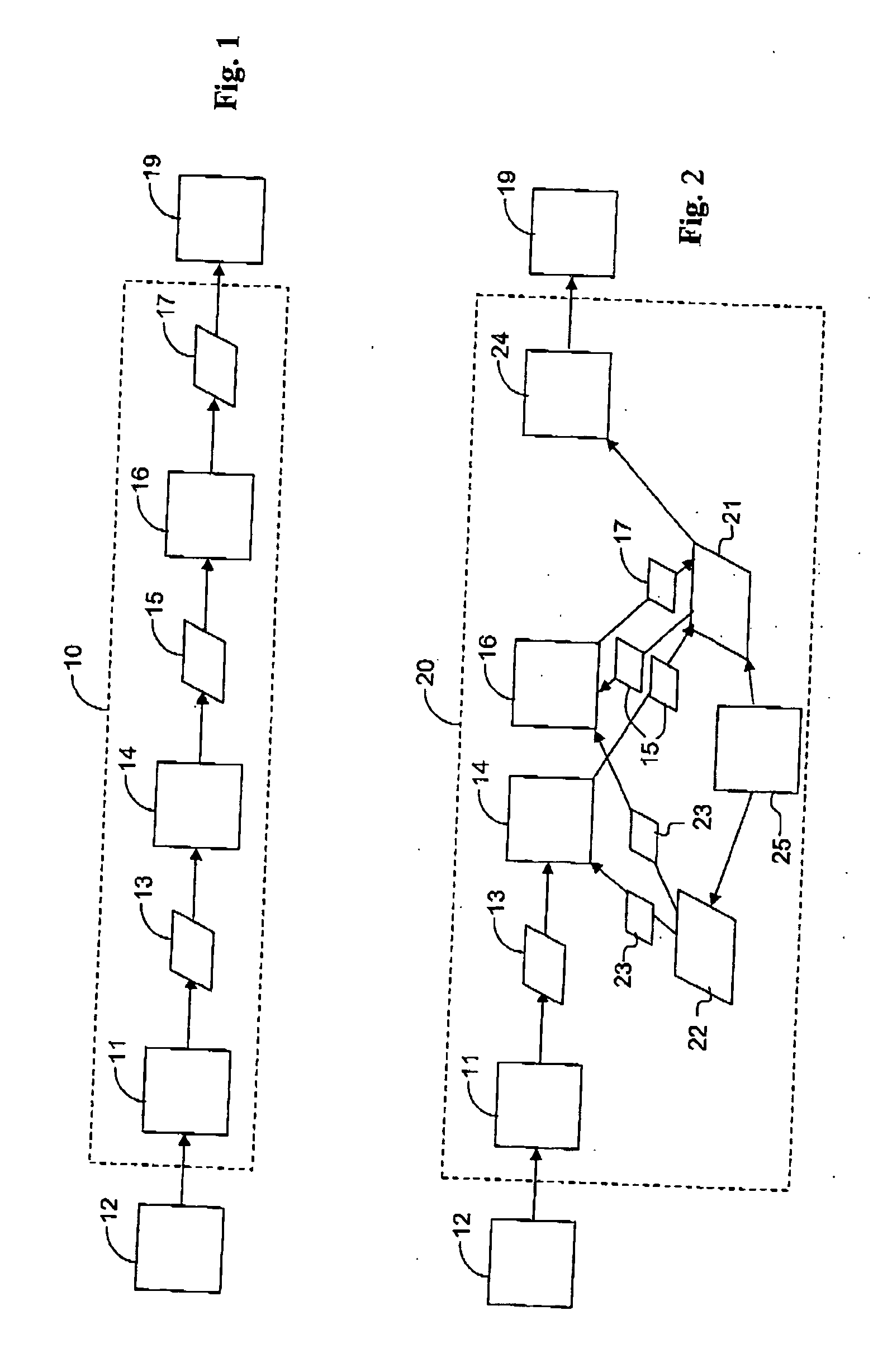
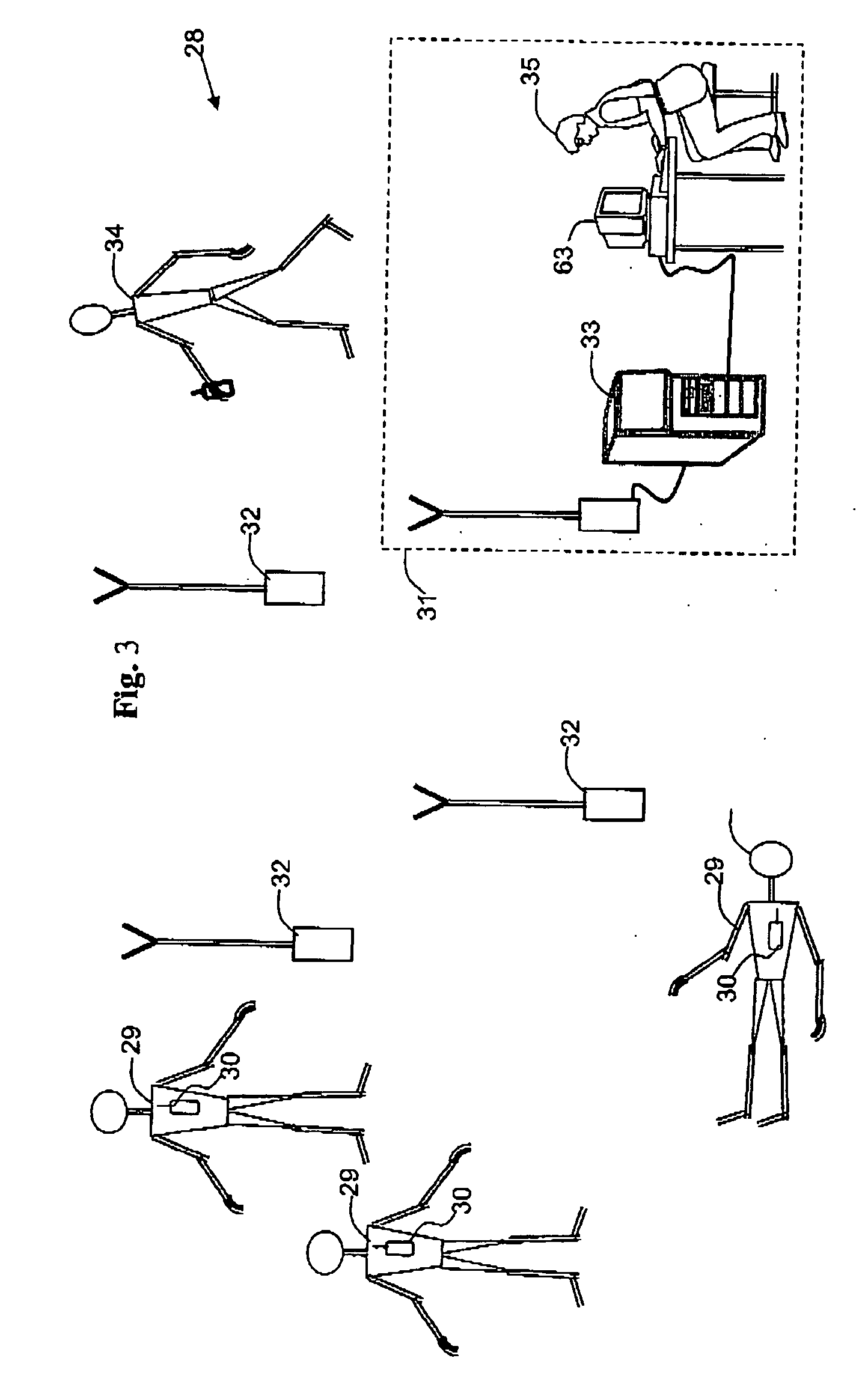
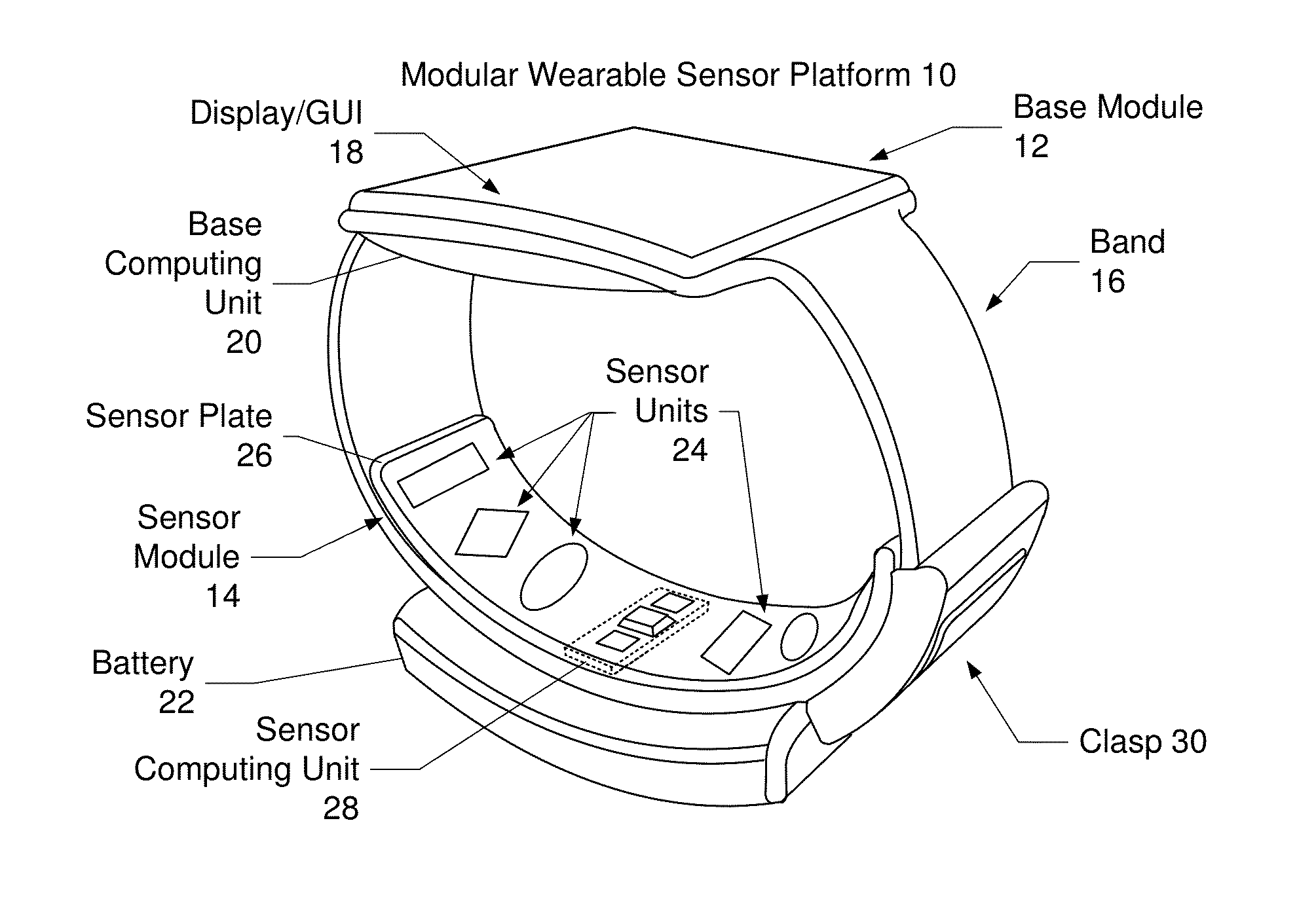
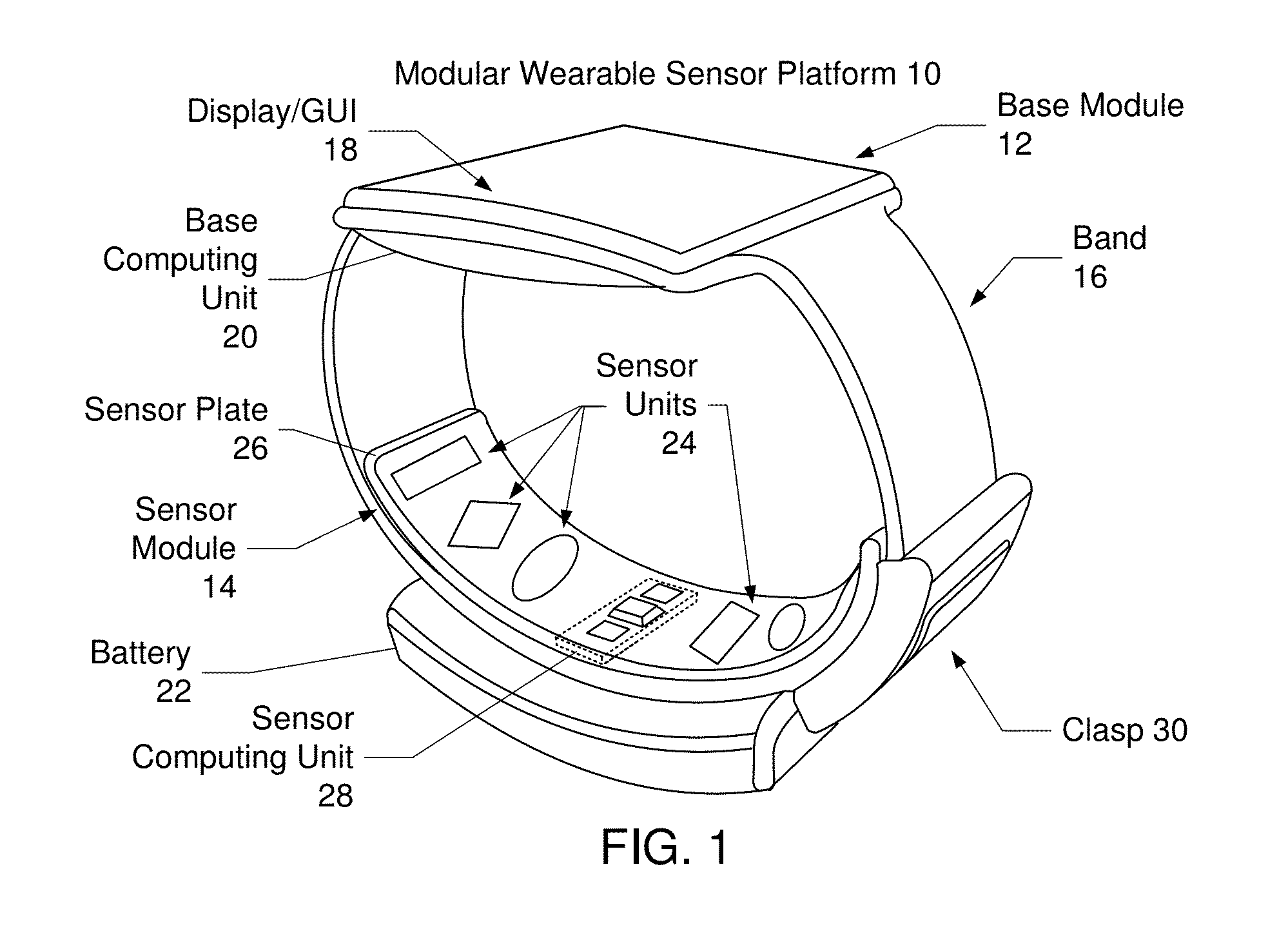
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149 results about "Physiologic measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physiologic measurement techniques used to measure bodily variations either directly or indirectly; examples are measurements of heart rate, mean arterial pressure, and total lung capacity.
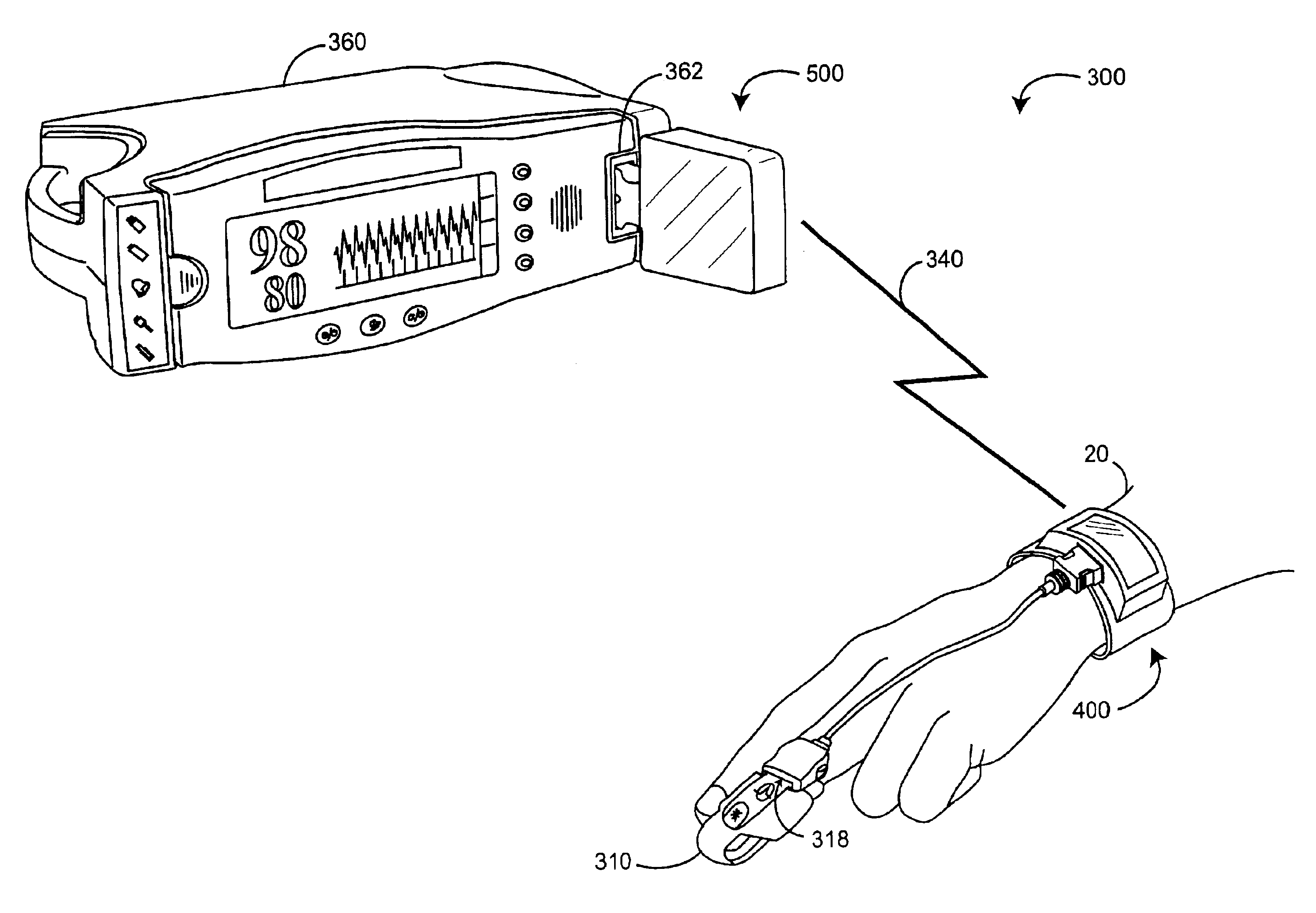
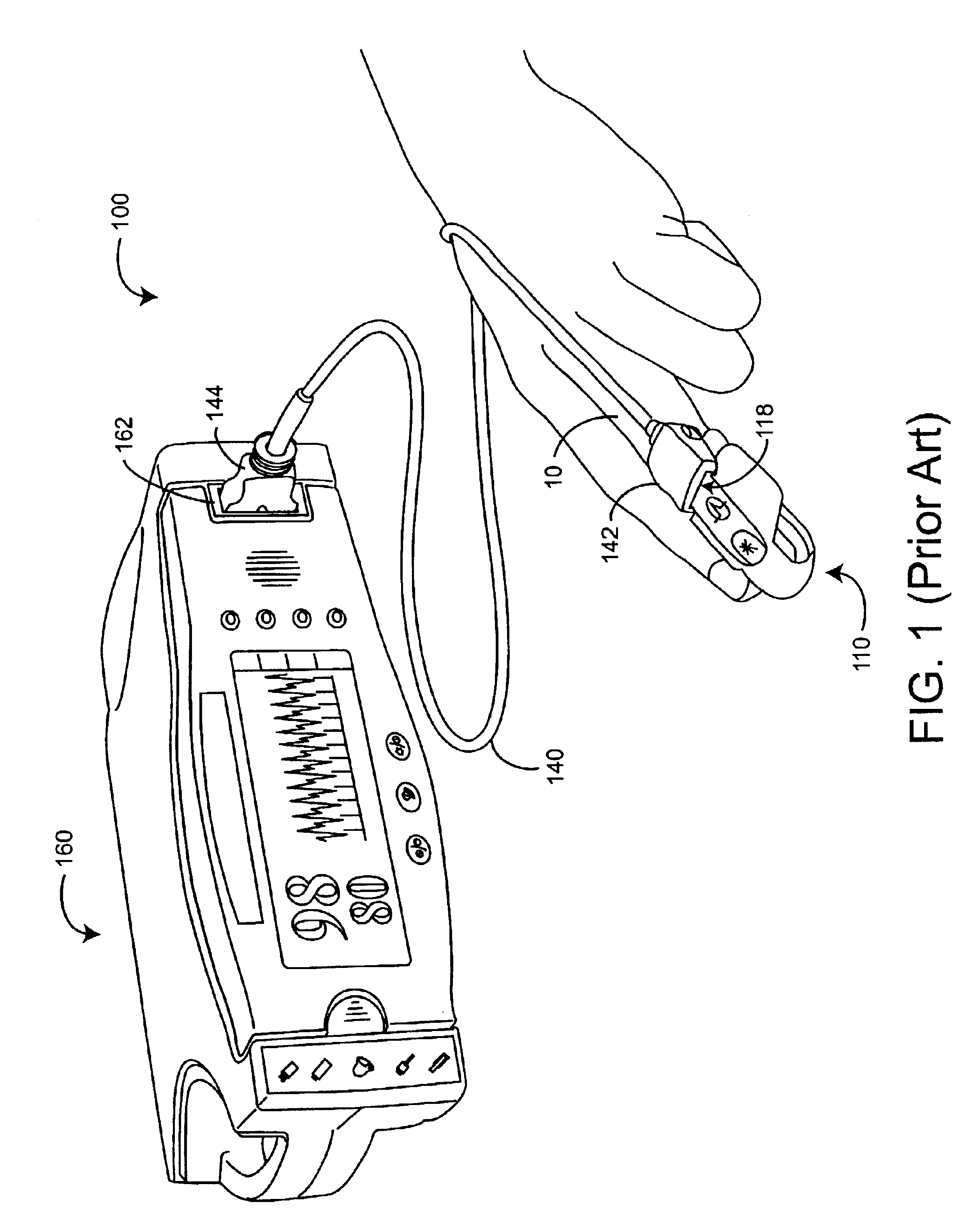
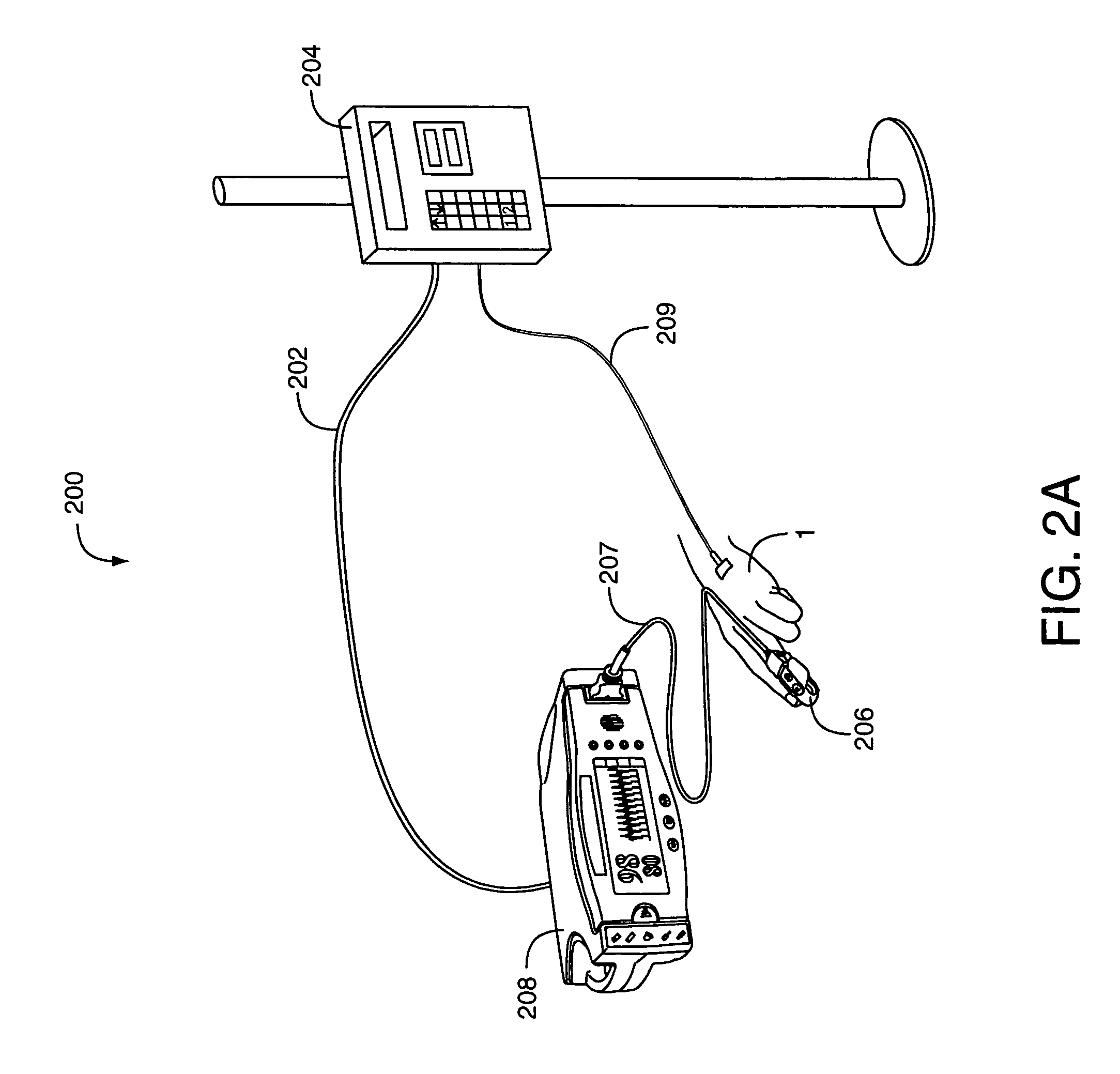
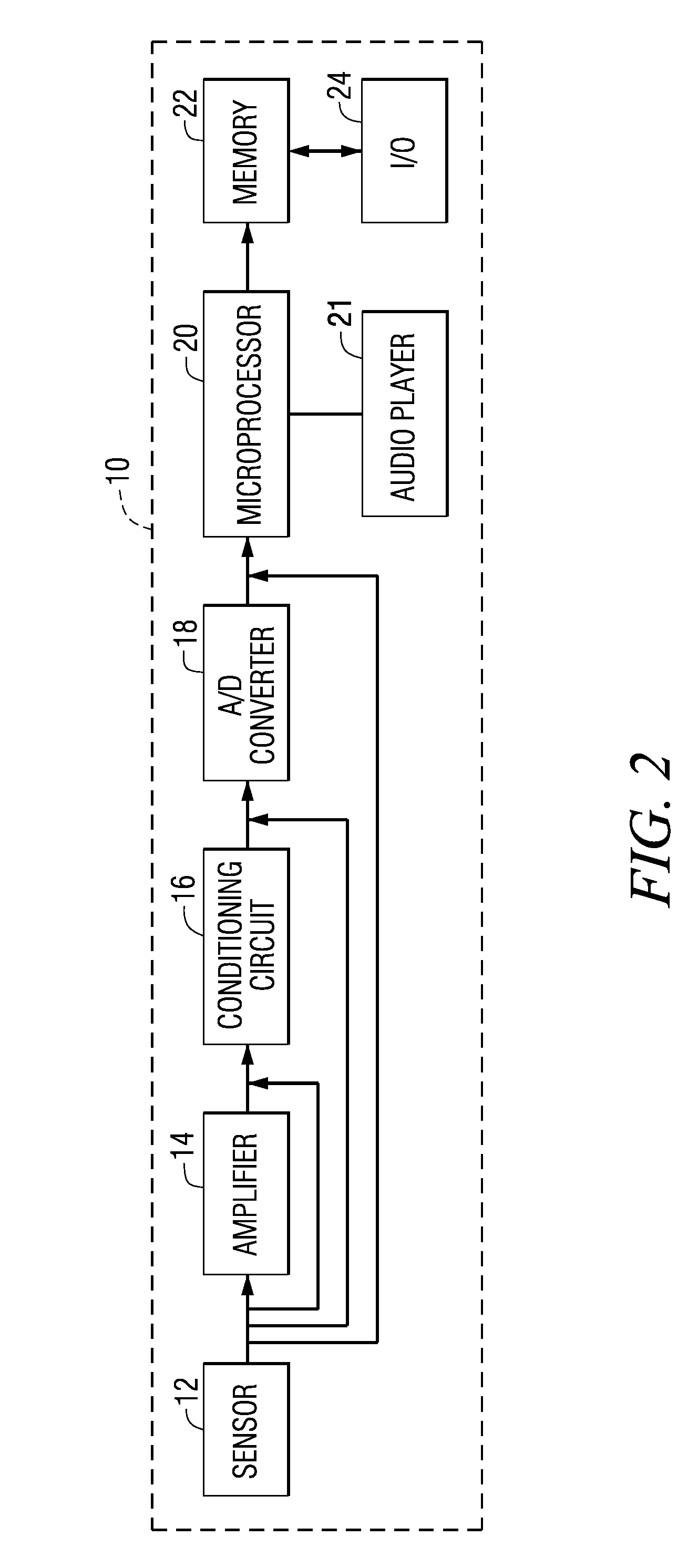
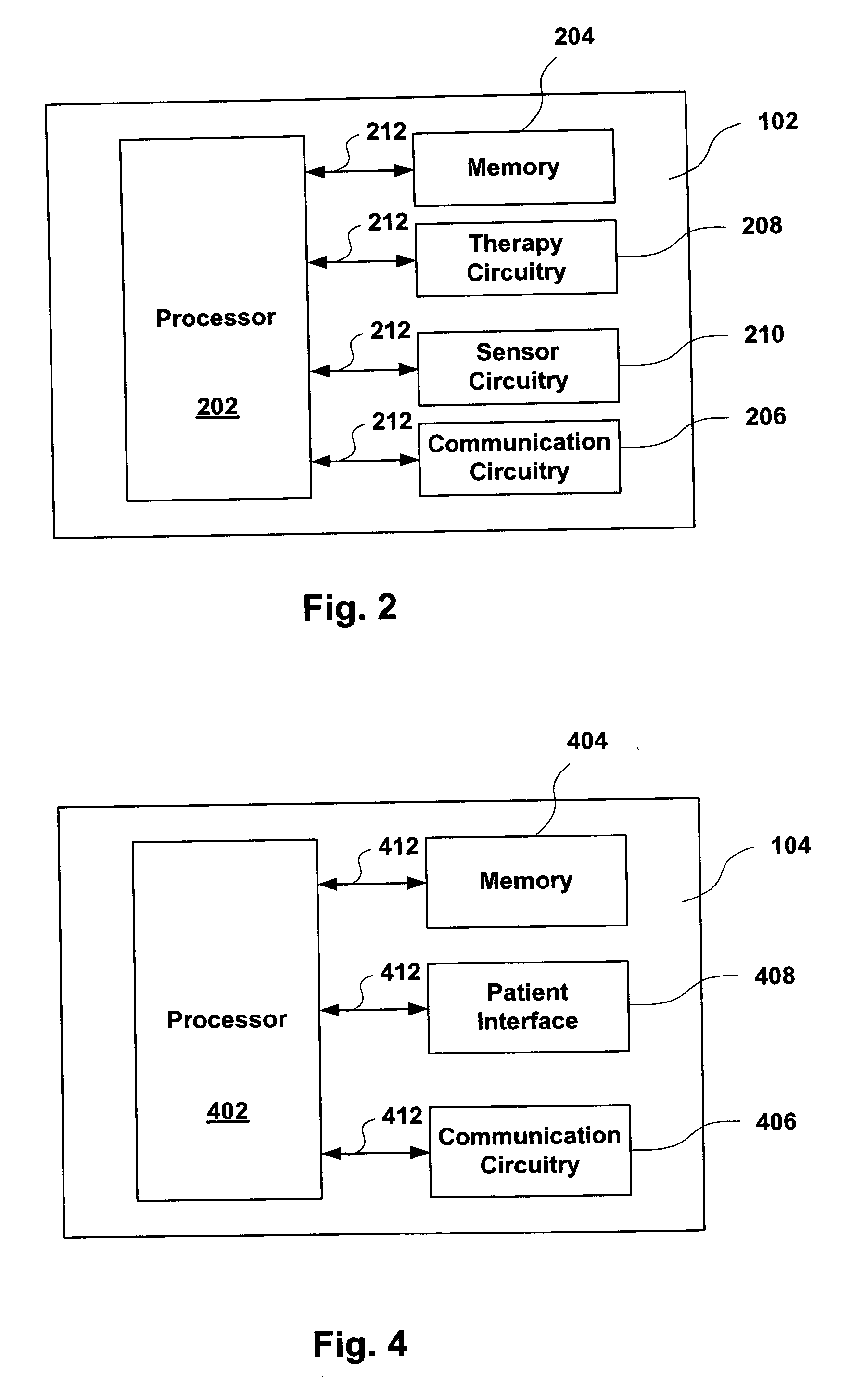
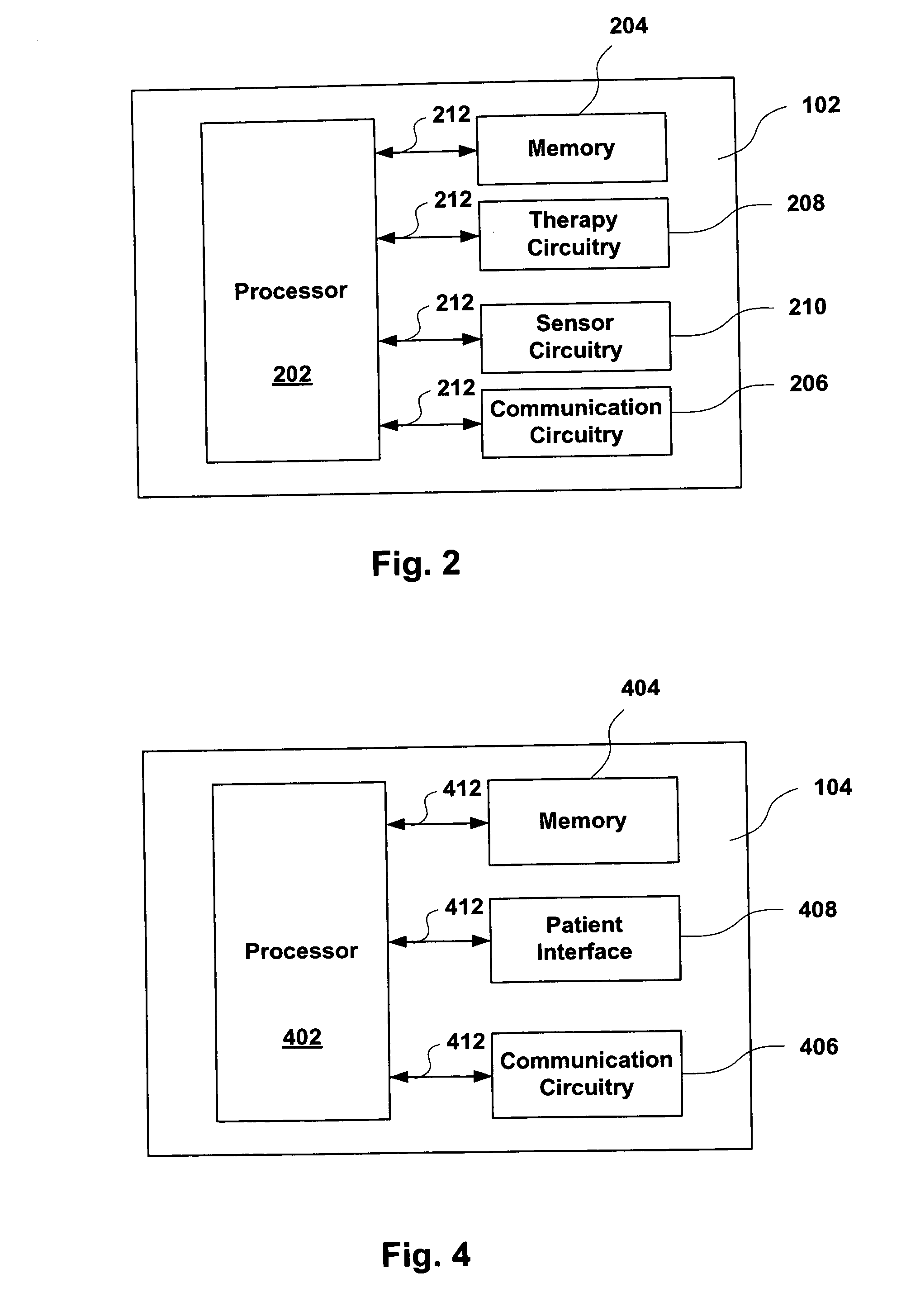
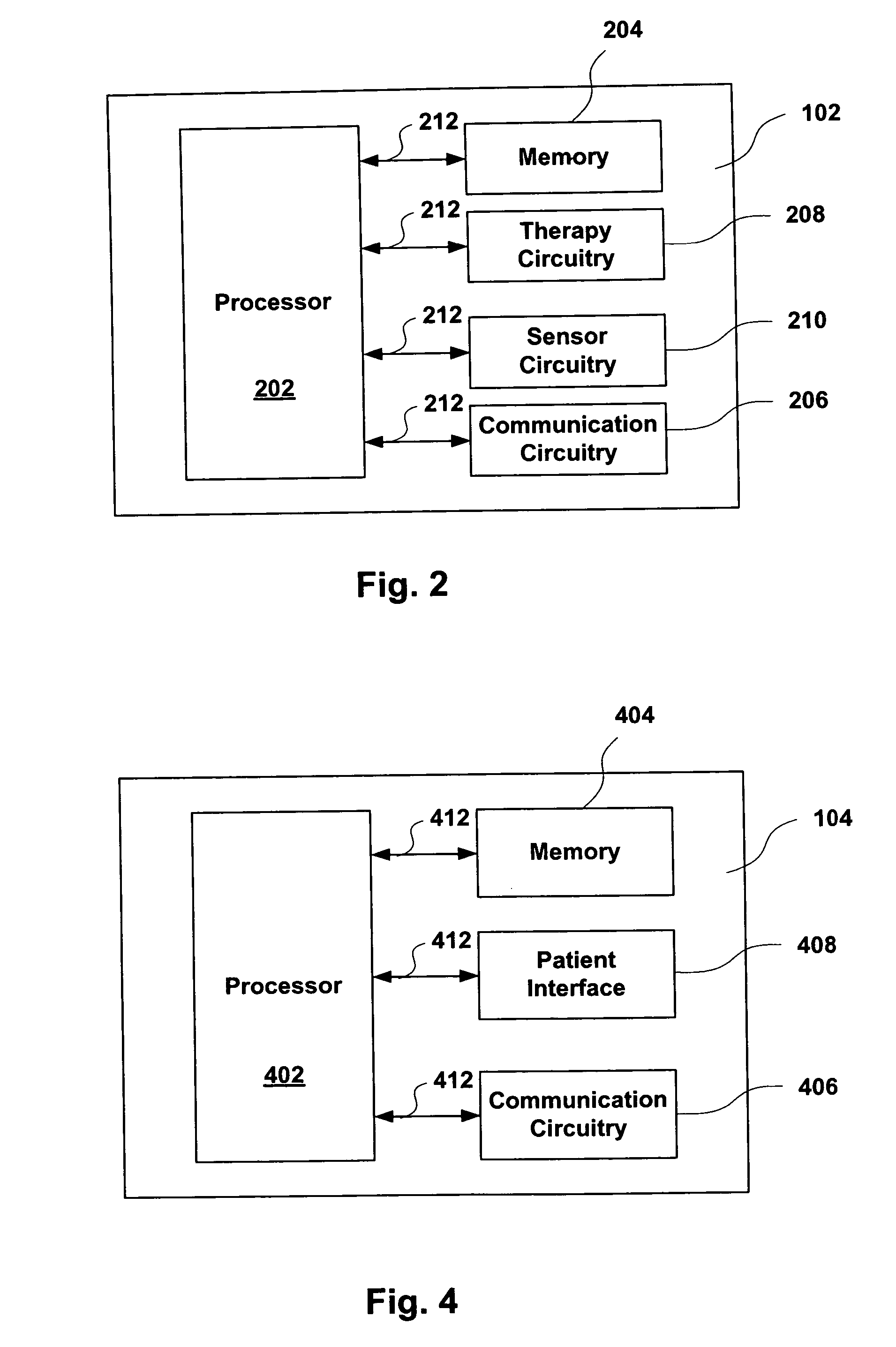
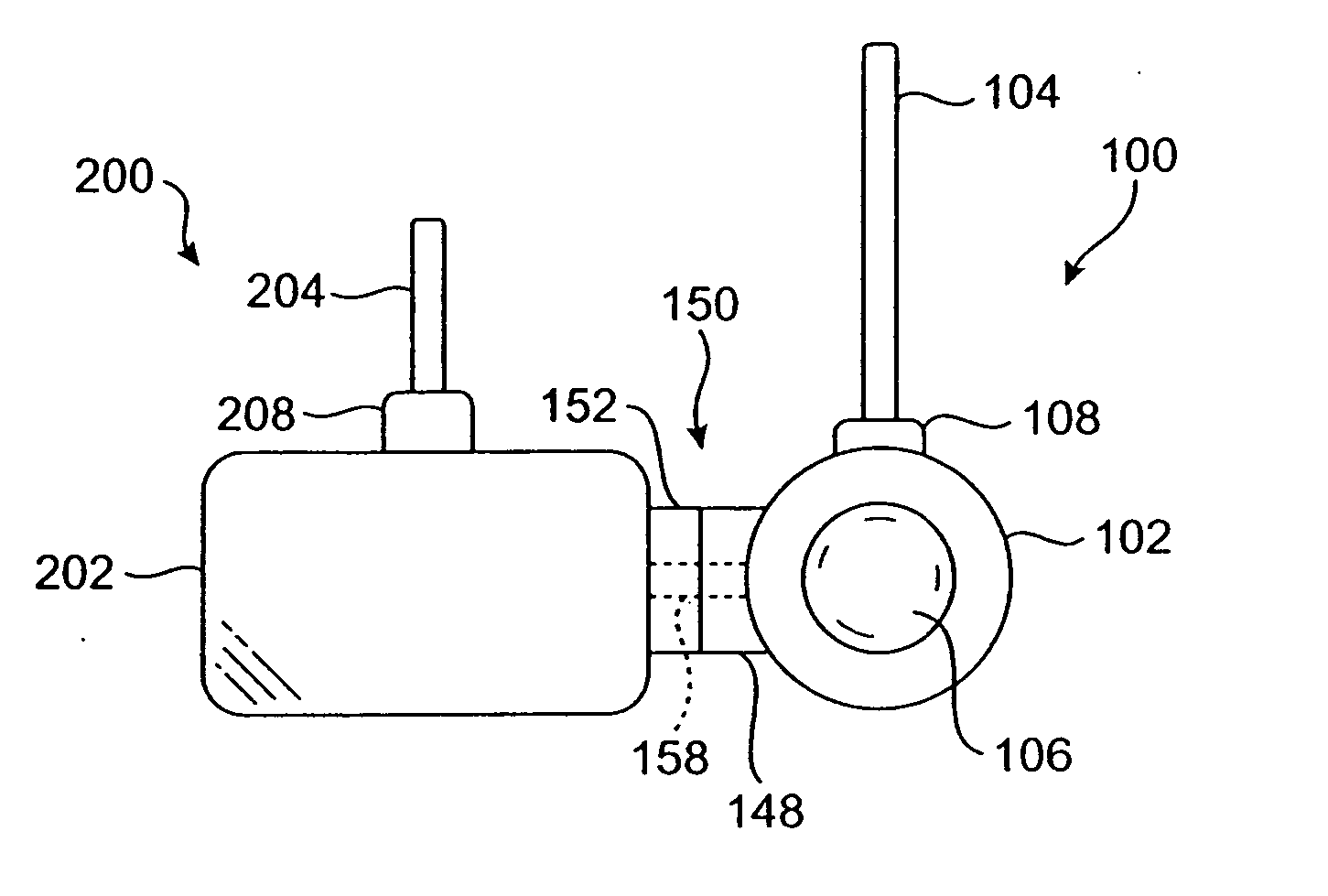
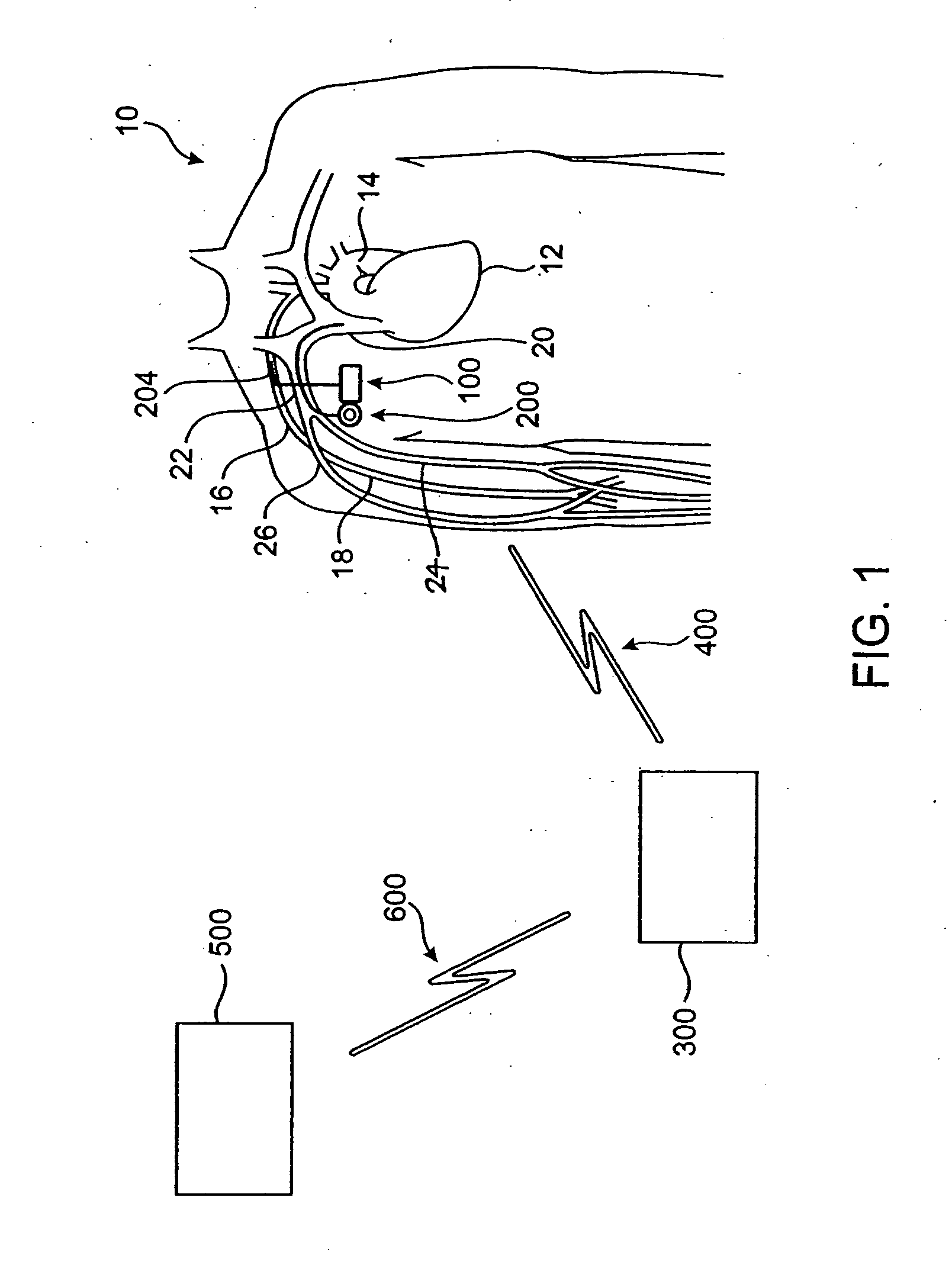
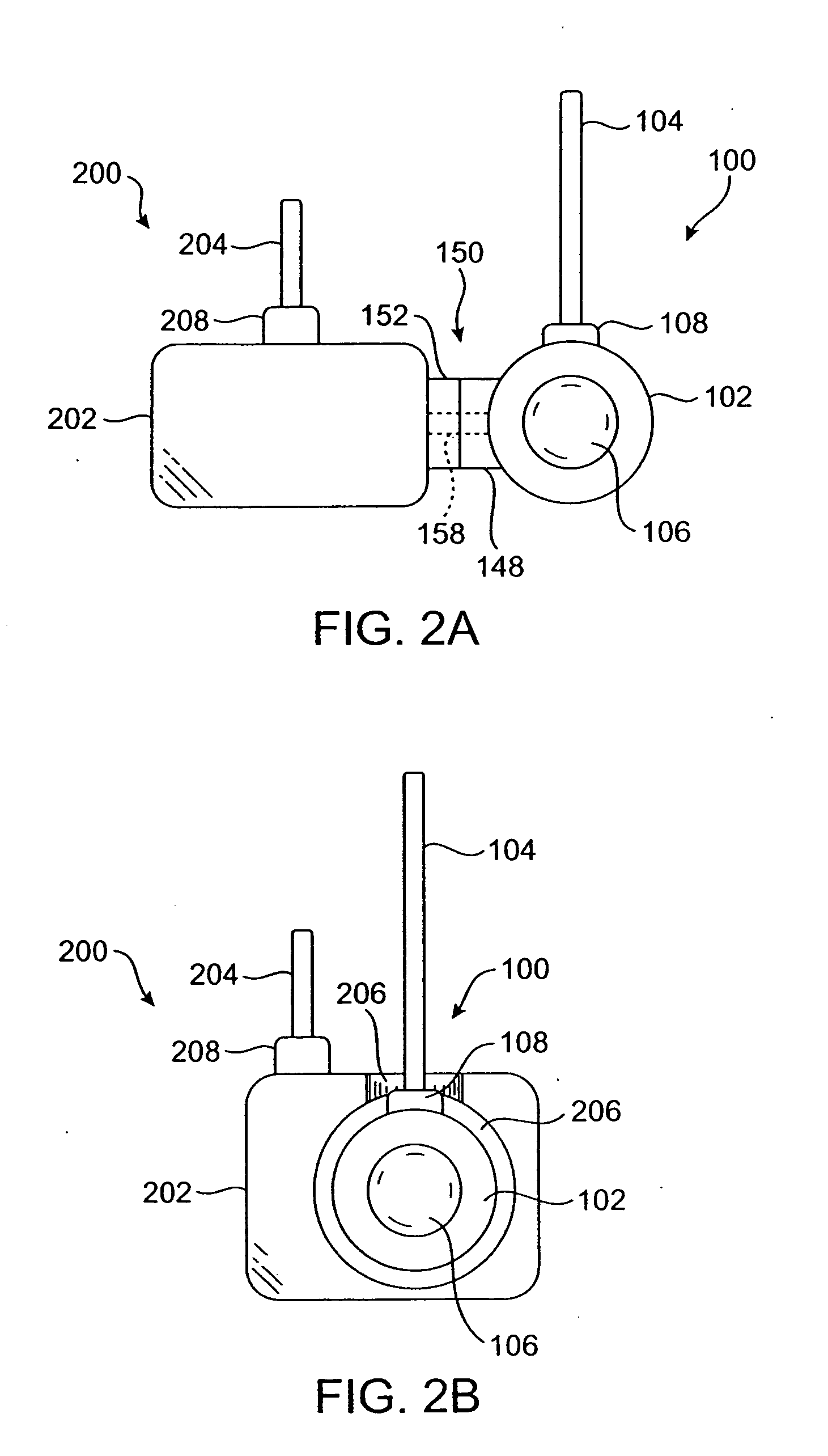
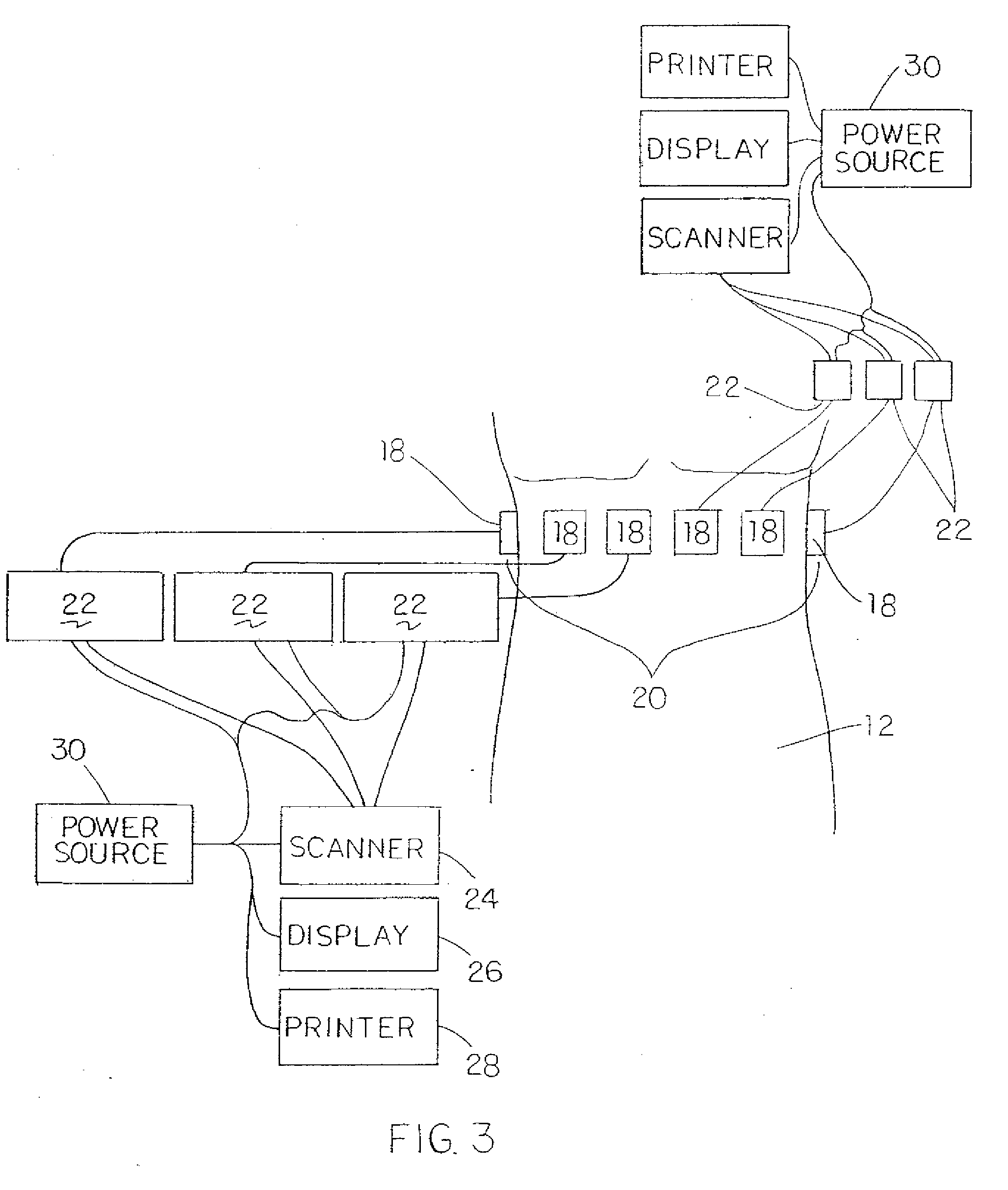
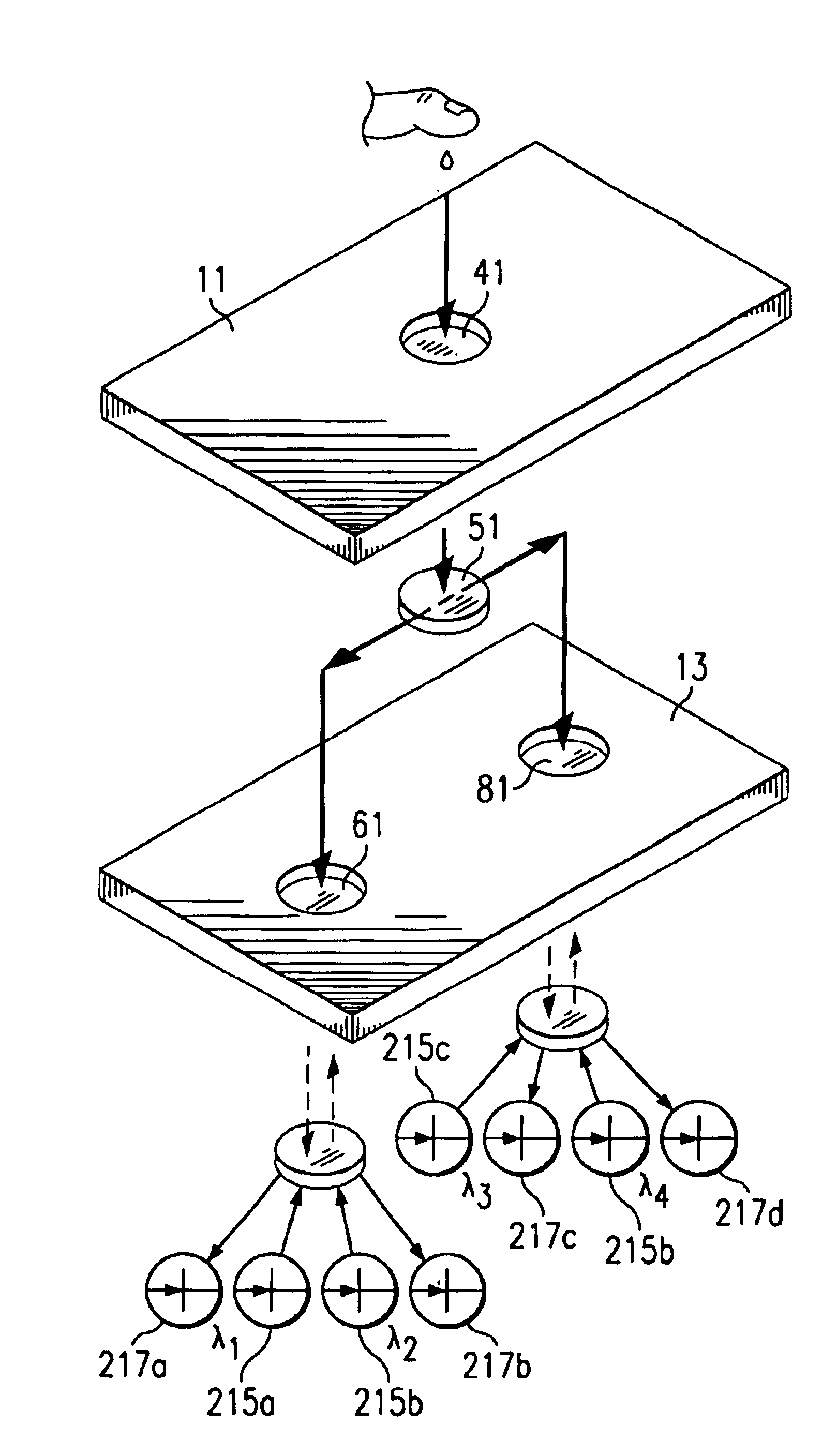
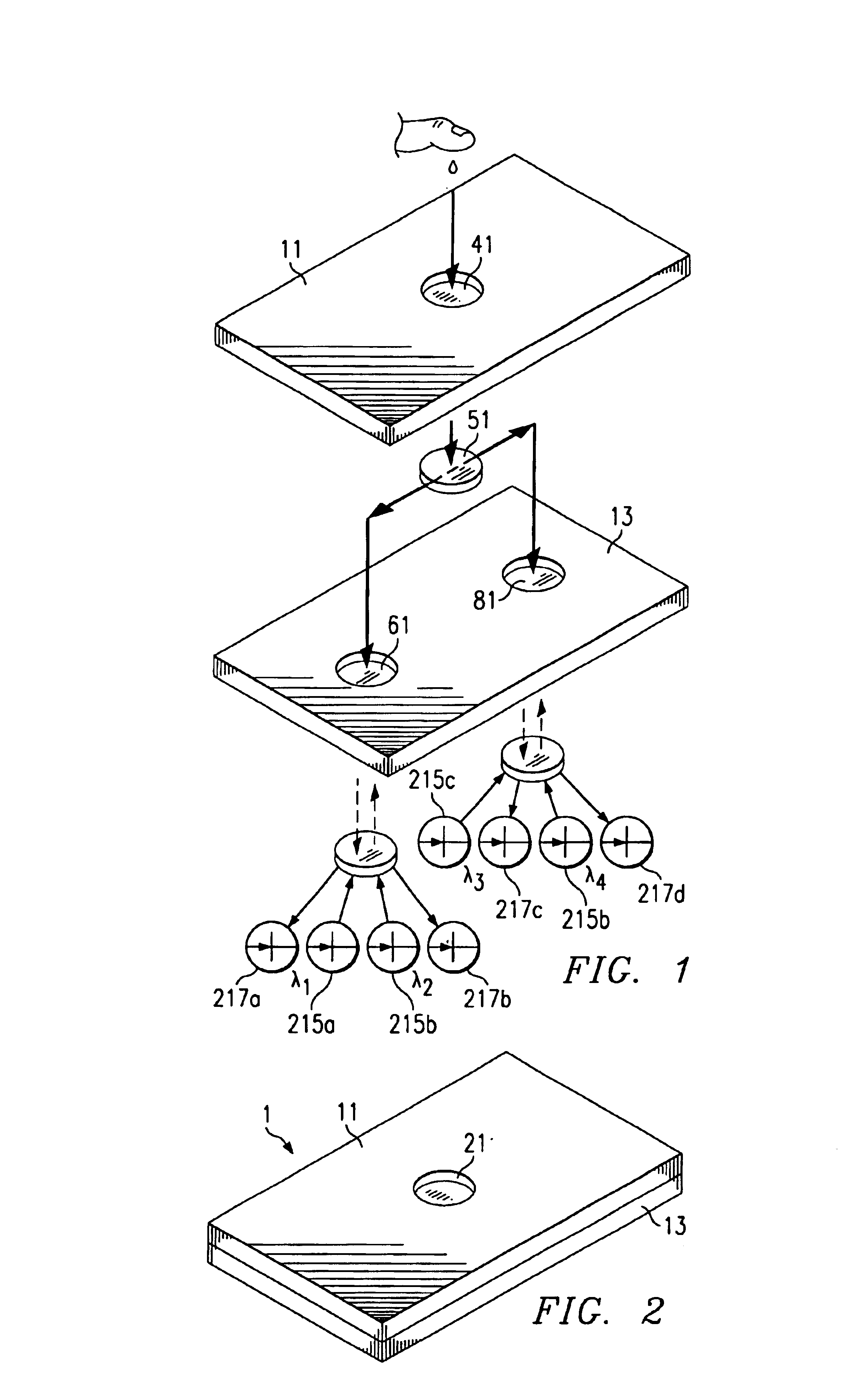
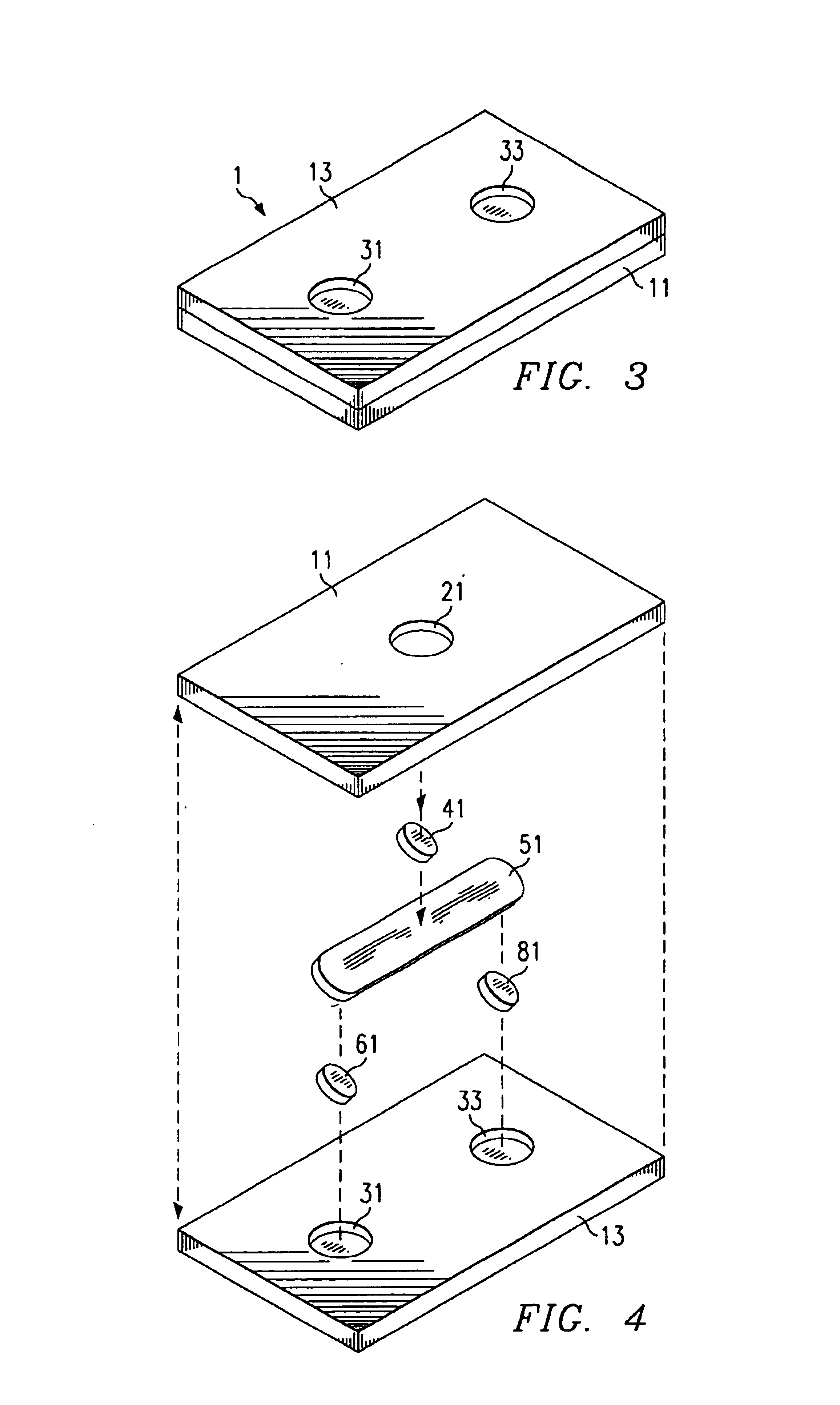
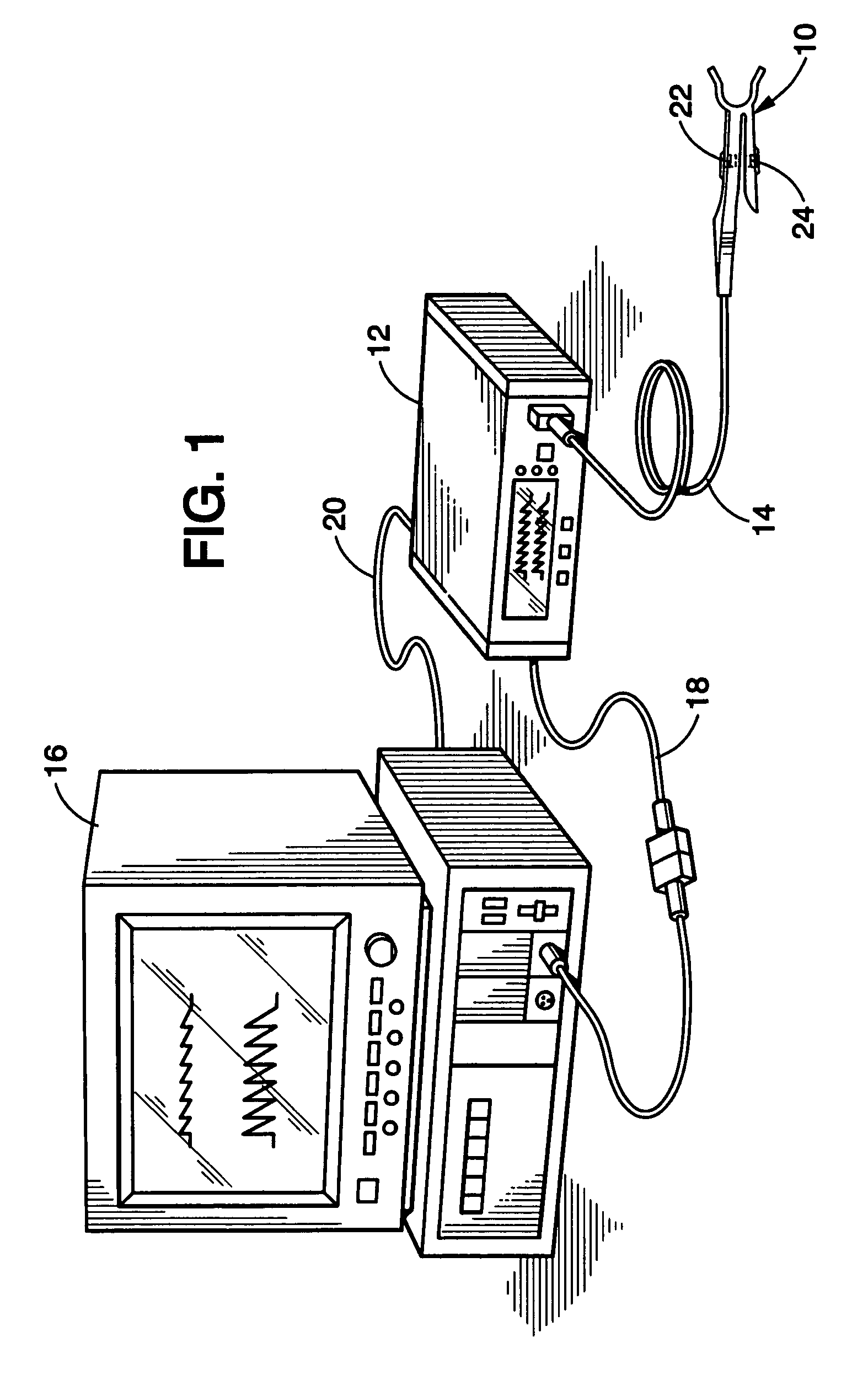
Physiological measurement communications adapter
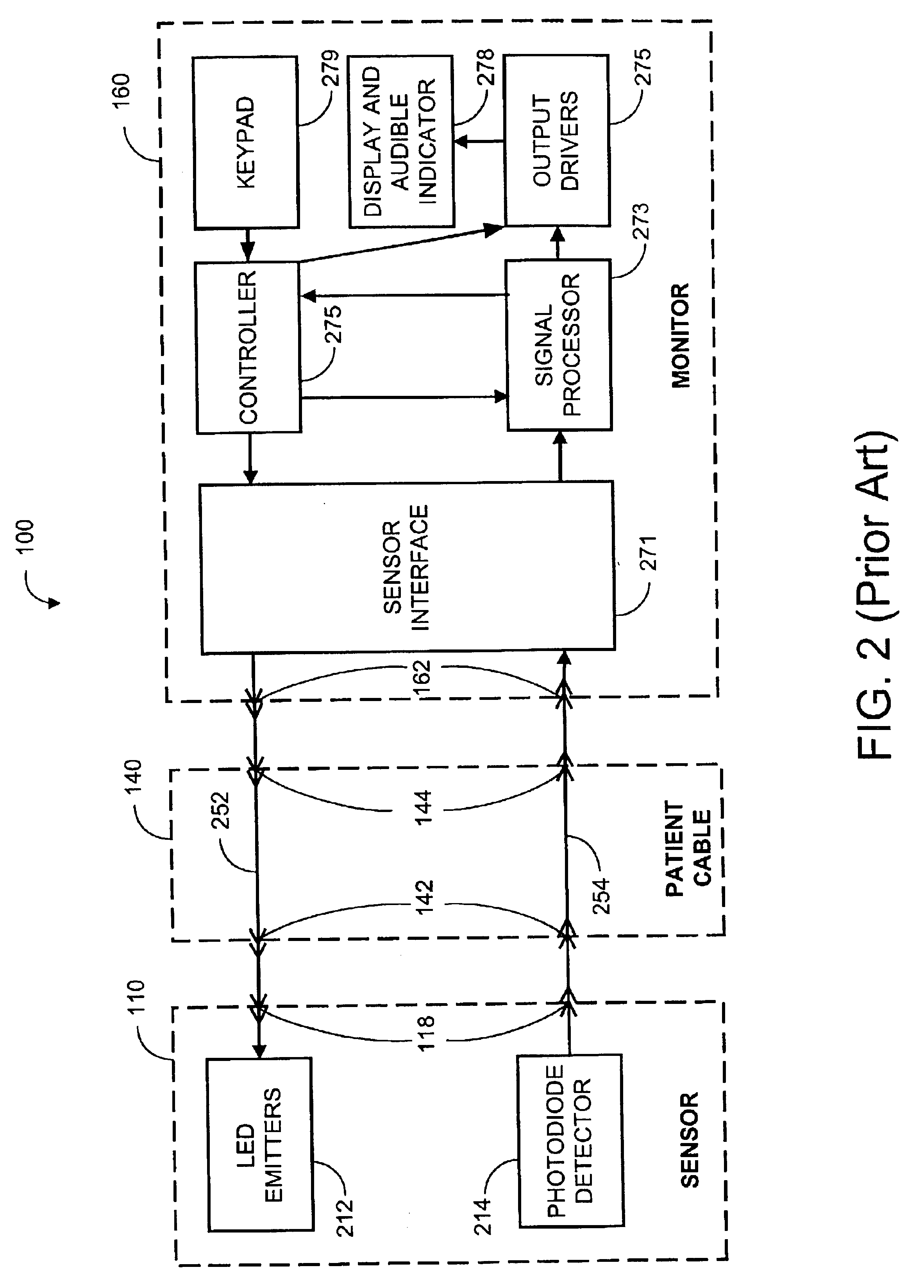
A sensor interface is configured to receive a sensor signal. A transmitter modulates a first baseband signal responsive to the sensor signal so as to generate a transmit signal. A receiver demodulates a receive signal corresponding to the transmit signal so as to generate a second baseband signal corresponding to the first baseband signal. Further, a monitor interface is configured to communicate a waveform responsive to the second baseband signal to a sensor port of a monitor. The waveform is adapted to the monitor so that measurements derived by the monitor from the waveform are generally equivalent to measurements derivable from the sensor signal. The communications adapter may further comprise a signal processor having an input in communications with the sensor interface, where the signal processor is operable to derive a parameter responsive to the sensor signal and where the first baseband signal is responsive to the parameter. The parameter may correspond to at least one of a measured oxygen saturation and a pulse rate.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
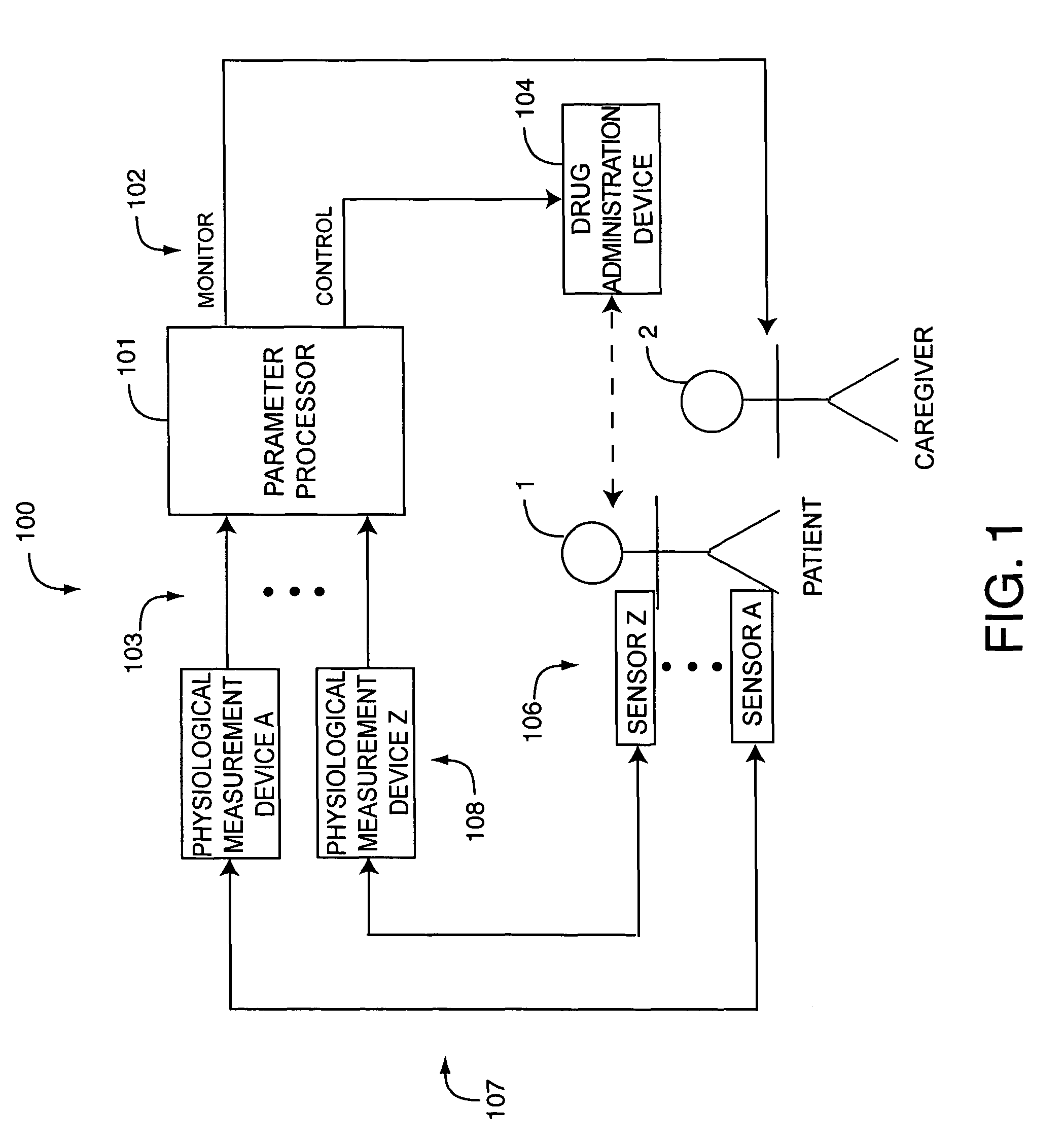
Drug administration controller
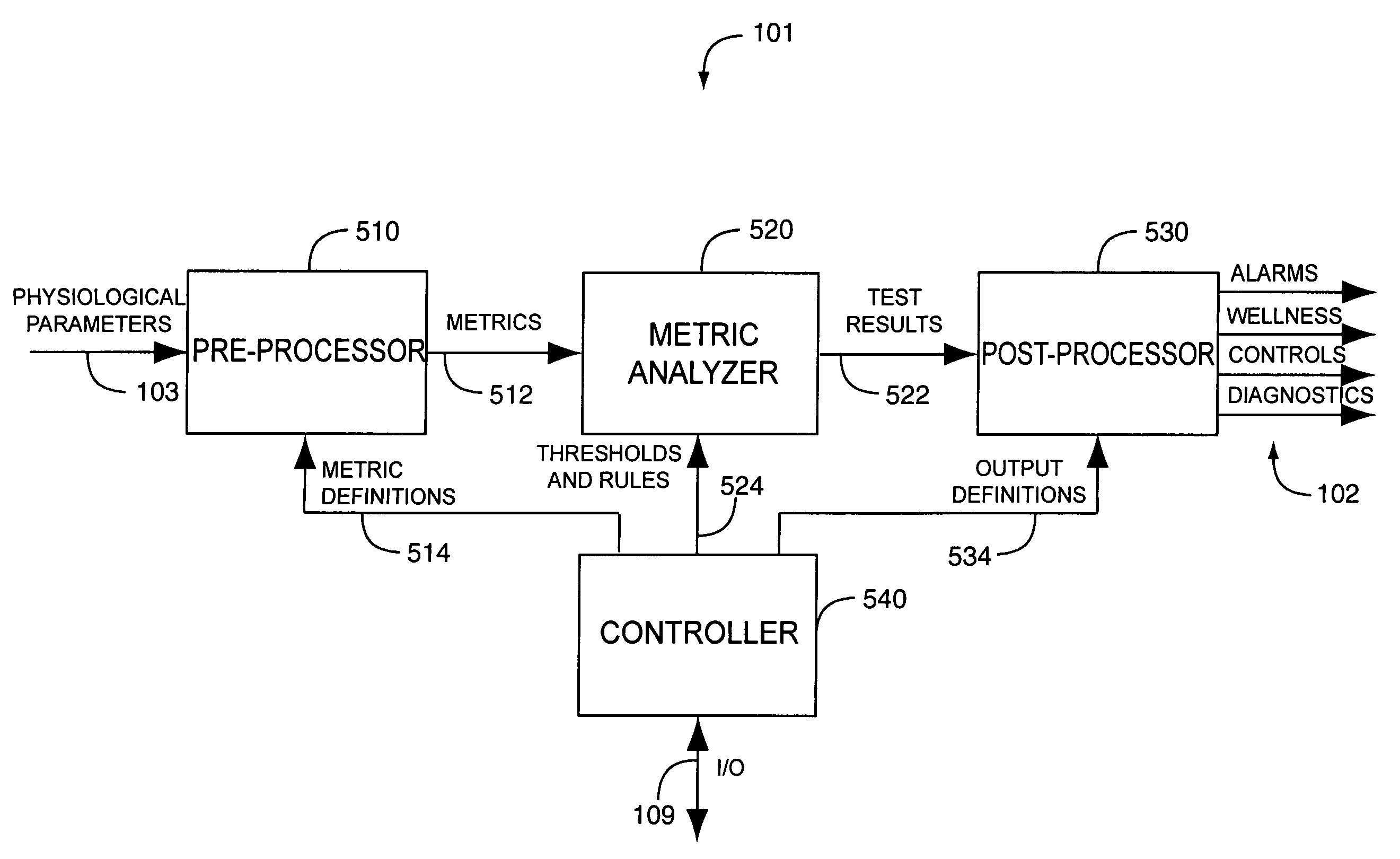
A drug administration controller has a sensor that generates a sensor signal to a physiological measurement device, which measures a physiological parameter in response. A control output responsive to the physiological parameter or a metric derived from the physiological parameter causes a drug administration device to affect the treatment of a person, such as by initiating, pausing, halting or adjusting the dosage of drugs administered to the person.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
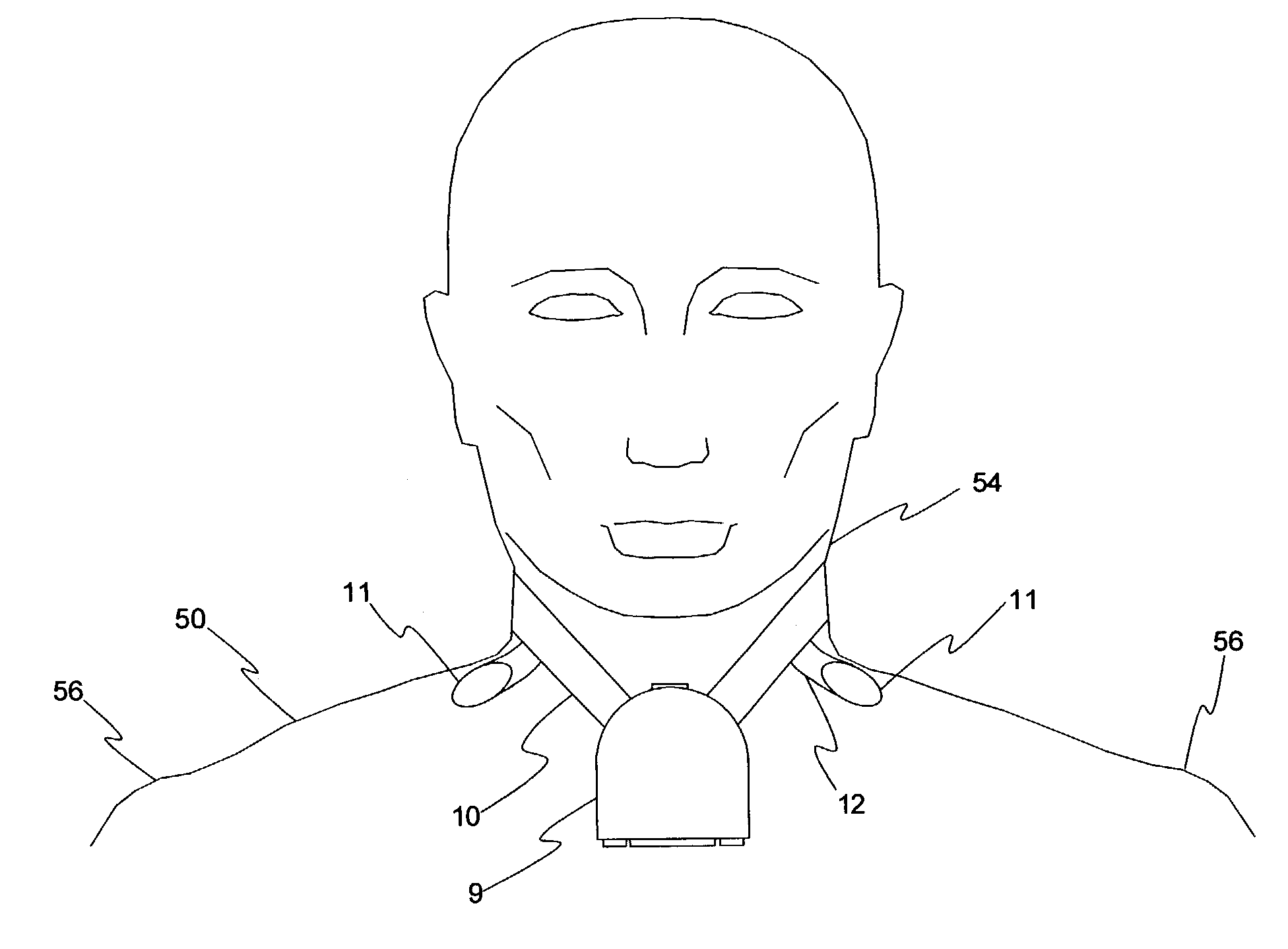
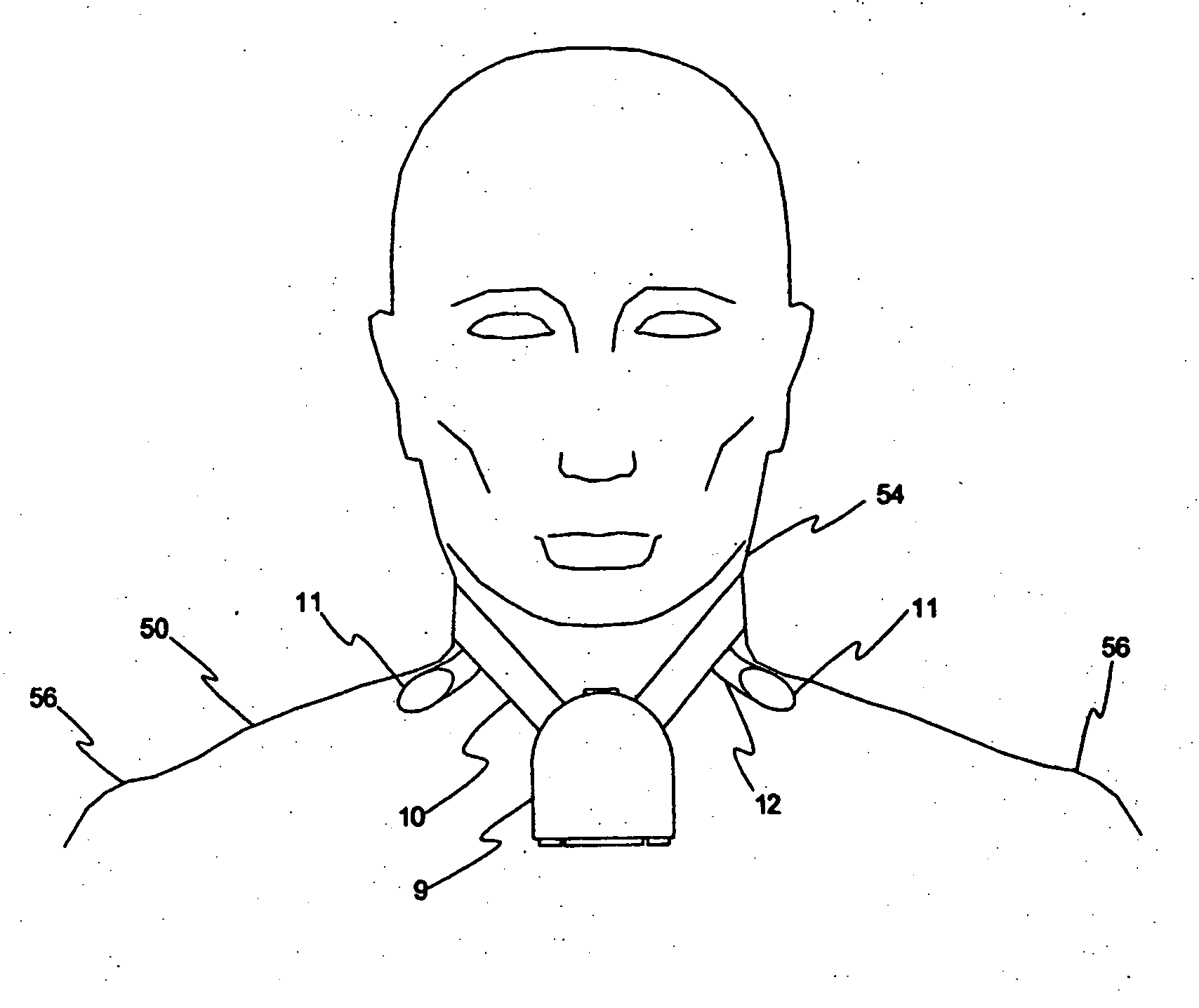
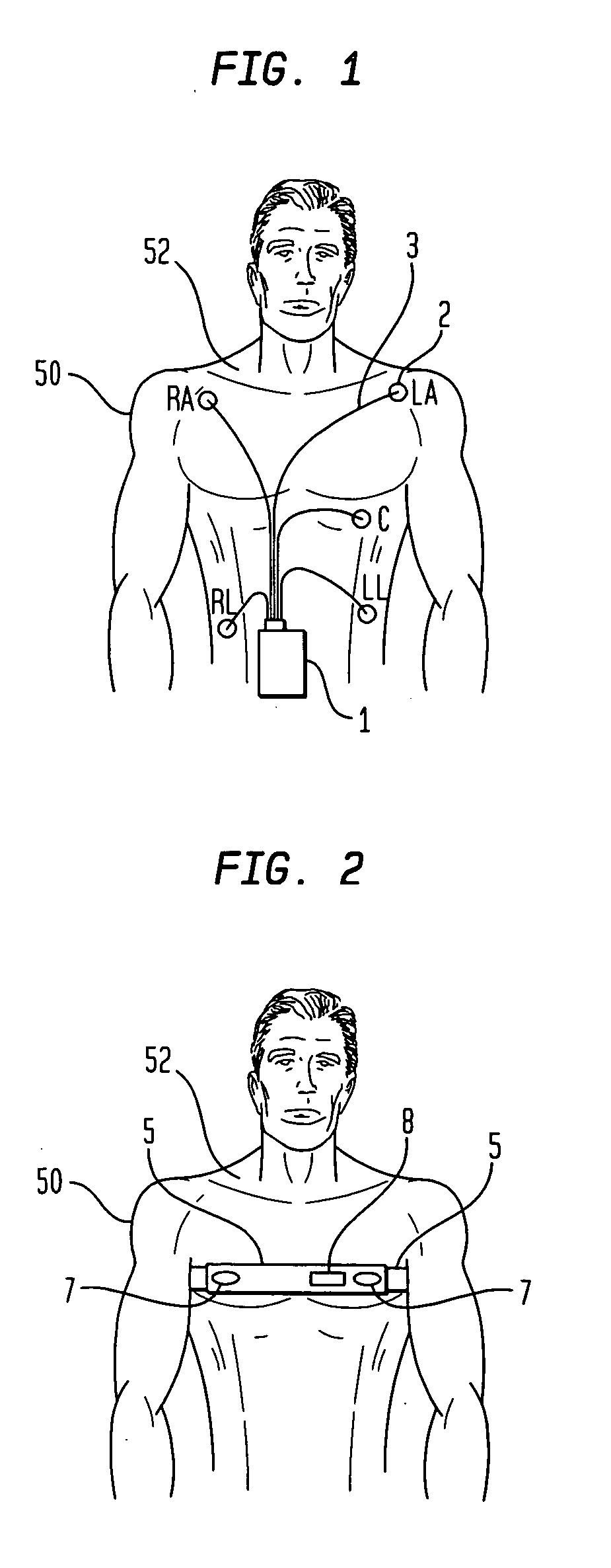
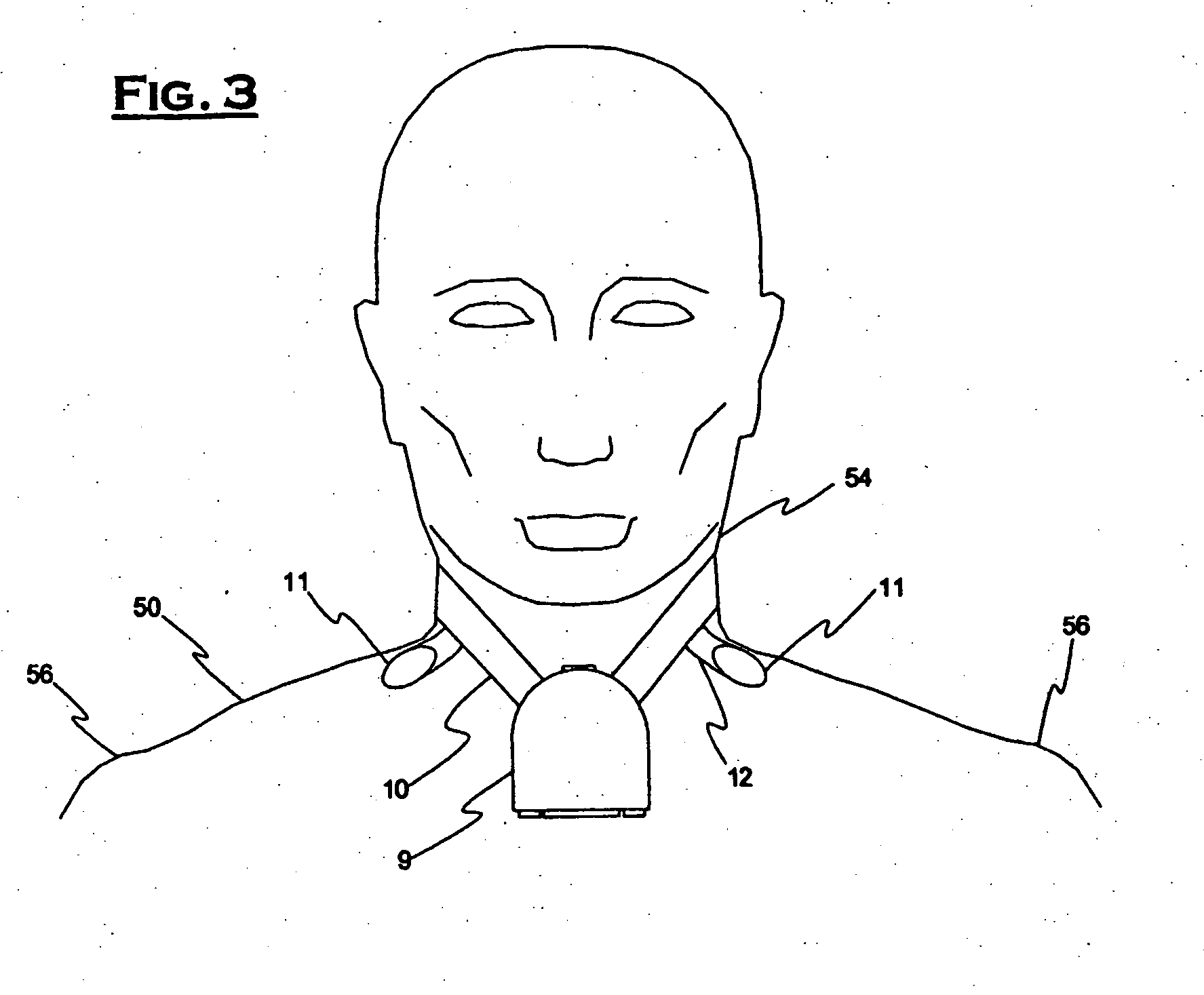
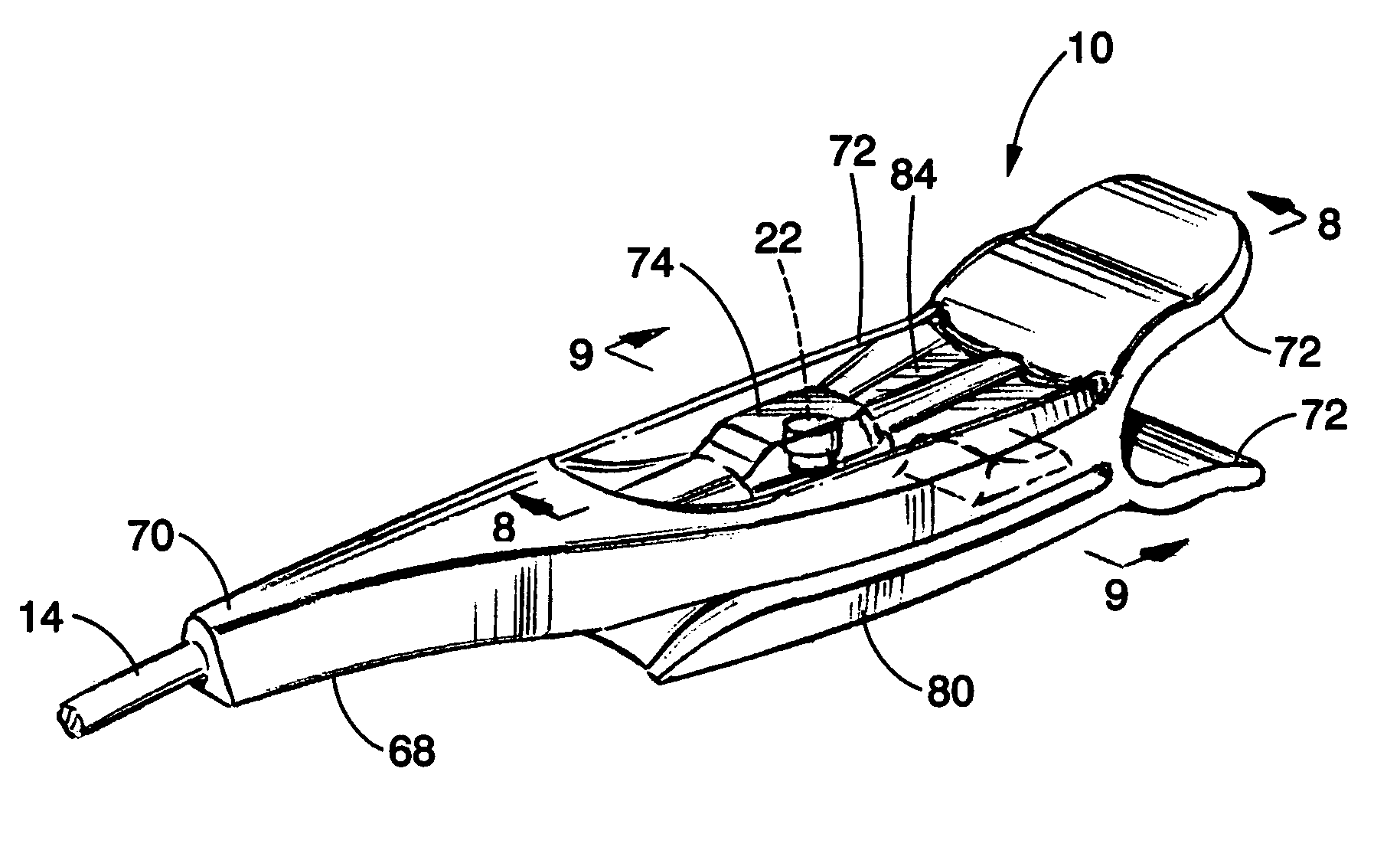
Patient-worn medical monitoring device
InactiveUS7257438B2Low costInsult to dignityDiagnostic signal processingElectrocardiographyElectricityEngineering
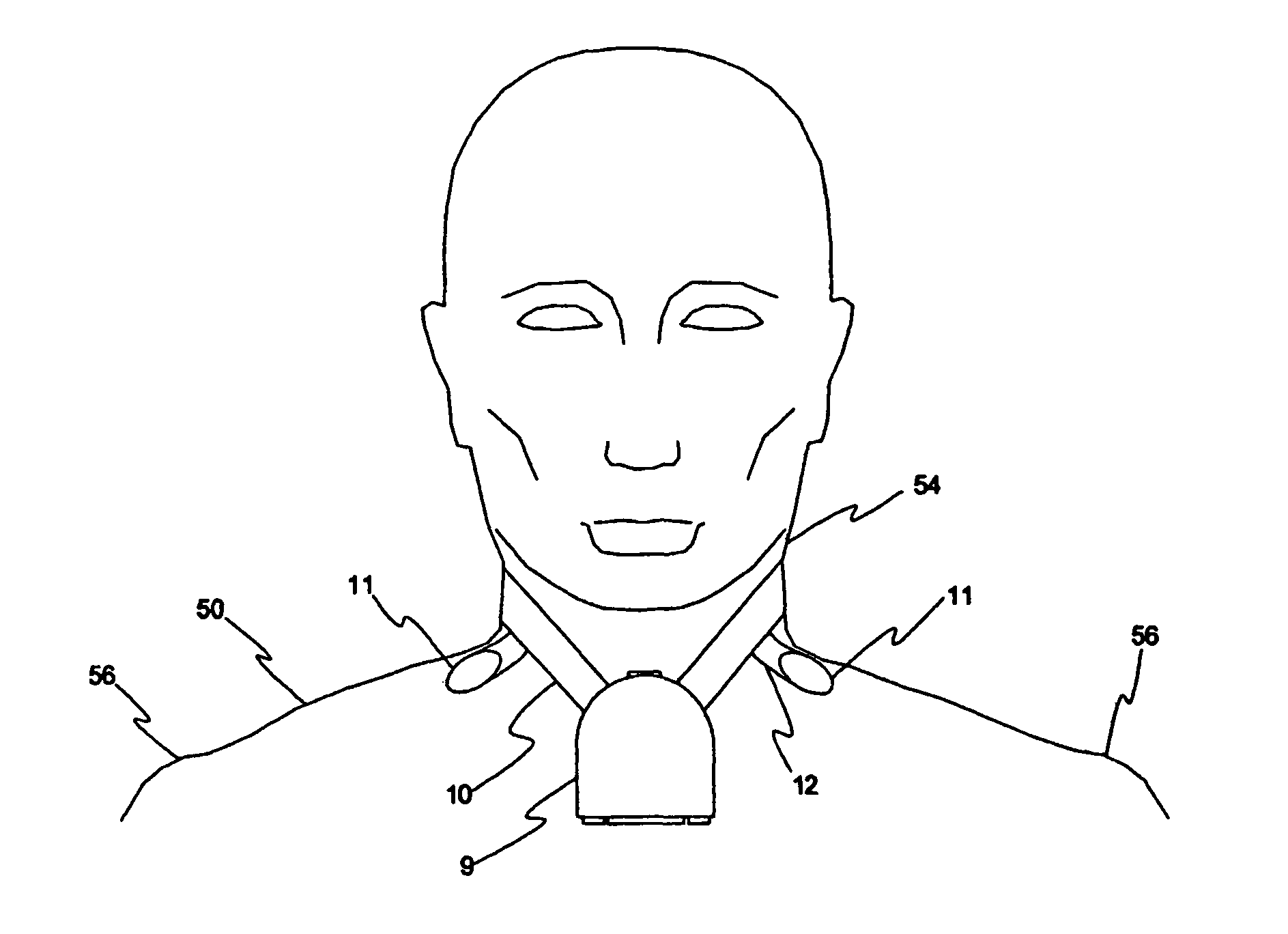
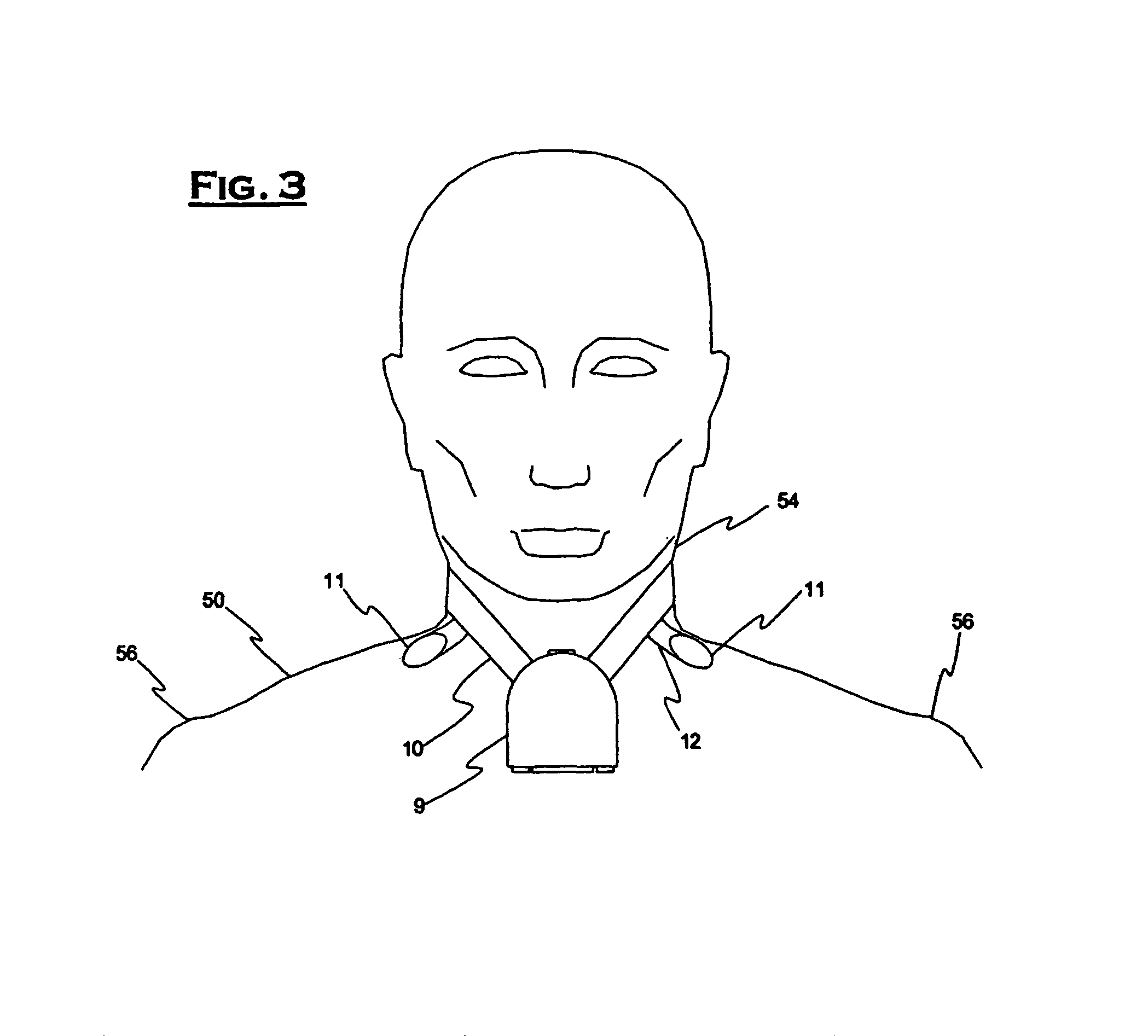
A medical monitor includes a lanyard and an electronic package supported in the manner of a pendant. The lanyard includes integral electrodes or other sensors for making physiological measurements, auxiliary components and connectors for electrically connecting the electrodes or sensors to the electronic package. The physiological measurements may be stored in the monitor for later readout, or may be transmitted, before or after processing, to a remote location.
Owner:DATASCOPE INVESTMENT
External ear-placed non-invasive physiological sensor
ActiveUS20090275813A1Lower latencyFast trackDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsExternal earsMedicine
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method and apparatus for determining critical care parameters
InactiveUS20120245439A1Prevent wrong actionElectrotherapyPerson identificationDiseaseResponse to injury
A physiological measuring system is disclosed that monitors certain physiological parameters of an individual through the use of a body-mounted sensing apparatus. The apparatus is particularly adapted for continuous wear. The system is also adaptable or applicable to calculating derivations of such parameters. A oxygen debt measuring embodiment is directed predicting an outcome in response to injury and illness. The technique allows for closed-loop resuscitation, early identification of illness and early corrective action.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV +1
Hyperspectral/multispectral imaging in determination, assessment and monitoring of systemic physiology and shock
ActiveUS20070024946A1Reduce and present informationHigh indexRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightWhole bodyBurn shock
The present invention provides a hyperspectral imaging system which demonstrates changes in tissue oxygen delivery, extraction and saturation during shock and resuscitation including an imaging apparatus for performing real-time or near real-time assessment and monitoring of shock, including hemorrhagic, hypovolemic, cardiogenic, neurogenic, septic or burn shock. The information provided by the hyperspectral measurement can deliver physiologic measurements that support early detection of shock and also provide information about likely outcomes.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
Method and circuit for indicating quality and accuracy of physiological measurements
InactiveUS20060030764A1Accurate detectionAccurate qualitySensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsPhysiological monitoringEngineering
Sensors and monitors for a physiological monitoring system having capability to indicate an accuracy of an estimated physiological condition. The sensor senses at least one physiological characteristic of a patient and is connectable to a monitor that estimates the physiological condition from signals detected by the sensor. The sensor includes a detector for detecting the signals from the patient which are indicative of the physiological characteristic. The sensor is associated with a memory configured to store data that defines at least one sensor signal specification boundary for the detected signals. The boundary is indicative of a quality of the signals and an accuracy of the physiological characteristic estimated from the signals by the monitor. The sensor further includes means for providing access to the memory to allow transmission of the data that defines the at least one sensor boundary to the monitor.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
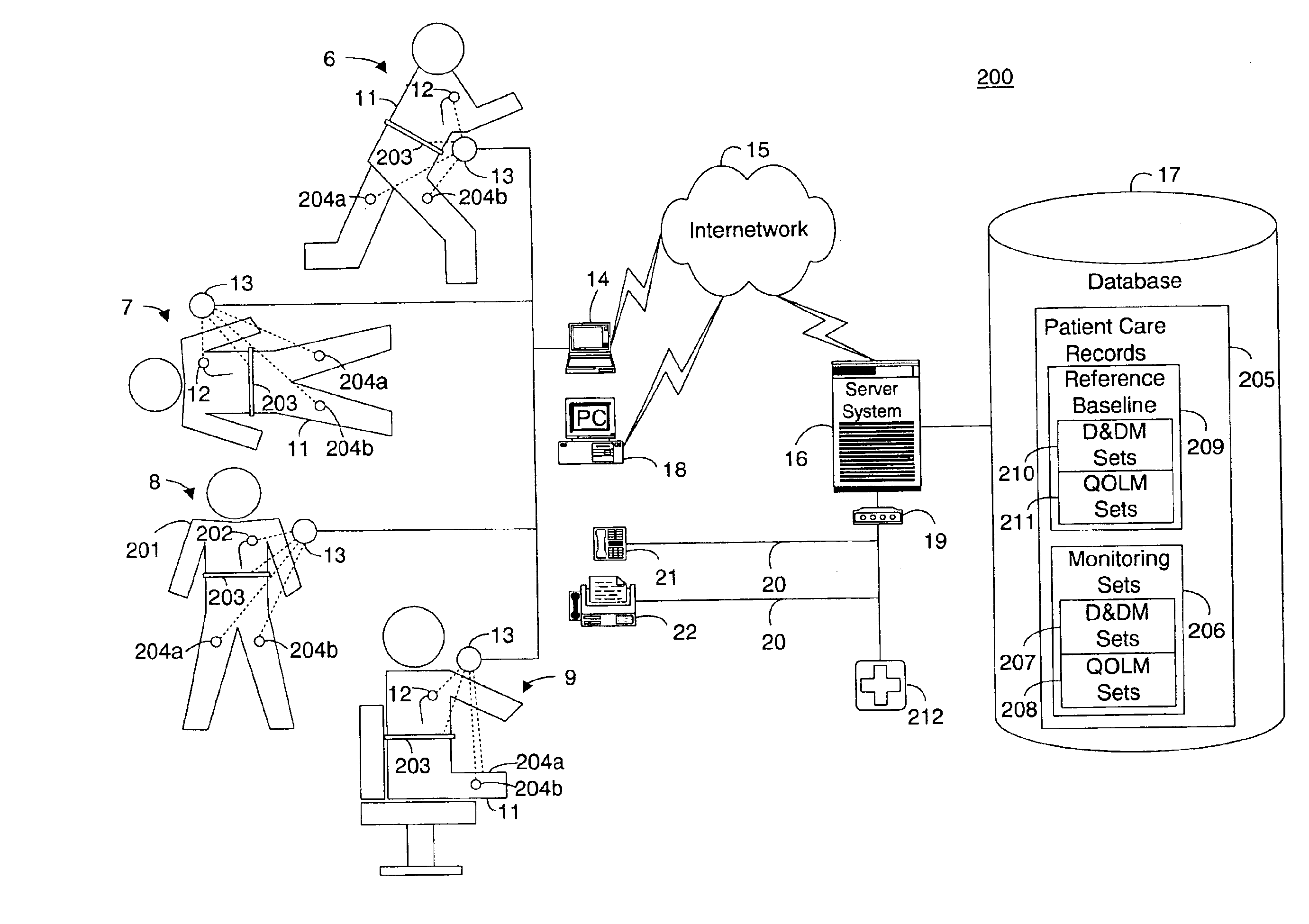
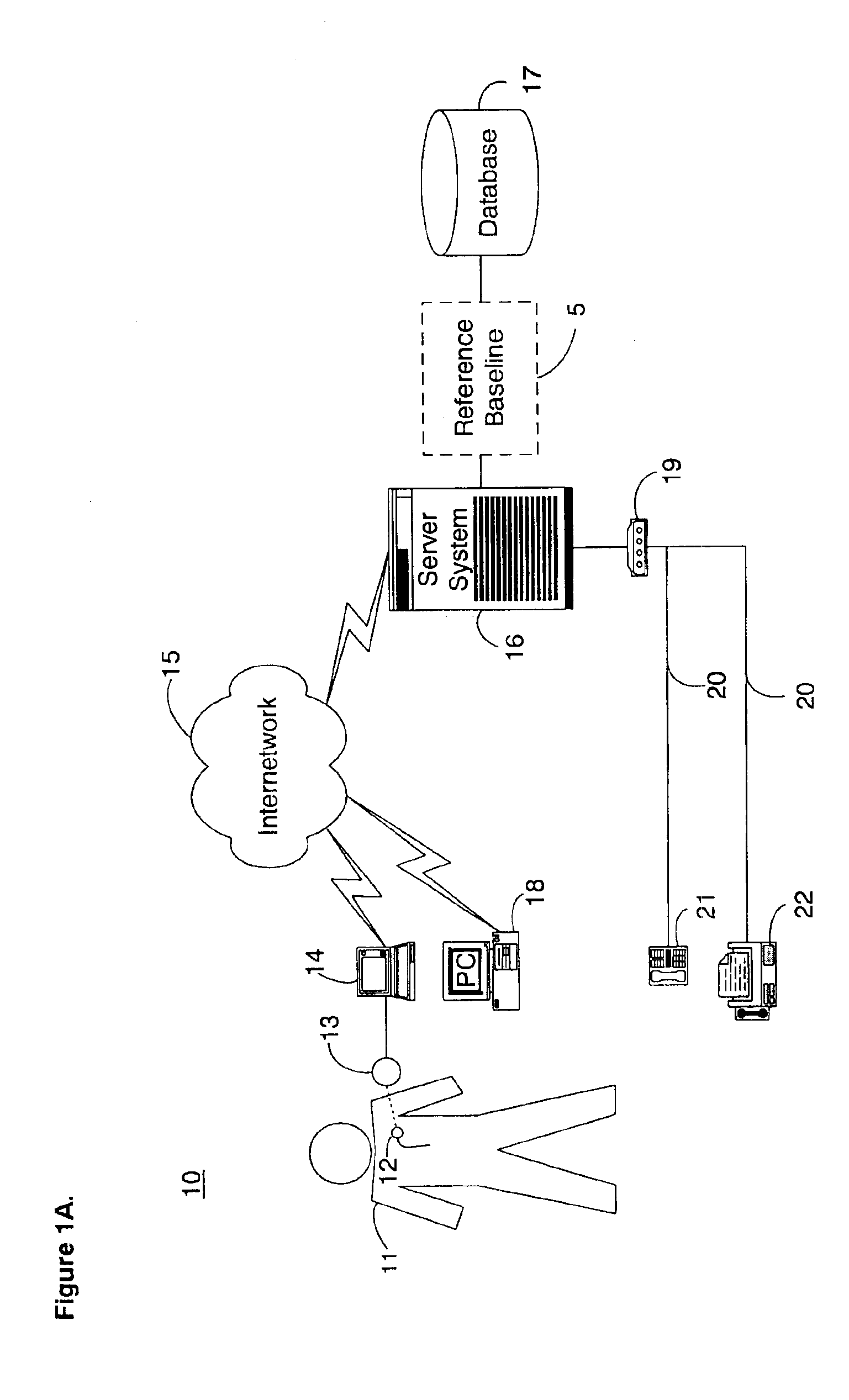
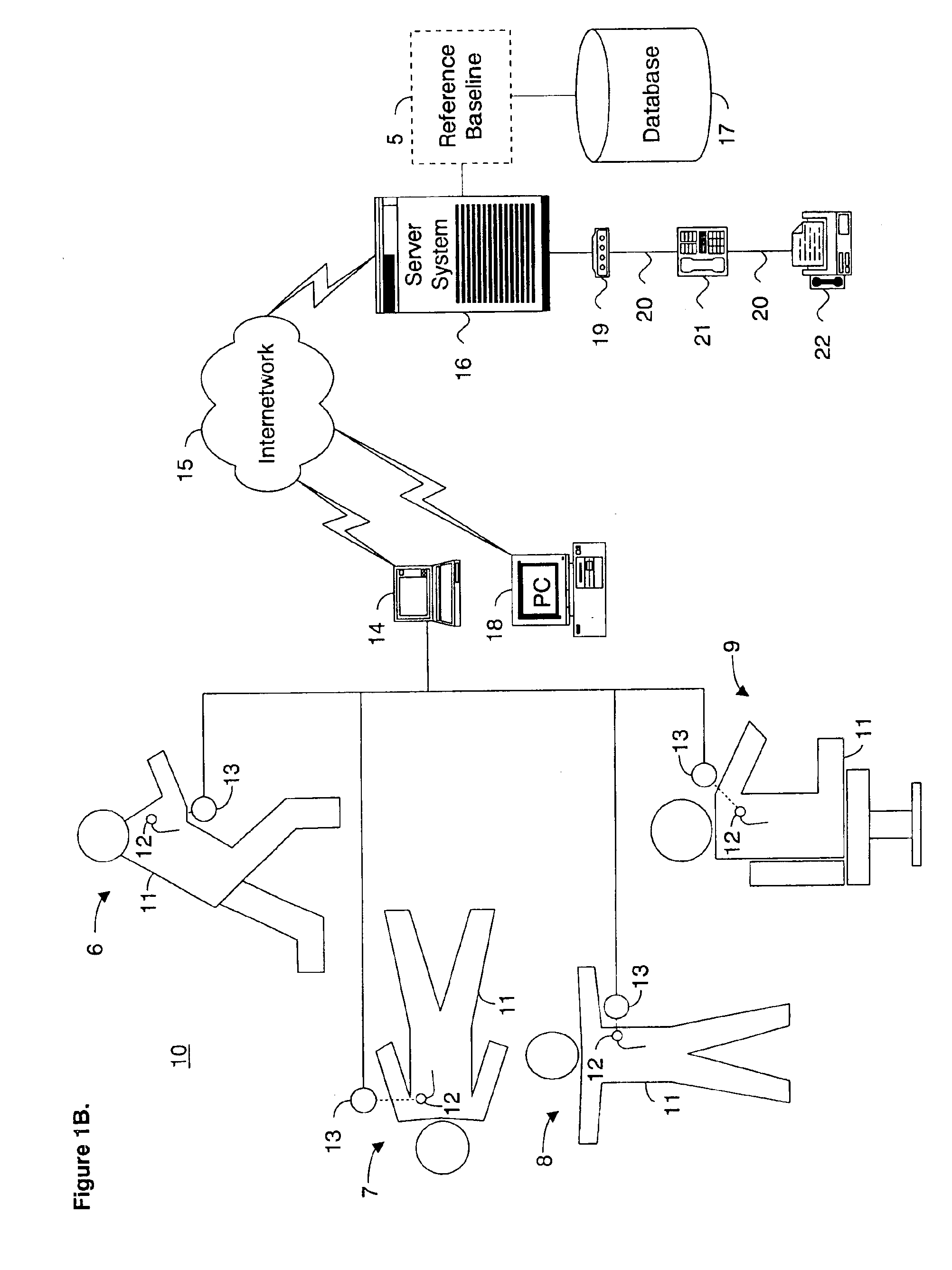
System and method for determining a reference baseline of regularly retrieved patient information for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS6887201B2Improve accuracyImproves chroniclingElectrotherapyHealth-index calculationEmergency medicinePatient status
A system for determining a reference baseline of regularly retrieved patient information for automated remote patient care is presented. A medical device having a sensor for monitoring at least one physiological measure of an individual patient regularly records and stores measures sets relating to patient information during an initial time period. A database collects one or more patient care records by organizing one or more patient care records and storing the collected measures set into such a patient care record for the individual patient. A server receives the collected device measures set from the medical device, processes the collected device measures set into a set of reference measures representative of at least one of measured or derived patient information, and stores the reference measures set into the patient care record as data in a reference baseline indicating an initial patient status.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
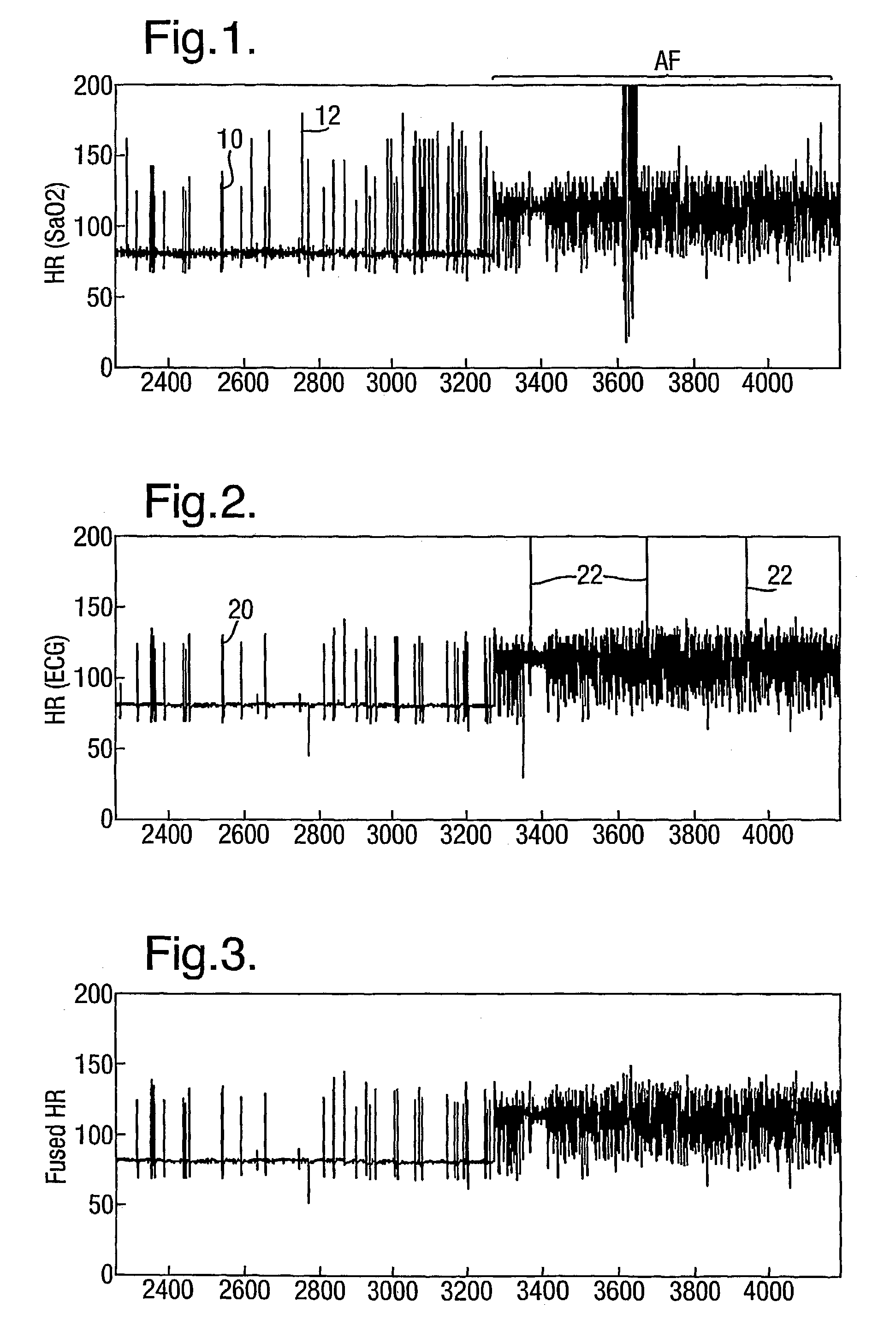
Combining measurements from different sensors
A method for combining measurements from two or more independent measurement channels, particularly physiological measurements such as heart rate. Independent measurements of heart rate, for instance by ECG and pulse oximetry, can be combined to derive an improved measurement eliminating artefacts on one channel. A model of the process generating the physiological parameter, e.g., the heart rate, is constructed and is run independently for each channel to generate predictions of the parameter. The measured values are compared with the predicted values and the differences are used as an indication of the confidence in the measurement. The measurements from the two channels are ombined using weights calculated from the respective differences.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
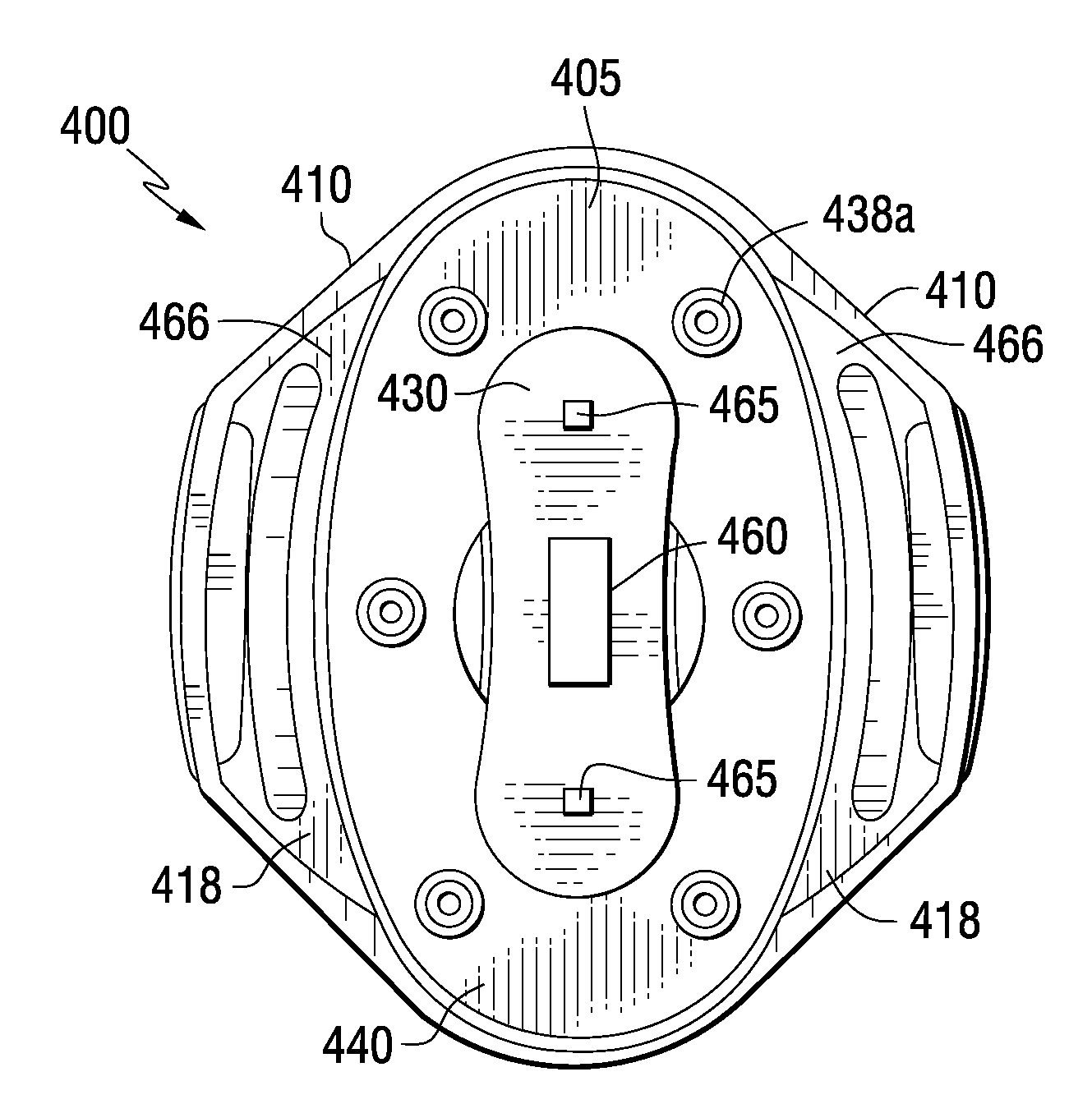
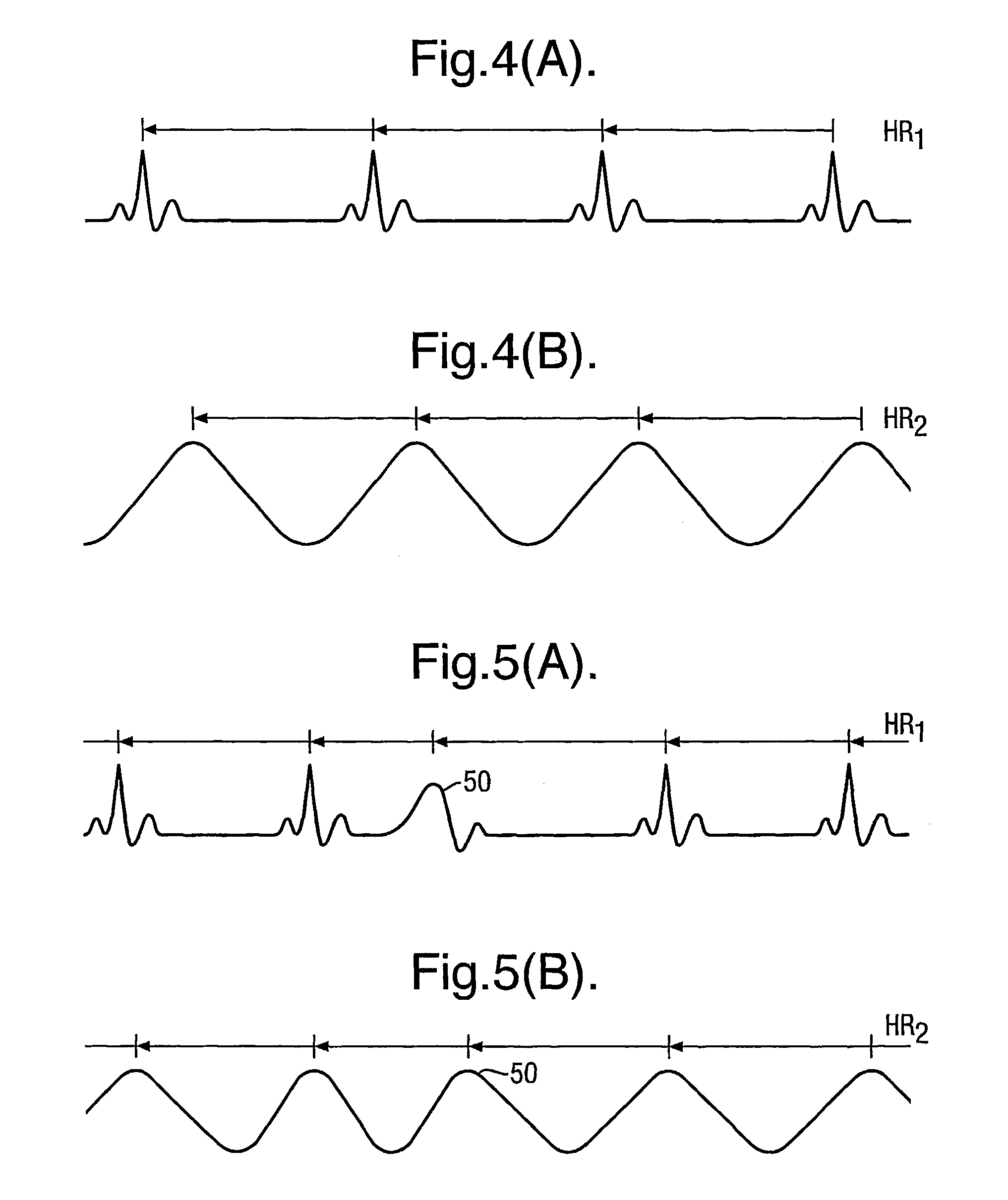
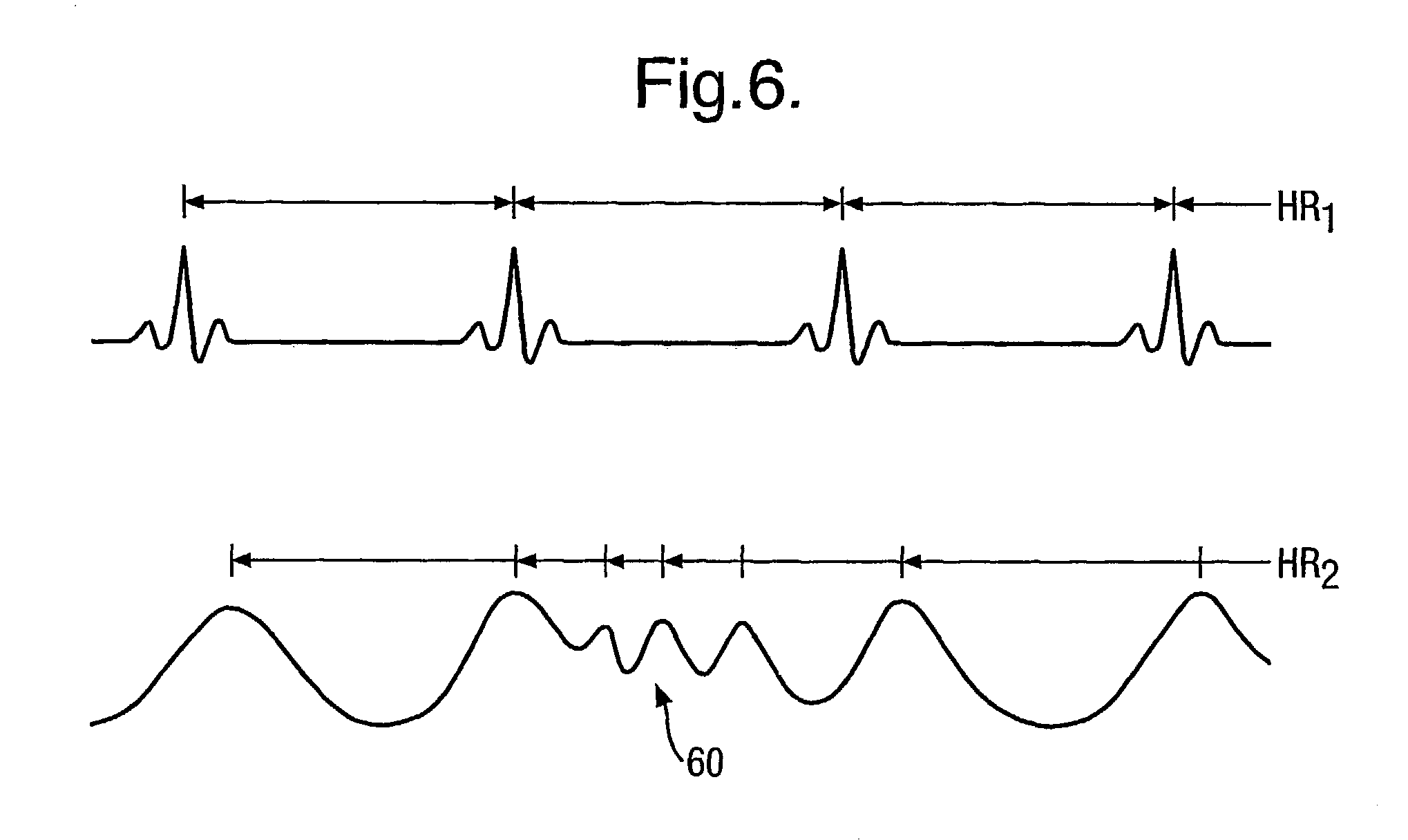
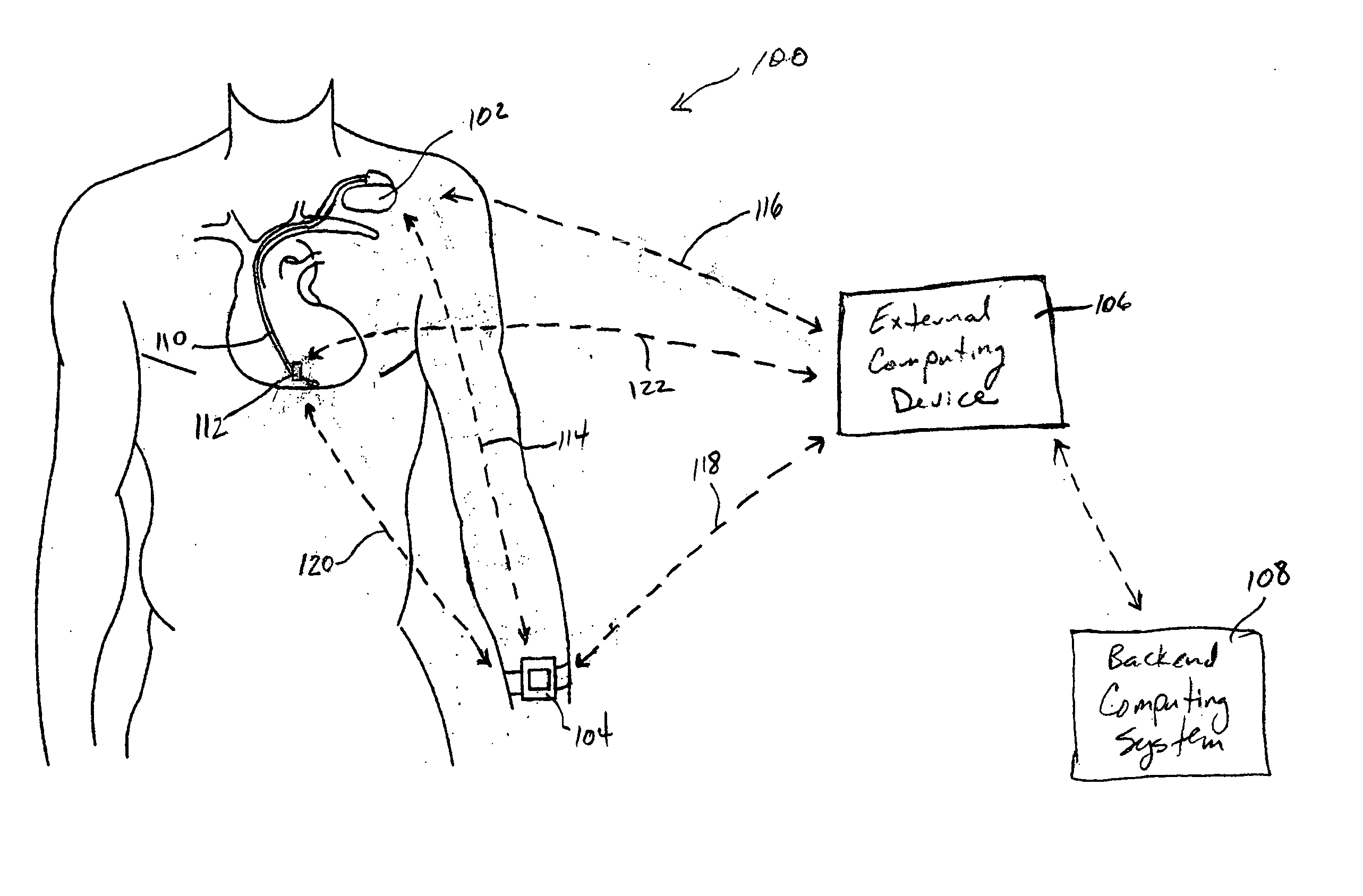
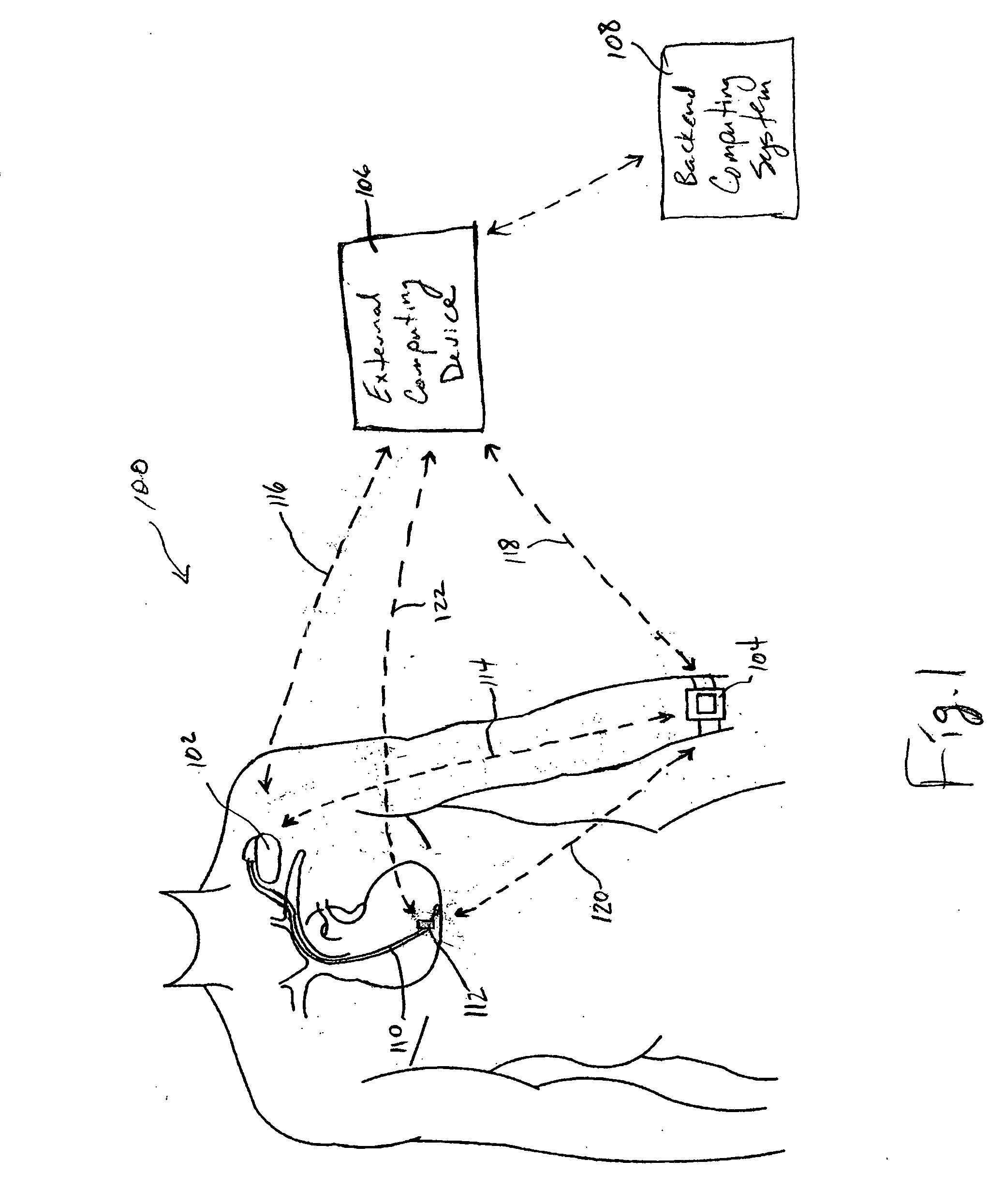
Systems and methods for deriving relative physiologic measurements
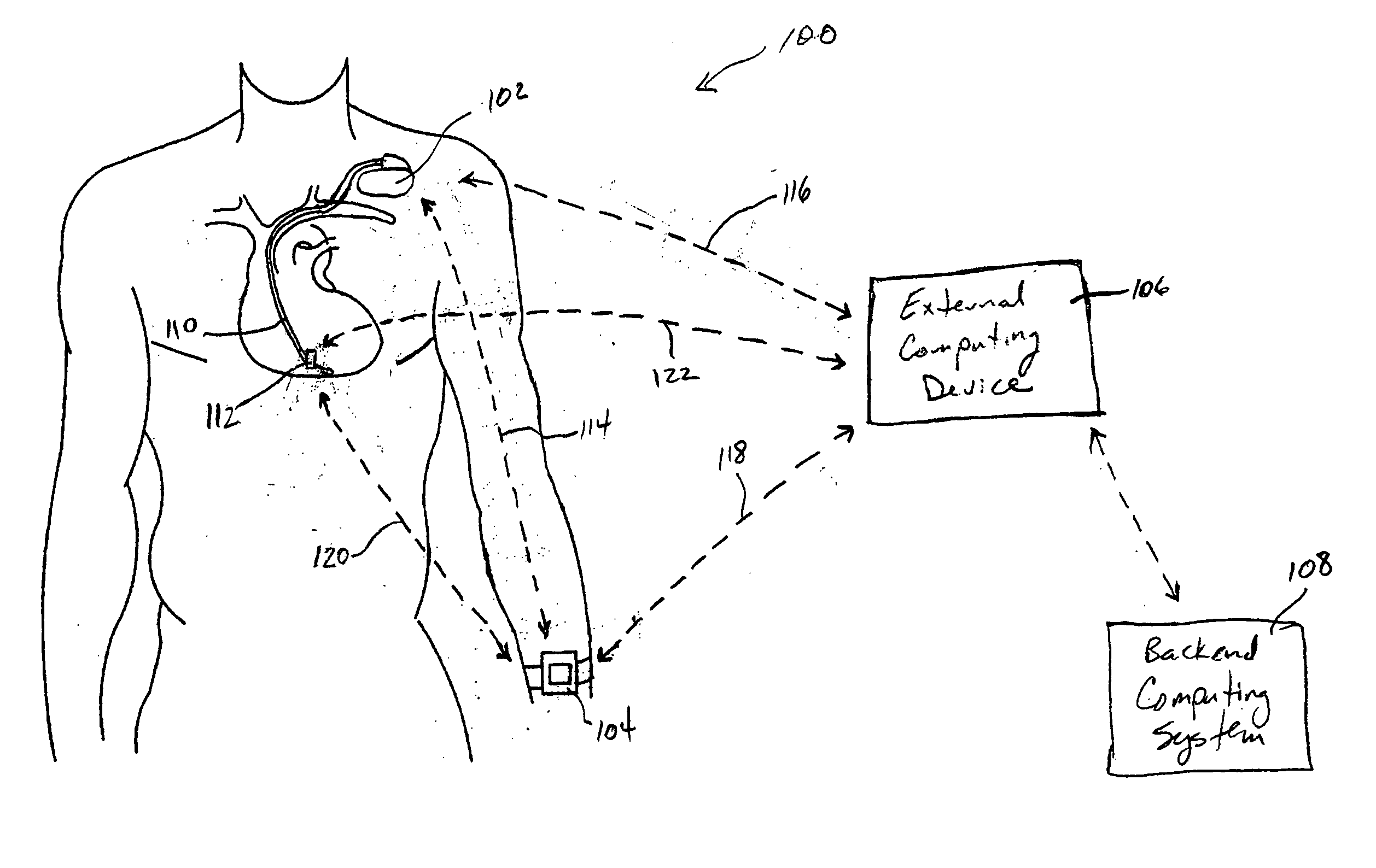
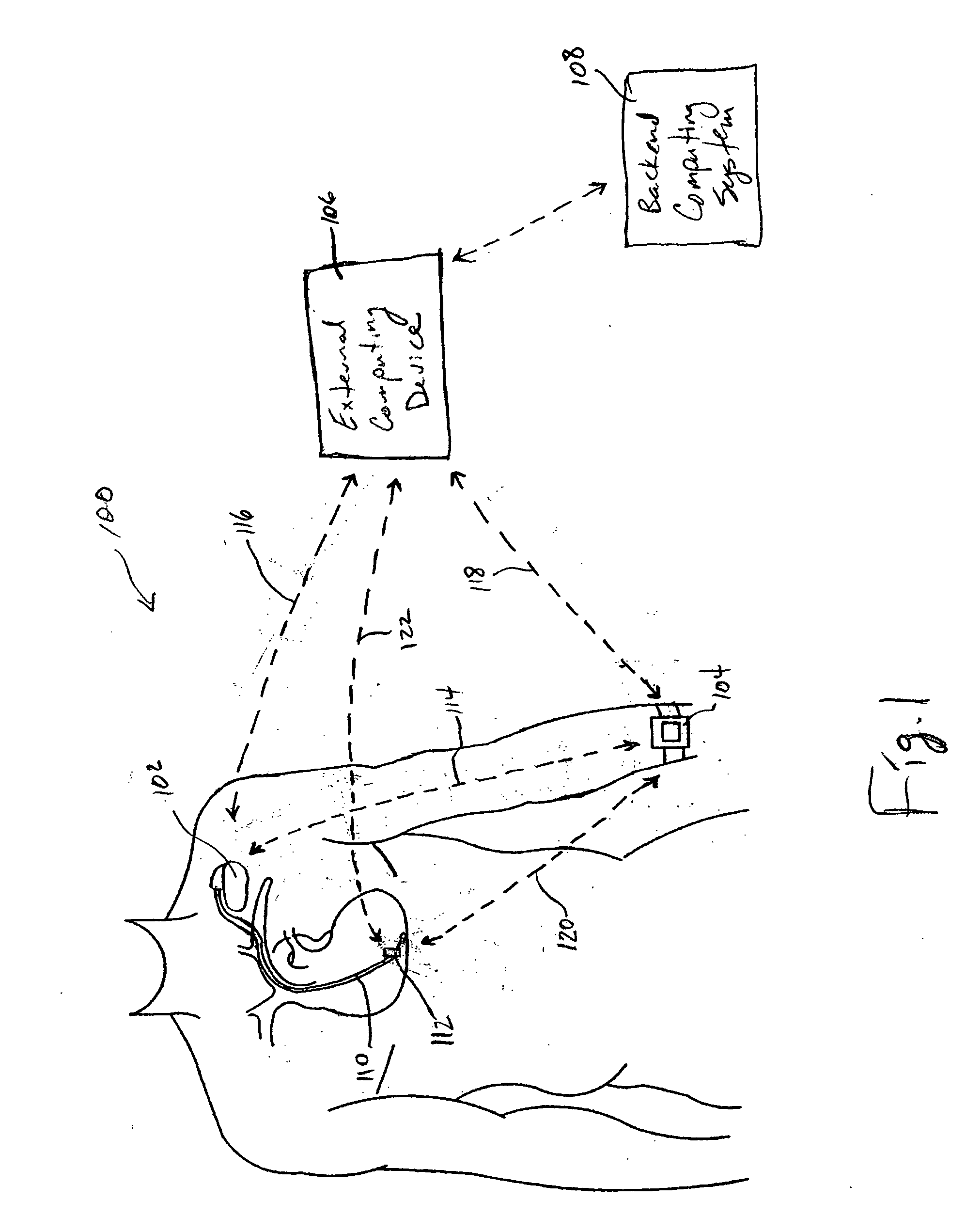
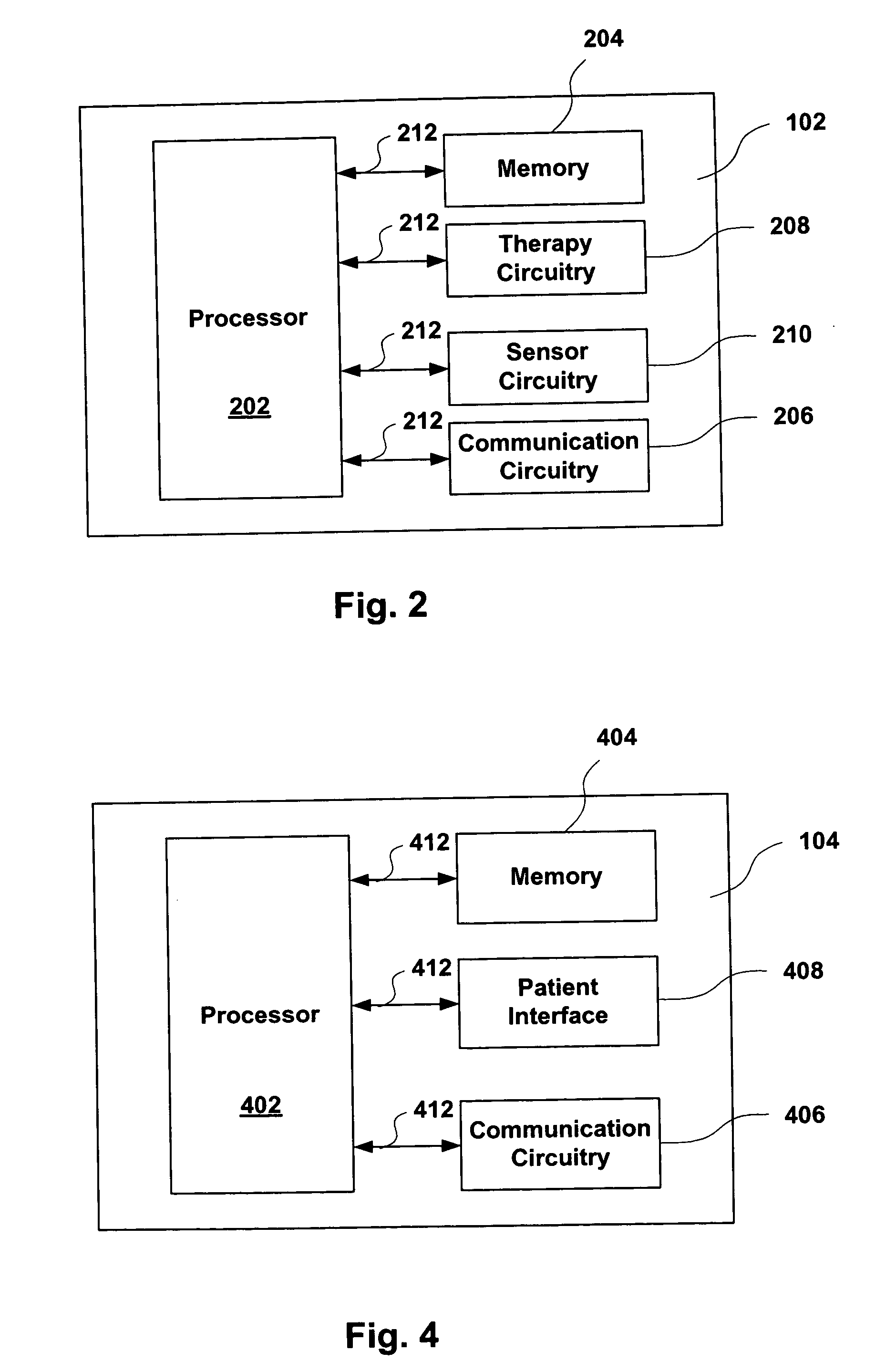
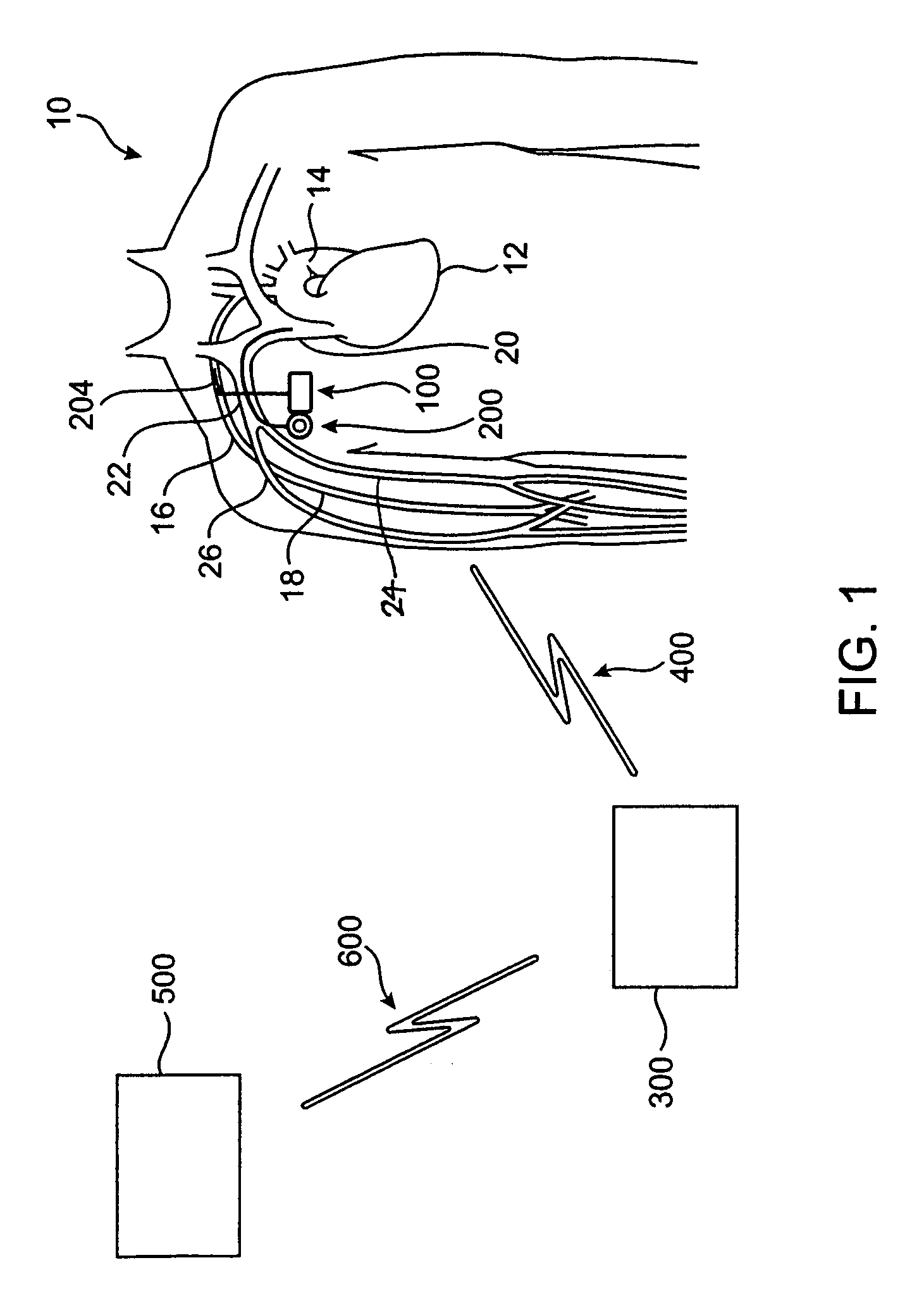
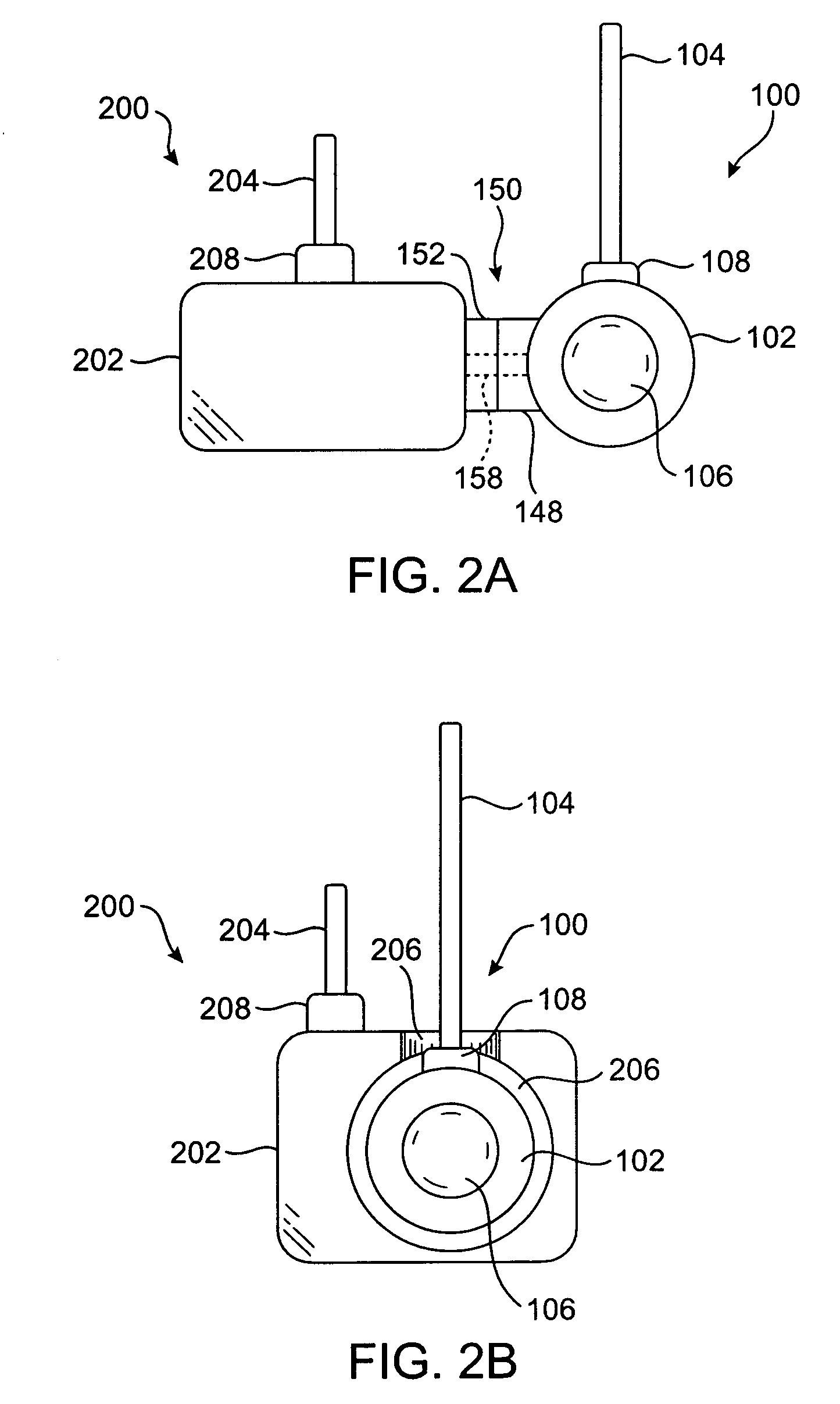
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a system for deriving physiologic measurement values that are relative to ambient conditions. In one embodiment, the system comprises an implantable medical device (“IMD”) and an external monitor. The IMD is adapted to determine an absolute physiologic parameter value within a patient's body, and communicate the absolute physiologic parameter value outside the patient's body, for example, to the external monitor. Further, the external monitor is adapted to receive the absolute physiologic parameter from the IMD and obtain an ambient condition value outside the body that can affect the absolute physiologic parameter value. The external monitor then calculates a relative physiologic parameter value from the ambient condition value and the absolute physiologic parameter value.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and methods for deriving relative physiologic measurements using an implanted sensor device
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a system for deriving physiologic measurement values that are relative to ambient conditions. In one embodiment, the system comprises an implantable medical device (“IMD”), which includes a main body; and a remote sensor system operable to measure an absolute physiologic parameter value within a patient's body. The system further comprises an external device, which can be operable to obtain an ambient condition value outside the patient's body that can affect the absolute physiologic parameter value, and communicate the ambient condition value to the remote sensor system. In accordance with one embodiment, the remote sensor system then can be further operable to receive the ambient condition value and calculate a relative physiologic parameter value from the ambient condition value and the absolute physiologic parameter value.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
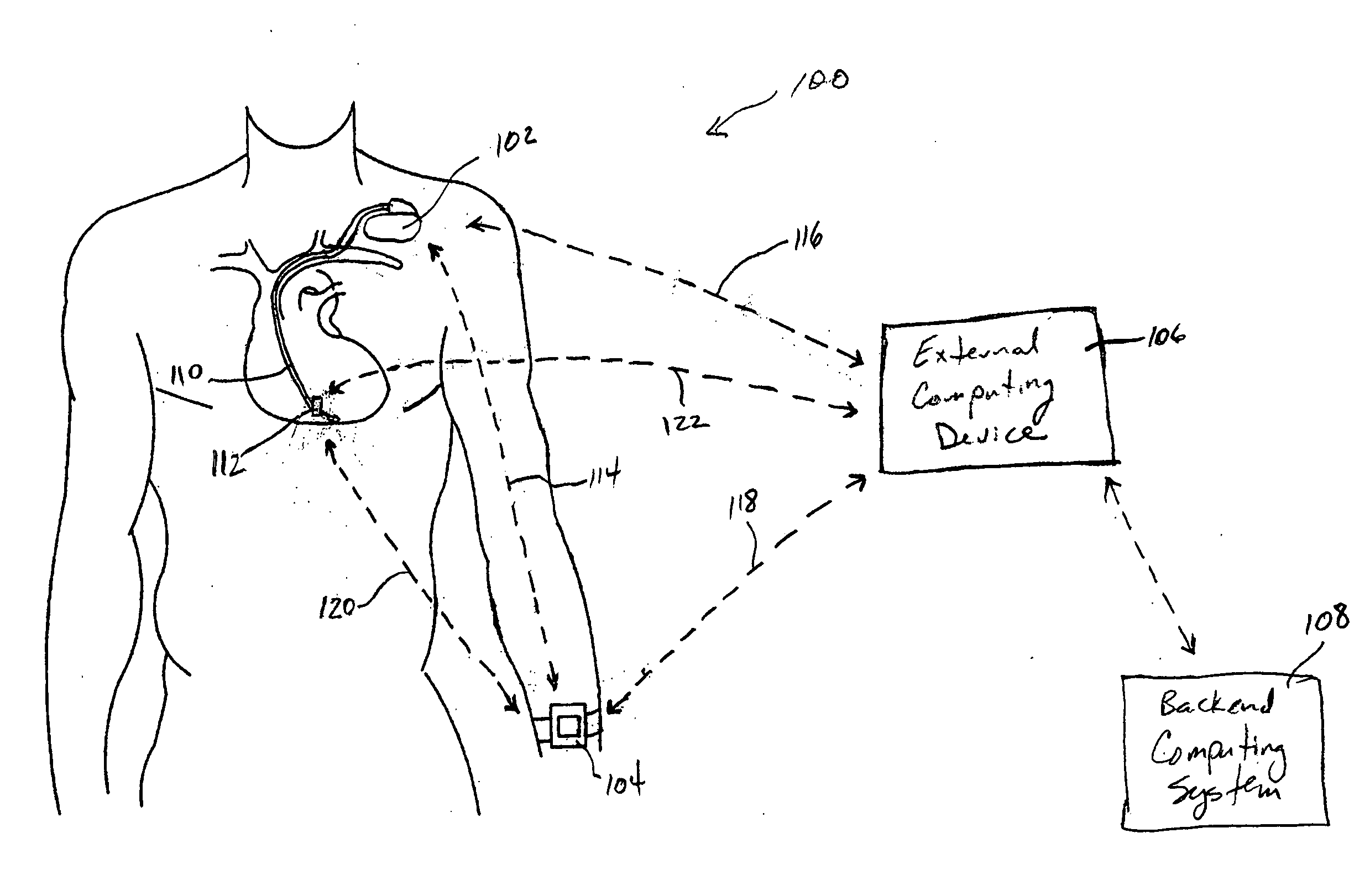
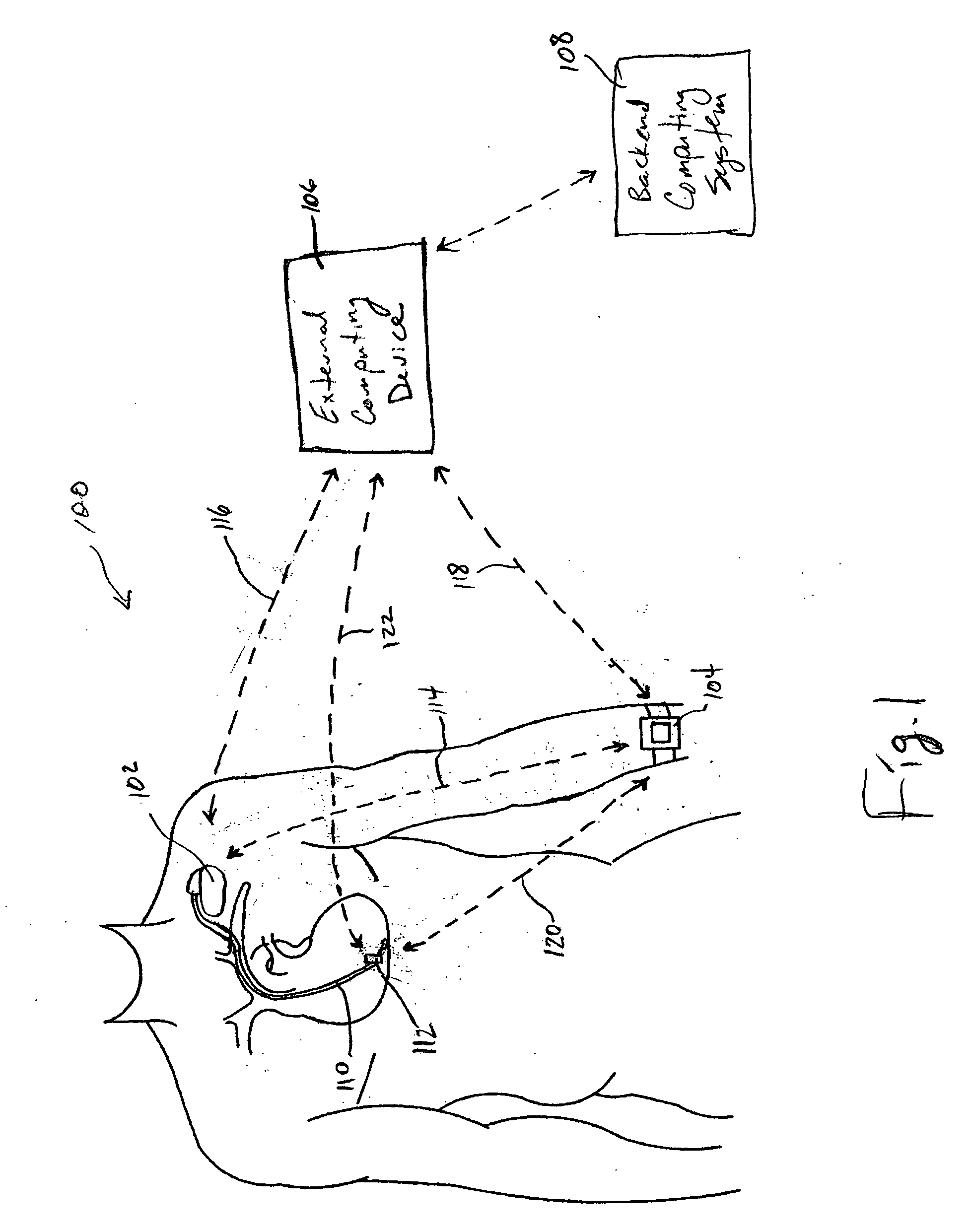
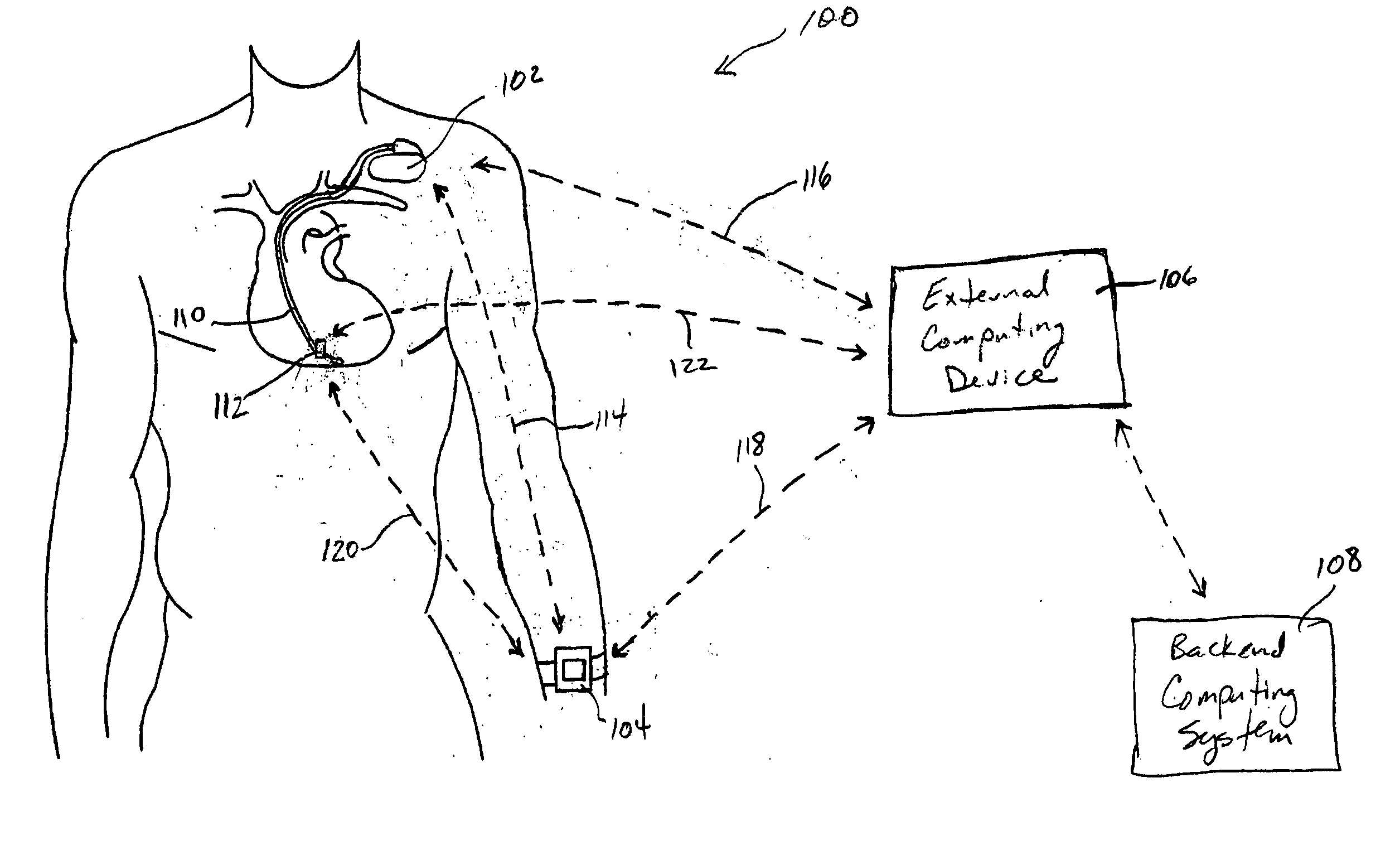
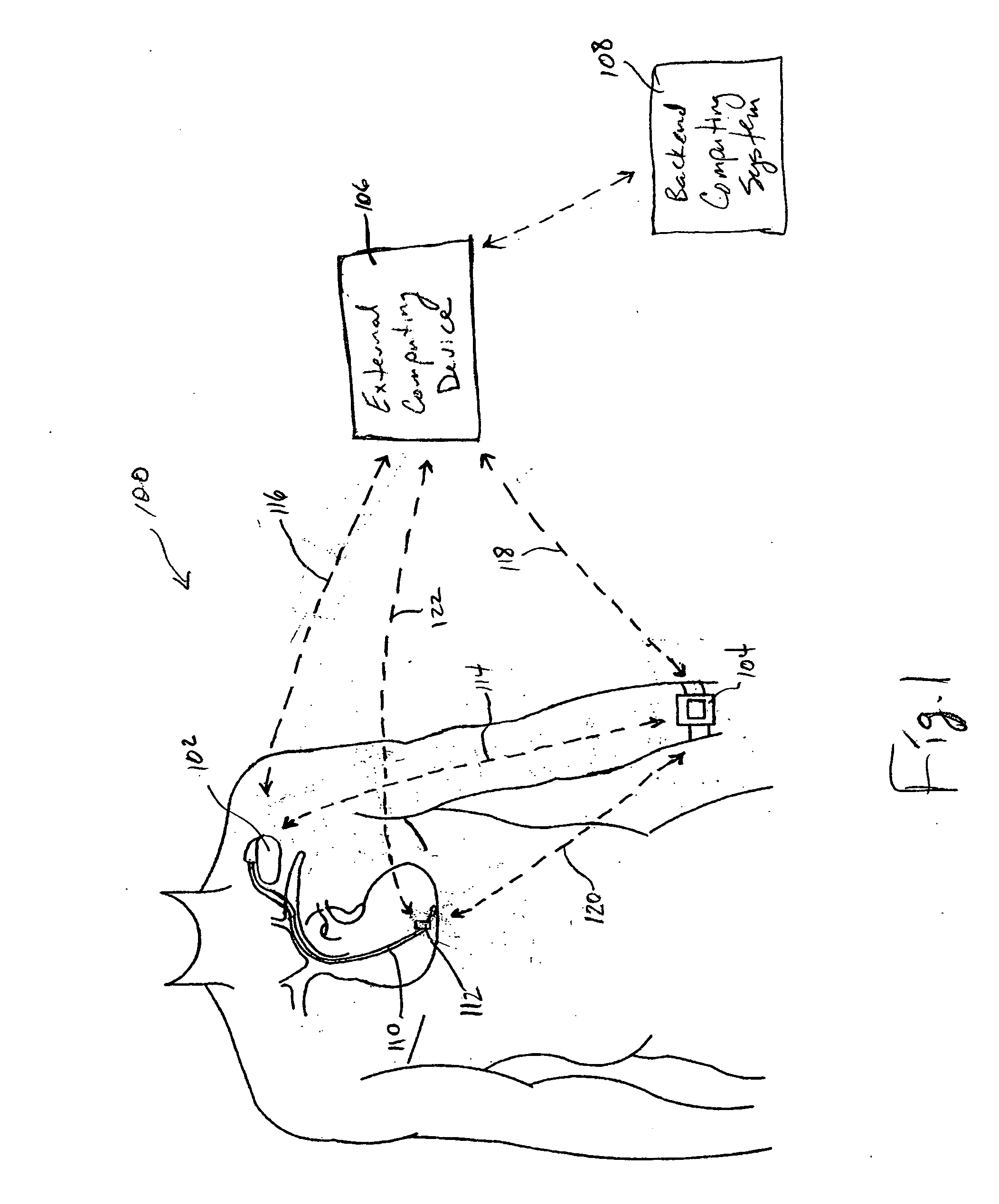
System and method for deriving relative physiologic measurements using an external computing device
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a system for deriving physiologic measurement values that are relative to ambient conditions. In one embodiment, the system comprises an implantable medical device (“IMD”) and an external computing device. The IMD is operable to determine an absolute physiologic parameter value within a patient's body, and communicate the absolute physiologic parameter value outside the patient's body, for example, to the external computing device. Further, the external computing device is operable to receive the absolute physiologic parameter from the IMD and obtain an ambient condition value outside the body that can affect the absolute physiologic parameter value. The external computing device then calculates a relative physiologic parameter value from the ambient condition value and the absolute physiologic parameter value.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Vascular access port with physiological sensor
InactiveUS7070591B2Easy to optimizeImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyMedical devicesCollection systemCommunication link
A combined vascular access port and physiologic parameter monitoring device. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be connected by a cooperative geometry. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be implanted at the same time and in the same anatomical location (e.g., subcutaneous pocket). The monitoring device may include a telemetry unit that transmits physiological measurement data to a local data collection system (e.g., carried by the patient or located in the patient's home), which may re-transmit the data to a remote data collection system (e.g., located at a physician's office or clinic) via a suitable communication link.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
Systems and methods for deriving relative physiologic measurements using a backend computing system
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a system for deriving physiologic measurement values that are relative to ambient conditions. In one embodiment, the system comprises an implantable medical device (“IMD”), an external computing device, and a backend computing system. The IMD determines an absolute physiologic parameter value within a patient's body, and communicates the absolute physiologic parameter value outside the patient's body, for example, to the external computing device. Further, the external computing device receives the absolute physiologic parameter from the IMD and communicates it to the backend computing system. The backend computing system receives the absolute physiologic parameter value and obtains an ambient condition value outside the body that can affect the absolute physiologic parameter value. The backend computing system then calculates a relative physiologic parameter value from the ambient condition value and the absolute physiologic parameter value, and in some embodiments, stores the relative physiologic parameter value in a storage location, such as a memory or database.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Patient-worn medical monitoring device
ActiveUS20070106167A1Low costCost of applicationDiagnostic signal processingElectrocardiographyElectricityEngineering
A medical monitor includes a lanyard and an electronic package supported in the manner of a pendant. The lanyard includes integral electrodes or other sensors for making physiological measurements, auxiliary components and connectors for electrically connecting the electrodes or sensors to the electronic package. The physiological measurements may be stored in the monitor for later readout, or may be transmitted, before or after processing, to a remote location.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
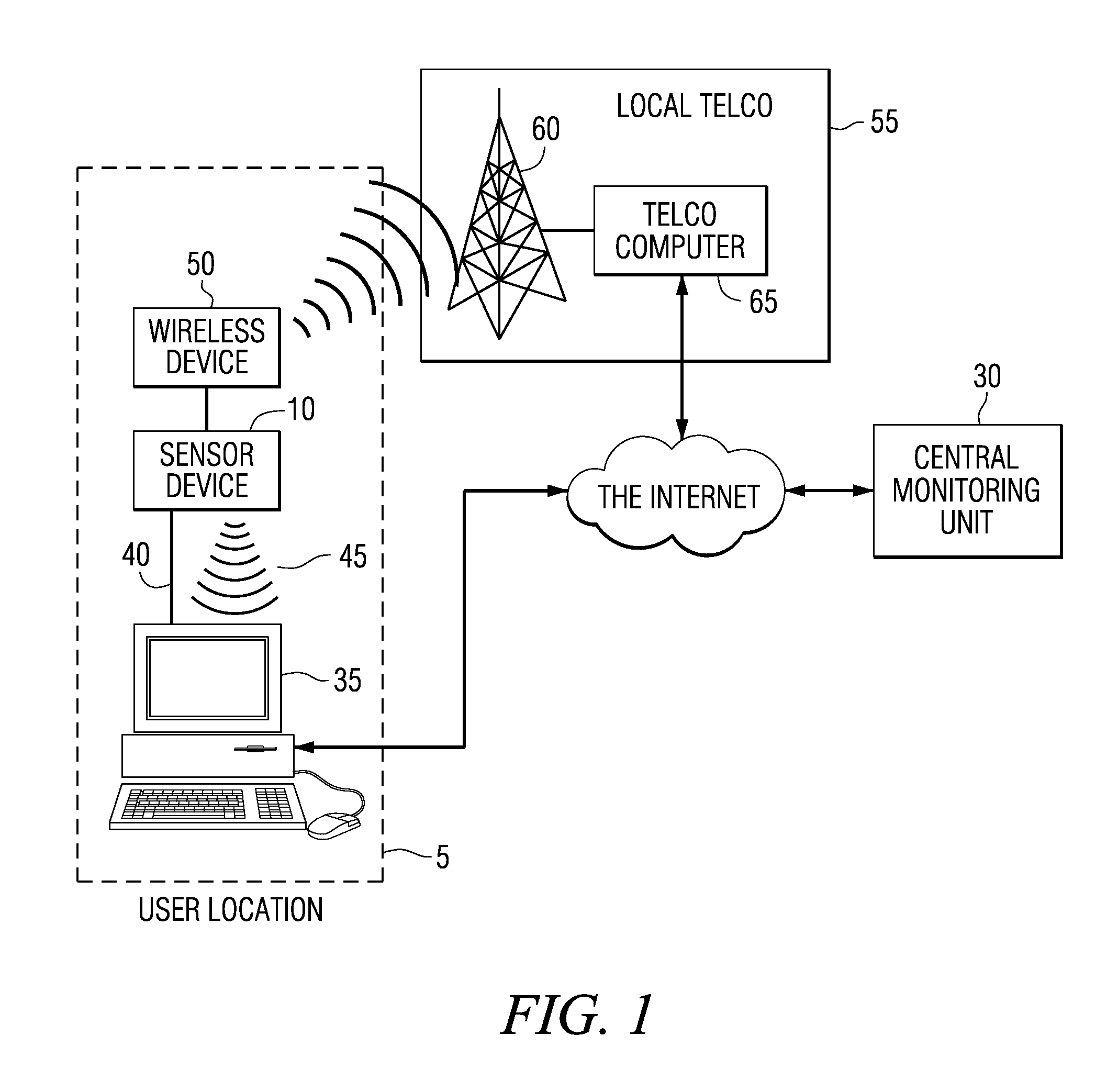
System and method for automatic monitoring of the health of a user
InactiveUS20050075542A1Easy to operateEarly detectionTelemedicineEvaluation of blood vesselsHealth conditionNon invasive
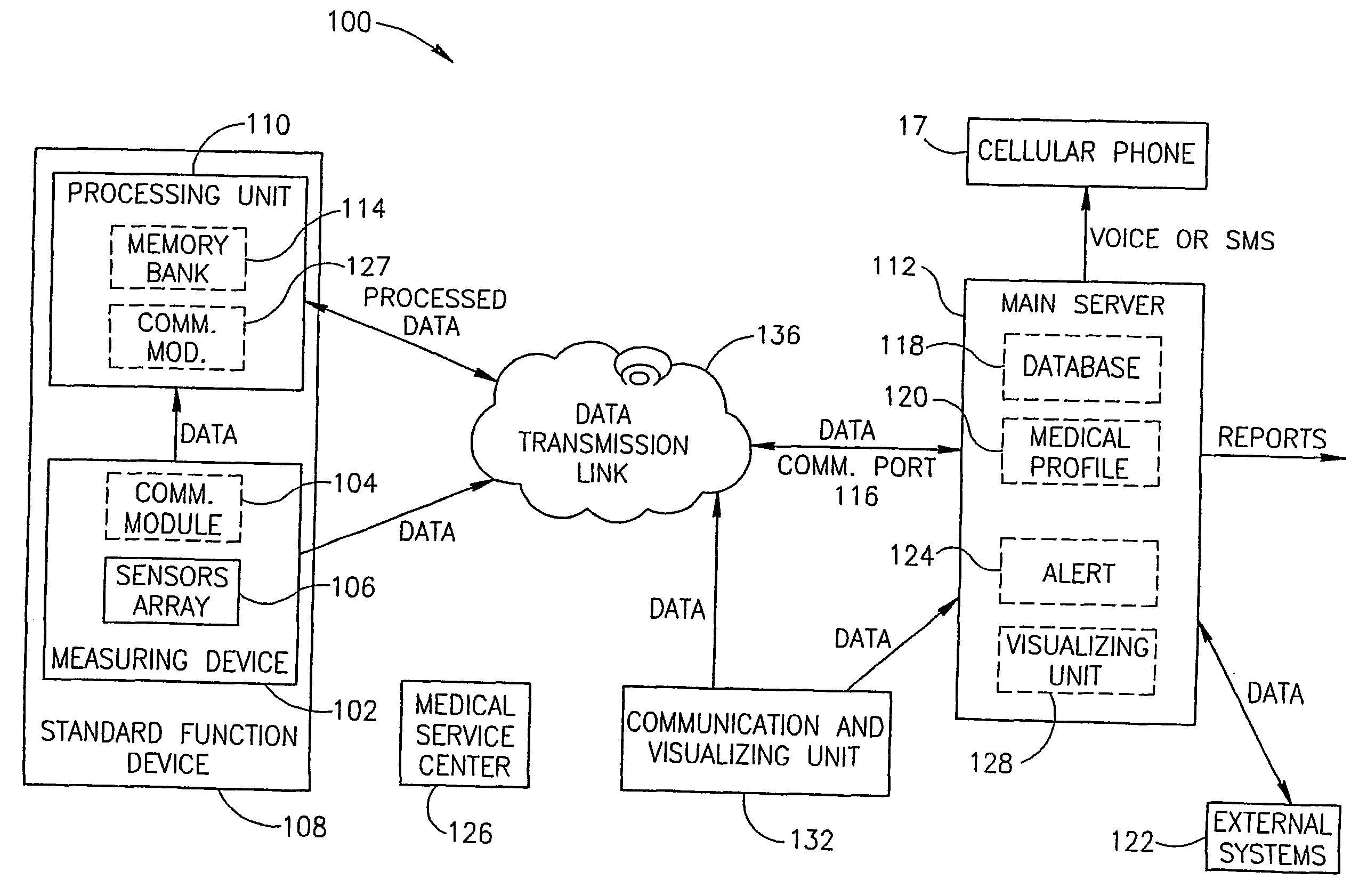
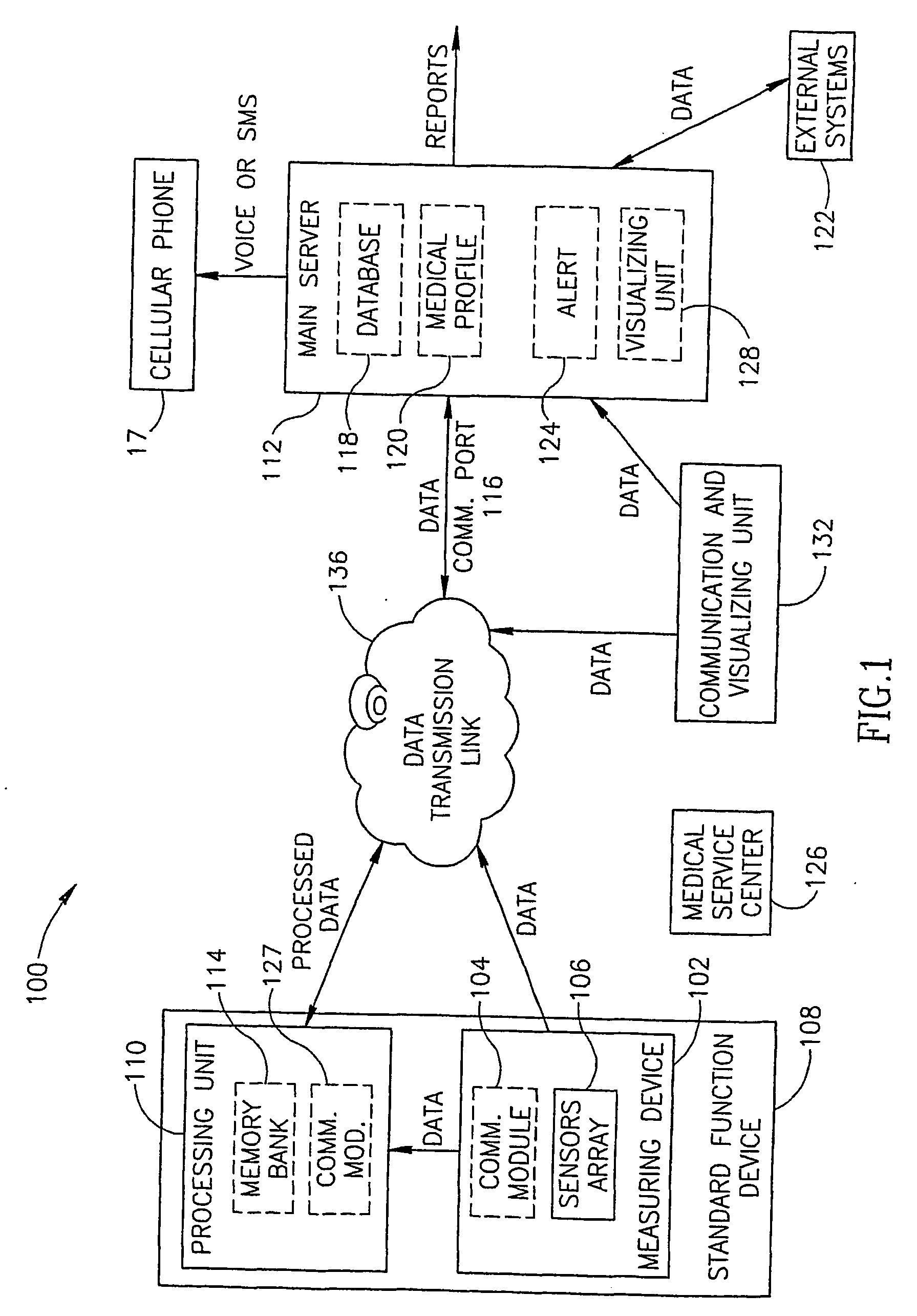
A system and method for automatically monitoring at least one physiological function of the user, without active intervention by the user, in a non-invasive manner. Such monitoring may be used to detect a deterioration in the health of the user. Preferably, the system according to the present invention features at least one physiological sensor for measuring the physiological parameter of the user to obtain the measurement of a physiological function, a local processing unit for extracting medical information from the physiological measurement, and a main server for processing the medical information in order to evaluate the health of the user. Such an evaluation is preferably performed by comparing medical information which has been obtained from a plurality of physiological measurements. Optionally and more preferably, the user is alerted if the evaluation detects a deterioration in at least one physiological function.
Owner:MEDIC4ALL INC
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining a physiological parameter
InactiveUS20100004517A1Accurate measurementThe result is accurateElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMeasurement deviceNon invasive
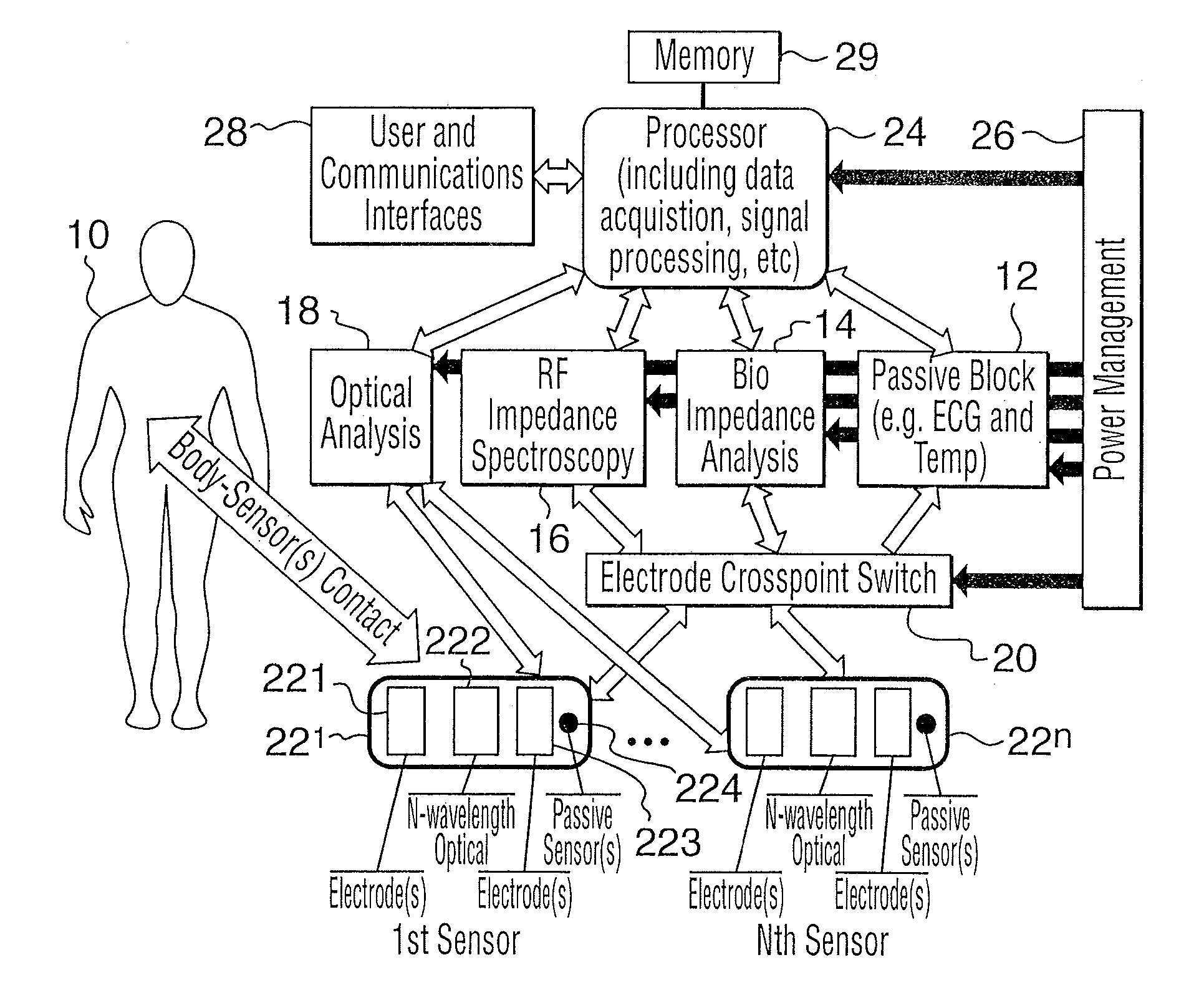
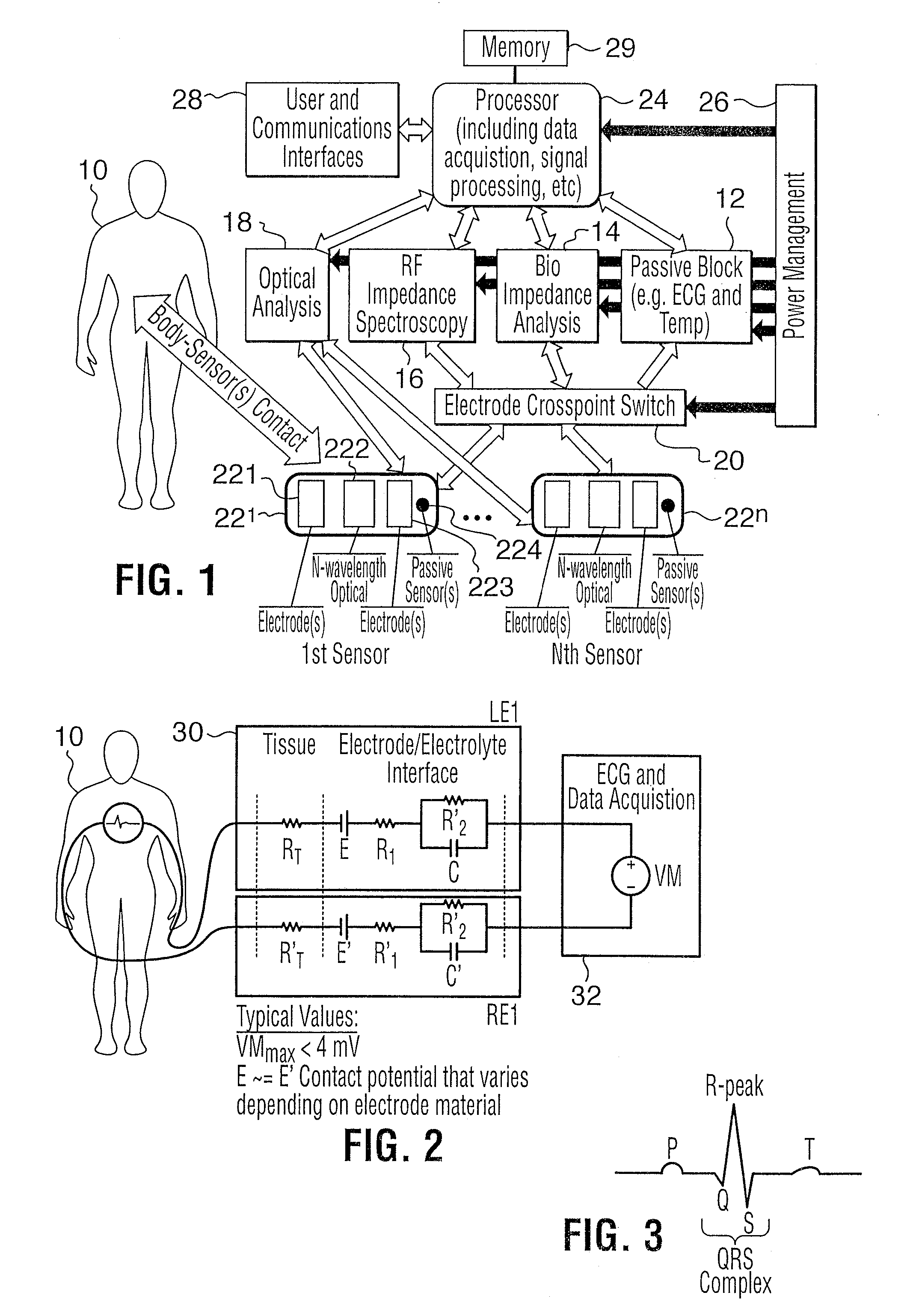
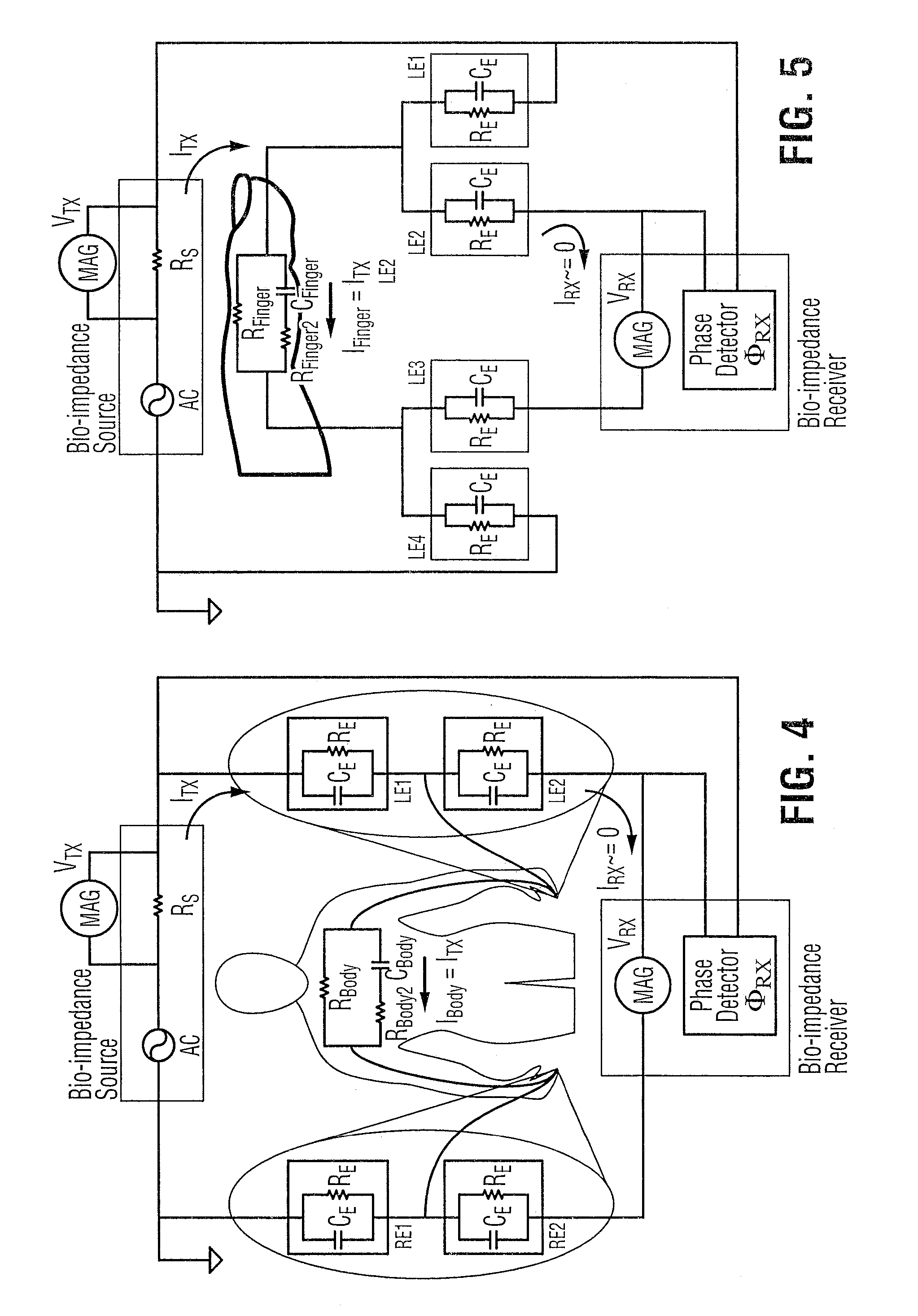
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the non-invasive analysis of physiological attributes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, cardiac output, respiratory response, body composition, and blood chemistry analytes including glucose, lactate, hemoglobin, and oxygen saturation. Using a combination of multi-functioning disparate sensors, such as optical and electrical, improvements are made over existing physiological measurement devices and techniques. The special configuration of one or more multi-functional sensors is used to non-invasively measure multi-wavelength optical plus one or more of ECG, Bio-impedance, and RF-impedance spectroscopic data. This information is used to develop self-consistent, non-linear algorithm in order to derive the physiological attributes while compensating for various forms of interfering effects including motion artifacts, sensor attachment variability, device component variability, subject physical and physiology variability, and various interfering physiological attributes.
Owner:BIOPEAK CORP
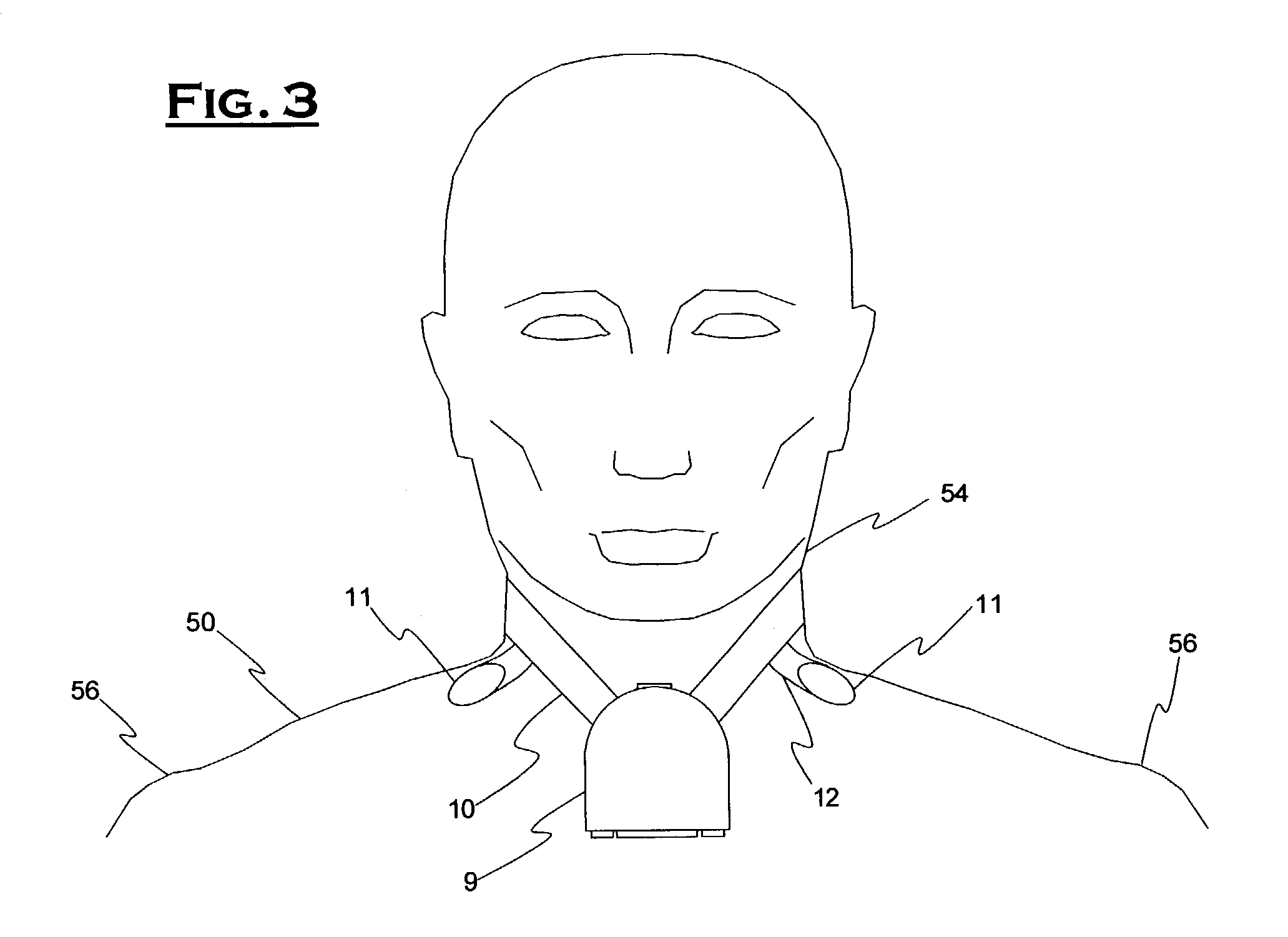
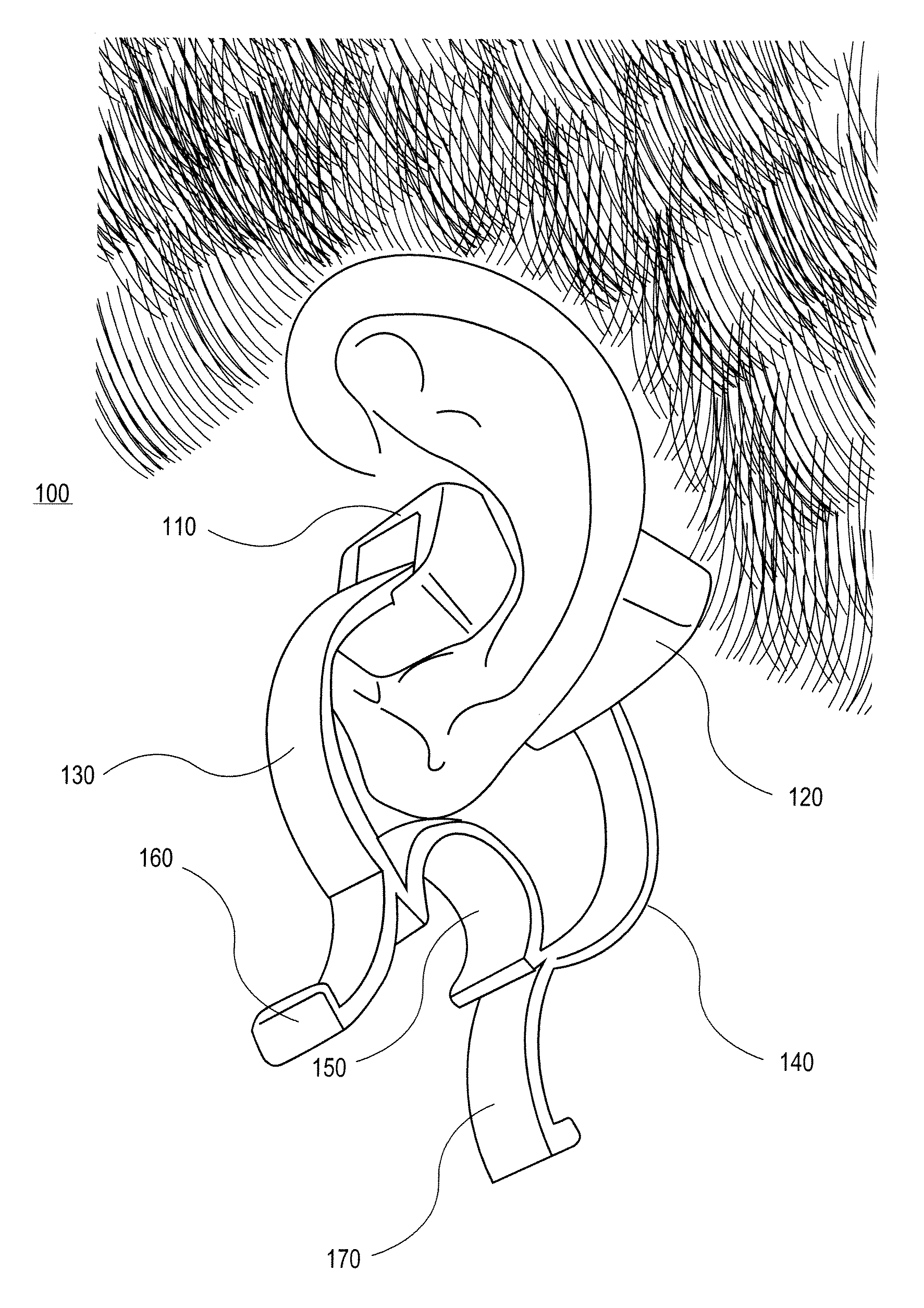
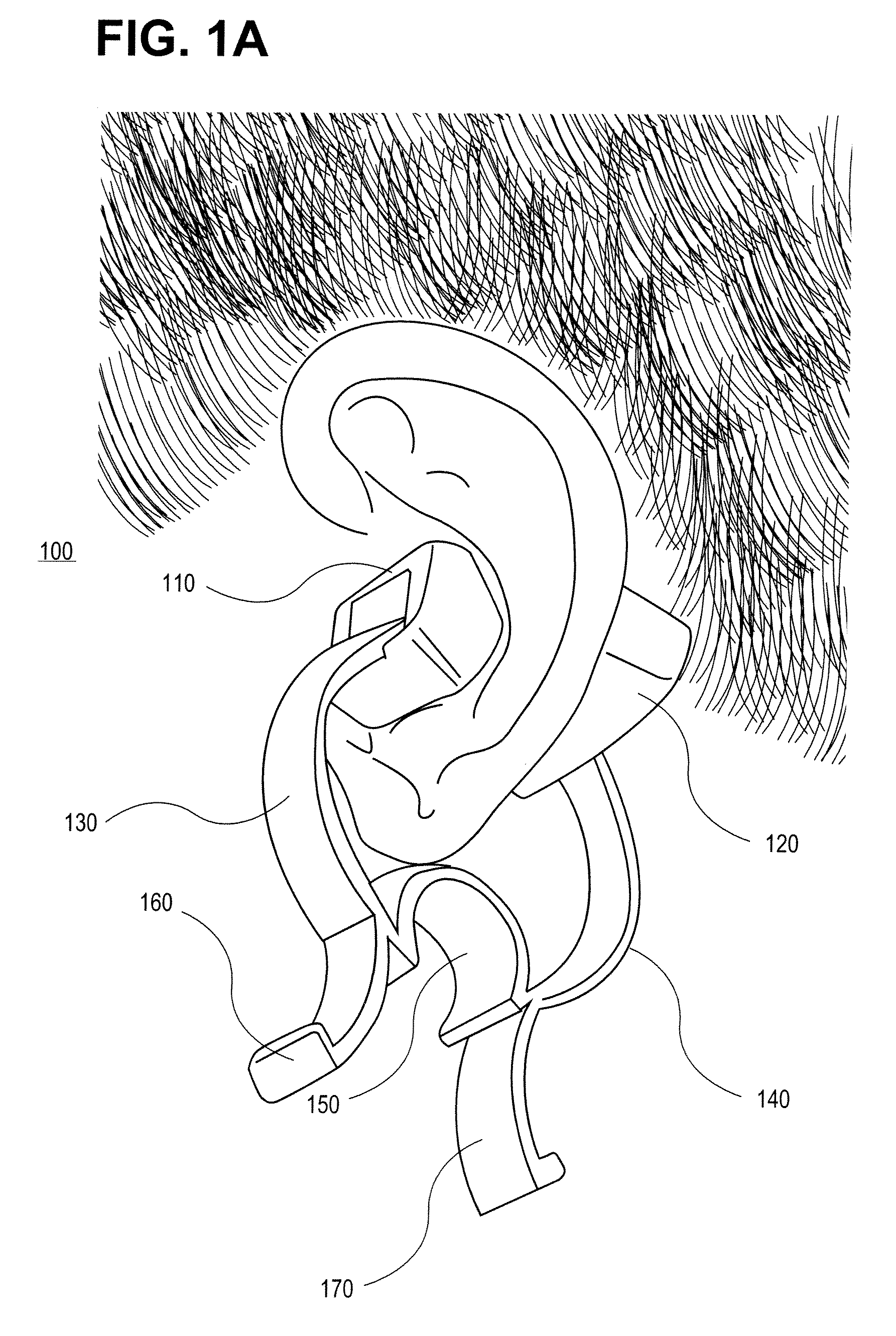
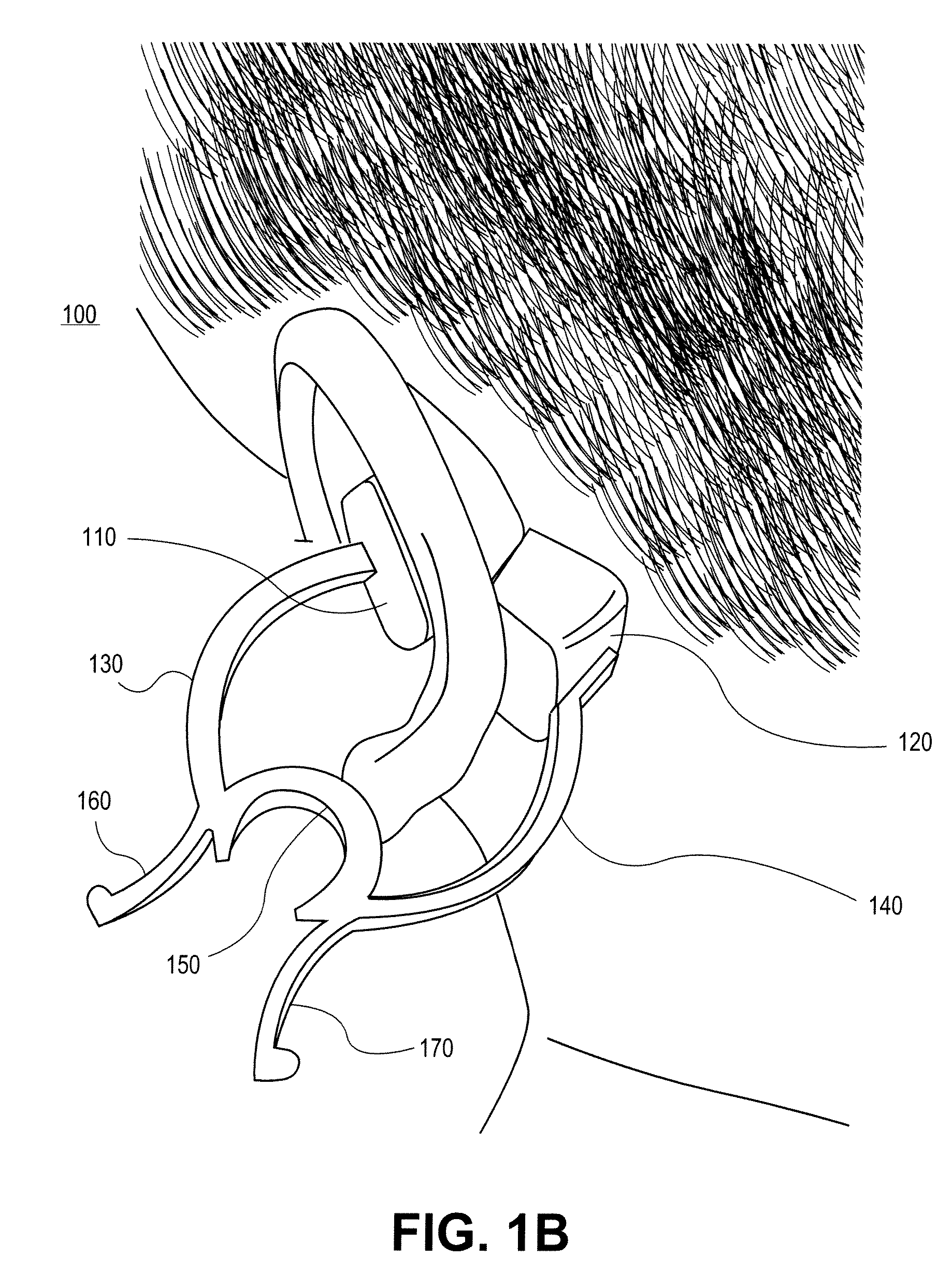
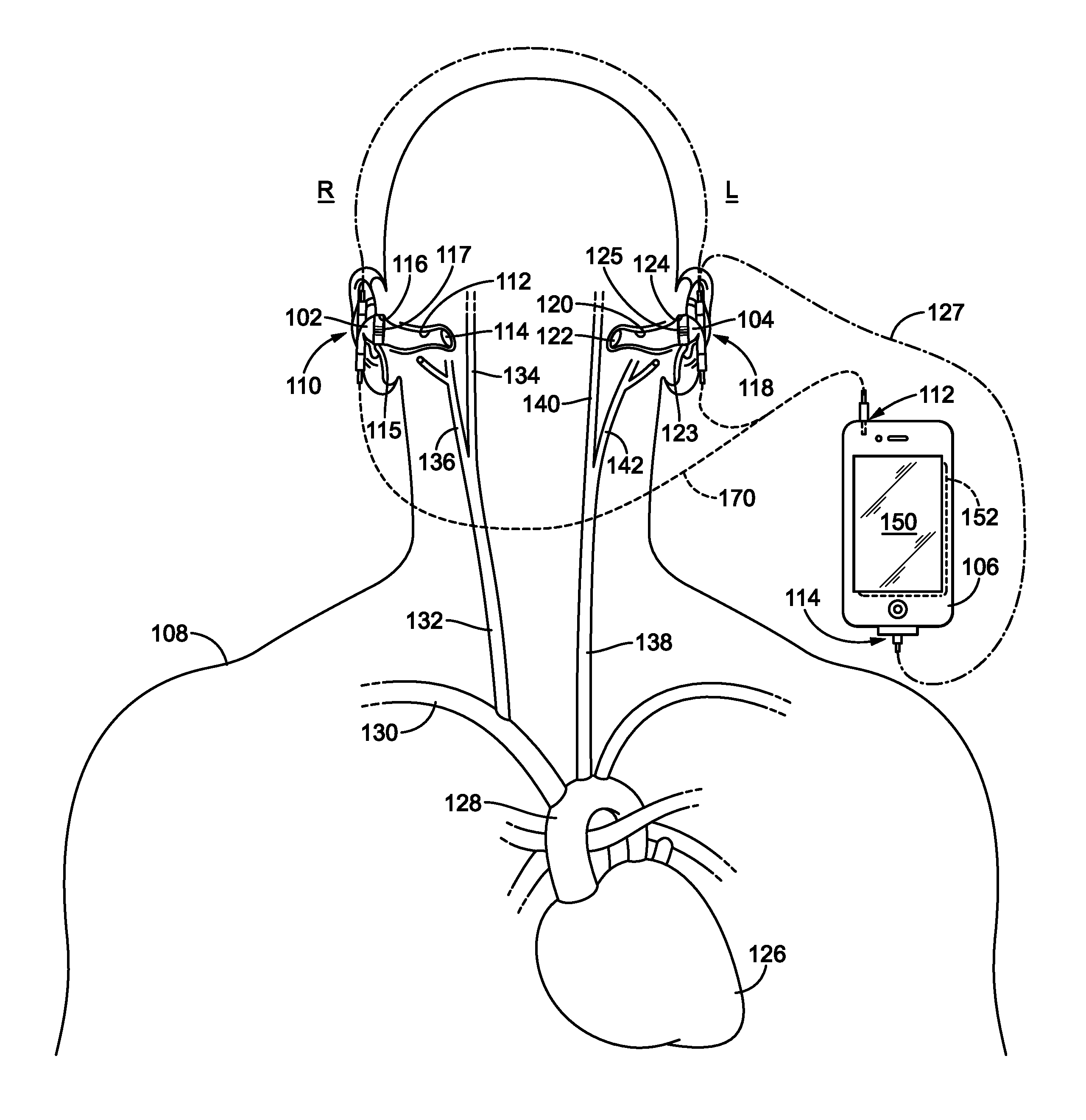
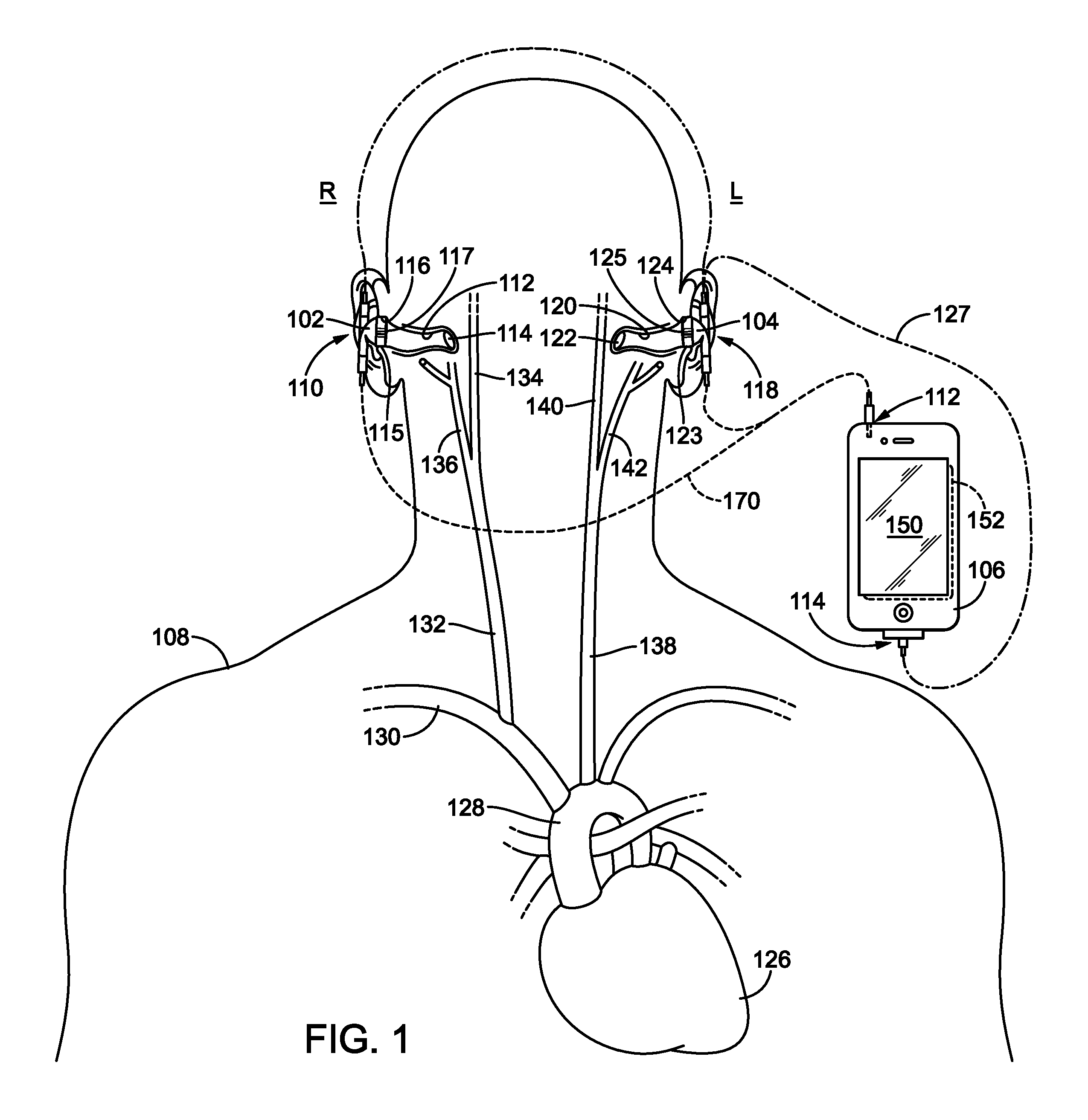
Obtaining physiological measurements using ear-located sensors
InactiveUS20140051940A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyControl signalEngineering
An apparatus and method for obtaining one or more physiological measurements associated with a user using ear-located sensors is disclosed herein. One or more of different types of sensors are configured to engage a user's ear. In some cases, the sensors will be included in one or both of a pair of earphones to capture physiological parameters. A portable device is configured to be in communication with the earphones to receive physiological parameters from the sensor(s) therein, and potentially to provide control signals to the sensors or other components in the earphones. The portable device determines physiological measurements corresponding to the received physiological parameters. The portable device is also configured to provide a user interface to interact with the user regarding the physiological measurements.
Owner:RARE LIGHT
Patient-worn medical monitoring device
ActiveUS8668643B2Low costInsult to dignityDiagnostic signal processingElectrocardiographyProcess measurementEngineering
One embodiment of a medical monitor includes a lanyard and an electronic package supported in the manner of a pendant. Another embodiment of a medical monitor attaches adhesively to a patient. Both embodiments include a reusable portion housing electronic components for processing measurements of the patient's physiological condition, and a disposable portion including a battery. The physiological measurements may be transmitted to a remote location along with a signal identifying the patient.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vascular access port with physiological sensor
InactiveUS20060178617A1Improve accuracyConvenient for physicianElectrocardiographyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTelecommunications linkCollection system
A combined vascular access port and physiologic parameter monitoring device. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be connected by a cooperative geometry. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be implanted at the same time and in the same anatomical location (e.g., subcutaneous pocket). The monitoring device may include a telemetry unit that transmits physiological measurement data to a local data collection system (e.g., carried by the patient or located in the patient's home), which may re-transmit the data to a remote data collection system (e.g., located at a physician's office or clinic) via a suitable communication link.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
System for automatic structured analysis of body activities
A personal emergency response system employs a structured terminology of body activities. Measurements of primary body activities using accelerometers, heart-bit monitors, etc. are converted to secondary and tertiary level body activities such as walk and fall, further sequenced and combined to determine a personal condition such as walk, stumble and fall, and to identify sequences of such conditions. The structured terminology enables a language supporting a functional description of body activities associated with physical and physiological measurements and enables a machine to understand physical activities.
Owner:COHEN
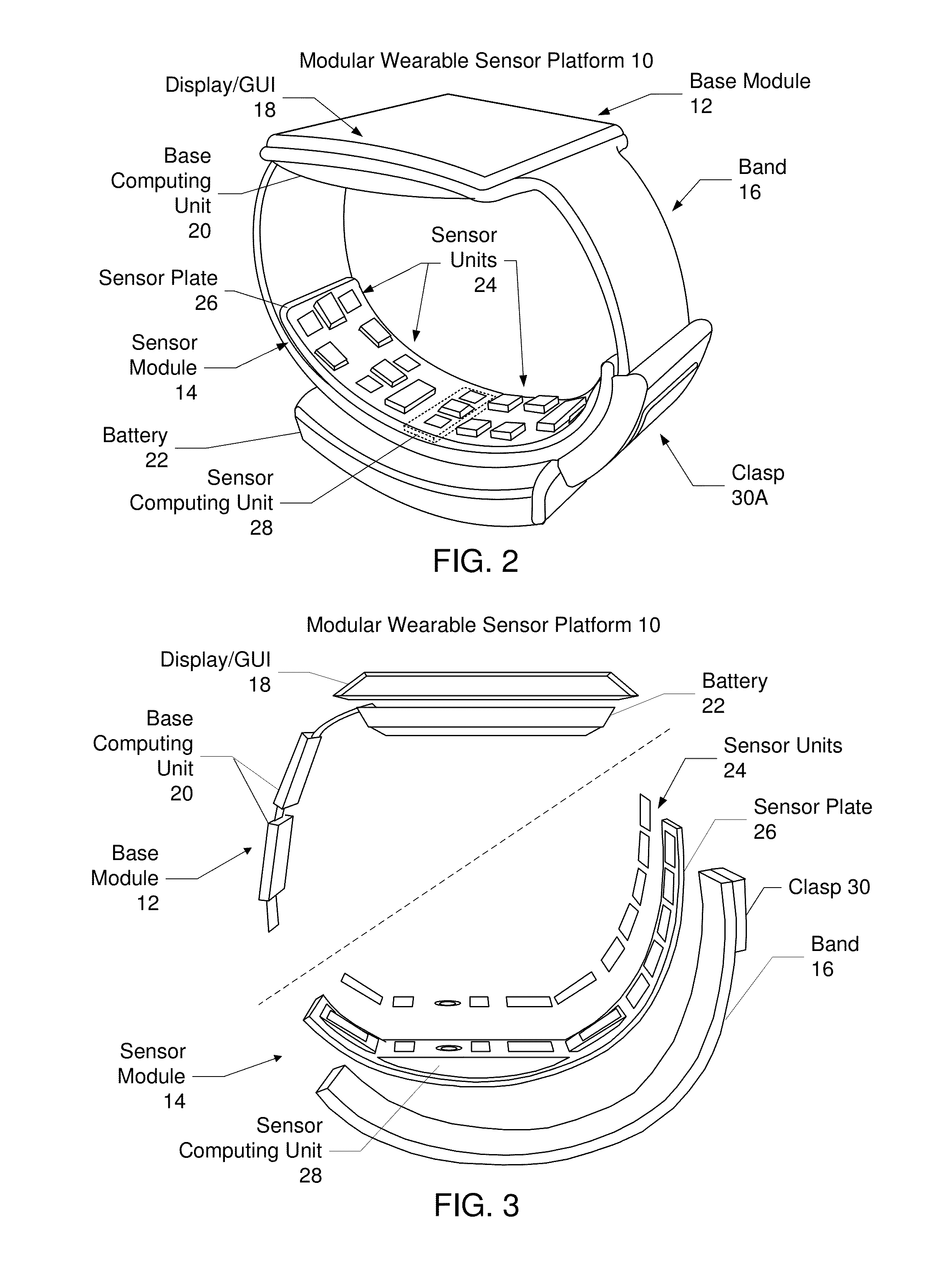
Confidence indicator for physiological measurements using a wearable sensor platform
Embodiments include a method and system for providing data to a user of a wearable sensor platform. The method may be performed by a least one software component executing on at least one processor. The method includes capturing data for the user using at least one sensor in the wearable sensor platform. The data includes physiological data and artifact data. The physiological data includes noise data therein. A confidence indicator for the data is determined based on at least one of the physiological data and the artifact data. A physiological data signal corresponding to the physiological data and the confidence indicator is provided to the user on the wearable device platform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bi-stable medical sensor and technique for using the same
InactiveUS20070032710A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical resistance and conductancePulse oximetry
A bi-stable sensor is provided that includes a frame upon which electrical and optical components may be disposed and a coating, such as an overmold coating, provided about the frame. A resistance-providing component is provided integral with or external to the coated bi-stable sensor such that the bi-stable sensor has two mechanically stable configurations that may be transitioned between by overcoming the resistance provided by the resistance-providing component and / or the by the coating. In one embodiment, the resistance-providing component comprises an elastic band provided about a hinge of the frame, either within or external to the coating. In one embodiment, the sensor may be placed on a patient's finger, toe, ear, and so forth to obtain pulse oximetry or other physiological measurements.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
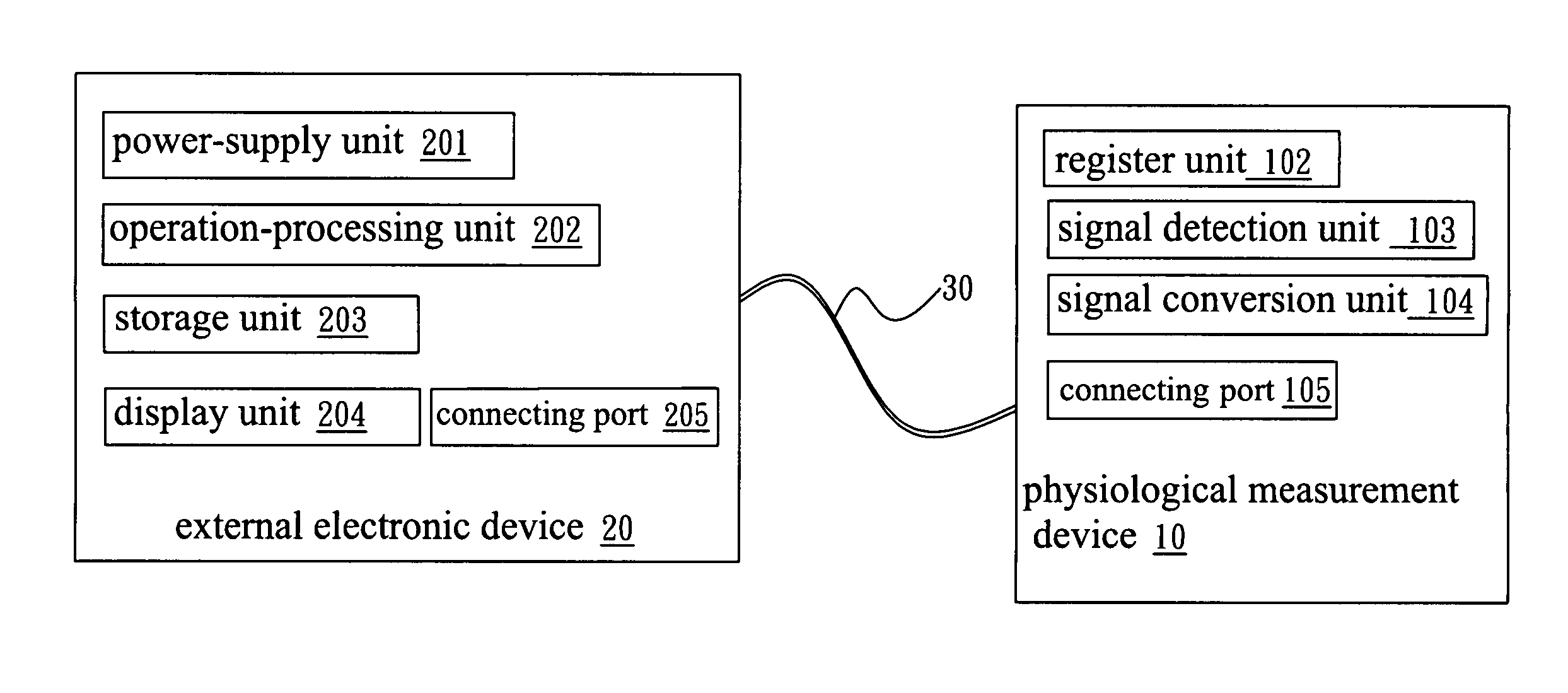
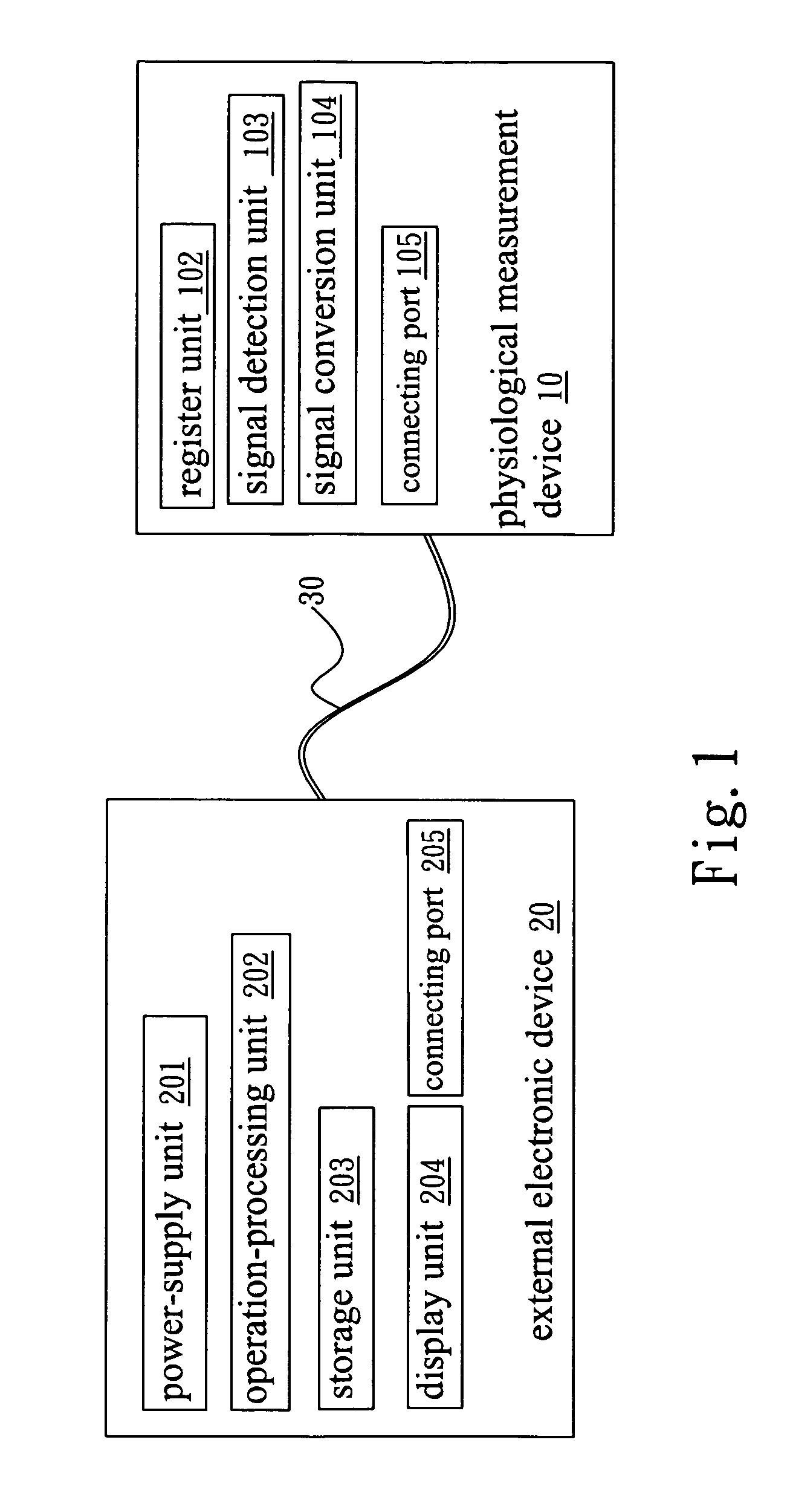
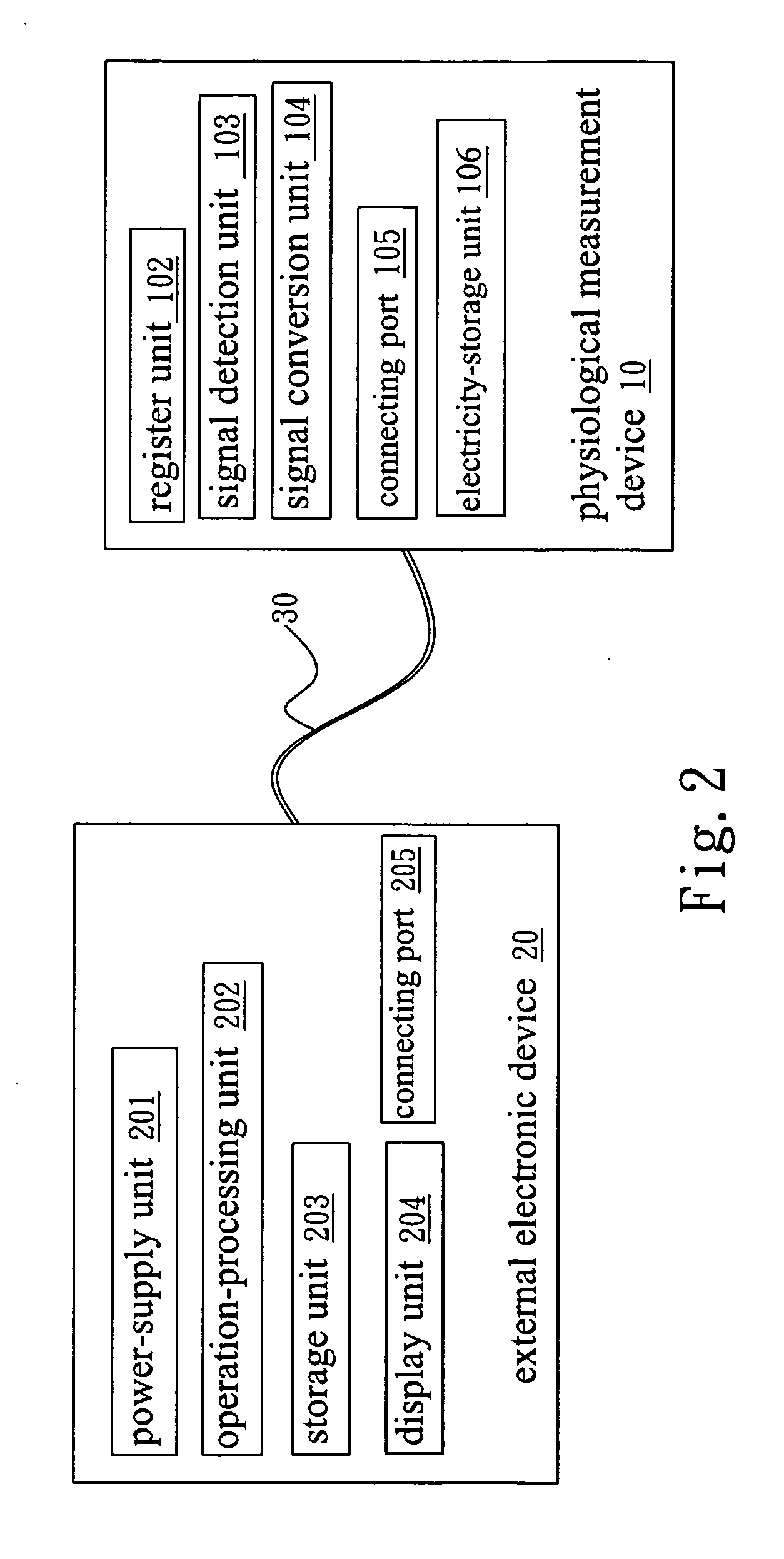
Simplified physiological measurement device
InactiveUS20070123783A1Reduce circuit complexityReduce in quantityEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterMeasurement deviceElectronic component
A simplified physiological measurement device utilizes a general port to receive power from an external electronic device and to transmit the signals obtained from physiological measurements to the external electronic device for calculation and display. Thereby, the mechanisms and electronic elements of the physiological measurement device can be obviously simplified, and the operational convenience can also be greatly promoted.
Owner:CHANG KUO YUAN
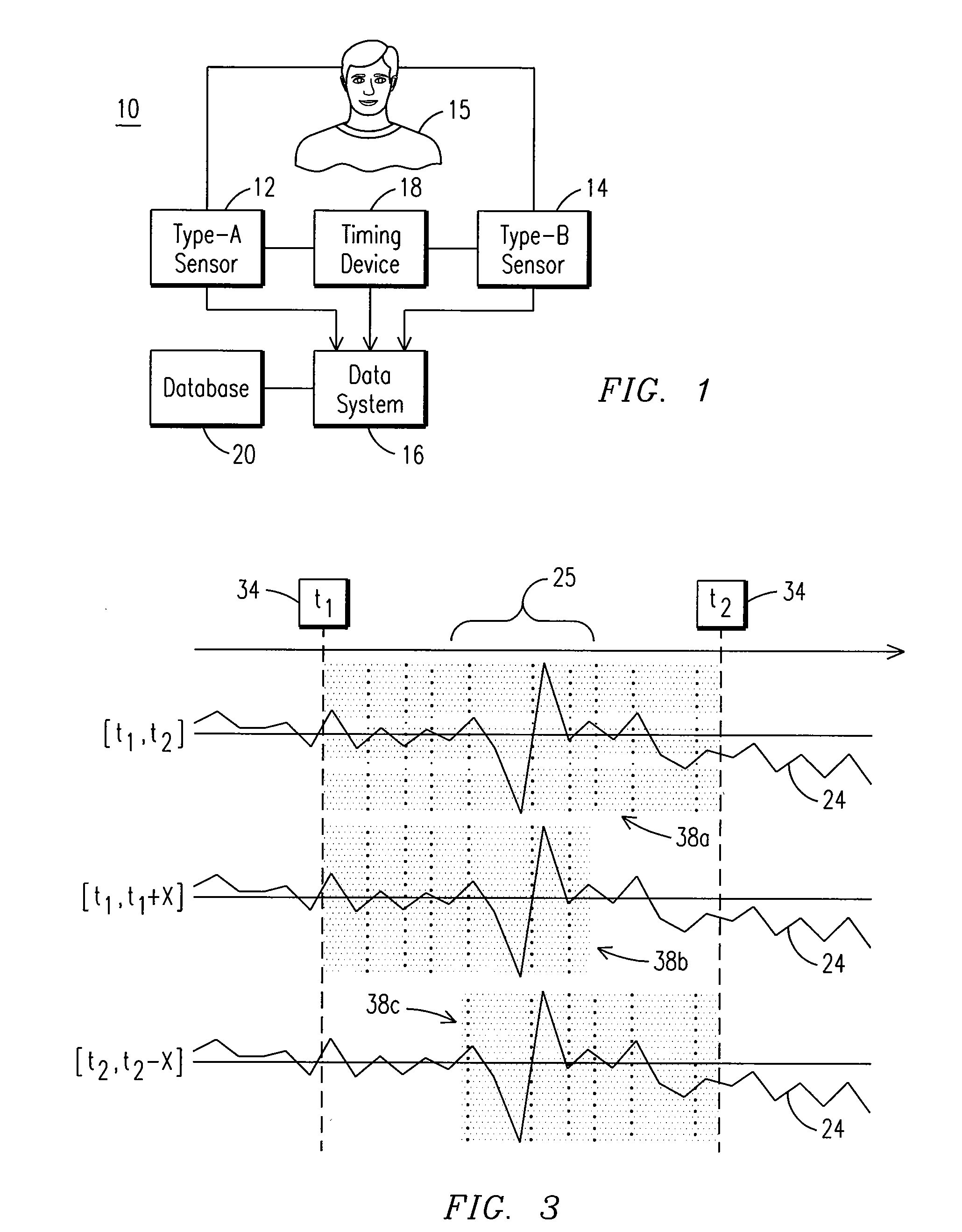
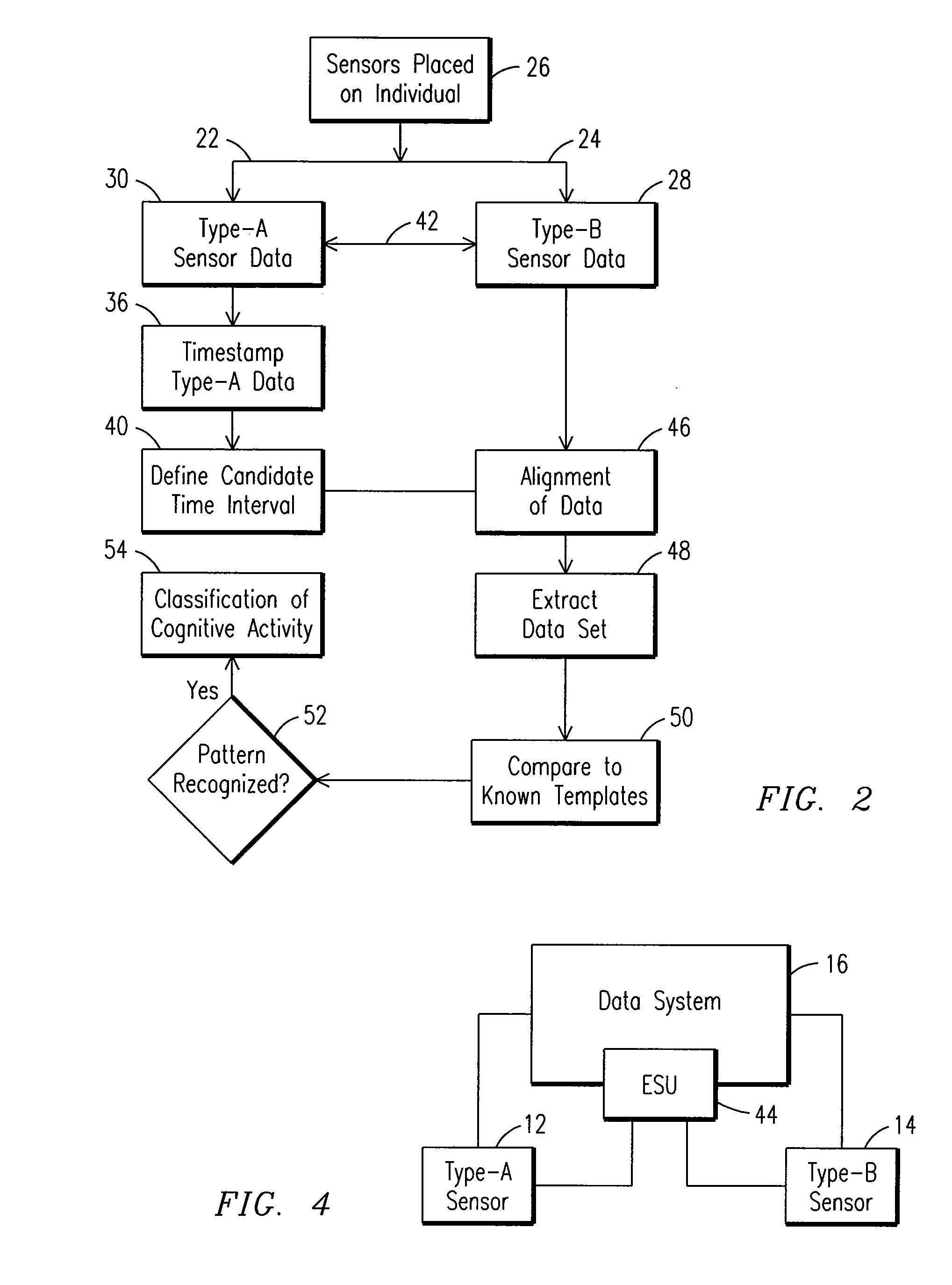
System And Method For The Real-Time Evaluation Of Time-Locked Physiological Measures
In one embodiment, a method is provided for classifying cognitive activity in an individual. In the method, a candidate time interval is identified from a first type of physiological data within which cognitive processing is expected to occur for the individual. In addition, a second type of physiological data is obtained that comprises data representative of a cognitive state of the individual. Further, the data representative of a cognitive state of the individual is extracted from the second type of physiological data based on the identified candidate time interval.
Owner:DESIGN INTERACTIVE +1
Multiparameter whole blood monitor and method
InactiveUS20090270695A1Increase turnaround timeRemove uncertaintyBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsPulse pressureIntravascular catheter
Owner:NEW PARADIGM CONCEPTS
Sizing and positioning technology for an in-the-ear multi-measurement sensor to enable NIBP calculation
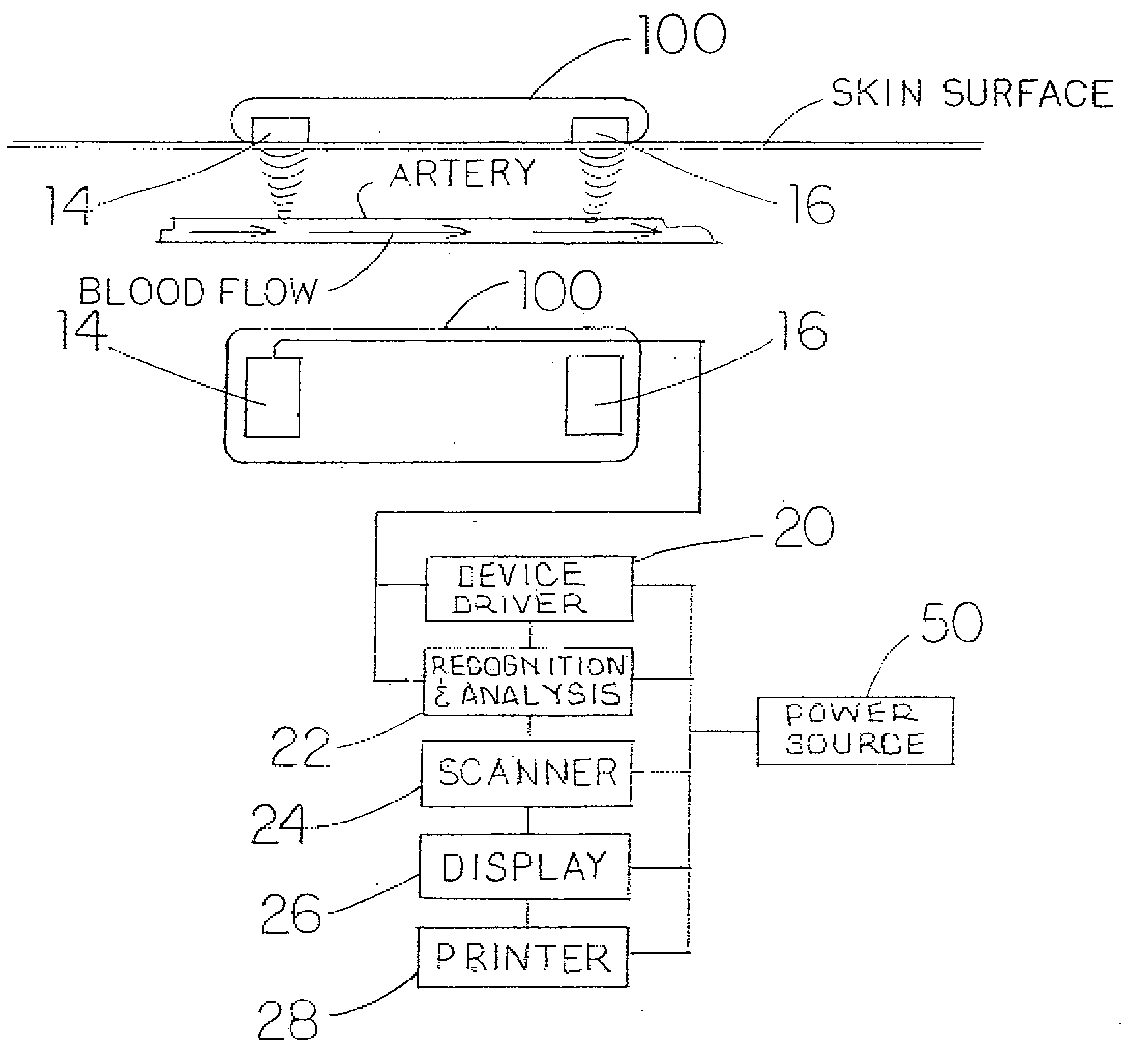
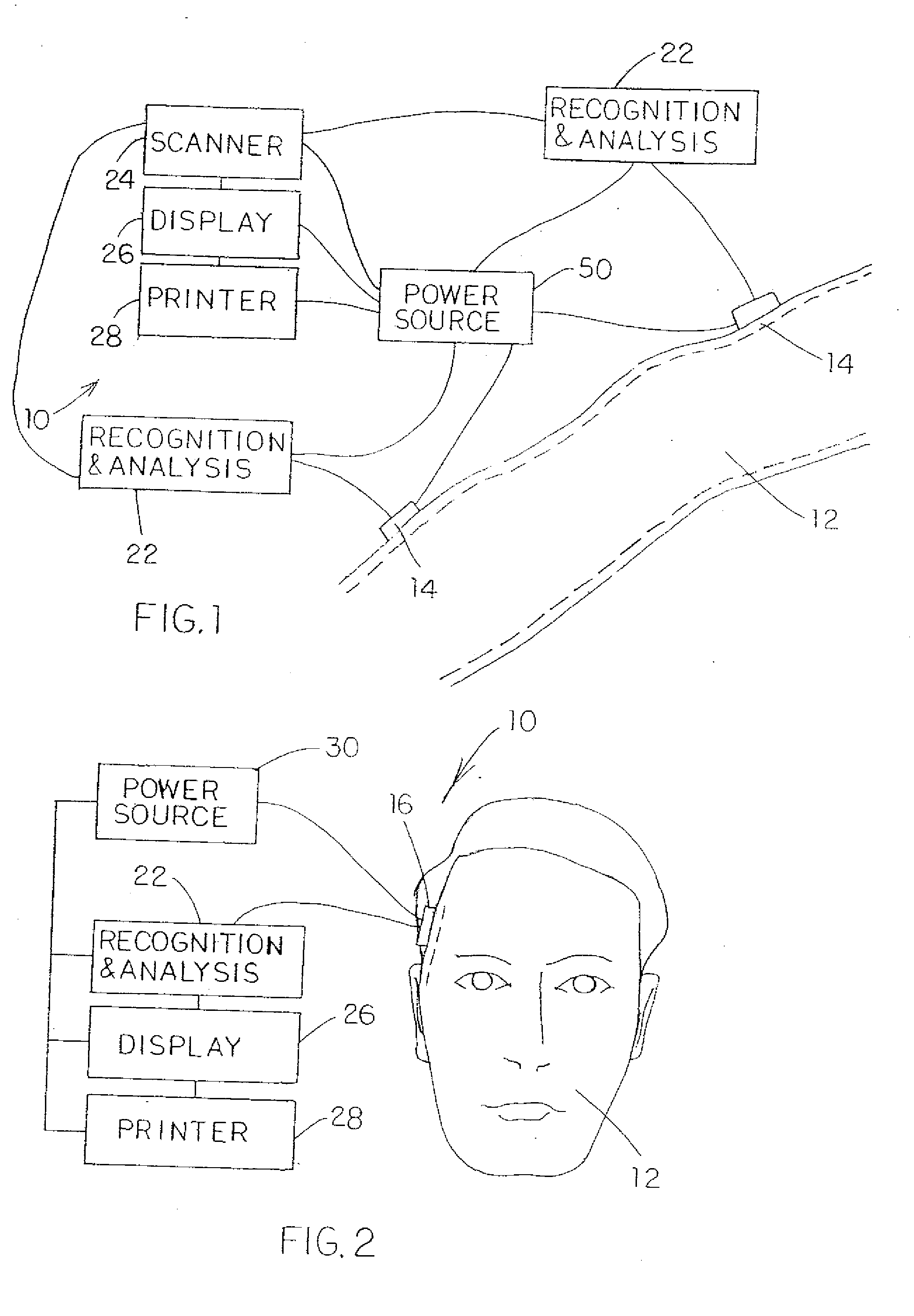
InactiveCN101212927ANon-invasive blood pressure measurementContinuous non-invasive measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterMeasurement deviceProximate
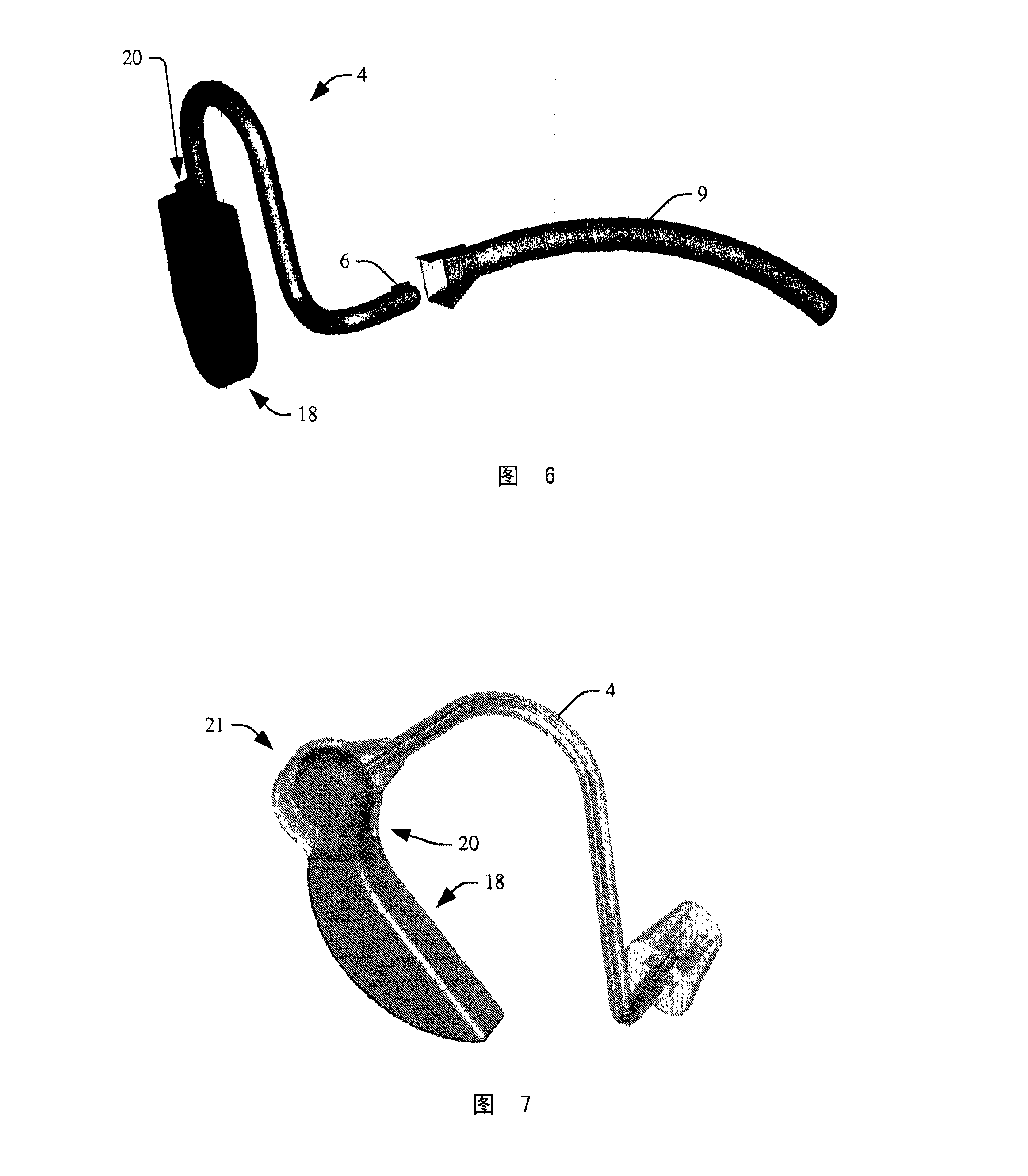
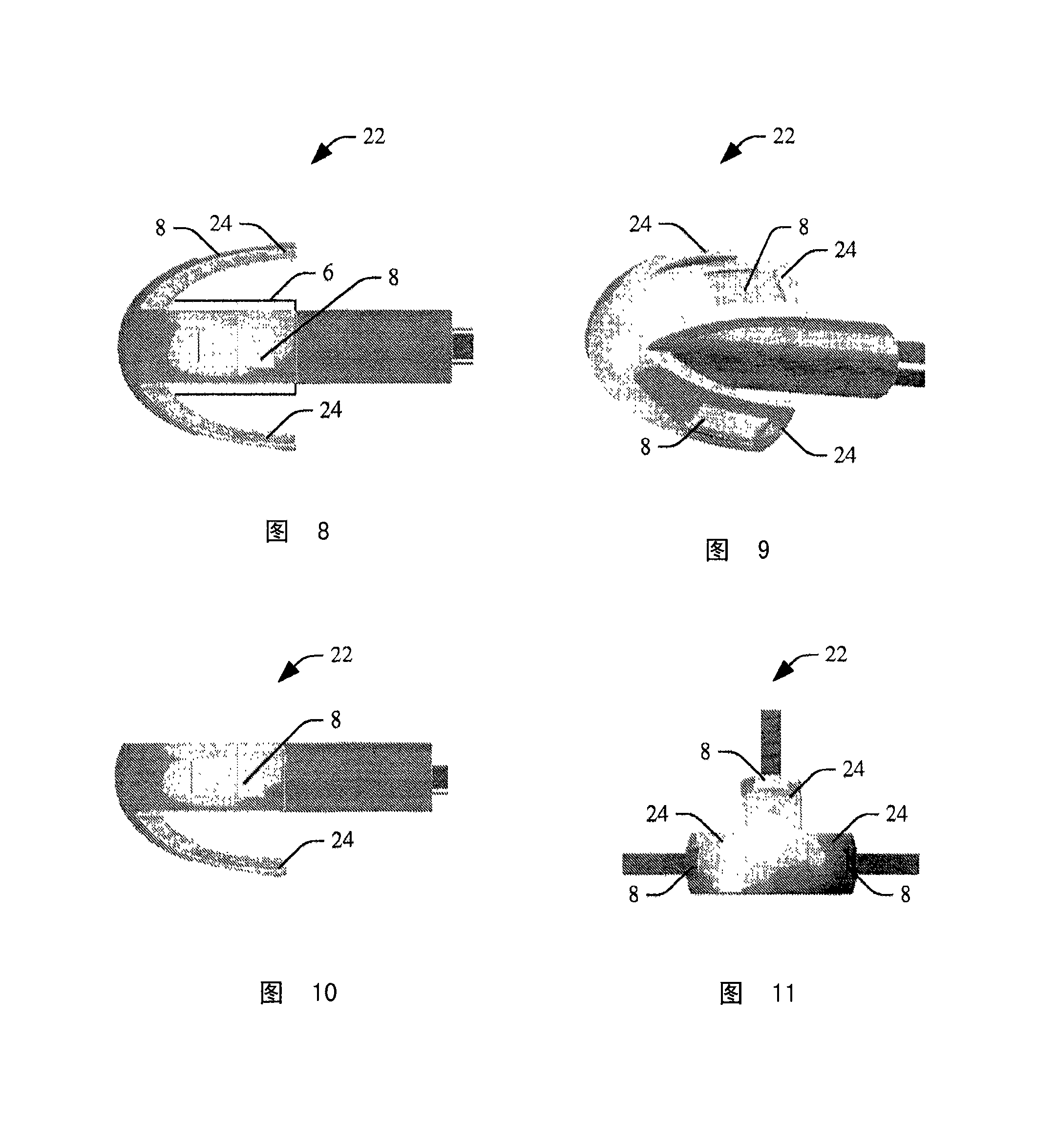
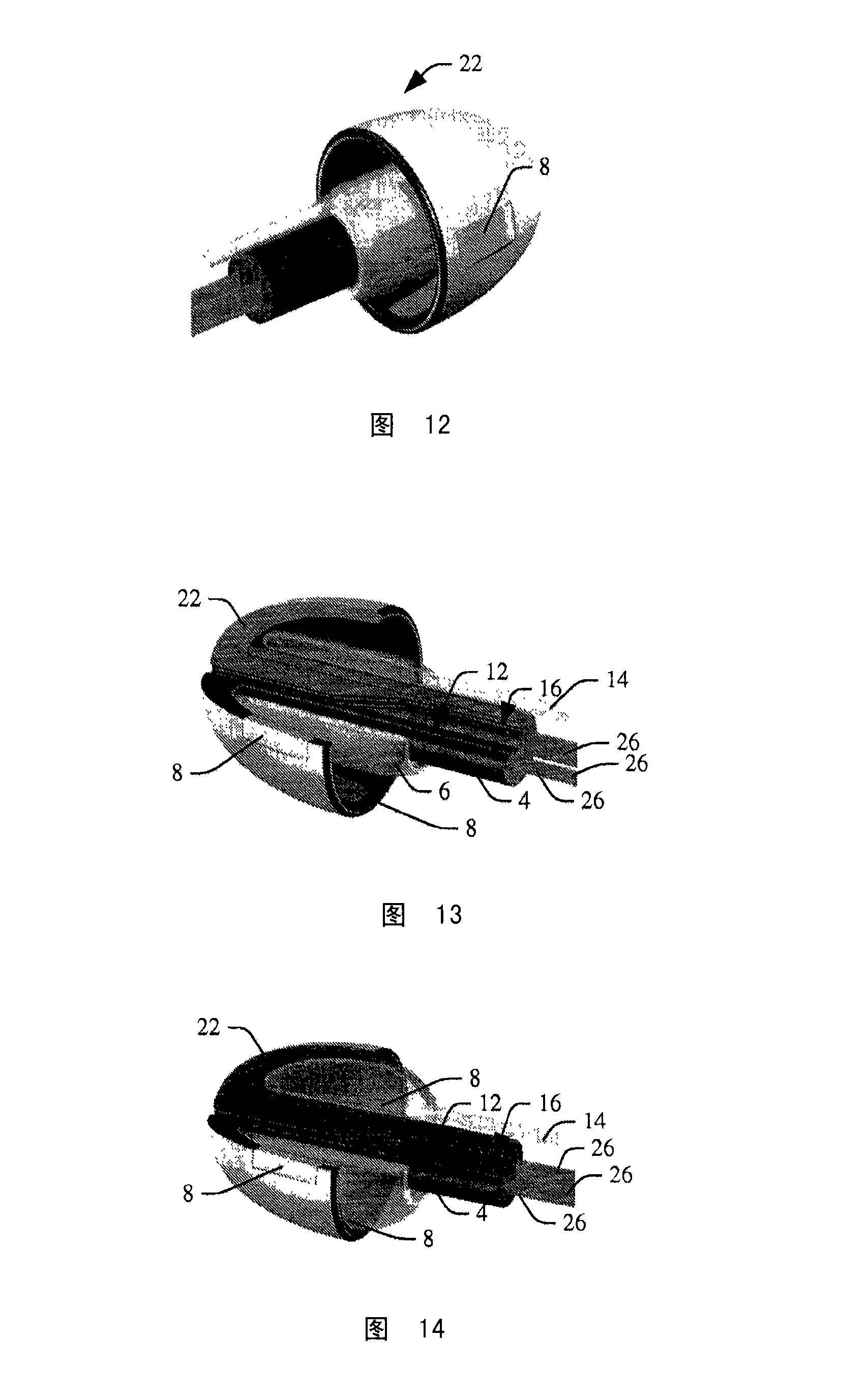
An in-the-ear (ITE) physiological measurement device (2) includes a structure (4) formed to be easily inserted into ear canals of various shapes and sizes. An inflatable balloon (6) surrounds the end of the structure (4) to be placed in the ear. Optionally, a mushroom-shaped tip (22) is attached to the end of the structure (4) and carries a plurality of sensors (8). Inflation of the balloon (6) radially expands the tip (22) to place the sensor (8) adjacent to the vascular tissue in the ear canal. Once in place, one or more sensors (8) sense physiological signals from vascular tissue and bone structures.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method, system, and apparatus for measurement and recording of blood chemistry and other physiological measurements
InactiveUS6844149B2Eliminate needMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood componentPorous medium
A multi-component test strip for analyzing a plurality of blood components in a single blood sample. The test strip comprises a porous medium having a sample receiving region, and two or more sample analysis regions. The sample receiving region is fluidically in series with the two or more sample analysis regions, and the two or more sample analysis regions are fluidically in parallel with each other. The two or more sample analysis regions contain indicating reagents specific to two or more specific blood components. Also disclosed is a system using the test strip for blood characterization, and a method of blood characterization and analysis.
Owner:PENDRAGON NETWORKS
Medical sensor and technique for using the same
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
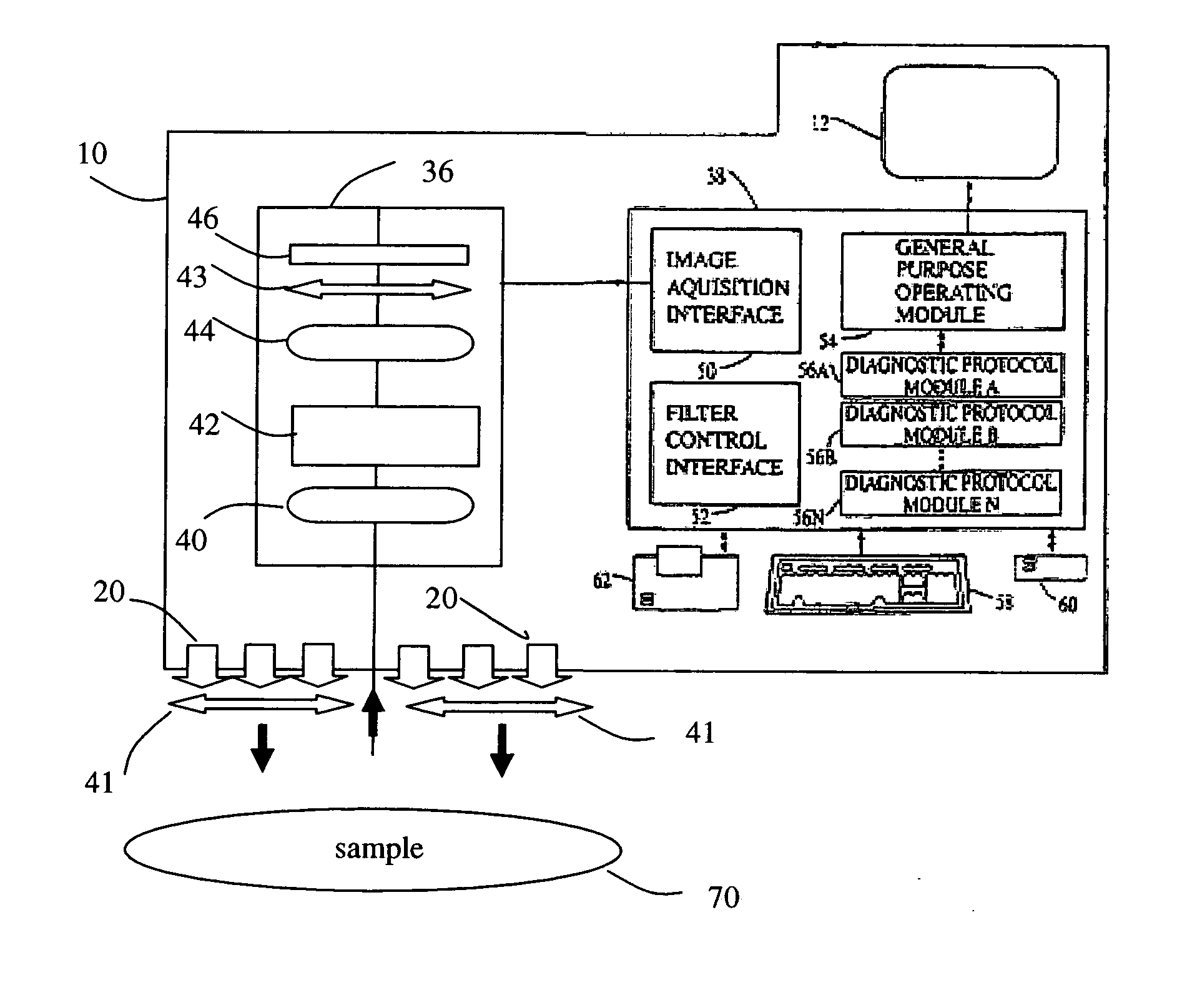
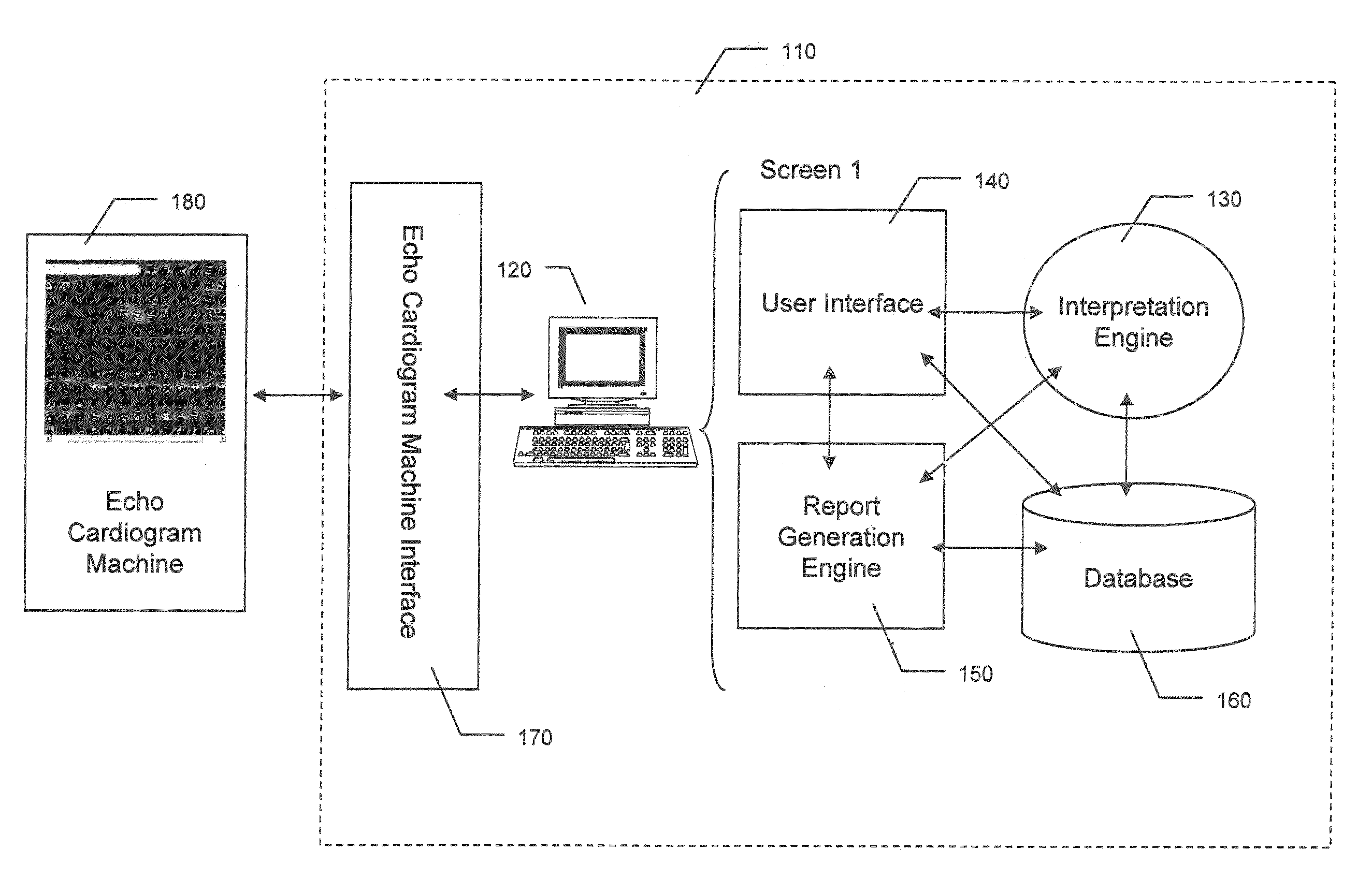
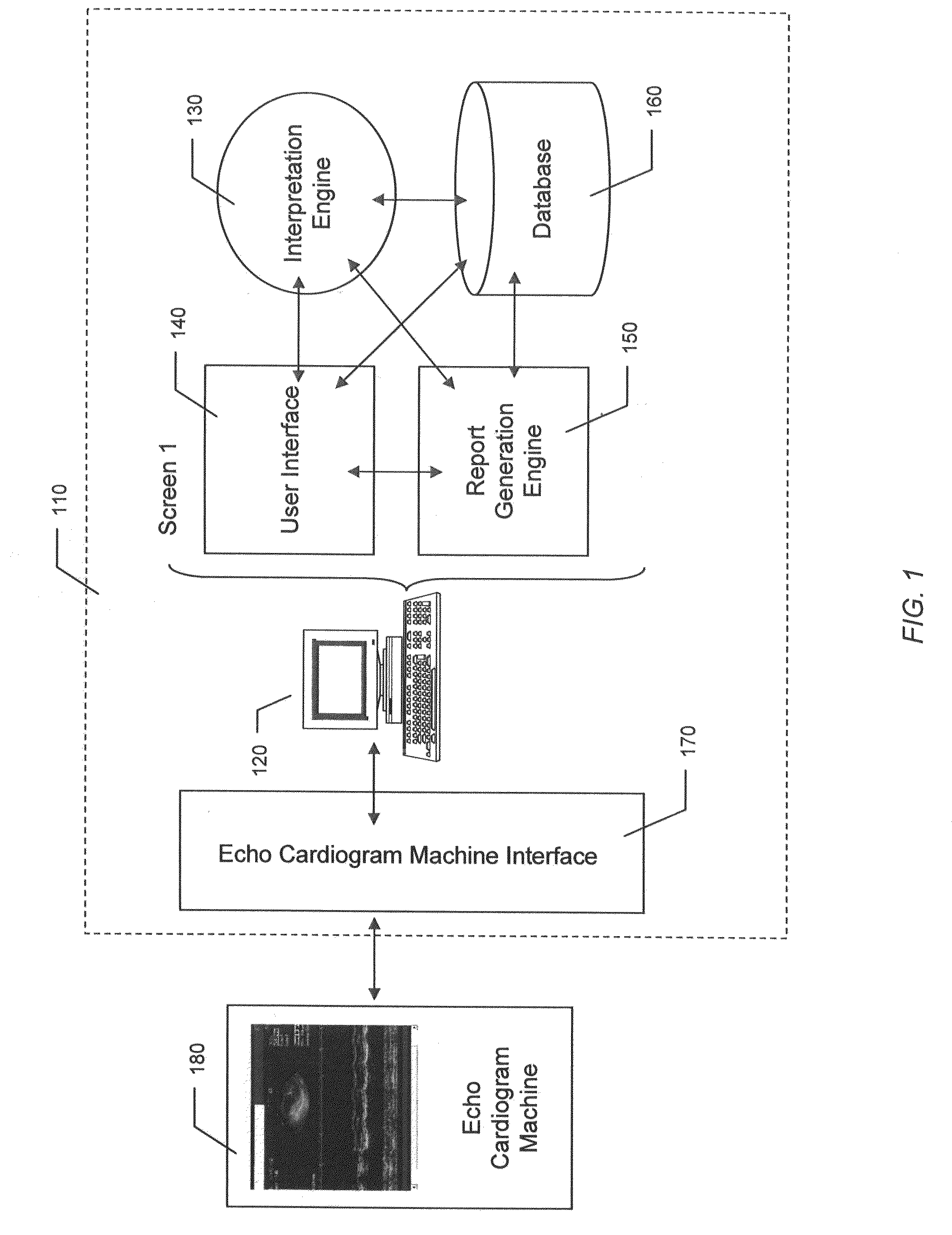
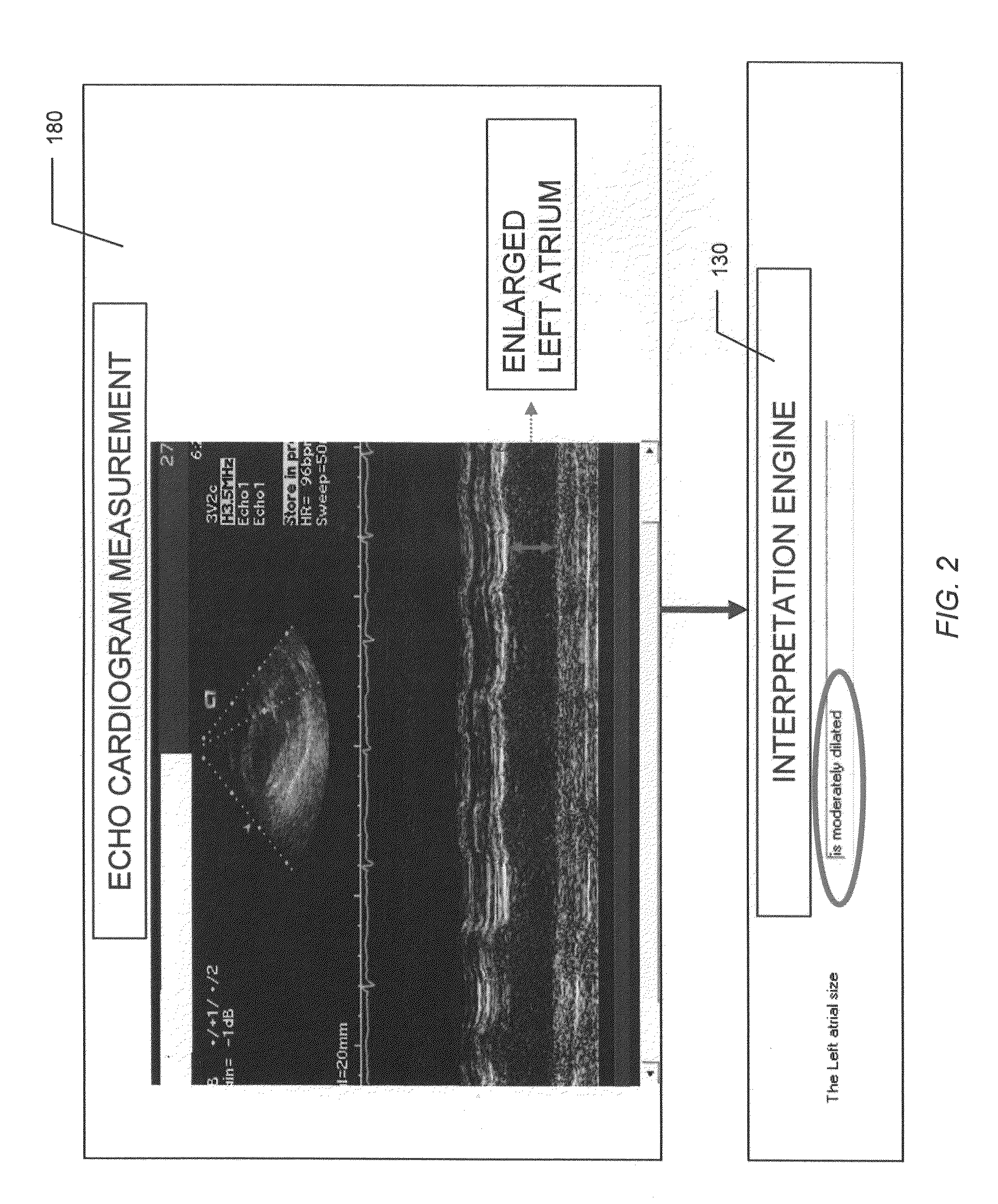
System and Method for Automated Medical Diagnostic Interpretation and Report Generation
InactiveUS20090171225A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionDimension measurementEngineering
Automated medical diagnostic interpretation and report generation for a non-invasive medical diagnostic test, such as an echo cardiogram, is provided. Various dimension measurements and physiological measurements from an echo cardiogram machine are transferred automatically to a computer over an echo cardiogram machine interface. The dimensions and physiological measurements are automatically interpreted by an intelligent interpretation engine running on a computer, generating various machine evaluations. The physician can approve the machine evaluations, overrule them, or make appropriate adjustments. Upon completion of the physician's review, the physician approved interpretations become diagnostic conclusions, and the report containing the results of the physician's review is generated by the report generation engine.
Owner:MEDNOVA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com