Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Esophageal Tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The tissue of the esophageal wall. It is composed of mucosa, a muscular coat, and a serosal surface.
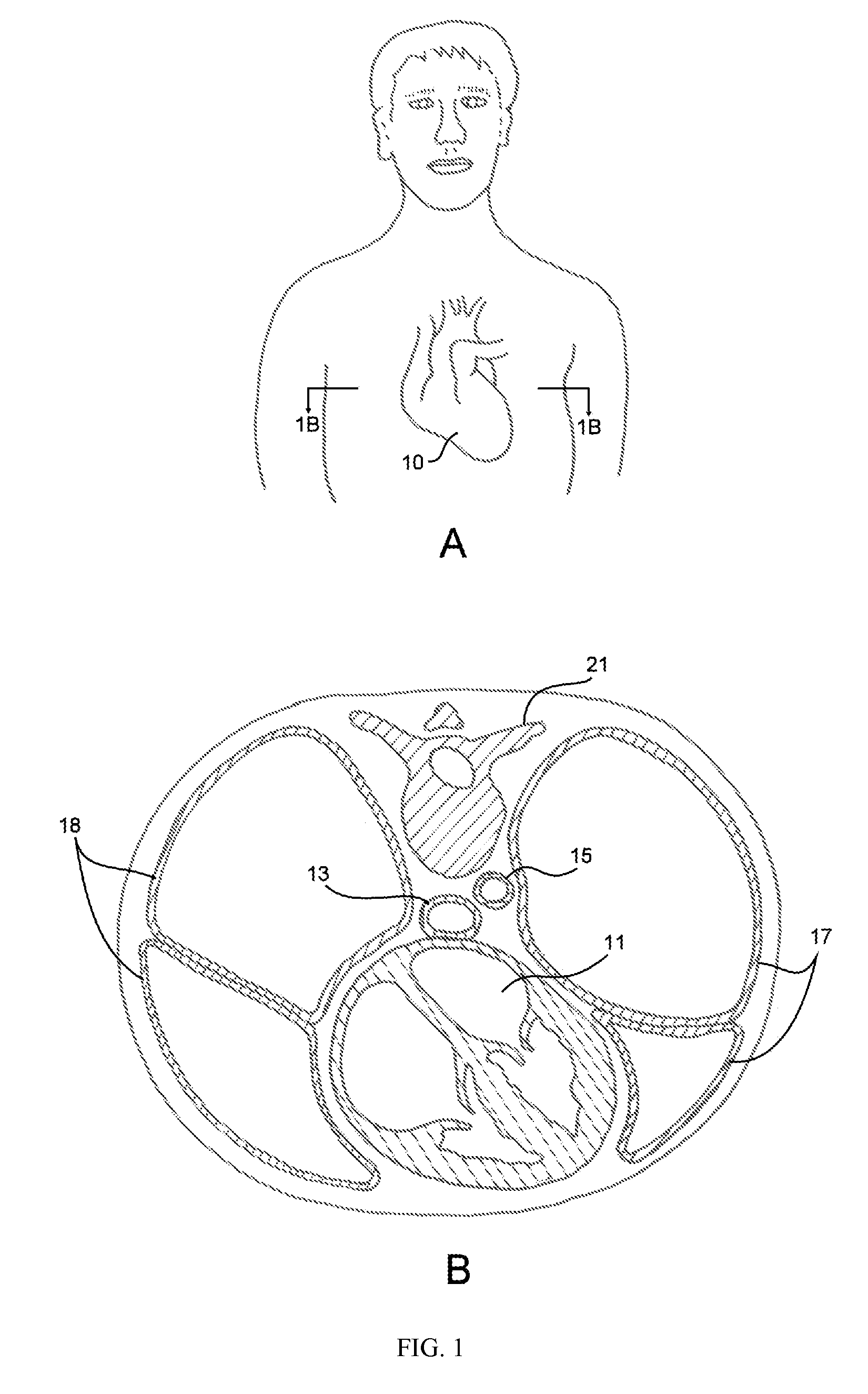
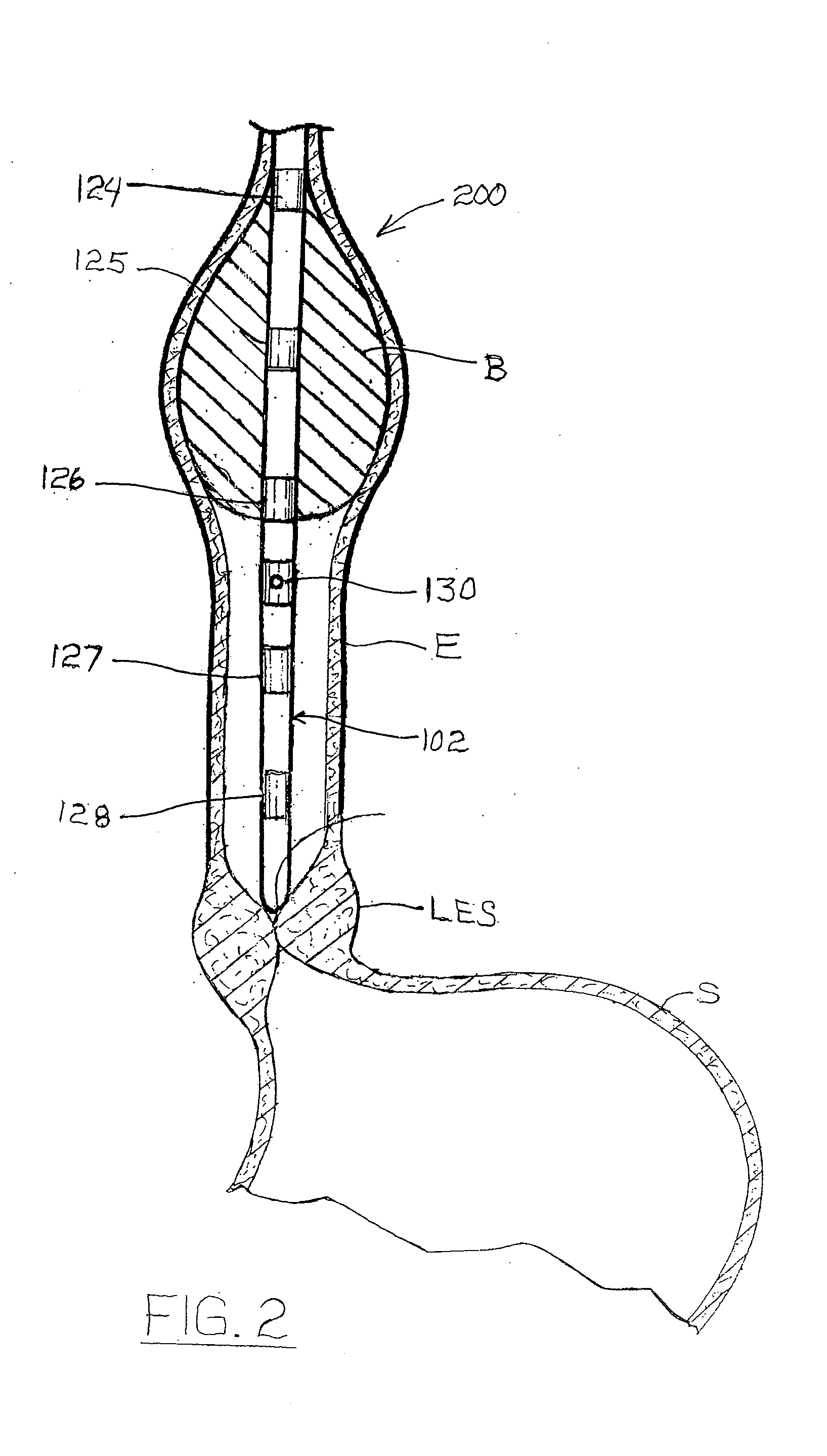
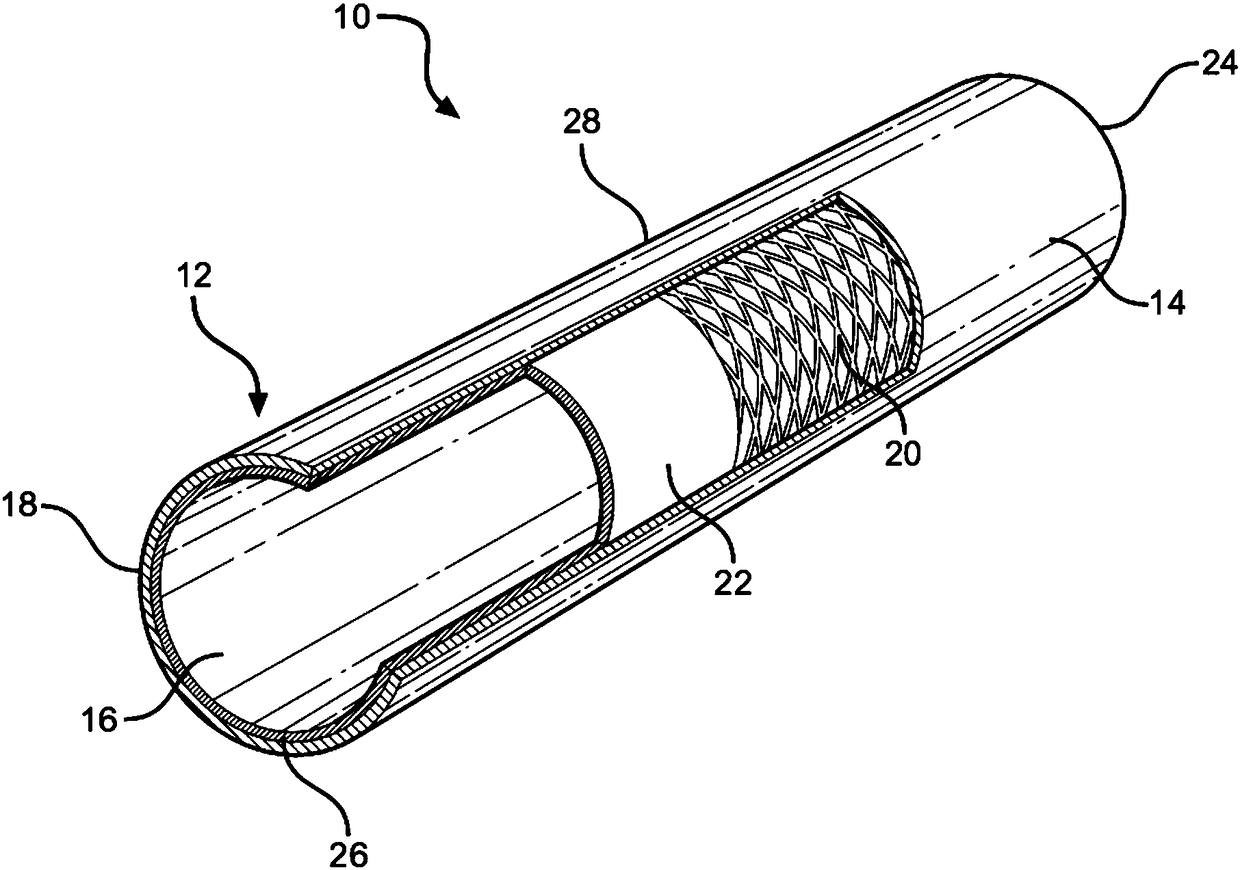
Apparatus and method for resectioning gastro-esophageal tissue
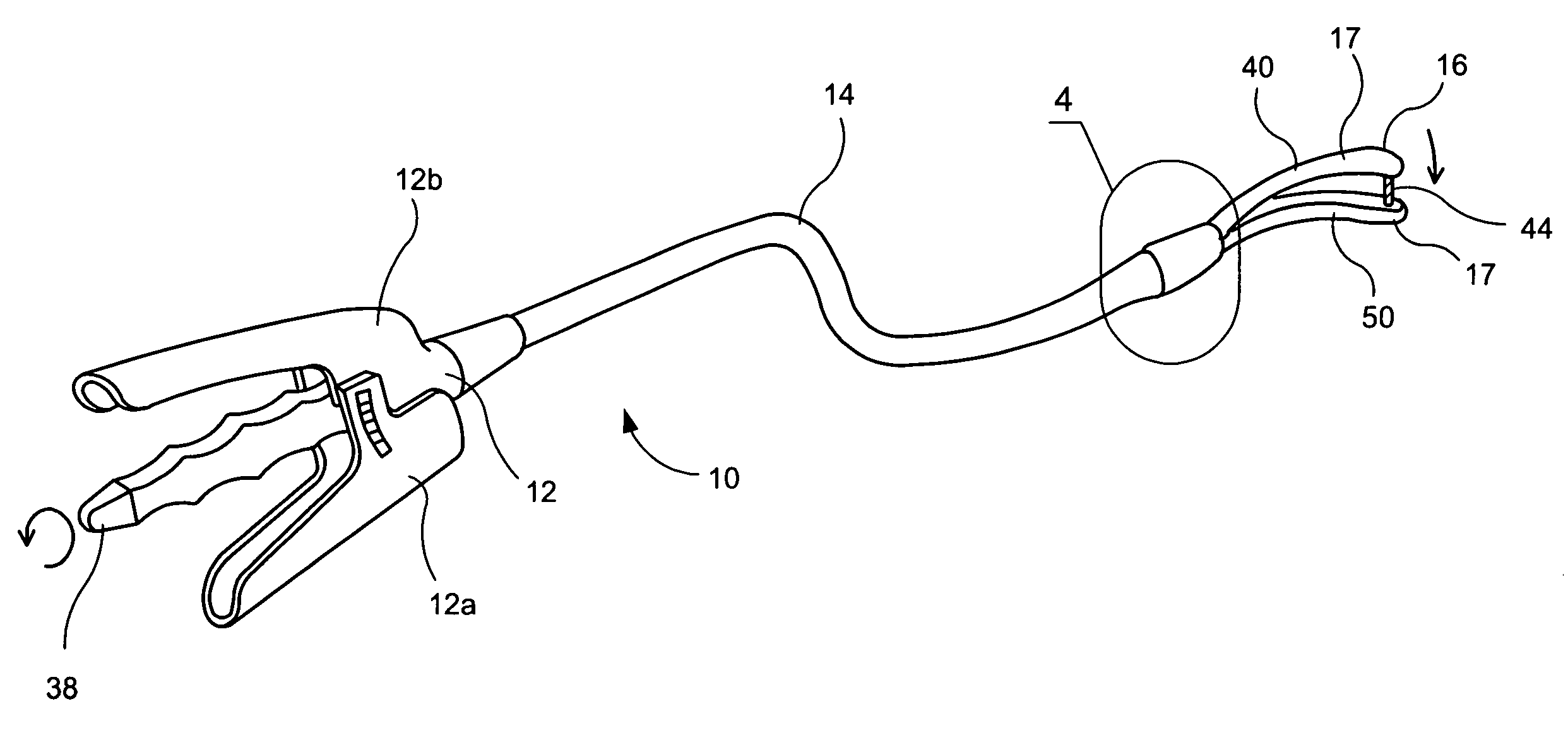
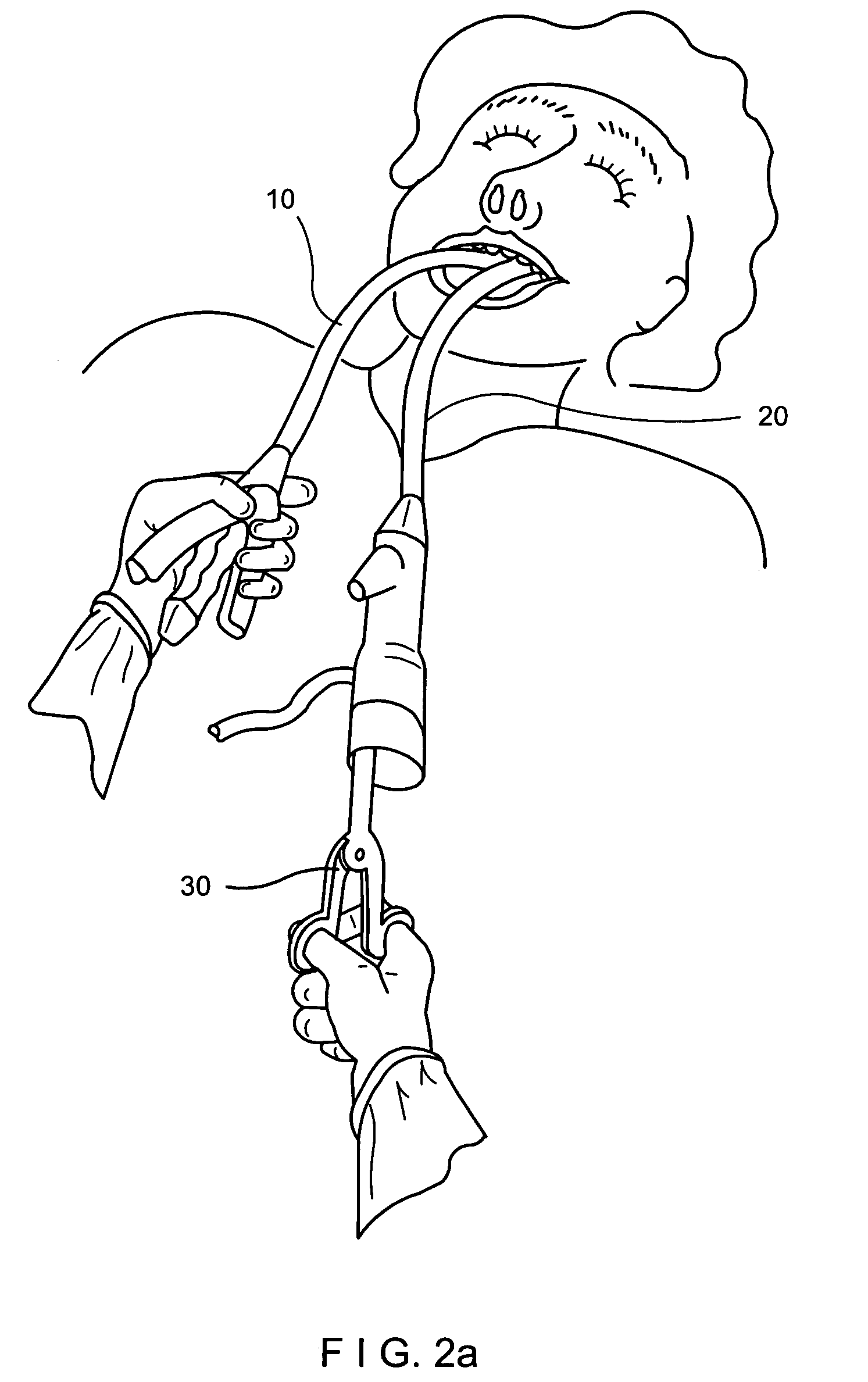
A system for stapling tissue comprises a flexible endoscope and an operative head including a pair of opposed, curved tissue clamping jaws sized to pass through an esophagus, the jaws being moveable with respect to one another between an open tissue receiving configuration and a closed tissue clamping configuration, a first one of the curved jaws including a stapling mechanism and a second one of the jaws including a staple forming anvil surface, the stapling mechanism including staple slots through which staples are fired arranged in a row extending from a proximal end of the first jaw to a distal end thereof in combination with a control handle which, when the operative head is in an operative position within one of a patient's stomach and esophagus, remains outside the patient, the control handle including a first actuator for moving the jaws relative to one another and a second actuator for operating the stapling mechanism.
Owner:REX MEDICAL LP
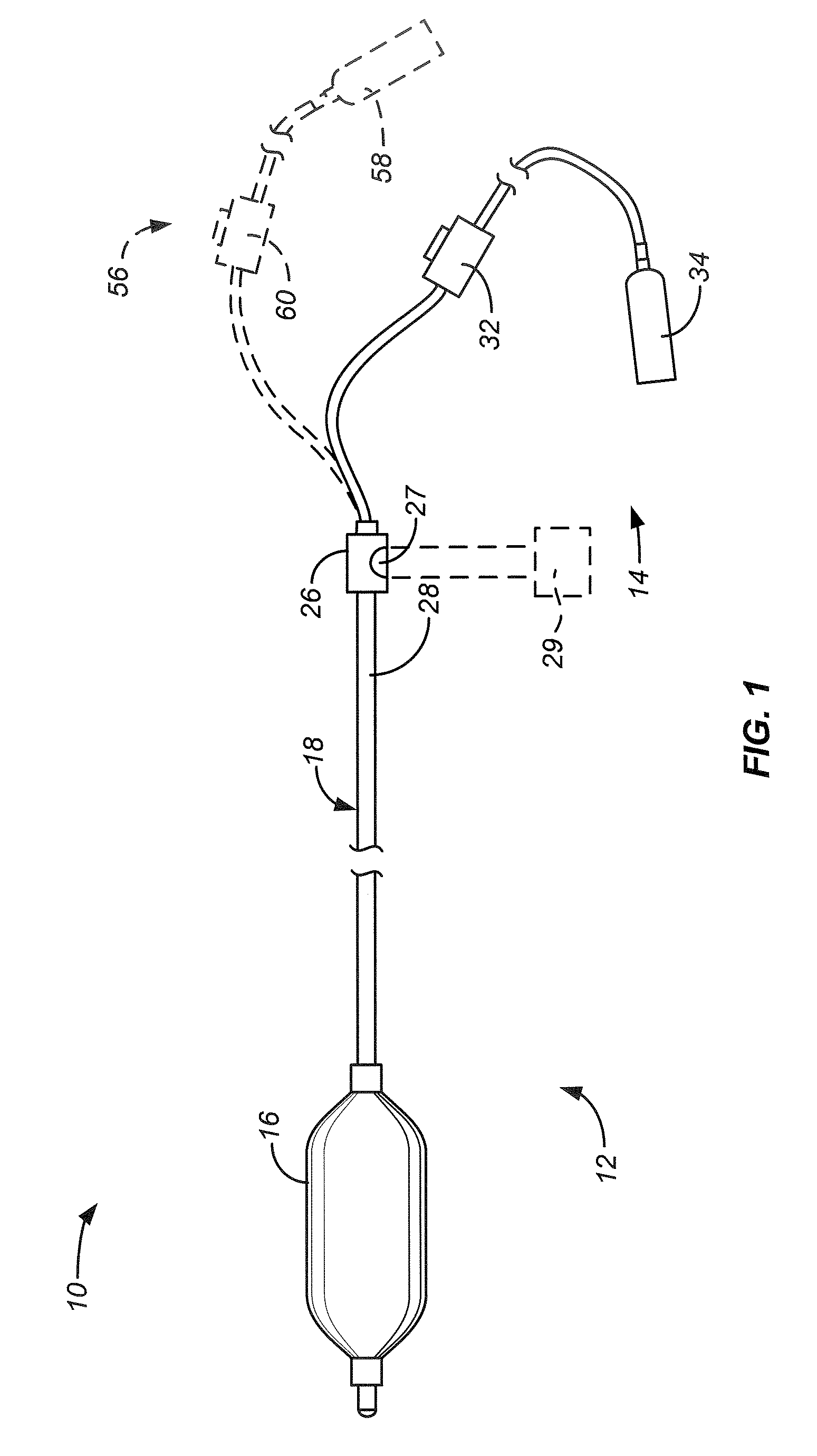
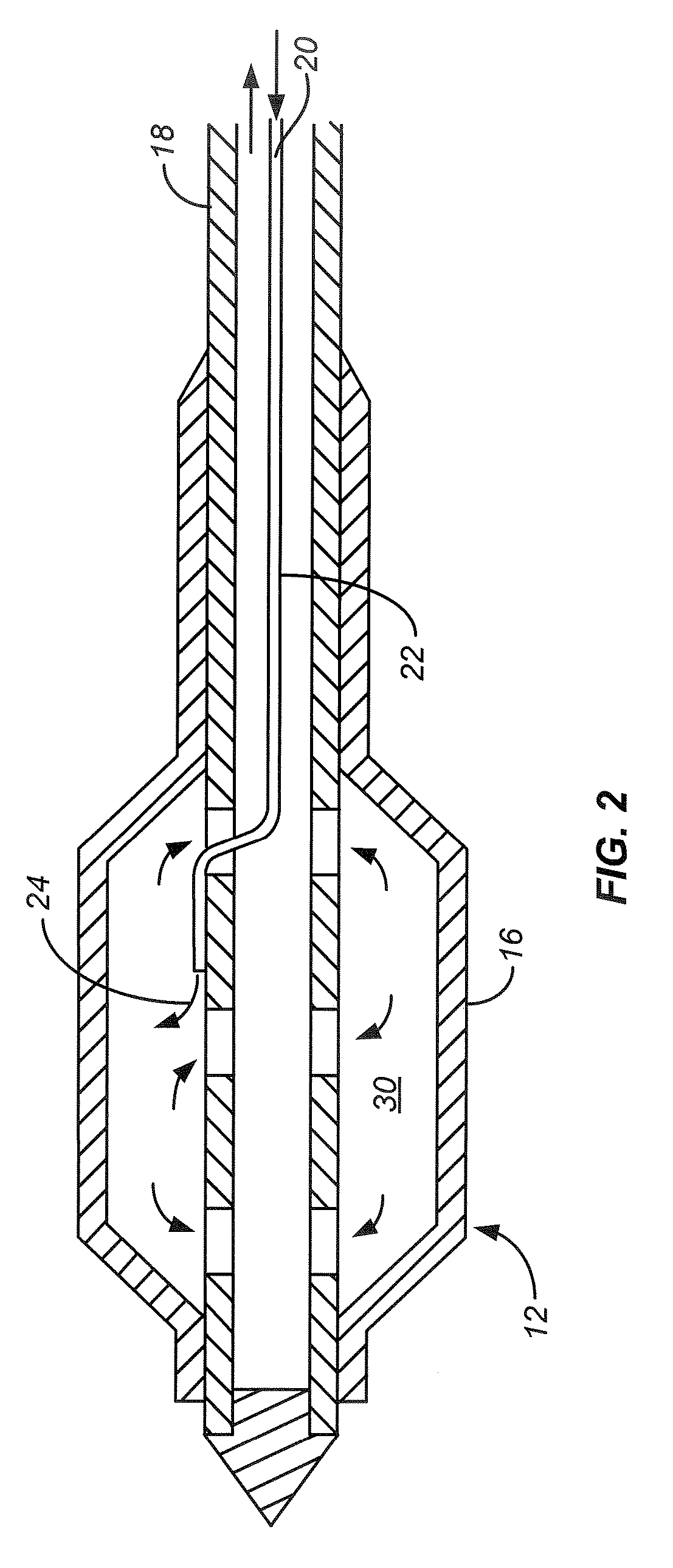
Device and method for esophageal cooling
InactiveUS20070055328A1Equally distributedDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsOesophageal injuryPreventing injury
The present invention includes a device and a method for preventing injury of the esophagus during thermal ablation of the left atrium. The device has an esophageal probe with a balloon tip for insertion into the esophagus of a patient. During usage, coolant passes into the esophageal probe and then fills its balloon. The coolant, when circulating through the balloon and an external cooling machine, protects the esophageal tissue in contact with the esophageal probe from thermal damage during ablation of the posterior wall of the left atrium of the heart, or other procedure.
Owner:MAYSE MARTIN L +1
Apparatus and method for resectioning gastro-esophageal tissue
A system for stapling tissue comprises a flexible endoscope and an operative head including a pair of opposed, curved tissue clamping jaws sized to pass through an esophagus, the jaws being moveable with respect to one another between an open tissue receiving configuration and a closed tissue clamping configuration, a first one of the curved jaws including a stapling mechanism and a second one of the jaws including a staple forming anvil surface, the stapling mechanism including staple slots through which staples are fired arranged in a row extending from a proximal end of the first jaw to a distal end thereof in combination with a control handle which, when the operative head is in an operative position within one of a patient's stomach and esophagus, remains outside the patient, the control handle including a first actuator for moving the jaws relative to one another and a second actuator for operating the stapling mechanism.
Owner:REX MEDICAL LP
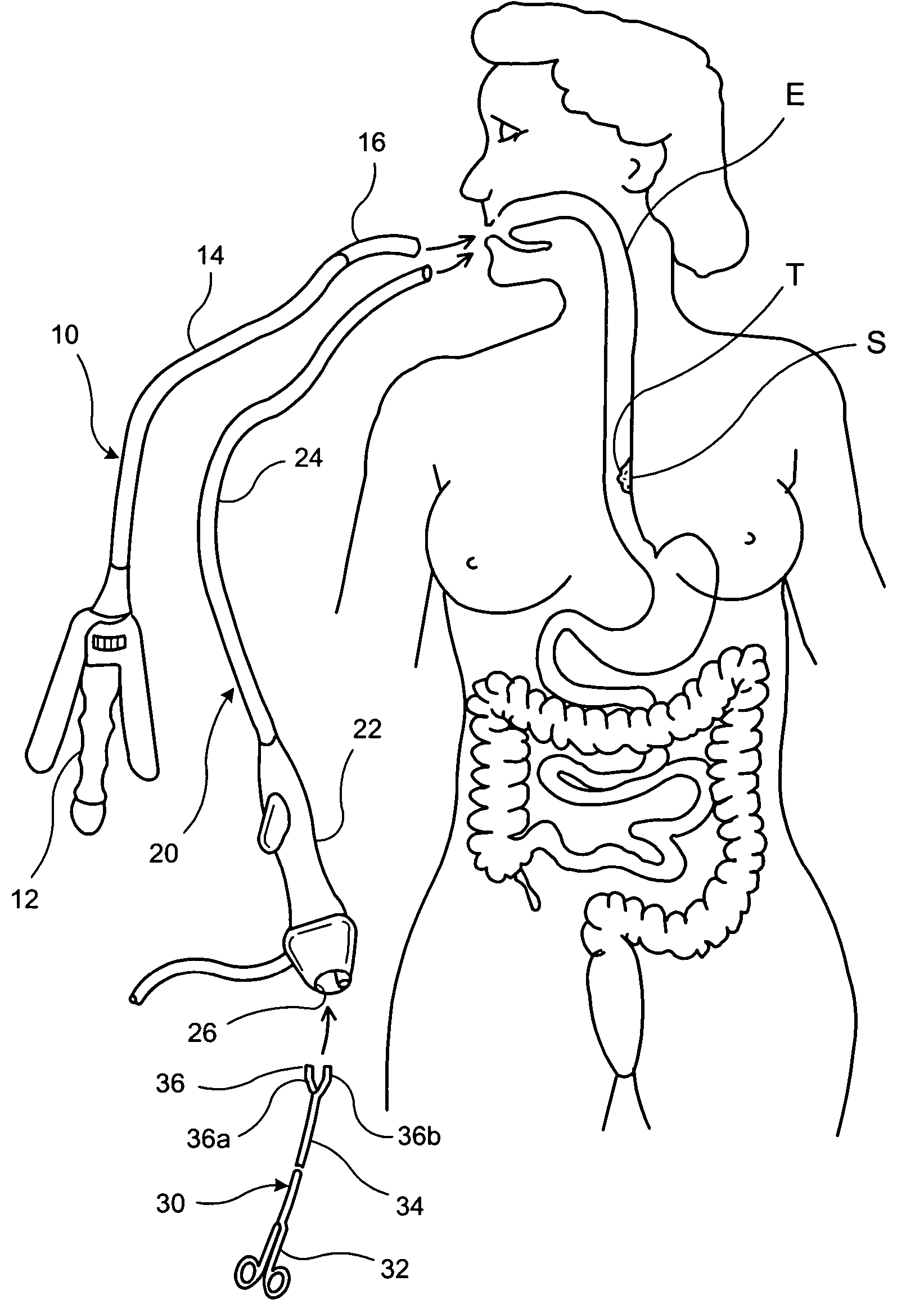
Methods and devices for folding and securing tissue
InactiveUS9173656B2Without compromising safetyHigh intrusion performanceStaplesNailsEsophagus wallMedical treatment
The present invention relates to devices, and methods for using the devices, to create and secure a tissue fold during an endoluminal medical procedure. The devices and methods may be used for folding and securing, for example, a fundus wall onto an esophagus wall or esophageal tissue in the region of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to reduce the diameter of the esophagus opening in that region. One aspect of the invention includes forming the tissue fold by closing a grasping arm that is pivotably connected to an overtube that has been positioned at the juncture of the fundus wall and esophagus wall. A further aspect of the invention includes tissue clips configured to be inserted and positioned through an endoluminal device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Barrett's Esophagus Cryogenic Ablation System
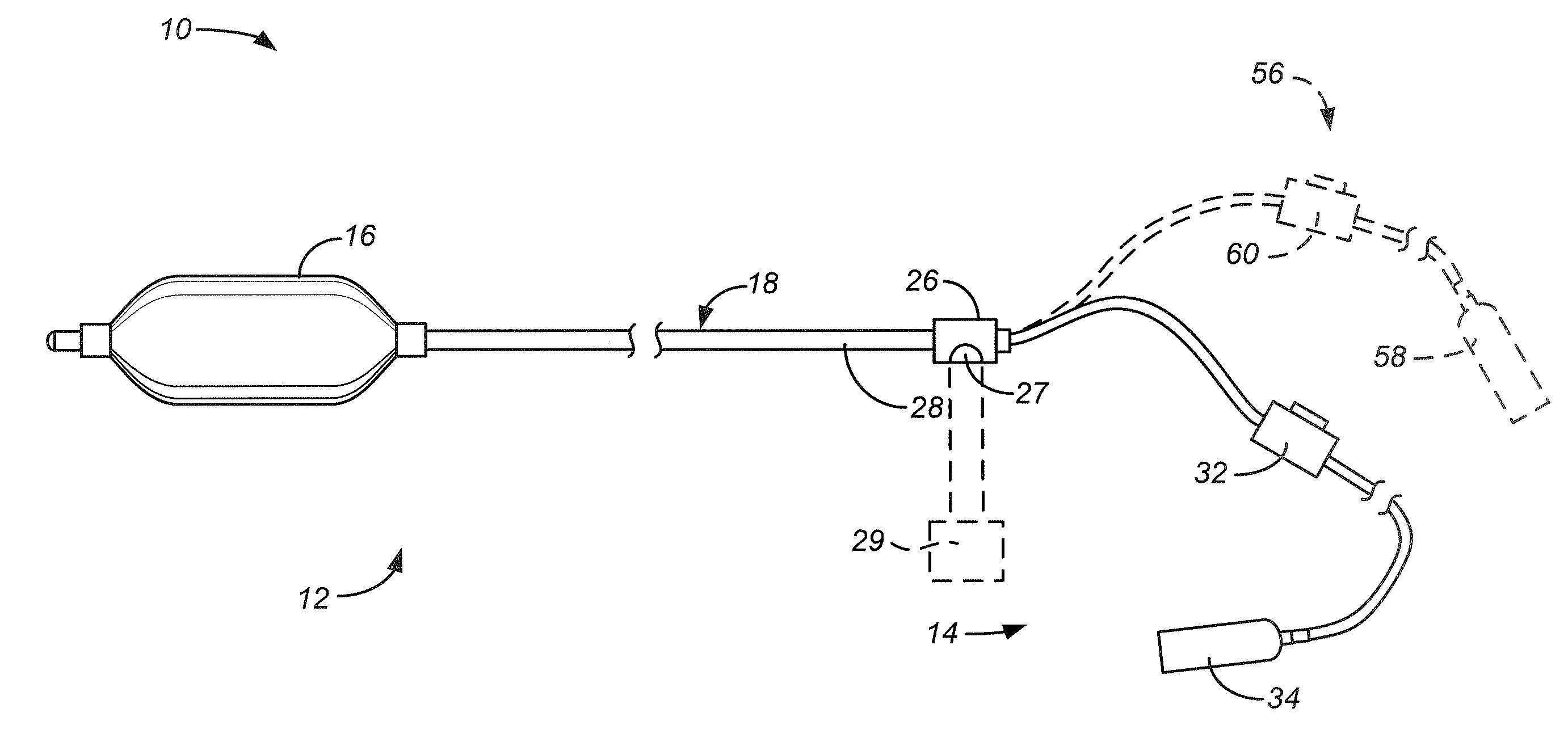
InactiveUS20070299433A1Avoid overexpansionControl expansionStentsBalloon catheterMedical deviceMedical treatment
A medical device for treating esophageal tissue comprises a catheter, a balloon, placeable within the esophagus of the patient, and a refrigerant. The refrigerant is deliverable into the interior of the balloon so to place the balloon into an expanded, cooled state so that the balloon can press against and cool esophageal tissue. In other examples the medical device may include means for limiting radial expansion of the balloon.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Esophageal waveform analysis for detection and quantification of reflux episodes
Owner:DIVERSATEK HEALTHCARE INC
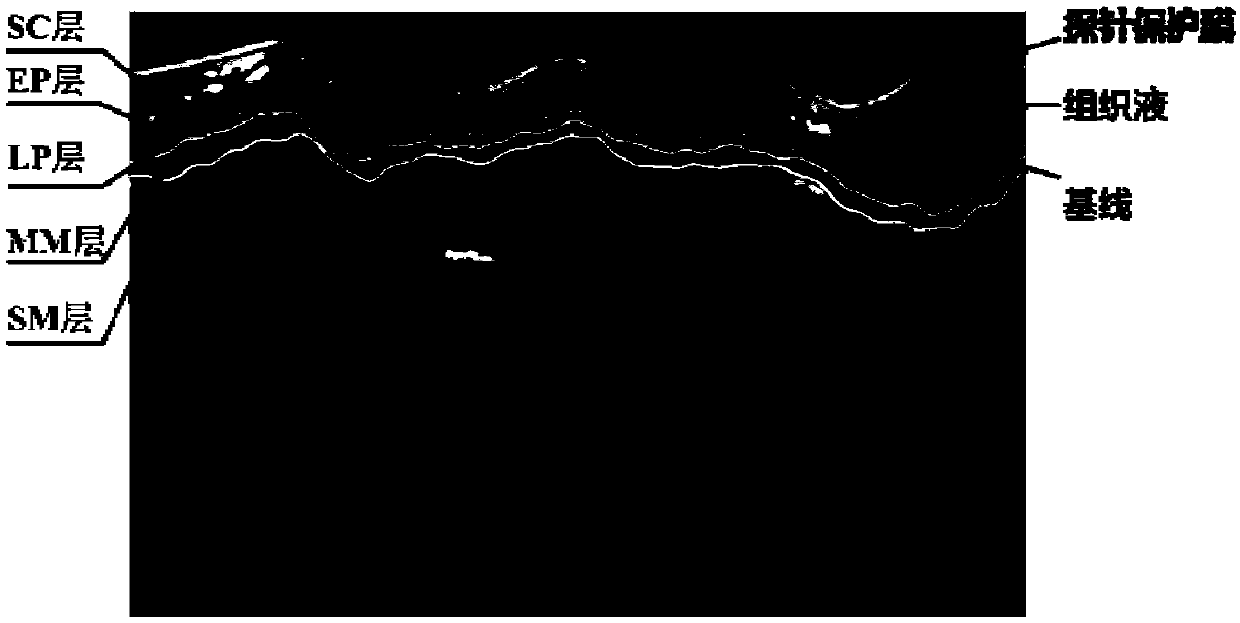
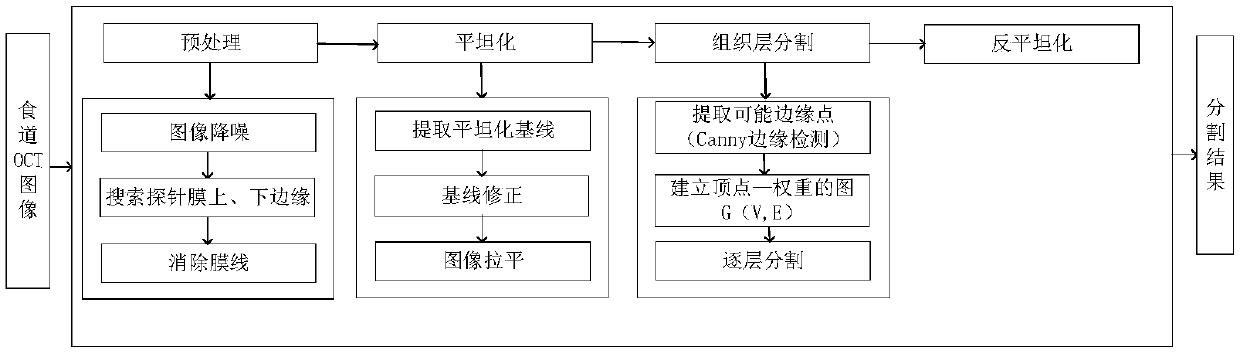
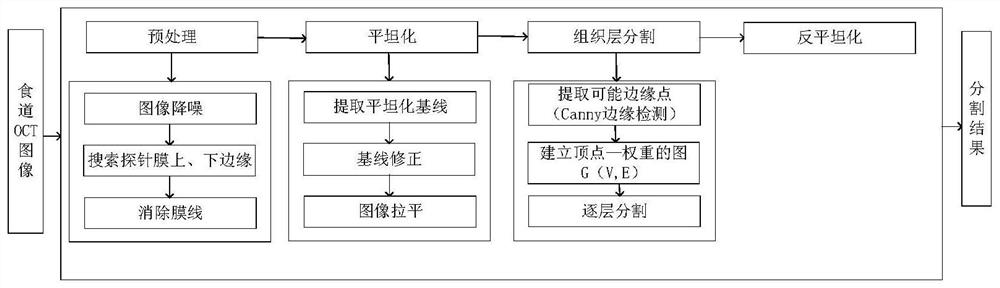
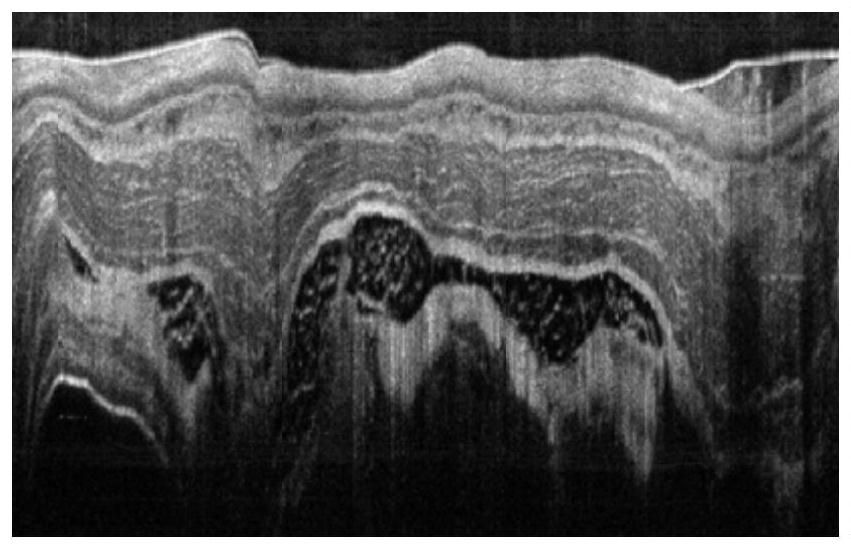
Automatic segmentation method and system of esophageal endoscopic OCT image hierarchy structure
ActiveCN108765388AImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationGradient operators
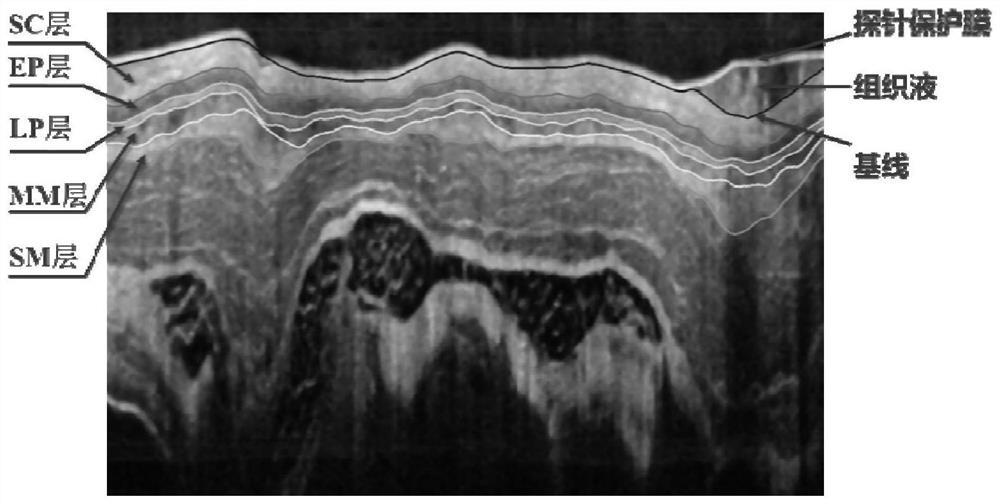
The invention discloses an automatic segmentation method and a system of an esophageal endoscopic OCT image hierarchy structure. The method comprises the following steps: image preprocessing, whereinan image is filtered and searched, and pixel values are complemented; image planarization, wherein the whole esophageal tissue in the image is straightened and corrected; segmentation of an image organization layer, wherein a current segmentation layer is used as a reference and the searching area of a next layer to be segmented is obtained in a mode of translating certain pixels downward and segmentation layer by layer is performed; image unplanarization, wherein the segmented image is inversely translated to obtain the final segmentation result. The invention provides a scheme for respondingto interference of a probe protective film, tissue liquid and the like, so as to avoid subsequent influences on tissue layer segmentation. The invention combines the Canny edge detection with the gradient operator, and proposes a new image segmentation method weight design scheme. The scheme uses the Canny operator to improve the precision of edge detection, and uses the gradient operator to compensate the missing edge in the Canny operator. The accuracy of segmentation is improved by combining the two operators.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Treatment for Gastroesophageal disease
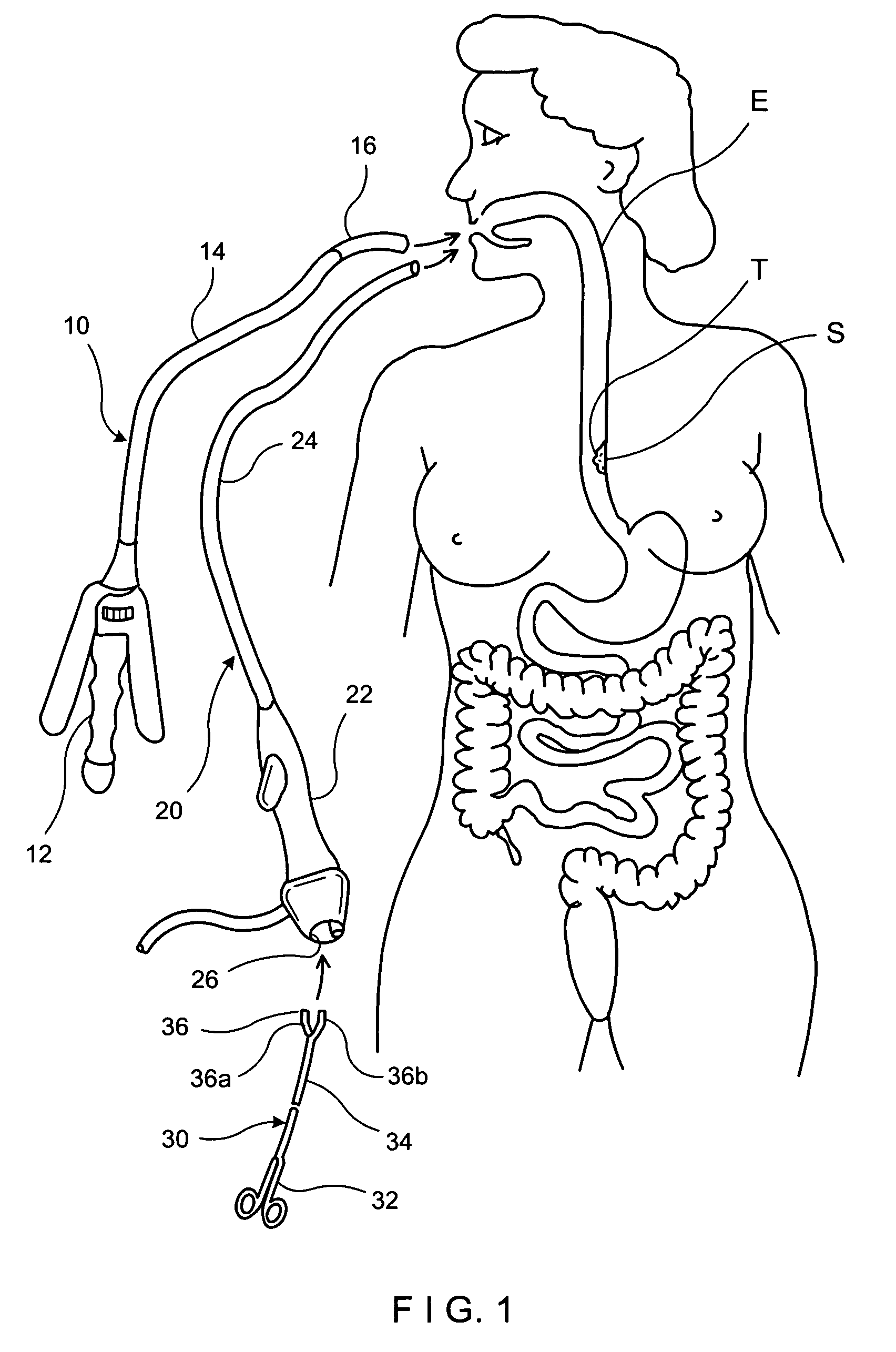
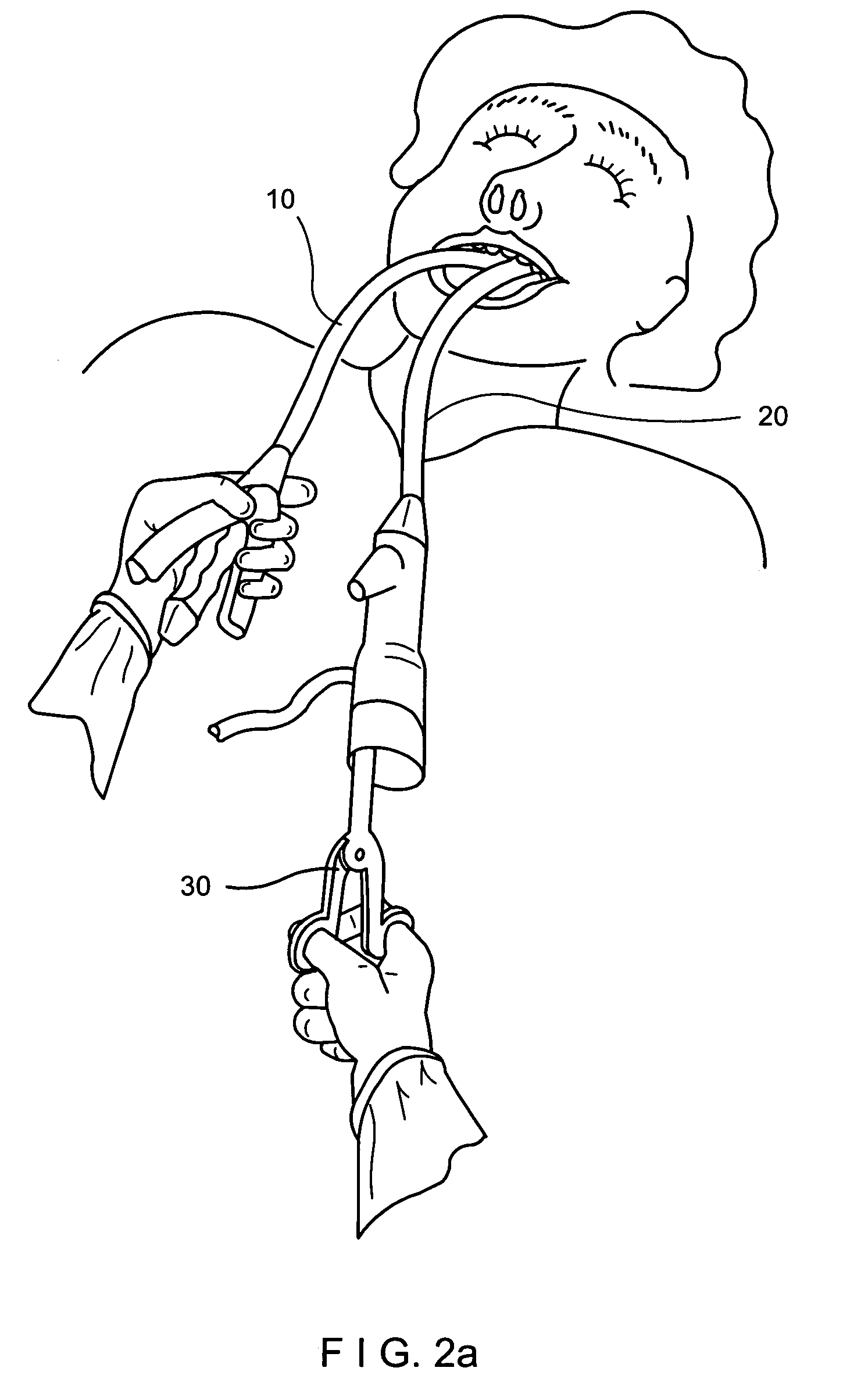
InactiveUS7047980B2Reduce frequencyReduce in quantityDiagnosticsSurgeryDistal portionBiomedical engineering
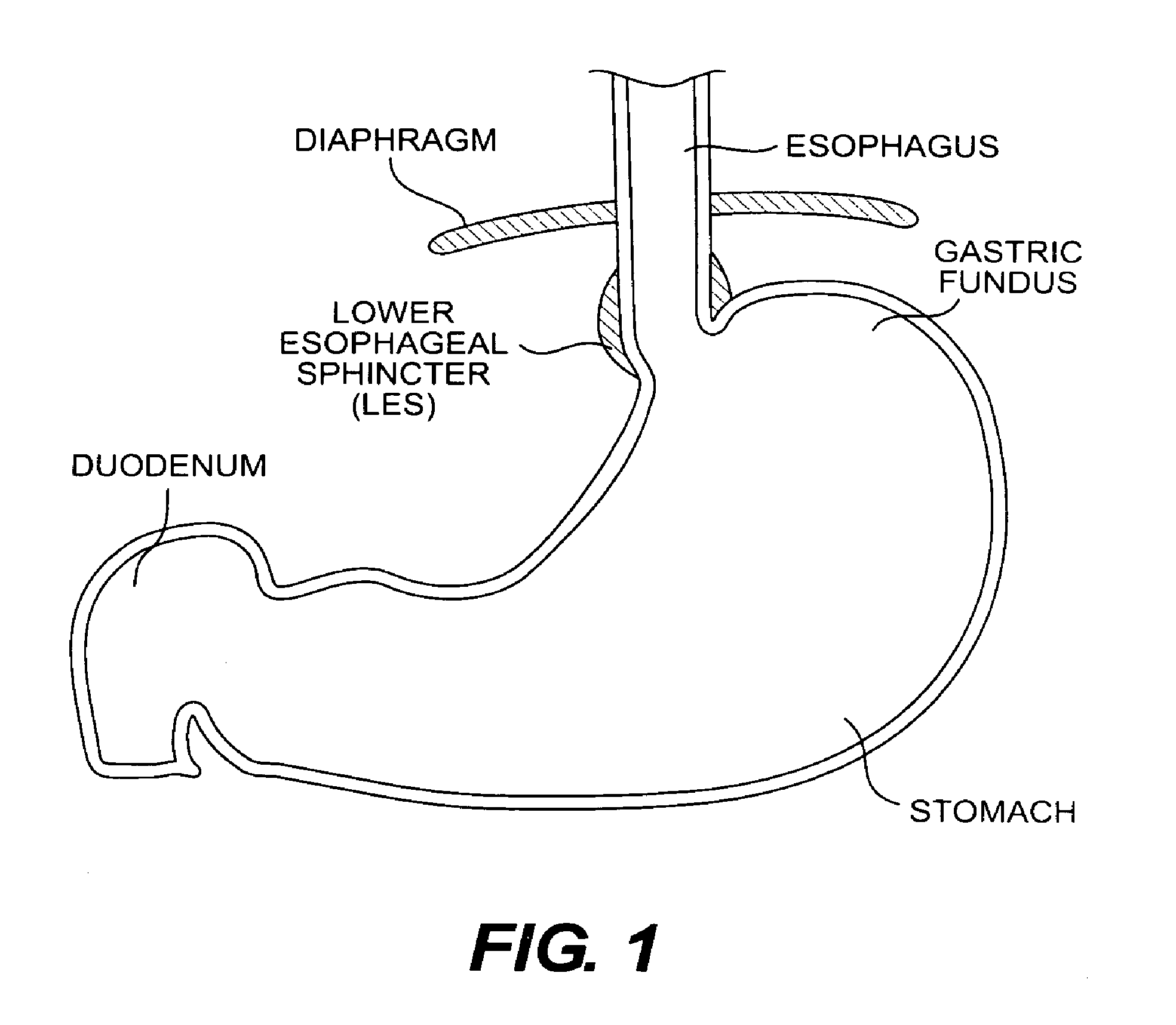
A system includes an implantable polymer for increasing the dimensions of layers of tissue. In one embodiment, the implantable polymer is delivered transorally using a scope and injection needle. The system allows for visualization and injection of polymer into the lower esophageal sphincter. Methods of treating gastroesophageal reflux disease include insertion of the distal portion of the injection needle into the esophageal tissue and injection of a polymer liquid to enlarge tissue dimensions. The polymer can be injected at several sites to distribute localized pressures and attain better distribution of the tissue bulking effect.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
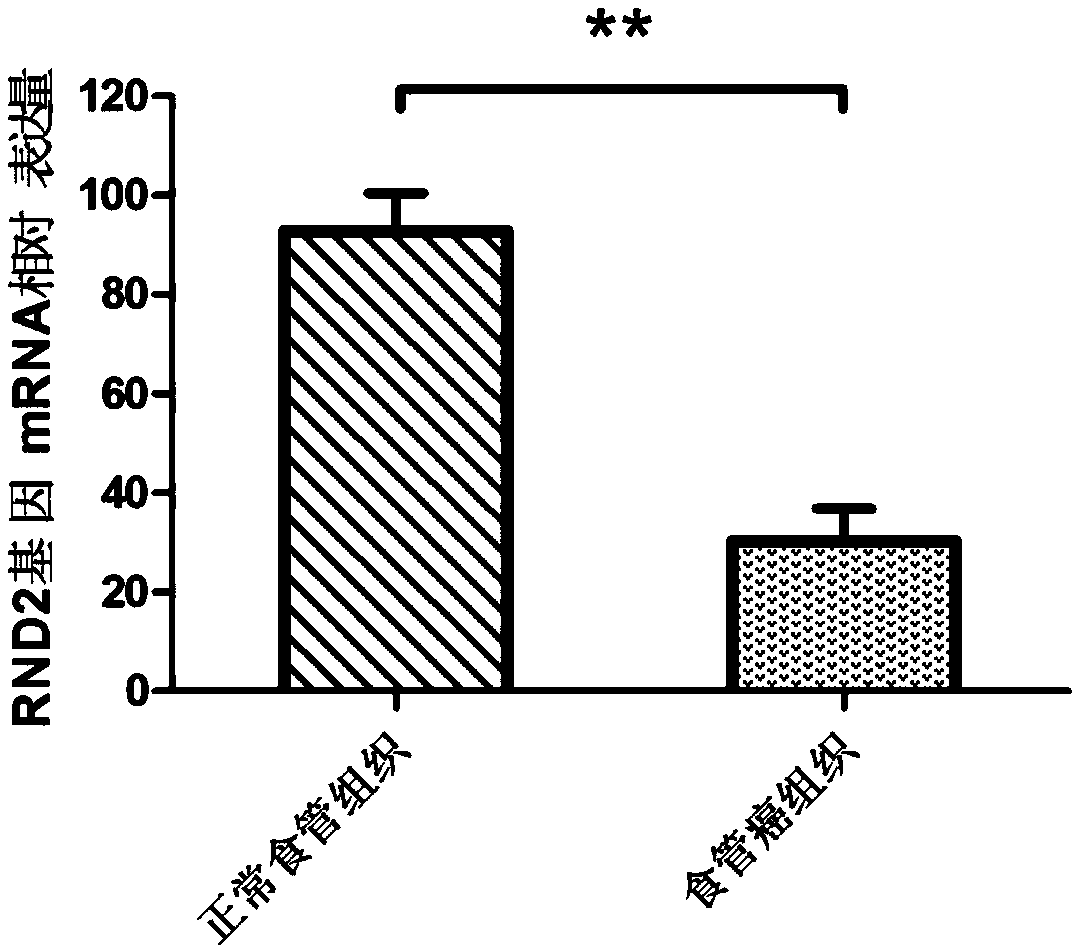
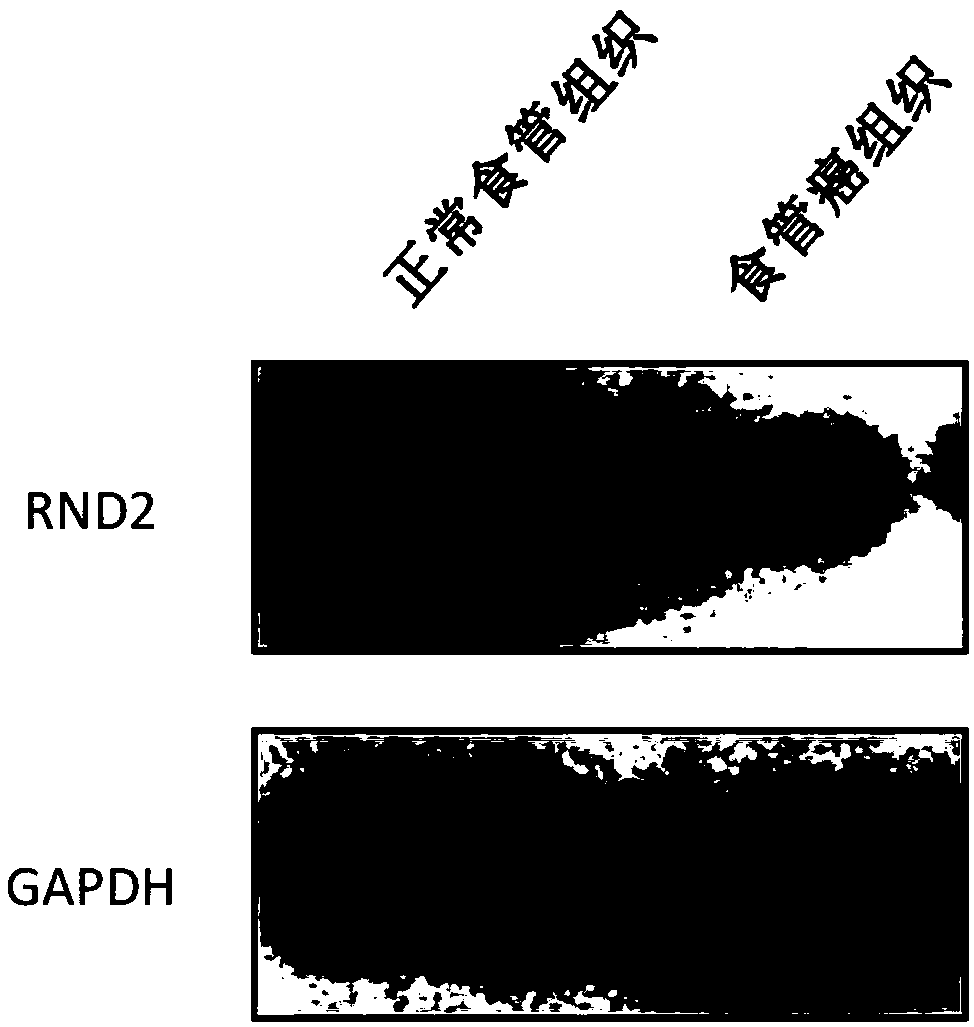
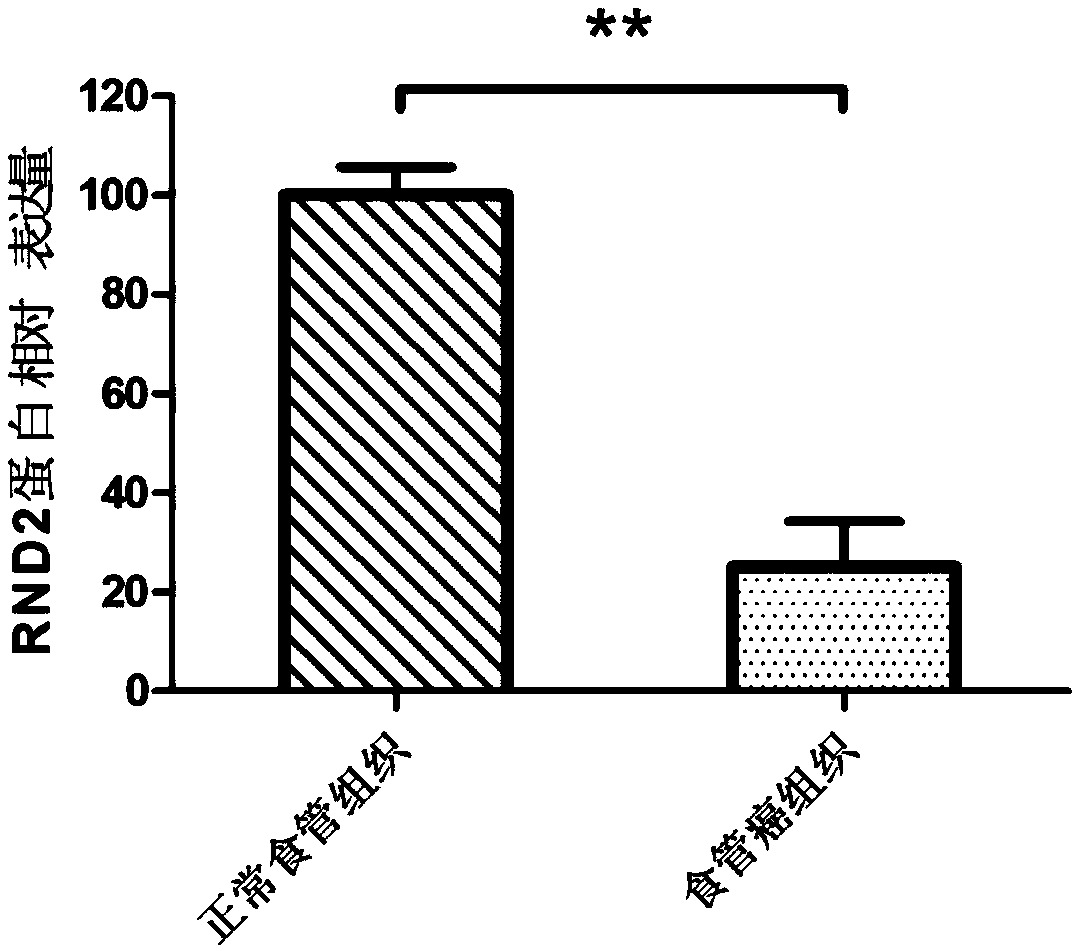
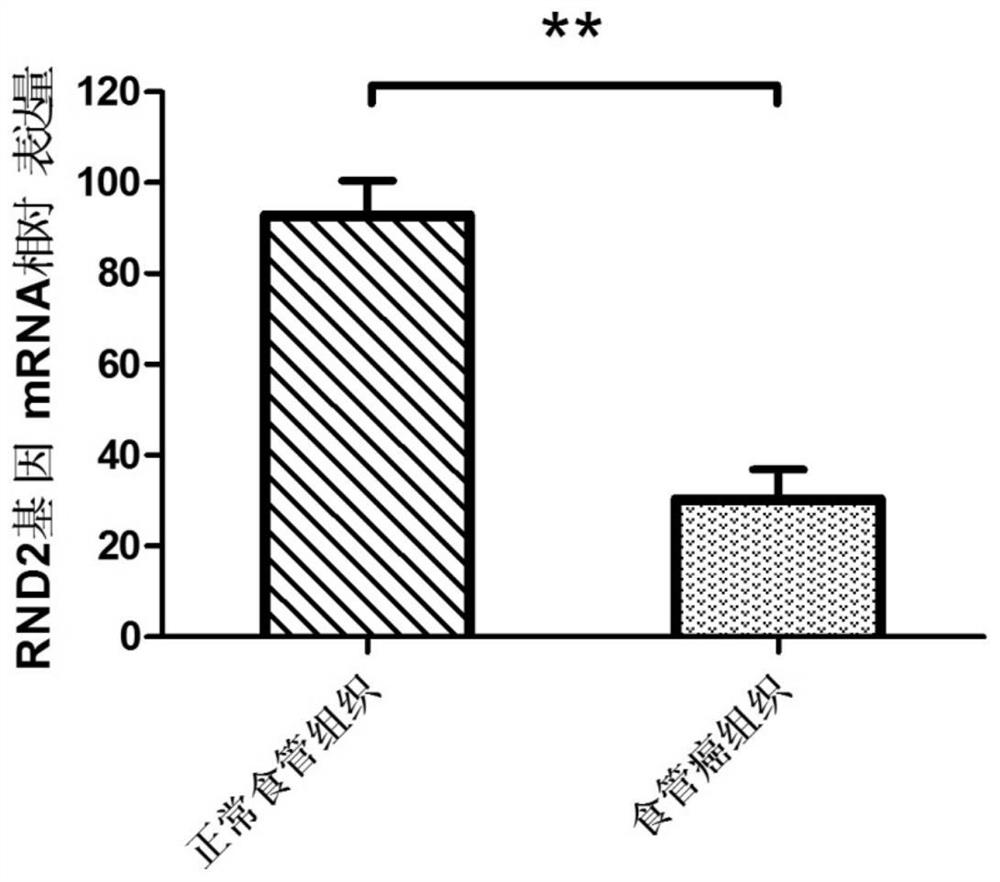
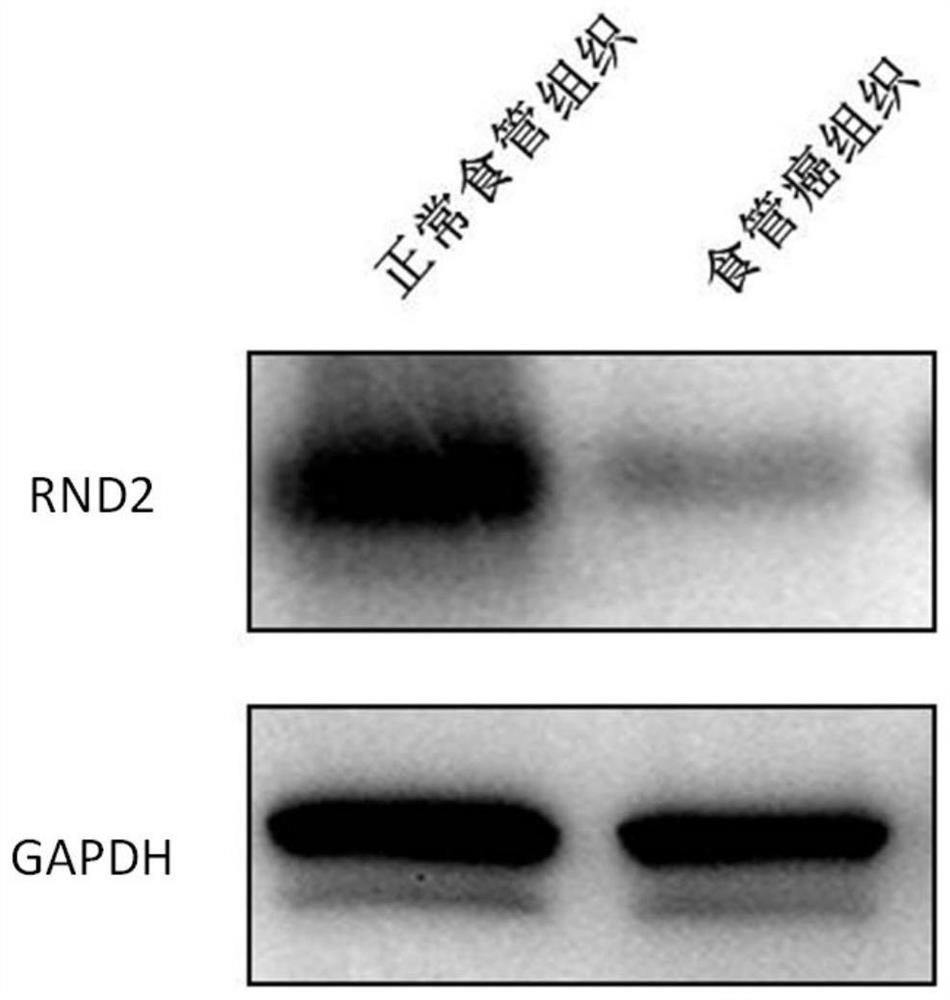
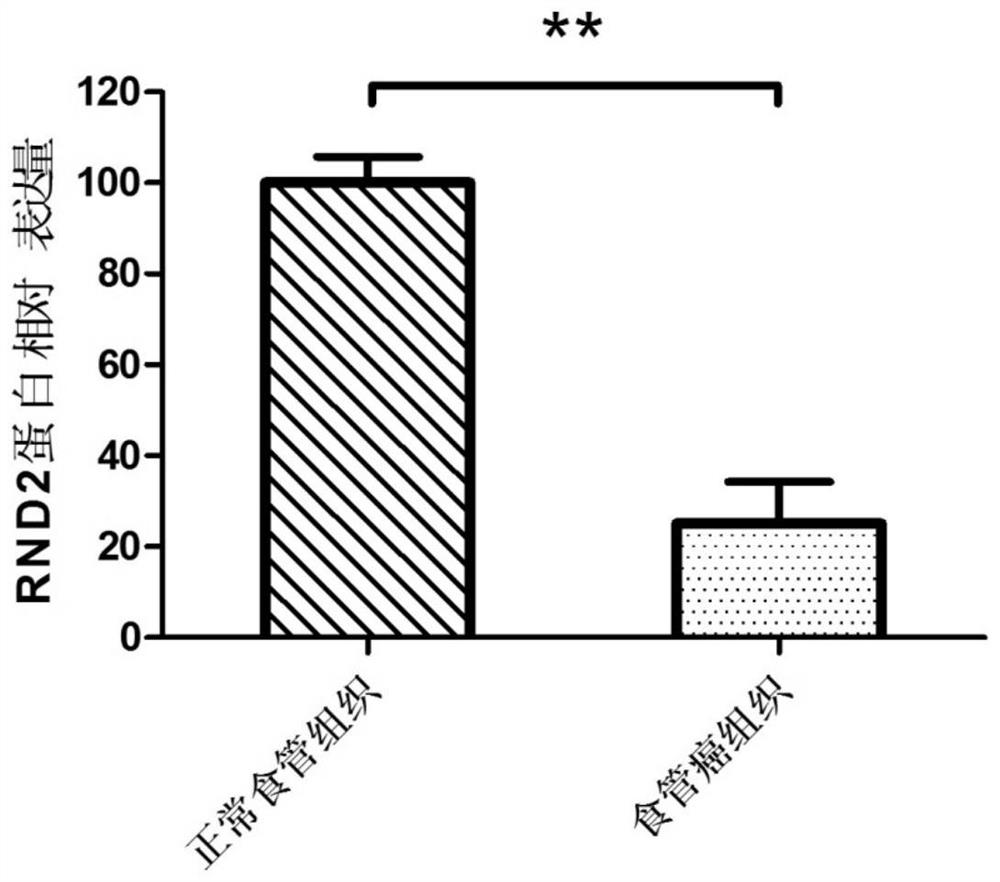
Preparation for detection, diagnosis or prognostic evaluation of esophageal cancer, medicament for treating esophageal cancer and application of RND2 gene
The invention relates to a preparation for detection, diagnosis or prognostic evaluation of an esophageal cancer, a medicament for treating the esophageal cancer and an application of an RND2 gene, and belongs to the technical field of tumor molecular biology. The preparation for detection, diagnosis or prognostic evaluation of the esophageal cancer disclosed by the invention comprises a detectionproduct for the mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) expression level of the RND2 gene, or a detection product for the expression amount of an RND2 protein; the RND2 protein belongs to the Rnd subfamilyof the Rho GTPase superfamily. The situation that the expression of the RND2 gene is related to the esophageal cancer is discovered by the invention for the first time. By detecting the expression ofthe RND2 in the esophageal tissue of a subject, whether the subject suffers from the esophageal cancer or not or whether the subject is at risk of suffering from the esophageal cancer or not can be judged. By improving the expression of the RND2 protein and supplementing the missing or deficiency of the endogenous RND2 protein, the esophageal cancer caused by lack of the RND2 protein can be treated or alleviated.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Esophageal tissue constructed by tissue engineering
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical engineering and specifically relates to an esophageal tissue constructed by tissue engineering. A tissue-engineered esophagus containing an epithelial layer and a dermal layer is consisted of scaffold materials and seed cells according to the basic principles and methods of tissue engineering. Vascular endothelial cells in the dermal layer directly participate in the establishment of a capillary network, and two revascularization methods are used to quickly communicate the capillary network in the dermal layer with the blood supply channel of a receptor, thus providing blood to the epithelium of the tissue-engineered esophagus. The esophageal tissue of the invention changes a former therapeutic mode of repairing damage by damage, and can be used for simplifying esophagectomy and one-stage reconstruction of digestive tracts, thus reducing medical trauma and benefiting the majority of patients with esophageal diseases.
Owner:DALIAN CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
Systems and methods for producing gastrointestinal tissues
Aspects of the disclosure relate methods and synthetic scaffolds for regenerating gastrointestinal tissue (e.g., esophageal tissue).
Owner:BIOSTAGE INC
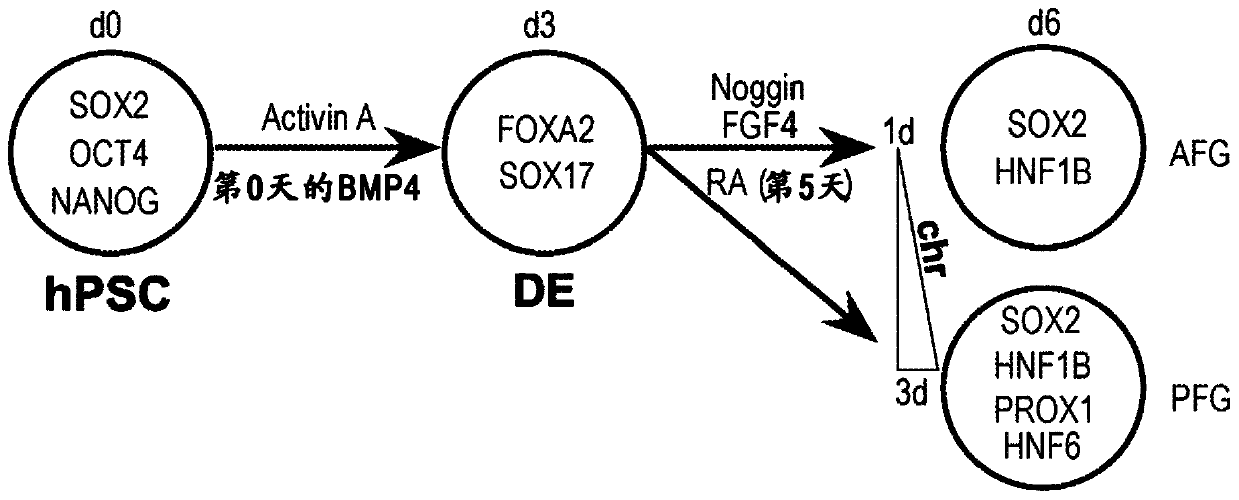
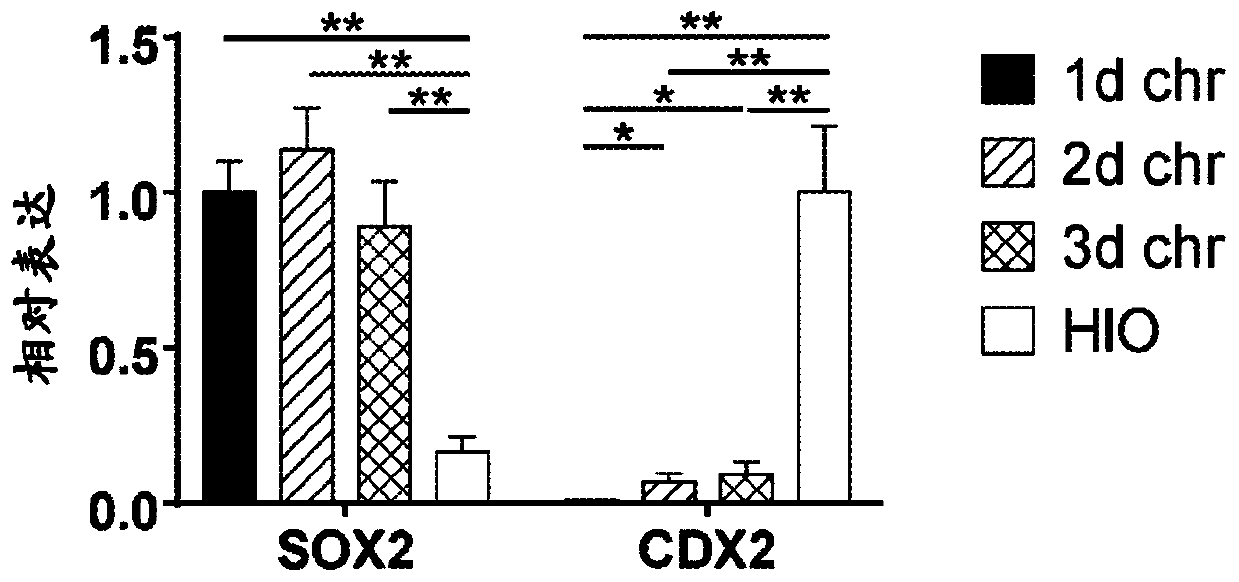
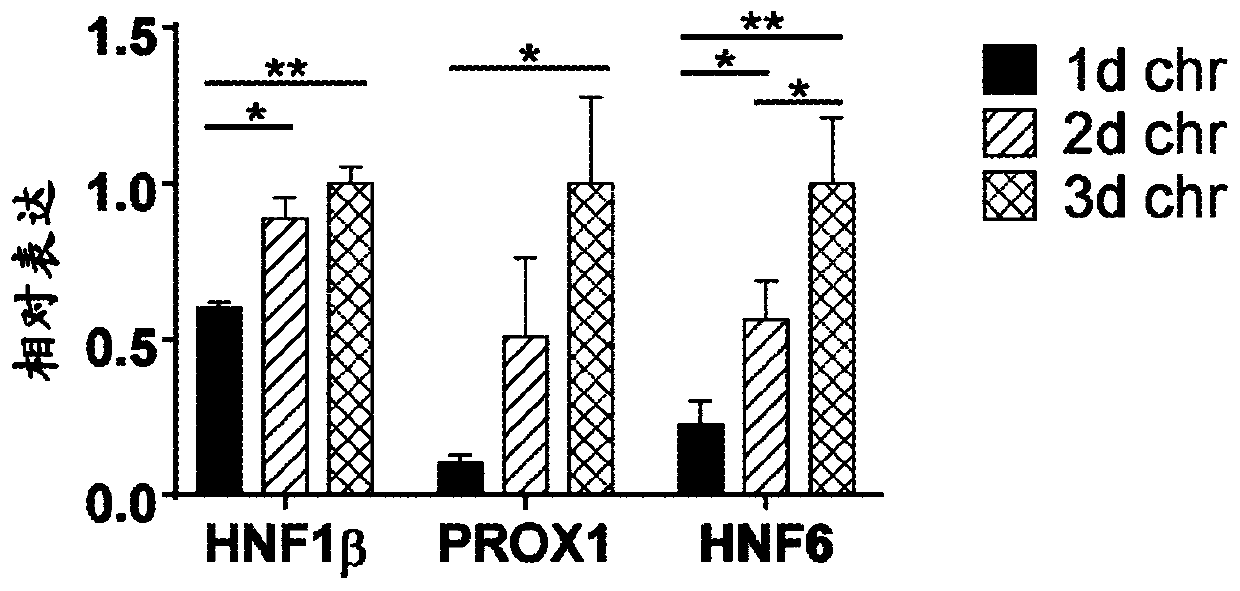
Esophageal tissue and/or organoid compositions and methods of making same
The instant disclosure relates to methods for converting mammalian definitive endoderm (DE) cells into specific tissue(s) or organ(s) through directed differentiation. In particular, the disclosure relates to formation of esophageal tissue and / or organoids formed from differentiated definitive endoderm.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
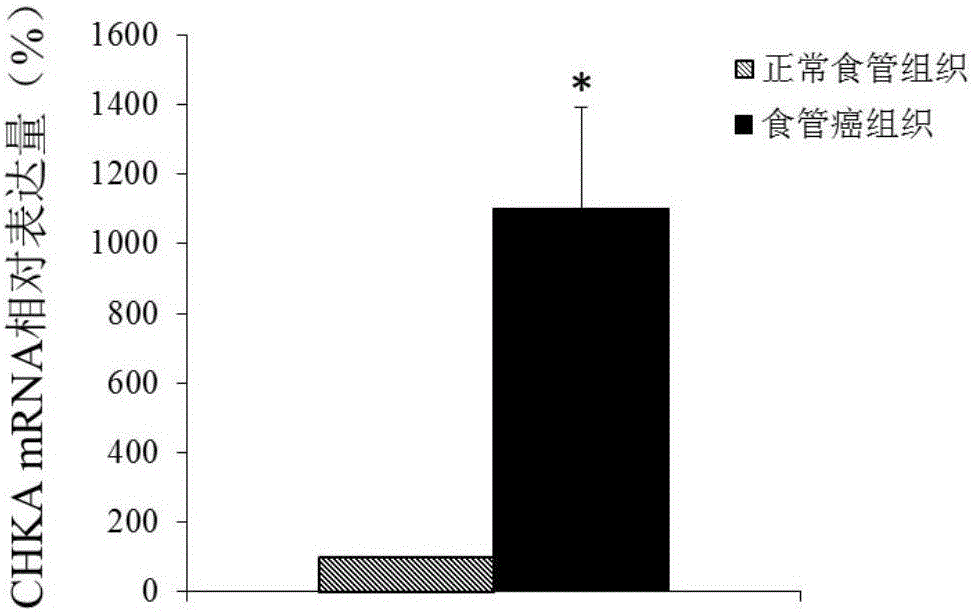
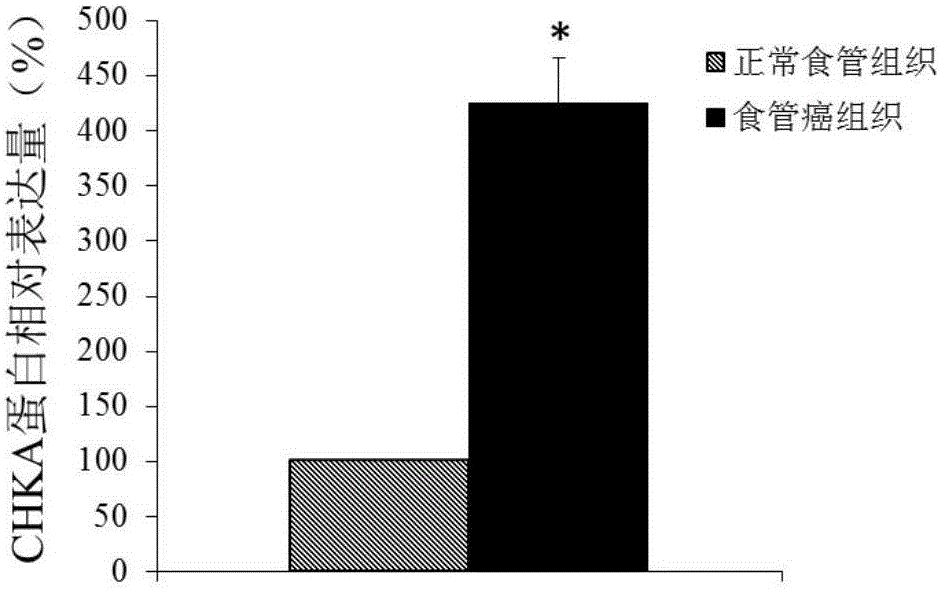
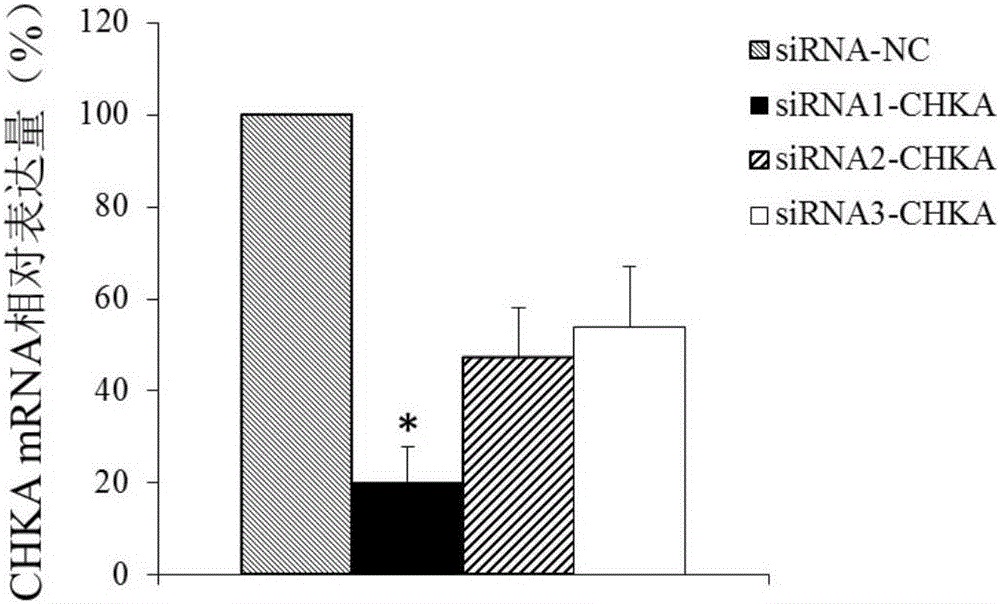
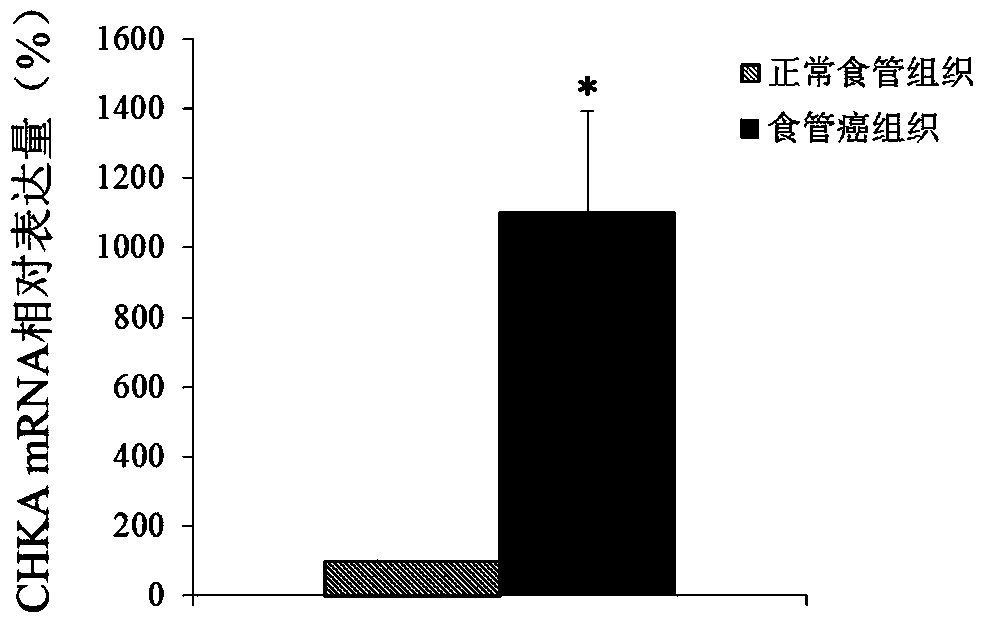
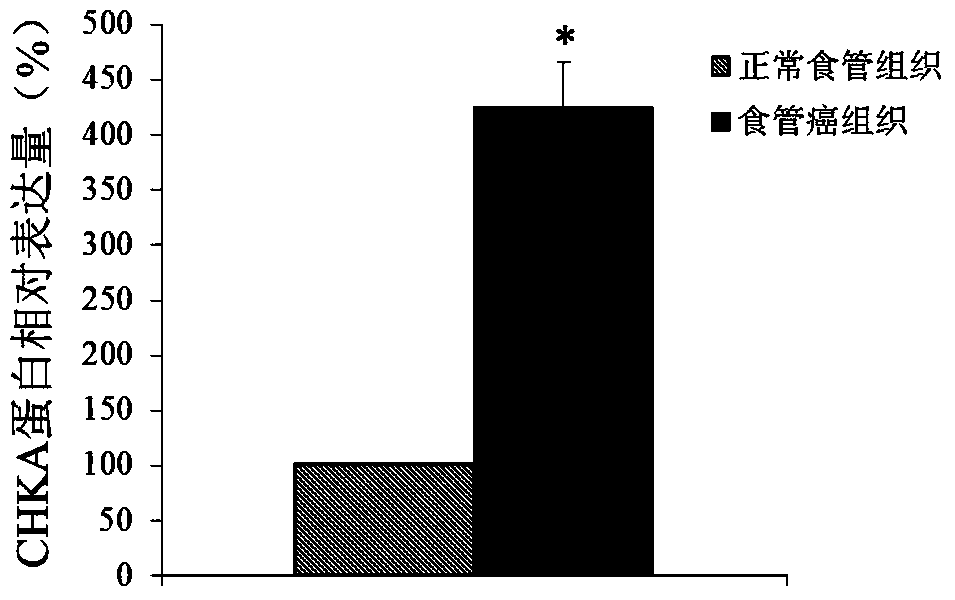
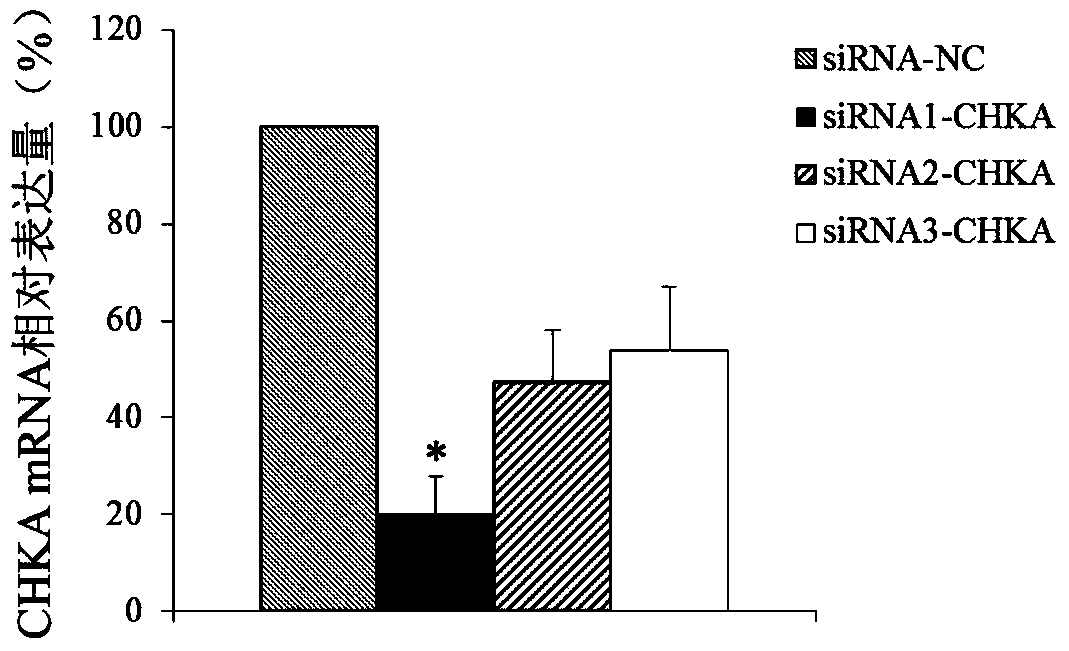
Application of CHKA gene to preparation of esophageal cancer diagnosis and treatment product
ActiveCN105886625ATimely diagnosisSpecific diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEsophageal cancerCancer research
The invention discloses a CHKA gene that can function as a molecular marker for early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Experiments prove that compared with normal esophageal tissues, the CHKA gene in esophageal cancer tissues has significantly increased expression, and RNA interference experiments prove that CHKA can affect proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. According to study results herein, it is possible to develop medicine to inhibit CHKA gene expression so as to clinically prevent and treat the esophageal cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Composition and method for determining of esophageal cancer
InactiveUS20110098185A1Simple and rapid methodSpecificNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEsophageal cancerMutant
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
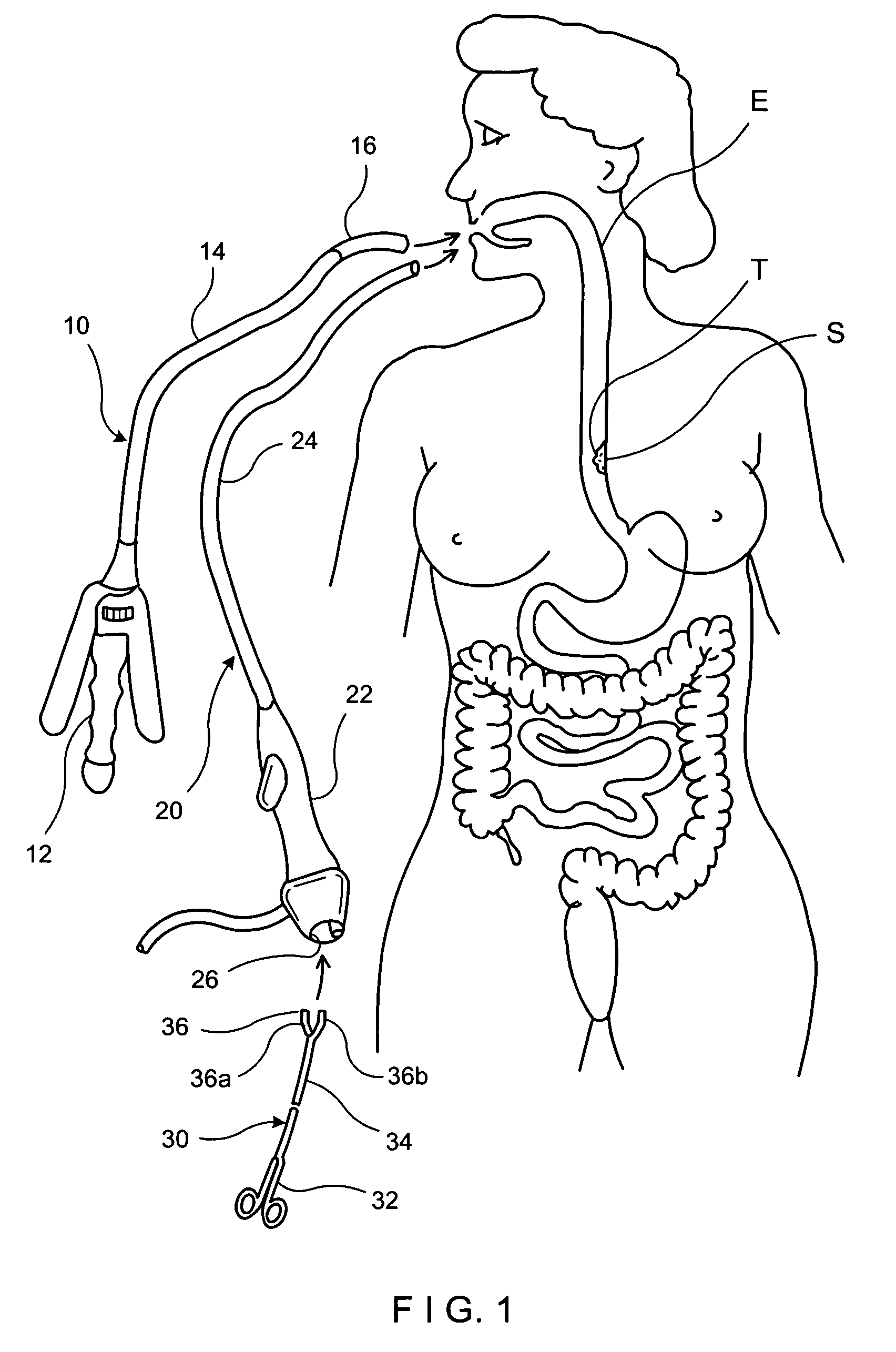
Methods and devices for folding and securing tissue
InactiveUS20130060264A1Without compromising safetyHigh intrusion performanceStaplesNailsEsophagus wallMedical treatment
The present invention relates to devices, and methods for using the devices, to create and secure a tissue fold during an endoluminal medical procedure. The devices and methods may be used for folding and securing, for example, a fundus wall onto an esophagus wall or esophageal tissue in the region of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to reduce the diameter of the esophagus opening in that region. One aspect of the invention includes forming the tissue fold by closing a grasping arm that is pivotably connected to an overtube that has been positioned at the juncture of the fundus wall and esophagus wall. A further aspect of the invention includes tissue clips configured to be inserted and positioned through an endoluminal device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Systems and methods for tracking spontaneous breathing in a mechanically ventilated patient
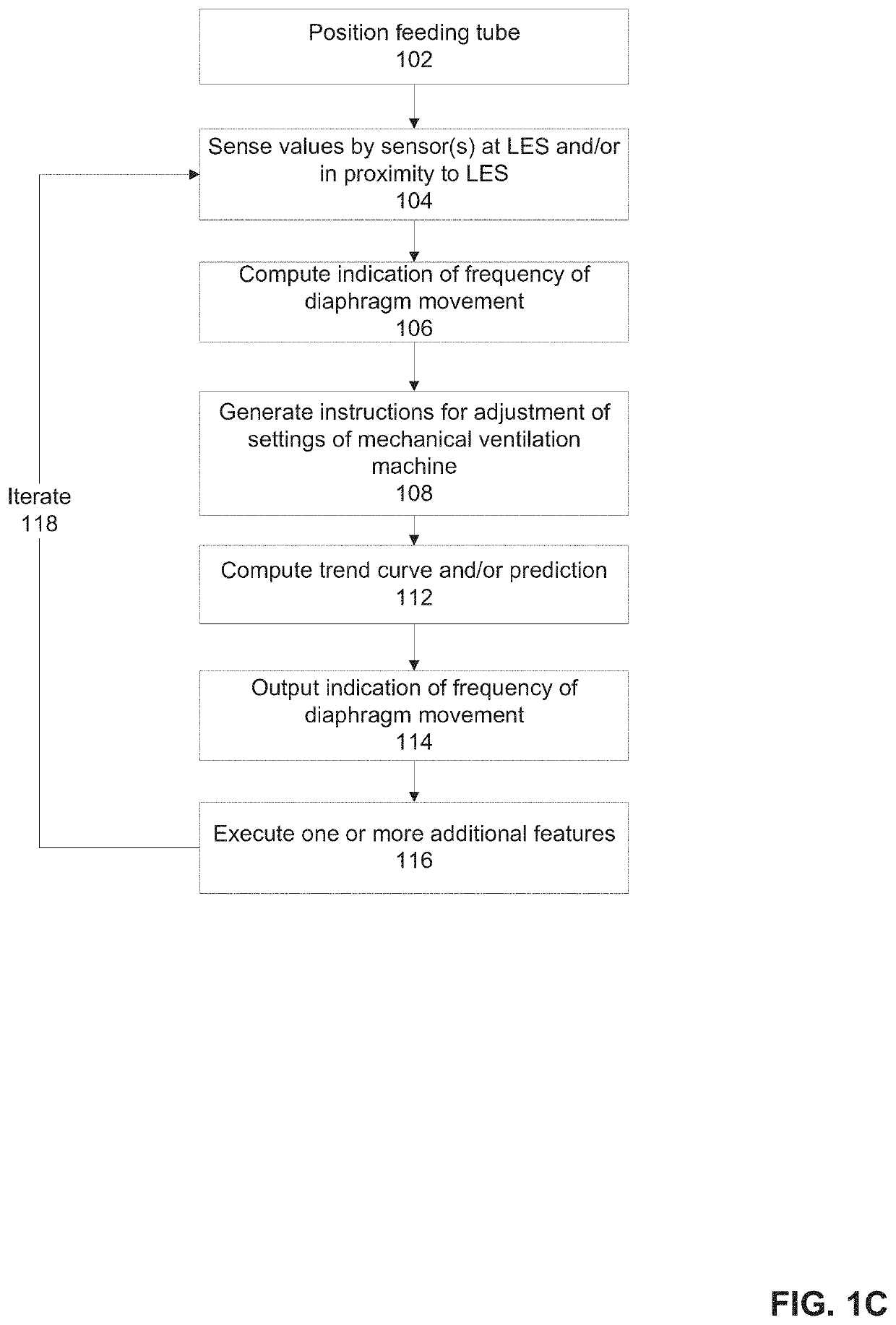
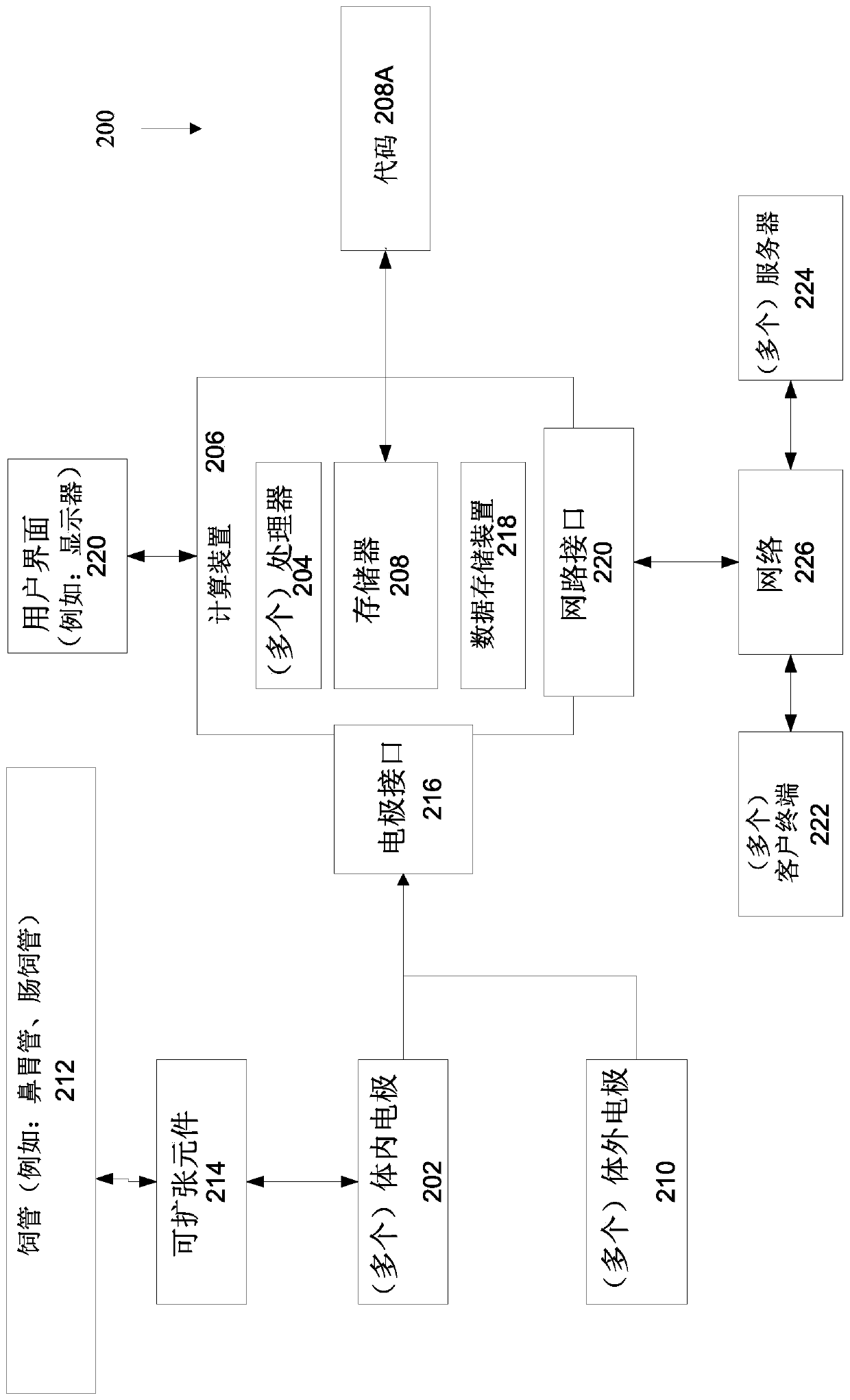
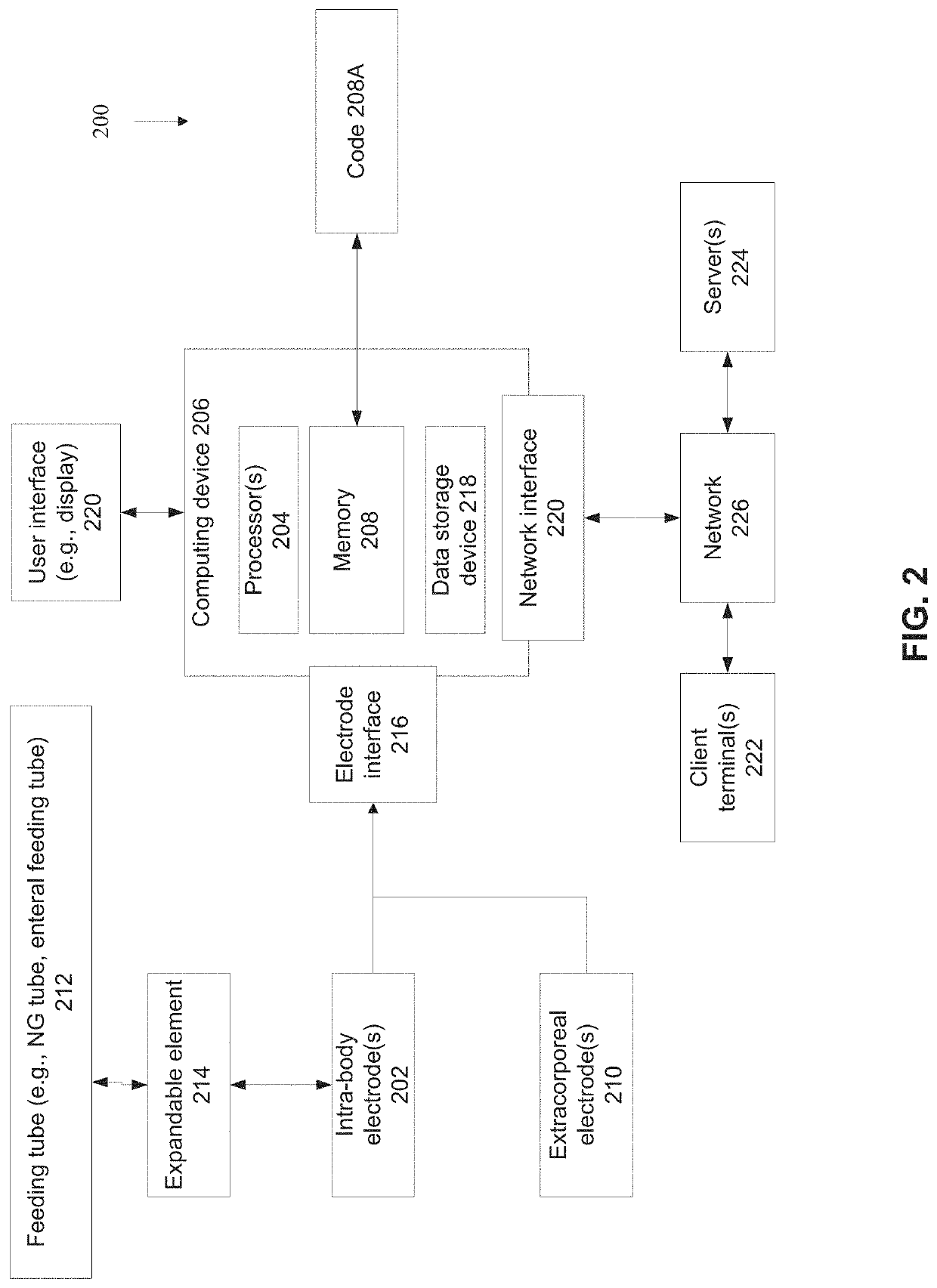
ActiveUS20210093815A1Improve performanceAdvanced technologyRespiratorsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAutonomous breathingSphincter
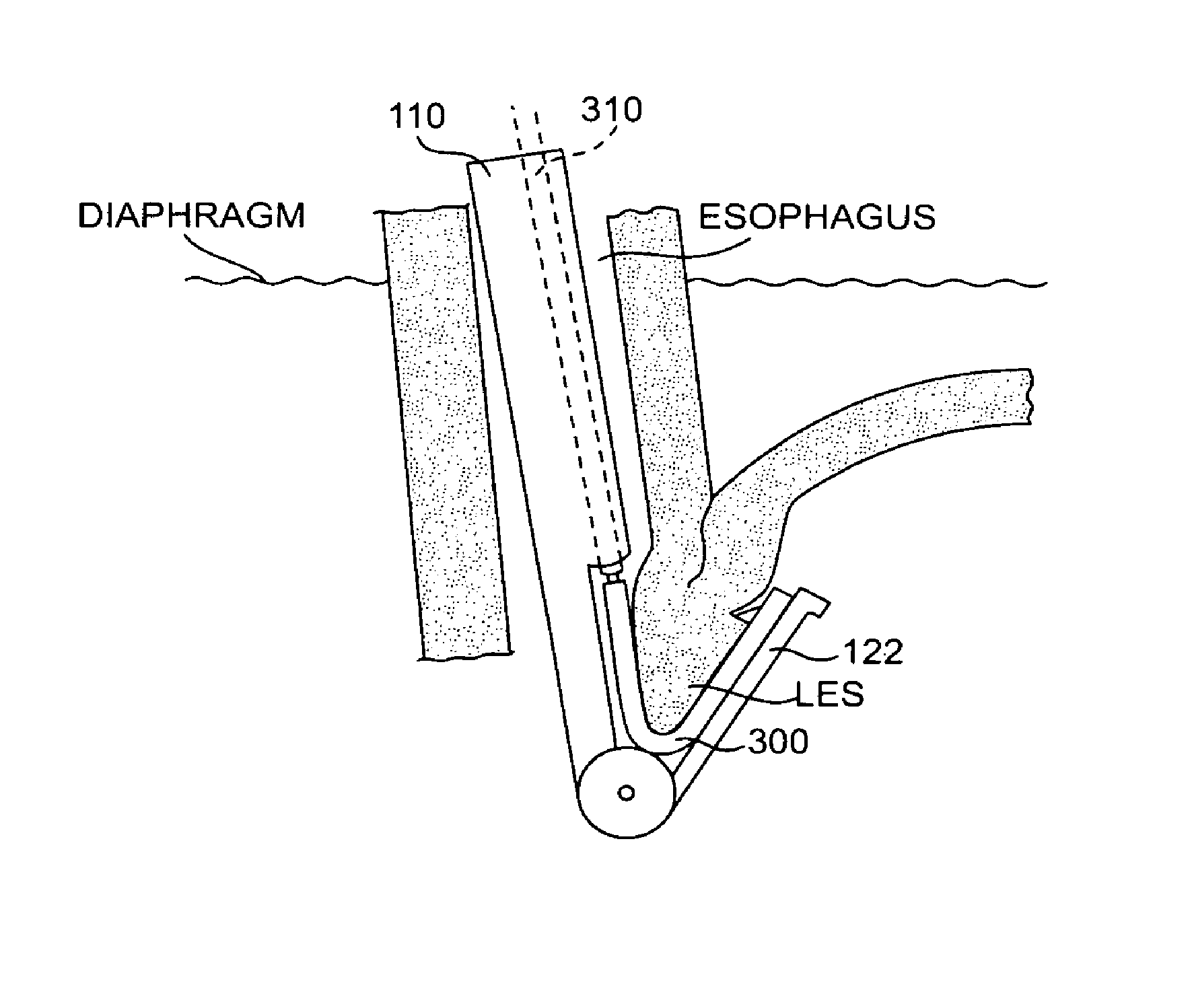
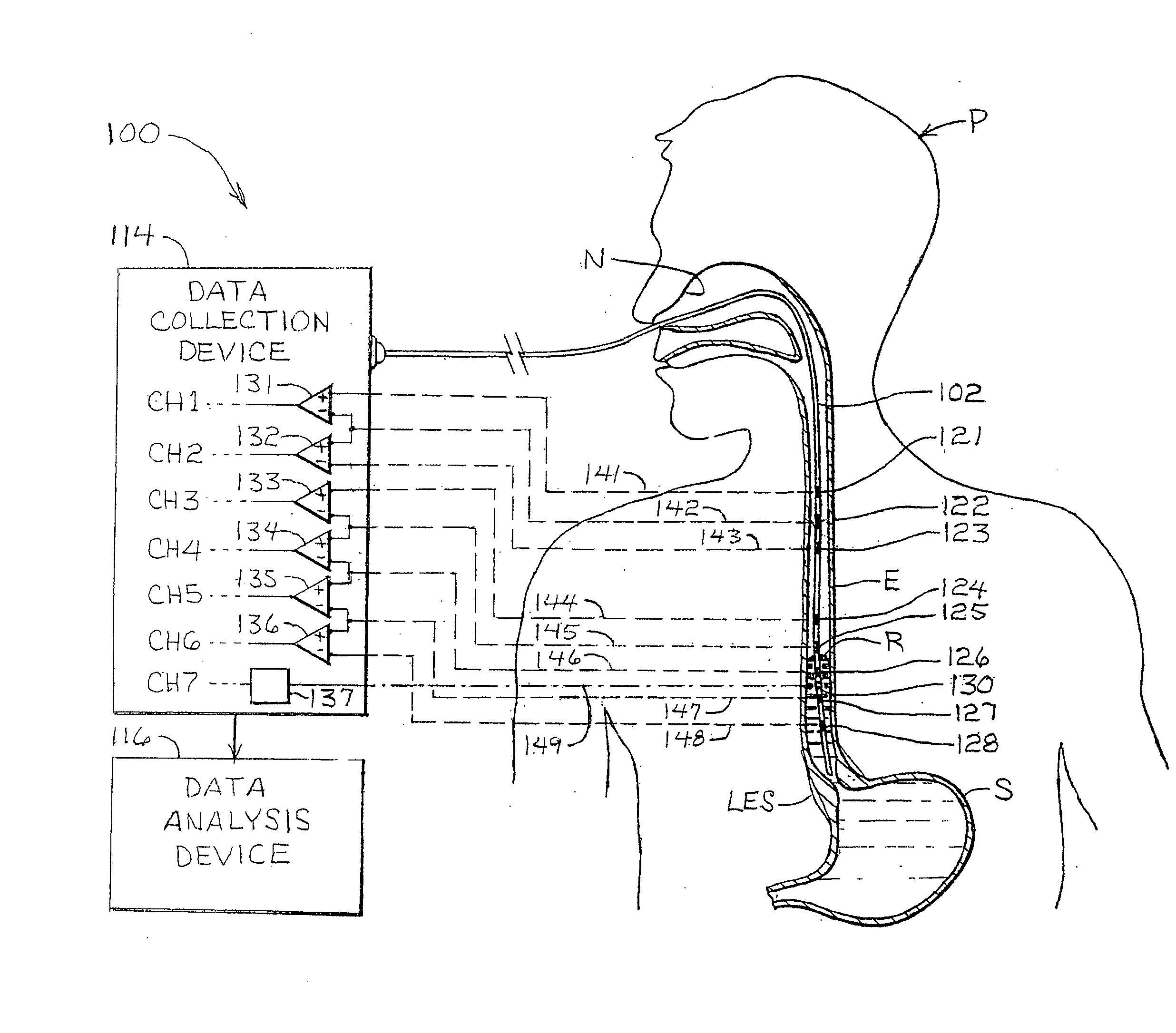
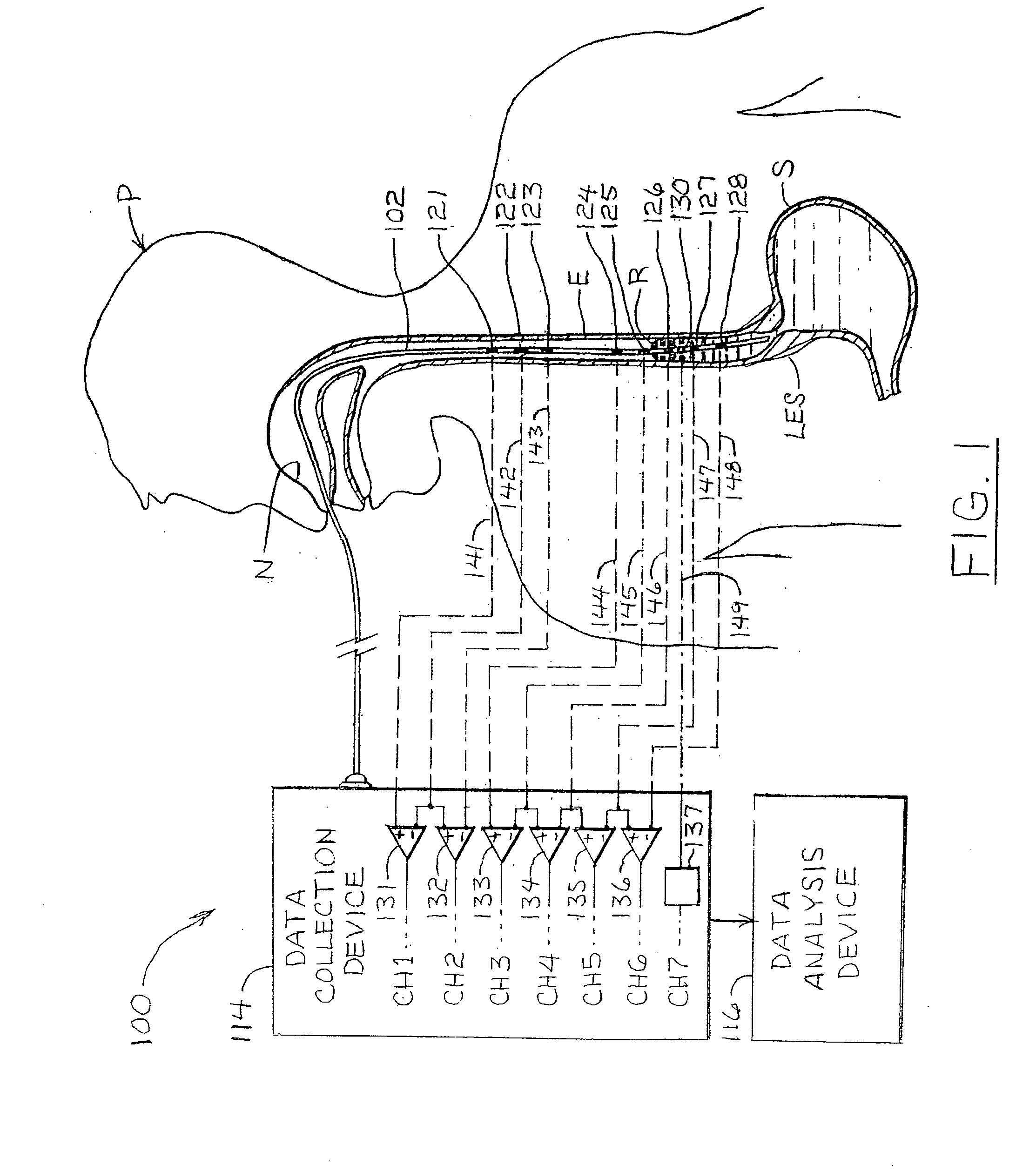
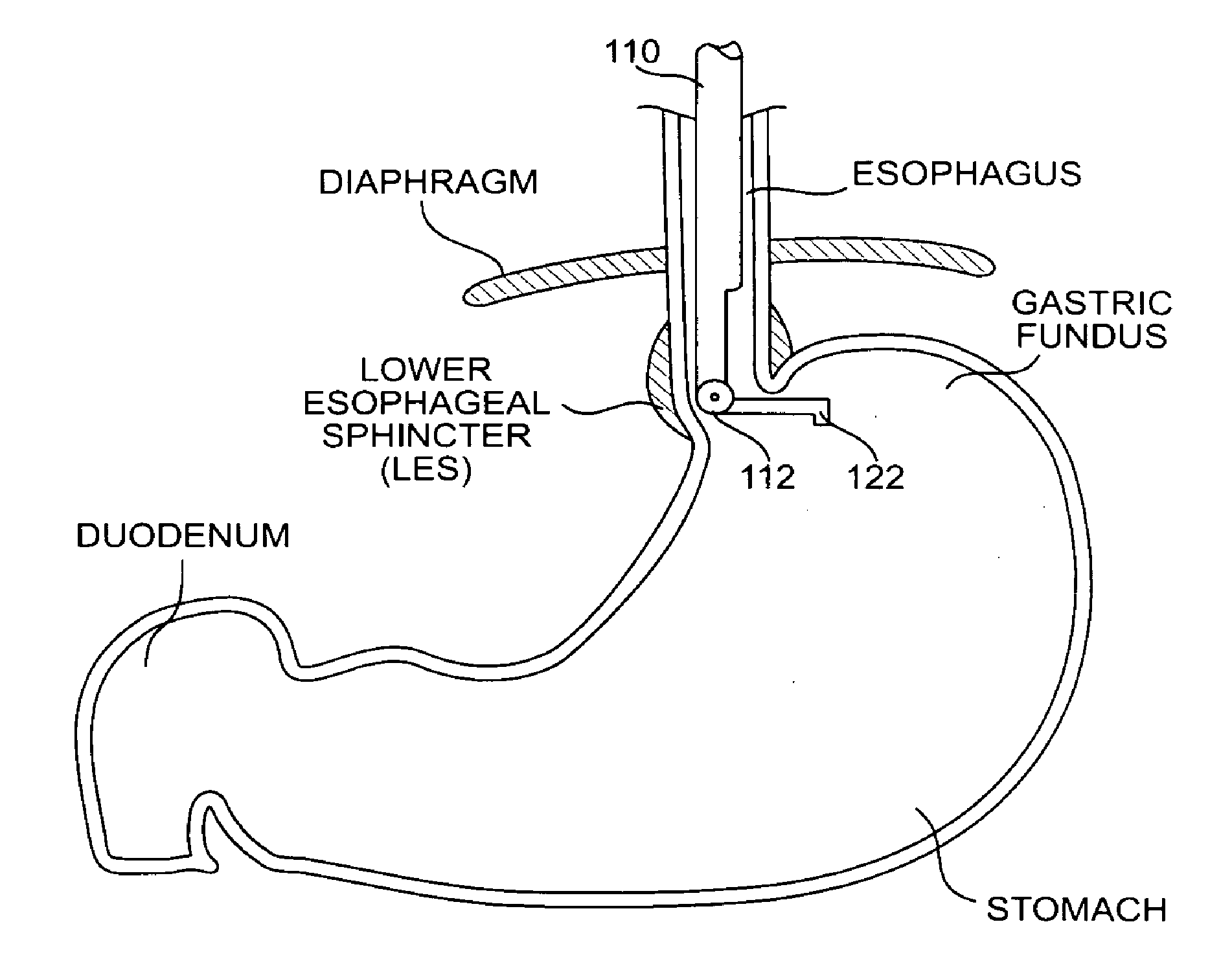
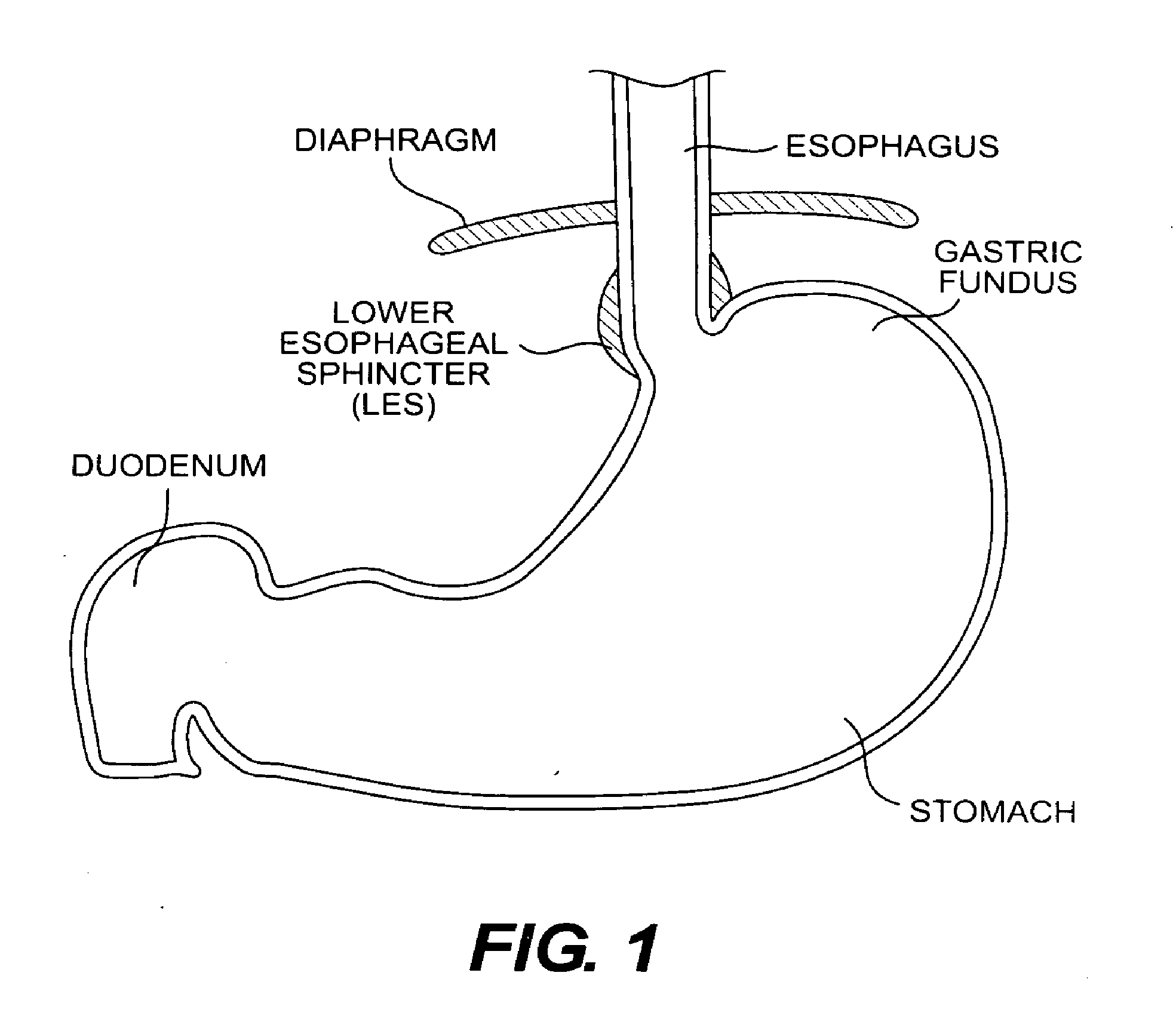
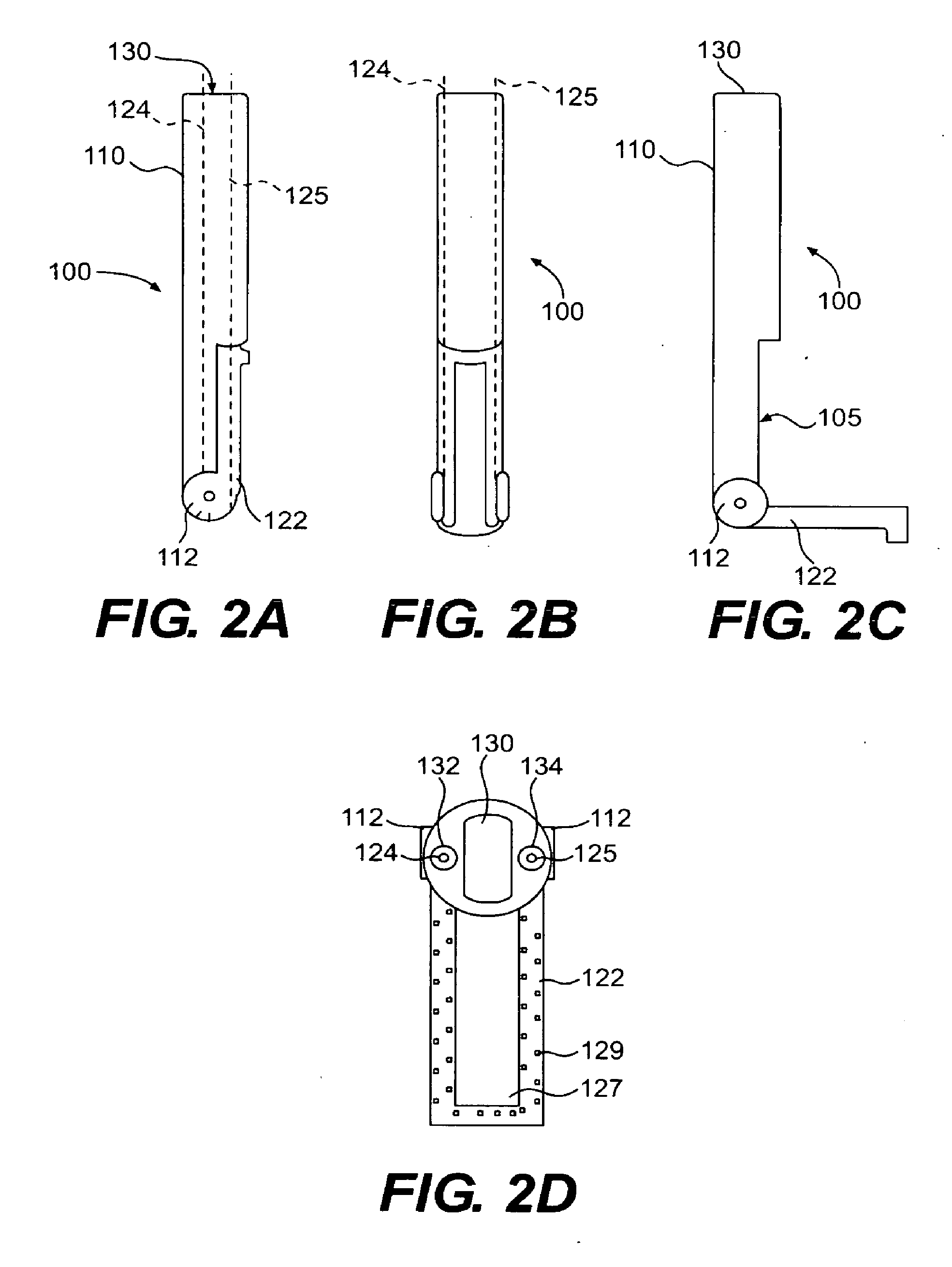
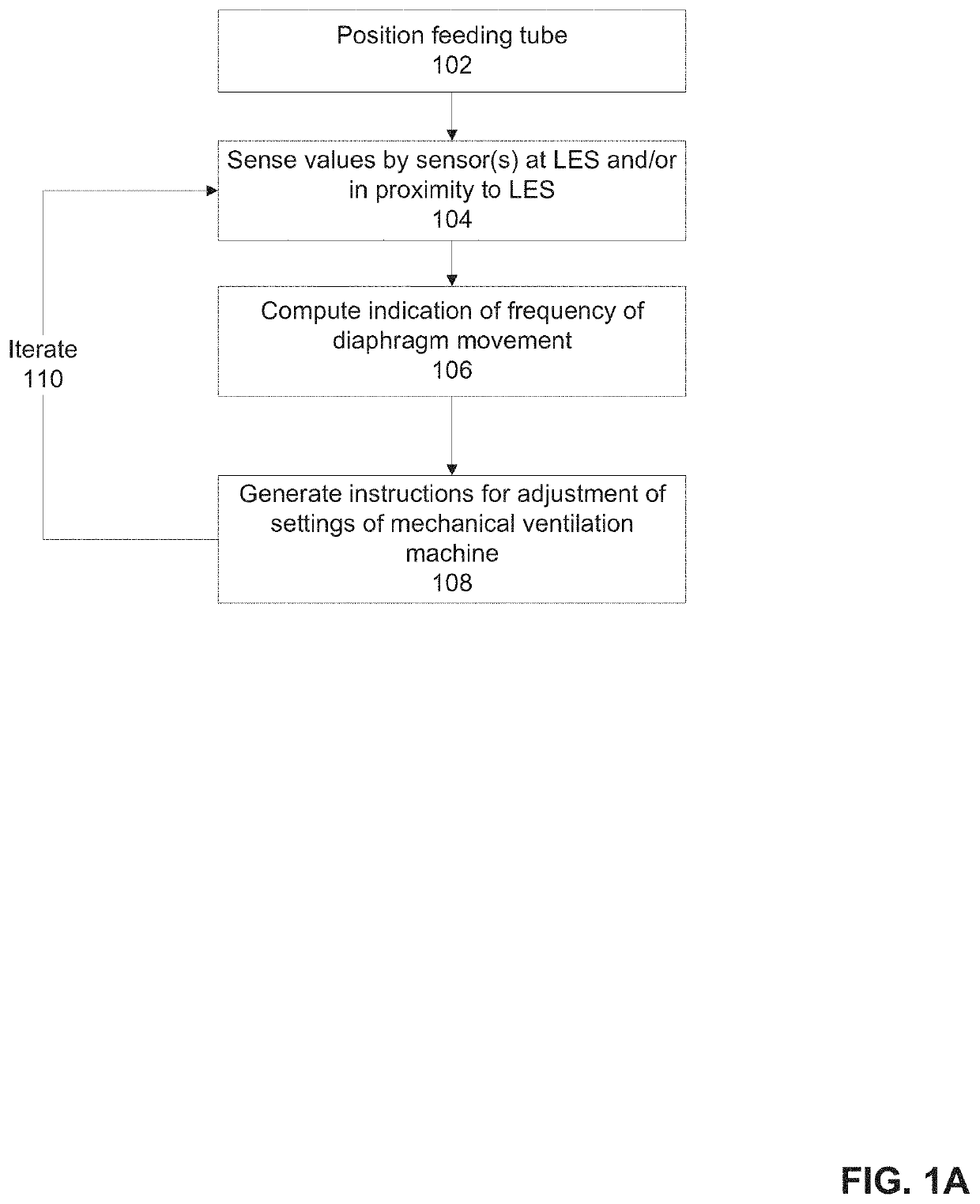
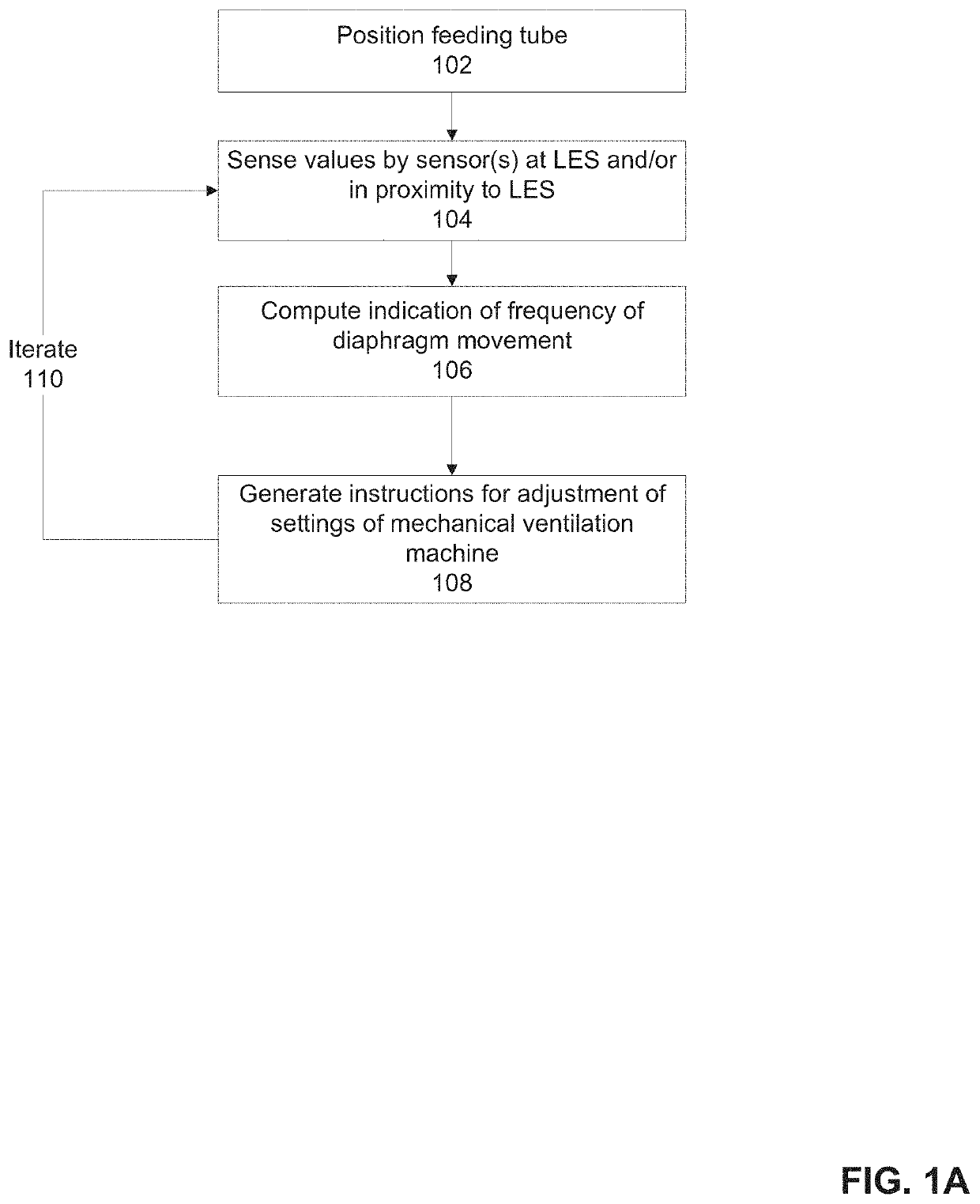
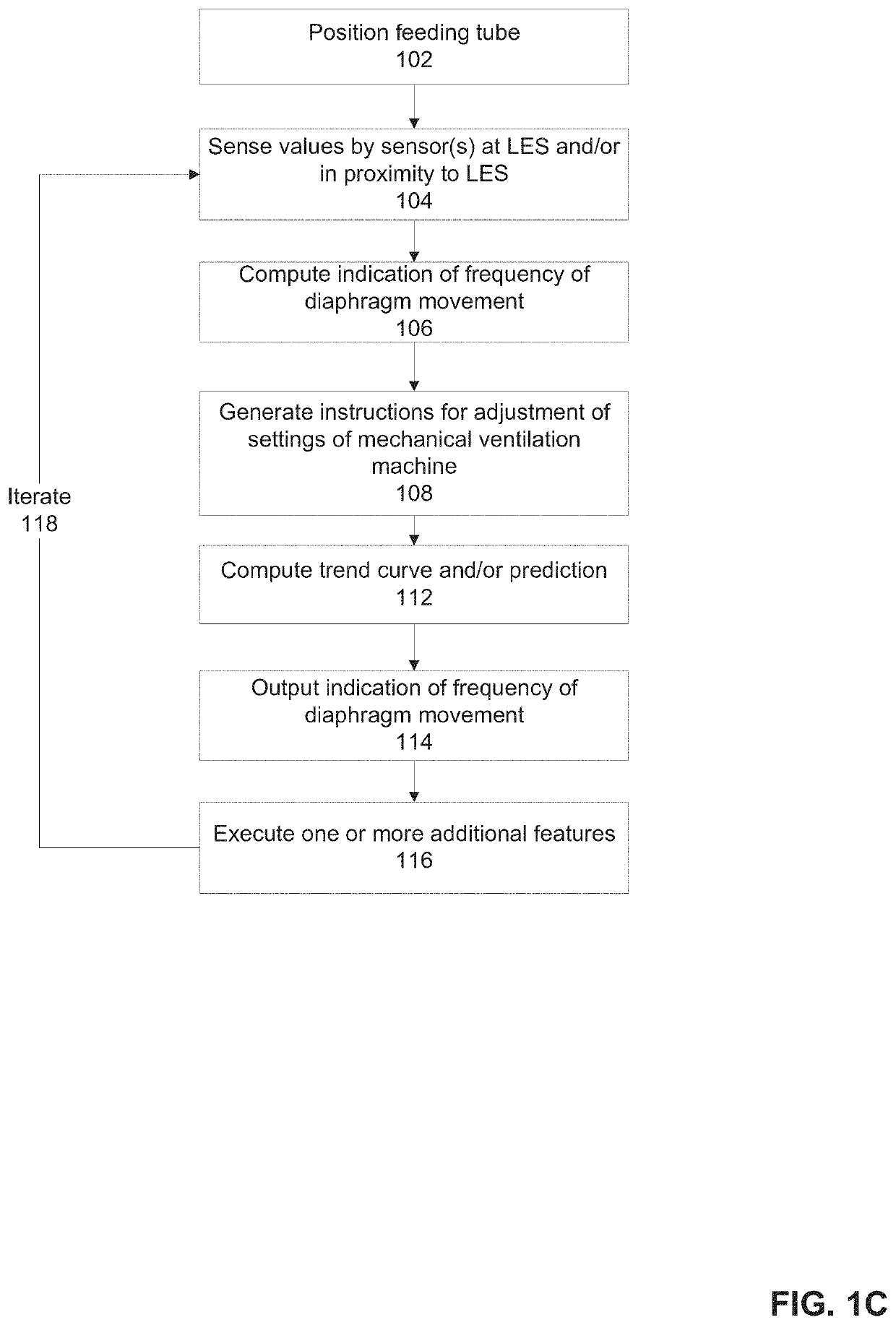
There is provided system for monitoring spontaneous breathing of a mechanically ventilated target individual, comprising: a feeding tube for insertion into a distal end of an esophagus of the individual, sensor(s) disposed on the feeding tube at a location such that the sensor(s) is located at the distal end of the esophagus of the individual when the feeding tube is in use, wherein the sensor(s) is positioned for sensing values by contact with the tissue of the esophagus including a lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and / or tissue in proximity to the LES, and code for computing an indication of a frequency band of diaphragm movement of the individual according to an analysis of values sensed by the sensor(s), and for adjustment of parameter(s) of a mechanical ventilator for mechanically ventilating the individual, wherein the instructions for adjustment are computed while the feeding tube is in use.
Owner:ART MEDICAL LTD
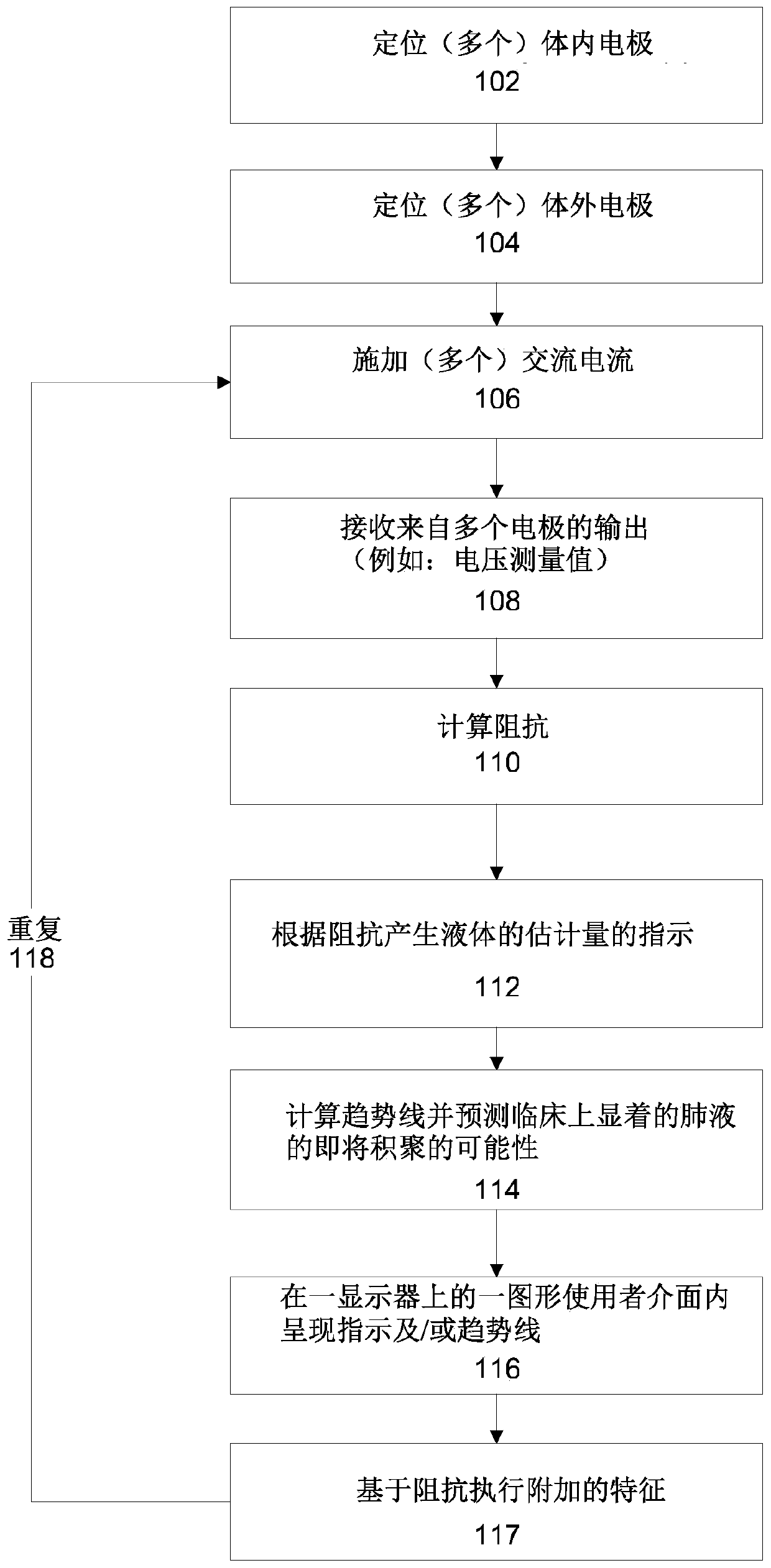
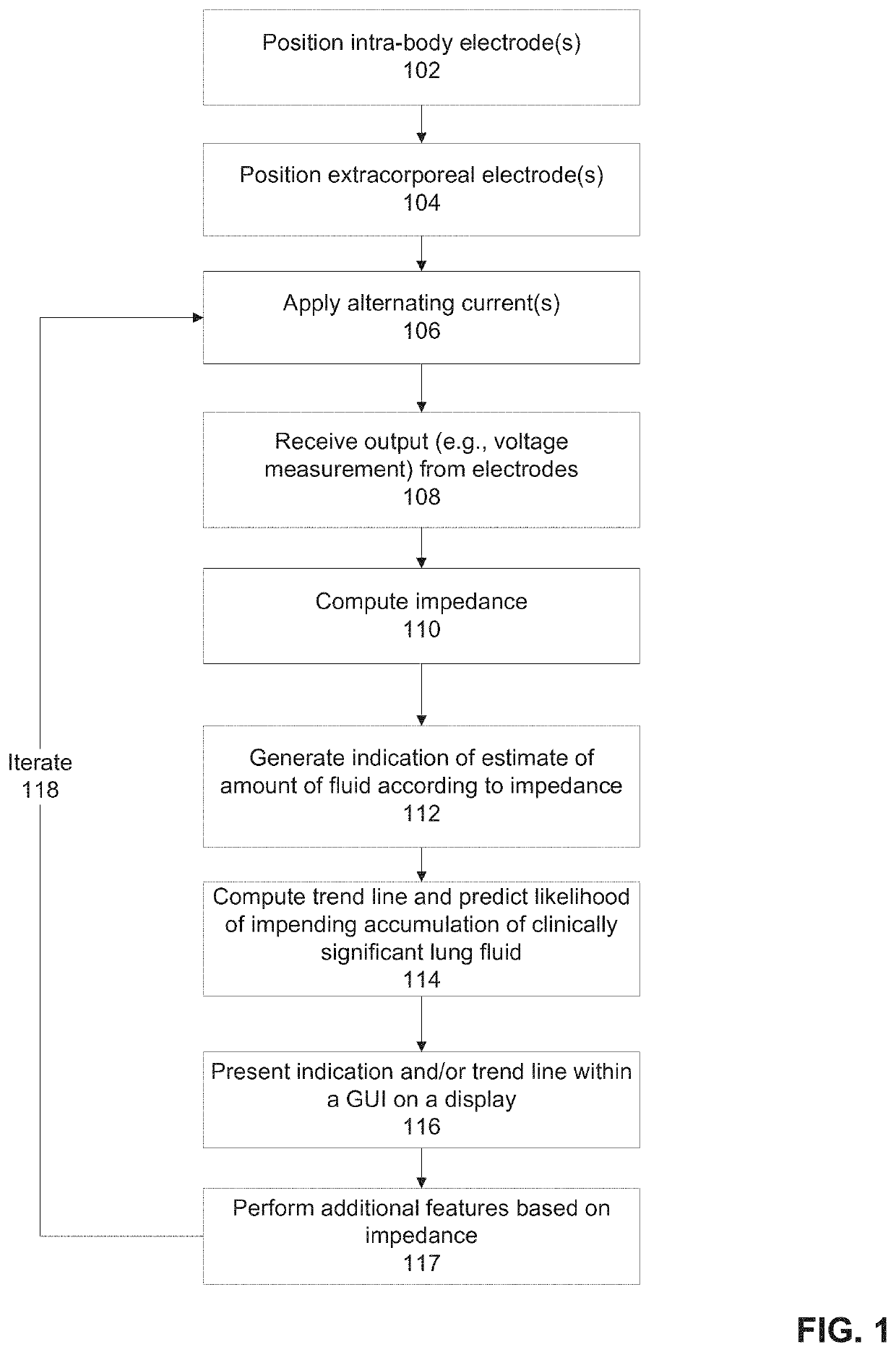
Systems and methods for sensing lung fluid
An apparatus for monitoring for accumulation of lung fluid comprises a feeding tube having first electrode(s) positioned thereon for electrical contact with tissue of an esophagus of a target patient including a lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and / or tissue in proximity to the LES, second electrode(s) sized and shaped for contacting skin of the target patient, and a non-transitory memory having stored thereon code instructions for applying alternating current(s) to pair(s) of first and second electrodes, measuring a voltage over the pair(s), and computing an estimate of a change of lung fluid relative to a baseline in lung(s) of the target patient according to the applied alternating current and measured voltage, wherein applying the at least one alternating current, measuring the voltage and computing the estimate of the change in lung fluid are iteratively executed for monitoring the target patient for accumulation of lung fluid while the feeding tube is in use.
Owner:ART MEDICAL LTD
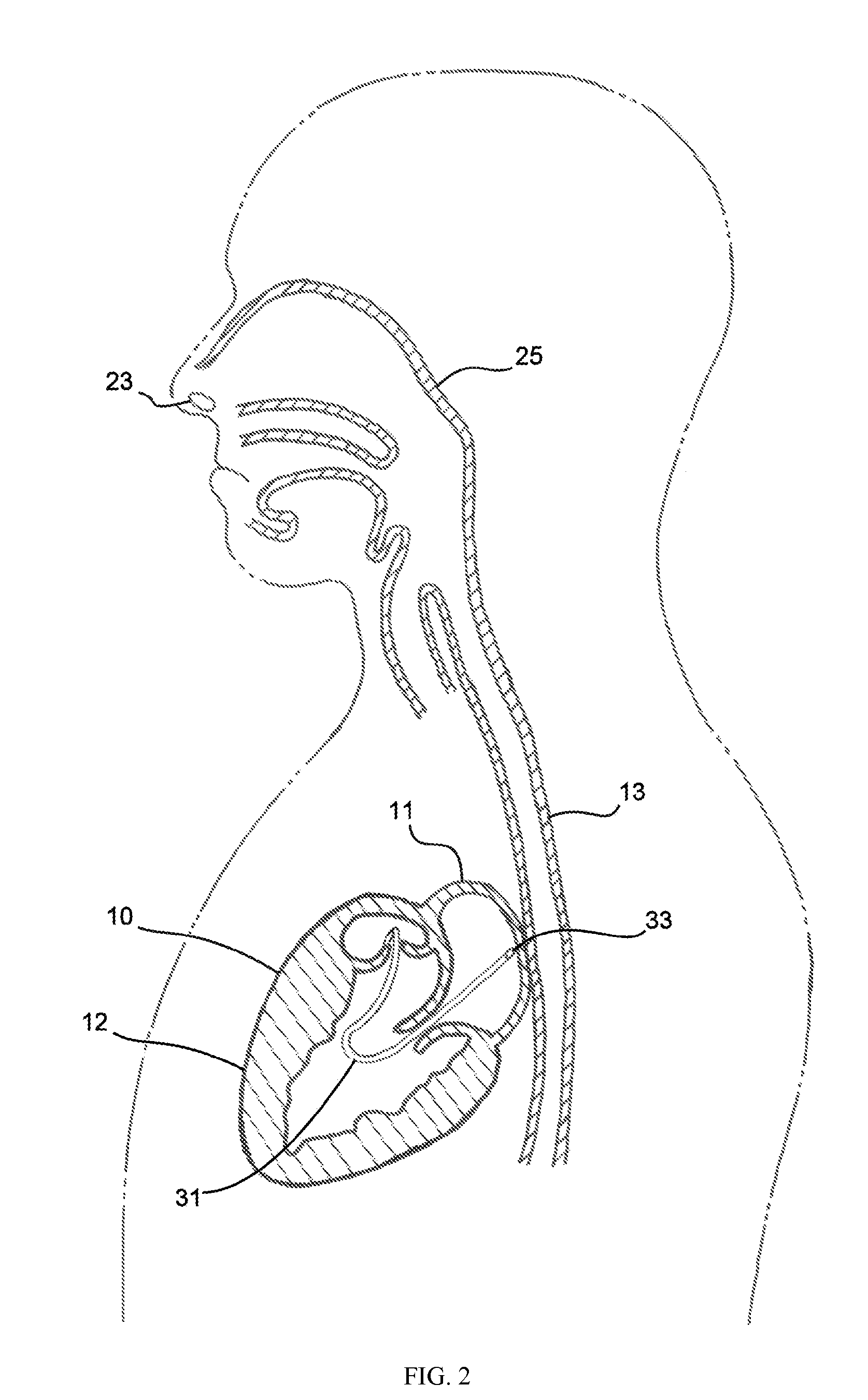
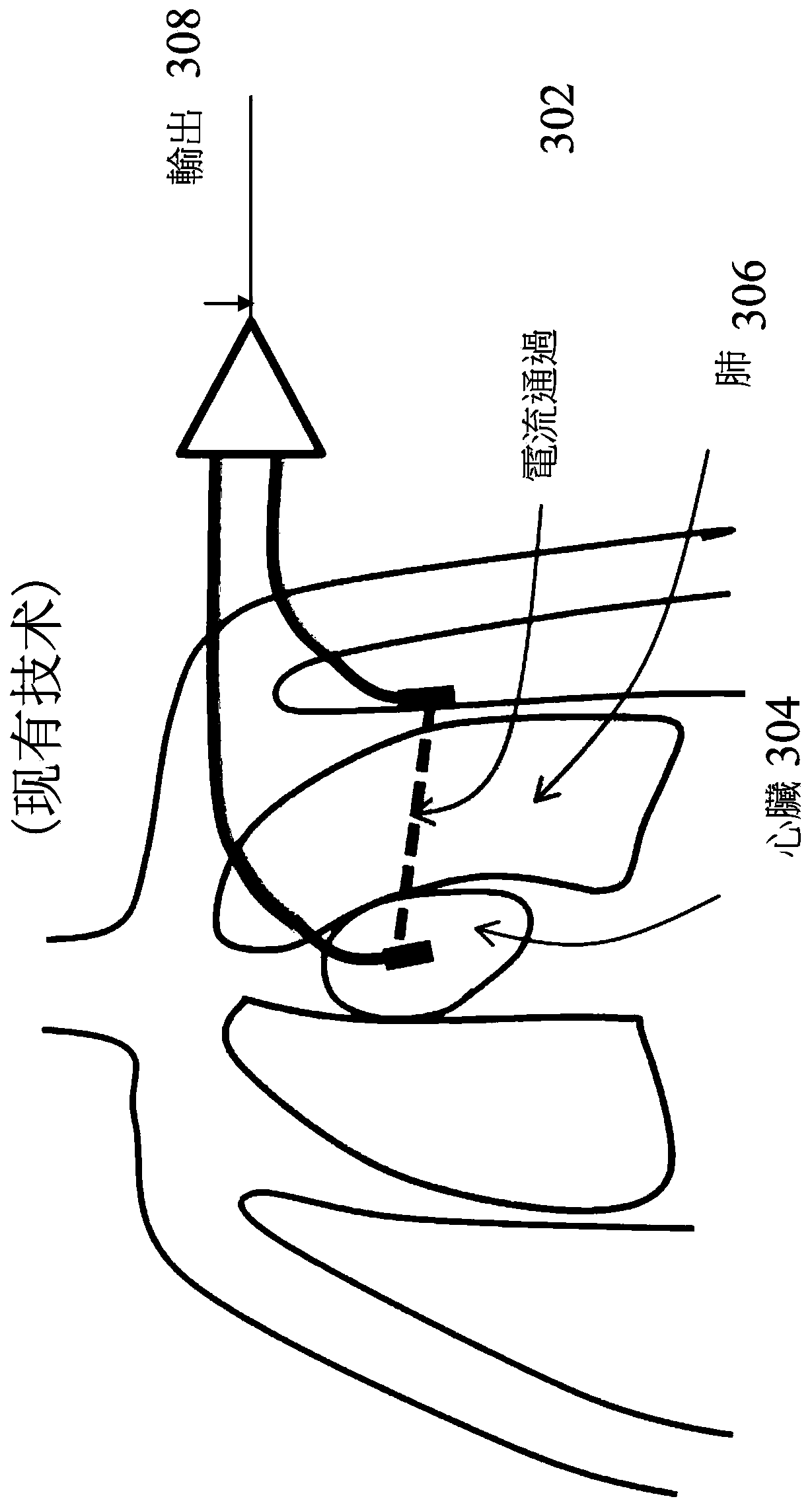
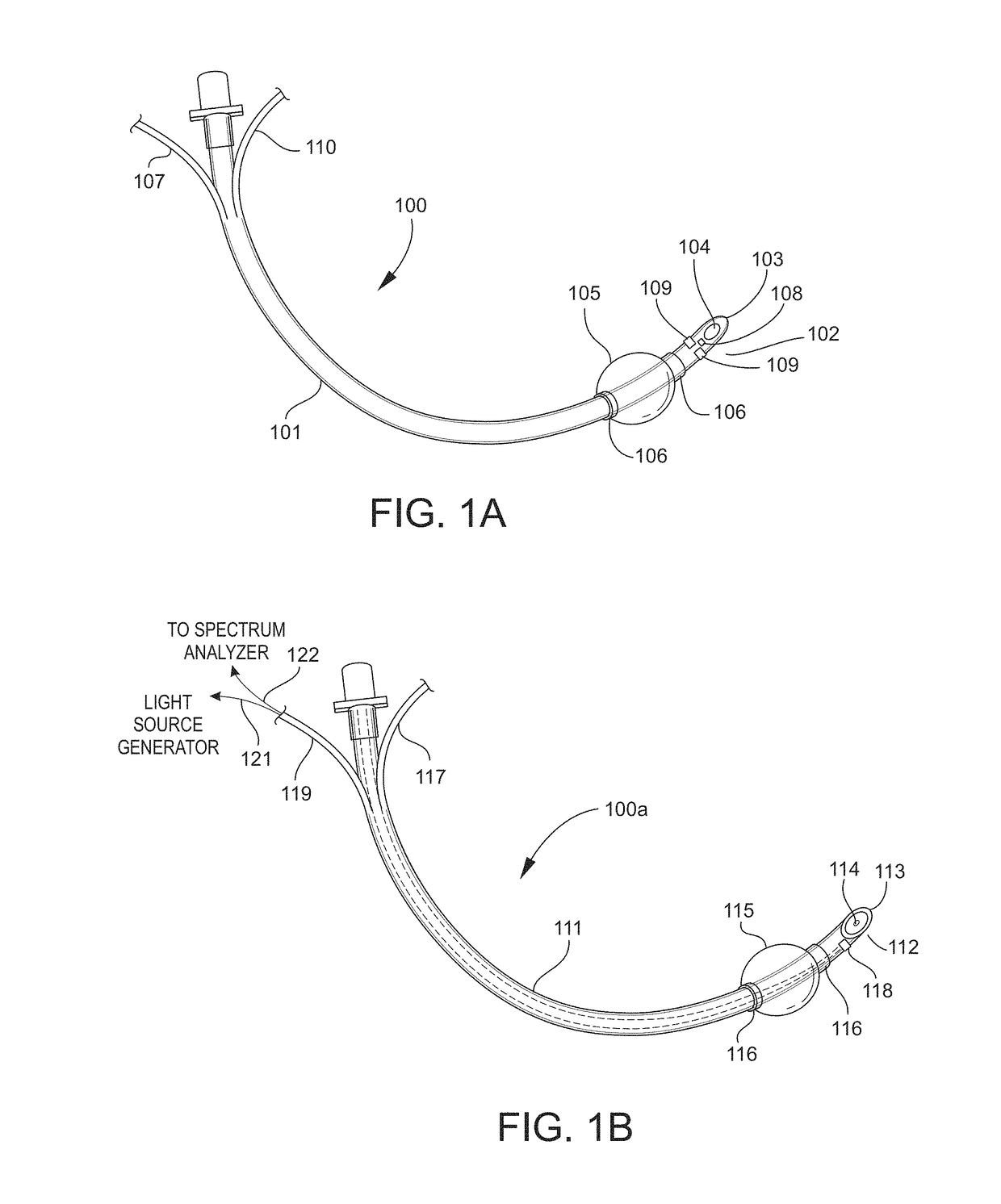
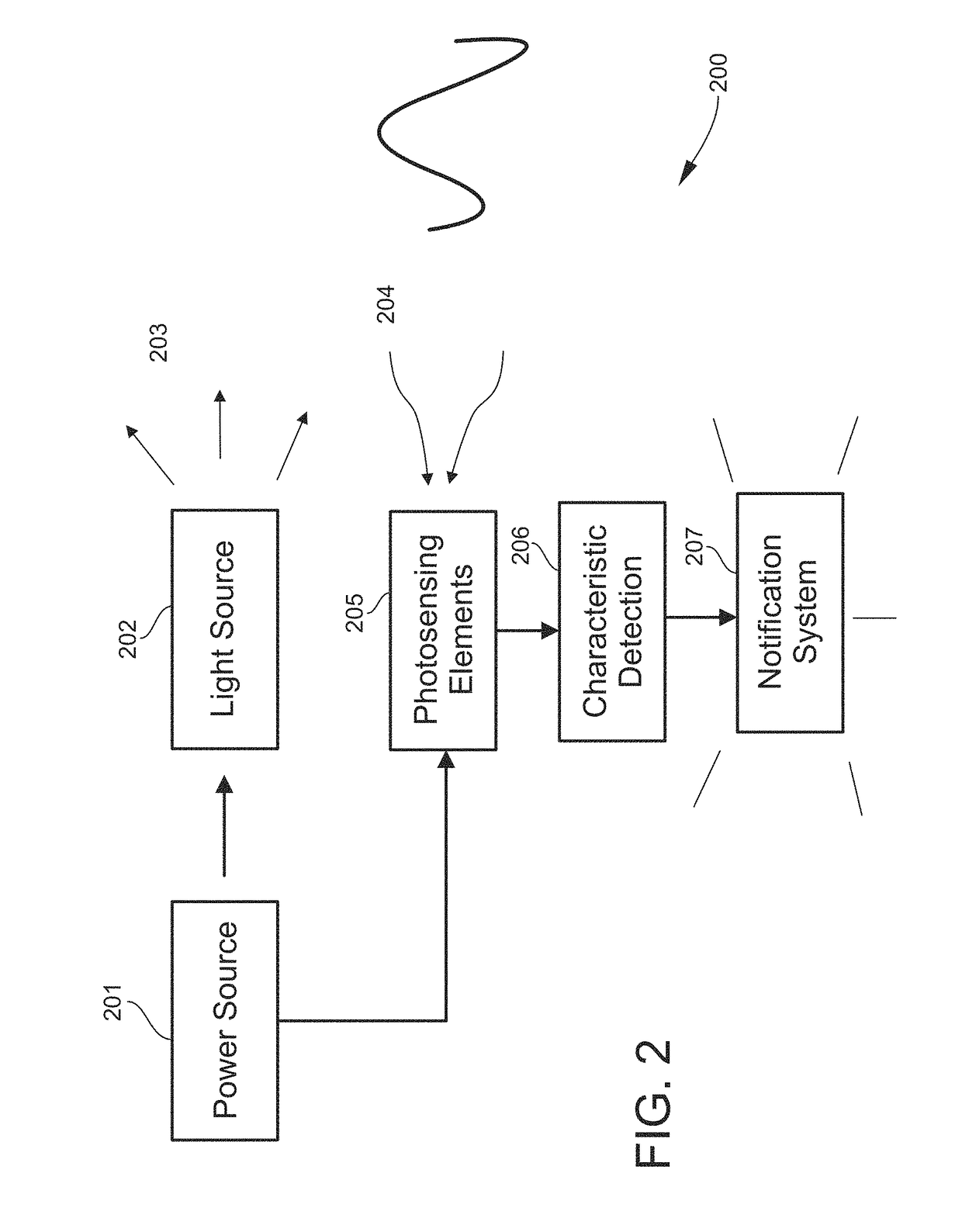
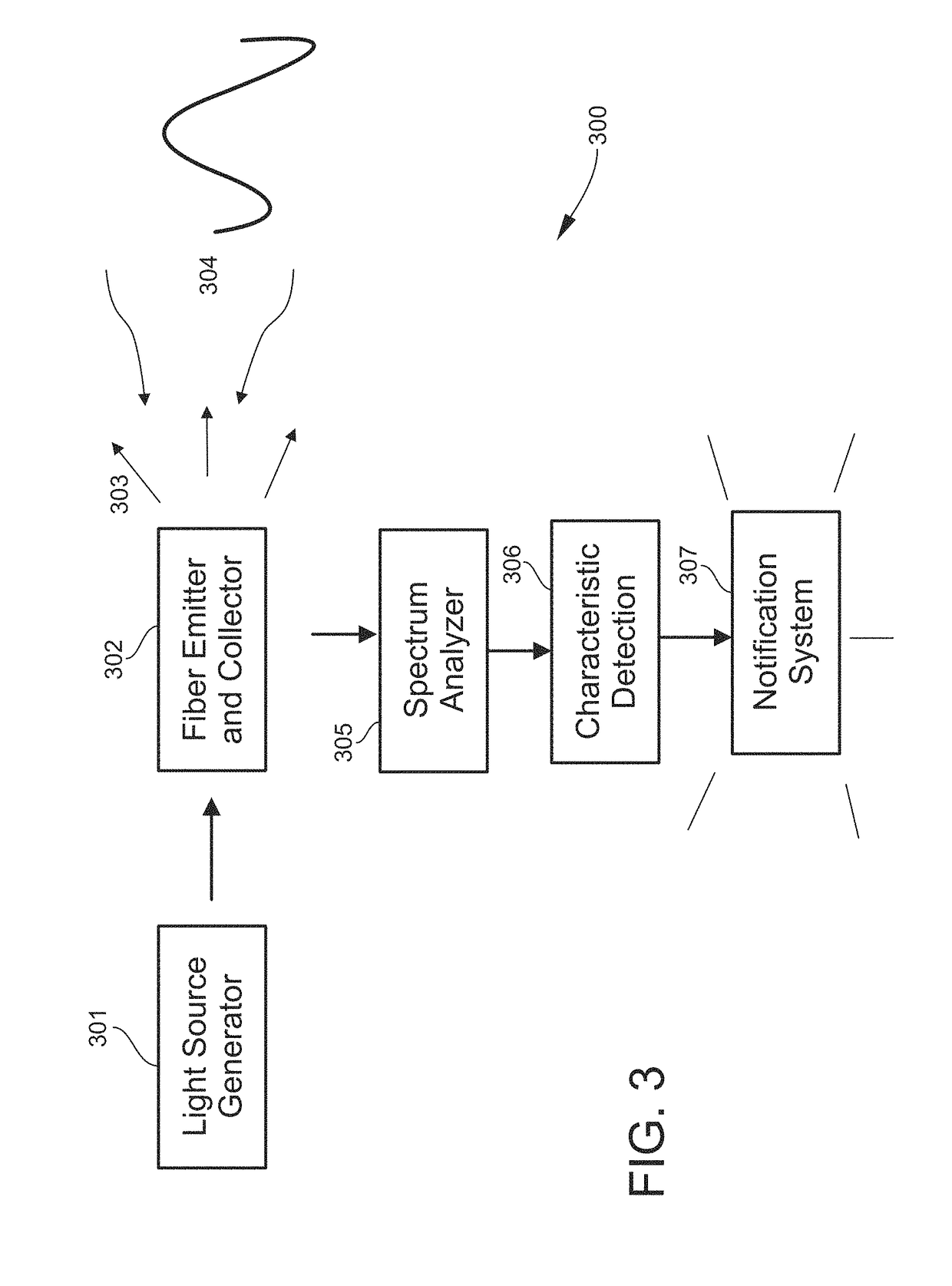
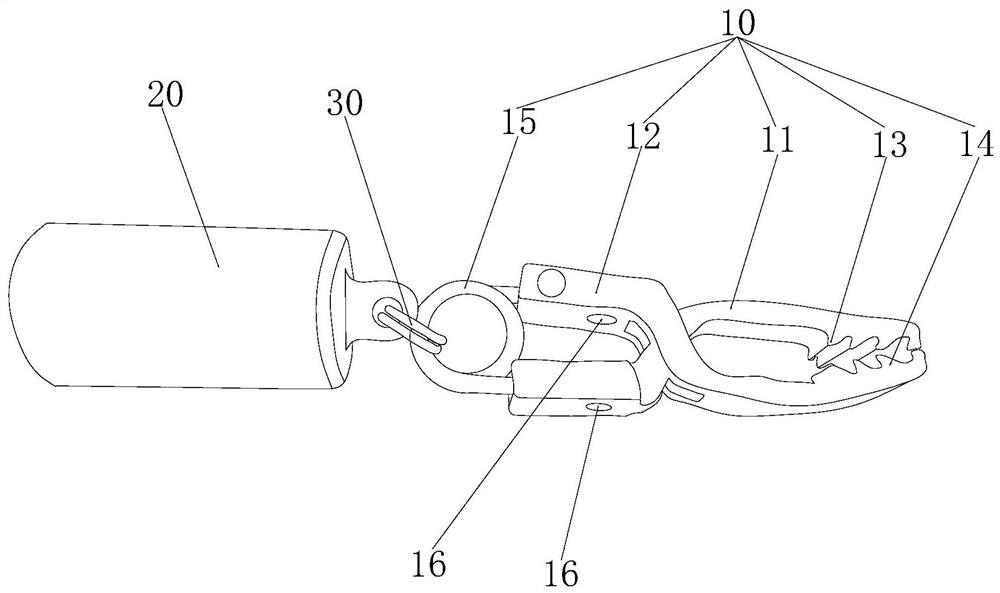
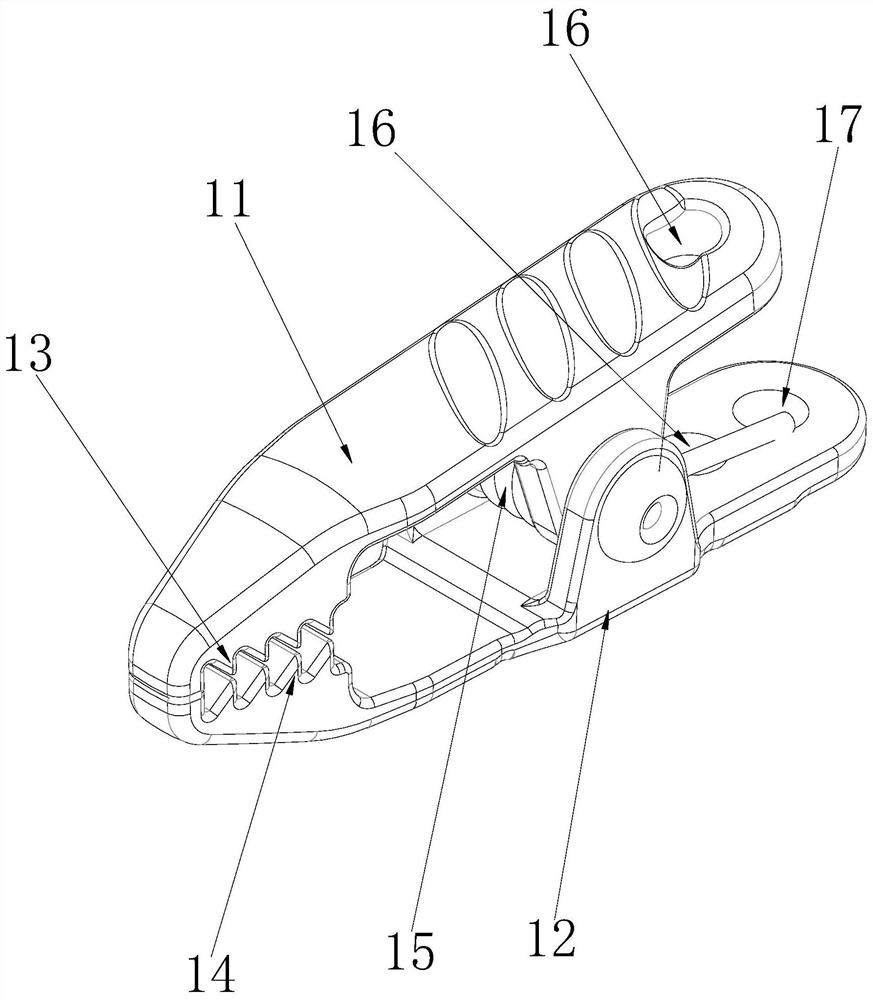
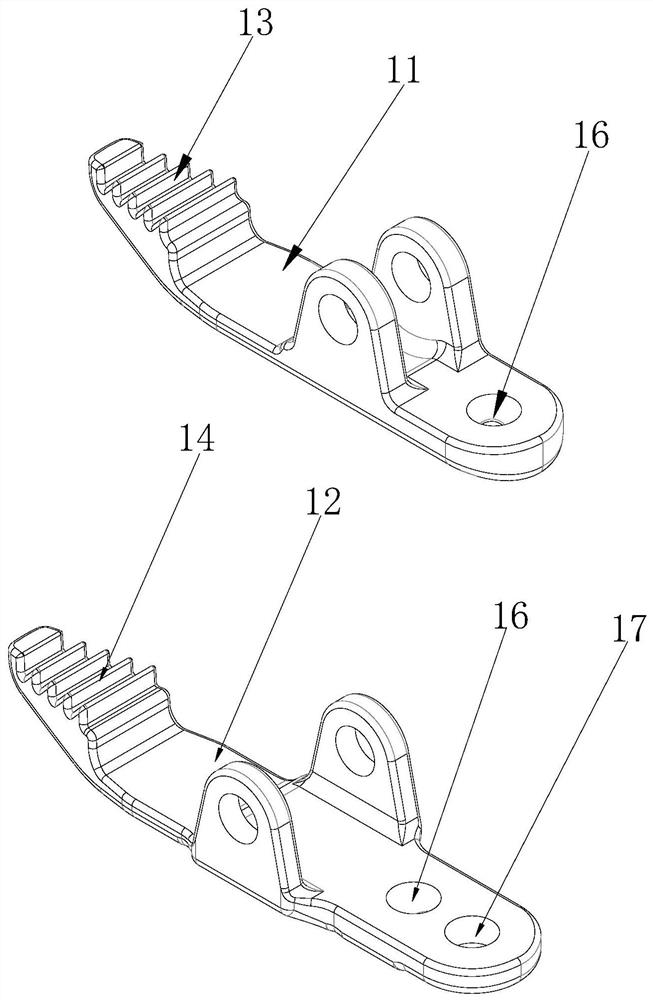
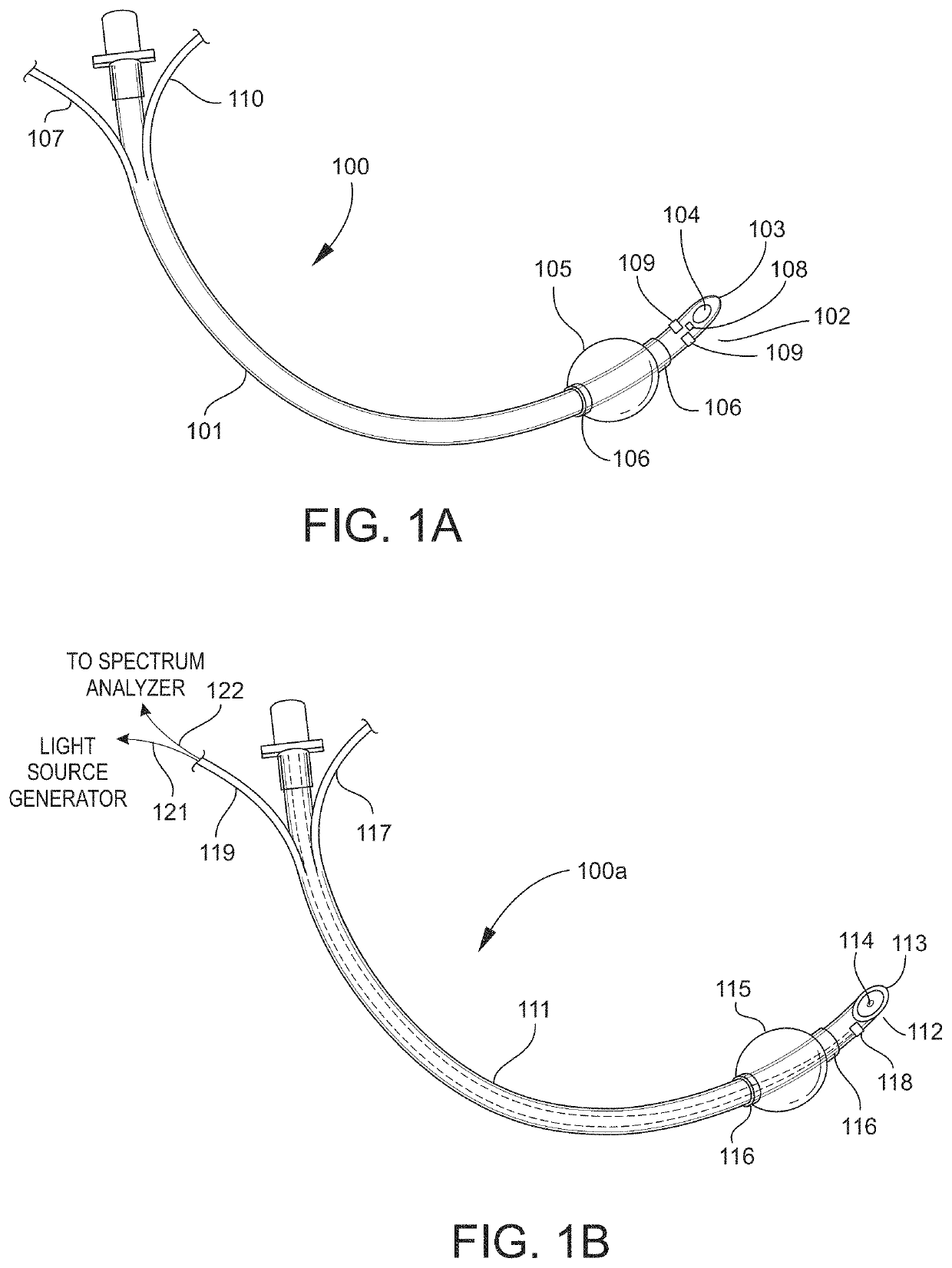
Airway Management Device for Identification of Tracheal and/or Esophageal Tissue
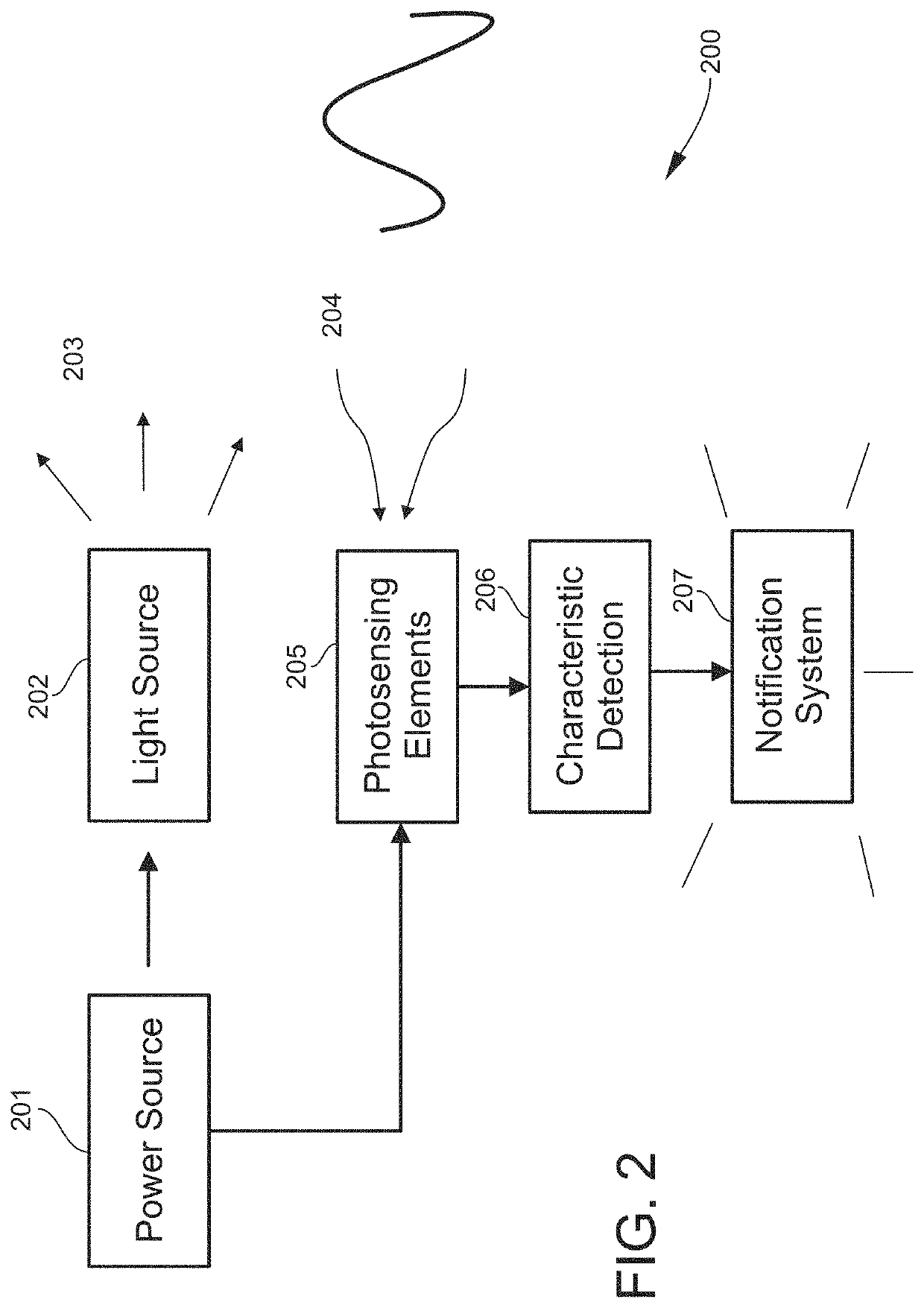
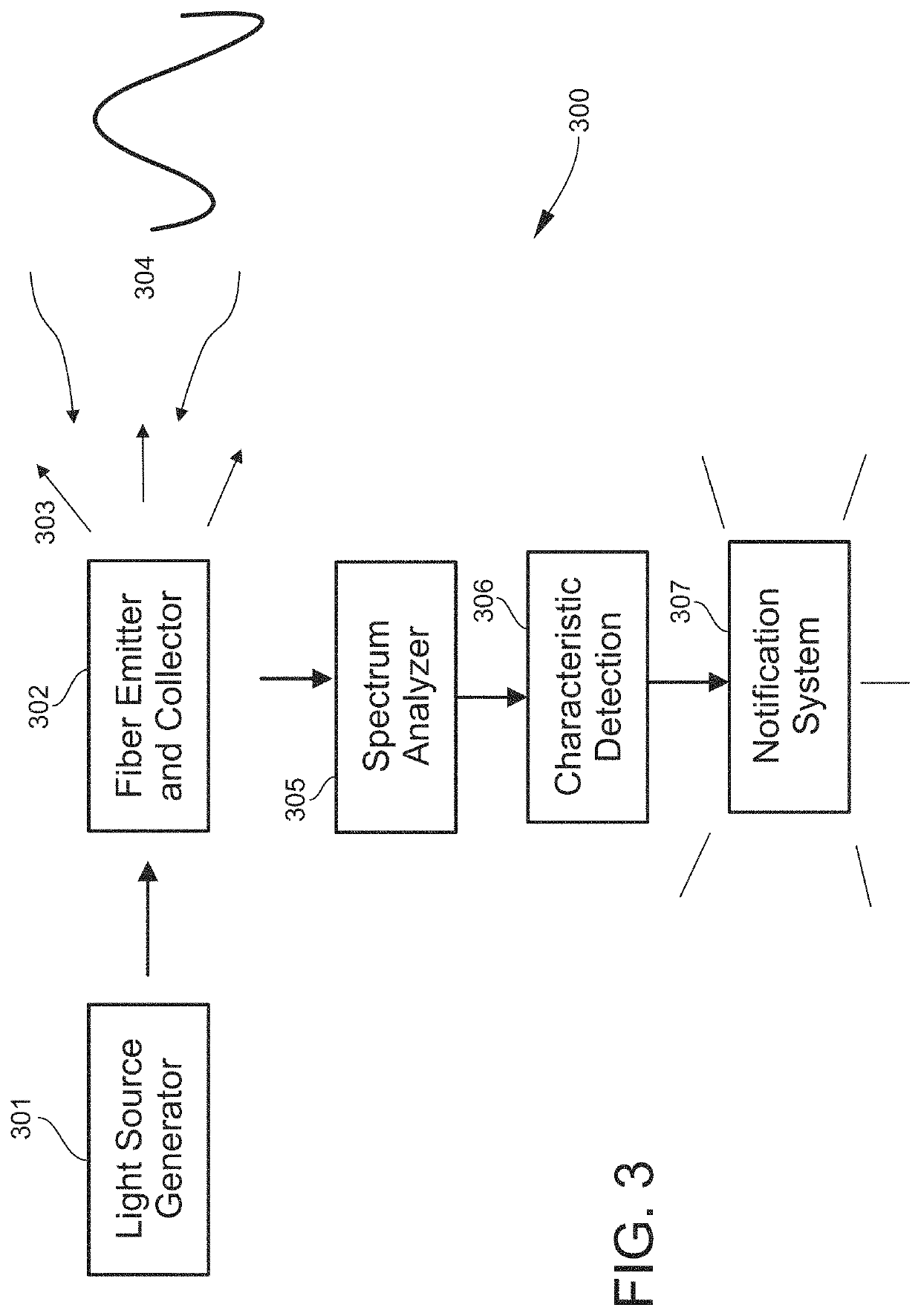
An airway management device (10) for a human or animal subject (20) includes an airway tube (101) having a first end for disposal external to the subject (20) and a second end (102) for disposal in a portion of an airway of the subject (20). A light emitting element (108) and a photo-sensing element (109) may be disposed at the second end (102) of the airway tube (101). The light emitting element (108) may be configured to transmit light to tissue adjacent to the light emitting element (108). The photo-sensing element (109) may be configured to receive reflectance spectra (204) from the tissue. The location of the second end (102) of the airway tube (101) may be determined from characteristics of the reflectance spectra (204) of the tissue.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Tissue clamp assembly and clamp forceps
PendingCN113662596ASolve problems that affect the normal operation of the operationSolve the real problemSurgical forcepsThoracoscopic procedureBiomedical engineering
The invention provides a tissue clamp assembly and clamp forceps, wherein the tissue clamp assembly comprises a tissue clamp and a traction magnet, the tissue clamp comprises a first clamping arm, a second clamping arm and a spring body, and the first clamping arm and the second clamping arm are hinged to each other; a first clamping part and a second clamping part are formed at the front end of the first clamping arm and the front end of the second clamping arm respectively, the first clamping part is provided with a first tooth-shaped chuck, the second clamping part is provided with a second tooth-shaped chuck, and the two ends of the spring body are connected with the first clamping arm and the second clamping arm respectively; corresponding clamping holes are formed in the rear end of the first clamping arm and the rear end of the second clamping arm; the traction magnet is connected with the tissue clamp through a connecting ring; the first tooth-shaped chuck and the second tooth-shaped chuck clamp human tissues under the action of the spring body; and the traction magnet is used for pulling the human tissues through the tissue clamp under the action of the attraction force of the external anchoring magnet. Therefore, when a single-hole thoracoscope operation is carried out, lung or esophageal tissue can be effectively pulled, and other surgical instruments cannot be collided or interfered.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Process for fabricating engineering esophagus imitating biochemistry tissue
InactiveCN101204592BGood maintenance functionGrowth Support and PromotionTubular organ implantsPolyesterFiber
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A preparation for detecting, diagnosing or evaluating prognosis of esophageal cancer, a drug for treating esophageal cancer and application of rnd2 gene
ActiveCN109517898BMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical drugEsophageal cancer
The invention relates to a preparation for detecting, diagnosing or evaluating prognosis of esophageal cancer, a drug for treating esophageal cancer and application of RND2 gene, belonging to the technical field of tumor molecular biology. The esophageal cancer detection, diagnosis or prognosis evaluation preparation of the present invention includes a detection product of RND2 gene mRNA expression level, or a detection product of RND2 protein expression level; RND2 protein belongs to the Rnd subfamily in the Rho GTPase superfamily, the present invention For the first time, it was discovered that the expression of RND2 gene is related to esophageal cancer. By detecting the expression of RND2 in the esophageal tissue of the subject, it can be judged whether the subject has esophageal cancer, or whether the subject has the risk of esophageal cancer. By increasing the expression of RND2 protein and supplementing the lack or insufficiency of endogenous RND2 protein, the esophagus cancer caused by RND2 protein deficiency can be treated or alleviated.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Esophageal heat transfer devices and methods for cardiac tissue ablation
PendingCN112236109APrevent or reduce the risk of heat injuryAchieve persistent damageSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesRat heartBiomedical engineering
Method and apparatus are disclosed for esophageal heat transfer devices and methods for cardiac tissue ablation procedures. An exemplary method includes collecting esophageal data via one or more sensing elements of an esophageal heat transfer device positioned within an esophagus of the patient. The exemplary method includes determining, based on the esophageal data and / or operator selected powersetting, a temperature setting and / or a flow rate setting for fluid flowing through the esophageal heat transfer device to maintain a target temperature of esophageal tissue adjacent to the ablationsite via a heat transfer region. The exemplary method includes adjusting, via the controller, a fluid source to provide the fluid to the esophageal heat transfer device at the temperature setting and / or a flow rate setting.
Owner:ADVANCED COOLING THERAPY INC
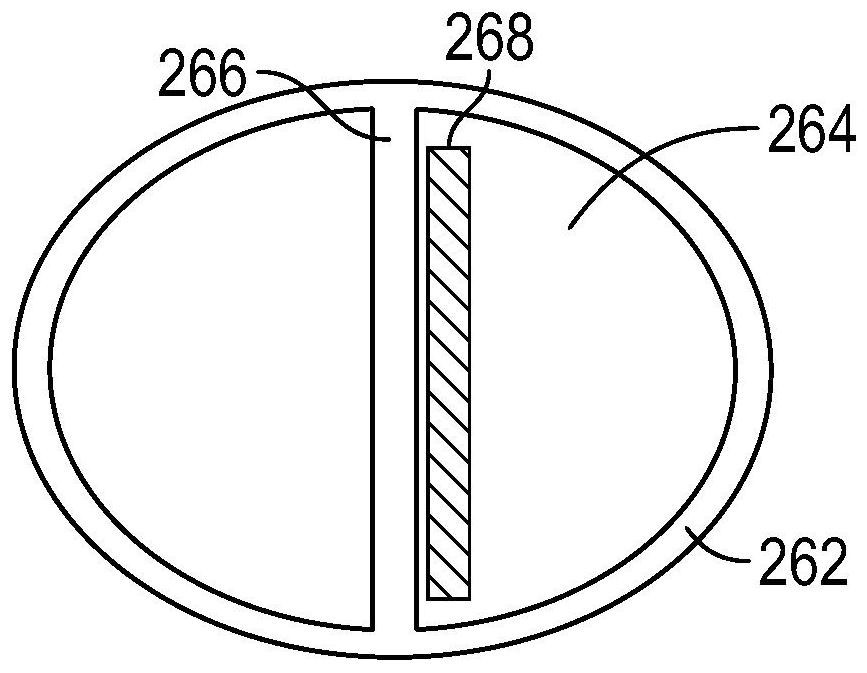
Decellularized small intestinal submucosa/polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer composite scaffold as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112891634ALess amount of residual DNALow immunogenicityTissue regenerationProsthesisCell phenotypeTissue repair
The invention discloses a decellularized small intestinal submucosa / polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer composite scaffold as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of tissue repair. The shape of the composite scaffold is similar to a layered structure of laryngeal pharynx and neck esophageal tissues. In the composite scaffold, the amount of residual DNA of the decellularized small intestinal submucosa is small, the composite scaffold has low immunogenicity and high biological activity, the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer is arranged in a nanofiber mode and can promote migration and growth of mucosa cells, and the composite scaffold has good mechanical properties. Through verification, interaction between cells and each layer of the scaffold is good, ideal cell proliferation and cell phenotypes are shown, and it is proved that the composite scaffold has a good tissue repair function.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL CENT LIHUILI HOSPITACL
Systems and methods for tracking spontaneous breathing in a mechanically ventilated patient
ActiveUS10967142B1Advanced technologyImprove performanceTracheal tubesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAutonomous breathingSphincter
There is provided system for monitoring spontaneous breathing of a mechanically ventilated target individual, including: a feeding tube for insertion into a distal end of an esophagus of the individual, sensor(s) disposed on the feeding tube at a location such that the sensor(s) is located at the distal end of the esophagus of the individual when the feeding tube is in use, wherein the sensor(s) is positioned for sensing values by contact with the tissue of the esophagus including a lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and / or tissue in proximity to the LES, and code for computing an indication of a frequency band of diaphragm movement of the individual according to an analysis of values sensed by the sensor(s), and for adjustment of parameter(s) of a mechanical ventilator for mechanically ventilating the individual, wherein the instructions for adjustment are computed while the feeding tube is in use.
Owner:ART MEDICAL LTD
Method and system for automatic segmentation of esophageal endoscopic oct image hierarchy
ActiveCN108765388BImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationGradient operators
The invention discloses an automatic segmentation method and a system of an esophageal endoscopic OCT image hierarchy structure. The method comprises the following steps: image preprocessing, whereinan image is filtered and searched, and pixel values are complemented; image planarization, wherein the whole esophageal tissue in the image is straightened and corrected; segmentation of an image organization layer, wherein a current segmentation layer is used as a reference and the searching area of a next layer to be segmented is obtained in a mode of translating certain pixels downward and segmentation layer by layer is performed; image unplanarization, wherein the segmented image is inversely translated to obtain the final segmentation result. The invention provides a scheme for respondingto interference of a probe protective film, tissue liquid and the like, so as to avoid subsequent influences on tissue layer segmentation. The invention combines the Canny edge detection with the gradient operator, and proposes a new image segmentation method weight design scheme. The scheme uses the Canny operator to improve the precision of edge detection, and uses the gradient operator to compensate the missing edge in the Canny operator. The accuracy of segmentation is improved by combining the two operators.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
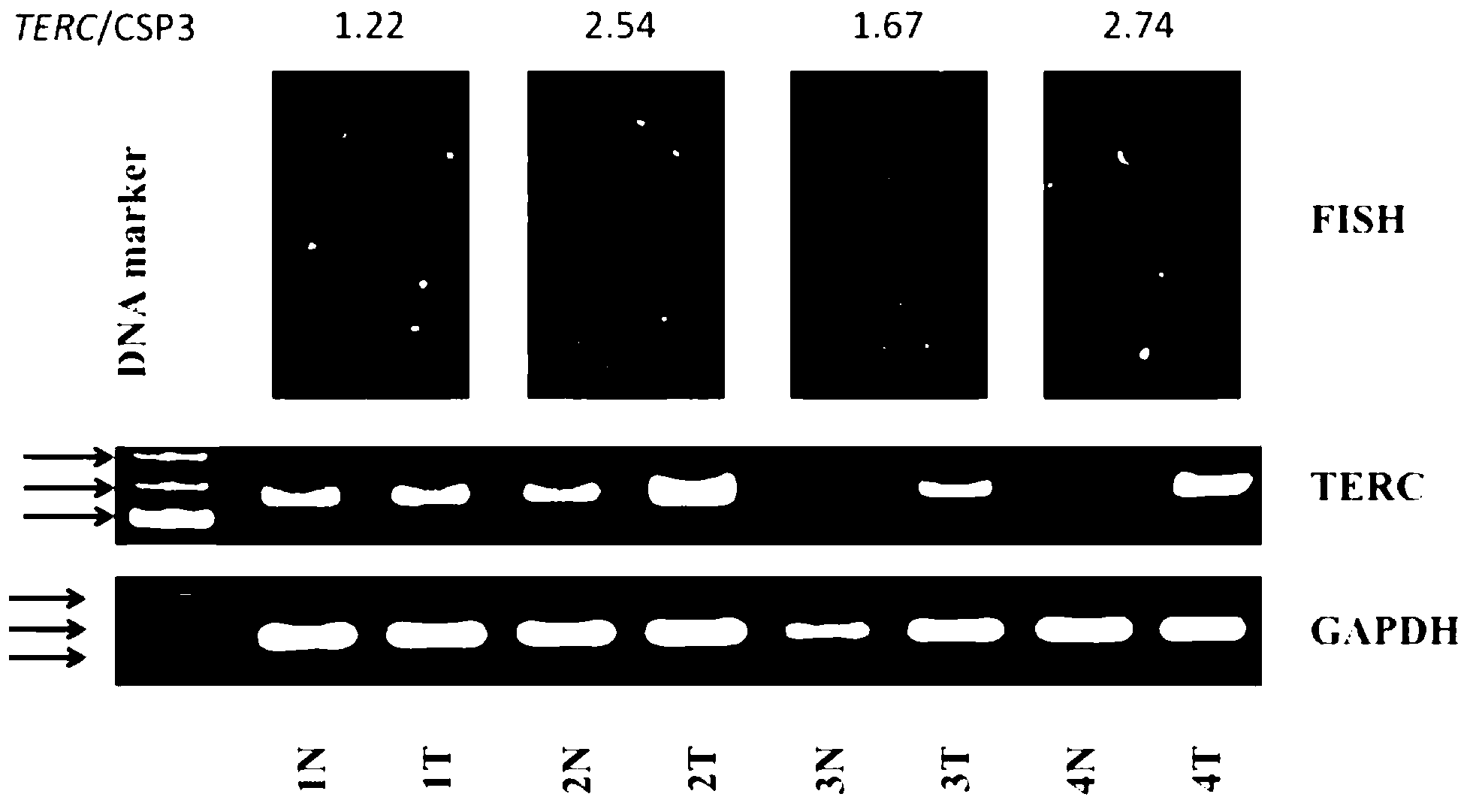
Florescent real-time quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for detecting amplification of TERC (Telomerase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) Component ) gene of esophageal cancer
InactiveCN102827927AShort detection cycleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerReference genes
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Systems and methods for sensing lung fluid and functionality
ActiveUS20210059604A1Improve performanceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAC - Alternating currentSphincter
An apparatus for monitoring for accumulation of lung fluid comprises a feeding tube having first electrode(s) positioned thereon for electrical contact with tissue of an esophagus of a target patient including a lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and / or tissue in proximity to the LES, second electrode(s) sized and shaped for contacting skin of the target patient, and a non-transitory memory having stored thereon code instructions for applying alternating current(s) to pair(s) of first and second electrodes, measuring a voltage over the pair(s), and computing an estimate of a change of lung fluid relative to a baseline in lung(s) of the target patient according to the applied alternating current and measured voltage, wherein the applying, the measuring, and the computing the estimate of the change in lung fluid are iteratively executed for monitoring the target patient for accumulation of lung fluid while the feeding tube is in use.
Owner:ART MEDICAL LTD
Application of chka gene in preparation of products for diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer
ActiveCN105886625BTimely diagnosisSpecific diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEsophageal cancerCancer research
The invention discloses a CHKA gene that can function as a molecular marker for early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Experiments prove that compared with normal esophageal tissues, the CHKA gene in esophageal cancer tissues has significantly increased expression, and RNA interference experiments prove that CHKA can affect proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. According to study results herein, it is possible to develop medicine to inhibit CHKA gene expression so as to clinically prevent and treat the esophageal cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
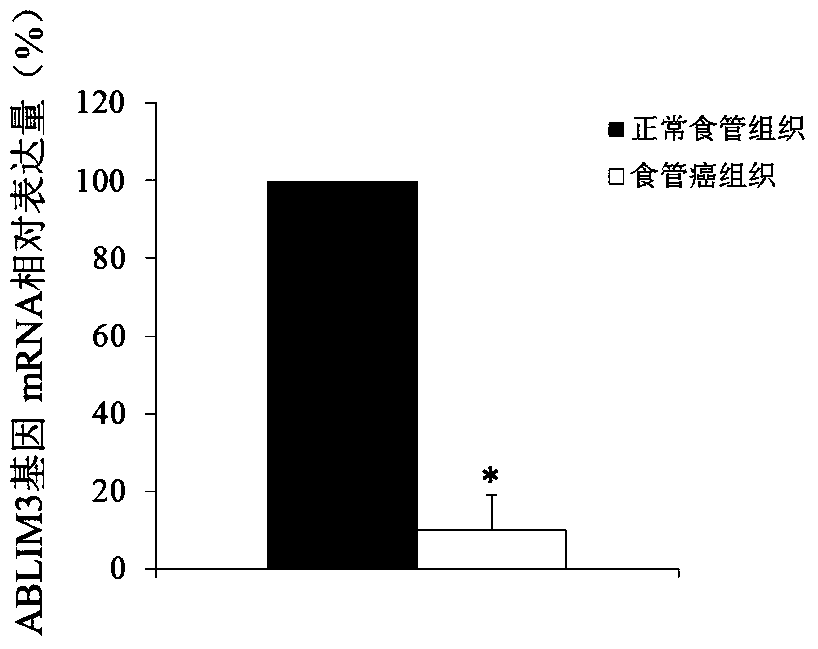
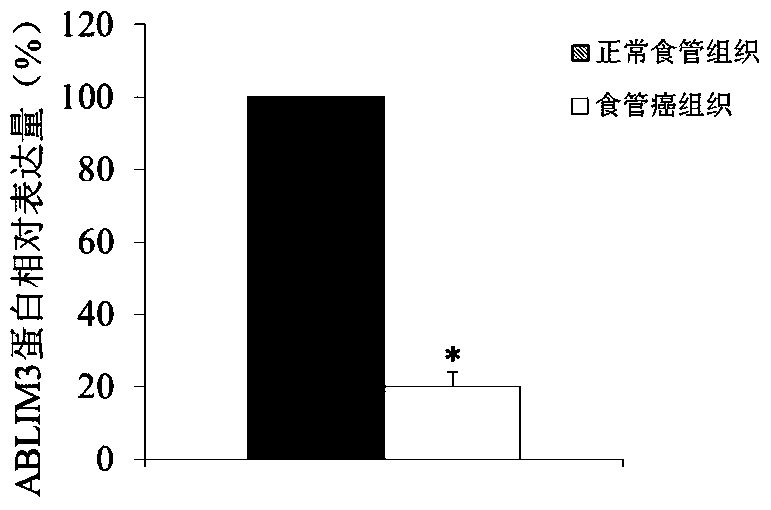
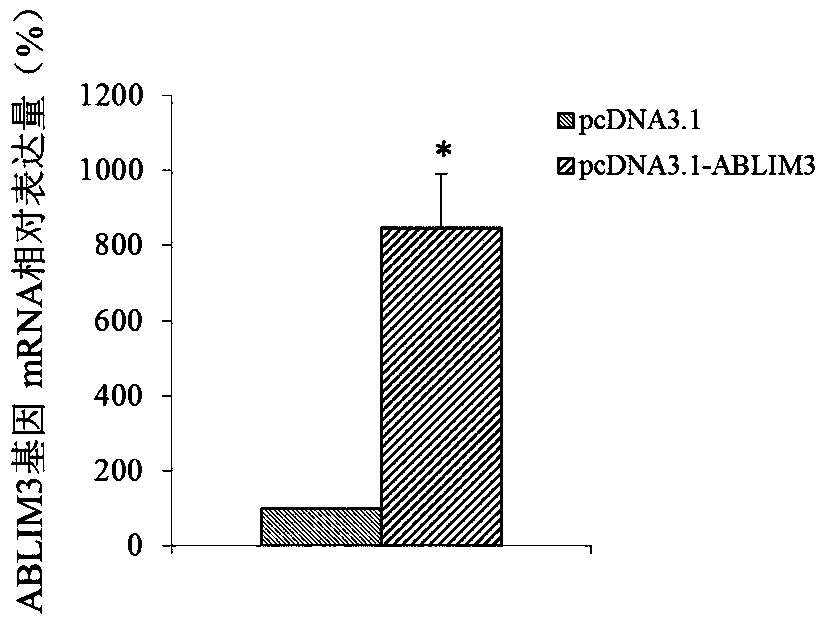
The use of ablim3 gene as a marker for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer
ActiveCN105861740BAchieve early diagnosisTimely genetic diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisWestern blotEsophageal cancer
The invention discloses a molecular marker-ABLIM3 gene and its expression product for early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. The present invention uses QPCR and Western blot methods to prove that the ABLIM3 gene is differentially expressed in esophageal cancer tissue and normal esophageal tissue, and can be used as an index for early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. In addition, the present invention also discloses that the ABLIM3 gene and its expression product can be used as a target for the treatment of esophageal cancer and used to guide the research and development of new drugs.
Owner:FOURTH HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Airway management device for identification of tracheal and/or esophageal tissue
An airway management device (10) for a human or animal subject (20) includes an airway tube (101) having a first end for disposal external to the subject (20) and a second end (102) for disposal in a portion of an airway of the subject (20). A light emitting element (108) and a photo-sensing element (109) may be disposed at the second end (102) of the airway tube (101). The light emitting element (108) may be configured to transmit light to tissue adjacent to the light emitting element (108). The photo-sensing element (109) may be configured to receive reflectance spectra (204) from the tissue. The location of the second end (102) of the airway tube (101) may be determined from characteristics of the reflectance spectra (204) of the tissue.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com