Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Arterial tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree.
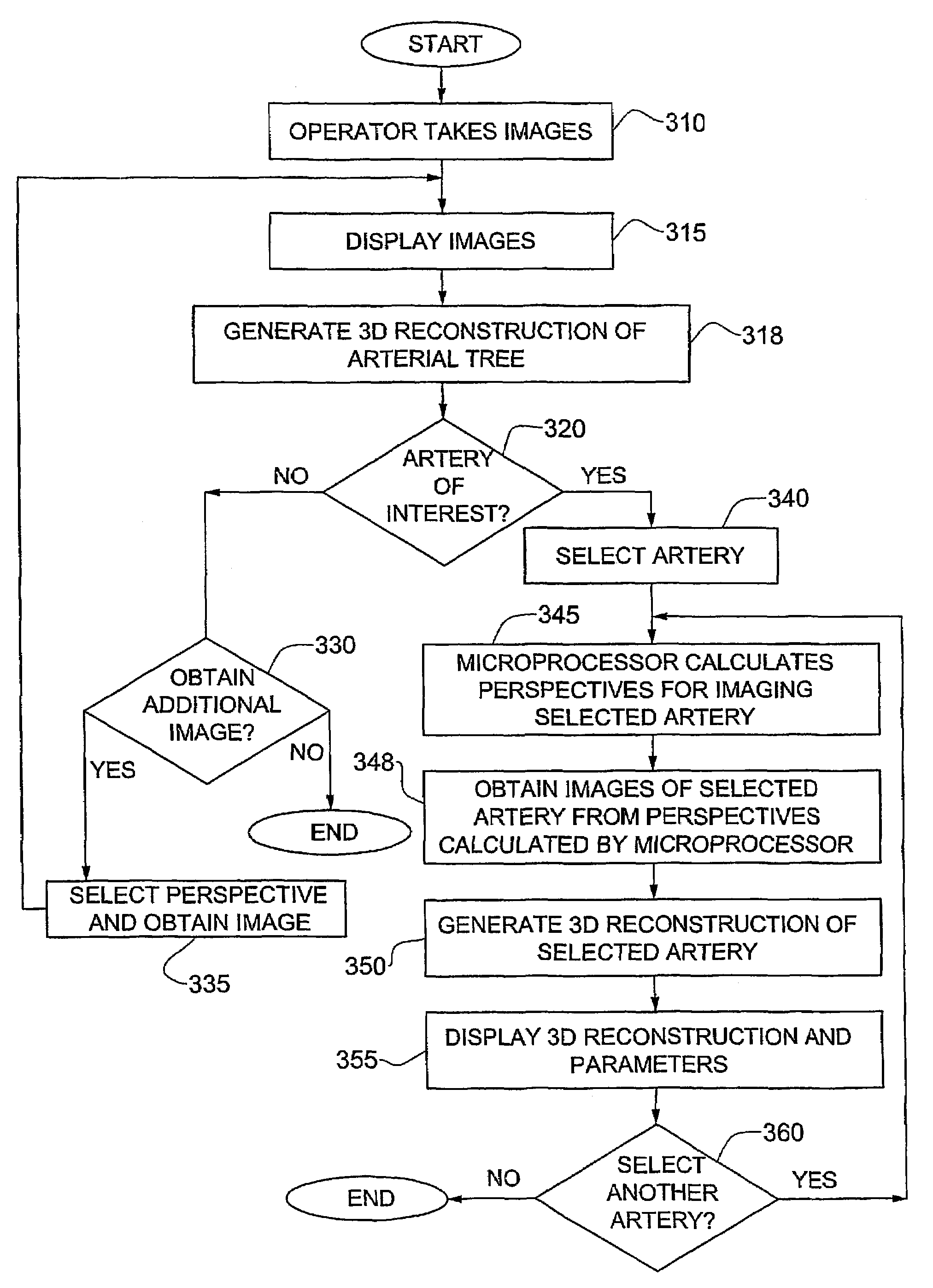
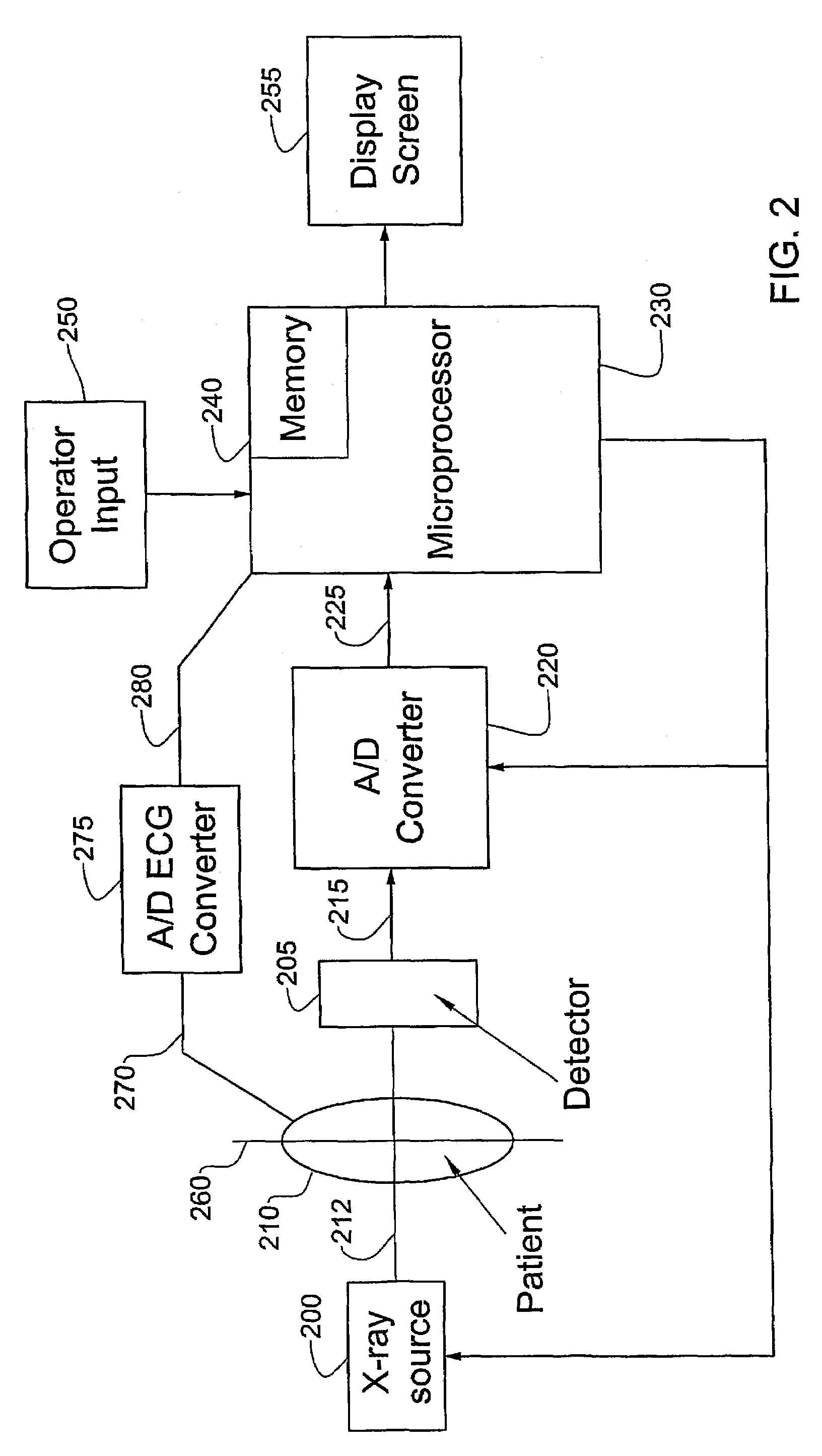
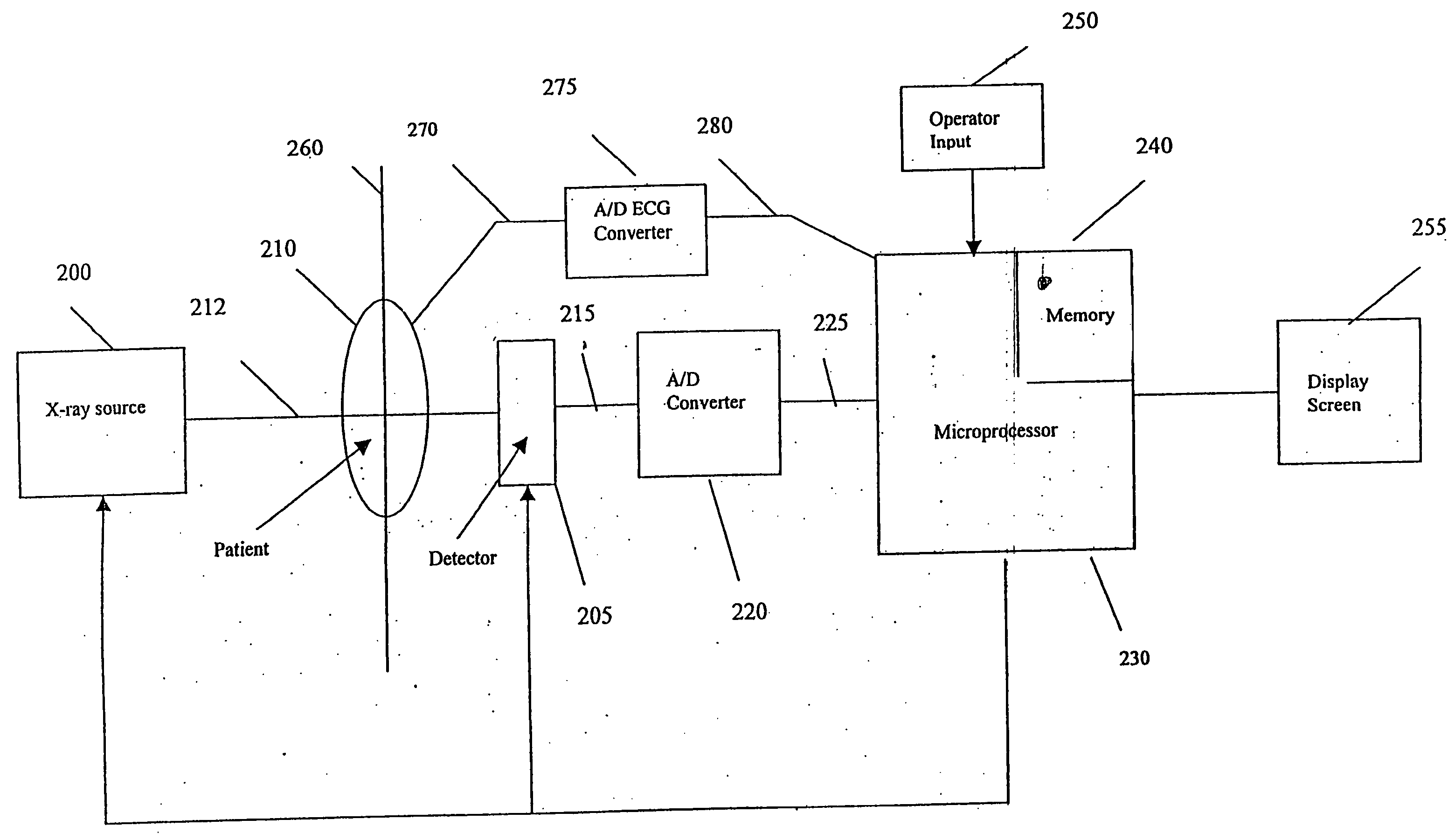
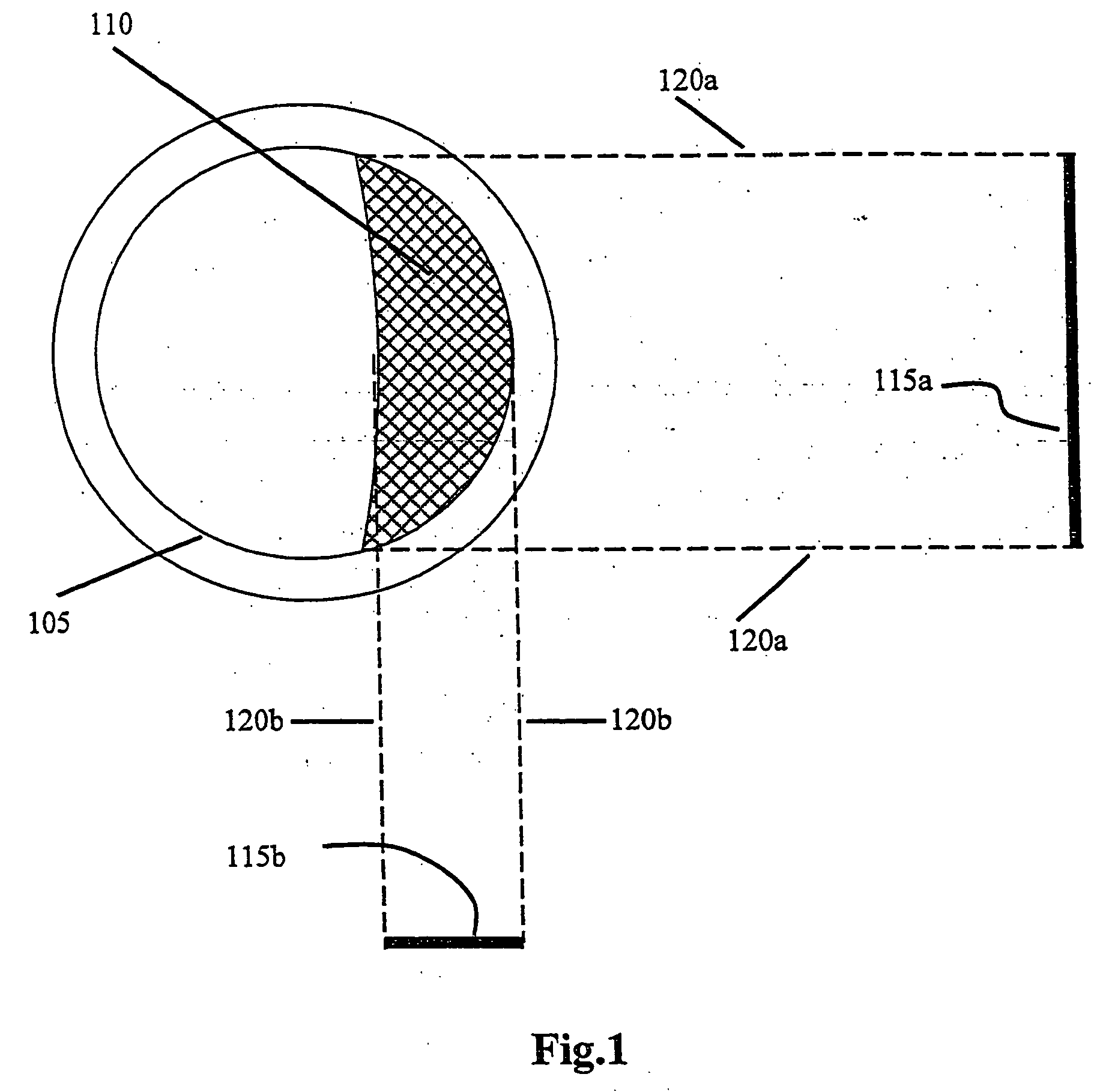
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of an artery
InactiveUS7321677B2Reduce exposureEasy accessBlood flow measurement devices2D-image generationArterial treeBlood vessel
A method and system for imaging an artery contained in an arterial tree. A microprocessor generates a three-dimensional reconstruction of the arterial tree from two or more angiographic images obtained from different perspectives. The orientation of the axis of the artery in the arterial tree is then determined, and a perspective of the artery perpendicular to the axis of the artery is determined. A three dimensional reconstruction of the artery from angiographic images obtained from the determined perspective is then generated.
Owner:PAIEON INC
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of an artery
InactiveUS20050008210A1Precise processingReduce exposureBlood flow measurement devices2D-image generationArterial treeBlood vessel
Owner:PAIEON INC
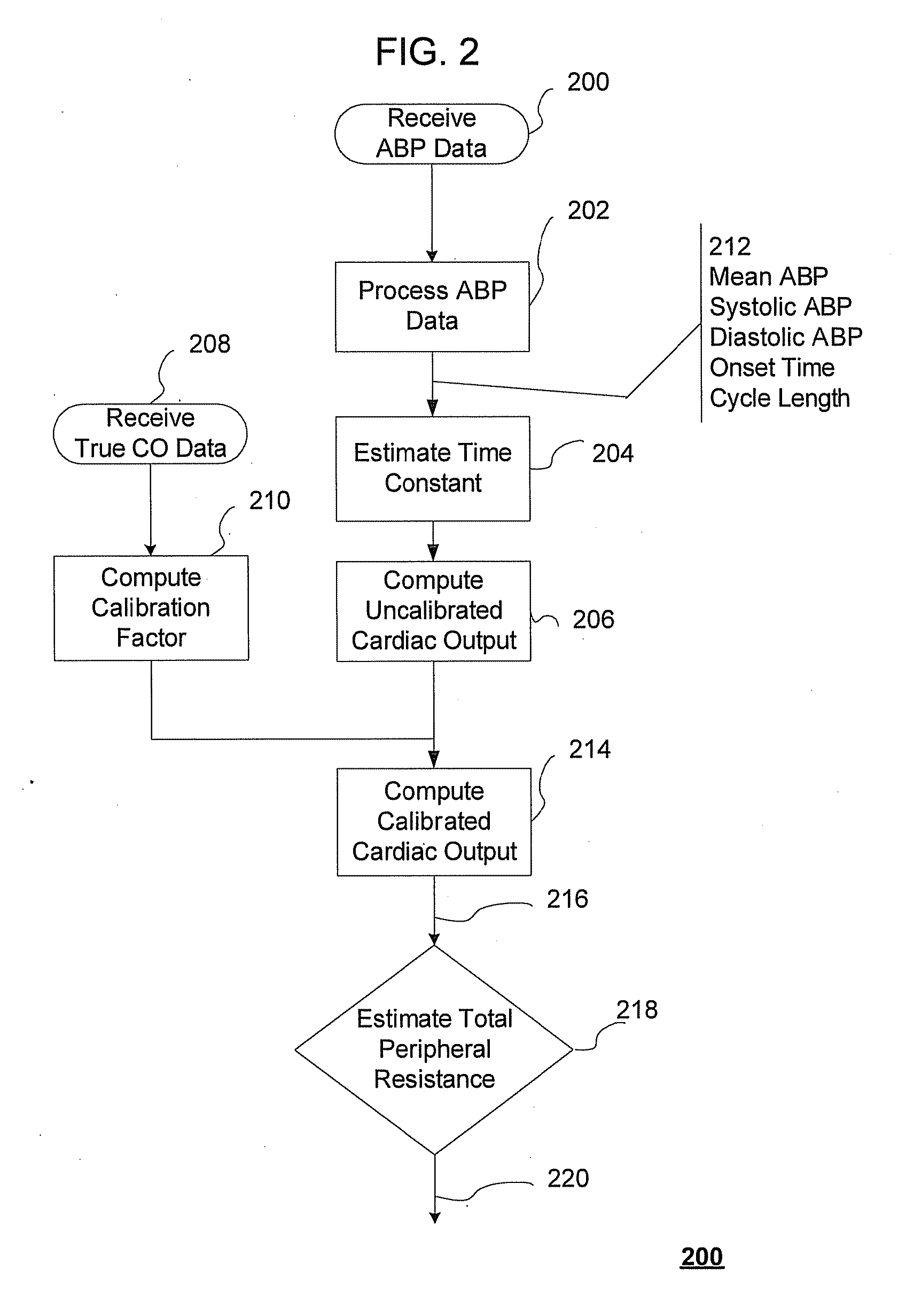
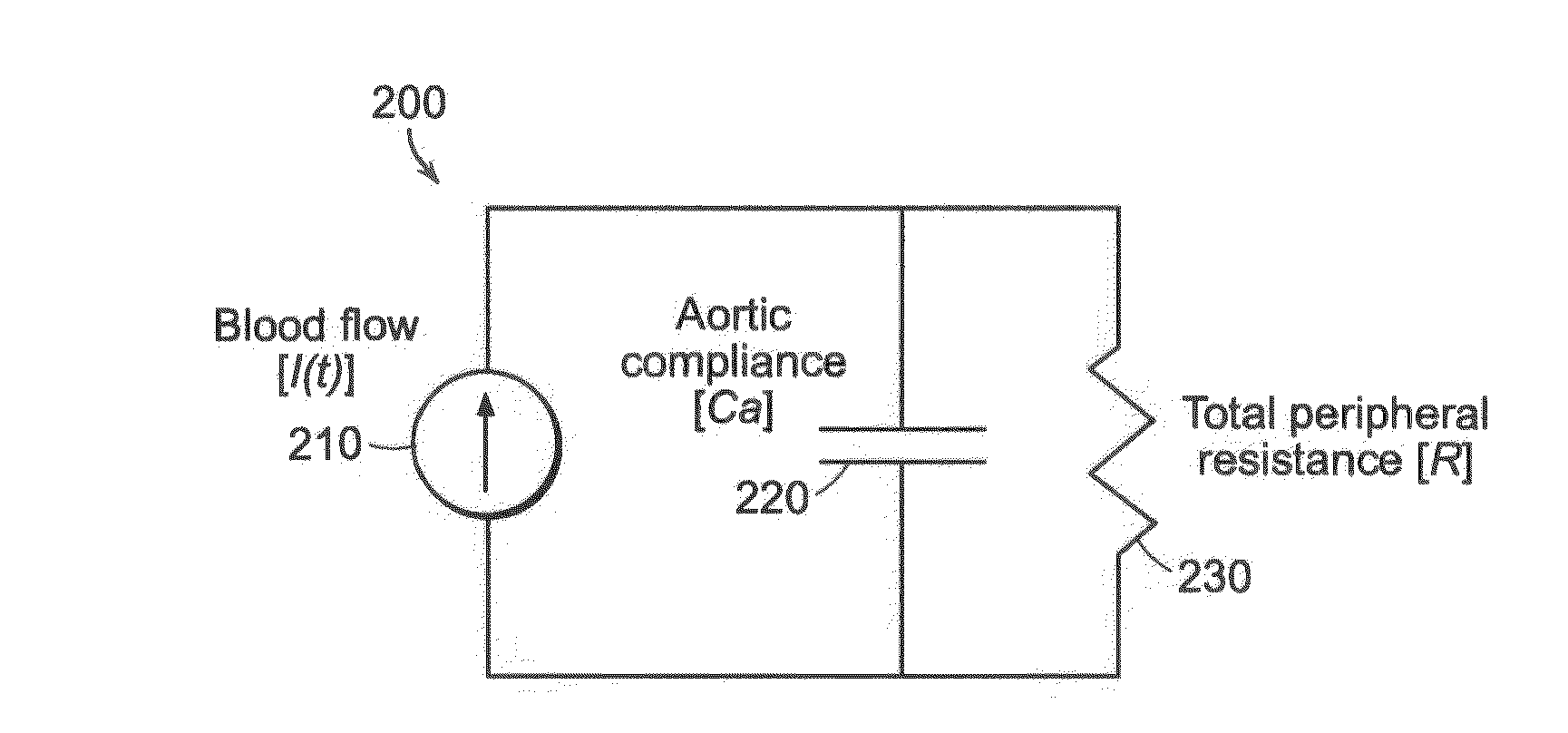
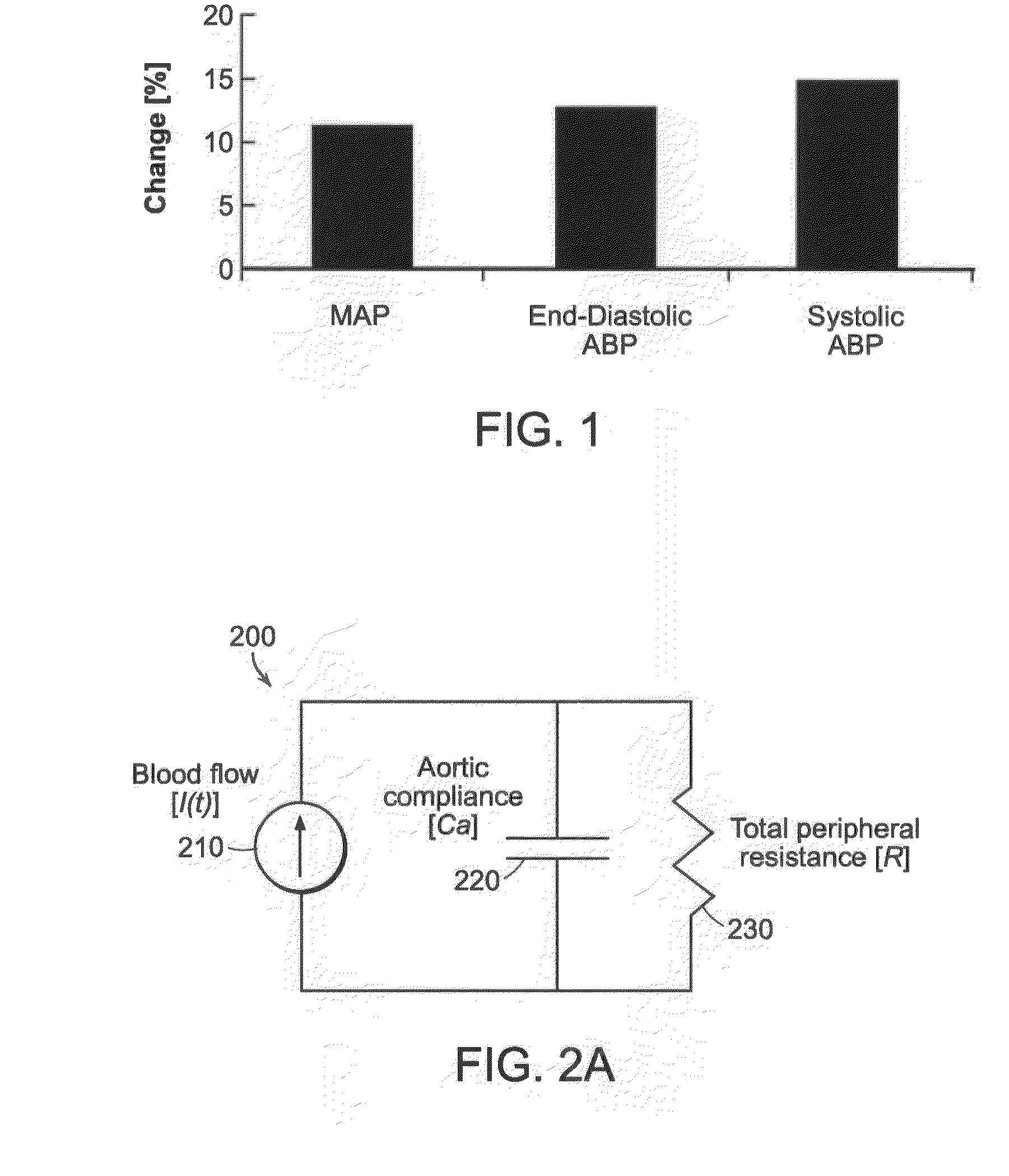
Systems and Methods for Model-Based Estimation of Cardiac Output and Total Peripheral Resistance
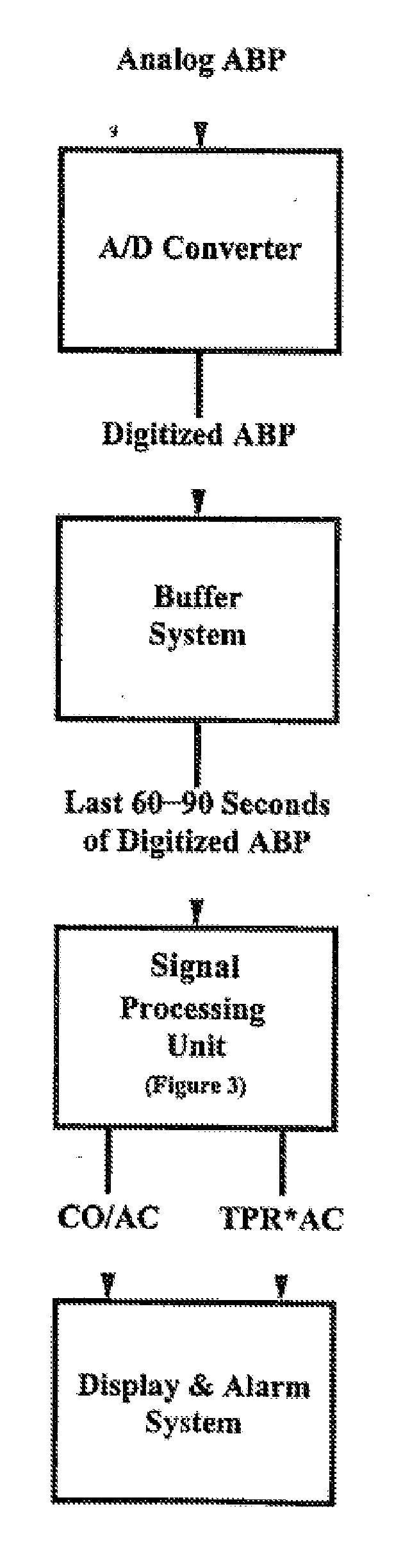
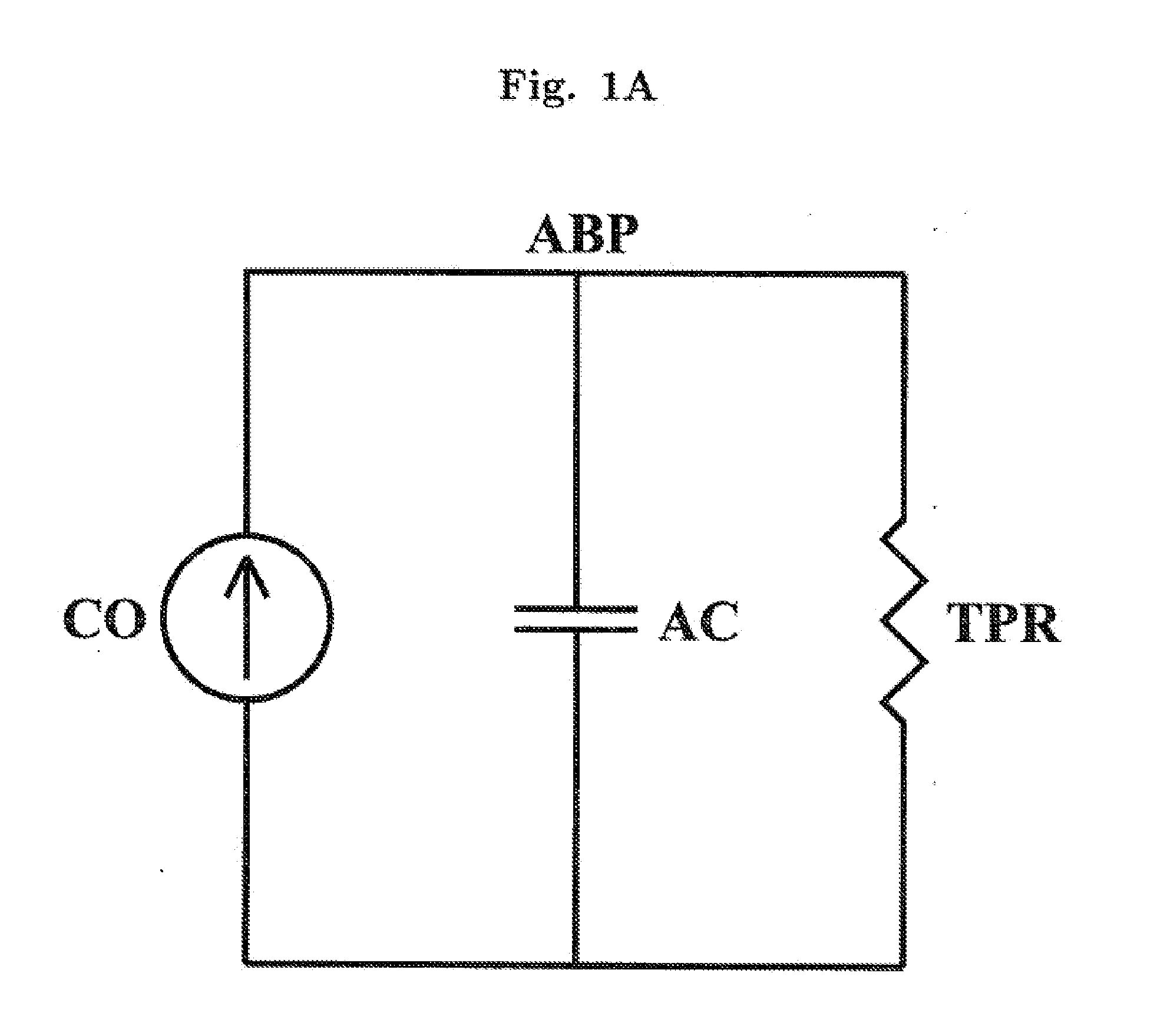
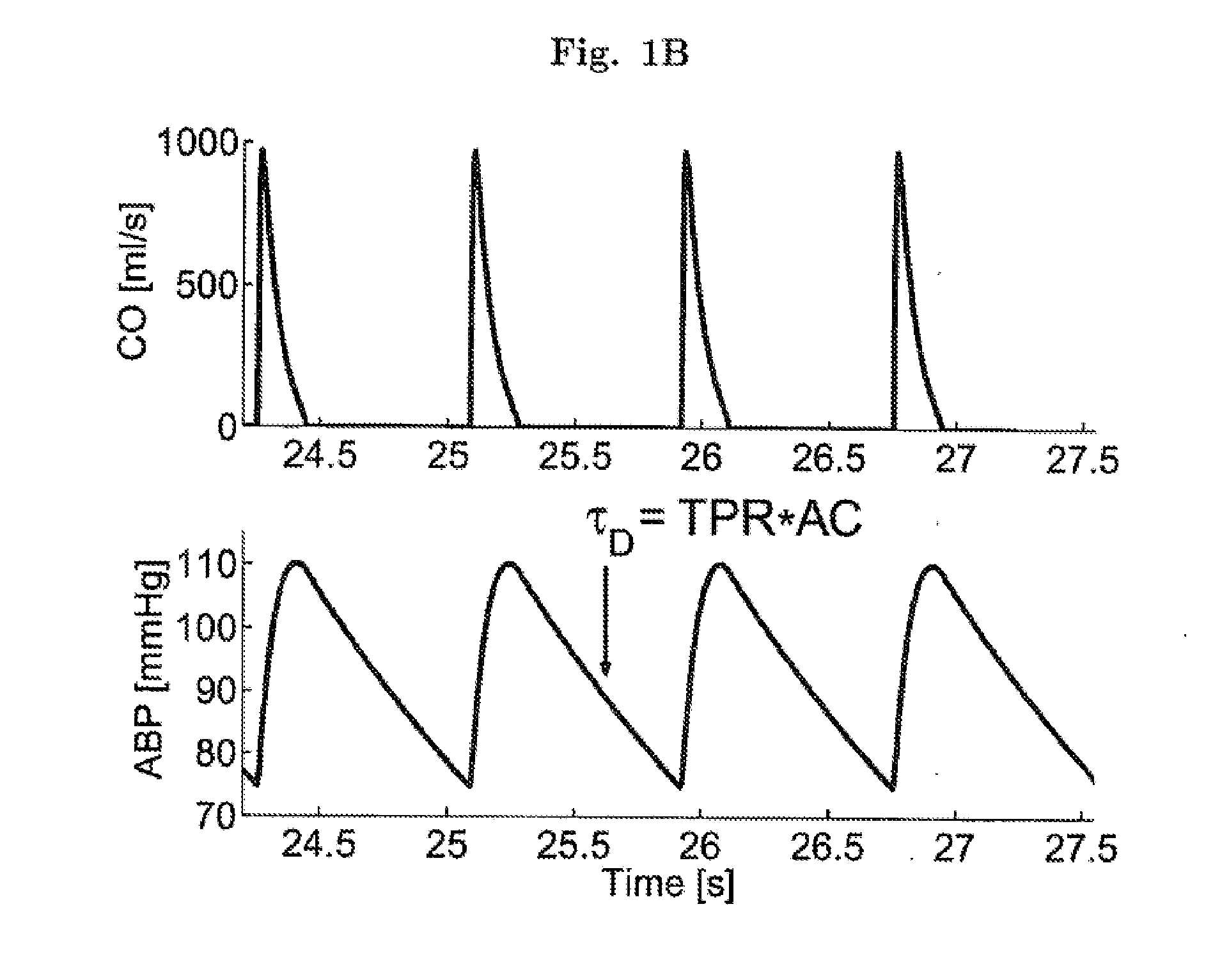
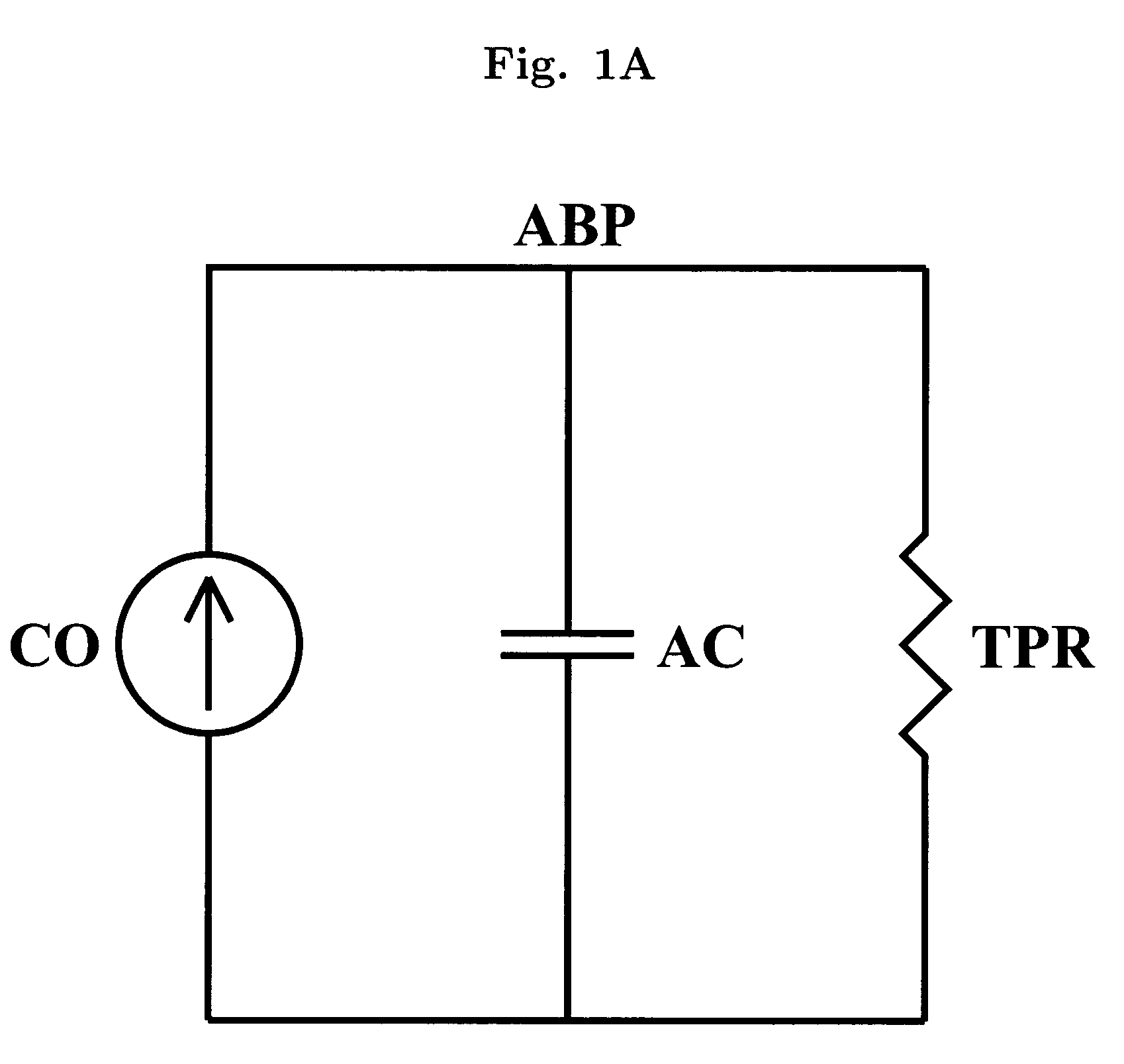
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac output and total peripheral resistance include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine intra-beat and inter-beat variability in arterial blood pressure and estimating from the variability a time constant for a lumped parameter beat-to-beat averaged Windkessel model of the arterial tree. Uncalibrated cardiac output and uncalibrated total peripheral resistance may then be calculated from the time constant. Calibrated cardiac output and calibrated total peripheral resistance may be computed using calibration data, assuming an arterial compliance that is either constant or dependent on mean arterial blood pressure. The parameters of the arterial compliance may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
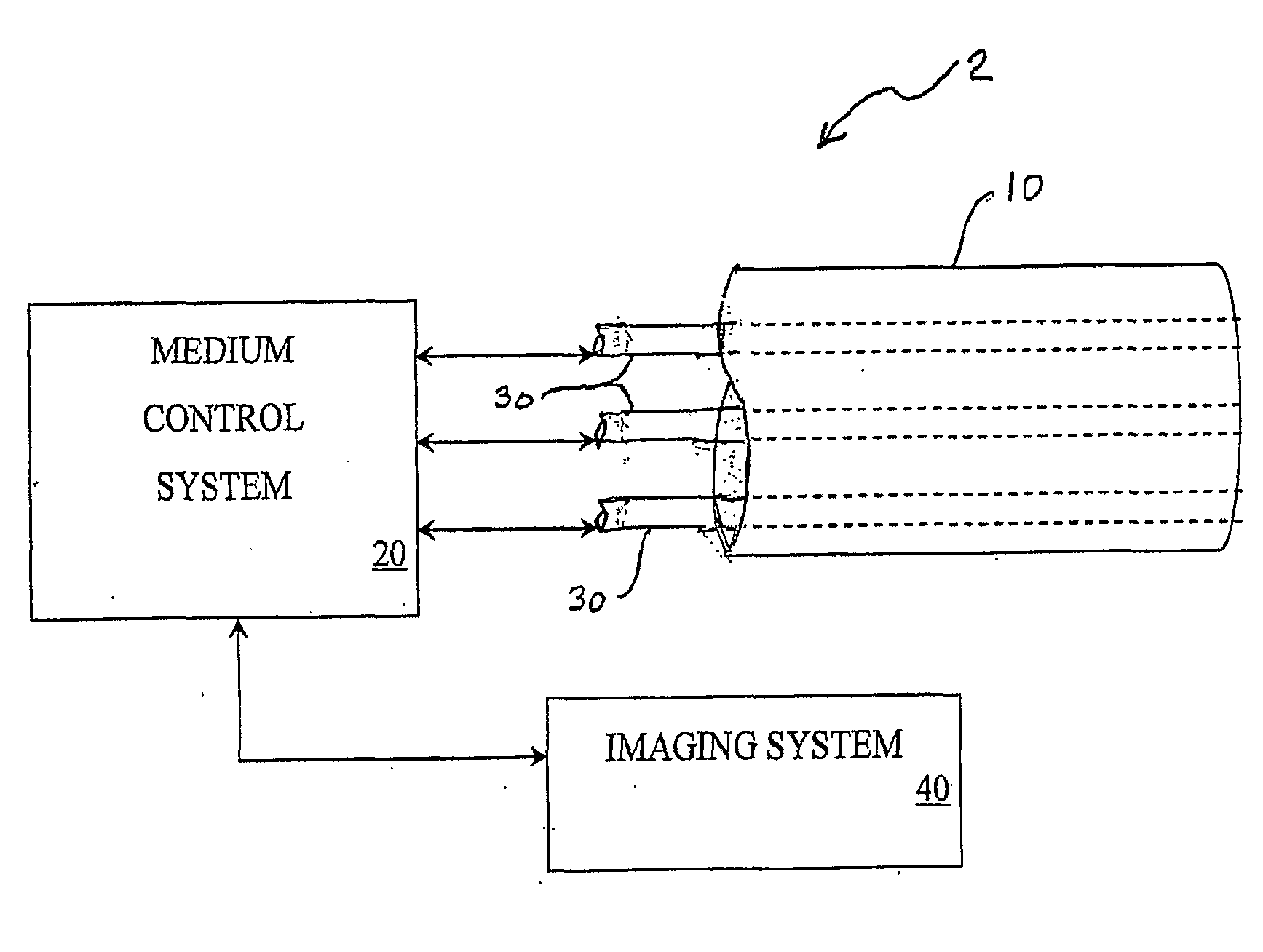
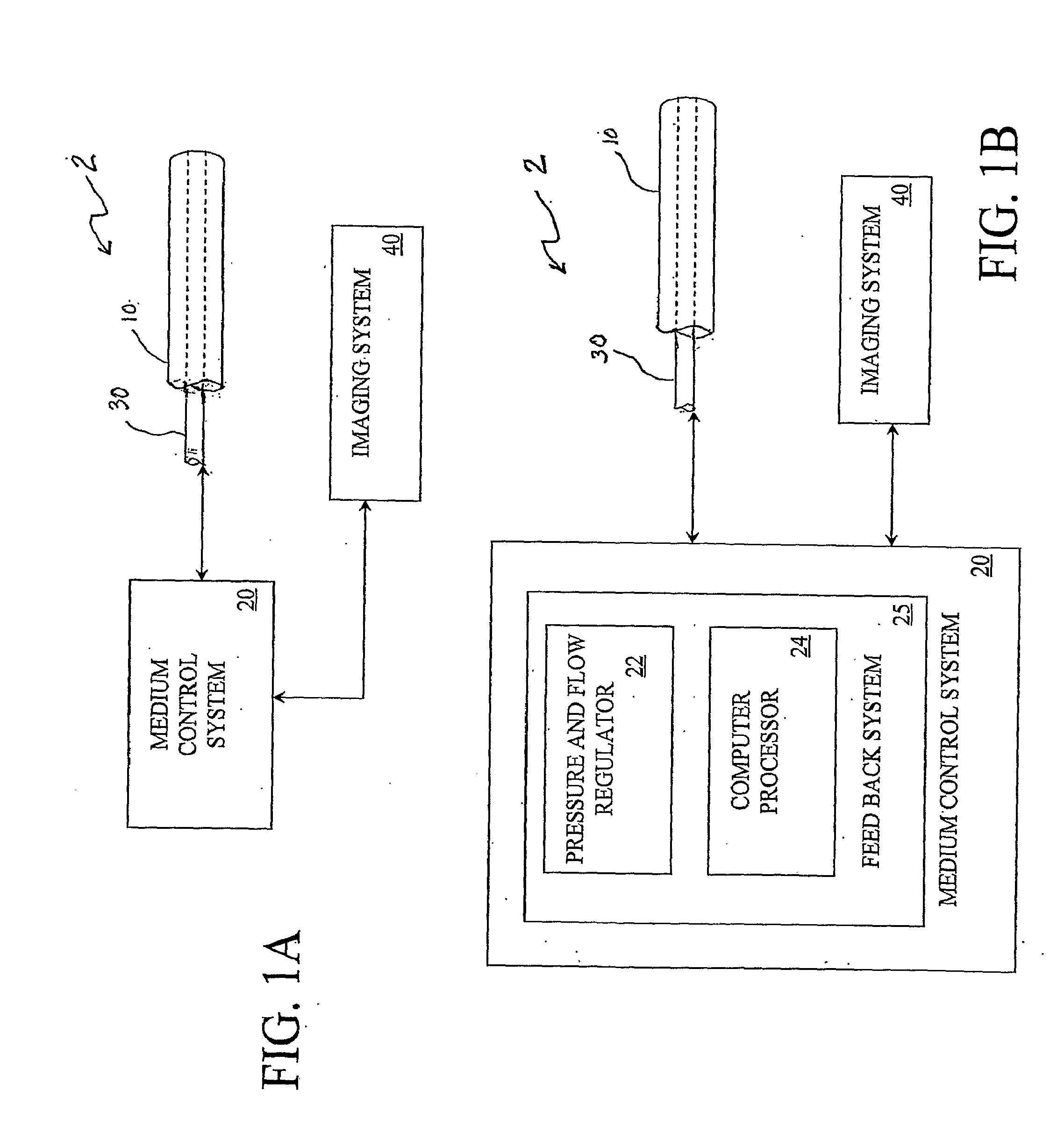
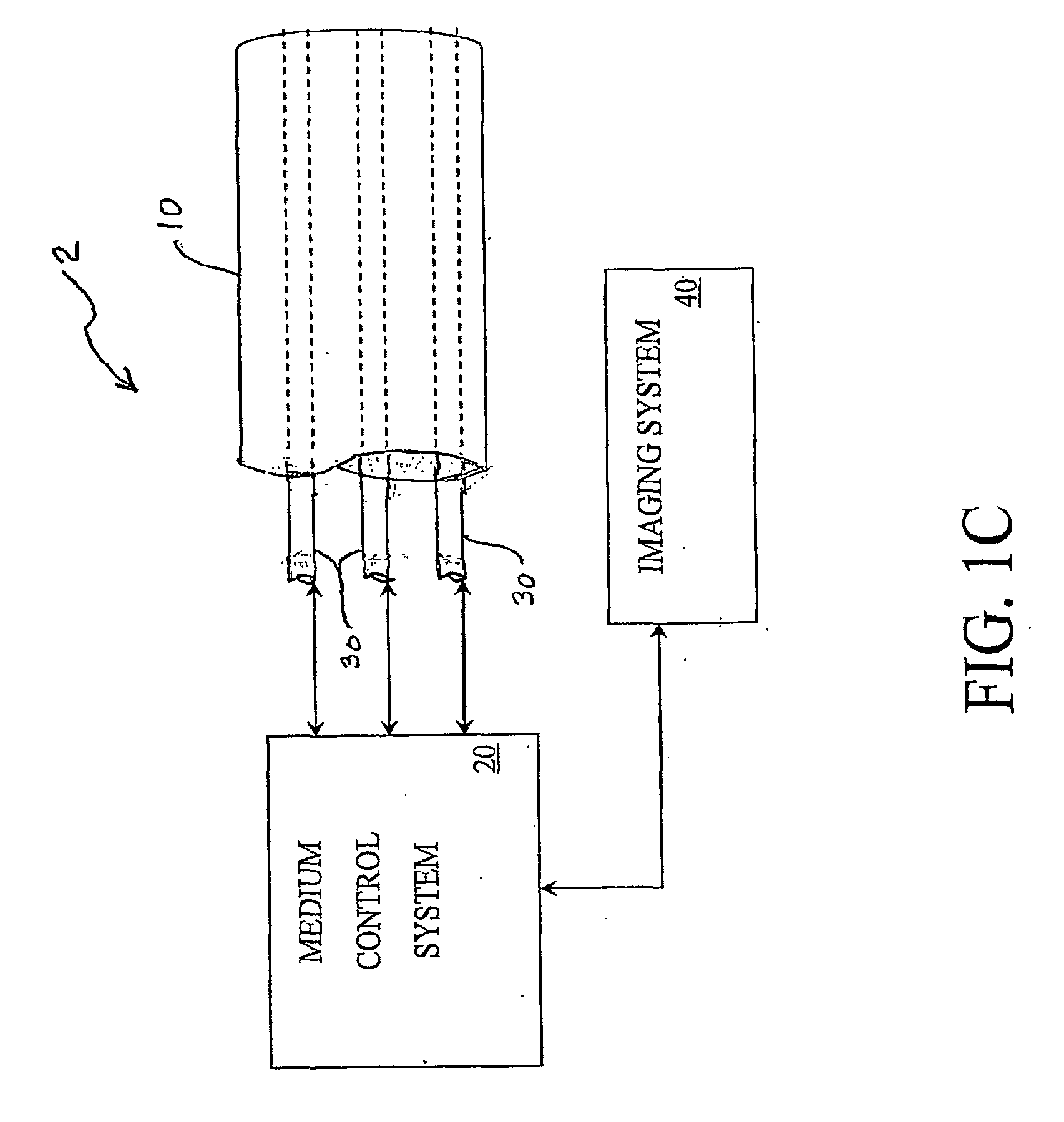
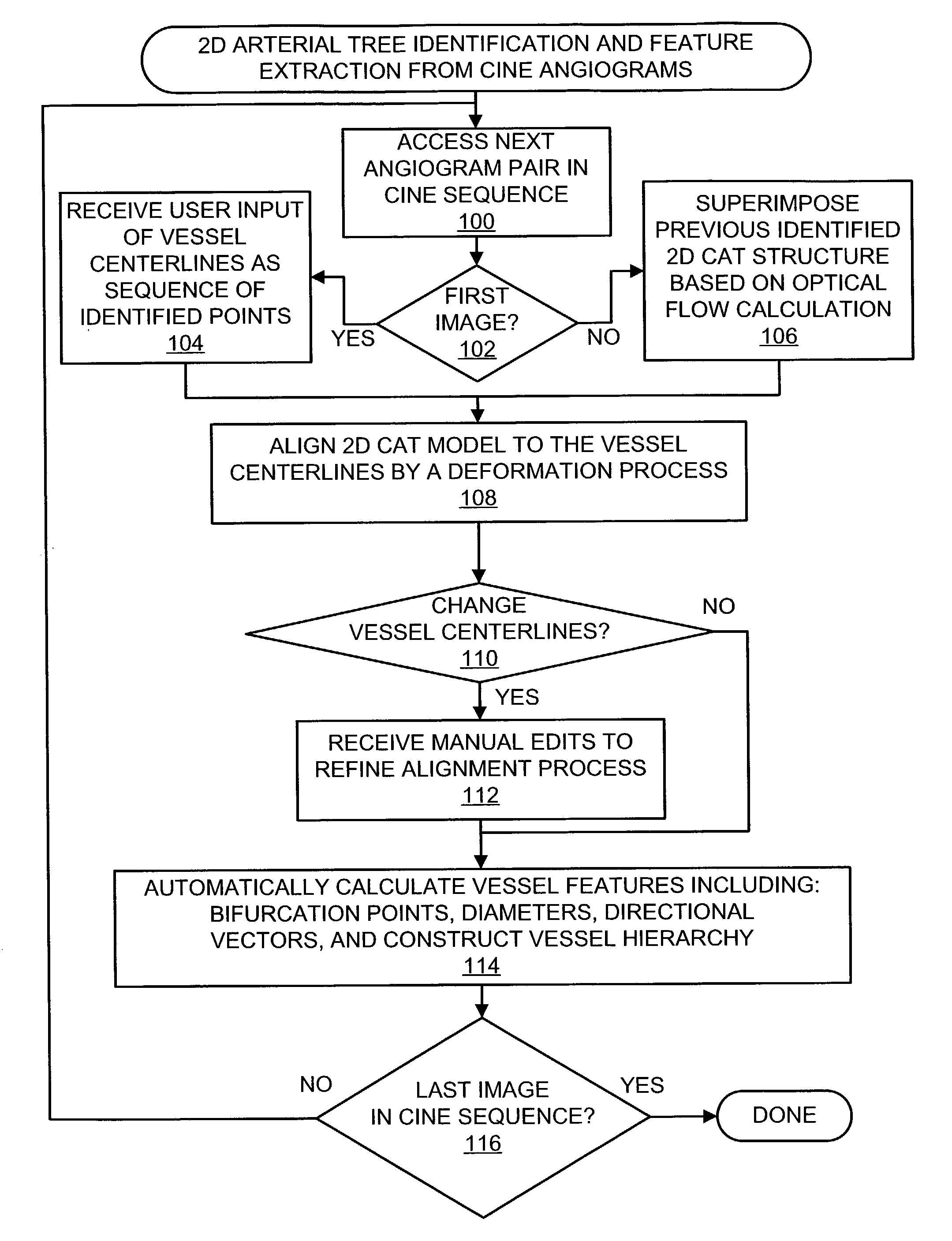
Multi-Port Catheter System with Medium Control and Measurement Systems for Therapy and Diagnosis Delivery
A series of embodiments of multi-lumen, multisegmented (or variable diameter) catheters and associated multi-channel flow control and measurement systems and methods for simultaneous delivery of a medium to a plurality of locations is described. The need for precise, stable reliable, and repeatable flow control in therapy delivery catheters is crucial to the efficacious treatment of the clinical manifestations of peripheral vascular disease (PVD) and other such maladies. Such treatments may involve the placement of multi-lumen catheters into peripheral arterial trees, with the subsequent need to govern the flow dynamics within each individual lumen of the multi-lumen device in such a way that an optimum distribution of the agent is achieved intra-arterially. Combinations of pumps, flow monitors, pressure monitors, feedback loops and related hardware and software collectively capable of achieving this goal are described. In other embodiments, this device and method could be used for infusions into tissues and solid organs, and microcoil systems can be added to the various components of the catheter systems to improve the imaging quality during MR-guided procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
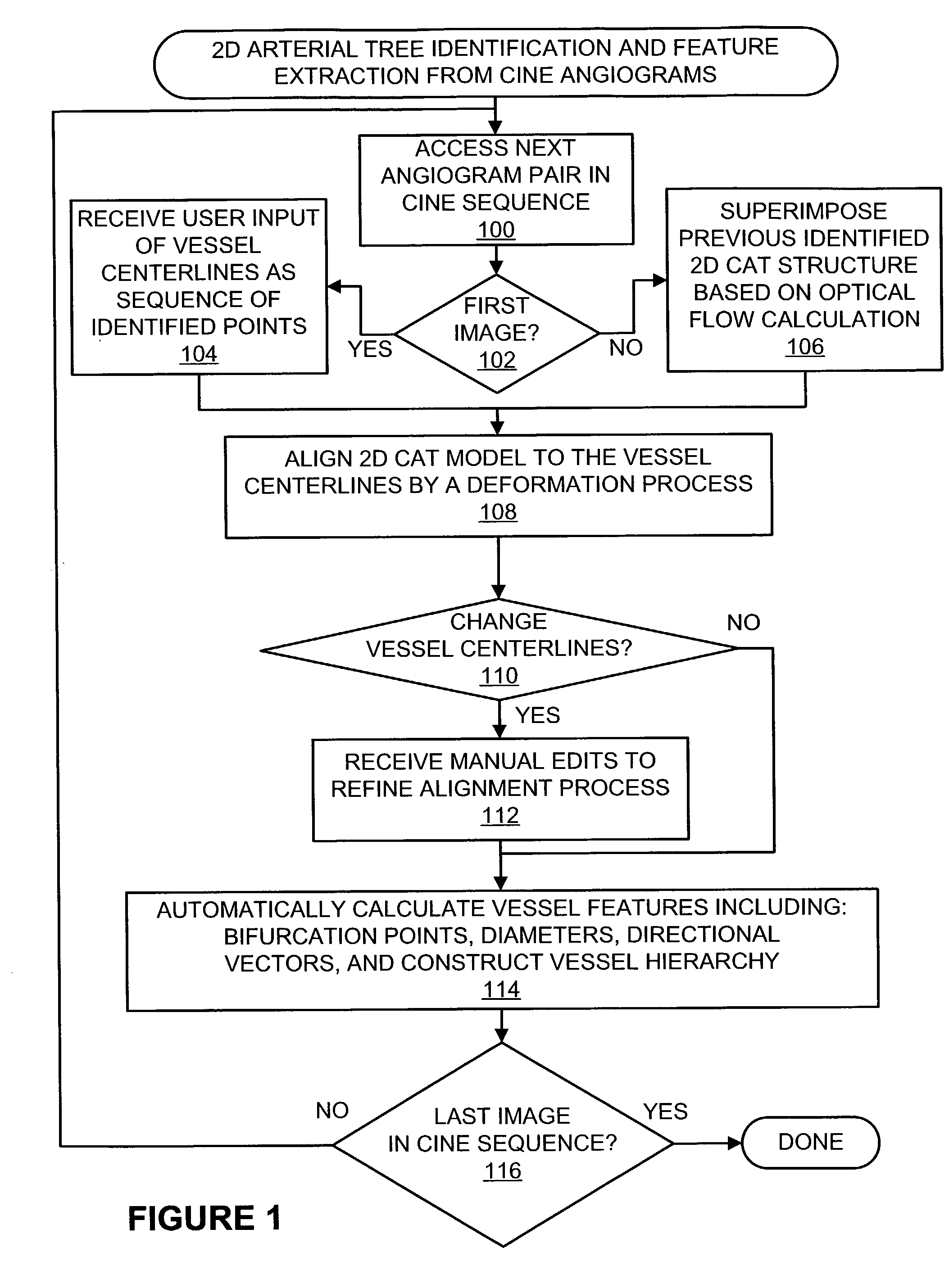
Methods and systems for display and analysis of moving arterial tree structures
ActiveUS7113623B2Improve patient outcomesImprove patient safetyImage enhancementImage analysisKinematicsCardiac cycle
Methods and systems for reconstruction of a three-dimensional representation of a moving arterial tree structure from a pair of sequences of time varying two-dimensional images thereof and for analysis of the reconstructed representation. In one aspect of the invention, a pair of time varying arteriographic image sequences are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional representation of the vascular tree structure as it moves through a cardiac cycle. The arteriographic image sequences maybe obtained from a biplane imaging system or from two sequences of images using a single plane imaging system. Another aspect of the invention then applies analysis methods and systems utilizing the three-dimensional representation to analyze various kinematic and deformation measures of the moving vascular structure. Analysis results may be presented to the user using color coded indicia to identify various kinematic and deformation measures of the vascular tree.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
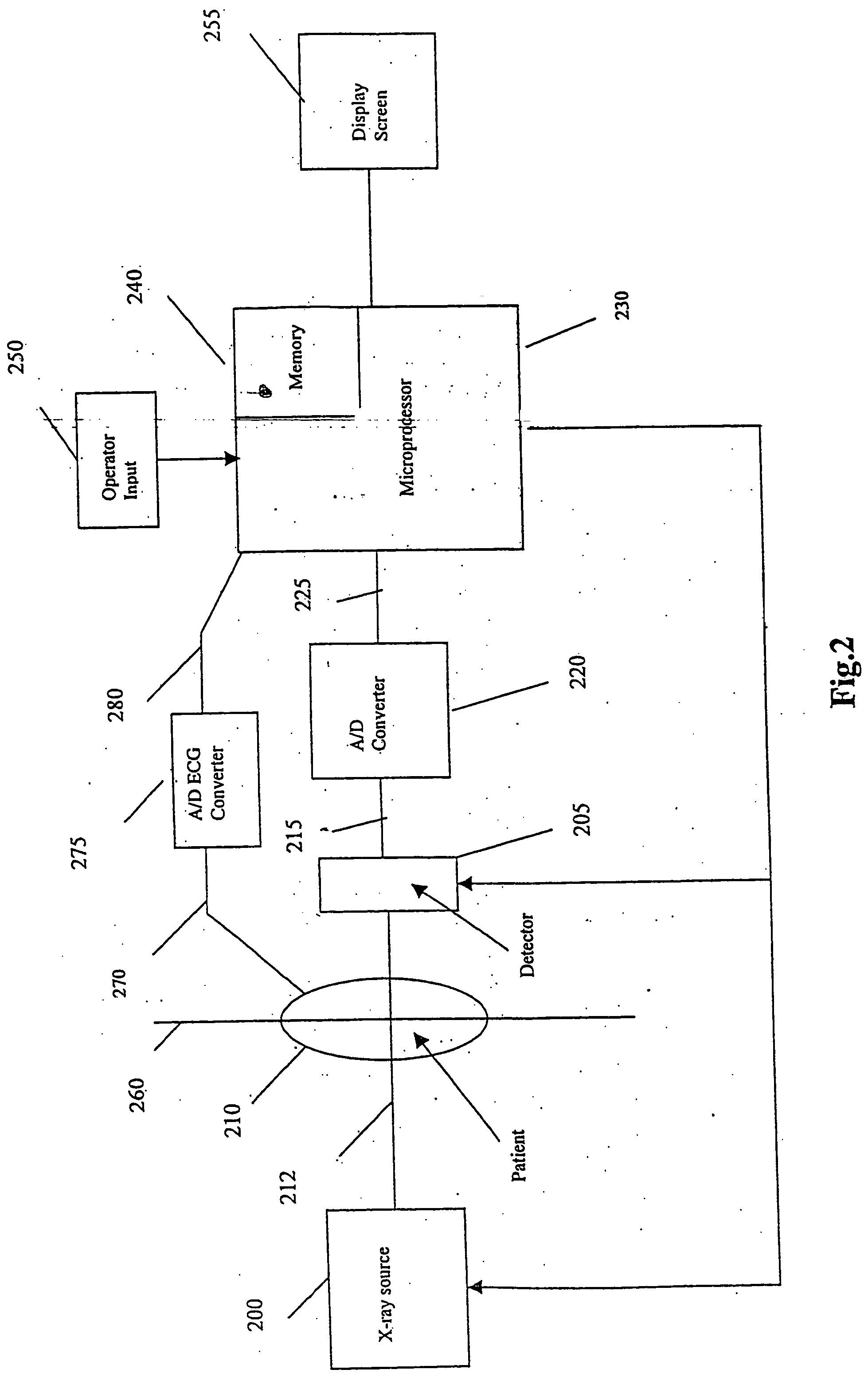
Method and apparatus for a continuous non-invasive and non-obstrusive monitoring of blood pressure
ActiveUS20090163821A1Improve accuracyContinuous trackingElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsArterial velocityArterial tree
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Method and apparatus for classification of coronary artery image data
InactiveUS20100082692A1Accurate and computationally efficient techniqueIncrease speedImage enhancementMedical data miningCoronary arterial treeBlood vessel feature
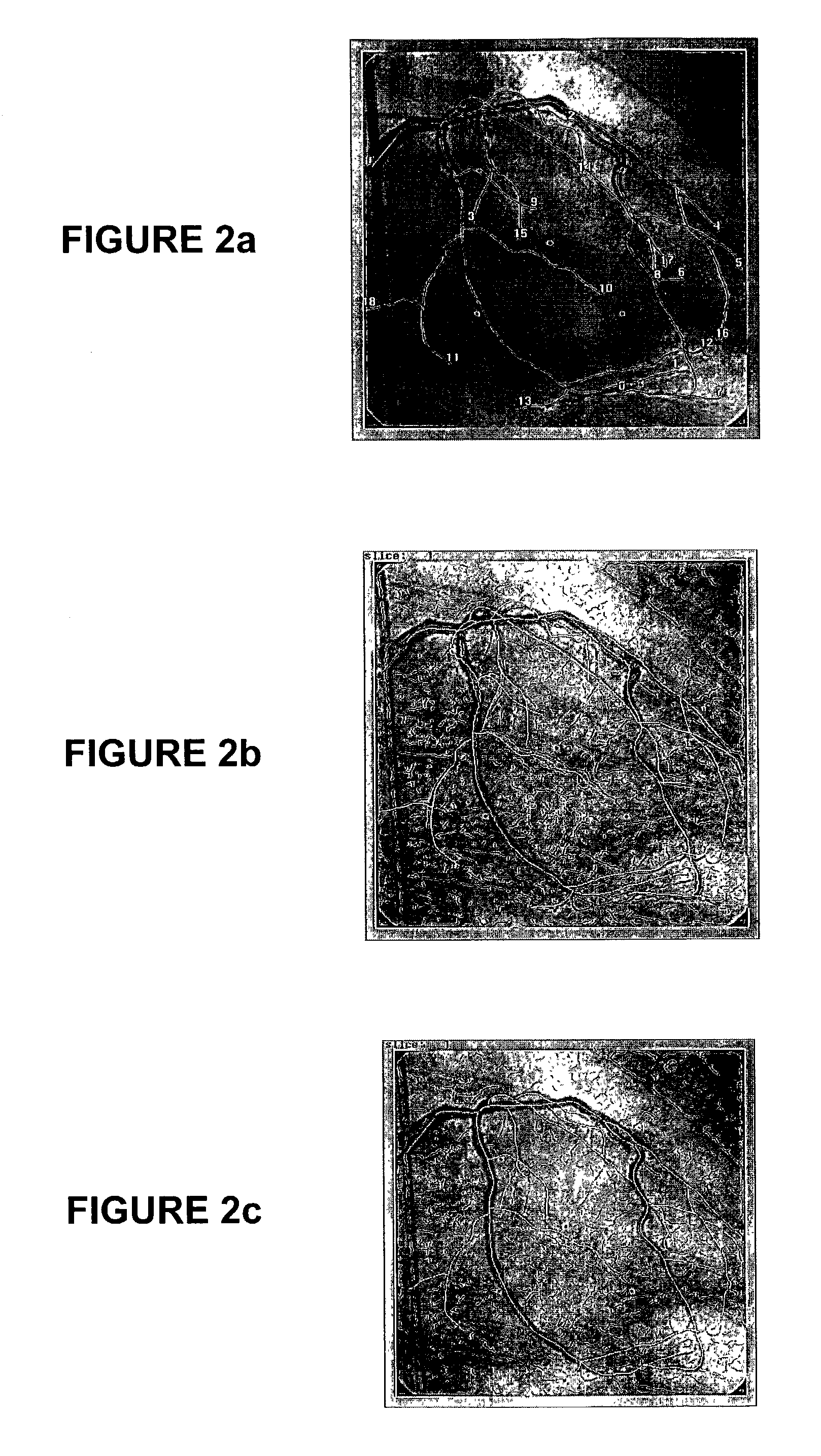
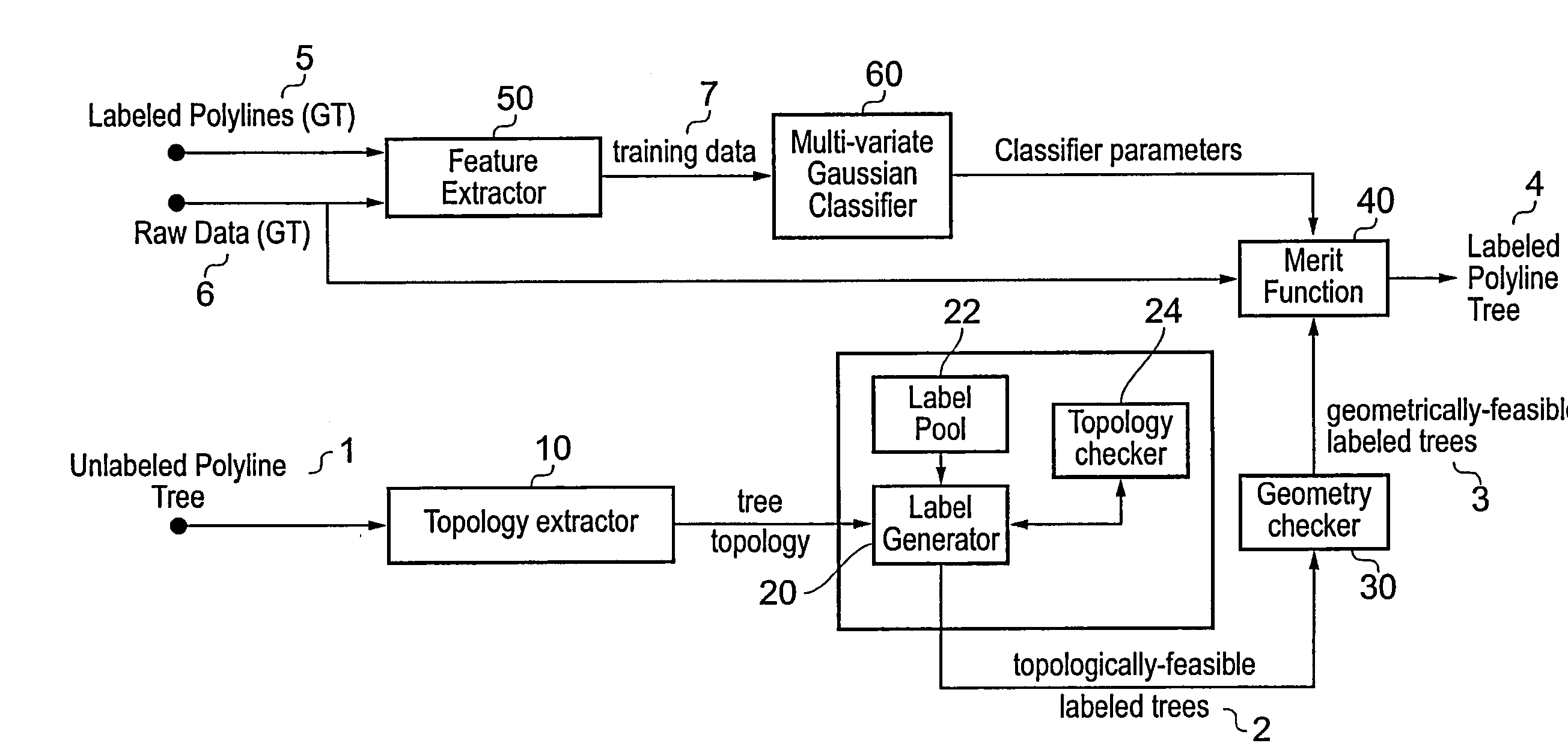
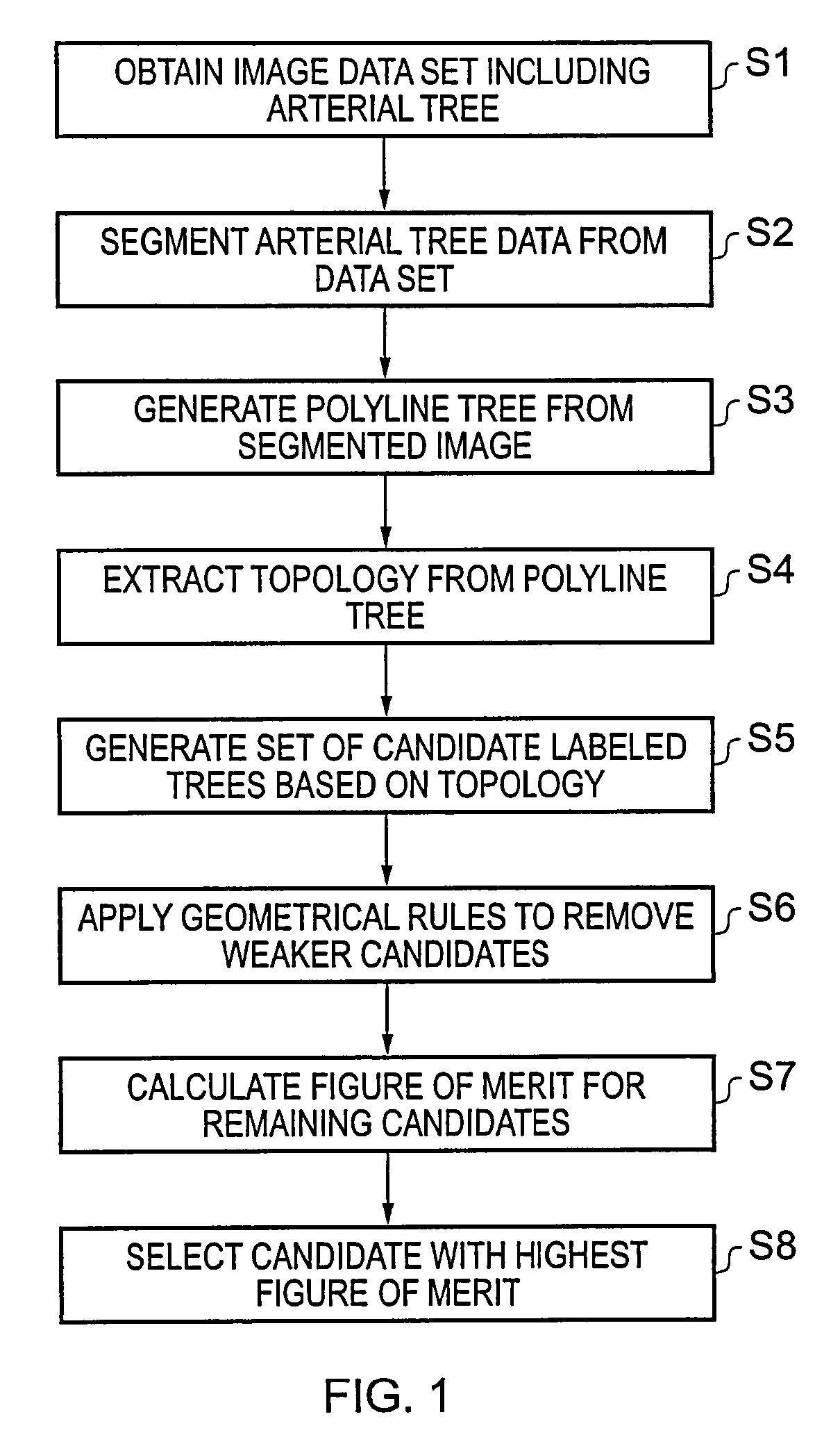
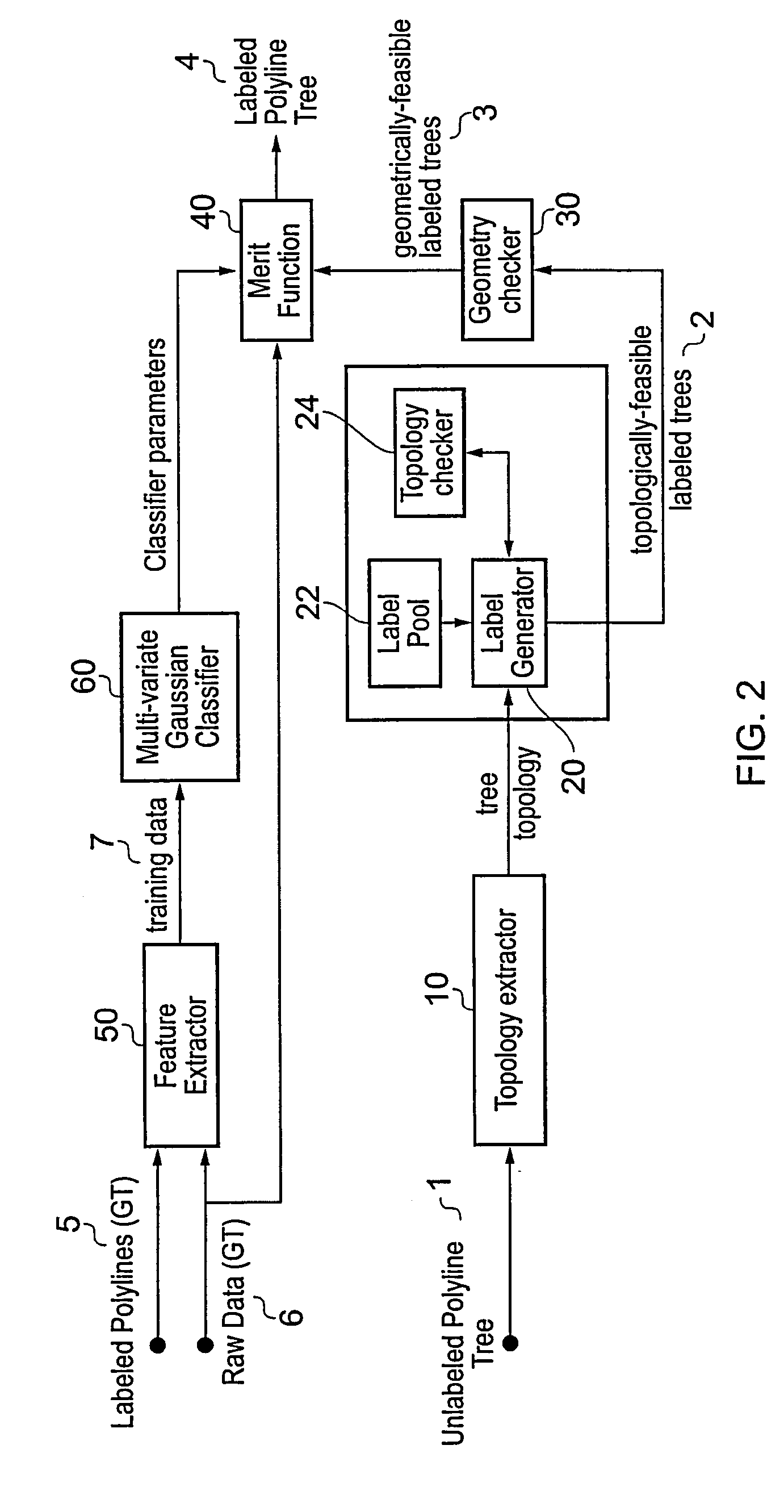
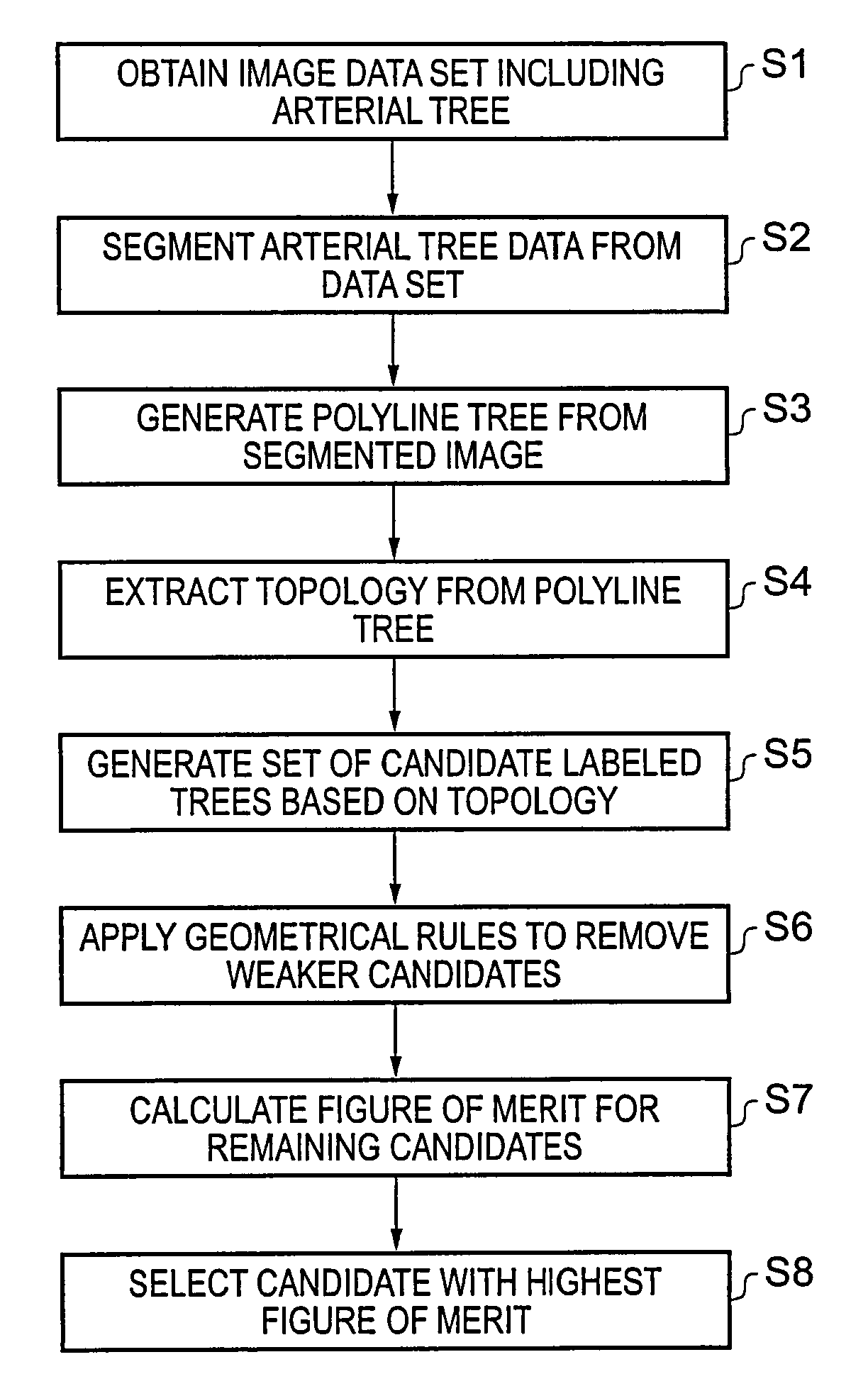
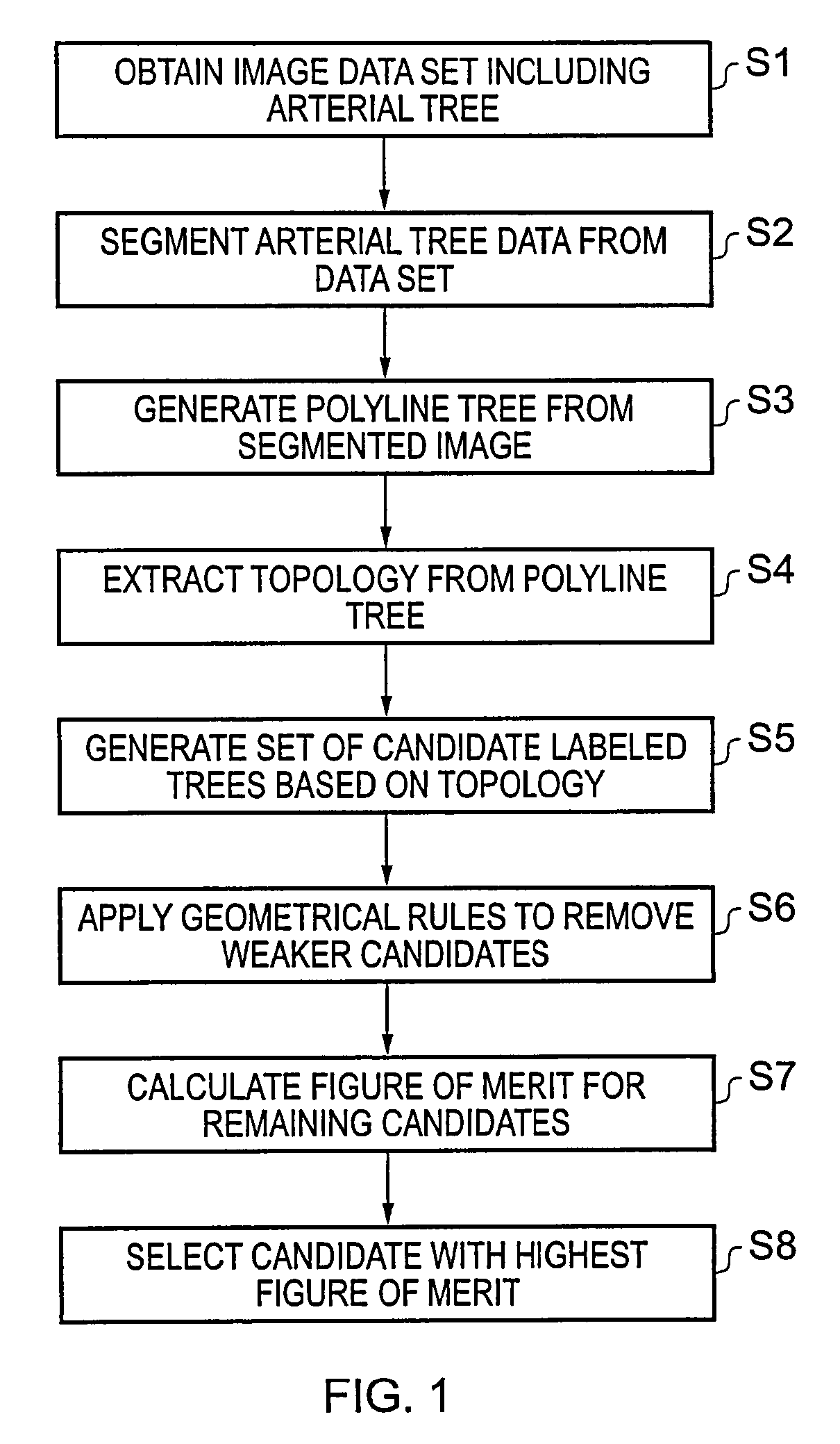
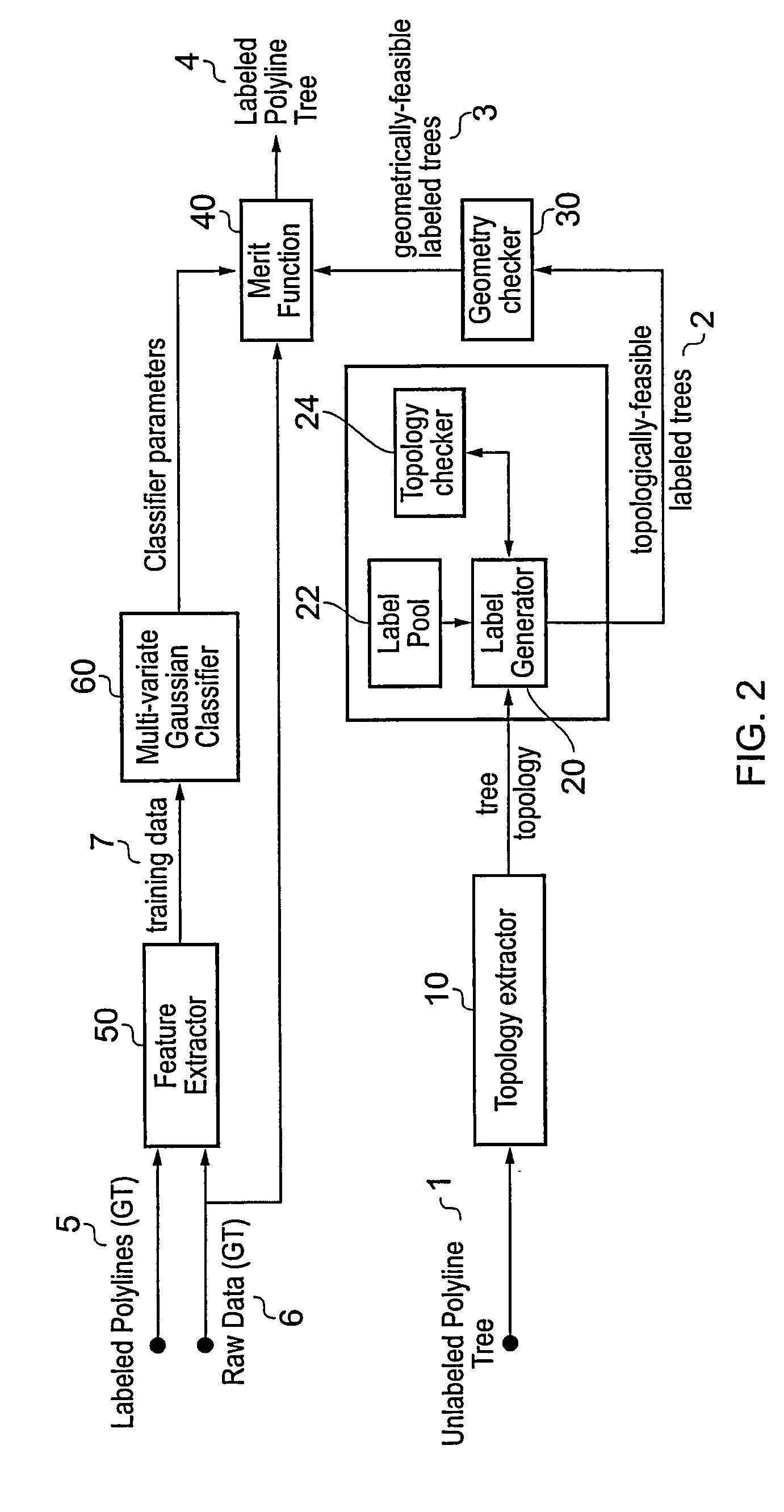
A polyline tree representation of a coronary artery tree imaged in a volume data set is obtained, and its topology is extracted to give a topological representation indicating the relative positions of vessels in the tree. The topological representation is compared with a set of topological rules to find possible anatomical classifications for each vessel, and a set of candidate labeled polyline trees is generated by labeling the polyline tree with labels showing each combination of possible anatomical classifications. Each candidate labeled tree is filtered according to a set of geometric rules pertaining to spatial characteristics of vessels in arterial trees, and any labeled tree not satisfying the geometric rules is rejected A figure of merit is calculated for each remaining candidate by comparing features of the vessels measured from the polyline tree and from the volume data set with features of correctly classified vessels in other data sets to determine the probable correctness of the labeling of each candidate, and the candidate with the best figure of merit is selected as showing the proper classification of the vessels.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Apparatus for determining cardiovascular parameters
InactiveUS7314449B2Reduced effectivenessReliable assessmentRespiratorsSurgeryAutonomous breathingTransmural pressure
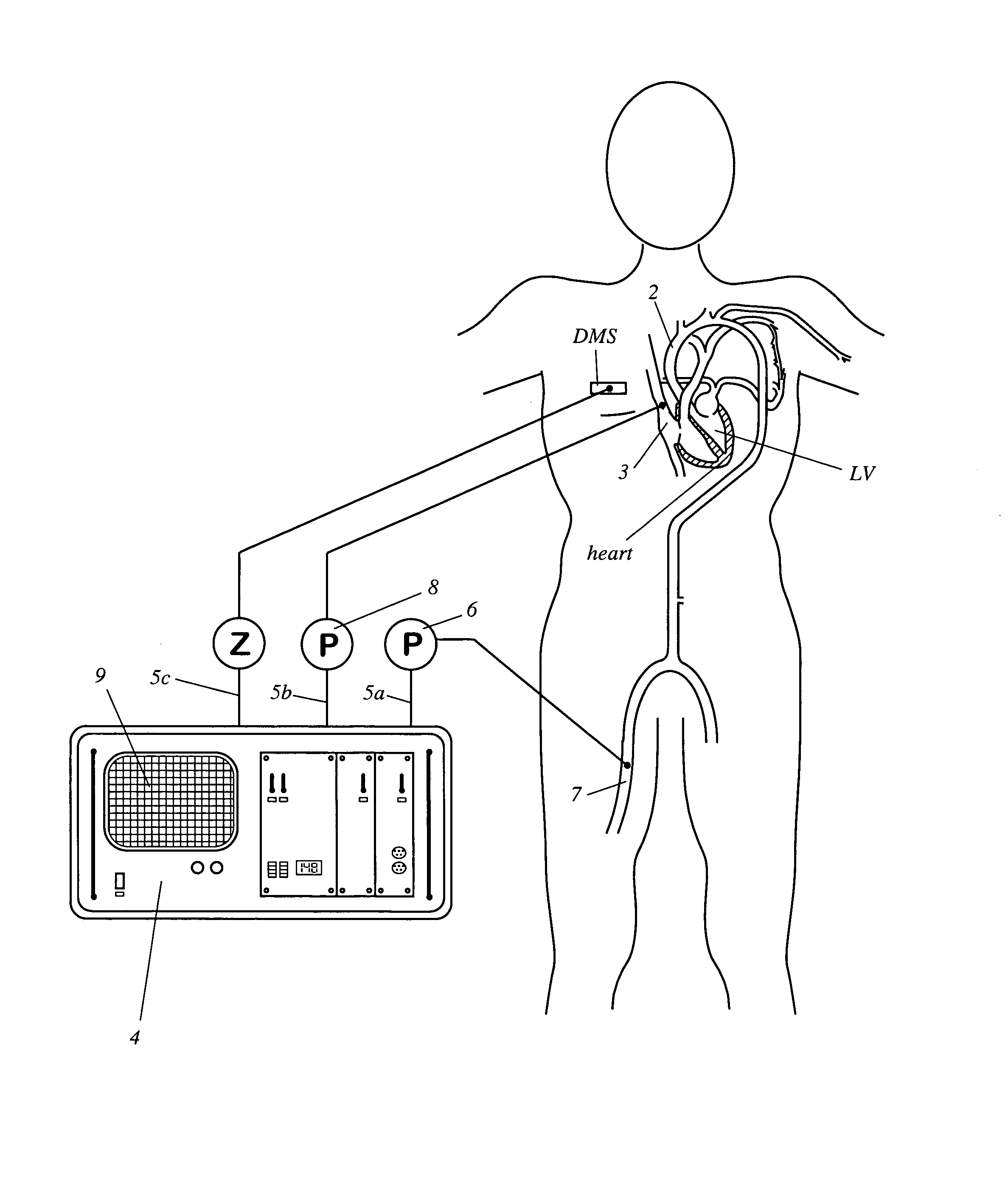
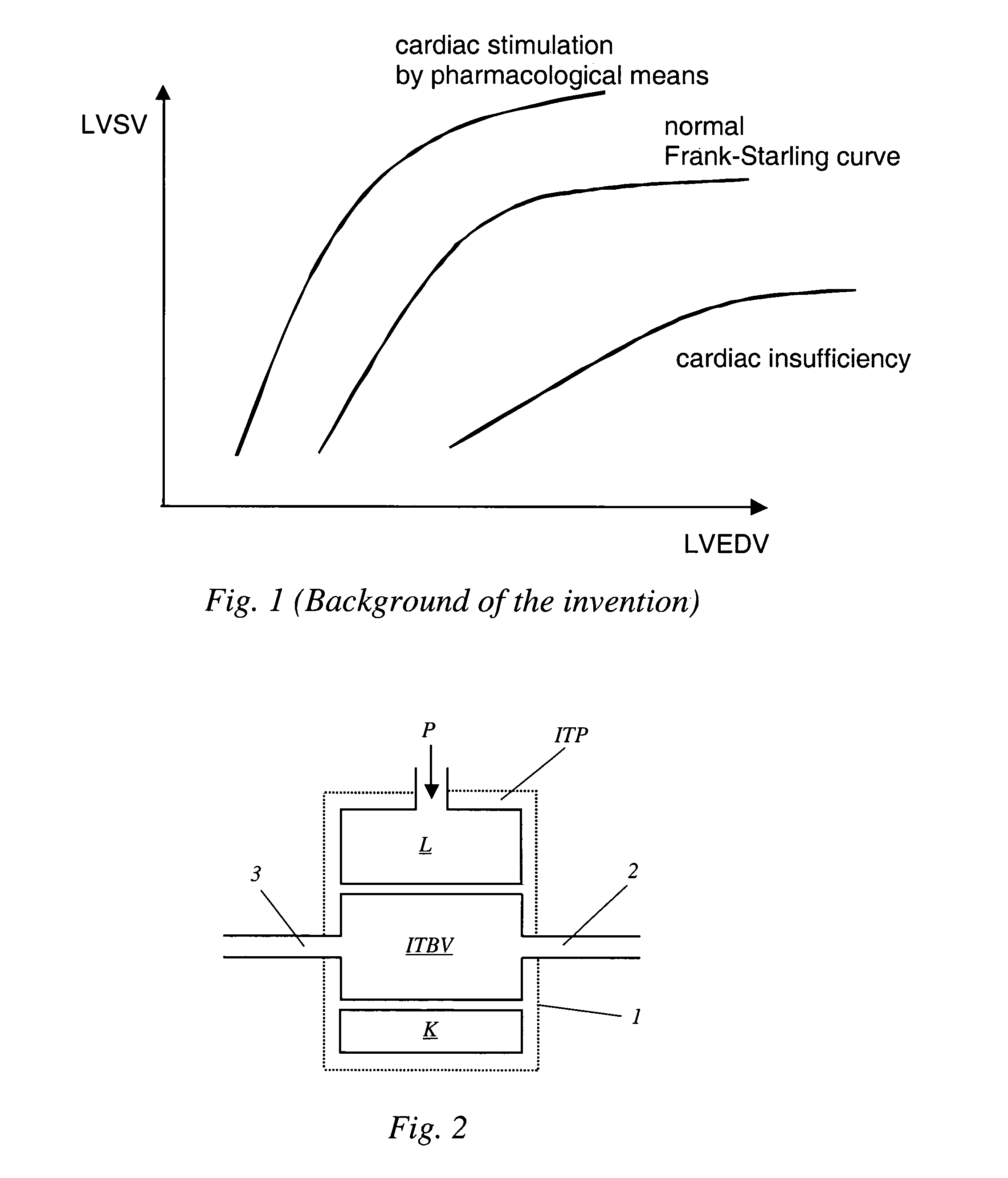
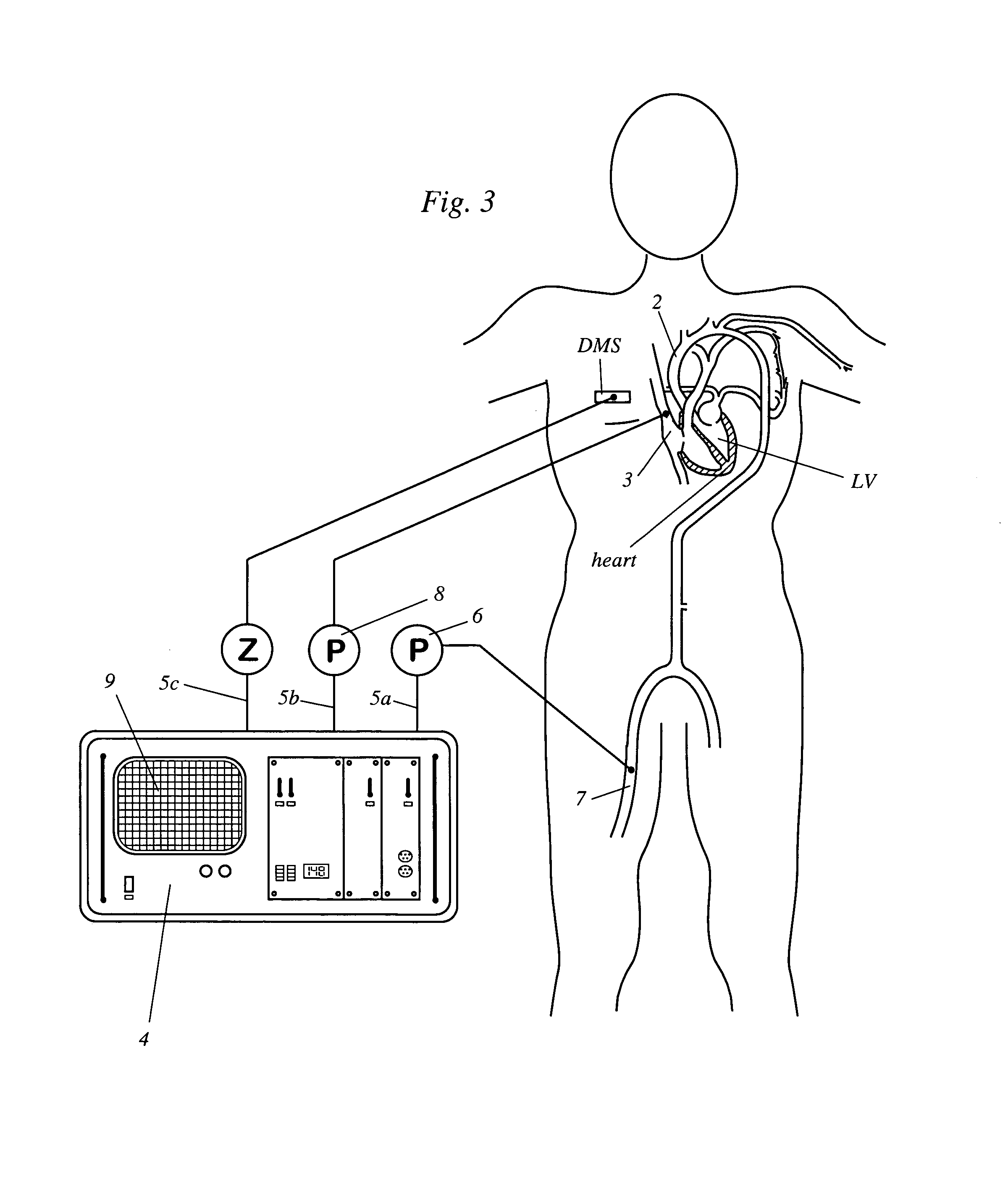
An apparatus that continuously monitors the arterial pressure measured by a pressure sensor in an artery, which pressure is regarded as the reading Pao that approximately corresponds to the aortal pressure. In principle, the arterial pressure can be measured in the aorta, near the aorta, or in the arterial tree. To provide a second reading, the apparatus, via the input channel, continuously monitors the central venous pressure (CVP), which is regarded as the reading PIT that approximately corresponds to the intrathoracic pressure (ITP). The third reading is provided via the input channel as a reading Z which expresses the thoracic compliance. Via known algorithms of the pulse contour analysis, the apparatus calculates the stroke volume variation, using as the determining pressure the transmural pressure which is calculated according to the formulaPtransmural=Pao−f(C)*PITThe cardiac volume responsiveness indicator (CVRI) is calculated for mechanical positive respiration according to the formulaCVRI=k*(SVV / ΔCVP)or for spontaneous breathing according to the formulaCVRI=l−m*(ΔCVP / SVV).
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYSTEMS SE
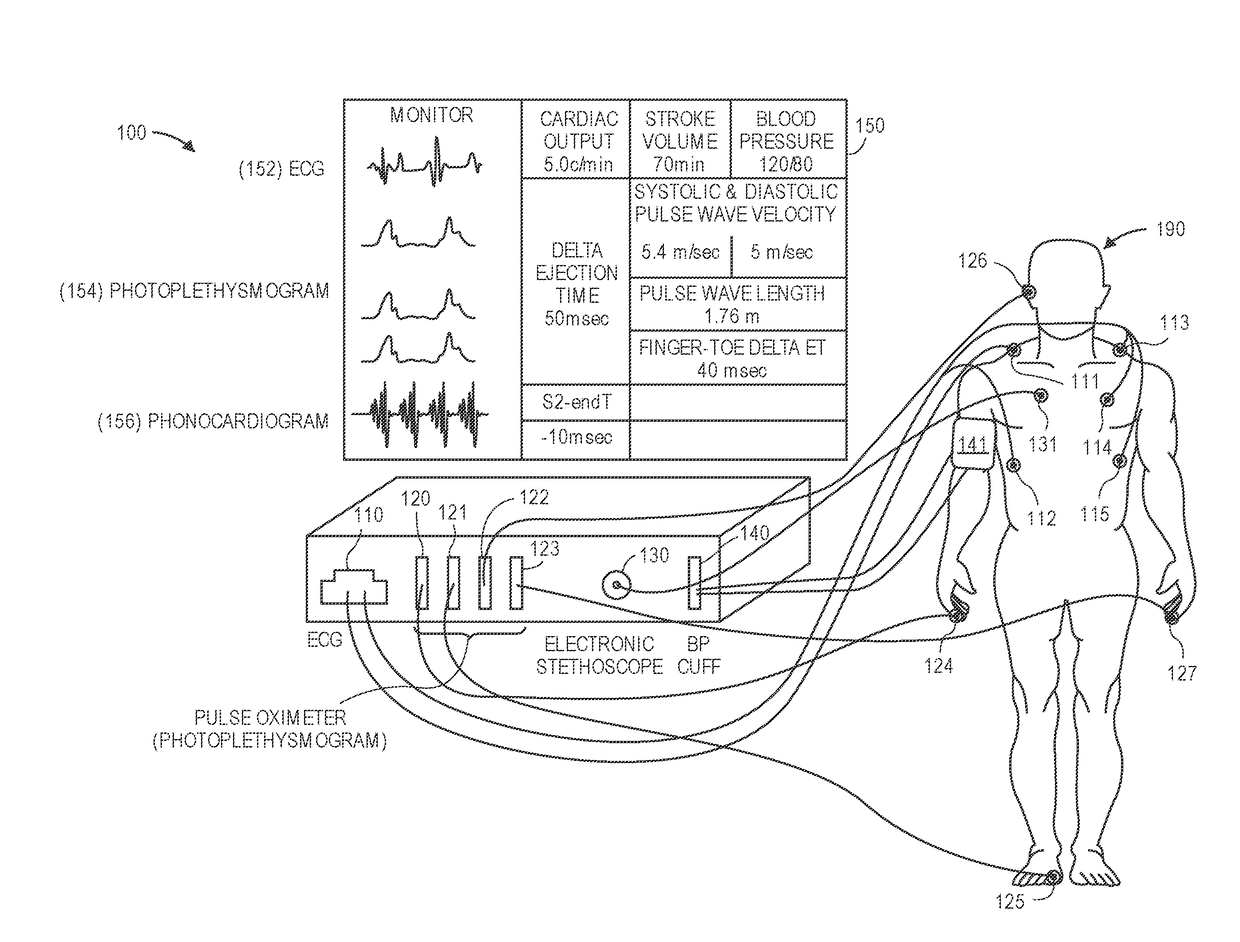
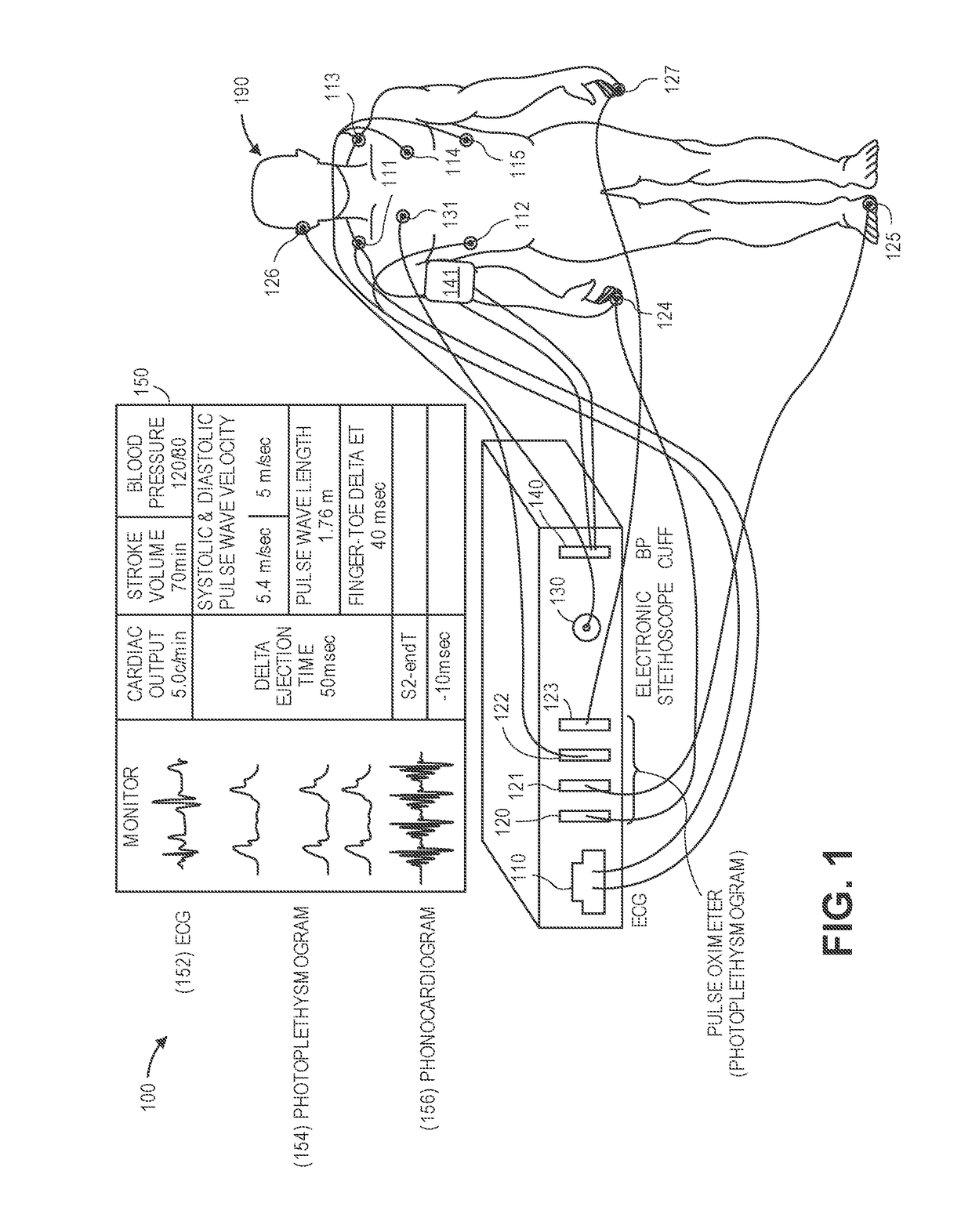
Methods and apparatus for determining cardiac output
ActiveUS20110034813A1Ease of evaluationElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsWhole bodyCardiac cycle
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for determining a dynamical property of the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree using long time scale information, i.e., information obtained from measurements over time scales greater than a single cardiac cycle. In one aspect, the invention provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac output (CO) from a single blood pressure signal measurement obtained at any site in the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree or from any related measurement including, for example, fingertip photoplethysmography.According to the method the time constant of the arterial tree, defined to be the product of the total peripheral resistance (TPR) and the nearly constant arterial compliance, is determined by analyzing the long time scale variations (greater than a single cardiac cycle) in any of these blood pressure signals. Then, according to Ohm's law, a value proportional to CO may be determined from the ratio of the blood pressure signal to the estimated time constant. The proportional CO values derived from this method may be calibrated to absolute CO, if desired, with a single, absolute measure of CO (e.g., thermodilution). The present invention may be applied to invasive radial arterial blood pressure or pulmonary arterial blood pressure signals which are routinely measured in intensive care units and surgical suites or to noninvasively measured peripheral arterial blood pressure signals or related noninvasively measured signals in order to facilitate the clinical monitoring of CO as well as TPR.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for classification of coronary artery image data
InactiveUS7941462B2Accurate and computationally efficient techniqueIncrease speedImage enhancementMedical data miningData setCoronary arterial tree
A polyline tree representation of a coronary artery tree imaged in a volume data set is obtained, and its topology is extracted to give a topological representation indicating the relative positions of vessels in the tree. The topological representation is compared with a set of topological rules to find possible anatomical classifications for each vessel, and a set of candidate labeled polyline trees is generated by labeling the polyline tree with labels showing each combination of possible anatomical classifications. Each candidate labeled tree is filtered according to a set of geometric rules pertaining to spatial characteristics of vessels in arterial trees, and any labeled tree not satisfying the geometric rules is rejected A figure of merit is calculated for each remaining candidate by comparing features of the vessels measured from the polyline tree and from the volume data set with features of correctly classified vessels in other data sets to determine the probable correctness of the labeling of each candidate, and the candidate with the best figure of merit is selected as showing the proper classification of the vessels.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Method and apparatus for a continuous non-invasive and non-obstrusive monitoring of blood pressure
ActiveUS8585605B2Improve accuracyContinuous trackingElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsArterial velocityArterial tree
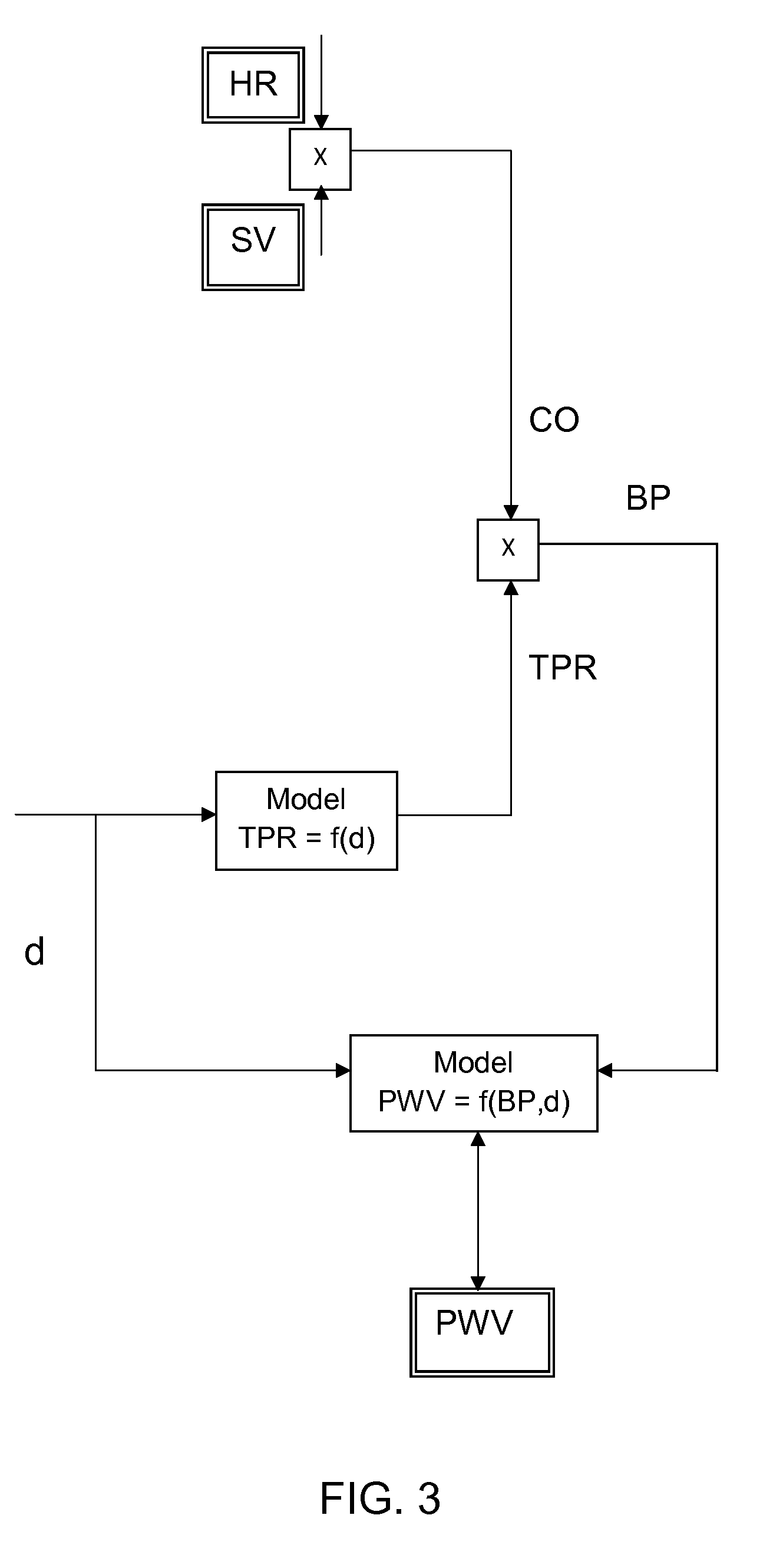
The invention provides a method and an apparatus for a continuous non-invasive and non-obstrusive monitoring of blood pressure. The method comprises the steps of: a) measuring the value (PW) of a Pulse Wave parameter, equal to or derived from the Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) parameter of a segment of the arterial tree of a subject, b) measuring the value (CO) of the Cardiac Output parameter, and c) determining the value (BP) of the blood pressure that satisfiesBP=argminBPd(PW,(CO,BP)),where PW is the value measured in step a), (CO, BP) corresponds to a predicted value of the Pulse Wave parameter computed according to a model of the segment of the arterial tree, the value (CO) of the Cardiac Output parameter measured in step b) and an hypothesized value of the blood pressure.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Image processing method for estimating a brain shift in a patient
InactiveUS20110257514A1Rapid and robust and precise responseImage enhancementImage analysisSurgical operationImaging processing
The disclosure relates to an image processing method for estimating a brain shift in a patient, the method involving: the processing of a three-dimensional image of the brain of a patient, acquired before a surgical operation, in order to obtain a reference cerebral arterial tree structure of the patient; the processing of three-dimensional images of the brain of the patient, acquired during the operation, in order to at least partially reconstitute a current cerebral arterial tree structure of the patient; the determination from the combination of the reference and current cerebral arterial tree structures, of a field of shift of the vascular tree representing the shift of the current vascular tree in relation to the reference vascular tree; the application of the determined field of shift of the vascular tree to a biomechanical model of the brain of the patient in order to estimate the brain shift of the patient; and the generation, from the estimated brain shift, of at least one image of the brain of the patient, in which the brain shift is compensated.
Owner:UNIV JOSEPH FOURIER +1
Method for determining a cardiac function
ActiveUS20090187110A1Accurate measurementIncrease pressureCatheterSensorsArterial velocityArterial tree
A method for determining a cardiac function, comprising (i) determining base anatomical characteristics associated with the subject, (ii) determining pulse delay to a first body site (PD01) and a second body site (PD02) as a function of the anatomical characteristics, wherein the distance via the arterial tree from the aortic valve to the first body site (PD01) is different than the arterial tree distance from the aortic valve to the second body site (PD02), (iii) determining pulse wave velocity between the first body site and the second body site (PWV12), (iv) determining pulse wave velocity between the aortic valve and the first body site (PWV01) as a function of PWV12, and the anatomical characteristics; and (v) determining the pre-ejection period (PEP) as a function of PD01 and PWV01.
Owner:CARDIAC PROFILES
Methods and apparatus for determining cardiac output
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for determining a dynamical property of the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree using long time scale information, i.e., information obtained from measurements over time scales greater than a single cardiac cycle. In one aspect, the invention provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac output (CO) from a single blood pressure signal measurement obtained at any site in the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree or from any related measurement including, for example, fingertip photoplethysmography.According to the method the time constant of the arterial tree, defined to be the product of the total peripheral resistance (TPR) and the nearly constant arterial compliance, is determined by analyzing the long time scale variations (greater than a single cardiac cycle) in any of these blood pressure signals. Then, according to Ohm's law, a value proportional to CO may be determined from the ratio of the blood pressure signal to the estimated time constant. The proportional CO values derived from this method may be calibrated to absolute CO, if desired, with a single, absolute measure of CO (e.g., thermodilution). The present invention may be applied to invasive radial arterial blood pressure or pulmonary arterial blood pressure signals which are routinely measured in intensive care units and surgical suites or to noninvasively measured peripheral arterial blood pressure signals or related noninvasively measured signals in order to facilitate the clinical monitoring of CO as well as TPR.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
Systems and methods for model-based estimation of cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac output and total peripheral resistance include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine intra-beat and inter-beat variability in arterial blood pressure and estimating from the variability a time constant for a lumped parameter beat-to-beat averaged Windkessel model of the arterial tree. Uncalibrated cardiac output and uncalibrated total peripheral resistance may then be calculated from the time constant. Calibrated cardiac output and calibrated total peripheral resistance may be computed using calibration data, assuming an arterial compliance that is either constant or dependent on mean arterial blood pressure. The parameters of the arterial compliance may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
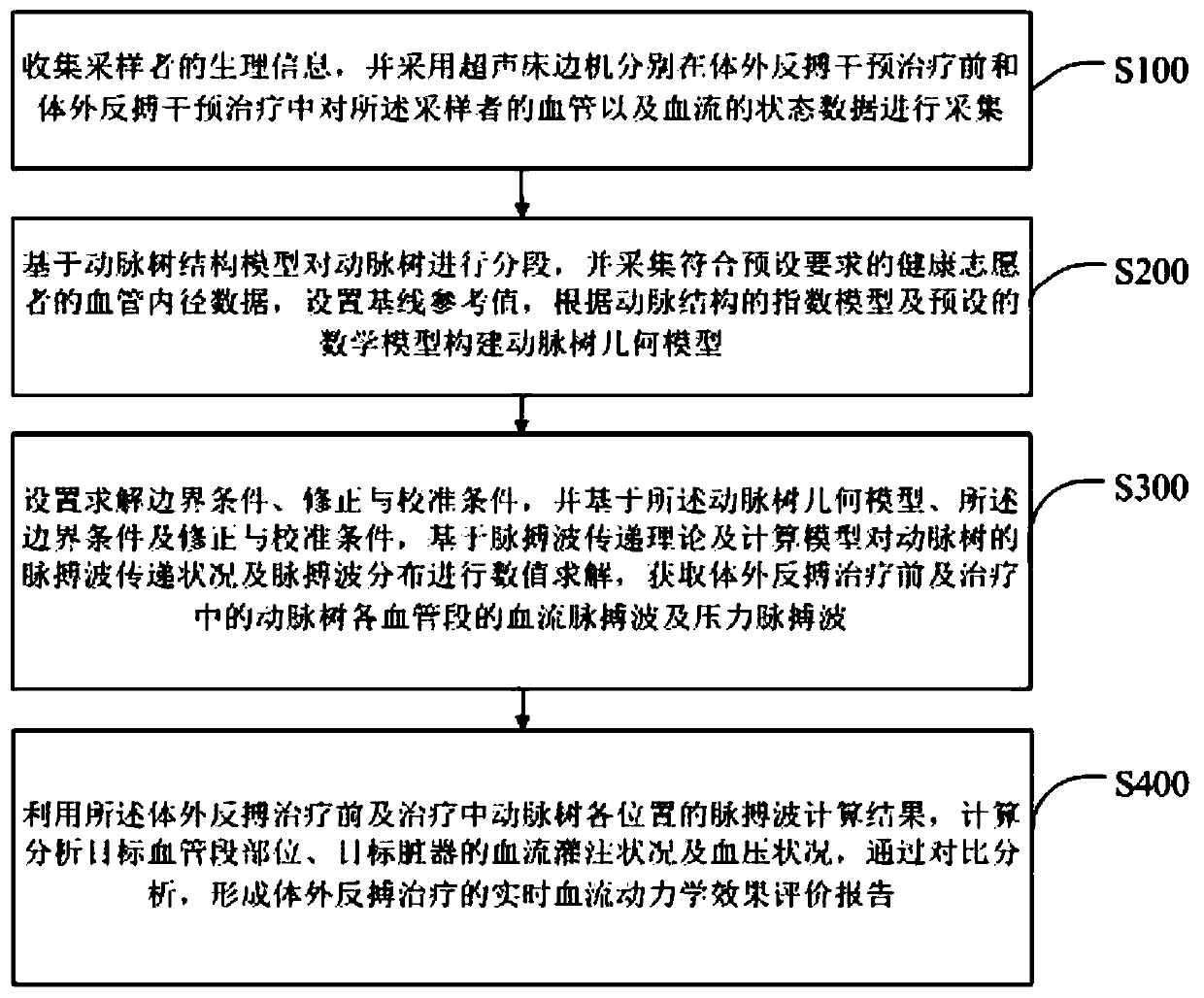
Method and device for detecting body haemodynamics response in in-vitro counterpulsation treatment
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting body haemodynamics response in in-vitro counterpulsation treatment. The detection method comprises the steps that physiological information ofa sampler is acquired, and blood vessel and blood flow state data before and in in-vitro counterpulsation treatment are acquired respectively; an arterial tree is segmented based on an arterial treestructure model, blood segment length and radius data of a healthy volunteer are acquired, a baseline reference value is set, and an arterial tree geometric solution model is constructed; and boundaryconditions and correction and calibration conditions are calculated and set, flow and pressure pulse wave distribution of each position of the arterial tree is calculated on the basis of the pulse wave transmission theory and the model, and the blood perfusion and blood pressure levels of target blood vessel segments and visceral organs before and in the in-vitro counterpulsation treatment are calculated. The method and device can be used for noninvasive, real-time and effective analysis of the immediate haemodynamics effect of the in-vitro counterpulsation intervention treatment, and break the technical bottleneck of lack of an effective immediate haemodynamics effect evaluation method in the current in-vitro counterpulsation treatment.
Owner:THE EIGHTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Novel device and method to measure ventricular arterial coupling and vascular performance
A device and method for analyzing of a disturbed pattern of pulse wave front results in a non-invasive, real-time diagnostic tool of arterial vascular performance on both a global and regional scale. The device provides a single number quantifying how well the arterial tree as a whole is coupled to receive and distribute a stroke volume of a single heartbeat. Changing heart rate, contractility, volume status, and afterload will change stroke volume and ejection time. Different vasculatures with different properties (e.g., size and intrinsic stiffness) will be best matched for different stroke volumes and ejection times to provide optimal coupling. The device will allow finding the optimal set of parameters for individual patient.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Systems and methods for model-based estimation of cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac output and total peripheral resistance include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine intra-beat and inter-beat variability in arterial blood pressure and estimating from the variability a time constant for a lumped parameter beat-to-beat averaged Windkessel model of the arterial tree. Uncalibrated cardiac output and uncalibrated total peripheral resistance may then be calculated from the time constant. Calibrated cardiac output and calibrated total peripheral resistance may be computed using calibration data, assuming an arterial compliance that is either constant or dependent on mean arterial blood pressure. The parameters of the arterial compliance may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
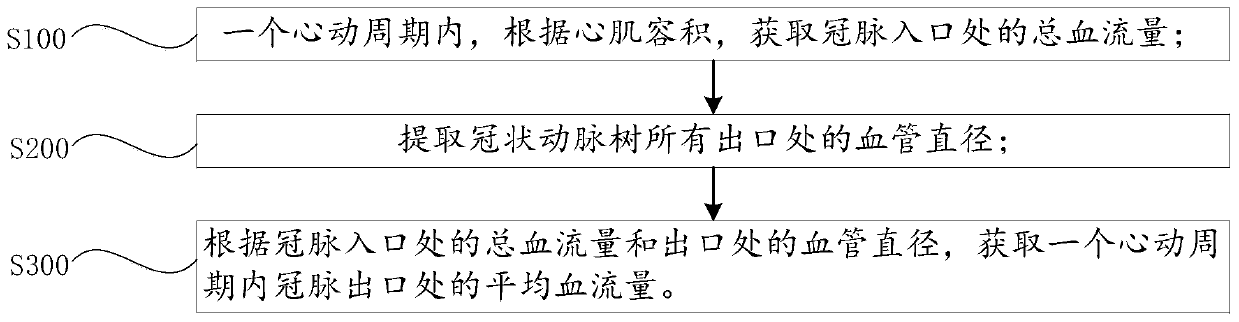
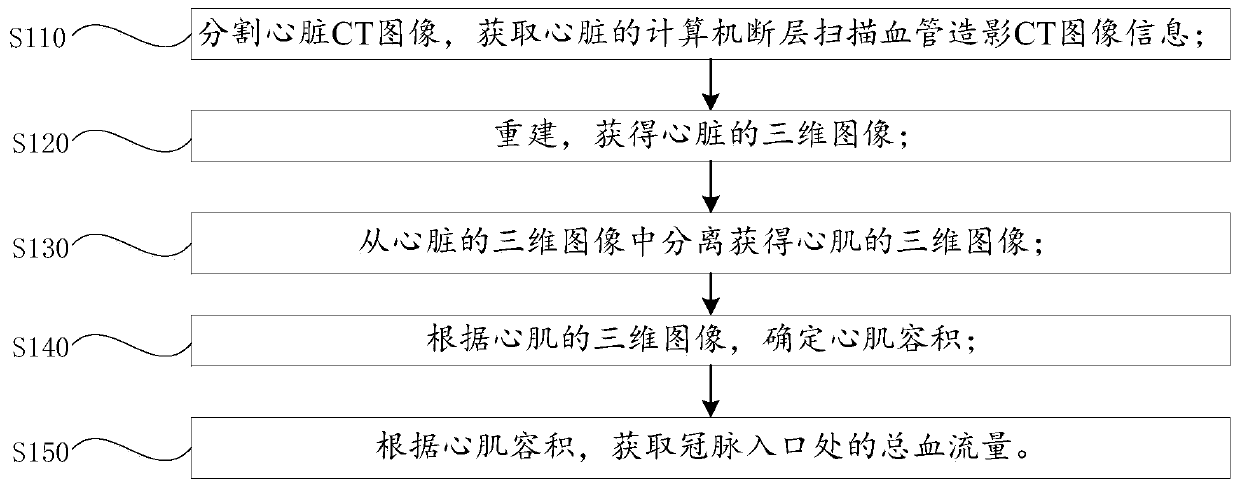
Method and device for obtaining average blood flow and flow rate at outlet of coronary artery, and system
InactiveCN110432886AEasy to operateAccurate measurementComputerised tomographsTomographyFine structureCoronary arterial tree
The application provides a method and device for obtaining average blood flow and flow rate at an outlet of a coronary artery, and a system. The method for obtaining the average blood flow at the outlet of the coronary artery in a cardiac cycle comprises the following steps of in one cardiac cycle, according to the volume of cardiac muscles, obtaining the total blood flow of an inlet of the coronary artery; extracting the blood vessel diameter of each of all the outlets of a corona arterial tree; and according to the total blood flow at the inlet of the coronary artery and the blood vessel diameter of the outlet of the coronary artery, obtaining the average blood flow at the outlet of the coronary artery in the cardiac cycle. The method disclosed by the application is a new non-invasive detection means, measuring the blood flow does not need to rely on a coronary artery ultrasonic technique, and according to the total blood flow at the inlet of the coronary artery and the blood vesseldiameter at the outlet, the average blood flow at the outlet of the coronary artery in one cardiac cycle can be obtained, so that the operation is easy, fine structure images can be distinguished, andthe measuring is more accurate.
Owner:SUZHOU RAINMED MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
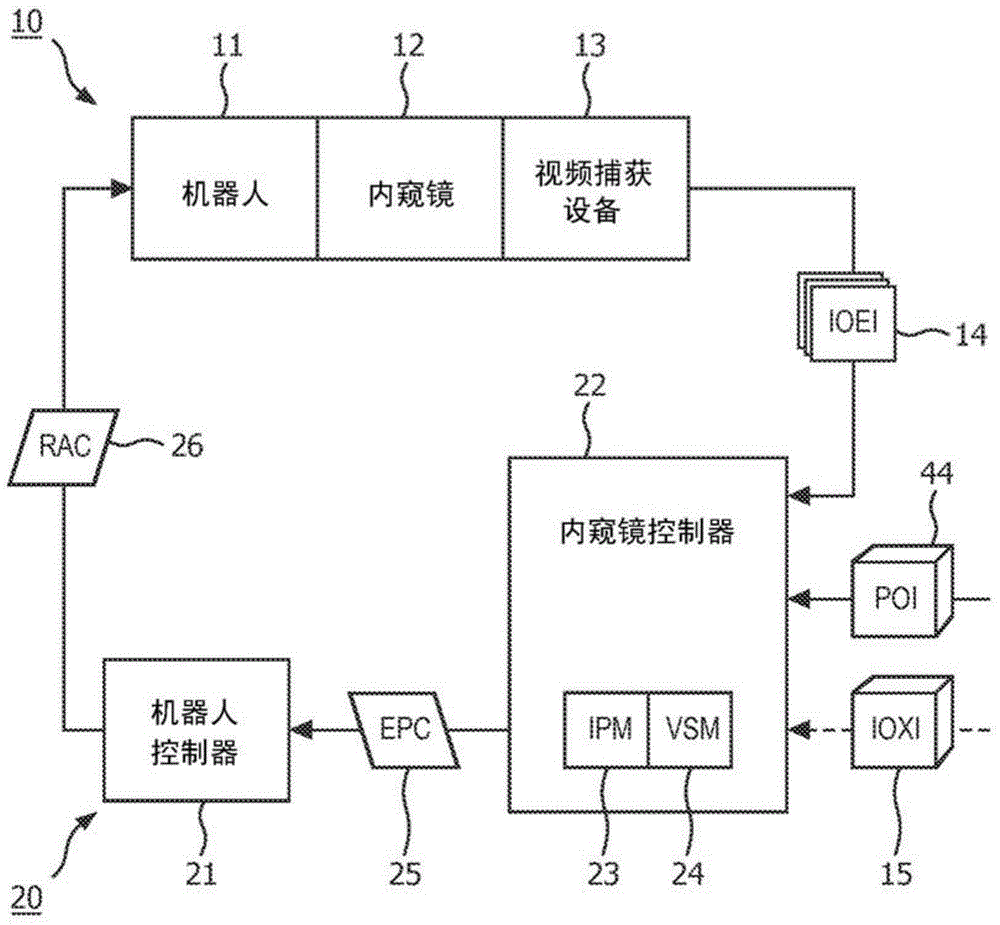
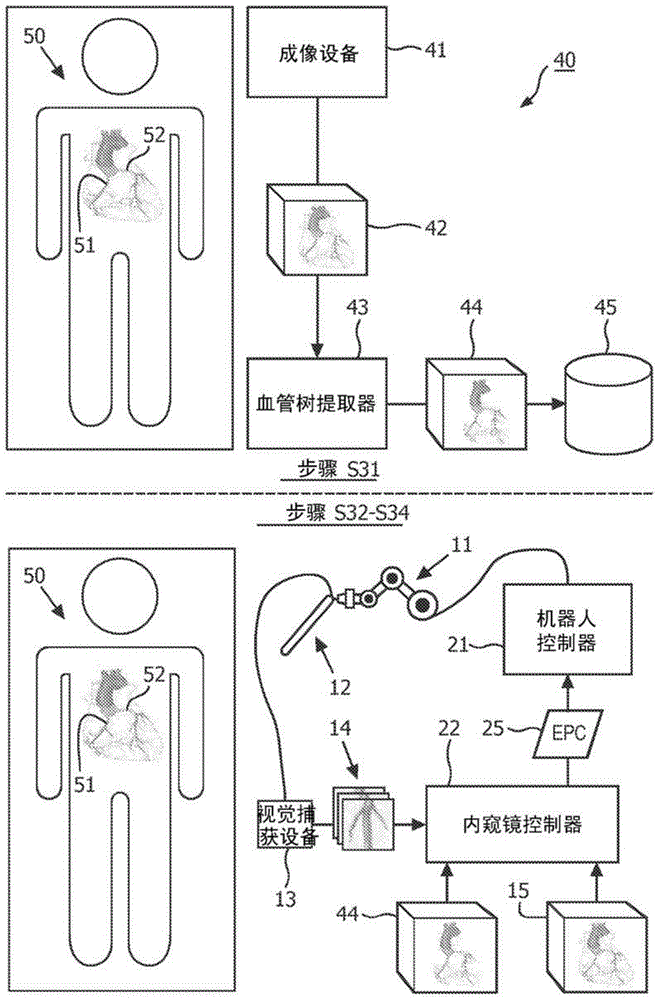
Endoscopic registration of vessel tree images
An image registration system an endoscope (12) and an endoscope controller (22). In operation, the endoscope (12) generates an intra-operative endoscopic image (14) of a vessel tree (e.g., an arterial tree or a venous tree) within an anatomical region, and the endoscope controller (22) image registers the intra-operative endoscopic image (14) of the vessel tree to a pre- operative three-dimensional image (44) of the vessel tree within the anatomical region. The image registration includes an image matching of a graphical representation of each furcation of the vessel tree within the intra-operative endoscopic image (14) of the vessel tree to a graphical representation of each furcation of the vessel tree within the pre-operative three-dimensional image (44) of the vessel tree.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for estimating changes of cardiovascular indices using peripheal arterial blood pressure waveform
ActiveUS20140358015A1Estimates are accurate and reliableEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial treeBlood arterial
The systems and methods described herein enable reliable estimation of cardiovascular indices on real-time, non-invasive or minimally-invasive, and heat-to-beat basis. Cardiovascular indices which can be estimated include: stroke volume (SV), which being limited to, cardiac output (CO) and total peripheral resistance (TPR). In various embodiments, one or more of these indices are estimated continuously, on a beat-to-beat basis, using peripheral arterial blood pressure (ABP) waveforms and certain parameters derived from the peripheral ABP waveforms. The derived parameters are substantially insensitive to distortions of the ABP waveform arising from tapered arterial branches throughout the arterial tree. The methods describe herein can provide a more accurate and reliable estimate of hemodynarnic parameters than existing techniques.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Detecting coronary stenosis through spatio-temporal tracking
Embodiments relate to detecting coronary stenosis through spatio-temporal tracking. Aspects include extracting a coronary artery tree from each of a sequence of angiogram images, creating a mean artery tree from the extracted coronary artery trees, and projecting the mean artery tree back onto each of the sequence of angiogram images to recover a complete coronary artery tree for each of the sequence of angiogram images. Aspects also include extracting one or more tubular sections from each of the sequence of angiogram images, estimating an arterial width for each of the one or more tubular sections from each of the sequence of angiogram images, and creating a spatio-temporal surface from the arterial widths of the one or more tubular sections over a time spanned by the sequence of angiogram images. Aspects further include detecting a minimum in the spatio-temporal surface and determining if the minimum is indicative of stenosis.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for determining a cardiac function
ActiveUS8834382B2Reduces and eliminates disadvantage and drawbackAccurate measurementCatheterSensorsArterial velocityArterial tree
A method for determining a cardiac function, comprising (i) determining base anatomical characteristics associated with the subject, (ii) determining pulse delay to a first body site (PD01) and a second body site (PD02) as a function of the anatomical characteristics, wherein the distance via the arterial tree from the aortic valve to the first body site (PD01) is different than the arterial tree distance from the aortic valve to the second body site (PD02), (iii) determining pulse wave velocity between the first body site and the second body site (PWV12), (iv) determining pulse wave velocity between the aortic valve and the first body site (PWV01) as a function of PWV12, and the anatomical characteristics; and (v) determining the pre-ejection period (PEP) as a function of PD01 and PWV01.
Owner:CARDIAC PROFILES
Image processing method for estimating a brain shift
InactiveUS9008381B2Rapid and robust and precise responseImage enhancementImage analysisSurgical operationImaging processing
Owner:UNIV JOSEPH FOURIER +1
Method for estimating changes of cardiovascular indices using peripheal arterial blood pressure waveform
ActiveUS9560977B2Estimates are accurate and reliableEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial treeBlood arterial
The systems and methods described herein enable reliable estimation of cardiovascular indices on real-time, non-invasive or minimally-invasive, and beat-to-beat basis. Cardiovascular indices which can be estimated include: stroke volume (SV), which being limited to, cardiac output (CO) and total peripheral resistance (TPR). In various embodiments, one or more of these indices are estimated continuously, on a beat-to-beat basis, using peripheral arterial blood pressure (ABP) waveforms and certain parameters derived from the peripheral ABP waveforms. The derived parameters are substantially insensitive to distortions of the ABP waveform arising from tapered arterial branches throughout the arterial tree. The methods describe herein can provide a more accurate and reliable estimate of hemodynamic parameters than existing techniques.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Radioembolism dose and injection position evaluation method based on fluid dynamics
PendingCN114880960AGuaranteed therapeutic effectDesign optimisation/simulationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyArterial treeOrgan damage
The invention relates to the technical field of interventional radiology arterial embolism, and discloses a radioembolism dose and injection position evaluation method based on fluid dynamics. Medical imaging images are acquired and preprocessed, and an artery tree is subjected to recognition and three-dimensional reconstruction by using the trained deep learning model and an accurate modeling method; segmenting and naming the reconstructed blood vessel; obtaining the flow of each blood vessel outlet of the embolism part based on fluid dynamics, and calculating embolism efficiency and organ injury conditions during injection at different embolism positions based on the flow of each blood vessel outlet of the embolism part; the method comprises the following steps: calculating the microsphere radiation quantity of each blood vessel outlet based on a flow ratio, then analyzing the radiation dose and distribution of the microspheres by using a statistical simulation method, drawing a radiation dose distribution three-dimensional cloud chart, and evaluating the damage degree of organs based on the radiation dose of the microspheres to ensure the treatment effect on tumors.
Owner:青岛埃米博创医疗科技有限公司
Method and device for detecting body hemodynamic response in external counterpulsation therapy
Owner:THE EIGHTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method and apparatus for eliminating atherosclerosis from a region of the arterial tree
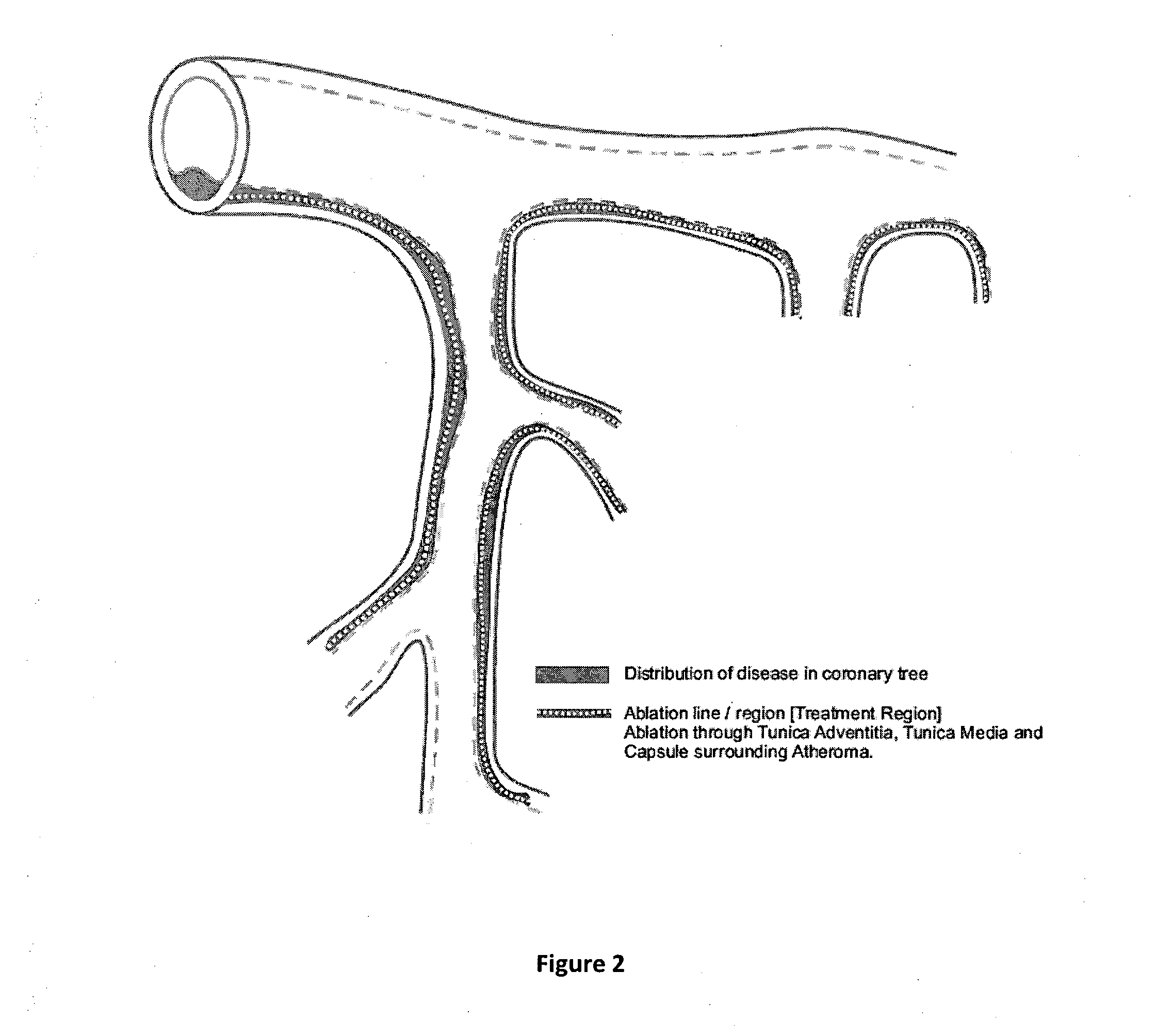
InactiveUS20140249517A1Eliminate the problemEliminating atherosclerosisDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsTunica AdventitiaRadiology
The present invetion provides a method and apparatus for elimination of atherosclerosis from an artery. According to the present invetion the diseased artery is approached from external side and ablate is approached in such a way that incision / cut pass through tunica adventitia and tunica media of the diseased artery and a fibrous capsule of the atherselerosis. On ablation / incision, the contents plaques are exposed to the natural defense of the body and are destroyed by the natural defense system. The plaque escaping out of the artery on the external surface of the artery may be wiped or washed away with saline during or after the ablation procedure. Then, natural healing of artery is allowed which eliminates atherosclerosis thoroughly.
Owner:SINGH AJOY I
Method for indirectly estimating and measuring arterial blood pressure by using PPG sensor
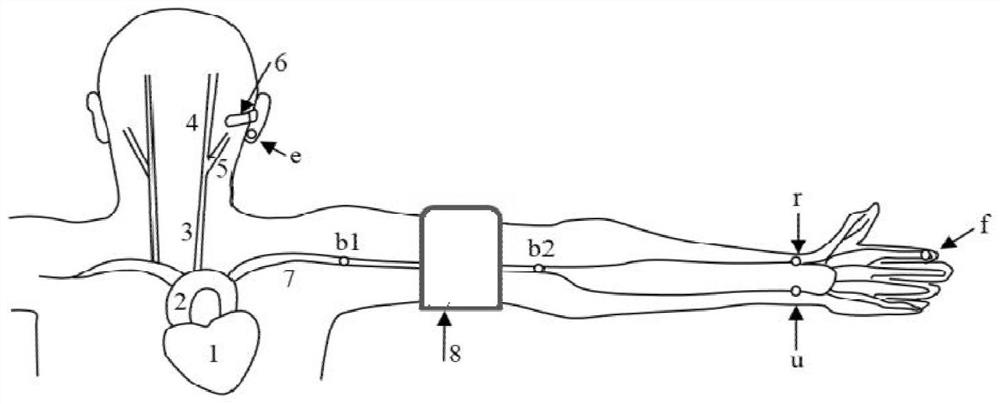
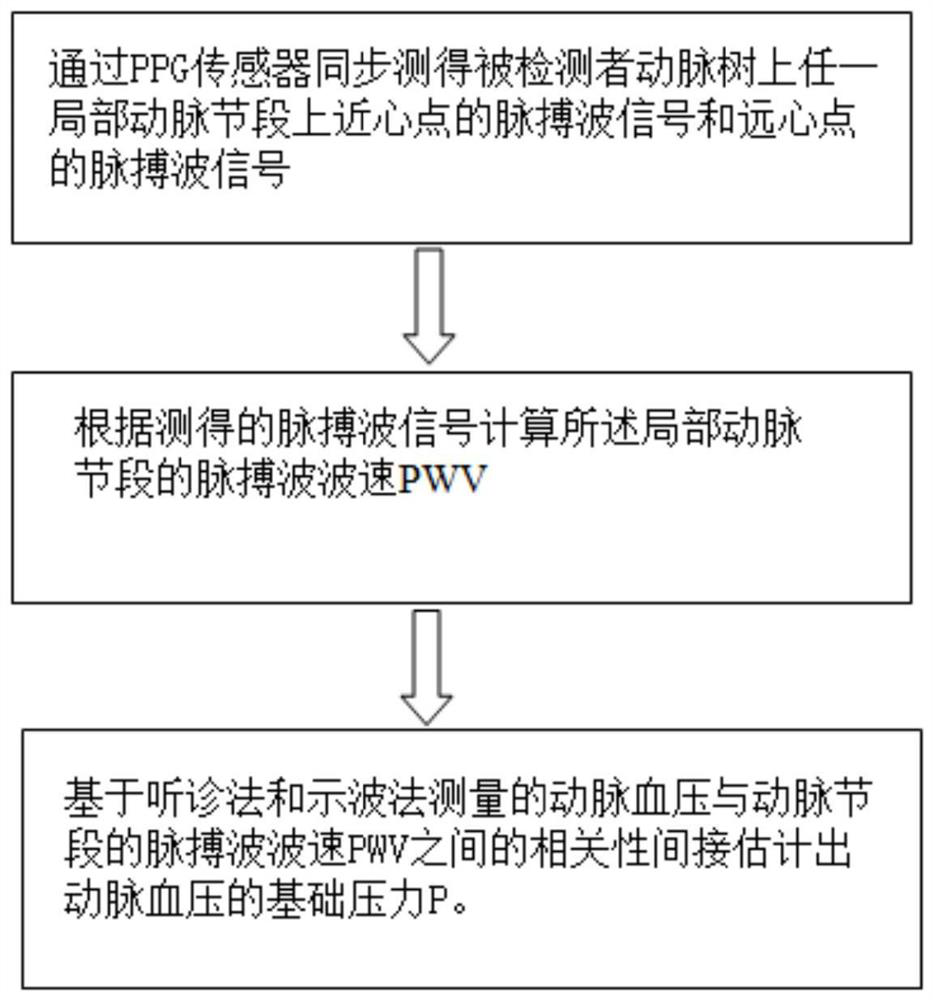
InactiveCN111789581ASpecific and comprehensive continuous state measurement informationEasy to operateEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyArterial velocityArterial tree
The invention discloses a method for indirectly estimating and measuring arterial blood pressure by using a PPG sensor. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, synchronously measuring a pulse wave signal of a point close to the heart and a pulse wave signal of a point away from the heart on any local arterial segment of an arterial tree of a subject through the PPG sensor; step 2, calculating a pulse wave velocity (PWV) of the local arterial segment according to the measured pulse wave signals; and step 3, according to the PWV obtained in the step 2, indirectly estimating the basic pressure P of an arterial blood pressure through correlation between the arterial blood pressure measured by an auscultation method and an oscillography method and the PWV of the related arterial segment. The method is noninvasive, free of oversleeves and invasion, free of management by specially-assigned persons and capable of being continuously used for a long time; an arterialblood flow does not need to be blocked when a systolic pressure is measured; the problems that long-time wearing is needed in actual detection operation, the monitoring difficulty is large, and disturbance to a patient is large are solved; and the effect of better actual operability is achieved.
Owner:感易(上海)传感技术有限公司
Endoscopic Registration of Vascular Tree Images
An image registration system, an endoscope (12) and an endoscope controller (22). During surgery, the endoscope (12) generates an intraoperative endoscopic image (14) of the vascular tree (e.g., the arterial or venous tree) within the anatomical region, and the endoscope controller (22) The intraoperative endoscopic image (14) is image registered with the preoperative three-dimensional image (44) of the vascular tree within the anatomical region. The image registration includes aligning a graphical representation of each branch of the vascular tree in the intraoperative endoscopic image (14) of the vascular tree with each branch of the vascular tree in the preoperative three-dimensional image (44) of the vascular tree. The graphic representation of the cross matches the image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com