Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Dashpot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
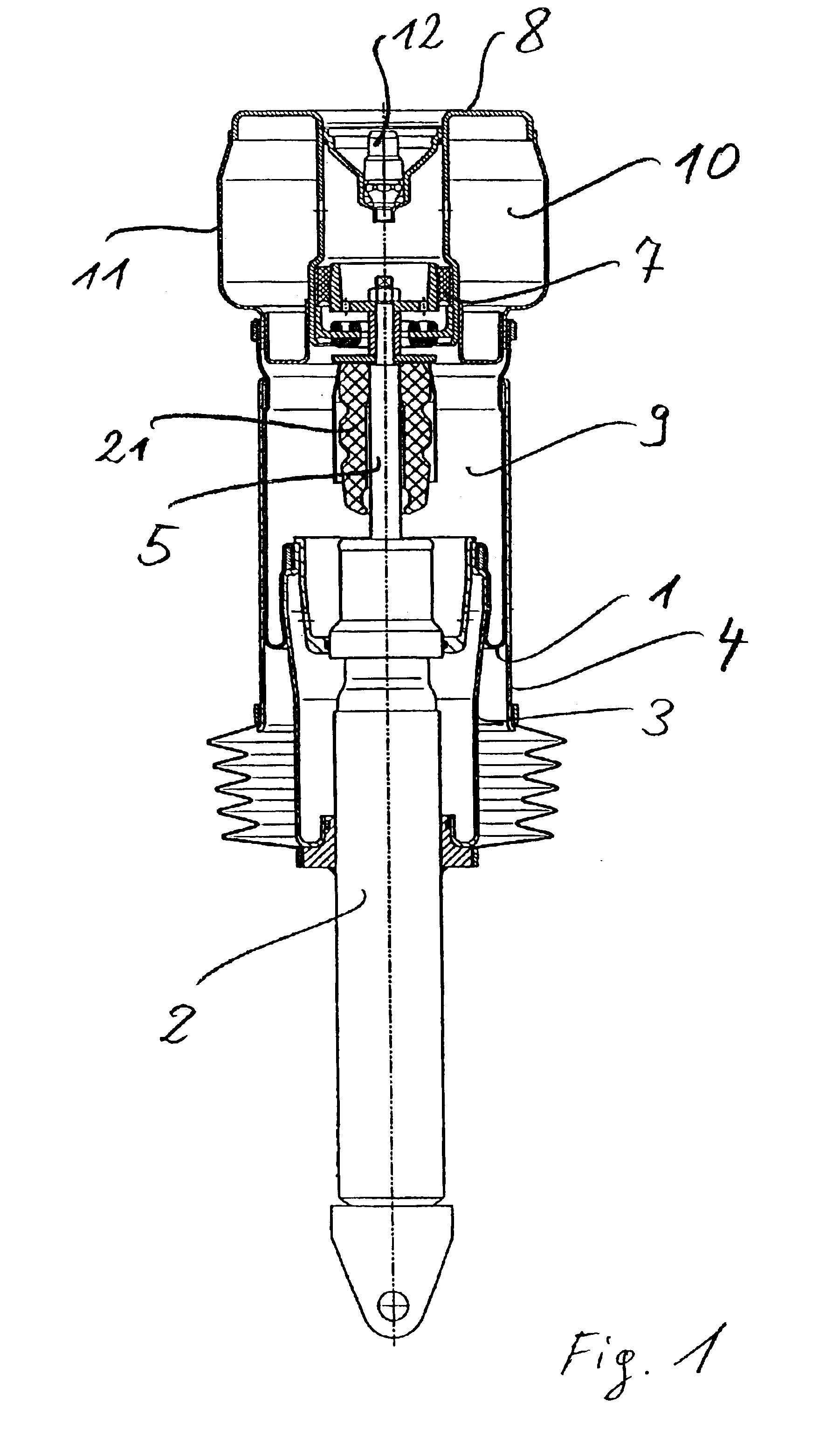
A dashpot is a mechanical device, a damper which resists motion via viscous friction. The resulting force is proportional to the velocity, but acts in the opposite direction, slowing the motion and absorbing energy. It is commonly used in conjunction with a spring (which acts to resist displacement). The process and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) symbol for a dashpot is .
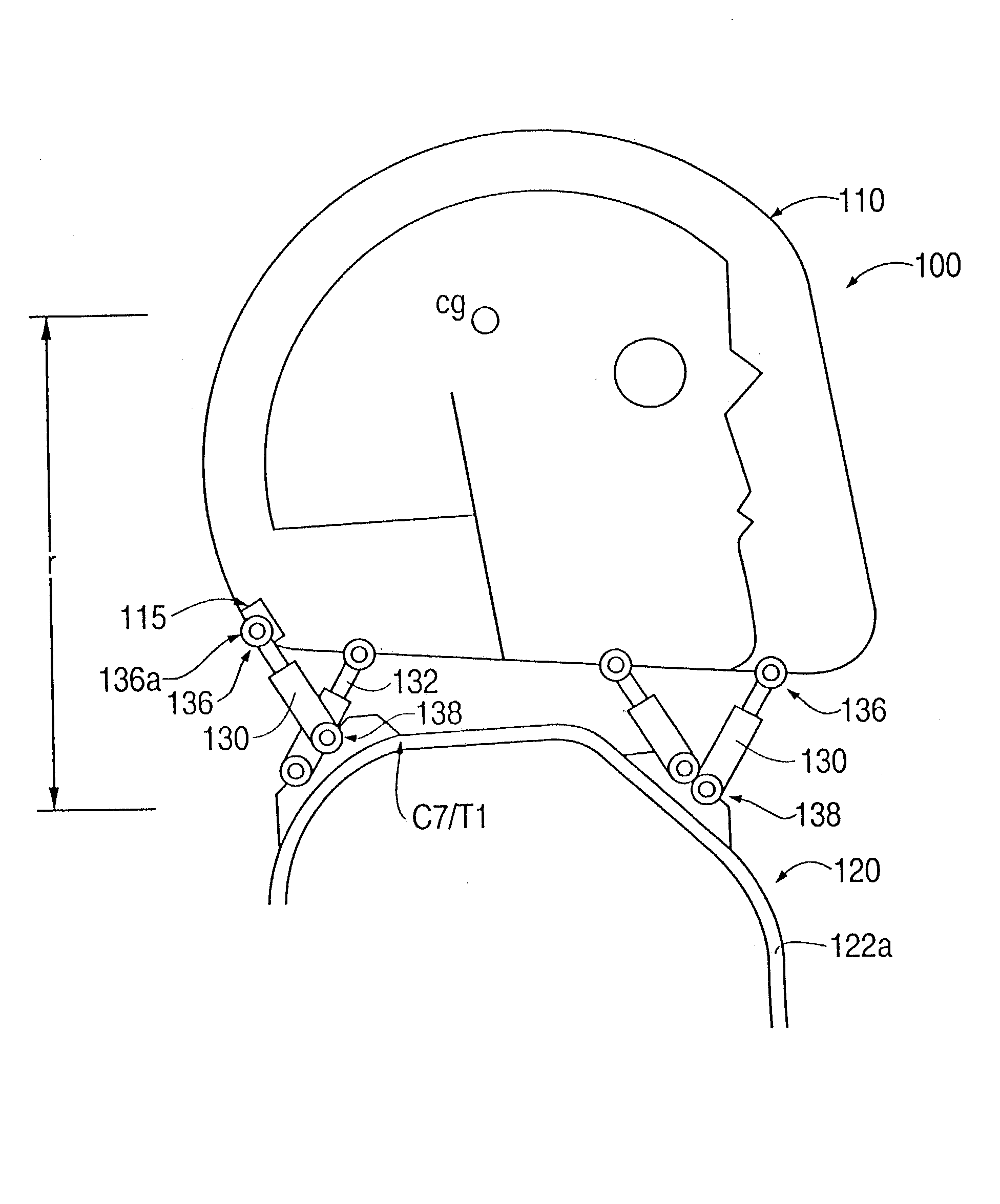
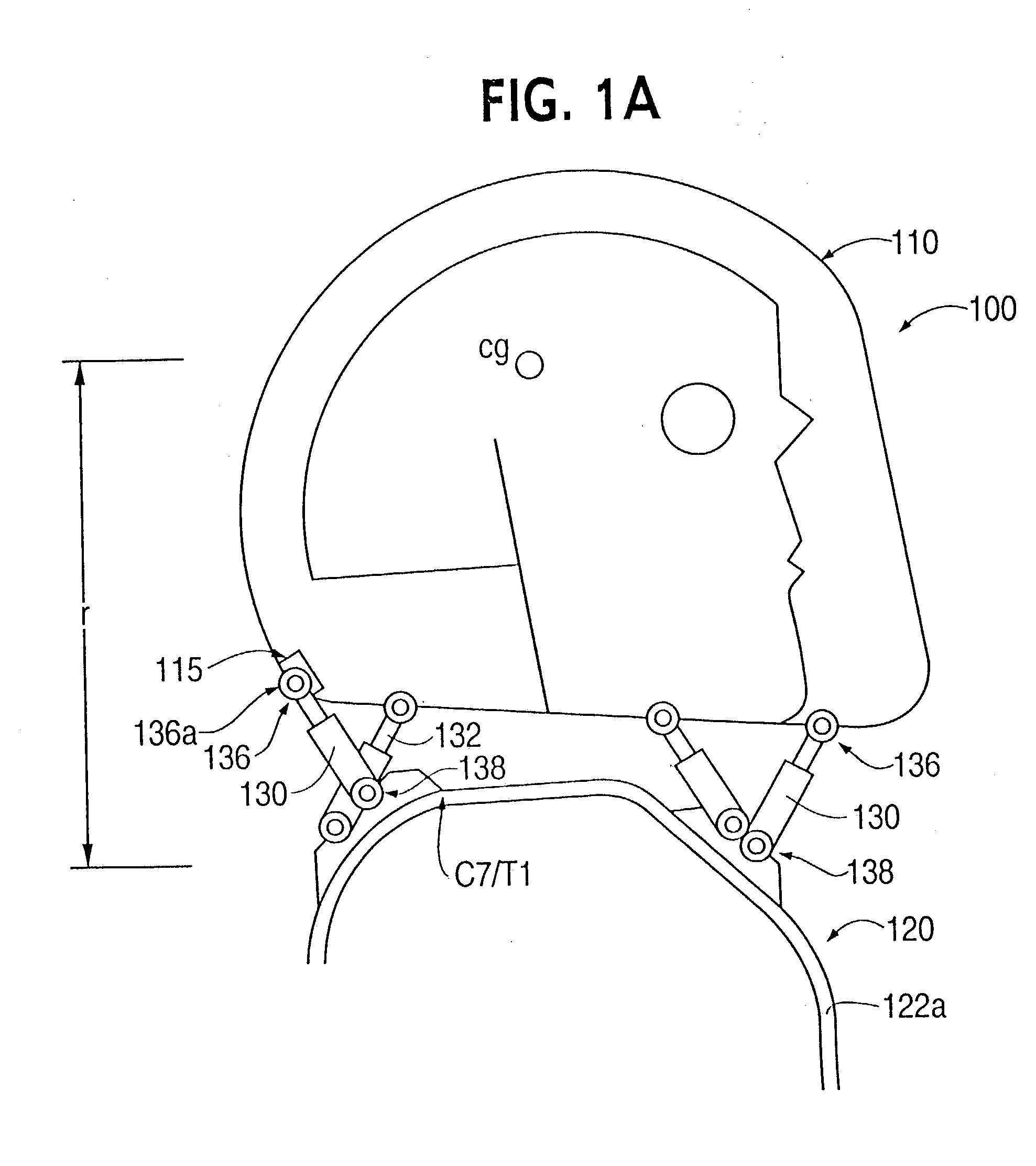
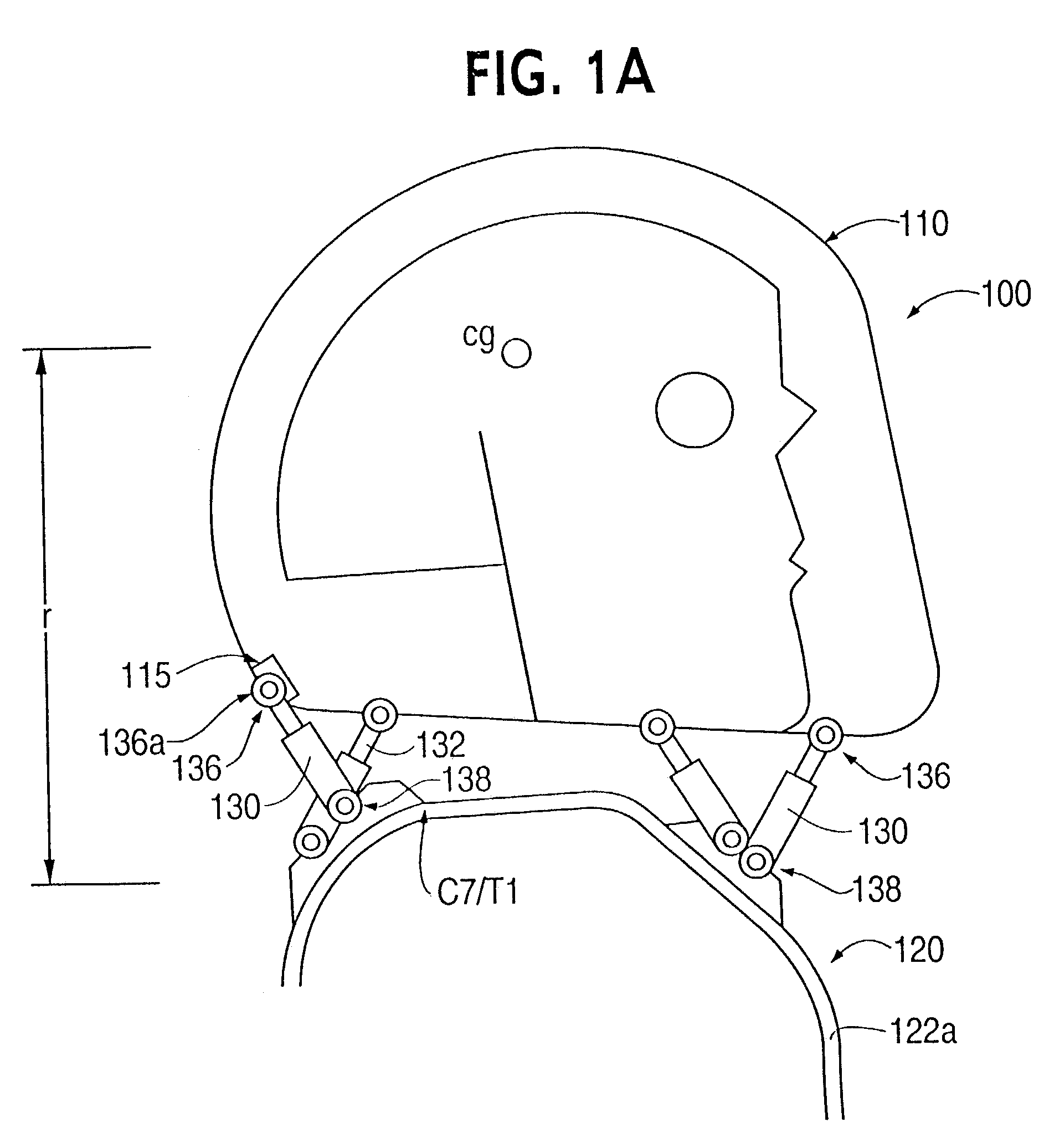
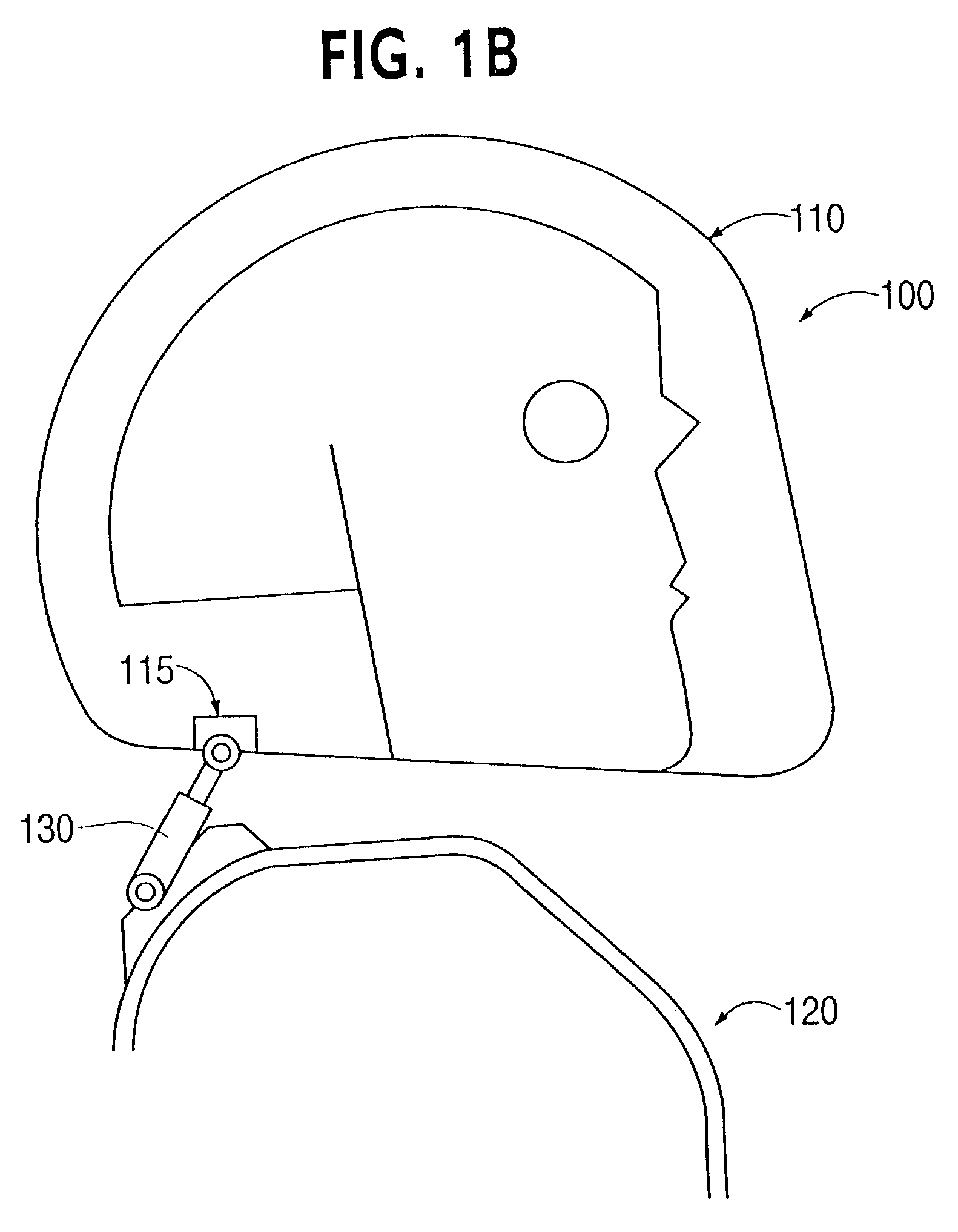
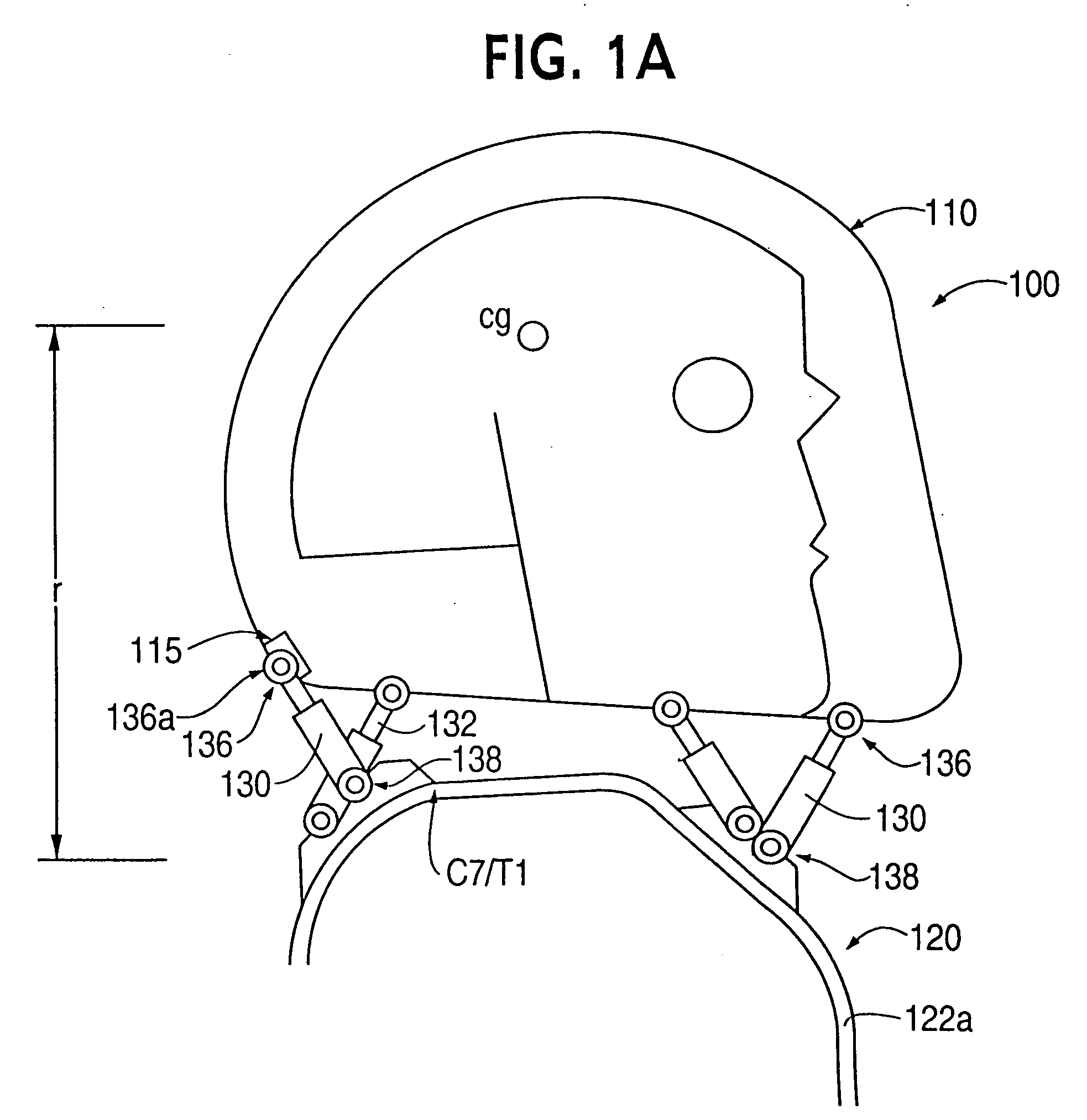
Head stabilizing system
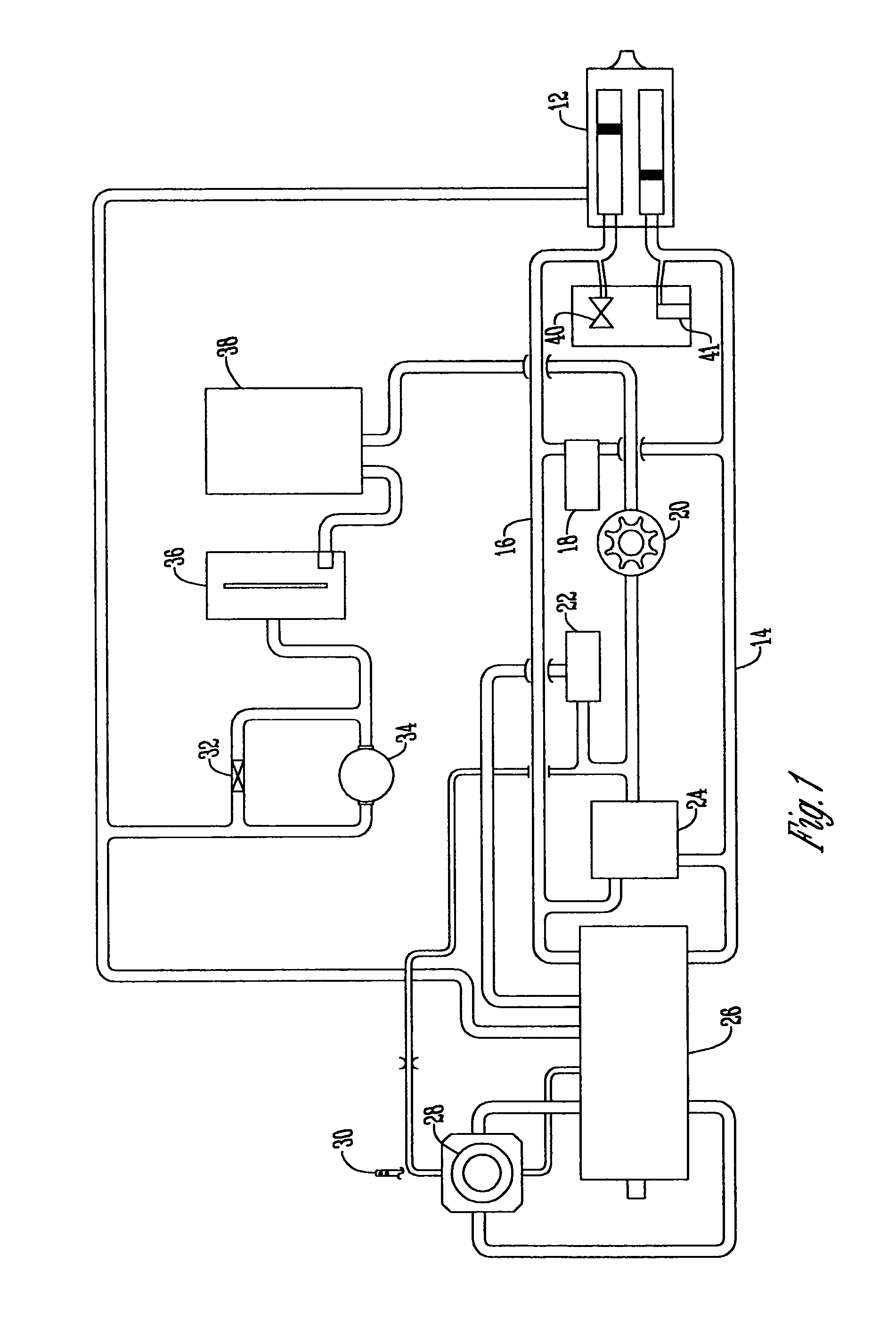
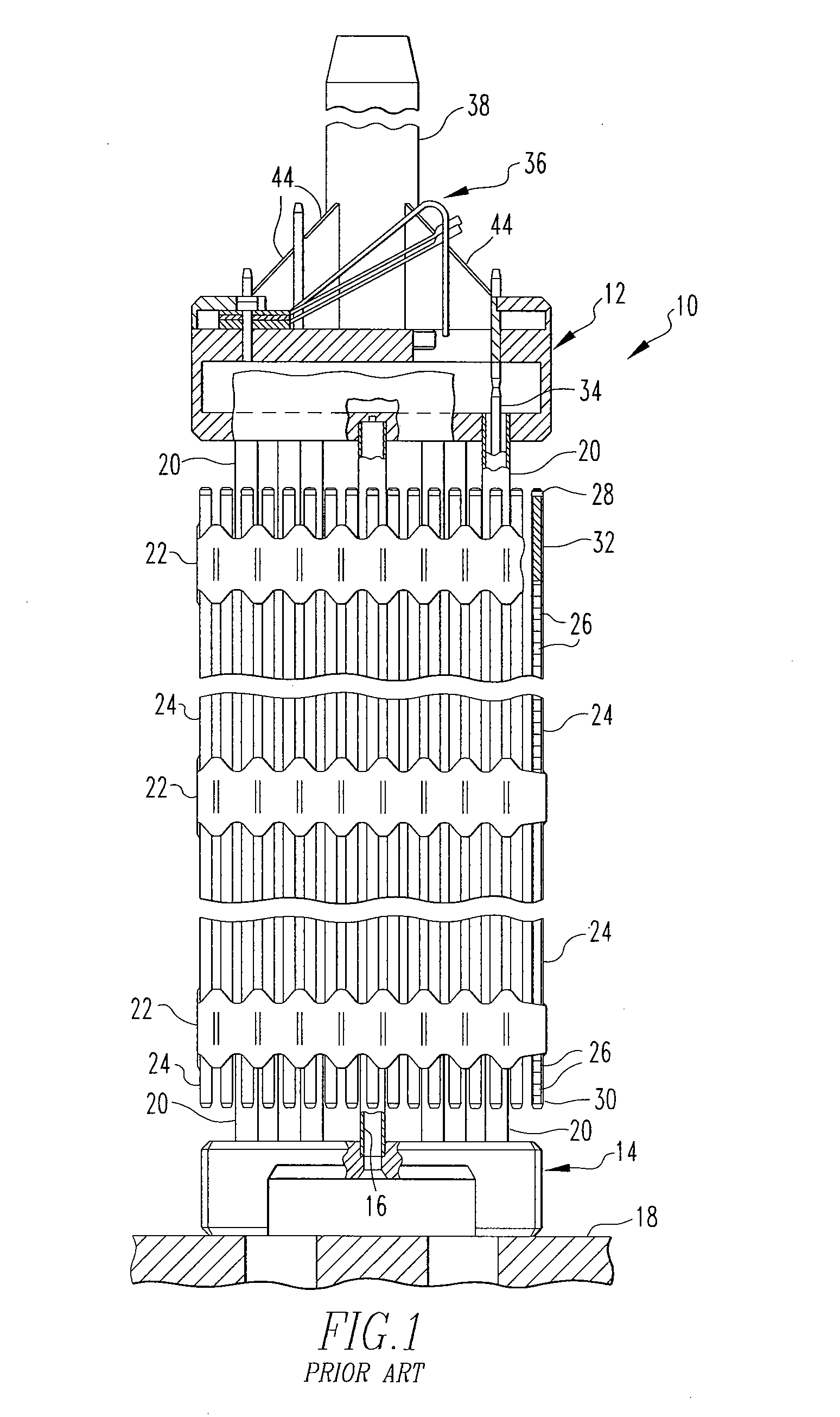
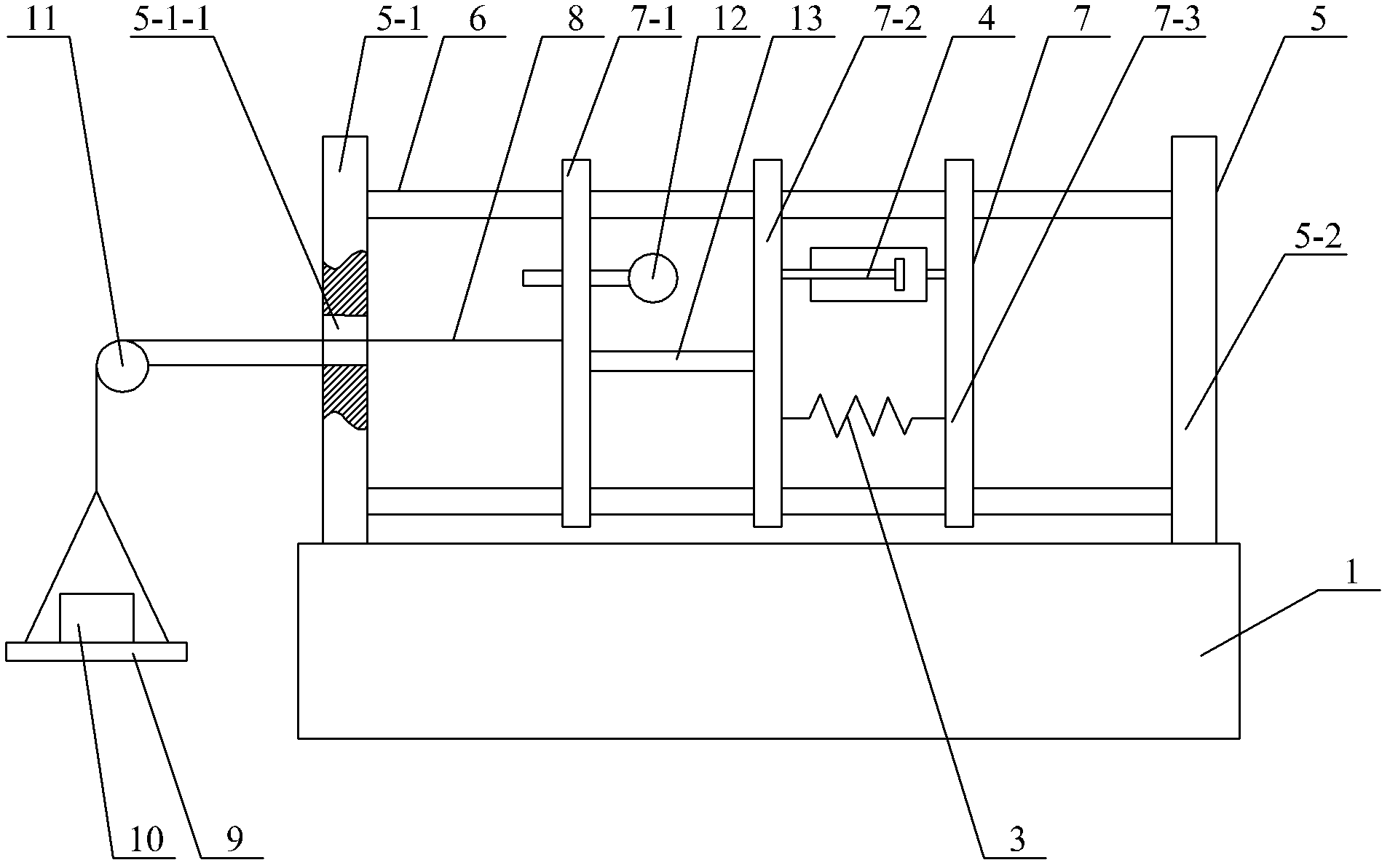
A head stabilizing system is provided. The head stabilizing system is intended to minimize loads on the head and the neck, some of which may be injurious or even fatal, by generating a reaction force that substantially opposes a force acting on the head and generated by rapid deceleration of a vehicle or a crash impact. The head stabilizing system includes a helmet, a connection structure, and at least one resisting member. The resisting member generates a reaction force that opposes the crash impact force, yielding a reduced net force on the head. This reaction force can be generated as a function of position, velocity or acceleration. The resisting member may include a tether, a dashpot, or a dashpot containing a controllable rheological fluid. The viscosity of the controllable rheological fluid can be automatically adjusted in response to changes in status of a vehicle or it's occupant.
Owner:BHC ENG
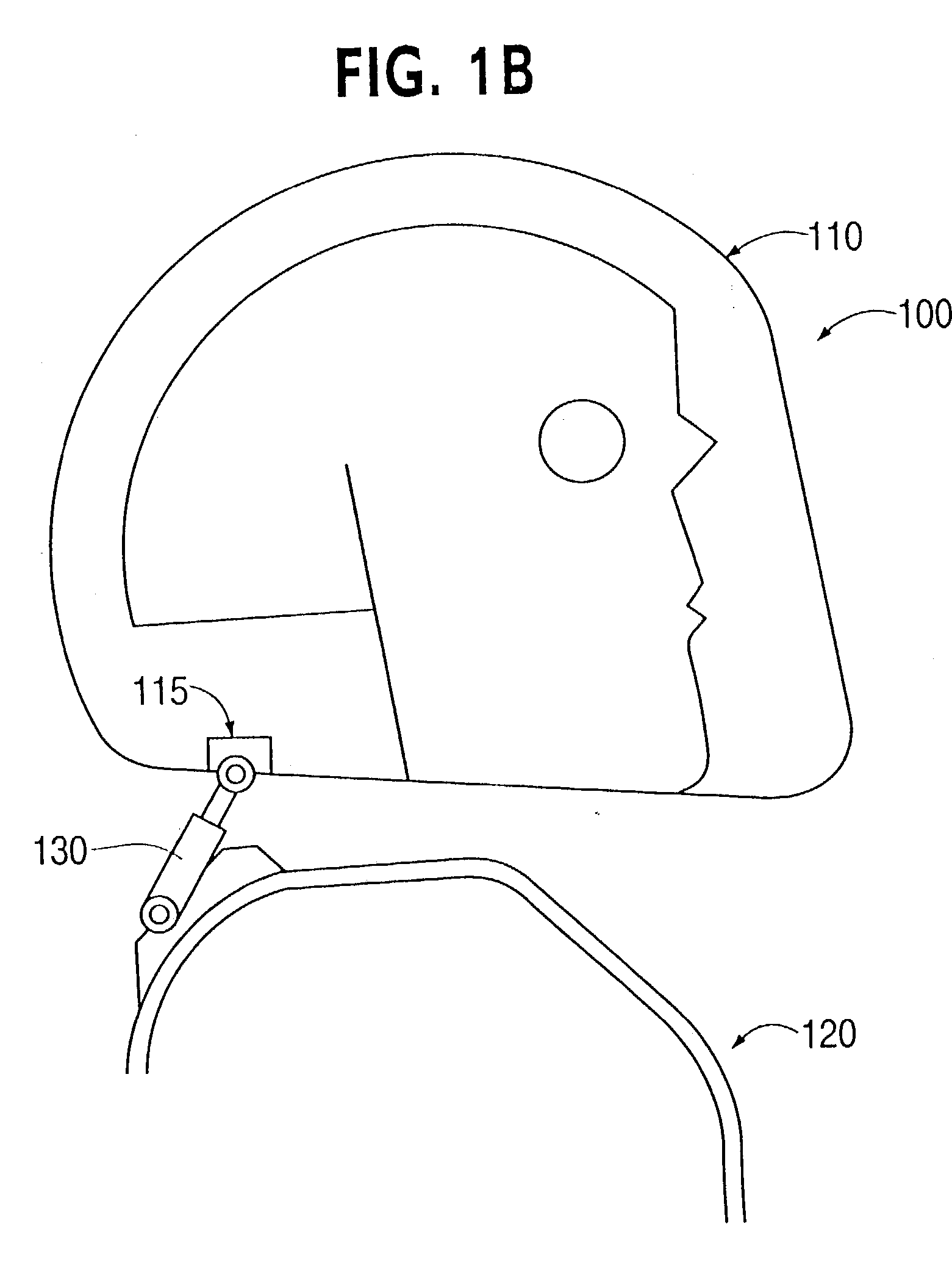
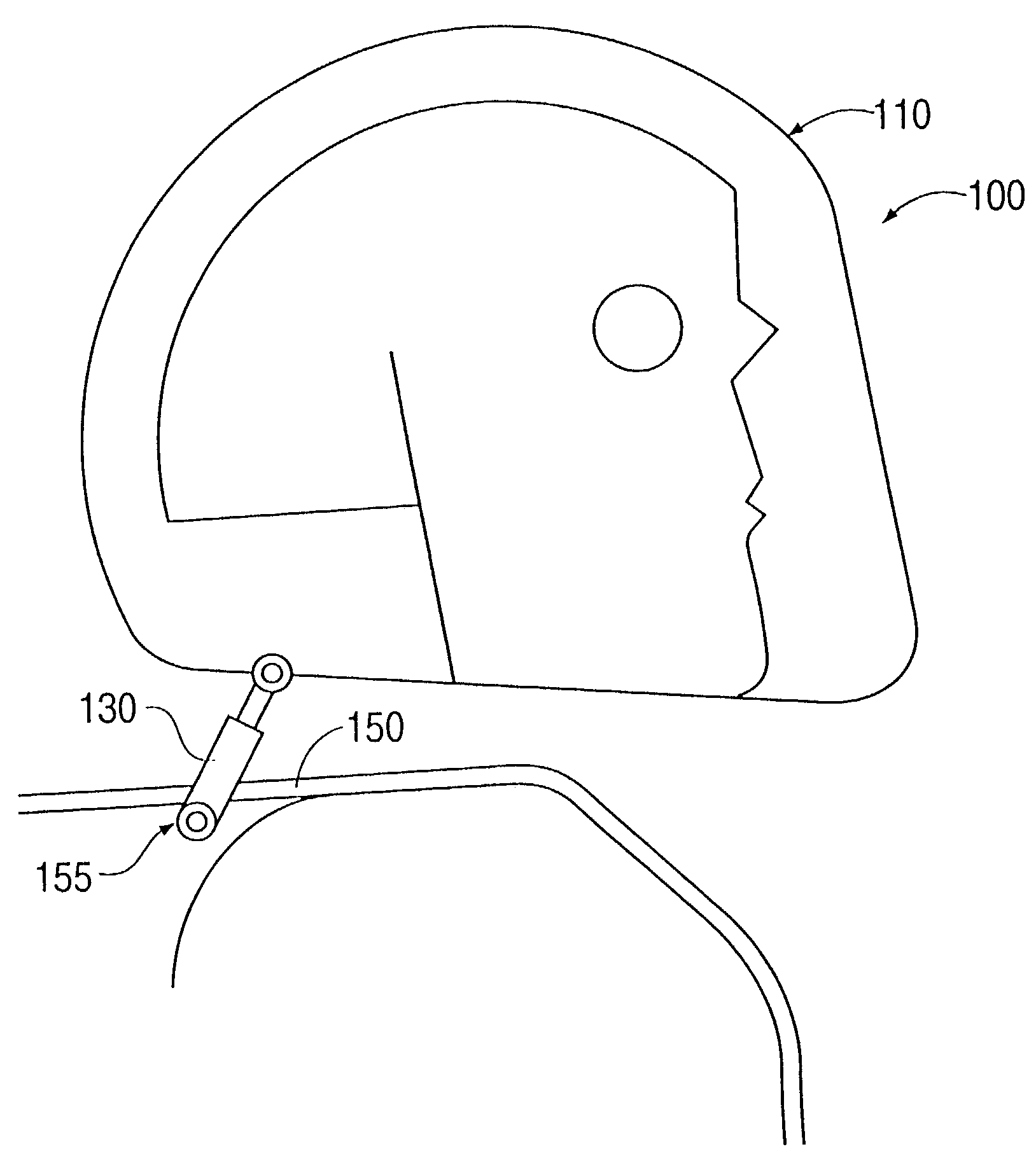
Head stabilizing system
Owner:BHC ENG
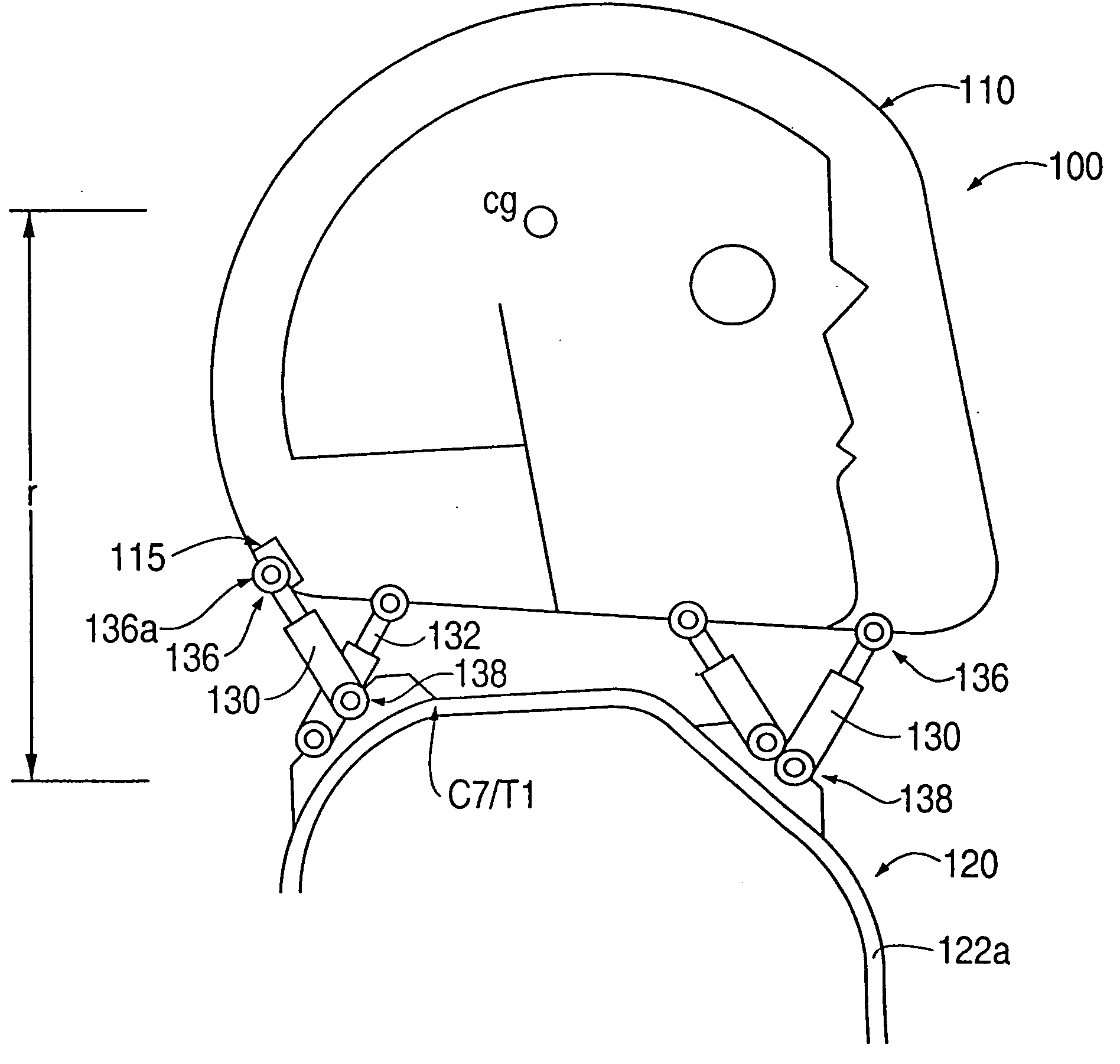
Head stabilizing system
A head stabilizing system is provided. The head stabilizing system is intended to minimize loads on the head and the neck, some of which may be injurious or even fatal, by generating a reaction force that substantially opposes a force acting on the head and generated by rapid deceleration of a vehicle or a crash impact. The head stabilizing system includes a helmet, a connection structure, and at least one resisting member. A mounting element is provided to be mounted onto the helmet to connect to the at least one resisting member. The mounting element is preferably attached to the helmet by an adhesive. The resisting member generates a reaction force that opposes the crash impact force, yielding a reduced net force on the head. This reaction force can be generated as a function of position, velocity or acceleration. The resisting member may include a tether, a dashpot, or a dashpot containing a controllable rheological fluid. The viscosity of the controllable rheological fluid can be automatically adjusted in response to changes in status of a vehicle or it's occupant.
Owner:BHC ENG
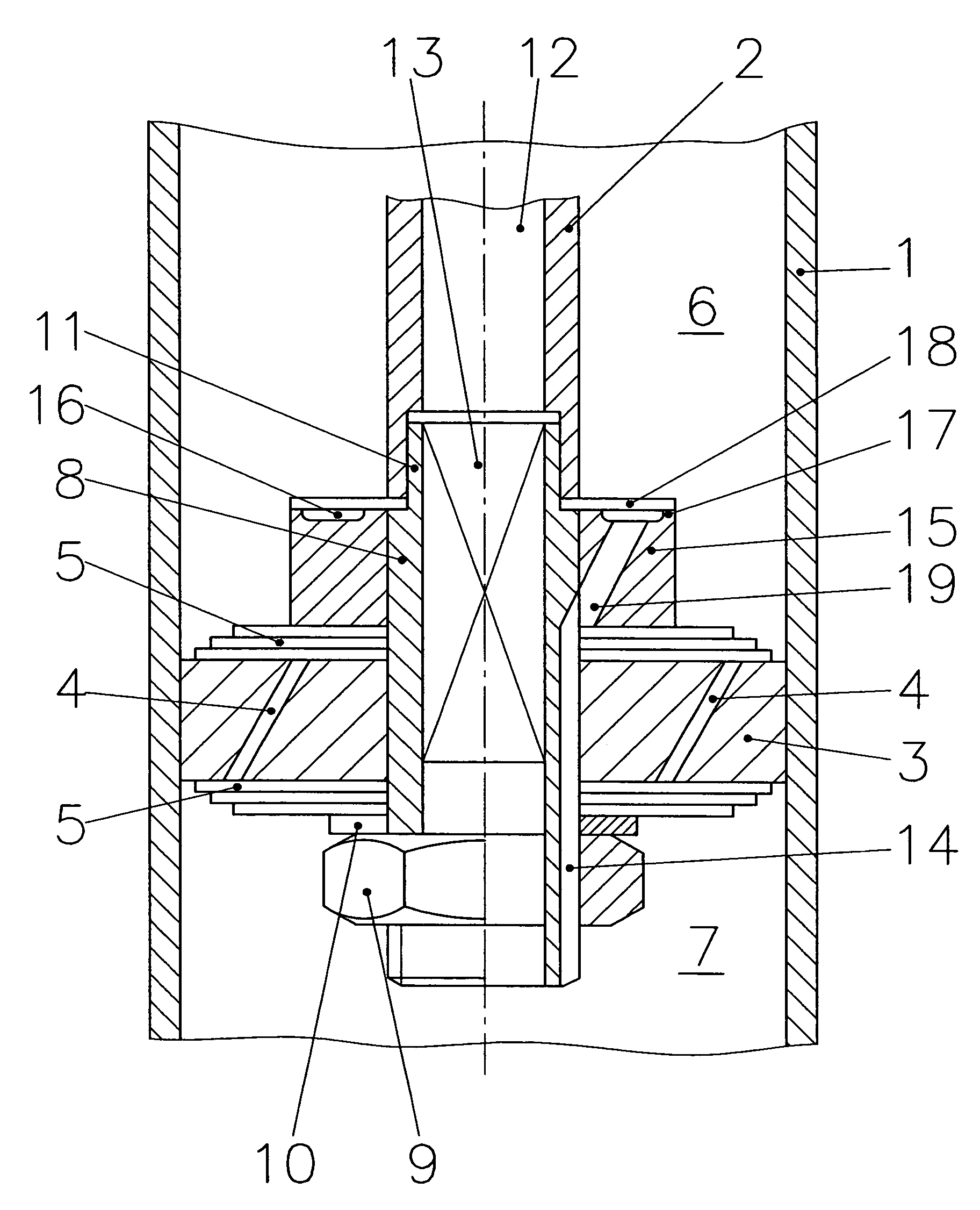
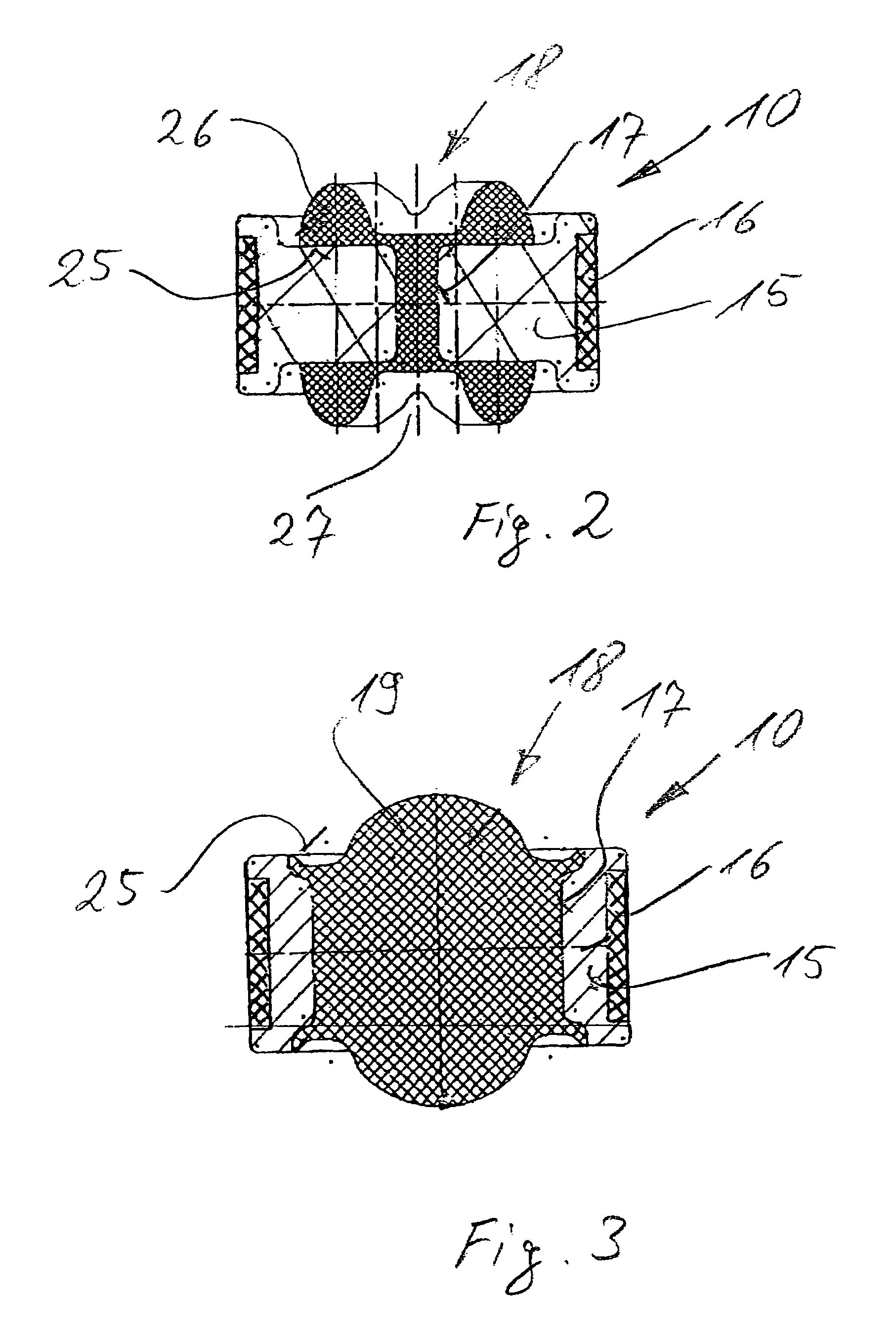
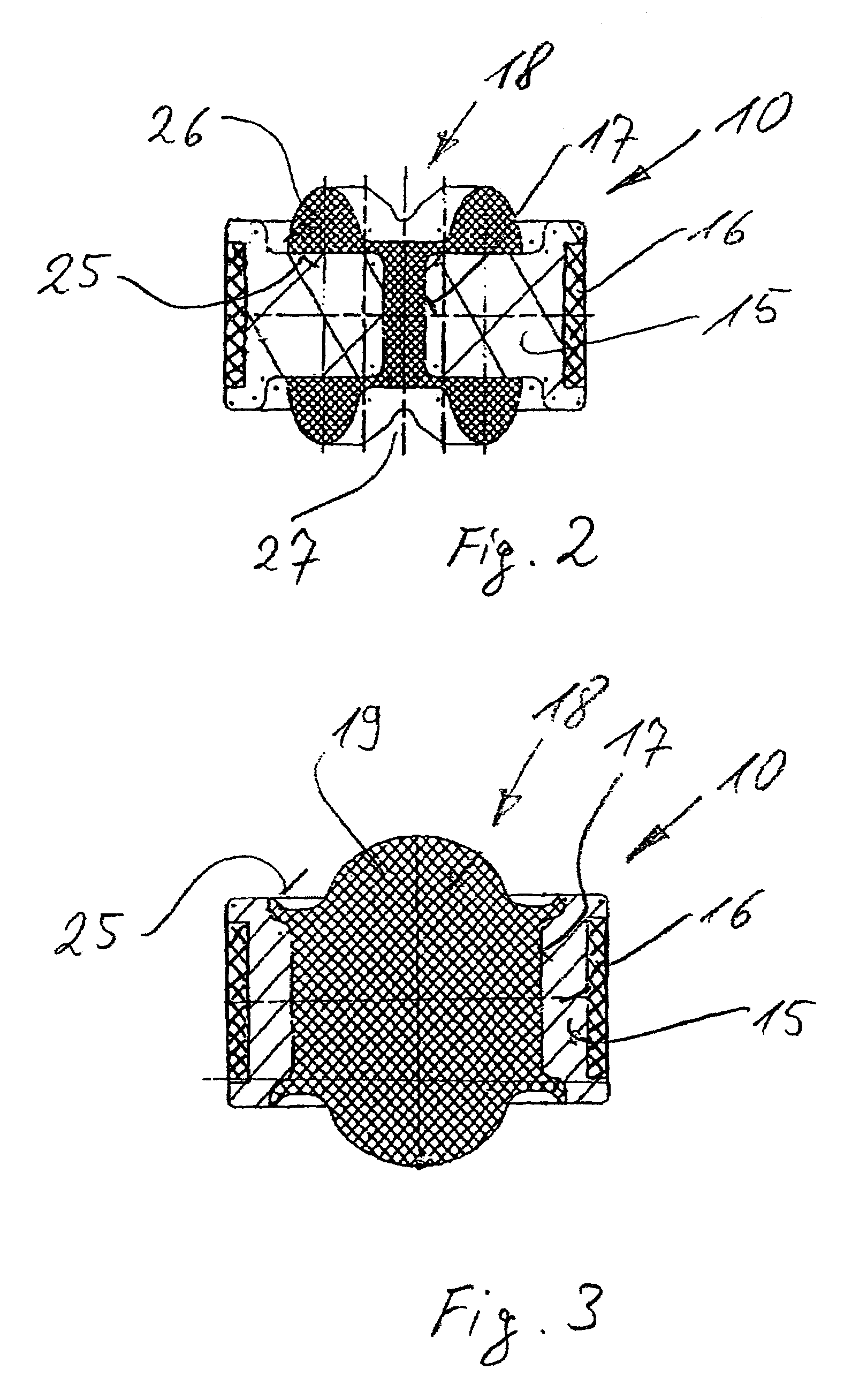
Blow-off valve for a hydraulic dashpot
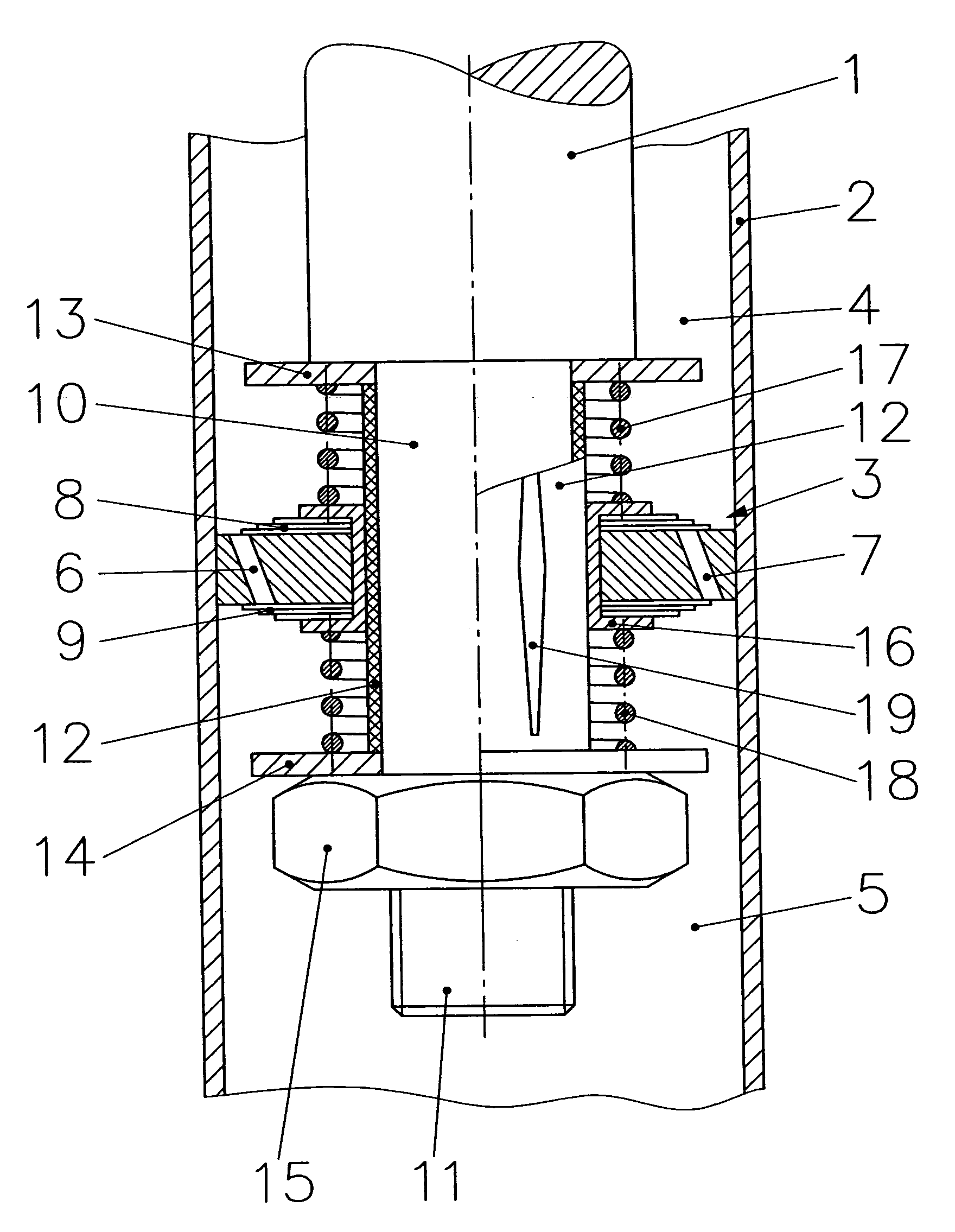
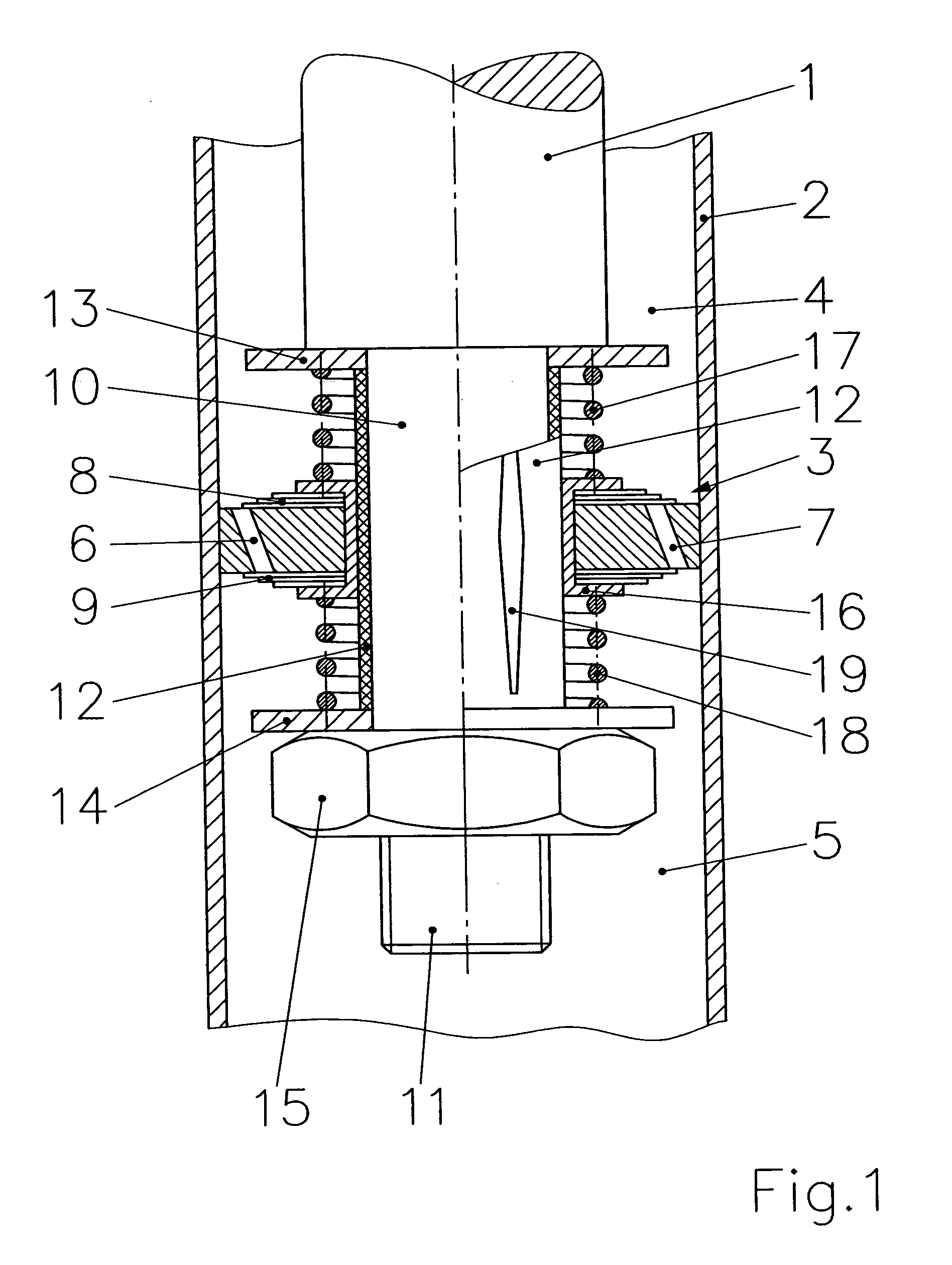
A blow-off valve for a hydraulic dashpot comprising a fluid charged cylinder (1) and a piston (3) that travels back and forth therein on the end of a piston rod. The piston partitions the cylinder into two compartments (6&7) and is provided with breaches (4) and shock-absorbing valves. The piston rod (2) or an extension (8) thereof is hollow and accommodates operating components (13).The object is a valve that can be accommodated along with the hydraulic lines that serve it outside the piston rod or an extension thereof.The outer surface of the piston rod is accordingly provided with at least one axial inwardly undulating groove (14) at least as long as the piston, including its fastenings and operating components, is high. Alternatively, the bore that extends through the piston rod or its extension and its fastenings and operating components is provided with a similar radially outward groove that can be closed off at the compression end by a spring-loaded valve.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Method for arranging a separating piston in a cavity and a device with such a separating piston
ActiveUS7975814B2Facilitate non-critical settingKeep the pressureSpringsAccumulator installationsDashpotControl theory
A steering damper system and method of regulating the fluid pressure of such a system are provided. The system can comprise a piston rod, a cylinder, a passage, and a damper portion. The damper portion can comprise a damper cavity, an outer piston, an inner piston, and a biasing component. The damper cavity can be in fluid communication with the passage. The outer piston can be slidably disposed in the damper cavity and define a chamber and a duct that is in fluid communication with the chamber and the passage. The inner piston can be slidably disposed in the chamber of the outer piston. The biasing component can exert an axial biasing force against the inner piston for regulating the pressure of fluid disposed in the system passing intermediate the passage, the damper cavity, and the chamber of the outer piston.
Owner:OHLINS
Fuel assembly and thimble screw of the same
InactiveUS7257185B1Avoid bending deformationAvoid deformationNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNuclear reactorDashpot
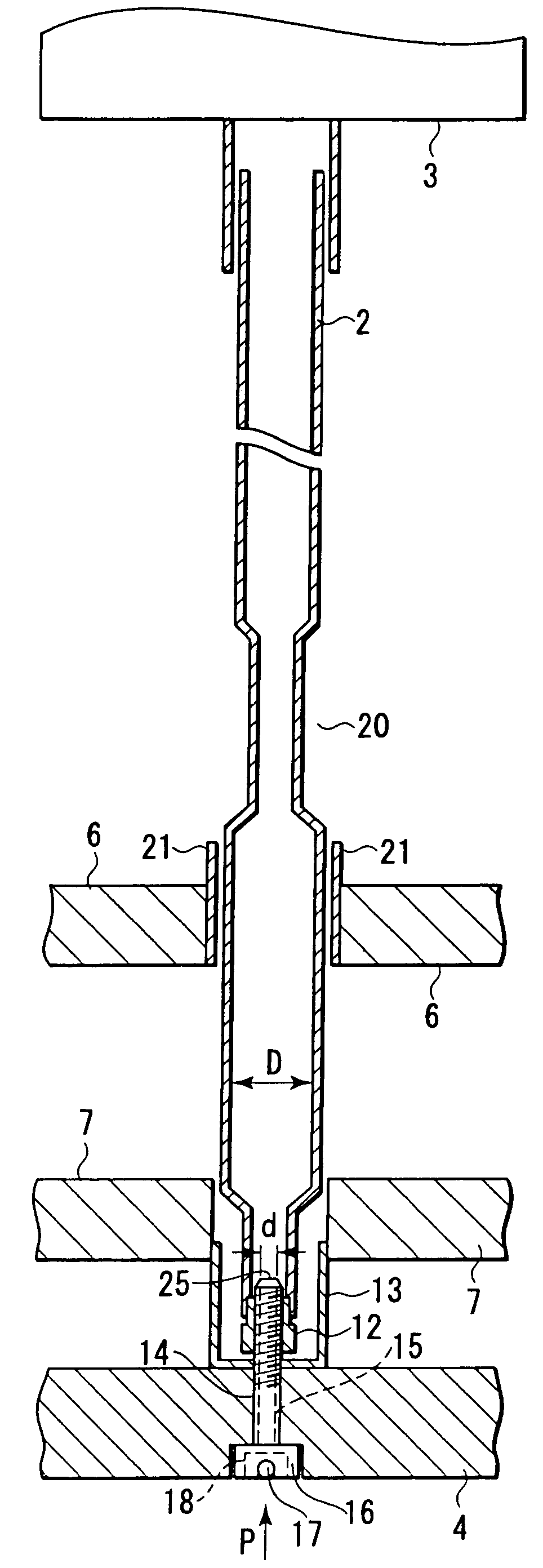
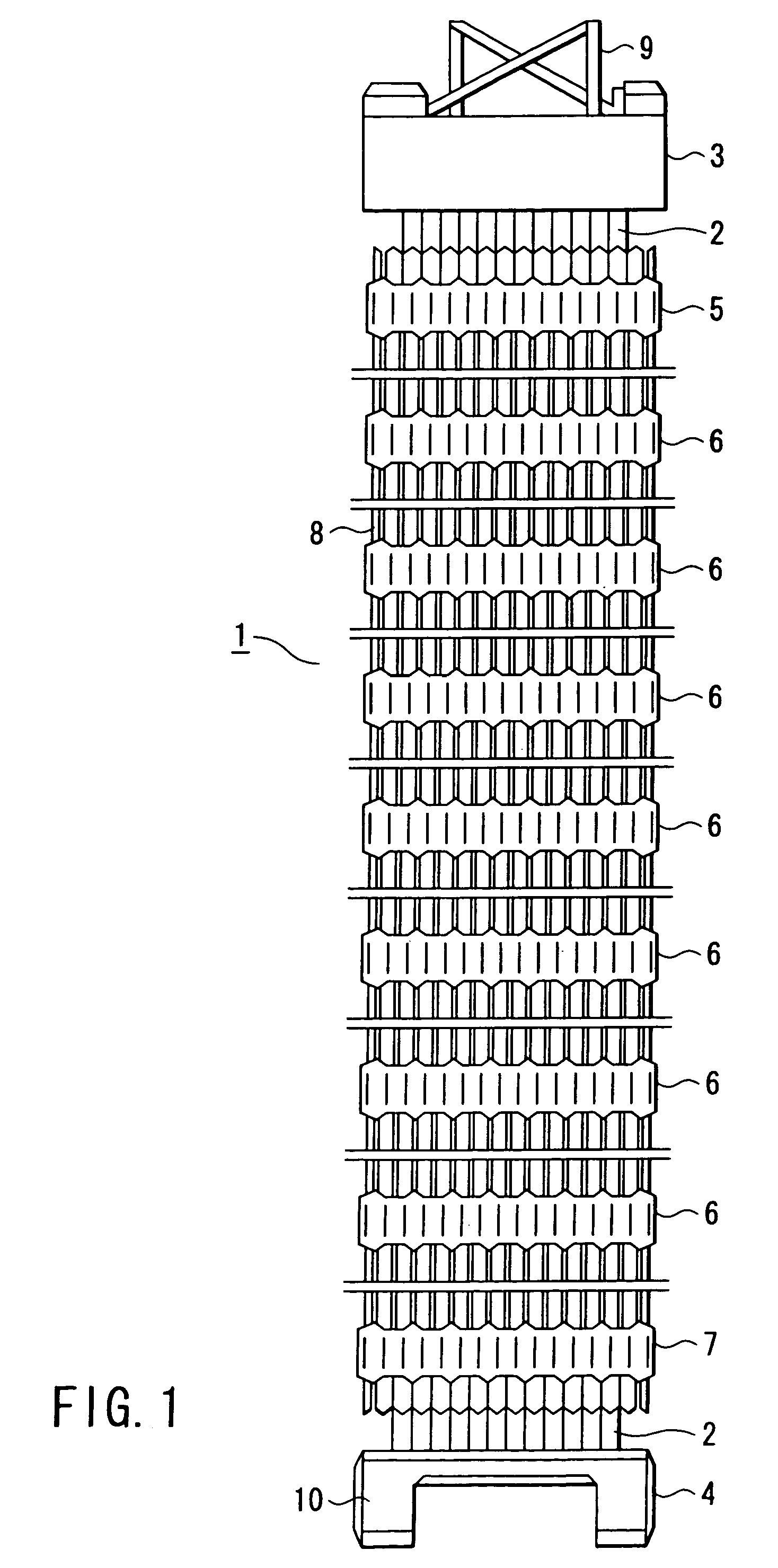
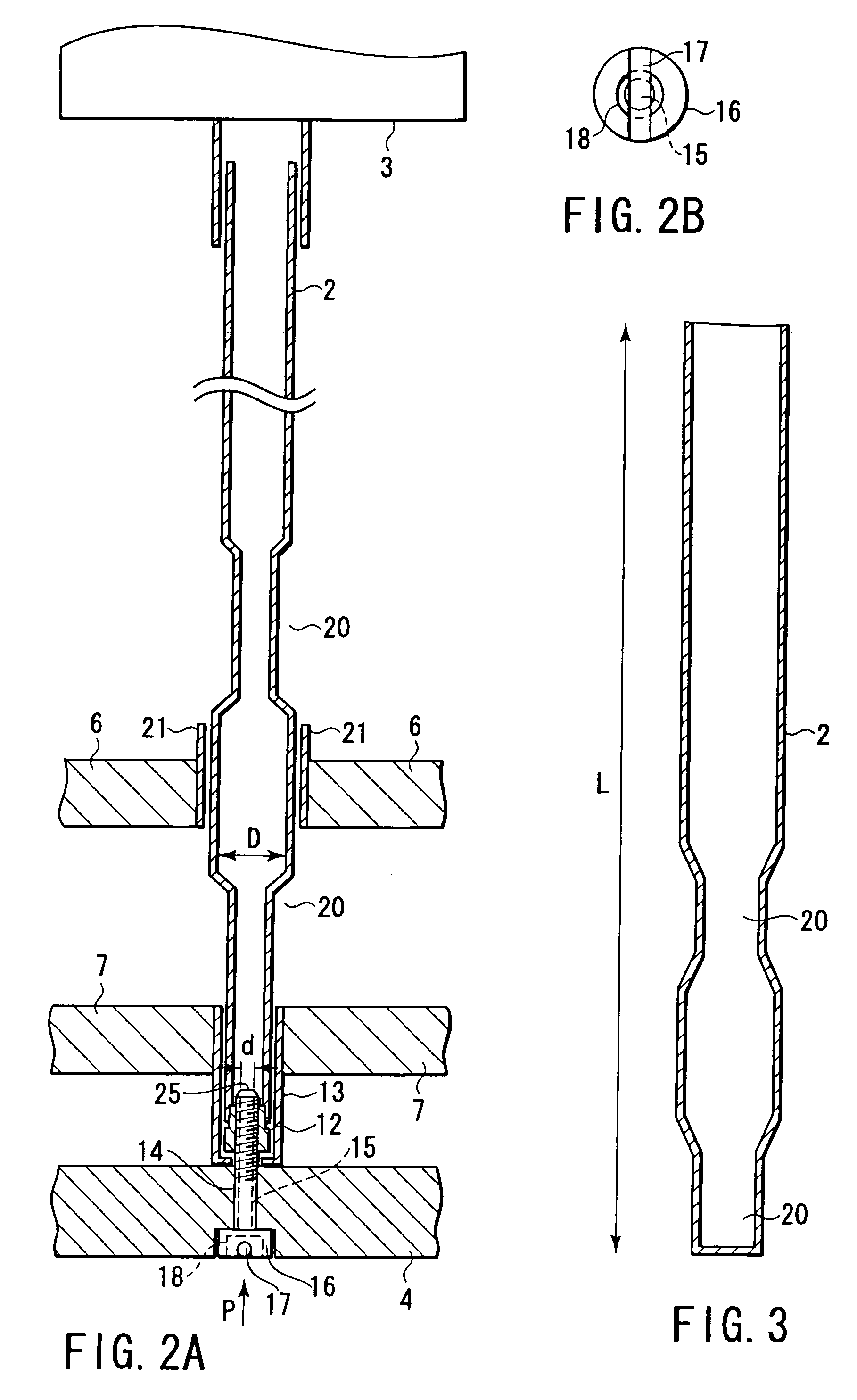
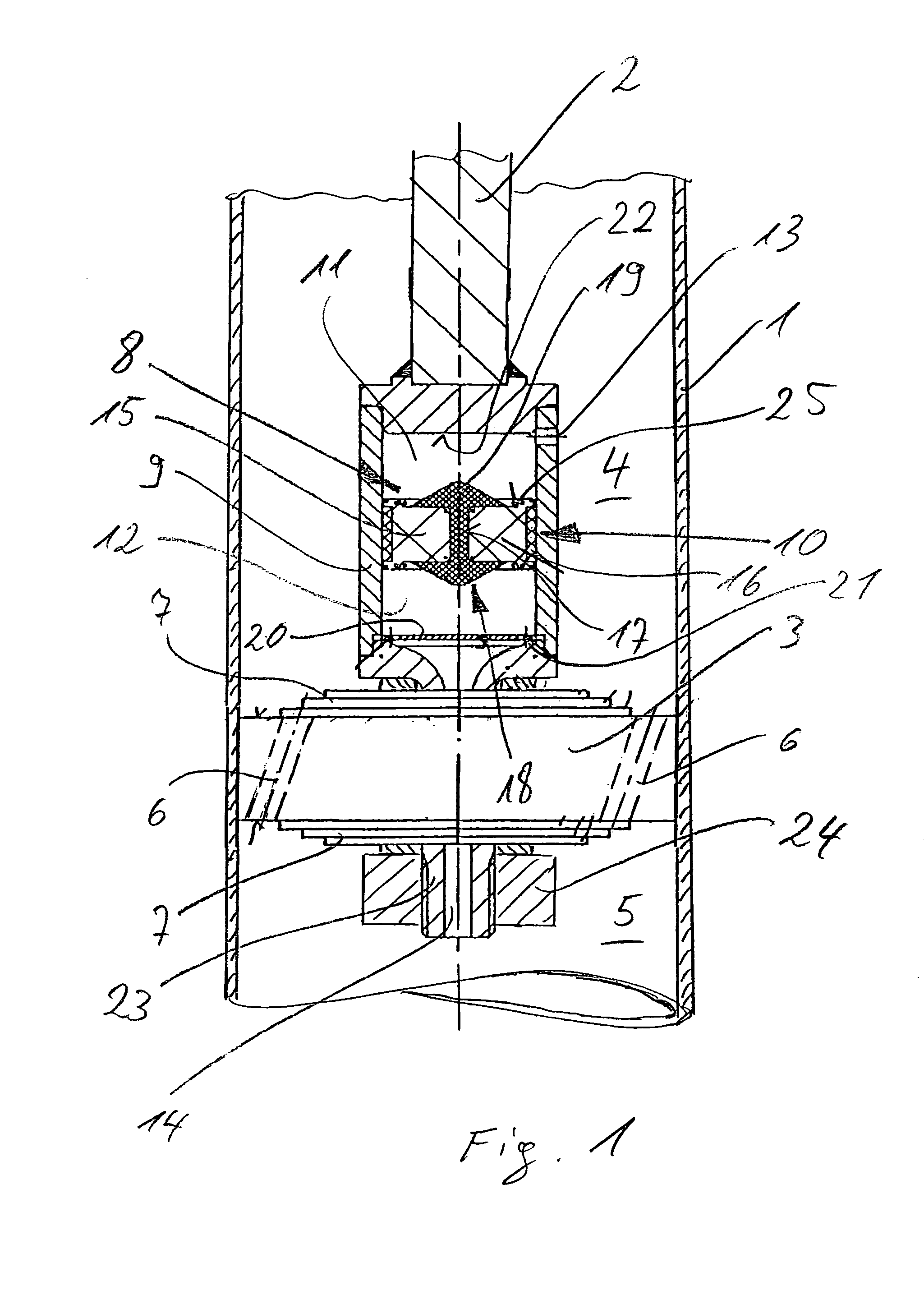
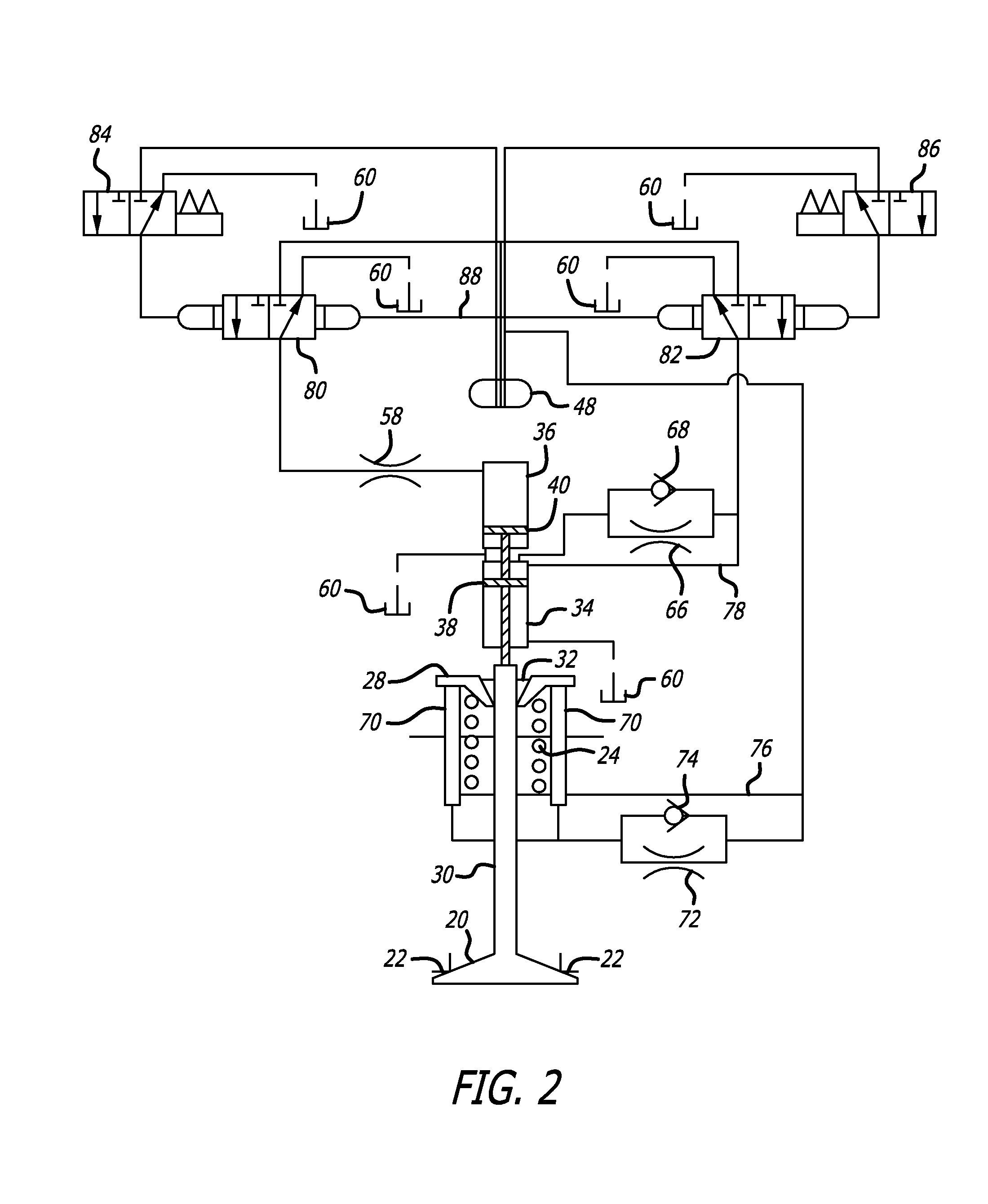
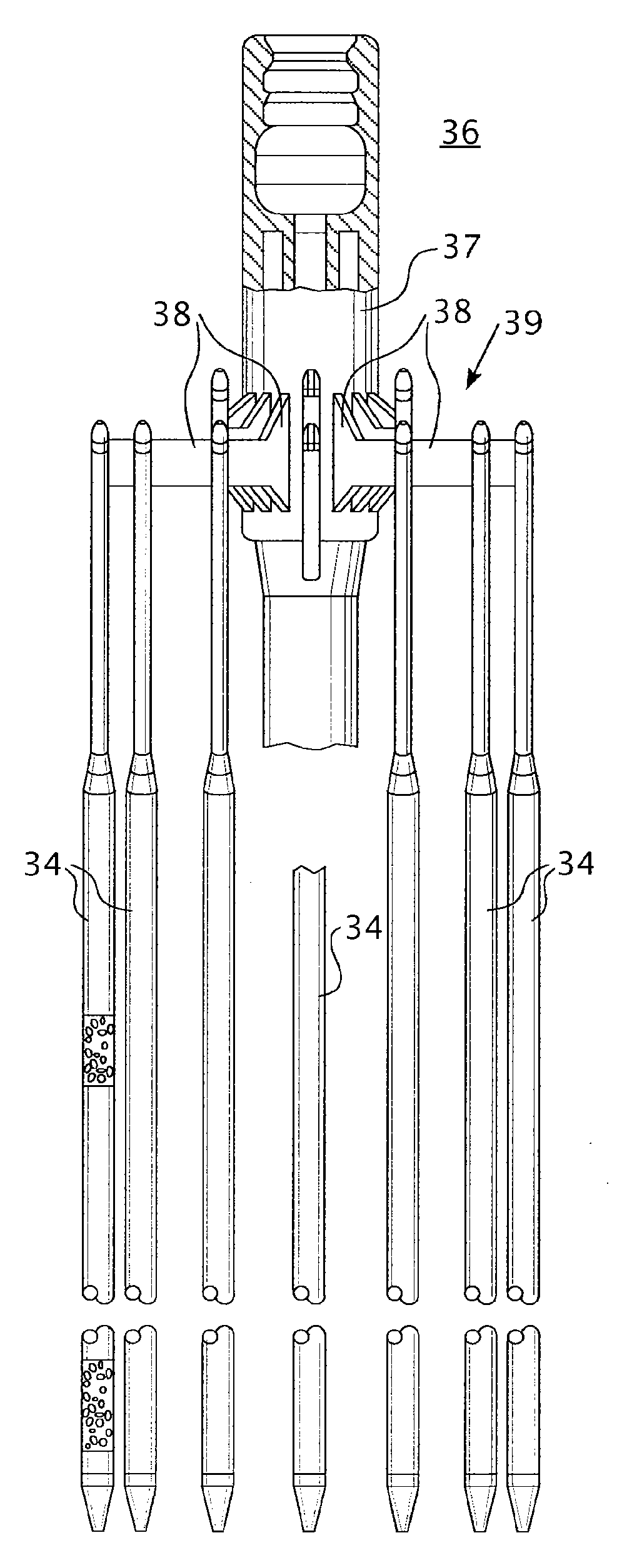
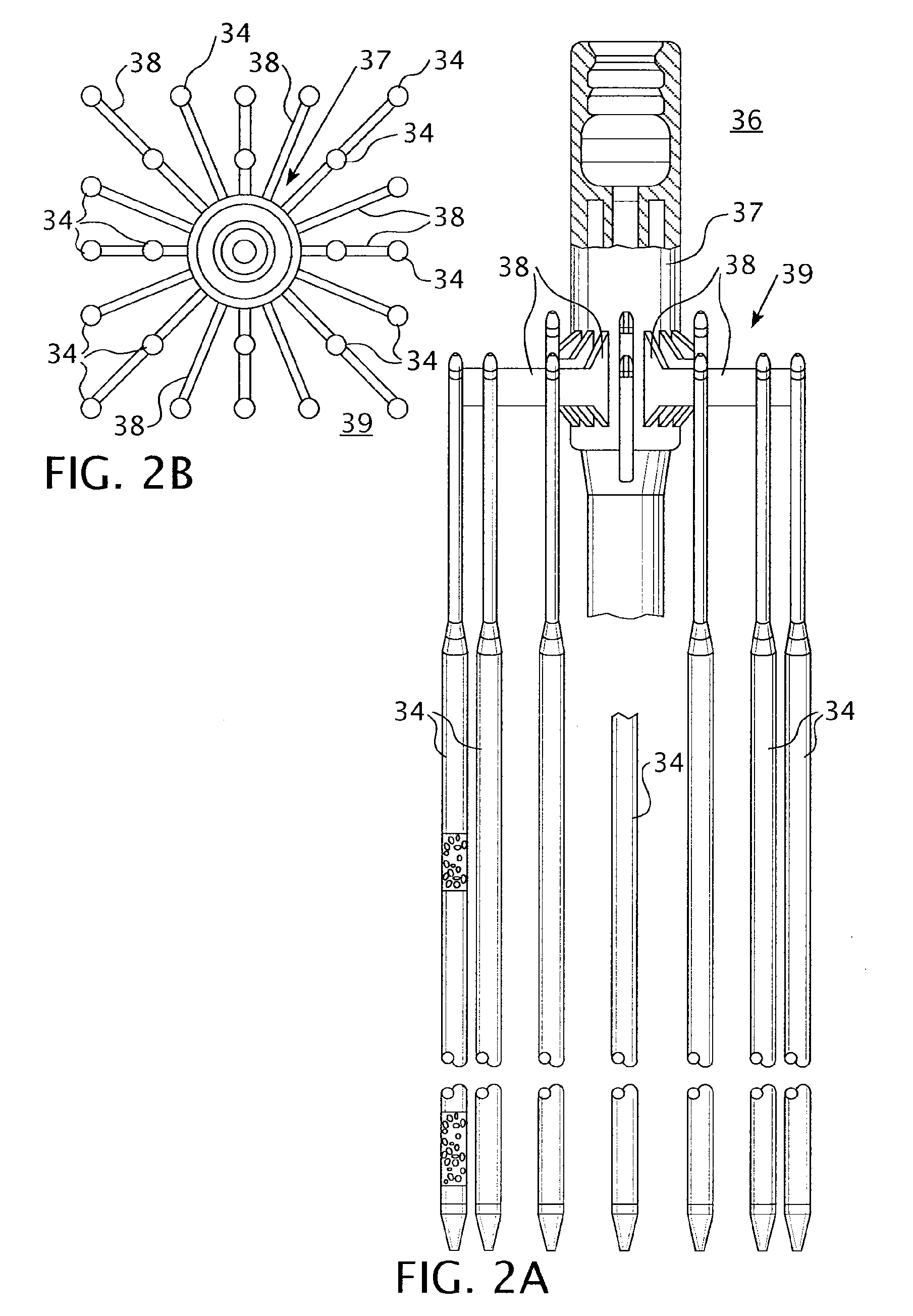
A fuel assembly includes a bottom nozzle set on a lower core plate of a nuclear reactor, a top nozzle with a hold down spring to urge the bottom nozzle against the lower core plate, guide thimbles which guide control rods, having passed through the top nozzle, toward the lower core plate, a dashpot formed on each of the guide thimbles to reduce the fall velocity of a corresponding one of the control rods, a thimble screw which connects each of the guide thimbles to the bottom nozzle, and a drain hole formed to extend through each of the thimble screw. The dashpot has a large-diameter portion with substantially the same diameter as that of each of the guide thimbles. The diameter d of the drain hole falls within a range of 0.04 D<d<0.08 D where D is an inner diameter of the large-diameter portion.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
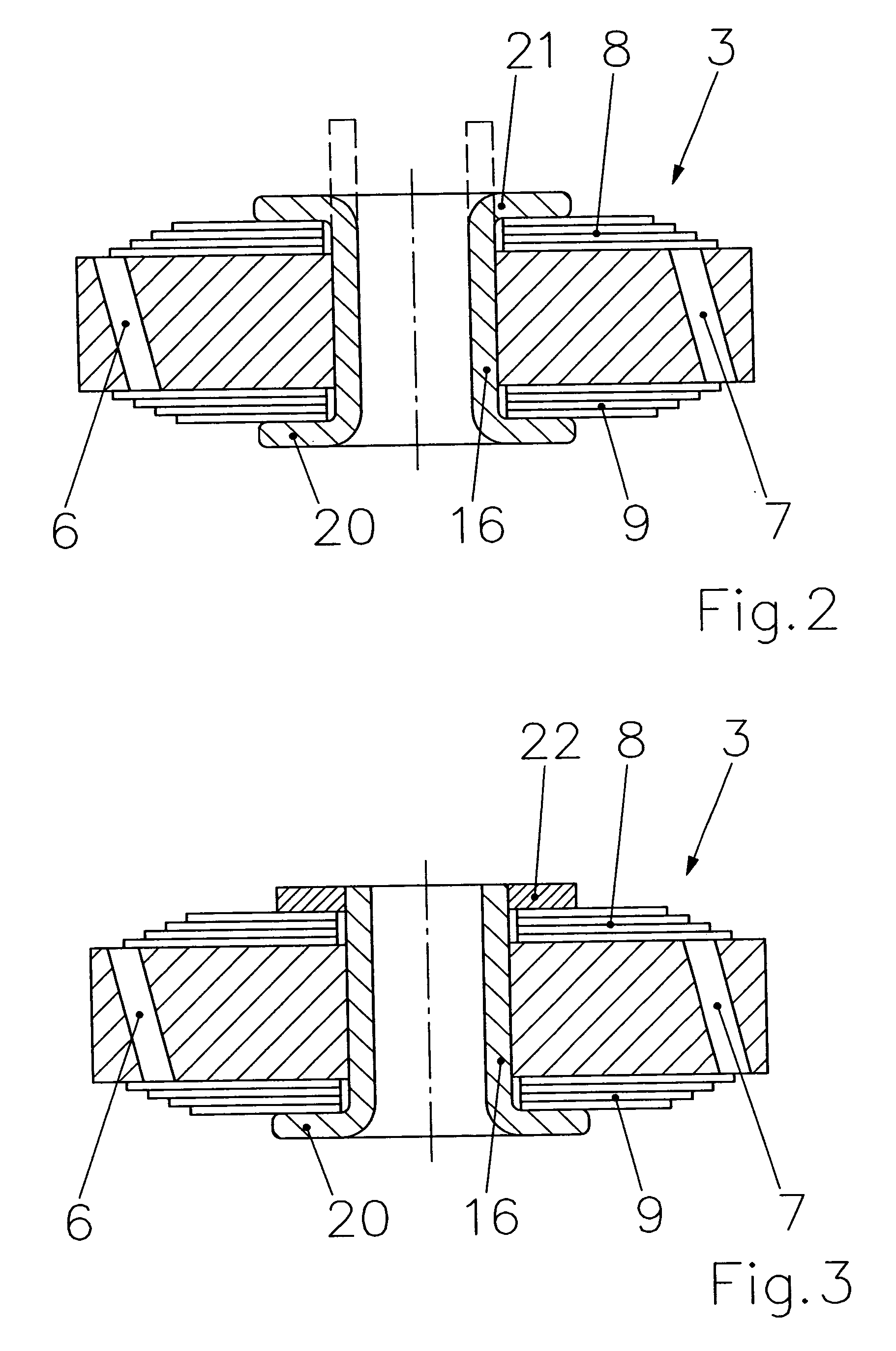
Dashpot with amplitude-dependent shock absorption
ActiveUS7255211B2Few local strainPerformance softSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsDashpotPiston
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN +1
Regulated dashpot with shock-absorption force controls
ActiveUS7699147B2Adjustable powerRiding comfort will be considerably improvedSpringsResilient suspensionsMobile vehicleDashpot
A regulable dashpot with shock-absorption force controls, especially intended for motor vehicles, with at least one flow-regulating system including one or more shock-absorption components for the compression phase and / or for the decompression phase. The object is to allow the dashpot to shift continuously between the hard and soft phases, whereby the valve-adjustment intervals can be varied at intervals that are not unnecessarily short or even unattainable. At least one valve assembly is accordingly supplied with variable flow impedance by a regulating valve (5 or 6).
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
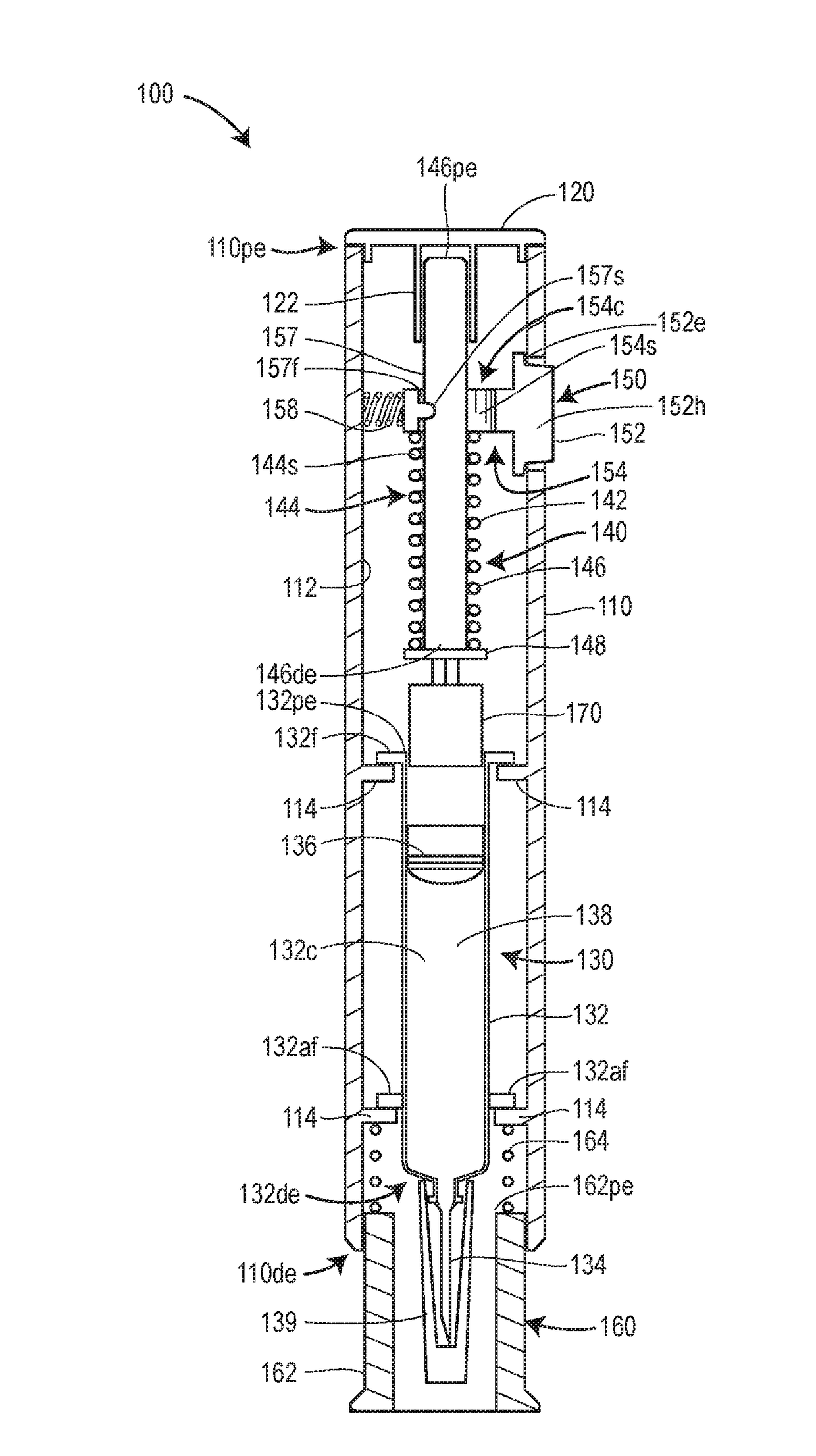
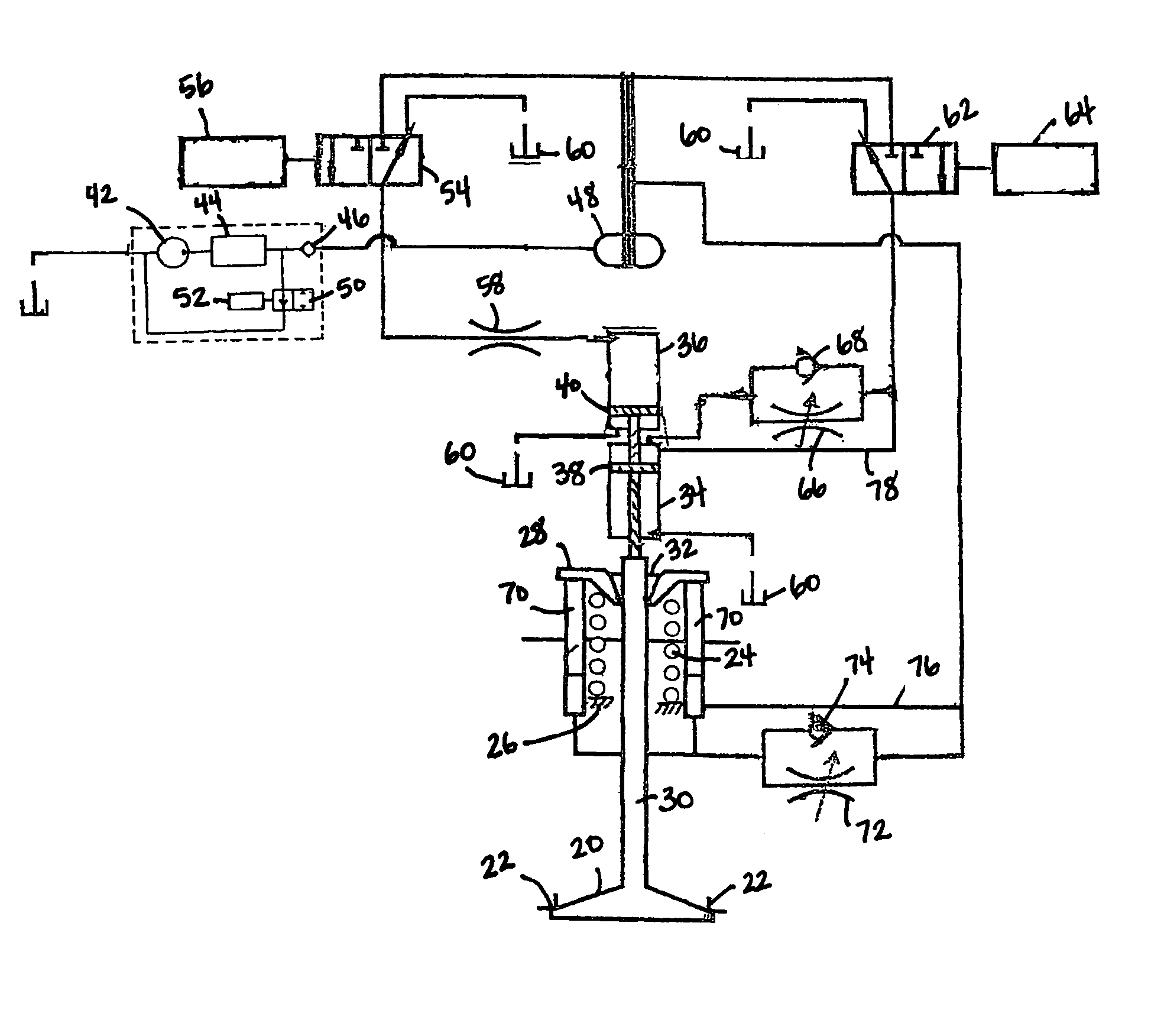
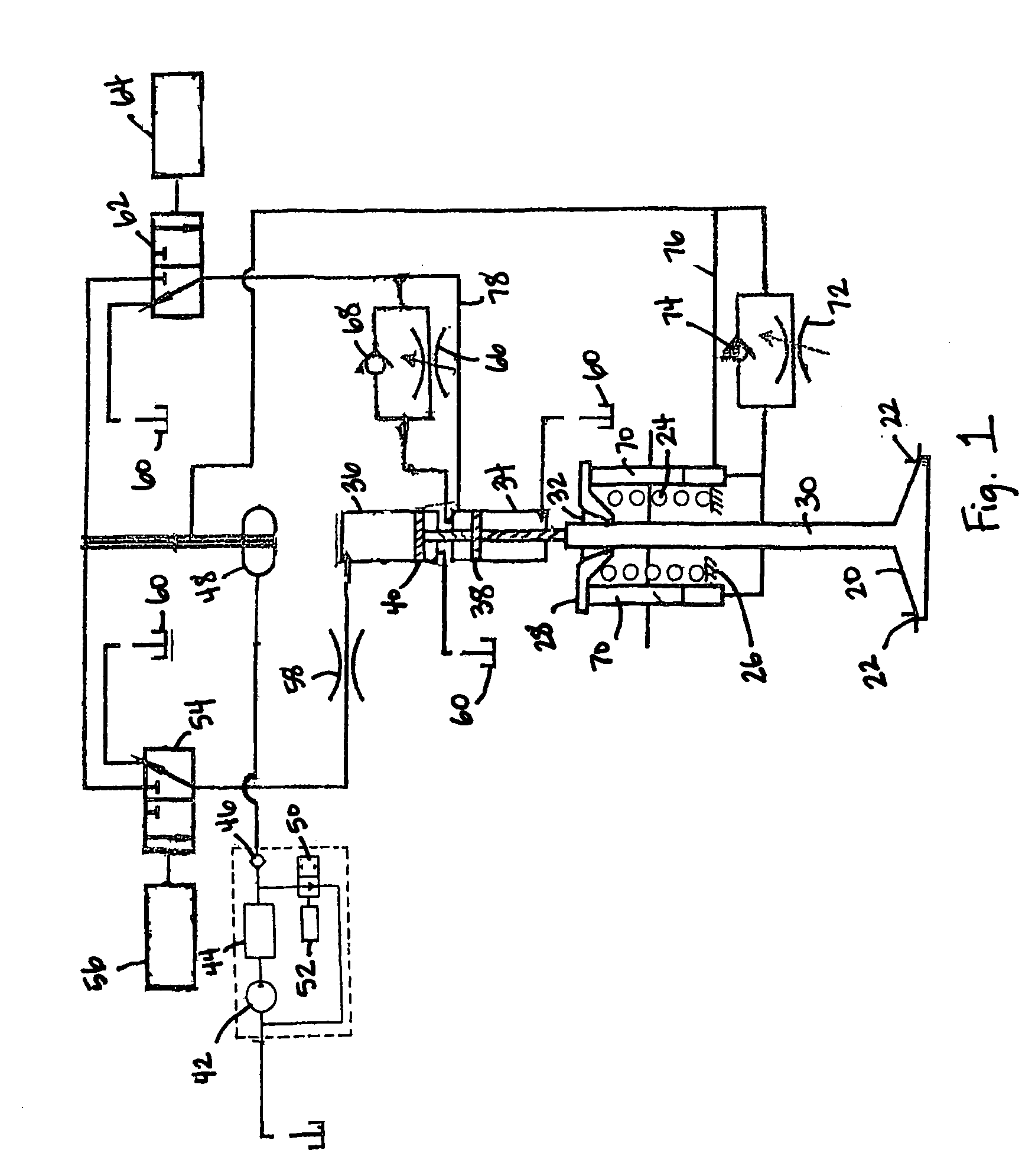
Autoinjector with shock reducing elements
An injection device, method, and system for drug delivery includes a primary container for storing a drug, the container having a stopper movably disposed in the container for expelling the drug, an injection drive mechanism comprising a plunger for acting on the stopper and an energy source for exerting a force on the plunger to cause the plunger to act on the stopper to expel the drug, the force causing the plunger to accelerate to a velocity prior to acting on the stopper, and a damping mechanism for reducing the velocity of the plunger prior to acting on the stopper. The damping mechanism can include a dashpot or an energy absorbing material associated with the plunger. Alternatively or additionally, the damping mechanisms can include absorbing material disposed between support members of an outer casing of the injection device and the primary container.
Owner:AMGEN INC
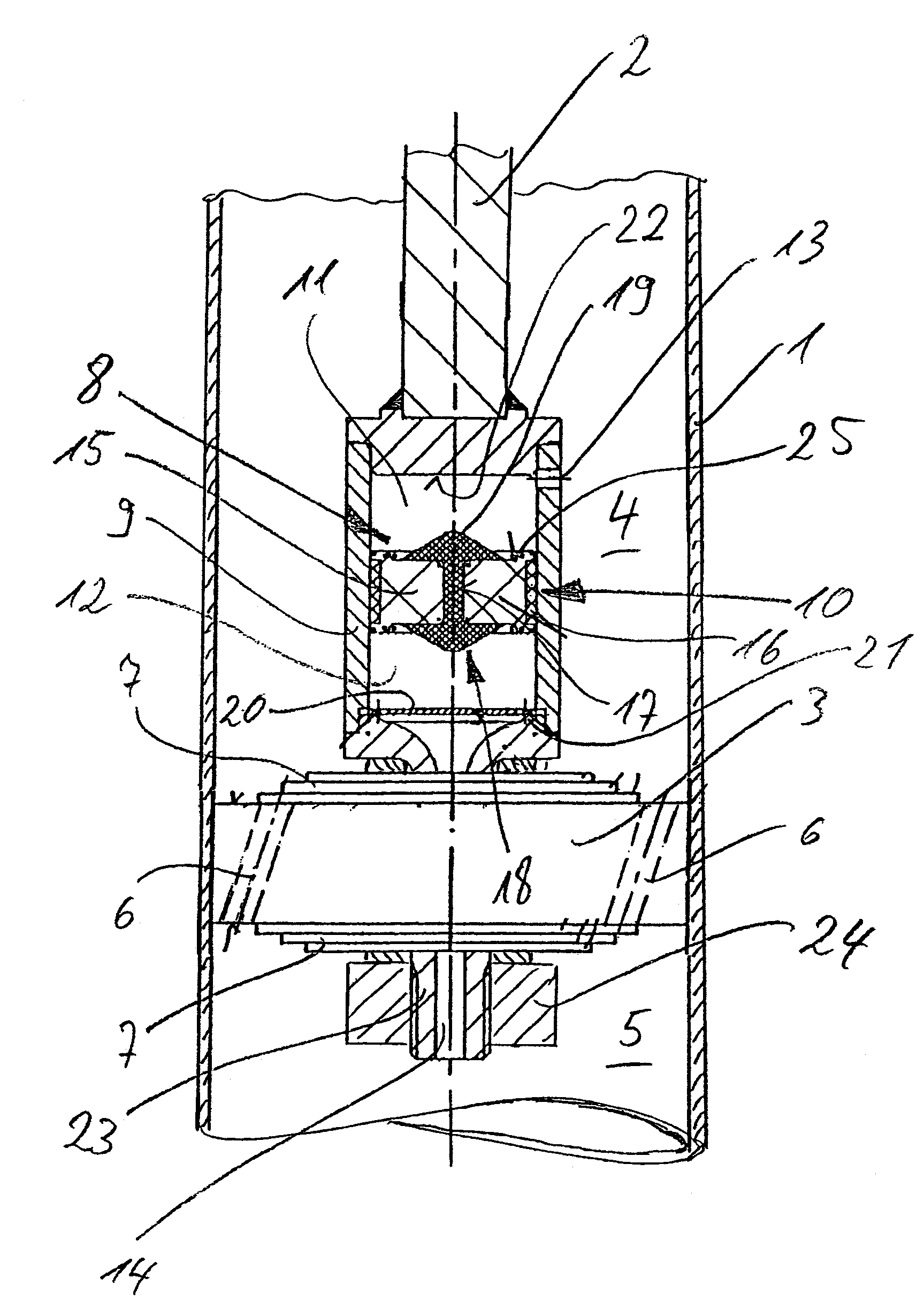
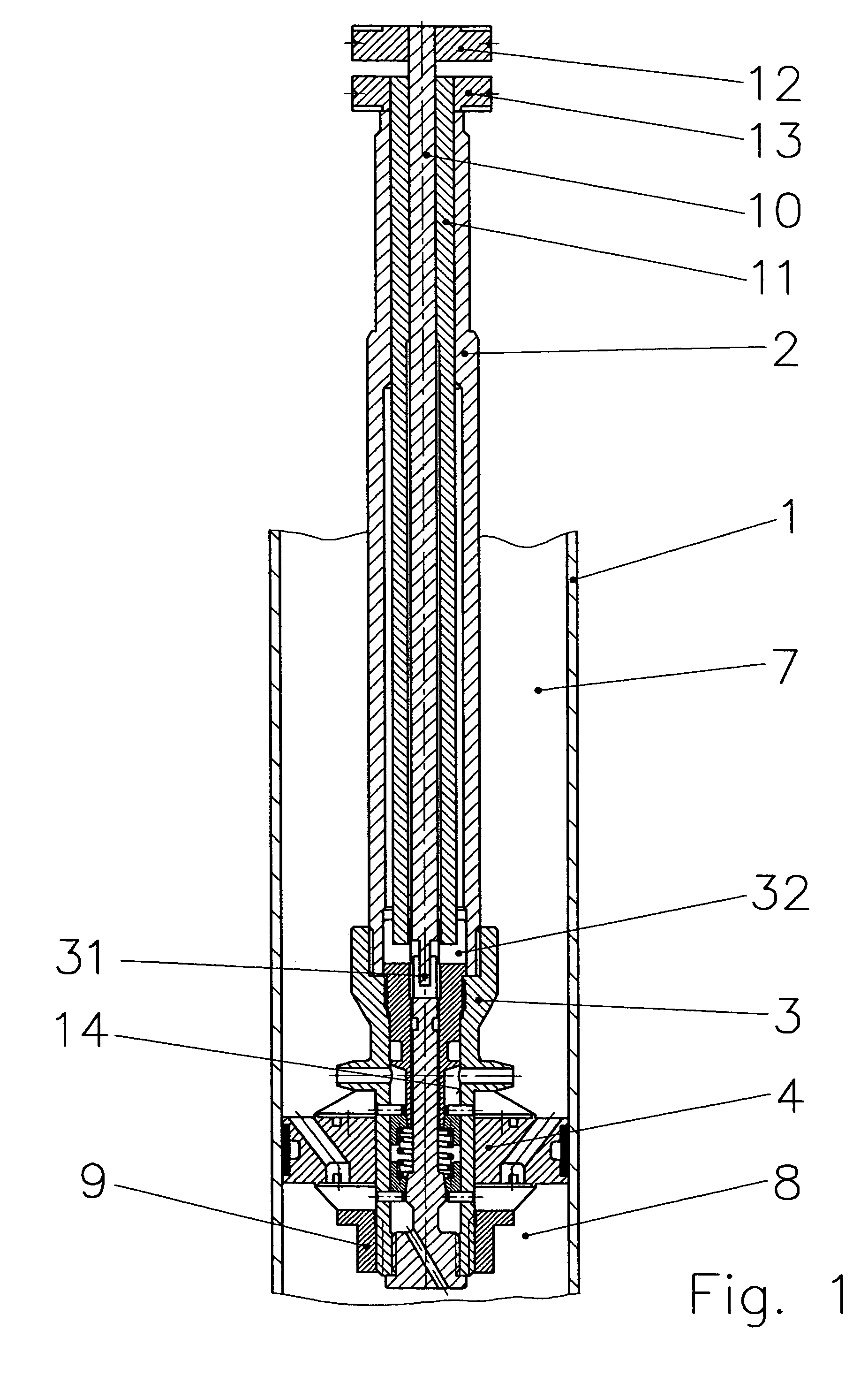
Assembly for a Hydraulic Dashpot
An assembly for a hydraulic dashpot. The dashpot is accommodated in an overall housing (1) and provided with a shock-absorbing piston (3) traveling back and forth inside the housing on one end of a piston rod (2) and partitioning the housing into two compartments (19&23), and a vibration-compensating piston (11) hydraulically paralleling the first piston and accommodated inside a subsidiary housing (10).The object of is to ensure a solid and reliable connection between the shock-absorbing piston and the piston rod while allowing as much of the piston rod as possible to find support inside the housing.The vibration-compensating piston is accordingly an annular piston and travels back and forth with its inner surface resting against a section (9) of the piston rod adjacent to the fastening for the shock-absorbing piston, and with its outer surface against the inner surface of the subsidiary housing.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Dual check-relief valve
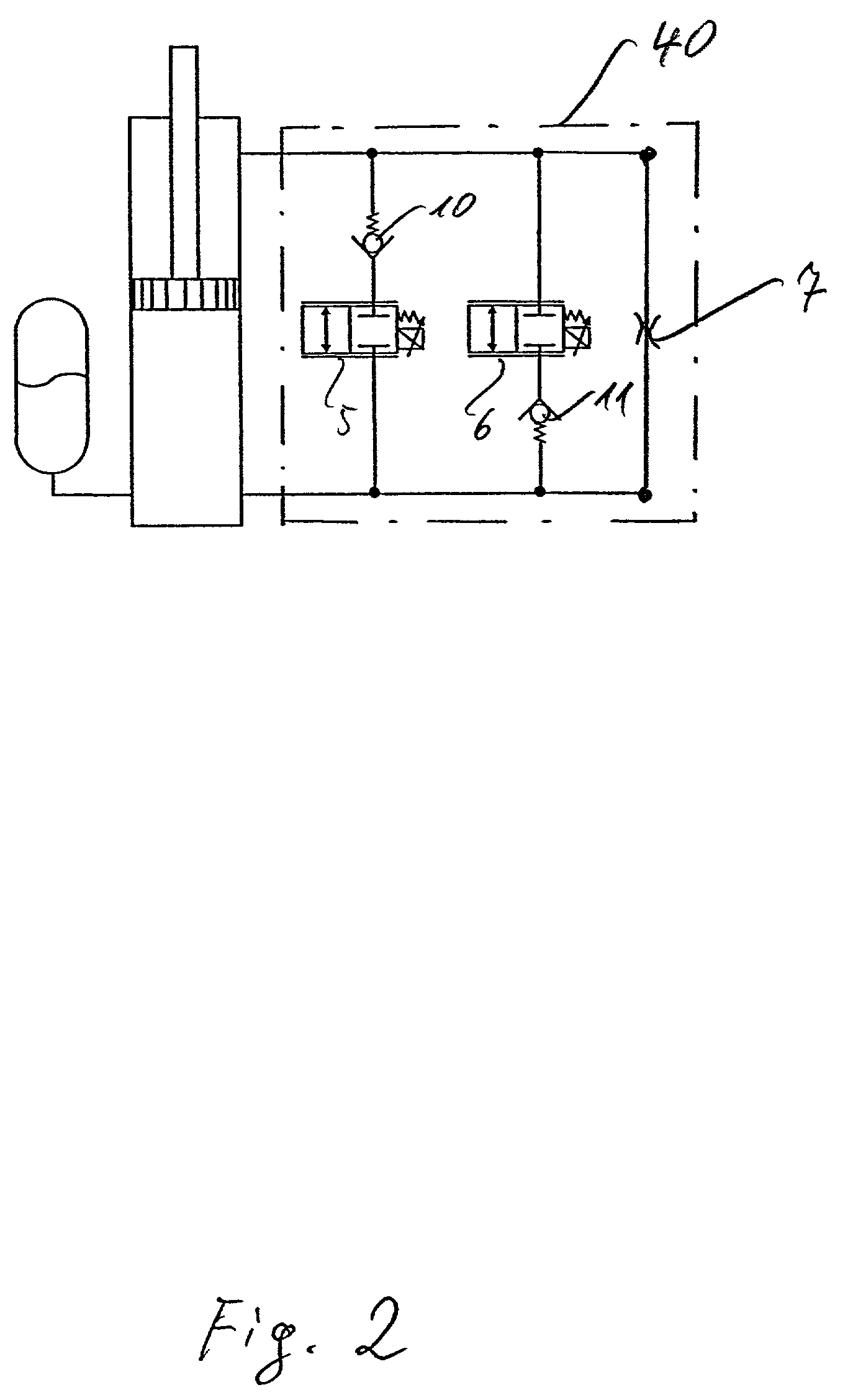
A dual check and high pressure relief valve that is able to perform the function of a hydrostatic high pressure relief valve and a check valve. The new valve has two poppets separated by a spring that are within two seats within a guide and secured by a plug. By adjusting the seats the relief pressure setting is set. The dual check and high pressure relief valve has three separate passageways that allow fluid flow between different combinations of the passages depending upon the function desired within the hydrostatic circuit. A dashpot is also included between the two poppets to provide positive dampening of the system.
Owner:SAUER DANFOSS NORDBERG
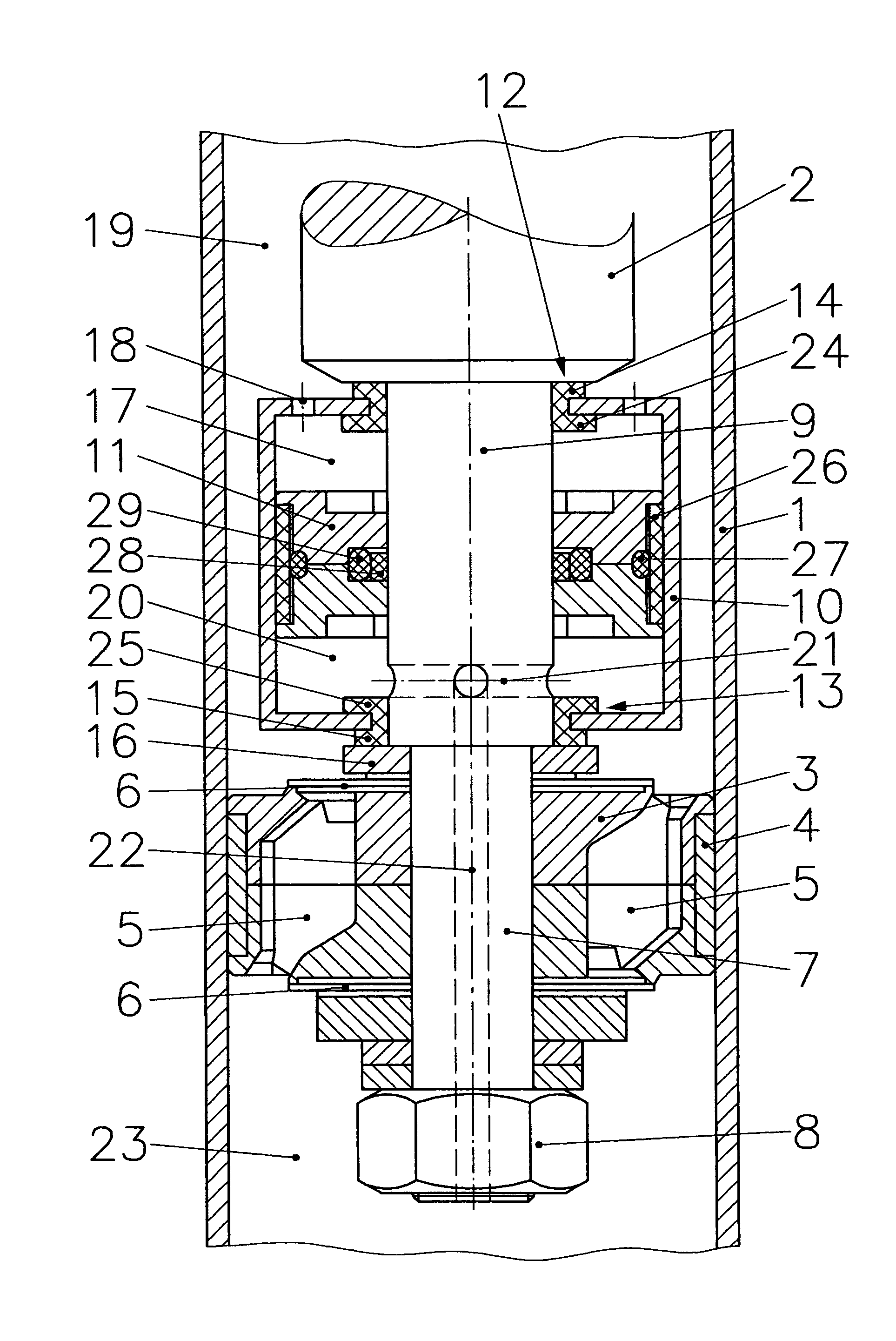
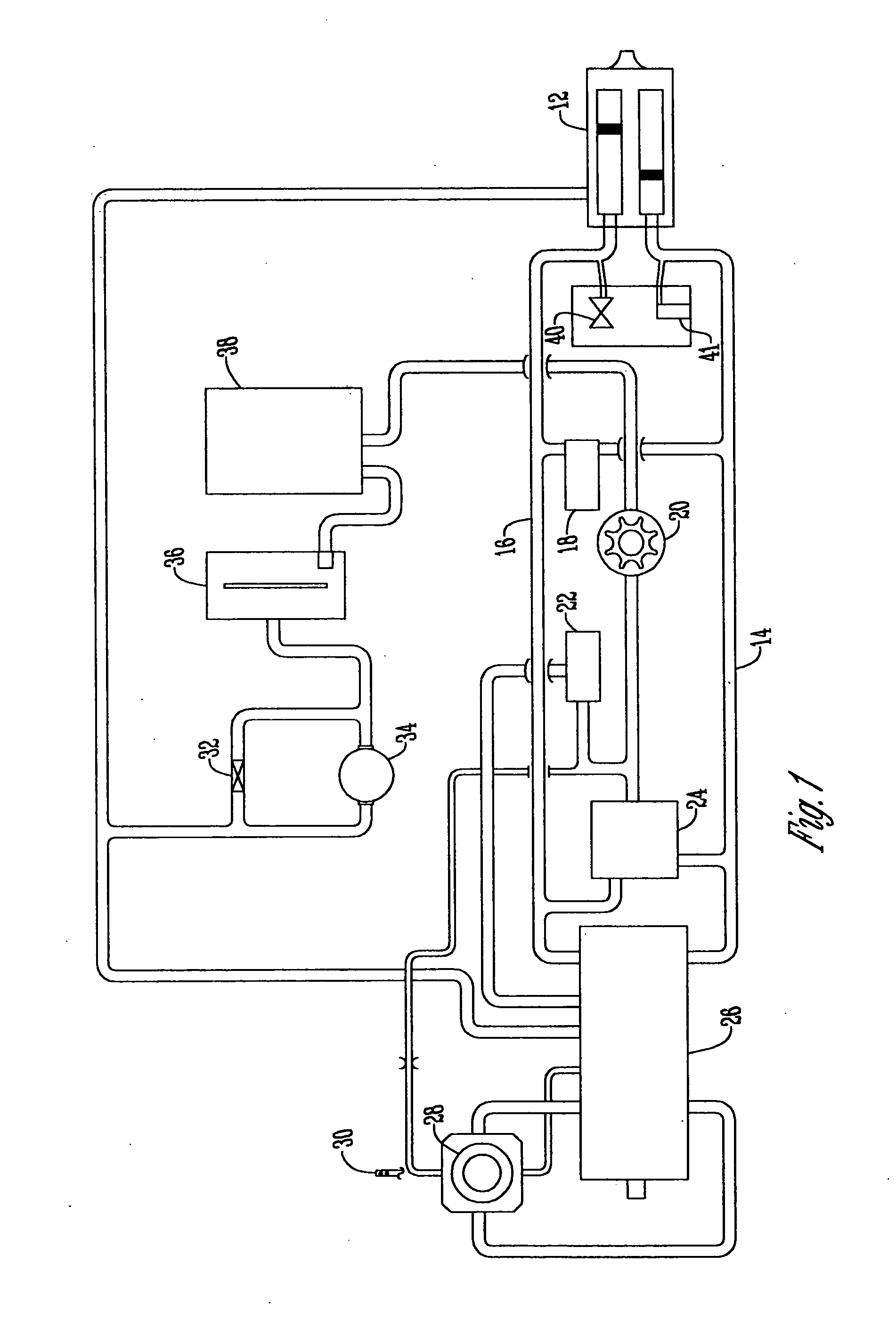
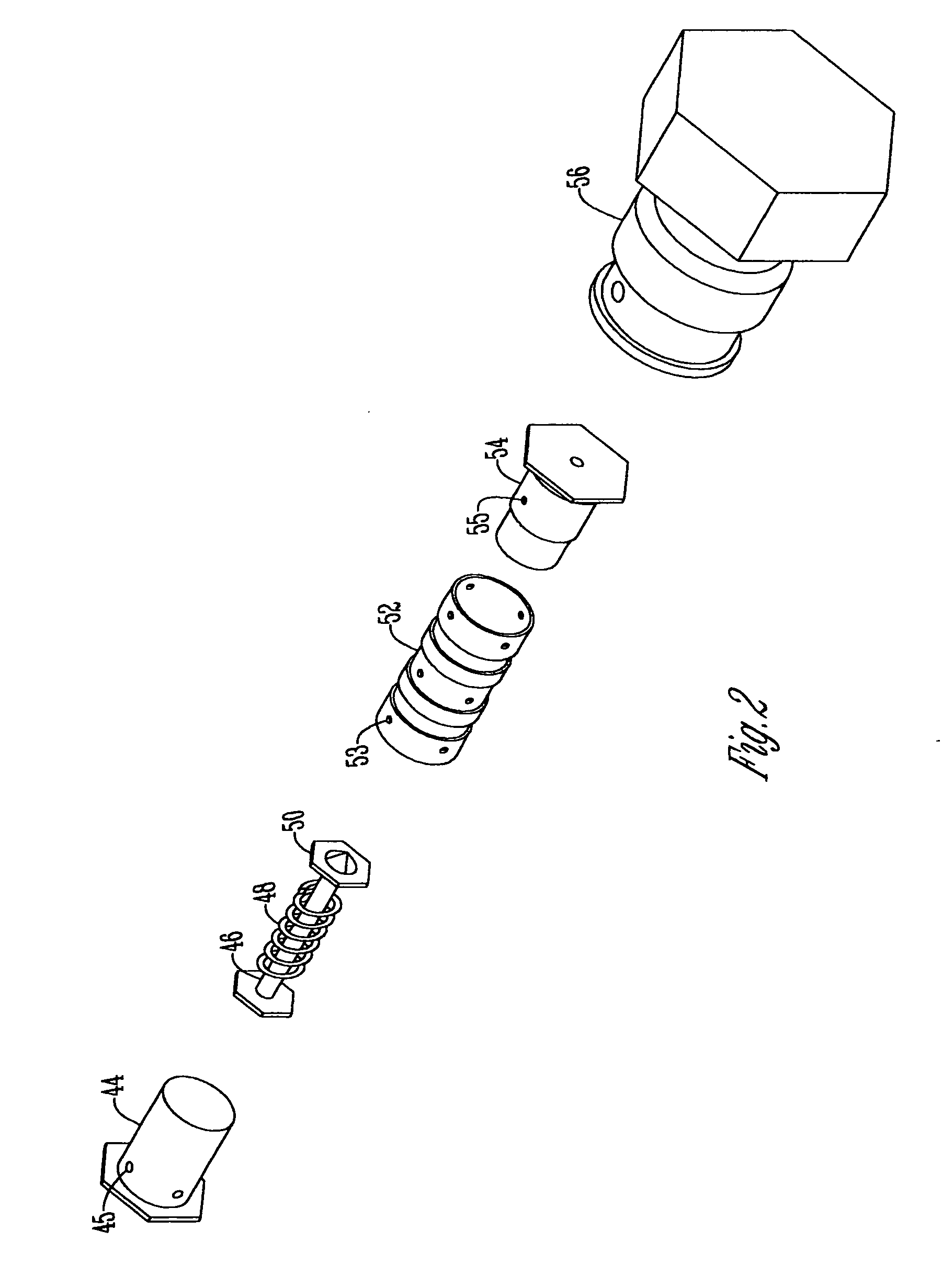
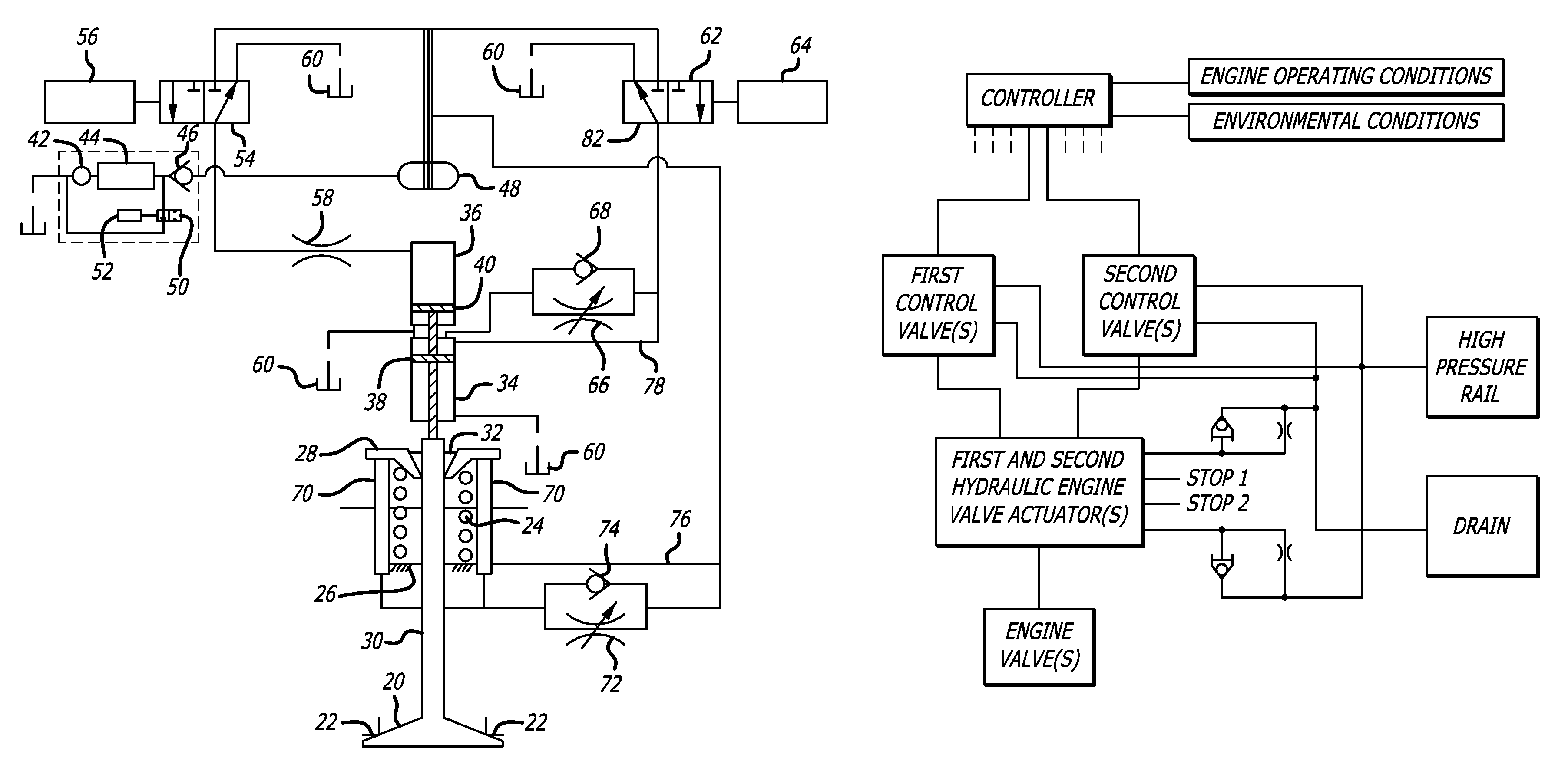
Hydraulic valve actuation systems and methods to provide multiple lifts for one or more engine air valves
Owner:STURMAN INDS
Nuclear reactor robust gray control rod
ActiveUS20090046824A1Low worthExcellent radiation-induced swelling characteristicNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactorDashpot
A control rod having a lower tip absorber material which exhibits substantially lower irradiation induced swelling than a second absorber material which extends above the lower tip absorber material. The lower tip absorber material having a substantially lower reactivity worth than the second absorber material, extends from a lower end plug of the control rod to an elevation just above a dashpot in a thimble guide tube in a nuclear fuel assembly when the control rod is fully inserted within the thimble guide tube.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
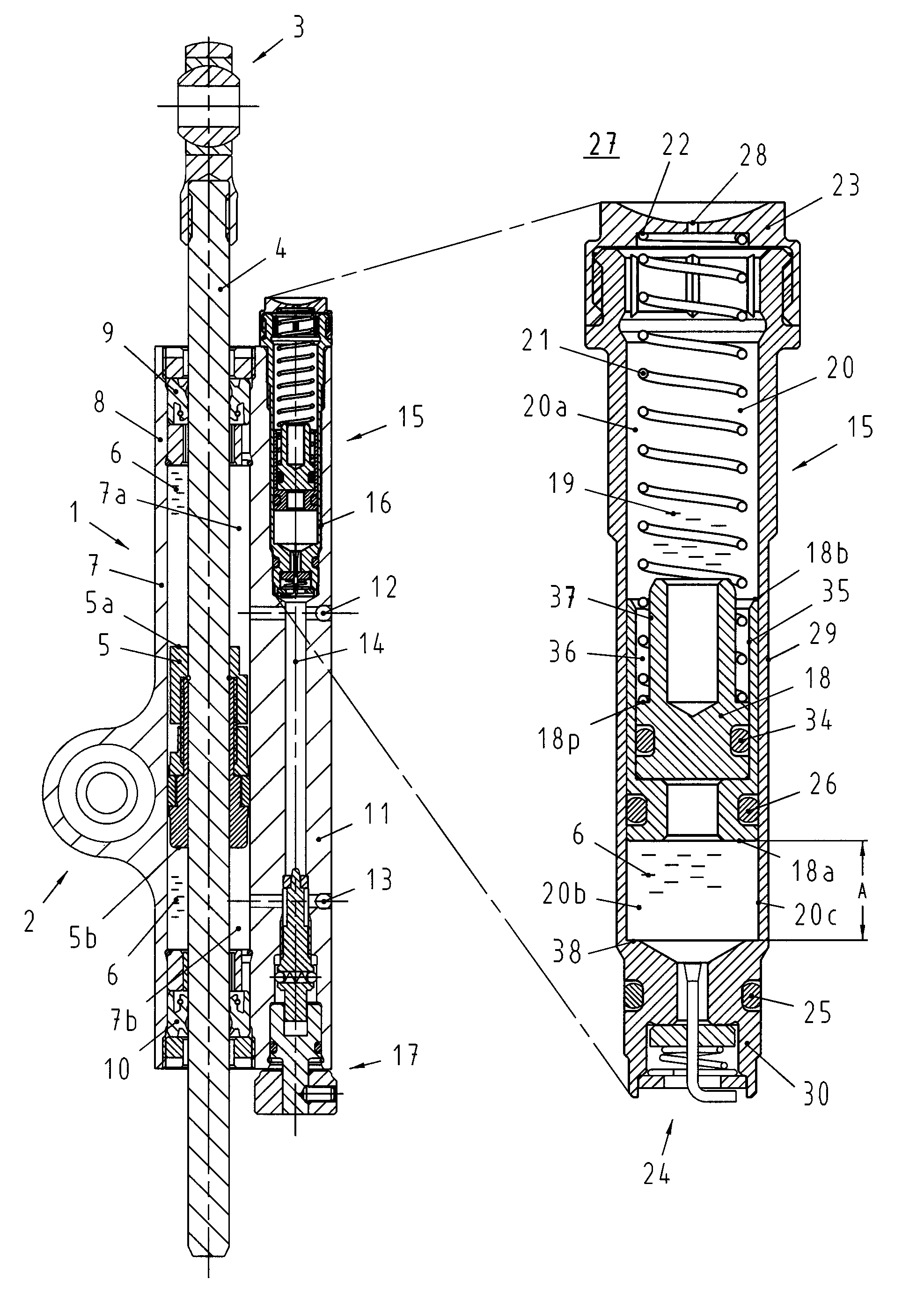
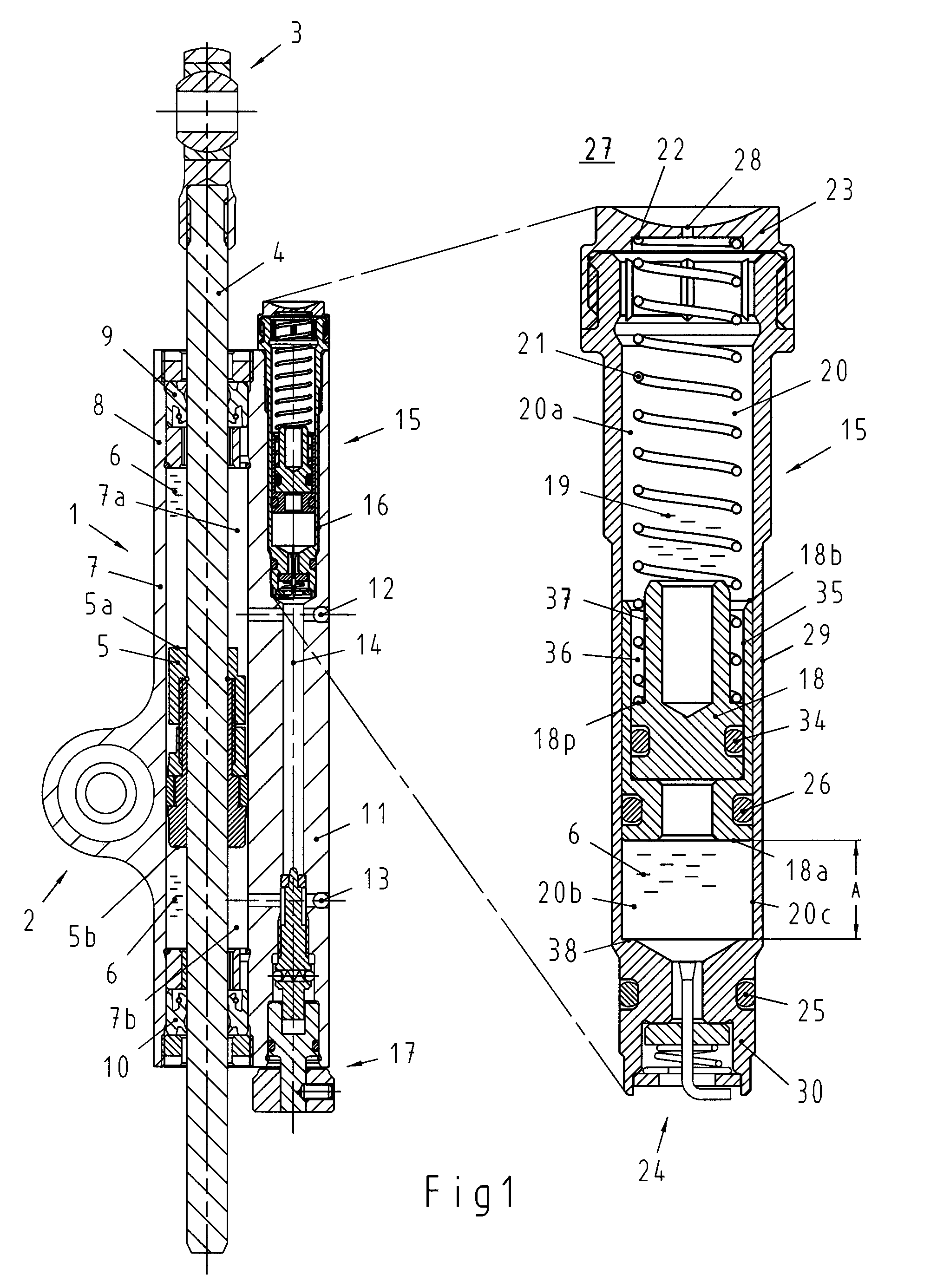
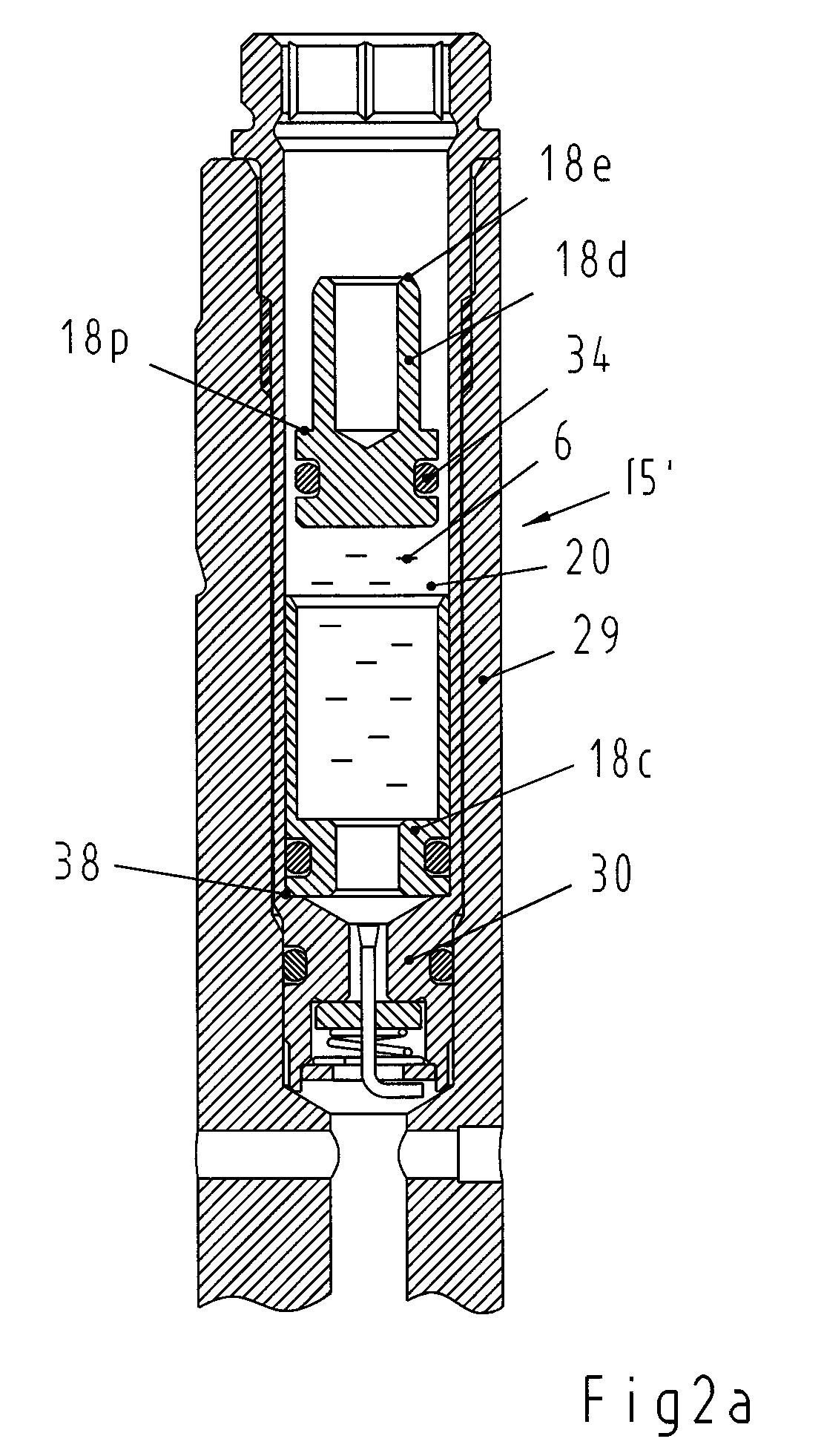
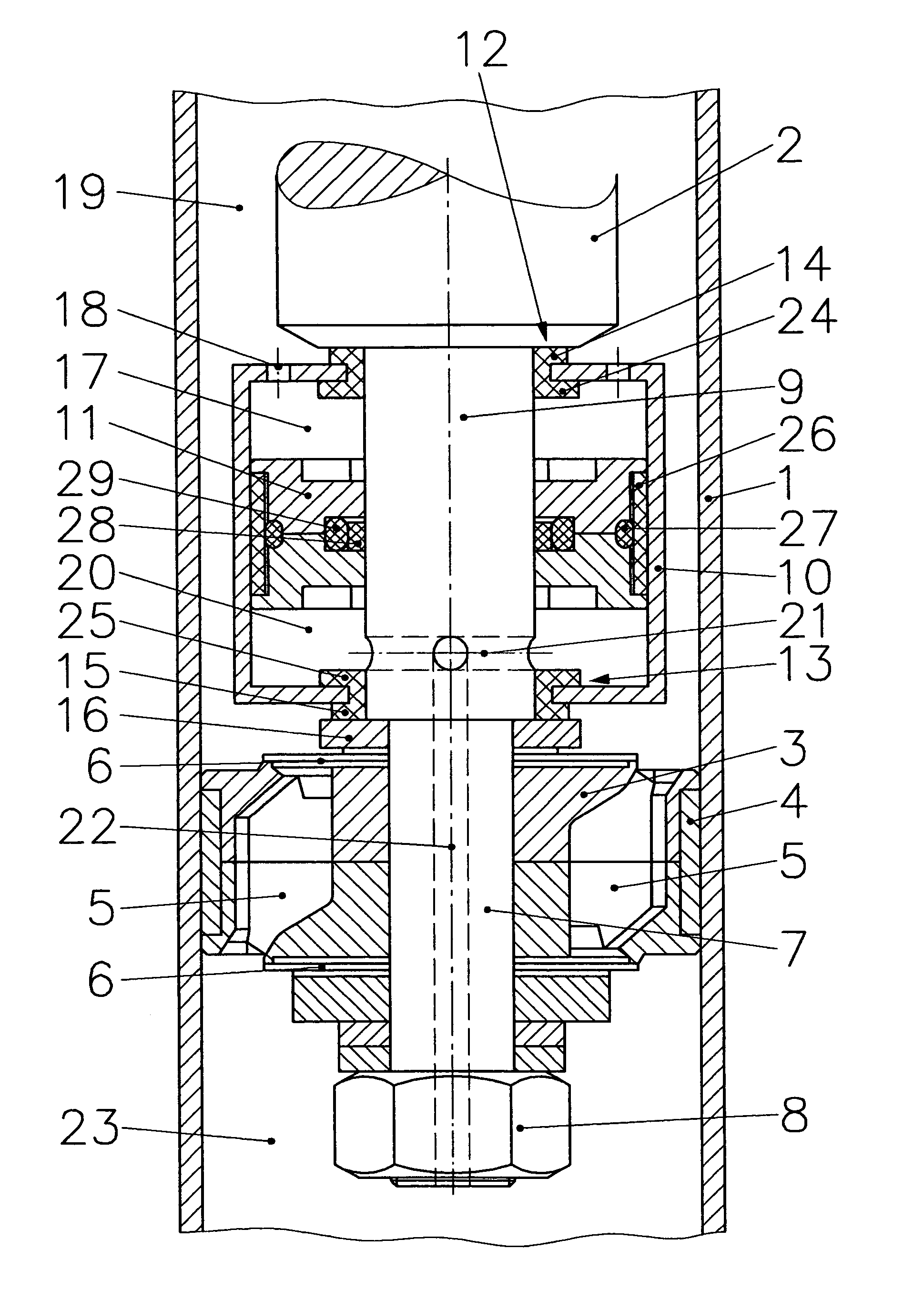
Subassembly for the amplitude-dependent absorption of shock
A subassembly for the amplitude-dependent absorption of shock, especially in a dashpot for a motor vehicle with a piston and an oscillating piston rod. The piston (3) is accommodated in a housing (2), partitioning the housing into two compartments (4&5), and travels up and down inside the housing, radially aligned and axially subject to motion-limiting tension, on the end of the piston rod (1). The object is a simple and reliable subassembly that takes up little additional space. The piston is accordingly axially tensioned between two springs (17&18).
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Pneumatic two-position two-way piston type multi-medium angle seat valve with buffer
InactiveCN101373030AEliminate shockEliminate vibration noiseSpindle sealingsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutomatic controlDashpot
Owner:SHANGHAI HONGXIANG MACHINERY MFG
Method and system of producing molded coal by coking organic castoff and weakly caking coal
The invention provides the method for producing molded coal with coking organic waste and baking coal. The method uses coking organic waste as binding agent, and then it is mixed with baking coal. The molded coal can be used as coking material. The method comprises baking coal breaker, coal dashpot, coking organic waste stirring device, coking organic waste dashpot, preliminary hybrid arrangement, homogeneous hybrid arrangement, and forming machine. The invention has the advantages of intimate mixing, high forming, solving environmental pollution, improving coke quality, save cost.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Dashpot with amplitude-dependent shock absorption
InactiveUS7441639B2Few local strainPerformance softSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsDashpotPiston
A dashpot featuring amplitude-dependent shock absorption, especially intended for the wheel of a vehicle and including a hydraulically parallel cylindrical pressure-compensation chamber (8). The pressure-compensation chamber is partitioned by an axially displaceable floating piston (10). At least one face (25) of the floating piston is provided with a resilient bumper (18). The object is a dashpot with a floating piston that arrives more gently at its limit inside the pressure-compensation chamber (8). The bumper is accordingly accommodated in an axial hollow (17) that extends through the body (15) of the floating piston.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Hydraulic valve actuation systems and methods to provide multiple lifts for one or more engine air valves
Hydraulic valve actuation systems and methods to provide multiple lifts for engine valves using fixed or hard stops at each lift. The fixed or hard stops provide a very repeatable selection of engine valve lifts dependent on engine operating conditions. For full valve lift, unidirectional hydraulic dashpots are used to decelerate the engine valve, both as it approaches the full lift fixed stop, and as the engine valve approaches the valve seat from the engine valve full lift position. Various embodiments and methods of operation are disclosed.
Owner:STURMAN INDS
Pneumatic-spring wheel-suspension leg
A pneumatic-spring wheel-suspension leg for motor vehicles. The leg comprises a bellows (1) that can be rolled up over a jacket (3) and accommodates a pneumatics chamber (9), a hydraulic dashpot inside the bellows or jacket, and a piston rod (5) that travels into and out of the dashpot and is attached axially and resiliently directly or indirectly at one end to the vehicle's chassis. The object is to relieve the dashpot of difficult attenuation tasks when a hard wheel suspension is necessary. The leg accordingly includes another pneumatics chamber (10) and the communication between the two pneumatics chambers can be partly or entirely blocked by a valve.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Hydraulic shock absorber
A hydraulic dashpot with a cylinder (1), a piston (4), and a bypass. The cylinder is charged with fluid. The piston partitions the cylinder into two compartments (7&8), travels back and forth therein on the end of a piston rod (2), and is provided with breaches and valves. The open cross-section of the bypass can be expanded and contracted and fixed in accordance with the direction the piston is traveling in, depending on whether the dashpot is in the compression or in the suction phase. The bypass is provided with an axially displaceable control component. One end of the control component comes to rest against a valve, its displacement being limited by stops. The bypass is accommodated in an axial bore through the piston rod. The bypass operates in conjunction with various outlets that open into the compartments. The control component is provided with at least one lateral flange and travels back and forth in at least one tube. The object is a smooth performance curve and low wear. The control component is accordingly in several parts, comprising at least two bypass control caps that axially travel up to stationary stops. The caps, in conjunction with axially variable components (18&21) that dictate the size of the open cross-section in both the compression and the suction phase, create a port.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP BILSTEIN
Magnetic vibration reducing method and vibration dampener
InactiveCN101067434AGood damping propertiesReduce volumeNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic springsMagnetic dampingDashpot
The magnetic damping method and the dashpot are to form the air space to generate the damping effect by the repellant formed between the magnetic poles. The dashpot is set with the up magnet and the down magnet according to the same polar between which the air space with the thickness changed by the load or vibration is formed from the repellant. The dashpot has the simple structure, low cost and not only decreases the vibration disturbance of 20Hz but below 20Hz.
Owner:张小建
Dual check-relief valve
A dual check and high pressure relief valve that is able to perform the function of a hydrostatic high pressure relief valve and a check valve. The new valve has two poppets separated by a spring that are within two seats within a guide and secured by a plug. By adjusting the seats the relief pressure setting is set. The dual check and high pressure relief valve has three separate passageways that allow fluid flow between different combinations of the passages depending upon the function desired within the hydrostatic circuit. A dashpot is also included between the two poppets to provide positive dampening of the system.
Owner:SAUER DANFOSS NORDBERG
Tube-in-tube threaded dashpot end plug
ActiveUS20080137798A1Guarantees proper engagementNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesDashpotEngineering
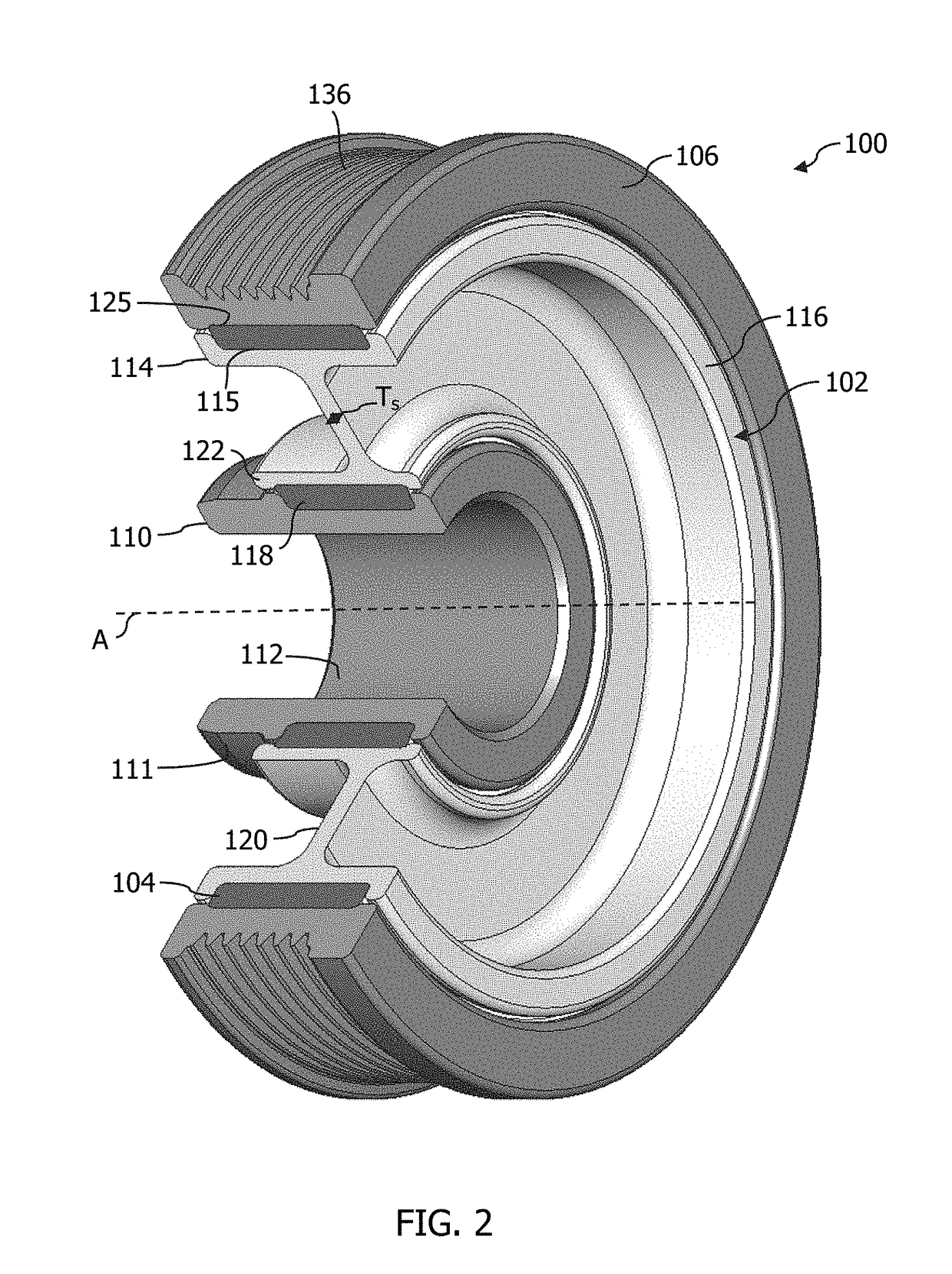
A nuclear fuel assembly having a tube-in-tube control rod guide tube design that incorporates an end plug that extends axially upward to an elevation above the lower most grid where it is sealed at its tipper end to the lower end of the control rod guide tube. The guide tube lower end plug has a threaded recess in its upper surface that mates with a corresponding dashpot end plug threaded extension that is formed as an insert in the lower end of the guide tube. A hole formed through the outer wall of the guide tube end plug at the elevation of the lower portion of the recess provides a positive inspection port for assuring the proper seating of the dashpot. A method of manufacture of such a fuel assembly is also disclosed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Measurement device of polymer viscoelastic model and measurement method of model element parameters
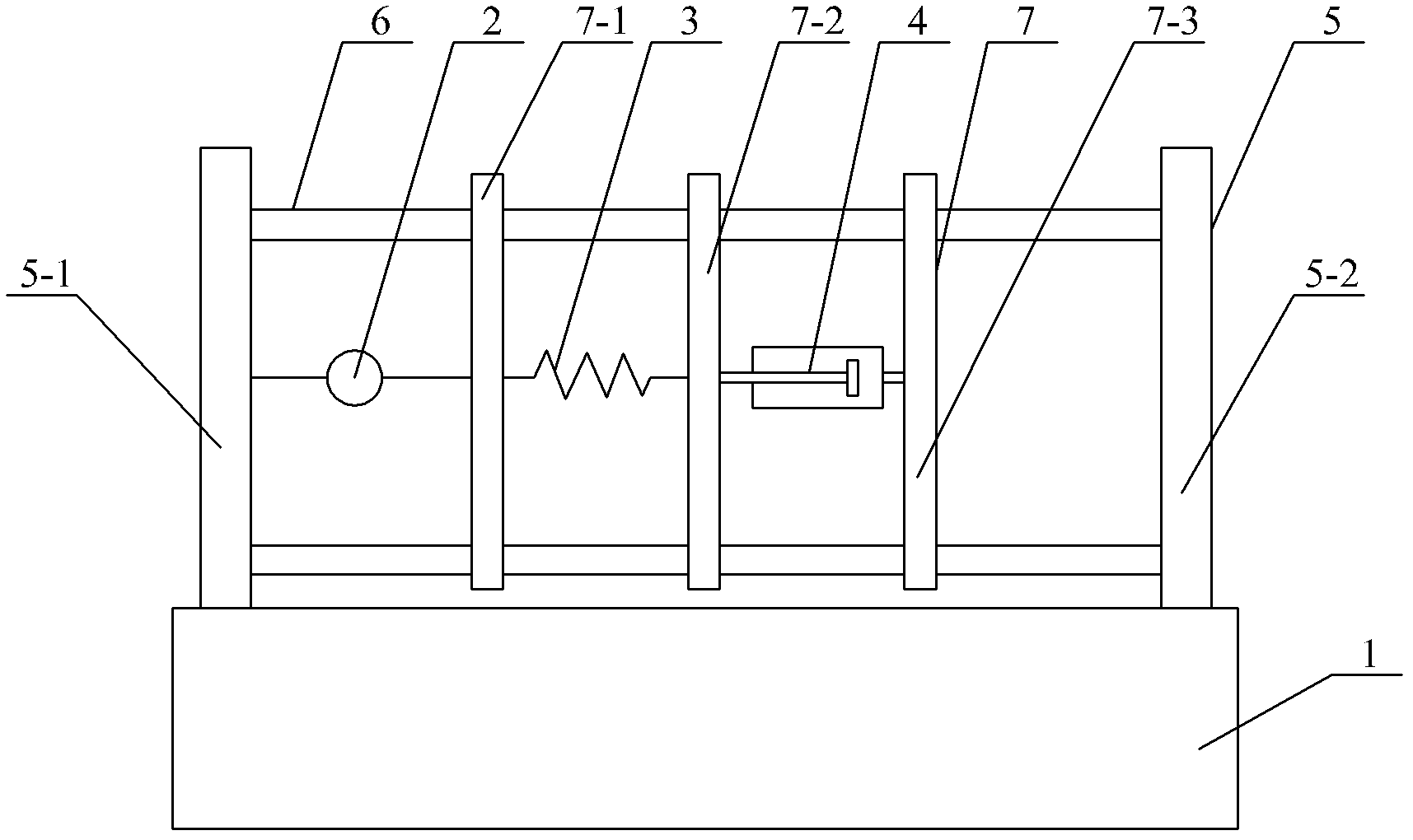
The invention relates to a measurement device of a polymer viscoelastic model and a measurement method of model element parameters, which relate to a measurement device of a viscoelastic model and a measurement method of model element parameters. The measurement device of the polymer viscoelastic model and the measurement method of the model element parameter are established to solve the problemsof a classic viscoelastic model that: the classic viscoelastic model is only an abstract model on paper and can not be a practical mechanical model. In the device of scheme 1: springs are connected with dashpots in series. In the device of scheme 2: springs are connected with dashpots in parallel. In the device of scheme 3: one of the two springs is connected with one of the two dashpots in series to form a Maxwell model, the other spring is connected with the other dashpot in parallel to form a Kelvin model and then the Kelvin model is connected with the Maxwell model in series. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining stress relaxation curves by the measurement device of the Maxwell model; obtaining creep curves by the measurement device of the Kelvin model; applying a constant stress sigma 0 on the measurement devices of four element mechanical models to obtain creep curves. The method can be used for establishing the practical polymer viscoelastic mechanical model.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Natural vacuum leak detection device with magnetic damping
InactiveUS20070256671A1Avoid communicationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelResonanceMagnetic damping
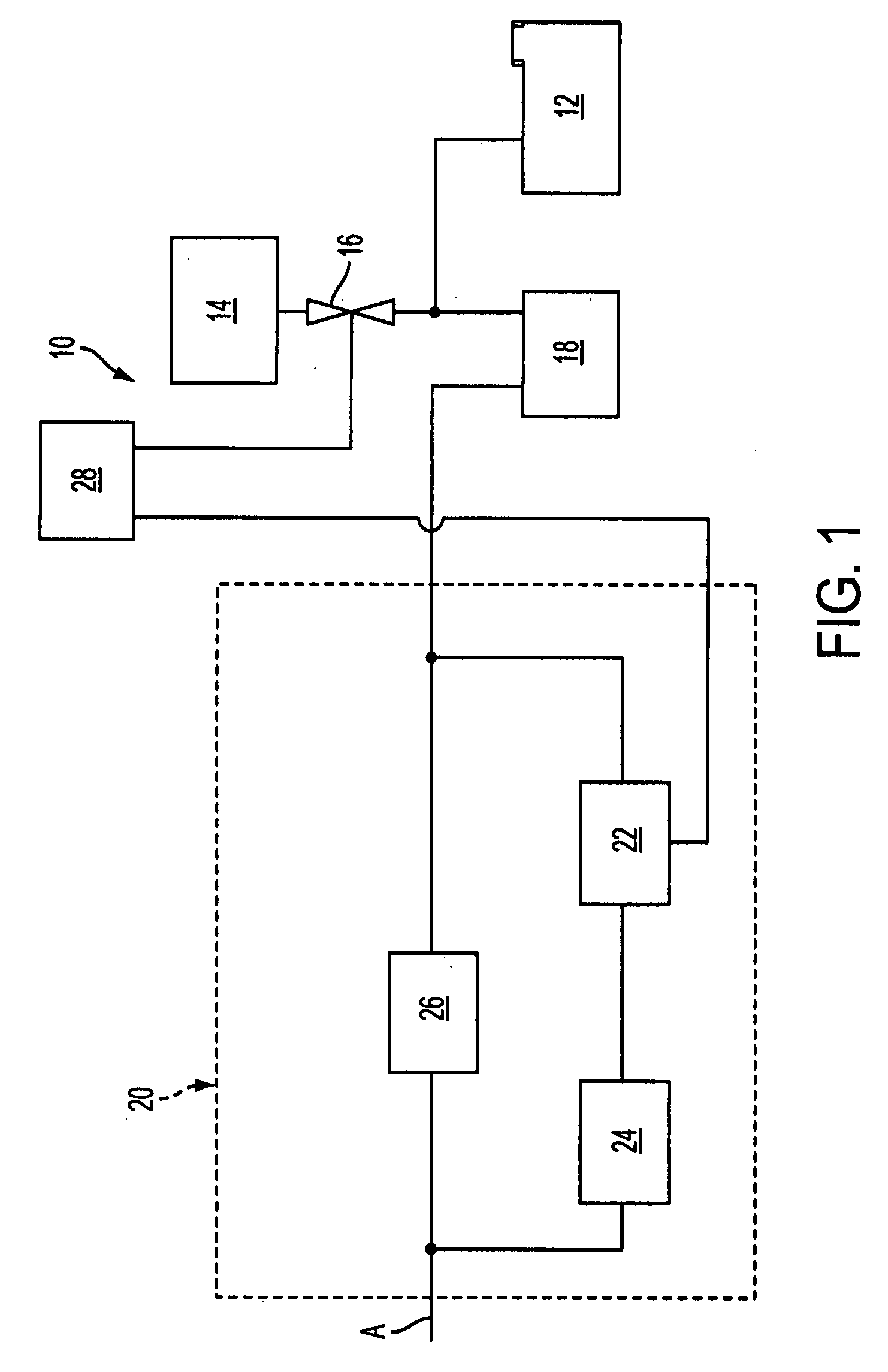
A pressure management apparatus (10) includes a housing (30) defining a fluid communication passage between first and second fluid ports (46, 48). A poppet (40) is disposed in the housing and is movable between first and second positions. The first position prevents fluid communication between the first and second ports and the second position permits fluid communication between the first and second ports. The poppet includes a structure (75) translatable along an axis relative to the housing. At least a portion of the structure includes a permanent magnet (72). A member (78) is fixed with respect to the housing and is associated with the structure. At least a portion of the member is of ferrous material such that the magnet is attracted to the member so that at least a portion of the poppet frictionally engages the member to create a dashpot damping of resonance of the poppet in the second position.
Owner:SIEMENS CANADA LTD
Pilger die and pilger mandrel for manufacturing dashpot tube for nuclear fuel assembly, method of manufacturing the pilger die and the pilger mandrel, and dashpot tube for nuclear fuel assembly
ActiveUS20120079864A1Improve efficiencyLow production costNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureDashpotZirconium alloy
A pilger die and a pilger mandrel which are used to produce a dashpot tube which can be used in a nuclear fuel assembly having an outer diameter of 31.75 mm or less and an inner diameter 25.654 mm or less, by processing a reduced expression zirconium alloy tube in two pilgering processes (a first step pass and a second step pass) using a single pilgering apparatus. Furthermore, provided are methods of manufacturing the pilger die and the pilger mandrel, and the dashpot tube for the nuclear fuel assembly. The dashpot tube can be manufactured by the single pilgering apparatus provided with the pilger die and the pilger mandrel.
Owner:KEPCO NUCLEAR FUEL CO LTD
Device for holding wafer shaped articles
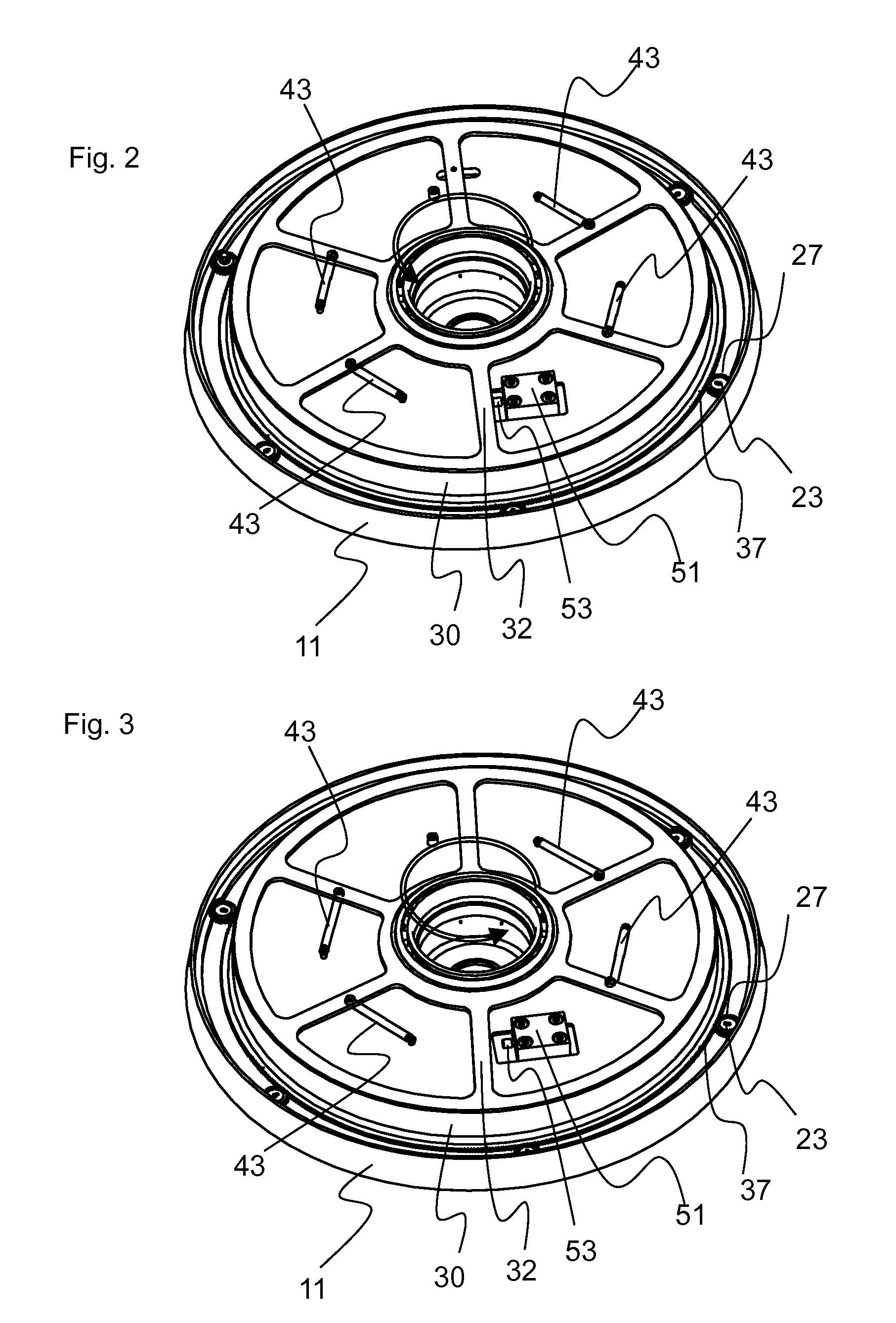
ActiveUS20110272874A1Working lifetimes be significantly shortenedImpairing desired controlled wafer shiftSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVicesDashpotControl arm
A spin chuck for holding semiconductor wafers includes one or more damping mechanisms to limit the force with which chuck pins impact the wafer edge following wafer shift. The damping mechanism may be a linear or rotary dashpot. The dashpot or dashpots are mounted on a surface of the chuck body and include a control arm that contacts a common gear ring that in turn drives the chuck pins during radially inward and outward movement.
Owner:LAM RES AG
Torsional vibration dampers
InactiveUS20170234419A1Reduce the total massIncreases reaction torqueTorsion springsPortable liftingElastomerDashpot
Torsional vibration dampers having a dual spring-dashpot system are disclosed that result in a lightweight hub and a lightweight inertia ring, which is concentric about the hub. The hub has a two-piece construction: a central hub defining an innermost sleeve that defines a bore for receiving a shaft; and a monolithic, generally-annular spoke defining an outermost ring concentric about and spaced radially outward from the central hub portion. A first elastomer member, which acts as a primary spring to damp torsional vibrations, is positioned concentrically against an inner surface or an outer surface of the outermost ring of the hub with the inertia ring concentrically positioned against the first elastomer member. A second elastomer member is positioned between and operatively couples the central hub to the annular spoke, thereby attributing a flexibility to the hub.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG
Tube-in-tube threaded dashpot end plug
A nuclear fuel assembly having a tube-in-tube control rod guide tube design that incorporates an end plug that extends axially upward to an elevation above the lower most grid where it is sealed at its tipper end to the lower end of the control rod guide tube. The guide tube lower end plug has a threaded recess in its upper surface that mates with a corresponding dashpot end plug threaded extension that is formed as an insert in the lower end of the guide tube. A hole formed through the outer wall of the guide tube end plug at the elevation of the lower portion of the recess provides a positive inspection port for assuring the proper seating of the dashpot. A method of manufacture of such a fuel assembly is also disclosed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Multifunction socket
The present invention discloses a multifunction socket and a socket box body. The socket box body comprises an outer frame, a flip cover, a bottom shell and sockets. The flip cover is a double-door structure, the flip cover is connected on the outer frame via a flipping structure, the outer frame is fixed on the bottom shell to form a box body, and a plurality of sockets are fixed in the box body. The flipping structure mainly comprises successively connected rotating shafts, torsion springs, hooks, a damper, the rotating shafts and a hook needle, and the flipping structure can realize back-and-forth movement and automatic fixation of the flip cover. According to the multifunction socket, the flipping structure can realize back-and-forth movement and automatic fixation of the flip cover; according to the structure, the occupied utilization area because of the size of the socket is greatly reduced; and meanwhile, the structure can effectively prevent the sockets and other modules from being exposed to the outside, and the structure can effectively prevent the sockets and other modules from contacting dust by closing "double doors" when the socket is not used.
Owner:美力达电子(昆山)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com