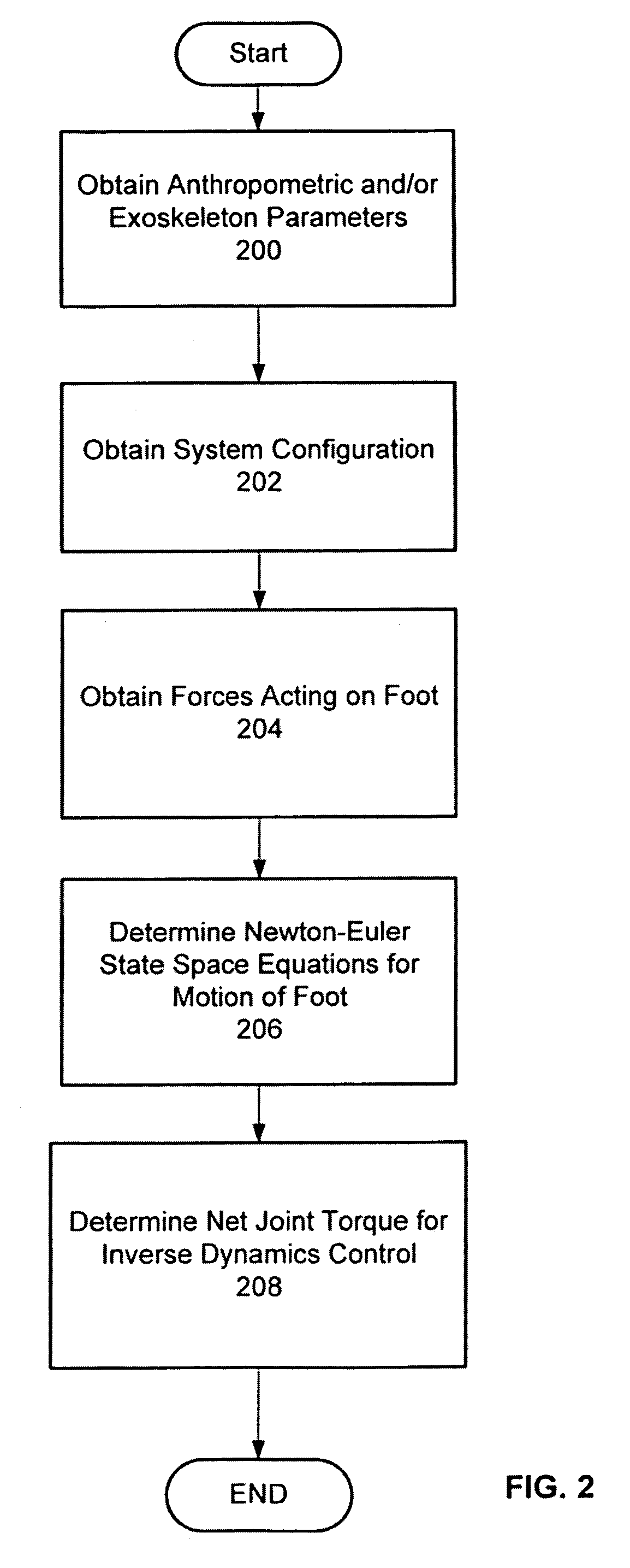
Techniques are provided for controlling a human-exoskeleton system including an ankle-foot orthosis by receiving system parameters for the human-exoskeleton system, receiving generalized coordinates such as an orientation of the foot, and determining a joint torque for controlling the ankle-foot orthosis to compensate for one or more components of forces acting on the foot. Forces selected for compensation include gravitational forces as well as external forces such as ground reaction forces. Techniques are provided for determining an ankle joint torque for partial or complete compensation of forces acting on the foot about an axis of rotation. The provided techniques mitigate the amount of interference between voluntary control and assist control, thereby allowing humans to quickly humans adapt to an exoskeleton system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
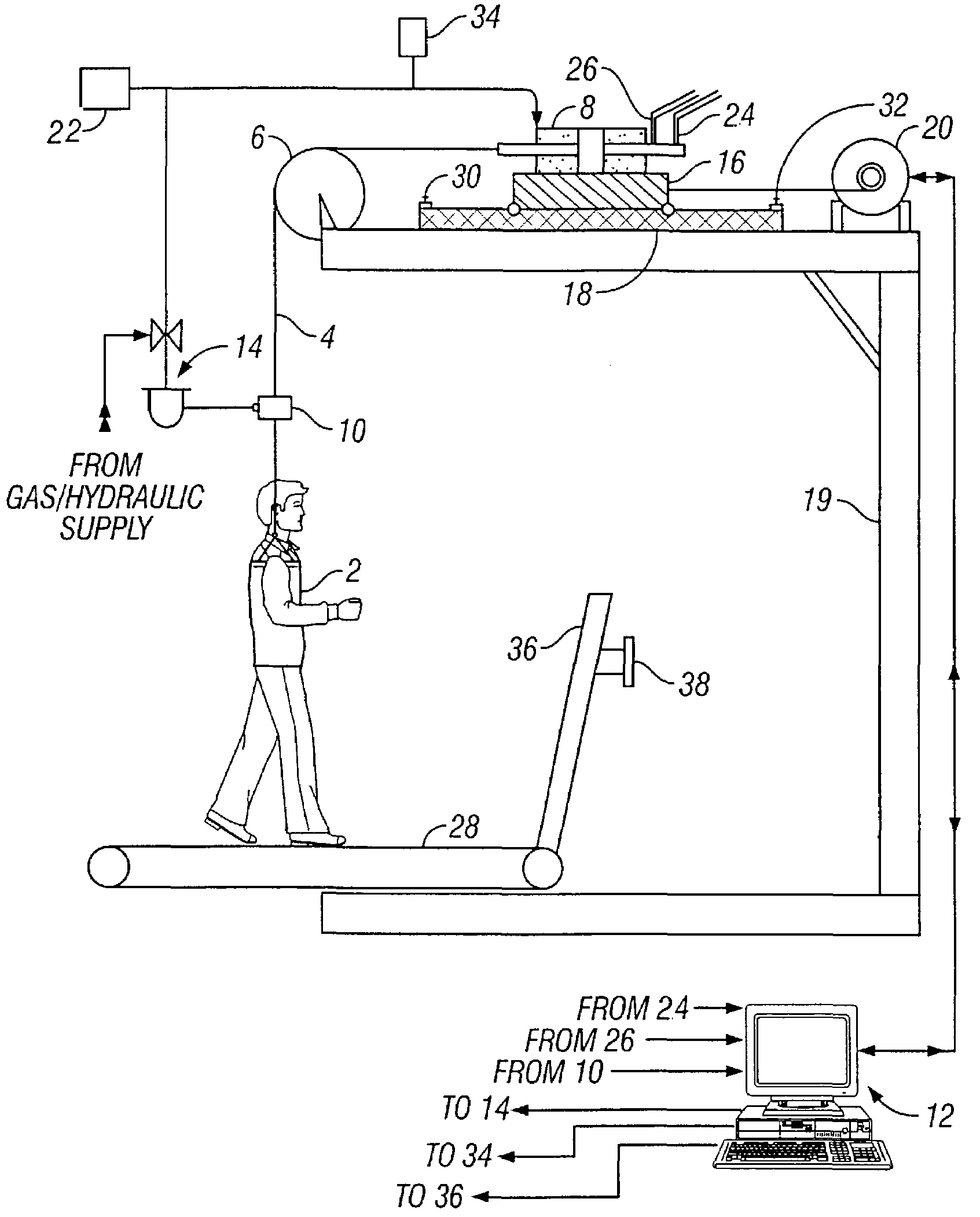
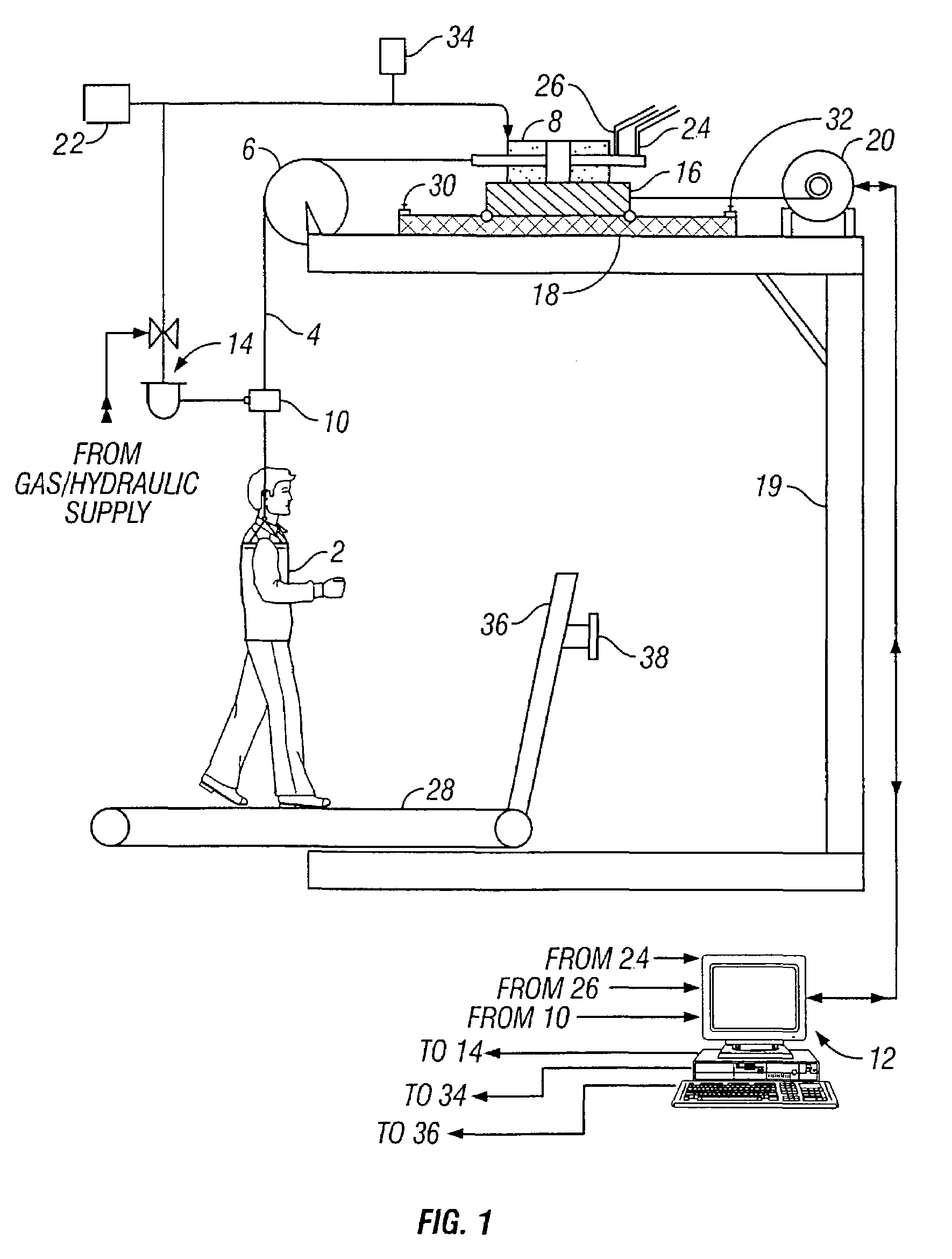
Closed-loop force controlled body weight support system
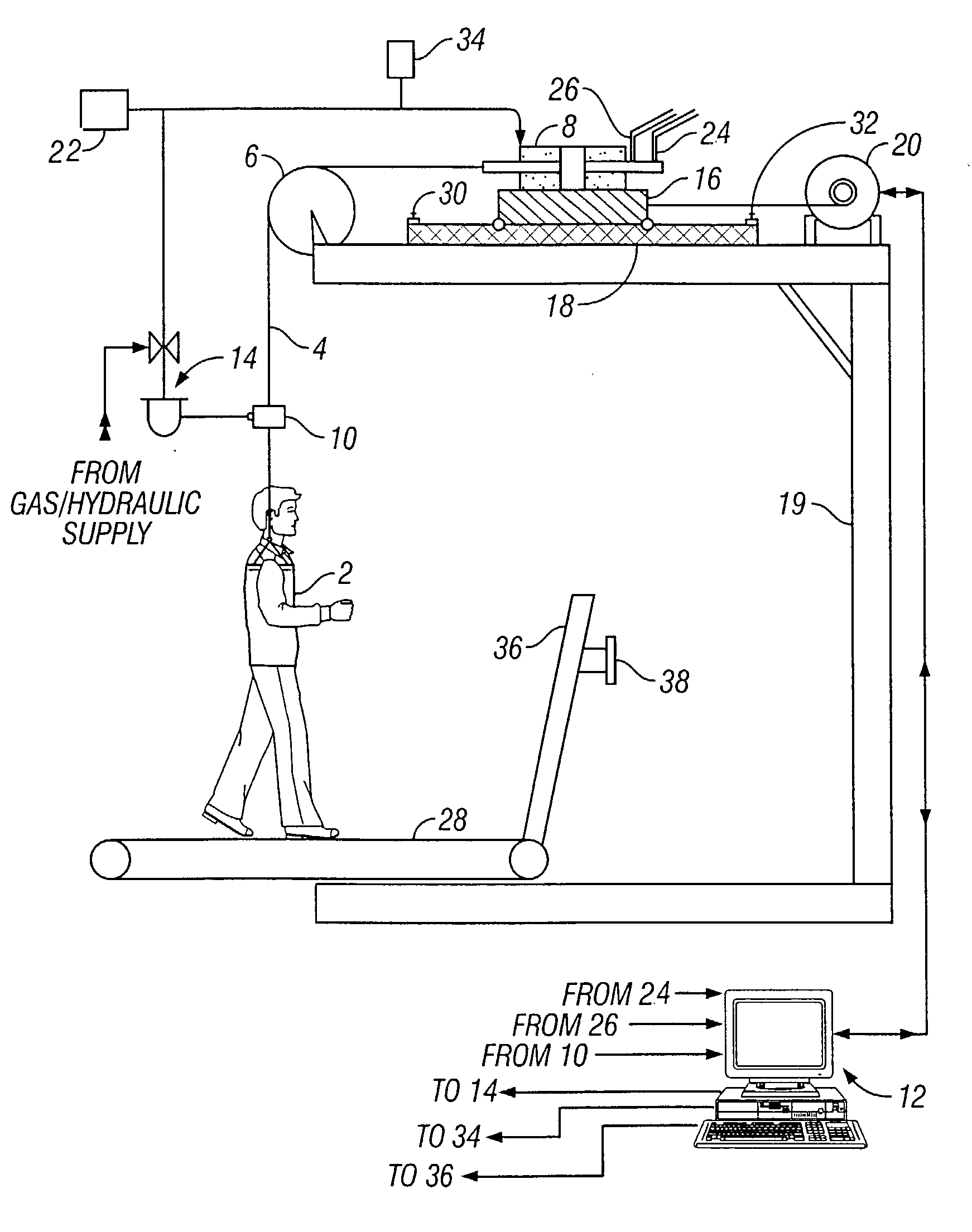
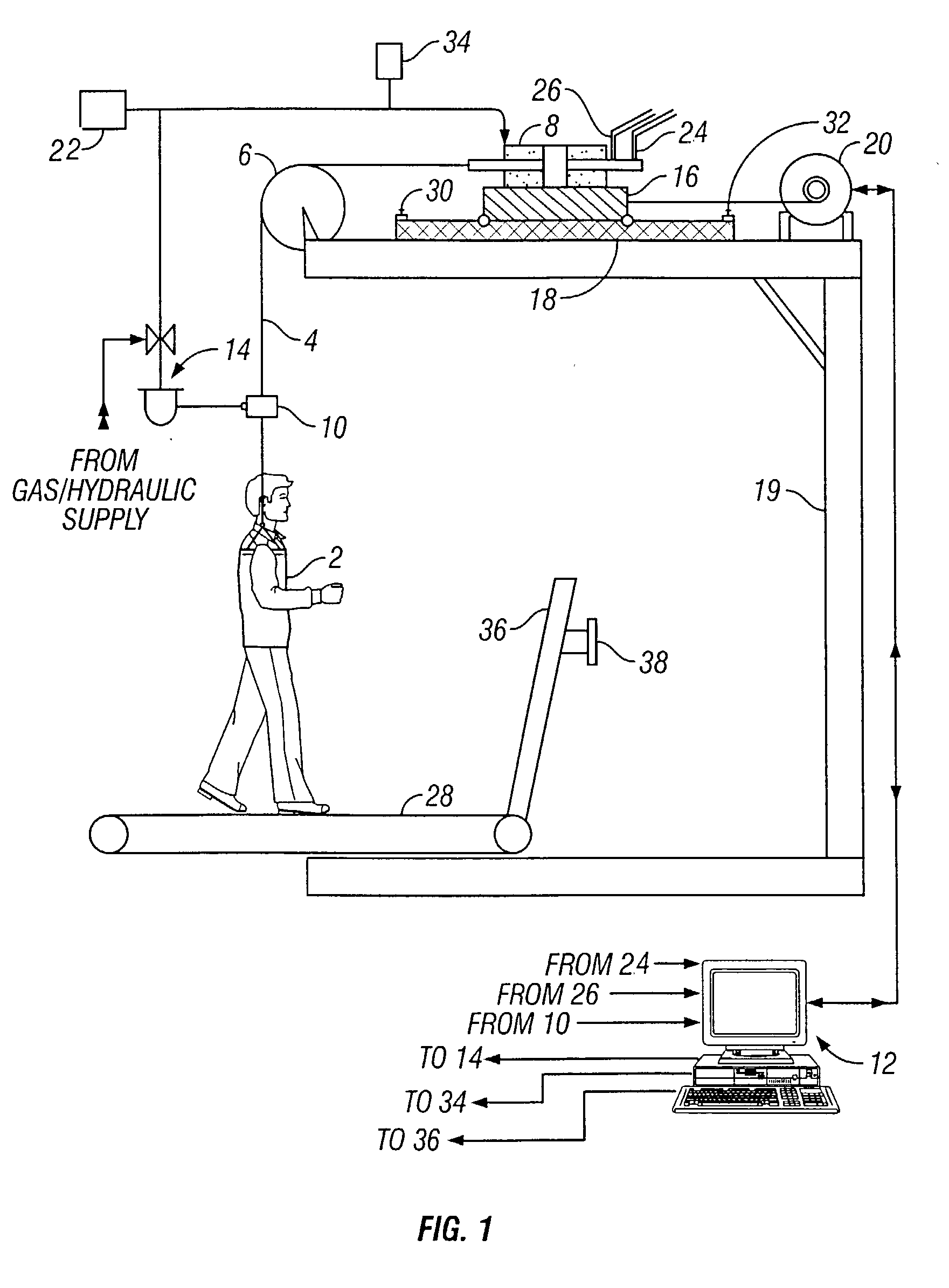
A body weight support system that monitors and controls the level of support force within a stepcycle to result in normative center of mass movement and ground reaction forces. The system comprises a harness connected to a lift line which in turn is connected to a means for advancing and retracting the lift line. A control system is configured to monitor load on the cable and to regulate lift line advancement and retraction in response to load information. The support system can be combined with a treadmill for locomotor training of a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Measuring forces in athletics
InactiveUS20070068244A1Accurate impactHigh sampling frequencyStructural/machines measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerEngineering
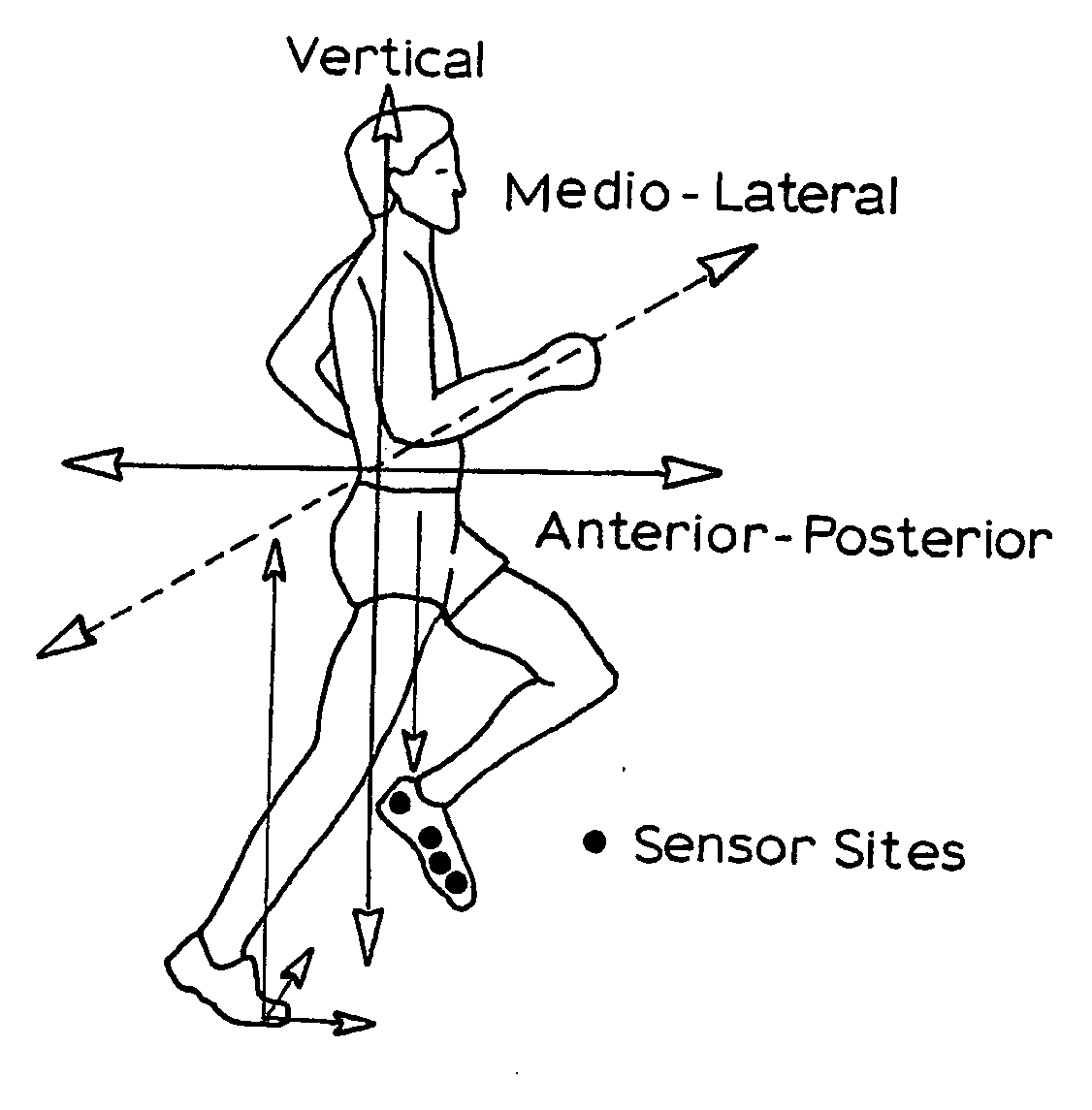
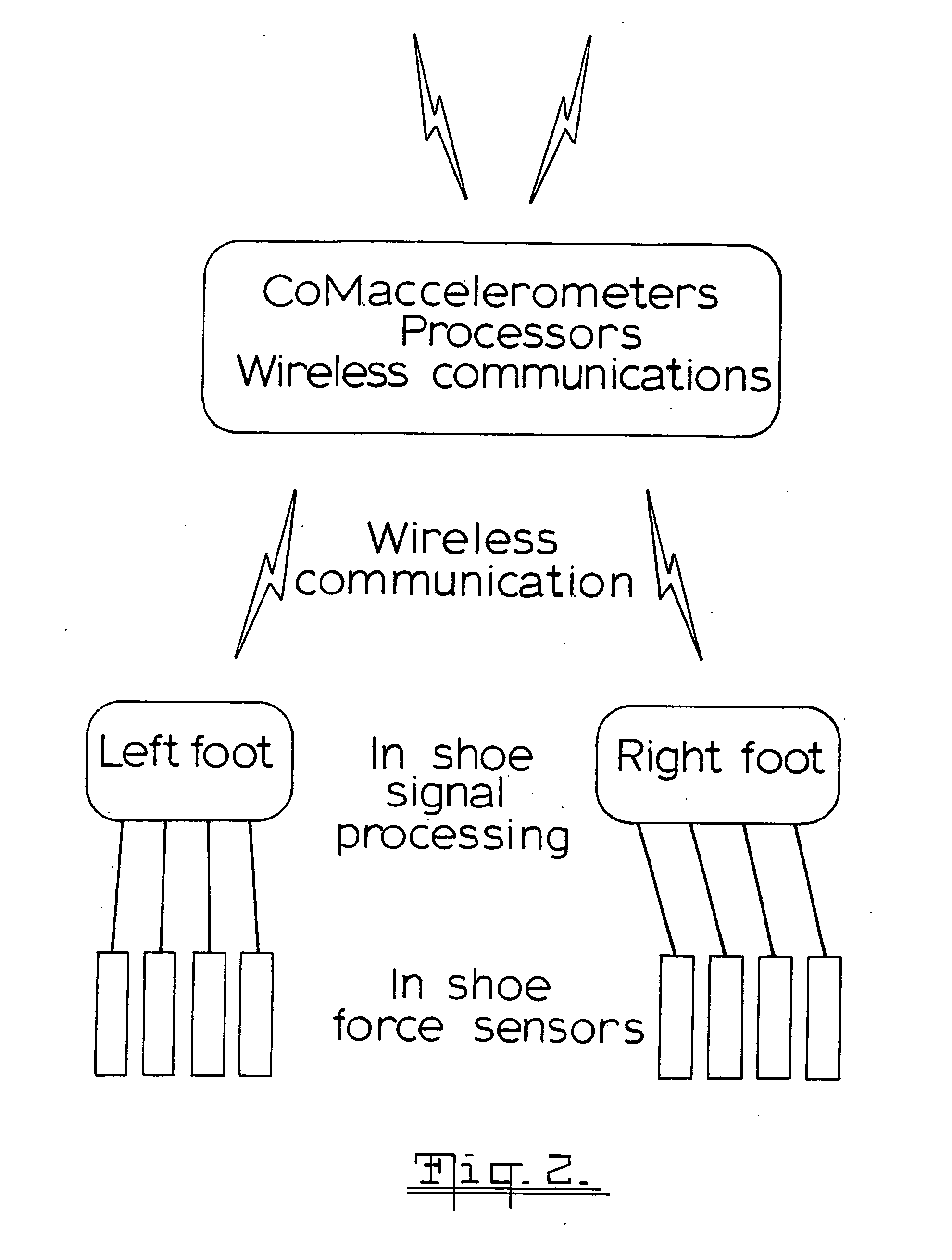
A system for measuring ground reaction force and analyzing the performance of an athlete in which force sensors are located in the athletes shoe and a three dimensional accelerometer is located adjacent the athletes centre of gravity and the signals from the accelerometer and the force sensors are recorded and used to derive the three orthogonal components of the ground reaction force (GRF). An artificial neural network is used to derive the three orthogonal components of GRIF
Owner:M B T L
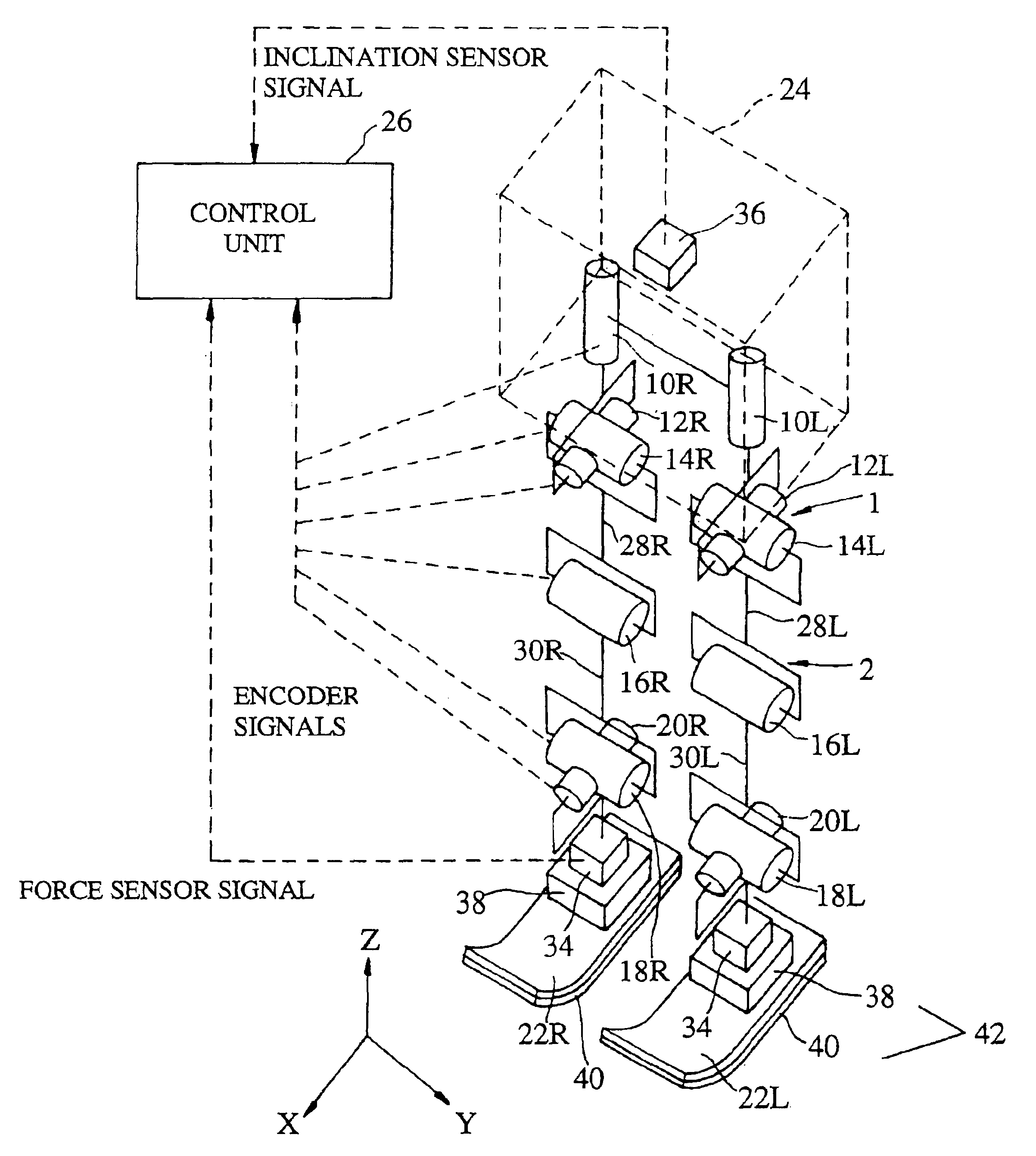
Attitude control device of mobile robot
InactiveUS7112938B2Maintain dynamic balancePostural stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlControl systemDynamic balance
A posture control system for a mobile robot. When an unexpected external force acts, the system is configured to control and stabilize the posture of the robot driving an arm link such that, in response to a first external force that is a component in a predetermined direction of an unexpected external force, a second external force acts on the arm link in a direction orthogonal to the predetermined direction. With this, when the mobile robot receives a reaction force, even if the posture becomes unstable or the robot receives an unexpected reaction force, it becomes possible to preserve the dynamic balance and to maintain a stable posture.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Four-leg robot mechanism based on bionic design
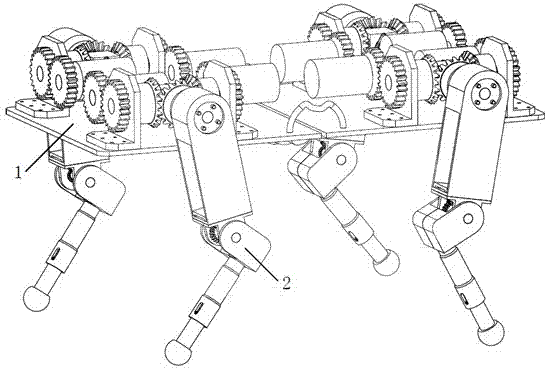
The invention relates to a four-leg robot mechanism based on a bionic design. The four-leg robot mechanism consists of a body frame and four legs. The body frame consists of a front plate and a rear plate, two sides of the body frame are provided with flexible handles, and the robot mechanism is convenient to convey; each leg comprises a hip, a huckle, a knee and a crural part; the hip realizes two freedom degrees by adopting a differential bevel gear; the hip and the huckle are connected by an expansion sleeve to realize fast and convenient assembly and disassembly; the bevel gear drive motion is adopted by the knee; the crural part comprises a large cylinder, a small cylinder, a conical spring and a force sensor; and the large cylinder and the small cylinder are connected through the conical spring, so that the external impact force generated in the walking process of the robot can be buffered, the force sensor on a sole can acquire ground acting force, and the external environment can be conveniently sensed in real time and the robot can be subjected to balanced control conveniently. Through the bionic design idea, a spinal cord and a flexible foot mechanism of the robot are stimulated and designed, the flexibility of the robot movement is improved, the impact of the ground to the robot is reduced, and the robot mechanism has a compact structure and is convenient to install.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Controller of legged mobile robot
InactiveUS20050110448A1Improve stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMobile robot controlDynamic models
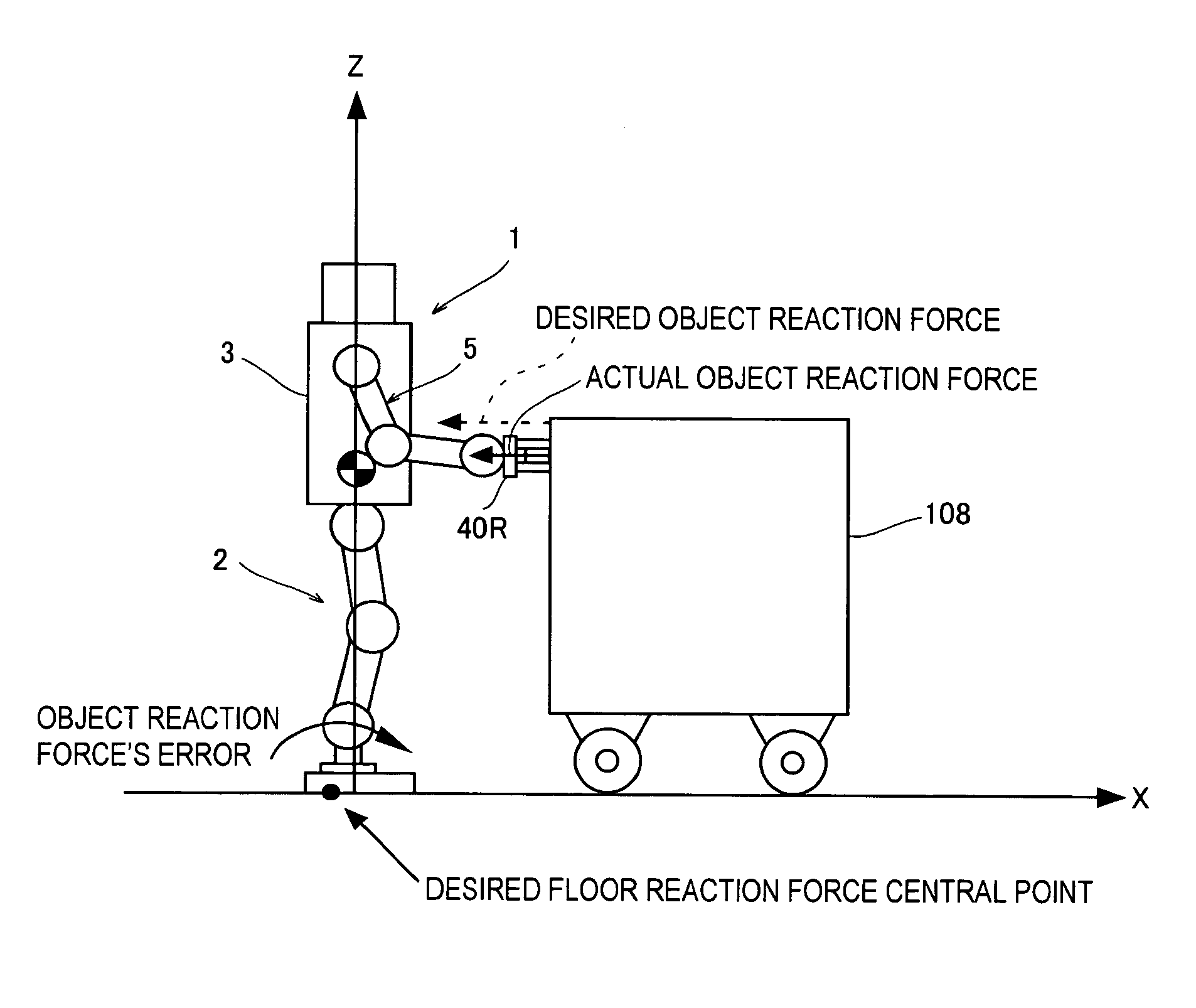
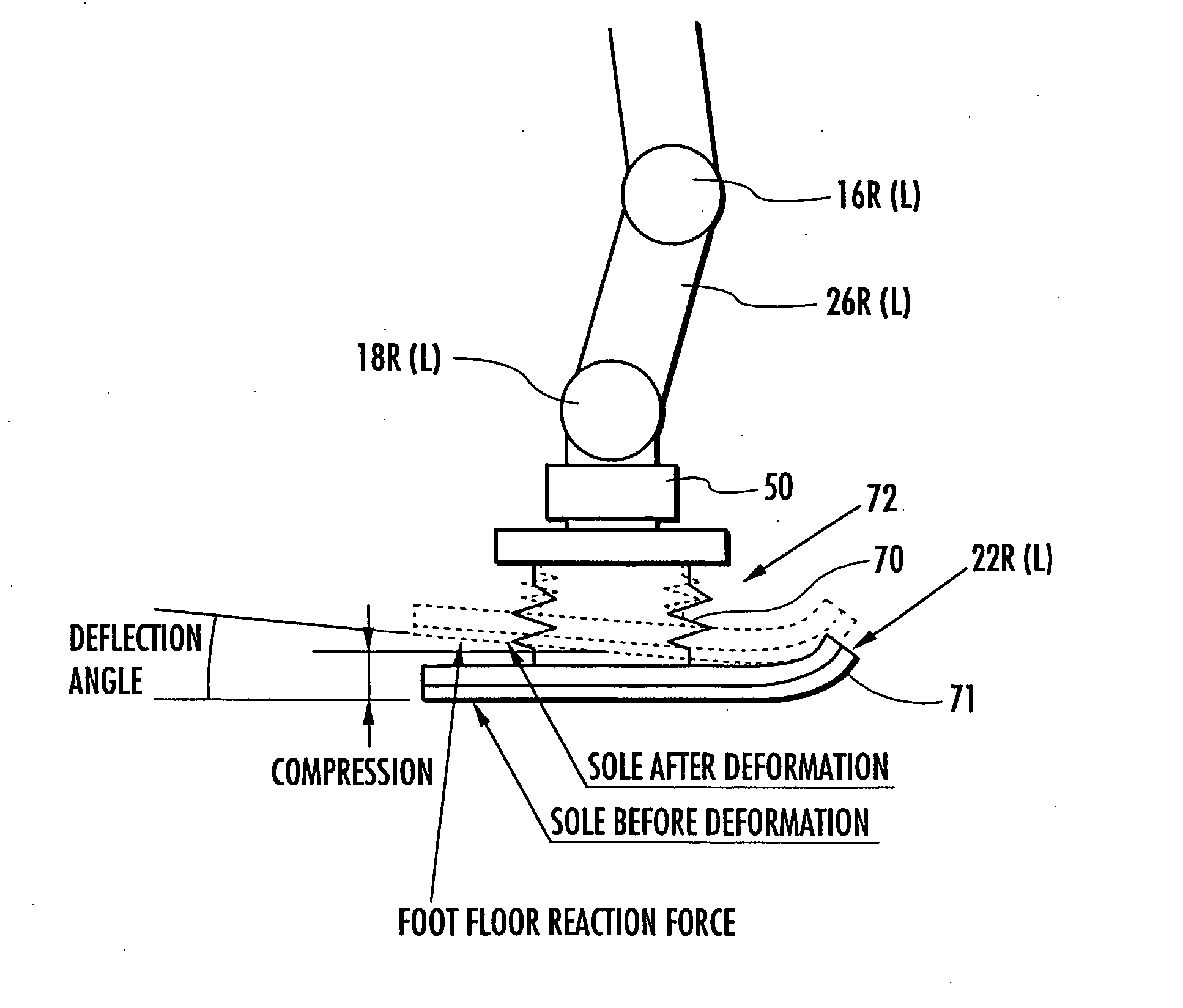
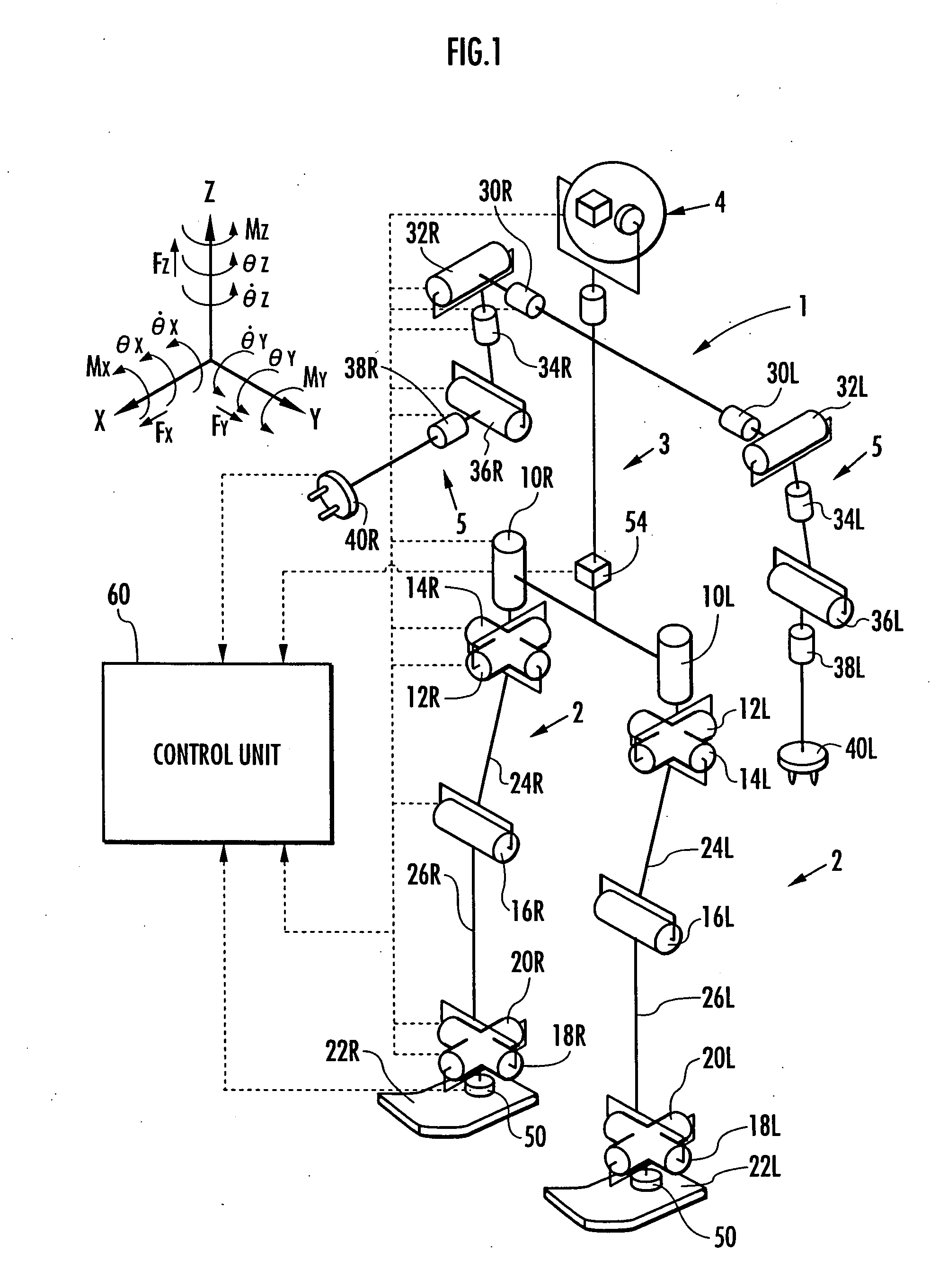
A control device for a legged mobile robot, in which a correction manipulated variable of a desired floor reaction force (desired floor reaction force's moment) is subsequently determined based on an error between an actual state quantity, such as a body posture angle, of the robot 1 and a desired state quantity of the same, and at the same time, a desired movement of the robot 1 is subsequently determined by the use of the correction manipulated variable and a dynamic model. At this time, a friction force component, which defines a frictional force between the robot 1 and a floor such as a translation floor reaction force's horizontal component, is set as a variable to be limited, and an allowable range of the variable to be limited is set. The desired movement is determined so that the variable to be limited remains within the allowable range and a resultant force of an inertial force and gravity, generated by the movement of the robot 1 on the dynamic model, balances with a floor reaction force obtained by correcting the desired floor reaction force by the correction manipulated variable. The desired movement is determined by adjusting a plurality of movement modes having mutually different generation ratios of a floor reaction force's moment and a translation floor reaction force.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
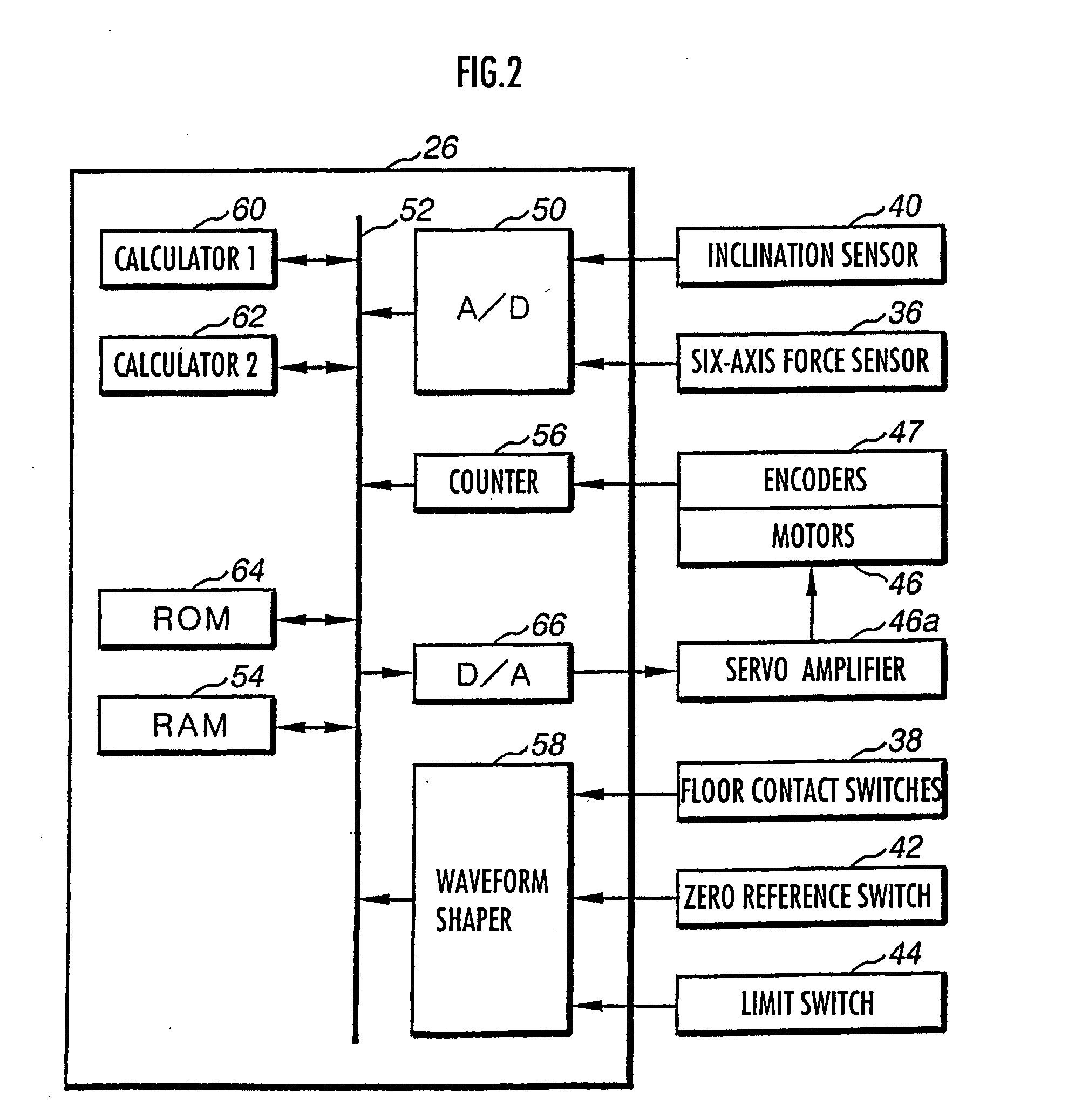
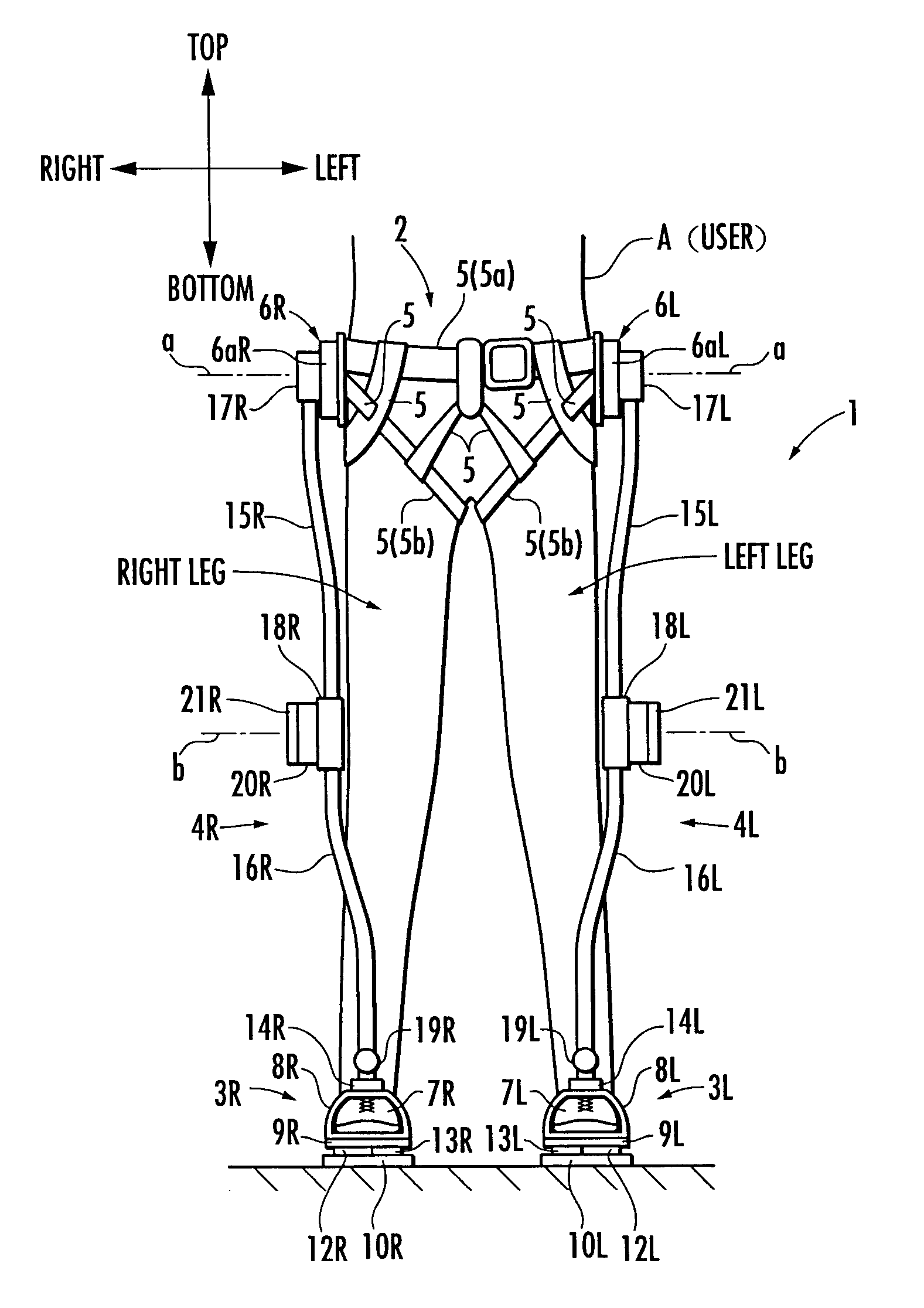
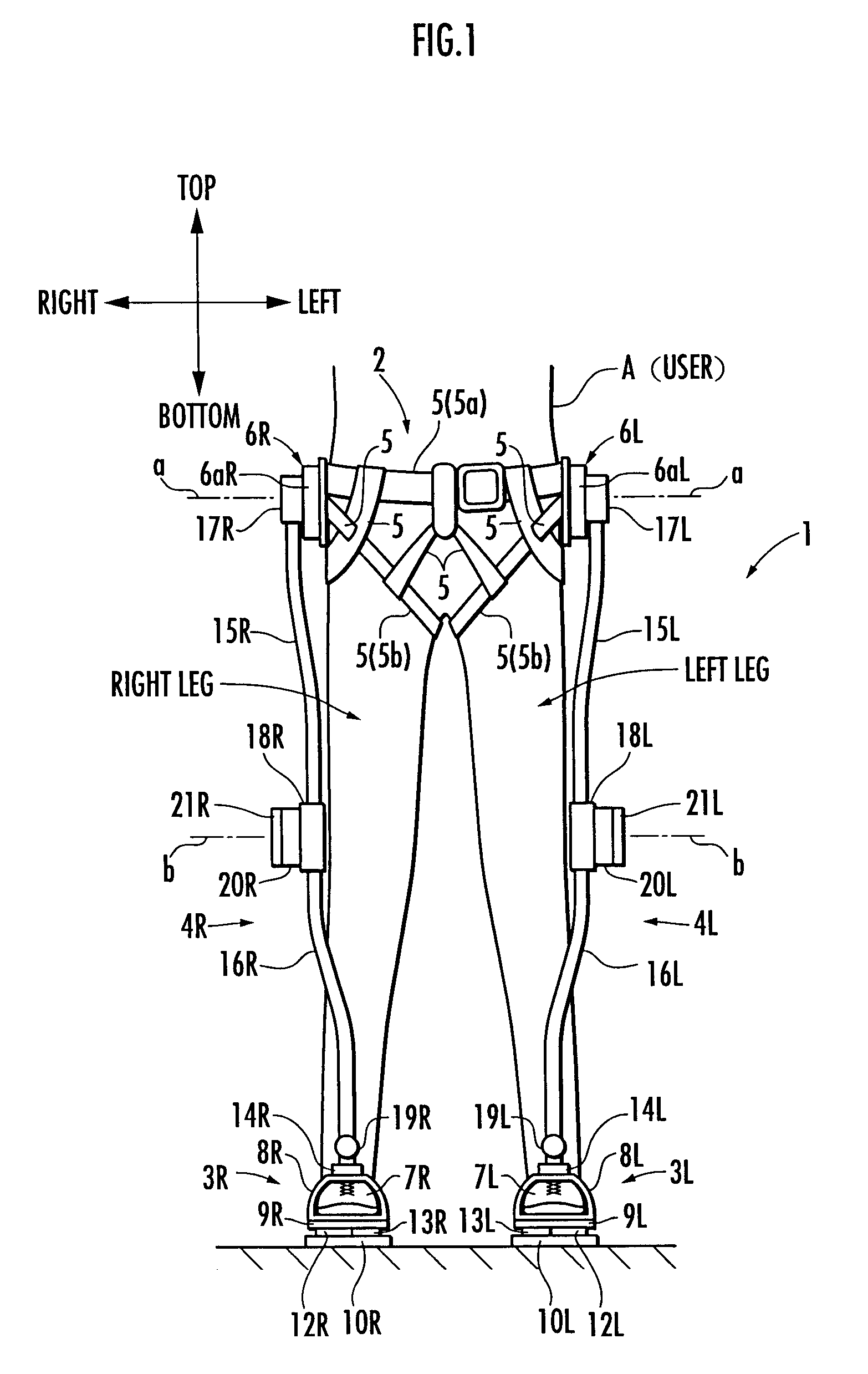
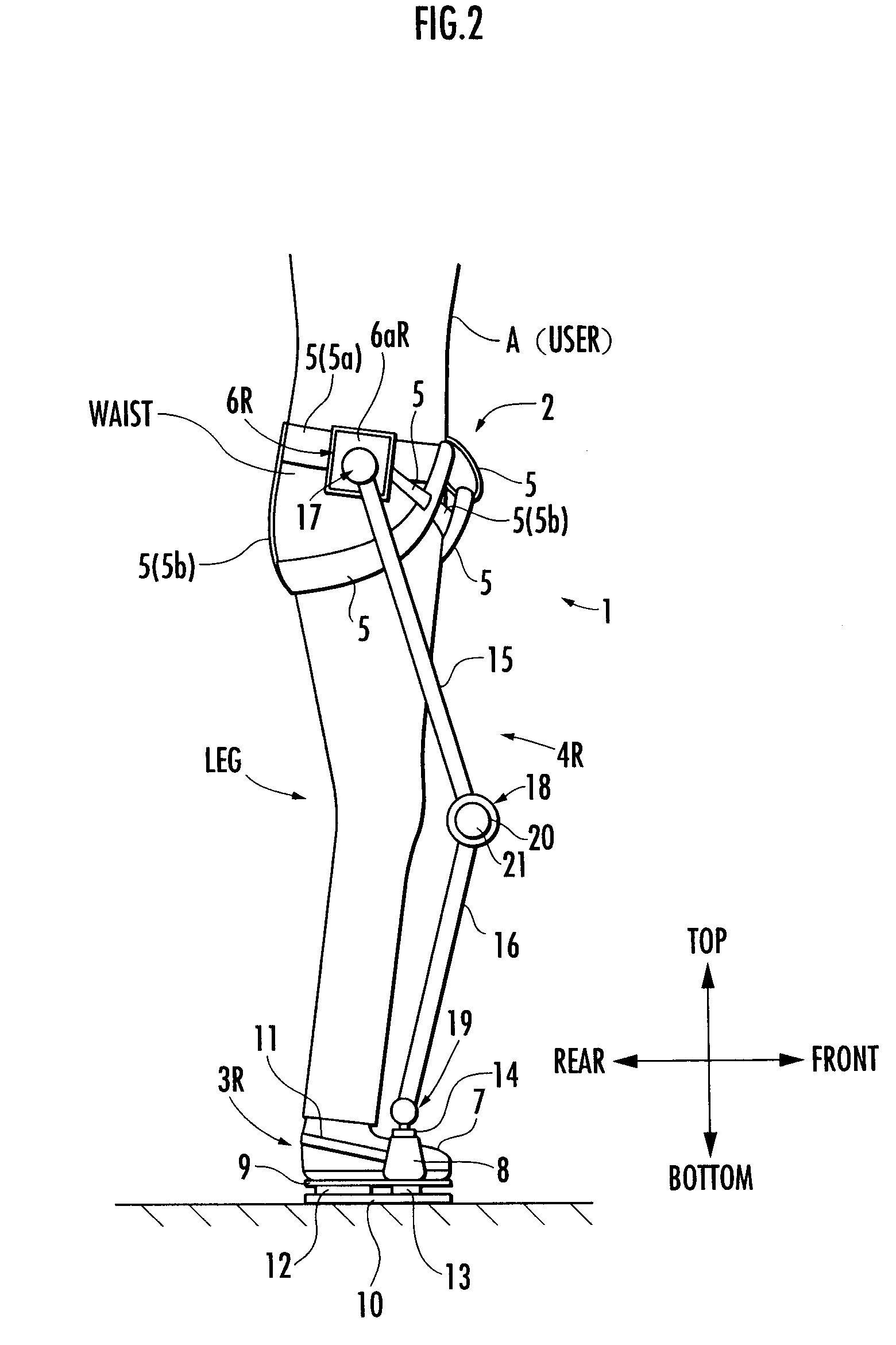
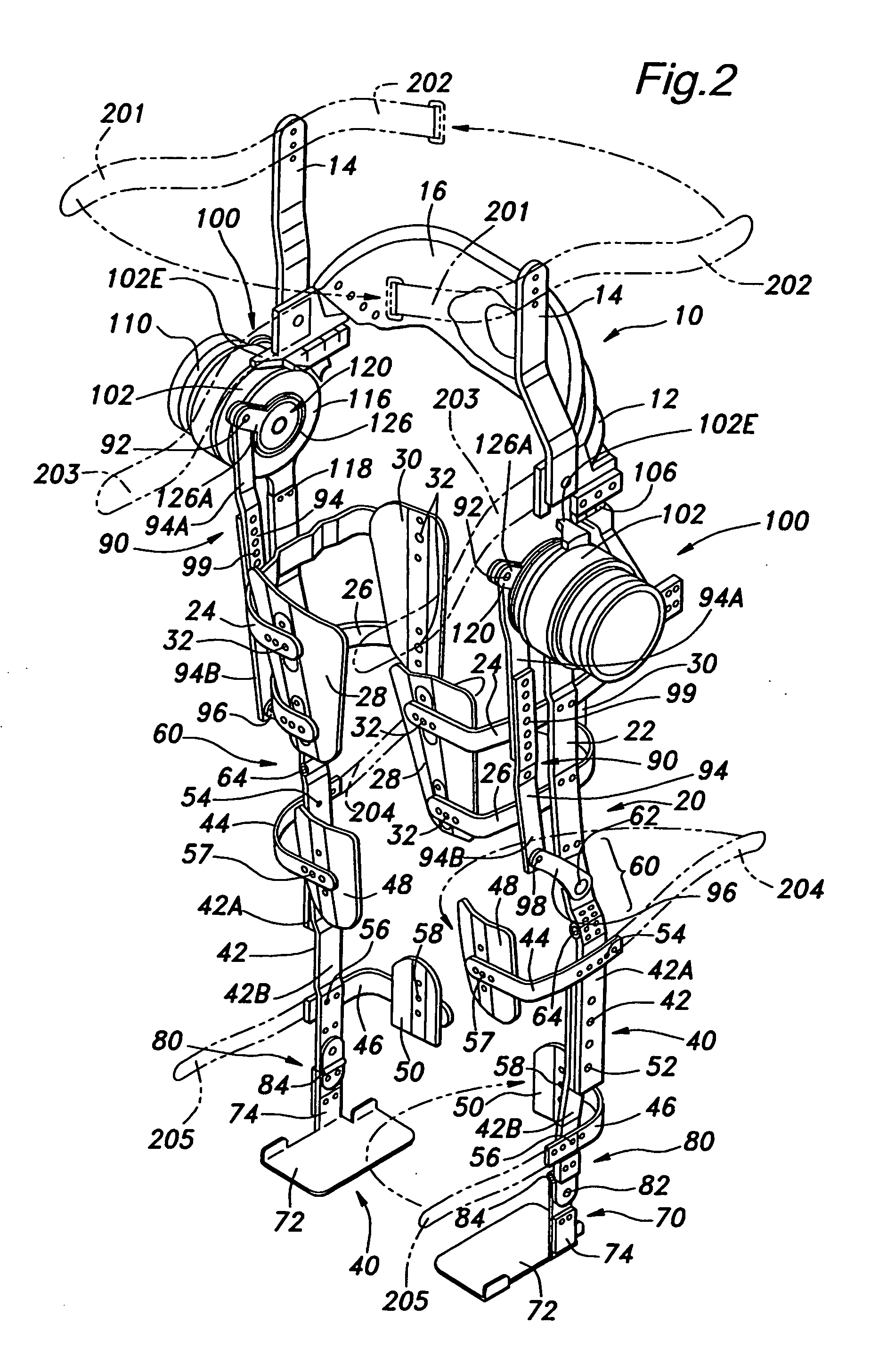
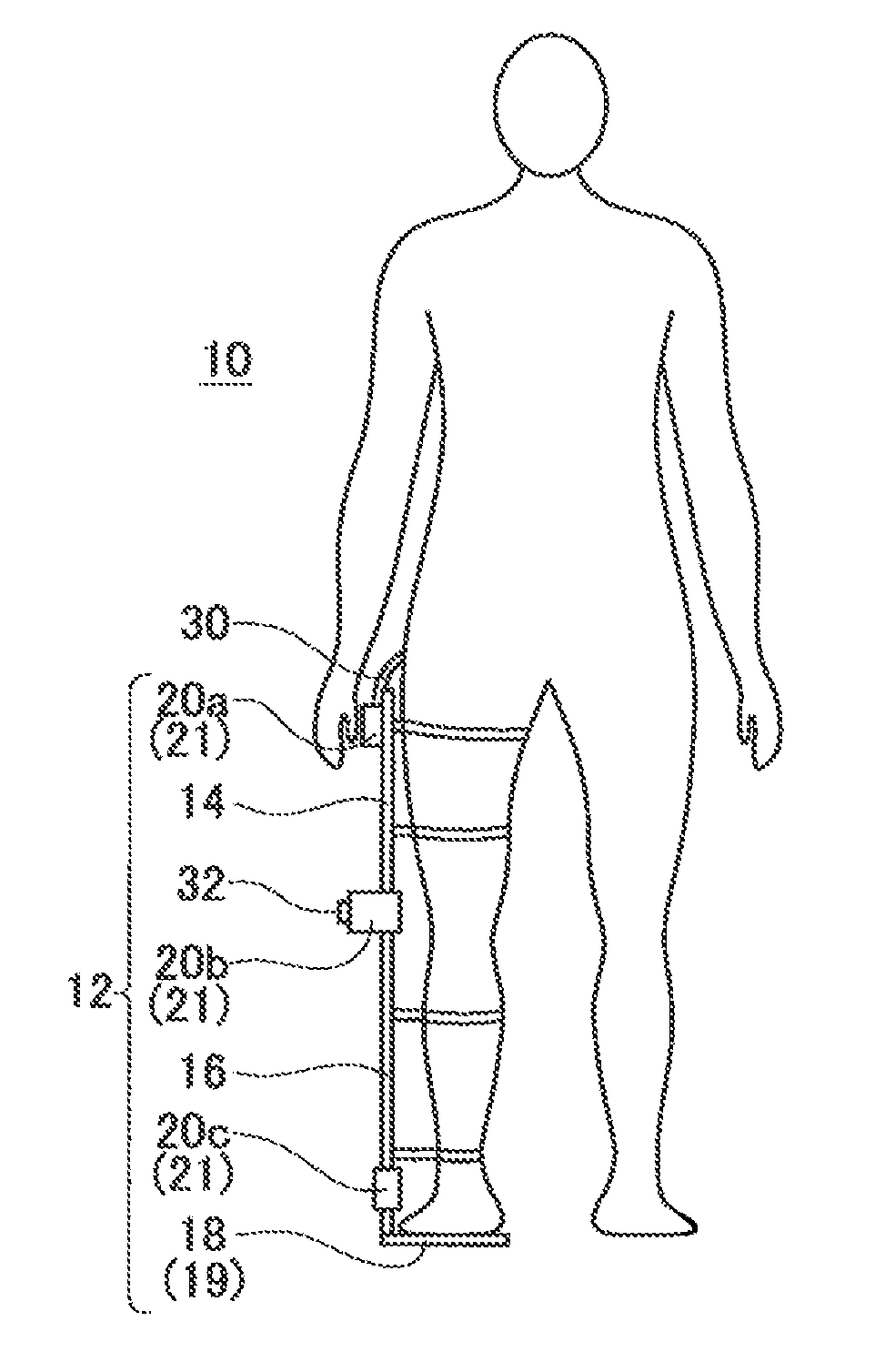
Walking assistance device
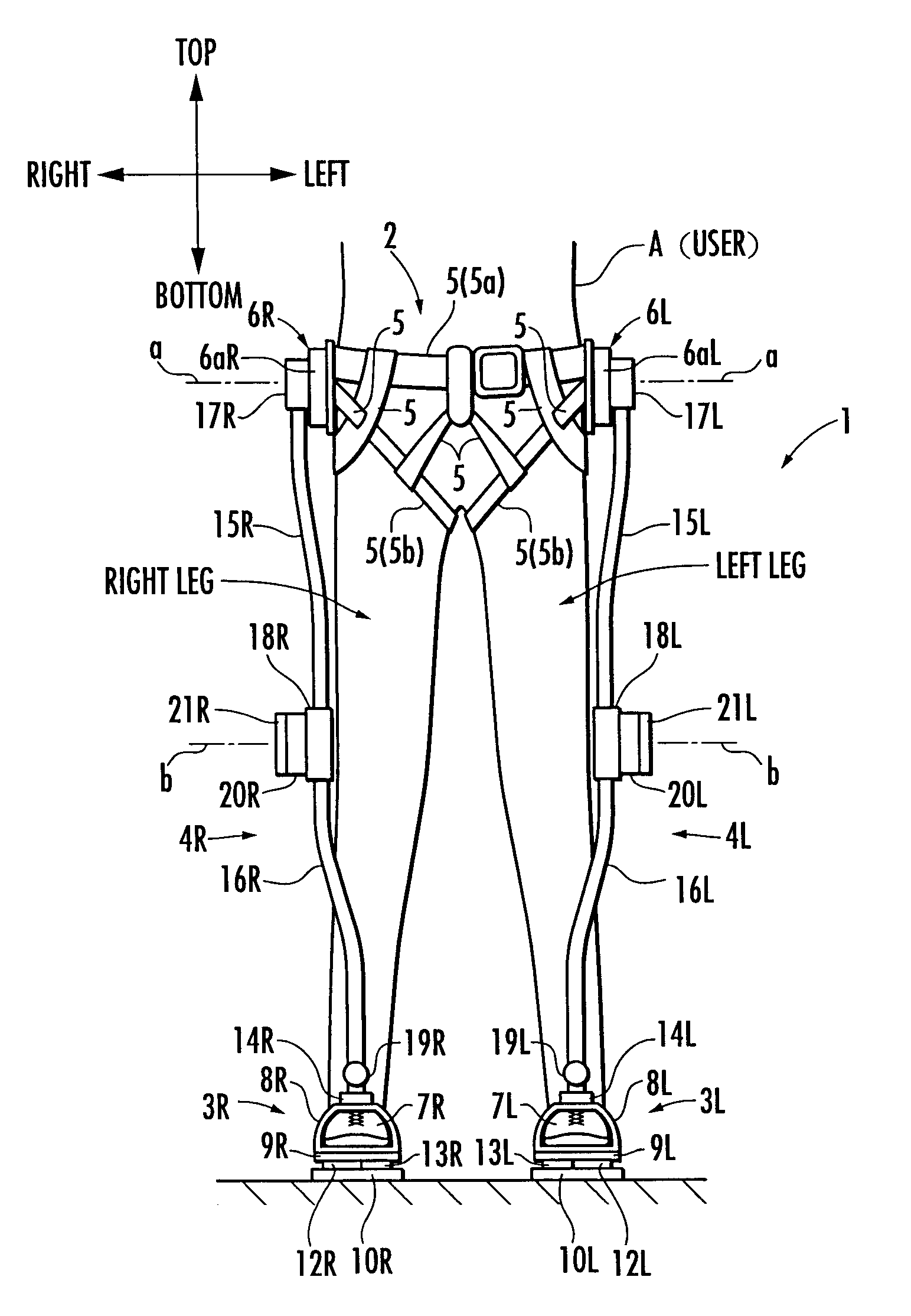
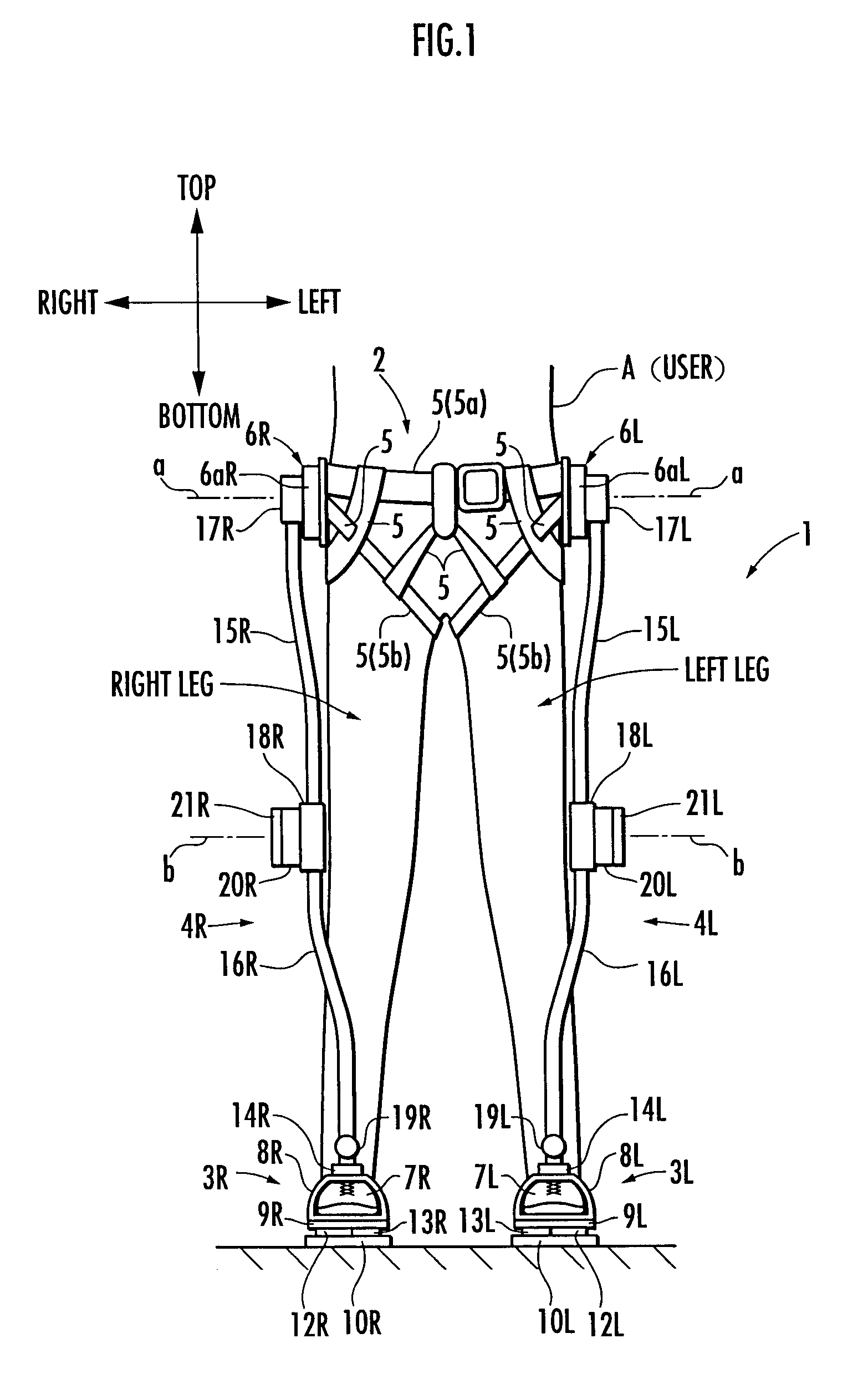
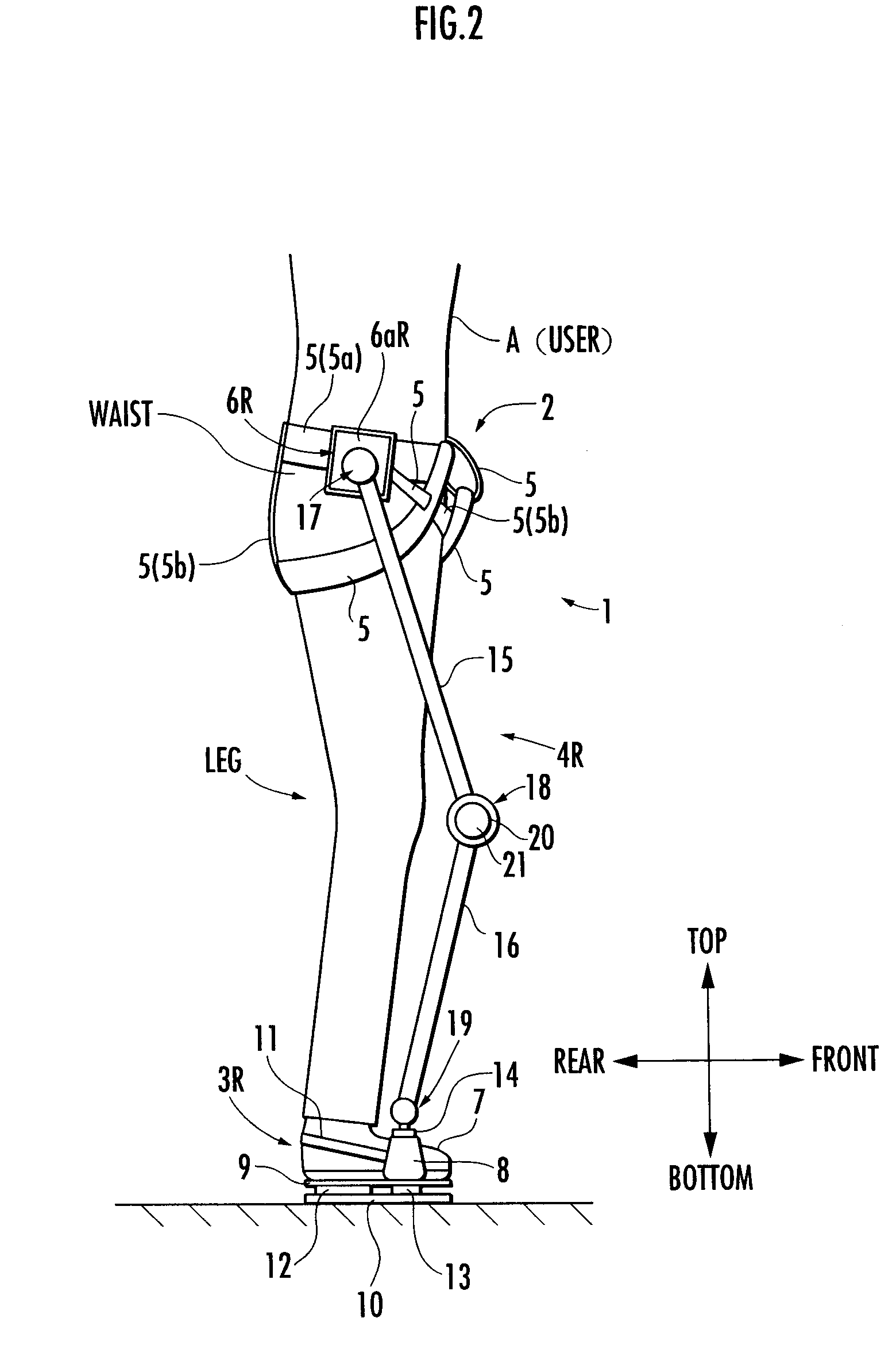
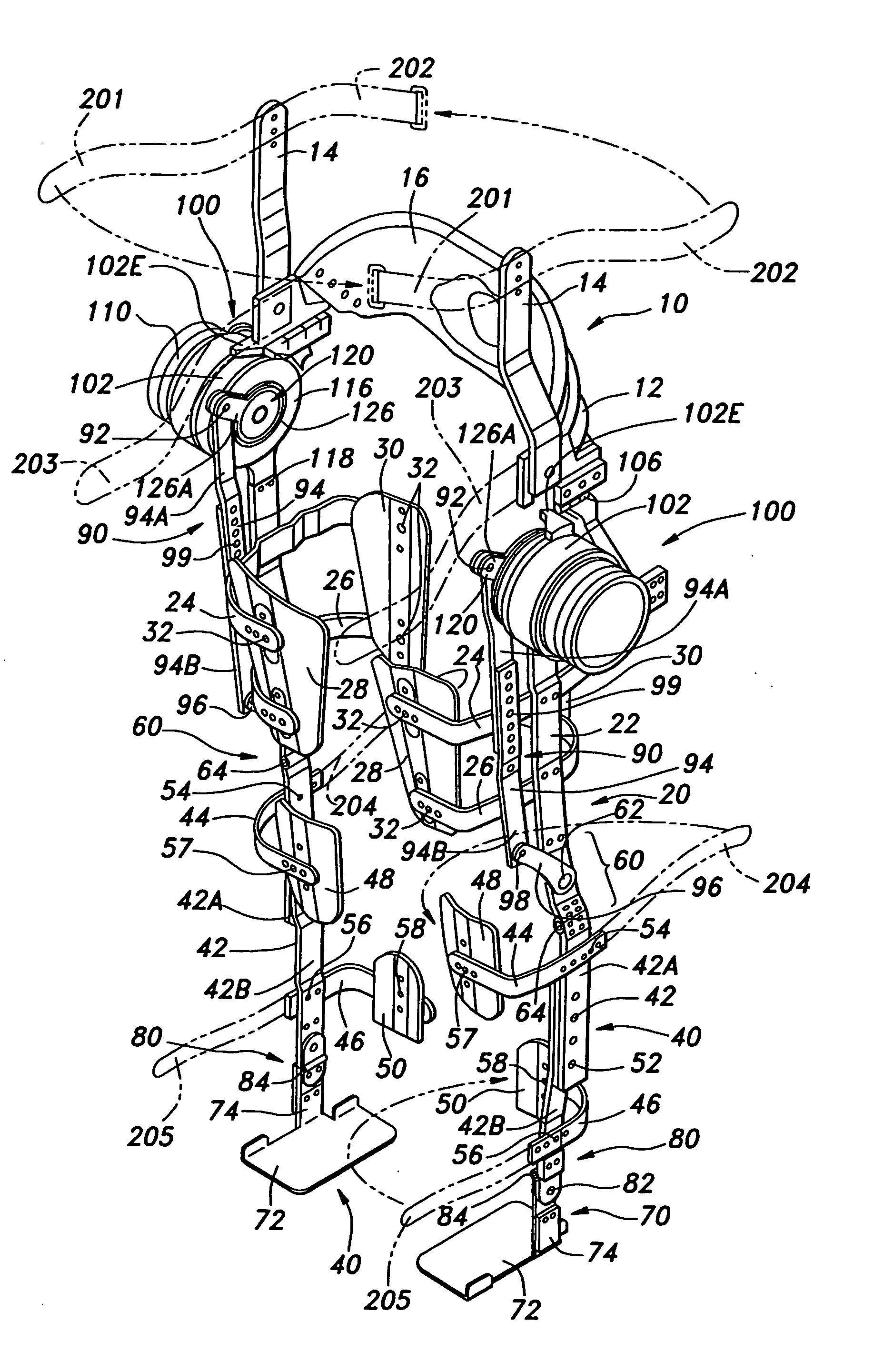
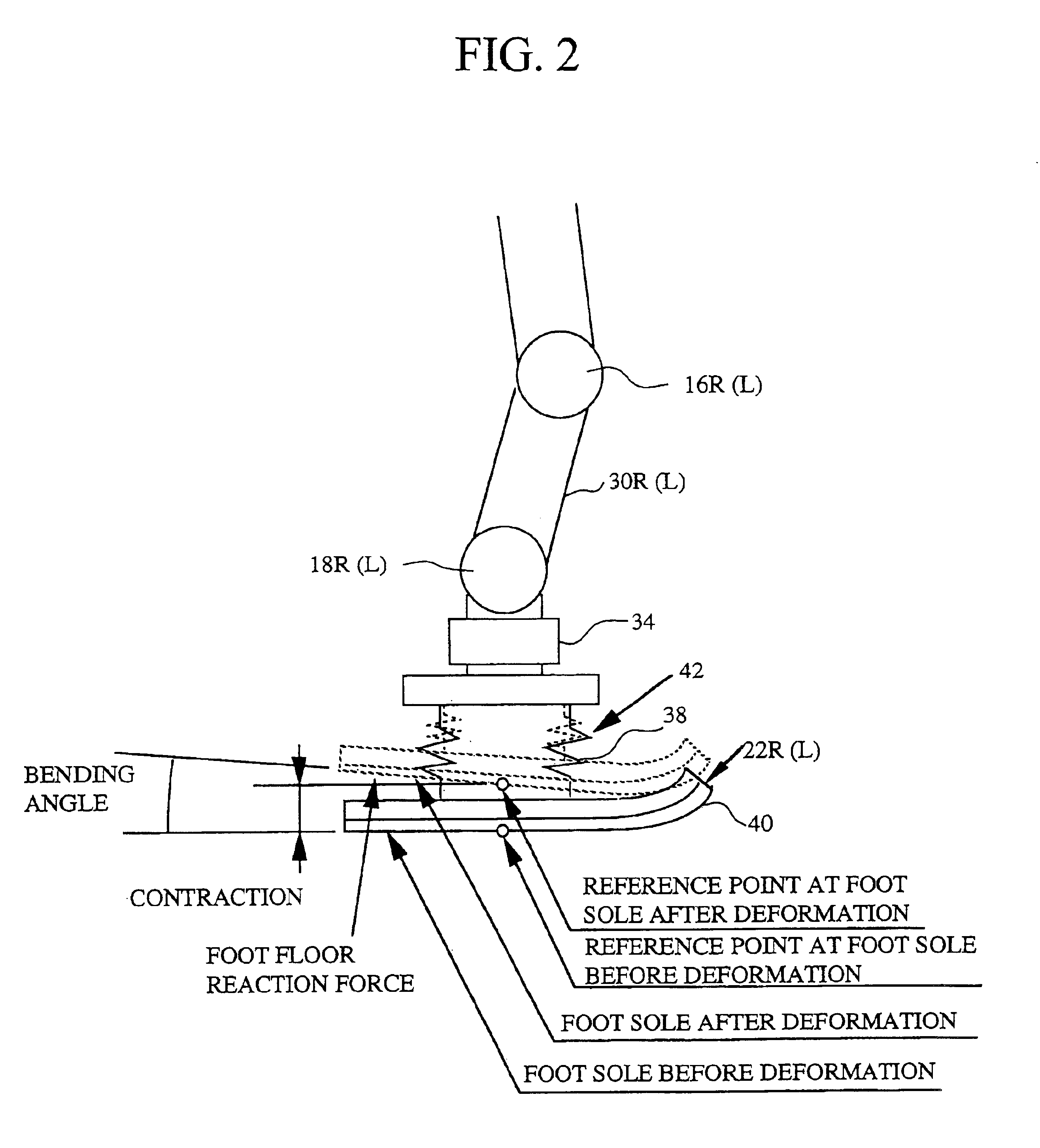
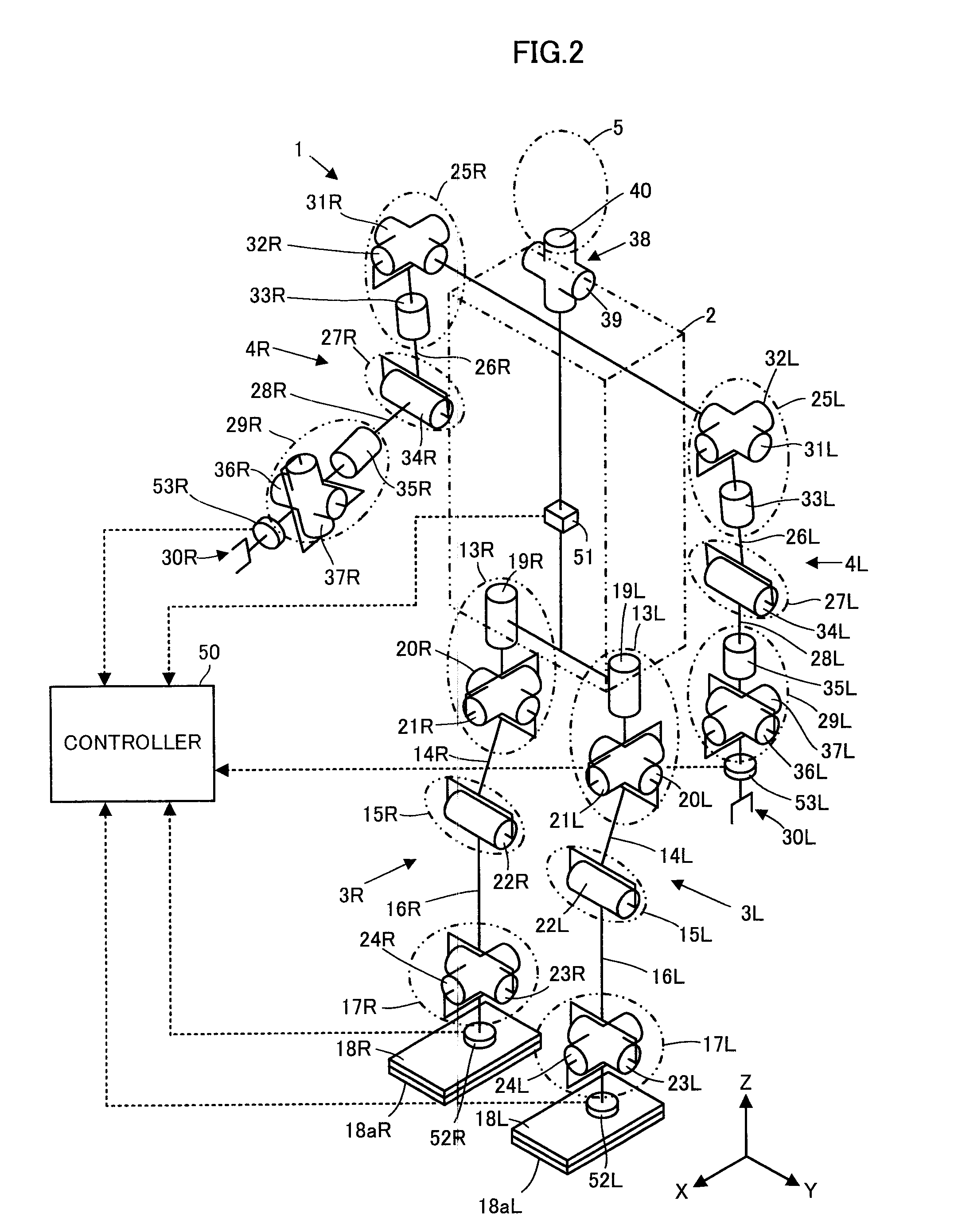
A walking assistance device (1) has a body-mounted assembly (2) installed on the waist of a user (A), foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) installed on feet, and leg links (4L, 4R) which connect the foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) to the body-mounted assembly (2). The foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) are provided with floor reaction force sensors (13L, 13R). Results obtained by multiplying the absolute values of floor reaction force vectors (three-dimensional vectors) detected by the floor reaction force sensors (13L, 13R) by a predetermined ratio are defined as target values of the magnitudes of the supporting forces transmitted to the leg links (4L, 4R) from the foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R). Actuators (20L, 20R) of the leg links (4L, 4R) are controlled such that the supporting forces having the magnitudes of the target values act on the leg links (4L, 4R) from the foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) through the intermediary of joints (19L, 19R).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Energy translating footwear mechanism for enhancing forward
InactiveUS20070283599A1Technique is effectiveEfficiently displacedSolesInsolesFoot strikeMuscular tension
Owner:MULLEN KRISTYNA +3
Walking assistance device
ActiveUS20090036815A1Reduce propulsion powerReduce loadChiropractic devicesWalking aidsEngineeringGround reaction force
A walking assistance device (1) has a body-mounted assembly (2) installed on the waist of a user (A), foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) installed on feet, and leg links (4L, 4R) which connect the foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) to the body-mounted assembly (2). The foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) are provided with floor reaction force sensors (13L, 13R). Results obtained by multiplying the absolute values of floor reaction force vectors (three-dimensional vectors) detected by the floor reaction force sensors (13L, 13R) by a predetermined ratio are defined as target values of the magnitudes of the supporting forces transmitted to the leg links (4L, 4R) from the foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R). Actuators (20L, 20R) of the leg links (4L, 4R) are controlled such that the supporting forces having the magnitudes of the target values act on the leg links (4L, 4R) from the foot-mounted assemblies (3L, 3R) through the intermediary of joints (19L, 19R).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Impact resistant structure for the helicopter and energy absorber used for the same
InactiveUS6959894B2Improve performanceHarmful initial load peak level is reducedPortable framesFuselage framesNacelleEngineering
An impact resistant structure of a helicopter having an energy absorber positioned under a floor of the helicopter and directly connected to a cabin frame of the helicopter. The energy absorber is arranged in accordance with a distribution of a ground reaction force on a general ground at a time of crash situation. The energy absorber also includes a plurality of independent hollow tubes of fiber reinforced composite material integrally formed by bundling only the hollow tubes. The hollow tubes are arranged so as to reduce a number of intersecting wall surfaces of the hollow tubes.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Closed-loop force controlled body weight support system
InactiveUS7381163B2Control fluctuationsRestrict levelComputer controlSimulator controlSupporting systemControl system
A body weight support system that monitors and controls the level of support force within a stepcycle to result in normative center of mass movement and ground reaction forces. The system comprises a harness connected to a lift line which in turn is connected to a means for advancing and retracting the lift line. A control system is configured to monitor load on the cable and to regulate lift line advancement and retraction in response to load information. The support system can be combined with a treadmill for locomotor training of a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
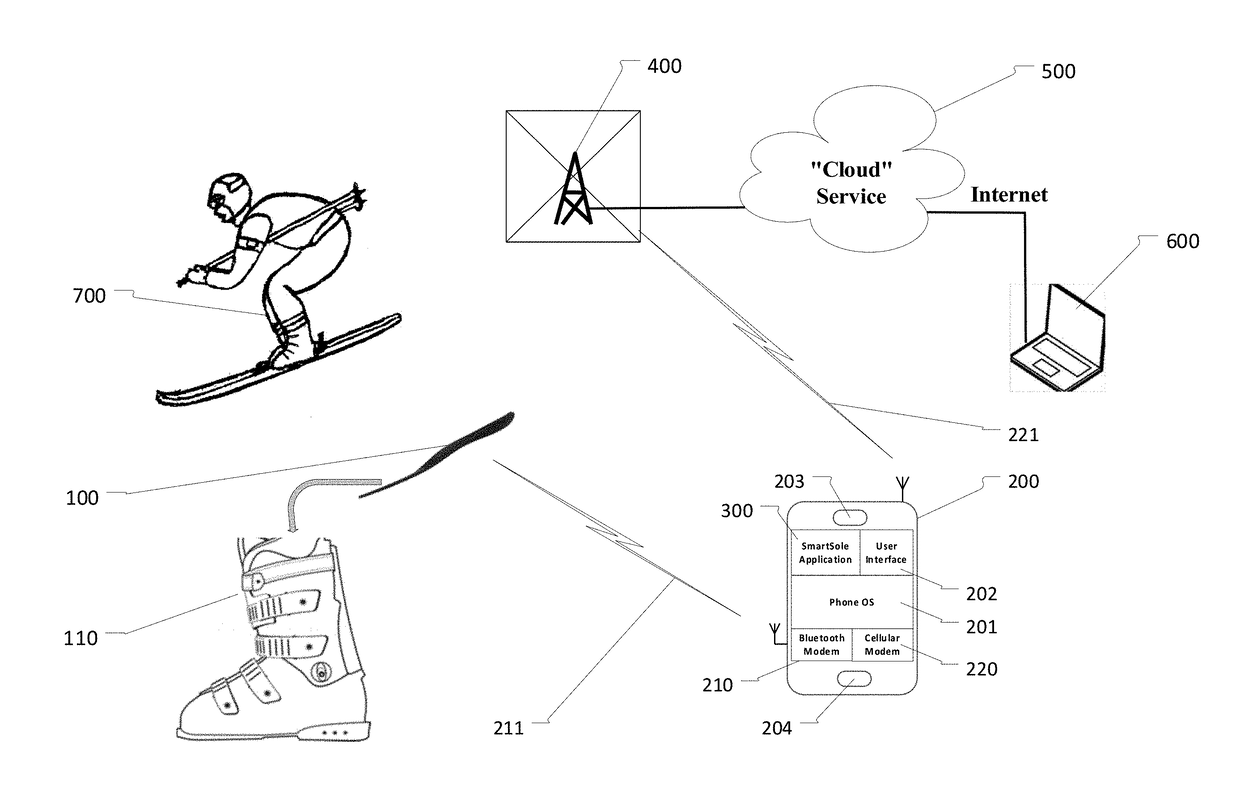
Method and Apparatus for Analysis of Gait and to Provide Haptic and Visual Corrective Feedback
InactiveUS20170225033A1Improve performancePhysical therapies and activitiesInsolesTouch PerceptionEngineering
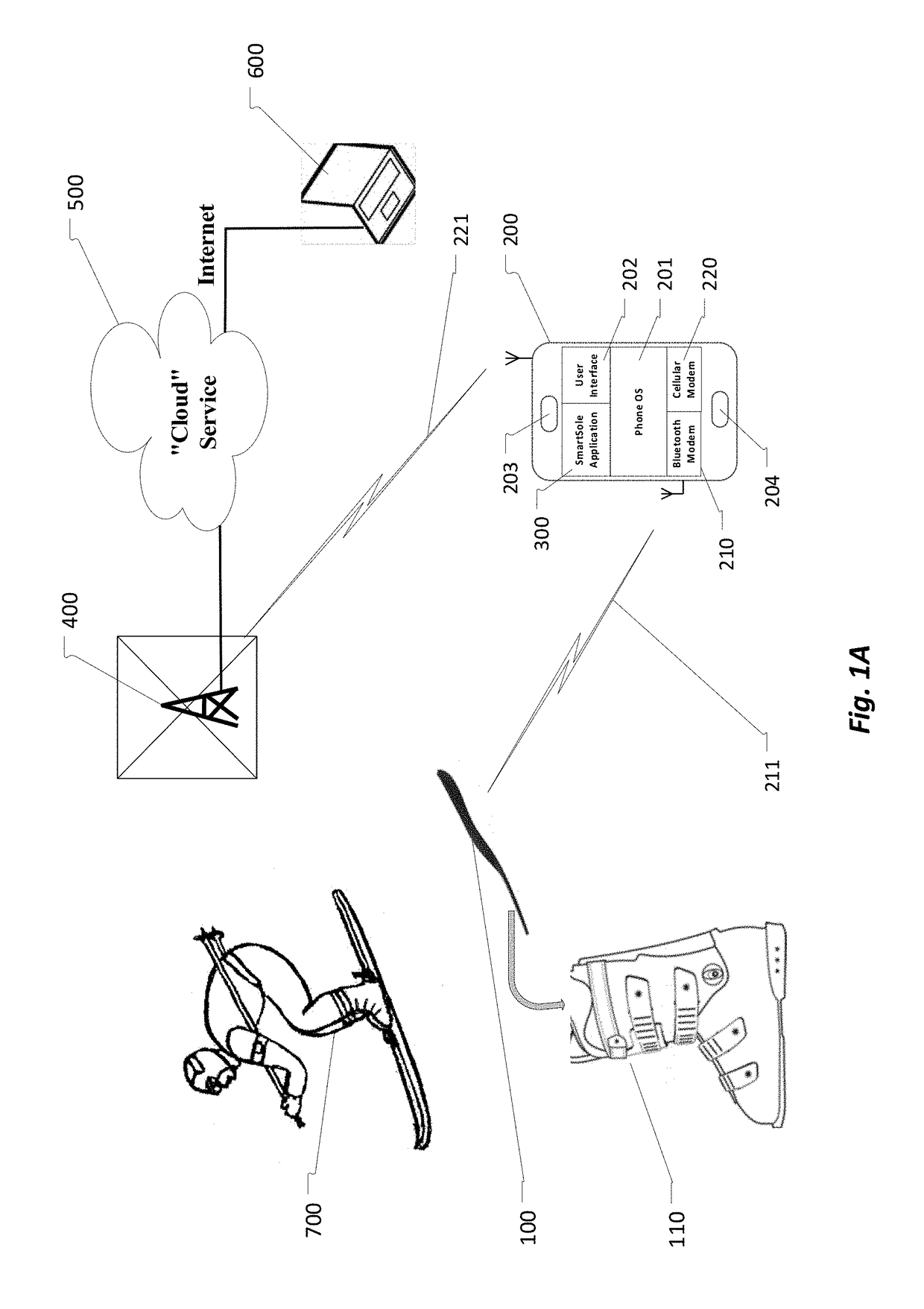
A system for analysis of user gait and to provide correction in form of haptic and visual feedback. This system comprises a motion and force sensors and a haptic actuator embedded in the user shoe insoles in communication with a smart-phone based analysis application, configured to calculate motion and orientation of the user feet in relation to the value, location and distribution of ground reaction forces measured by sensors located in the shoe insoles and after analysis of said forces and motion, to provide haptic feedback to the user foot instructing about the location (and timing) of pressure the user must apply to achieve an optimal gait.
Owner:IPCOMM
Rehabilitation device and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20100076360A1Effective walking trainingPromotes reconstruction of cerebral tissueElectroencephalographyPerson identificationControl objectiveEngineering
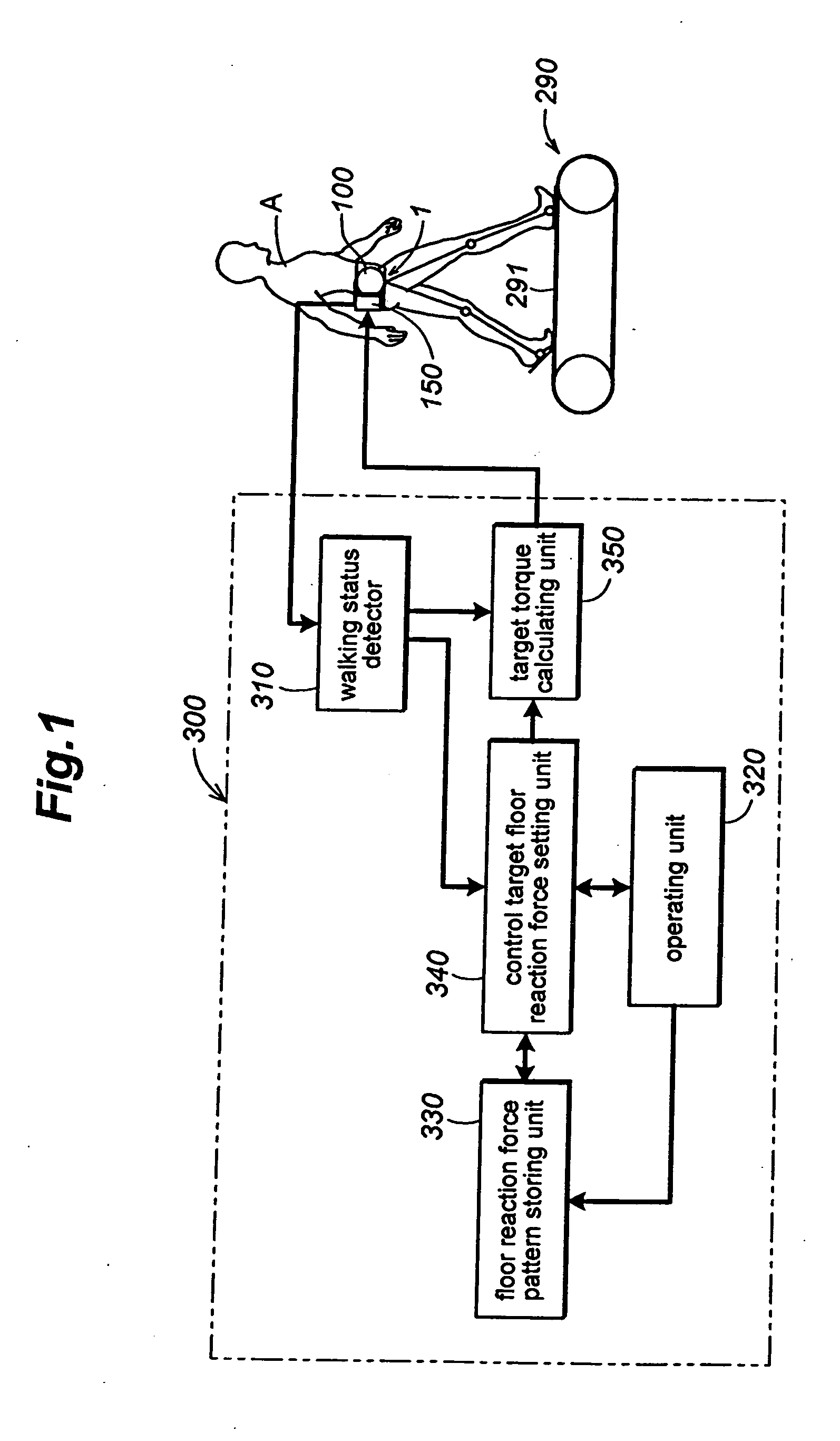
The present invention provides a rehabilitation device using a walking assistance device (1) having an actuator which generates and provides torque to a lower limb joint of a wearer wearing the walking assistance device (1), comprising a floor reaction force pattern storing unit (330) configured to store a reference floor reaction force pattern; a control target floor reaction force setting unit (340) for determining a control target floor reaction force based on the floor reaction force pattern stored in the floor reaction force pattern storing unit (330); a target torque calculating unit (350) for calculating a target torque of the actuator to achieve the control target floor reaction force determined by the control target floor reaction force setting unit (340); and an actuator output controller (150) for controlling output of the actuator such that the actuator generates a torque matching the target torque calculated by the target torque calculating unit (350); wherein the floor reaction force that the wearer receives is increased and decreased by the application of torque generated by the actuator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus and method for analysing a golf swing
This invention is an apparatus and method for measuring or analysing a golf swing. Measurement or analysis is made relative to energy generation and transfer through a player's body and club. The measurement or analysis data is principally obtained from the player's ground-reaction forces. Processed signals are analysed with an artificial intelligence system. Ground-reaction forces relate to reaction forces which occur between a standing surface and the player's feet. The apparatus and method measures or analyses a golf swing in an automatic manner or in an automatic and interactive manner.
Owner:布莱恩·弗朗西斯·穆尼
Controller of legged mobile robot
InactiveUS6969965B2Improve stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlNet forceDynamic models
A control device for a legged mobile robot, in which a correction manipulated variable of a desired floor reaction force (desired floor reaction force's moment) is subsequently determined based on an error between an actual state quantity, such as a body posture angle, of the robot 1 and a desired state quantity of the same, and at the same time, a desired movement of the robot 1 is subsequently determined by the use of the correction manipulated variable and a dynamic model. At this time, a friction force component, which defines a frictional force between the robot 1 and a floor such as a translation floor reaction force's horizontal component, is set as a variable to be limited, and an allowable range of the variable to be limited is set. The desired movement is determined so that the variable to be limited remains within the allowable range and a resultant force of an inertial force and gravity, generated by the movement of the robot 1 on the dynamic model, balances with a floor reaction force obtained by correcting the desired floor reaction force by the correction manipulated variable. The desired movement is determined by adjusting a plurality of movement modes having mutually different generation ratios of a floor reaction force's moment and a translation floor reaction force.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Gait generation device for legged mobile robot
ActiveUS20060247800A1Reliably securing stabilityStable and reliableComputer controlSimulator controlDynamic modelsDynamic balance
A vertical component or the like of a floor reaction force moment to be applied to a robot 1 is defined as a restriction object amount, and the permissible range of the restriction object amount is set. A provisional motion of the robot that satisfies a predetermined dynamic balance condition is determined on a predetermined dynamic model, and if a restriction object amount determined by the provisional motion deviates from the permissible range, then the motion of a desired gait is determined by correcting the provisional motion by changing the angular momentum changing rate of the robot from the provisional motion while limiting the restriction object amount to the permissible range on the dynamic model.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Head stabilizing system
Owner:BHC ENG
System and method of controlling a legged locomotion robot
ActiveUS7881824B2Reduce the amount of calculationEffective calculationComputer controlSimulator controlObject pointEngineering
The lumbar part of a robot as a controlled-object point where the mass amount becomes maximum is set as the origin of a local coordinate, an acceleration sensor is disposed at the controlled-object point to directly measure the attitude and acceleration at that position to control the robot to take a stable posture on the basis of a ZMP. Further, at each foot which touches the walking surface, there are provided a floor reaction force sensor and acceleration sensor to directly measure a ZMP and force, and a ZMP equation is formulated directly at the foot nearest to a ZMP position. Thus there can be implemented a stricter and quick control of the robot for a stable posture.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Gait pattern generating device for legged mobile robot
InactiveUS6876903B2Drawback can be obviatedEvenly combinedProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlTurn angleDynamic models
A gait generation system of a legged mobile robot, in particular a biped robot that has the dynamic model expressing the relationship between the motion of the body and leg and the floor reaction force, and provisionally determines the current time gait parameters including at least parameters that determine leg trajectory and the like in response to a demand, supposes the parameters of a periodic gait, corrects the current time gait parameters such that the body trajectory determined from the dynamic model and the parameters of the current time gait, etc., converges to a body trajectory determined from the parameters of the periodic gait, and determines instantaneous values of the current time gait based on the corrected current time gait parameter. With this, the system can generates a gait of any stride, turning angle and walking period, including the floor reaction force acting on the legged mobile robot, that satisfies the dynamic equilibrium condition. Further, the system can generates a gait in such a manner that the displacement and velocity of each robot part are continues at the boundary of the generated gait and that succeeding thereto, can generate a gait that is high in the margin of stability, can predict future behavior of the robot and generate a gait such that no disadvantages such as posture divergence occurs.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Momentum-Based Balance Controller For Humanoid Robots On Non-Level And Non-Stationary Ground
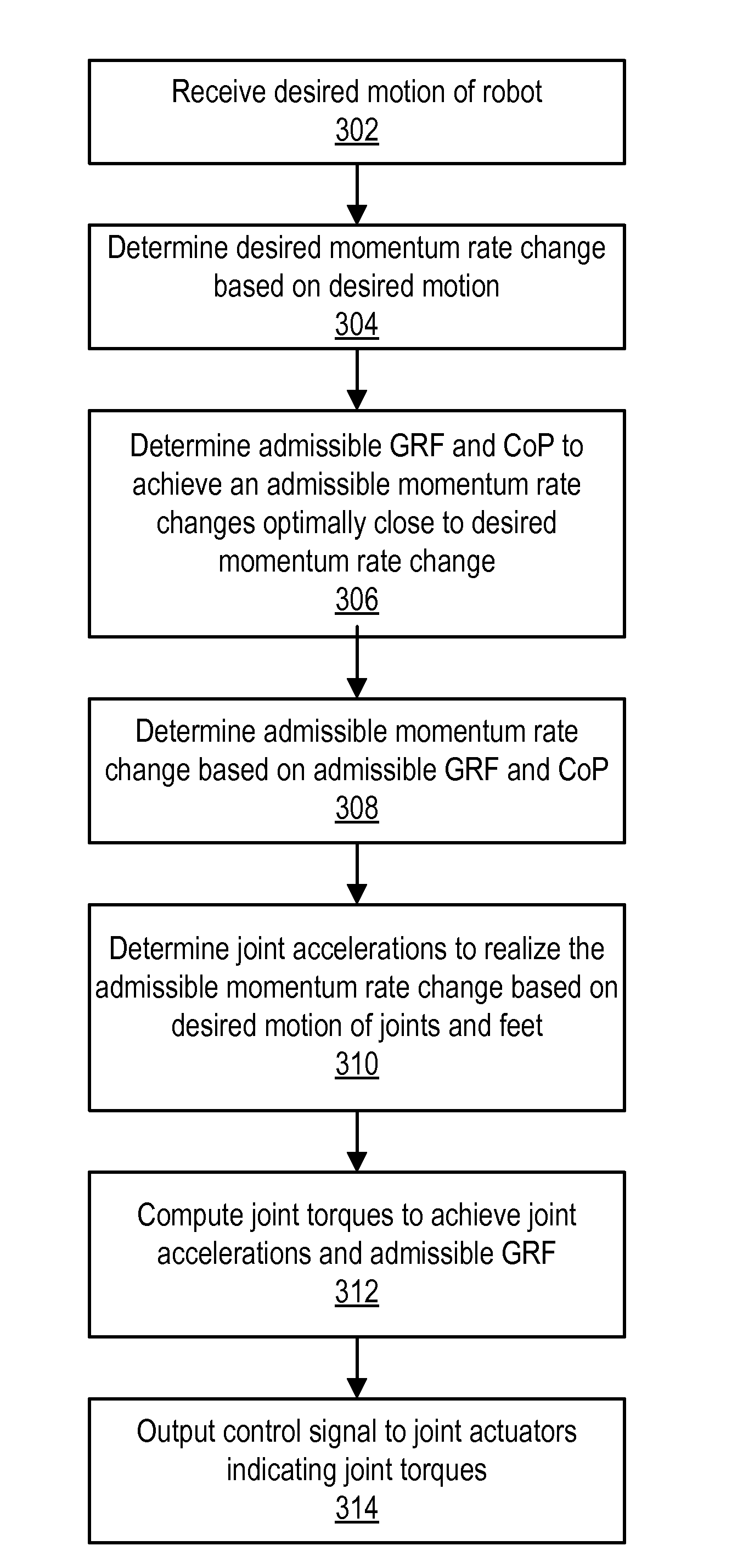
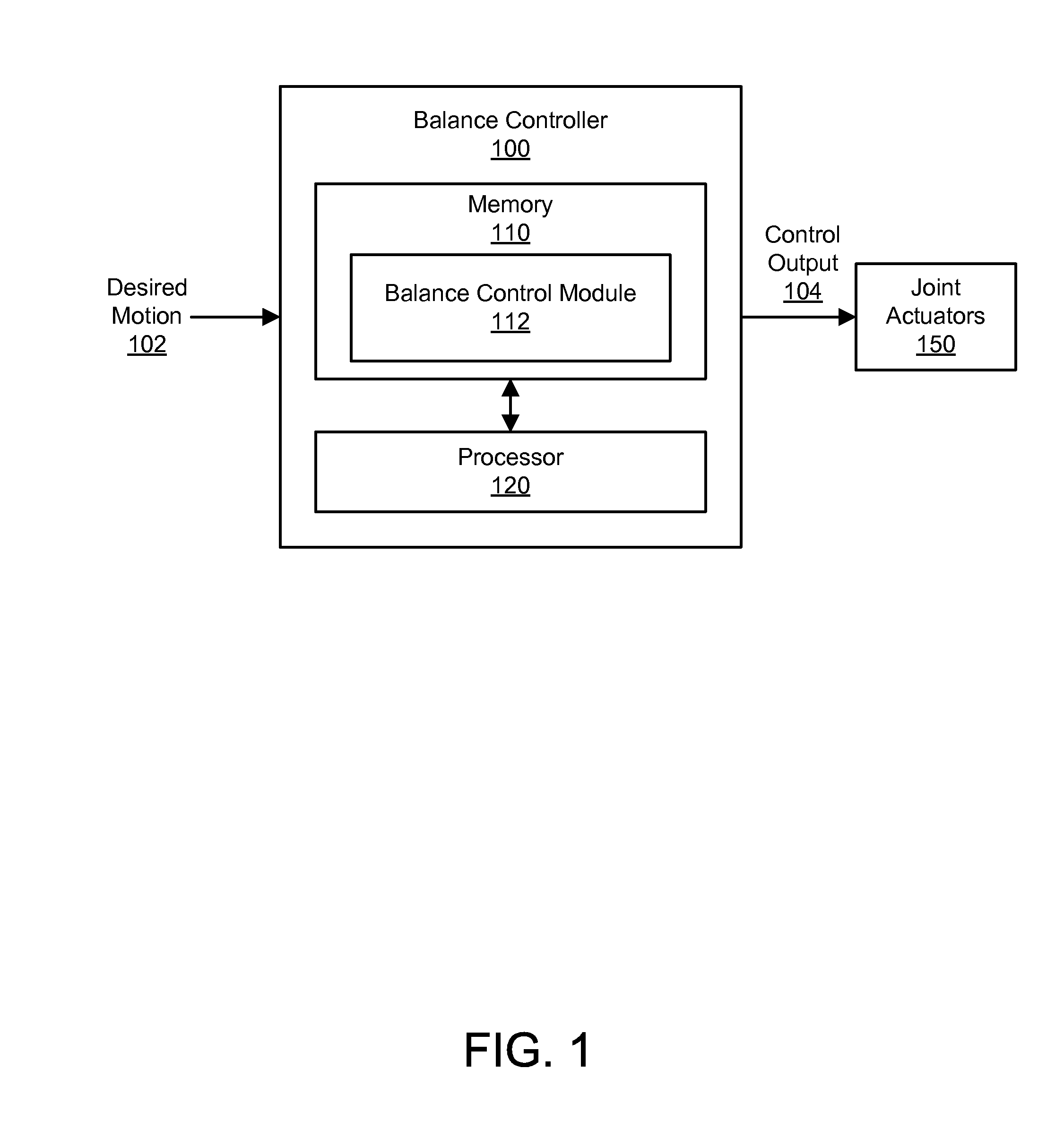
A momentum-based balance controller controls a humanoid robot to maintain balance. The balance controller derives desired rates of change of linear and angular momentum from desired motion of the robot. The balance controller then determines desired center of pressure (CoP) and desired ground reaction force (GRF) to achieve the desired rates of change of linear and angular momentum. The balance controller determines admissible CoP, GRF, and rates of change of linear and angular momentum that are optimally close to the desired value while still allowing the robot to maintain balance. The balance controller controls the robot to maintain balance based on a human motion model such that the robot's motions are human-like. Beneficially, the robot can maintain balance even when subjected to external perturbations, or when it encounters non-level and / or non-stationary ground.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Basketball Insole
An insole which provides cushioning and support to a user's foot subjected to a high magnitude of ground reaction forces (GRF) encountered in playing court sports, such as basketball, is herein disclosed. The insole comprises a base having a bottom side which defines recesses adapted to receive pads having particular properties. The location and materials of the various pads and pods work together to provide ground reaction force modulation to the user's foot which is highly desirable for users engaged in basketball and similar activities.
Owner:IMPLUS FOOTCARE
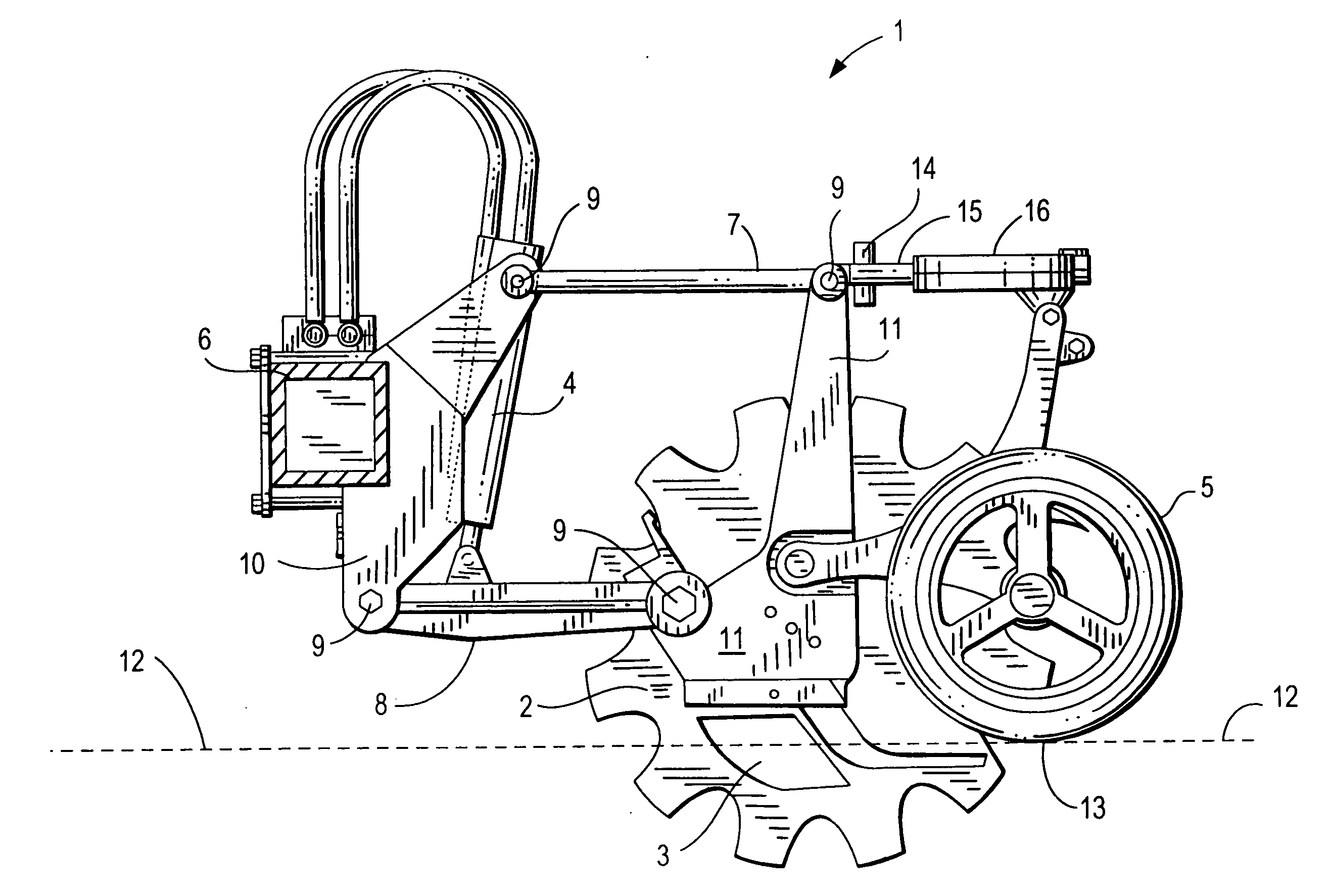
Adaptive advance drive control for milling machine
ActiveUS8128177B2Slow downReduce reaction forceSlitting machinesRoads maintainenceControl systemMotive power
An adaptive advance control system for a construction machine senses the reaction forces applied by the ground surface to a milling drum, and in response to the sensed changes in those reaction forces controls the motive power applied to an advance drive of the machine. Early and rapid detection of such changes in reaction forces allow the control system to aid in preventing lurch forward events of the construction machine.
Owner:WIRTGEN GMBH
Mobile object controller and floor surface estimator
ActiveUS20120303162A1Efficiently determinedSmooth changeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMatrix representation
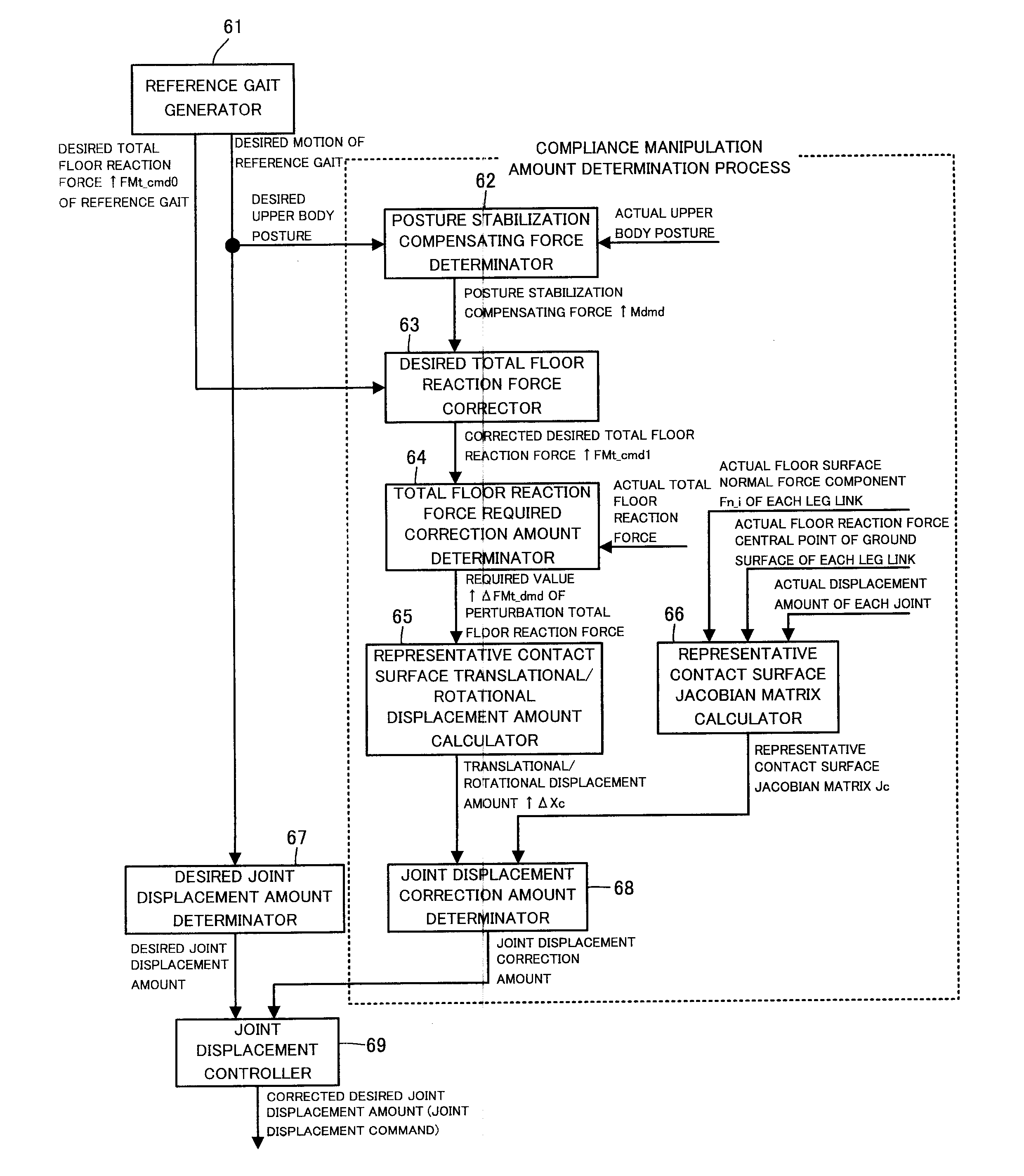
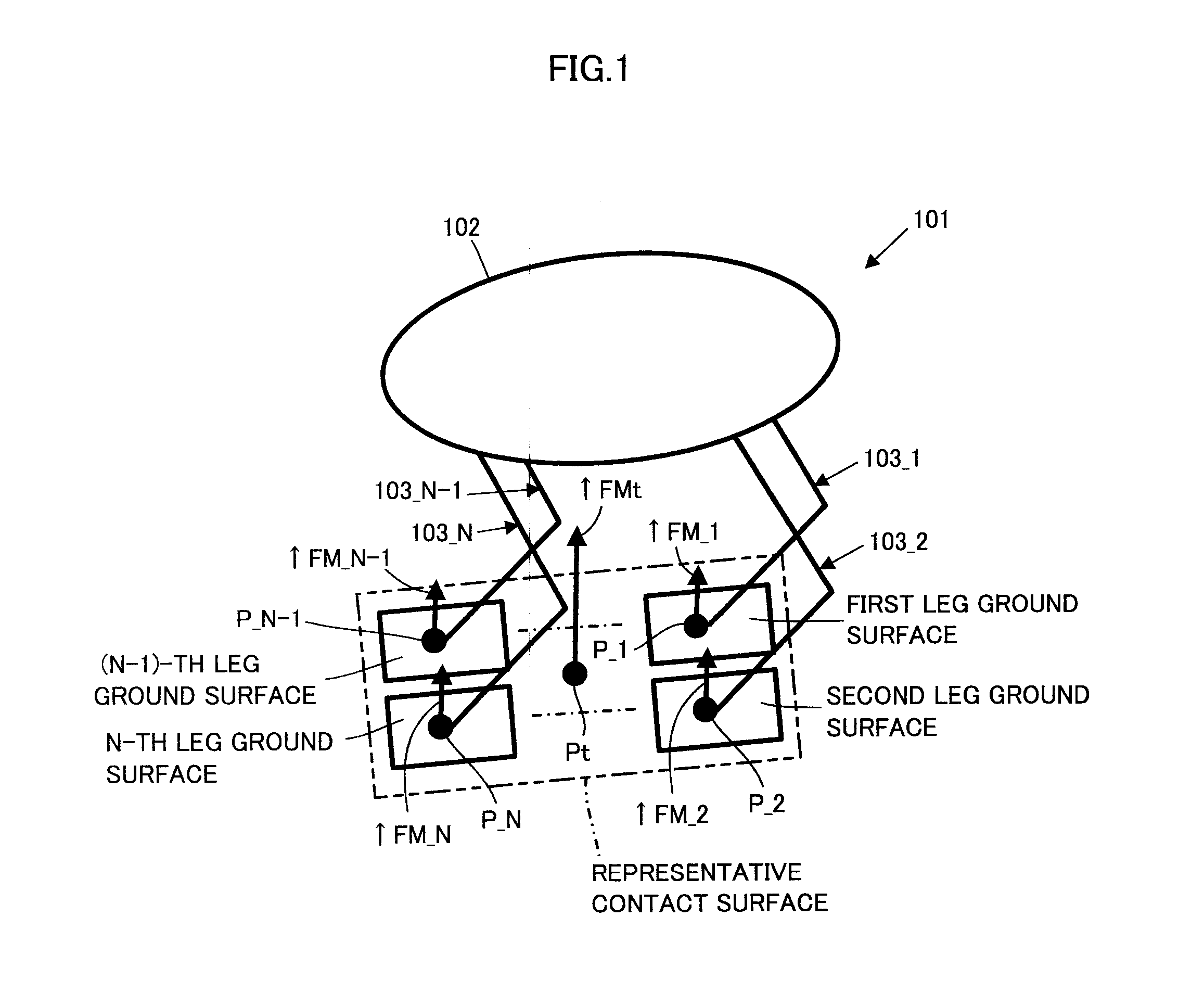
A total floor reaction force required correction amount by which an error between an observed value of a total floor reaction force acting on a mobile object 101 and a desired total floor reaction force approaches zero is converted to a spring displacement amount of a position / posture of a representative contact surface representative of ground surfaces of the mobile object 101. A correction amount of a displacement amount of each joint of the mobile object 101 is determined by multiplying the spring displacement amount by a pseudo inverse matrix of a Jacobian matrix representing a relation between a change amount of the position and posture of the representative contact surface per unit time and a change amount of a generalized variable vector per unit time. The displacement amount of each joint is controlled according to a corrected desired joint displacement amount obtained by correcting a desired joint displacement amount.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Energy translating mechanism incorporated into footwear for enhancing forward momentum and for reducing energy loss
InactiveUS7287340B2Reduce the risk of injuryEfficiently displacedSolesInsolesFoot strikeMuscular tension
The present invention provides soles, platforms, or inserts incorporated into footwear, preferably athletic footwear, designed to promote a more efficient running technique by an energy-translating sole comprising one or more angular displacement members, balance-thrust members, and counterbalance as well as conventional features. Systems and methods of the present invention promote more efficient running technique by facilitating foot-strike to occur at a point under and behind the runner's center of gravity. This may be accomplished, for example, by a foot-strike member, angular displacement member and balance-thrust member working cooperatively to displace the runner's center of gravity and translate gravitational, inertial and ground reaction forces, as well as muscular tension forces, into linear momentum.
Owner:MULLEN KRISTYNA +3
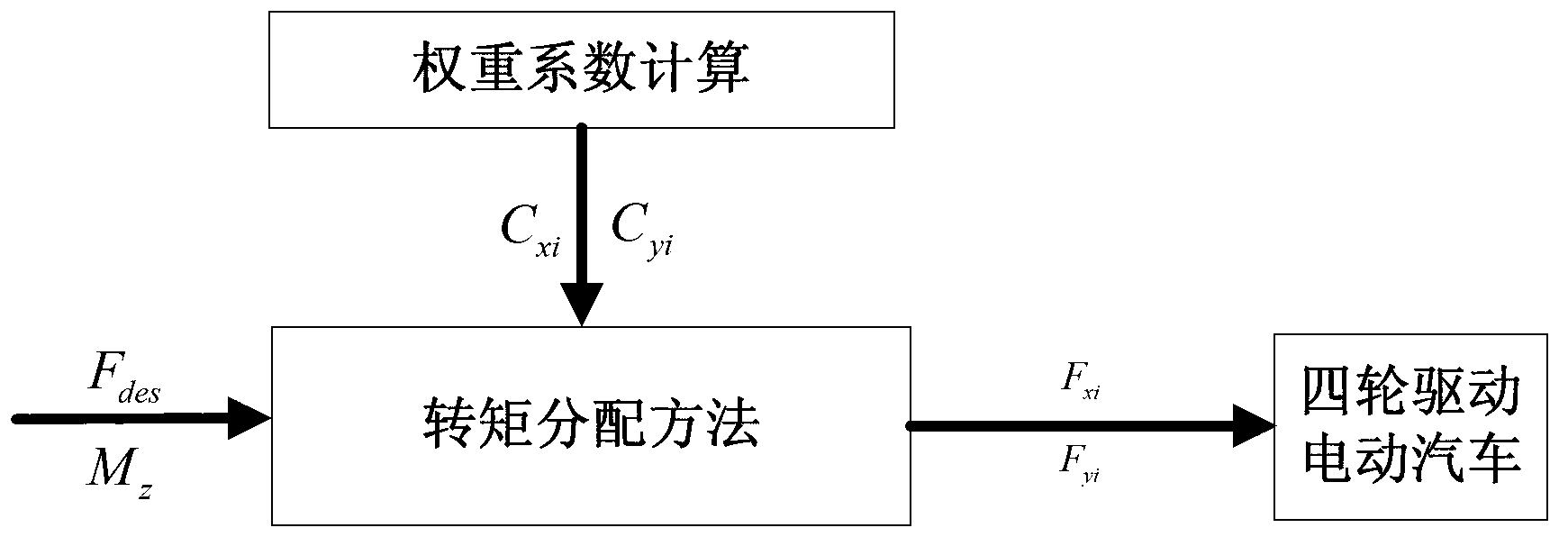
Torque distribution method of four-wheel drive electric vehicle
InactiveCN103303157AGuaranteed stabilityOptimize the weight coefficientSpeed controllerTransverse forceWeight coefficient
The invention provides a torque distribution method of a four-wheel drive electric vehicle, which comprises the following steps: considering parameters such as front wheel longitudinal force and transverse force, back wheel tyre longitudinal force, tyre friction coefficient, tyre load, tyre radius and maximal driving torque of a wheel hub motor, optimizing weight coefficient of the parameters, meanwhile considering the driving force limit condition of a drive motor, adopting a linear analytic method, providing a stable distribution and optimization method, guaranteeing the stability and controllability of a vehicle body, and utilizing ground friction force to the maximal limit.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
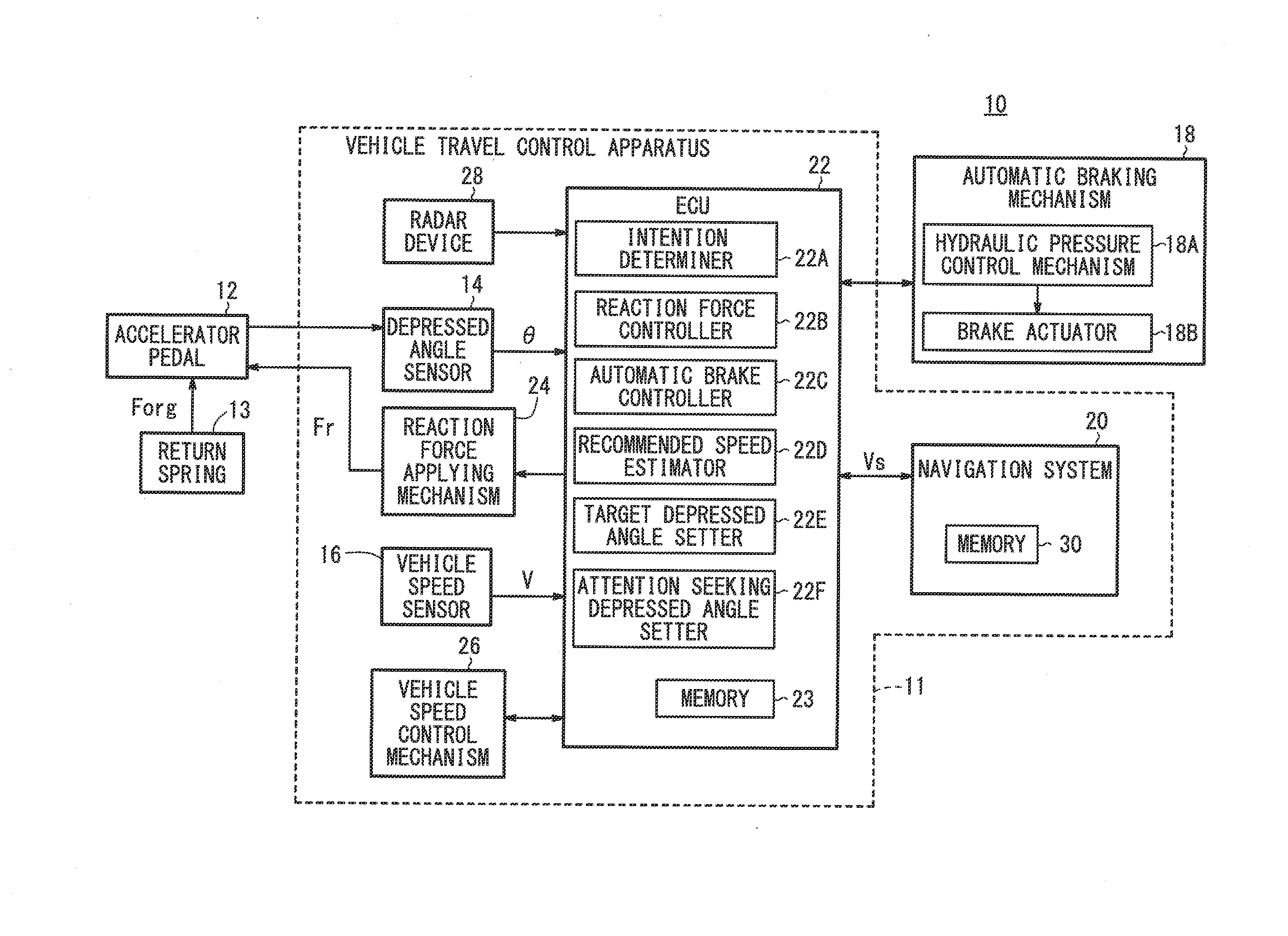
Vehicle travel control device
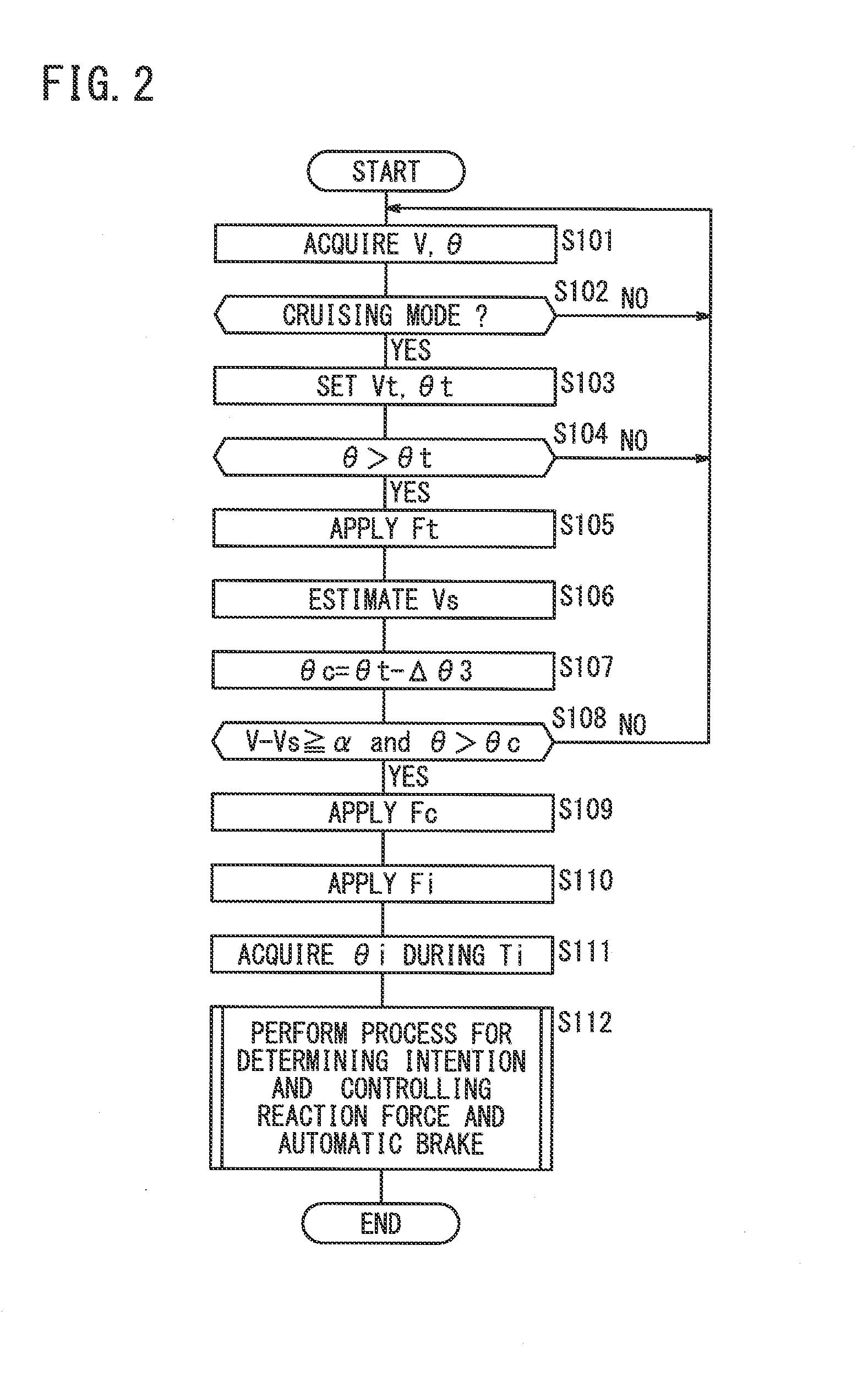
ActiveUS20130173113A1Rapid responseDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsEngineeringControl unit
A vehicle travel control device can accurately determine a driver's intention to adjust the vehicle speed. After applying attention attracting reaction force corresponding to outside circumstances and the like to an accelerator pedal through a reaction force application mechanism, a reaction force control unit outputs intention determining reaction force that is used to determine the driver's intention to adjust the vehicle speed and is smaller than the attention attracting reaction force, and determines the intention to adjust the vehicle speed on the basis of the accelerator pedal operation amount of the driver while the intention determining reaction force is being applied to the accelerator pedal through the reaction force application mechanism.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Walking assist device
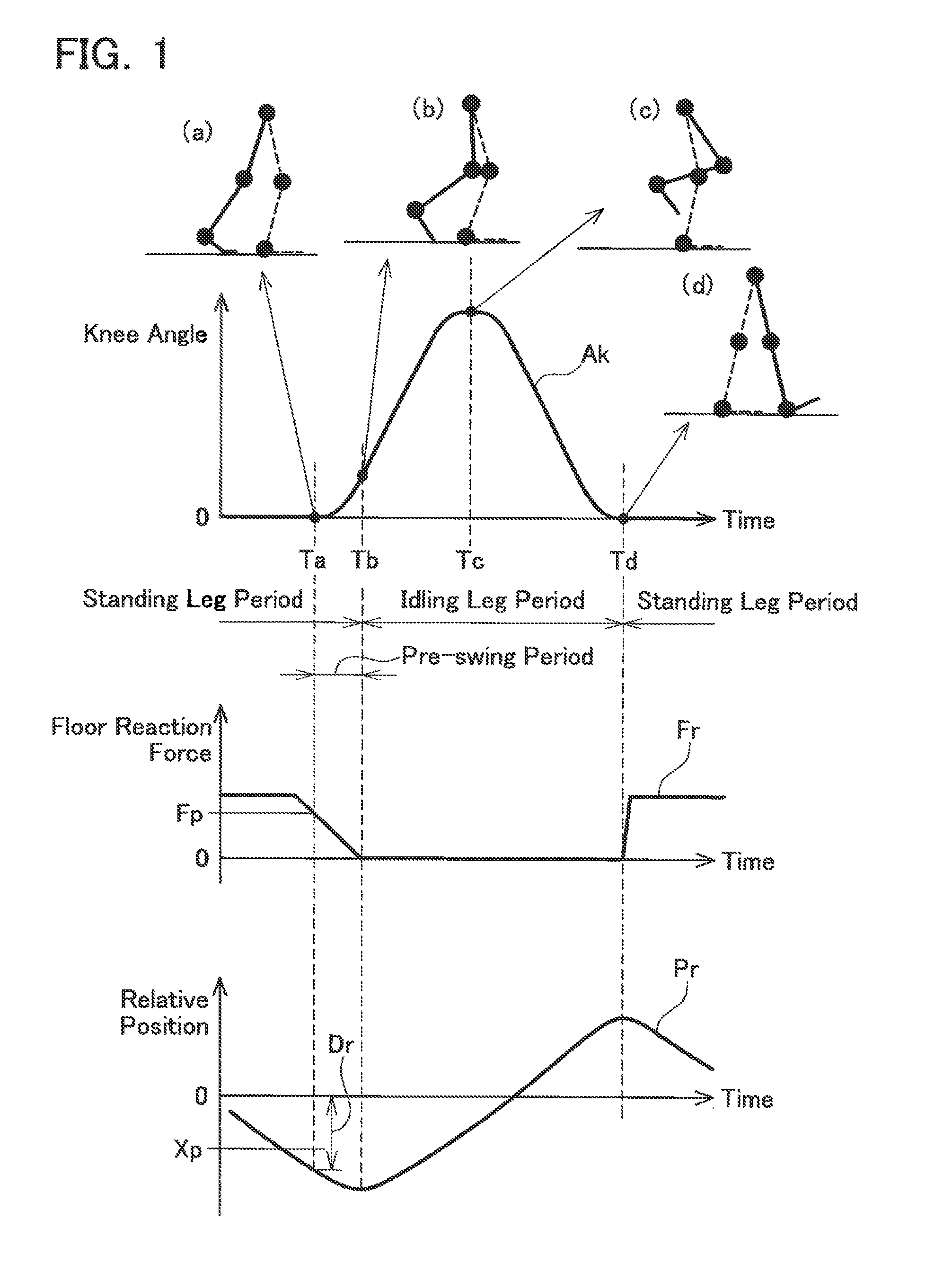
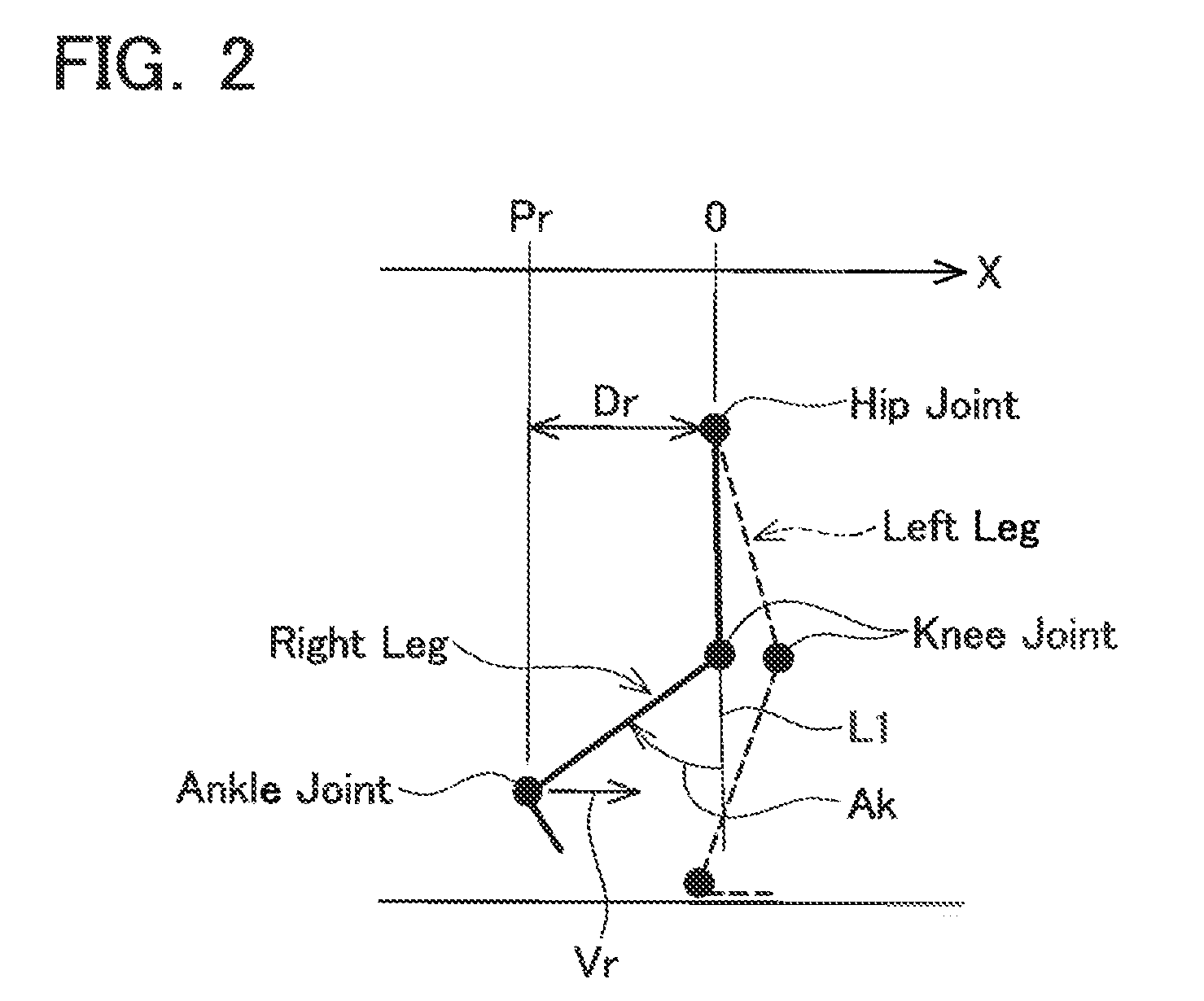
ActiveUS20120226203A1Feeling of discomfort can be reduceReduce reaction forceChiropractic devicesWalking aidsKnee JointEngineering
To provide a walking assist device which can apply torque to a knee joint at a suitable timing. A walking assist device includes an actuator, a reaction force sensor and an angle sensor. The walking assist device is fitted to a user's leg. The actuator is able to apply torque to a knee joint of one leg of the user. The reaction force sensor detects a reaction force that the foot of the one leg receives from the floor. The angle sensor detects a hip joint angle of the one leg around a pitch axis. The walking assist device specifies a timing to start applying the torque to the knee joint in a direction that swings the lower leg backward, based on the detected reaction force and the detected hip joint angle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Gait generation device for legged mobile robot
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com