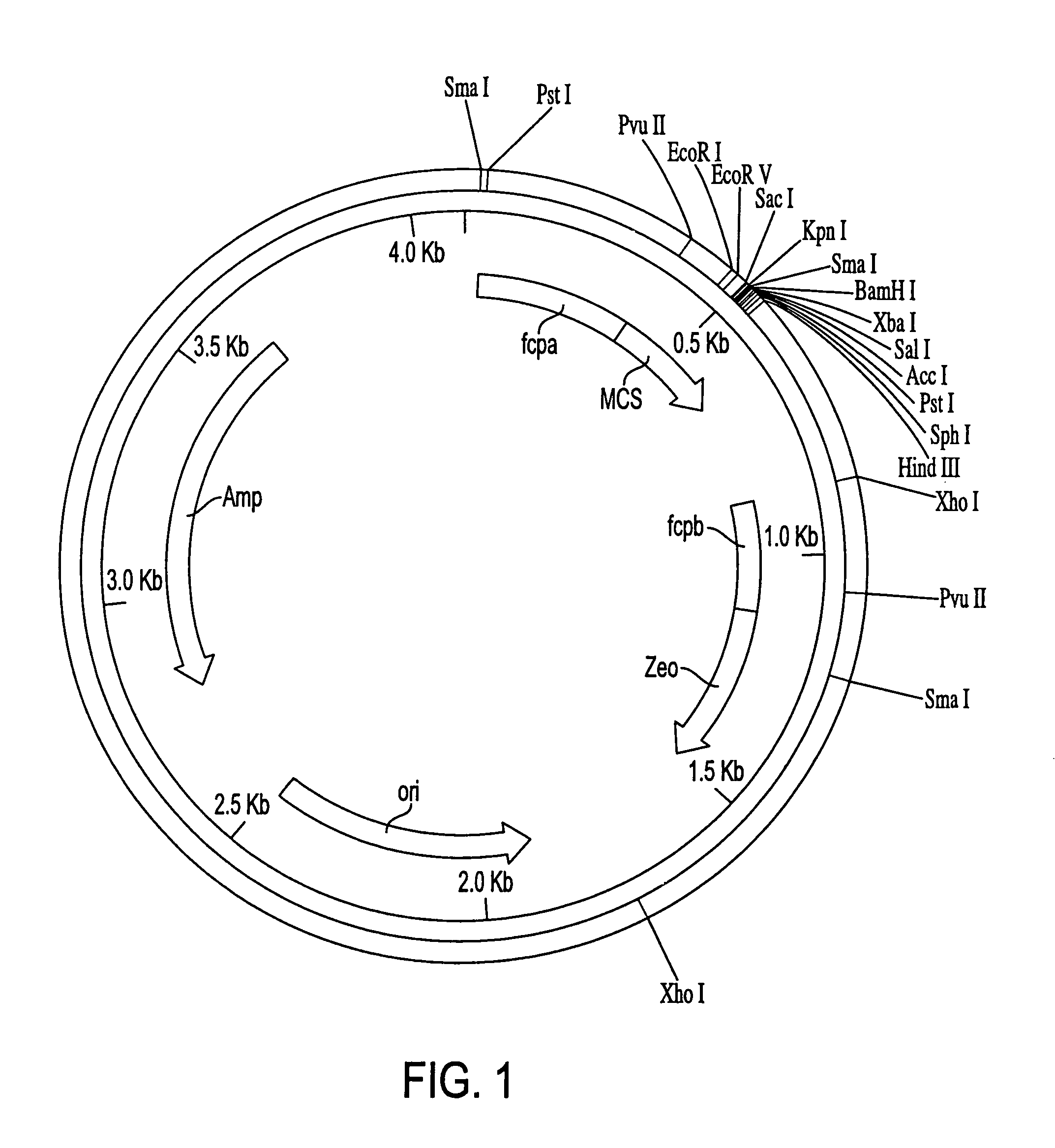
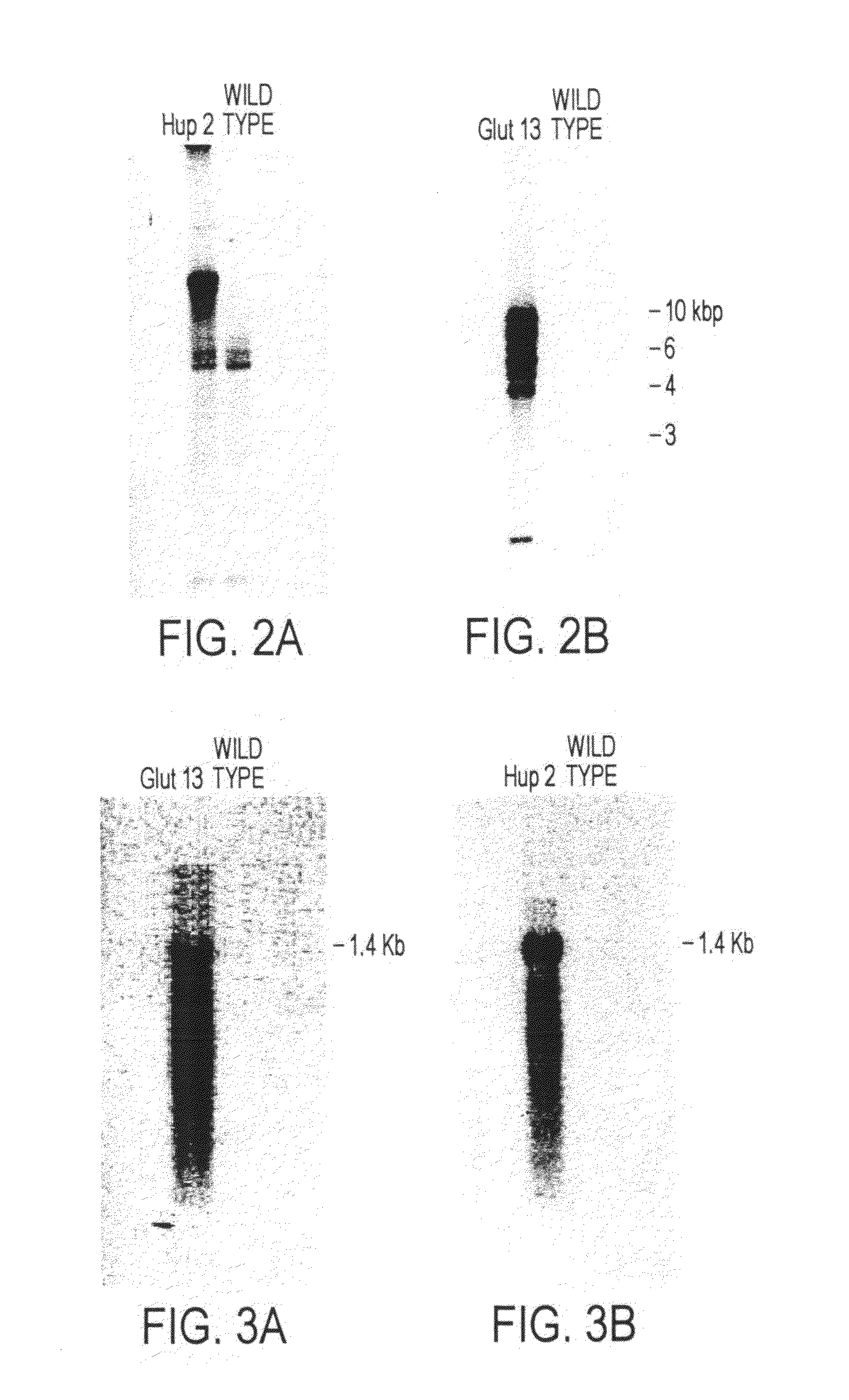
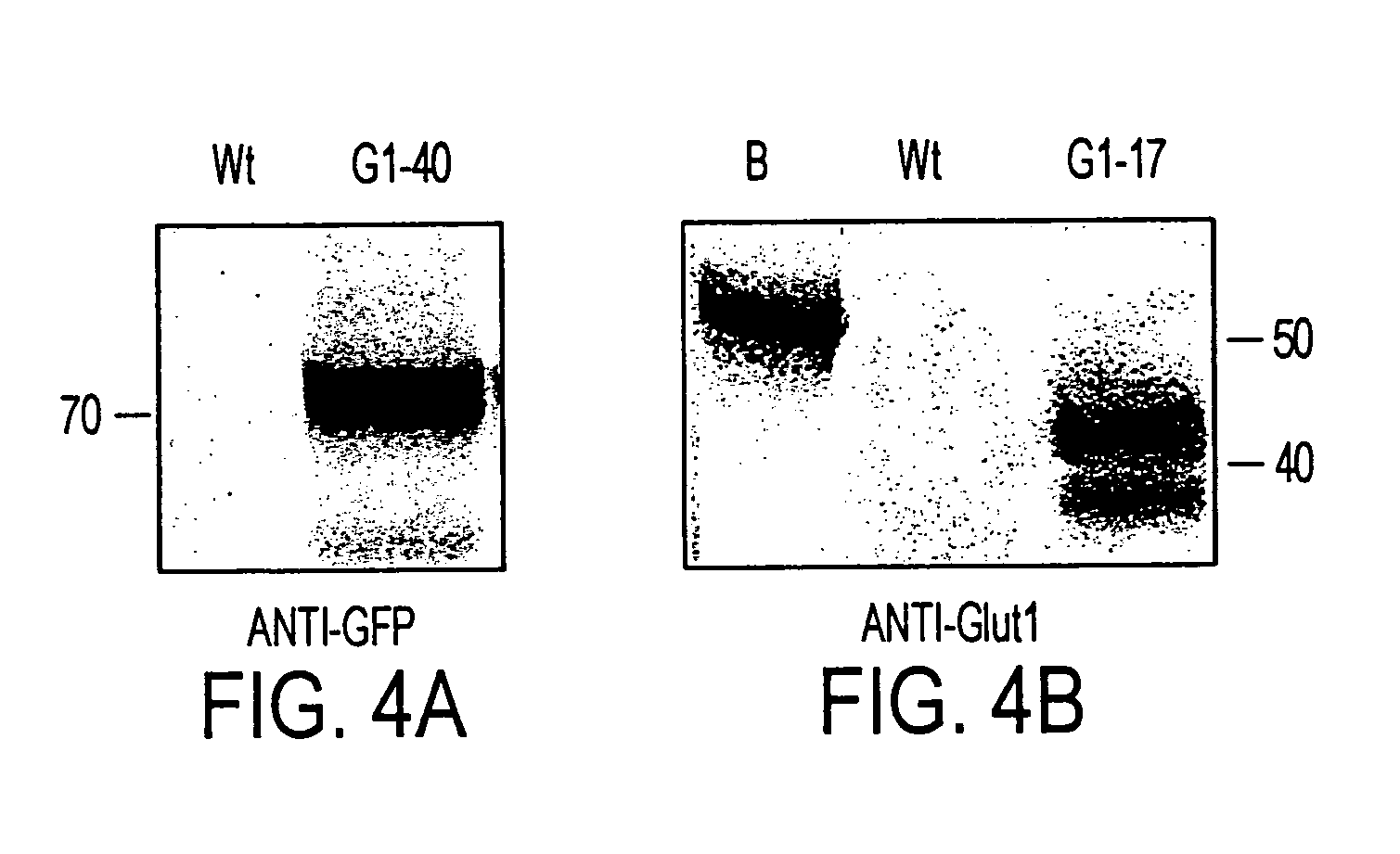
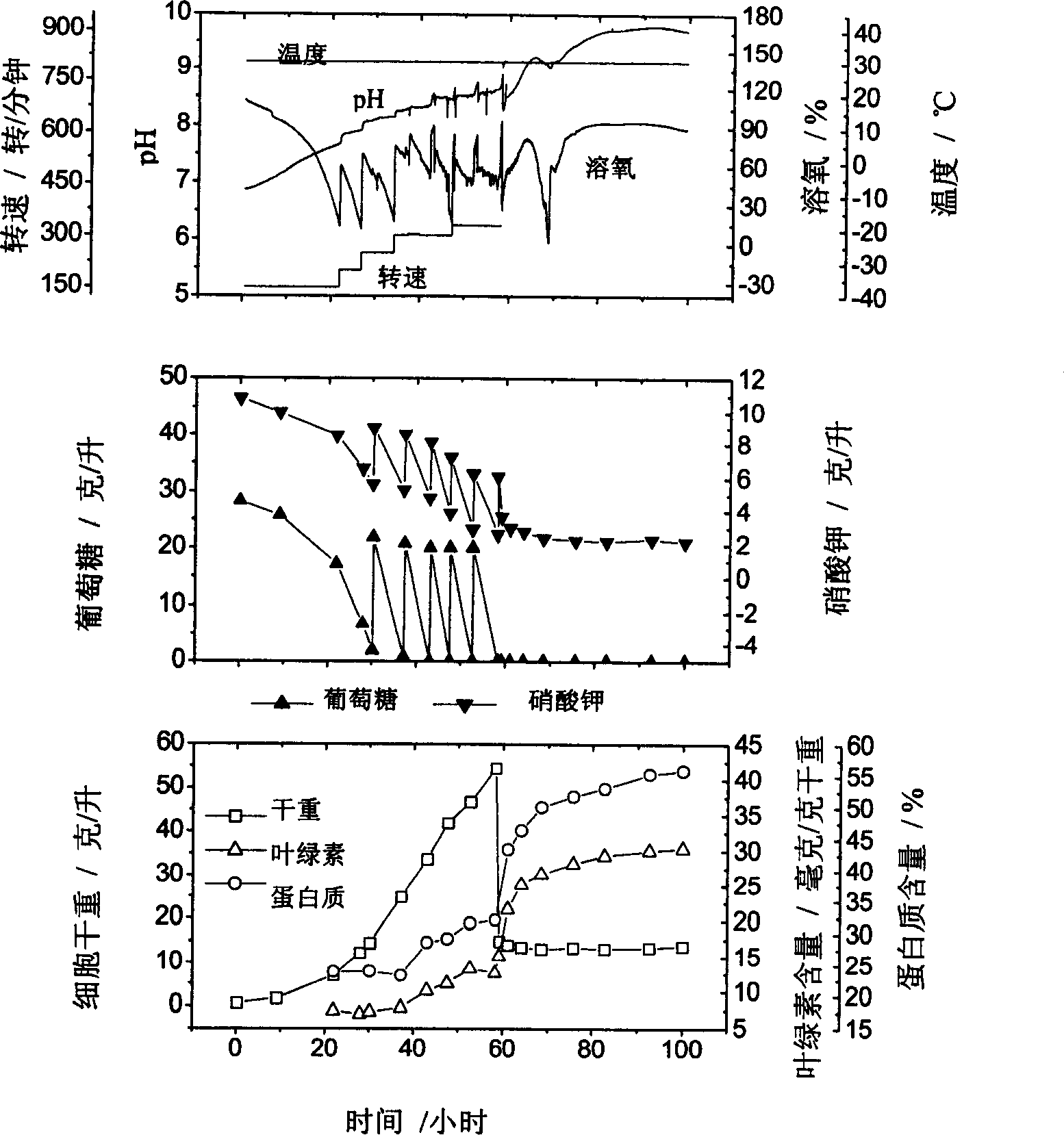
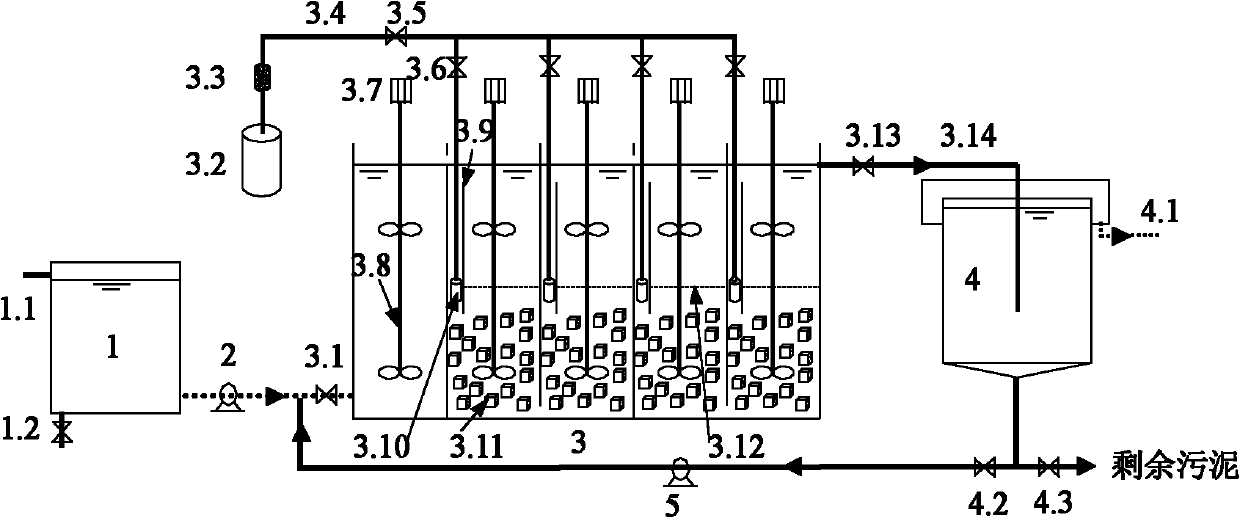
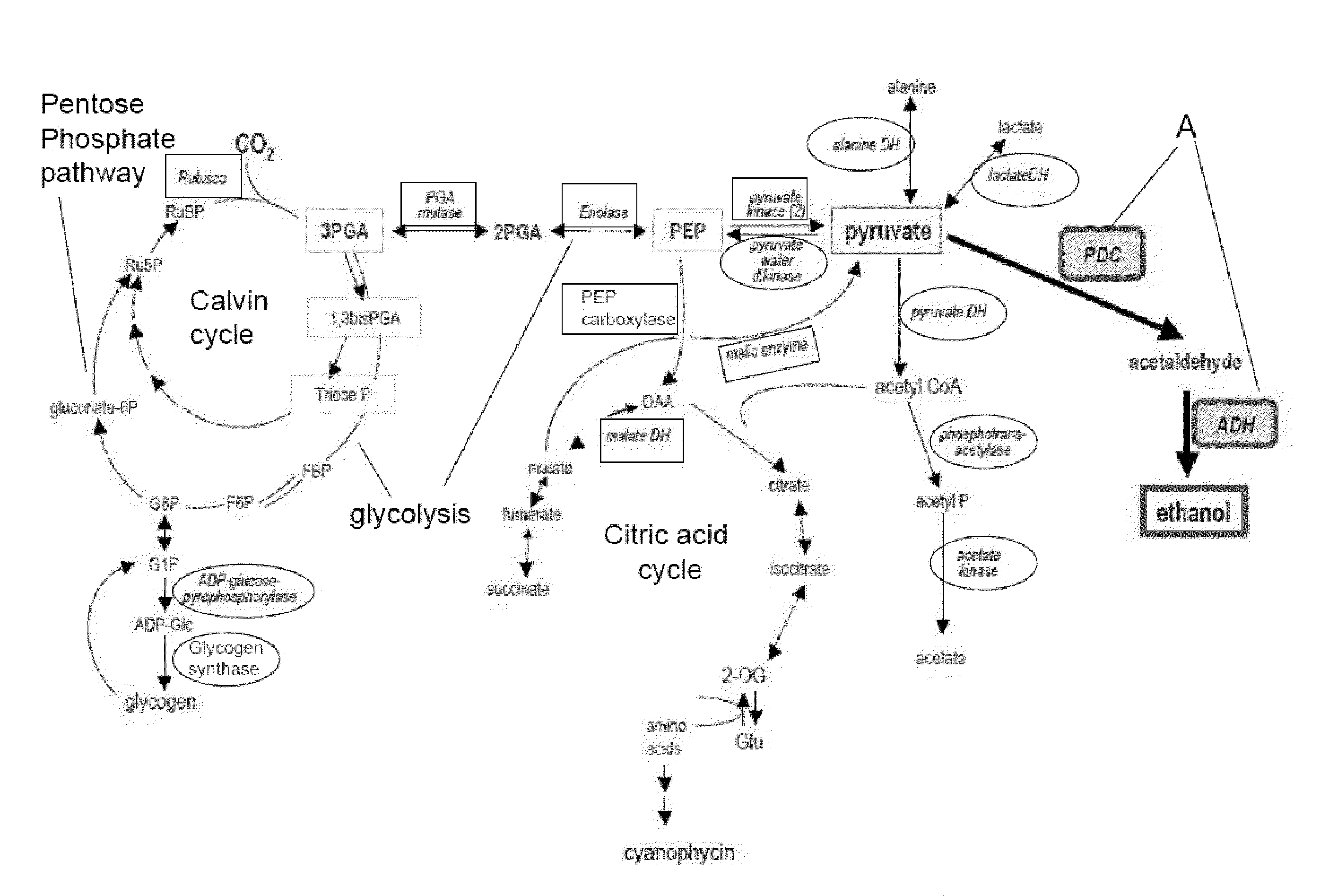
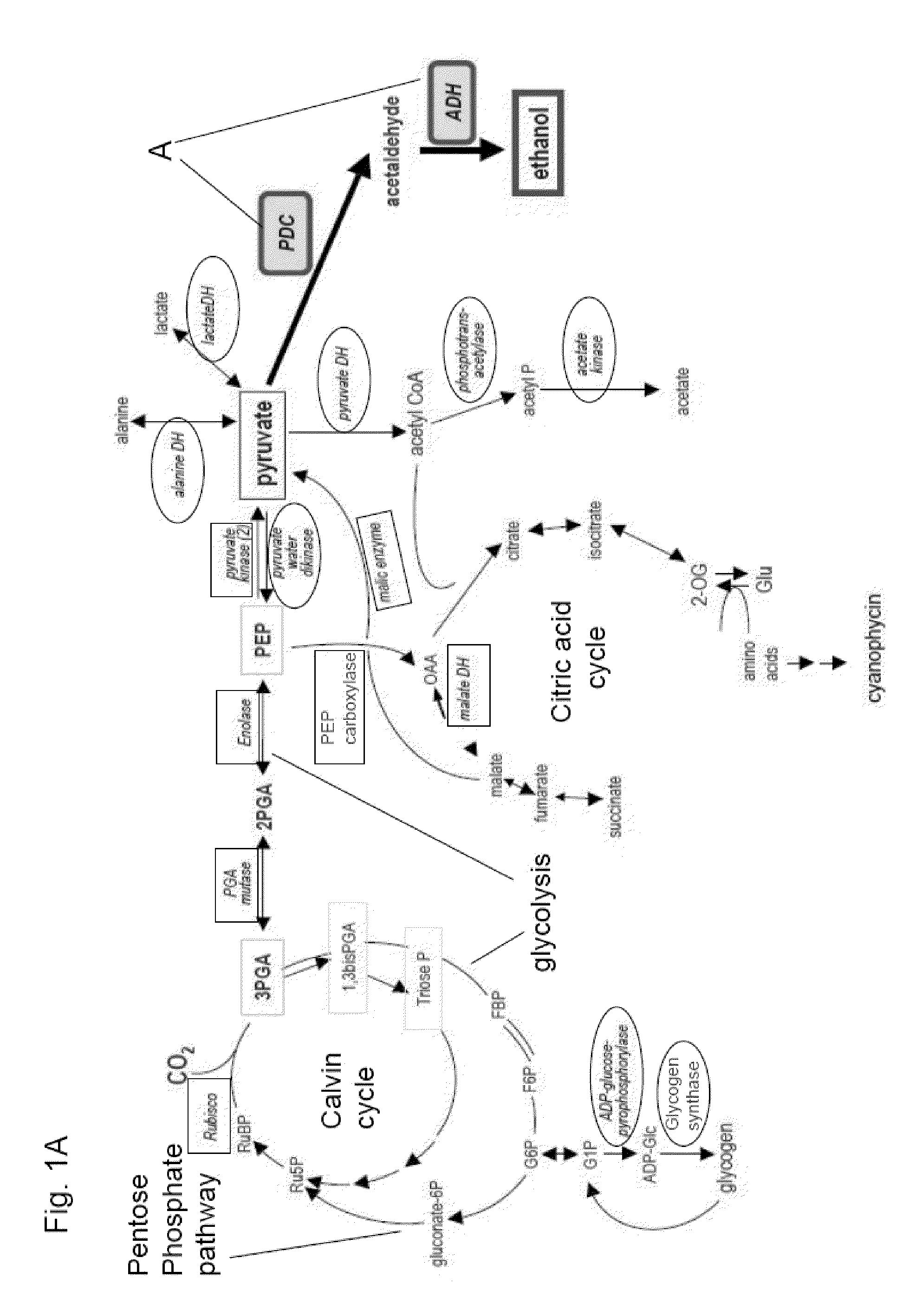
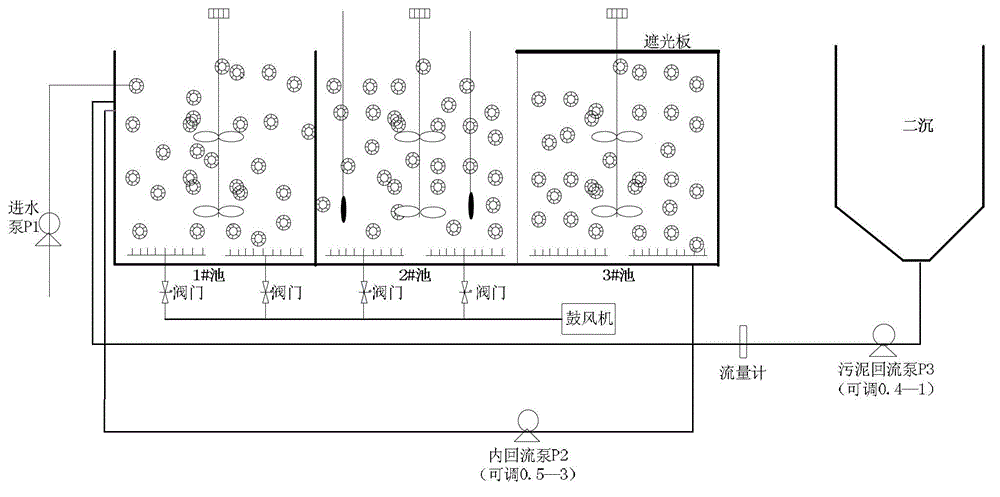
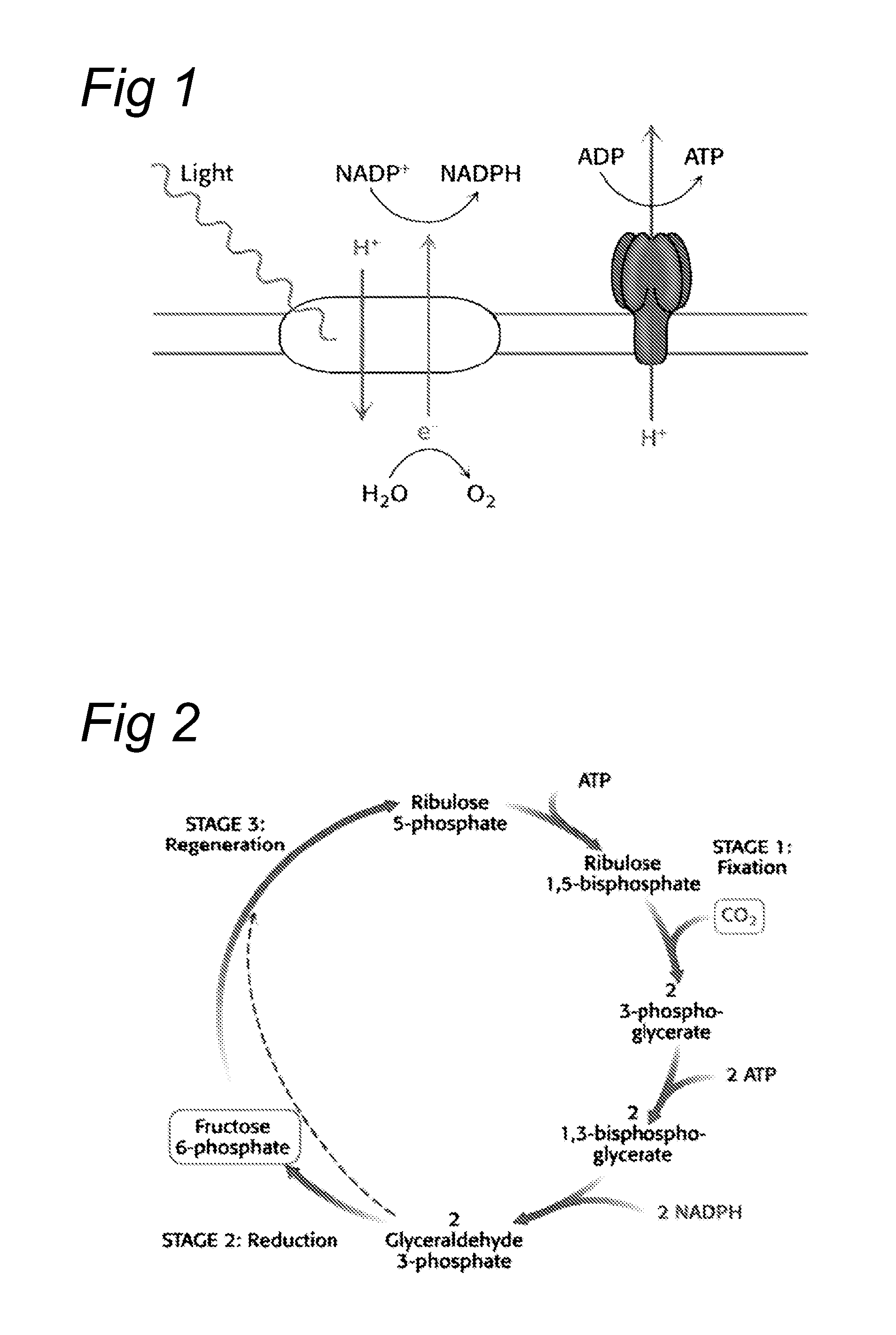
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Autotroph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An autotroph or primary producer, is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) from simple substances present in its surroundings, generally using energy from light (photosynthesis) or inorganic chemical reactions (chemosynthesis). They are the producers in a food chain, such as plants on land or algae in water (in contrast to heterotrophs as consumers of autotrophs). They do not need a living source of energy or organic carbon. Autotrophs can reduce carbon dioxide to make organic compounds for biosynthesis and also create a store of chemical energy. Most autotrophs use water as the reducing agent, but some can use other hydrogen compounds such as hydrogen sulfide. Some autotrophs, such as green plants and algae, are phototrophs, meaning that they convert electromagnetic energy from sunlight into chemical energy in the form of reduced carbon.
Trophic conversion of obligate phototrophic algae through metabolic engineering
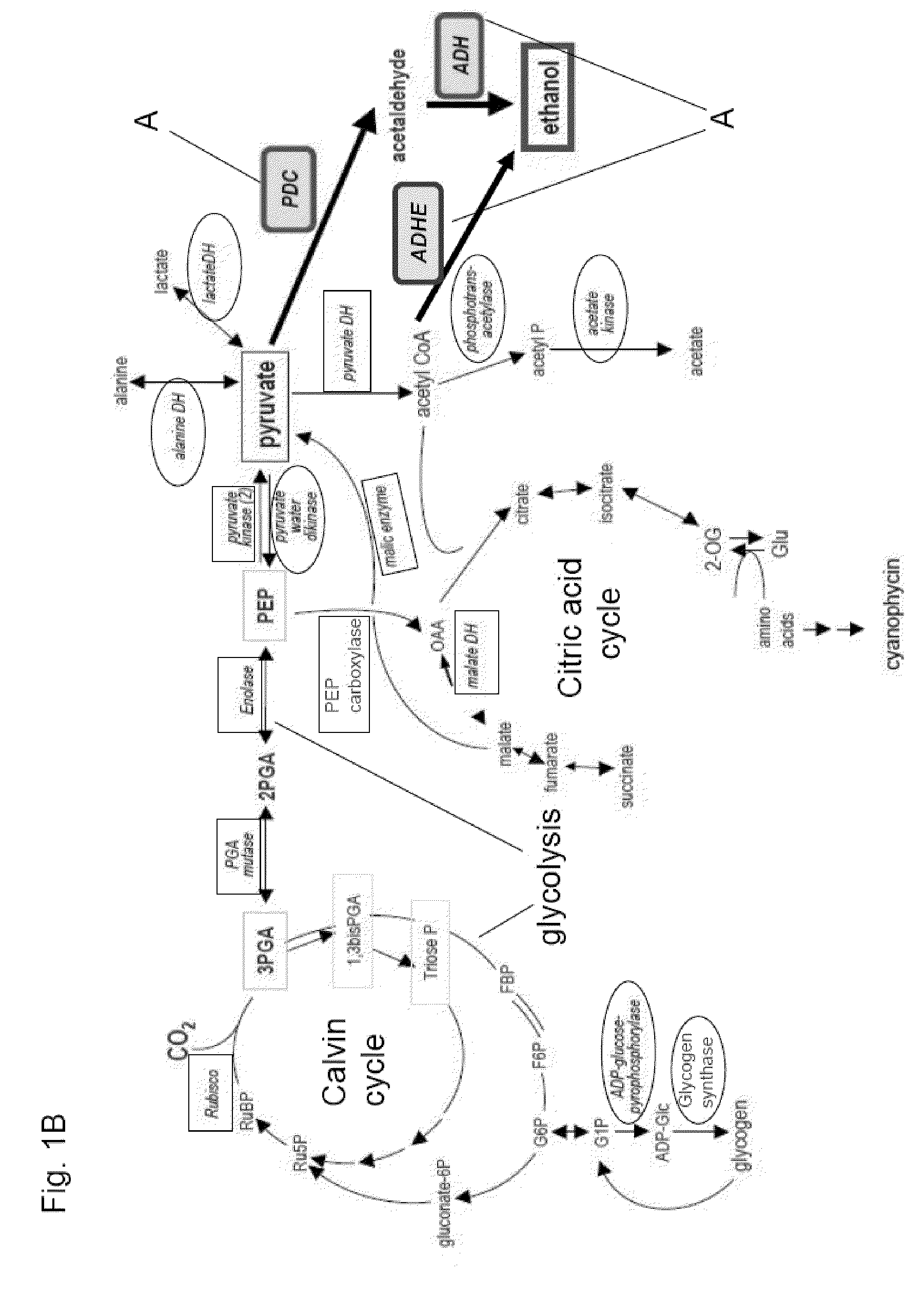
Most microalgae are obligate photoautotrophs and their growth is strictly dependent on the generation of photosynthetically-derived energy. In this study it is shown that the microalga Phaeodaclylurn tricornutum can be engineered to import glucose and grow in the dark through the introduction of genes encoding glucose transporters. Both the human and Chlorella kessleri glucose transporters facilitated the uptake of glucose by P. tricornutum, allowing the cells to metabolize exogenous organic carbon and thrive, independent of light. This is the first successful trophic conversion of an obligate photoautotroph through metabolic engineering, and it demonstrates that methods of cell nourishment can be fundamentally altered with the introduction of a single gene. Since strains transformed with the glucose transport genes are able to grow non-photosynthetically, they can be exploited for the analysis of photosynthetic processes through mutant generation and characterization. Finally, this work also represents critical progress toward large-scale commercial exploitation of obligate phototrophic algae through the use of microbial fermentation technology, eliminating significant limitations resulting from light-dependent growth.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
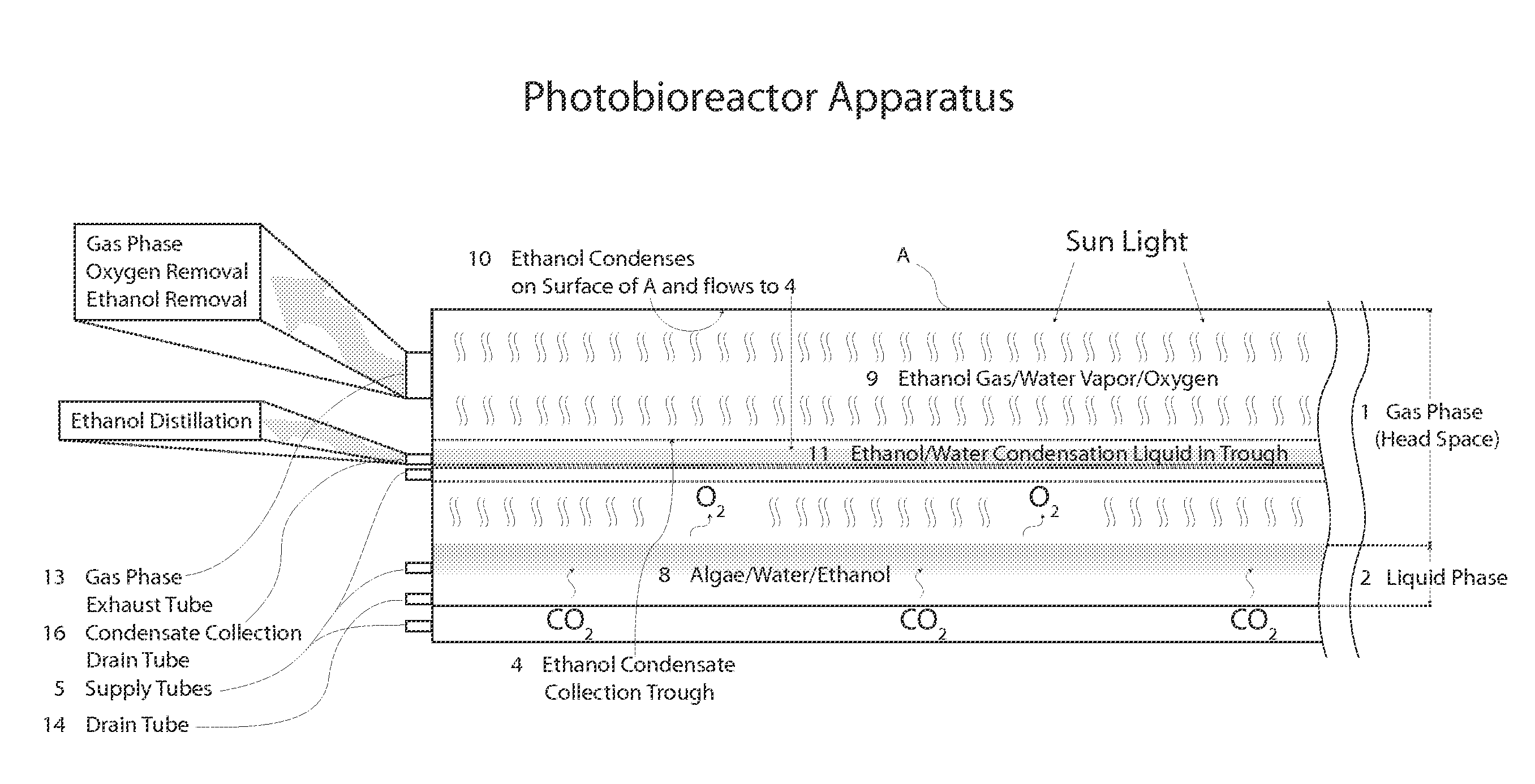
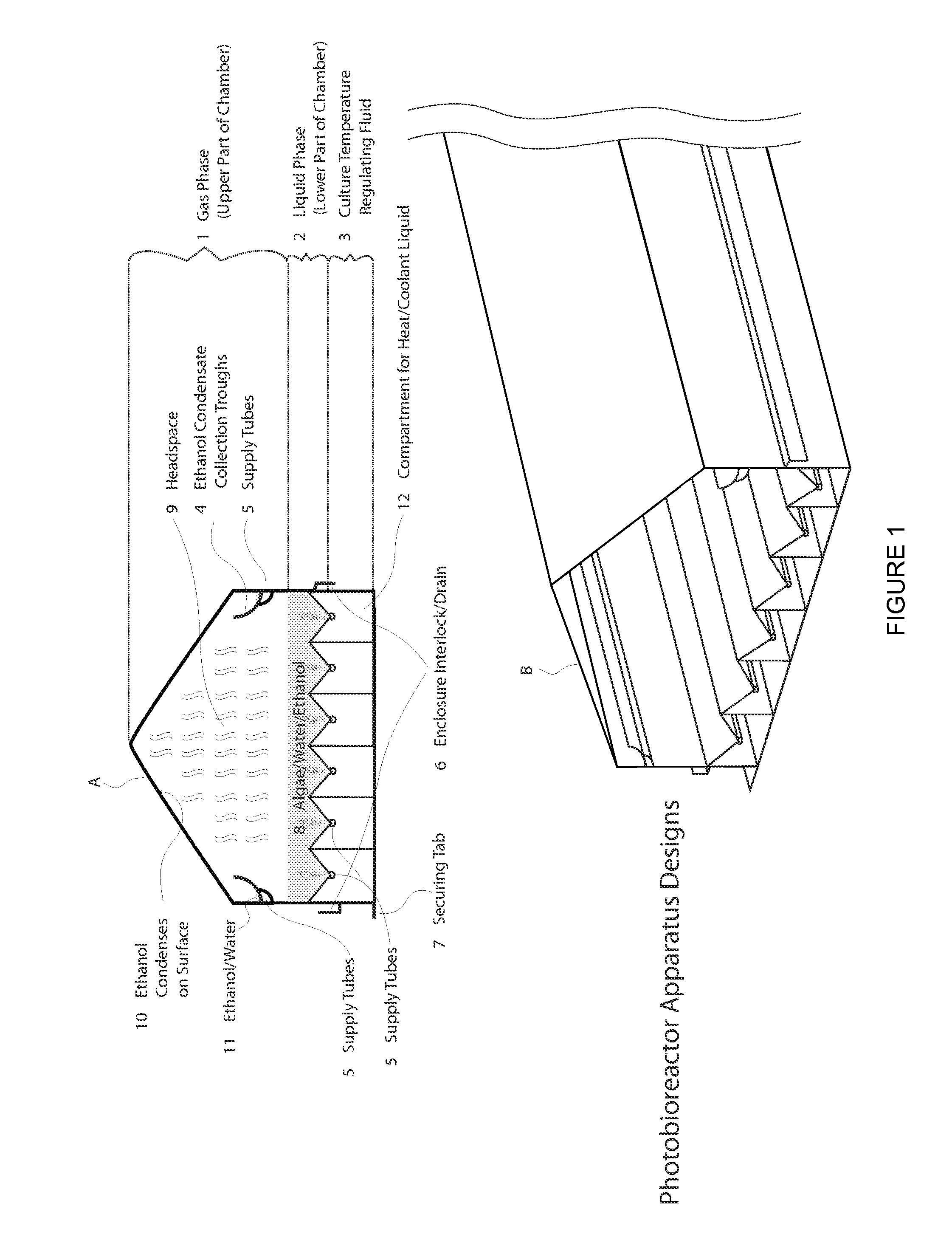
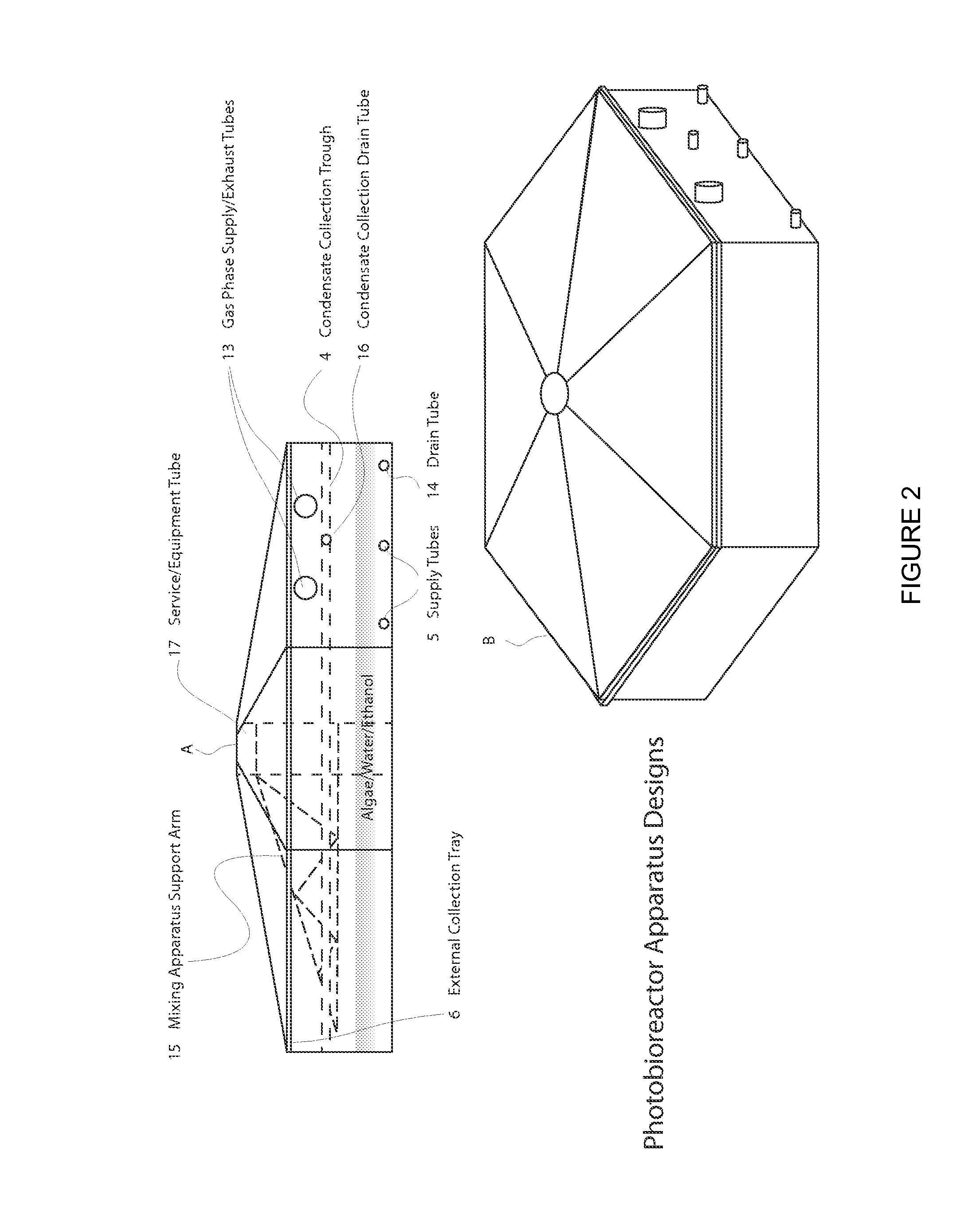
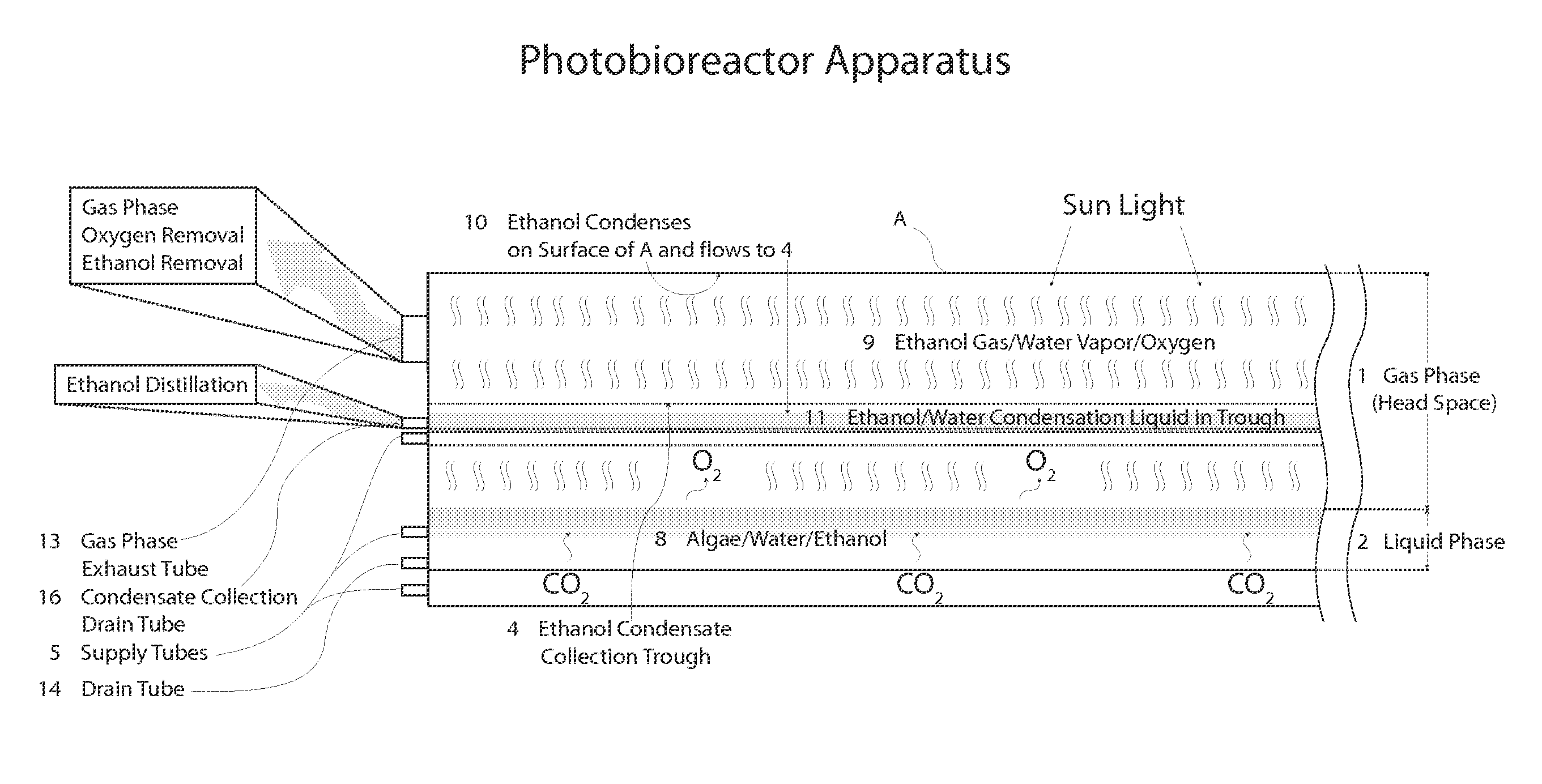
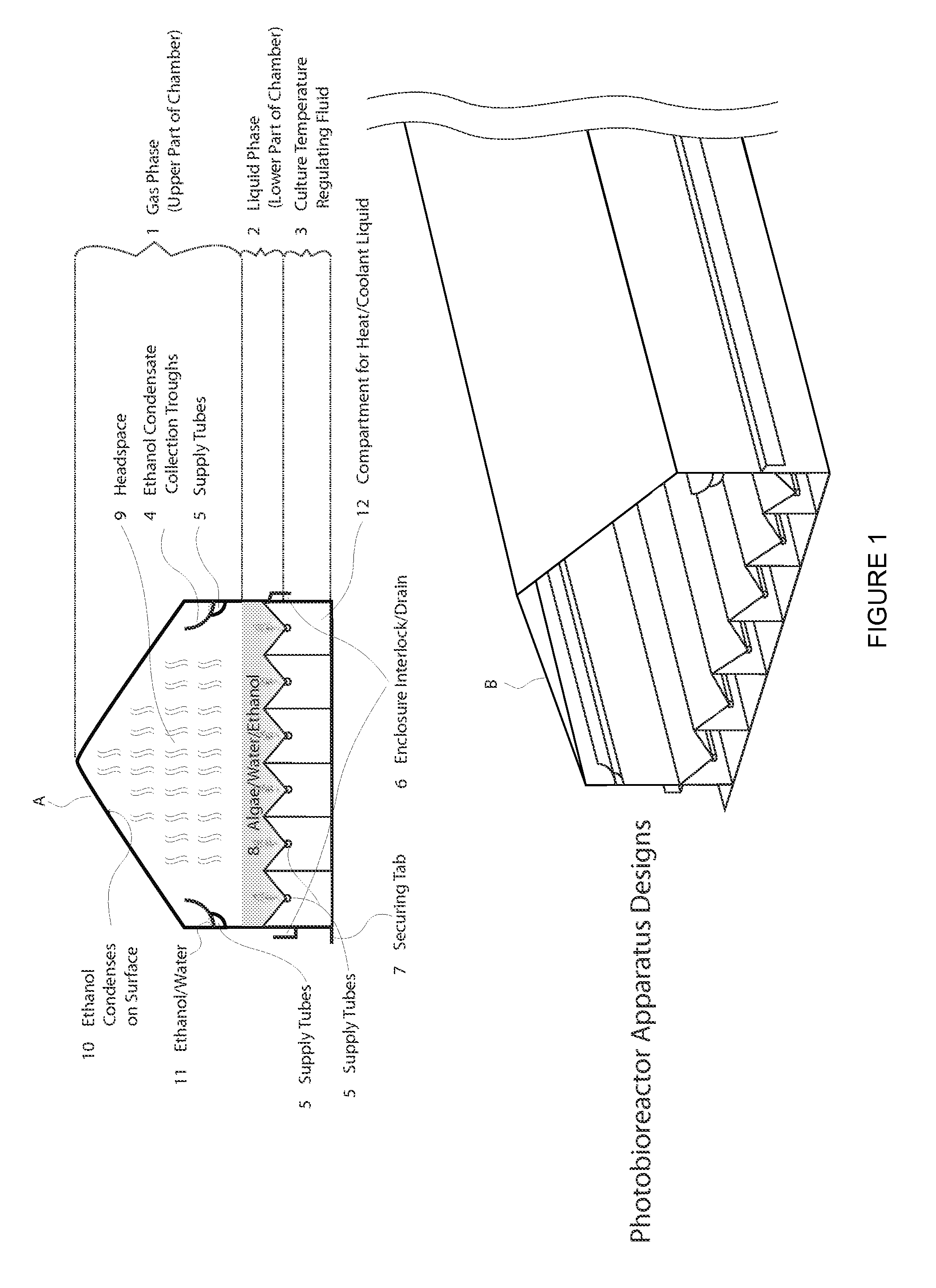
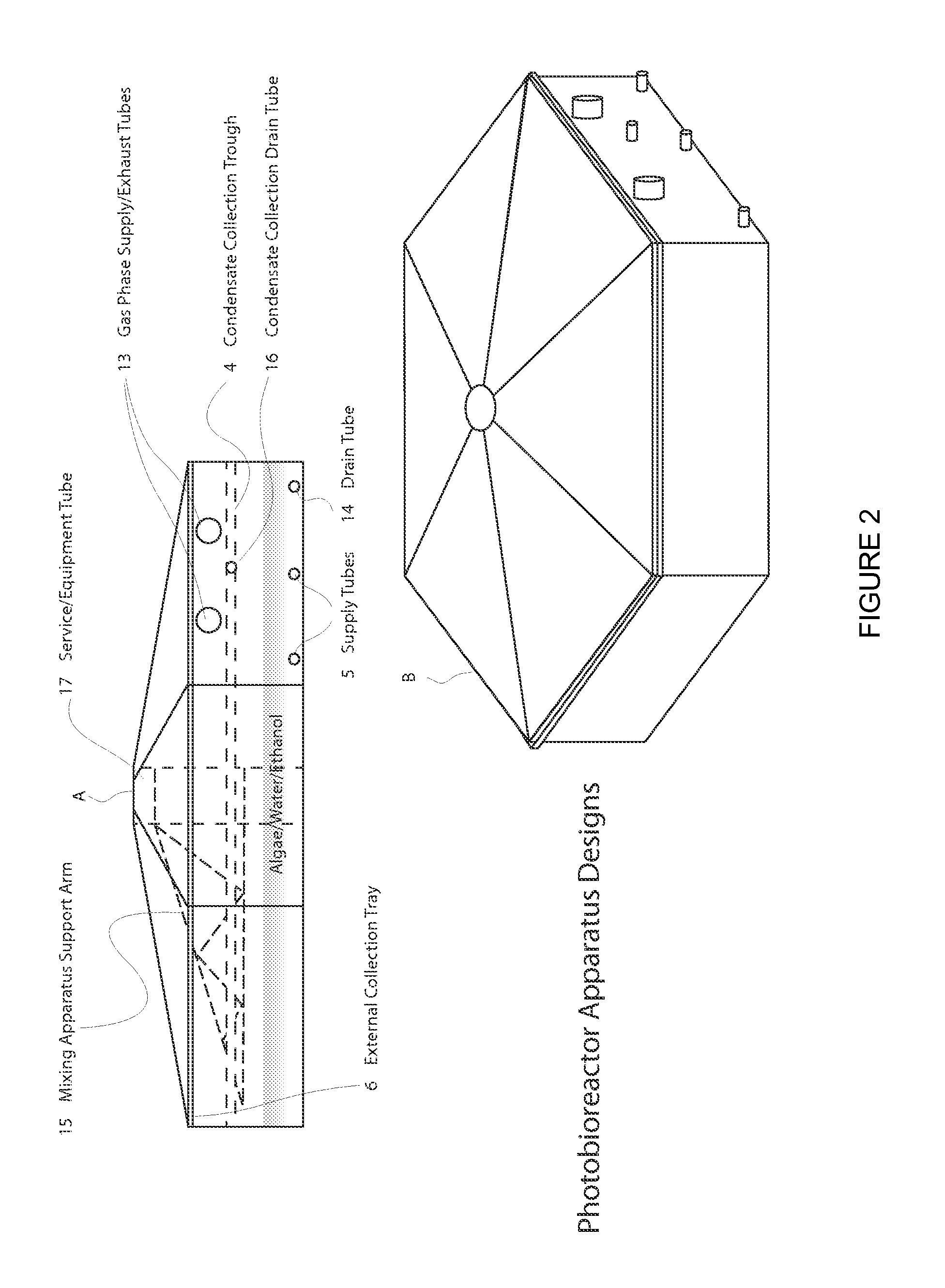
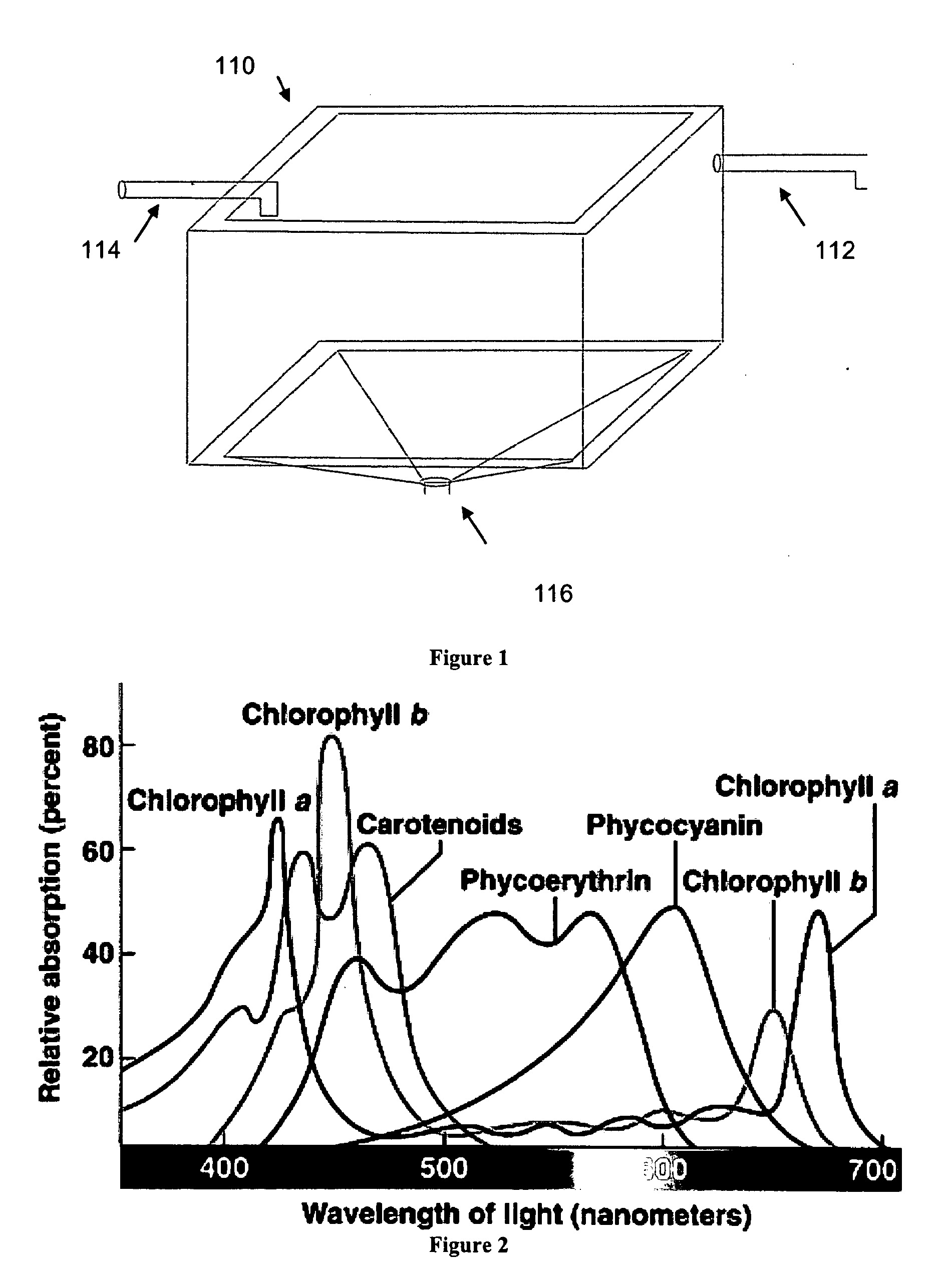
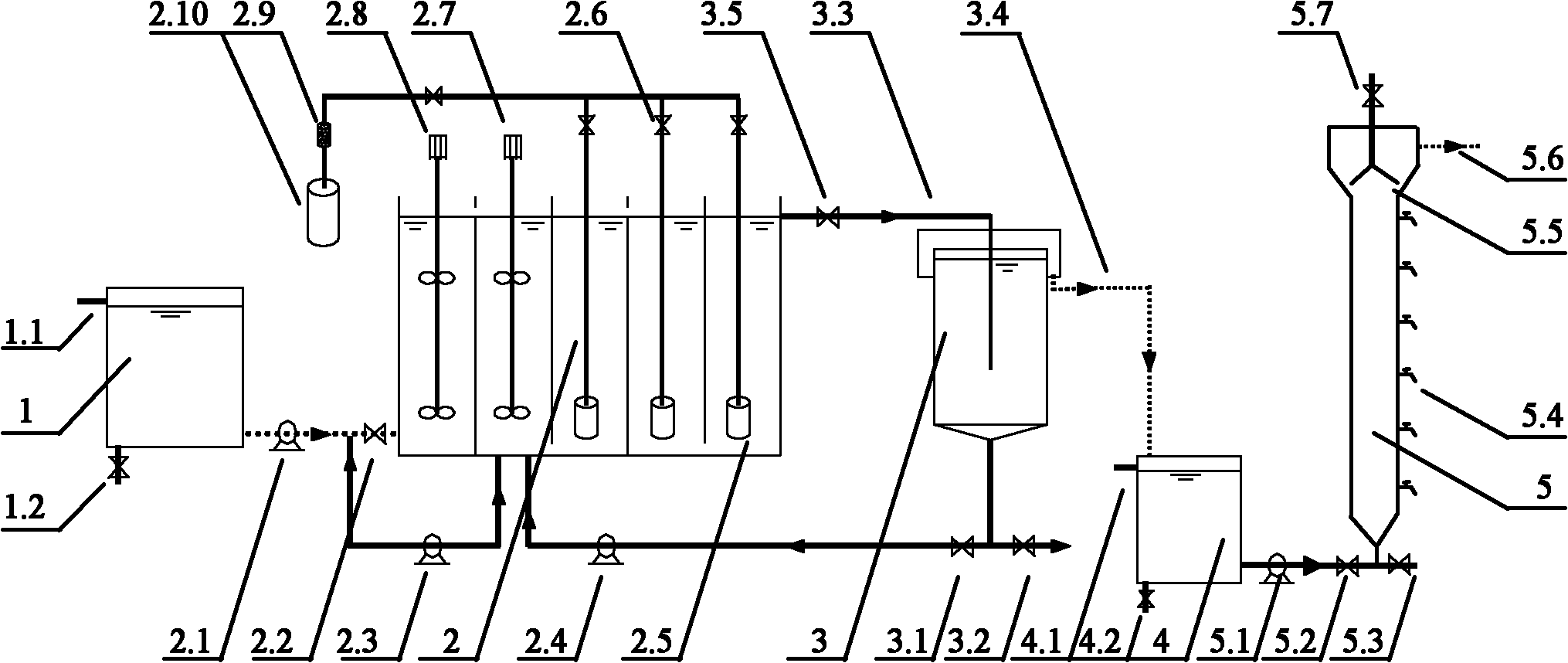
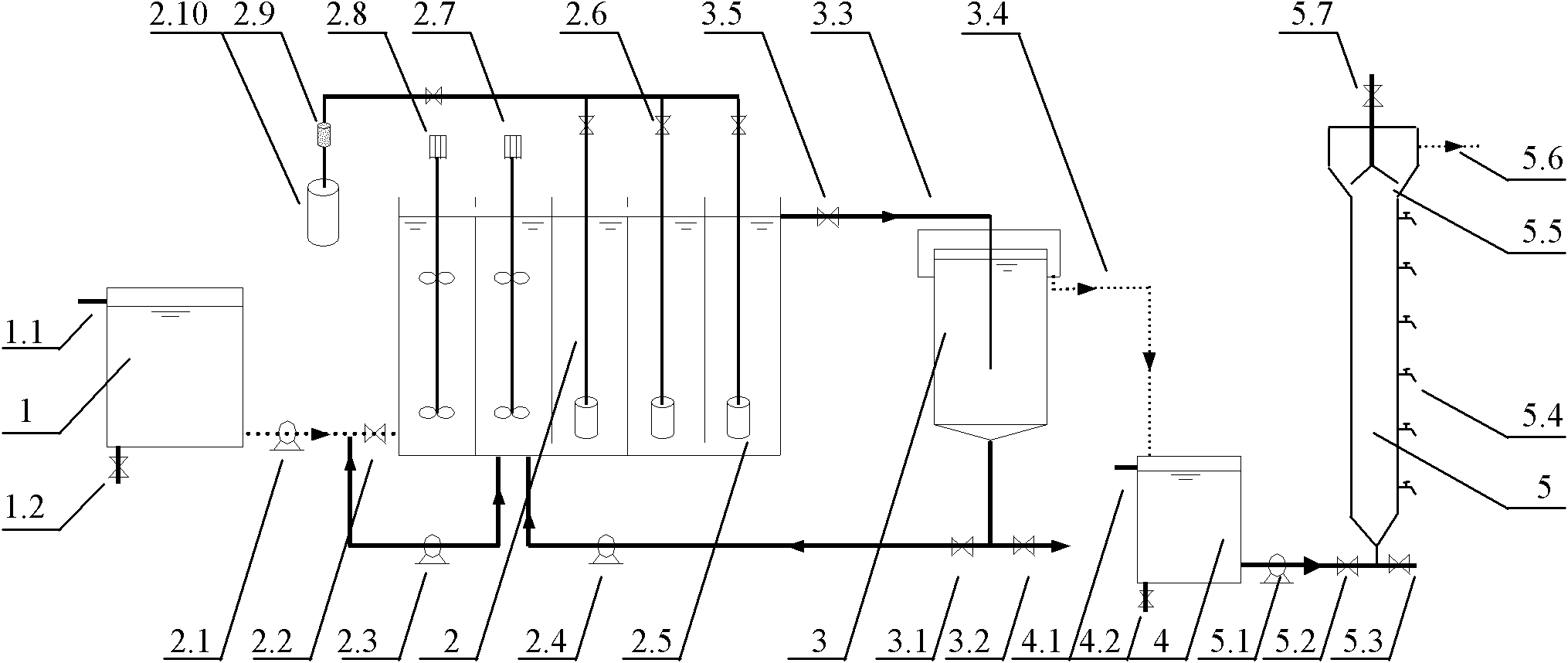
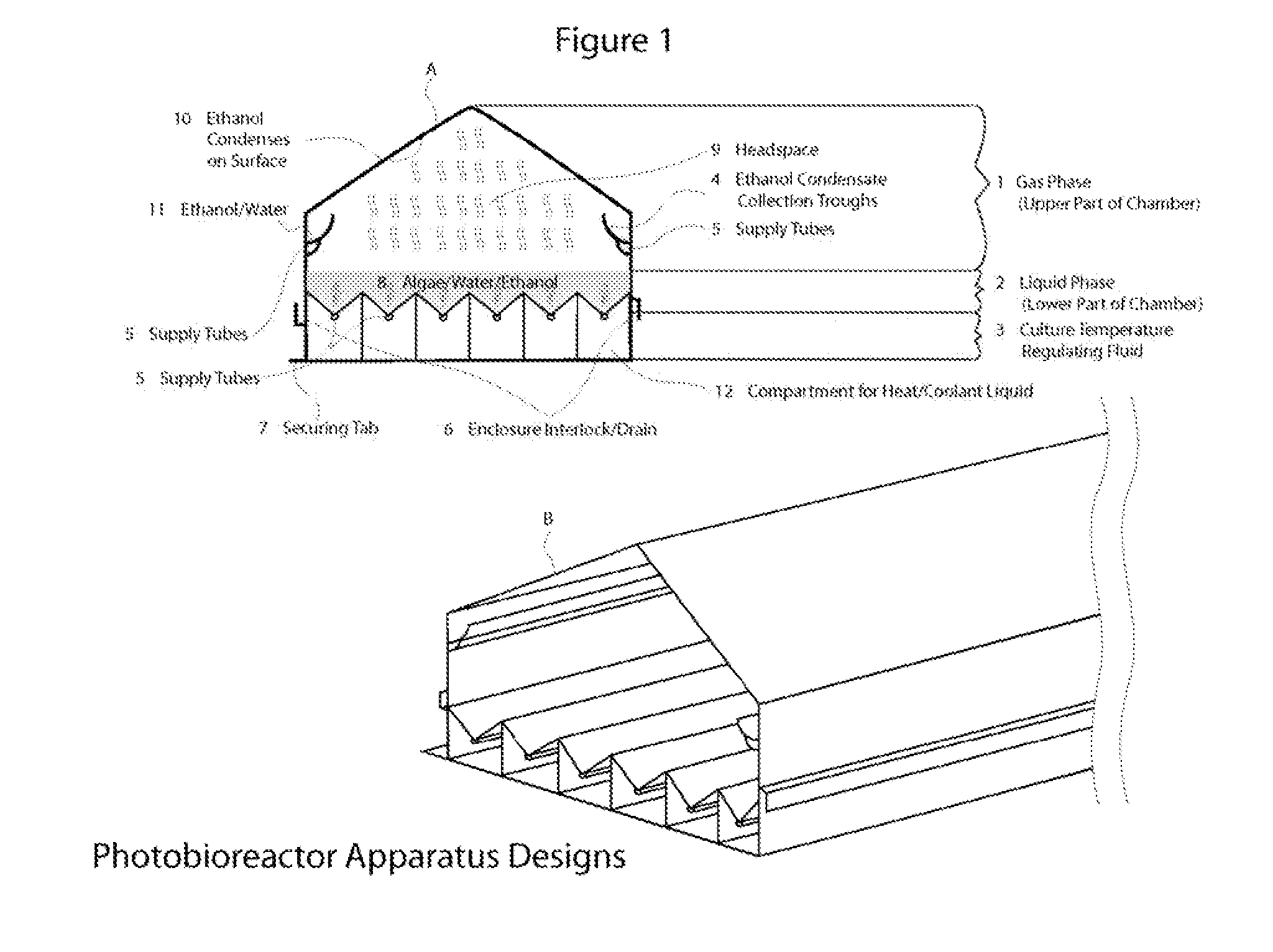
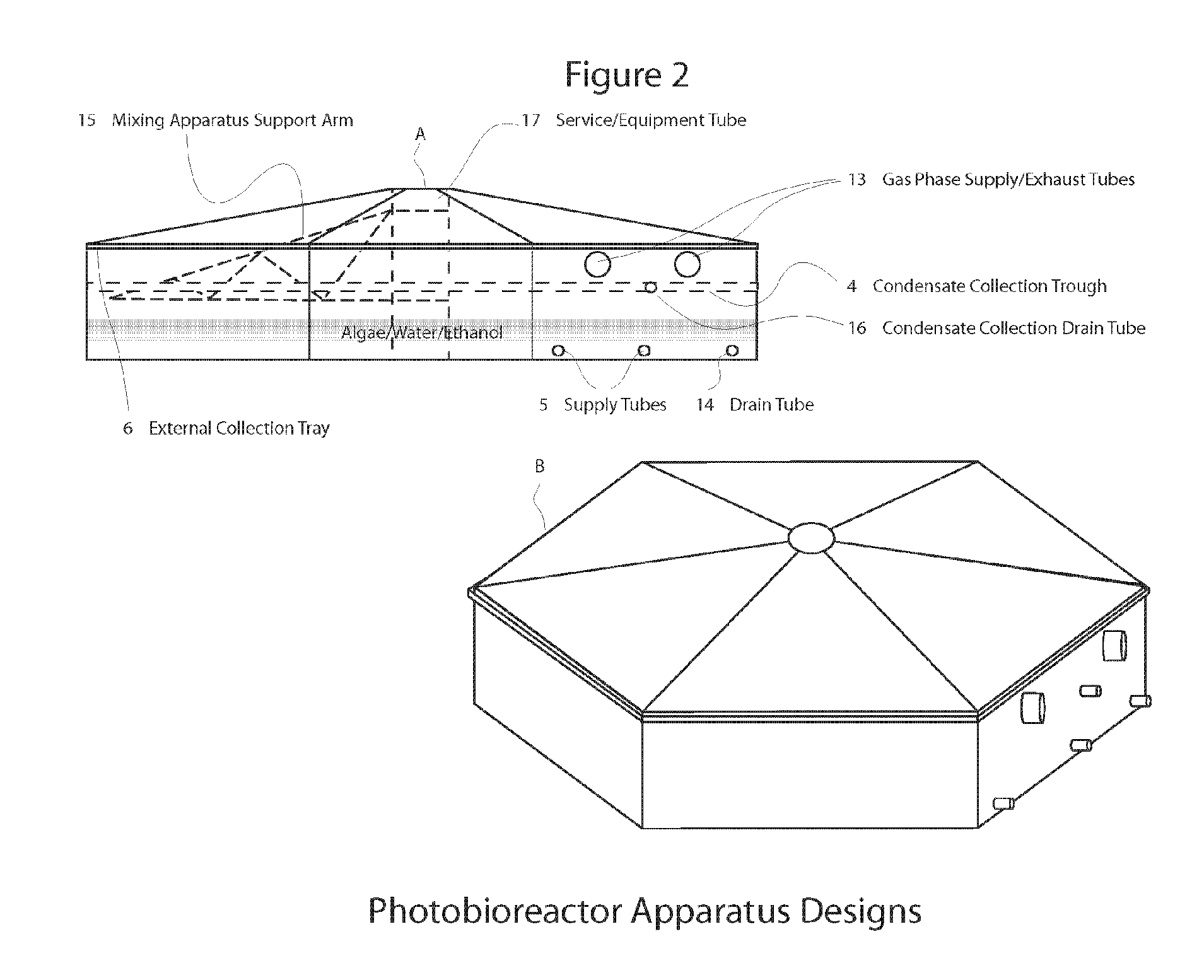
Closed photobioreactor system for continued daily in situ production, separation, collection, and removal of ethanol from genetically enhanced photosynthetic organisms
InactiveUS20080153080A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotobioreactorOrganism
Owner:ALGENOL BIOFUELS SWITZERLAND
Closed photobioreactor system for continued daily in situ production, separation, collection, and removal of ethanol from genetically enhanced photosynthetic organisms
InactiveUS7682821B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyPhotobioreactor
Owner:ALGENOL BIOFUELS SWITZERLAND
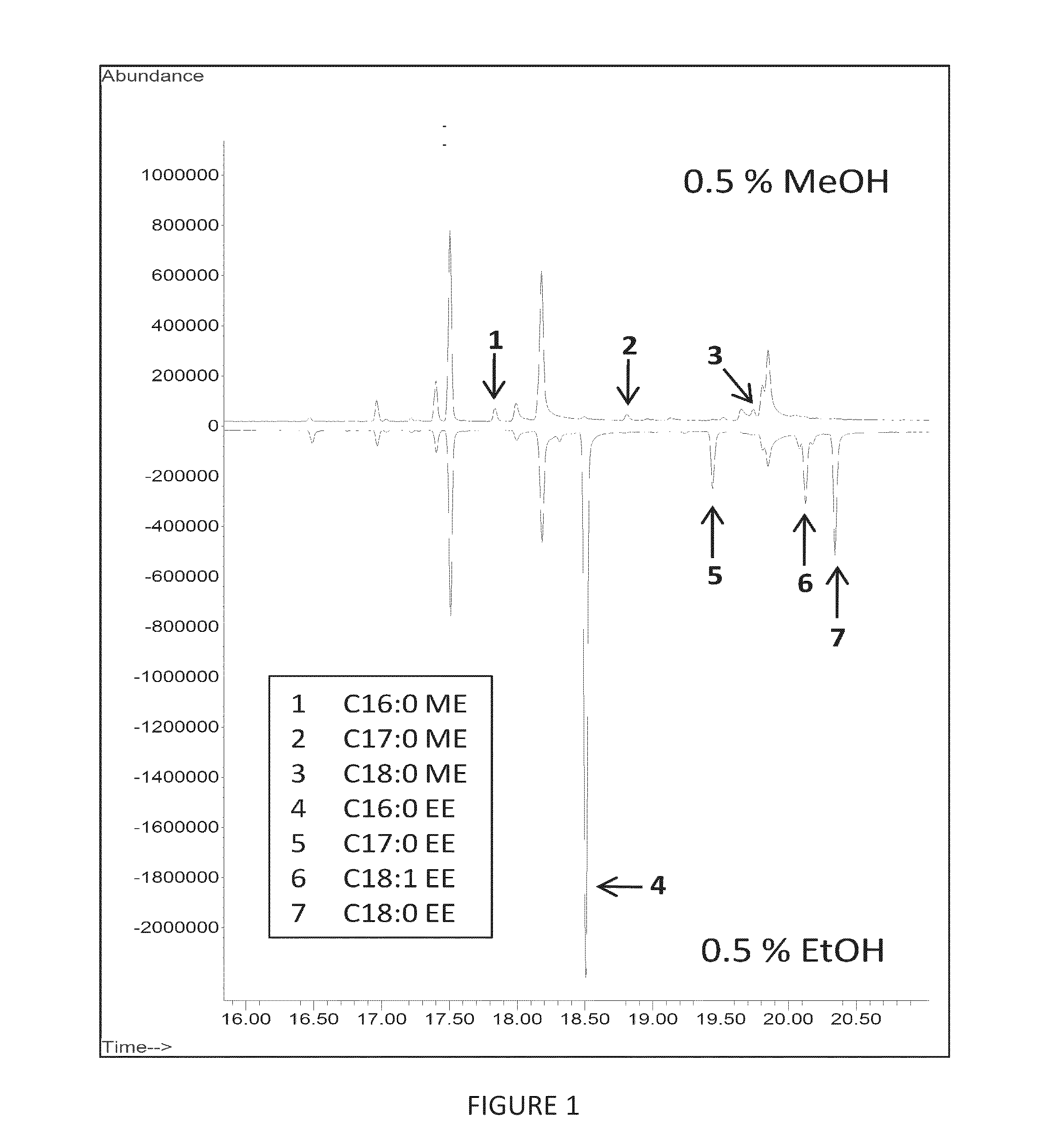
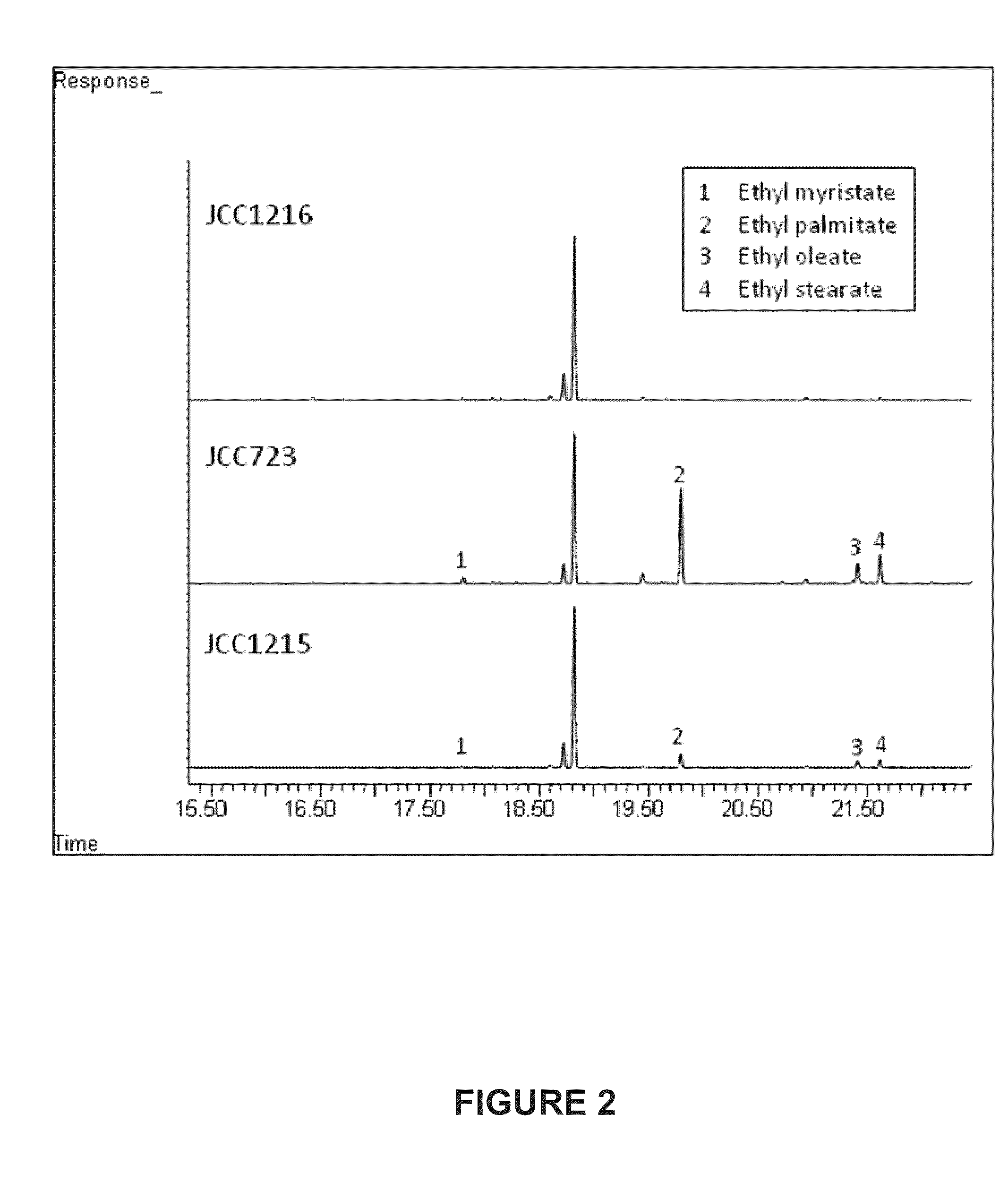
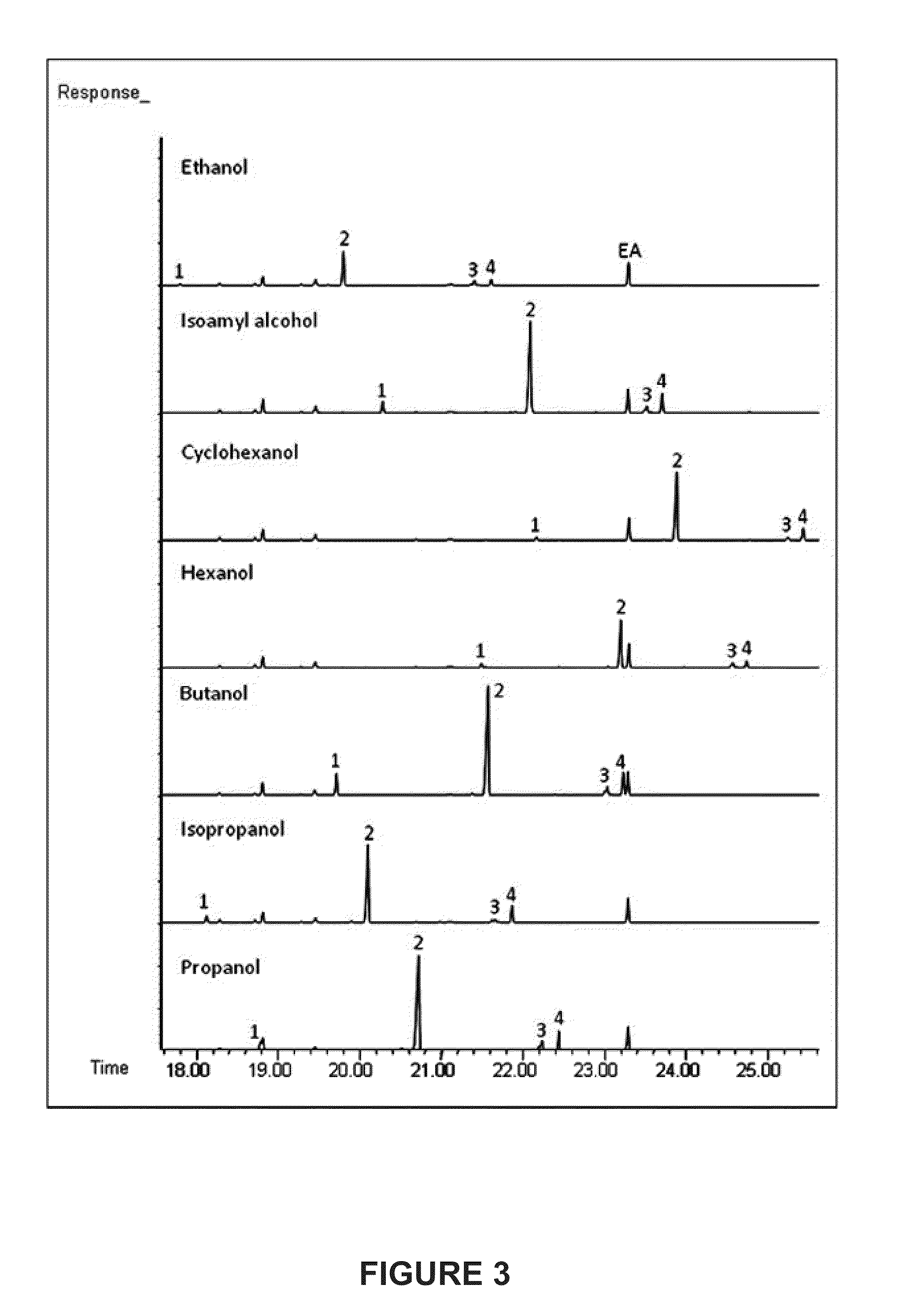
Methods and Compositions for the Recombinant Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids and Esters
The present disclosure identifies methods and compositions for modifying photoautotrophic organisms, such that the organisms efficiently convert carbon dioxide and light into compounds such as esters and fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the compounds produced are secreted into the medium used to culture the organisms.
Owner:JOULE UNLTD INC +1
Bioreactor
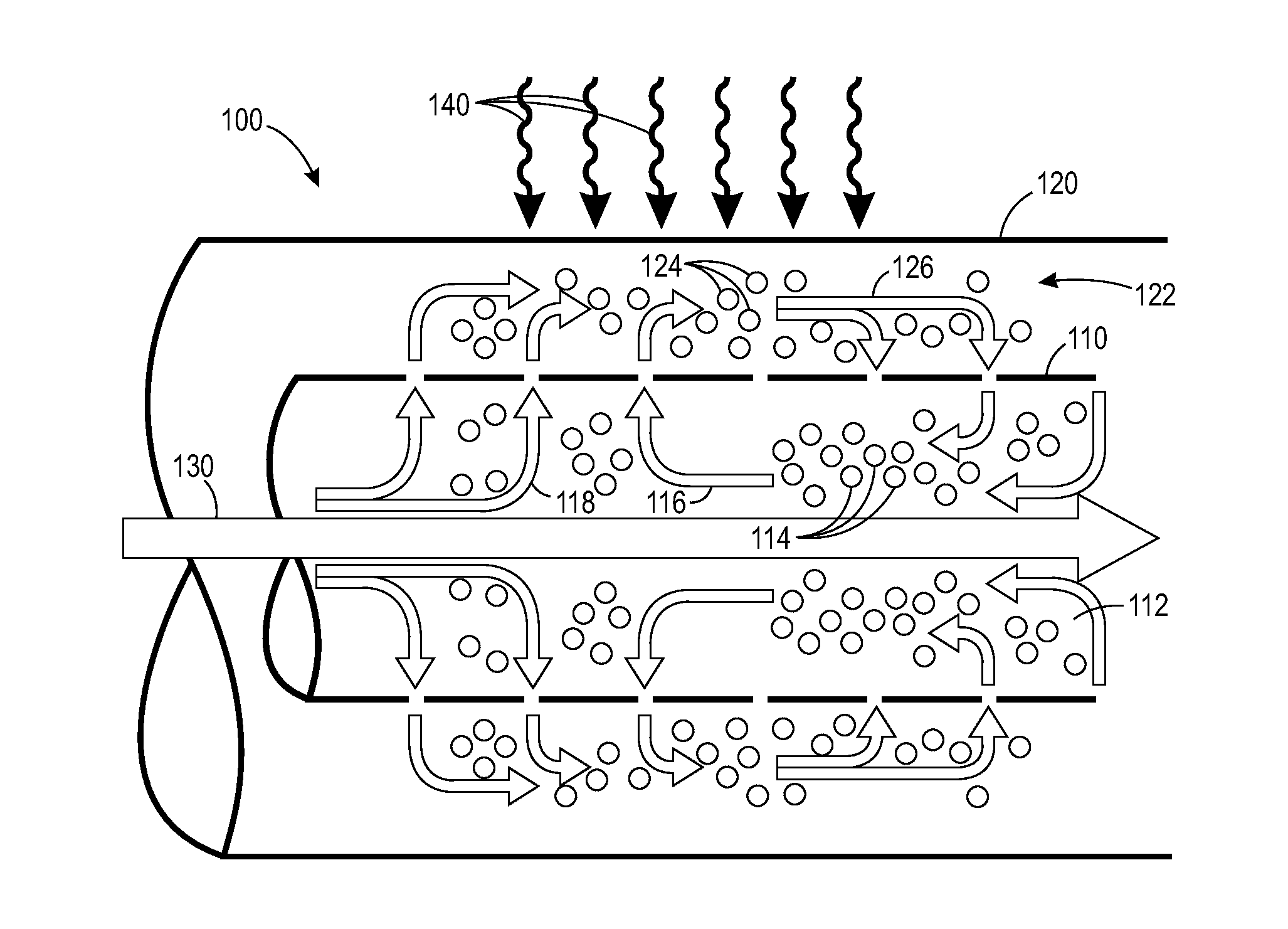
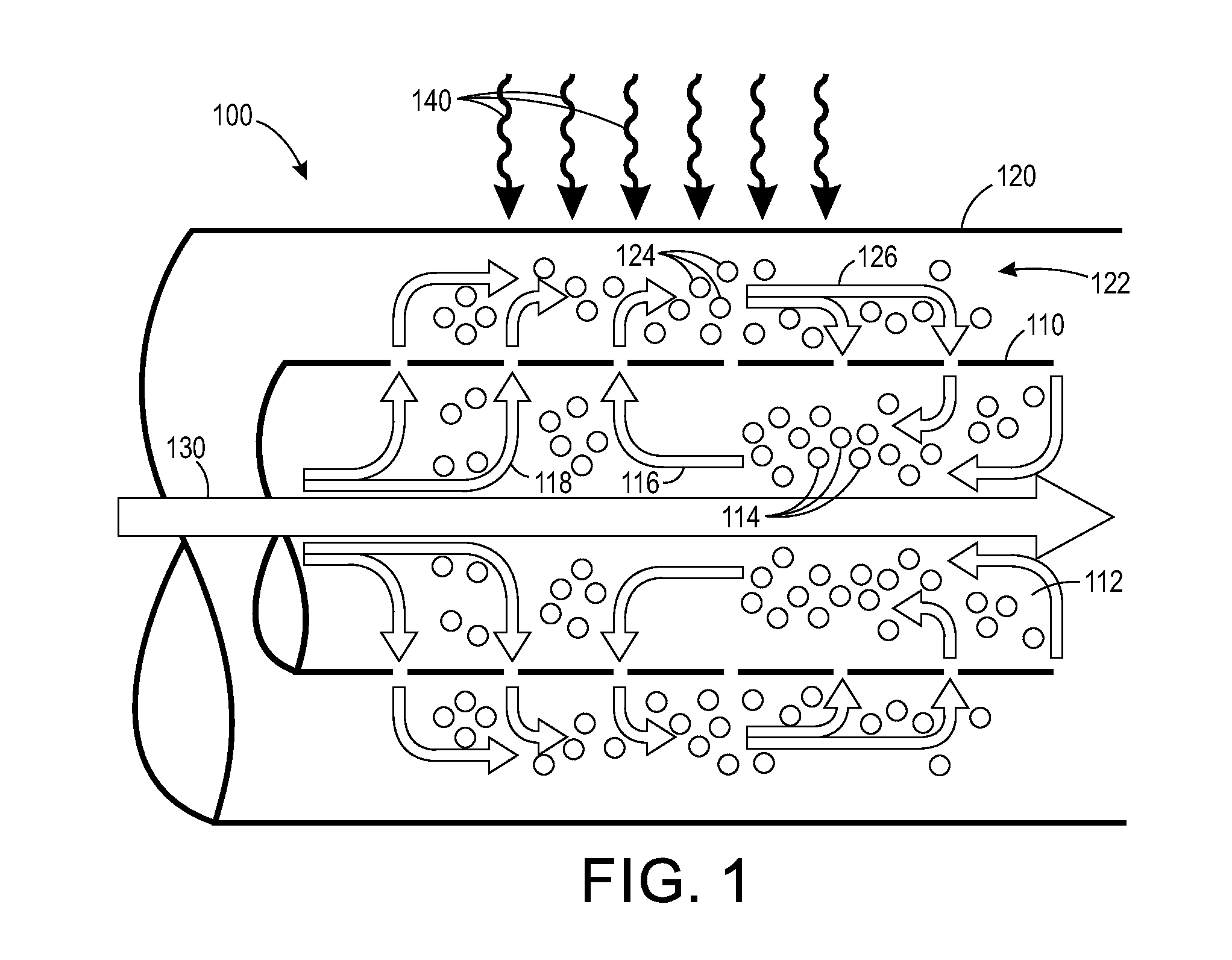
InactiveUS20100255458A1Maximizing growth rateMaximize growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSolar heating energyOrganismBioreactor
The invention provides devices and methods for the growth of photoautotrophic organisms. The devices and methods address issues related to the design of bioreactors, selection of a photoautotrophic organism, growth of the photoautotrophic organisms, extraction of biomass products, and / or use of the biomass products as a renewable energy source.
Owner:ALGAEDYNE CORPORTION
Photo bioreactor and cultivation system for improved productivity of photoautotrophic cell cultures
InactiveUS20110070632A1High and nearly constant conversion efficiencyImprove disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProduction ratePhotobioreactor
This invention relates to open or close top photobioreactor apparatus for improved productivity with a small footprint, that can be placed in varied temperature zones, above or below ground on land or in water or use in space-station for conducting aqueous aerobic or anaerobic; continues or batch wise cultivation and harvesting of photoautotrophic organism's.More particularly this invention concerns with a novel means and process for uniform optical dispersion and optical enhancement by utilizing a solar energy collection unit attached to a photo-emitting system which emits full spectrum or specific wavelength light substantially uniformly and radially along its length.
Owner:BIOCETANE
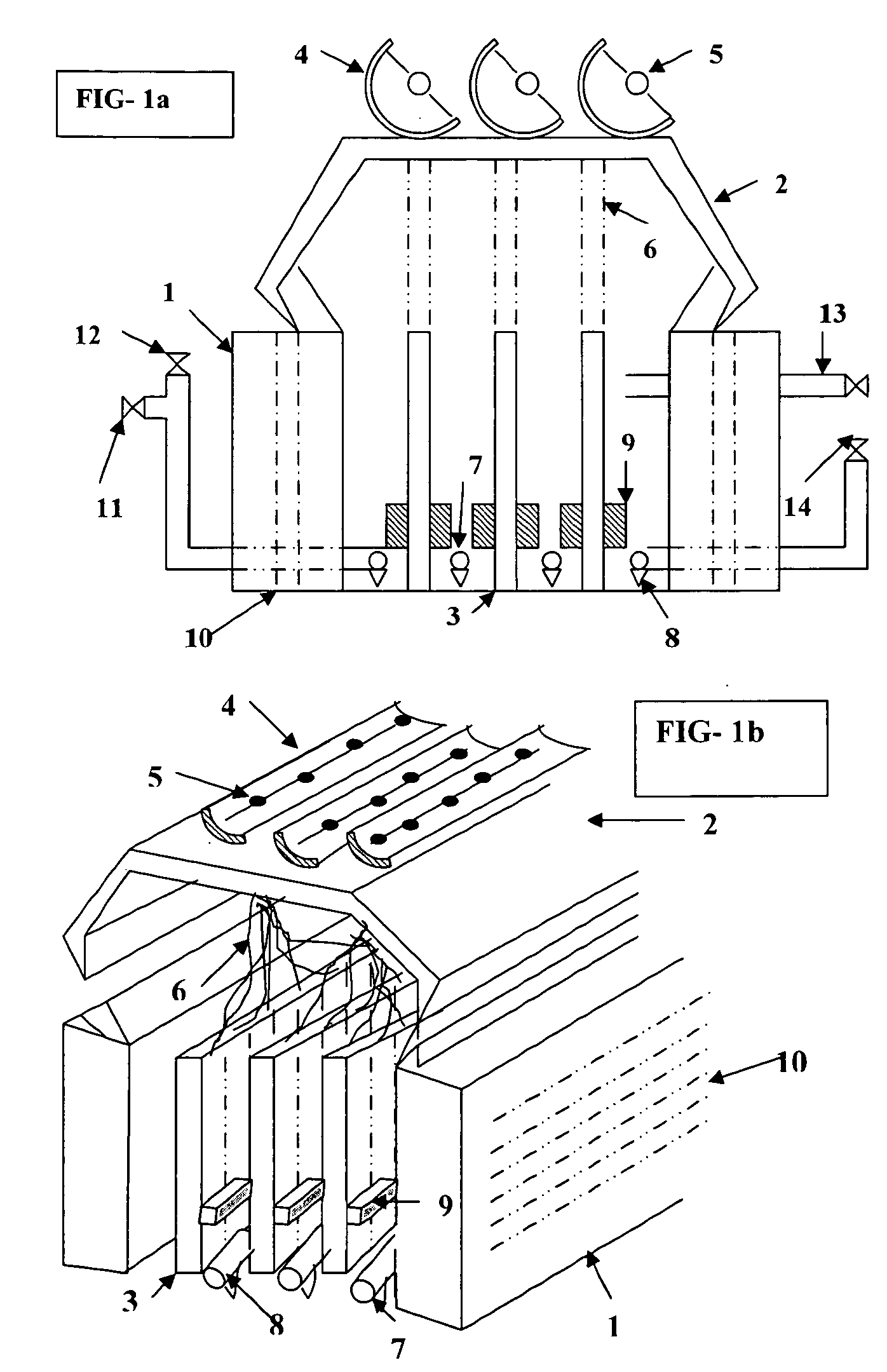
Combined denitrification apparatus and method by shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation of sludge-digestion liquid
ActiveCN101289264AImprove nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiencyLow construction costTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater bathsSludge
The invention discloses a device for autotrophic nitrogen removal by combining A / O shortcut nitrification of sludge digestion liquid and anaerobic ammonium oxidation of granular sludge and a method thereof. The device of the invention comprises a digestion liquid tank, an A / O shortcut nitrification tank, a sedimentation tank, a middle water tank, an anaerobic ammonium oxidation tank, wherein, the digestion liquid tank is communicated with a first cancellus as an anoxic zone of the A / O shortcut nitrification tank by the inlet pump of the A / O shortcut nitrification tank; the sedimentation tank the upper part of which is communicated with the middle water tank by a water pipe is provided with a central pipe and the anaerobic ammonium oxidation tank is provided with a water bath sleeve and a granular sludge bed. In addition, the method of the invention comprises the following steps of starting the A / O shortcut nitrification tank; starting the anaerobic ammonium oxidation tank of the granular sludge; operating an autotrophic biological nitrogen removal system in series after the starting of the A / O shortcut nitrification tank and the anaerobic ammonium oxidation tank is respectively completed. The device and the method of the invention are applicable to the shortcut nitrification and the nitrogen removal of the sludge digestion liquid in a sewage treatment plant and have the advantages of advanced technology, simple structure of the device, convenient operation and good treatment effect of water purification.
Owner:BEIJING DRAINAGE GRP CO LTD
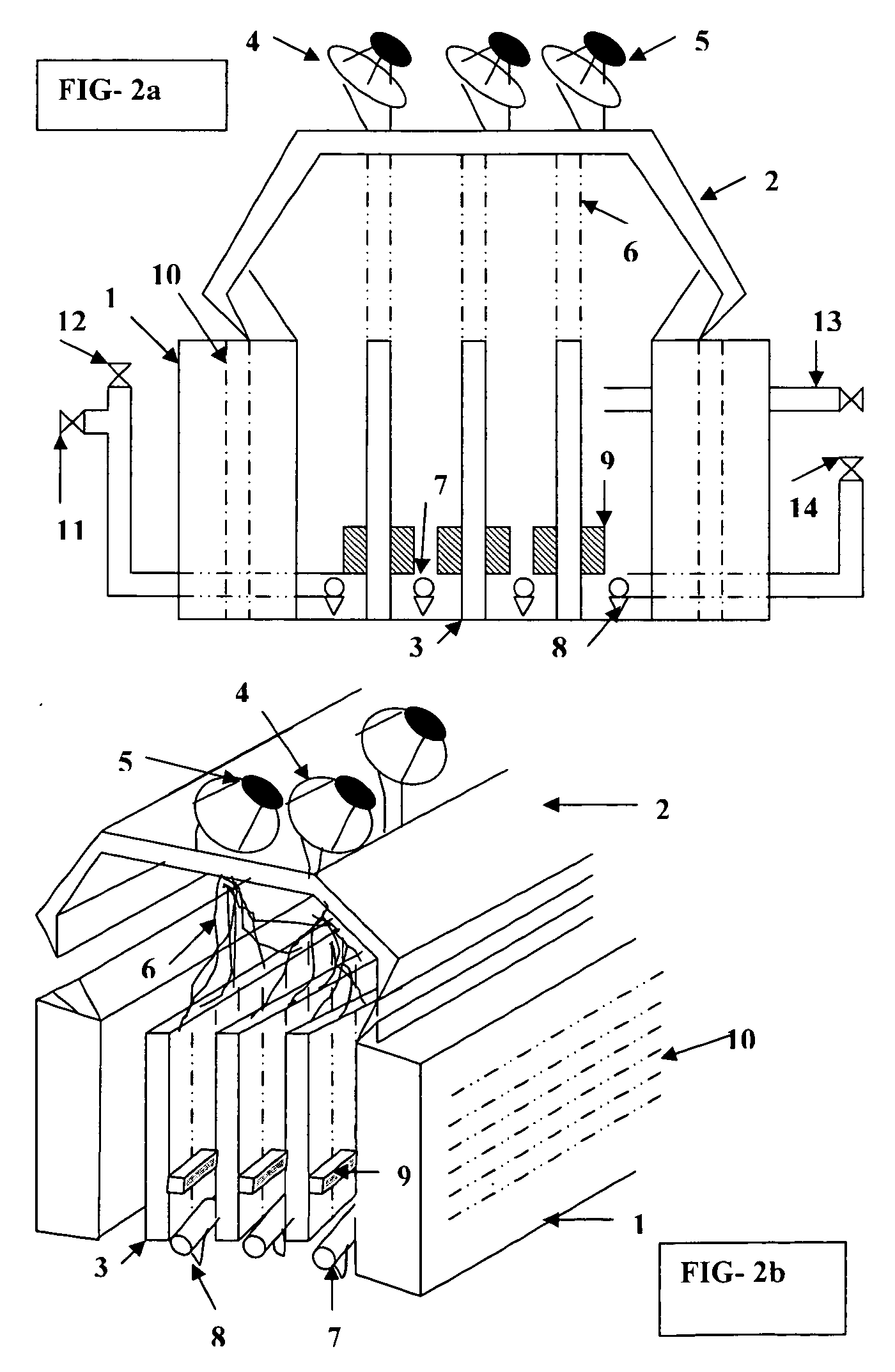
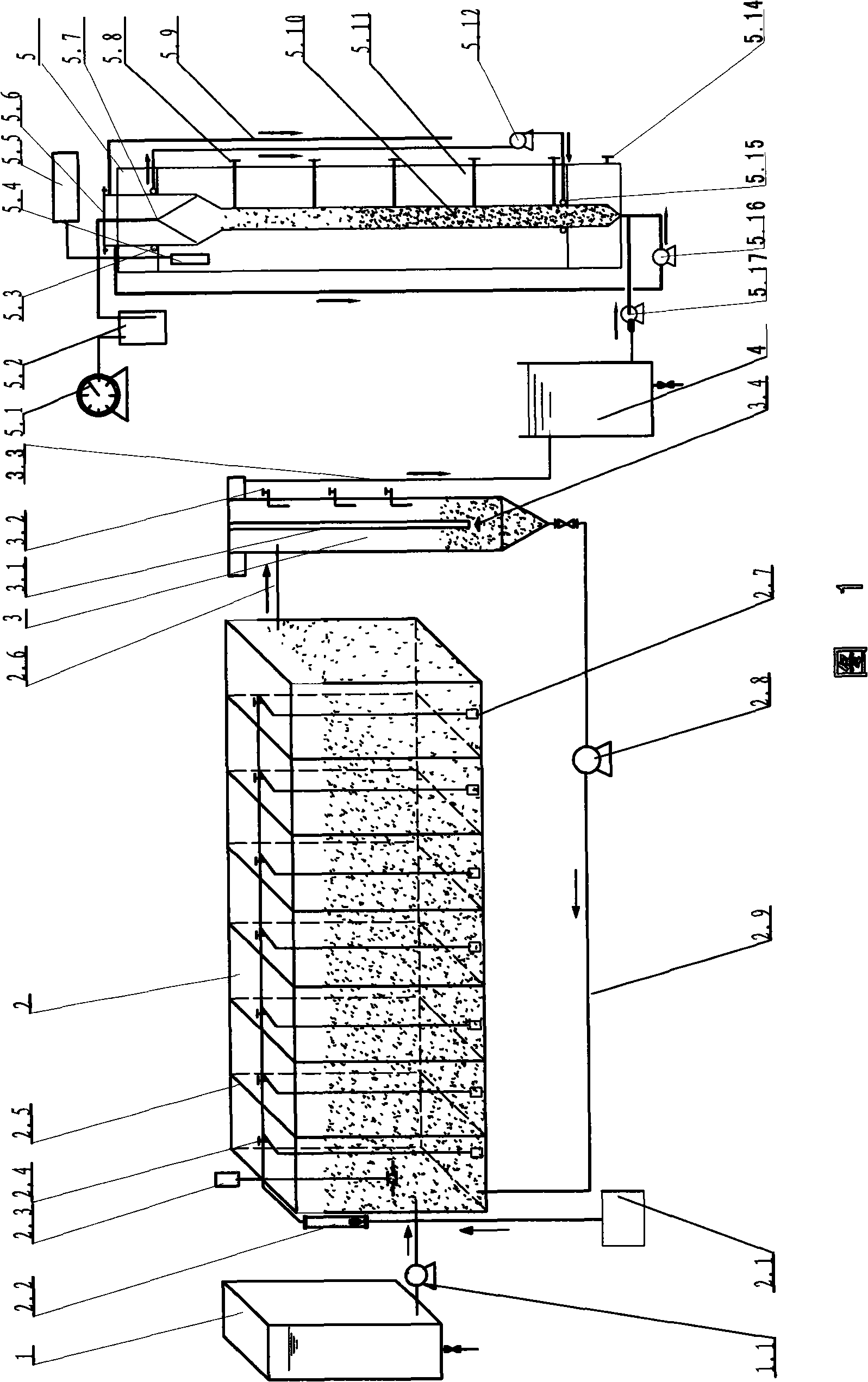
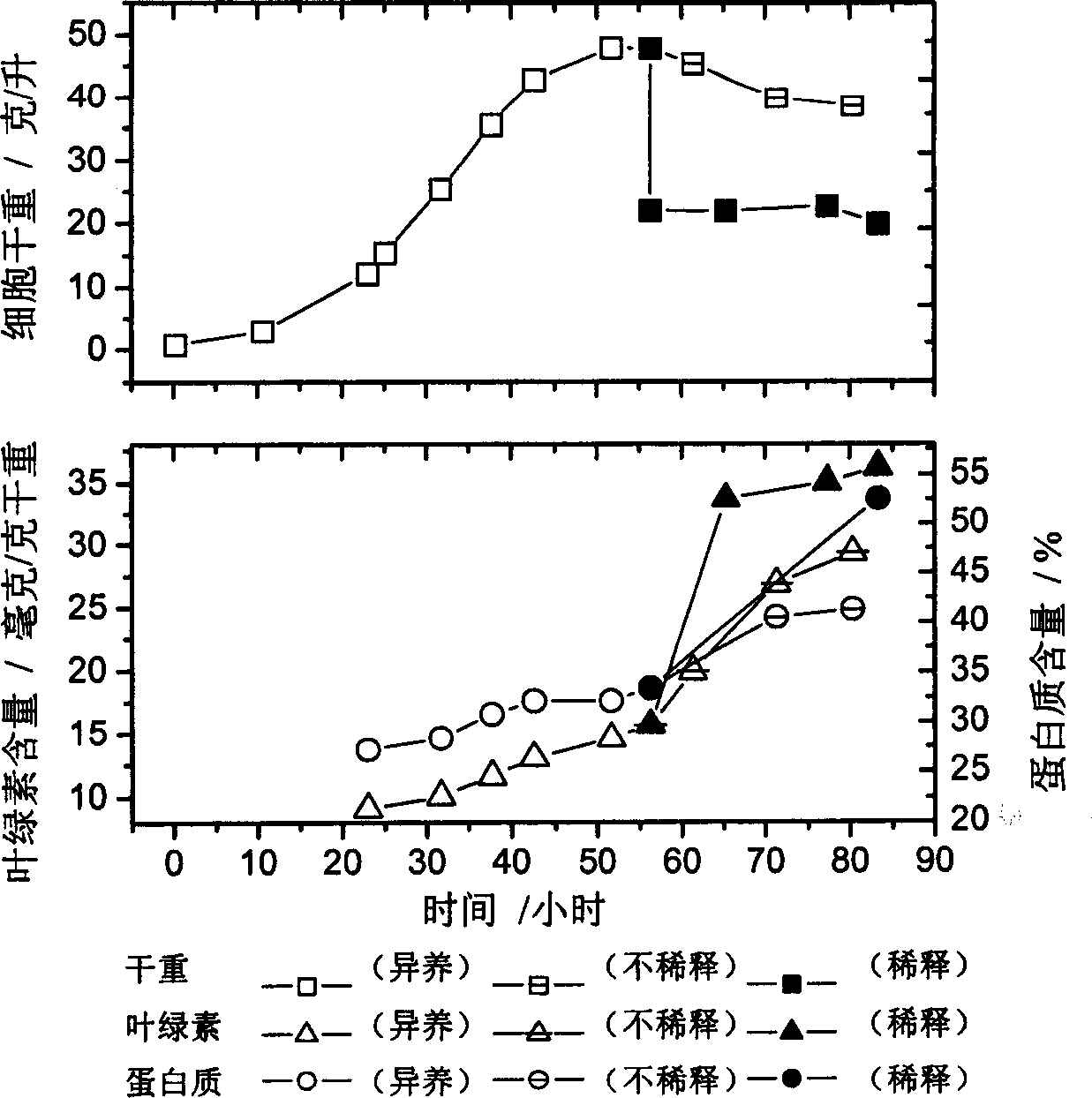
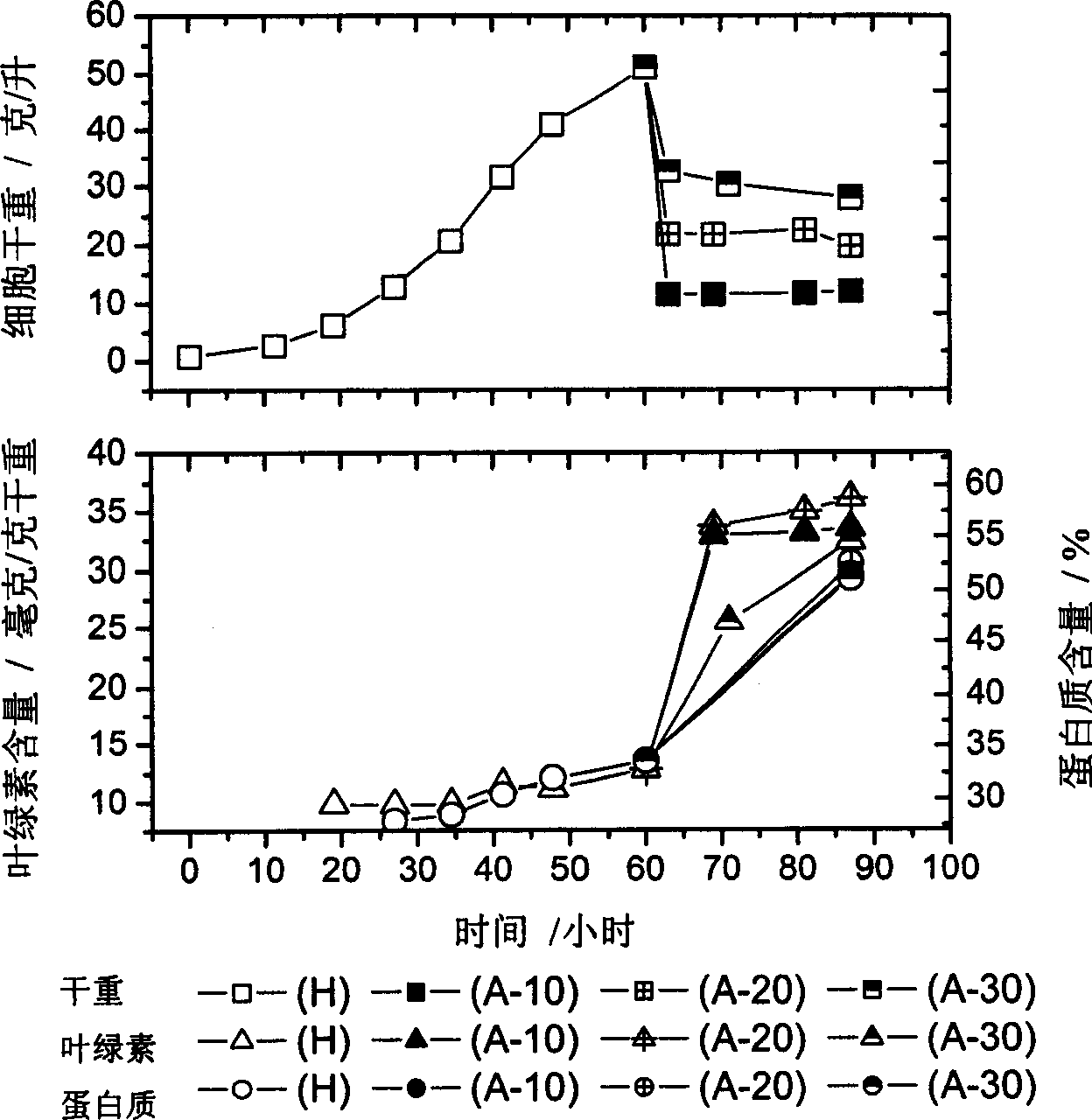
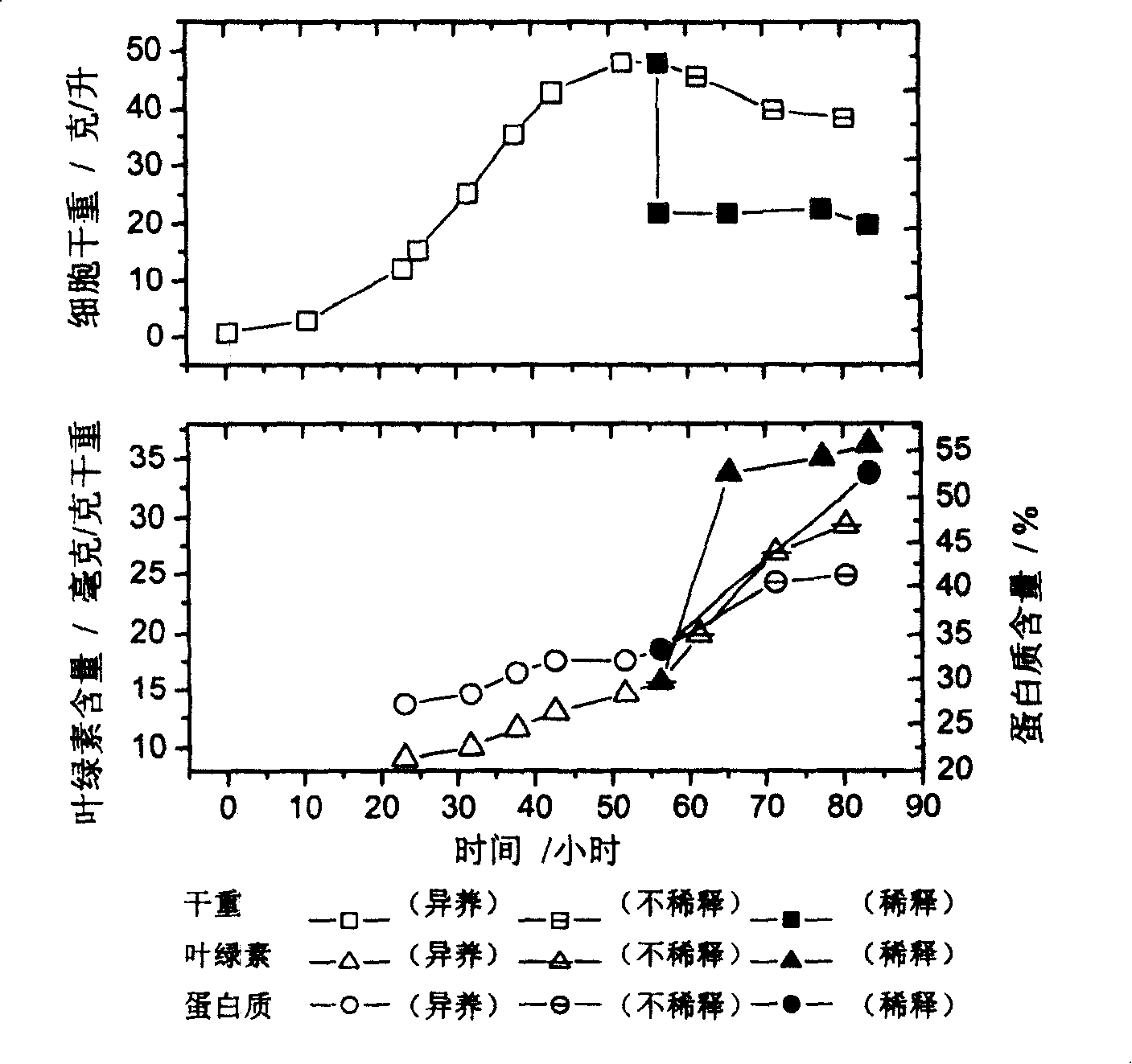
Method for culturing chlorella with high-density and high-quality
The invention discloses a small ball algae cultivation method with high density and high quality, which comprises the following phases: high-density heterotrophy cultivation, high-density algae liquid dilution and photo-autotroph cultivation. The invention makes the small ball algae reach high-density level within shorter cultivation period, which improves the small ball algae quality.
Owner:JIAXING ZEYUAN BIOLOGICAL PROD
Device and method for denitrification of single stage autotroph in low-cellulose nitrate (CN) high-ammonia nitrogen waste water
ActiveCN102101720AAchieve separationEasy to controlTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesCelluloseSludge
The invention discloses a device and a method for denitrification of single stage autotroph in low-cellulose nitrate (CN) high-ammonia nitrogen waste water. The device comprises a raw water tank, a water inlet pump, a reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank and a sludge reflux pump, wherein overcurrent holes are arranged in the water flow direction of the reactor in an up-and-down alternative form and connected with various grid chambers, an anoxic zone grid chamber is arranged at the front end of the reactor, and an aerobic zone grid chamber is arranged at the back end of the reactor; the anoxic zone grid chamber is provided with a stirrer and an agitator blade; the aerobic zone grid chamber is provided with the stirrer, the agitator blade, an aeration riser pipe and an intermediate perforated clapboard; and the aeration riser pipe is internally provided with an aeration head, and sponge filling material is filled below the intermediate perforated clapboard, wherein filling ratio is 30-50%. In the method, shortcut nitrification is achieved above the aerobic zone through low dissolved oxygen (DO is 0.5 <-1>mg / L) and free ammonia (FA) inhibition so that ammonia nitrogen is converted to nitrite nitrogen; and anoxicammoxidation biomembrane acts on the lower part of the aerobic zone, the nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen are converted to nitrogen, thereby achieving denitrification of autotroph. The method has the advantages of low oxygen consumption, less sludge output and no extra carbon source.
Owner:彭永臻
Genetically Modified Cyanobacteria for the Production of Ethanol
InactiveUS20100068776A1Increased biosynthetic levelsImprove the level ofBacteriaBiofuelsPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
The invention provides novel compositions of matter for the production of ethanol from carbon dioxide and water. Particularly, the invention provides photoautotrophic organisms having a first and second genetic modification, wherein the first genetic modification improves the ethanol production from organisms having the second genetic modification.
Owner:ALGENOL BIOFUELS
Low-carbon urban sewage biological phosphorus removal and autotrophic biological nitrogen removal device and method
ActiveCN102101746AReduce doseEmission reductionEnergy based wastewater treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentOxygenChemistry
The invention discloses a low-carbon urban sewage biological phosphorus removal and autotrophic biological nitrogen removal device and a low-carbon urban sewage biological phosphorus removal and autotrophic biological nitrogen removal method. The device comprises a raw water tank, a biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank, an intermediate water tank and an anammox reactor, wherein the biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor is a university of cape town (UCT) reactor without internal returning of digestive fluid; the secondary secondary sedimentation tank is a radial-flow sedimentation tank; and the anammox reactor is an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. The method comprises: introducing urban sewage first to the anaerobic zone of the biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor for phosphorus release, then to an anoxic zone of the biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor for denitrification and phosphorus absorption and finally to an aerobic zone for aerobic phosphorus absorption and half shortcut nitrification; subjecting mixed liquid containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen to sludge and water separation in the secondary sedimentation tank; and introducing the water to the anammox UASB reactor for autotrophic biological nitrogen removal under anammox action. When the method is used, process aeration can be reduced, energy consumption can be reduced, and carbon source is saved. The method is suitable for treating low-carbon sewage.
Owner:彭永臻
Closed photobioreactor system for continued daily in situ production of ethanol from genetically enhanced photosynthetic organisms with means for separation and removal of ethanol
InactiveUS20100068801A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotobioreactorOrganism
Owner:ALGENOL BIOFUELS SWITZERLAND
Dual-compartment bioreactor for use in wastewater treatment and algal production
ActiveUS20160122705A1Reduce and eliminate for oxygen toxicityReduce and eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlgaeBiology
A dual compartment bioreactor system includes a heterotrophic bioreactor, an autotrophic bioreactor, and a membrane between the autotrophic bioreactor and the heterotrophic bioreactor. The autotrophic bioreactor includes a transparent outer wall. Each population benefits from the products of the metabolism of the other. Methods for wastewater treatment and algal production utilize the system.
Owner:XEROX CORP
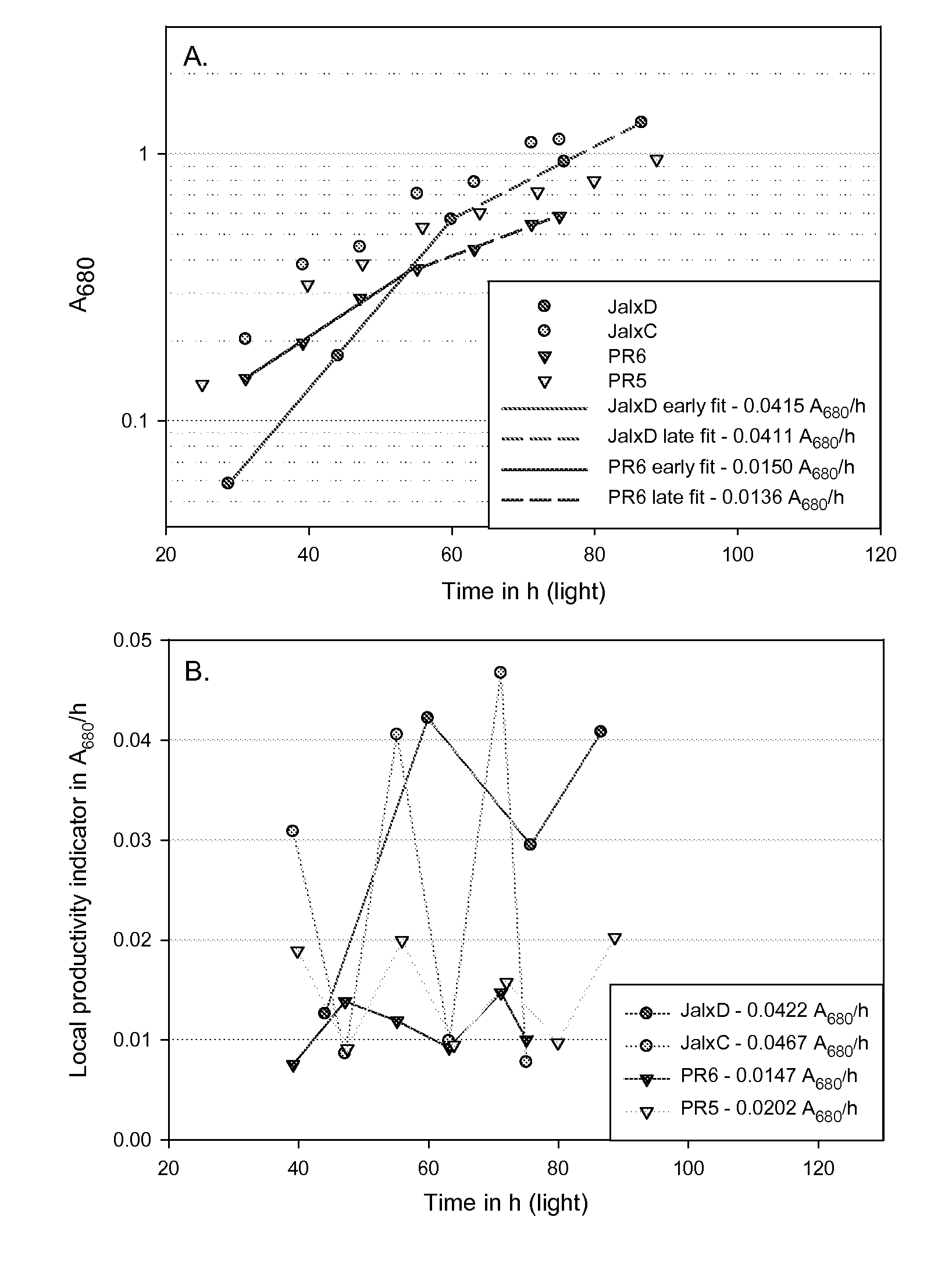
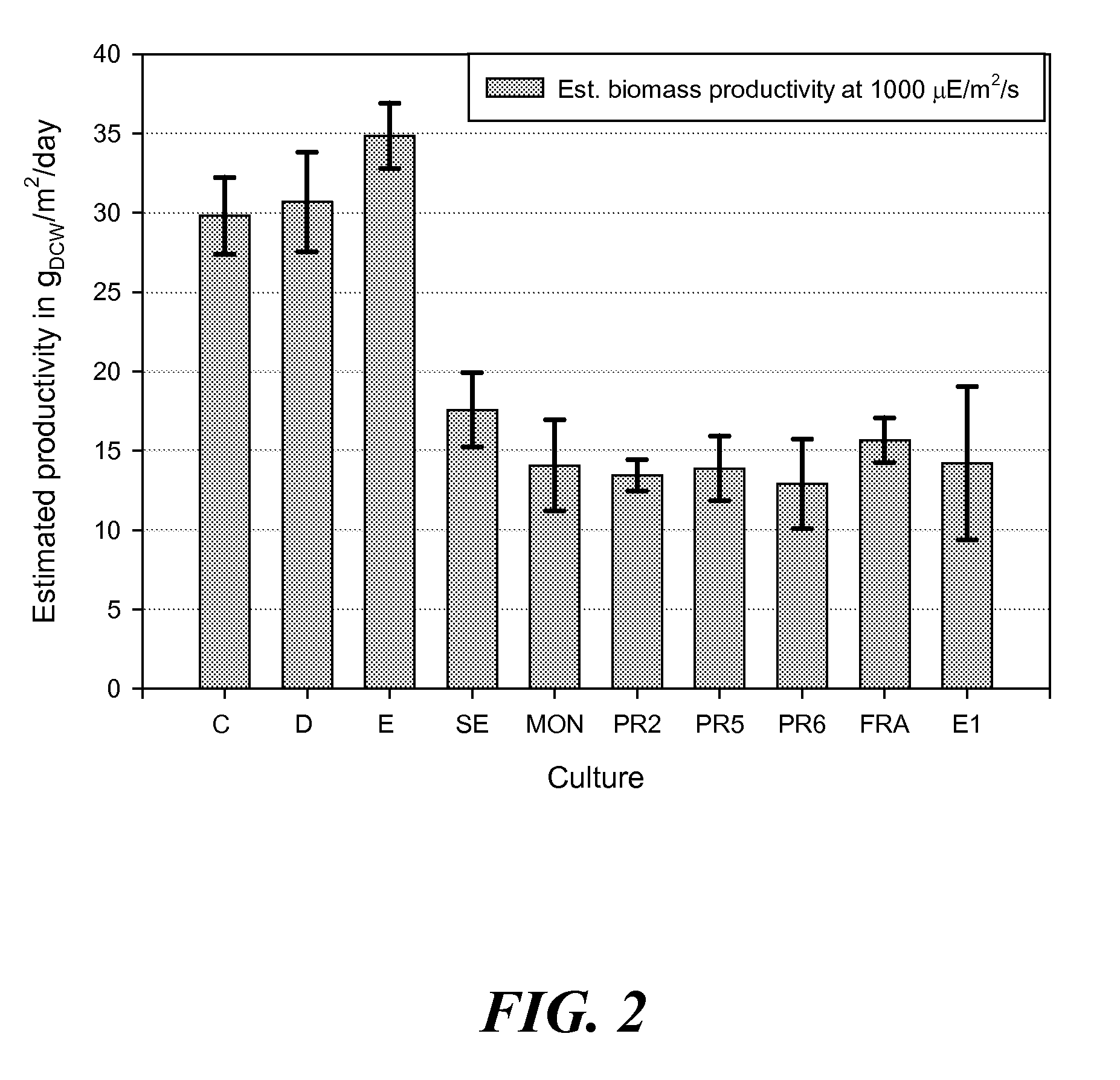
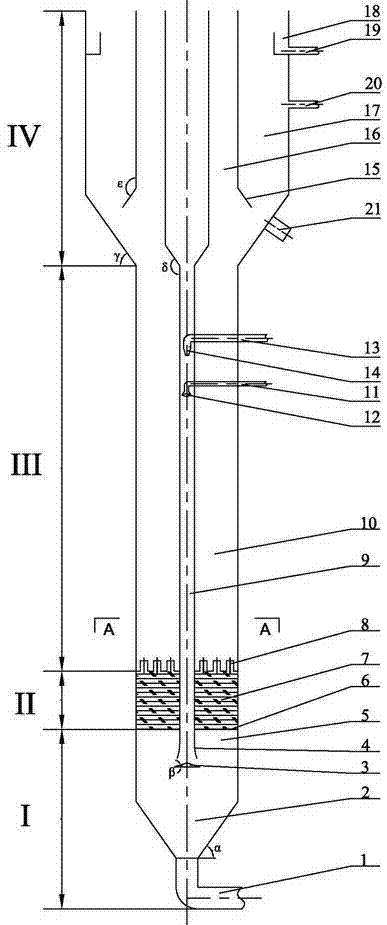
Methods for estimating intrinsic autotrophic biomass yield and productivity in unicellular photosynthetic algae
InactiveUS20100107487A1Algae productsComputation using non-denominational number representationProduction rateGram
A robust methodology is described herein for determining the algae biomass photoautotrophic yield (in gram of biomass synthesized per μmole of absorbed photons), which is useful for reliable biomass productivity estimates for selecting, comparing, and optimizing algae cultures for large-scale production. Another method is provided herein to increase dissolved inorganic carbon concentration and alleviate limitations common in aerated small-scale batches. This carbonate addition method allows for a more accurate determination of the algae culture photoautotrophic yield under small-scale experimental conditions. Also provided herein is a method for estimating a light spectrum-dependent scatter-corrected algae-specific absorption cross section, which permits the use of Beer's law to estimate the fraction of photons absorbed by a given algae culture. Determination of the algae photoautotrophic yield and absorption cross section enable a full photobioreactor parameterization and the resulting capacity to achieve highly controlled nutrients-supply conditions.
Owner:HOLLAND ALEXANDRA D
Method and device for removing nitrate in aquaculture seawater through heterotrophism and autotrophy series connection denitrification
ActiveCN106495323AAchieve removalReduce generationWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHigh concentrationSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a method and a device for removing nitrate in aquaculture seawater through heterotrophism and autotrophy series connection denitrification. The device comprises a heterotrophic organism denitrification unit, an autotrophic organism denitrification unit and an outlet water filtering unit, wherein the heterotrophic organism denitrification unit comprises a heterotrophic denitrification bioreactor; the autotrophic organism denitrification unit comprises an autotrophic denitrification bioreactor; the outlet water filtering unit comprises a solid filtering device; aquaculture seawater to be treated is sequentially introduced into the heterotrophic denitrification bioreactor, the autotrophic denitrification bioreactor and the solid filtering device, and the removal of nitrate in the aquaculture seawater can be realized. The method and the device have the advantages that on the premise of maintaining high-concentration dissolved oxygen of inlet water, the removal of nitrate in circulation aquaculture seawater is realized; the generation of nitrous acid in the outlet water is strictly controlled; the consumption of organic carbon sources and the generation quantity of sulfate radicals are reduced; the treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Authigenic ferric salt chemical phosphorus removal-anaerobic ferrous oxidization biological denitrification integrated device
InactiveCN103693806AAchieve recyclingSolve the problem of insufficient carbon sourcesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationNitrogen removal
The invention discloses an authigenic ferric salt chemical phosphorus removal-anaerobic ferrous oxidization biological denitrification integrated device. The device is provided with a chemical flocculation settling area, a ferrous salt supplement area, a nitrogen and phosphorus removal area and a three-phase separation area from bottom to top, wherein the chemical flocculation settling area is provided with a solid-liquid separation phosphorus removal area and a slowly flocculating phosphorus removal area, the ferrous salt supplement area is provided with a zero-valent iron filling area, the nitrogen and phosphorus removal area is provided with a rapidly settling phosphorus removal area and a ferrous oxidization biological nitrogen removal area from inside to outside, the three-phase separation area is provided with a gas release area and a settling area, and the settling area is provided with a biological sludge discharge port, a reflux port, an overflow weir and a water outlet. According to the device, the matrix of the phosphorus removal process and the nitrogen removal process can be recycled; by using biological denitrificatio and authigenic ferric salt chemical phosphorus removal agent, the cost for removing phosphorus is lowered; zero-valent iron such as cheap iron residue / scrap iron is dissolved by acid ferric salt phosphorous removal reaction solution so as to provide ferrous salt matrix for biological denitrification, and the purpose of processing waste with waste is achieved; by using autotroph for denitrification, the problem of insufficient carbon source in biological denitrification of wastewater is effectively solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Trophic conversion of obligate phototrophic algae through metabolic engineering
InactiveUS20080138851A1Stable populationUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganismBiology
Most microalgae are obligate photoautotrophs and their growth is strictly dependent on the generation of photosynthetically-derived energy. In this study it is shown that the microalga Phaeodaclylurn tricornutum can be engineered to import glucose and grow in the dark through the introduction of genes encoding glucose transporters. Both the human and Chlorella kessleri glucose transporters facilitated the uptake of glucose by P. tricornutum, allowing the cells to metabolize exogenous organic carbon and thrive, independent of light. This is the first successful trophic conversion of an obligate photoautotroph through metabolic engineering, and it demonstrates that methods of cell nourishment can be fundamentally altered with the introduction of a single gene. Since strains transformed with the glucose transport genes are able to grow non-photosynthetically, they can be exploited for the analysis of photosynthetic processes through mutant generation and characterization. Finally, this work also represents critical progress toward large-scale commercial exploitation of obligate phototrophic algae through the use of microbial fermentation technology, eliminating significant limitations resulting from light-dependent growth.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Methods and compositions for the recombinant biosynthesis of fatty acids and esters
Owner:JOULE UNLTD TECH
Device and method for treating pharmaceutical waste water through synchronous biological denitrification and devulcanization and autotrophic biological denitrification
InactiveCN102351366AReduce dosePrevent overacidificationMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater treatmentAutotroph
The invention relates to a device and a method for treating pharmaceutical waste water through synchronous biological denitrification and devulcanization and autotrophic biological denitrification. The device is provided with a synchronous denitrification and devulcanization pool, an anaerobic methane generation pool, a partial nitrosification pool, an autotrophic biological denitrification pool and a water outlet pool. The method comprises the steps that: 1) anaerobic digested sludge is added to the synchronous denitrification and devulcanization pool; 2) outlet water of the synchronous denitrification and devulcanization pool enters the anaerobic methane generation pool; 3) outlet water of the anaerobic methane generation pool enters the partial nitrosification pool; 4) outlet water of the partial nitrosification pool enters the autotrophic biological denitrification pool through a middle settling pool; and 5) mixed liquid in the autotrophic biological denitrification pool flows into the water outlet pool after the sludge and water separation in a final setting pool. Through the cooperative action of the synchronous biological denitrification and devulcanization, anaerobic methane generation and autotrophic biological denitrification processes, the deep treatment of the pharmaceutical waste water is realized, and the method and the device are suitable for the standard reaching treatment and the regeneration of the pharmaceutical waste water. The device structure and the operation method are perfect, the energy is saved, the cost is low, the waste water treatment effect is good, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:BEIJING TANSI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO
Wastewater nitrogen removal treatment method based on photoelectrocatalysis-autotrophic biofilm
InactiveCN104671589ARealize synchronous removalStrong complementarityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogen removalBiofilm
The invention discloses a wastewater nitrogen removal treatment method based on a photoelectrocatalysis-autotrophic biofilm. The method is that wastewater to be treated is fed into a reaction chamber to be subjected to nitrogen removal treatment; at least part of the reaction chamber is manufactured from a light transmission material; a visible-light response photoanode is arranged in the reaction chamber, and a cathode of an autotrophic denitrifying biofilm develops in the reaction chamber; the pH of the wastewater is regulated to be 7 to 8 during the nitrogen removal treatment, then the wastewater is fed into the reaction chamber, 1 to 3V working voltage is applied across the photoanode and the cathode, the visible light irradiates through the light transmission part of the reaction chamber until the concentration of ammonia nitrogen and the concentration of nitrate nitrogen decrease to reach the set target value, and then the reacted wastewater is drained from the reaction chamber. According to the wastewater nitrogen removal treatment method, the autotrophic biofilm denitrifying and photoelectric catalyzing technologies are carried out, so that the shortage that the ammonia-nitrogen wastewater cannot be treated by the autotrophic biofilm denitrifying technology, and the nitrate-nitrogen wastewater cannot be treated by the photoelectric catalyzing technology can be overcome, and various nitrogen elements can be synchronously removed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Novel partial-nitrosation anaerobic ammoxidation integrated reactor
InactiveCN103896395AActive influenceAchieve UnicomWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesRefluxSludge
The invention discloses a novel partial-nitrosation anaerobic ammoxidation integrated reactor which comprises a main reaction area, an upper three-phase separator and an air ascending chamber, wherein the main reaction area is internally sequentially provided with a sludge fluidization area, a middle biomembrane area and an upper biomembrane area from bottom to top, and the main reaction area is externally sequentially provided with a bottom water inlet, an air inlet and an upper water outlet from bottom to top; a three-phase separator area internally sequentially comprises a biomembrane area and an air collecting chamber from bottom to top; and the three-phase separator is externally provided with a sediment area. The novel partially-nitrosation anaerobic ammoxidation integrated reactor disclosed by the invention can realize the subarea culture of nitrosation and anaerobic ammoxidation in a single reactor, thereby preventing the influence of certain environment factors on anaerobic ammoxidation bacteria and nitrosation bacteria; and the novel partially-nitrosation anaerobic ammonia oxidation integral reactor realizes the combination of various areas through a self-reflux function, thereby realizing the denitrification of wastewater autotrophs.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological nitrogen removal combination device
ActiveCN105254134AImprove denitrification effectReduce the impactMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention provides a biological nitrogen removal combination device. The biological nitrogen removal combination device comprises a water inflow water tank, an oxygen-poor denitrification tank, an aerobiotic nitrification tank, a middle settling tank and an autotroph nitrogen removal tank, all of which are sequentially connected. The device has the effects that by the adoption of the device, part of organic matter having the adverse effect on anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria can be consumed, meanwhile, nitrate nitrogen generated in the autotroph nitrogen removal tank is removed, the overall nitrogen removal effect of a system is improved, and the total nitrogen removal rate is increased to 90%-97% from 80%-85%. The oxygen consumption of the autotroph nitrogen removal tank during oxidation of ammonia and nitrogen is reduced by 80%-95%, aeration intensity is reduced accordingly, and the influences of DO on the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria are lowered. The content and activity of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria and ammonia oxidizing bacteria in sludge of the autotroph nitrogen removal tank are improved. The nitrogen volume removal load rate of the device can reach 2.5-10 kg / (m<3>.d), gas-solid-liquid three-phase separation is completed in one reactor, no settling tank needs to be independently arranged, and reactor units are reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN ENEW ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENGCO LTD
Sewage treatment method using micro-aerobic autotroph to remove nitrogen
InactiveCN102942290ALow running costEasy to operateMultistage water/sewage treatmentTotal nitrogenOxygen
The invention discloses a sewage treatment method using micro-aerobic autotroph to remove nitrogen. The method comprises the following steps of 1. carrying out micro-aerobic oxidizing on organic matters in sewage, and meanwhile realizing partially synchronous nitrification, denitrification and nitrosification; 2. strictly controlling dissolved oxygen, proportionally converting ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen, and making the ratio of the ammonia nitrogen to the nitrite nitrogen in the discharged sewage approach to 1; and 3. enriching the anaerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria, and ensuring that the ammonia nitrogen and the total nitrogen in the discharged sewage reach standards. The method has the advantages that the existing urban sewage with low carbon-nitrogen ratio and the sewage with high ammonia nitrogen ratio can be treated highly efficiently, the technology is simple, the operation is convenient, the method is suitable for large-scale engineering, and the good economical, social and environmental benefits are realized.
Owner:QINGDAO SPRING WATER TREATMENT
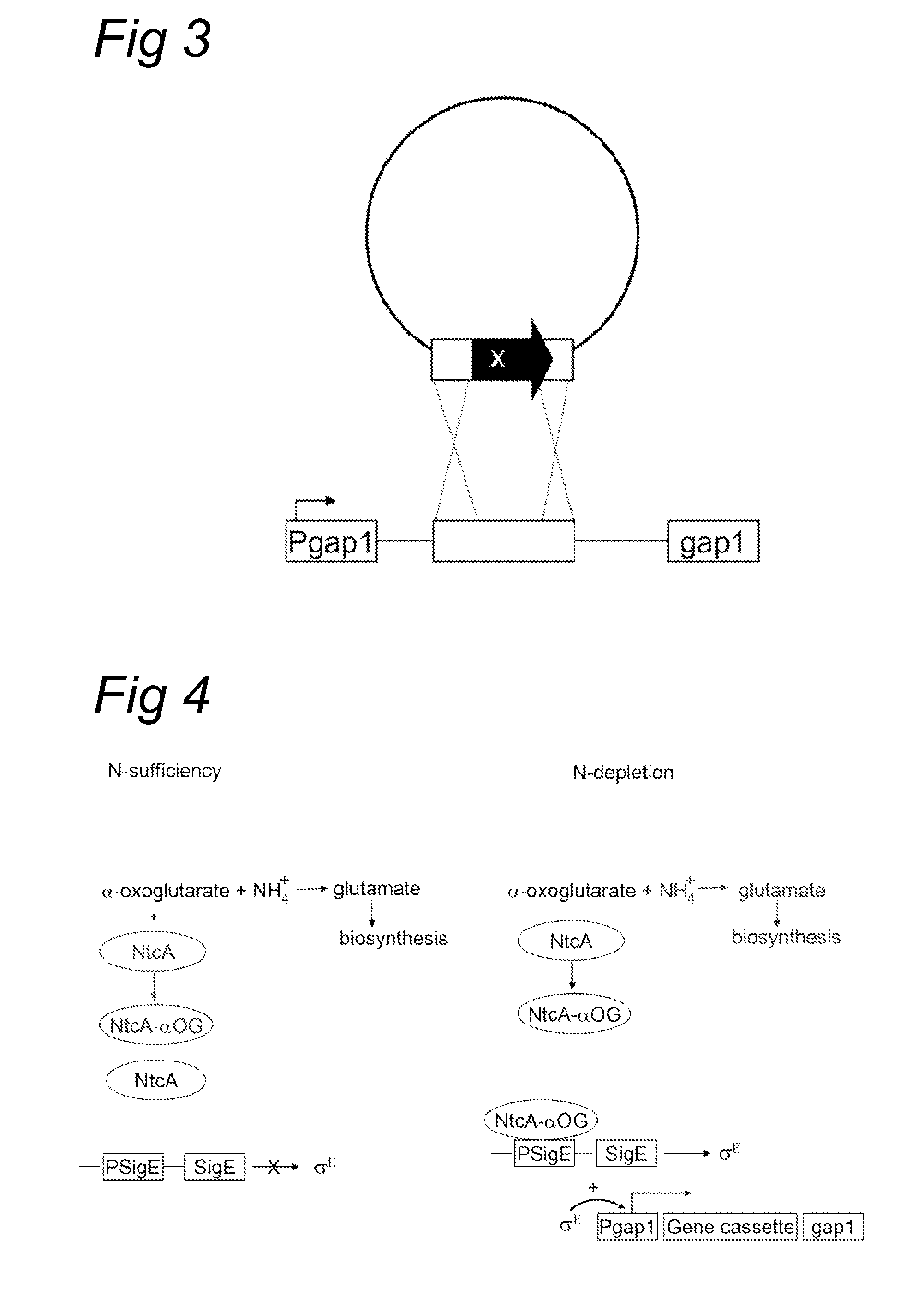
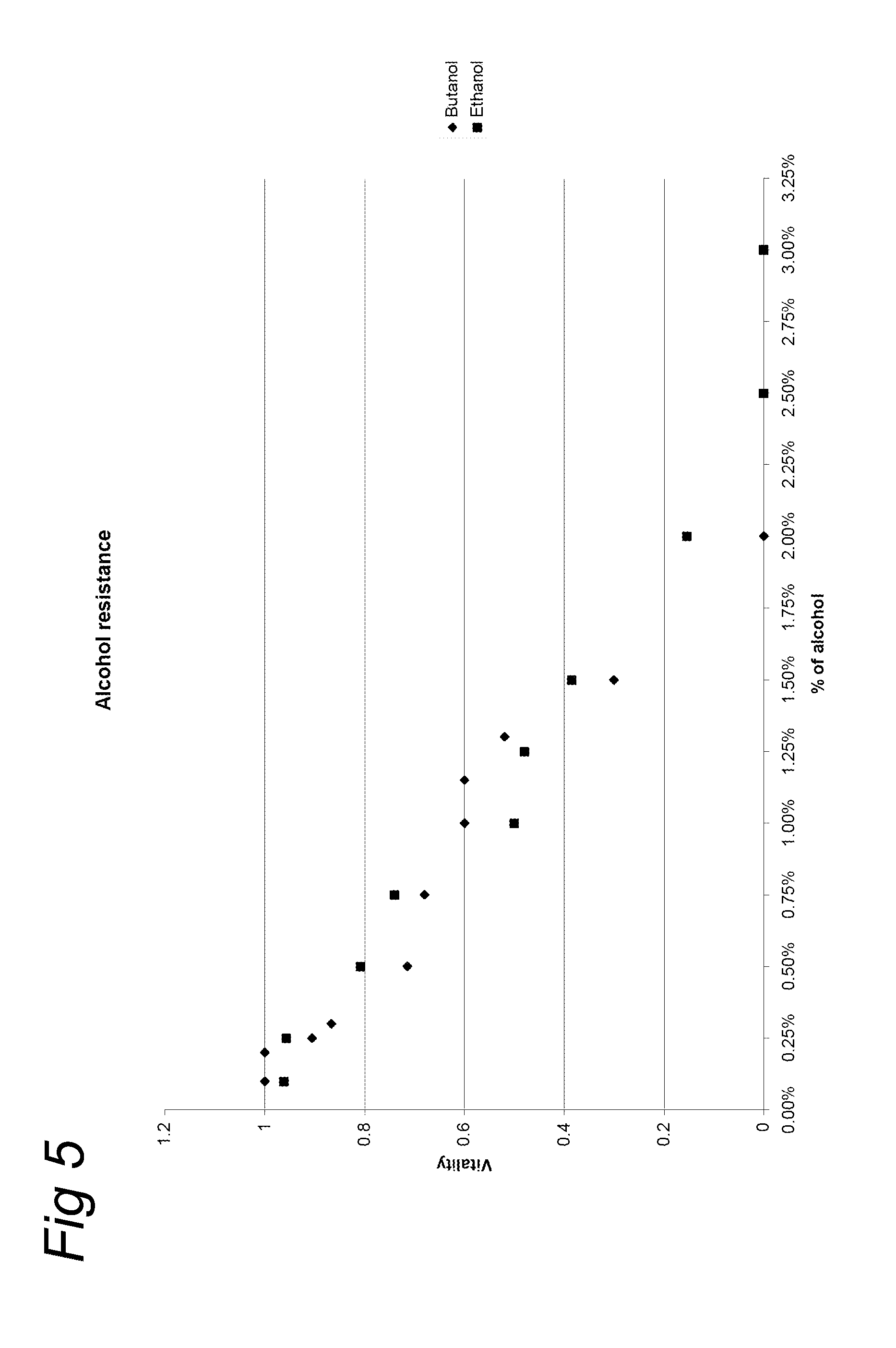
Light-driven co2 reduction to organic compounds to serve as fuels or as industrial half products by an autotroph containing a fermentative gene cassette
ActiveUS20110212498A1Not sensitiveSufficient expressionBacteriaUnicellular algaeSimple Organic CompoundsCyanobacteria
A process of producing an organic compound and / or an intermediary compound as defined herein by feeding carbon dioxide to a culture of a cyanobacterial cell and subjecting the culture to light, wherein the cell is capable of expressing a nucleic acid molecule, wherein the expression of the nucleic acid molecule confer on the cell the ability to convert a glycolytic intermediate into the organic compound and / or into the intermediary compound and wherein the nucleic acid molecule is under the control of a regulatory system which responds to a change in the concentration of a nutrient in the culture.
Owner:PHOTANOL +1
Method for dissolving medium/low grade phosphate ore powder by utilizing acidophilic heterotroph and acidophilic autotroph
The invention relates to a method for dissolving medium / low grade phosphate ore powder by utilizing acidophilic heterotroph and acidophilic autotroph. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) activating an acidophilic heterotroph original bacterial solution to obtain an acidophilic heterotroph activated bacterial solution; 2) activating an acidophilic autotroph original bacterial solution to obtain an acidophilic autotroph activated bacterial solution; 3) mixing the acidophilic heterotroph activated bacterial solution and the acidophilic autotroph activated bacterial solution to acclimate: mixing the two bacterial solutions according to a volume ratio of 1: (0.5-1.5) to obtain a mixed bacterial solution and acclimating the mixed bacterial solution to obtain an acclimated bacterial solution; and 4) performing the biological dissolution of medium / low grade phosphate ore powder: adjusting the pH value of the culture solution D, adding the acclimated bacterial solution, and then placing the container in a 30-35 DEG C thermostatic shaker to perform shaking cultivation at 120-180rpm for 15-20 days and obtain soluble phosphorus. The method is characterized by high phosphorus-dissolving rate, simple technology and low production cost.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for treating high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater by autotrophic denitrification process
InactiveCN105800873AHigh processing loadIncrease manpower and material resourcesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationSludge
The invention relates to a method for treating high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater by a autotrophic denitrification process, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment and recycling. The method is characterized by being a completely autotrophic biological denitrification process based on nitrite, wherein by virtue of the action of ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB), ammonia is oxidized into nitrite; and by virtue of the action of anaerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria (AAOB), the residual ammonia and nitrite are converted into nitrogen gas. According to the method, a biological fluidized bed filler is added into a CANON tank, so that the ammonia nitrogen treatment load is improved, and therefore, the method is an efficient and energy-saving ammonia nitrogen wastewater treatment process. Active sludge can be recycled, so that the method has remarkable environmental benefits and economic benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
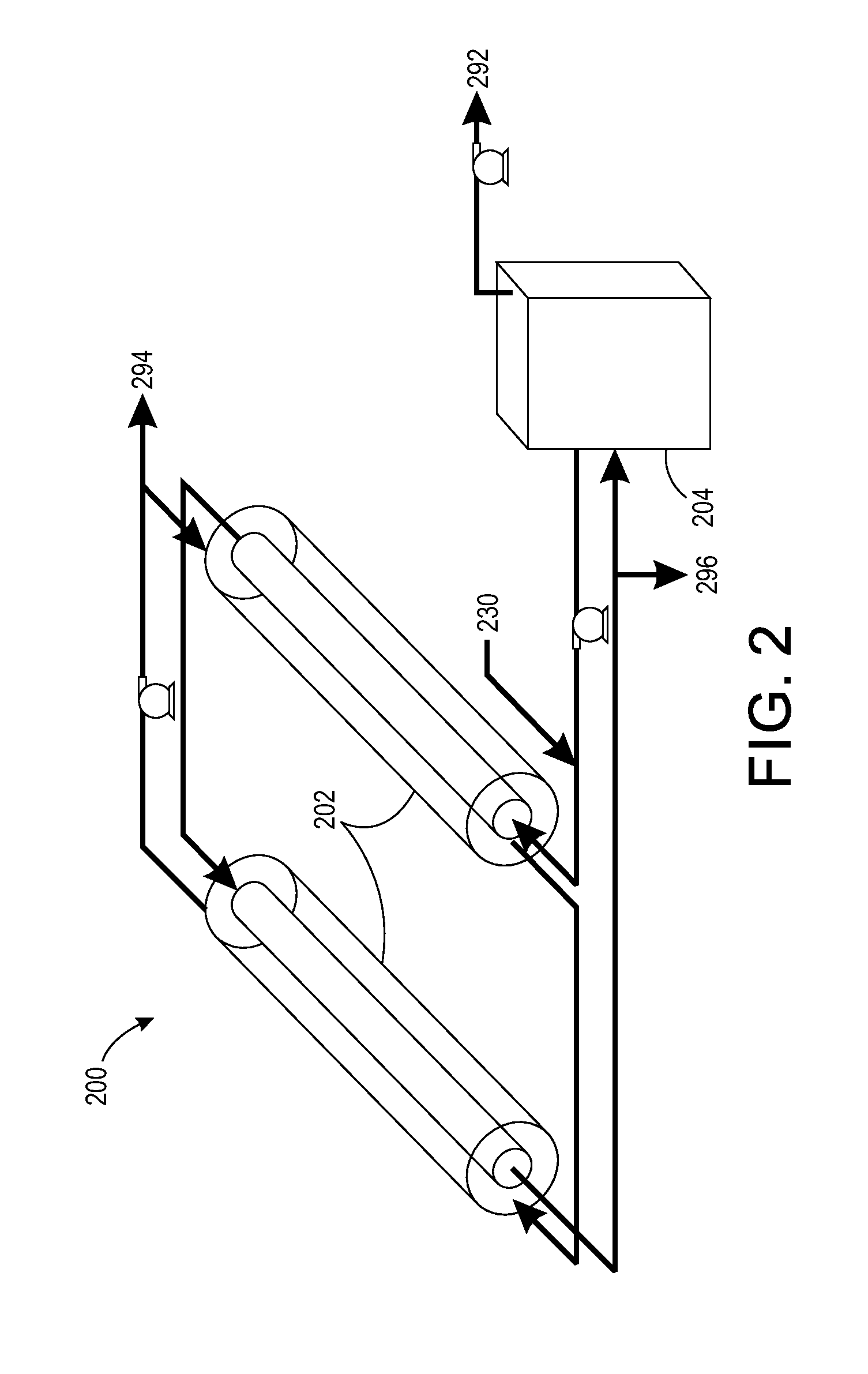
A method for separating solid particles from a waterbody
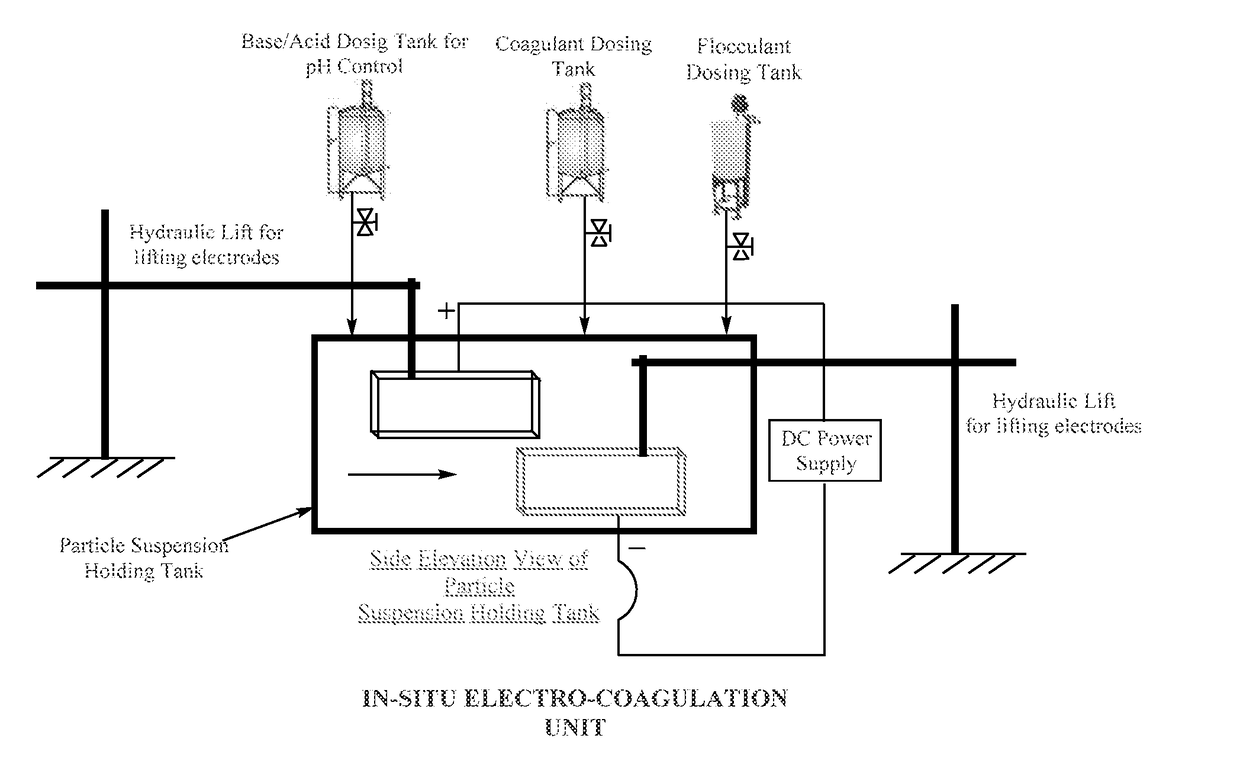
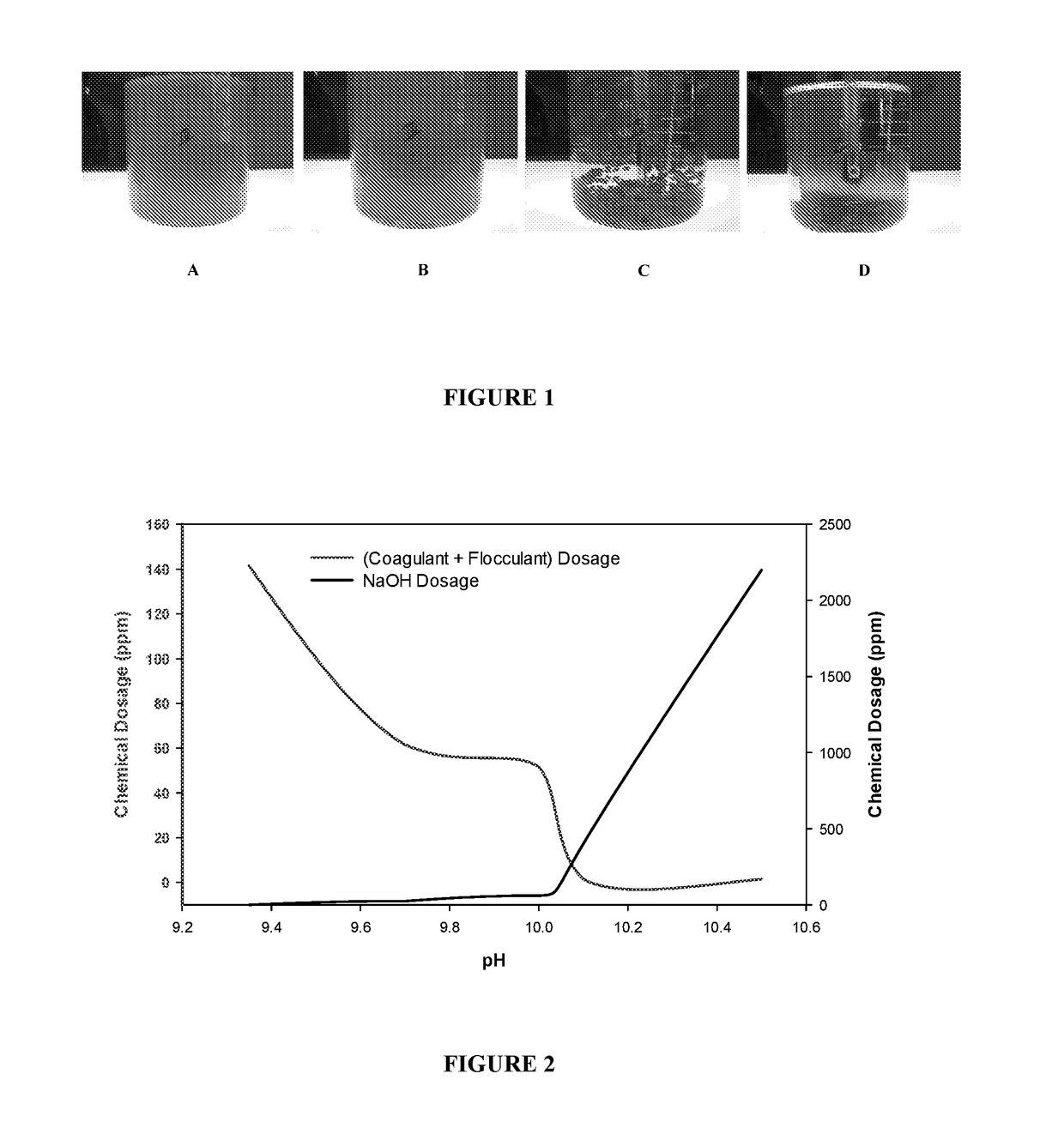
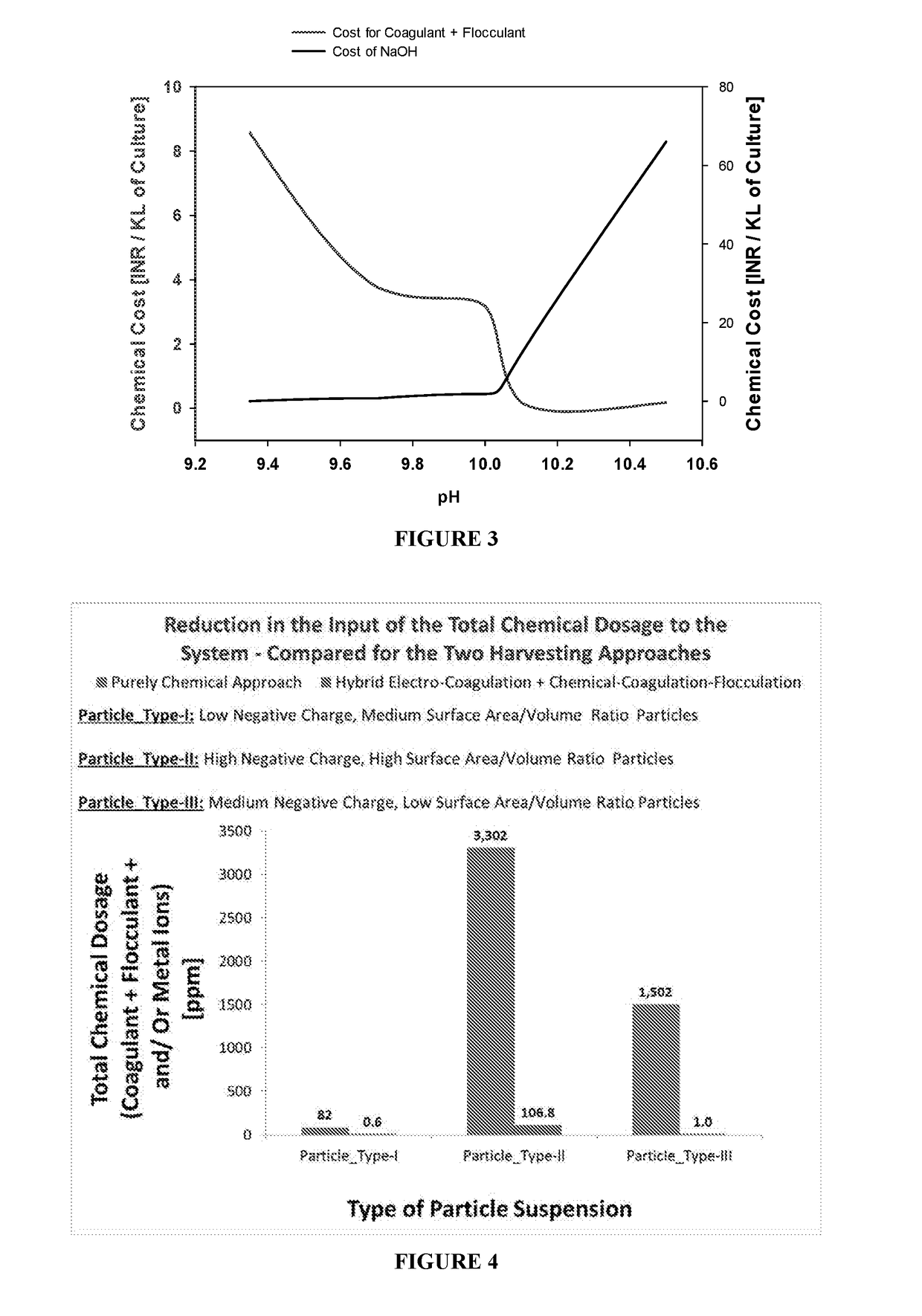
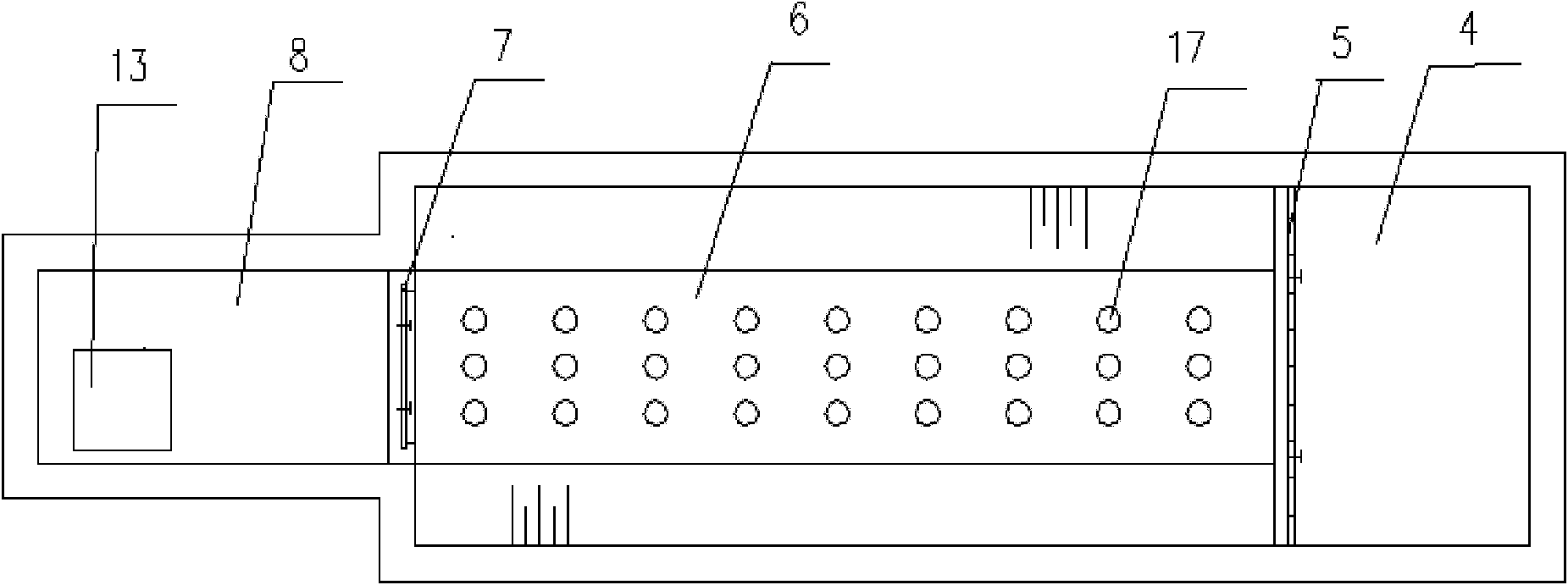
ActiveUS20170266587A1Treatment involving filtrationSoil-shifting machines/dredgersElectro coagulationSolid particle
The present disclosure relates to a method for separation of solid particles from a waterbody. Preferably, the present disclosure relates to a method, wherein a combination of chemicals including coagulant(s) and flocculant(s) are employed for said separation of solid particles, wherein suitable examples of solid particles are living organisms and non-living matter, wherein living organisms include autotrophs such as phototrophs, which are either microscopic or macroscopic in nature (algae). The disclosure thus particularly relates to method of chemical coagulation and flocculation for separating solid particles, preferably either algae or bacteria or both from a waterbody. The present disclosure also provides for an alternate method, wherein the aforesaid method of coagulation and flocculation is combined with electro-coagulation and / or pH modulation strategies for separation of said solid particles in any sequence.
Owner:RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED
Water treatment method and device based on photoautotroph film
InactiveCN102086080AImprove light utilizationEasy flow controlMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesWater discharge
The invention discloses a water treatment method and device based on a photoautotroph film. The whole body of the device is arranged from eastern to western along the flow direction and successively comprises a pre-precipitation area, a treatment area and a water discharging area, wherein the three areas are adjacently connected, and weirs are arranged among the three areas; an water inlet pipe is arranged on the side wall of the pre-precipitation area, and a return pipe is provided with a reflux valve; bionic biological film carriers are evenly planted in a treatment pool, and the bionic biological film carriers consist of main carriers and carrier floating balls, wherein the main carriers are mutually connected and fixed at the bottom of treatment pool, and the carrier floating balls are light and transparent; water enters the pre-precipitation area through the water inlet pipe to preliminarily remove inorganic particles, and then overflows to the treatment area for treatment by weirs and flows into the water discharging area through the weirs; part of the treated water in the water discharging area flows back to the pre-precipitation area through the return pipe under the action of a reflux pump, and the reflux ratio is controlled by the reflux valve; and the rest water is discharged by a water discharging pump in the water discharging area. In the invention, the illumination utilization ratio is high, a precipitation pool does not need to be arranged additionally, and the occupied area is reduced; and besides the energy consumption required by reflux, light energy is asingle energy source of the device, and the device has the characteristics of low carbon content and low energy consumption.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Method for culturing chlorella with high-density and high-quality
The invention discloses a small ball algae cultivation method with high density and high quality, which comprises the following phases: high-density heterotrophy cultivation, high-density algae liquid dilution and photo-autotroph cultivation. The invention makes the small ball algae reach high-density level within shorter cultivation period, which improves the small ball algae quality.
Owner:JIAXING ZEYUAN BIOLOGICAL PROD
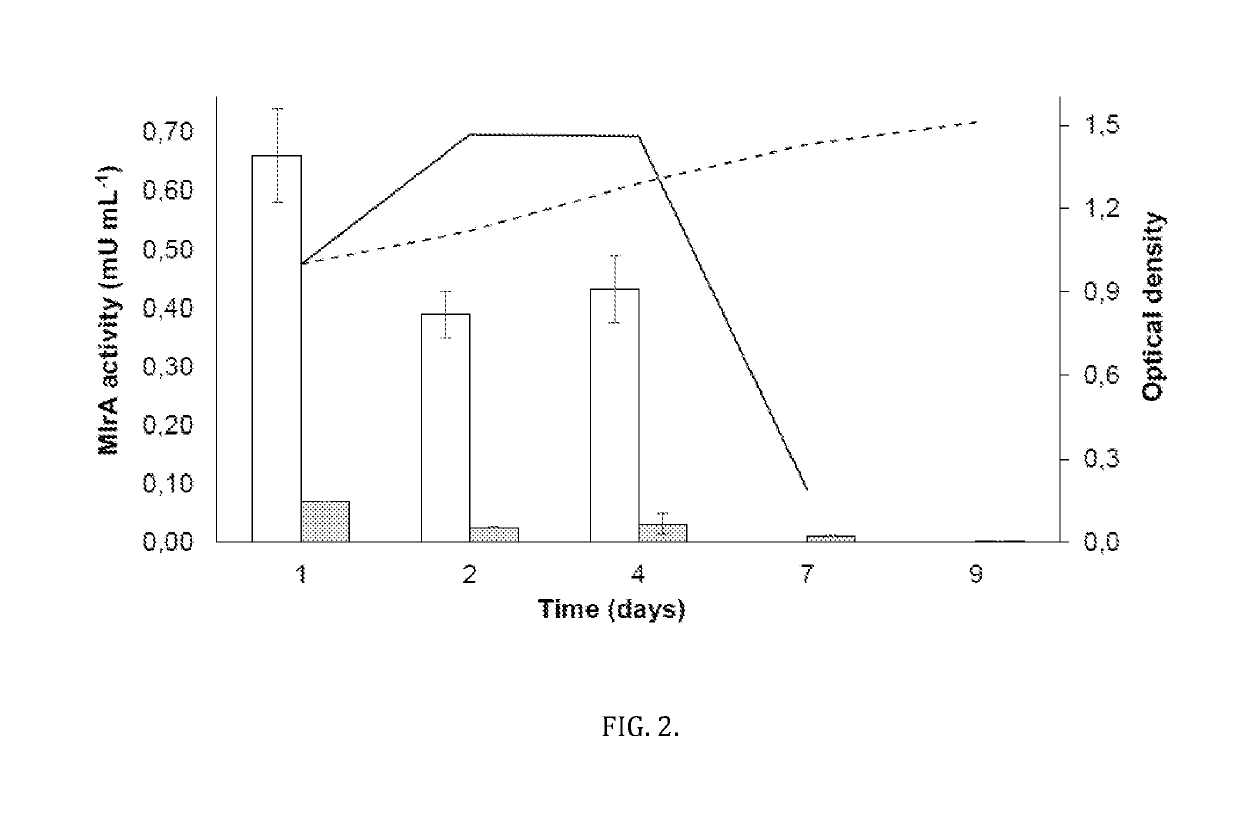
Biocatalyst comprising photoautotrophic organisms producing recombinant enzyme for degradation of harmful algal bloom toxins
The invention comprises a photoautotrophic organism, generally having simpler nutritional requirements than heterotrophic organisms, utilized as a chassis for the heterologous expression and function of enzymes, or derivatives of said enzymes, that show activity toward the degradation / detoxification of toxins known to be associated with and specific to harmful algal blooms. As an example, a cyanobacterial strain (Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803) modified to express Sphingomonas sp. USTB-05 MlrA enzyme functionality, showing the capability of degrading microcystins (results shown here) and nodularins, is presented. Under modelled natural conditions, results indicate that heterologous enzymatic activity against microcystin-LR is more stable over time when utilizing a photoautotrophic chassis in comparison to use of a heterotrophic bacterial strain. In addition, both the viability and cell density of the photoautotrophic host is maintained for a significantly longer period of time, compared to a heterotrophic host.
Owner:DEXTER JASON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com