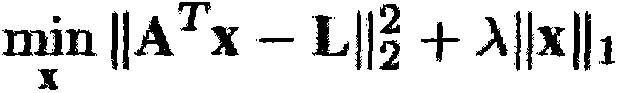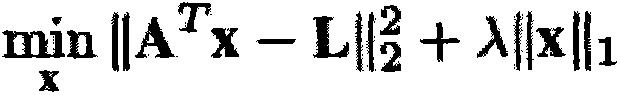Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Depth order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
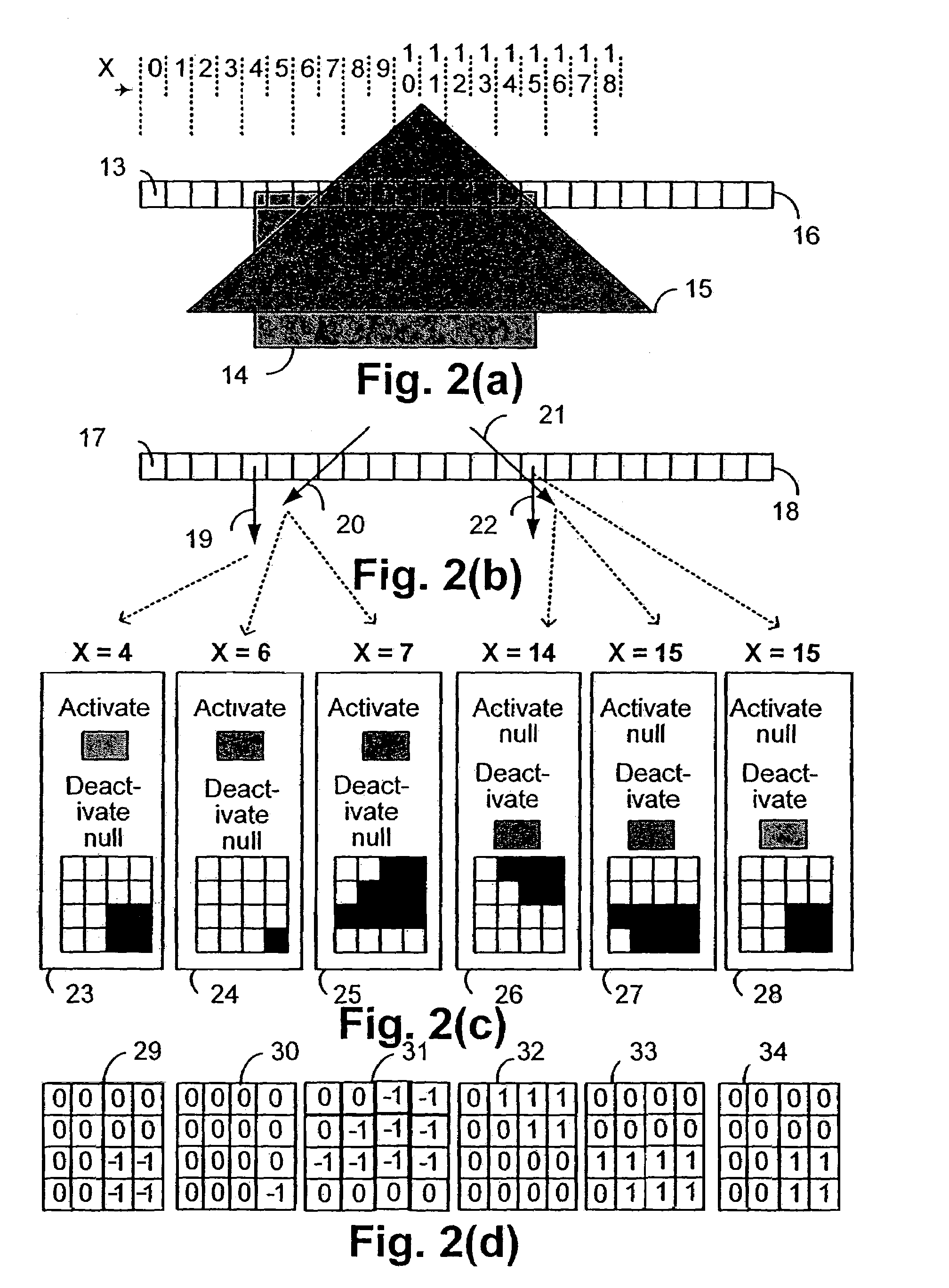
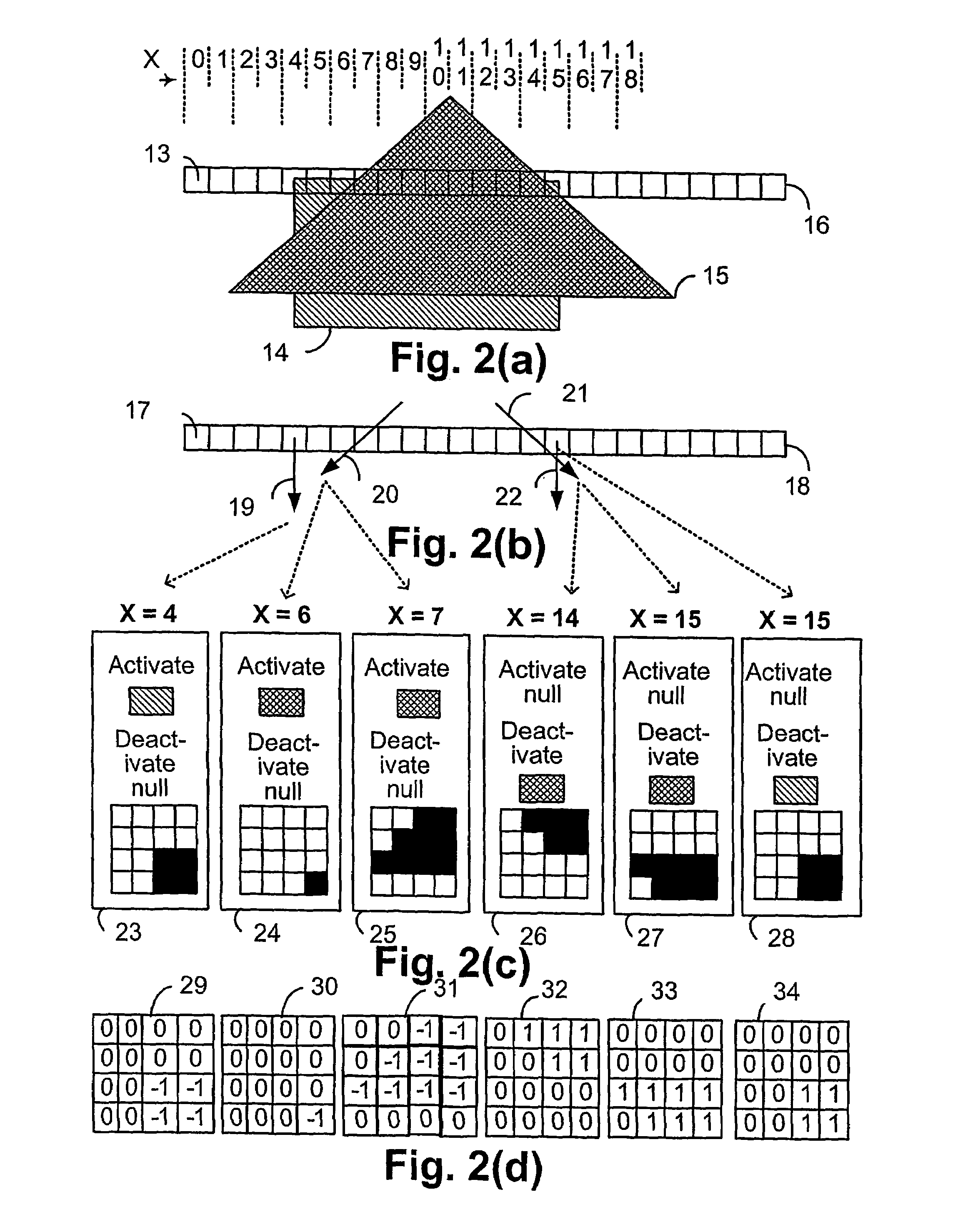
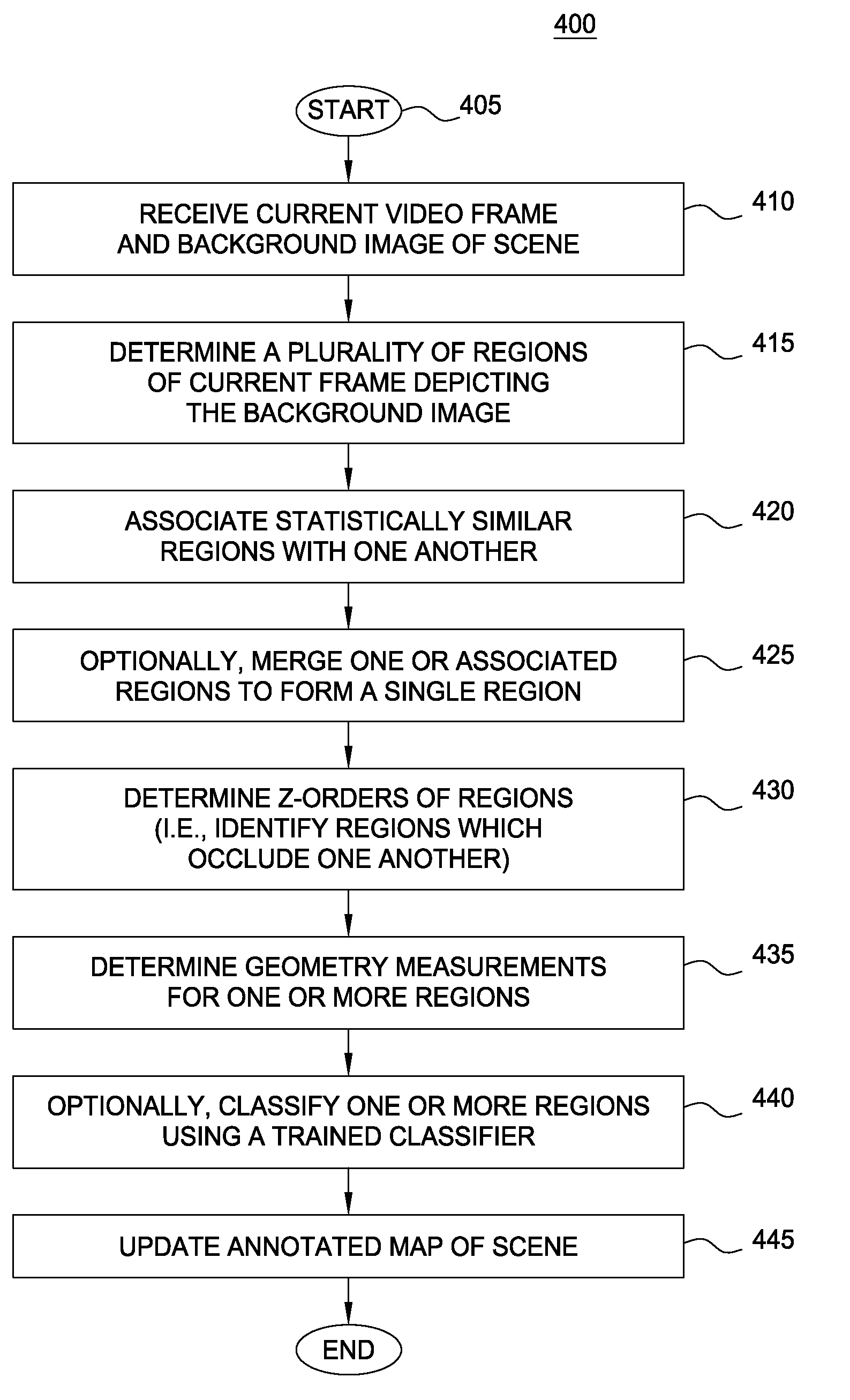
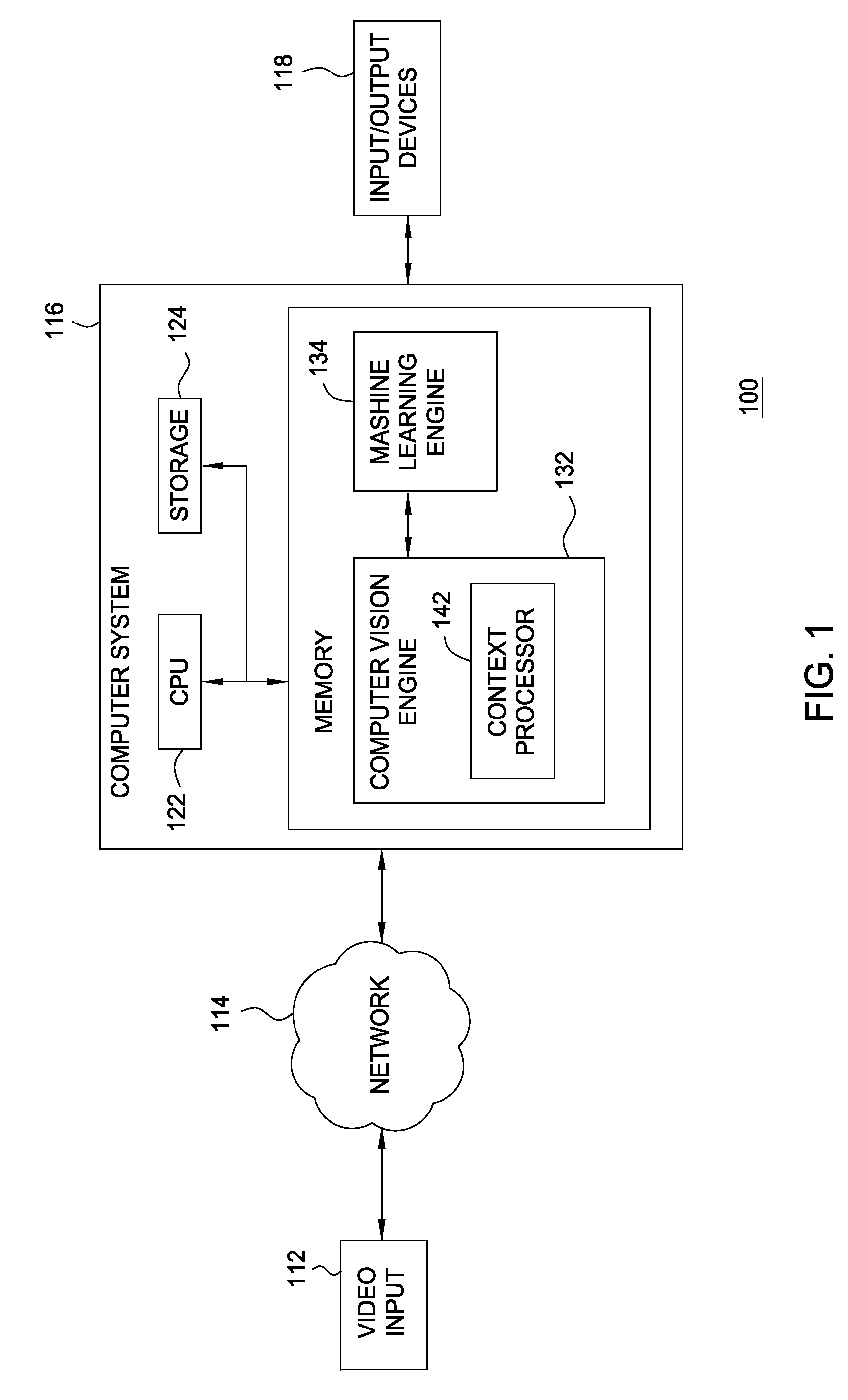
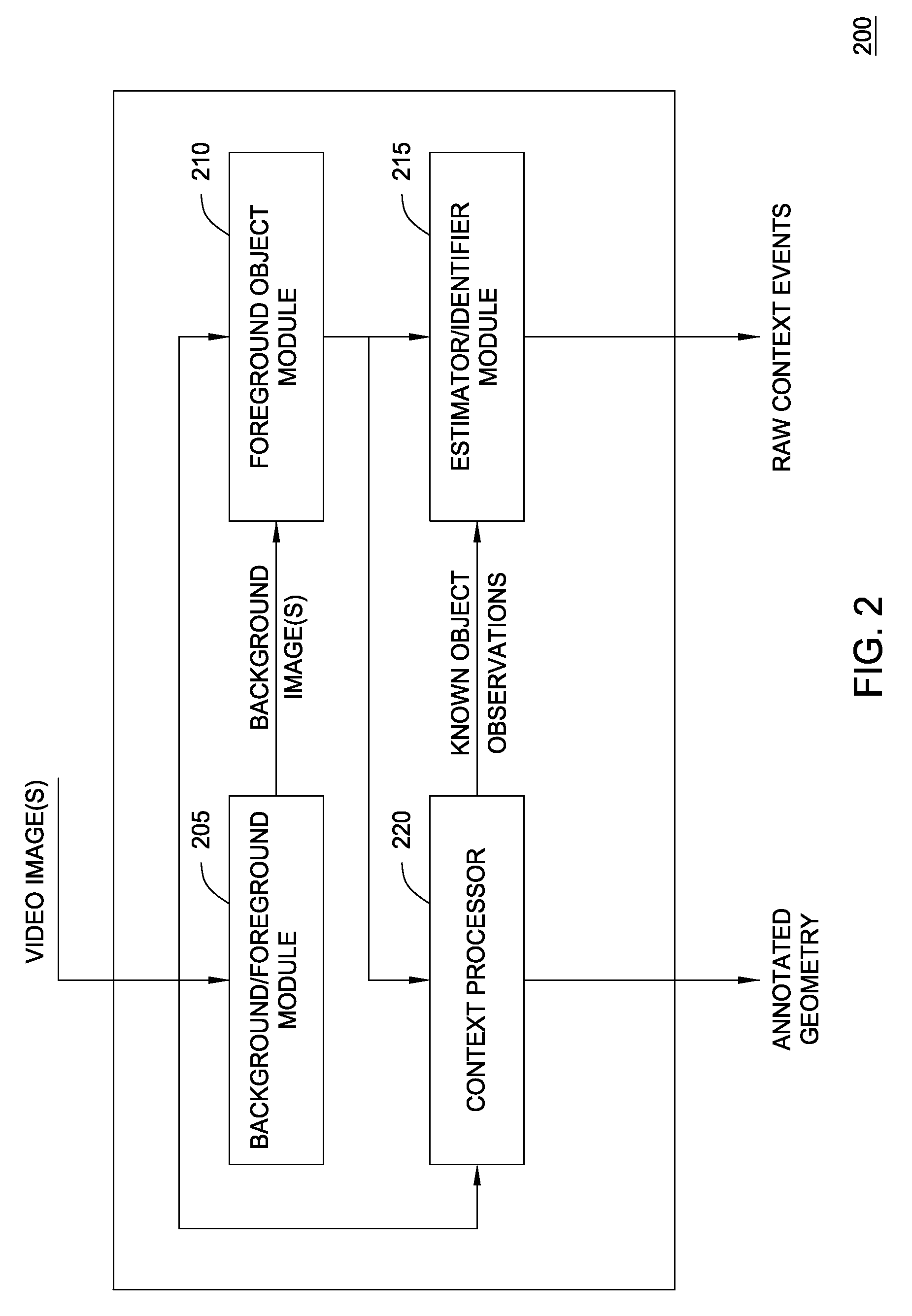
Context processor for video analysis system
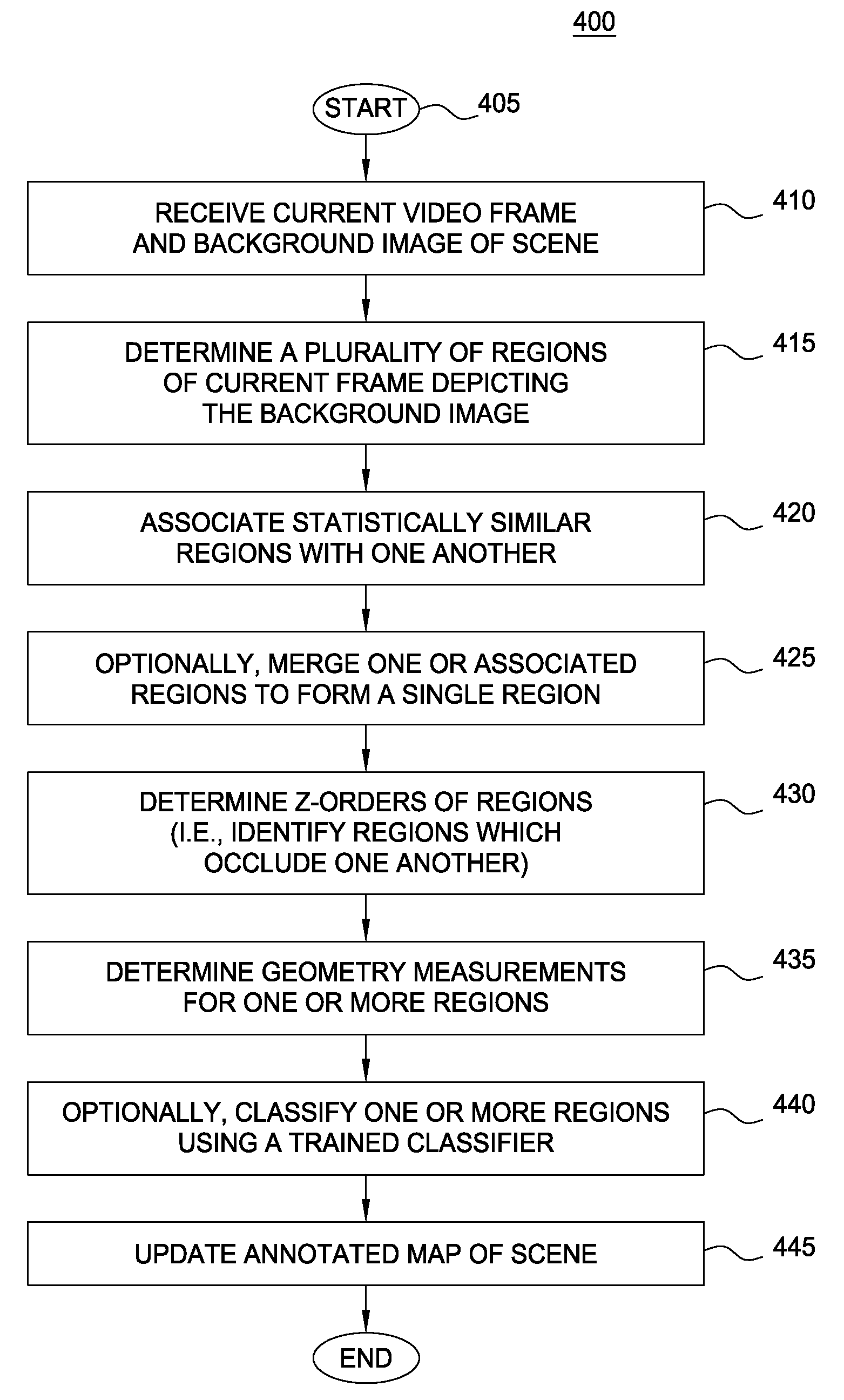
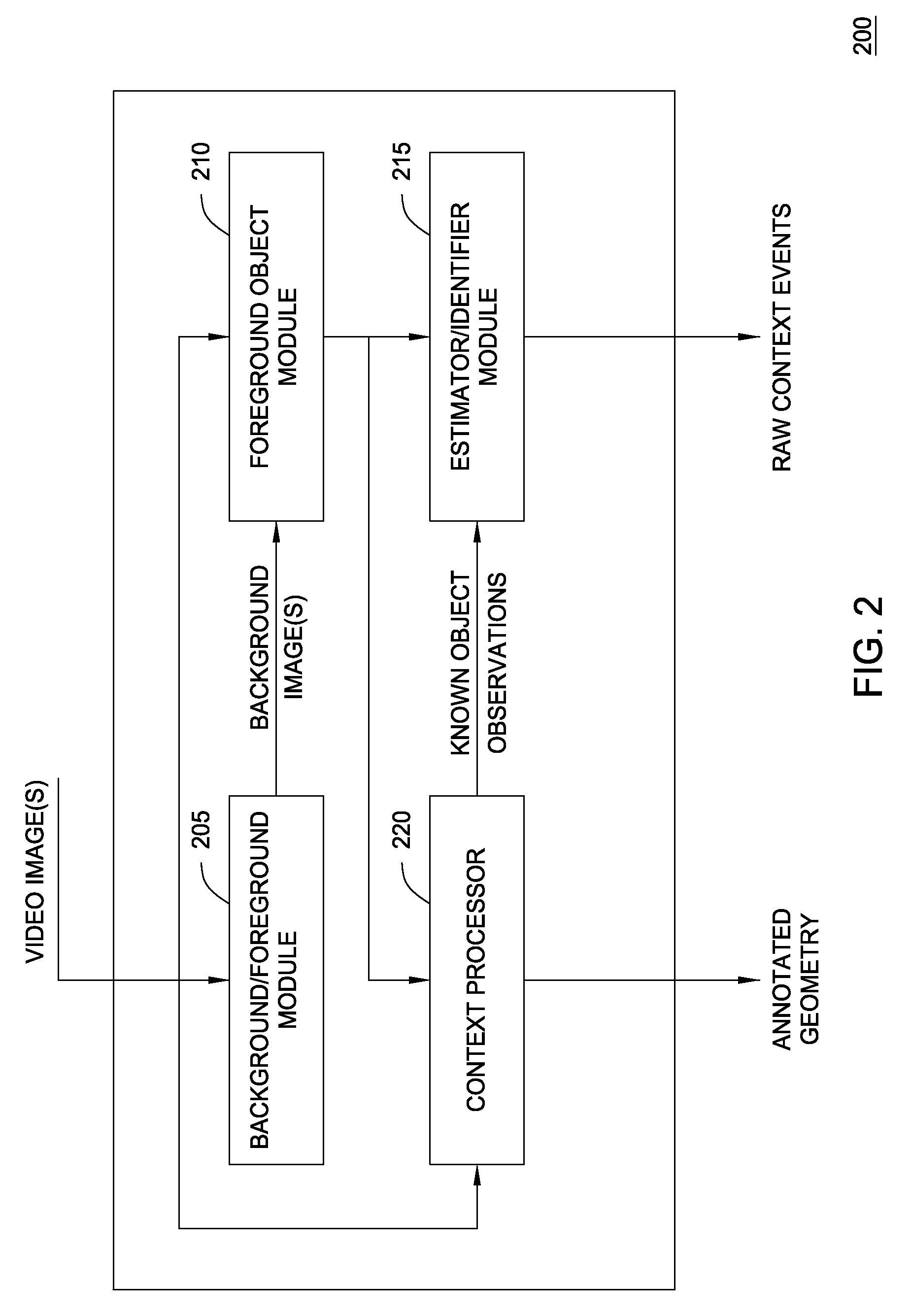
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and a system for mapping a scene depicted in an acquired stream of video frames that may be used by a machine-learning behavior-recognition system. A background image of the scene is segmented into plurality of regions representing various objects of the background image. Statistically similar regions may be merged and associated. The regions are analyzed to determine their z-depth order in relation to a video capturing device providing the stream of the video frames and other regions, using occlusions between the regions and data about foreground objects in the scene. An annotated map describing the identified regions and their properties is created and updated.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
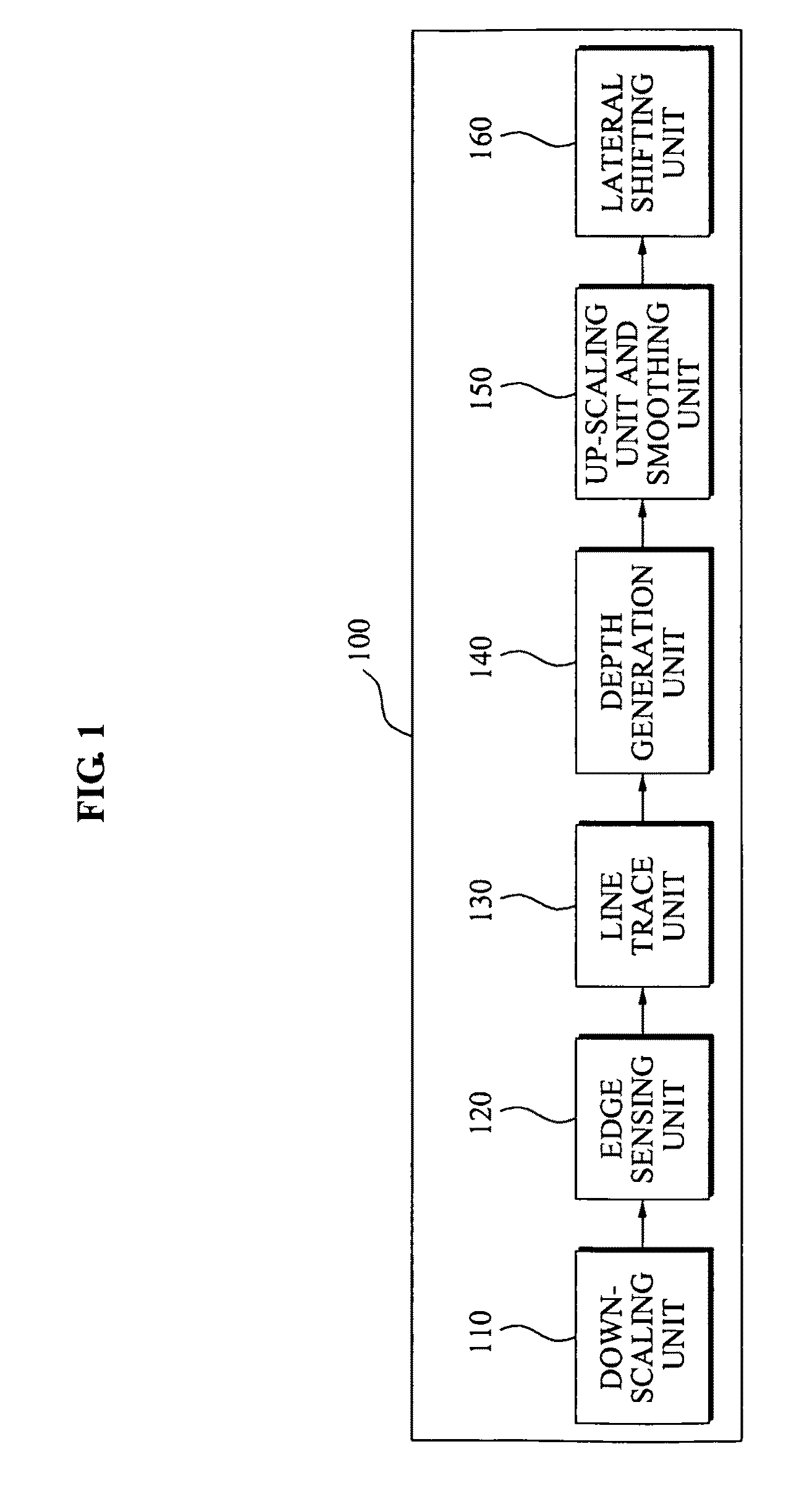
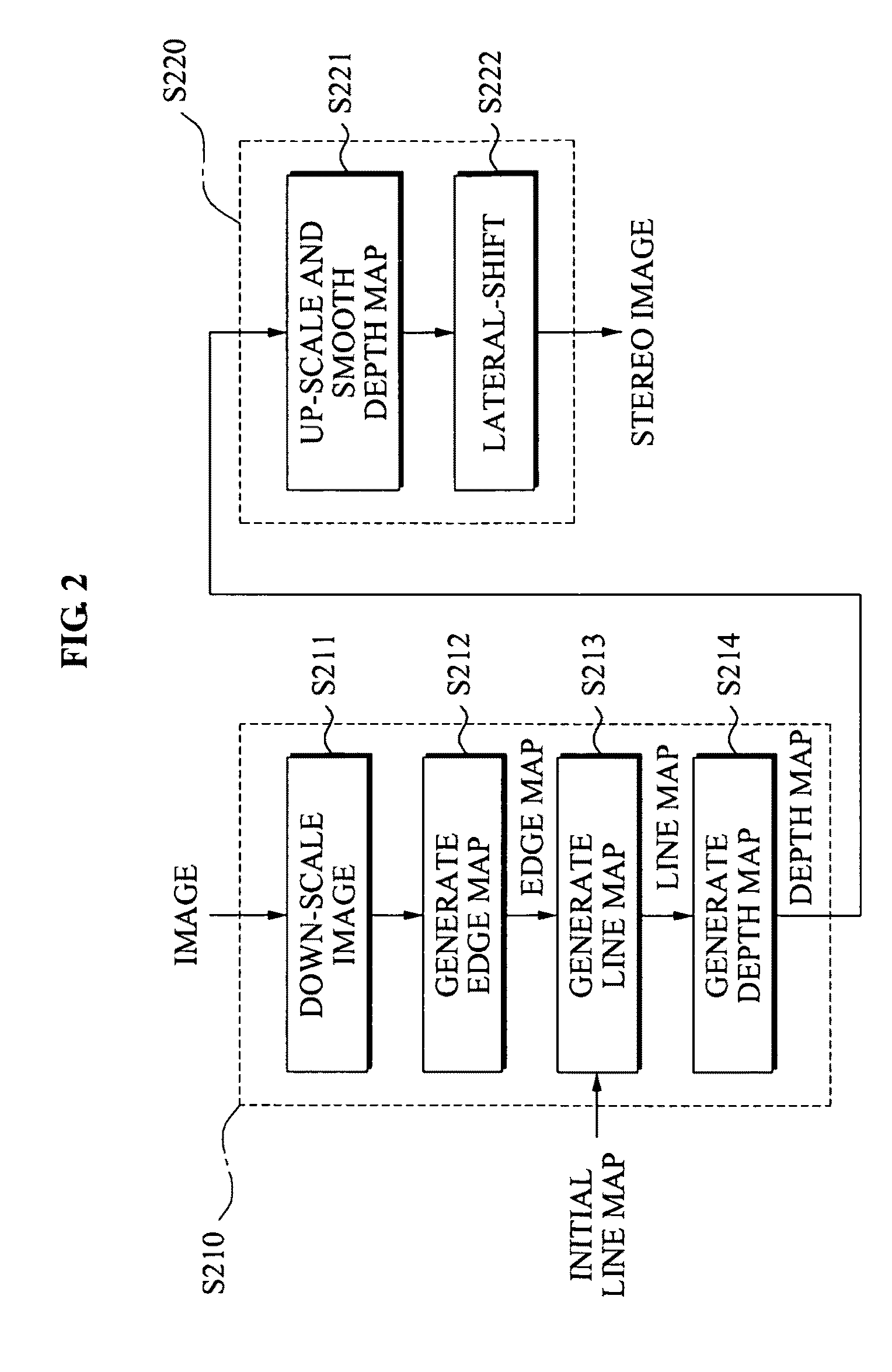
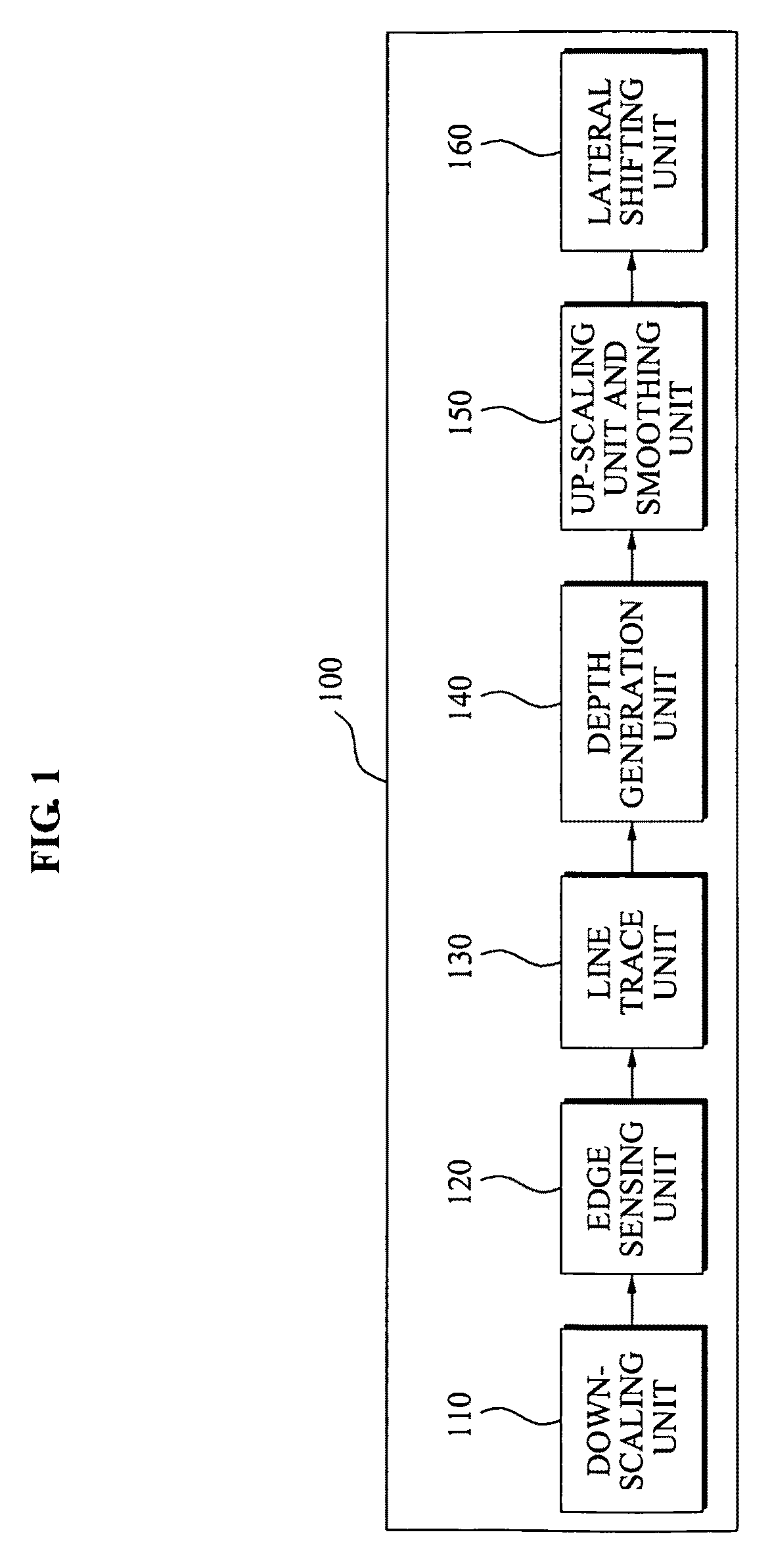
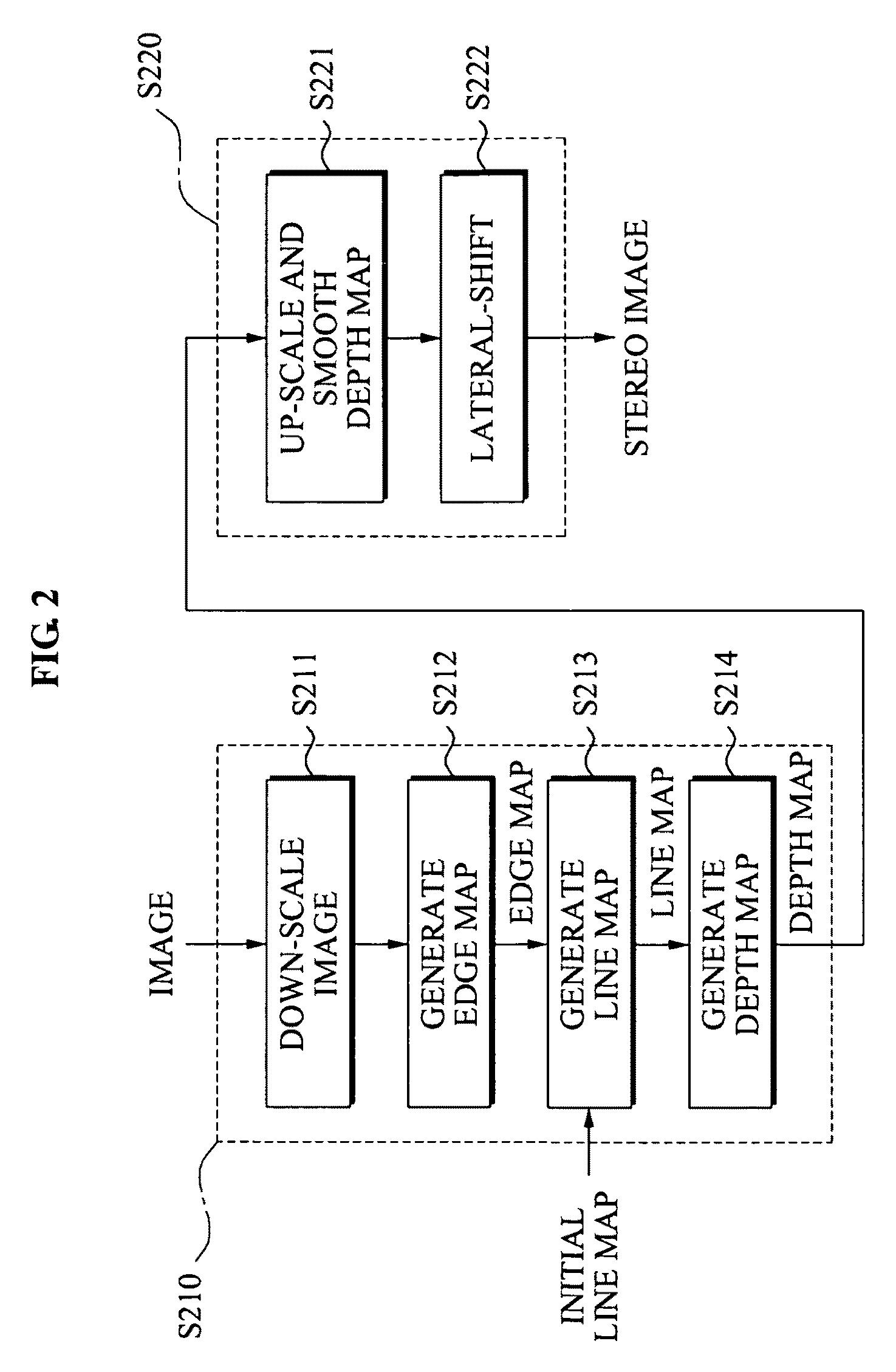
Conversion method and apparatus with depth map generation
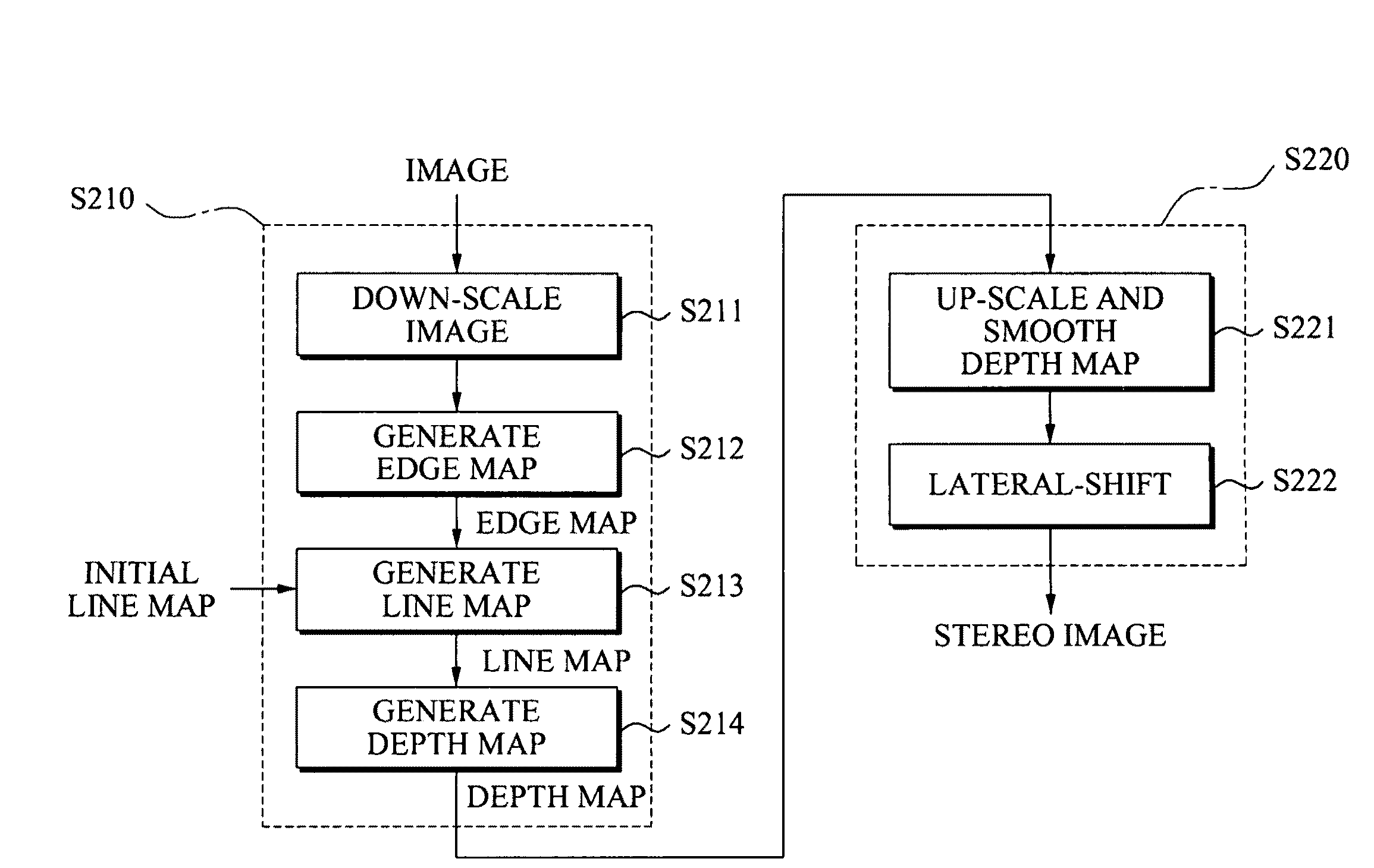
A conversion method and apparatus with a generating of a depth map for two dimensional (2D)-to-three dimensional (3D) conversion. A depth order may be restored based on a line tracing and an edge map generated from an input image, and a stereo image may be generated using depth information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rendering successive frames in a graphic object system
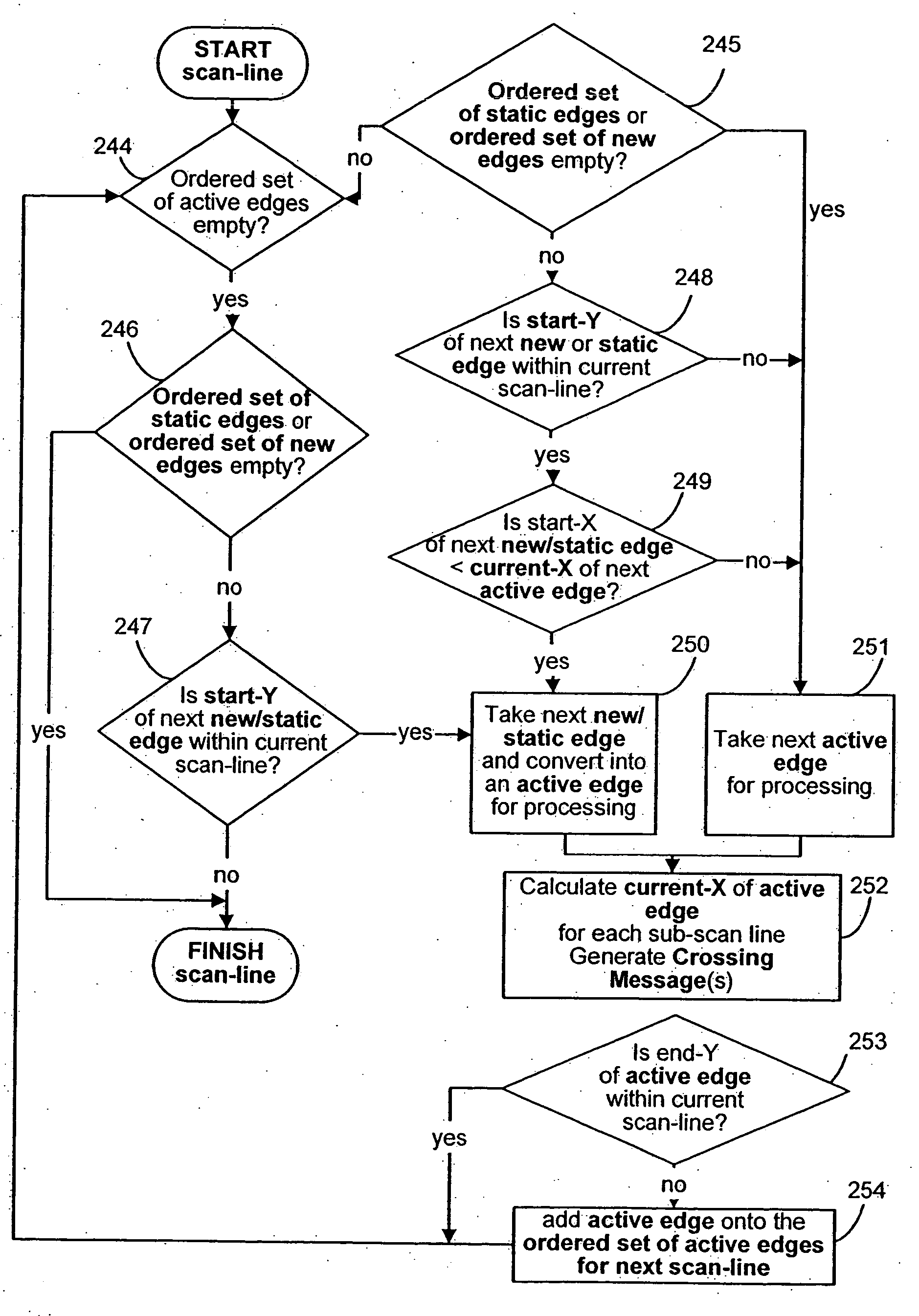
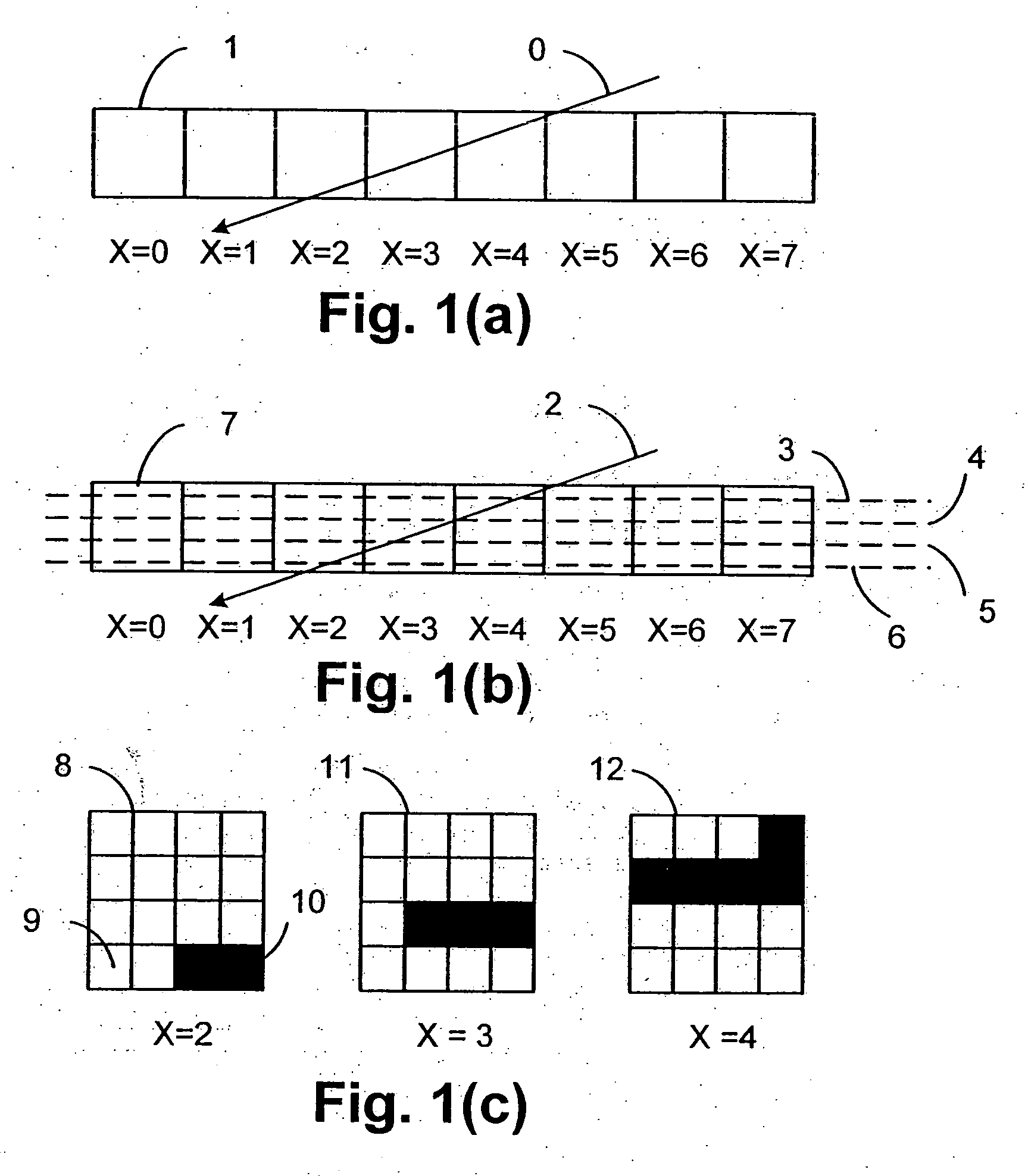
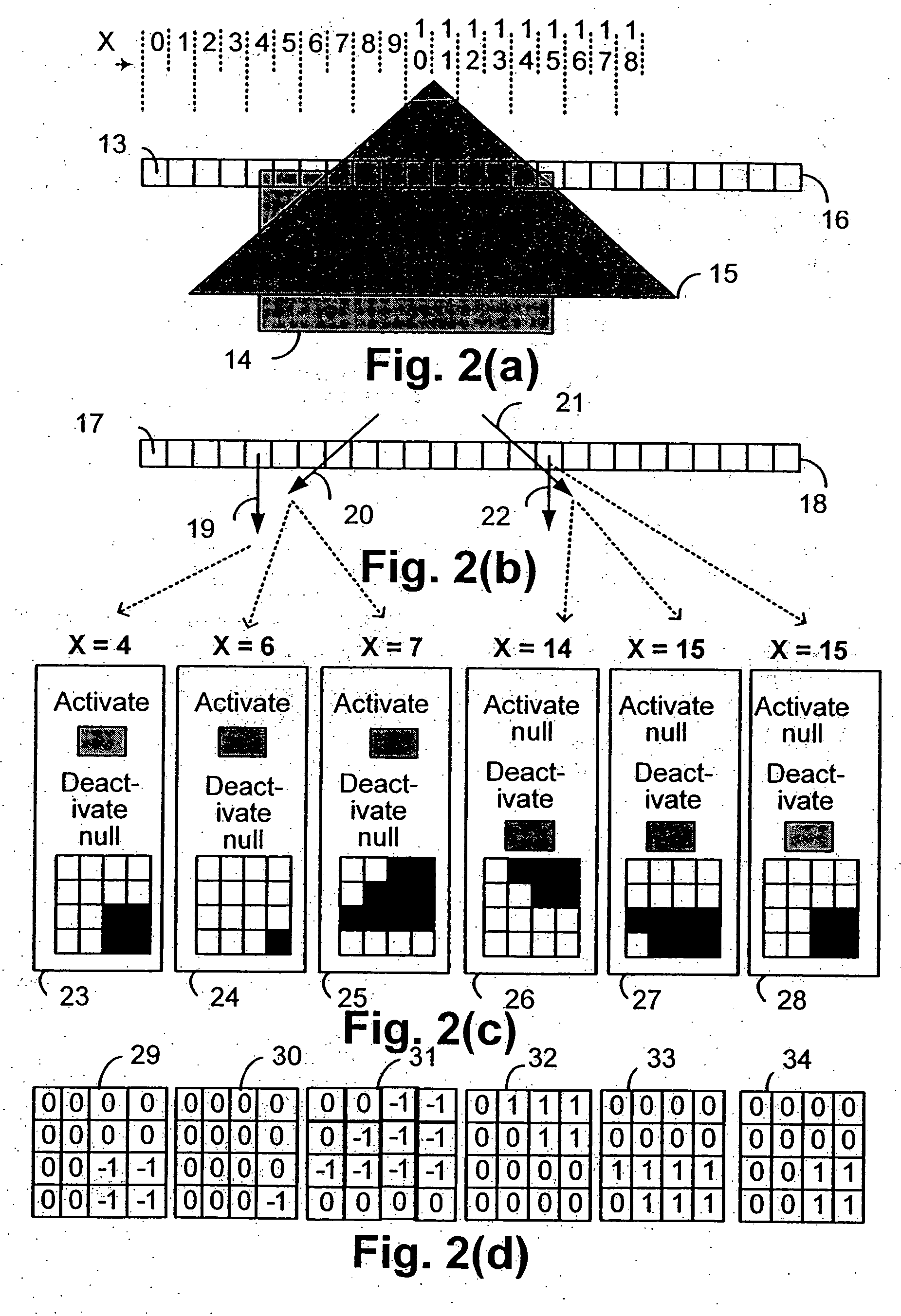
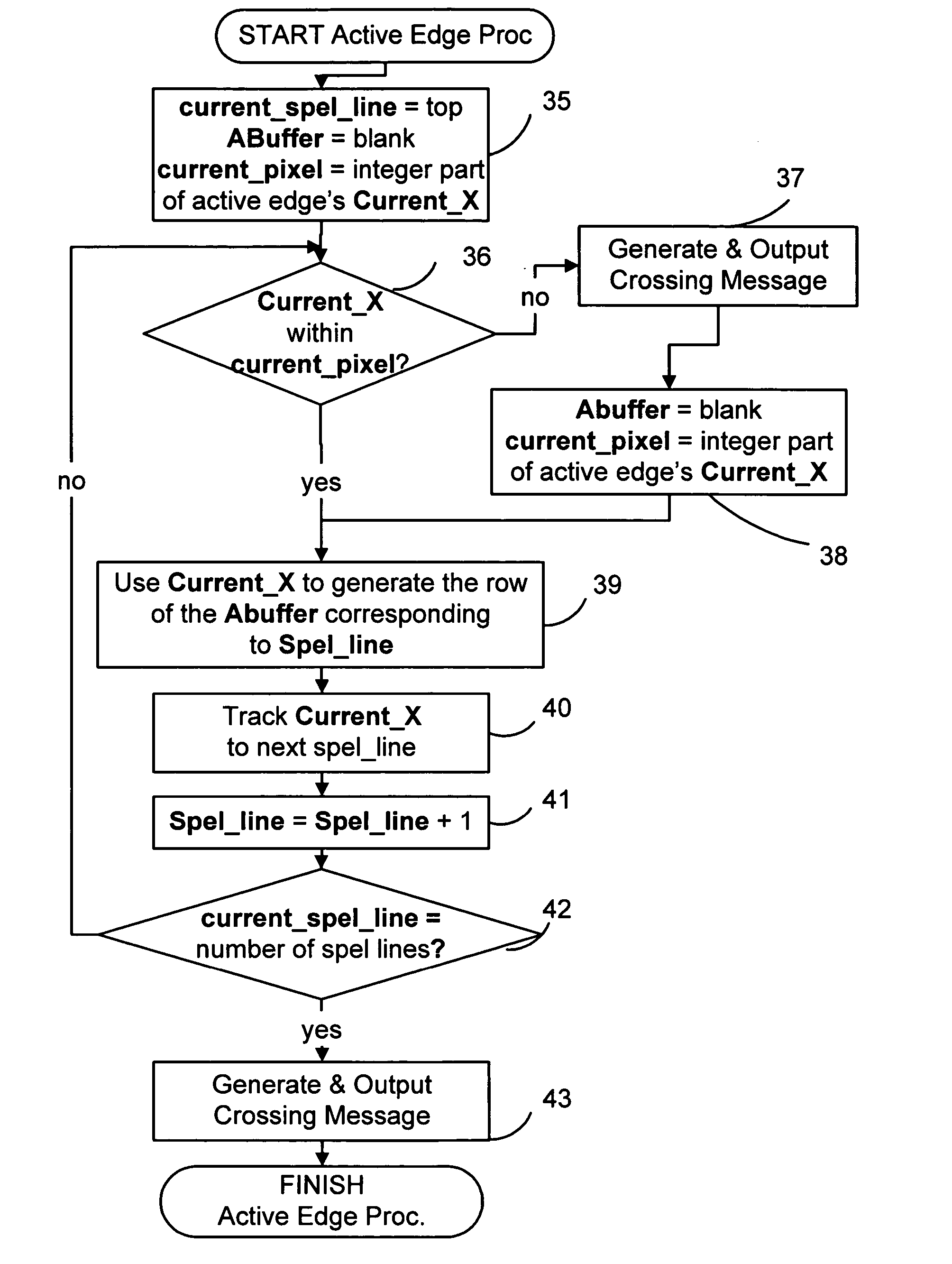
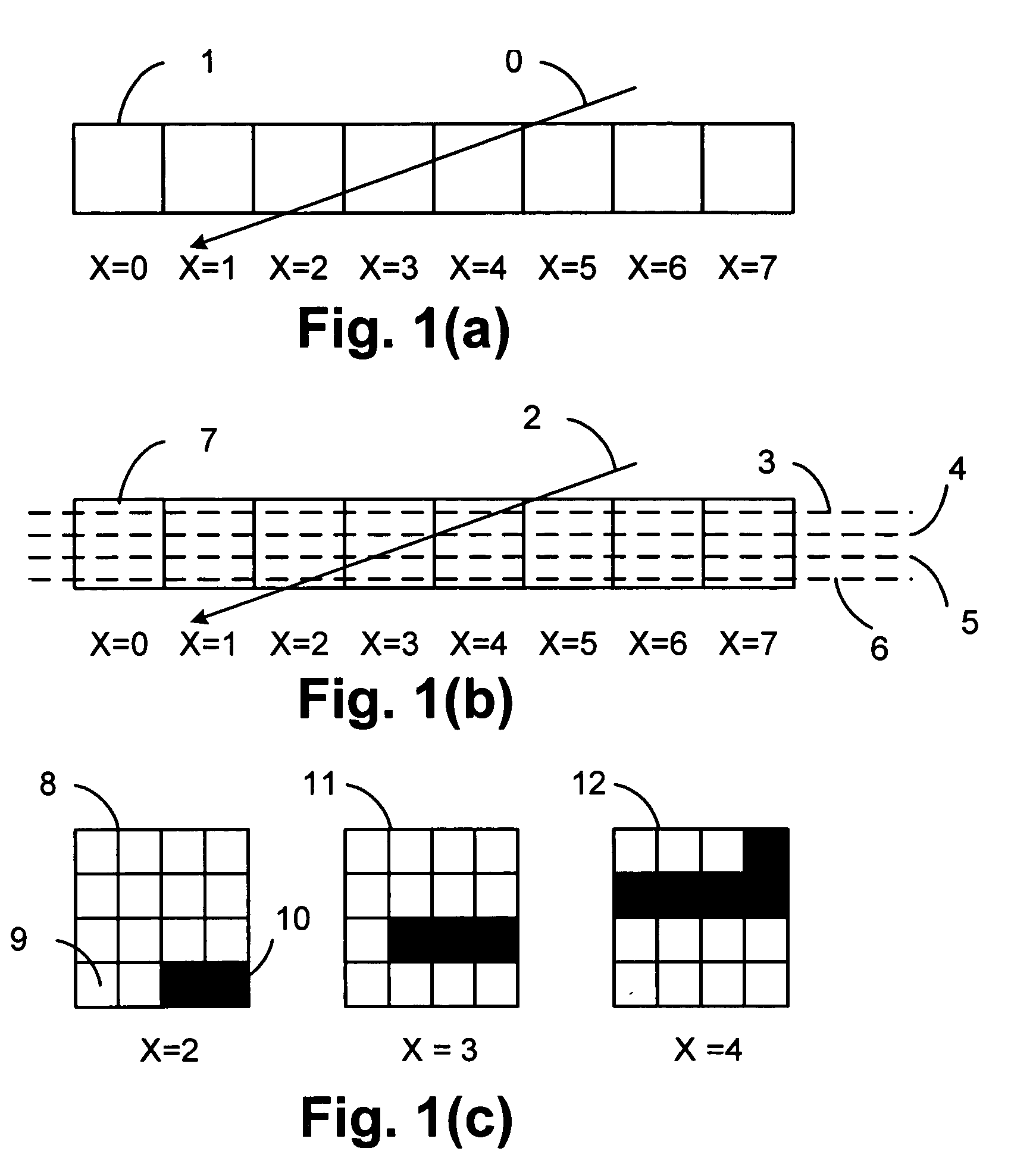
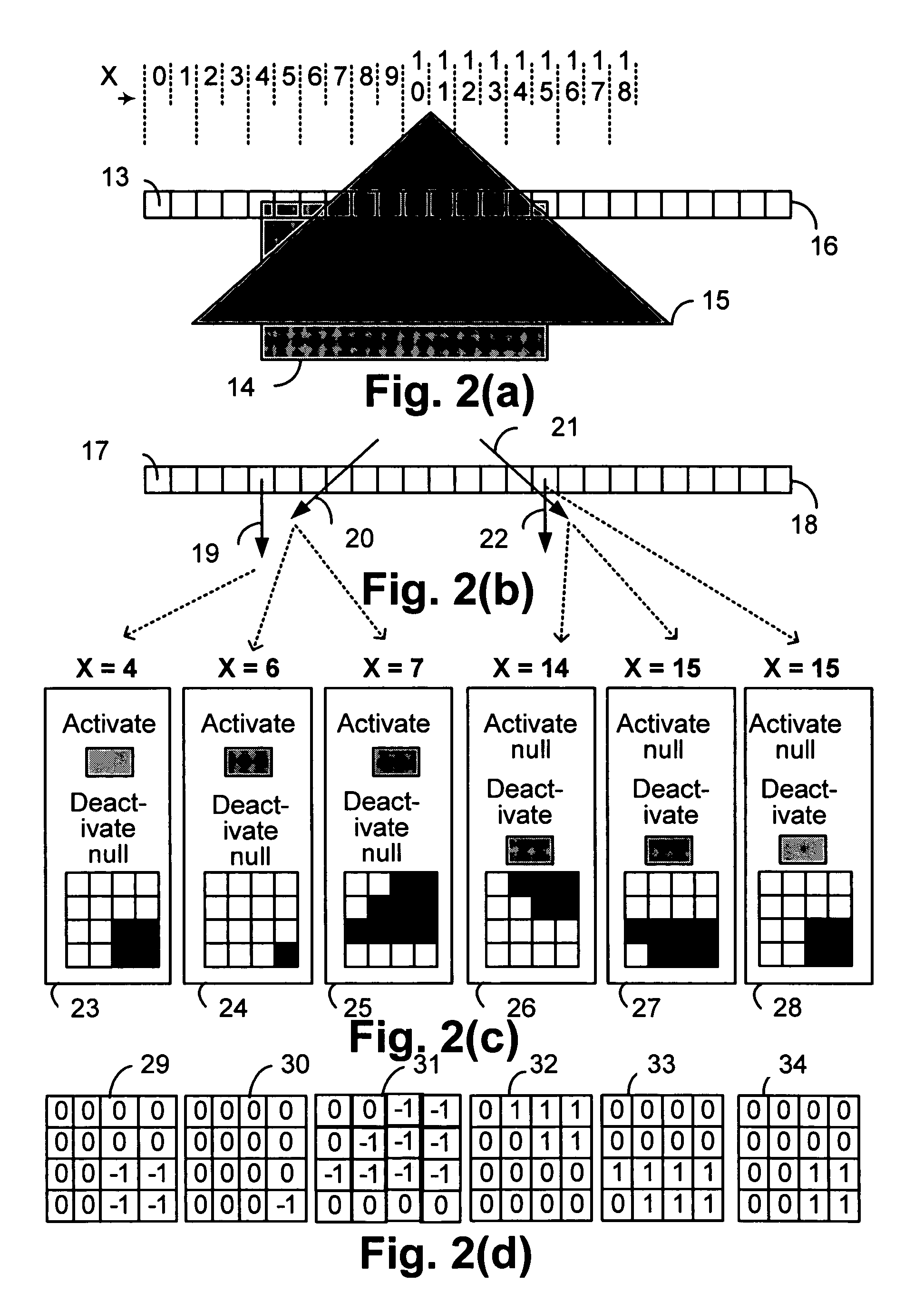
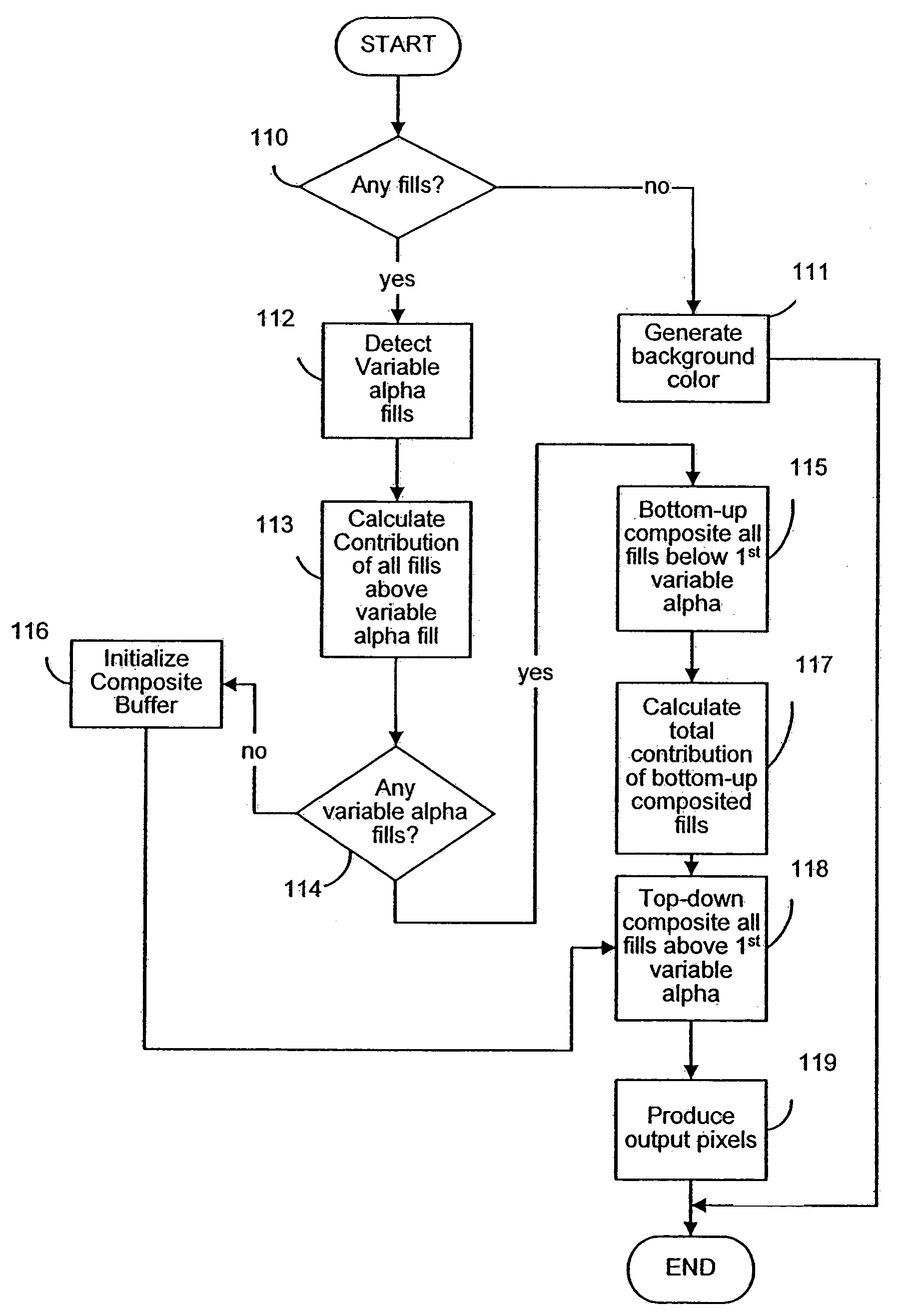
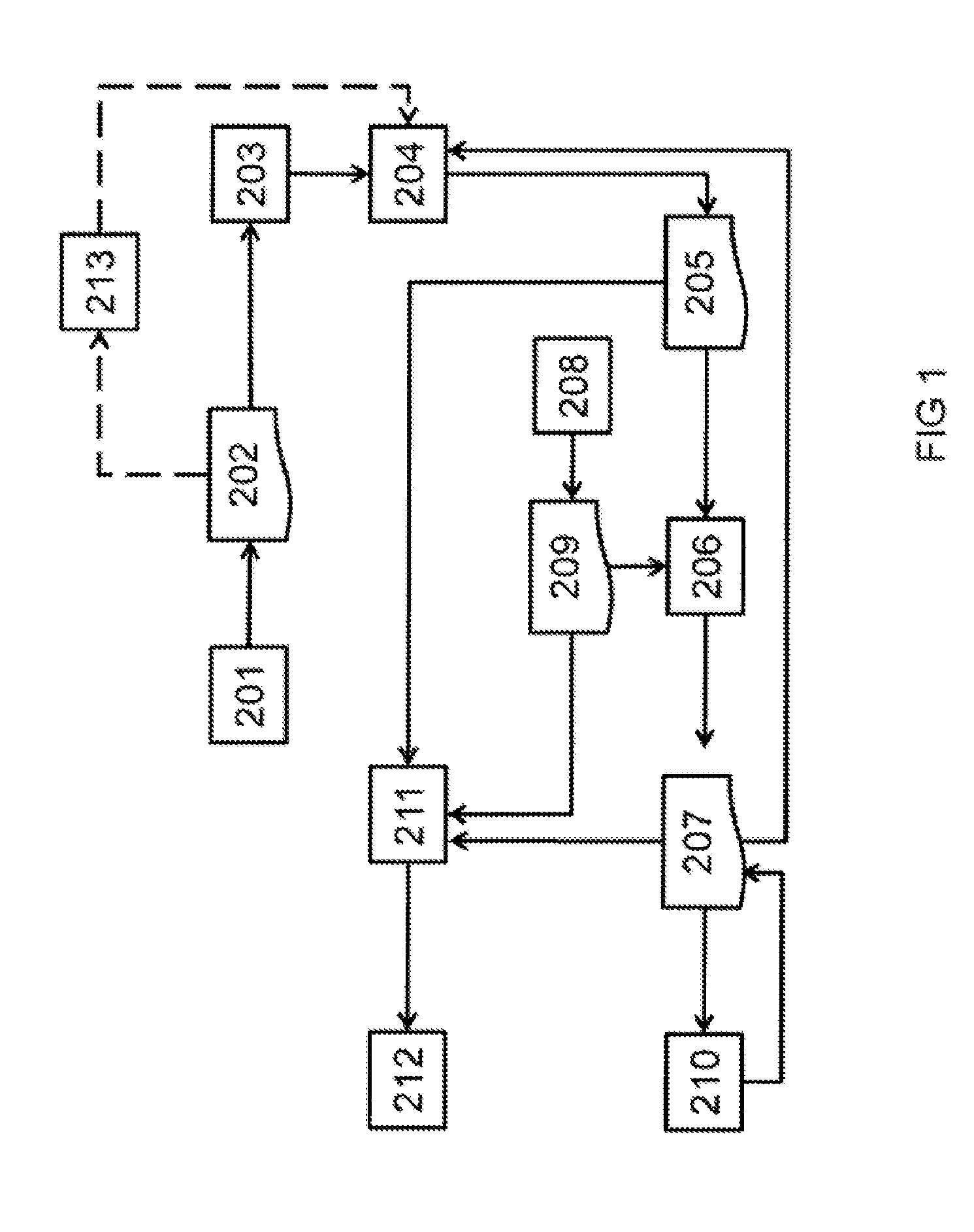
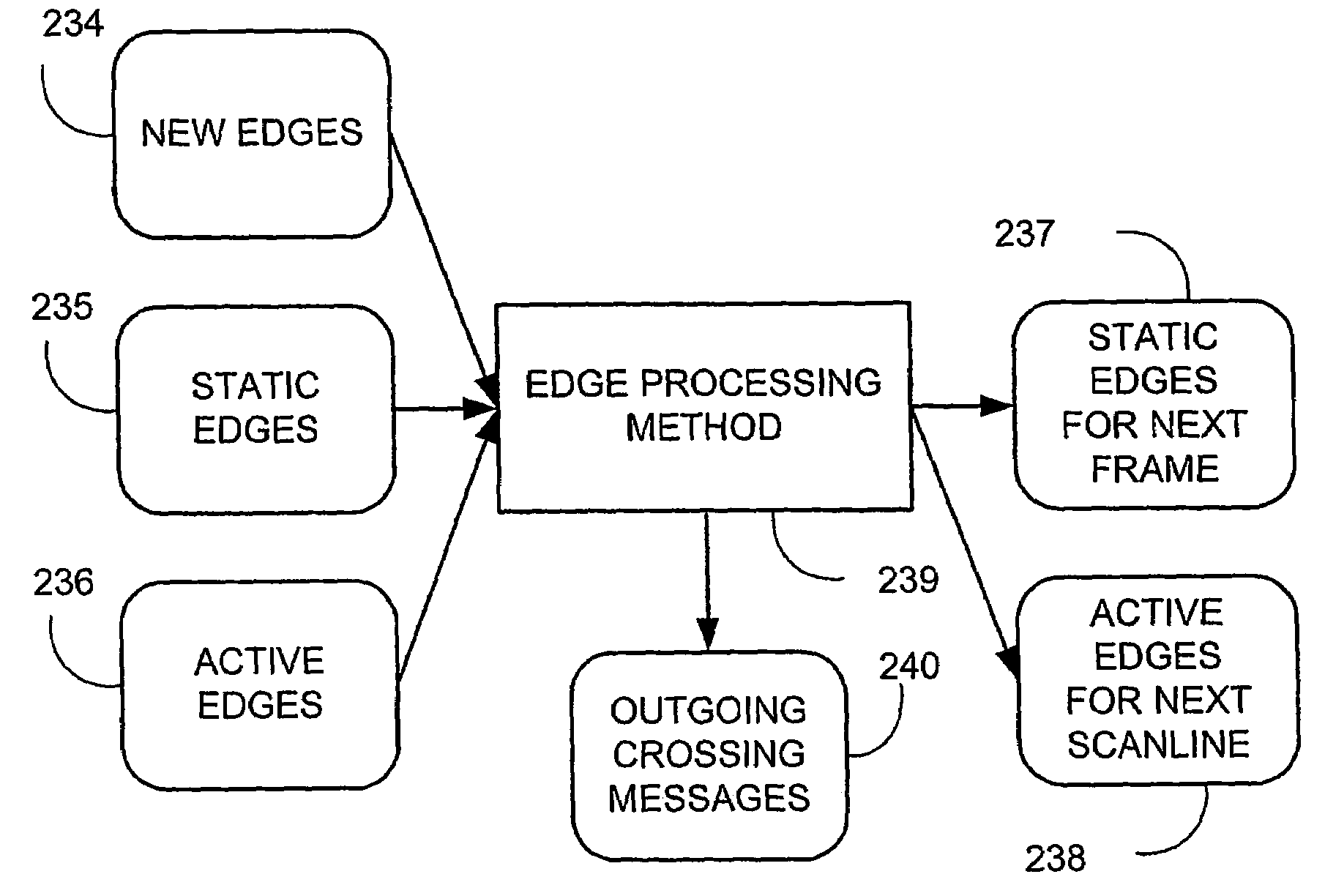
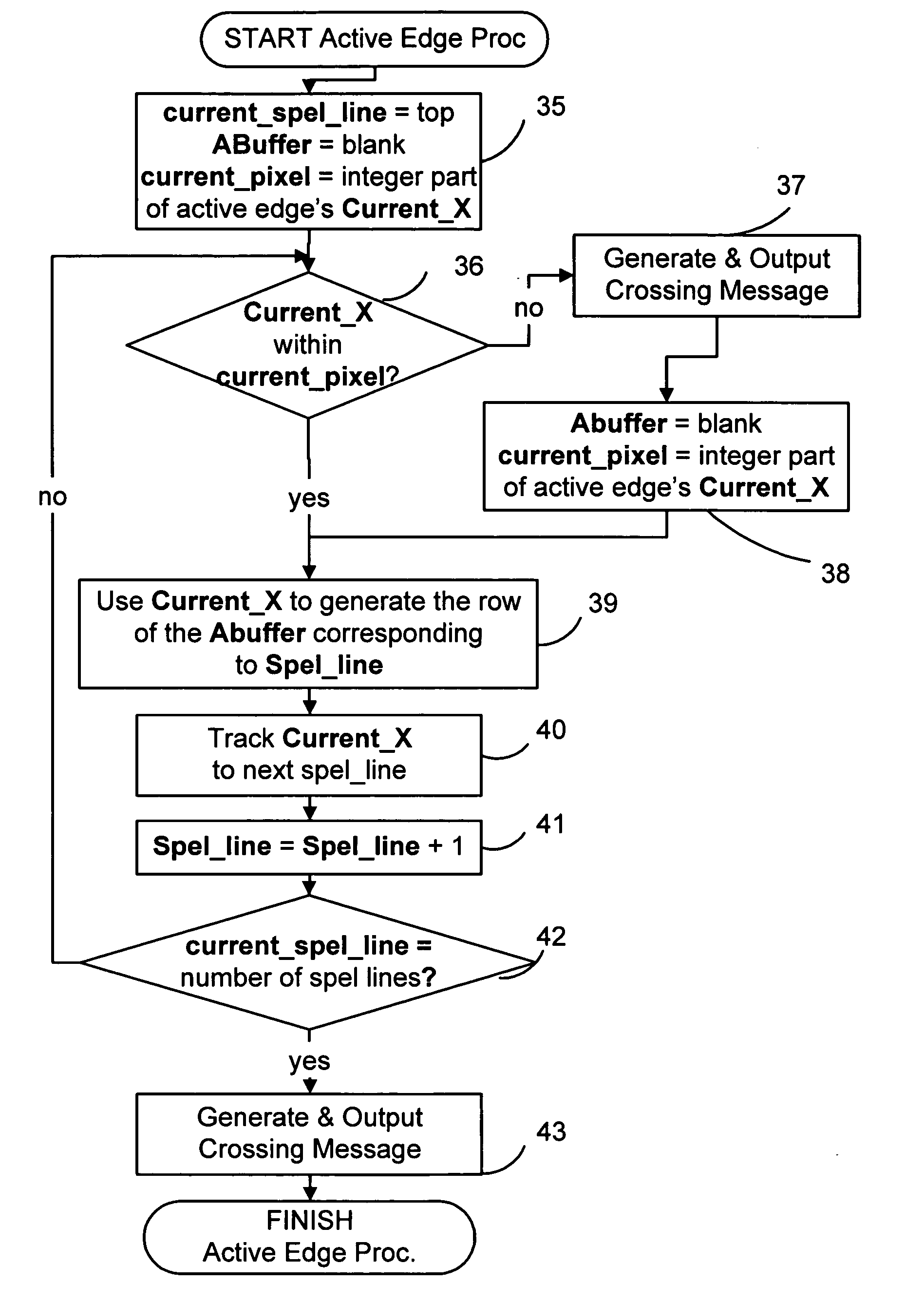
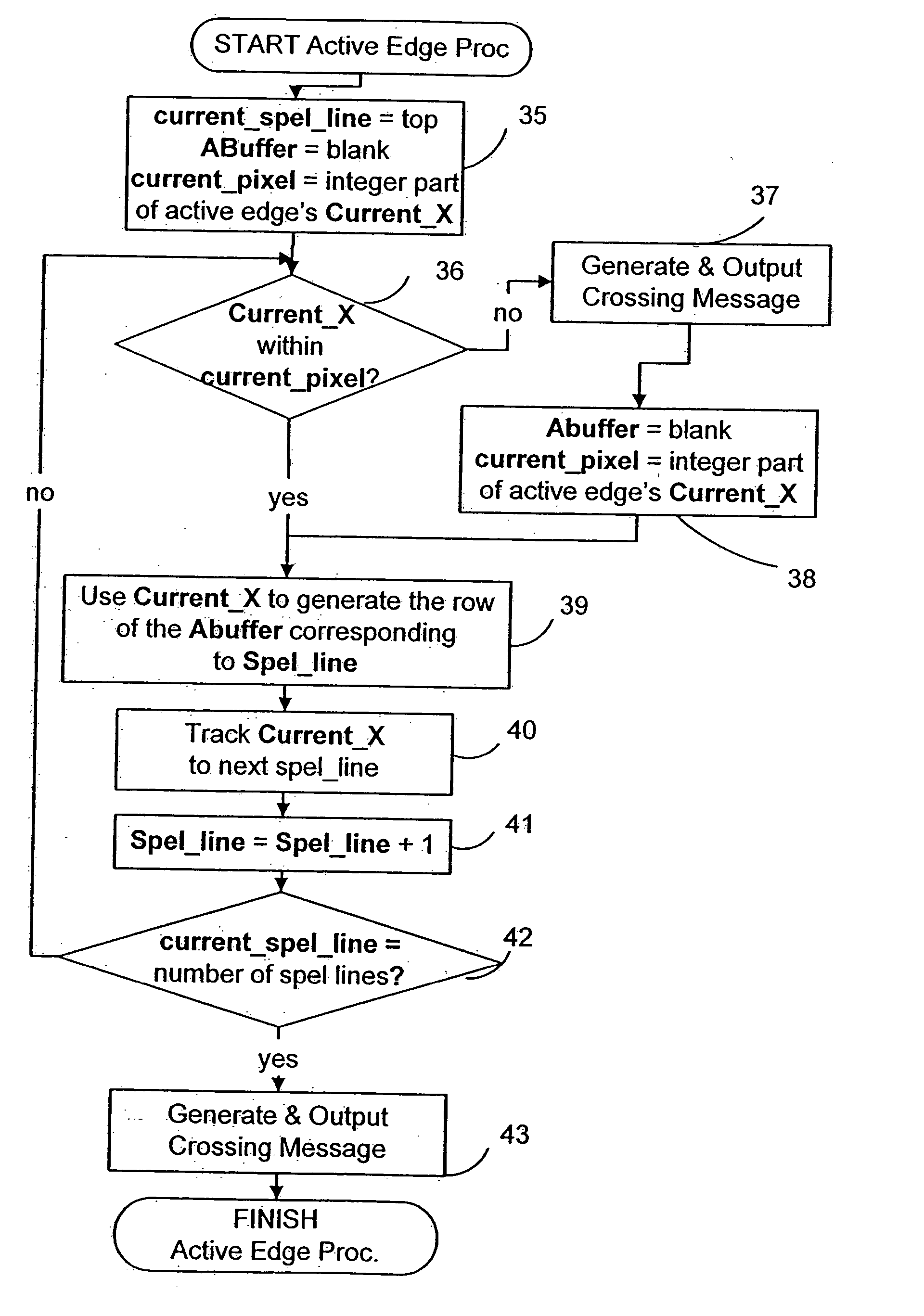
Disclosed is an imaging engine system (699) generally intended for the reproduction of graphical object images using apparatus having limited computing resources, such as so-called “thin clients”. Numerous developments of traditional image processing and rendering enable high quality image generation. One such development takes advantage of temporal coherence between one frame in an animation sequence and the succeeding frame. In particular, there will often be some edges (233, 235) of graphical objects that remain “static” across several contiguous frames. One example of this includes those edges used to draw image background detail. Another development performs antialiasing during scan line rendering of a graphic object image where sub-pixel resolution coverage bit-masks (A-buffers 29-34) are generated for a limited number of scan lines at a time. Preferably the A-buffers are generated for only one pixel at a time. Another development relates to rendering a scan line of a graphic object image in a scan line renderer for a span of pixels lying between two x-order consecutive edges intersecting the scan line. For the span of pixels, this development maintains a subset of depths present in the rendering, the subset being those depths that are present on the span and being maintained in depth order (590) and subject to removal of depths where the corresponding depth is no longer active. In another development a compositing stack (6101-6107) of image layers to be rendered in a raster scan fashion is simplified. Rendering is operable over a run of two or more pixels within which a relationship between graphical objects contributing to the layers does not change. The layers are first divided into groups (6110, 6112, 6114), with each group being separated by a layer having variable transparency (6111, 6113). For a top one of the groups, layers having constant colour in the run are reduced to a single equivalent colour (6115, 6116, 6117) having an associated accumulated contribution. Many other developments are disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
Antialiasing compositing in graphic object rendering
Disclosed is an imaging engine system (699) generally intended for the reproduction of graphical object images using apparatus having limited computing resources, such as so-called “thin clients”. Numerous developments of traditional image processing and rendering enable high quality image generation. One such development takes advantage of temporal coherence between one frame in an animation sequence and the succeeding frame. In particular, there will often be some edges (233, 235) of graphical objects that remain “static” across several contiguous frames. One example of this includes those edges used to draw image background detail. Another development performs antialiasing during scan line rendering of a graphic object image where sub-pixel resolution coverage bit-masks (A-buffers 29-34) are generated for a limited number of scan lines at a time. Preferably the A-buffers are generated for only one pixel at a time. Another development relates to rendering a scan line of a graphic object image in a scan line renderer for a span of pixels lying between two x-order consecutive edges intersecting the scan line. For the span of pixels, this development maintains a subset of depths present in the rendering, the subset being those depths that are present on the span and being maintained in depth order (590) and subject to removal of depths where the corresponding depth is no longer active. In another development a compositing stack (6101-6107) of image layers to be rendered in a raster scan fashion is simplified. Rendering is operable over a run of two or more pixels within which a relationship between graphical objects contributing to the layers does not change. The layers are first divided into groups (6110, 6112, 6114), with each group being separated by a layer having variable transparency (6111, 6113). For a top one of the groups, layers having constant color in the run are reduced to a single equivalent color (6115, 6116, 6117) having an associated accumulated contribution. Many other developments are disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
Mixed-order compositing for images having three-dimensional painting effects
ActiveUS9142056B1Texturing/coloringCathode-ray tube indicatorsBrush strokeIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
Rendering 3D paintings can be done by compositing brush strokes embedded in space. Image elements are rendered into an image representable by a pixel array wherein at least some of the image elements correspond to simulated painting strokes. A method may include determining stroke positions in a 3D space, determining stroke orders, and for each pixel to be addressed, determining a pixel color value by determining strokes intersections with a view ray for that pixel, determining a depth order and a stroke order for intersecting fragments, each fragment having a color, alpha value, depth, and stroke order, assigning an intermediate color to each of the fragments, corresponding to a compositing of nearby fragments in stroke order, and assigning a color to the pixel that corresponds to a compositing of the fragments using the intermediate colors assigned to the fragments. The compositing may be done in depth order.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC +1
Image converting device and three-dimensional image display device including the same
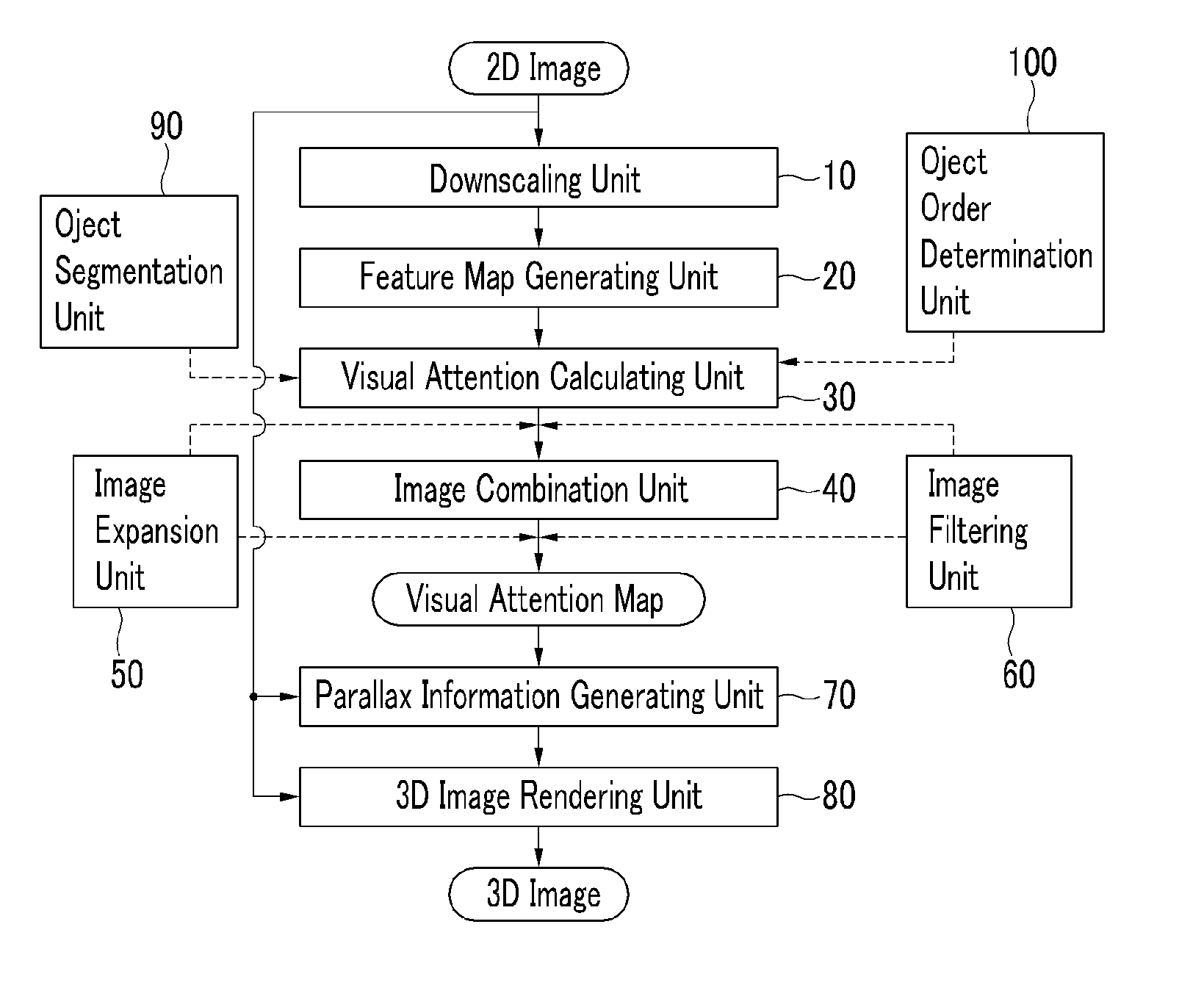
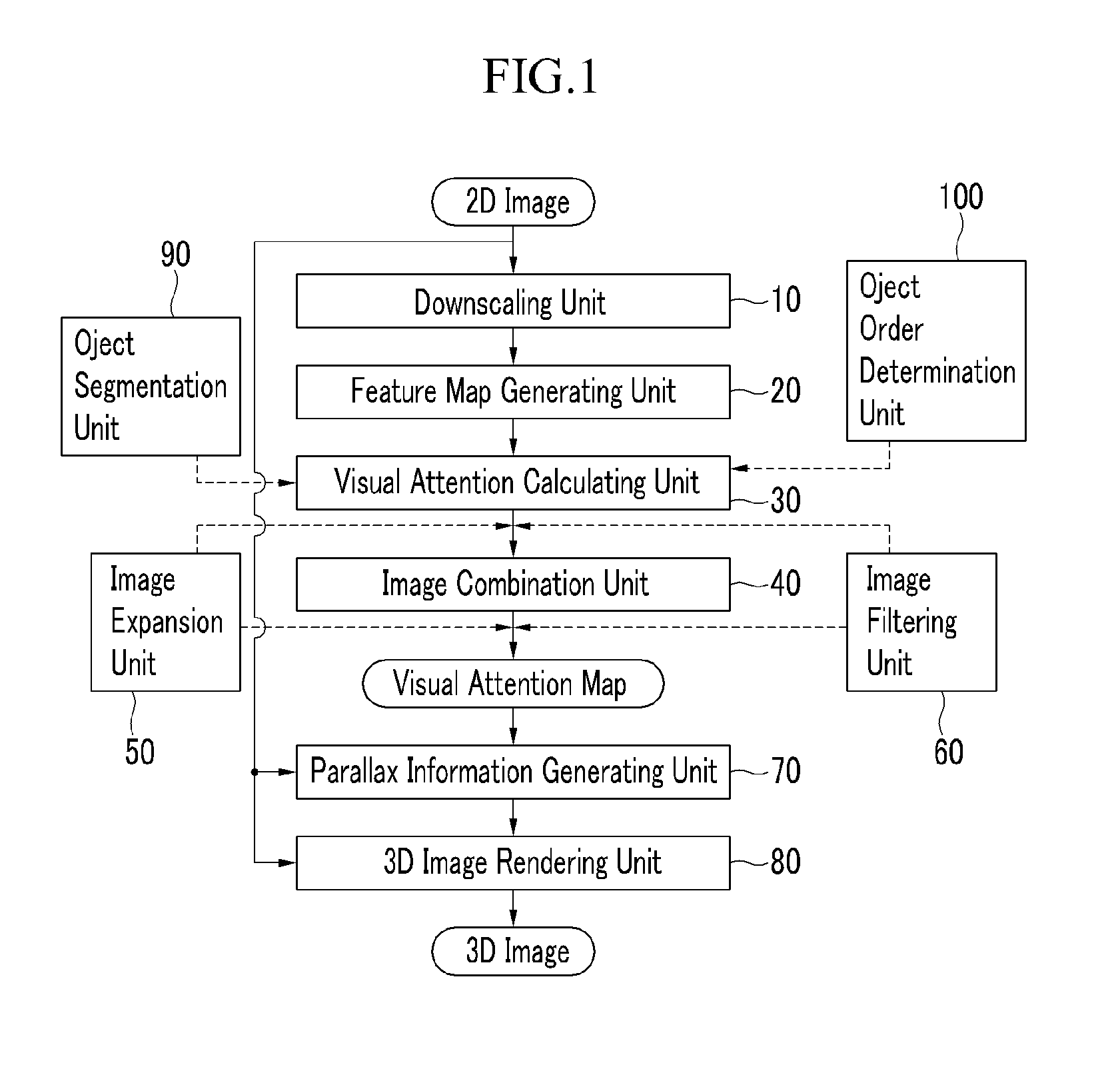
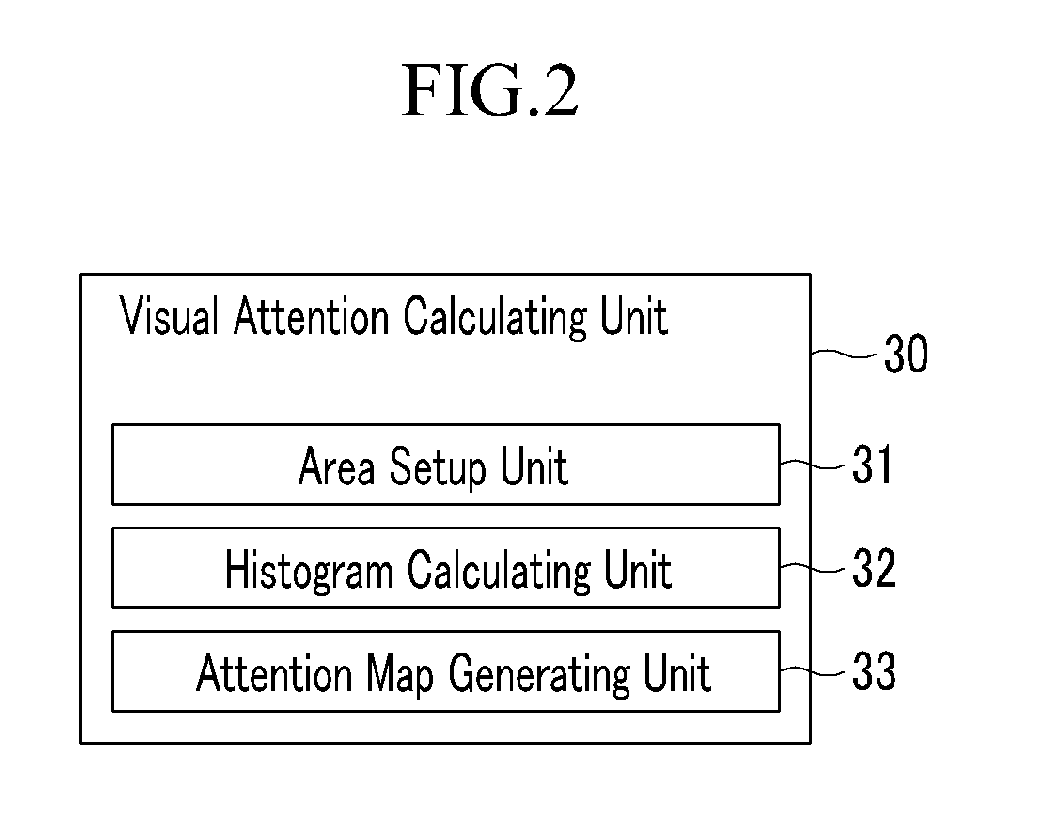
InactiveUS20110249886A1Reduce the amount of calculationReduce the amount of memoryCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsFeature mappingVisual perception
An image converting device includes; a downscaling unit which downscales a two-dimensional image to generate at least one downscaling image, a feature map generating unit which extracts feature information from the downscaling image to generate a feature map, wherein the feature map includes a plurality of objects, an object segmentation unit which divides the plurality of objects, an object order determining unit which determines a depth order of the plurality of objects, and adds a first weight value to an object having the shallowest depth among the plurality of objects, and a visual attention calculating unit which generates a low-level attention map based on visual attention of the feature map.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Optimising compositing calculations for a run of pixels
Owner:CANON KK
Method of tracking objects in a video sequence
A video surveillance system (10) comprises a camera (25), a personal computer (PC) (27) and a video monitor (29). Video processing software is provided on the hard disk drive of the PC (27). The software is arranged to perform a number of processing operations on video data received from the camera, the video data representing individual frames of captured video. In particular, the software is arranged to identify one or more foreground blobs in a current frame, to match the or each blob with an object identified in one or more previous frames, and to track the motion of the or each object as more frames are received. In order to maintain the identity of objects during an occlusion event, an appearance model is generated for blobs that are close to one another in terms of image position. Once occlusion takes place, the respective appearance models are used, in combination with a depth factor representing the depth order of the occluded objects, to segment the resulting group blob into regions which are classified as representing one or other of the merged objects.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
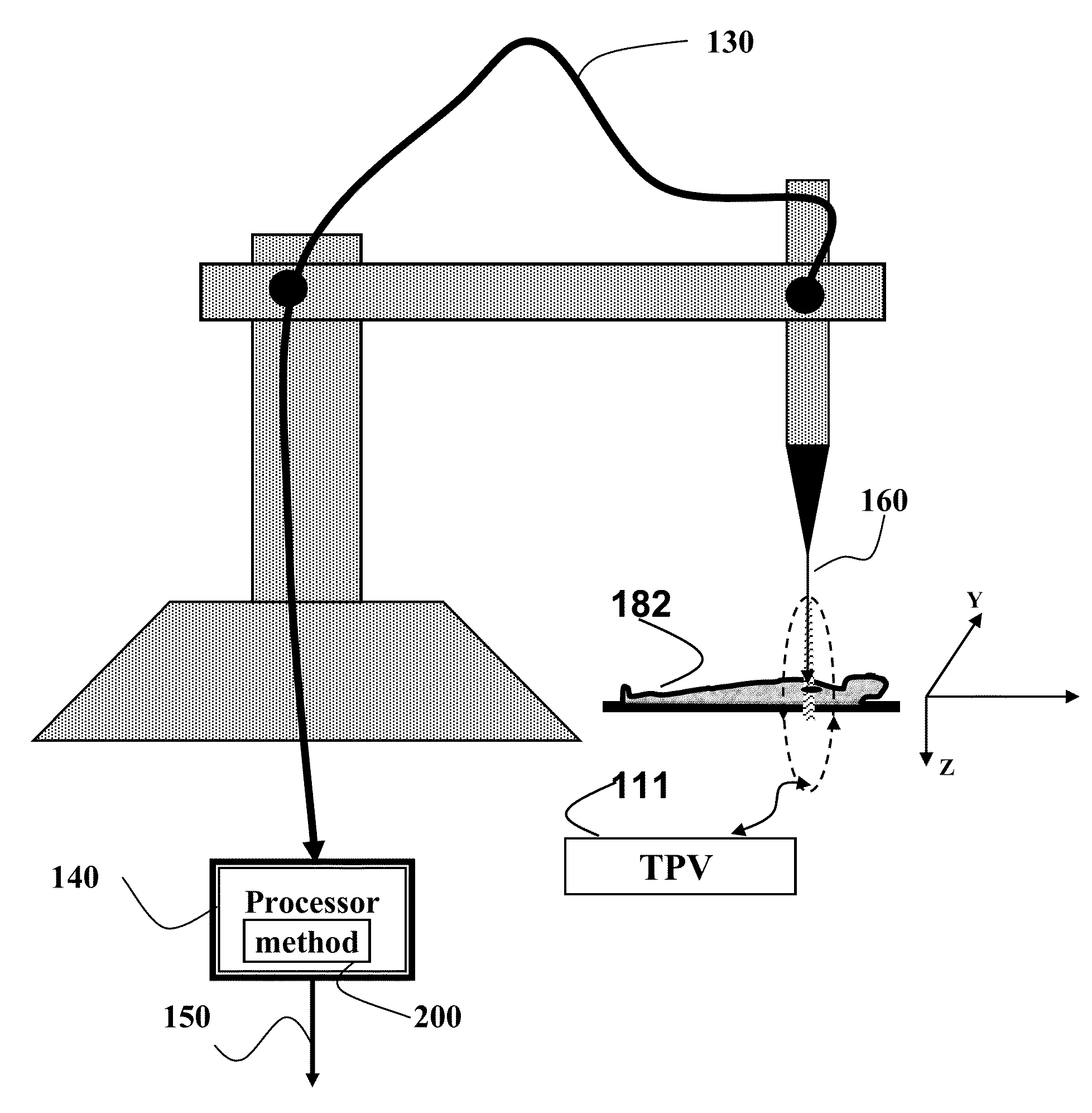
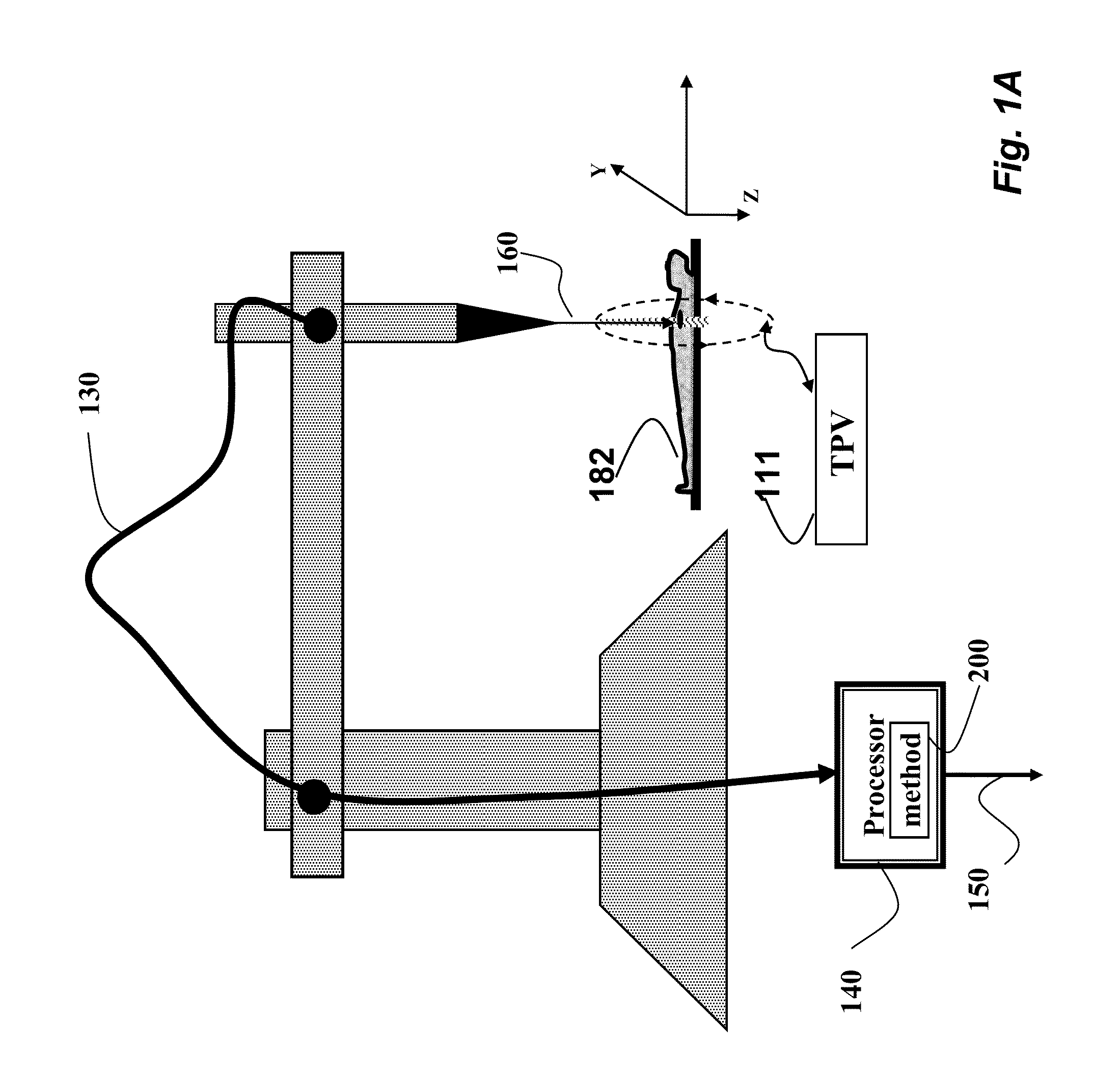
Method for Determining Paths of Particle Beams Through 3D Tissue Volumes
ActiveUS20110280372A1Ultra-fast acceptable solutionChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle beamEngineering
A path of a particle beam is determined through a 3D planning treatment volume (PTV), wherein the PTV includes a set of slices in a depth order, and each slice includes a set of locations. For each slice, the set of locations are grouped into a set of lines along a selected direction, wherein each line is a straight line and includes a starting location and an ending location, and each line is connected to one or two other lines, and the connecting connects two lines to either the starting location or the ending location of the lines to form a tour, and the tours are connected through the slices in the depth order to form the path of the particle beam.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Training method and system comprising mixed real and virtual images
ActiveUS20110027761A1Reduce riskAvoid damageCosmonautic condition simulationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSimulationVirtual appliance
Training method for the simulation of an operation performed by at least one device which is part of a real apparatus, wherein the method comprises providing to display means overlaid images under controlled depth order of a virtual apparatus, and real images of said device, and providing a simulated response to control means, based on data of the position and behavior of said device and on data of the position and behavior of said virtual apparatus.
Owner:EADS CONSTRS AERONAUTICAS
Method for tracking depths in a scanline based raster image processor
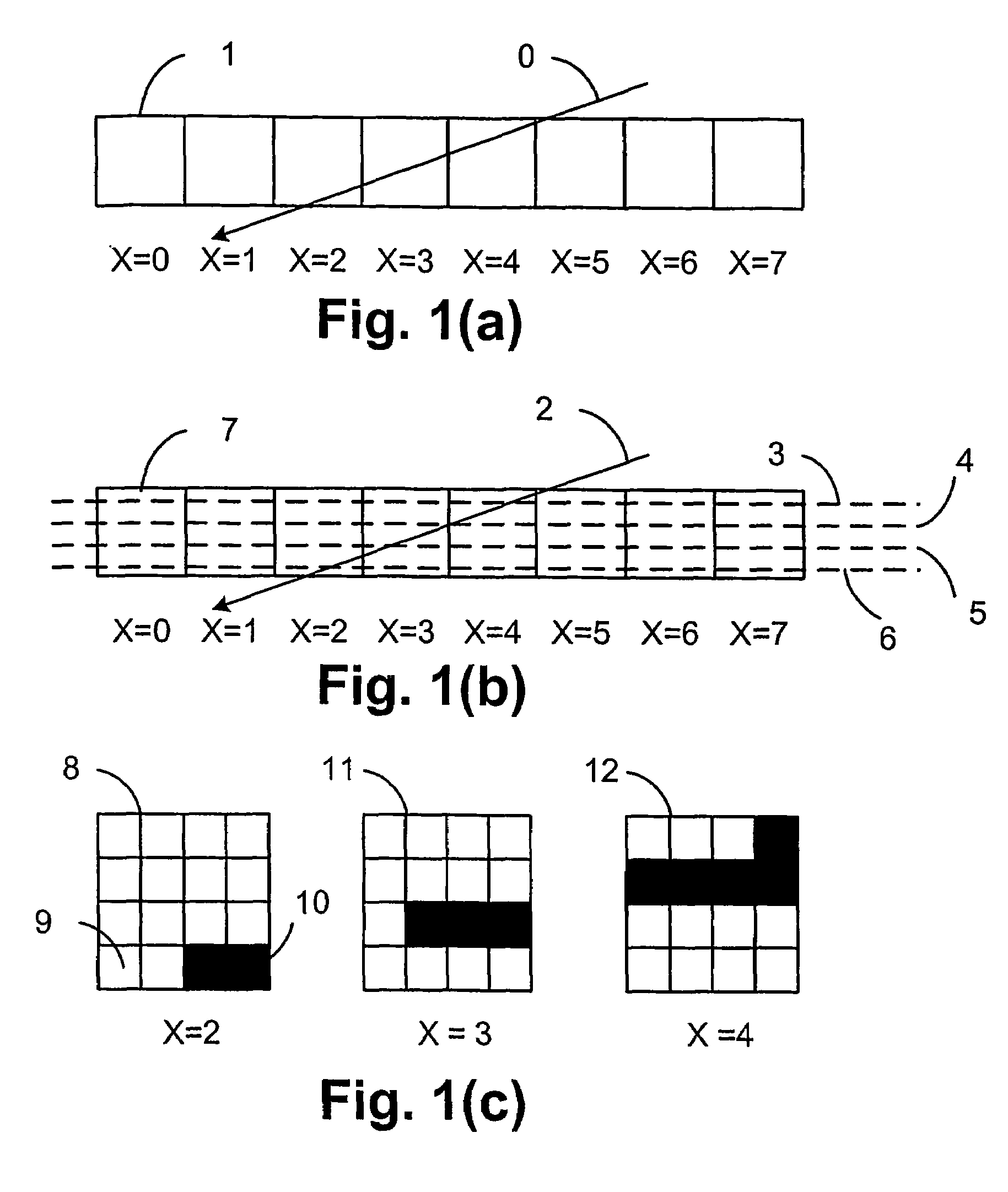
ActiveUS7425955B2More disadvantageFilling planer surface with attributes3D-image renderingGraphicsGrating
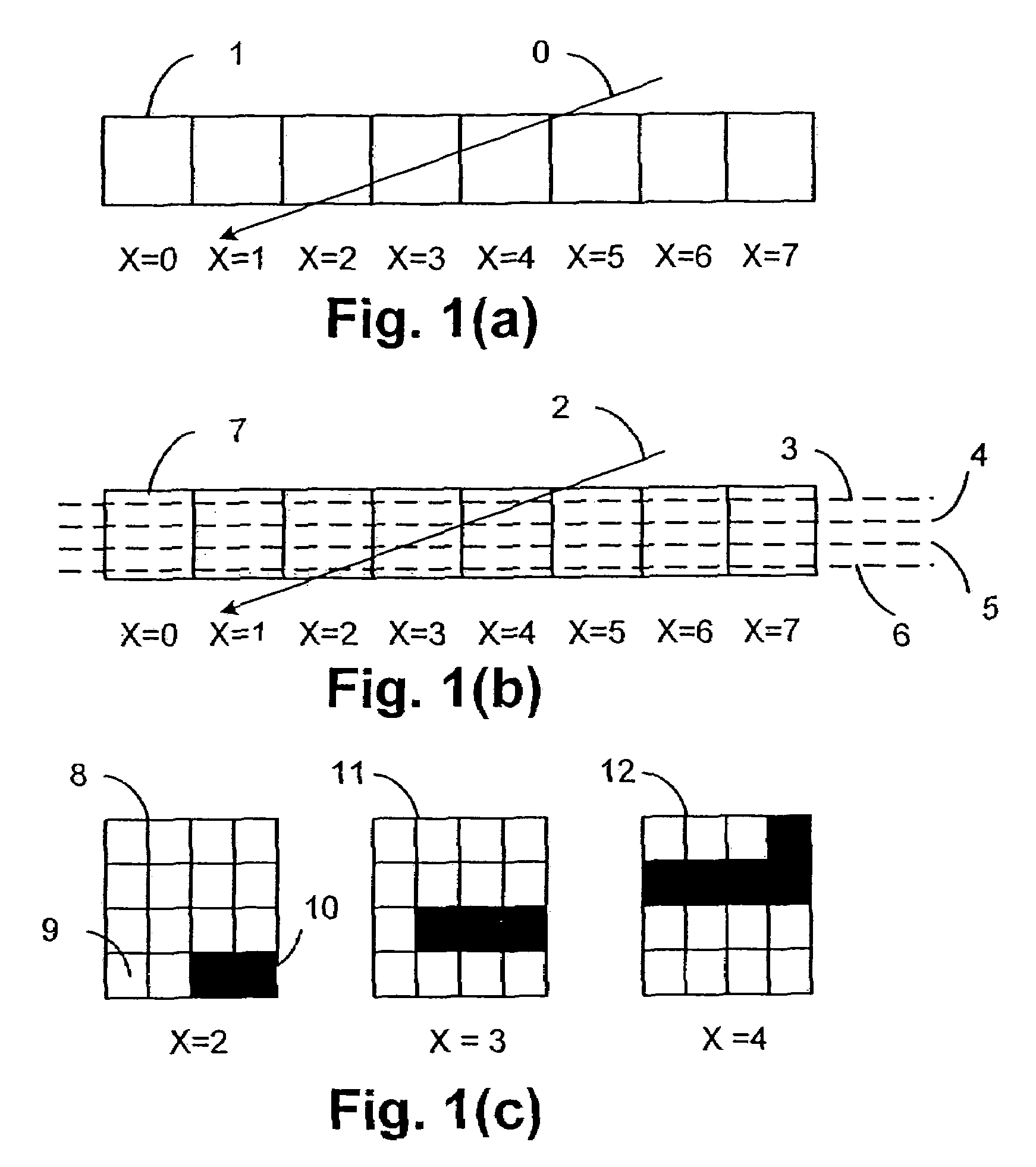
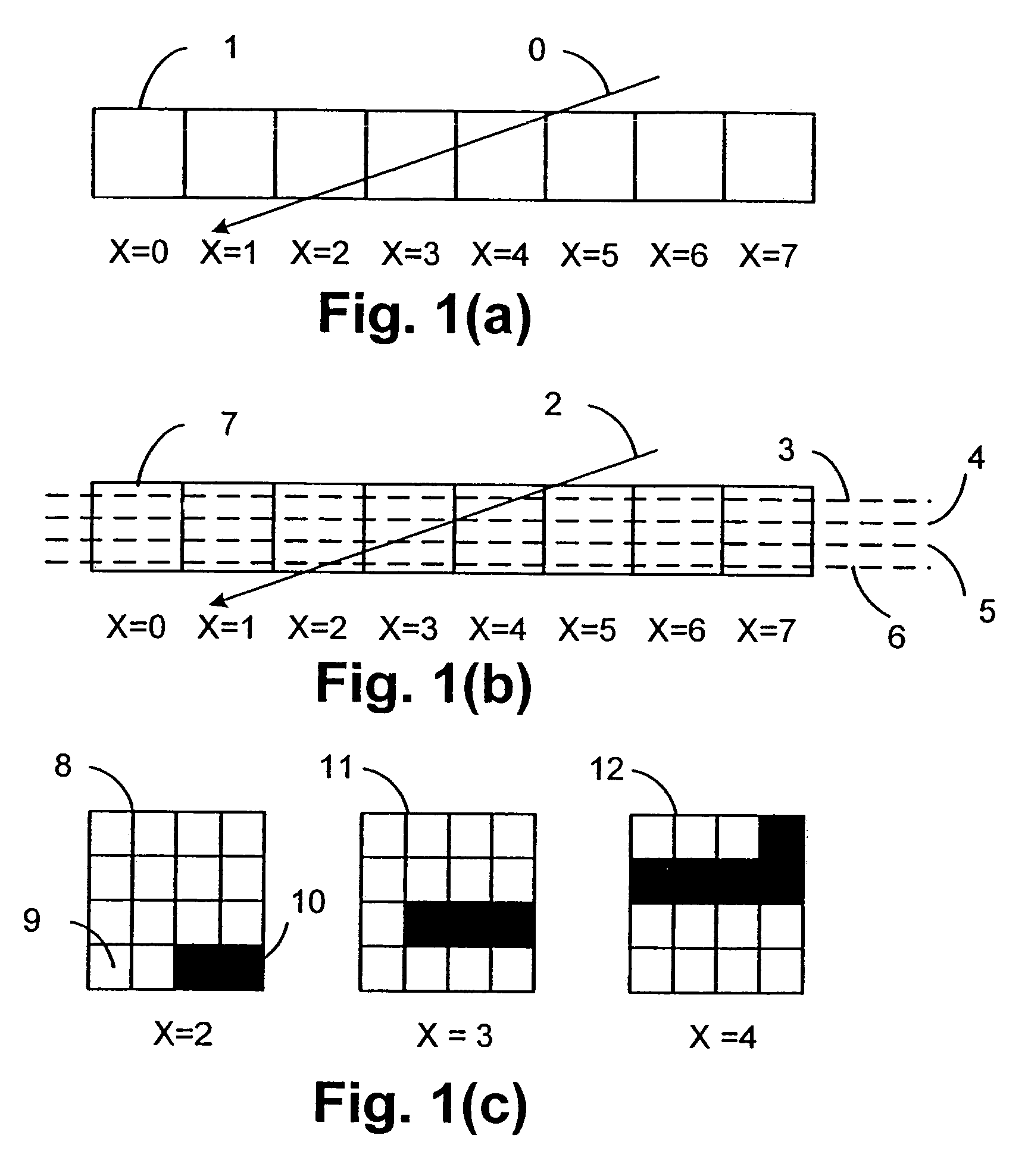
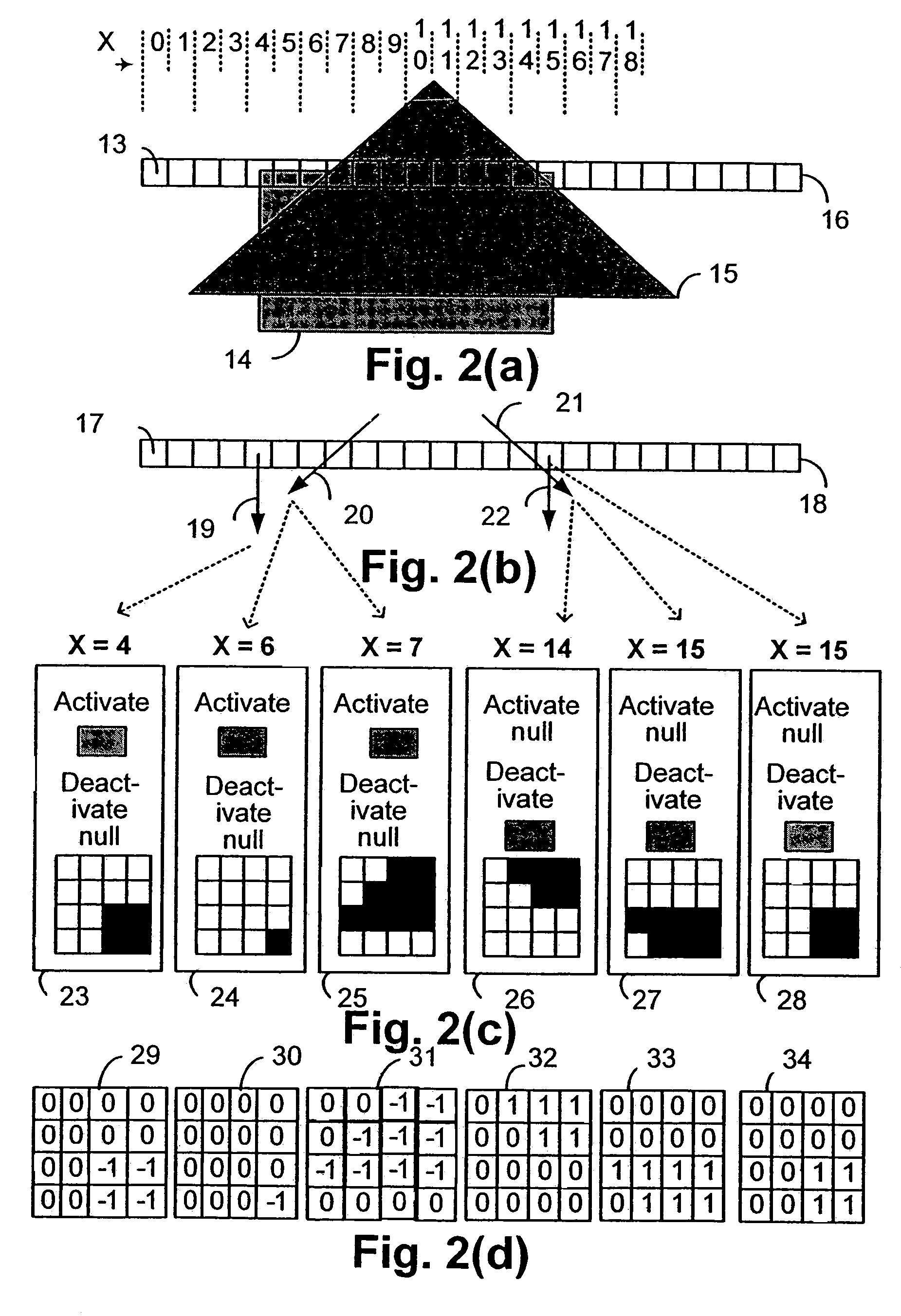
A method of rendering a scan line of a graphic object image in a scan line renderer for spans of pixels laying between consecutive x-ordered edges intersecting the scan line includes maintaining a set of depths present in the rendering of the scan line, with the set being maintained in depth order. For each span, the set contains at least those depths that are active in the span, and the set is subject to removal of at least one depth at a subsequent span on the scan line where the corresponding depth is no longer active.
Owner:CANON KK
Context processor for video analysis system
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and a system for mapping a scene depicted in an acquired stream of video frames that may be used by a machine-learning behavior-recognition system. A background image of the scene is segmented into plurality of regions representing various objects of the background image. Statistically similar regions may be merged and associated. The regions are analyzed to determine their z-depth order in relation to a video capturing device providing the stream of the video frames and other regions, using occlusions between the regions and data about foreground objects in the scene. An annotated map describing the identified regions and their properties is created and updated.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Optimising compositing calculations for a run of pixels
InactiveUS20050017984A1More disadvantage2D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSub-pixel resolutionGraphics
Disclosed is an imaging engine system (699) generally intended for the reproduction of graphical object images using apparatus having limited computing resources, such as so-called “thin clients”. Numerous developments of traditional image processing and rendering enable high quality image generation. One such development takes advantage of temporal coherence between one frame in an animation sequence and the succeeding frame. In particular, there will often be some edges (233, 235) of graphical objects that remain “static” across several contiguous frames. One example of this includes those edges used to draw image background detail. Another development performs antialiasing during scan line rendering of a graphic object image where sub-pixel resolution coverage bit-masks (A-buffers 29-34) are generated for a limited number of scan lines at a time. Preferably the A-buffers are generated for only one pixel at a time. Another development relates to rendering a scan line of a graphic object image in a scan line renderer for a span of pixels lying between two x-order consecutive edges intersecting the scan line. For the span of pixels, this development maintains a subset of depths present in the rendering, the subset being those depths that are present on the span and being maintained in depth order (590) and subject to removal of depths where the corresponding depth is no longer active. In another development a compositing stack (6101-6107) of image layers to be rendered in a raster scan fashion is simplified. Rendering is operable over a run of two or more pixels within which a relationship between graphical objects contributing to the layers does not change. The layers are first divided into groups (6110, 6112, 6114), with each group being separated by a layer having variable transparency (6111, 6113). For a top one of the groups, layers having constant color in the run are reduced to a single equivalent color (6115, 6116, 6117) having an associated accumulated contribution. Many other developments are disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
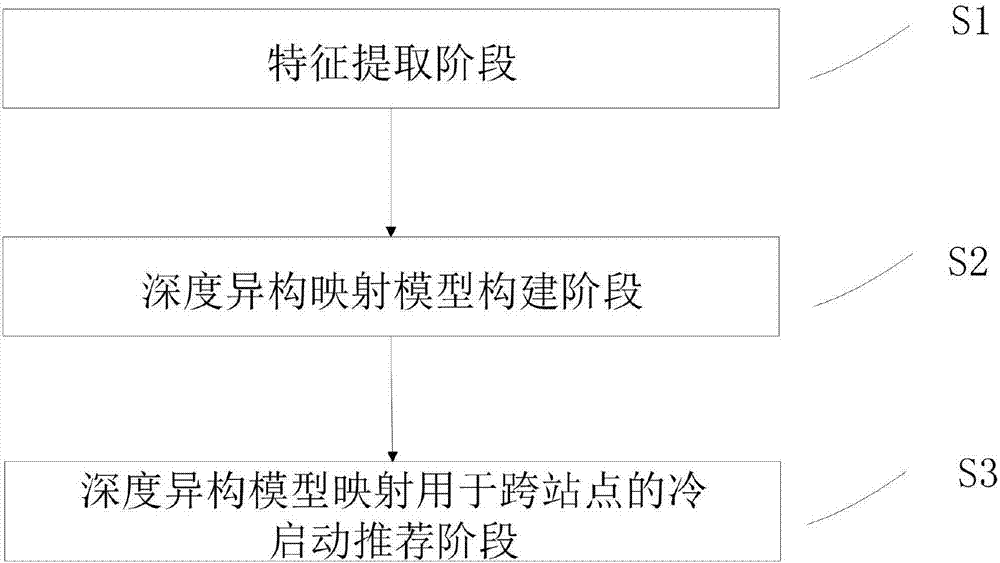
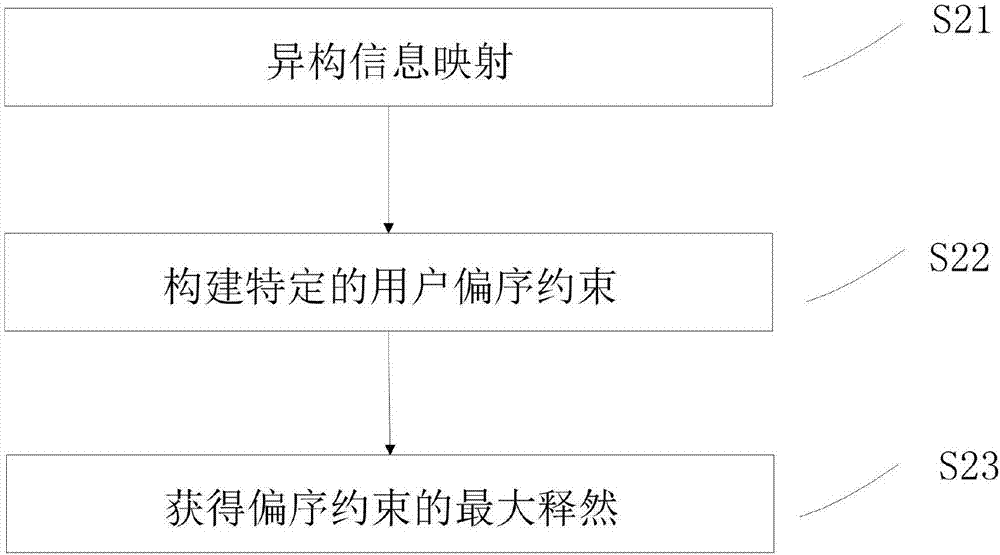
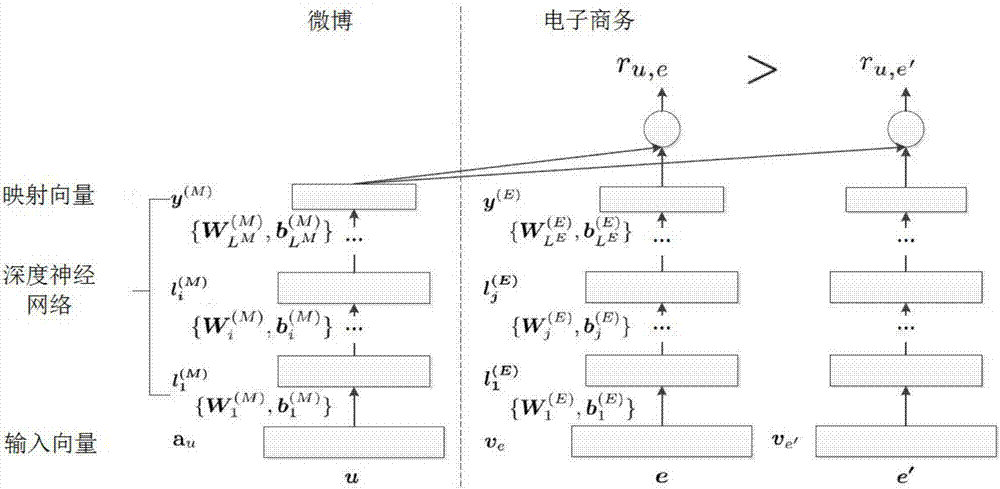
Cross-site cold-start recommendation method based on deep learning
InactiveCN107103499AImprove recommendation efficiencyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMarketingPurchasingDepth order
The invention provides a cross-site cold-start recommendation method based on deep learning. The method achieves the recommendation of a product for a new user through the information of the new user of an e-commerce website in a social network without the historical record of the user, and can obtain the interest point of the user in a detailed manner through the social information of the user. The method comprises the steps: constructing a depth ordering model based on the user's preference; completing the conversion of the e-commerce website user information and the social network user information through the constructed model, searching the purchasing behavior similar to the habitual purchase behavior of the user in the super-user node information, and completing the recommendation, thereby improving the recommendation efficiency.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
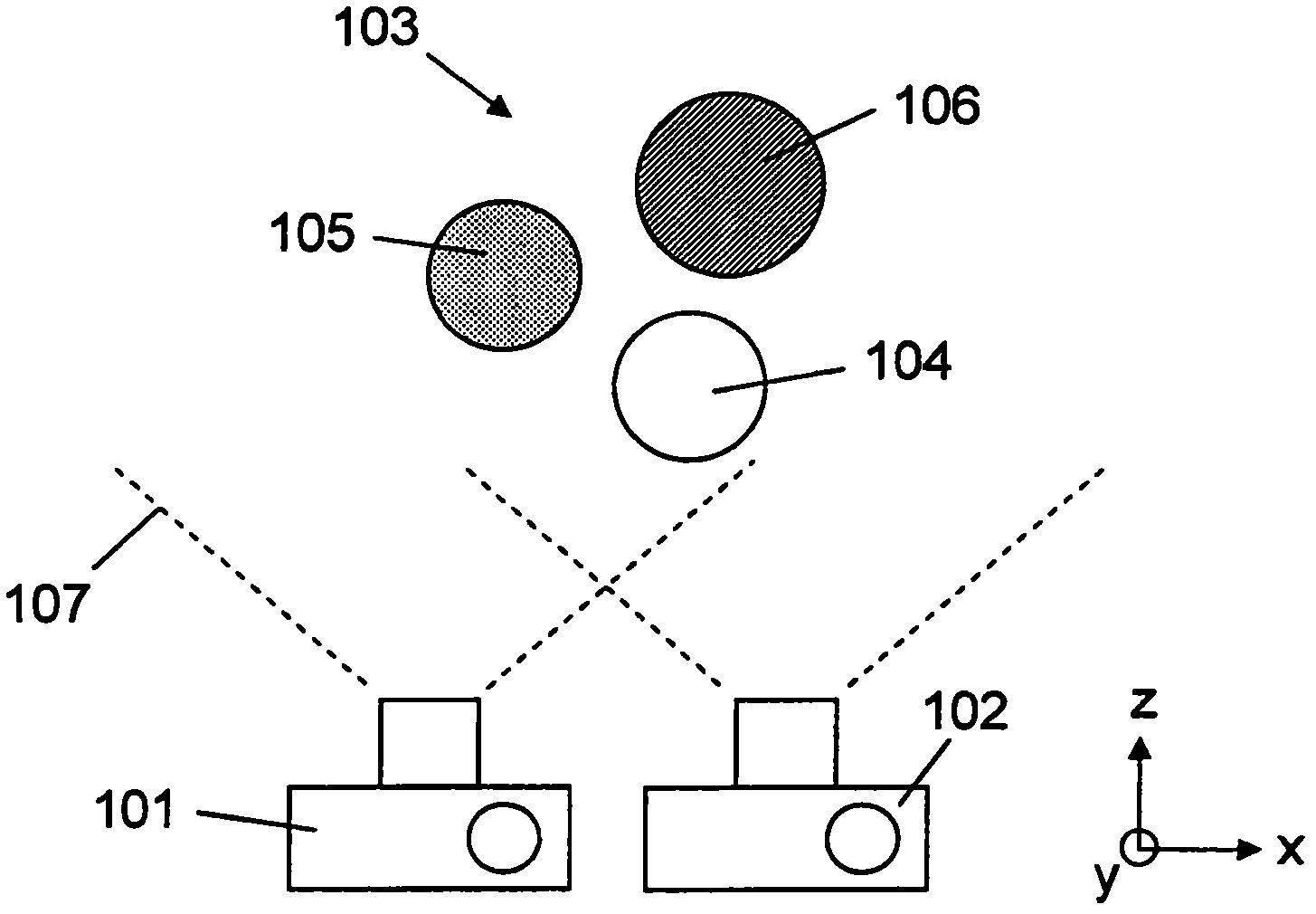
A processor, apparatus and associated methods
A processor configured to receive respective image data, representative of images, of the same subject scene from two or more image capture sources spaced apart at a particular predetermined distance; identify corresponding features from the respective image data; determine the change in position of the identified features represented in the respective image data; and identify the depth-order of the identified features according to their determined relative change in position to allow for depth-order display of the identified features according to their determined relative change in position.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Civilian defense digital camouflage net and method
ActiveCN103278046AImprove survivabilityBlurred boundariesCamouflage devicesProtective buildings/sheltersSurvivabilityCut flowers
The invention relates to the technical field of civilian defense and camouflage and discloses a civilian defense digital camouflage net and method. The camouflage net is composed of multiple different camouflage net units and annular ropes. A large net is formed by weaving and connecting the different camouflage nets through the annular rope arranged on the periphery of each camouflage net unit. Each camouflage net unit is composed of a bottom net and a net face. Each net face is made of cut-flower composite base cloth which prevents infrared rays and radar and has a color system of shallow gray, deep gray, jade green, brown and soil color, wherein the color system imitates a background. The civilian defense digital camouflage net can be rapidly assembled according to on-spot backgrounds and seasons, civilian defense primary objectives are merged with the surrounding backgrounds and survival capability of the objectives is improved. Based on the relevant principle of blocking a perception depth order in visuality, square corners and adjacent spots are used for blocking so that observers have an illusion that distances from the spots are different and spatial layering feelings are generated. Boundaries of the digital camouflage spots are not clear and the camouflage net has smooth continuous curves which are not easy to identify by the eyes.
Owner:UNIT 61489 OF PLA
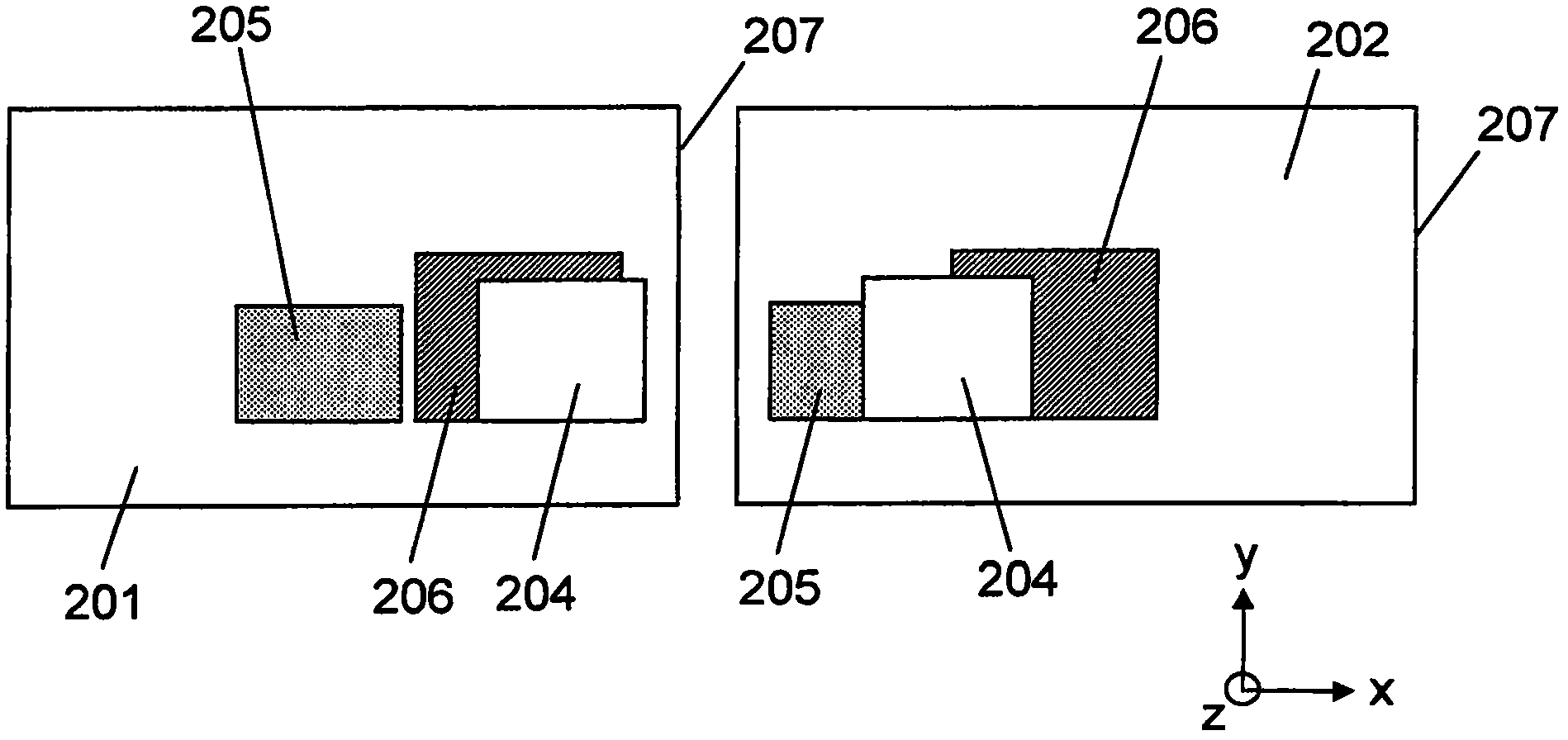
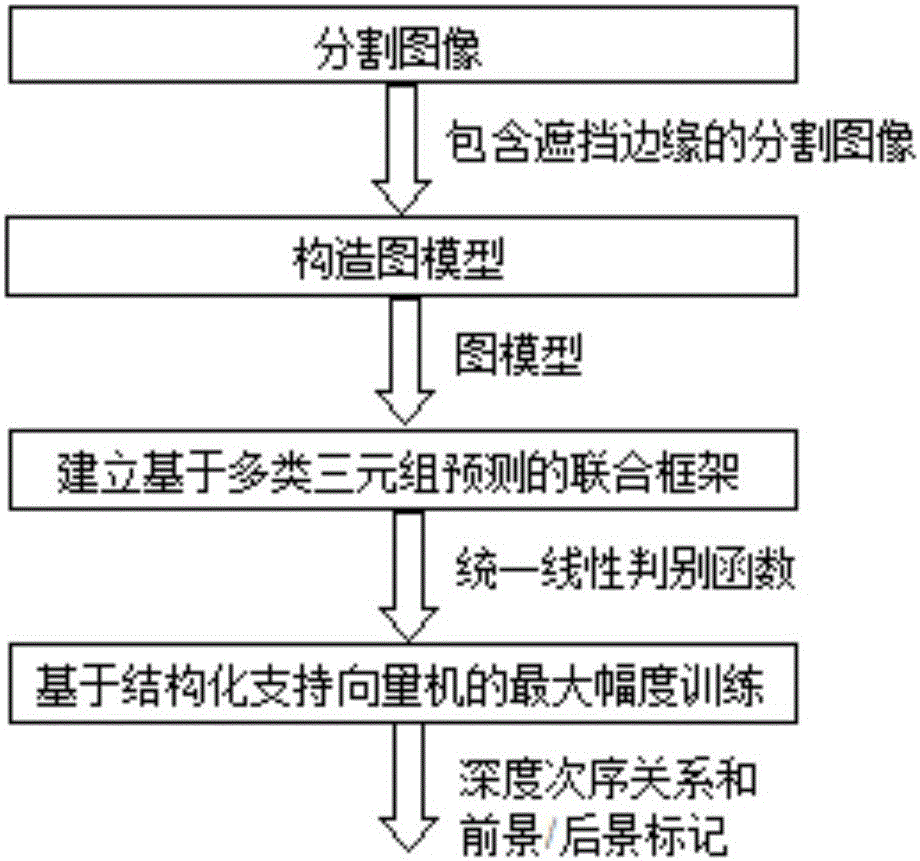
Combined learning method for foreground region marking and depth order inferring
InactiveCN105809671AImprove effectivenessImage enhancementImage analysisStructured support vector machineData set
The invention discloses a combined learning method for foreground region marking and depth order inferring, including the following steps: conducting image segmentation, building image models for the segmented images, building a combined framework based on the predictions of a variety of three tuples, and carrying out training with maximal amplitude on the basis of a structured support vector machine so as to obtain the deep order relationship of each region in the images and the foreground and background markings; The invention makes modifications and improvements to the limitations and deficiencies from one signal predication by deeply estimating monocular images and reviewing and summarizing the foreground region markings, puts forward an estimated combination of framework and makes effective and correct use of some graph verification code algorithms from Geometric Context data set and Cornell Depth Order data set. And a more effective prediction result can be achieved through the method.
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY
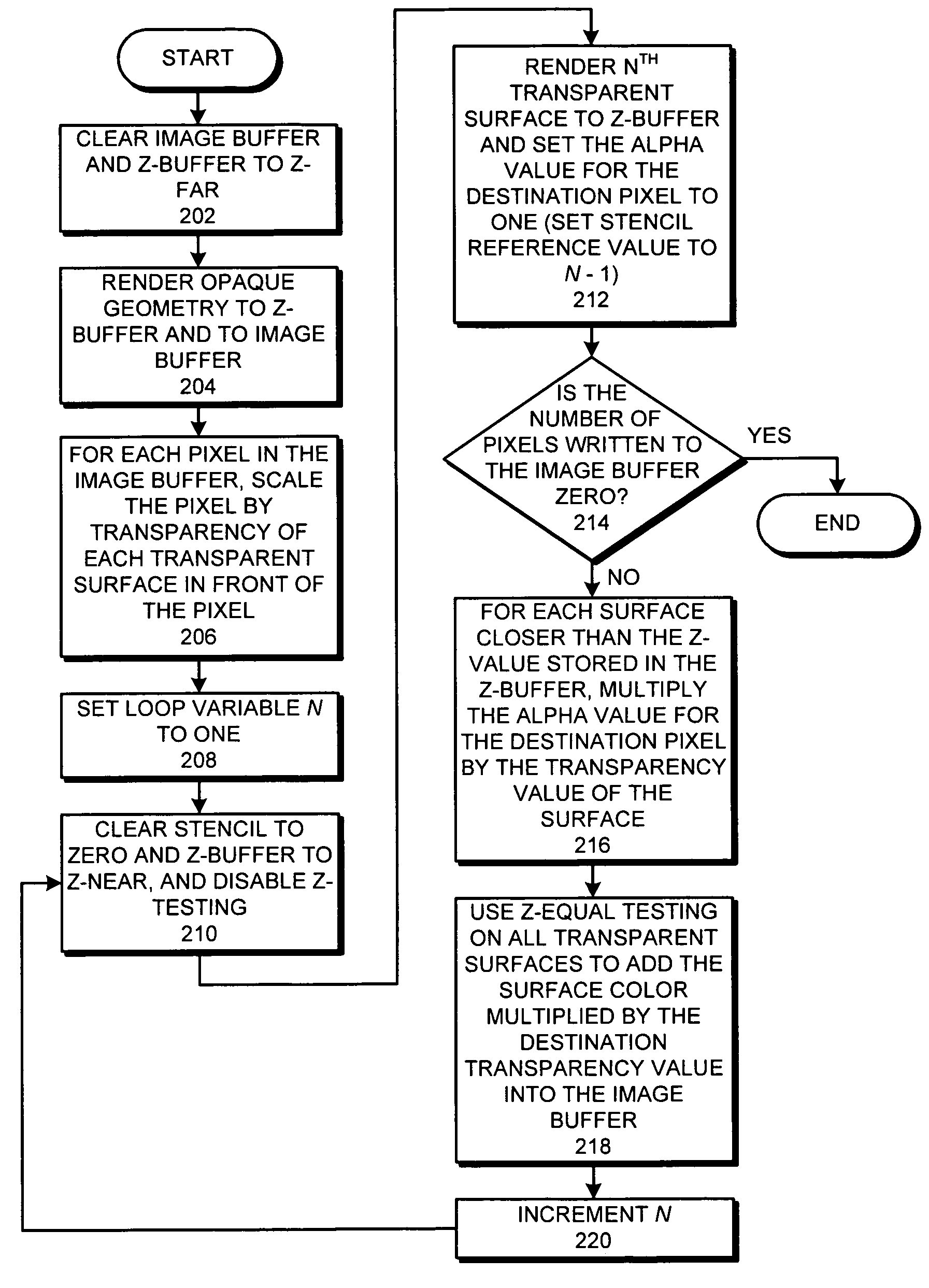
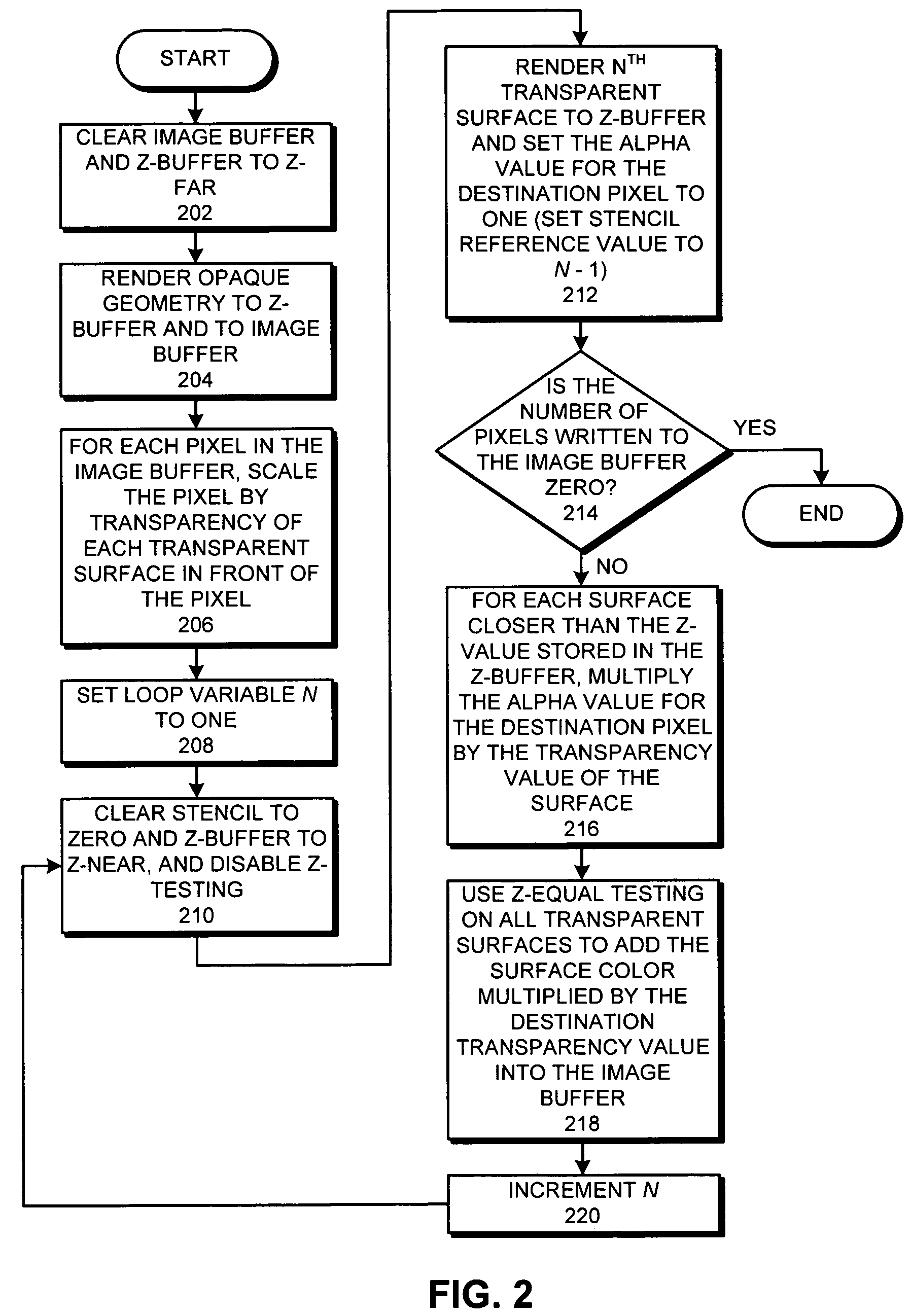
Method and apparatus for rendering semi-transparent surfaces
A system that renders a three-dimensional model which contains semi-transparent surfaces. During operation, the system renders the semi-transparent surfaces in the three-dimensional model by performing the following operations iteratively for each semi-transparent surface in draw-order instead of depth-order: (1) rendering the semi-transparent surface to a Z buffer, (2) calculating a cumulative transparency value for each pixel of the semi transparent surface as a function of the transparency value for each opaque and semi-transparent surface that intersects the pixel and is in front of the Z-value for the pixel in the Z-buffer, (3) attenuating a surface color value for each pixel in the semi-transparent surface by the cumulative transparency value for the pixel, and (4) adding the attenuated surface color value to a corresponding pixel value in the image buffer.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Rendering successive frames in a graphic object system
Owner:CANON KK
Method and system for designing depth of seismic source excitation well
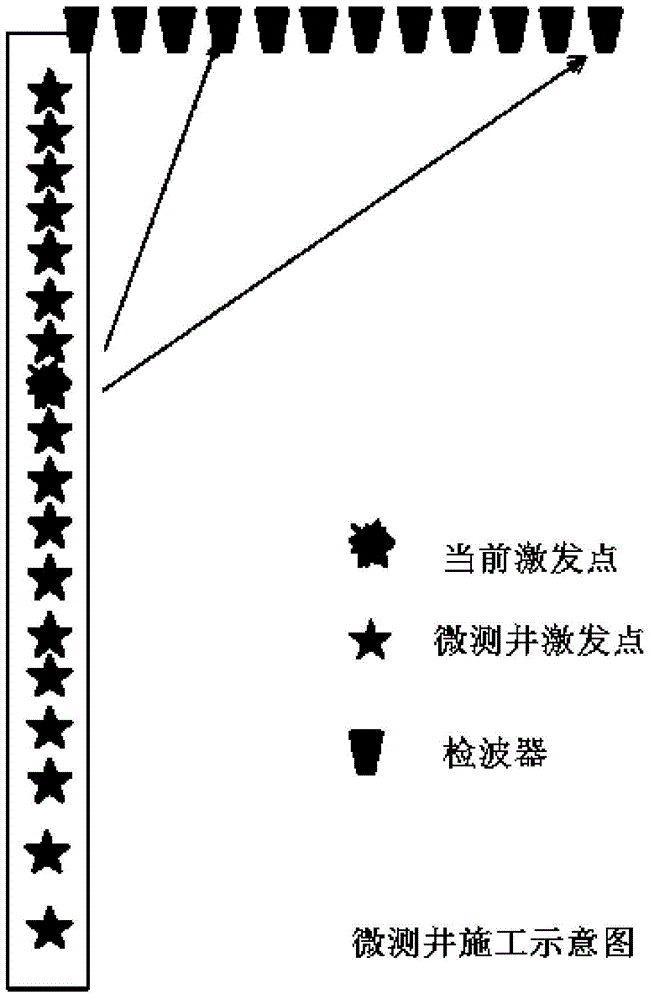
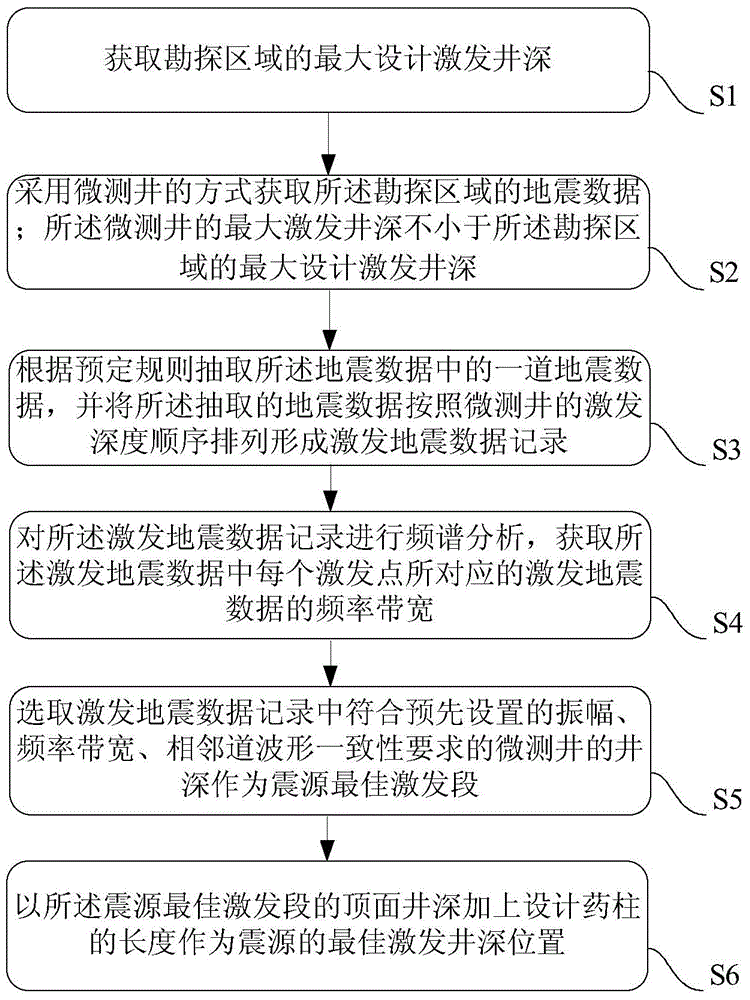
InactiveCN104459799AImprove stimulation effectLarge amplitudeSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingDepth in a wellSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method and system for designing the depth of a seismic source excitation well. The method includes the steps of S1, obtaining the maximum designed depth of the excitation well in an exploration region; S2, obtaining seismic data of the exploration region in a micro-logging mode; S3, extracting a set of seismic data in the seismic data according to a preset rule, and arranging the extracted seismic data according to the micro-logging excitation depth order to form an excitation seismic data record; S4, carrying out frequency spectrum analysis on the excitation seismic data record to obtain the frequency bandwidth of the excitation seismic data; S5, selecting the micro-logging well depth, meeting a preset amplitude, frequency bandwidth and adjacent channel waveform coincidence requirement, in the excitation seismic data record to serve as an optimal seismic source excitation segment. By means of the method and system, the reasonable seismic source excitation well depth can be obtained through design in a complex earth surface region, the seismic source excitation effect can be improved, and the signal to noise ratio of collected seismic data can be improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
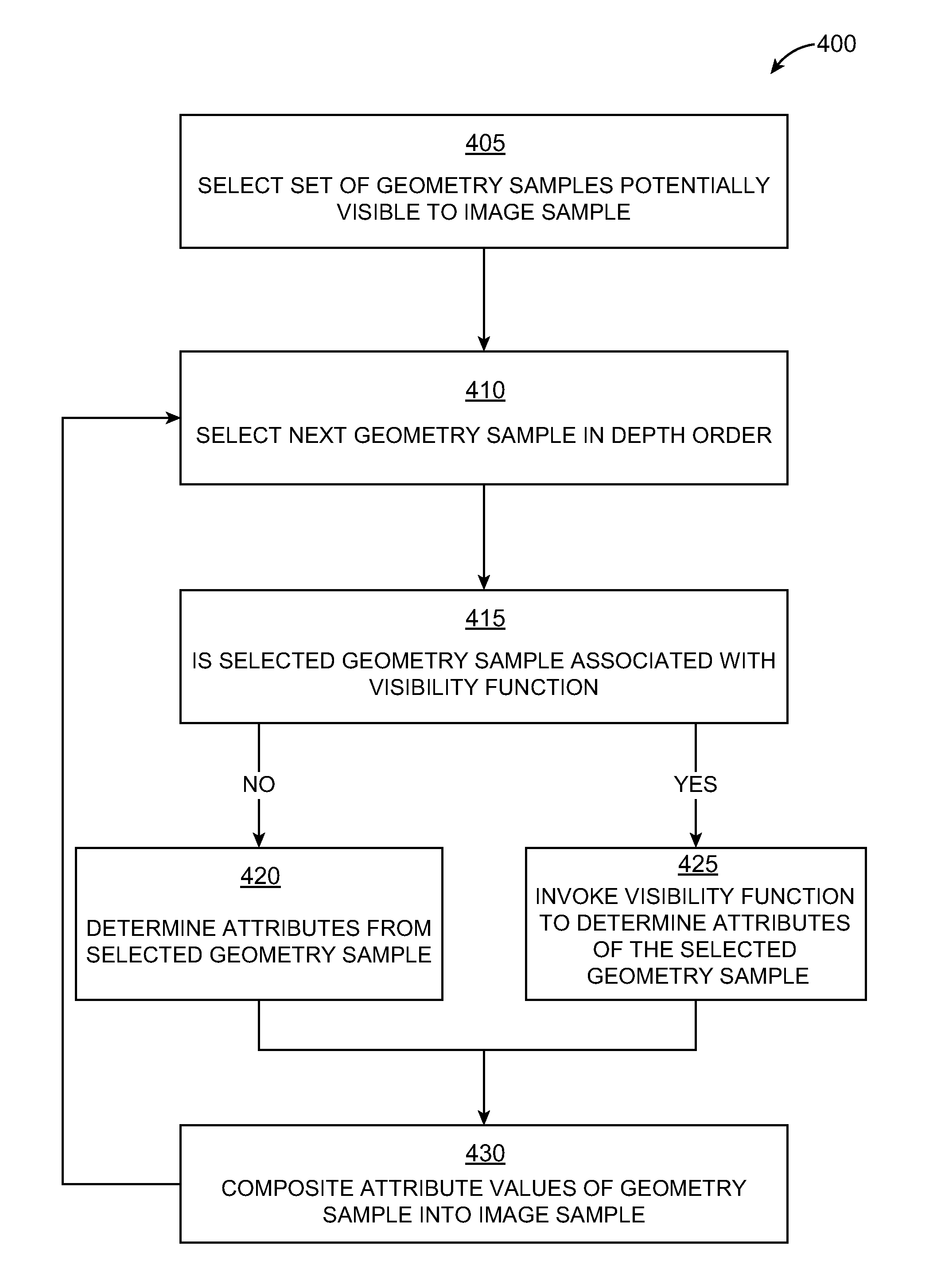
Programmable visible surface compositing
InactiveUS8026915B1Drawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVisible surfaceVisibility function
Programmable or user-defined visibility functions can be defined to achieve rendering effects and eliminate rendering errors. A renderer traverses the set of geometry samples potentially visible to an image sample. Rather than accumulate opacity and color in strict depth order, the renderer can invoke visibility functions associated with some or all of the geometry samples. Each geometry sample's visibility function can access attributes of any other geometry sample associated with the image sample. Furthermore, each geometry sample's visibility function can identify the position of its associated geometry sample and any other geometry samples in the depth sequence of geometry samples associated with an image sample. A visibility function can return any arbitrary value based on attributes of its associated geometry sample, attributes of other geometry samples associated with the image sample, and / or the position of geometry samples in the depth sequence associated with the image sample.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
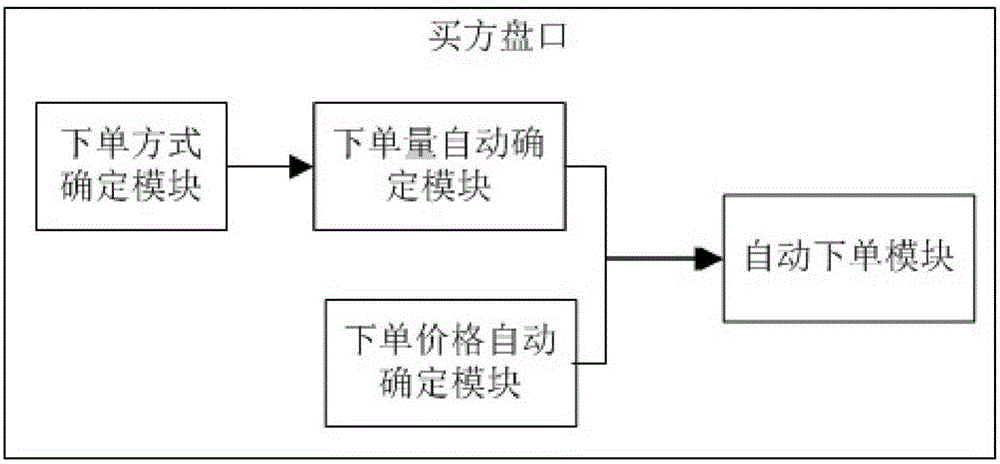
Financial transaction 1-click ordering platform
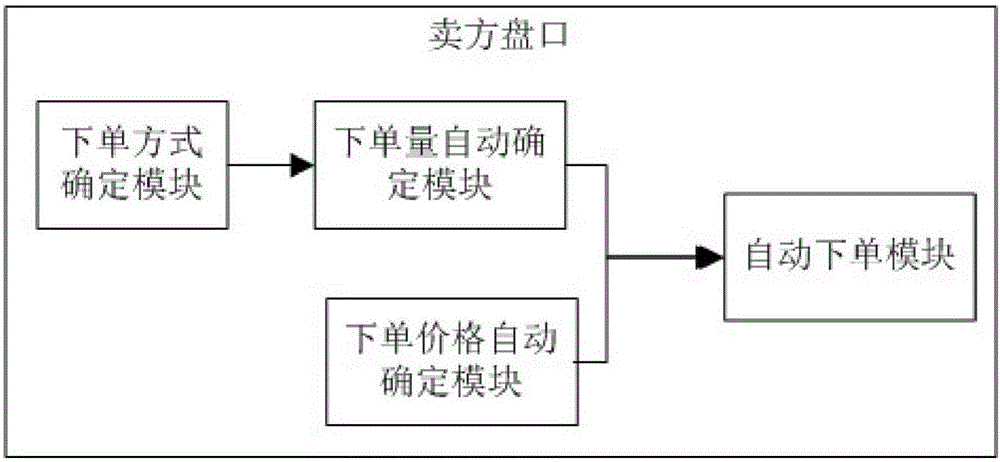
InactiveCN105809540AMeet the needs of high-frequency tradingFast TradingFinanceOrder formFinancial transaction
The present invention relates to a financial transaction lightning hand platform, including a buyer's handicap and a seller's handicap. Both the buyer's handicap and the seller's handicap include: an order determination module: it is used to determine whether the order is multiple order, deep order or Keyboard order and default order quantity under various order methods; order price automatic determination module: it is used to automatically determine the order price according to the position of the mouse; order quantity automatic determination module: it is used to determine the order price according to the The order method determined by the order method determination module and the default order quantity under various order methods automatically determine the actual order quantity; the automatic order module: it is used to automatically determine the actual order quantity based on the order price and the actual order quantity. Place an order. The financial transaction lightning hand platform can place orders directly on the buyer's market and the seller's market. The order is convenient and fast, so that it can realize one-click order and fast transaction.
Owner:北京火币天下网络技术有限公司
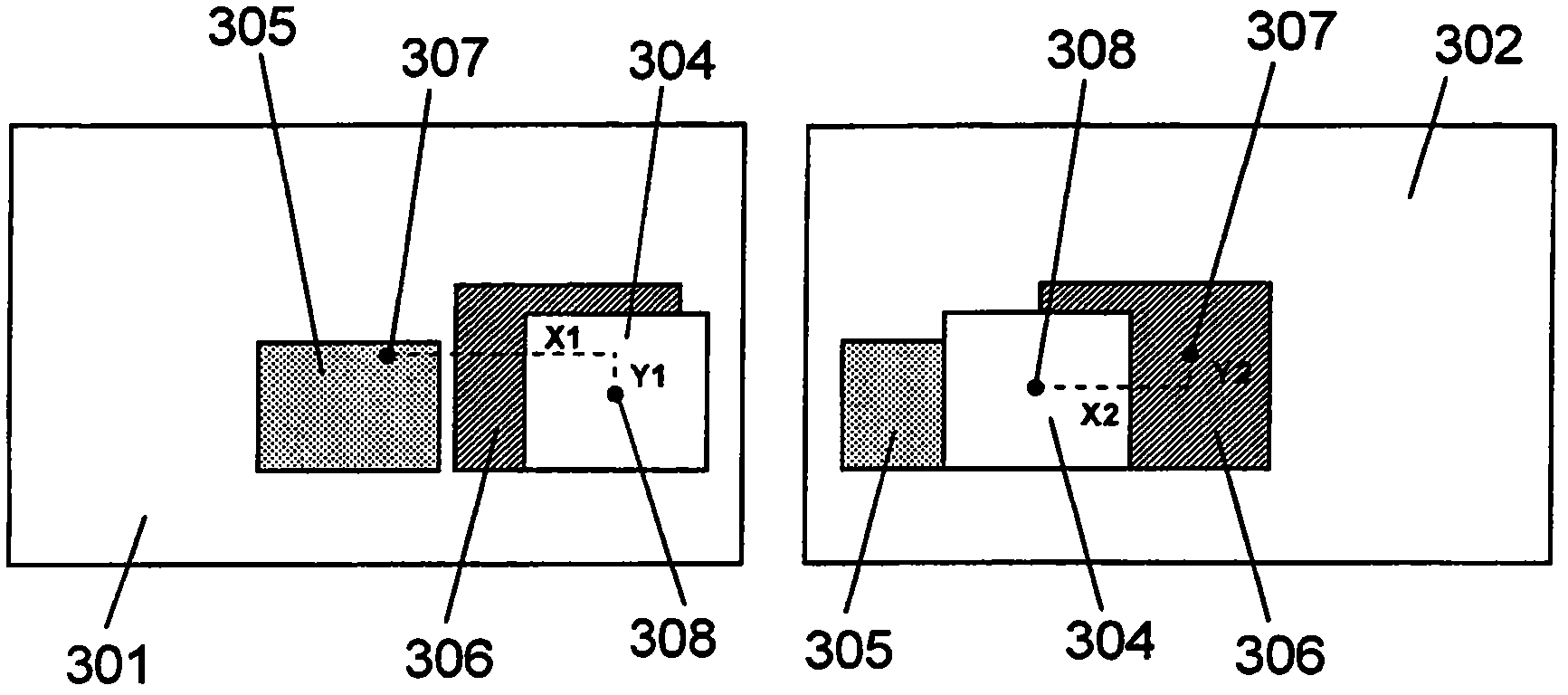
Depth order reasoning method based on occlusion feature learning
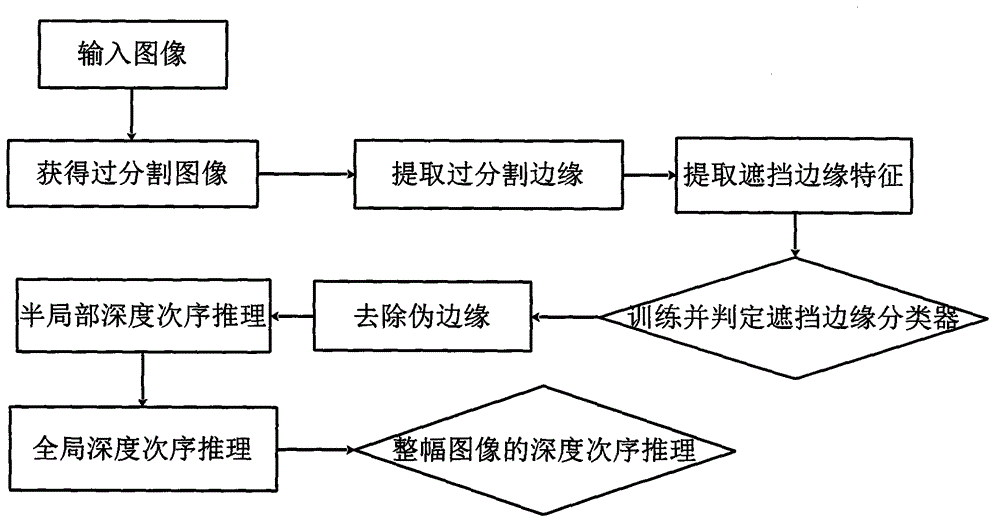
InactiveCN106157293ANarrow down the search spaceImprove judgment efficiencyImage analysisMargin classifierBerkeley algorithm
The present invention provides a deep order reasoning method based on occlusion feature learning, comprising the following steps: obtaining an over-segmented image through the Berkeley algorithm, using an occlusion edge classifier to extract over-segmented edges from common edges; after color model processing, Extract occlusion edge features; select sparse-based classifiers, train and determine occlusion edges; remove false edges by fusing same-layer regions, and avoid misjudgment problems in the process of occlusion edge classifiers; adopt a new triple description operator to realize semi-local depth order reasoning; finally, through modeling, describe the local depth order as a partial order relationship, and use the relevant knowledge of graph theory to transform the global depth order reasoning into a kind of The problem of effective path, so as to complete the depth order reasoning of the whole image.
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY
Conversion method and apparatus with depth map generation
A conversion method and apparatus with a generating of a depth map for two dimensional (2D)-to-three dimensional (3D) conversion. A depth order may be restored based on a line tracing and an edge map generated from an input image, and a stereo image may be generated using depth information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Binary-tree based object depth order evaluation method in monocular image
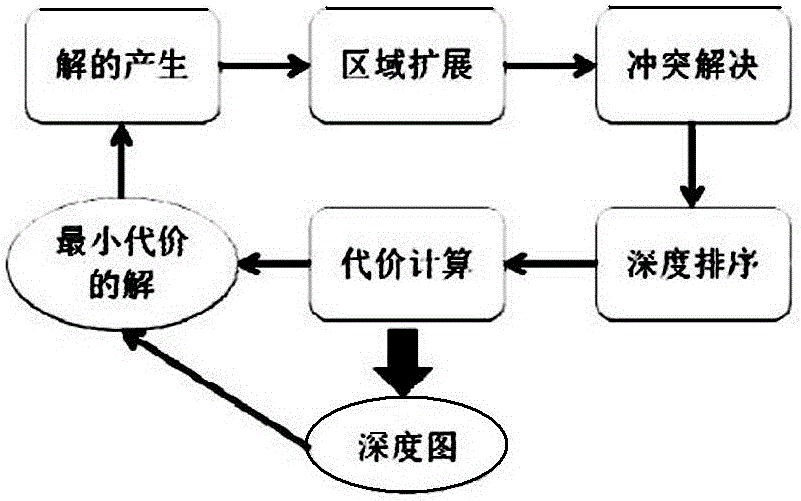
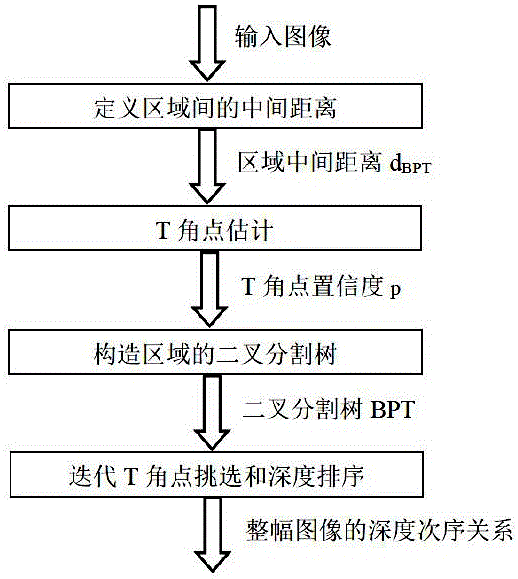
InactiveCN105719288AGuaranteed convergenceImprove robustnessImage analysisBinary treeComputer science
The invention discloses a binary-tree based object depth order evaluation method in a monocular image. The evaluation method comprises steps of 1: defining middle distances among image regions; 2: evaluating T angle point confidence for T angle points formed at junctures of the image regions; 3: according to the middle distances and the T angle point confidence, constructing a binary partitioning tree so as to obtain a regional model of the image; and 4: selecting an optimal T angle point set and finishing depth ordering so as to obtain a depth order graph. Thus, a depth levelrestoration effect is achieved.
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY
Training method and system comprising mixed real and virtual images
ActiveUS8911236B2Avoid damageReduce riskAircraft componentsCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulationVirtual device
Owner:EADS CONSTRS AERONAUTICAS
Method and device for calculating depth order of monocular image
ActiveCN107993239AIntegrity guaranteedImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionMonocular image
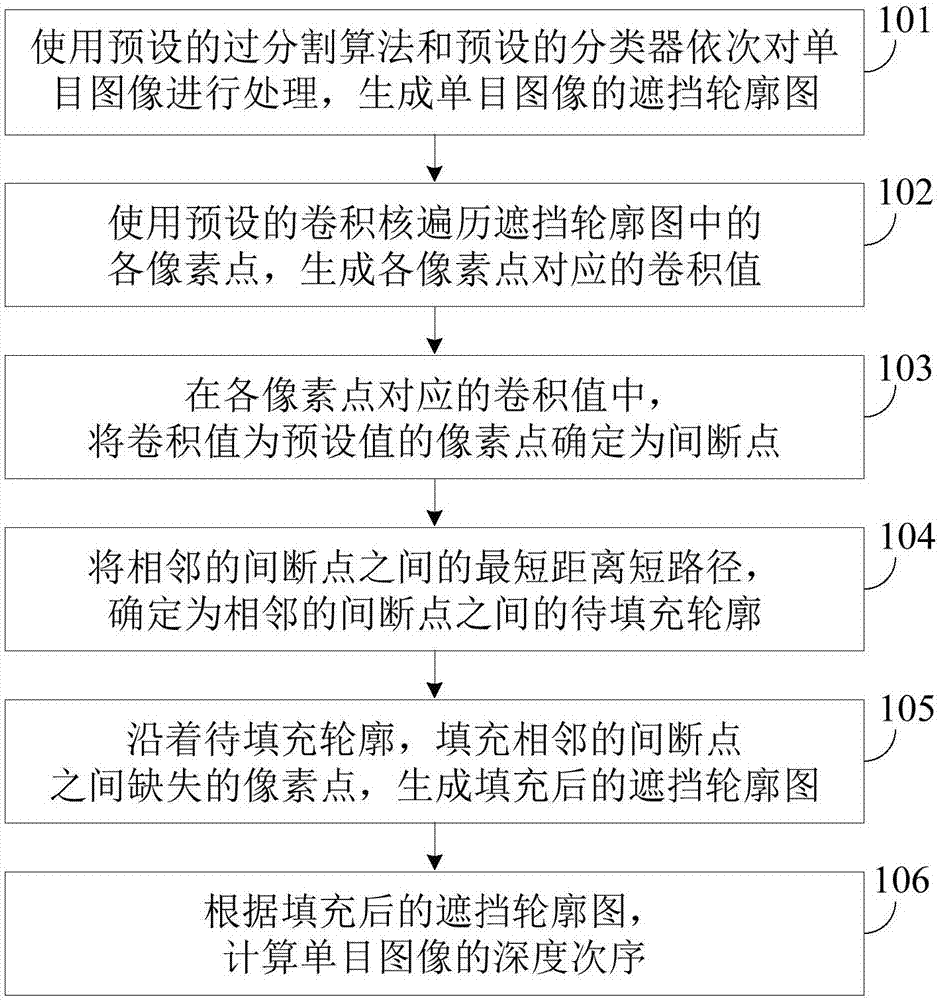
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for calculating a depth order of a monocular image. The method includes using a preset over-segmentation algorithm and a preset classifierto sequentially process a monocular image to generate a masking contour map of the monocular image; using a preset convolution kernel to traverse each pixel in the masking contour map to generate a convolution value corresponding to each pixel; in the convolution value corresponding to each pixel, determining the pixels with the convolution value being a preset value as discontinuity points whichare pixels located at the two ends of the missing pixel in the masking contour map; determining a shortest path between the adjacent discontinuity points as a to-be-filled contour between the adjacentdiscontinuity points; along the to-be-filled contour, filling the missing pixel between the adjacent discontinuity points, and generating a filled masking contour map; and calculating the depth orderof the monocular image according to the filled masking contour map. By application of the method and device for calculating the depth order of the monocular image, the depth order of the monocular image can be accurately calculated.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A digital camouflage camouflage net and method for civil air defense
ActiveCN103278046BImprove survivabilityBlurred boundariesCamouflage devicesProtective buildings/sheltersCut flowersRadar
The invention relates to the technical field of civilian defense and camouflage and discloses a civilian defense digital camouflage net and method. The camouflage net is composed of multiple different camouflage net units and annular ropes. A large net is formed by weaving and connecting the different camouflage nets through the annular rope arranged on the periphery of each camouflage net unit. Each camouflage net unit is composed of a bottom net and a net face. Each net face is made of cut-flower composite base cloth which prevents infrared rays and radar and has a color system of shallow gray, deep gray, jade green, brown and soil color, wherein the color system imitates a background. The civilian defense digital camouflage net can be rapidly assembled according to on-spot backgrounds and seasons, civilian defense primary objectives are merged with the surrounding backgrounds and survival capability of the objectives is improved. Based on the relevant principle of blocking a perception depth order in visuality, square corners and adjacent spots are used for blocking so that observers have an illusion that distances from the spots are different and spatial layering feelings are generated. Boundaries of the digital camouflage spots are not clear and the camouflage net has smooth continuous curves which are not easy to identify by the eyes.
Owner:UNIT 61489 OF PLA
Manufacture of semiconductor device
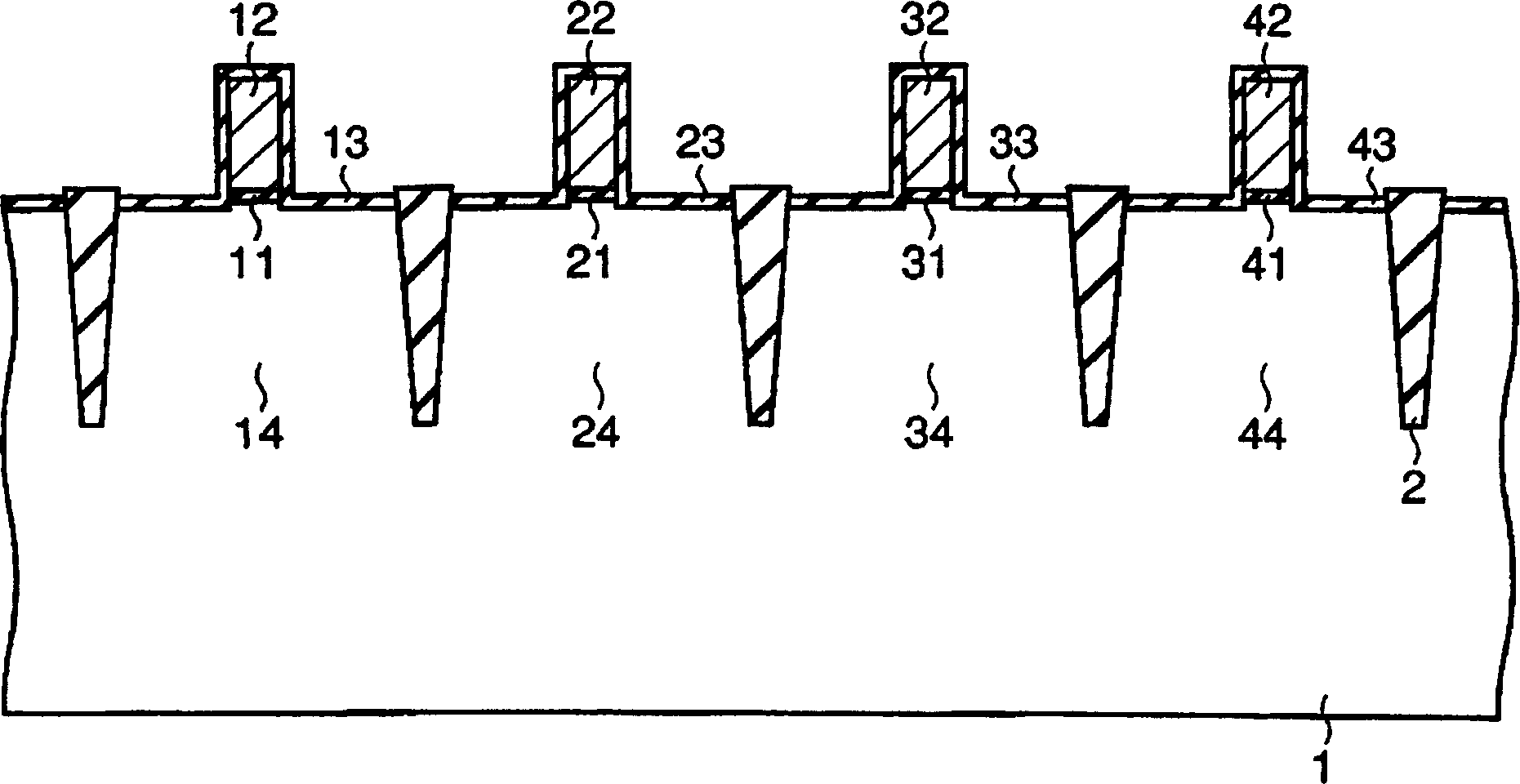
InactiveCN1645595AInhibitory drive abilityReduce impurity concentrationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringImpurity
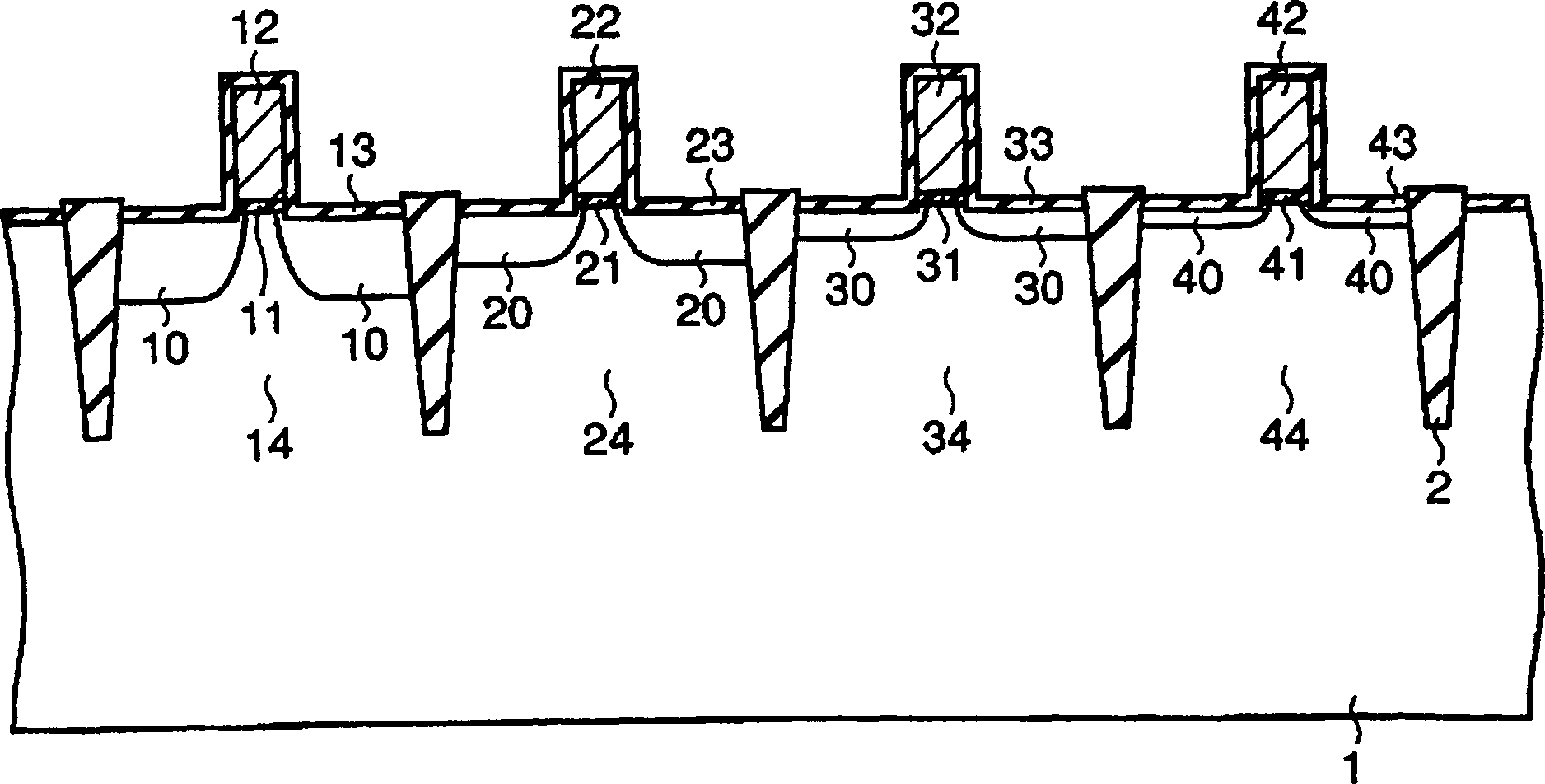
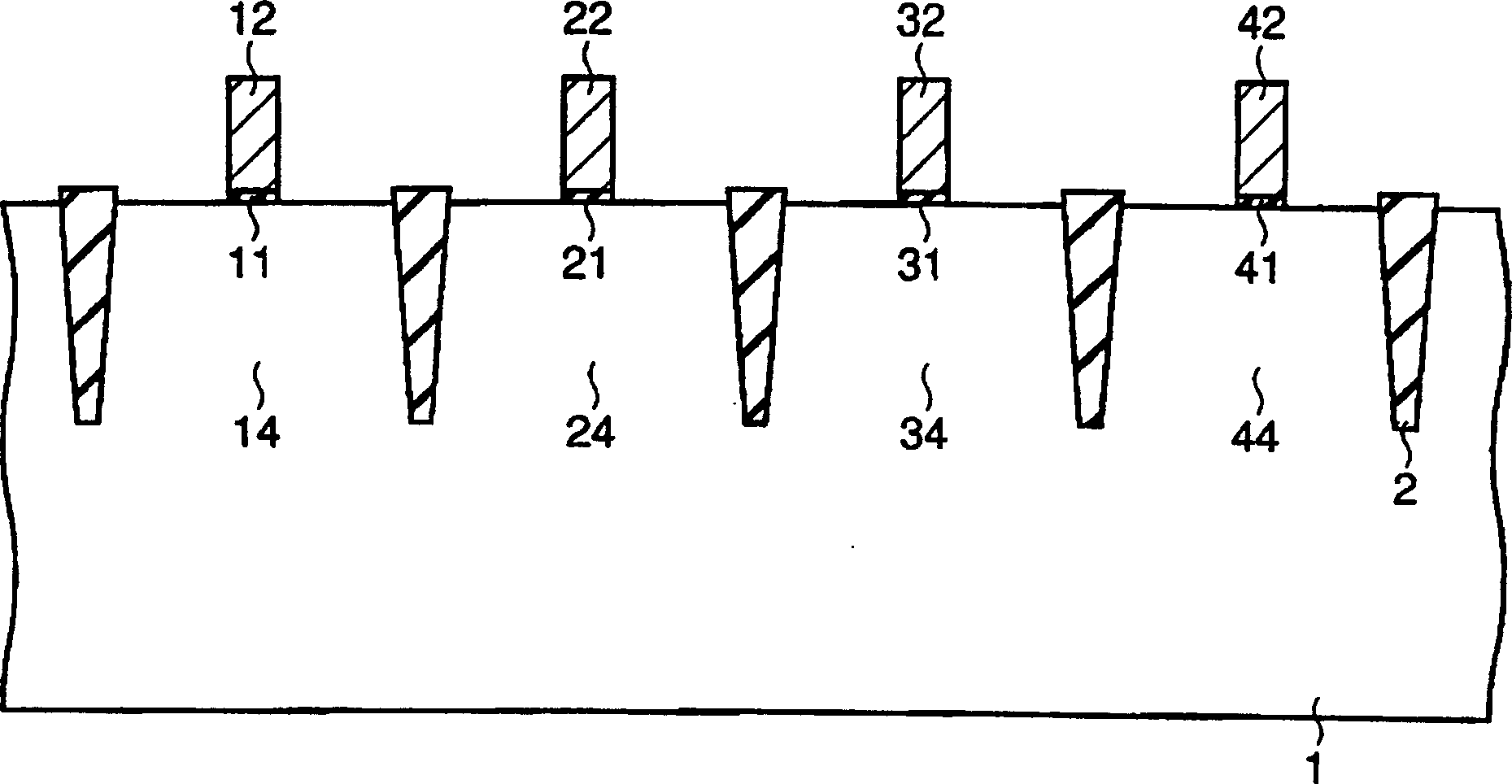
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of semiconductor devices, which can suppress a decline of impurity density in LDD region with shallow junction depth. The method in which a plurality of MOS transistors are formed on a semiconductor substrate of semiconductor devices, includes a process of forming a plurality of gate electrodes on the semiconductor substrate corresponding to each MOS transistor, and a process of forming LDD regions on surface of the semiconductor substrate at both sides of each MOS transistor according to depth order of junction depth of LDD regions of the above-mentioned MOS transistors.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com