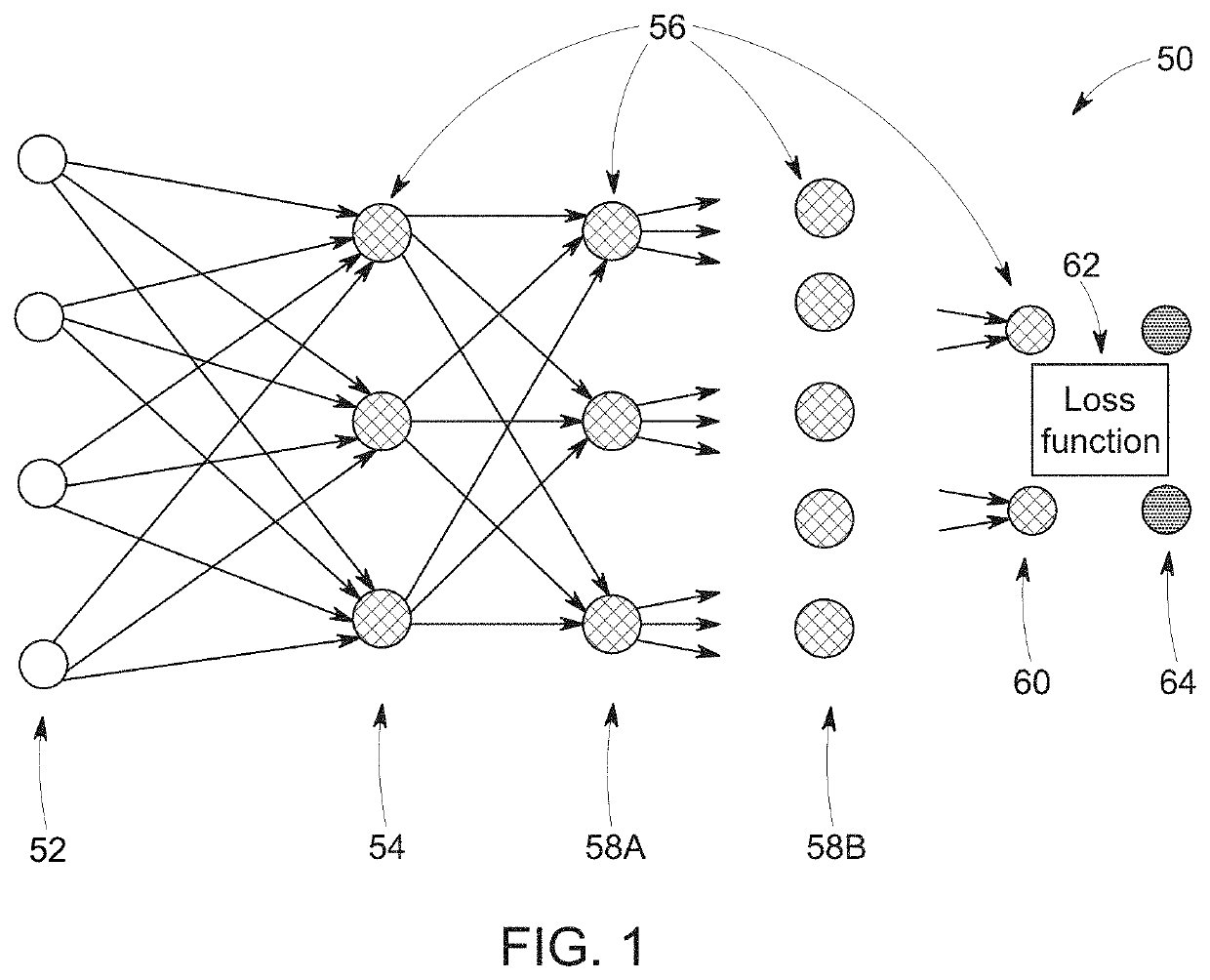
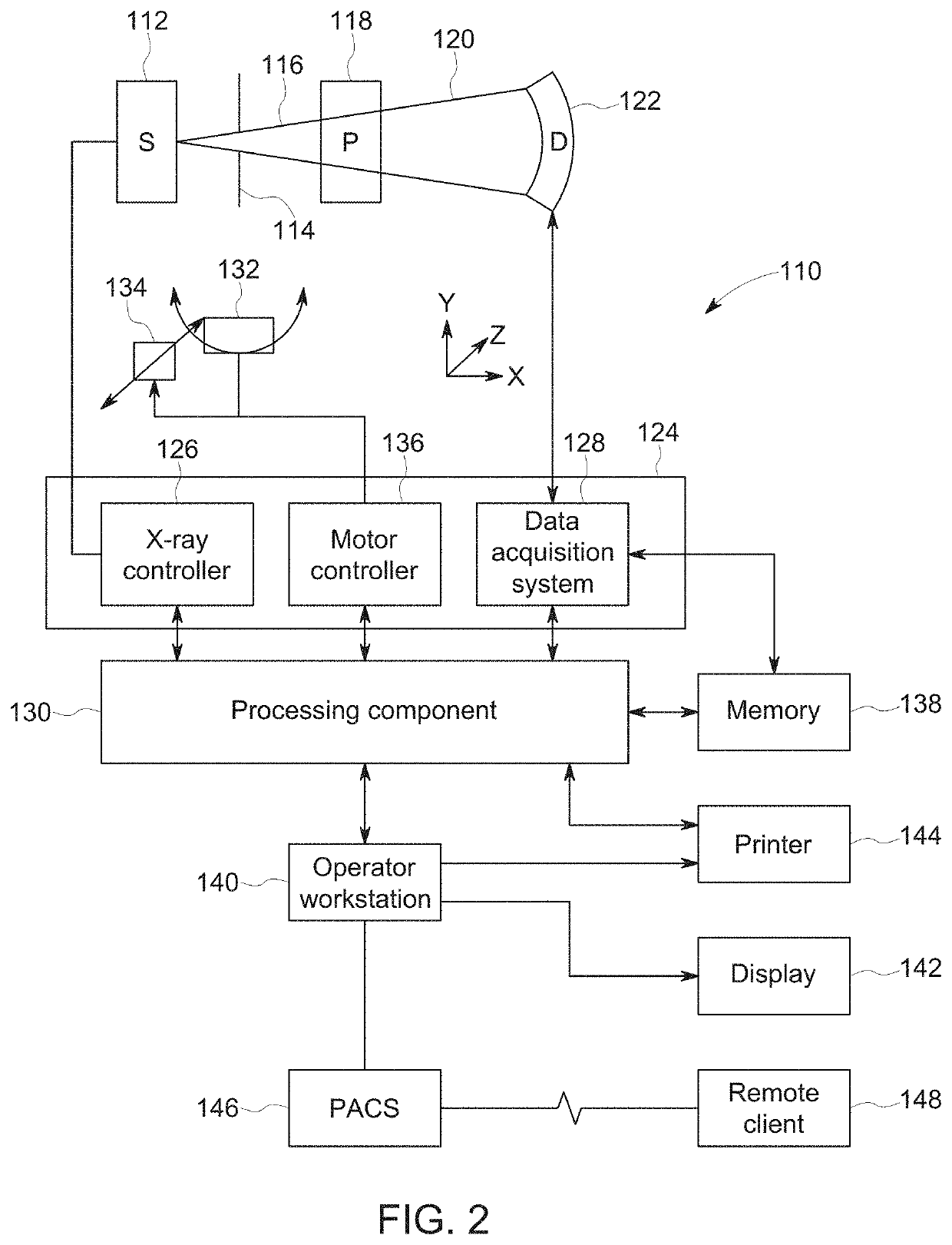
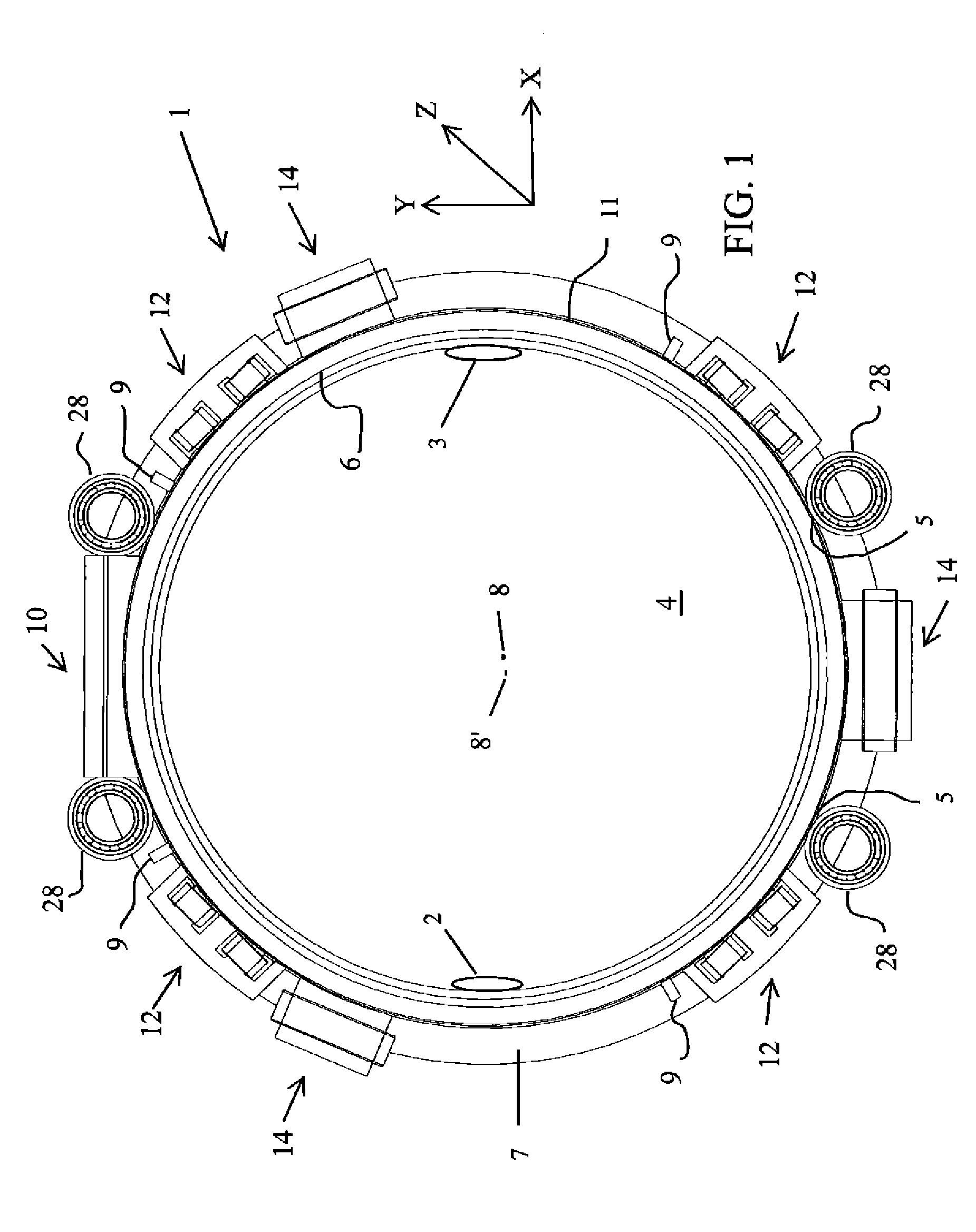
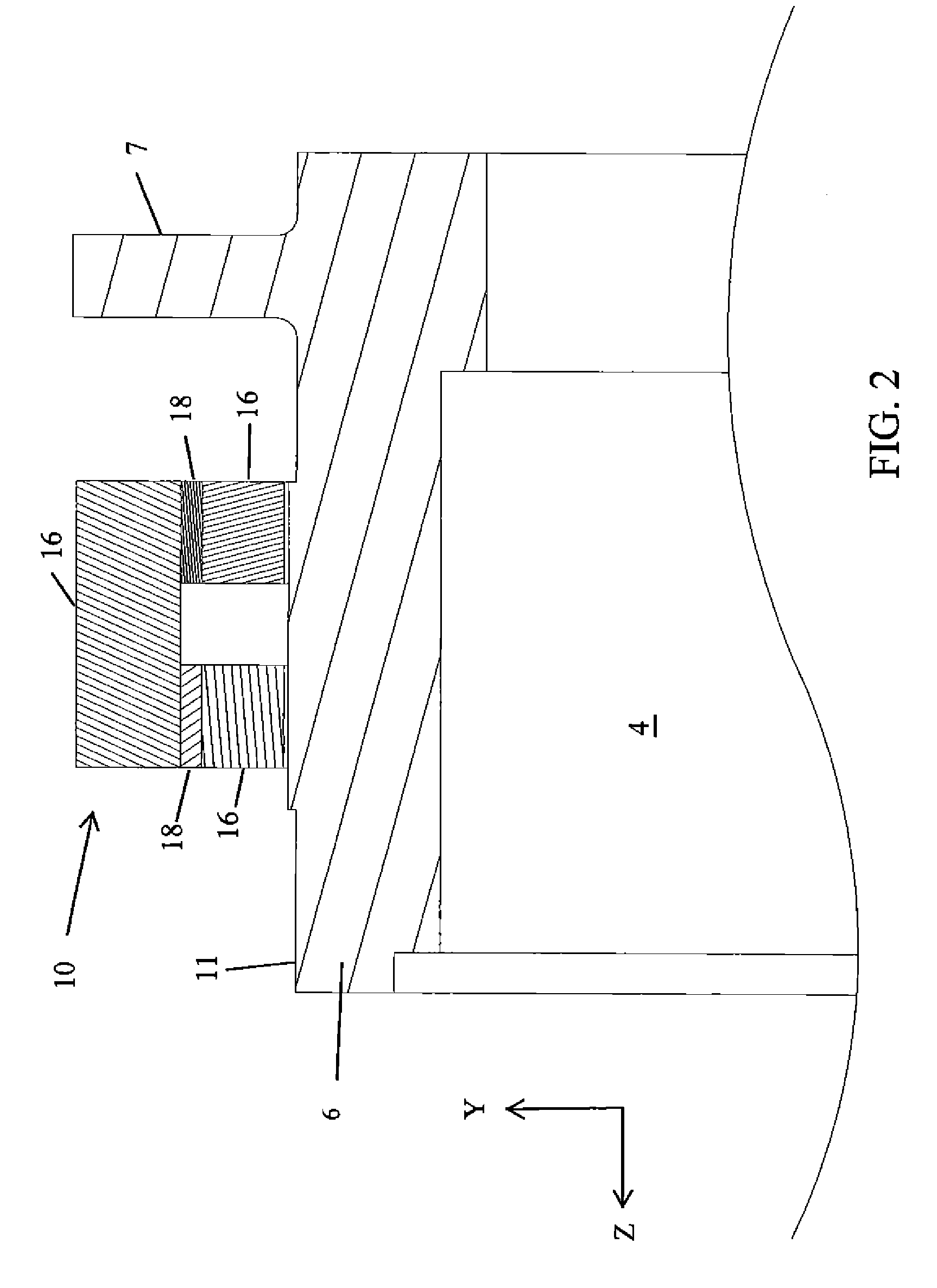
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Diagnostic scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
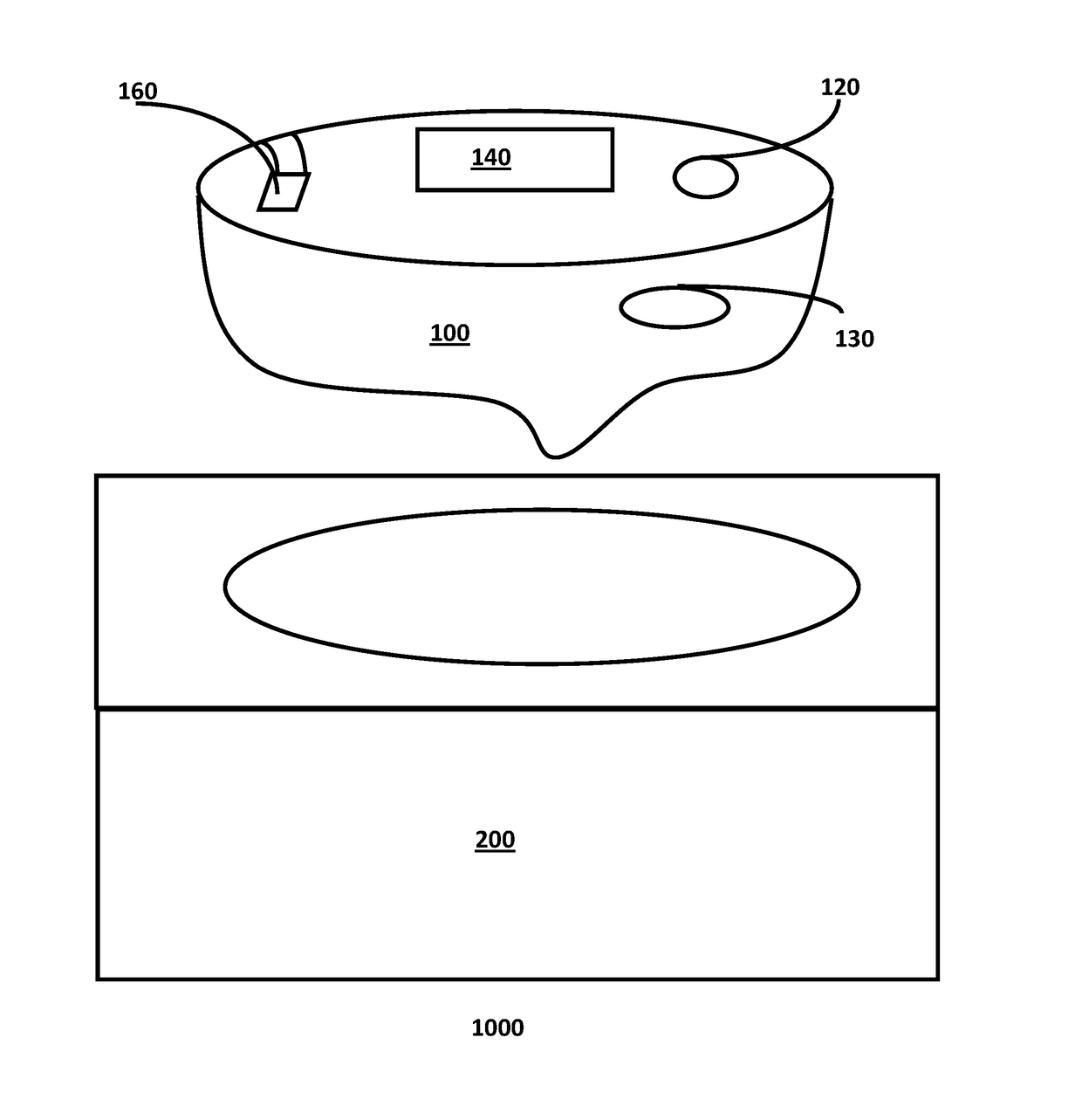
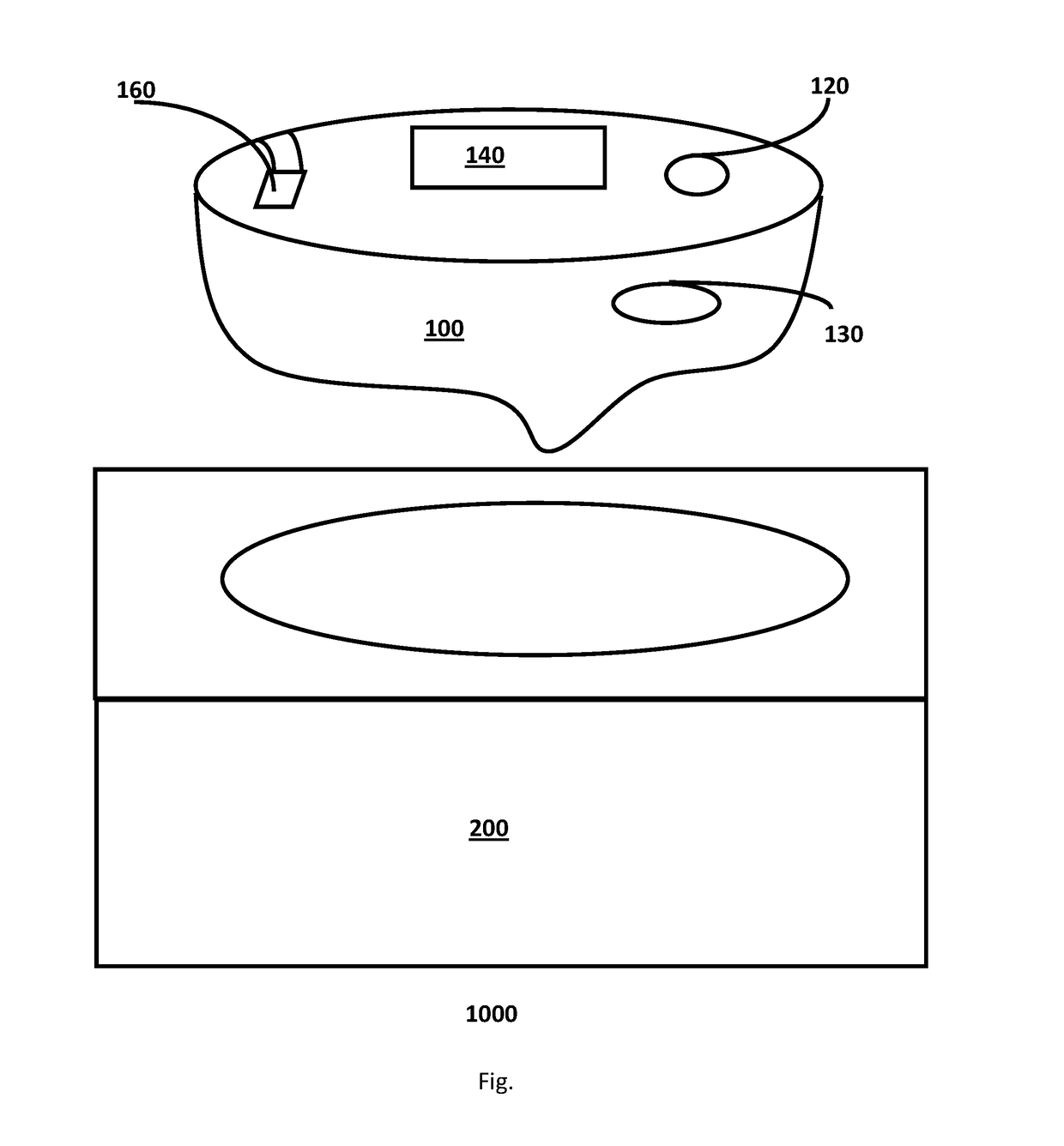
Method and system for guided, efficient treatment
InactiveUS20130024213A1Accurate and efficientAccurate diagnosisRadiation diagnosis data transmissionMedical imagesDashboardMedical record
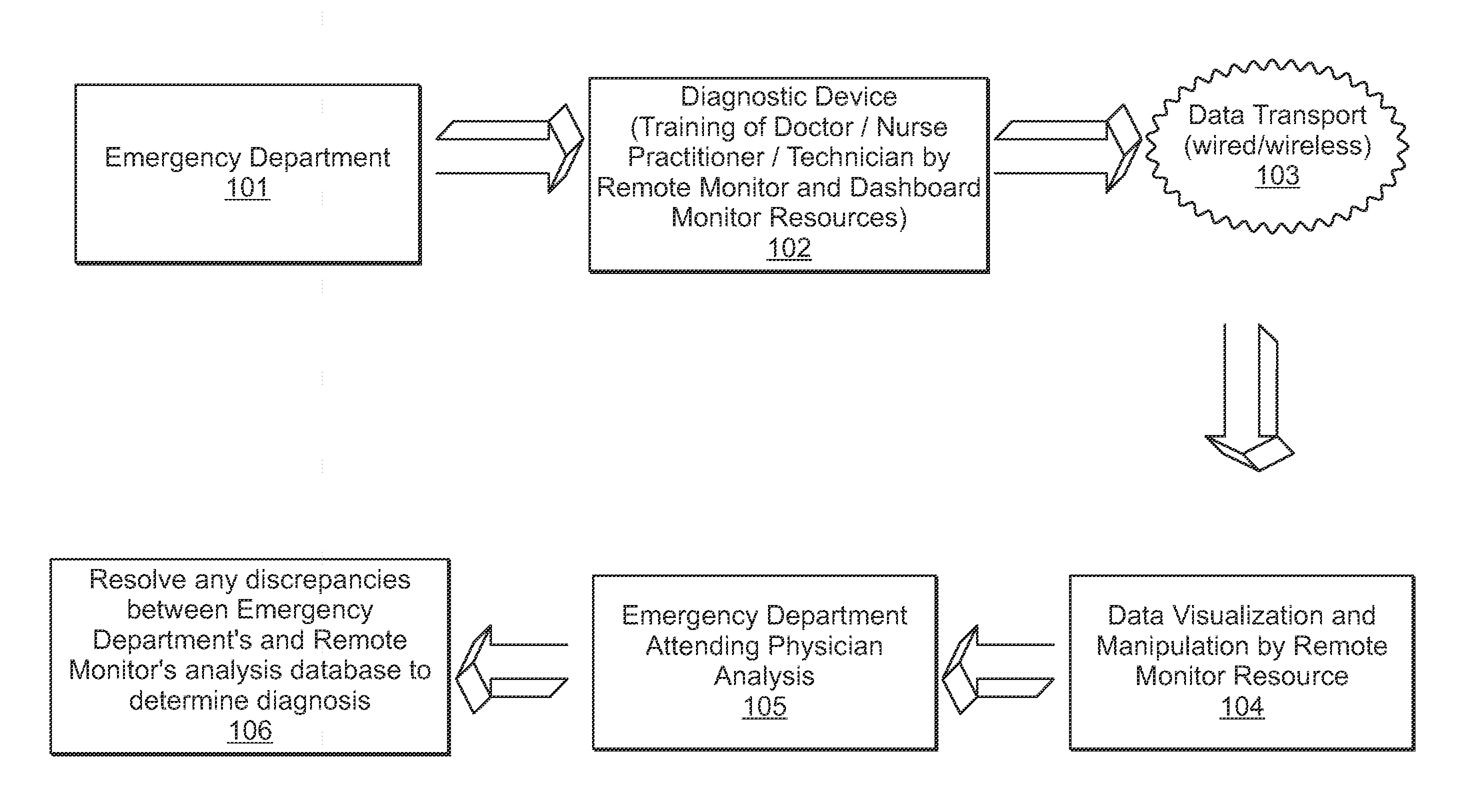
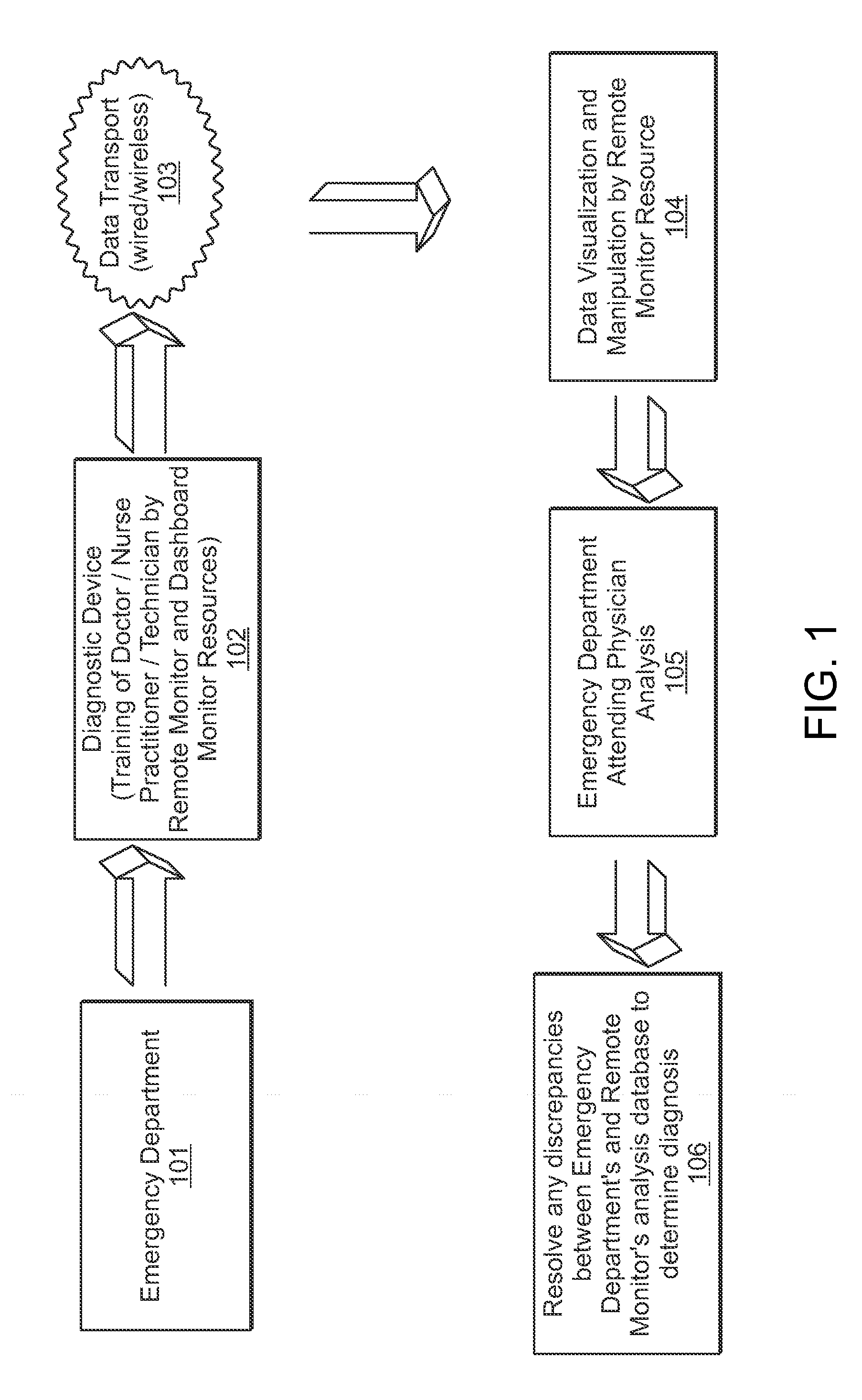
A system and method is provided in which medical treatment of a patient is effected in a systematic and guided fashion. From a patient's symptoms and electronic medical record, a specific diagnostic test may be recommended. Upon execution of the diagnostic test, the diagnostic scan results may be forwarded to a remote location for assistance in analysis. Once analyzed, the results are transmitted to the attending medical personnel. The results, and information which led to the decision to have a diagnostic test, are also sent to a repository for use in future diagnoses and other determinations. A monitor or dashboard is used to keep track of the various steps of the procedure, to provide on the job guidance in using a diagnostic test device, and the ensure a specific efficiency and protocol are followed. A remote location of experts may also be monitoring the dashboard, as a quality control.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
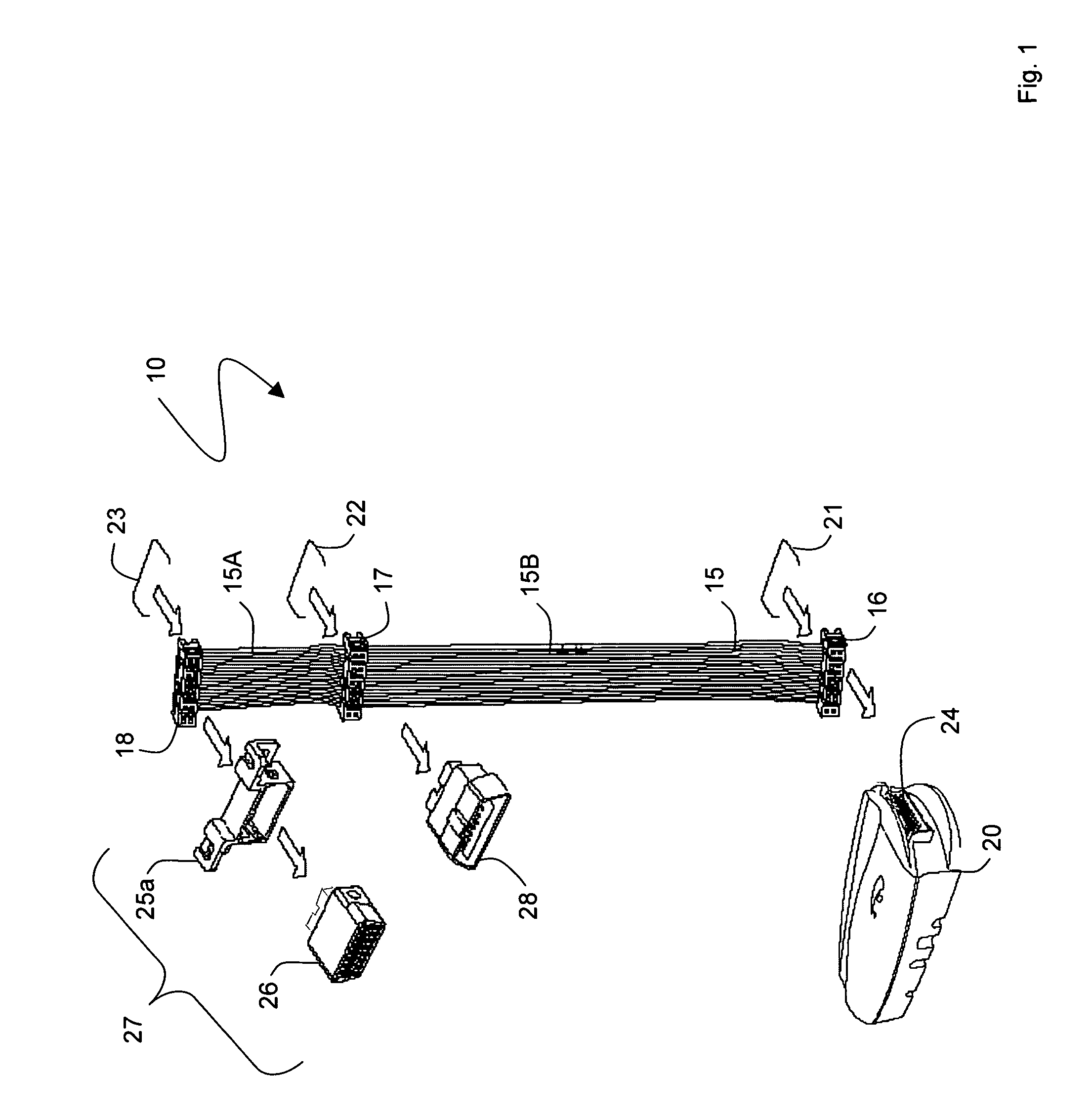
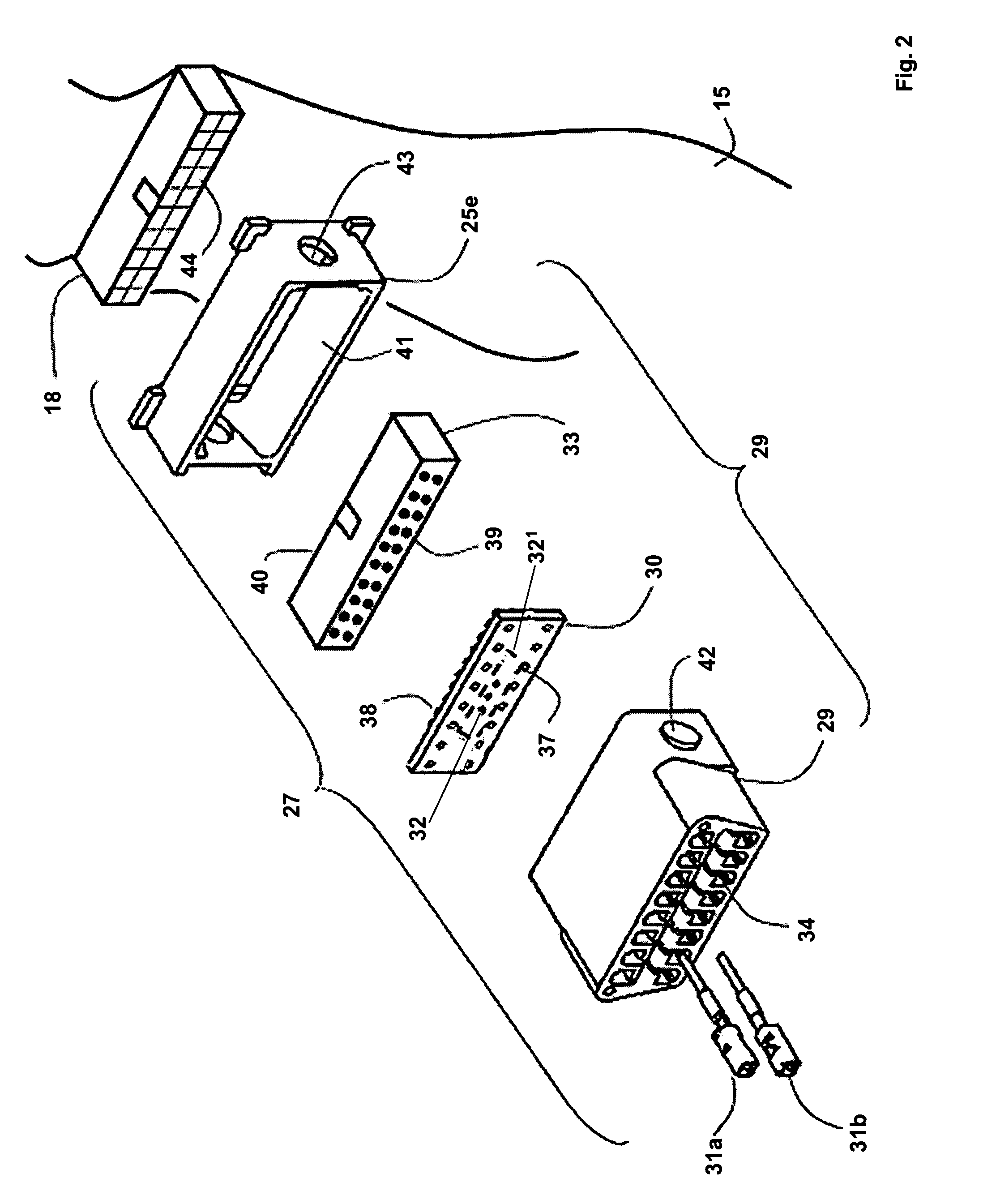
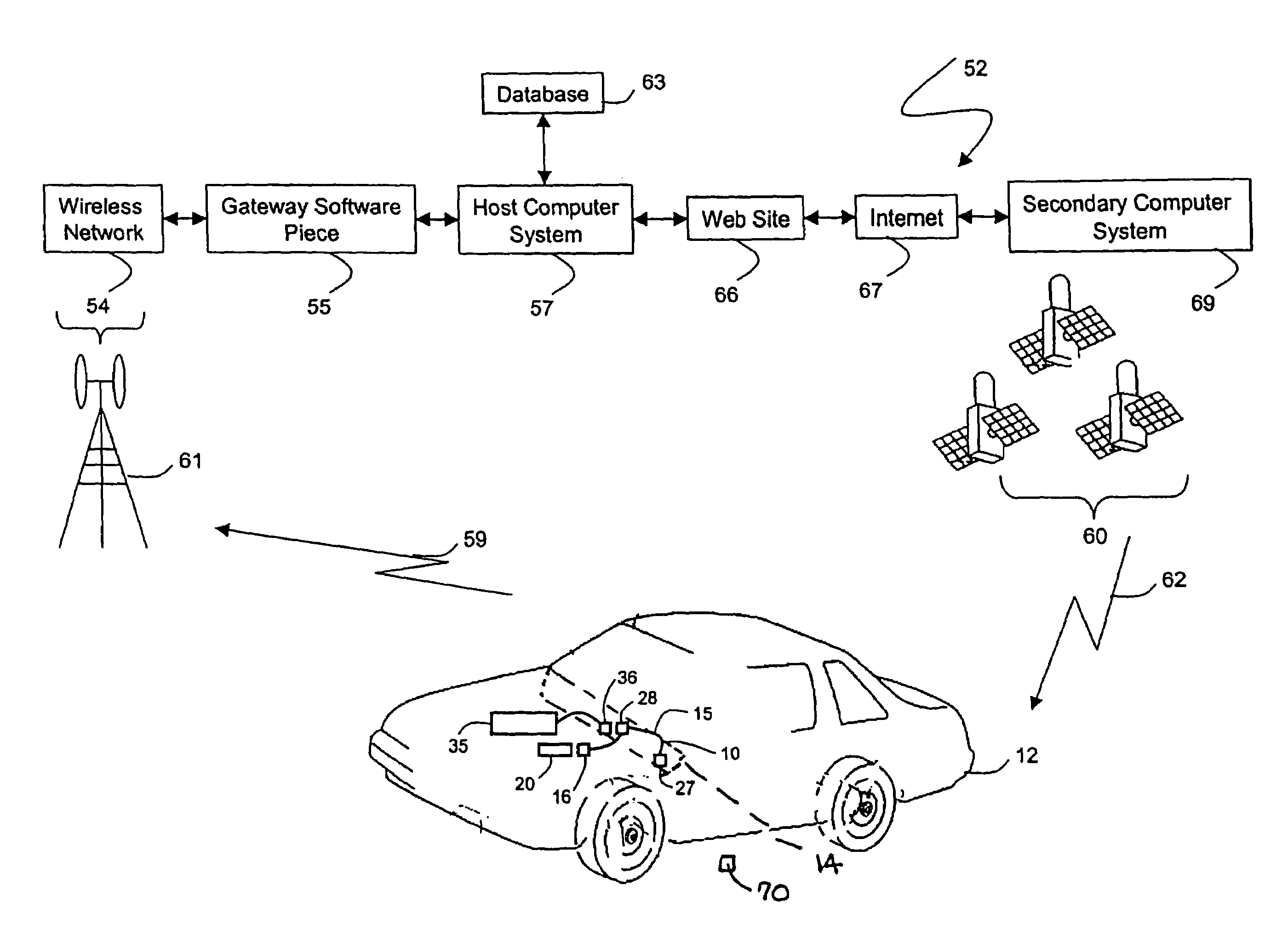
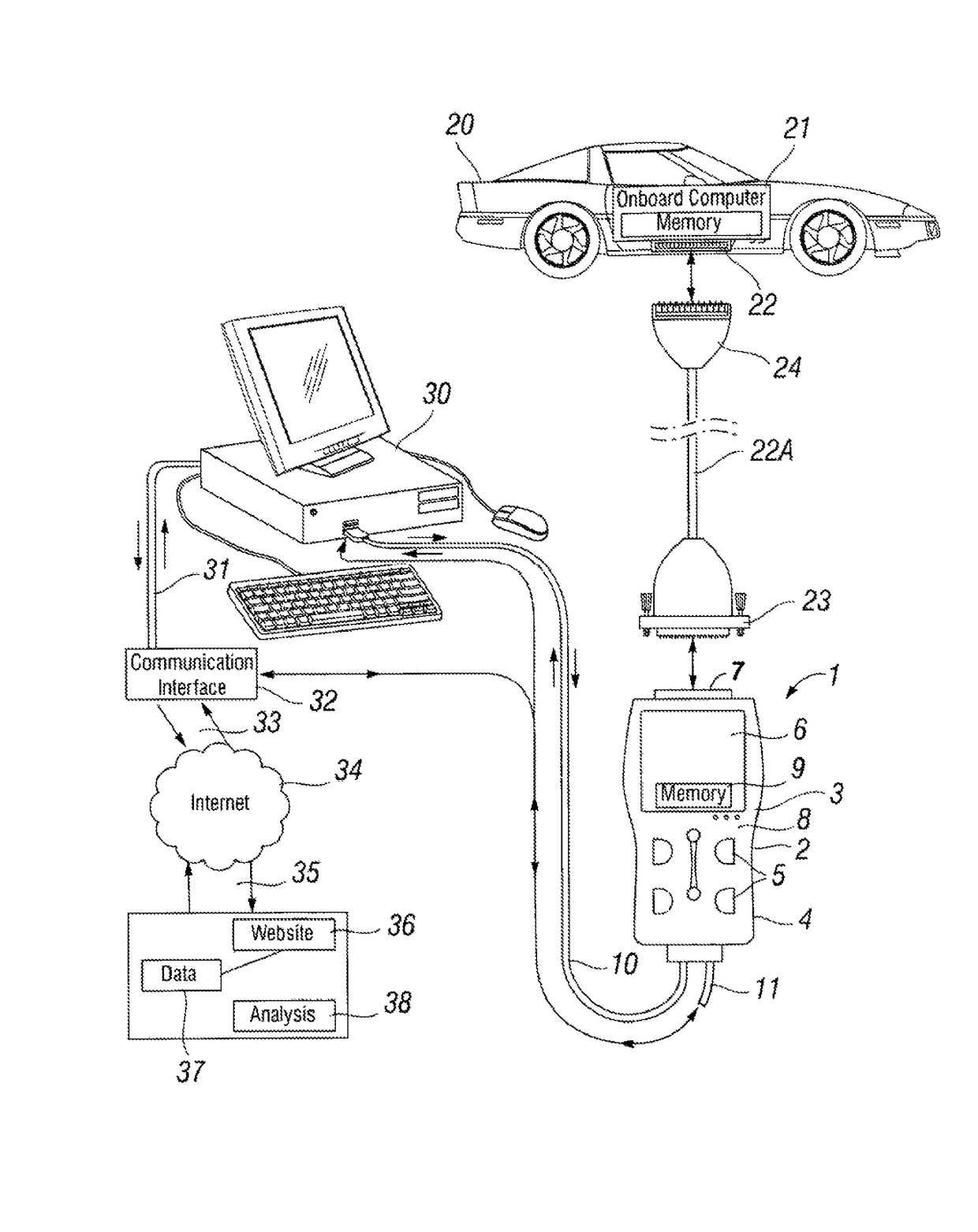
In-vehicle wiring harness with multiple adaptors for an on-board diagnostic connector
ActiveUS7225065B1Facilitate electrically couplingVehicle testingVehicle connectorsIn vehicleEngineering
An embodiment provides a wiring harness that connects a telematics device to a host vehicle. One embodiment of the wiring harness may include: 1) a cable featuring a plurality of wires; 2) a first connector featuring a snap-on adaptor that attaches to a connector core with a pin configuration that mates with a diagnostic scan tool; 3) a second connector that connects to an in-vehicle diagnostic system; and 4) a third connector that connects to the telematics device. A wiring kit embodiment and method embodiments for coupling a telematics device to a host vehicle are also disclosed.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
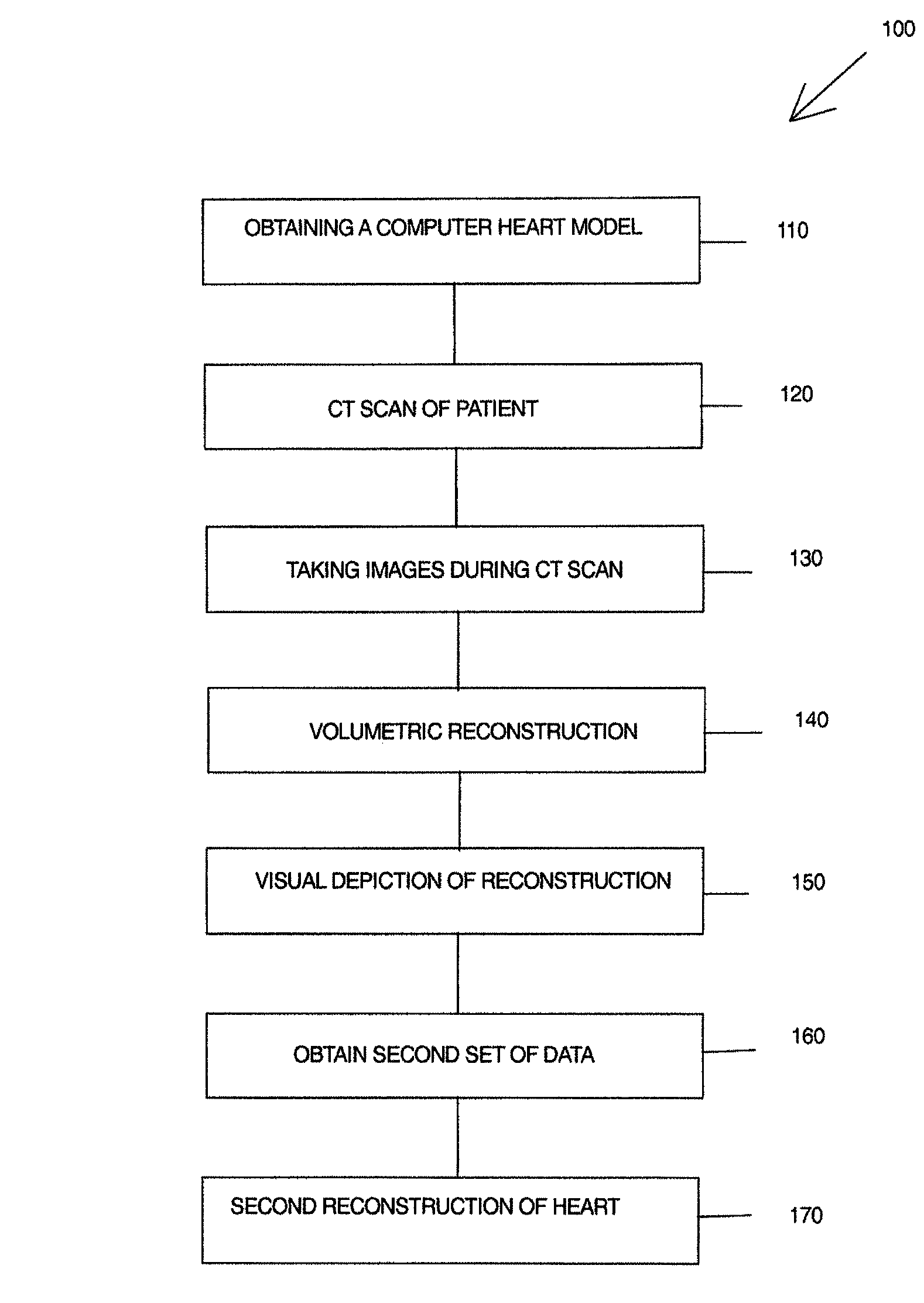
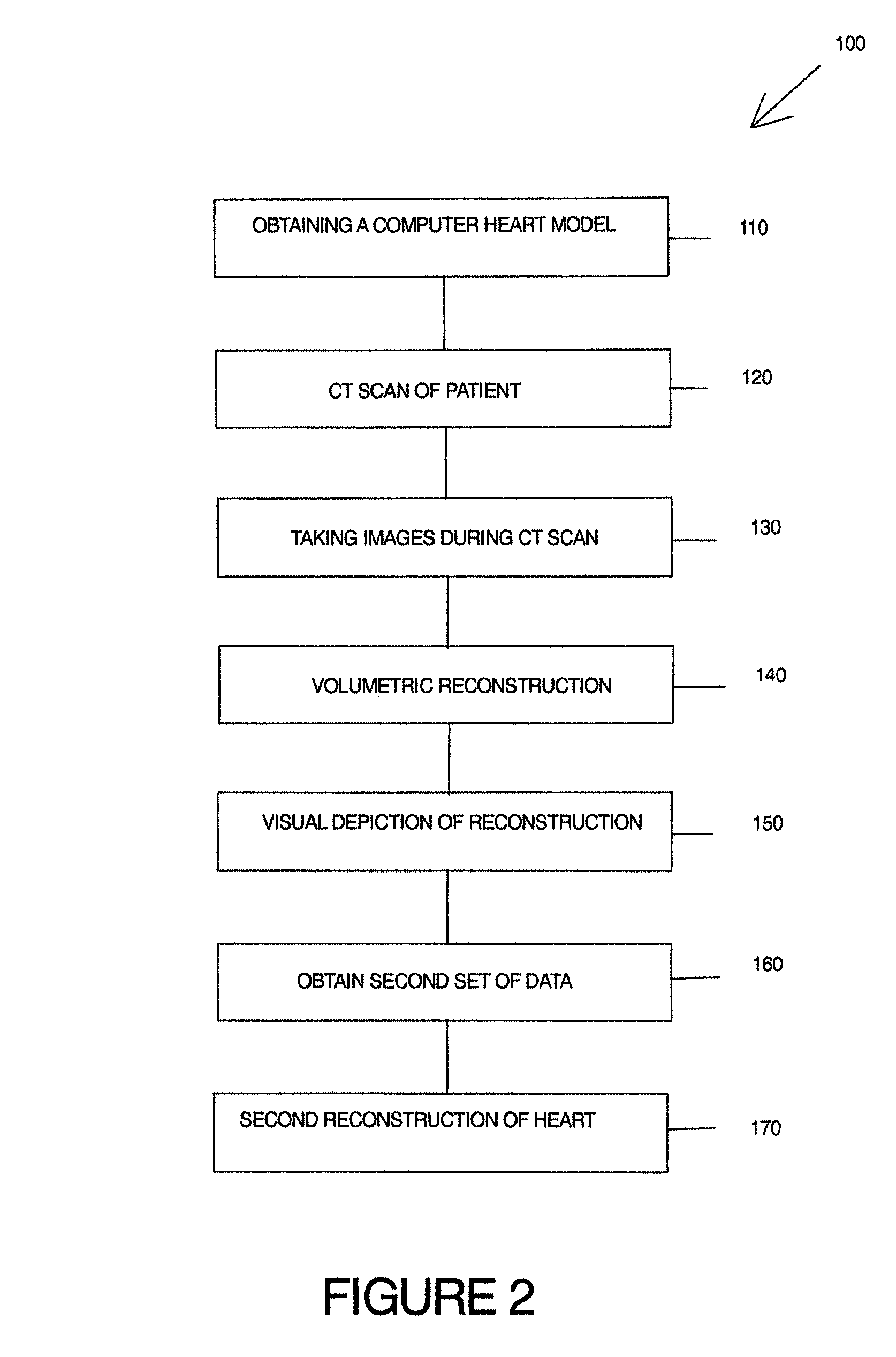
Model-based heart reconstruction and navigation
ActiveUS7773719B2Provide structureMinimize exposureImage enhancementImage analysisBase heartData set
A method to obtain a patient based organ model from patient data, having steps of obtaining a computerized organ model based upon at least one data set of patients, the computerized organ model having a set of classifiers that are used to determine physical parameters of the patients heart, placing the patient in a diagnostic scanner device, taking representative data images of a patients organ while changing position of the image scan, the data images taken with ECG synchronization; and preparing the patient based organ model by evaluating the representative data images of the patients organ with the set of classifiers in the computerized organ model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
In-vehicle wiring harness with multiple adaptors for an on-board diagnostic connector
An embodiment provides a wiring harness that connects a telematics device to a host vehicle. One embodiment of the wiring harness may include: 1) a cable featuring a plurality of wires; 2) a first connector featuring a snap-on adaptor that attaches to a connector core with a pin configuration that mates with a diagnostic scan tool; 3) a second connector that connects to an in-vehicle diagnostic system; and 4) a third connector that connects to the telematics device. A wiring kit embodiment and method embodiments for coupling a telematics device to a host vehicle are also disclosed.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
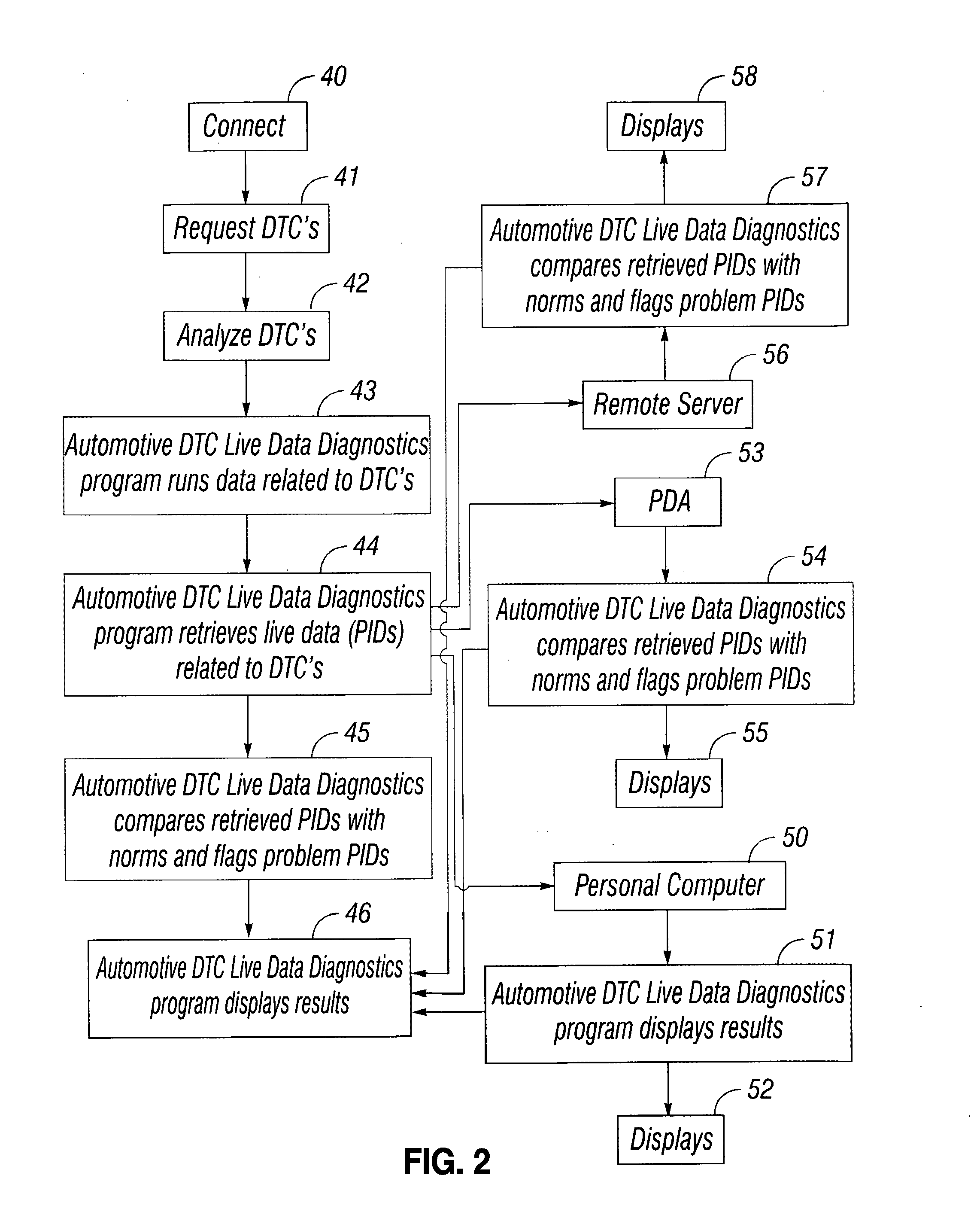
Handheld Scan Tool with Fixed Solution Capability
ActiveUS20130204485A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCode moduleTelecommunications link
A diagnostic scan tool is provided including a connect / configure module for establishing a communication link between the scan tool and a vehicle electronic control unit (ECU). A vehicle specification module operates to identify a vehicle under test in response to receipt of a vehicle identification number (VIN). A trouble code module receives digital trouble codes (DTCs) from the ECU. A freeze frame data module retrieves freeze frame data from the ECU, the retrieved freeze frame data being functionally associated with a highest priority DTC. A database lists possible vehicle defect solutions, indexed to the VIN and the DTCs. A digital signal processor is operative to derive the highest priority DTC from analysis of the retrieved freeze frame data. The digital signal processor further being operative to regulate selection of a most likely vehicle defect solution associated with the VIN and the highest priority DTC.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
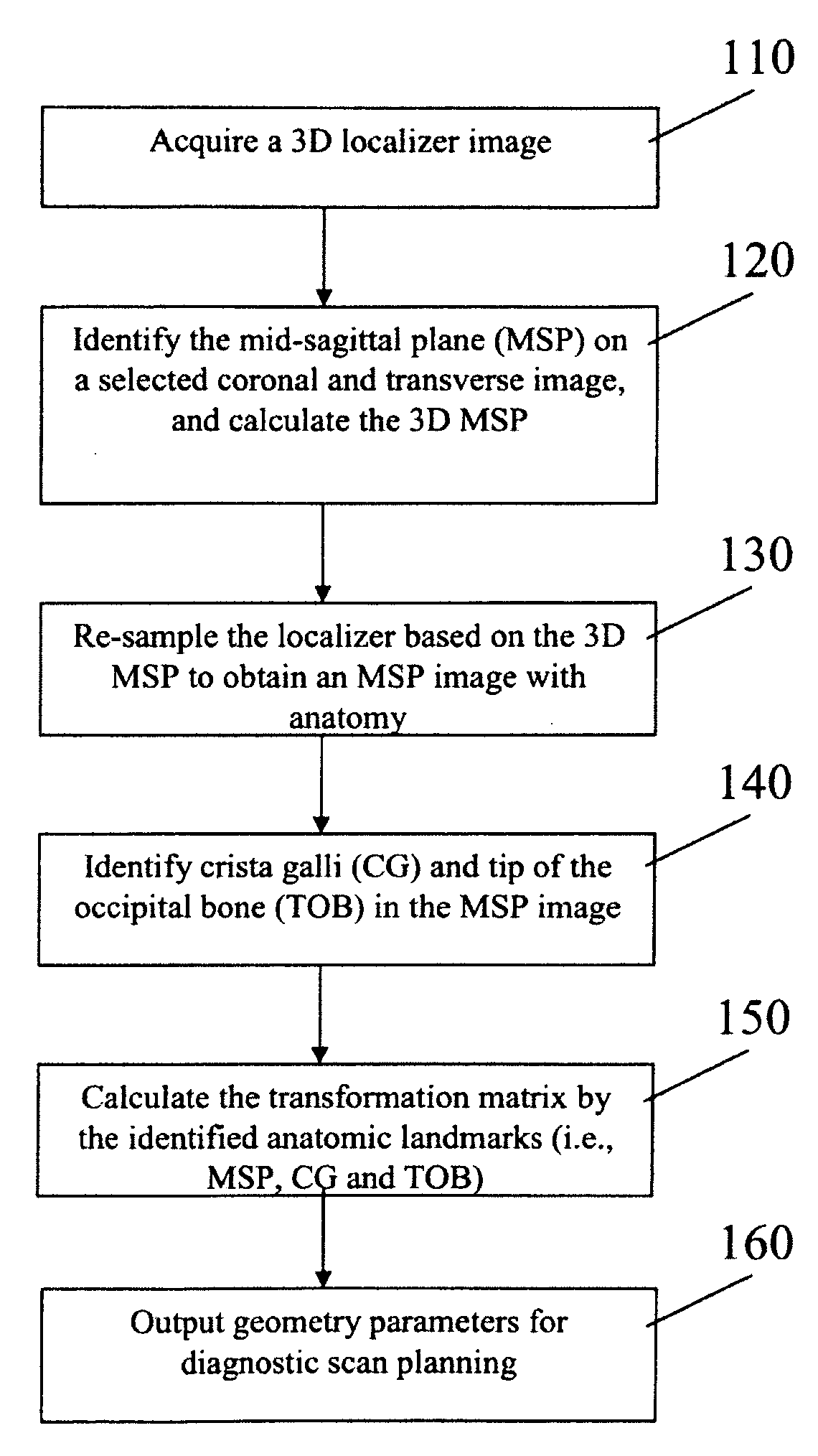
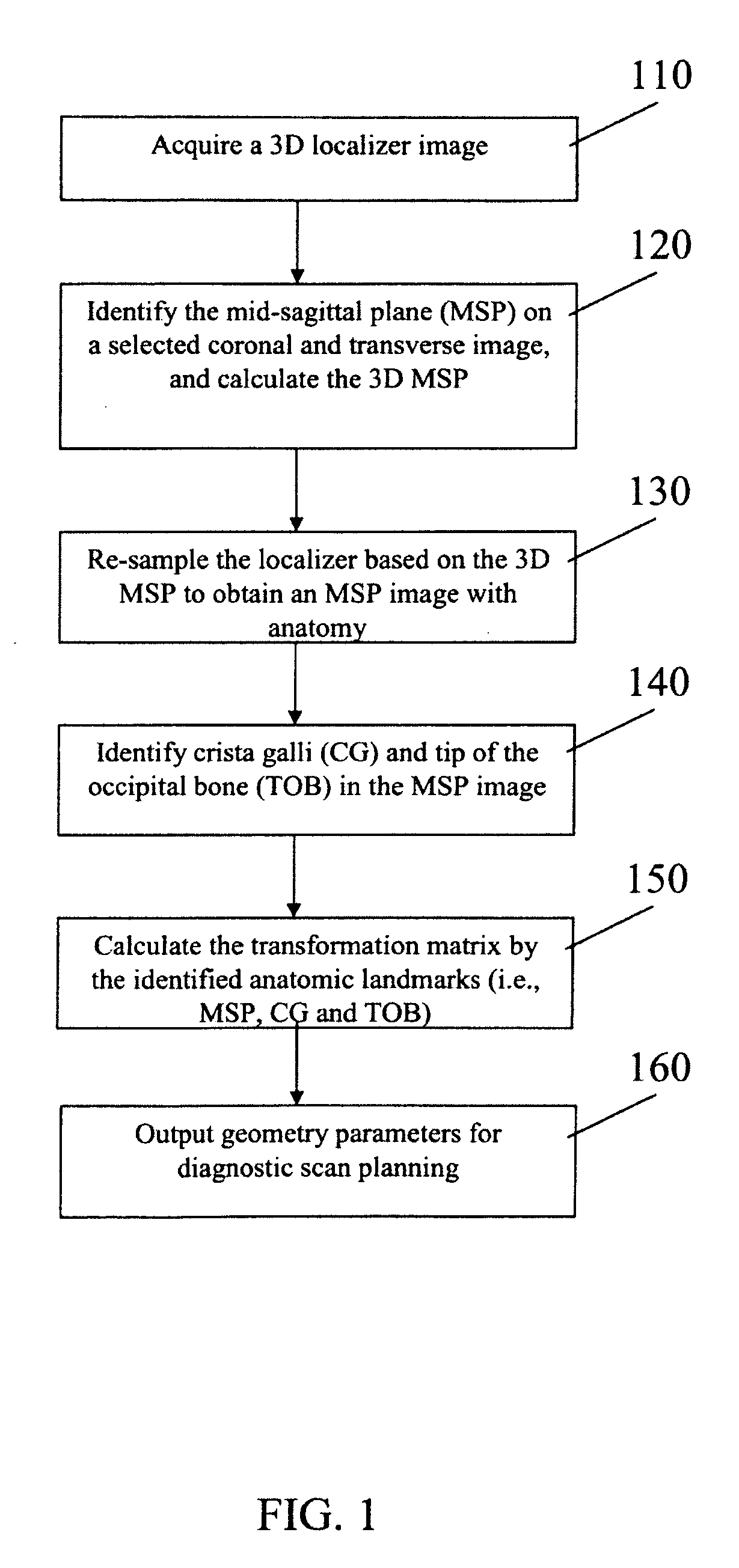
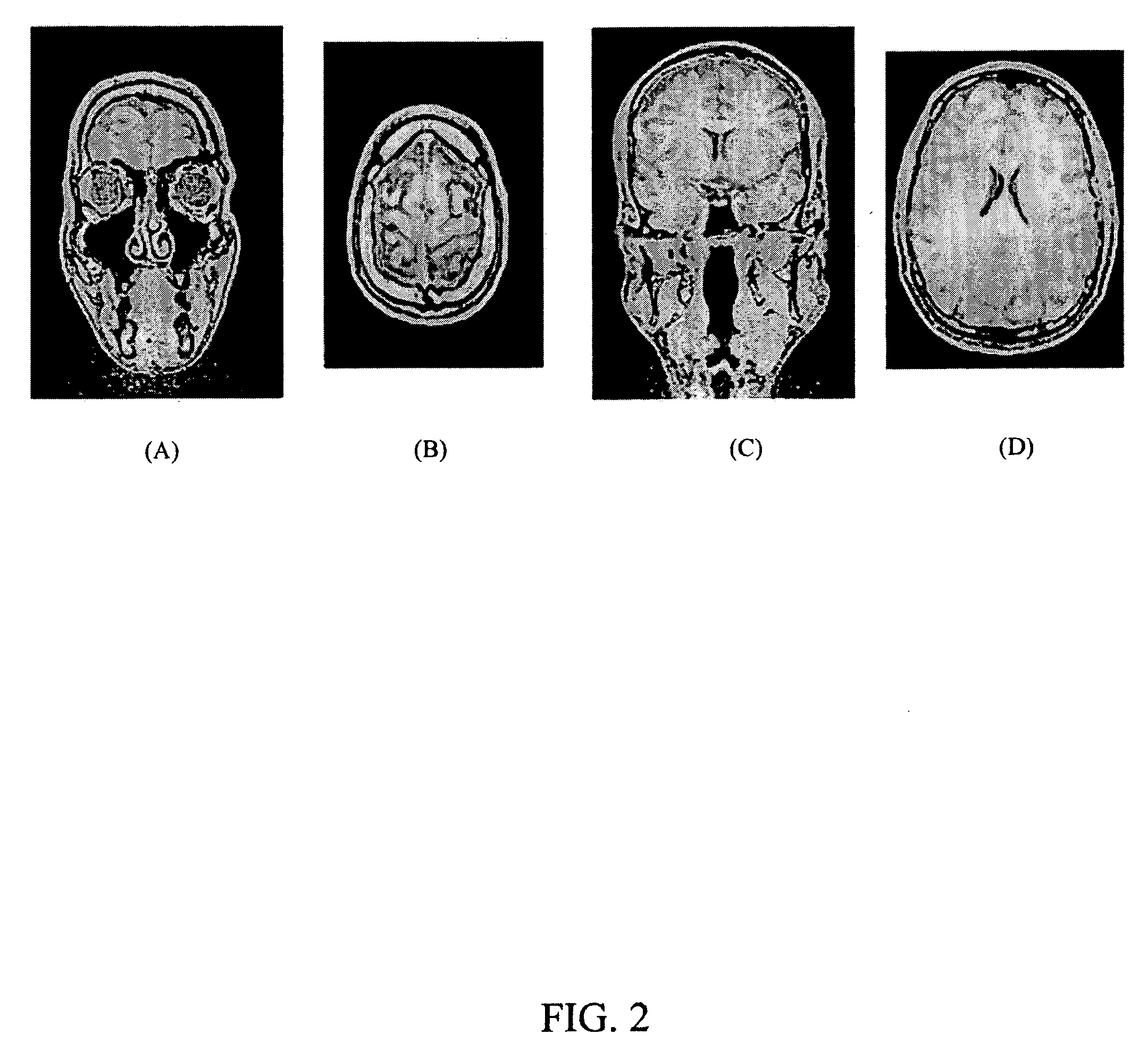
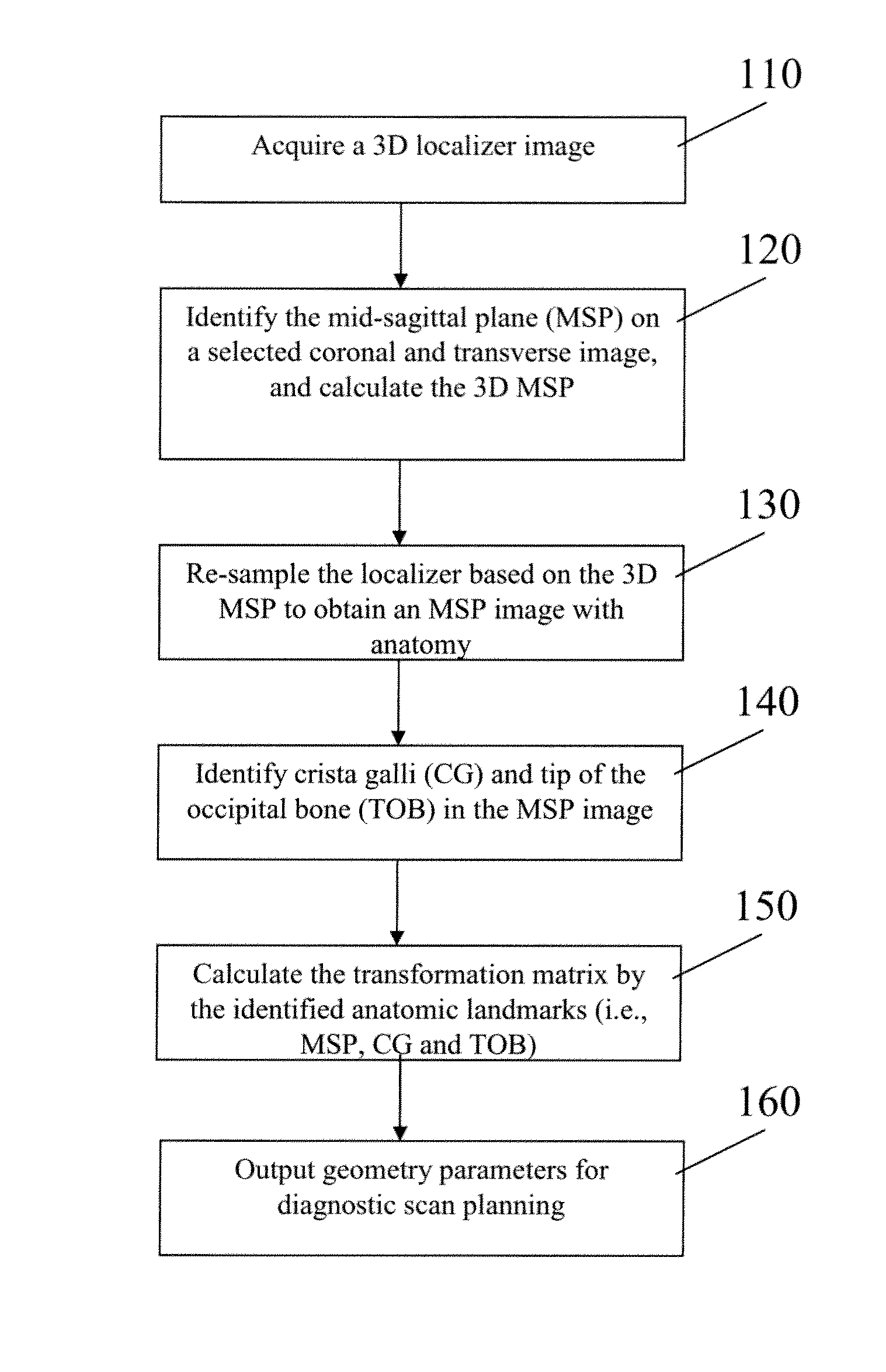
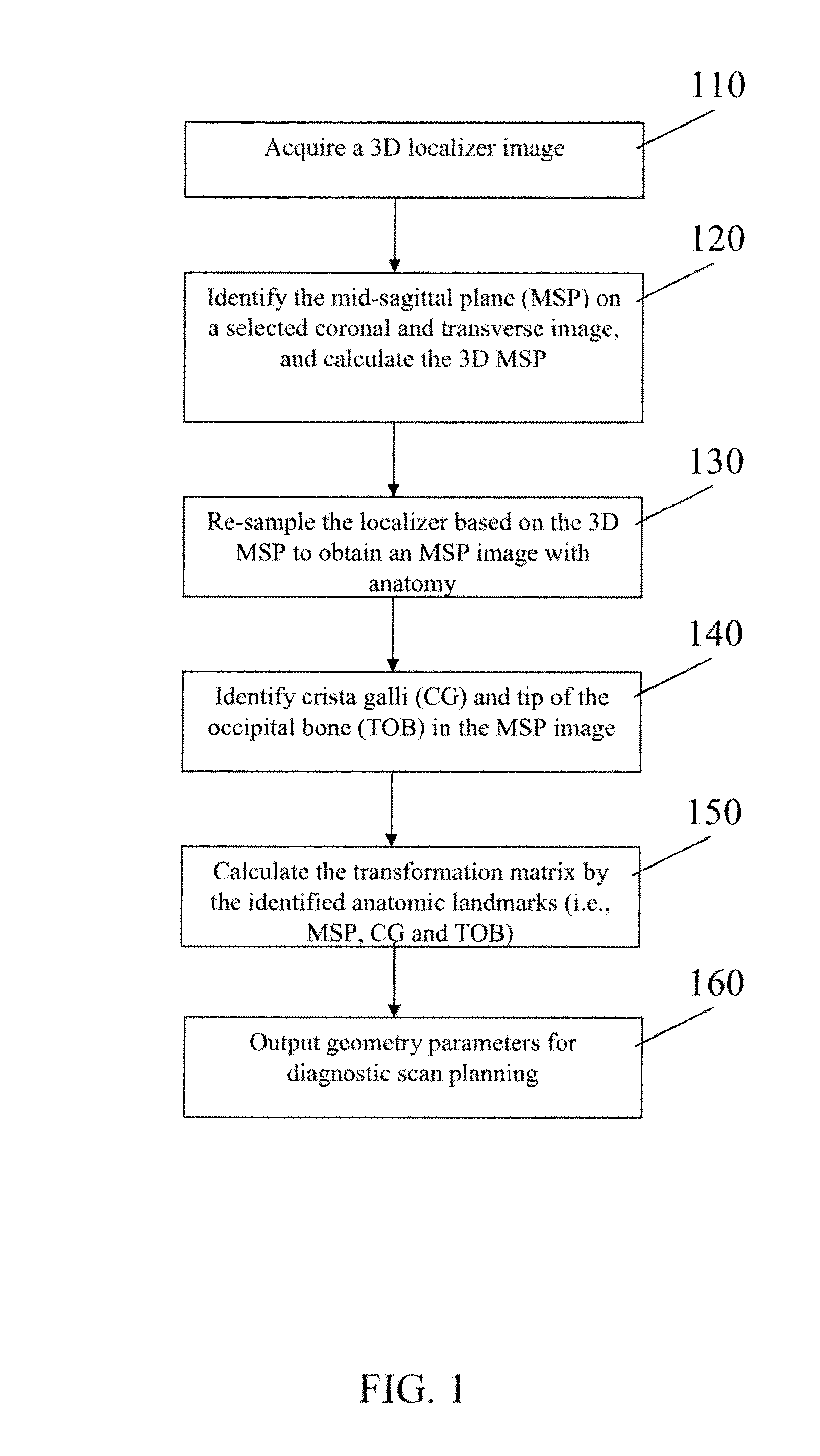
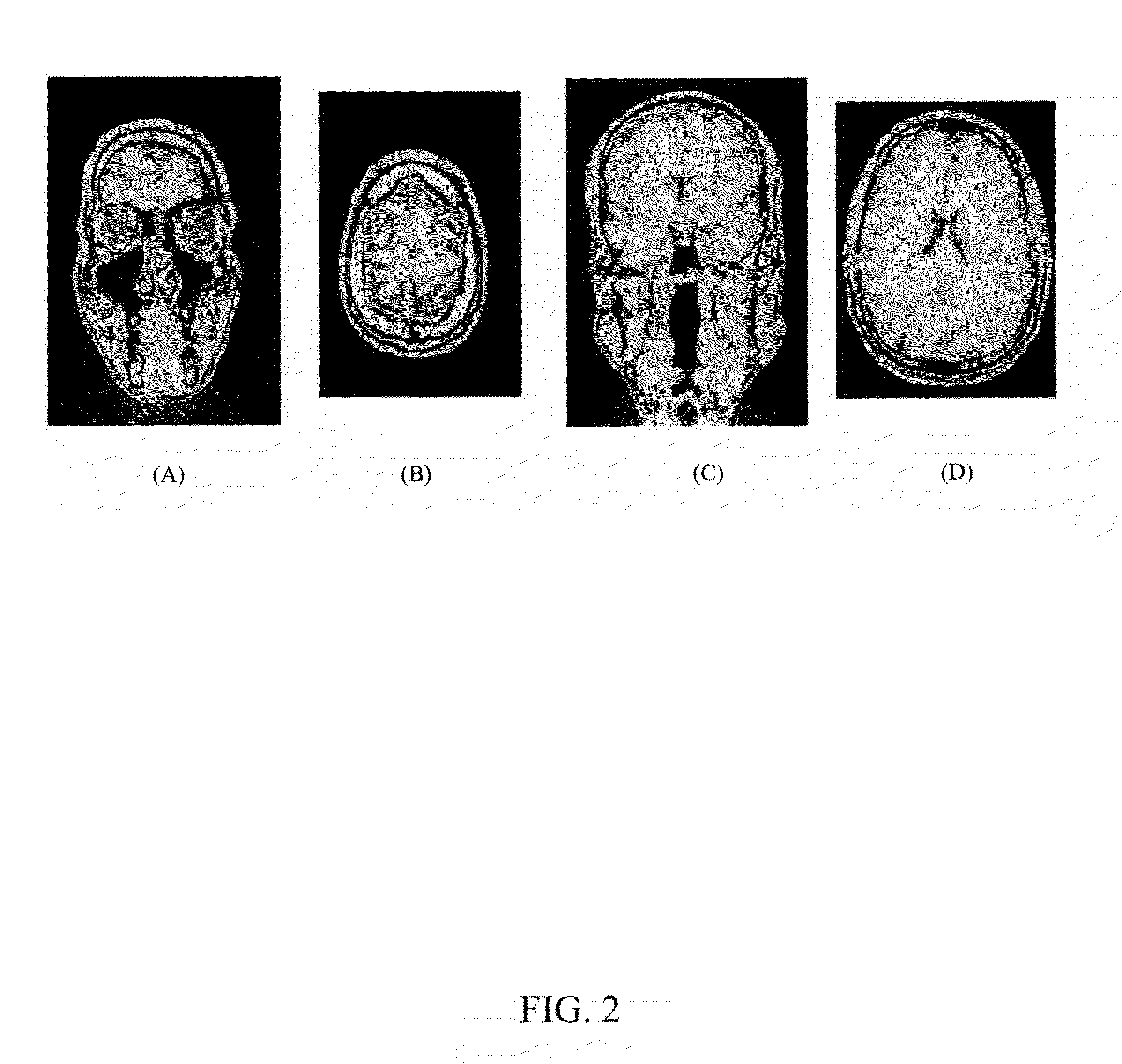
Automatic Alignment of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Brain Scan By Anatomic Landmarks
InactiveUS20090093706A1Maximize magnitudeMinimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringBrain scanningSagittal plane
A method to automatically align magnetic resonance (MR) brain scans for diagnostic scan planning, including: acquiring a three-dimensional (3D) localizer image of a patient; selecting a two-dimensional (2D) coronal view and a 2D transverse view from the localizer image; identifying a mid-sagittal plane (MSP) line in each of the coronal and transverse views and calculating a 3D MSP based on the MSP lines; reconstructing the localizer image based on an equation for the 3D MSP to obtain an image of the MSP of the patient's brain; identifying crista galli (CG) and tip of the occipital bone (TOB) in the image of the MSP of the patient's brain; calculating a transformation matrix based on the MSP, CG and TOB in the image and using the transformation matrix to obtain a scan plan for the patient; and outputting the scan plan for the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Handheld scan tool with fixed solution capability
ActiveUS8909416B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCode moduleTelecommunications link
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
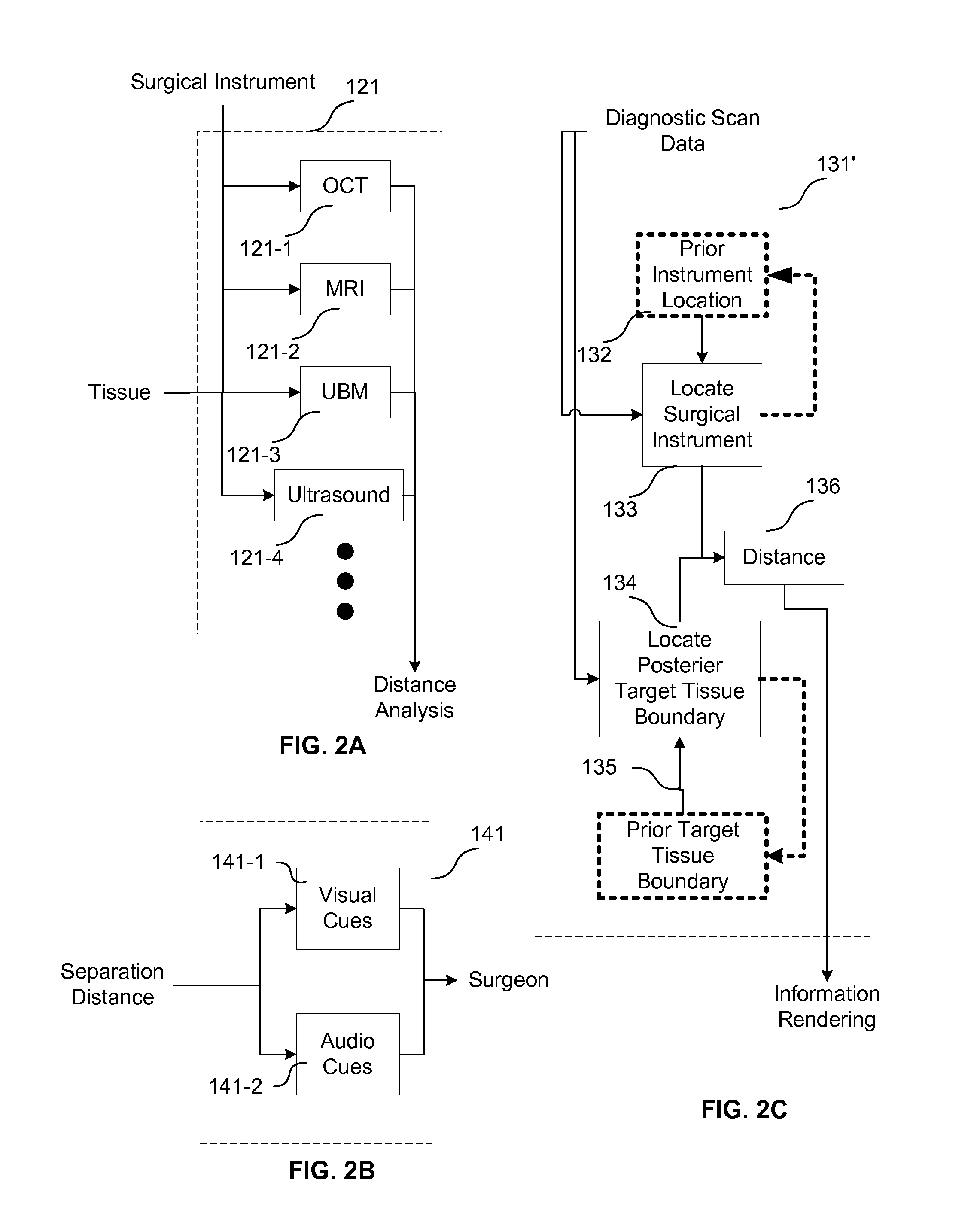
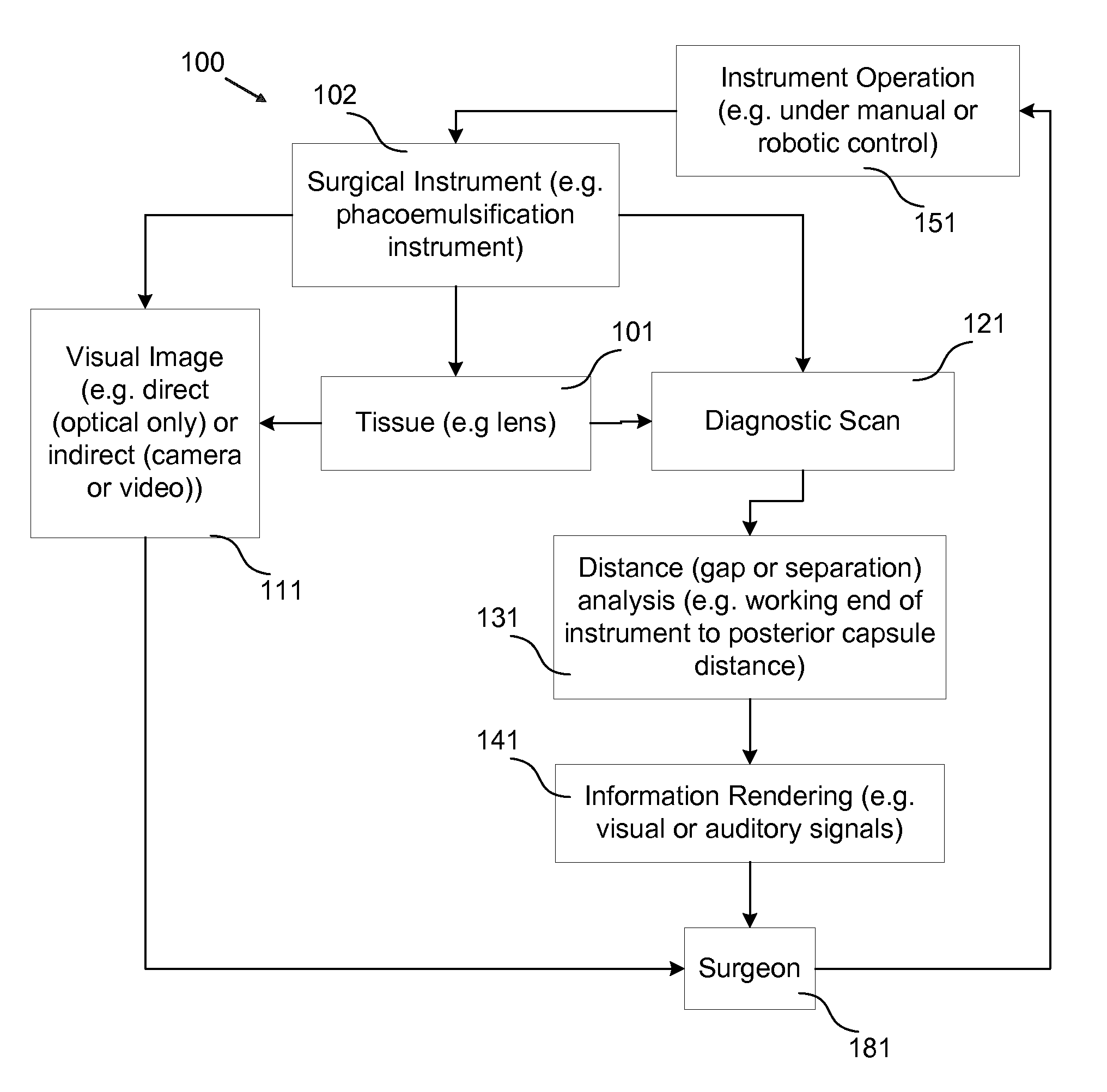
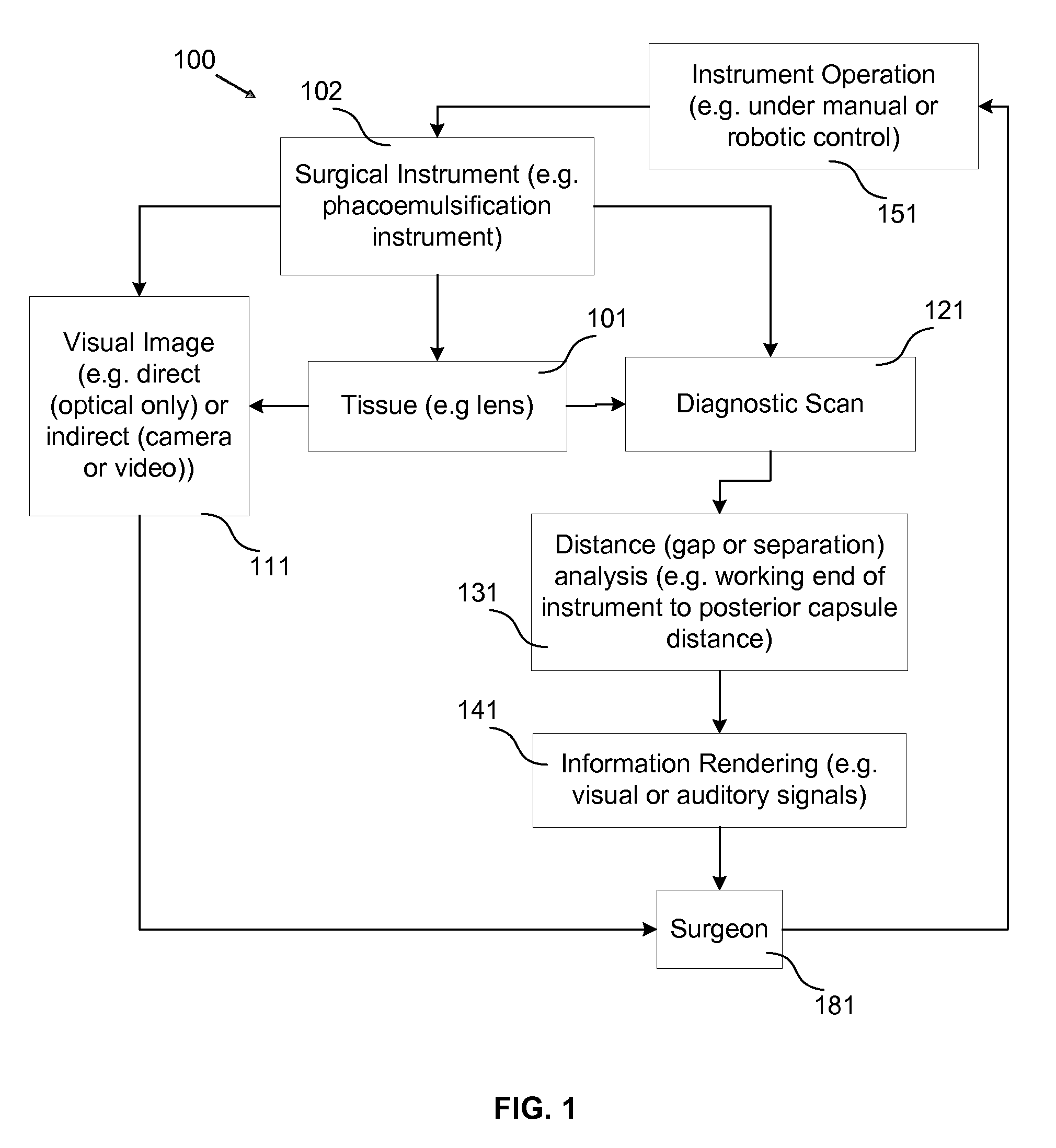
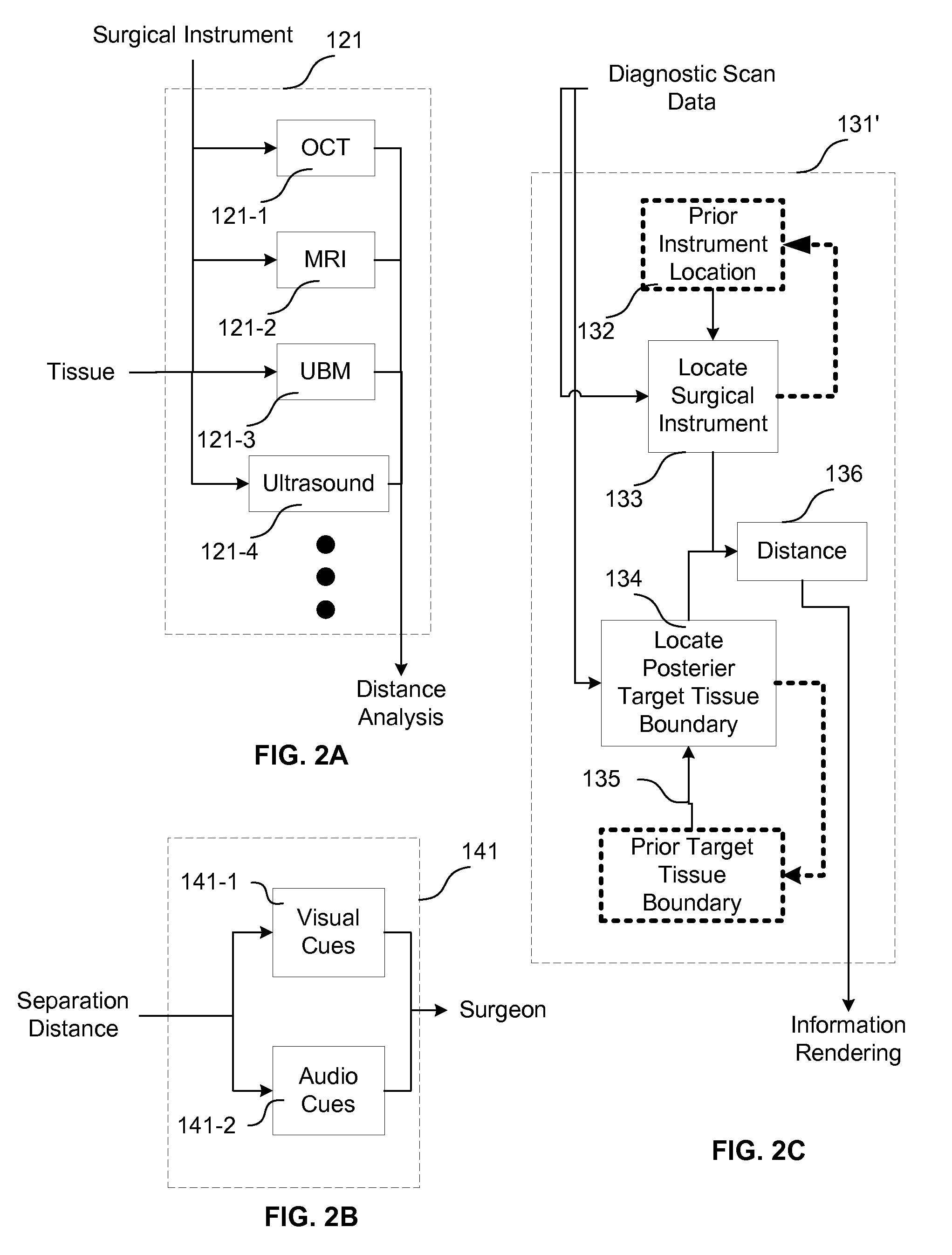
Surgical Procedures Using Instrument to Boundary Spacing Information Extracted from Real-Time Diagnostic Scan Data
InactiveUS20120022546A1Less riskAddressing slow performanceIncision instrumentsEye surgeryImage ViewSurgical department
Specific embodiments of the invention are directed to improved phacoemulsification procedures involving the use of processed non-visual three-dimensional data (i.e. diagnostic scan data) to provide a surgeon with additional guidance (i.e. more than that generally obtained from visual observation of the working area) concerning the distance separating a working end of a phacoemulsification instrument and the posterior portion of the capsule of the eye during surgical procedures involving the removal of the crystalline lens of an eye (e.g. a cataract removal procedure). Such separation (i.e. distance or gap) information may be used to aid the surgeon in cutting or scoring the lens to a desired depth while minimizing the risk of penetrating the posterior portion of the capsule with the working end of the instrument. Some embodiments provide for the visual and / or auditory conveyance of distance information to the surgeon wherein visual information may be conveyed by overlaying it with real visual images of actual surface features viewed by the surgeon. Additional embodiments provide for overlaying visual representations of selected three-dimensional structure information (e.g. depths of troughs cut into the lens) with the real surface feature images viewed by the surgeon.
Owner:VANTAGE SURGICAL SYST
Hand held data retrieval device with fixed solution capability
ActiveUS20150105972A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCode moduleTelecommunications link
A diagnostic scan tool is provided including a connect / configure module for establishing a communication link between the scan tool and a vehicle electronic control unit (ECU). A vehicle specification module operates to identify a vehicle under test in response to receipt of a vehicle identification number (VIN). A trouble code module retrieves digital trouble codes (DTCs) from the ECU. A freeze frame data module retrieves freeze frame data from the ECU, the retrieved freeze frame data being functionally associated with a highest priority DTC. A database lists possible vehicle defect solutions, indexed to the VIN and the DTCs. A digital signal processor is operative to derive the highest priority DTC from analysis of the retrieved freeze frame data. The digital signal processor further being operative to regulate selection of a most likely vehicle defect solution associated with the VIN and the highest priority DTC.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
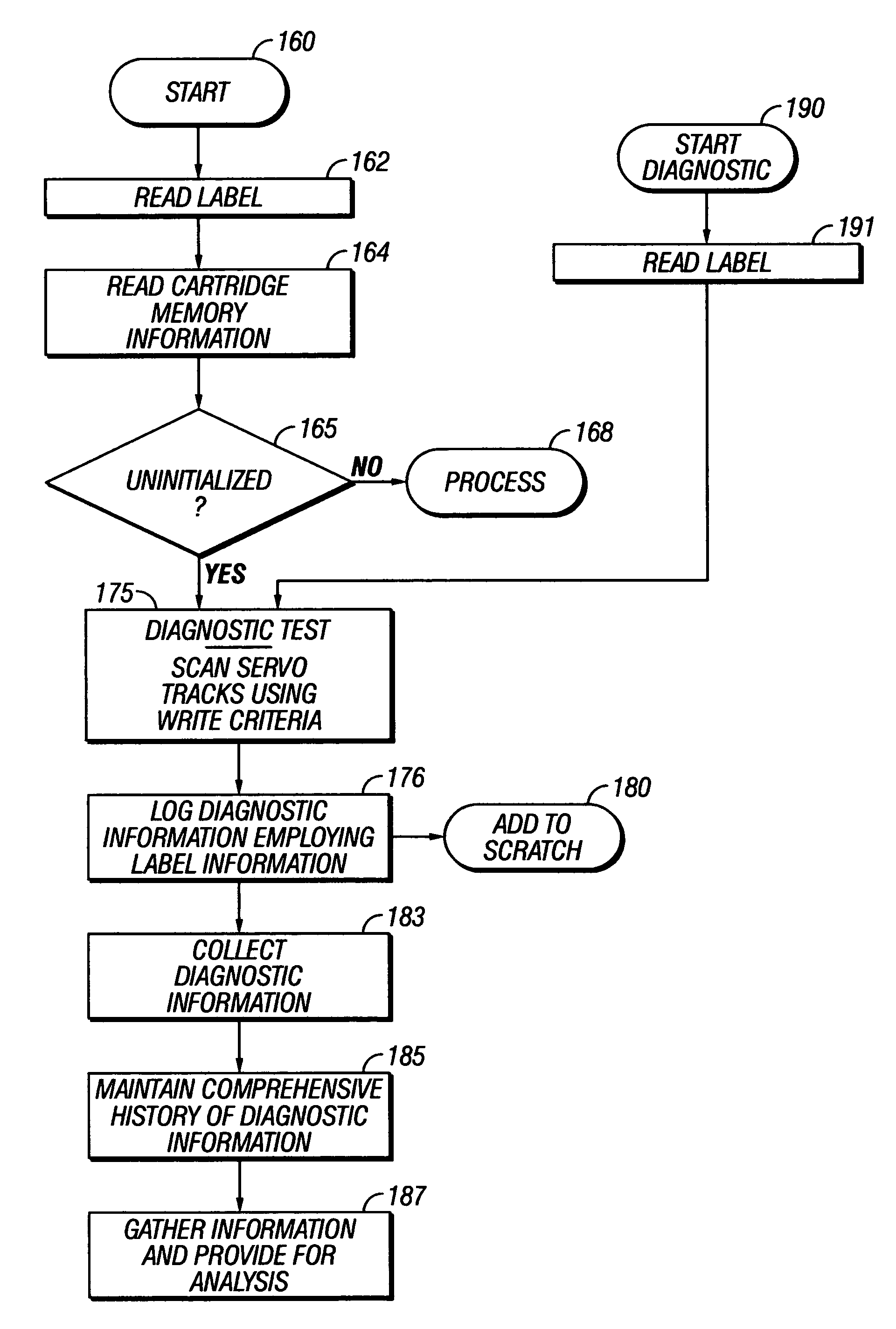
Automated data storage library magnetic tape diagnostic
InactiveUS7116506B1Flat record carrier combinationsRecord information storageMagnetic tapeMagnetic tape data storage
Diagnostic information is provided in an automated data storage library which stores magnetic tape data storage cartridges. Uninitialized magnetic tape data storage cartridges are identified; a diagnostic scan is conducted by a drive of the library of the servo tracks on magnetic tape of an identified cartridge using write criteria for a diagnostic test; the results of the diagnostic test are logged by the drive; and the logged results of the diagnostic test are collected at the library controller.
Owner:IBM CORP
Surgical procedures using instrument to boundary spacing information extracted from real-time diagnostic scan data
InactiveUS8945140B2Less riskAddressing slow performanceEye surgerySurgical navigation systemsOperative Surgical ProceduresSurgical department
The present disclosure is directed to improved phacoemulsification procedures involving the use of processed non-visual three-dimensional data (i.e. diagnostic scan data) to provide a surgeon with additional guidance concerning the distance separating a working end of a phacoemulsification instrument and the posterior capsule of the eye during a surgical procedure involving the removal of the crystalline lens of an eye. Such information is implemented to aid the surgeon in cutting or scoring the lens to a desired depth while minimizing the risk of penetrating the posterior portion of the capsule with the working end of the instrument. Some embodiments provide for the visual and / or auditory conveyance of distance information to the surgeon. Additional embodiments can provide for overlaying visual representations of selected structure information with the images provided to the surgeon.
Owner:VANTAGE SURGICAL SYST
Precision Applicator
An applicator comprises a first structural element which has a shape determined according to a digital geometric representation of a target structure, the applicator further comprises an active agent located according to a diagnostic scan of the target structure.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Automatic alignment of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scan by anatomic landmarks
InactiveUS8190232B2Maximize magnitudeMinimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringBrain sectionLandmark
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
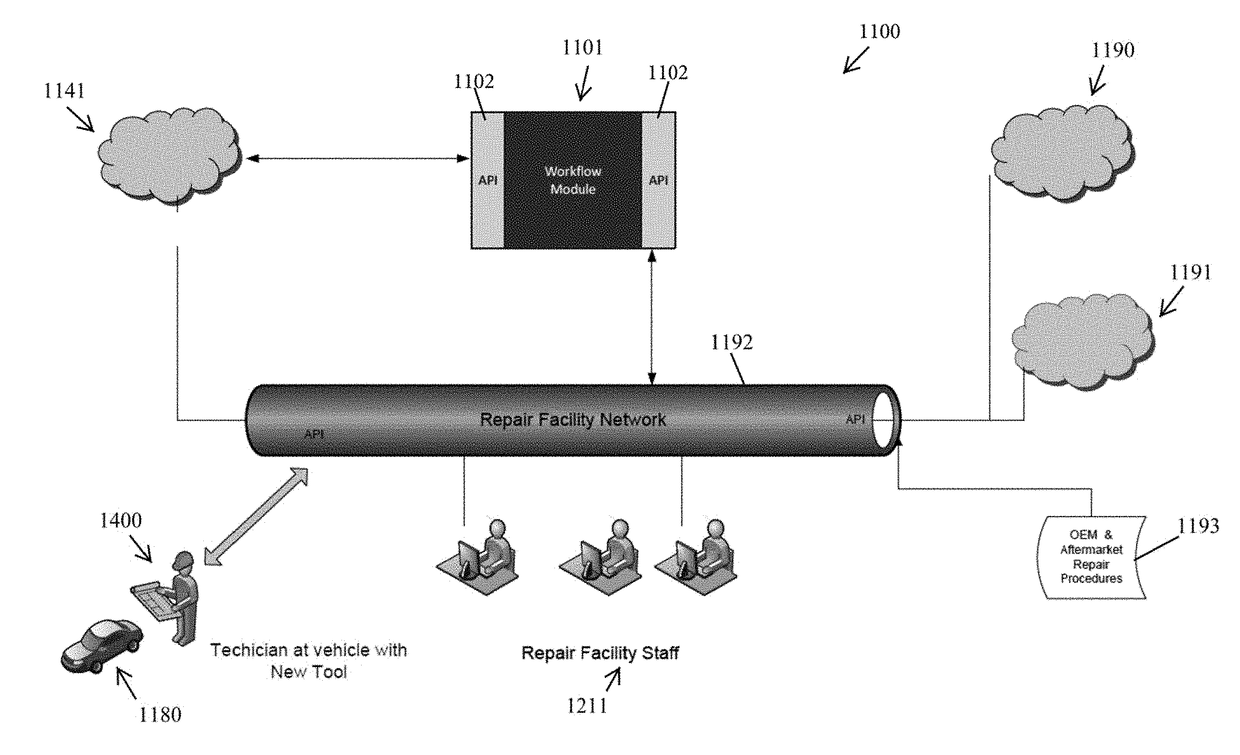
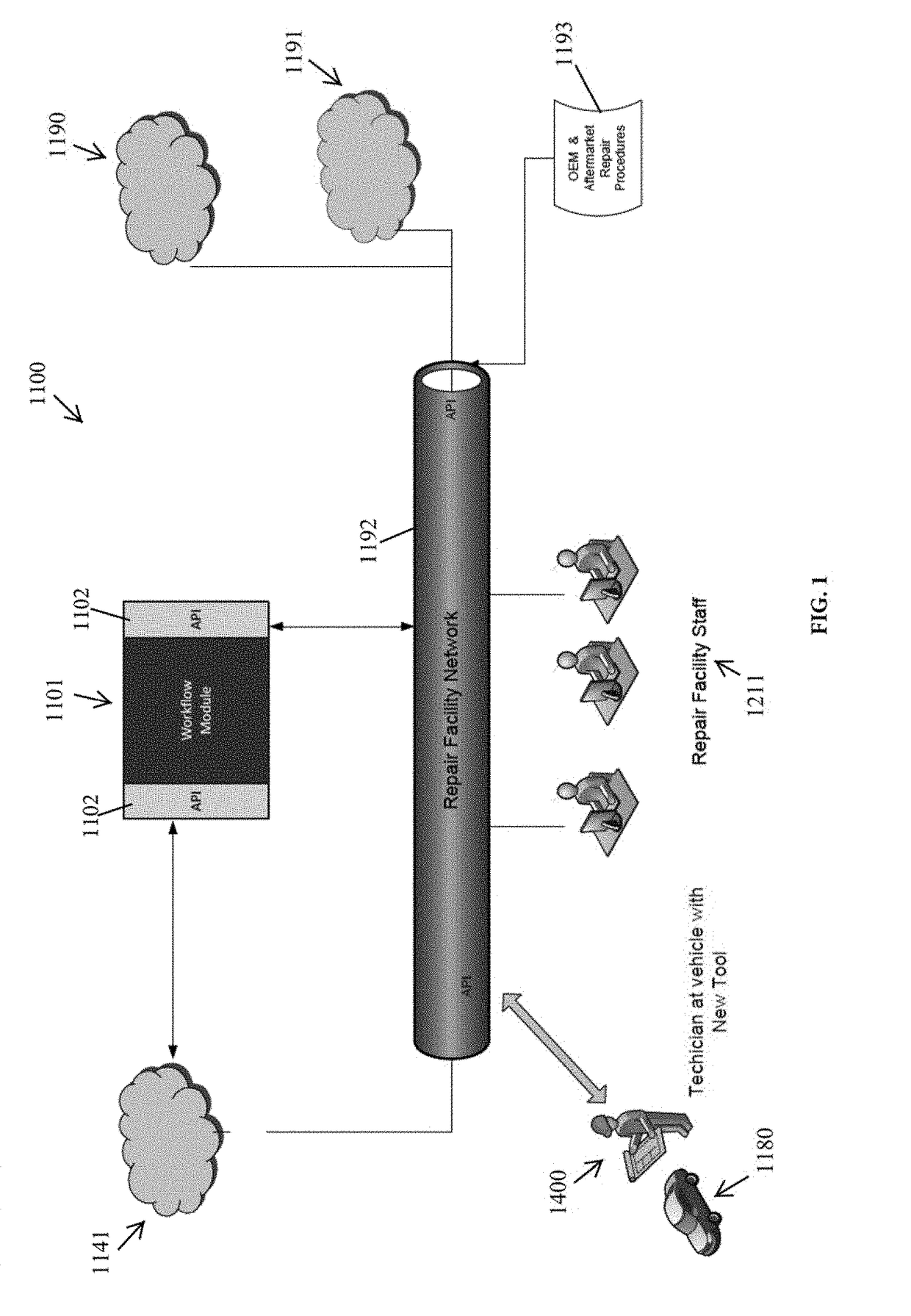
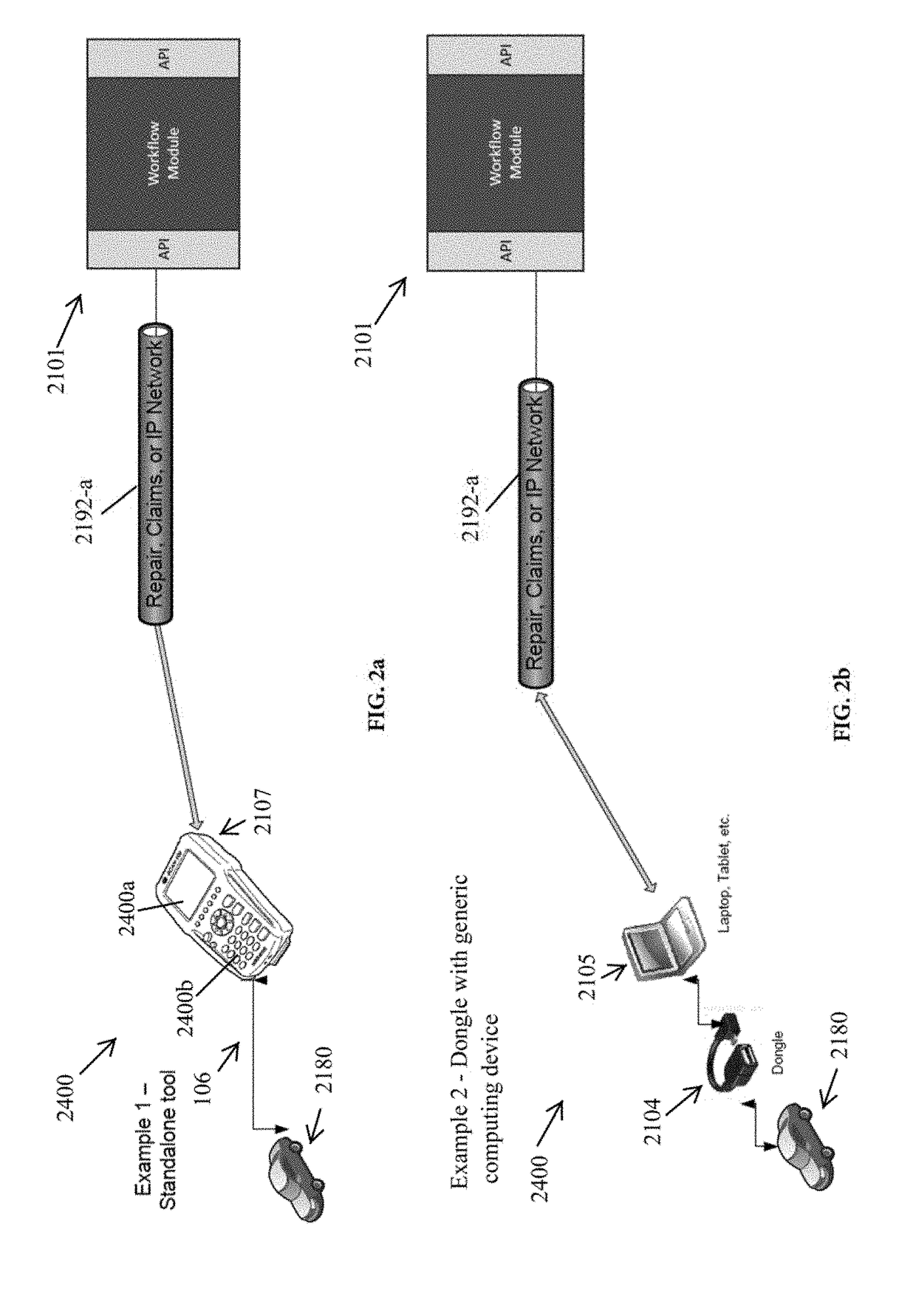
Systems and methods for use of diagnostic scan tool in automotive collision repair
ActiveUS20170301154A1Enable utilizationAccurate and timely decisionRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesBilling/invoicingData streamDecision taking
A new automotive collision repair technology is provided, including system and data flow architectures that are designed to provide enhanced data and enhanced data flow in the context of vehicle diagnosis and repair, particularly when repairs are necessary due to collisions. In some examples, the data flow through the network is streamlined, to avoid network congestion, to use fewer computer and network resources and / or to enable the utilization of smaller databases. In other examples, enhanced access to data in real-time and near real-time enabled by a Workflow Module supports more accurate and timely decisions on vehicle repair. An advantage of this new automotive collision repair technology is that it enables proper and proven repairs, which in turns increases operation safety of repaired vehicle and people safety.
Owner:MITCHELL INT INC
System and method for automated magnetic resonance scan prescription for optic nerves
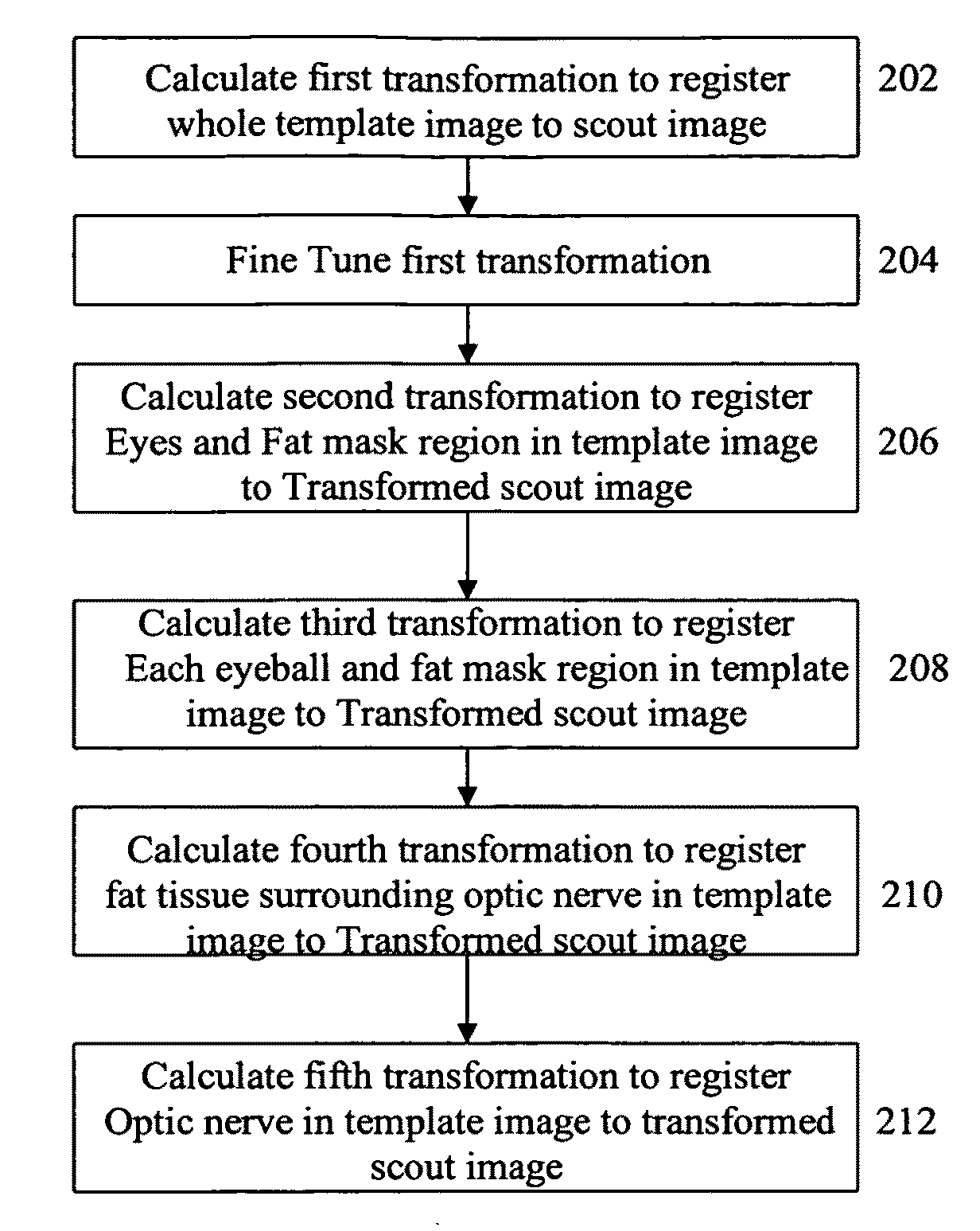
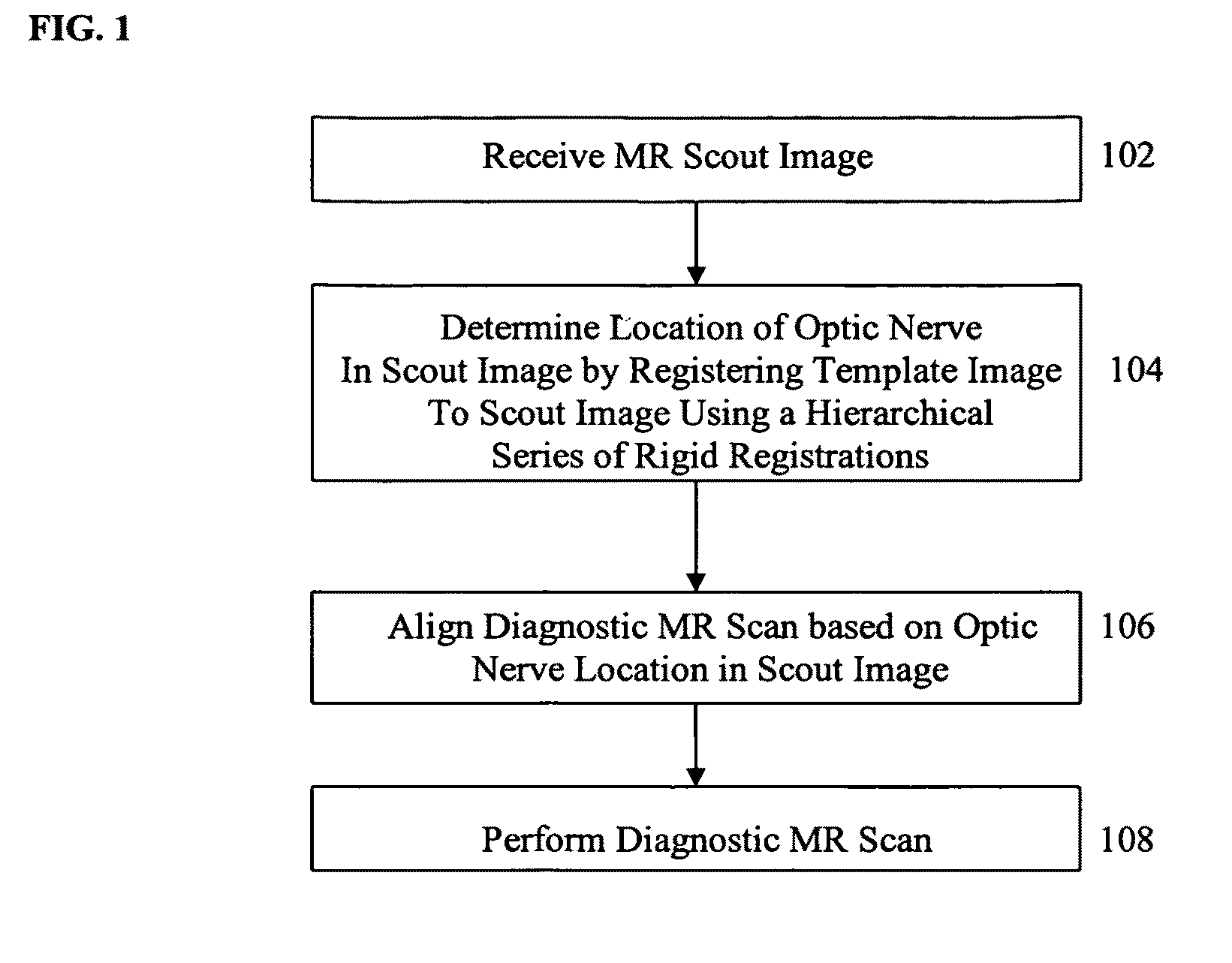
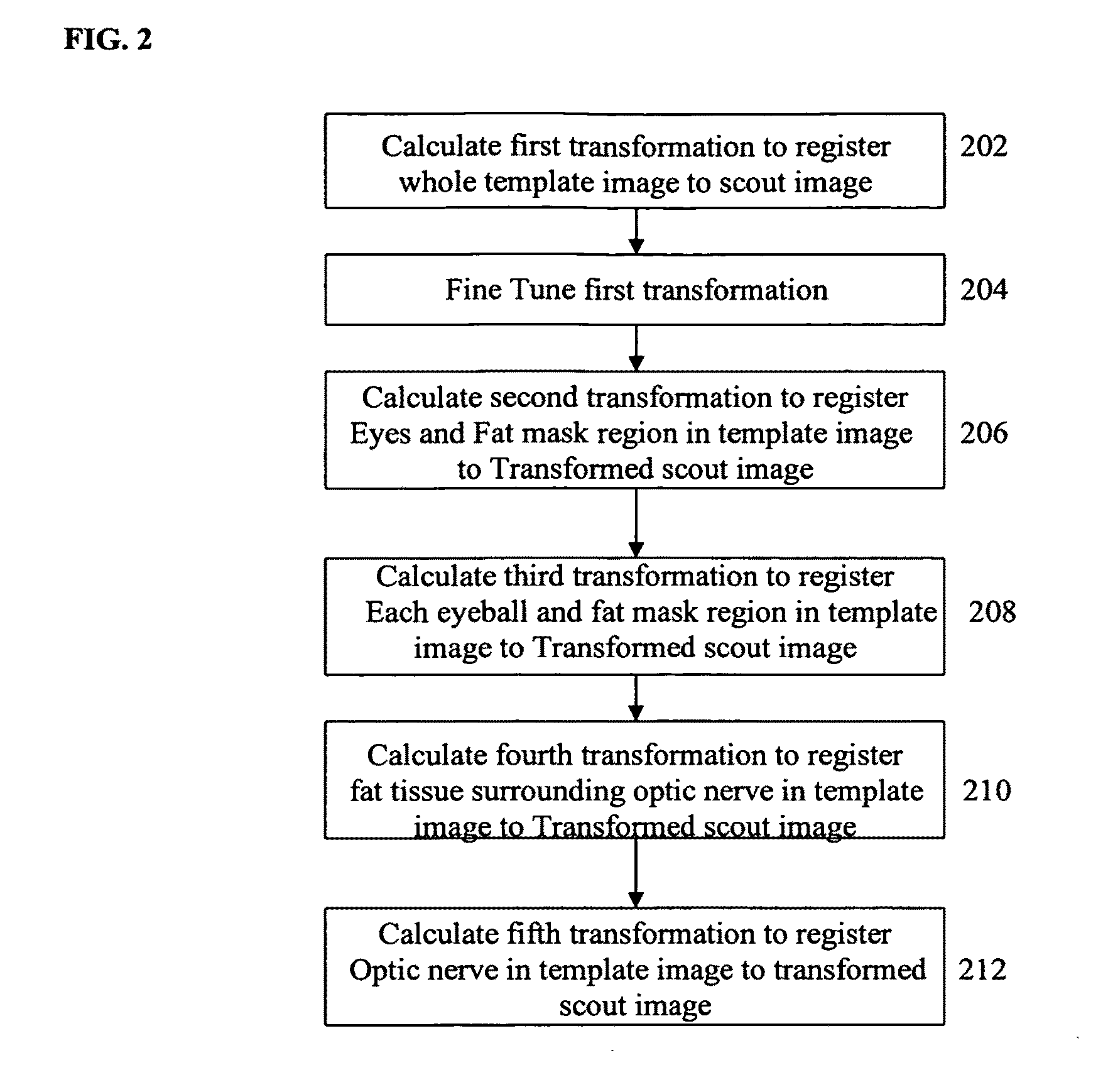
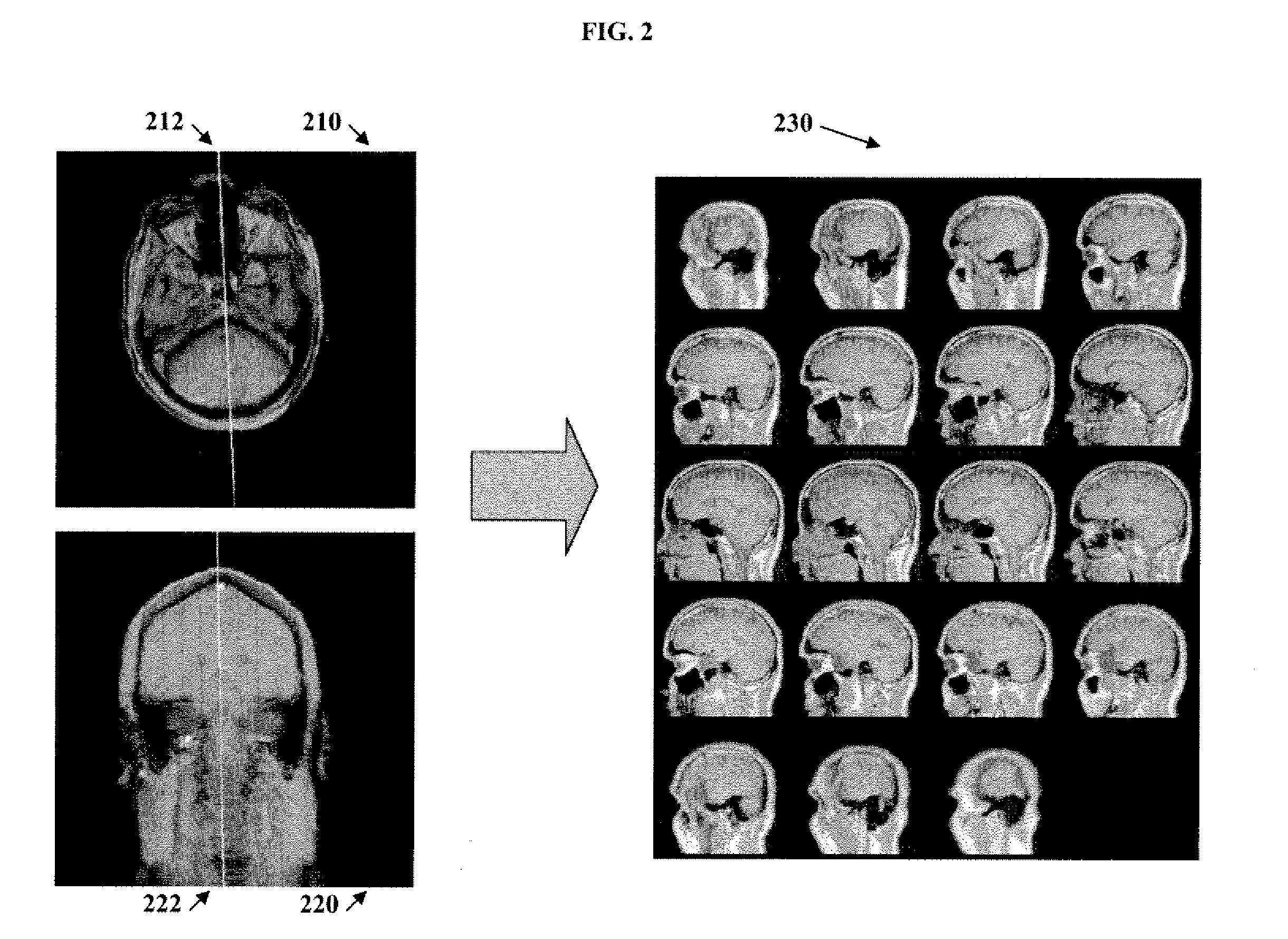
A method and system for automated magnetic resonance (MR) scan prescription is disclosed. A 3D MR scout image is obtained by an initial MR scan. The location of an optic nerve in the scout image is determined by registering a template image to the scout image using a hierarchical series of rigid registrations. The hierarchical series of rigid registrations utilizes a coarse to fine scheme to register regions in the template image to the scout image, starting with the whole template image and finishing with the optic nerve. A diagnostic MR scan is then aligned based on the location of the optic nerve in the scout image, and the diagnostic scan is performed resulting in a high quality diagnostic 3D MR image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Magnetic Resonance Brain Scan Planning
InactiveUS20080071163A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionSagittal planeMR - Magnetic resonance
A method and system for automatic MR brain scan planning is disclosed. The method utilizes a set of 2D orthogonal localizer images to determine scanning planes for 3D diagnostic MR scans. A location of the mid-sagittal plane (MSP) is detected in each of a transversal localizer image and a coronal localizer image. A sagittal scanning plane is determined based on the location of the MSP in the transversal and coronal localizer images. A diagnostic sagittal MR scan is then acquired based on the sagittal scanning plane. The corpus callosum CC is segmented in a sagittal MR image slice resulting from the diagnostic sagittal MR scan. A transversal scanning plane can be determined based on a location of the CC in the sagittal MR image slice and the location of the MSP in the coronal localizer image, and a coronal scanning plane can be determined based on the location of the CC in the sagittal MR image slice and the location of the MSP in the transversal localizer image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Identification of regions of interest and extraction of time value curves in imaging procedures
A method of extracting at least one time-value curve to determine a protocol in an imaging procedure using an imaging system, includes: determining a first N-dimensional data set of pixel values of a portion of a body of the patient at a first time using the imaging system, wherein N is an integer; determining at least a second N-dimensional data set of pixel values of the portion at a second time using the imaging system; computing a predetermined number of correlated segments of the imaged portion corresponding to a predetermined number of regions of interest of the patient by computing a similarity metric of a time series of pixel values; computing the at least one time-value curve for at least one of the regions of interest; and determining a protocol for a diagnostic scan using the image system based at least in part upon data from the time value curve.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Hand held data retrieval device with fixed solution capability
A diagnostic scan tool is provided including a connect / configure module for establishing a communication link between the scan tool and a vehicle electronic control unit (ECU). A vehicle specification module operates to identify a vehicle under test in response to receipt of a vehicle identification number (VIN). A trouble code module retrieves digital trouble codes (DTCs) from the ECU. A freeze frame data module retrieves freeze frame data from the ECU, the retrieved freeze frame data being functionally associated with a highest priority DTC. A database lists possible vehicle defect solutions, indexed to the VIN and the DTCs. A digital signal processor is operative to derive the highest priority DTC from analysis of the retrieved freeze frame data. The digital signal processor further being operative to regulate selection of a most likely vehicle defect solution associated with the VIN and the highest priority DTC.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
Methods and systems for computed tomography
Methods and systems are provided for automatic exposure control in computed tomography imaging systems. In one embodiment, a method comprises in response to an object-specific dose metric input by a user via a user interface operably coupled to a scanner, predicting an image quality of a diagnostic scan, calculating an output level of a source of the scanner for the image quality, and performing the diagnostic scan at the output level when the image quality is higher than a threshold. In this way, patient-specific image quality settings may be determined.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and System for Dose-Optimized Computed Tomography Scanning of a Target Organ
ActiveUS20180228450A1Health-index calculationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsComputed tomographyConfidence interval
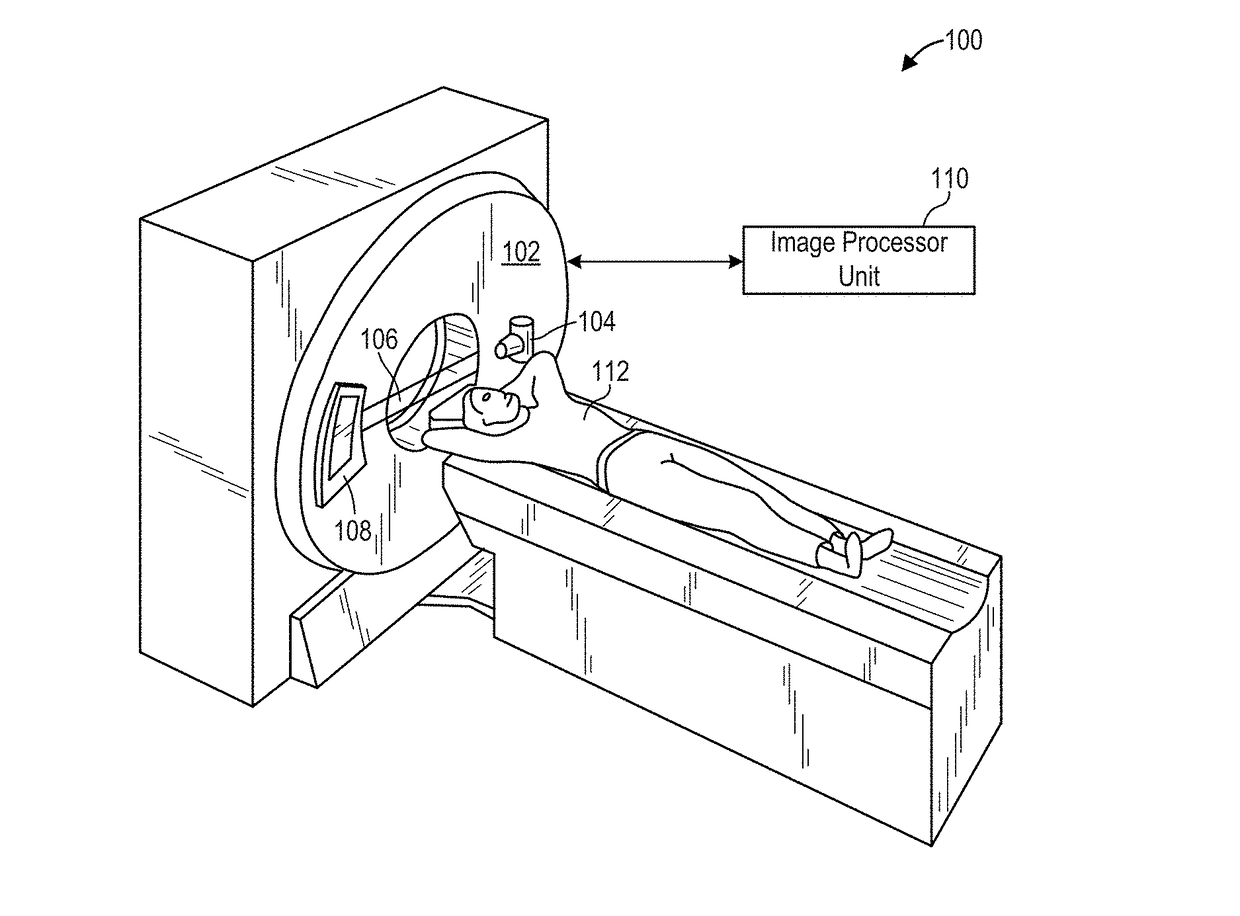
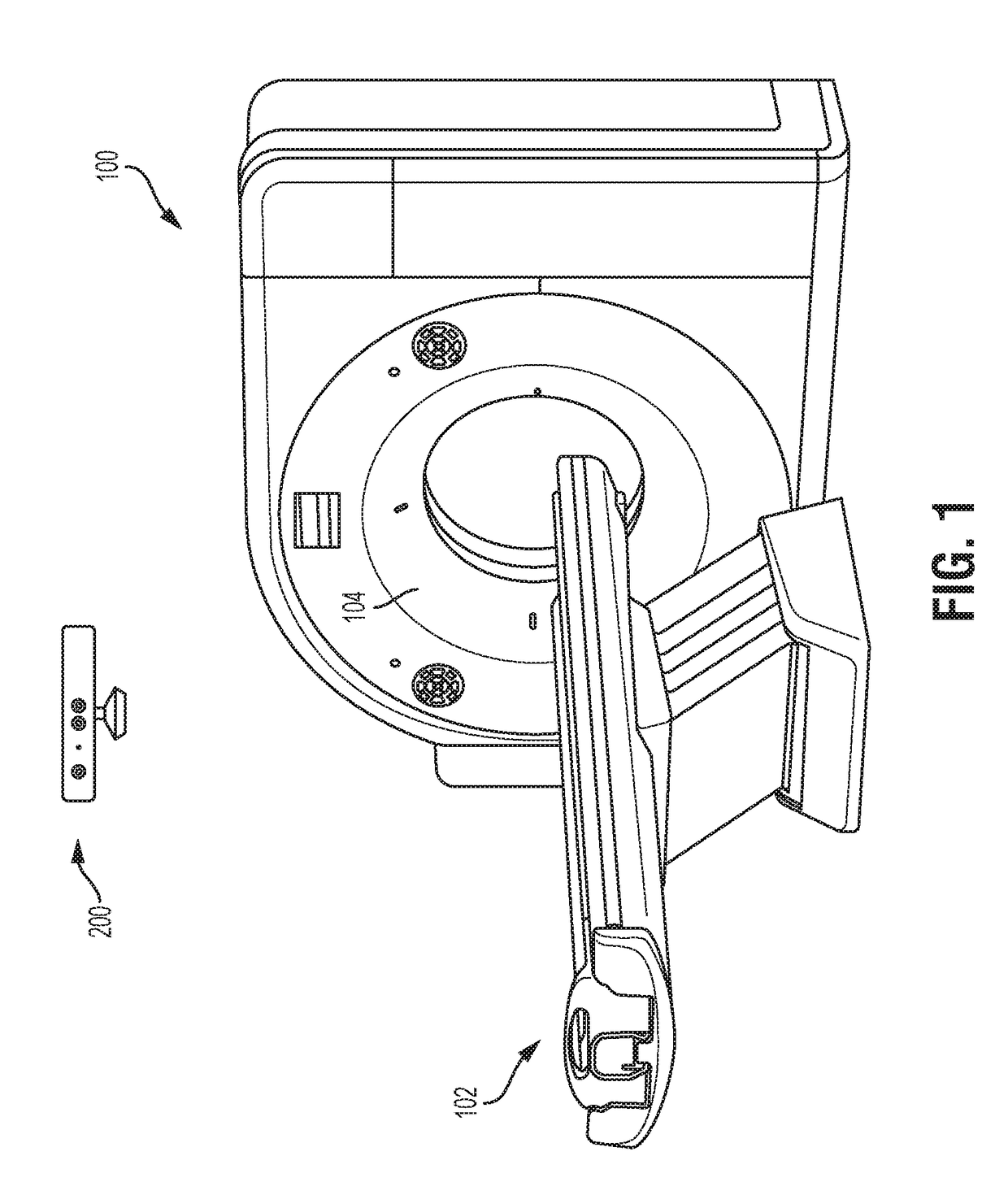
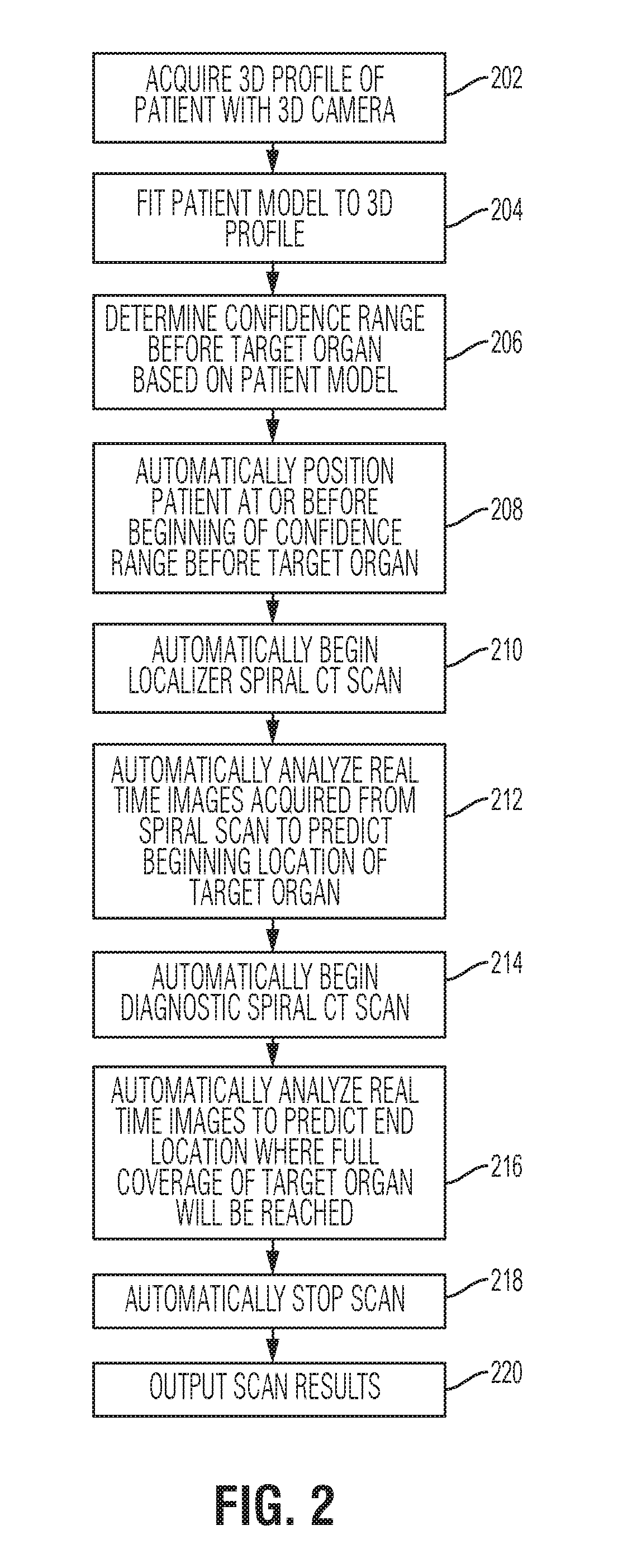
A method and system for dose-optimized acquisition of a computed tomography (CT) scan of a target organ is disclosed. A localizer spiral CT scan is started at a beginning of a confidence range before a target organ. Real-time localizer scan images are automatically analyzed to predict a beginning location of the target organ based on the real-time localizer scan images. A diagnostic spiral CT scan is automatically started at the predicted beginning location of the target organ. Real-time diagnostic scan images are automatically analyzed to predict an end location of the target organ where full coverage of the target organ will be reached. The diagnostic spiral CT scan is automatically stopped in response to reaching the predicted end location of the target organ. A 3D profile can be acquired using a 3D camera and used to determine the confidence range before the target organ.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
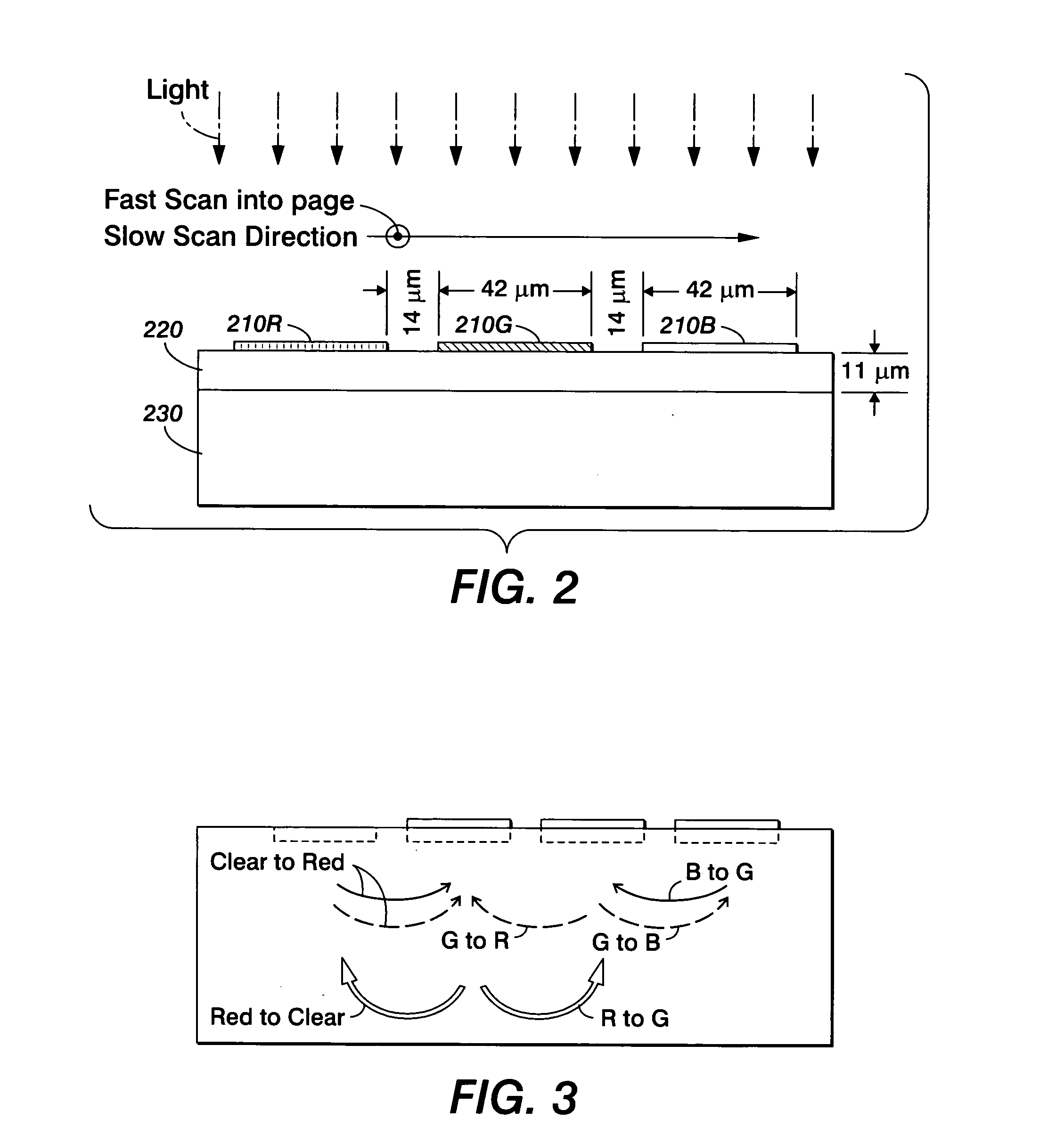
Method for correcting scanner non-uniformity
InactiveUS20070247681A1More complex electronic devicesSimpler electro-mechanical systemsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer scienceDiagnostic scan
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for correcting scanner non-uniformity
InactiveUS7692832B2More complex electronic devicesSimpler electro-mechanical systemsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSpatial changeComputer science
Owner:XEROX CORP
Identification of regions of interest and extraction of time value curves in imaging procedures
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
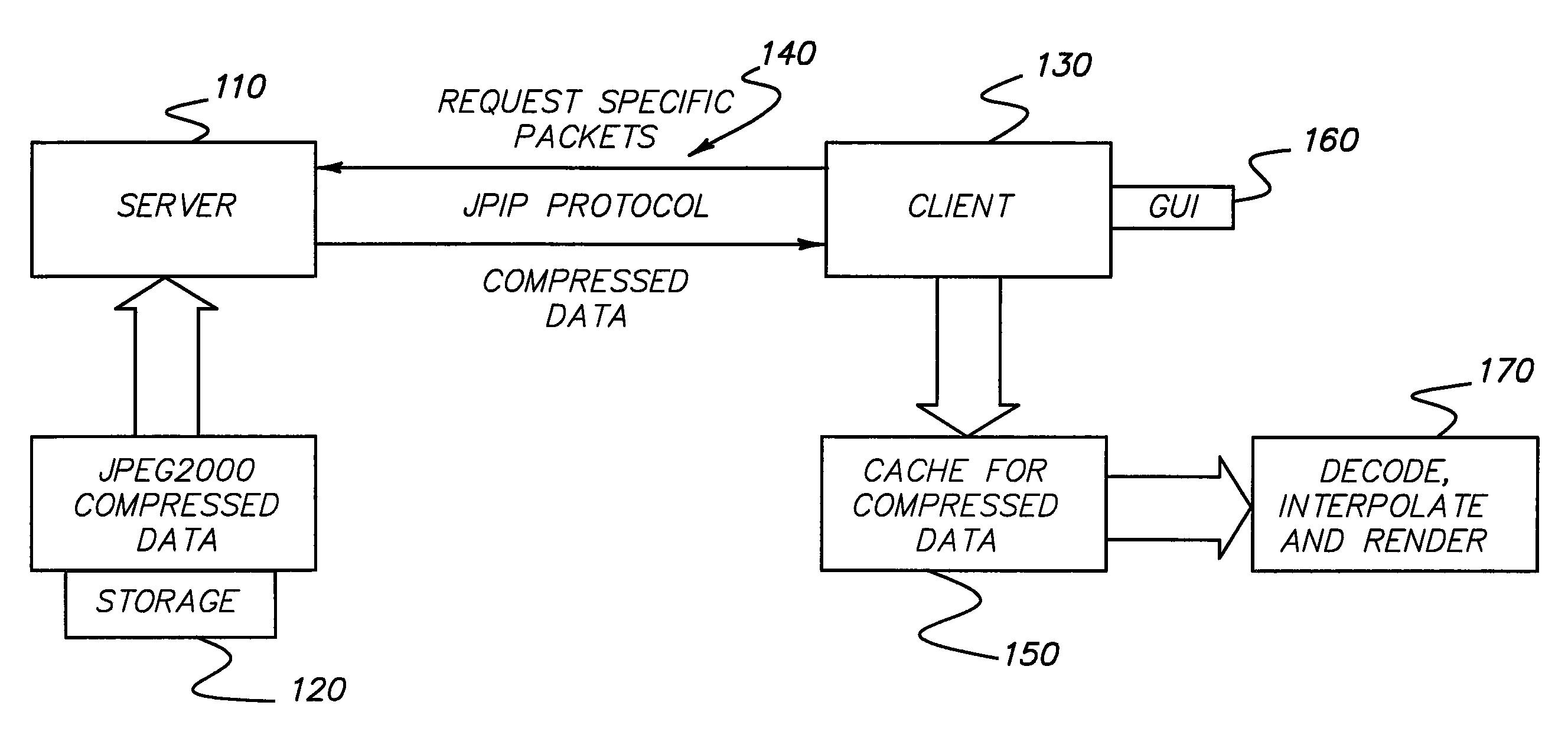
System and method for rendering an oblique slice through volumetric data accessed via a client-server architecture
InactiveUS7502501B2More responsiveMinimize bandwidthCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsNetworking protocolVolumetric data
A system renders oblique slices through volumetric data accessed via a network using a client-server architecture. The system includes a server for processing and storing volumetric data comprising axial slices obtained from a diagnostic scanning system, a client for processing user requests related to specific views of the volumetric data, and a network protocol for connecting the client with the server over the network and obtaining data from the server for use by the client. A processing stage at the client specifies an oblique slice and communicates particulars of the oblique slice to the server, thereupon obtaining axial slice data from the server specifically for portions of the axial slices that are needed to render the oblique slice. Memory at the client stores the axial slice data, and a rendering stage at the client renders the oblique slice from the axial slice data in the memory.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
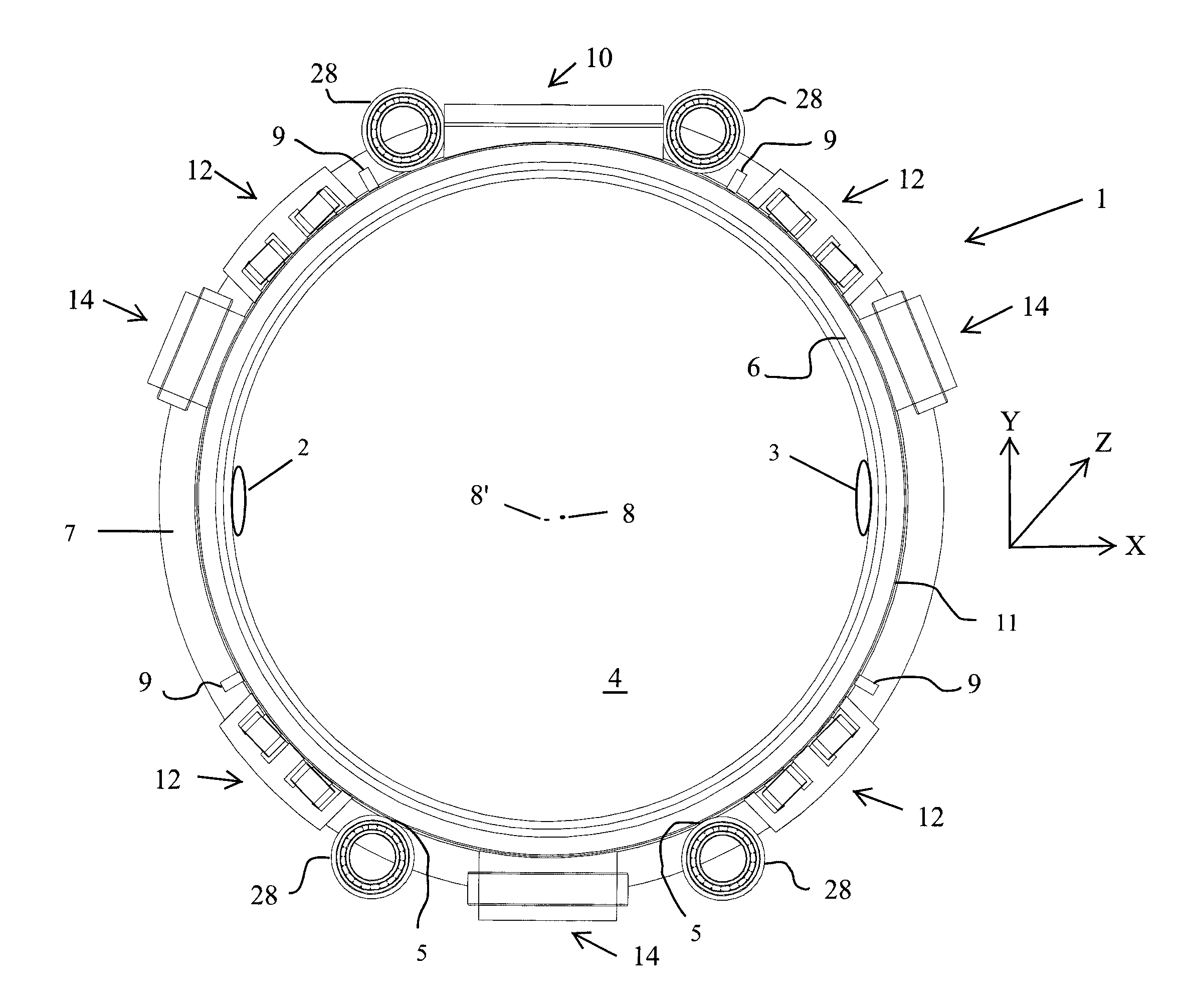
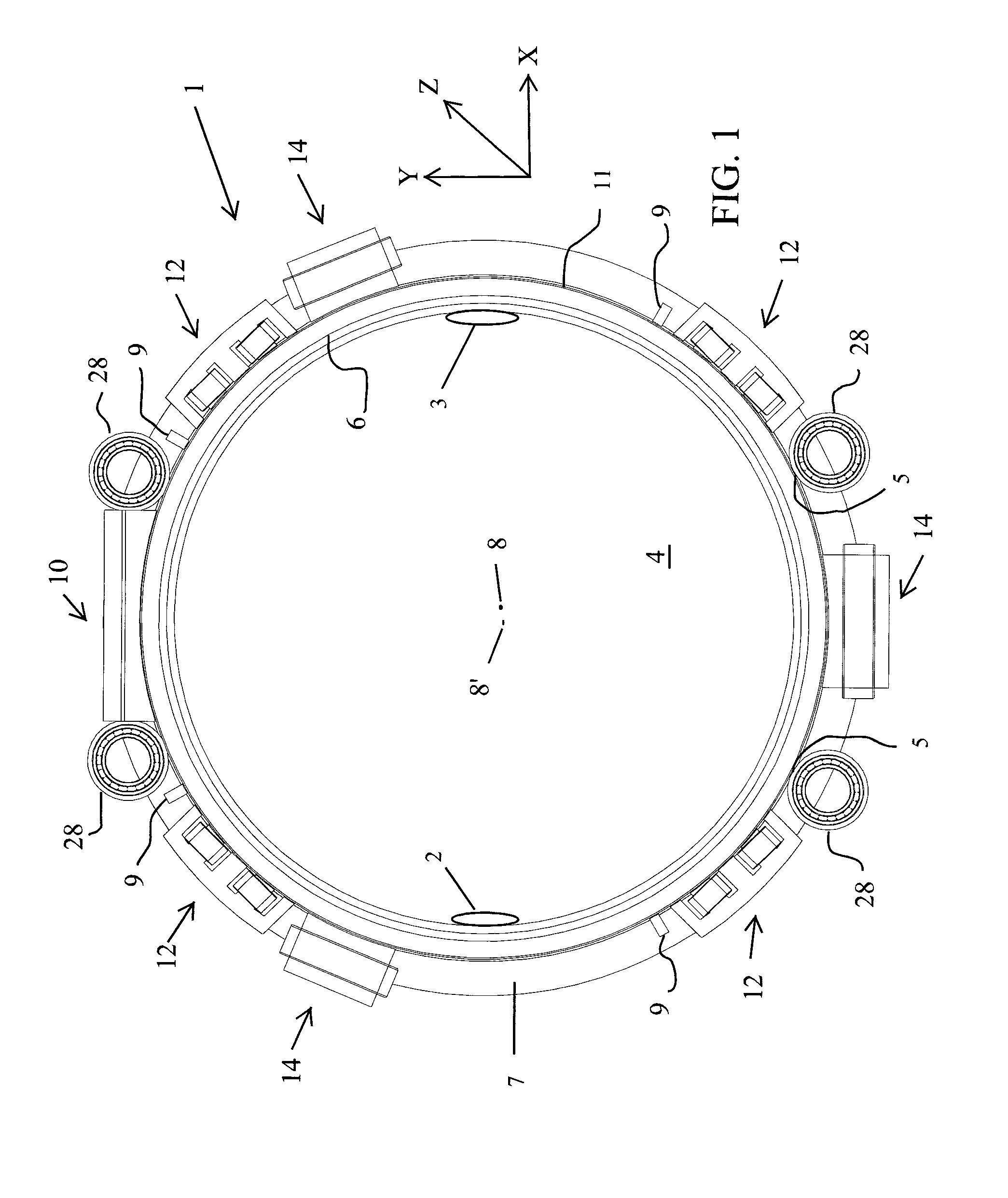
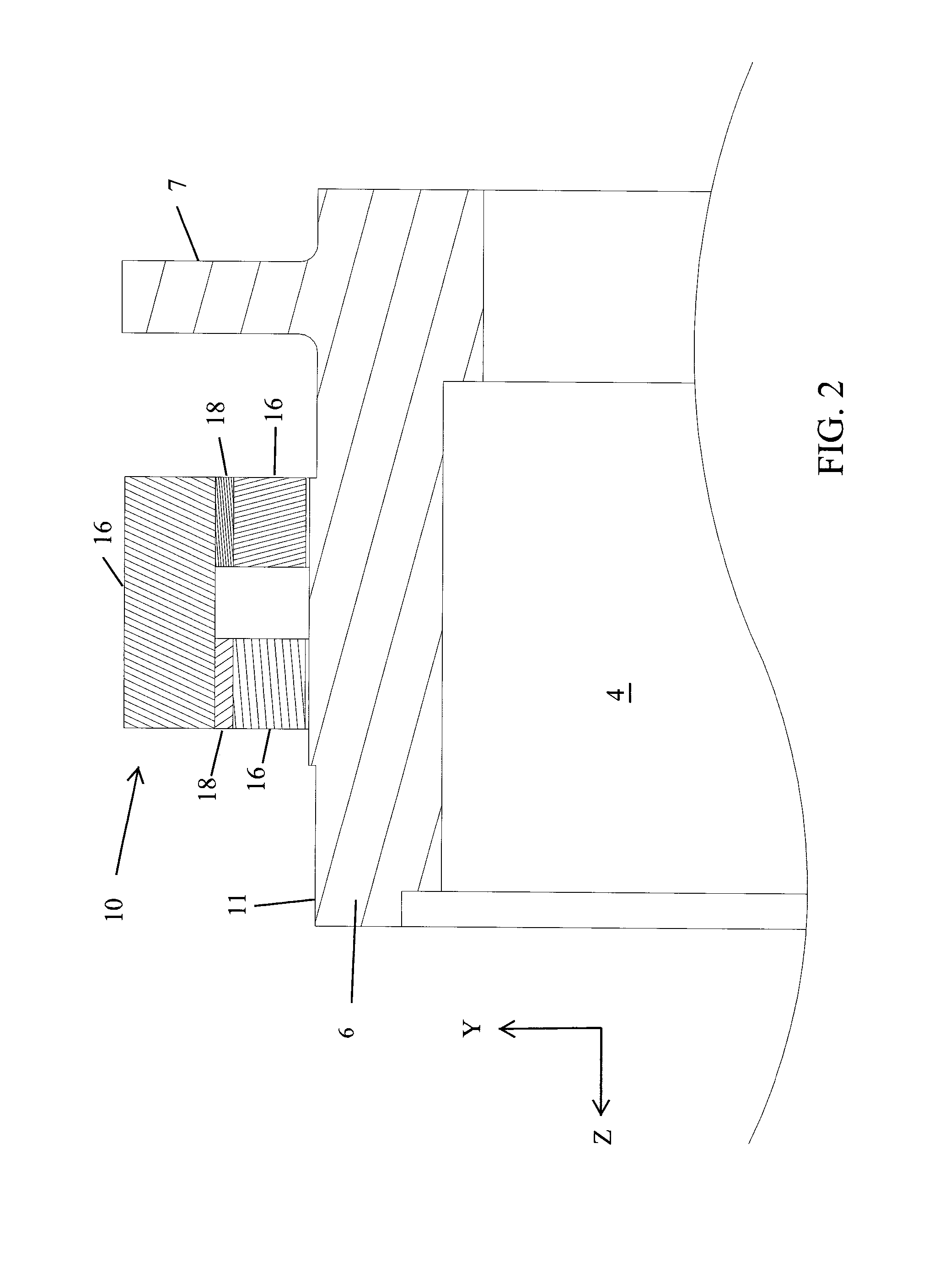
Diagnostic scanning apparatus
ActiveUS20140270051A1Reduced and no lubrication requirementMinimizing and eliminating amountMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRolling contact bearingsEngineeringActuator
A diagnostic scanning apparatus includes a hollow rotor sized to receive a patient. First and second flanges are connected to and extend radially outward from the rotor in a spaced-apart relationship, each of the first and second flanges including, at least in part, a magnetically-permeable material. A radiation source is affixed to the first flange and / or the rotor. A first axial actuator generates a variable magnetic field, is fixedly disposed adjacent to the first flange and can magnetically pull the first flange in a first axial direction of the rotor. A second axial actuator generates a variable magnetic field, is fixedly disposed adjacent to the second flange and can magnetically pull the second flange in a second axial direction of the rotor that is opposite of the first axial direction. The first and second axial actuators are both at least substantially disposed between the first and second flanges.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +2
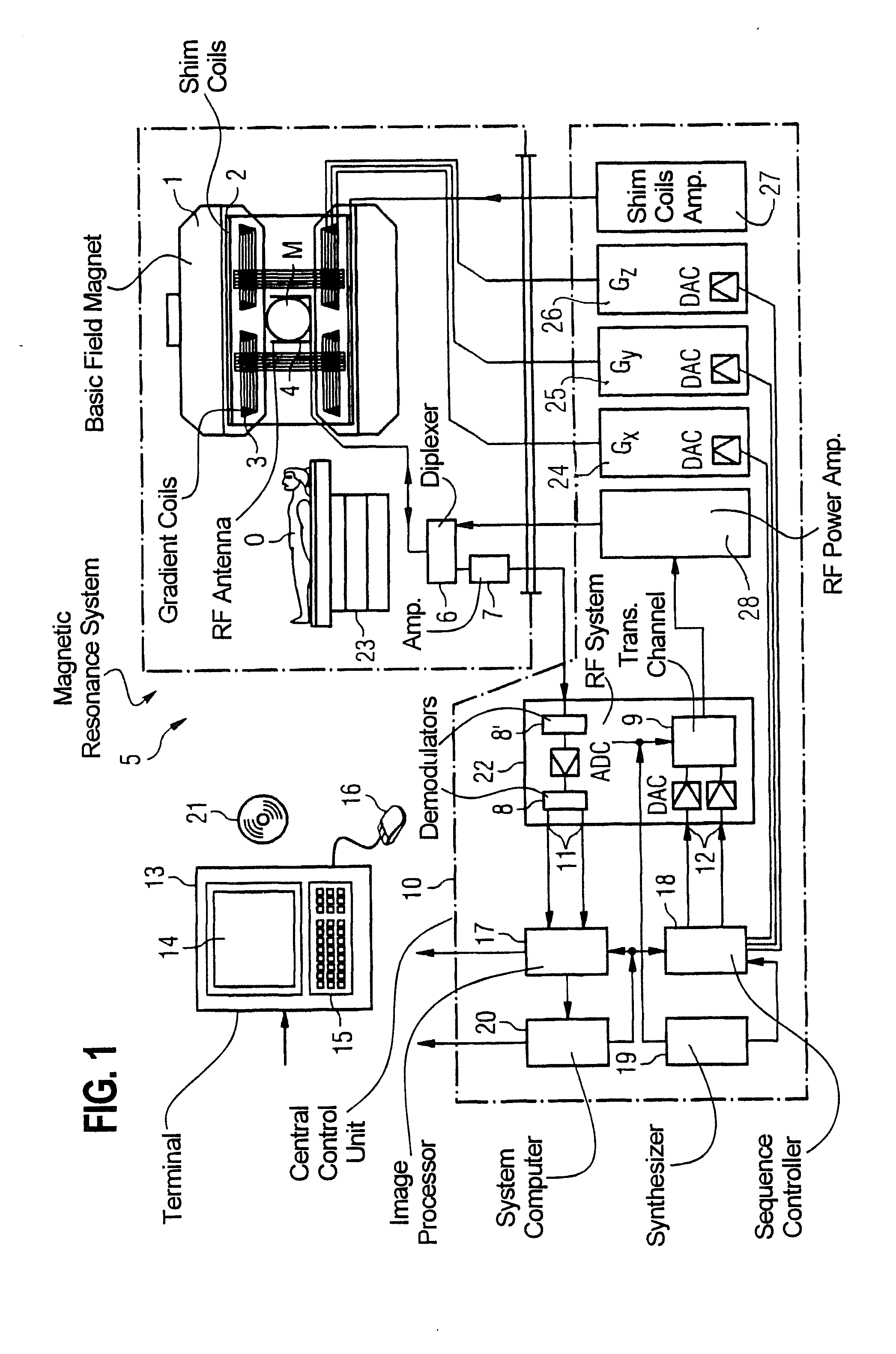
Method and apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance images in a session, with acquisition of a consistently valid reference scan
InactiveUS20160038054A1Extended durationAvoid unnecessary repetitionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMri image
In a magnetic resonance (MR) imaging method and apparatus, multiple diagnostic scans are obtained of an examination subject during an imaging session. An initial reference scan of the subject is obtained at the beginning of the session and, as the session proceeds, an automatic determination is made before each diagnostic scan is obtained as to whether the immediately preceding reference scan is still valid, primarily be checking whether an amount of patient movement has occurred that renders the immediately preceding reference scan invalid. Either a new reference scan is obtained before the next diagnostic scan, or, if still valid, the immediately preceding reference scan is used for the next diagnostic scan.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Coil sensitivity estimation for parallel imaging
InactiveCN1910470AWeakening rangeReduce phase errorMagnetic measurementsImaging techniqueGradient echo
In a parallel or SENSE imaging technique in an MRI system (40), a calibration scan is conducted to generate a calibration image (86) indicative of sensitivity profiles of parallel imaging coils (76a, . . . ,76n) also in the regions where the magnetic field is distorted. This is accomplished by using a phase refocusing imaging protocol such as a spin echo technique, or by using a gradient echo technique where the echo time is very short. In addition, the phase encode direction of the calibration scan and a diagnostic imaging scan shall be matched. A diagnostic imaging scan is conducted using a diagnostic scan protocol to generate a diagnostic image representation from each parallel imaging coil. A SENSE processor (90) reconstructs a final diagnostic image (92) from the diagnostic image representations and the coil sensitivity profiles.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Data-based scan gating
In accordance with the present disclosure, the present technique finds a diagnostic scan timing for a non-static object (e.g., a heart or other dynamic object undergoing motion) from raw scan data, as opposed to reconstructed image data. To find the scan timing, a monitoring scan of a patient's heart is performed. In the monitoring scan, the patient dose may be limited or minimized. As the projection data is acquired during such a monitoring scan, the projection data may be subjected to sinogram analysis in a concurrent or real-time manner to determine when to start (or trigger) the diagnostic scan.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
Diagnostic scanning apparatus
ActiveUS8270563B2Shorten the timeIncrease rotation speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLinear bearingsRotational axisMagnetic bearing
An apparatus includes an annular rotor that rotates about a rotational axis. A magnetic bearing system influences the position of the annular rotor in three-dimensional space and includes at least three actuators, wherein at least one actuator generates a force for lifting the annular rotor in a vertical direction, at least one actuator influences the position of the annular rotor in the radial direction of the annular rotor and at least assists in maintaining an annular gap between at least one non-magnetic bearing and the annular rotor during operation and at least one actuator influences the position of the annular rotor in an axial direction of the annular rotor. At least one radiation source may be fixedly mounted on the annular rotor.
Owner:AB SKF
Method and apparatus for phase calibration of an MRI pulse
ActiveUS20080036460A1Clear and artifact-free imageWide range of usesMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPulse sequenceDiagnostic scan
The present invention concerns a method and an apparatus for phase-calibrating an MRI pulse sequence which is used to calculate a linear phase and a constant phase to perform phase calibration on the scanned data, wherein a corresponding pre-scan without a phase encoding gradient is performed before a diagnostic scan. A reference echo is selected from the echoes obtained in the pre-scan. On the basis of the reference echo the constant phase is calculated to be used in performing the phase calibration in the scan. The constant phase that is obtained is correct and not affected by phase jumping. A further image reconstruction performed on the phase-calibrated data produces clear and artifact-free images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com