Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Path dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Path dependence is the dependence of economic outcomes on the path of previous outcomes, rather than simply on current conditions. In a path dependent process, “history matters” — it has an enduring influence.
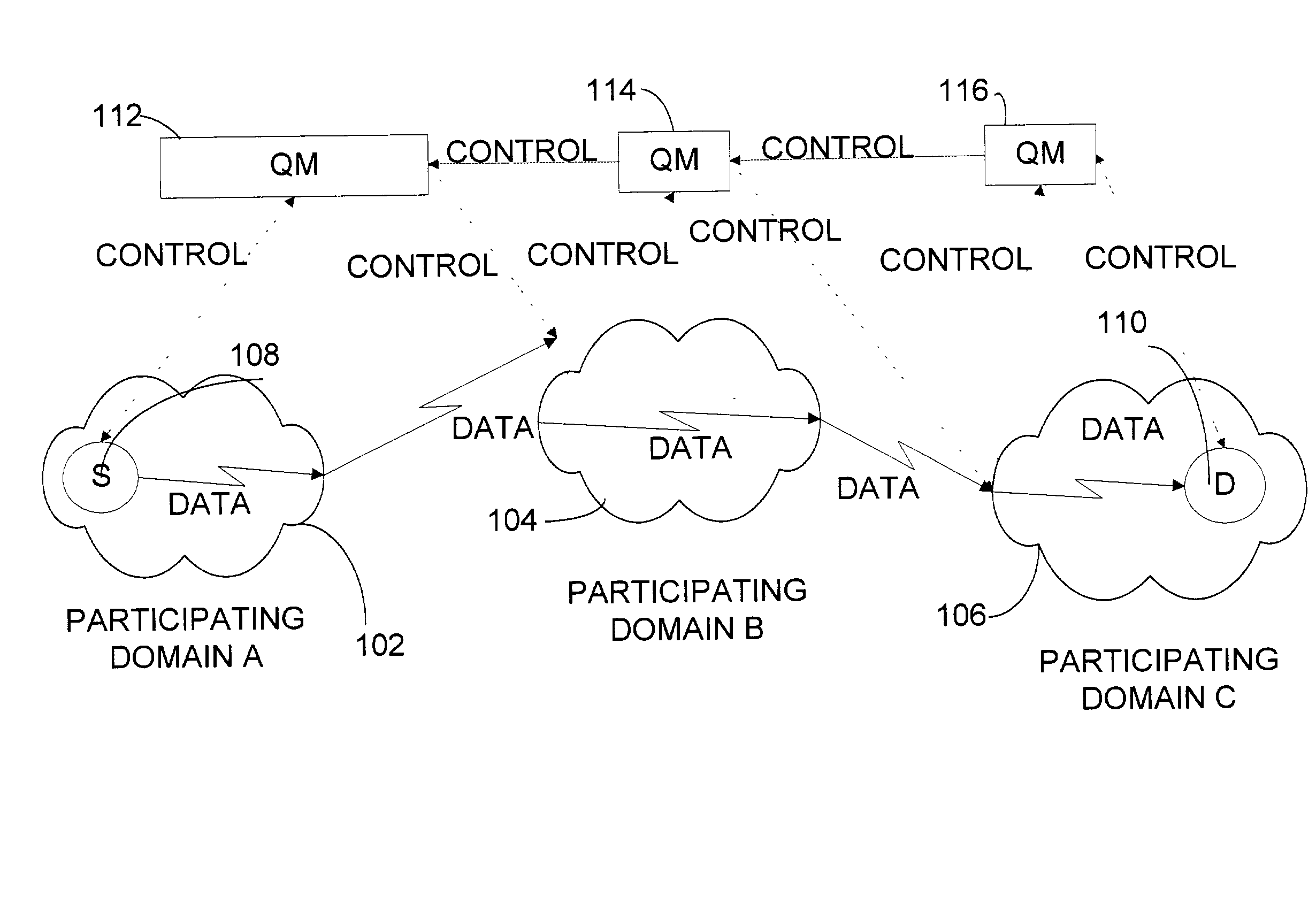
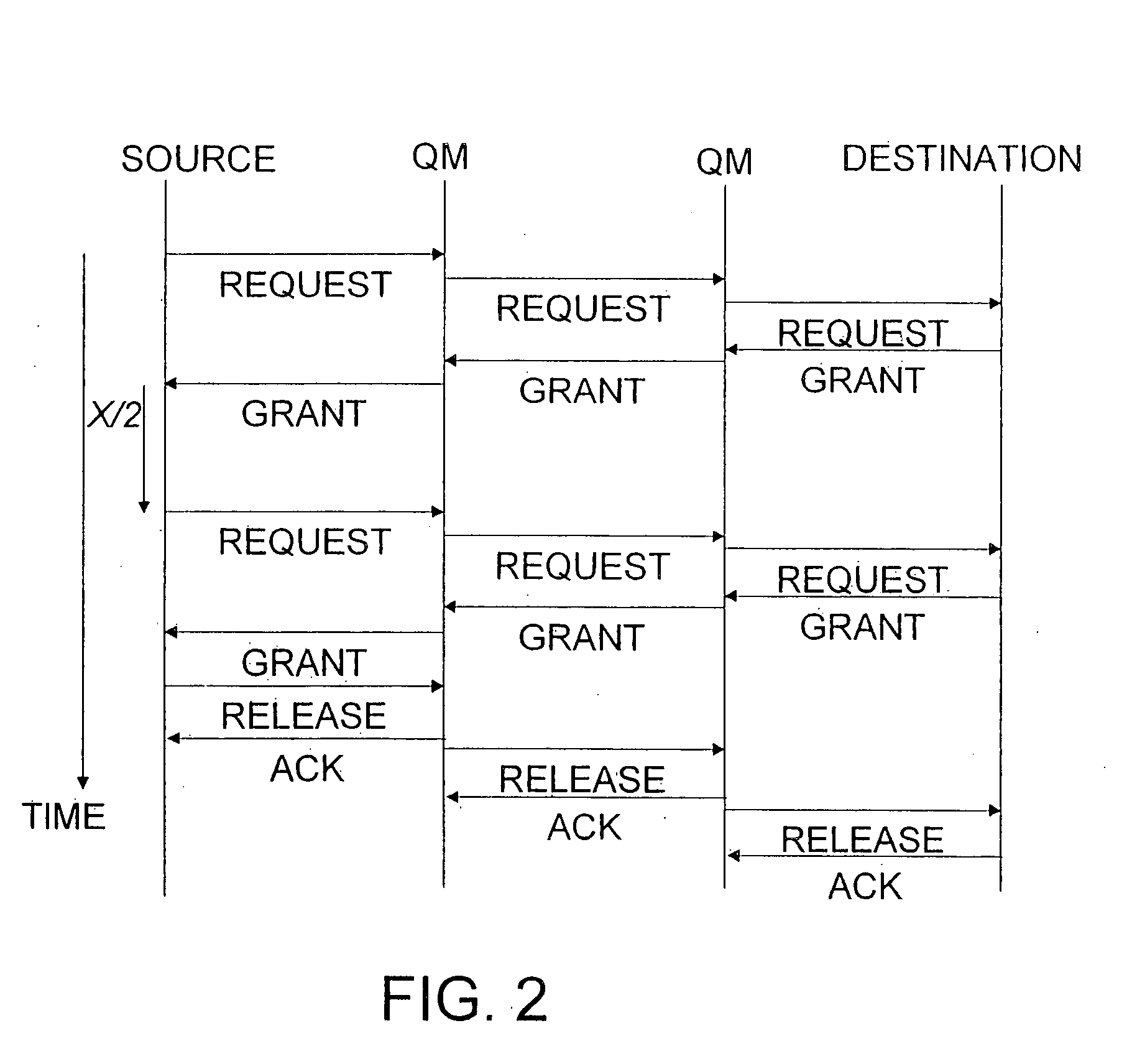
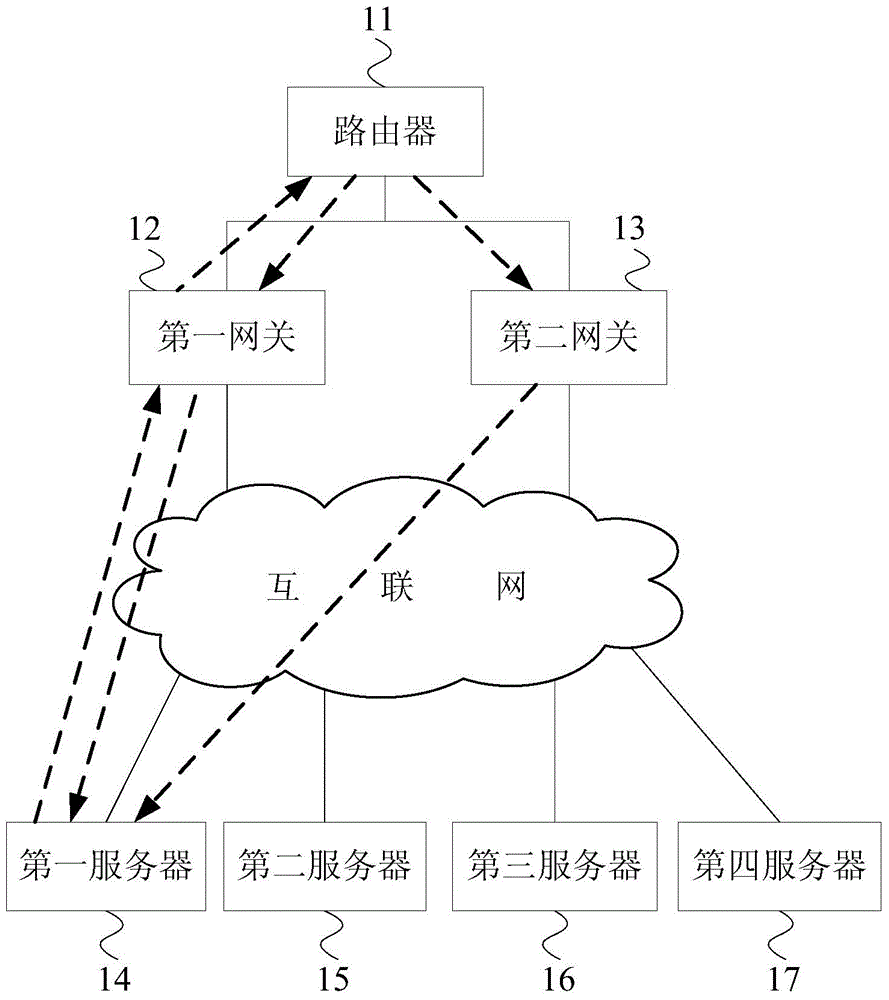
Method and system for providing a mobile IP network with non-path dependent intra domain quality of service
InactiveUS7269657B1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsDomain nameQuality of service
A system and method for providing quality of service (QoS) service over a mobile IP network with dynamic domains, multiple or distributed QoS managers per domain and / or with network congestion feedback being used to establish an estimated total domain bandwidth which is used for regulating access to a domain.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Hearing device and method for choosing a program in a multi program hearing device
The invention concerns a hearing device having an input transducer and an output transducer with a signal path therebetween, signal processing means connected in said signal path for influencing a signal in the signal path dependent on a PPS (processing parameter set), and a PPS memory accessible by the signal processor means for storing a number of different PPS's for use by the signal processing means. The system has means for monitoring the acoustic environment in a learning mode, where the user chooses the PPS to be used in the signal processing. Later in an automatic mode the hearing aid system chooses the PPS based on a comparison of the current acoustic environment with the monitored environment in the learning phase.
Owner:OTICON
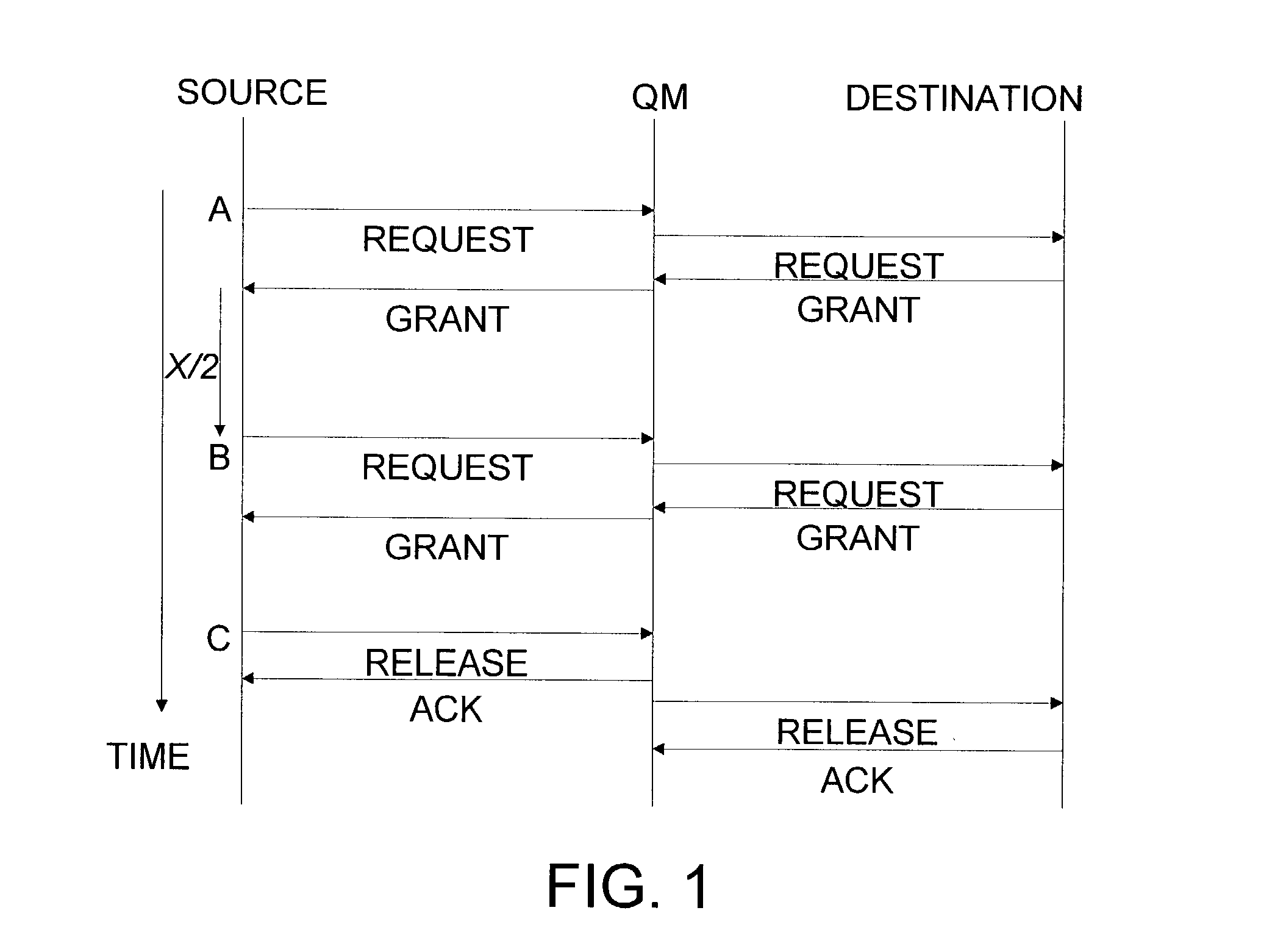
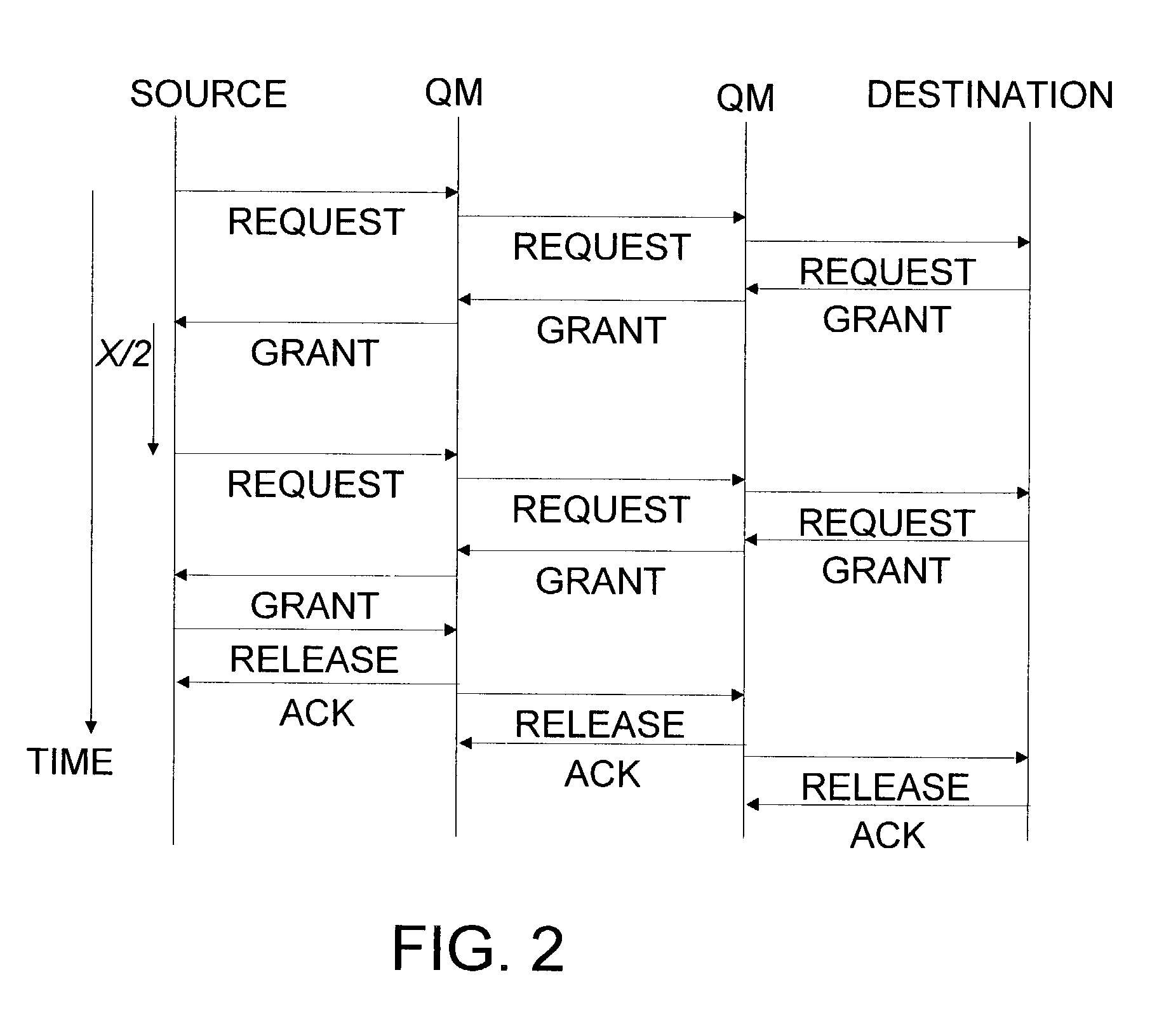
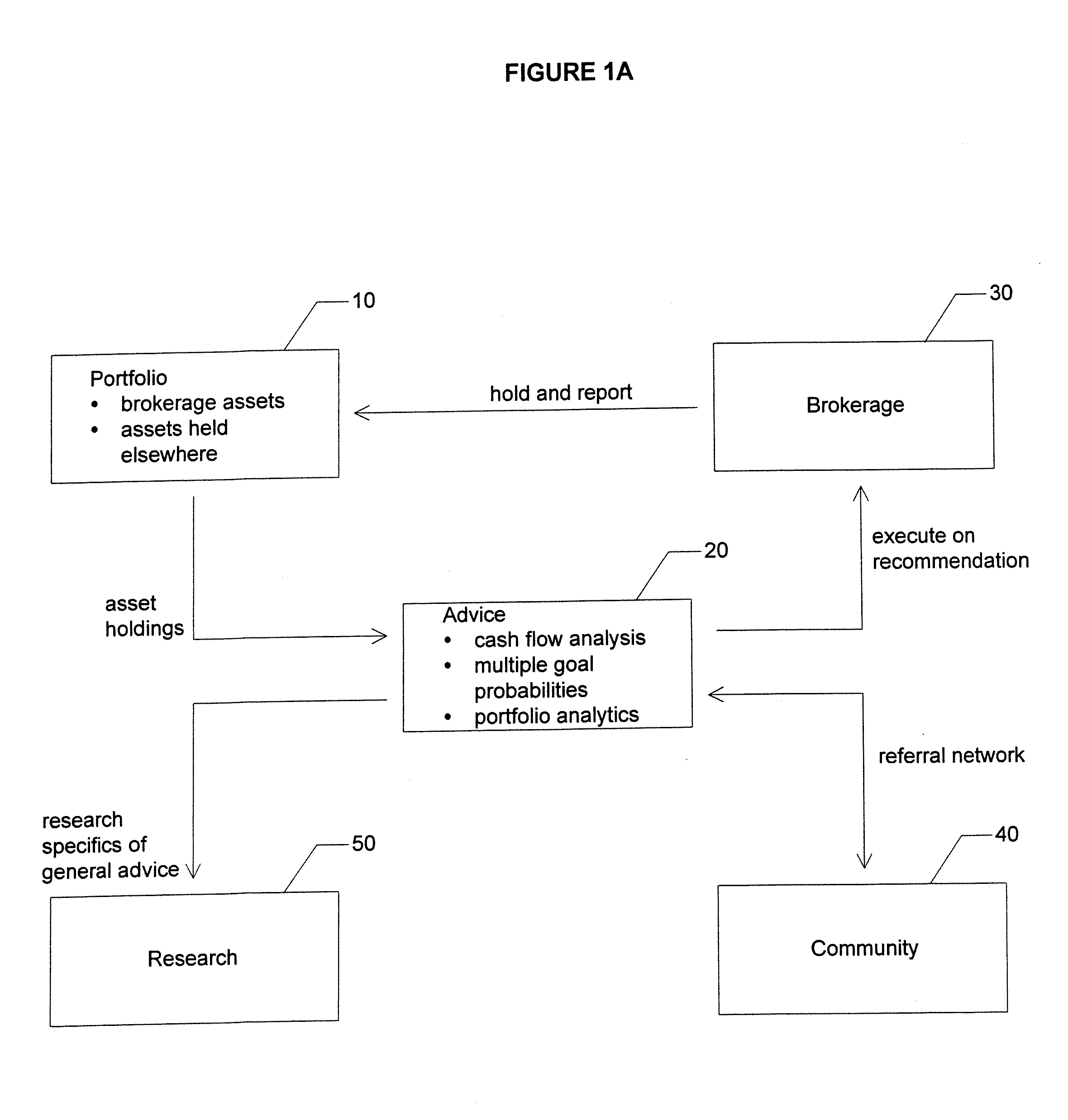
Method and system for computing path dependent probabilities of attaining financial goals
Owner:RISKMETRICS GROUP
Image object ranking
Automatic vision system object indexing and image database query system using both path-dependent and path-independent features of moving objects within a sequence of images. Feature vectors of both average over frames of an object traversing the field of view plus average over blocks of a grid for a path association. Color histograms may be an included feature.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
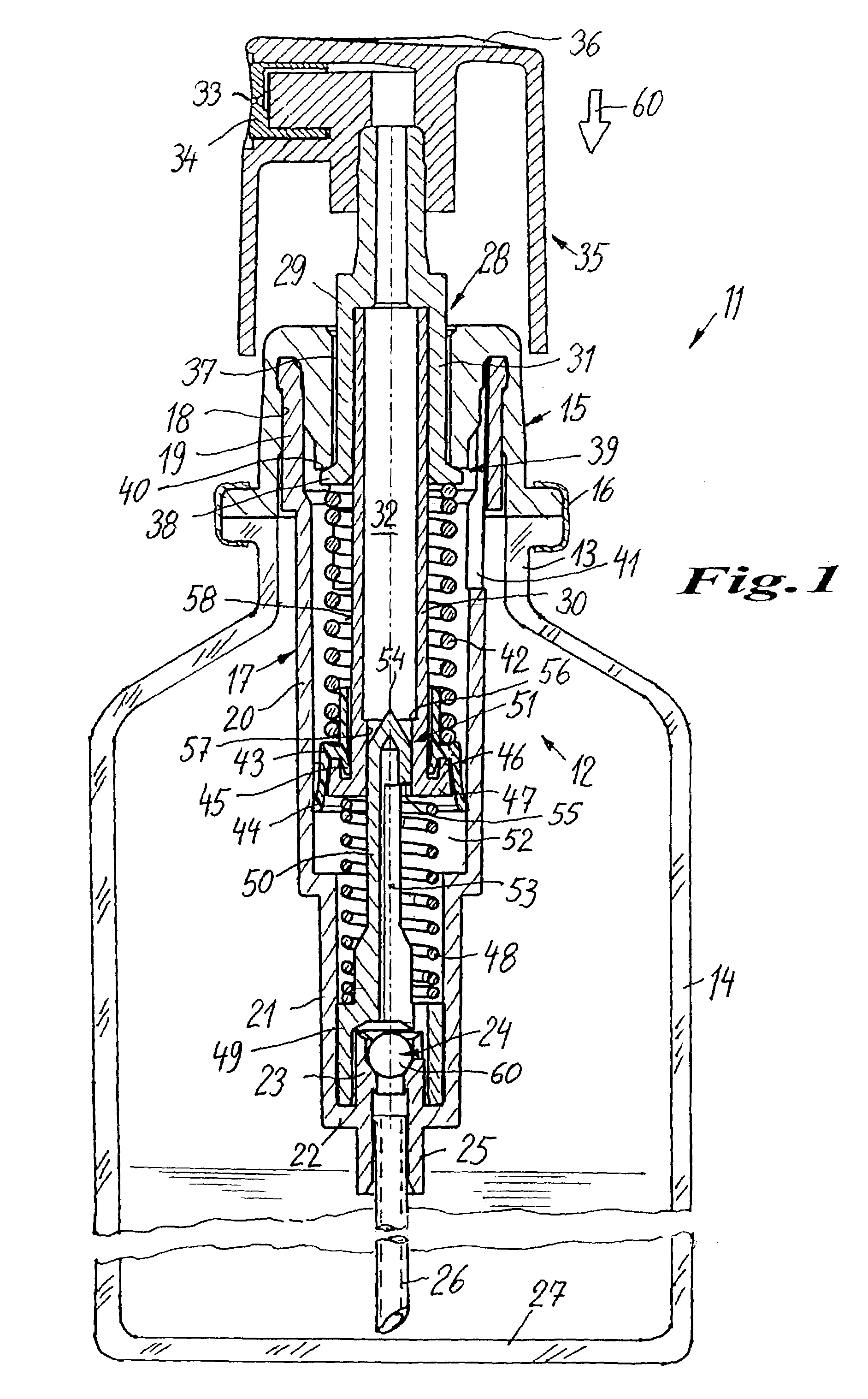
Dispenser for the discharge of flowable media
InactiveUS7066359B2Simple and appropriateSpring tension is relatively constantClosuresDispensing apparatusPump chamberEngineering
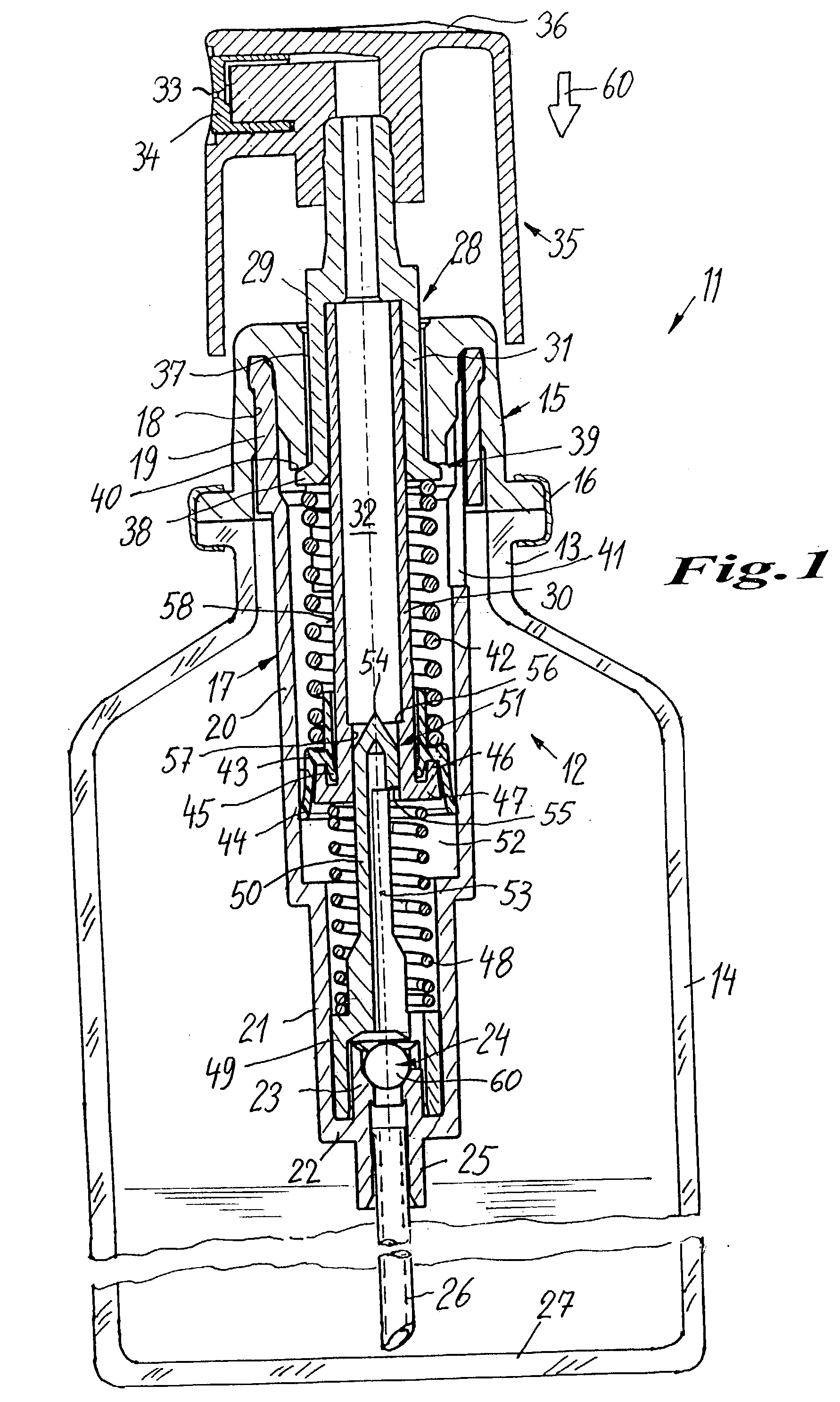
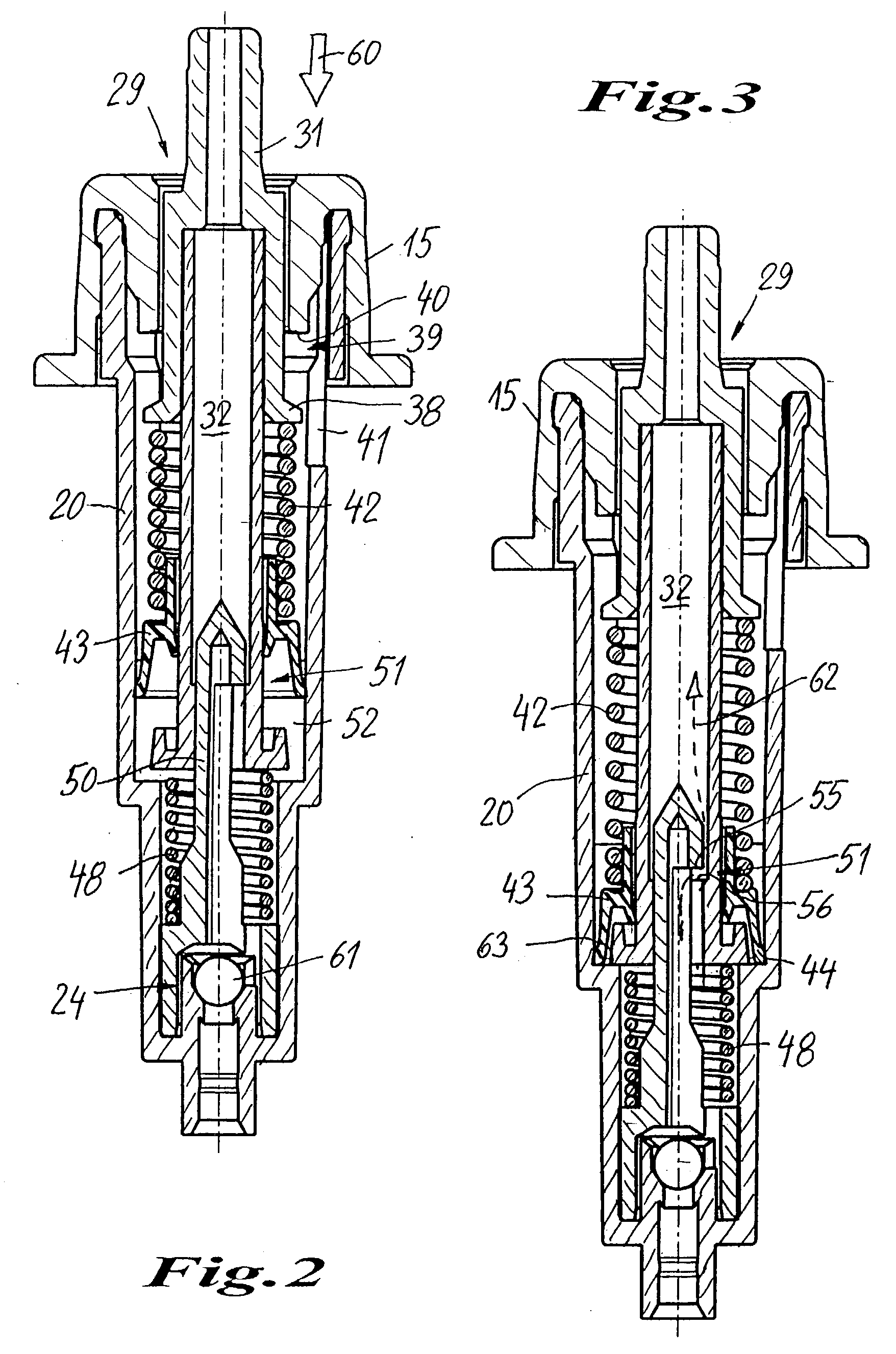
A dispenser for flowable media is provided, which operates in user-independent manner with respect to the pressure buildup and dosage quantity. On pressing on an operating head (35) a piston rod (29) is forced into a pump cylinder. As the pump chamber (52) is sealed by means of a delivery valve (51), which operates in path-dependent manner as a slide valve, under the action of a spring (42) pressing on the piston collar (43), a pressure builds up in the pump chamber (52), which is released following a predetermined length of travel on opening the delivery valve. A relatively constant pressure can be obtained over the entire discharge phase through the pretension of spring (42).
Owner:APTAR RADOLFZELL
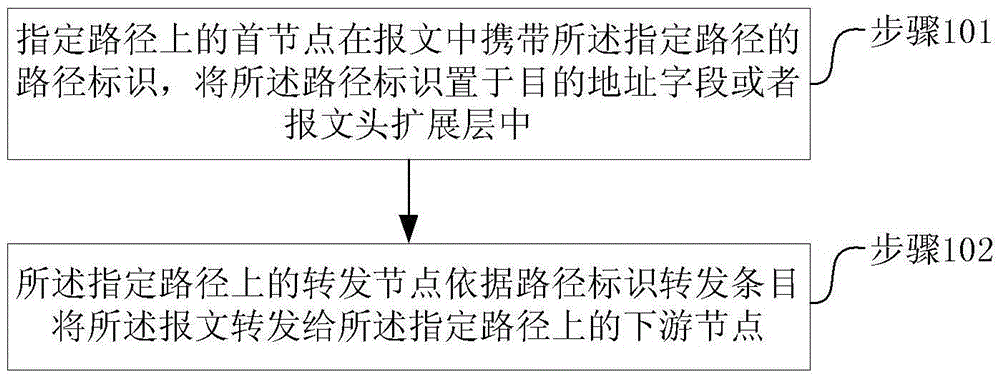
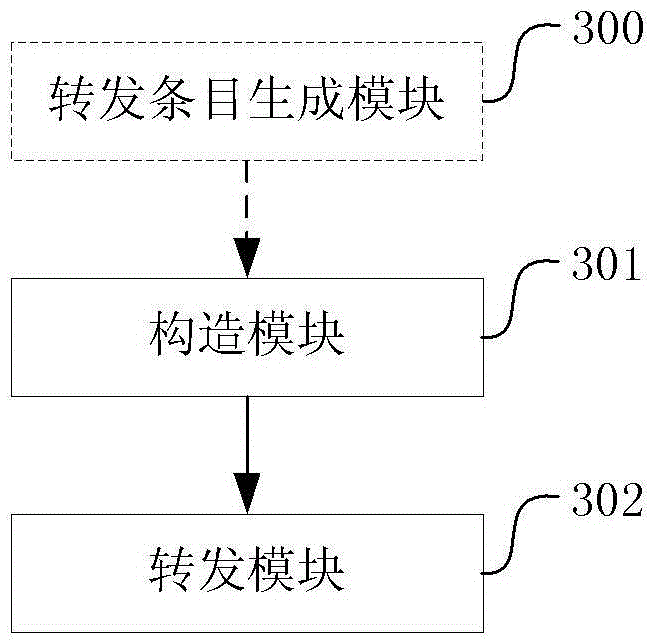
Message transmission method, apparatus and system
ActiveCN106656781AImprove forwarding efficiencyData switching networksPath dependentDistributed computing
In order to solve the technical problems of the prior art, the invention provides a message transmission method, apparatus and system which can increase the forwarding efficiency wherein the method comprises the following steps: carrying by the first node of a designated path the path identifier of the designated path in the message; placing the path identifier in a message header extension layer or a destination address field or an outer layer tag wherein the path identifier is used to direct the forwarding of the message; and after the message carries the path identifier, forwarding the message to the downstream node of the designated path by the forwarding path of the designed path according to the path identifier forwarding entry. According to the technical schemes proposed by the embodiments of the invention, the forwarding node relies directly on the path identifier to check table and forward without other processing on the package of the message head, therefore, increasing the forwarding efficiency.
Owner:ZTE CORP
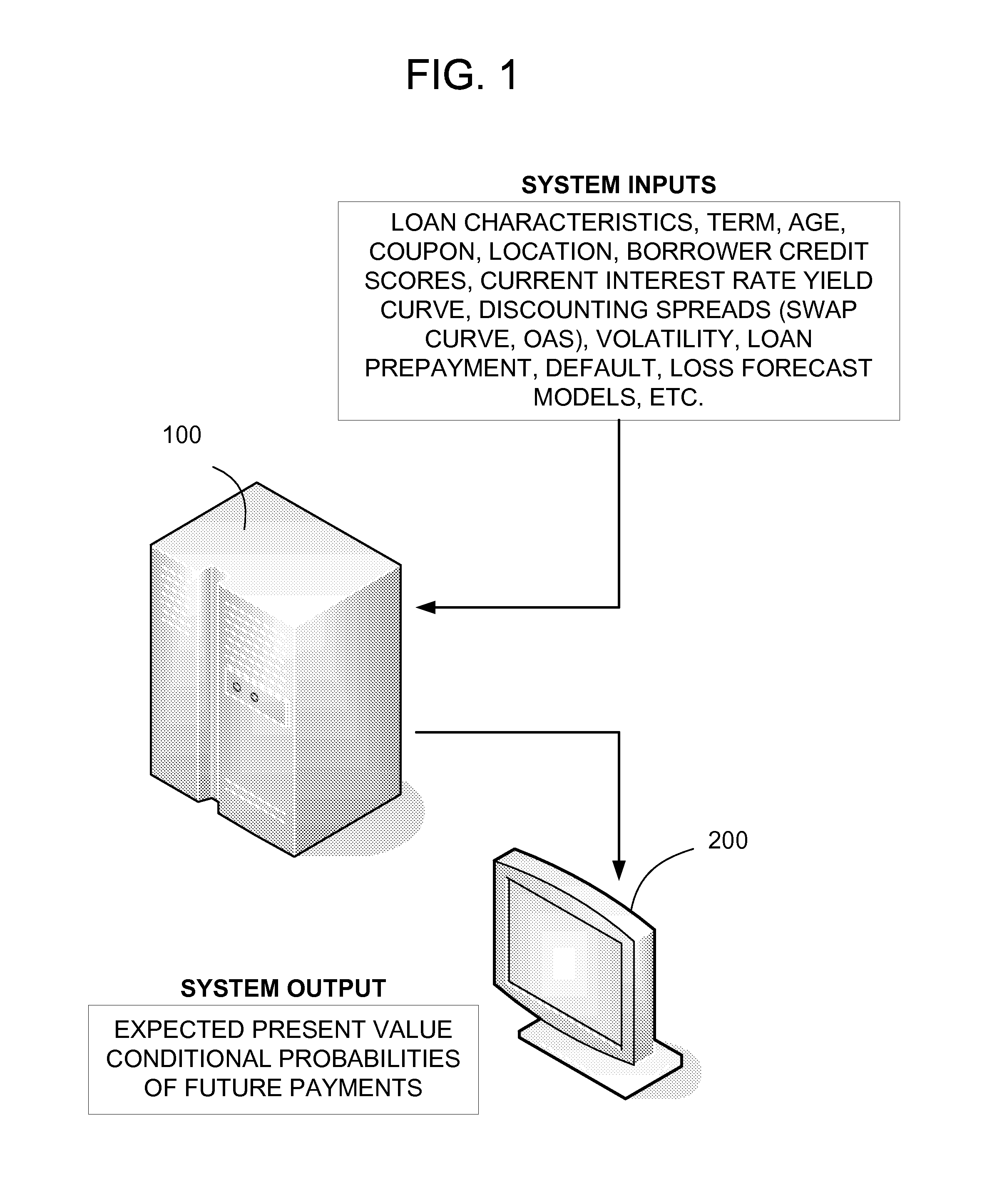
Methods and apparatus for iterative conditional probability calculation methods for financial instruments with path-dependent payment structures
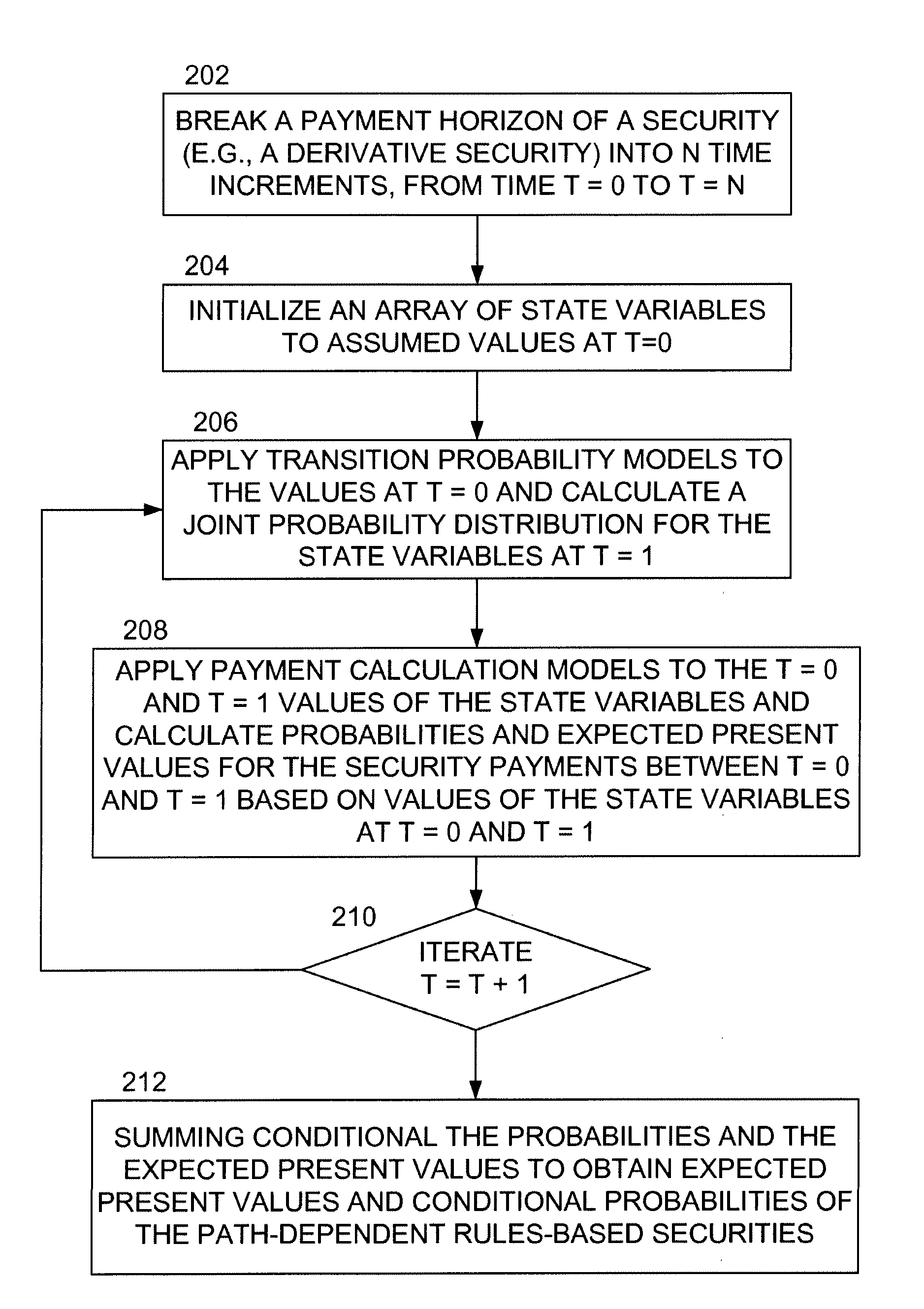
Methods and apparatus provide for calculating expected present values and conditional probabilities of future payments of path-dependent rules-based securities or derivative contracts using iterative conditional probability calculation methods, including: (a) breaking a payment horizon of the securities or derivative contracts into N time increments over time t=0 to t=N; (b) initializing an array of state variables to assumed values at t=0; (c) applying transition probability models to the assumed values of the state variables at time t=0 and calculating a joint probability distribution for the state variables at time t=1; (d) applying payment calculation models to both the t=0 and t=1 values of the state variables and calculating probabilities and expected present values for the securities or derivative contracts payments occurring between t=0 and t=1 based on values of the state variables at times t=0 and t=1; (e) repeating steps (c)-(d) iteratively at each time t and calculating joint probability distributions for the state variables, probabilities, and expected present values of the the securities or derivative contracts payments occurring between times t and t+1 based on values of the state variables at times t and t+1; and (f) summing the probabilities and the expected present value calculations across time and values of the state variables to obtain the expected present values and conditional probabilities of the future payments of the path-dependent rules-based securities or derivative contracts.
Owner:HUGHES FEFFERMAN SYST
Method and system for providing a mobile IP network with non-path dependent intra domain quality of service
InactiveUS20080056178A1Improve abilitiesEfficient changeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesDomain nameQuality of service
A system and method for providing quality of service (QoS) service over a mobile IP network with dynamic domains, multiple or distributed QoS managers per domain and / or with network congestion feedback being used to establish an estimated total domain bandwidth which is used for regulating access to a domain.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Multi-stage machine-learning models to control path-dependent processes
Provided is a process, including: obtaining a first training dataset of subject-entity records; training a first machine-learning model on the first training dataset; forming virtual subject-entity records by appending members of a set of candidate action sequences to time-series of at least some of the subject-entity records; forming a second training dataset by labeling the virtual subject-entity records with predictions of the first machine-learning model; and training a second machine-learning model on the second training dataset.
Owner:CEREBRI AI INC
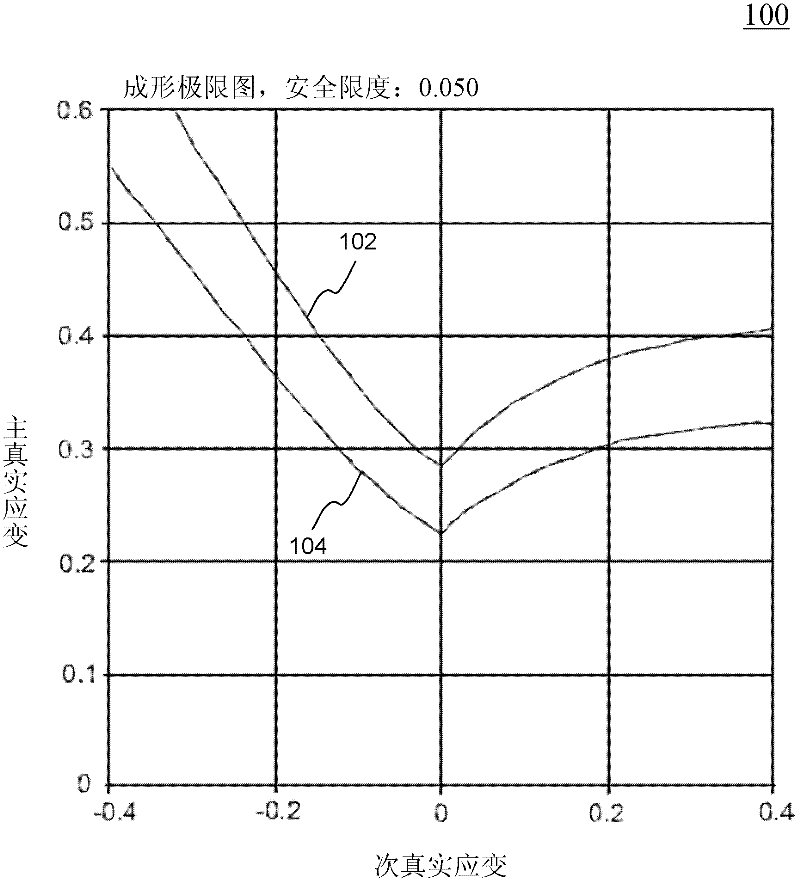
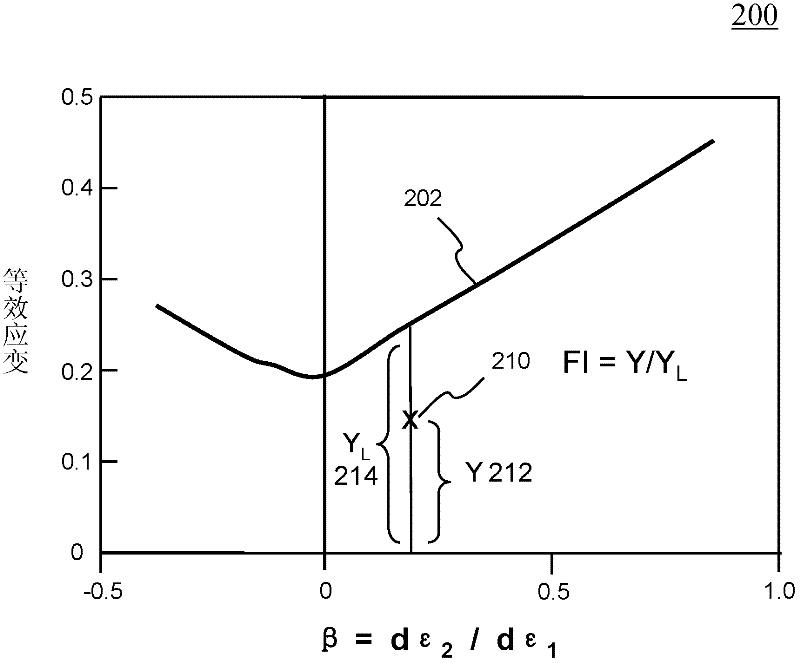
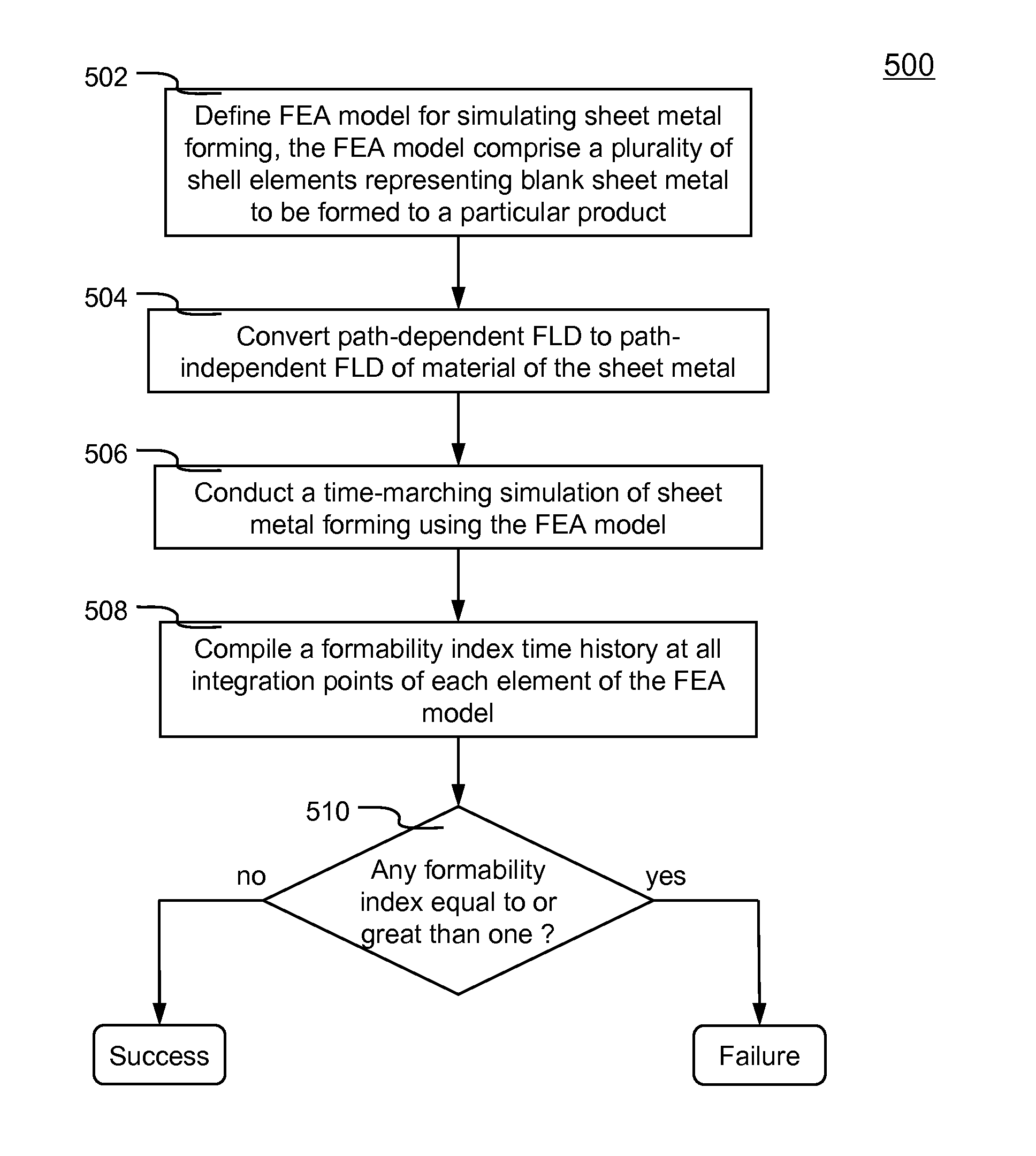
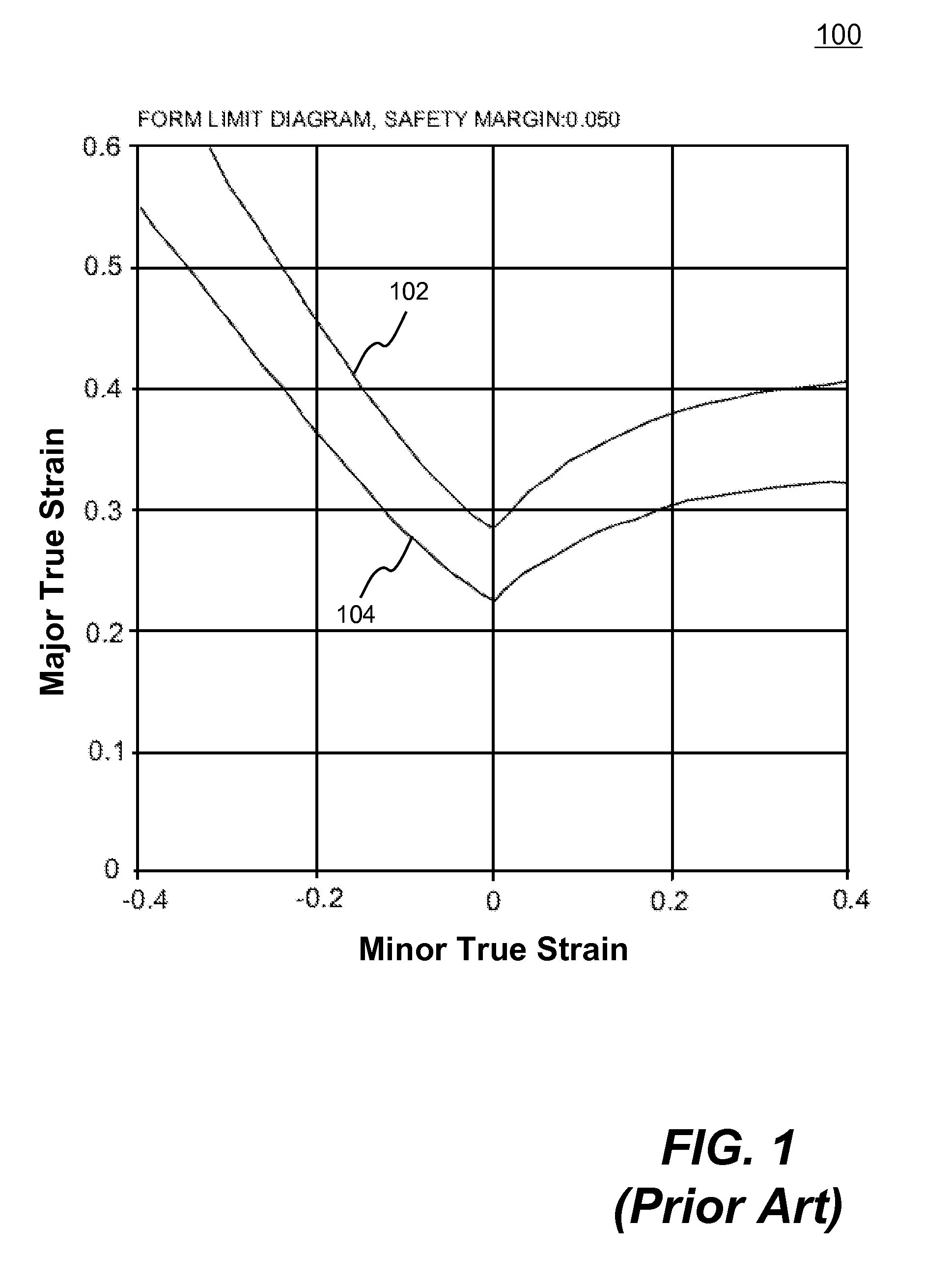
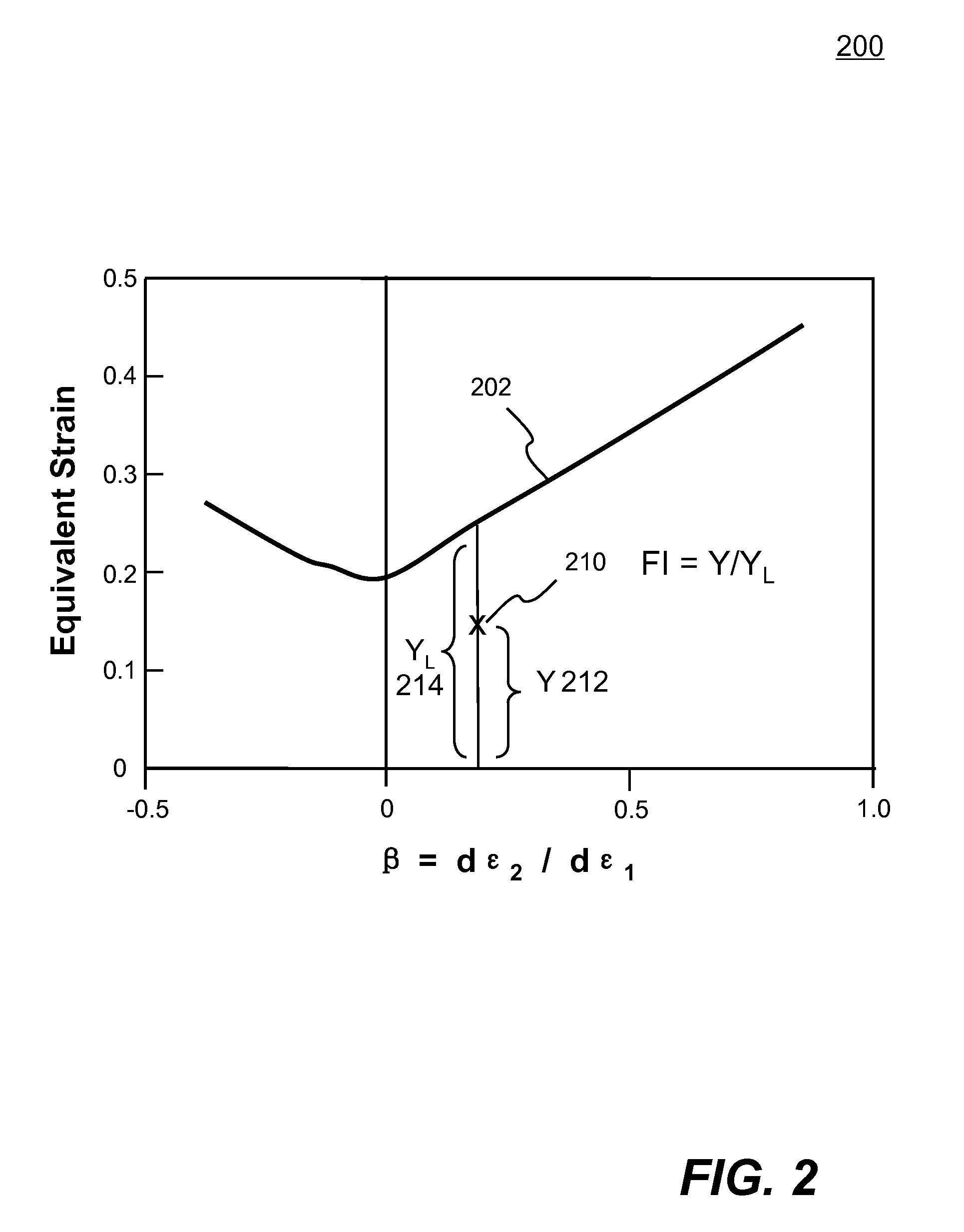
Method and system for numerically simulating and predicting necking failure in sheet metal forming
InactiveCN102262688AEasy to useEasy to observeDesign optimisation/simulationAerodynamics improvementForming limit diagramElement analysis
Systems and methods of predicting sheet metal forming failure using numerical simulations (e.g., finite element analysis) are disclosed. A FEA model is defined for a particular sheet metal forming process. Blank sheet metal is modeled with a plurality of shell elements. Additionally, a deformation path-dependent forming limit diagram (FLD) is converted to a path-independent FLD. A time-marching simulation of the sheet metal forming process is conducted using the FEA model. At each solution cycle, equivalent strain at each integration point of shell element is checked against the corresponding forming limit strain value of the path-independent FLD. The ratio of the equivalent strain and the forming limit strain is defined as formability index. A time history of the formability index of each shell element is saved into a file and displayed to a monitor upon user's instructions. When a particular element's formability index reaches one or higher, a localized necking is predicted.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Network protection switching mechanisms and methods of network protection
ActiveUS8358929B2High speedMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsControl communicationsNetwork control
A network protection switching mechanism comprises a plurality of optical switches located at a plurality of nodes; a plurality of optical communication paths between said switches; switch based fault detectors located as part of at least two switches which generate detection results representative of the identification of a fault; switch based controllers located as part of said at least two switches; and internal switch-communication means between said fault detectors and said controllers which facilitate the transmission of detection results from said fault detectors to said controllers; wherein said controllers directly cause switching to an alternative optical communication path dependent upon the receipt of said detection results; whereby autonomous switch based protection without dependence on either inter-switch control communication or higher level network control communication is achieved.
Owner:HUBERSUHNER POLATIS LTD
Methods and apparatus for iterative conditional probability calculation methods for financial instruments with path-dependent payment structures
Methods and apparatus provide for calculating expected present values and conditional probabilities of future payments of path-dependent rules-based securities or derivative contracts using iterative conditional probability calculation methods, including: (a) breaking a payment horizon of the securities or derivative contracts into N time increments over time t=0 to t=N; (b) initializing an array of state variables to assumed values at t=0; (c) applying transition probability models to the assumed values of the state variables at time t=0 and calculating a joint probability distribution for the state variables at time t=1; (d) applying payment calculation models to both the t=0 and t=1 values of the state variables and calculating probabilities and expected present values for the securities or derivative contracts payments occurring between t=0 and t=1 based on values of the state variables at times t=0 and t=1; (e) repeating steps (c)-(d) iteratively at each time t and calculating joint probability distributions for the state variables, probabilities, and expected present values of the securities or derivative contracts payments occurring between times t and t+1 based on values of the state variables at times t and t+1; and (f) summing the probabilities and the expected present value calculations across time and values of the state variables to obtain the expected present values and conditional probabilities of the future payments of the path-dependent rules-based securities or derivative contracts. By using the foregoing iterative conditional probability calculation methods it is possible to evolve a composite state variable CSV in a path-independent manner and use CSV to calculate present value cash-flow of a path-dependent rules-based security.
Owner:HUGHES FEFFERMAN SYST
Call path dependent authentication
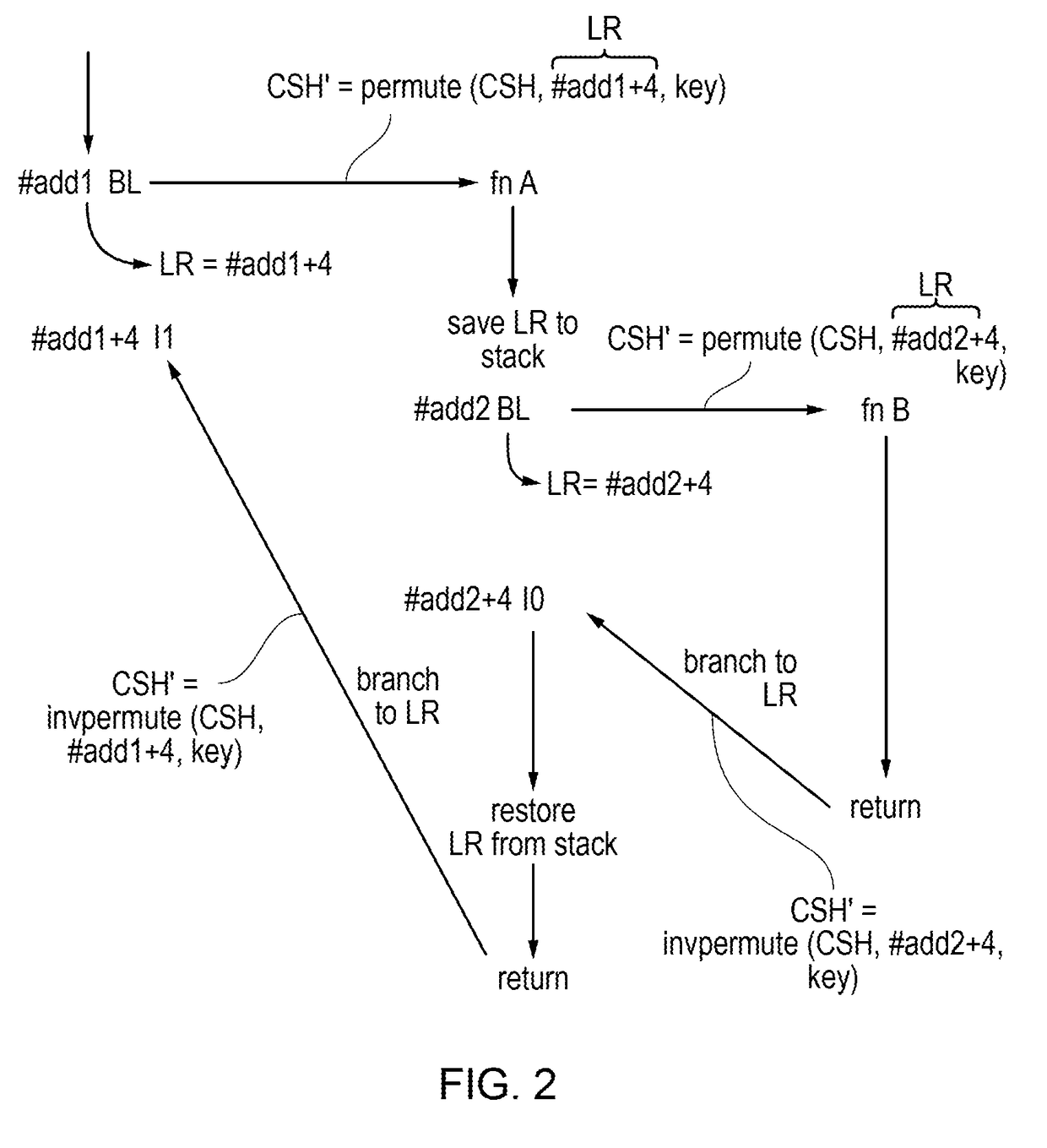
ActiveUS20190087566A1Digital data protectionDigital data authenticationComputer hardwareError processing
A call path identifier is maintained which is permuted in response to a calling instruction for calling a target function, based on a function return address. The call path identifier is used as a modifier value for authentication code generating and checking instructions for generating and checking authentication codes associated with source values. In response to the authentication code checking instruction, if an expected authentication code mismatches a previously generated authentication code for a source value then an error handling response is triggered. This is useful for preventing attacks where address pointers which are valid in one part of the code are attempted to be reused in other parts of code.
Owner:ARM LTD
Network Protection Switching Mechanisms and Methods of Network Protection
ActiveUS20100027989A1Increase network reliabilityImprove availabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsControl communicationsNetwork control
A network protection switching mechanism comprises a plurality of optical switches located at a plurality of nodes; a plurality of optical communication paths between said switches; switch based fault detectors located as part of at least two switches which generate detection results representative of the identification of a fault; switch based controllers located as part of said at least two switches; and internal switch-communication means between said fault detectors and said controllers which facilitate the transmission of detection results from said fault detectors to said controllers; wherein said controllers directly cause switching to an alternative optical communication path dependent upon the receipt of said detection results; whereby autonomous switch based protection without dependence on either inter-switch control communication or higher level network control communication is achieved.
Owner:HUBERSUHNER POLATIS LTD
Dispenser for the discharge of flowable media
InactiveUS20040000567A1Simple and compact structureSimple and appropriateContracting/expanding measuring chambersClosuresPump chamberEngineering
A dispenser for flowable media is provided, which operates in user-independent manner with respect to the pressure buildup and dosage quantity. On pressing on an operating head (35) a piston rod (29) is forced into a pump cylinder. As the pump chamber (52) is sealed by means of a delivery valve (51), which operates in path-dependent manner as a slide valve, under the action of a spring (42) pressing on the piston collar (43), a pressure builds up in the pump chamber (52), which is released following a predetermined length of travel on opening the delivery valve. A relatively constant pressure can be obtained over the entire discharge phase through the pretension of spring (42).
Owner:APTAR RADOLFZELL
Configuration representation and modeling using configuration spaces
ActiveUS7953779B1Facilitate useful presentationOther databases browsing/visualisationCommerceGraphicsAutomatic transmission
Configuration spaces facilitate the useful presentation of data, particularly configuration data used for representing configured products. Products include features and common features can be grouped by families. For example, an automobile can include a transmission family. The transmission family could include features such as automatic transmission and 4-speed manual transmission. Configuration spaces can be achieved by consolidating selected data without loosing useful information. The degree of consolidation achieved can be significant enough to permit display of data using conventional display technology. Configuration spaces break down the “universe” of possible configurations into constituent spaces defined by groups of rules for a selected feature. Common dependencies between the selected feature and related features can be consolidated to produce a more minimal form of the data used for representing the selected features and related features. Configuration spaces can provide a useful graphical view of the breakdown of all rules written for a single feature or multiple features. The data present in this view can be analyzed to, for example, study the dependency paths of an existing configuration and better understand the impact of revising configuration relationships. Thus, configuration spaces aid in the creation and modification of configuration models.
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
Message forwarding method, apparatus, and system
The invention provides a message forwarding method, an apparatus, and a system. The method includes: a first message sent by a gateway is received and analyzed, and a source IP address and a source MAC address of the first message are obtained; a host cache table is inquired, and when the host cache table does not have a mapping relation between the source IP address and the source MAC address, the mapping relation between the source IP address and the source MAC address is saved in the host cache table; according to the first message, a response message is generated, the host cache table is inquired, and a first destination MAC address corresponding to a first destination IP address in the response message is obtained; and according to the first destination MAC address corresponding to the first destination IP address in the response message, the response message is forwarded to an external network via the gateway. According to the message forwarding method, the apparatus, and the system, as long as paths dependent on bidirectional messages are consistent, operating business can work in a normal manner.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Sheet Metal Forming Failure Prediction Using Numerical Simulations
InactiveUS20110295570A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationForming limit diagramElement analysis
Systems and methods of predicting sheet metal forming failure using numerical simulations (e.g., finite element analysis) are disclosed. A FEA model is defined for a particular sheet metal forming process. Blank sheet metal is modeled with a plurality of shell elements. Additionally, a deformation path-dependent forming limit diagram (FLD) is converted to a path-independent FLD. A time-marching simulation of the sheet metal forming process is conducted using the FEA model. At each solution cycle, equivalent strain at each integration point of shell element is checked against the corresponding forming limit strain value of the path-independent FLD. The ratio of the equivalent strain and the forming limit strain is defined as formability index. A time history of the formability index of each shell element is saved into a file and displayed to a monitor upon user's instructions. When a particular element's formability index reaches one or higher, a localized necking is predicted.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Polarization coding quantum cryptography system
ActiveUS20100158252A1Stable characteristicsKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationQuantum channelOptoelectronics
Provided is a polarization coding quantum cryptography system. The quantum cryptography includes a light source, a quantum channel, an optical path selector, and a path-dependent polarization selector. The light source generates a signal light. The quantum channel is used as a path to transmit the signal light to a receiver unit. The optical path selector is disposed between the light source and the quantum channel to transmit the signal light to one of a plurality of propagation paths. The path-dependent polarization selector is disposed between the optical path selector and the quantum channel. Herein, the path-dependent polarization selector is configured to determine the polarization direction of the signal light according to the propagation path of the signal light.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
High efficiency redundancy architecture in SRAM compiler
A yield enhancement circuit substitutes a redundant sub-circuit for a faulty sub-circuit in an integrated circuit such as memory. The yield enhancement circuit has a plurality of fault indication devices, which is associated with one sub circuit of the integrated circuits such that one fault indication device is activated to generate a fault signal to express the existence of a fault within the faulty sub-circuit. Additionally selected adjacent fault indication devices generate the fault signal to express the existence of the fault within the faulty circuit. A fault detection device determines the existence of the faulty sub-circuit and transmits a redundancy implementation signal to a plurality of redundancy activation circuits. Each redundancy activation circuit selectively transfers input / output signals to a designated path dependent on the expression of the existence of a fault within the integrated circuit.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for optimization of redundant link usage in a multi-shelf network element
InactiveUS7710866B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionCritical timeTime sensitive
A method and apparatus for optimizing redundant link usage allows a portion of the wasted bandwidth in a redundant link system to be utilized for additional data traffic without compromising the ability of the system to respond to and correct for a failure of a link. In one embodiment, one of two independent, individually addressable links is selected as a nominal communication path, and the other as a standby communication path. The path independent traffic is sent via the nominal communication path, while the path dependent data is sent via the nominal communication path or the standby path, in accordance with the dependence of the traffic. In another embodiment, critical time sensitive traffic is sent via a nominal and standby time sensitive paths, while normal traffic is sent via nominal normal path, and non-critical traffic is sent via a standby normal path.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method for determining a torque characteristic of an automated friction clutch
InactiveUS20090090591A1Accurately determineLess effectMechanical actuated clutchesSlip couplingMobile vehicleRest position
A method for determining a torque characteristic of a friction clutch located in a drive train of a motor vehicle in the force flow between a drive engine and a transmission and which is closed in its rest position. At least two marker points of a regulating-path-dependent torque characteristic are determined, one of which is determined at a slipping limit of the clutch. To enhance determination of the torque characteristic, a first marker point is determined with the clutch engaged, the transmission in neutral and the engine running, by slowly disengaging the clutch until a reduction in the speed of the transmission input shaft relative to the engine speed is detected. A corresponding pair of values of this marker point with the known braking torque of the input shaft and the set position are used for adapting an existing characteristic.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
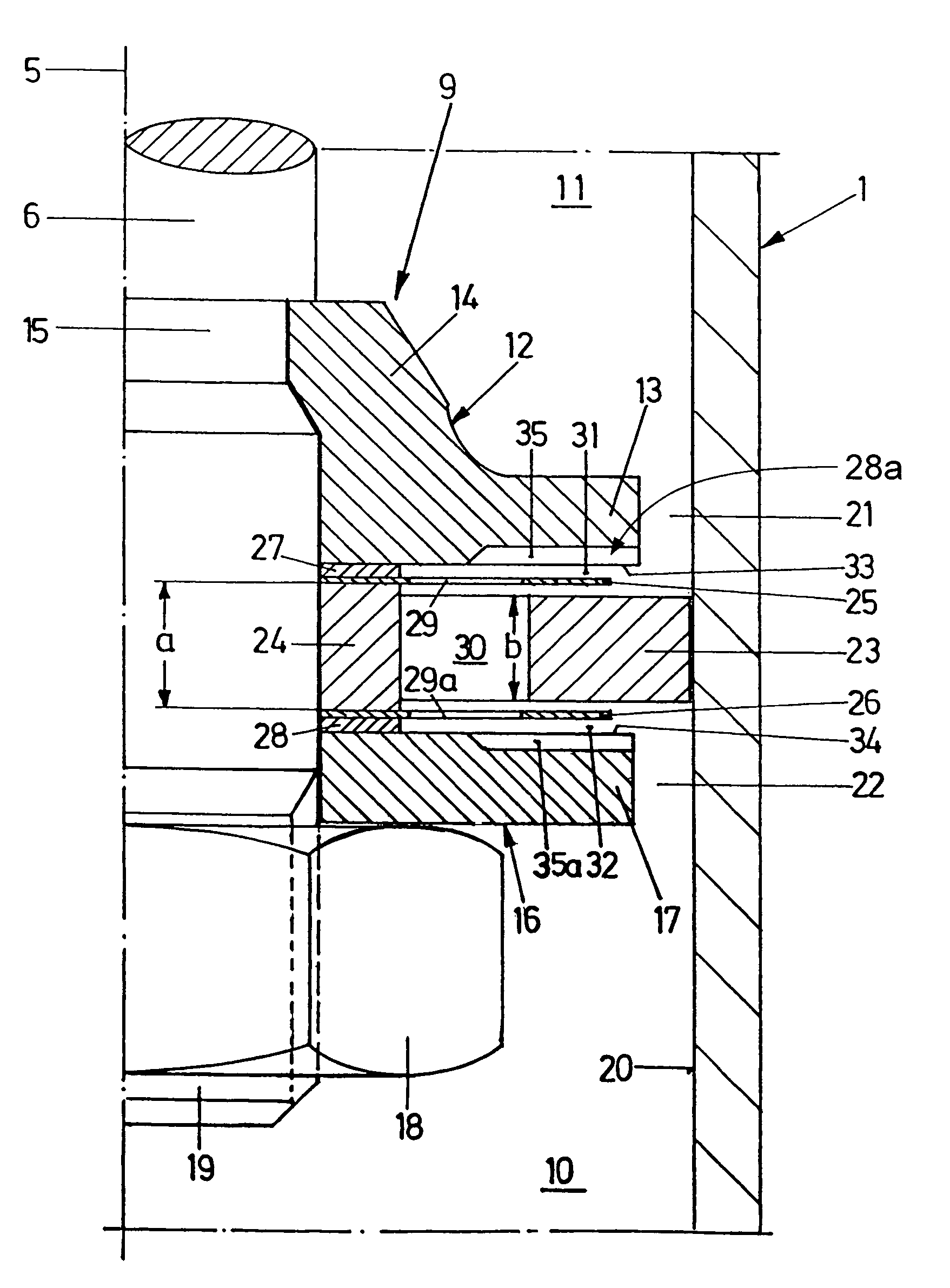
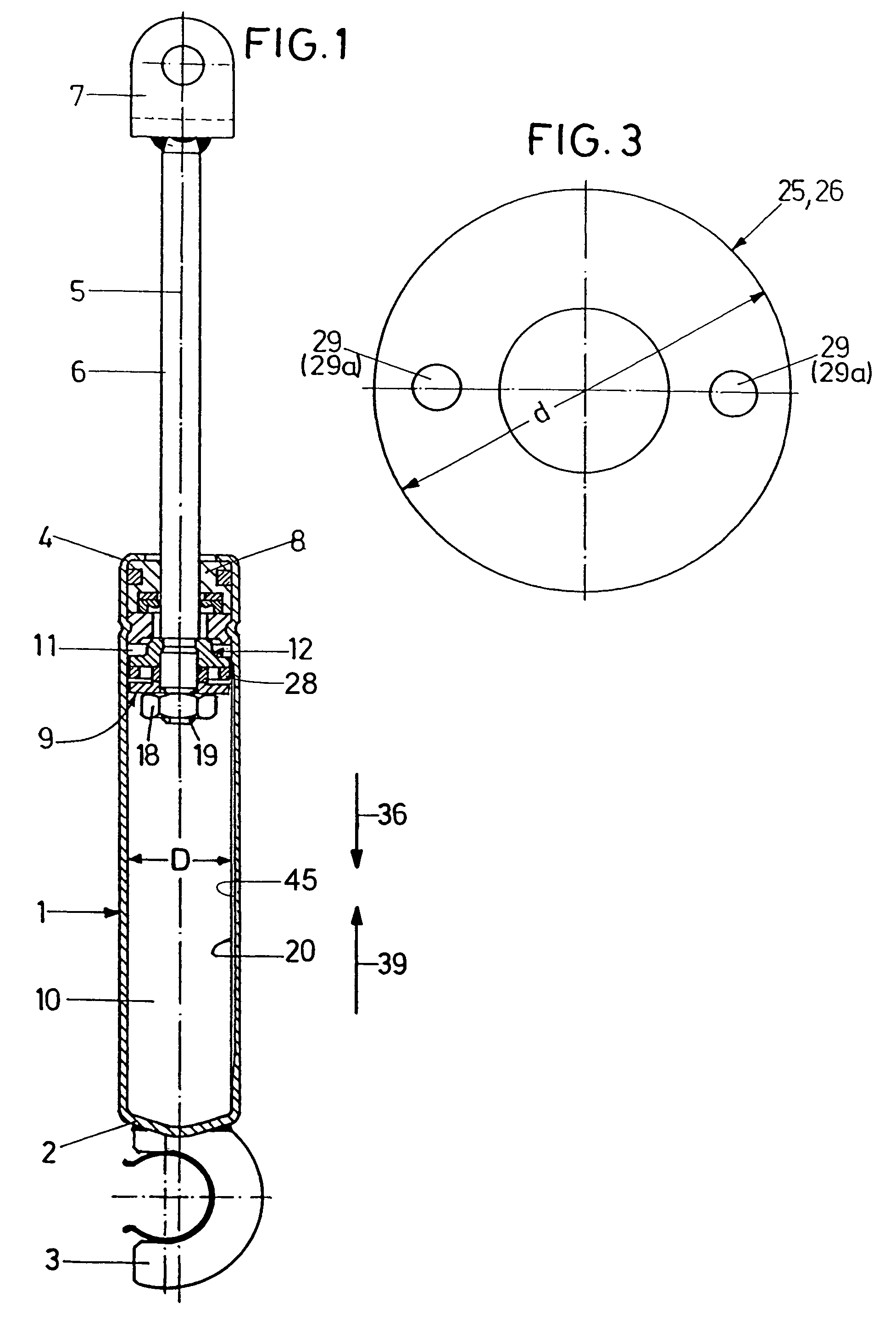
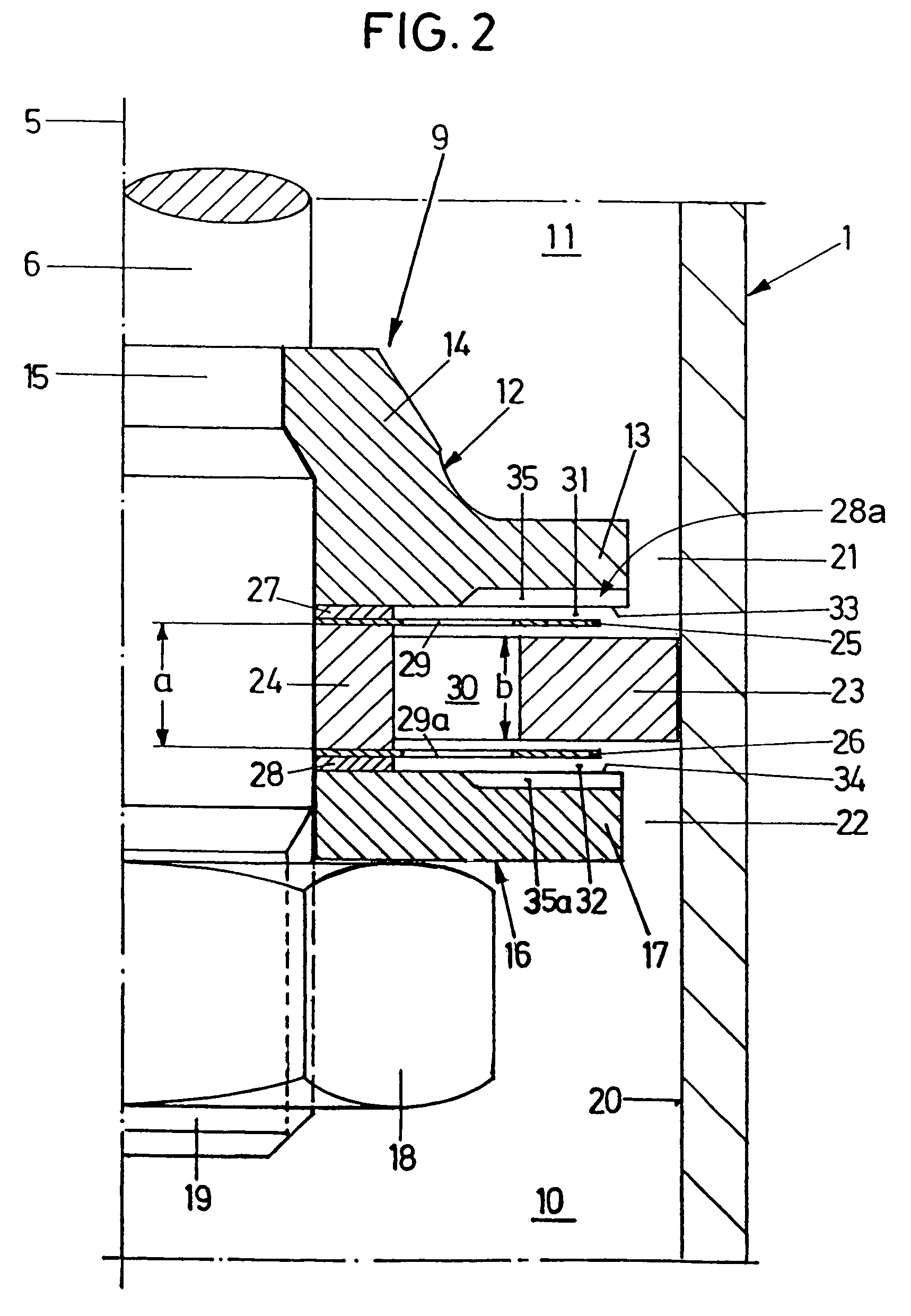
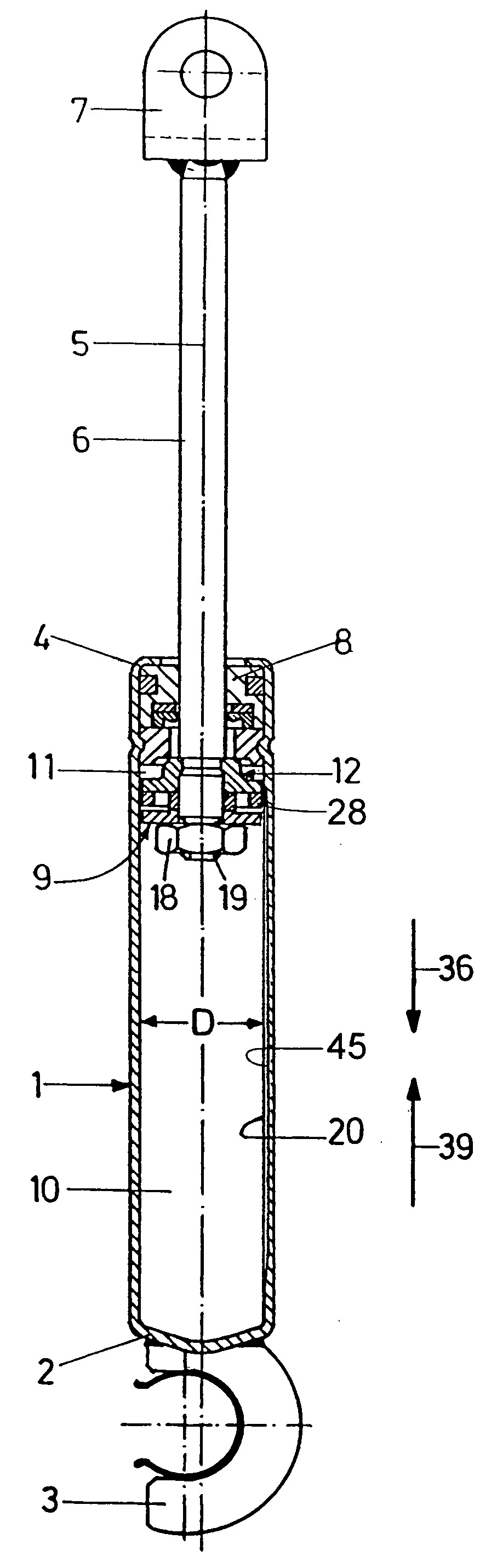
Gas spring
InactiveUS7073642B2Excellently controllable stroke behaviourNegatively affectedLiquid springsGas based dampersGas springEngineering
A gas spring comprises a cylindrical casing, in which a piston rod is guided for displacement concentric of a central longitudinal axis. A damping piston is mounted on the piston rod, dividing the interior of the casing into two sectional casing chambers. A filling of compressed gas is provided inside the casing. A damping device is provided for velocity-dependent damping of a motion of stroke of the damping piston and another damping device is provided for path-dependent damping of a motion of stroke of the damping piston. The result is a gas spring of excellently controllable stroke behaviour.
Owner:SUSPA
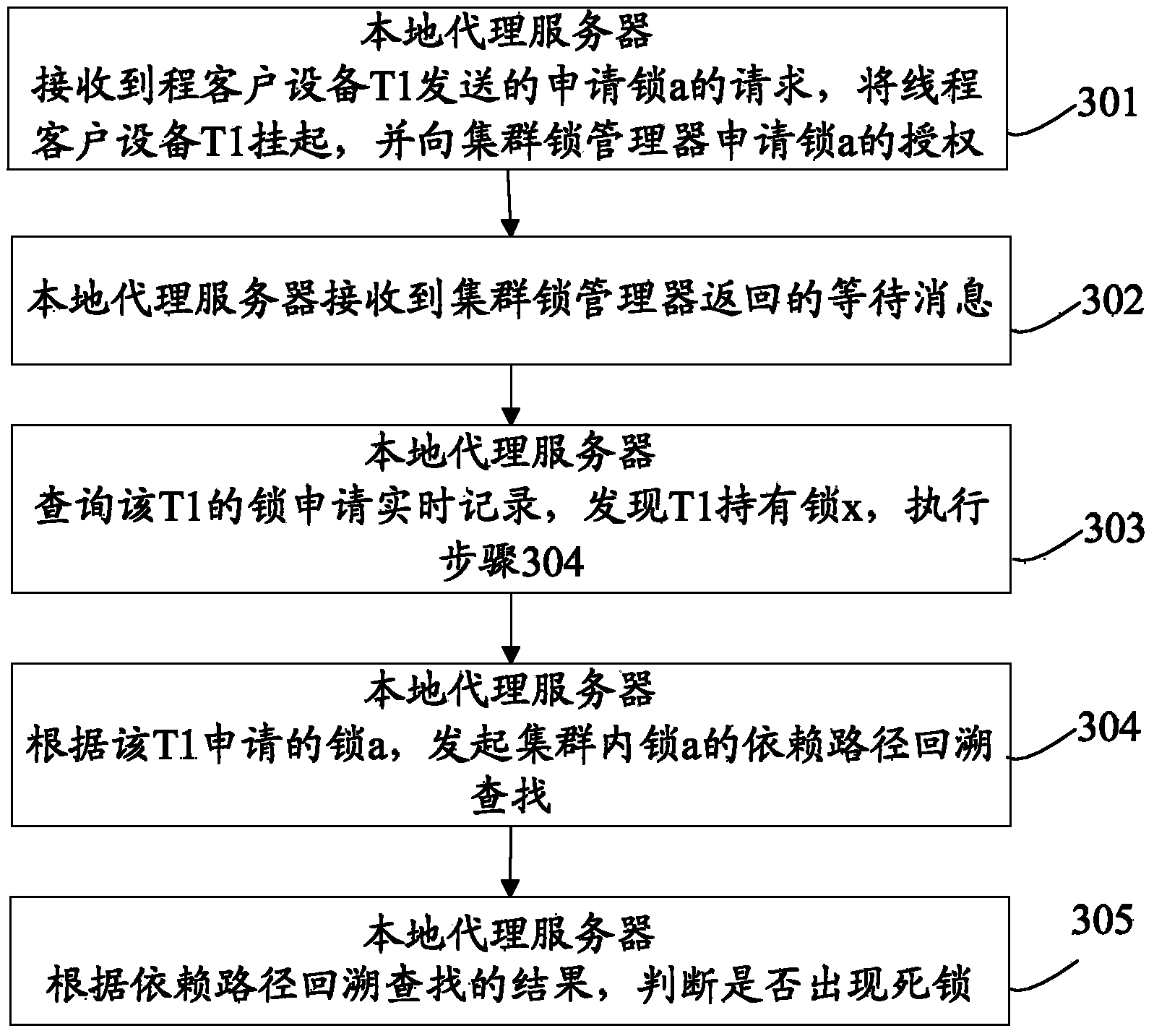
Deadlock detecting method, equipment and system
ActiveCN103678122ATimely processingRealize real-time detectionMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware testing/debuggingLock managerProxy server
The invention discloses a deadlock detecting method, equipment and system and belongs to the technical field of clusters. The method includes: receiving an application of a first lock from first thread client equipment; transmitting an authorization request to a cluster lock manager according to the application so as to apply for the authorization of the first lock; receiving the waste message returned by the cluster lock manager; inquiring the local lock application real-time records, and starting backtracking search of the dependence path of the first lock in a cluster if the fact that the first thread client equipment holds a second lock is discovered; judging whether deadlock occurs or not according to the search result. The method has the advantages that when the thread client equipment applies to hang a certain lock, a proxy server searches whether the client equipment holds another lock or not, if so, the backtracking search of the dependence path of applied lock is started, real-time detection of deadlock is achieved, and the method is simple and efficient.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Gas spring
InactiveUS20050045438A1Excellently controllable stroke behaviourNegatively affectedLiquid springsGas based dampersGas springEngineering
A gas spring comprises a cylindrical casing, in which a piston rod is guided for displacement concentric of a central longitudinal axis. A damping piston is mounted on the piston rod, dividing the interior of the casing into two sectional casing chambers. A filling of compressed gas is provided inside the casing. A damping device is provided for velocity-dependent damping of a motion of stroke of the damping piston and another damping device is provided for path-dependent damping of a motion of stroke of the damping piston. The result is a gas spring of excellently controllable stroke behaviour.
Owner:SUSPA
Method and system for computing path dependent probabilities of attaining financial goals
Owner:RISKMETRICS GROUP
Network protection switching mechanisms and methods of network protection
A network protection switching mechanism comprises a plurality of optical switches located at a plurality of nodes; a plurality of optical communication paths between said switches; switch based fault detectors located as part of at least two switches which generate detection results representative of the identification of a fault; switch based controllers located as part of said at least two switches; and internal switch- communication means between said fault detectors and said controllers which facilitate the transmission of detection results from said fault detectors to said controllers; wherein said controllers directly cause switching to an alternative optical communication path dependent upon the receipt of said detection results; whereby autonomous switch based protection without dependence on either inter-switch control communication or higher level network control communication is achieved.
Owner:POLATIS
Relational reasoning method, device and equipment based on deep neural network
ActiveCN109902301AImprove accuracyInference methodsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmArtificial intelligence
The invention discloses a relation reasoning method based on a deep neural network. The method comprises the steps of after obtaining sample sentences, constructing a syntactic dependency tree consisting of a plurality of words according to a preset fusion rule, then respectively extracting a main feature of the syntactic dependency tree on a shortest dependency path and an auxiliary feature on anon-shortest dependency path, finally carrying out feature fusion on the main feature and the auxiliary feature according to the preset fusion rule, and obtaining a relation reasoning result accordingto the fusion result. Visibly, according to the method, the characteristics of the syntactic dependency tree on the shortest dependency path and the non-shortest dependency path are extracted respectively and fused, and due to the fact that the auxiliary characteristics have a certain auxiliary effect on the reasoning result, the accuracy of relation reasoning is remarkably improved by effectively utilizing the main characteristics and the auxiliary characteristics of the syntactic dependency tree. In addition, the invention further provides a relation reasoning device and equipment based onthe deep neural network and a computer readable storage medium, and the effects of the relation reasoning device and equipment correspond to the effects of the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for generating function call code based on call stack and dependent path
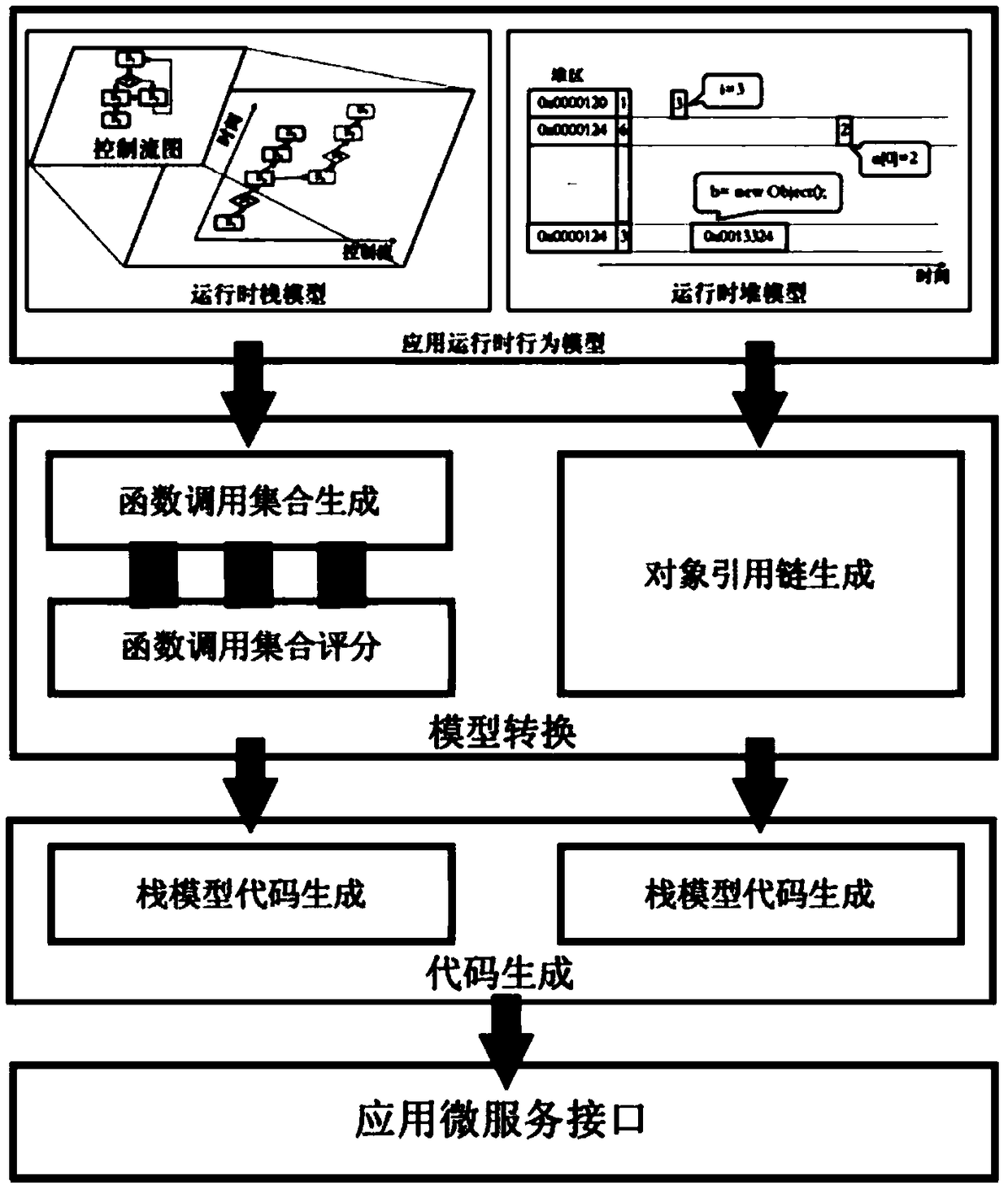
ActiveCN109240666ASolve the problem of complex execution sequenceCreation/generation of source codeCall stackPath dependent
The invention discloses a method and a system for generating a function calling code based on a calling stack and a dependent path, By monitoring the running of Android applications, the applied behavioral reflection runtime model is obtained, and the target object containing the target data is annotated in the runtime stack model of the behavioral reflection runtime model, All function call setsof the target object are generated, and each function call set is graded according to the difficulty of generating function call code using each function call set, and the function call set is recommended according to the graded function call set to generate function call code. The invention can generate a code corresponding to a function call, For each new object that is not constructed, the functions that are called before the object are quickly found out, and the functions that take the object as parameters and the function call stack are combined to form a plurality of functions, and on this basis, a scheme with high possibility of code generation is recommended, which effectively solves the problem of complex execution sequence in the development of Android application micro-services.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Device and method for a combined interferometry and image-based determination of geometry, especially for use in micro system engineering
ActiveUS7545505B2Simple and rapid changeoverGood correlationMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansDetector arrayOptoelectronics
The apparatus according to the invention comprises an object lens which can operate in at least two different measuring modes. In a first, interference mode a workpiece is measured by means of interference optometry. In a second, imaging measuring mode an optical image is produced, for example, on a camera-like detector array and may be applied to an image processing routine. Switching between the two measuring modes is performed by the type of illumination of the object lens and an element which is disposed preferably in the reference beam path of an interferometer and which activates or deactivates the reference beam path dependent on the spectral composition of the utilized light. In this manner a simple and rapid changeover between the two measuring modes is provided, without the need for replacing or even for moving the object lens. Apart from the rapidity of changeover, a good correlation is achieved between the measuring data which are yielded by the interferometry and by the image processing and which are obtained in one and the same reference coordinate system.
Owner:CARL MAHR HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com