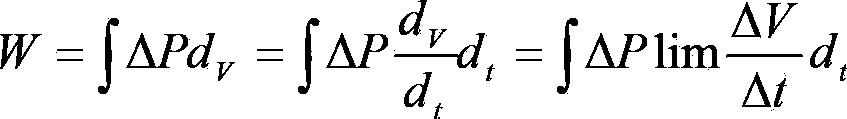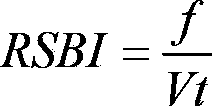Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139 results about "Autonomous breathing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
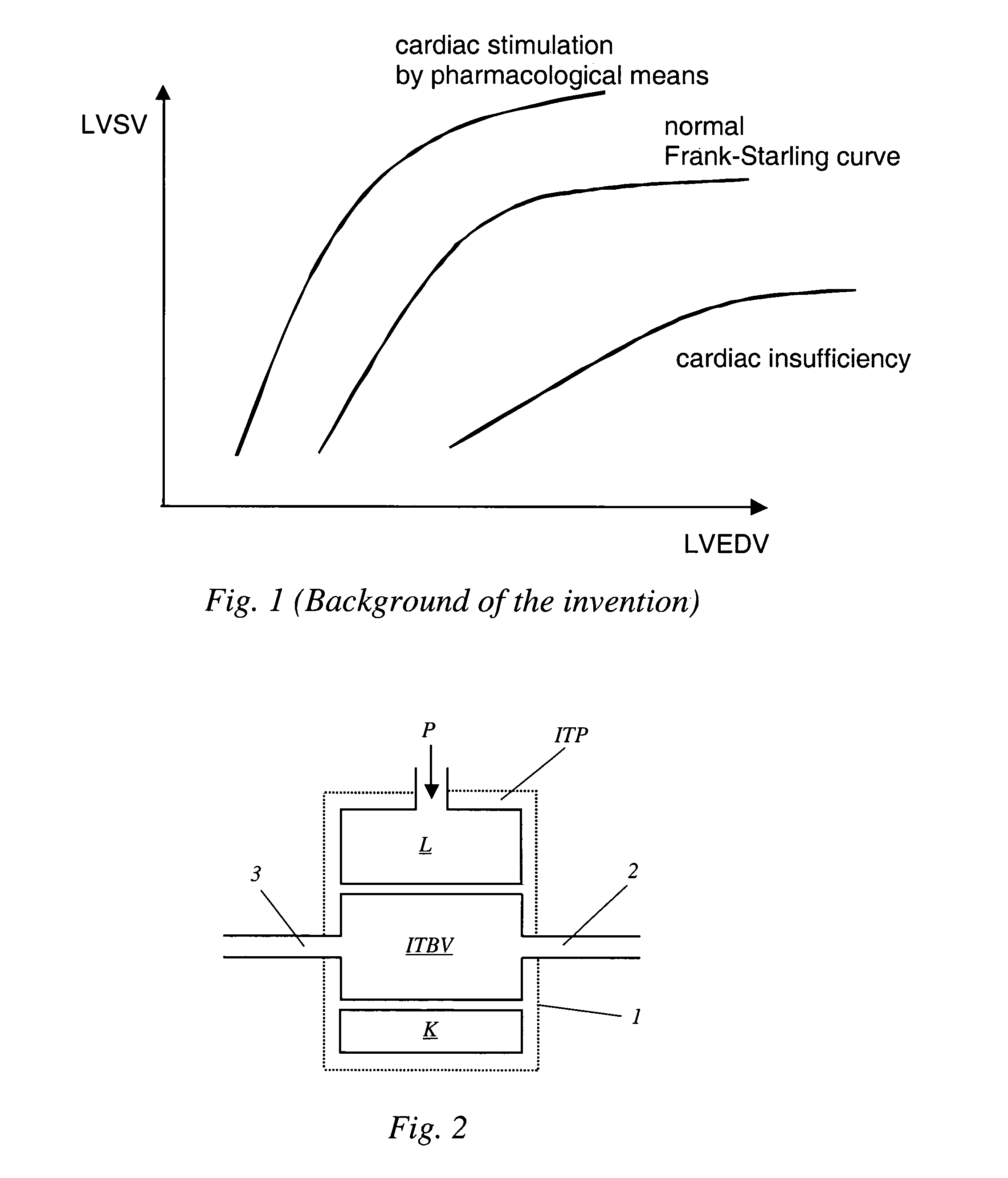
Breathing is controlled by the autonomic nervous system (or automatic nervous system), a part of the CNS responsible for bodily processes that function without conscious thought, such as breathing or beating of the heart.
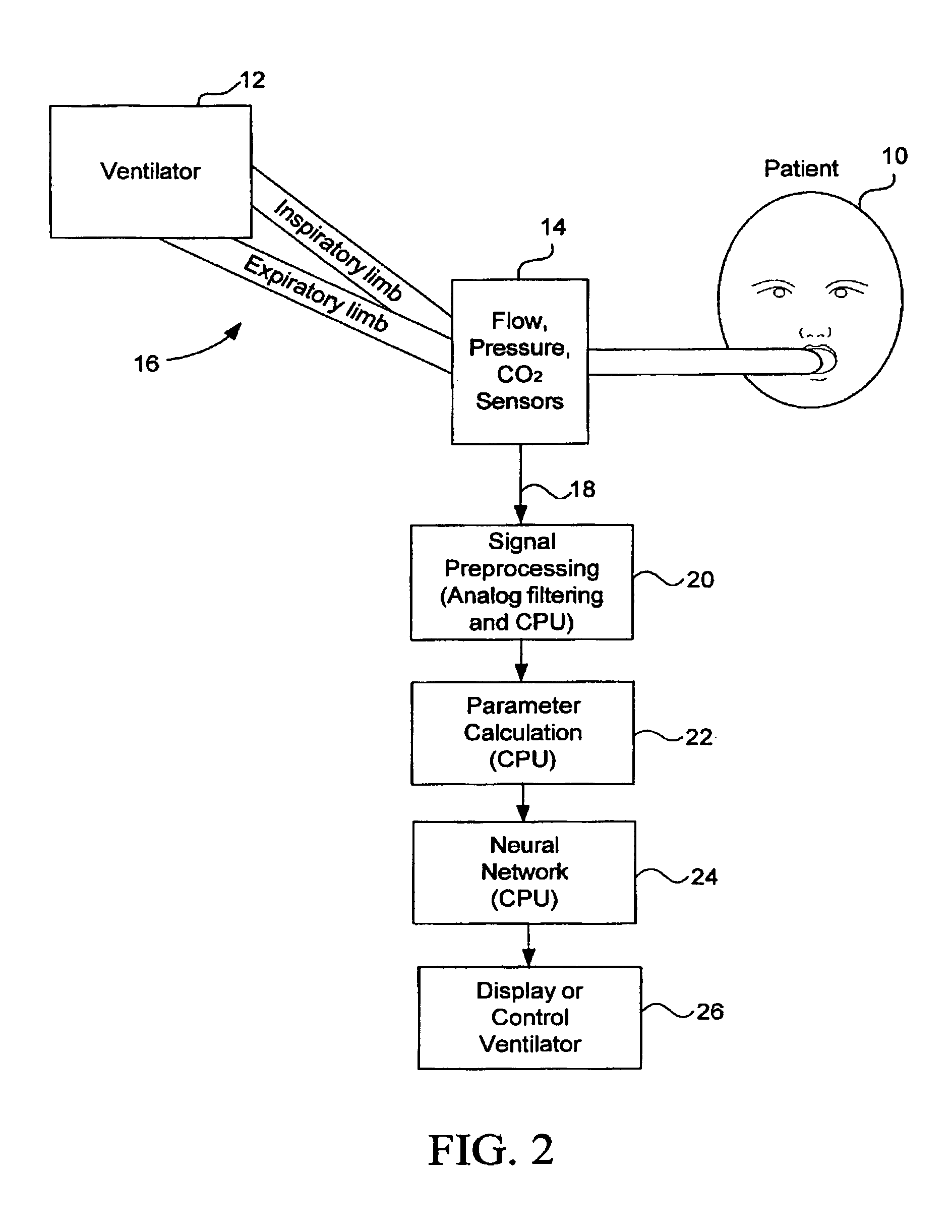
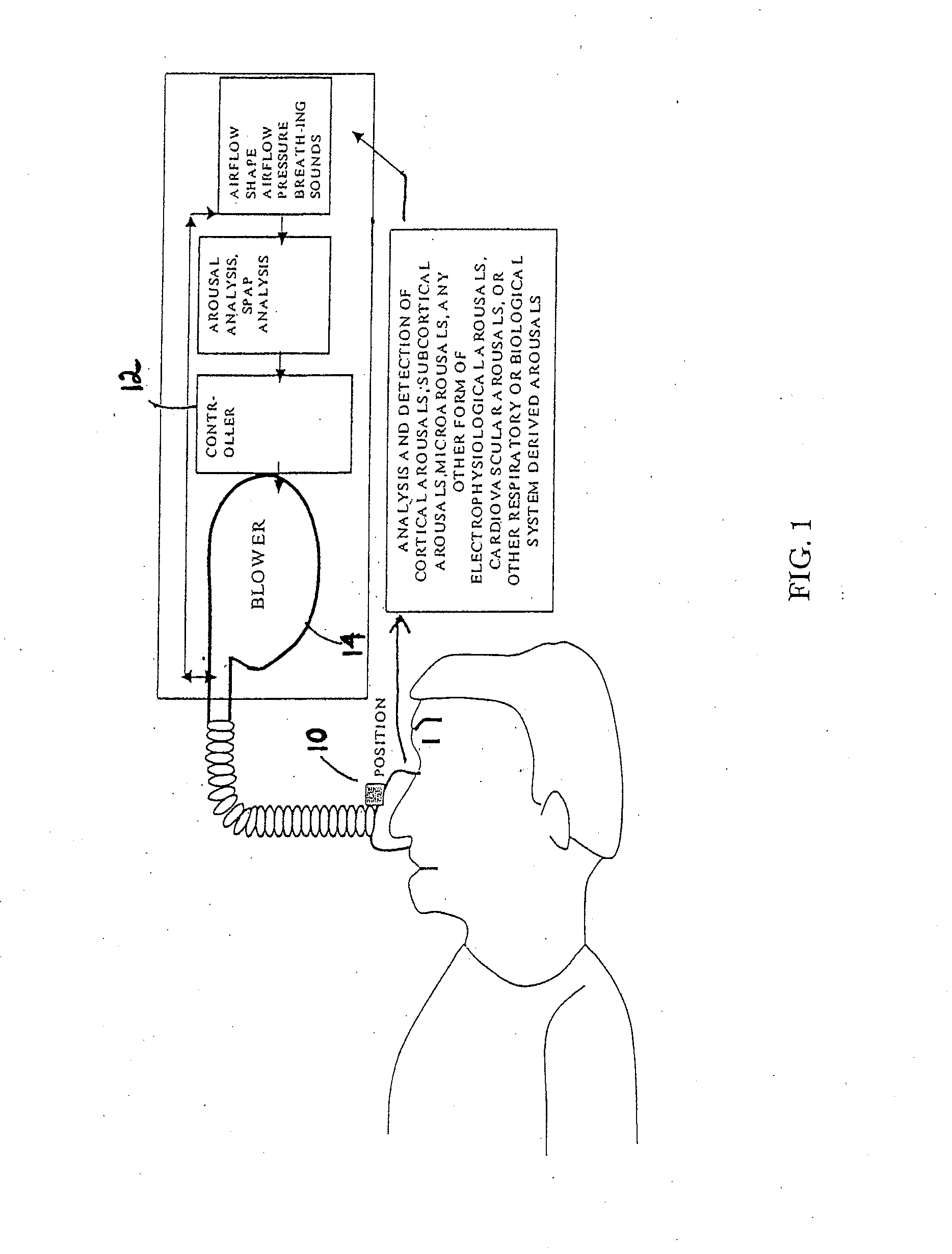
System and method for optimized delivery of an aerosol to the respiratory tract
InactiveUS20070157931A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingAerosol deposition
The present disclosure relates to systems, methods, and devices for controlling delivery of aerosolized formulations to patients in need of treatment, which optimizes aerosol deposition to the respiratory tract of the patient and can be adapted for use in spontaneously breathing patients or in those requiring mechanical ventilation.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
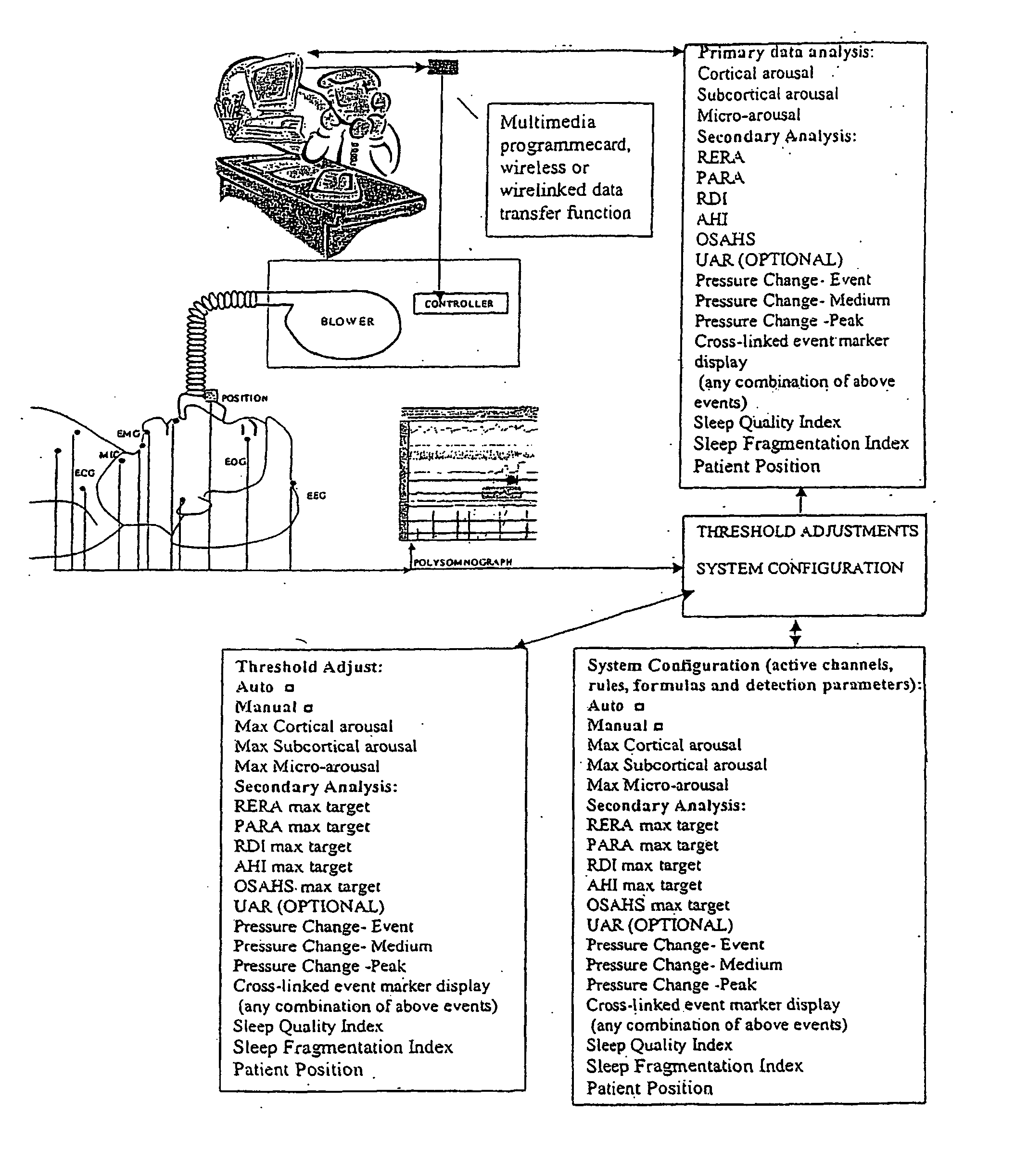
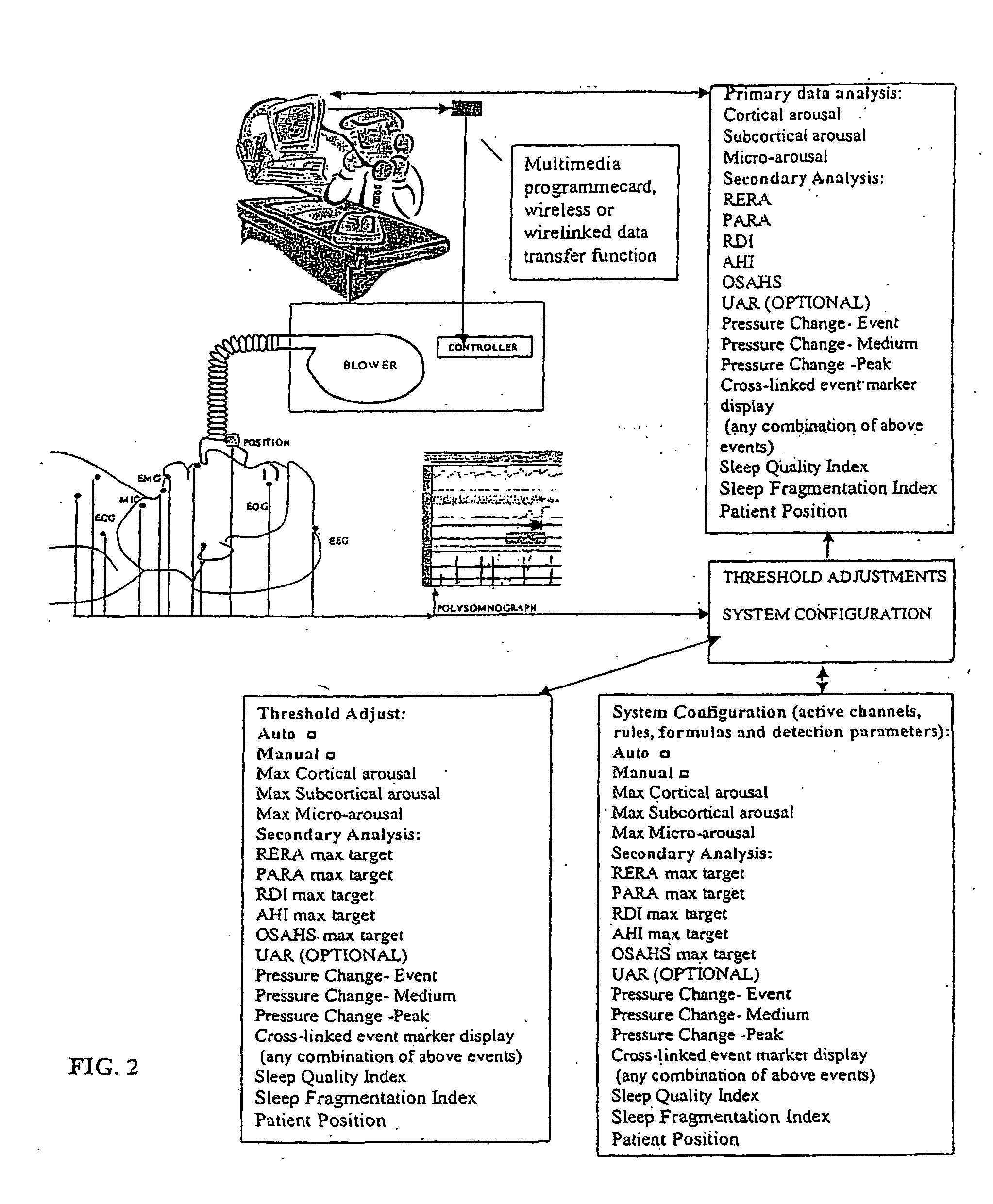
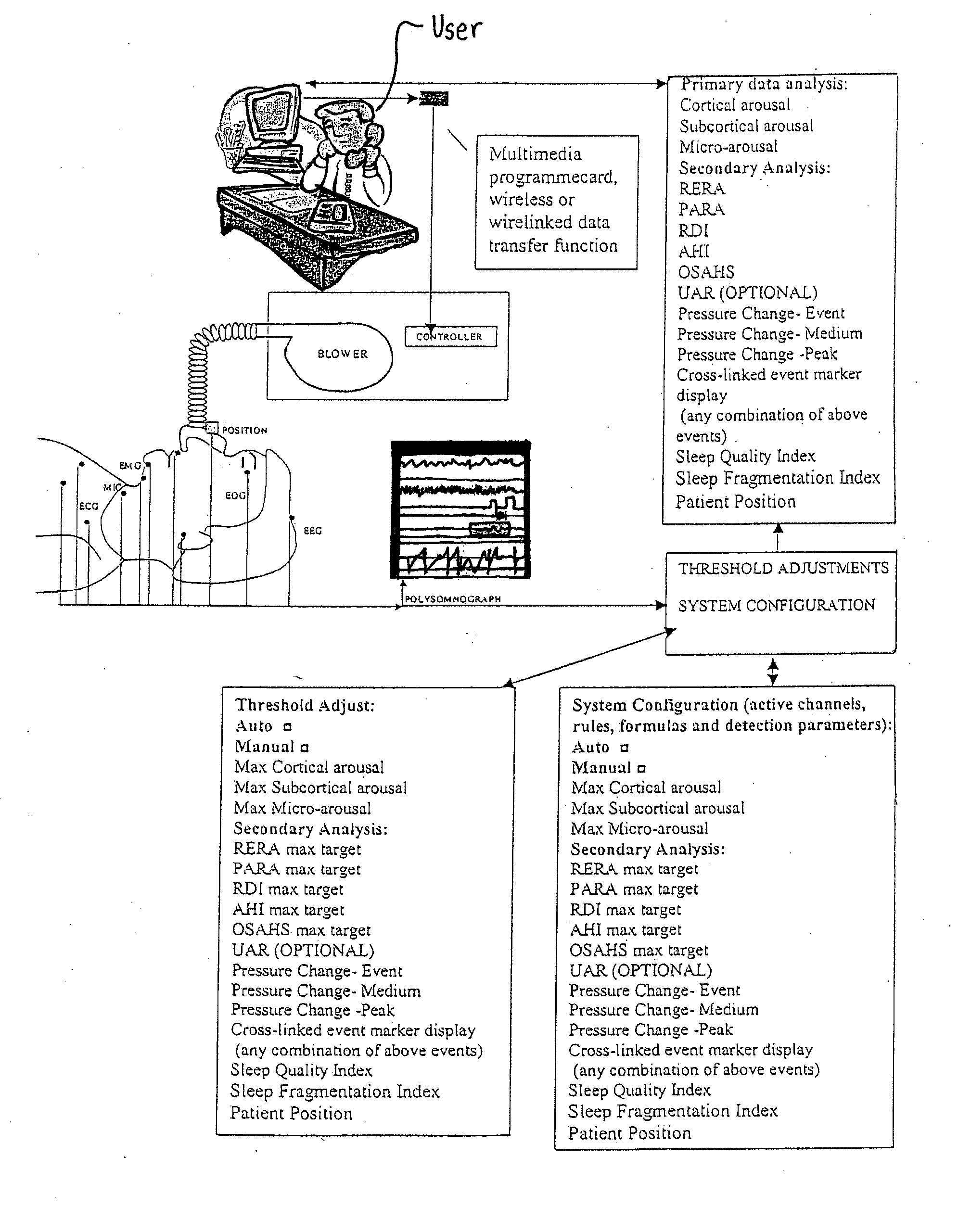
Method and apparatus for maintaining and monitoring sleep quality during therapeutic treatments
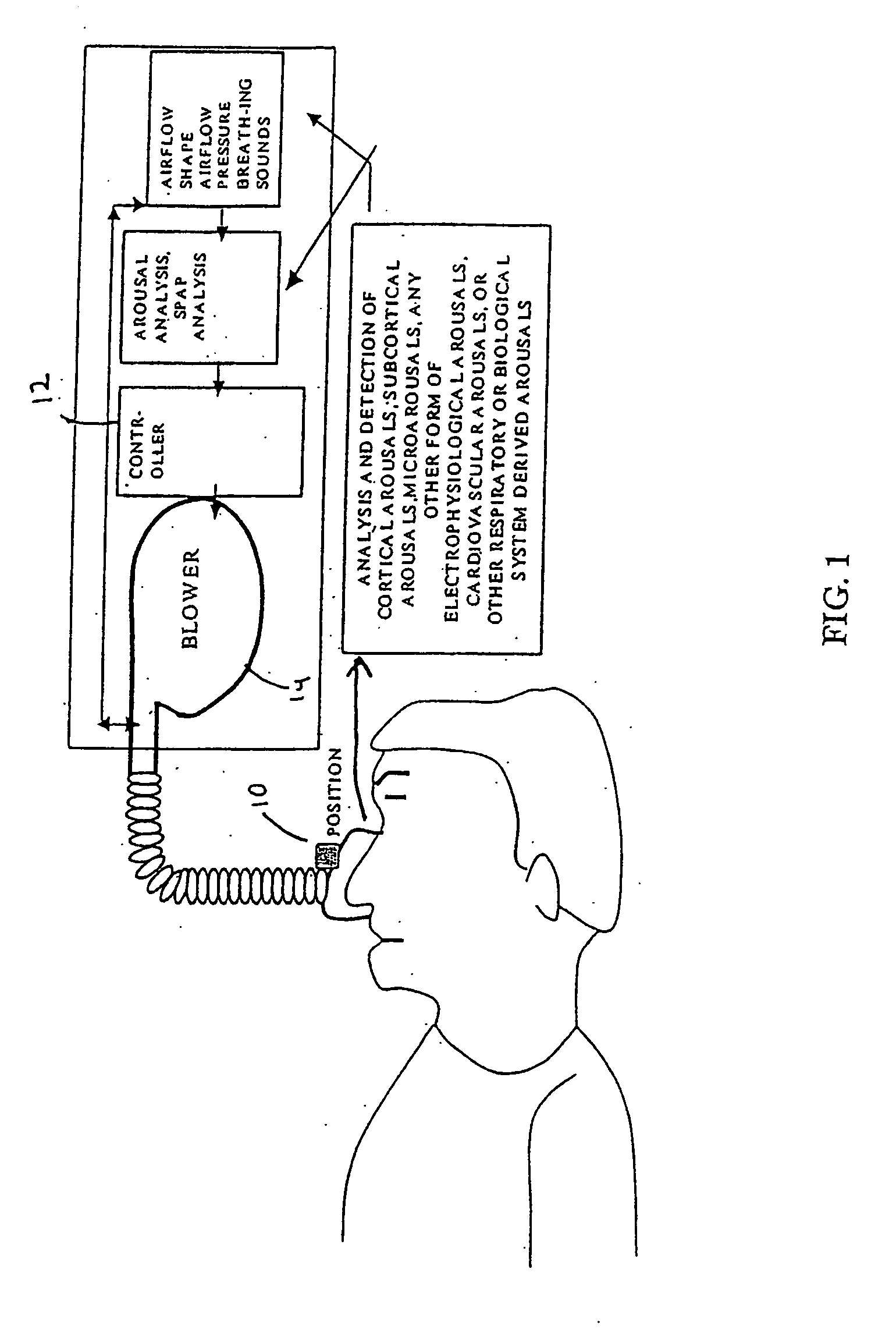
ActiveUS20050217674A1Reduce or eliminate both sleep breathing disorders and sleep fragmentationRespiratorsElectrocardiographyAutonomous breathingTherapeutic Devices
The present invention monitors and interprets physiological signals and spontaneous breathing events to detect the onset of arousal. Once the onset of arousal is determined, the present invention determines adjustments that are needed in the operation of a therapeutic device to avoid or minimize arousals. In one embodiment, the present invention includes one or more sensors which detect a patient's physiological parameters, a controller which monitors and determines the onset of arousal based on the physiological variables received from the sensor, and a therapeutic treatment device which is controlled by the controller. The sensor can be a combination of one or more devices which are able to monitor a physiological parameter that is used by the present invention to determine the onset of arousal or the onset of a sleep disorder. The sensors can be integrated into one unit or may operate independent of the others.
Owner:COMPUMEDICS
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation for treating airway obstructions
ActiveUS20100252042A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingControl cell
A system for reducing airway obstructions of a patient may include a ventilator, a control unit, a gas delivery circuit with a proximal end in fluid communication with the ventilator and a distal end in fluid communication with a nasal interface, and a nasal interface. The nasal interface may include at least one jet nozzle, and at least one spontaneous respiration sensor in communication with the control unit for detecting a respiration effort pattern and a need for supporting airway patency. The system may be open to ambient. The control unit may determine more than one gas output velocities. The more than one gas output velocities may be synchronized with different parts of a spontaneous breath effort cycle, and a gas output velocity may be determined by a need for supporting airway patency.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for continuous measurement of flux of gases in the lungs during breathing
ActiveUS20050217671A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingEngineering
A method of calculating the flux of any gas (x) in a CBC circuit for a ventilated or a spontaneous breathing subject, for example said gas(x) being; a) an anesthetic such as but limited to; i)N2O; ii) sevoflurane; iii) isoflurane; iv) halothane; v) desflurame; or the like b) Oxygen; c) Carbon dioxide; or the like utilizing the following relationships; Flux of gas(x)=SGF (FSX−FEX) wherein SGF=Source of gas flow into the breathing circuit (CBC circuit) in liters / minute as read from the gas flow meter as set by the anesthesiologist; FSX=Fractional concentration of gas X in the source gas (which is set by the anesthesiologist); FEX=Fractional concentration of gas X in the end expired gas as determined by a portable gas analyzer, or the like.
Owner:THORNHILL SCI INC
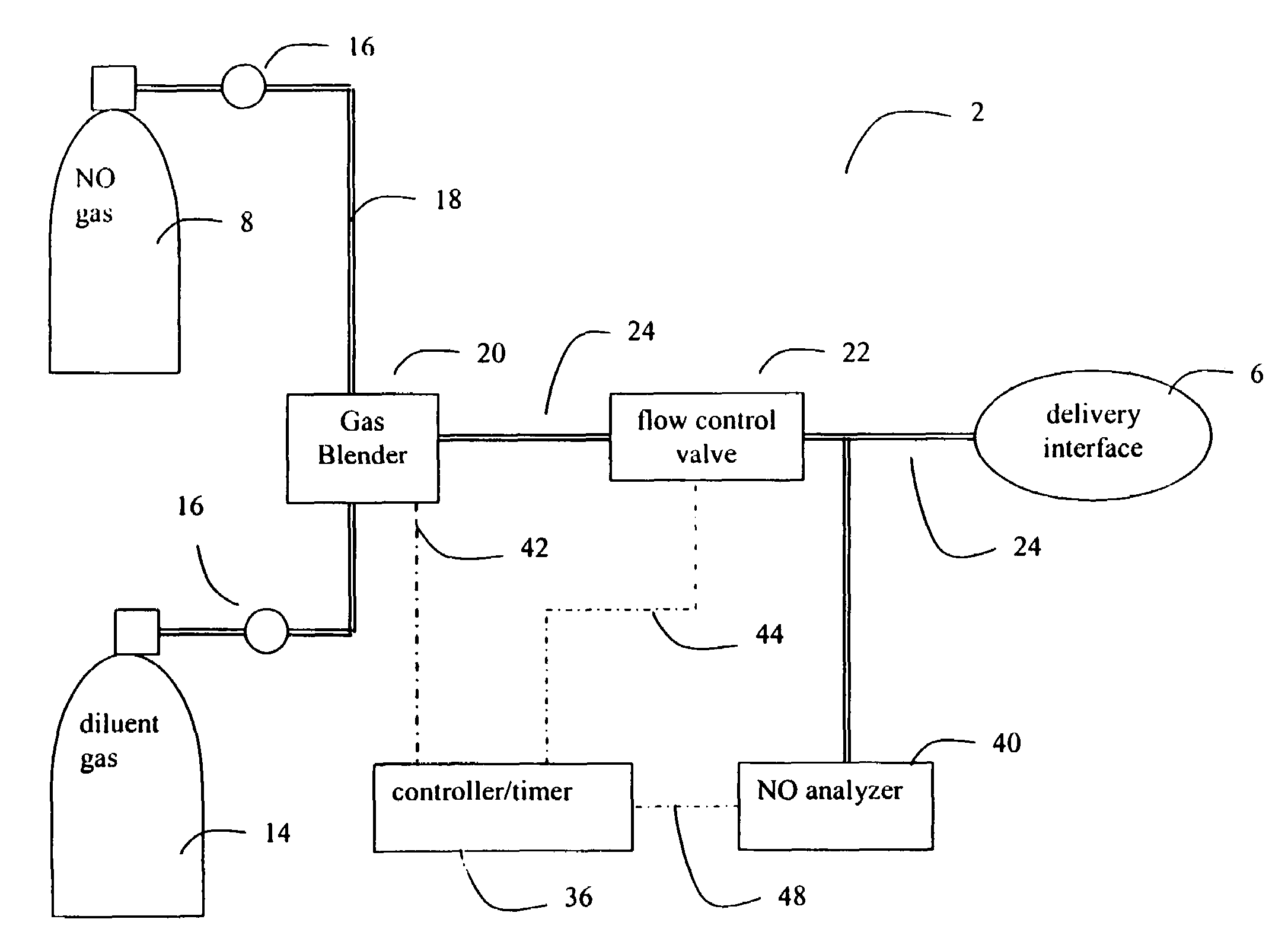
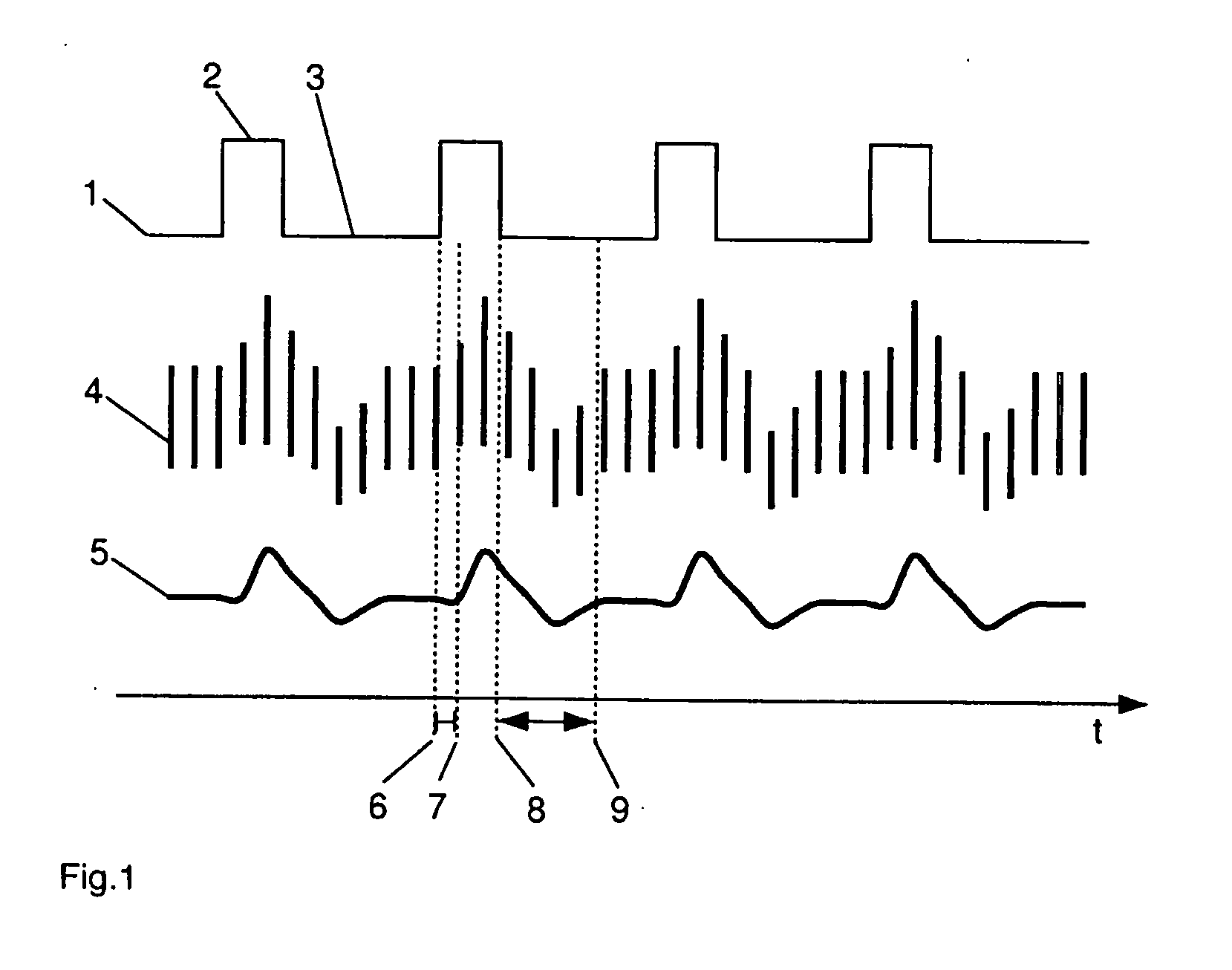
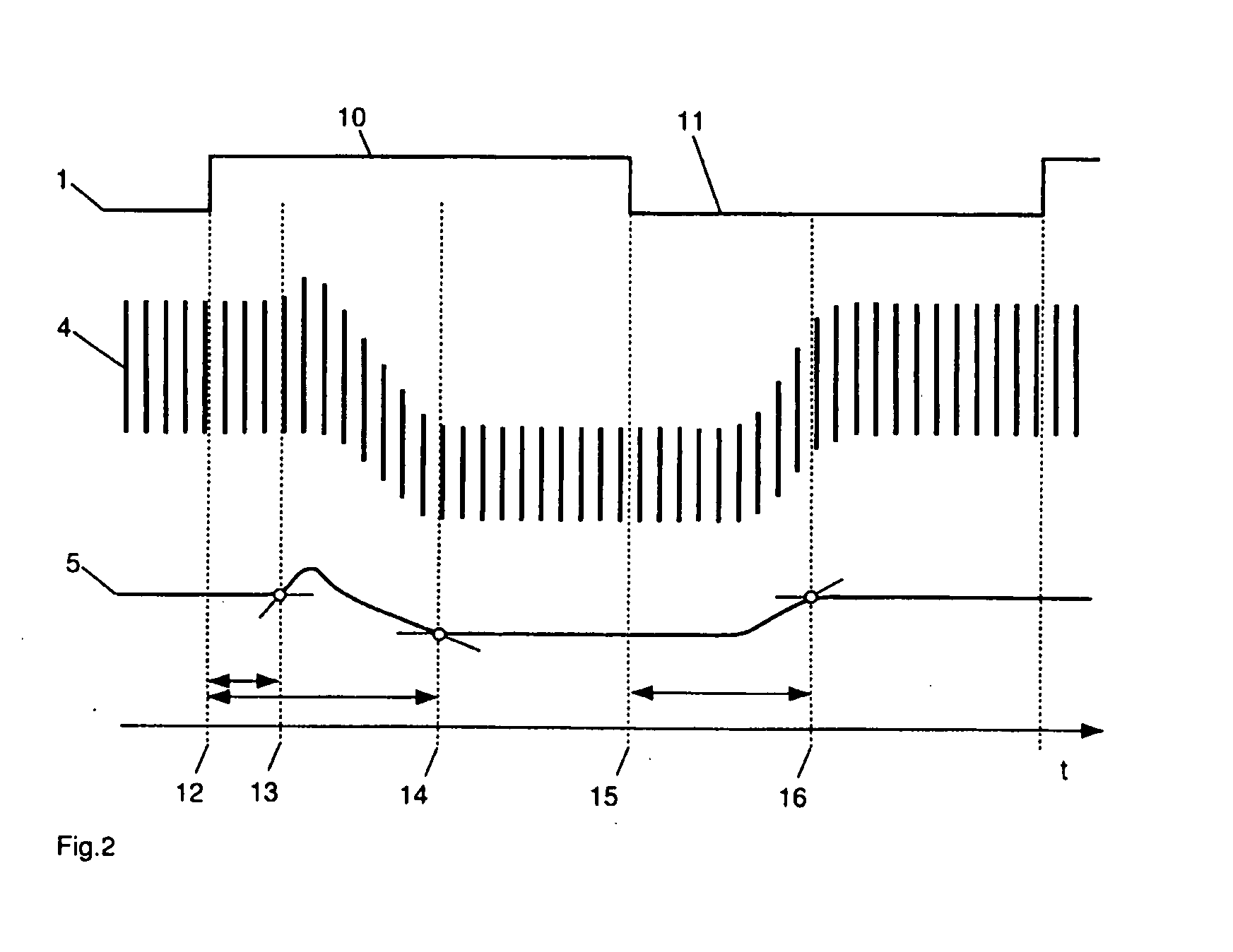
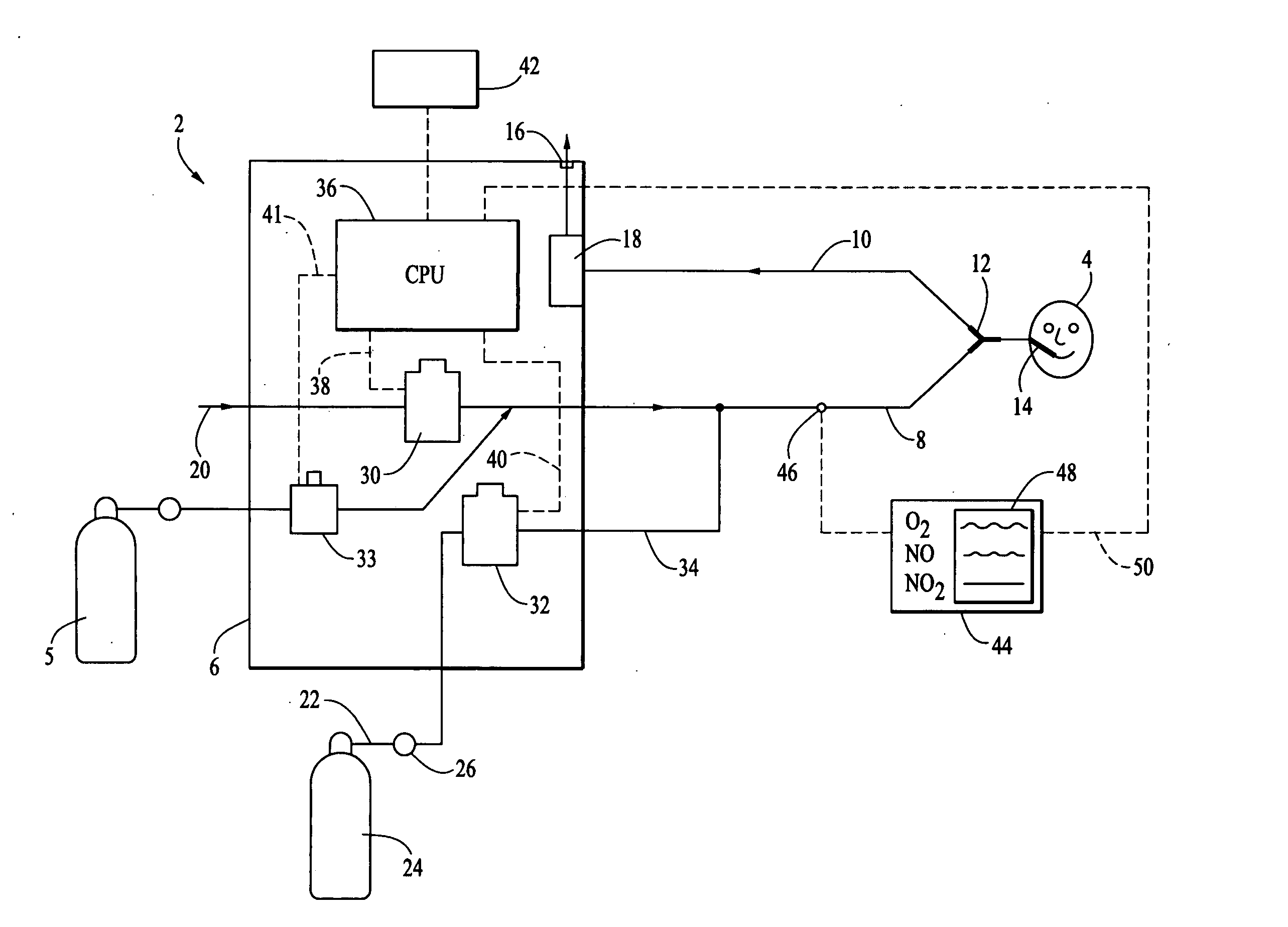
Method and apparatus for delivery of inhaled nitric oxide to spontaneous-breathing and mechanically-ventilated patients with intermittent dosing
InactiveUS7516742B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingNitric oxide
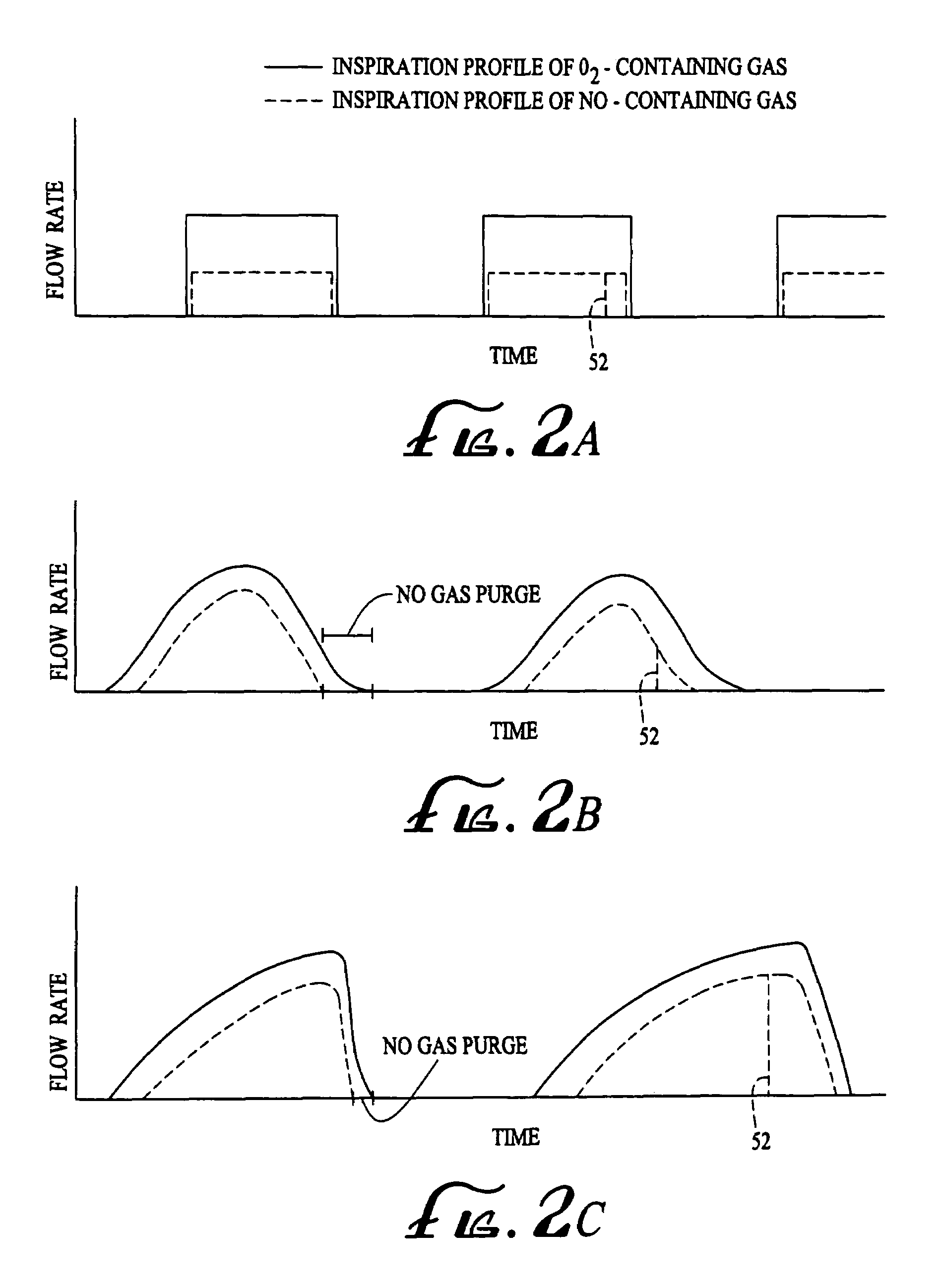
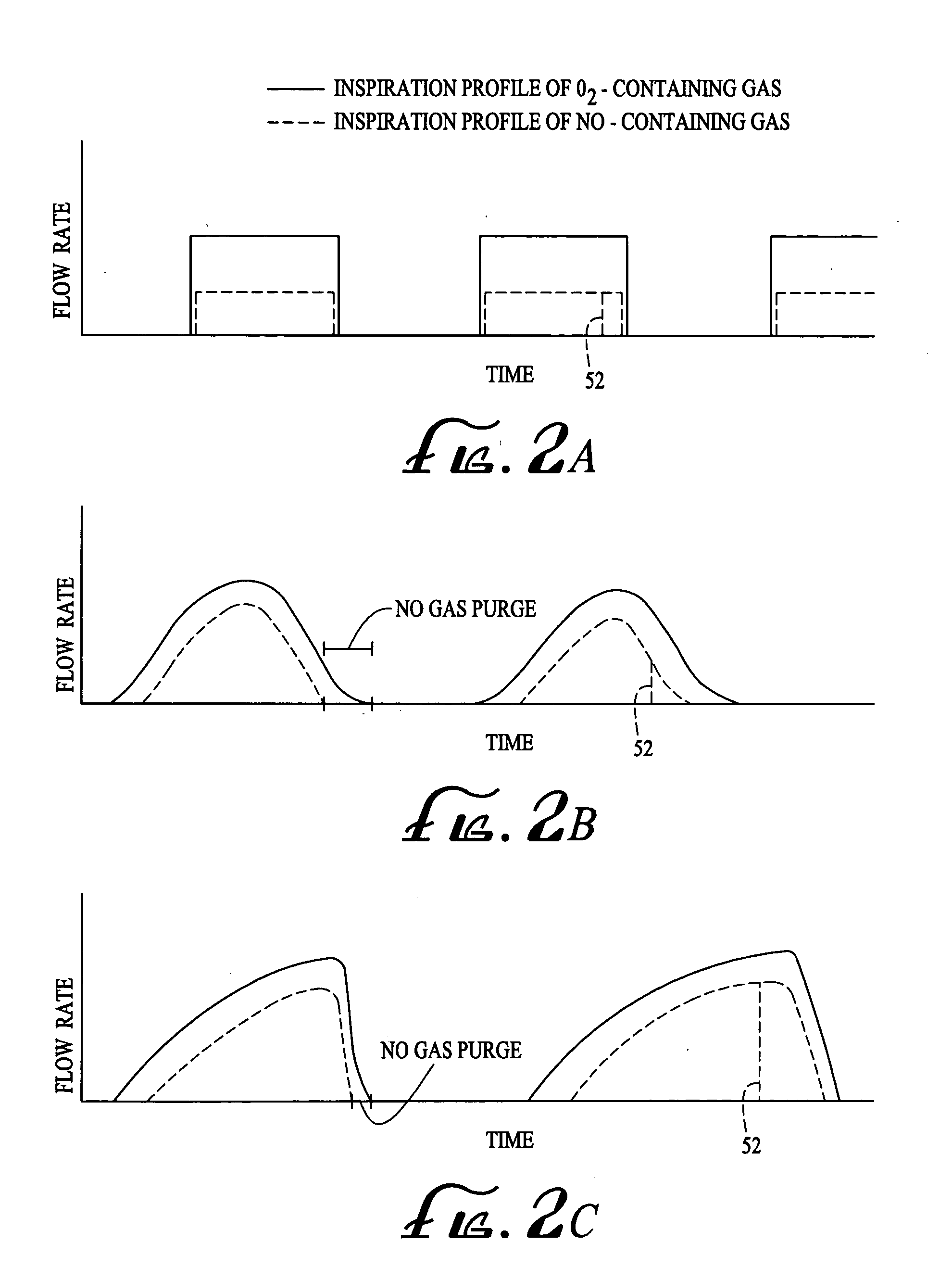
A device and method is disclosed for delivering NO to a patient. The device utilizes a single controller that controls two separate flow controllers to deliver an oxygen-containing gas and a NO-containing gas to the patient to provide NO-containing gas at a flow profile that is proportional or quasi-proportional to a flow profile of the oxygen-containing gas throughout patient inspiration. The controller further comprises logic for setting a nitric oxide delivery profile comprising at least two different concentrations of nitric oxide containing gas and for automatically switching between the at least two different concentrations of nitric oxide containing gas on a timed basis.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 207 INC +1
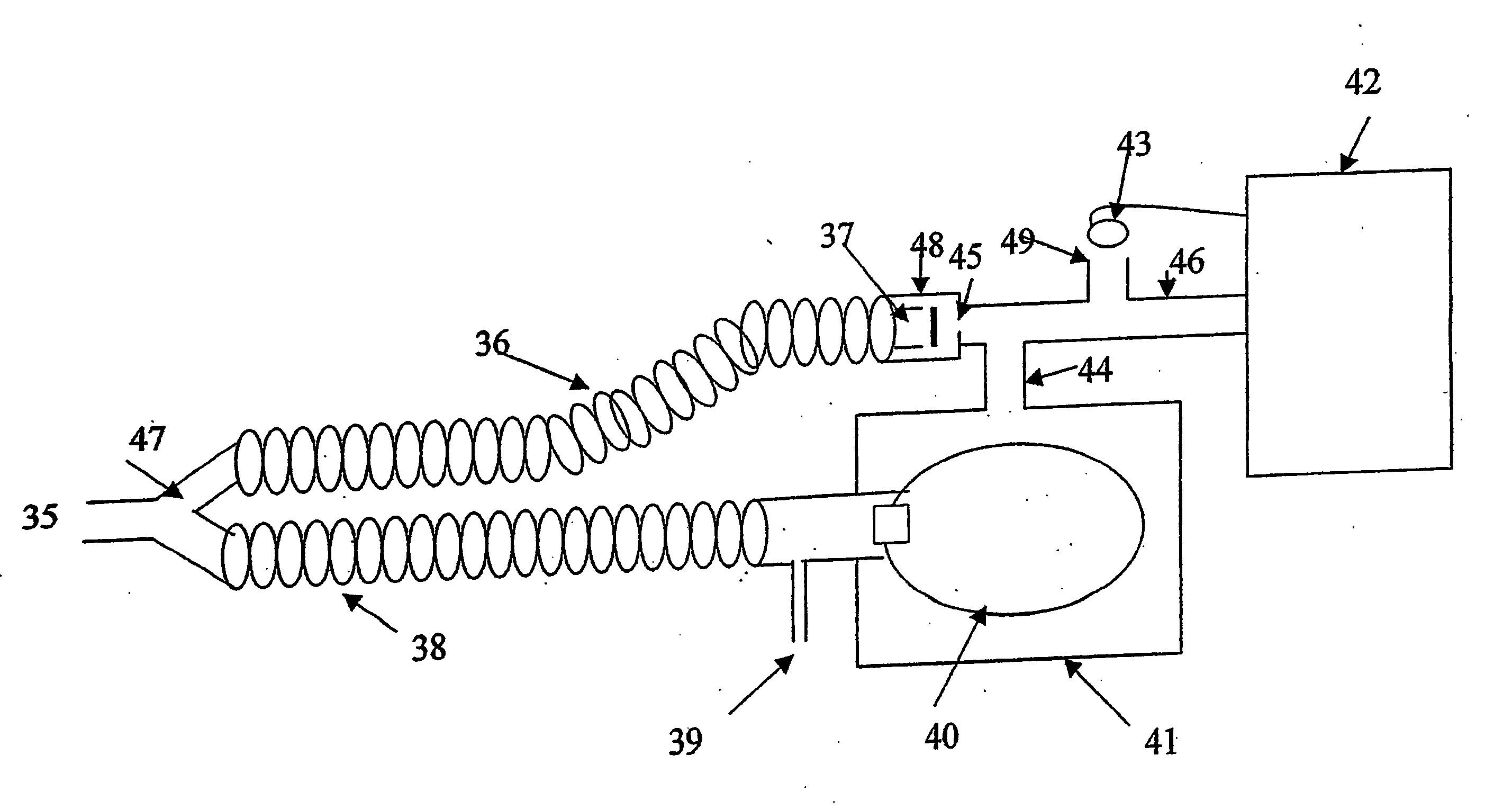
System and elements for managing therapeutic gas administration to a spontaneously breathing non-ventilated patient
InactiveUS20040163647A1Reduce in quantityLower the volumeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksAutonomous breathingBiomedical engineering
A system controls and manages administration of a therapeutic gas, such as NO, O2, or the like, to a spontaneously breathing, non-ventilated patient such that concentrated NO is as low as reasonably possible while delivering the desired amount of NO to the distal portions of the lungs. The system includes an entrainment cell that provides remote, turbulent mixing with low temporal latency and can be used with a nasal cannula or a mask. The entrainment cell uses room air to dilute the therapeutic gas; however, supplementary gases can also be used. A baffle can be included to promote mixing and a flow sensor can also be used if desired. Multiple ports can be included in the entrainment cell. An equalizing valve is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
Method and apparatus for predicting work of breathing
ActiveUS7425201B2Non-invasively predicting (estimatingAvoid muscle fatigueRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingMathematical model
A method of creating a non-invasive predictor of both physiologic and imposed patient effort from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using an adaptive mathematical model. The patient effort is commonly measured via work of breathing, power of breathing, or pressure-time product of esophageal pressure and is important for properly adjusting ventilatory support for spontaneously breathing patients. The method of calculating this non-invasive predictor is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
Out flow resistance switching ventilator and its core methods
InactiveUS20080011301A1Ensure ventilation safetyIncrease spaceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingFlow resistivity
An out flow resistance switching ventilator and its methodology for providing mechanical ventilation support to the respiratory failure patient are claimed. Based on the continuous out flow impounding ventilation mechanism, the apparatus provides ventilation by switching flow resistance between two different levels at a continuous gas flow system outlet valve controlled by patient's spontaneous breathing or preset mandatory parameters, resulting in airway pressure levels switching, and therefore creating lung volume switching, which is totally different from either volume ventilation or pressure ventilation mechanism utilized in the current conventional ventilators.
Owner:QIAN YUANCHENG
Methods and apparatus for the sytematic control of ventilatory support in the presence of respiratory insufficiency
ActiveUS20070163590A1Reduce gainHigh gainOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksAutonomous breathingMedicine
A method and apparatus for providing ventilatory assistance to a spontaneously breathing patient An error signal (56) is computed that is the difference between a function of respiratory airflow (54) over a period of time and a target value (52). Using a servo loop, air is delivered to the patient at a pressure that is a function of the error signal, the phase of the current breathing cycle, and a loop gain that varies depending on the magnitude of the error signal. The loop gain increases with the magnitude of the error signal, and the gain is greater for error signals below a ventilation target than for error signals above the ventilation target value. The target value (52) is an alveolar ventilation that takes into account the patient's physiologic dead space.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and apparatus for non-invasive prediction of intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEPi) in patients receiving ventilator support
ActiveUS20050284476A1Accurate detectionQuantitative precisionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingAir volume
The present invention describes a method and apparatus for non-invasive prediction of the “intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure” (PEEPi) which is secondary to a trapping of gas, over and above that which is normal in the lungs; the presence of PEEPi imposes an additional workload upon the spontaneously breathing patient. Several indicators or markers are presented to detect and quantify PEEPi non-invasively The markers may include an expiratory air flow versus expiratory air volume trajectory, an expiratory carbon dioxide flow versus expiratory air volume trajectory, an expiratory carbon dioxide volume to expiratory air volume ratio, an expiratory air flow at onset of inhalation, a model of an expiratory waveform, a peak to mid-exhalation airflow ratio, duration of reduced exhaled airflow, and a Capnograph waveform shape.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG
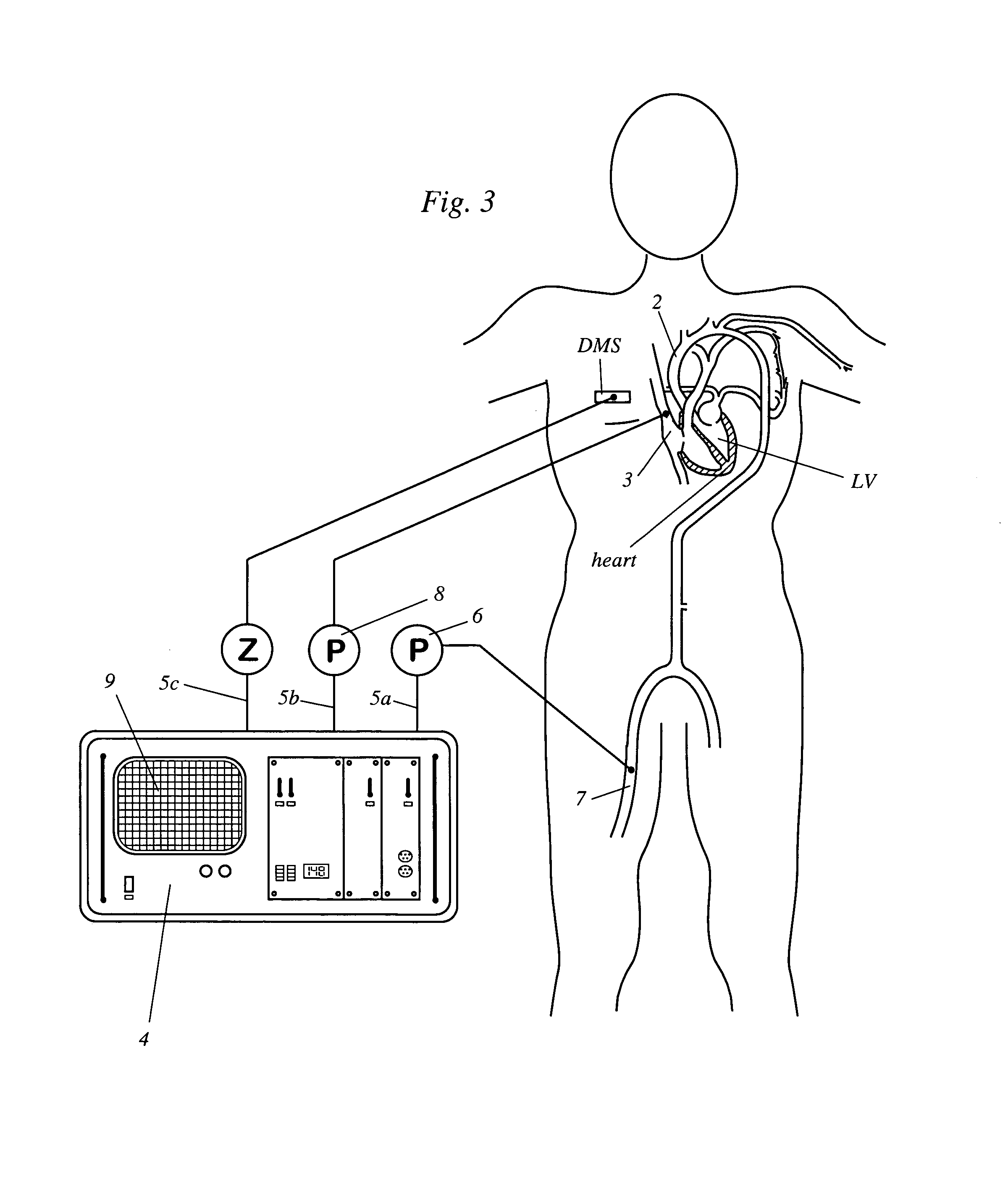
Apparatus and computer program for determining a patient's volemic status represented by cardiopulmonary blood volume
InactiveUS20080045845A1The implementation process is simpleLess laborRespiratorsCatheterAutonomous breathingNormal blood volume
An apparatus for determining a patient's volemic status can make use of a physiological heart-lung interaction during spontaneous breathing or mechanical ventilation. Further, a computer program for determining the patient's volemic status has instructions for carrying out the steps of generating data of a physiological heart-lung interaction during spontaneous breathing or mechanical ventilation, and determining the patient's volemic status when making use of the data of the physiological heart-lung interaction, when run on a computer.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCE IPRM AG
Method and apparatus for delivery of inhaled nitric oxide to spontaneous-breathing and mechanically-ventilated patients
InactiveUS20050076907A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingNitric oxide
A device and method is disclosed for delivering NO to a patient. The device utilizes a single controller that controls two separate flow controllers to deliver an oxygen-containing gas and a NO-containing gas to the patient. The flow profiles of the oxygen-containing gas and the NO-containing gas are controlled by the controller. In one aspect of the invention, the flow profile of the NO-containing gas is proportional to the flow profile of the oxygen-containing gas throughout patient inspiration. In this regard, the patient receives a steady concentration of NO. In another aspect of the invention, the flow profile of the NO-containing gas is quasi-proportional to the flow profile of the oxygen-containing gas. In this regard, the NO-containing gas flow profile is altered to provide an increased concentration of NO either at the beginning or end of inspiration. In one aspect, the delivery device is used with mechanically-ventilated patients. In the other aspect of the delivery device, the device is used with spontaneously-breathing patients. The device and method, in a preferred embodiment, further contemplates using a gas purge or air flush feature to remove enriched-oxygen and / or NO from the device.
Owner:STENZLER ALEX
Tracheal catheter and prosthesis and method of respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS20050034721A1Improve the quality of lifeEfficient methodTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingOxygen
The invention is relative to a method and an apparatus for supporting the respiration of a patient and to a tracheal prosthesis. According to the invention the spontaneous respiration of a patient is detected by sensors and at the end of an inhalation procedure an additional amount of oxygen is administered to the lungs via a jet gas current. This improves the absorption of oxygen during inhalation. If required, the exhalation procedure of the patient can be arrested or slowed by a countercurrent in order to avoid a collapse of the respiration paths in this manner. This procedure is realized by an apparatus comprising an oxygen pump that can be connected to an oxygen source and comprising a tracheal prosthesis that can be connected via a catheter. The spontaneous respiration of the patient is detected by sensors connected to a control unit for activating the oxygen pump. The tracheal prosthesis comprises a tubular support body with a connection for the catheter and two of the sensors are associated with the support body. The tracheal prosthesis and the jet catheter that is integrated or can be introduced are dimensioned so that the patient can freely breath and speak without restriction.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
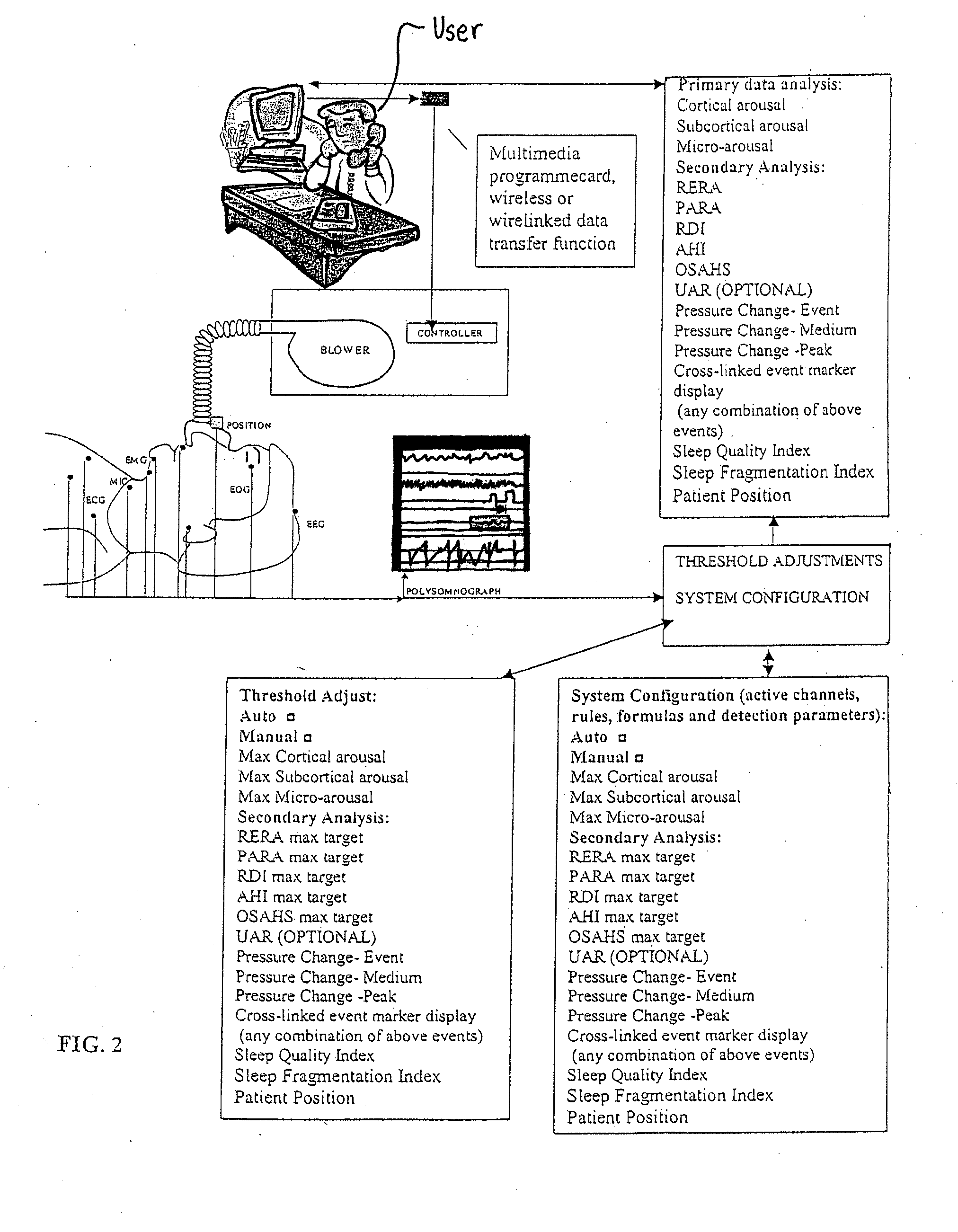
Method and apparatus for maintaining and monitoring sleep quality during therapeutic treatments
ActiveUS20110192400A9Reduce or eliminate both sleep breathing disorders and sleep fragmentationRespiratorsElectrocardiographyAutonomous breathingPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention monitors and interprets physiological signals and spontaneous breathing events to detect the onset of arousal. Once the onset of arousal is determined, the present invention determines adjustments that are needed in the operation of a therapeutic device to avoid or minimize arousals. In one embodiment, the present invention includes one or more sensors which detect a patient's physiological parameters, a controller which monitors and determines the onset of arousal based on the physiological variables received from the sensor, and a therapeutic treatment device which is controlled by the controller. The sensor can be a combination of one or more devices which are able to monitor a physiological parameter that is used by the present invention to determine the onset of arousal or the onset of a sleep disorder. The sensors can be integrated into one unit or may operate independent of the others.
Owner:COMPUMEDICS
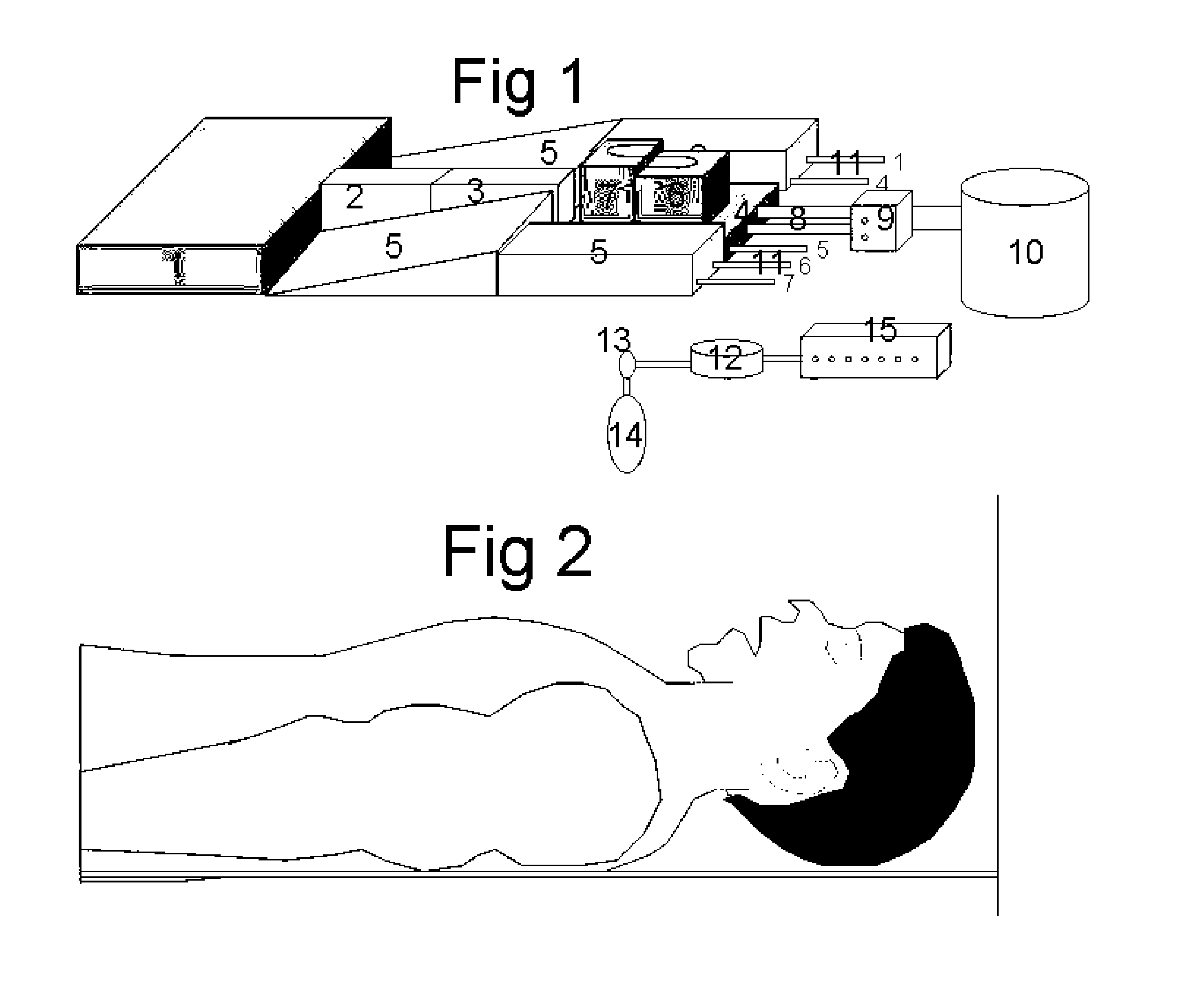
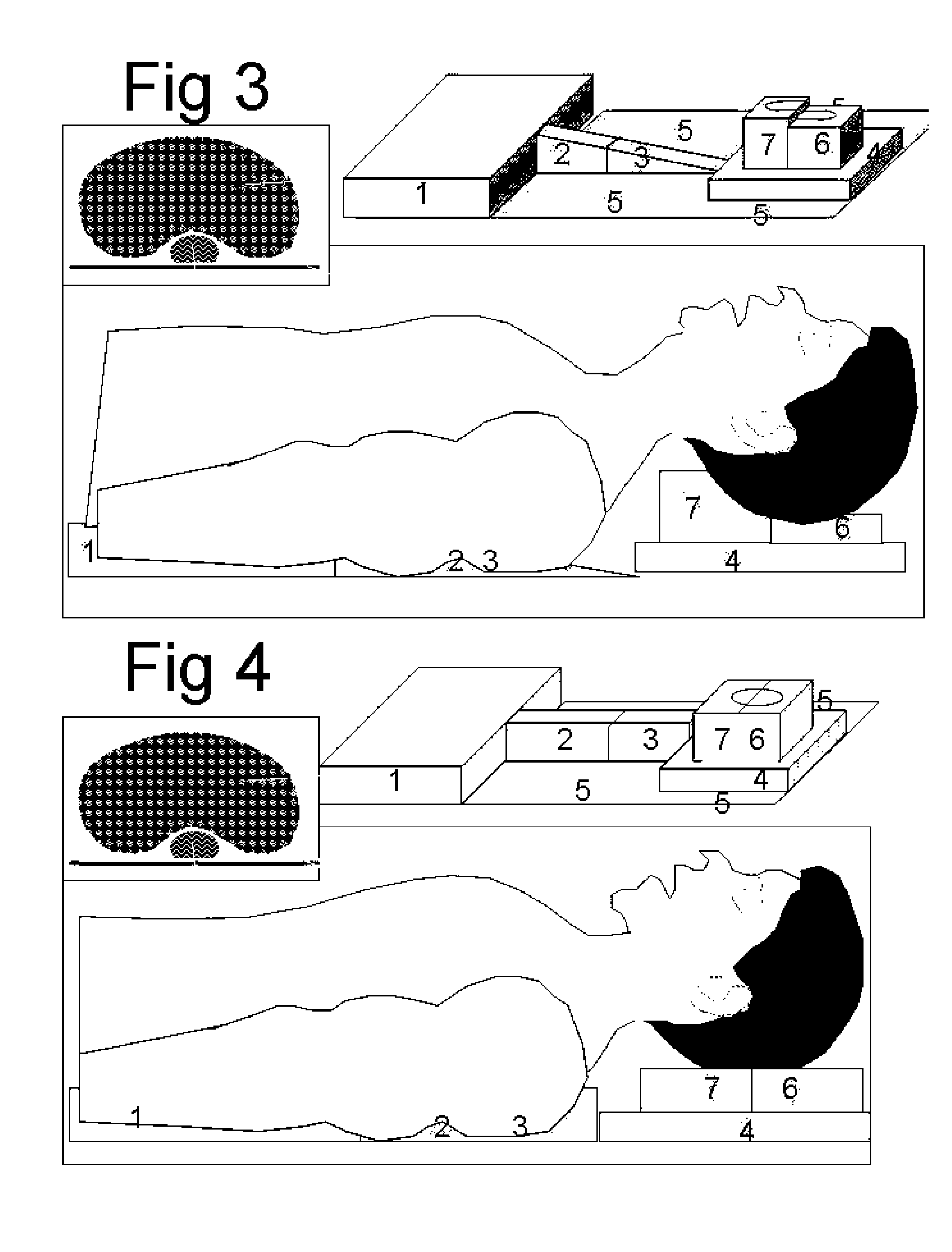
Intubation positioning, breathing facilitator and non-invasive assist ventilation device
InactiveUS20070181122A1Easy intubationEasy alignmentRespiratorsOperating tablesSpinal columnAssisted ventilation
This invention can be used in three different ways for patients who are lying down in bed or on the operating table. First it facilitates the endotracheal intubation, secondly it facilitates the spontaneous breathing of obese patients and thirdly it assists the spontaneous inspiration and expiration in a non-invasive way. This invention device is positioned under the patient before he is asleep without disturbing him. It allows a gradual elevation of the lower and or upper thorax, a gradual elevation of the head giving a flexion of the neck and a gradual hyperextension of the head. After intubation the position is returned to normal without need for removing the invention device. This invention elevates the spinal column and therefore the thorax is no more compressed and the ribs can move free. Inspiration requires less force and the patient can be breathing easier even when lying down. In this invention the spinal column elevation can also be inflated in a synchronized way with the respiration of the patient. During inspiration the spinal column is elevated, facilitating the inspiration. During expiration the elevation is lowered, facilitating the expiration. The work of breathing is reduced for the patient resulting in larger minute volume ventilation or less oxygen consumption.
Owner:MULIER JAN PAUL
Method and apparatus for breathing during anesthesia
InactiveUS6123072AEliminate the problemMinimize movementRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingWhole body
A method and apparatus are provided for ventilation of patients during general anesthesia. Breathing gas is supplied to the patient during anesthesia at a controlled volume above the functional residual capacity of the patient's lungs. The patient is allowed to spontaneously respire when the volume of breathing gas is above the functional residual capacity. The pressure of the breathing gas is periodically reduced to facilitate expulsion of carbon dioxide-containing gas from the patient. The system promotes alveolar ventilation, carbon dioxide excretion, oxygenation and respiratory monitoring in patients who receive general anesthesia.
Owner:DOWNS JOHN B
Acoustic Ventilation and Respiratory Booster Machine
InactiveUS20140190481A1Improve ventilationLess injuriousTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingHuman–machine interface
An acoustic ventilator using feedback control is designed to generate and exert a desired mixture of pressure oscillations into a supply of gas entering a subject's airways to maintain optimal ventilation and perfusion in the lungs. According to the subject's biological specifications and real-time medical condition, computers and human interface control the vibrations in intensity and frequency along with the pressure and composition of blended gases in order to enhance oxygenation and CO2 clearance. Acoustic ventilation will cause the ventilating gases to diffuse through the subject's lungs without the aid of a separate ventilator, and with or without spontaneous breathing.
Owner:JAM MOHAMMAD R
Method for use with the pressure triggering of medical ventilators
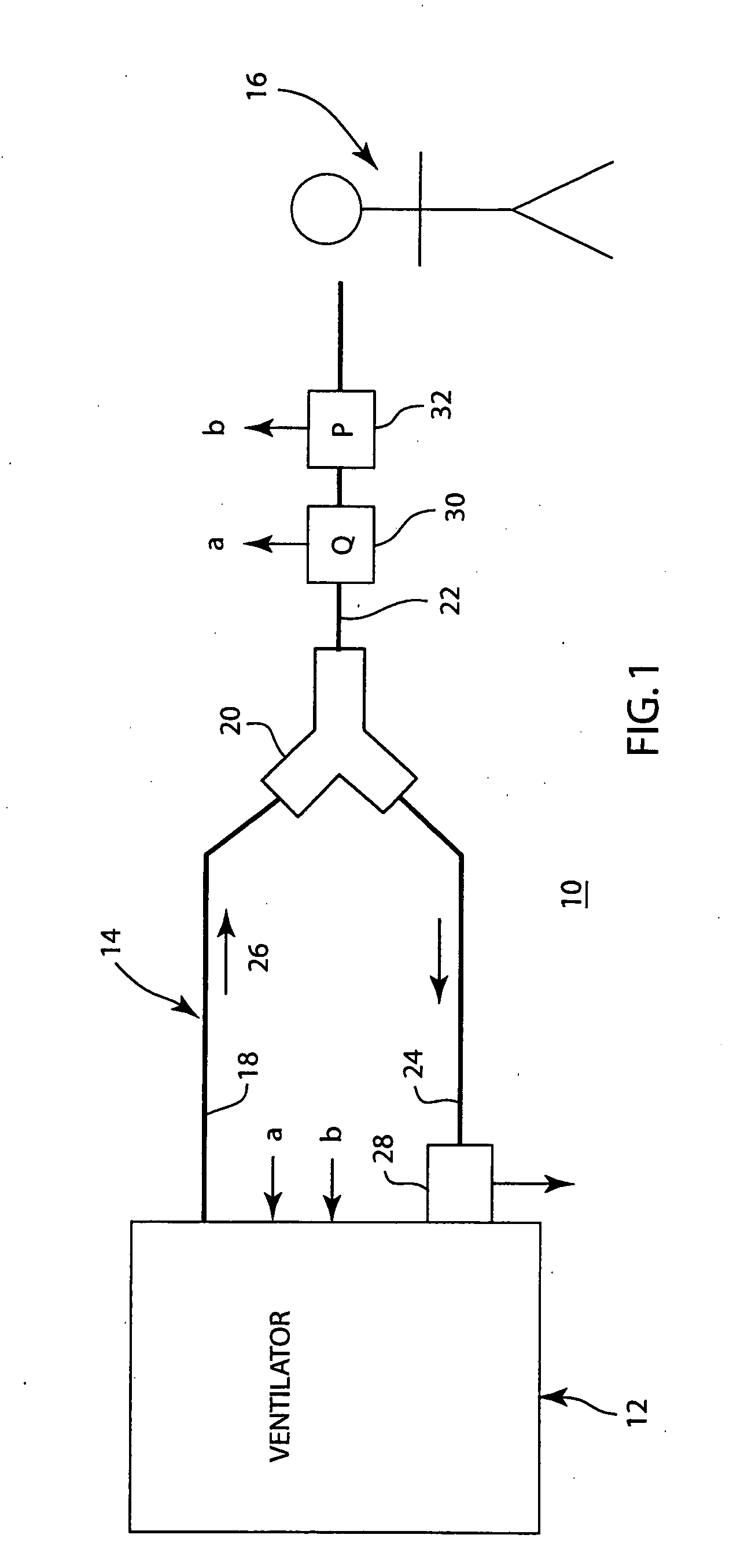
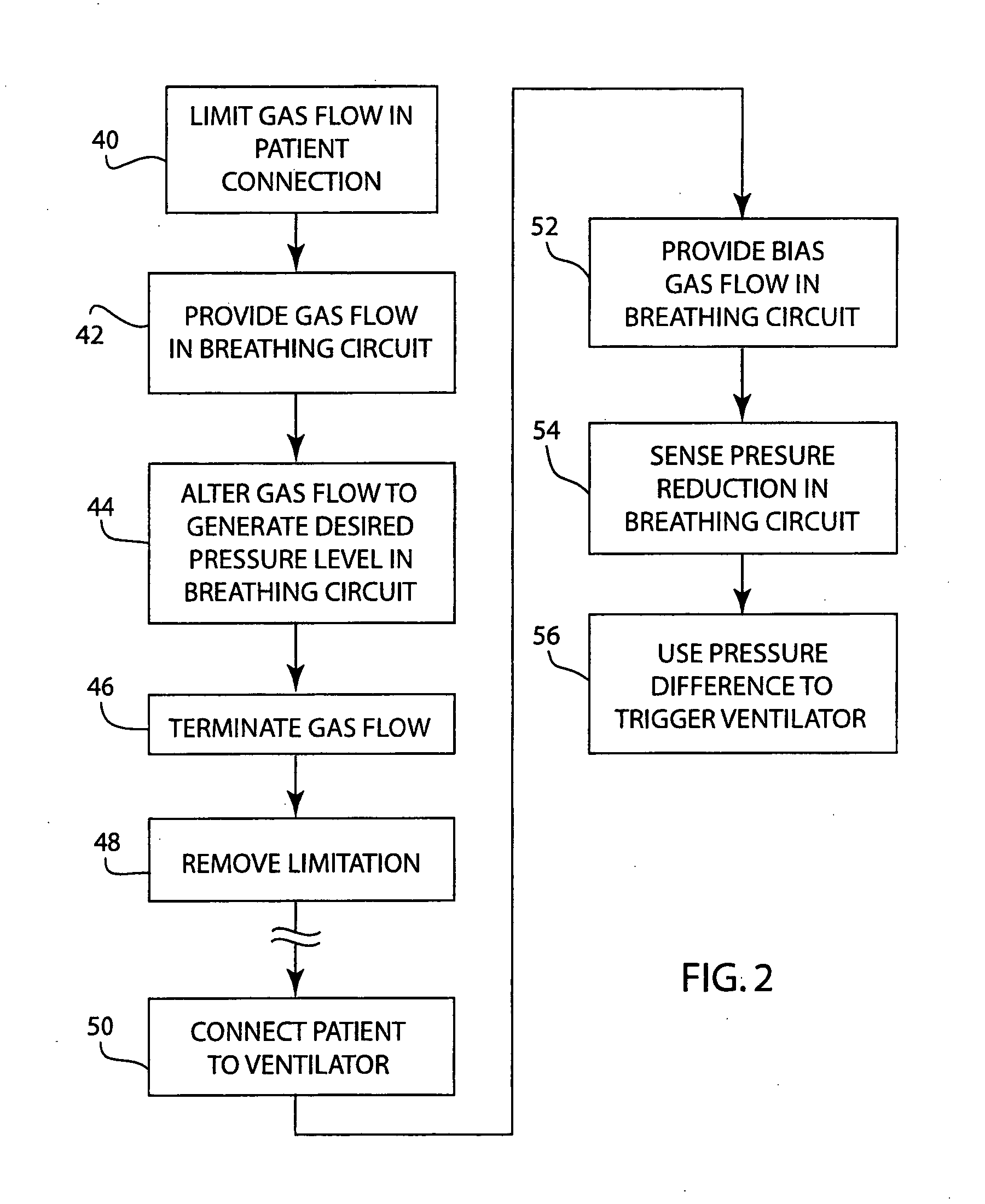
ActiveUS20070044798A1Increased pressure sensitivityDesign economyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingInhalation
A method for providing a pressure reference level for pressure triggering a ventilator responsive to a spontaneous breathing attempt by a patient. In the method, the patient connection of the breathing circuit is capped or plugged. A gas flow is then provided through the breathing circuit and is altered to an amount that causes the flow resistance properties of the breathing circuit to generate a desired gas pressure in the breathing circuit suitable for use as a reference pressure by the ventilator for pressure responsive triggering. During the operation of the ventilator, gas flow in a corresponding amount serves as a bias flow in the breathing circuit to assist breathing by the patient. The bias flow also generates the reference pressure level in the breathing circuit. A reduction in pressure from the pressure level resulting from inhalation by the patient triggers the operation of the ventilator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and computer program for determining a patient's volemic status represented by cardiopulmonary blood volume
InactiveUS20120179051A1The implementation process is simpleLess laborRespiratorsEvaluation of blood vesselsAutonomous breathingNormal blood volume
An apparatus for determining a patient's volemic status can make use of a physiological heart-lung interaction during spontaneous breathing or mechanical ventilation. Further, a computer program for determining the patient's volemic status has instructions for carrying out the steps of generating data of a physiological heart-lung interaction during spontaneous breathing or mechanical ventilation, and determining the patient's volemic status when making use of the data of the physiological heart-lung interaction, when run on a computer.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES IPRM AG
Nasal interface apparatus and systems for use with a respiratory assist device
ActiveUS20150250973A1Increase airway pressureLight weightRespiratory masksBreathing masksAssisted ventilationAutonomous breathing
An ambulatory assist ventilation (AA V) apparatus and system are disclosed for the delivery of a respiratory gas to assist the spontaneous breathing effort of a patient with a breathing disorder. The AA V system includes a compressed respiratory gas source, a respiratory assist device for controlling respiratory gas flow to the patient, a patient circuit tubing and a low profile nasal interface device, which does not have a dead space or hollow area where C02 can collect, for delivering the respiratory gas to the patient, wherein the nasal interface device is fluidly connected to the respiratory assist device via tubing for receiving the respiratory gas therefrom.
Owner:INOGEN INC
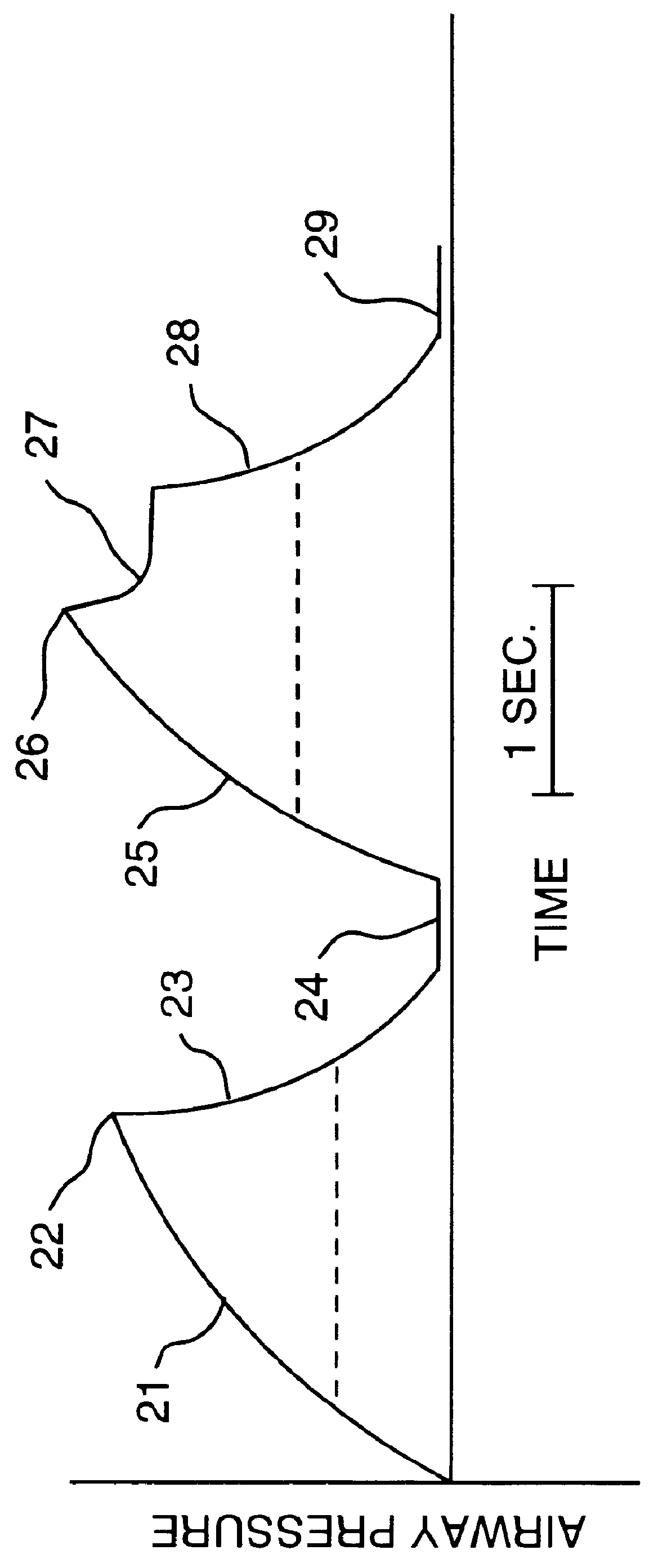
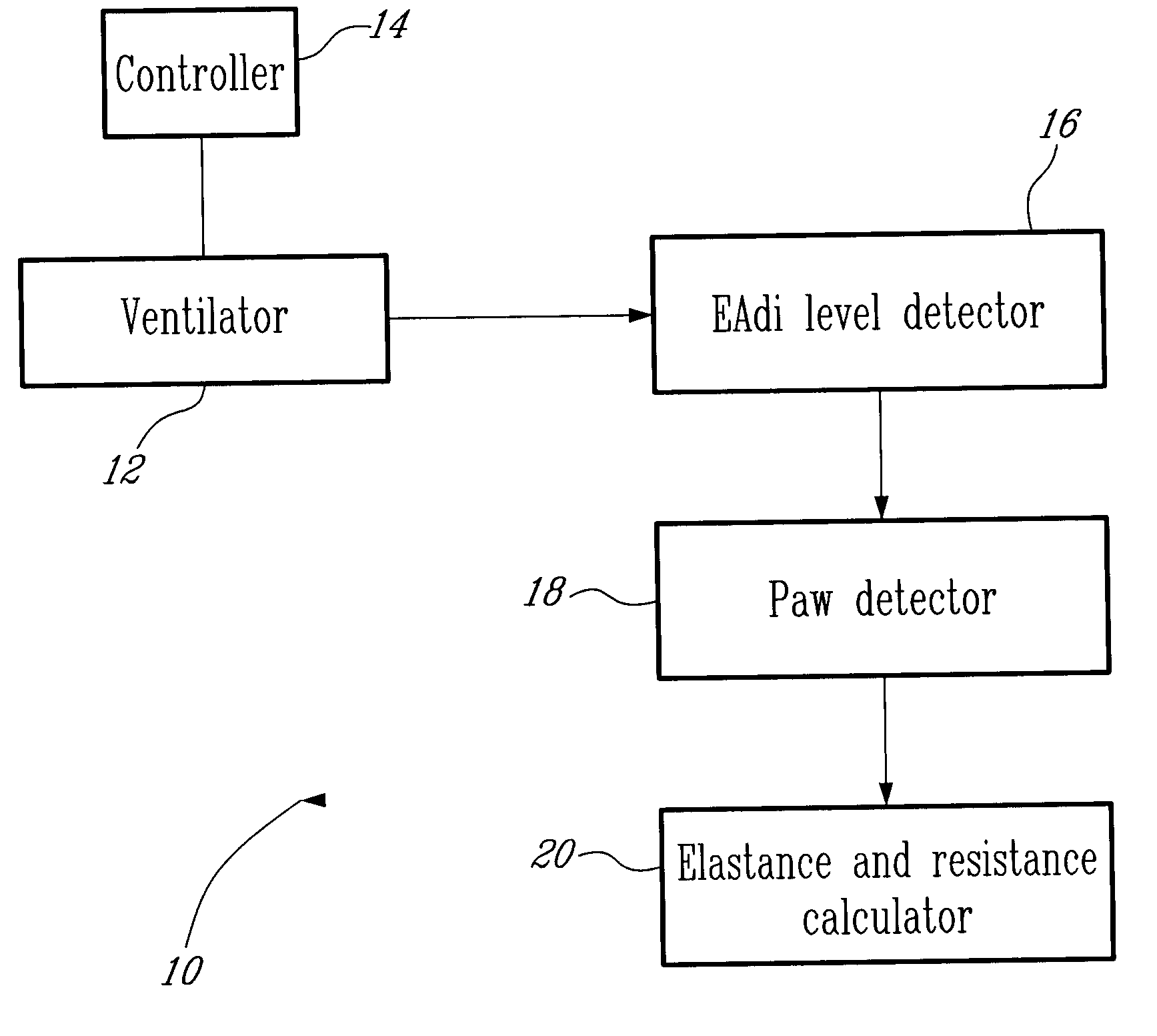
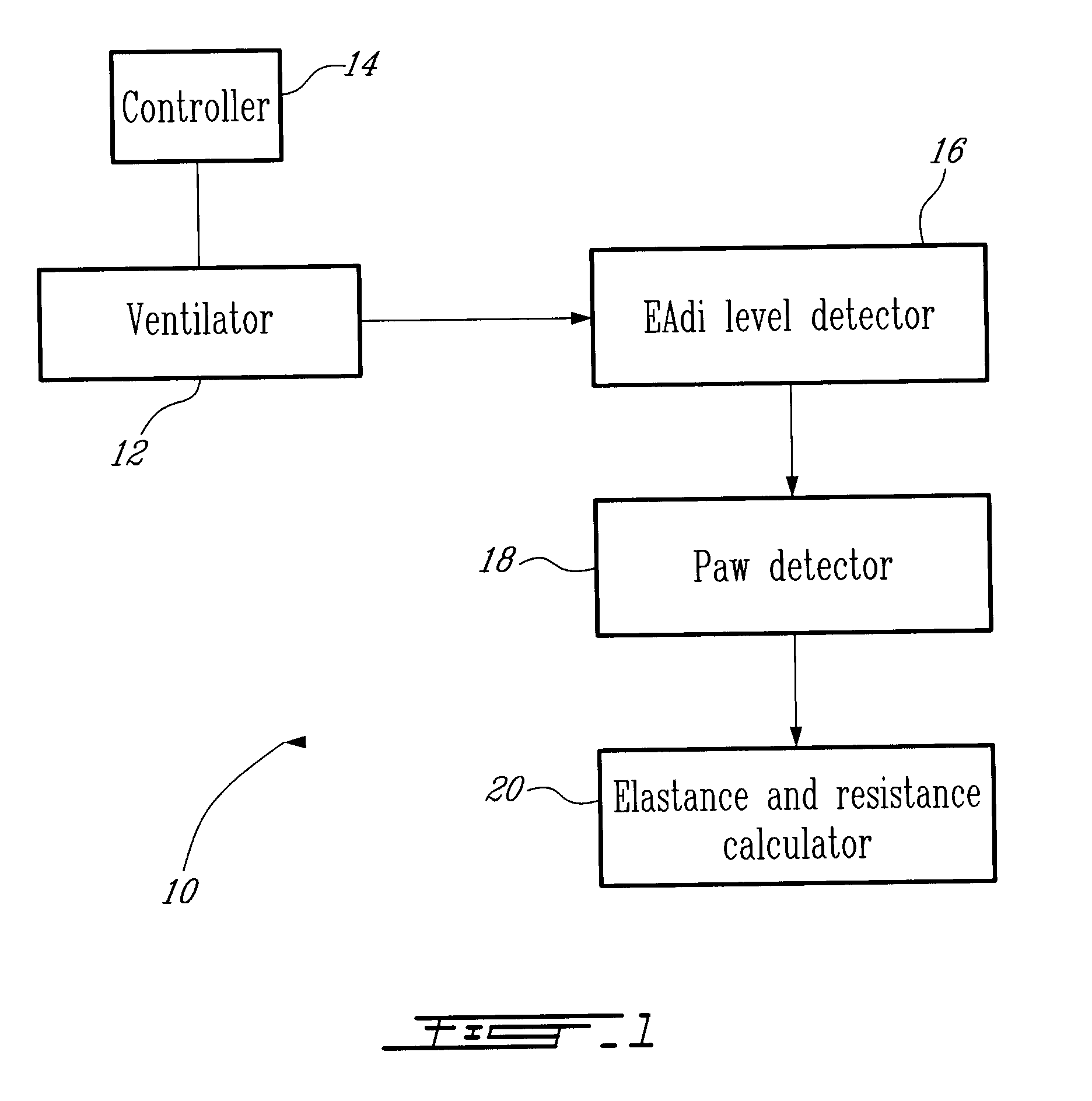
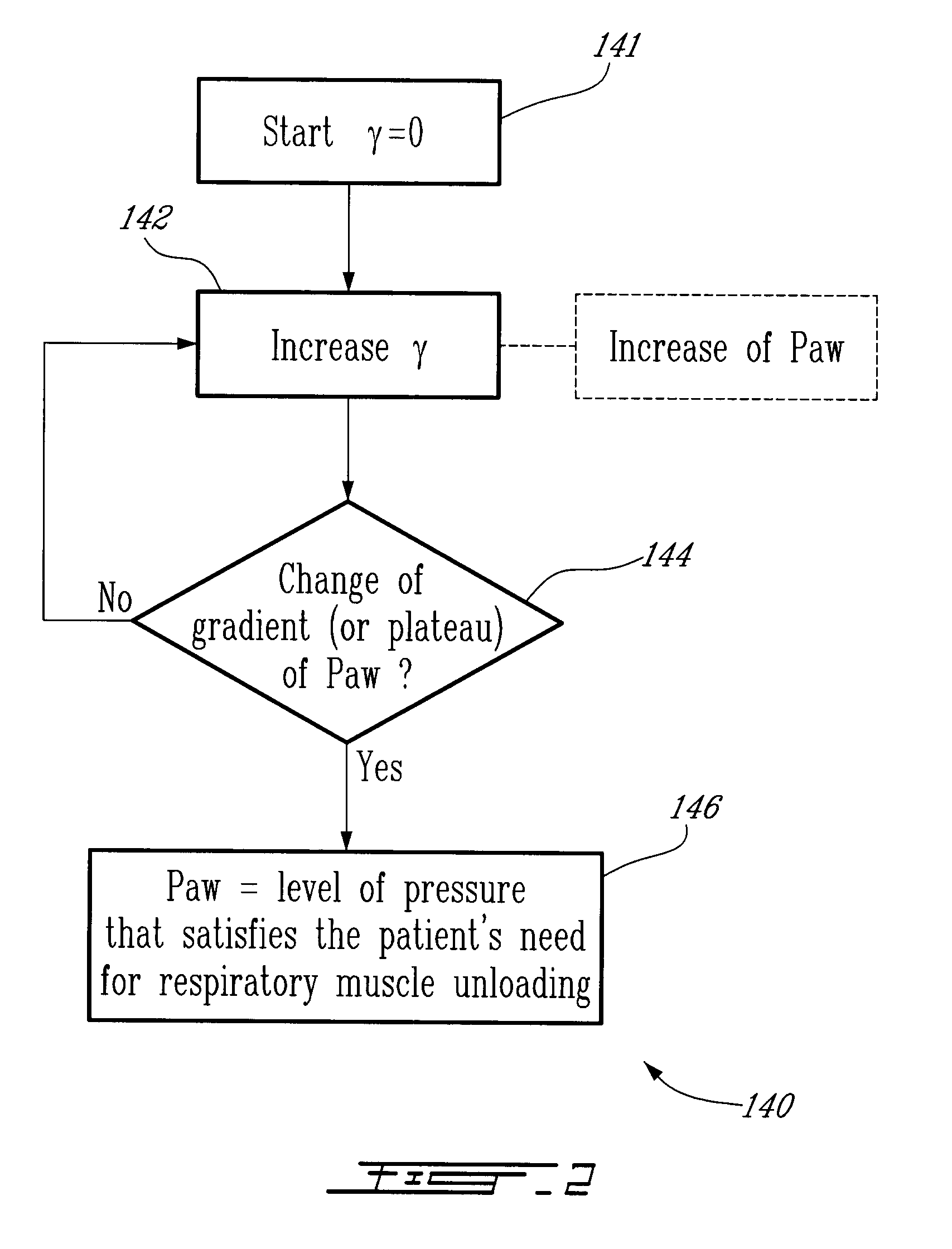
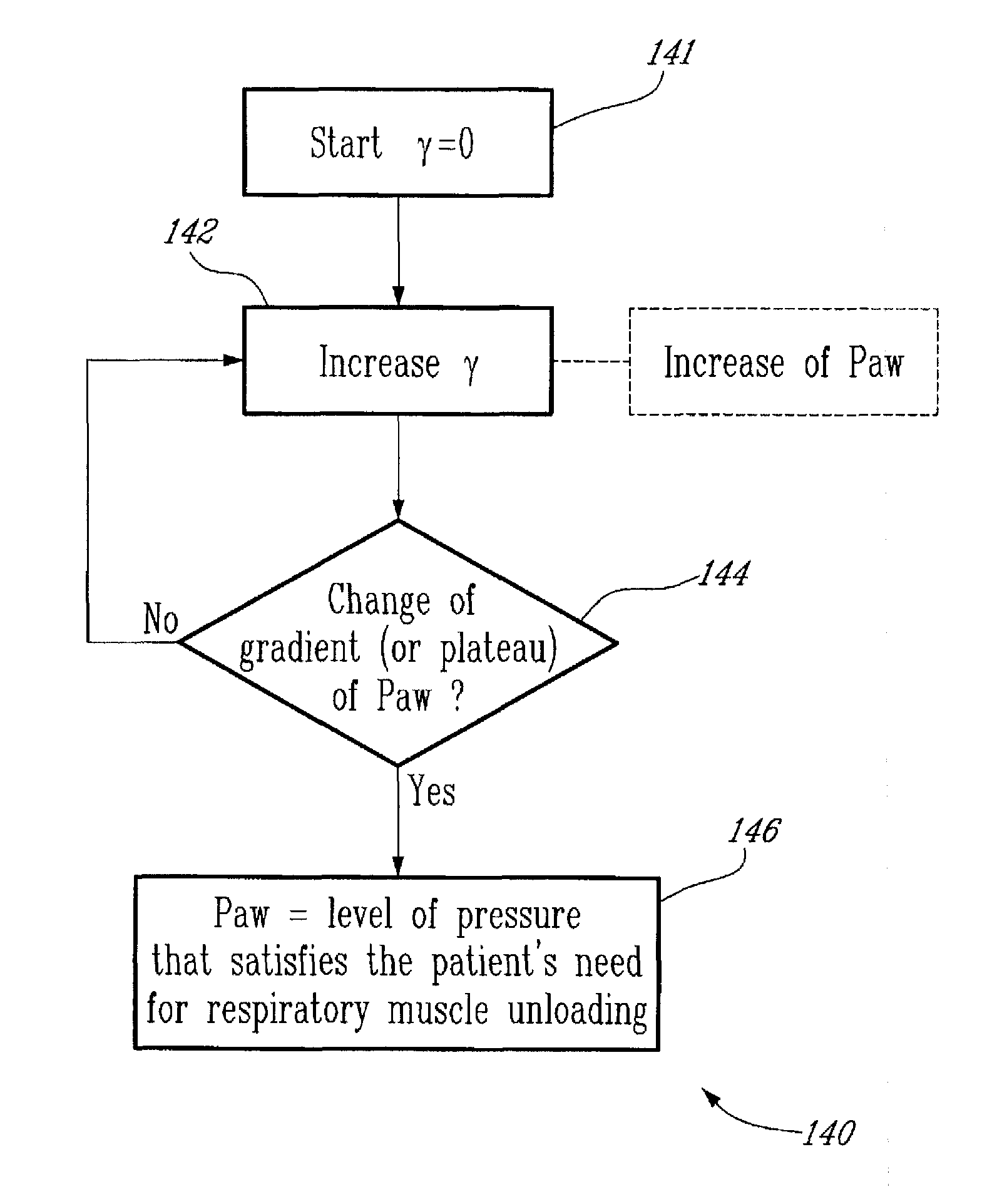
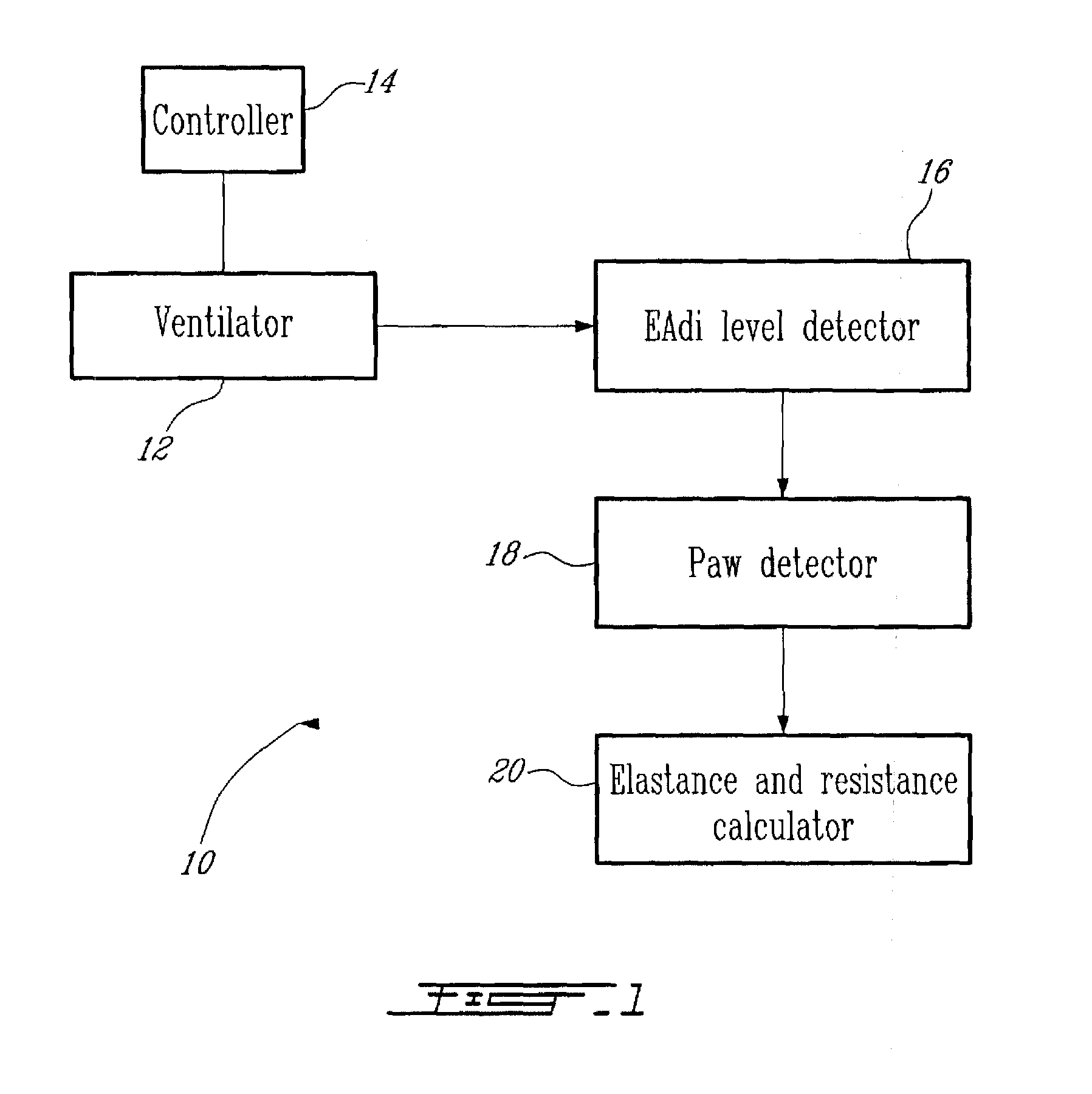
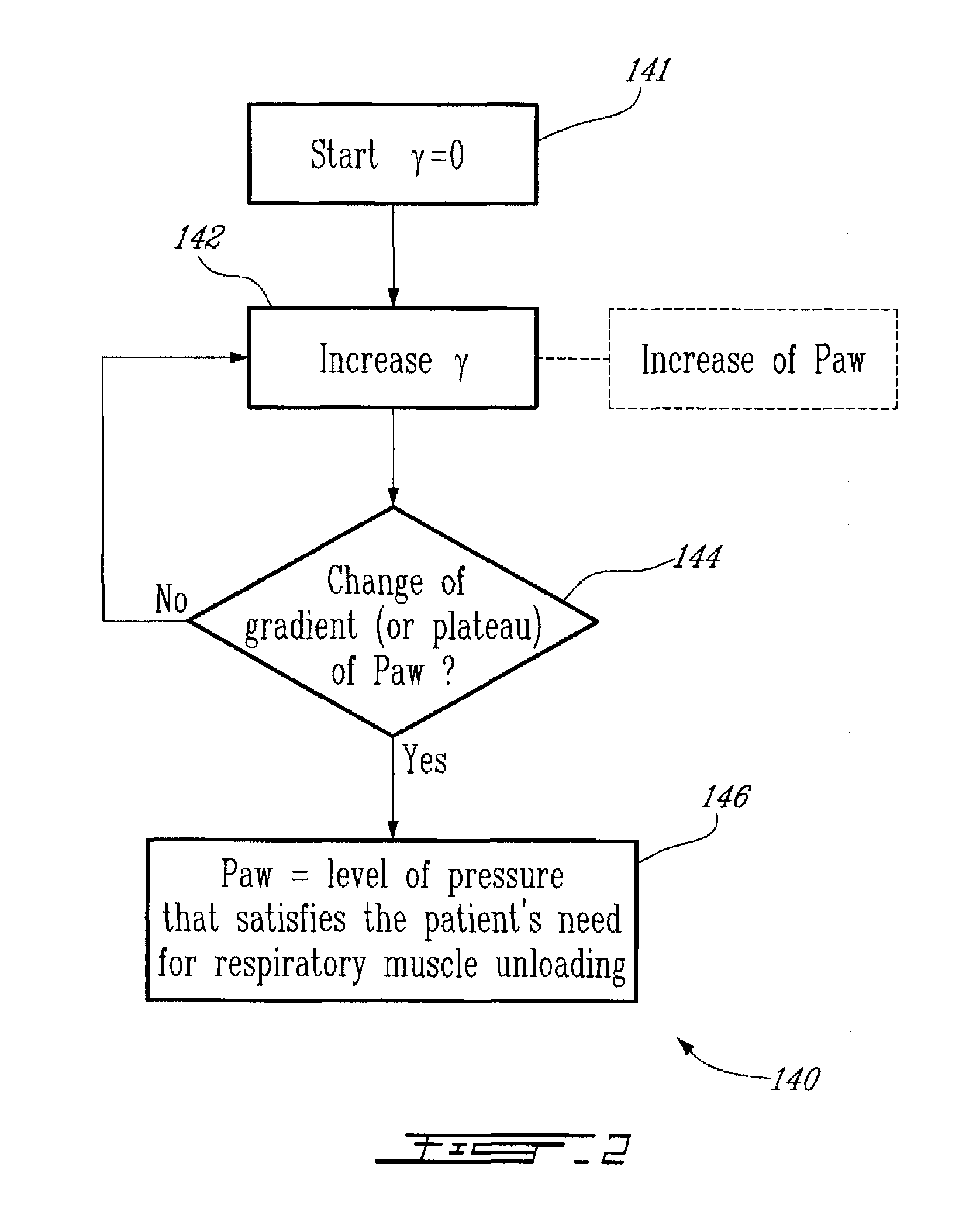
Method and System for Determining Dynamically Respiratory Features in Spontaneoulsy Breathing Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilatory Assist
ActiveUS20100228142A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingAirway pressures
A method for determining dynamically a respiratory feature in a spontaneously breathing patient receiving mechanical ventilatory assist comprises: modifying a level of mechanical ventilatory assist to the patient, measuring an airway pressure, detecting a change of gradient of the measured airway pressure and determining the respiratory feature based on the measured airway pressure upon detecting the change of gradient of the airway pressure. Furthermore, the method also comprises: measuring a respiratory neural drive of the patient and detecting a lowest level of the measured respiratory neural drive for determining the respiratory feature based on the detected lowest level of respiratory neural drive.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
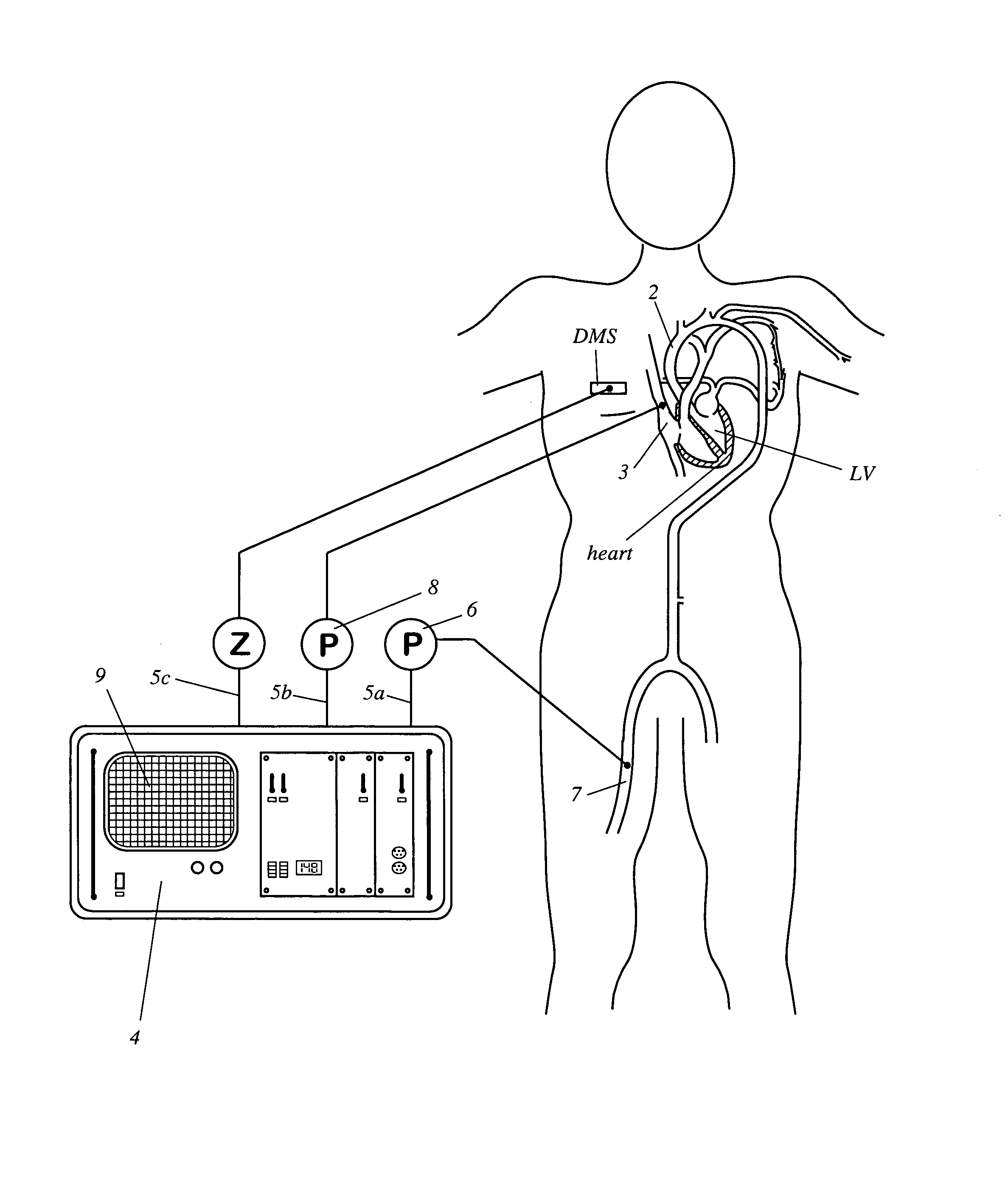
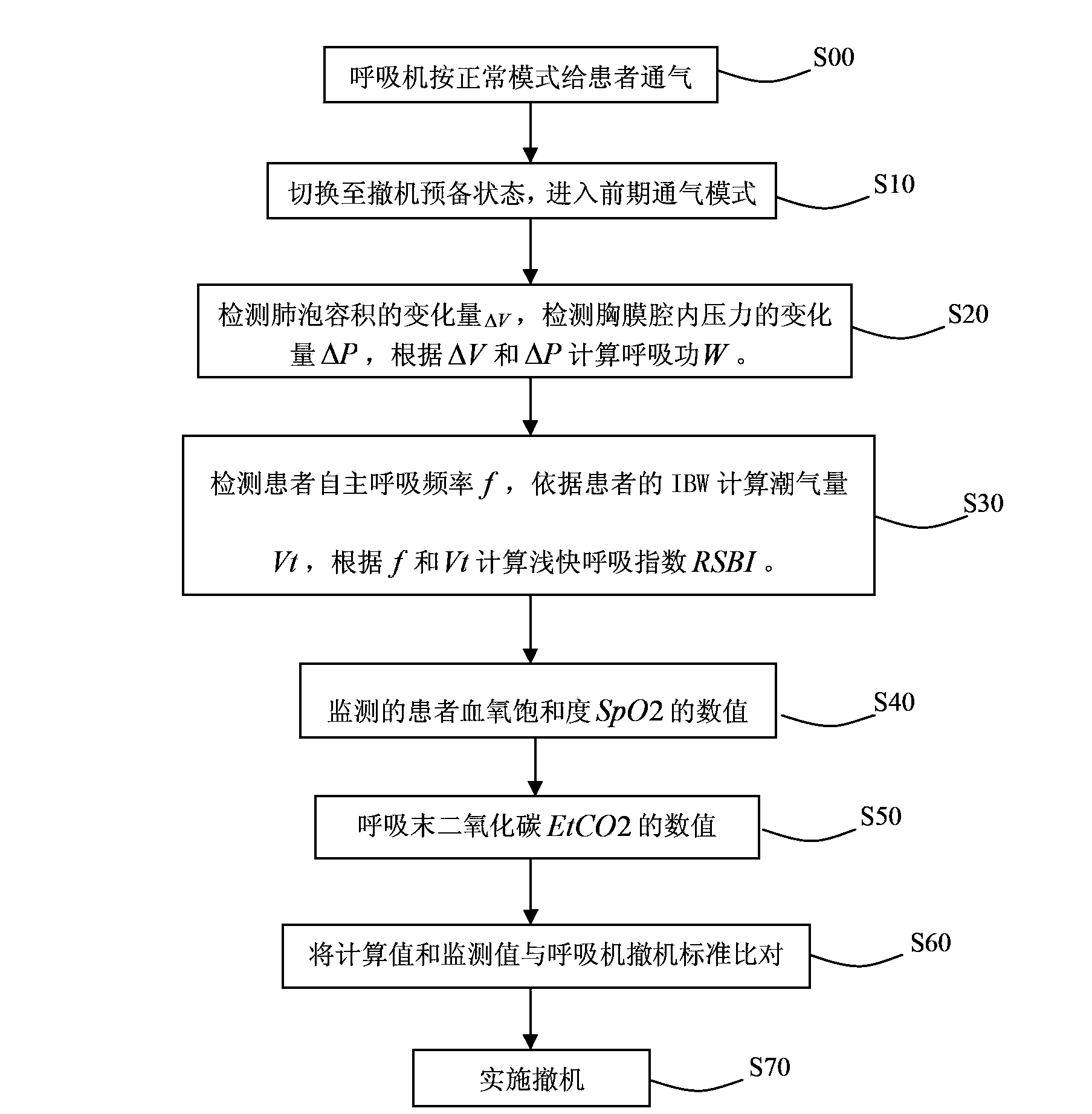
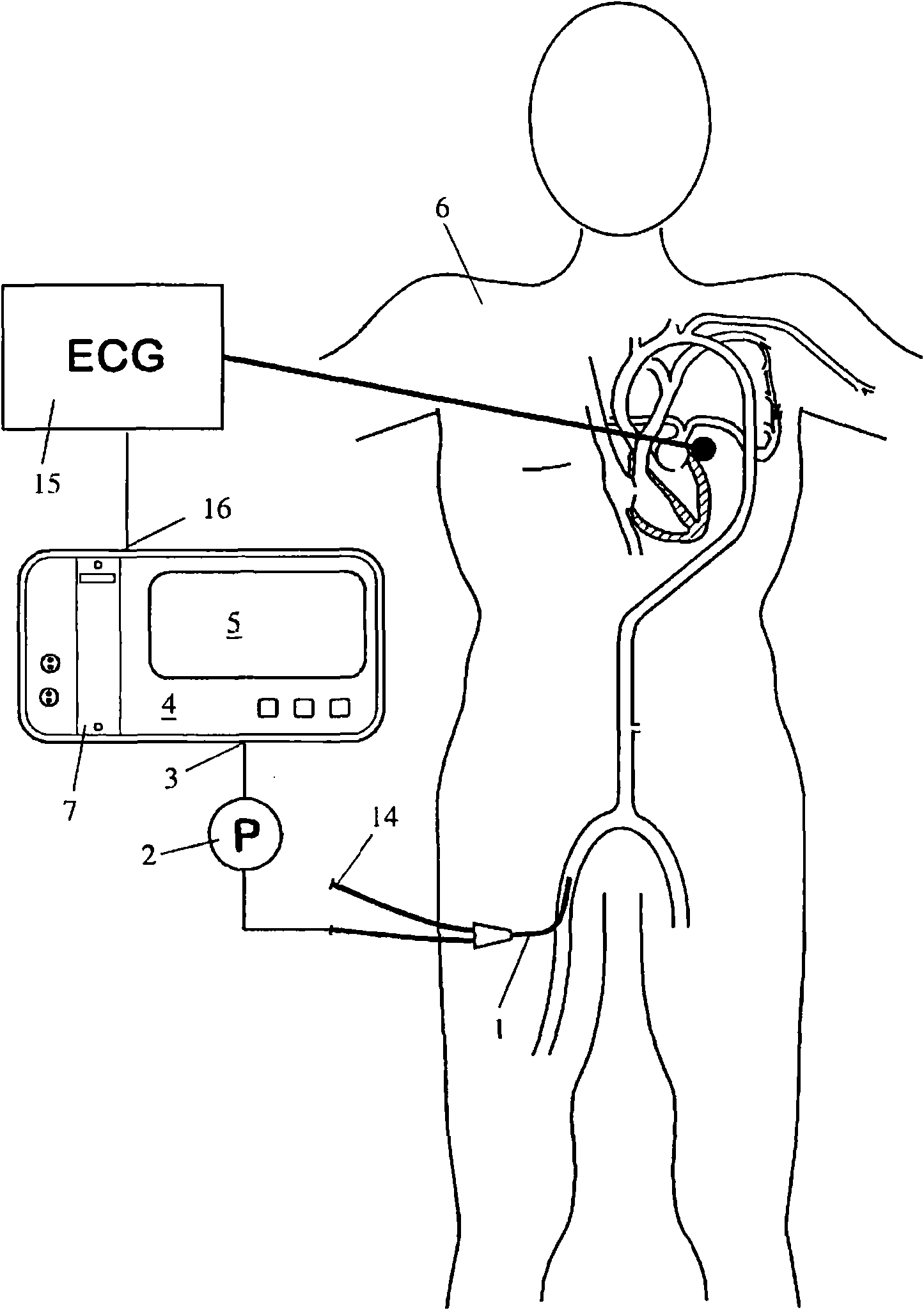
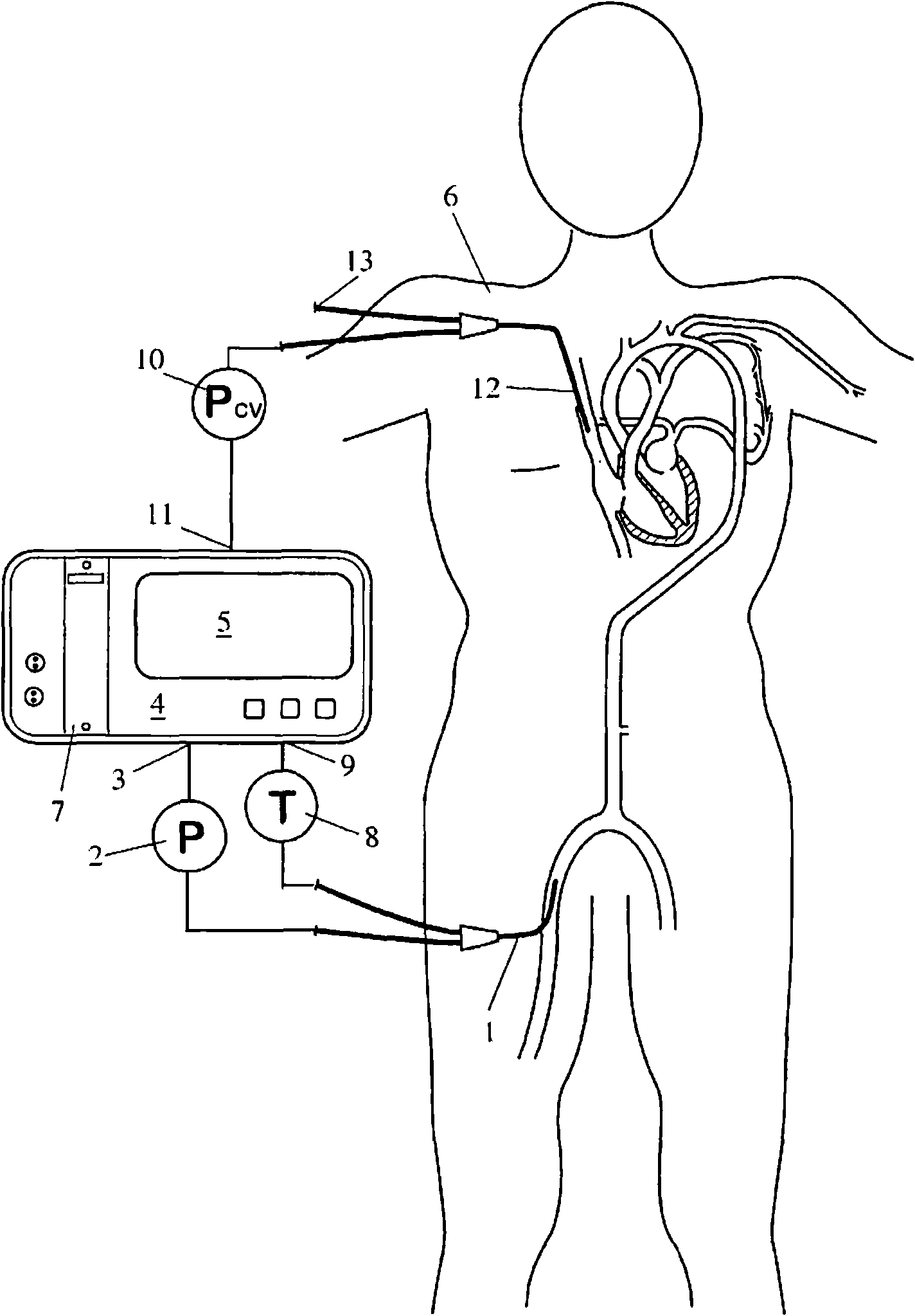
Apparatus for determining cardiovascular parameters
InactiveUS7314449B2Reduced effectivenessReliable assessmentRespiratorsSurgeryAutonomous breathingTransmural pressure
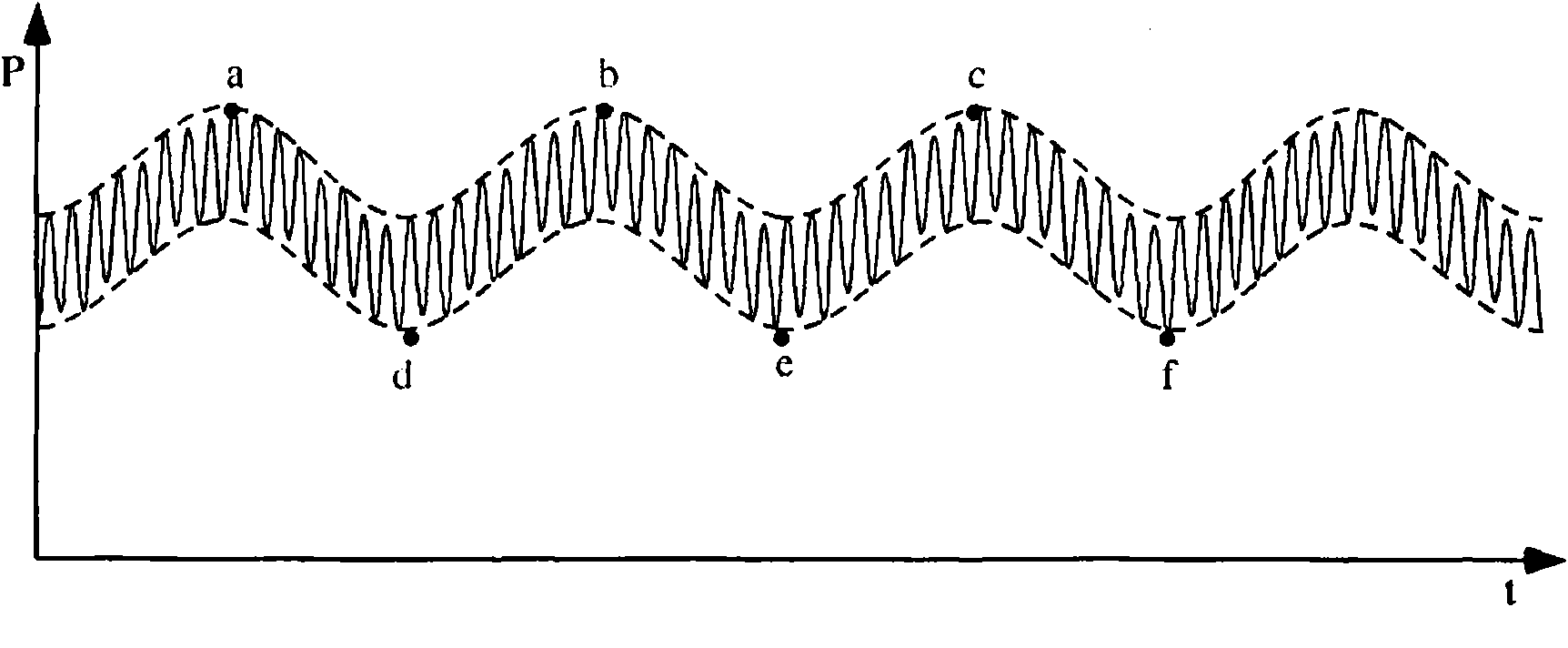
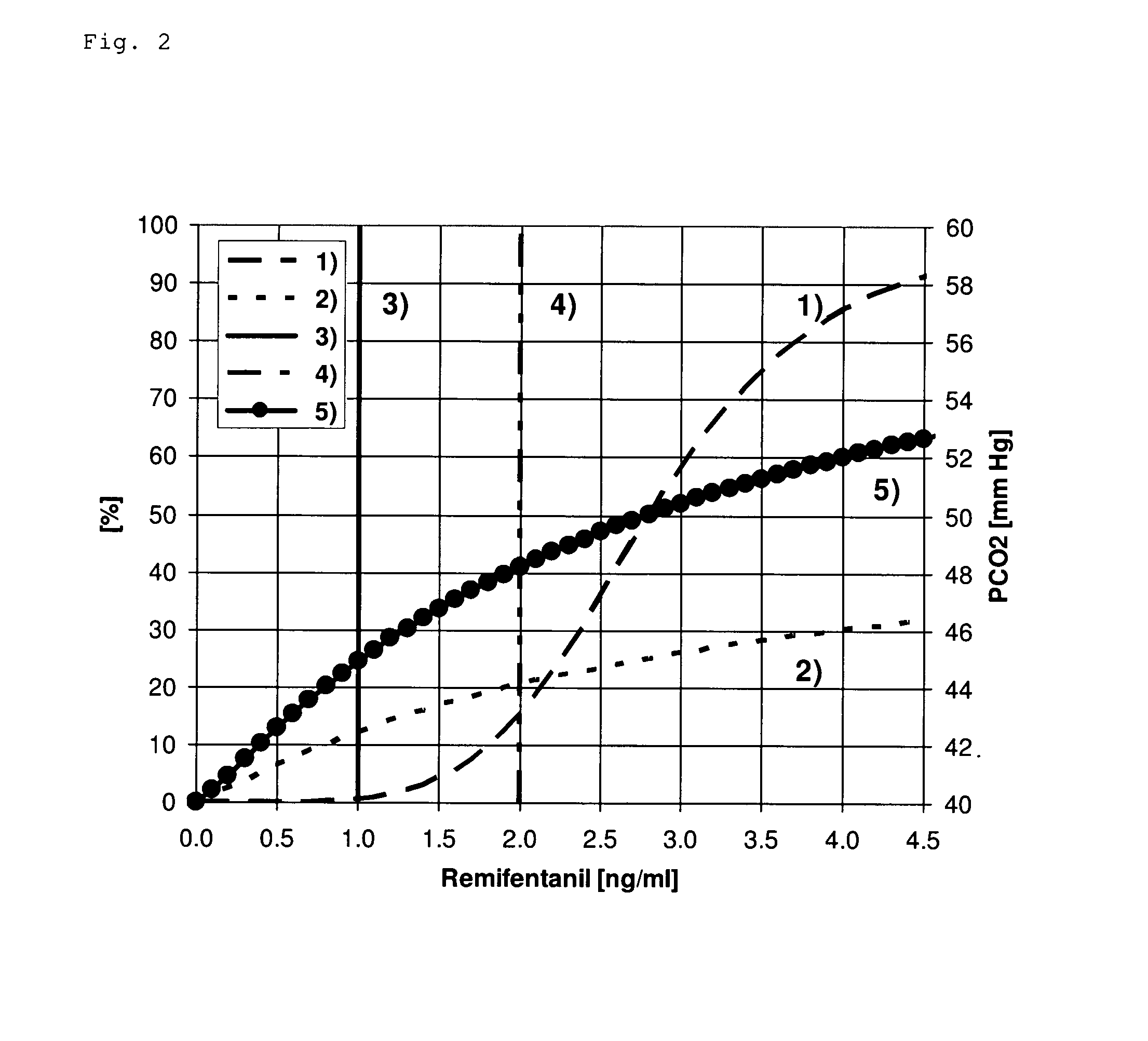
An apparatus that continuously monitors the arterial pressure measured by a pressure sensor in an artery, which pressure is regarded as the reading Pao that approximately corresponds to the aortal pressure. In principle, the arterial pressure can be measured in the aorta, near the aorta, or in the arterial tree. To provide a second reading, the apparatus, via the input channel, continuously monitors the central venous pressure (CVP), which is regarded as the reading PIT that approximately corresponds to the intrathoracic pressure (ITP). The third reading is provided via the input channel as a reading Z which expresses the thoracic compliance. Via known algorithms of the pulse contour analysis, the apparatus calculates the stroke volume variation, using as the determining pressure the transmural pressure which is calculated according to the formulaPtransmural=Pao−f(C)*PITThe cardiac volume responsiveness indicator (CVRI) is calculated for mechanical positive respiration according to the formulaCVRI=k*(SVV / ΔCVP)or for spontaneous breathing according to the formulaCVRI=l−m*(ΔCVP / SVV).
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYSTEMS SE
Weaning method and weaning device for intelligent breathing machine
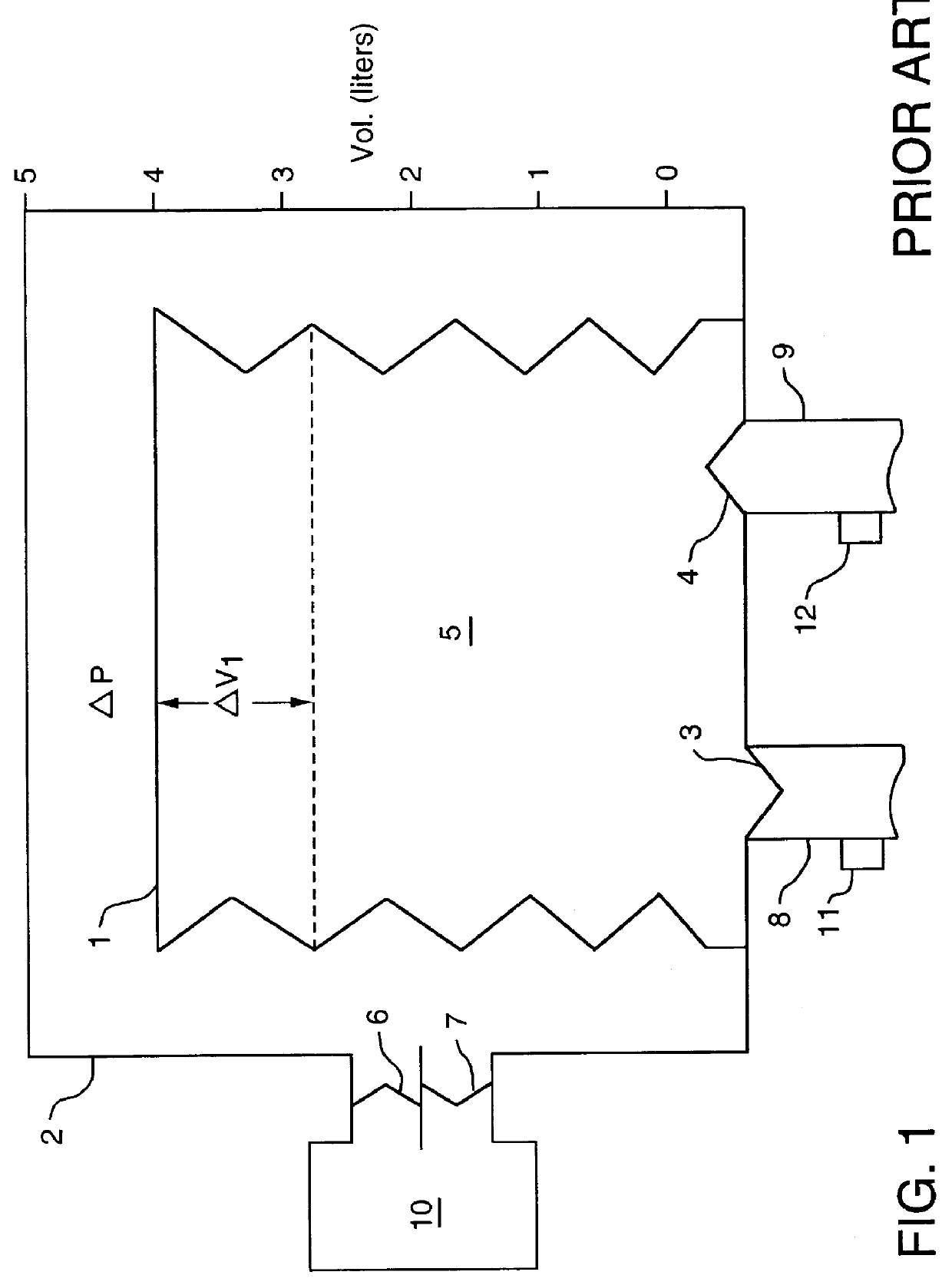
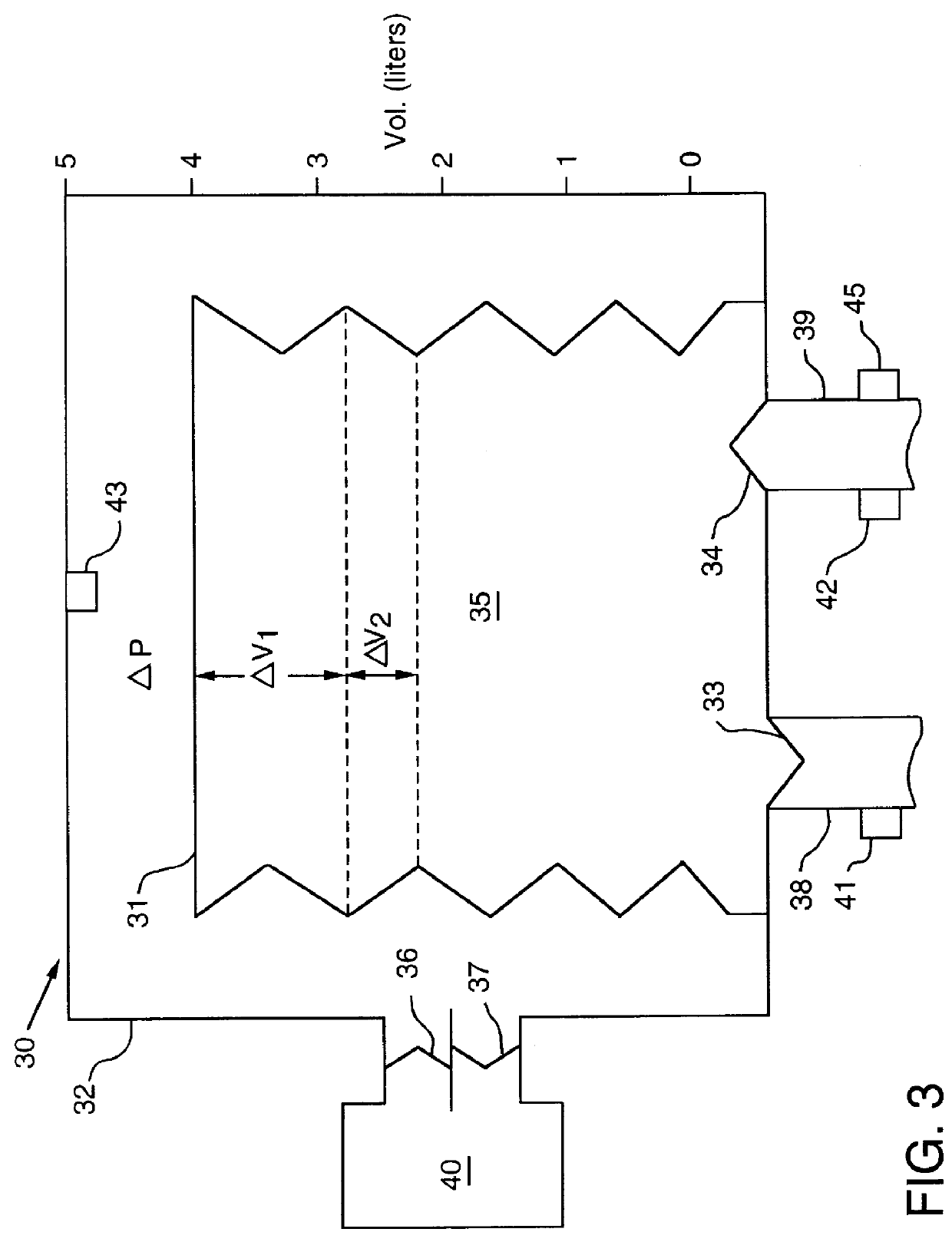
ActiveCN103893866AHigh degree of automationImprove measurement accuracyRespiratorsWeaningInternal pressure
The invention discloses an intelligent breathing machine and a weaning method for the intelligent breathing machine. A ventilation effect can be automatically realized by the intelligent breathing machine before weaning is carried out. The weaning method includes examining variation delta V of the volumes of the pulmonary alveoli of a patient, variation delta P of the internal pressure of the pleural cavity of the patient and the spontaneous breathing frequency f of the patient at first; computing work W of breathing and a rapid-shallow-breathing index RSBI of the patient by the aid of examined values; monitoring a numerical value of the blood oxygen saturation degree SpO2 of the patient and a numerical value of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 of the patient; comparing computed values and the monitored values to weaning standards of the breathing machine; implementing weaning if the weaning standards of the breathing machine are met; implementing secondary weaning judgment if the weaning standards of the breathing machine are not met. The intelligent breathing machine, the weaning method and a weaning device have the advantages that various key indexes of vital signs of the patient are monitored automatically, so that whether weaning is implemented or not can be comprehensively judged, and the weaning judgment accuracy can be improved; a good clinical effect can be realized by the weaning method, and the weaning method and the weaning device bring convenience for medical staff to accurately implement weaning operation according to weaning information.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
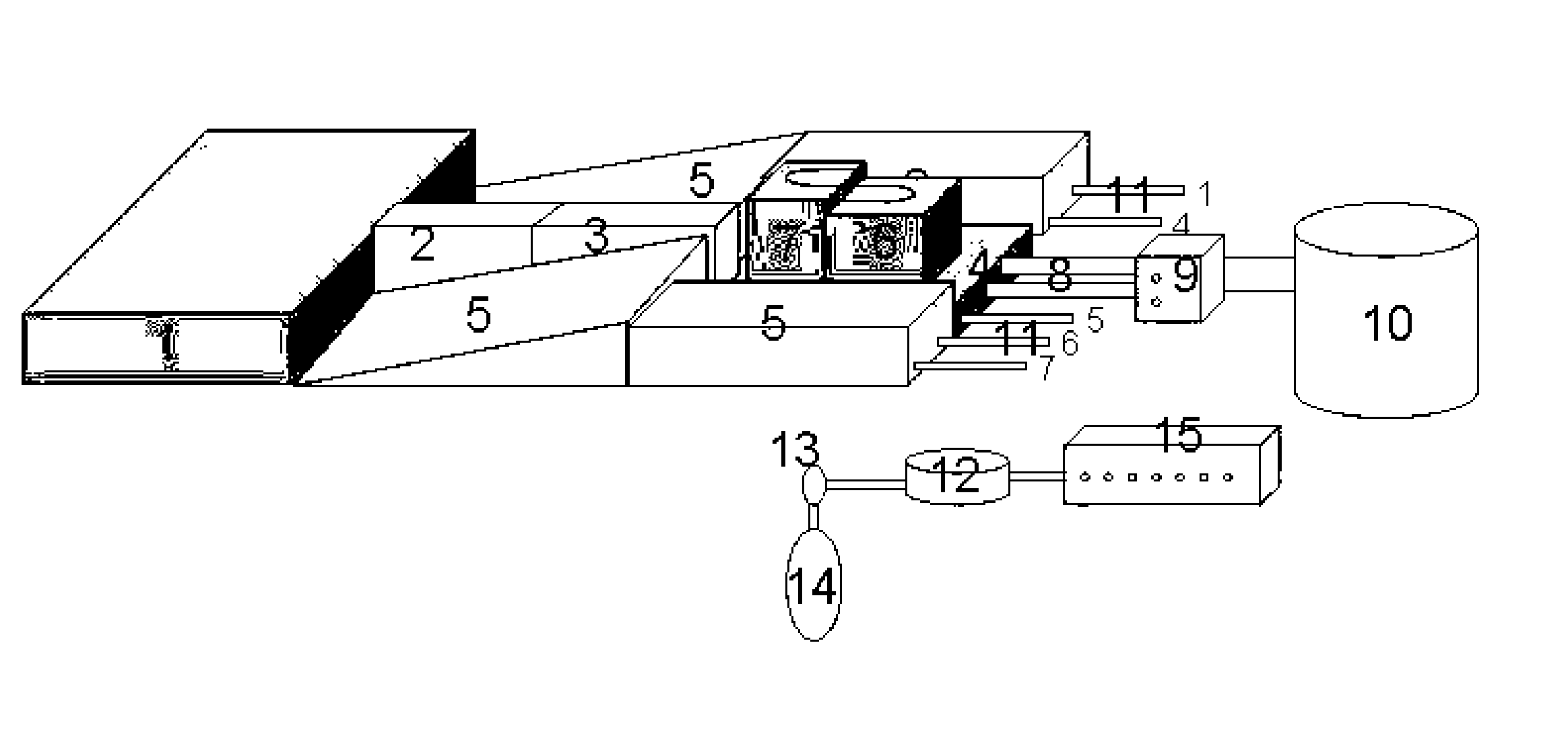
Apparatus for actively simulating autonomous respiration of human body in vitro and gas analyzing method employing the same
The invention, which belongs to the psychological research filed of respiratory medicine, relates to an apparatus for actively simulating autonomous respiration of a human body in vitro and a gas analyzing method employing the same. The apparatus includes a circulating gas circuit formed by a driving respirator, a dual-cavity simulation lung device and a head dead space model; and the output end of the dual-cavity simulation lung device is connected with the head dead space model by a gas analyzing device. The gas analyzing method comprises the following steps that: data are collected; integration is carried out on results by multiplication of obtained real-time oxygen concentration inside the apparatus and inspiration / expiration flow rates so as to obtain oxygen fluxes and tidal volumes of expiration / inspiration in each respiratory cycle; and division operation is carried out on the oxygen fluxes and tidal volumes to obtain mean effective inspired oxygen concentration in inspiratory / expiratory phases. According to the invention, the apparatus having a compact structure can be applied to scientific research and training of various ventilation modes; and the applied gas analyzing method enables a detection result to be accurate and to approach a real one.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICIAL UNIV +1
Method and system for determining dynamically respiratory features in spontaneously breathing patients receiving mechanical ventilatory assist
ActiveUS8551009B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingAirway pressures
A method for determining dynamically a respiratory feature in a spontaneously breathing patient receiving mechanical ventilatory assist comprises: modifying a level of mechanical ventilatory assist to the patient, measuring an airway pressure, detecting a change of gradient of the measured airway pressure and determining the respiratory feature based on the measured airway pressure upon detecting the change of gradient of the airway pressure. Furthermore, the method also comprises: measuring a respiratory neural drive of the patient and detecting a lowest level of the measured respiratory neural drive for determining the respiratory feature based on the detected lowest level of respiratory neural drive.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Apparatus and method for determining physiologic parameters of a patient
InactiveCN101919690AElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsDecreased mean arterial pressureArterial catheter
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for determining physiologic parameters of a patient. The apparatus comprises a patient monitor reading in a pressure signal from a pressure sensor measuring an arterial pressure of the patient employing an arterial catheter. The patient monitor can also read in an electrocardiography signal from an ECG device The patient monitor determines curve characteristics indicative for a breathing state and / or a heart rhythm state of the patient and switches from a first volume responsiveness indication state to a second volume responsiveness indication state, if a first condition is met by the curve characteristics, and from the second volume responsiveness indication state to the first volume responsiveness indication state, if a second condition is met. Thus, two visually and / or audibly distinguishable indication states are provided depending on - whether the relevant curve characteristics indicate that the patient is in an arrhythmic condition, and / or - whether the relevant curve characteristics indicate that the patient is breathing spontaneously.
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYST
Safety valve and breathing apparatus
ActiveCN105617527AReduce or eliminate pollutionEasy to disassembleRespiratorsValvesAutonomous breathingMedicine
The invention discloses a safety valve and a breathing apparatus. The safety valve comprises a base, a driving part and a quick release assembly, wherein the quick release assembly comprises a main airway, an autonomous breathing airway and an opening and closing part, wherein the autonomous breathing airway extends to the outside of the safety valve in a sealed manner and is communicated with an external environment; the main airway and the autonomous breathing airway are both arranged on the quick release assembly, so that airflow is isolated from the base and the driving part and is completely not contacted with the base and the driving part, and the condition that air in the autonomous breathing airway moves to the base, the driving part or other parts in the breathing apparatus and pollutes the parts is reduced or completely eliminated. Furthermore, the quick release assembly taken as a part, directly contacted with air, in the safety valve can be dismounted from the base conveniently, and is disinfected and sterilized independently and easily.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Monitoring and control for a laryngeal mask airway device
The disclosed method of monitoring the cuff pressure of an LMA provides an estimation of a patient's anesthetic state. Cuff pressure tends to rise and fall during IPPV and spontaneous breathing. One of the disclosed methods activates an alarm if an instantaneous value of the cuff pressure exceeds selected levels. This method may also automatically adjust the selected levels. One of the disclosed methods activates an alarm if activity of the cuff pressure as observed over a period of time exceeds a selected level.
Owner:INDIAN OCEAN MEDICAL INC
System for Controlling Administration of Anaesthesia
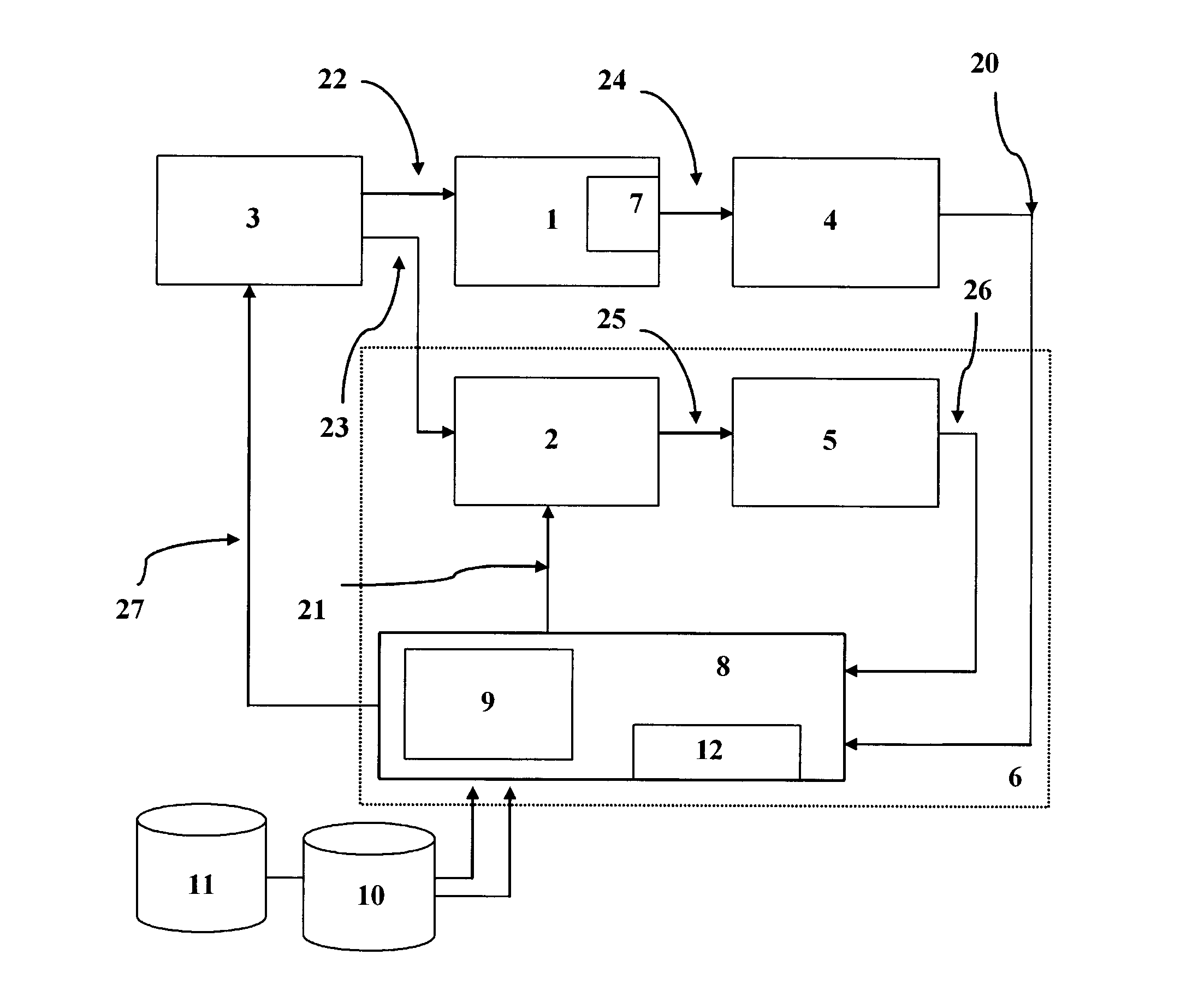
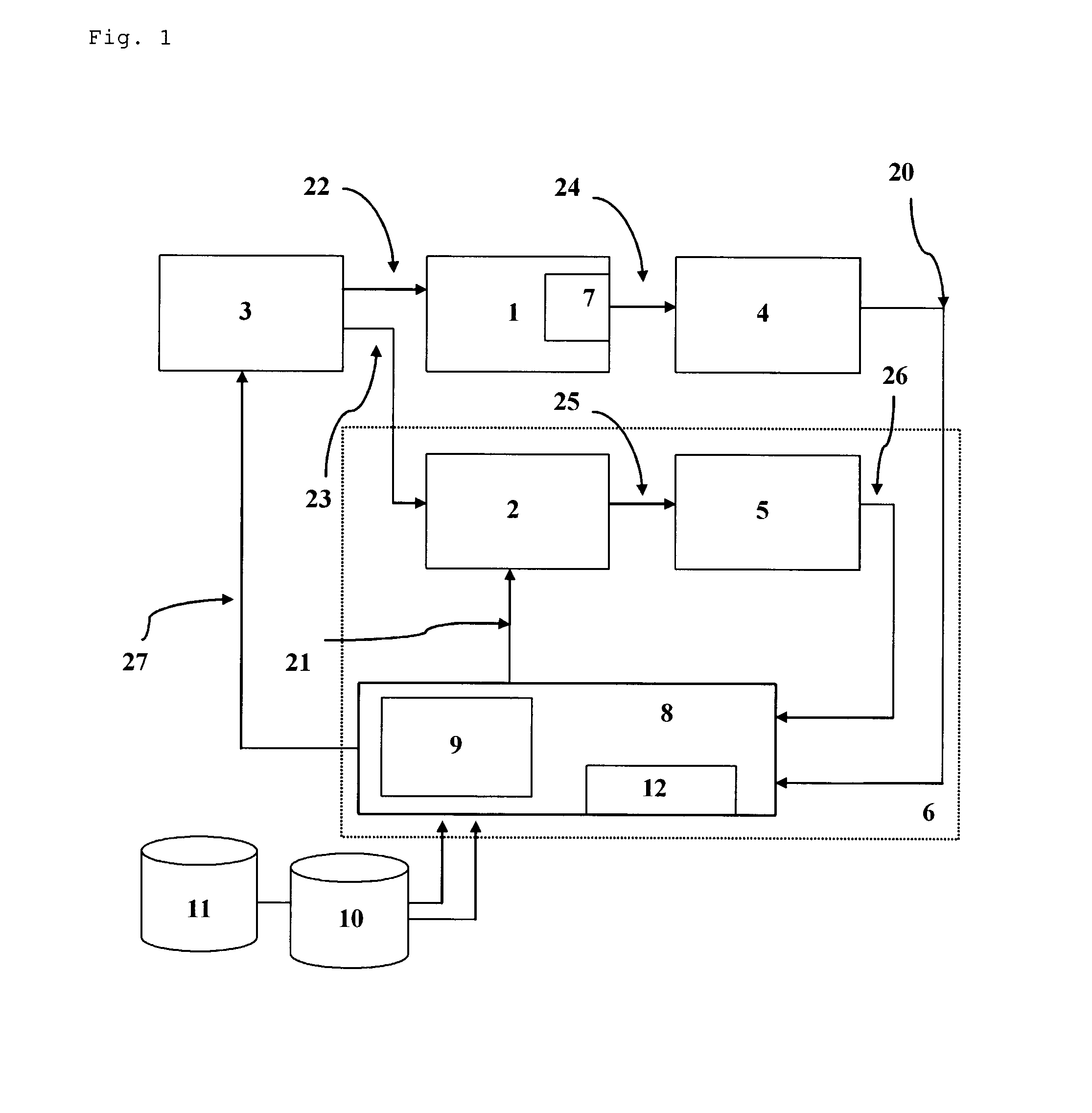
InactiveUS20100212666A1Simplifying drug administrationImprove patient safetyRespiratorsMedical devicesAutonomous breathingControl signal
A system for controlling administration of a respiratory depressant drug or mixture of drugs to a spontaneously breathing patient comprises a drug delivery unit (3), being adapted for indexed or continuous and automatic titration of a respiratory depressant drug or mixture of such drugs to said patient (1), and a control apparatus (6), receiving measurement signals (20) relative to the respiratory state of said patient (1) and issuing control signals (27) to said drug delivery unit (3), wherein the control apparatus is adapted to keep said measurement signals relative to the respiratory state to a predetermined condition and thereby providing adequate sedation and / or analgesia to said patient.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN +1
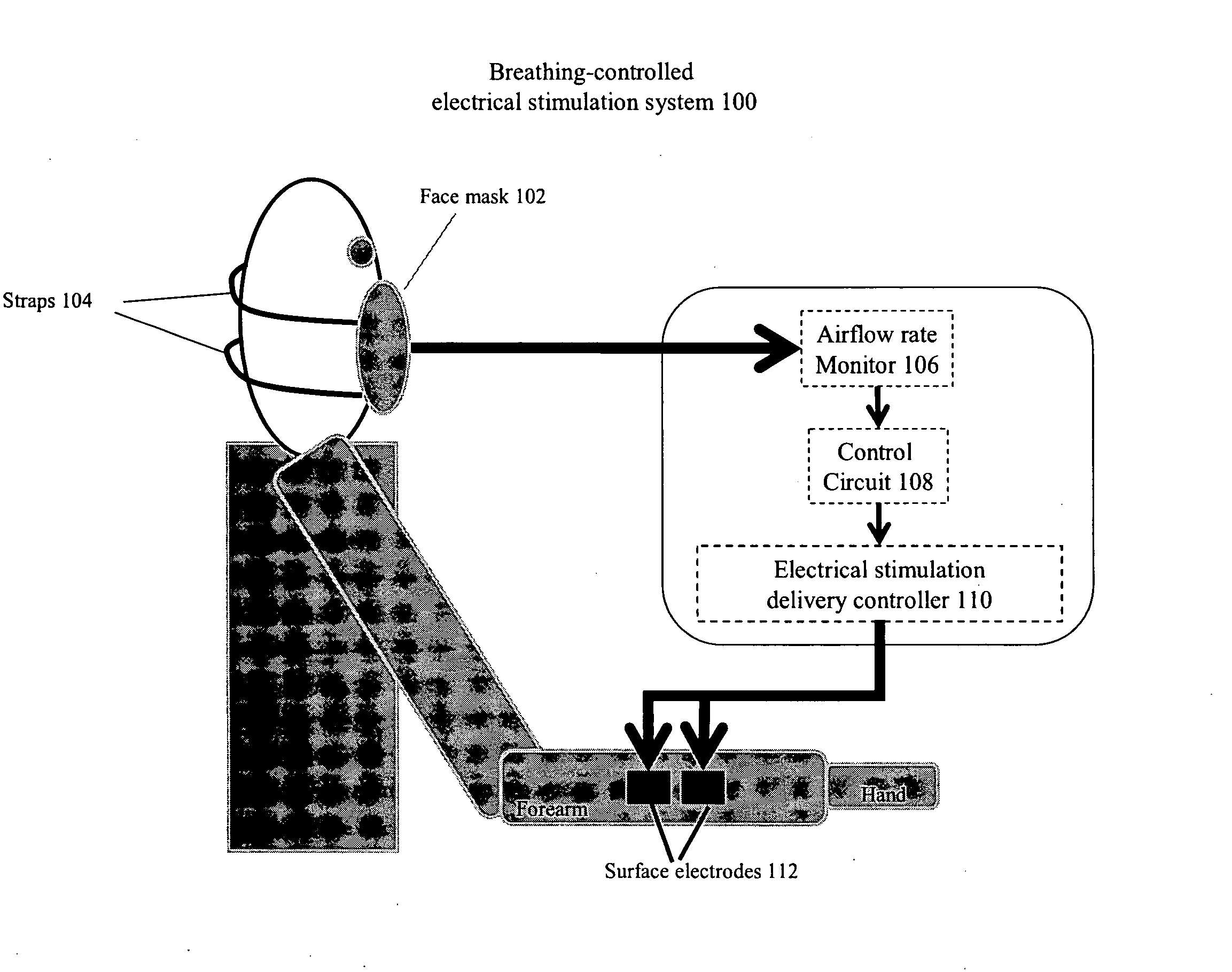
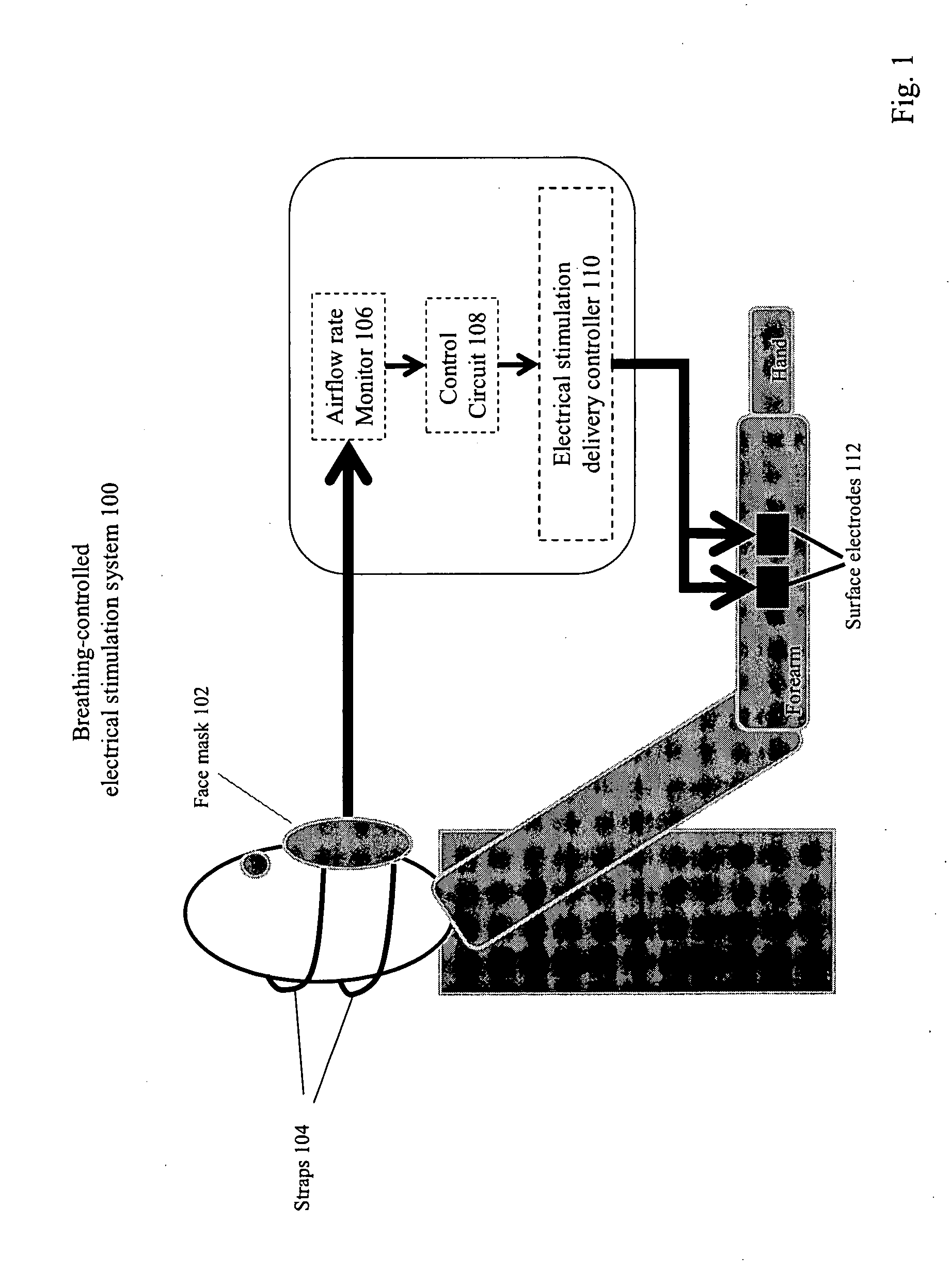
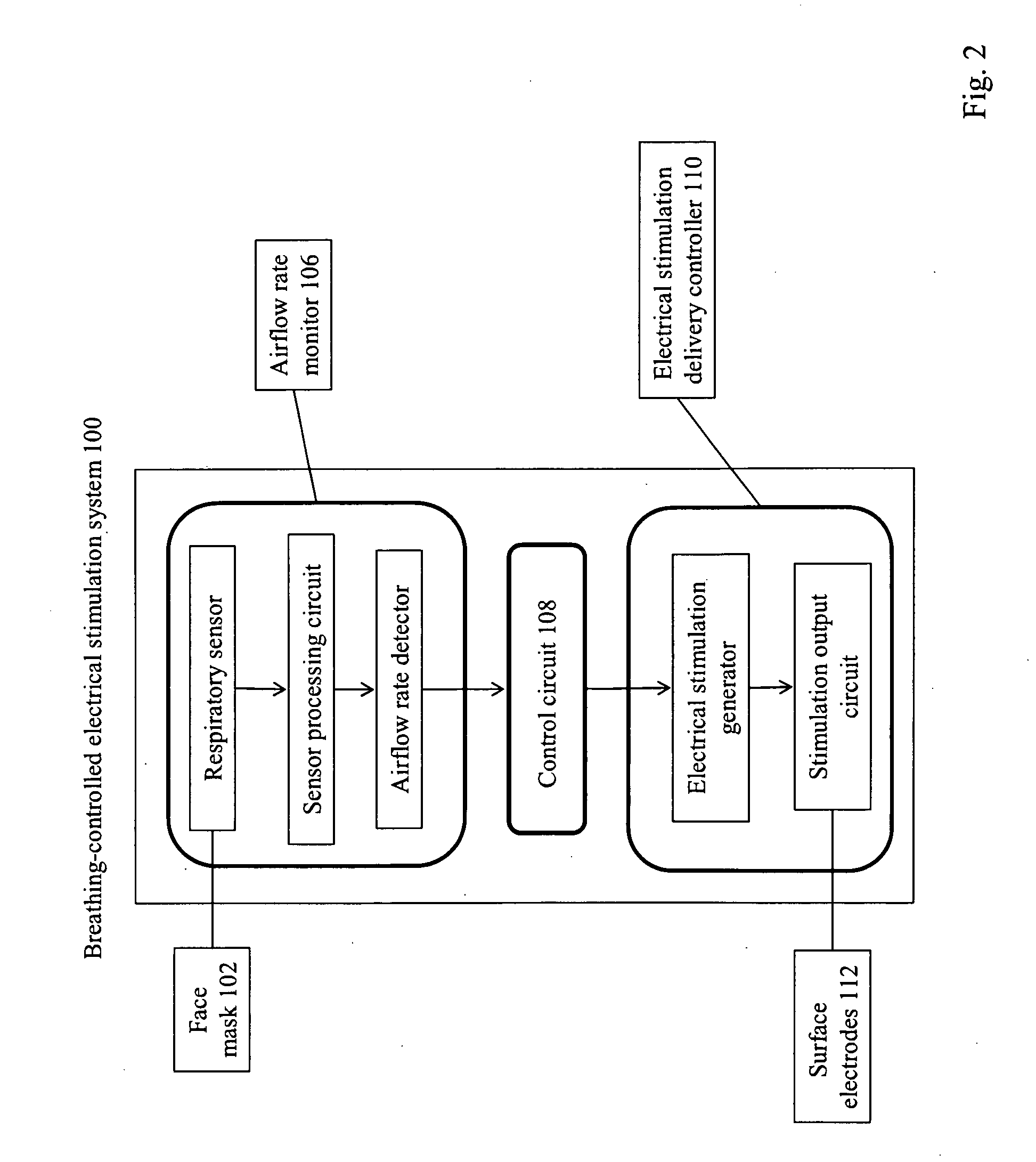
Method and Apparatus of Breathing-Controlled Electrical Stimulation for Skeletal Muscles
ActiveUS20090326606A1Improve efficiencyAvoid excessive problemElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationAutonomous breathing
Methods and devices are provided such that electrical stimulation can be delivered to a patient's skeletal muscles in response to certain respiratory signals, such as when voluntary breathing is detected.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com