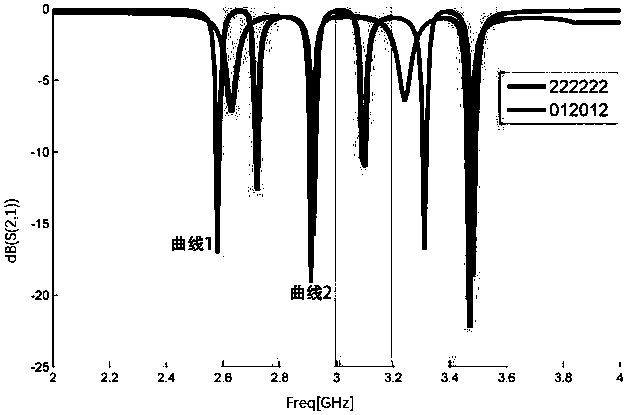
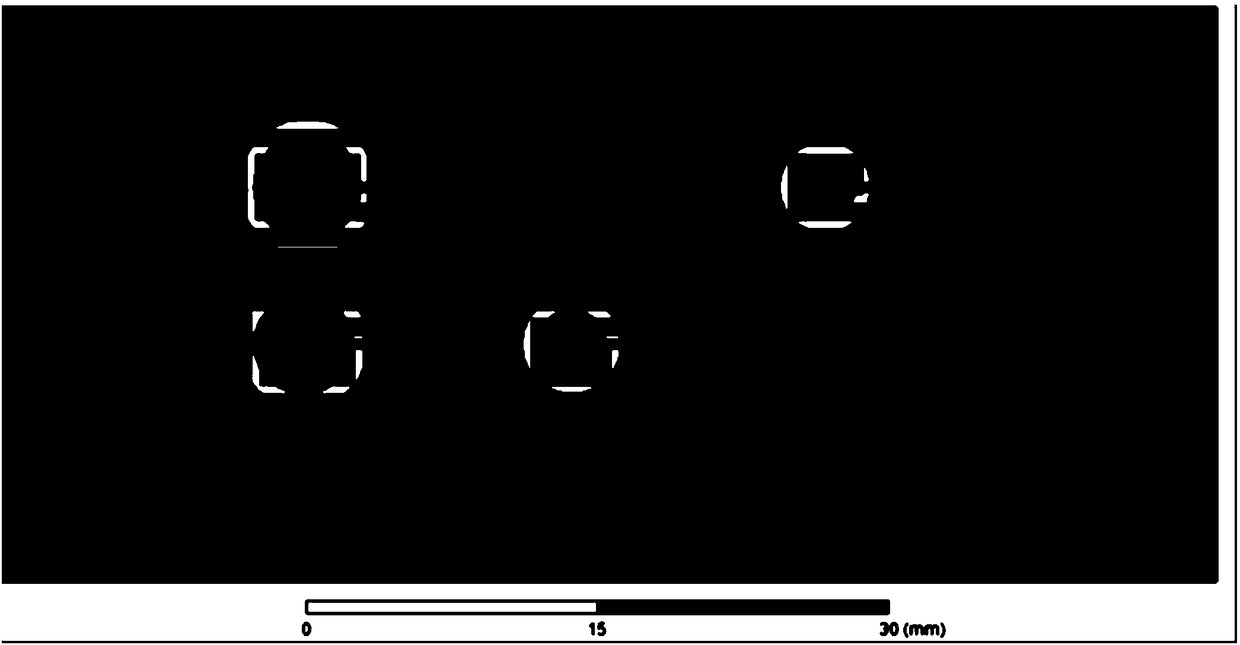
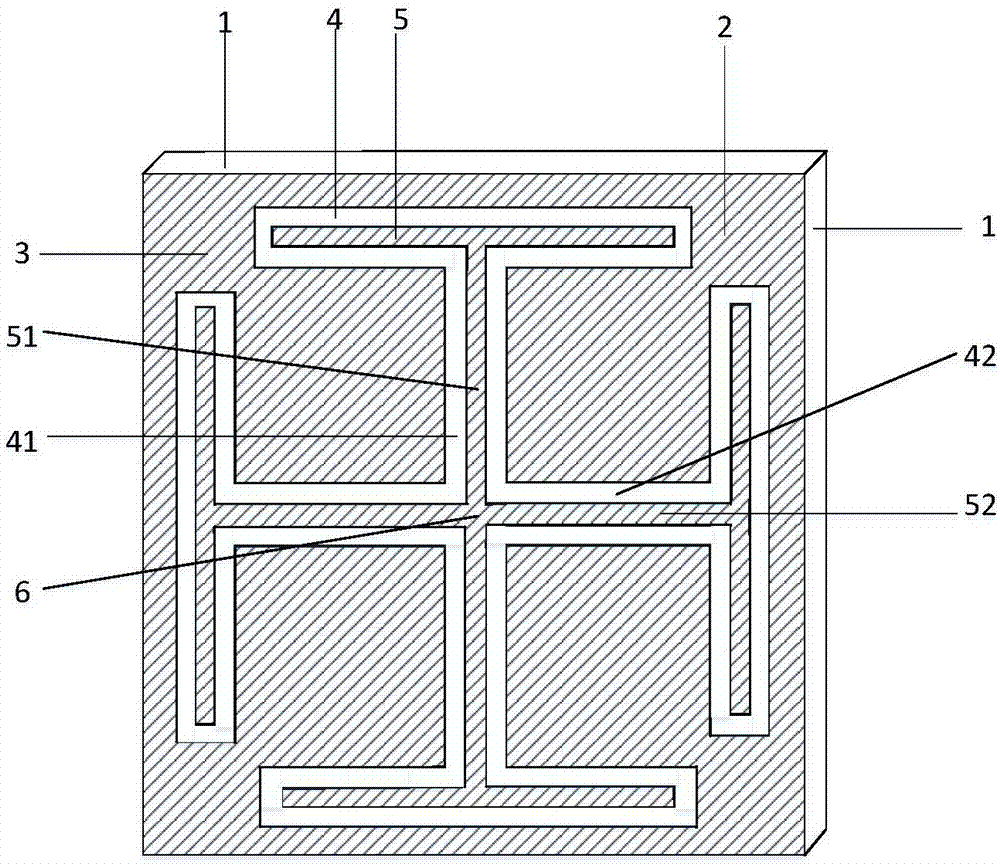
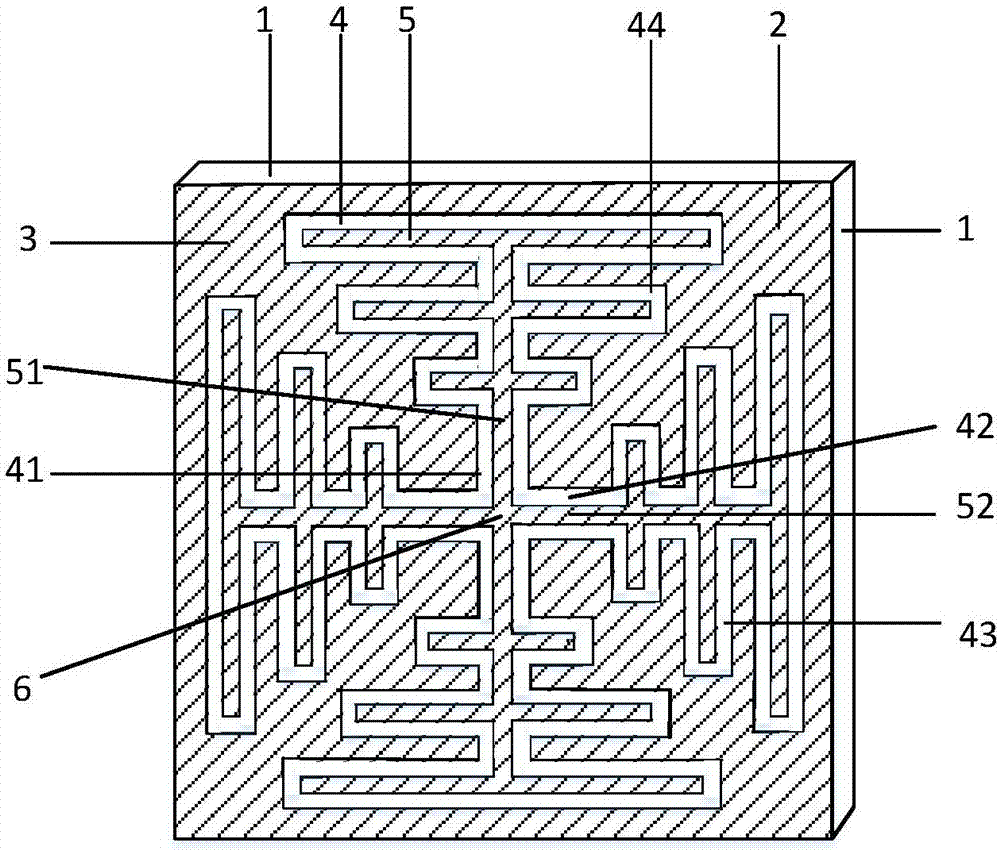
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Chipless RFID" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
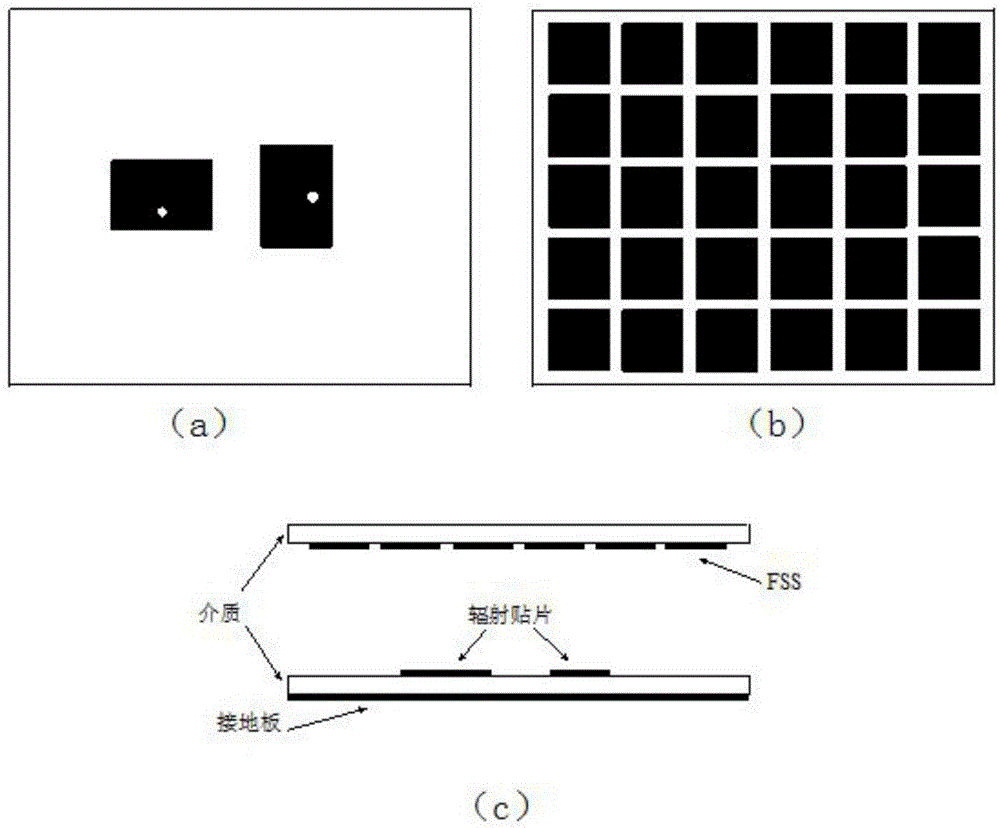
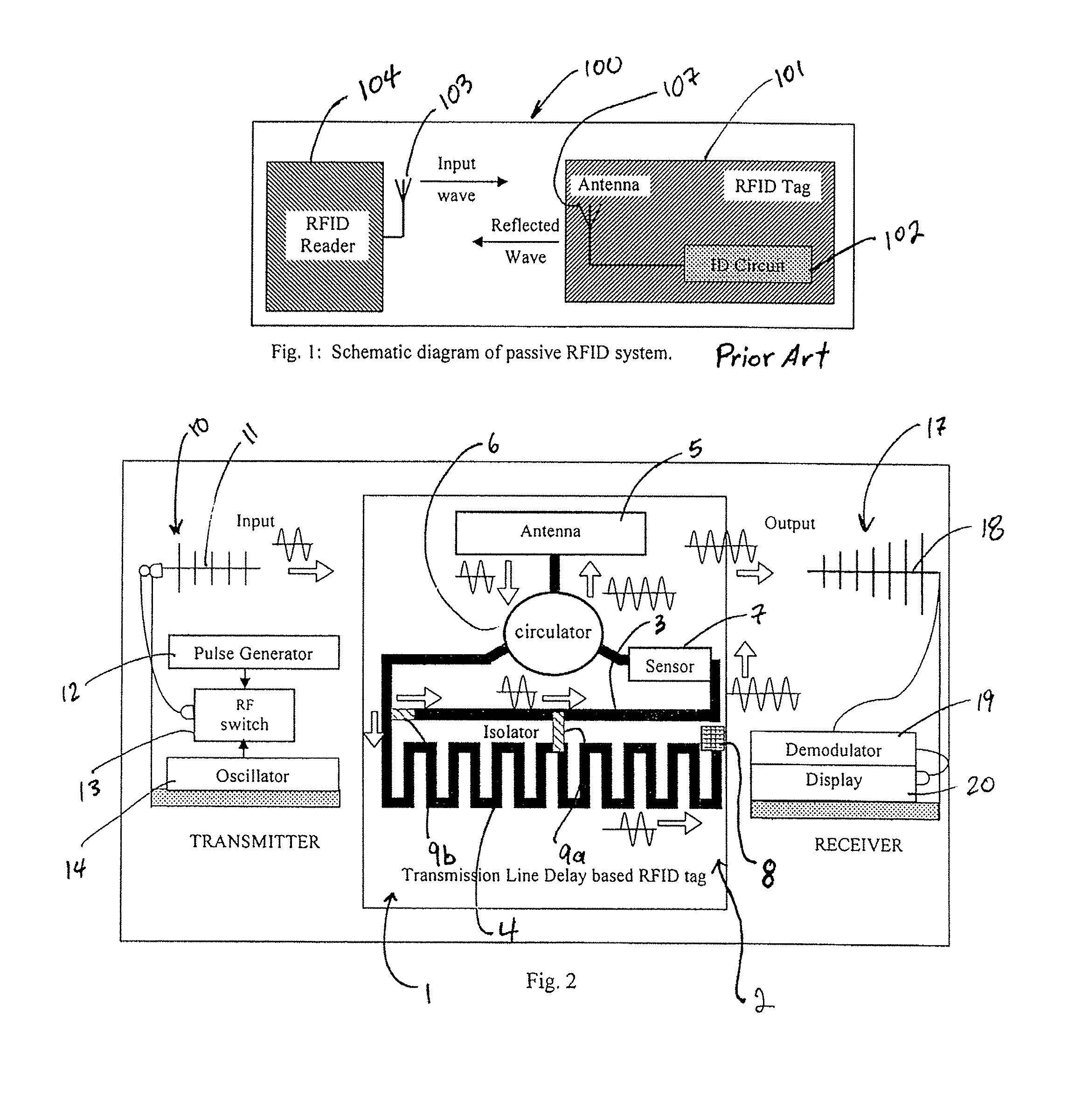
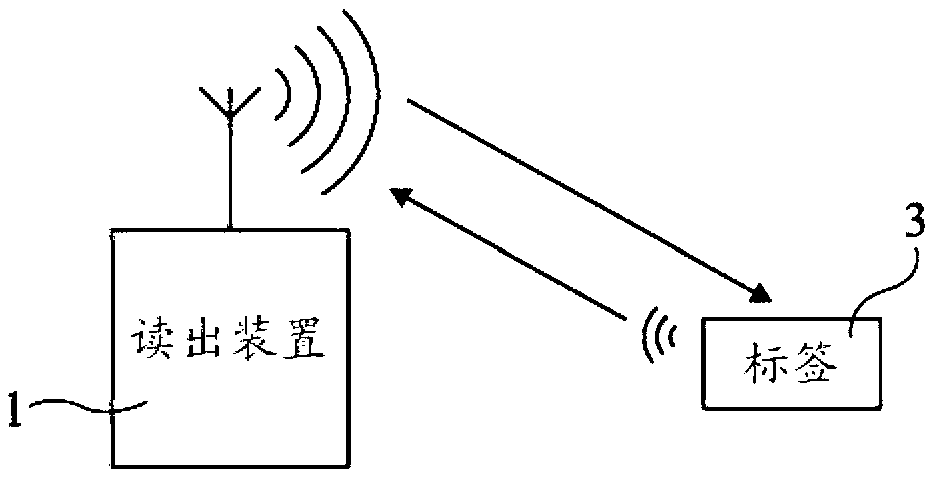
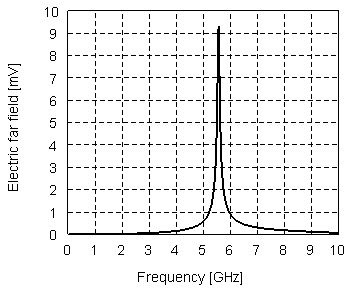
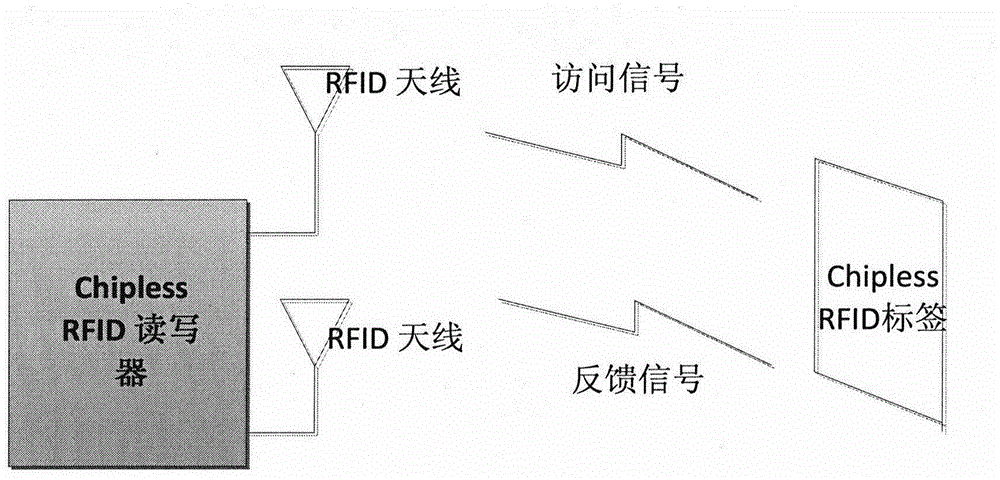
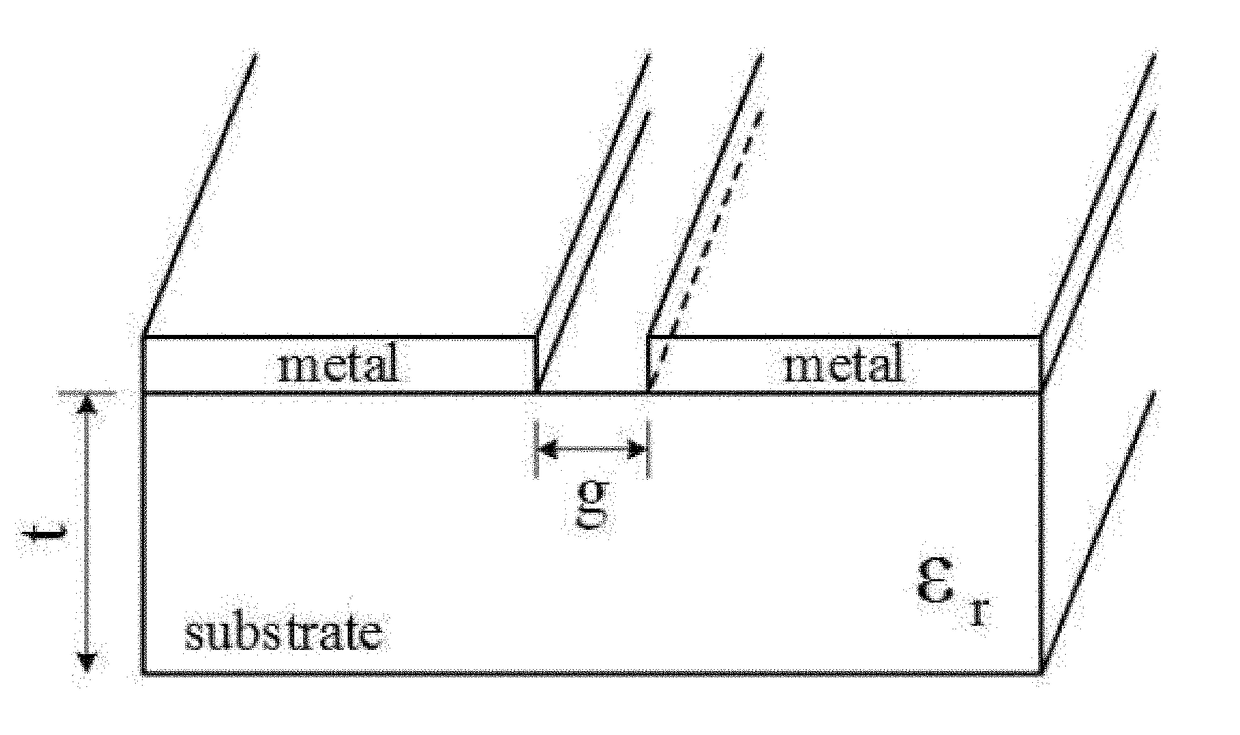
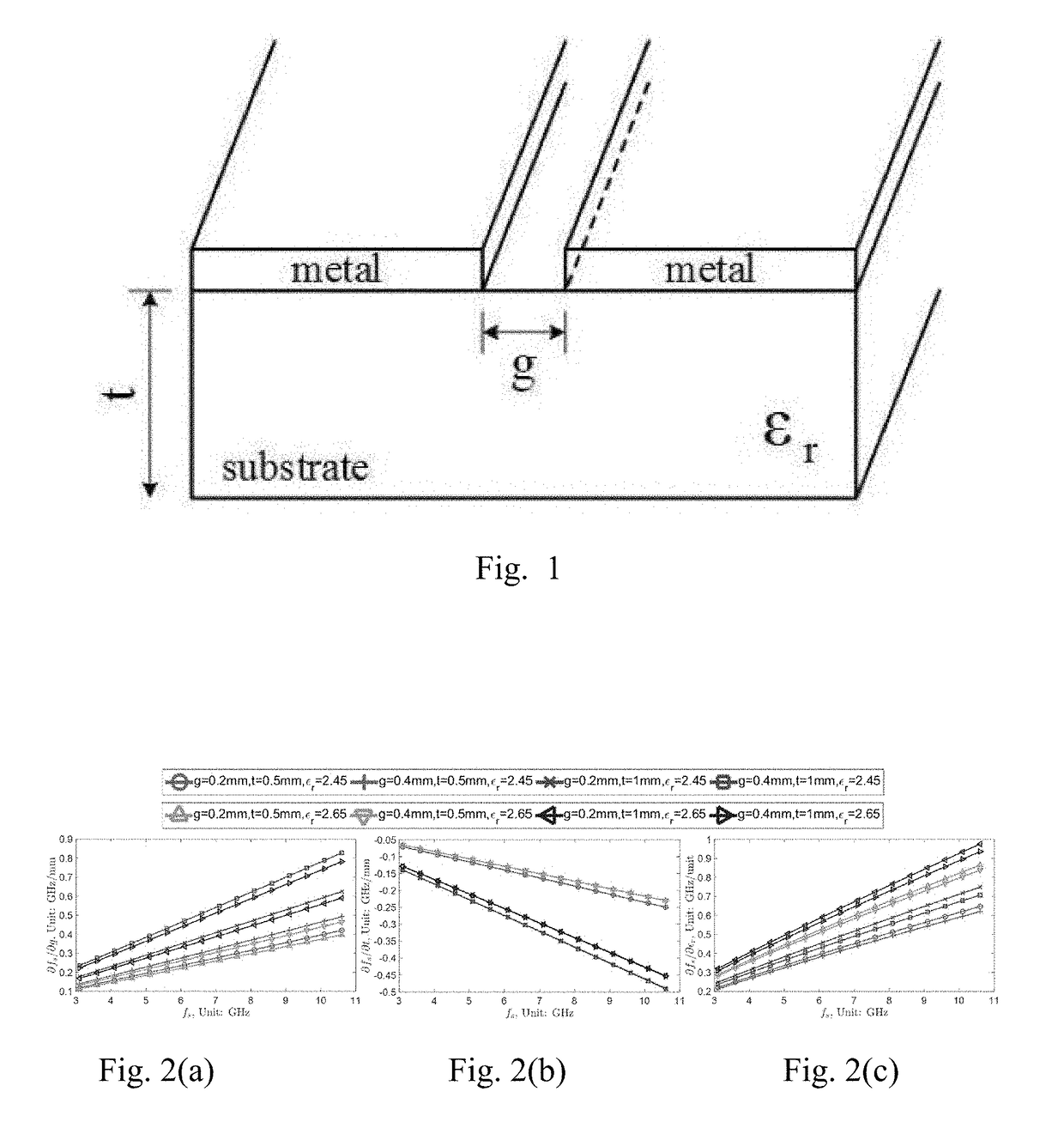
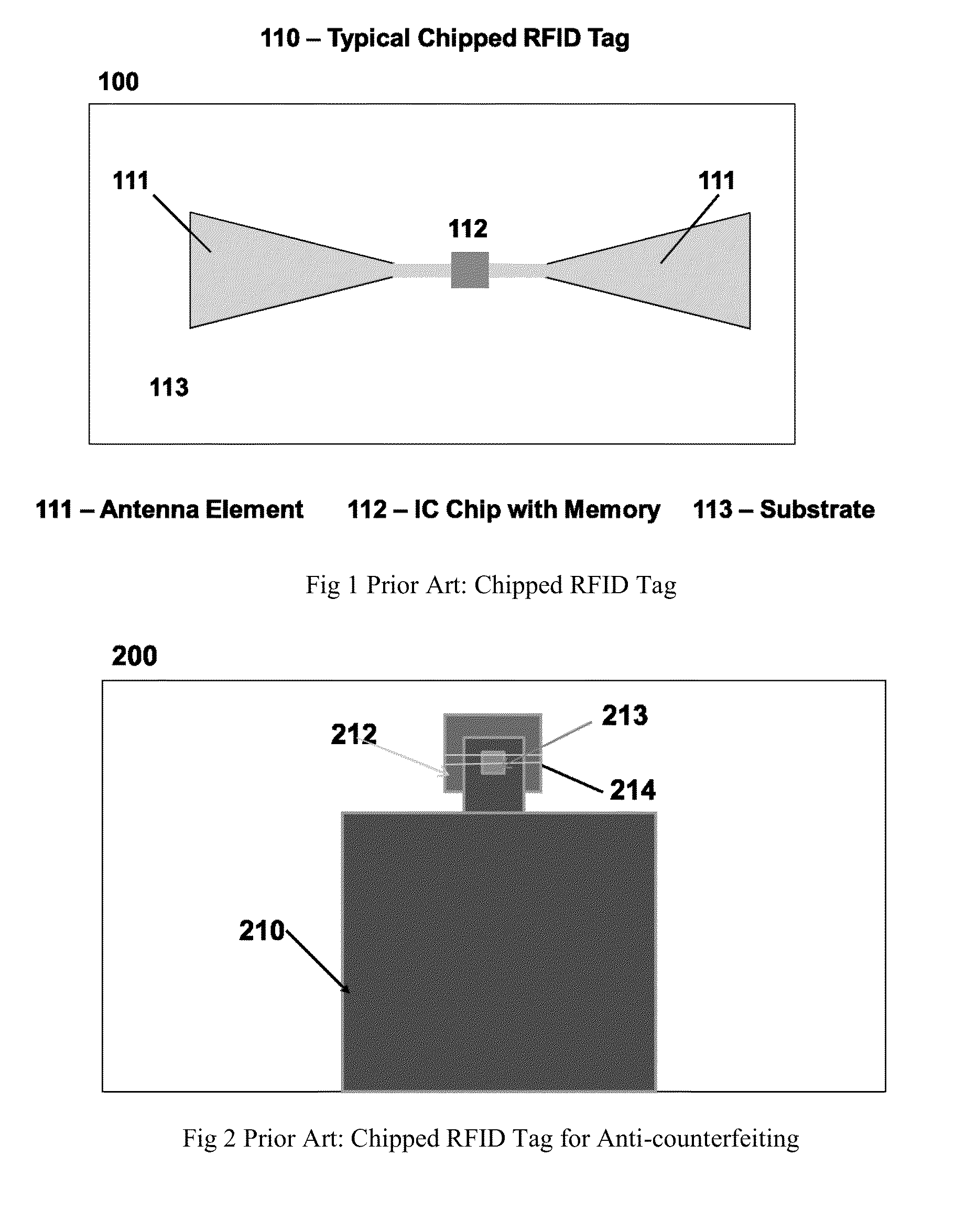
Chipless RFID tags are RFID tags that do not require a microchip in the transponder. RFIDs offer longer range and ability to be automated, unlike barcodes that require a human operator for interrogation. The main challenge to their adoption is the cost of RFIDs. The design and fabrication of ASICs needed for RFID are the major component of their cost, so removing ICs altogether can significantly reduce its cost. The major challenges in designing chipless RFID is data encoding and transmission.
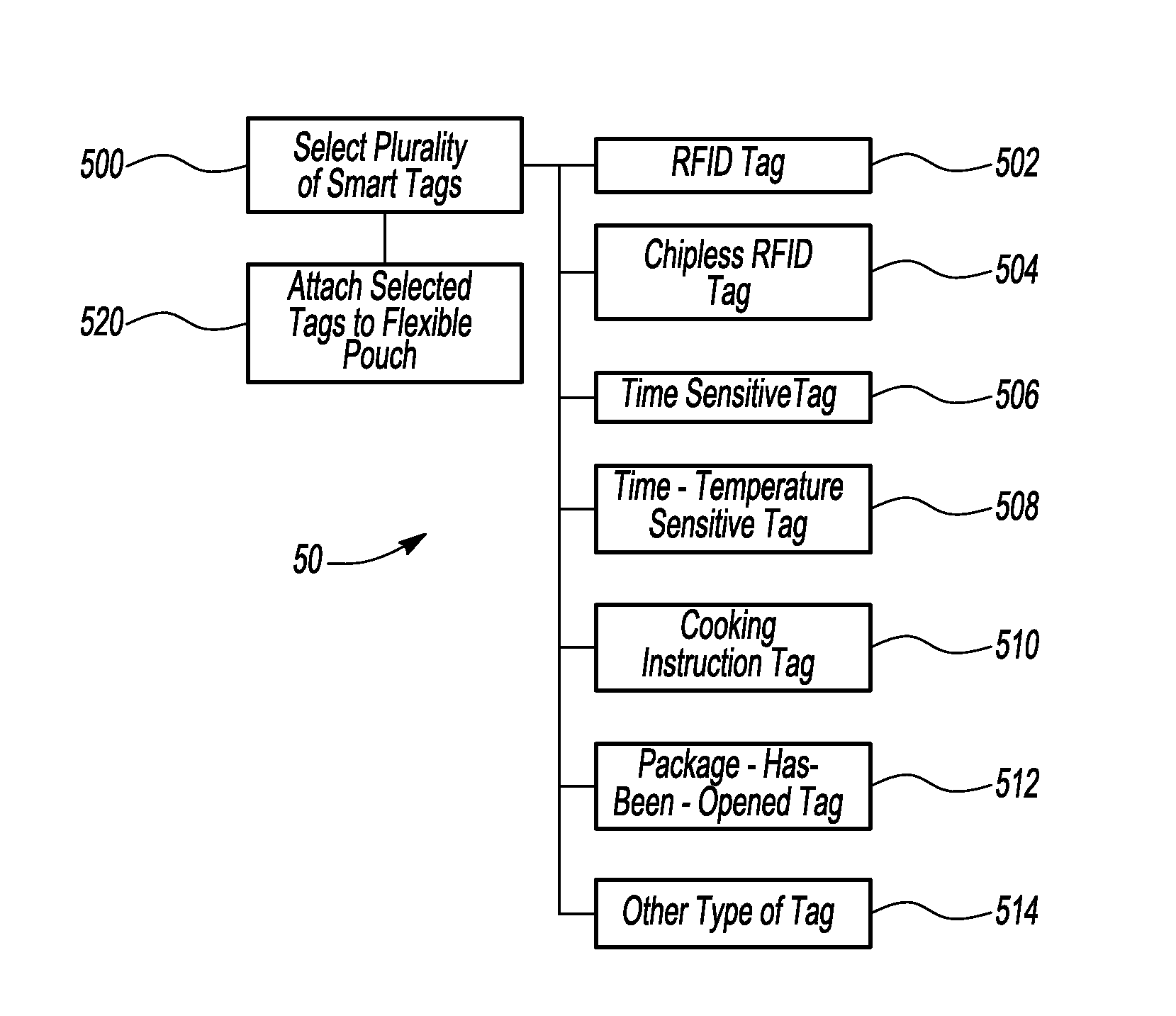
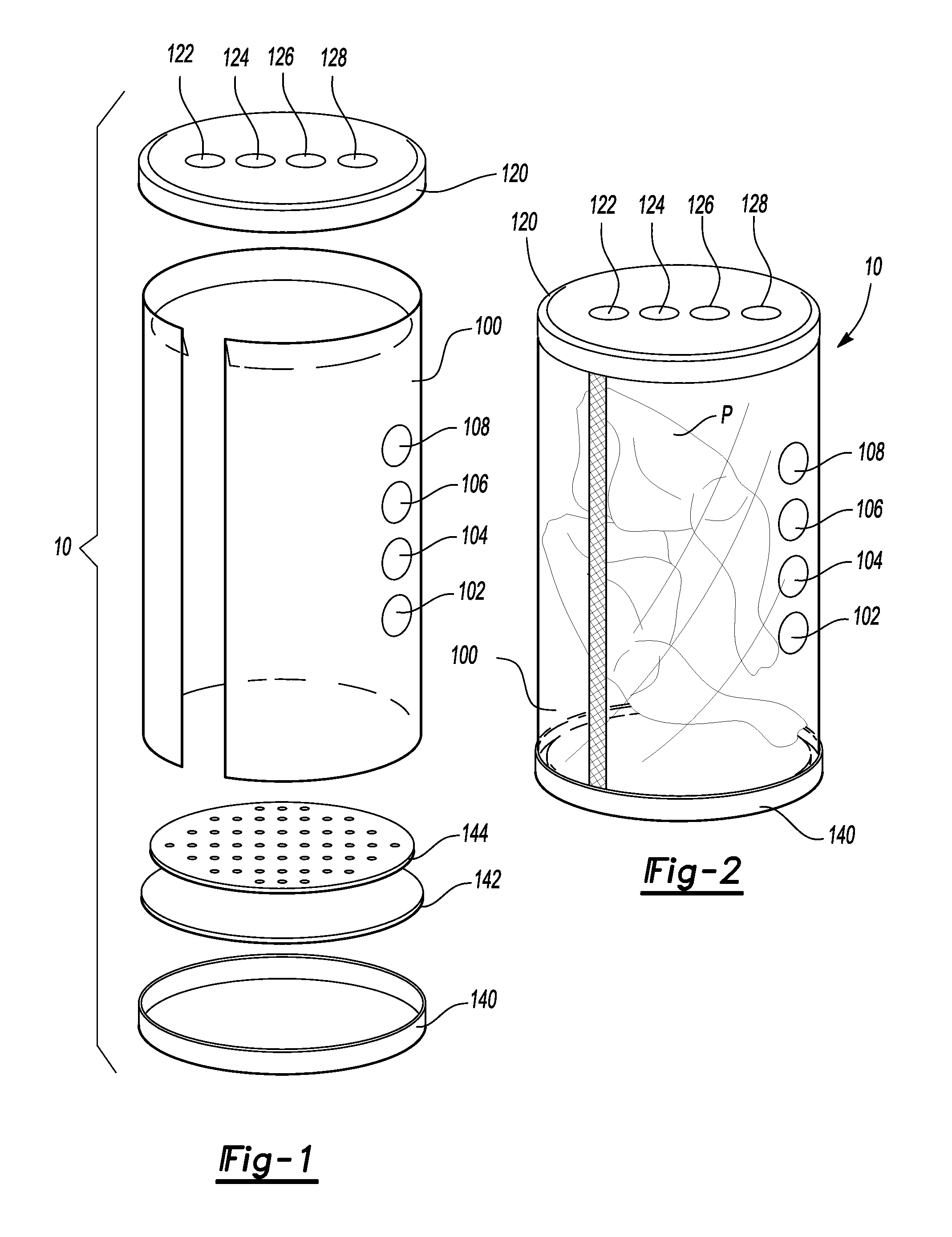
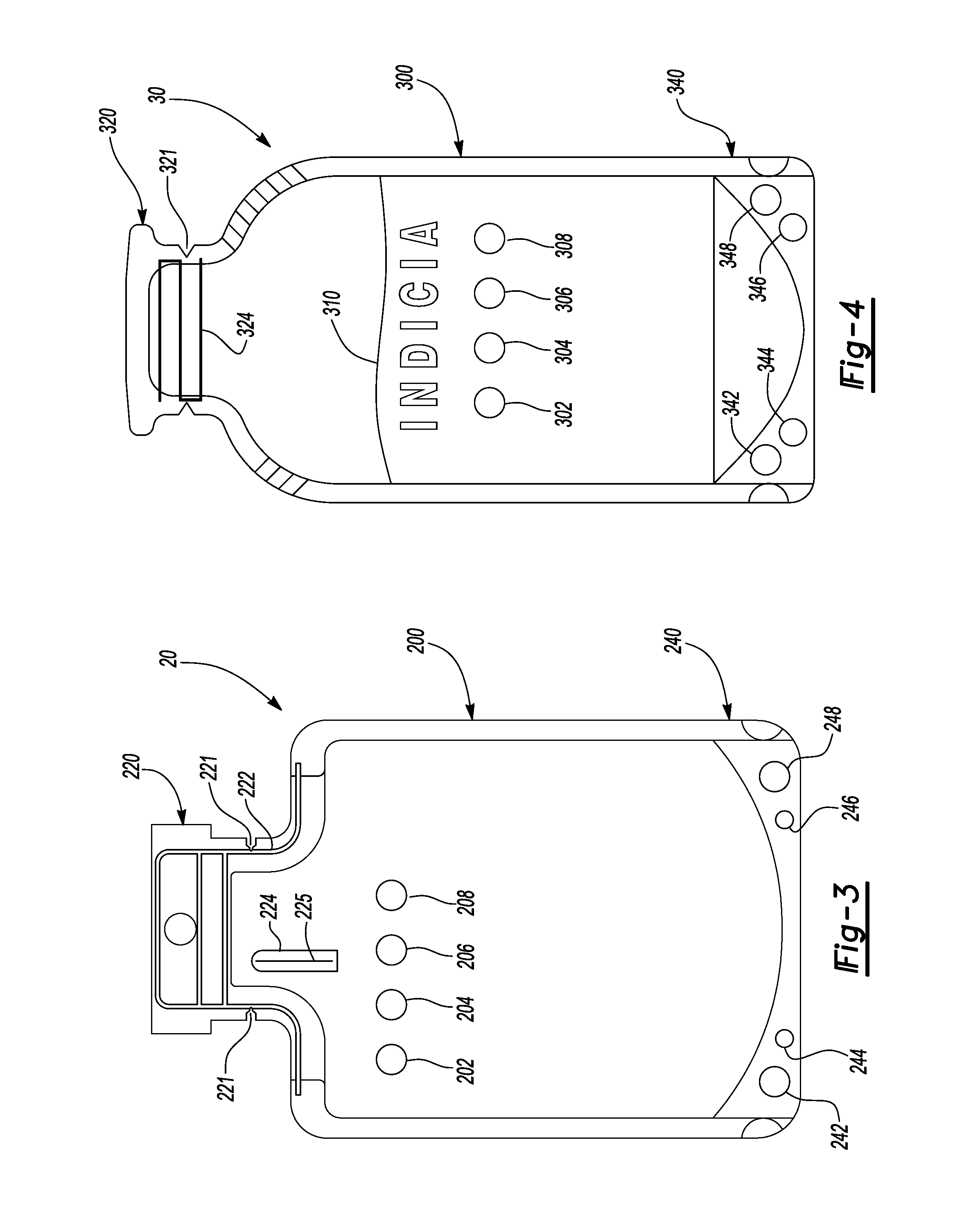
Flexible pouch with smart tags
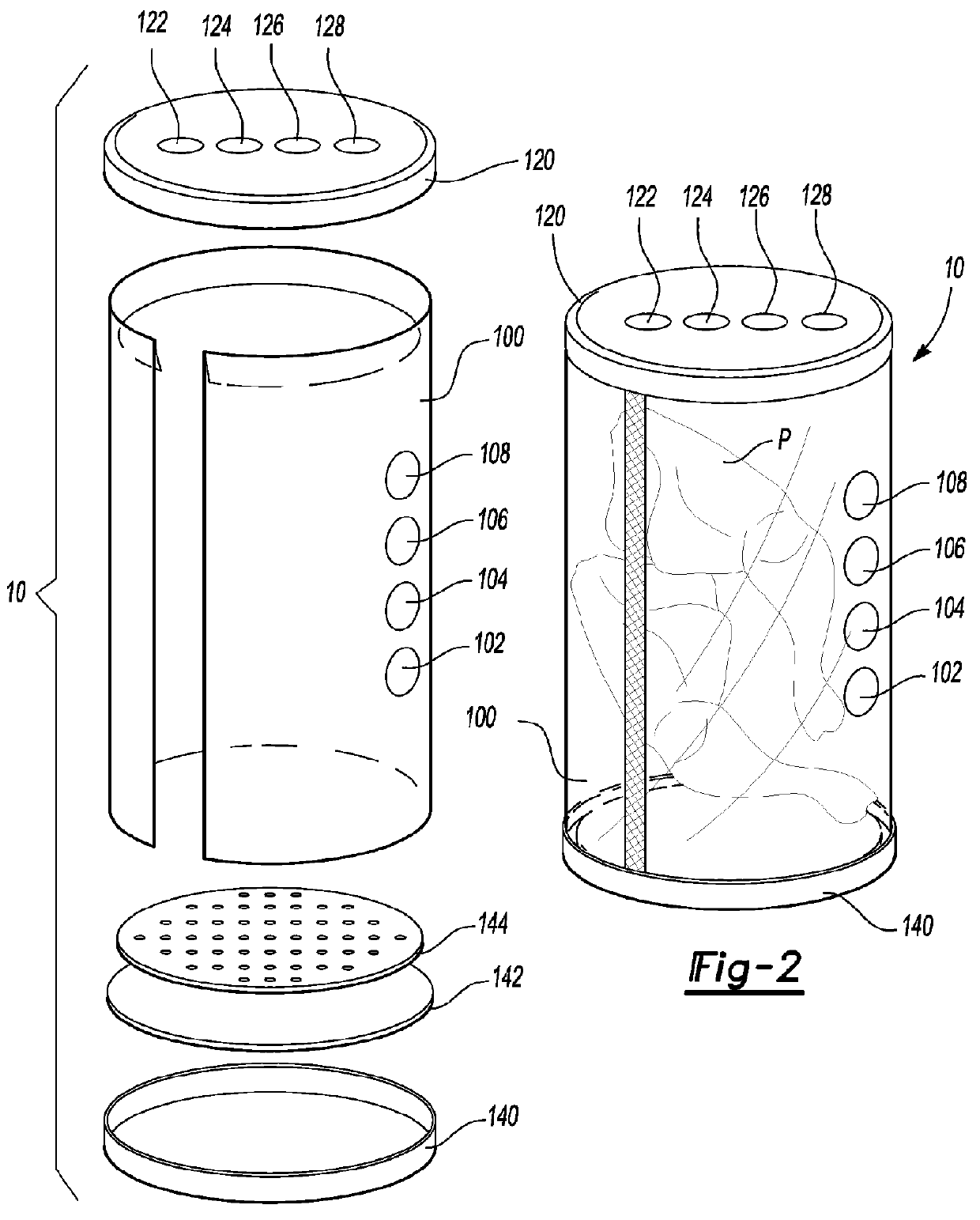
The present invention discloses a smart pouch that has a flexible pouch with a plurality of smart tags attached thereto. The plurality of smart tags can include one or more of the following: a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag, a chipless RFID tag, a time sensitive tag, a time-temperature sensitive tag, a package-has-been-opened tag, a cooking instructions tag, and the like. A signal provided by the plurality of smart tags to a reader can provide a plurality of information to the reader and the information can be related to the flexible pouch and any content, product, etc., that may be contained therewithin. In addition, at least one of the plurality of smart tags can be located within an air pocket.
Owner:POUCH PAC INNOVATIONS
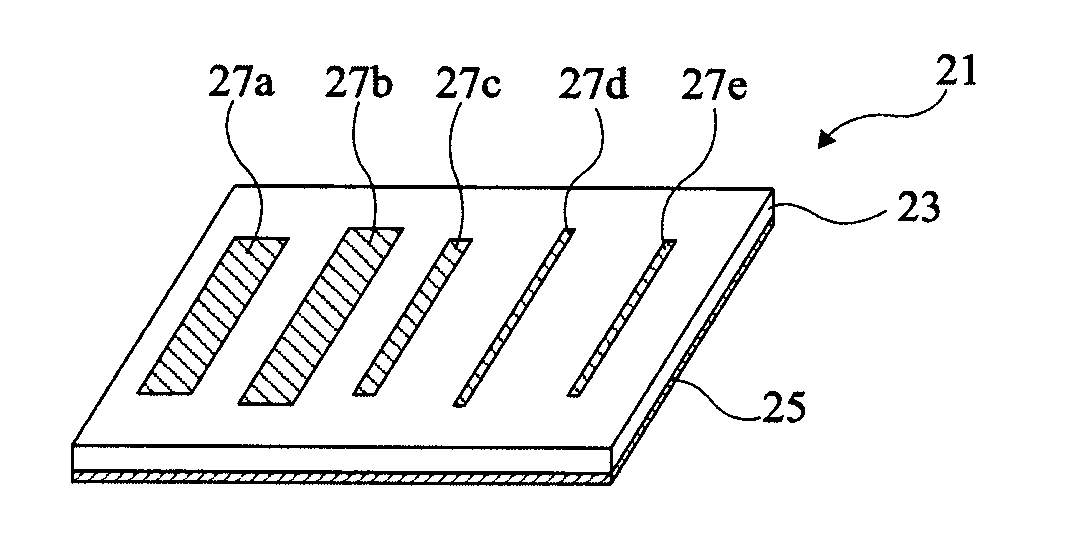
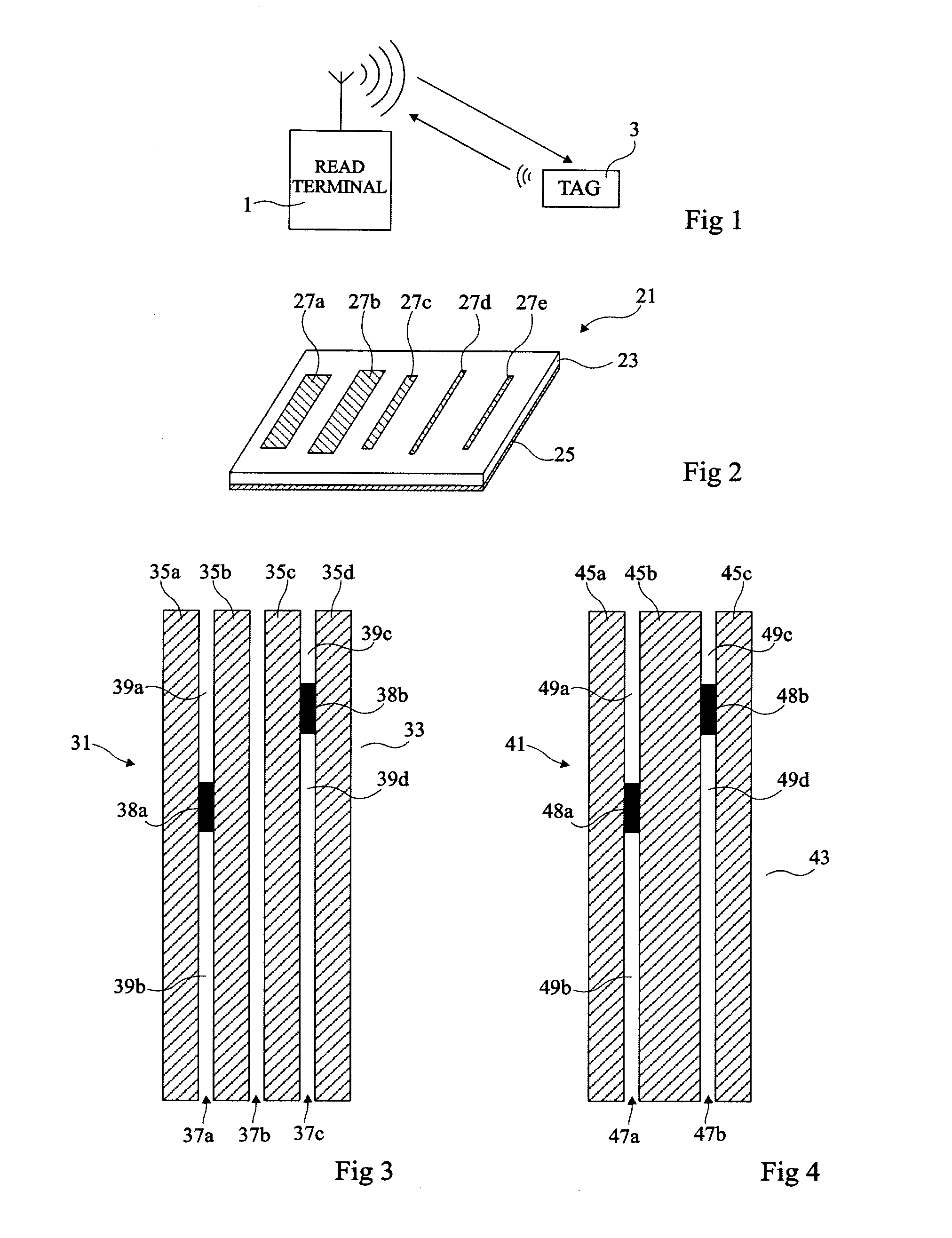
Chipless passive RFID tag
ActiveUS20130015248A1Less expensiveEasy to manufactureRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalChipless RFIDElectrical and Electronics engineering
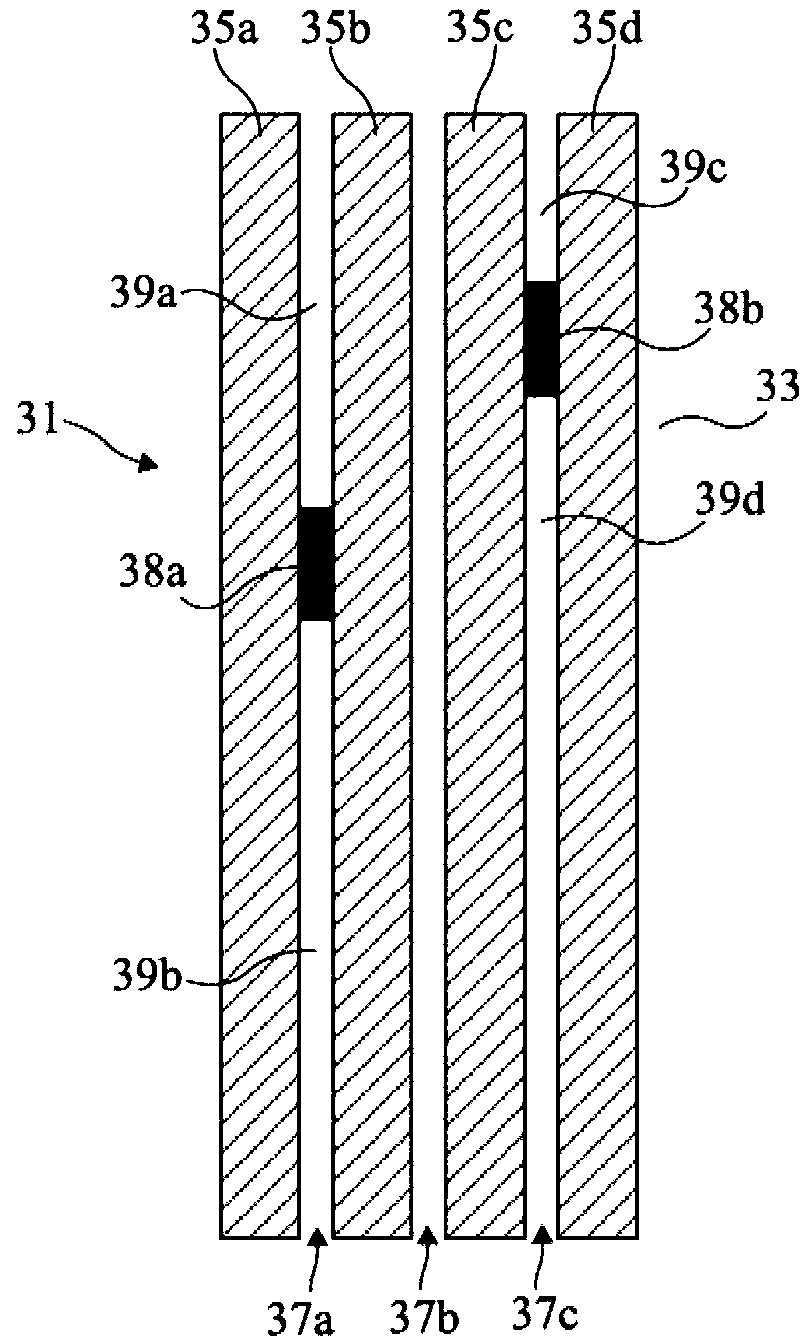
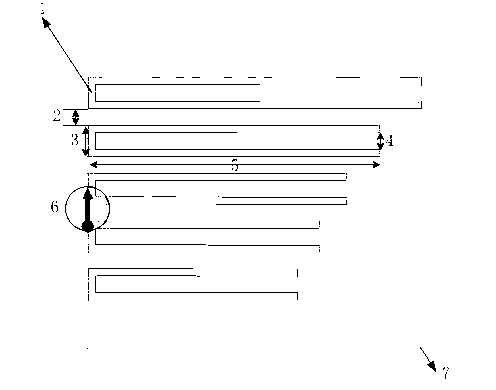
A chipless RFID tag comprises a plurality of disjoint parallel conducting bands formed on a dielectric support, in which conducting bridges interlink neighboring conducting bands, the conducting bridges delimiting, between the conducting bands, portions of dielectric bands of distinct lengths, each portion of dielectric brand determining a resonant frequency of the tag, the set of resonant frequencies of the tag defining an identification code.
Owner:INSTITUT NAT POLYTECHN DE GRENOBLE +1
Manufacturing technology of chipless radio frequency identification (RFID) radio frequency tag
ActiveCN103065180AReduce dosageSave energyAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsHot stampingChipless RFID
The invention discloses a manufacturing technology of a chipless radio frequency identification (RFID) radio frequency tag. According to the invention, a vacuum evaporation method or a cold and hot stamping process is used to manufacture the chipless RFID radio frequency tag. A technology process comprises the following steps: according to a requirement, designing an antenna structure of the chipless RFID radio frequency tag; then taking PVC, PP, PET, paper, a plastic and the like as a base material; using the vacuum evaporation method or the cold and hot stamping process to transfer a conductive metal to a surface of the base material; finally carrying out film coating and packaging so as to obtain the chipless RFID radio frequency tag. The chipless RFID radio frequency tag manufactured by using the above process possesses excellent folding resistance and good toughness. And the tag possesses the following advantages that manufacturing cost is low; an operation technology is simple and easy to operate and so on. A wide application prospect is possessed.
Owner:哈尔滨大东方新材料科技股份有限公司
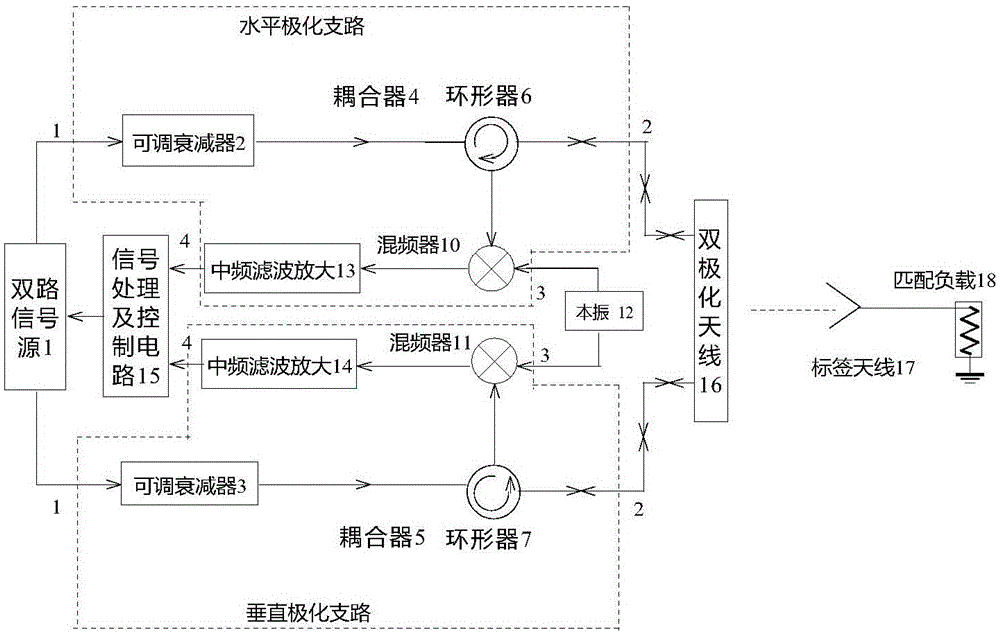
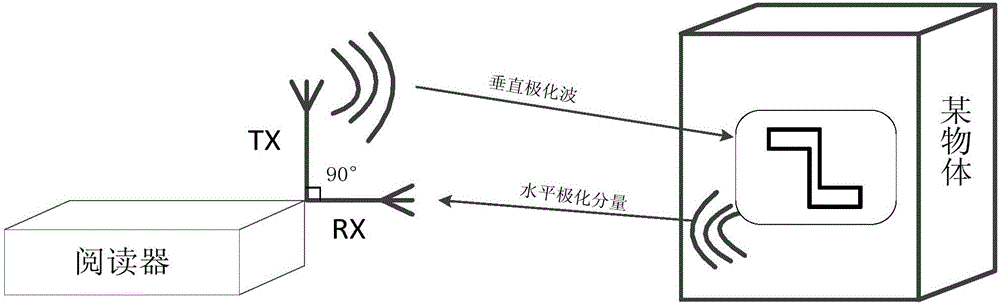
Polarized RFID system without chips
ActiveCN105139047ASimple structureSolve the signal leakage problemCo-operative working arrangementsChipless RFIDLocal oscillator signal
The invention provides a polarized RFID (radio frequency identification) system without chips. The polarized RFID system without chips comprises a double channel signal source, a horizontal polarization branch circuit, a vertical polarization branch circuit, a dual polarization antenna, and a signal processing and control circuit, wherein the double channel signal source can generate two channels of radiofrequency signals with the same frequency and controllable phase at will; the horizontal polarization branch circuit adjusts the amplitude of the first channel of radiofrequency signal during the signal emission process, and performs frequency mixing for a reflected signal and a local oscillator signal during the process of receiving the reflected signal, and performs filtering and amplification when the frequency conversion is taken down; the vertical polarization branch circuit adjusts the amplitude of the second channel of radiofrequency signal during the signal emission process, and performs frequency mixing for a reflected signal and a local oscillator signal during the process of receiving the reflected signal, and performs filtering and amplification when the frequency conversion is taken down; the dual polarization antenna emits two channels of radiofrequency signals with adjustable amplitude and phase, and can stimulate a pair of linear polarization electromagnetic waves which are vertical in the polarized direction; the two channels of linear polarization electromagnetic waves can be overlaid with any polarized electromagnetic waves, and can receive the reflected signal; and the signal processing and control circuit is used for adjusting the phase difference between two channels of radiofrequency signals, and is used for coding the reflected signal.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
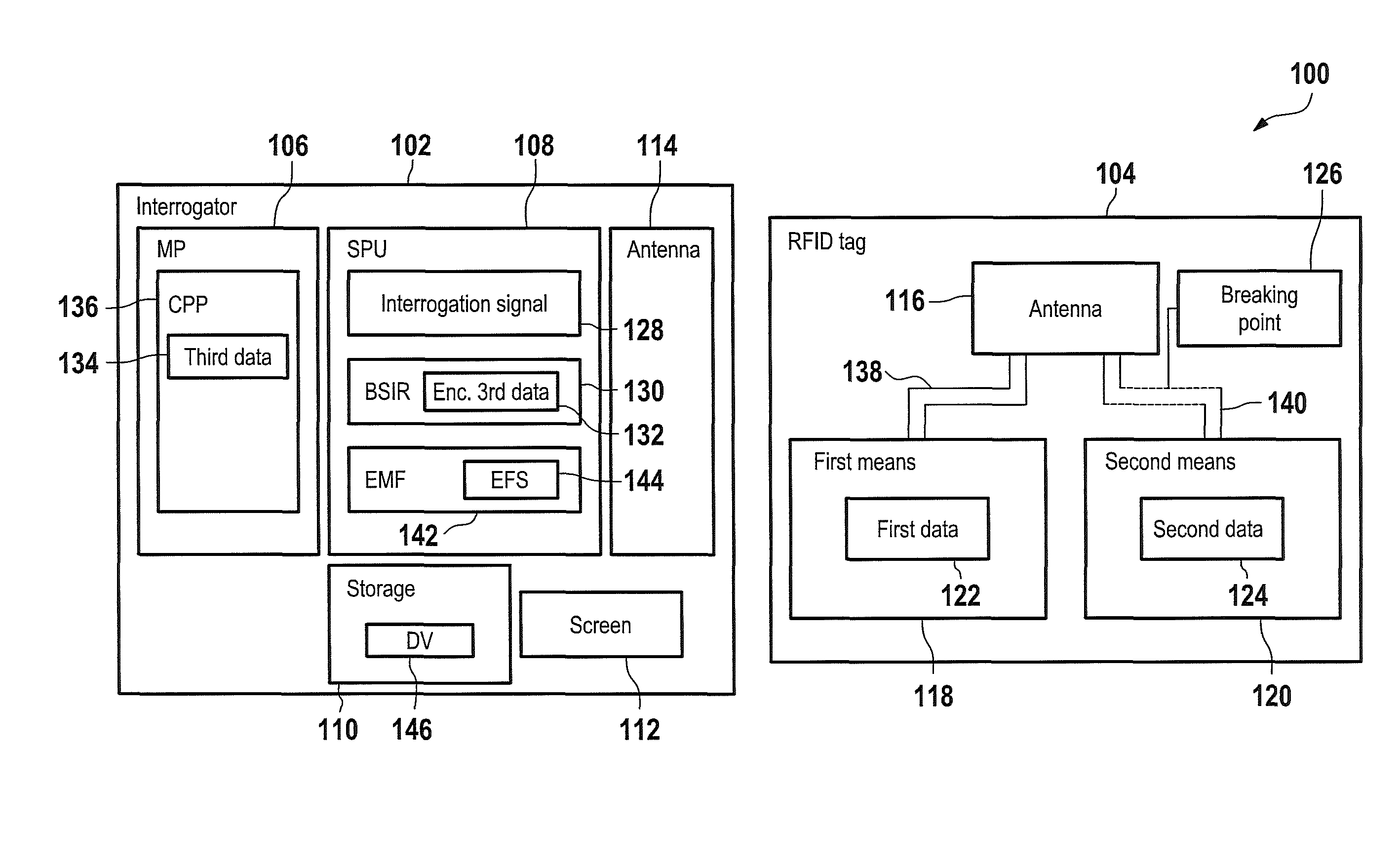
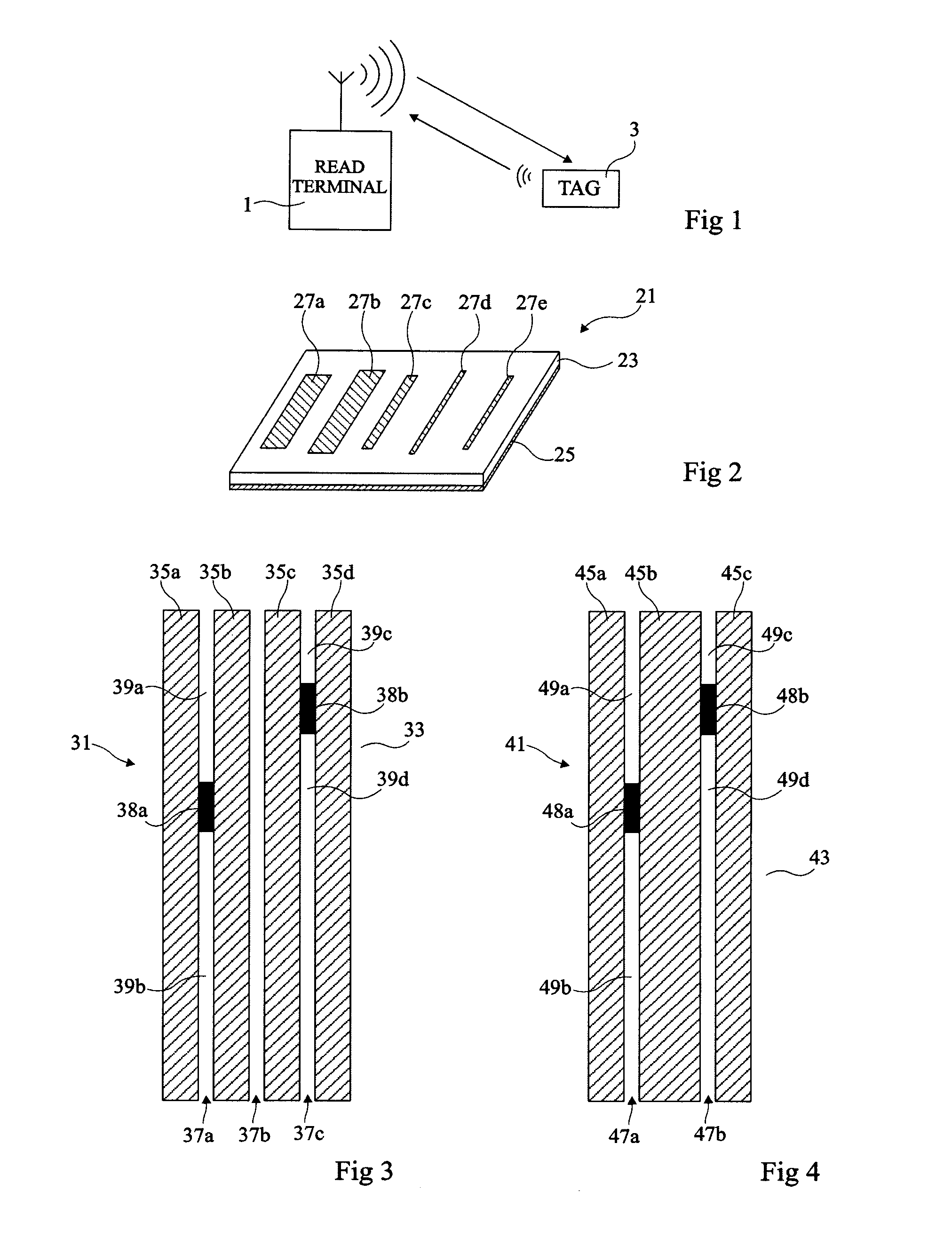
Chipless RFID tag and method for communicating with the RFID tag
InactiveUS20080084276A1Near-field in RFIDNear-field systems using receiversChipless RFIDRadio frequency signal
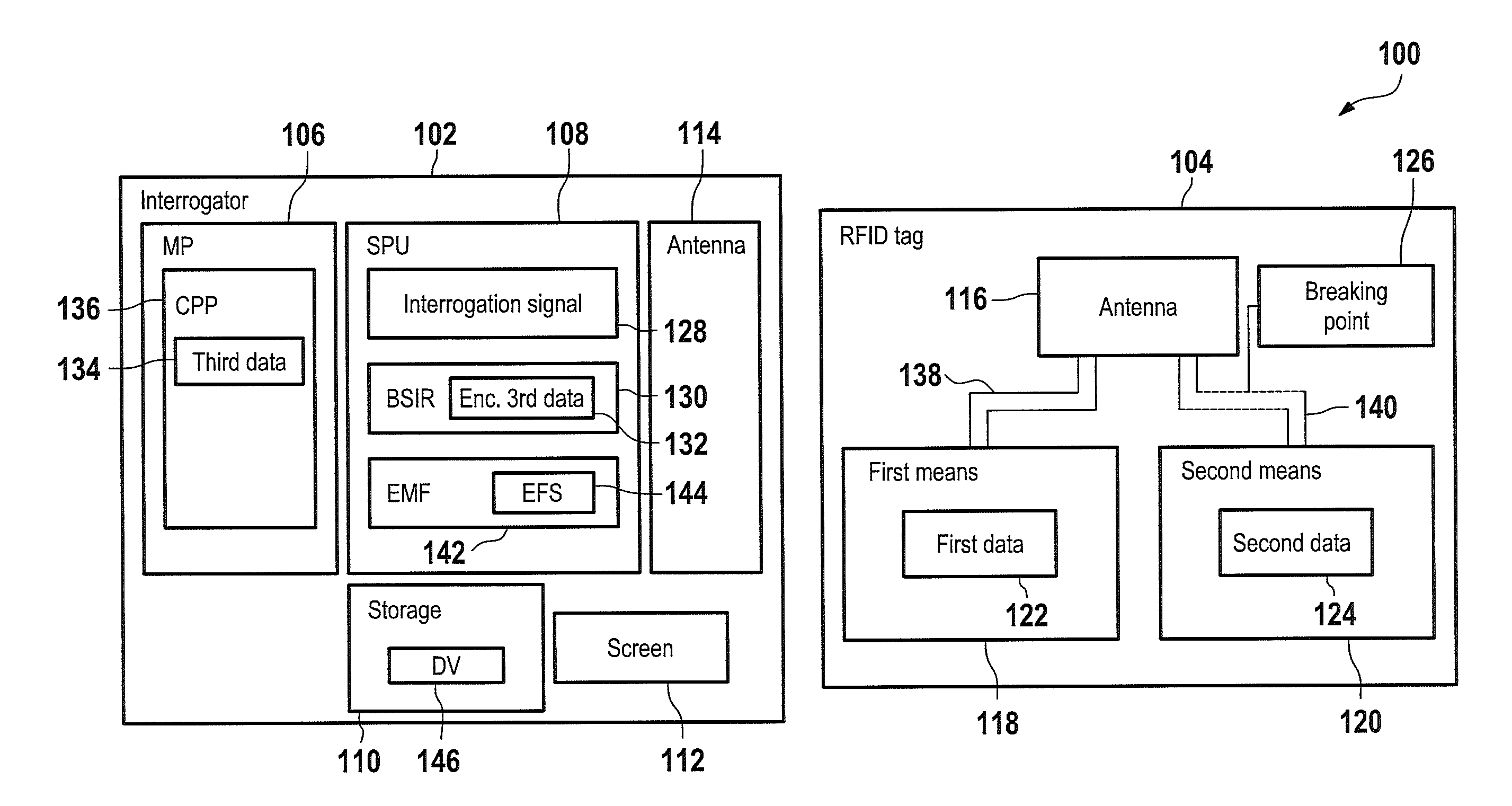
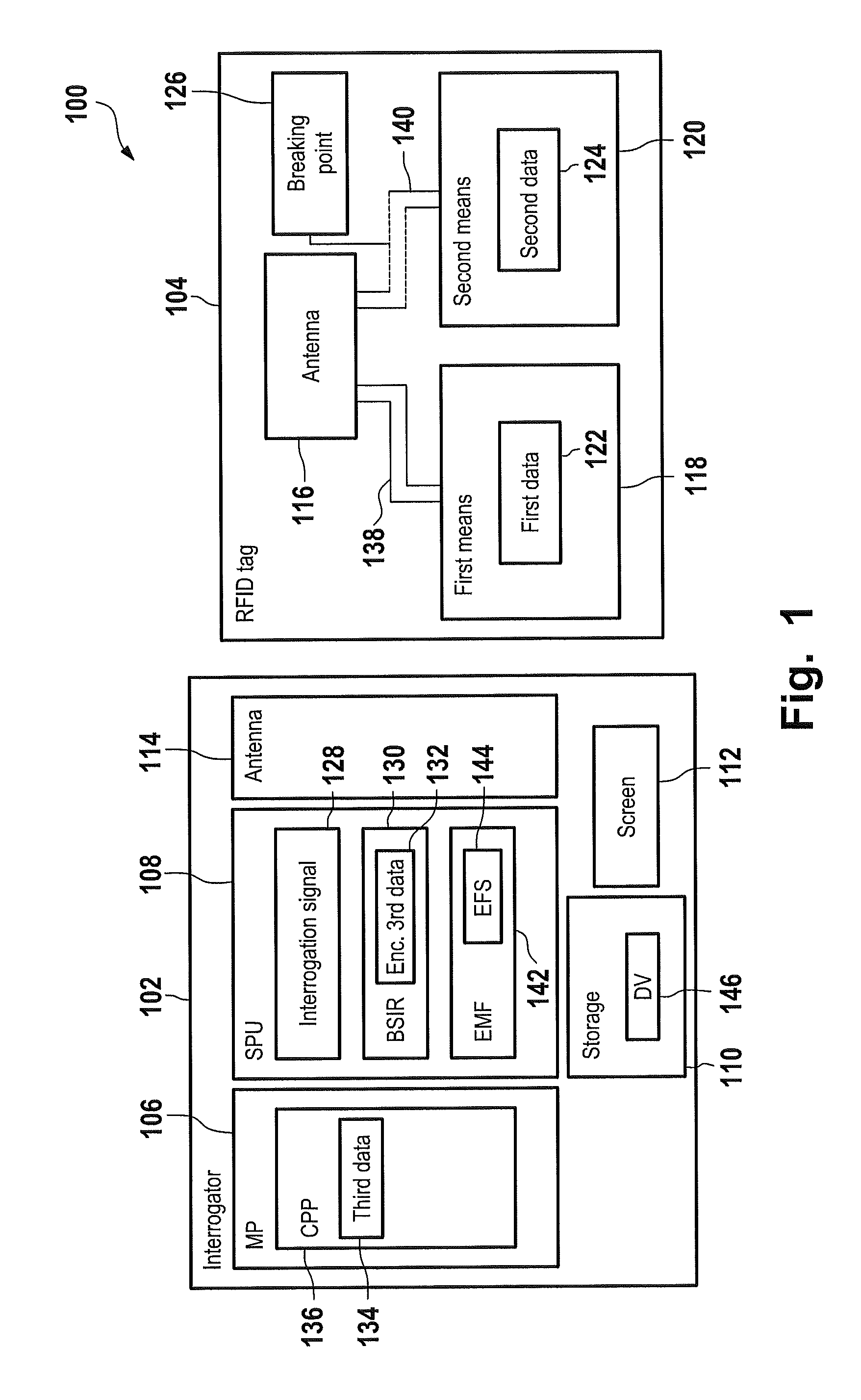
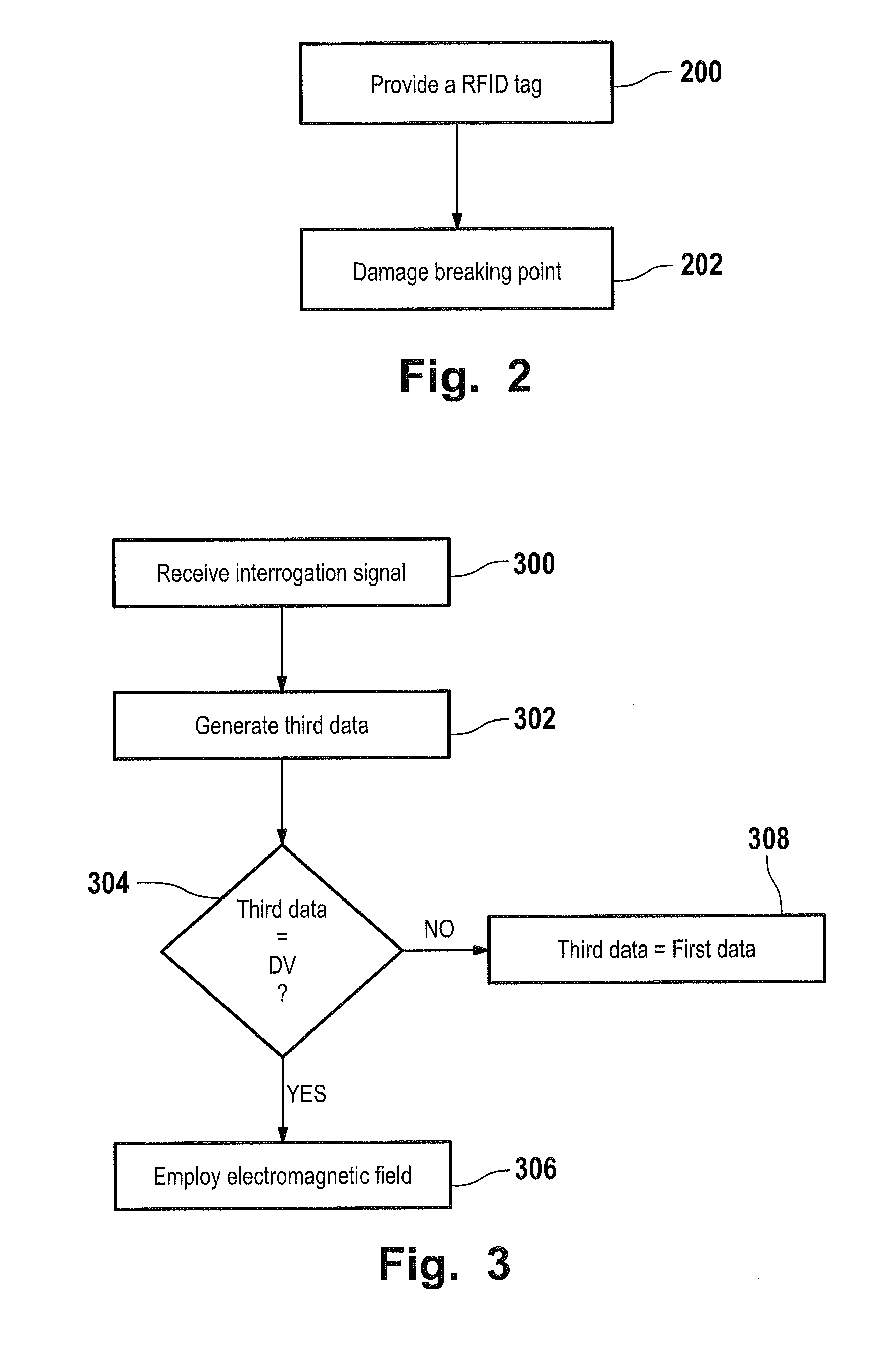
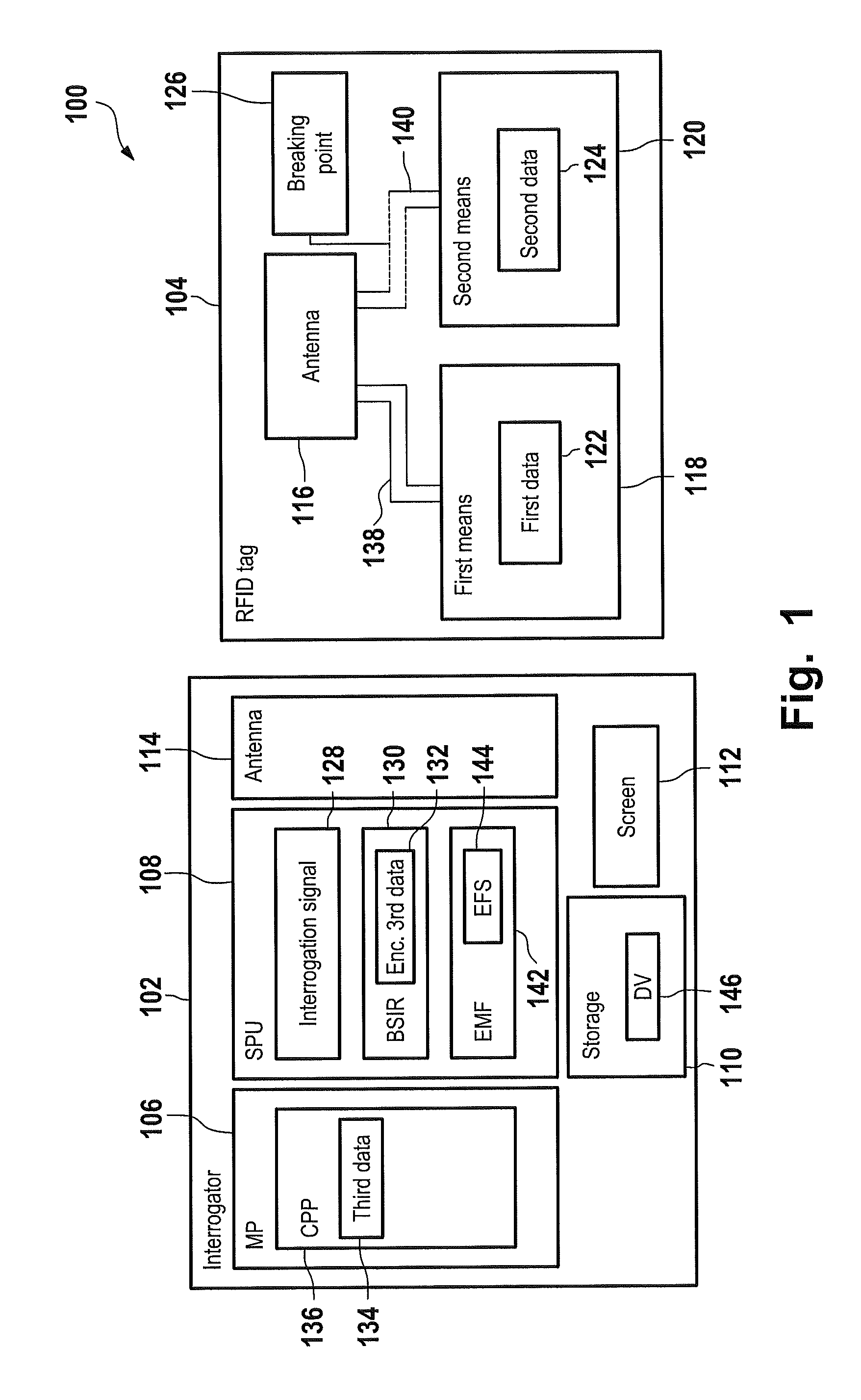
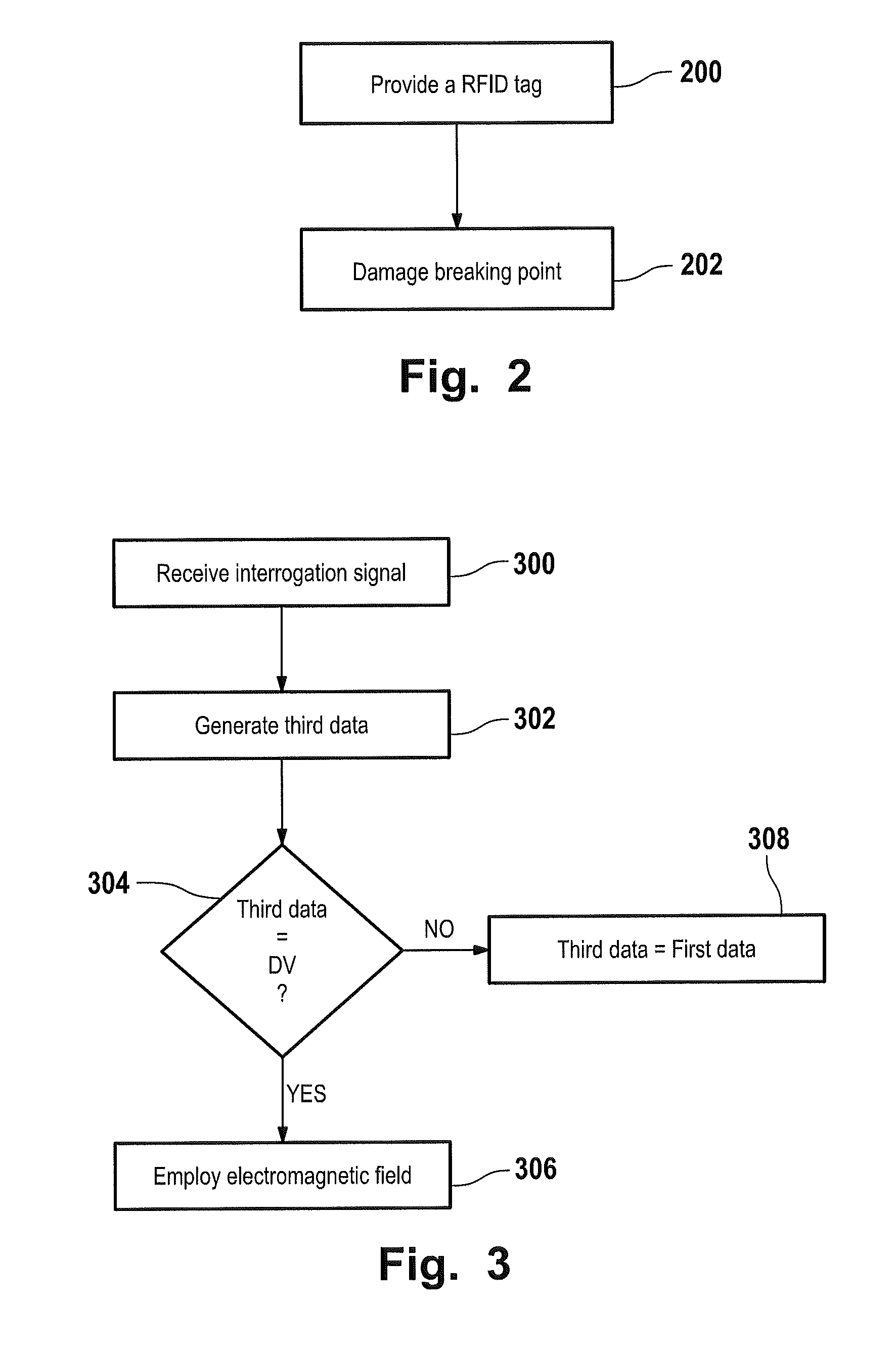
A radio frequency identification (RFID) tag and a method and system for communicating with the RFID tag. The RFID tag includes a first and second structure respectively holding first data and second data that is complementary to the first data. The RFID tag does not include a microchip. An electromagnetic radio frequency signal is transmitted from an interrogator to the RFID tag. The interrogator receives, from the RFID tag, a response signal including third data being the first data or a combination of the first data and the second data. The interrogator extracts the third data from the response signal. A default value equal to the combination of the first data and the second data is stored in the interrogator. If the interrogator determines that the third data is unequal / equal to the default value, then a screen of the interrogator displays that the RFID tag is enabled / not enabled.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ultra-wideband dual-polarization chipless RFID label
ActiveCN106096707ALow costImprove spectrum utilizationAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsChipless RFIDMain diagonal
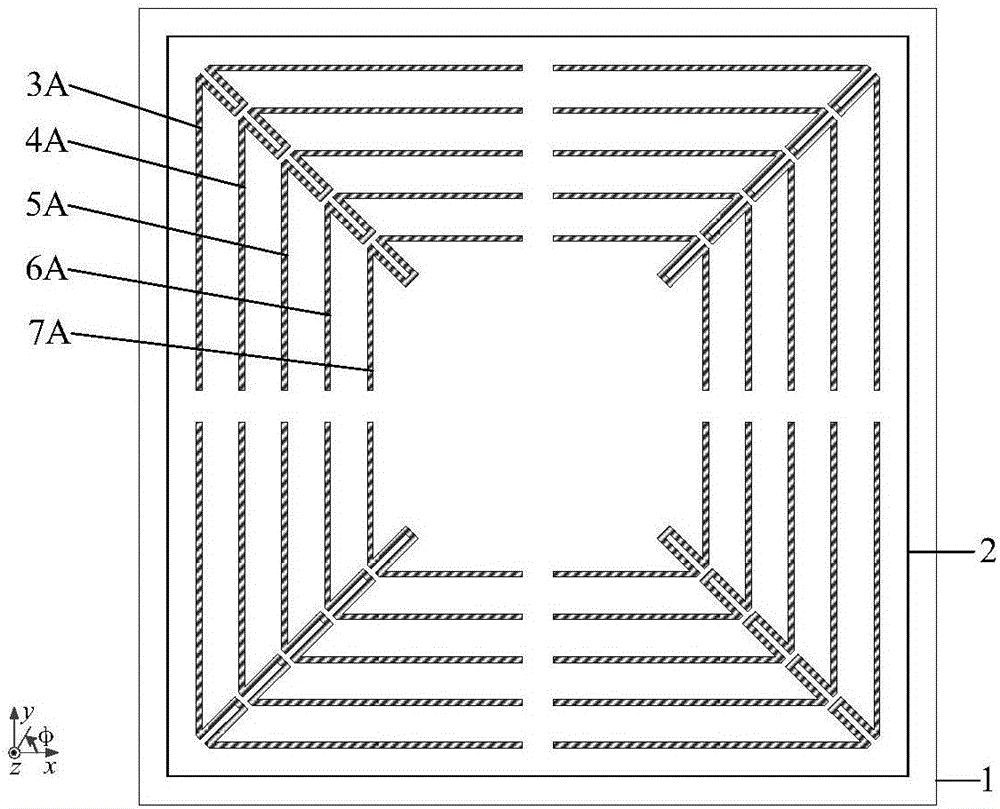
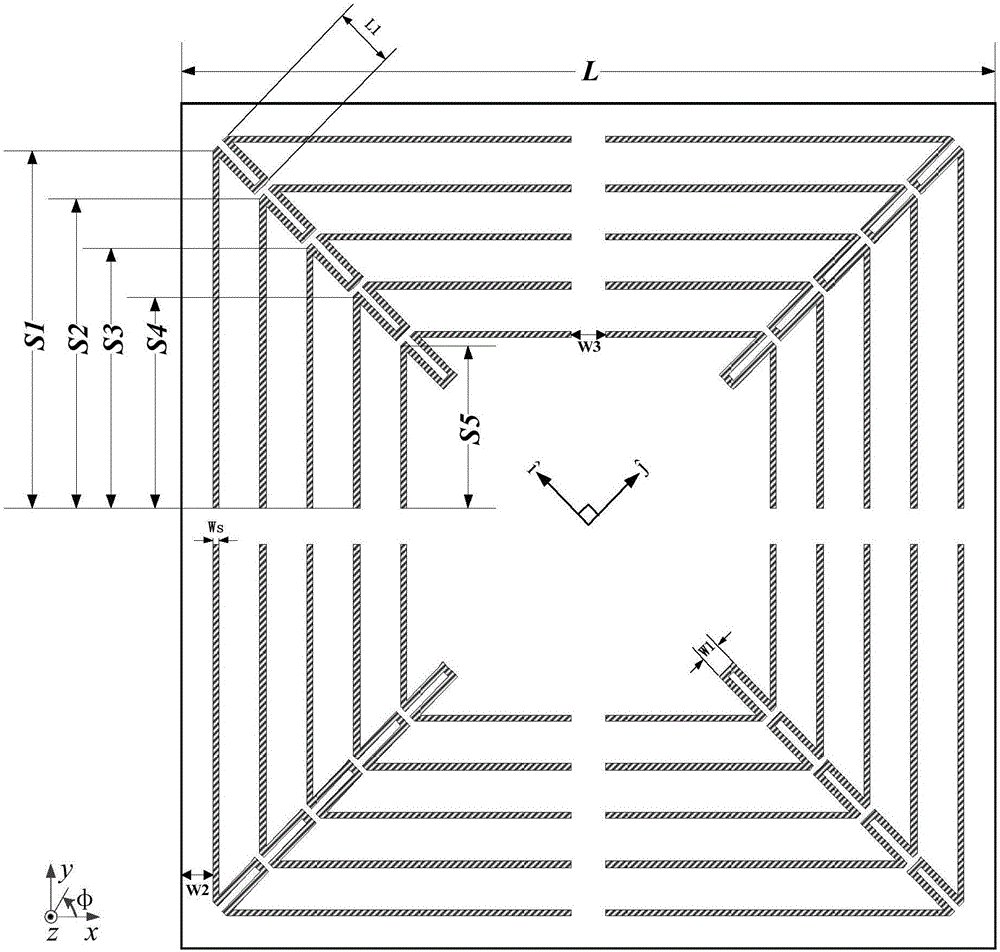
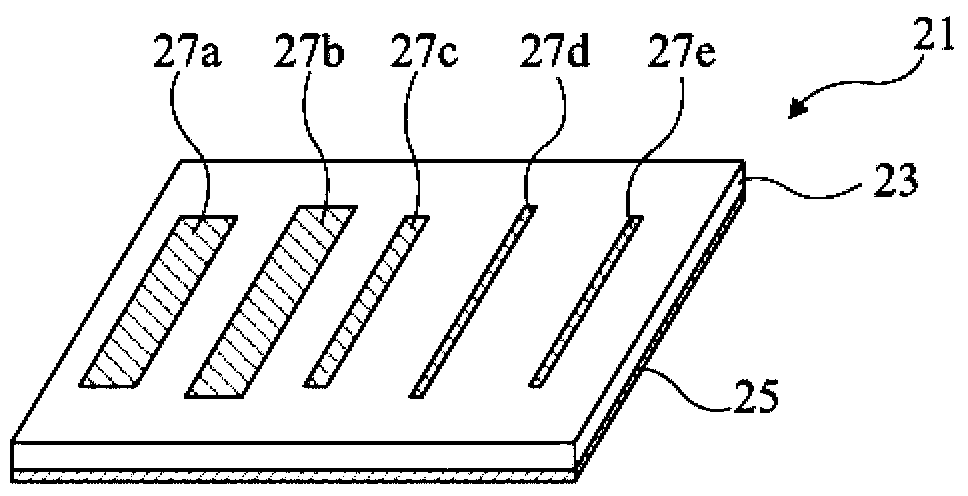
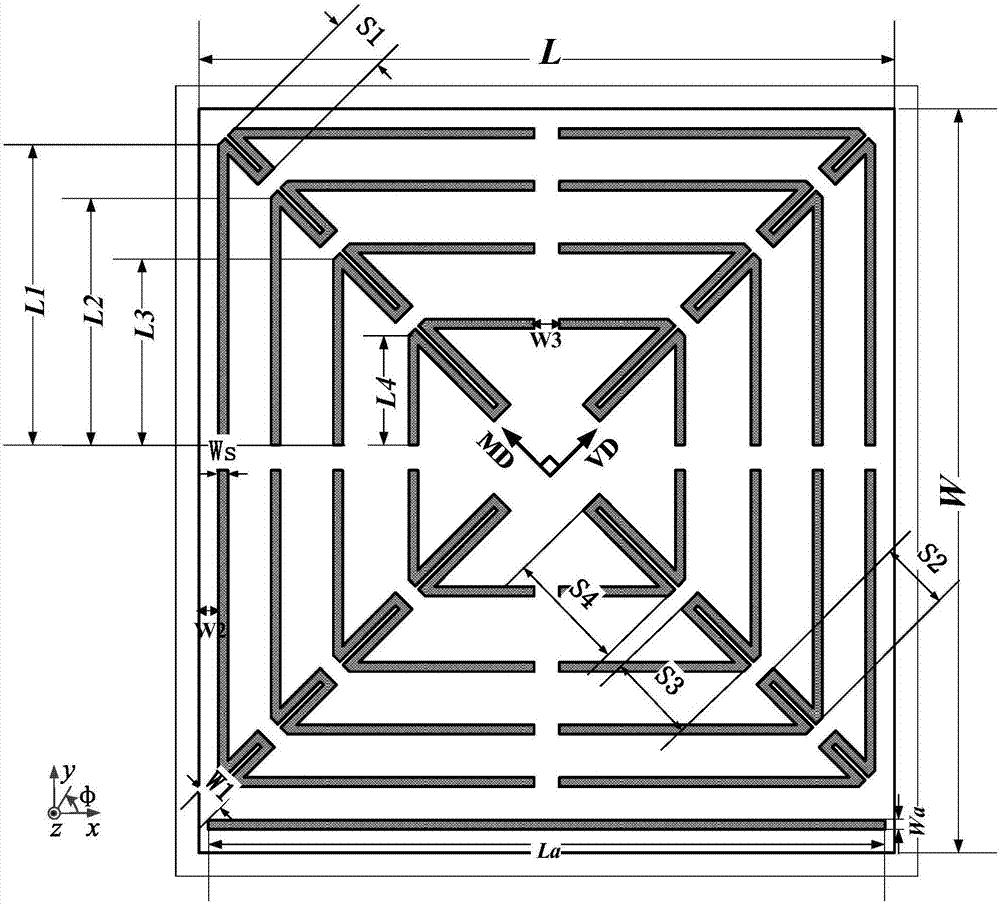
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband dual-polarization chipless RFID label. The ultra-wideband dual-polarization chipless RFID label comprises an antenna radiation unit and a medium substrate. The antenna radiation unit is arranged on the upper surface of the medium substrate. The antenna radiation unit is formed by a square paster. The square paster is provided with four open groove structures including first, second, third and fourth open groove structures. The first and third open groove structures are arranged on a main diagonal of the square paster and are centrally symmetric with respect to the square paster. The second and fourth open groove structures are arranged on an auxiliary diagonal of the square paster and are centrally symmetric with respect to the square paster. The label antenna has the advantages that miniaturization is realized, the capacity is large, the polarization isolation is high, the bandwidth efficiency is high, and printing is easy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Printing system architecture for encoding chip-less RFID tags in real time
ActiveCN106250963AAntenna supports/mountingsConductive pattern formationChipless RFIDFrequency spectrum
Provided is a method for encoding chipless RFID tags in real-time. The method includes exposing a chipless RFID transponder to a conductive material, the RFID transponder comprising an antenna and a plurality of resonant structures, the plurality of resonant structures together defining a first spectral signature. Each of the plurality of resonant structures includes a respective one of a frequency domain. The method also includes depositing a conductive material on at least one of the resonant structures to short the at least one of the resonant structures. The remainder of the plurality of resonant structures that are not shorted by the conductive material define a second spectral signature for the RFID transponder.
Owner:XEROX CORP
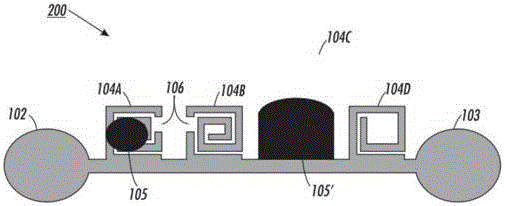
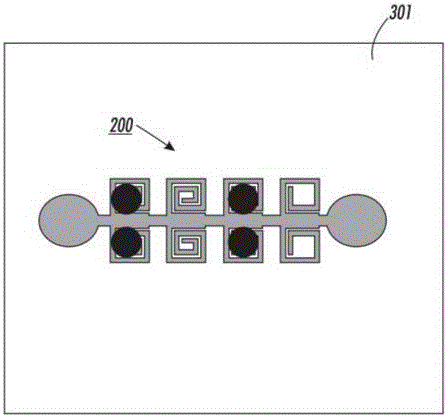
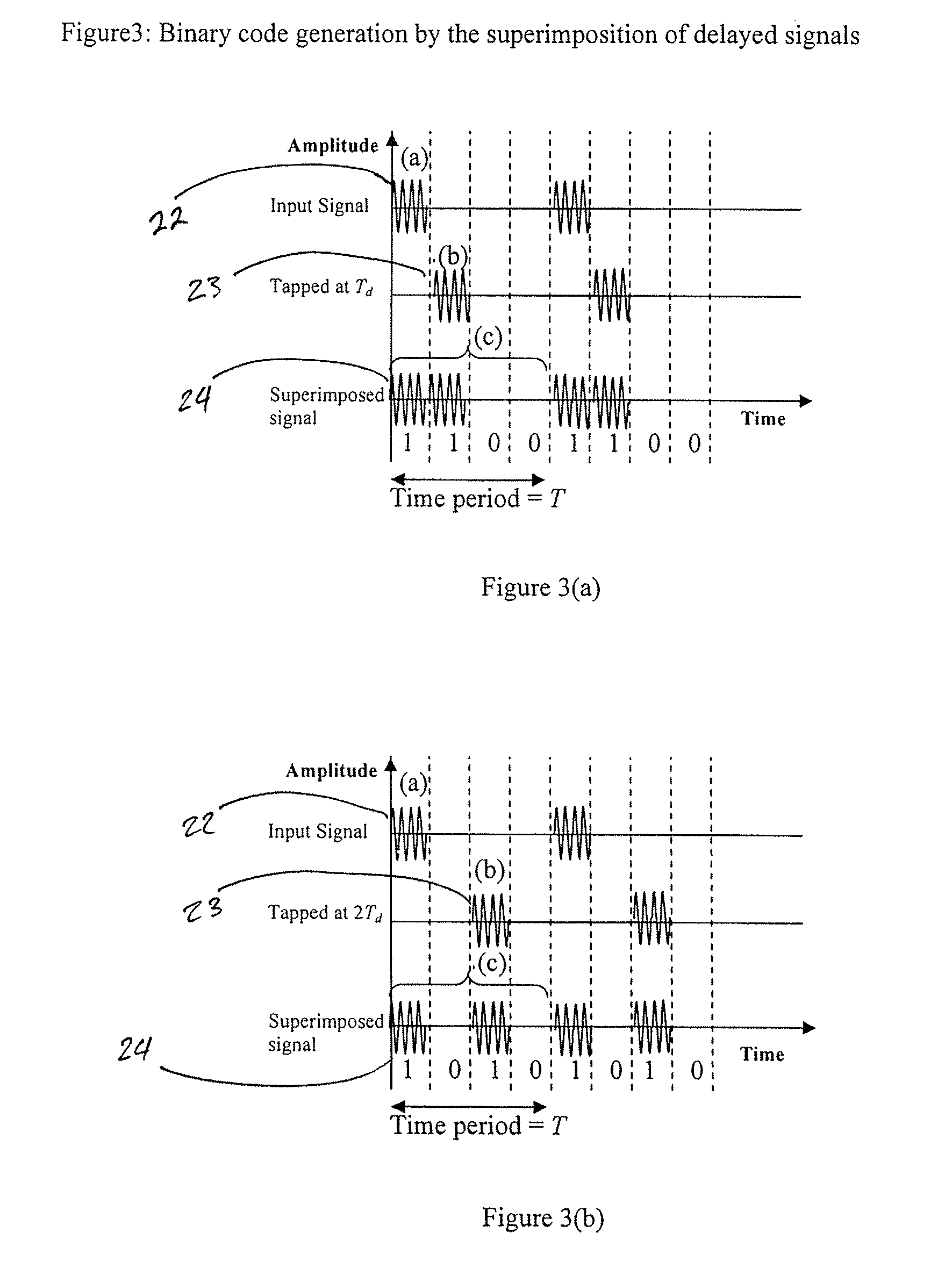
Transmission delay based RFID tag
InactiveUS8736452B1Uniform impedanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChipless RFIDTime domain
A chipless RFID tag system having a transmitter sending an input signal and a tag substrate. An ID generation circuit on the tag relies on microstrip transmission line patterns which are pre-designed to generate a unique code. The ID generating circuit may be designed based upon the transmission line properties, including signal delay, and / or reflection, and / or phase change. The tag may be formed on a flexible substrate having at least one microstrip and the microstrip having a first portion with a first impedance and a second portion with a second impedance different from the first impedance. The tag may further include a microstrip antenna for communication with the transmitter and a receiver system. The tag may also include sensors for detection of desired substances of interest. The system may further include a receiver detecting at least two reflections from an interface of first and second impedances and identifying relative time domain positions of the reflections to one another.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH RES CORP
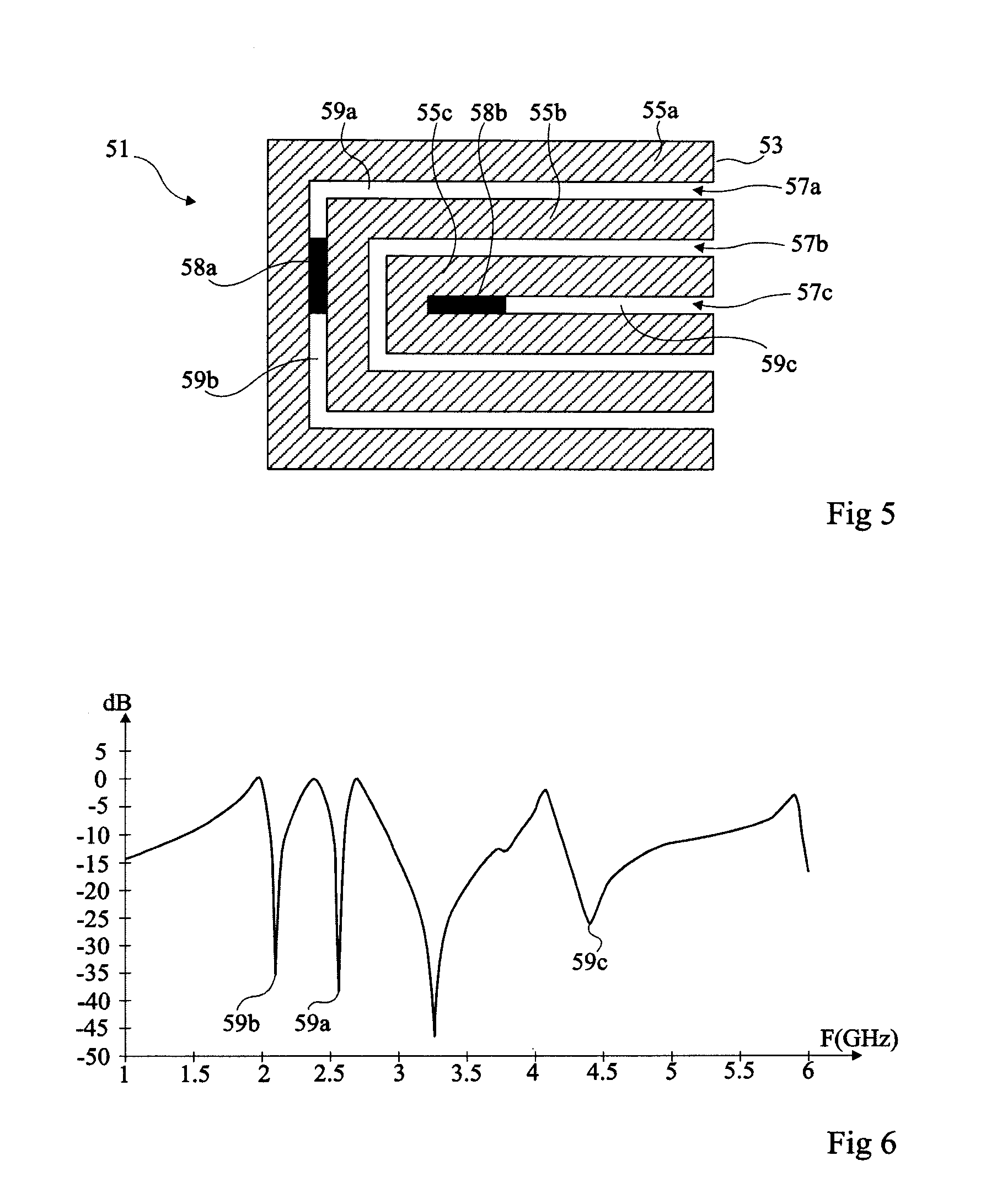
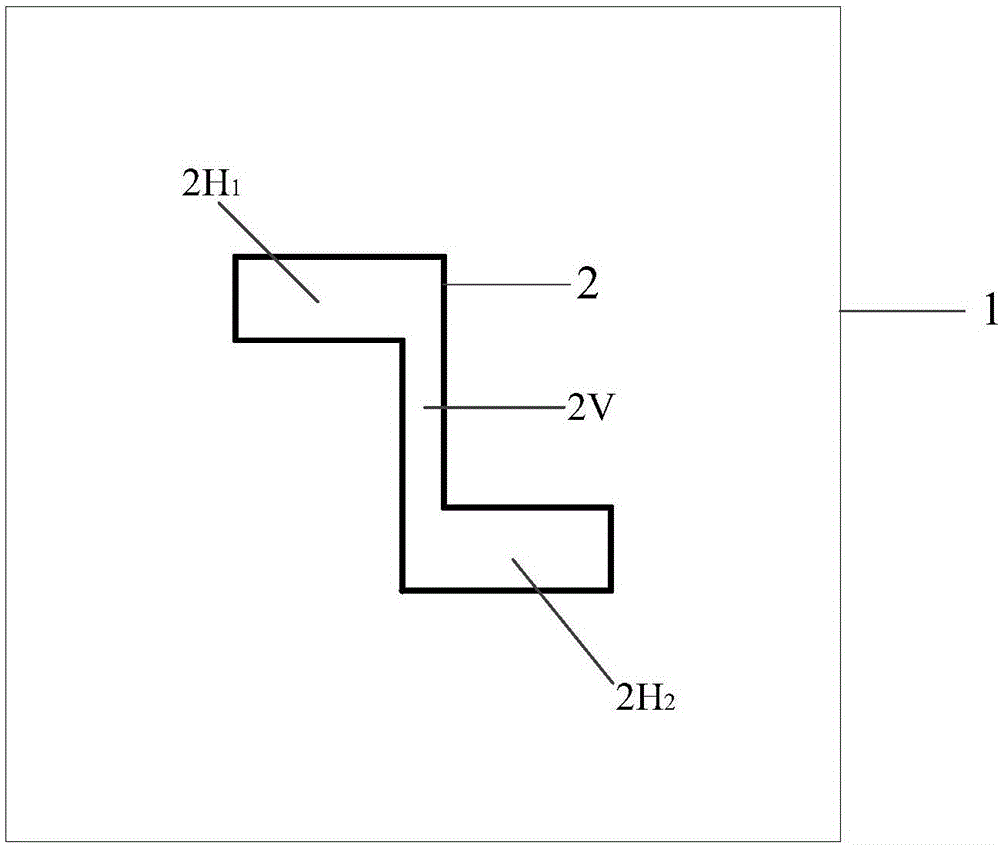
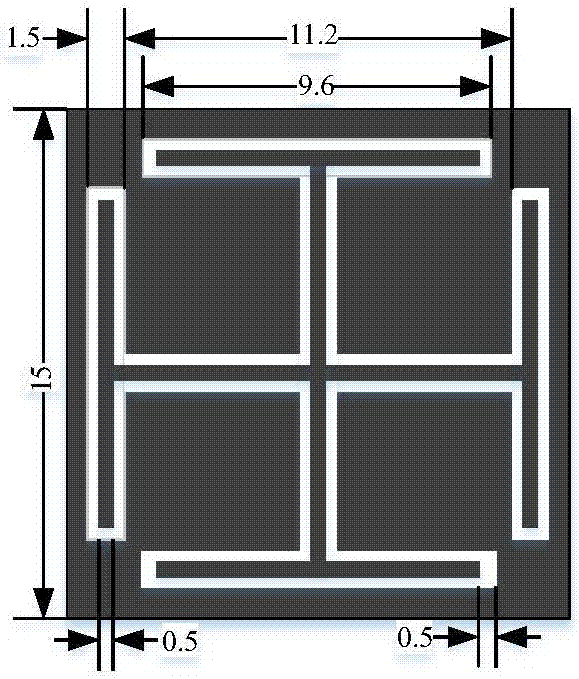
Z-shaped depolarized chipless RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag and system
ActiveCN106295775AImprove isolationImprove anti-interference abilityAntenna supports/mountingsMemory record carrier reading problemsChipless RFIDDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a Z-shaped depolarized chipless RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag and a system. The tag comprises a tag patch unit, a metal floor and a single-layer dielectric substrate, wherein the tag patch unit is located on the upper surface of the single-layer dielectric substrate, the metal floor is located on the lower surface of the single-layer dielectric substrate, the tag patch unit is composed of two transverse branches and one longitudinal branch, the two transverse branches are respectively perpendicular to two ends of the longitudinal branch, and the tag patch unit is of a Z-shaped structure. The tag has the advantages that the tag is small, strong in anti-interference capability, easy to detect in a practical environment, simple in structure, easy to produce in batch and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
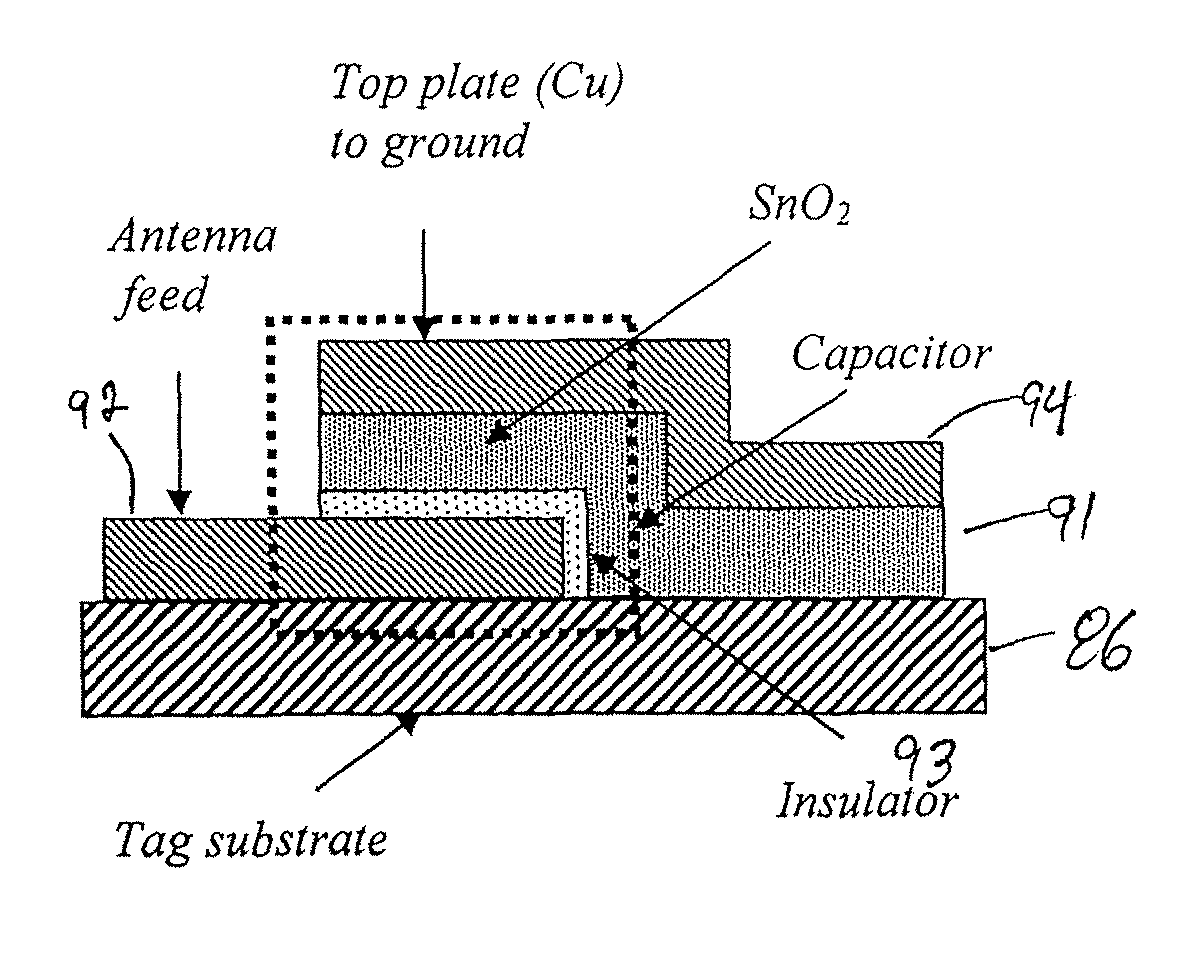
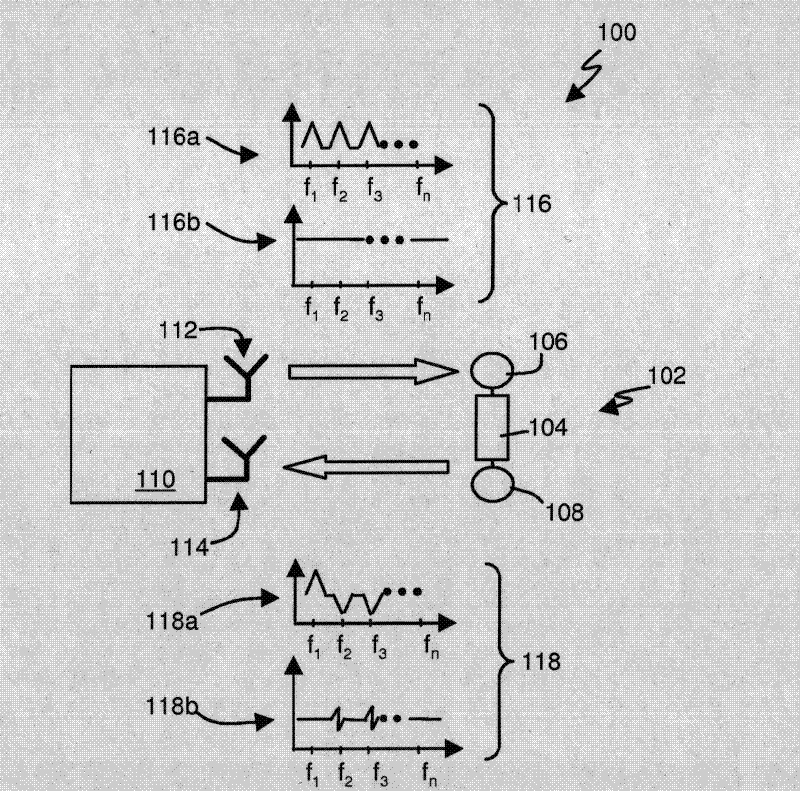
Chip-less radio frequency identification systems using metamaterials and identification methods thereof
InactiveUS20100134254A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh resolutionMultiplex system selection arrangementsCo-operative working arrangementsChipless RFIDFrequency spectrum
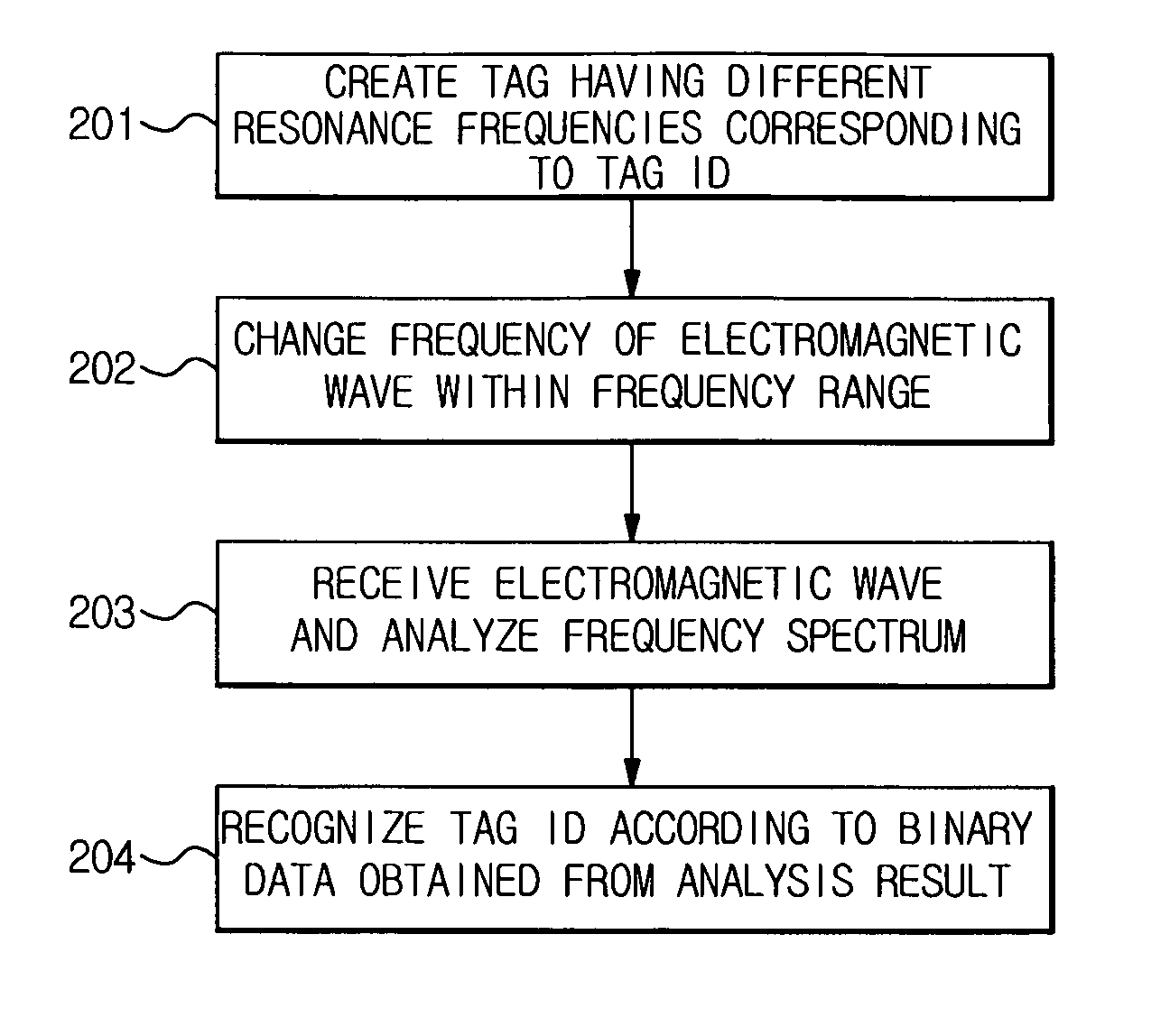
A chip-less RFID system, using metamaterial, may include a tag and a reader. The tag may include the metamaterial. The metamaterial may have at least two resonance frequencies. The reader may change a frequency of a first electromagnetic wave to be transmitted to the tag. The reader may recognize an identification (ID) of the tag by receiving a second electromagnetic wave from the tag that corresponds to the first electromagnetic wave. An identification method of chip-less RFID systems, using metamaterial, may include creating a tag that includes the metamaterial, the metamaterial having different resonance frequencies, changing a frequency of a first electromagnetic wave to be transmitted to the tag by a reader, and analyzing a frequency spectrum of a second electromagnetic wave from the tag that corresponds to the first electromagnetic wave.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Chipless RFID tag and method for communicating with the RFID tag
InactiveUS8068010B2Near-field in RFIDNear-field systems using receiversChipless RFIDRadio frequency signal
A radio frequency identification (RFID) tag and a method and system for communicating with the RFID tag. The RFID tag includes a first and second structure respectively holding first data and second data that is complementary to the first data. The RFID tag does not include a microchip. An electromagnetic radio frequency signal is transmitted from an interrogator to the RFID tag. The interrogator receives, from the RFID tag, a response signal including third data being the first data or a combination of the first data and the second data. The interrogator extracts the third data from the response signal. A default value equal to the combination of the first data and the second data is stored in the interrogator. If the interrogator determines that the third data is unequal / equal to the default value, then a screen of the interrogator displays that the RFID tag is enabled / not enabled.
Owner:IBM CORP
Manufacturing technology of chip-free RFID label
ActiveCN105160381ALow costImprove folding resistanceAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsChipless RFIDManufacturing technology
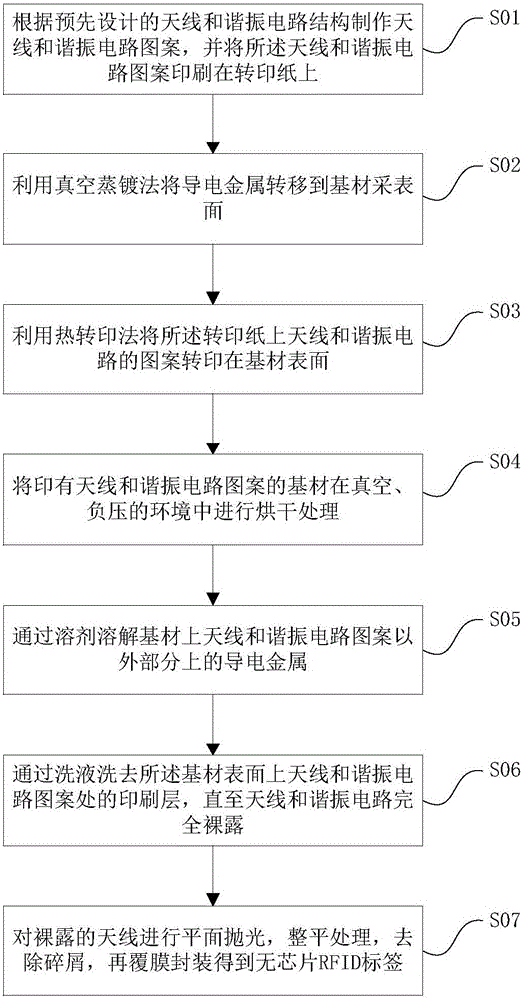
The invention relates to a manufacturing technology of a chip-free RFID label, which comprises the steps of printing an antenna and a resonance circuit pattern on a piece of transfer paper; transferring a conductive metal onto a base material surface through vacuum vaporization method; transferring the printing of the antenna and the resonance circuit pattern on the transfer paper onto the base material surface; drying the base material with the antenna and the resonance circuit pattern; washing the conductive metal on the base material apart from the antenna and the resonance circuit pattern through a solvent; washing a printing layer on the base material surface apart from the antenna and the resonance circuit pattern through a washing lotion until the antenna and the resonance circuit are fully exposed; and plane polishing and levelling the exposed antenna, removing chips and overlaying film for packaging to obtain a chip-free RFID label. According to the manufacturing technology of the chip-free RFID label, the RFID label cost is greatly reduced; a chip-free RFID label can be obtained; advantages like excellent flexibility resistance and good toughness, low manufacturing cost and simple and good operation technology are provided; and wide application prospect is provided.
Owner:WUHAN WEDO INFORMATION & TECH
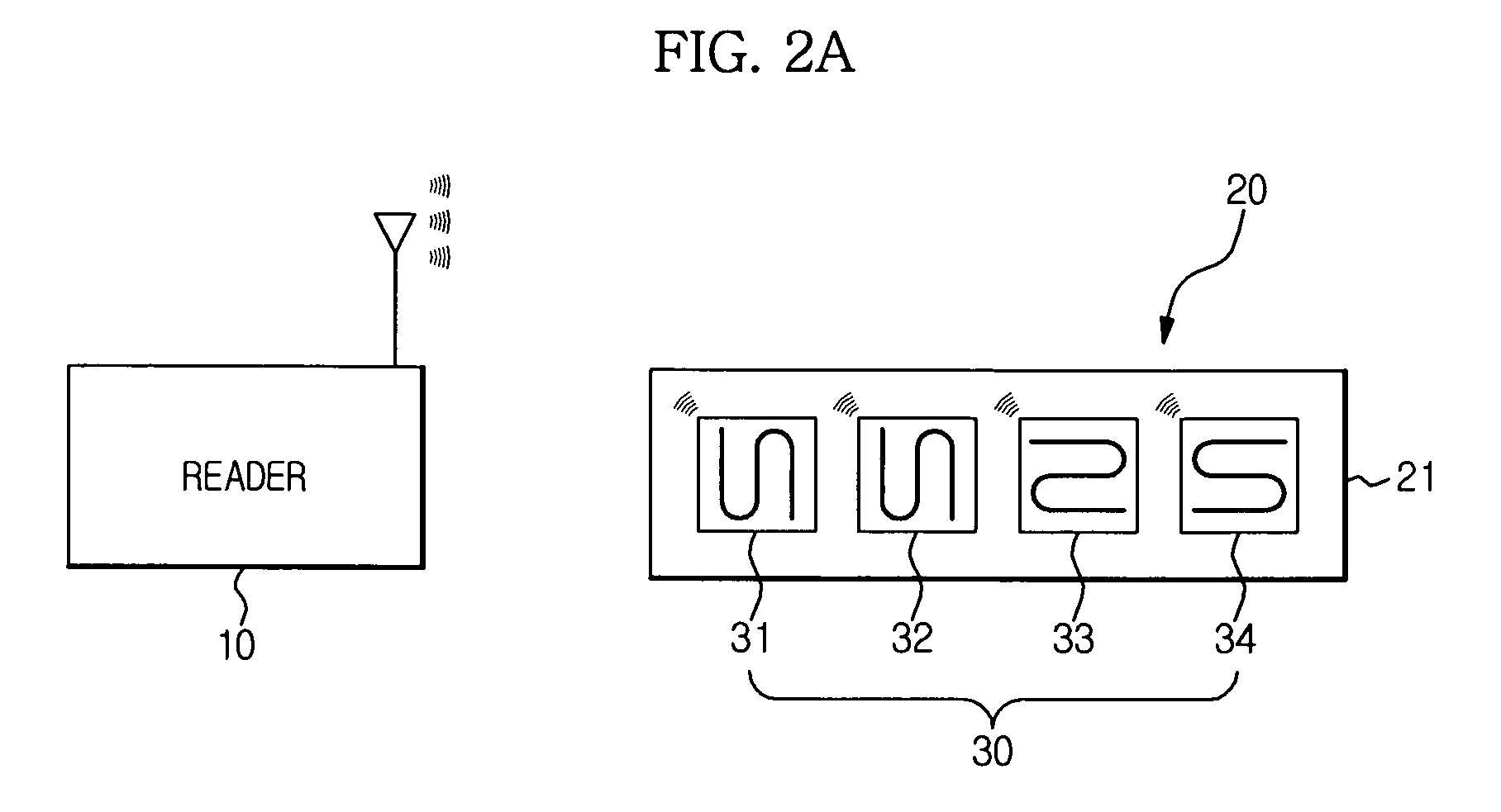
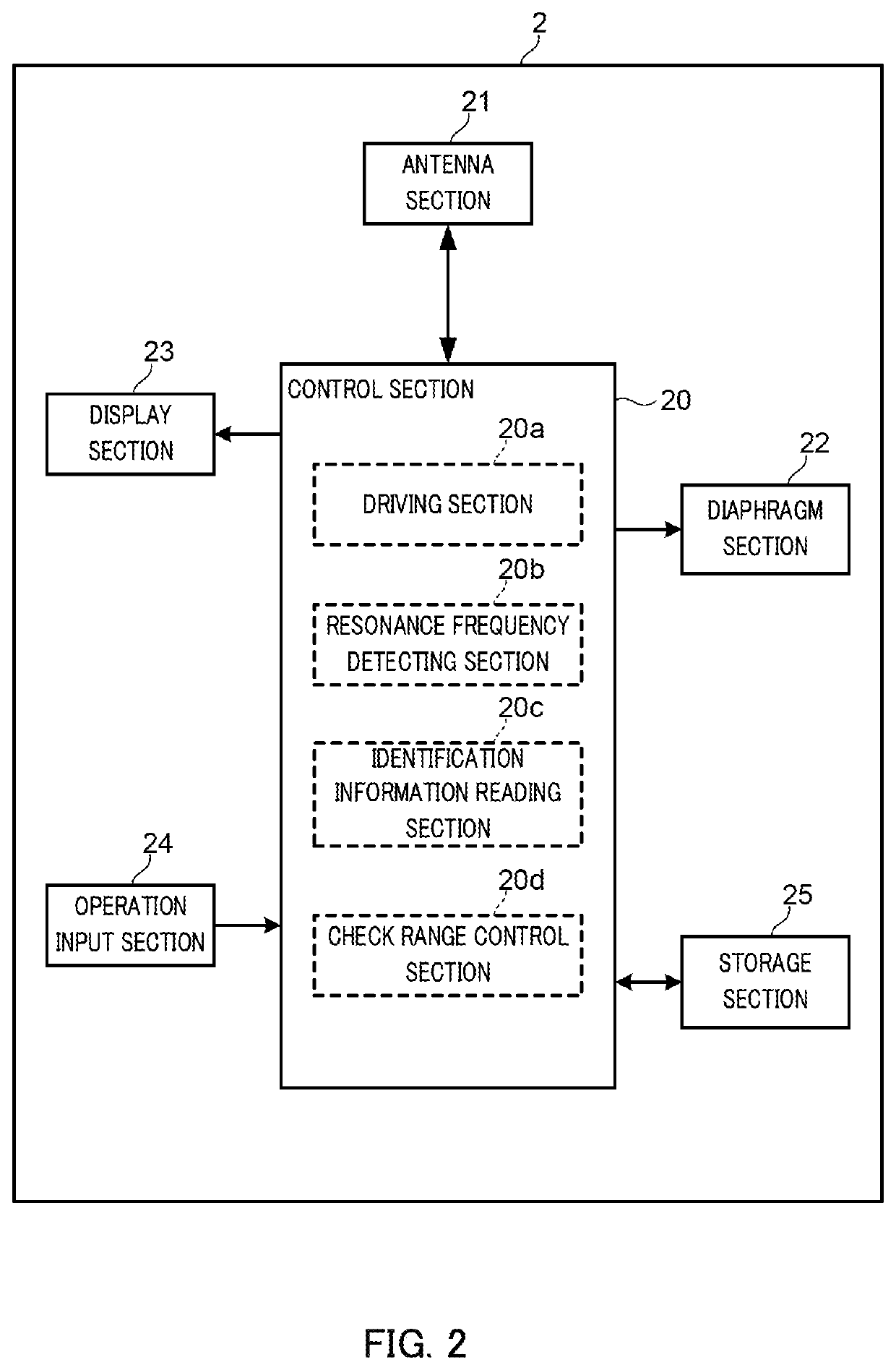
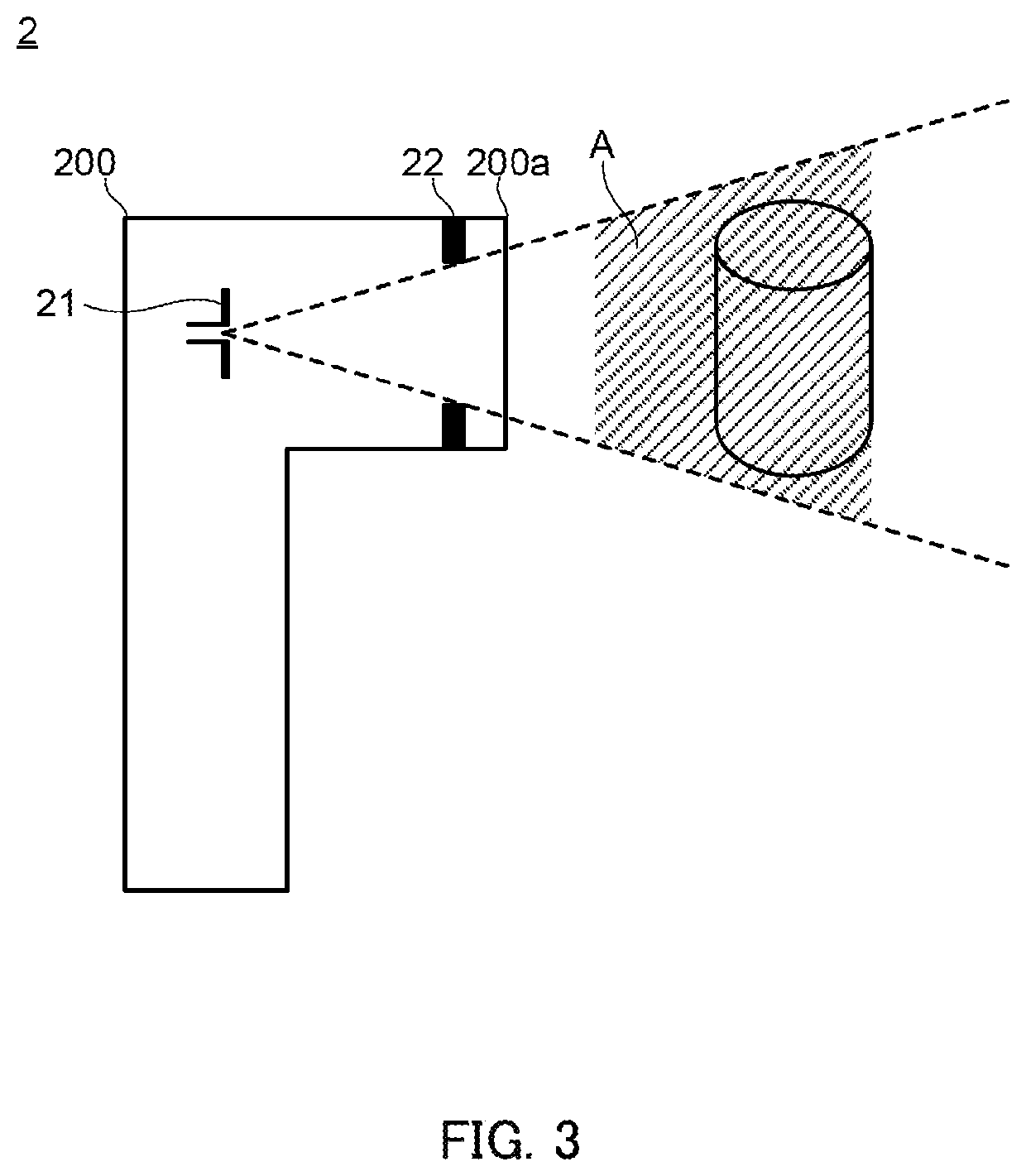
Tag Reader, RFID System, and Method for Reading Identification Information
ActiveUS20200250387A1Increase information densityImprove accuracyRecord carriers used with machinesAntennasChipless RFIDEngineering
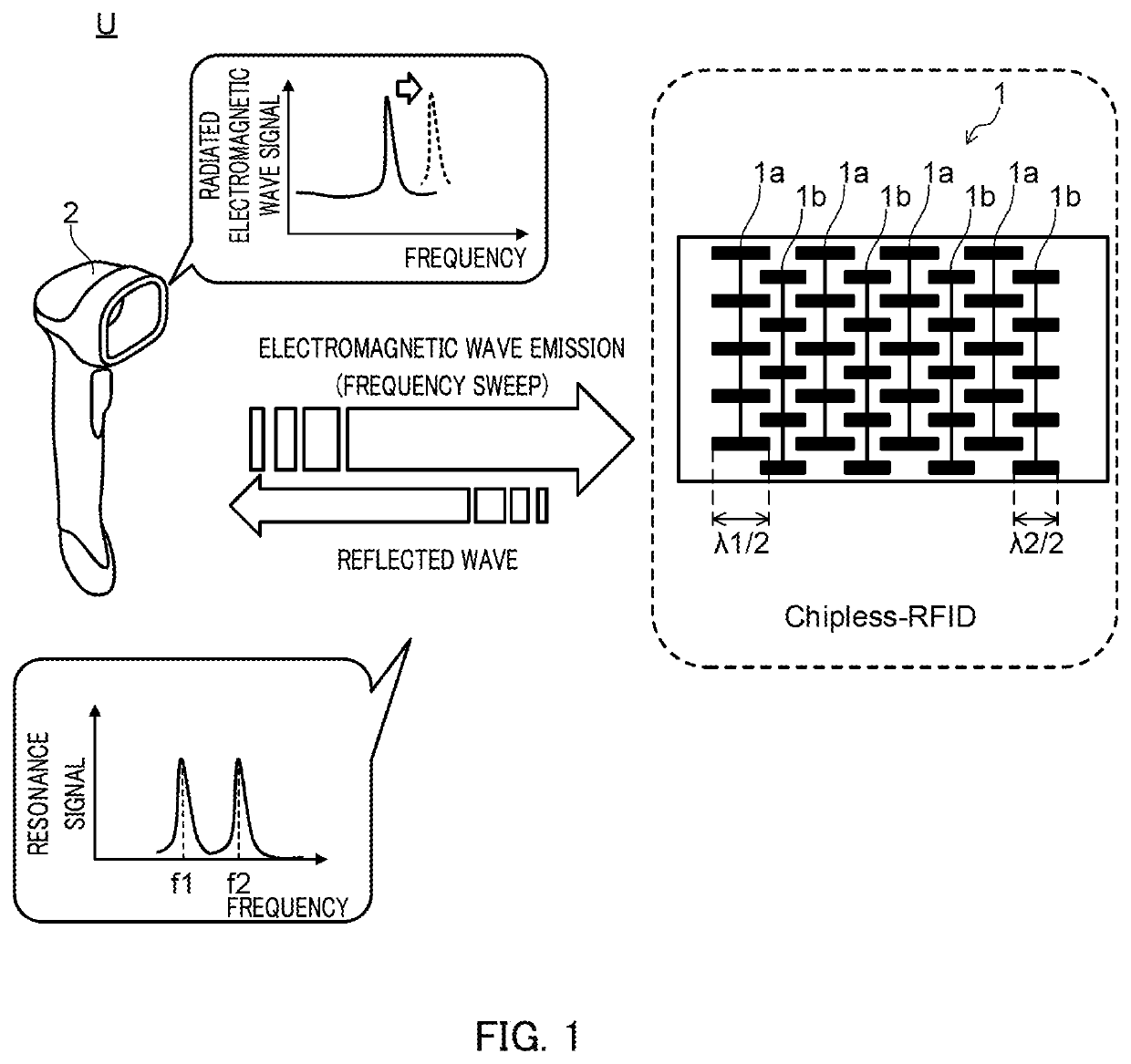
This tag reader can be applied to a chipless RFID tag having a plurality of resonance frequencies that are associated with identification information. The tag reader is provided with: a radiation unit that radiates electromagnetic waves within a predetermined millimeter wave or microwave frequency band so as to cause sweeping of the radiation frequency; and a detection unit that detects the plurality of resonance frequencies of a chipless RFID tag on the basis of the reflection characteristics of waves reflected from the chipless RFID tag when the electromagnetic waves are radiated.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
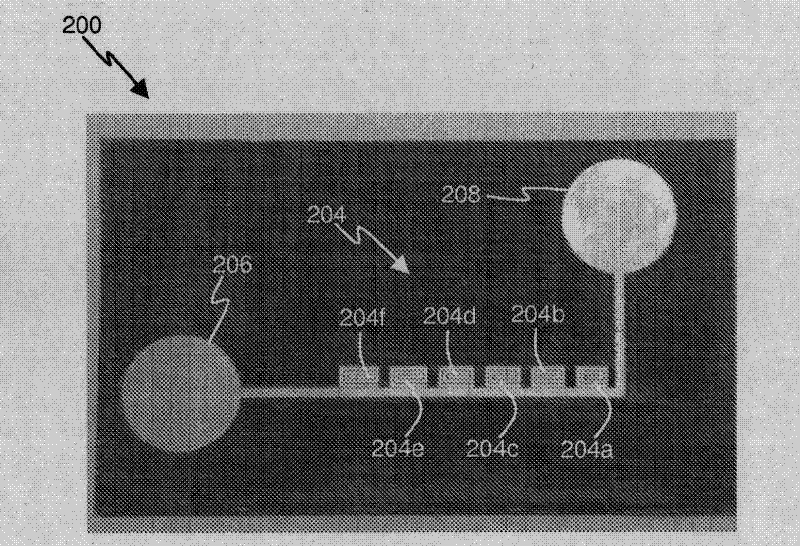
Radio frequency transponder
InactiveCN102057533AResistance/reactance/impedenceRadiating elements structural formsChipless RFIDSpiral resonator
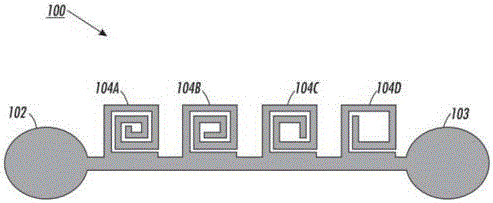
Information is encoded in a resonator / antenna structure, which may be interrogated in order to retrieve the information via radio frequency (RF) excitation. The resonator / antenna structure comprises a multiresonator including a plurality of substructures, and exhibits a plurality of resonances in the RF domain. Characteristic frequencies of the resonances depend upon the substructures, which may be modified in accordance with information to be encoded within the resonator / antenna structure. The resonator / antenna may be formed as a conductive structure disposed upon a dielectric substrate, and may be useful for encoding information within chipless RFID tags, security documents, negotiable instruments, and so forth. A variety of suitable multiresonator structures are disclosed, including multi-stop-band filters comprising cascaded spiral resonators, a 'wheel and spoke' structure, an interleaved resonant circuit, and a fractal resonator structure.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
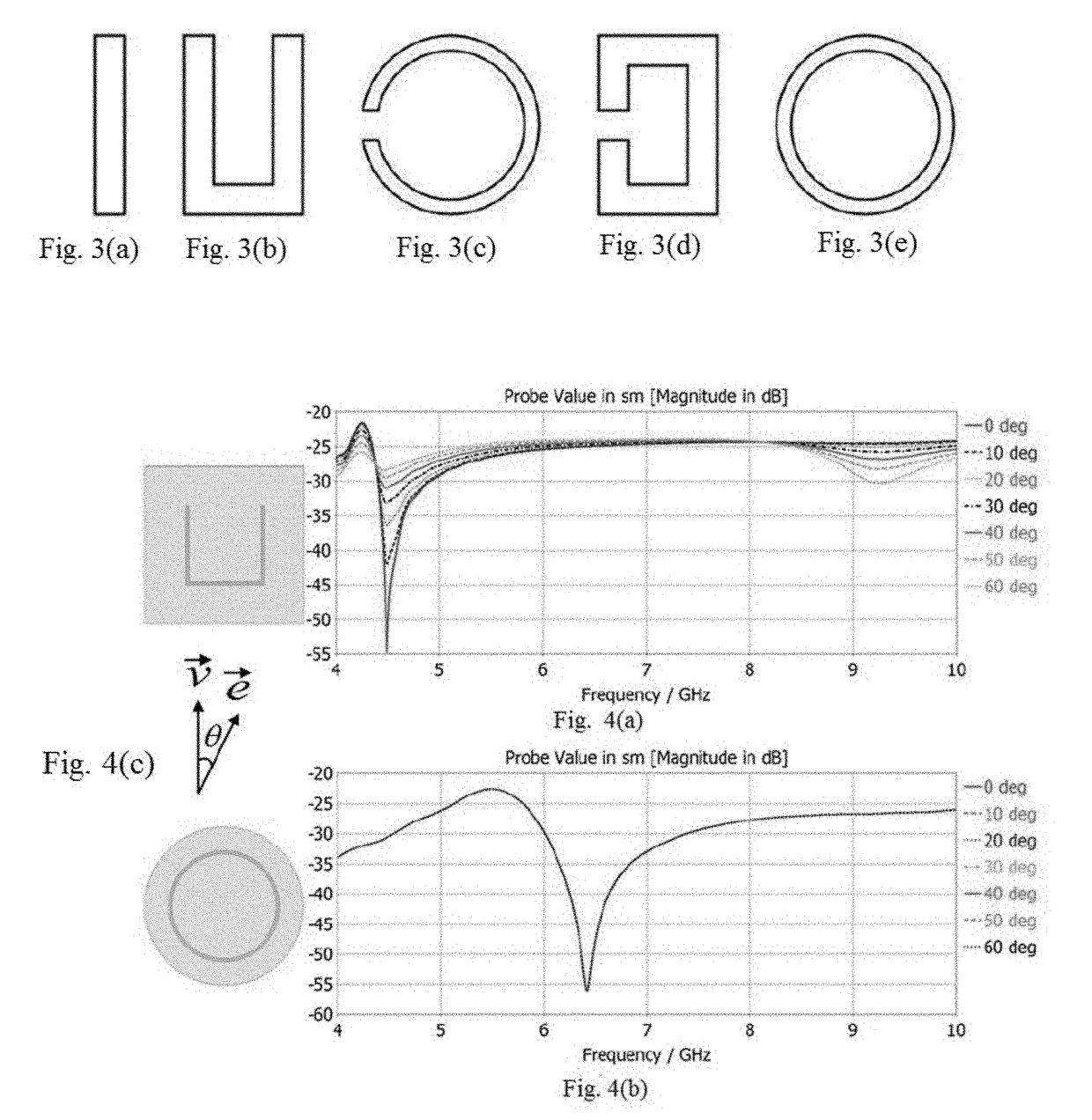
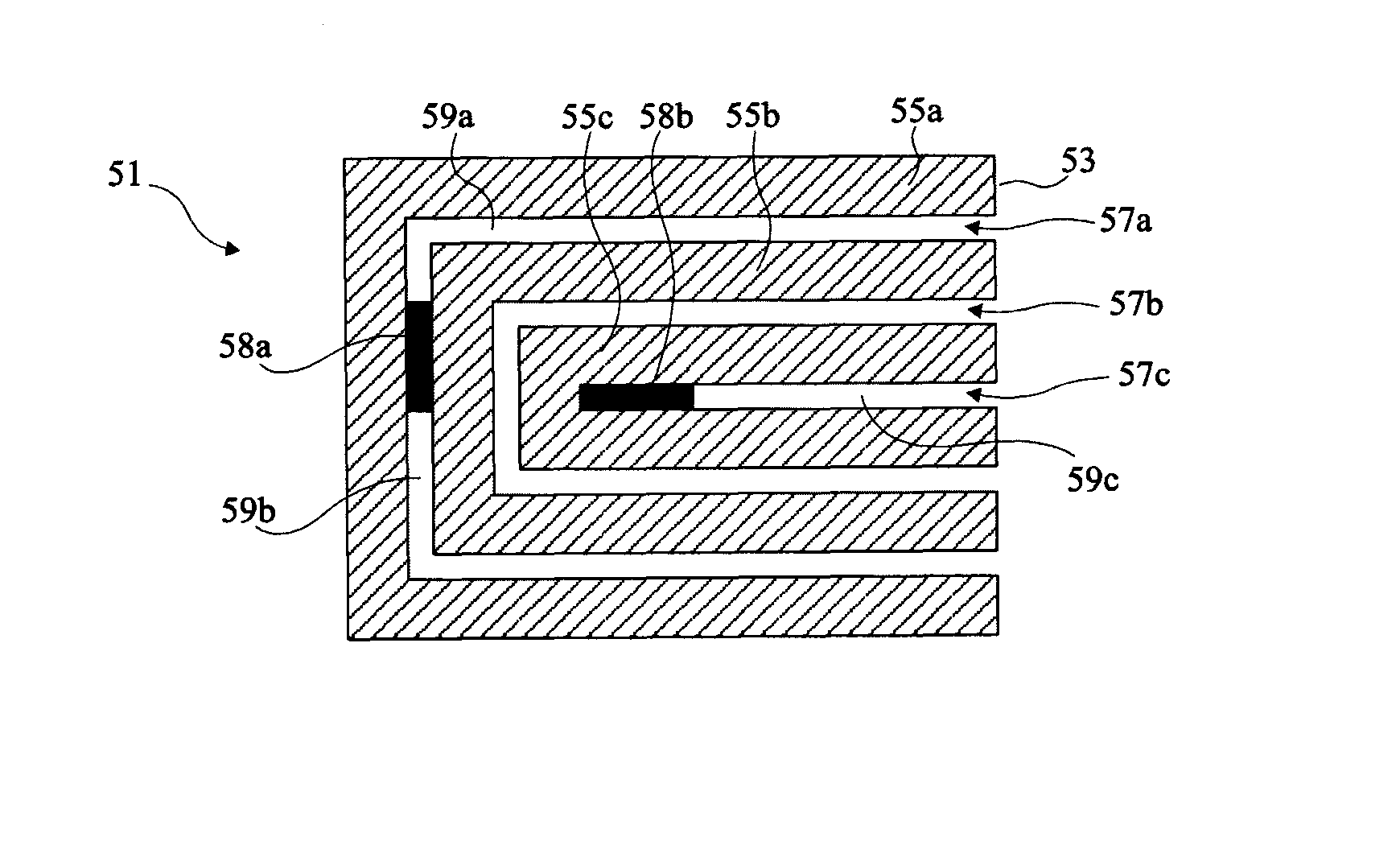
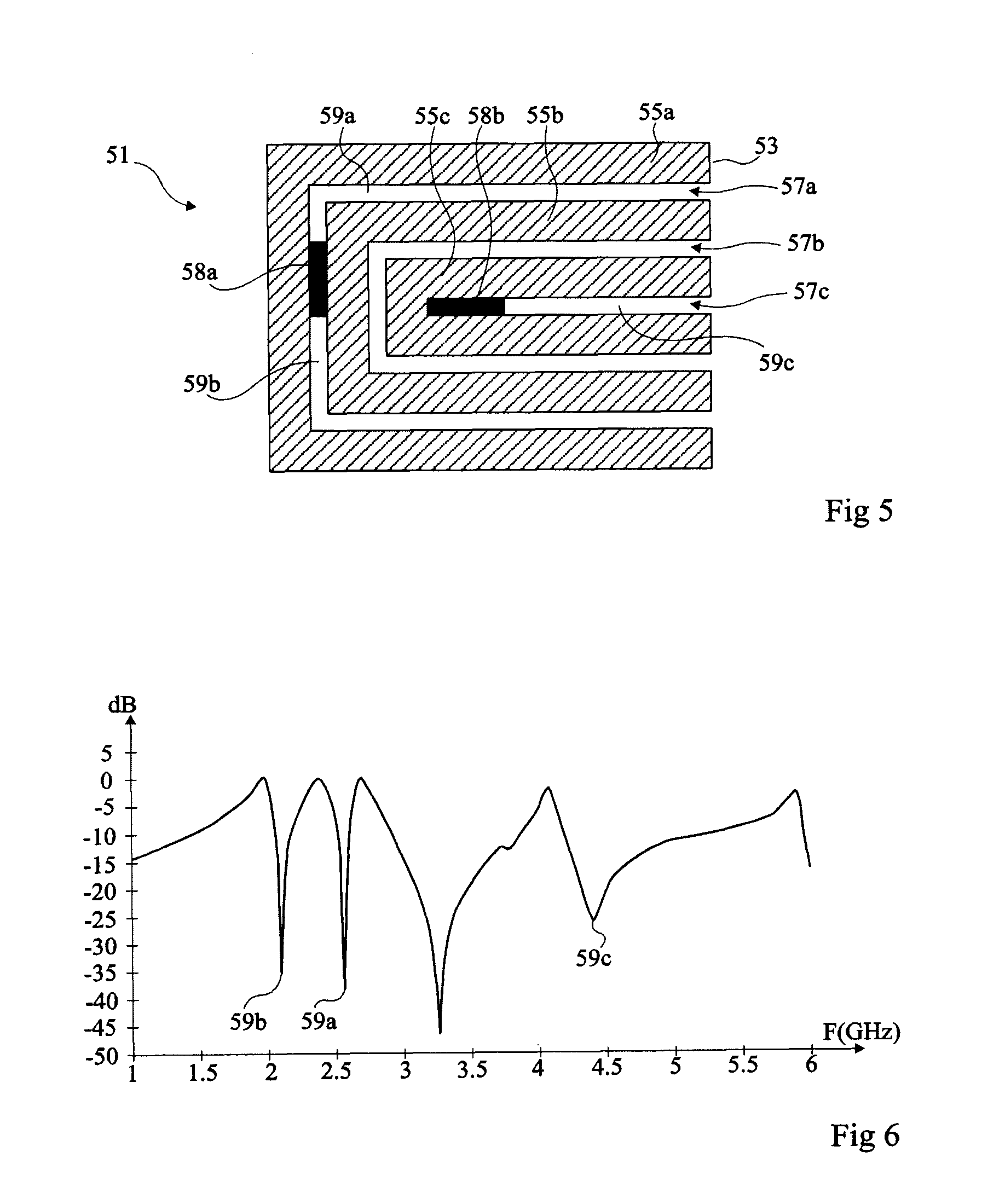
Reconfigurable resonators for chipless RFID applications
InactiveUS10211498B1Design economyResonatorsRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDEngineering
The reconfigurable resonators for chipless RFID applications provide spiral resonators for a multiple resonator passive RFID transponder tag. Each spiral resonator includes a U-shaped frame of conductive material and has a plurality (K−1) of parallel adjusting or shorting elements disposed between the legs of the U-shaped frame. Each resonator has one leg coupled to a transmission line adapted for connection between a receiving antenna and a transmitting antenna (in some embodiments, a single antenna may be used for both receiving and transmitting), and one of the adjusting or shorting elements may be selectively connected to the opposing leg of the frame to configure the resonator to resonate at one of (K−1) different resonant frequencies (K frequencies if none of the elements are connected) by a short metal jumper strip to change the length of the spiral resonator.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Chipless passive rfid tag
InactiveCN102884540AAvoid disadvantagesRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm electric actuationChipless RFIDEngineering
A chipless RFID tag comprises a plurality of disjoint parallel conducting bands formed on a dielectric support, in which conducting bridges interlink neighboring conducting bands, the conducting bridges delimiting, between the conducting bands, portions of dielectric bands of distinct lengths, each portion of dielectric brand determining a resonant frequency of the tag, the set of resonant frequencies of the tag defining an identification code.
Owner:INSTITUT NAT POLYTECHN DE GRENOBLE +1
Chipless radio frequency identification (RFID) electronic tag based on pole identification
InactiveCN103218647ASimple structureReduce energy consumptionRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDNatural resonance
The invention discloses a chipless radio frequency identification (RFID) electronic tag based on pole identification. The chipless RFID electronic tag based on the pole identification is composed of a plurality of folded dipole basic resonance units with different physical sizes, and each basic resonance unit is capable of generating unique resonance characteristics in a specific frequency range. Tag structures with different data codes can be acquired through combination of all the resonance units with different lengths, widths and folded position-center distances. When detecting is carried out, ultra wide band (UWB) impulse pulsed electromagnetic wave is used for a drive signal, and a singularity expansion method (SEM) based on stag scattered signals is adopted to acquire pole parameters which correspond with stag structure parameters. Identity data with the stags are distributed on complex frequency (poles) related to natural resonance, and then identification of the chipless RFID electronic tag can be achieved through a specific coding and decoding method.
Owner:何毅 +2
Flexible pouch with smart tags
The present invention discloses a smart pouch that has a flexible pouch with a plurality of smart tags attached thereto. The plurality of smart tags can include one or more of the following: a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag, a chipless RFID tag, a time sensitive tag, a time-temperature sensitive tag, a package-has-been-opened tag, a cooking instructions tag, and the like. A signal provided by the plurality of smart tags to a reader can provide a plurality of information to the reader and the information can be related to the flexible pouch and any content, product, etc., that may be contained therewithin. In addition, at least one of the plurality of smart tags can be located within an air pocket.
Owner:POUCH PAC INNOVATIONS
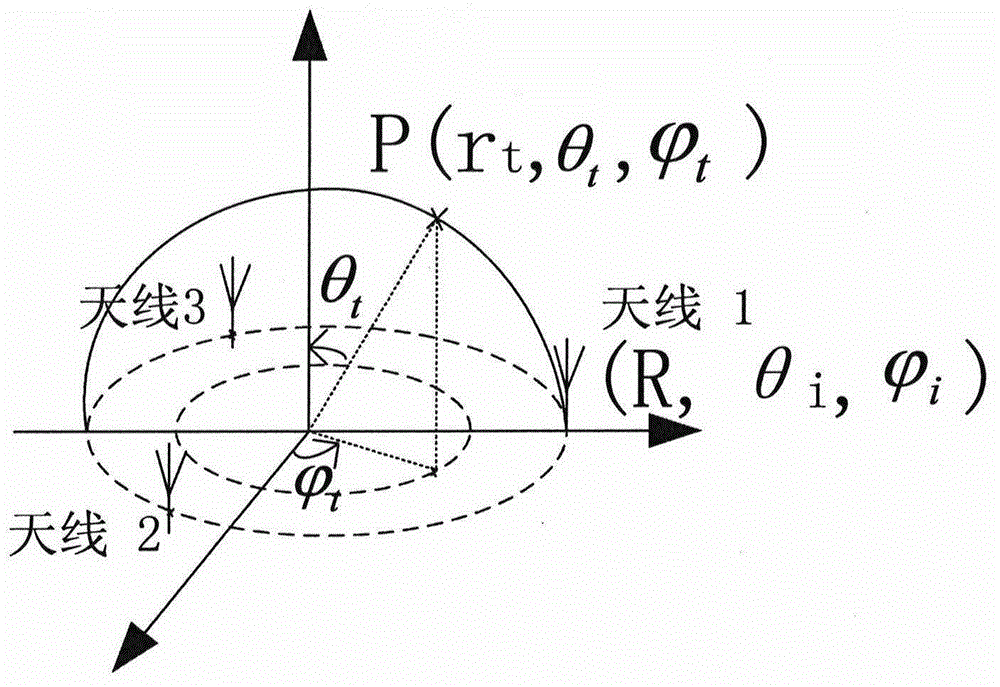
3D localization method of Chipless RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) on the basis of printing electronic technology
InactiveCN104899617ACo-operative working arrangementsRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDMathematical model
The invention discloses a 3D localization method of Chipless RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) on the basis of a printing electronic technology, and belongs to the field of wireless communication and the Internet of Things. The technology comprises a Chipless RFID printing method, a Chipless RFID design method with a high information capacity and a 3D localization method of Chipless RFID. A Chipless RFID tag structure with the high information capacity is designed, researched nano-silver particle reagent is used as printing ink to realize a purpose that a required device is printed on paper or PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) materials, at least three reader antennae are utilized for reading distance between the antennae and the tag structure, a corresponding mathematic model is established, and the information of a position where the tag is positioned is estimated. The 3D localization technology, which is realized by the printing electronic technology, of the Chipless RFID has the following advantages: a) tag processing is simple and convenient; b) the Chipless RFID tag is high in information capacity storage; c) the 3D localization method uses a traditional localization technology and a literature "Chipless RFID Tag Localization" method as references to propose the localization method of the Chipless RFID, and Chipless RFID localization can be realized.
Owner:杨军 +1
Ucr: an unclonable environmentally-sensitive chipless RFID tag
ActiveUS20180121689A1Increase temperaturePaper-money testing devicesRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDEmbedded system
Chipless RFID tags and methods of using the same are provided. Each RFID tag provided herein can generate a unique and unclonable (unclonable chipless RFID, or UCR) identifier from its intrinsically random manufacturing process. The UCR device can monitor increase in storage temperature beyond that which is appropriate for a specific commodity to which the device is attached.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
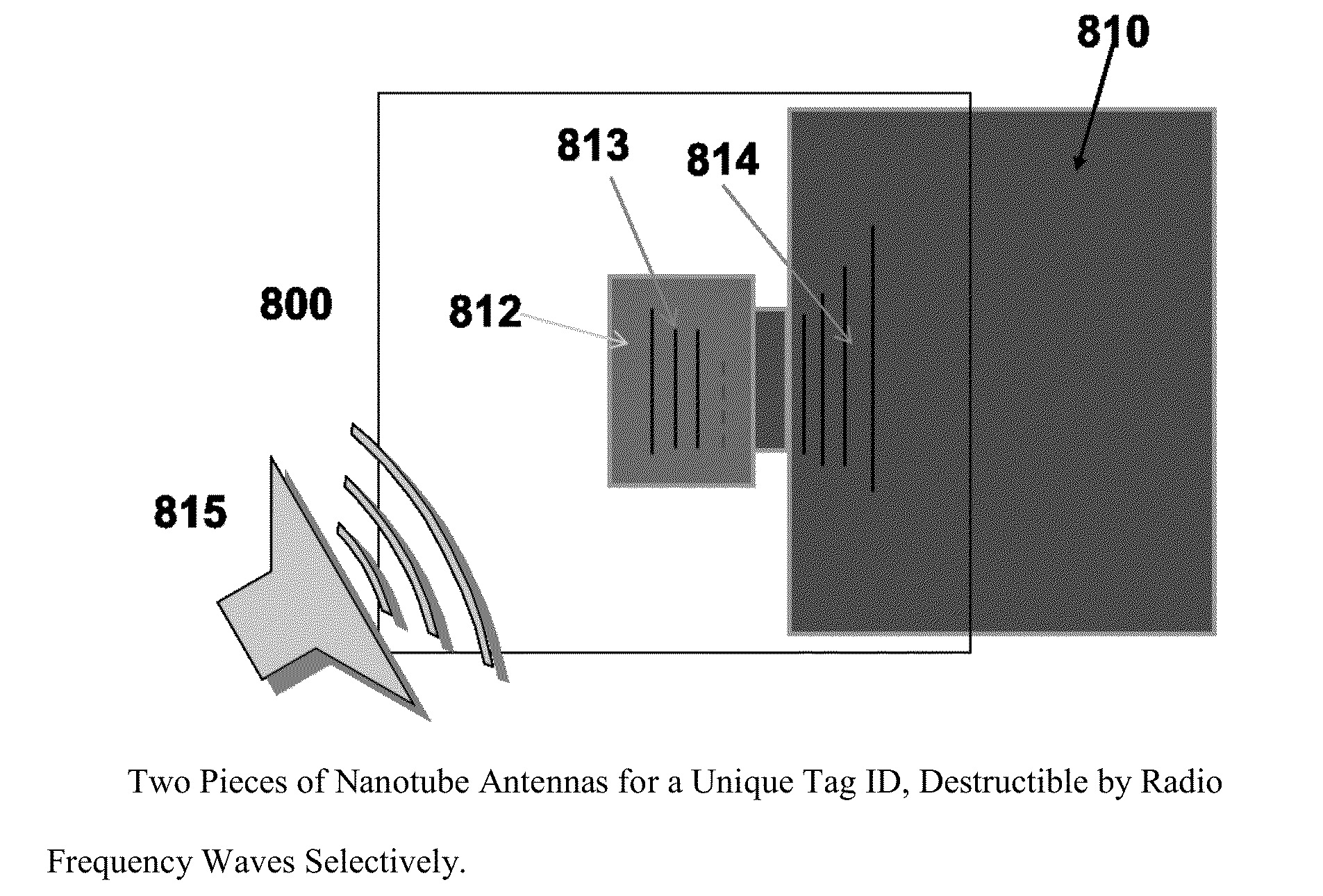
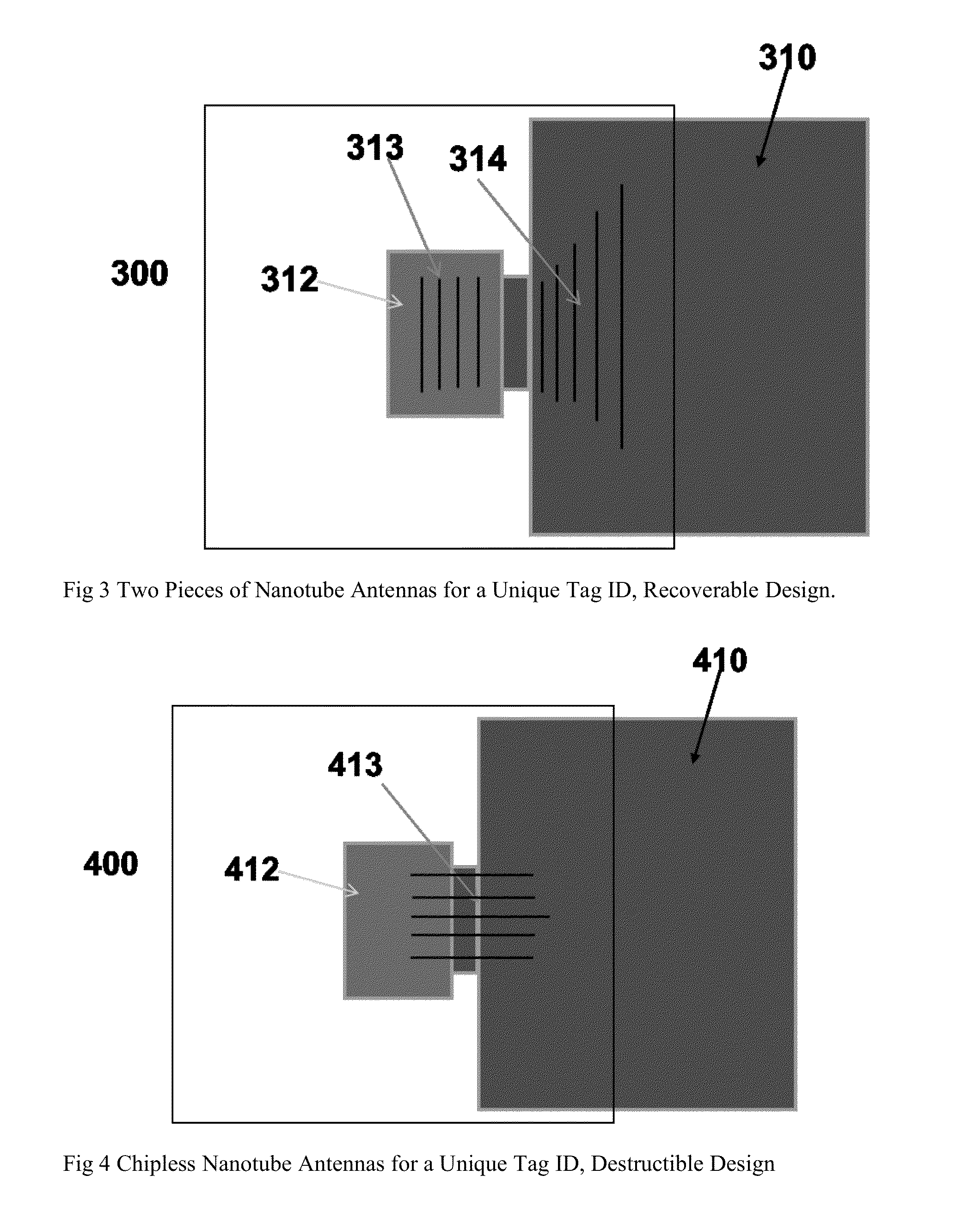
Chipless nanotube electromagnetic identification system for Anti-counterfeiting, authorization, and brand protection
InactiveUS20150076235A1Small sizeSufficient securityRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDElectricity
Chipless RFID nanotube tags (300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900) with anti-counterfeiting capability are designed into one piece, mostly two pieces, three pieces, or multiple pieces of nanotube antenna elements on at least two dielectric substrates (310 / 312, 510 / 512,810 / 812, 910 / 912 / 913 / 916 etc.) for providing brand product protection, authorization, anti-counterfeiting, and even recycling, and tag process control purposes.
Owner:QIAN ZHENGFANG +1
Omnidirectional chipless RFID tag based on angle positioning
ActiveCN107392298ALow costLarge capacityRecord carriers used with machinesHigh level techniquesChipless RFIDDielectric substrate
The invention discloses an omnidirectional chipless RFID tag based on angle positioning. The RFID tag comprises an antenna radiating patch structure and a dielectric substrate structure. The antenna radiating patch structure is located on the upper surface of the dielectric substrate structure. The antenna radiating patch structure is composed of a rectangular patch printed with an upper coding unit and a lower positioning unit, wherein the lower positioning unit is located directly below the upper coding unit. The omnidirectional chipless RFID tag provided by the invention has the advantages of omnidirectionality, miniaturization, large capacity, high spectrum utilization, easy printing and the like, and is applicable to the field of Internet of Things.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
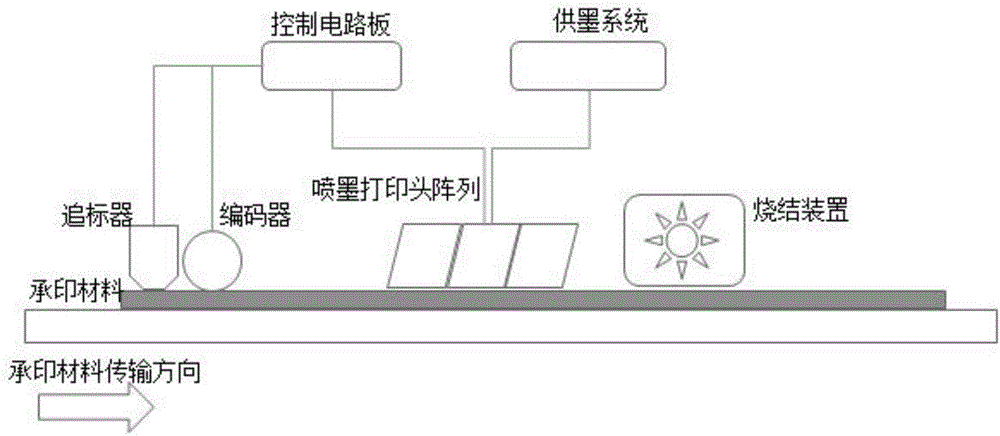
System and method for inkjet manufacturing of variable Chipless RFID
The invention relates to a system and method for inkjet manufacturing of a variable Chipless RFID. The system comprises an inkjet printing head, a function ink material, a sintering device, a mark chasing device, an encoder, a control circuit board, an industrial control machine and a data server. According to the method, the Chipless RFID data scheme stored in the data server is transmitted to the industrial control machine, the industrial control machine converts server data into printing signals so as to be transmitted to the control circuit board, the control circuit board determines the position of a printing base material and the transmission speed according to signals fed back by the mark chasing device and the encoder, a spraying head is controlled to print the function material ink on the base material to form a Chipless RFID line type, the resonance characteristic of the Chipless RFID can be achieved through the sintering device, and due to data online transmission and inkjet printing, Chipless RFIDs are different. According to the system and method, the aim that inkjet printing manufacturing has the unique Chipless RFID is achieved, the Chipless RFID can serve as an independent system and also can serve as an embedding structure of a printing or packaging and other machines.
Owner:高志强
Information capacity expansion method for chipless RFID electronic tag
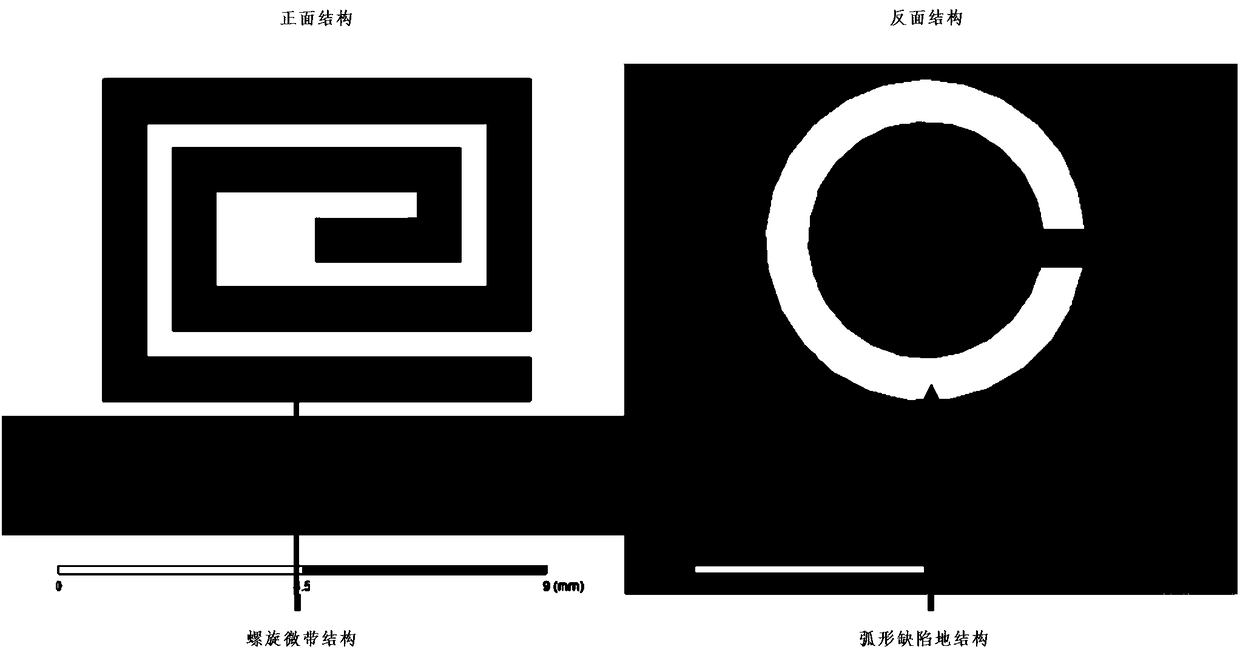
PendingCN108133253AIncrease information capacityIncrease capacityRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDFrequency characteristic
The invention discloses an information capacity expansion method for a chipless RFID electronic tag and relates to an optimization technology for chipless RFID tags. According to the method, information capacity of the chipless RFID electronic tag is expanded, an arc-shaped defected ground structure is innovatively added against the defect that a chipless RFID tag of an original structure has small capacity, the tag realizes hybrid coding by use of frequency characteristics and amplitude characteristics of signals, and therefore the information capacity of the tag is increased.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Galvanic process for making printed conductive metal markings for chipless rfid applications
InactiveCN101442882AAvoid problems associated with printing particulate matterLow costLiquid surface applicatorsRadiating elements structural formsChipless RFIDHalf-reaction
A process for printing a metal wire pattern on a substrate, including: printing a first salt solution including a metal ion that will undergo a reduction half-reaction; printing a second salt solution containing an oxidizing agent that will undergo an oxidation half-reaction in contact with the first salt solution, resulting in the reduction of the metal ions of the first salt solution; and allowing the first and second salt solutions to react by a galvanic reaction, causing reduced metal ions of the first salt solution to precipitate as a solid, on the substrate.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Fractal technology-based chipless RFID (radio frequency identification) tag and RCS (radar cross section) amplitude coding method thereof
InactiveCN107292371AReduce RCS peakAdjust frequencyAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsMetal stripsChipless RFID
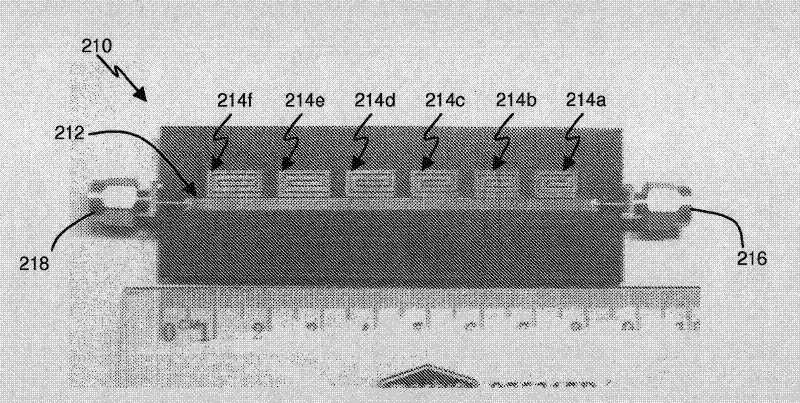
The invention discloses a fractal technology-based chipless RFID (radio frequency identification) tag and an RCS (radar cross section) amplitude coding method thereof. The tag comprises a dielectric substrate and a plurality of resonators, wherein the upper surface is provided with a metal layer, the resonators are arranged on the metal layer of the dielectric substrate, and the resonator comprises a slit in the metal layer and metal strips in the slit, wherein the slit includes a central vertical slit and a central transverse slit intersecting with each other perpendicularly at an intersection. The tag is characterized in that the at least one resonator structure is subjected to fractal technology processing: a plurality of transverse slits are uniformly distributed at two sides of the central transverse slit additionally with the central transverse slit adopted as a symmetry axis; a plurality of vertical slits are uniformly distributed at two sides of the central vertical slit additionally with the central transverse slit adopted as a symmetry axis; and a vertical metal strip in the central vertical slit intersects with a center transverse metal strip in the central transverse slit at an intersection. The tag of the invention has the advantages of high frequency spectrum utilization, un-correlation to polarization directions, single-layer structure, simplicity and easiness in processing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Chipless passive RFID tag
ActiveUS8556184B2Less expensiveEasy to manufactureRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalChipless RFIDEngineering
A chipless RFID tag comprises a plurality of disjoint parallel conducting bands formed on a dielectric support, in which conducting bridges interlink neighboring conducting bands, the conducting bridges delimiting, between the conducting bands, portions of dielectric bands of distinct lengths, each portion of dielectric brand determining a resonant frequency of the tag, the set of resonant frequencies of the tag defining an identification code.
Owner:IDYLLIC TECH
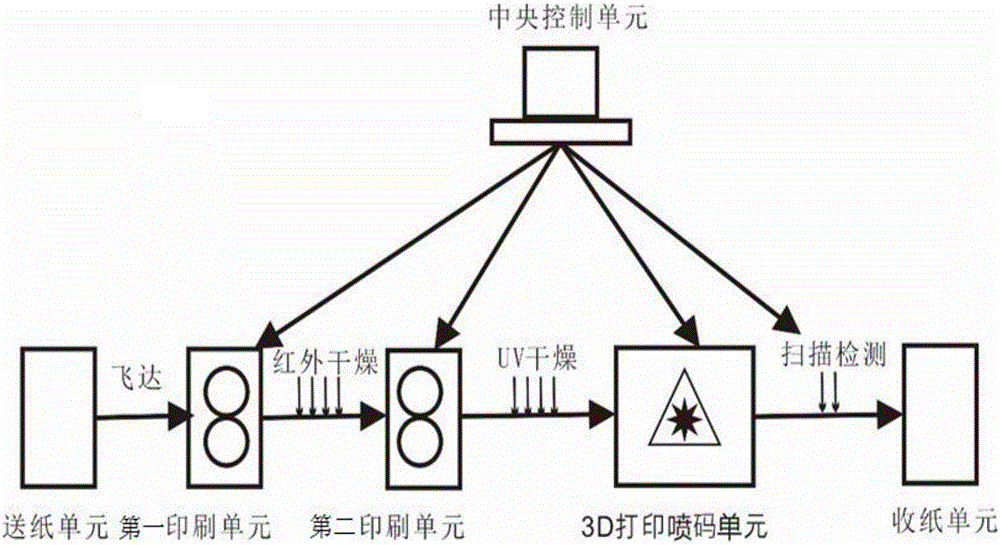
Printing system and printing method for chip-free RFID electronic label
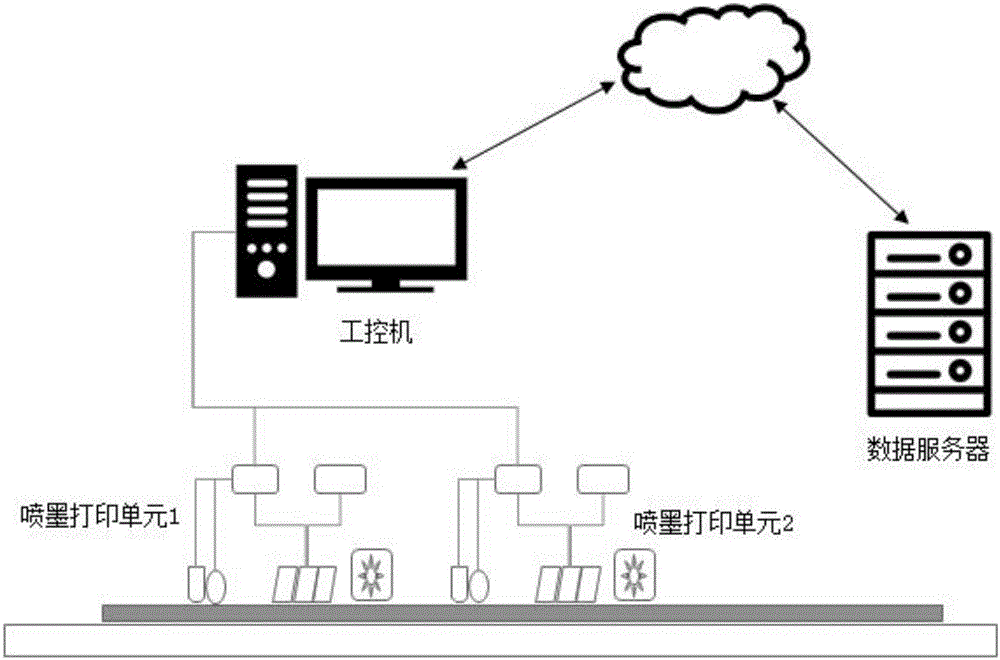
ActiveCN106739535ALow costReduce human errorTypewritersOther printing apparatusChipless RFIDEngineering
The invention discloses a printing system and a printing method for a chip-free RFID electronic label. The printing system comprises a central control unit, a paper feeding unit, a printing unit, a 3D printing code-spraying unit and a paper collecting unit, wherein the paper feeding unit, the printing unit and the 3D printing code-spraying unit and the paper collecting unit are all connected with the central control unit. The problems of electronic label printing in the prior art that an electronic chip is implanted in a corresponding electronic label bag, then printing and packaging of the electronic label are performed through equipment; a waste rate is high due to equipment or manual error during a printing and packaging process; besides, the electronic chip is high in cost, low in anti-falsification and easy to embezzle; and the position of the electronic label chip is difficult to adjust are solved.
Owner:贵州劲嘉新型包装材料有限公司
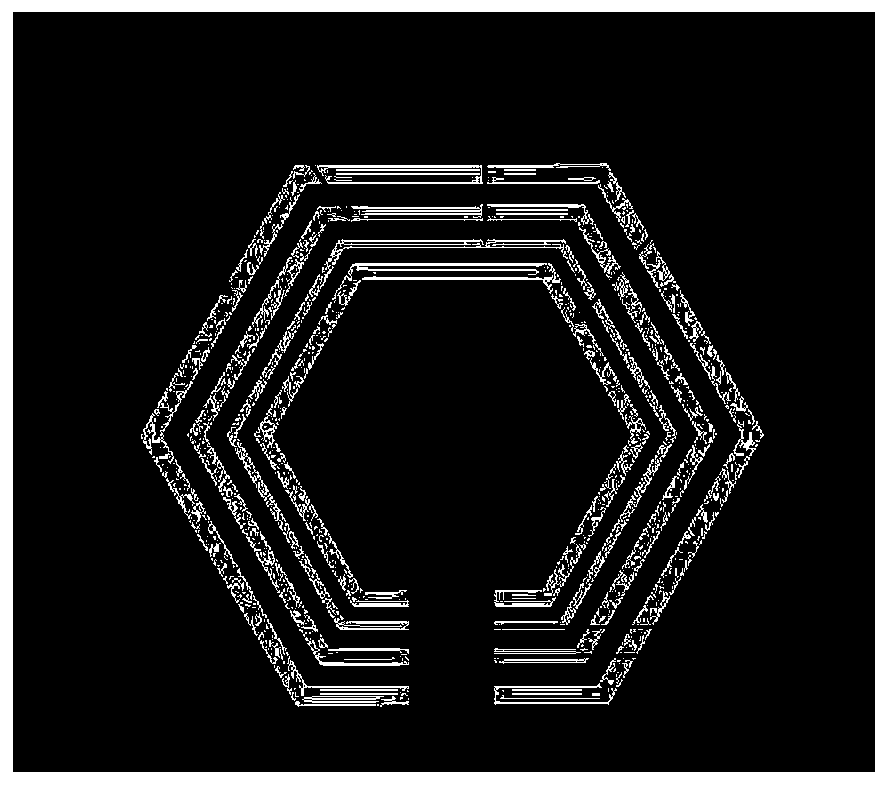
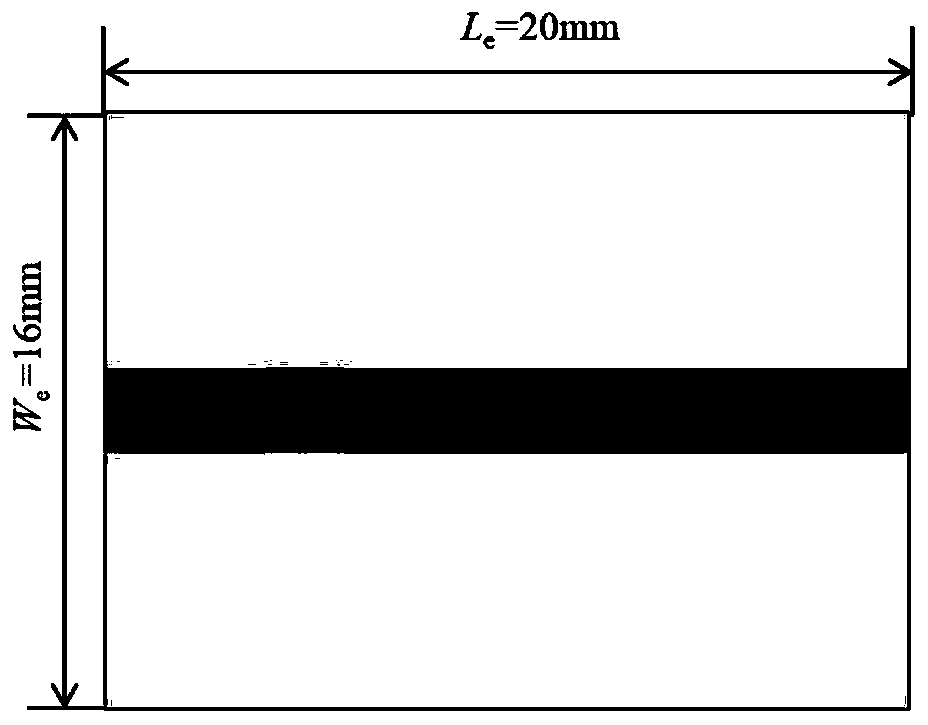
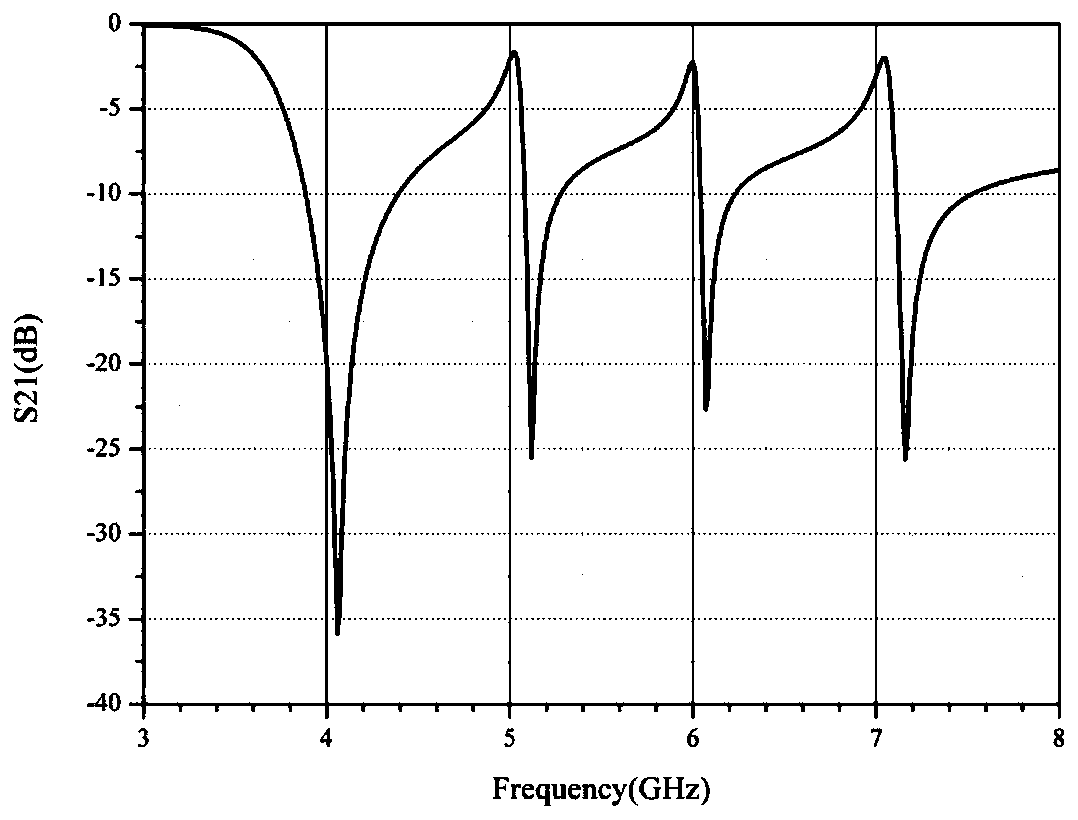
A chipless RFID tag based on CSRR
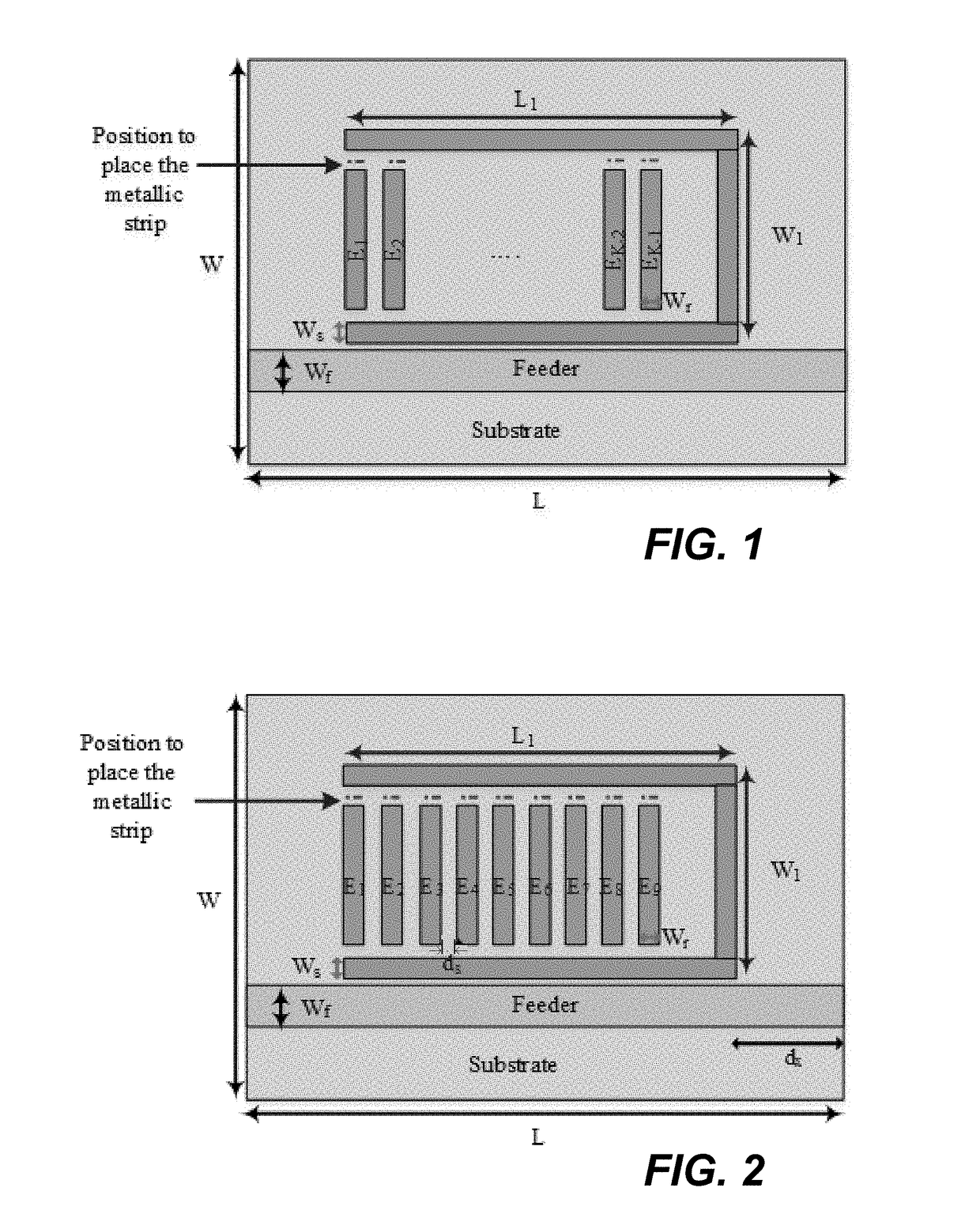
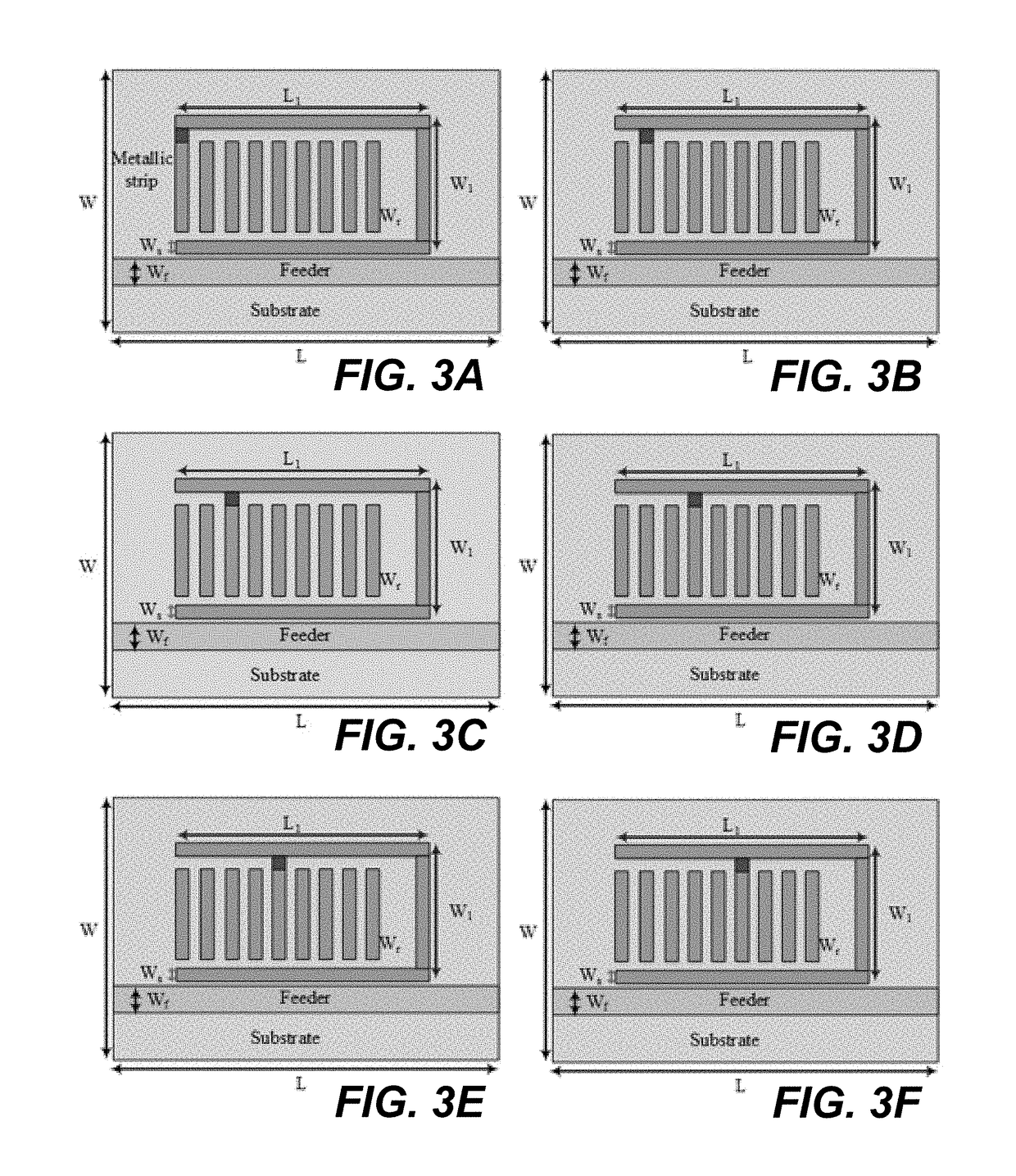
The invention provides a chipless RFID tag based on a CSRR. The chipless RFID tag includes a dielectric plate, ta coupling microstrip line arranged on one surface of the dielectric plate, and a micro-strip resonance unit arranged on the other surface of the dielectric plate; the micro-strip resonance unit comprises a plurality of nested micro-strip resonators; wherein each micro-strip resonant unit is of a regular hexagon structure with an opening in one side and an opening in the same direction, specific digit coding is achieved by setting the specific number of the micro-strip resonators, each micro-strip resonator is set to be in a resonant or short-circuit state to achieve two-digit coding, and the characteristic impedance of the coupling micro-strip line is 50 ohm. According to the invention, the capacity expansion of the chipless tag is realized by increasing the number of the micro-strip resonators, and the expandability is flexible. By reducing the interval between the resonantfrequencies generated by the microstrip resonators, the capacity of the chipless RFID tag can be improved by maximizing the number of the resonators within a specific frequency range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chipless RFID tag based on four-state coupled line resonator and optimization system of chipless RFID tag
ActiveCN110659712ALow costReduce spectrumCo-operative working arrangementsRecord carriers used with machinesChipless RFIDIntelligent management
The invention discloses an optimization system of a chipless RFID tag. The optimization system comprises an RFID tag, a reader-writer and a back-end server; the reader-writer is used for reading the RFID tag and transmitting data to the back-end server in a wireless or wired manner; the rear-end server is used for completing data processing and automatic intelligent management and control, whereinthe RFID tag comprises a patch antenna and the multi-resonator model, the multi-resonator model comprises more than one four-state coupling line resonator, and the four-state coupling line resonatorshave four states and are respectively coded. The chipless RFID tag provided by the invention has the good effects of optimal bandwidth, efficient and accurate identification and expandability, has the characteristics of wide identification range, direction independence and the like, and effectively improves the overall performance of a chipless RFID tag system.
Owner:盐城农农炽辉科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com