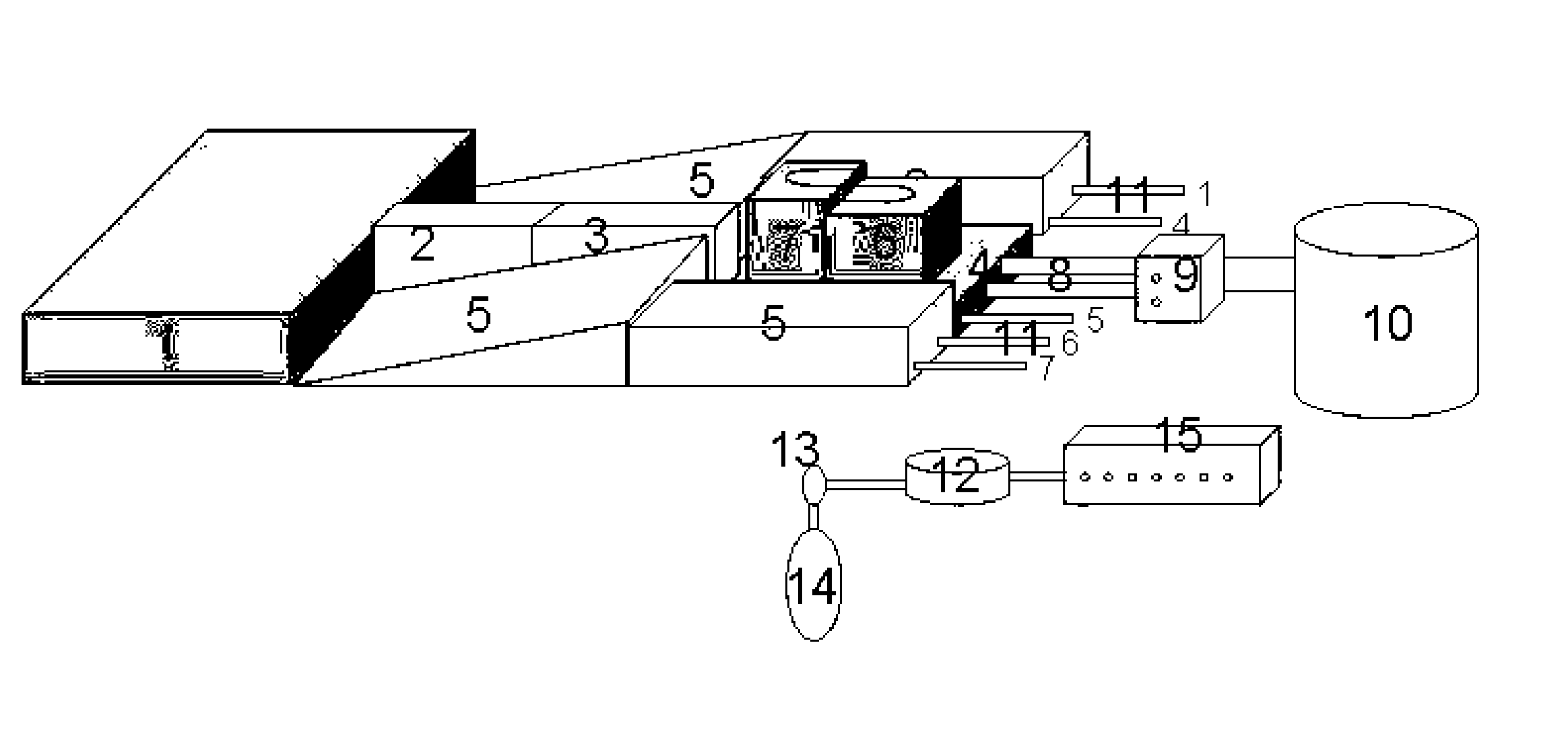
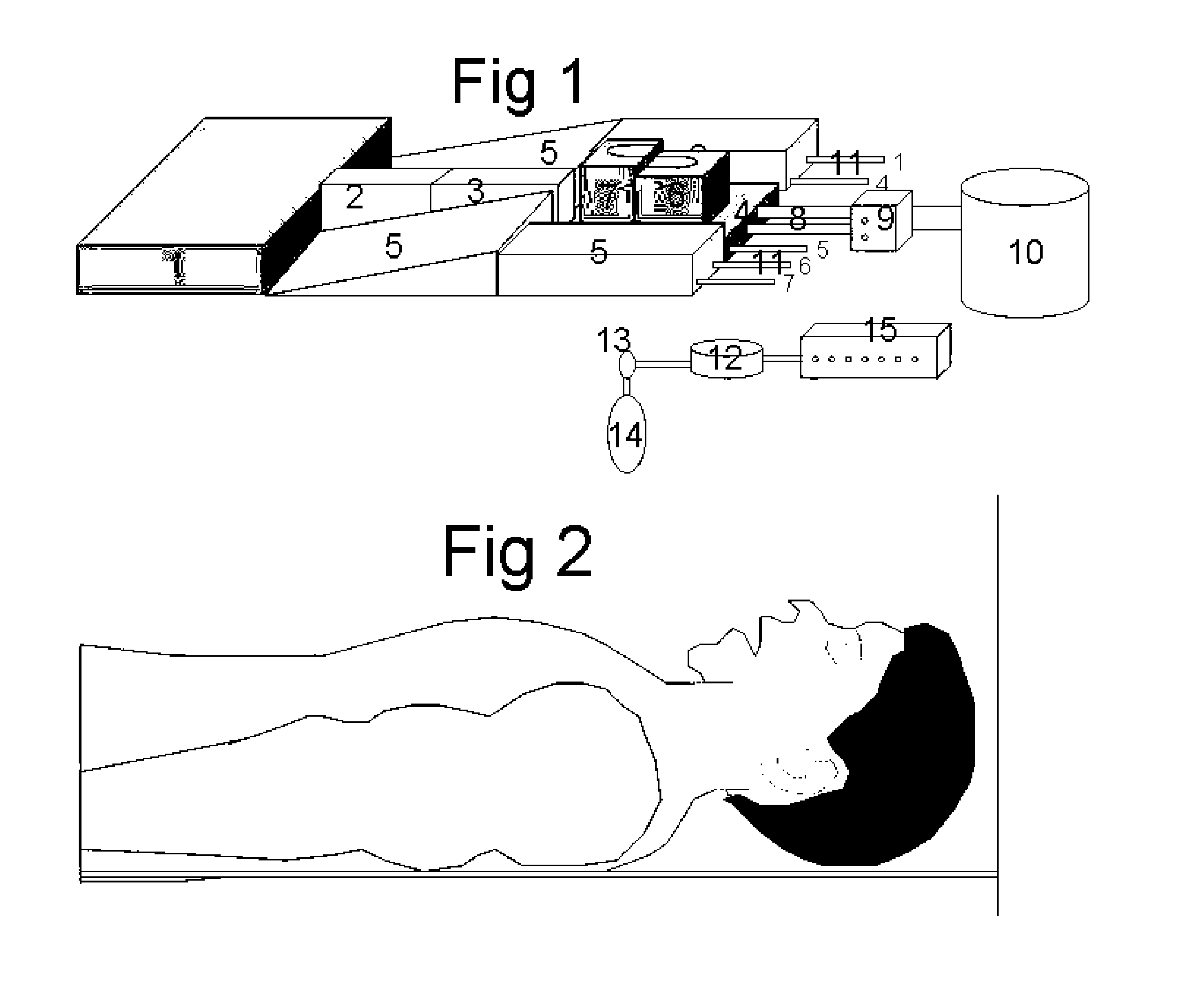
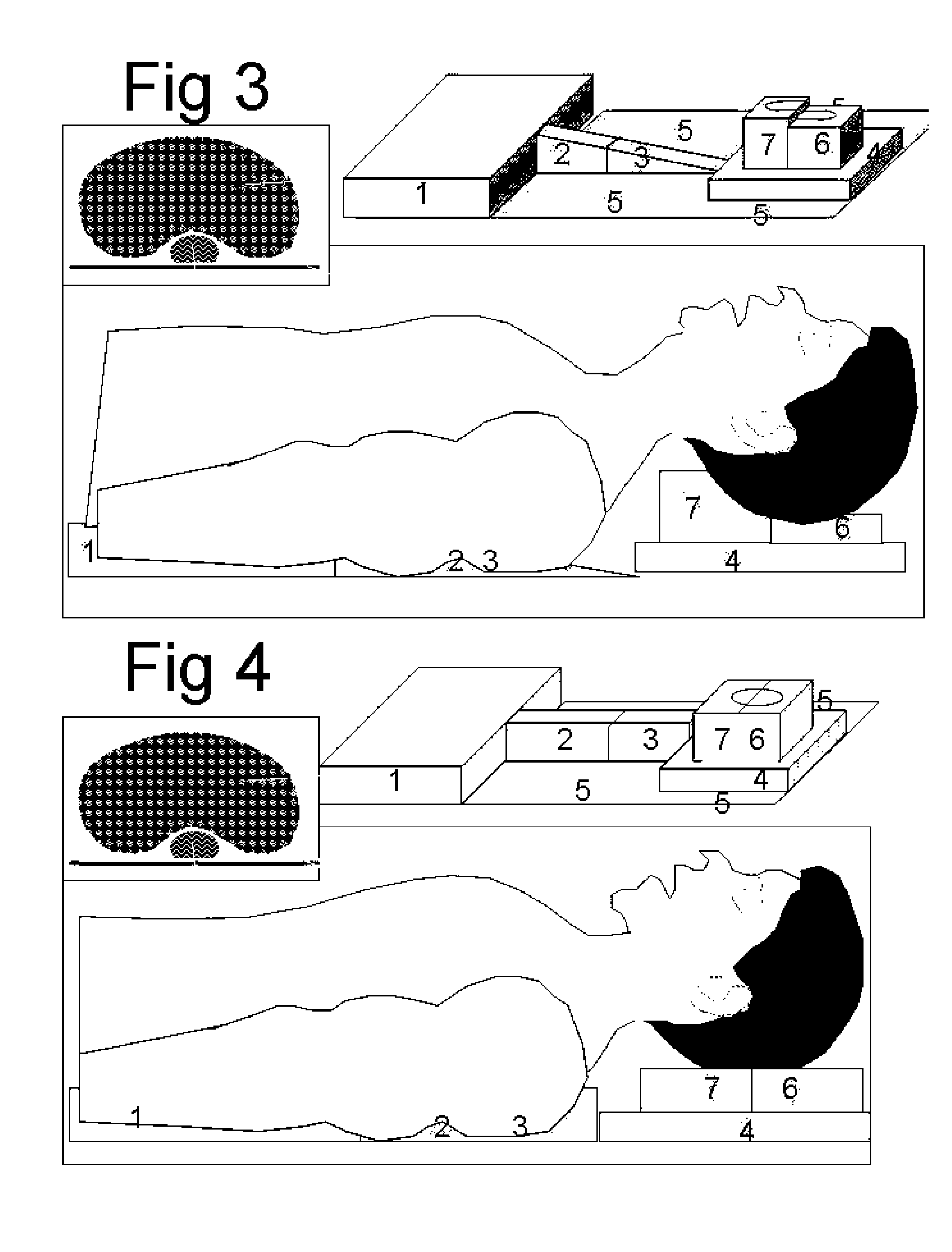
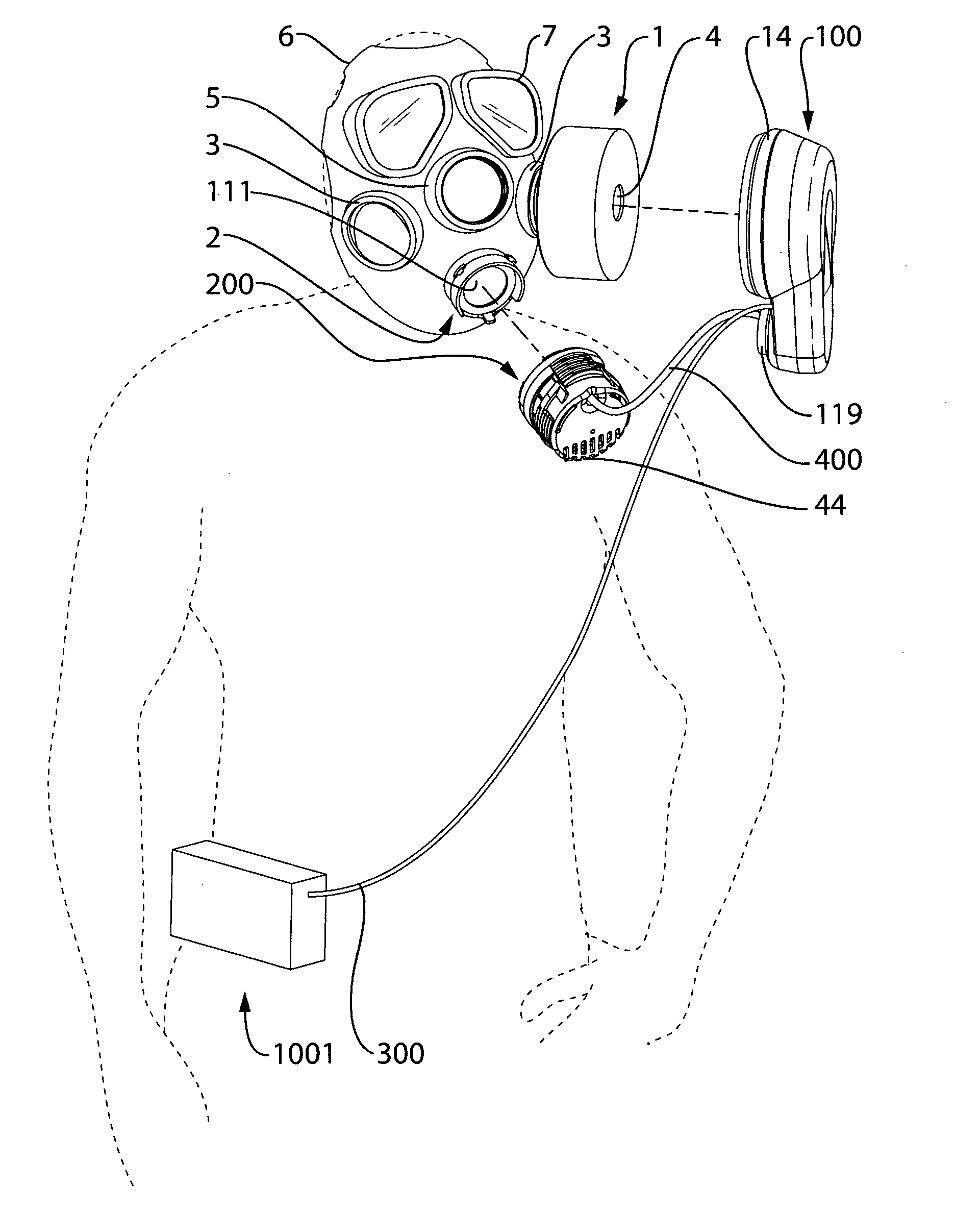
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Assisted ventilation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
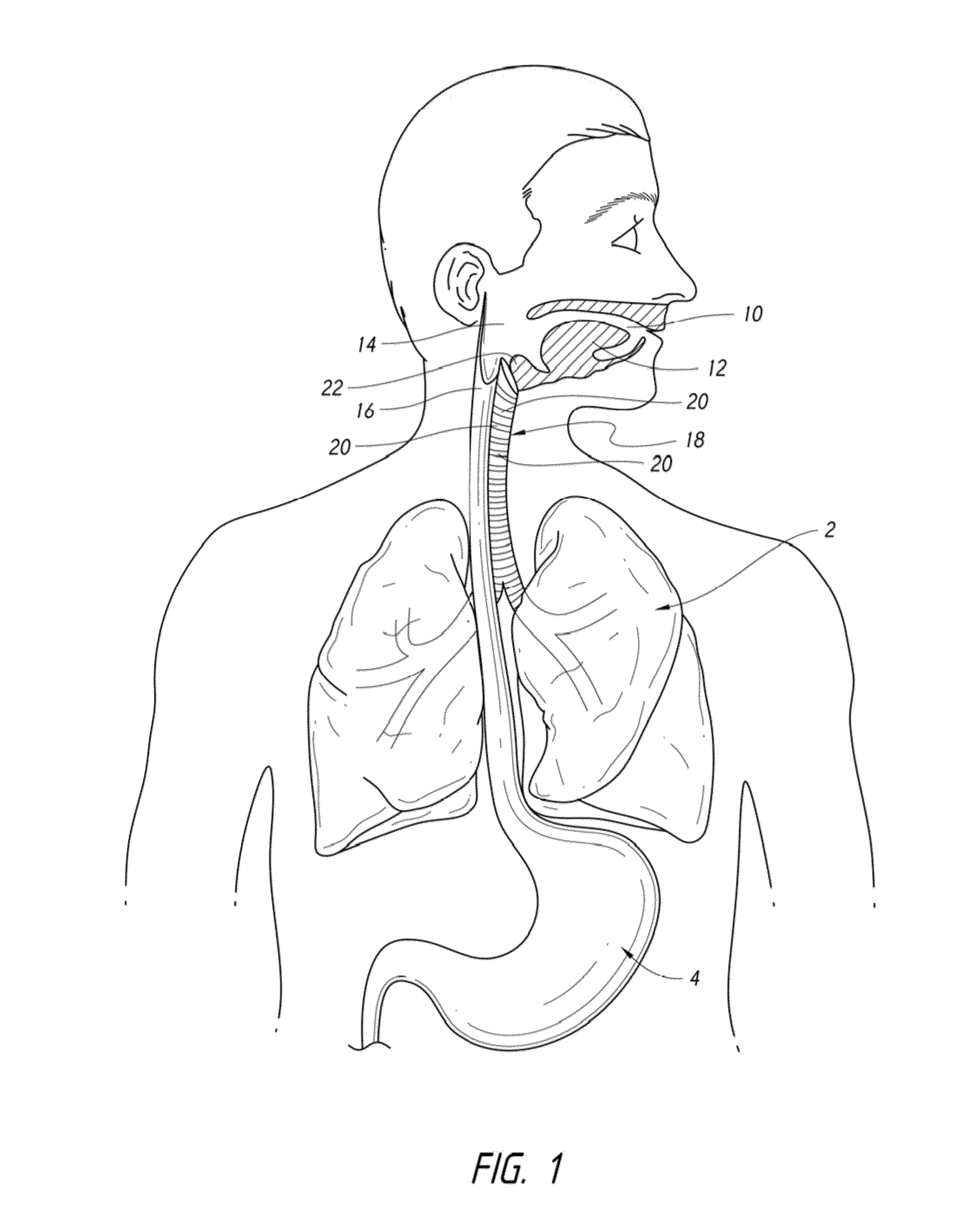
Assisted ventilation. Definition of assisted ventilation. Assisted ventilation is where the practitioner offers ventilatory support to a patient whose alveolar ventilation is inadequate to maintain normal partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
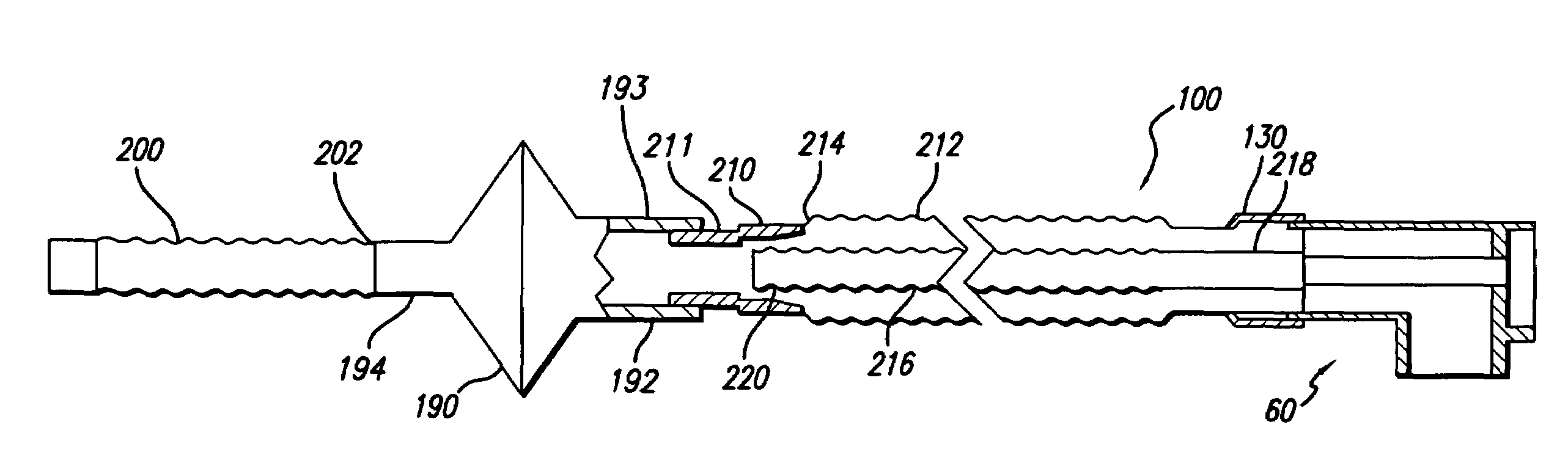
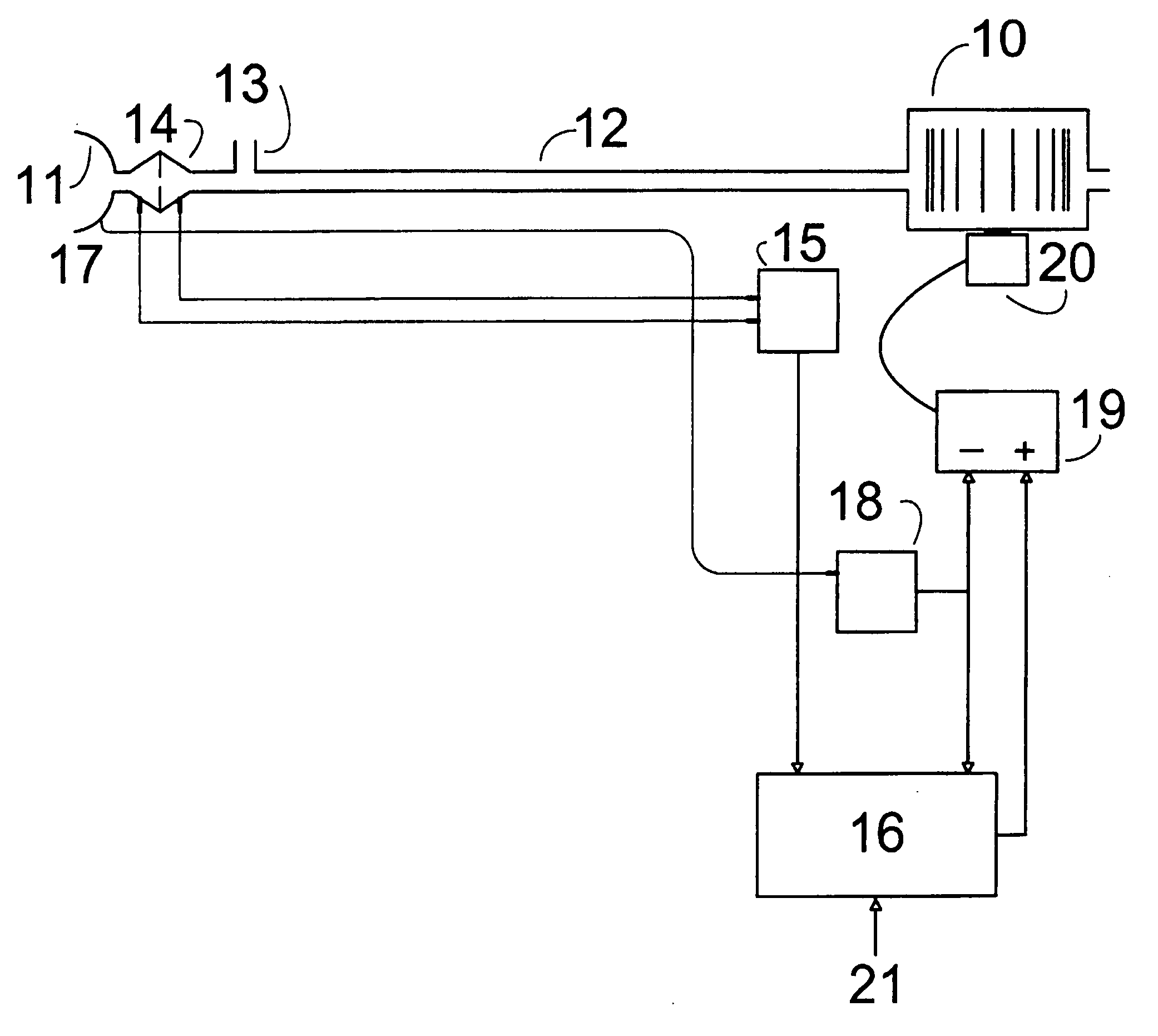
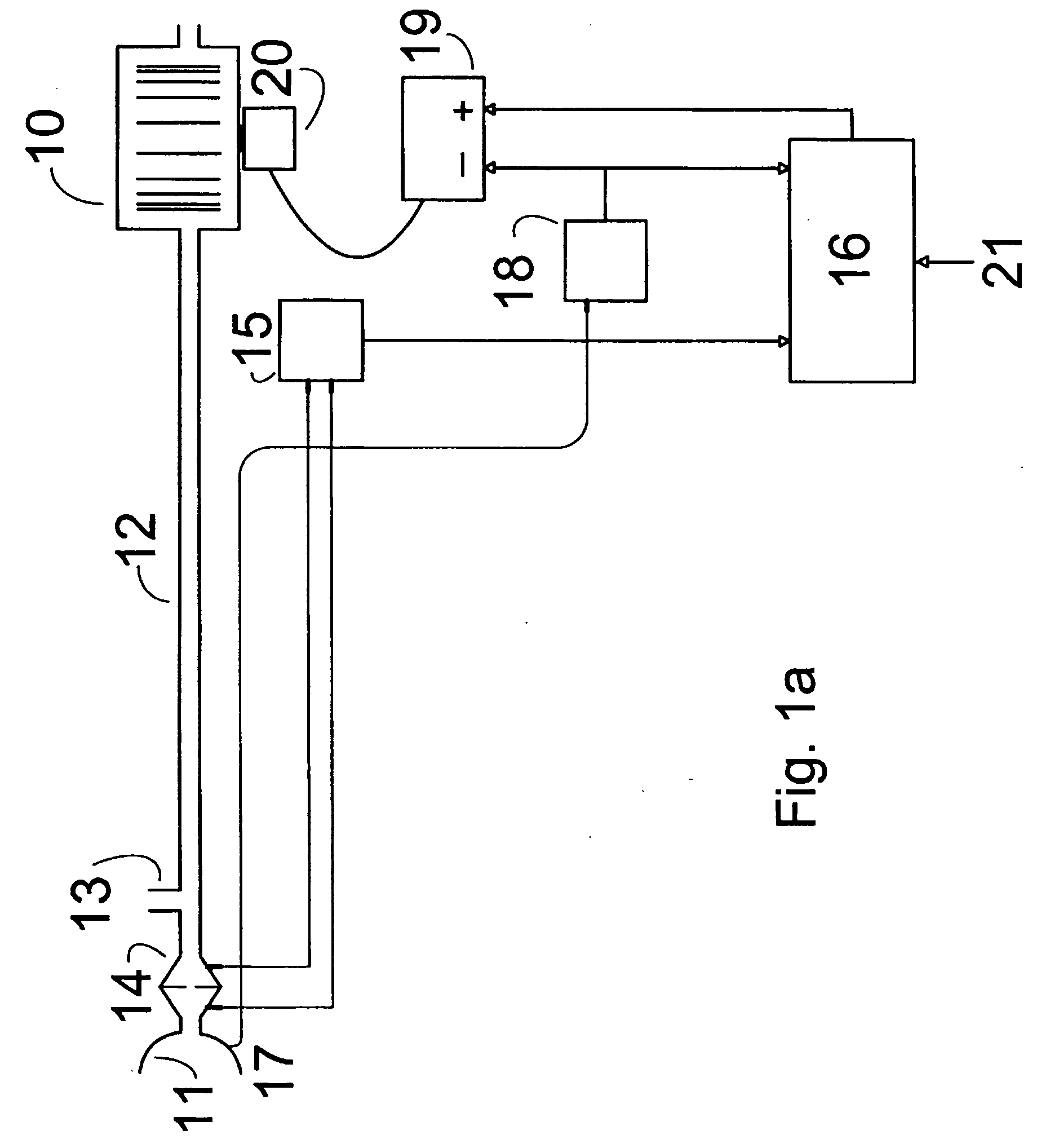
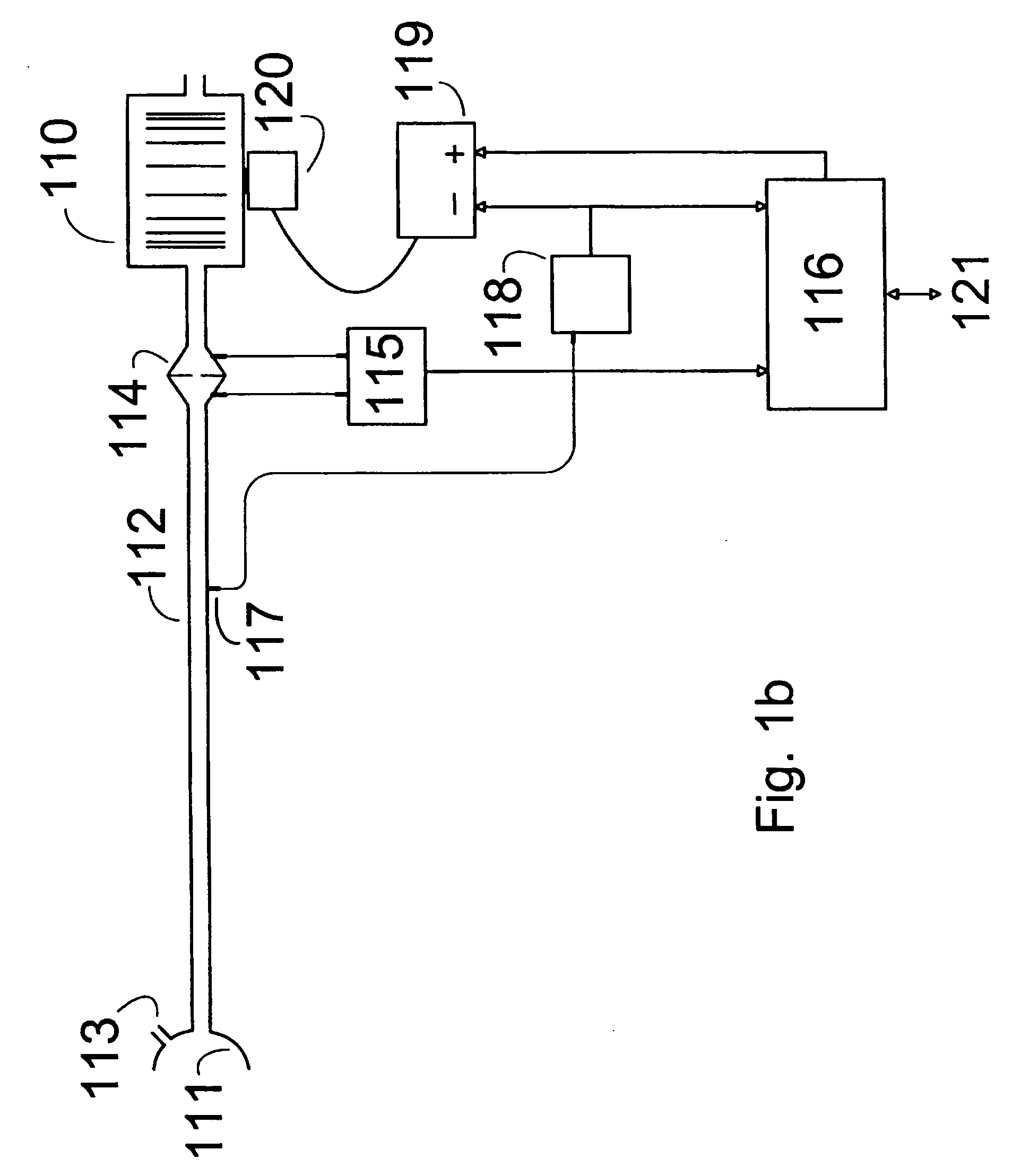
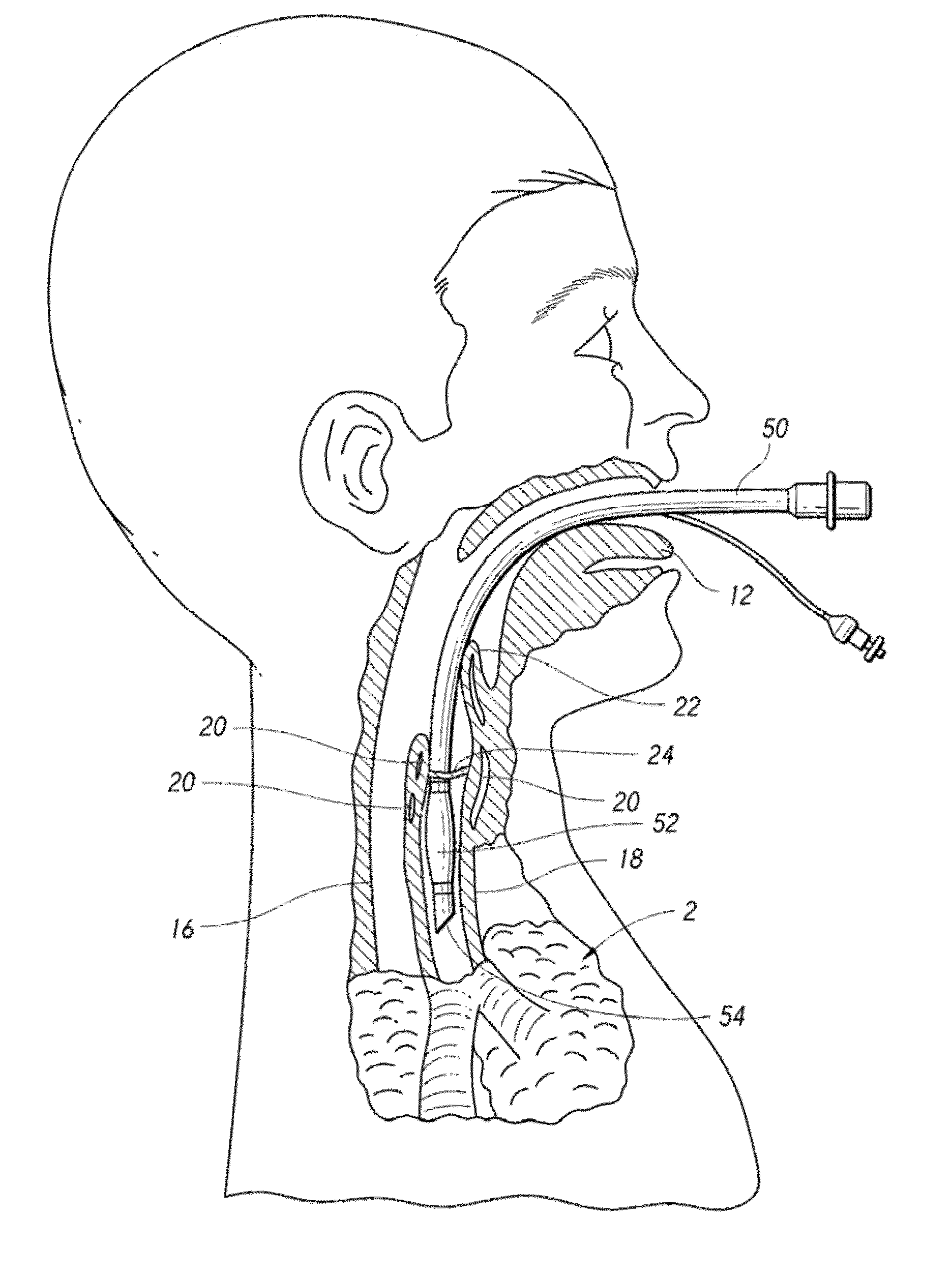
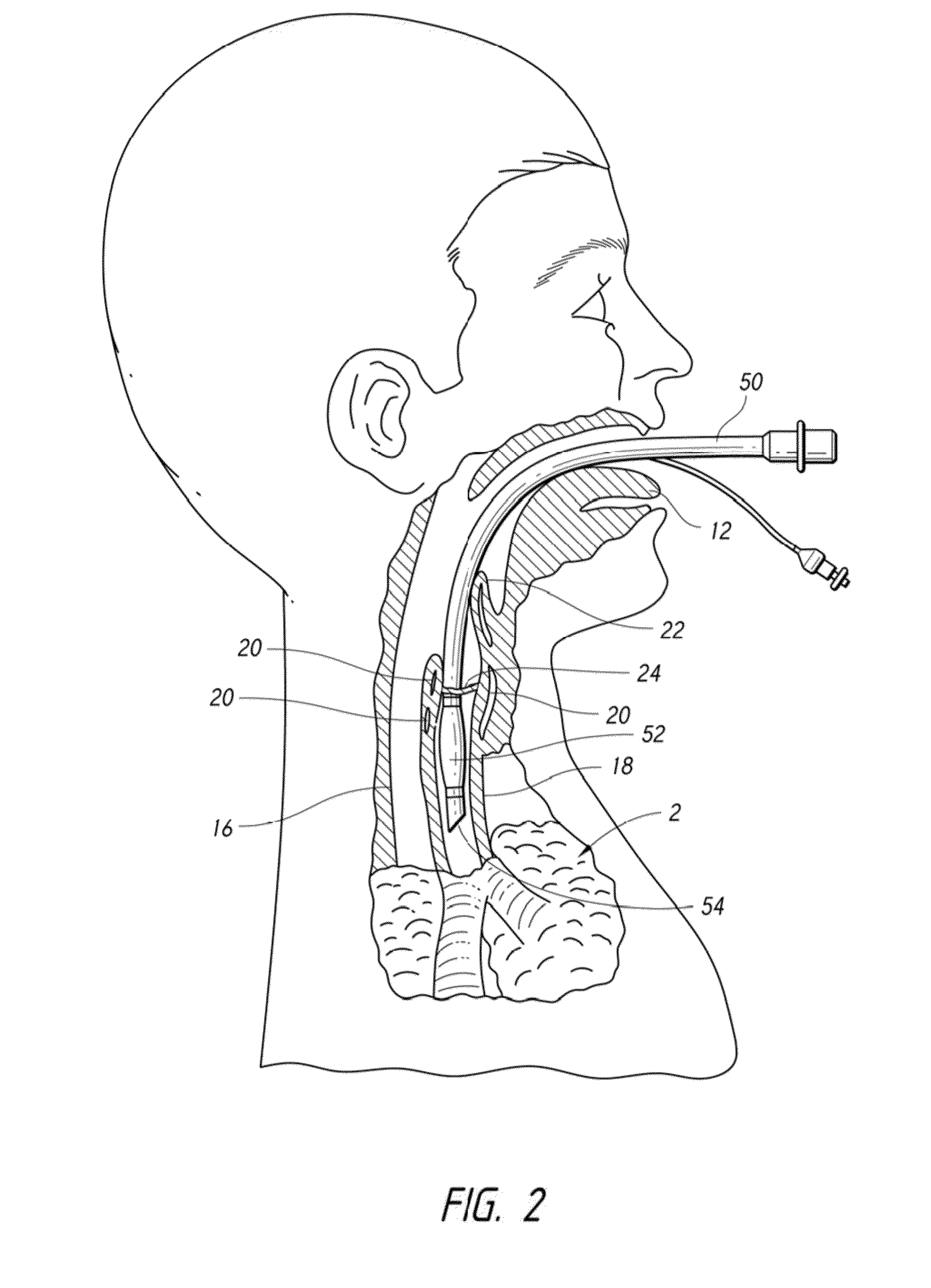
Methods and devices for minimally invasive respiratory support
ActiveUS20080135044A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationCatheter
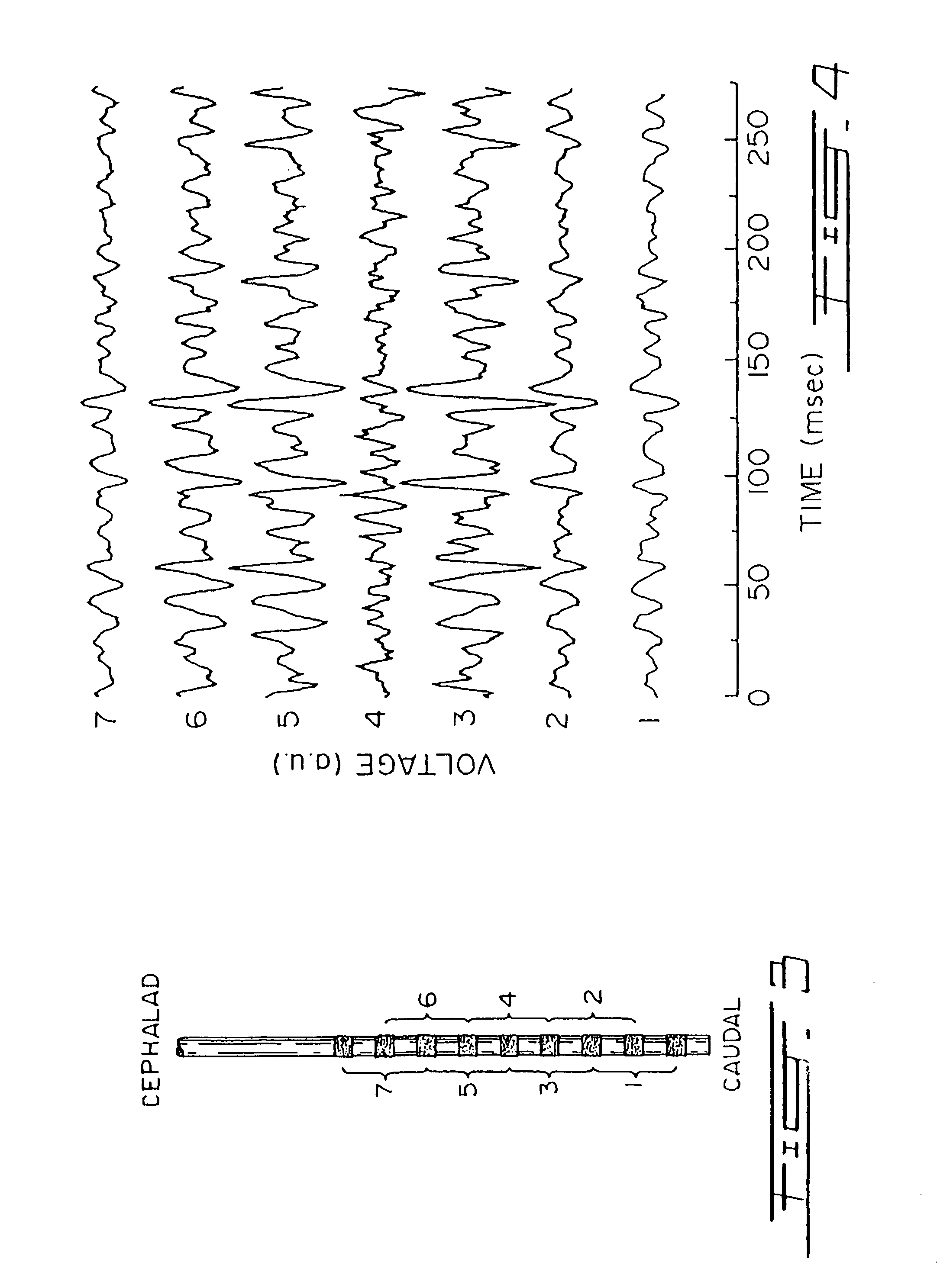
Modes, methods, systems and devices are described for providing assisted ventilation to a patient, including wearable ventilation systems with integral gas supplies, special gas supply features, ventilation catheters and access devices, and breath sensing techniques.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and apparatus for determining respiratory system resistance during assisted ventilation
InactiveUS6837242B2Simple methodReduces to determineRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationEngineering
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
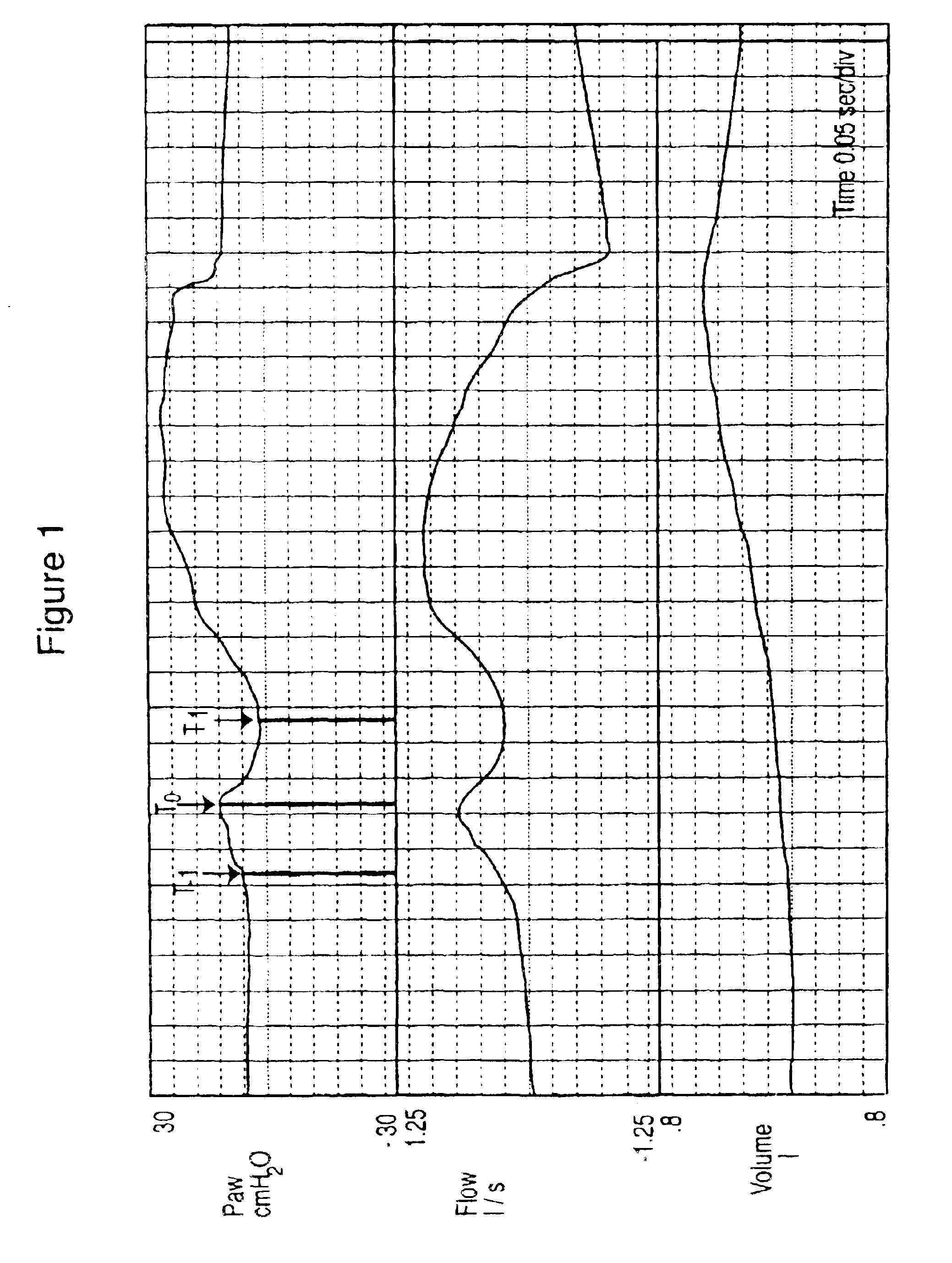
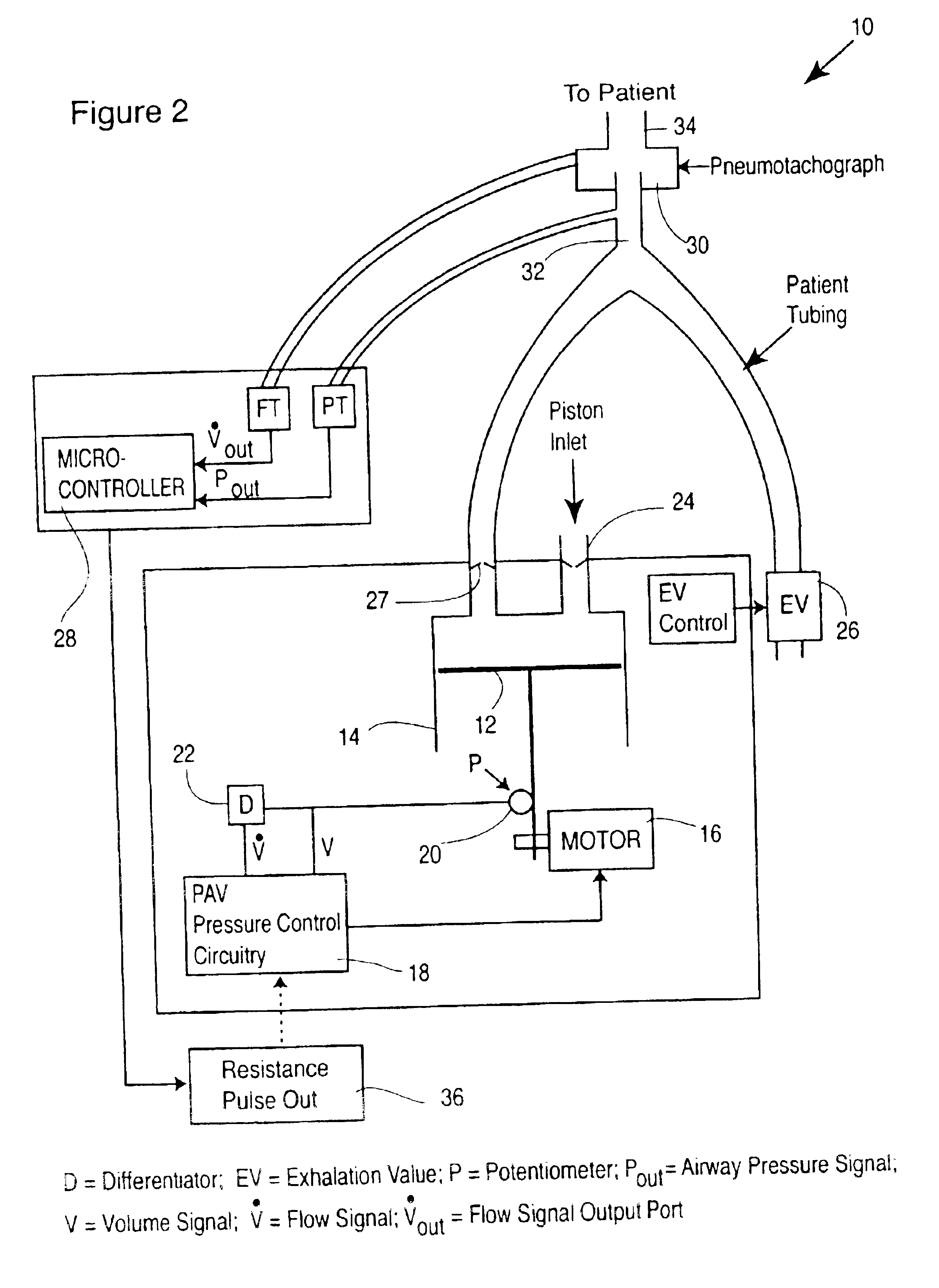
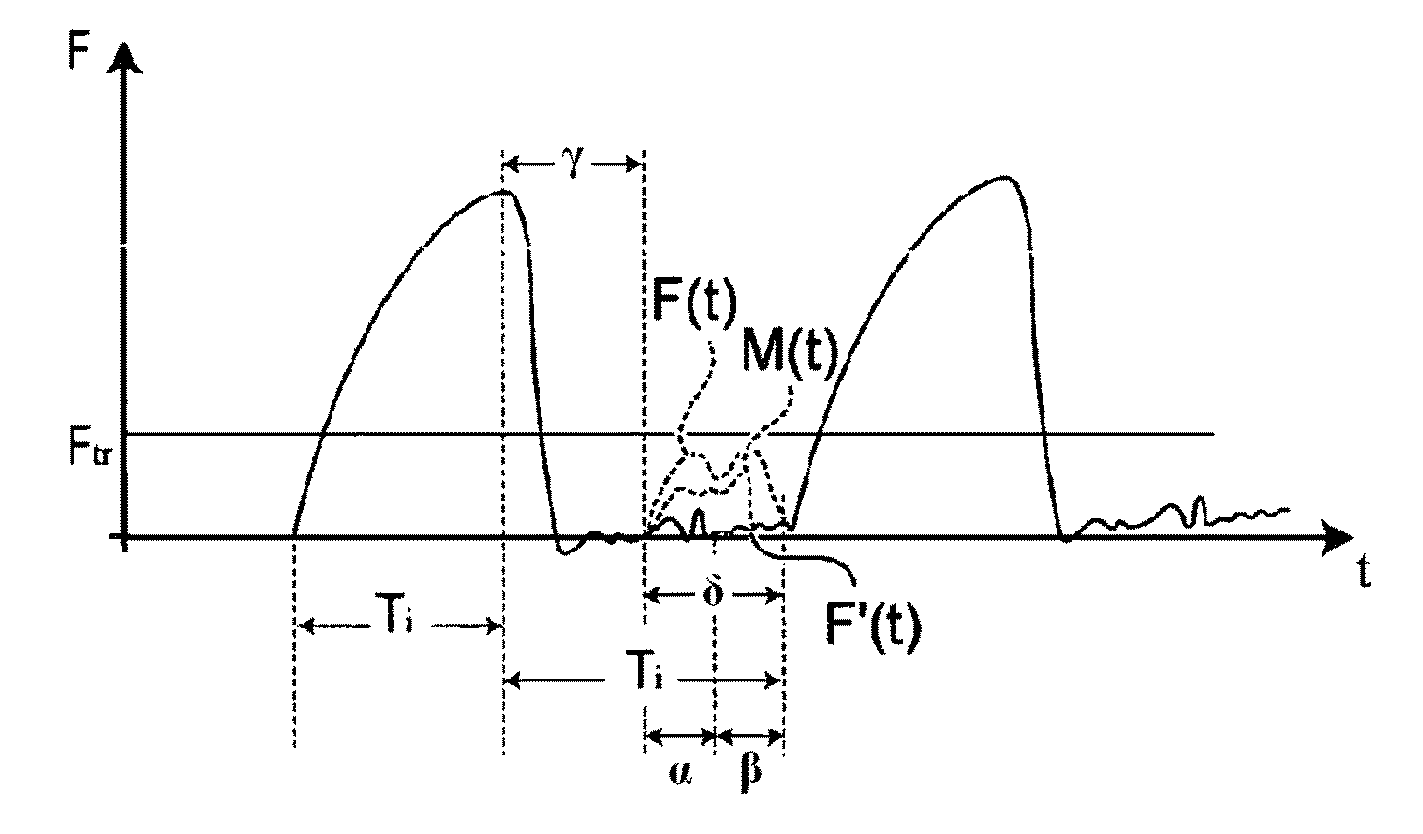
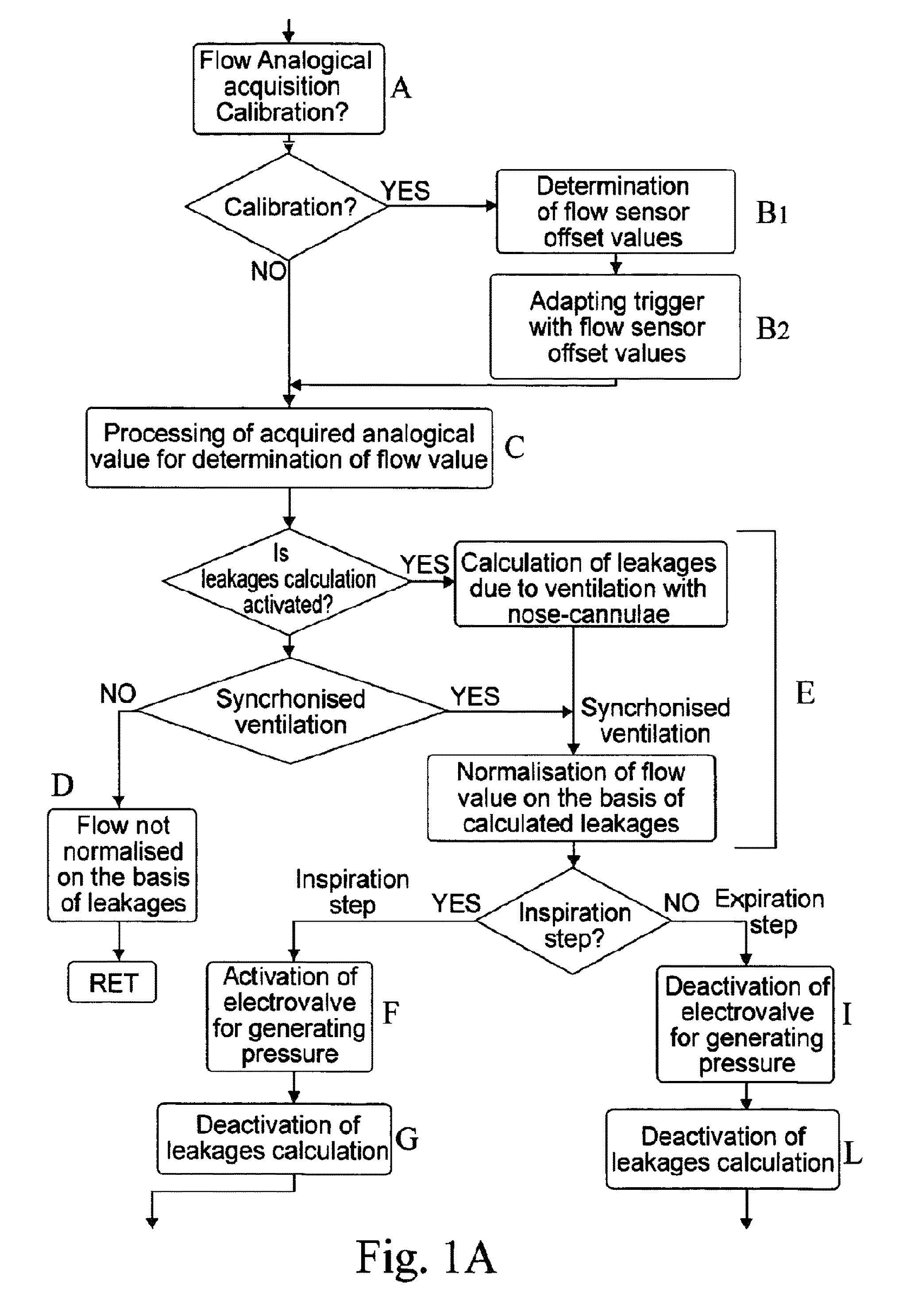
Method and relevant apparatus for nasal ventilation, particularly for flow-synchronised neonatal assisted ventilation
ActiveUS7814906B2Stable and uniform signalUnified operationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationNasal cavity
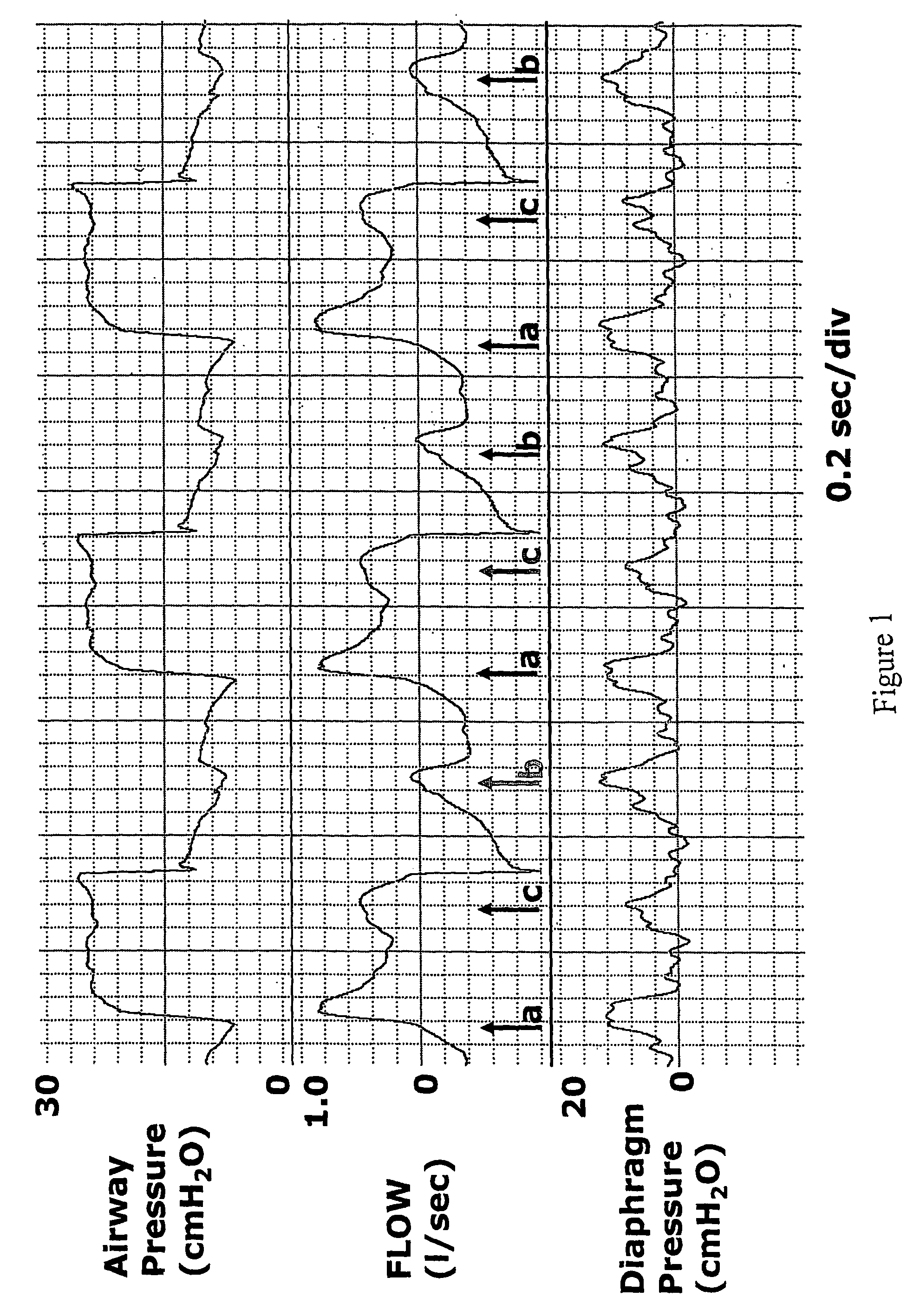
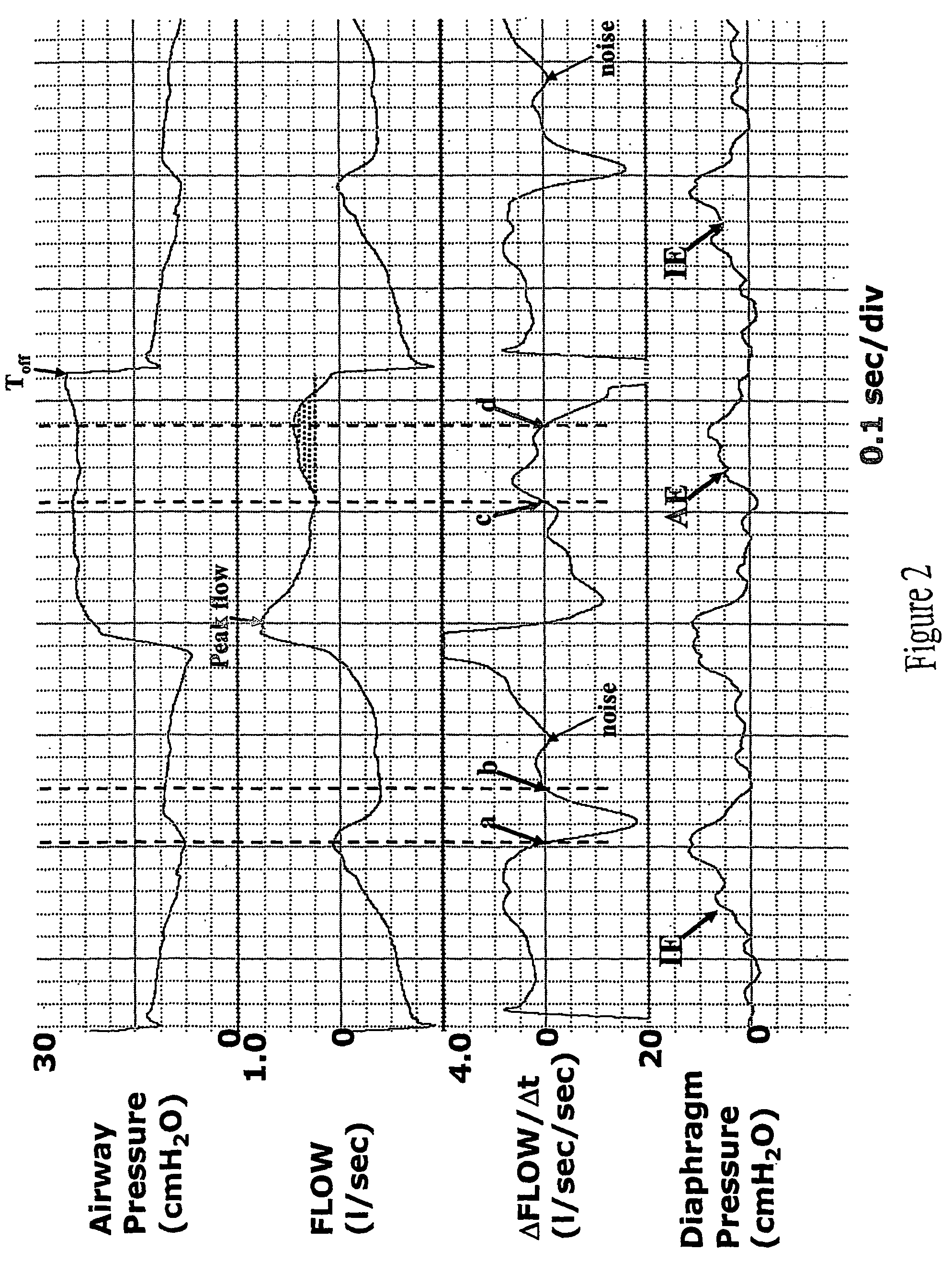
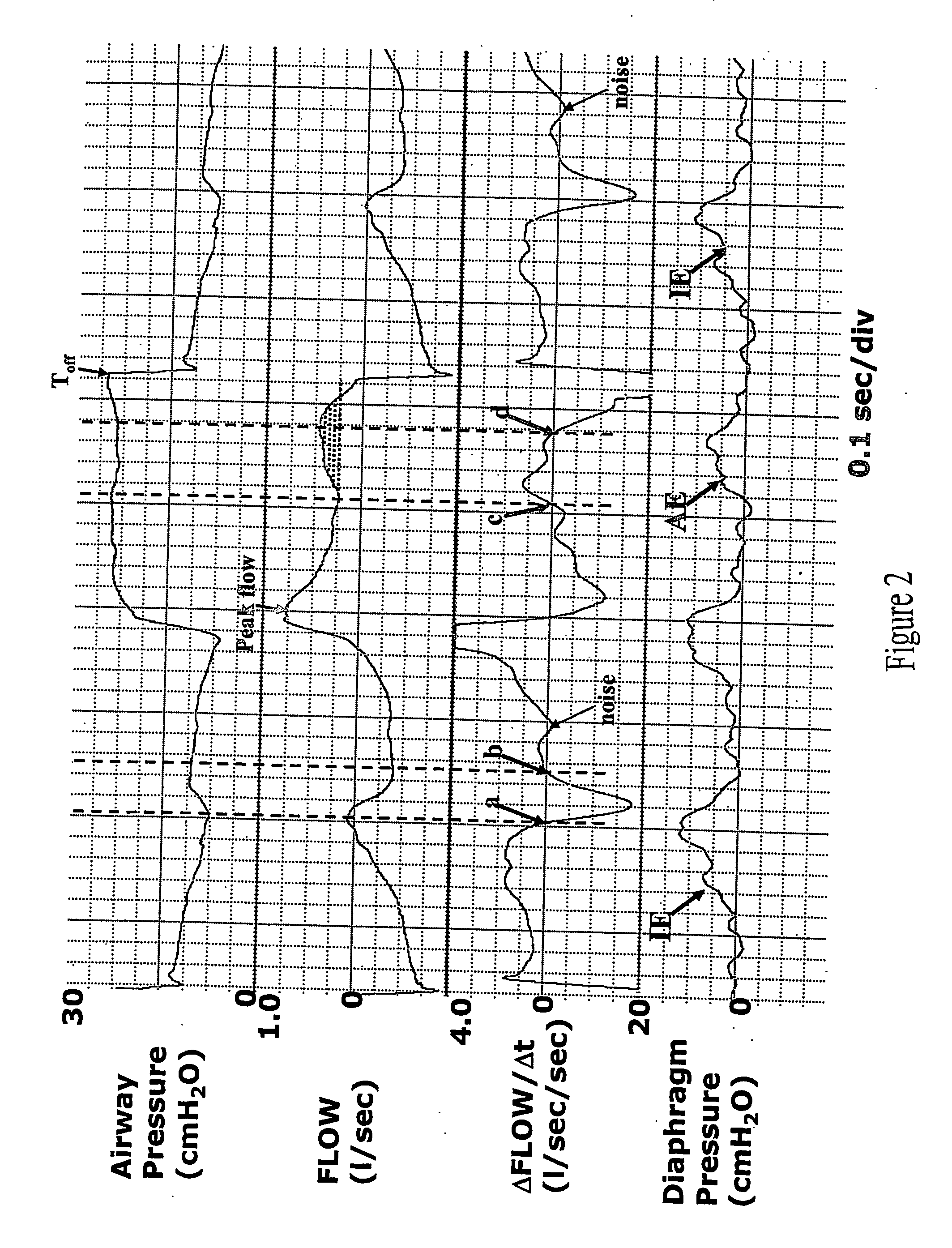
In a method for nasal ventilation and relevant apparatus, particularly for flow-synchronized neonatal assisted ventilation, wherein F(t) is a signal proportional to the ventilation flow, the following steps are performed:(a) inspiration, having a time length Ti, during which air is introduced at an inspiration pressure;(b) expiration, having a time length Te, during which the introduction of air is interrupted;(c) return to step (a);with a flow threshold Ftr, during the expiration step (b) the following steps are provided:(b1) a waiting step having a time length γ before activation of computation of the leakages; and(b2) a step of leakage computation, having a time length δ, so that γ+δ=Te, wherein if a normalized signal F′ (t), obtained by a processing by way of an algorithm of the surveyed signal F(t), exceeds the threshold Ftr, a spontaneous respiration activity is detected and the inspiration step (a) is reactivated.
Owner:GINEVRI SRL
Proportional pressure assist ventilation controlled by a diaphragm electromyographic signal
InactiveUS6920878B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationInspiratory Capacity
A closed loop system uses (a) the intensity of the diaphragm electromyogram (EMG) for a given inspiratory volume; (b) the inspiratory volume for a given EMG intensity; or (c) a combination of (a) and (b); in view of controlling the level of gas flow, gas volume or gas pressure delivered by a mechanical (lung) ventilator. The closed loop ventilator system enables for automatic or manual adjustment of the level of inspiratory support in proportion to changes in the neuro-ventilatory efficiency such that the neural drive remains stable at a desired target level. An alarm can also be used to detect changes in neuroventilatory efficiency in view of performing manual adjustments.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Synchrony between end of ventilator cycles and end of patient efforts during assisted ventilation
InactiveUS7819815B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationInhalation
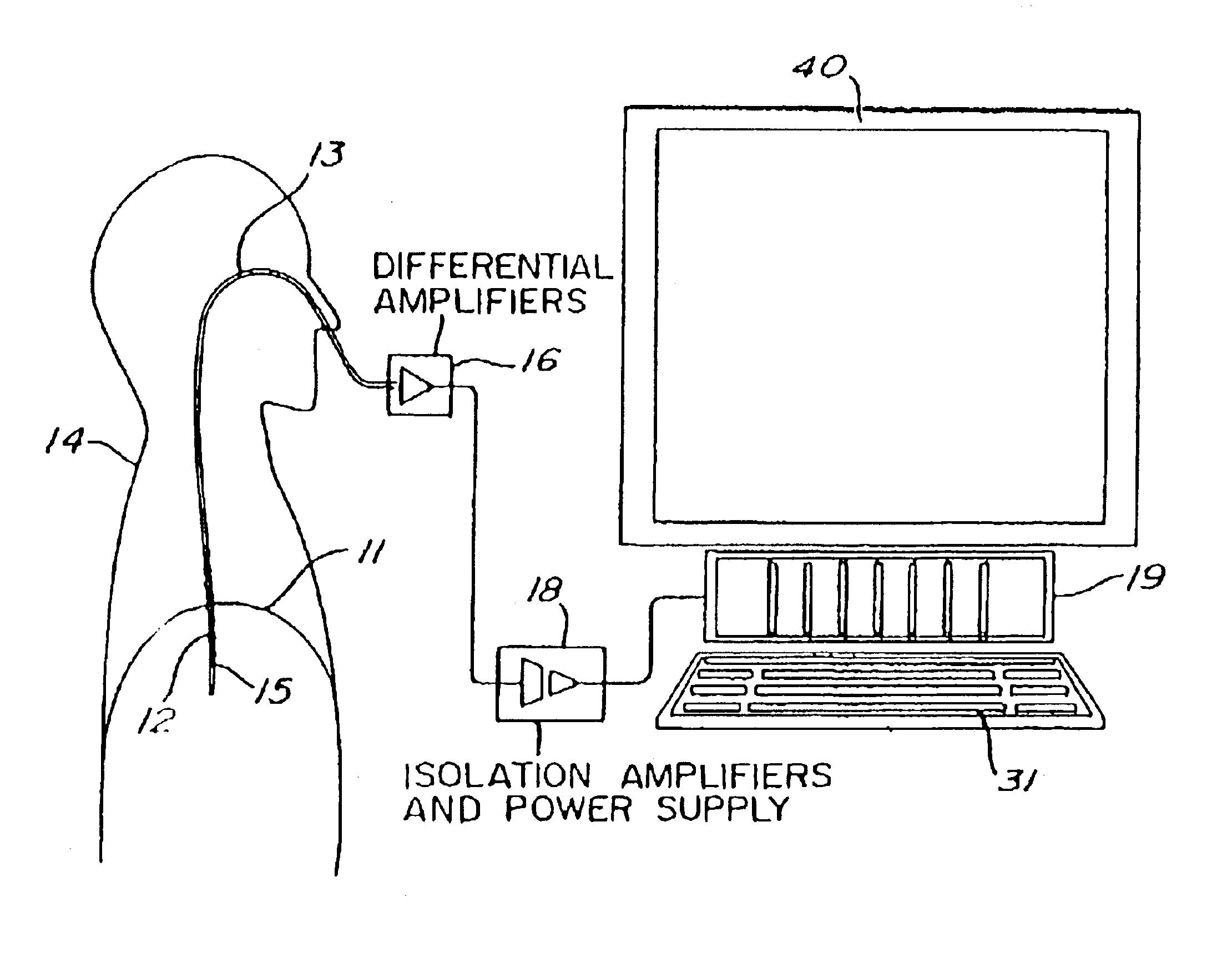
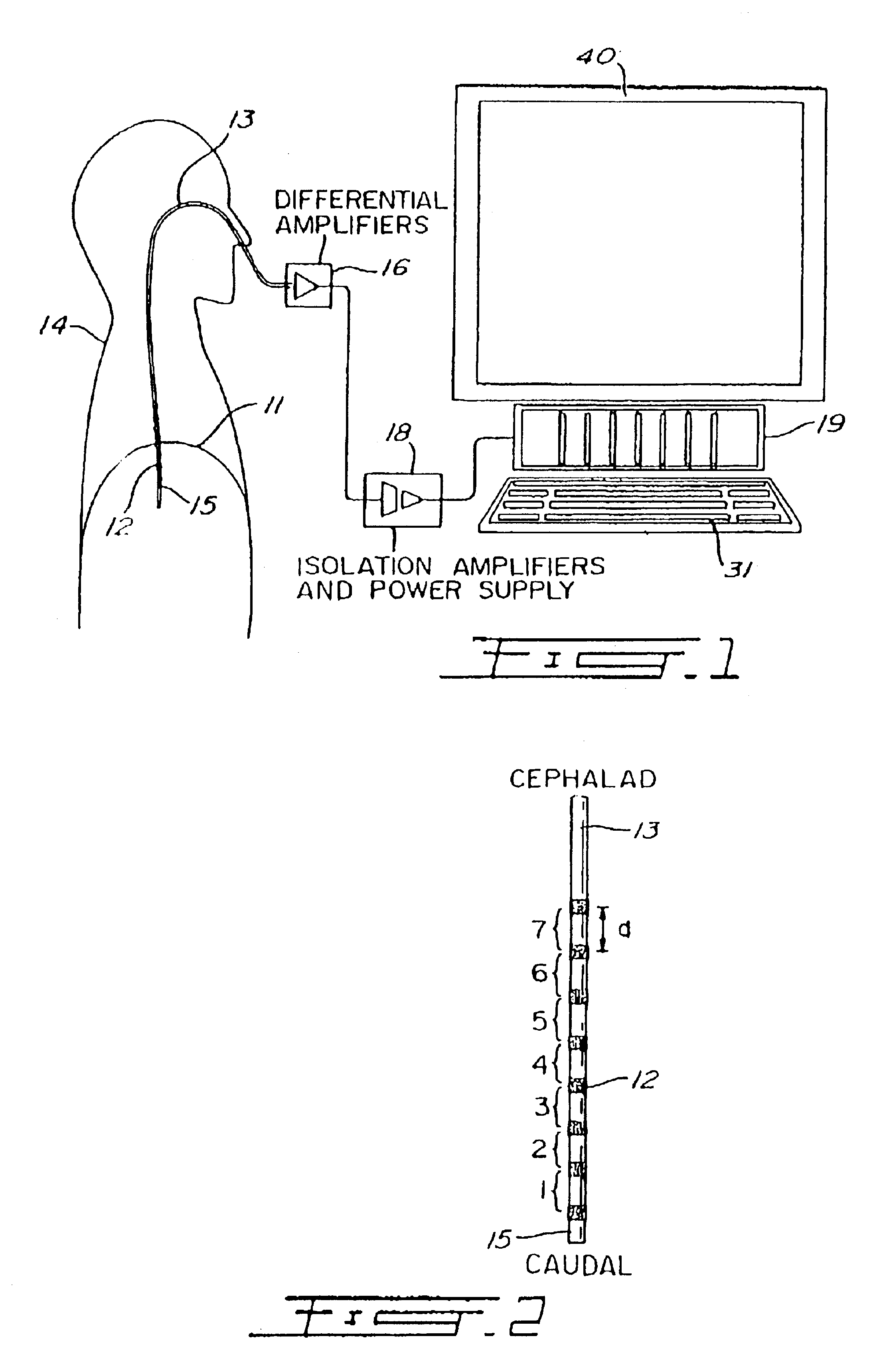
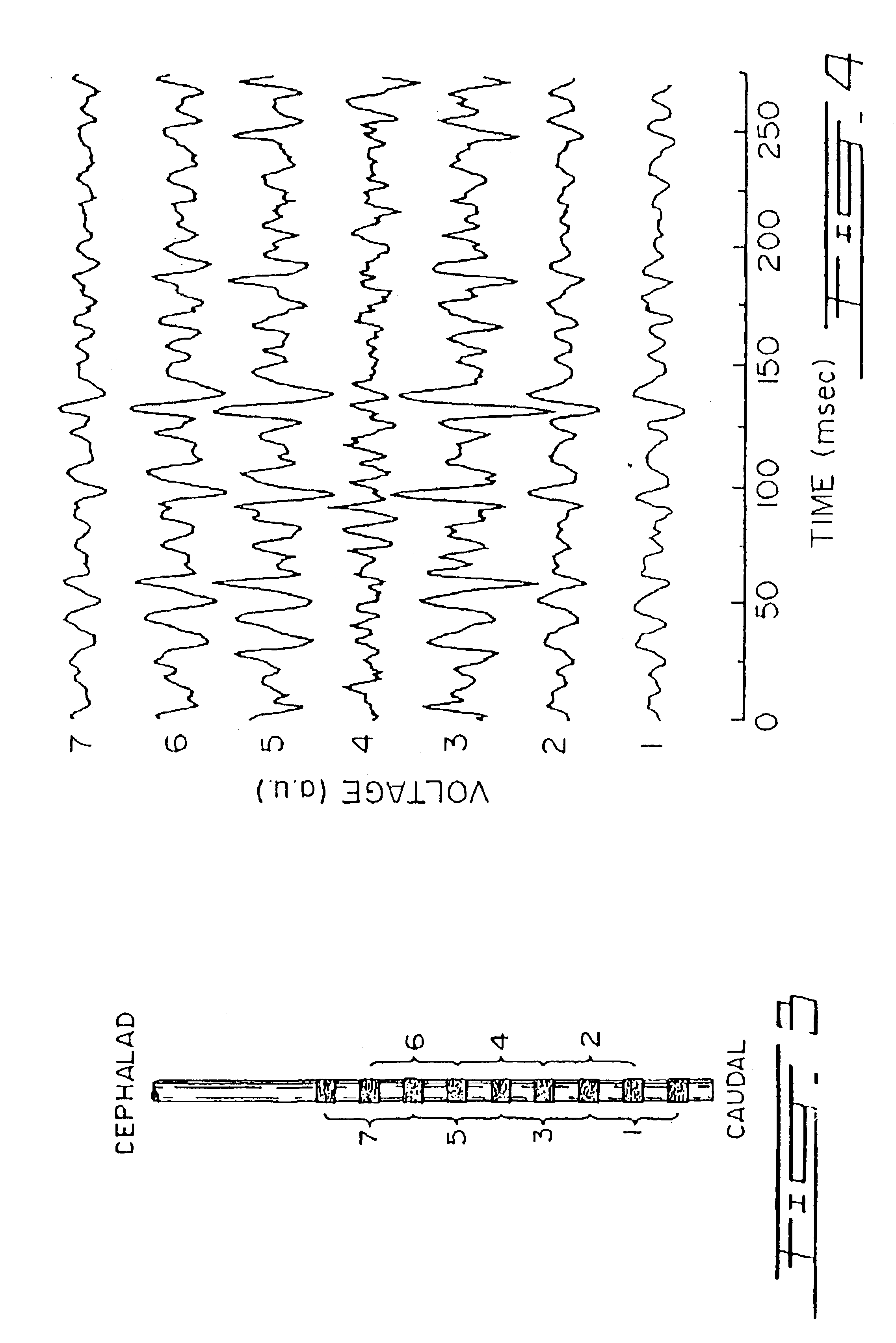
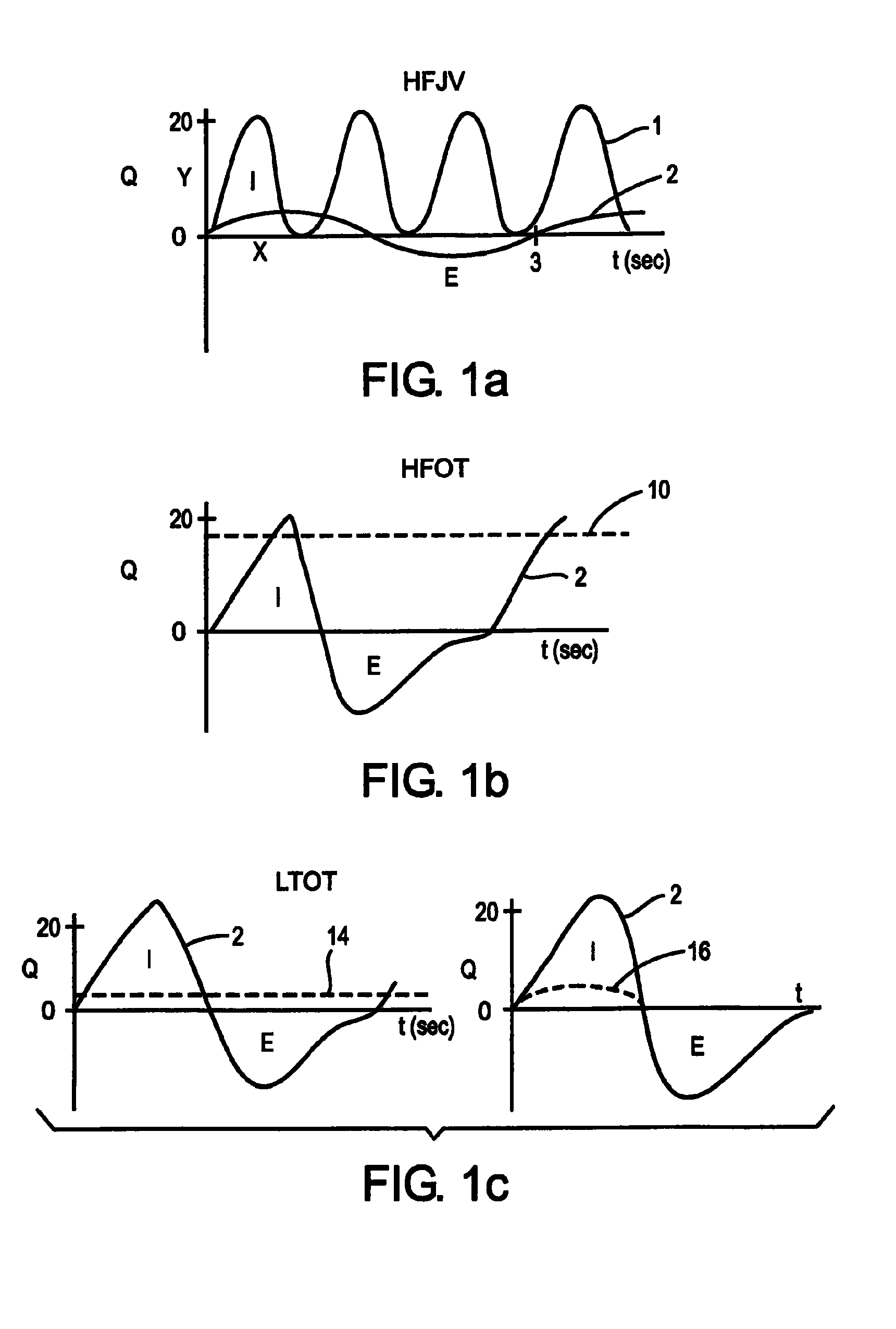
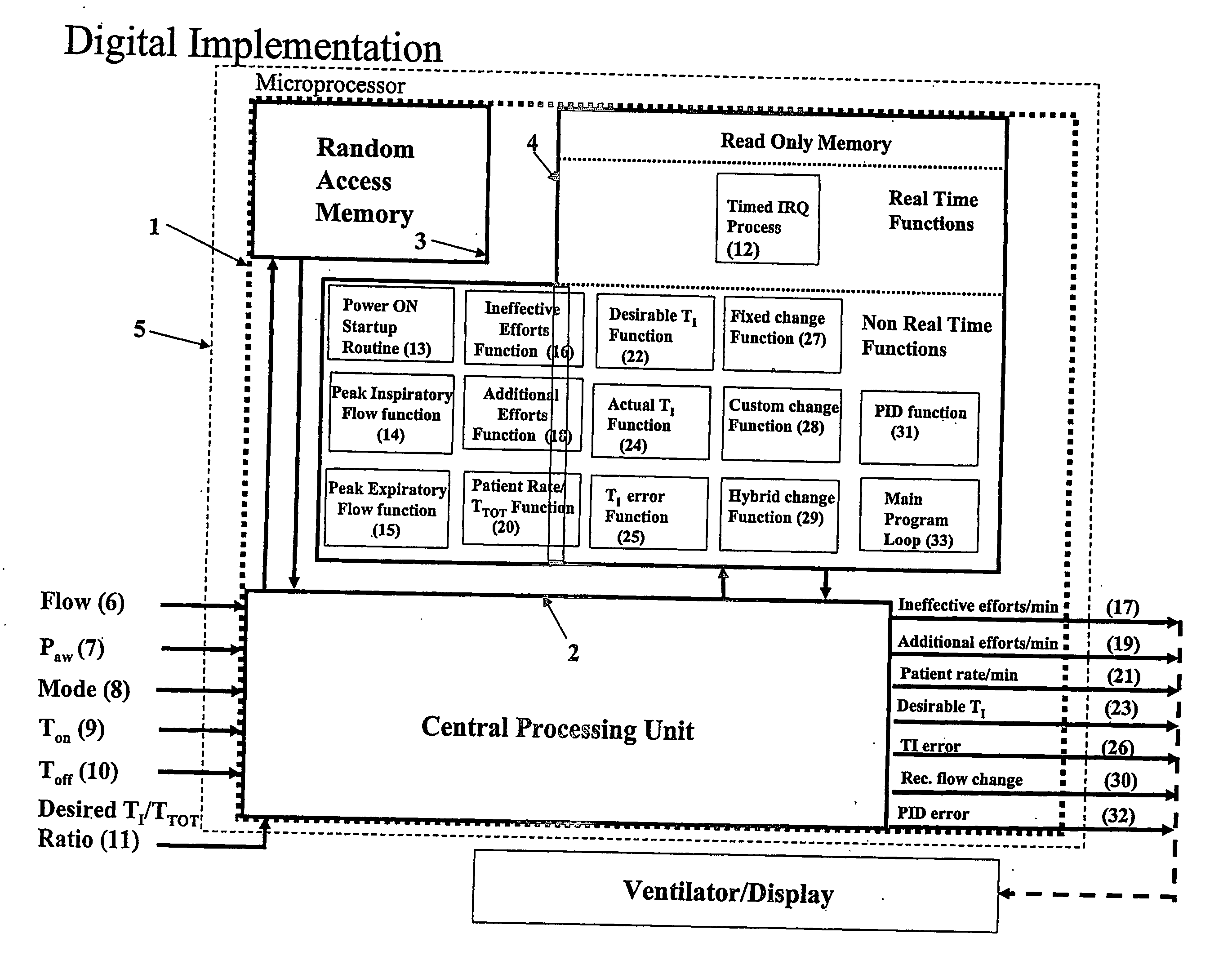
Automatic ongoing adjustment of the cycling-off time of ventilator inflation phase during assisted ventilation in accordance with true respiratory rate of a patient. Electrical signals are generated corresponding to the gas flow exchanged between patient and ventilator (flow) and / or to airway pressure (Paw) and the true respiratory rate of the patient (patient RR) is determined on an ongoing basis from the flow and / or Paw. The current average cycle duration of patient respiratory efforts (current patient TTOT) is estimated from patient RR. A current desirable duration of the inhalation phase (desirable TI) is calculated from the product of current patient TTOT a TI / TTOT ratio chosen to be in the physiological range, usually 0.25 to 0.50. The ventilator phase is caused to terminate in accordance with the desirable TI.
Owner:YRT
Electromagnet-assisted ventilation cover for an electronic equipment enclosure
ActiveUS7345875B2Simply and inexpensive to implementCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersAssisted ventilationEngineering
A ventilation assembly for an electronic equipment enclosure. The ventilation assembly includes a housing having at least one ventilation port, and a cover movable between an open position and a closed position. The cover is positioned over the ventilation port when the cover is in the closed position. The ventilation assembly further includes at least one electromagnet for selectively securing the cover in the closed position.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
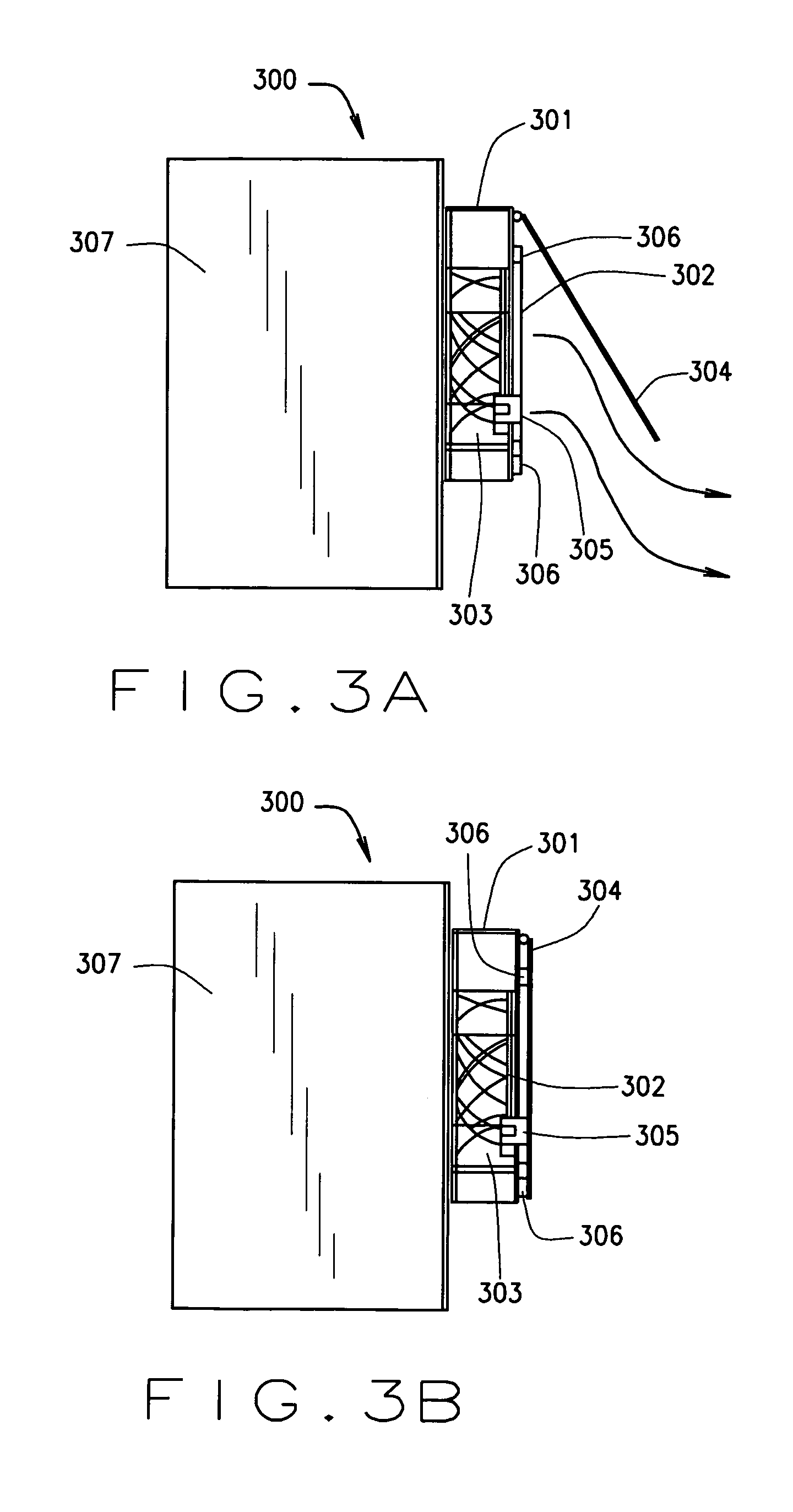
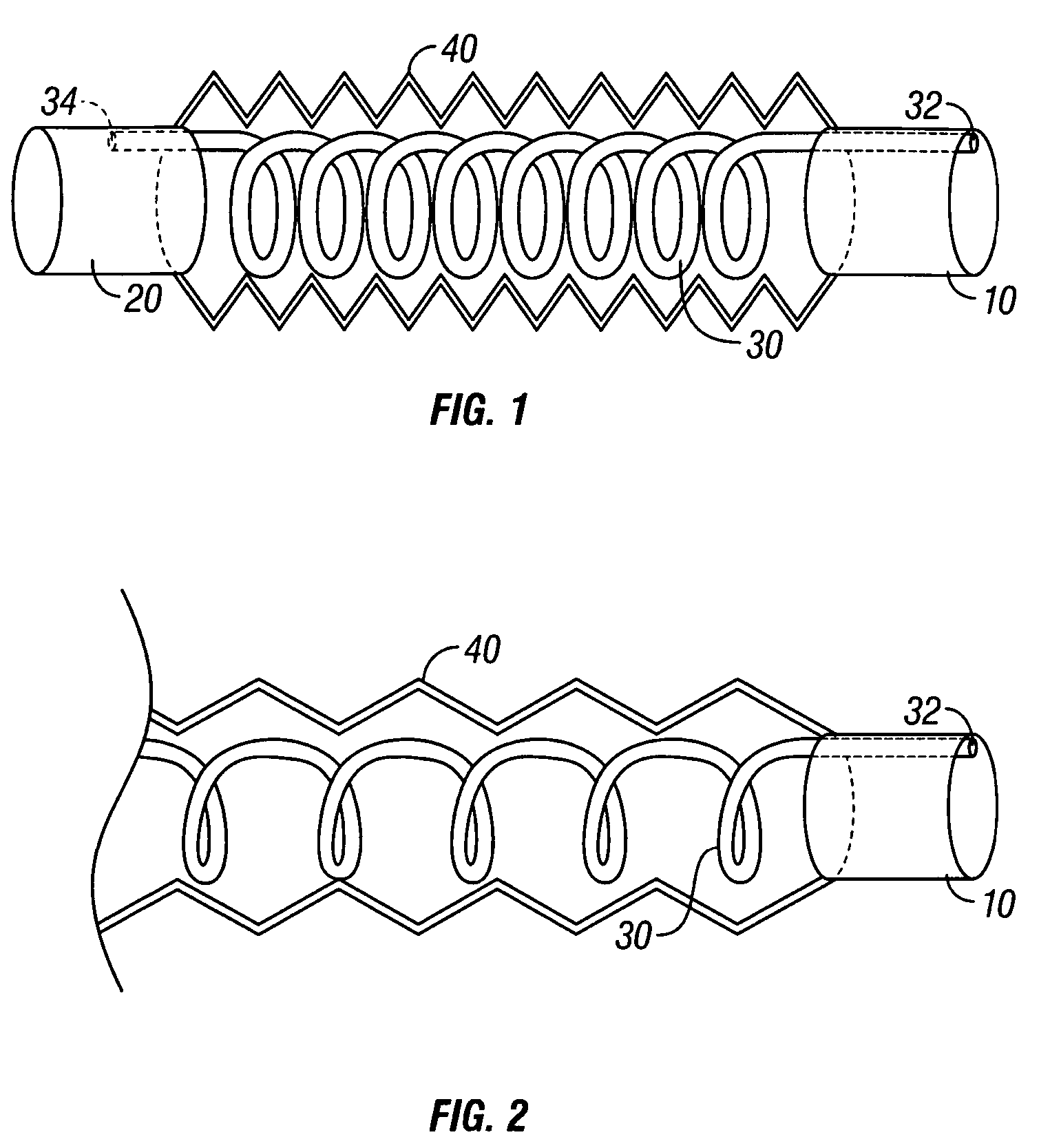
Multilumen unilimb breathing circuit with detachable proximal fitting
InactiveUS7418965B2Avoids hypocapnia and hypoxiaReadily attachableRespiratorsSurgeryAssisted ventilationBreathing circuit tube
Owner:AMBU AS
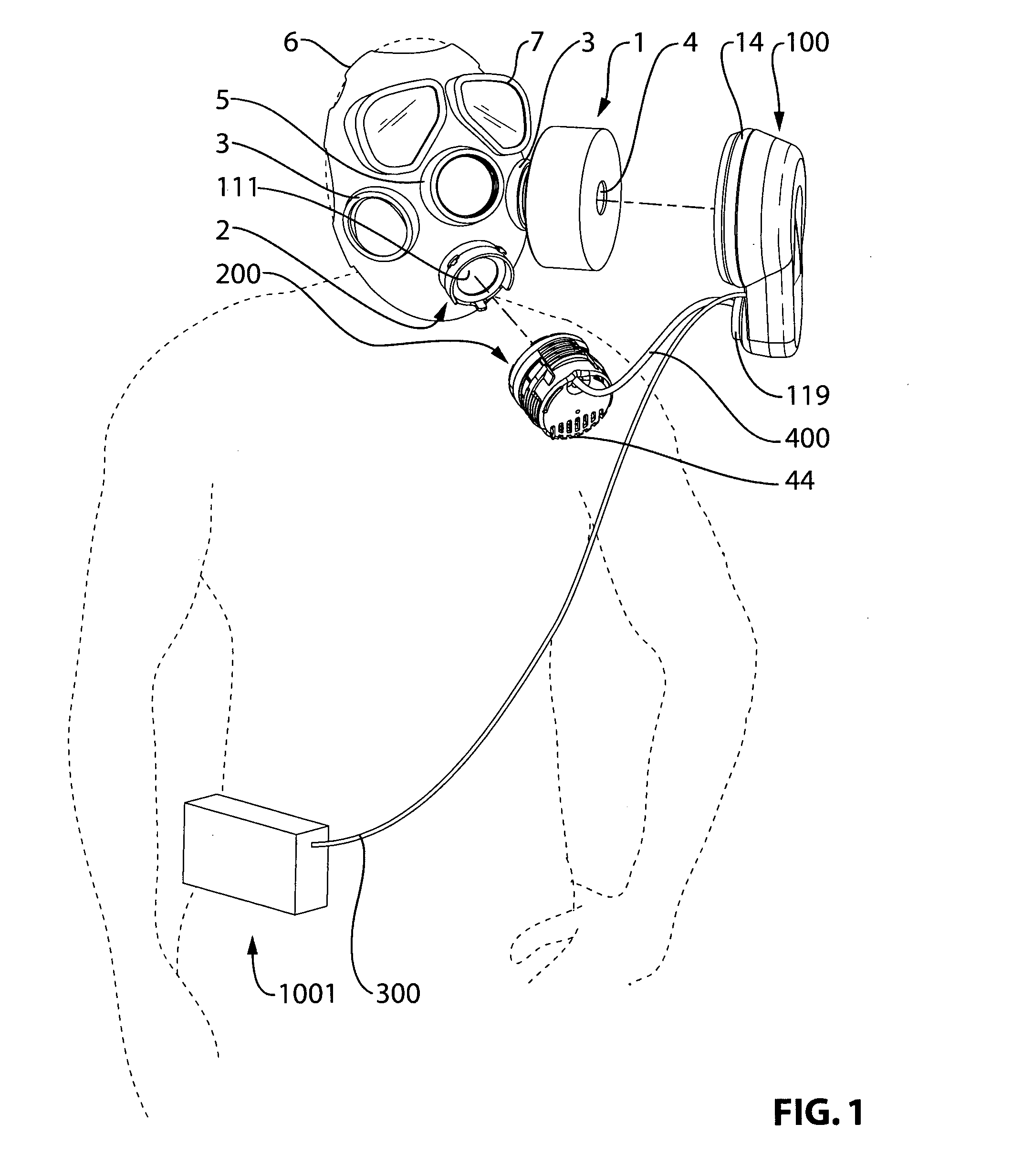
Assisted ventilation to match patient respiratory need
InactiveUS20060150974A1Reduce noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksAssisted ventilationTransducer
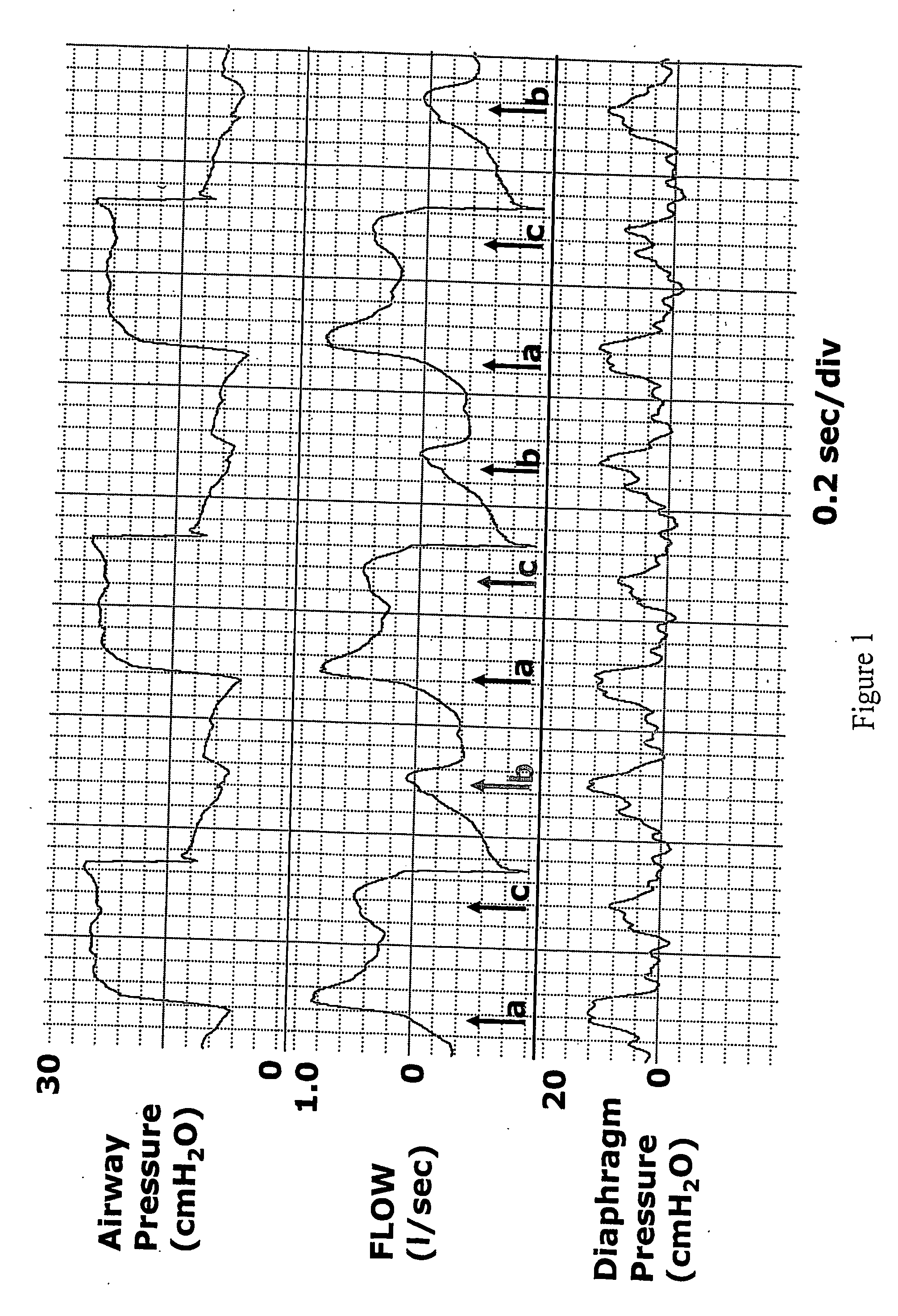
The apparatus provides for the determination of the instantaneous phase in the respiratory cycle, subject's average respiration rate and the provision of ventilatory assistance. A microprocessor (16) receives an airflow signal from a pressure transducer (18) coupled to a port (17) at a mask (11). The microprocessor (16) controls a servo (19), that in turn controls the fan motor (20) and thus the pressure of air delivered by the blower (10). The blower (10) is coupled to a subject's mask (ii) by a conduit (12). The invention seeks to address the following goals: while the subject is awake and making substantial efforts the delivered assistance should be closely matched in phase with the subject's efforts; the machine should automatically adjust the degree of assistance to maintain at least a specified minimum ventilation without relying on the integrity of the subject's chemoreflexes; and it should continue to work correctly in the pesence of large leaks.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Methods and devices for minimally invasive respiratory support
ActiveUS8381729B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationAssisting ventilation
Modes, methods, systems and devices are described for providing assisted ventilation to a patient, including wearable ventilation systems with integral gas supplies, special gas supply features, ventilation catheters and access devices, and breath sensing techniques.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Synchrony between end of ventilator cycles and end of a patient efforts during assisted ventilation
InactiveUS20060278223A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationInhalation
Automatic ongoing adjustment of the cycling-off time of ventilator inflation phase during assisted ventilation in accordance with true respiratory rate of a patient. Electrical signals are generated corresponding to the gas flow exchanged between patient and ventilator (flow) and / or to airway pressure (Paw) and the true respiratory rate of the patient (patient RR) is determined on an ongoing basis from the flow and / or Paw. The current average cycle duration of patient respiratory efforts (current patient TTOT) is estimated from patient RR. A current desirable duration of the inhalation phase (desirable TI) is calculated from the product of current patient TTOT a TI / TTOT ratio chosen to be in the physiological range, usually 0.25 to 0.50. The ventilator phase is caused to terminate in accordance with the desirable TI.
Owner:YRT
Proportional pressure assist ventilation controlled by a diaphragm electromyographic signal
InactiveUS7021310B1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationInspiratory Capacity
A closed loop system uses (a) the intensity of the diaphragm electromyogram (EMG) for a given inspiratory volume; (b) the inspiratory volume for a given EMG intensity; or (c) a combination of (a) and (b); in view of controlling the level of gas flow, gas volume or gas pressure delivered by a mechanical (lung) ventilator. The closed loop ventilator system enables for automatic or manual adjustment of the level of inspiratory support in proportion to changes in the neuro-ventilatory efficiency such that the neural drive remains stable at a desired target level. An alarm can also be used to detect changes in neuroventilatory efficiency in view of performing manual adjustments.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Intubation positioning, breathing facilitator and non-invasive assist ventilation device
InactiveUS20070181122A1Easy intubationEasy alignmentRespiratorsOperating tablesSpinal columnAssisted ventilation
This invention can be used in three different ways for patients who are lying down in bed or on the operating table. First it facilitates the endotracheal intubation, secondly it facilitates the spontaneous breathing of obese patients and thirdly it assists the spontaneous inspiration and expiration in a non-invasive way. This invention device is positioned under the patient before he is asleep without disturbing him. It allows a gradual elevation of the lower and or upper thorax, a gradual elevation of the head giving a flexion of the neck and a gradual hyperextension of the head. After intubation the position is returned to normal without need for removing the invention device. This invention elevates the spinal column and therefore the thorax is no more compressed and the ribs can move free. Inspiration requires less force and the patient can be breathing easier even when lying down. In this invention the spinal column elevation can also be inflated in a synchronized way with the respiration of the patient. During inspiration the spinal column is elevated, facilitating the inspiration. During expiration the elevation is lowered, facilitating the expiration. The work of breathing is reduced for the patient resulting in larger minute volume ventilation or less oxygen consumption.
Owner:MULIER JAN PAUL
Method and apparatus for ventilation assistance
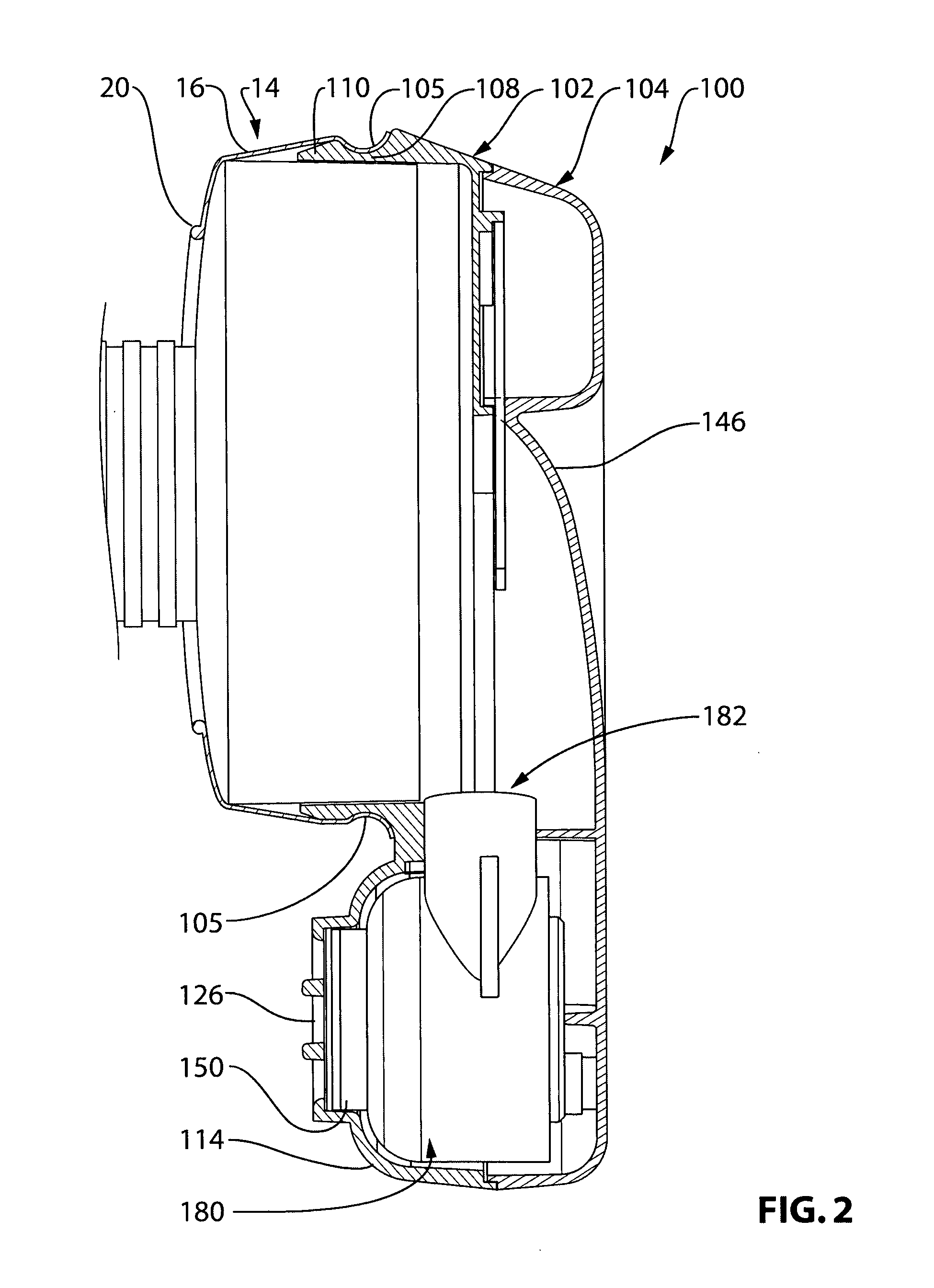
InactiveUS20100101575A1Avoid pollutionEnhance biased airflowRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMating connectionAtmospheric air
A mask interface device is provided for a protective mask of the type having a mask filter and a mask expiratory port, the mask expiratory port having an expiratory port valve of the type that is normally closed and openable upon expiration, the mask filter having an inspiratory air inlet, the mask interface device comprising: a mask interface assembly mountable to the mask and having a mounting interface for mounting an air pressure generator in fluid communication with the inspiratory inlet of the mask filter; and an expiratory port interface assembly mountable to the mask expiratory port and comprising at least one opening for venting expired gas to atmosphere and a one-way valve that is positioned to control the flow of expired gas out through the at least one opening, and wherein the one-way valve is set to an opening pressure that provides positive end expiratory pressure or PEEP. Optionally, this opening pressure is between 2.5 and 20 cm H2O. Optionally, the mask interface device interface directly with the mask filter. In one embodiment of the invention, this interface does not require the filter to have a mating connection and is therefore is universal for a broad class of filters, for example cylindrical filters that project from the mask.
Owner:FEDORKO LUDWIK +1
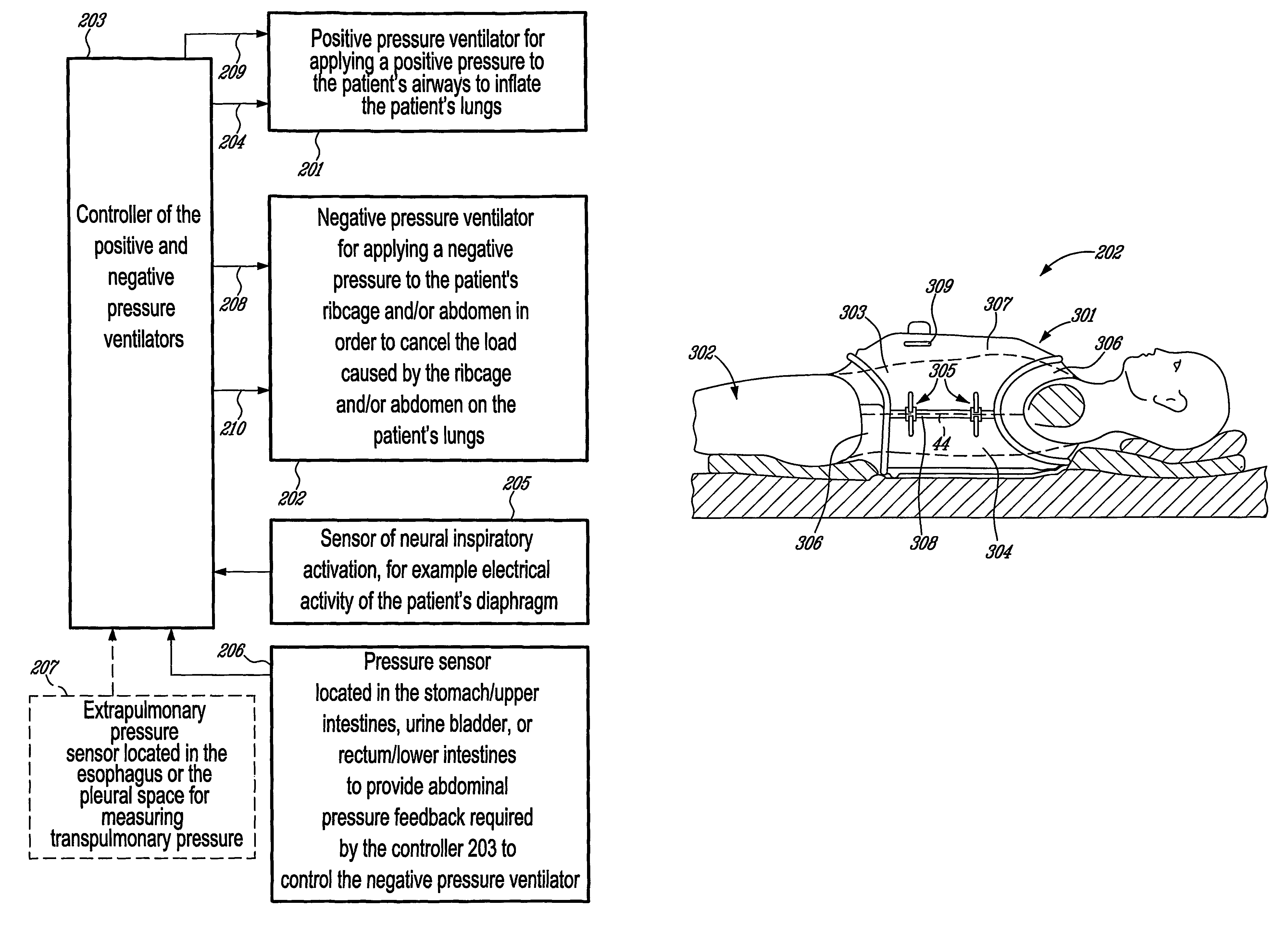
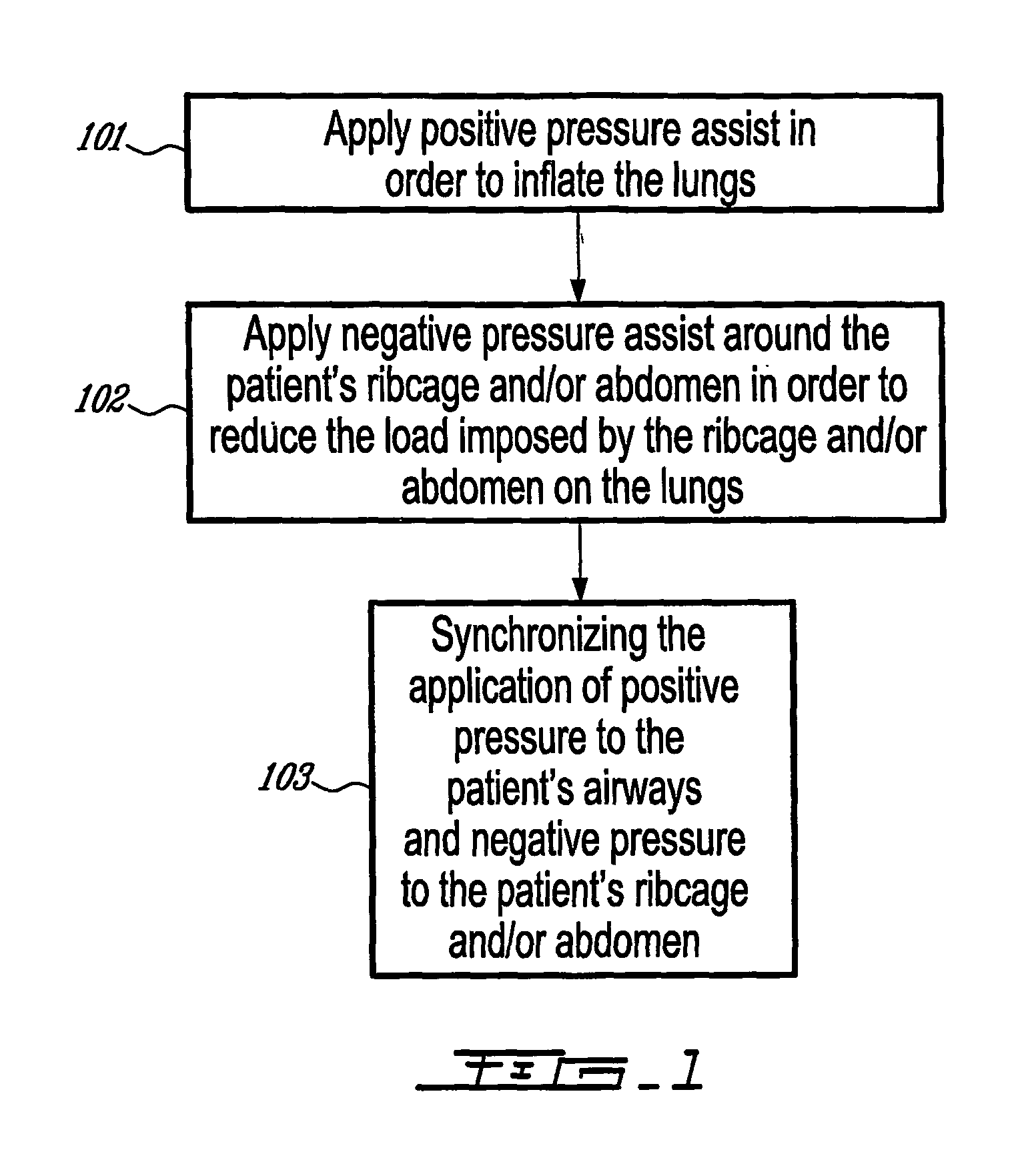
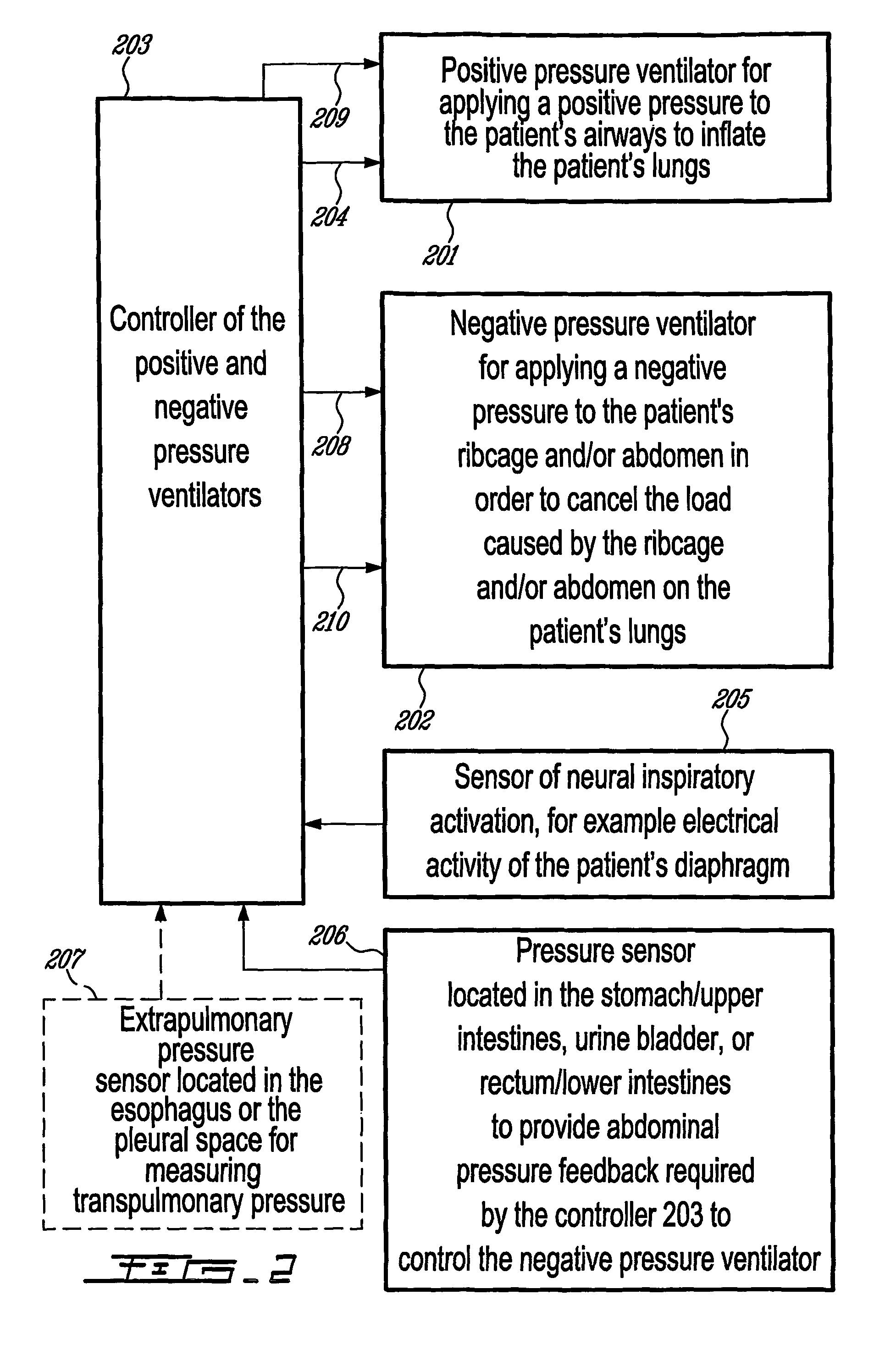
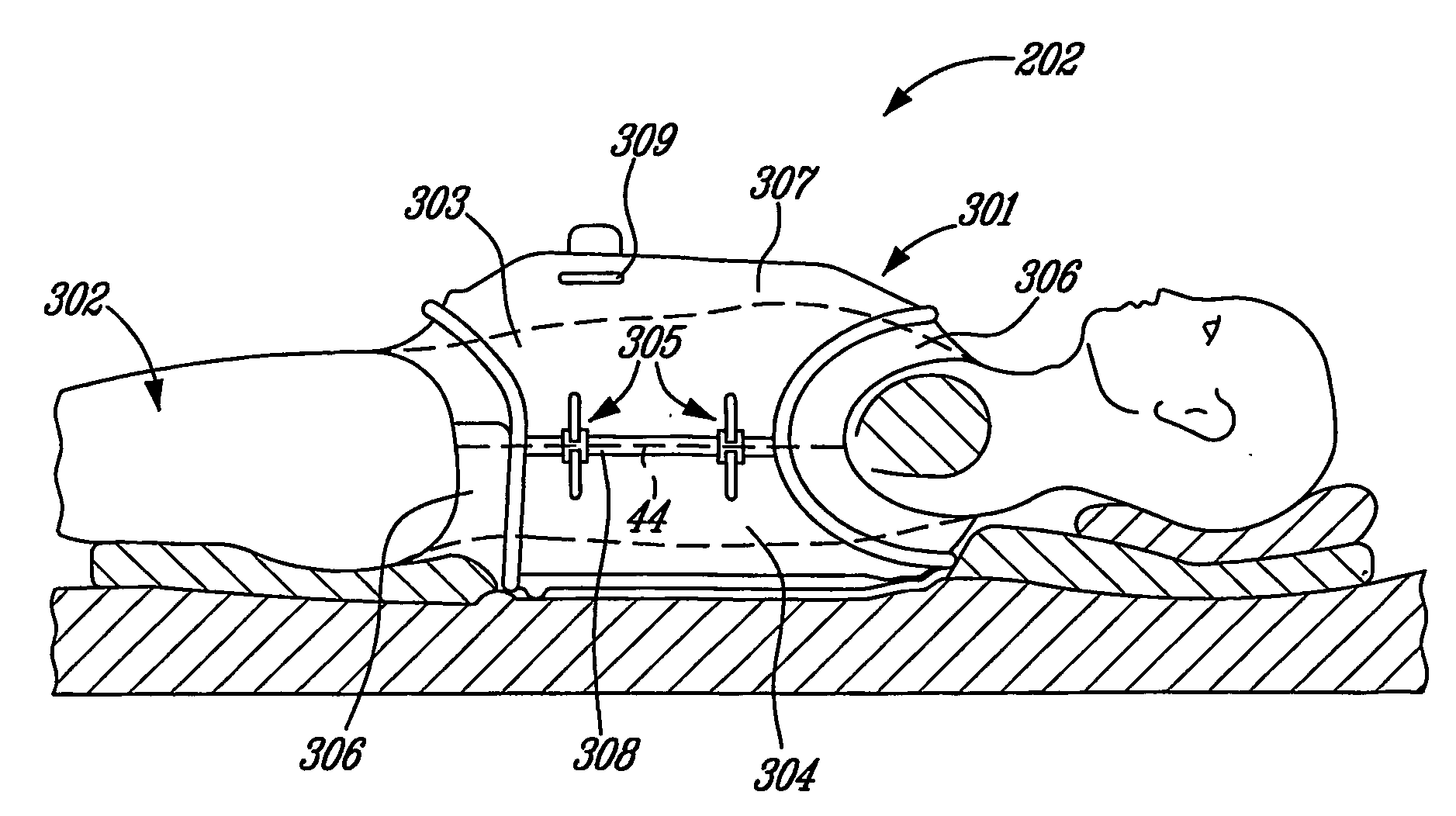
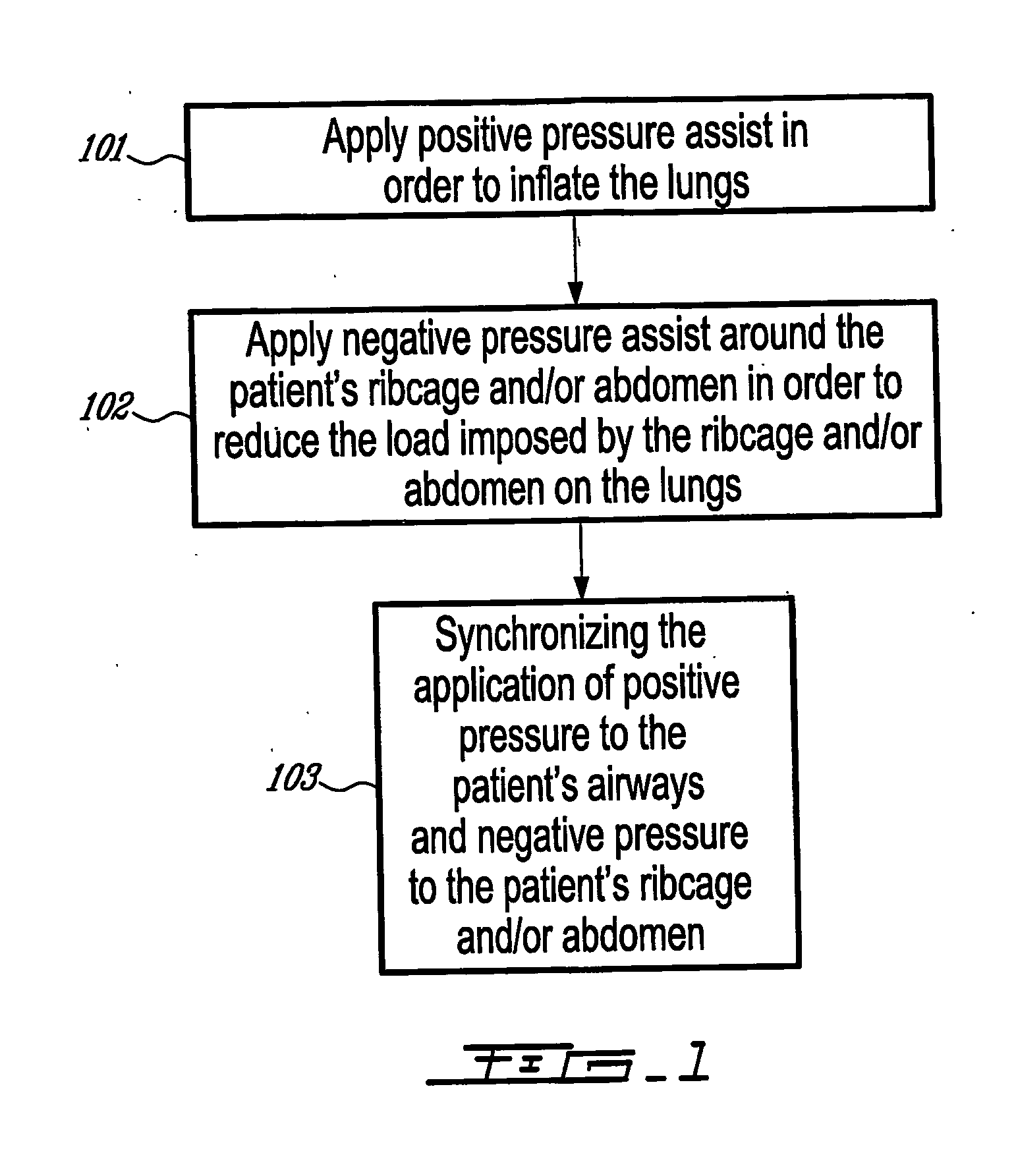
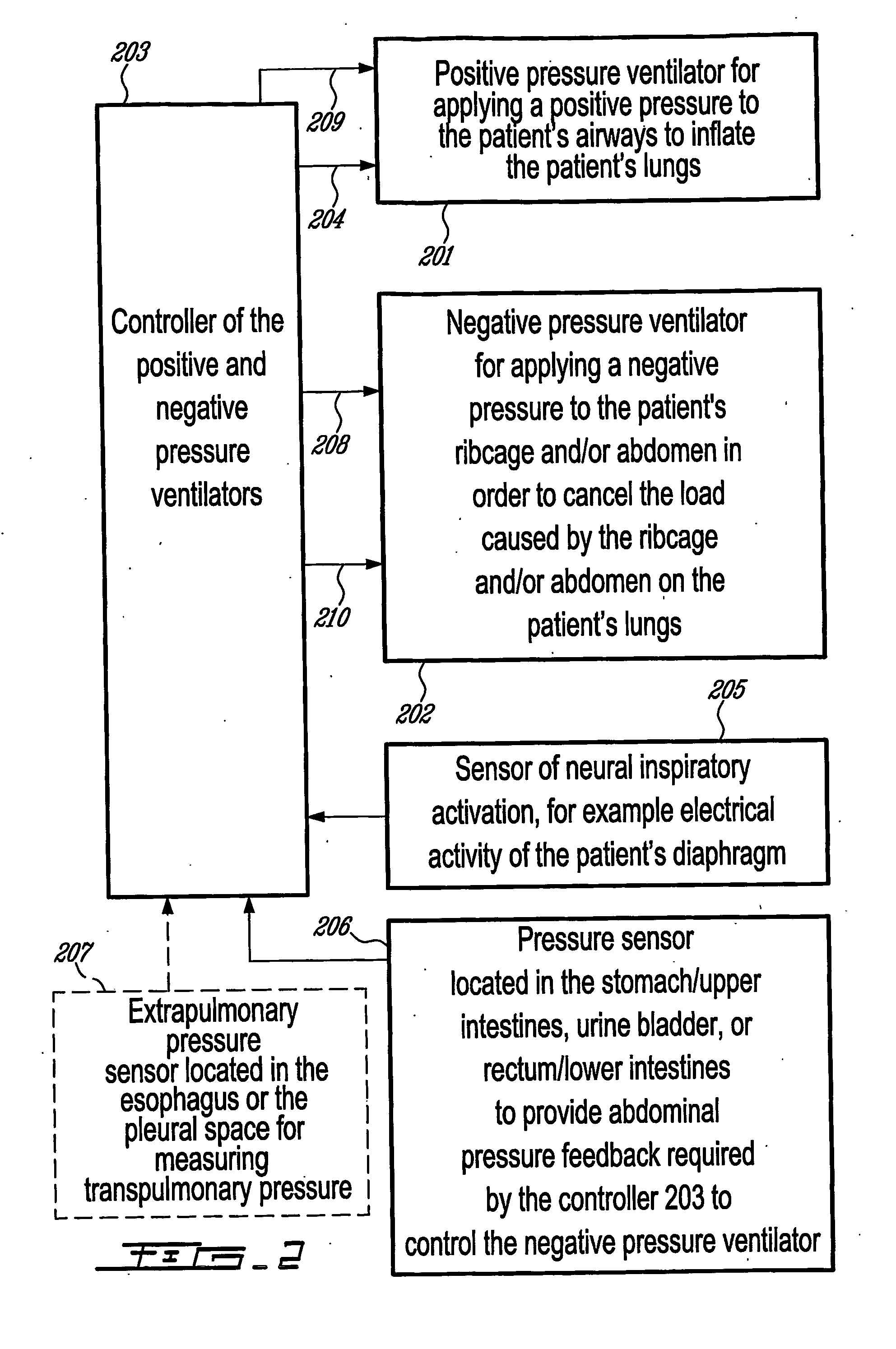
Combined positive and negative pressure assist ventilation
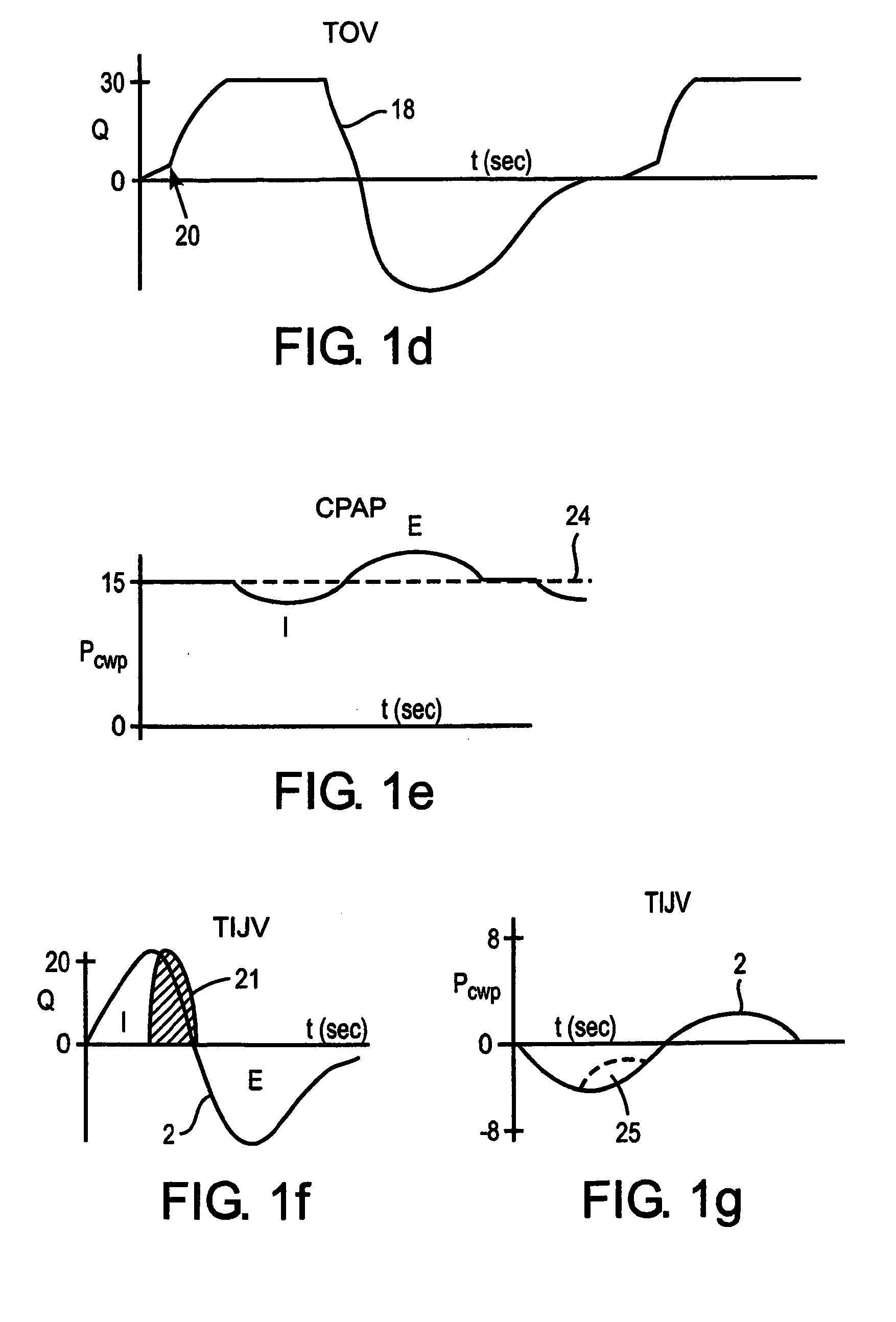
The present invention relates to a method of delivering combined positive and negative pressure assist ventilation to a patient, wherein a positive pressure is applied to the patient's airways to inflate the patient's lungs, a negative pressure is applied around the patient's ribcage and / or abdomen in order to reduce a load imposed by the ribcage and / or abdomen on the patient's lungs, and application of the positive and negative pressures is synchronized. The present invention also relates to a system for delivering combined positive and negative pressure assist ventilation to a patient, comprising a positive pressure ventilator connected to the patient's airways for applying a positive pressure to the patient's airways to inflate the patient's lungs, a negative pressure ventilator installed on the patient's ribcage and / or abdomen for applying a negative pressure around the patient's ribcage and / or abdomen in order to reduce a load imposed by the ribcage and / or abdomen on the patient's lungs, and a controller for synchronizing operation of the positive and negative pressure ventilators.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Multilumen unilimb breathing circuit with detachable proximal fitting
InactiveUS20050022828A1Improve securityReduce the possibilityRespiratorsSurgeryAssisted ventilationBreathing circuit tube
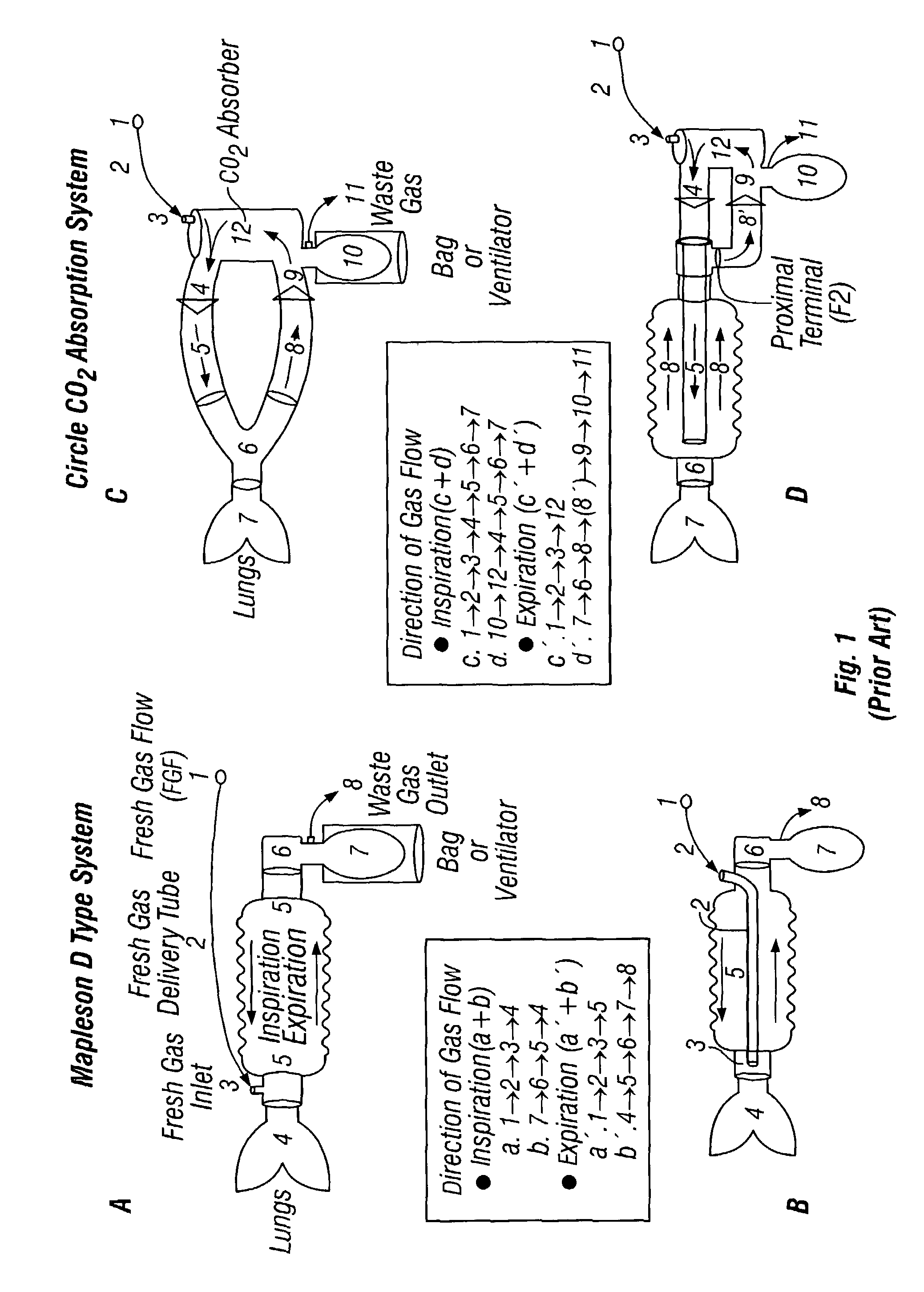
A multilumen unilimb breathing circuit with a detachable proximal fitting for providing respiratory gases to and receiving expiratory gases from a patient. The circuit has unique fittings for connection to patient devices or assisted ventilation systems and components. Despite many teachings away in the prior art from making breathing circuit tubing detachable from the proximal terminal, the proximal end of the rigid multilumen proximal fitting can be attached and detached by a user at a site of use to a mating multilumen proximal terminal while its distal end can be attached to multiple lumens formed of flexible tubing for carrying gases to and from a patient. The present invention introduces for the first time to the multilumen unilimb circuit art a detachable proximal fitting.
Owner:AMBU AS
Combined Positive and Negative Pressure Assist Ventilation
InactiveUS20080115786A1Reduce loadRespiratorsElectrotherapyAssisted ventilationPositive airway pressure
The present invention relates to a method of delivering combined positive and negative pressure assist ventilation to a patient, wherein a positive pressure is applied to the patient's airways to inflate the patient's lungs, a negative pressure is applied around the patient's ribcage and / or abdomen in order to reduce a load imposed by the ribcage and / or abdomen on the patient's lungs, and application of the positive and negative pressures is synchronized. The present invention also relates to a system for delivering combined positive and negative pressure assist ventilation to a patient, comprising a positive pressure ventilator connected to the patient's airways for applying a positive pressure to the patient's airways to inflate the patient's lungs, a negative pressure ventilator installed on the patient's ribcage and / or abdomen for applying a negative pressure around the patient's ribcage and / or abdomen in order to reduce a load imposed by the ribcage and / or abdomen on the patient's lungs, and a contmller for synchronising operation of the positive and negative pressure ventilators.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
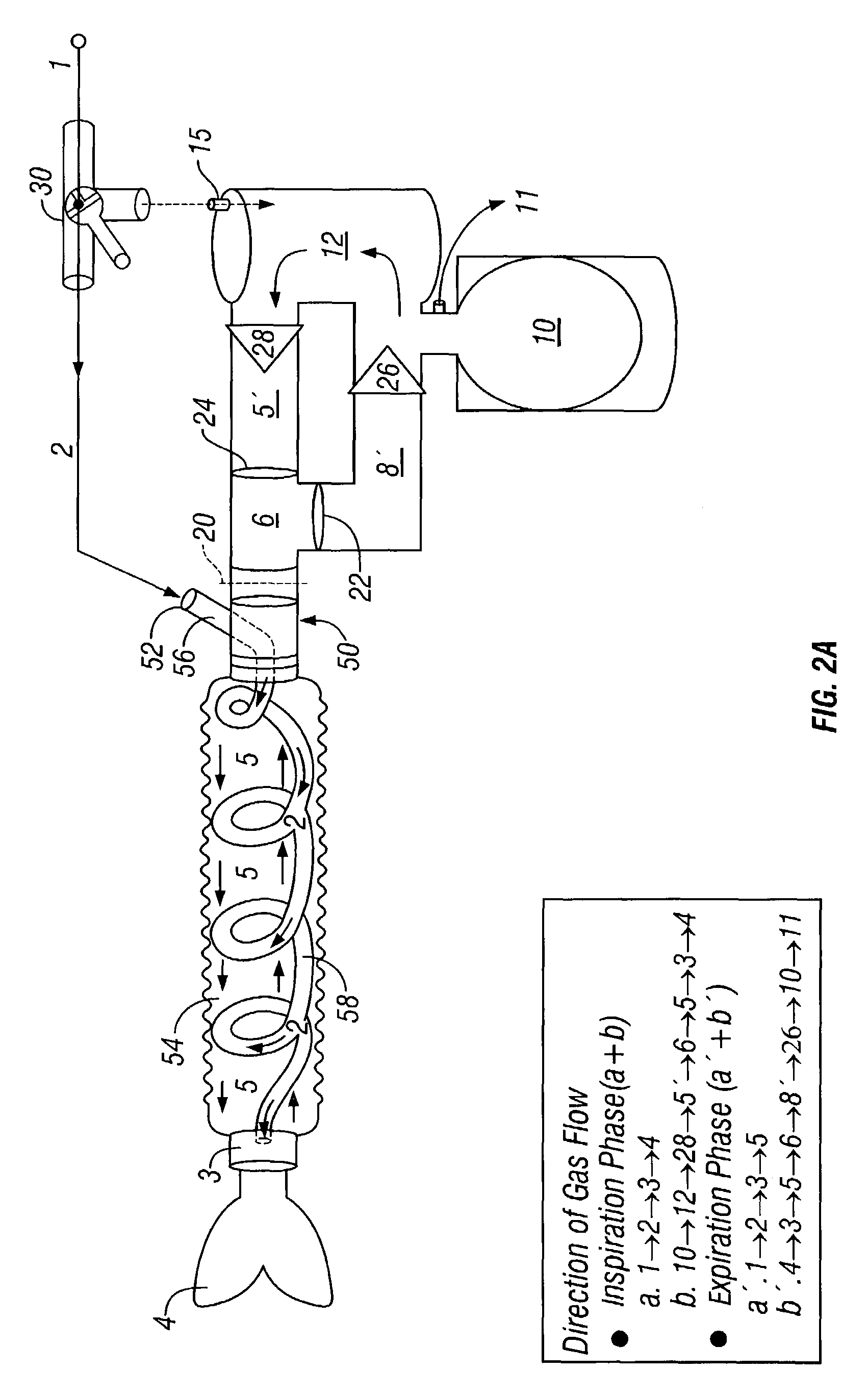
Breathing circuits having unconventional respiratory conduits and systems and methods for optimizing utilization of fresh gases
InactiveUS7261105B2Avoid obstructionMinimize disconnection riskRespiratorsSurgeryAssisted ventilationBreathing gas
A breathing circuit comprising first and second conduits is disclosed, wherein at least one of the conduits is a non-conventional conduit. A multilumen unilimb breathing circuit is also disclosed having first and second conduits, wherein when the proximal ends of said first and second conduits are each connected to an inlet and outlet fitting, respectively, movement of the distal end of the first conduit causes a corresponding movement of the distal end of the second conduit. In an embodiment, inner and outer flexible conduits are formed of pleated tubing that is axially extendable and compressible to form a unilimb multilumen respiratory circuit. The pleating provides for axial extension and contraction. The multilumen respiratory circuit can provide a variable rebreathing volume. In an embodiment, at least one tube in a multilumen respiratory conduit is radially collapsible and radially expandable to a maximum radius for carrying respiratory gases to and from a patient. Also disclosed are methods and systems of optimizing utilization of fresh gases during artificial or assisted ventilation, including administering anesthesia.
Owner:AMBU AS
Nasal interface apparatus and systems for use with a respiratory assist device
ActiveUS20150250973A1Increase airway pressureLight weightRespiratory masksBreathing masksAssisted ventilationAutonomous breathing
An ambulatory assist ventilation (AA V) apparatus and system are disclosed for the delivery of a respiratory gas to assist the spontaneous breathing effort of a patient with a breathing disorder. The AA V system includes a compressed respiratory gas source, a respiratory assist device for controlling respiratory gas flow to the patient, a patient circuit tubing and a low profile nasal interface device, which does not have a dead space or hollow area where C02 can collect, for delivering the respiratory gas to the patient, wherein the nasal interface device is fluidly connected to the respiratory assist device via tubing for receiving the respiratory gas therefrom.
Owner:INOGEN INC
Electromagnet-assisted ventilation cover for an electronic equipment enclosure
ActiveUS20060285291A1Simply and inexpensive to implementCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersAssisted ventilationAssisting ventilation
A ventilation assembly for an electronic equipment enclosure. The ventilation assembly includes a housing having at least one ventilation port, and a cover movable between an open position and a closed position. The cover is positioned over the ventilation port when the cover is in the closed position. The ventilation assembly further includes at least one electromagnet for selectively securing the cover in the closed position.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Boosted-ventilation direct air cooling tower
InactiveCN103712473AAdd adjustment functionImprove overall heat transfer coefficientSteam/vapor condensersAssisted ventilationCooling tower
The invention belongs to the field heat exchange, and relates to a boosted-ventilation direct air cooling tower, in particular to an air-cooling power generation air cooling island and an air driving mode. Due to winter-summer difference and day-night difference of air temperature, frequent natural wind and multiple changes of wind speed and wind direction, a pure natural ventilation and simple mechanical-assisted ventilation air cooling tower is difficult to meet current air cooling requirements. Condensation triangles composed of axial flow fans, finned tubes and the like are disposed around the lower portion of a natural ventilator. Cooling capacity of the air cooling tower in summer is greatly enhanced, damage of strong wind is weakened greatly, excess draft in the air cooling tower in winder can be utilized, energy is recovered through the axial flow fans, and hot air in the tower can be pumped out by reverse rotation of the fans to melt the accidentally-frozen fined tubes. The boosted-ventilation direct air cooling tower can be matched with direct air cooling and indirect air cooling units in various sizes.
Owner:李宁
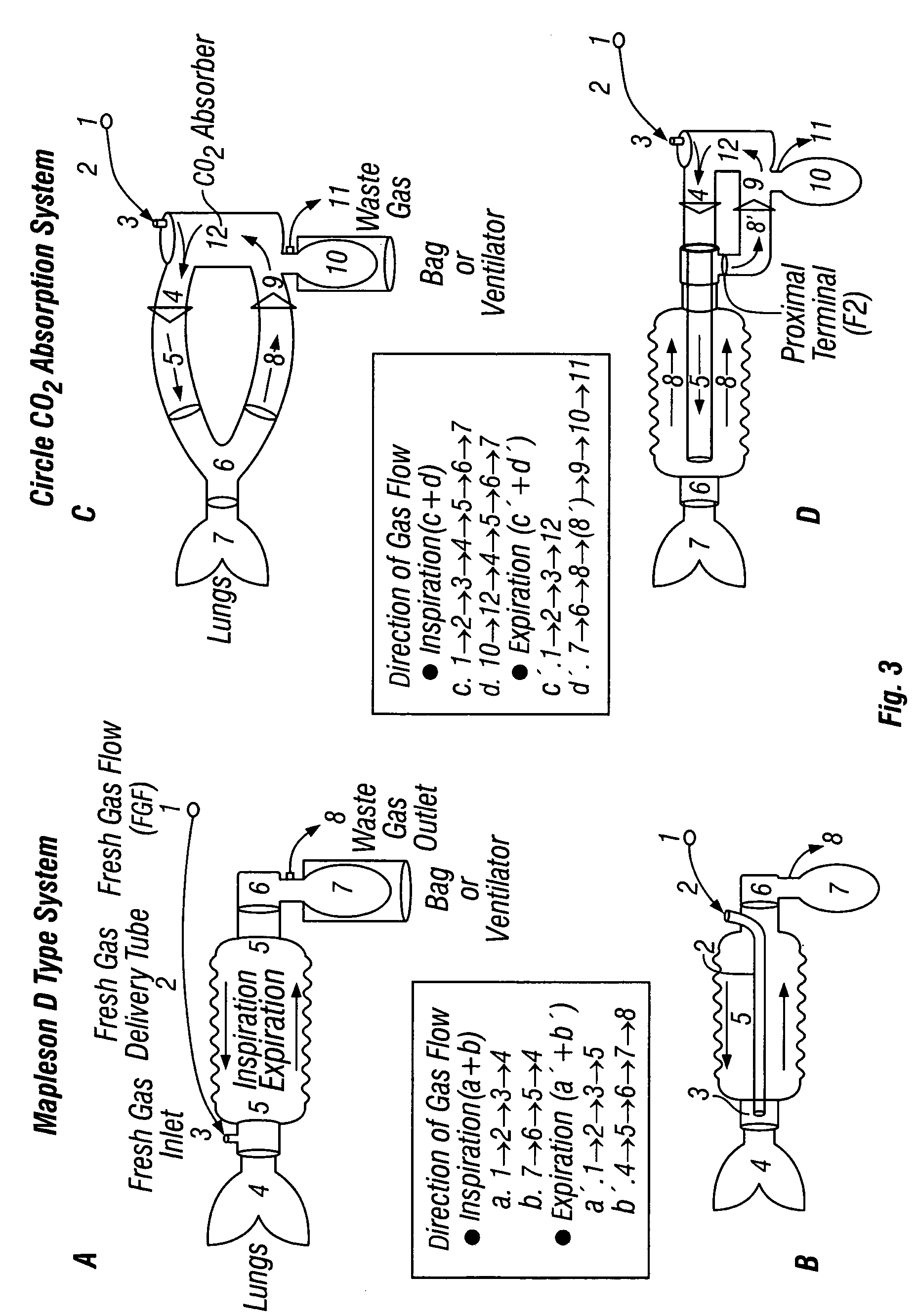
Breathing systems with post-inspiratory valve fresh gas flow input, components for implementing same, and methods of use
InactiveUS7717109B2Simple and safe processUtilization of fresh gases is optimizedRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationBreathing circuit component
A system for providing anesthesia or assisted ventilation that has a post-inspiratory valve fresh gas flow input is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a fresh gas flow diverter valve is provided to permit an operator to provide fresh gas flow proximally or distally of the inspiratory valve. Also disclosed is an adaptor and other breathing circuit components for forming a system of the present invention. A method of providing anesthesia or assisted ventilation using low flow fresh gas is disclosed.
Owner:AMBU AS
Process and device for generating an alarm during a machine-assisted patient ventilation
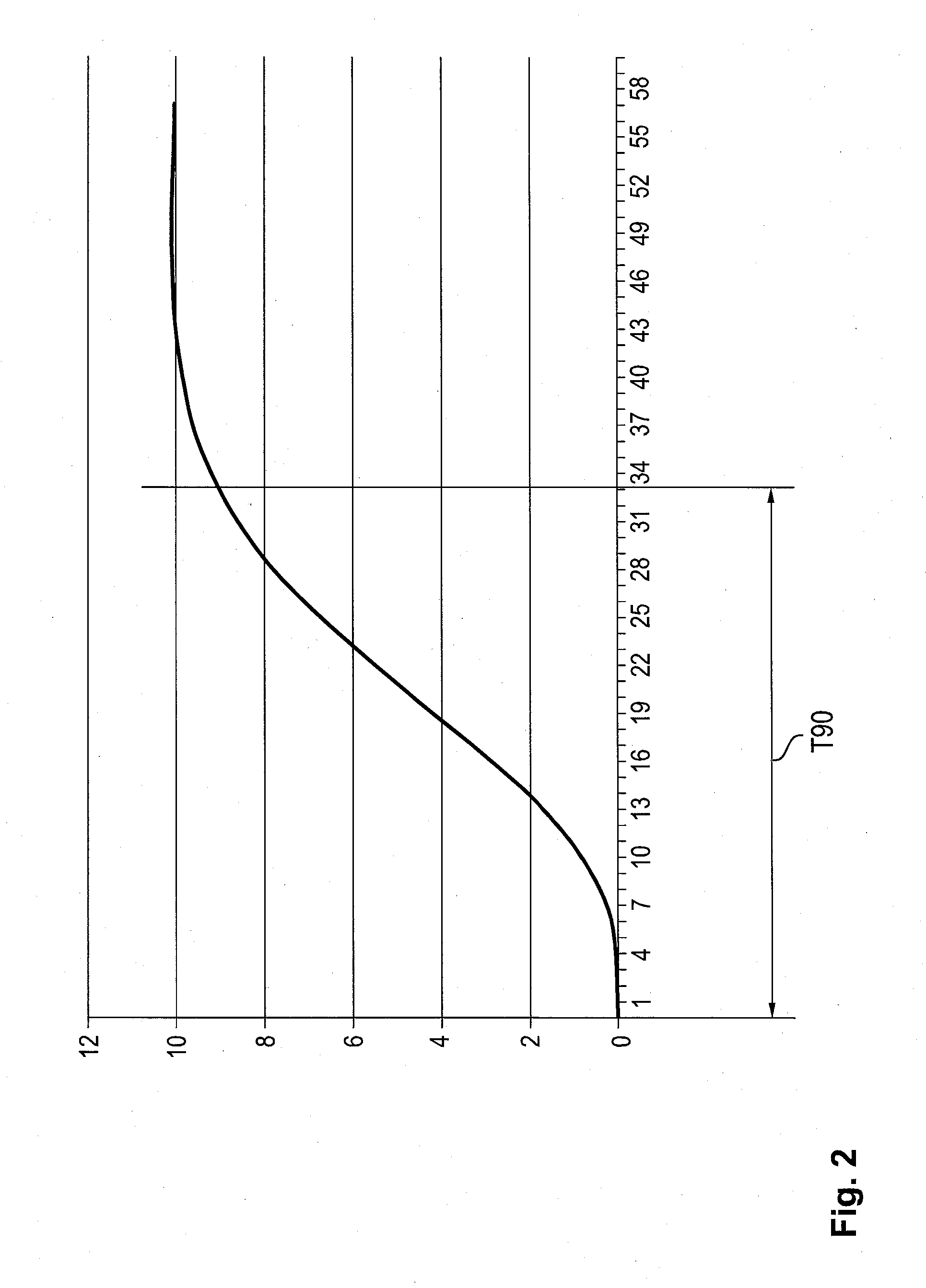
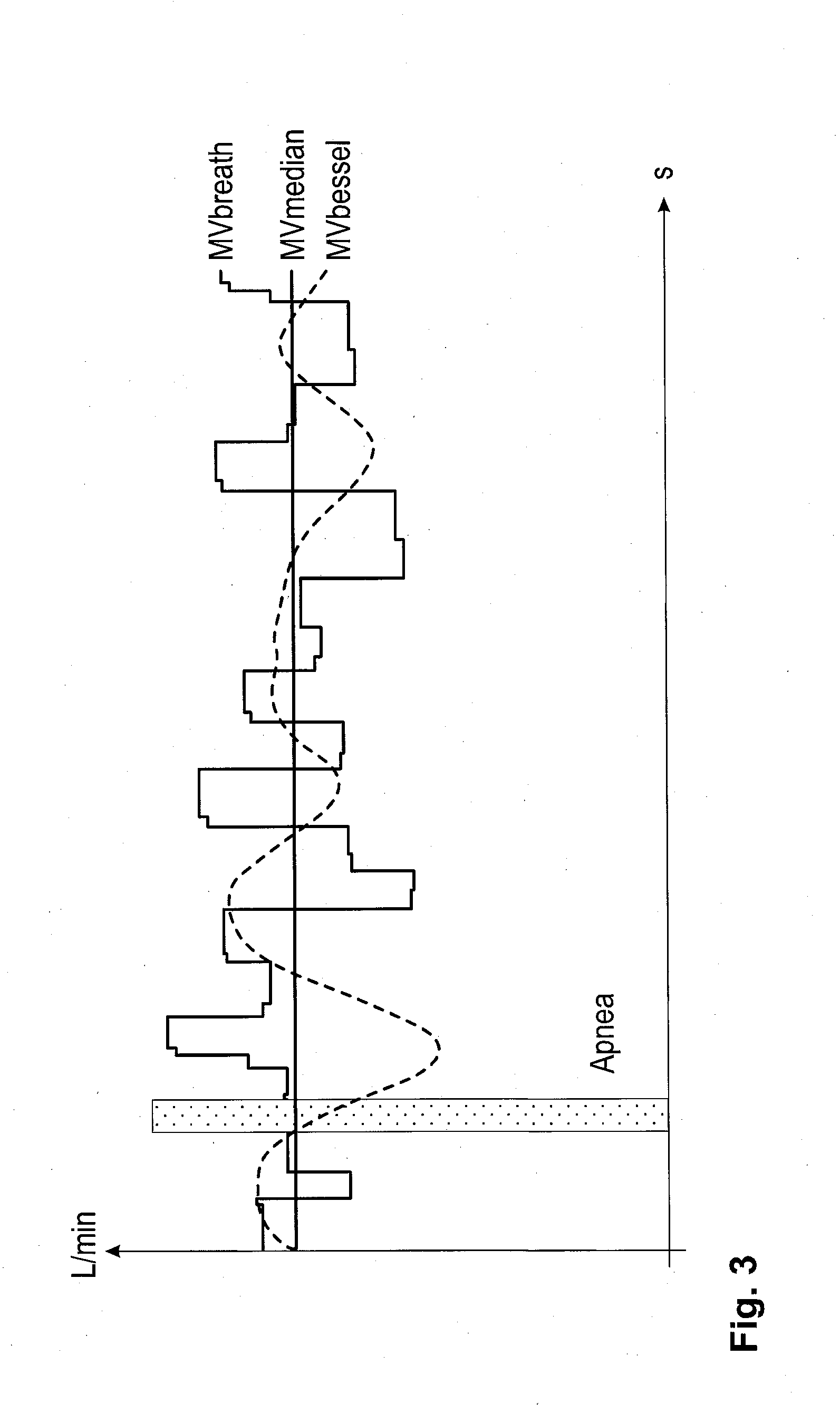
ActiveUS20150258290A1Increasing danger potentialReduce in quantityRespiratorsRespiratory device testingAssisted ventilationCritical limit
A device and process generates an alarm during a machine-assisted ventilation of a patient. A minute volume is measured and a median of the minute volume and a lower critical limit value of the minute volume and a time delay are determined and are recorded in a control device. A reference signal is determined as a function of the lower critical limit value for the minute volume and the time delay based on the median of the minute volume. From the reference signal an alarm limit value located below the lower critical limit value as well as a value for a maximum tolerated duration of apnea of the patient are derivable. An alarm signal is generated both during an undershooting of the lower critical limit value over a period of time that is longer than the established time delay and during an undershooting of the alarm limit value.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Apparatus and method for improved assisted ventilation
ActiveUS20150265790A1Improved patient careAccurate operationTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesResuscitation procedureAssisted ventilation
Devices and methods for allowing for improved assisted ventilation of a patient. The methods and devices provide a number of benefits over conventional approaches for assisted ventilation. For example, the methods and devices described herein permit blind insertion of a device that can allow ventilation regardless of whether the device is positioned within a trachea or an esophagus. In addition, the methods and device allow for timed delivery of ventilations based on a condition of a thoracic cavity to increase the amount and efficiency of blood flow during a resuscitation procedure.
Owner:COLABS
Apparatus and method for improved assisted ventilation
ActiveUS20130146051A1Easy to identifyPrevent crashHeart defibrillatorsMedical devicesAssisted ventilationAssisting ventilation
Devices and methods for allowing for improved assisted ventilation of a patient. The methods and devices provide a number of benefits over conventional approaches for assisted ventilation. For example, the methods and devices described herein permit blind insertion of a device that can allow ventilation regardless of whether the device is positioned within a trachea or an esophagus.
Owner:COLABS
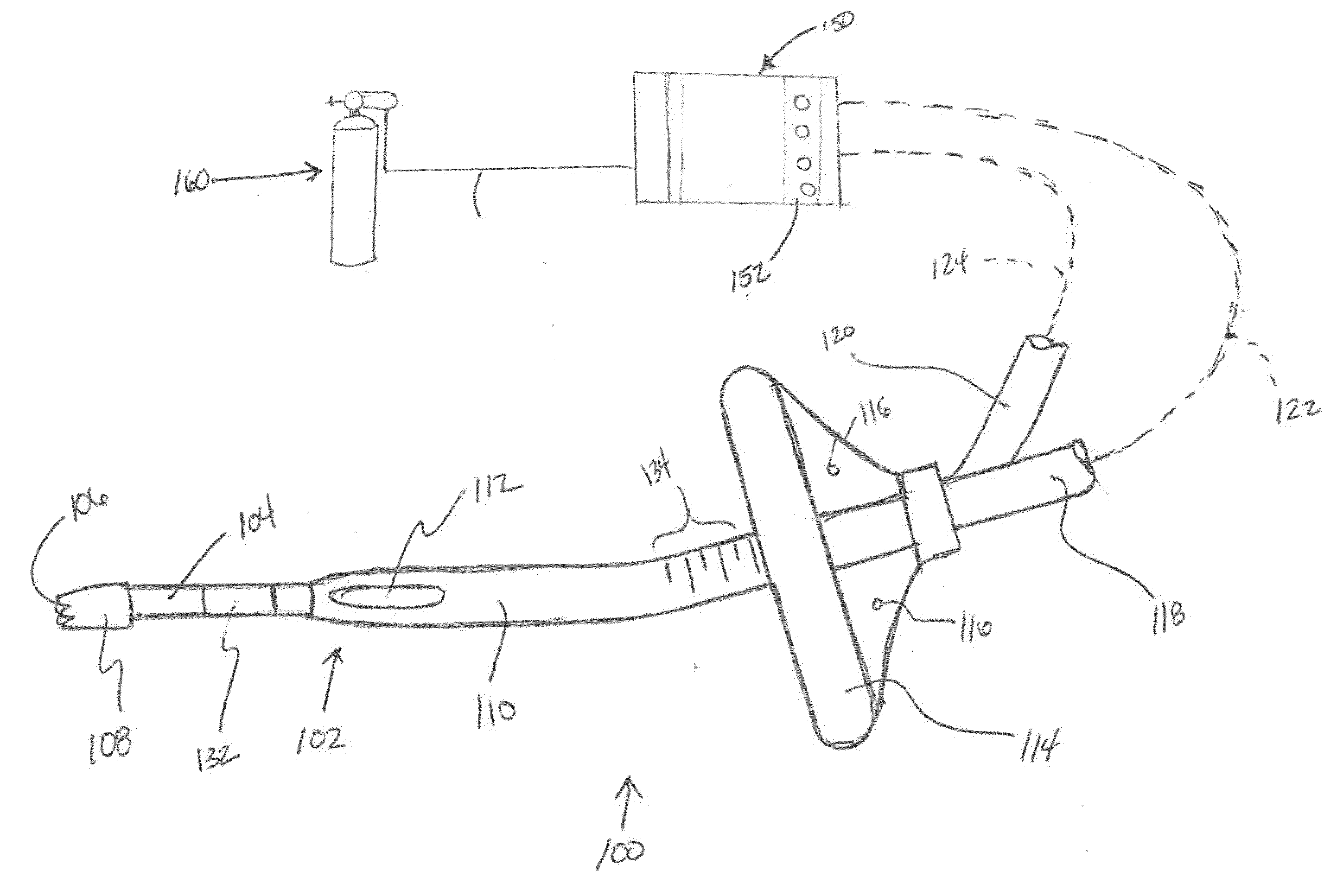
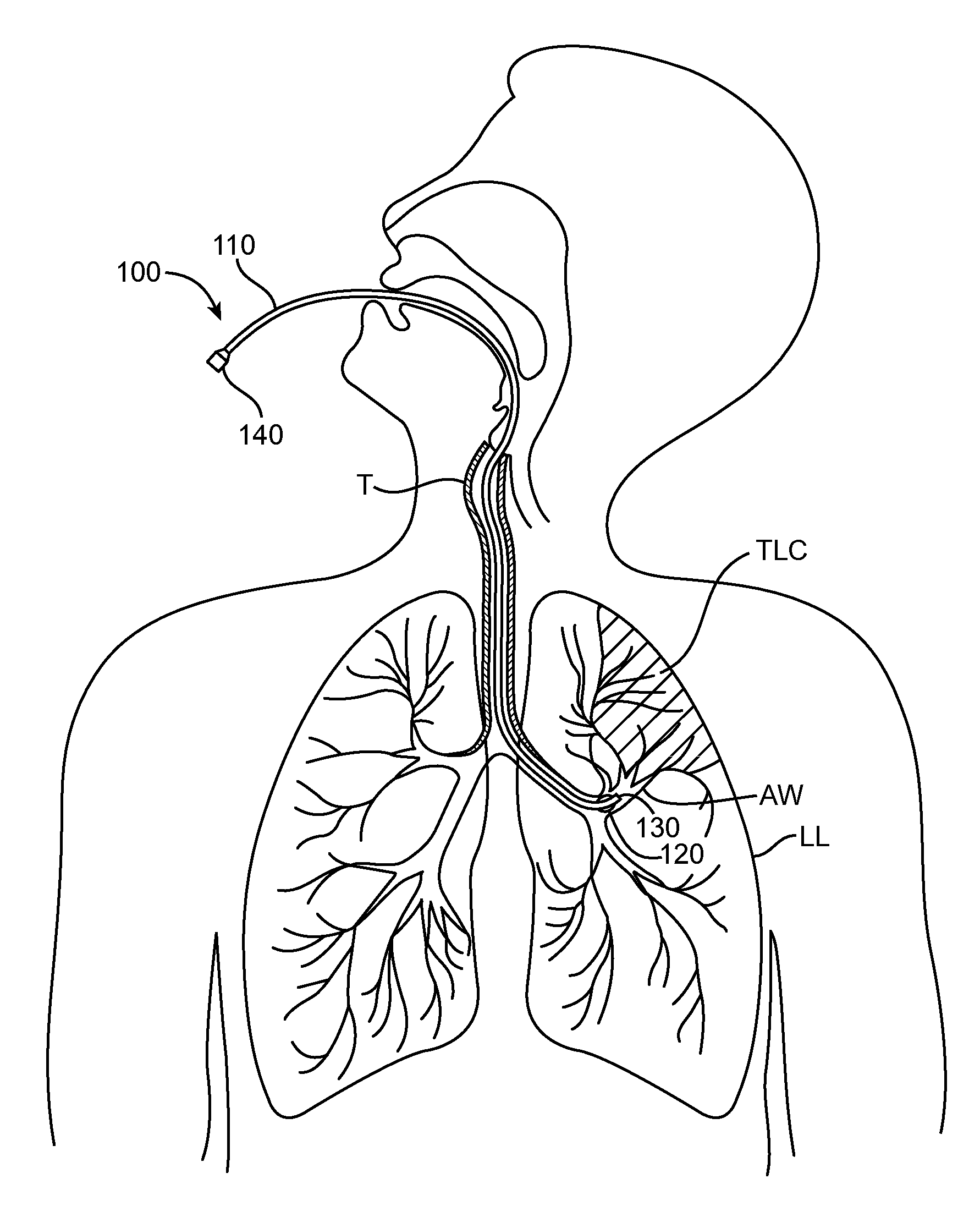
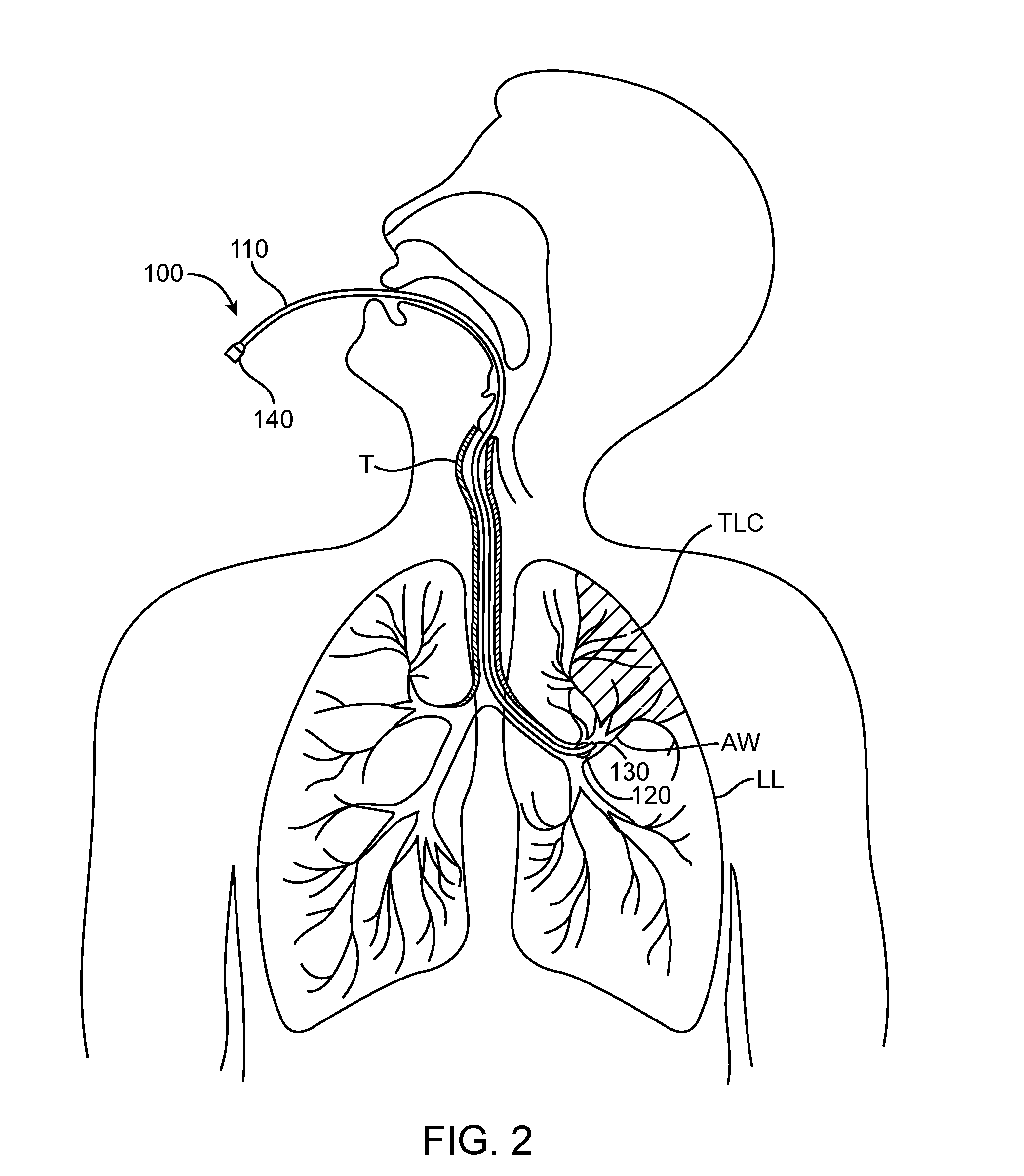
Methods and systems for endobronchial diagnostics
Methods and systems for targeting, accessing and diagnosing diseased lung compartments are disclosed. The method comprises introducing a diagnostic catheter with an occluding member at its distal end into a lung segment via an assisted ventilation device; inflating the occluding member to isolate the lung segment; and performing a diagnostic procedure with the catheter while the patient is ventilated. The proximal end of the diagnostic catheter is configured to be attached to a console. The method may also comprise introducing the diagnostic catheter into the lung segment; inflating the occluding member to isolate the lung segment; and monitoring blood oxygen saturation. The method may further comprise introducing the diagnostic catheter into the lung segment; determining tidal flow volume in the lung segment; determining total lung capacity of the patient; and determining a flow rank value based on the tidal flow volume of the lung segment and the total lung capacity.
Owner:PULMONX
Multifunctional automatic cardio-pulmonary resuscitation first-aid equipment
InactiveCN105616138AIncrease success rateGuaranteed validityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAssisted ventilationAutomatic control
Multifunctional automatic cardio-pulmonary resuscitation first-aid equipment comprises a base, a platform, a pressing plate, a connecting rod, a screw nut, a ball screw, a stand column, a servo motor, a host, a touch screen, a manual input device, an automatic defibrillation device, a heart rate detection sensor, a cooling gas generation device and a hood provided with a hollow interlayer, wherein the front end of the screw nut is connected with the pressing plate through the connecting rod; the automatic defibrillation device is connected with the host; the heart rate detection sensor is connected with the host; the hood provided with the hollow interlayer is connected with the cooling gas generation device. The equipment has the advantages as follows: accurate pressing depth and pressing frequency of a patient can be automatically controlled in the emergent treatment process of cardiac arrest, waveforms of ventricular fibrillation are automatically recognized, defibrillation is triggered, smoothness of an airway is kept, mechanical assisted ventilation is provided, the dependence on a special doctor in the emergent treatment process is reduced, the accuracy and the automatic degree are improved, the cardio-pulmonary resuscitation effectiveness is guaranteed, brain death is reduced, and the multifunctional automatic cardio-pulmonary resuscitation first-aid equipment can be applied in a wide range.
Owner:SHENGJING HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICAL UNIV
Test conjoined electrolytic bath provided with assisted ventilation chamber
InactiveCN103323508AReduce disturbanceReduce signal to noise ratioMaterial electrochemical variablesAssisted ventilationElectricity
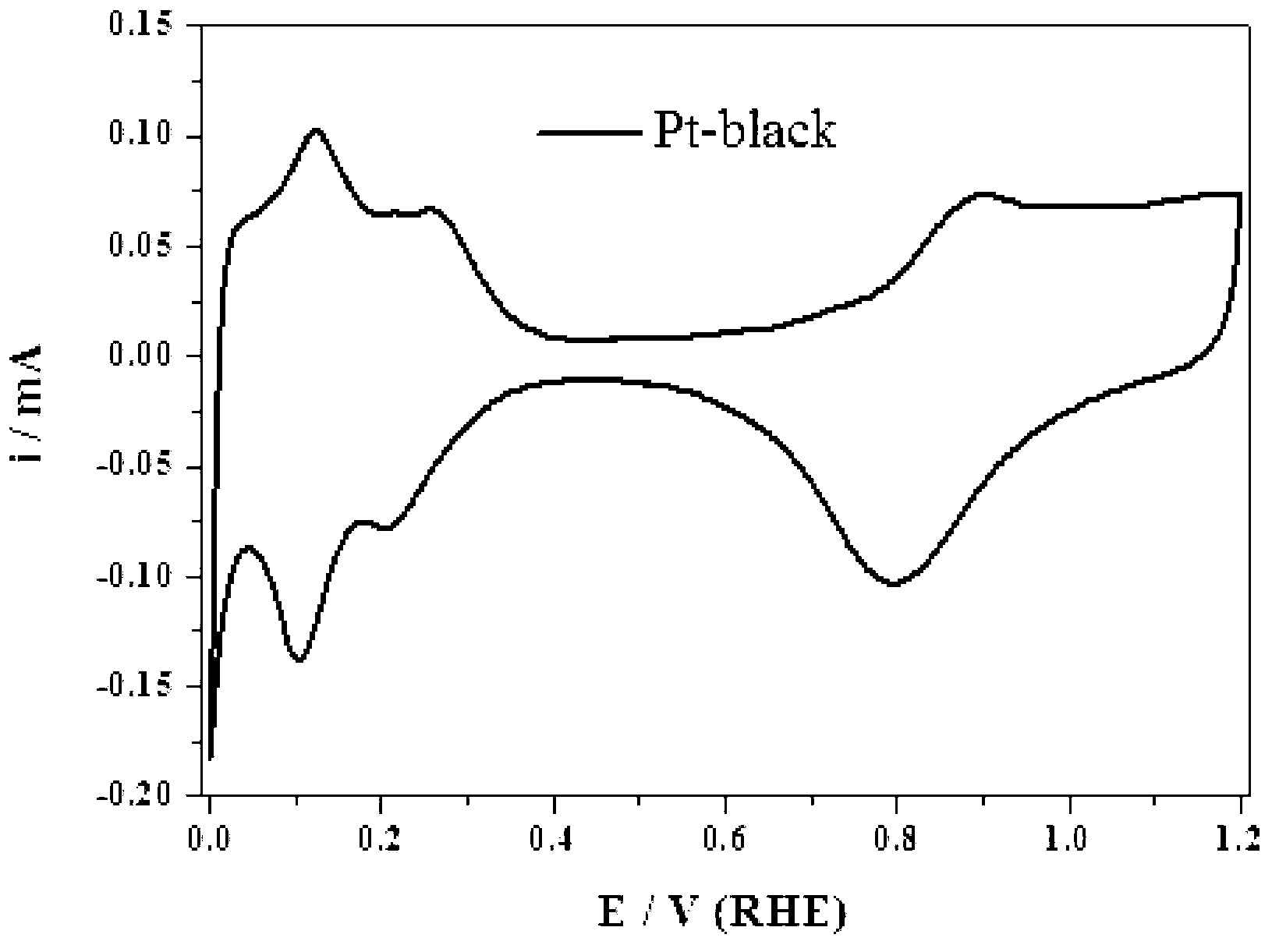
A test conjoined electrolytic bath provided with an assisted ventilation chamber is suitable for the electric performance test field of a fuel-cell catalyst. The test conjoined electrolytic bath mainly comprises three parts, namely a test pool, an assisted ventilation chamber and a reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber. The test pool is provided with a working electrode, a counter electrode with a platinum sheet and a glass core mounted at an inlet air pipe end. The reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber contains a reference hydrogen reference electrode liquid storage tube, a connecting pipe arranged between the reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber and the test pool, and a reference hydrogen reference electrode provided with an inlet air pipe and a platinum black plated platinum sheet. The reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber is connected with the test pool through the connecting pipe. The assisted ventilation chamber is provided with the inlet air pipe. The connecting pipe is fixed between the assisted ventilation chamber and a test cabinet. And the inlet air pipe faces a port of the connecting pipe. A porous glass plug is also arranged inside the connecting pipe.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Air incoming pipeline structure adapted to ventilation system
ActiveCN108917082AEfficient use ofImprove utilization efficiencyDucting arrangementsLighting and heating apparatusAssisted ventilationEngineering
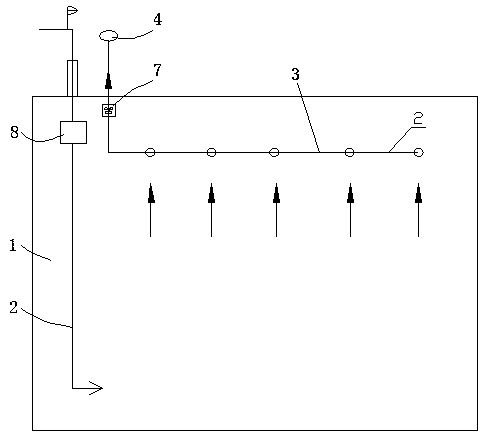
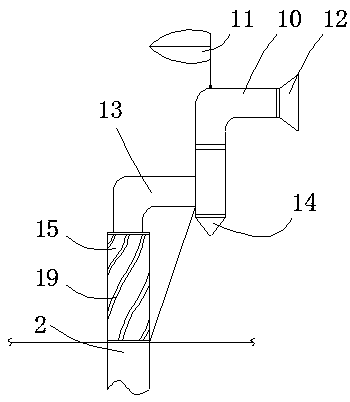
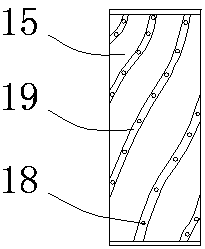
The invention discloses an air incoming pipeline structure adapted to a ventilation system. The air incoming pipeline structure comprises an air incoming pipeline communicating the inside with the outside of a room. The air incoming pipeline structure is characterized in that an air incoming structure for assisting air incoming is arranged at an outer port, positioned outside the room, of the airincoming pipeline and comprises an air incoming barrel in vertical arrangement, the lower half of the air incoming barrel is communicated with the air incoming pipeline, the upper end of the air incoming barrel is provided with an air incoming section in a horizontal direction, and the outer end of the air incoming section is an air incoming end. The air incoming pipeline structure can better utilize natural wind power for assisted ventilation, so that utilization efficiency of the natural wind power is improved, energy consumption is lowered, and the air incoming pipeline structure is especially suitable for implementation, popularization and application in buildings of regions with developed wind power.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Ventilator for Rapid Response to Respiratory Disease Conditions
InactiveUS20100306992A1Increasing oxygen pressureEnsure safetyRespiratorsWave amplification devicesDiseaseAssisted ventilation
The present specification discloses a ventilator system that can be manufactured quickly with minimal skill requirements and rapidly deployed in response to epidemic respiratory disease conditions. In one embodiment, the ventilator, having a minimal number of controls, is used to give ventilation or mechanical breathing to a patient suffering ARDS. The mechanical ventilation is based on pressure control and has variable pressure, breathing rate, and oxygenation. Preferably, the ventilator is rapidly deployable, easy and intuitive to operate, and capable of sustaining at least 75% of epidemic respiratory distress victims who require assisted ventilation until resuming normal breathing.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE INC
Sudden cardiac arrest first-aid integrated device
ActiveCN107233204AImprove survival rateSimplify rescue difficultyRespiratorsHeart defibrillatorsAssisted ventilationEcg signal
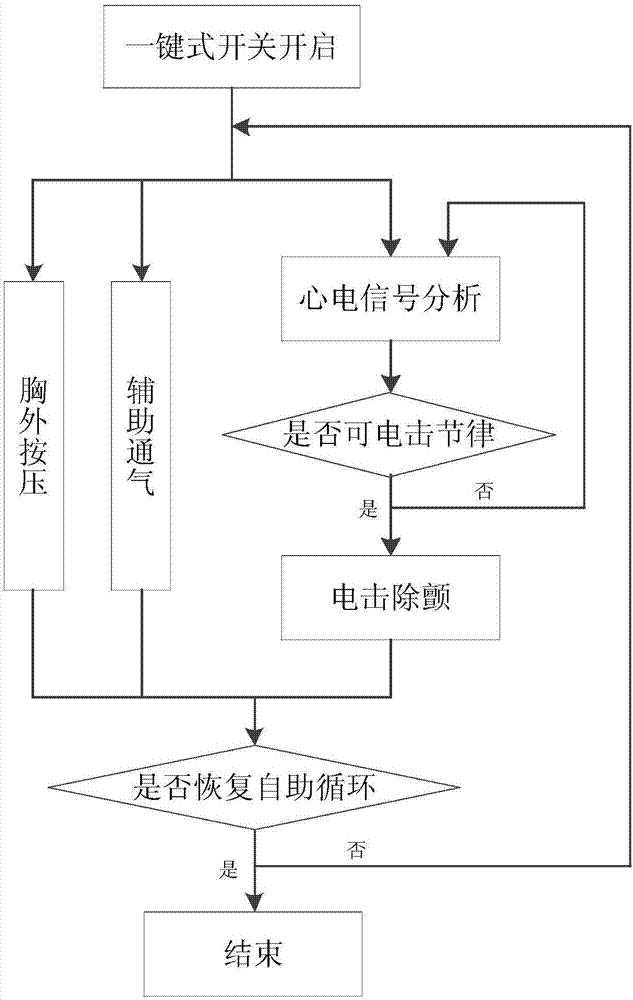
The invention discloses a sudden cardiac arrest first-aid integrated device. The device comprises a microprocessor, an external chest compression module, a respiration assisting module and an external defibrillation module, wherein the microprocessor sends a work starting instruction to the external defibrillation module, the external chest compression module and the respiration assisting module at the same time; the external chest compression module and the respiration assisting module conduct external chest compression and assisted ventilation respectively in the proportion of 30:2; the external defibrillation module collects electrocardiogram signals, the microprocessor conducts interference noise filtering on the electrocardiogram signals, distinguishes ECG rhythm types and judges whether electric defibrillation can be conducted, and if yes, the microprocessor controls the external defibrillation module to automatically send out electric shock; in the whole analysis and electric shock process, continuous chest compression and electrocardiogram signal analysis before electric defibrillation are synchronously implemented, and people do not need to stop chest compression before electric defibrillation; the external chest compression module and the respiration assisting module carry out continuous chest compression and assisted ventilation. First-aid personnel can achieve cardio-pulmonary resuscitation one-click operation by using the device, the rescue difficulty is greatly reduced, and the survival rate of a sudden cardiac arrest patient is increased.
Owner:李城钰
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com