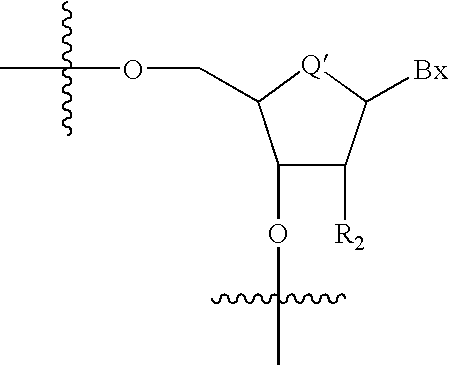
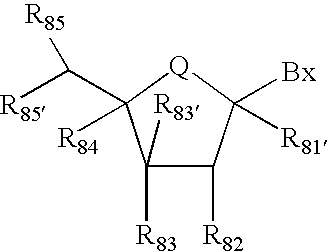
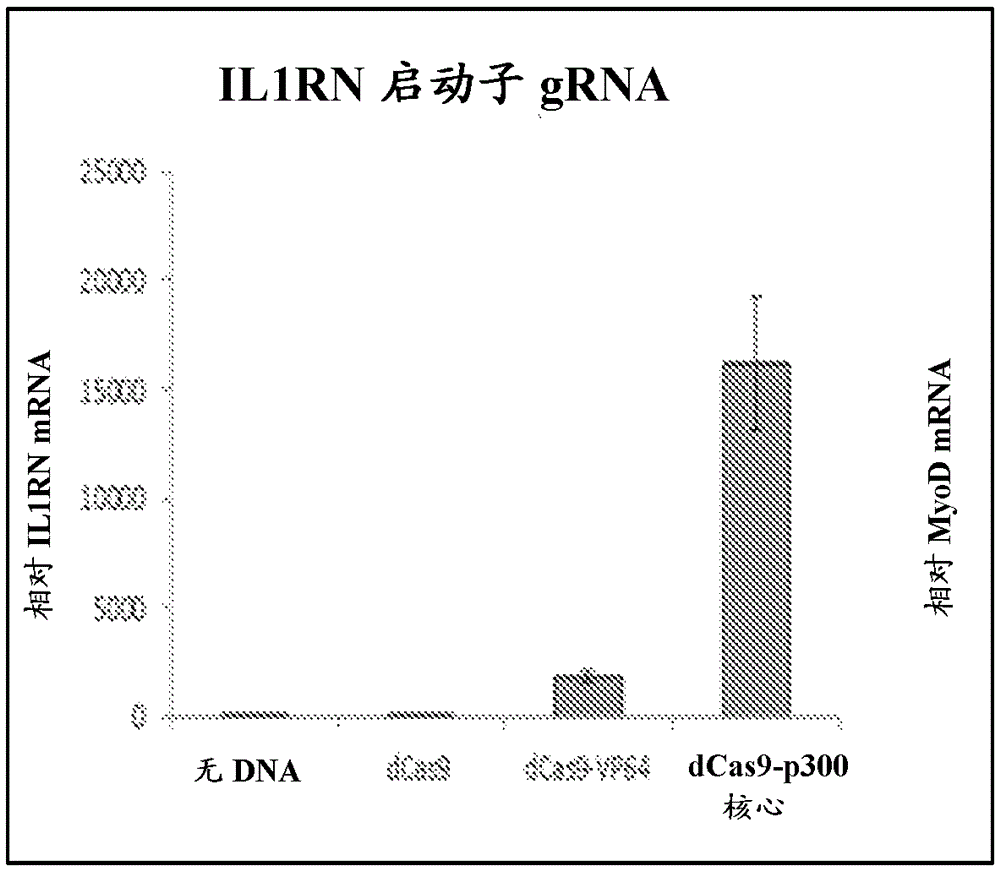
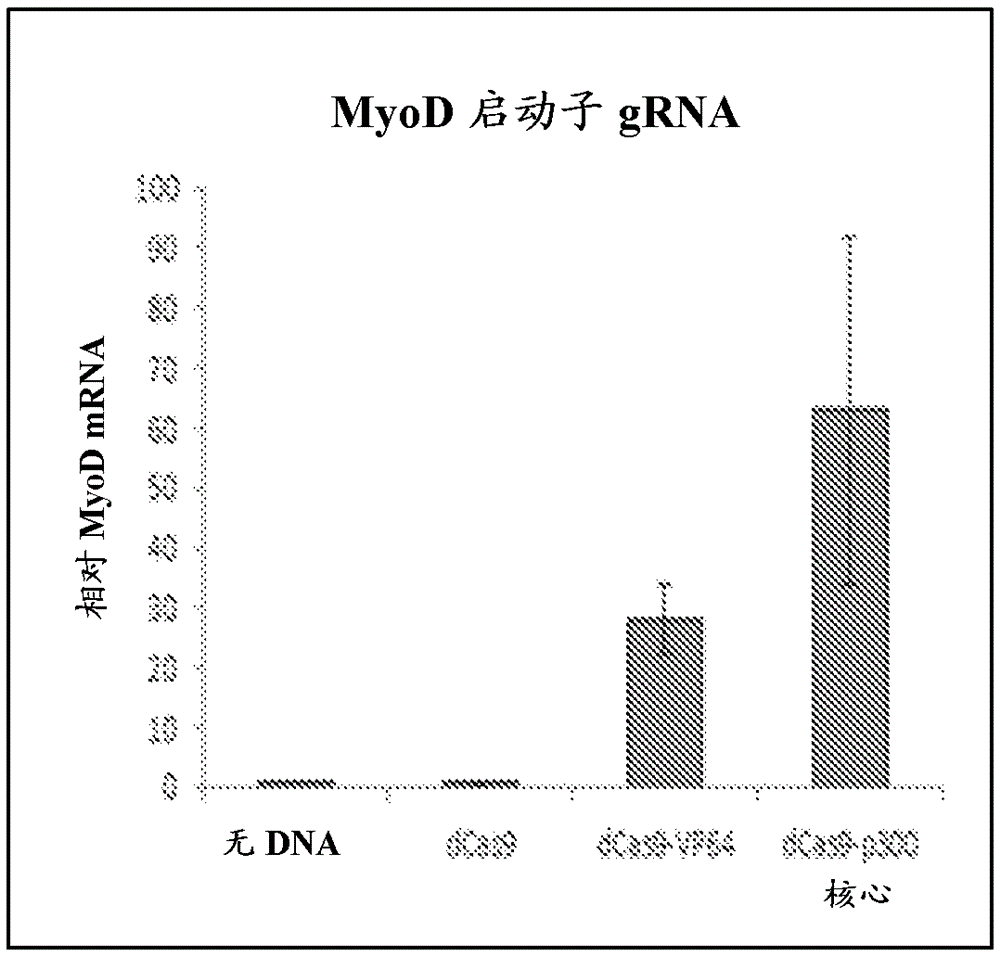
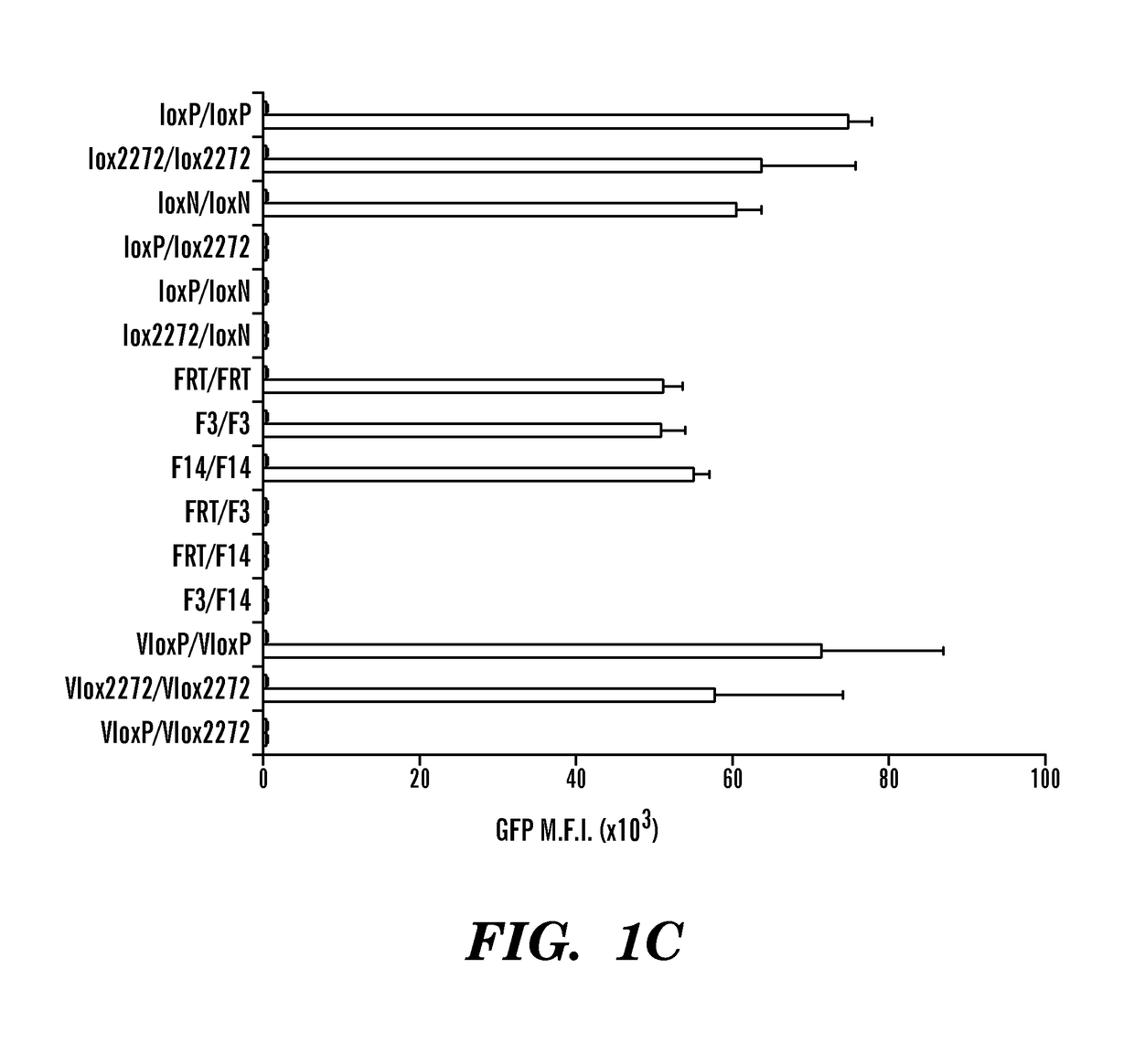
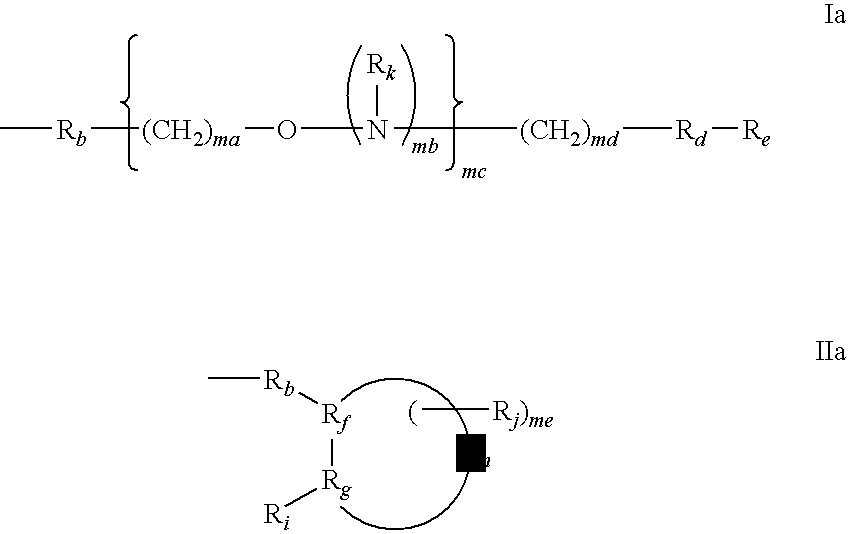
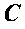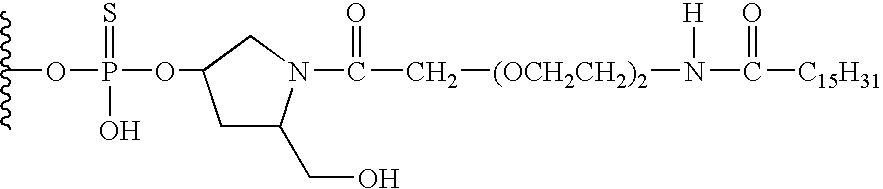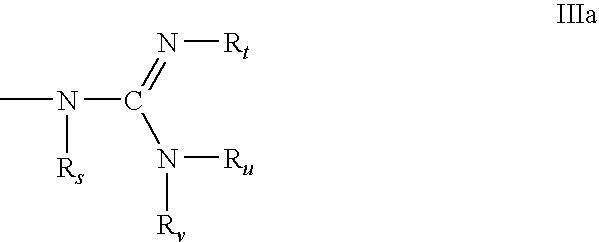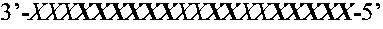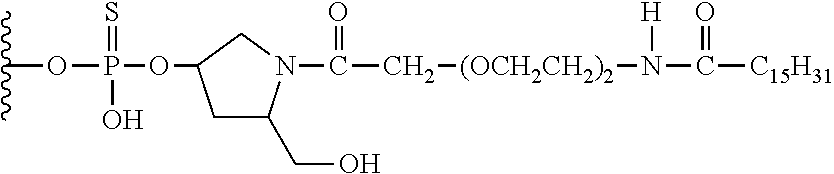Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Genetic modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
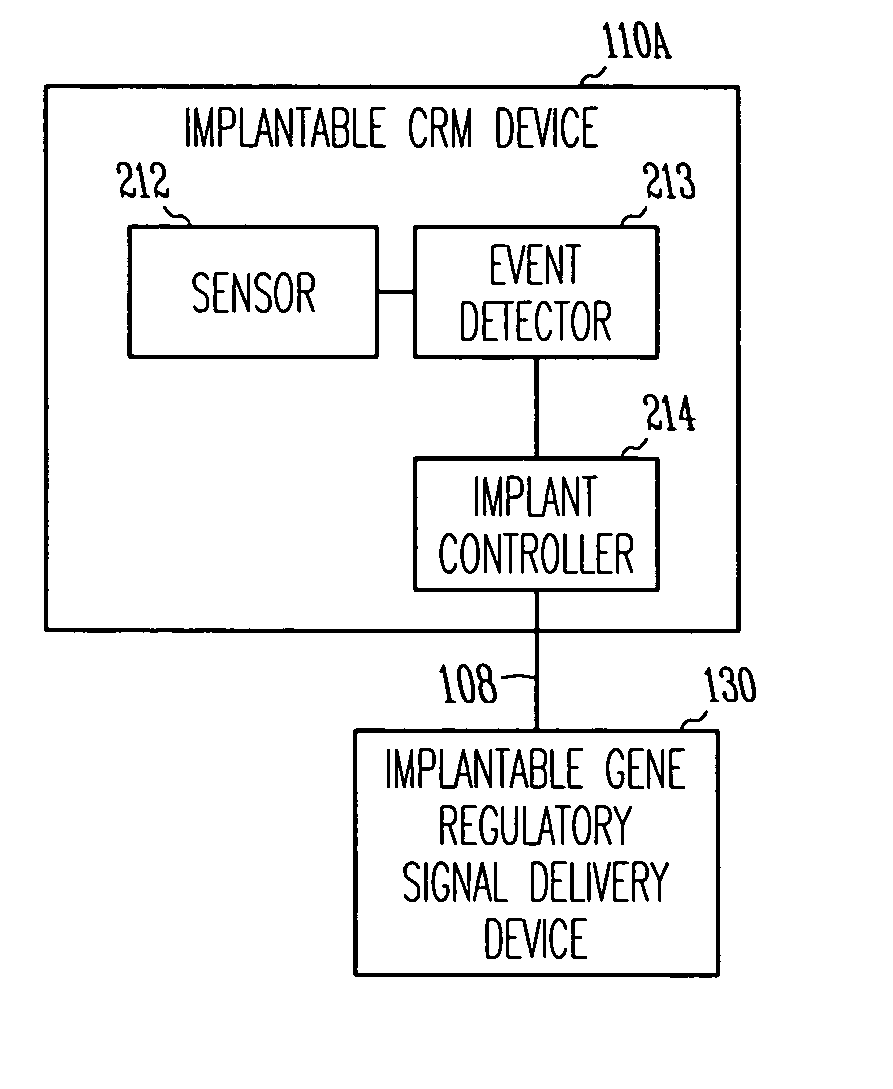
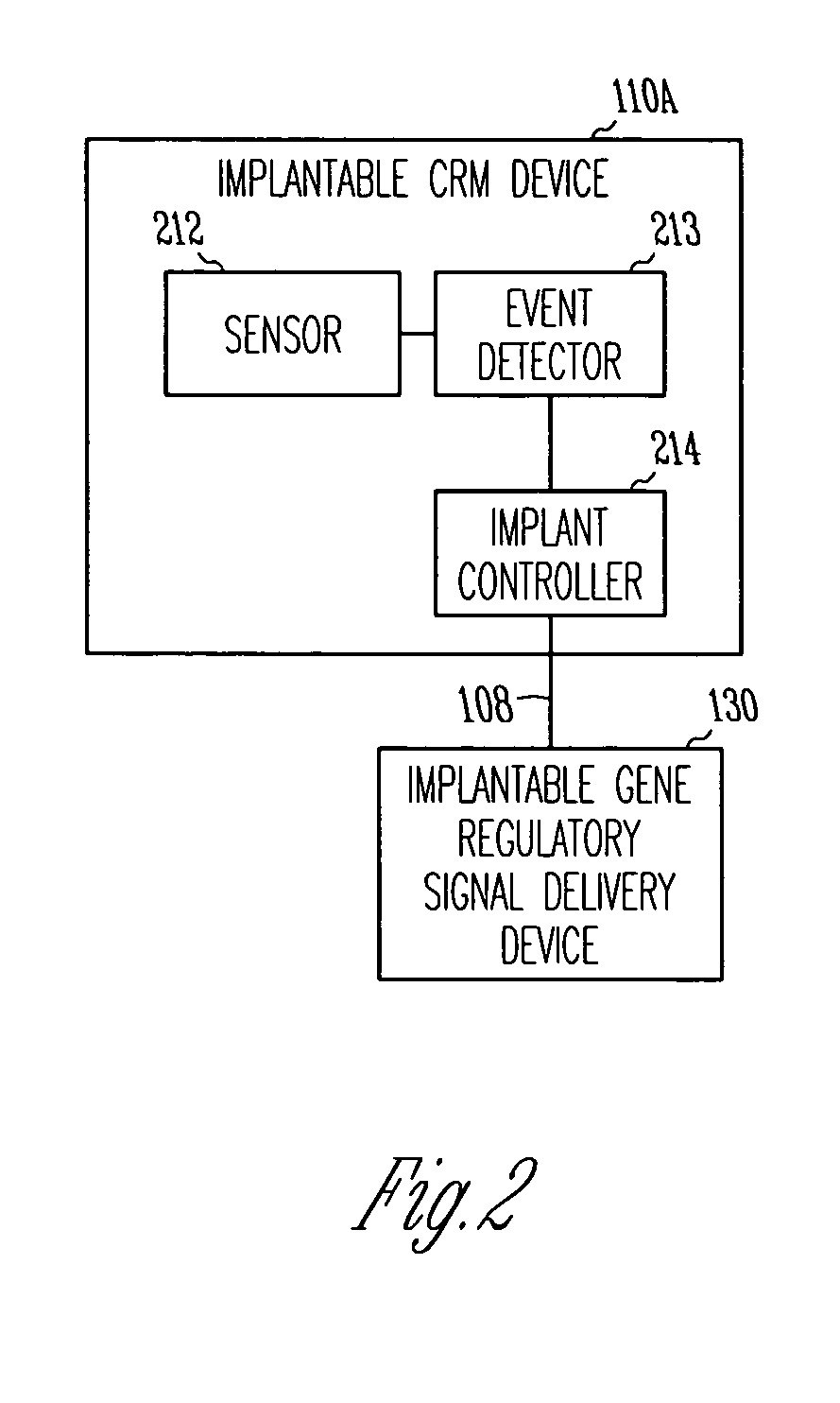
Method and apparatus for device controlled gene expression
InactiveUS20050192637A1Readily be titratedPreventing and inhibiting and cardiac conditionGenetic material ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsForms of energyRegulator gene
A gene regulatory system controls gene therapy by emitting one or more forms of energy that regulate gene expression by triggering promoters. The system includes a sensor to sense a signal indicative of a need for the gene therapy as well as responses to the gene therapy. The regulation of the gene expression is controlled based on the sensed signal and / or a user command. In one embodiment, the system delivers one or more electrical therapies in conjunction with the gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Exosome transfer of nucleic acids to cells
InactiveUS20070298118A1Avoiding adverse immune reactionImprove isolationSpecial deliveryGenetic material ingredientsGenetic MaterialsExosome
Owner:CODIAK BIOSCI
Double strand compositions comprising differentially modified strands for use in gene modulation
InactiveUS20070123484A1Suppress gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideRibonucleosideTRIM Motif
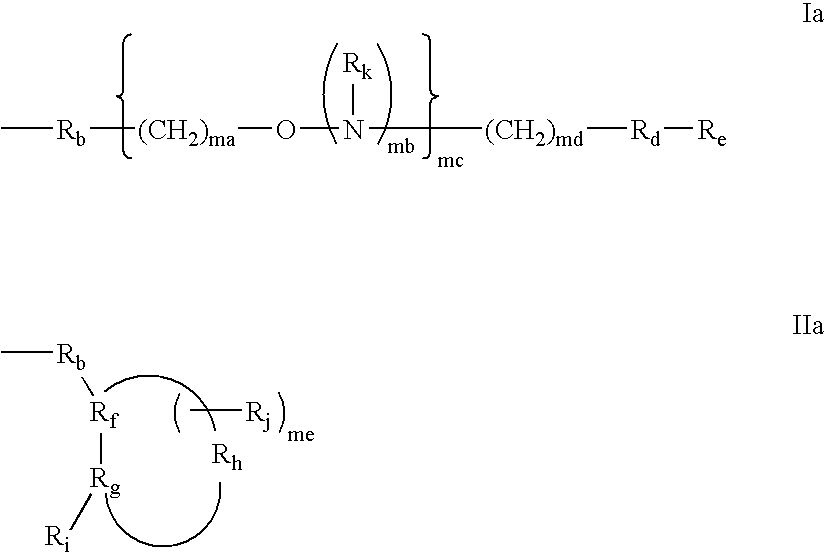
The present invention provides double stranded compositions wherein each strand is modified to have a motif defined by positioning of β-D-ribonucleosides and sugar modified nucleosides. More particularly, the present compositions comprise one strand having an alternating motif and another strand having a hemimer motif, a blockmer motif, a fully modified motif or a positionally modified motif. At least one of the strands has complementarity to a nucleic acid target. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes. In preferred embodiments the compositions of the present invention hybridize to a portion of a target RNA resulting in loss of normal function of the target RNA. The present invention also provides methods for modulating gene expression.
Owner:BHAT BALKRISHEN +4
Double strand compositions comprising differentially modified strands for use in gene modulation
The present invention provides double stranded compositions wherein each strand is modified to have a motif defined by positioning of β-D-ribonucleosides and sugar modified nucleosides. More particularly, the present compositions comprise one strand having an alternating motif and another strand having a hemimer motif, a blockmer motif, a fully modified motif or a positionally modified motif. At least one of the strands has complementarity to a nucleic acid target. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes. In preferred embodiments the compositions of the present invention hybridize to a portion of a target RNA resulting in loss of normal function of the target RNA. The present invention also provides methods for modulating gene expression.
Owner:BHAT BALKRISHEN +4
Sugar surrogate-containing oligomeric compounds and compositions for use in gene modulation
InactiveUS20040171031A1Modifies effectImprove efficiencySugar derivativesHydrolasesCompound sRNA-induced silencing complex
Compositions comprising first and second oligomers are provided wherein at least a portion of the first oligomer is capable of hybridizing with at least a portion of the second oligomer, at least a portion of the first oligomer is complementary to and capable of hybridizing to a selected target nucleic acid, and at least one of the first or second oligomers includes a modification comprising a sugar surrogate. Oligomer / protein compositions are also provided comprising an oligomer complementary to and capable of hybridizing to a selected target nucleic acid and at least one protein comprising at least a portion of an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), wherein at least one nucleoside of the oligomer has a sugar surrogate modification.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Rna-guided gene editing and gene regulation
Disclosed herein are Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) / CRISPR-associated (Cas) 9-based system related compositions and methods of using said CRISPR / Cas9-based system related compositions for altering gene expression and genome engineering. Also disclosed herein are compositions and methods of using said compositions for altering gene expression and genome engineering in muscle, such as skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
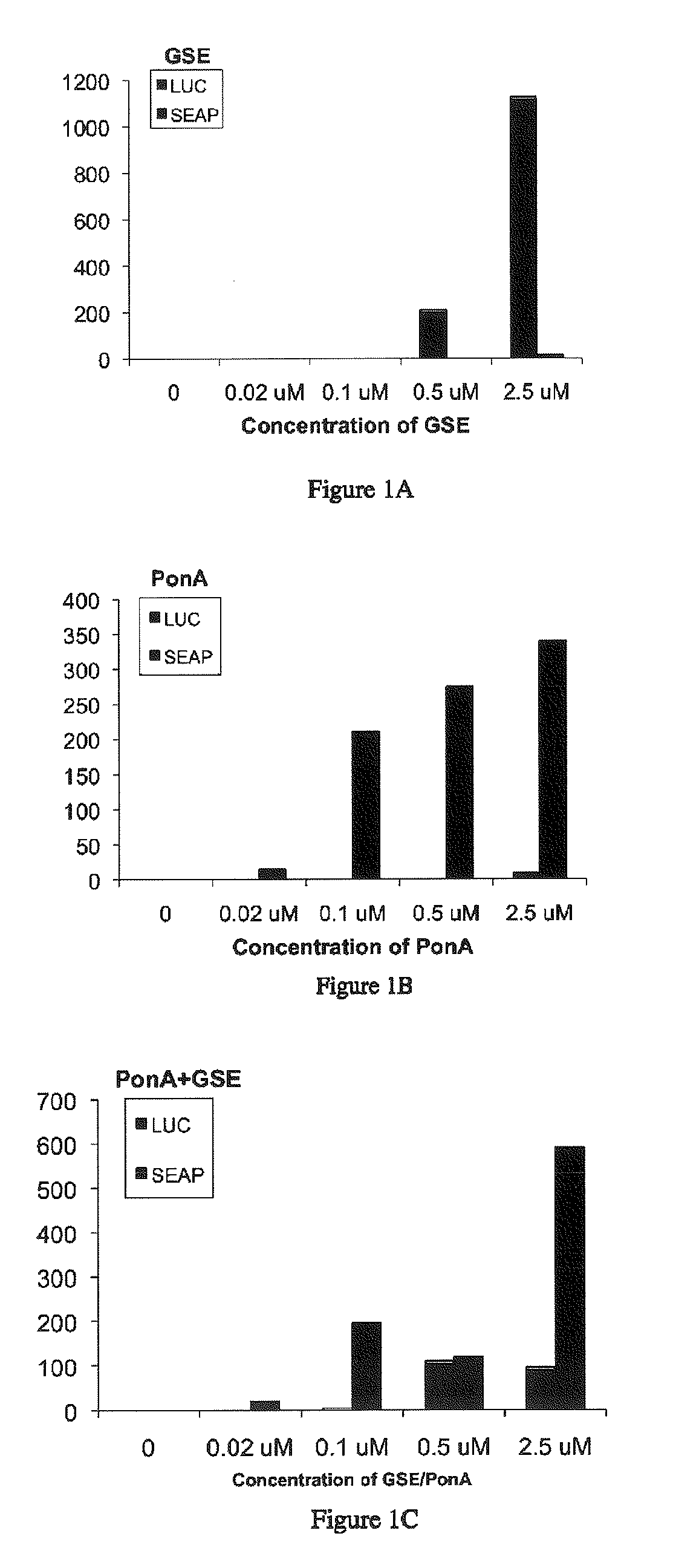
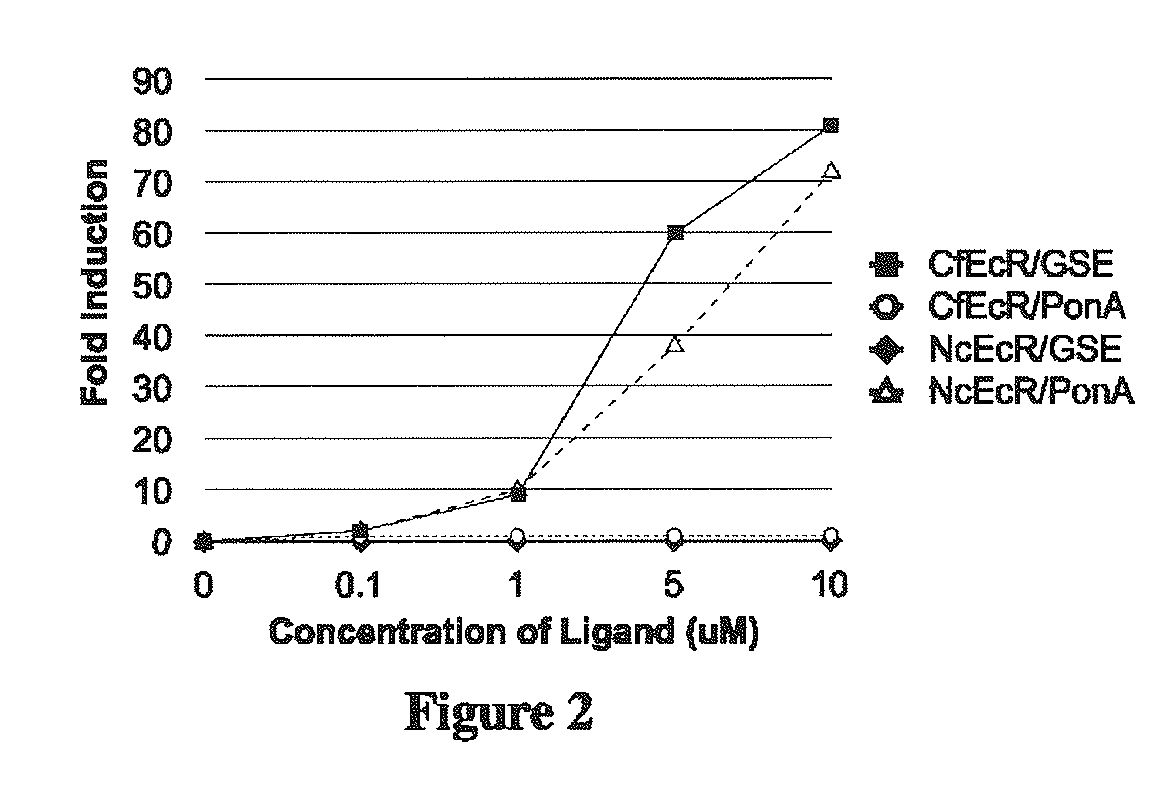
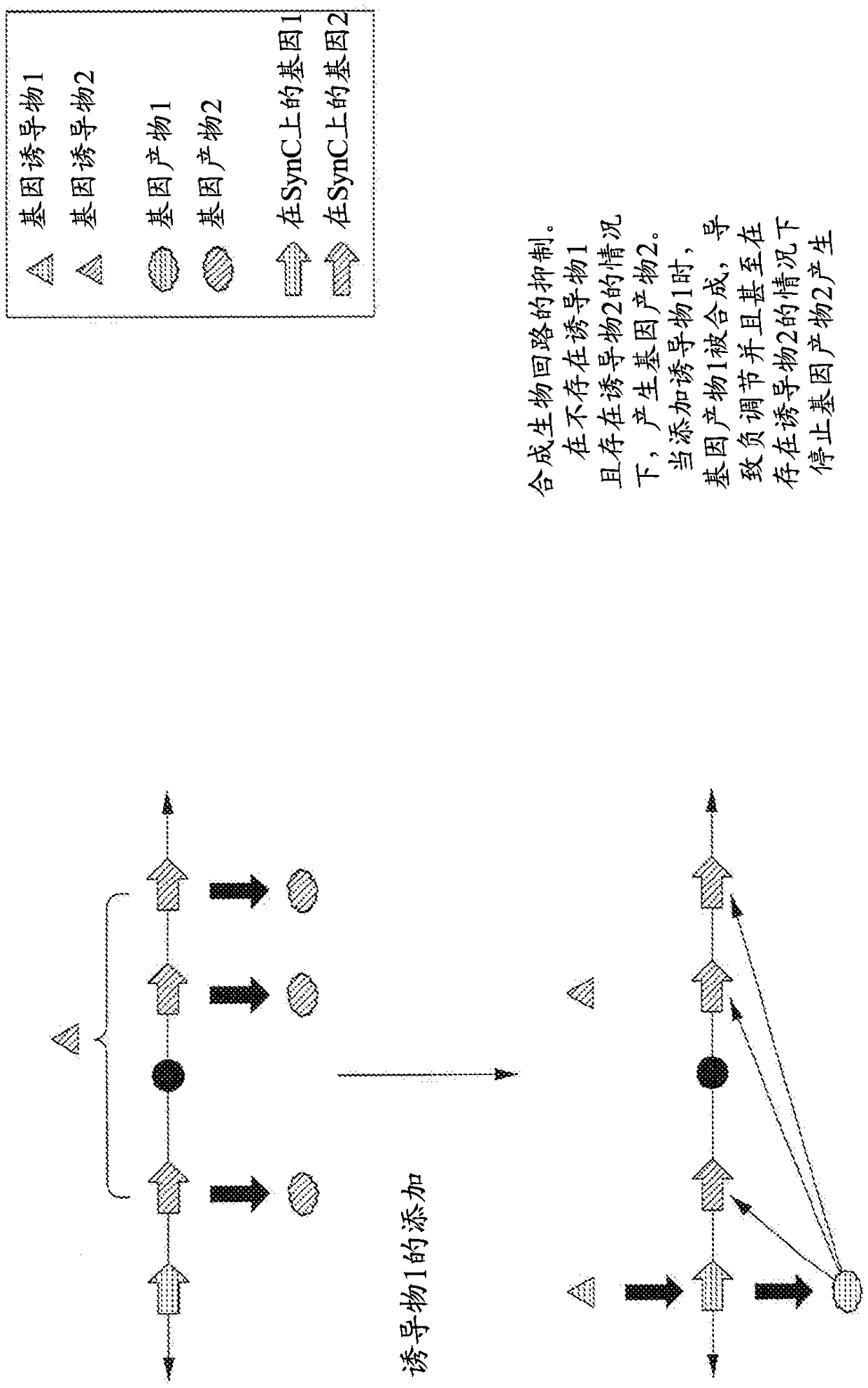
Multiple Inducible Gene Regulation System
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. More specifically, the present invention relates to a multiple inducible gene regulation system that functions within cells to simultaneously control the quantitative expression of multiple genes.
Owner:RHEOGENE HLDG
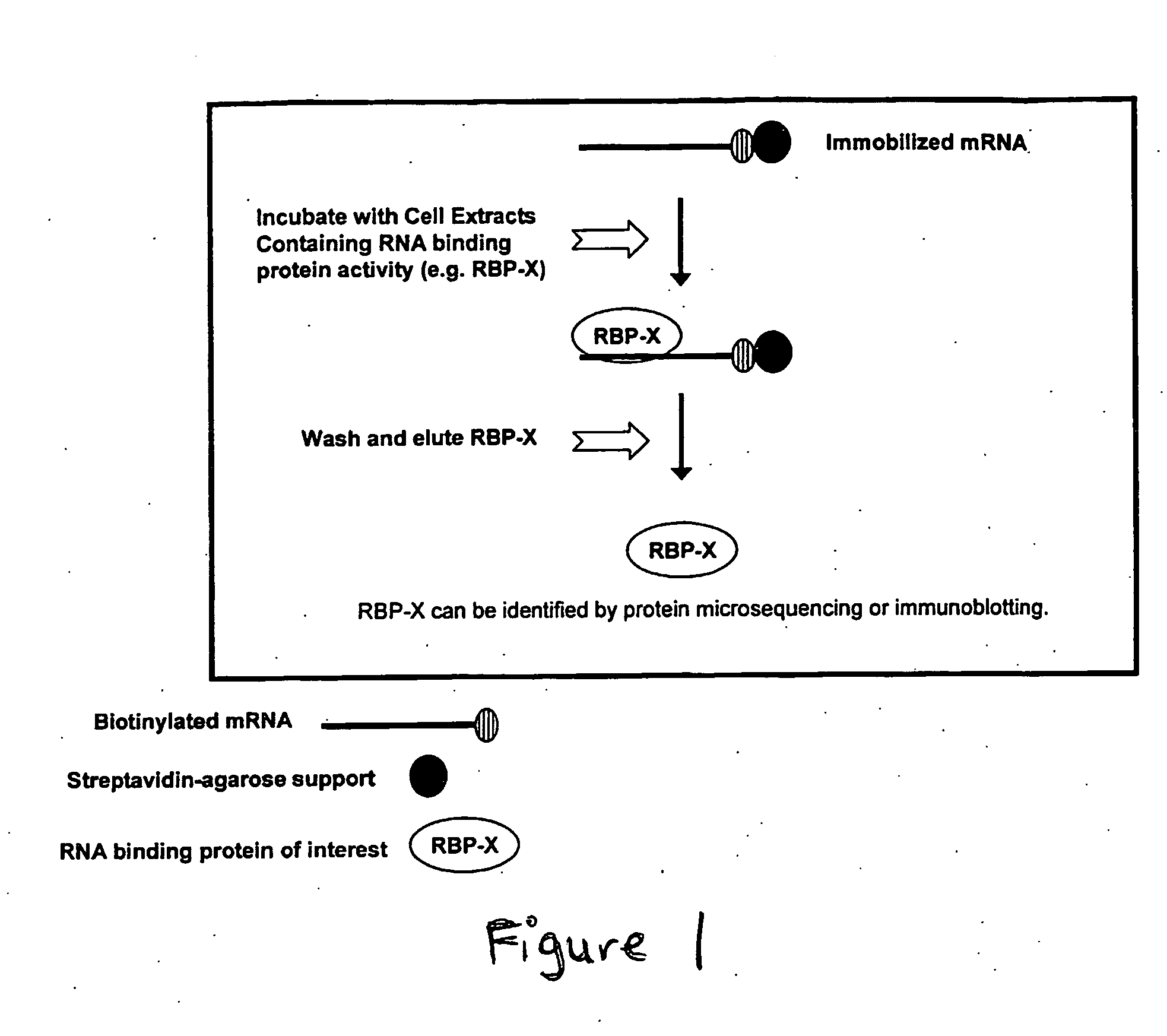
Methods for identifying therapeutic targets involved in glucose and lipid metabolism
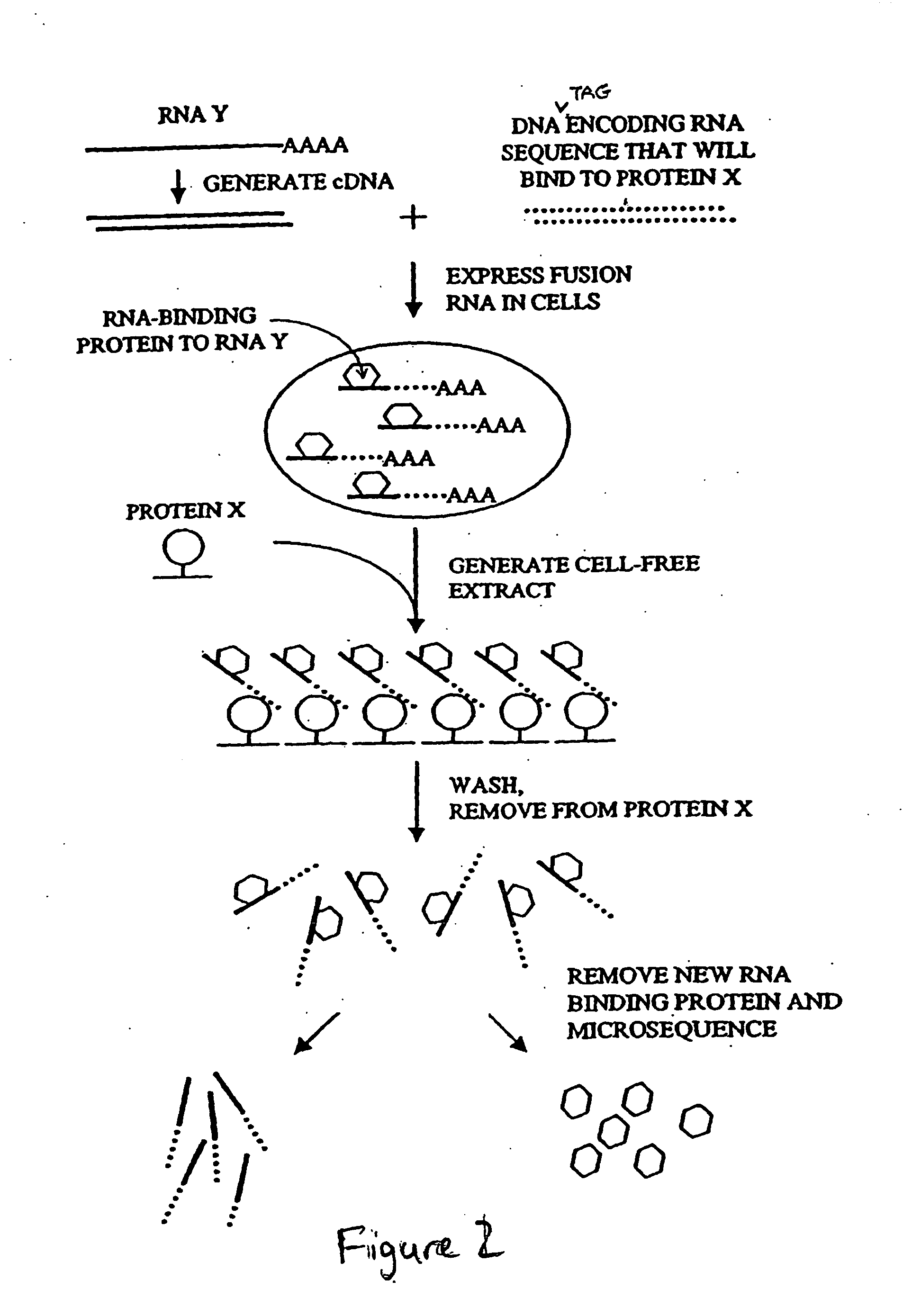
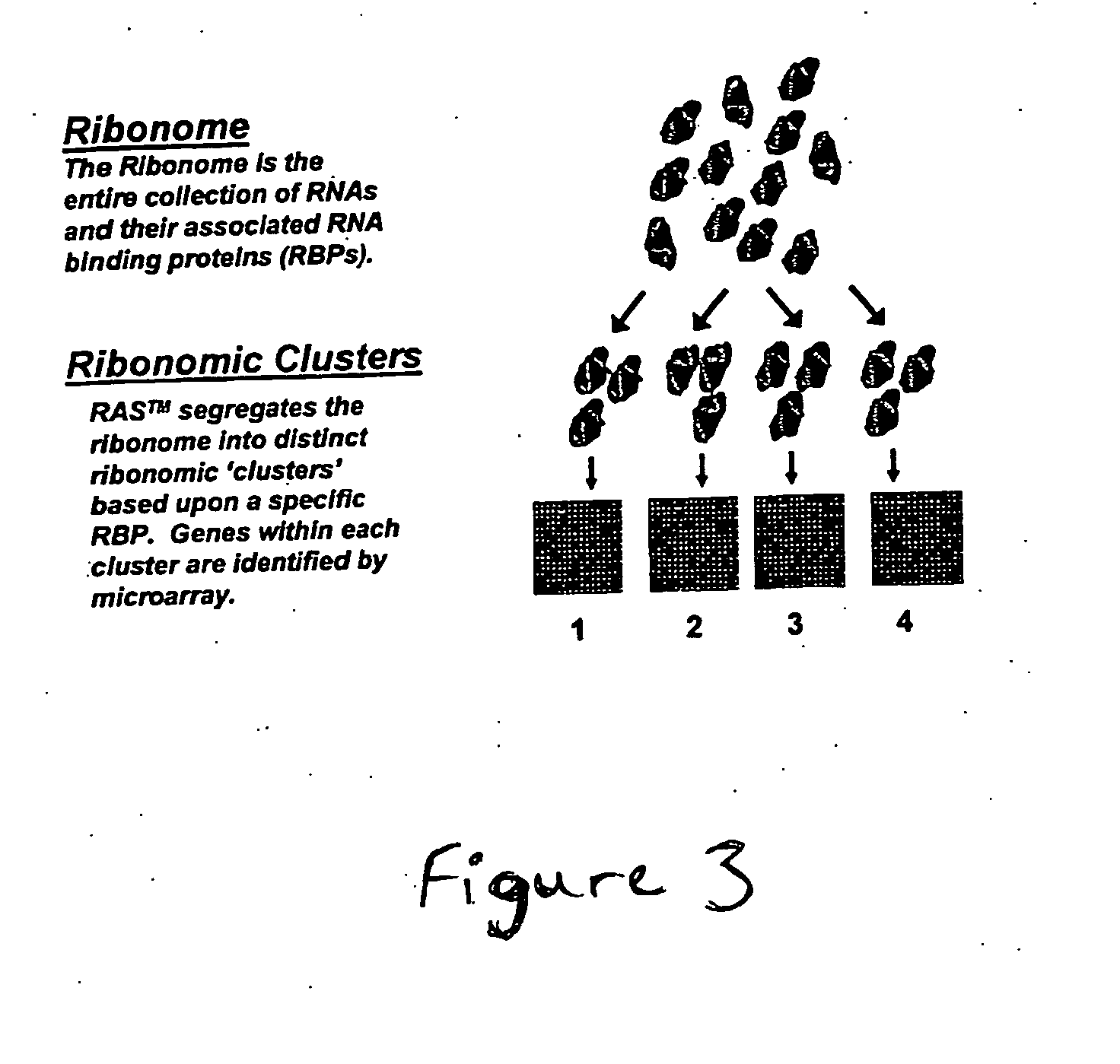
The identification and evaluation of mRNA and protein targets associated with RNA binding proteins or mRNP complexes is described. In particular, the invention provides methods for identifying RNA binding proteins associated with physiological pathways that participate in glucose and lipid metabolism and mRNAs that exhibit coordinated gene regulation across those M pathways. Candidate targets are provided that are useful for the diagnosis or treatment of diseases related to diseases, such as disease related to aberrant glucose and lipid metabolism, such as, for example, obesity, diabetes, and hypoglycemia.
Owner:RIBONOMICS
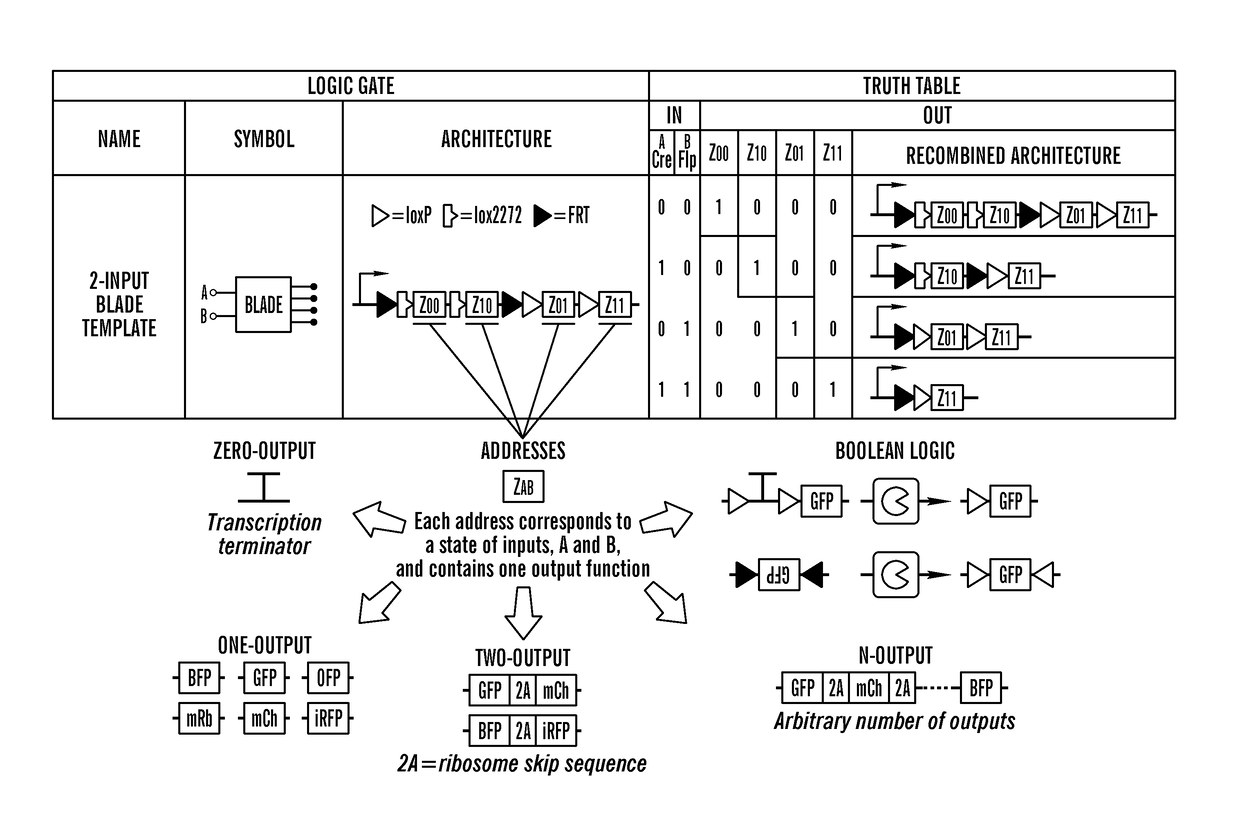
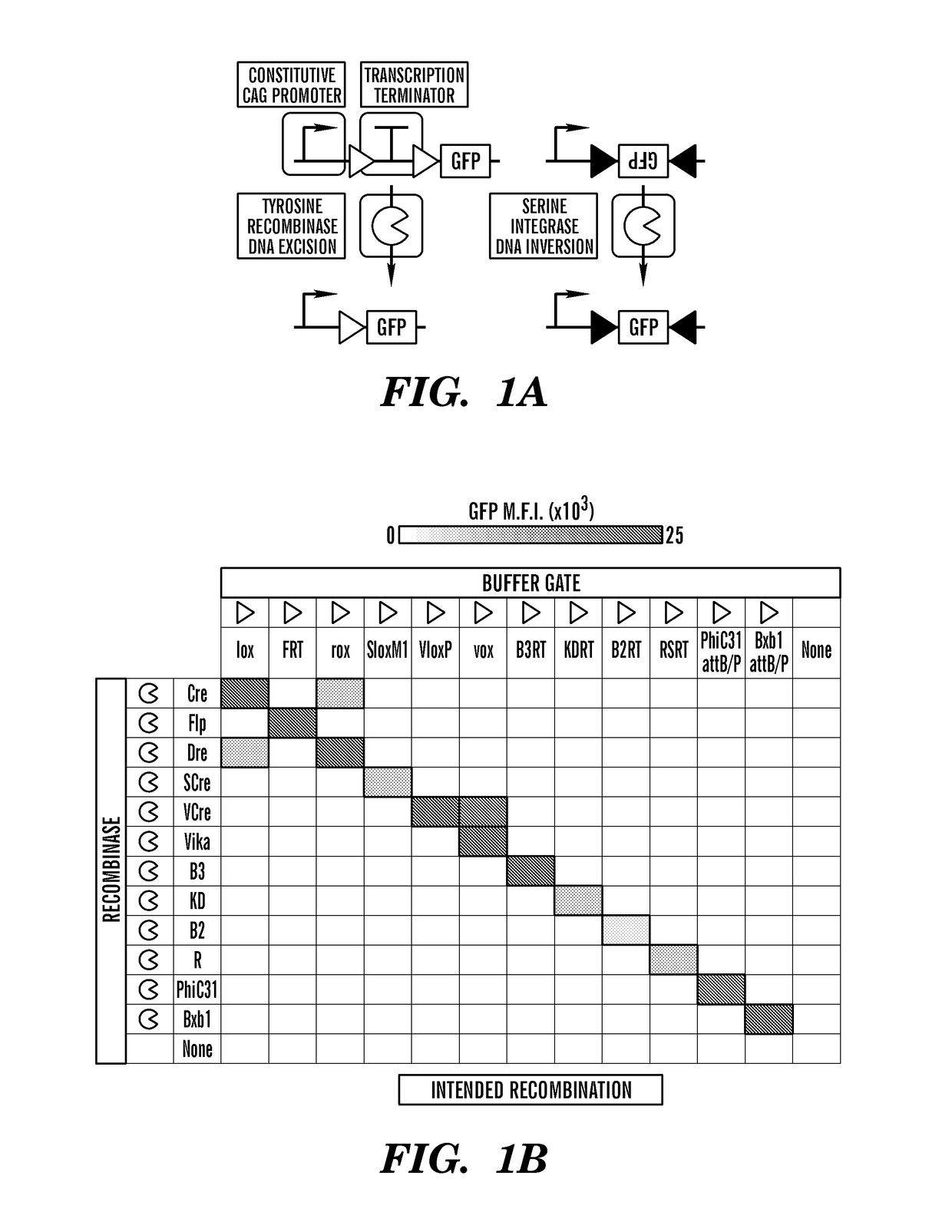
DNA recombinase circuits for logical control of gene expression
ActiveUS20170183654A1Stable changeEfficient assemblyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyT cellCell therapy
The invention provides, inter alia, recombinase-based systems that provide for integrated logic and memory in living cells such as mammalian cells. The nucleic acid cassettes, switches, and systems described herein allow for control of gene expression or gene regulation. The invention also provides nucleic acid-based switches for adopted T-cell therapy.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Conjugated double strand compositions for use in gene modulation
InactiveUS20090306178A1Increased nuclease resistanceIncrease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsDrug compositionsRegulator geneDouble strand
The present invention provides conjugated double stranded compositions wherein each strand is modified to have a motif defined by positioning of β-D-ribonucleosides and / or sugar modified nucleosides. More particularly, the present compositions comprise a linked conjugate group on one strand and a non hybridizing region of 2′-modified nucleosides on the other strand. Each strand further comprises one or more phosphorothioate internucleoside linkage. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes. In preferred embodiments the compositions of the present invention hybridize to a portion of a target RNA resulting in loss of normal function of the target RNA. The present invention also provides methods for modulating gene expression.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Brachypodium distachyon drought-resistant gene and expression vector as well as coding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN108103074AImprove toleranceGuaranteed absorptionBacteriaPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPeroxidase
The invention provides a brachypodium distachyon drought-resistant gene and an expression vector as well as coding protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is the sequenceshown by SEQ ID NO.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to the sequence shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The protein is obtained by coding the gene of claim 1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown by SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is used for improving application of the plant tolerance to drought stress. The gene provided by the invention regulates the plant to close pores to reduce the moisture lost in transpiration; a stronger root system is obtained in a drought condition so as to guarantee moisture absorption; moreover, the gene can improve the activity of such enzymes as catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in the antioxidase system and eliminate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in time, thereby reducing the oxidative damage of cells caused by the ROS and improving the plant tolerance to drought.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Double strand compositions comprising differentially modified strands for use in gene modulation
Owner:BHAT BALKRISHEN +5
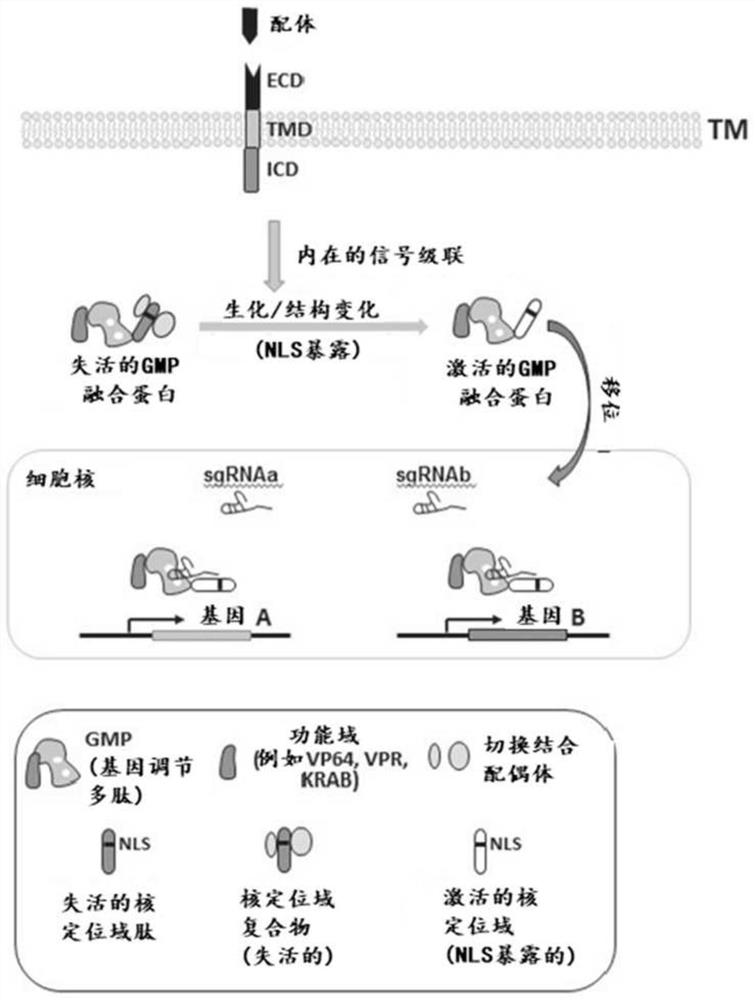
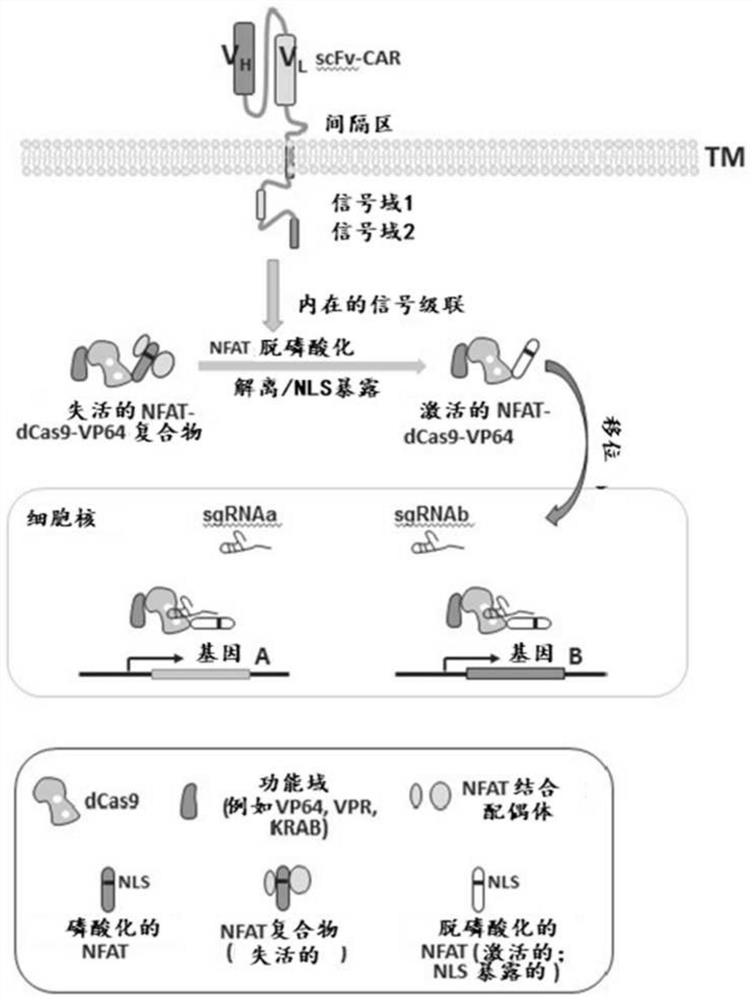
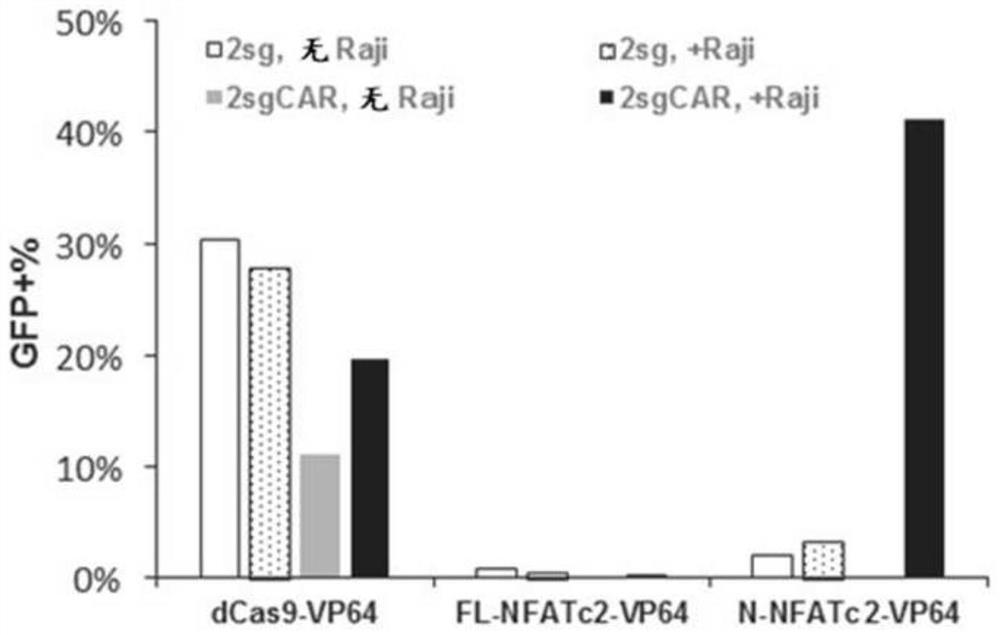
Gene regulation via conditional nuclear localization of gene modulating polypeptides
PendingCN112512594APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyHeterologousExtracellular signal
The present disclosure provides a system for regulating expression of a target polynucleotide in a cell. The system may comprise a chimeric polypeptide comprising a gene modulating polypeptide fused in-frame with a heterologous nuclear localization domain. The heterologous nuclear localization domain may be operable to translocate the chimeric polypeptide to a cell nucleus upon activation by an active cellular signaling pathway. The cellular signaling pathway may be inducible in response to an extracellular signal. In response to the extracellular signal, the chimeric polypeptide may localizeto the cell nucleus and the gene modulating polypeptide may regulate expression of a target polynucleotide in the cell nucleus.
Owner:REFUGE BIOTECH INC
In vivo gene regulation by the combination of knock-in-teto sequence into the genome and tetracycline-controlled trans-suppressor (TTS) protein
InactiveUS20130061343A1Easy to integrateEfficiently findSugar derivativesNucleic acid vectorDiseaseTetracycline Control
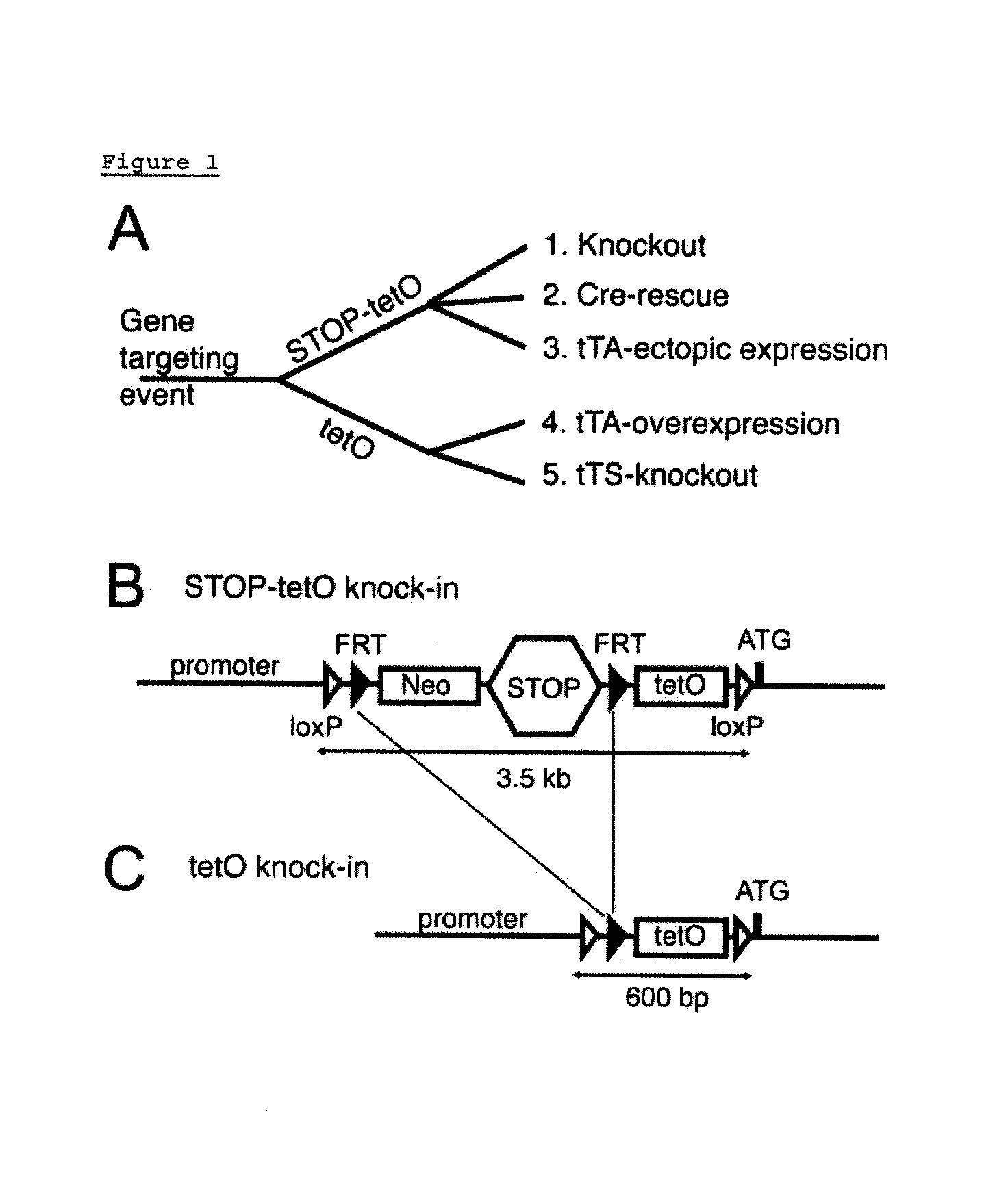
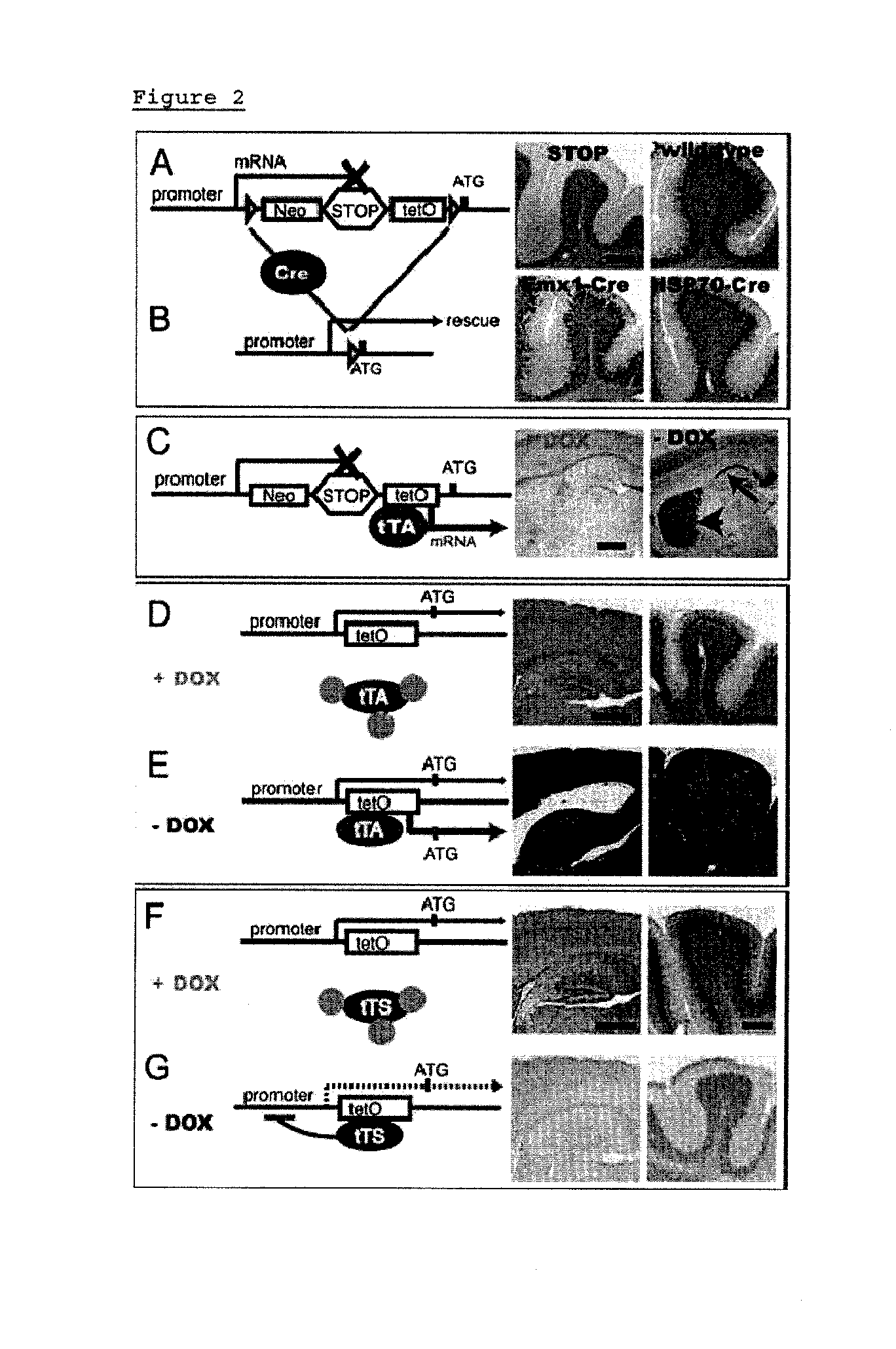
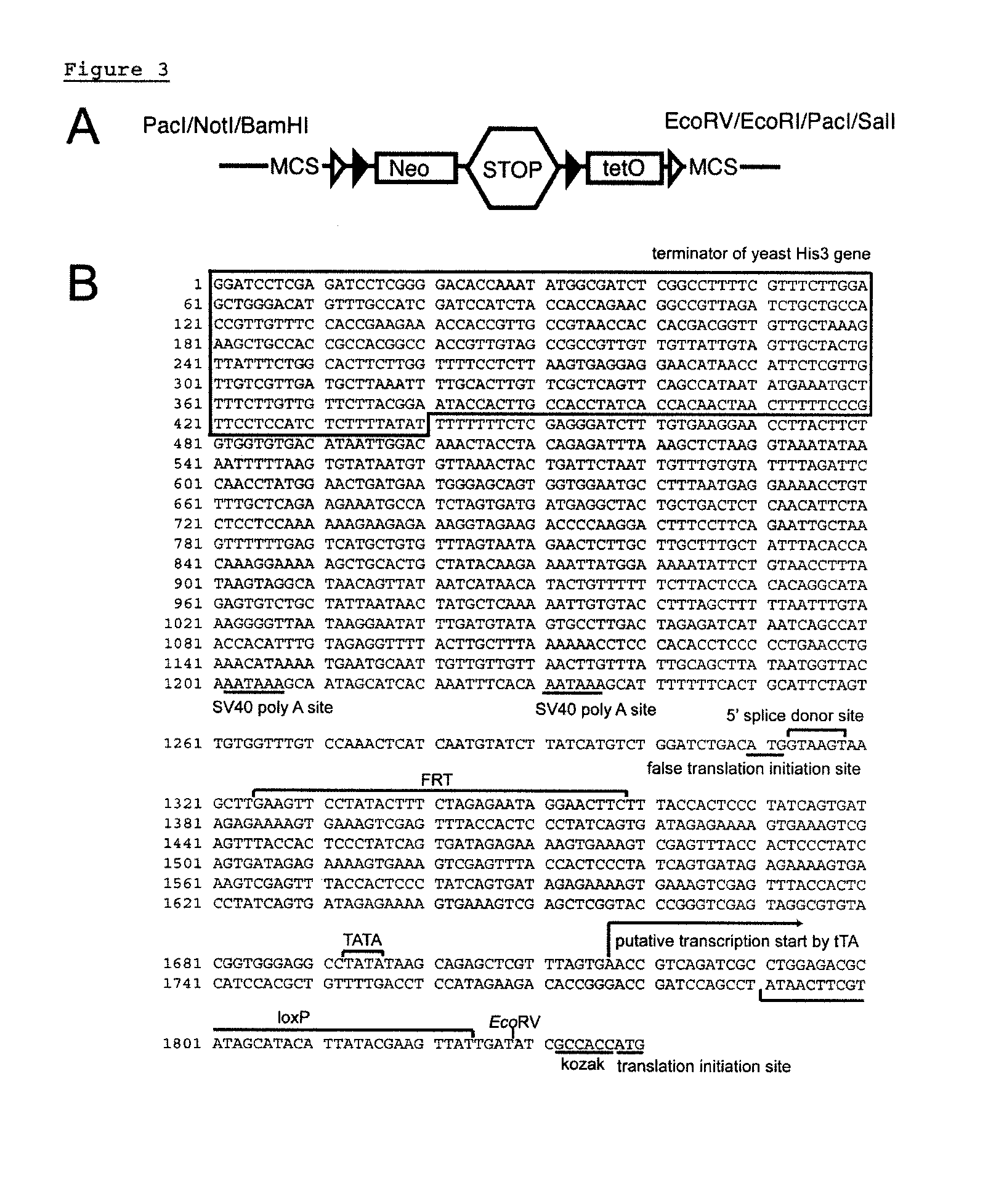
Disclosed is a FAST (Flexible Accelerated STOP TetO-knockin) system, an efficient method for manipulating gene expression in vivo to rapidly screen animal models of disease. This invention further discloses a single gene targeting event yielding 2 distinct knockin mice—STOP-tetO and tetO knockin—which permit generation of multiple strains with variable expression patterns: 1) knockout, 2) Cre-mediated rescue; 3) tTA-mediated misexpression; 4) tTA-mediated overexpression; and 5) tTS-mediated conditional knockout / knockdown. Using the FAST system, multiple gain- and loss-of-function strains can therefore be generated on a timescale not previously achievable. These strains can then be screened for clinically-relevant abnormalities. The flexibility and broad applicability of the FAST system is demonstrated by targeting several genes encoding proteins implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders: Mlc1, Neuroligin 3, the serotonin 1A receptor, and the serotonin 1B receptor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
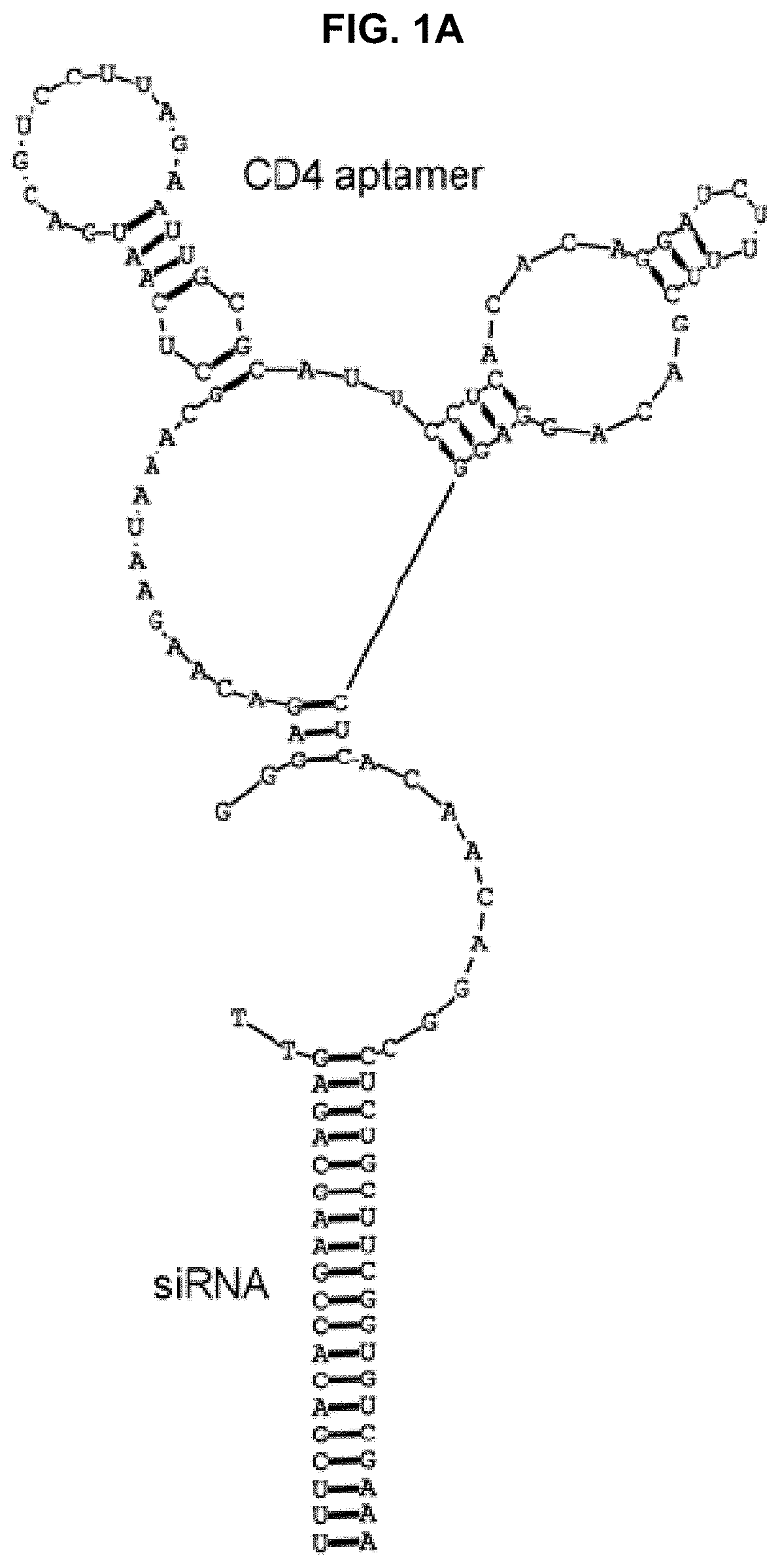
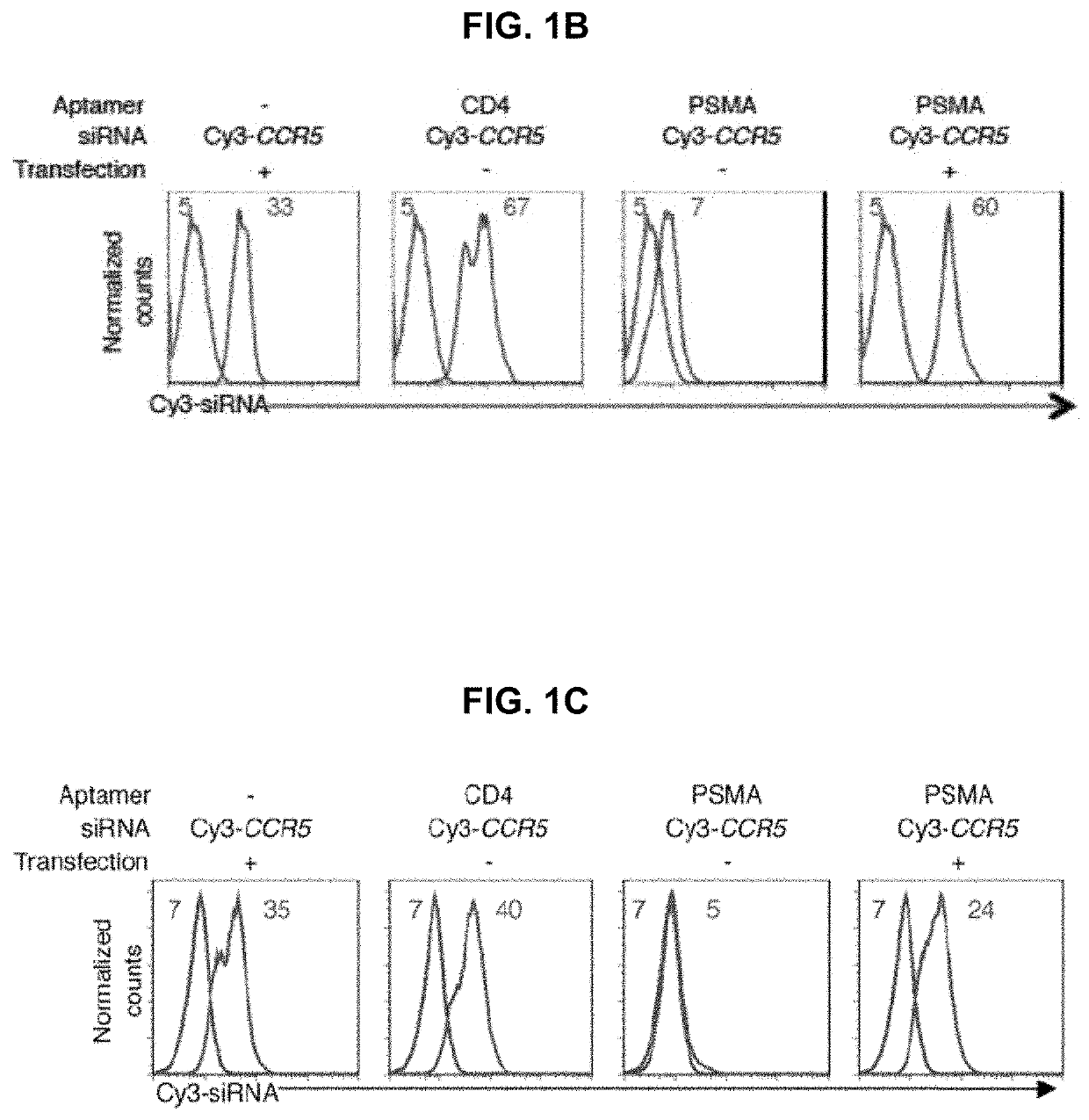
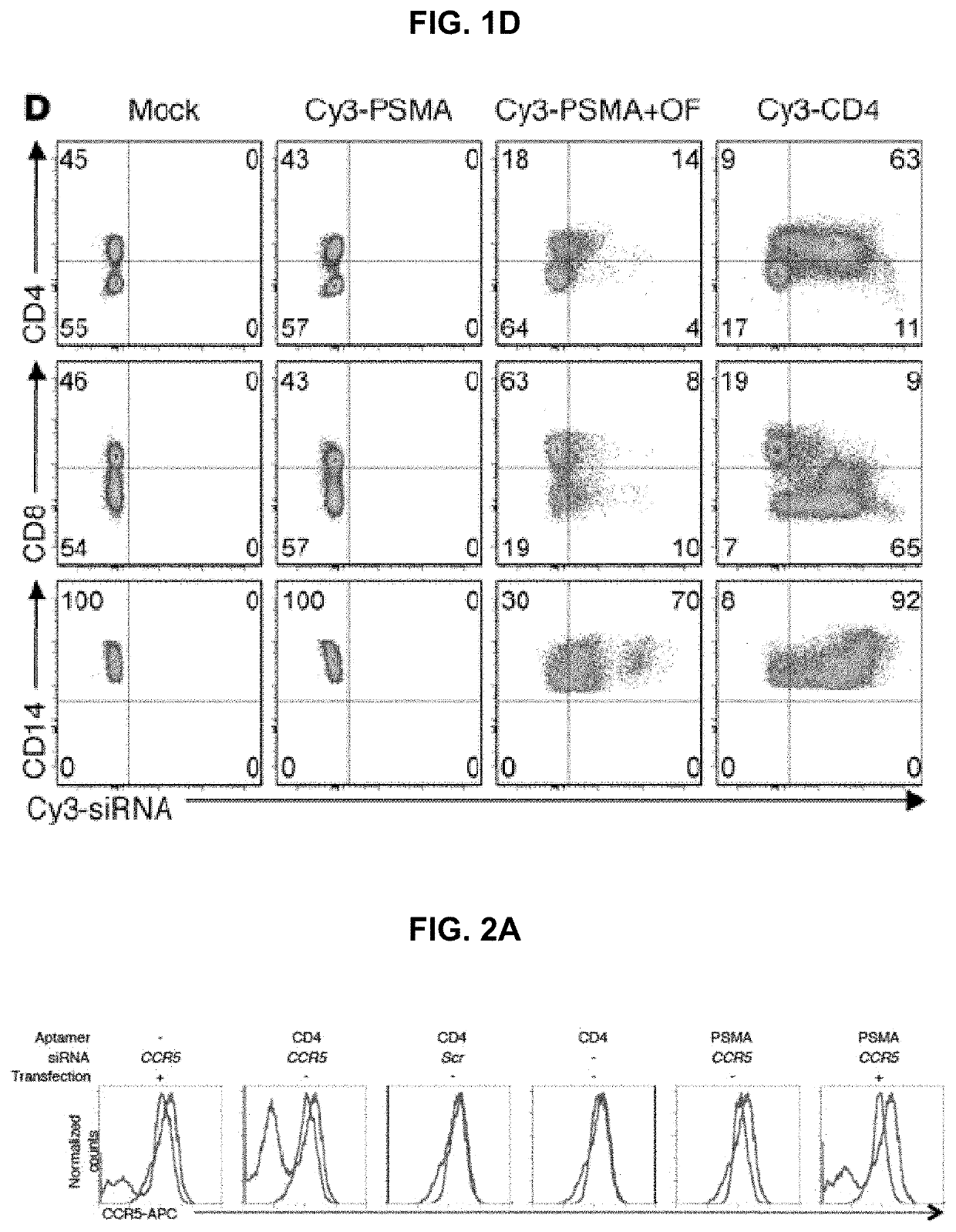
Tau modulators and methods and compositions for delivery thereof
The present disclosure is in the field of diagnostics and therapeutics for Alzheimer's Disease that concerns in vivo genetic modulation of a disease gene.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Methods for reprogramming cells and uses thereof
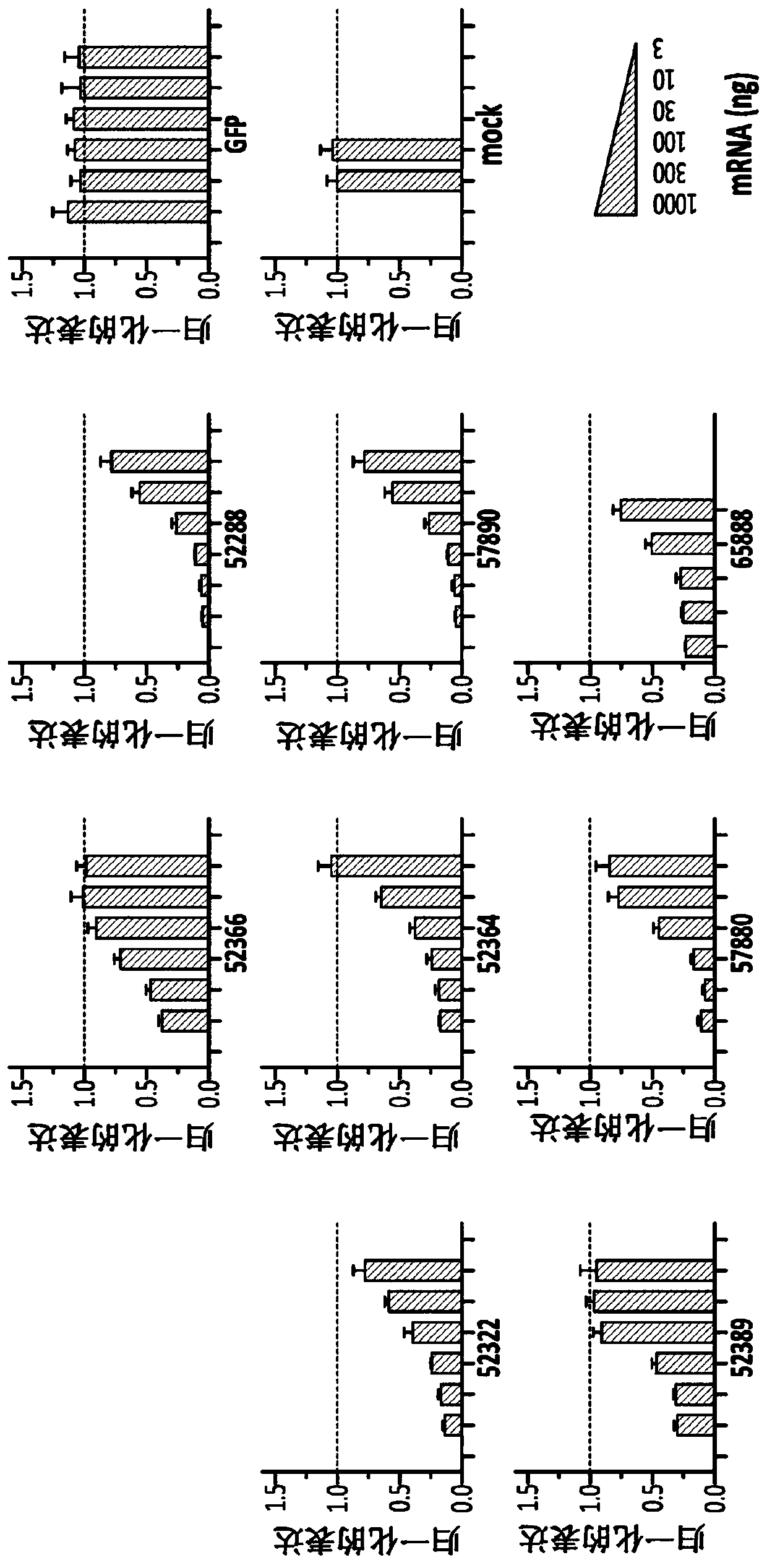
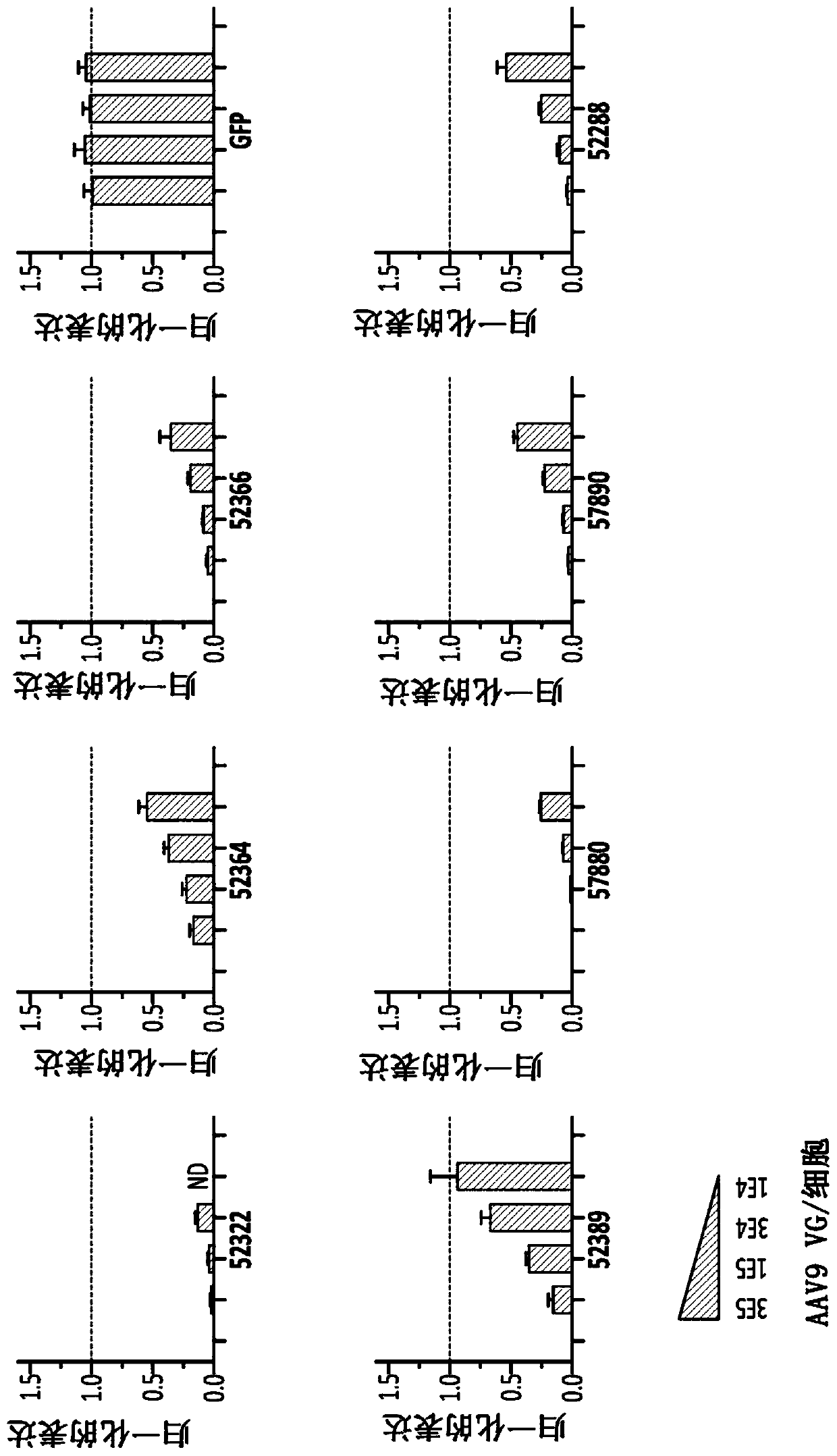
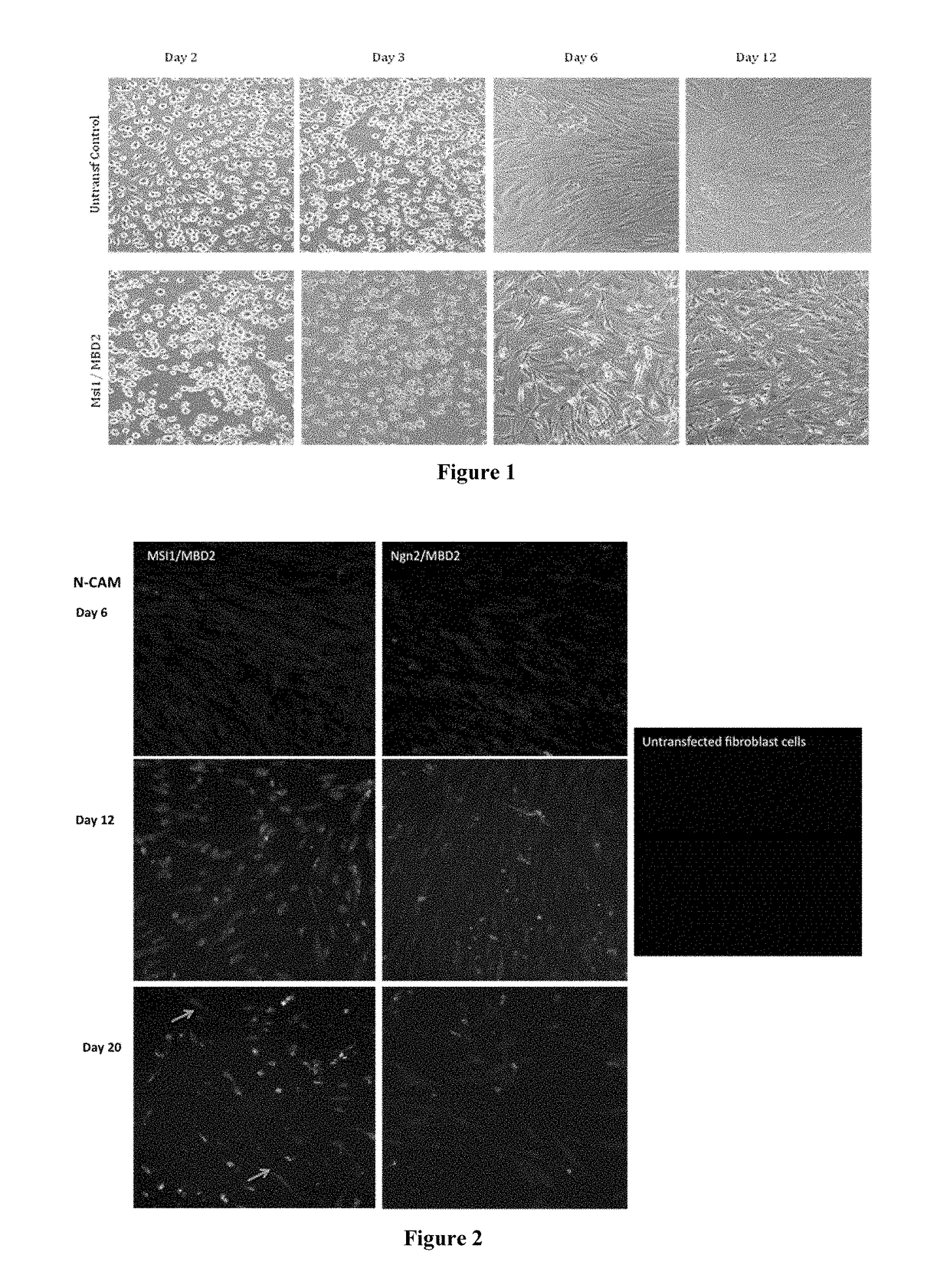
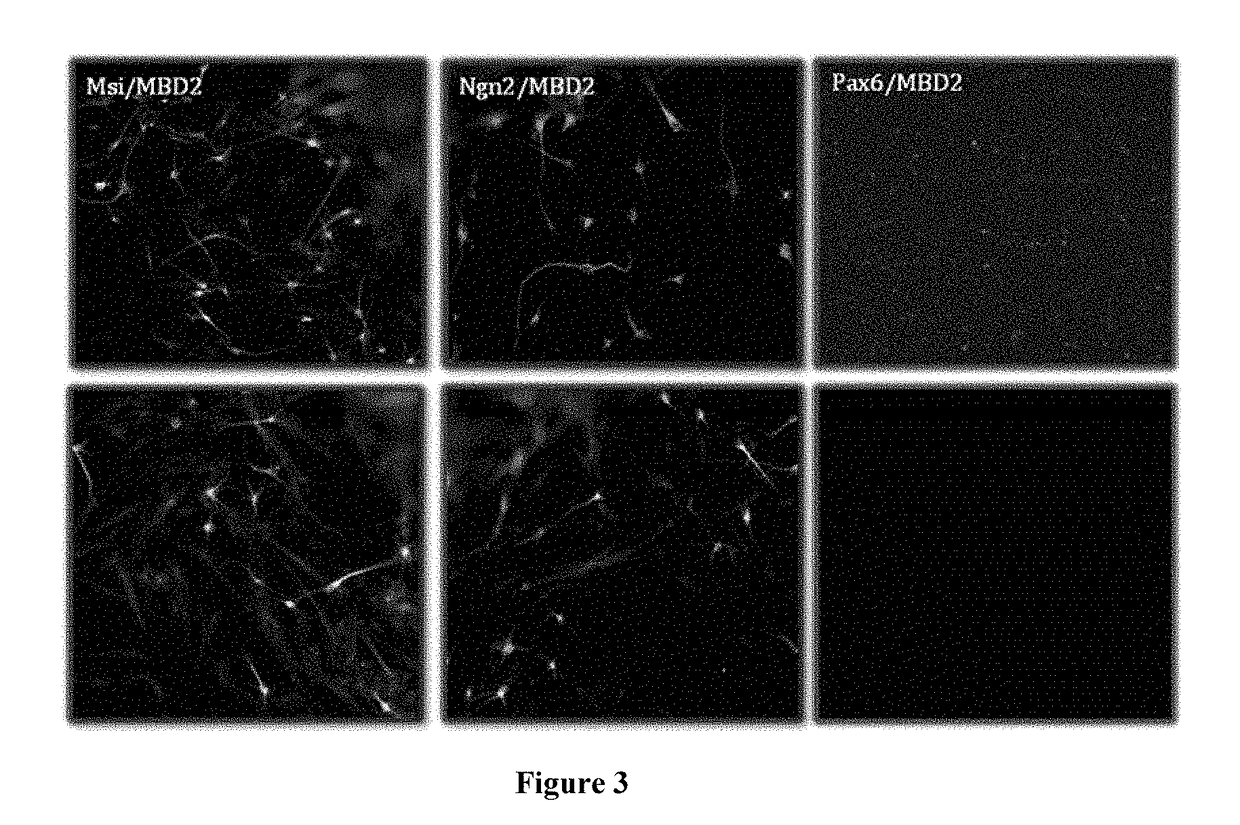
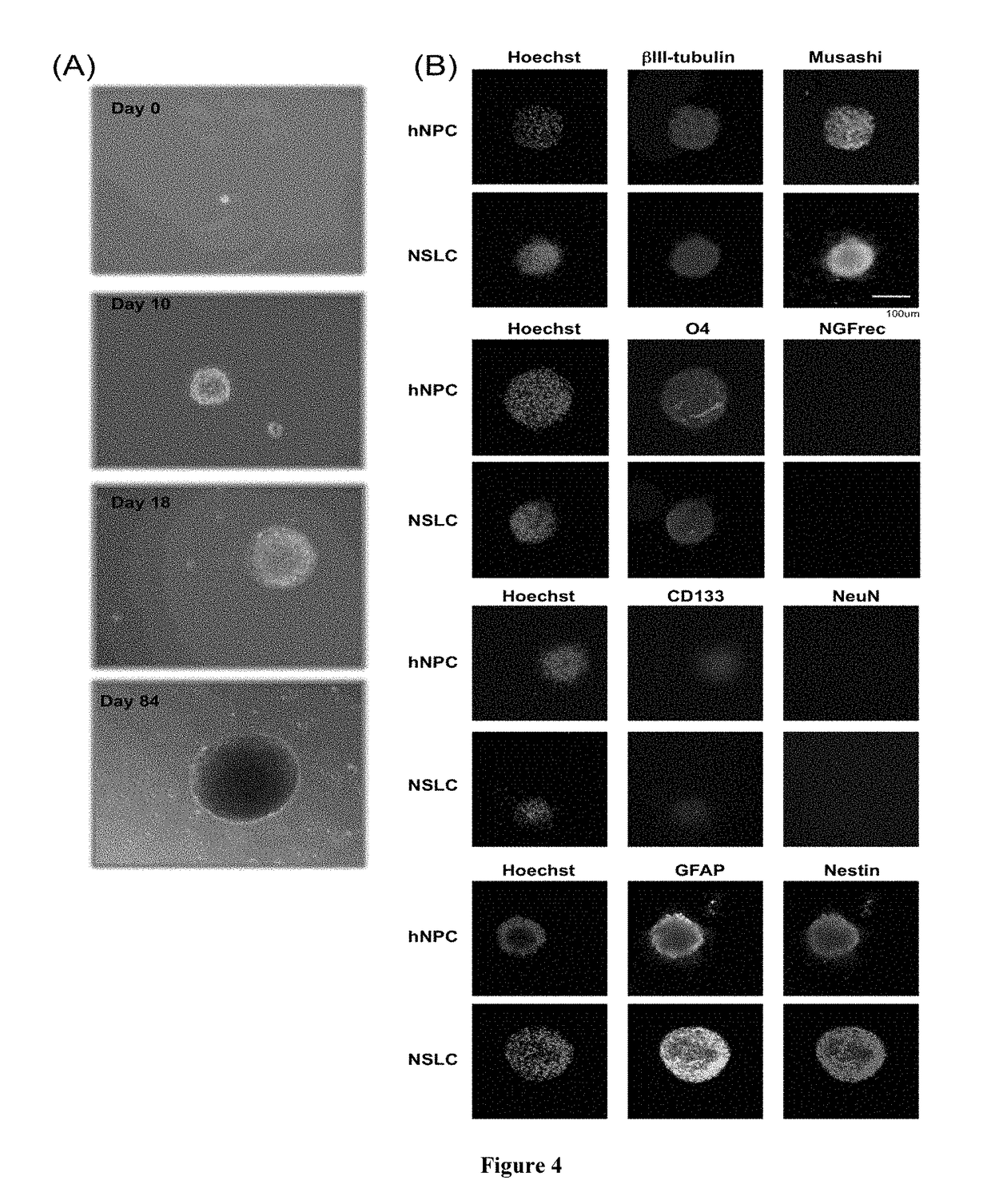
A method of obtaining a neural multipotent, unipotent or somatic cell, including: i) providing a cell of a first type which is not a neural multipotent, unipotent or somatic cell; ii) increasing expression of at least one neural multipotent or unipotent gene regulator in the cell of a first type, to a level at which the at least one neural multipotent or unipotent gene regulator is capable of driving transformation of the cell of a first type into the neural multipotent, unipotent or somatic cell, wherein the at least one multipotent or unipotent gene regulator is Musashi1 (Msi1), Neurogenin 2 (Ngn2), or both Msi1 and Ngn2; and iii) placing or maintaining the cell in a neural cell culture medium and maintaining sufficient intracellular levels of the at least one multipotent or unipotent gene regulator for a sufficient period of time to allow a stable neural multipotent, unipotent or somatic cell to be obtained.
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
Double strand compositions comprising differentially modified strands for use in gene modulation
The present invention provides double stranded compositions wherein each strand is modified to have a motif defined by positioning of β-D-ribonucleosides and sugar modified nucleosides. More particularly, the present compositions comprise one strand having a gapped motif and another strand having a gapped motif, a hemimer motif, a blockmer motif, a fully modified motif, a positionally modified motif or an alternating motif. At least one of the strands has complementarity to a nucleic acid target. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes. In some embodiments, the compositions of the present invention hybridize to a portion of a target RNA resulting in loss of normal function of the target RNA. The present invention also provides methods for modulating gene expression.
Owner:BHAT BALKRISHEN +5
Double strand compositions comprising differentially modified strands for use in gene modulation
The present invention provides double stranded compositions wherein the first strand is modified to have a particular motif and the second strand is modified a selected motif. More particularly, the present compositions comprise an antisense strand that is modified to have a positional / full motif and the sense strand is modified to have an alternating motif, a hemimer motif, a blockmer motif, a gapped motif, a positional motif, a positional / full motif or a fully modified motif. Each strand further comprises one or more phosphorothioate internucleoside linkage. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
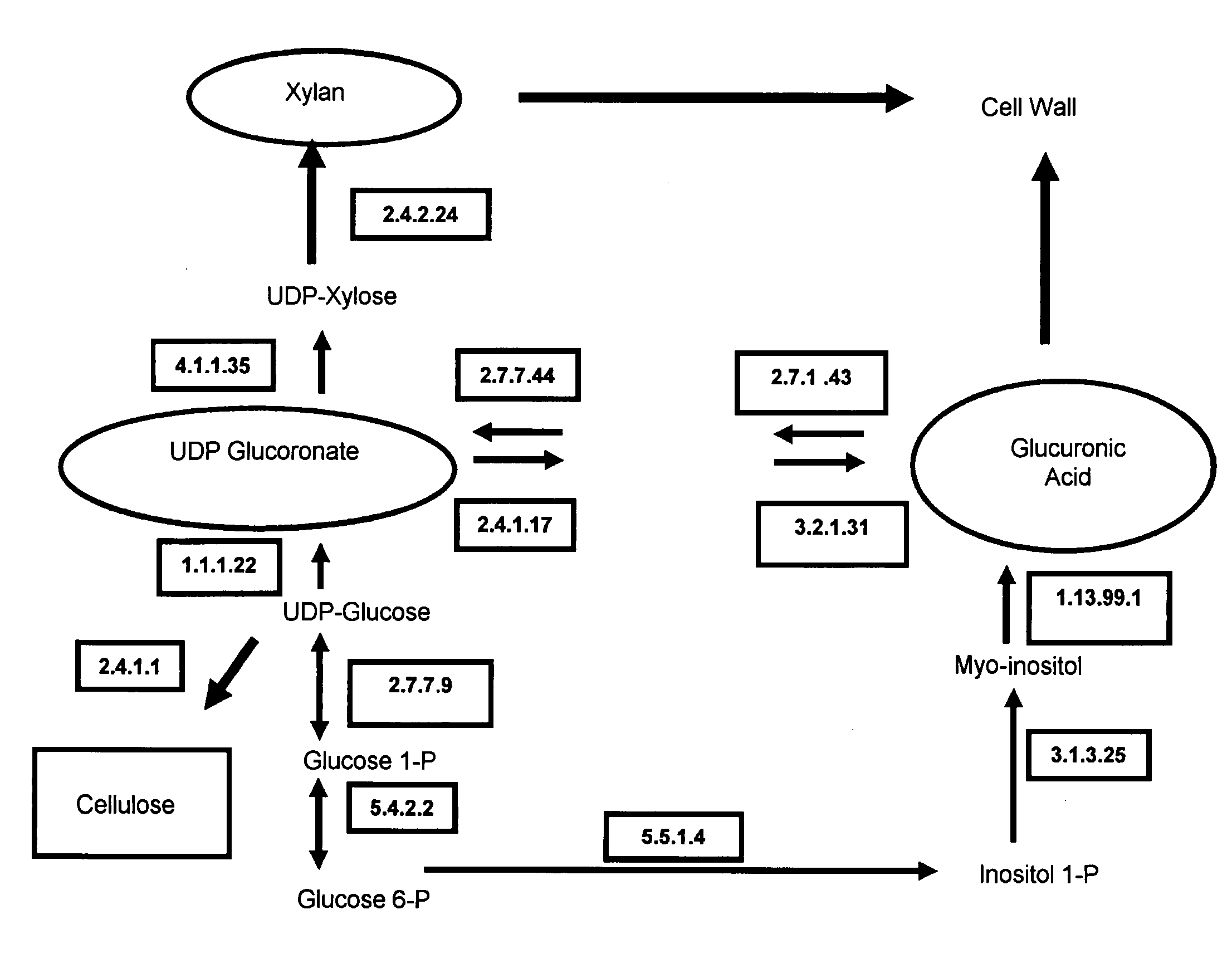
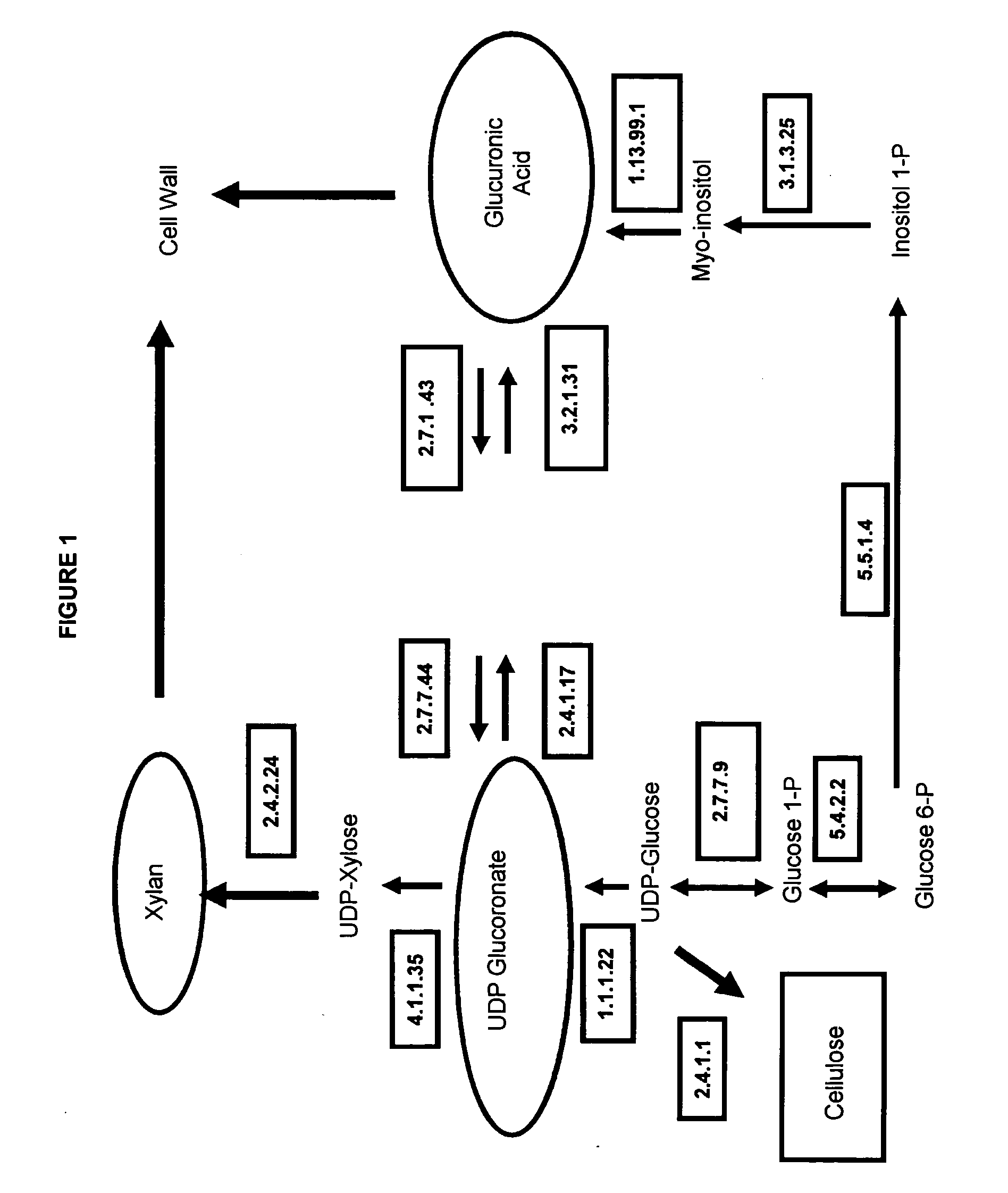
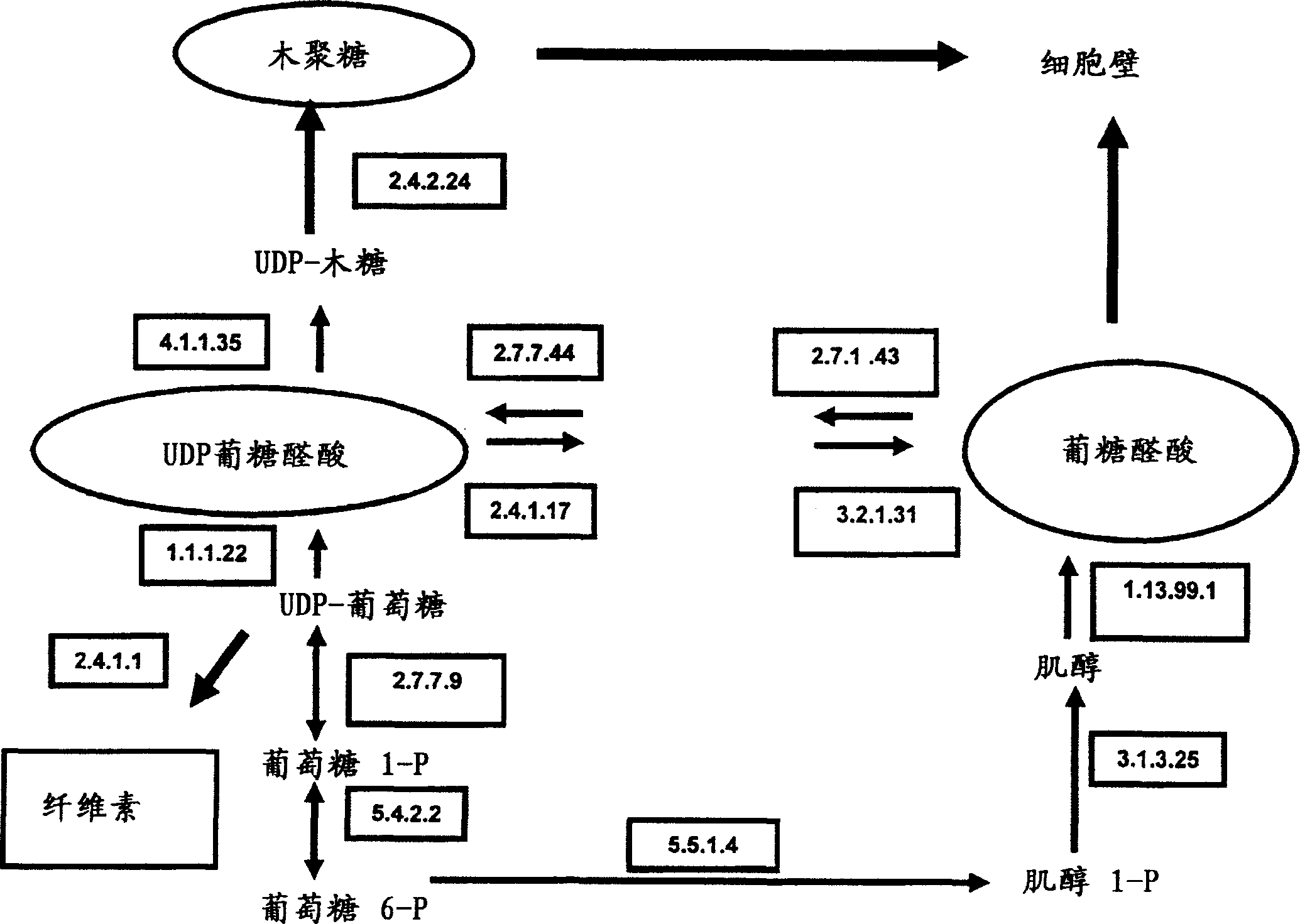
Method for the Genetic Modulation of the Biosynthesis of Hemicelluloses, Cellulose and Uronic Acids in Plant Cells Using Gene Expression Cassettes
InactiveUS20080277080A1Change outputImproves wood qualityNon-fibrous pulp additionHydrolasesPlant cellUronic acid
The present invention refers to gene expression cassettes encoding enzymes involved in the metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of hemicelluloses, cellulose and / or uronic acids, and to a method for genetic transformation of plant cells through the introduction of one or more gene expression cassettes from the present invention, and the overexpression and repression of these genes in plants.More particularly, the present invention refers to a method for introducing expression cassettes in plants. Additionally, the present invention refers to genetically modified plants.The present invention also refers to the attainment of the genetically modified plant, its derived plants and seeds, as well as the wood, paper and cellulose from this plant.
Owner:SUZANO PAPEL E CELULOSE +2
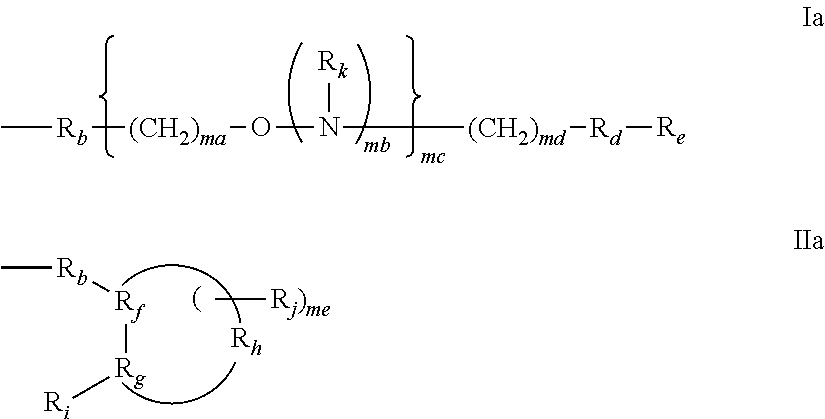
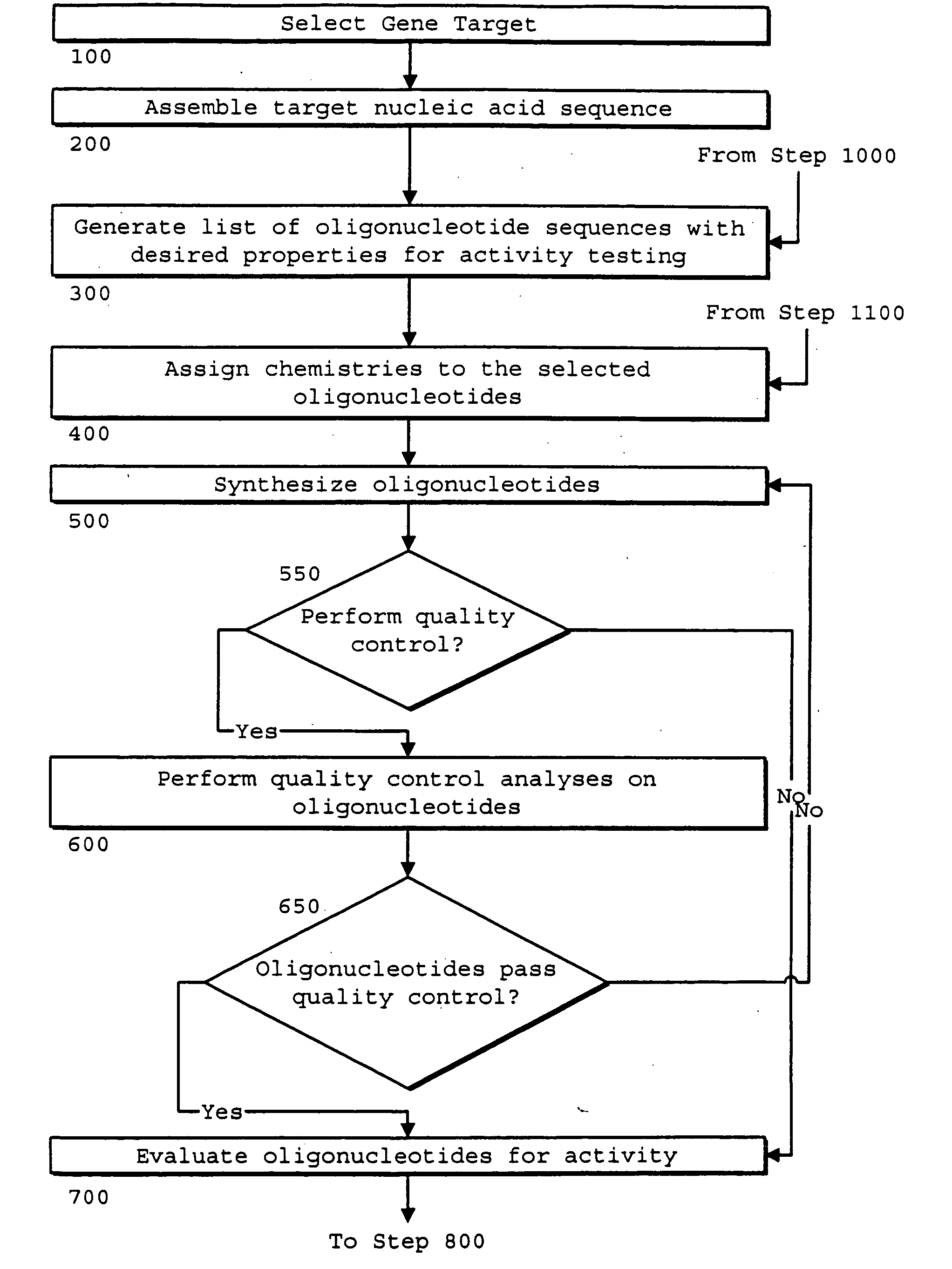
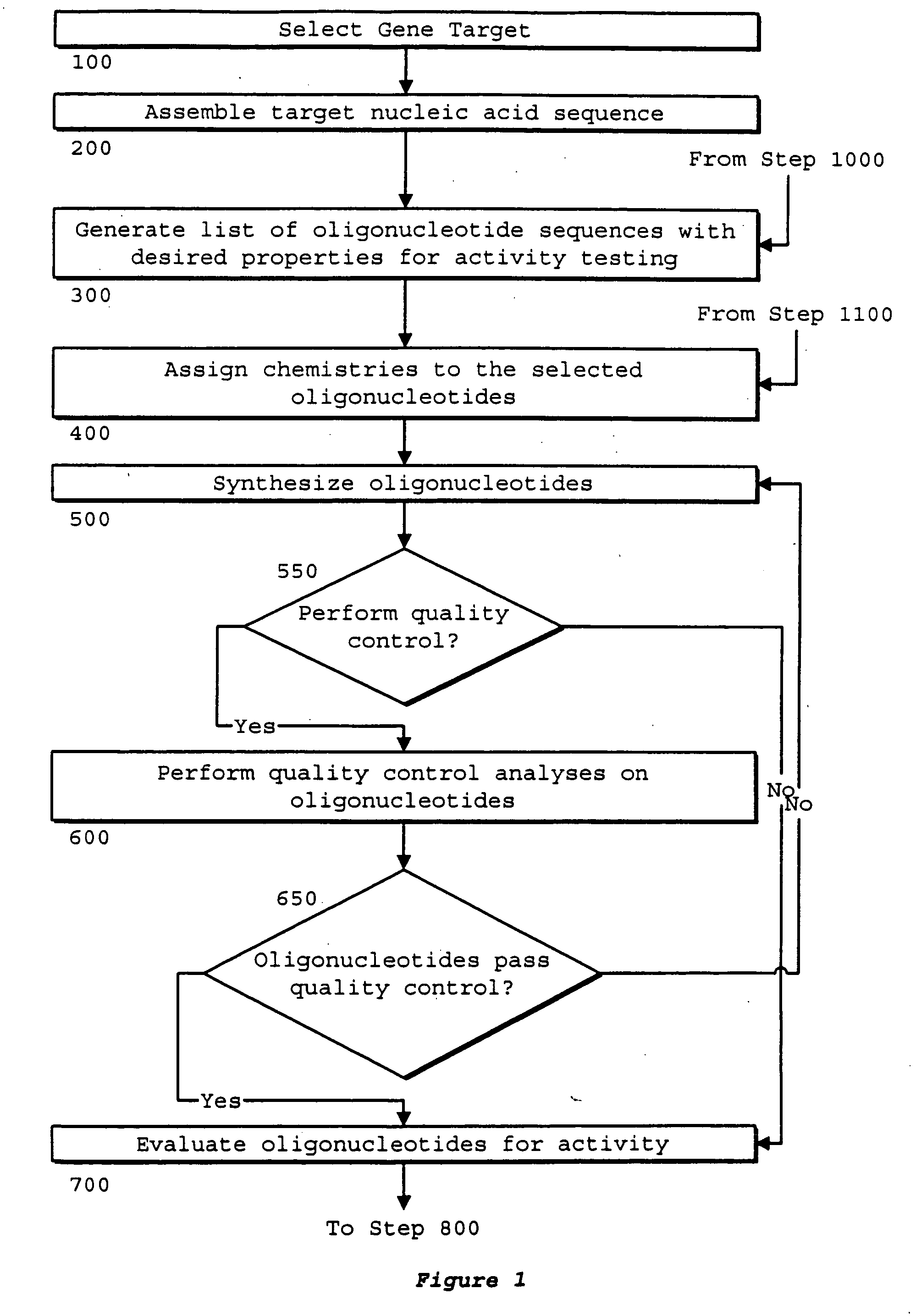
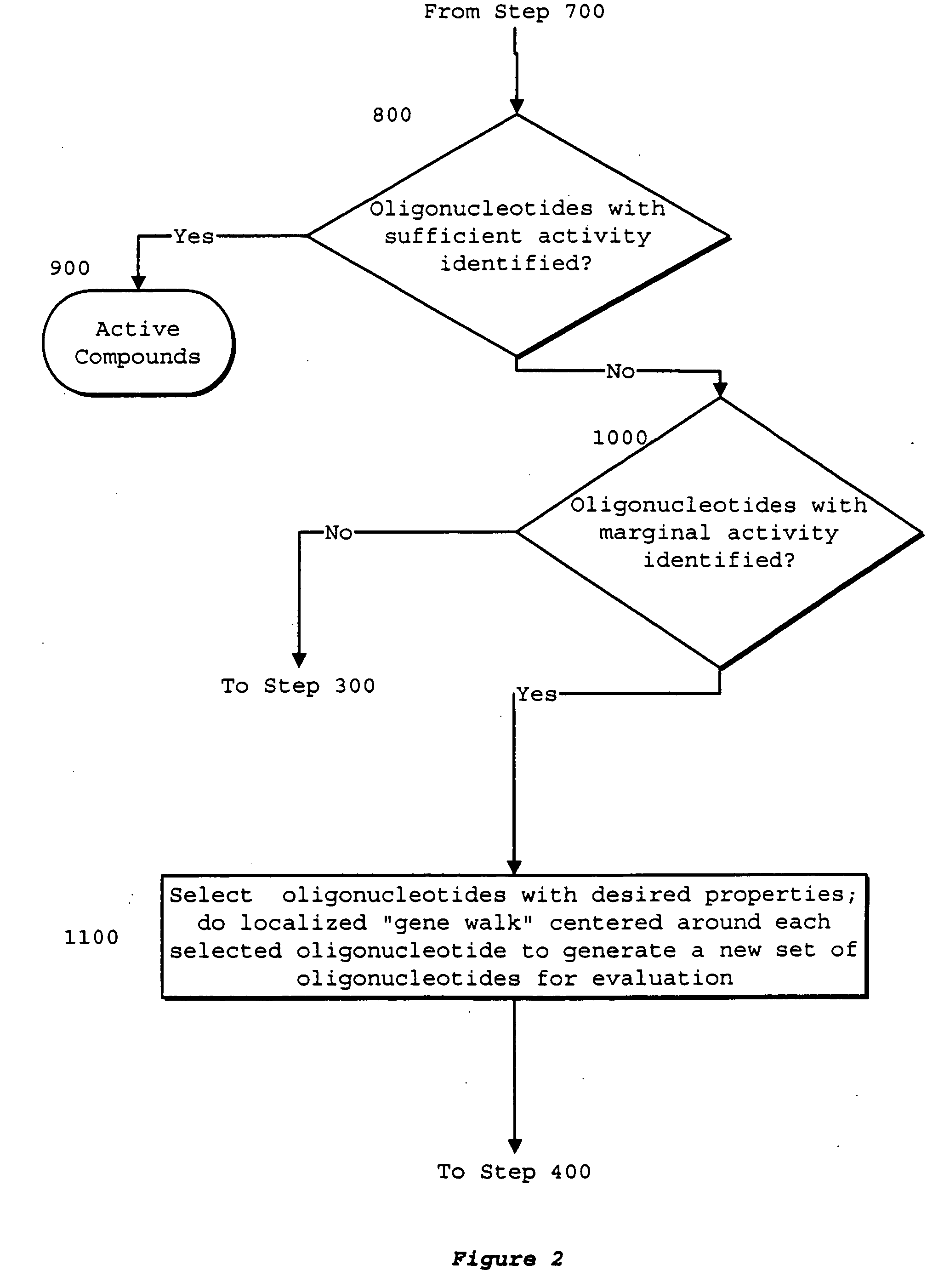
Identification of genetic targets for modulation by oligonucleotides and generation of oligonucleotides for gene modulation
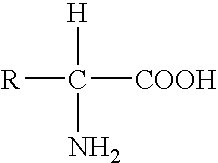
InactiveUS20060069518A1Organic chemistry methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleobase
Interative, preferably computer based iterative processes for generating synthetic compounds with desired physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties, i.e., active compounds, are provided. During iterations of the processes, a target nucleic acid sequence is provided or selected, and a library of candidate nucleobase sequences is generated in silico according to defined criteria. A “virtual” oligonucleotide chemistry is chosen and a library of virtual oligonucleotide compounds having the selected nucleobase sequences is generated. These virtual compounds are reviewed and compounds predicted to have particular properties are selected. The selected compounds are robotically synthesized and are preferably robotically assayed for a desired physical, chemical or biological activity. Active compounds are thus generated and, at the same time, preferred sequences and regions of the target nucleic acid that are amenable to oligonucleotide or sequence-based modulation are identified.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
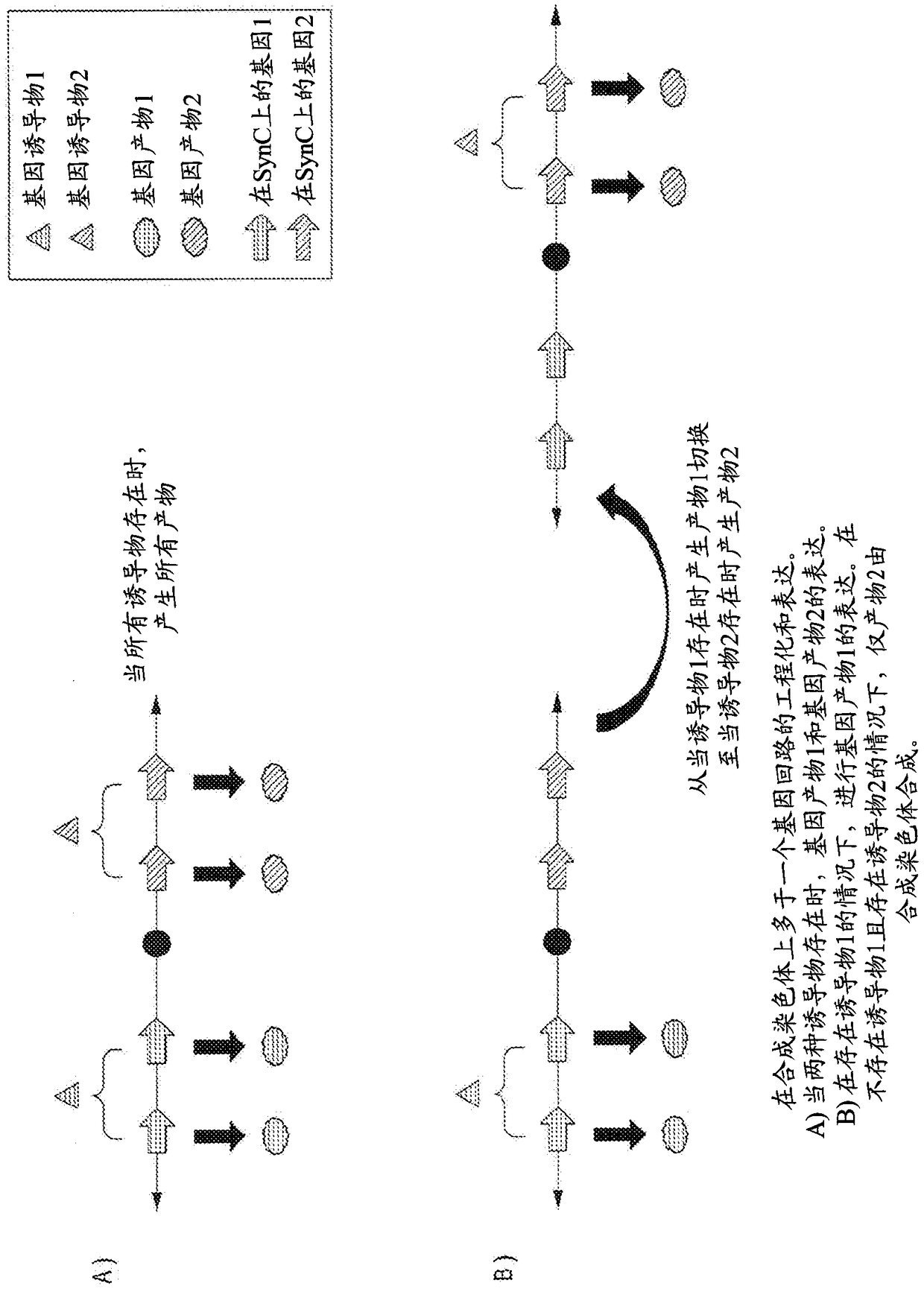
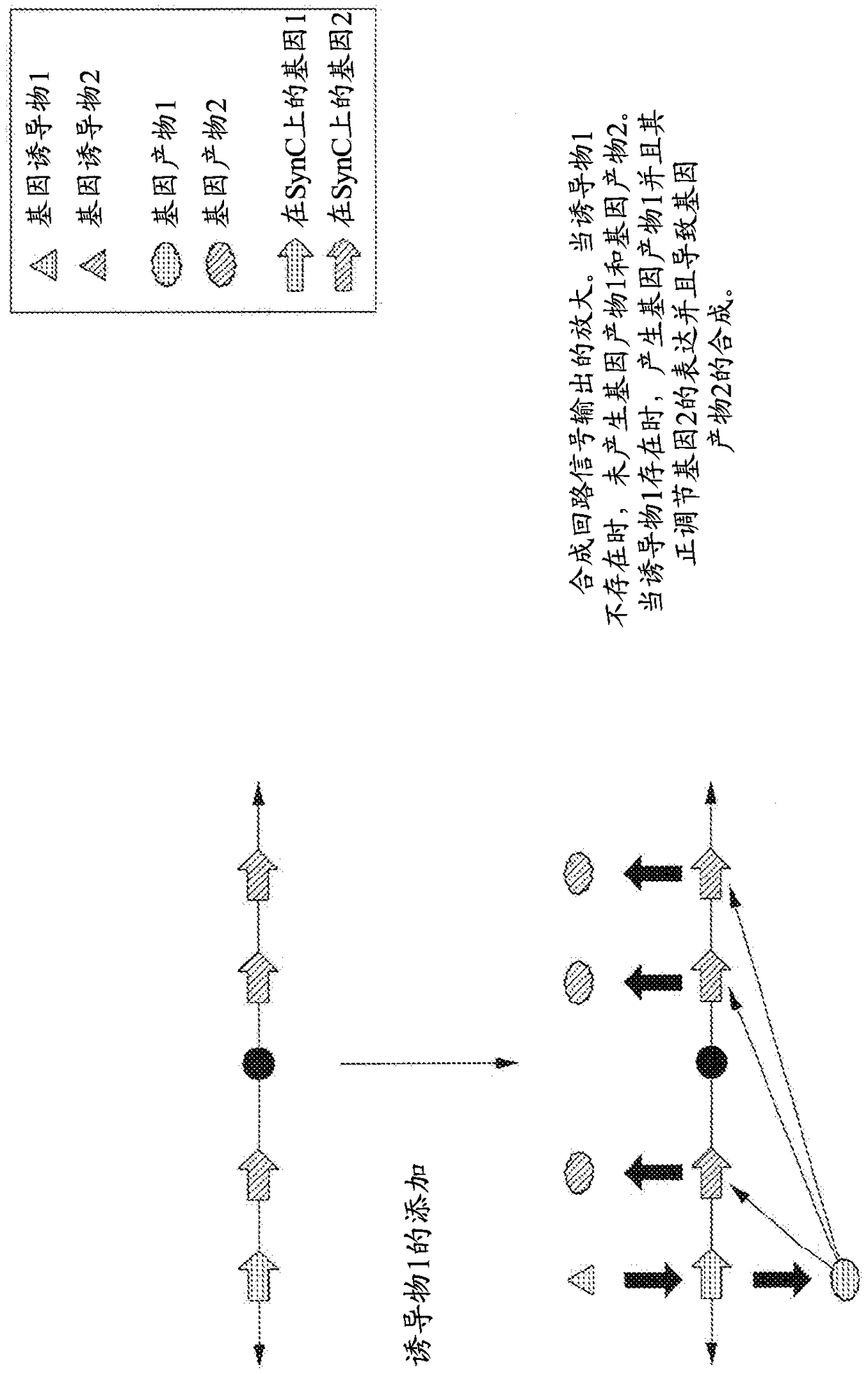
Methods for creating synthetic chromosomes having gene regulatory systems and uses thereof
The present invention encompasses compositions and methods to allow one to deliver and express multiple genes under the control of multiple gene regulatory components in a recipient cell via a synthetic chromosome. The engineering of synthetic chromosomes to contain multiple gene control units permits the construction of complex biological circuits.
Owner:SYNPLOID BIOTEK LLC
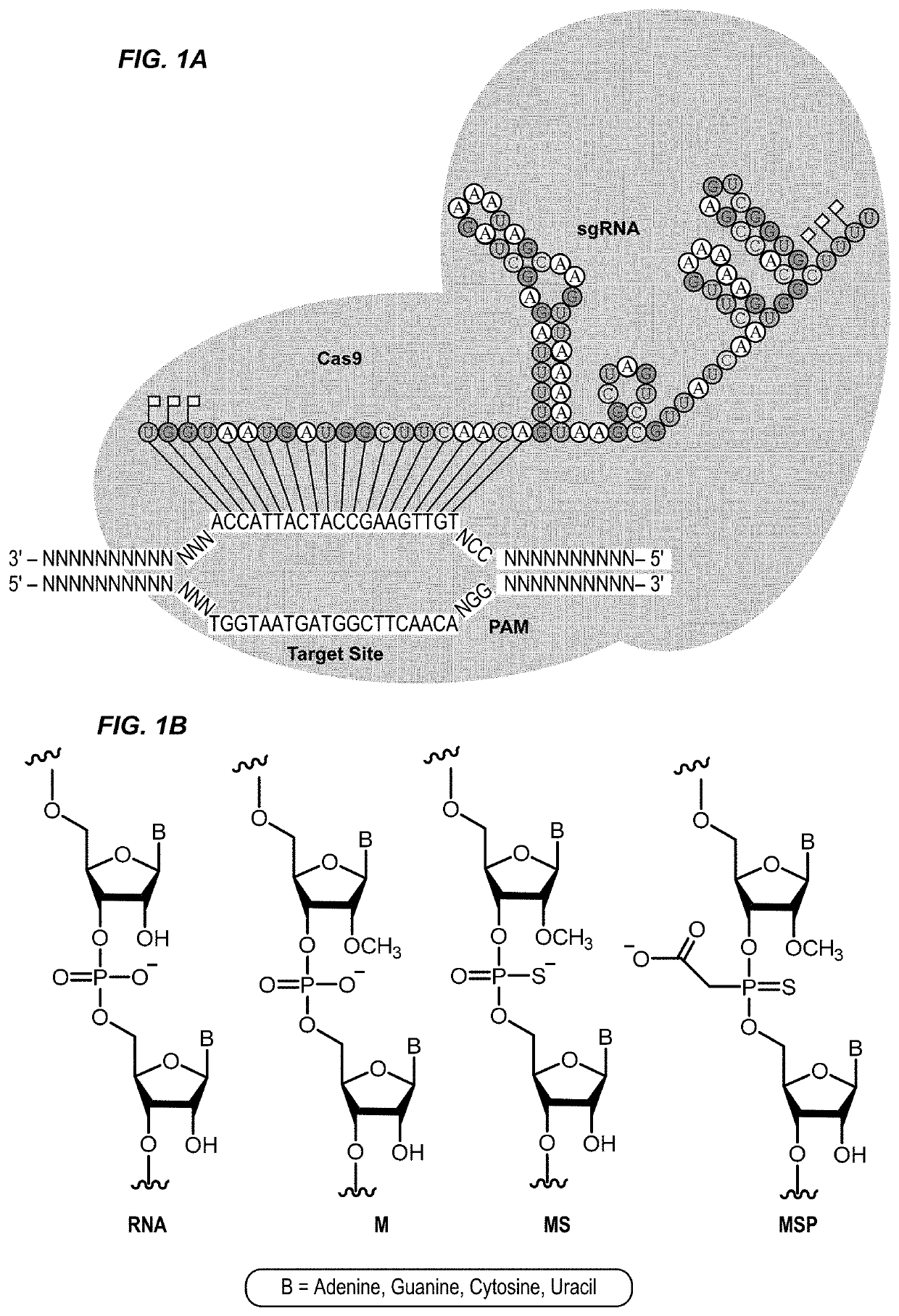
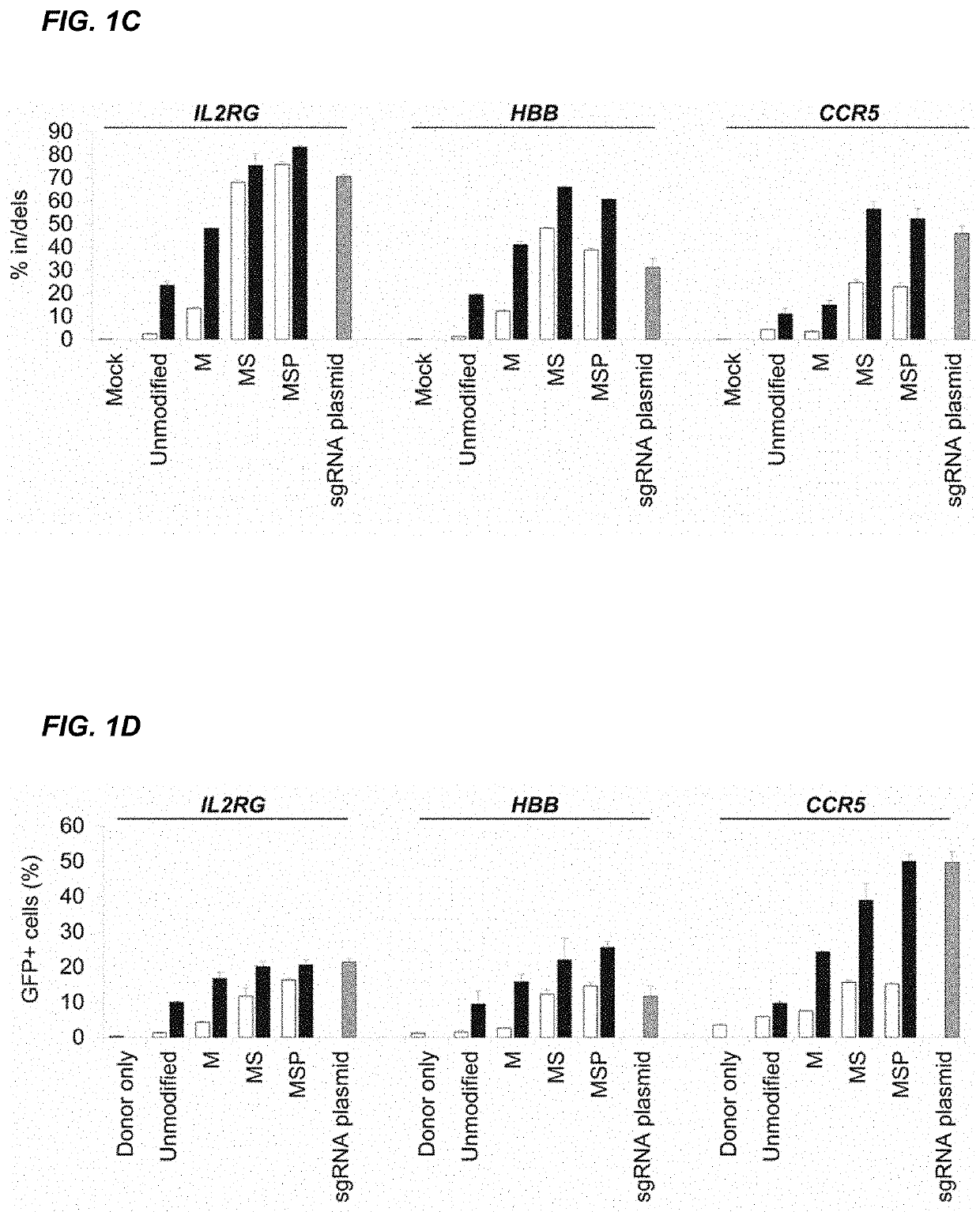
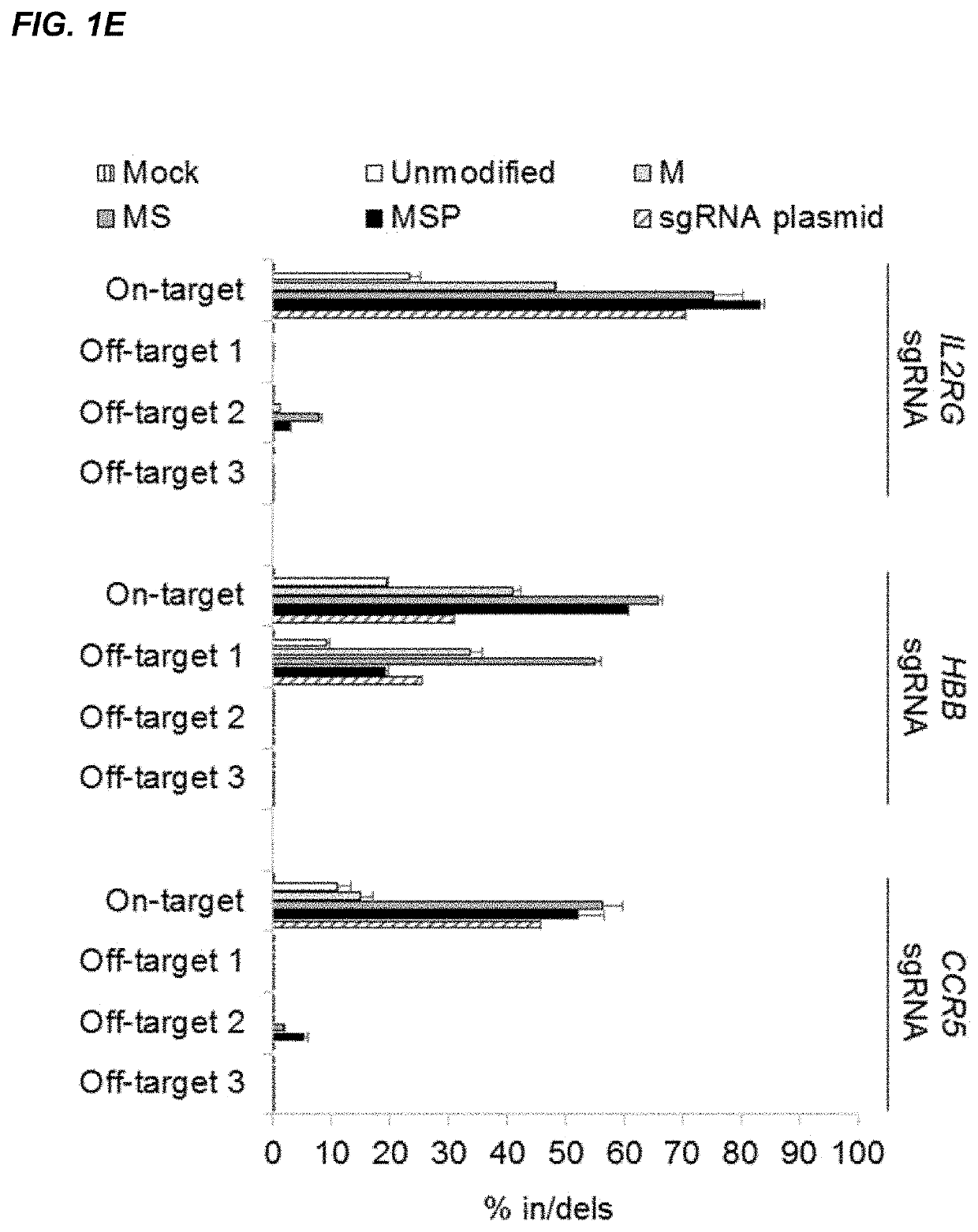
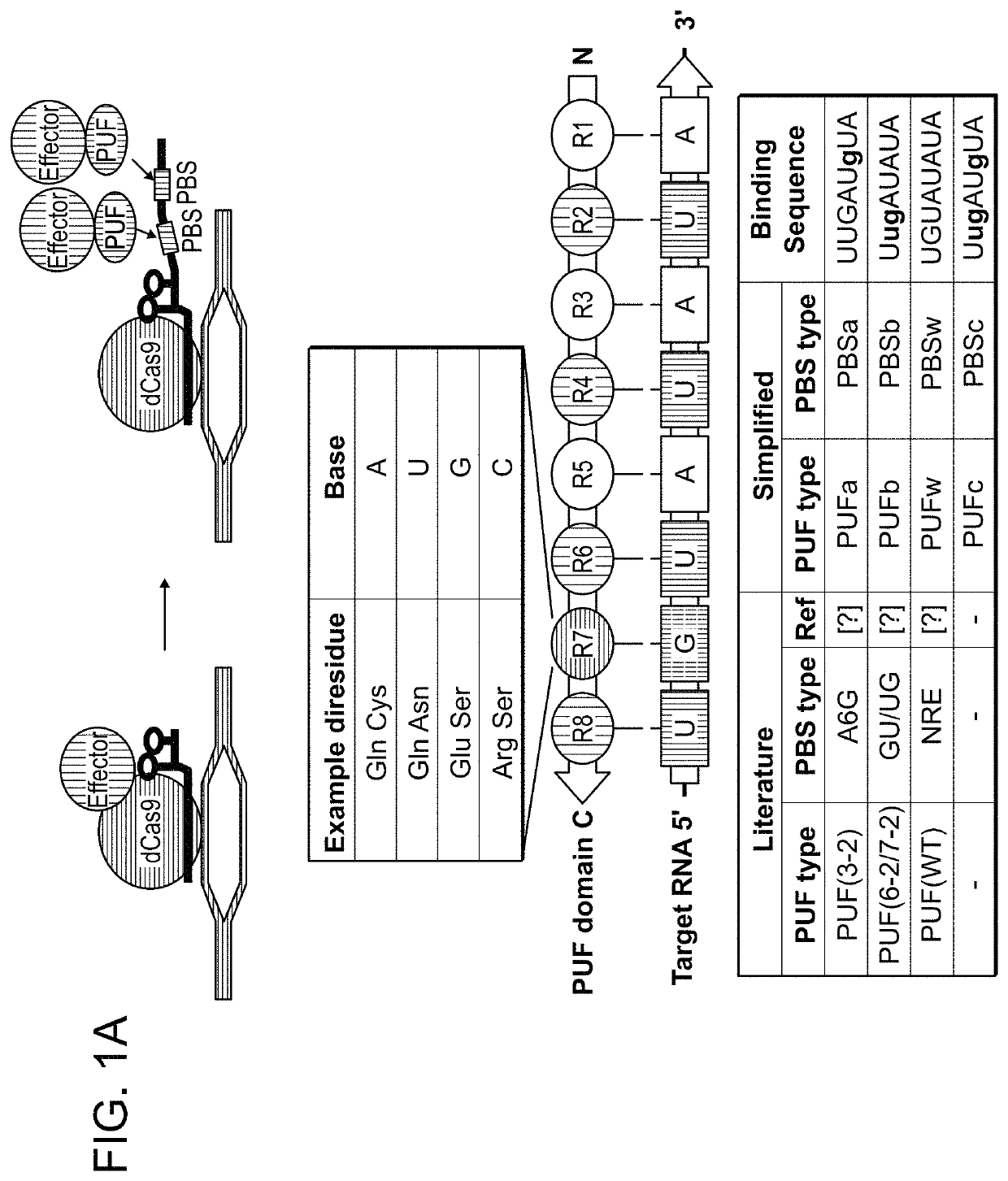
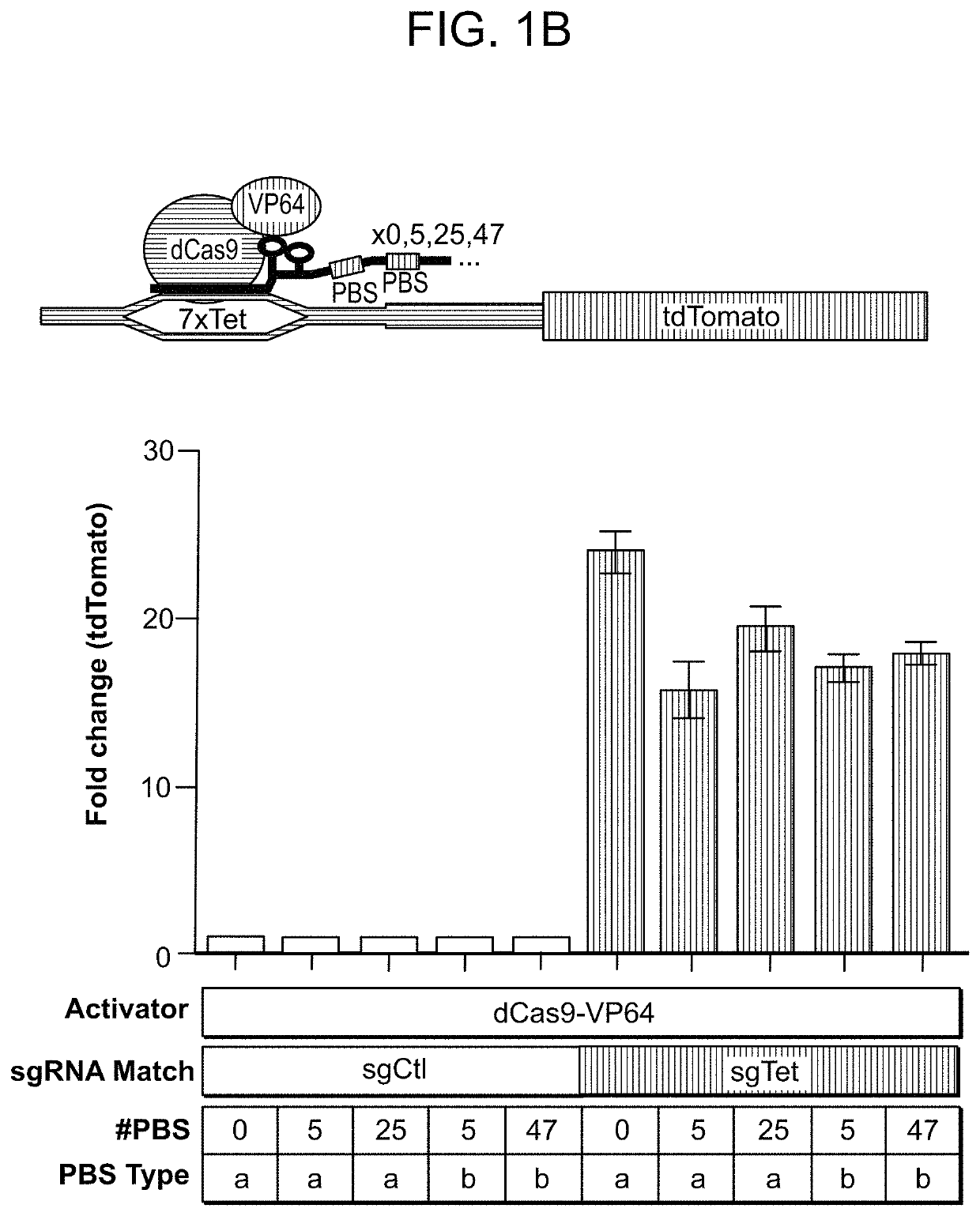
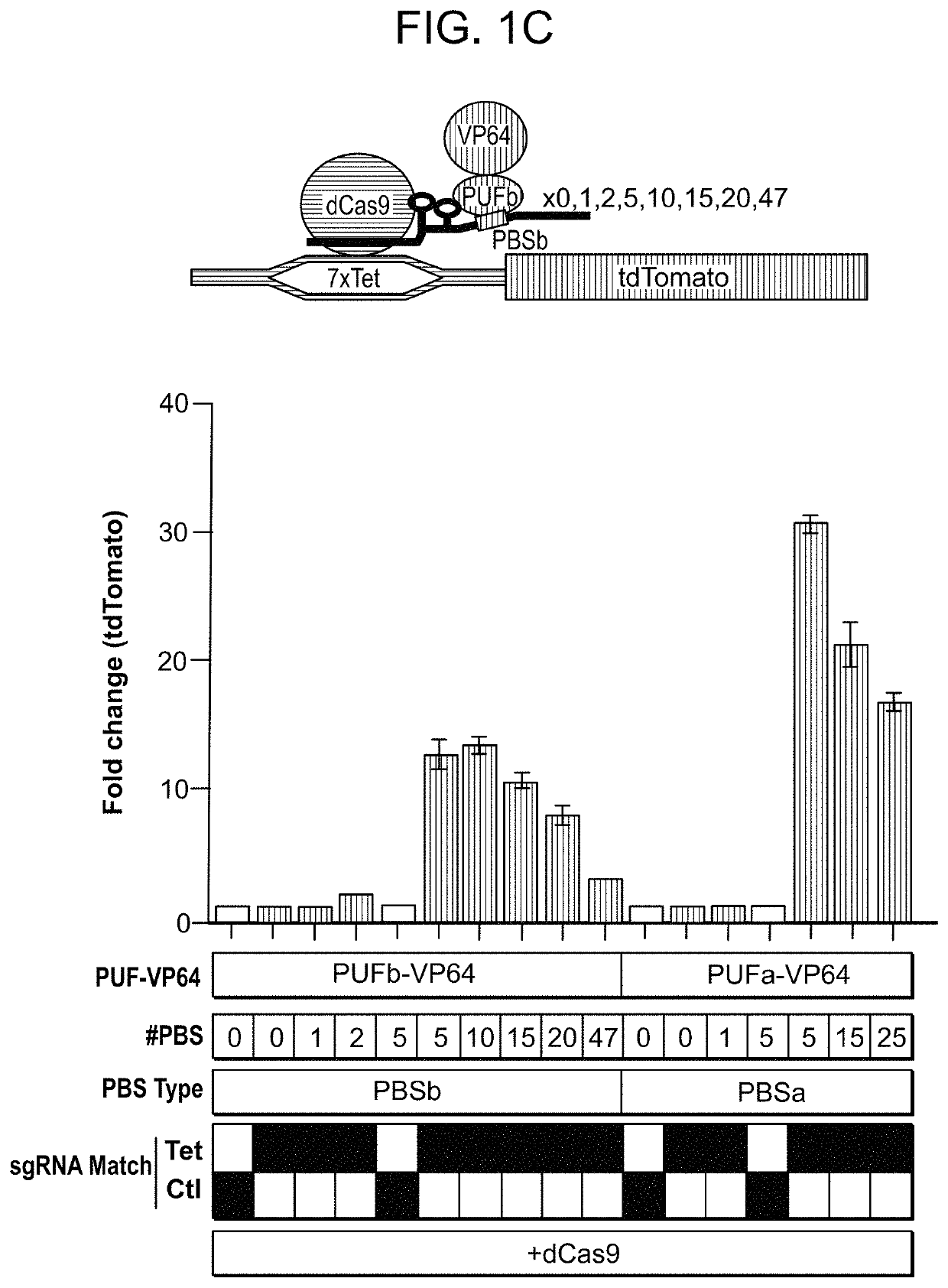
Chemically modified guide rnas for crispr/cas-mediated gene regulation
ActiveUS20220195425A1Increased activationGrowth inhibitionSenses disorderNervous disorderInducer CellsGenetic modulation
Provided herein are methods for inducing CRISPR / Cas-based gene regulation (e.g., genome editing or gene expression) of a target nucleic acid (e.g., target DNA or target RNA) in a cell. The methods include using modified single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that enhance gene regulation of the target nucleic acid in a primary cell for use in ex vivo therapy or in a cell in a subject for use in in vivo therapy. Additionally, provided herein are methods for preventing or treating a genetic disease in a subject by administering a sufficient amount of a modified sgRNA to correct a mutation in a target gene associated with the genetic disease.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method to restore or improve cognitive functions
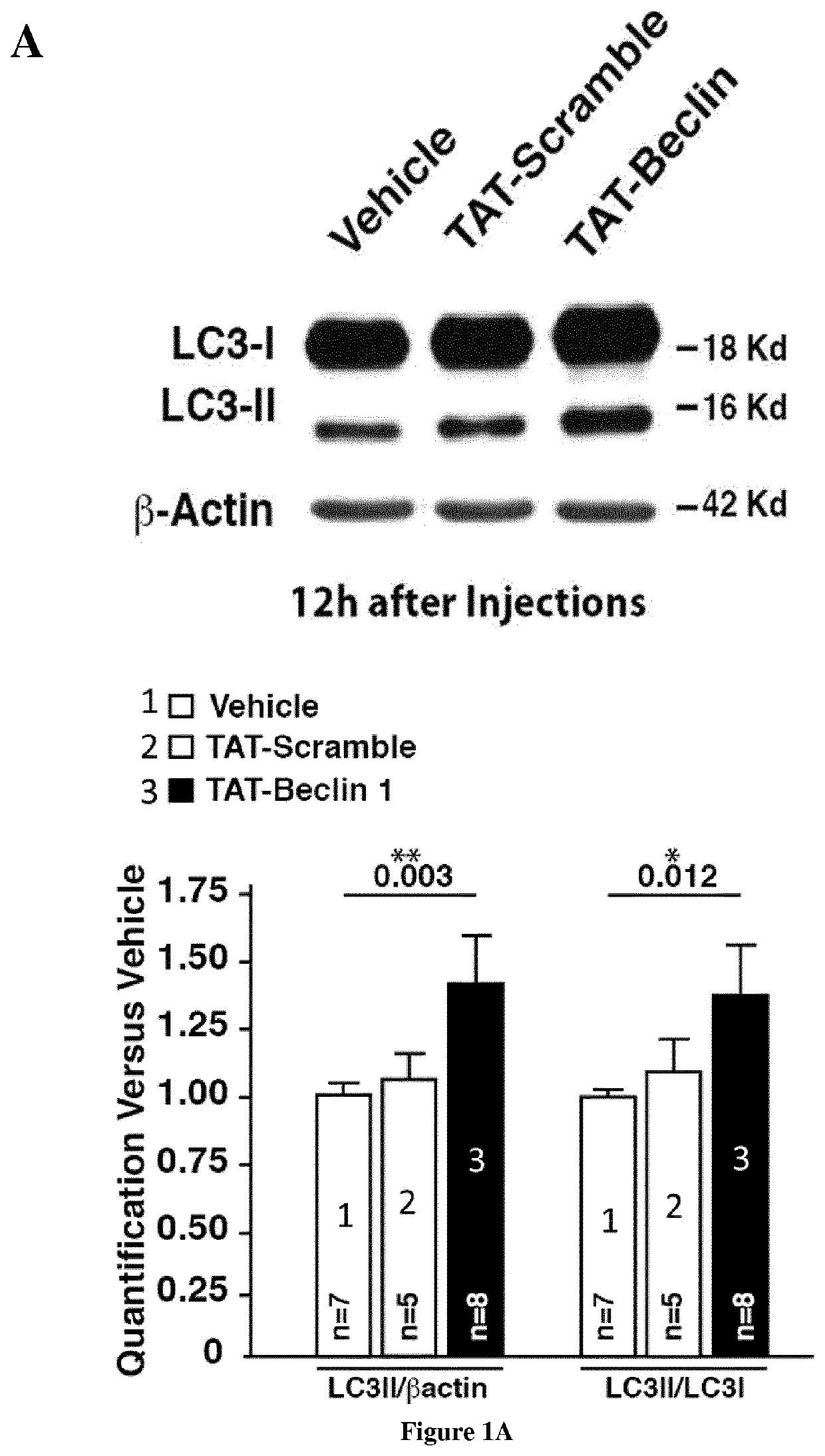
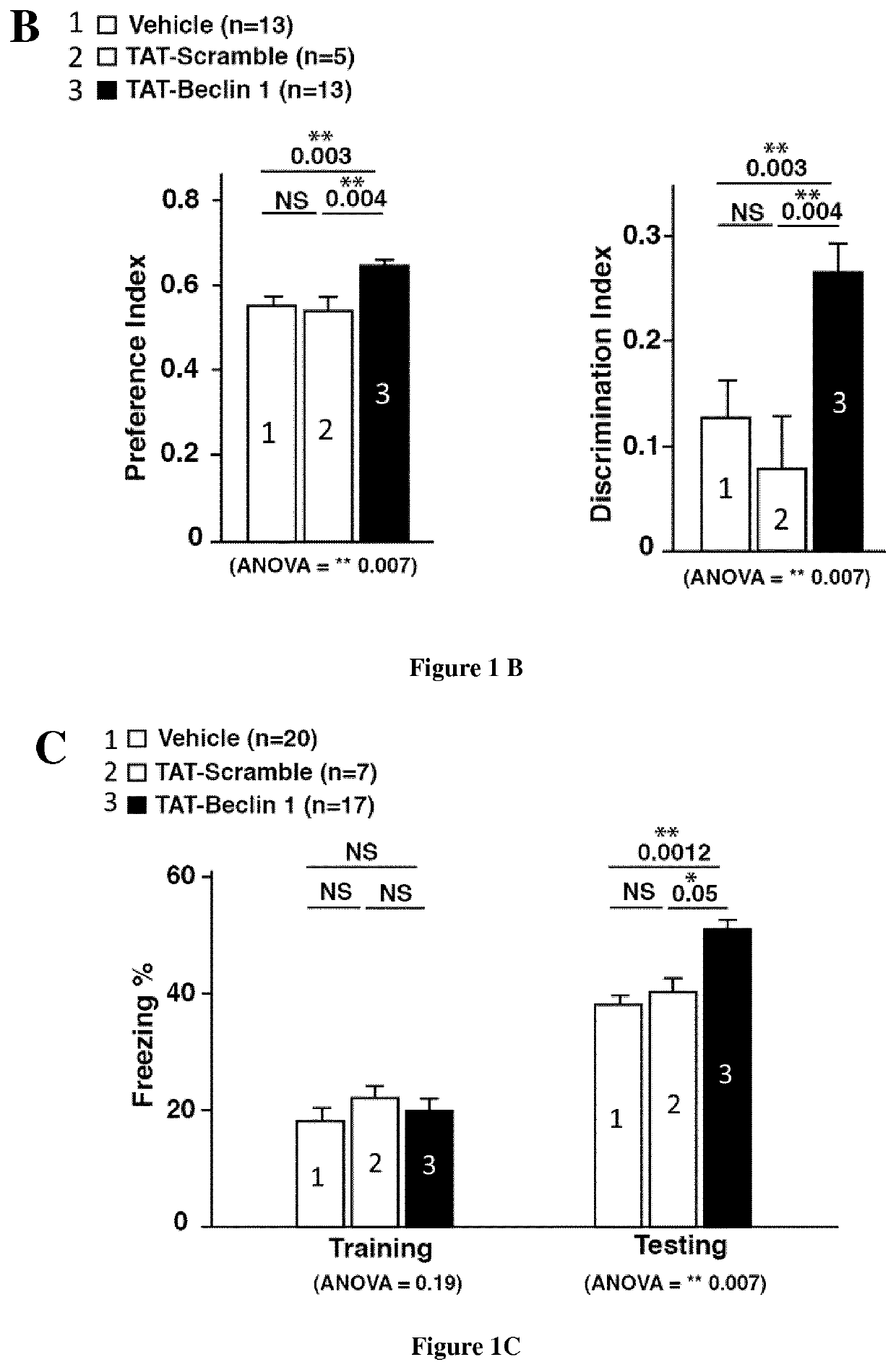
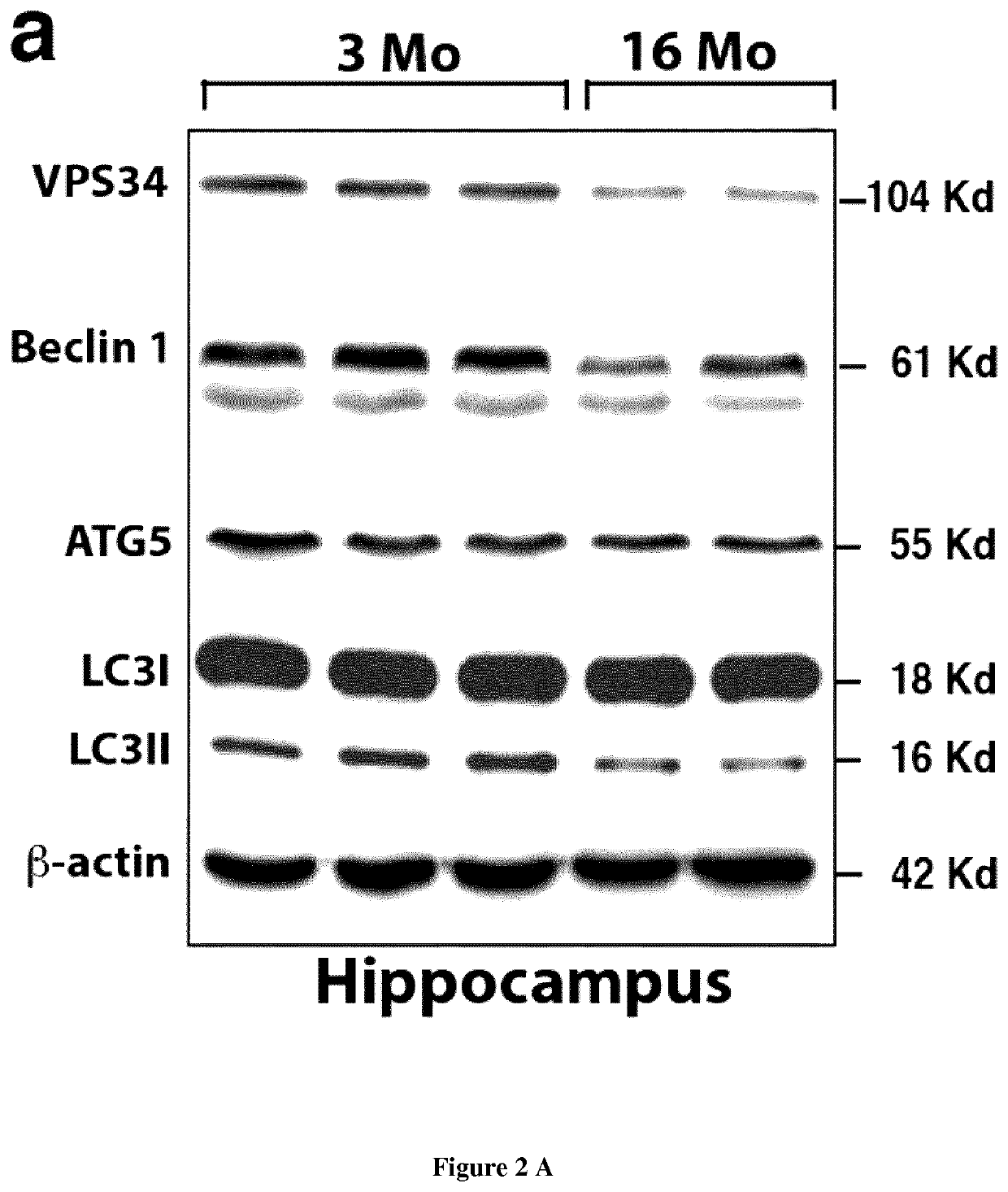
PendingUS20210379146A1Induce autophagyReverse age-related memory declineNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmacometricsMouse Hippocampus
The present invention relates to the field of memory and cognitive functions. Here the inventors show that memory stimulations induce autophagy in the mouse hippocampus, while local pharmacological and genetic modulations of hippocampal autophagy strongly influence memory acquisition. More, the inventors observe that hippocampal autophagy declines during aging and they find that restoring autophagy specifically in the hippocampus of aged mice, following autophagy inducers (such as TAT-Beclin-1), can significantly reverse age-related memory decline. Their results reveal a novel physiological role of autophagy in regulating hippocampal-dependent memory functions, and demonstrate the potential therapeutic benefits of modulating autophagy in order to prevent and / or reverse the deleterious effects of aging on cognitive function. The present invention relates to an activator of the autophagy for use in the restoration and / or improvement of cognitive functions in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
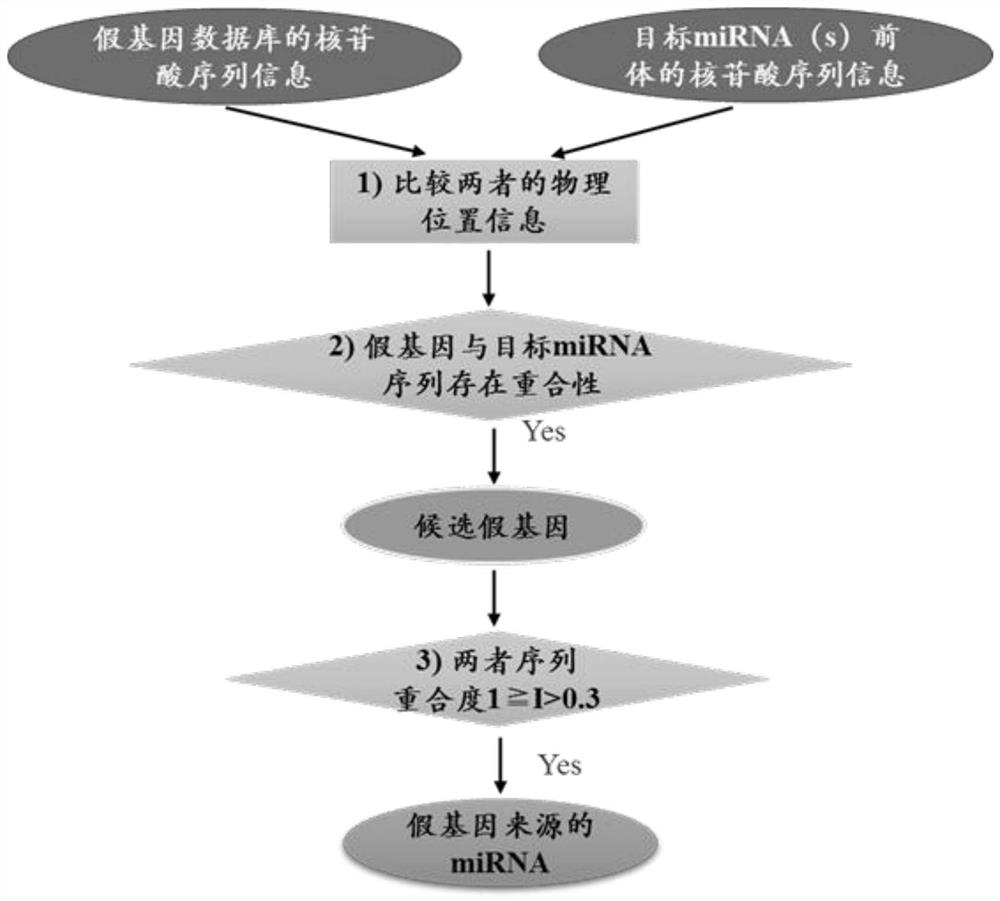
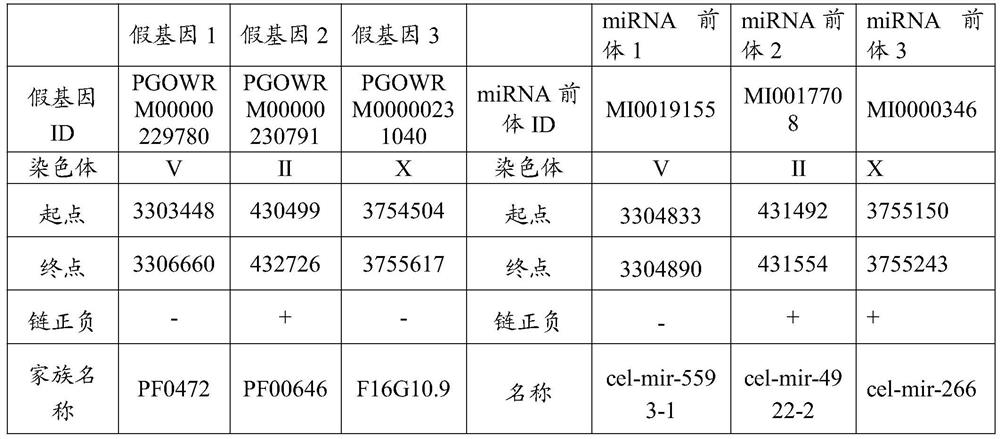
A method for detecting the source of miRNA
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Compositions comprising alternating 2'-modified nucleosides for use in gene modulation
The present invention provides compositions comprising at least one oligomeric compound comprising an alternating motif and further include a region that is complementary to a nucleic acid target. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes. In preferred embodiments the compositions of the present invention hybridize to a portion of a target RNA resulting in loss of normal function of the target RNA. The present invention also provides methods for modulating gene expression.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Three-component CRISPR/Cas complex system and uses thereof
ActiveUS11434484B2Lack nuclease activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainGenomeDNA
The invention described herein provides compositions and reagents for assembling a tripartite complex at a specific location of a target DNA. The invention also provides methods for using the complex to, for example, label a specific genomic locus, to regulate the expression of a target gene, or to create a gene regulatory network.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
Method for the genetic modulation of the biosynthesis of hemicelluloses, cellulose and uronic acids in plant cells using gene expression cassettes
The present invention refers to gene expression cassettes encoding enzymes involved in the metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of hemicelluloses, cellulose and / or uronic acids, and to a method for genetic transformation of plant cells through the introduction of one or more gene expression cassettes from the present invention, and the overexpression and repression of these genes in plants. More particularly, the present invention refers to a method for introducing expression cassettes in plants. Additionally, the present invention refers to genetically modified plants. The present invention also refers to the attainment of the genetically modified plant, its derived plants and seeds, as well as the wood, paper and cellulose from this plant.
Owner:SUZANO PAPEL E CELULOSE +2
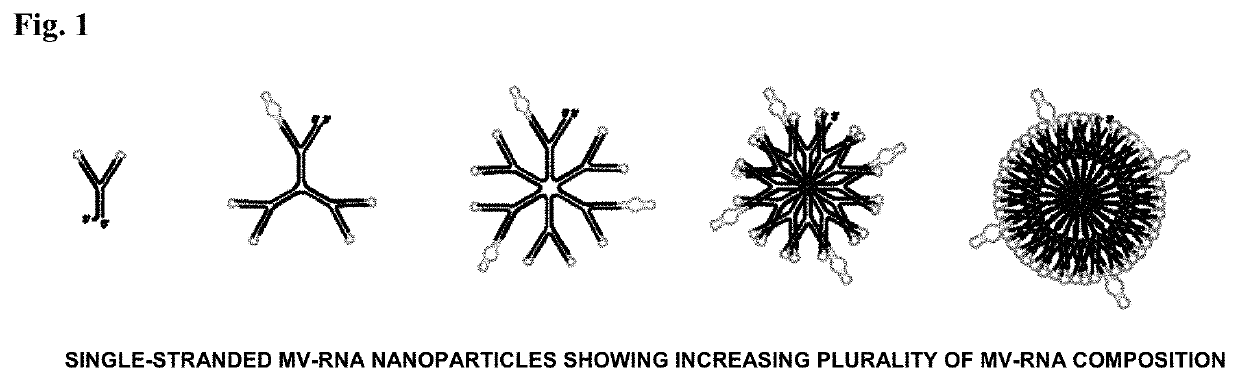
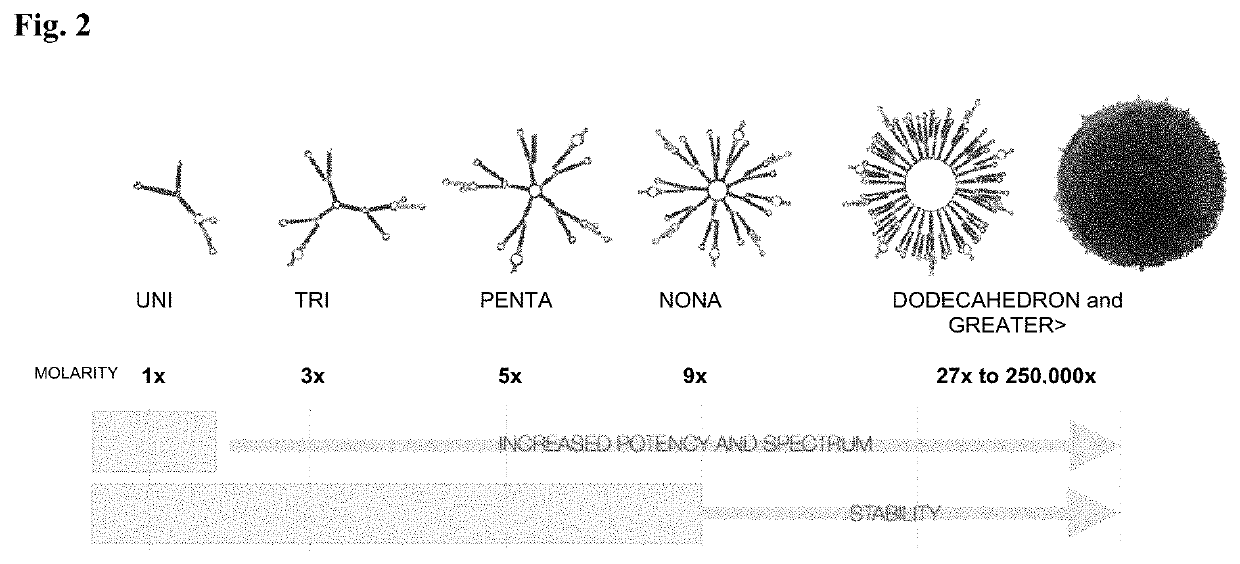
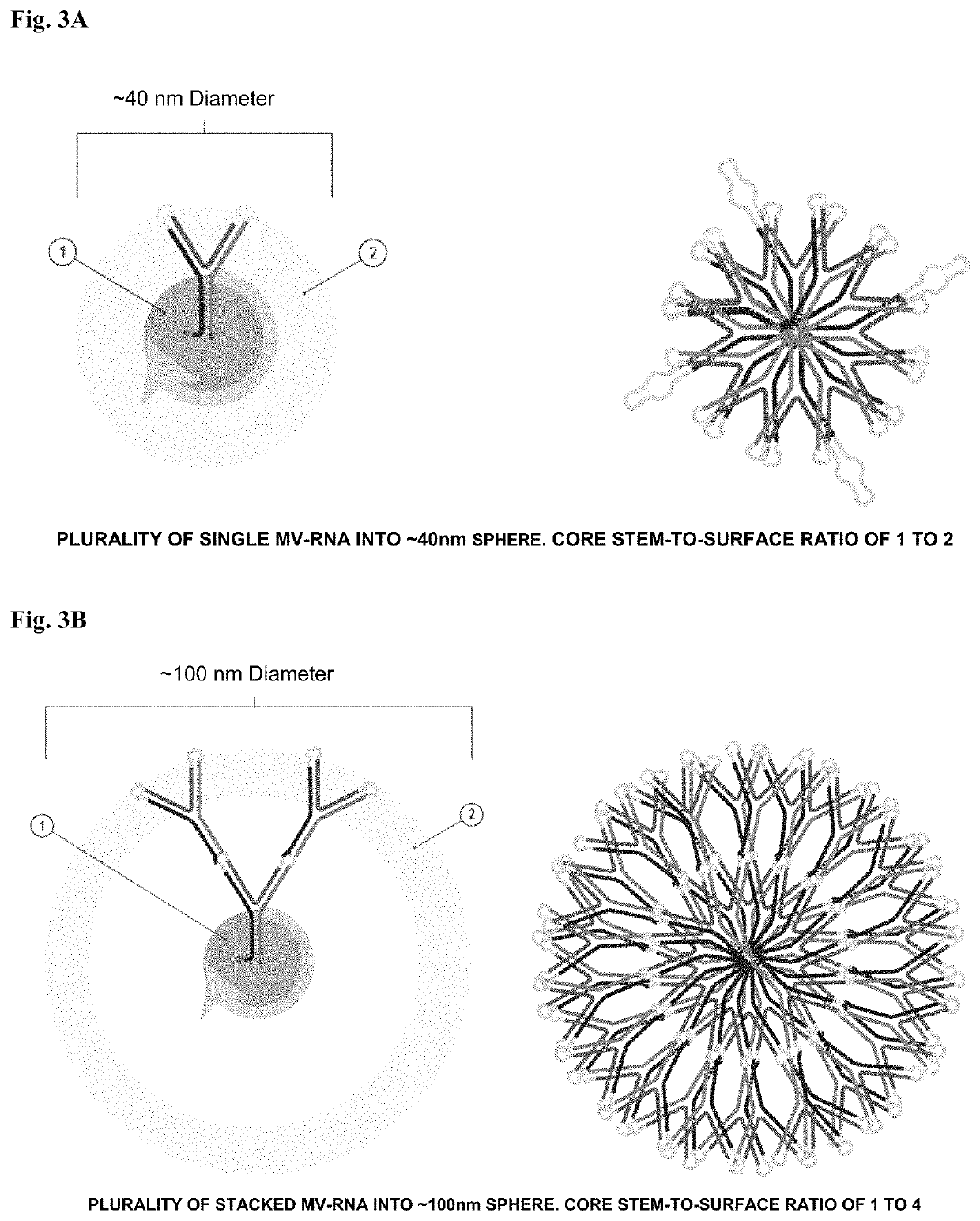
Polynucleotide nanoparticles for the modulation of gene expression and uses thereof
ActiveUS10731157B2Precision releaseHigh productPowder deliveryAntineoplastic agentsNucleotideExpression gene
The present invention is directed to novel self-forming polynucleotide nanoparticles, and the use of such nanoparticles and compositions comprising the same for gene modulation in a variety of organisms.
Owner:HALO BIO RNAI THERAPEUTICS
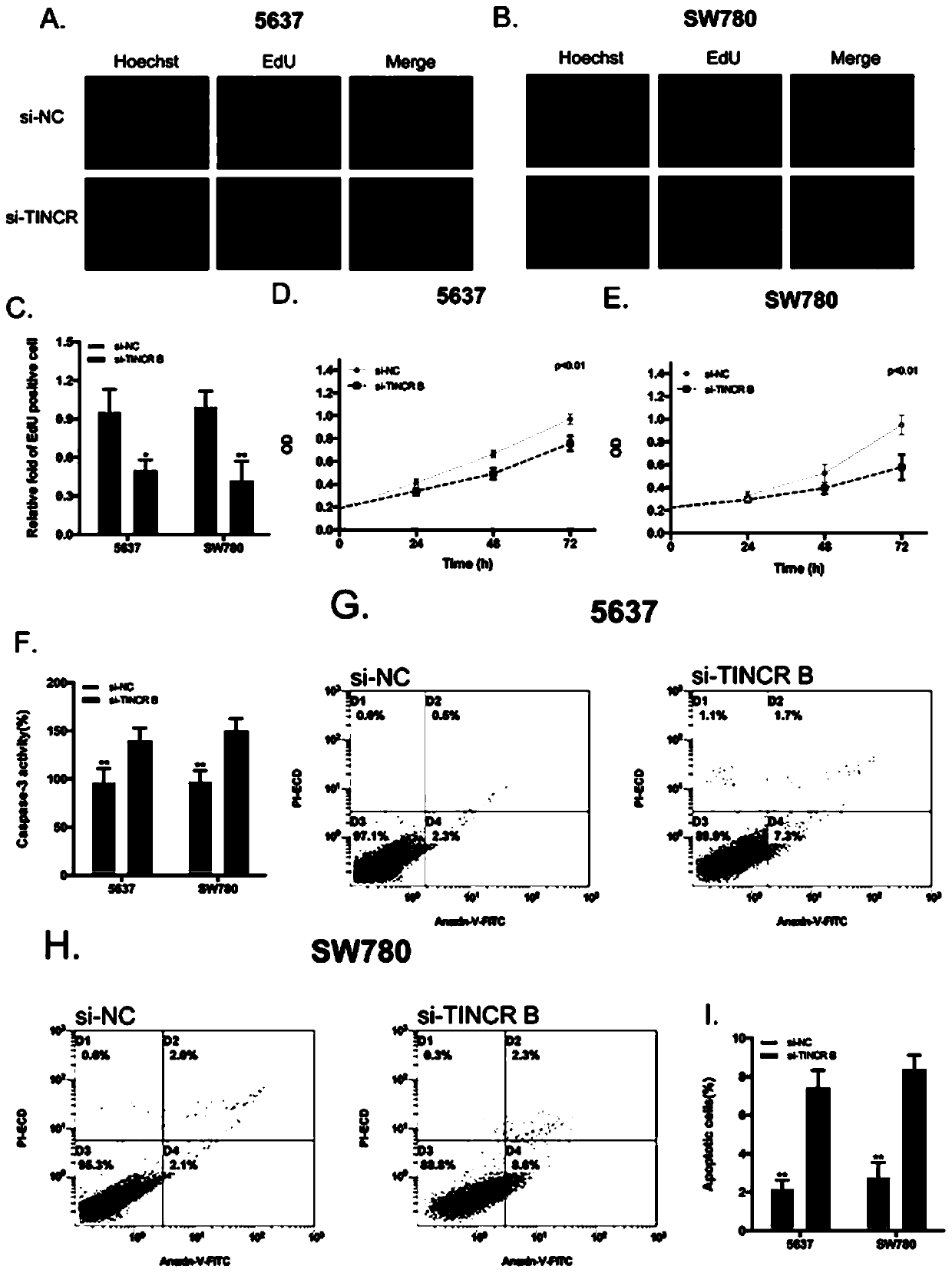
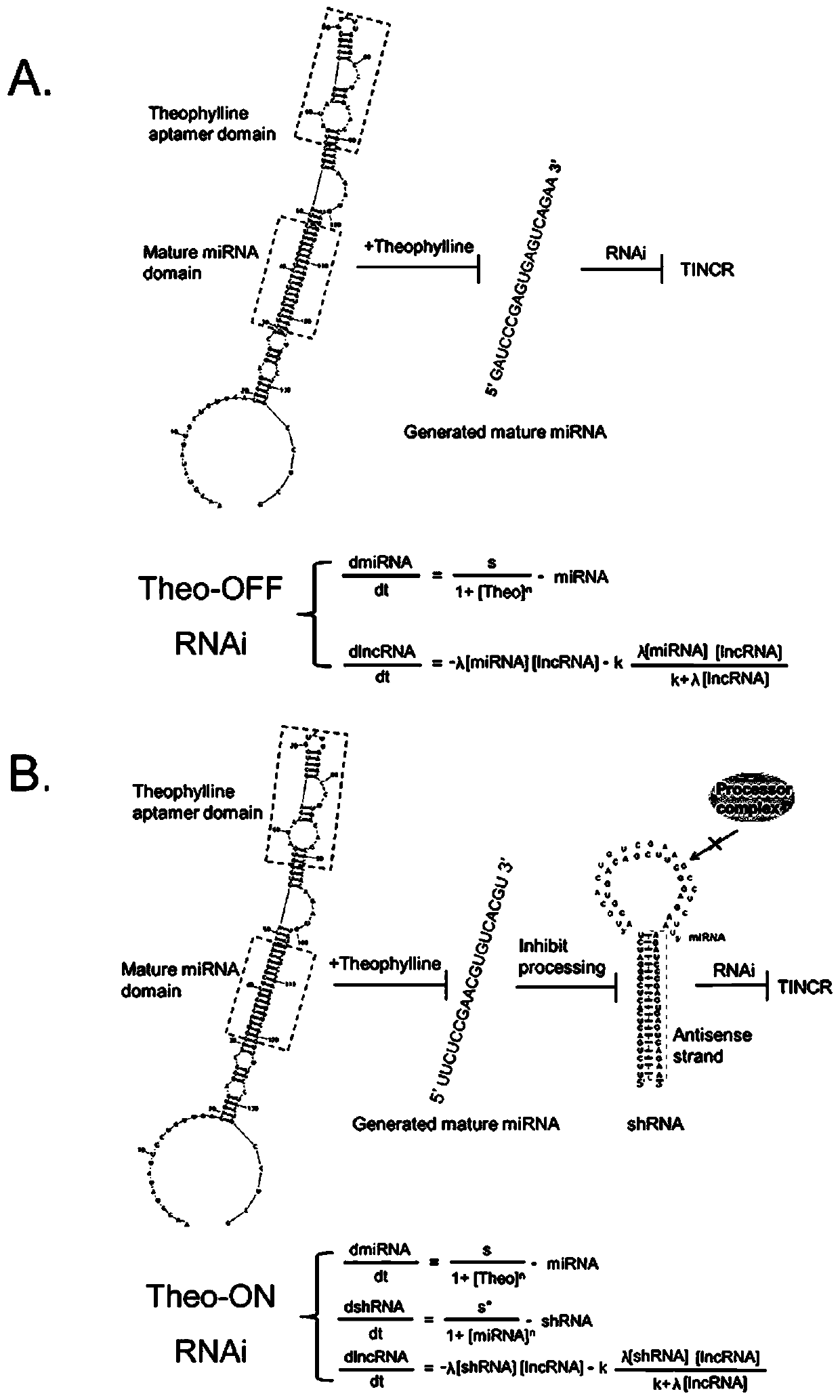
A kind of theophylline-induced RNA interference switch system and its gene regulation method and application
ActiveCN106318972BInhibit progressOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAptamerTheophylline
The invention discloses a theophylline-induced RNA disturbance on-off system and gene control method and use thereof. The theophylline-induced RNA disturbance on-off system at least comprises an RNA disturbance shutter. The RNA disturbance shutter is in itself an artificial miRNA fore-body or is transferred to an artificial miRNA fore-body. The artificial miRNA fore-body includes miRNA fore-body and the theophylline RNA aptamer of the annular section that is mixed with the miRNA fore-body; the theophylline RNA aptamer can be combined with theophylline to obstacle the interference effect of RNA. The RNA disturbance on-off system of the invention can activate or suppress RNA noise channel according to the theophylline concentration and dependence, thereby controlling the expression of target genes.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com