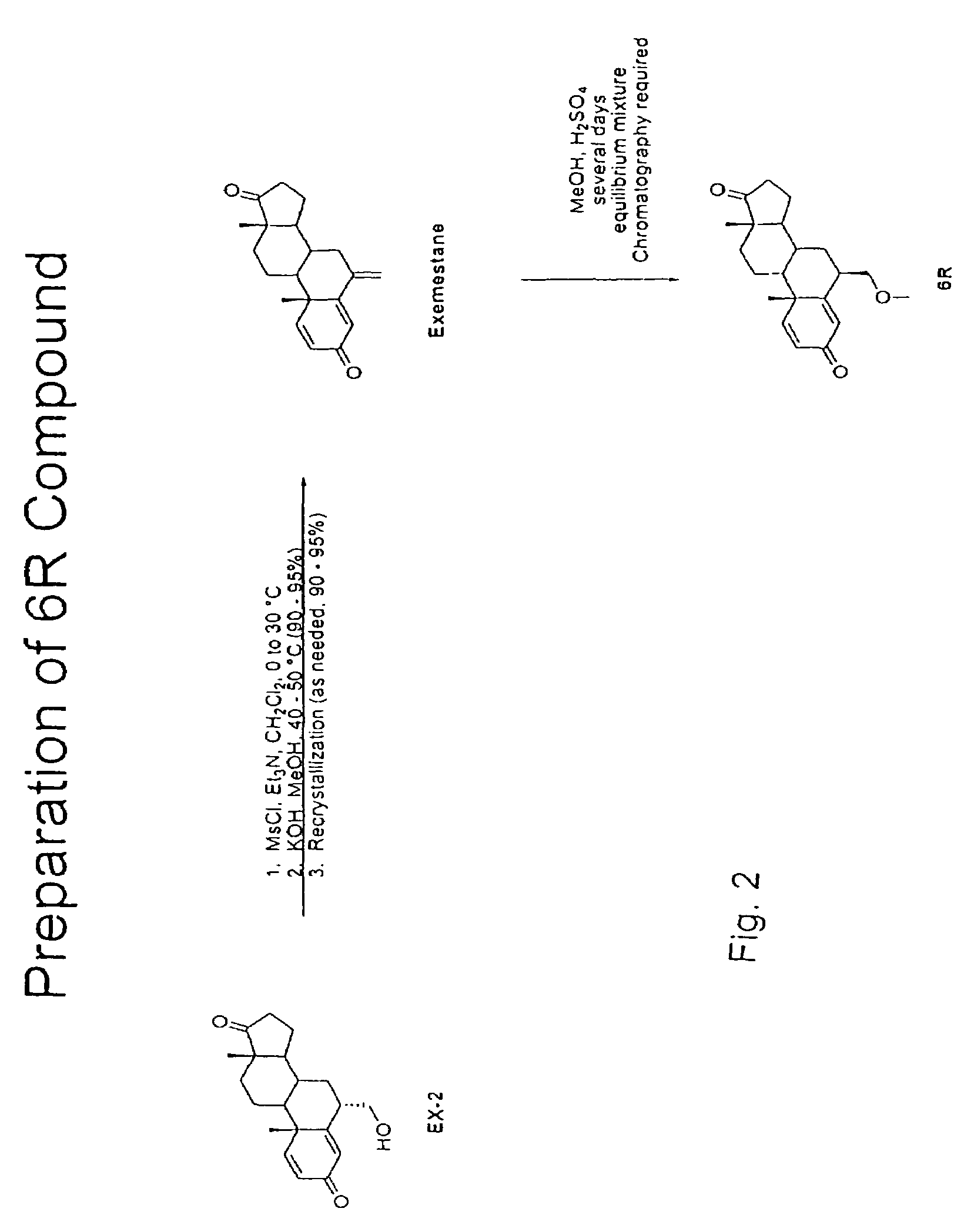
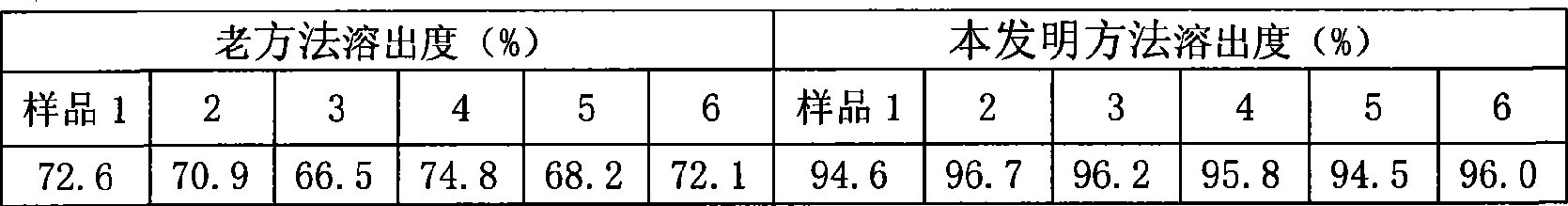
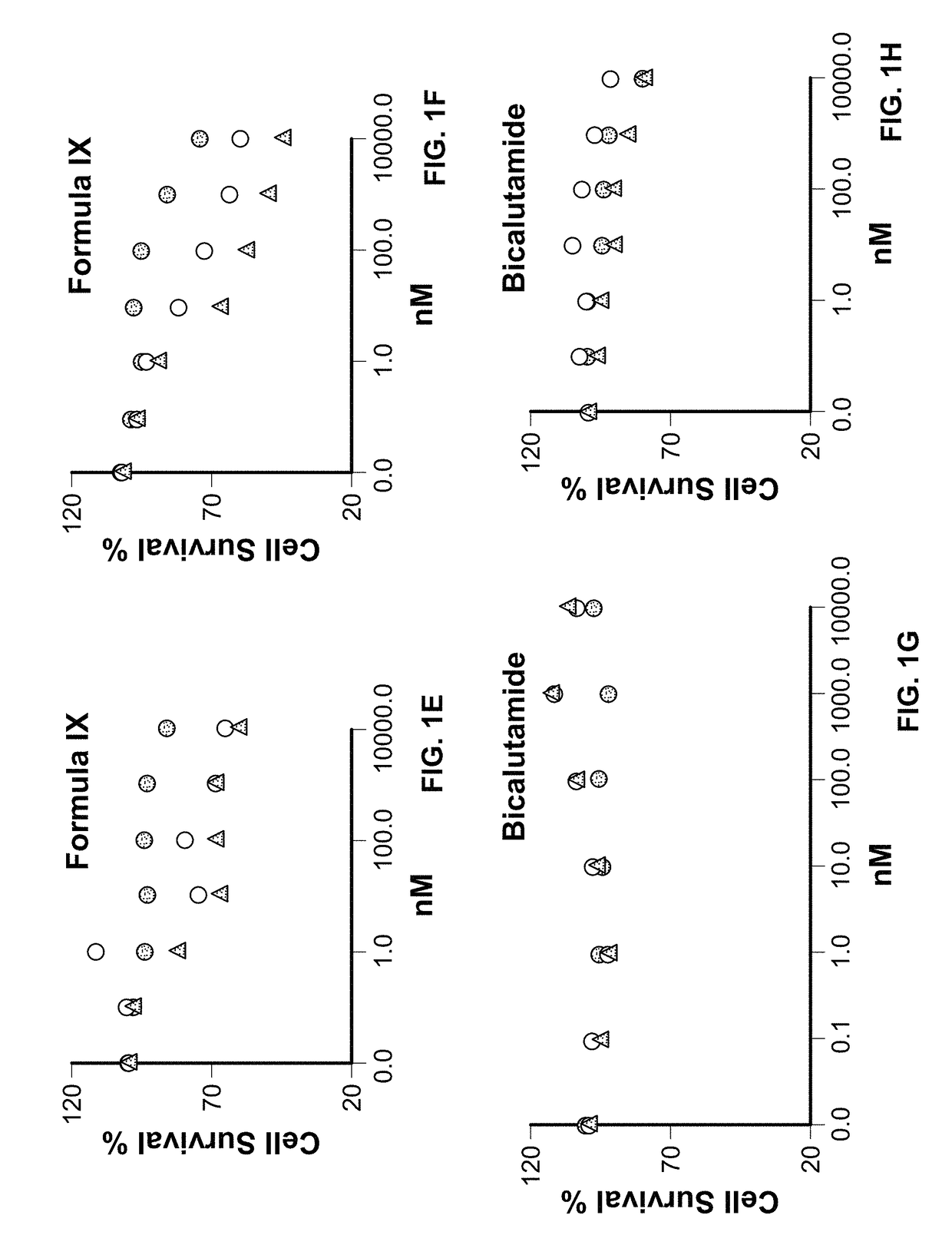
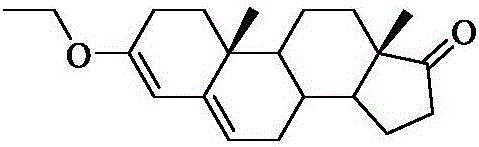
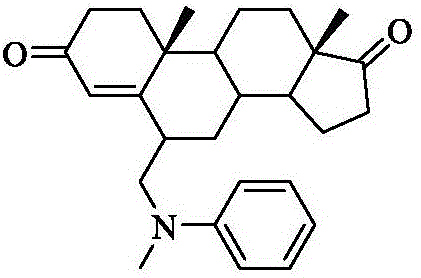
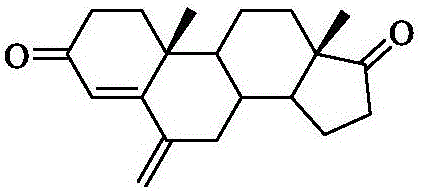
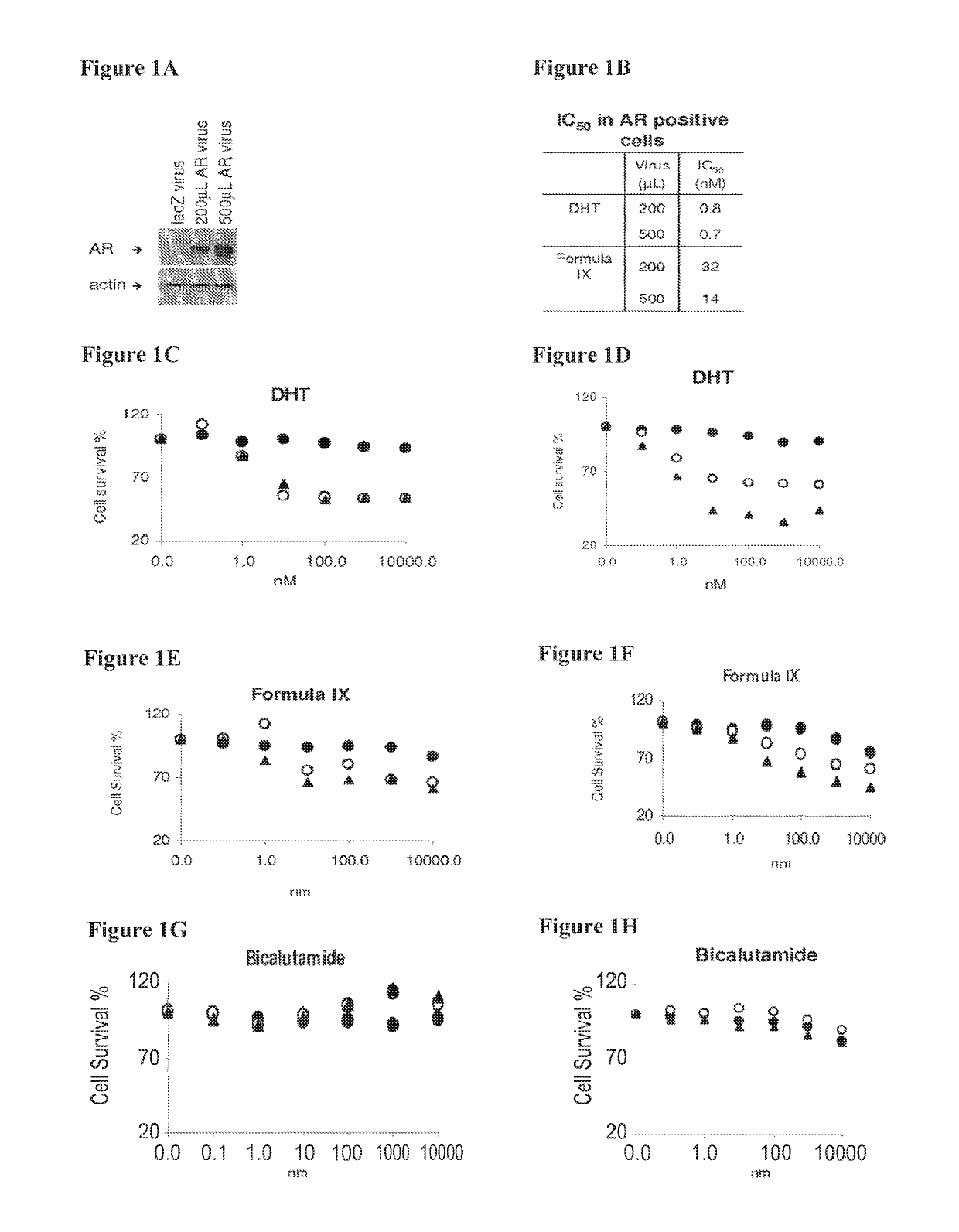
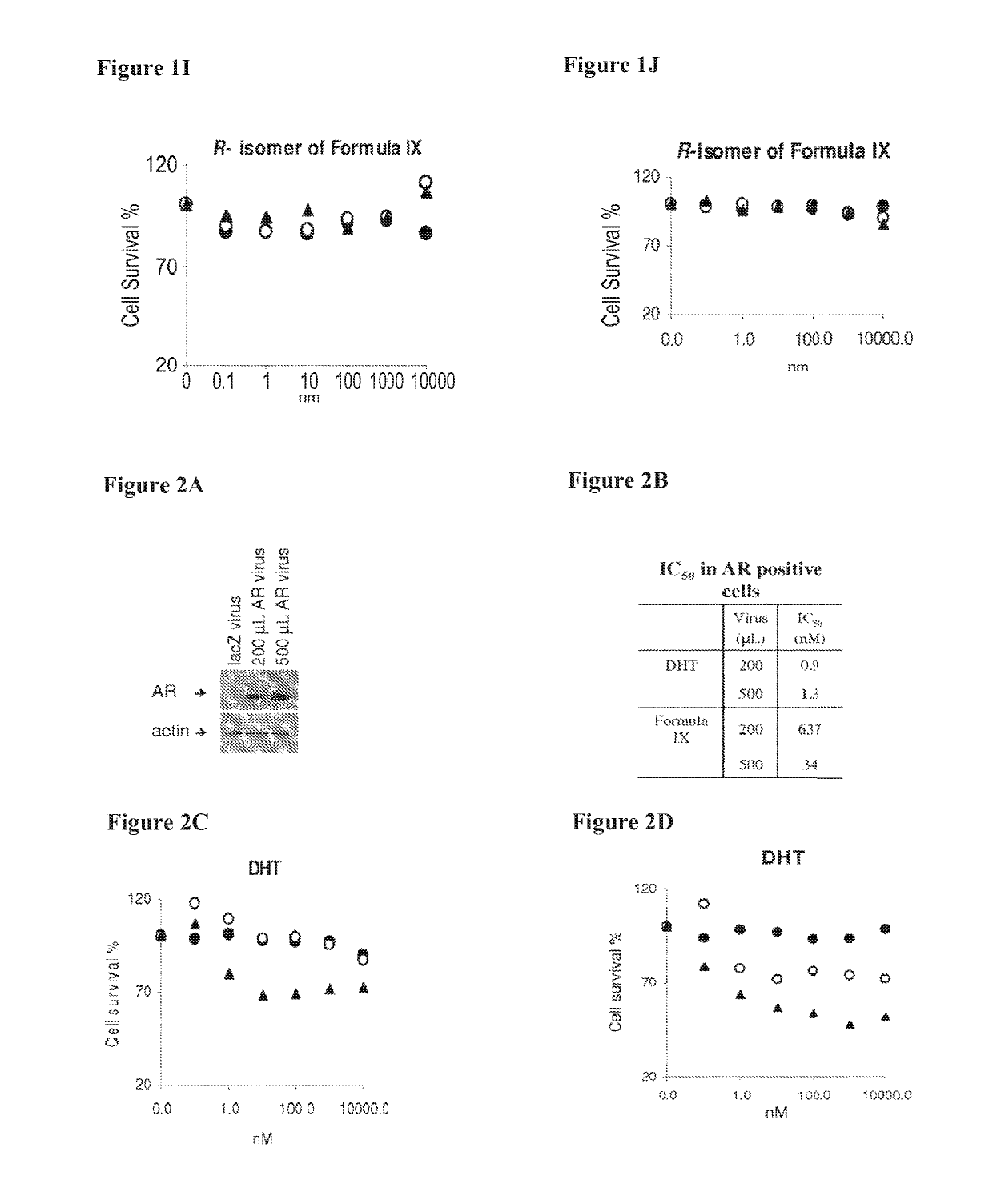
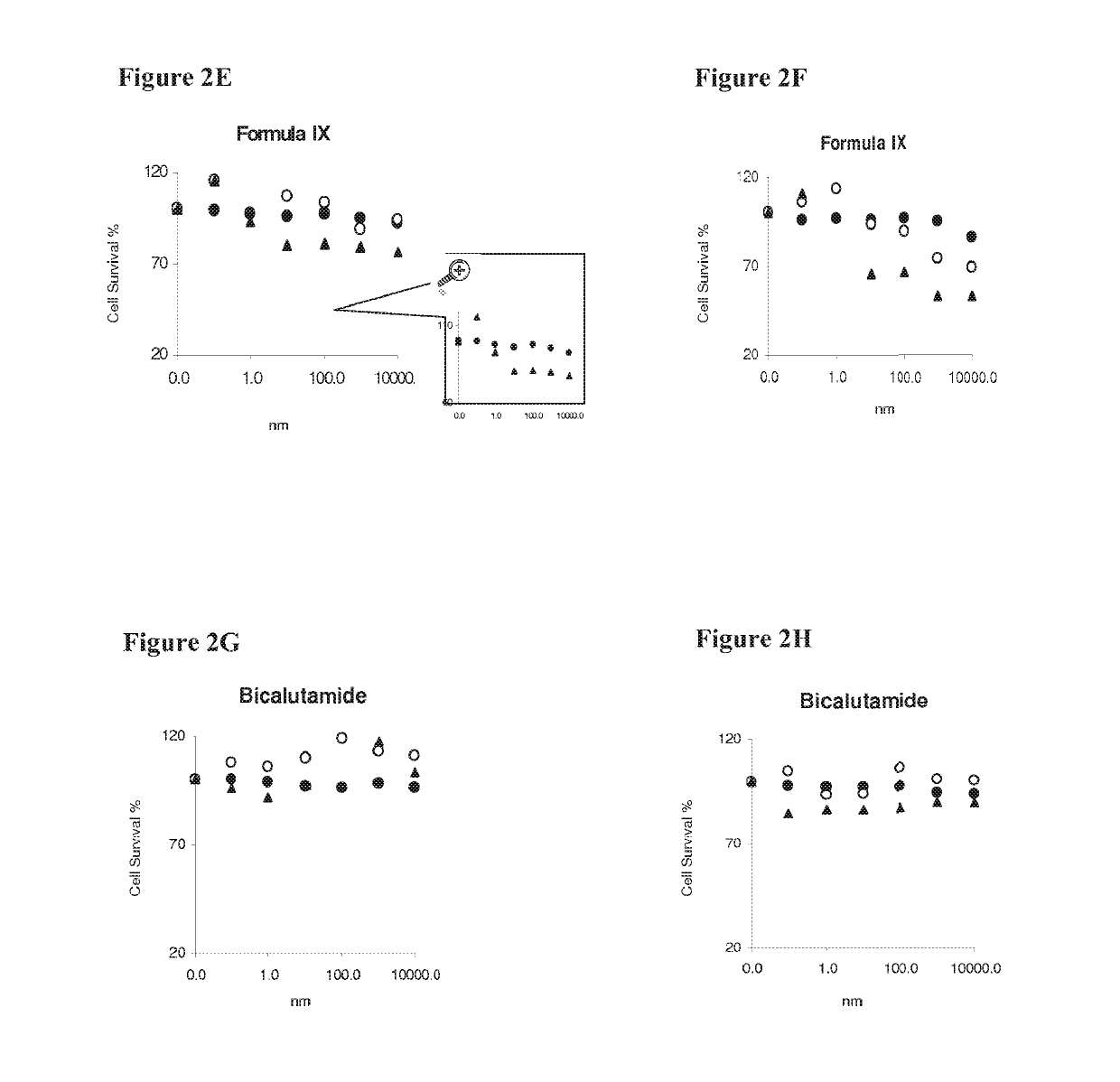
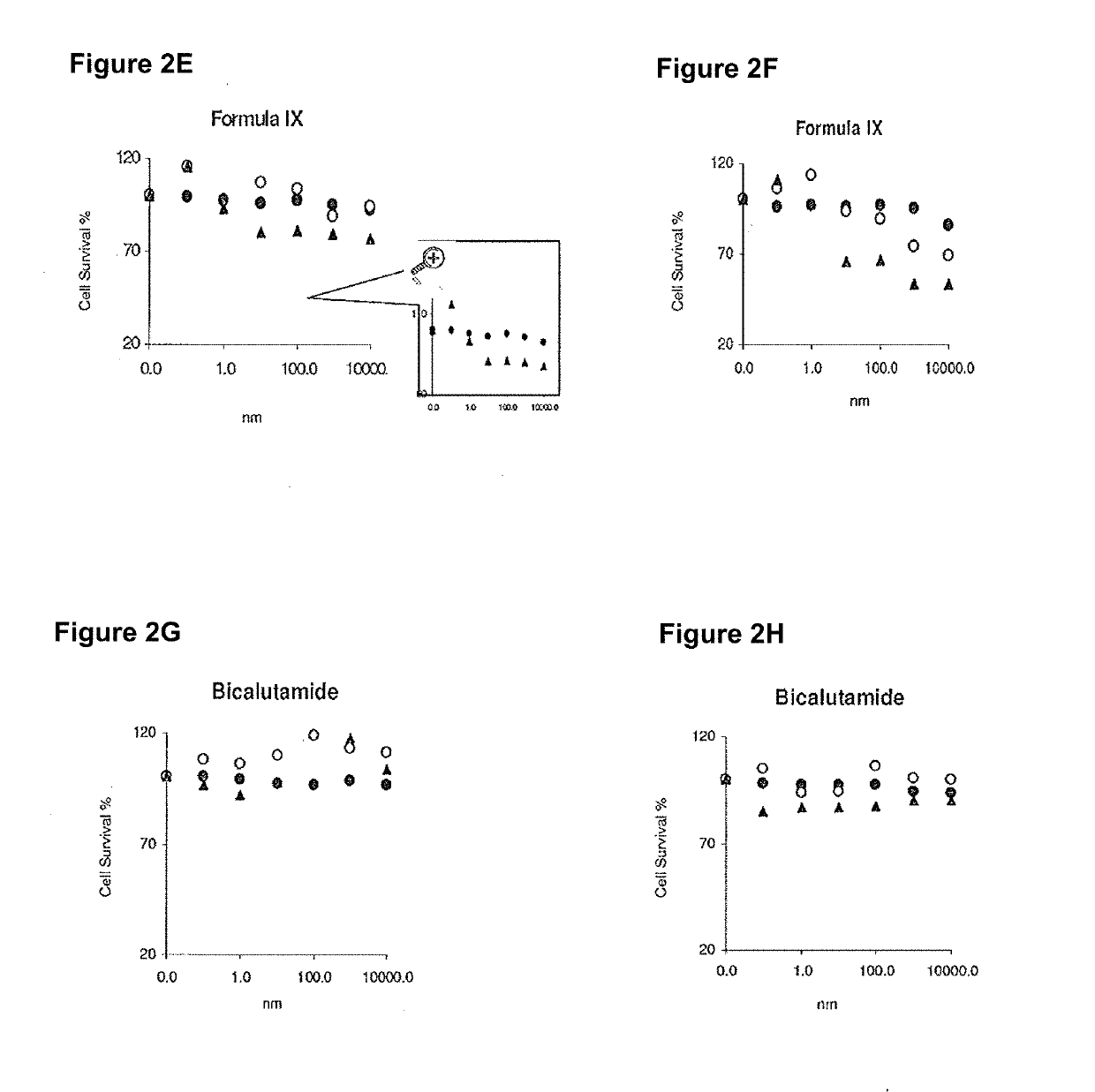
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Exemestane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This medication is used to treat certain types of breast cancer (such as hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer) in women after menopause. Exemestane is also used to help prevent the cancer from returning.
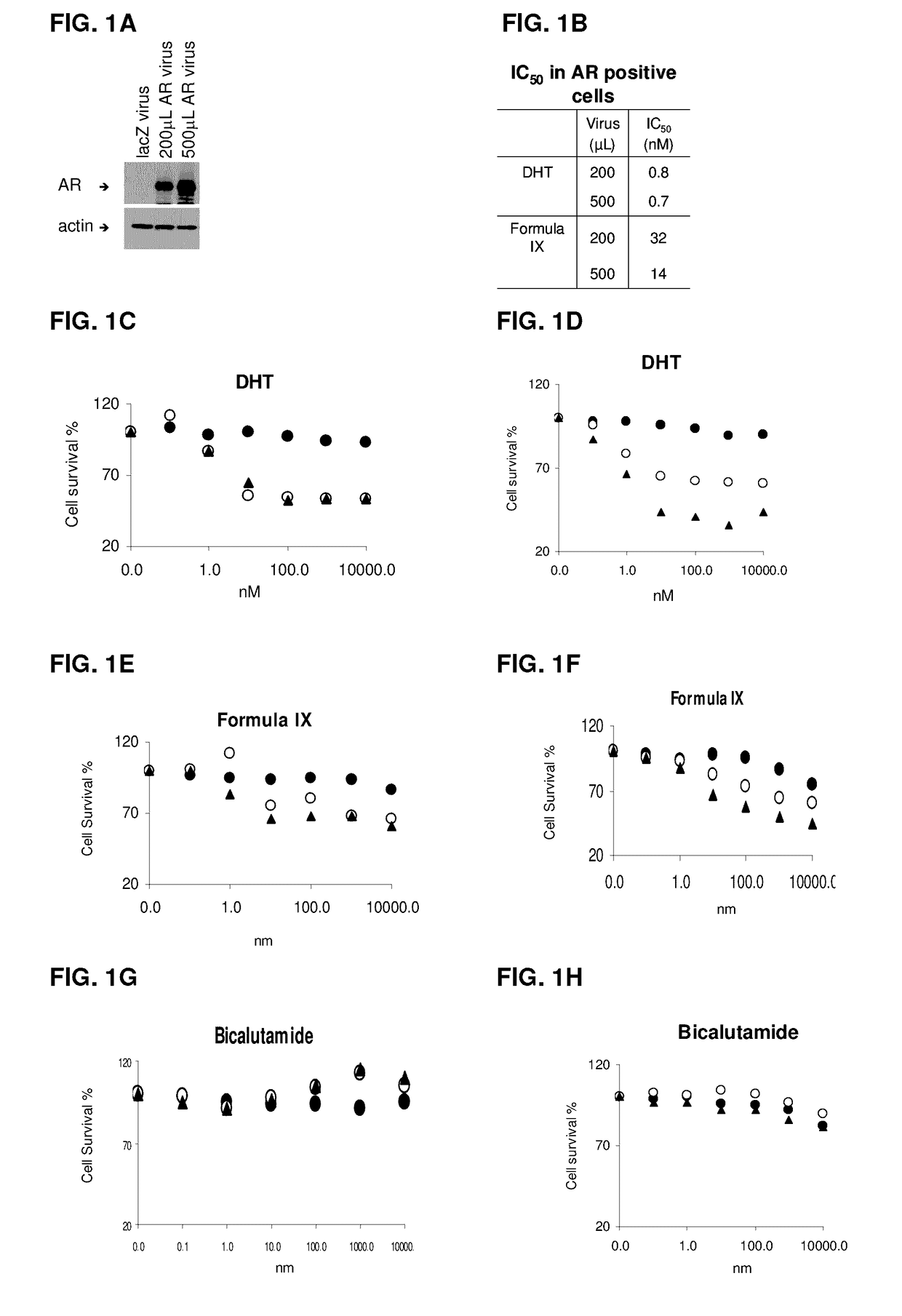
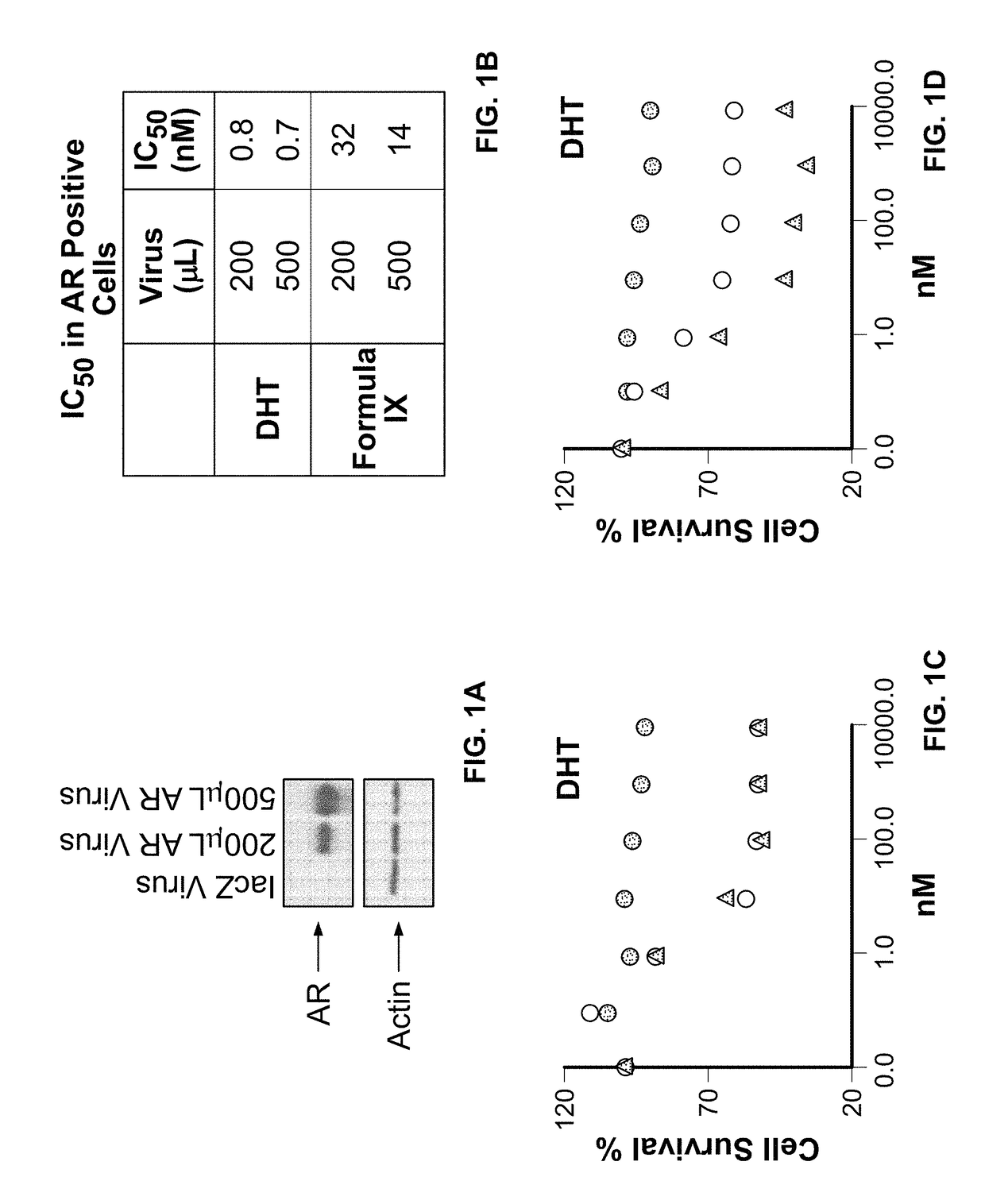
Method of treating estrogen receptor (ER) -positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulator (SARMS)
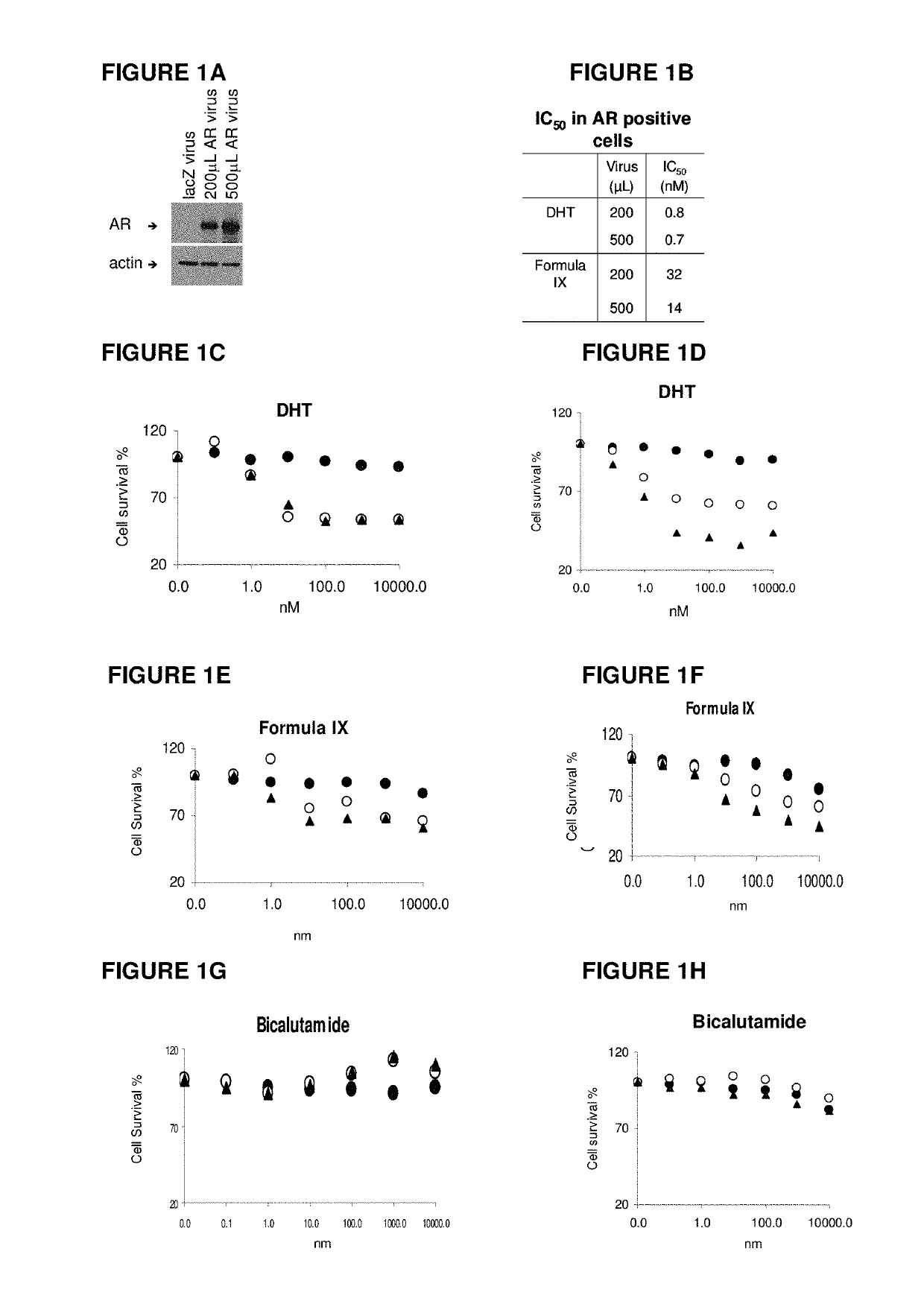
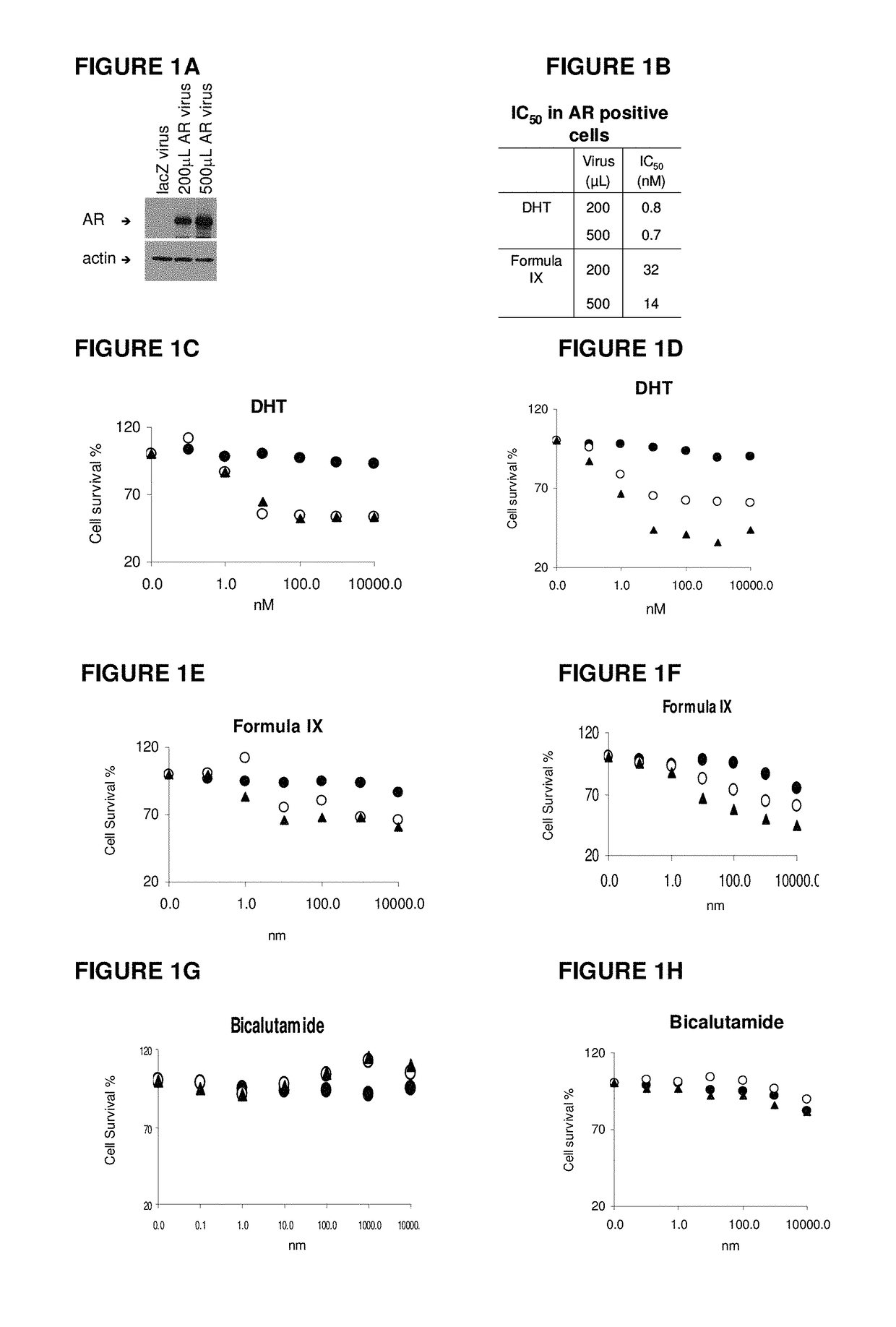
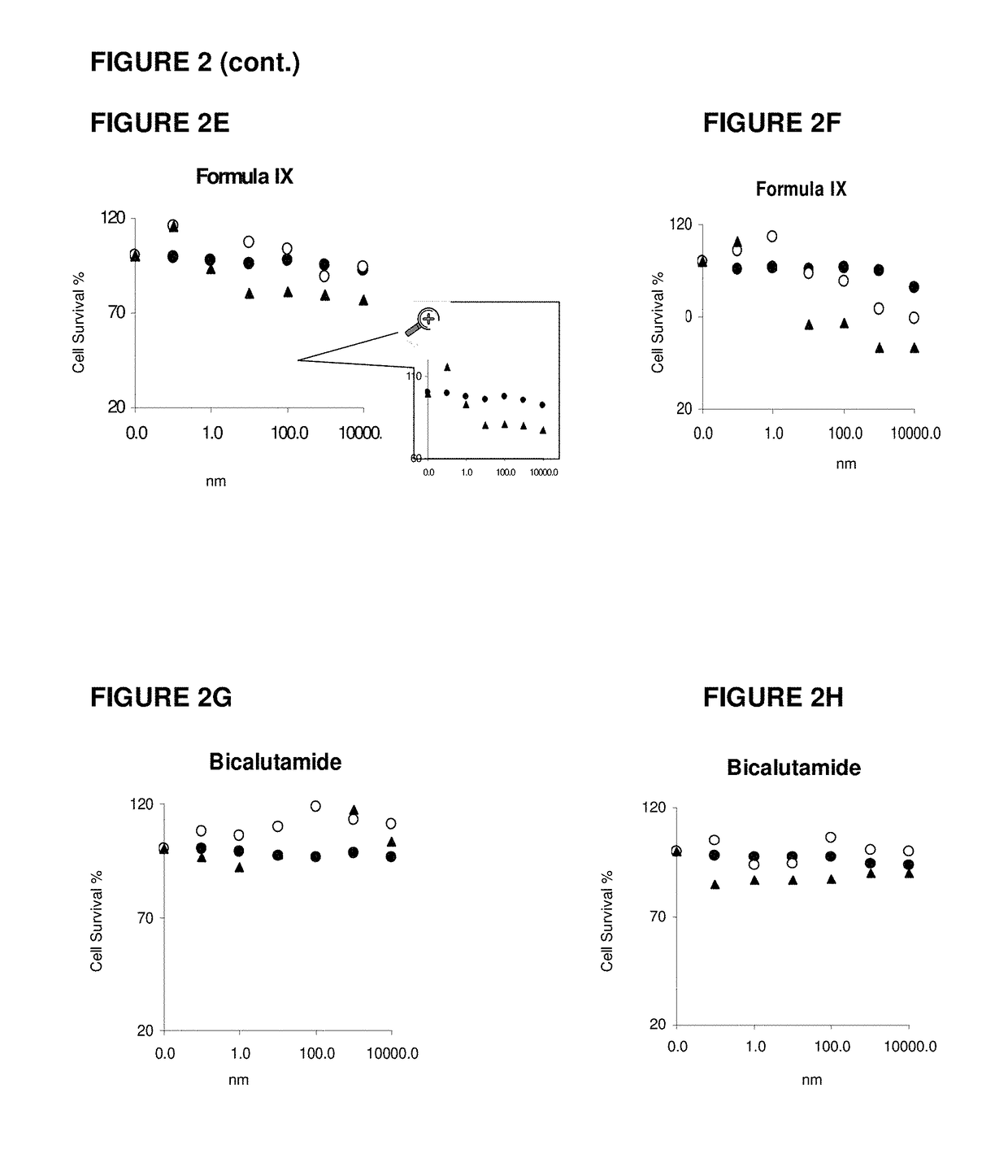
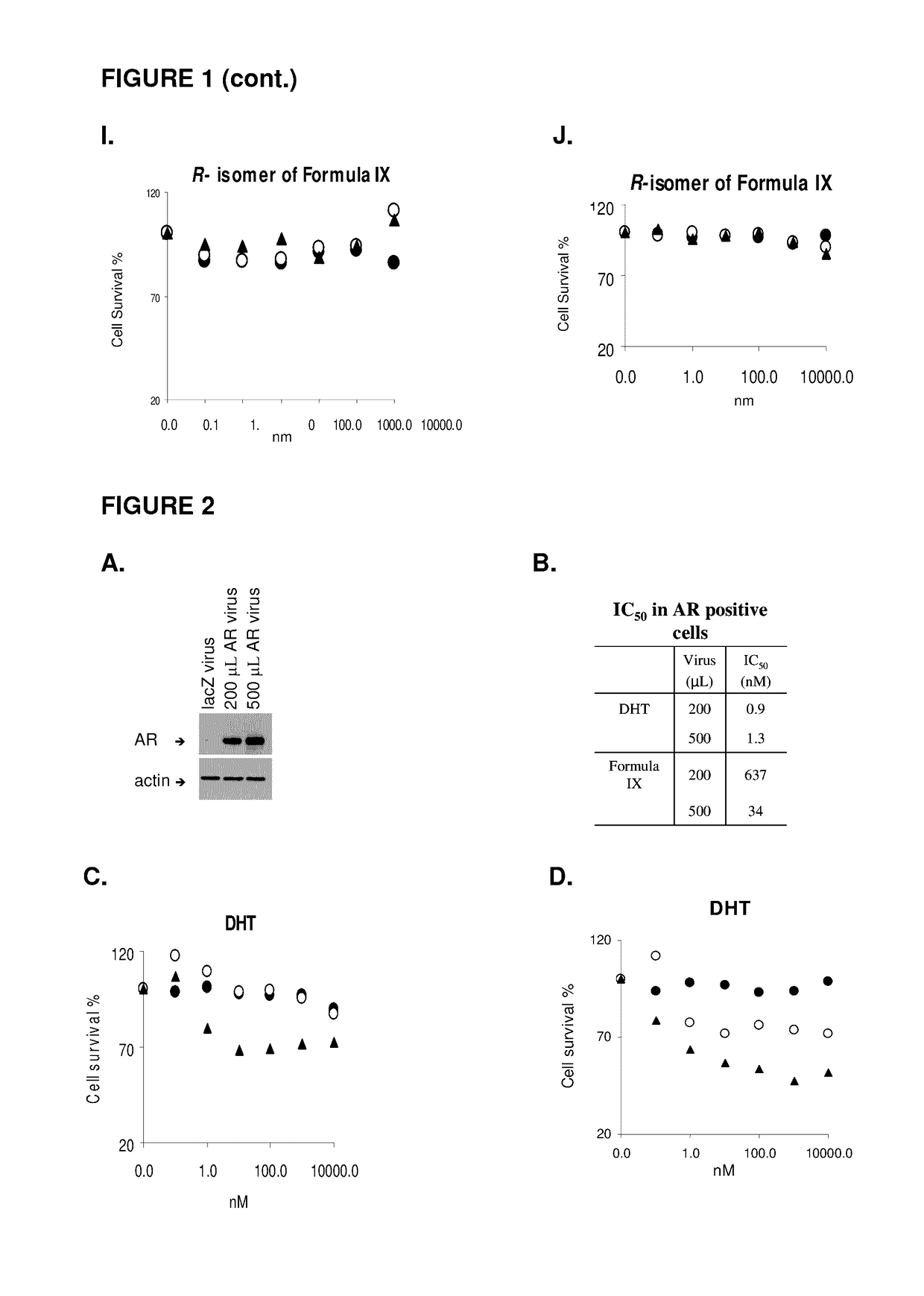
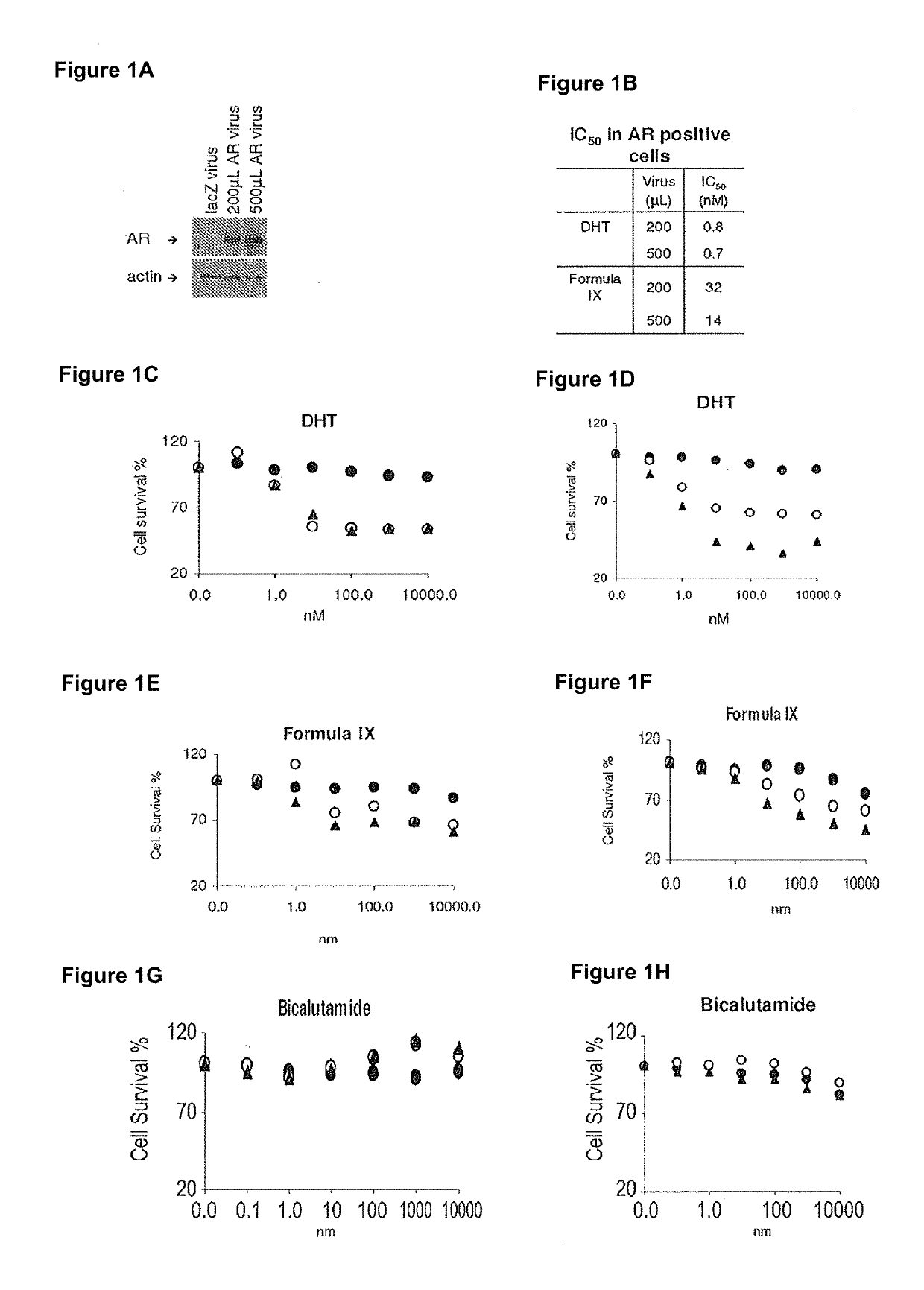
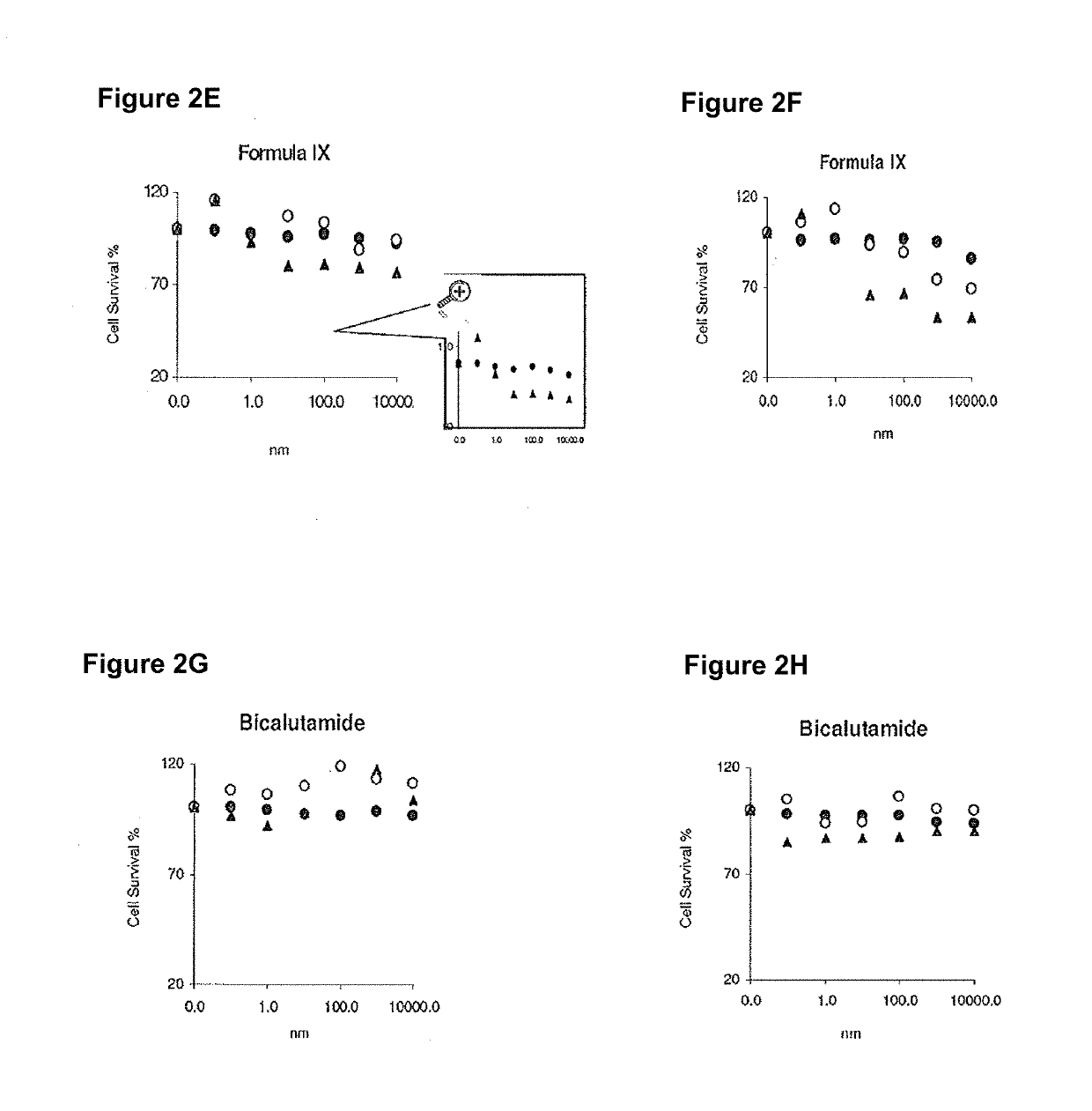
This invention relates to the treatment of androgen receptor-positive breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Accordingly, this invention provides methods of: a) treating a subject suffering from breast cancer; b) treating a subject suffering from metastatic breast cancer; c) treating a subject suffering from refractory breast cancer; d) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive breast cancer; e) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive refractory breast cancer; f) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; g) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; h) treating a subject suffering from triple negative breast cancer; i) treating a subject suffering from advanced breast cancer; j) treating a subject suffering from breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; k) treating, preventing, suppressing or inhibiting metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; l) prolonging survival of a subject with breast cancer, and / or m) prolonging the progression-free survival of a subject with breast cancer; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a SARM compound of this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
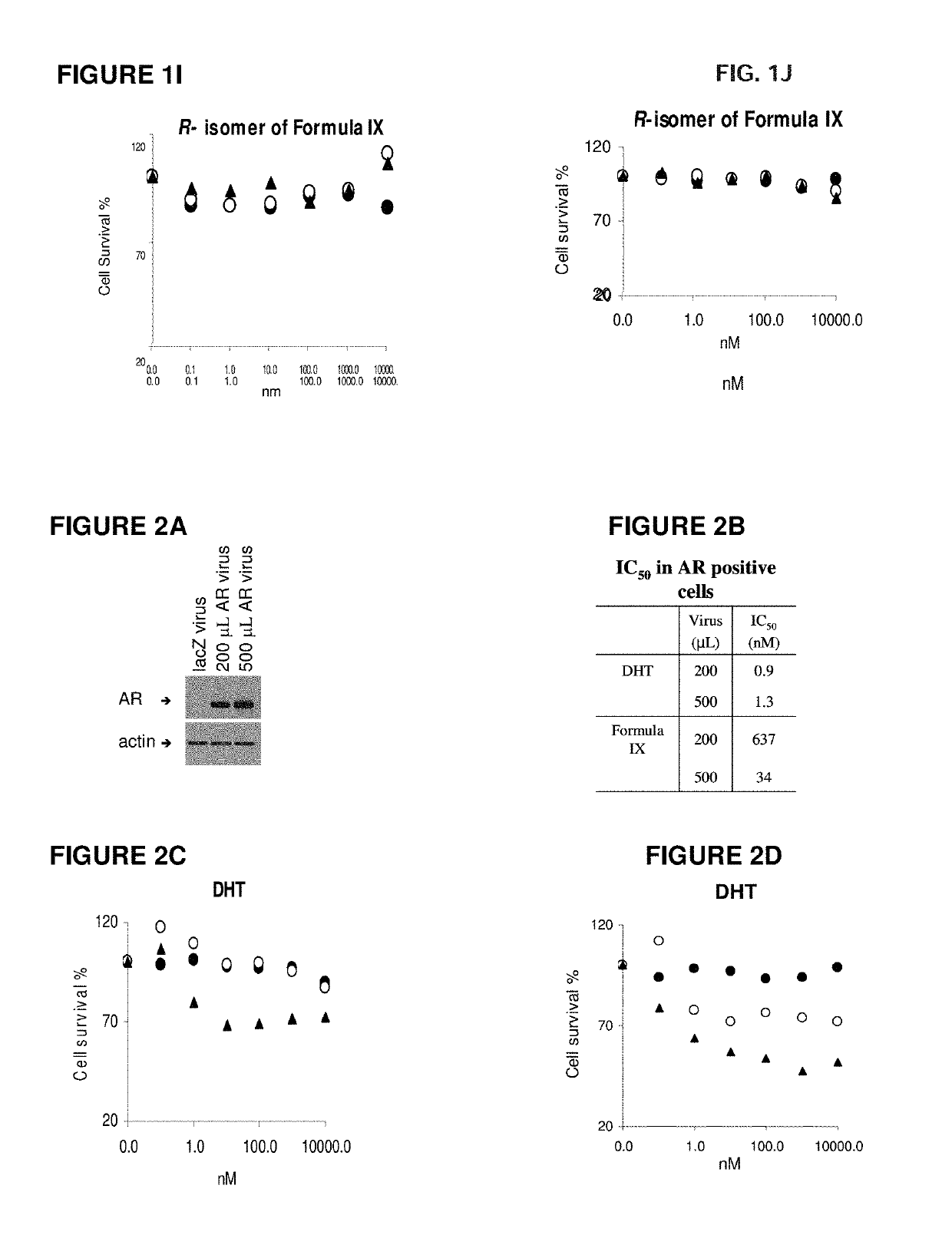
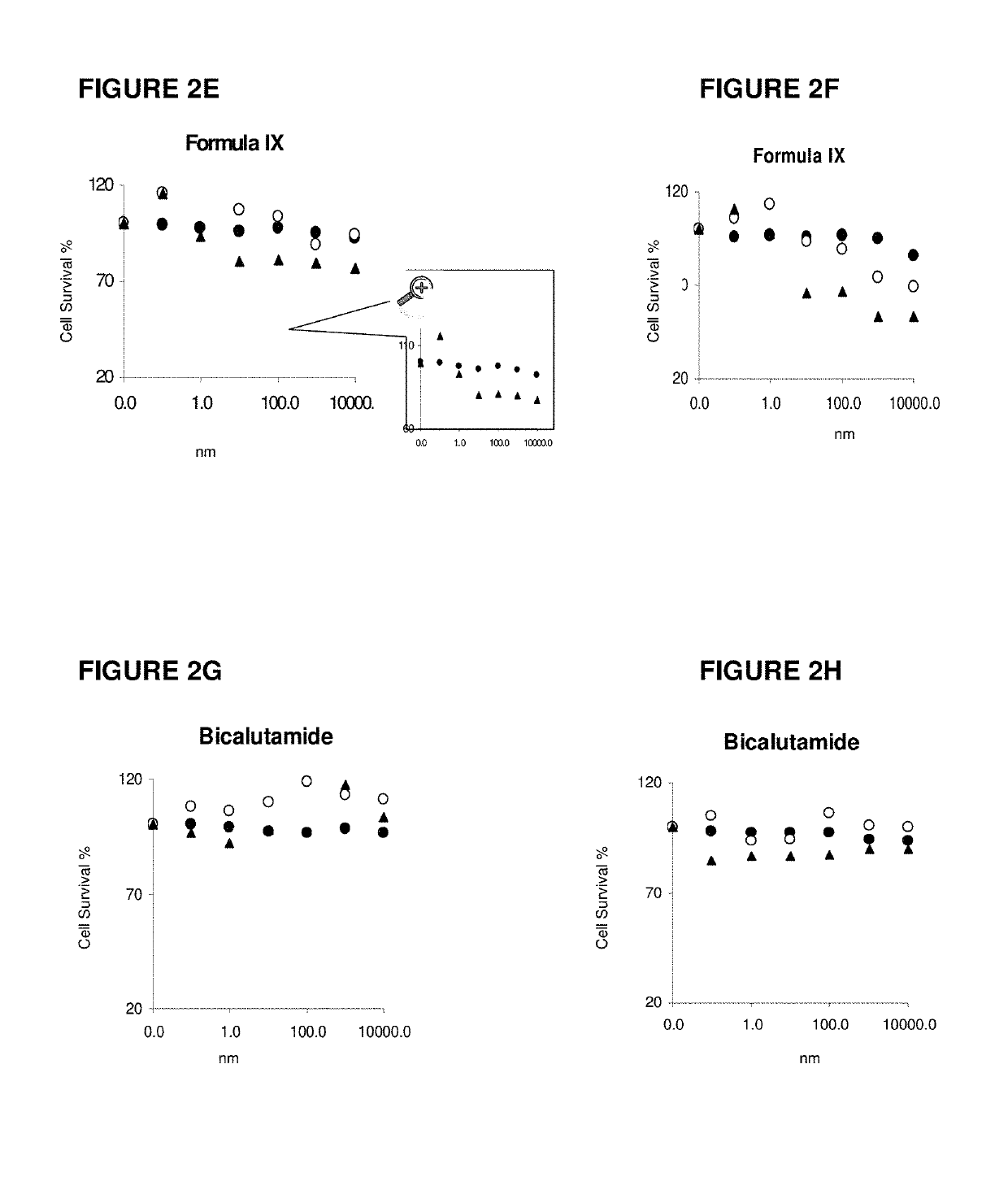
Method of treating androgen receptor (AR) -positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulator (SARMS)
ActiveUS20140350102A1Treating and preventing and suppressing and inhibiting metastasisProlonged progression-free survivalBiocideOrganic chemistryToremifeneLymphatic Spread
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
(S)-6-methyloxaalkyl exemestane compounds and related methods of use
6-Methyloxaalkyl exemestane compounds and related compositions, as can be used, chemotherapeutically, to inhibit growth and proliferation of cancer cells.
Owner:ENDECE LLC
CTLA-4 antibody and aromatase inhibitor combination of treatment for breast cancer
InactiveCN101052655AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAromatase inhibitorCTLA4 Protein
The invention relates to administration of an anti-CTLA4 antibody, particularly human antibodies to human CTLA4, such as those having amino acid sequences of antibodies 3.1.1, 4.1.1, 4.8.1, 4.10.2, 4.13.1, 4.14.3, 6.1.1, 11.2.1, 11.6.1, 11.7.1, 12.3.1.1, 12.9.1.1, and 10DI (MDX-010), in combination with an aromatase inhibitor, for treatment of breast cancer. More particularly, the invention relates to administration of an anti-CTLA4 antibody and exemestane for treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:PFIZER PROD INC
Exemestane compounds, compositions and related methods of use
Owner:ENDECE LLC
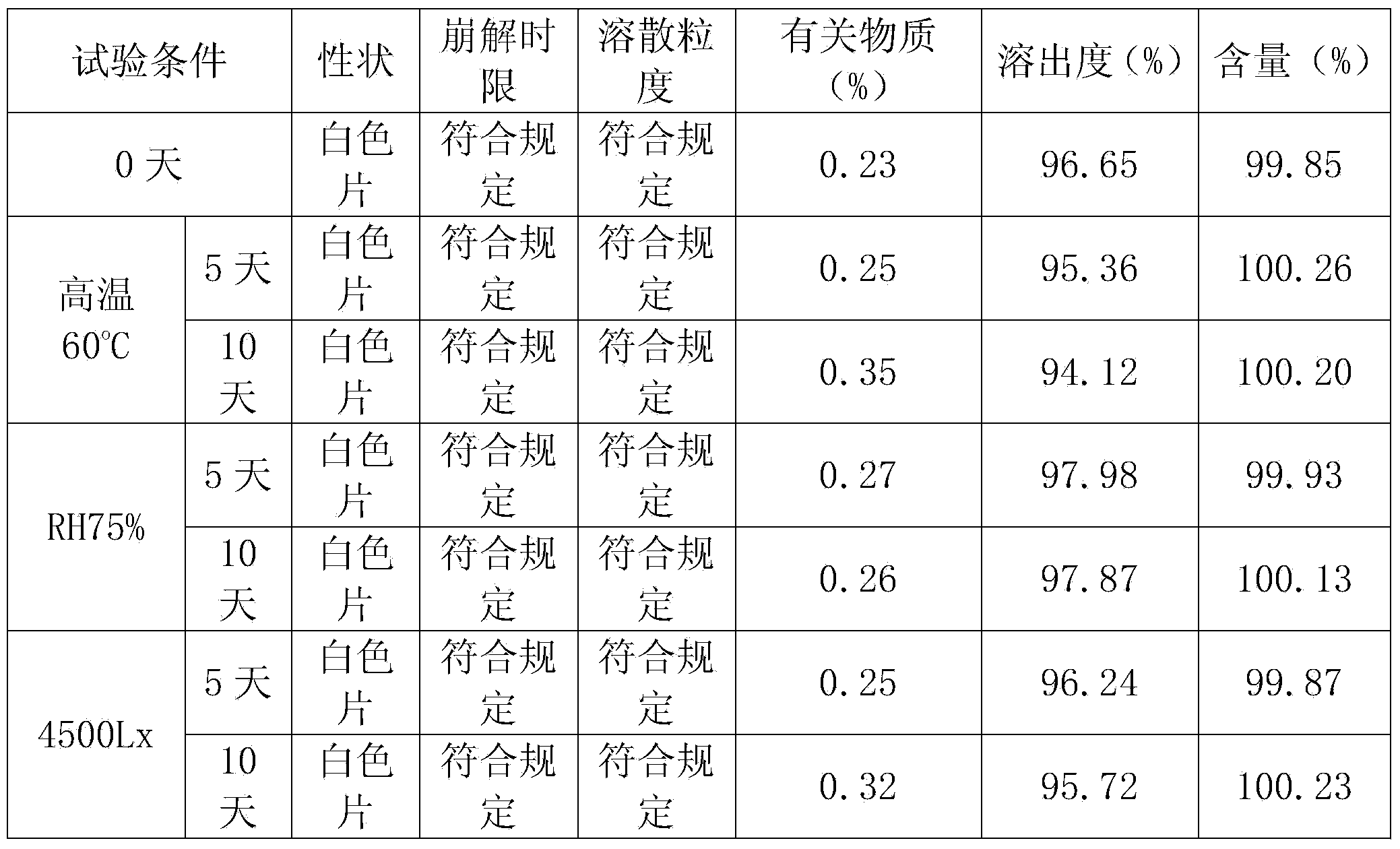
Exemestane tablet and technique for preparing the same
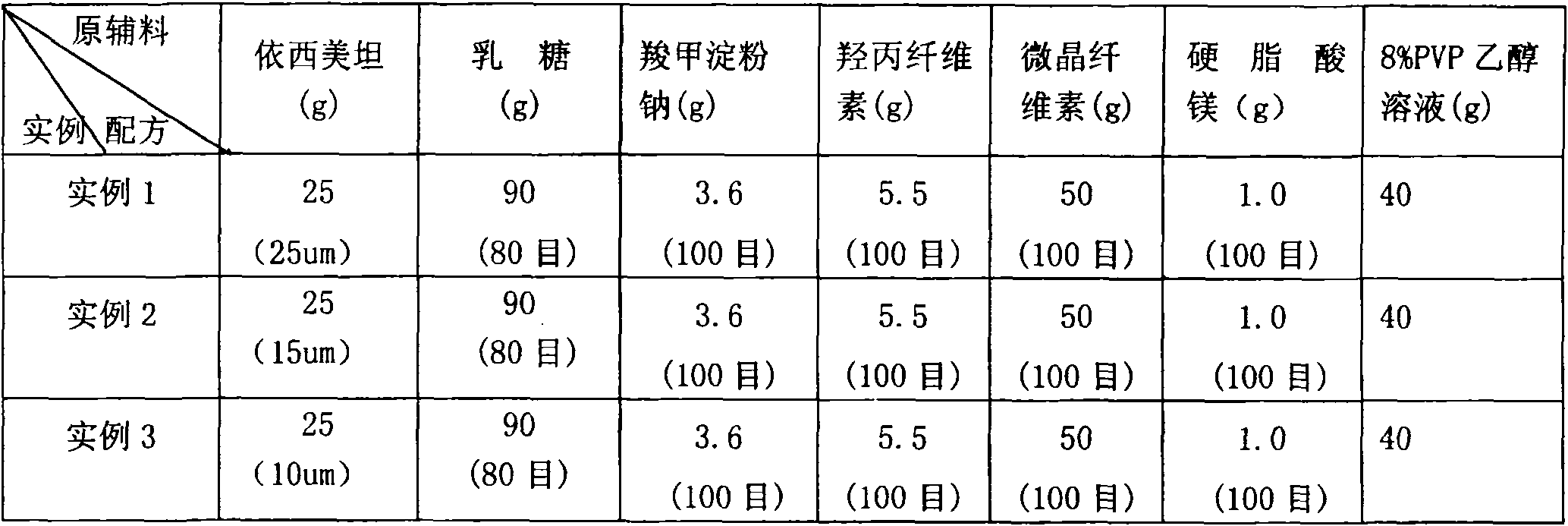
The invention relates to aromasin tablet and preparation method of same. The invention reduces the dosage of carboxyrnethyl starch sodium and hyprolose, and increases the dosage of microcrystalline cellulose. The aromasin is micronized which overcomes the shortage of the current technical process. The invention provides products of better quality and dissolution rate, and capable being used in industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI FOSUN PHARMA DEV CO LTD +1
Exemestane intermediate and preparation method therefor and application thereof
InactiveCN105017370AClear structureClear physical and chemical propertiesSteroidsStructural formulaMethyl group
The invention relates to an exemestane intermediate, particularly 6-(N-methyl-N-phenyl)-amine methyl-4-ene-3,17-androstanedione and a preparation method therefor and application thereof. The structural formula of the exemestane intermediate is a formula shown in the description. The 6-(N-methyl-N-phenyl)-amine methyl-4-ene-3,17-androstanedione prepared by the method provided by the invention can be used for preparing 6-methylene-4-ene-3,17-androstanedione through elimination reaction and the 6-methylene-4-ene-3,17-androstanedione is further oxidized to prepare exemestane. By using the intermediate provided by the invention to prepare exemestane, the purity and yield of exemestane are remarkably improved, the long-term troubled problem on the yield and purity of synthesized exemestane in the field is solved, and industrial practices verify that the exemestane intermediate has extreme value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY +1
Exemestane synthesis technology
InactiveCN105622694AIncrease profitOvercome the problems of many processes and heavy workloadSteroidsKetoneChemistry
The invention discloses an exemestane synthesis technology. The technology comprises the steps of 6-methylene-androst-4-en-3,17-dione synthesis, crude exemestane synthesis and purification. The technology has the advantages of simple route, easily available raw materials, high yield, and suitableness for domestic industrial production.
Owner:赵建英
Exemestane intermediate oxime compound, and preparation method and application thereof
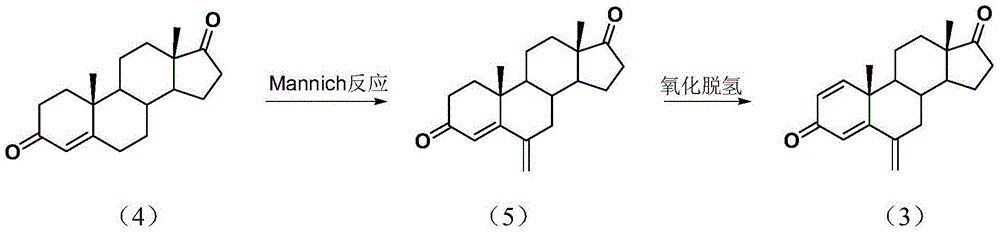
InactiveCN105294807ASimple process routeRaw materials are easy to getSteroidsMannich reactionIsoamyl alcohol
The invention discloses an exemestane intermediate 17-oximino-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-one, and a preparation method and an application thereof. Most of existing methods have the defect of low total yield, and are not suitable for industrial production. The invention discloses the exemestane intermediate 17-oximino-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-one with a novel structural formula. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dimethylamine hydrochloride and paraformaldehyde are refluxed with water in isoamyl alcohol; 17-oximino-androstadienone is added for carrying out a Mannich reaction, such that 17-oximino-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-one is obtained; and exemestane can be prepared through the hydrolysis of 17-oximino-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-one. The method is simple, and has high industrialization value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY +1
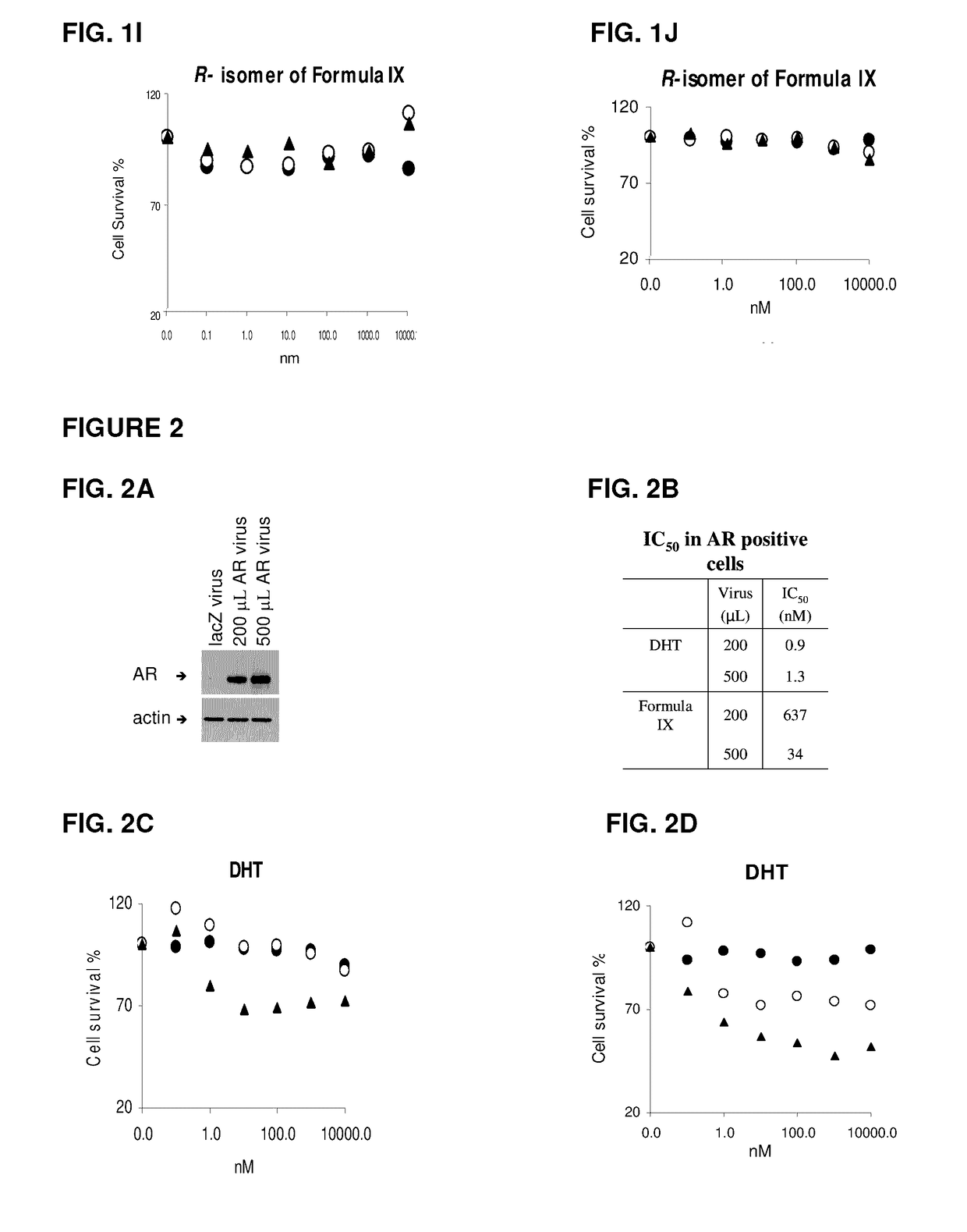
Method of treating her2-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMS)
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer; advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, palbociclib (Ibrance), trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; and / or HER2-positive; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20150209426A1Prevented increase in phospho AKTPronounced inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsEverolimusPancreatic hormone
A method for treating breast cancer with an insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor antagonist in combination with exemestane and everolimus.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Exemestane intermediate 17,17-ethyldioxy-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-ketone and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105085599ASimple process routeRaw materials are easy to getKetal steroidsMannich reactionIsoamyl alcohol
The invention discloses an exemestane intermediate 17,17-ethyldioxy-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-ketone and its preparation method and application. Most existing methods have low overall yield and are not suitable for industrial production. The invention provides an exemestane intermediate 17,17-ethyldioxy-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-ketone with a new structural formula. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, dimethylamine hydrochloride and paraformaldehyde undergo reflux carrying water in isoamyl alcohol; and then, androstadienone ethylene glycol ketal is added to carry out an Mannich reaction so as to prepare 17,17-ethyldioxy-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-ketone, and 17,17-ethyldioxy-6-methyleneandrost-1,4-diene-3-ketone is hydrolyzed to prepare exemestane. The method is simple and has industrial value.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY +1
Method of treating HER2-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMS)
ActiveUS10258596B2MicrocapsulesNitrile/isonitrile active ingredientsToremifeneHER2 Positive Breast Cancer
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer; advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, palbociclib (Ibrance), trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; and / or HER2-positive; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Method of treating androgen receptor (AR)-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulator (SARMs)
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer; advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Exemestane sustained-release capsule
InactiveCN103948570AReduce the total dose of medicationGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAdhesiveSustained Release Capsule
The invention discloses an exemestane sustained-release capsule. The exemestane sustained-release capsule is composed of 5-20wt% of exemestane, 58-95wt% of excipient, 3-10wt% of film coating material, 0-10wt% of wetting agent and 1-2wt% of adhesive; and a preparation method for the same comprises the step of preparing by (1) an extrusion rounding method, (2) a powder coating method, and (3) a liquid deposition method to obtain the exemestane sustained-release capsule.
Owner:赵辉
Method of treating androgen receptor (AR)-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulator (SARMs)
This invention relates to the treatment of androgen receptor-positive breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Accordingly, this invention provides methods of: a) treating a subject suffering from breast cancer; b) treating a subject suffering from metastatic breast cancer; c) treating a subject suffering from refractory breast cancer; d) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive breast cancer; e) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive refractory breast cancer; f) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; g) treating a subject suffering from AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; h) treating a subject suffering from triple negative breast cancer; i) treating a subject suffering from advanced breast cancer; j) treating a subject suffering from breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; k) treating, preventing, suppressing or inhibiting metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; l) prolonging survival of a subject with breast cancer, and / or m) prolonging the progression-free survival of a subject with breast cancer; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a SARM compound of this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Preparation method of exemestane
The invention discloses a preparation method of exemestane, relates to the field of an anti-cancer drug, and particularly relates to exemestane. The preparation method of the exemestane includes stepsof preparing 6-methylene androstenone glycol acetone; under the nitrogen protection, orderly adding paraformaldehyde, dimethylamine hydrochloride and isoamyl alcohol in a four-opening reaction bottle; heating and backflowing water for 2 hours; adding androstenone glycol acetone, preserving temperature and stirring at 140 DEG C; performing high performance liquid chromatography tracking detectionreaction; finishing reaction for 15 hours, and cooling to room temperature; adding distilled water to wash; after layering, drying it by anhydrous magnesium sulfate, depressurizing and recycling solvent; performing column chromatography on silica gel to obtain white solid; secondly, preparing exemestane; orderly adding 6-methylene androstenone glycol acetone, p-toluenesulfonic acid and tetrahydrofuran in a four-opening bottle under the nitrogen protection. The preparation method is simple in technical route, easy to obtain raw materials, low in cost, high in yield, and overcomes the defects existed in the prior art; therefore, the preparation method is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:SHAANXI QIYUAN TECH DEV
Method of treating er mutant expressing breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMS)
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer; advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) (tamoxifen, toremifene, raloxifene), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist (goserelin), aromatase inhibitor (AI) (letrozole, anastrozole, exemestane), cyclin-dependent kinase 4 / 6 (CDK 4 / 6) inhibitor (palbociclib (Ibrance), ribociclib (Kisqali), abemaciclib (Vorzenio)), mTOR inhibitor (everolimus), trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, neratinib (Nerlynx), olaparib (Lynparza) (an inhibitor of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP)), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; HER2-positive; and / or treating a subject suffering from ER mutant expressing breast cancer, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Exemestane tablet and technique for preparing the same
The invention relates to aromasin tablet and preparation method of same. The invention reduces the dosage of carboxyrnethyl starch sodium and hyprolose, and increases the dosage of microcrystalline cellulose. The aromasin is micronized which overcomes the shortage of the current technical process. The invention provides products of better quality and dissolution rate, and capable being used in industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI FOSUN PHARMA DEV CO LTD +1
Compositions comprising exemestane and novel methods of use
ActiveUS20170196887A1Strong synergyIncrease attractivenessHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntipyreticEtiologyEnzyme Gene
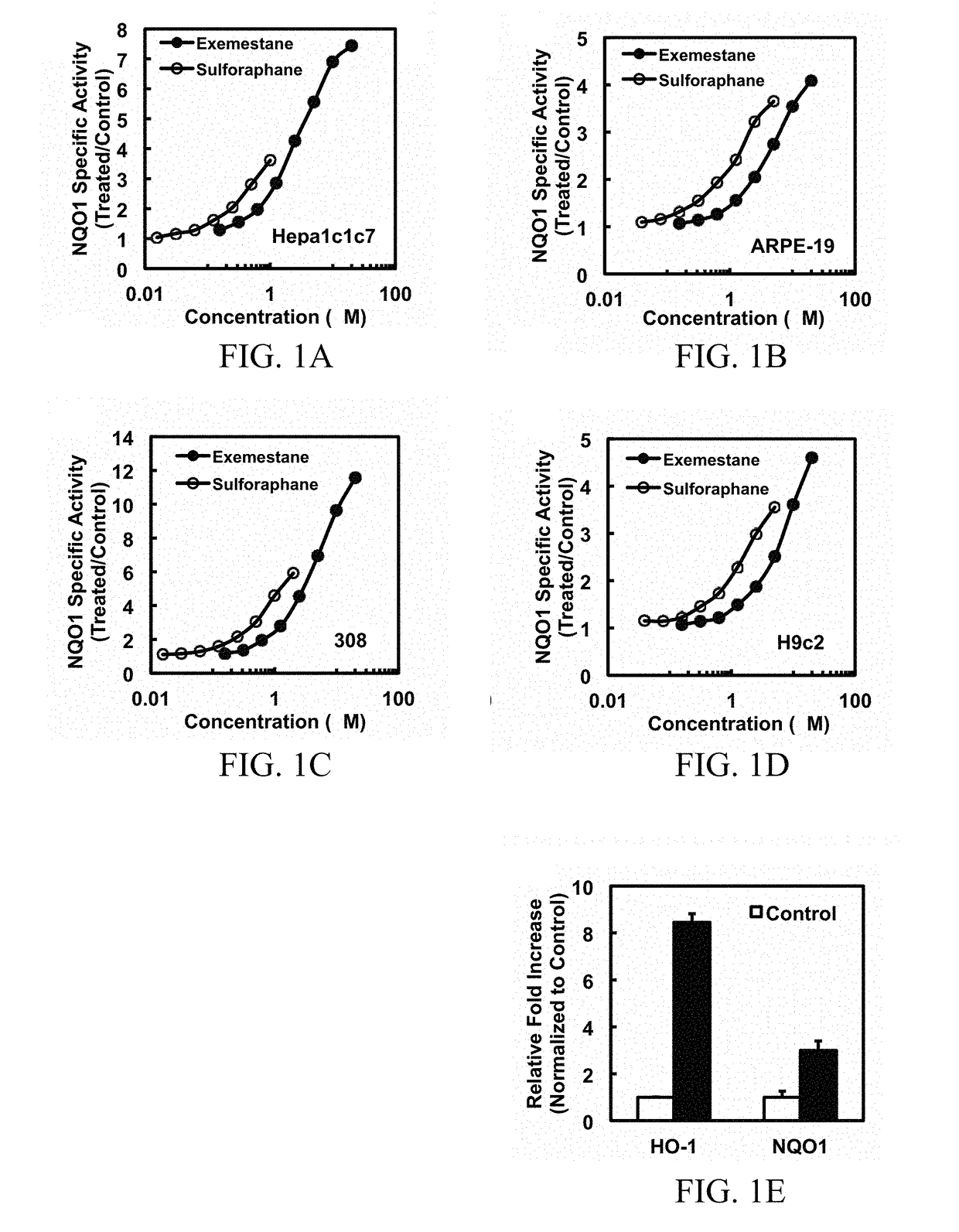
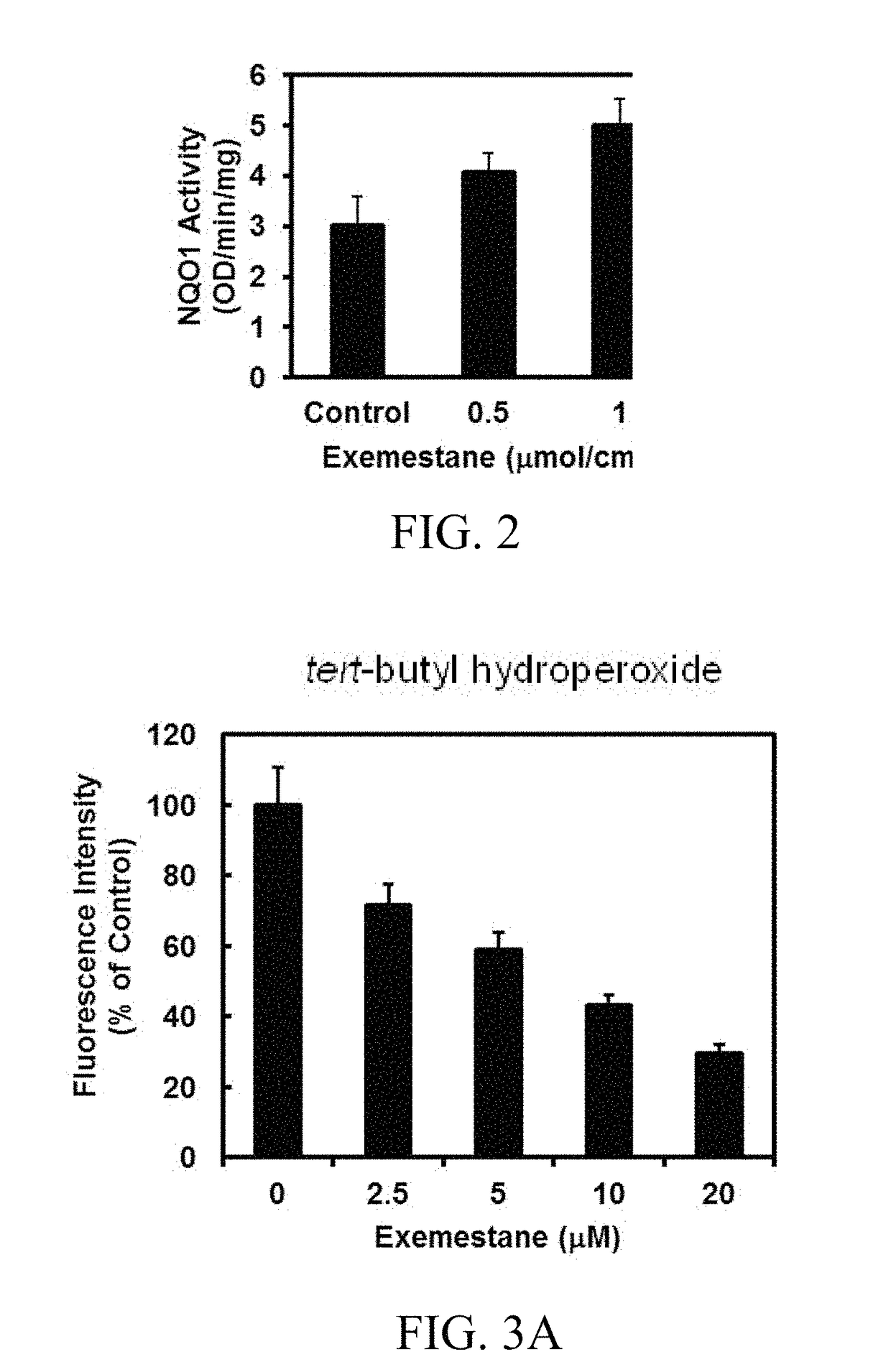
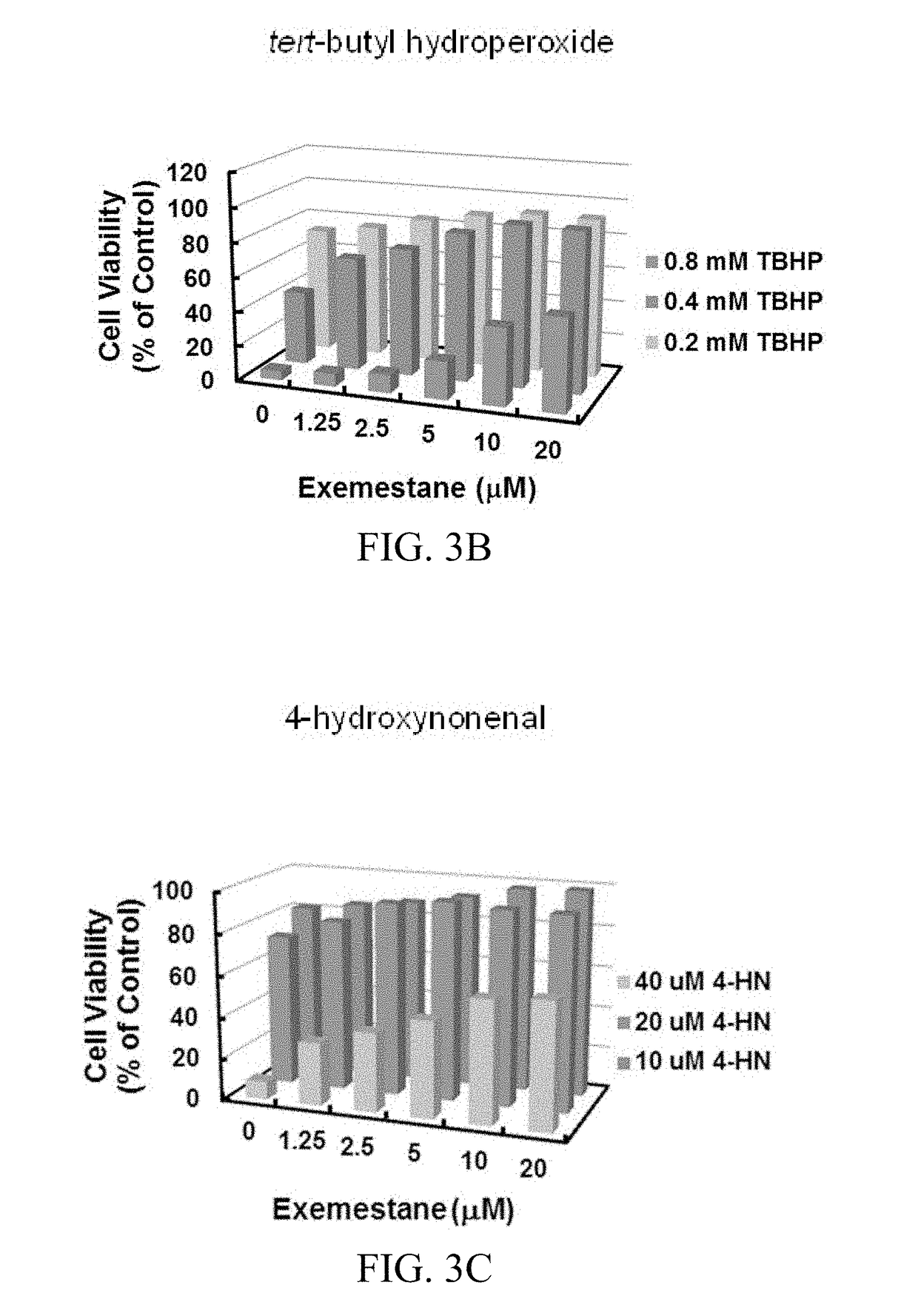
In addition to its potent mechanism-dependent inhibition of estrogen biosynthesis, in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention, it has now been found that exemestane has novel chemoprotective properties which have hitherto not been explicitly recognized. The present invention provides methods for the use of compositions comprising exemestane for chemoprotection against a wide variety of non-mammary tumors (and possibly other chronic diseases) that are not estrogen-dependent, but have oxidative stress, inflammation and electrophile-damaging etiologies. The present invention also shows that exemestane shows powerful synergism with other classes of Nrf2-activators and phase 2 enzyme gene activators, including, for example sulforaphane (an isothiocyanate), shikonin (a naphthoquinone), zerumbone (a cyclic sesquiterpene) and resveratrol (a stilbene derivative), which increases the attractiveness of exemestane's novel uses.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of treating androgen receptor (AR)-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulator (SARMs)
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Exemestane orally disintegrating tablet and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an exemestane orally disintegrating tablet and a preparation method thereof. The exemestane orally disintegrating tablet comprises a principal ingredient of exemestane and auxiliary ingredients of disintegrating agents, fillers and corrective agents. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing, directly tabletting, coating and the like. Exemestane orally disintegrating tablets have the following advantages: the tablets can disintegrate or be soluble in mouth without water and enter digestive tracts with a swallowing act, and the behavior in vivo is consistent with that of common tablets; the exemestane orally disintegrating tablets have the characteristics of convenience for taking, quick absorption, high bioavailability and the like; patient adaptabilities can be improved and clinical medicine choices for doctors and patients can be increased.
Owner:赵辉
Method of treating estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulator (SARMS)
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Industrial production method of exemestane
An industrial production method of exemestane comprises the following steps: adding androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione, anhydrous ethanol, triethyl orthoformate and p-toluenesulfonic acid into a reactor, stirring above added materials, carrying out rotary drying, and crystallizing the obtained dried mixture to obtain an intermediate YXMT01; sequentially adding the intermediate YXMT01, anhydrous ethanol, tetrahydrofuran, 37% formaldehyde, N-toluidine and p-toluenesulfonic acid into the reactor, and carrying out rotary drying to obtain an intermediate YXMT02; sequentially adding the intermediate YXMT02, ethyl acetate and hydrochloric acid into the reactor, precipitating, carrying out suction filtration to obtain white solid, and re-crystallizing the white solid with toluene to obtain an intermediate YXMT03; and sequentially adding the intermediate YXMT03, toluene and IBX into the reactor, stirring the added substances, cooling the obtained substance, concentrating the obtained filtrate, and re-crystallizing the obtained concentrate to obtain white solid YXMT. The method has the advantages of avoiding of uncontrollability of a one-kettle method in industrial production, cheap sources of raw materials, easiness in control of the process operation, high yield, stable quality, and suitableness for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING CHENGONG PHARM CO LTD
Application of aromatase inhibitor in preparation of anti-cirrhosis or anti-liver fibrosis drugs
The invention relates to application of an aromatase inhibitor in preparation of anti-cirrhosis or anti-liver fibrosis drugs. The aromatase inhibitor particularly can be exemestane, formestane, letrozole or anastrozole, and they can all reach good effects in anti-fibrosis and anti-cirrhosis aspects.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Method of treating HER2-positive breast cancers with selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMS)
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer; advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed SERM (tamoxifen, toremifene), aromatase inhibitor, palbociclib (Ibrance), trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, exemestane (Aromasin), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; and / or HER2-positive; comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Non-invasive method of evaluating breast cancers for selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) therapy
This invention relates to the treatment of breast cancer in a subject, for example a female subject. Including methods of: treating metastatic breast cancer; refractory breast cancer; AR-positive breast cancer; AR-positive refractory breast cancer; AR-positive metastatic breast cancer; AR-positive and ER-positive breast cancer; triple negative breast cancer; advanced breast cancer; breast cancer that has failed selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) (tamoxifen, toremifene, raloxifene), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist (goserelin), aromatase inhibitor (AI) (letrozole, anastrozole, exemestane), cyclin-dependent kinase 4 / 6 (CDK 4 / 6) inhibitor (palbociclib (Ibrance), ribociclib (Kisqali), abemaciclib (Vorzenio)), mTOR inhibitor (everolimus), trastuzumab (Herceptin, ado-trastuzumab emtansine), pertuzumab (Perjeta), lapatinib, neratinib (Nerlynx), olaparib (Lynparza) (an inhibitor of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP)), bevacizumab (Avastin), and / or fulvestrant treatments; metastasis in a subject suffering from breast cancer; HER2-positive; treating a subject suffering from ER mutant expressing breast cancer and / or treating breast cancer in a subject, by first determining the 18F-16β-fluoro-5α-dihydrotestosterone (18F-DHT) tumor uptake and identifying said subject as having AR-positive breast cancer based on 18F-DHT tumor uptake, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) compound.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Synthetic method of exemestane
ActiveCN112409432AReduce usageSimplify the subsequent purification processSteroidsBulk chemical productionPtru catalystOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a synthetic method of exemestane. The method comprises the following steps: by taking 6-methyleneandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione as a raw material, directly carrying out selective [delta]1,2 dehydrogenation reaction on the raw material in an organic solvent under the protection of nitrogen, in the presence of an inorganic base and in the presence of an organic phosphorus ester compound as a ligand under the condition of heating reflux under the catalysis of a catalyst, and after the reaction is carried out for a period of time, and carrying out post-treatment to obtain the exemestane. Compared with a traditional synthesis method, the route has the advantages that 1,2 selective dehydrogenation is carried out on 6-methyleneandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione through the catalyst to prepare the exemestane, the use of benzoquinone oxidants, Jones oxidants and the like is avoided, the subsequent purification process is simplified, the yield is increased, and the pollution problem in the production process is reduced.
Owner:SHAANXI SCI TECH UNIV
Synthesis of New Potent Aromatase Inhibitors Through Biocatalysis of Anti-Cancer Drugs, Atamestane, Drostanolone Enanthate, and Exemestane
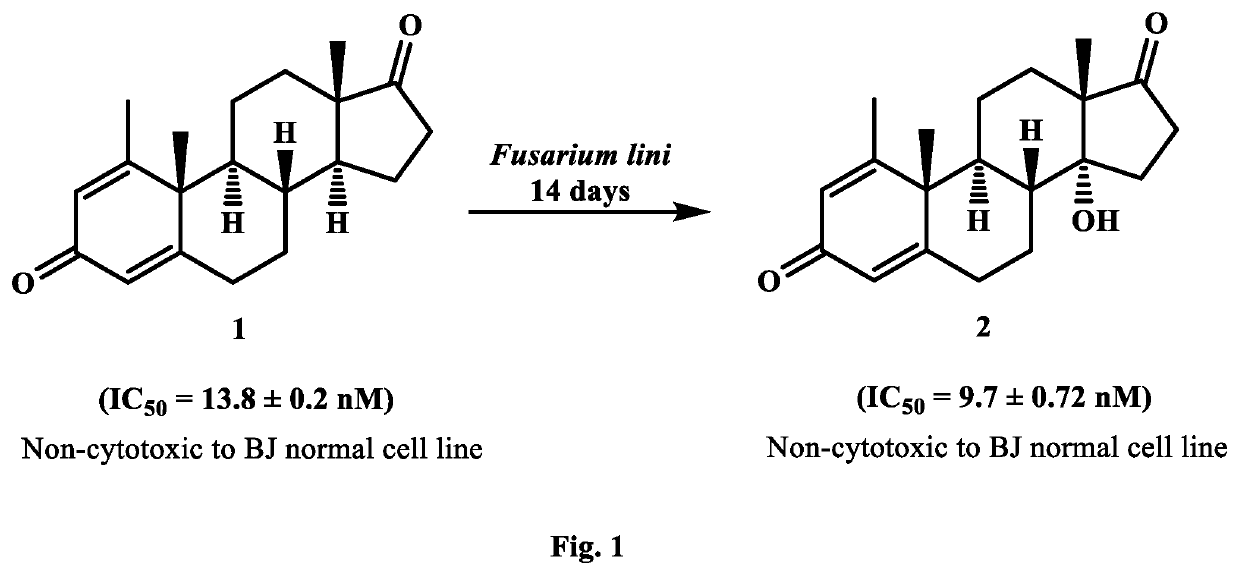
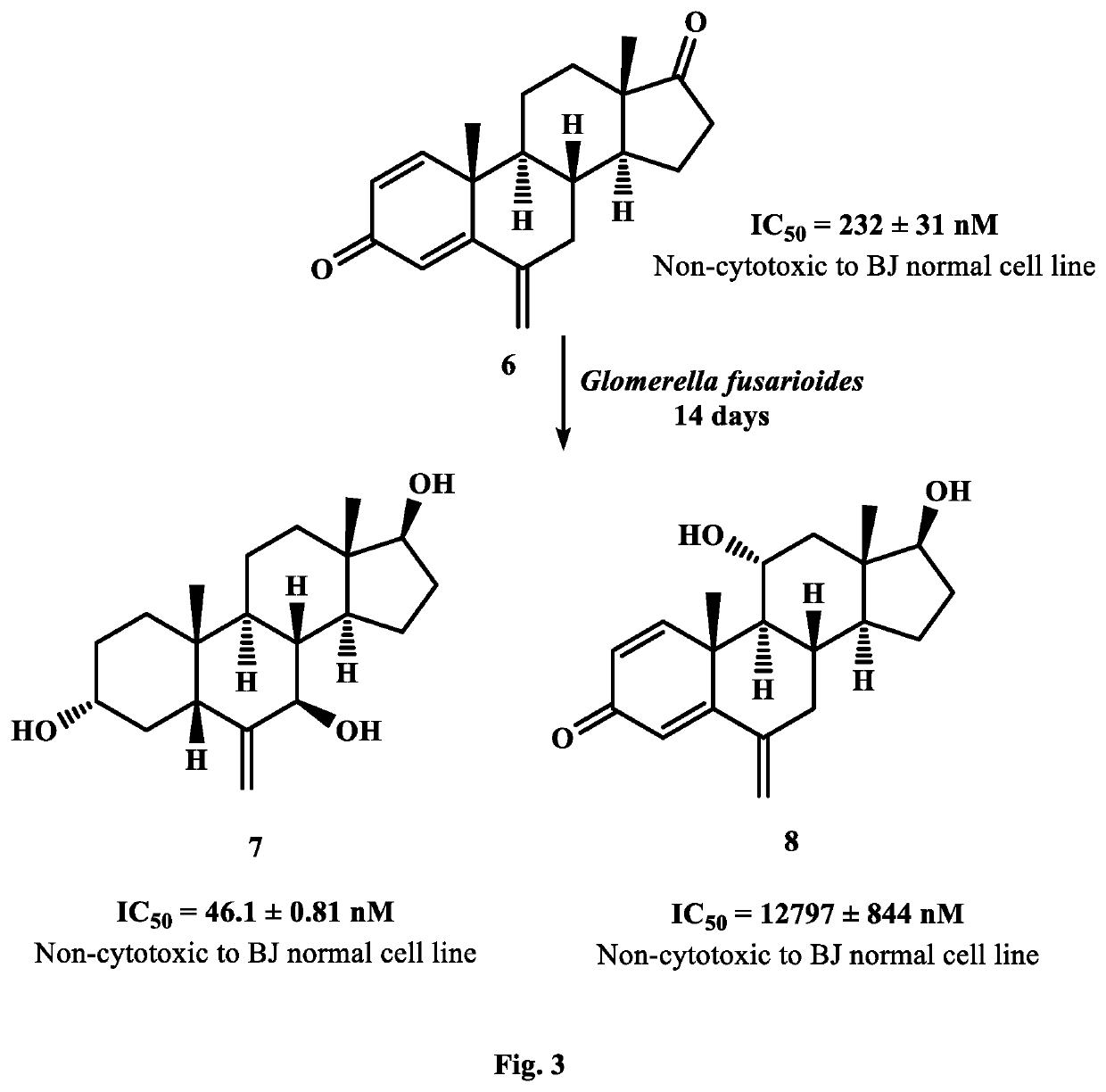
New analogues of anti-cancer drugs atamestane (1), drostanolone enanthate ((3), and exemestane (6) were synthesized through biotransformation. New derivatives, 14α-hydroxy-1-methylandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione ((2) (IC50, 9.7±0.72 nM) of 1 (IC50, 13.8±0.2 nM), and 2-methylandrosta-12β,17β-dihydroxy-1,4-diene-3-one (4) (IC50, 4.23±0.133 nM) of 3 (IC50, 6.4±0.06 nM) showed a potent inhibition against human aromatase enzyme and thus have the potential to treat ER+ breast-cancers and other related diseases. New metabolites, 2α-methyl-9α,17β-dihydroxy-5α-androstan-3-one ((5) (IC50=793.0±29.9 nM) of 3, 6-methylene-3α,7β,17β-trihydroxy-5β-androstane (7) (IC50, 46.1±0.81 nM), and 11α,17β-dihydroxy-6-methylene-androsta-1,4-diene-3-one (8) (IC5O=12797.0±844 nM) of exemestane (6) (IC50=232.0±31 nM) also showed a remarkable anti-aromatase activity. Aromatase is an enzyme, involves in the synthesis of estrogen (ER). Increased amount of ER due to overexpression of aromatase in the body, promotes cancerous cells growth in breast. Therefore, aromatase enzyme is a key target for the discovery of chemotherapeutic agents against ER+ breast-cancers.
Owner:WAHAB ATIA TUL +5
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com