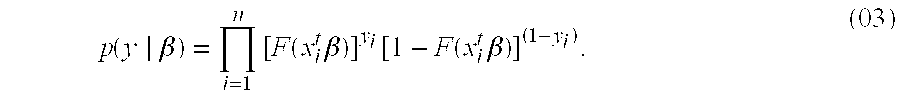Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Genetic screen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A genetic screen or mutagenesis screen is an experimental technique used to identify and select for individuals who possess a phenotype of interest in a mutagenized population. Hence a genetic screen is a type of phenotypic screen. Genetic screens can provide important information on gene function as well as the molecular events that underlie a biological process or pathway. While genome projects have identified an extensive inventory of genes in many different organisms, genetic screens can provide valuable insight as to how those genes function.
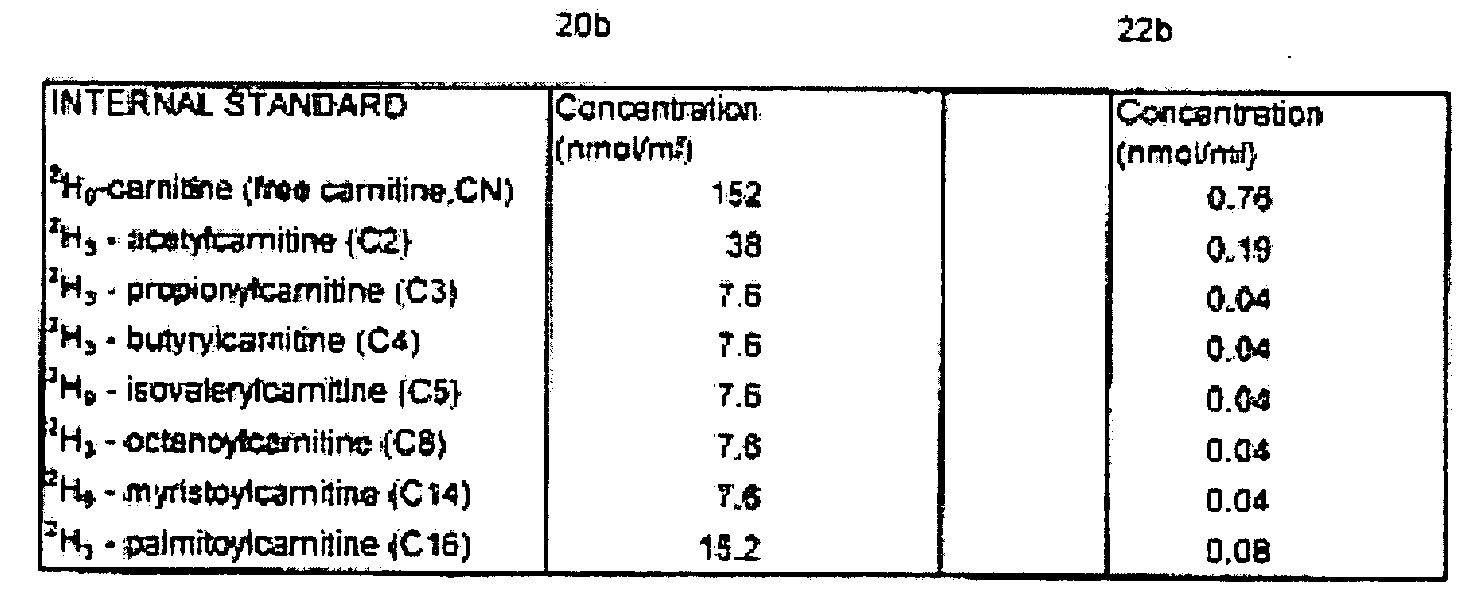
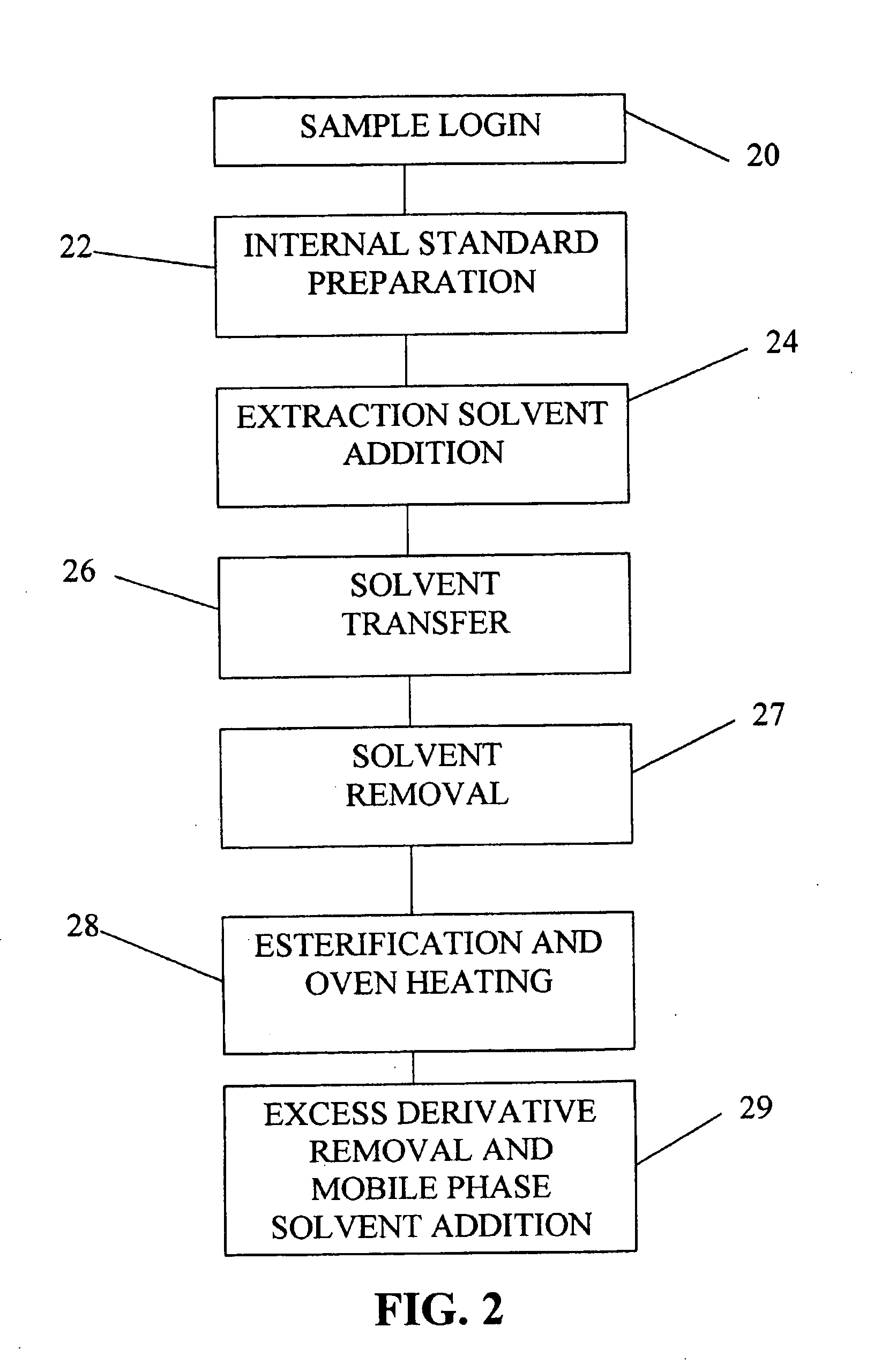
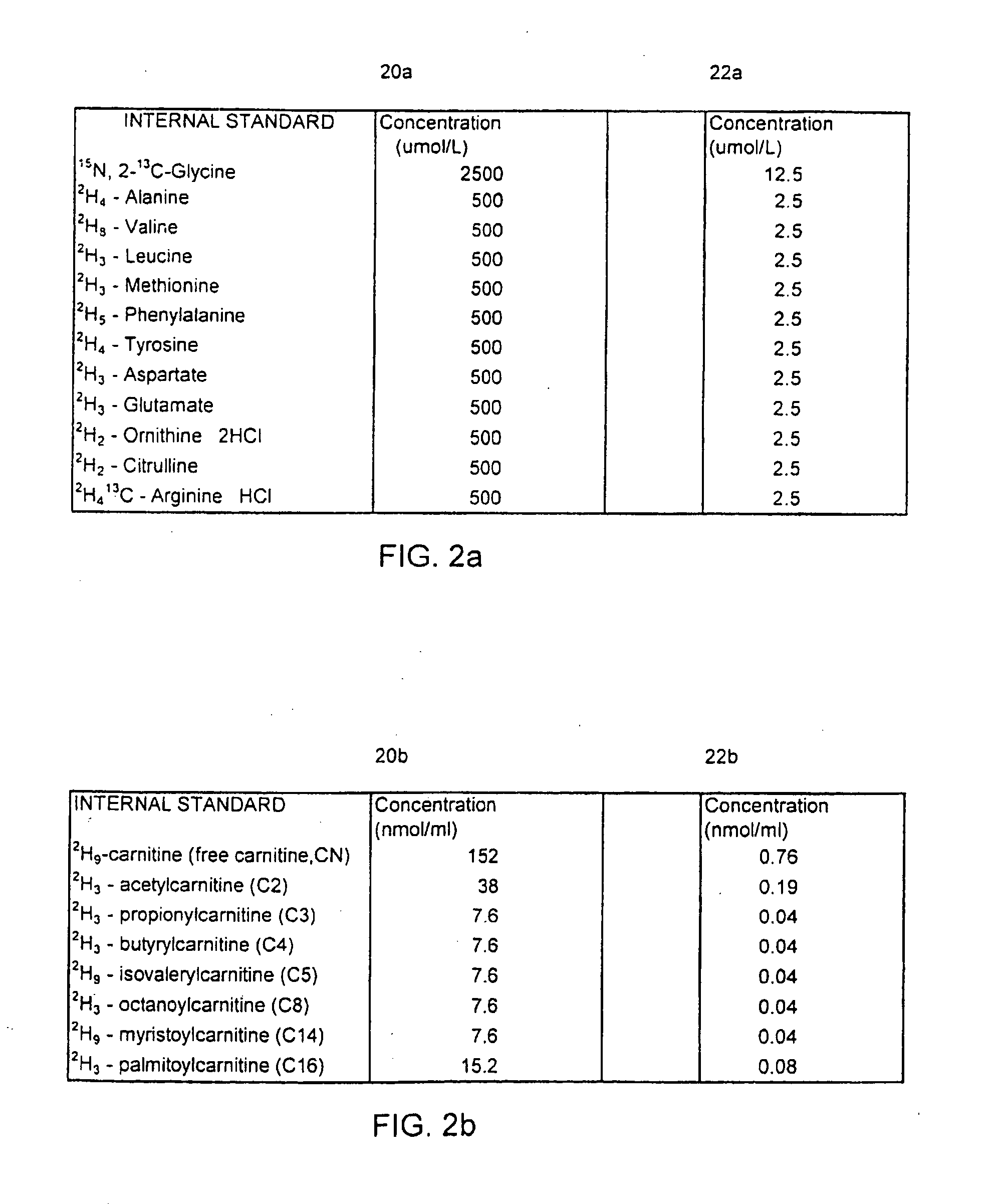
Clinical method for the genetic screening of newborns using tandem mass spectrometry and internal standards therefor
InactiveUS20060008922A1Simple methodRapid sample throughputParticle separator tubesDisease diagnosisMetaboliteTandem mass spectrometry
A method for screening newborns using electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. The method improves the current protocols that use tandem mass spectrometry by assuring accurate and consistent results at the clinical level through enhanced quality controls and quality assurance protocols as applied to the scan profiling and sample preparation of blood spots from newborns. Specific additives are used in precise concentrations of internal standards, employing detailed controls adapted to distinguish twenty metabolites, which are scanned and vigorously compared to known spectra results. Revealing peaks, metabolite concentration, and scan intensities in the quality assurance steps are then compared to a range of thresholds to determine whether or not the sample is contaminated, drug-ridden, diagnosable, or unacceptable. All spectra results and quality assurance flags are organized in spreadsheet form and exported to a database where values are compiled and stored for daily output results and trend analysis. The method provides for high-throughput and quality results, having a consistent predictability for genetically testing newborns efficiently and accurately.
Owner:PERKINELMER GENETICS
Clinical method for the genetic screening of newborns using tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060014297A1Simple methodRapid sample throughputParticle separator tubesDisease diagnosisMetaboliteTandem mass spectrometry
A method for screening newborns using electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. The method improves the current protocols that use tandem mass spectrometry by assuring accurate and consistent results at the clinical level through enhanced quality controls and quality assurance protocols as applied to the scan profiling and sample preparation of blood spots from newborns. Specific additives are used in precise concentrations of internal standards, employing detailed controls adapted to distinguish twenty metabolites, which are scanned and vigorously compared to known spectra results. Revealing peaks, metabolite concentration, and scan intensities in the quality assurance steps are then compared to a range of thresholds to determine whether or not the sample is contaminated, drug-ridden, diagnosable, or unacceptable. All spectra results and quality assurance flags are organized in spreadsheet form and exported to a database where values are compiled and stored for daily output results and trend analysis. The method provides for high-throughput and quality results, having a consistent predictability for genetically testing newborns efficiently and accurately.
Owner:PERKINELMER GENETICS
Non-invasive prenatal genetic screen
The present invention provides methods and kits useful for genetic testing or screening of fetuses using nucleic acid samples isolated from cervical mucus samples of fetus hosts.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
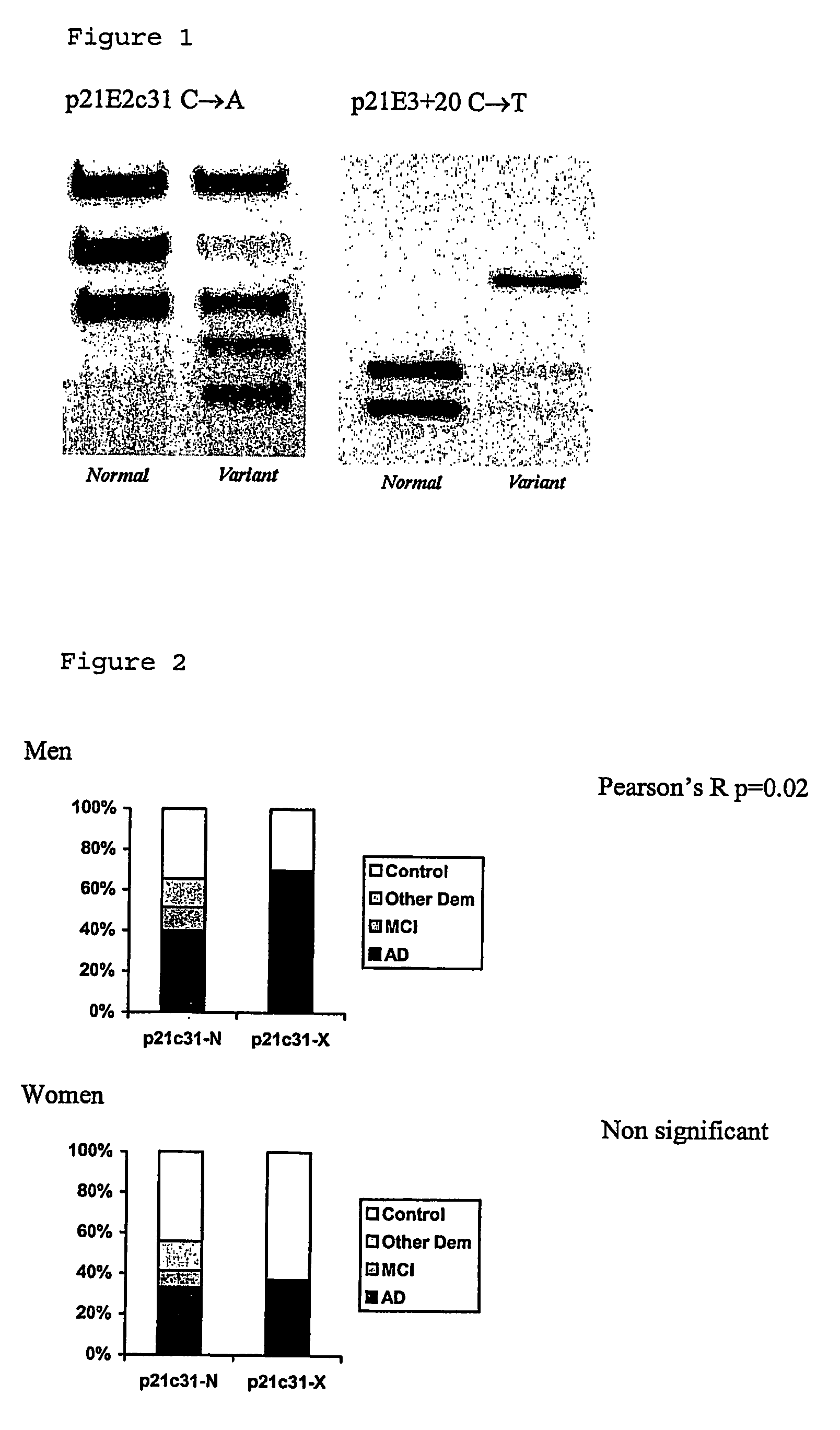
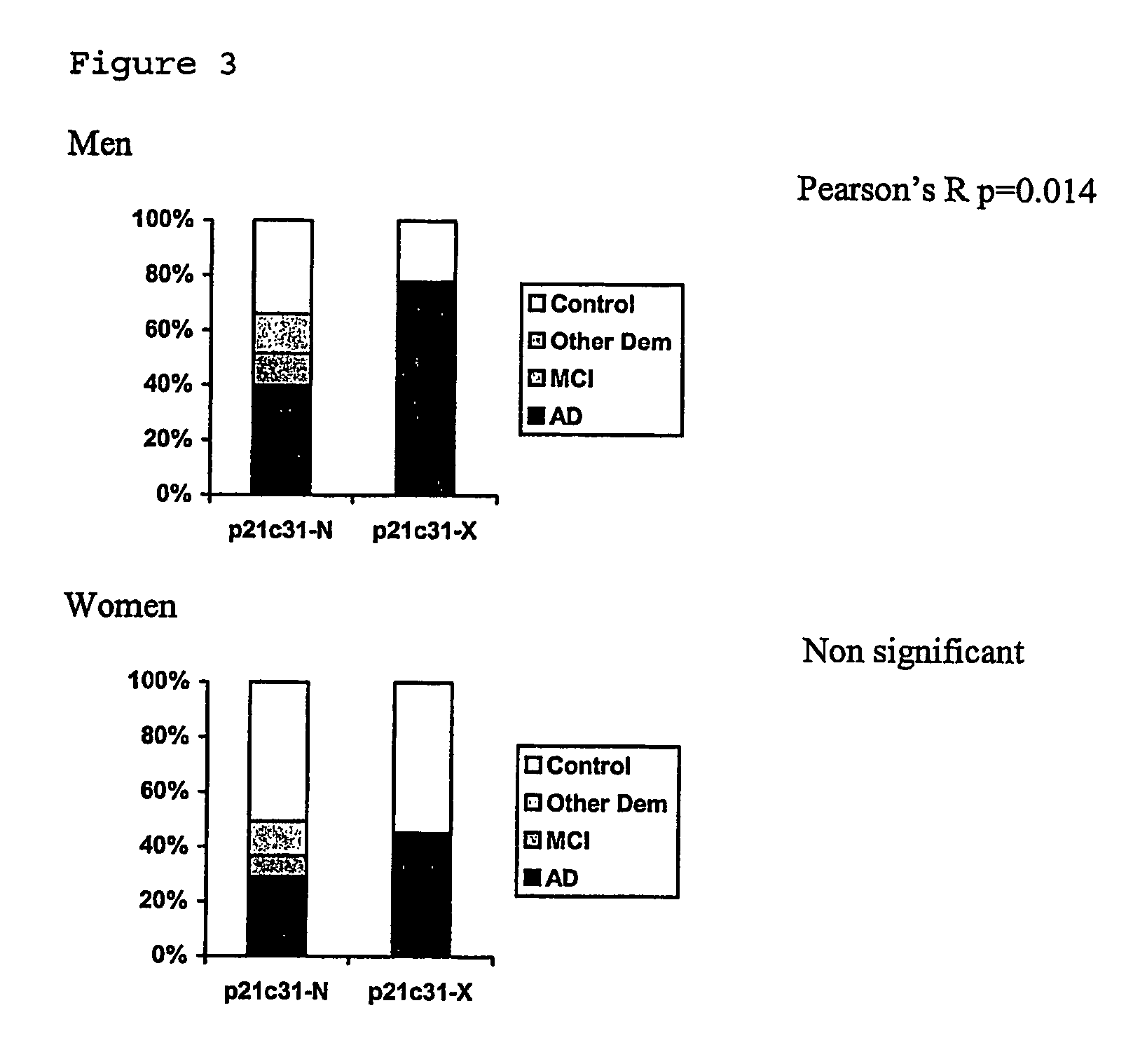
Susceptibility gene for alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20070072184A1Increased riskReduction in age of onset of AlzheimerSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenotyping
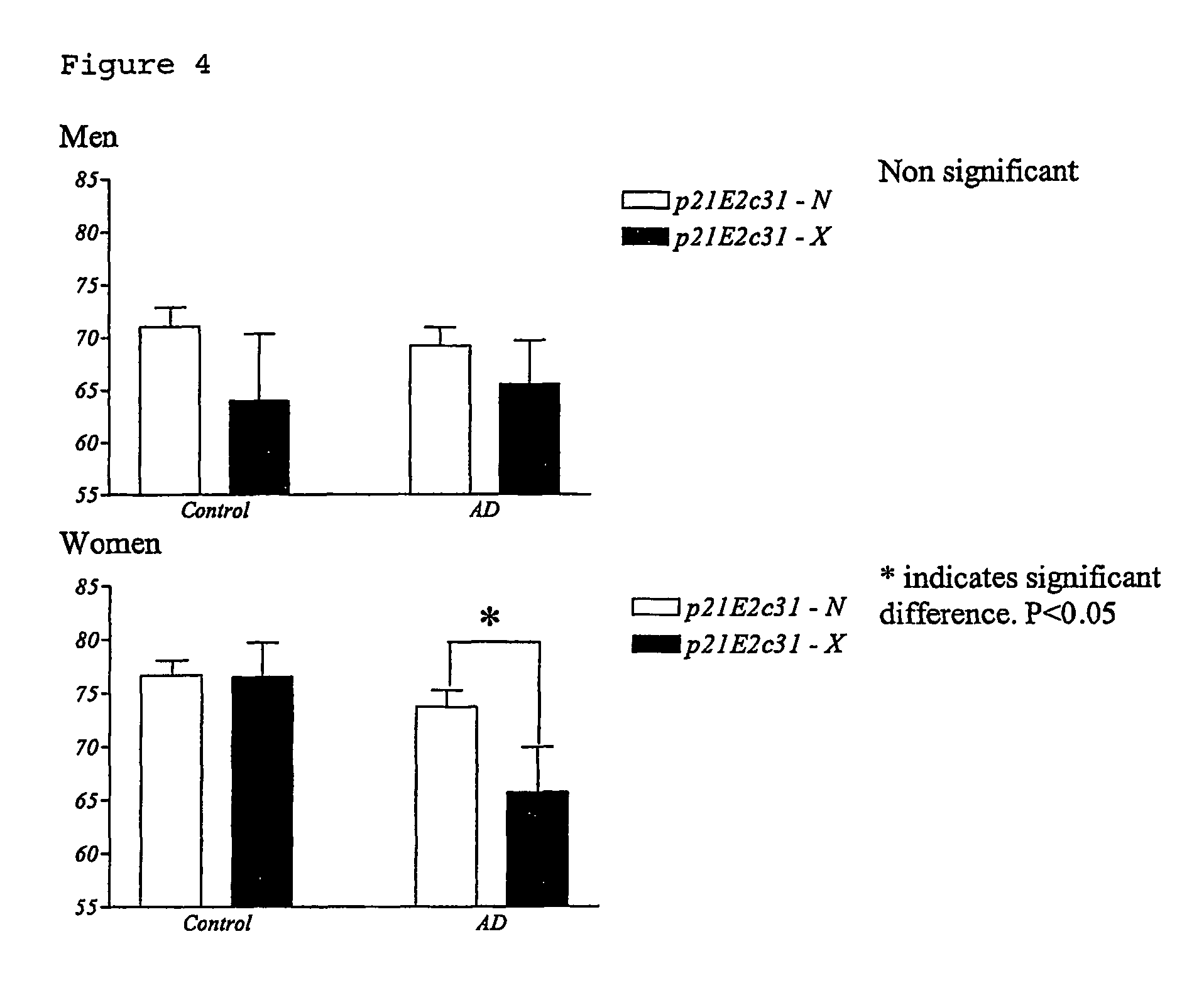
The invention relates to genetic screens for susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease. In particular, the invention provides genetic screens based on genotyping of the p21E2c31 polymorphism and / or the p21E3+20 C / T polymorphism in the p21cip 1 gene.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
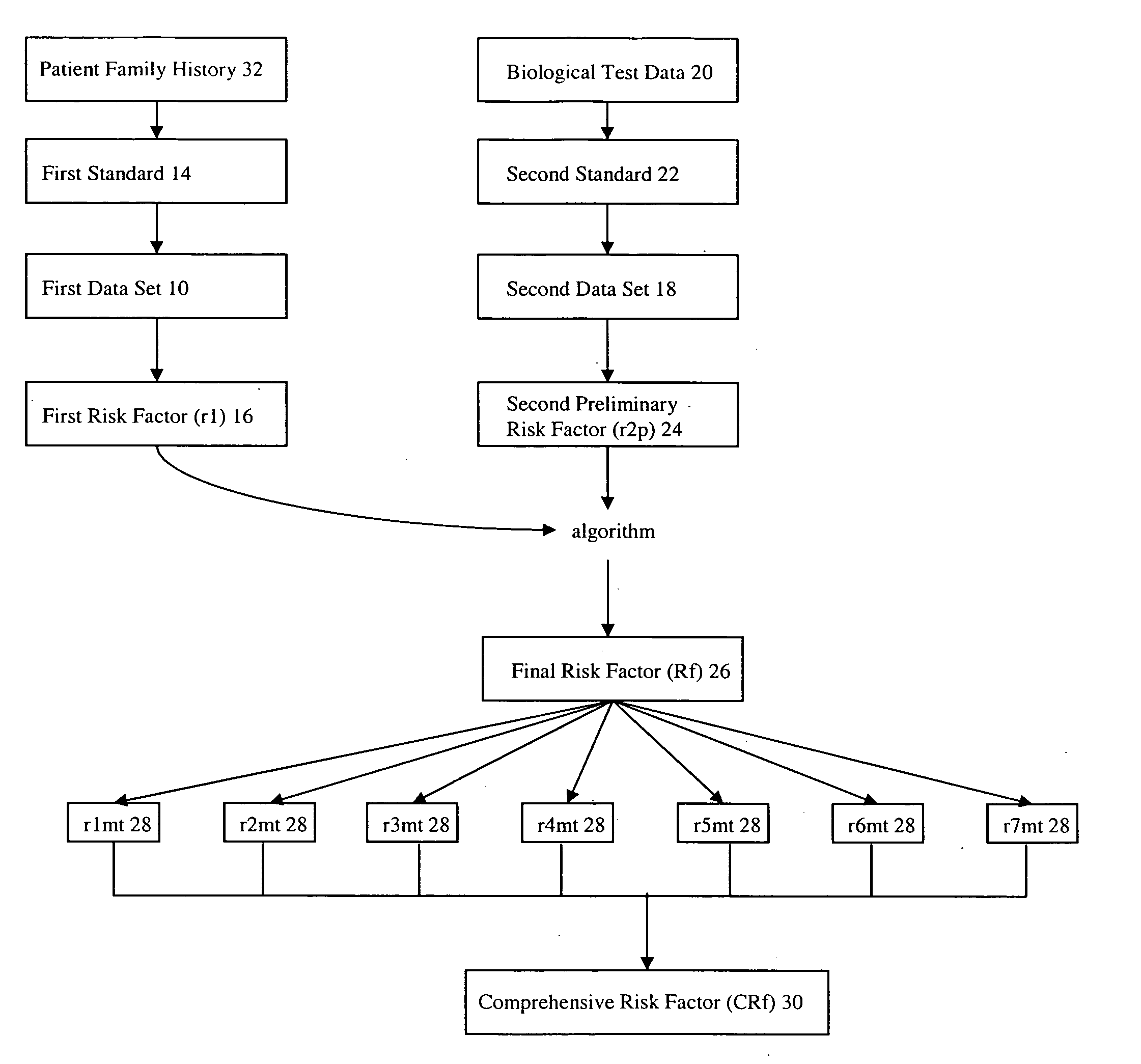
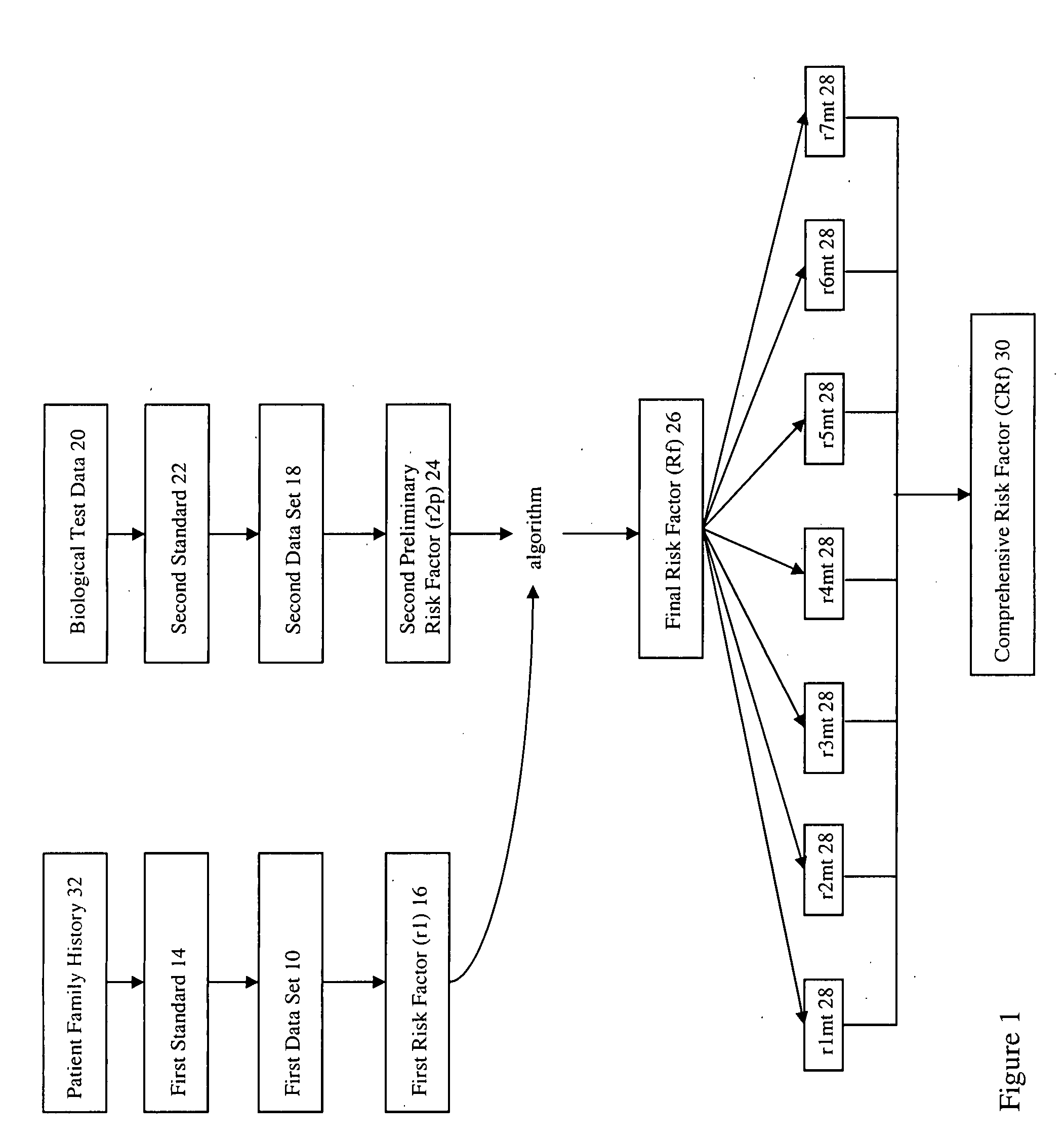
Method of genetic screening and analysis
InactiveUS20090030723A1Improve forecast accuracyData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationAnalysis methodGenetic disorder
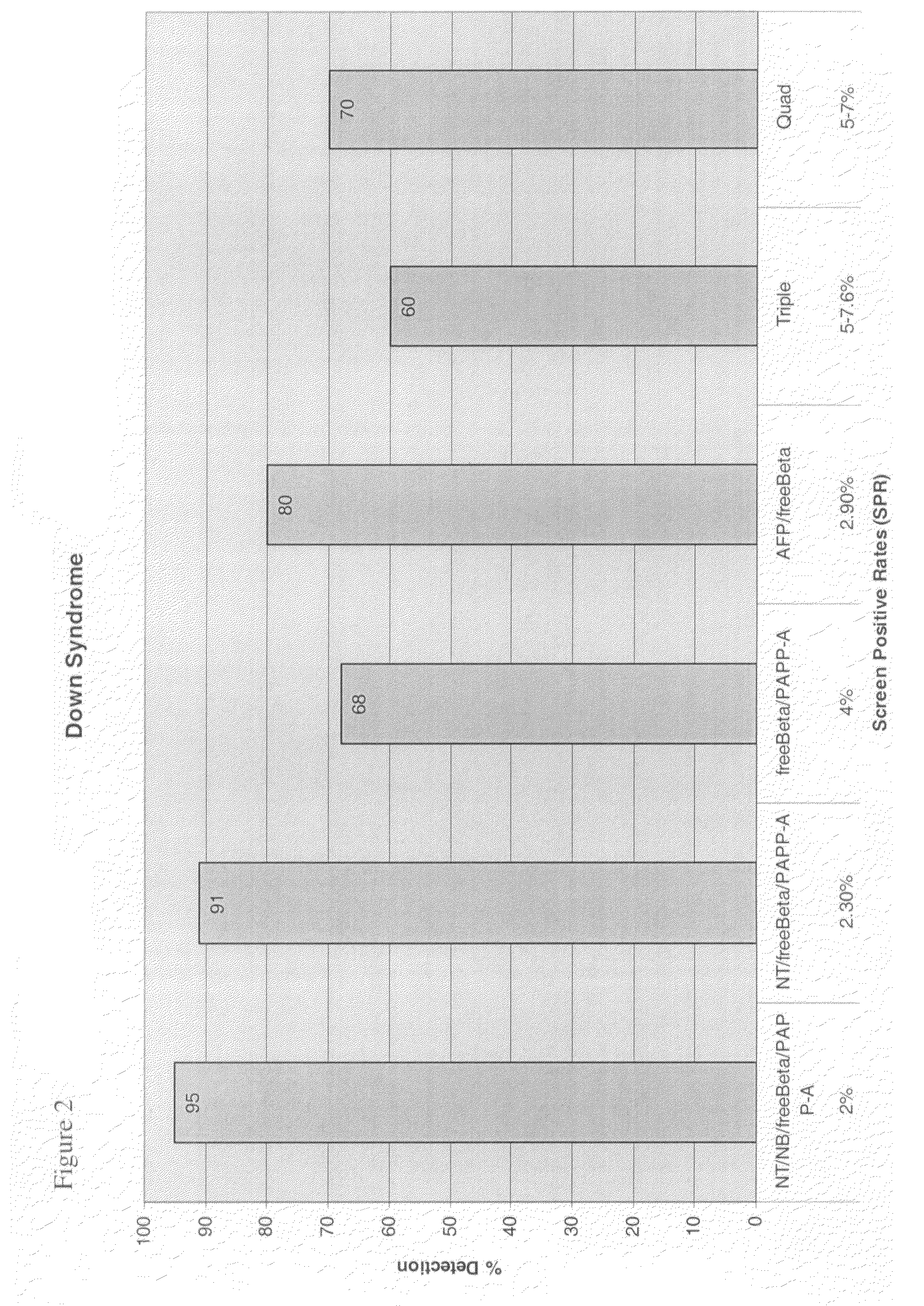
A method of genetic screening and analysis, particularly for prenatal genetic screening to determine a risk estimate or probability of genetic disorders for a specific pregnancy integrating a patient's family history data (r1) with a patient's biological test data (r2p) to generate a final prenatal risk factor (Rf). A comprehensive risk factor (CRf) is generated by running a multiplicity of tests on the Rf for screening various genetic disorders.
Owner:GENECARE MEDICAL GENETICS CENT
Compositions and methods for mammalian genetics and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120190011A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorGene productMammalian cell
The invention provides compositions and methods for performing mammalian cell genetics, e.g., genetic screens, using near-haploid cells. The invention further provides genes and gene products isolated using the inventive methods and methods of use thereof.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Genetic Screen for Interaction Interface Mapping
InactiveUS20080044815A1Quick identificationReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAssayInteraction interface
Owner:PHYLOGICA
Non-invasive prenatal genetic screen
InactiveUS20100261188A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic Screening (procedure)Non invasive
The present invention provides methods and kits useful for genetic testing or screening of fetuses using nucleic acid samples isolated from cervical mucus samples of fetus hosts.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Gene for regulating plant height of Gossypium hirsutum, and application thereof
InactiveCN108396031AStrong specificityRealize regulationPlant peptidesFermentationGenomic sequencingMolecular breeding
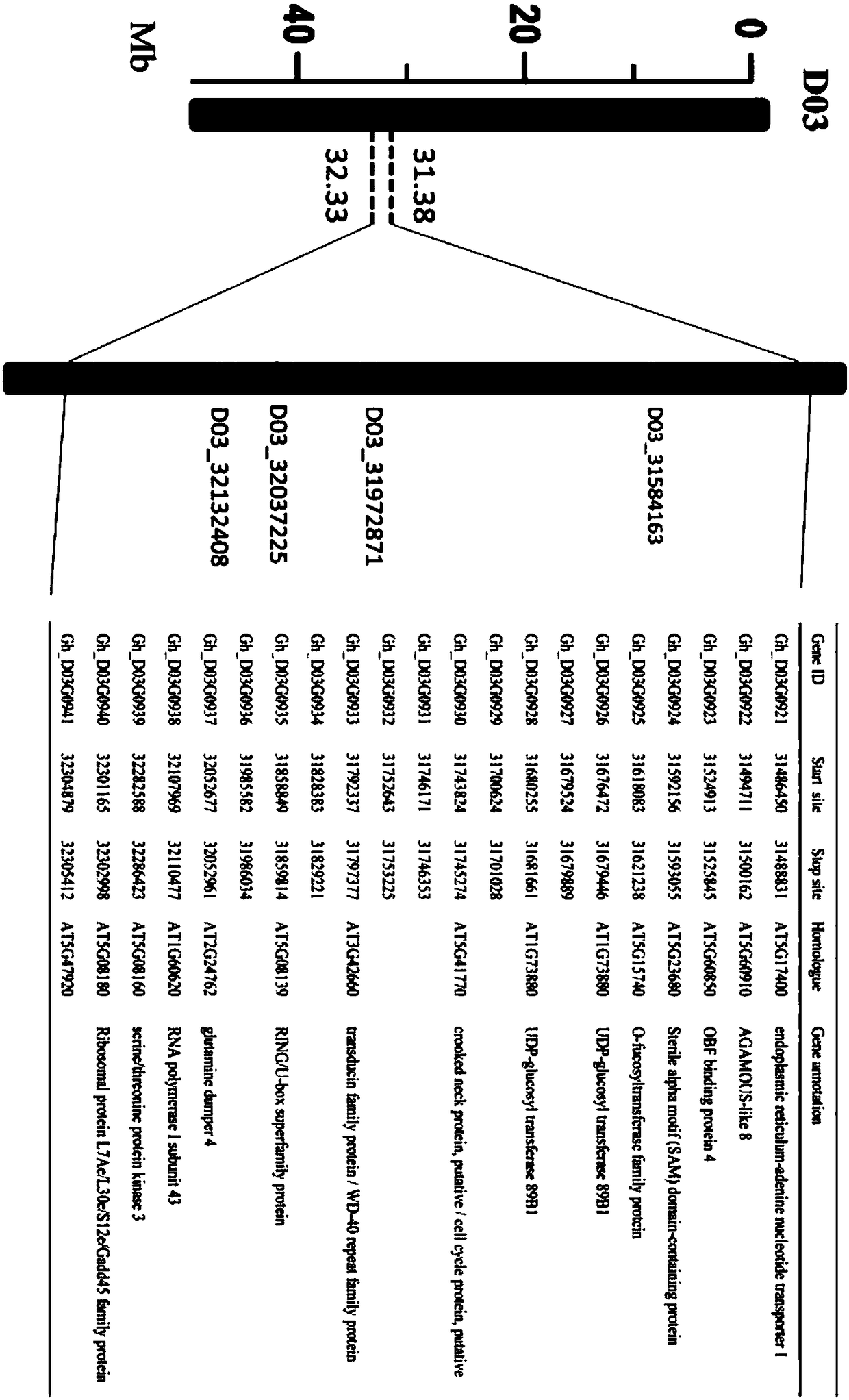
The invention relates to the field of plant height genes, and concretely relates to a gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum, and an application thereof. The base sequence of the CDS of the gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and a specific base sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. A large number of SNPs covering the whole genome of Gossypium spp. are developed based on an SLAF-seq reduced representation sequencing technology by utilizing 355 natural populations of Gossypium hirsutum, genetic genes of theplant height are parsed by adopting a GWAS technology through the 3-year and 2-site phenotypic identification of plant height traits, and the genetic screens are screened to obtain the gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum. A result of verification of the functions of the gene by using a virus-induced gene silencing technology shows that the plant height can be controlled by regulating the expression of the gene, so the gene lays a foundation for developing the molecular breeding of the Gossypium hirsutum.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV +1
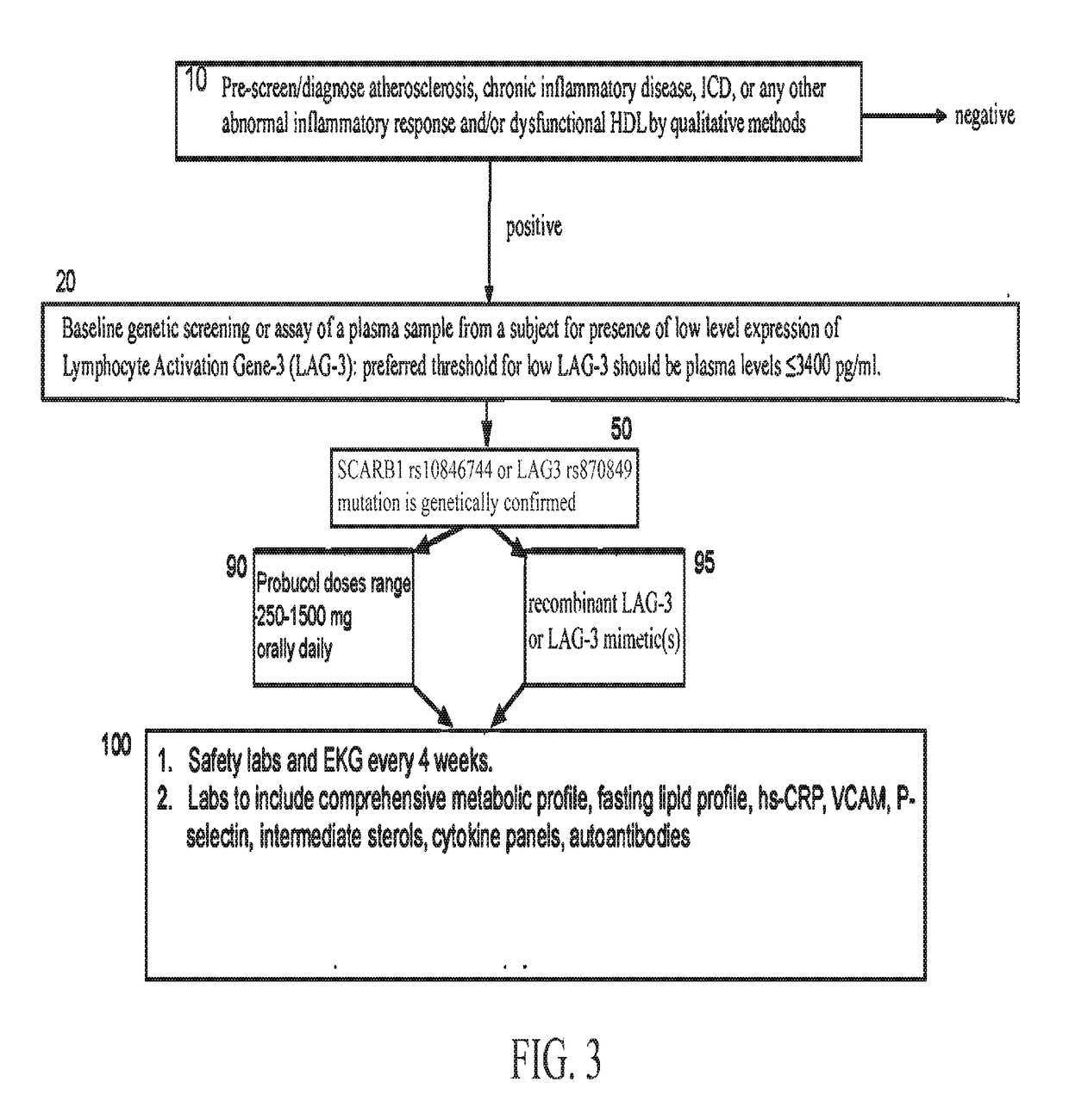
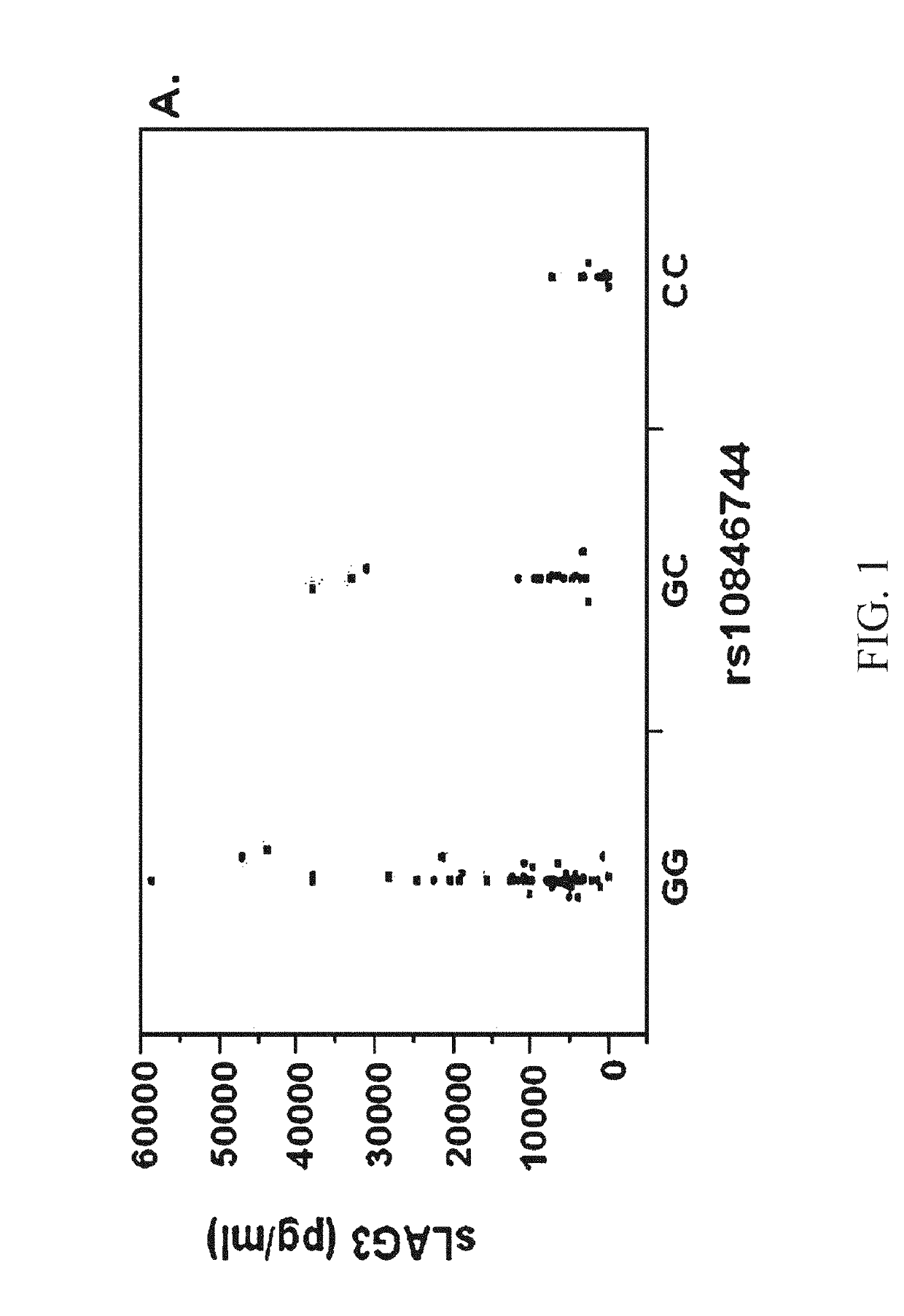
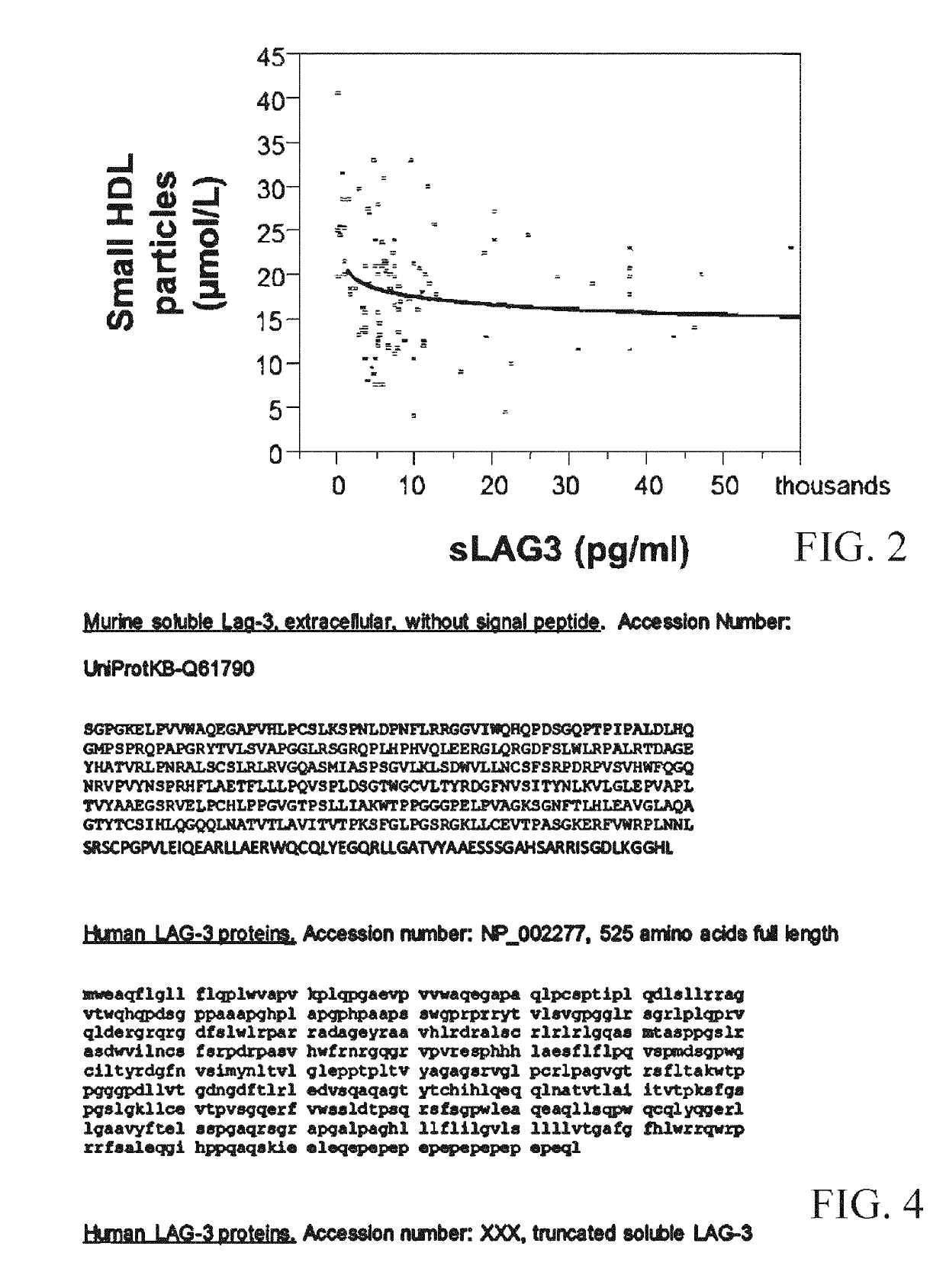
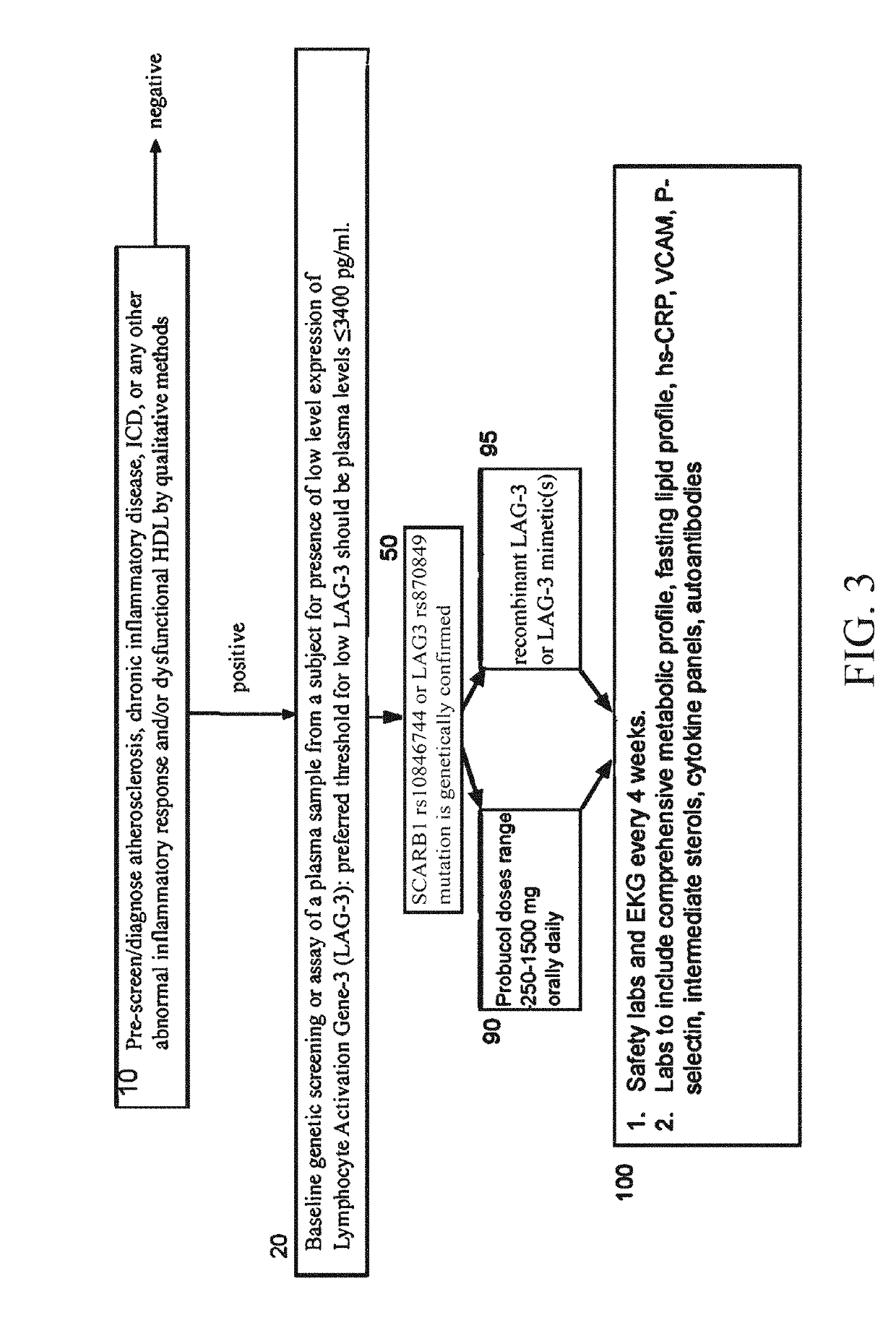
Use of recombinant lymphocyte activation gene-3 as a companion therapeutic for patients at risk for cardiovascular disease and other chronic inflammatory diseases
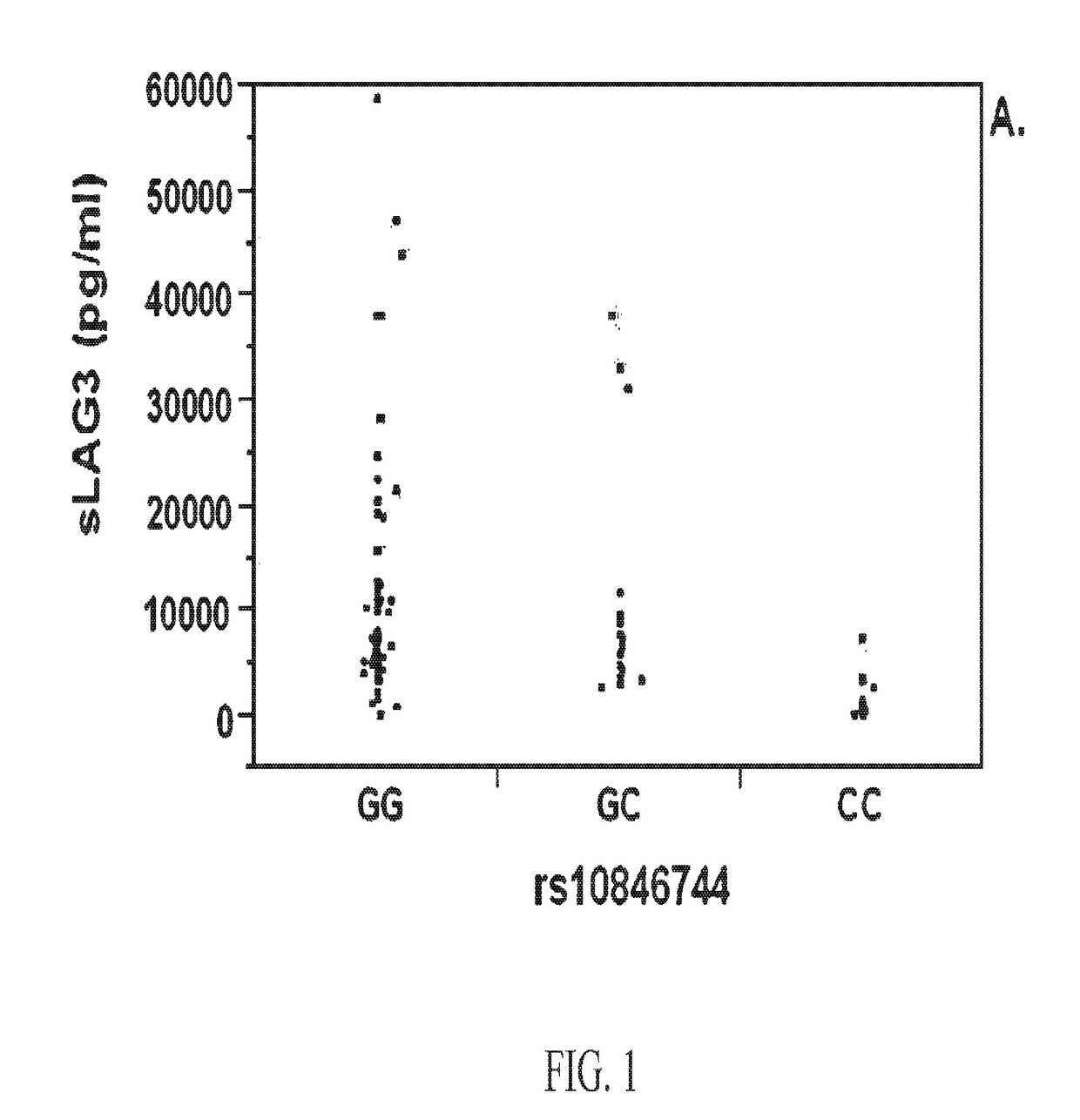
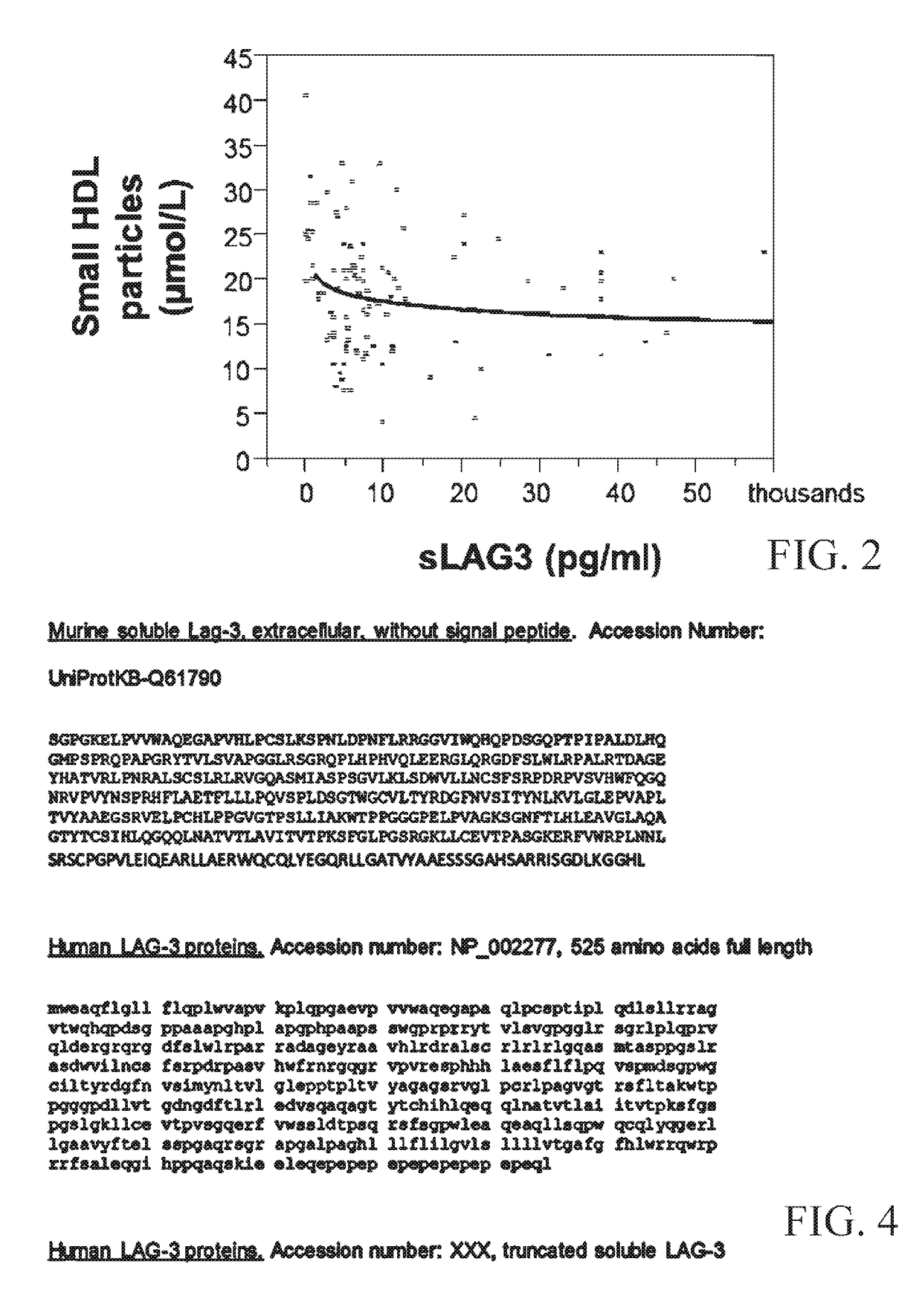
A method for classifying patients at risk for cardiovascular disease, other chronic inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular and / or non-cardiovascular morbidity and mortality based on a risk assessment for lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3) protein deficiency, and for mediating the risk using recombinant lymphocyte activation gene-3 or LAG3 mimetic as a companion therapeutic alone or in combination with a statin and / or an anti-hyperlipidemic drug. The risk assessment is two-prong, beginning with a qualitative determination whether a subject has or is predisposed to abnormal expression of inflammasomes, heightened risk for inflammation and / or to dysfunctional HDL, followed by a quantitative assay or genetic screen for a polymorphism that occurs in the coding sequence of the LAG3 gene. Given positive indication, recombinant LAG3 and / or LAG3 mimetic is used alone or in combination with the therapeutic use of a cholesterol mediating drug for treatment.
Owner:RODRIGUEZ OQUENDO ANNABELLE
Use of recombinant lymphocyte activation gene-3 as a companion therapeutic for patients at risk for cardiovascular disease and other chronic inflammatory diseases
Owner:RODRIGUEZ OQUENDO ANNABELLE
Genetic functions required for gene silencing in maize
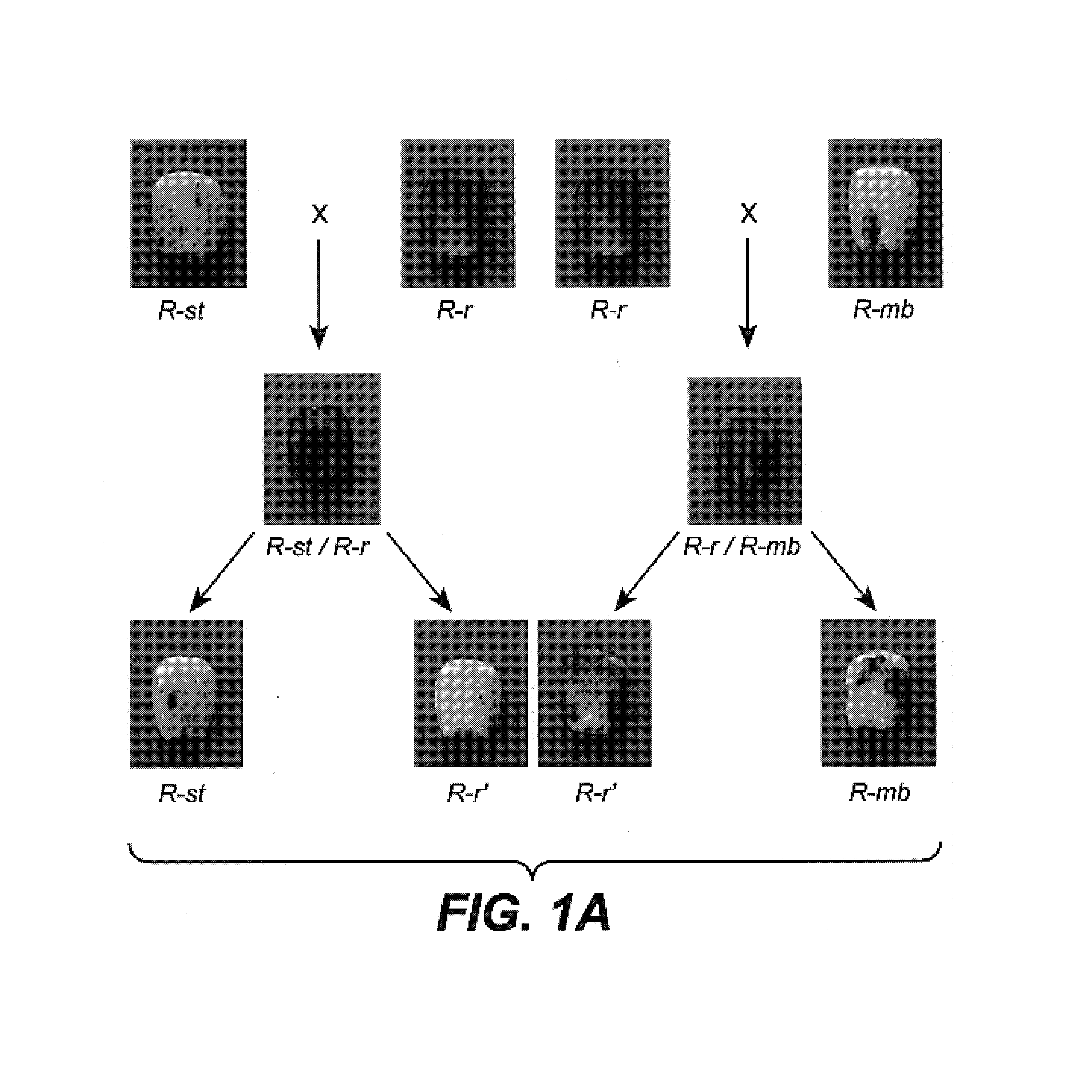
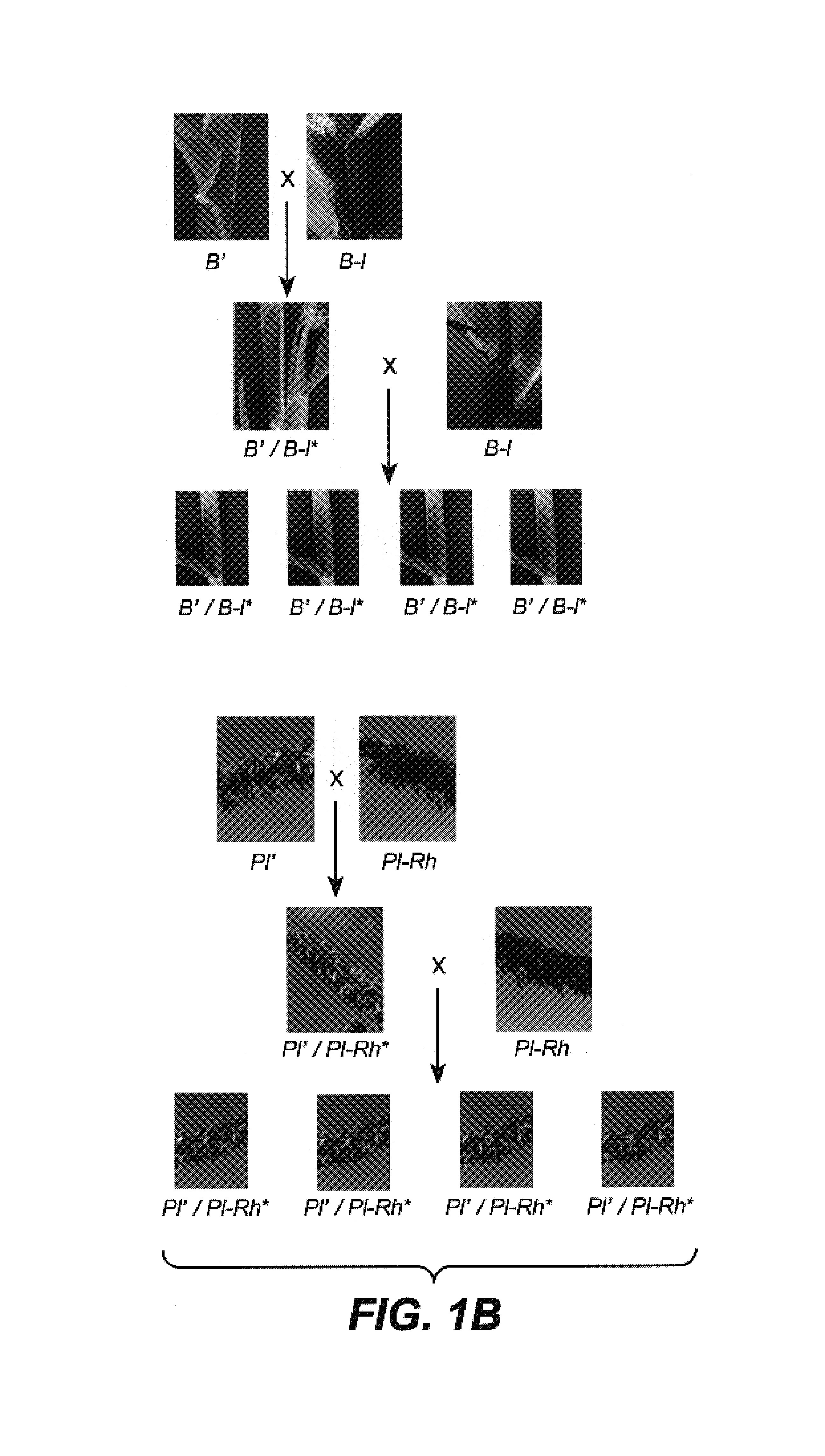
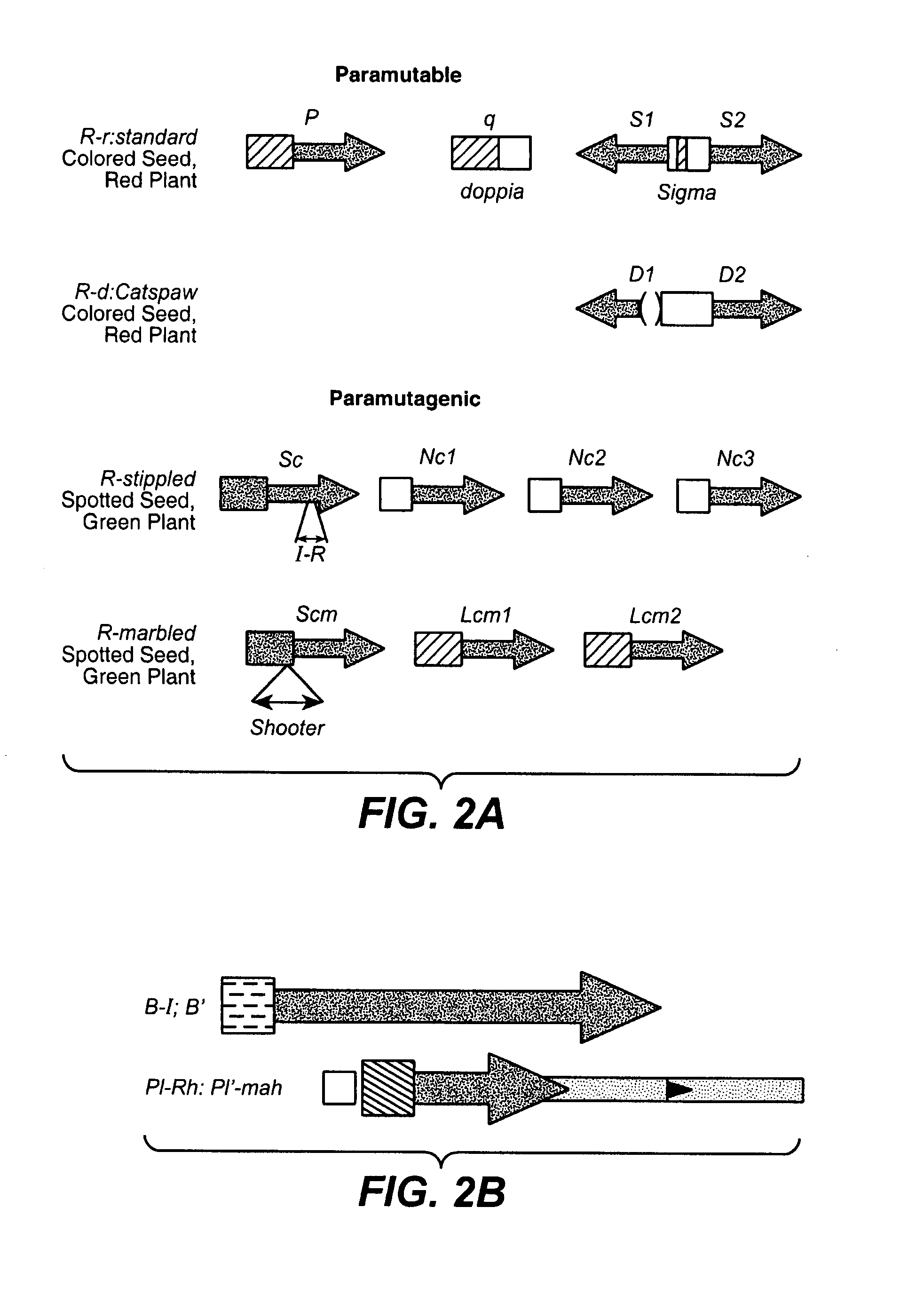
InactiveUS7264970B2Reduce establishmentSlow changeFused cellsOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic functionHybrid seed
Transgenic silencing is a little understood process by which genes introduced into plants are turned off or silenced. Genetic screens were designed to identify corn mutants with reduced gene silencing activity. Such mutant corn lines include Mop1-1; Mop1-2EMS; Mop2-1, mop3-1; CC2343, rmr1-1; rmr1-2; rmr2-1; rmr6-1; rmr7-1; rmr7-2; rmr8-1; rmr9-1; Mop1-4; Mop1-5; and rmr11-1 and seeds derived therefrom, the plants are useful for corn breeding programs to produce inbred and hybrid seed with reduced gene silencing activity.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +2
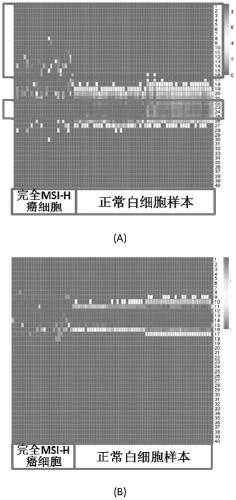
A microsatellite biomarker combination, detection kit and use thereof
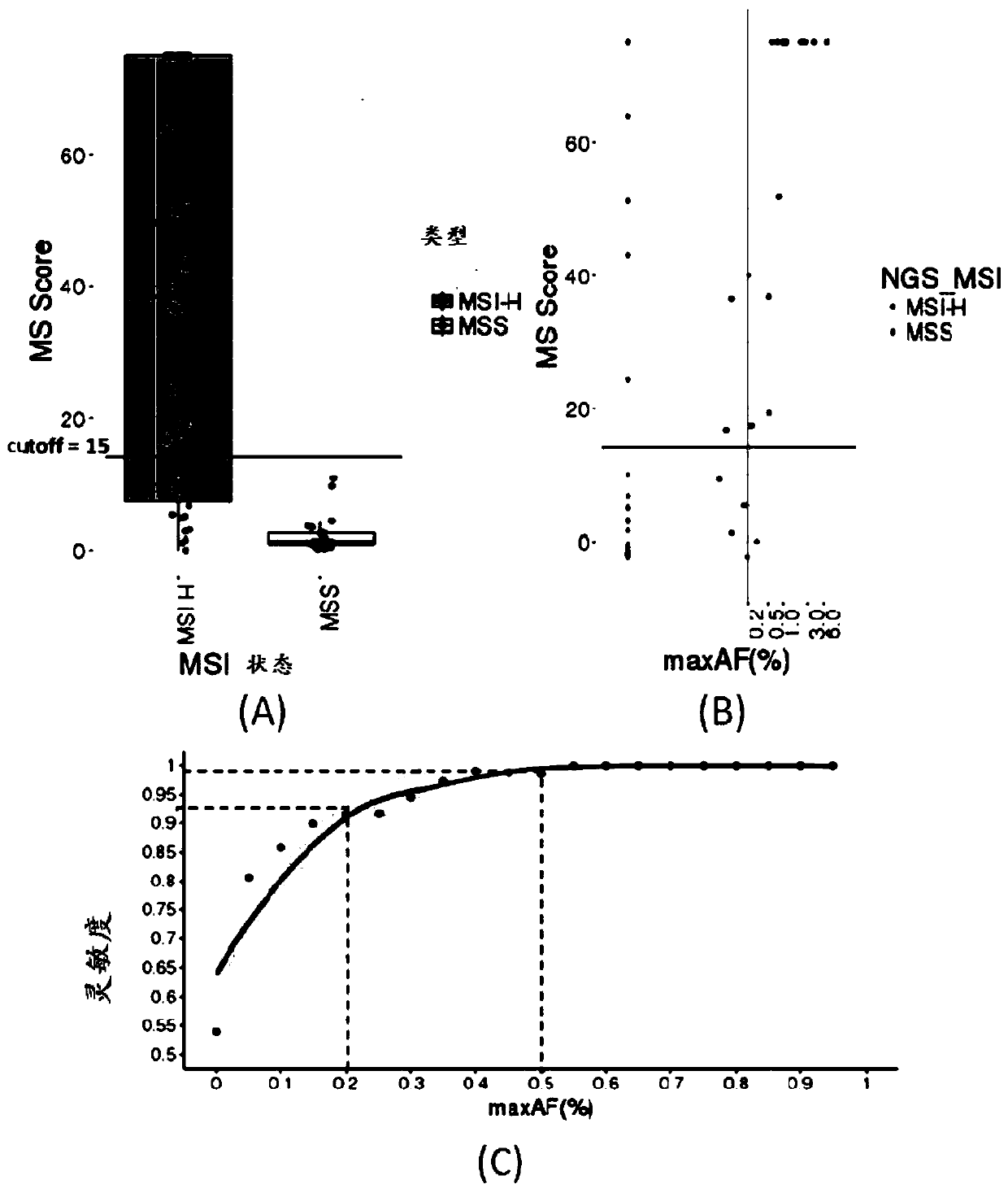
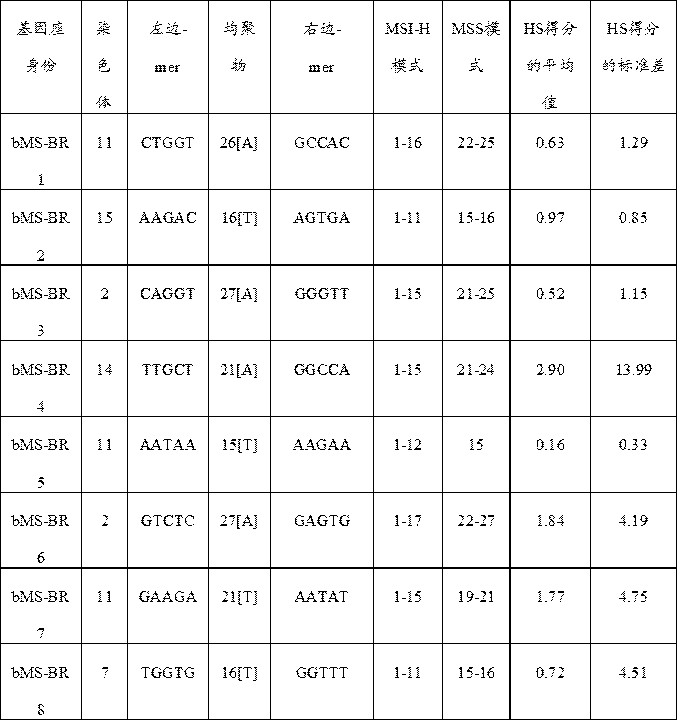
The present invention relates to biomarker combinations, kits for their detection, and their detection in plasma samples of microsatellite instability (MSI) and non-invasive detection of cancer, preferably colorectal (eg bowel), gastric or endometrial cancer. Use in diagnosis, prognostic assessment, treatment selection, or genetic screening. This application provides for the first time a plasma MSI detection method that can determine the microsatellite (MS) status of a sample with high accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BURNING ROCK DX CO LTD
Method of predicting chemotherapeutic responsiveness of cancer
ActiveUS20100292087A1% efficiencyPredict prognosisLibrary screeningAnalogue computers for chemical processesAlkaloidWilms' tumor
Disclosed is a method of predicting clinical tumor outcome by providing gene expression from a tumor sample. The method utilizes a novel genetic screen to identify genes that contribute to chemotherapeutic responsiveness, using formalin fixed paraffin embedded clinical samples of epithelial cancer, specifically serous ovarian cancer. The method is useful in predicting tumor responsiveness to chemotherapeutics, including alkylating agents, cisplatin, antimetabolites, plant alkaloids, and antitumor antibiotics. A microarray screen showed formalin fixed paraffin embedded samples can identify genes related to chemotherapeutic response with 86% efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Dilated cardiomyopathy gene detection marker and application thereof
ActiveCN114507727AMany disease-causing genesIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhysiologyGenetics
The invention provides an application of gene mutation in preparation of a dilated cardiomyopathy detection kit. The gene mutation is SGCB c.243 + 6Agt; and T variation sites. SGCB c.243 + 6Ag < t >; the homozygous mutation of the T site can be used for gene diagnosis or auxiliary diagnosis of clinical dilated cardiomyopathy, genetic screening is provided for families carrying dilated cardiomyopathy pathogenic variation, and the possibility is provided for realizing prenatal and postnatal rearing.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
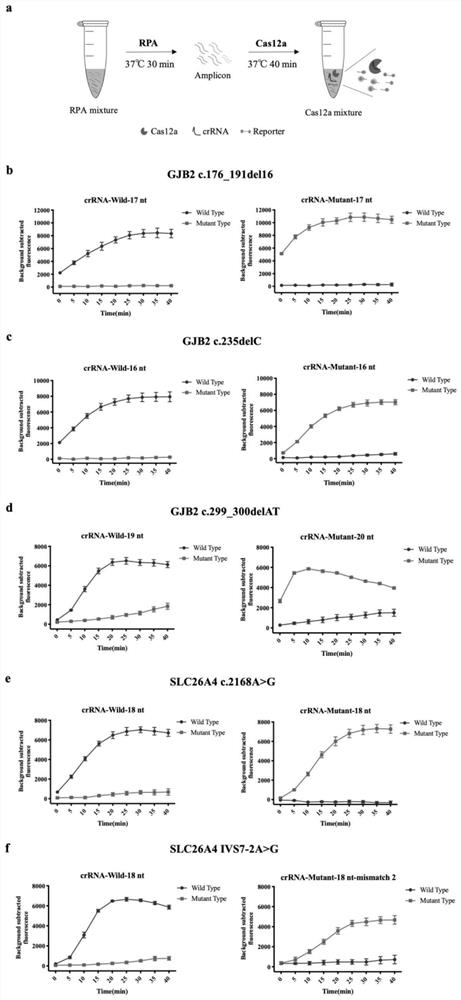
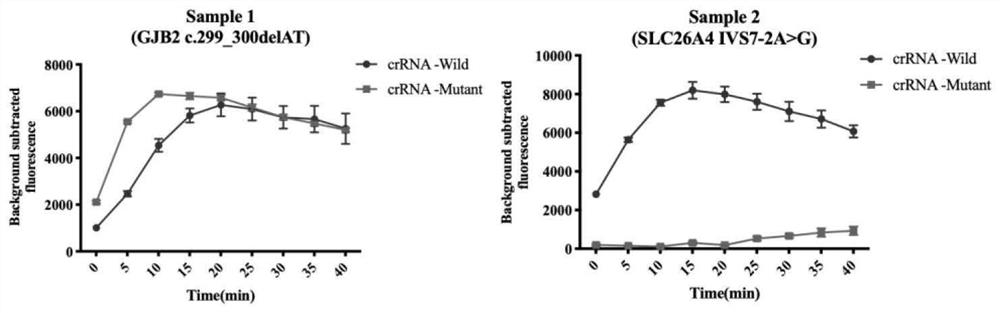
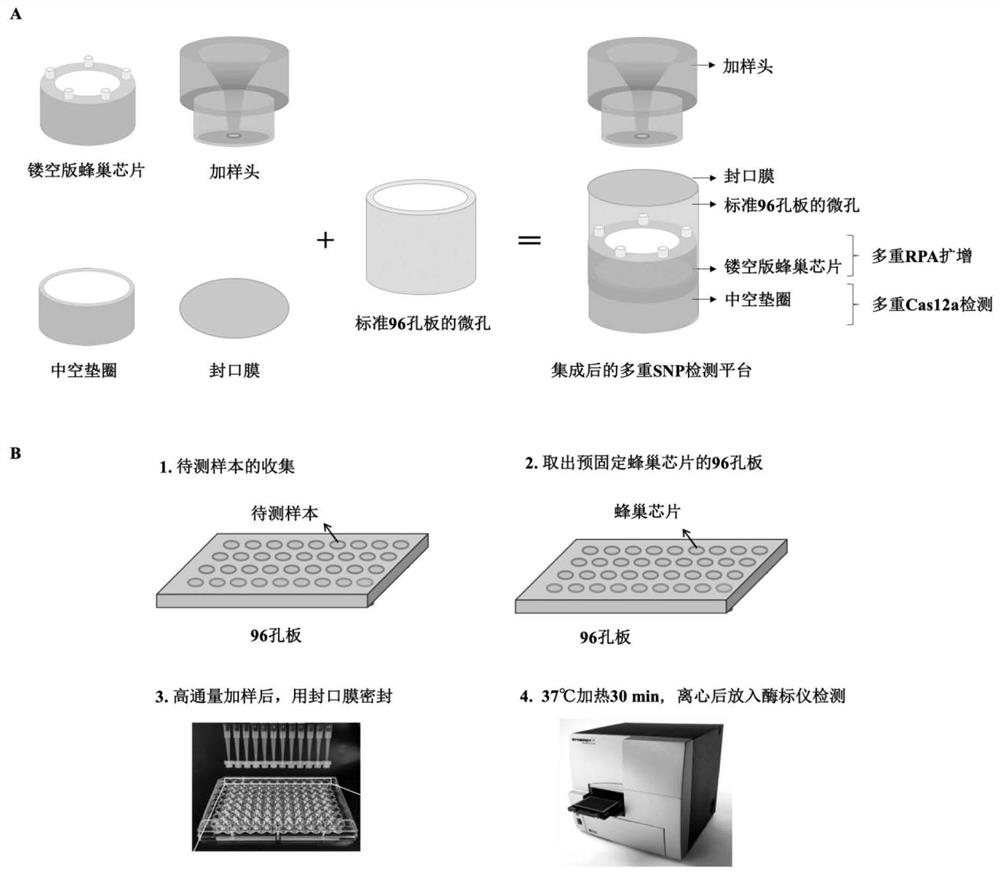
crRNA combination for multiple detection of hereditary hearing loss, kit and method theref
PendingCN113265457AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a crRNA combination for multiple detection of hereditary hearing loss, a kit and a method thereof. The crRNA combination targets five SNP sites of deafness genes GJB2 and SLC26A4 at the same time, and comprises nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.6, SEQ ID No.8 and SEQ ID No.10. According to the multiple detection kit for hereditary hearing loss, a Cas12a detection reaction system is arranged in a micropore of a pore plate, multiple RPA amplification is performed in a hollow honeycomb chip, and the hollow honeycomb chip and the bottom of the micropore are physically isolated by using a hollow gasket, so that two reactions of multiple RPA amplification and Cas12a detection are firstly isolated and then fused; one-step and multiple detection is realized, and aerosol pollution possibly caused by uncovering detection is also avoided. The method also realizes high-throughput detection, at most 96 samples are detected in one reaction, 5 SNP loci are distinguished at the same time, and the method is suitable for large-scale genetic screening.
Owner:上海抗码芯瑞生物科技有限公司
Susceptibility gene for Alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS7842455B2Increased riskReduction in age of onset of AlzheimerSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSusceptibility geneGenomic screening
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Screens and assays for agents useful in controlling parasitic nematodes
InactiveUS7064243B2Reduce expressionReduce processing stepsPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyAssay
The invention provides a method of identifying anti-nematode compounds and further provides transgenic nematodes that may be used to practice the method. In particular, the invention provides a screen for compounds that inhibit a nematode secretion pathway e.g, compounds that inhibit the secretion of proteins by nematodes. The transgenic nematodes express reporters for nematode secreted proteins. In preferred embodiments of the invention the screen is performed using C. elegans, i.e., certain embodiments of the invention utilize C. elegans and C. elegans secretory pathways as a model system for parasitic nematodes and parasitic nematode secretion pathways. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions that may be used in the treatment and prevention of nematode infection in humans and animals and anti-nematode agents that may be used to protect plants from plant-parasitic nematodes. In addition, the invention provides a genetic screen for identifying additional targets for anti-nematode compounds.
Owner:CAMBRIA PHARMA
Method for the identification of genes involved in neurodegenerative processes
InactiveUS20110214191A1Progressive arrhythmicityReduced expression levelNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementLate onsetSleep wake
A method for the identification of genes involved in neurodegenerative processes, detectable by the late onset of a phenotype associated with neurodegeneration, by means of a genetic screen of deregulated genes, which comprises the measurement of sleep-wake cycle activity schemes in different stages of life, young and adult, of individuals of an animal model, such as Drosophila. A mutant fly whose genome comprises a disruption in its enabled gene, with decrease of the enabled gene expression, and exhibiting a late onset neurodegenerative phenotype in adulthood.
Owner:INIS BIOTEC LLC +2
Genetic test for PSE-susceptible turkeys
InactiveUS20050272362A1Good quality meatCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesWater holding capacityBiology
This invention relates to methods and compounds for the improvement of turkey meat and turkey populations, but not limited to, a genetic screen to select for turkeys that produce a better quality of meat characterized by a higher postmortem pH and better water holding capacity.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Compositions and methods for mammalian genetics and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190376079A1Nucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene productMammalian cell
The invention provides compositions and methods for performing mammalian cell genetics, e.g., genetic screens, using near-haploid cells. The invention further provides genes and gene products isolated using the inventive methods and methods of use thereof.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Method of predicting chemotherapeutic responsiveness of cancer
Disclosed is a method of predicting clinical tumor outcome by providing gene expression from a tumor sample. The method utilizes a novel genetic screen to identify genes that contribute to chemotherapeutic responsiveness, using formalin fixed paraffin embedded clinical samples of epithelial cancer, specifically serous ovarian cancer. The method is useful in predicting tumor responsiveness to chemotherapeutics, including alkylating agents, cisplatin, antimetabolites, plant alkaloids, and antitumor antibiotics. A microarray screen showed formalin fixed paraffin embedded samples can identify genes related to chemotherapeutic response with 86% efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
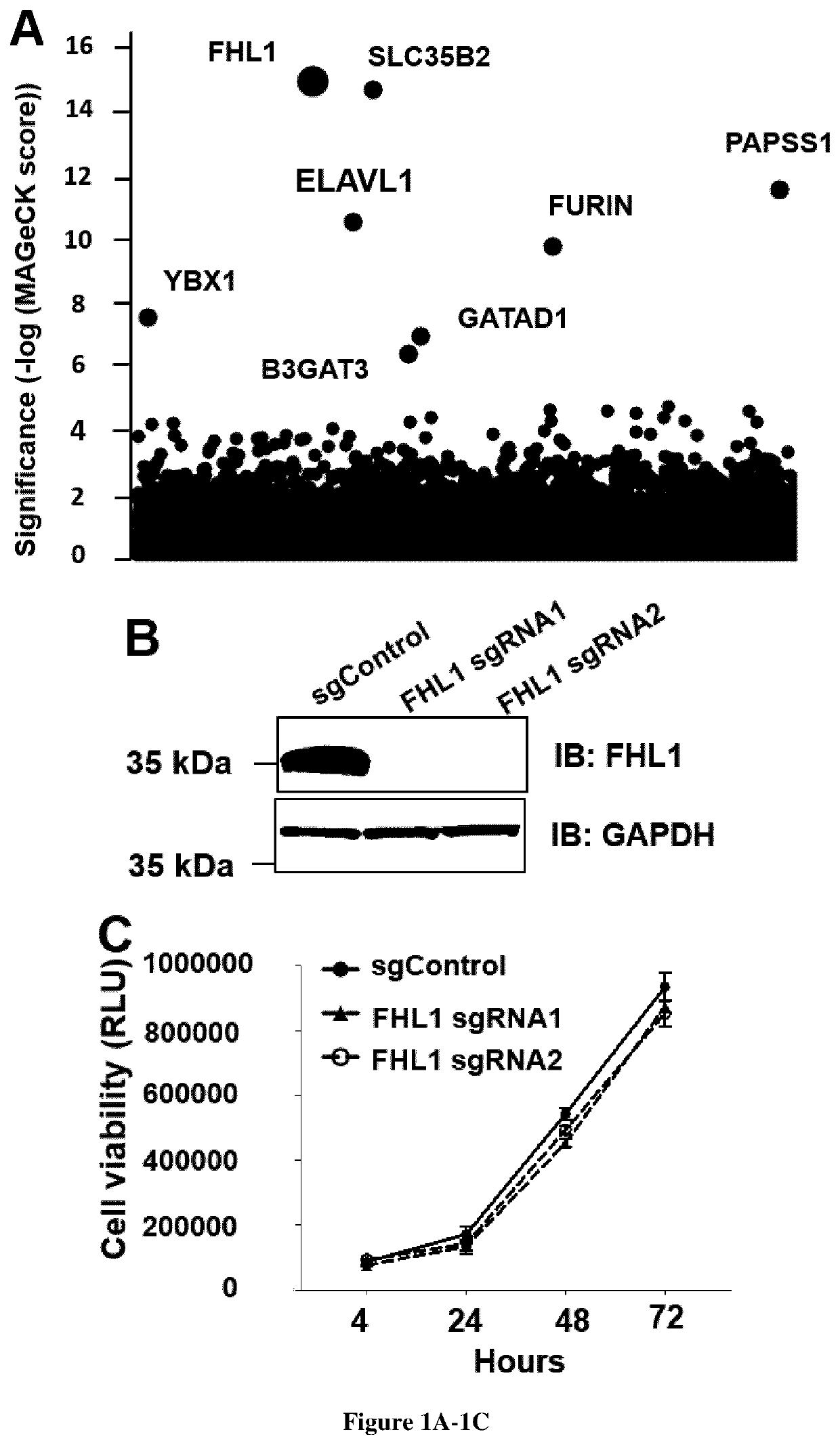
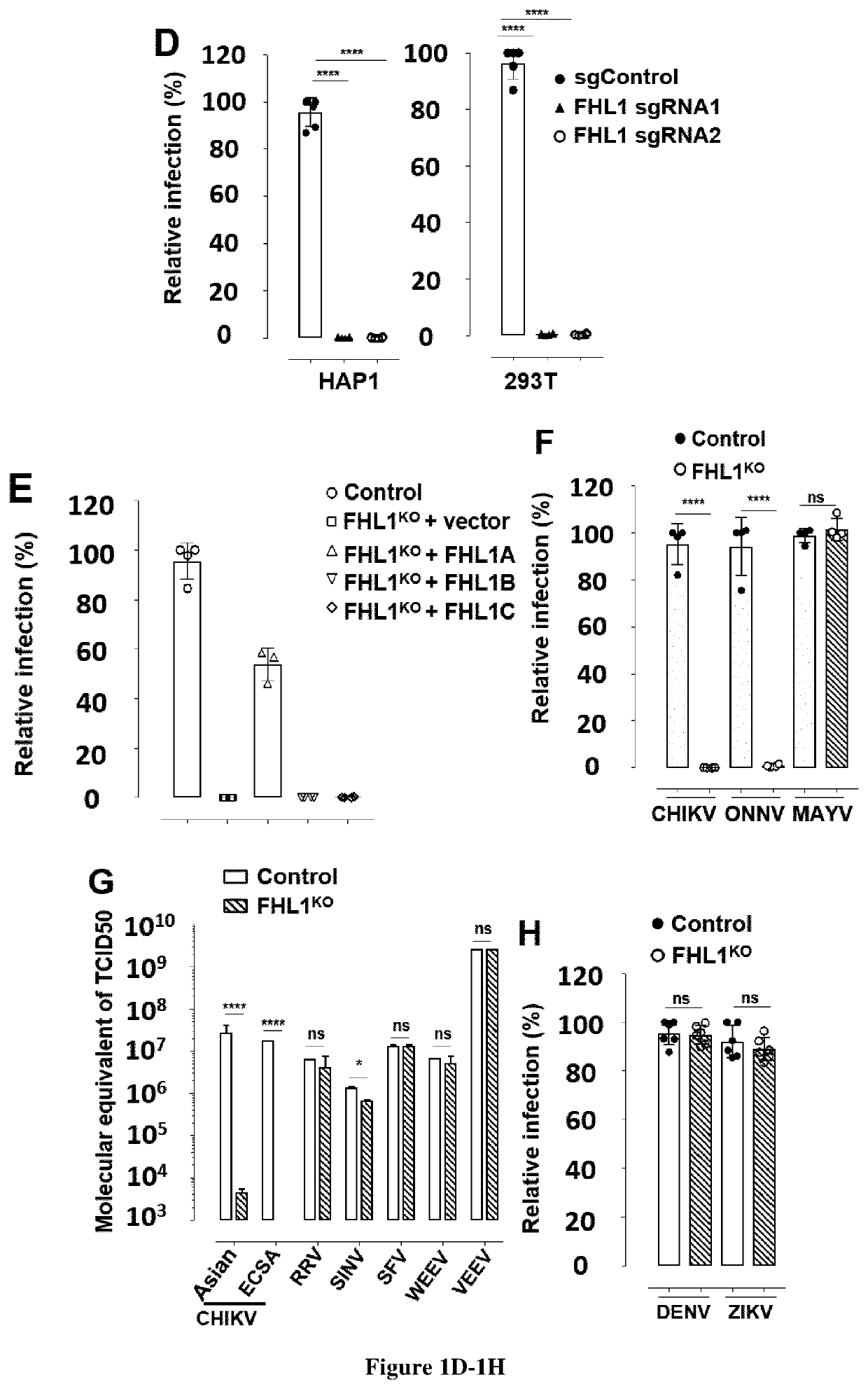
Methods for screening inhibitors against chikungunya virus and for determining whether subjects are predisposed to infection by said virus
PendingUS20220098681A1Easily commercially availableInhibit bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviralsChikungunyaNon steroid anti inflammatory drug
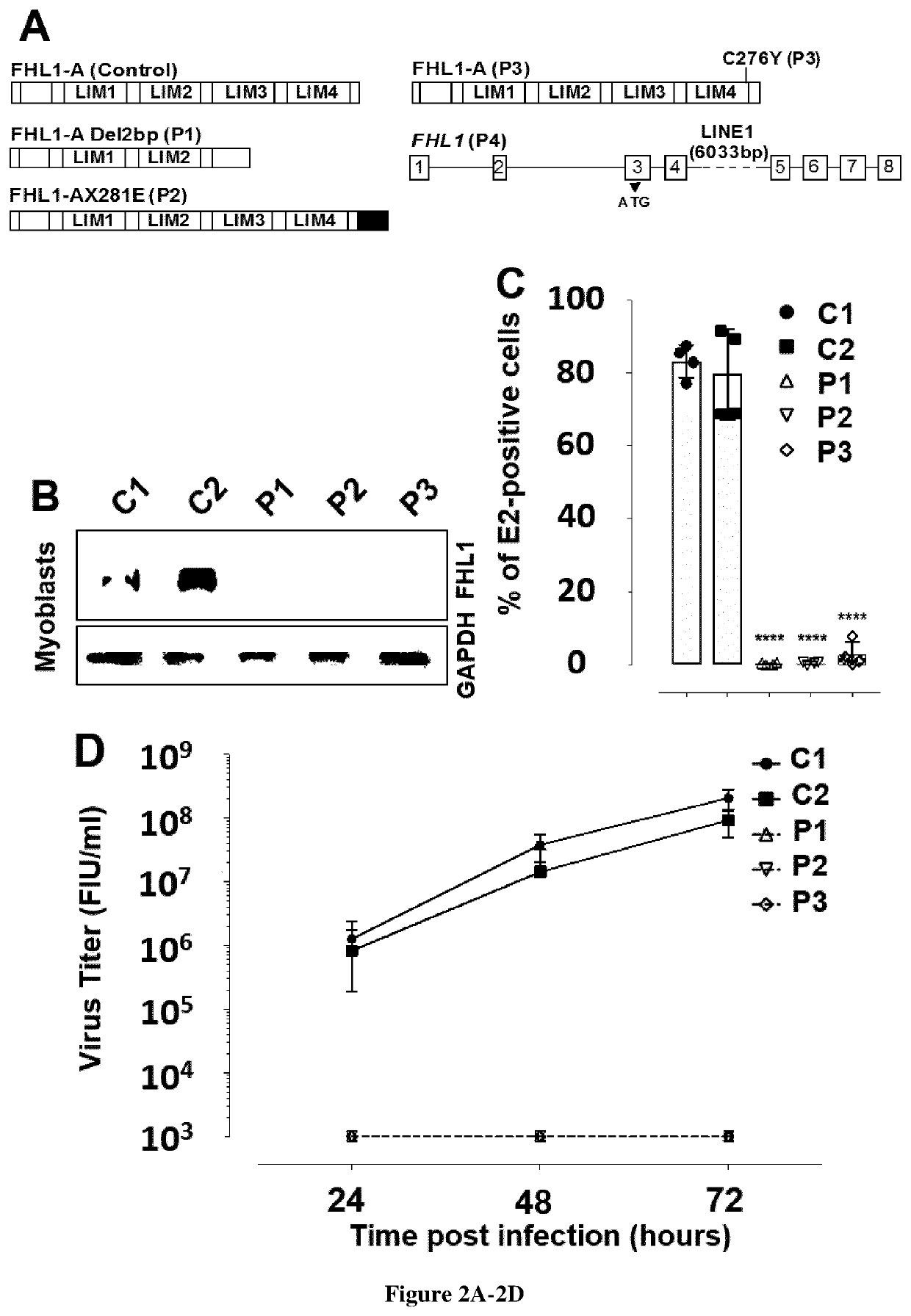
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) has caused recent outbreaks associated with severe morbidity. Currently no vaccine or treatment exists to protect humans from CHIKV infection. Treatment is therefore purely symptomatic and is based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Accordingly, there is a high medical need exists to have new methods of screening of compounds which could inhibit chikungunya virus. Further to a CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screen the inventors now identify the four and a half LIM domains protein 1 (FHL1) has an essential host factor for CHIKV infection. In particular, they show that primary myoblast and fibroblast from FHL1 deficient patient are resistant to CHIKV infection. They also demonstrate that depletion of FHL1 prevents CHIKV replication. Finally, they show that CHIKV non-structural protein 3 interacts specifically with FHL1A through its hypervariable domain. Thus compounds that are capable of inhibiting the interaction between the non-structural protein 3 and FHL1 would be suitable for inhibiting the replication capacity of the virus. Determining the expression level of FHL1 and / or identifying some genetic variant would also be suitable for determining whether some subjects are predisposed to CHIKV infection.
Owner:UNIVERSITÉ PARIS CITÉ +2
Genetic test for PSE-susceptible turkeys
InactiveUS7432057B2Good quality meatCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesBiotechnologyZoology
This invention relates to methods and compounds for the improvement of turkey meat and turkey populations, but not limited to, a genetic screen to select for turkeys that produce a better quality of meat characterized by a higher postmortem pH and better water holding capacity.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Methods of identifying essential protein domains
PendingUS20180023139A1Generate efficientlyEfficiently mutationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic screenProtein domain
Provided herein, in some aspects, are methods of determining whether a candidate protein, more specifically a functional domain of a candidate protein, is essential for viability of cells of interest using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CPJSPR)-Cas9 technology which holds great promise for genetic screening and for the discovery of therapeutic targets.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
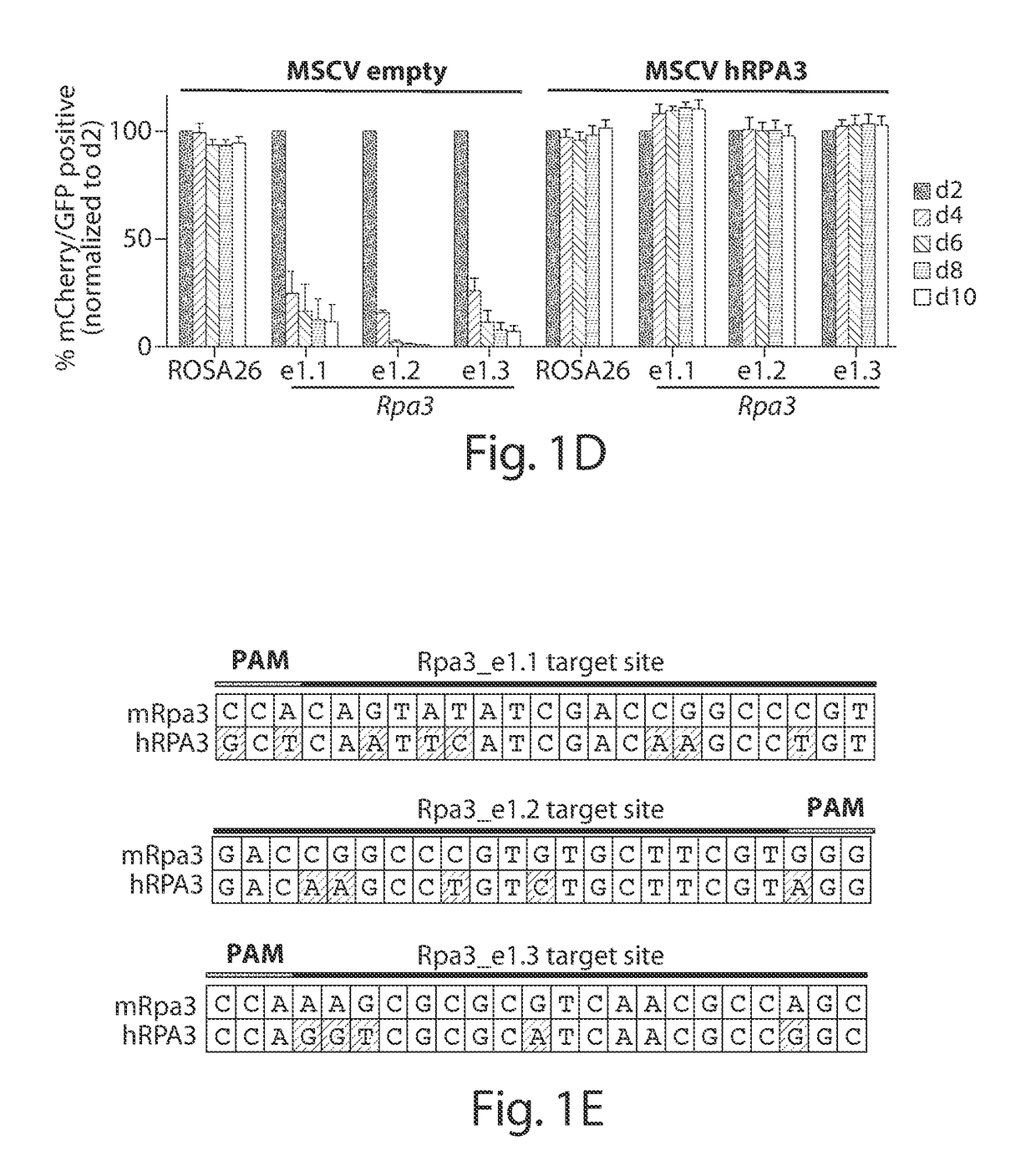
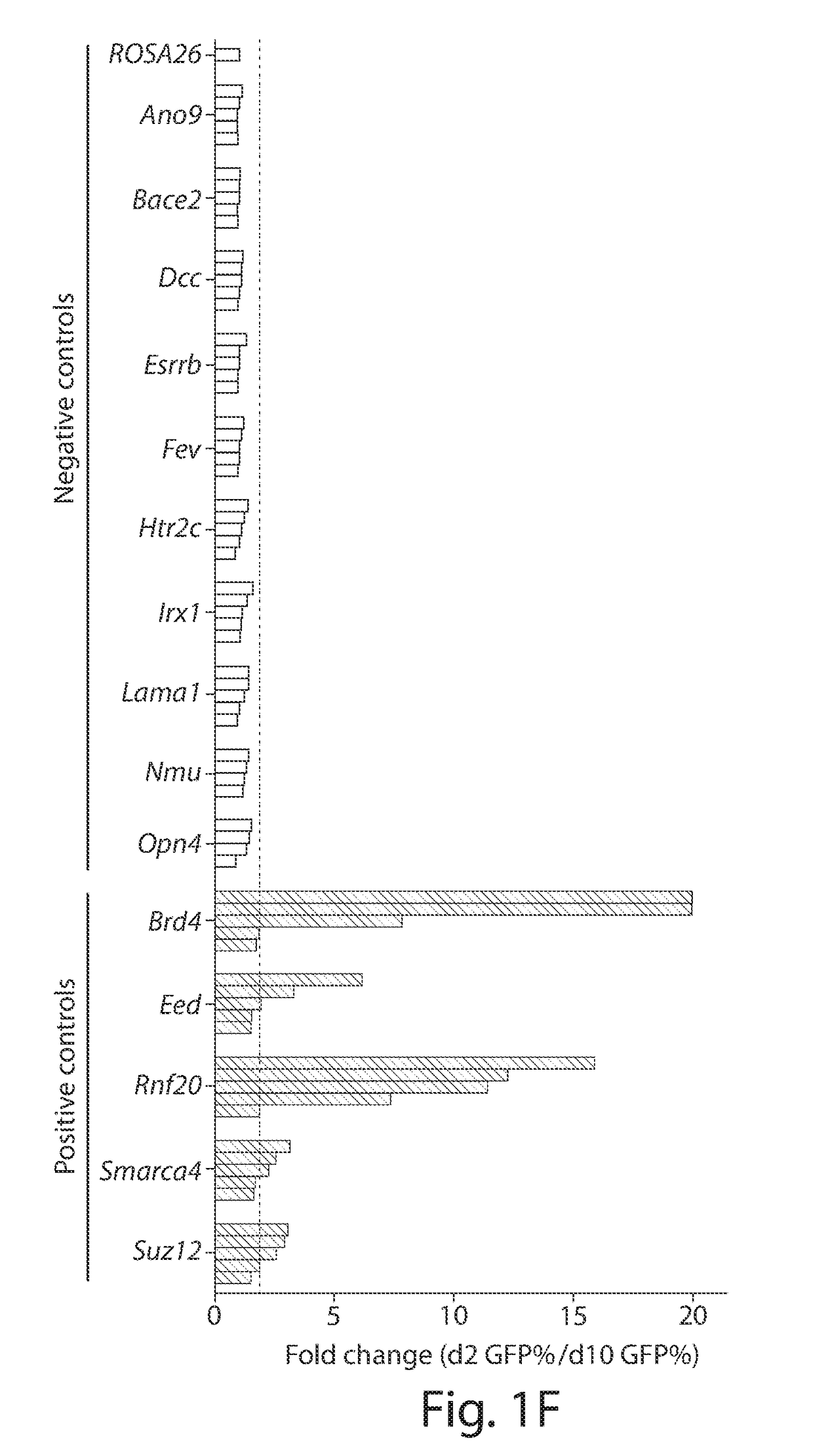
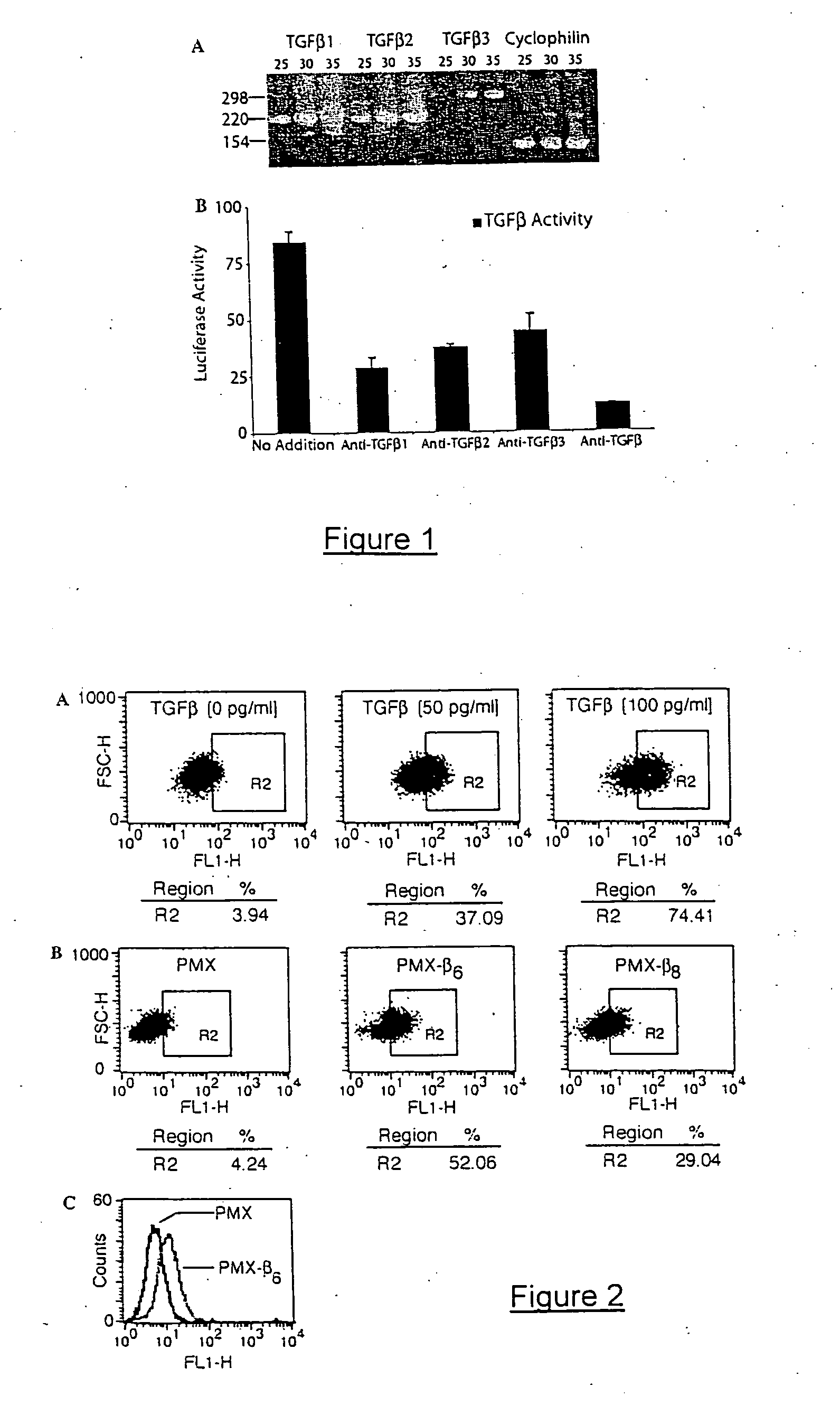
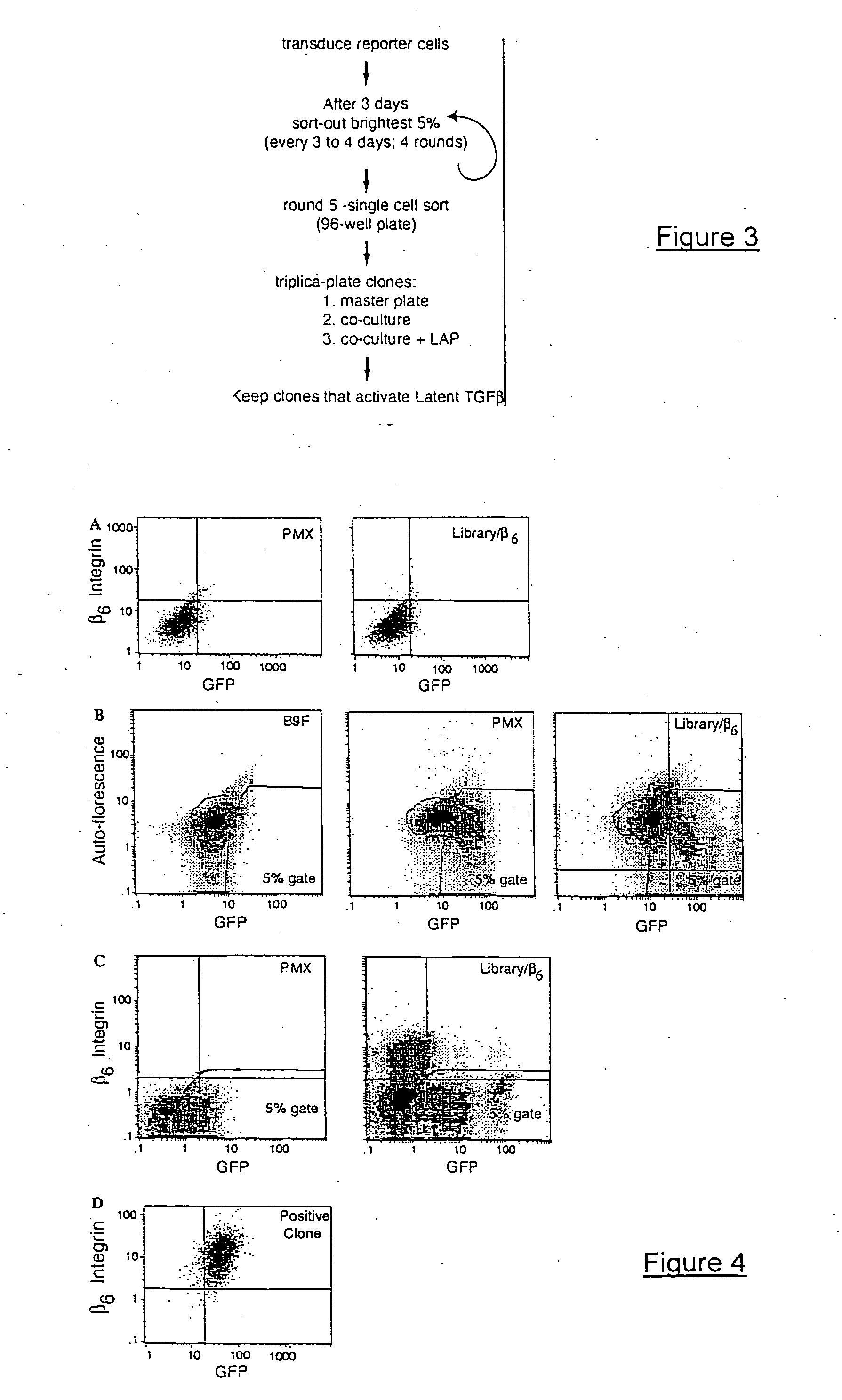
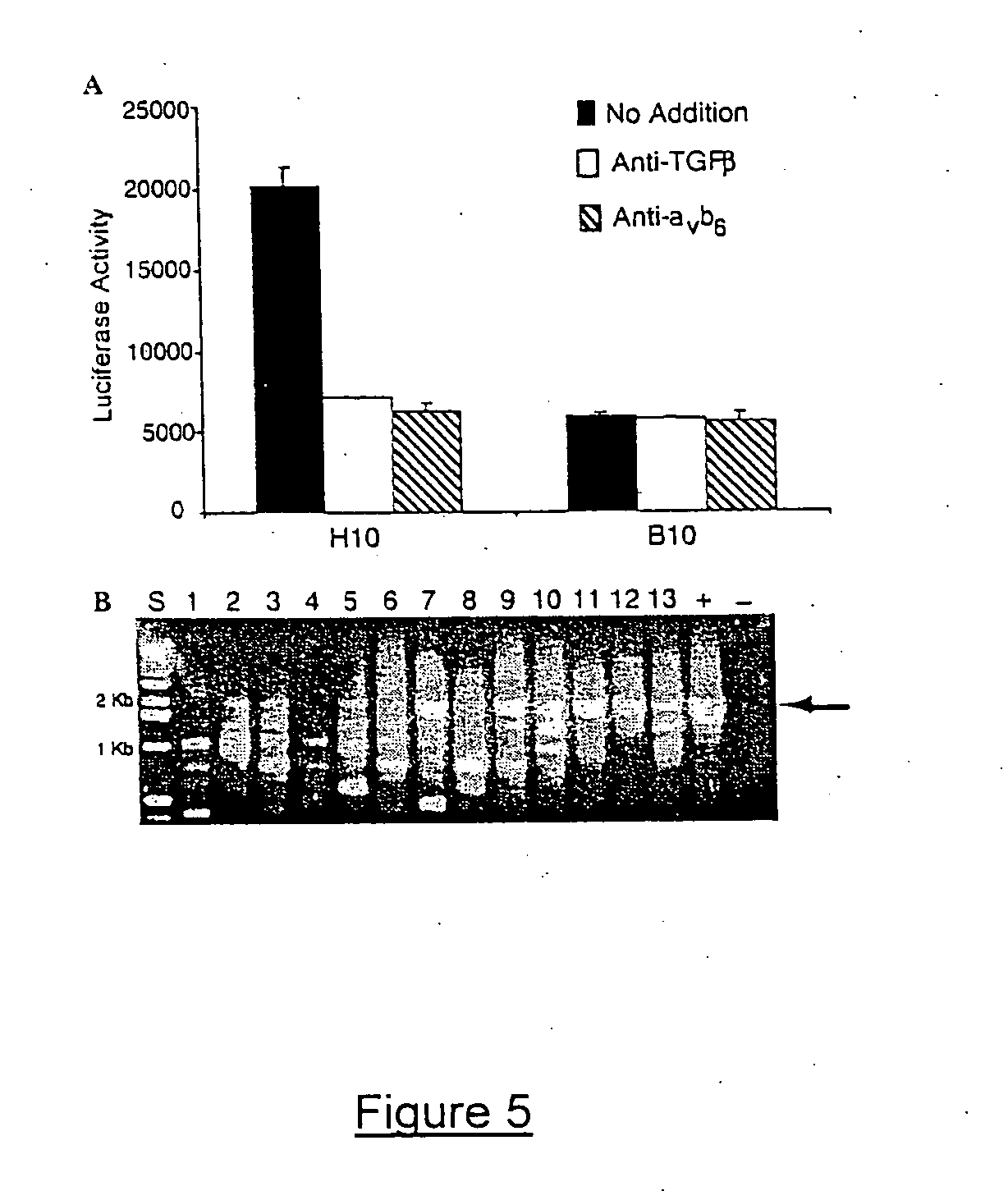
Genetic screen for bioactive peptides
A method of screening for a protein involved in the extracellular regulation of latent TGFβ activation by transducing a cell line with a retroviral cDNA library to create a reporter cell line that produces green fluorescent protein (GFP) in response to TGF-β signaling; growing individual clones created by the reporter cell line; co-culturing each individual clone with a second TGF-β reporter cell line that produces luciferase in response to TGF-β, wherein the luciferase production identifies positive clones; and identifying a mechanism of latent TGF-β activation that is employed by the positive clones. A TGFβ reporter cell line including a cell line; and a retroviral cDNA library, wherein the reporter cell line produces GFP in response to TGF-β signaling. A method of screening for gene products involved in a biological process.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Methods of reducing levels of tau
InactiveUS9696306B2Halogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsHydrocarbon active ingredientsDiseaseDirected differentiation
Successful CNS drug discovery requires a scalable, highly physiological neuronal model. Using directed differentiation of mouse embryonic stem (mES) cells, including mES cells isolated from a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a highly homogeneous primary neuronal model amenable to phenotypic assays for production and synaptotoxicity of amyloid β-peptide was developed. This model furnishes a highly physiological and AD-relevant platform suitable for high throughput small molecule and functional genetic screens, providing specific small molecule compounds identified by such screens.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Kit and method of using same
PendingCN114730610AReliable detectionImprove bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsInsertion deletionNucleotide
A kit for genetic screening for use in a device, wherein the kit performs a wet laboratory assay at the time of operation. The assays include processing a genetic material derived from one or more cell exons and detecting single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertion deletions, and copy number variations (CNVs) in genetic DNA readings from the genetic material. The kit can be performed as a single assay for processing the genetic material. The kit includes a software product executable on computing hardware to cause the computing hardware to invoke an algorithm to process the genetic DNA readings by comparing portions of the genetic DNA readings to DNA sequence transcripts in order to determine a probability of occurrence of the DNA sequence transcripts in the DNA reading data. The algorithm is used to simultaneously detect both SNVs and CNVs in the genetic DNA readings from the genetic material, and annotate clinically relevant CNVs.
Owner:コンジェニカリミテッド
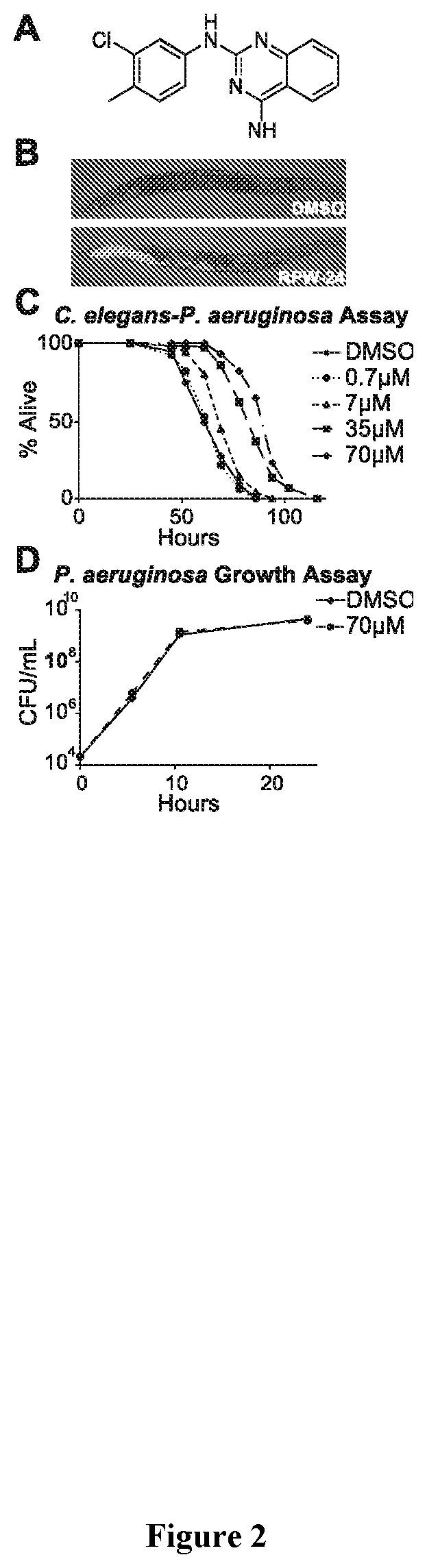
Antihelminthic medications for pathogenic nematodes
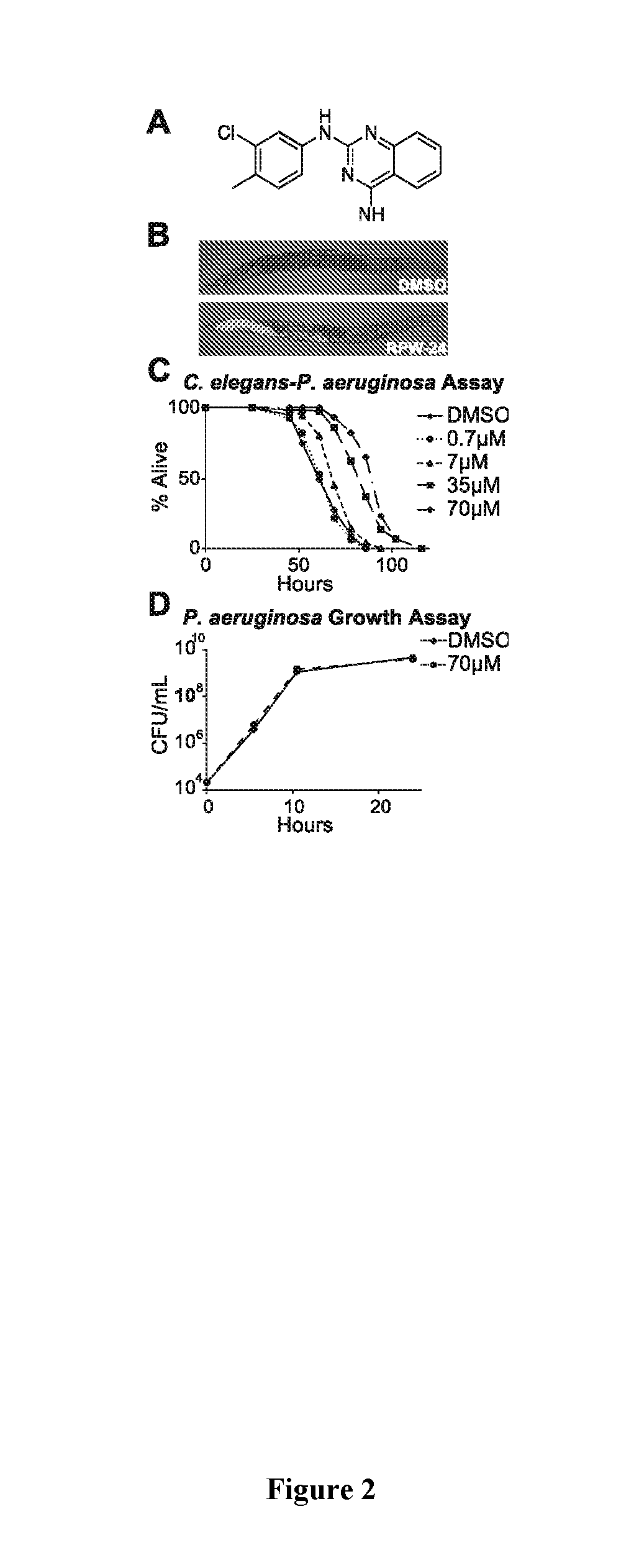
Inappropriate activation of innate immune responses in nematode intestinal epithelial cells underlies the pathophysiology of some inflammatory disorders. Immunostimulatory xenobiotics are known to protect nematodes from bacterial infection (e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa). Conversely, these same xenobiotics are toxic to uninfected nematodes. These xenobiotics were subjected to a forward genetic screen in uninfected nematodes to identify nematode mutants that were resistant to the deleterious effects of these xenobiotics. These resistant nematode strains contained hypomorphic mutations in each of the known components of the p38 MAP kinase cassette (tir-1, nsy-1, sek-1 and pmk-1), demonstrating that hyperstimulation of p38 MAPK innate immune responses may be responsible for the induced toxicity. A second genetic screen using dominant activators of the p38 MAPK pathway identified a single allele that had a gain-of-function (gf) mutation in nsy-1, the MAP kinase kinase kinase that acts upstream of p38 MAPK pmk-1.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Antihelminthic Medications For Pathogenic Nematodes
Inappropriate activation of innate immune responses in nematode intestinal epithelial cells underlies the pathophysiology of some inflammatory disorders. Immunostimulatory xenobiotics are known to protect nematodes from bacterial infection (e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa). Conversely, these same xenobiotics are toxic to uninfected nematodes. These xenobiotics were subjected to a forward genetic screen in uninfected nematodes to identify nematode mutants that were resistant to the deleterious effects of these xenobiotics. These resistant nematode strains contained hypomorphic mutations in each of the known components of the p38 MAP kinase cassette (tir-1, nsy-1, sek-1 and pmk-1), demonstrating that hyperstimulation of p38 MAPK innate immune responses may be responsible for the induced toxicity. A second genetic screen using dominant activators of the p38 MAPK pathway identified a single allele that had a gain-of-function (gf) mutation in nsy-1, the MAP kinase kinase kinase that acts upstream of p38 MAPK pmk-1.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com