Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "QuakeFinder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
QuakeFinder is a company focused on developing a system for earthquake prediction. QuakeFinder operates as a project of aerospace engineering firm Stellar Solutions, and by subscriptions and sponsorships from the public.
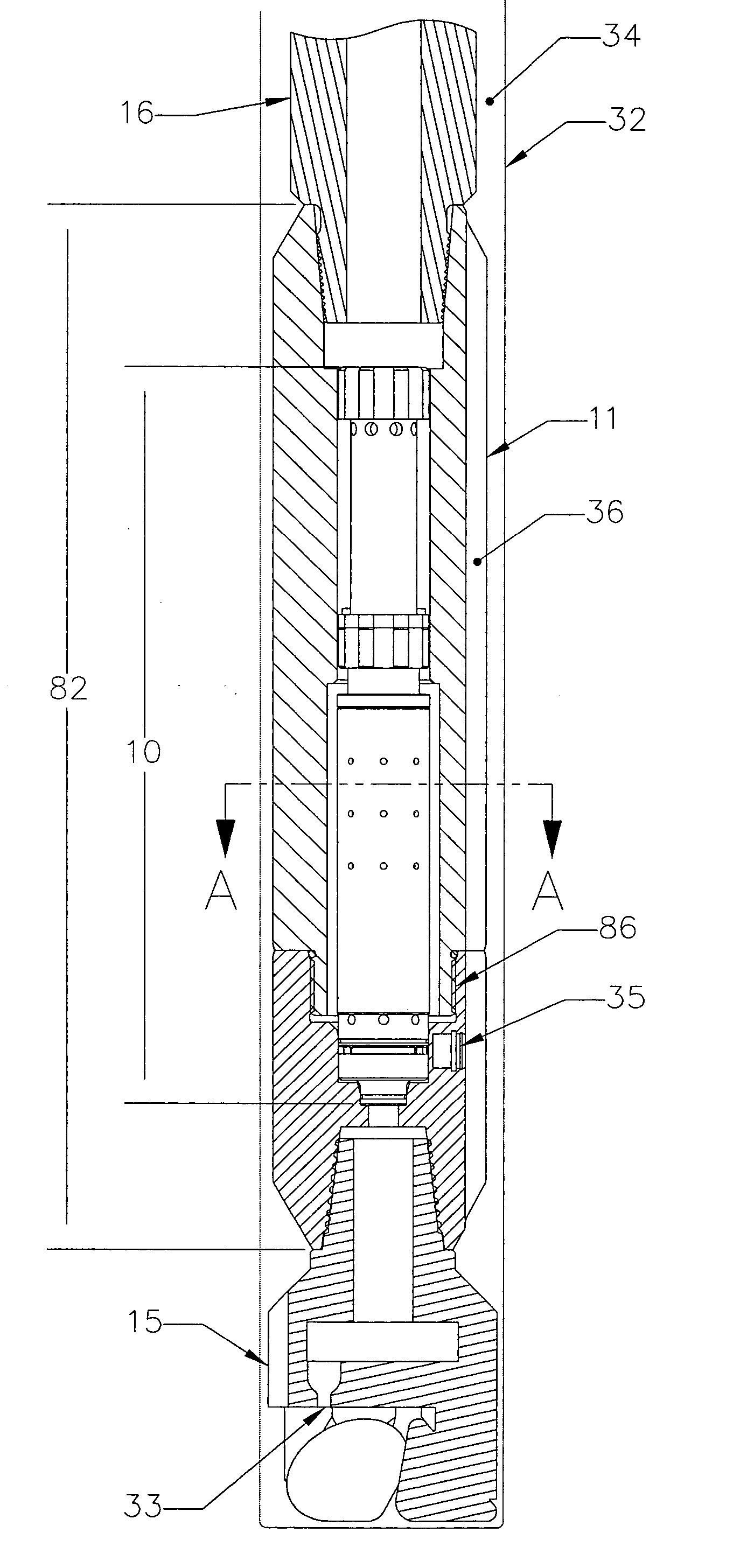
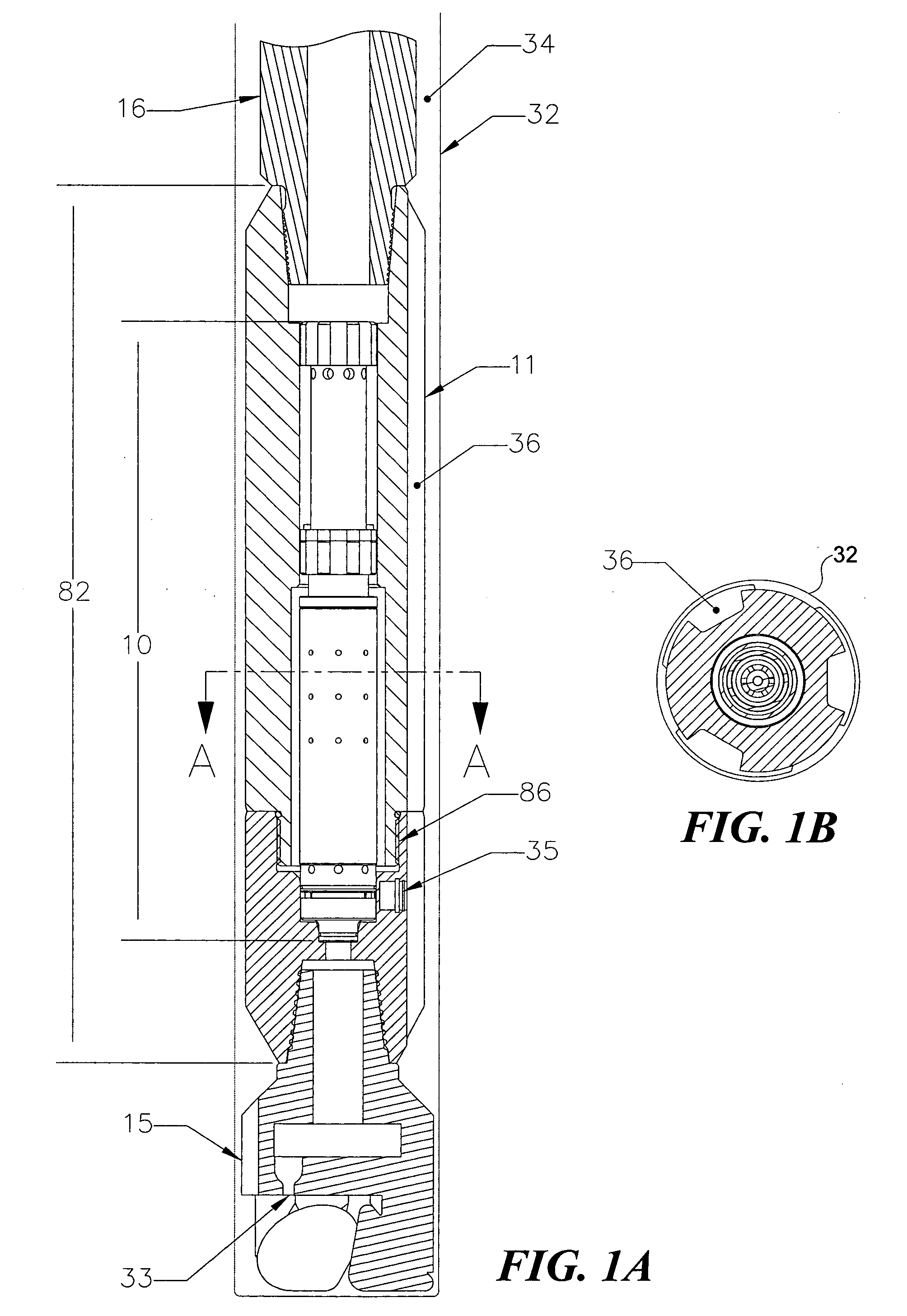
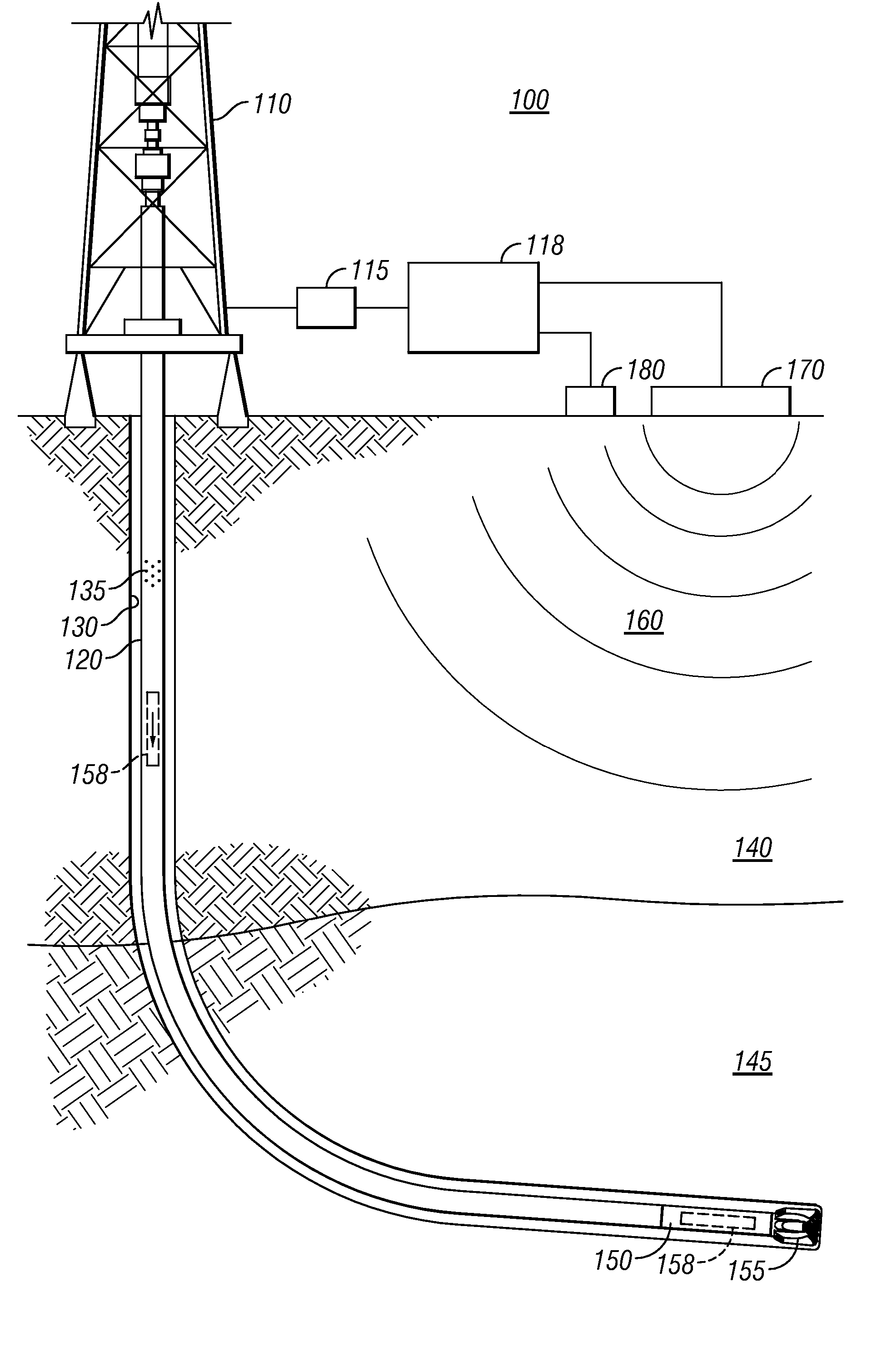
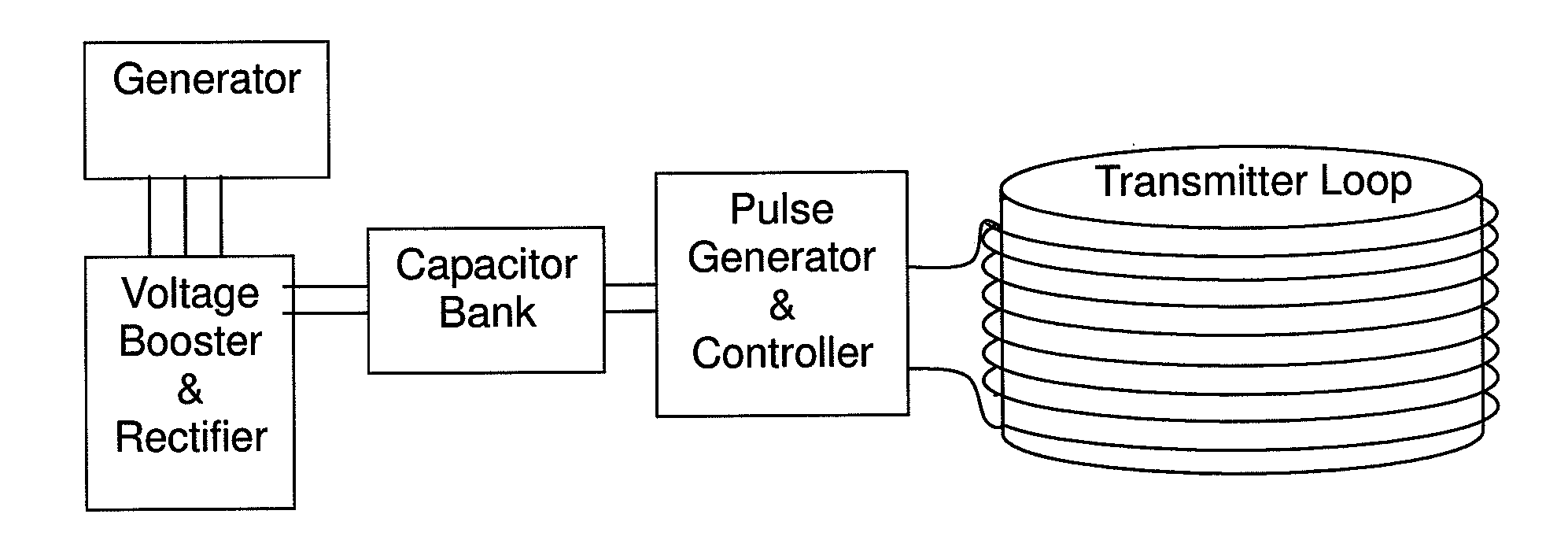
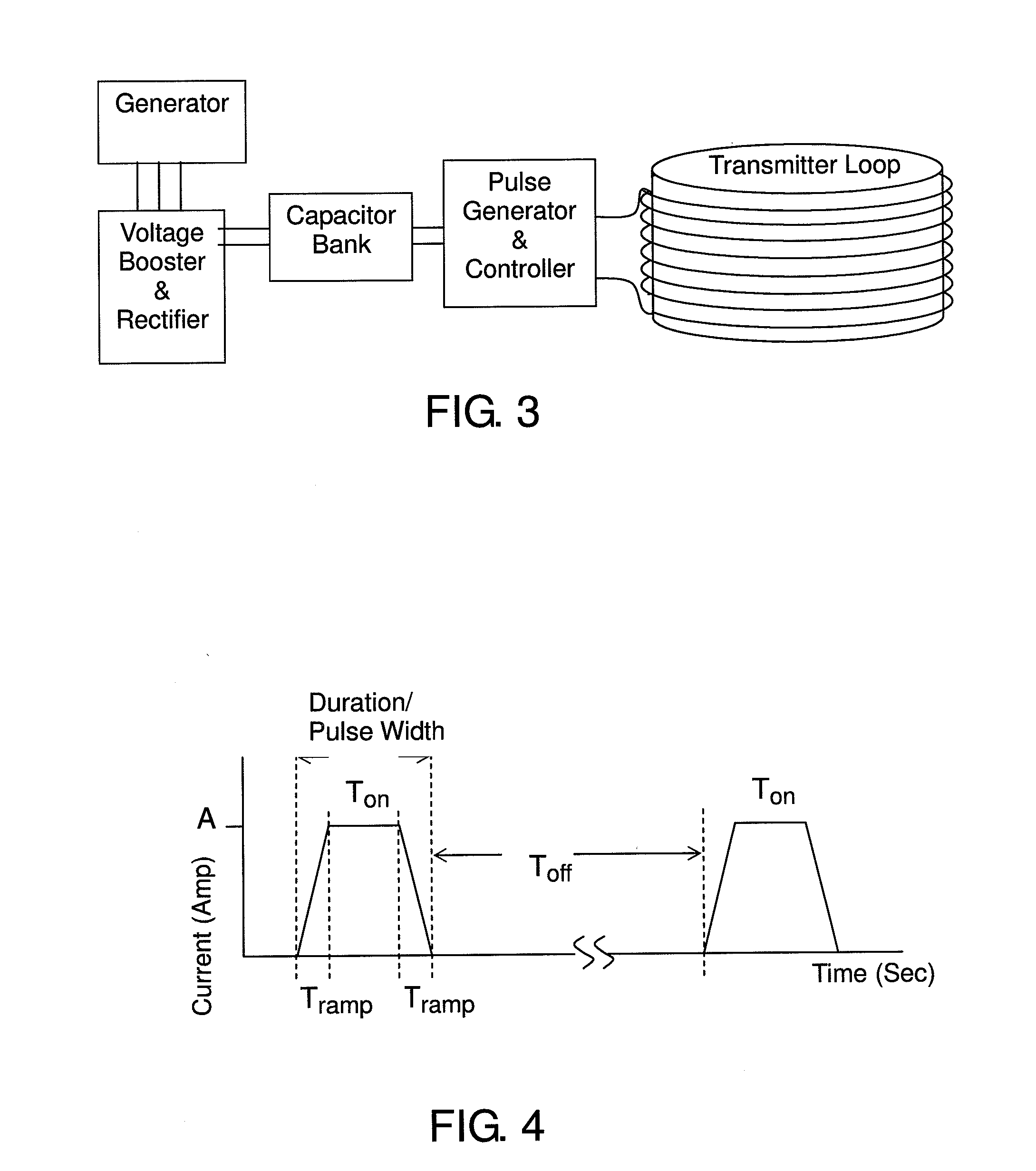
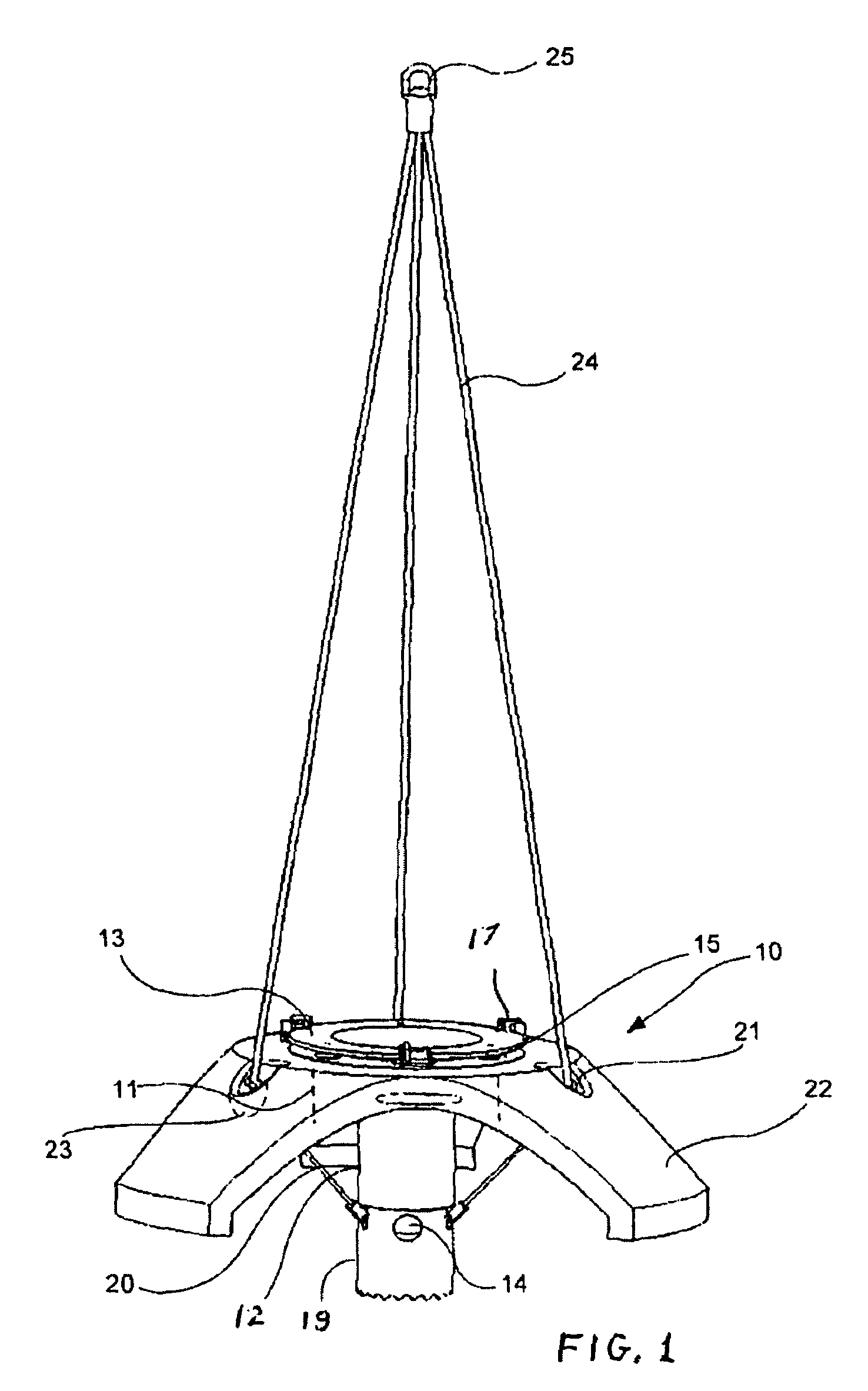
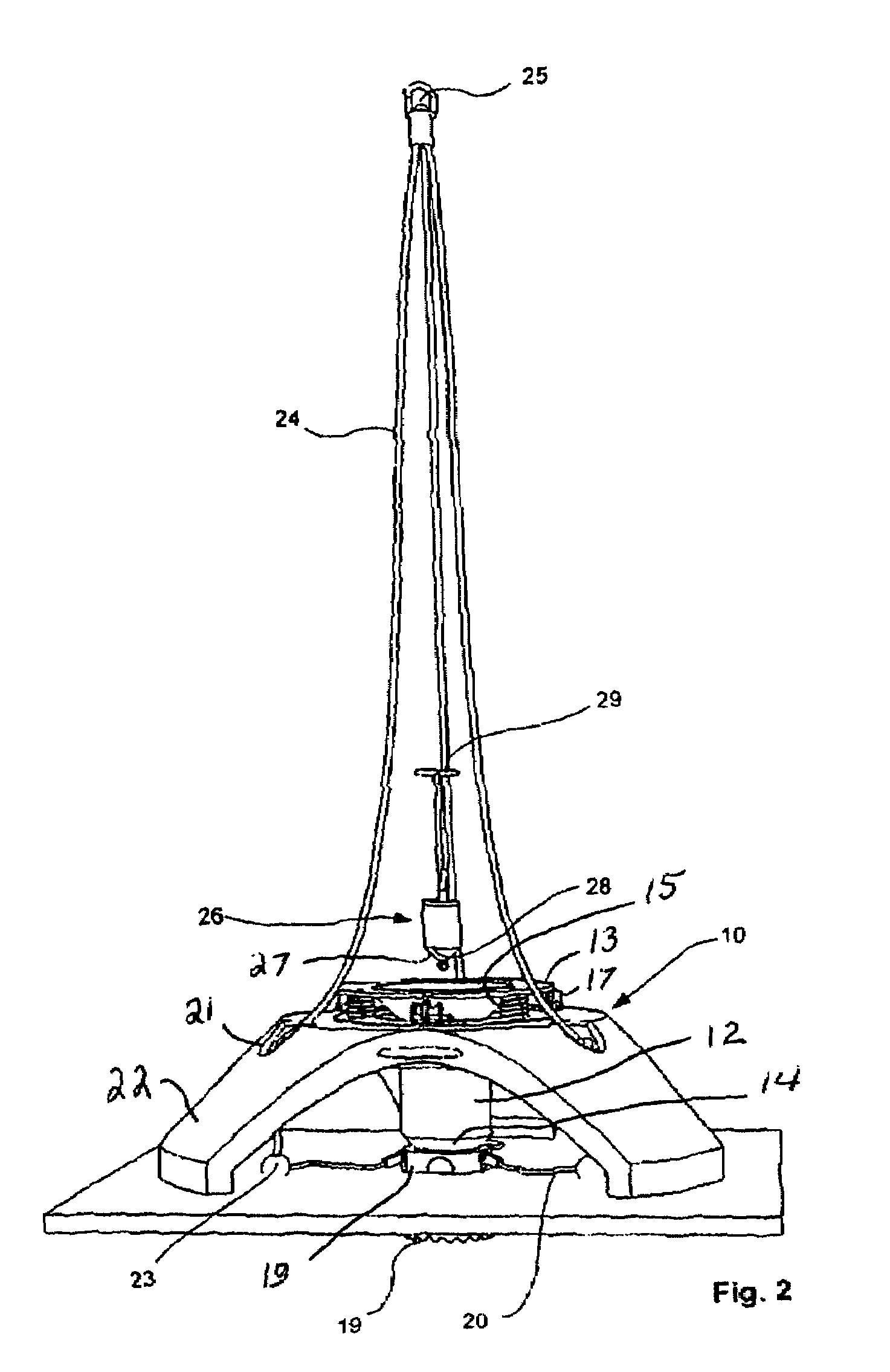
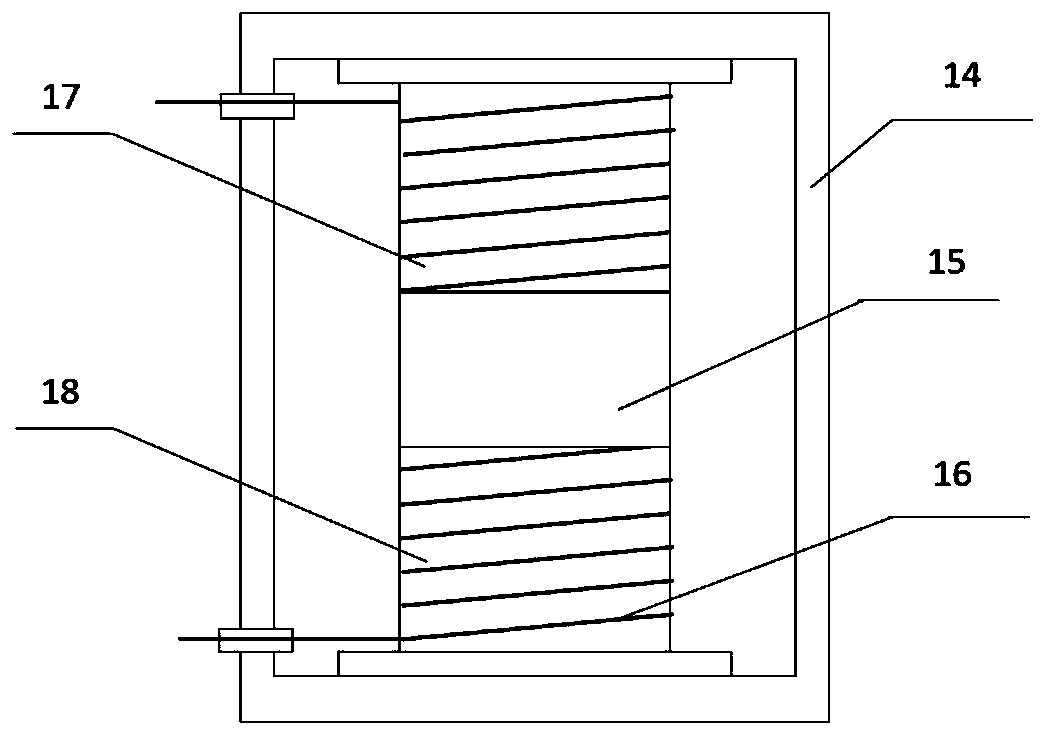
Hydraulic impulse generator and frequency sweep mechanism for borehole applications
ActiveUS20050178558A1Travel can be limitedEliminate water hammer effectSurveyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGeophoneSeismic velocity
This invention discloses a valve that generates a hydraulic negative pressure pulse and a frequency modulator for the creation of a powerful, broadband swept impulse seismic signal at the drill bit during drilling operations. The signal can be received at monitoring points on the surface or underground locations using geophones. The time required for the seismic signal to travel from the source to the receiver directly and via reflections is used to calculate seismic velocity and other formation properties near the source and between the source and receiver. This information can be used for vertical seismic profiling of formations drilled, to check the location of the bit, or to detect the presence of abnormal pore pressure ahead of the bit. The hydraulic negative pressure pulse can also be used to enhance drilling and production of wells.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
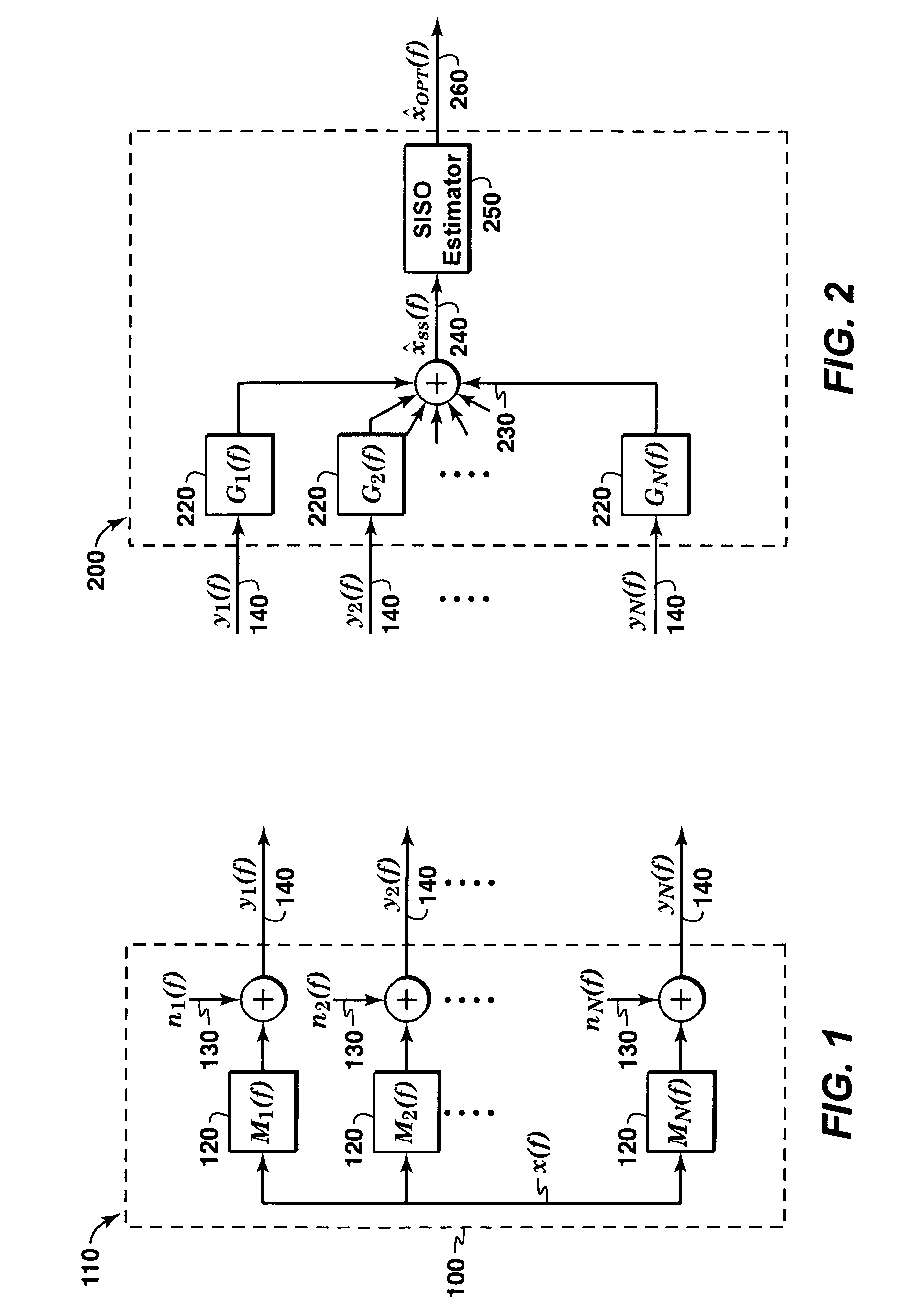
Method for combining seismic data sets
ActiveUS20060190181A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeophoneHydrophone
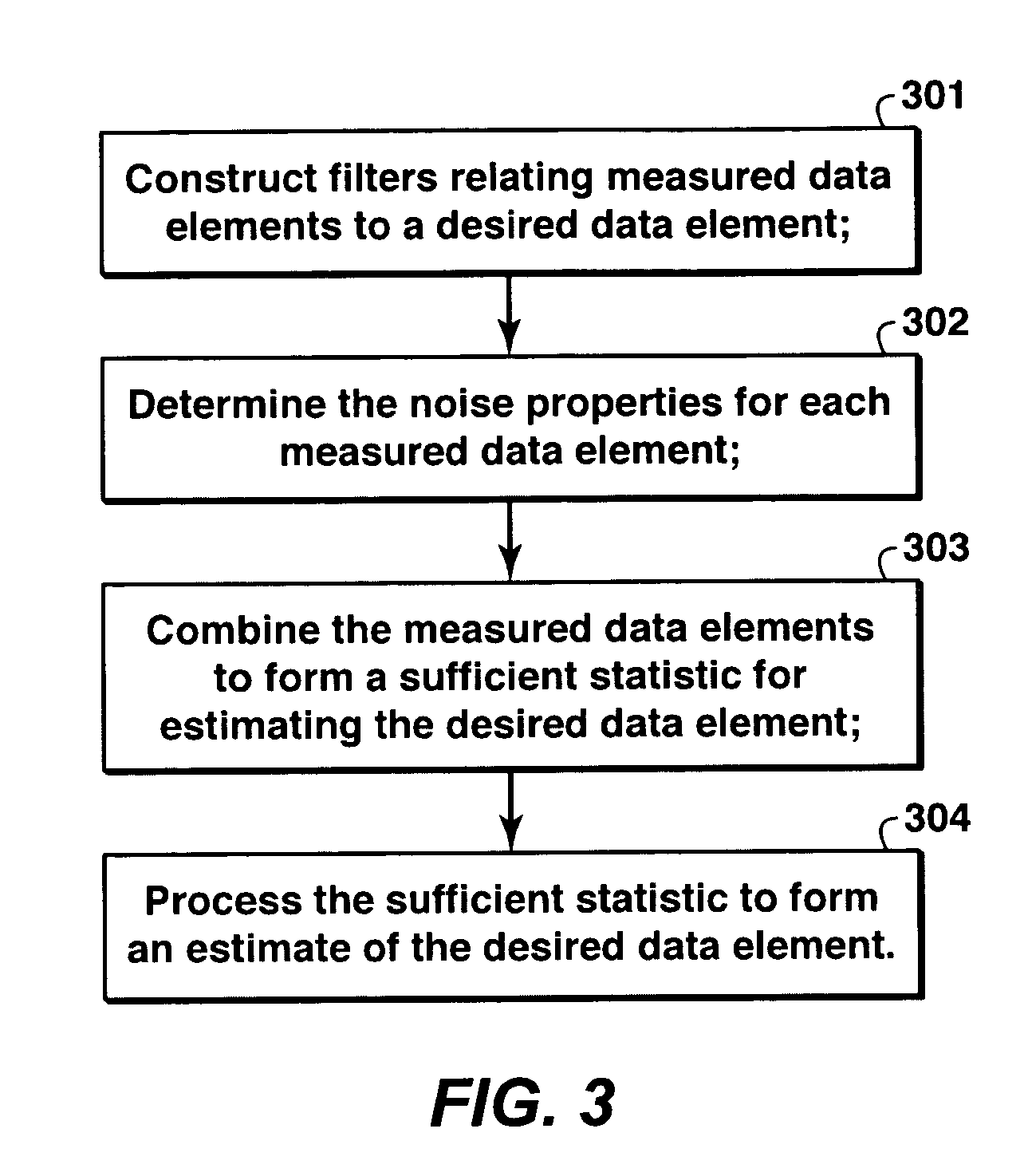
A method is disclosed for combining seismic data sets. This method has application in merging data sets of different vintages, merging data sets collected using different acquisition technologies, and merging data sets acquired using different types of sensors, for example merging hydrophone and geophone measurements in ocean bottom seismic data. In one embodiment, a desired data trace is to be determined from a set of measured data traces, and the following steps are applied: (a) model filters are constructed which express the deterministic relationship between the desired data trace and each available measured trace that depends on the desired data trace; (b) the noise properties associated with each measured data trace are determined; (c) a sufficient statistic for the desired data trace is formed by application of an appropriate filter to each measured trace and summing the filter outputs; (d) the sufficient statistic is further processed by a single-input single-output estimator to construct an estimate of the desired data trace from the sufficient statistic.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method and apparatus for land based seismic data acquisition
ActiveUS7561493B2Minimize the possibilityEliminate needSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal recordingGeophoneLand based
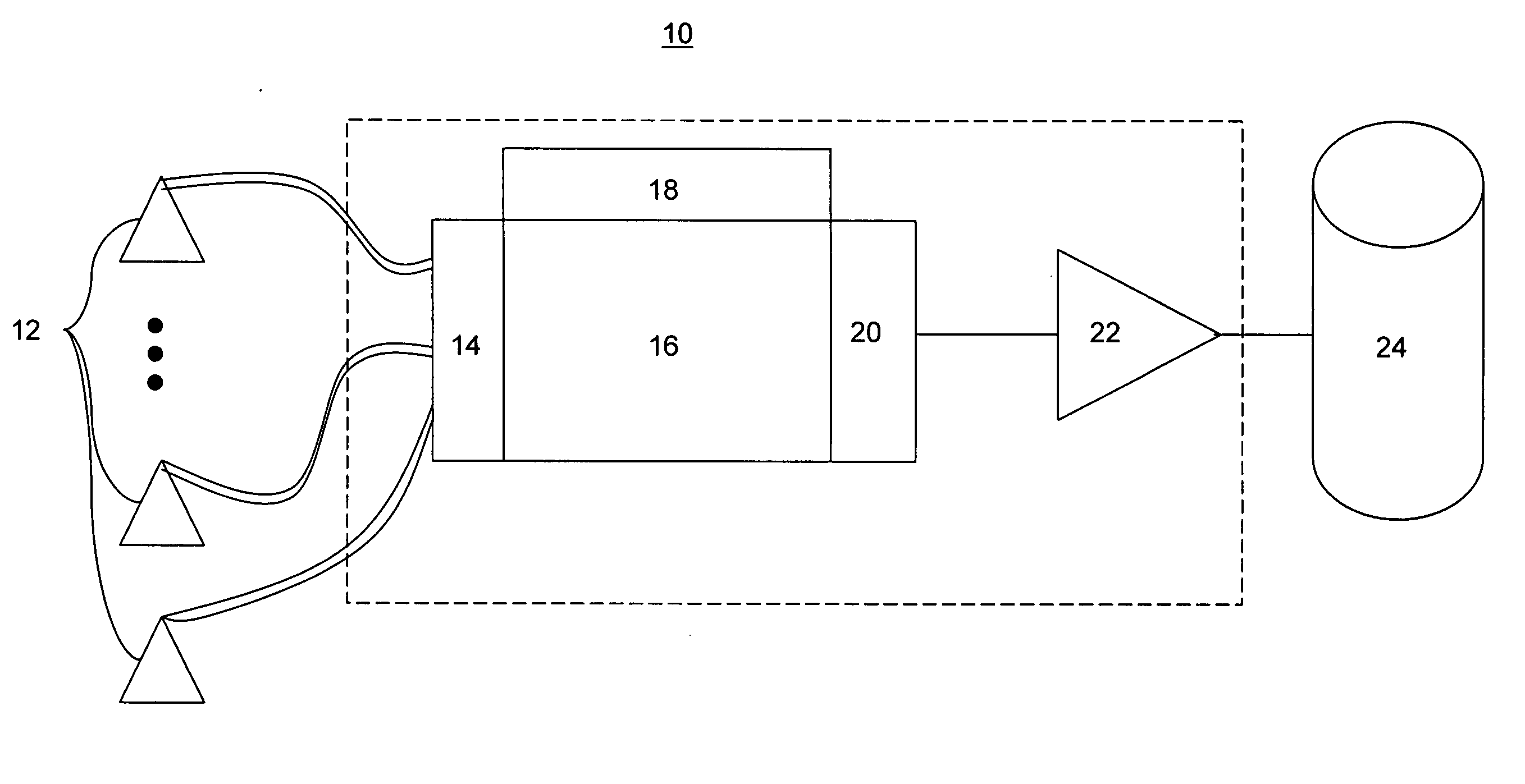
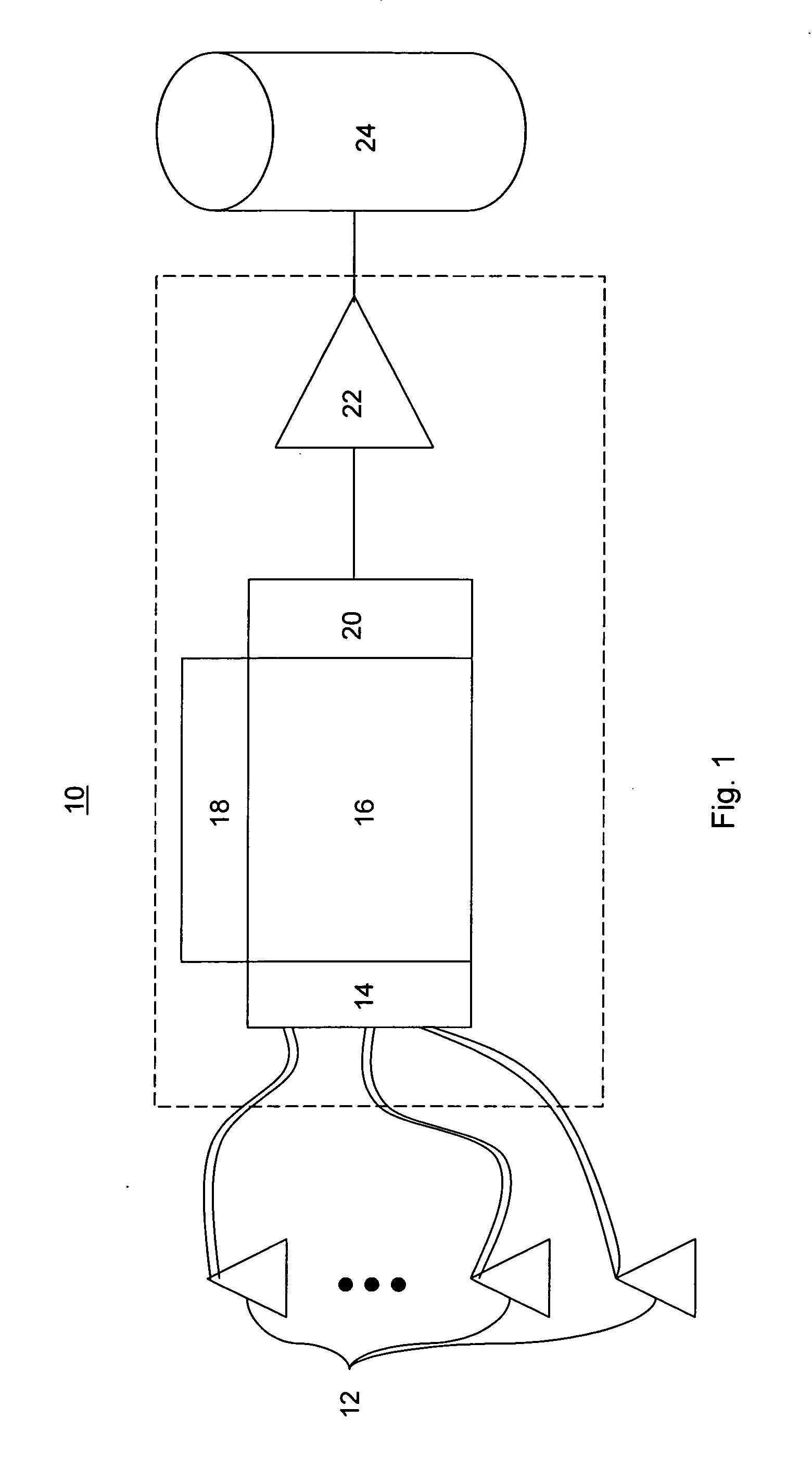
A seismic exploration method and unit comprised of continuous recording, self-contained wireless seismometer units or pods. The self-contained unit may include a tilt meter, a compass and a mechanically gimbaled clock platform. Upon retrieval, seismic data recorded by the unit can be extracted and the unit can be charged, tested, re-synchronized, and operation can be re-initiated without the need to open the unit's case. The unit may include an additional geophone to mechanically vibrate the unit to gauge the degree of coupling between the unit and the earth. The unit may correct seismic data for the effects of crystal aging arising from the clock. Deployment location of the unit may be determined tracking linear and angular acceleration from an initial position. The unit may utilize multiple geophones angularly oriented to one another in order to redundantly measure seismic activity in a particular plane.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
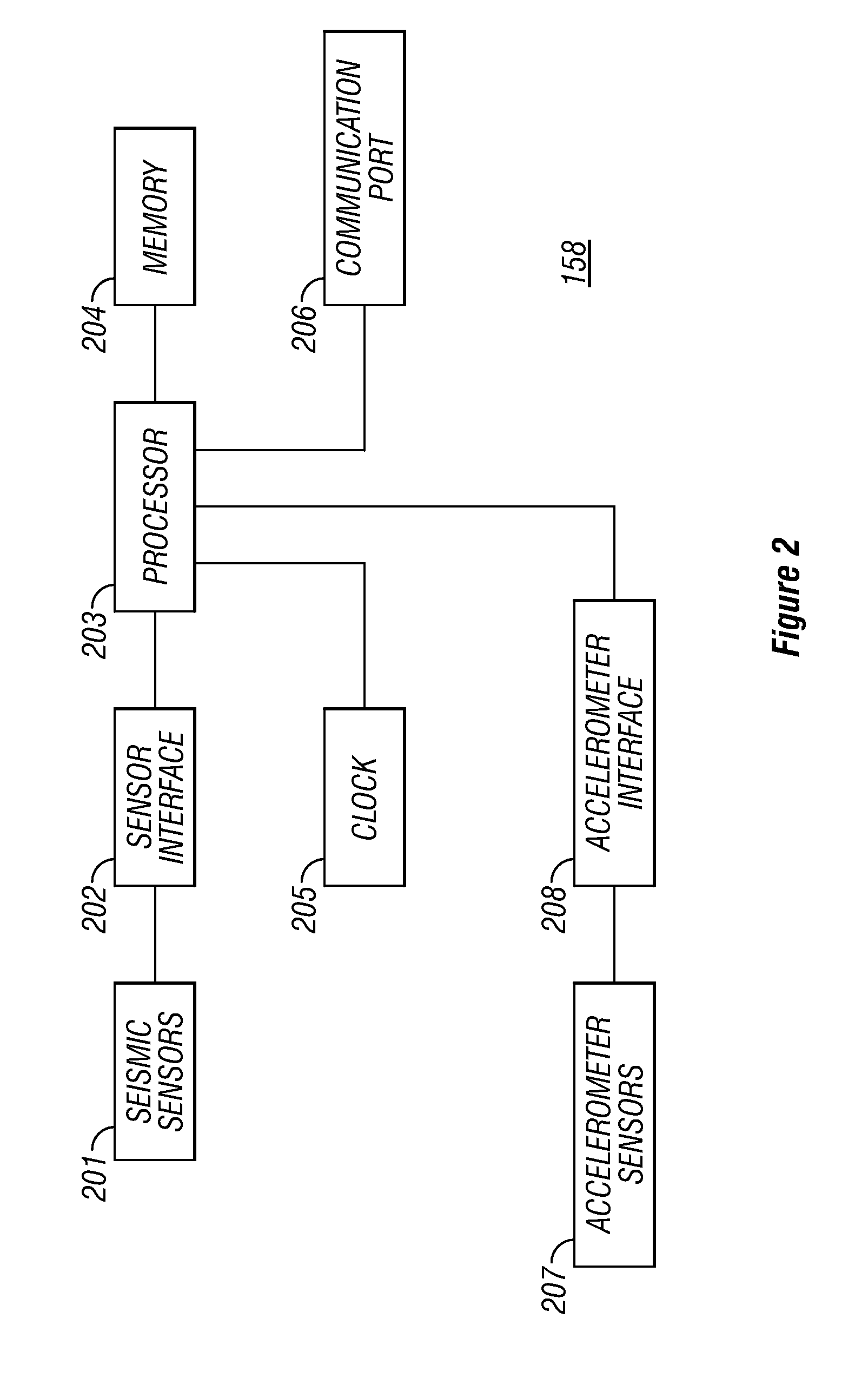
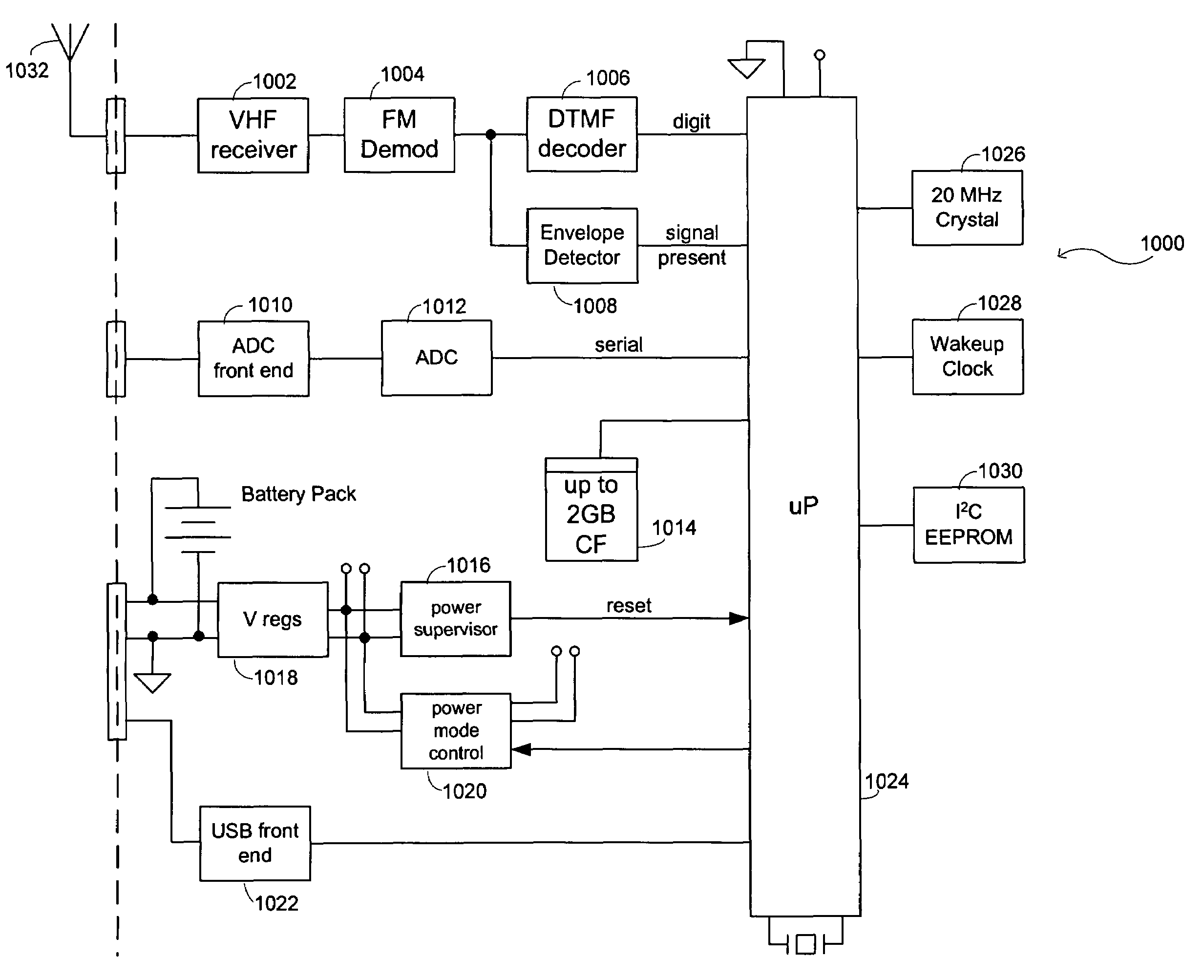
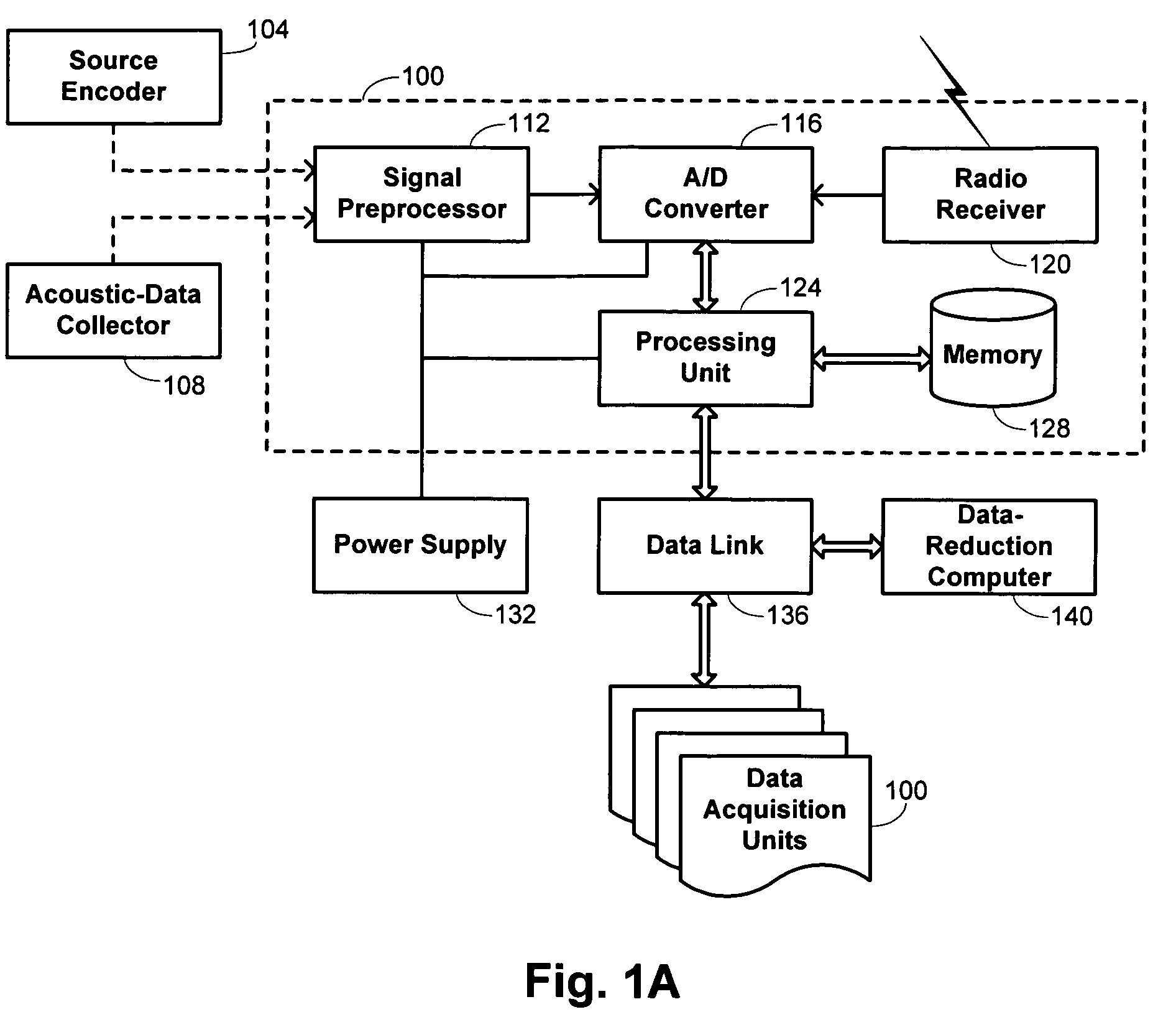
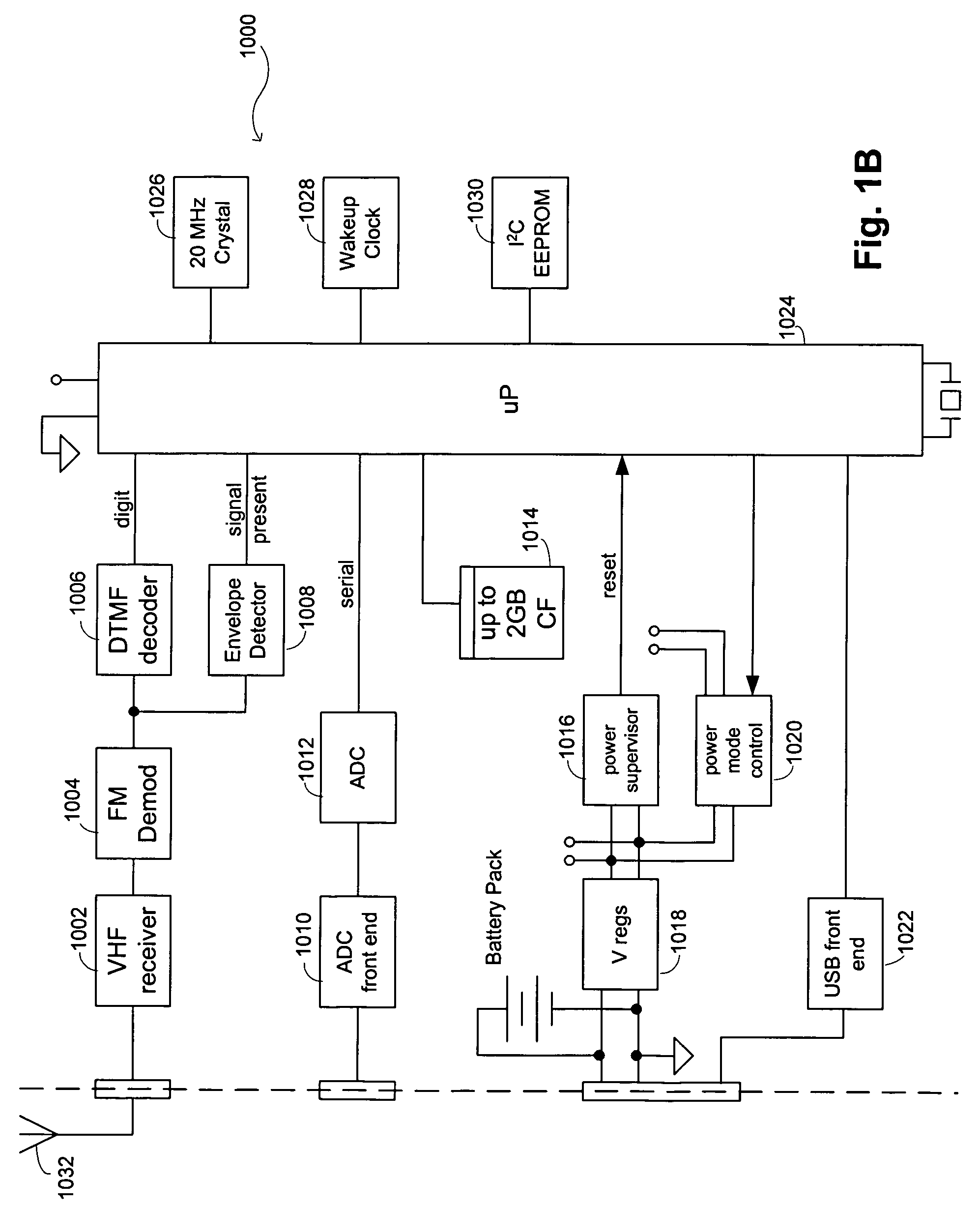
Seismic-data acquisition methods and apparatus
A self-contained data acquisition unit is provided for acquiring seismic data. The unit has a microprocessor and an antenna adapted to receive an electromagnetic signal. A decoder is connected with the microprocessor and adapted to convert received electromagnetic signals to dual-tone multiple-frequency (“DTMF”) digits. A geophone interface is provided with a geophone for collecting acoustic data incident on the geophone. A memory is connected with the geophone interface for storing a representation of the collected acoustic data and for storing a representation of a reference electromagnetic signal to be used in synchronizing acoustic data collected by other data acquisition units. A battery power source is connected with the microprocessor.
Owner:ASCEND GEO
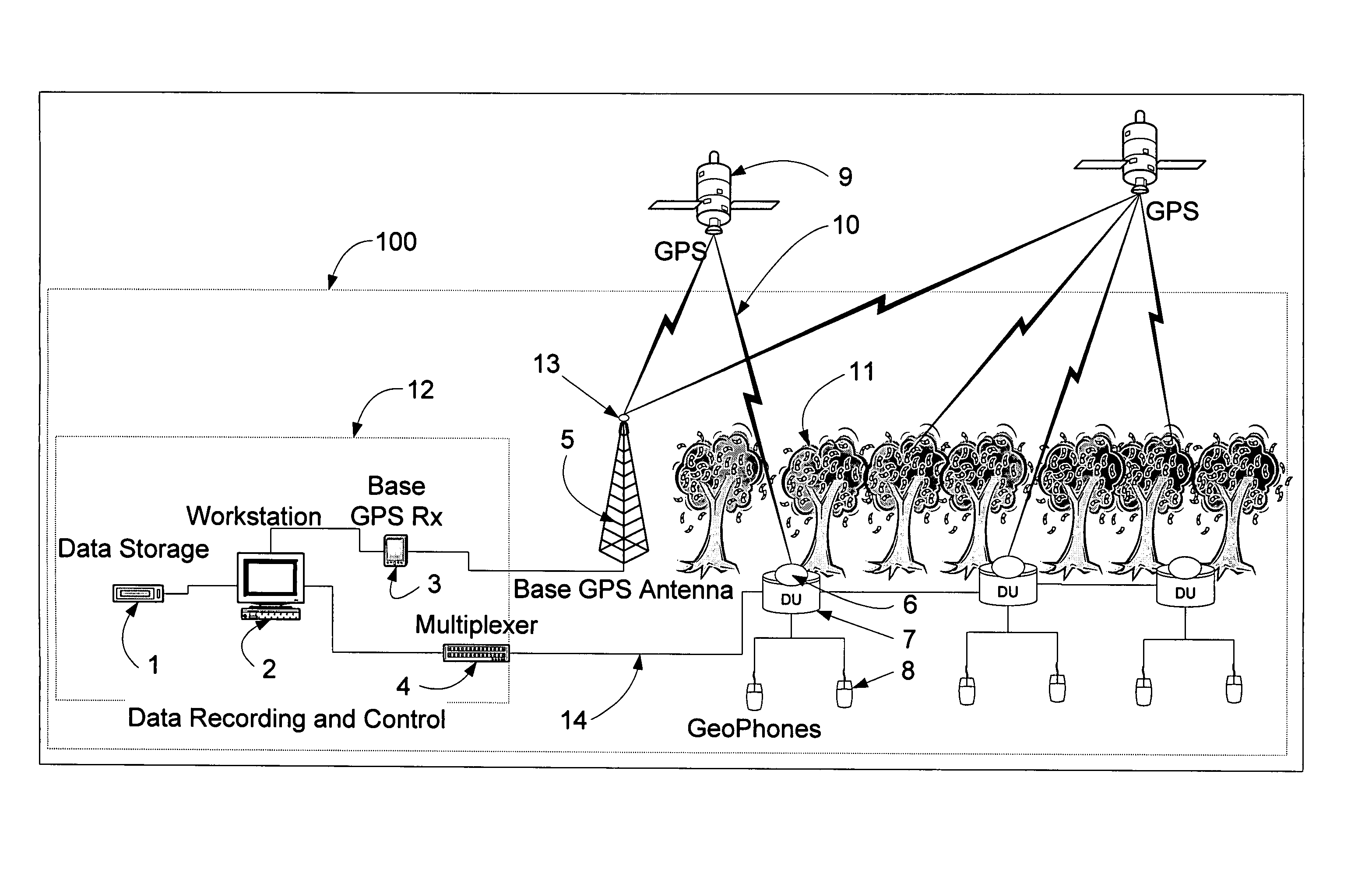
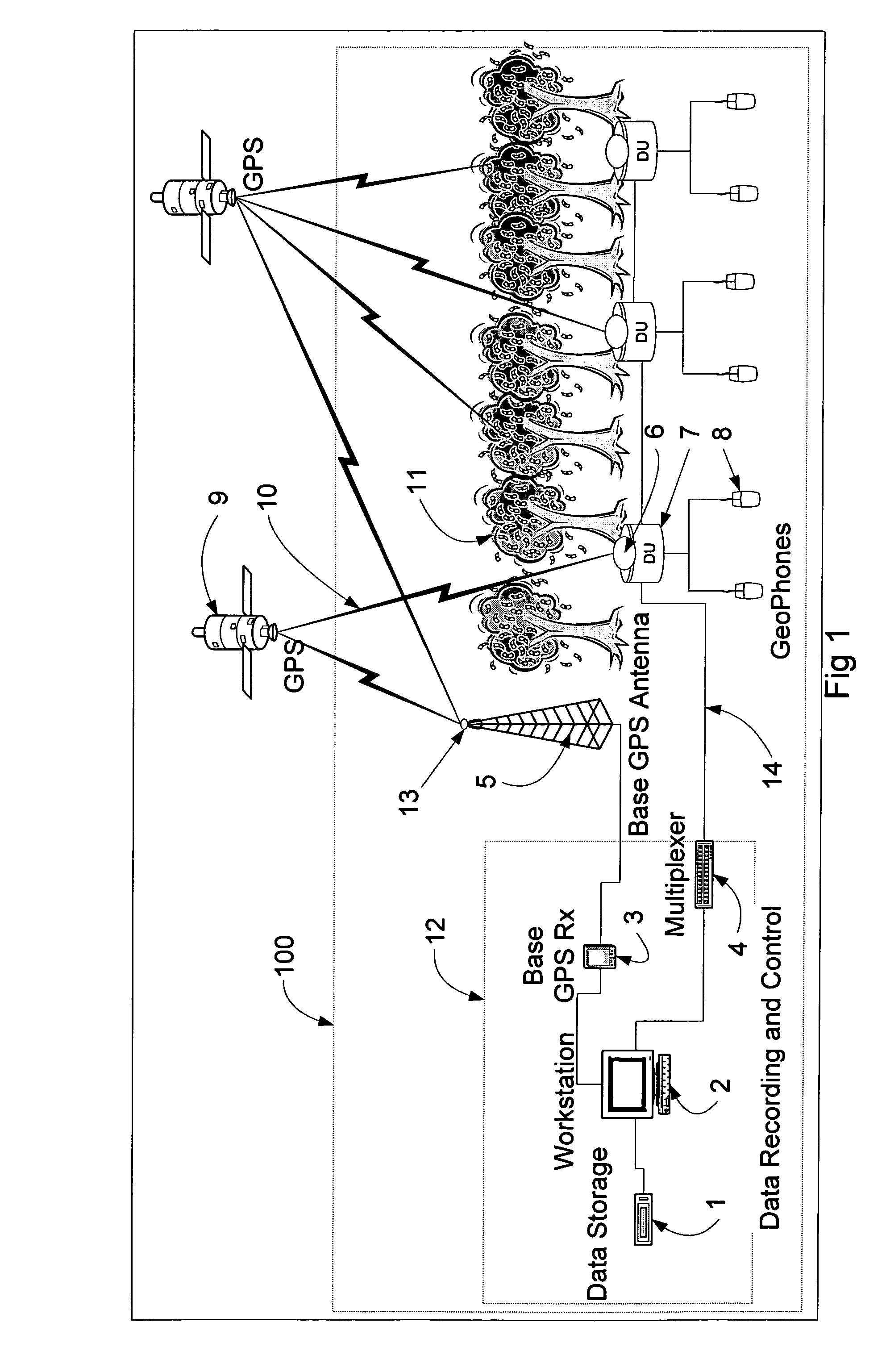
Seismic measuring system including GPS receivers
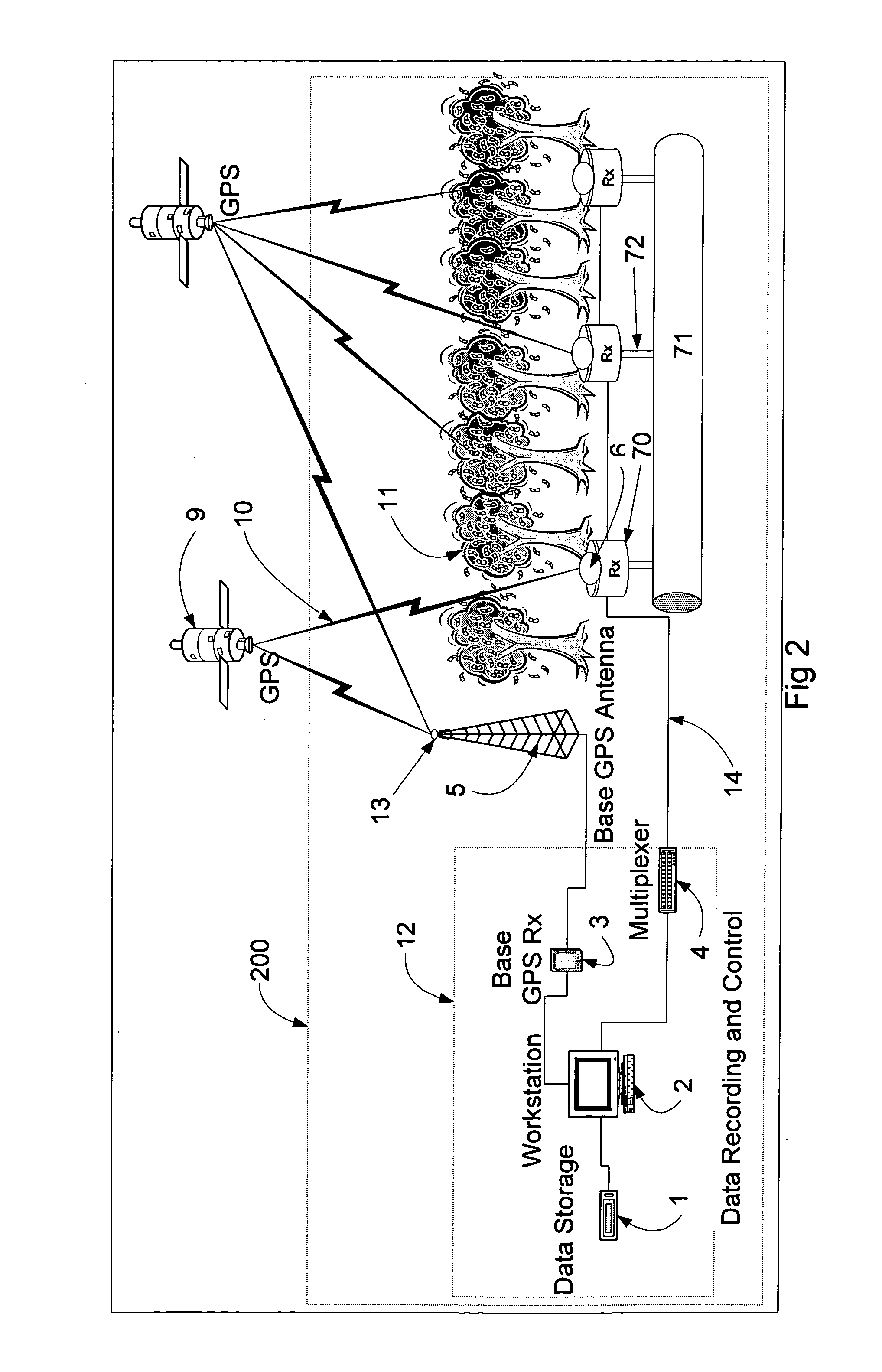
ActiveUS20050033519A1Improve acquisitionImprove tracking performanceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic data acquisitionGeophoneTime information
A system for analyzing three-dimensional seismic data includes a plurality of digitizer units, each with a configuration of geophones, a data recording and control center, a base GPS receiver with an associated antenna with a substantially unrestricted view of the sky and at the respective digitizer units low-power slave GPS receivers that acquire and track GPS satellite signals using tracking assistance information provided by the base GPS receiver. The slave GPS receivers use the tracking assistance information to acquire and track GPS satellite signals that may be relatively weak at the receivers, due to conditions at the site, such as foliage canopies and so forth. The system processes range information provided by the slave GPS receivers over an extended period of time. In this way, the precise positions of the respective slave GPS receivers, and thus, the digitizer units, can be calculated, even if the slave GPS receivers are able to observe and collect data from sets of two or more satellites for only three or four relatively short time intervals at various sky positions during the extended period. The slave GPS receivers then locally produce for the digitizer units timing signals that are based on the GPS codes and synchronized across the system. If a given slave GPS receiver cannot, at a given time, track any GPS satellite signals, a nearby slave GPS receiver supplies the timing information required for the geophone data gathering operations.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
Electromagnetic and its combined surveying apparatus and method
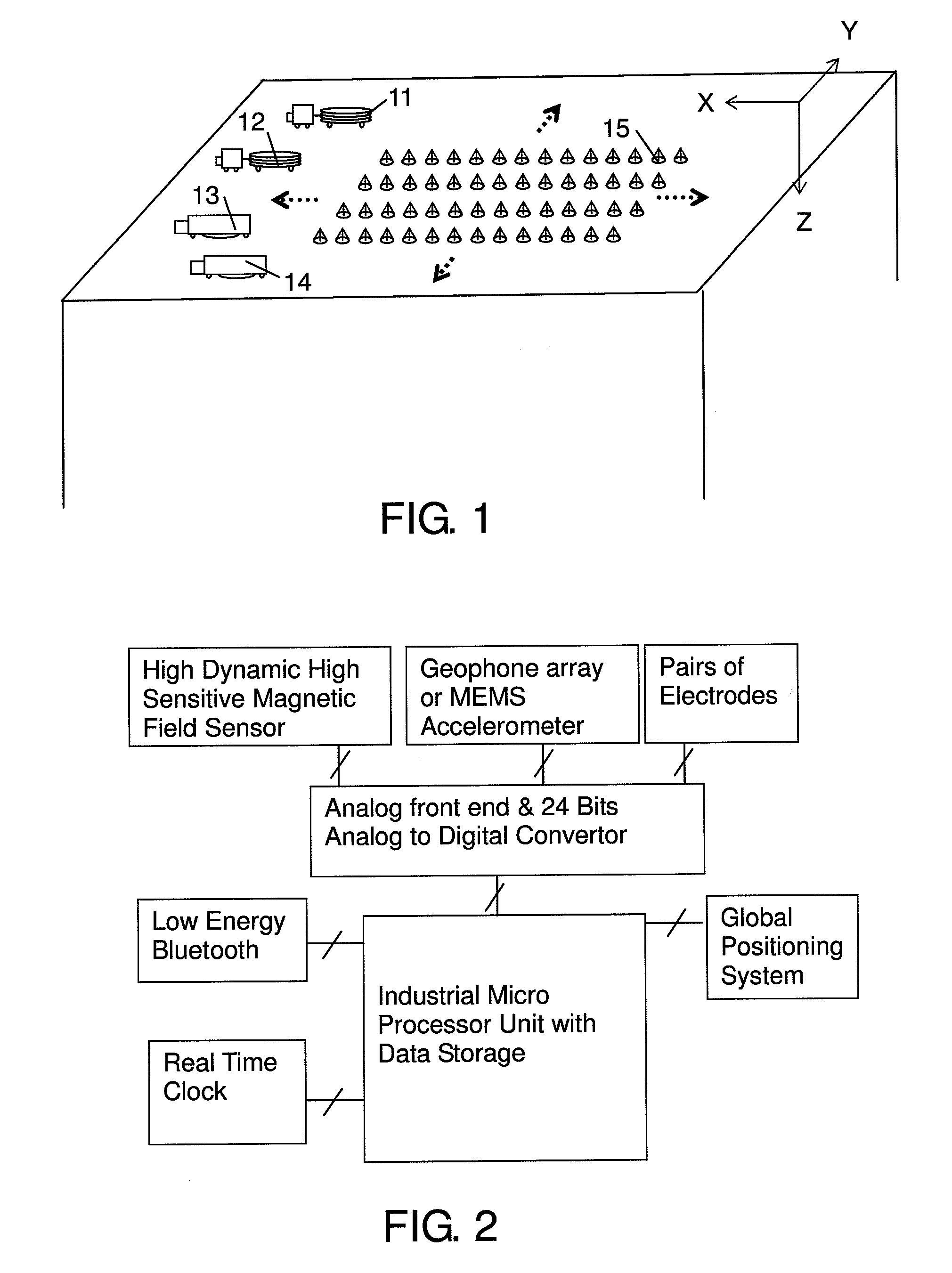
ActiveUS20120262179A1Easy to implementEasy to moveSeismologyDetection using electromagnetic wavesGeophoneAccelerometer
An electromagnetic and its combined surveying apparatus and method, utilizing small-sized one or three-dimensional magnetic field sensors with high dynamic range and high sensitivity, which can be used together with highly populated receivers for the electromagnetic exploration. The electrical field could be derived from the vertical component of the magnetic field of the highly populated receivers and the magneto-telluric data could be derived by measuring the three components of the magnetic data. Moreover, by means of connecting the same populated receivers with geophones or MEMS accelerometers, and moving the seismic sources together with the mobile electromagnetic source, seismic survey could be carried out. It is therefore able to undertake the interpretation of the seismic, electromagnetic and magneto-telluric data and perform a combined field exploration
Owner:WHAN WEN J
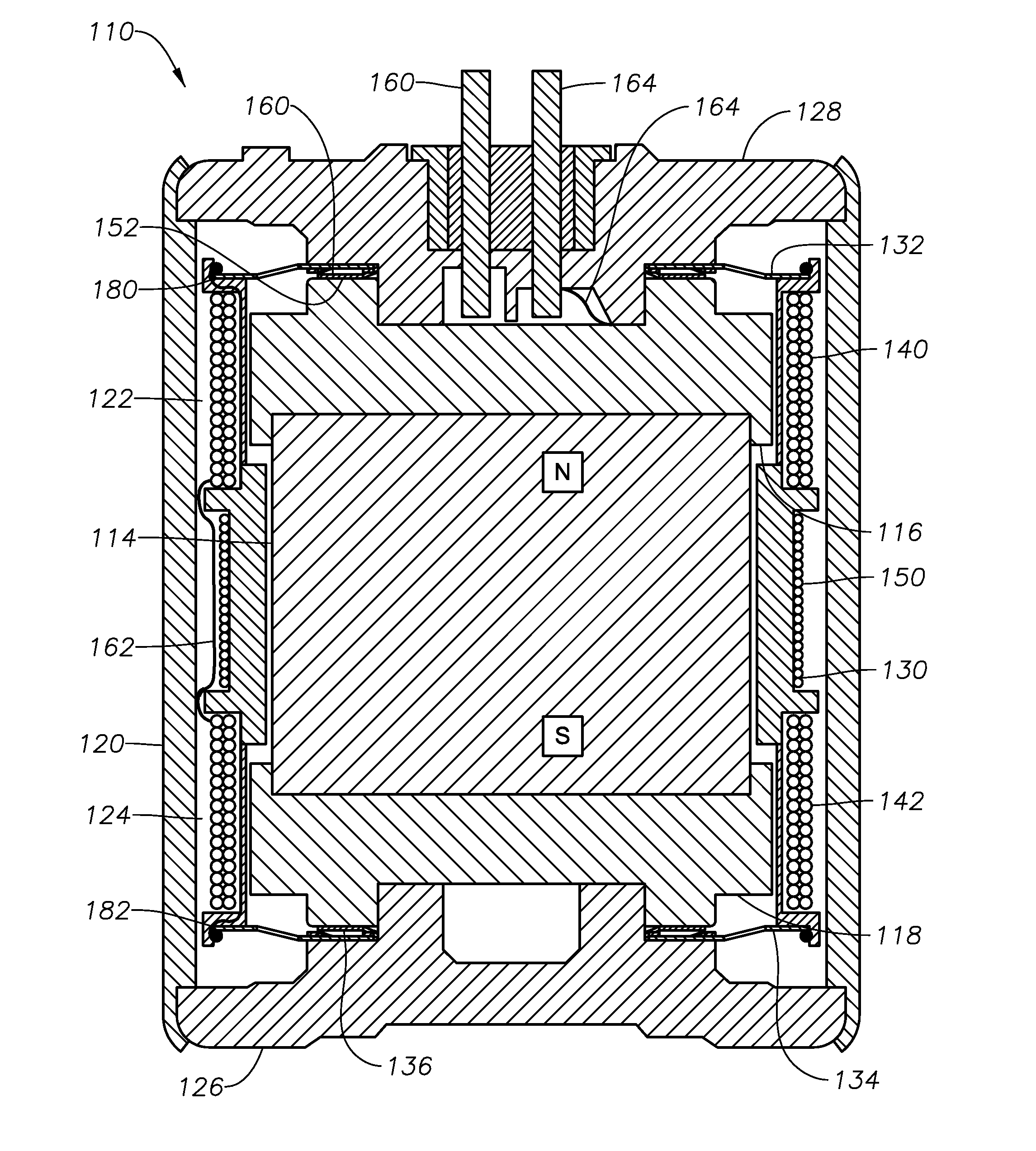
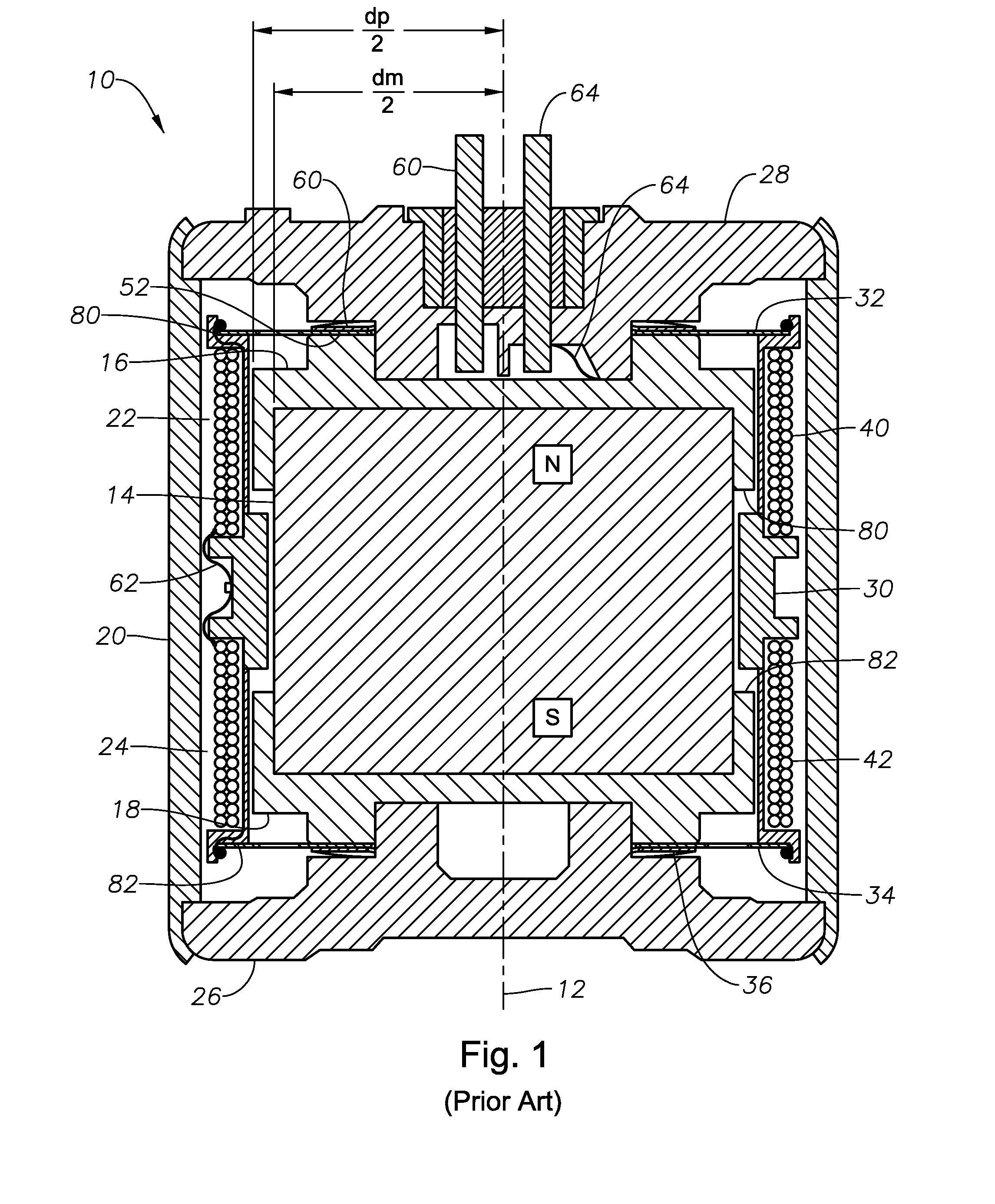
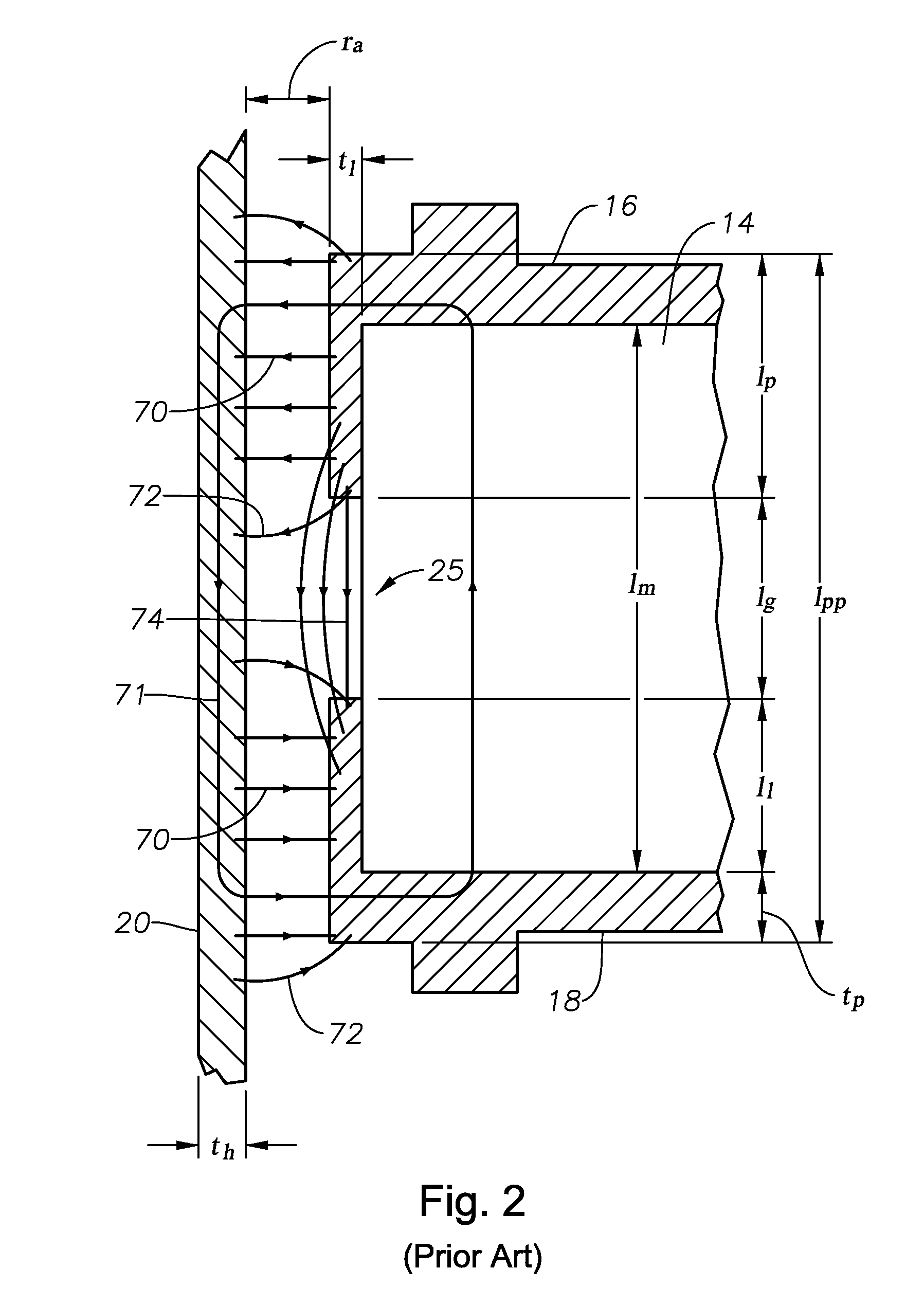
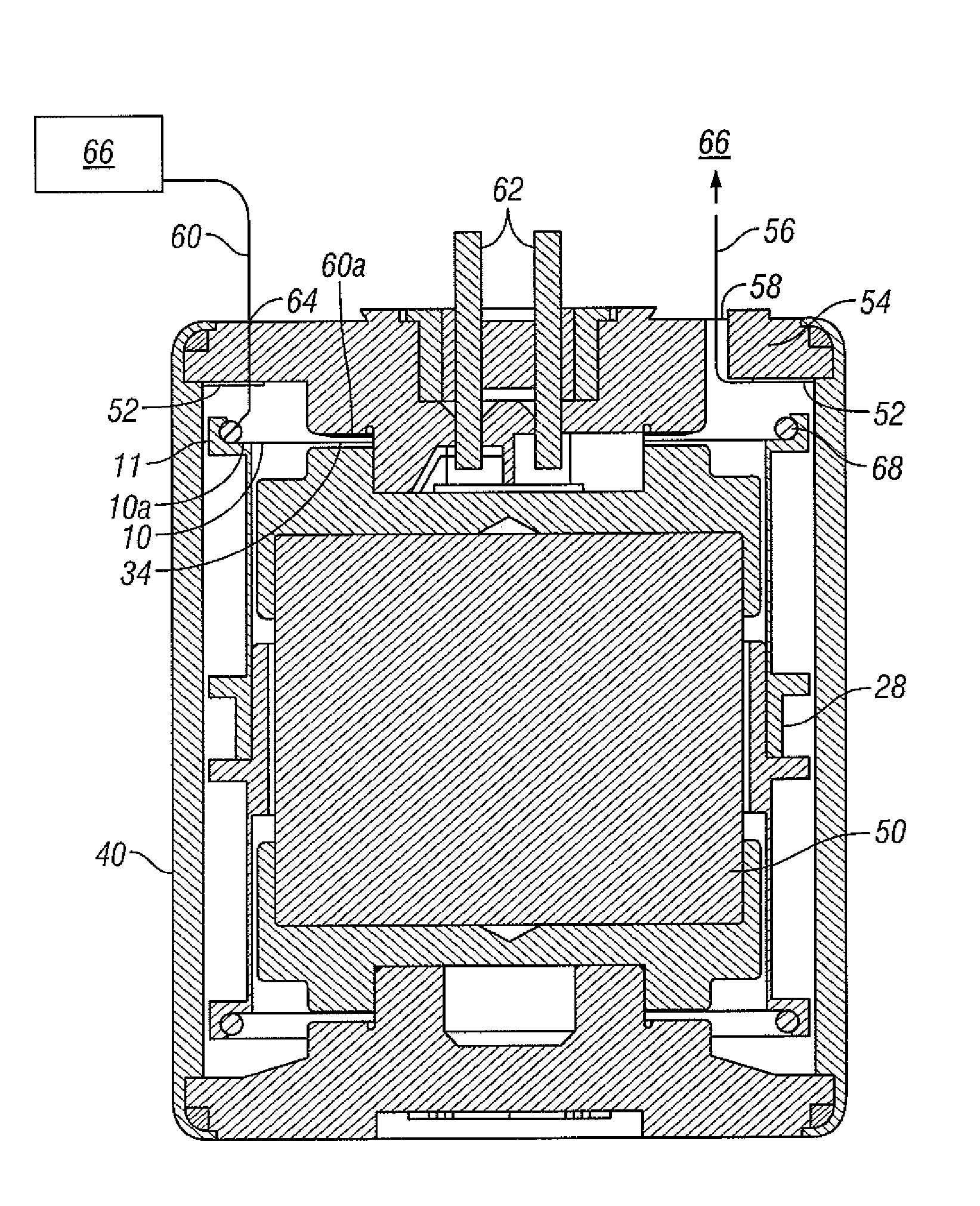
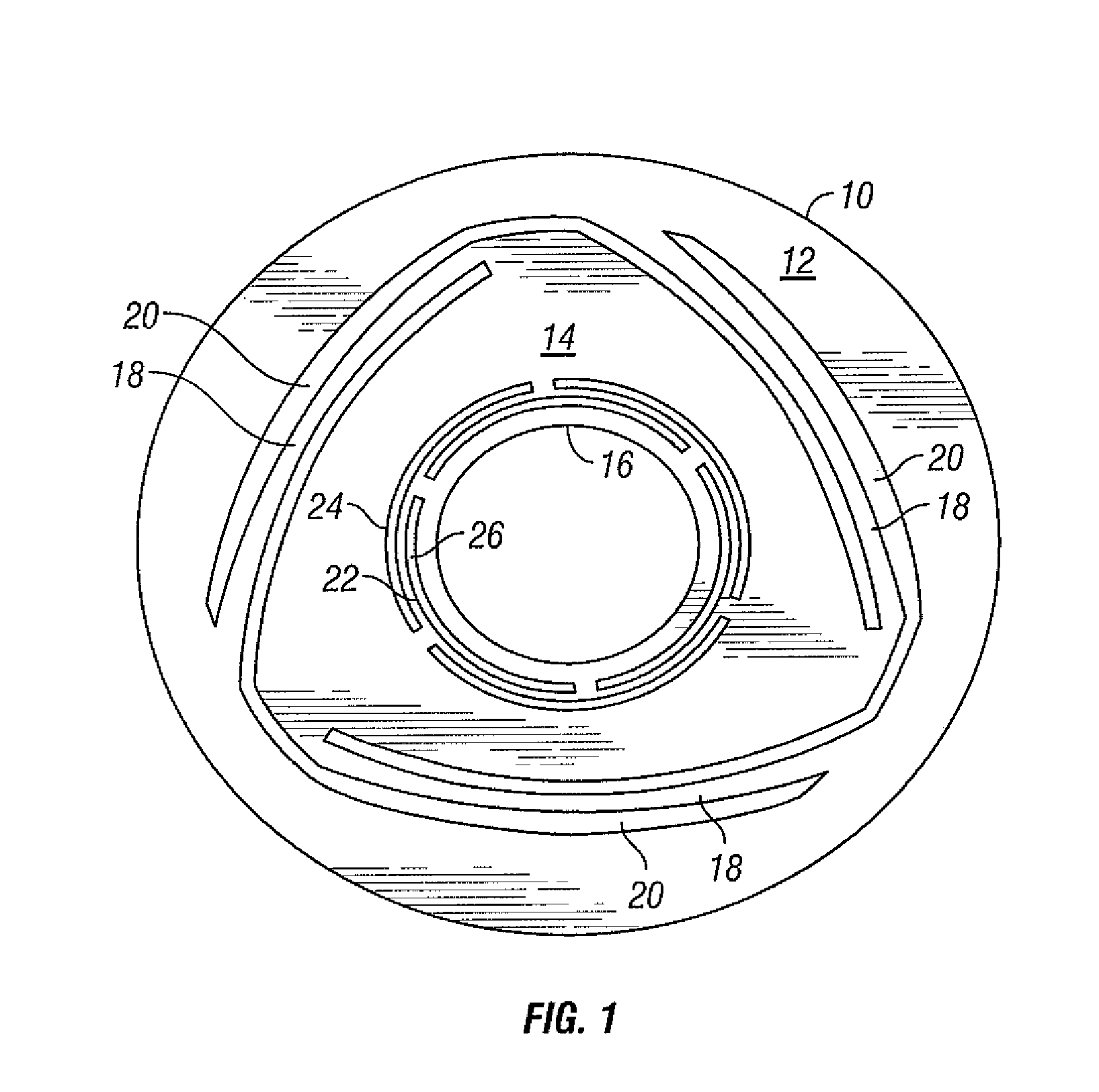
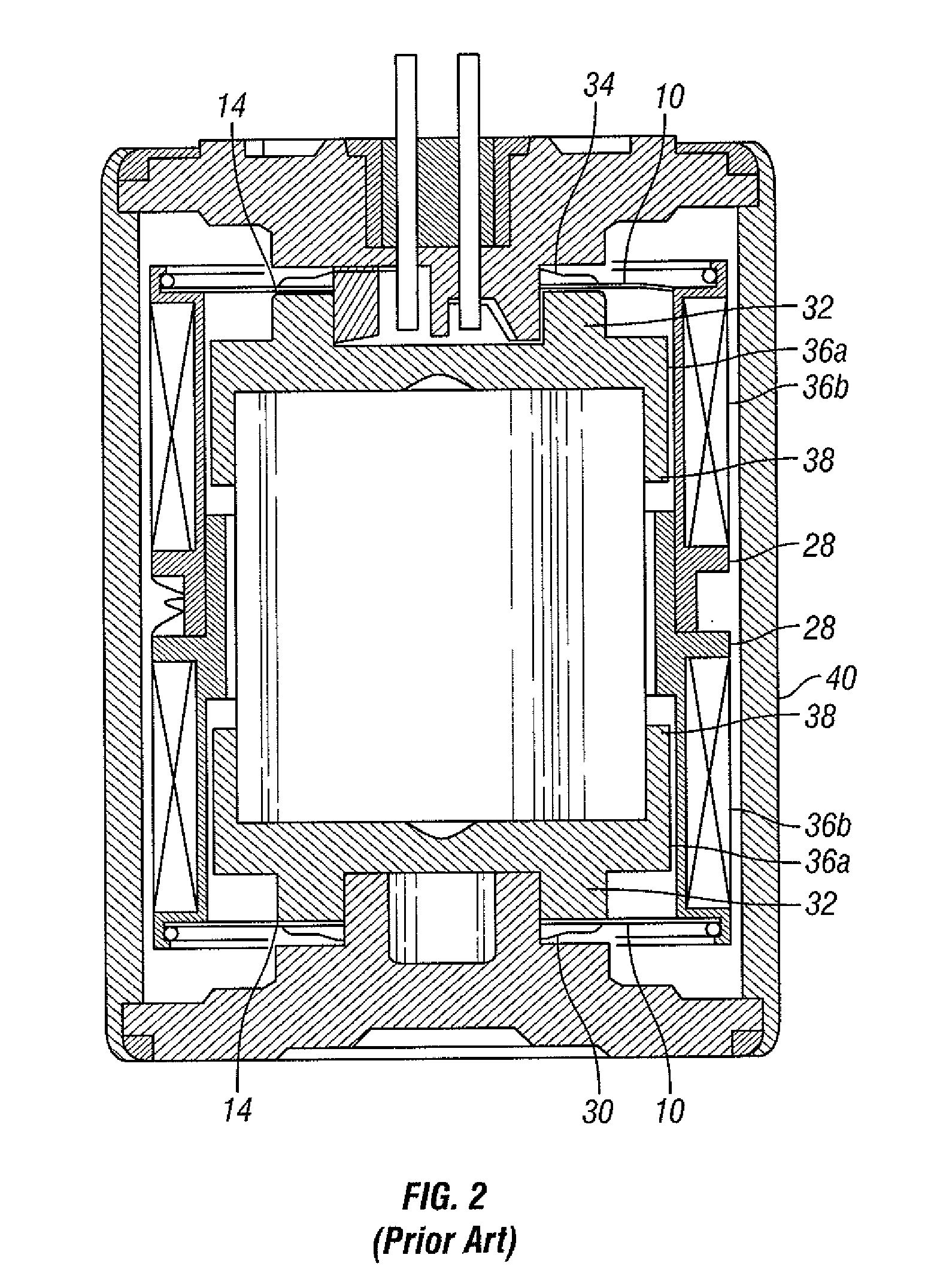
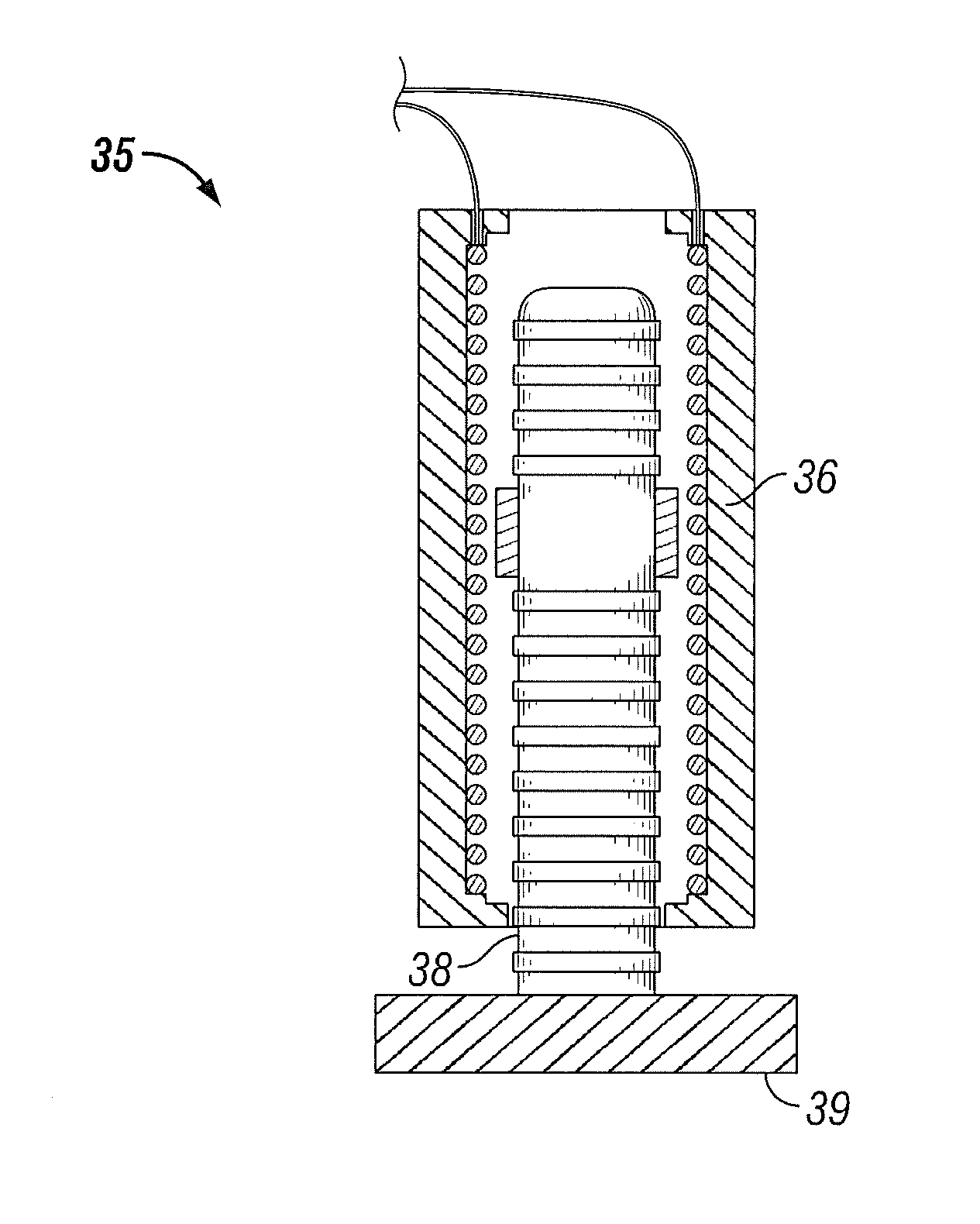
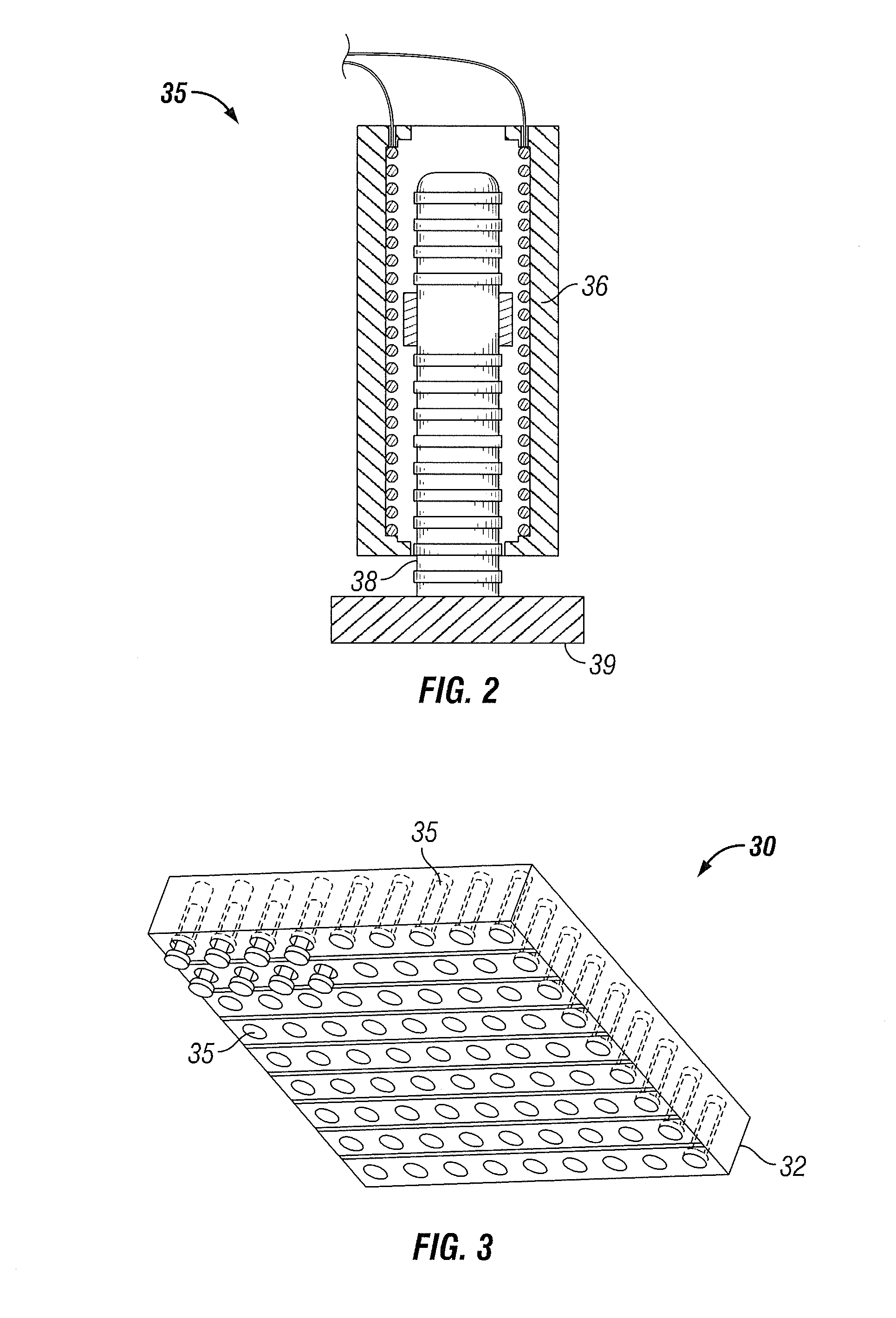
Vertical geophone having improved distortion characteristics
ActiveUS20110007609A1Minimize geophone distortionSimplifies tuningElectrical transducersSeismologyGeophoneEngineering
A vertical geophone that includes a lower frequency spring, which forms part of the geophone electrical circuit, that is positioned directly on the lower end cap This arrangement eliminates the “spring supported by a spring” arrangement of prior art geophones to minimize geophone distortion and simplify tuning of the frequency springs. A contact spring is positioned between the lower frequency spring and the lower pole piece for forming part of the geophone electrical circuit. One surface of contact spring includes a plurality of wiper surfaces that ensure consistent sliding electrical contact against either the bottom surface of the lower pole piece or the upper surface of the lower frequency spring. The obverse surface of the contact spring is preferably spot welded to the other adjacent member.
Owner:GEOSPACE TECH
Sensor arrangement and method for the installation and moving of this
ActiveUS7224641B2Effective and reliable seismic monitoringWave based measurement systemsSeismic signal receiversGeophoneSeismic survey
Arrangement for use for seismic surveys of geological formations in a seabed, where a plurality of such arrangements, which are provided with sensor units 26, are placed on the seabed for collecting pressure waves and shear waves reflected from the geological formations. There exist arrangements for transferring seismic data to a surface receiver placed on a vessel, an offshore installation, or an onshore installation. Each sensor unit 26 is held by a carrier 10 and is connected to a cylindrically skirt-shaped structure 19 adapted to be led down into the seabed, and each sensor unit 26 comprises at least one geophone. The carrier 10 comprises a holder 12 for the cylindrically skirt-shaped structure 19, which structure 19 shall penetrate down into the seabed, as this holder 12 is adapted to be moved between a lower position and an upper position, to be able to be mechanically released from the skirt-shaped structure 19.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
Seismic modem
A system for the transmission of data by seismic wave, the system having at least one transmitting unit, that at least one transmitting unit comprising a first processing unit encoding a first signal, the first processing unit being coupled to a digital to analog converter, an amplifier amplifying the first signal, and a seismic pressure wave inducer transmitting the first signal to a geological feature; and at least one receiving unit, the receiving unit comprising at least one receiver coupled to the geological feature for receiving the first signal, and an analog to digital converter whereby the first signal is transferred from the geophone and is conveyed to a second processing unit, the second processing unit being configured to identify and decode the first signal.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Seismic monitoring
ActiveUS9759824B2Mitigate disadvantageAvoid the needSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSeismic signal receiversGeophoneRegion of interest
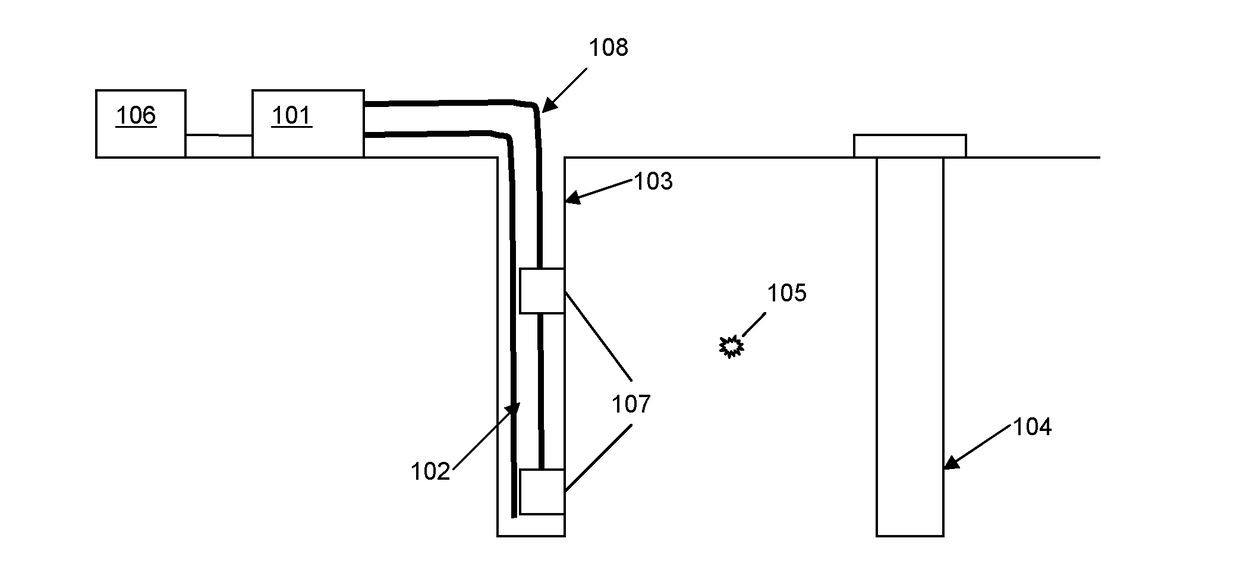
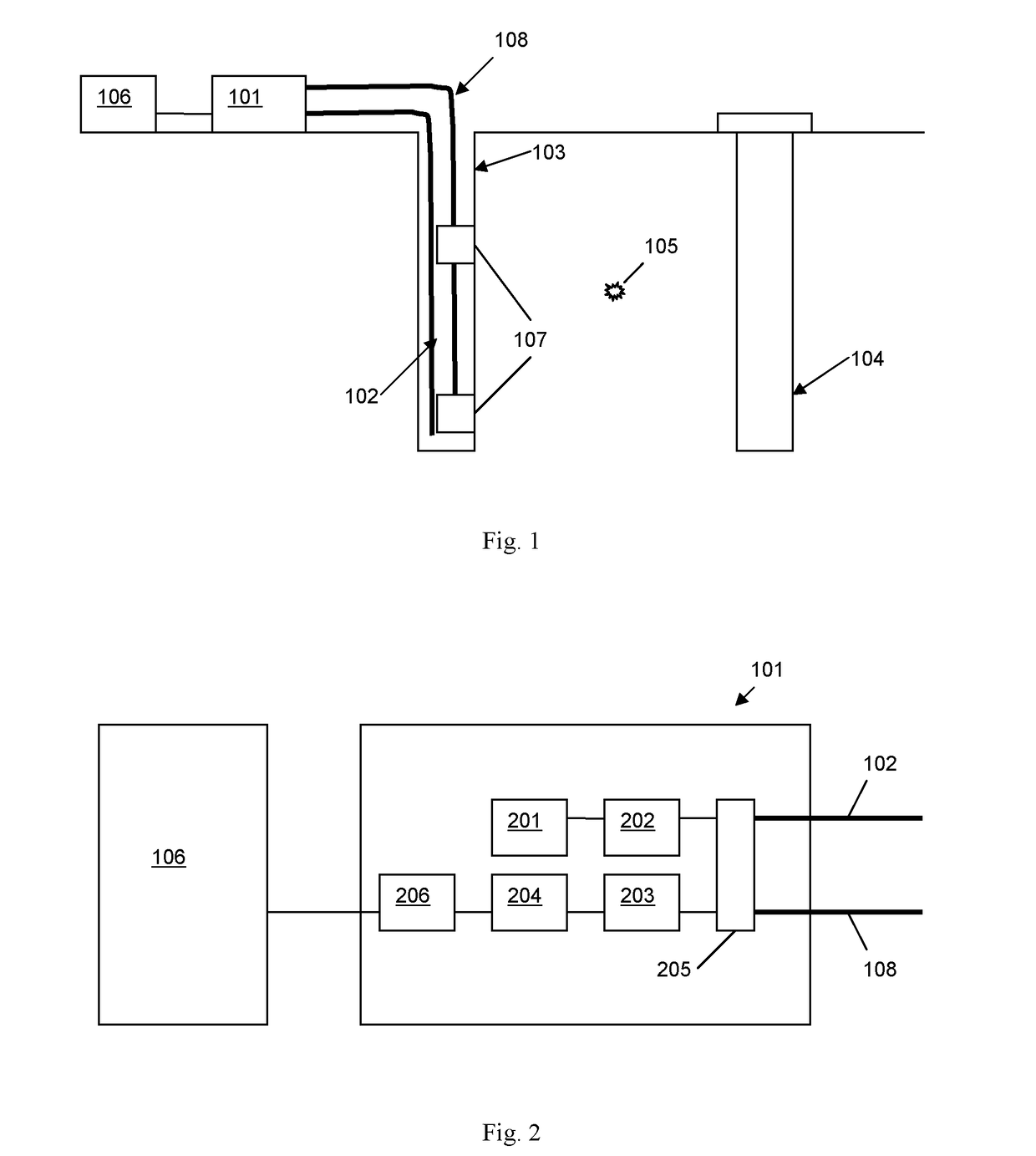
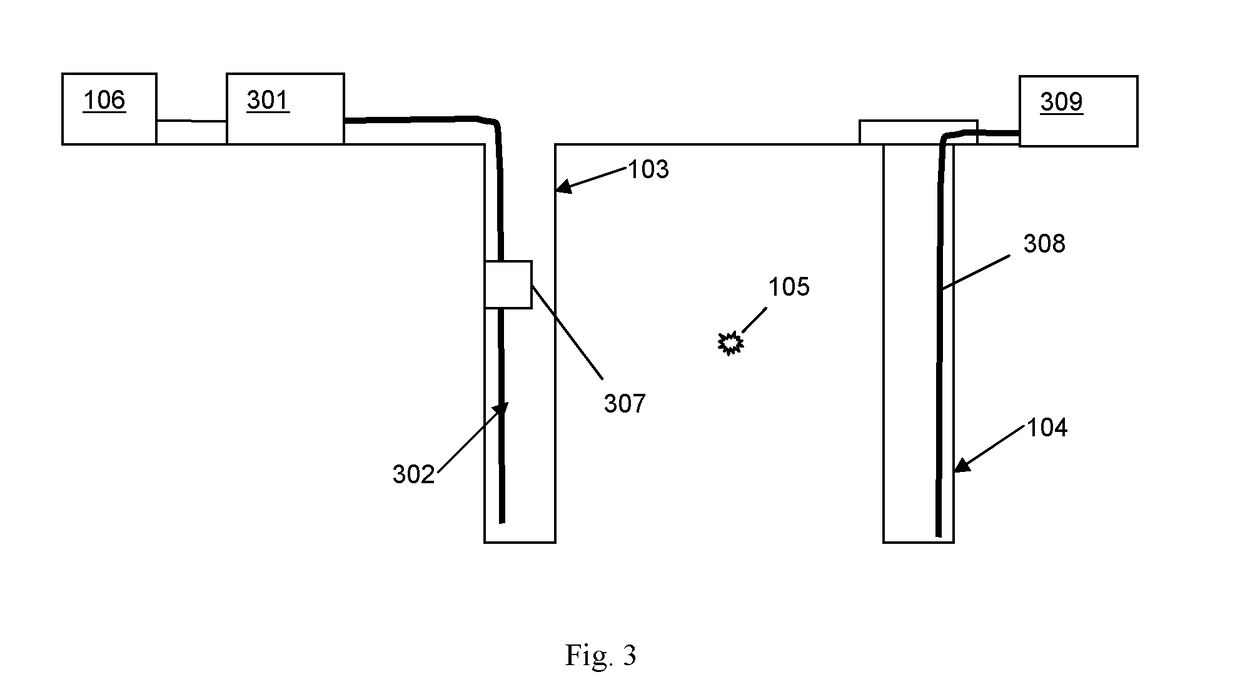
The application describes methods and apparatus for seismic monitoring using fiber optic distributed acoustic sensing (DAS). The method involves interrogating a first optical fiber (102) deployed in an area of interest to provide a distributed acoustic sensor comprising a plurality of longitudinal sensing portions of fiber and also monitoring at least one geophone (107) deployed in the area of interest. The signal from the at least one geophone is analyzed to detect an event of interest (105). If an event of interest is detected the data from the distributed acoustic sensor acquired during said event of interest is recorded. The geophone may be co-located with part of the sensing fiber and in some embodiments may be integrated (307) with the sensing fiber.
Owner:OPTASENSE HLDG LTD
Bottom module for seismic survey
InactiveUS20130028047A1Expand the scope of useReduction of laboriousnessSeismology for water-covered areasElectricityHydrophone
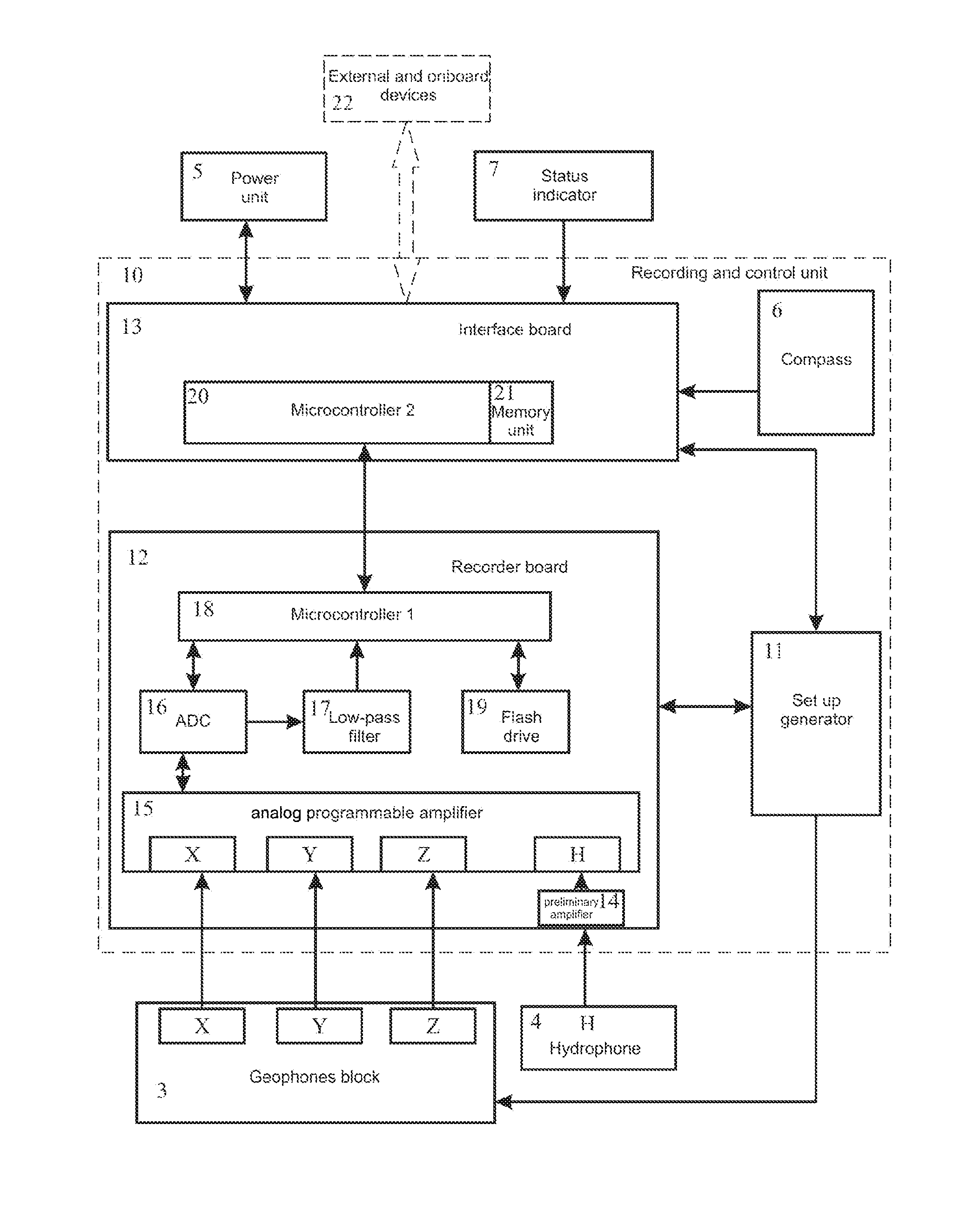
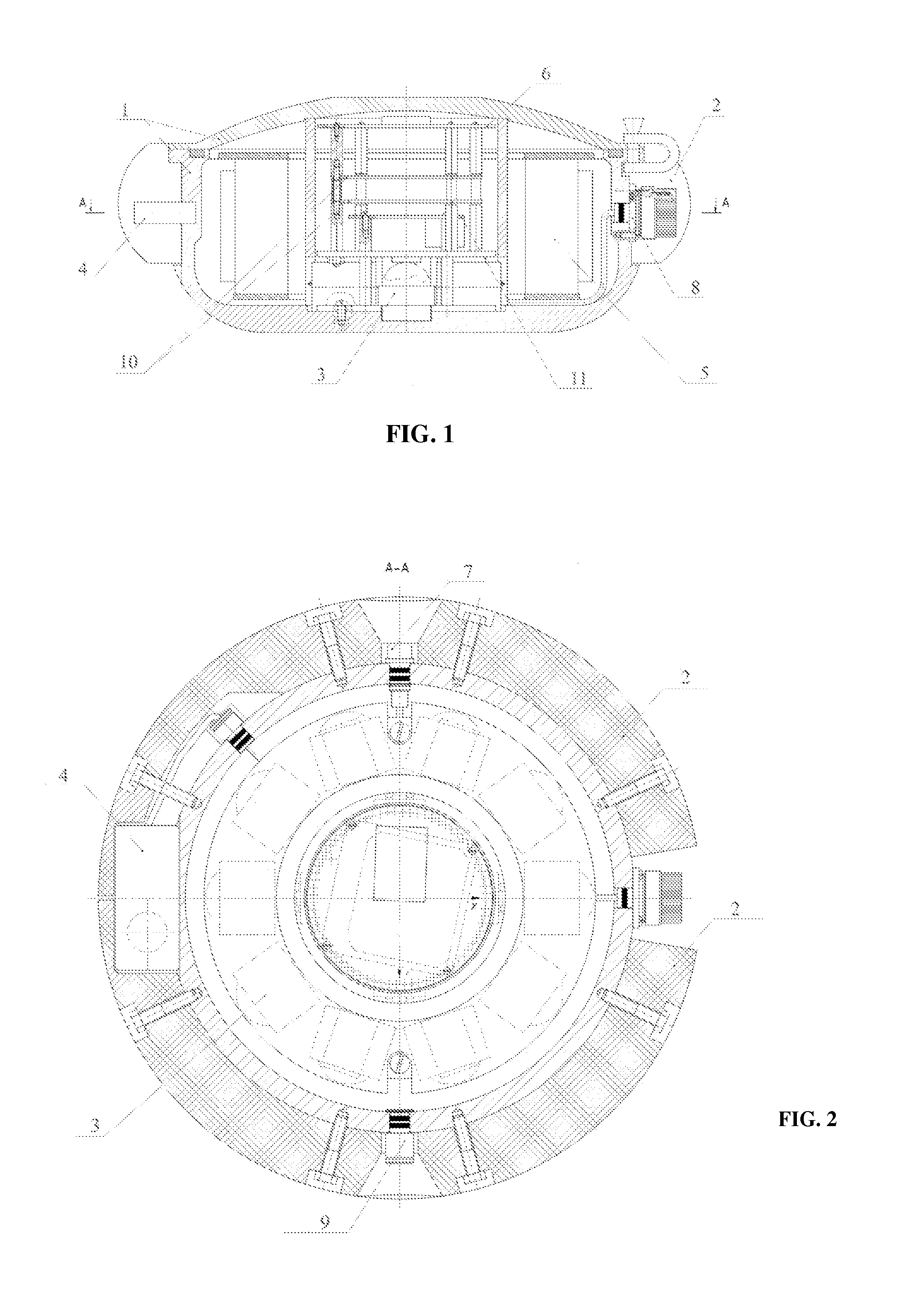
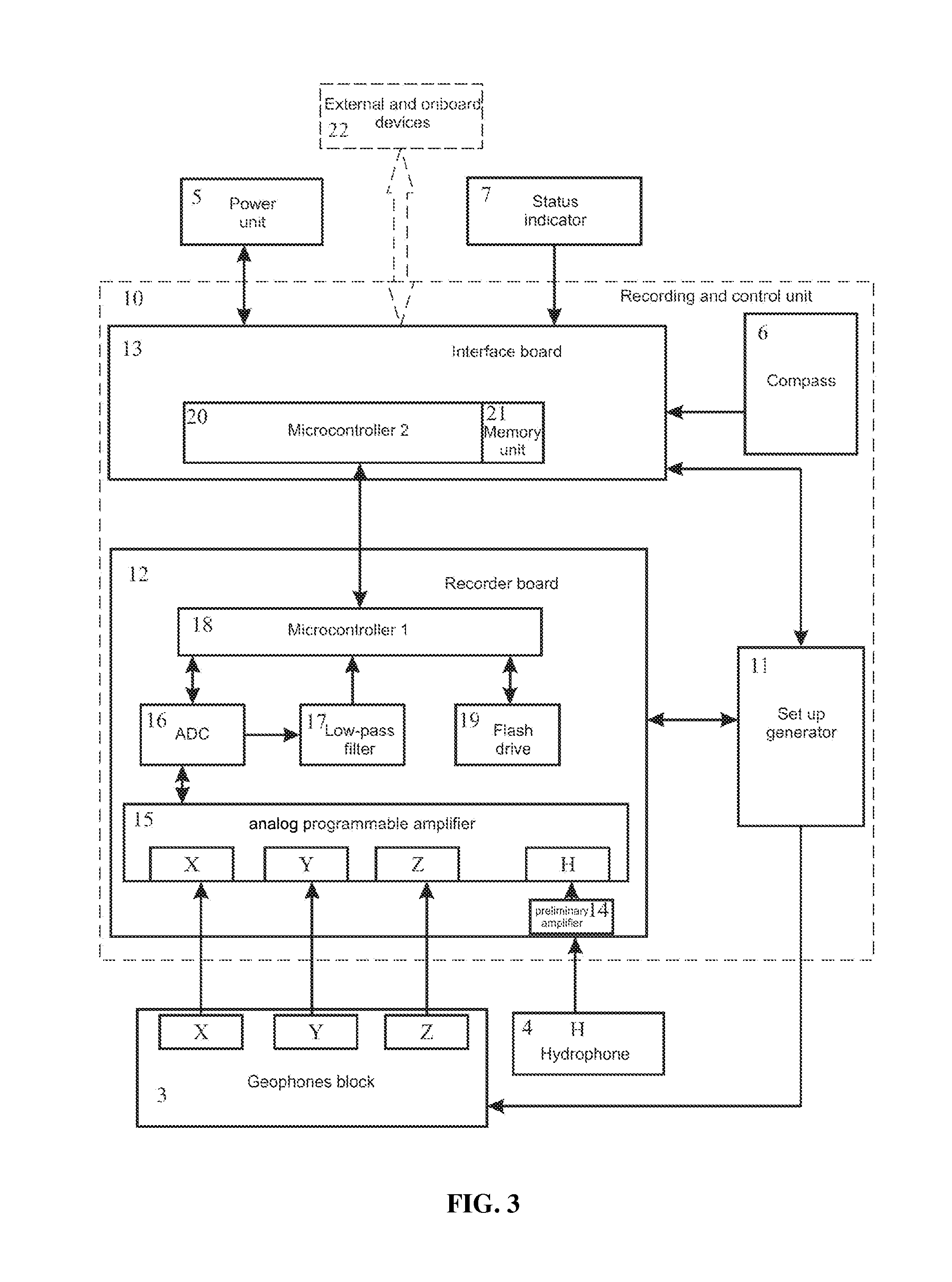
A system is proposed for conducting efficient marine seismic surveys in different climatic conditions for water depths of 0-500 meters, in near-shore zones and on the land for obtaining seamless profiles. The system includes at least one bottom module (BM) and onboard devices located on a vessel. The BM can be submerged from the vessel onto a bottom ground and lifted up on the board. The BM includes a case provided with roundings on its upper surface and its bottom area, to which case are mounted damping elements, a hydrophone and a geophone block for receiving seismic data, a vacuum port, a hermetic electrical socket, and equipment arranged inside the case, including—a clock generator,—a digital compass providing angle data,—an interface board essentially reading the seismic and angle data and transmitting thereof to the onboard devices, and—a recorder board communicating with the geophones, hydrophone, and interface board.
Owner:TULUPOV ANDREJ VLADIMIROVICH
Lateral stress pore pressure probe used for testing soil static lateral pressure coefficient
InactiveCN103174122ASolve the defect that the static lateral pressure coefficient of the soil layer cannot be measuredConvenient in situ static side pressure coefficientIn situ soil foundationConvertersPore water pressure
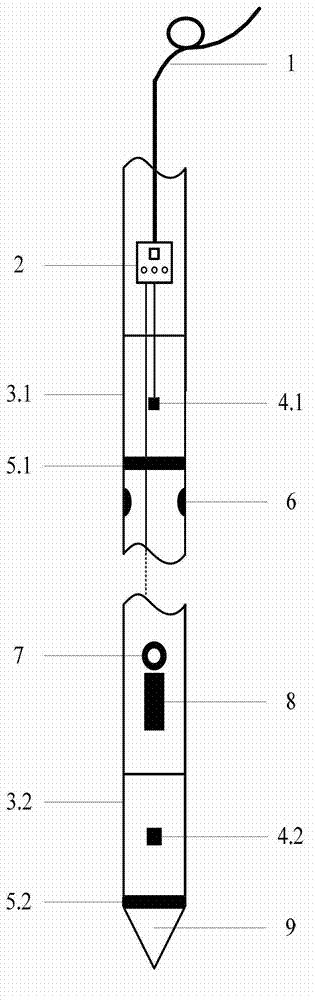
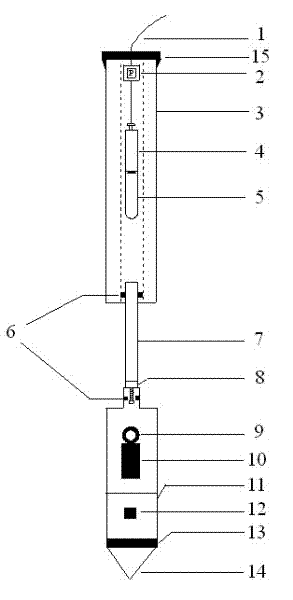
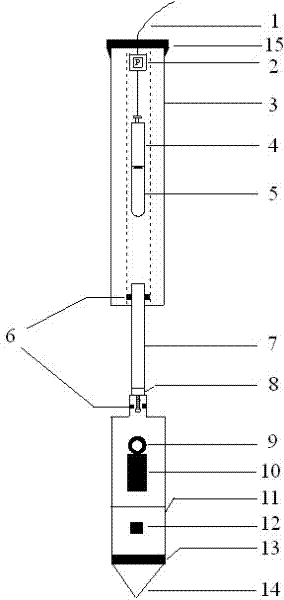
The invention discloses a lateral stress pore pressure probe used for testing a soil static lateral pressure coefficient. An analog-digital converter (2) is arranged on the top portion of the upper half section of the probe, a side wall upper friction drum (3.1), an upper pore pressure filtering ring (5.1) and a pair of lateral stress sensors (6) are sequentially arranged on the lower portion of the analog-digital converter (2) from top to bottom, the lateral stress sensors (6) are symmetrically arranged on the outer wall of a feeler lever, and an upper pore space water pressure sensor (4.1) is arranged in the middle of the side wall upper friction drum (3.1). A three-component seismic detector (7), a clinometer (8), a side wall lower friction drum (3.2), a lower pore pressure filtering ring (5.2) and a cone probe (9) are sequentially arranged on the lower half section of the probe from top to bottom, and a lower pore space water pressure sensor (4.2) is arranged on the middle portion of the side wall lower friction drum (3.2). Signal and data transmission is achieved through connection of a coaxial-cable (1) and the analog-digital converter (2) arranged on the top portion of the probe. The lateral stress pore pressure probe has the advantages of being in-situ, rapid, continuous, economical and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Omnidirectional vector seismic data processing method and apparatus, computer-readable storage medium and device
The invention discloses an omnidirectional vector seismic data processing method and apparatus, a computer readable storage medium and a device, applied to an omnidirectional vector geophone. Wherein the method comprises: collecting omnidirectional vector seismic data of the omnidirectional vector geophone, and performing a pre-processing operation on the omnidirectional vector seismic data; performing pressure and shear waves separation operation on the omnidirectional vector seismic data after the data is subject to the pre-processing operation, to obtain pressure wave data and shear wave data; sequentially performing space vector calculation, a wave field recovery operation and an imaging operation on the pressure wave data and the shear wave data, and then performing modeling to obtain a pressure wave velocity model and a shear wave velocity model. The invention solves the problem of the existing seismic exploration technology that cannot measure and process divergence data and curl data of seismic wave field, so as to improve construction, lithology, fluid exploration accuracy and reliability and promote seismic exploration to be developed from structural exploration to lithology exploration and fluid exploration.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
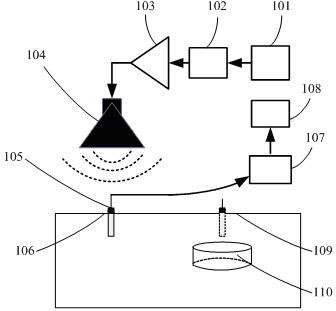
Device and method for measuring resonance intensity of land mine
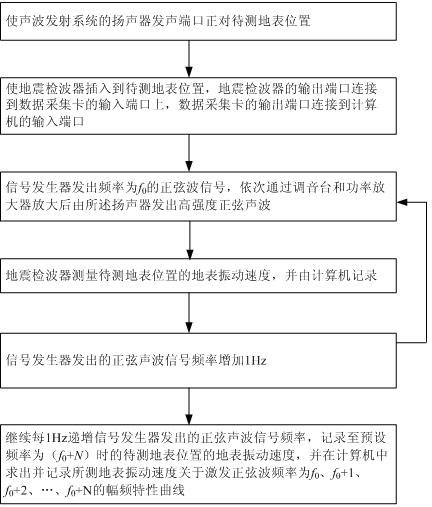
InactiveCN102540245AWork around limitations of increased sensitivityQuick measurementVibration measurement in solidsSeismologyMeasurement deviceData acquisition
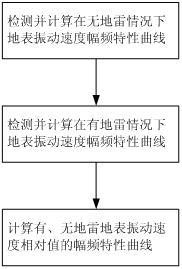
The invention discloses a device for measuring resonance intensity of land mine. The device includes a signal generator, a sound console, a power amplifier and a loudspeaker, wherein the signal generator is connected with the sound console, the power amplifier and the loudspeaker sequentially through leads to form a sound wave emission system. The device further includes a seismic detector, a data acquisition card and a computer, wherein the seismic detector is connected with the computer via the data acquisition card through a data line to form a ground surface vibration speed detection system. A method for measuring resonance intensity of the land mine by using the device particularly comprises the following steps of: 1) detecting and calculating a ground surface vibration speed amplitude-frequency characteristic curve under the condition without the land mine; 2) detecting and calculating a ground surface vibration speed amplitude-frequency characteristic curve under the condition with the land mine; and 3) evaluating a specific value of the two curves in the steps to acquire a ground surface vibration speed relative value amplitude-frequency characteristic curve under the conditions with and without the land mine. By the measuring device and the measuring method, the resonance intensity of the land mine can be measured precisely and quickly.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Determination of geophone coupling
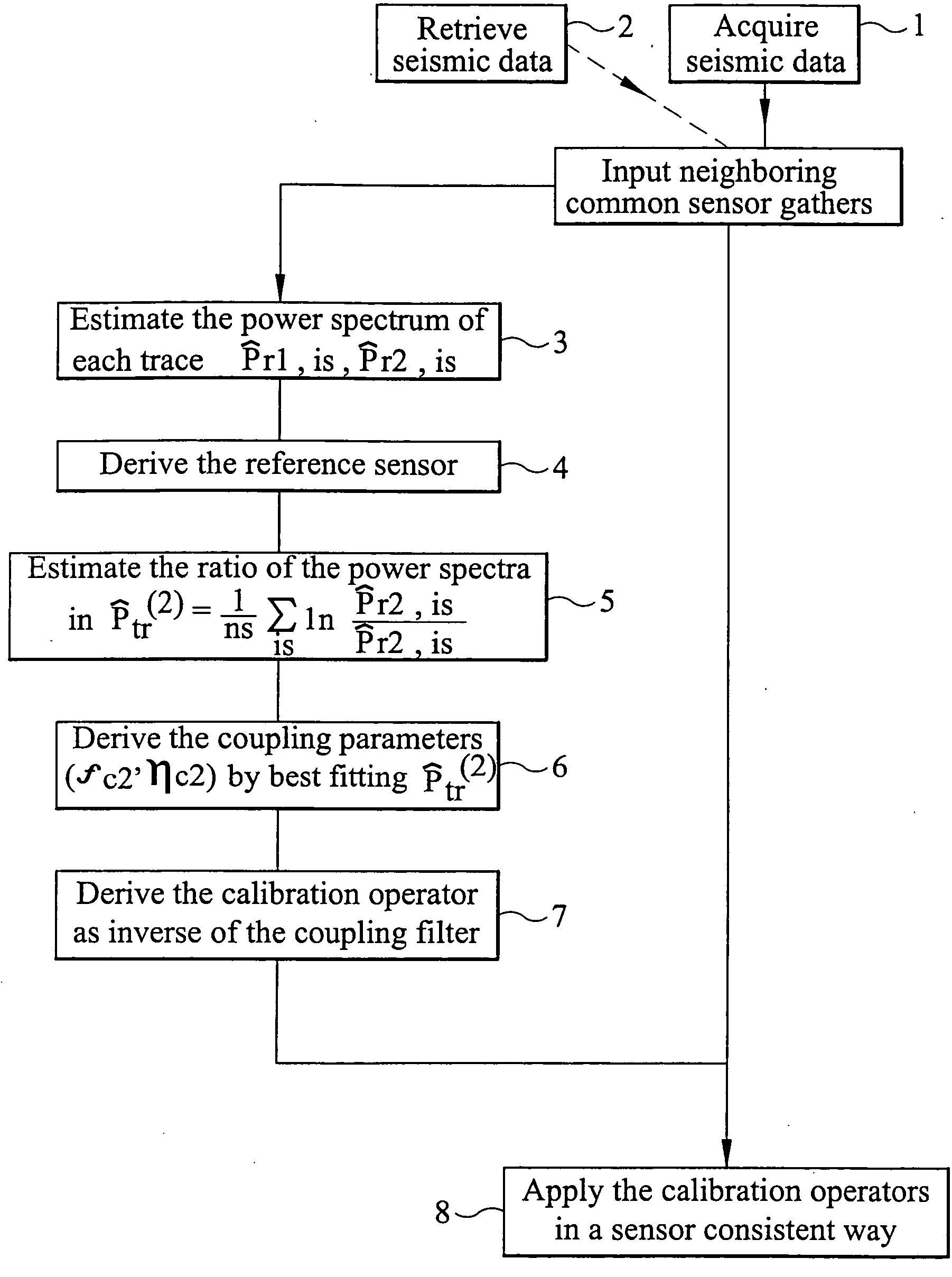
ActiveUS20050114034A1The process is fast and accuratePoor couplingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesStatic/dynamic balance measurementGeophoneCoupling
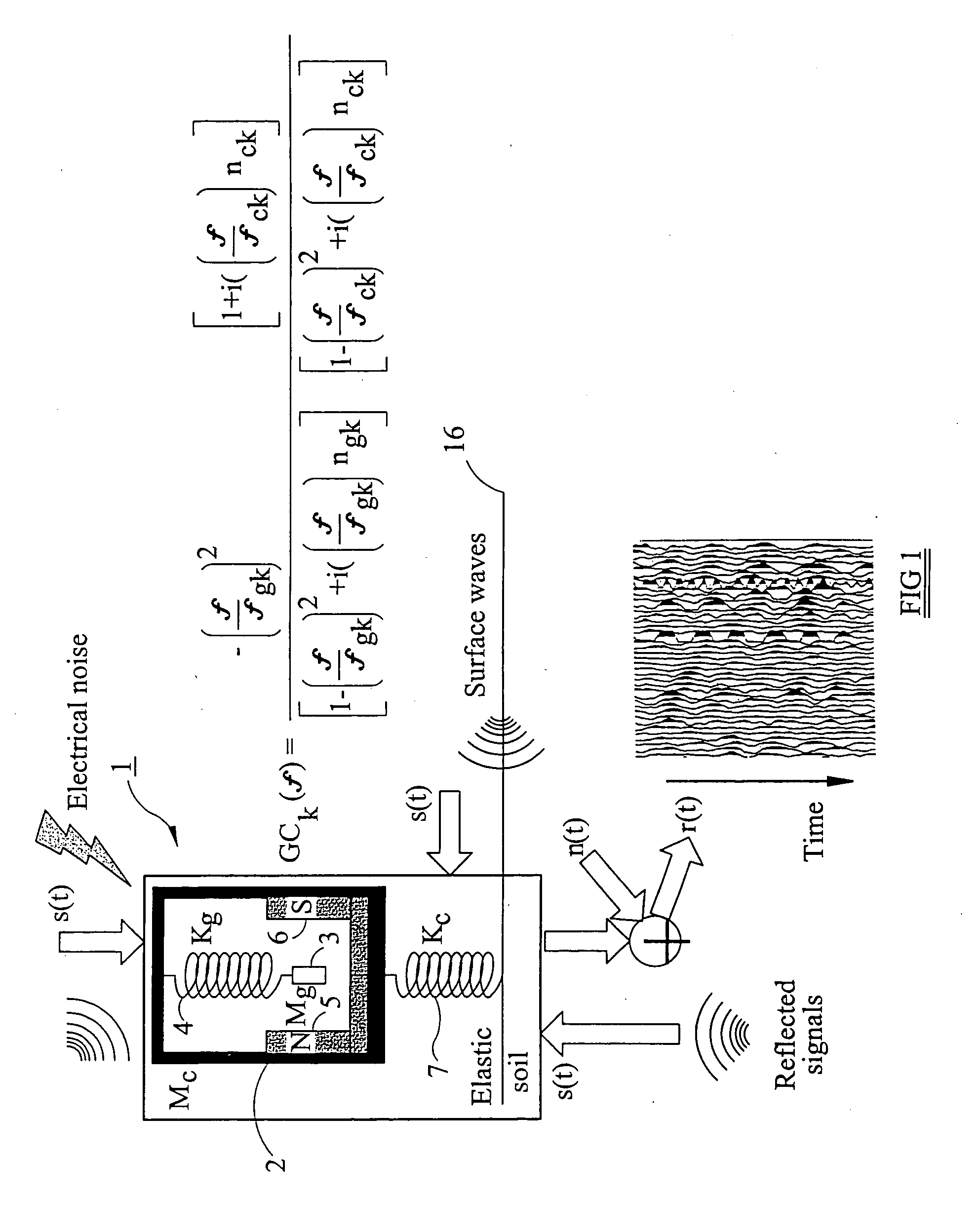
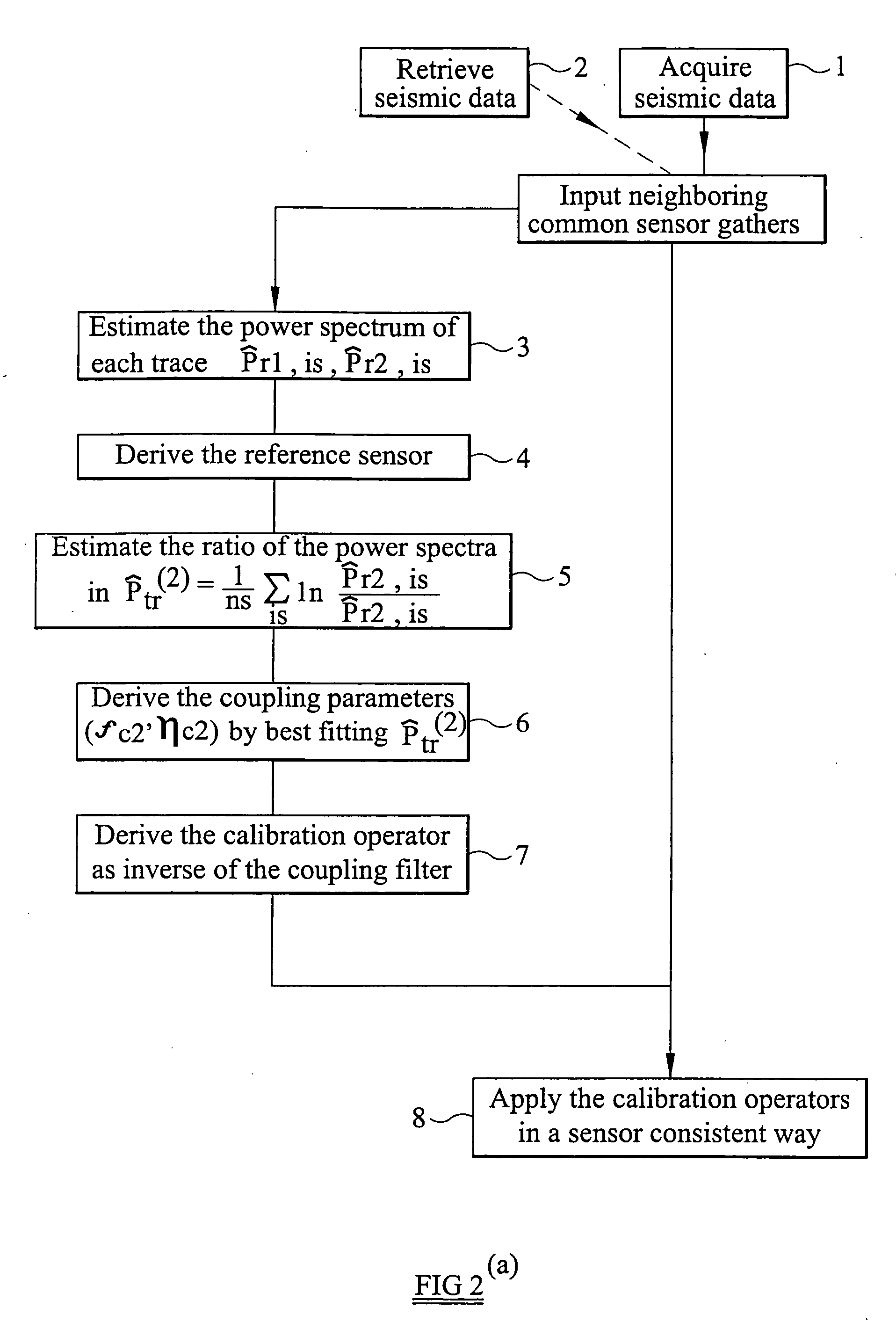
Information about coupling of a seismic receiver is obtained from a power spectrum for a record acquired at a seismic receiver. In one method, the power spectrum for the record is compared with a reference power spectrum, which may be known a priori or which may be determined from the power spectra of records acquired by a group of receivers. In an alternative method, one receiver of a group of receivers is designated as a reference receiver, and the power spectra of records acquired by other receivers in the group are compared with a power spectrum for the reference receiver. The obtained information about the coupling of a receiver may be used to determine a coupling correction operator for the receiver, and this operator can be applied to seismic data acquired by the receiver to correct for the effects of imperfect coupling of the receiver.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Environmental geotechnical piezocone penetration test probe capable of extracting gas samples and gas sample extracting method
ActiveCN102518107ASolve the defect of not being able to take gas samplesIn situ soil foundationGeophoneSoil science
The invention relates to an environmental geotechnical piezocone penetration test probe capable of extracting gas samples and a gas sample extracting method. A sealing cover (15) is arranged at the top of the probe, and a cable (1) penetrates out from the sealing cover; the upper half section of the probe is a hollow cylindrical probe rod (3), and a pore pressure sensor (2), a small-sized hose pump (4) and a sampling container (5) are arranged in the probe rod in the upper half section; a probe rod (7) with a polypropylene porous filter screen is disposed on the middle section of the probe, and an upper O-shaped ring (6) is connected with the probe rod with the polypropylene porous filter screen and the hollow cylindrical probe rod (3); and a copper threaded opening connector (8) at the lower portion of the probe is connected with the middle probe rod, a three-component seismic detector (9) is disposed under the copper threaded opening connector (8), and a gradiograph (10), a side wall friction barrel (11), a temperature sensor (12), a pore pressure filtering ring (13) and a conical probe (14) are arranged under the three-component seismic detector (9). The probe has the advantages that the probe can be located at an original position, is fast, accurate and economical and the like, and is a powerful sampling tool for an environmental geotechnical engineering CPTU (piezocone penetration test).
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
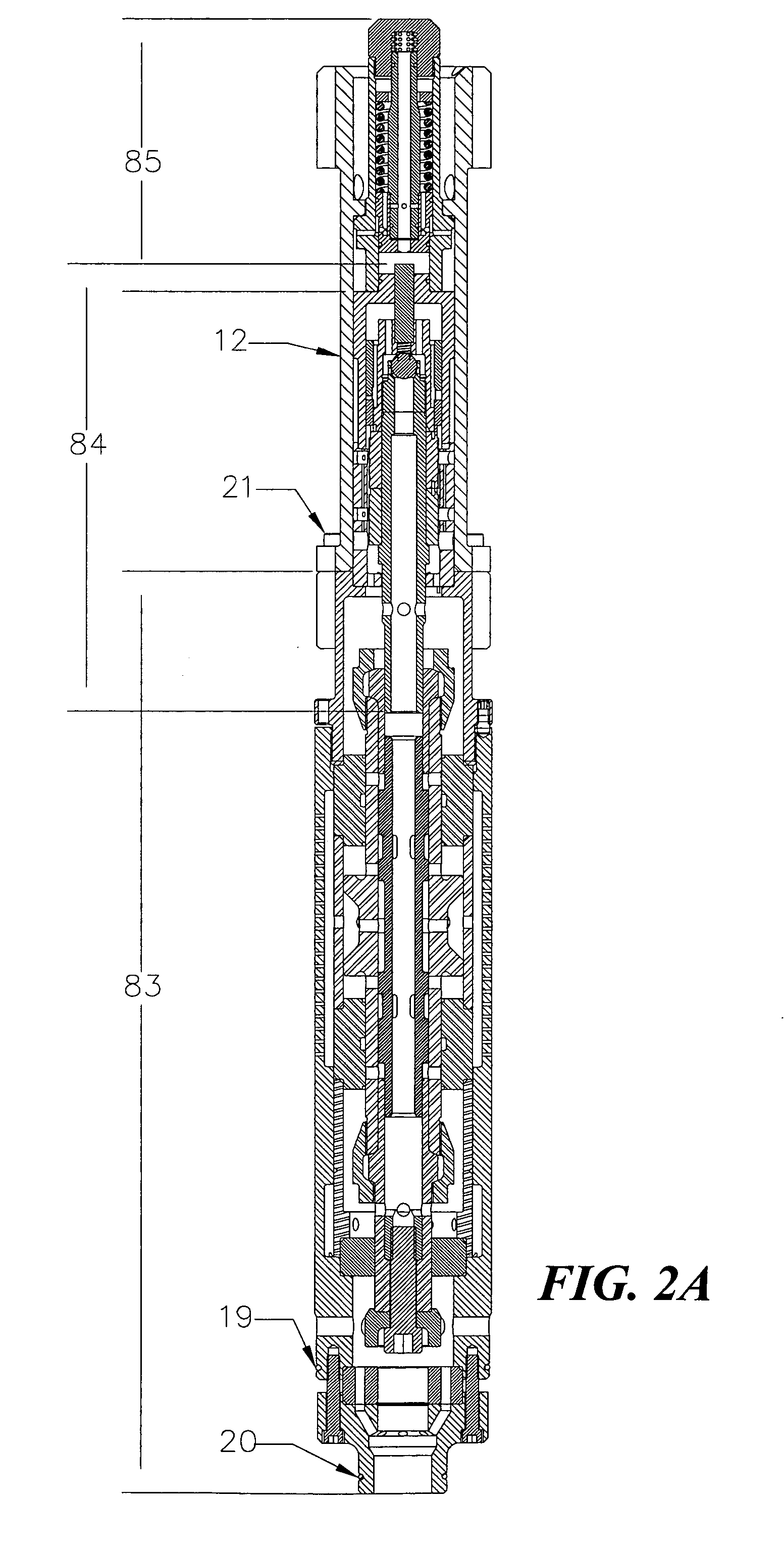
Geophone with mass position sensing
ActiveUS20070223314A1Increase the effective surface areaElectrical transducersSeismic signal receiversGeophoneMotion sensing
A motion sensing element with position sensing includes a case, a magnet positioned within the case, a spring assembly having an electrically conductive member and a coil assembly coupled to the spring assembly. The coil assembly and magnet are moveable with respect to one another. A capacitor plate is proximate the electrically conductive member with a distance between the capacitor plate and electrically conductive member being variable as the magnet and coil assembly move. Leads connect the capacitor plate and electrically conductive member to a sensing circuit for estimating the relative positions of the magnet and coil assembly.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
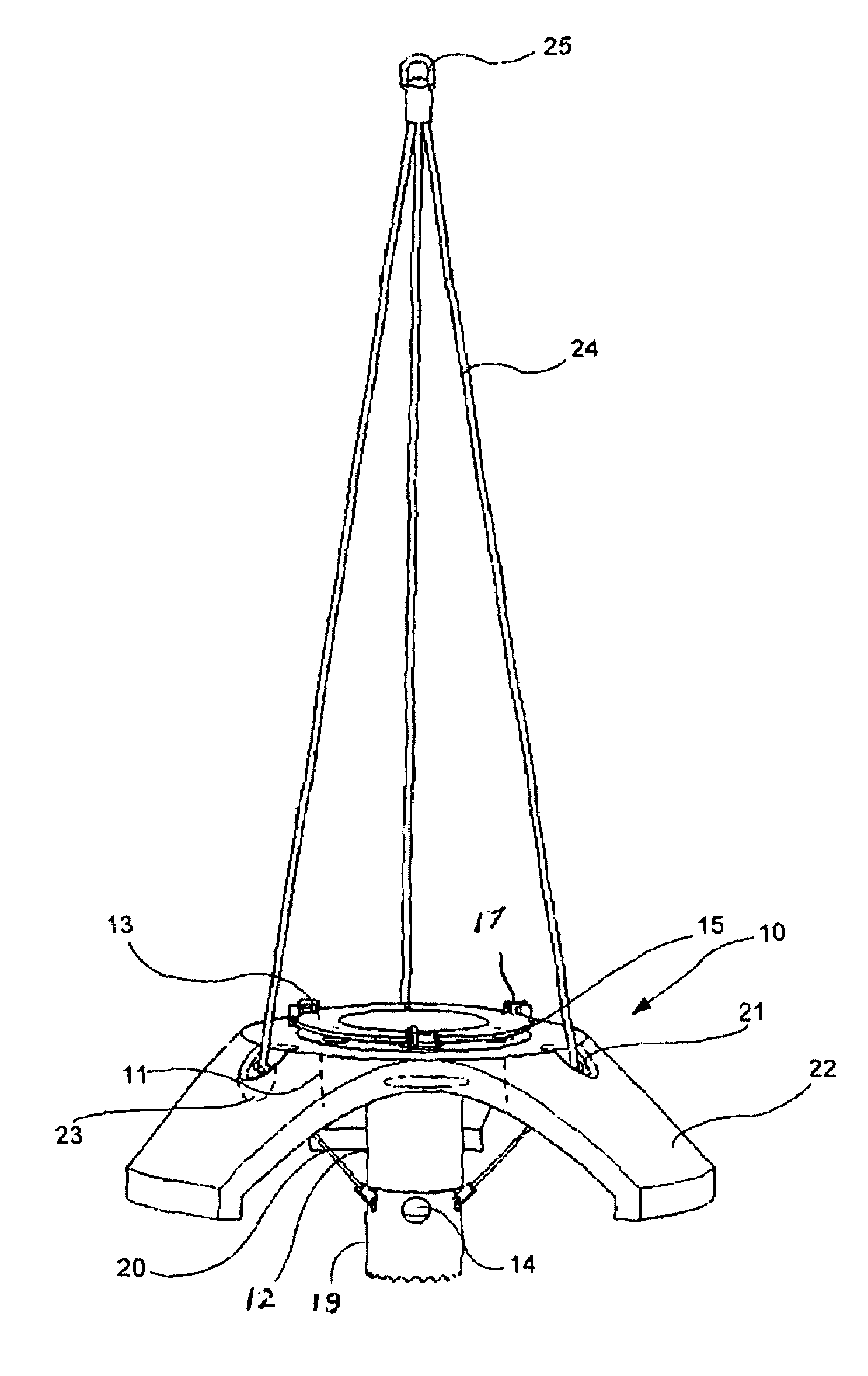
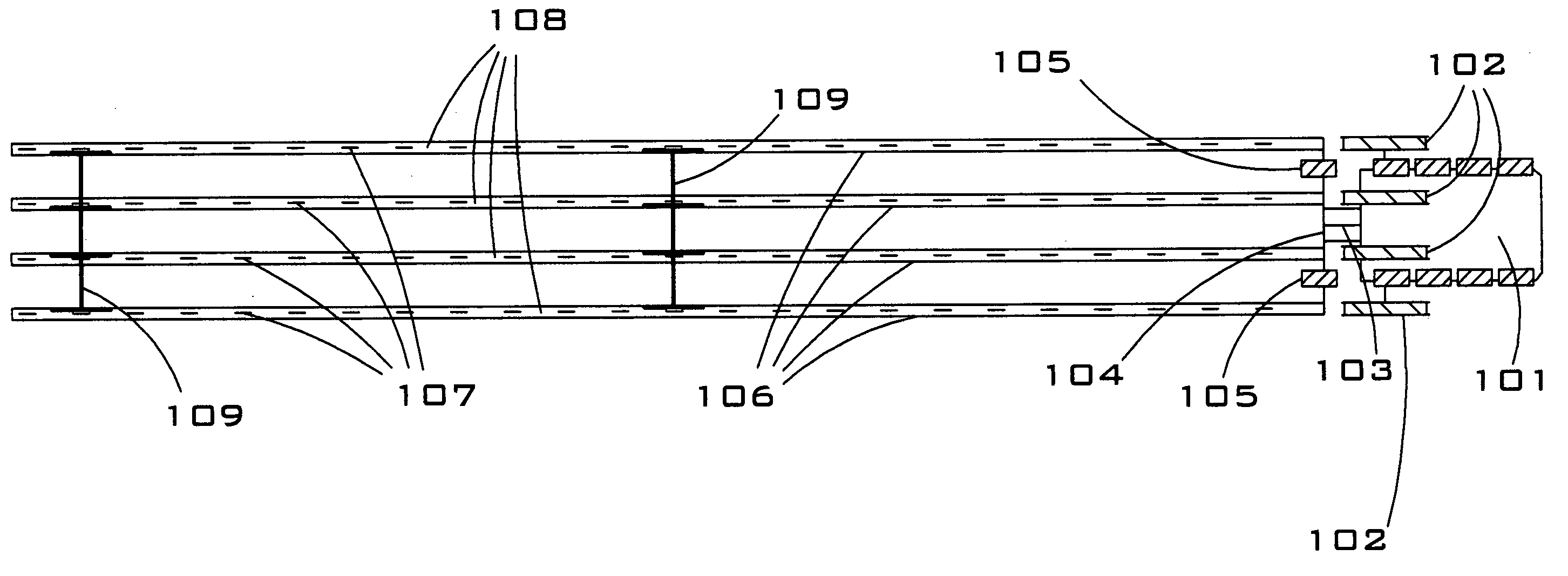
Rapidly deployable, three-dimensional seismic recording system
InactiveUS20050249039A1Improve stabilityFacilitates rapid deploymentTransducer detailsSeismic data acquisitionGeophoneEngineering
A mobile, easily deployable, three-dimensional seismic recording system suitable for shallow seismic reflection or refraction surveys. The system comprises a towing unit, a reel assembly system, a towing frame, and one or more streamers. Each streamer comprises a rubber mat and a plurality of geophones. The geophones are placed on top of the rubber mat, a hole is cut in the rubber mat beneath each geophone, and each geophone is held in place on the rubber mat by a rubber pad that is placed on top of the geophone and secured to the rubber mat with a plurality of bolts. Streamer spacers, each of which comprises a plurality of frames and a cross-bar connecting the frames, are used to secure the streamers to each other when a measurement is being taken. A method for taking seismic measurements using the seismic recording system described herein.
Owner:MONTANA TECH OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTANA +1
System for transmission of seismic data
ActiveUS8228759B2Readily and easily affixedTransmissionWireless architecture usageSeismic signal transmissionControl signalEngineering
The transmission system combines a self-contained, wireless seismic acquisition unit and a wireless, line of site, communications unit to form a plurality of individual short-range transmission networks and also a mid-range, line of sight transmission network. Each seismic unit has a power source, a short-range transmitter / receiver disposed within a casing and a geophone disposed within the casing. Each wireless communications unit is formed of an elongated support structure on which is mounted an independent power source, mid-range radio transmitter / receiver; and a short-range transmitter / receiver configured to wirelessly communicate with the short-range transmitter / receiver of the acquisition unit. Preferably, when deployed, the acquisition unit is buried under the surface of the ground, while the wireless communications unit is positioned in the near vicinity of the buried unit so as to vertically protrude above the ground. The acquisition unit and the wireless communications unit communicate by short-range transmissions, while the wireless communications unit communicates with other seismic acquisition systems using mid-range radio transmission. When multiple seismic acquisition unit / wireless communications units are deployed in an array, the system can pass collected seismic and quality control data in relay fashion back to a control station and / or pass timing and control signals out to the array.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
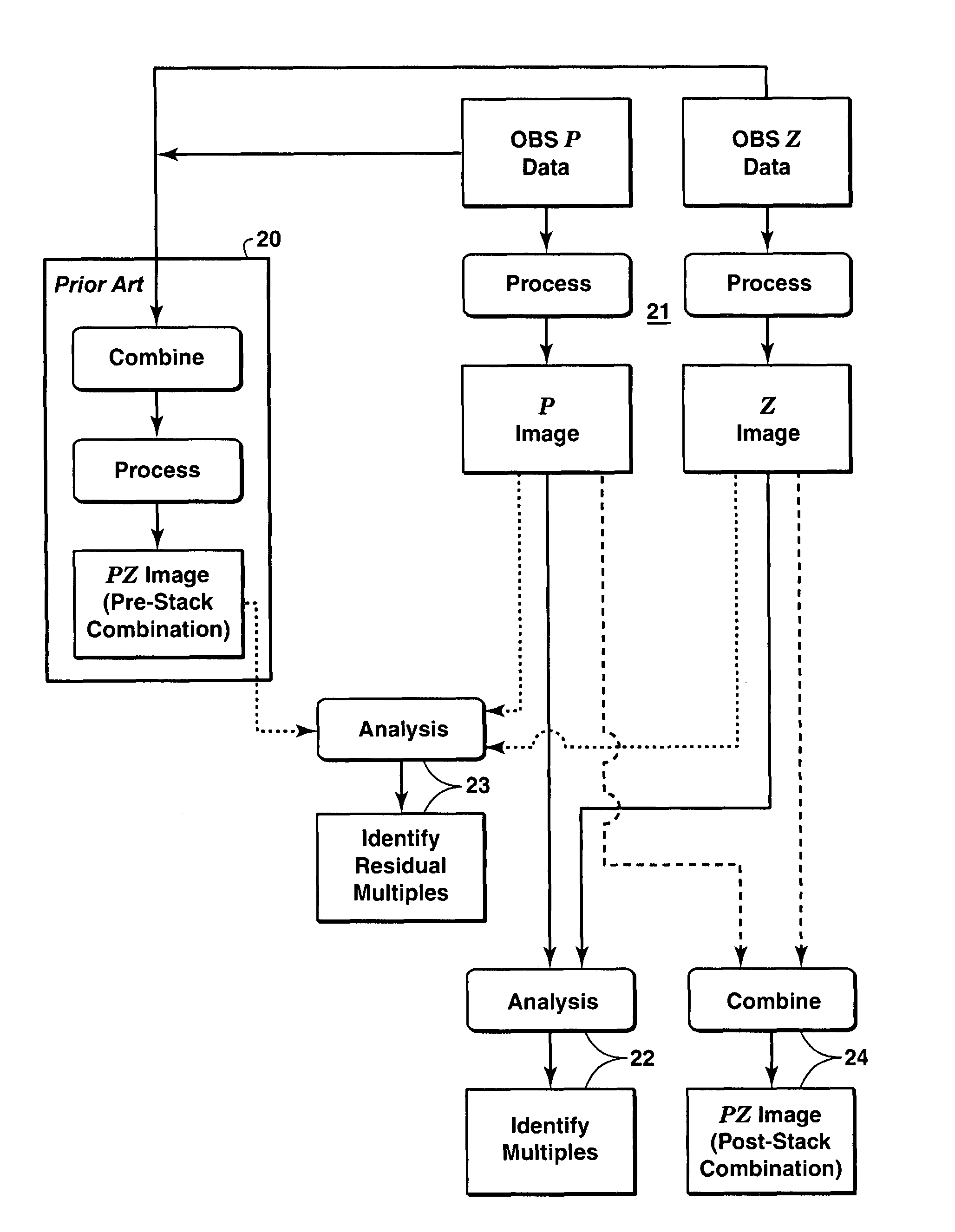
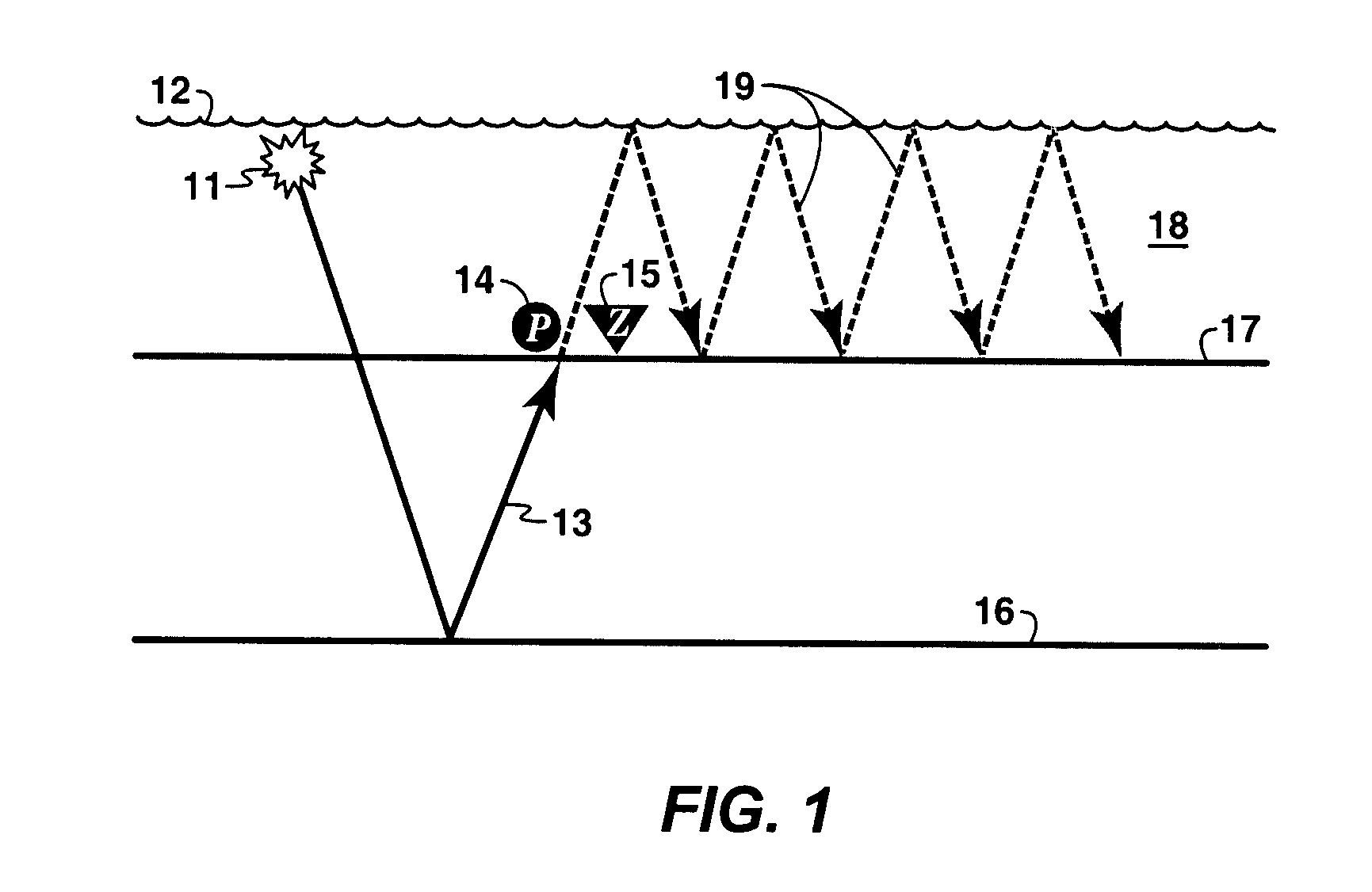
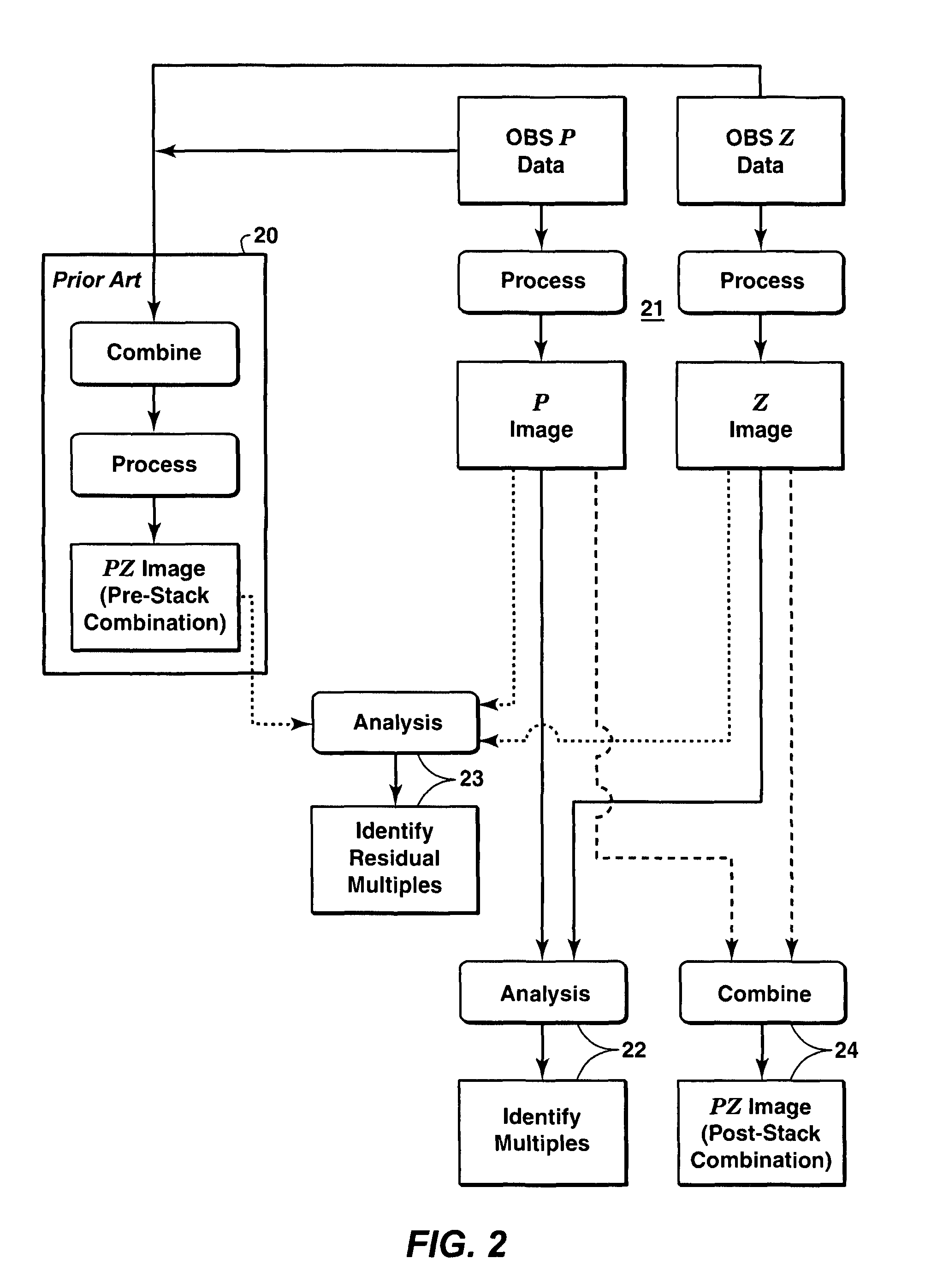
Identification and suppression of multiples in ocean bottom seismic data
A method for identifying and suppressing water column reverberations (“multiple reflections”) in two-component ocean bottom seismic data is disclosed. The method involves processing the hydrophone (P) data and the geophone (Z) data separately to produce two stacked images of the subsurface (21). Analyzing the stacked P-image and the stacked Z-image together can be used to identify multiple reflections (22). Analyzing the stacked / ′-image and the stacked Z-image together with an image of the subsurface created from hydrophone and geophone data combined in the usual way (PZ-image) (20) can be used to identify residual multiples in the PZ image (23). The stacked P and Z images can be combined using an existing PZ combination technique to suppress multiples (24). The efficiency of the PZ combination technique at suppressing multiples is increased because of the higher signal-to-noise ratio of stacked data.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Distinctive land seismic sweep
ActiveUS20130286780A1Effectively to impartBiocideSeismic data acquisitionAcoustic energyHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The invention is an electric sweep type seismic vibrator source of the type used in seismic prospecting for hydrocarbons. The source uses an engine and generator combination to create electric power for all systems on the source such as driving a frame of linear electric motors that direct a rod or piston to contact the ground in a recurring fashion along with driving the source from location to location through a survey area. Preferably a foot is arranged on the bottom end of the rod or piston for contact with the ground and by engaging the grid of motors to push down against the ground in a rapid progression, acoustic energy is created and delivered into the ground for geophones to sense and record. However, the rapid progression of pulses or sweep of seismic energy is delivered in a distinctive fashion as compared to a conventional upsweep or downsweep and the distinctiveness is also achieved by creating a designed cadence or timing such that each pulse in a series of pulses is not delivered in a regular timing. Several similar seismic sources may be employed where each is provided with its own distinctive series of pulses such that each may be identified within the data record and source separation from a number of seismic sources may be accomplished.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Optical fiber ground earthquake detection method and system
ActiveCN110703316ASimple structureLow costSeismic signal receiversConverting sensor output opticallyRayleigh scatteringEarthquake detection
The present invention discloses an optical fiber ground earthquake detection method and system. The method comprises: fixing several optical fiber earthquake detectors on a sensing optical cable at intervals to form a row of sensing units, combining several rows of sensing units to form an optical fiber earthquake detector network; laser emitted by a laser device enters an optical branching deviceand is split into several rows of pulsed light signals, the pulsed light signals separately enter several circulators, and each path of pulsed light is uni-directionally transmitted to a port II by aport I in a circulator, and enters each row of sensing units; the pulsed light signals are transmitted on the detector to generate Rayleigh scattering light, the Rayleigh scattering light and Rayleigh backscattering light are transmitted to the port II of the circulator, are output by a port III of the circulator, are converted into an electrical signal after detection of a photoelectric detector, the electrical signal enters a signal processing module, and the signal process module extracts a vector or three-dimensional earthquake signal according to a demodulated vibration signal. The method and the system can implement reusing and network formation of detectors, and can implement large-range quasi-distributed vector or three-dimensional earthquake signal detection.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Seismic modem
A system for the transmission of data by seismic wave, the system having at least one transmitting unit, that at least one transmitting unit comprising a first processing unit encoding a first signal, the first processing unit being coupled to a digital to analog converter, an amplifier amplifying the first signal, and a seismic pressure wave inducer transmitting the first signal to a geological feature; and at least one receiving unit, the receiving unit comprising at least one receiver coupled to the geological feature for receiving the first signal, and an analog to digital converter whereby the first signal is transferred from the geophone and is conveyed to a second processing unit, the second processing unit being configured to identify and decode the first signal.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Seismic detector for pull-type crawler
ActiveCN103278844ARigid packaging requirements are goodEnhanced couplingSeismic signal receiversGeophoneStructural engineering
The invention relates to a seismic detector for a pull-type crawler, which comprises a shell and a grounding end connected with the front end of the shell and arranged outside a rubber belt track; the shell is arranged at the inside of the rubber belt track, and the grounding end and the shell are connected to be fixed on the rubber belt track; a detector core is rigidly fixed in the inner cavity of the shell and is closed by a thread end cover arranged at the tail end of the detector core; the bottom end of the detector core is provided with a signal lead; during seismic measuring, as the detector core body and the shell package are rigidly fixed and the shell of the detector and the ground form an absolute mass body, the detector can better measure the particle vibration of the earth surface. The seismic detector is suitable for the rigid packaging requirements between the shell and all vibration-type and other mechanical sensor core bodies. A contact, which is coupled with the ground, of the detector with the minitype structure is connected onto the mobile rubber belt track by threads, so the seismic detector is stable in work, reliable, efficient, suitable for various geological surfaces to carry out geophysical prospecting, low in manufacturing cost, simple and conveniently connected with a lower computer.
Owner:安徽吉思勘仪器科技有限公司
Dynamic positioning method and system of submarine geophone and geophone
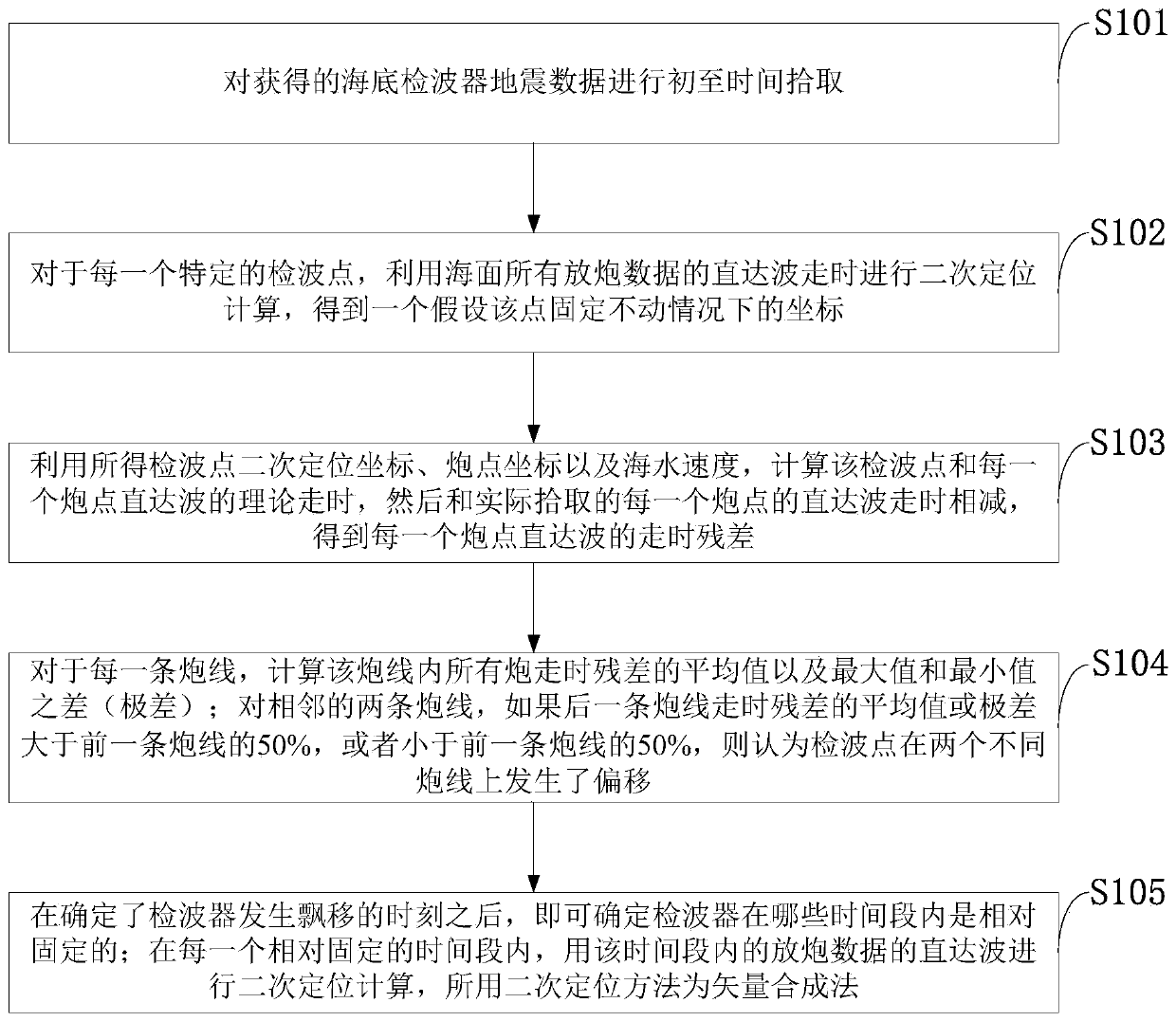
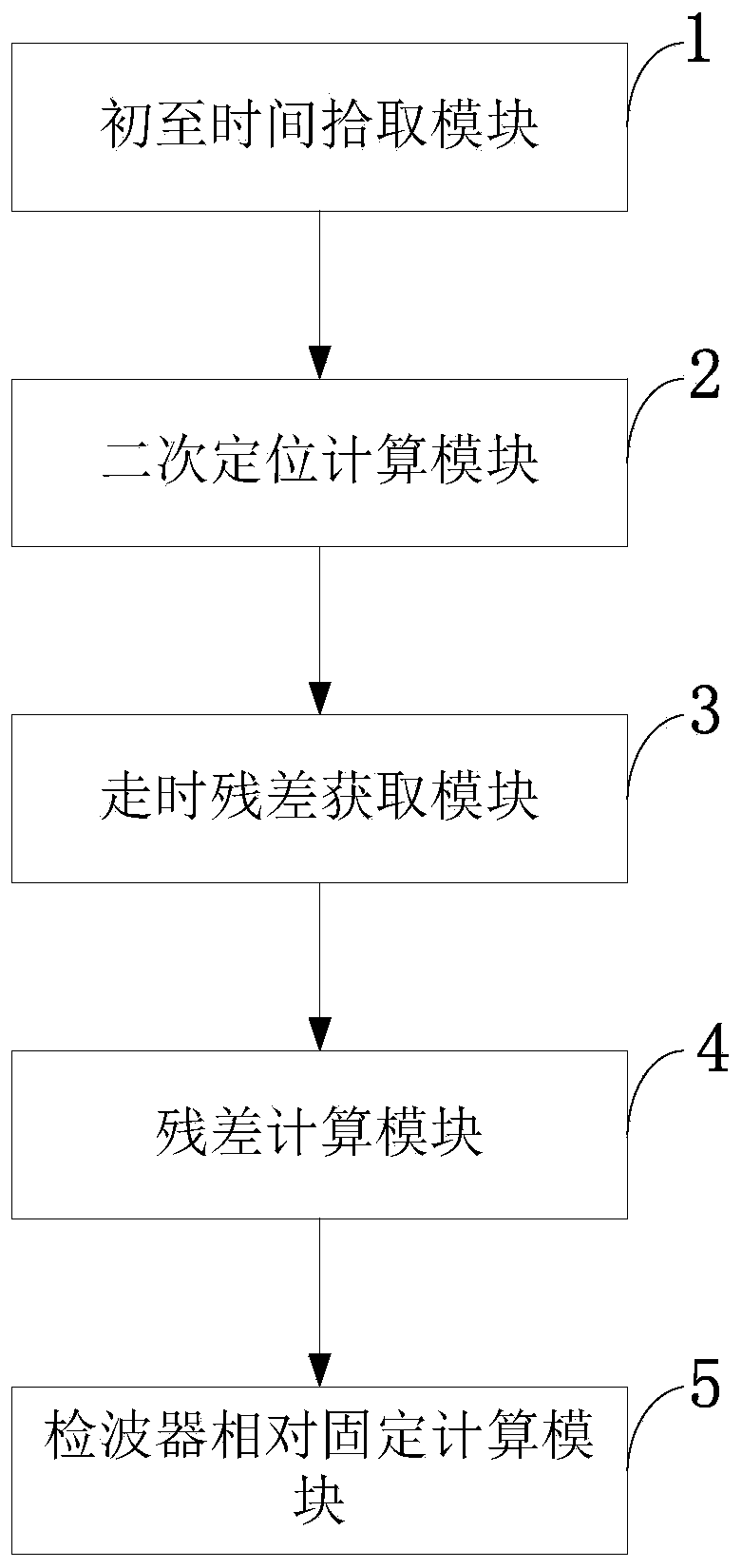
ActiveCN110780350ASeismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasGeophoneDynamic positioning
The invention belongs to the technical field of ocean seismic exploration, and discloses a dynamic positioning method and system of a submarine geophone and the geophone. The dynamic positioning method comprises the steps of picking up first arrival time of submarine geophone seismic data; performing secondary positioning calculation on each special detection point according to direct wave traveltime of all shot data of a sea surface to obtain coordinate under the condition that the point is assumed to be fixed; calculating theoretical travel time of direct waves of the detection point and each shot point according to the obtained secondary positioning coordinate of the detection point, the coordinates of shot points and a seawater speed, and subtracting the theoretical travel time from direct wave travel time, actually picked up, of each shot point to obtain travel time residue of the direct wave of each shoot point; calculating an average value and a range of travel time residue ofall shots in each shot line; and determining a moment when the geophone moves according to an average value and a range of travel time residue of an adjacent shot line, and determining when the geophone is relatively fixed within certain time. By the dynamic positioning method, a foundation is laid for subsequent high-accuracy imaging.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +3
System for automatically detecting and sorting spring pieces for seismic detector
InactiveCN102632042AEliminate accumulated errorsHigh measurement accuracySortingStrength propertiesGeophoneControl system
The invention relates to a system for automatically detecting and sorting spring pieces for a seismic detector. The system comprises a controller system, a measuring mechanism and a sorting mechanism, and is characterized in that: the measuring mechanism and the sorting mechanism synchronously work under control of the control system, namely when the measuring mechanism detects the current spring piece and calculates an elastic coefficient, a supporting force and a sorting coordinate of the spring piece, the sorting mechanism takes the last detected spring piece from a piece carrying plate, and hangs the taken spring piece on the corresponding hanging pin on a sorting board according to a coordinate value of the spring piece on the sorting board, which is sent by a controller. In a measuring process, when the measured spring piece is taken away, an operator only places the spring piece to be detected on the piece carrying plate and turns on a measuring button, so that the following detecting and sorting processes are not intervened by the operator. A plurality of machines can be operated by one person and the system has the advantages of high precision, high speed, high efficiency, simpleness in operation and low labor intensity.
Owner:王锁弘
High-resolution earthquake detector and manufacturing method thereof
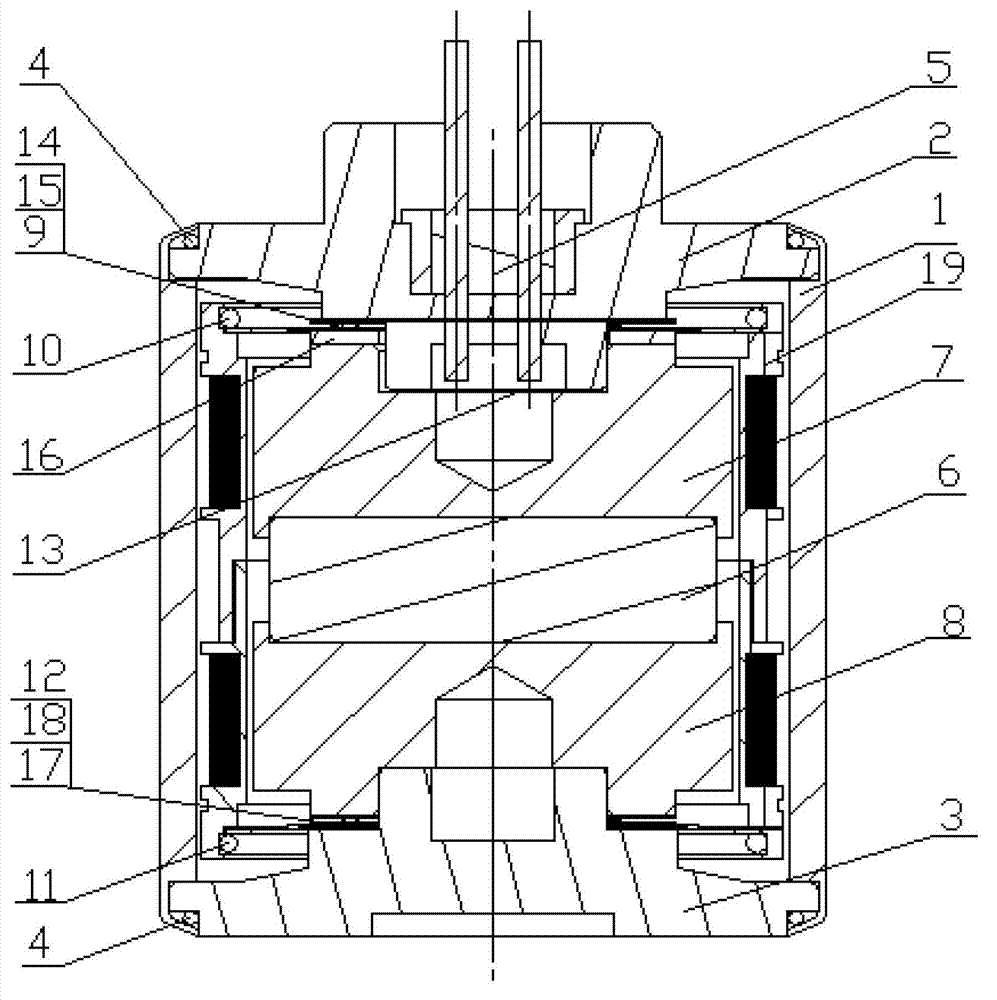
ActiveCN102901980ASmall distortionReduce consistencySeismic signal receiversLow distortionImage resolution
The invention relates to a high-resolution earthquake detector and a manufacturing method thereof. With the adoption of a detector structure, an upper cover with a guide positioning part, a magnetic system consisting of upper and lower magnetic boots and magnetic steel, a spring-mass system consisting of a coil frame with a winding and a spring, a lower cover, and a shell are coaxial in an assembling process, so that the detector distortion can be effectively reduced. The matching condition ensures that inner and outer rings of upper and lower spring sheets are at a horizontal position after being assembled; the upper and the lower spring sheets are not additionally stressed by external force; and each part inside the detector with a sealed opening is compactly matched without release, so that the distortion of the detector can be reduced. The natural frequency of single spring can be directly detected, and the two springs with equal frequencies can be selected to be matched in pair, so as to ensure the consistency of the spring, and reduce the allowance range and the distortion. With the adoption of a method for directly testing the frequency, the natural frequency of the earthquake detector can be tested before the opening of the detector is sealed, so that the allowance range of the detector can be further reduced.
Owner:BEIJING HUAHANG RADIO MEASUREMENT & RES INST
Microseism ground monitoring device and seismic source positioning method
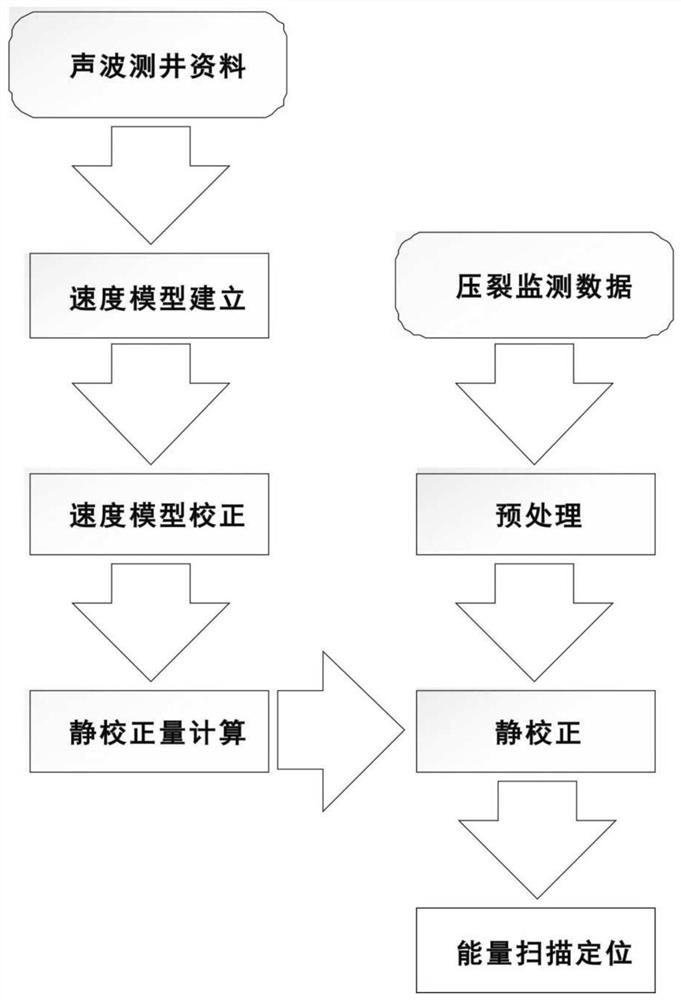
PendingCN111796327AOptimize layoutLow costSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal processingComputer hardwareData acquisition
The invention discloses a microseism ground monitoring device and a seismic source positioning method. The microseism ground monitoring device comprises a data acquisition and processing module, a signal transmission module and a power supply module. The data acquisition and processing module comprises a geophone used for receiving a microseism analog signal; the geophone is connected with a signal conditioning module, which is connected with an A / D conversion module; the A / D conversion module is connected with a processor module, which is respectively connected with a data storage module anda global navigation satellite module; the processor module is connected with the signal transmission module; and the power supply module is connected with the data acquisition and processing module and is used for supplying power to the data acquisition and processing module. According to the invention, a superimposed energy scanning imaging technology which does not need to extract the first arrival of a signal event is adopted to carry out ground seismic source positioning, and the seismic source position can be effectively determined on the premise of not high requirement on signal source quality; microseism real-time positioning and monitoring can be supported through the server; and meanwhile, a mobile 4G signal is adopted, and the advantage of low signal transmission cost is achieved.
Owner:CENT FOR HYDROGEOLOGY & ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY CGS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com