Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Digital protective relay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
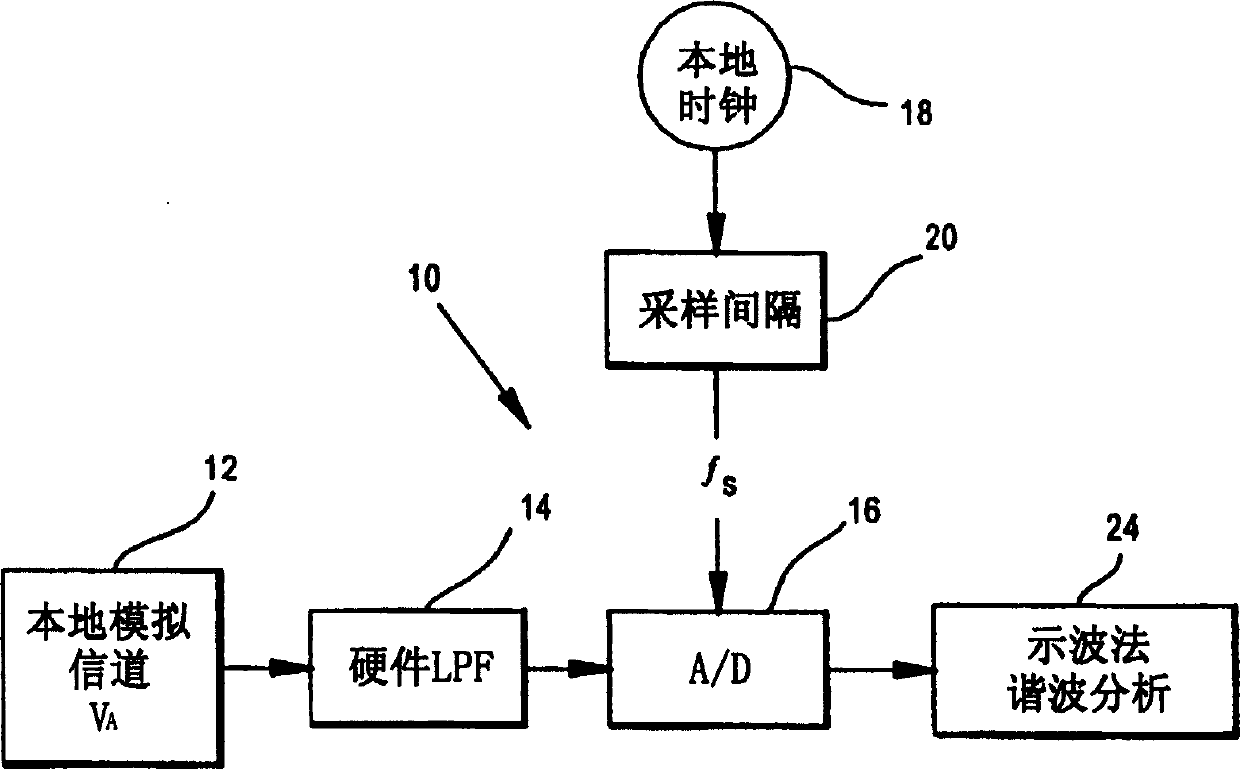
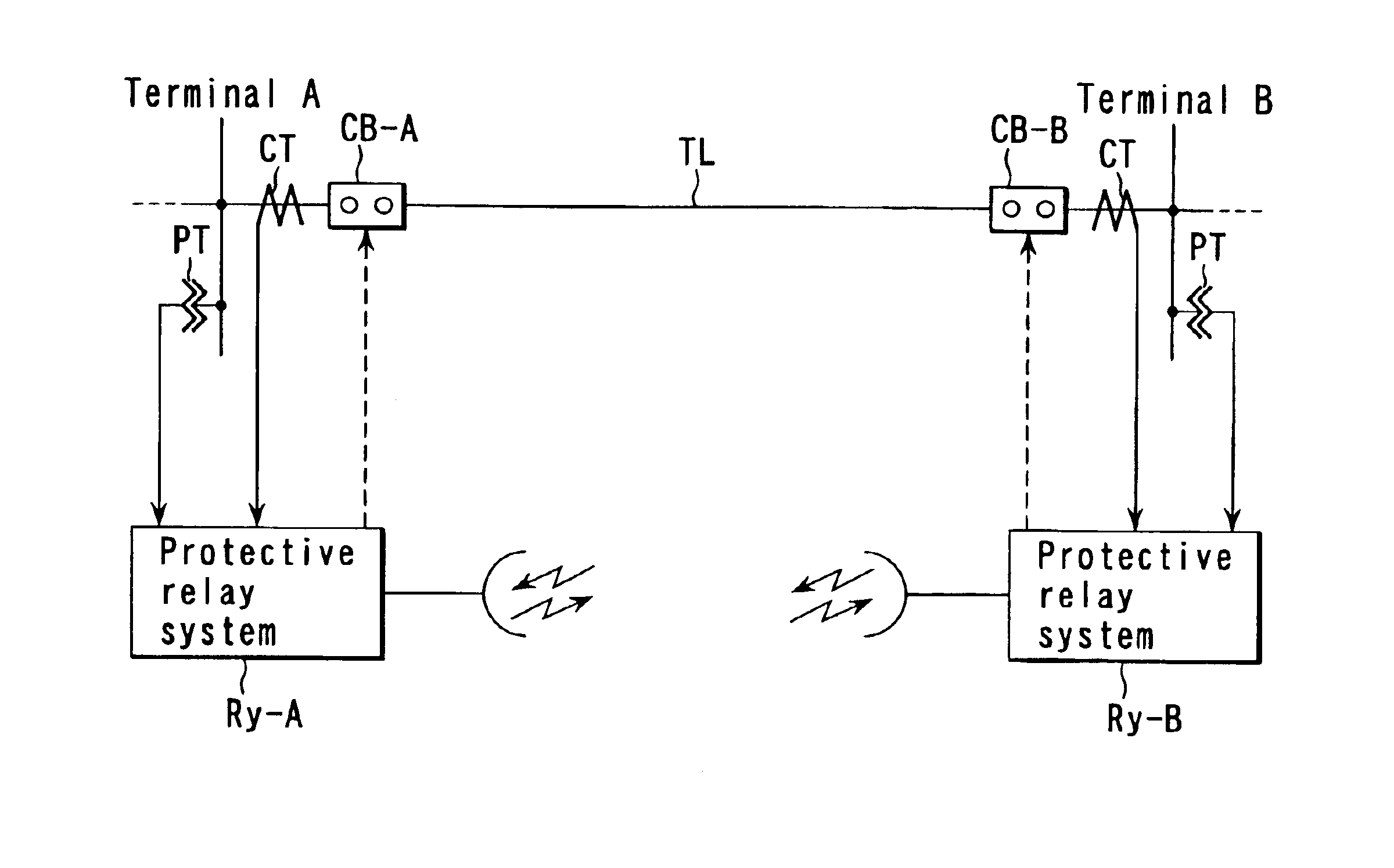
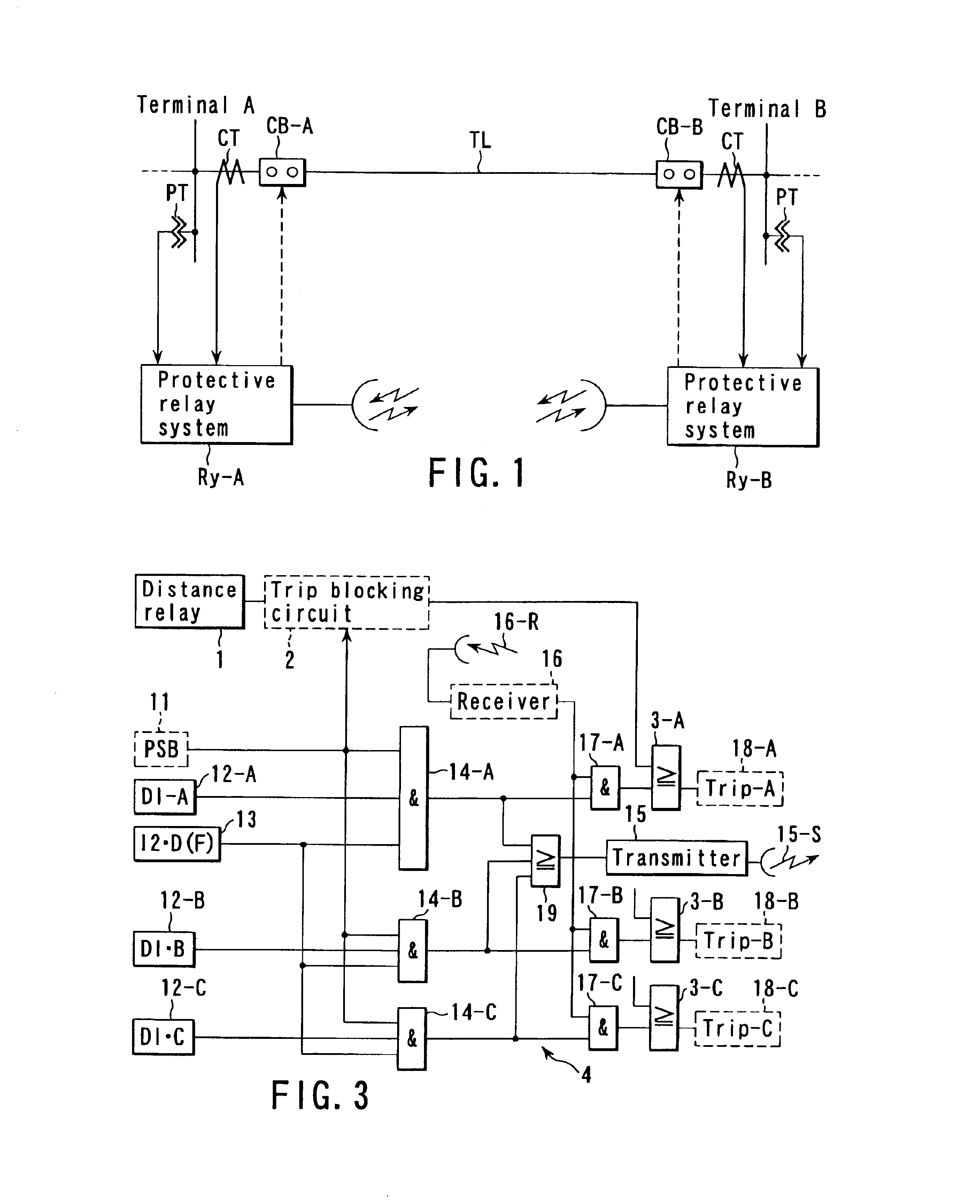
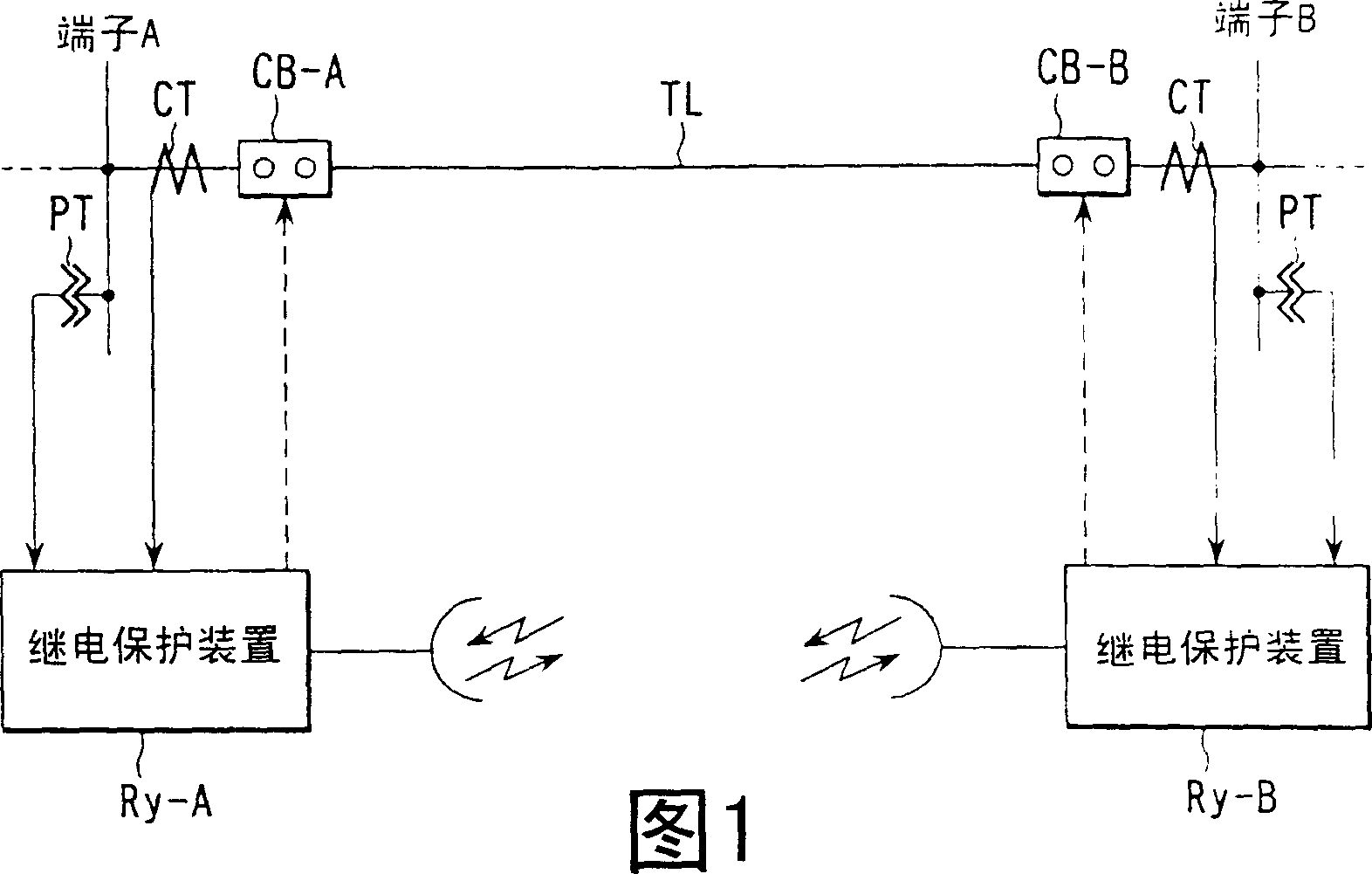
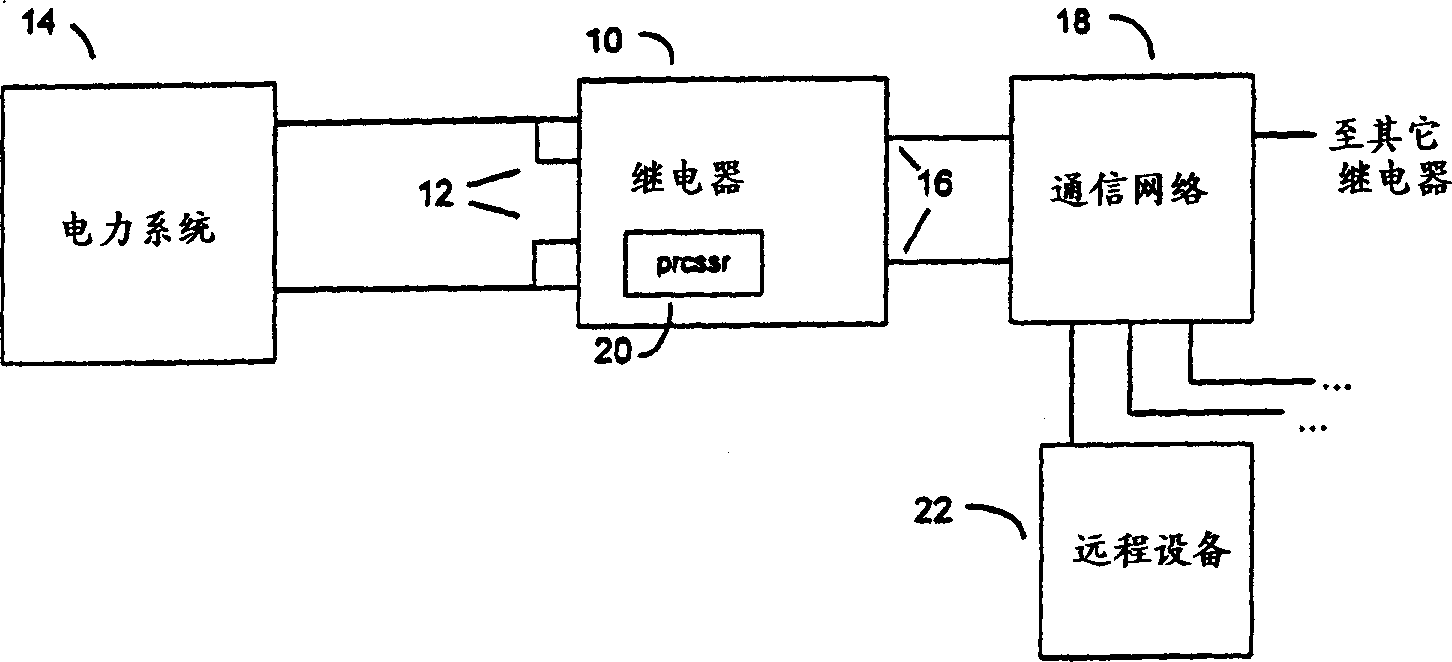
In utility and industrial electric power transmission and distribution systems, a digital protective relay is a computer-based system with software-based protection algorithms for the detection of electrical faults. Such relays are also termed as microprocessor type protective relays. They are functional replacements for electro-mechanical protective relays and may include many protection functions in one unit, as well as providing metering, communication, and self-test functions.
Protective relay with synchronized phasor measurement capability for use in electric power systems
InactiveUS6845333B2Current/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital protective relayEngineering
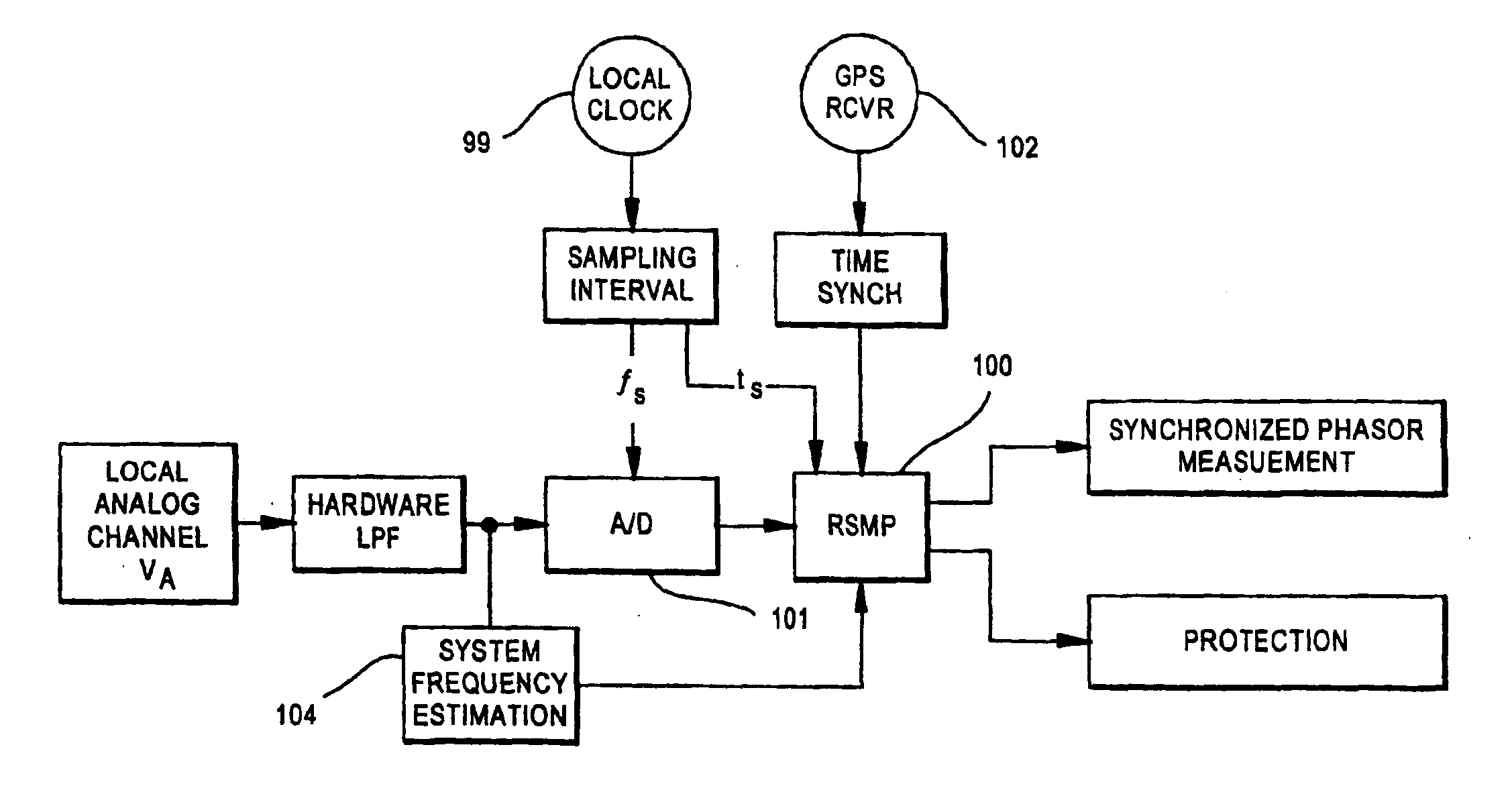
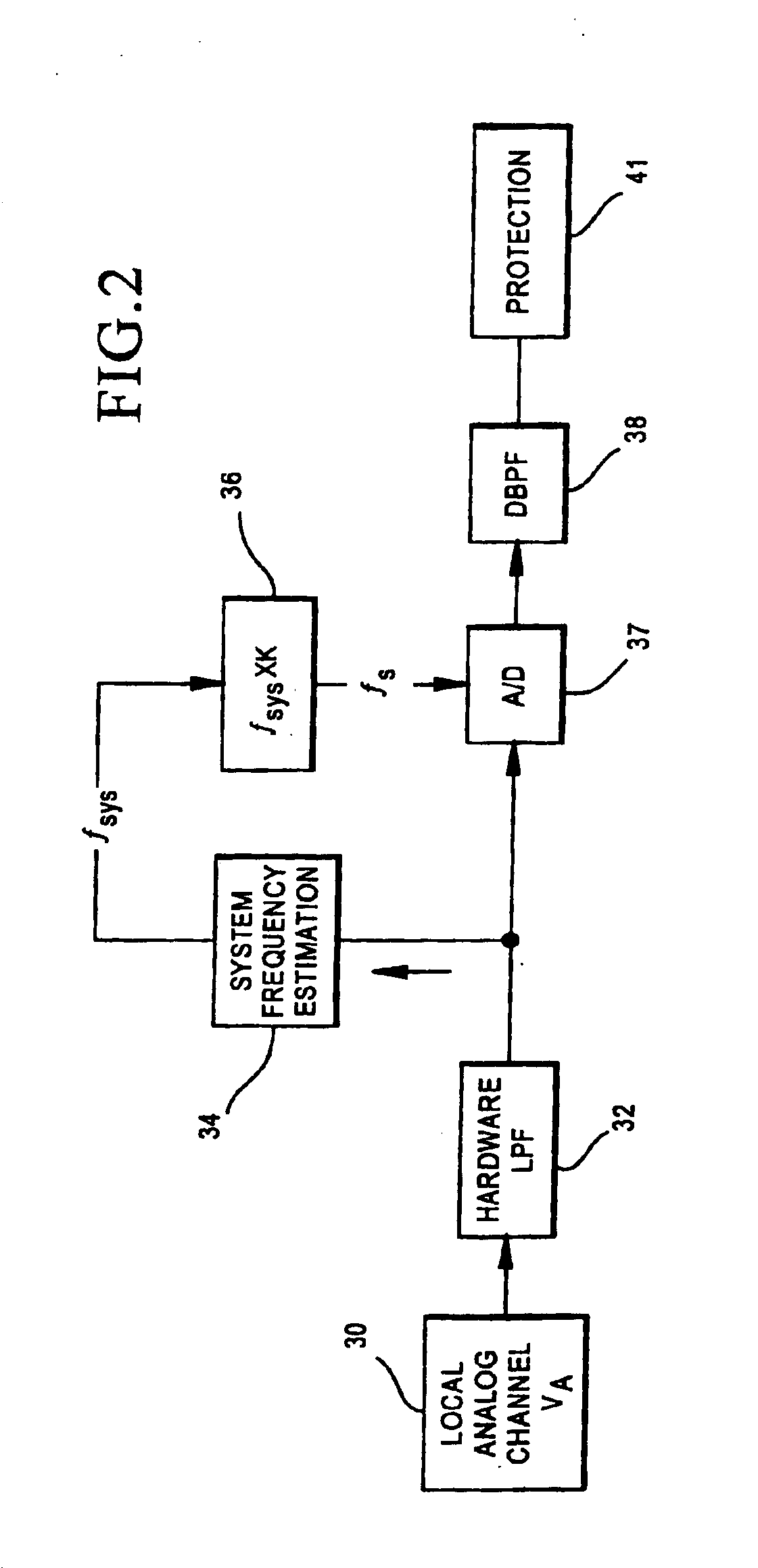
The relay system obtains voltage and current values from a power line and uses a first sampling element to sample the voltage and current values at selected intervals of time. The resulting sampled signals are used for power system-wide protection, control, monitoring and metering. The sampled signals are then resampled at a rate which is a selected multiple of the power system frequency. The results of the resampling are used by processing circuitry for protection functions including fault determinations.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
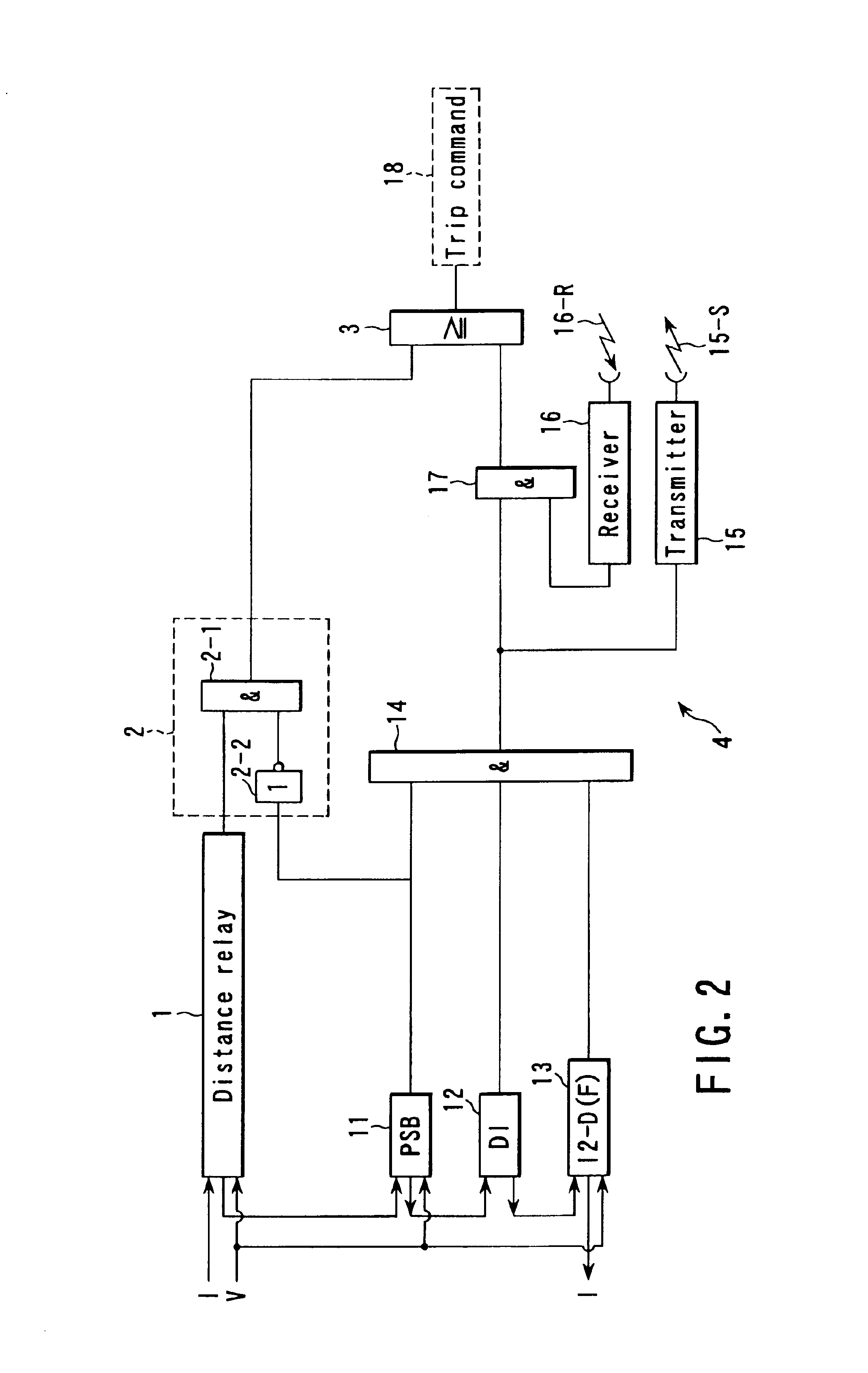
Digital protective relay system
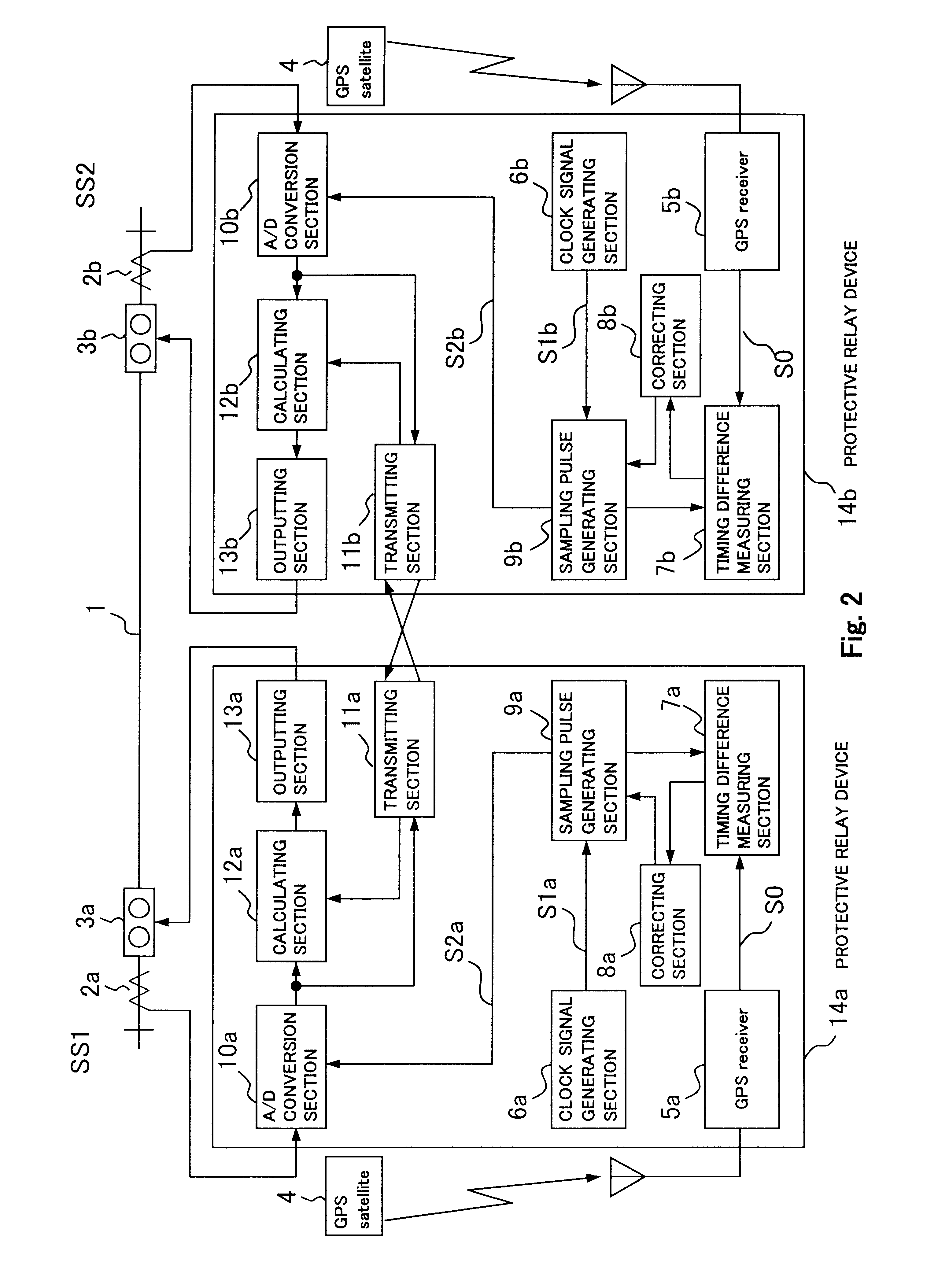
InactiveUS6678134B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceEmergency protective arrangement detailsDigital protective relayTime lag
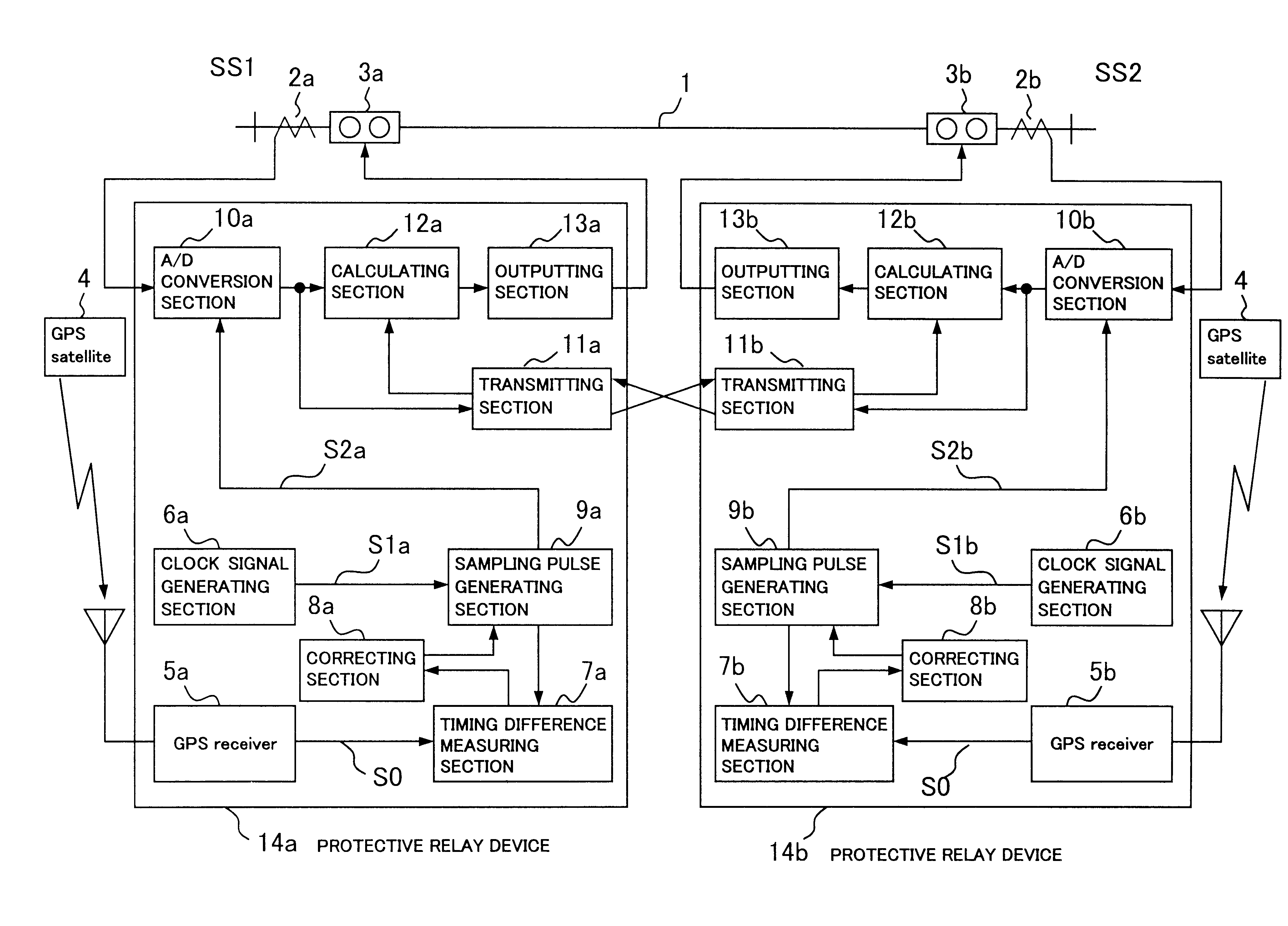
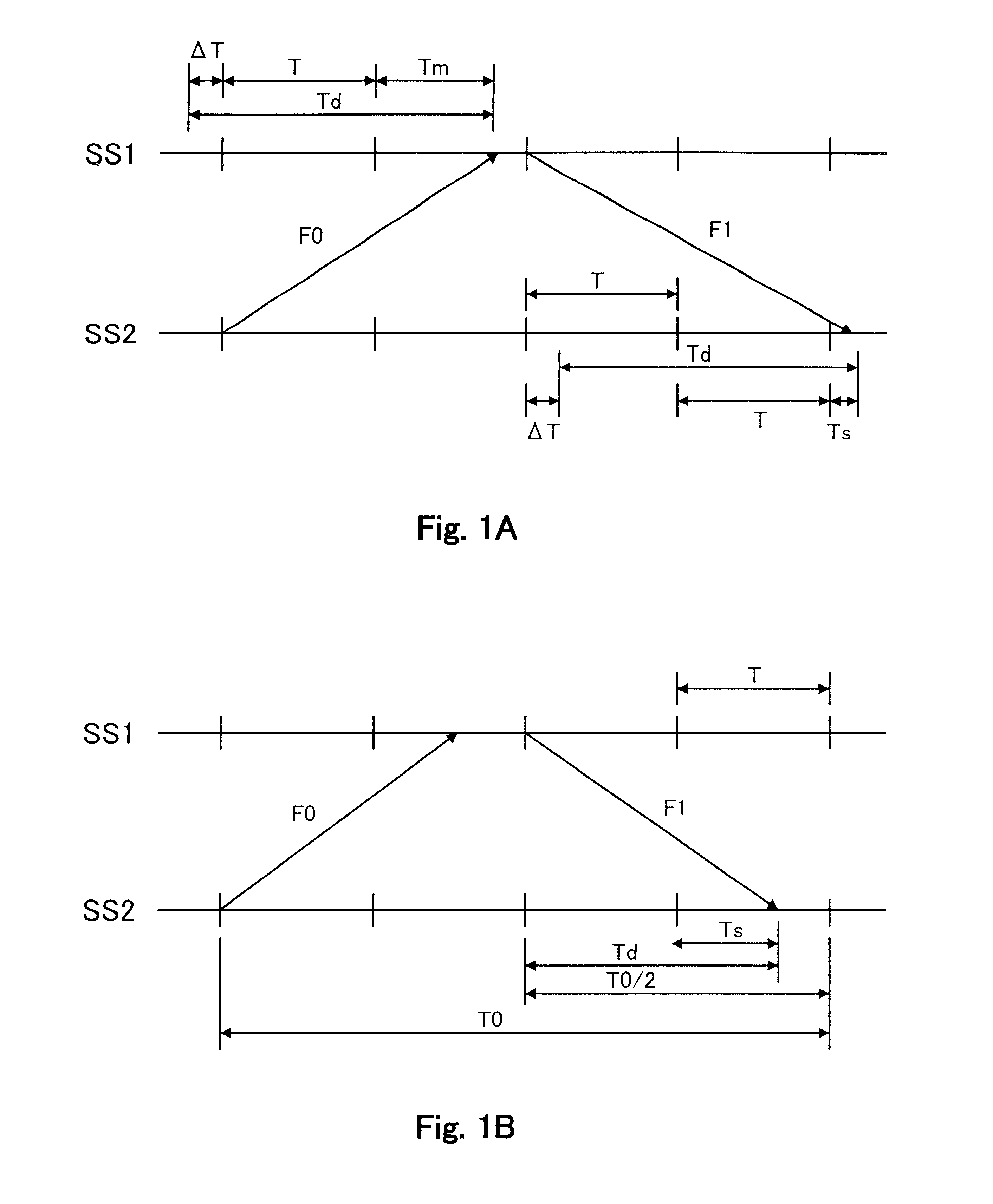
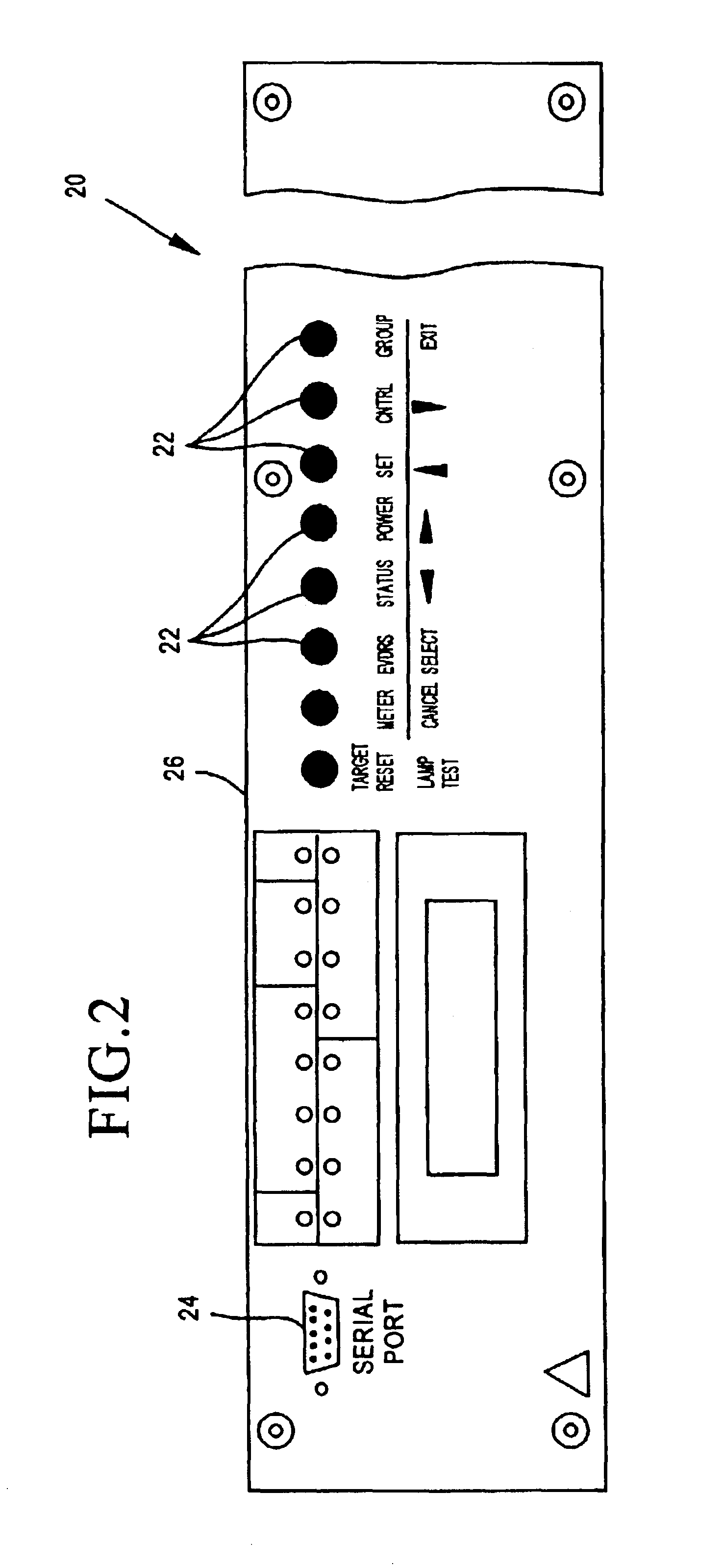
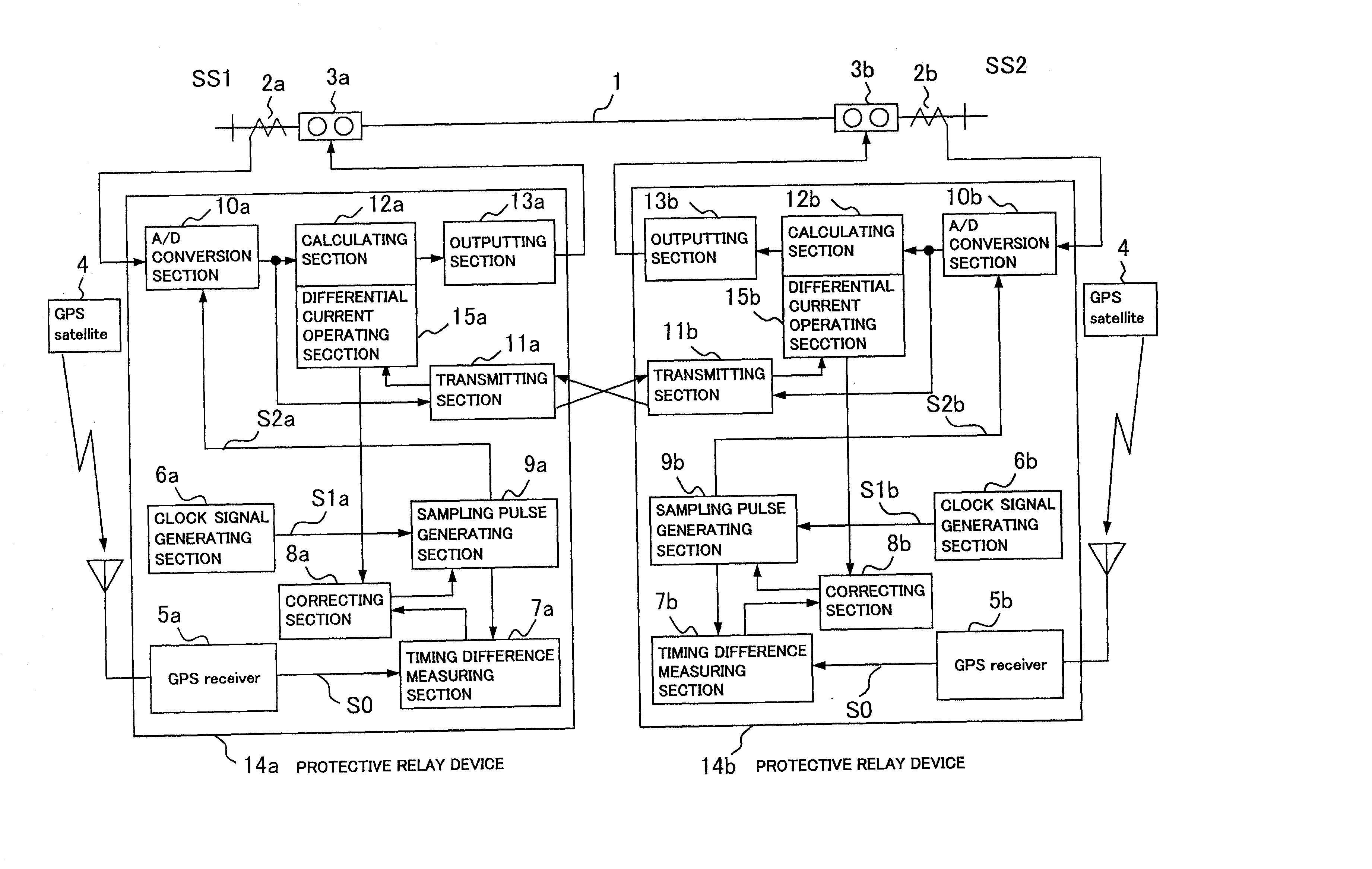
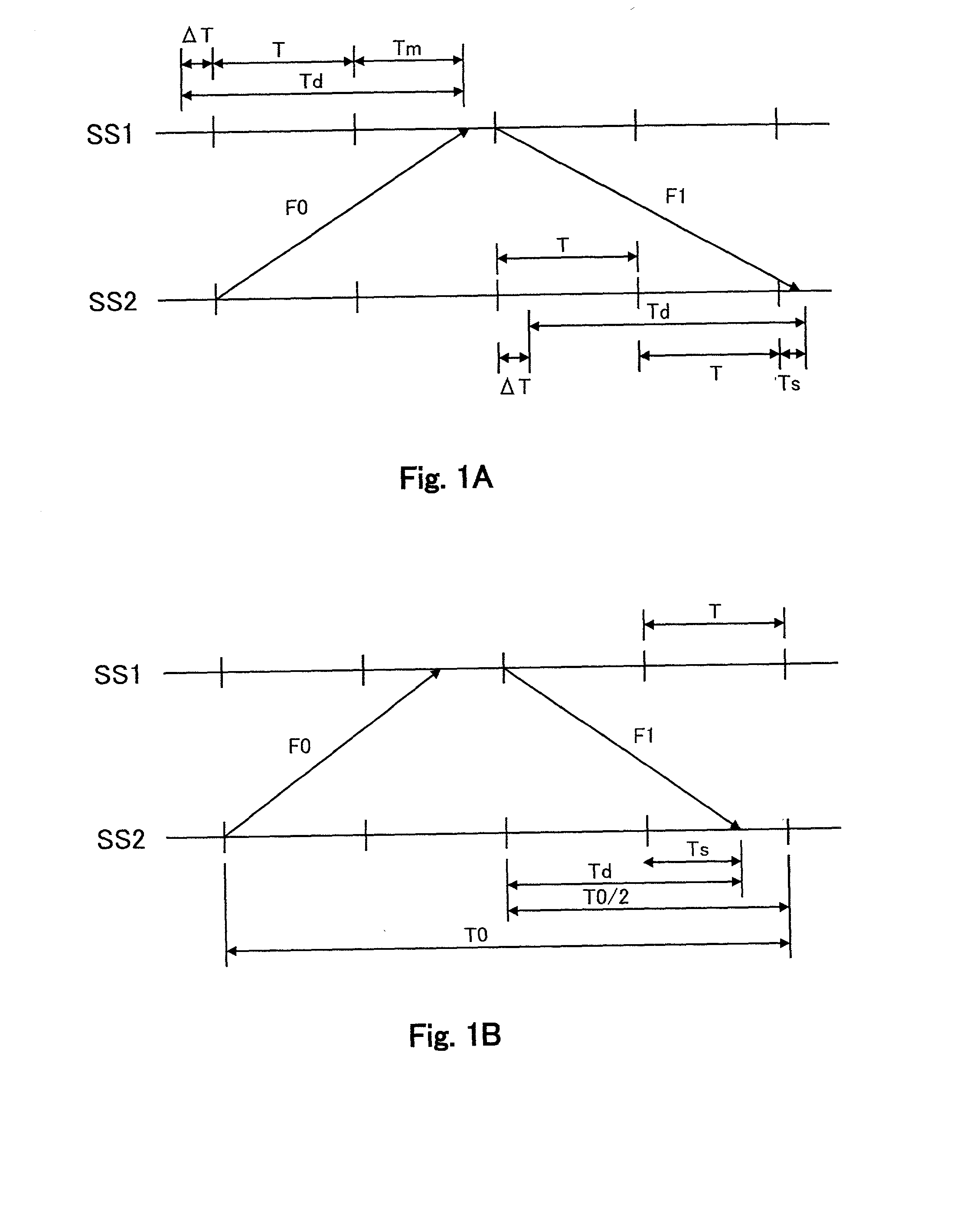
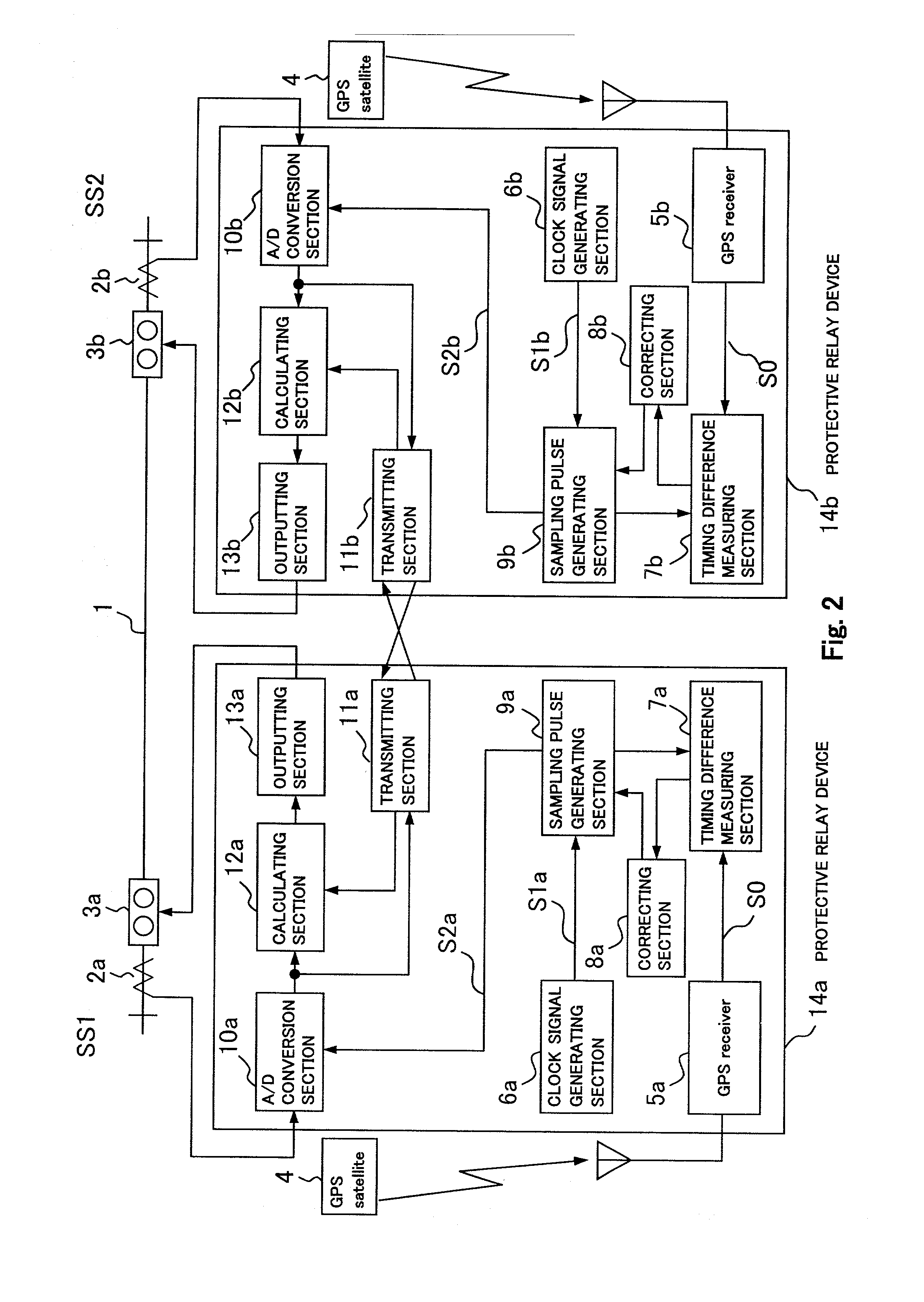
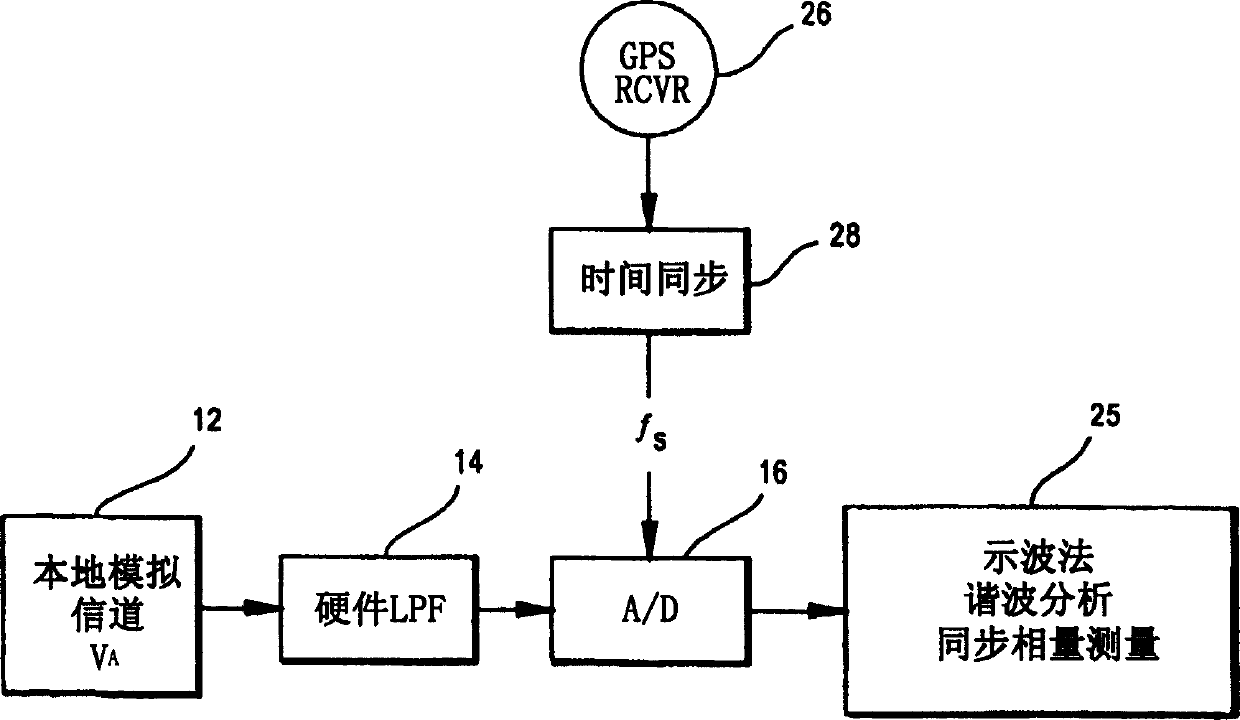
A digital protective relay system is capable of making sampling timing the same among plural protective relay device which operate independent from each other by using a signal from a GPS satellite. The sampling timing is made the same regardless of the time lag from which it is sent downstream with the concomitant transmission delay time in the case of data communications, or regardless of the time lag from which it is sent upstream.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Bus total overcurrent system for a protective relay
InactiveUS6839210B2Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDigital protective relayEngineering
A power system bus total overcurrent system is used with a part of a power system which includes two buses and first and second power line portions which extend between them. A protective relay system includes protective relays for each of the first and second power line portions, located near the two buses, wherein the relays determine the total current into and out of each bus. The bus total overcurrent system includes first and second communication lines between each pair of relays and another communication line which extends between the first and second communication lines. In a current balance arrangement, the relays measure difference current using the same communication line arrangement between the two pairs of relays to determine a fault condition. Fault determinations are made in each case by the protection algorithms from total and difference currents.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
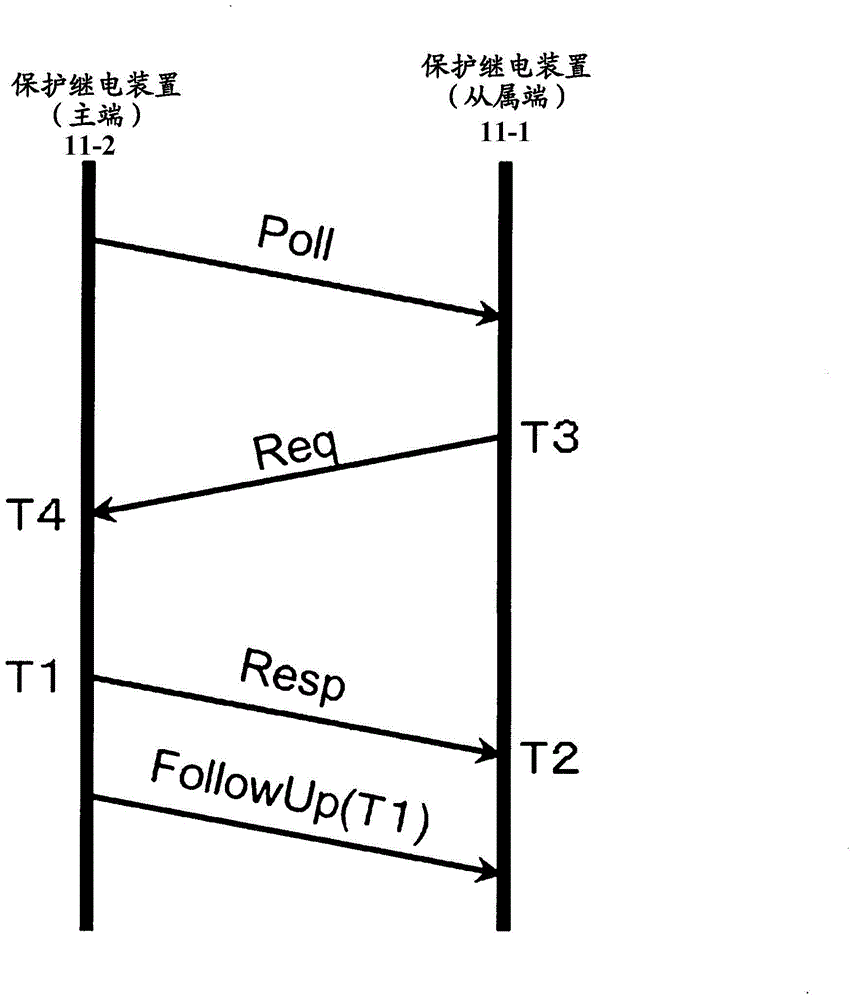
Multi-slave clock sampling value multi-interface synchronizing system based on IEEE1588
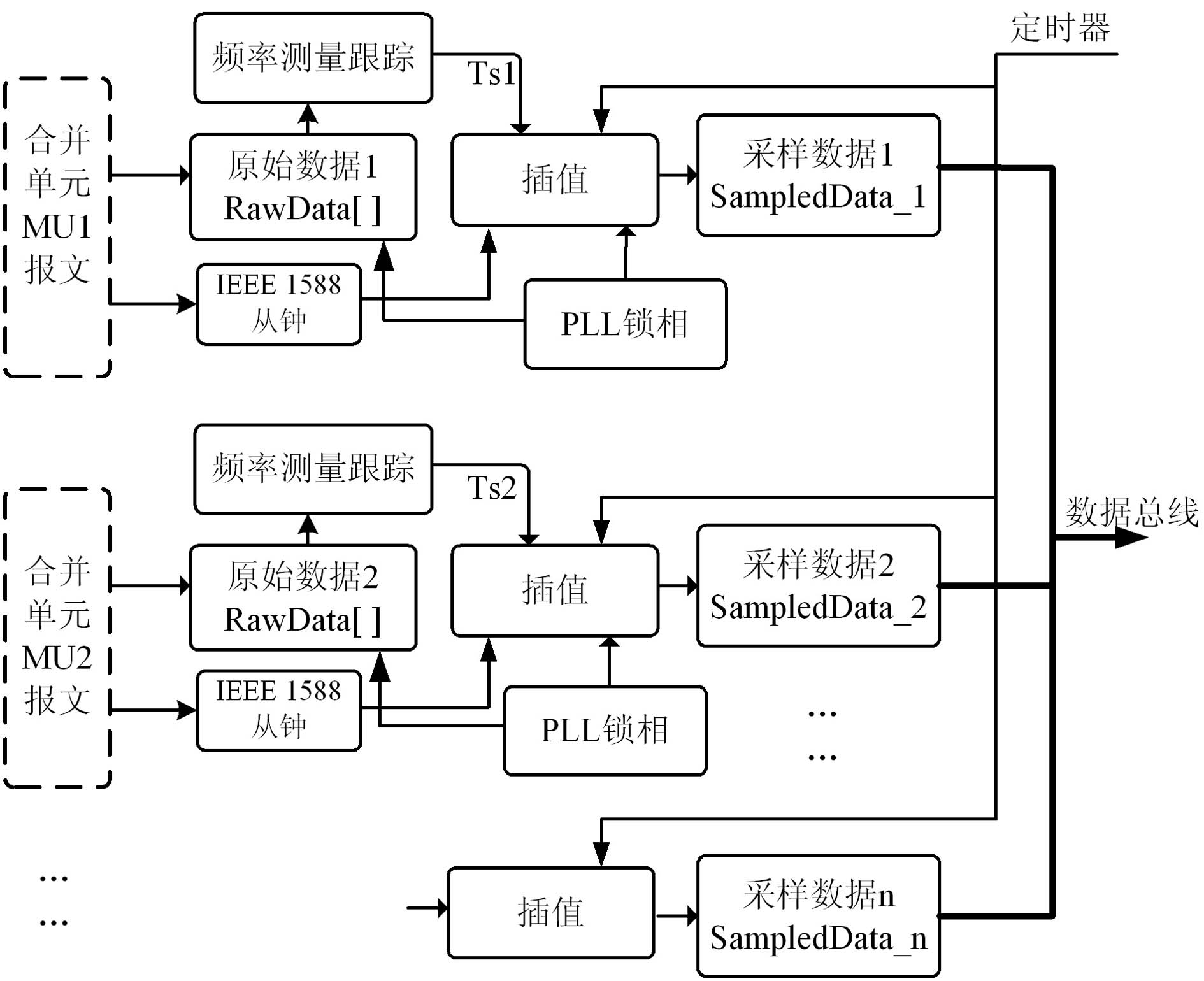
The invention discloses a sampling value multi-interface synchronizing system based on IEEE1588, which is characterized by comprising a universal IEEE1588 clock interface and a universal multi-sampling value synchronizing interface, wherein the universal IEEE1588 clock interface is a communication receiving module provided with a plurality of IEEE1588 slave clock interfaces, and the number of theslave clocks can be automatically expanded according to the number of master clocks; and the universal multi-sampling value synchronizing interface is a communication interface which can form internetworking connection with merging units and comprises an Ethernet data receiving module, a software sampling and interpolating module, a phase-locked loop (PLL) module, a frequency tracking module and a multi-interface sampling value synchronizing module. The system of the invention can be used for electronic equipment requiring sampling synchronization, such as a digital protective relay device, an electric energy meter, an electric energy quality monitoring device and the like, thereby providing a convenient solution for the problem that the sampling value internetworking transmission in the prior art depends on the global sampling synchronous source.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +1
Primary cut-out state monitoring method
The invention discloses a primary cut-out state monitoring method, which comprises following steps: using existing fault recording apparatus and digital protective-relay device in converting station automatic system to record normal divided brake current decay process; using recorded data to calculate circuit breaker opening time; then estimating circuit breaker state according to opening time of circuit breaker and opening time trend in some time.
Owner:苏盛 +2
Digital protective relay for power systems with operator-initiated record keeping capability
InactiveUS6920028B2Parameter calibration/settingEmergency protective arrangement detailsDigital protective relayRecord keeping
A digital protective relay for power systems includes a memory location for storing information entered by an operator concerning the operation of the relay. Conventional reports of the relay will include a reference to such operator-entered information. This information will include particular actions taken by the operator relative to the relay, as well as notes made by the operator on particular actions and / or entry of and changes to the relay settings. The entered information can be conveniently retrieved by the operator.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Digital protective relay system
InactiveUS20020057544A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceEmergency protective arrangement detailsDigital protective relayTime lag
A digital protective relay system is capable of making sampling timing the same among plural protective relay device which operate independent from each other by using a signal from a GPS satellite. The sampling timing is made the same regardless of the time lag from which it is sent downstream with the concomitant transmission delay time in the case of data communications, or regardless of the time lag from which it is sent upstream.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
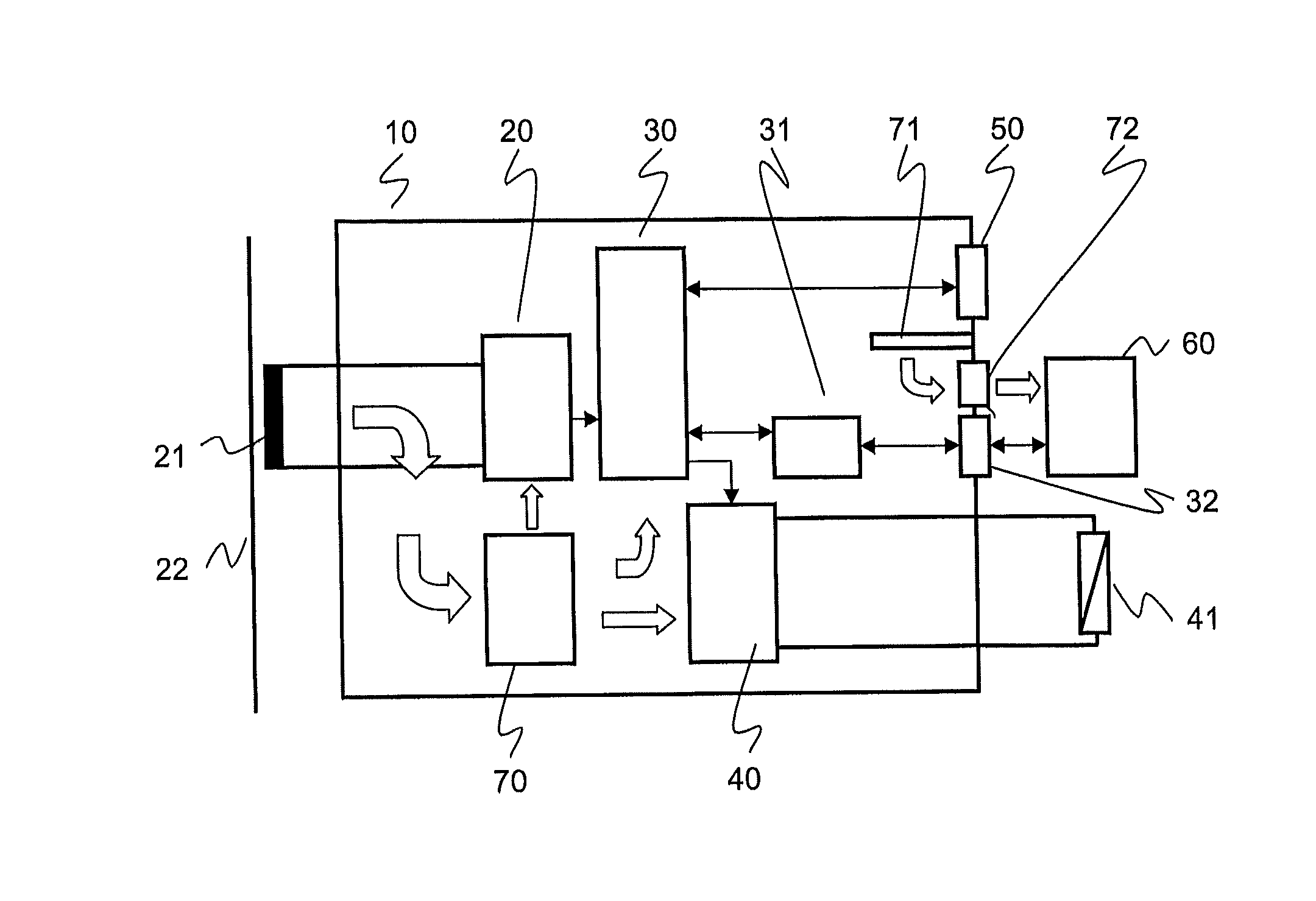
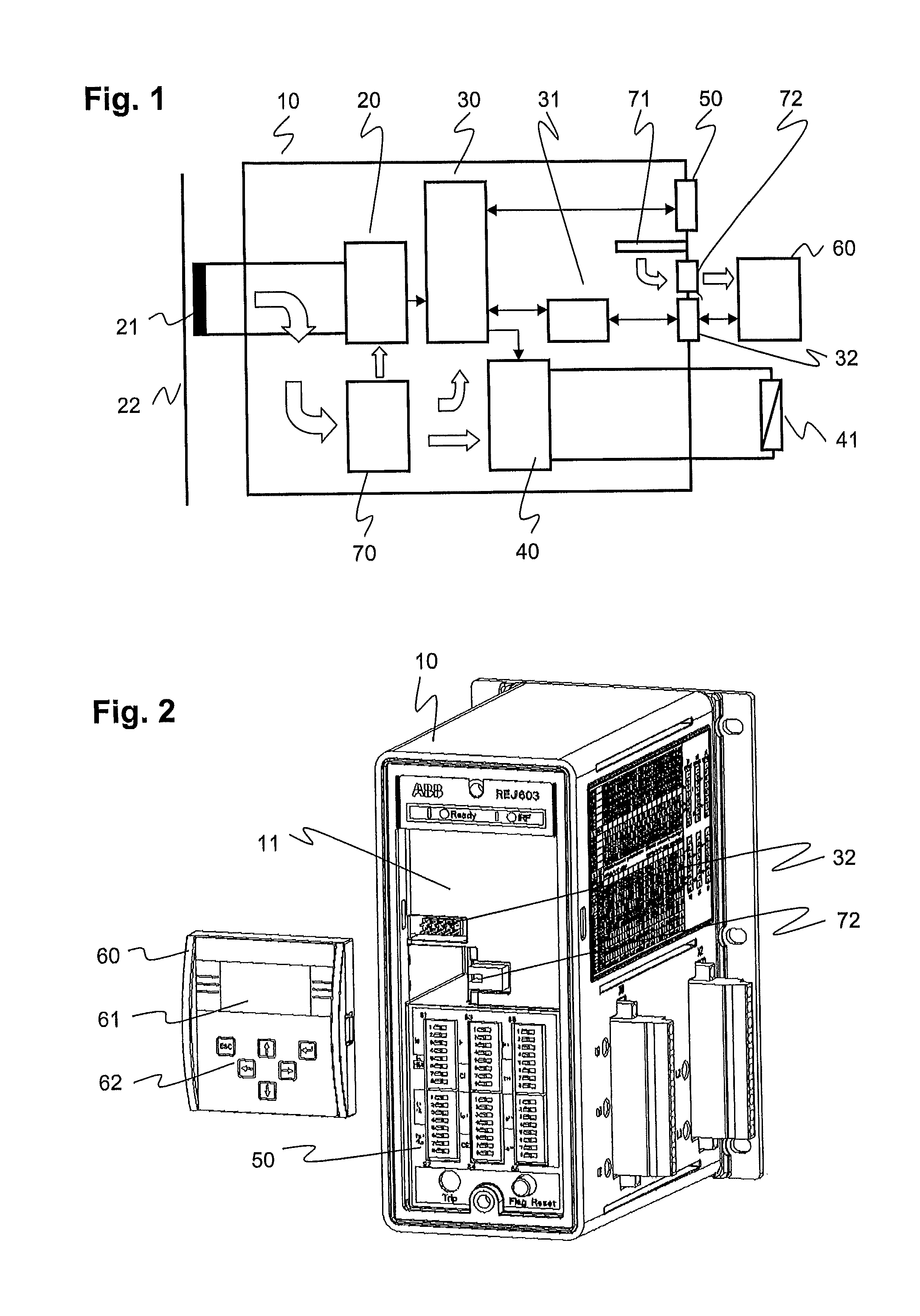
Protective relay and human-machine interface therefor
ActiveUS20100296221A1Parameter calibration/settingCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsHuman–machine interfaceDelayed time
A fully operational digital protective relay or Intelligent Electronic Device (IED) are provided for protecting electrical equipment of a power distribution system. The relay includes an input module, a processing module and an output module. Signals received from current transformers connected to the input module are evaluated by the processing module, and in reaction thereto, trip signals can be output to an actuator of a circuit breaker via the output module. A base Human Machine Interface (HMI) enables a user to enter operating parameters such as a delay time or nominal current to the processing module. Optionally, a further HMI may be attached to the protective relay and connected, via a suitable interface for data exchange, to the processing module for the purpose of displaying protection-related information to a user. This further HMI is both optional and detachable. For example, the further HMI can be repeatedly attached to and detached from the protection device. The detachable HMI provides for an increased flexibility in the use of the protective relay, as a user may adapt its interfacing capability by acquiring a detachable HMI of the type and at the time that best suits his evolving needs.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Protective relay with synchronized phasor measurement capability for use in electric power systems
InactiveCN1646927AMeasurement using ac-dc conversionEmergency protection detectionDigital protective relayPhasor measurement unit
The relay system obtains voltage and current values from a power line and uses a first sampling element to sample the voltage and current values at selected intervals of time. The resulting sampled signals are used for power system-wide protection, control, monitoring and metering. The sampled signals are then resampled at a rate which is a selected multiple of the power system frequency. The results of the resampling are used by processing circuitry for protection functions including fault determinations.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Information dependent data transmission for pilot protective relays
InactiveUS6686857B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital protective relayWave shape
Owner:ABB INC
Protective relay for power systems having fault distance measurement filter logic
ActiveUS7345862B2Improve performanceEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDigital protective relayControl circuit
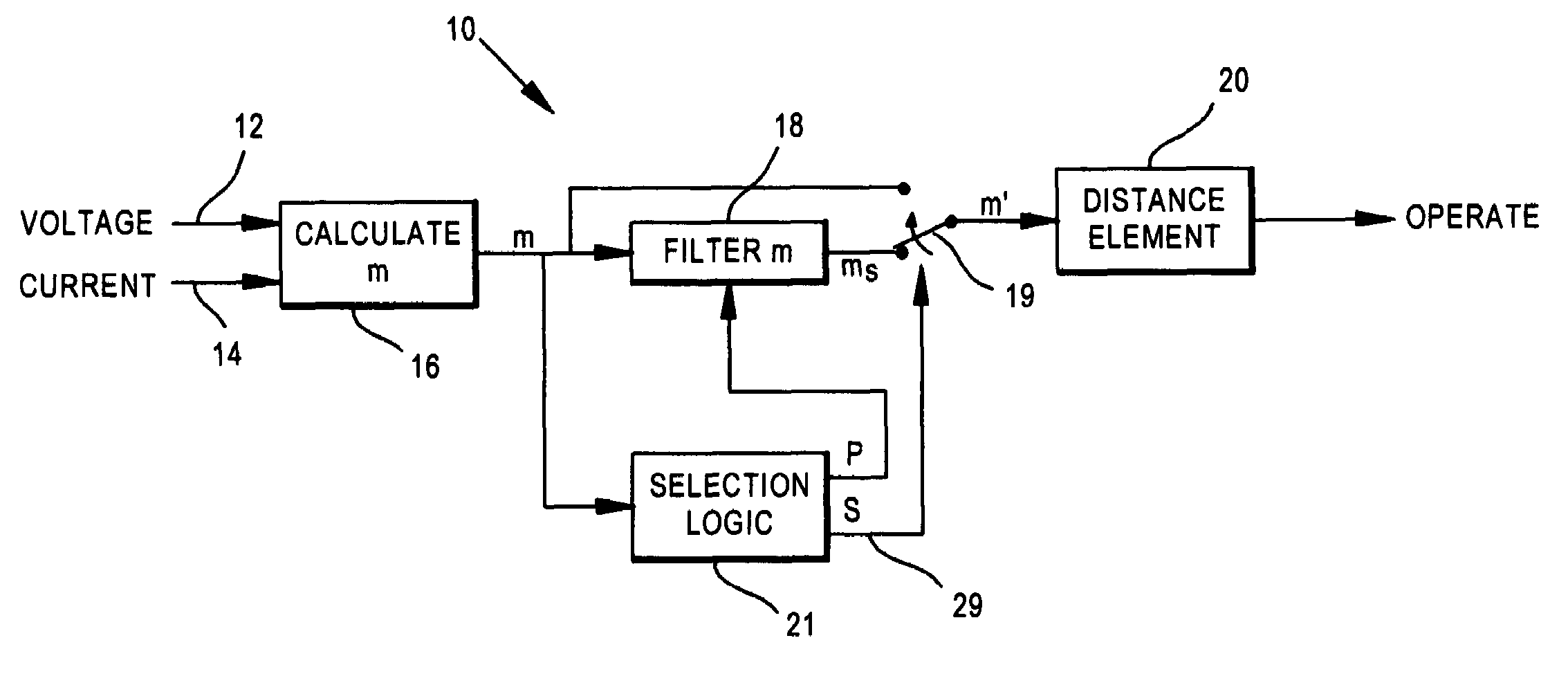
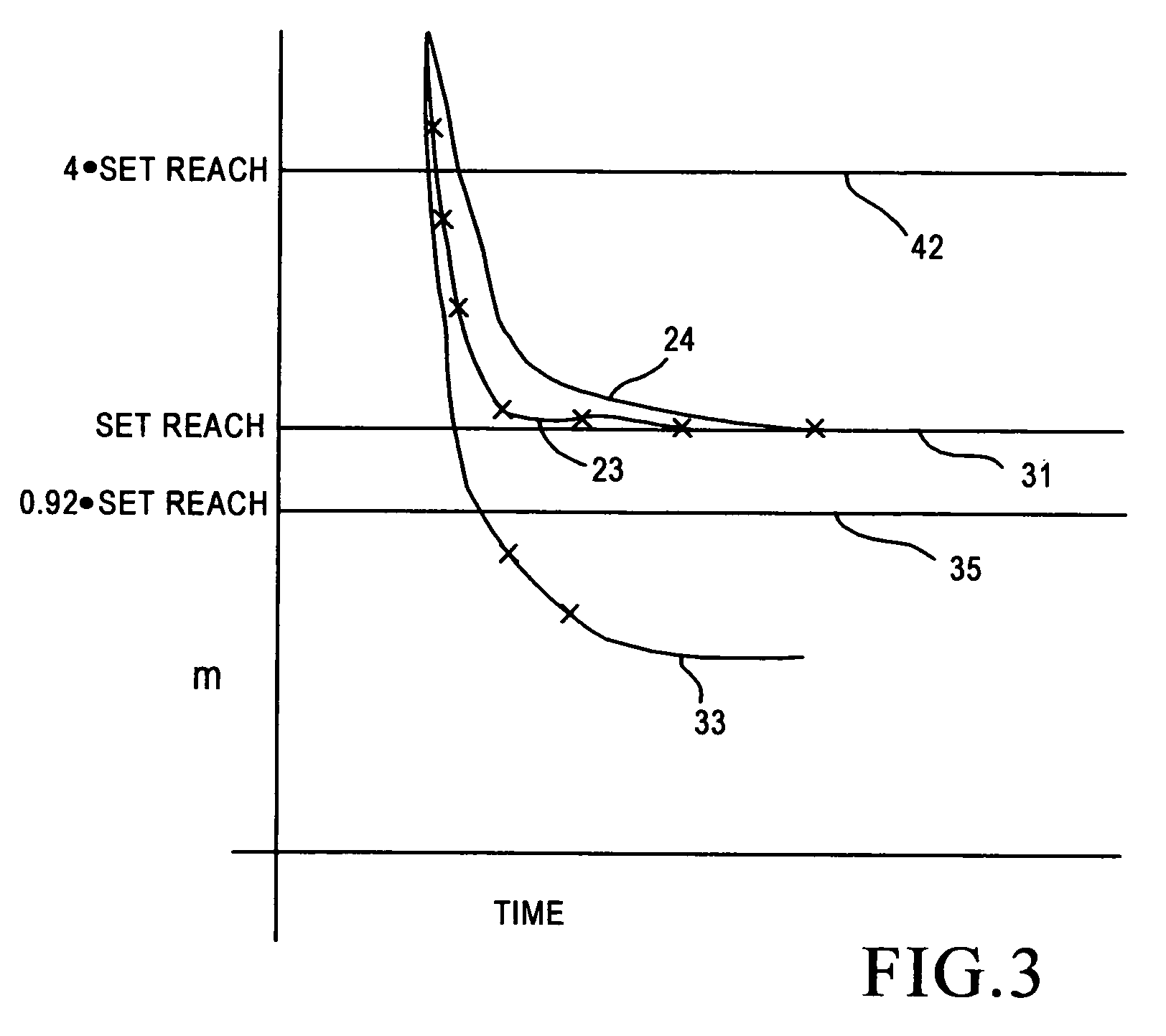
The system is used in a distance-type protective relay which includes a calculation circuit responsive to voltage and current values from a power line to produce a quantity which is analogous to the distance between the relay and a fault on the line, referred to as an m quantity. This quantity is then applied to a distance element / circuit for comparison of said quantity with a setting reach value for a zone one distance protection to determine whether the fault is within zone one protection. The system includes a filter circuit which filters the quantity before it reaches the distance element, resulting in a smoothing of said quantity and rejection of noise therefrom. The system further includes a control circuit which determines whether the filter is to be used in the system in a particular situation, depending upon whether when the value of the quantity is above a selected percentage of the setting reach value.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Digital protection relay, digital protection relay test device, and digital protection relay test method
InactiveUS20150200534A1Safe and easy testElectrical testingArrangements responsive to excess currentDigital protective relayElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Digital protective relay device and data transmission device for the same
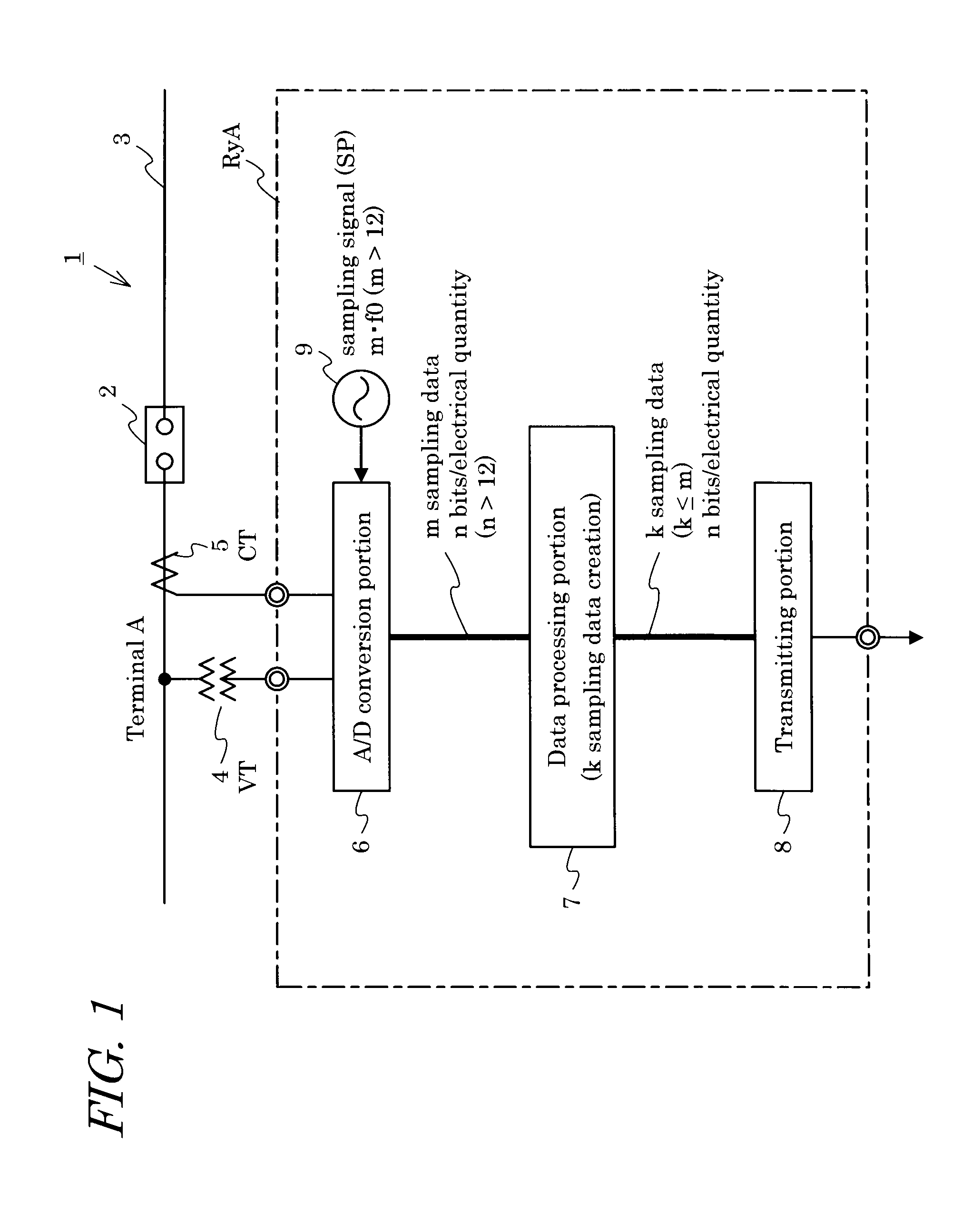
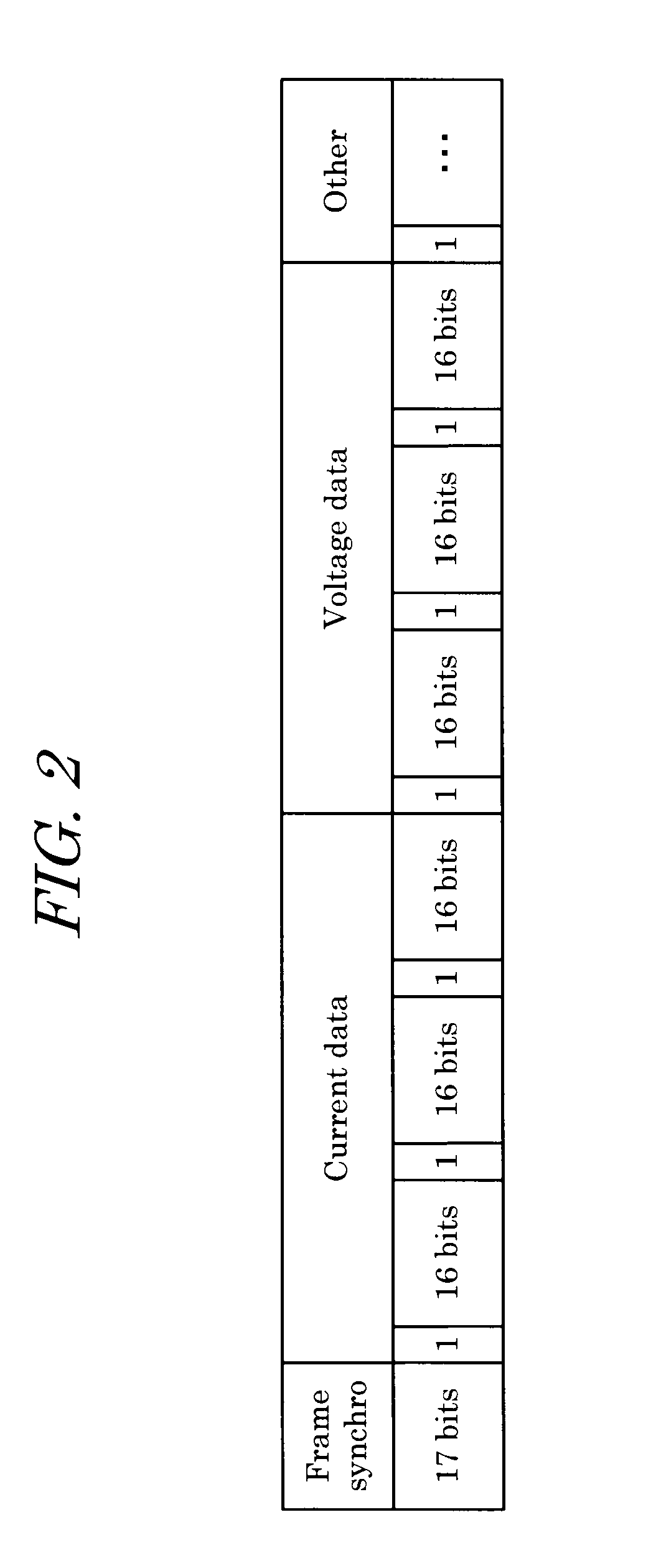
InactiveUS20110013676A1High-precision and highly functionalMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlDigital dataDigital protective relay
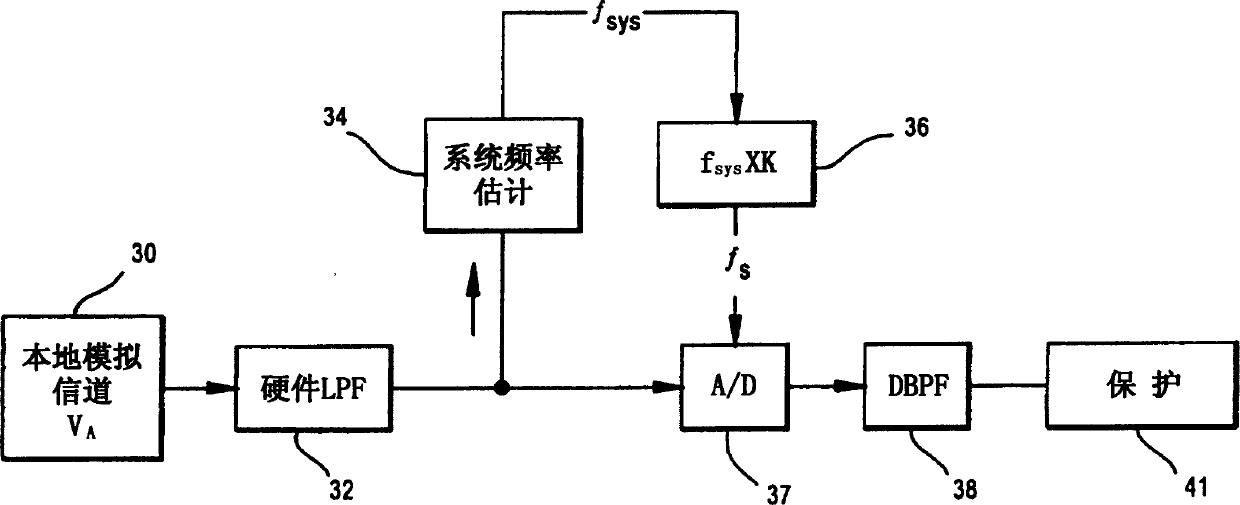
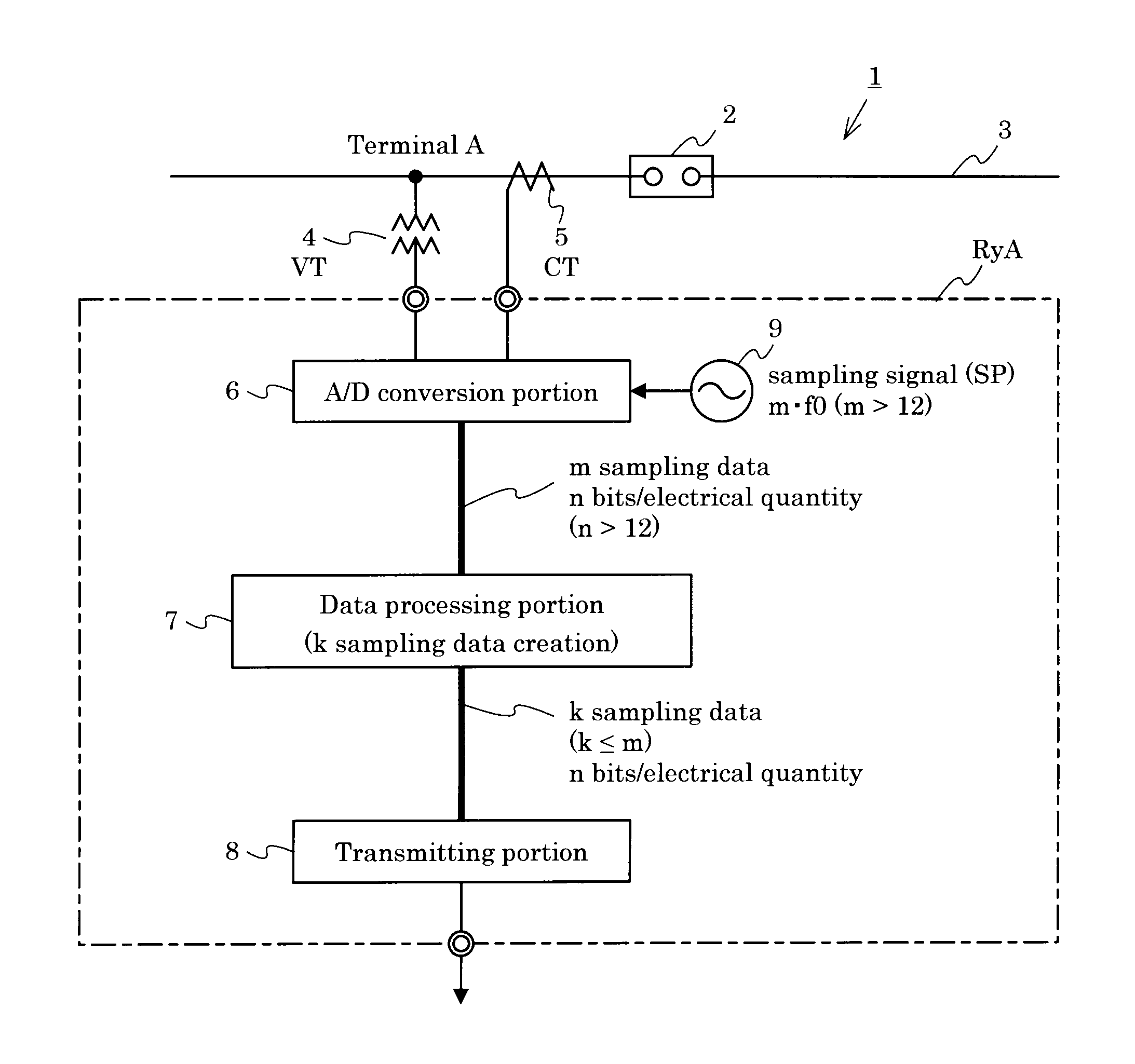
Provided is a high-precision and highly functional digital protective relay device and a data transmission device for a digital protective relay device, by enabling transmission of large amounts of system electrical quantity data. The data transmission device for a digital protective relay device, the transmission device comprising: an analog / digital conversion portion 6, which, after sampling a system electrical quantity signal acquired from an electric power system at m times the fundamental frequency f0 (m>12) thereof, performs conversion into n-bit digital data (n>12); a data processing portion 7, which converts m sampling data of n bits with frequency m·f0, obtained by the analog / digital conversion portion, into k sampling data with frequency k·f0 (k≦m) at or below the former frequency; and a transmitting portion 8, which transmits k sampling data obtained by the data processing portion to another protective relay device in a prescribed transmission format.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
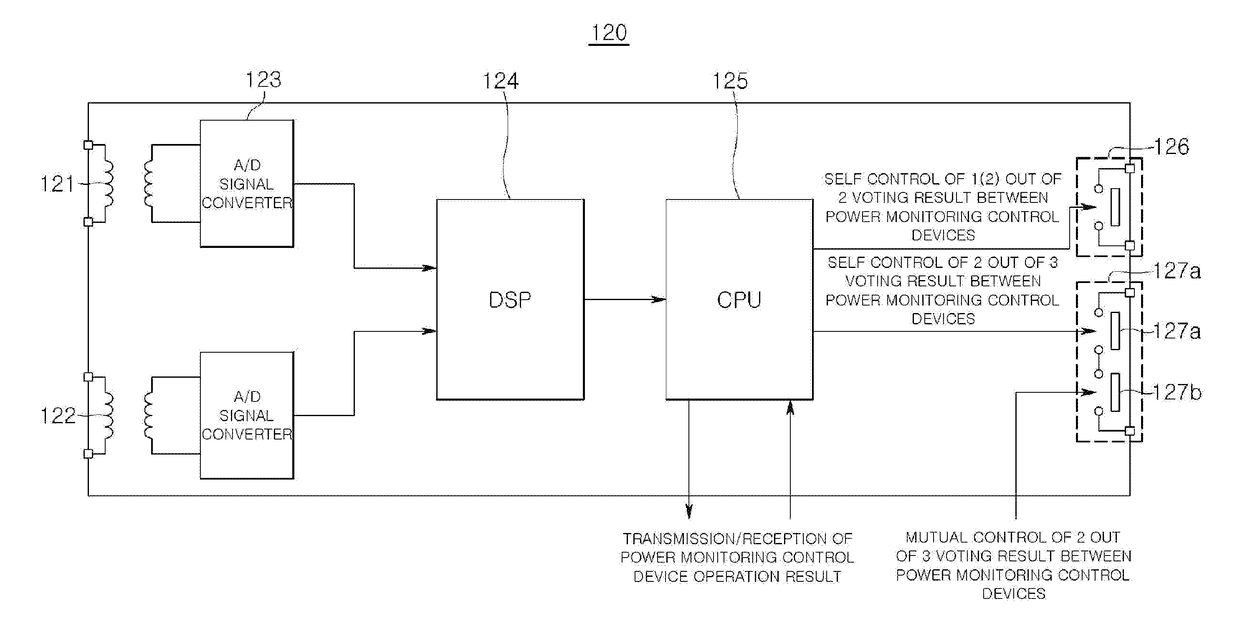
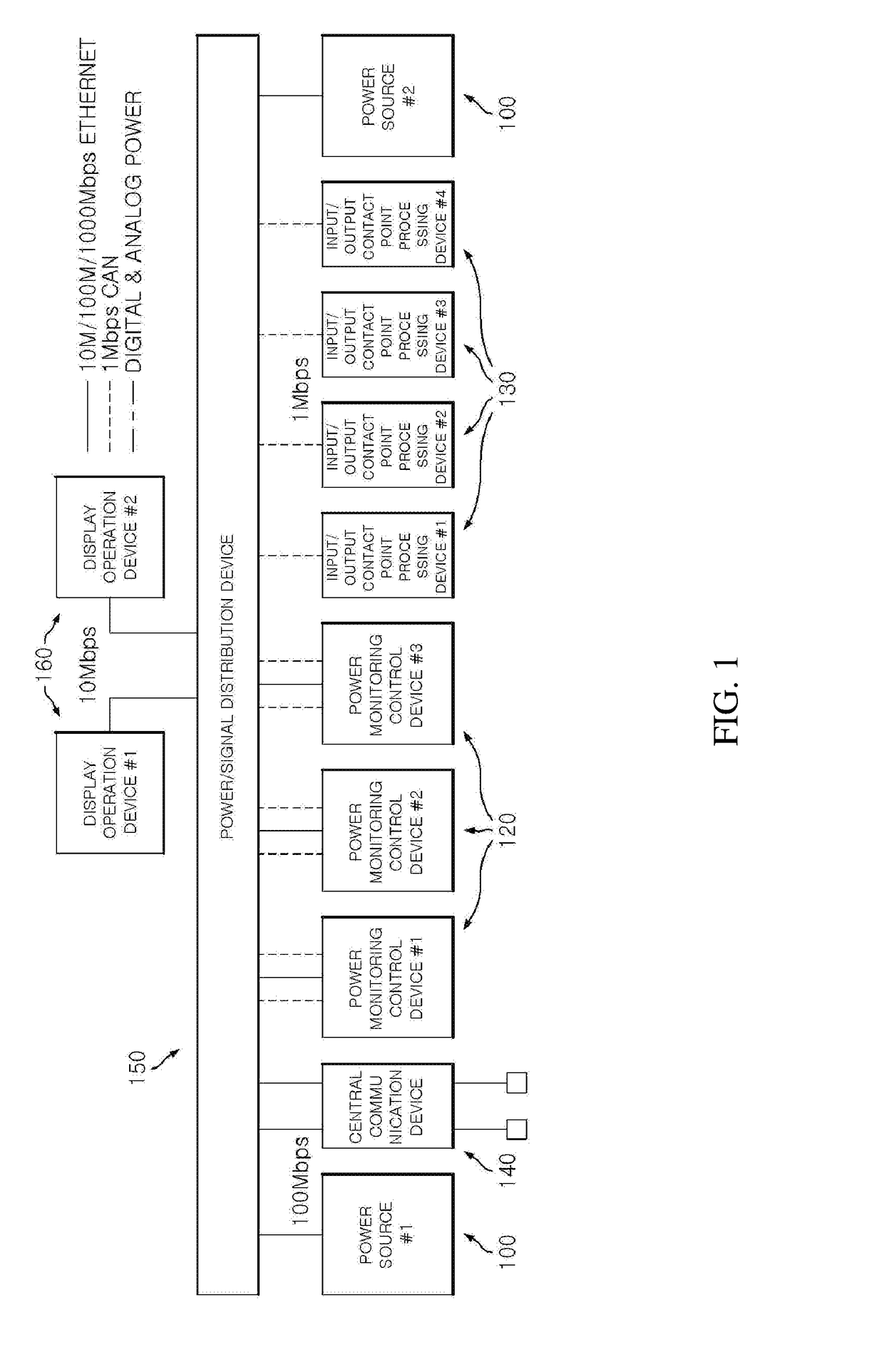
Triple redundant digital protective relay and operating method therefor
ActiveUS20170365992A1Avoid malfunctioningReduce stepsBus-bar/wiring layoutsEmergency protective arrangement detailsDigital protective relayStructure of Management Information
Provided are a triple redundant digital protective relay and an operating method therefor. The triple redundant digital protective relay according to the present invention includes: three power monitoring control devices which have a triple redundant structure and control a circuit breaker for separating a failed power system based on a 2 out of 3 voting using real-time mutual data communication; and a central communication device which acquires data related to an operating state of the power system from the three power monitoring control devices and manages the acquired data related to the operating state of the power system.
Owner:YPP
Protective relay system
InactiveUS6873508B2Eliminate pointArrangements responsive to excess currentDigital protective relayNegative phase
In a protective relay system according to an aspect of the present invention, a direction of a fault is correctly determined during system oscillation using one of a negative-phase-sequence relay and a zero-phase-sequence relay. A circuit breaker is tripped only when an internal fault is determined at both terminals to be protected using a carrier signal. Thus, even though a fault occurs during system oscillation, the circuit breaker can be tripped against the internal fault.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Visual dynamic monitoring system for operating states of protective relay system
InactiveUS20130282323A1Improve reliabilityAvoid powerResistance/reactance/impedenceEmergency protection data processing meansTime informationDigital protective relay
A visual dynamic monitoring system for operating states of a protective relay system, which is applied to a computer based relay includes: collecting information of a voltage input circuit & a current input circuit and internal hardware & software of protection relay, as well as a tripping and closing circuit, to obtain real-time informations completely reflecting operating states of the protective relay system; analytically calculating the real-time information mentioned above according to the designed protection principle, forming logical relations having a time sequential characteristic among the real-time information with a result by the analytically calculating; and dynamically displaying the operating states of the protective relay system, so as to providing a supporting data for implementing an evaluation of the operating states of the protective relay system.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIHAO AUTOMATION CO LTD
Protective relay for power systems having fault distance measurement filter logic
ActiveUS20050094335A1Improve performanceEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDigital protective relayEngineering
The system is used in a distance-type protective relay which includes a calculation circuit responsive to voltage and current values from a power line to produce a quantity which is analogous to the distance between the relay and a fault on the line, referred to as an m quantity. This quantity is then applied to a distance element / circuit for comparison of said quantity with a setting reach value for a zone one distance protection to determine whether the fault is within zone one protection. The system includes a filter circuit which filters the quantity before it reaches the distance element, resulting in a smoothing of said quantity and rejection of noise therefrom. The system further includes a control circuit which determines whether the filter is to be used in the system in a particular situation, depending upon whether when the value of the quantity is above a selected percentage of the setting reach value.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
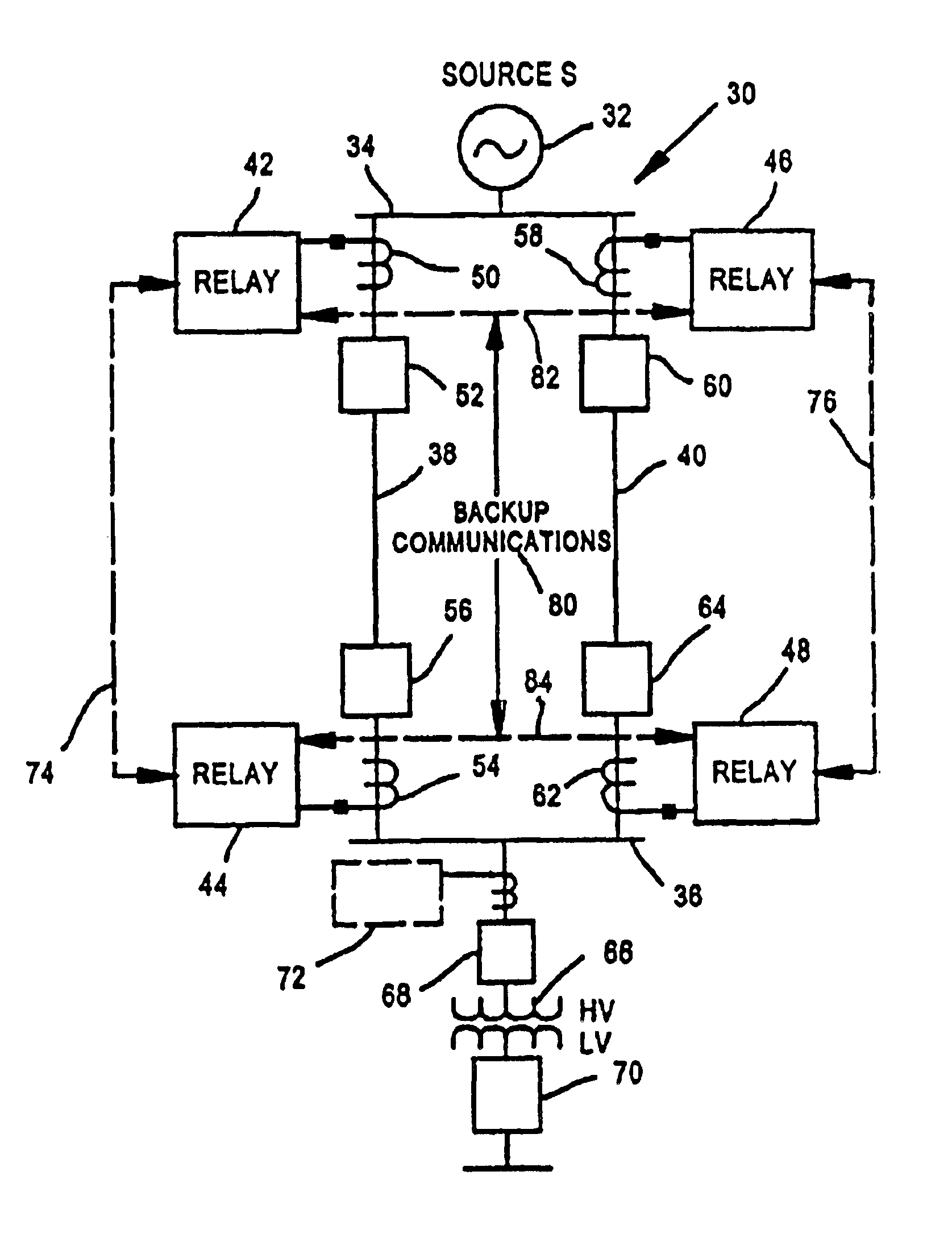
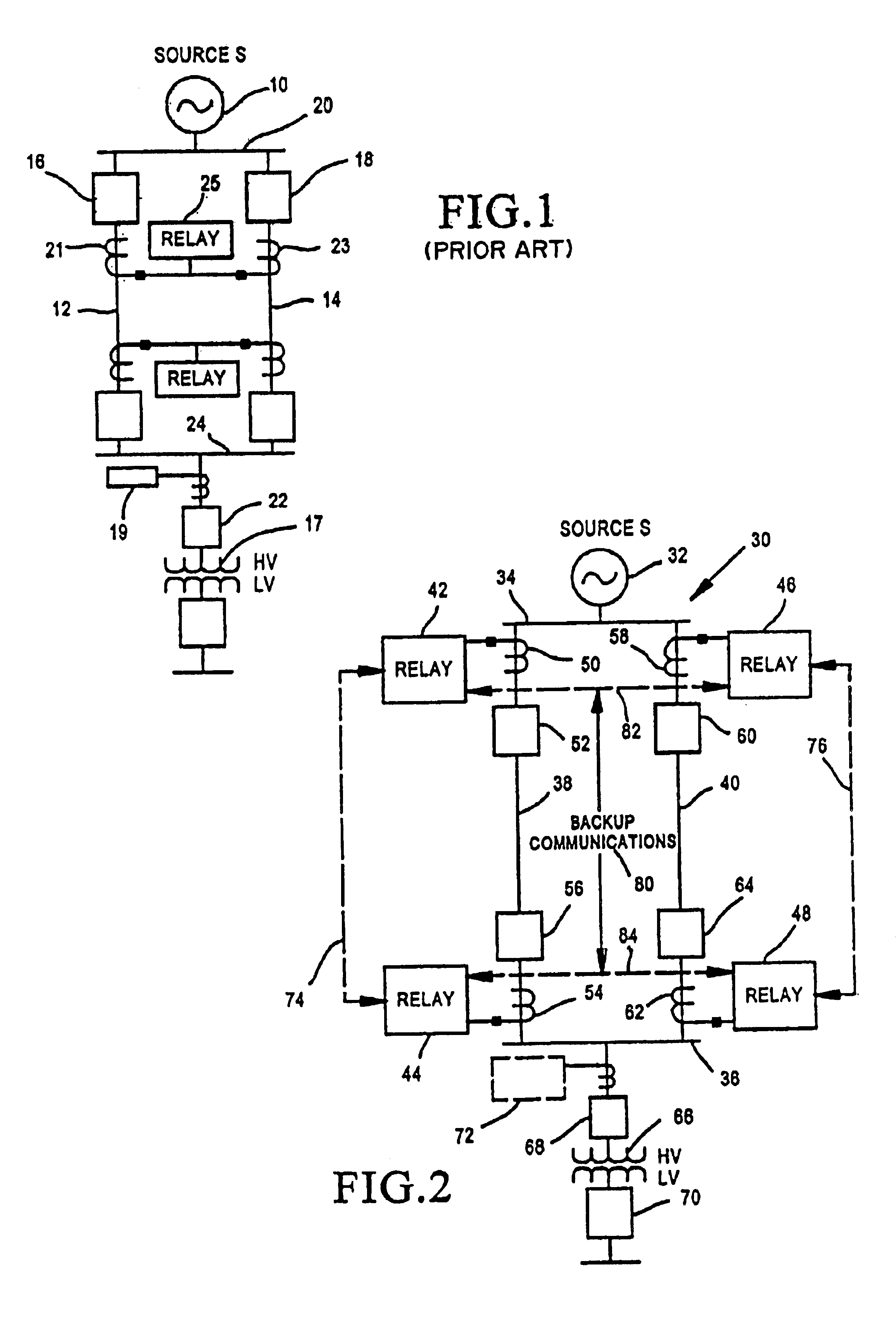
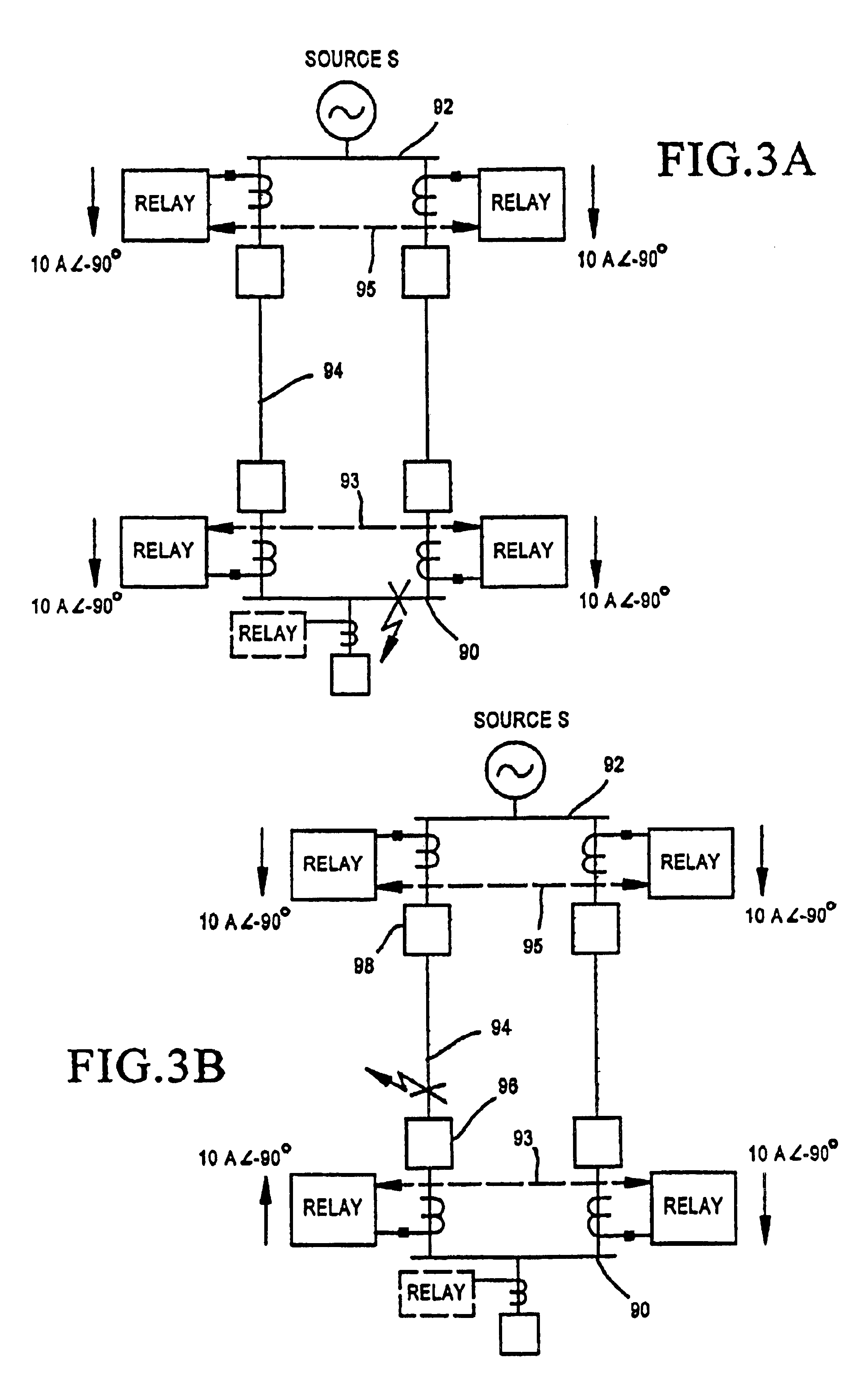
Relay protection device
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Protection system for electrical power distribution system using directional current detection and logic within protective relays
InactiveCN103155328AReduce consumptionEmission reductionSteering by propulsive elementsPropulsive elementsDigital protective relayPower flow
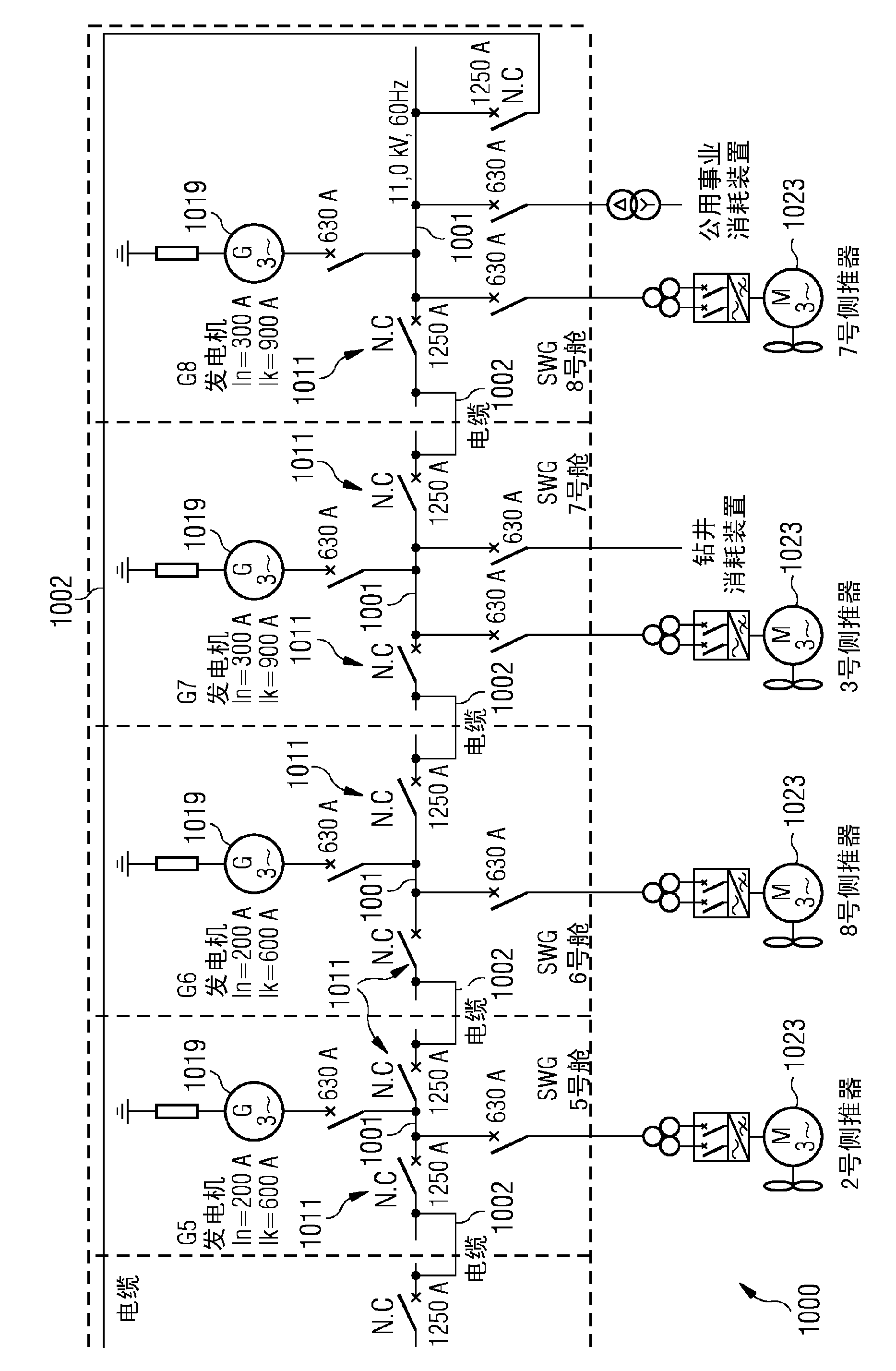
It is described a power distribution system for a dynamically positioned vessel. The power distribution system comprises: a plurality of busses (101,103,105,107) comprising a first bus (103) to which a load (123) is connectable; a plurality of switches (109,111,113,115) comprising a first switch (111) and a second switch (113), wherein the plurality of busses is connected via the plurality of switches in an interjacent manner to form a ring (117), the first bus is connected in between the first switch and the second switch. The power distribution system is configured to open the first switch and concurrently open the second switch, if a first current (149) flowing via the first switch in a direction towards the first bus is above a predetermined current threshold for longer than a predetermined time duration and a second current (143); flowing via the second switch in a direction towards the first bus is above the predetermined current threshold for longer than the predetermined time duration, thereby disconnecting the first bus from the ring while all other buses remain connected together. Further a method of power distribution and a vessel are provided.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
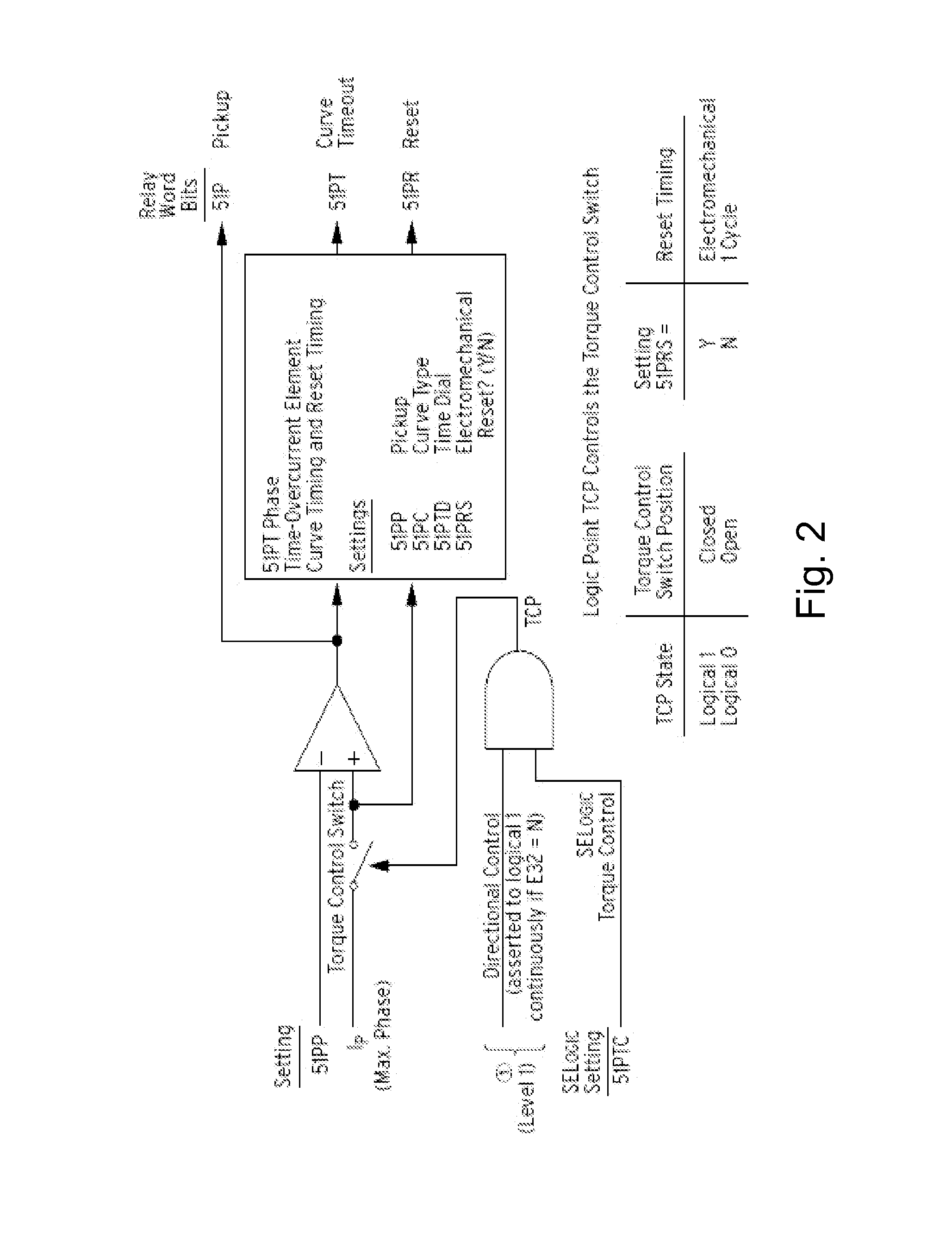
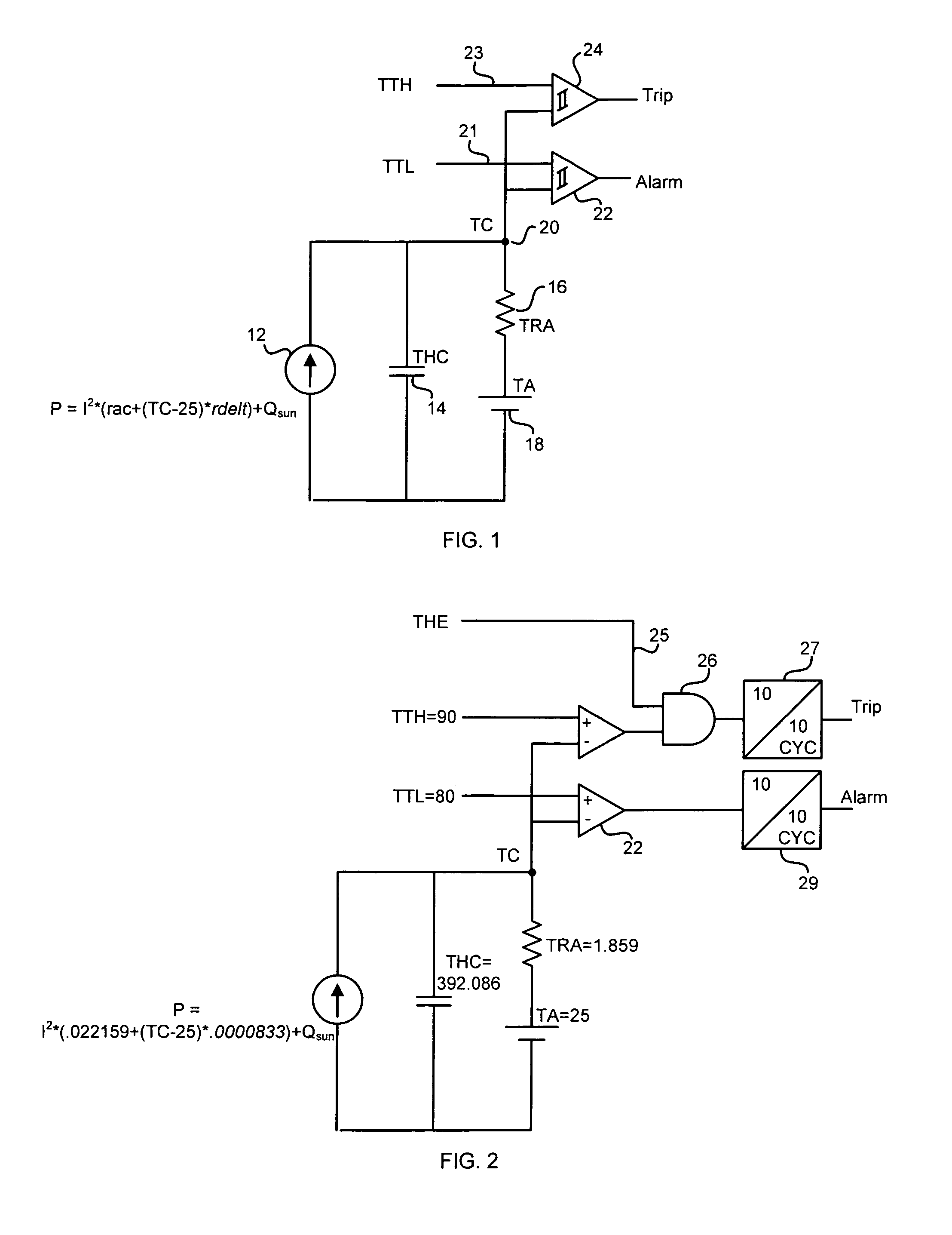
Distance protective relay using a programmable thermal model for thermal protection
ActiveUS7239496B2Parameter calibration/settingEmergency protective arrangements responsive to undesired changesDigital protective relayElectrical conductor
The system includes a distance protective relay for power lines which includes a logic capability which is responsive to settings entered into the relay by an end user to implement the value of those settings into stored thermal model equations which emulate the temperature of the power line conductor. The logic within the relay is organized and has the capability of receiving the setting values entered by the user and to use those in the logic equations to determine the temperature of the conductor.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
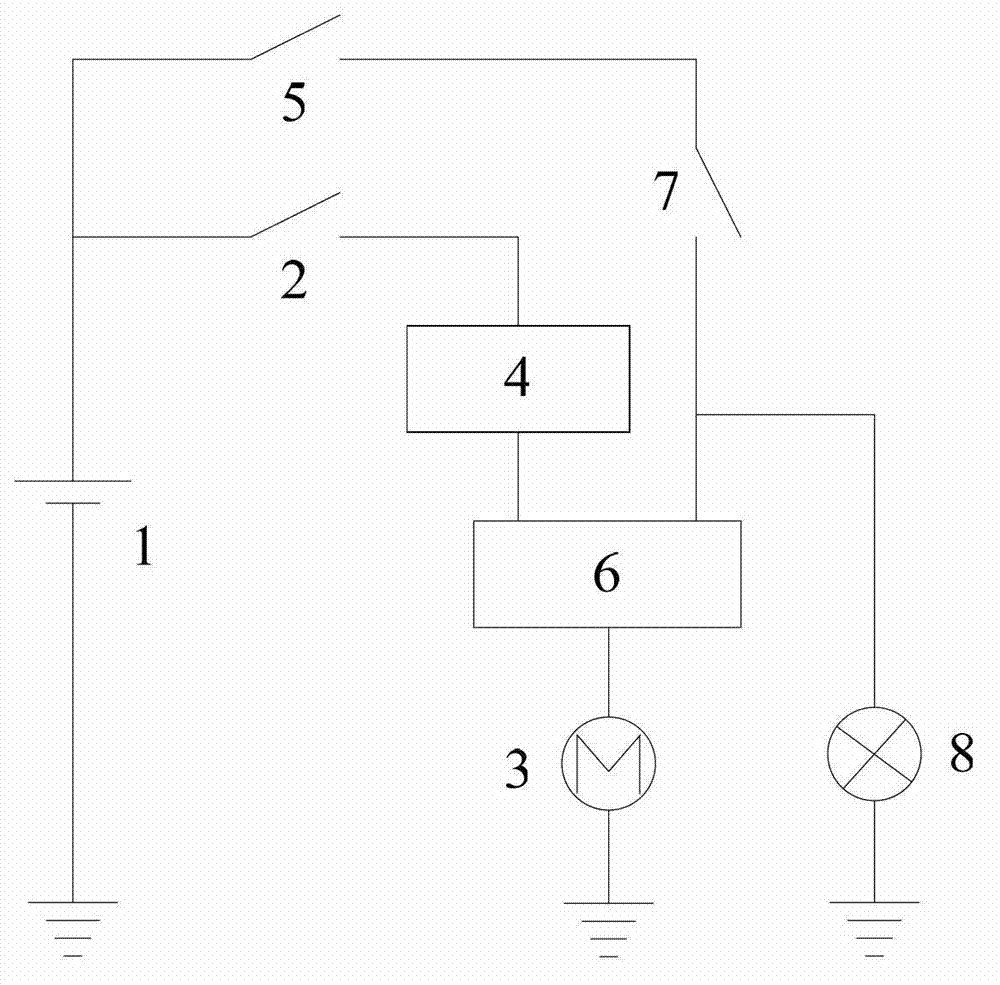
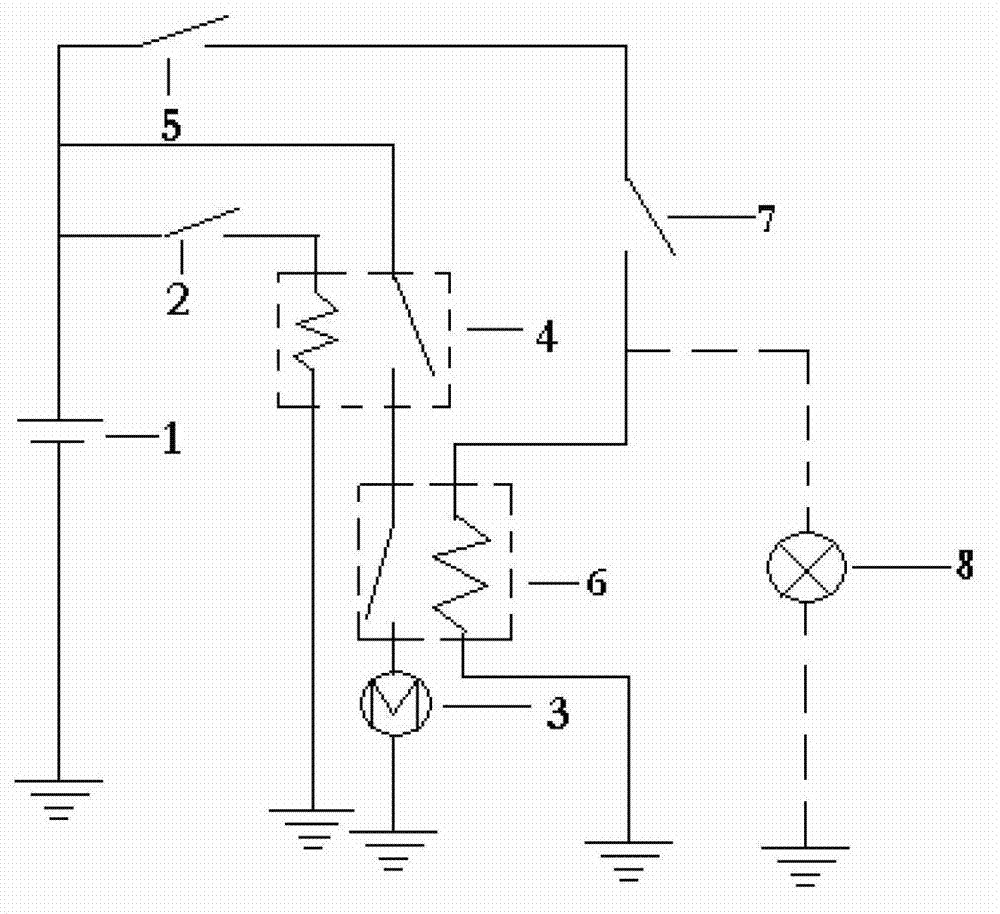
Start-up protection circuit for automobile engine
InactiveCN102953894AImprove protectionSimple structureElectric motor startersMachines/enginesDigital protective relayEngineering
The invention discloses a start-up protection circuit for an automobile engine, which belongs to the technical field of protection of an automobile starter. The circuit comprises a storage battery, an ignition switch starting gear, a starter, a starting relay, an ignition switch igniting gear, a protective relay and a normally closed oil pressure switch. One output of the storage battery is connected with the starter after sequentially passing through the ignition switch starting gear, the starting relay and the protective relay while the other output of the storage battery is connected with the starter after sequentially passing through the ignition switch starting gear, the normally closed oil pressure switch and the protective relay. According to the start-up protection circuit for the automobile engine provided by the invention, the starter is powered off automatically after the starter starts successfully, so that the starter is protected more safely.
Owner:WUXI INST OF COMMERCE
Protective relay and human-machine interface therefor
ActiveUS7974064B2Parameter calibration/settingCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsHuman–machine interfaceElectrical devices
A fully operational digital protective relay or Intelligent Electronic Device (IED) are provided for protecting electrical equipment of a power distribution system. The relay includes an input module, a processing module and an output module. Signals received from current transformers connected to the input module are evaluated by the processing module, and in reaction thereto, trip signals can be output to an actuator of a circuit breaker via the output module. A base Human Machine Interface (HMI) enables a user to enter operating parameters such as a delay time or nominal current to the processing module. Optionally, a further HMI may be attached to the protective relay and connected, via a suitable interface for data exchange, to the processing module for the purpose of displaying protection-related information to a user. This further HMI is both optional and detachable. For example, the further HMI can be repeatedly attached to and detached from the protection device. The detachable HMI provides for an increased flexibility in the use of the protective relay, as a user may adapt its interfacing capability by acquiring a detachable HMI of the type and at the time that best suits his evolving needs.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Multiple communications protocols in a protective relay
InactiveCN1302464AImprove communication performanceAdvanced Protection ControlParameter calibration/settingEmergency protective arrangement detailsDigital protective relayPower-system protection
A protective relay and power system protection method which incorporates multiple user-selectable communications protocols over multiple communications ports. The relay can support multiple communications protocols over a single communications port, and can support simultaneous formatting and communication over multiple communications ports using different protocols. By supporting a full array of communication protocols in each relay, protective control functionality is enhanced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
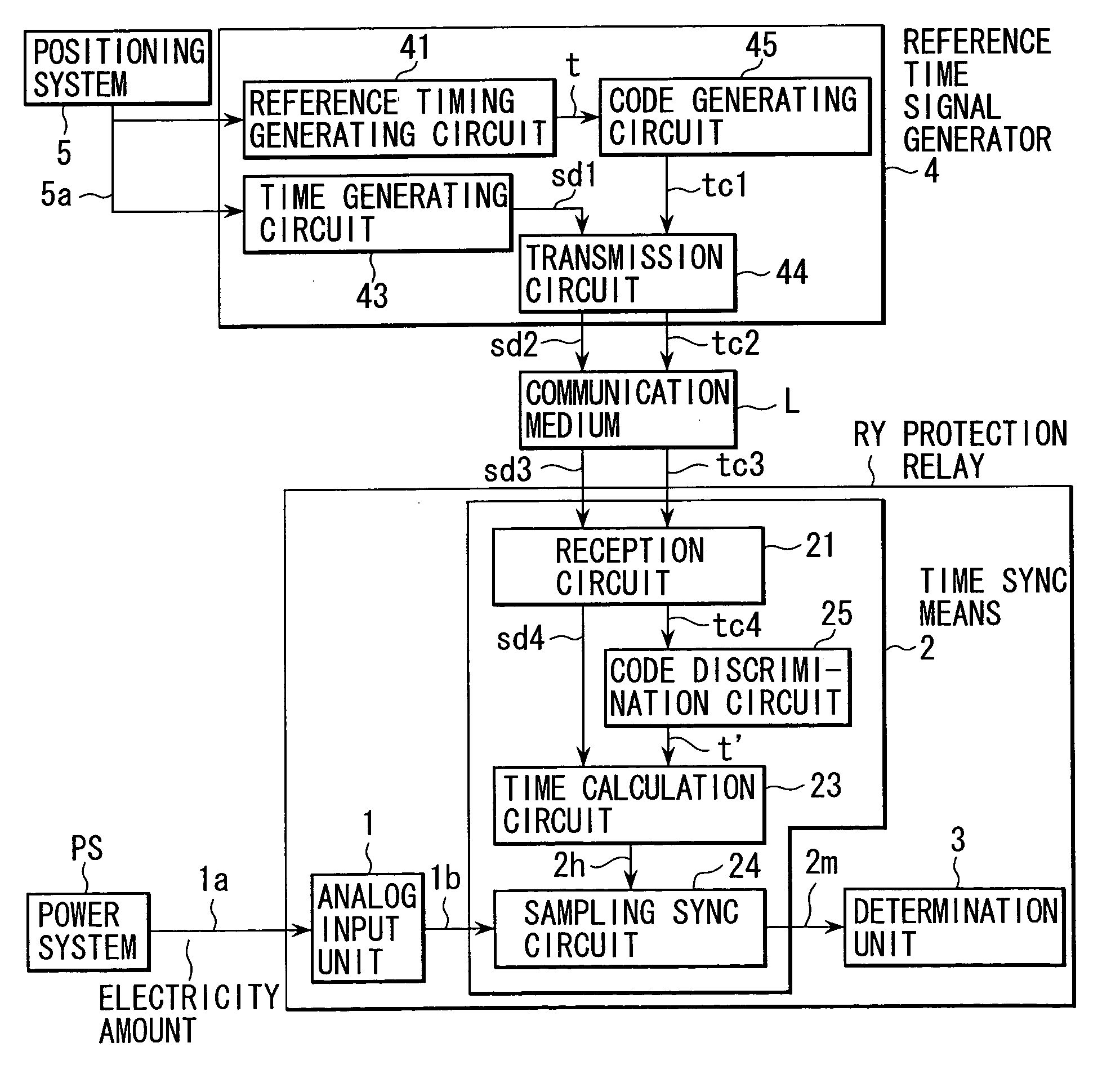
Digital protection relay with time sync function
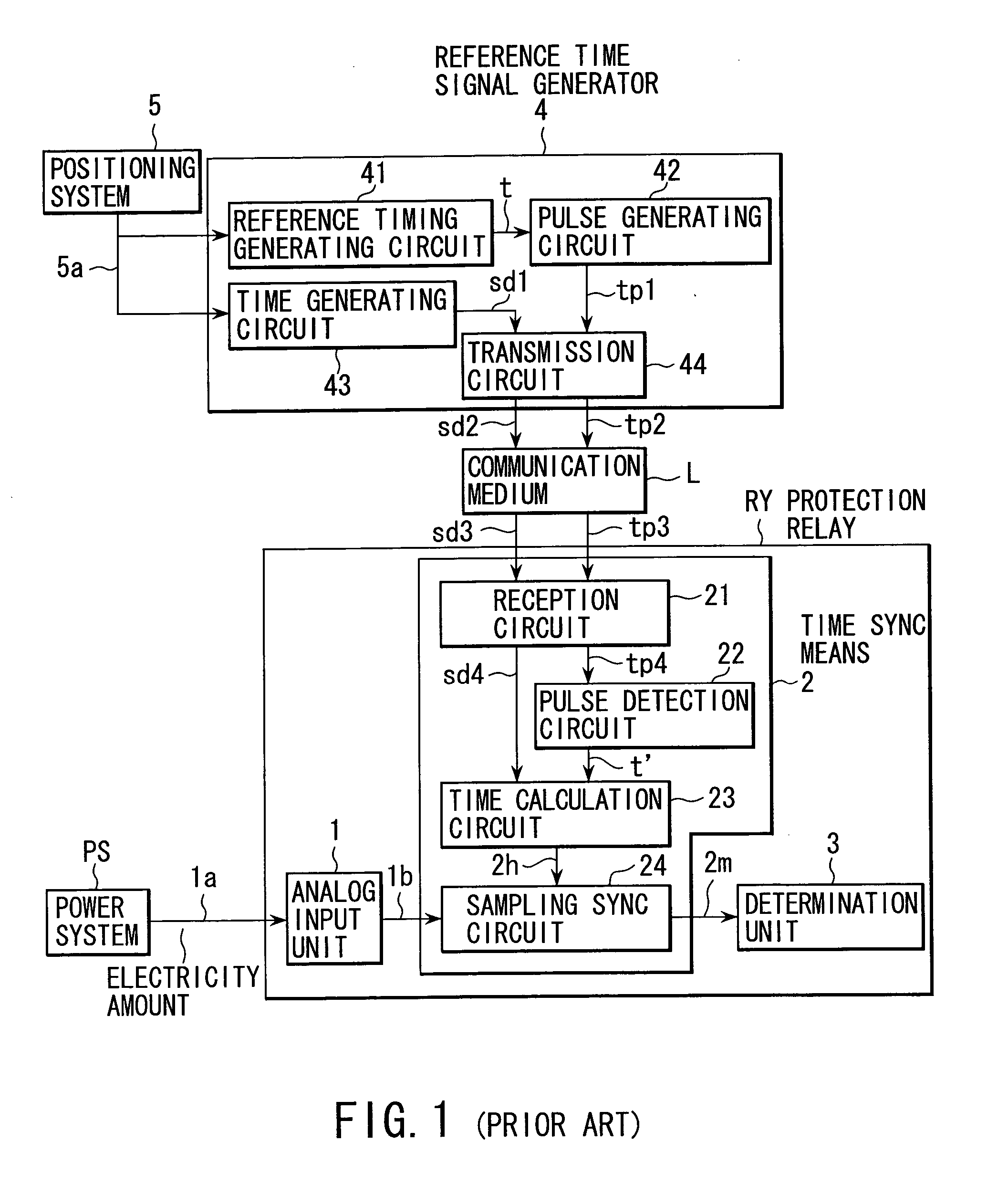
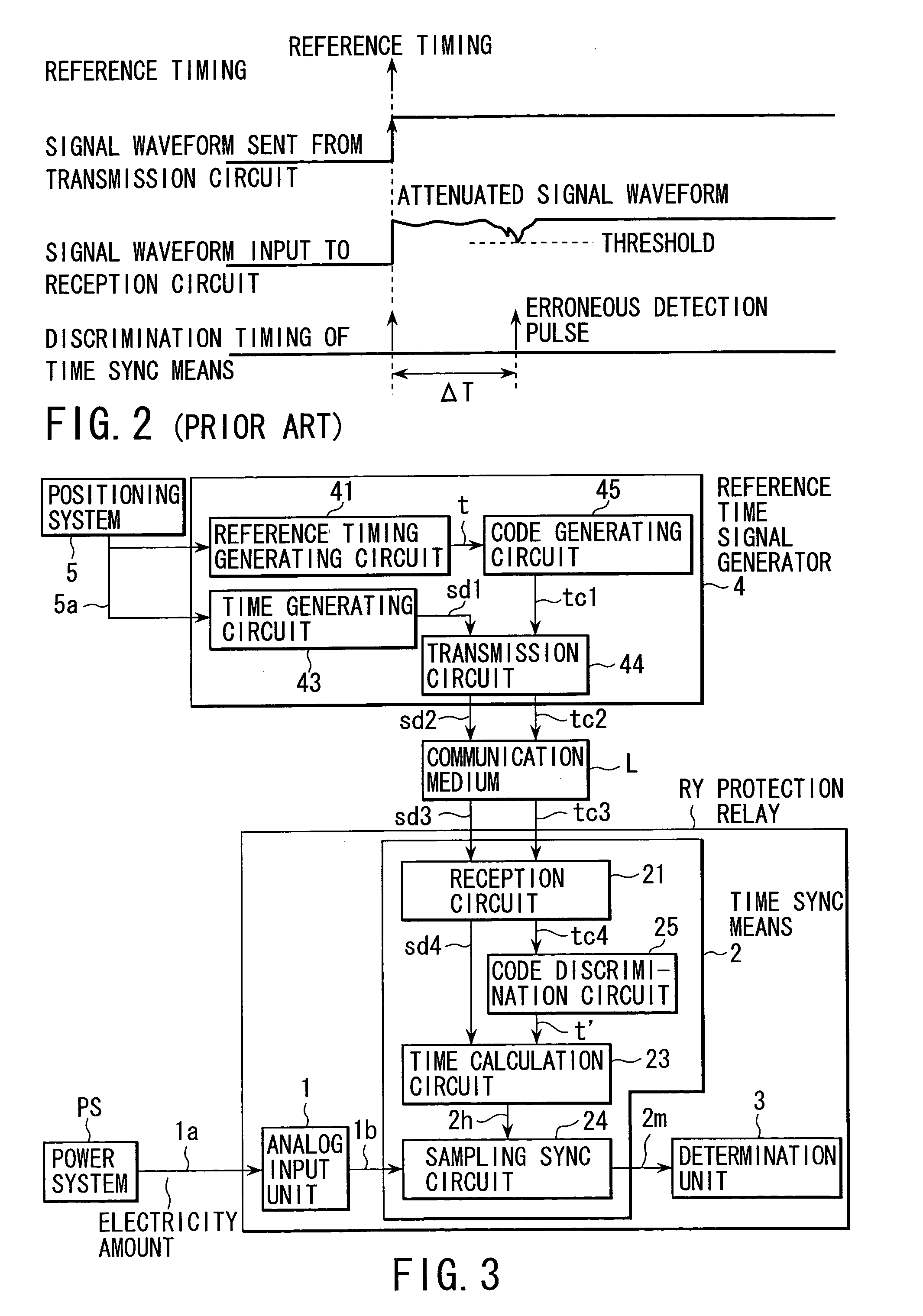
InactiveUS7199989B2Eliminate errorsElectrical testingEmergency protection data processing meansElectricityDigital protective relay
In a digital protection relay with a time sync function, the sampling timing of which is specified based on a reference timing transmitted from a time signal generator to a time sync unit, with a determination value. The time sync unit includes a reception circuit that receives a discrimination code and time data transmitted from the time signal generator, a code discrimination circuit that discriminates the reference timing on condition that the received discrimination code coincides with a desired code, a time calculation circuit that calculates the sampling timing on the basis of the discriminated reference timing and the time data, and a sampling sync circuit that specifies the sampling timing of a digital quantity of electricity on the basis of the calculated sampling timing.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Protective relay system and protective relay device
InactiveCN104919669AAchieve protectionEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDigital protective relayElectricity
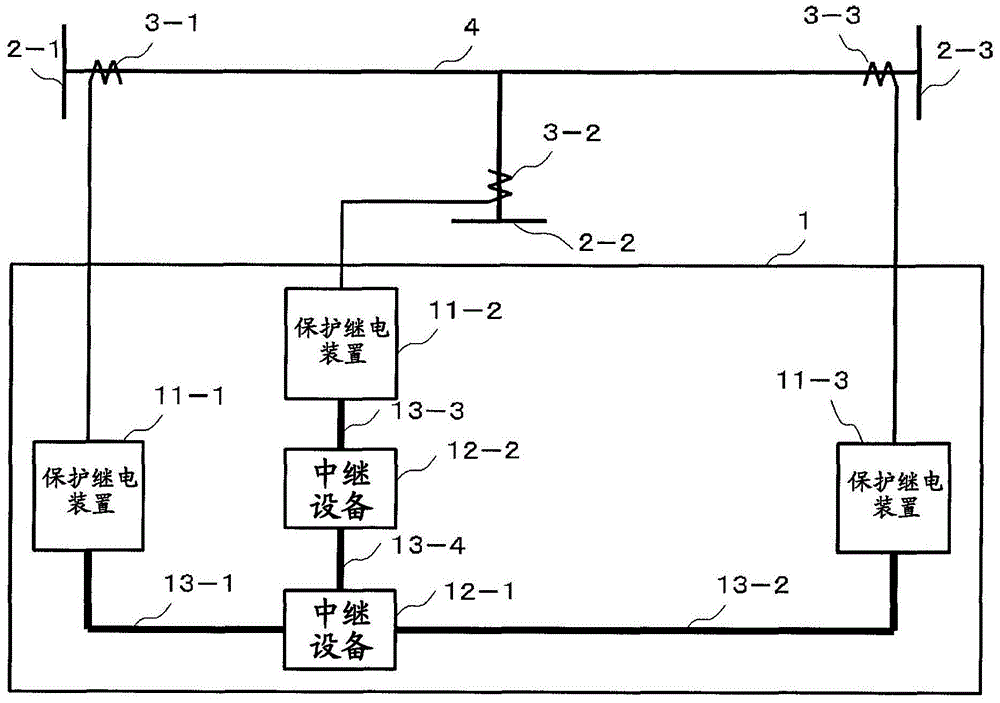
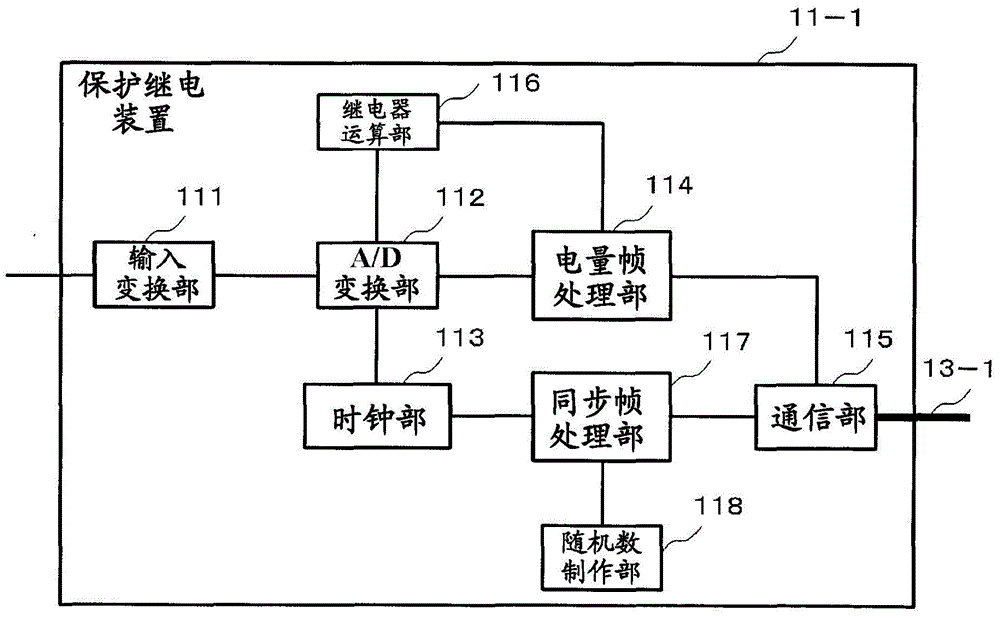
The purpose of the embodiment according to the present invention is to provide a protective relay system, a protective relay device, and a time synchronization method such that highly-accurate time synchronization between devices can be achieved. The embodiment according to the present invention relates to a protective relay system having a plurality of protective relay devices which protect a power grid on the basis of data pertaining to the amount of electricity in the power grid, said protective relay devices communicating with each other over a network. Each protective relay device comprises: a clock generation unit for periodically indicating the timing for sampling data pertaining to the amount of electricity in the power grid; a relay calculation unit for performing relay calculation on the basis of the sampled electricity amount data, and the electricity amount data received through the network; a random number generation unit for generating random numbers; and a synchronization frame processing unit for determining the timing for transmitting a synchronization frame to other protective relay devices over the network on the basis of the random number generated by the random number generation unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Verification system of grounding direction protective relay
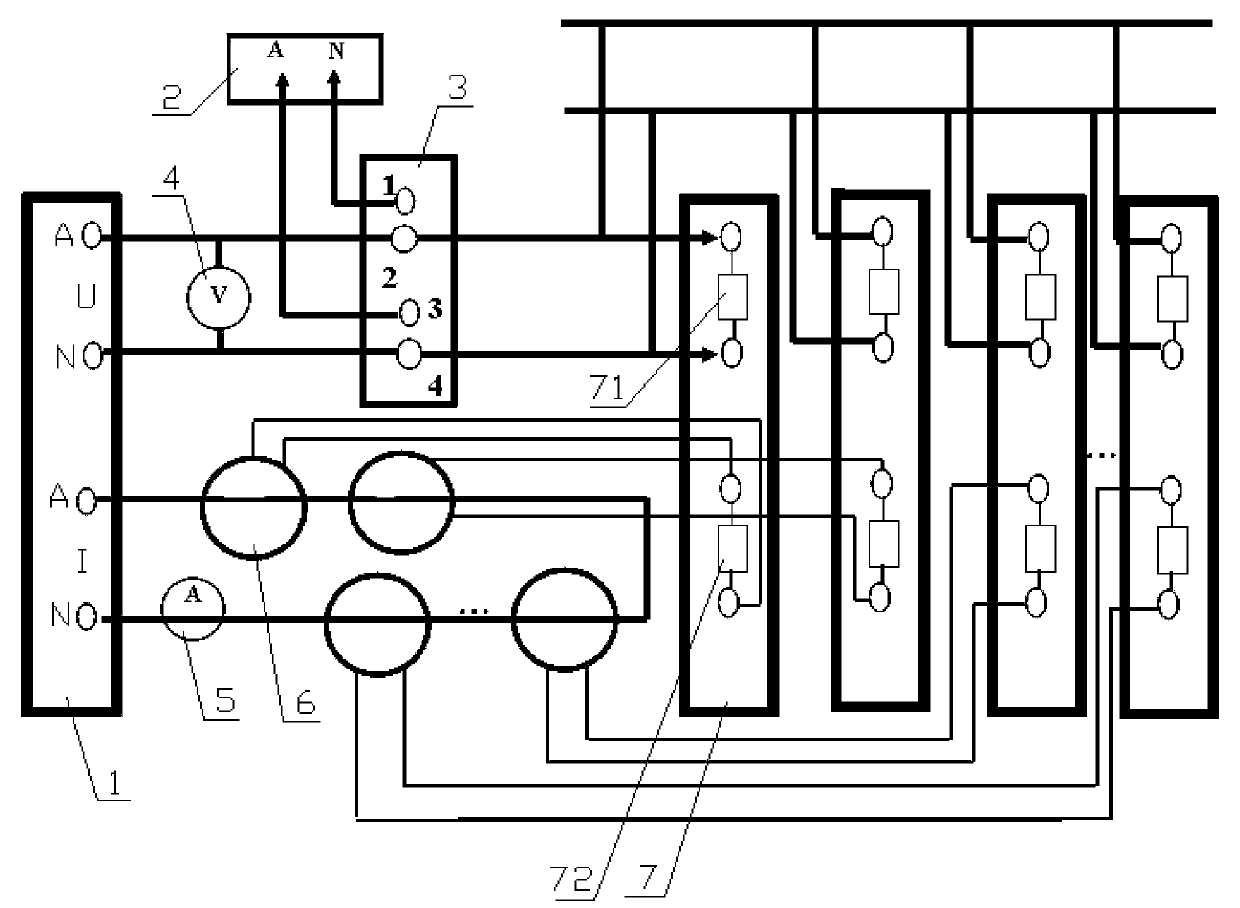
ActiveCN103630831AReduce labor intensityVerify correctnessCircuit interrupters testingDigital protective relayPower flow
The invention discloses a verification system of grounding direction protective relays; a secondary side of a zero sequence voltage transformer in the verification system is connected with a first wiring terminal and a third wiring terminal of a plug-in; an A-phase end and an N-phase end of a verification instrument voltage channel are respectively connected with a plurality of voltage coils of verified relays through a second wiring terminal and a fourth wiring terminal of the plug-in, and the phase end and the coil have same polarity; a voltage meter is connected in parallel with the A-phase end and the N-phase end of the verification instrument voltage channel; a plurality of zero sequence current transformers and ammeters are connected in series in sequence between the A-phase end and the N-phase end of the verification instrument voltage channel, and have same polarity; a plurality of output ends of the zero sequence current transformers are respectively connected in sequence with the plurality of current coils of the verified relays, and the output ends and the coils have same polarity. The verification system can simultaneously verify all grounding direction protective relays of one busbar; the zero sequence current transformers and the zero sequence voltage transformers are connected in the system; wiring correctness can be verified in the verification process, thereby reducing labor intensity of the verification work, and improving verification efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOSTEEL IND TECHNOLOGICAL SERVICE
Digital protective relay
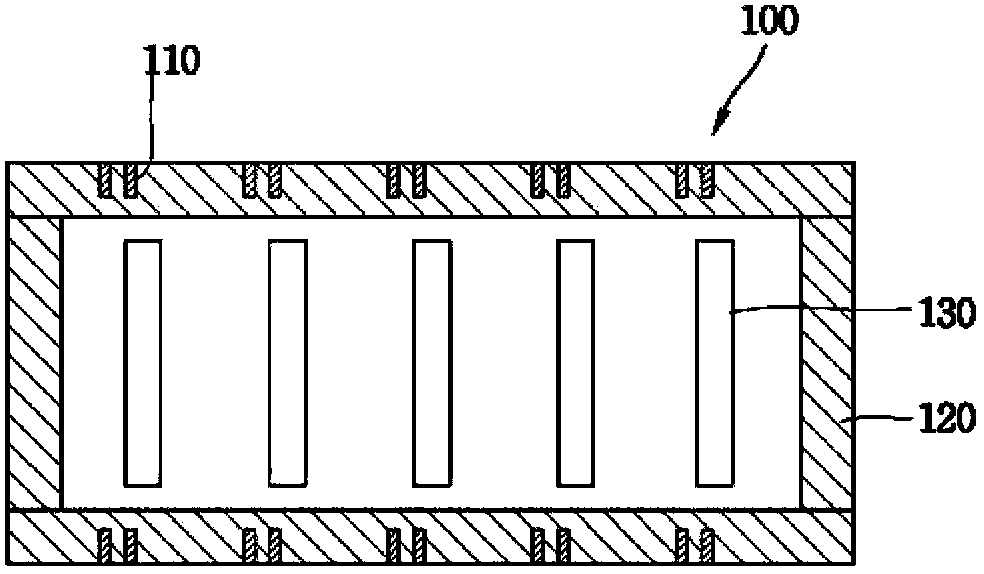
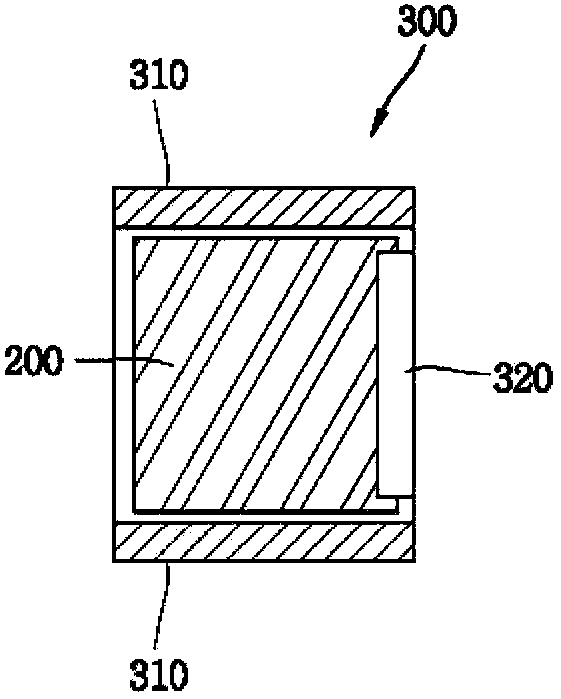
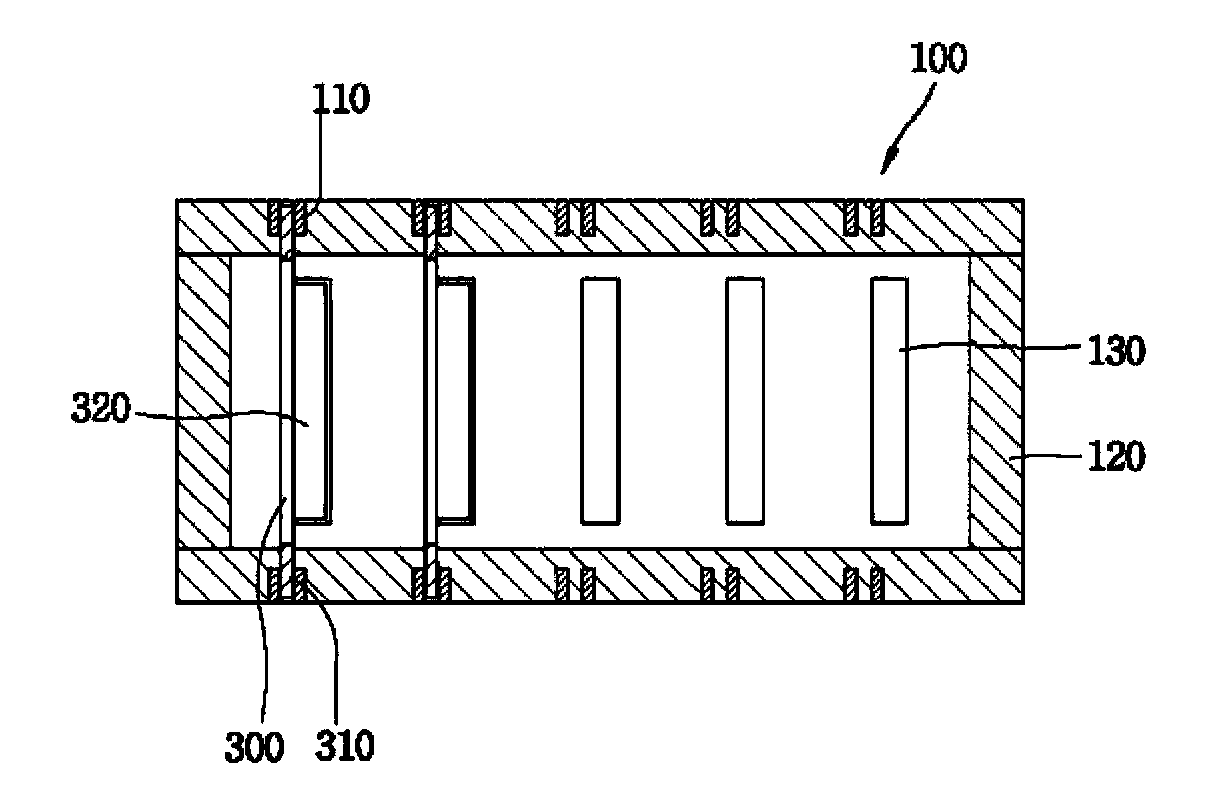
ActiveCN103369829APrinted circuit groundingCross-talk/noise/interference reductionDigital protective relayElectromagnetic interference
A digital protective relay includes at least one daughter PCB (300) having an electronic circuit which generates electromagnetic interference noise or high frequency noise; and a backplane printed circuit board (100) having, on an upper surface thereof, a plurality of first connectors (130) for connection with the daughter PCB (300), the backplane PCB (100) being connected to the daughter PCB through the first connectors (130), and providing a noise discharge path (120) along which the electromagnetic interference noise or the high frequency noise from the daughter PCB flows to an external ground.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Primary cut-out state monitoring method
InactiveCN100383547CImprove economyEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCircuit interrupters testingDigital protective relayPower grid
The invention discloses a primary cut-out state monitoring method, which comprises following steps: using existing fault recording apparatus and digital protective-relay device in converting station automatic system to record normal divided brake current decay process; using recorded data to calculate circuit breaker opening time; then estimating circuit breaker state according to opening time of circuit breaker and opening time trend in some time.
Owner:苏盛 +2
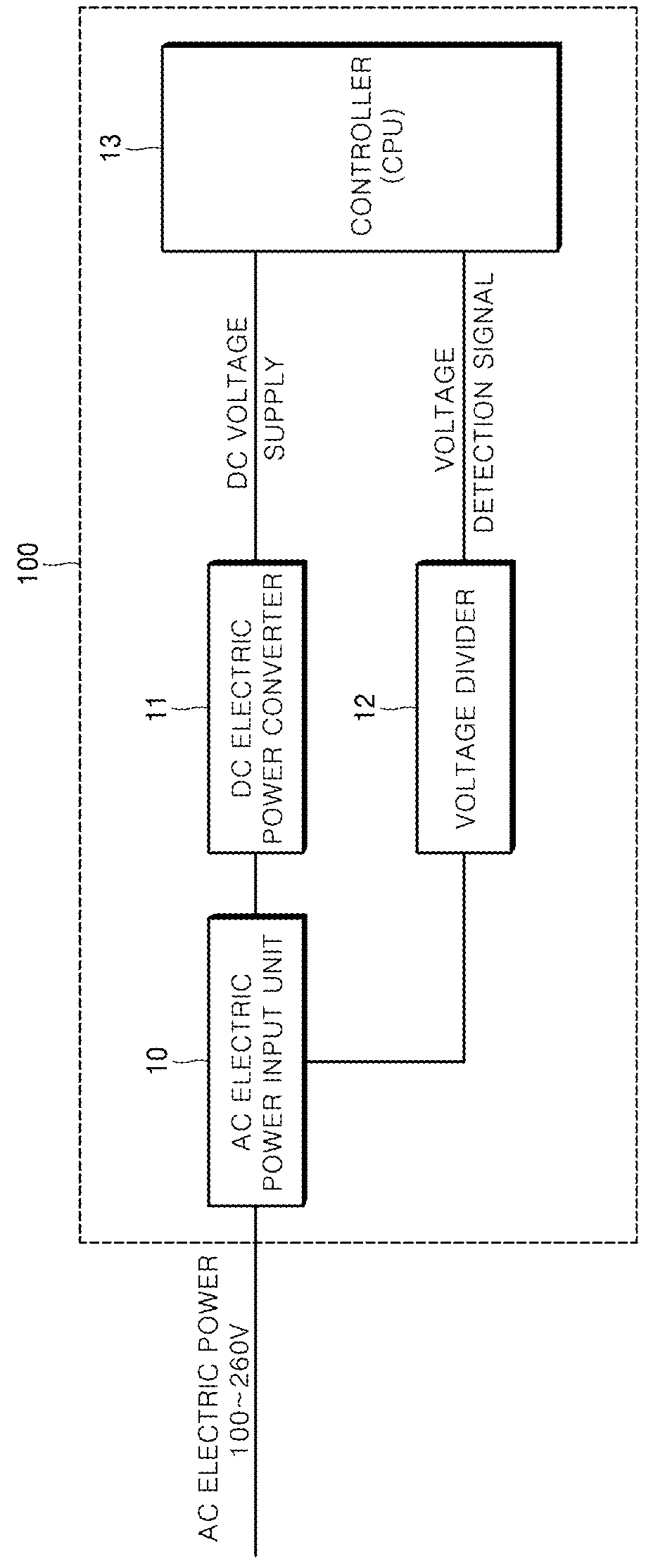
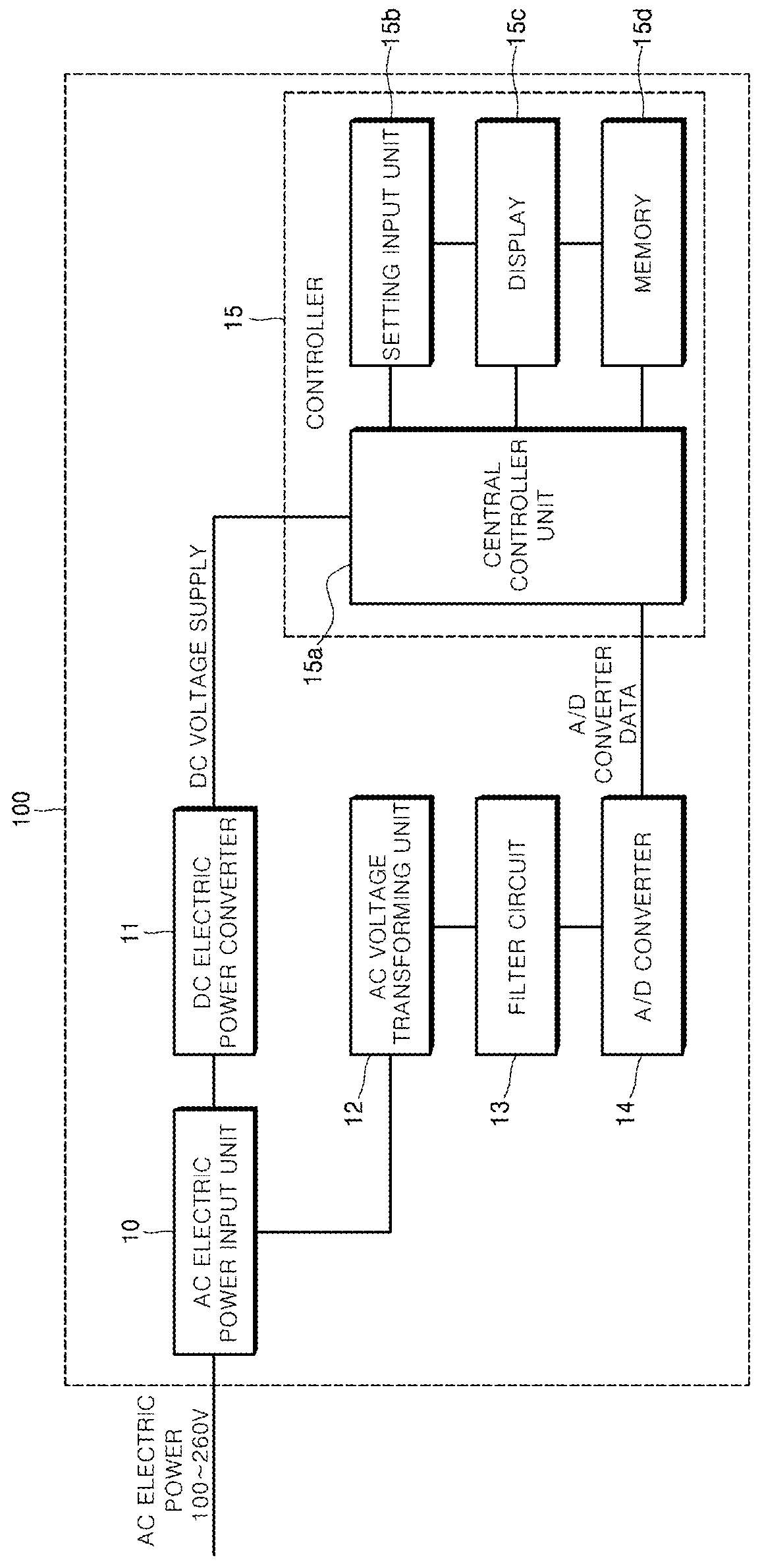
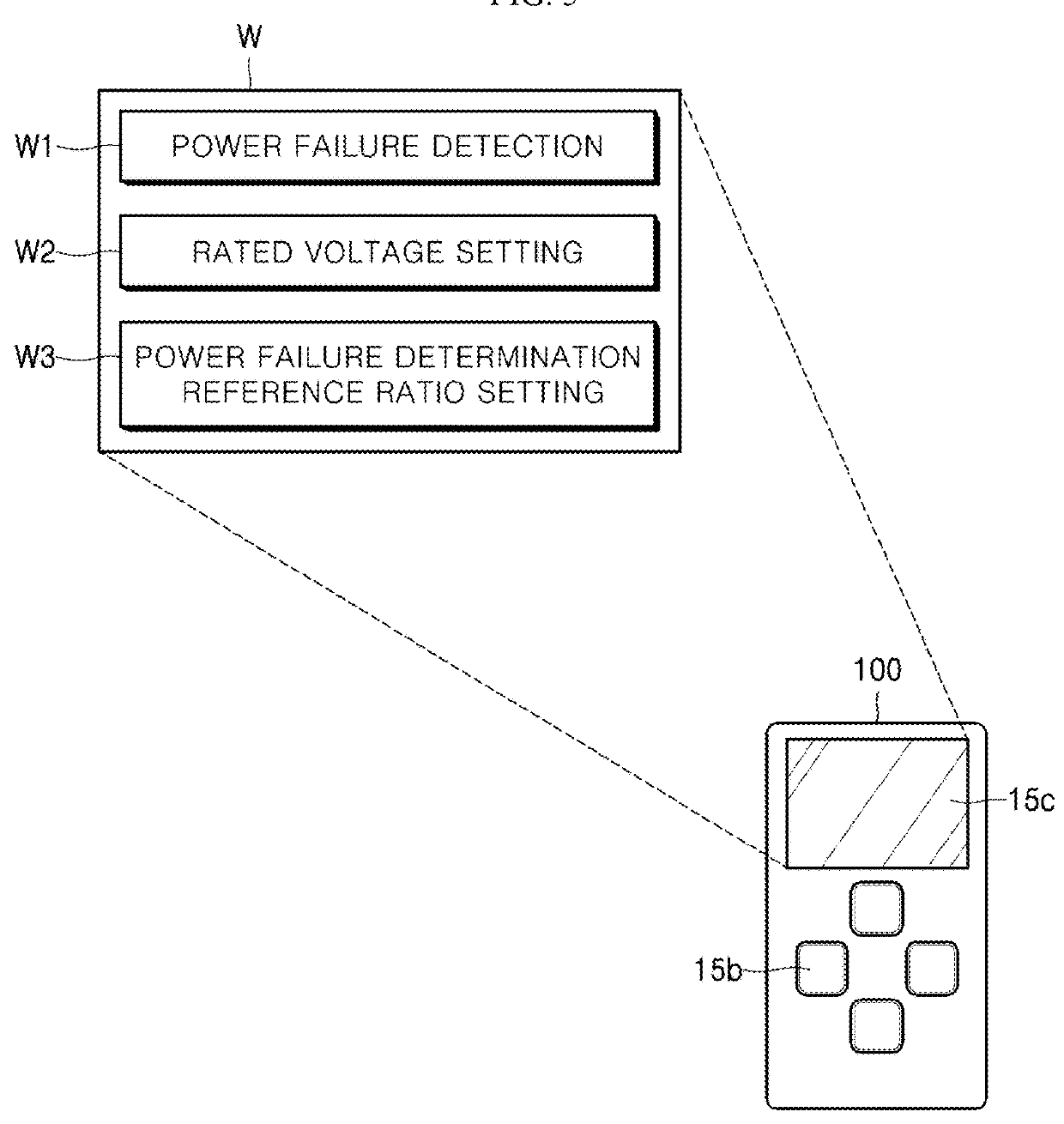
Power failure monitoring device of digital protection relay
ActiveUS9997048B2Accurately determineImproper operationParameter calibration/settingCurrent/voltage measurementDigital protective relayVoltage reference
Embodiments of a power failure monitoring device of a digital protection relay capable of preventing a relay operation error and a data loss by determining a power failure when an electric power voltage being detected is dropped to be equal to or less than a prestored power failure reference voltage to enable a controller to perform a power failure preparation operation are provided.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
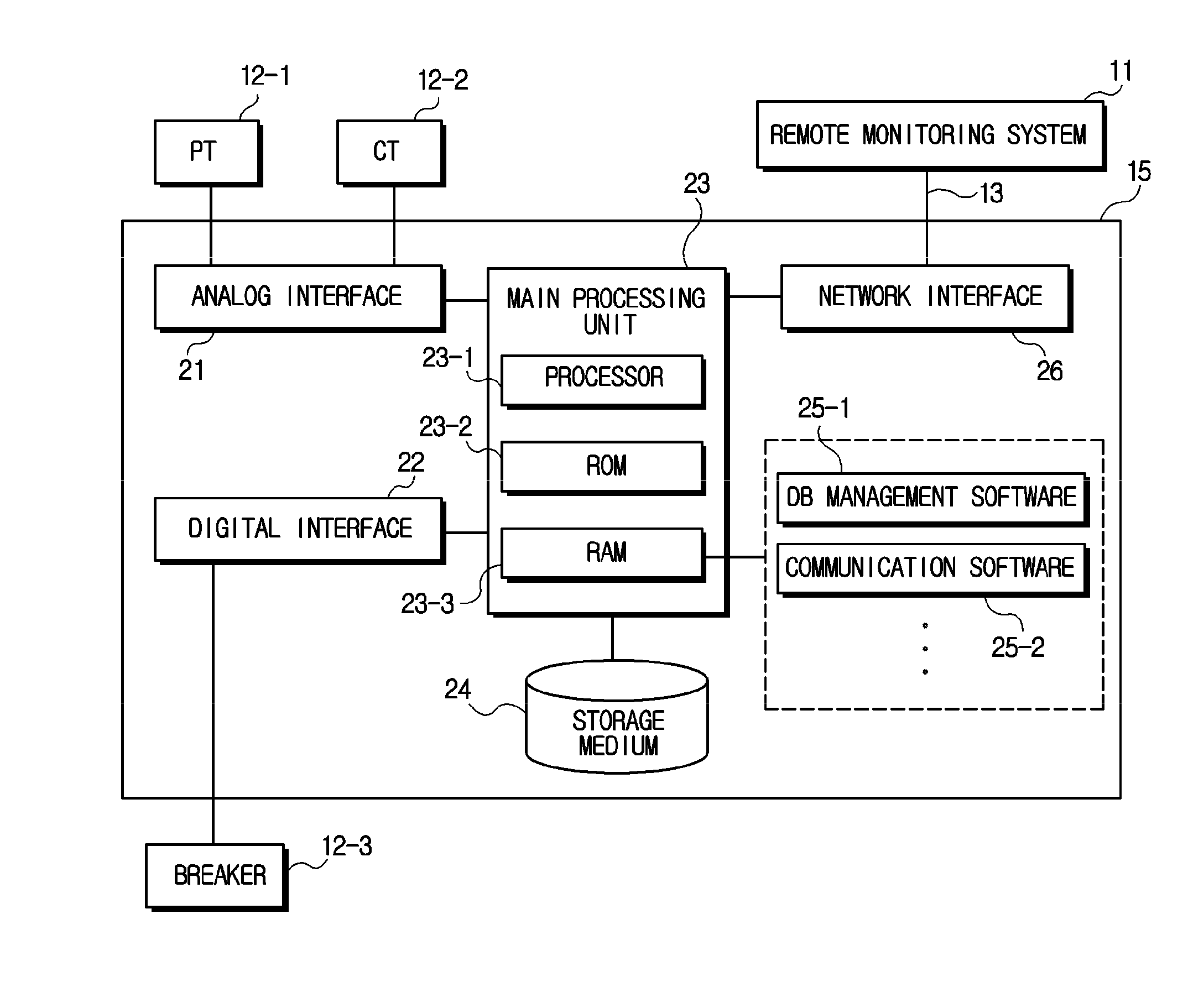
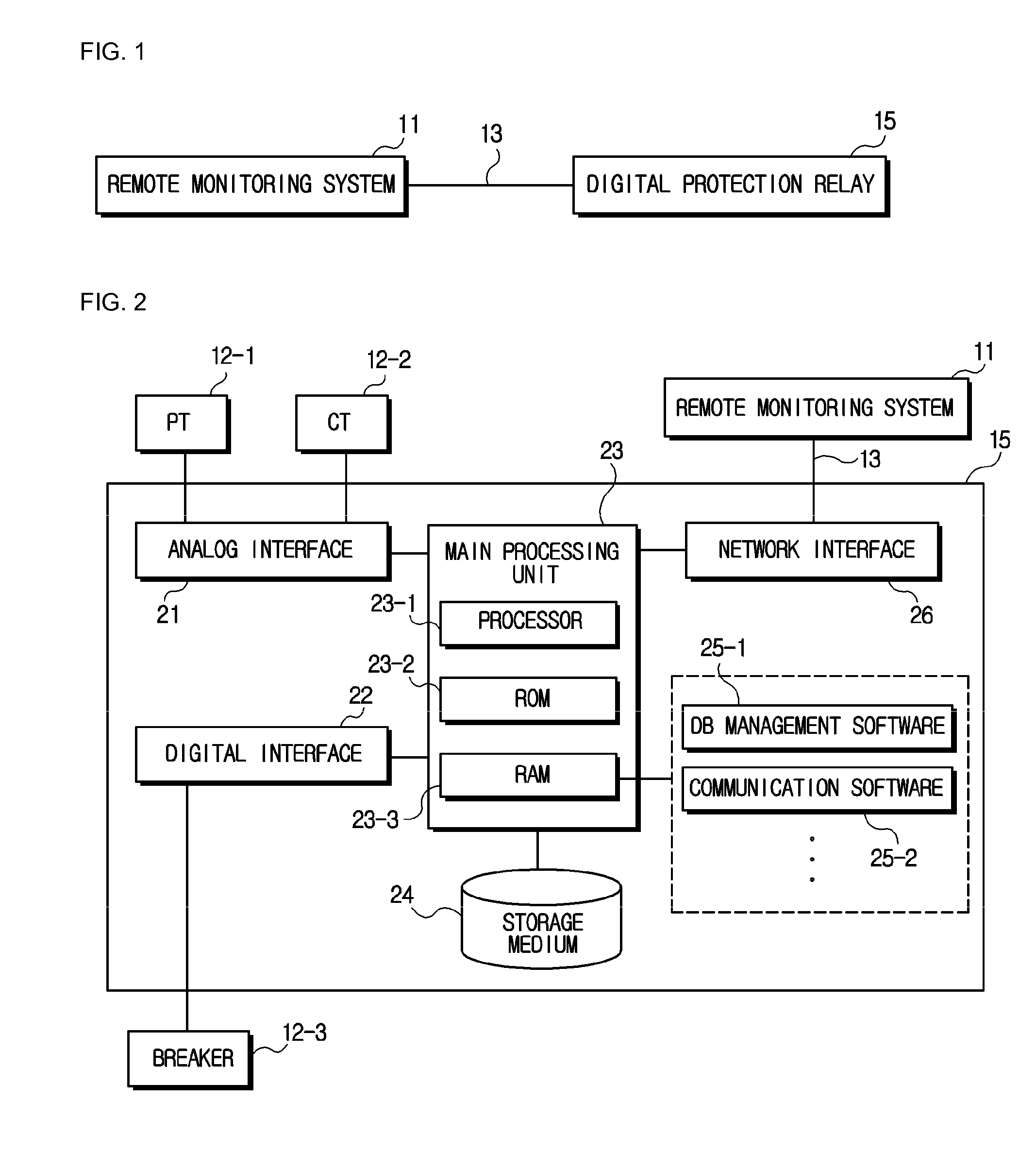
Remote communication system and method
InactiveUS20110276839A1Unnecessary to performNot easy to changeFault responseEmergency protective arrangement detailsDigital protective relayMonitoring system
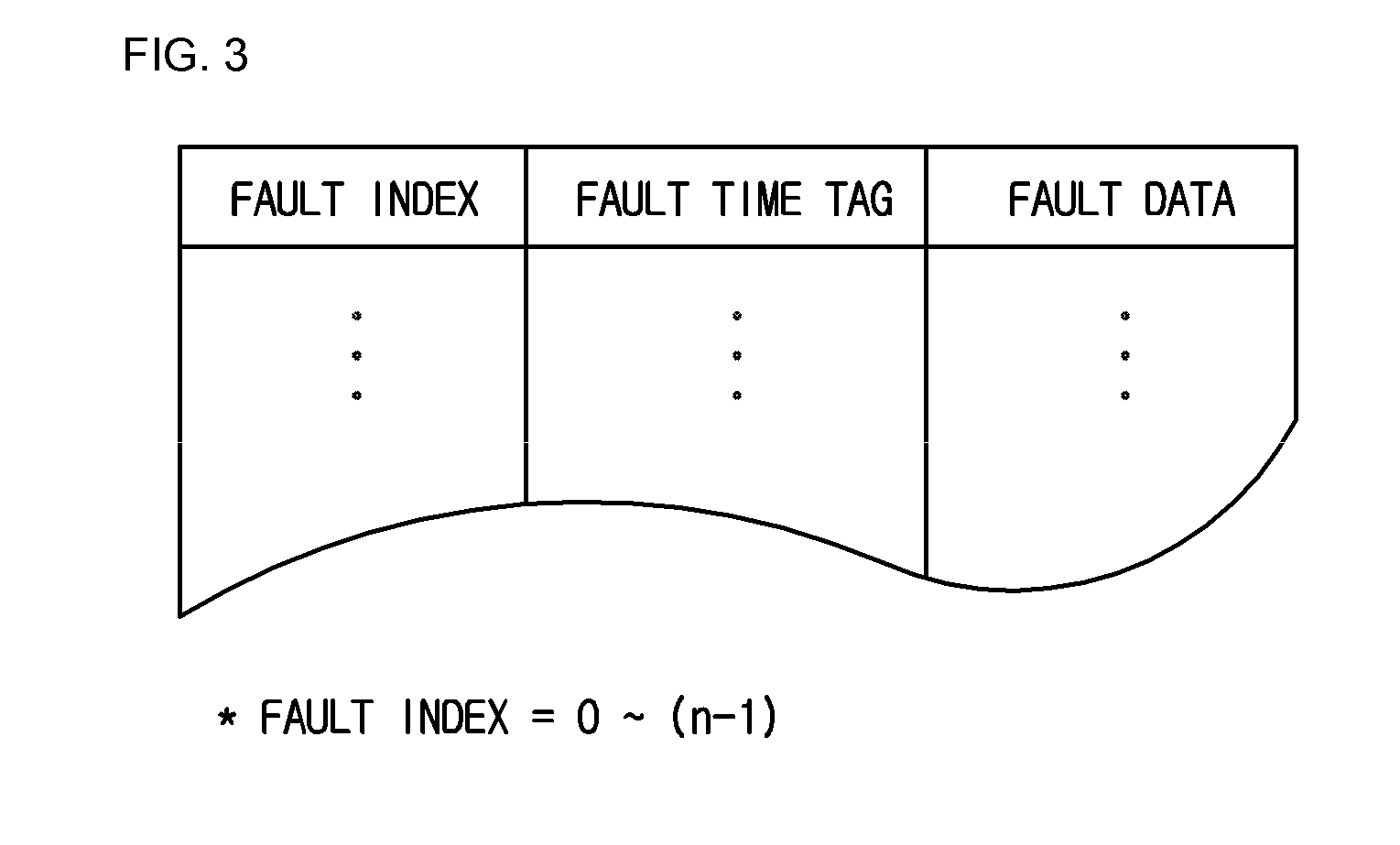
Disclosed is a remote communication system and method. A remote communication system includes a digital protection relay and a remote monitoring system. The digital protection relay stores and maintains fault indices for identifying a predetermined number of faults that have occurred, fault time tags corresponding to the fault indices and fault data corresponding to the fault indices. The remote monitoring system sets a fault index, a fault time tag, a fault data block size to be communicated at a time and a fault data block index for specifying a fault data block to be communicated, and requests the digital protection relay of a fault data block.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com