Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Leader election" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
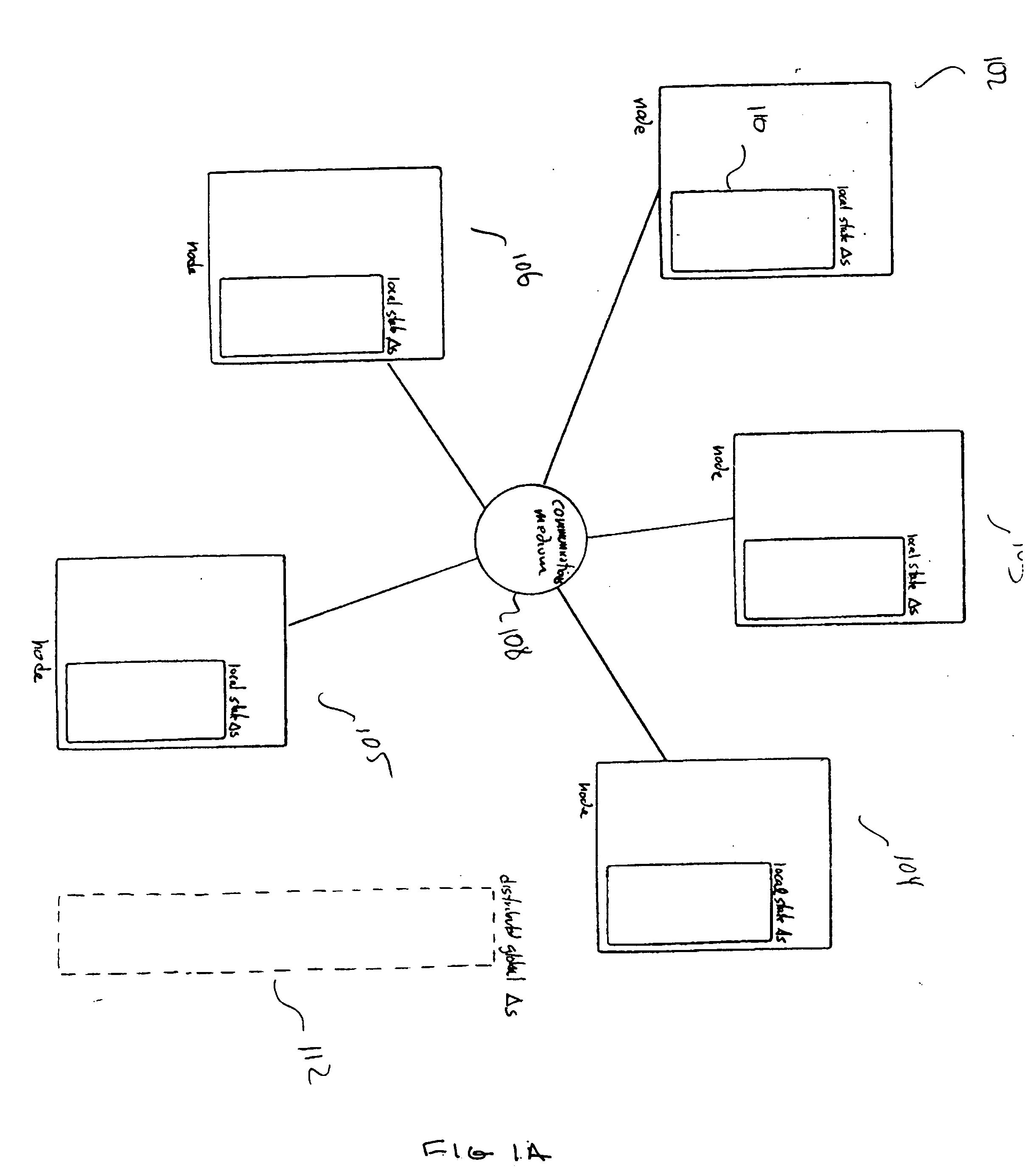
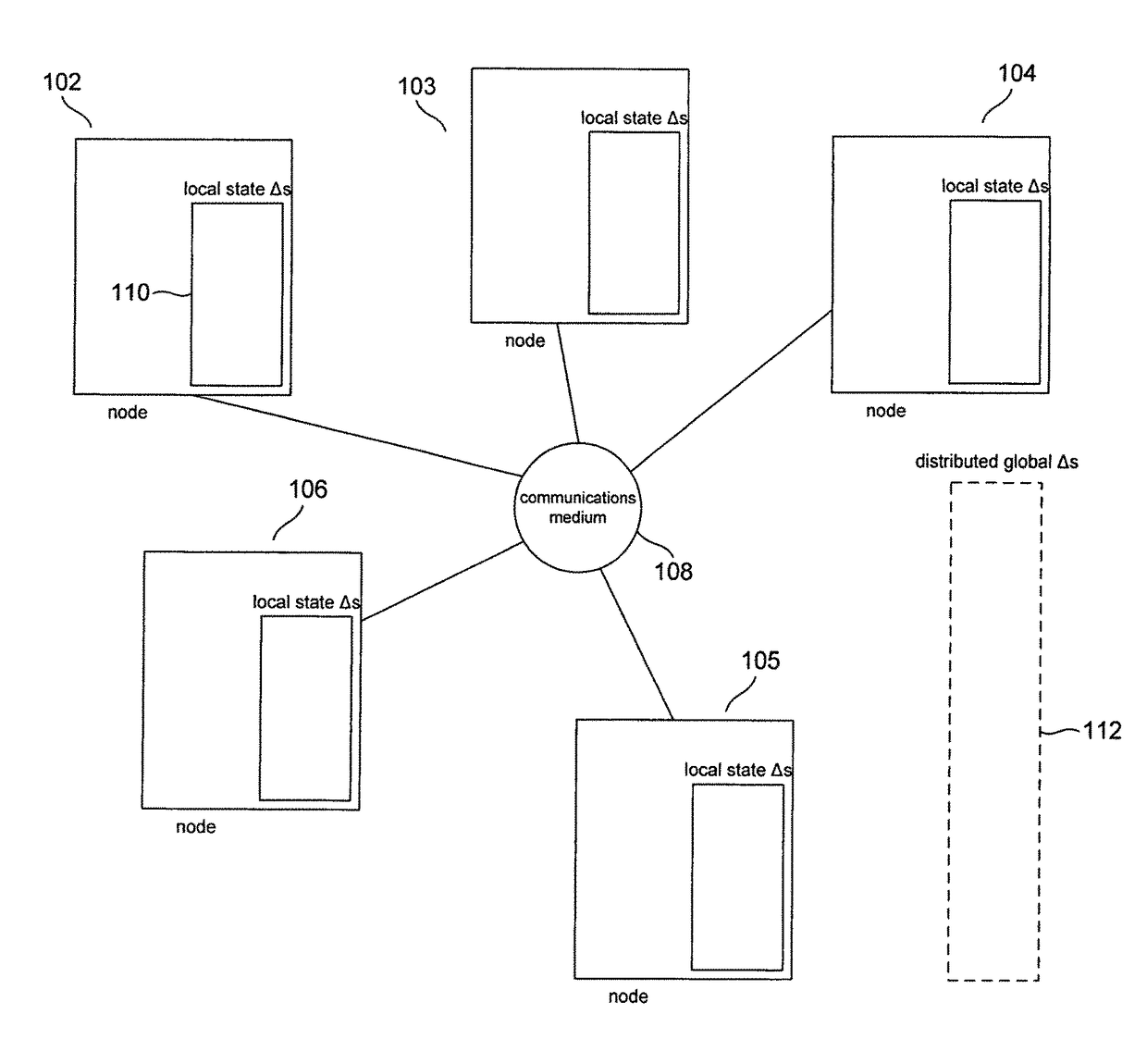
In distributed computing, leader election is the process of designating a single process as the organizer of some task distributed among several computers (nodes). Before the task is begun, all network nodes are either unaware which node will serve as the "leader" (or coordinator) of the task, or unable to communicate with the current coordinator. After a leader election algorithm has been run, however, each node throughout the network recognizes a particular, unique node as the task leader.
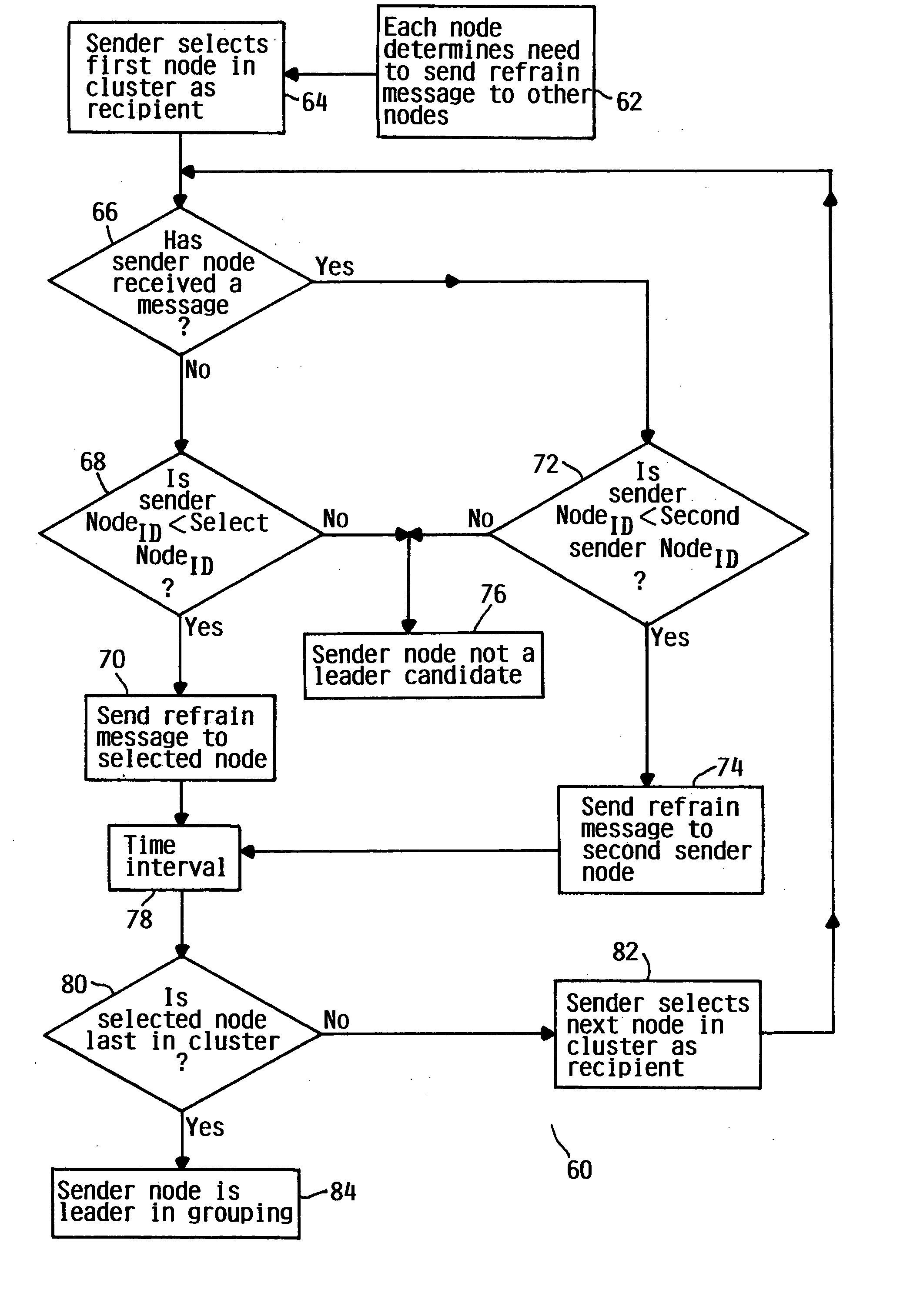
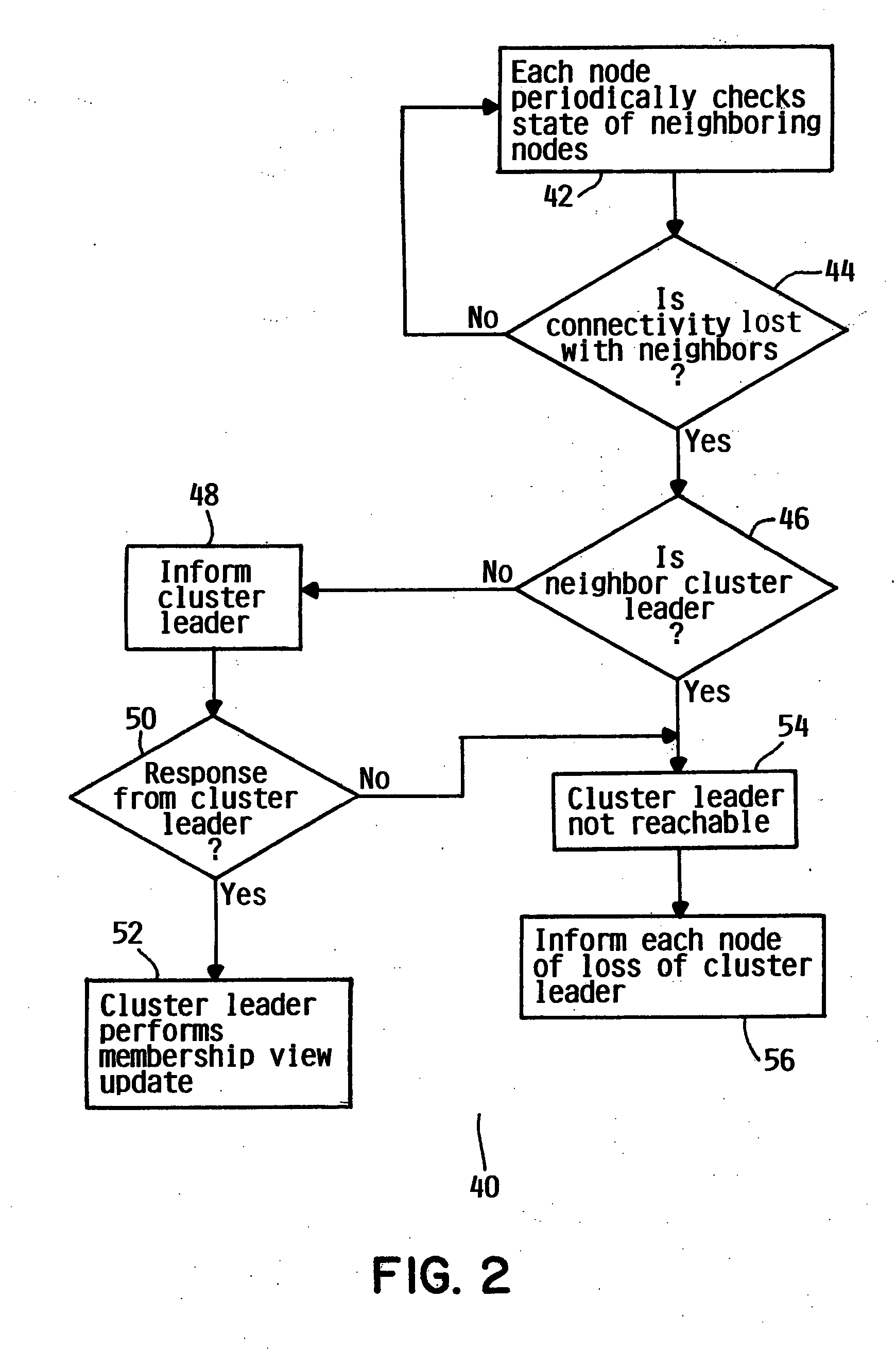
Reliable leader election in storage area network
InactiveUS20050132154A1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsLeader electionStorage area network
A method and system for election of a cluster leader in a storage area network is provided Each node in a grouping of storage area network nodes communicates with each of the nodes on a periodic basis to determine if any of the nodes have failed (42). In the event of a cluster fault, each node may request a position of cluster leader. A pruning protocol (60) is invoked to ensure efficient convergence of a single cluster leader candidate to favor a majority grouping leader candidate to become the new cluster leader. In the event the leader candidate from the majority grouping has failed to become the new cluster leader, a minority grouping leader candidate can become the cluster leader. Following the pruning protocol, a voting protocol (100) is invoked followed by lock of the quorum disk (138) by the elected cluster leader candidate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Distributed-leader-election service for a distributed computer system
ActiveUS20080071853A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionLeader electionComputerized system
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for leadership allocation in a distributed computer system. In certain embodiments of the present invention, a leader-election-service process runs within each node of a distributed computer system, together cooperatively providing a distributed-leader-election service. The distributed-leader-election service employs a distributed consensus service to manage distributed state information related to roles and leadership allocation within a distributed computer system. Client processes within each node interface with the leader-election-service process of the node in order to assume leadership of particular roles within the distributed computer system. Leadership-allocation management is thus centralized, within each node. In alternative embodiments, the distributed-leader-election service may be implemented as a collection of library routines that run in the context of client processes.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
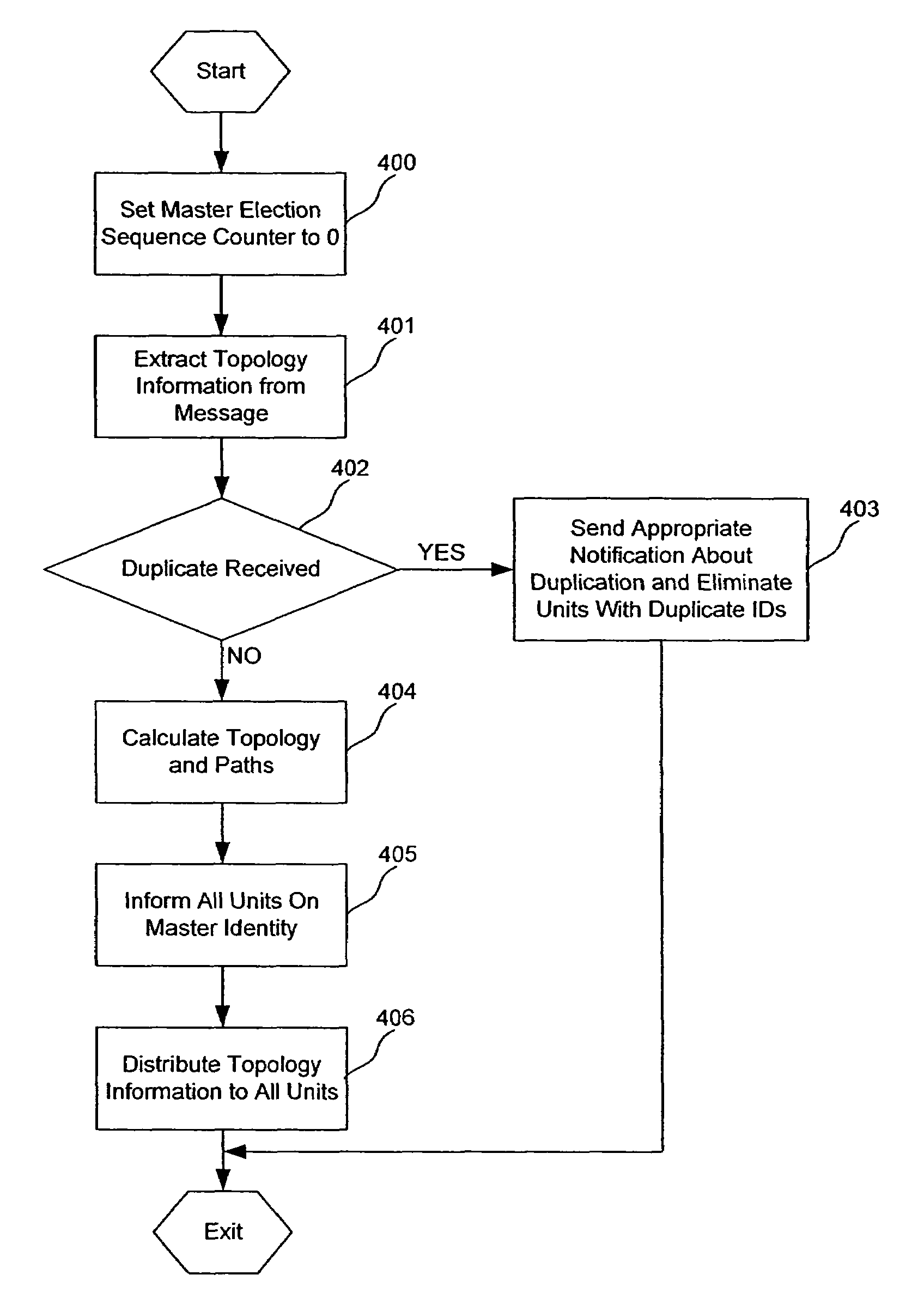
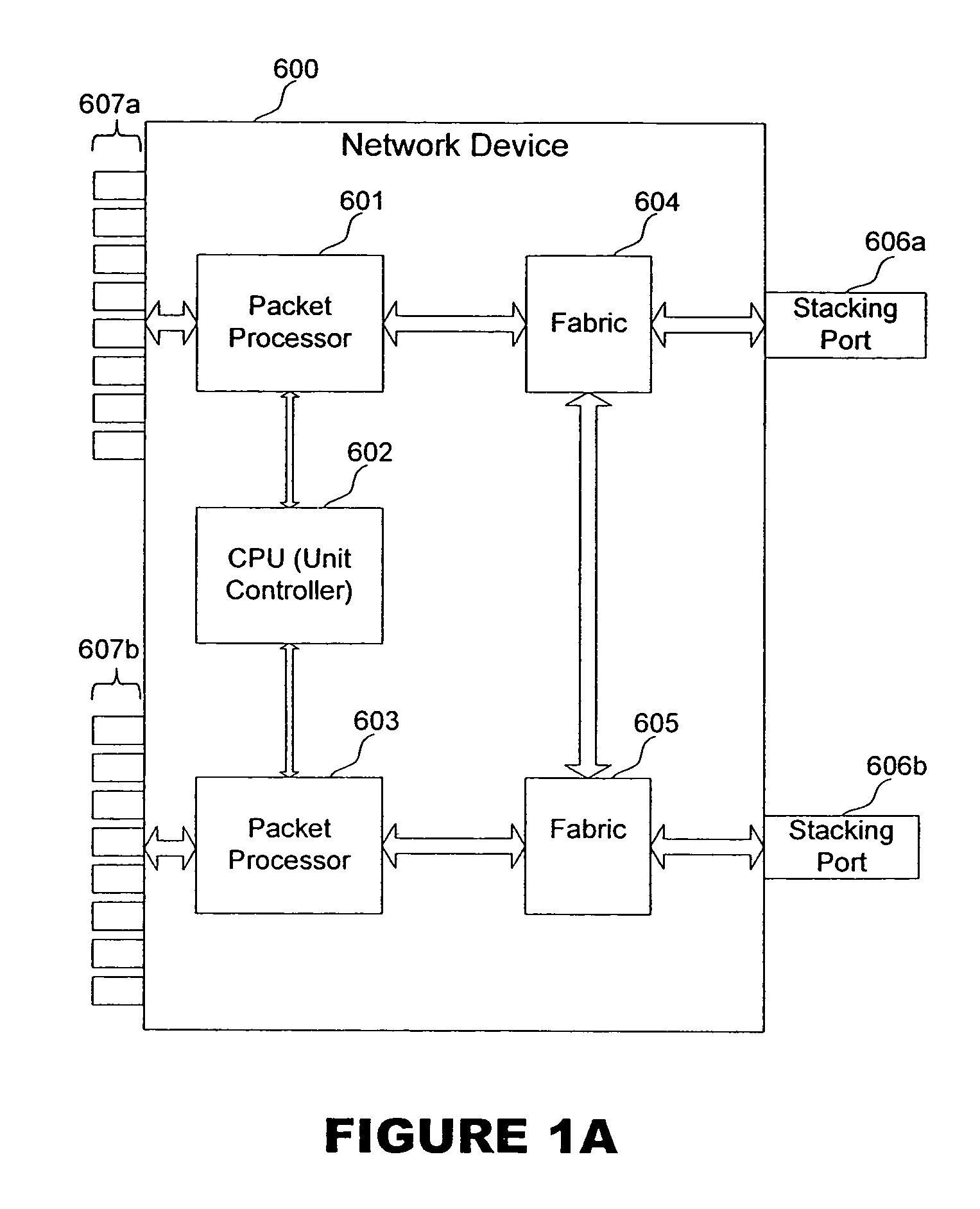
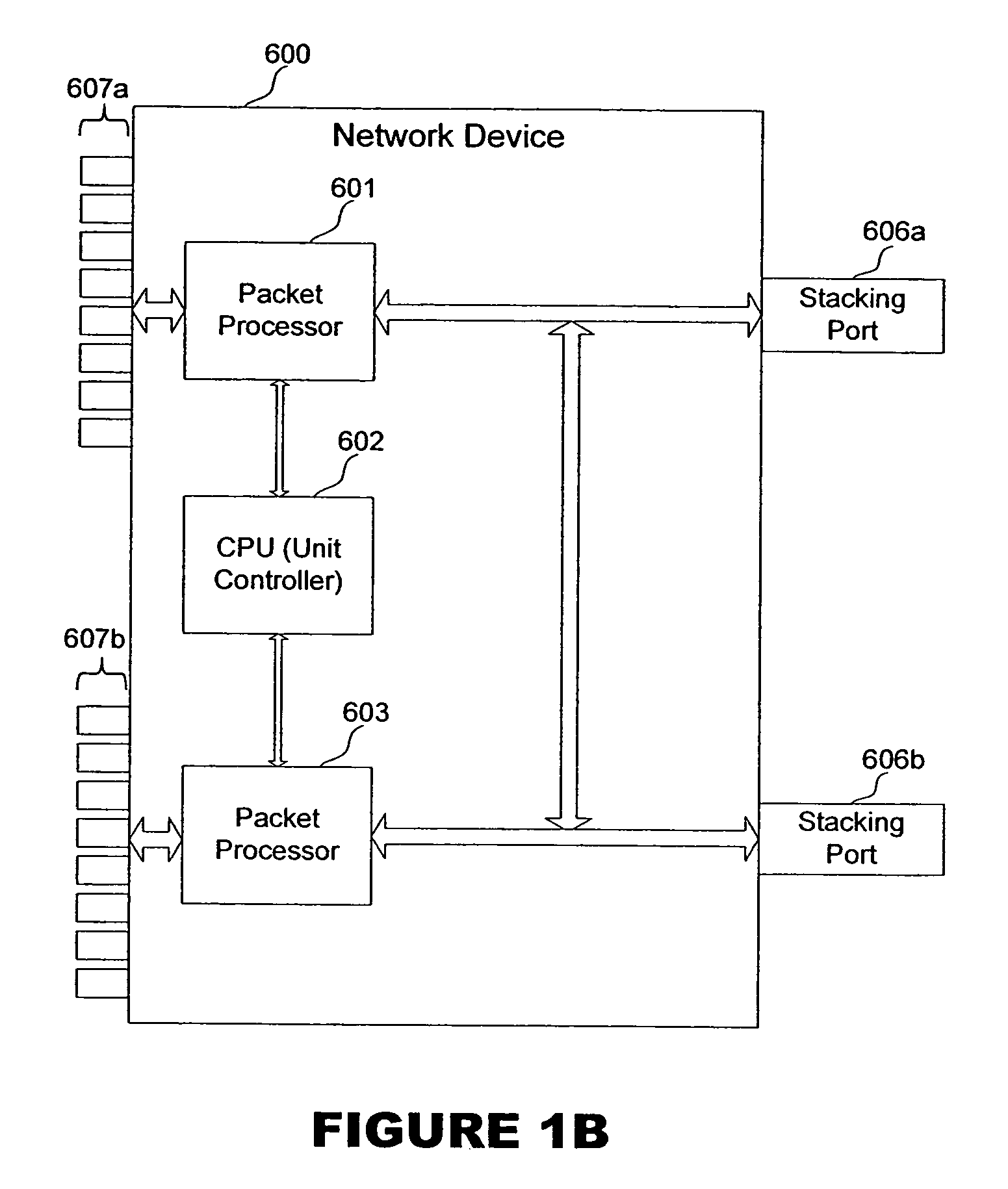
Apparatus and method for master election and topology discovery in an Ethernet network
An apparatus, method and computer memory for electing a master unit from multiple candidate units on a ring or chain topology network is provided. Master proposal data packets are transmitted onto a plurality of stacking links. At least one message data packet is received on the one candidate unit. A candidate unit is elected as the master unit if it receives message data packets corresponding to the transmitted master proposal data packets.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
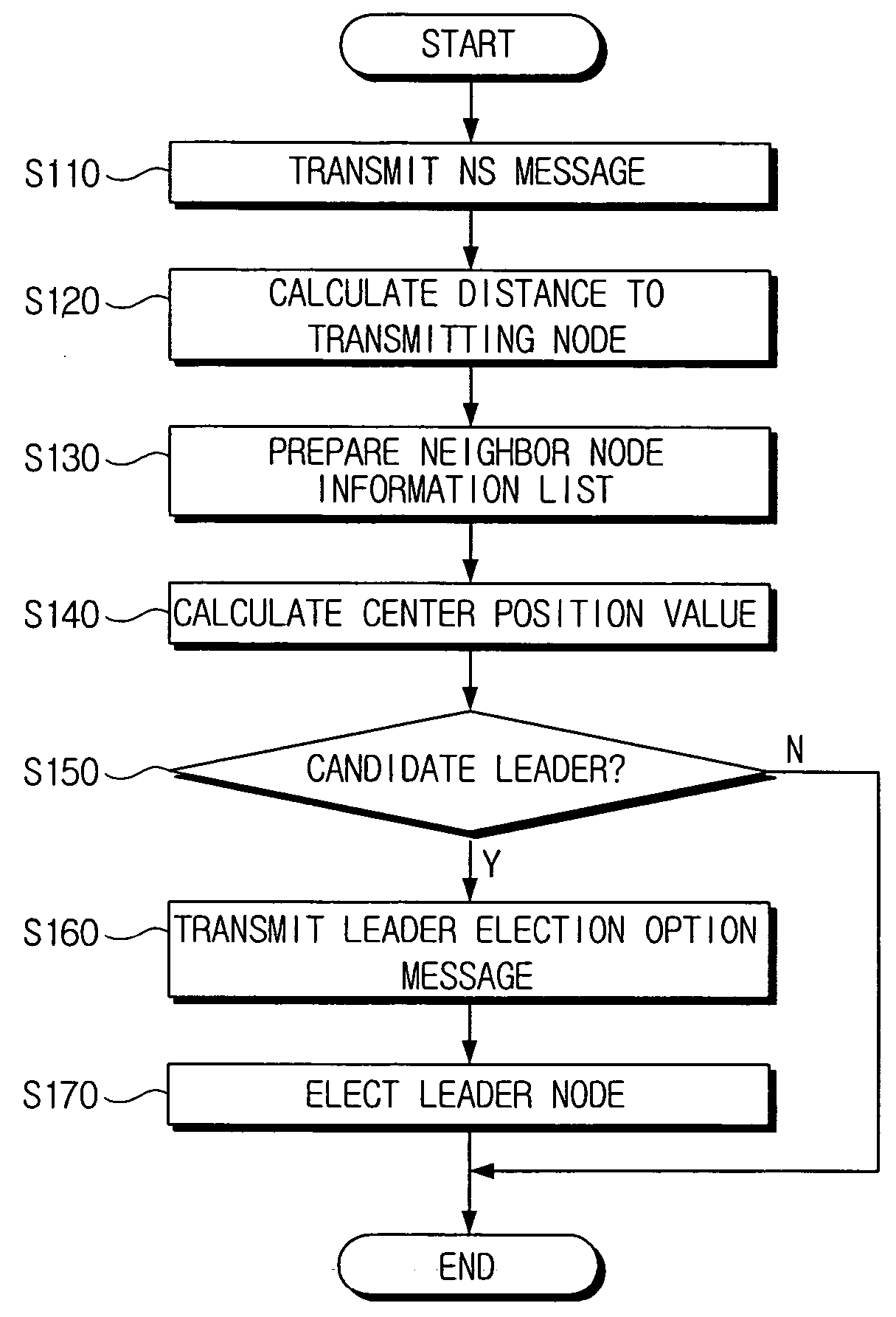
Method of electing a leader in an ad-hoc network
ActiveUS20050094574A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationLeader electionSelf-organizing network
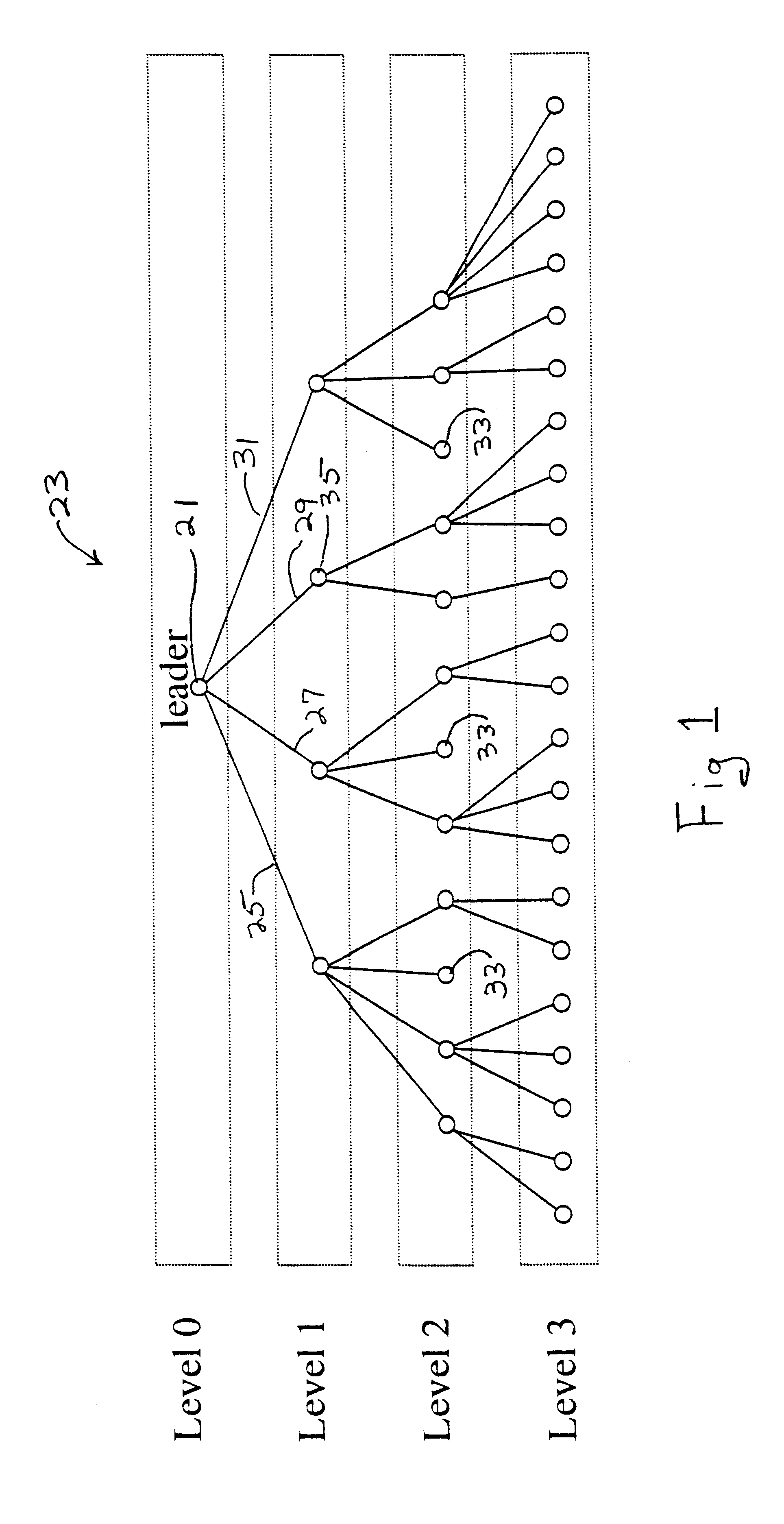
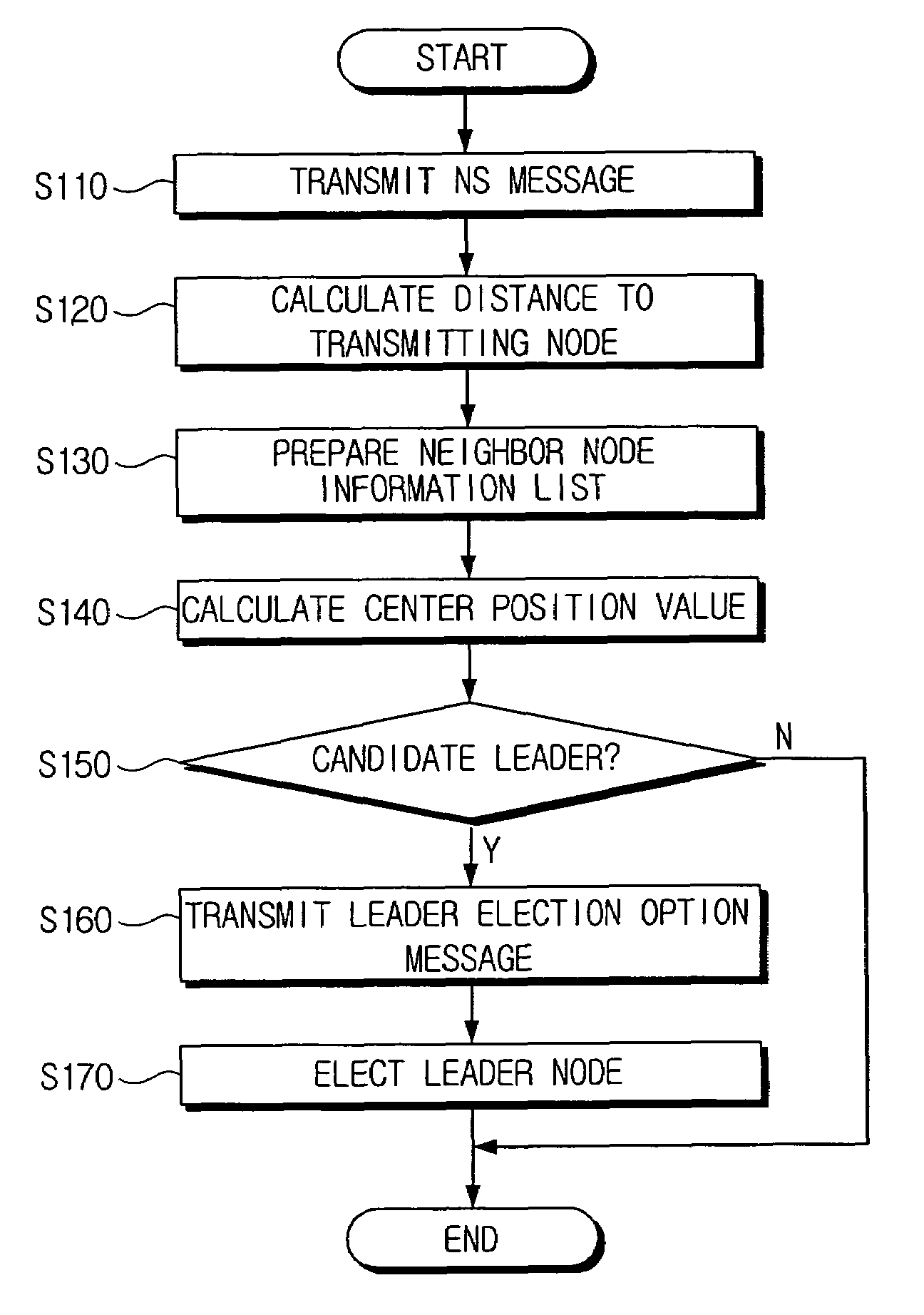
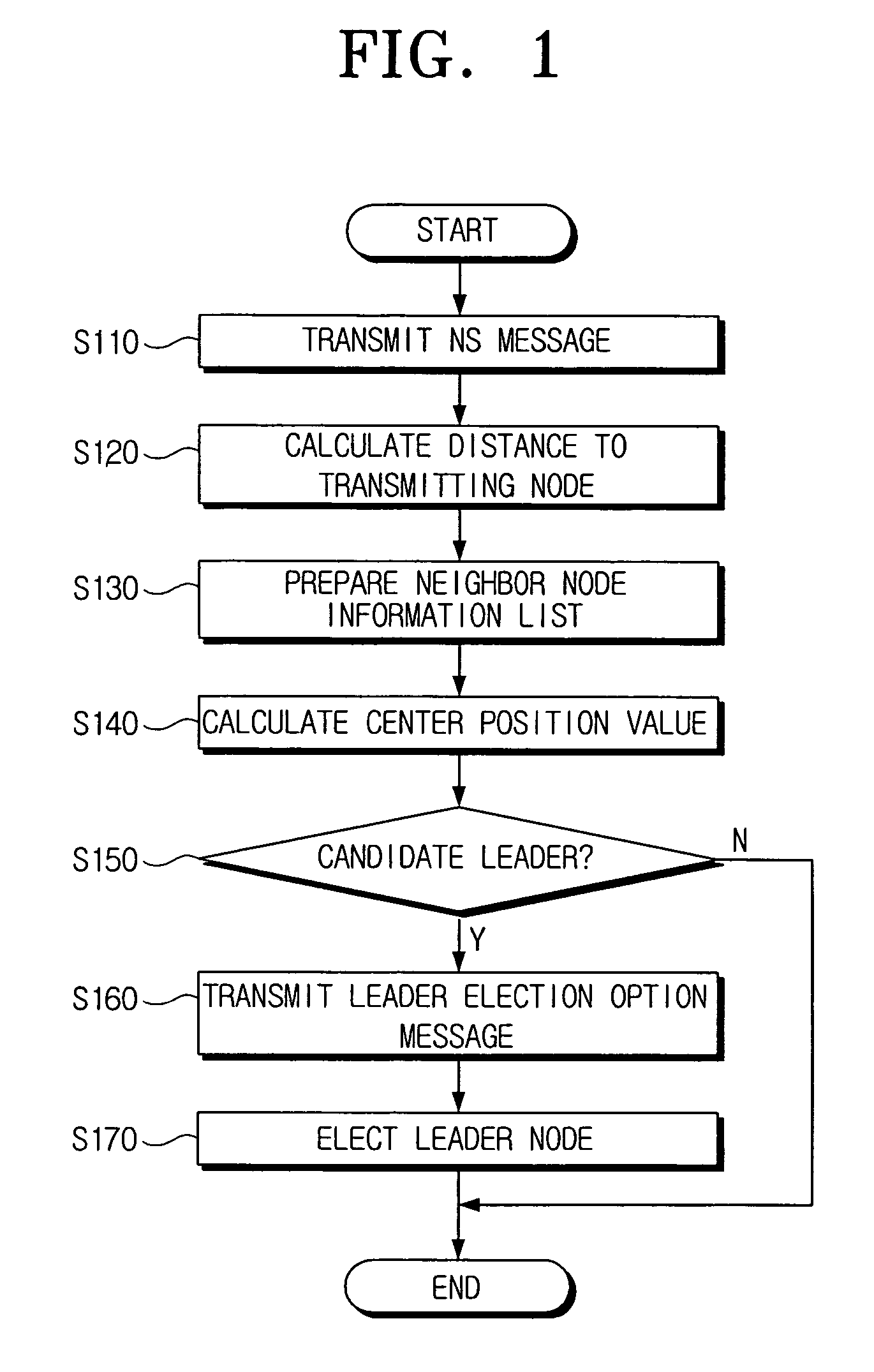
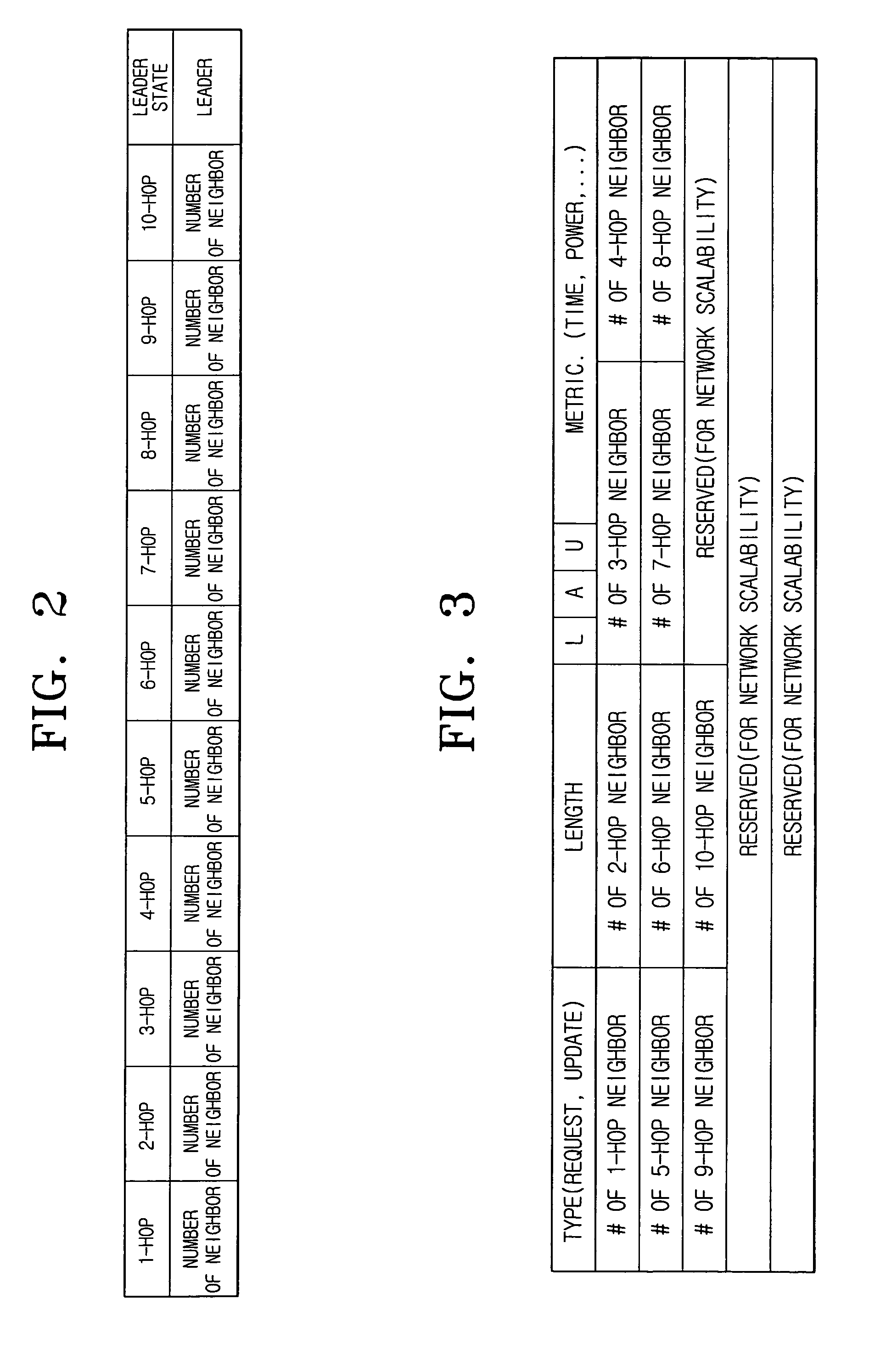
A method of electing a leader node in an ad-hoc network including a plurality of nodes in the ad-hoc network transmitting node solicitation (NS) messages and calculating distances between the plurality of nodes using information included in the NS messages, determining whether the plurality of nodes are candidate leaders by calculating center position values based on the distances calculated by each of the nodes, and electing the leader node based on information included in leader election option messages transmitted by each candidate leader.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
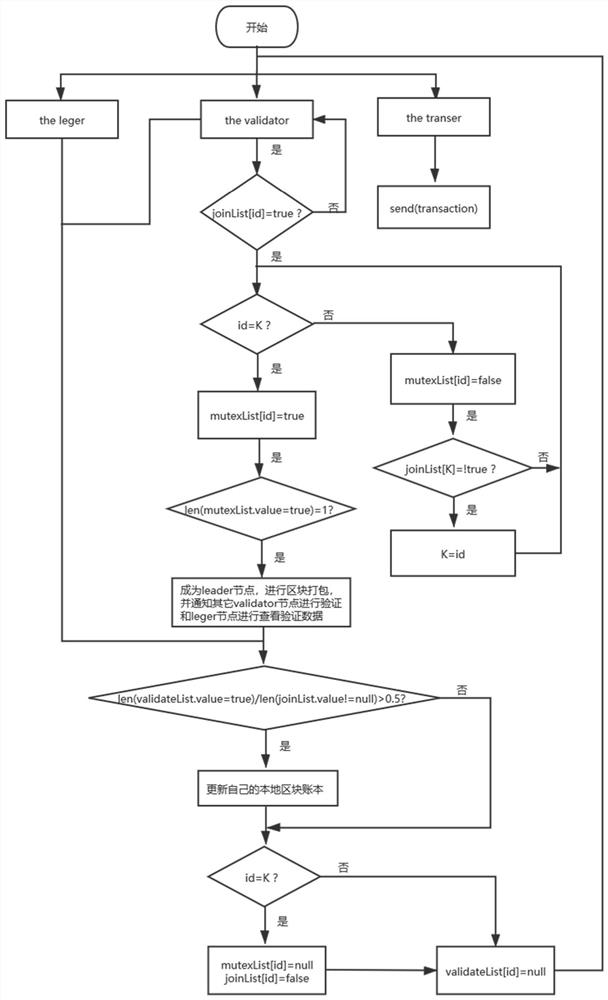
Reputation-based PBFT consensus system and method, and block chain data processing system
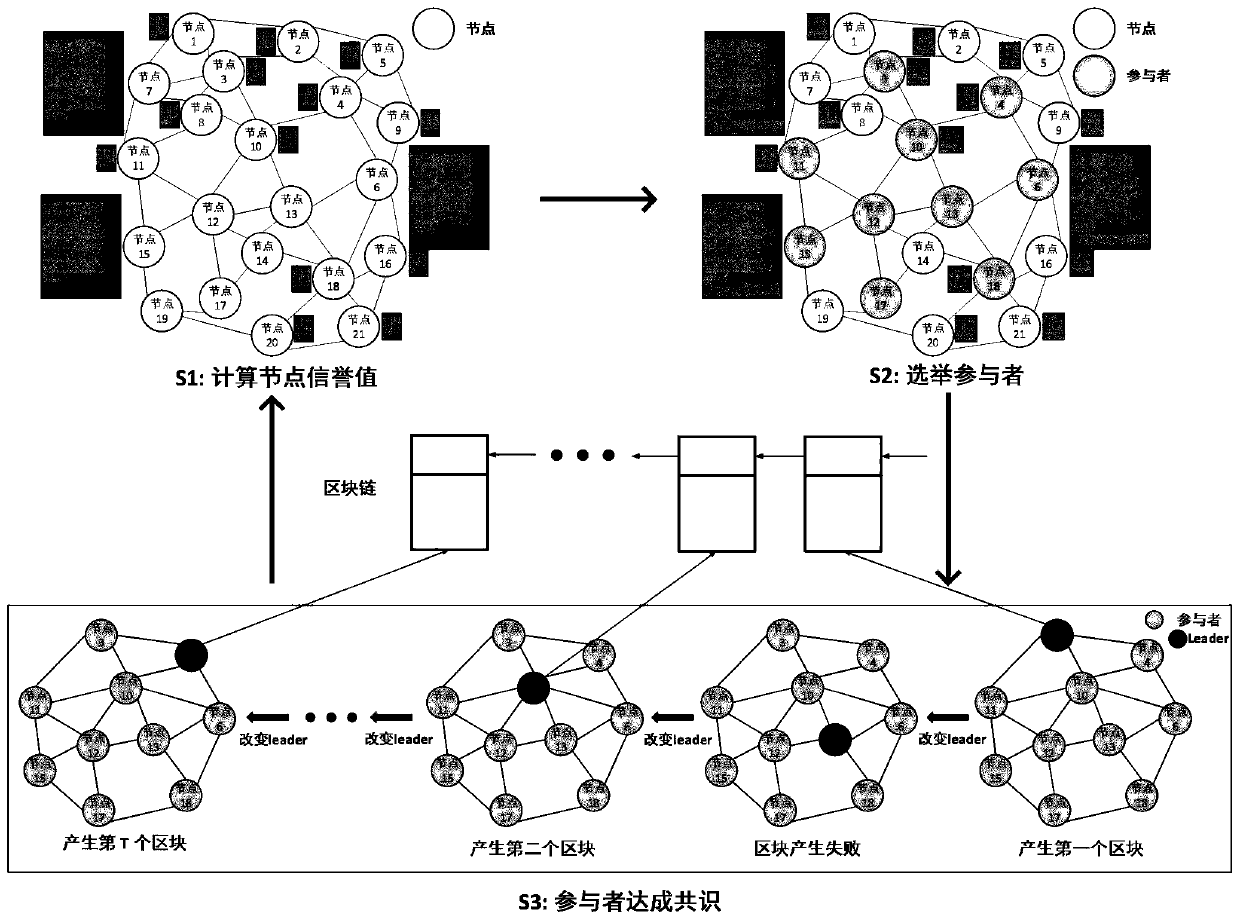
The invention belongs to the technical field of block chains, and discloses a reputation-based PBFT consensus system and method, and a block chain data processing system. The method comprises the steps of designing a lightweight reputation evaluation model, and calculating a mixed reputation value of the node based on node importance and service feedback; selecting a part of nodes of which the reputation values are higher than a threshold value as participants of a classical practical occupancy fault-tolerant consensus mechanism; and running a PBFT consensus mechanism in the participant, achieving a consensus based on a new leader election and transaction verification method, and broadcasting a consensus result. Due to the fact that the classical PBFT consensus mechanism is limited in expandability, consensus is not affected by the network scale. Due to the fact that a node reputation evaluation method and a participant election method are added, the method has higher safety compared with a classical PBFT. The calculated node reputation can guide the next transaction, so that the computing power for evaluating the node reputation is effective computing power.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for strong-leader election in a distributed computer system
InactiveUS20080071878A1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsLeader electionComputerized system
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for strong-leader election in a distributed computer system. In certain embodiments of the present invention, nodes employ a distributed consensus service, such as Paxos, to seek election of leader at or near the expiration of each of a set of successive lease periods. A current leader seeks re-election prior to expiration of the current lease, thus favoring continued re-election of the current leader until and unless the current leader fails or surrenders the leadership role.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
A method for implementing a network scalability block chain
InactiveCN109544334AImprove scalabilityImprove securityFinanceEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesLeader electionChain structure
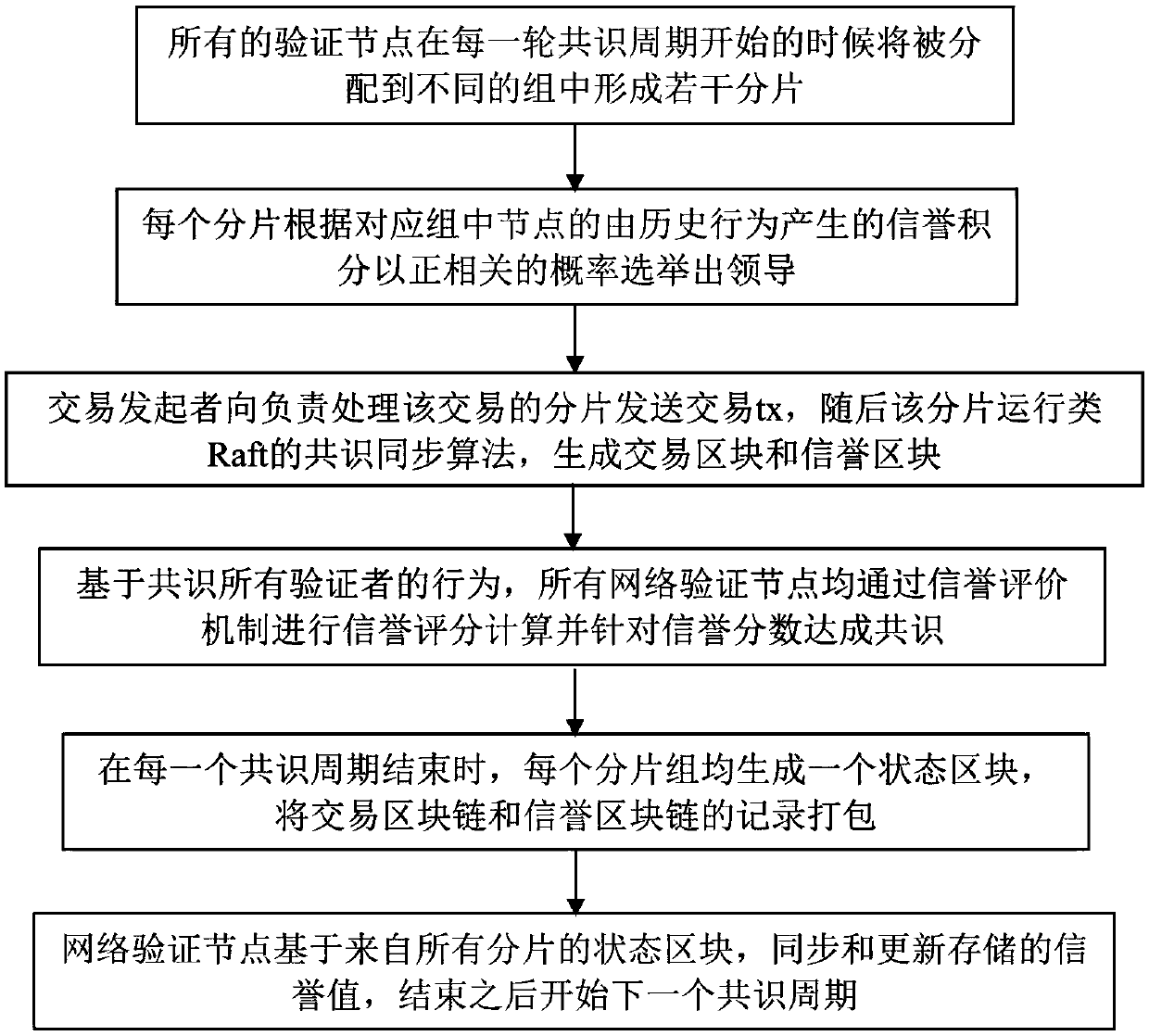
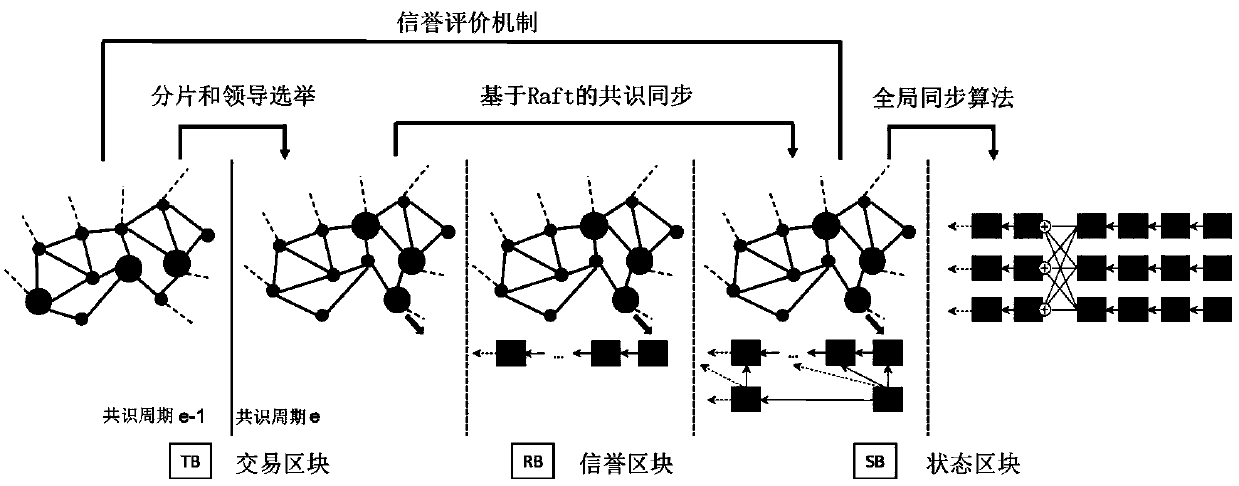
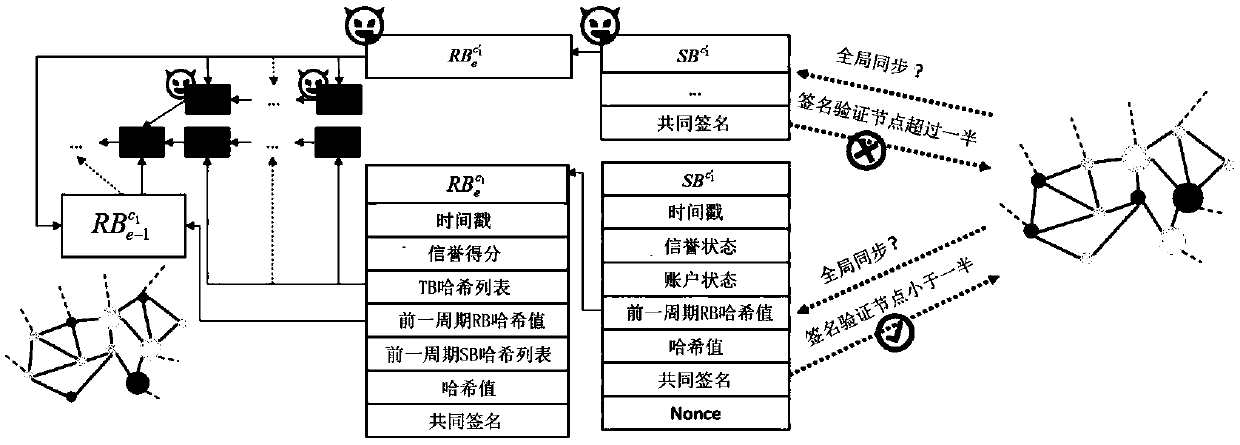
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for implementing a network scalability block chain, which comprises the following steps: slicing and leadership election, consensus synchronization based on slicing leadership, reputation evaluation mechanism and global synchronization algorithm. The embodiment of the invention proposes a parallel chain structure, which separates the transaction and the consensus into two chains, so as to improve the scalability of the block chain network. The consensus part is carried out in the reputation chain. The network of reputation chain pays attentionto the security and supports the high-speed transaction of the network of transaction chain with proper speed. Based on the advantages of the reputation evaluation mechanism, the embodiment of the invention proposes a network slicing method based on the reputation evaluation mechanism. After the network slicing, the honest and excellent performance node has a greater probability to become the leader of the slicing, so as to realize the high throughput of the network without reducing the safety of the block chain network.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUSHTREE TECH CO LTD
Technique for establishing a virtual backbone in an ad hoc wireless network
InactiveUS6839541B2Efficient processReduce the burden onNear-field transmissionNetwork topologiesLeader electionWireless mesh network
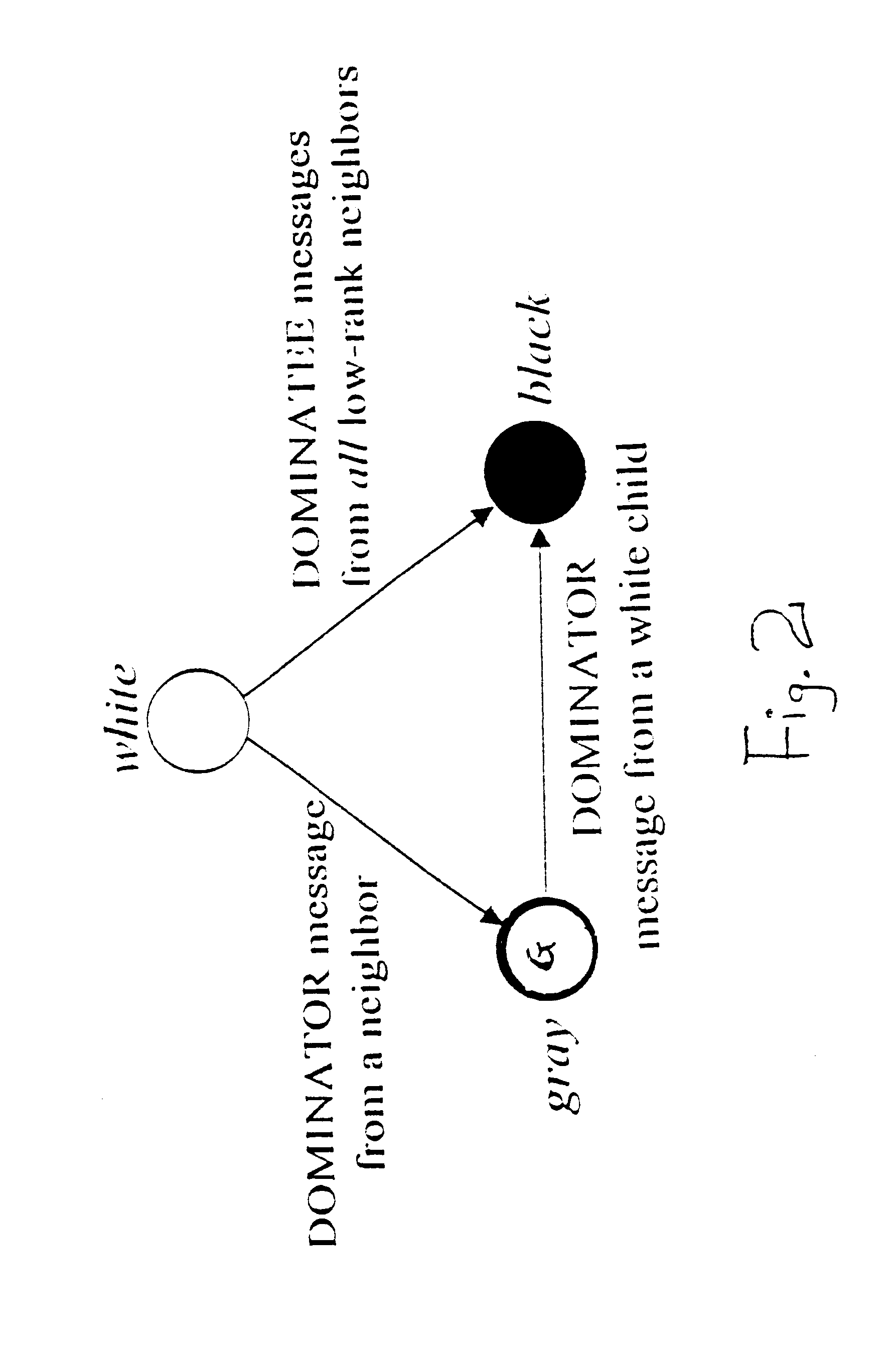
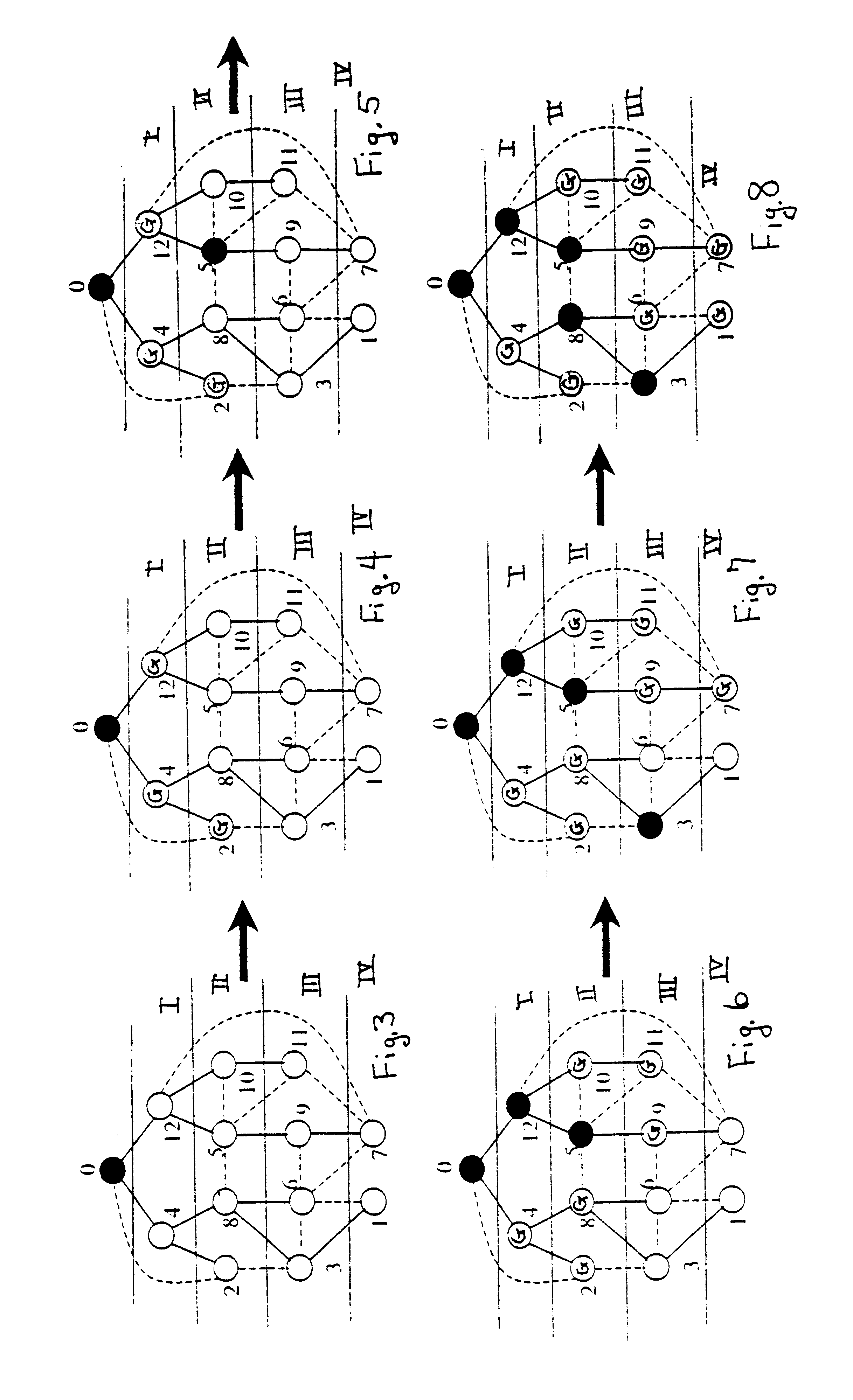
An algorithm on a computer readable medium for efficiently creating a message efficient virtual backbone in a wireless ad hoc network utilizes three phases to establish an efficient network among the independent transceivers of a wireless ad hoc network. Independent transceivers within the transmission range of each other are neighbors. A leader election and tree construction phase constructs a tree of neighboring transceivers with one transceiver being designated the root and with each transceiver establishing and recording its location in the tree structure and the identifiers of its neighbors; and reporting when the tree is established. A level calculation phase determines the level of each transceiver away from the root transceiver, with each transceiver recording the level of its neighbors. Precedence for each transceiver is established with consideration of each transceiver's tree level and identifier, with tree level being paramount in deciding precedence; and reporting when the levels of the tree are established. A backbone construction phase establishes all transceivers as a dominator or a dominatee, with the dominators forming the network backbone and the dominatees all being neighbors to a dominator. Within the network each transceiver only needs to know the information of its neighboring transceivers.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
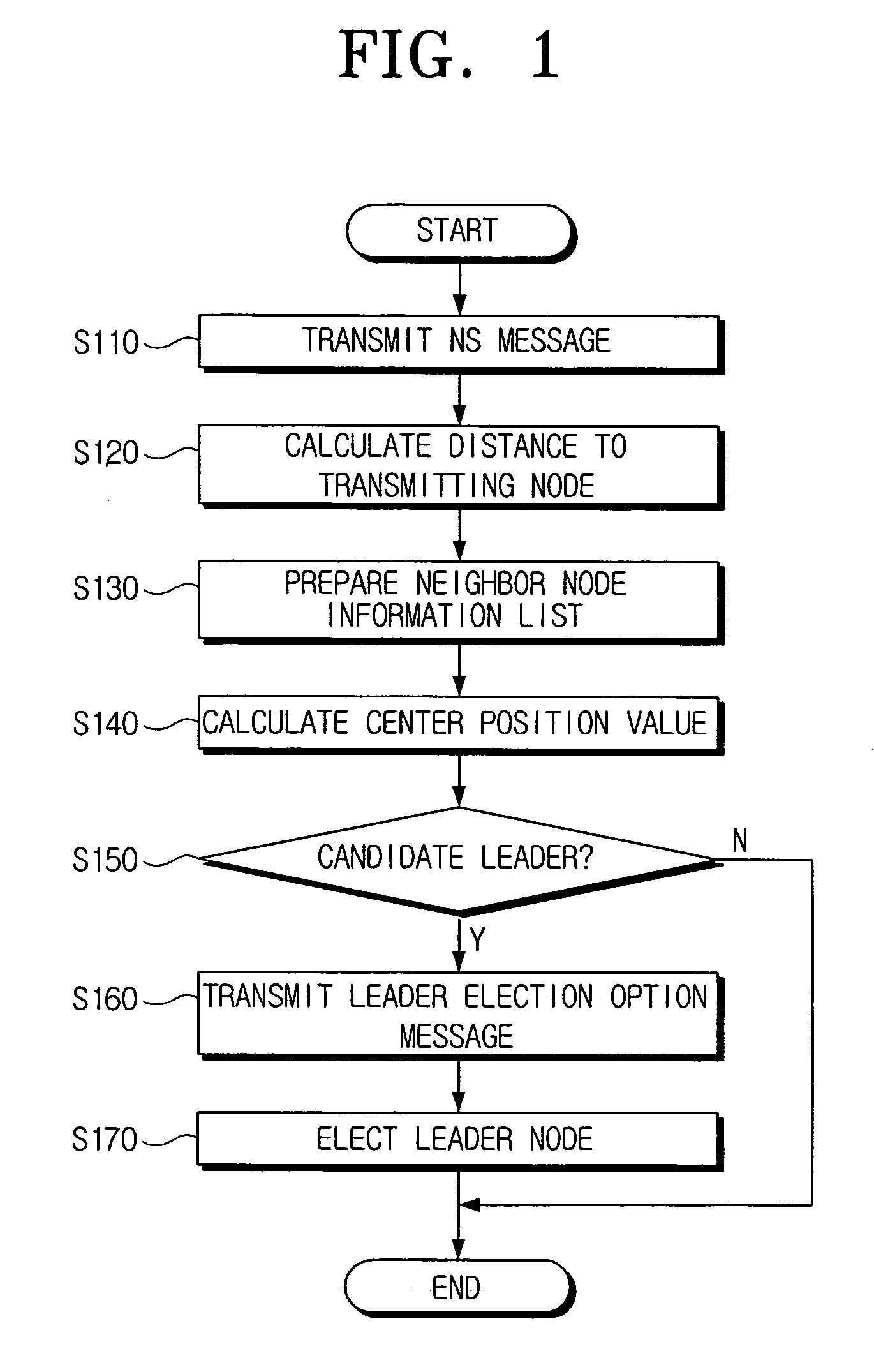
Method of electing a leader in an ad-hoc network
ActiveUS7532585B2Network topologiesData switching by path configurationLeader electionSelf-organizing network
A method of electing a leader node in an ad-hoc network including a plurality of nodes in the ad-hoc network transmitting node solicitation (NS) messages and calculating distances between the plurality of nodes using information included in the NS messages, determining whether the plurality of nodes are candidate leaders by calculating center position values based on the distances calculated by each of the nodes, and electing the leader node based on information included in leader election option messages transmitted by each candidate leader.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Egregious error mitigation system
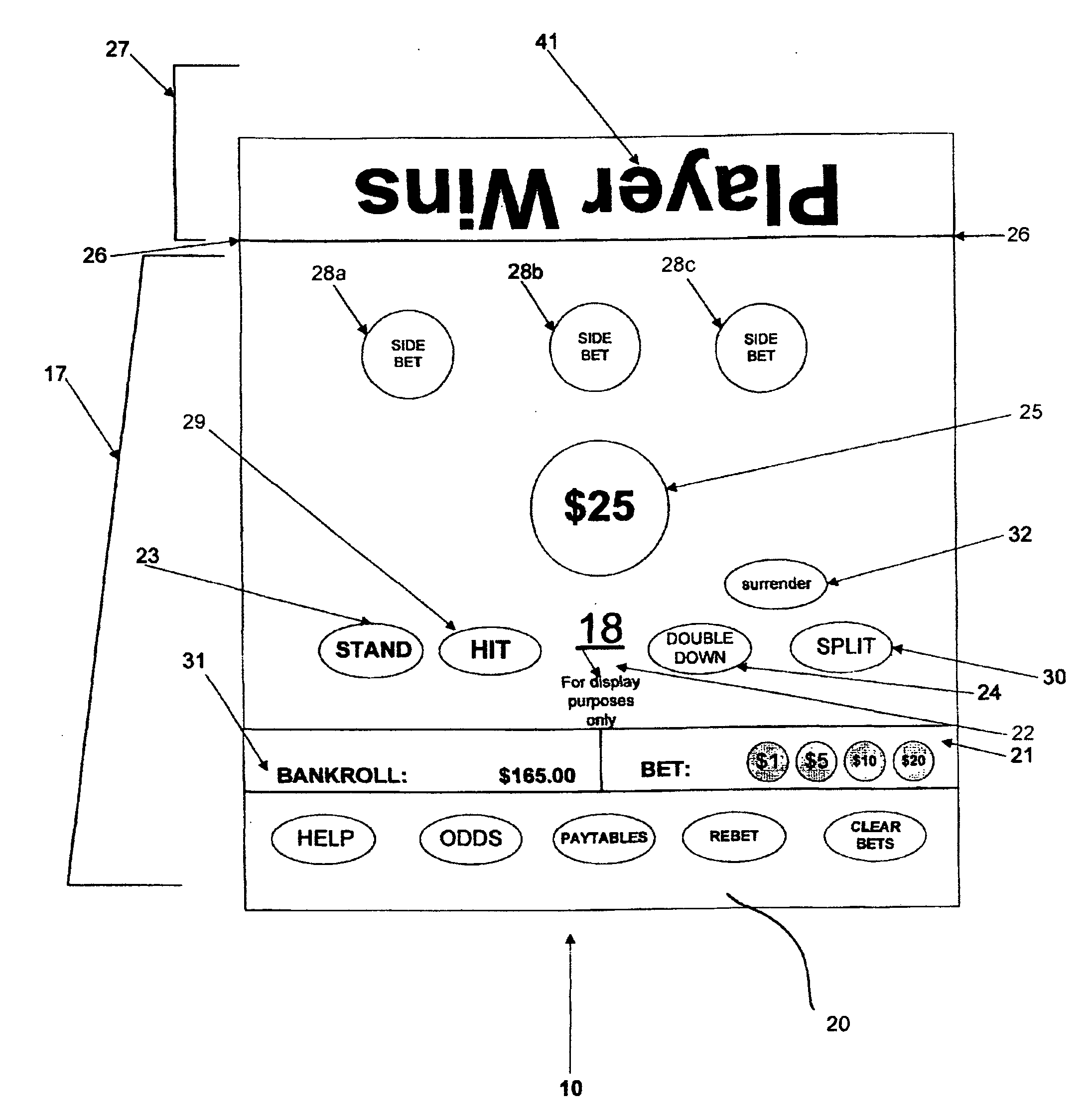
ActiveUS20100113120A1Card gamesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingLeader electionDisplay device
A playing card gaming system is disclosed that provides the player with an opportunity to withdraw a game play decision that is less advantageous to a player than at least one other play decision. The system includes a player interface that displays a prompt when a less advantageous decision is made. The display may include an area that provides the dealer with a visual indication that the player is being asked to confirm an election. A card delivery system with a playing card information reader provides card information to the system. A game processor determines if player elections are disadvantageous.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
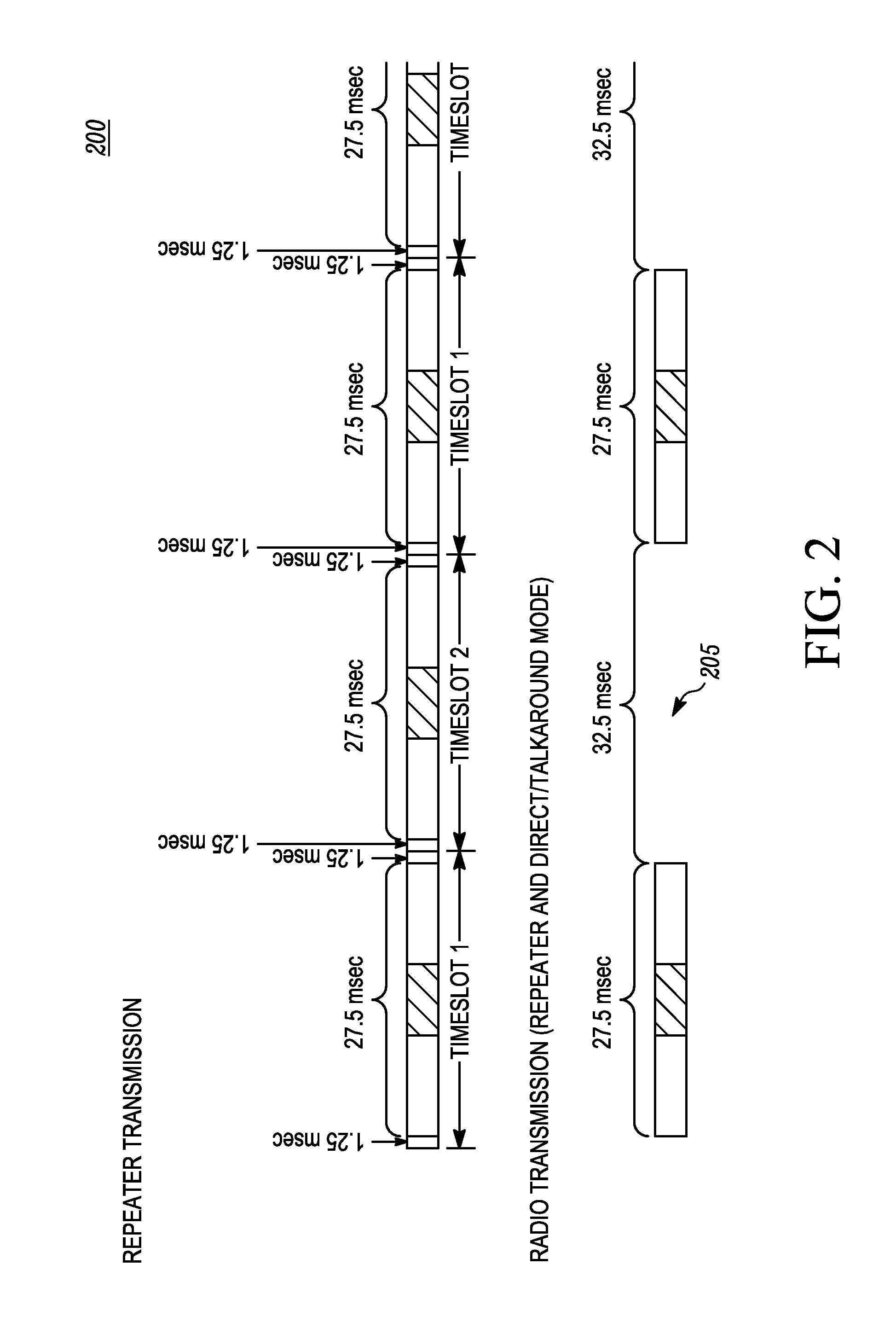
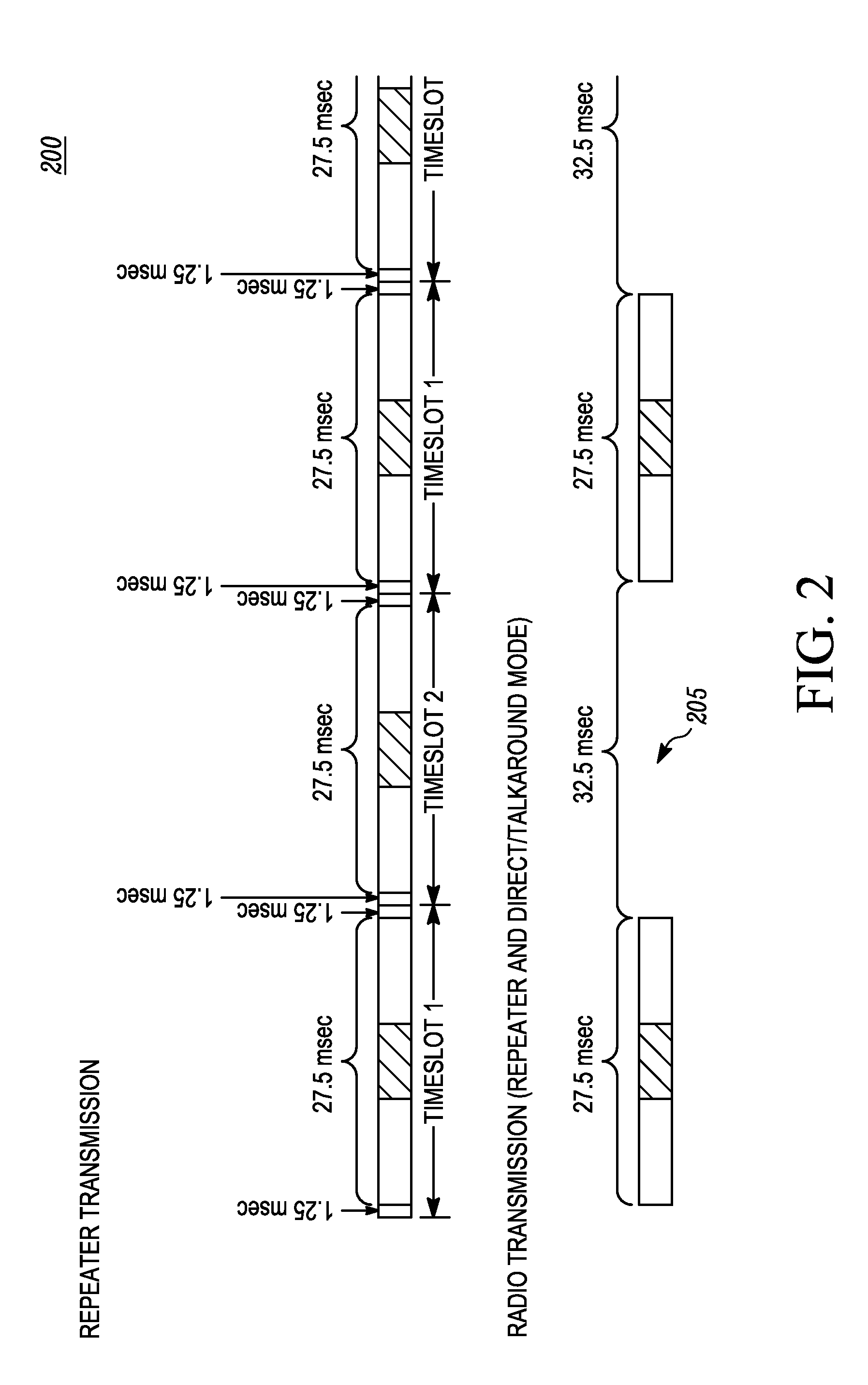
Method for synchronizing direct mode time division multiple access (TDMA) transmissions
ActiveUS20110255527A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexLeader electionTelecommunications
A method for synchronizing the direct mode TDMA transmission of a set of radios by following a selected radio as the leader includes: receiving, by a radio, a communication from an other radio; identifying, by the radio, a leader according to a leadership election rule using the received communication from the other radio and a current leader information; setting, by the radio, the identified leader as its leader; and synchronizing, by the radio, a time slot boundary with a time slot boundary defined by the leader.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
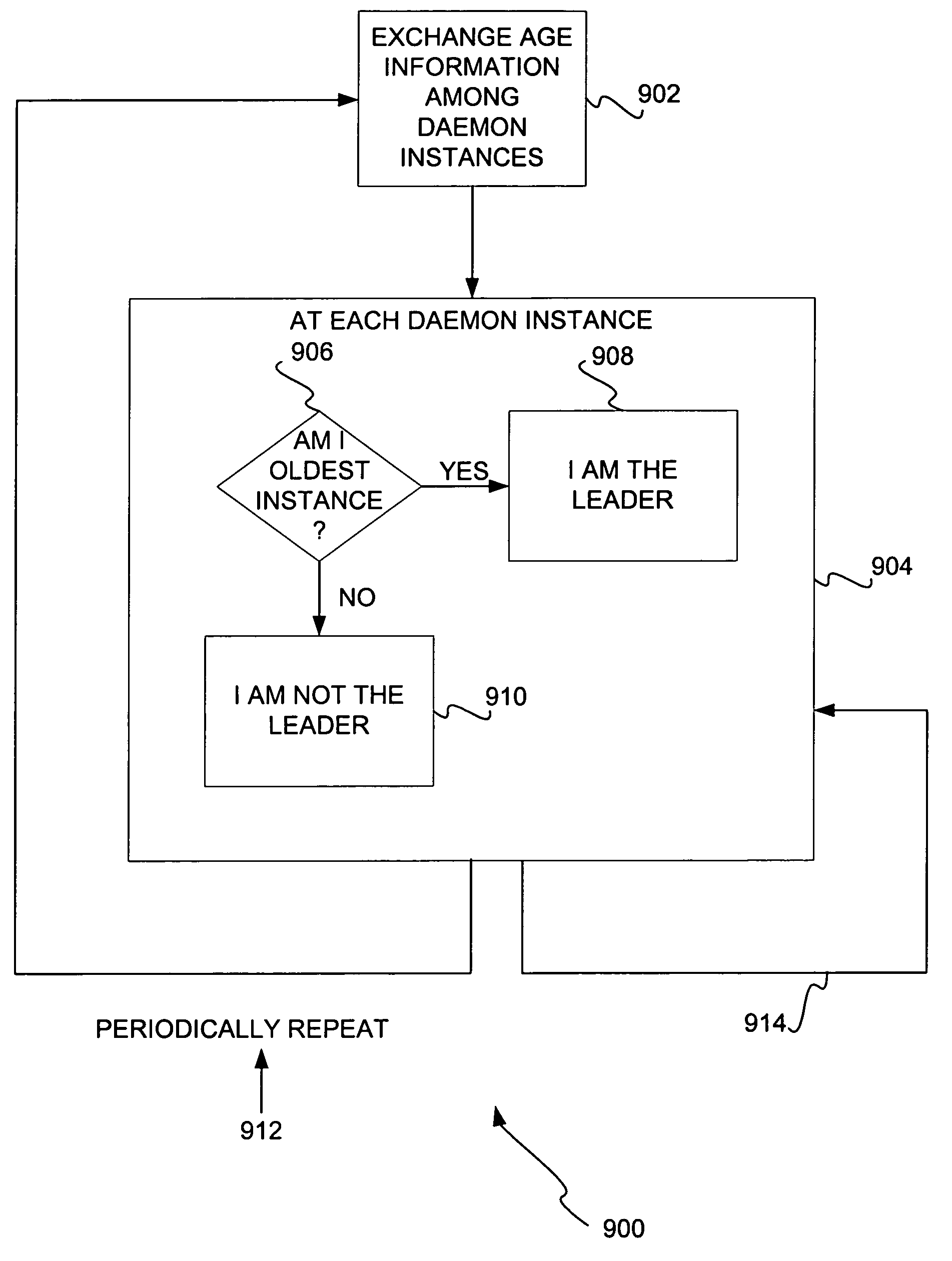
Weak leader election
InactiveUS7139790B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLeader electionOperations research
A weak leader election approach to determine which of a number of redundant nodes is the leader node is disclosed. The redundant nodes exchange information particular to them, such as age information. Based on the information received from the other nodes, each node determines whether it is the leader. Where the information is age information, a criteria that can be used to make this determination is that the oldest node is the leader. Each redundant node knows only whether it is the leader node. Redundant nodes that are not the leader do not know which node is the leader node.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
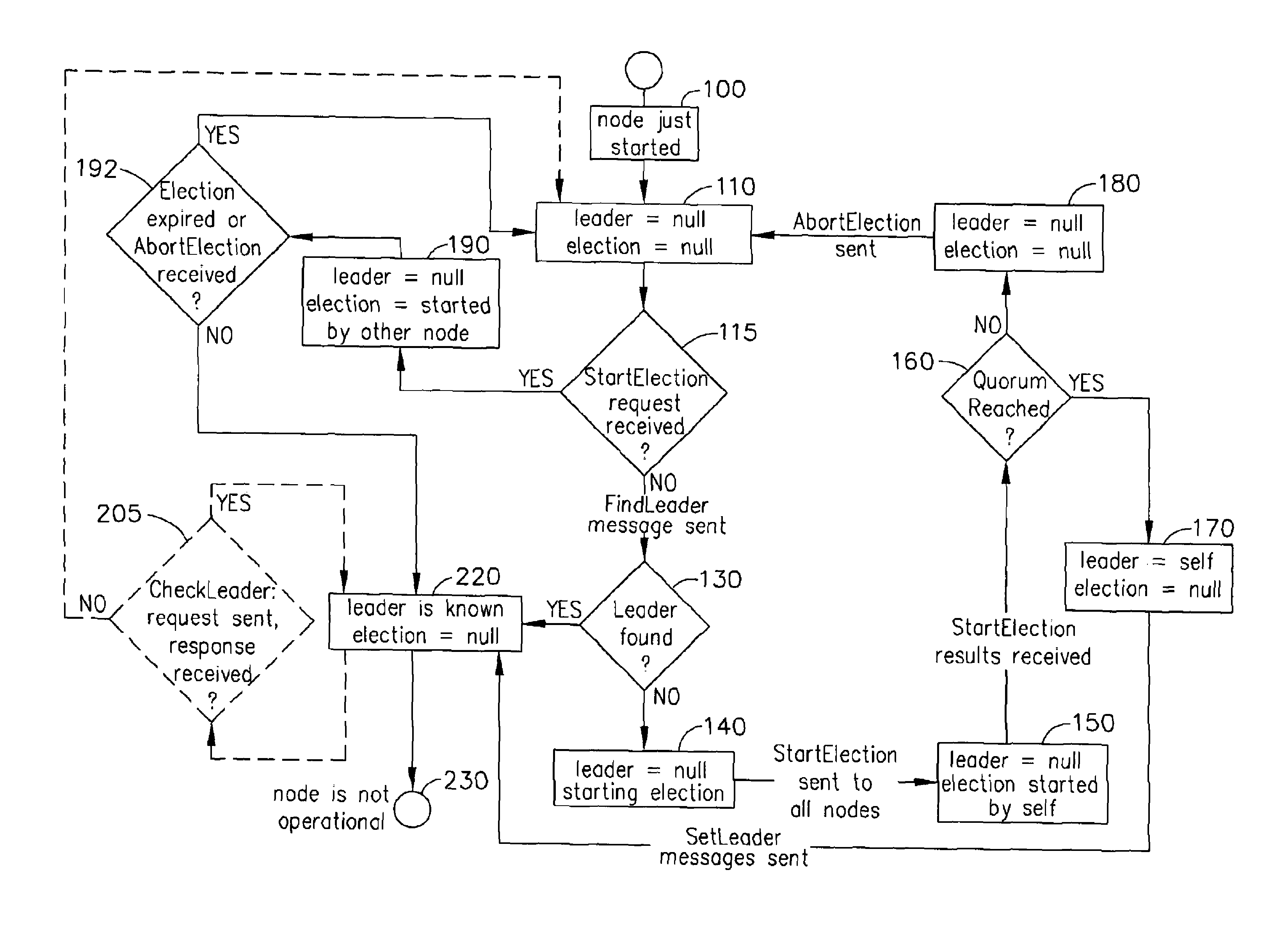
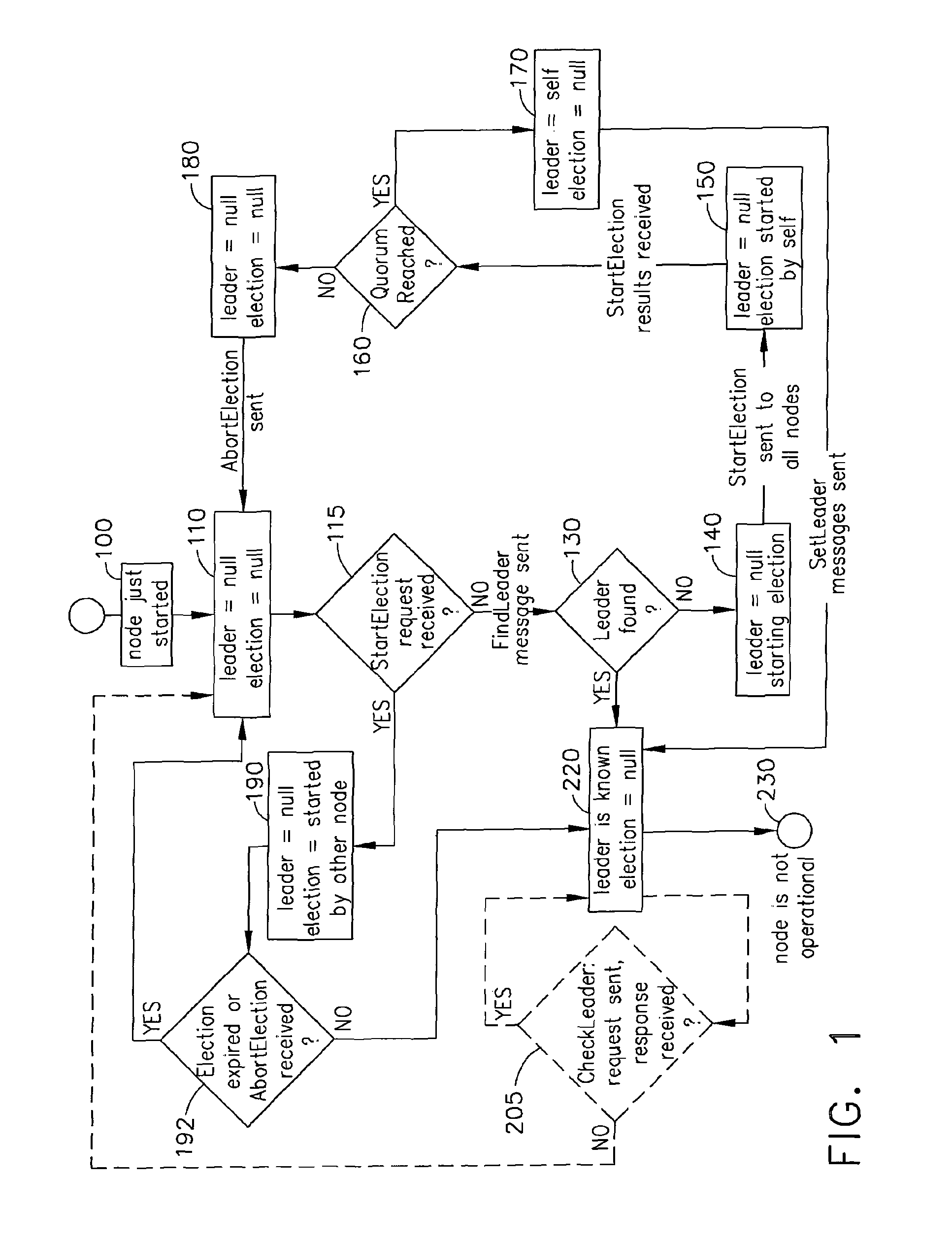
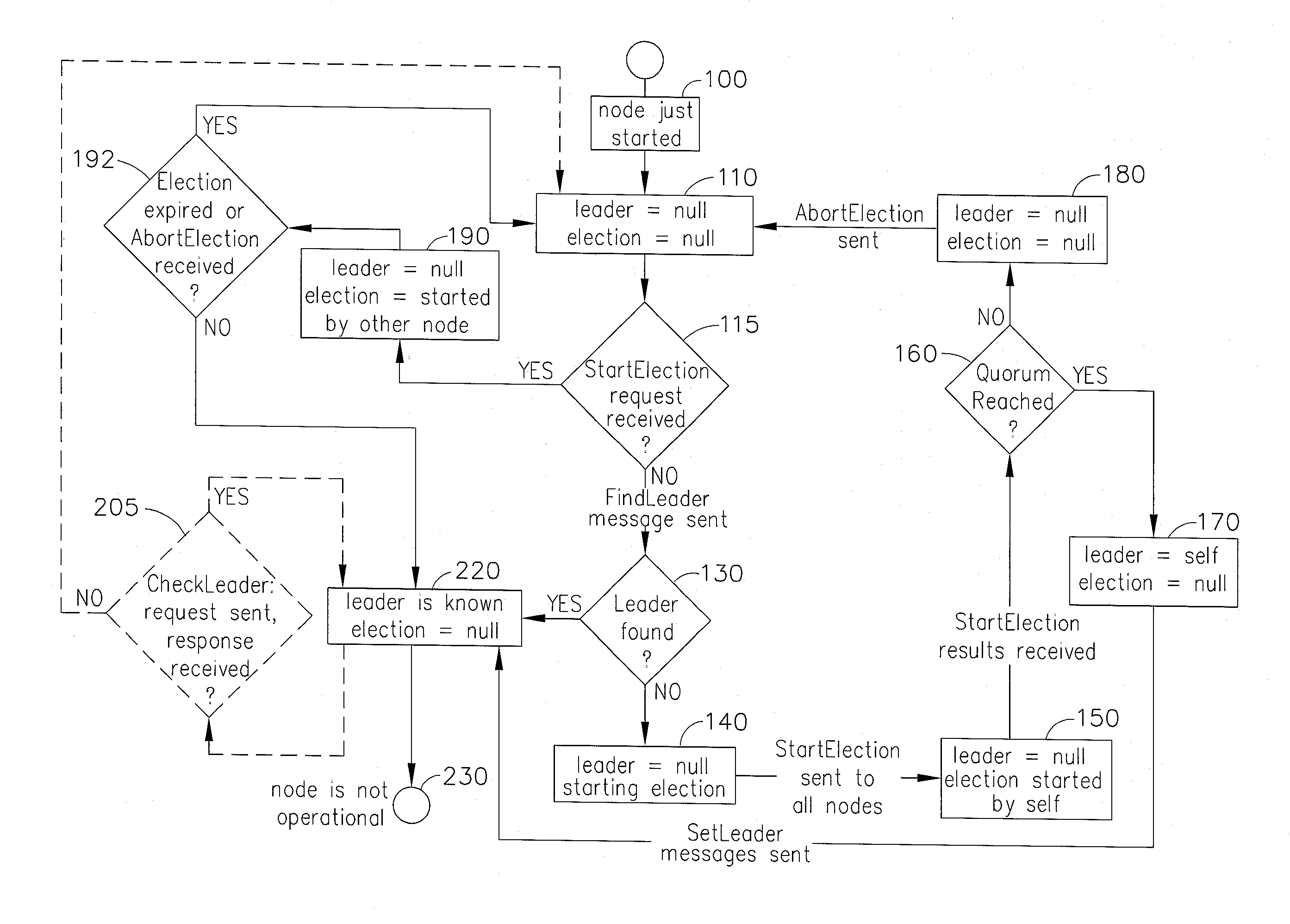
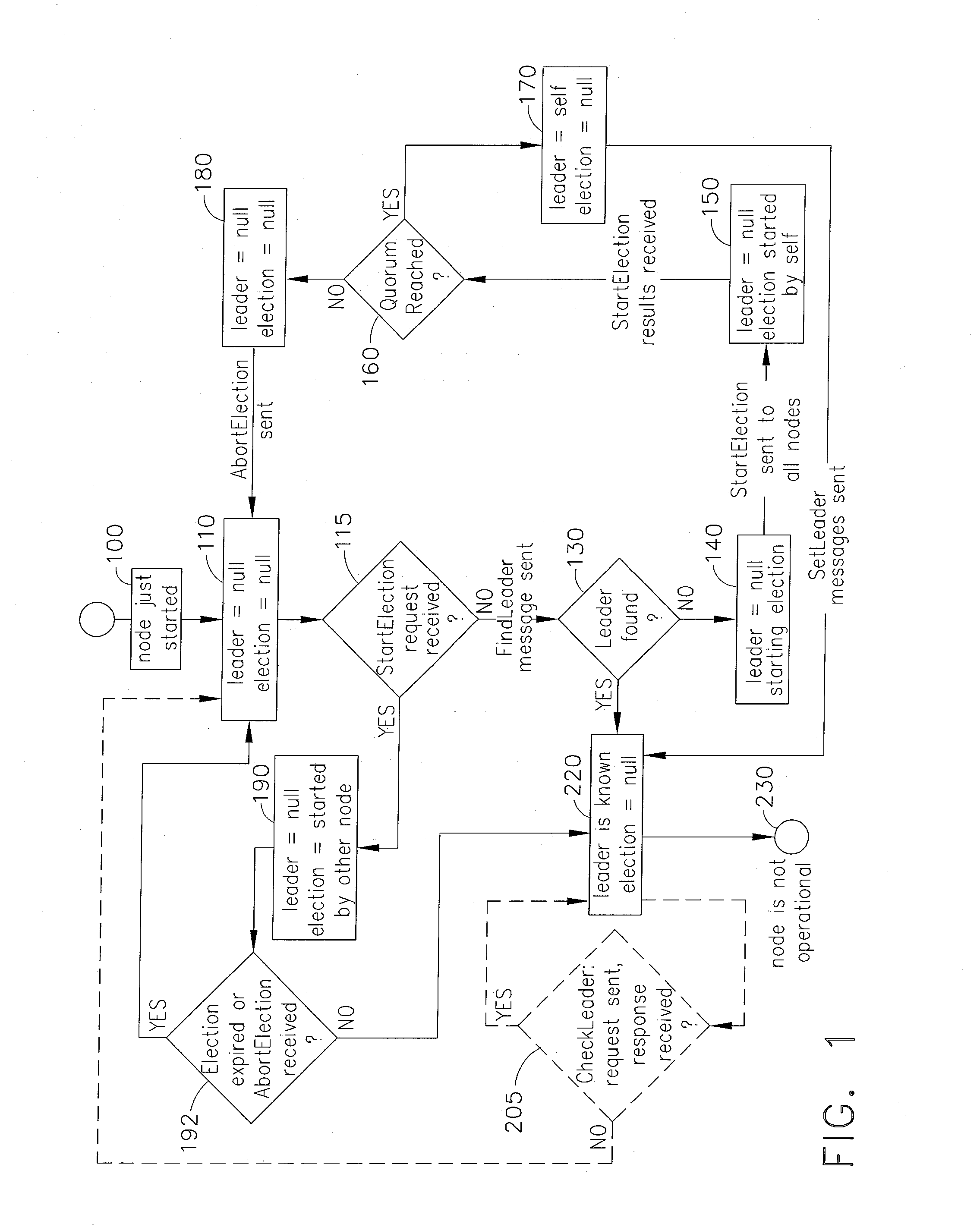
Systems and methods of providing fast leader elections in distributed systems of simple topologies
Systems and computer-implemented methods of electing a new leader node in distributed systems of simple topologies connecting a plurality of nodes on at least one computer system. The computer-implemented method comprises several steps including at least one node, which detected the absence of a leader, starting a first round for its approval as an Approved Election Initiator. If a quorum accepts the StartElection request during the first round, then the Election Initiator starts a second round to set the leader. If a quorum of all nodes has not been reached during the first round, then the first round fails. The method repeats until a leader is set and is repeated each time a node discovers that the network does not have an active leader. Also provided herein is a computer readable medium having computer executable instructions stored thereon for performing the computer-implemented method.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
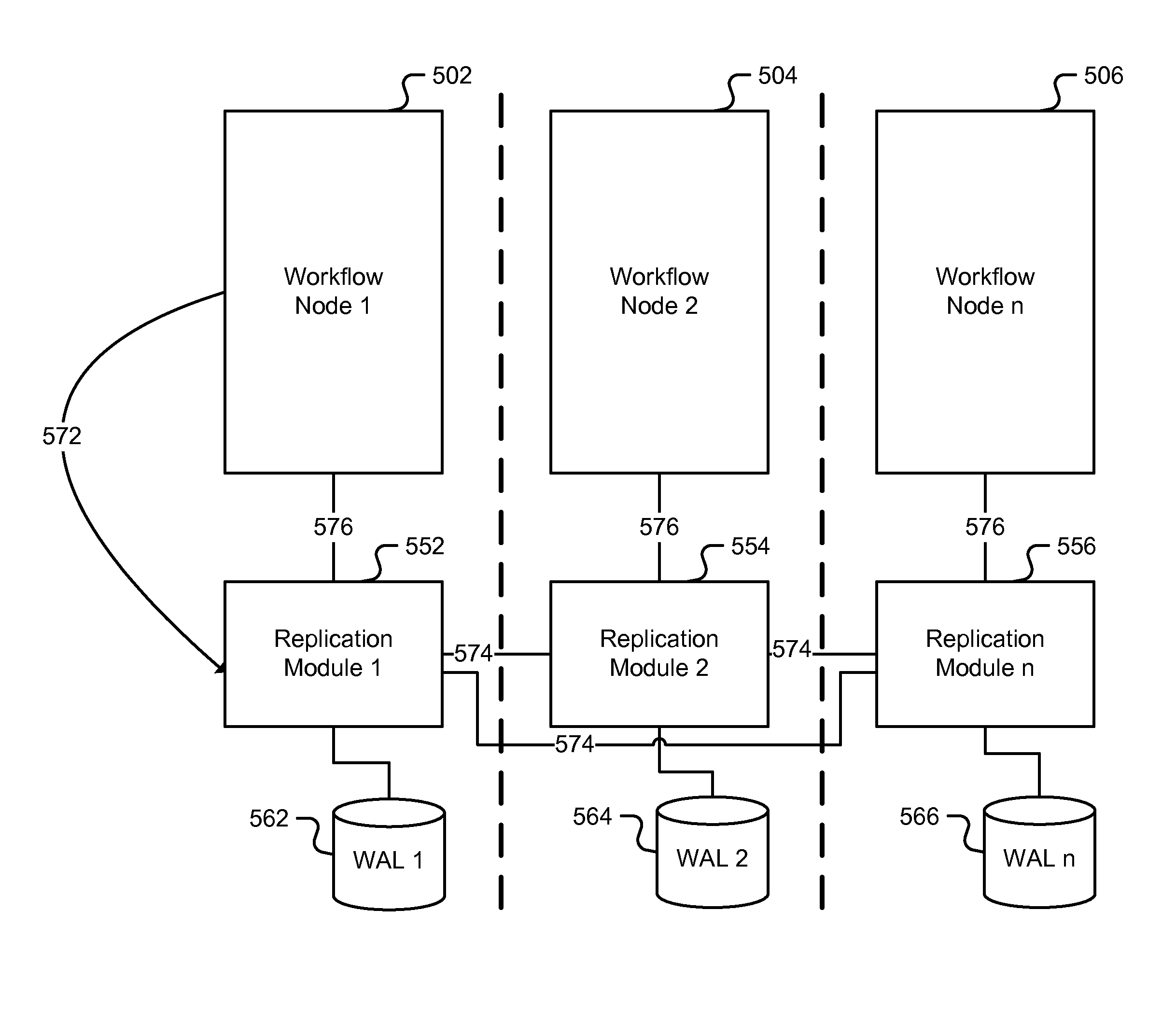
Model framework to facilitate robust programming of distributed workflows
ActiveUS20140304380A1Digital computer detailsNon-redundant fault processingLeader electionParallel computing
A method is disclosed. A finite state machine model for a single system workflow is replicated across a plurality of distributed nodes associated with a leader election protocol. A leader is determined amongst the plurality of distributed nodes to perform a next action of the finite state machine model based at least in part on the leader election protocol. One or more nodes amongst the plurality of distributed nodes are configured to submit a timeout ticket if the next action of the finite state machine model does not appear to have been performed by the leader within a prescribed time.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Systems and Methods of Providing Fast Leader Elections in Distributed Systems of Simple Topologies
ActiveUS20120124412A1Fast efficient simpleFault toleranceTransmissionRedundant hardware error correctionLeader electionComputerized system
Systems and computer-implemented methods of electing a new leader node in distributed systems of simple topologies connecting a plurality of nodes on at least one computer system. The computer-implemented method comprises several steps including at least one node, which detected the absence of a leader, starting a first round for its approval as an Approved Election Initiator. If a quorum accepts the StartElection request during the first round, then the Election Initiator starts a second round to set the leader. If a quorum of all nodes has not been reached during the first round, then the first round fails. The method repeats until a leader is set and is repeated each time a node discovers that the network does not have an active leader. Also provided herein is a computer readable medium having computer executable instructions stored thereon for performing the computer-implemented method.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Cluster election design method
InactiveCN103491168AHigh availability serviceImprove continuous working abilityTransmissionLeader electionCluster based
The invention discloses a cluster election design method. In the election process, when a node processor initiates an election, the other nodes receive an election request and then judge the size of an initiator p_id of the a_id, if the a_id is smaller than the p_id, the node processor initiates the election again, if the a_id is larger than the p_id, the nodes reply the ack, and the nodes show to agree that the node processor is used as the leader node. When more than half of the nodes reply the ack, the node processor becomes the new leader. If the election is initiated for more than 5 seconds, the half of nodes still do not reply the ack, and a new leader is not generated, the node processor initiates the election again until the new leader is generated. According to the election algorithm based on the cluster nodes, the leader election among the cluster nodes is achieved, after the leader fails, the new election is initiated again, the high available service of a cluster can be ensured, and the continuous working capability of the cluster is improved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
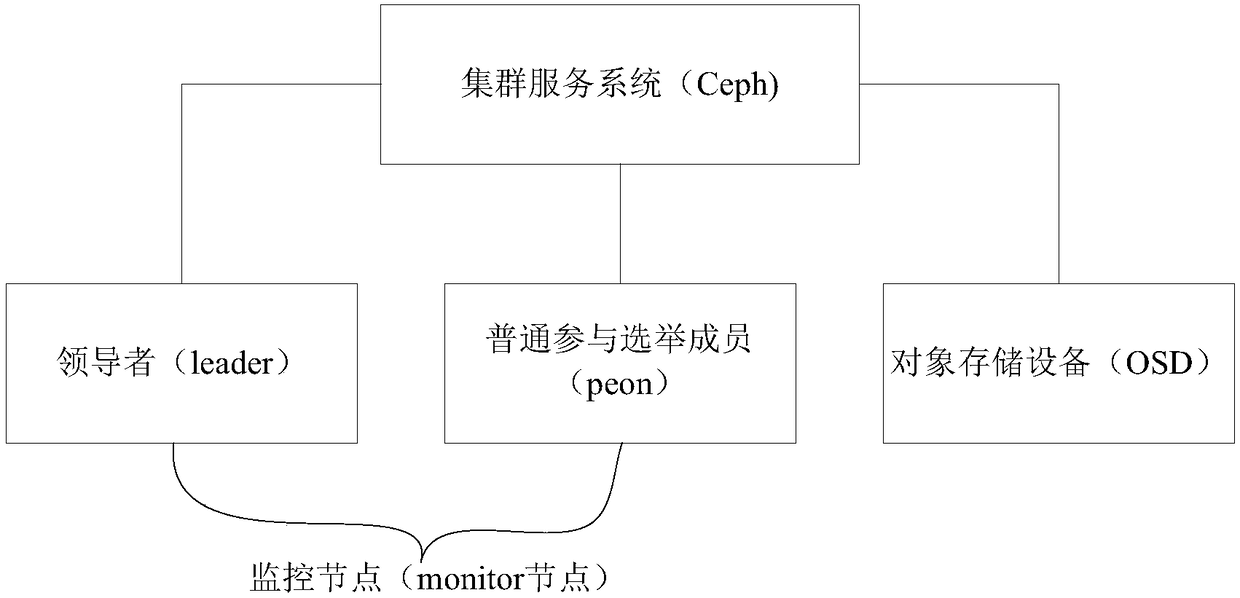
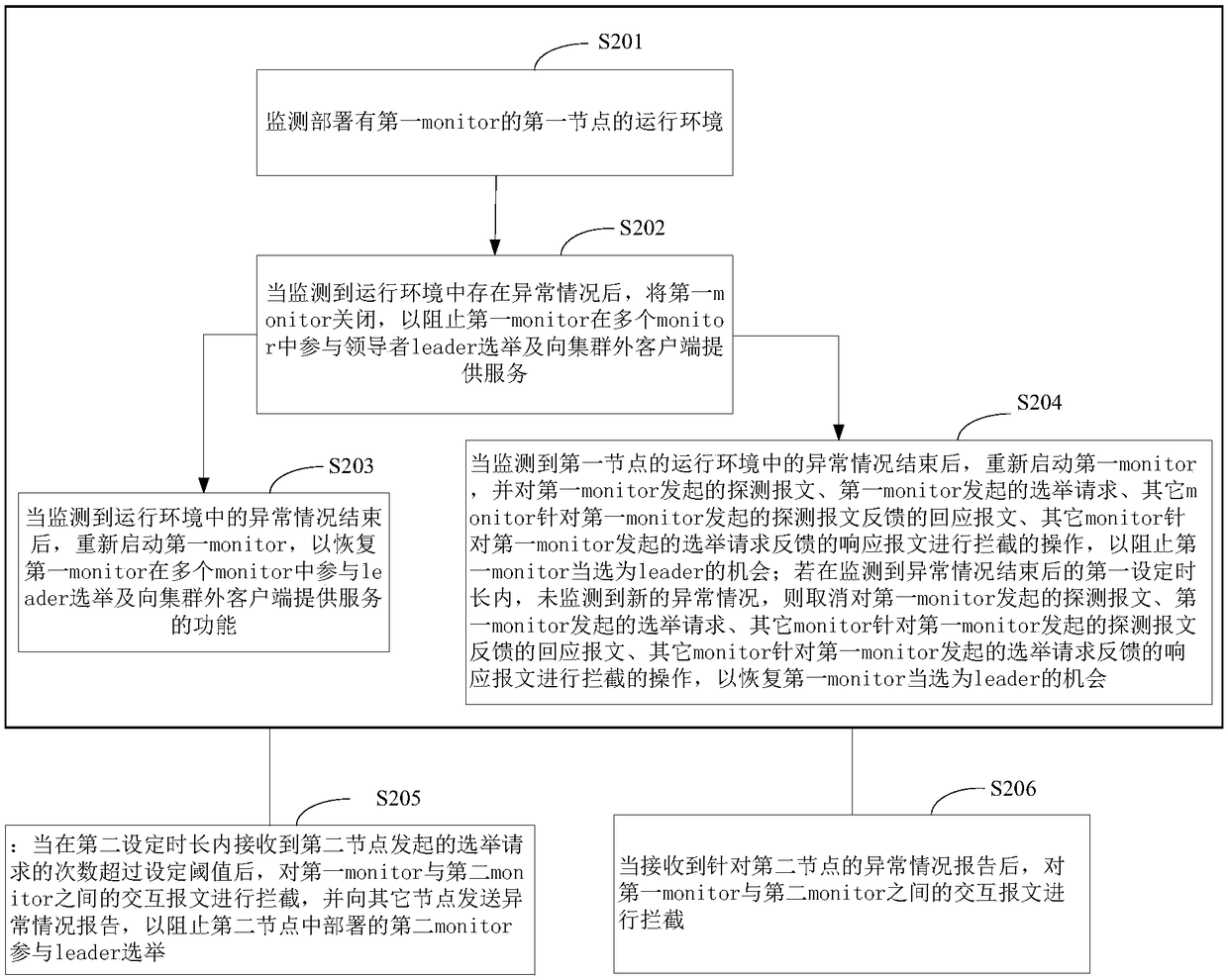
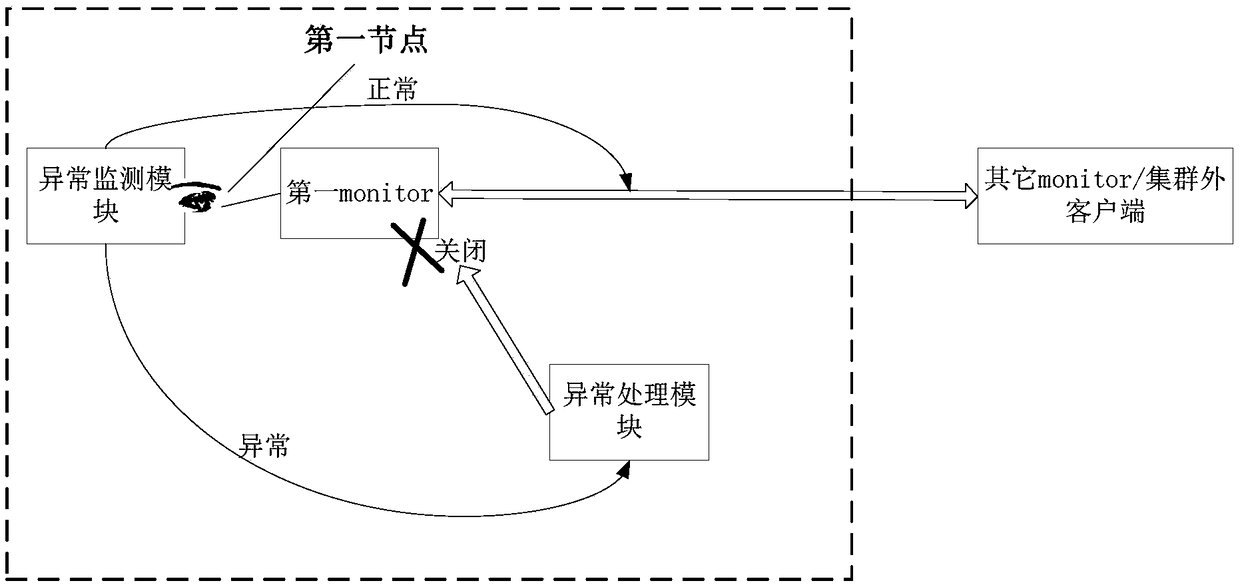
Election control method and device
InactiveCN108494585AAvoid interruptionGuaranteed SustainabilityData switching networksLeader electionDependability
The application relates to the technical field of the data communication, and especially relates to an election control method and device, an election method and device. The method is applied to a node deployed with a target monitor procedure in a cluster service system, and comprises the following steps: monitoring an operation environment of a first node deployed with a first monitor; turning off the first monitor when monitoring that the abnormal situation is existent in the operation environment, thereby preventing the first monitor for participating the leader election in multiple monitors and providing service for the client outer of the cluster; therefore, the situation of continuously and repeatedly entering the election state is avoided when the operation state and the operation environment of the monitor are abnormal, and the interruption of the whole cluster service is avoided; furthermore, the service cannot be provided for the client under the problem existence state, thesystem resource is saved, and the data reliability in the distributed storage cluster is improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
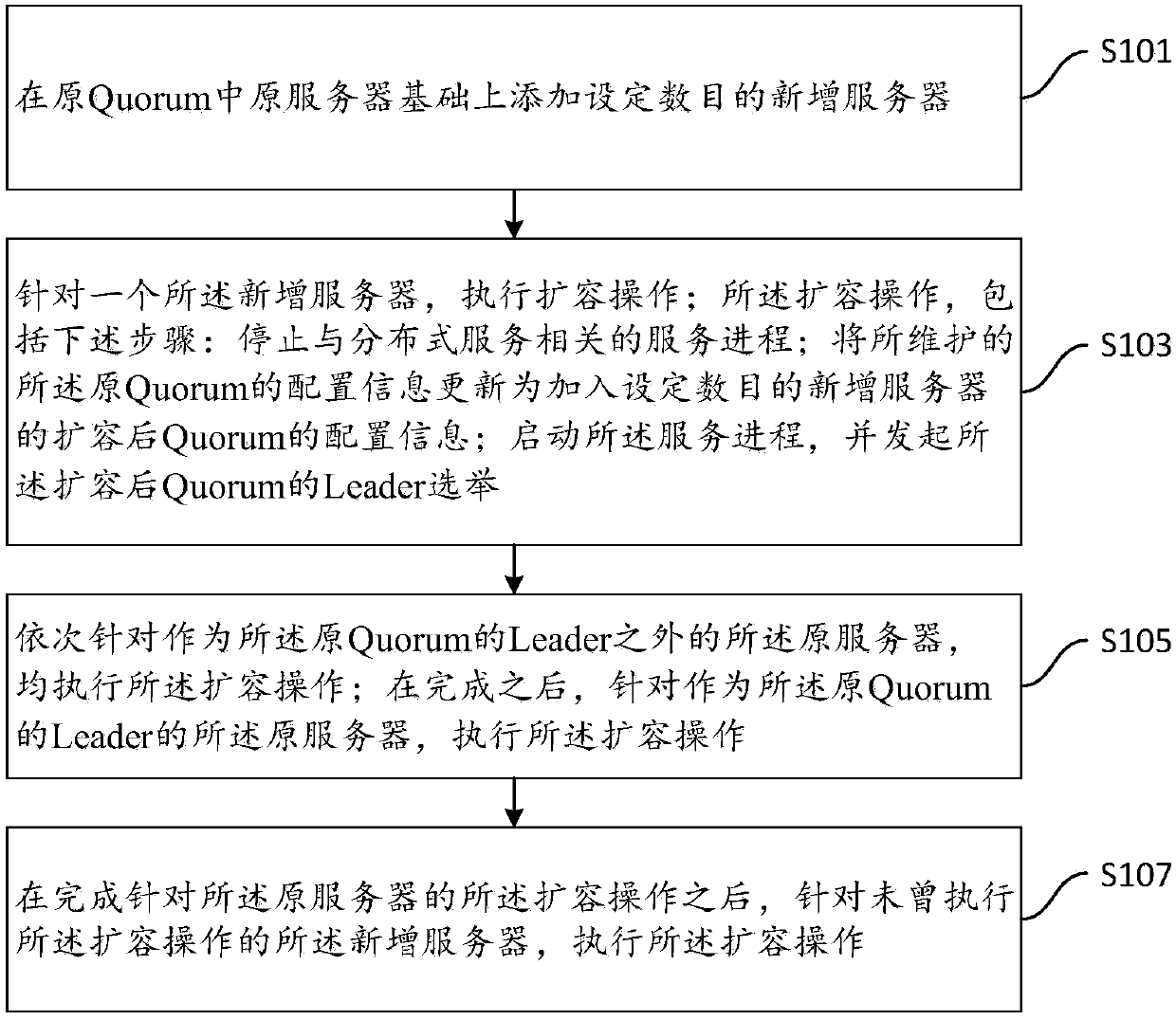
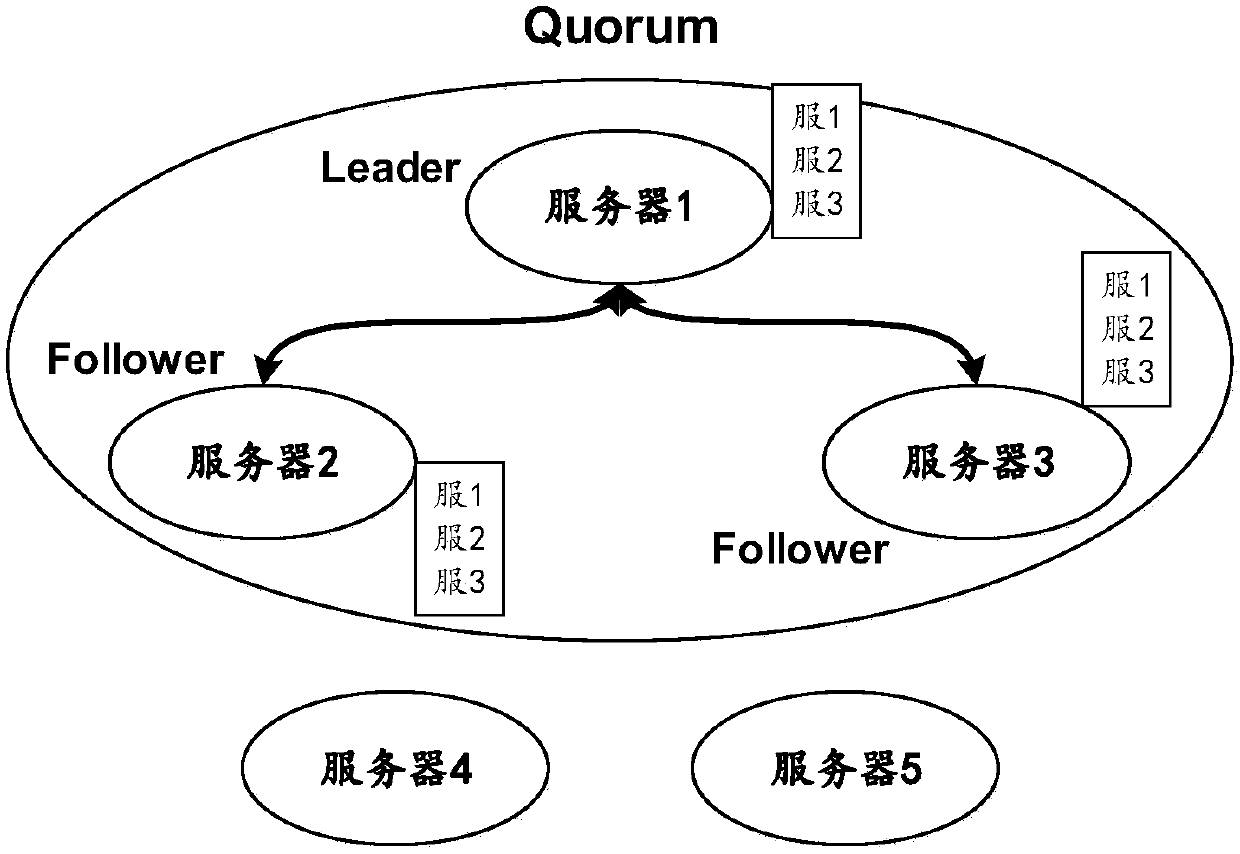
Paxos-protocol-based distributed consistency system online capacity expanding and online capacity reducing method and device
ActiveCN107919977AFast and reliable expansion methodImprove user experienceData switching networksSecuring communicationLeader electionDistributed services
The invention provides a Paxos-protocol-based distributed consistency system online capacity expanding method comprising the steps that the preset number of new servers are additionally arranged on the basis of the original servers in the original Quorum; capacity expanding operation is performed on one new server; the capacity expanding operation comprises the following steps: the service processrelated to the distributed services is stopped; the configuration information of the capacity-expanded Quorum including all the original servers and the preset number of new servers is updated; the service process is started and Leader election for the capacity-expanded Quorum is initiated; the capacity expanding operation is performed for each original server apart from the Leader of the original Quorum and the capacity expanding operation is performed for the Leader of the original Quorum after completion; and the capacity expanding operation is performed on the new servers of which capacity expanding is not performed. The problems of the present cold capacity expanding method that the distributed system services are paused in the capacity expanding process can be solved. The inventionalso provides a Paxos-protocol-based distributed consistency system online capacity reducing method.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
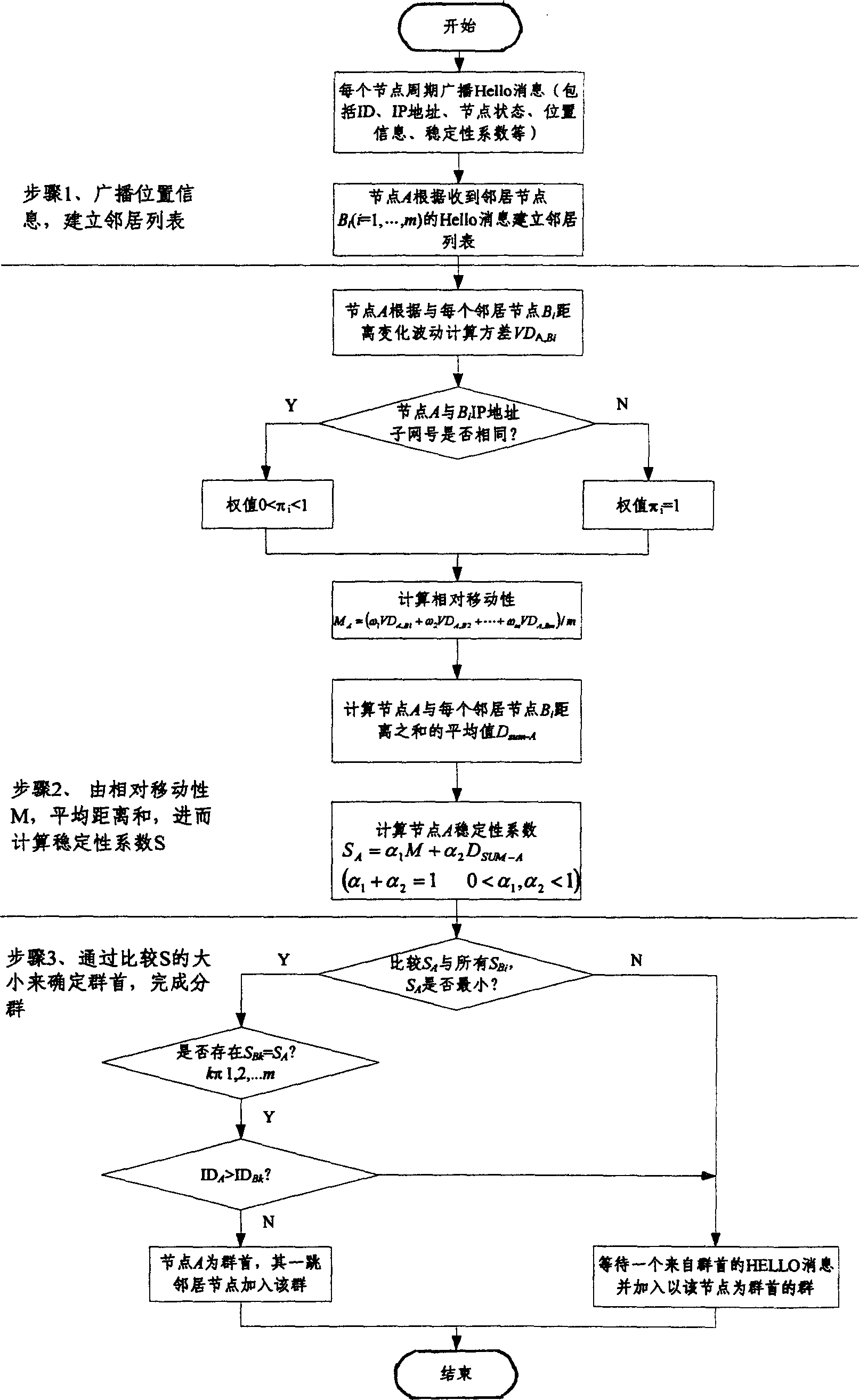
Cluster chief election method based on node type for ad hoc network
InactiveCN1863130AImprove stabilityReduce the number of iterationsNetworks interconnectionLeader electionStability coefficient
The invention is a node type-based group leader selecting method, applied to ad hoc network, considering node types, i.e. administrative units the nodes belong to and combining with speed and distance of relative movement, advancing a synthetic group leader index: stability coefficient S, and using the stability coefficient to make group leader selection and subgroup formation. The subgroup network composed of the method can reduce number of group leader changing times at network division, improving network stability. And it can effectively reduce the number of group leader changing times, achieving network stabilizing purpose.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Consensus method suitable for wireless block chain network
ActiveCN110913501AGuaranteed normal transmissionUniqueness guaranteedTransmissionHigh level techniquesLeader electionCarrier signal
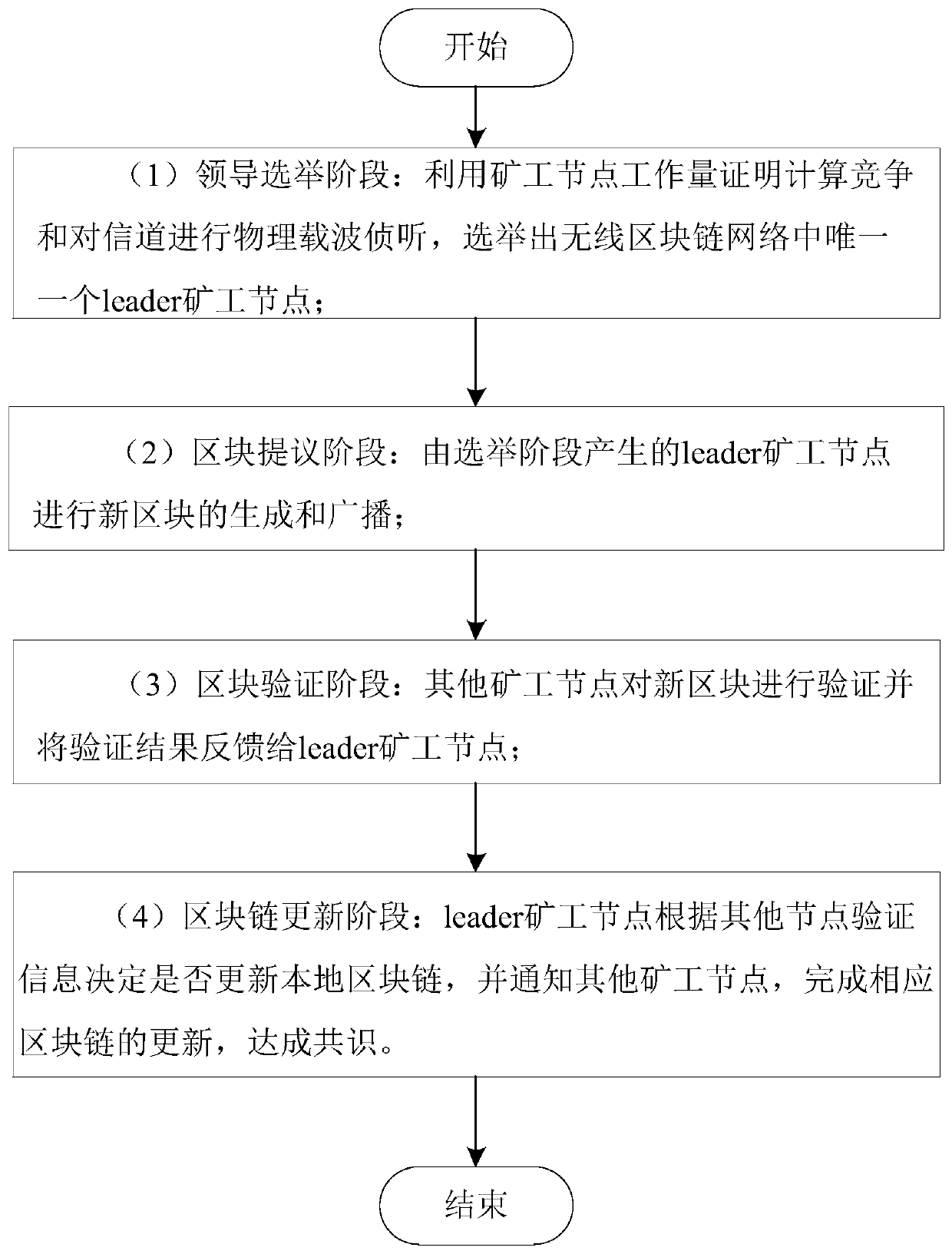
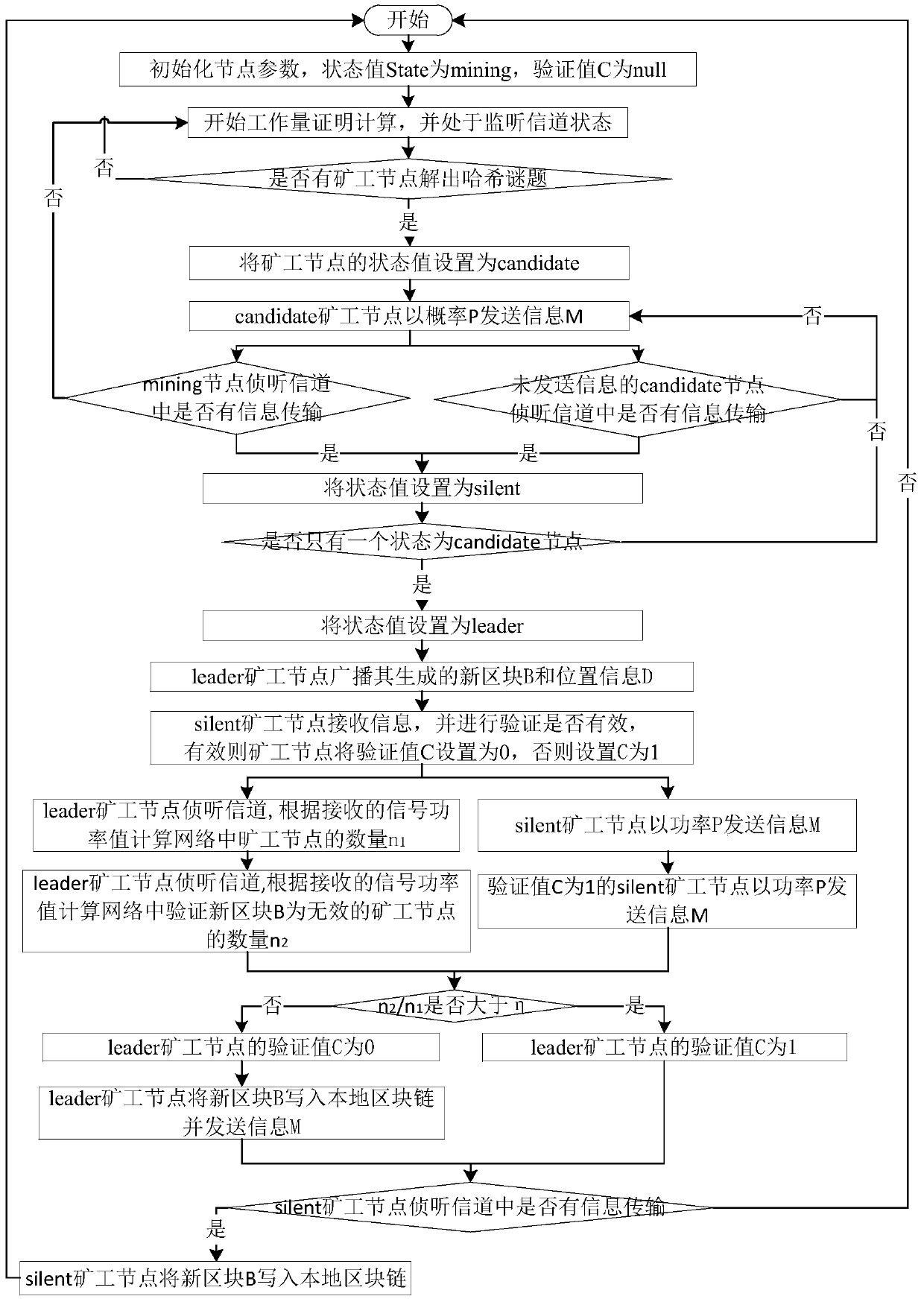
The invention discloses a consensus method suitable for a wireless block chain network. The consensus method comprises the following steps: (1) a leader election stage: electing a unique leader minernode in the wireless block chain network; (2) a block proposal stage: generating and broadcasting a new block by the leader miner node generated in the election stage; (3) a block verification stage:verifying the new block by other miner nodes and feeding back a verification result to the leader miner node; and (4) a block chain updating stage: the leader miner node deciding whether to update thelocal block chain according to the verification information of other nodes to achieve a consensus. According to the method, under the conditions that transmission information between miner nodes is uncertain and a transmission channel is unstable, through methods such as proof of work calculation, physical carrier sensing and setting of inter-node transmission rules, all nodes in the whole blockchain network reach consensus in the optimal operation round number, and the bifurcation problem in the block chain network is avoided to a certain extent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Optimizing the distribution of electrical energy
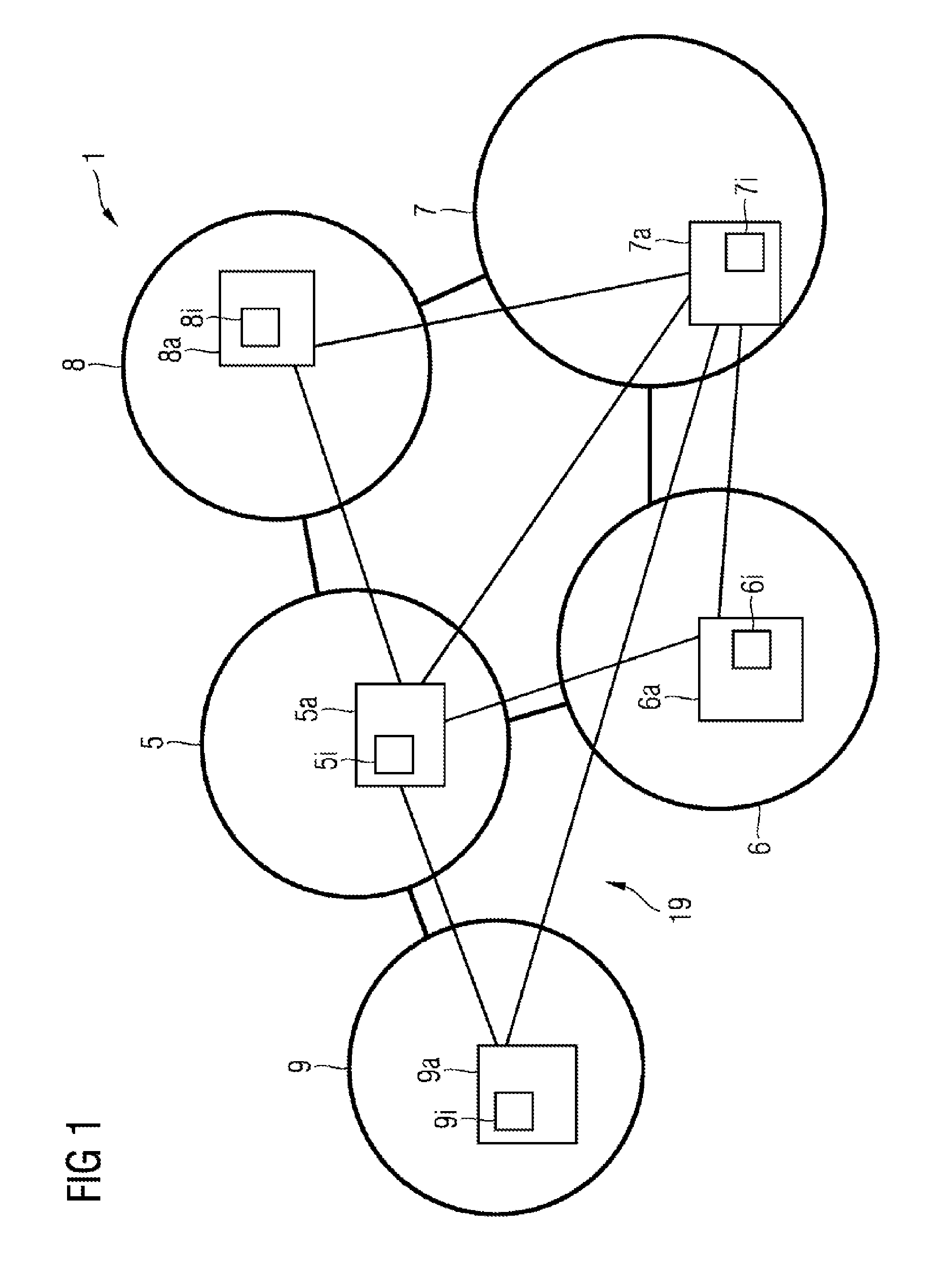
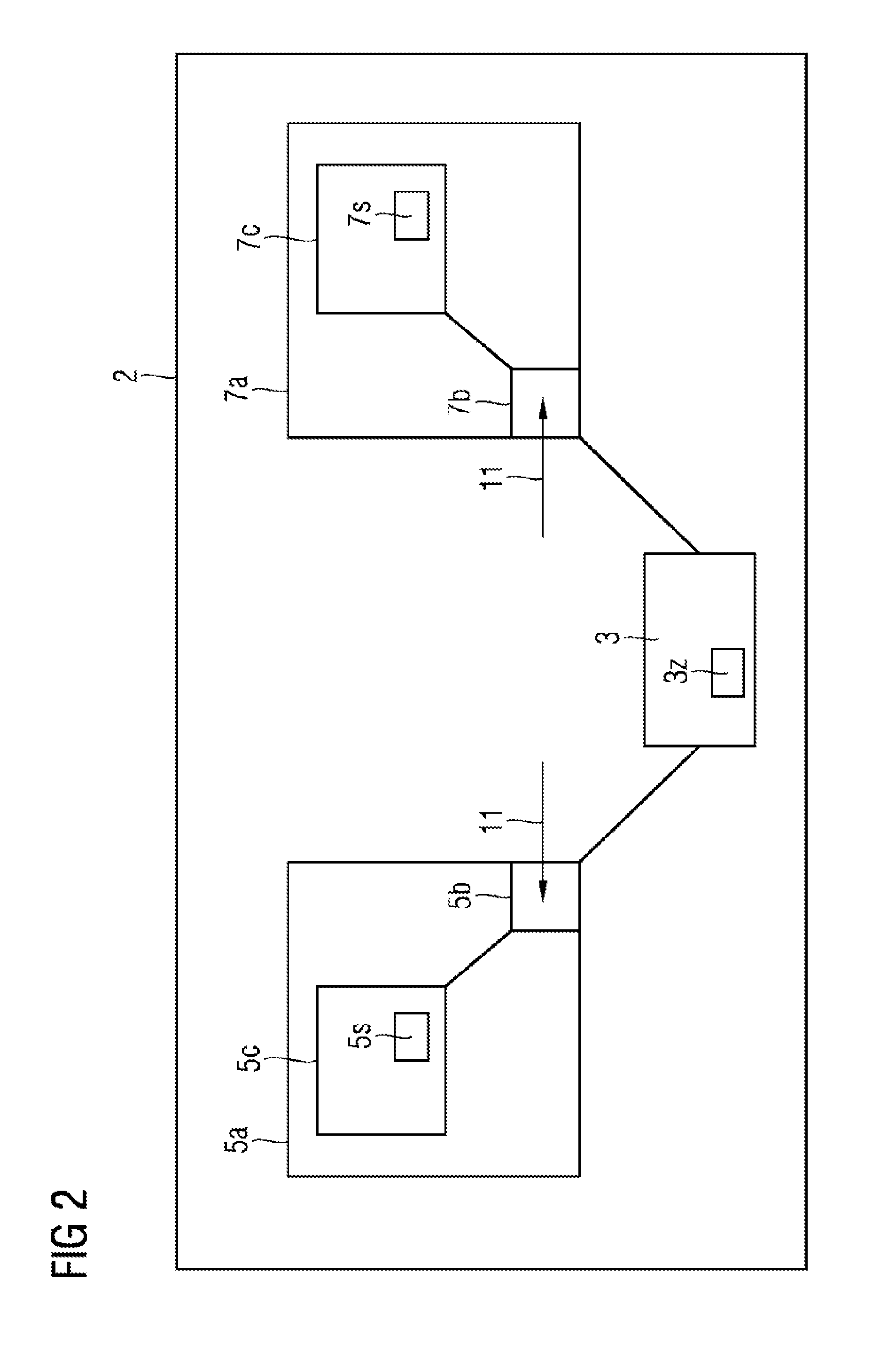
The invention relates to methods and systems for optimizing the distribution of electrical energy in an electrical power supply system (I) which comprises autonomous supply system regions (5, 6, 7, 8, 9), comprising the method steps of:—receiving input data (II) by at least two dispatcher instances (5a, 7a), wherein the input data (II) represents energy intervals (5i, 6i, 7i, 8i, 9i) which are requested by the autonomous supply system regions (5, 6, 7, 8, 9);—calculating at least one solution (5s, 7s) of the distribution of electrical energy to the supply system regions (5, 6, 7, 8, 9) by each of the at least two dispatcher instances (5a, 7a);—selecting one of the calculated solutions (5s, 7s) for the distribution of electrical energy in the power supply system (I) by means of a leader election. The invention relates to the technical field of distributing electrical energy and can be used, for example, for smart grids.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Distributed-leader-election service for a distributed computer system
ActiveUS9596301B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionLeader electionComputerized system
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for leadership allocation in a distributed computer system. In certain embodiments of the present invention, a leader-election-service process runs within each node of a distributed computer system, together cooperatively providing a distributed-leader-election service. The distributed-leader-election service employs a distributed consensus service to manage distributed state information related to roles and leadership allocation within a distributed computer system. Client processes within each node interface with the leader-election-service process of the node in order to assume leadership of particular roles within the distributed computer system. Leadership-allocation management is thus centralized, within each node. In alternative embodiments, the distributed-leader-election service may be implemented as a collection of library routines that run in the context of client processes.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and/or method for maintaining highly-available, consistent, partition-tolerant clusters using client voters
ActiveUS20200028750A1Improve availabilityImprove fault toleranceData switching networksLeader electionHigh availability
Certain example embodiments relate to a distributed computing system including servers organized in a cluster and clients. One server is elected leader and is responsible for maintaining consensus information among the other servers. Each server is configured to determine whether a new leader election is to take place. If so, the respective server requests votes for a new leader from the other server(s) and determines whether it has won by a clear majority. Depending on the implementation, votes from eligible client devices are counted, either in a main election together with server votes, or in a tie-break election (if needed) after server votes. Once a server has won, the other servers are informed accordingly. It therefore is possible to maintain a highly-available, consistent, partition-tolerant cluster in the distributed computing systems, using client voters.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
Model framework to facilitate robust programming of distributed workflows
ActiveUS8732282B1Digital computer detailsNon-redundant fault processingLeader electionFinite-state machine
A method is disclosed. A finite state machine model for a single system workflow is replicated across a plurality of distributed nodes associated with a leader election protocol. A leader is determined amongst the plurality of distributed nodes to perform a next action of the finite state machine model based at least in part on the leader election protocol. One or more nodes amongst the plurality of distributed nodes are configured to submit a timeout ticket if the next action of the finite state machine model does not appear to have been performed by the leader within a prescribed time.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
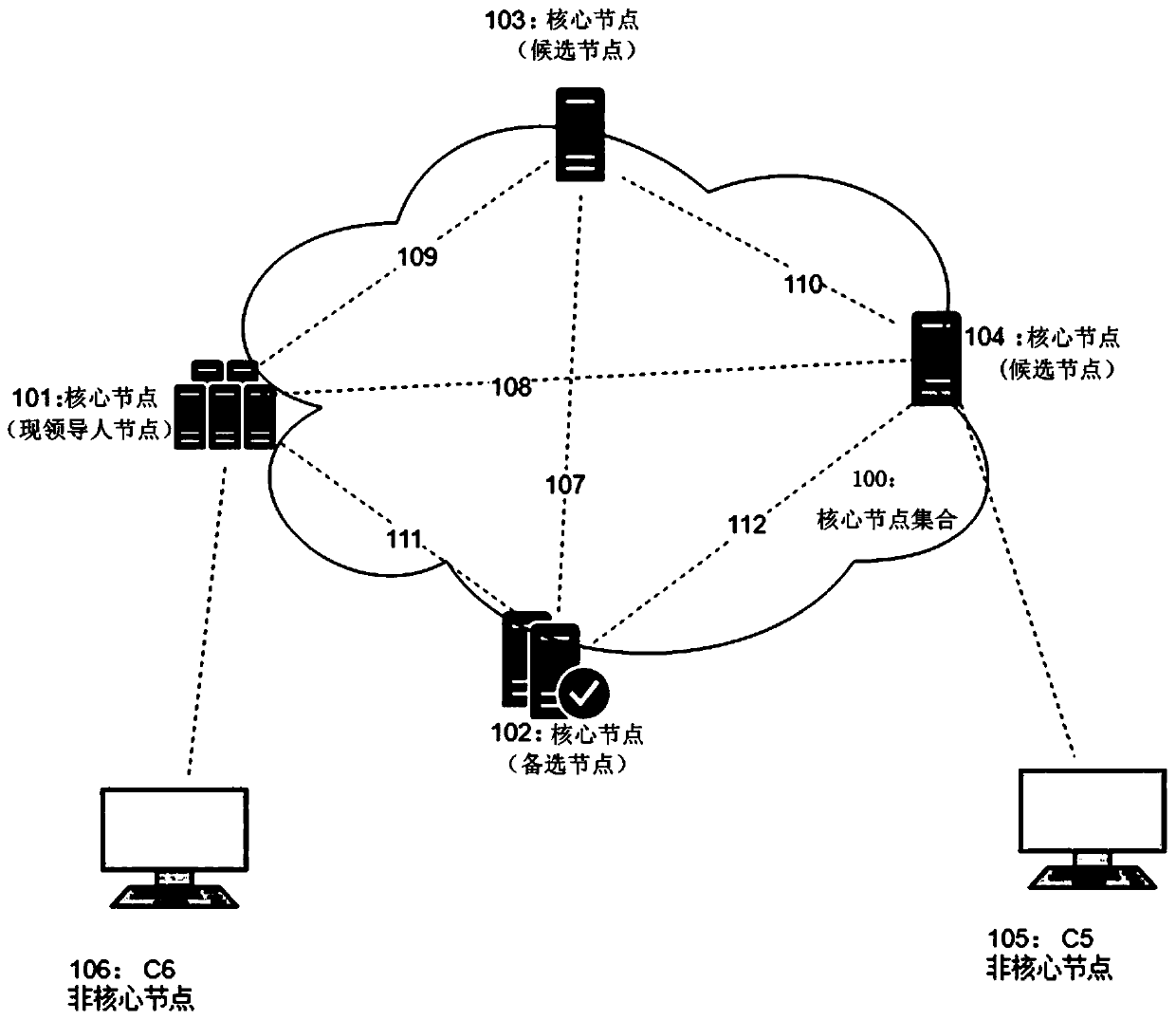
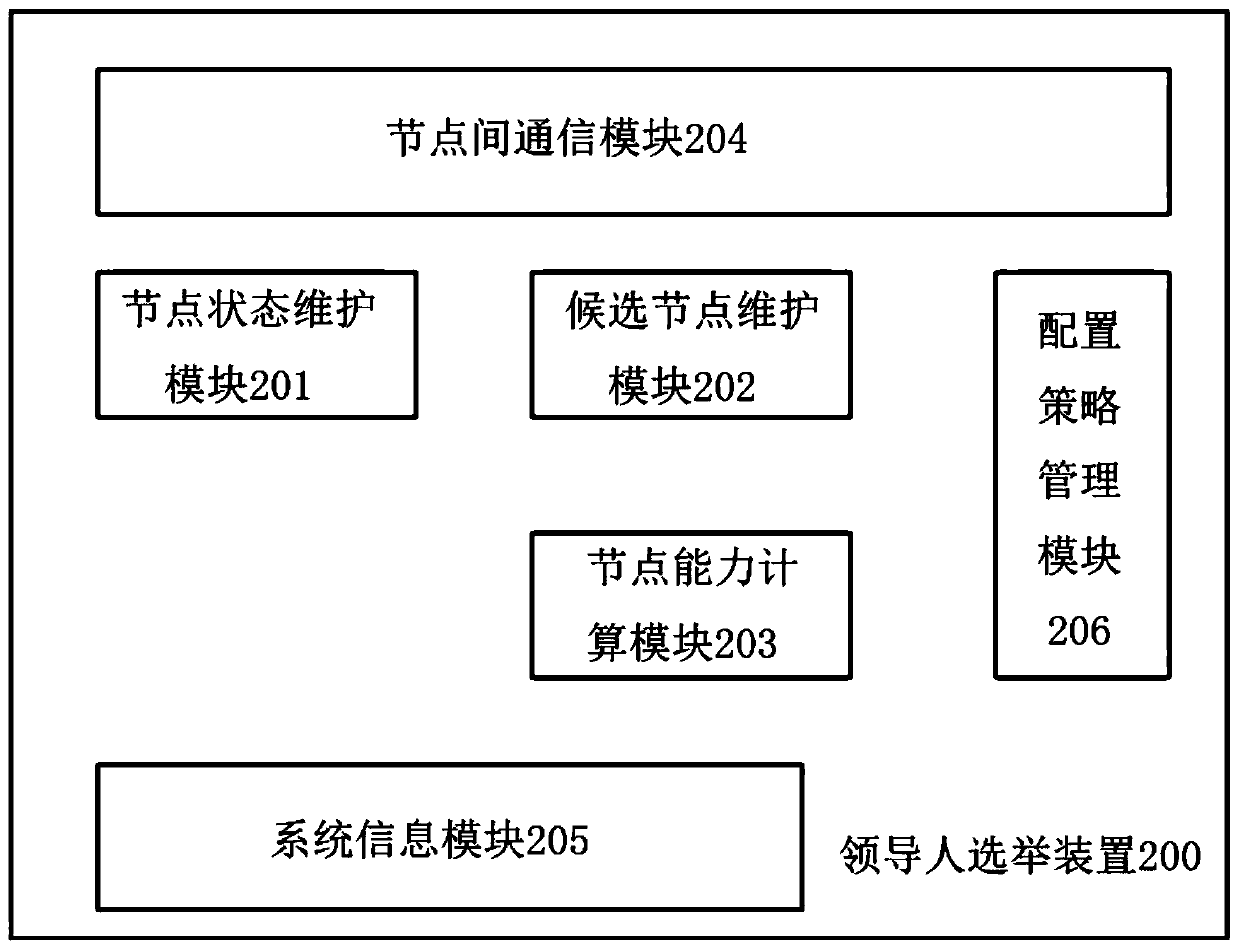
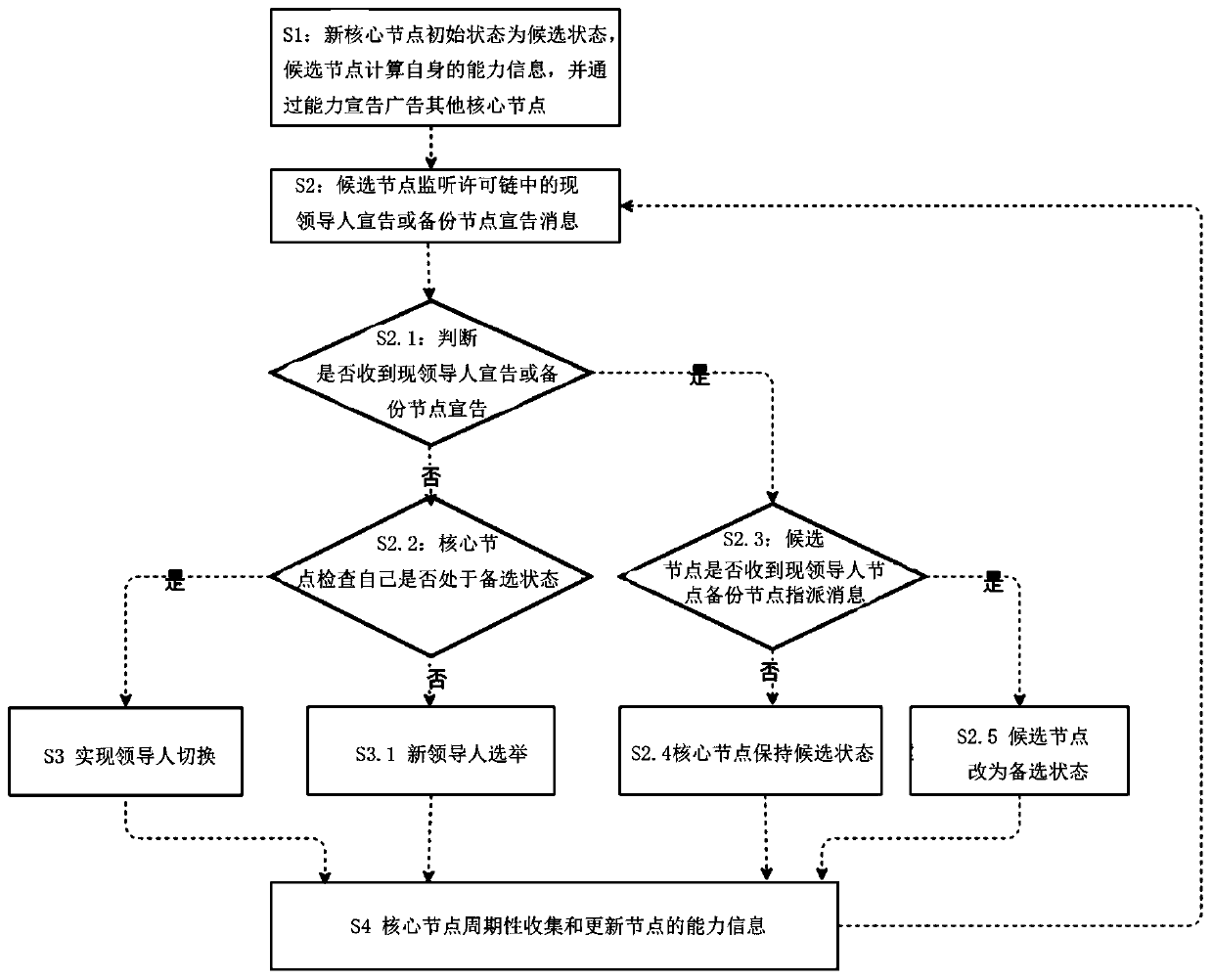
A blockchain leader election method and a blockchain leader election device
InactiveCN109728941AImplement node replacementAvoid absenceData switching networksLeader electionEmergency condition
The invention provides a blockchain leader election method and a blockchain leader election device. According to the method, the backup node is determined in advance according to the node capability and the established strategy, so that leader node alternation is quickly realized after expiration or under emergency conditions, the core node can be quickly converted into the selected node, and a new leader node is quickly selected in a voting manner, so that the leader vacancy in a permission chain is prevented. Therefore, the leader is high in alternation speed and high in efficiency, and themethod and device can select a relatively complex node selection rule, and give consideration to the effect, the efficiency and the flexibility.
Owner:王春峰
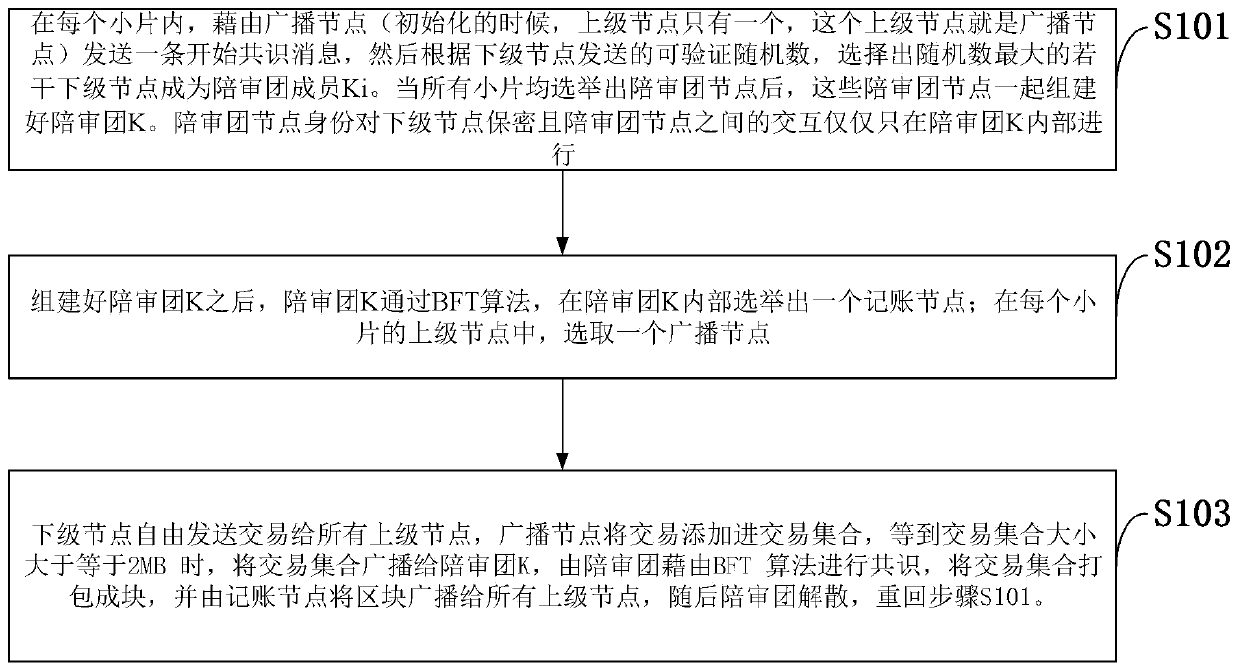
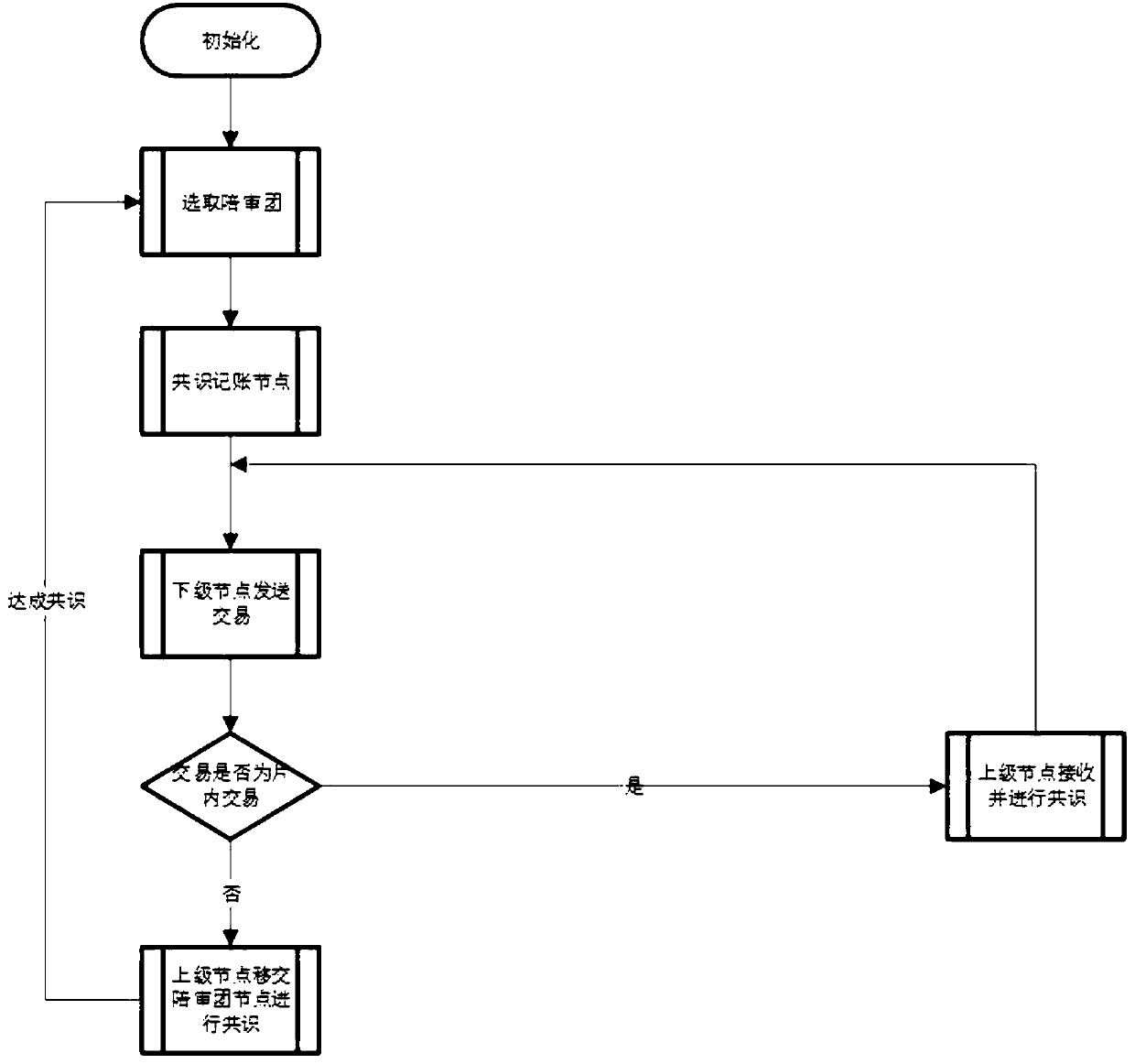
Hierarchical consensus method based on accompanying group system and blockchain data processing system
ActiveCN110400218AConstraint errorImprove TPSSpecial service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationNODALData processing system
The invention belongs to the technical field of distributed computing, and discloses a hierarchical consensus method based on an accompanying group system, and a block chain data processing system, and the method comprises the steps: selecting a plurality of subordinate nodes with the maximum random number as accompanying group members Ki according to verifiable random numbers transmitted by the subordinate nodes; after the accompanying group K is established, electing, by the accompanying group K, an accounting node in the accompanying group K through a leader election algorithm; selecting one broadcast node from the superior nodes of each small piece; freely sending transactions by the subordinate nodes to all the superior nodes, packaging the received transactions by the broadcast nodes, and performing, by the accompanying group, consensus by means of a BFT algorithm; and packaging the transaction set after consensus into blocks, and broadcasting the blocks to all superior nodes bythe accounting node, and then disintegrating the accompanying group. According to the method and the system, the original huge transaction quantity is dispersed into each fragment and is processed between the accompanying group members, so that the purpose of improving tps is achieved, and the Byzantine error is effectively restricted at the same time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
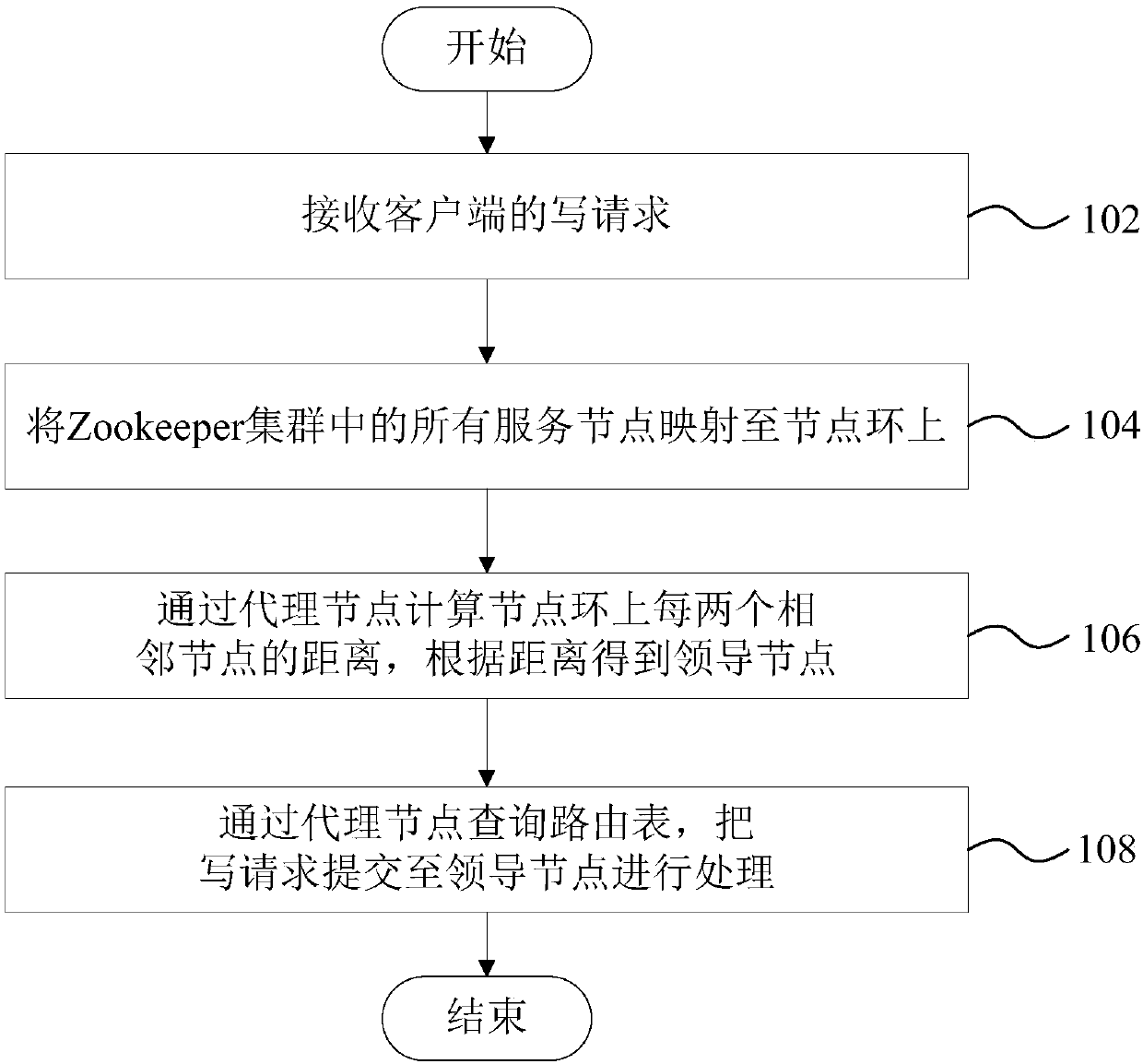
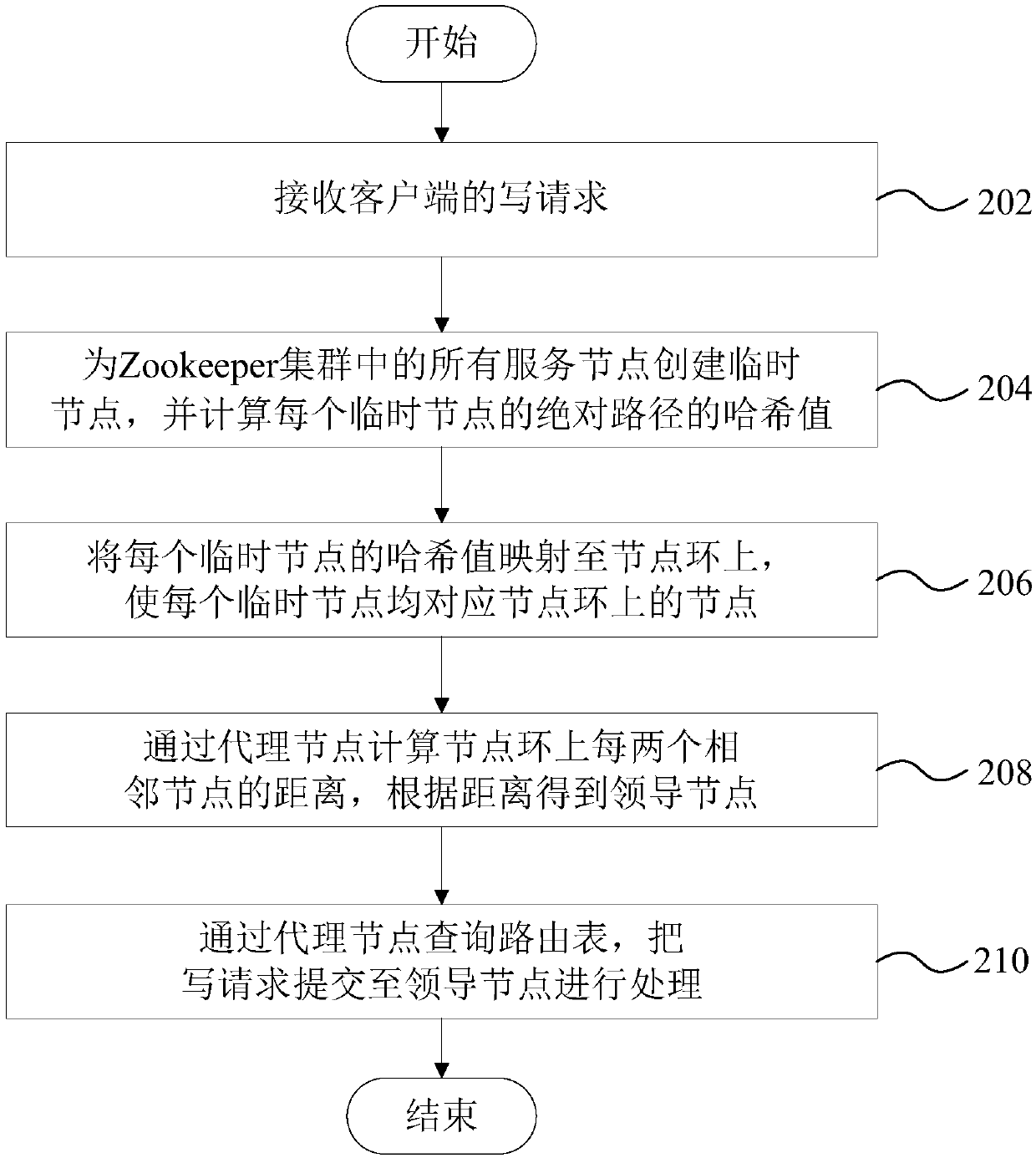
Request coordination method and device based on Zookeeper, computer device and storage medium
ActiveCN109951508AImprove acceleration performanceImprove fault toleranceTransmissionLeader electionRouting table
The invention discloses a request coordination method and device based on a Zookeeper, a computer device and a storage medium. The request coordination method based on the Zookeeper comprises the following steps: receiving a write request of a client; mapping all the service nodes in the Zookeeper cluster to a node ring; calculating the distance between every two adjacent nodes on the node ring through the agent node, and obtaining a leader node according to the distance; and querying the routing table through the agent node, and submitting the write request to the leader node for processing.According to the embodiment of the invention, the requirement on the number of servers in the existing Leader election of the ZooKeeper cluster is made up, and the transverse expansion capability andfault tolerance of the ZooKeper cluster are improved. And the proxy node is introduced to inquire the routing table to quickly route the client request, so that the problem of low efficiency caused bya main writing mode of the existing client or the problem of data consistency caused by writing in any mode are avoided.
Owner:中国移动通信集团重庆有限公司 +1
Self-organizing community system
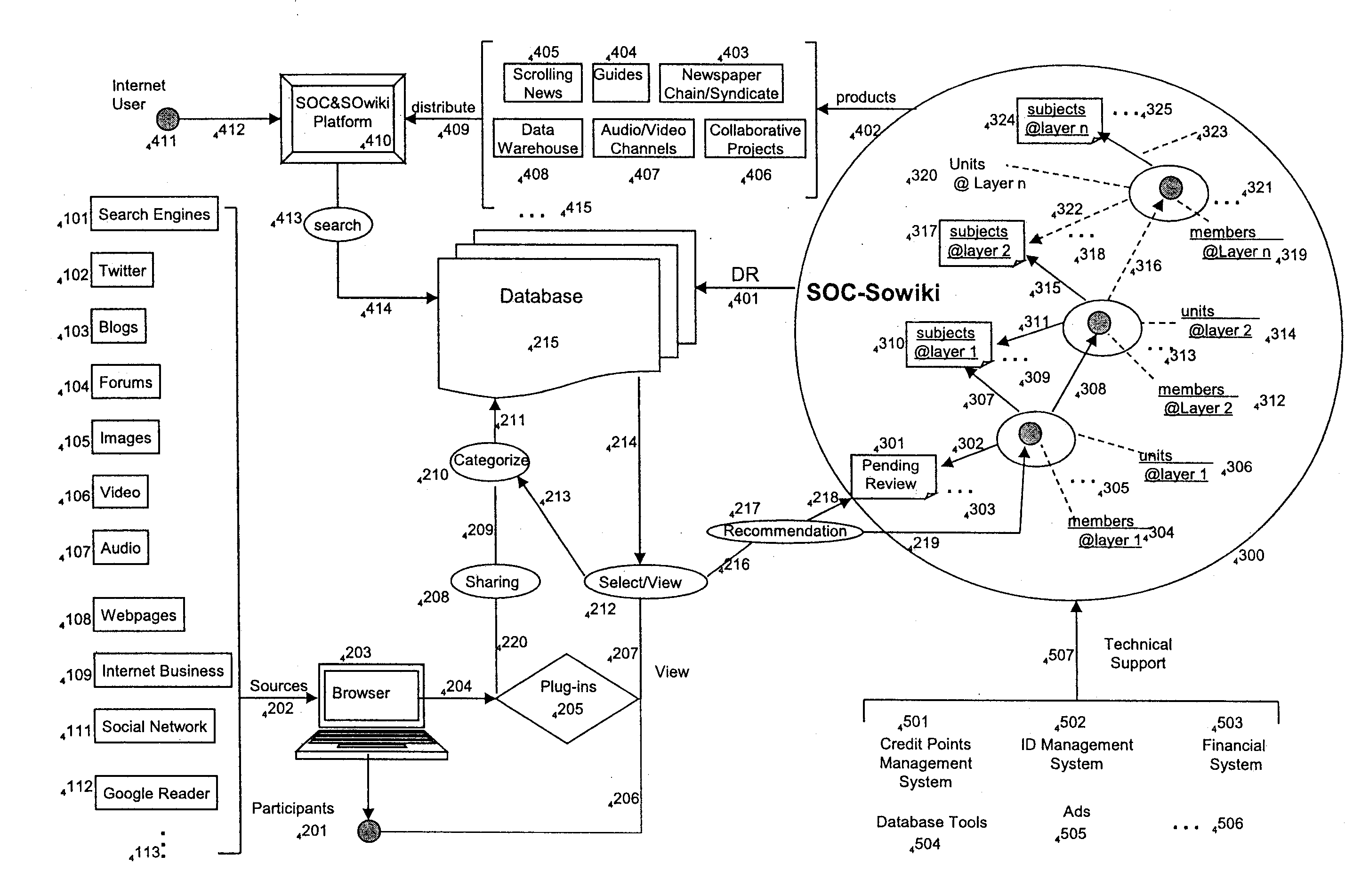
ActiveUS20120047133A1Address information overloadLow costWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsLeader electionCommunity system
The invention provides self-organization methodologies and system for internet users to build web-based organizational hierarchical structure that is constituent of units within which direct and sufficient communication can be fulfilled. Each unit is administrated autonomously through the democratic-decision process, and processes information internally. The members of unit can designate or replace its leader anytime though election; the leader elect of a unit will then become a member of its direct upper unit in the structure, representing its unit to participate in the management and election of upper unit and to bring the consolidated results of its unit to the upper unit for further consolidation; recursively, a hierarchical structure is to form from bottom to upper progressively, and to produce different level of end products at different layer. Taking the advantage of self-organization methodologies, the SOC & SOwiki platform and systems are to be designed and implemented to support various applications of SOC & SOwiki structures that are created to satisfy different social needs or business models.
Owner:WANG LIXIONG
Novel block chain consensus method based on shared storage
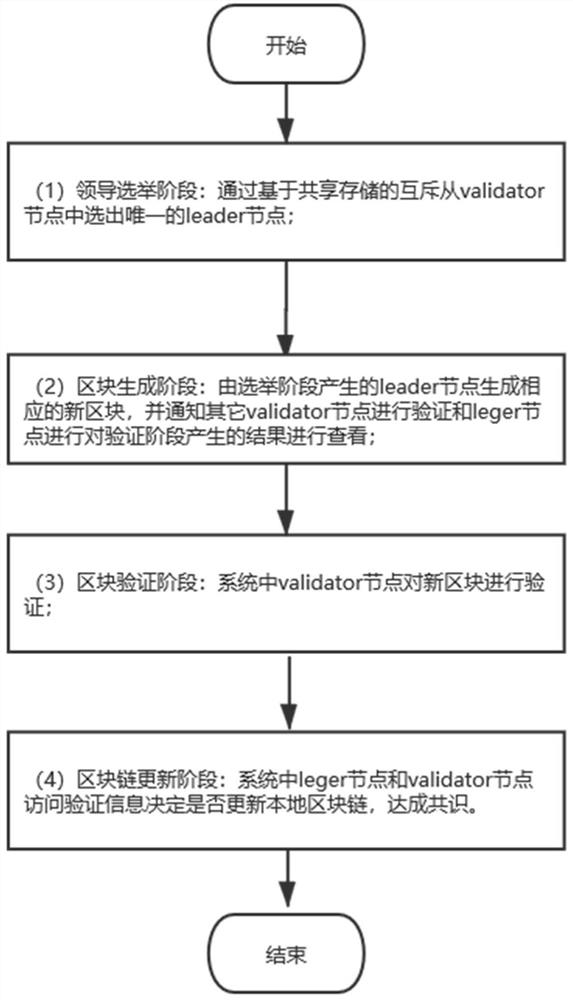
ActiveCN112187866AUniqueness guaranteedAvoid forksInterprogram communicationData switching networksLeader electionInformation transmission
The invention discloses a novel blockchain consensus method based on shared storage. The novel blockchain consensus method comprises the following steps: S1, a leader election stage: selecting a unique leader node from validator nodes through mutual exclusion based on the shared storage; S2, a block generation stage: generating a corresponding new block by the leader node generated in the electionstage, and notifying other validator nodes to carry out verification and the leader node to check a result generated in the verification stage; S3, a block verification stage: verifying the new blockby the validator node in the system; S4, a blockchain updating stage: enabling a leger node and a validator node in the system to access the verification information to determine whether to update the local blockchain or not to achieve a consensus. The method has the advantages that a shared storage mode is used for replacing a traditional P2P communication mode, a unique leger node is selected through a mutual exclusion algorithm, resource waste caused by selection of a main node of a transmission block chain can be avoided while the information transmission frequency is reduced, and the whole block chain network achieves consensus at low cost.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for synchronizing direct mode time division multiple access (TDMA) transmissions
ActiveUS20120287921A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexLeader electionTelecommunications
A method for synchronizing the direct mode TDMA transmission of a set of radios by following a selected radio as the leader includes: receiving, by a radio, a communication from an other radio; identifying, by the radio, a leader according to a leadership election rule using the received communication from the other radio and a current leader information; setting, by the radio, the identified leader as its leader; and synchronizing, by the radio, a time slot boundary with a time slot boundary defined by the leader.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com