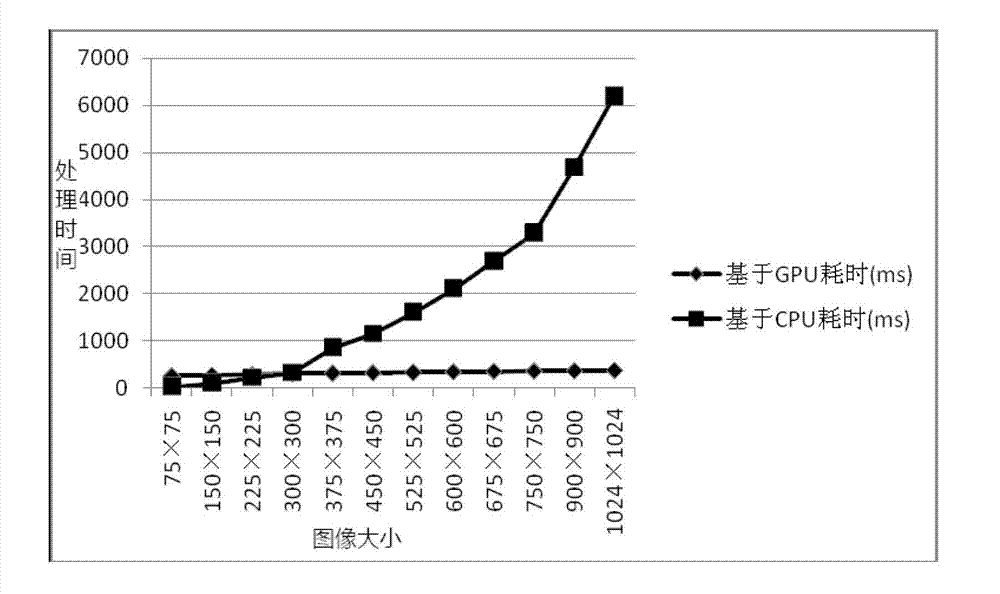
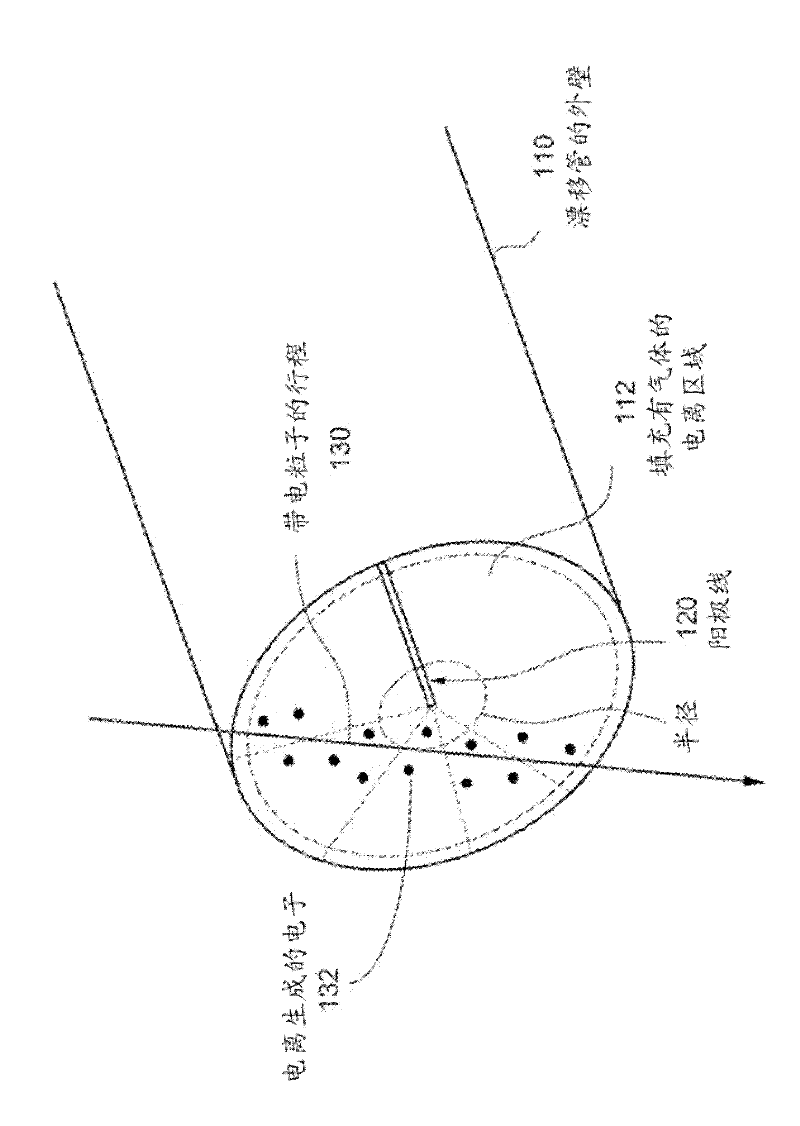
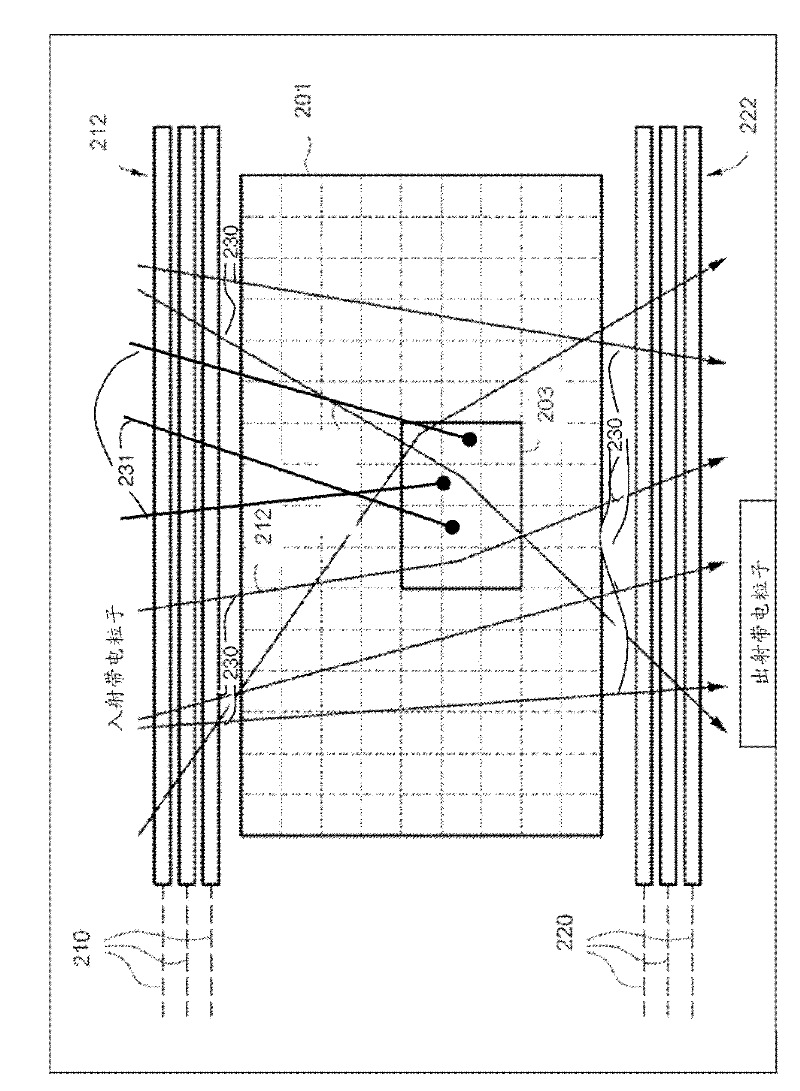
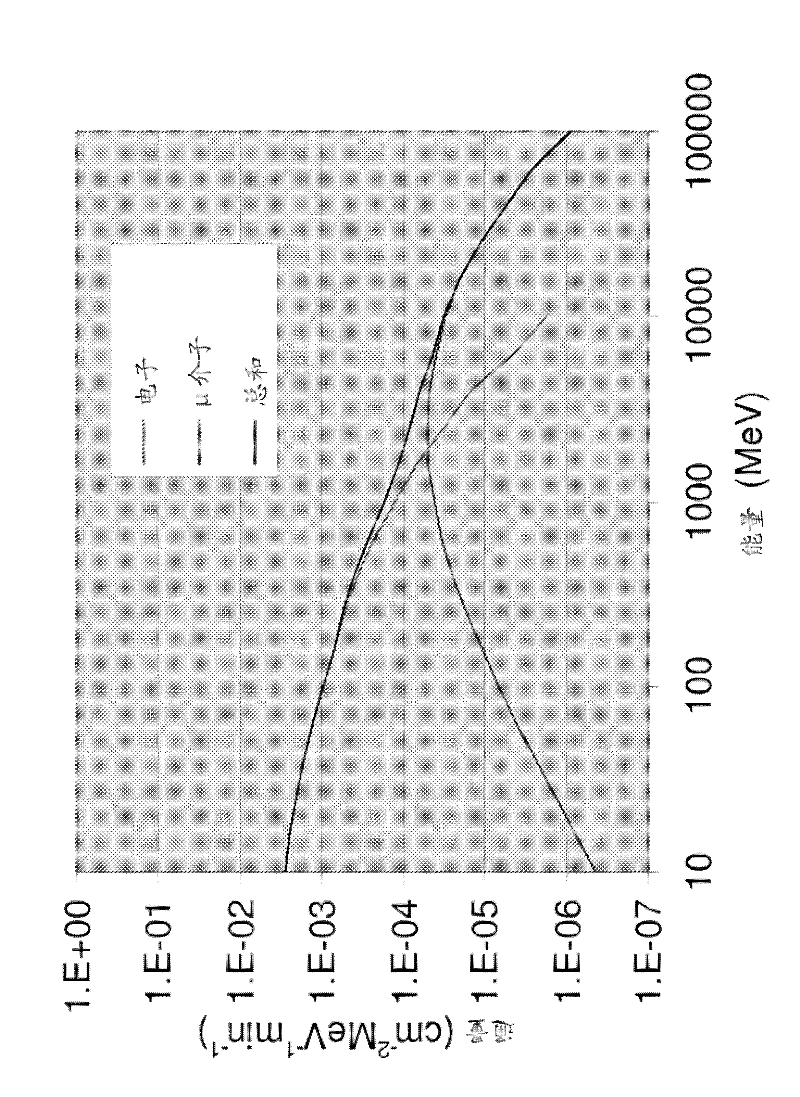
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143 results about "Cosmic ray" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cosmic rays are high-energy protons and atomic nuclei which move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the sun, from outside of the solar system, or even from distant galaxies. Upon impact with the Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays can produce showers of secondary particles that sometimes reach the surface. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidence that a significant fraction of primary cosmic rays originate from the supernova explosions of stars. Active galactic nuclei also appear to produce cosmic rays, based on observations of neutrinos and gamma rays from blazar TXS 0506+056 in 2018.
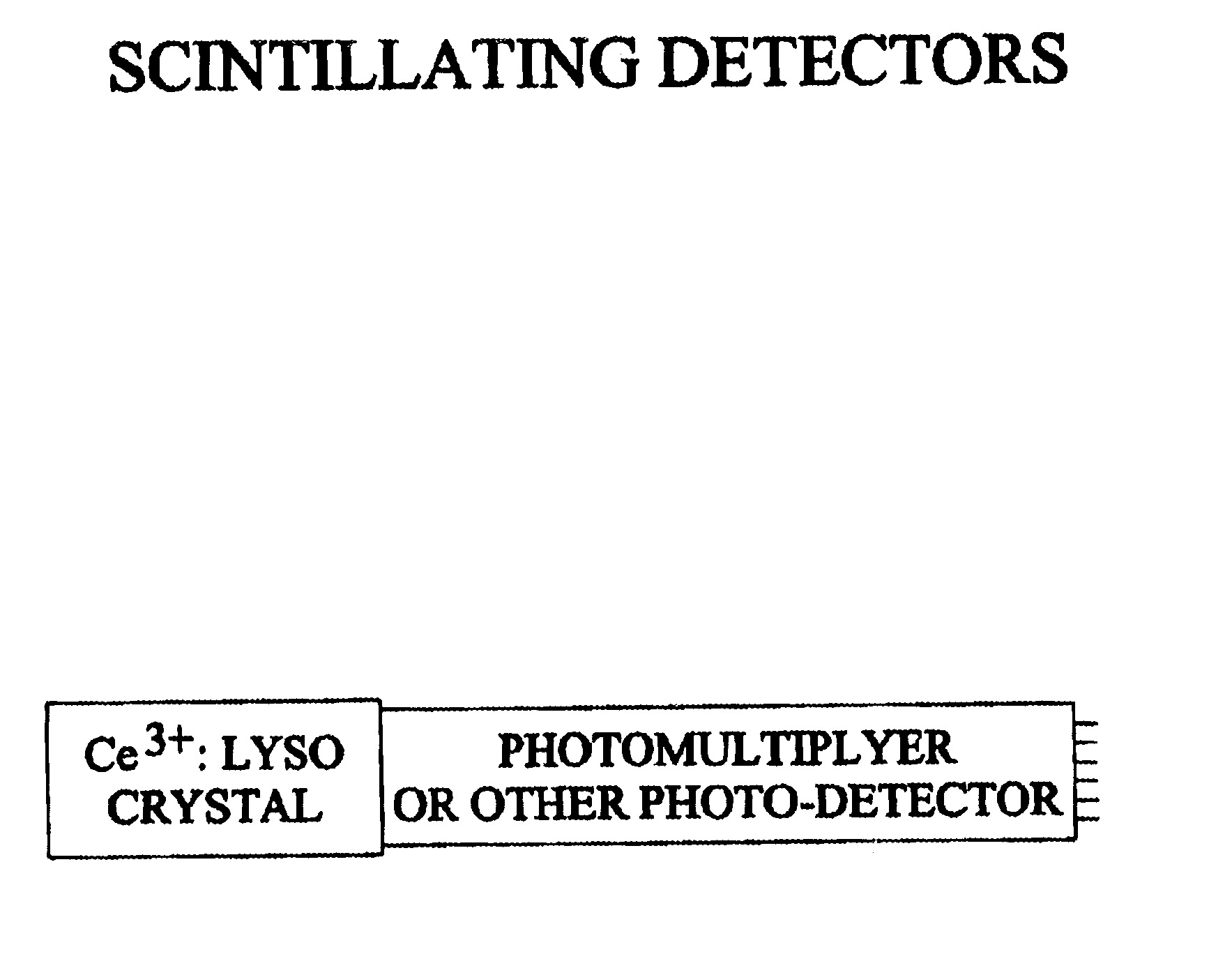
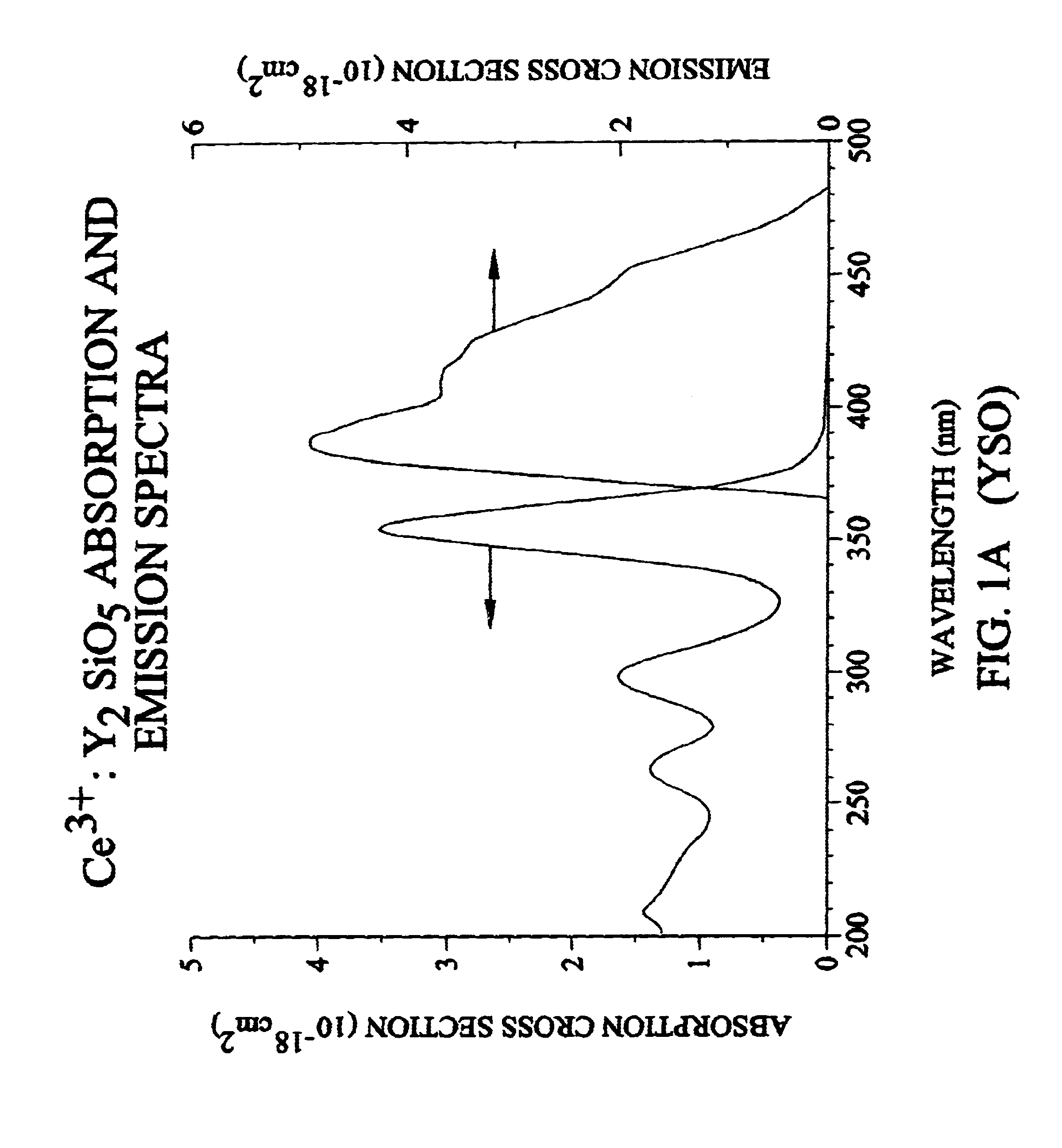
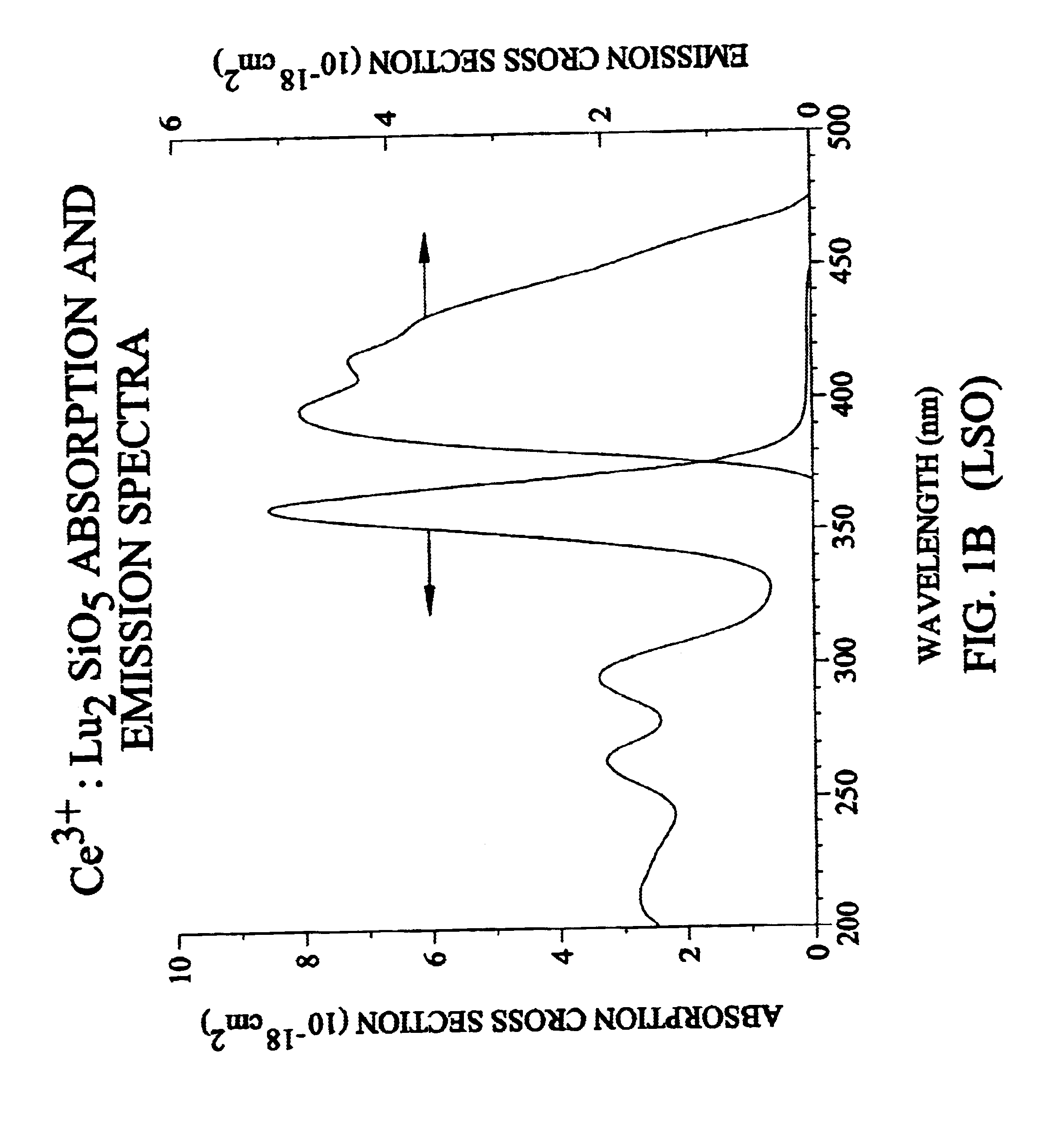
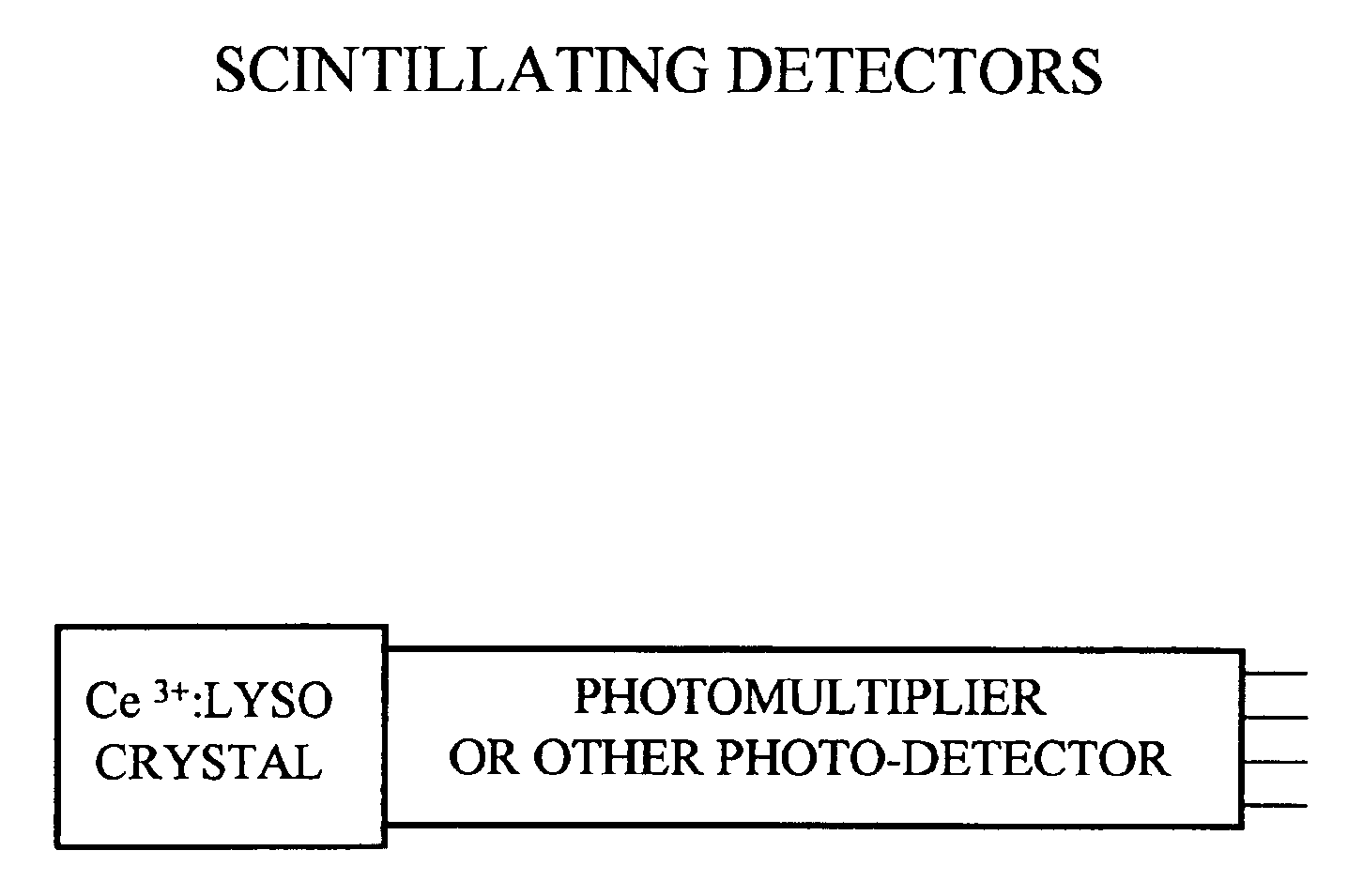
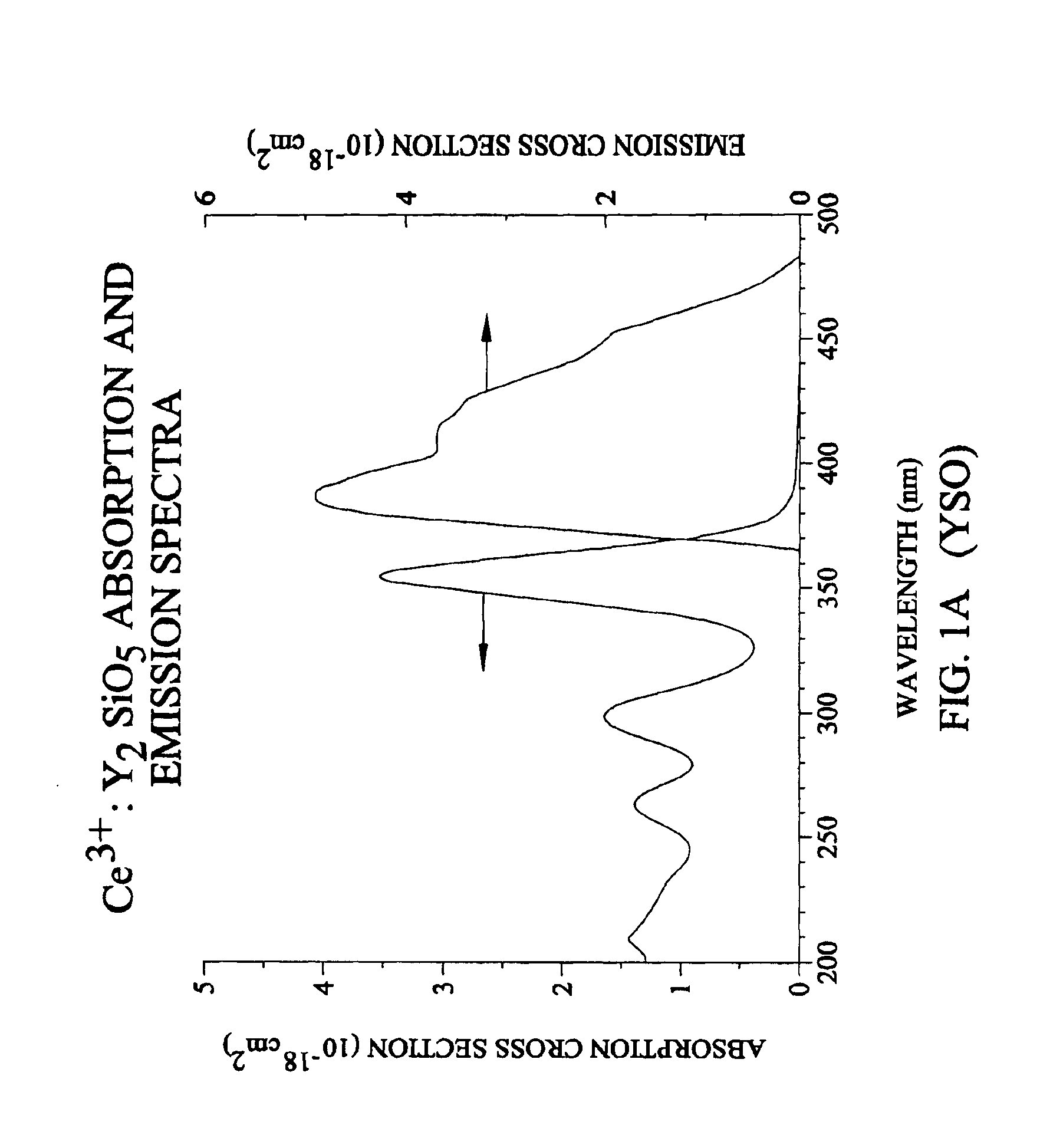
Lutetium yttrium orthosilicate single crystal scintillator detector
InactiveUS6624420B1Improve performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent compositionsLutetiumHigh energy
A single crystal having the general composition, Ce2x(Lu1-yYy)2(1-x)SiO5 where x=approximately 0.00001 to approximately 0.05 and y=approximately 0.0001 to approximately 0.9999; preferably where x ranges from approximately 0.0001 to approximately 0.001 and y ranges from approximately 0.3 to approximately 0.8. The crystal is useful as a scintillation detector responsive to gamma ray or similar high energy radiation. The crystal as scintillation detector has wide application for the use in the fields of physics, chemistry, medicine, geology and cosmology because of its enhanced scintillation response to gamma rays, x-rays, cosmic rays and similar high energy particle radiation.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA +2
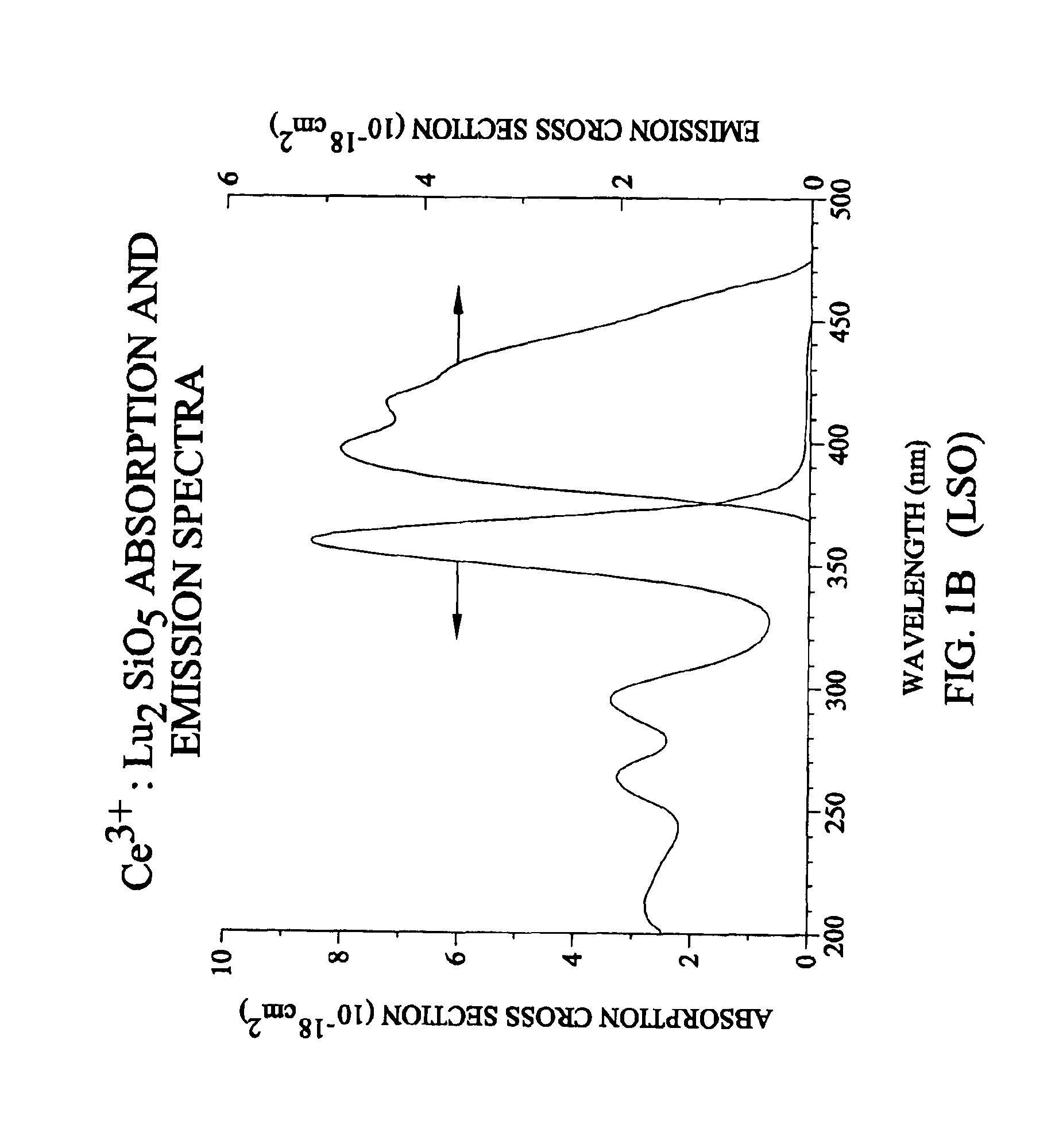
Lutetium yttrium orthosilicate single crystal scintillator detector
InactiveUS6921901B1Improve performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent compositionsLutetiumHigh energy
A single crystal having the general composition, Ce2x(Lu1-yYy)2(1-x)SiO5 where x=approximately 0.00001 to approximately 0.05 and y=approximately 0.0001 to approximately 0.9999; preferably where x ranges from approximately 0.0001 to approximately 0.001 and y ranges from approximately 0.3 to approximately 0.8. The crystal is useful as a scintillation detector responsive to gamma ray or similar high energy radiation. The crystal as scintillation detector has wide application for the use in the fields of physics, chemistry, medicine, geology and cosmology because of its enhanced scintillation response to gamma rays, x-rays, cosmic rays and similar high energy particle radiation.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
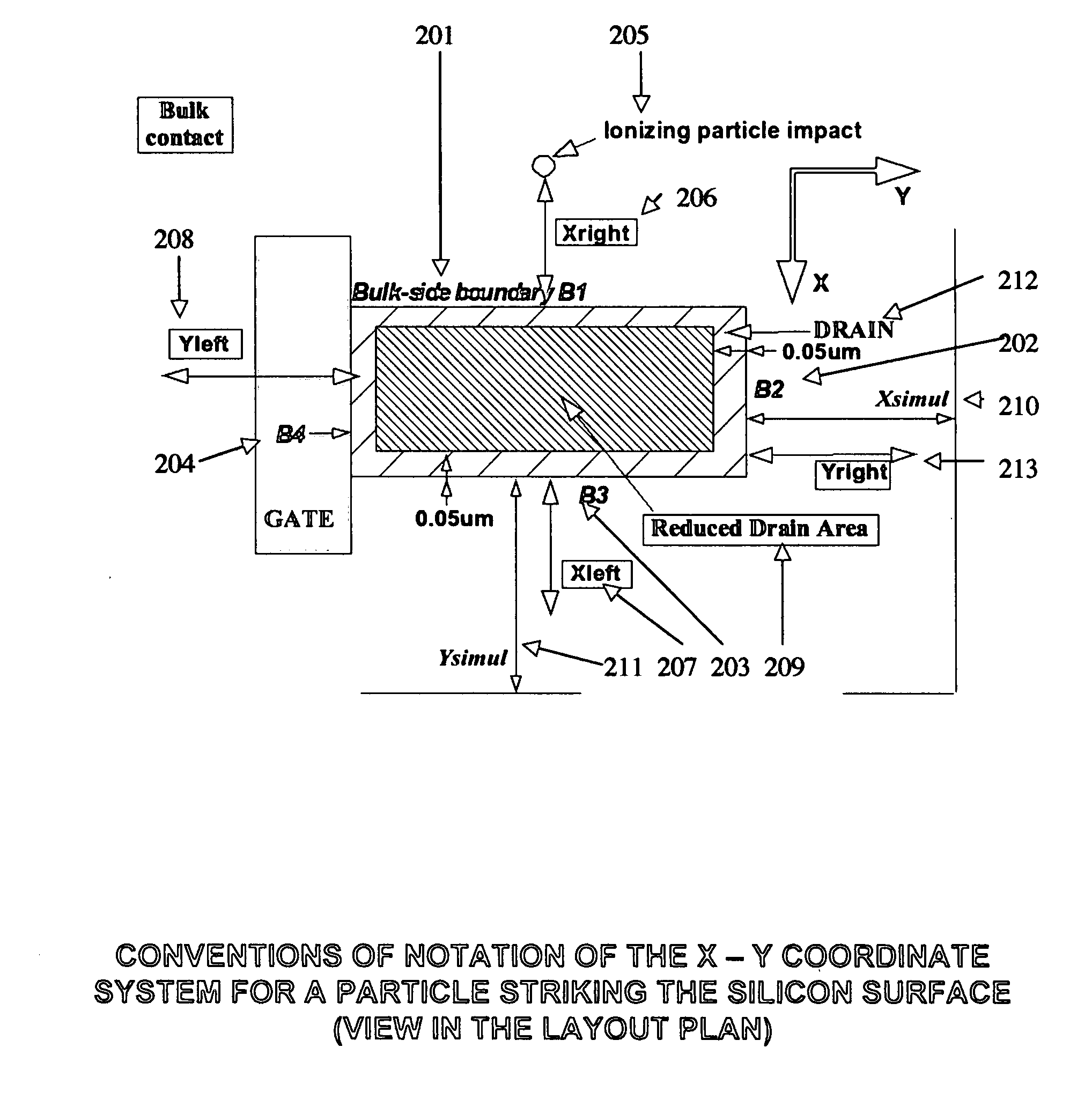
Apparatus and method for the determination of SEU and SET disruptions in a circuit caused by ionizing particle strikes
InactiveUS20080077376A1Accurate and fast simulation methodHigh speedAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationElectricityAlpha particle
This application discloses a new, and useful computer implemented method and apparatus that can be used for the determination of SEU and SET disruptions in a cell or circuit, caused by ionizing particle strikes, including those caused by neutrons (cosmic rays), alpha particles or heavy ions. The method of the present invention includes a fast simulation tool (“TFIT”), which calculates the electrical effect of a particle's impact to a cell, or a circuit. The method is used to predict the soft error rate (SER) calculations and the FIT (number of failures-in-time) performance of designated test cell's design, depending on the type of particle environment specified. The method is designed to simulate the response of the cell or circuit to the stimuli caused by a particle strike. These stimuli are modeled as a “current source” placed between the drain and the source of each struck transistor.
Owner:IROC TECH
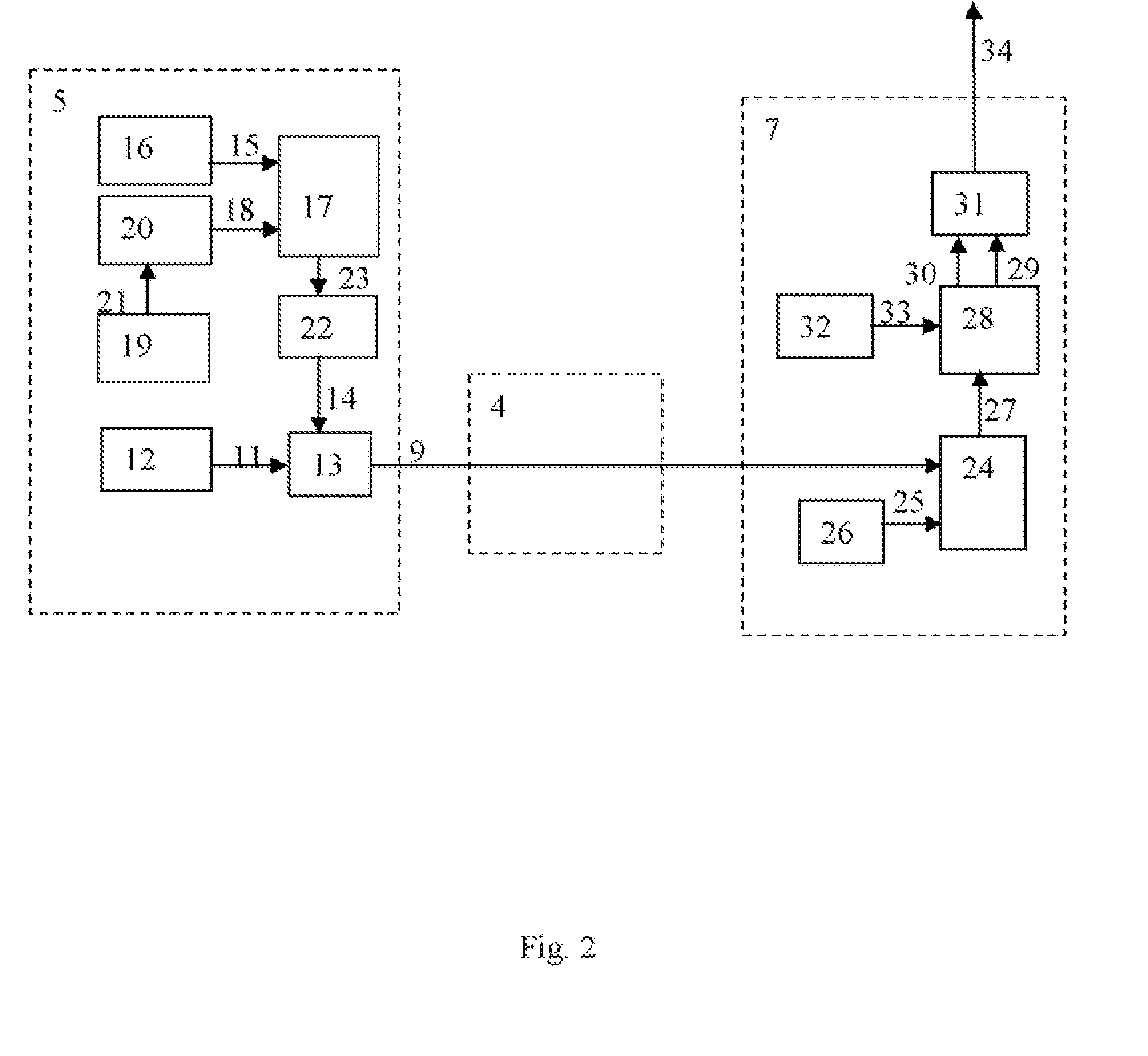
Imaging based on cosmic-ray produced charged particles
ActiveUS8536527B2Improve fidelityImprove resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyComputational physics
Techniques, apparatus and systems for obtaining tomographic images of a volume of interest by using charged particle tomography detection systems.
Owner:DECISION SCI INT CORP +1
Coherent optical transceiver and coherent communication system and method for satellite communications
InactiveUS20080025728A1Fast elimination of additive noiseSatellite communication transmissionTransmission monitoringDigital signal processingTransceiver
An optical transceiver is provided for optical communications with additive noise compensation. The system and method are disclosed for the additive noise cancellation, which is typically a vibration noise, caused by moving platform, where the transceiver is located. The transceiver comprises an additive noise sensor and a digital signal processing (DSP) unit which implements variable step size technique to adjust the filter weight in the least square estimate of the noise signal. In the preferred embodiment the digital signal processing is applied both at the transmission and the receiving side. The optical device is packed for ground-satellite and inter-satellite communications applications with resistance to high-energy X-rays, gamma rays and cosmic rays. The optical device sustains its operation characteristics under launch load.
Owner:CELIGHT
Multifunctional radiation shield for space and aerospace applications
InactiveUS20070194256A1Easy to carryLow chemical activityNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsX-raySpaceflight
Owner:SPACE MICRO A CORP OF DELAWARE
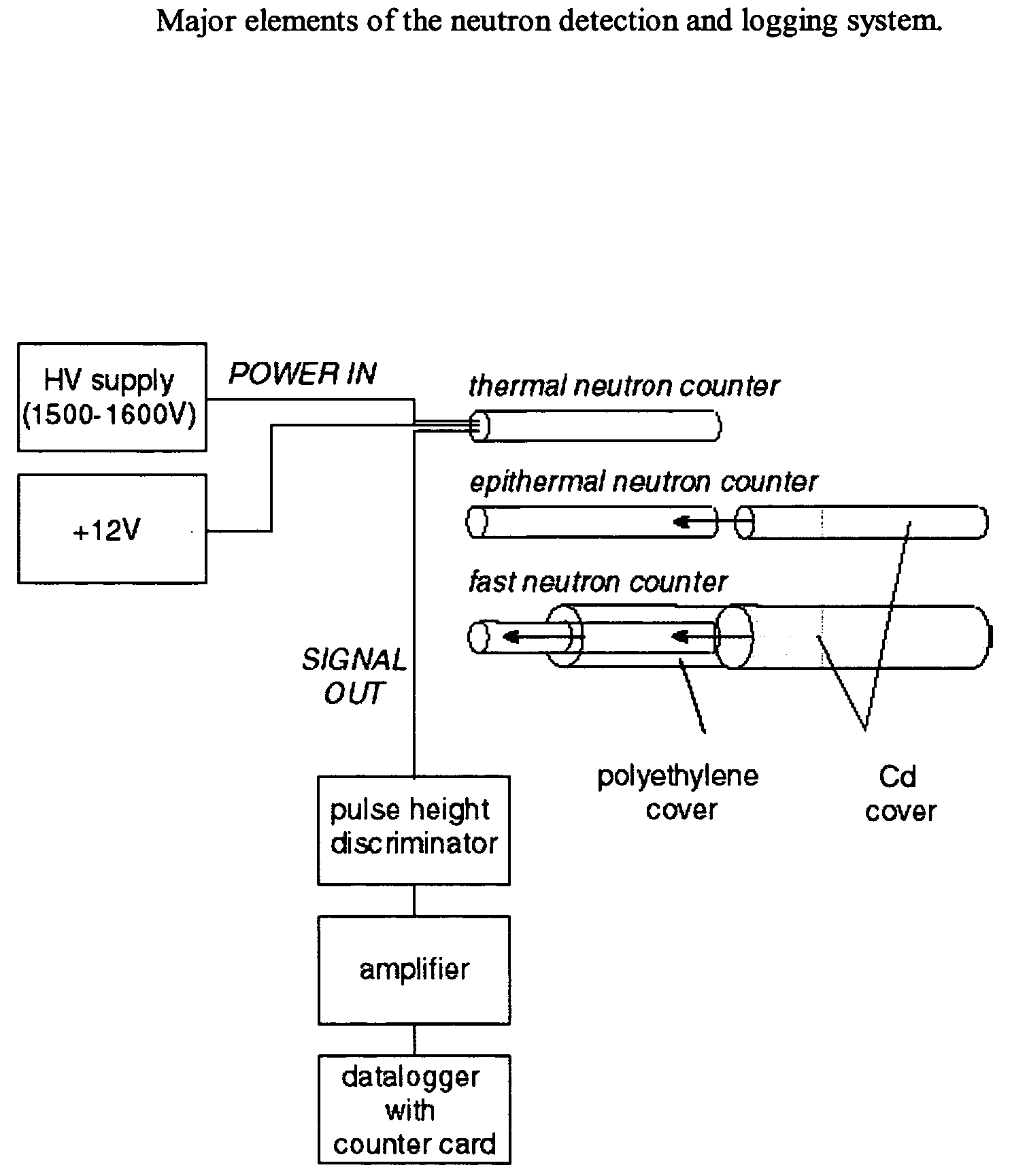
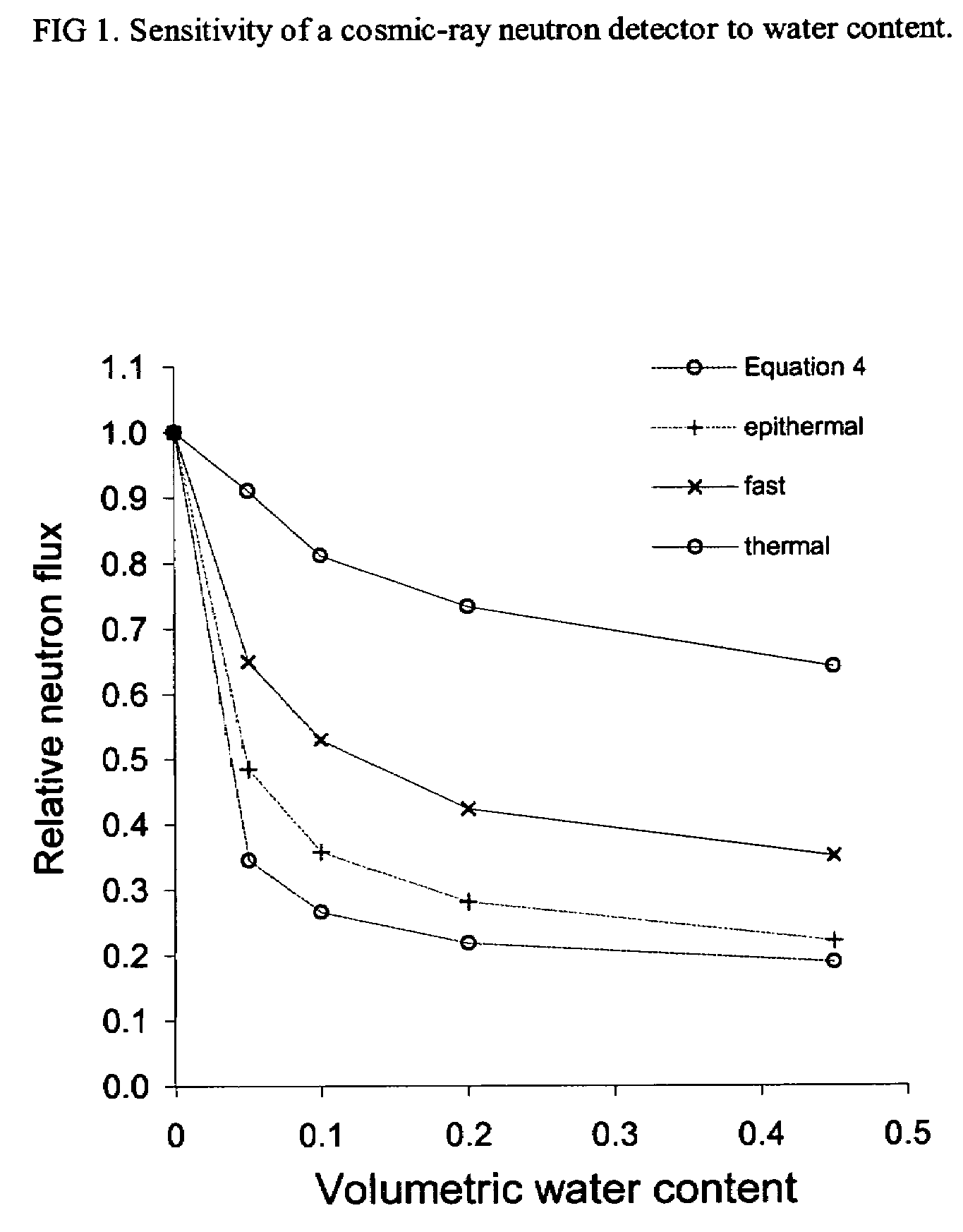
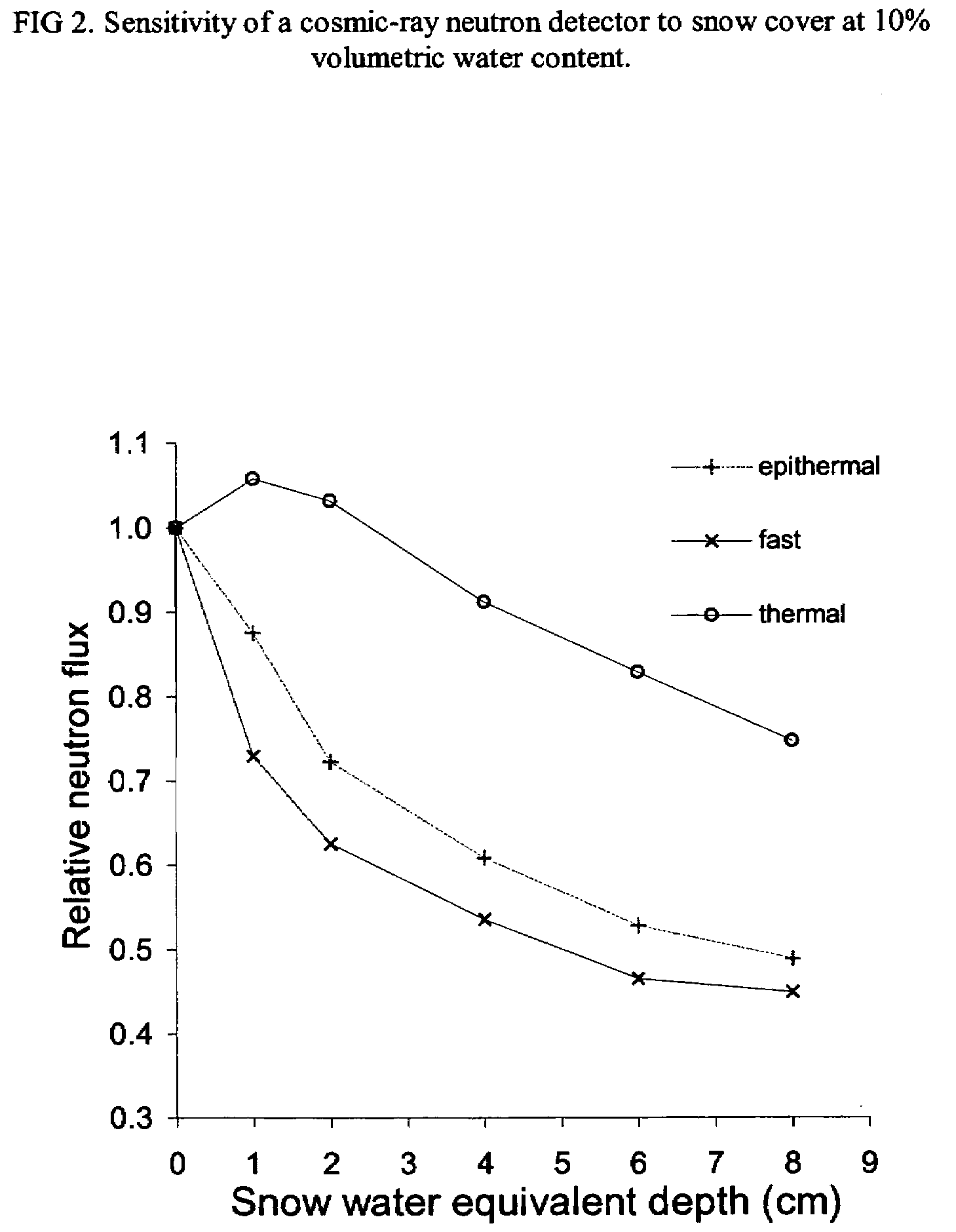
Non-invasive method for measuring soil water content or snow water equivalent depth using cosmic-ray neutrons
InactiveUS20080087837A1Weaken energySlow rate of increaseMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSnowpackThermal energy
The present invention is directed toward the determination of soil water content and the water equivalent depth of snow deposited on top of the ground. The apparatus for measuring soil water content consists of one or more cosmic-ray neutron detectors located above the soil surface. The detectors record neutrons in the thermal, epithermal or fast energy bands. Snow water equivalence is determined by using a thermal neutron detector and an epithermal or fast neutron detector. Neutron count rates for all three energy bands decrease monotonically with increasing soil water content. Epithermal and fast neutron count rates decrease monotonically with increased snow water equivalent depth, but thermal neutron count rates increase at first and then decrease with increasing snow cover.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF UNLV OF ARIZONA
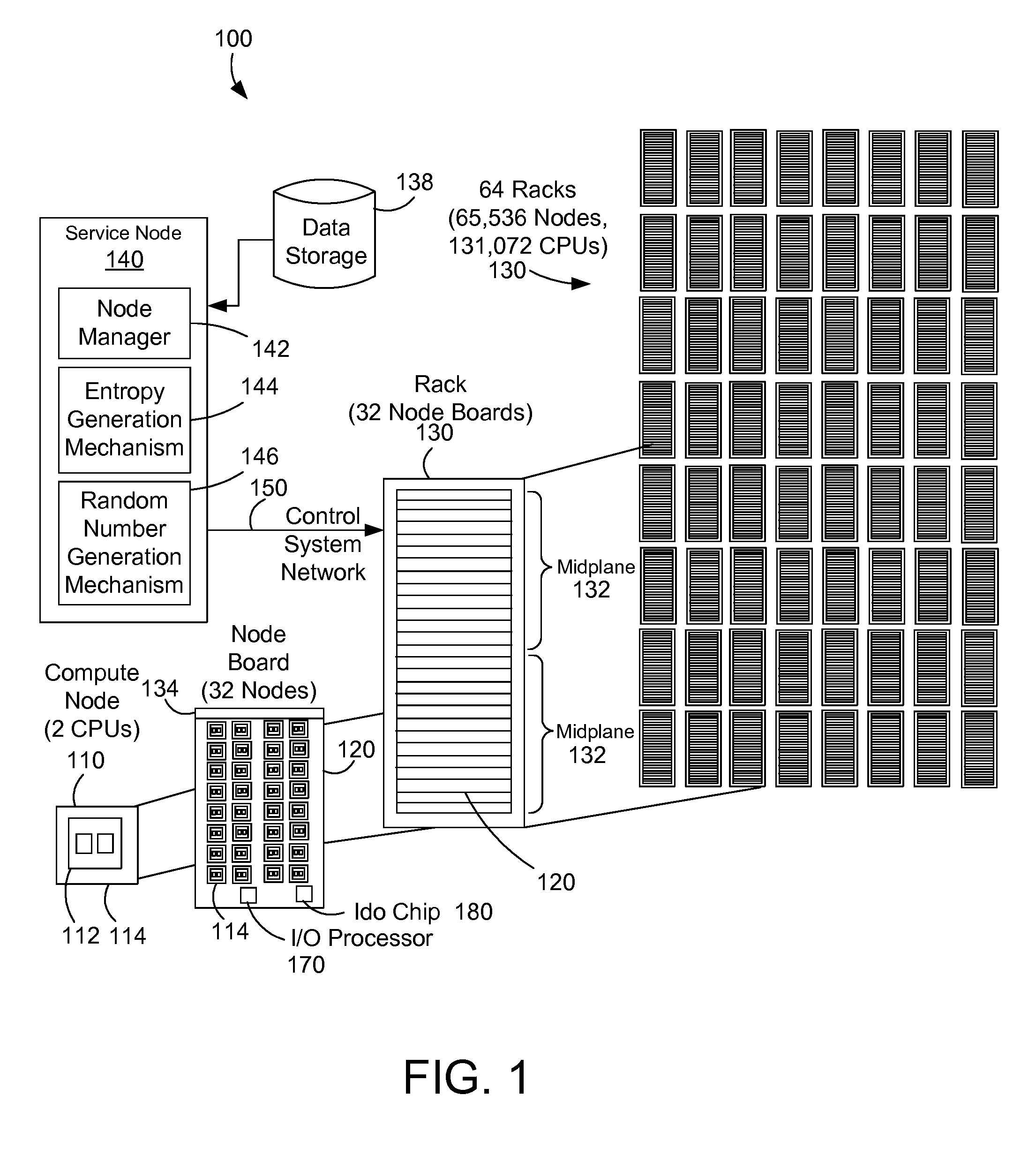
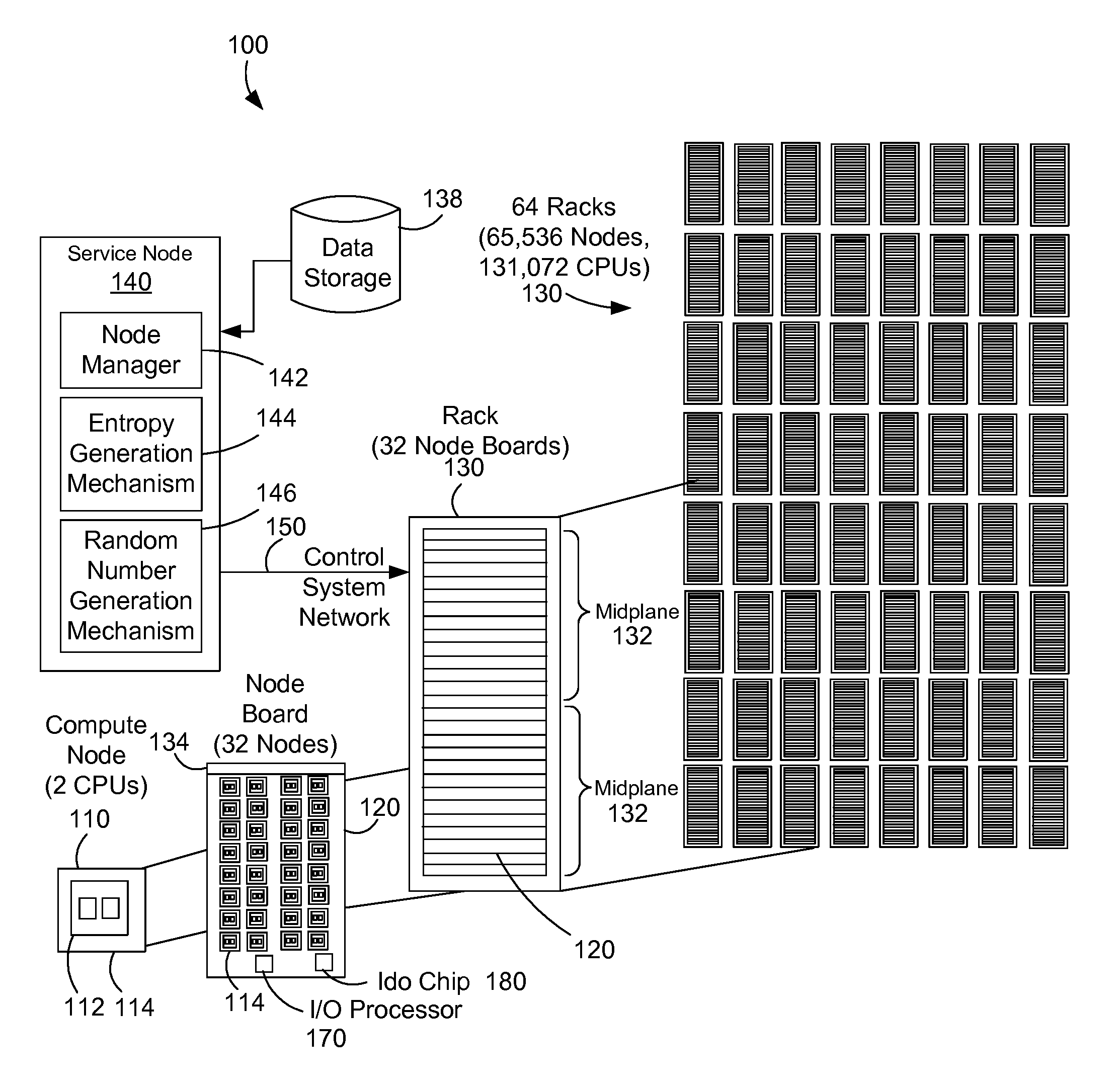
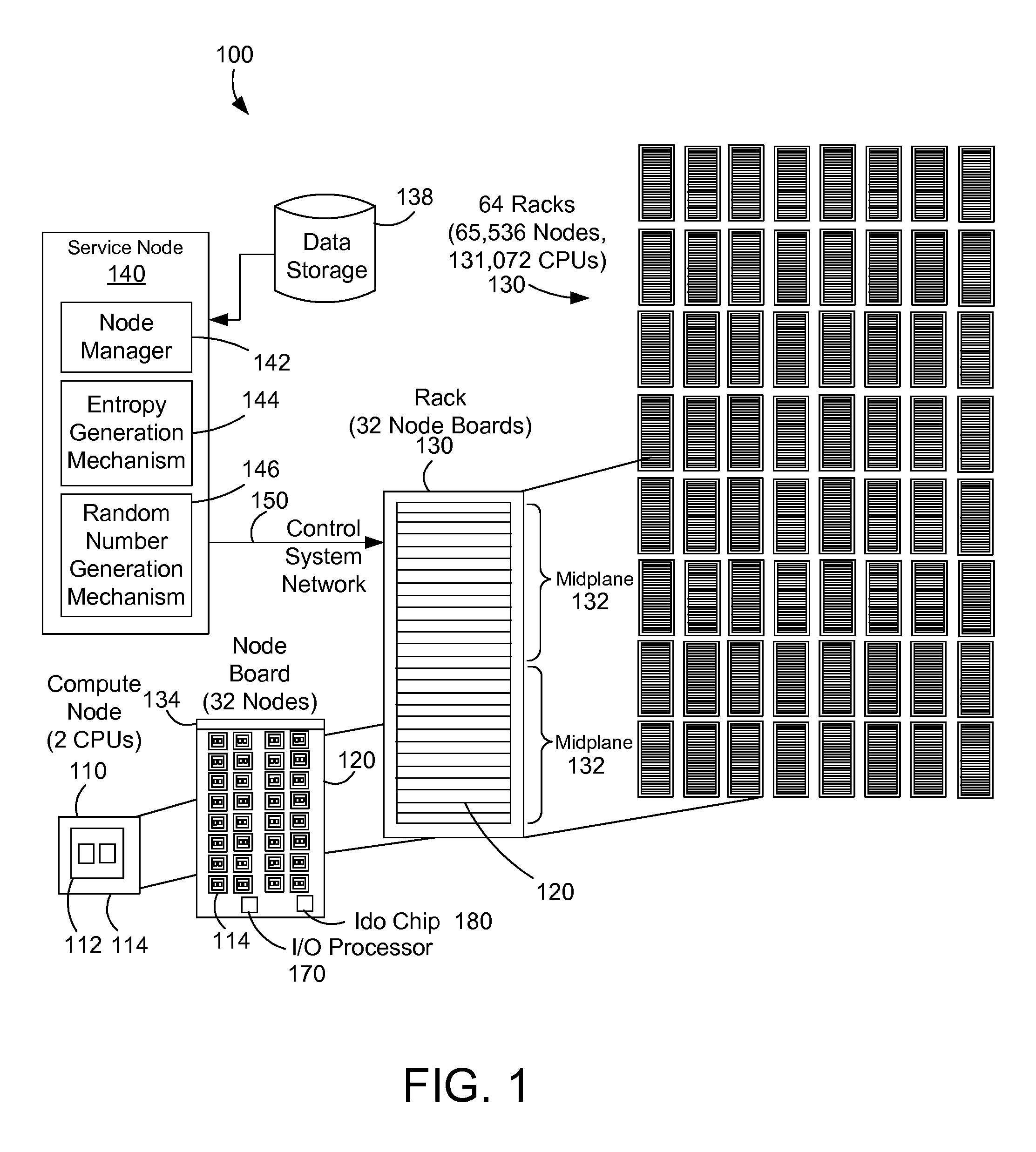
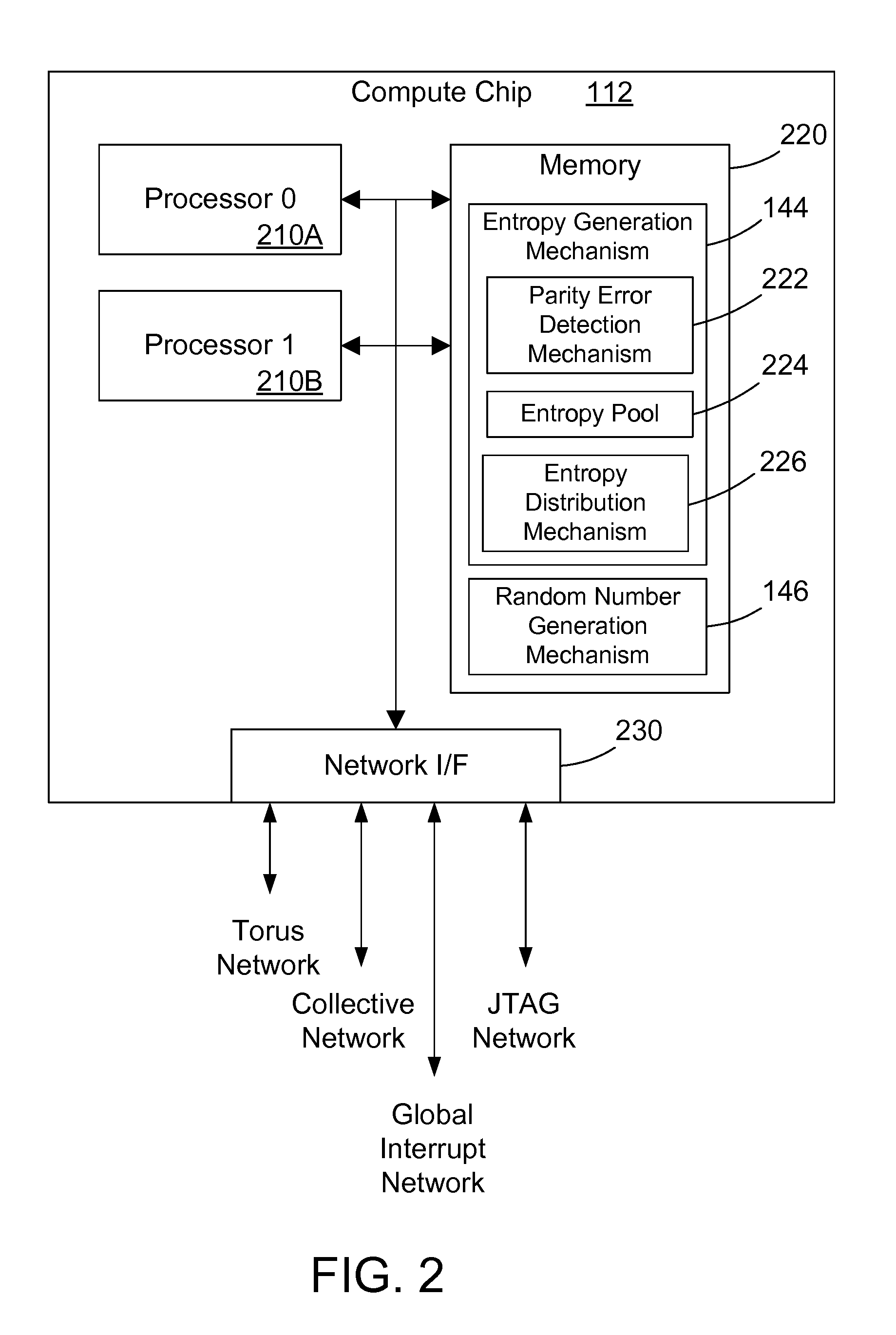
Adding entropy for improved random number generation in a computer system
InactiveUS20100306296A1Quality improvementRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsRelevant informationAlpha particle
A parallel computer system adds entropy to improve the quality of random number generation by using parity errors as a source of entropy because parity errors are influenced by external forces such as cosmic ray bombardment, alpha particle emission, and other random or near-random events. By using parity errors and associated information to generate entropy, the quality of random number generation in a parallel computer system is increased.
Owner:IBM CORP
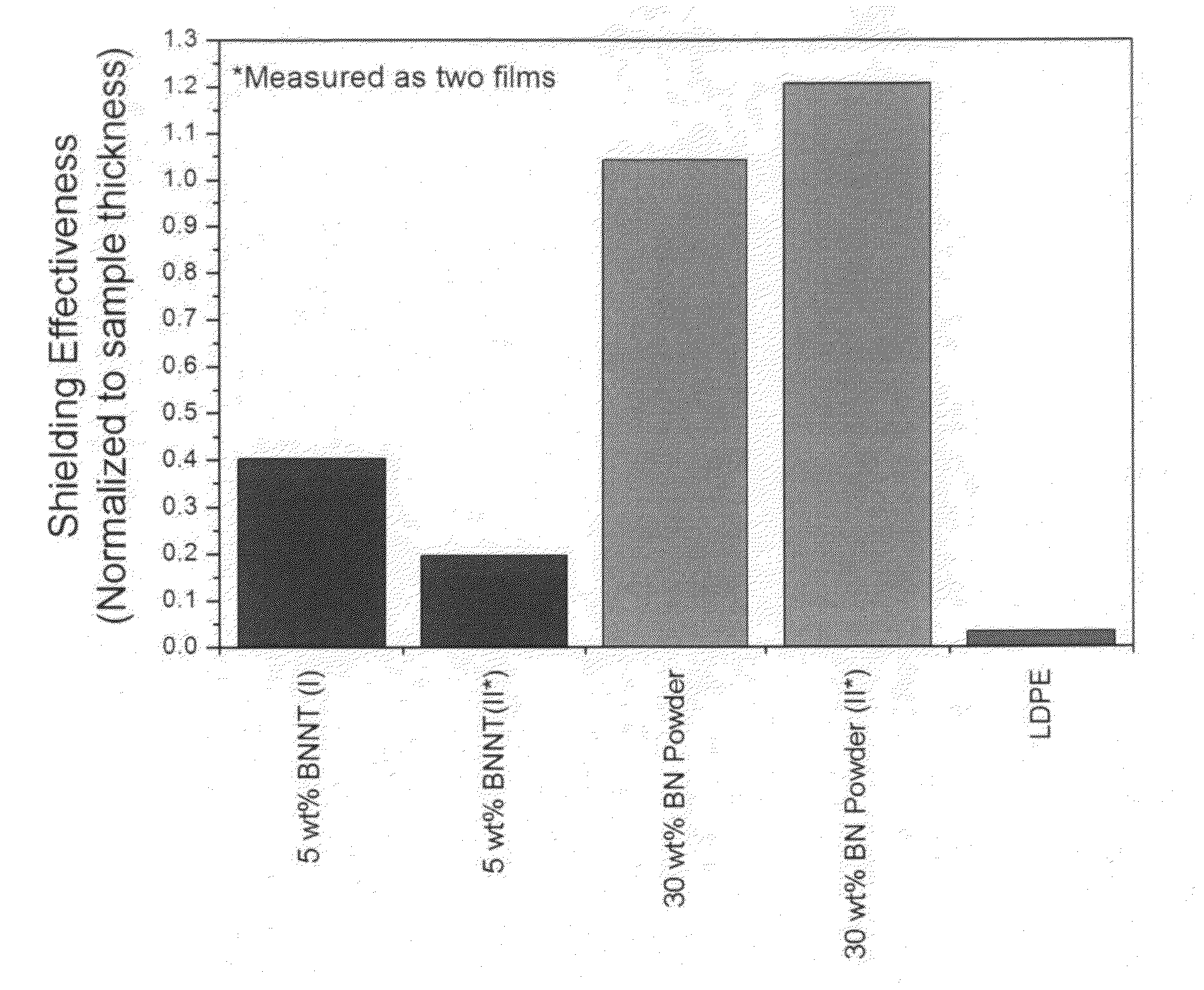
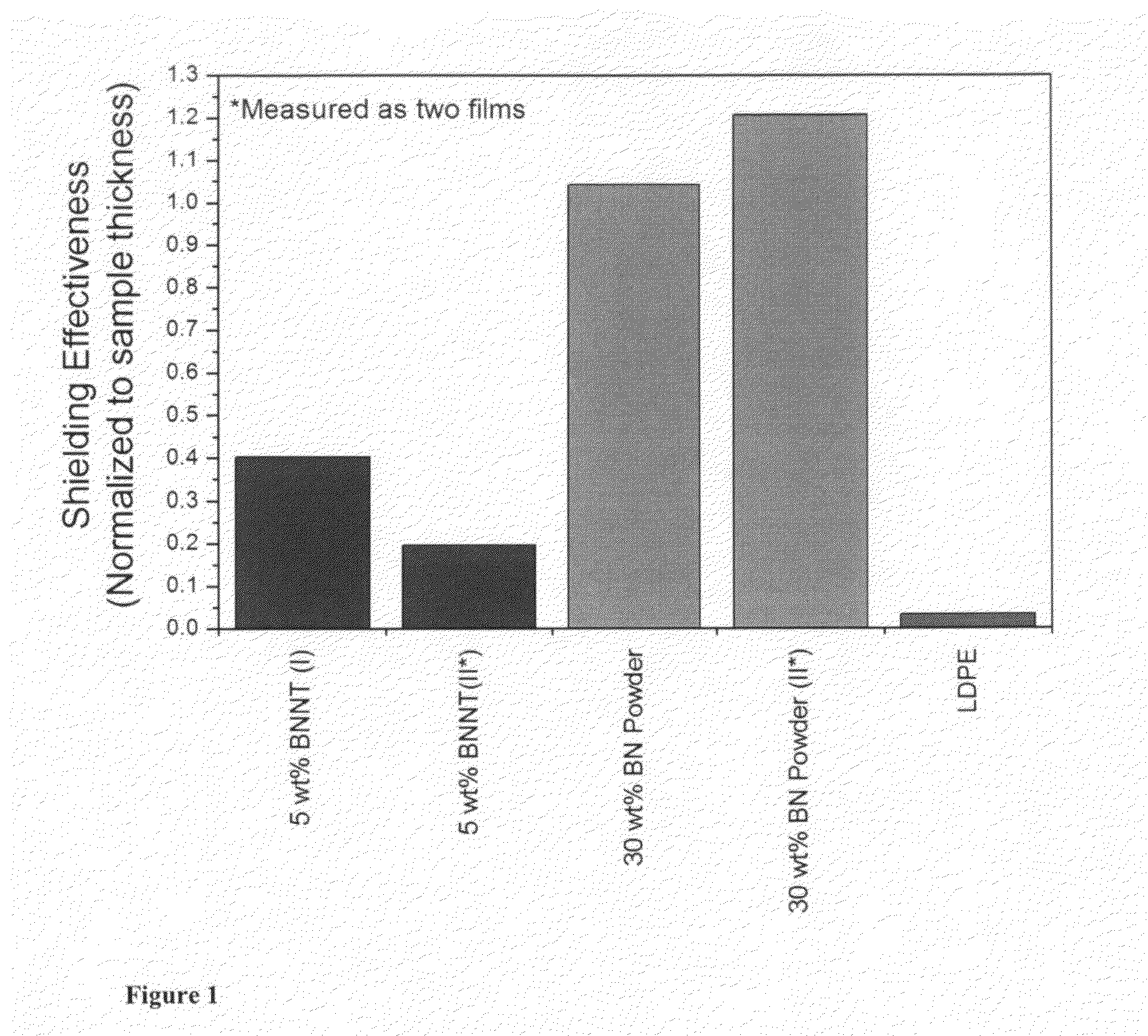
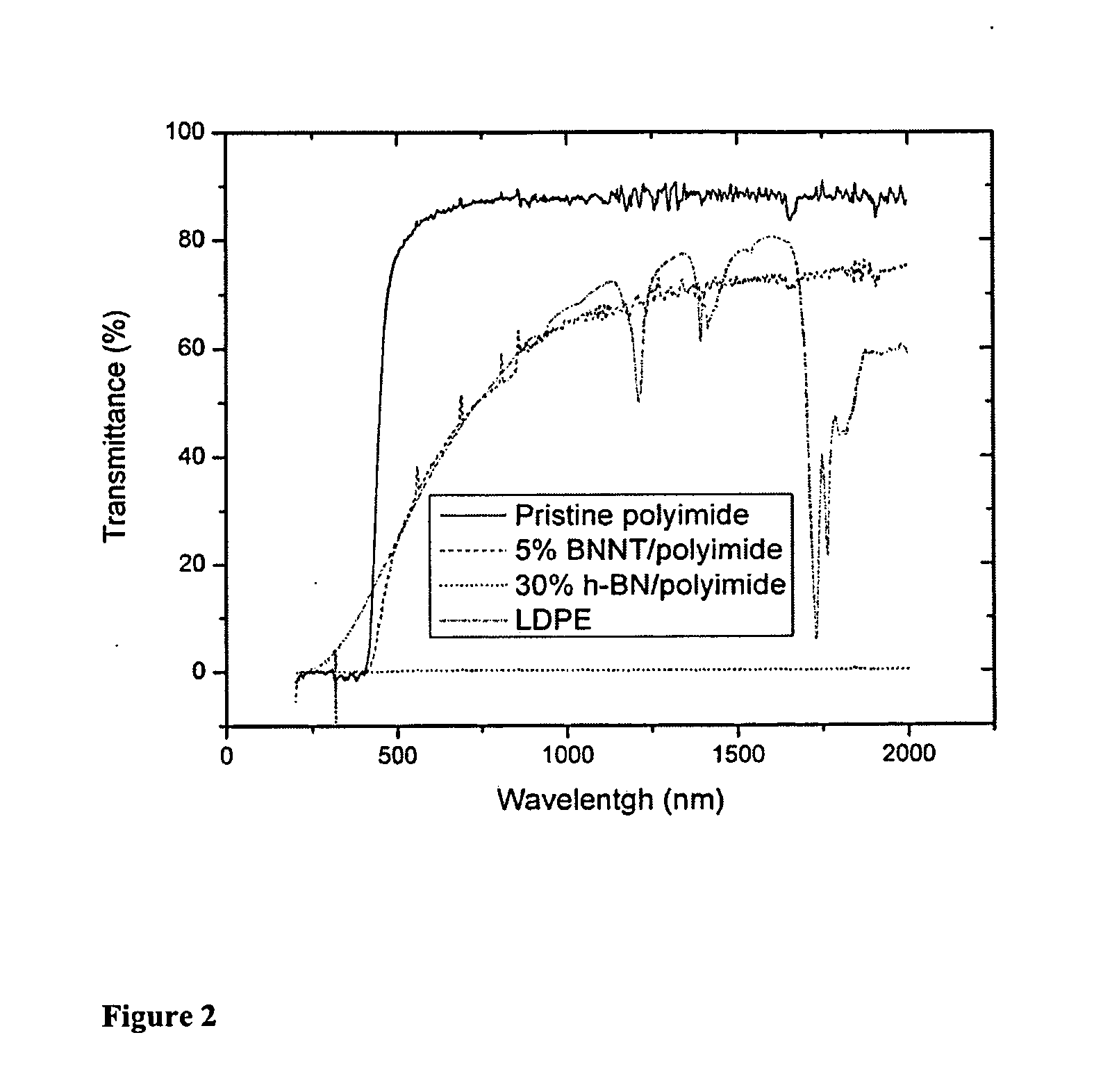
Boron nitride and boron nitride nanotube materials for radiation shielding
Effective radiation shielding is required to protect crew and equipment in various fields including aerospace, defense, medicine and power generation. Light elements and in particular hydrogen are most effective at shielding against high-energy particles including galactic cosmic rays, solar energetic particles and fast neutrons. However, pure hydrogen is highly flammable, has a low neutron absorption cross-section, and cannot be made into structural components. Nanocomposites containing the light elements Boron, Nitrogen, Carbon and Hydrogen as well dispersed boron nano-particles, boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) and boron nitride nano-platelets, in a matrix, provide effective radiation shielding materials in various functional forms. Boron and nitrogen have large neutron absorption cross-sections and wide absorption spectra. The incorporation of boron and nitrogen containing nanomaterials into hydrogen containing matrices provides composites that can effectively shield against neutrons and a wide range of radiation species of all energies without fragmentation and the generation of harmful secondary particles.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC +1
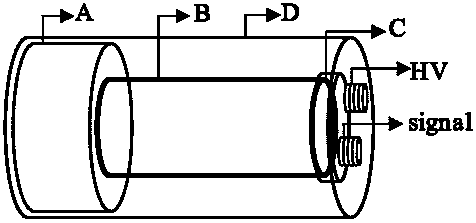
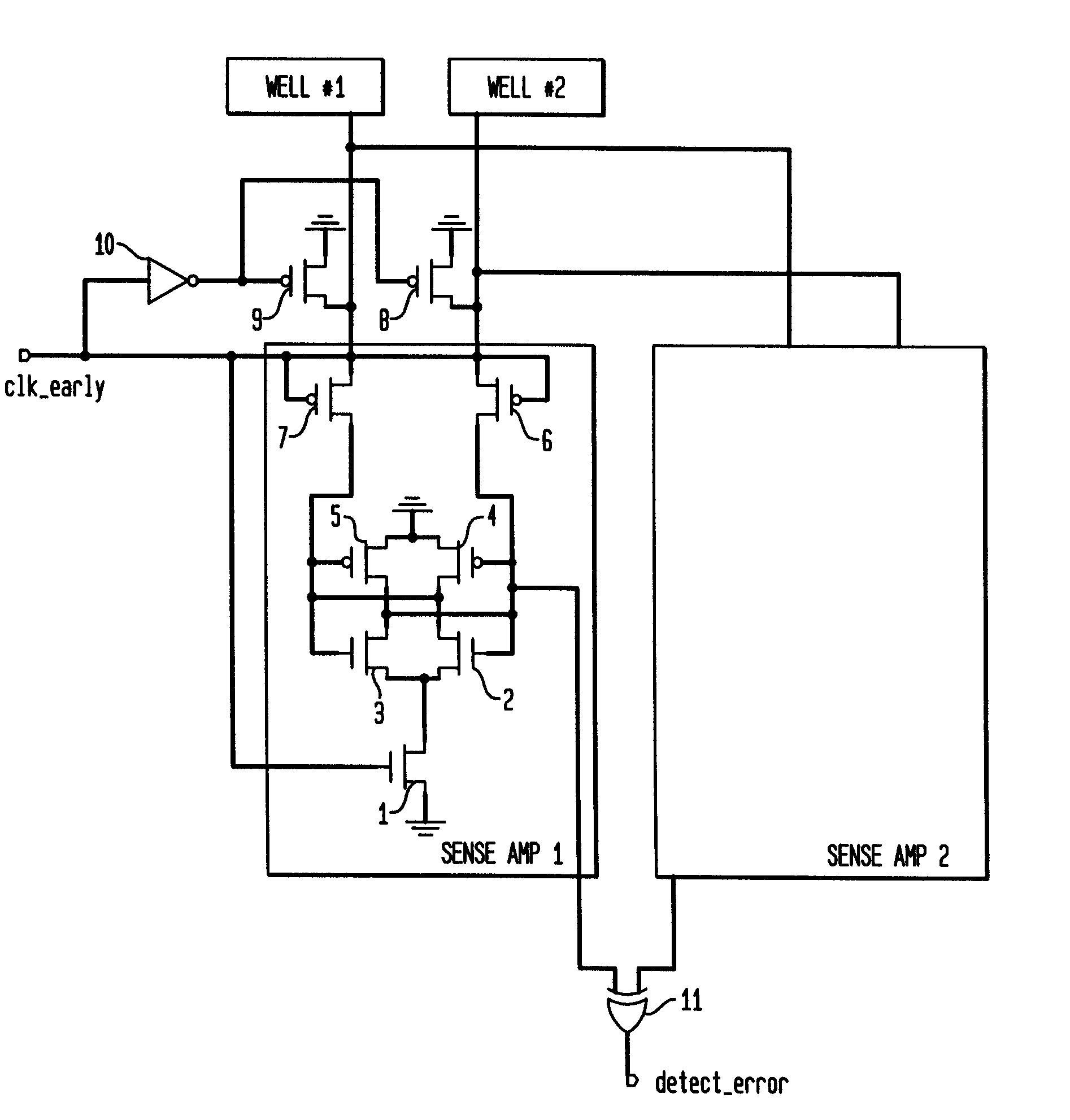
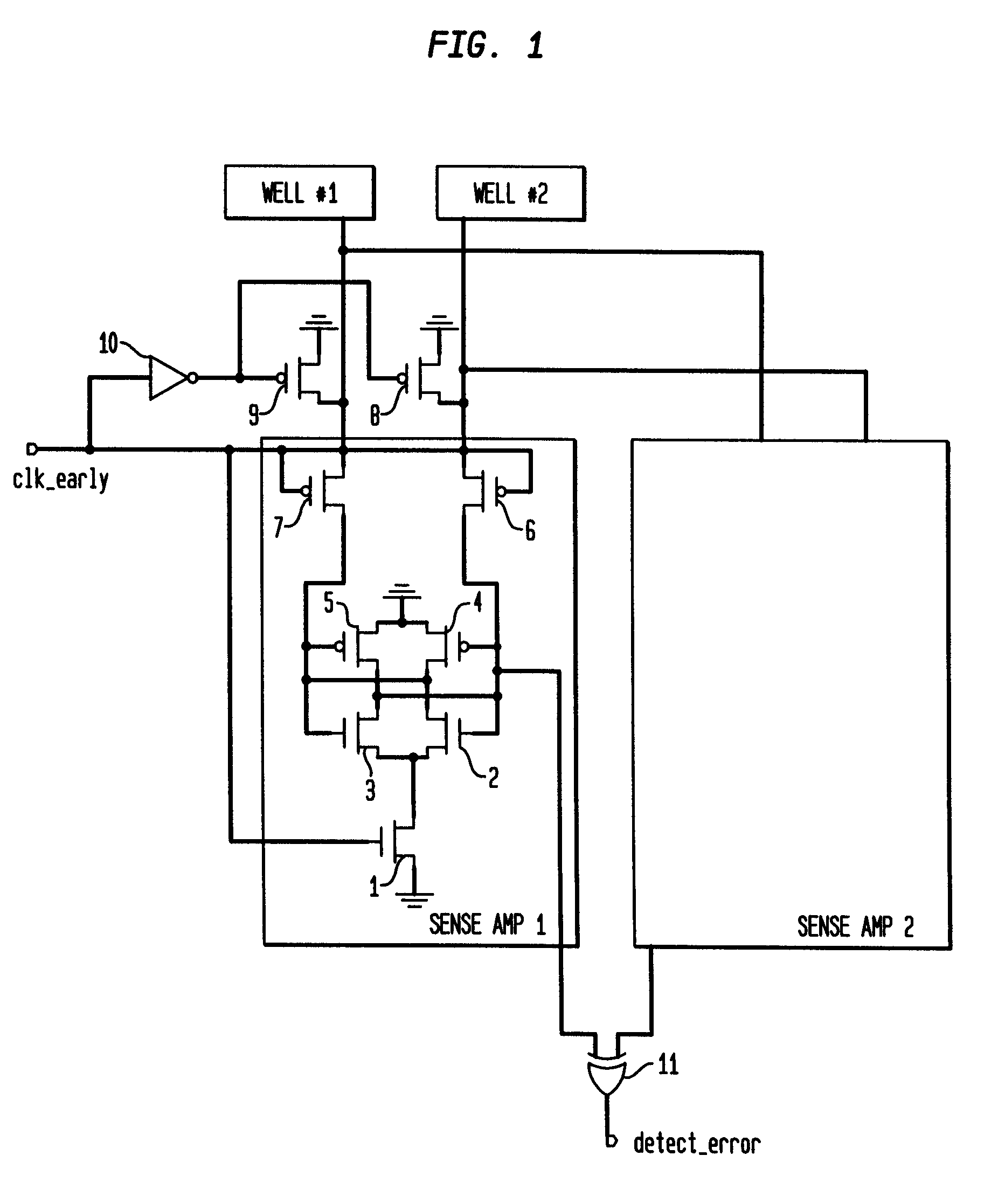
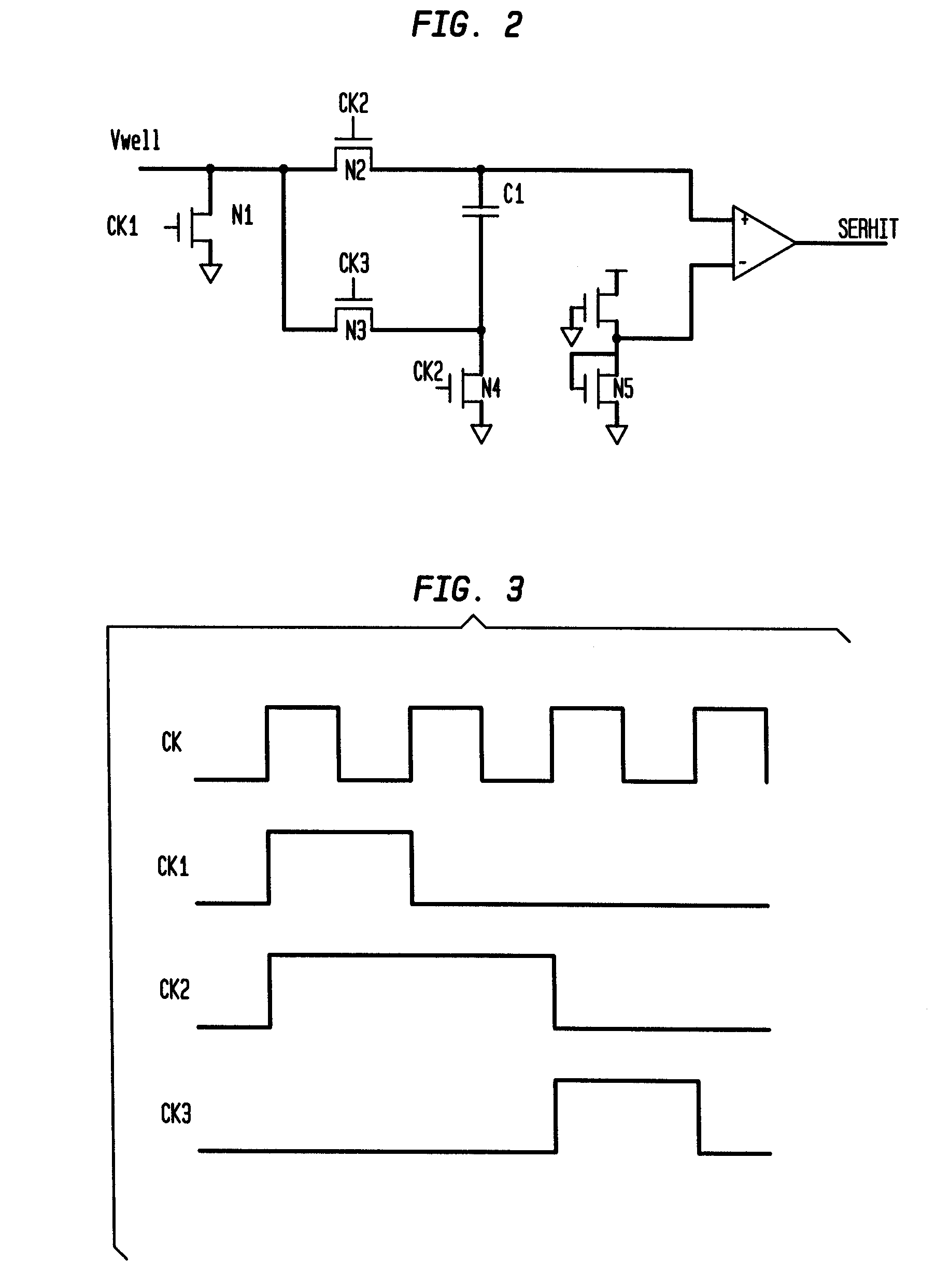
Detector for alpha particle or cosmic ray
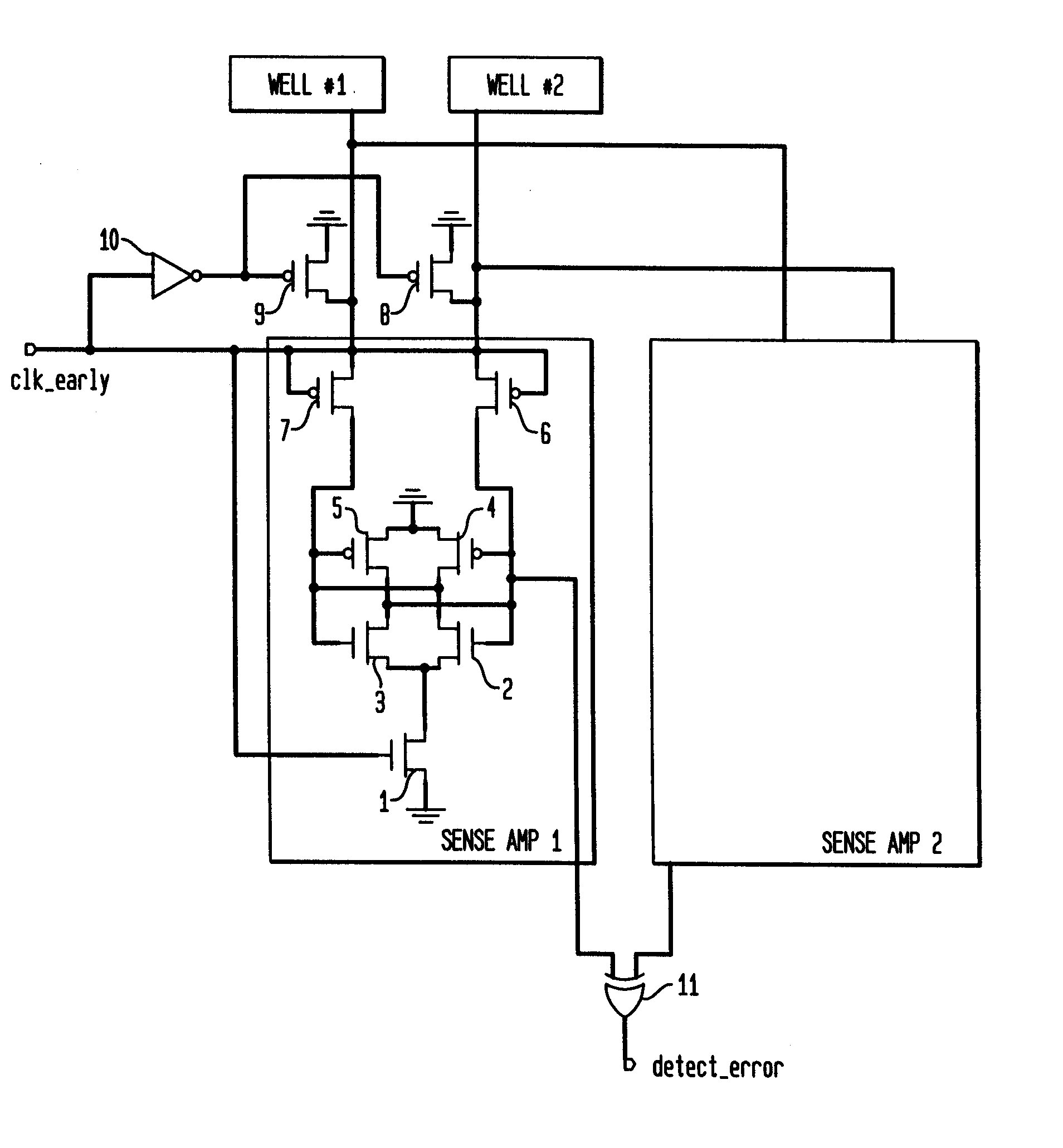
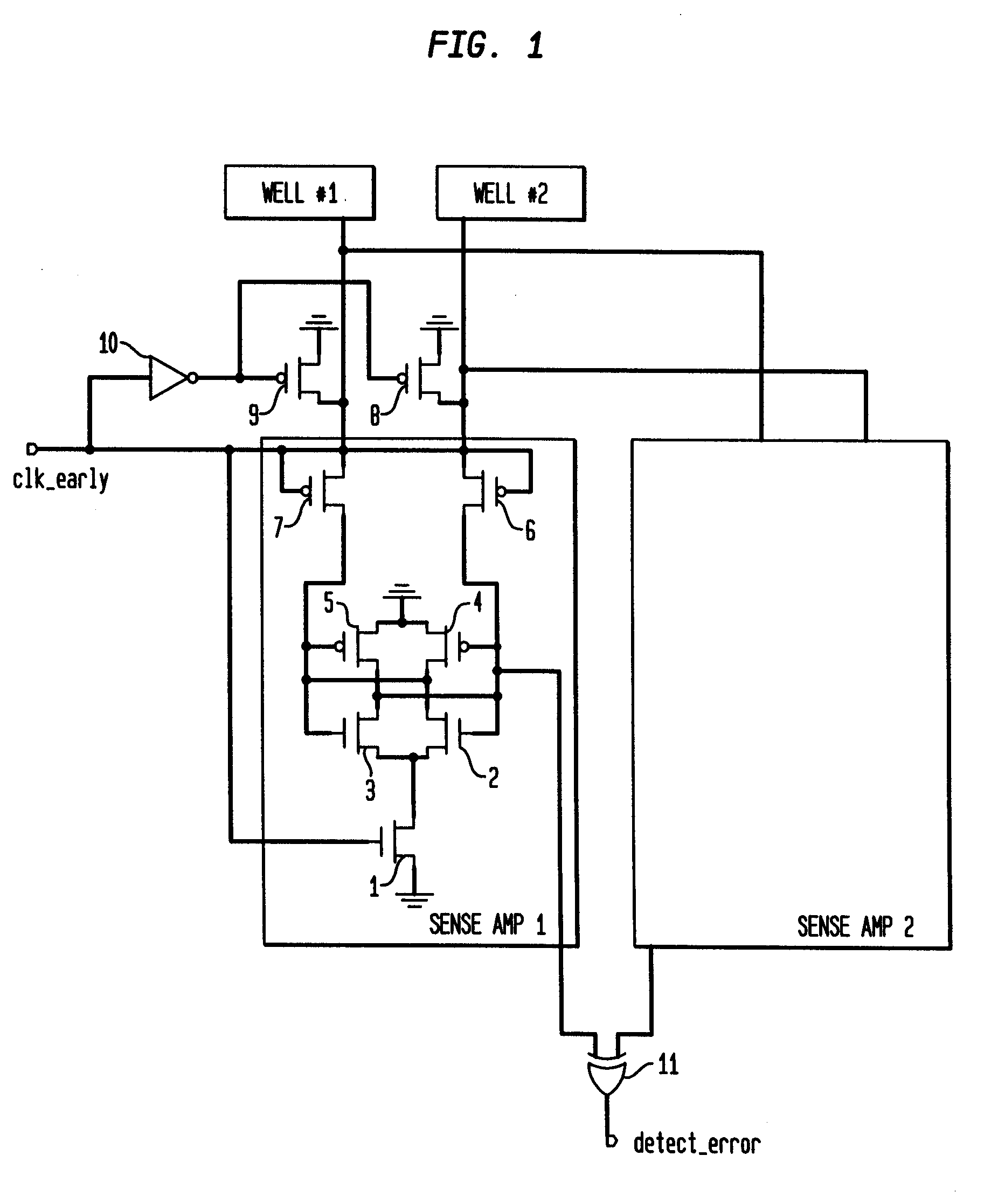
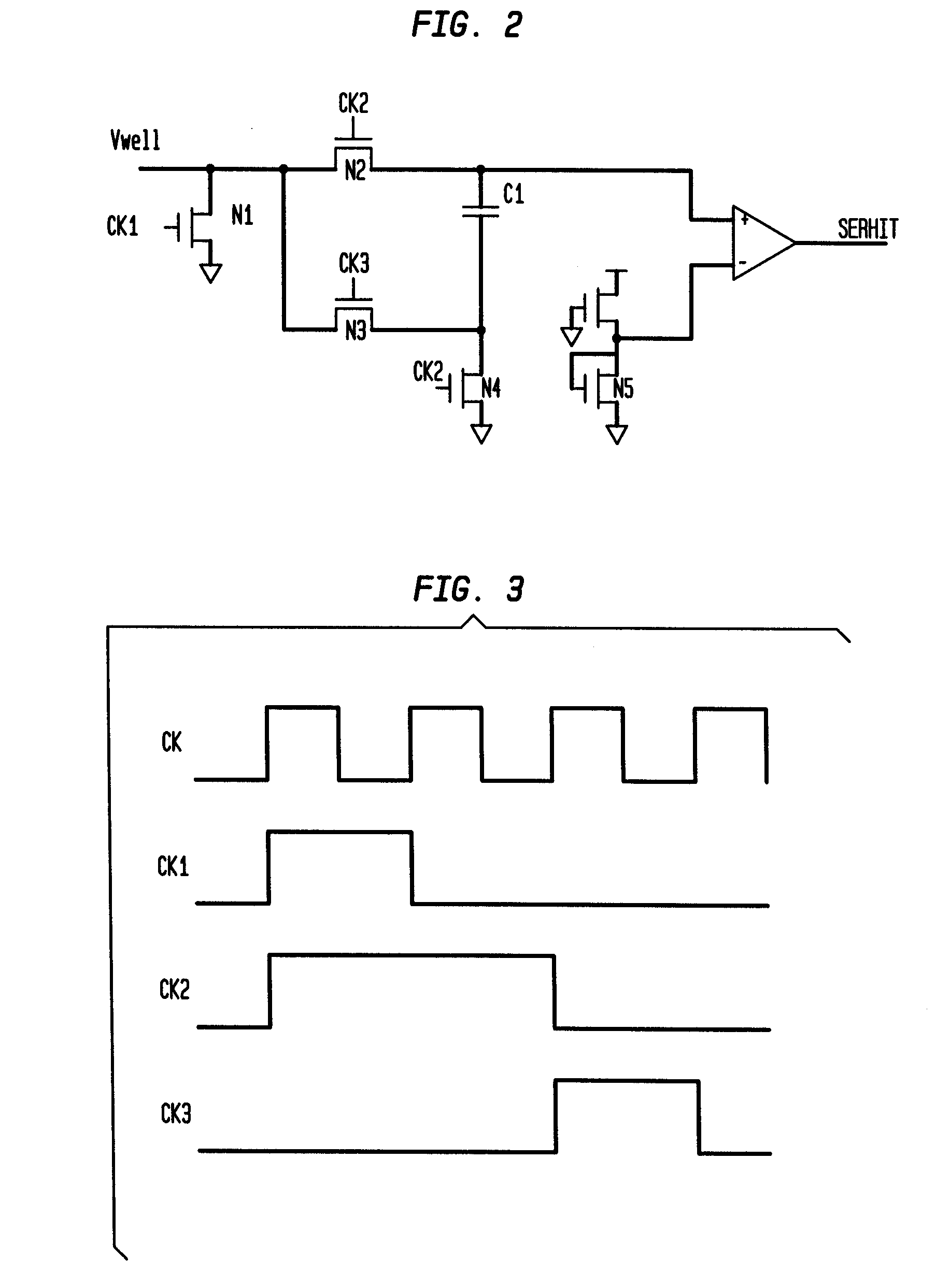
A detector circuit and method for detecting a silicon well voltage or current to indicate an alpha particle or cosmic ray strike of the silicon well. One significant application for the detection circuit of the present invention is for the redundancy repair latches that are used in SRAMs. The redundancy repair latches are normally written once at power-up to record failed latch data and are not normally written again. If one of the latches changes states due to an SER (Soft Error Rate-such as a strike by an alpha particle or cosmic ray) event, the repair data in the redundancy latches of the SRAM would now be incorrectly mapped. The detector circuit and method monitors the latches for the occurrence of an SER event, and responsive thereto issues a reload of the repair data to the redundancy repair latches. A first embodiment of the detector circuit differentially detects the floating voltages of first and second silicon wells during periods of non-operation of the circuits fabricated in the first and second silicon wells. In a second embodiment, a detector circuit monitors the background voltage level of a single silicon well over first and second consecutive periods of time. A second application for the detection circuit is for traditional logic circuits.
Owner:IBM CORP
Spectrometric data cleansing
ActiveUS7233870B1Spectral/fourier analysisRecognisation of pattern in signalsNoise spectroscopyNoise spectrum
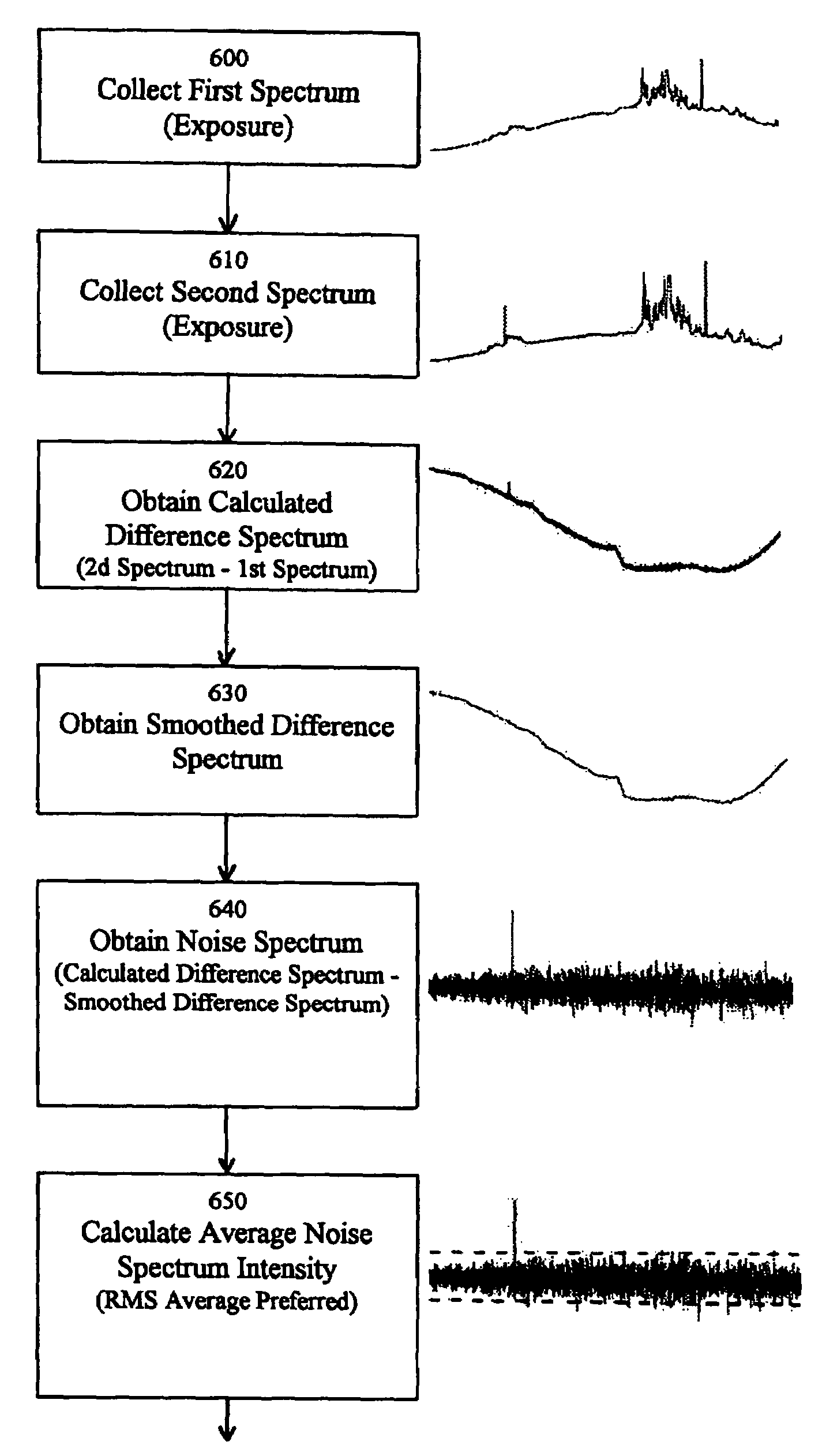
Spectra obtained from spectrographic readings from a sample can be filtered for artifacts, e.g., distorted data points arising from cosmic ray interference, by subtracting one spectrum from another to obtain a difference spectrum; smoothing the difference spectrum; and then calculating the difference between the smoothed and unsmoothed difference spectra to obtain a noise spectrum. The resulting noise spectrum, which represents localized differences between the original spectra, can then be reviewed for readings which exceed the norm by some predetermined amount (e.g., readings which exceed the average level of the noise spectrum by some percentage). These excessive readings constitute distorted data points, and the corresponding points on the spectra can have their values adjusted to eliminate the excessive readings, thereby removing the artifacts.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS SCI INSTR LLC
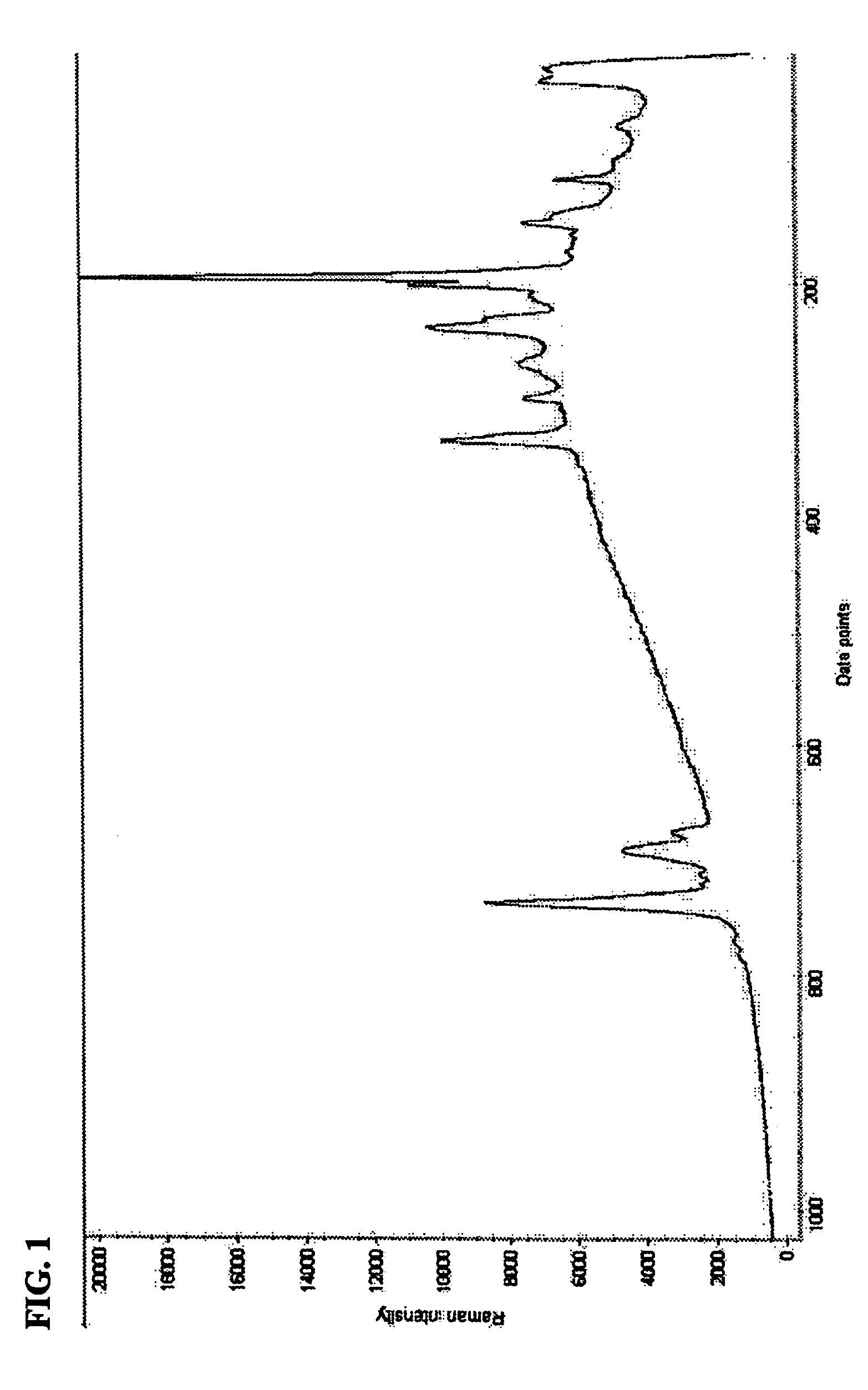
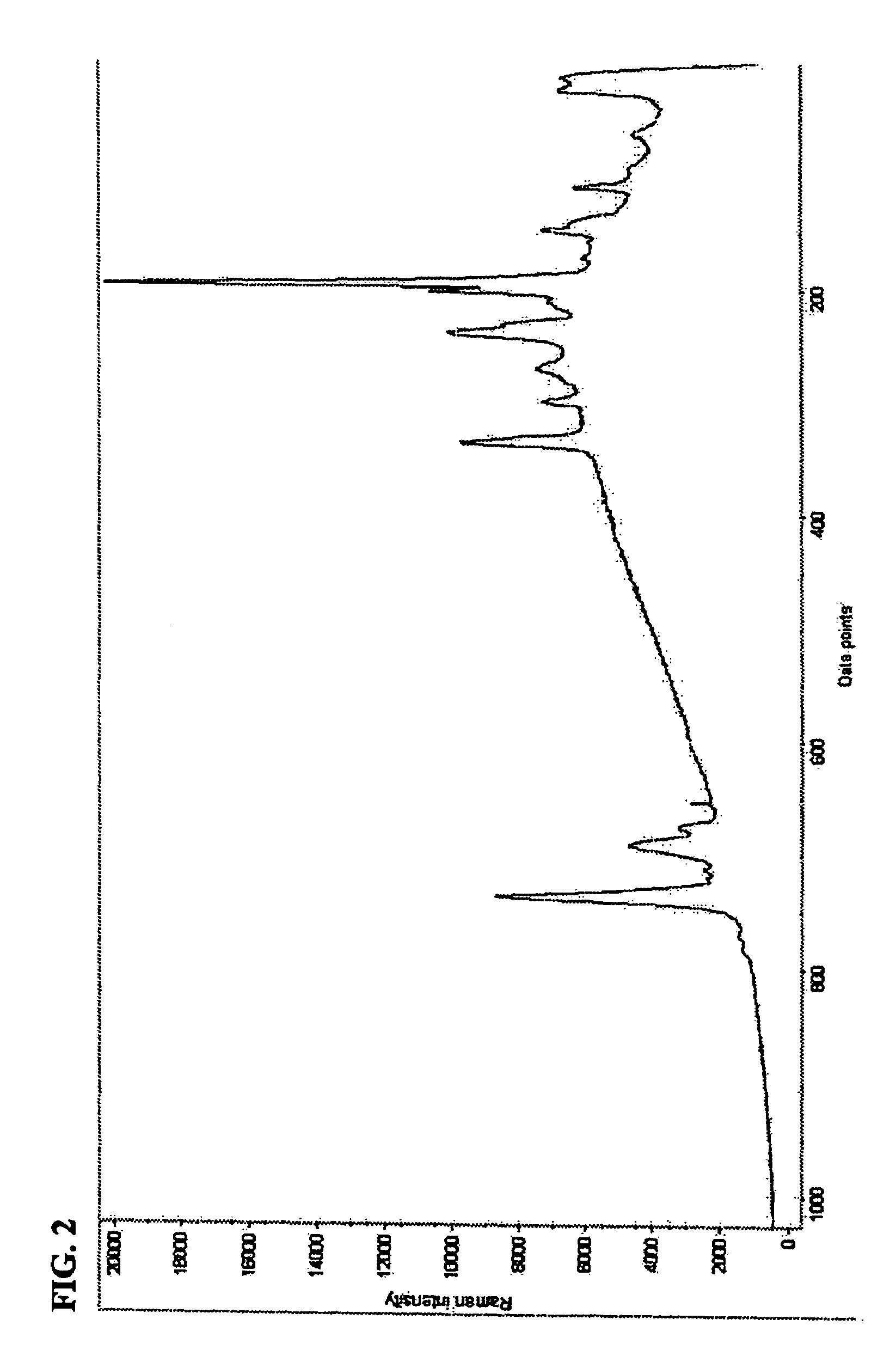
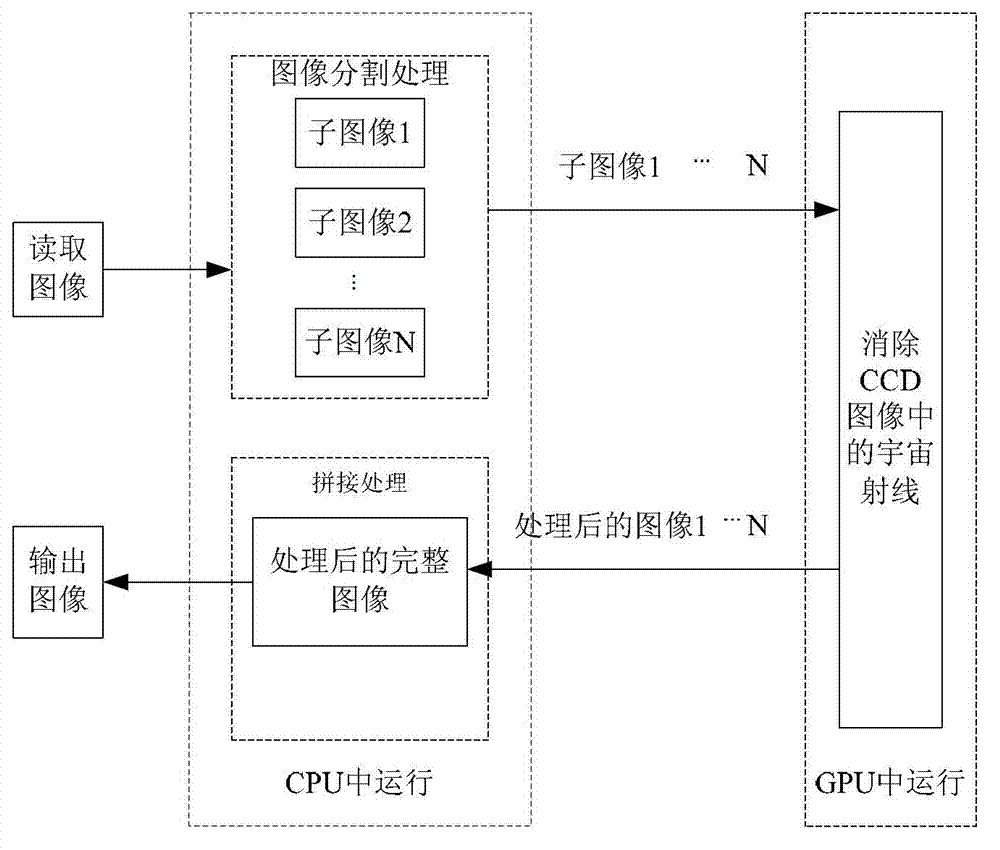
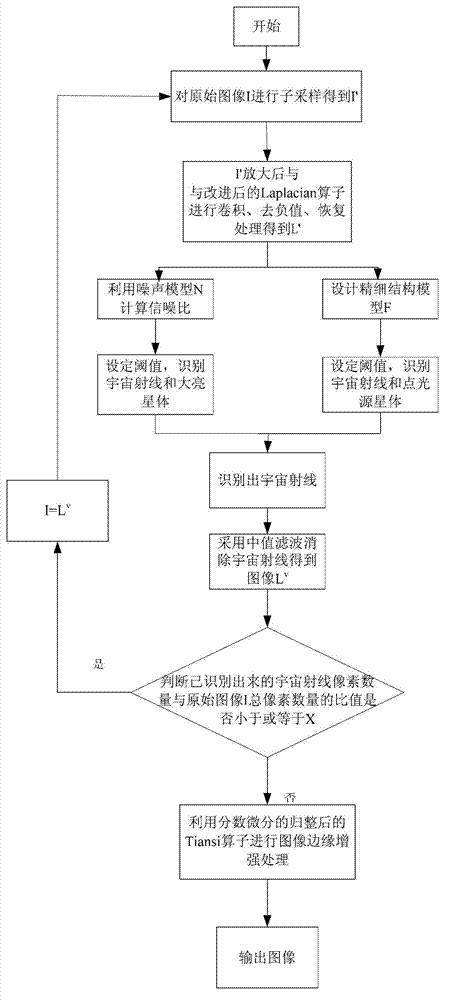
Method for removing cosmic rays in charge-coupled device (CCD) astronomic image
InactiveCN102881003AIncrease the amount of informationQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisFractional differentialComputer vision
The invention discloses a method for removing cosmic rays in a charge-coupled device (CCD) astronomic image. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing sub-sampling on an original image I to obtain a sub-sampled image; (2) improving a Laplacian operator, amplifying the sub-sampled image, performing convolution operation on the amplified sub-sampled image and the improved Laplacian operator, removing a negative value, and recovering an original size to obtain a Laplacian image L'; (3) identifying cosmic rays in the Laplacian image L'; (4) removing the cosmic rays in the Laplacian image L'; and (5) performing image edge enhancement processing on the image in which the cosmic rays are removed by utilizing a fractional differential normalized Tiansi operator. According to the method, the identification rate of the cosmic rays is greatly increased, a part influenced by the cosmic rays in a star can be maximally retained, and the processing quality of the image is improved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Imaging based on cosmic-ray produced charged particles
ActiveCN102203637AMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementTomographyComputational physics
Techniques, apparatus and systems for obtaining tomographic images of a volume of interest by using charged particle tomography detection systems.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY +1
Water Cerenkov light high-energy particle detector
ActiveCN102981180ASimple structureMake up for the shortcomingsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentHigh energyData acquisition
The invention relates to a water Cerenkov light high-energy particle detector which comprises a Cerenkov light generation device, a light collection device, a photoelectric conversion device and a data acquisition device. The light collection device and the photoelectric conversion device are mounted in the water Cerenkov light high-energy particle detector. When velocities of charged particles entering the detector are greater than a phase velocity of light in water, Cerenkov light can be generated. The generated water Cerenkov light is collected by the light collection device in the detector, and passes through the photoelectric conversion device; and light signals can be converted into electrical signals. The output electrical signals after undergoing analog-digital conversion are stored and recorded by the data acquisition device finally. The water Cerenkov light high-energy particle detector is mainly used for detecting the particle quantity and the energy of relativistic particles, and applicable to the research of high-energy gamma astronomy and high-energy cosmic rays.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
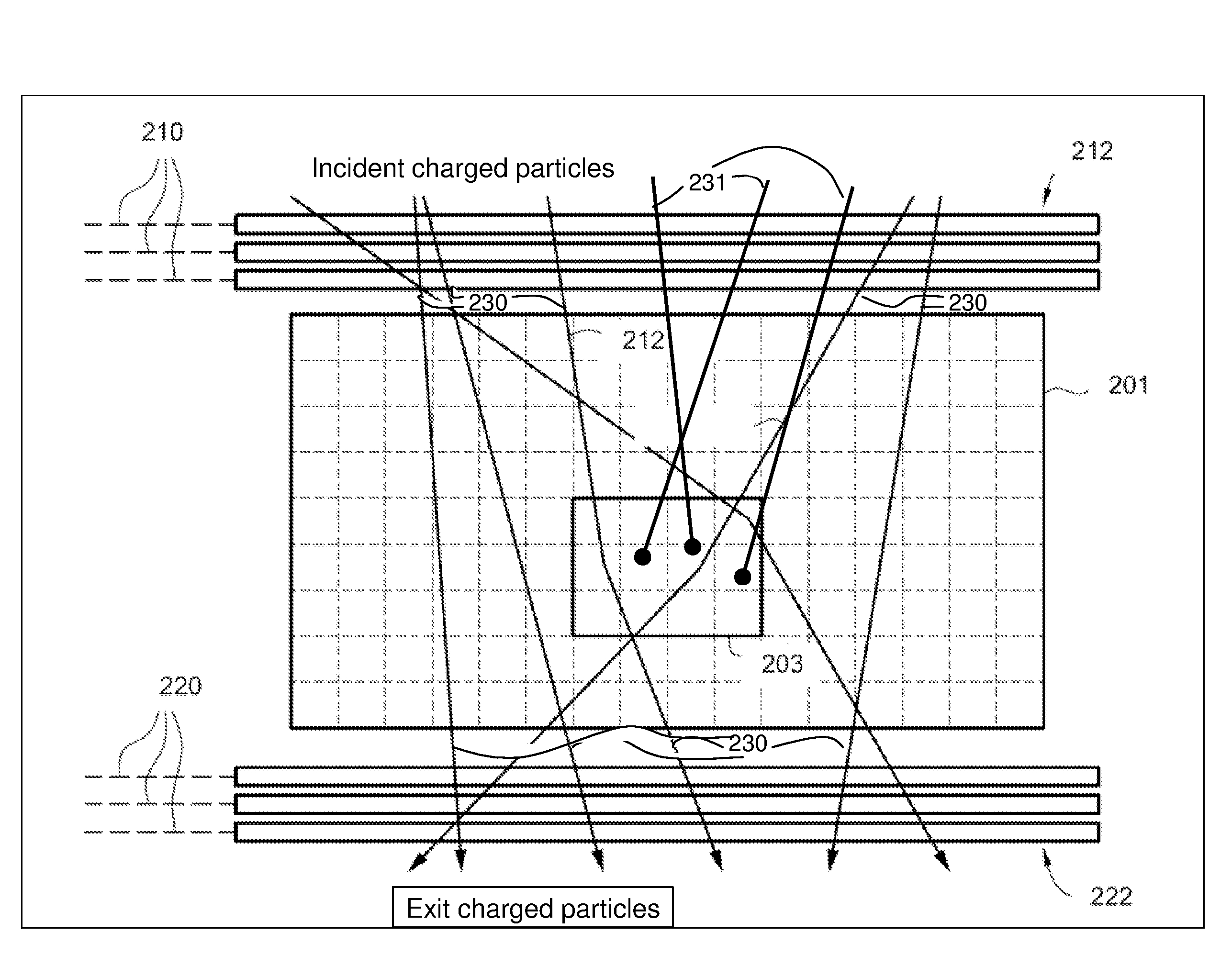
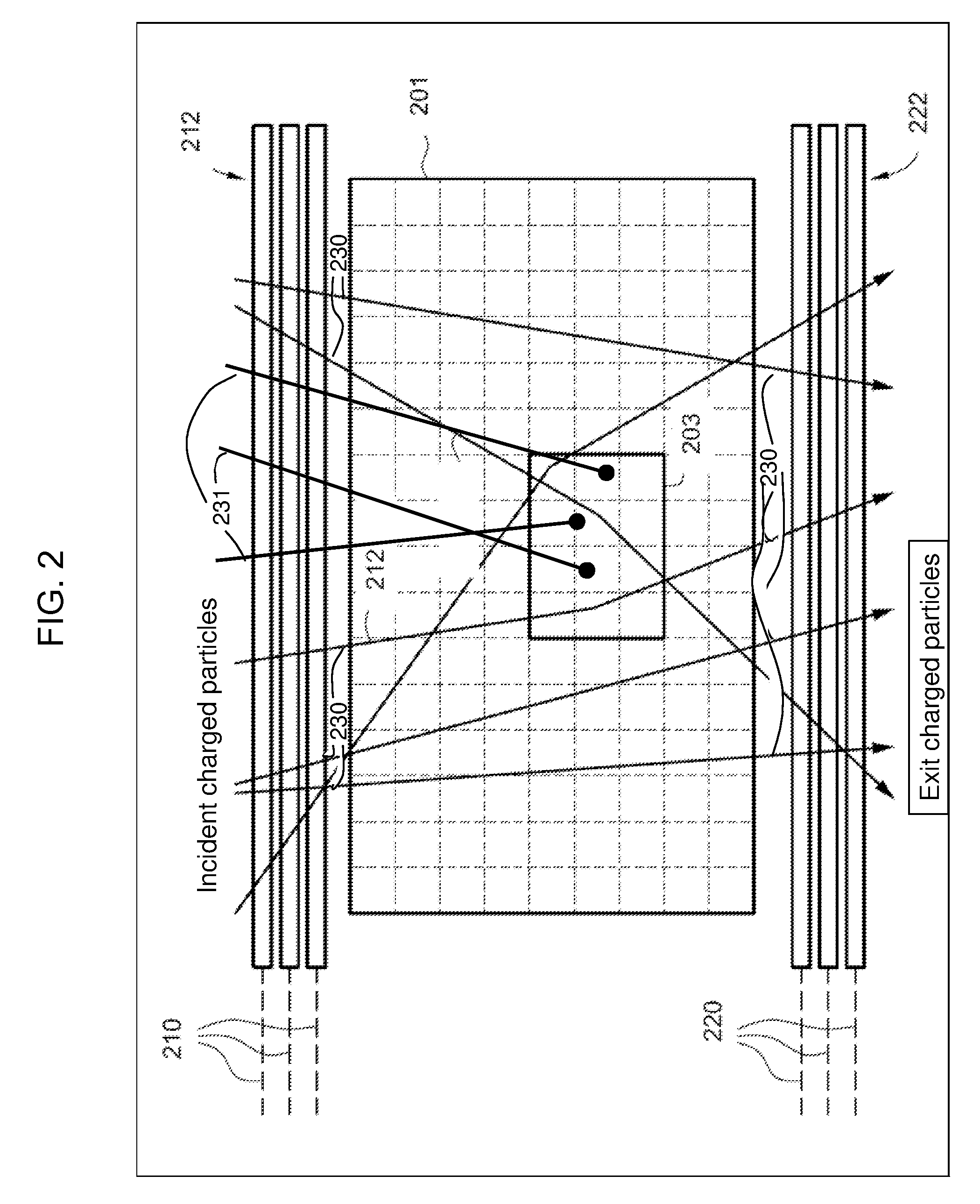
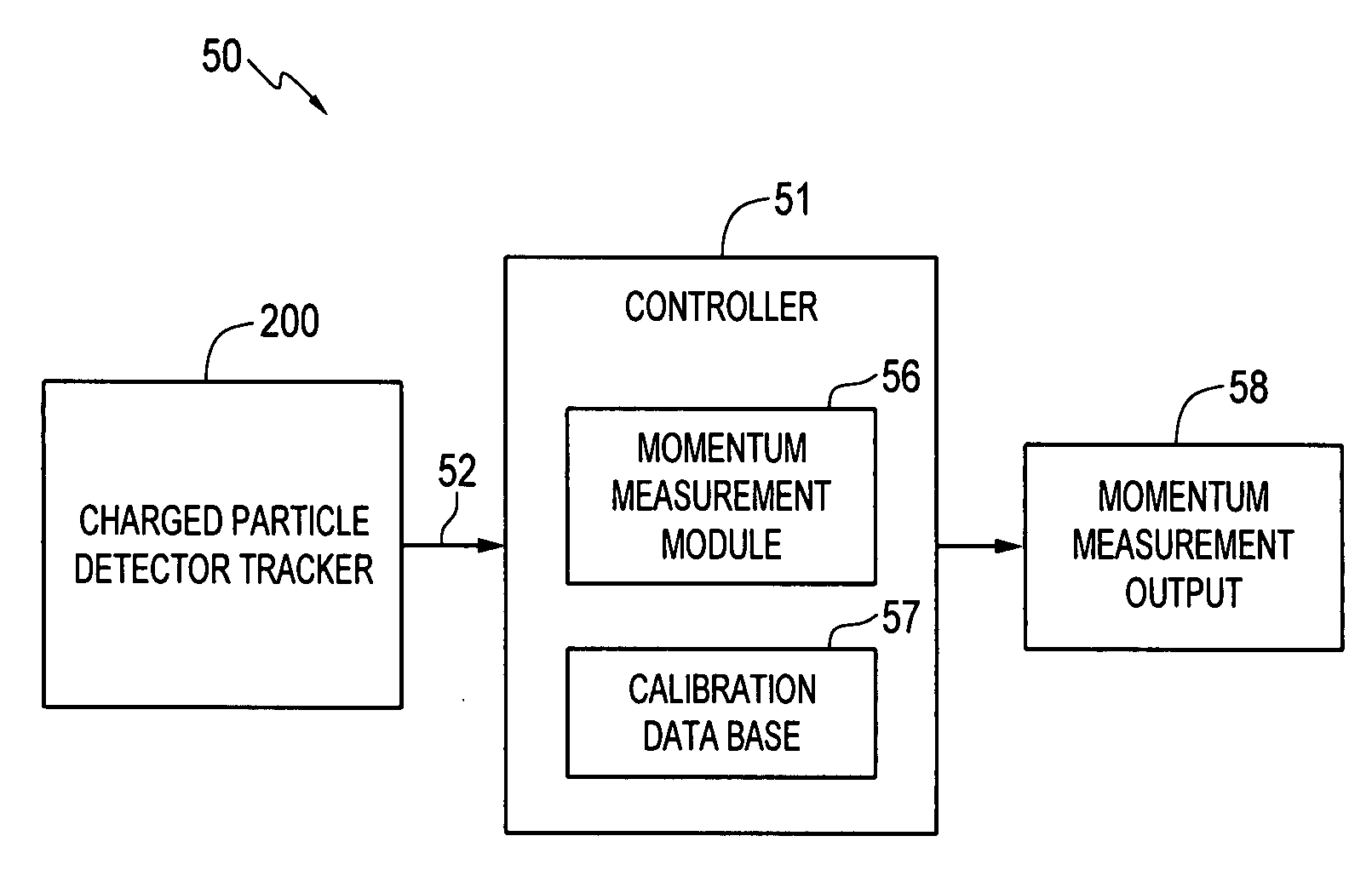
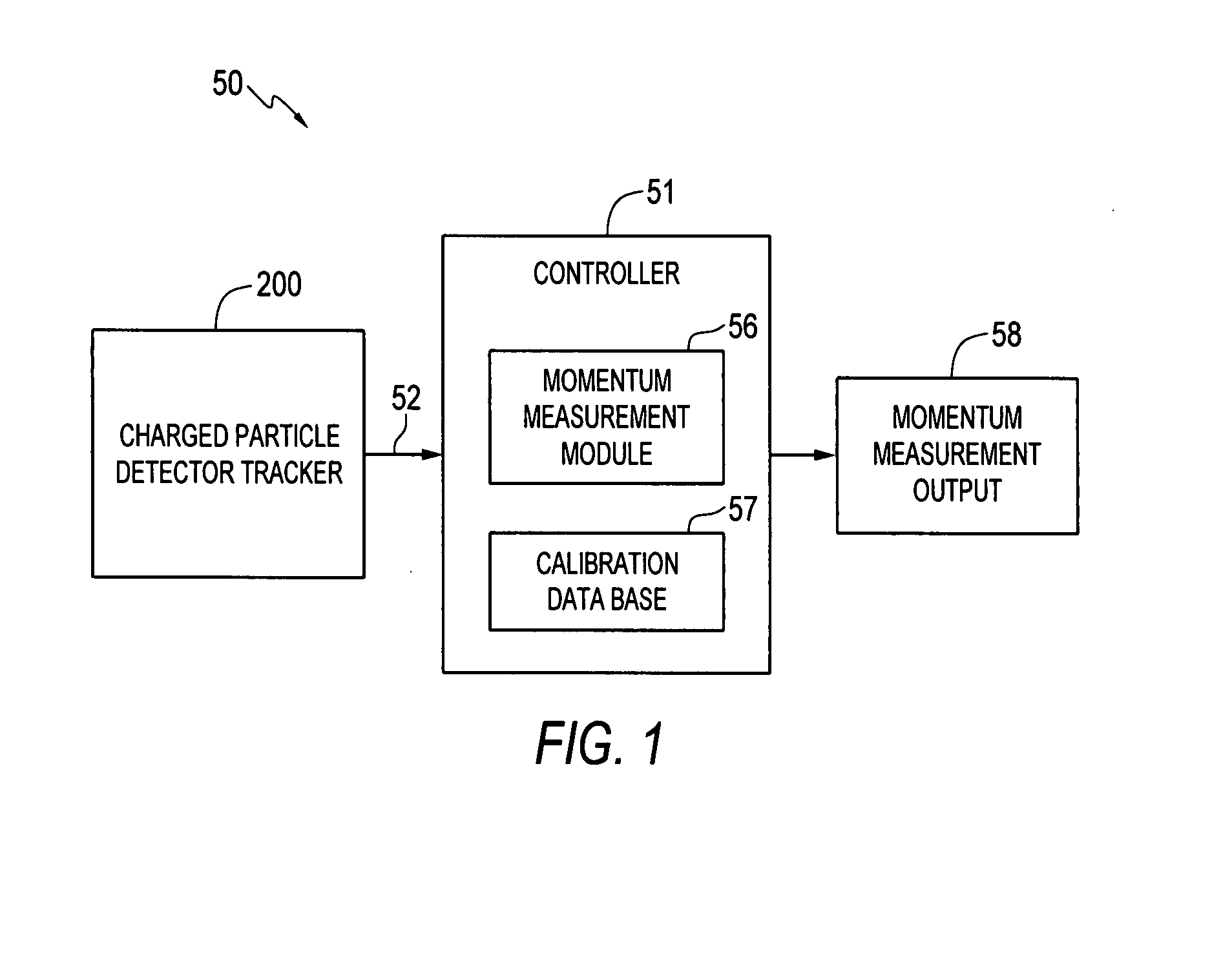
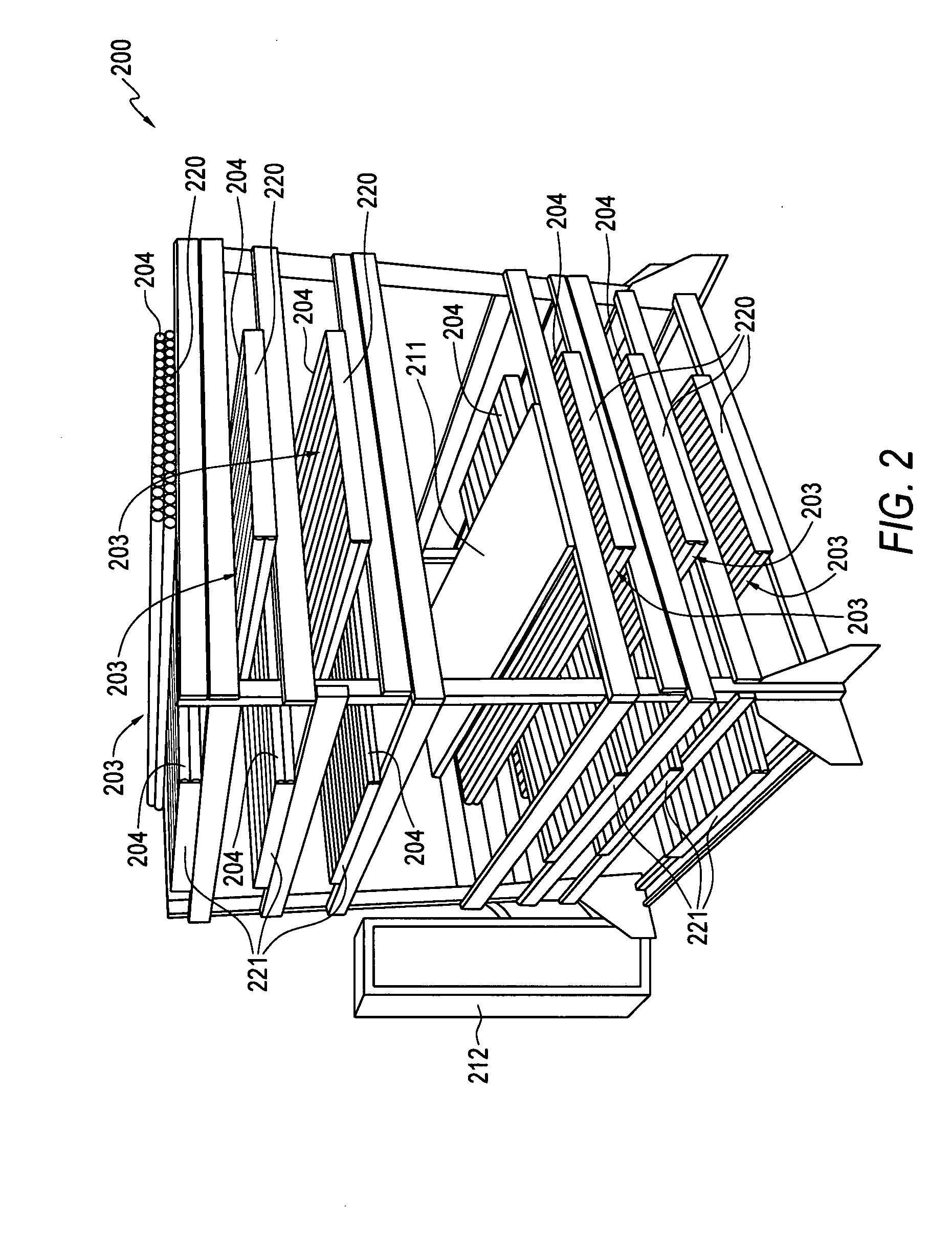
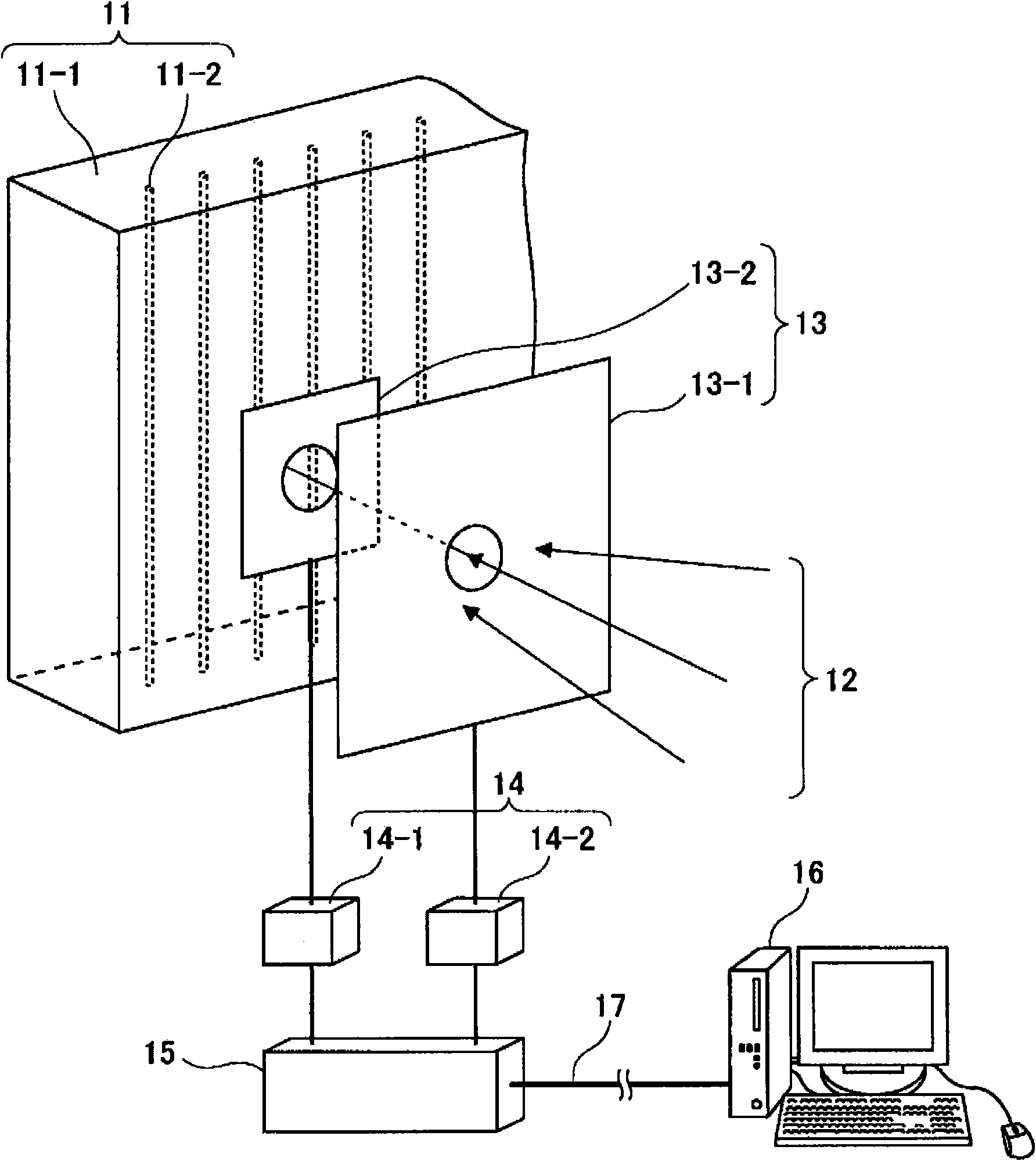
Measuring momentum for charged particle tomography
ActiveUS20080265156A1Reduce noiseSufficient massThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMomentumTomography
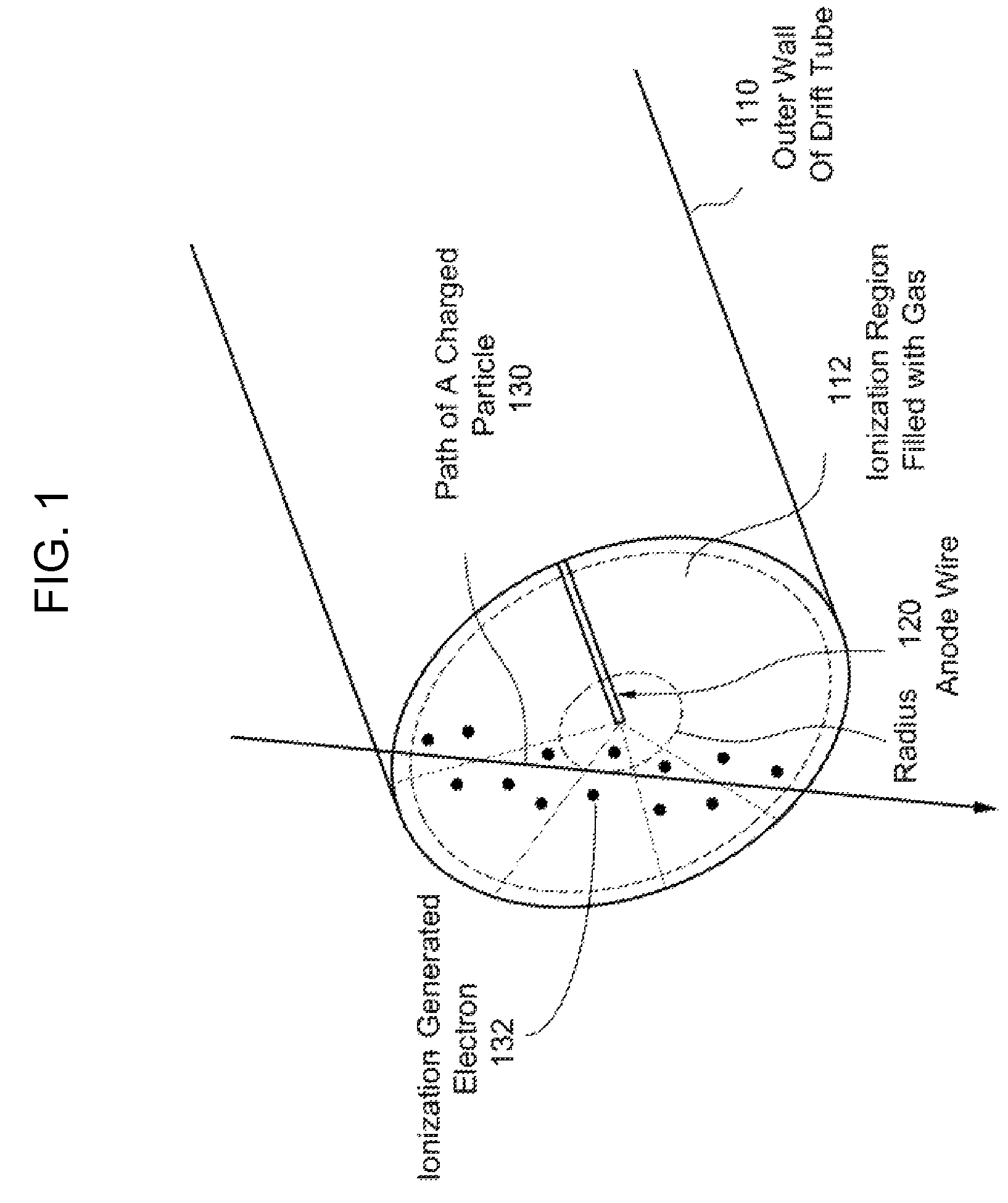
Methods, apparatus and systems for detecting charged particles and obtaining tomography of a volume by measuring charged particles including measuring the momentum of a charged particle passing through a charged particle detector. Sets of position sensitive detectors measure scattering of the charged particle. The position sensitive detectors having sufficient mass to cause the charged particle passing through the position sensitive detectors to scatter in the position sensitive detectors. A controller can be adapted and arranged to receive scattering measurements of the charged particle from the charged particle detector, determine at least one trajectory of the charged particle from the measured scattering; and determine at least one momentum measurement of the charged particle from the at least one trajectory. The charged particle can be a cosmic ray-produced charged particle, such as a cosmic ray-produced muon. The position sensitive detectors can be drift cells, such as gas-filled drift tubes.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
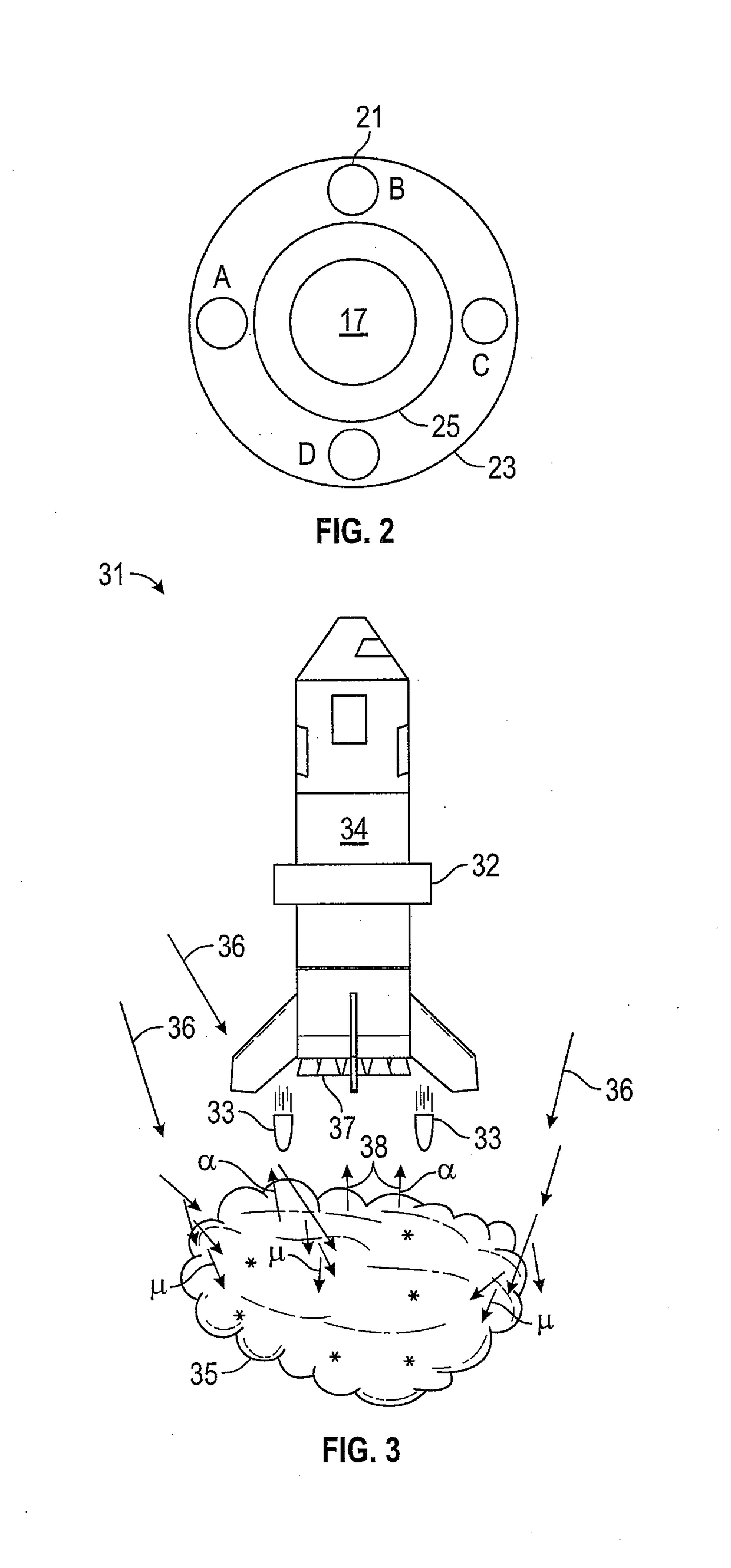
Spacecraft landing and site-to-site transpsort for a planet, moon or other space body
ActiveUS20180134417A1Increase volumeIncrease the areaAmmunition projectilesCosmonautic ground equipmentsEngineeringCLOUD experiment
A method, operable in the presence of ambient cosmic rays, is provided for braking a craft upon approach to a planet, moon or other space body, e.g. in preparation for landing. Deuterium-containing particle fuel material is projected in a specified direction outward of the craft, which interacts with both the cosmic rays and their principal decay product muons to generate energetic micro-fusion products that produce a braking thrust on the craft for a specified trajectory. The micro-fusion products may push directly against the craft, e.g. upon a pressure plate, or upon a sail or parachute connected to the craft, to decelerate the craft. A prepositioned automated landing system at a landing site may project the fuel material toward the craft based on telemetry tracking of an incoming craft and likewise directly disperse the material cloud to form a braking cushion at the landing site. The micro-fusion landing system may be part of a site-to-site transport, where the craft was launched using either conventional chemical rockets or micro-fusion for accelerating thrust.
Owner:DREXLER JEROME
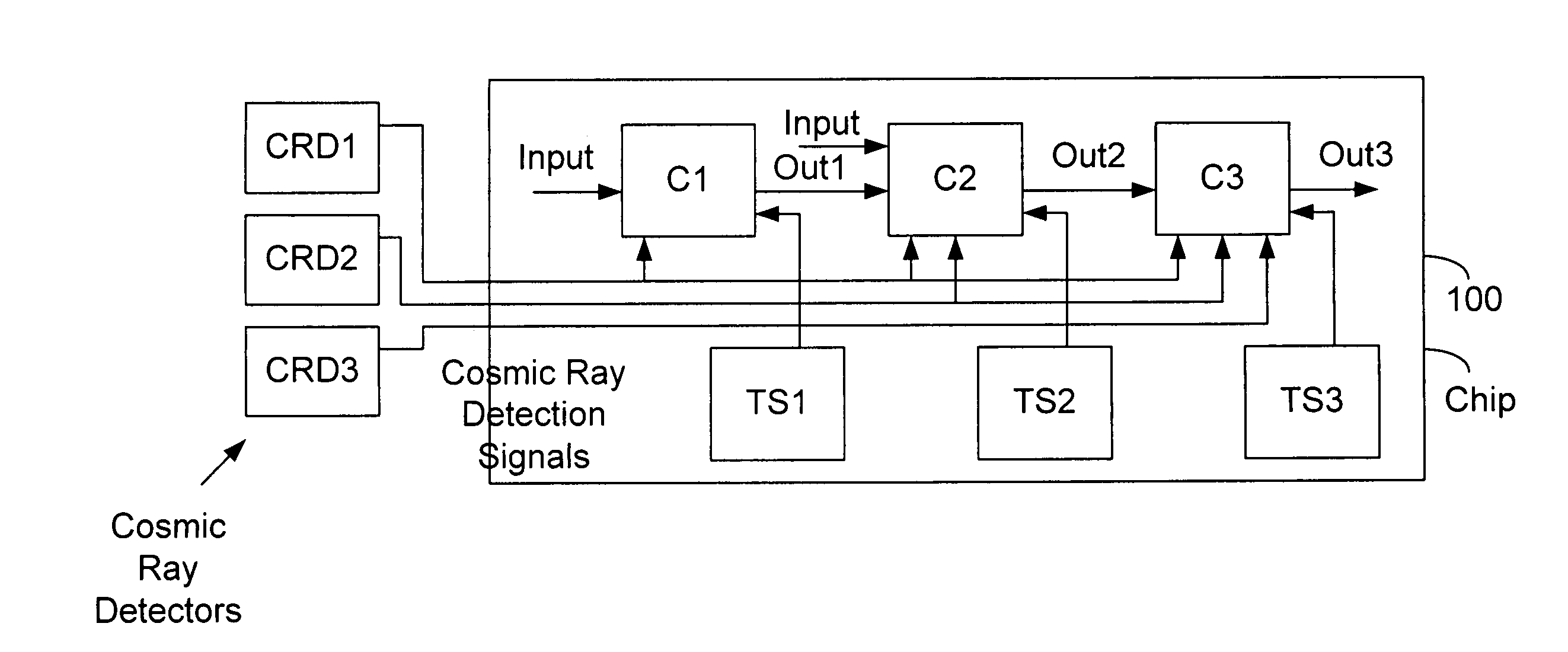
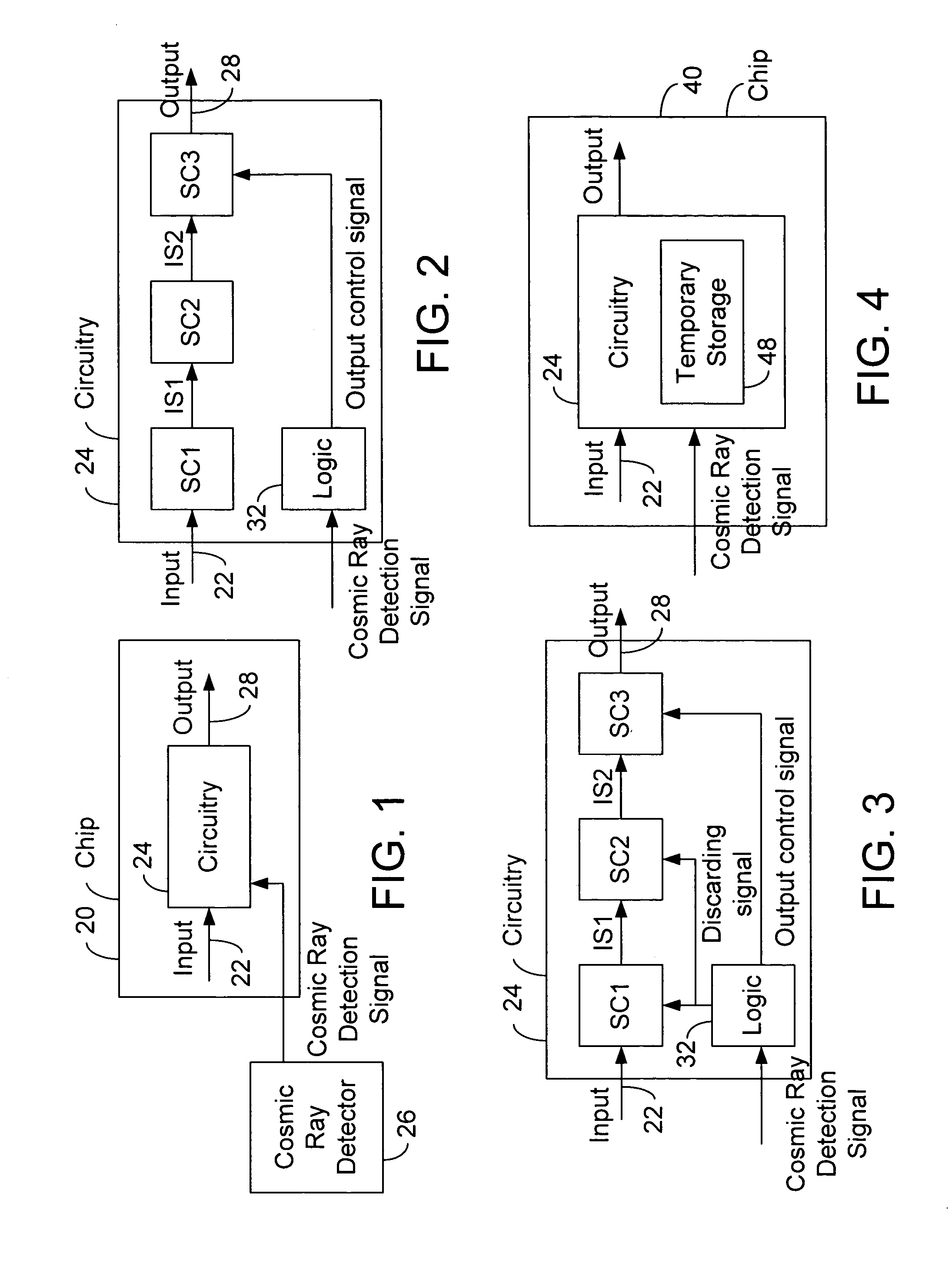
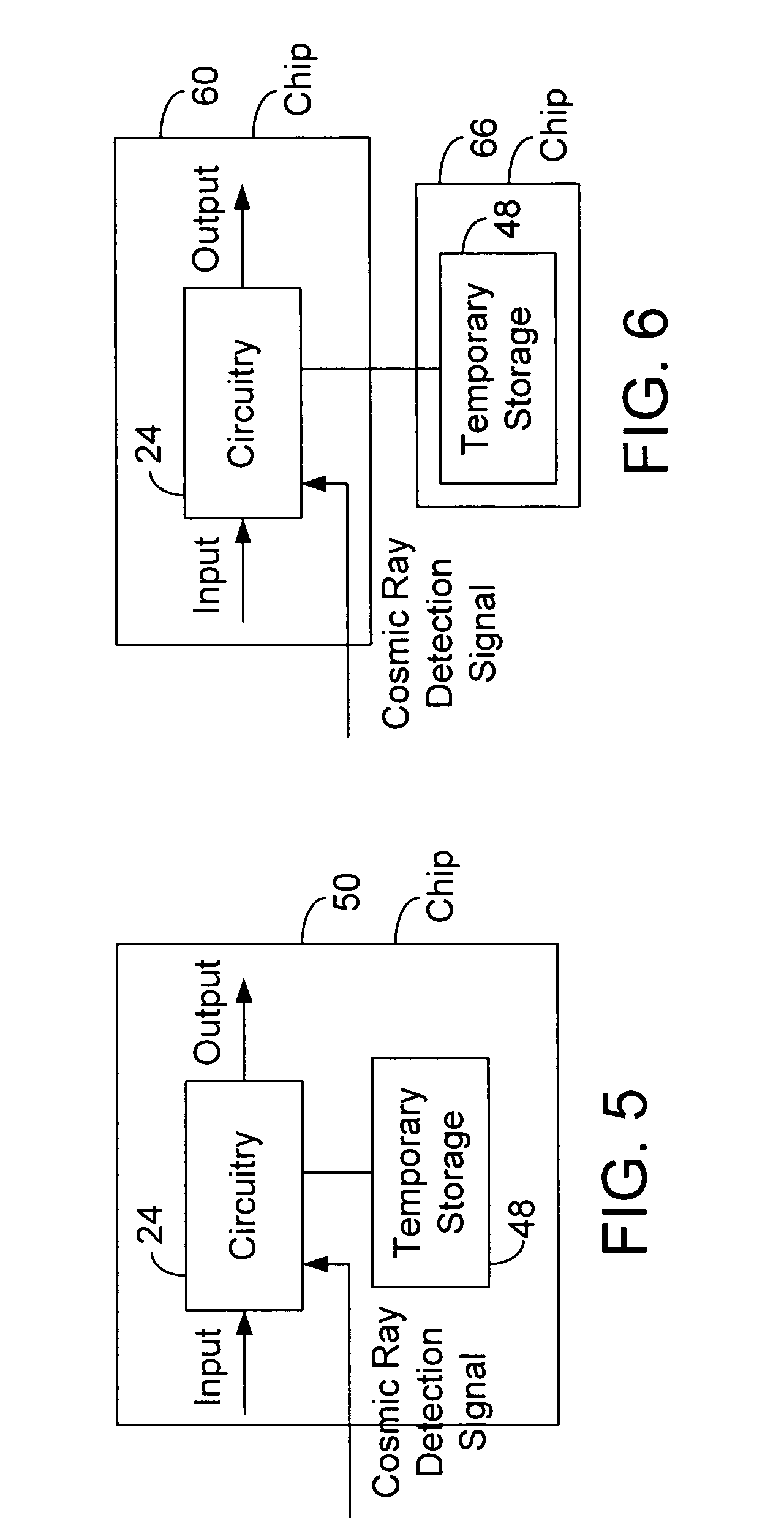
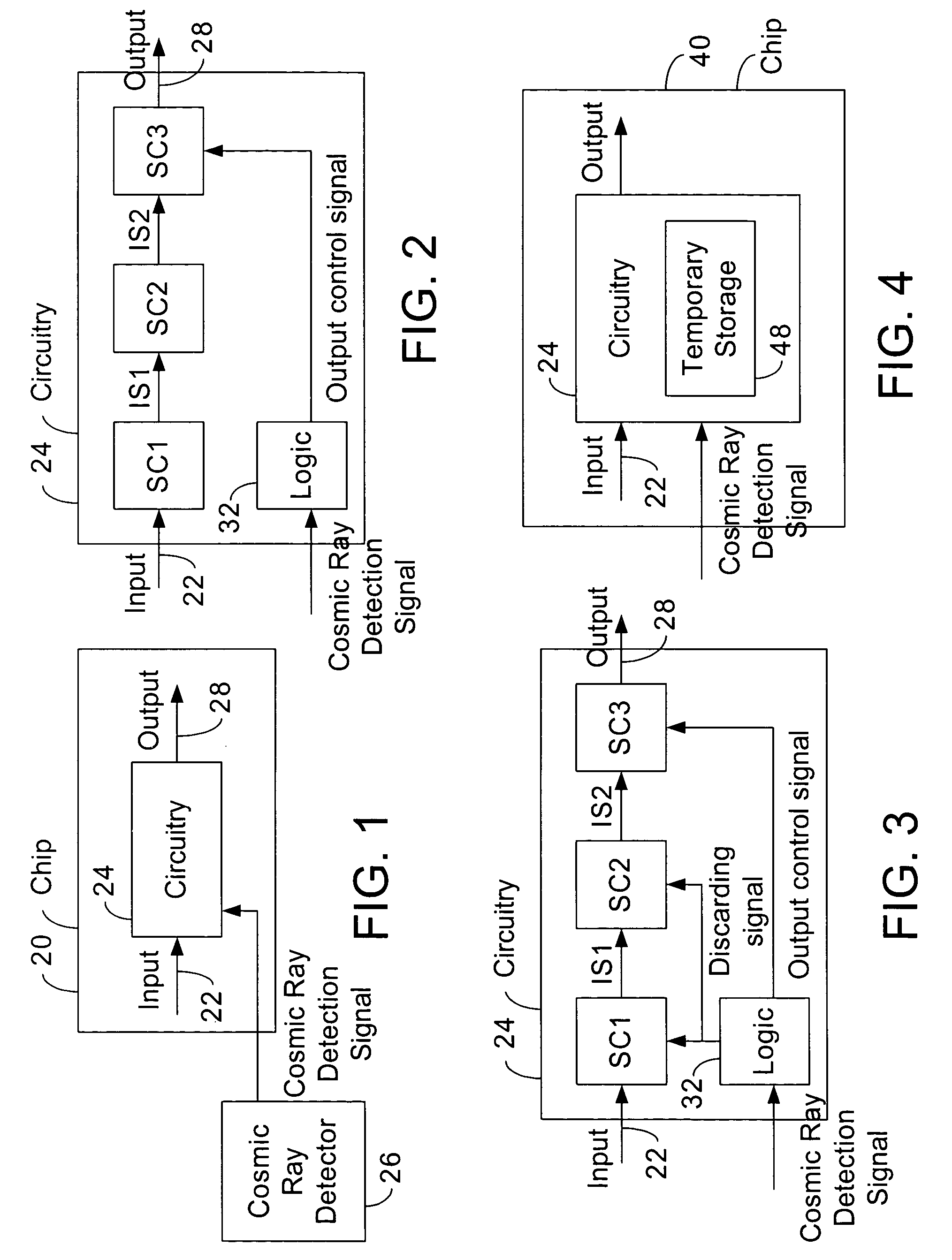
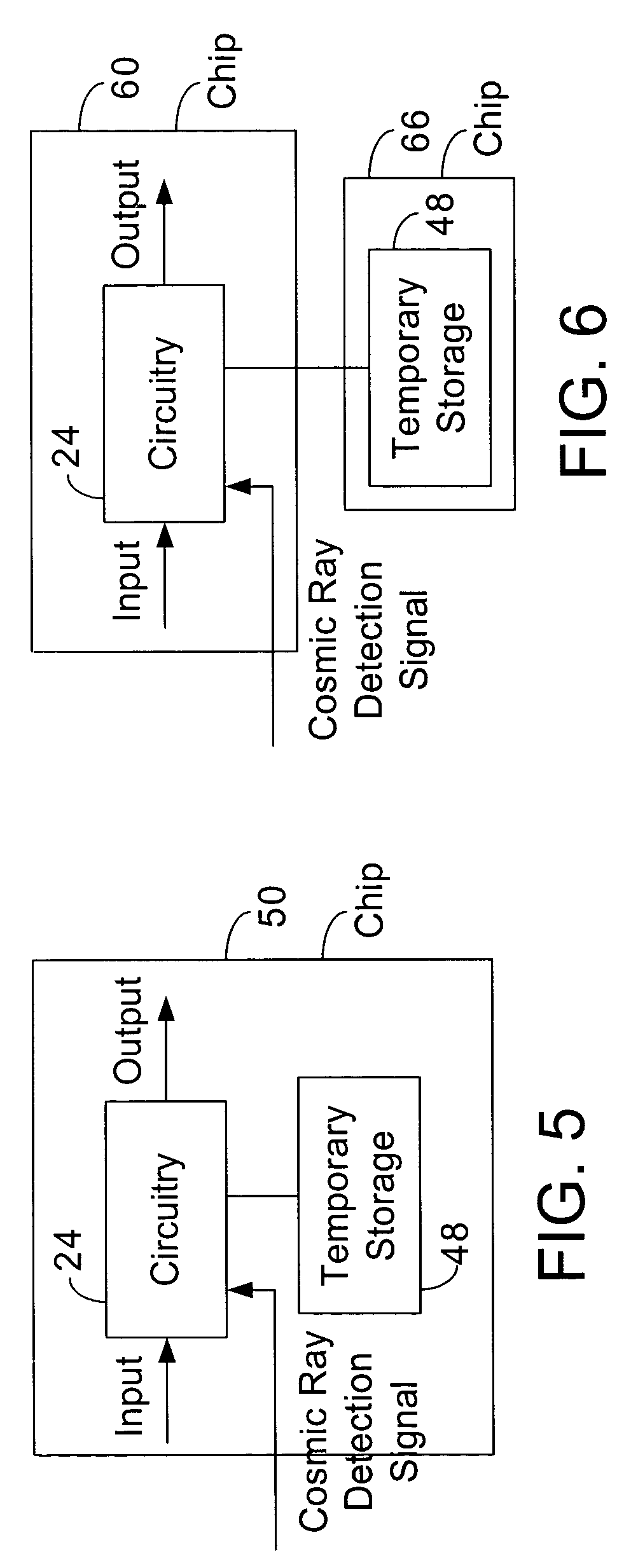
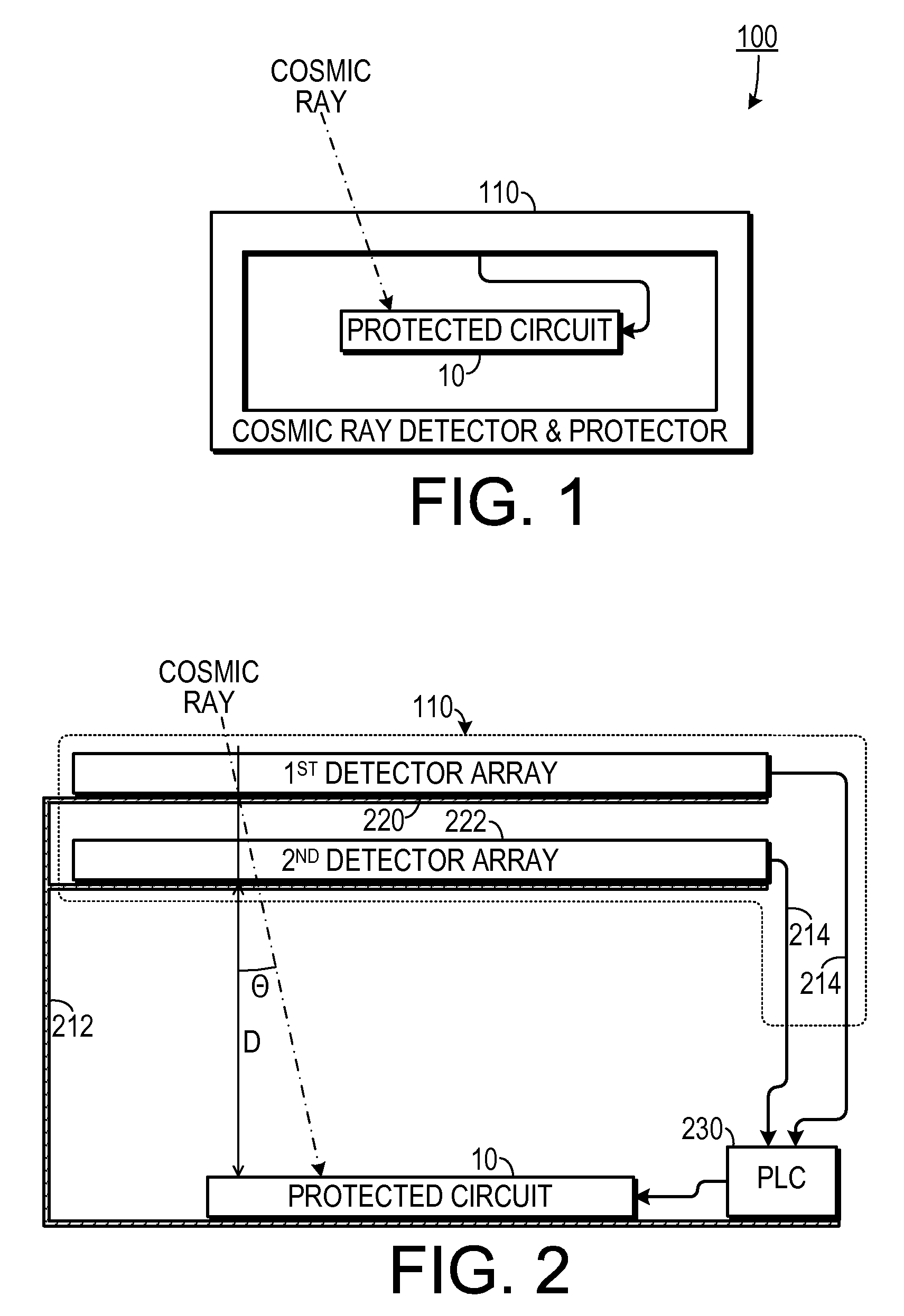
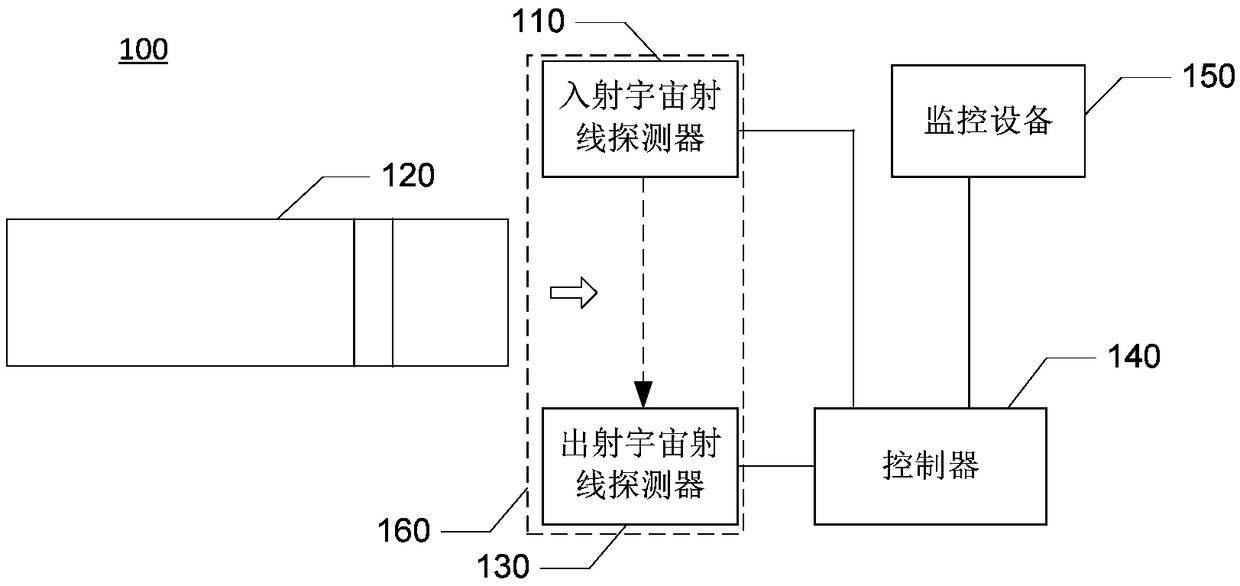
System with response to cosmic ray detection
In some embodiments, a system includes a cosmic ray detector to detect cosmic rays and to generate cosmic ray detection signals indicative of the detected cosmic rays. The system also includes first circuitry to receive input signals and to produce output signals, and wherein the first circuitry speculates that the cosmic ray detector will not detect cosmic rays, but in response to the cosmic ray detection signals, the first circuitry re-performs at least some operations. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
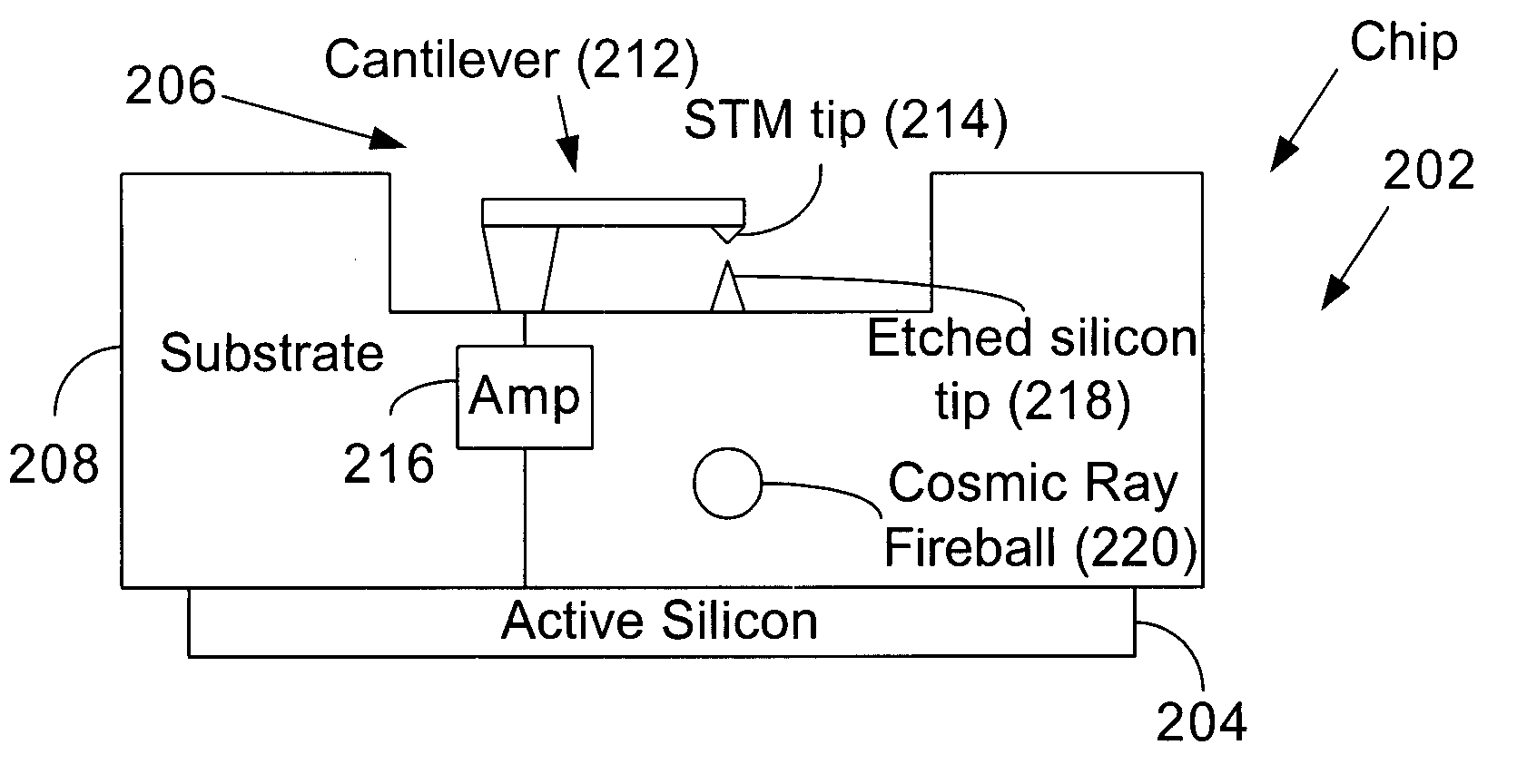
Cosmic ray detectors for integrated circuit chips
InactiveUS20060000981A1Error detection/correctionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCantileverIntegrated circuit
In some embodiments, a cosmic ray detector includes a cantilever with a first tip. The detector also includes a second tip and circuitry to provide a signal indicative of a distance between the first and second tips being such as would be caused by a cosmic ray interaction event. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
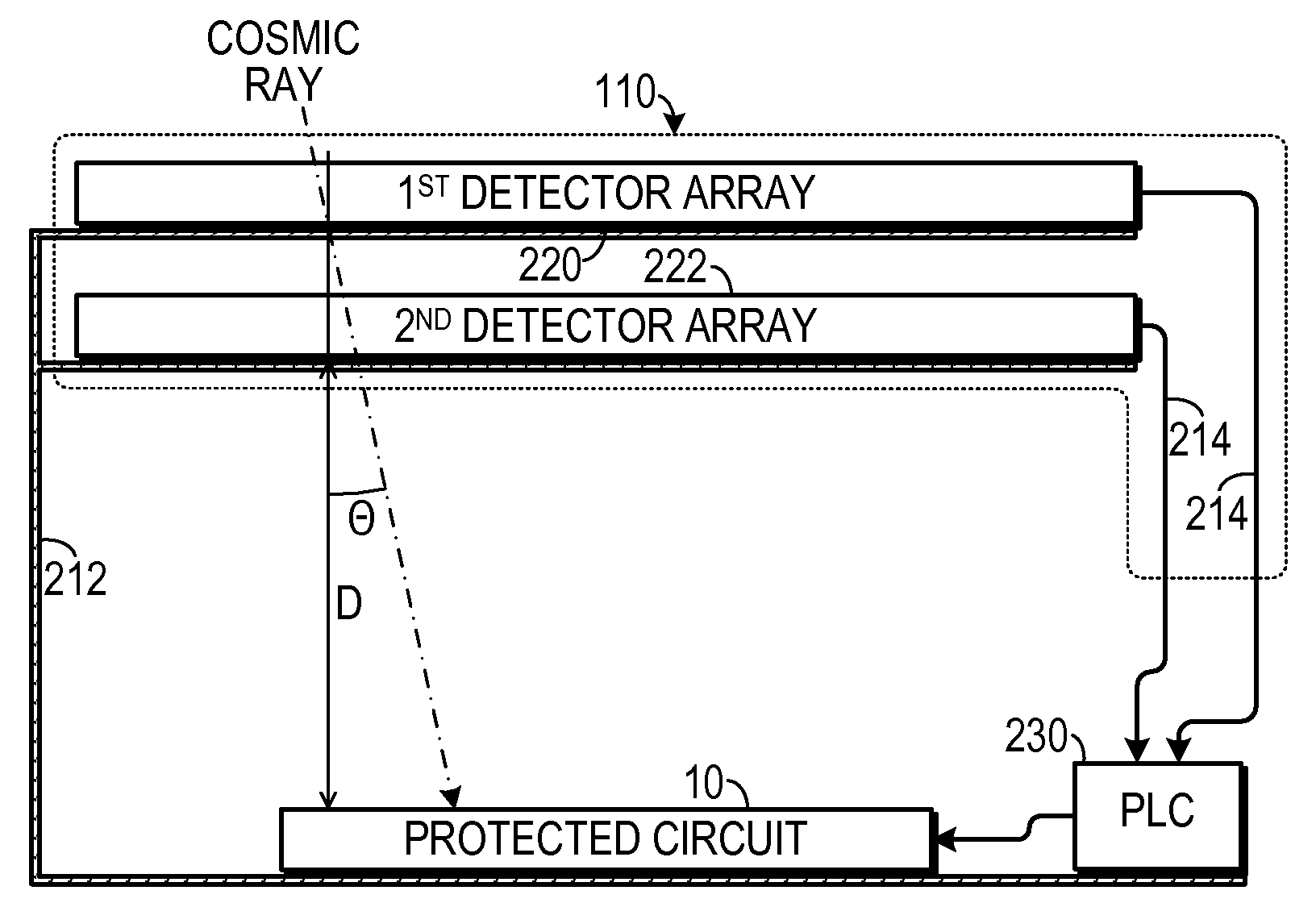
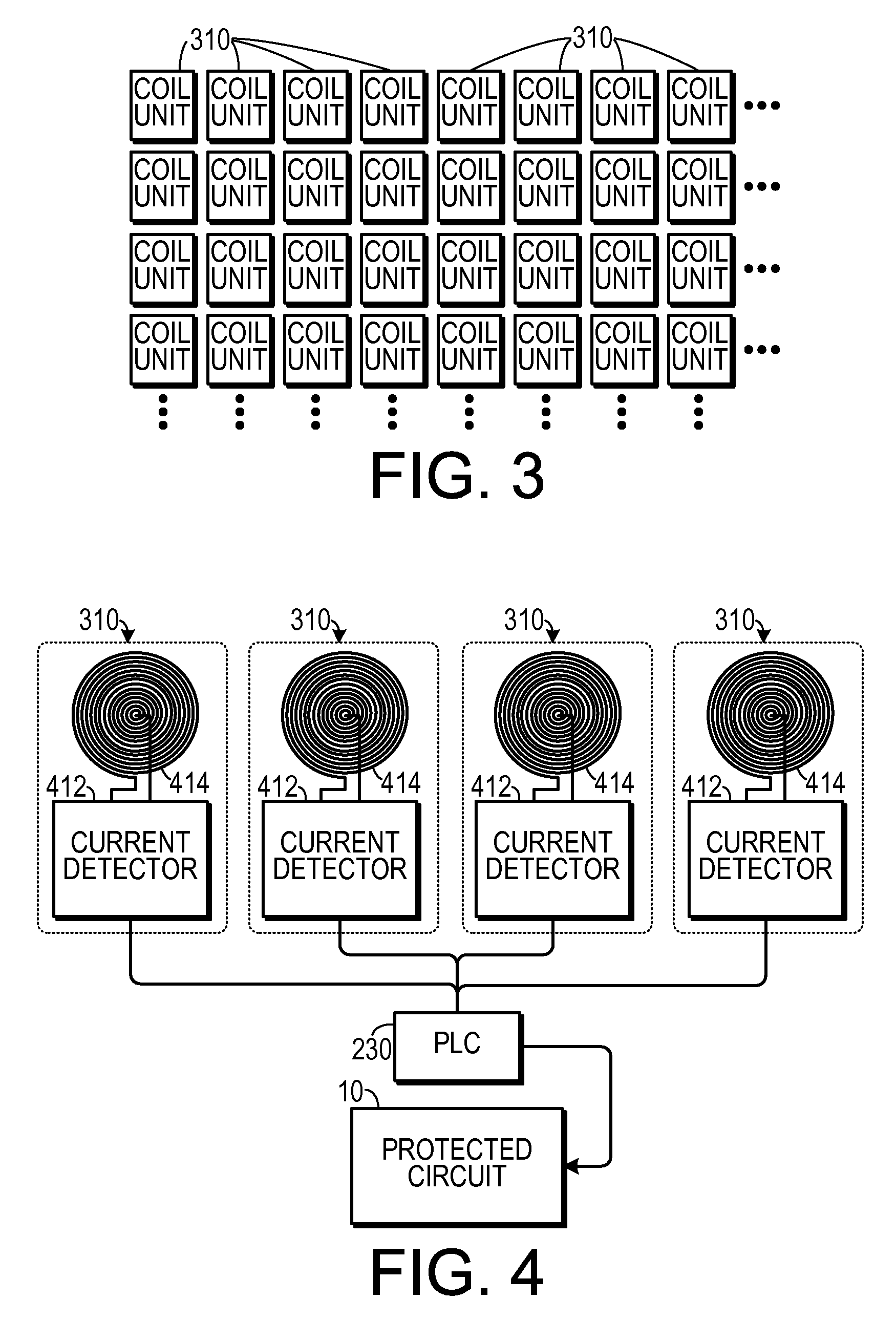
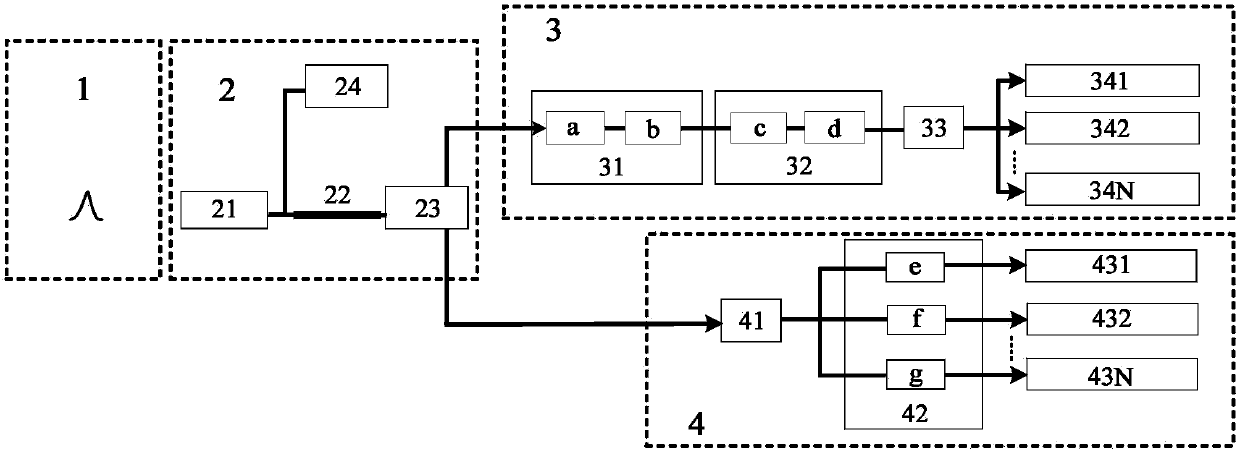
Magnetic Induction Grid as an Early Warning Mechanism for Space Based Microelectronics
InactiveUS20090231771A1Overcome disadvantagesMagnetic/electric field screeningArrangements responsive to excess currentEngineeringElectron
A system for protecting an electronic device from cosmic rays includes a frame in which the circuit is disposed, a cosmic ray detection circuit and a protection circuit. The cosmic ray detection circuit is supported by the frame and is spaced apart from the circuit. The cosmic ray detection circuit is configured to assert an incoming cosmic ray signal when a cosmic ray interacts with the cosmic ray detection device. The protection circuit is coupled to the incoming cosmic ray signal and is configured to cause the electronic device to enter a protected state when the cosmic ray signal is asserted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Scintillation detector system for system trigger and waveform measurement and method thereof
InactiveCN104020484ASolve false triggersSolve the problem of waveform measurement distortionRadiation intensity measurementUltrasound attenuationTime domain
The invention discloses a scintillation detector system for system trigger and waveform measurement and a method thereof. The technical problem that a single scintillation detector system realizes system trigger and pulse full-waveform measurement diagnosis during waveform measurement in a pulse radiation field is solved. The system has the following main characteristics: on one hand, the influence of cosmic rays and dark noise on the trigger function of a detector is effectively avoided by the adoption of a passive filter technology; and on the other hand, the influence of time-domain reflectometry caused by impedance mismatching on full-waveform measurement of the detector is effectively overcome by full utilization of the unique performance of a passive broadband attenuator in attenuation of both forward and backward signals. Meanwhile, a low noise amplifier is utilized to amplify signals, and it is guaranteed that signal amplitude of the line is unchanged. Thus, reliable trigger is guaranteed, and it is guaranteed that a filter circuit will not influence full-waveform measurement of another line. Efficiency of the detector system is effectively raised, and the system has a function of reliably monitoring running status at real time.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
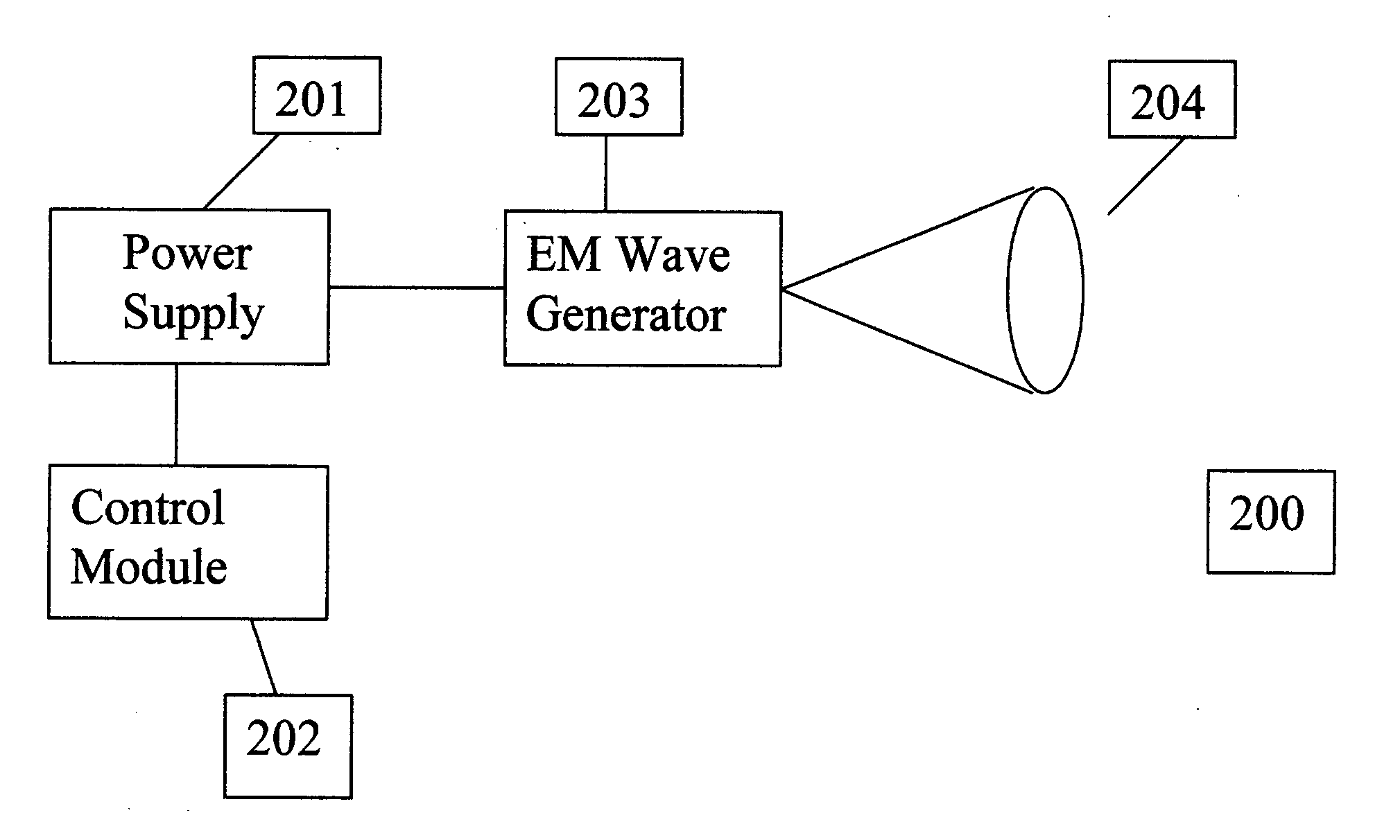
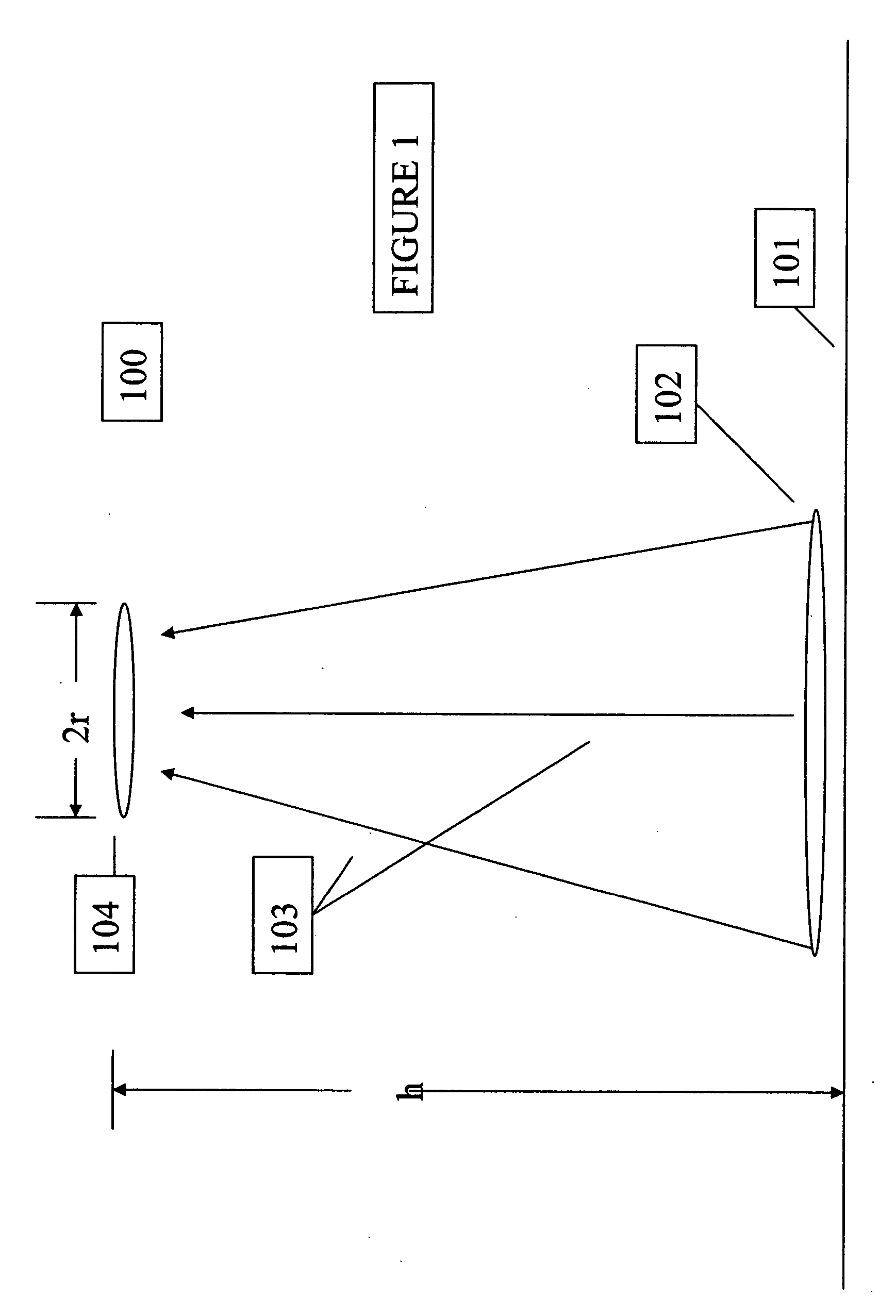
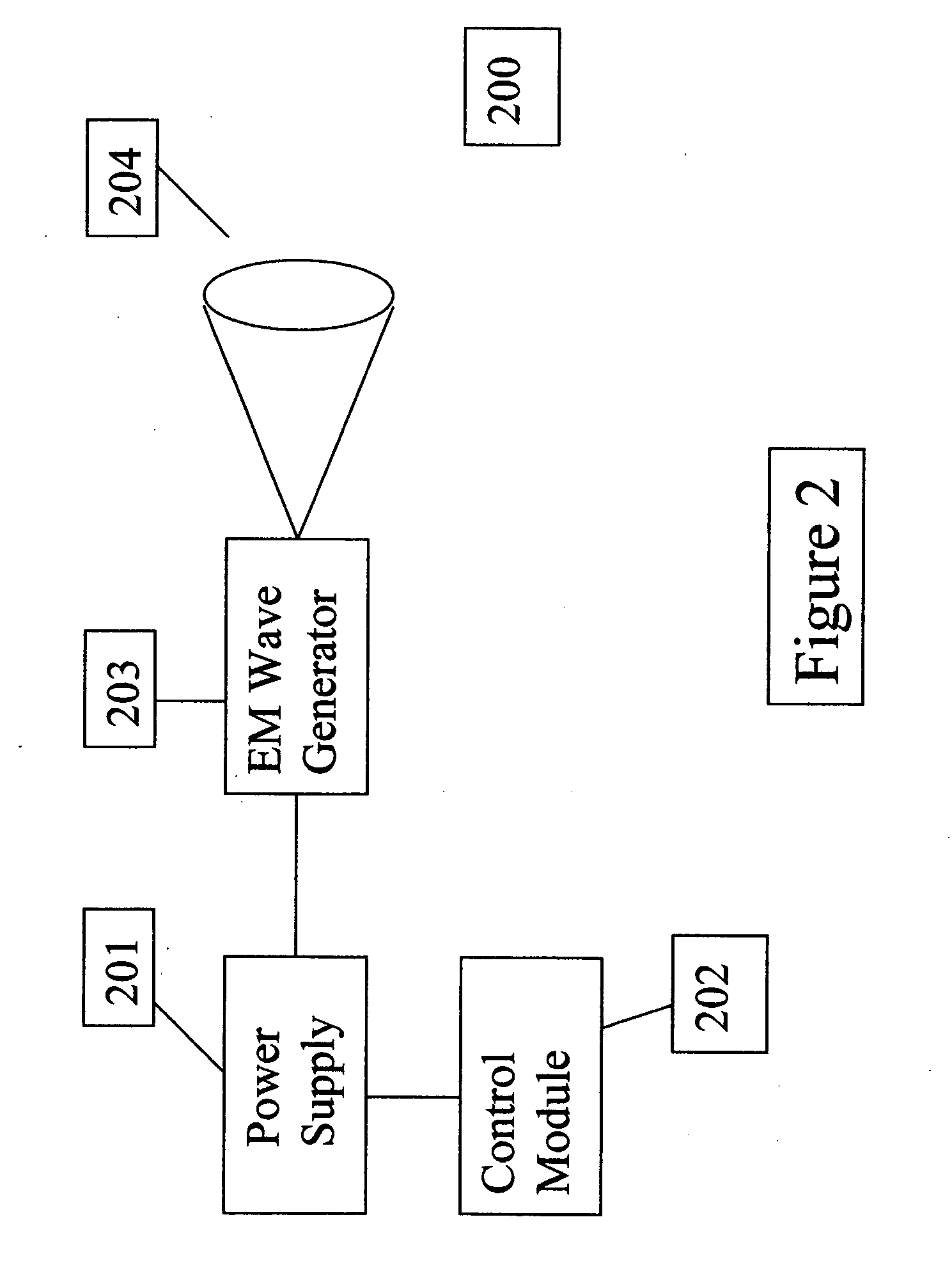
Cosmic particle ignition of artificially ionized plasma patterns in the atmosphere
InactiveUS20070238252A1Reduced to practiceReduced Power RequirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWeather influencing devicesAtmospheric sciencesIonization
This invention is a method and apparatus for creating artificially ionized regions in the atmosphere utilizing ionization trails of cosmic rays and micro-meteors to ignite plasma patterns in electric field patterns formed by ground based electromagnetic wave radiators. The applications are useful for telecommunications, weather control, lightening protection and defense applications. The invention lowers the power requirements for forming artificial ionized regions in the atmosphere by a factor of up to 1600 times lower than those required in existing designs and projections for creation of artificial ionized regions in the atmosphere.
Owner:EASTLUND BERNARD
Detector for alpha particle or cosmic ray
A detector circuit and method for detecting a silicon well voltage or current to indicate an alpha particle or cosmic ray strike of the silicon well. One significant application for the detection circuit of the present invention is for the redundancy repair latches that are used in SRAMs. The redundancy repair latches are normally written once at power-up to record failed latch data and are not normally written again. If one of the latches changes states due to an SER (Soft Error Rate-such as a strike by an alpha particle or cosmic ray) event, the repair data in the redundancy latches of the SRAM would now be incorrectly mapped. The detector circuit and method monitors the latches for the occurrence of an SER event, and responsive thereto issues a reload of the repair data to the redundancy repair latches. A first embodiment of the detector circuit differentially detects the floating voltages of first and second silicon wells during periods of non-operation of the circuits fabricated in the first and second silicon wells. In a second embodiment, a detector circuit monitors the background voltage level of a single silicon well over first and second consecutive periods of time. A second application for the detection circuit is for traditional logic circuits.
Owner:IBM CORP
Triboelectrification and electrostatic dissipation detection analysis device for space environment
ActiveCN108872726AReal-time acquisition of triboelectricityReal-time access to friction performanceElectrical measurementsElectricitySpace environment
The invention relates to the technical field of triboelectrification, and especially relates to a triboelectrification and electrostatic dissipation detection analysis device for a space environment.The device comprises a vacuum system, a cosmic ray radiation system, an alternating temperature system, a sliding friction and contact separation friction integrated drive unit, and an electrostatic detection system. The device can achieve the observation and analysis of the triboelectrification and electrostatic discharge parameters of a material in the space environment in real time, and has a higher application value for the selection and design of the triboelectrification and electrostatic discharge and electrostatic resistant materials of a spacecraft.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for simulating space astronomy cosmic ray observation image
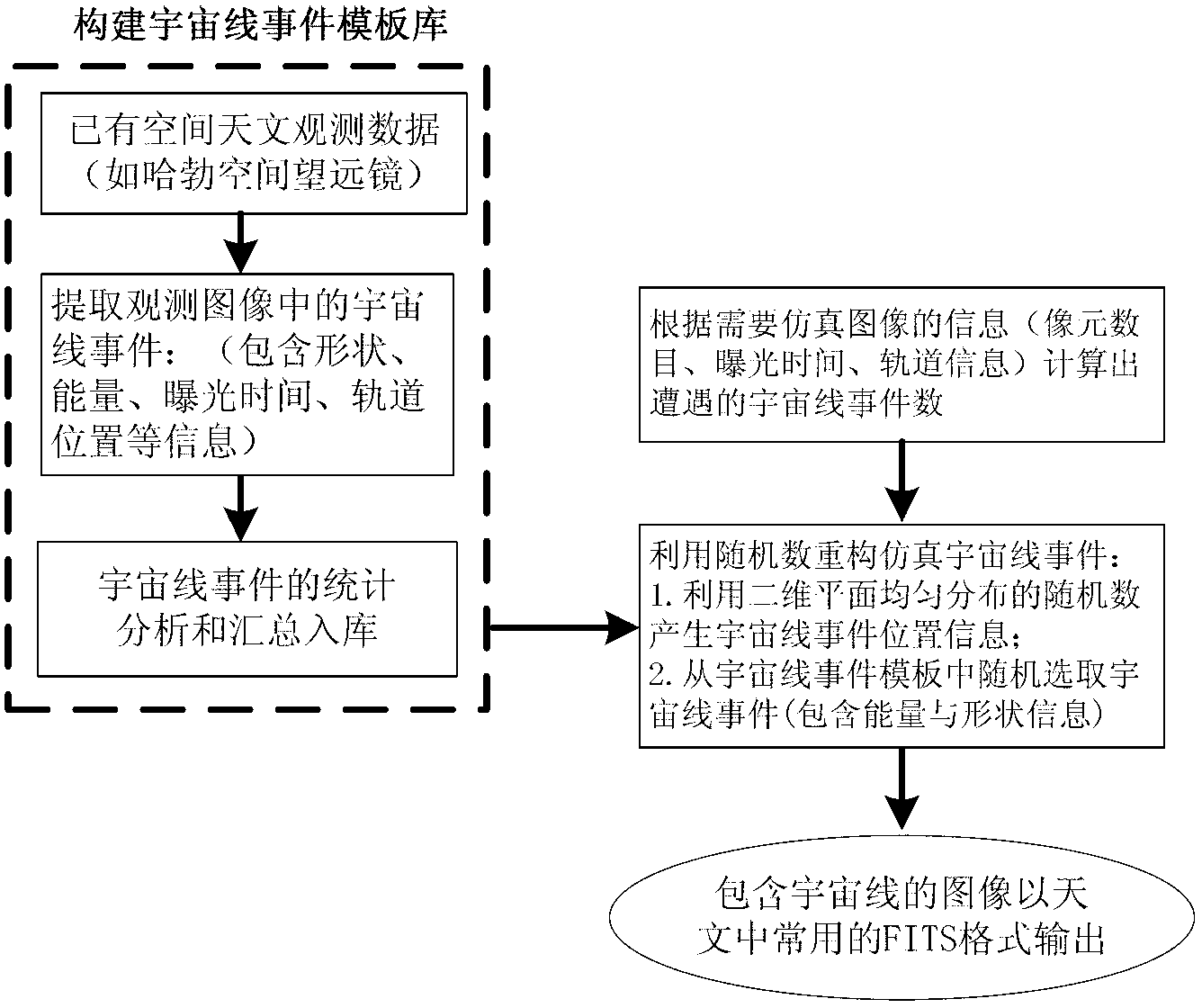
InactiveCN103324812AThe characteristic parameters are true and reliableThe number of image spots is real and reliableSpecial data processing applicationsComputer visionTelescope
The invention discloses a method for simulating a space astronomy cosmic ray observation image. The method comprises a first step of choosing existing space telescope images according to the characters of a space astronomy observation instrument which needs simulating, a second step of grouping the space telescope images according to different orbital positions in the process of observing, wherein each group of images are processed by the following steps, firstly, all cosmic ray events in the images are extracted to establish cosmic ray event template libraries, and secondly, the statistic analysis is carried out on the cosmic ray event template libraries established for each group of images, the statistic process is carried out on the quantity of encountered events on a CCD target face in unit picture element area and in unit time, the quantity of the encountered events is recorded as the cosmic ray encounter rate CRsRate, and the statistic process is carried out on the energy distribution of the cosmic ray events and the number of picture elements occupied by each cosmic ray event, a third step of extracting the cosmic ray events from the cosmic ray event template libraries according to the information of images to be simulated, a fourth step of generating simulation cosmic ray images through the extracted cosmic ray events in the third step, the remaining picture elements, except the cosmic ray events, in the images serve as the background, and the value of the remaining picture elements is set to be zero.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method, device and system for inspecting object based on cosmic ray
ActiveCN105700029AQuality improvementImprove security inspection efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentObject basedRadio imaging
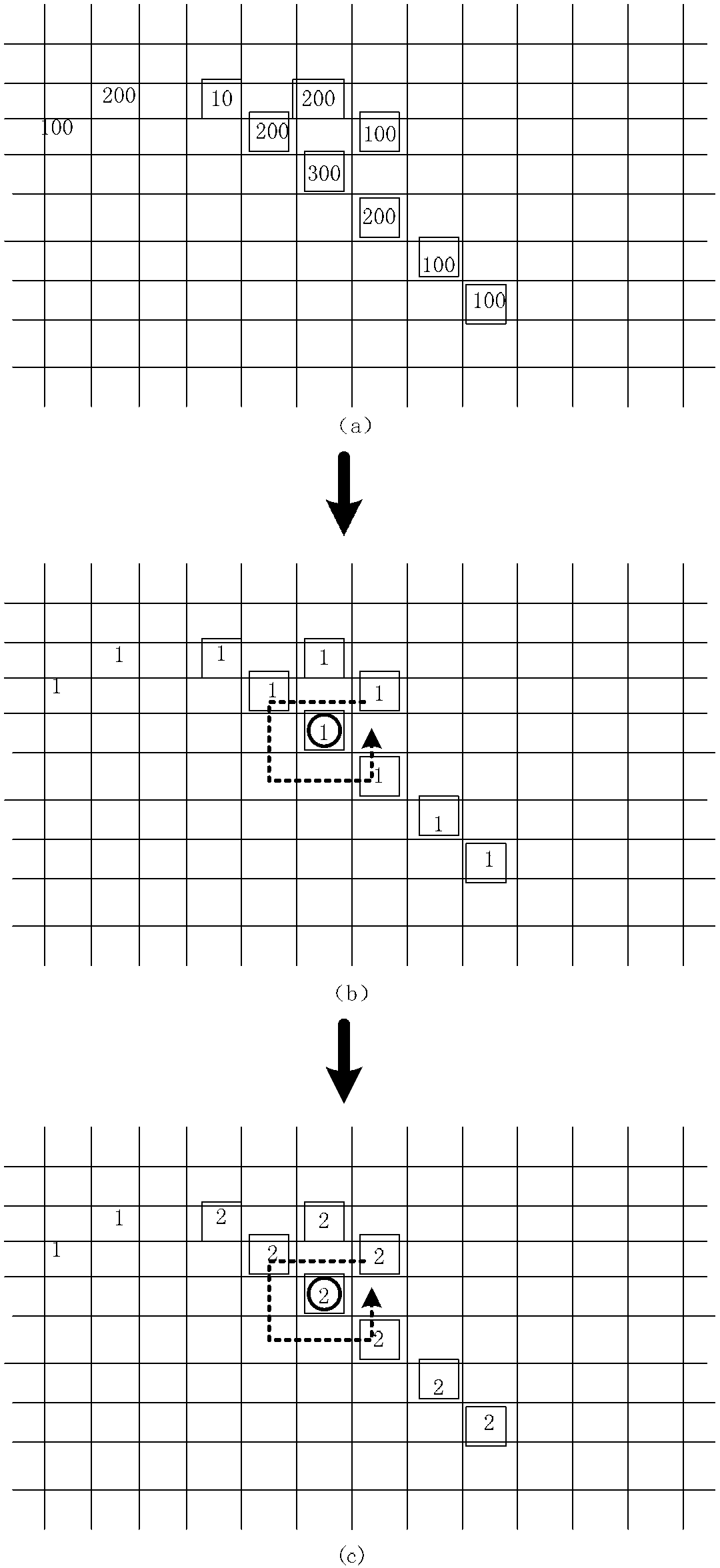
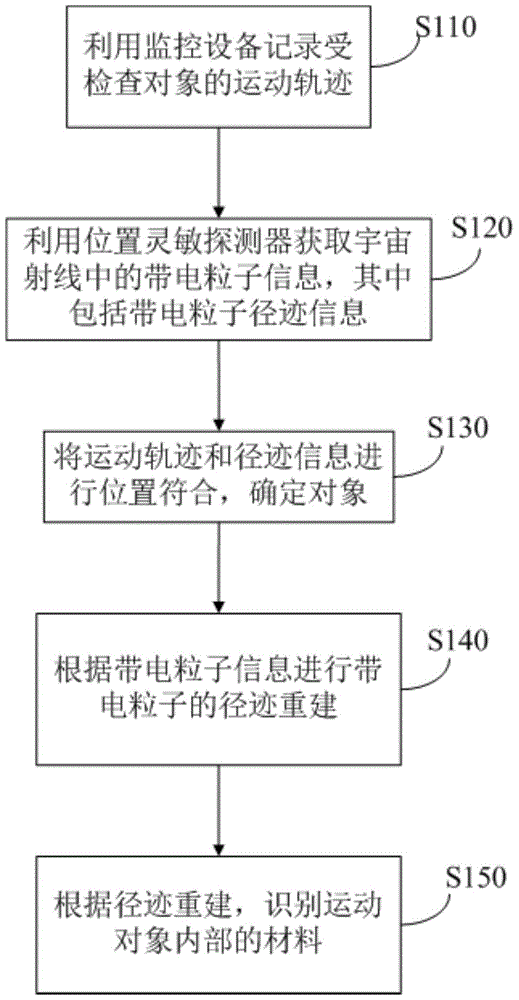
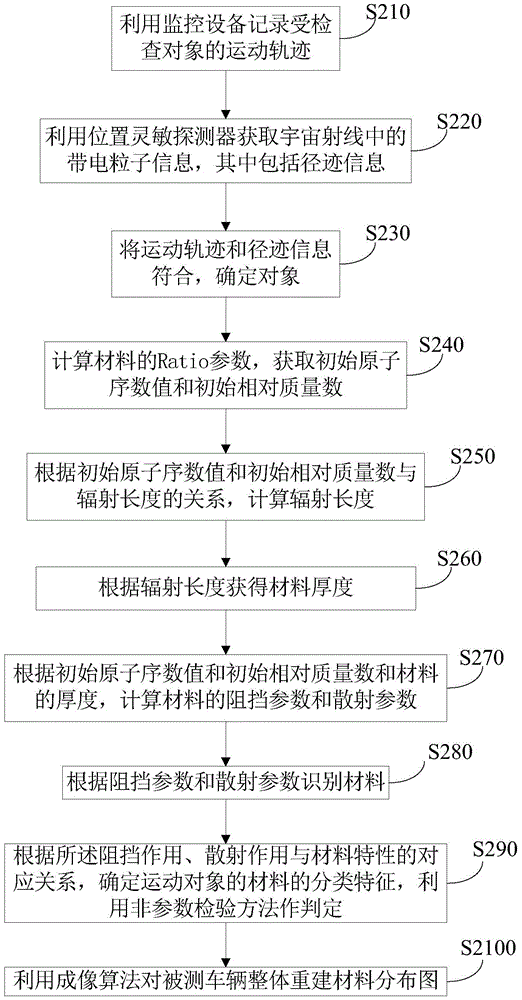
The invention relates to a method, device and system for inspecting an object based on a cosmic ray, and belongs to the technical field of radio imaging and safety inspection. The method comprises the steps: recording the movement track of an inspected object through the record of monitoring equipment; obtaining the information of charged particles in the cosmic ray through employing a position sensitivity detector, wherein the information of the charged particles comprises the track information of the charged particles; carrying out the position according of the movement track and the track information, and determining the object; carrying out the track remodeling of the charged particles according to the information of the charged particles; and recognizing the internal material of the movement object according to the track remodeling. The method inspects a moving person, and can detect a nuclear material, narcotics and explosives carried by the person.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
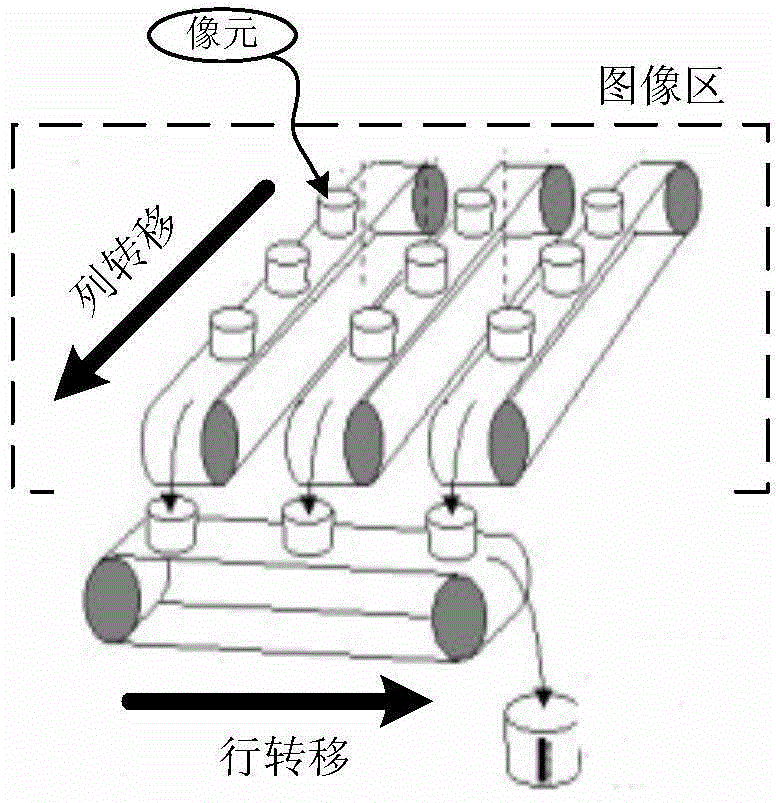
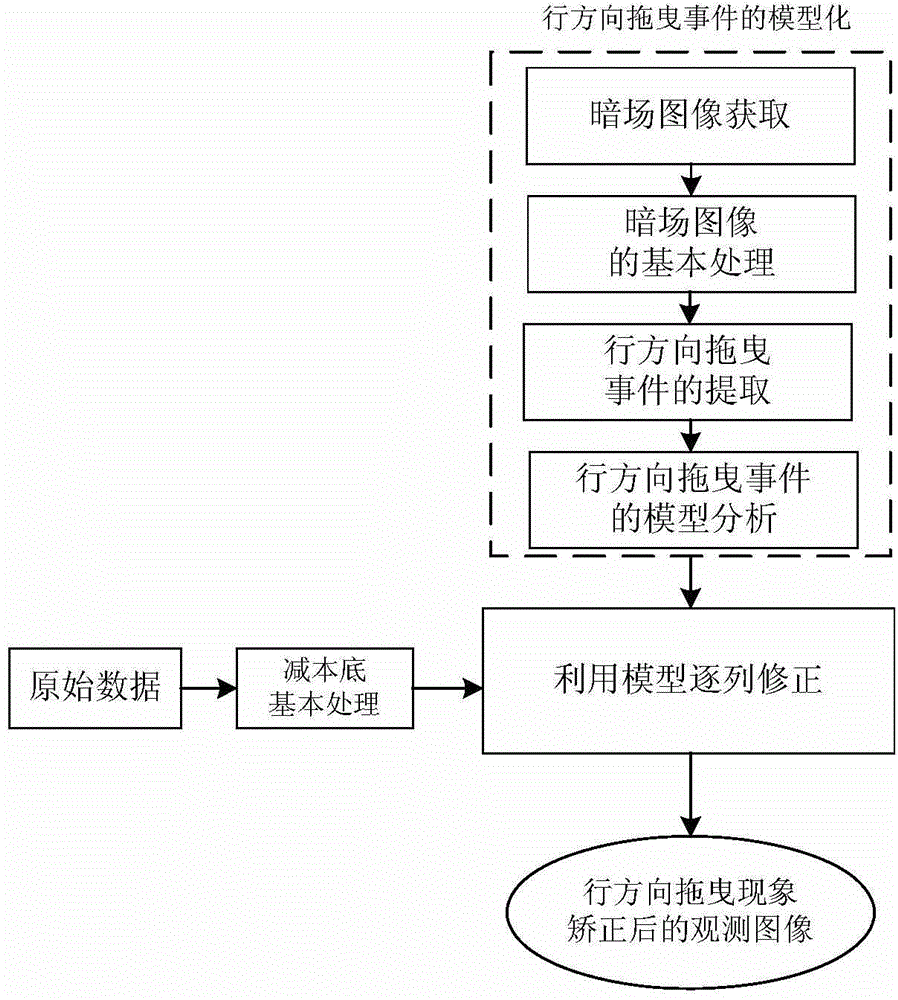
Method for correcting line-direction dragging of image observed by lunar-based astronomical telescope
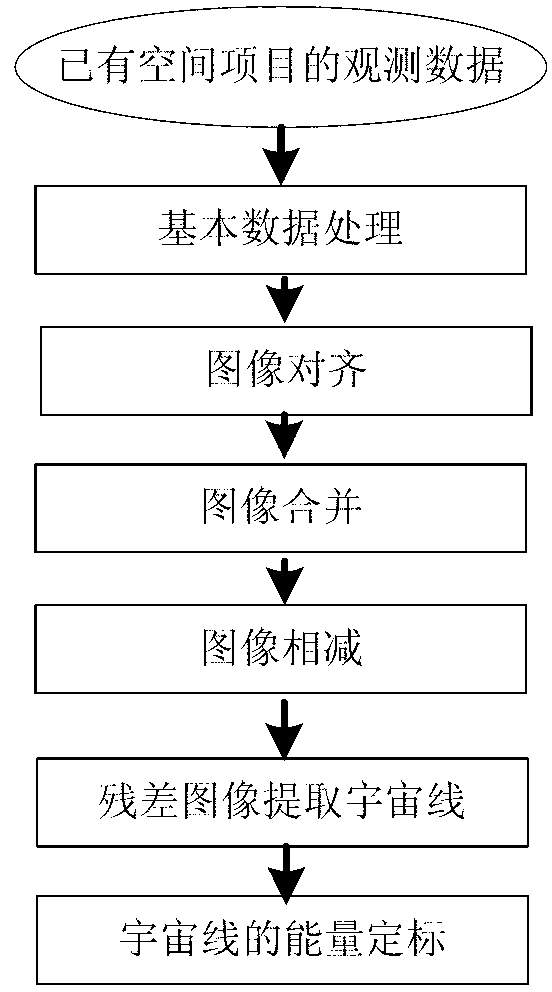
InactiveCN104574269AEasy to implementEasy accessGeometric image transformationModel parametersAstronomical telescopes
A method for correcting line-direction dragging of an image observed by a lunar-based astronomical telescope comprises the steps of 1, acquiring a dark field image and processing the dark field image to obtain a super dark field image with cosmic ray interference eliminated; 2, extracting line-direction dragging events from the super dark field image; 3, conducting model fitting analysis on all the dragging events extracted in the step 2, so that model parameters are obtained; 4, conducting background subtraction on a primal space observation CCD image, and correcting the image obtained after background subtraction row by row by means of the model parameters obtained in the step 3, so that correction of line-direction dragging of the image observed by the lunar-based astronomical telescope is achieved.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adding entropy for improved random number generation in a computer system
InactiveUS20130086136A1Quality improvementRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsRelevant informationAlpha particle
A parallel computer system adds entropy to improve the quality of random number generation by using parity errors as a source of entropy because parity errors are influenced by external forces such as cosmic ray bombardment, alpha particle emission, and other random or near-random events. By using parity errors and associated information to generate entropy, the quality of random number generation in a parallel computer system is increased.
Owner:IBM CORP
Device and method for realizing high sensitivity detection on radioactive gas nuclide activity
InactiveCN106405615AImprove shielding effectReduce backgroundX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentBeta gamma coincidenceRadioactive gas
The invention discloses a device and a method for realizing high sensitivity detection on radioactive gas nuclide activity and solves a problem that cosmic rays generate coincidence background counting in a coincidence measurement system. The device comprises an inflatable beta detector, a gamma detector, an anti cosmic ray detector set and a digital coincidence circuit, wherein the beta detector and the gamma detector are arranged in a lead shield, the beta detector is arranged on the gamma detector in a bottom down mode, the anti cosmic ray detector set is used for shielding coincidence signals generated by the cosmic rays in the beta detector and the gamma detector, the anti cosmic ray detector set comprises five anti cosmic ray detectors which are respectively arranged at a top portion and periphery of the lead shield, output signals of the anti cosmic ray detectors, output signals of the beta detector and output signals of the gamma detector are respectively transmitted to the digital coincidence circuit to acquire gamma detector original spectra, anti cosmic ray gamma spectra, beta-gamma coincidence spectra and anti cosmic ray beta-gamma coincidence spectra. The device is advantaged in that radioactive gas nuclide detection sensitivity can be greatly improved.
Owner:北京放射性核素实验室
Method and apparatus for reconstructing particle track, and inspection method and inspection device
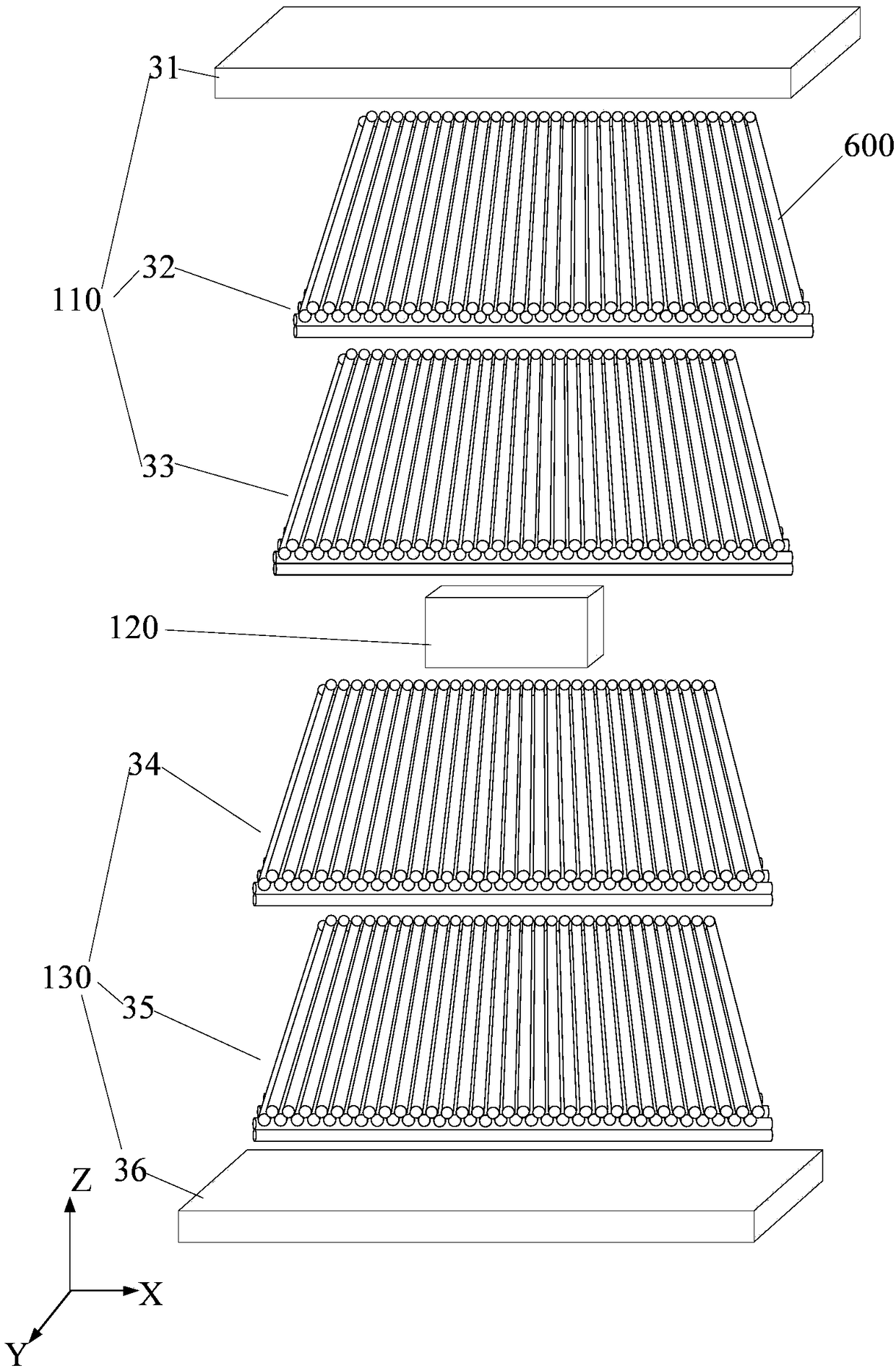
PendingCN109283588AAccurate reconstructionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionDrift tubeScintillator
A method and apparatus for reconstructing a track of cosmic ray particles, and an inspection method and inspection apparatus are disclosed. The method includes: detecting cosmic ray particles by usinga cosmic ray particle detector, wherein the cosmic ray particle detector includes at least one scintillator and a plurality of drift tubes, and charged particles in at least two of the plurality of drift tubes are drifted under the action of the cosmic ray particles; using at least one scintillator to record the time null point of the cosmic ray particles incident on the cosmic ray particle detector; calculating the drift time of the charged particles in the at least two drift tubes according to the time null point; determining positions at which the cosmic ray particles are incident on the at least two drift tubes on the basis of the calculated drift time; and fitting the track of the cosmic ray particles according to the determined positions at which the cosmic ray particles are incident on the at least two drift tubes.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD
Nondestructive inspection apparatus and nondestructive inspection method for composite structure
InactiveCN101971010ALow costUsing wave/particle radiation meansRadiation intensity measurementStress radiographyTime constant
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com