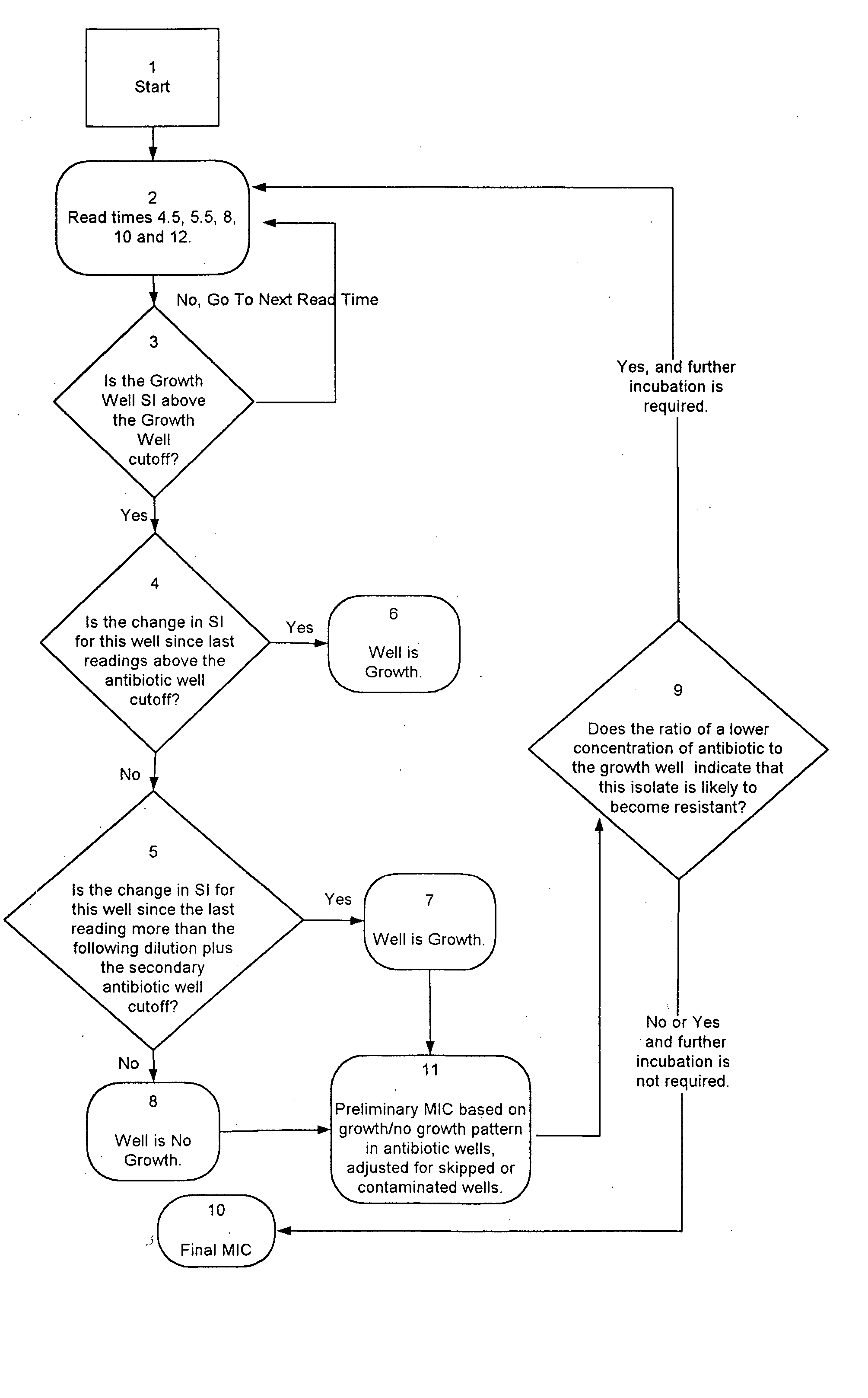
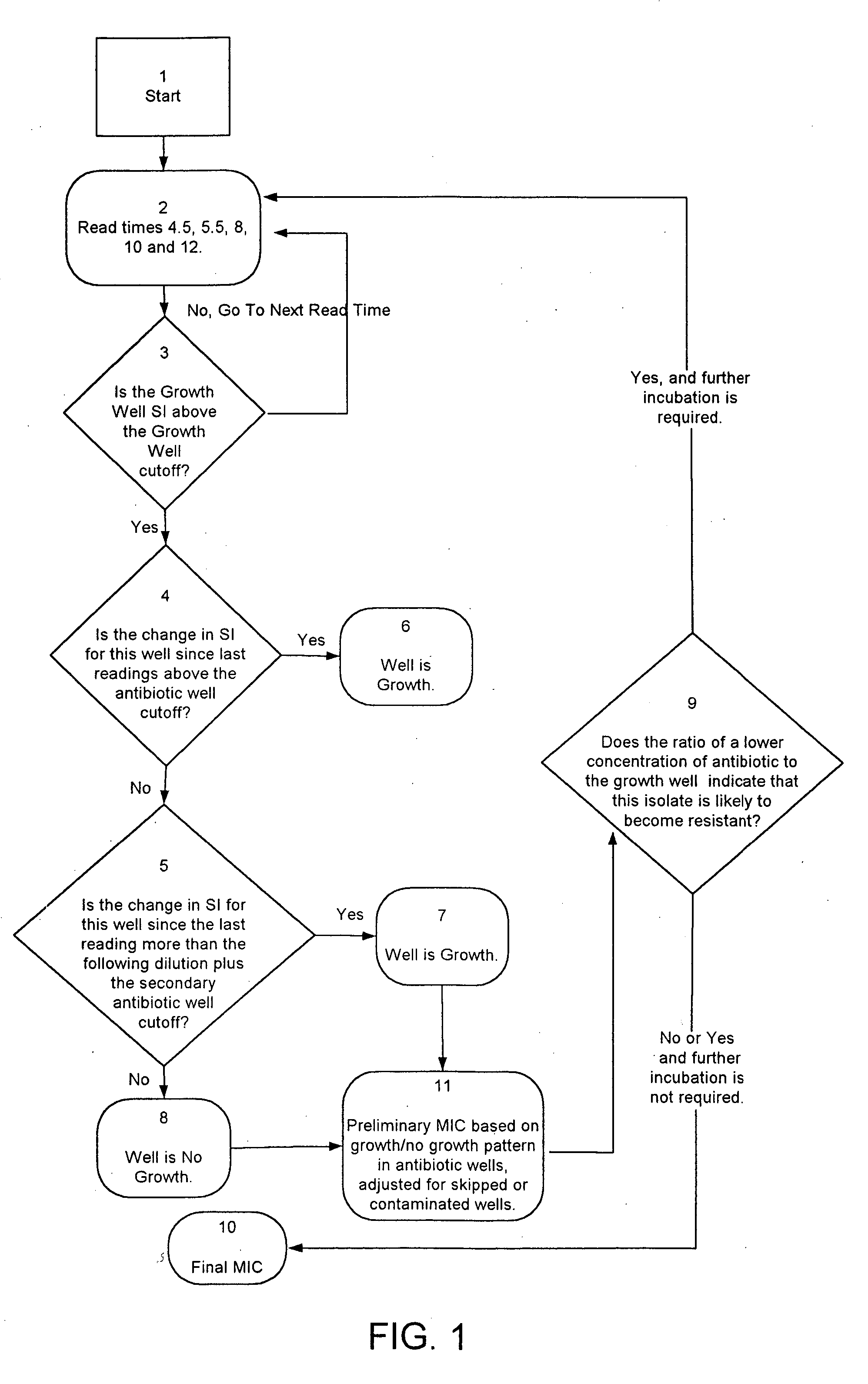
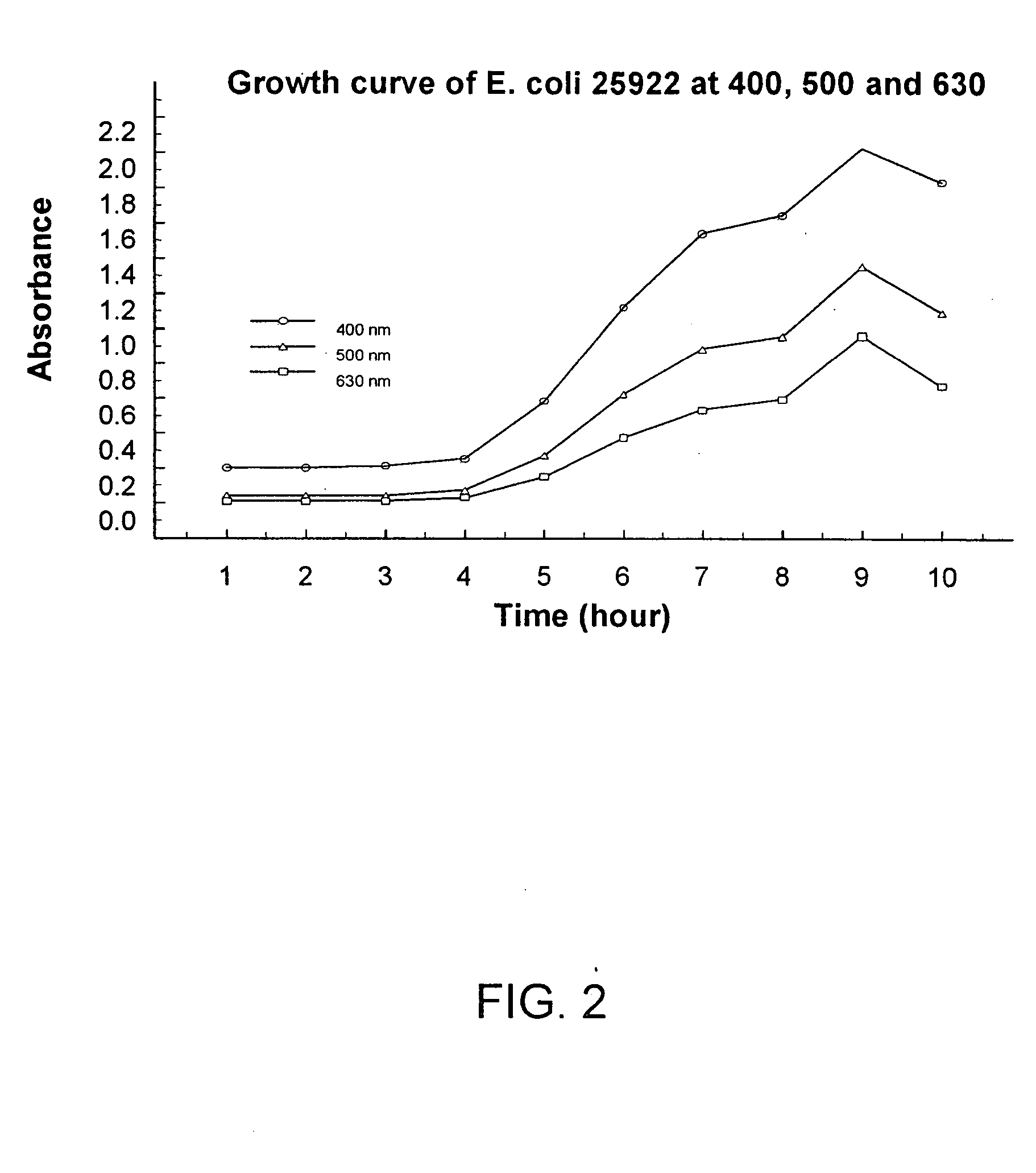
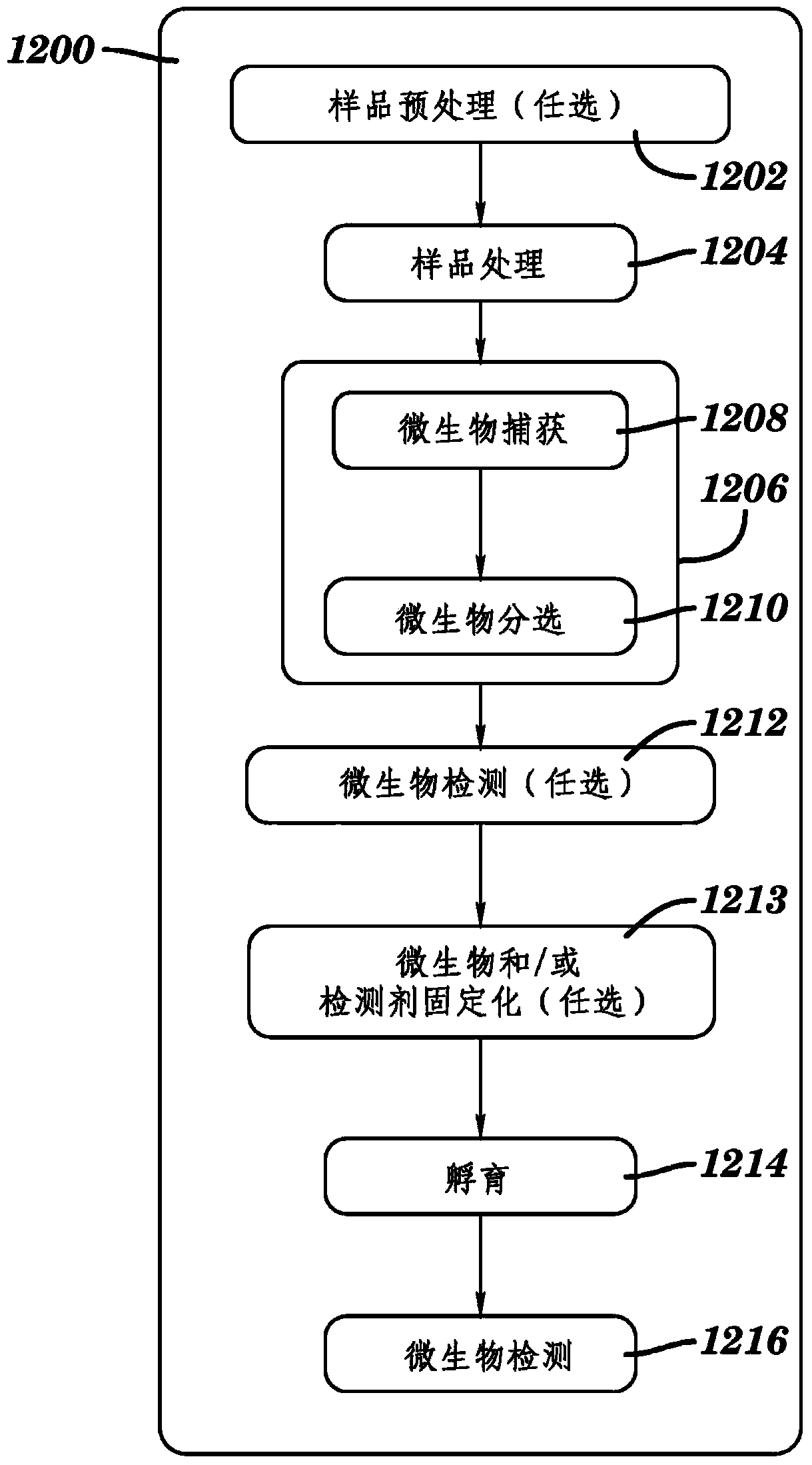
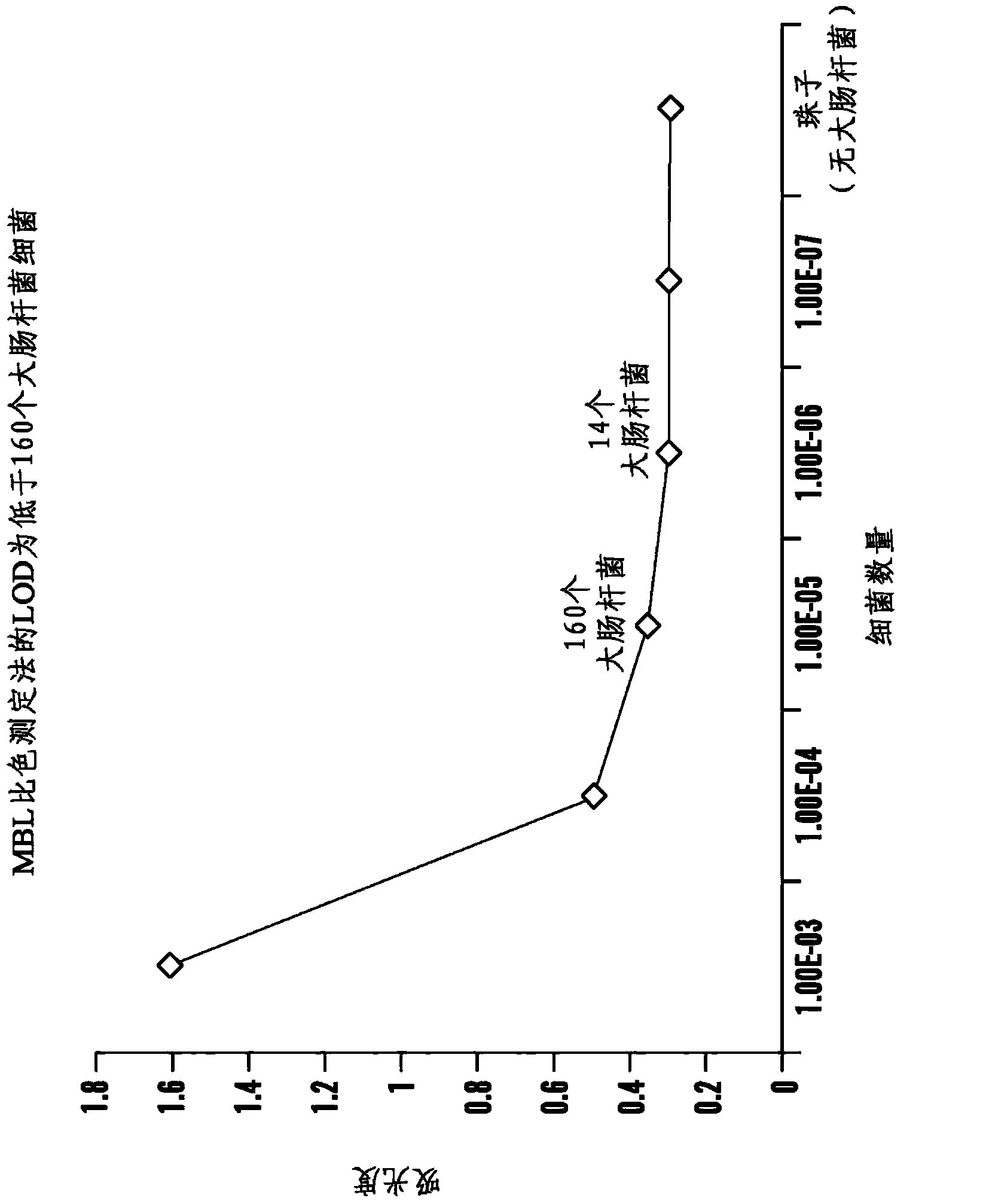
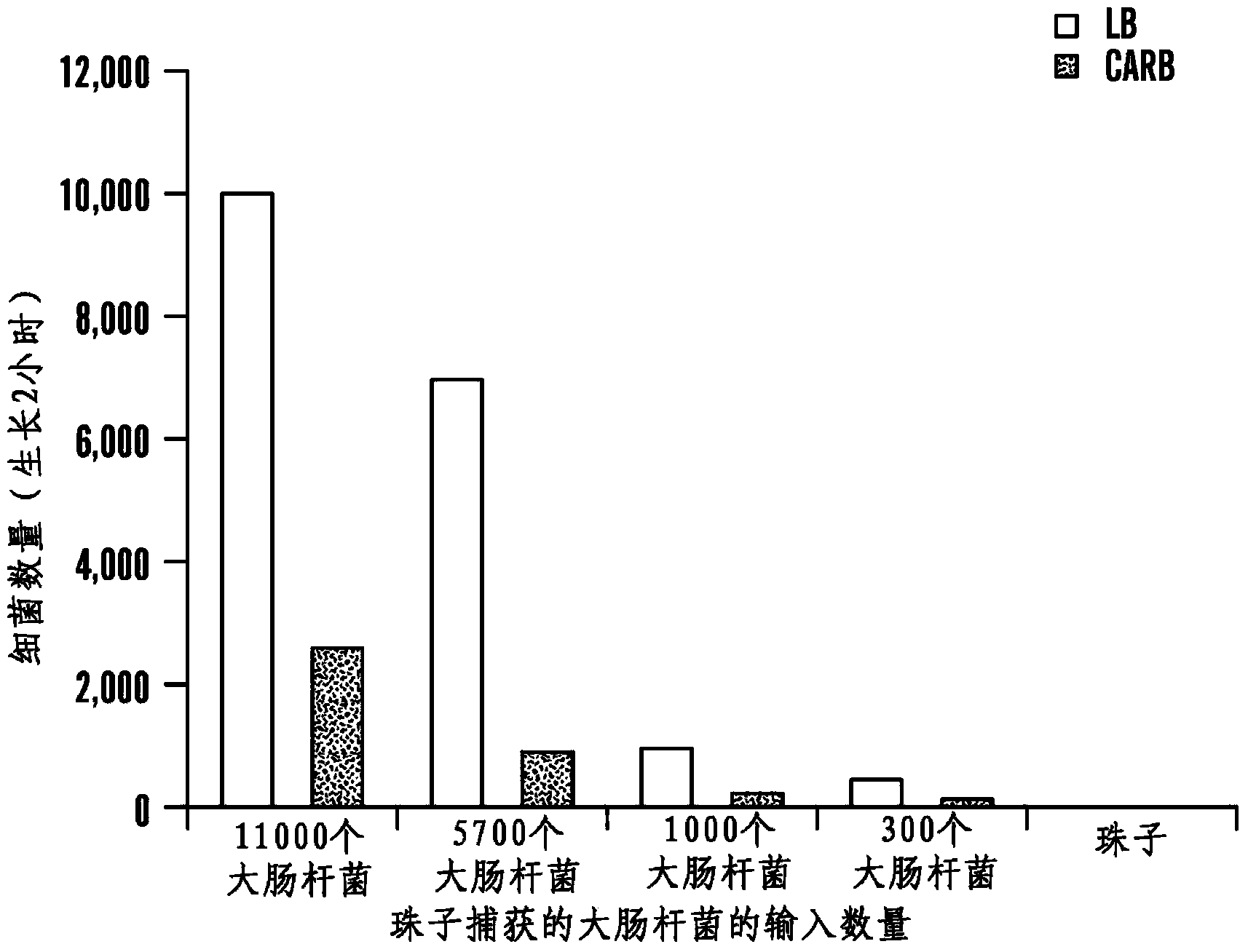
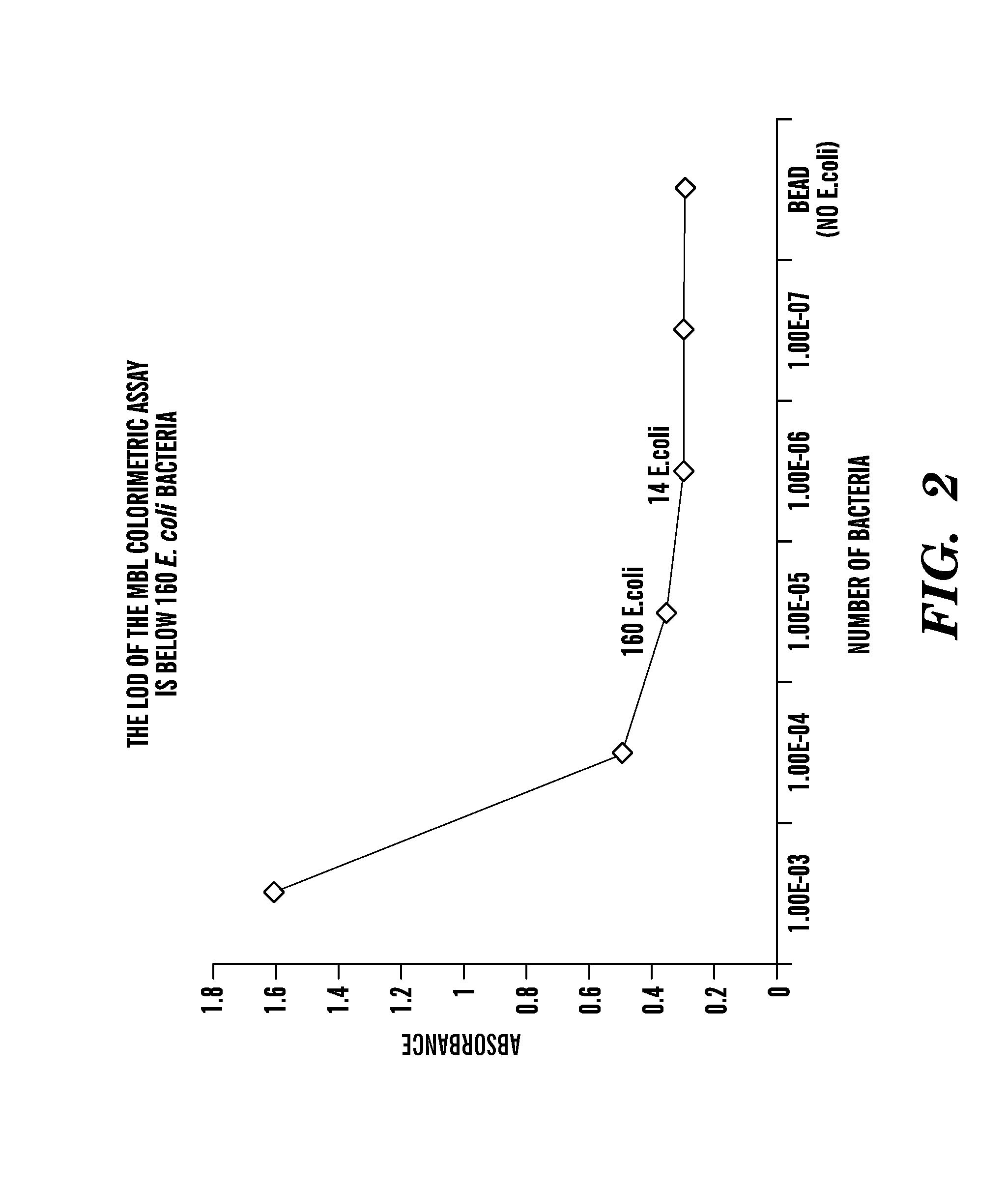
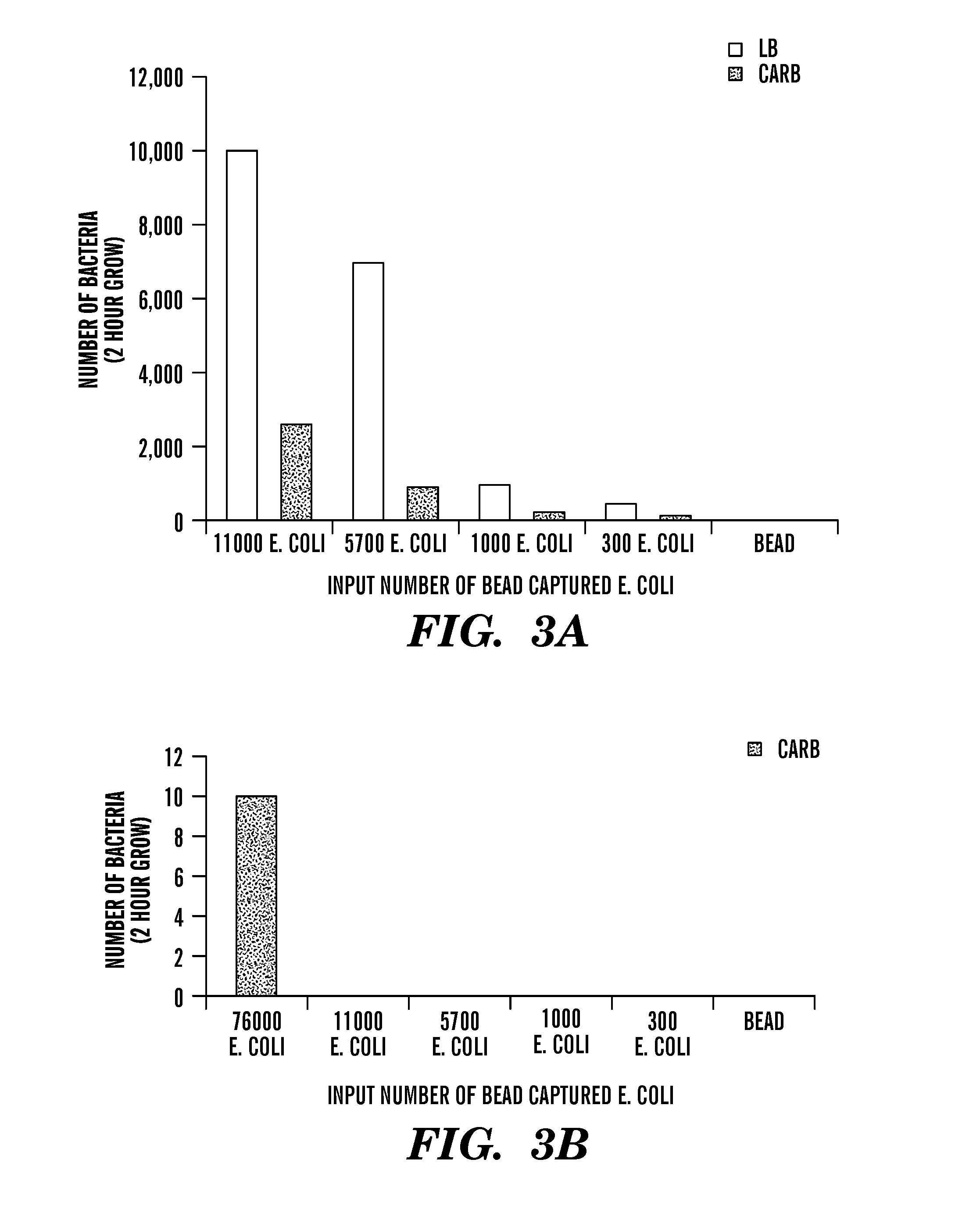
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85 results about "Antibiotic susceptibilities" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
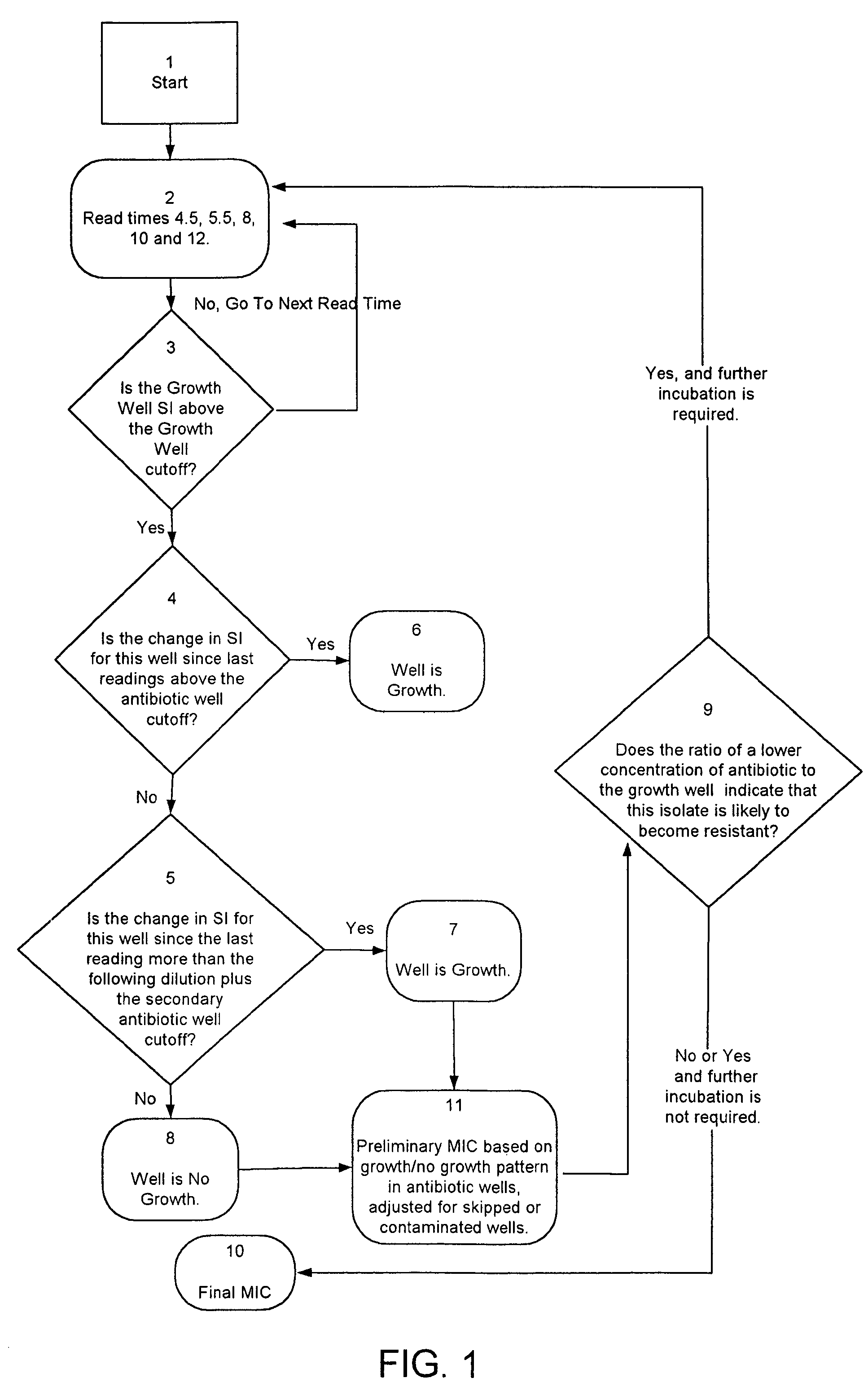
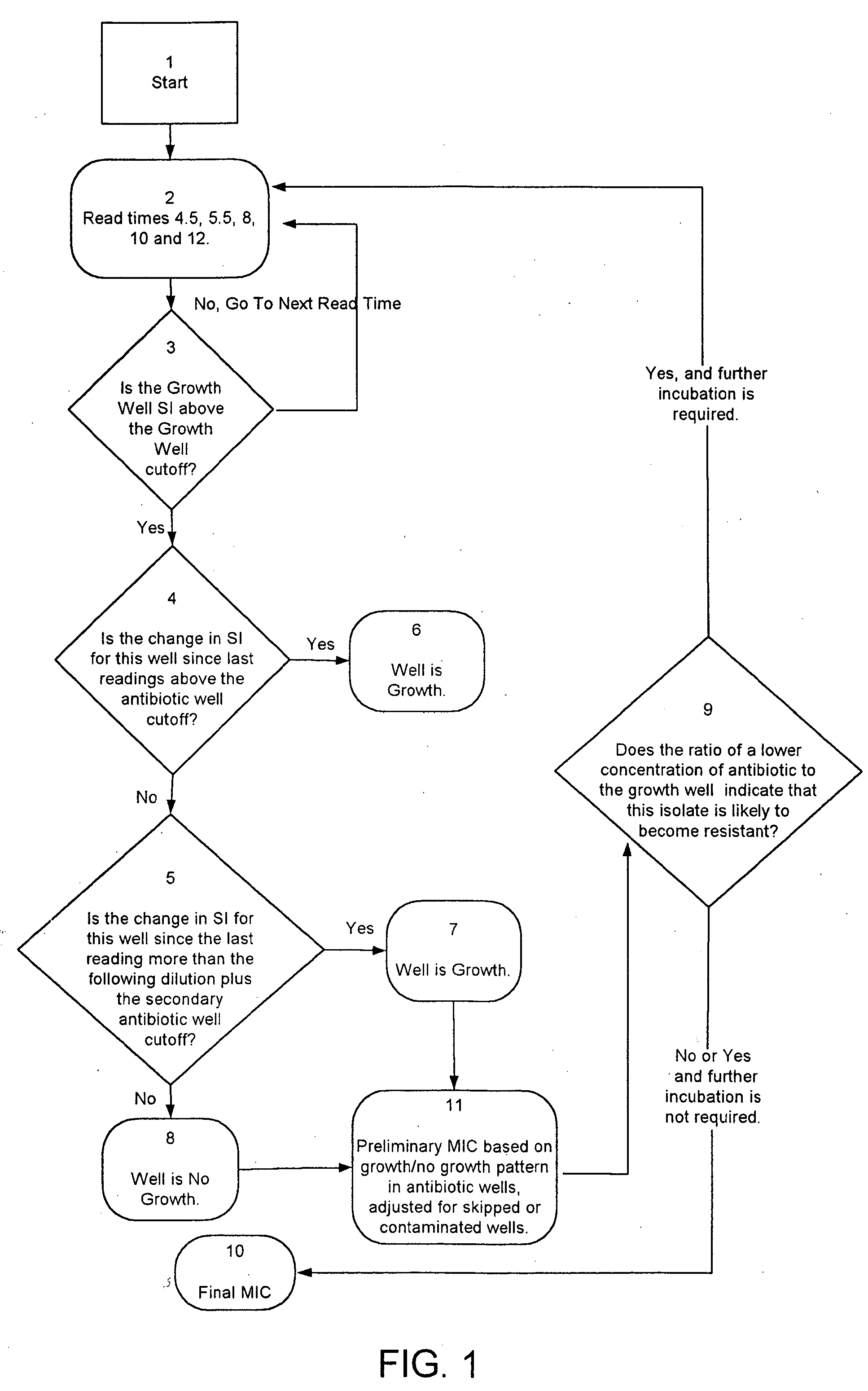
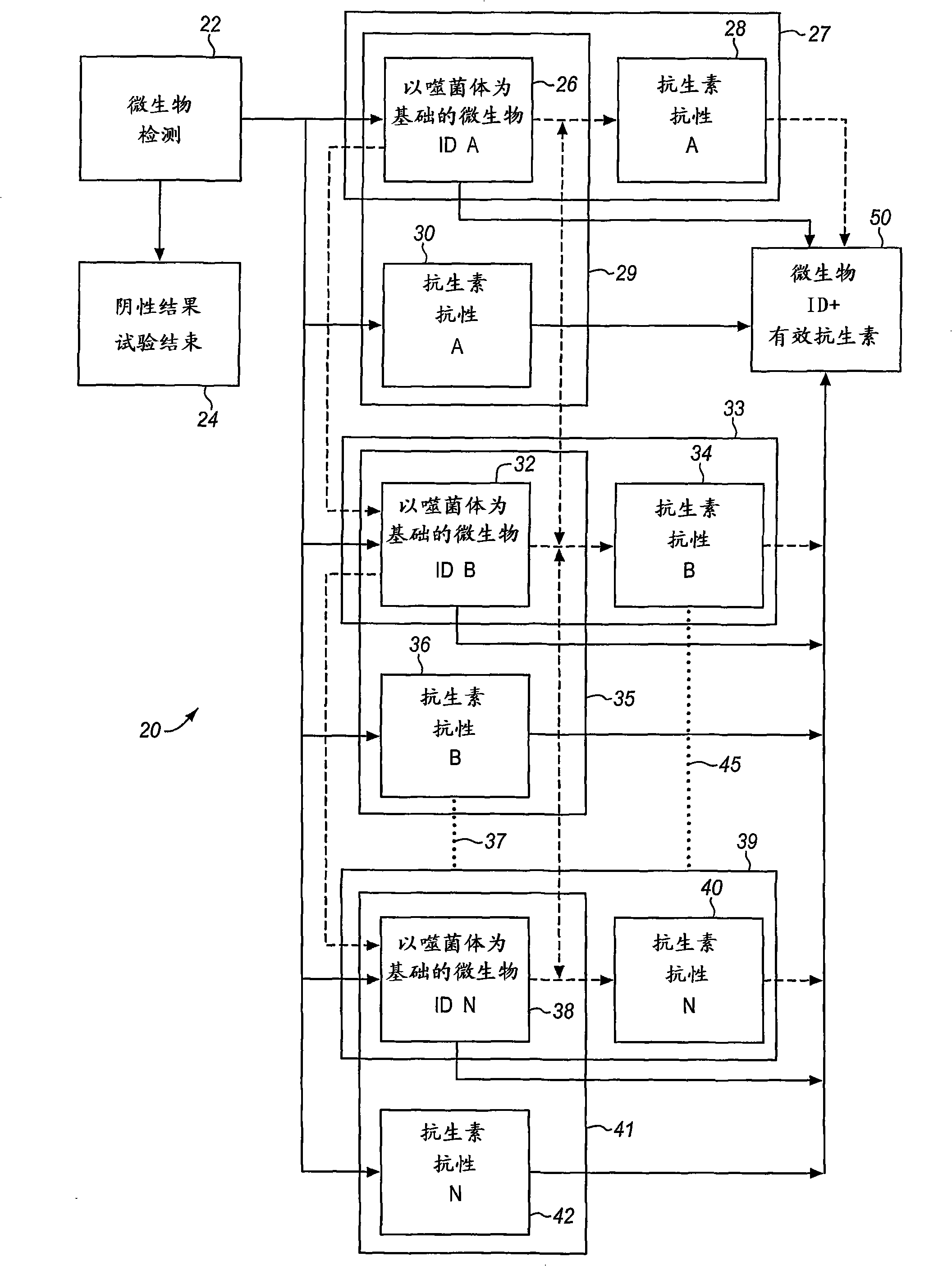
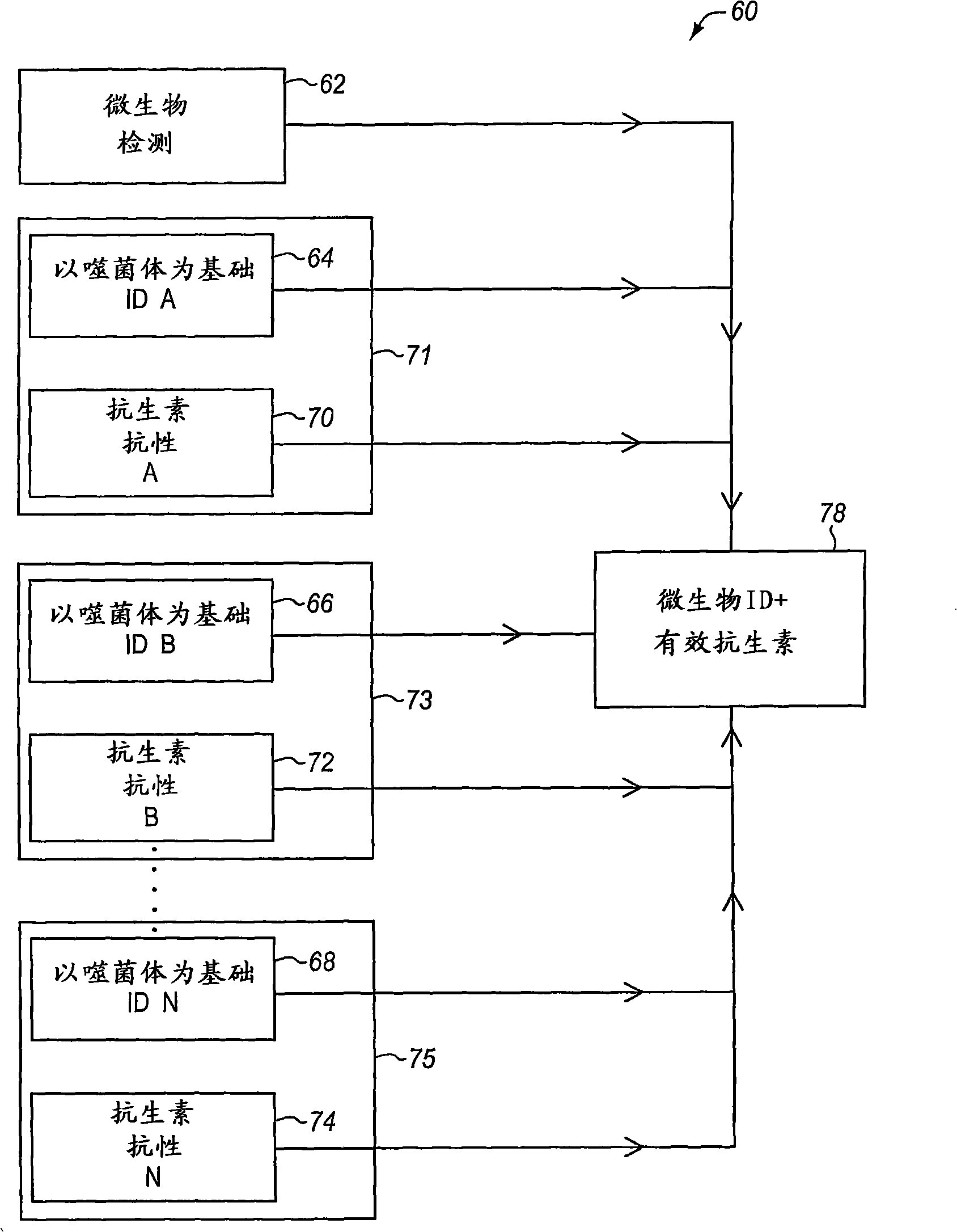
Combined rapid susceptibility assay and microorganism identification system
InactiveUS20050095665A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismHybrid system
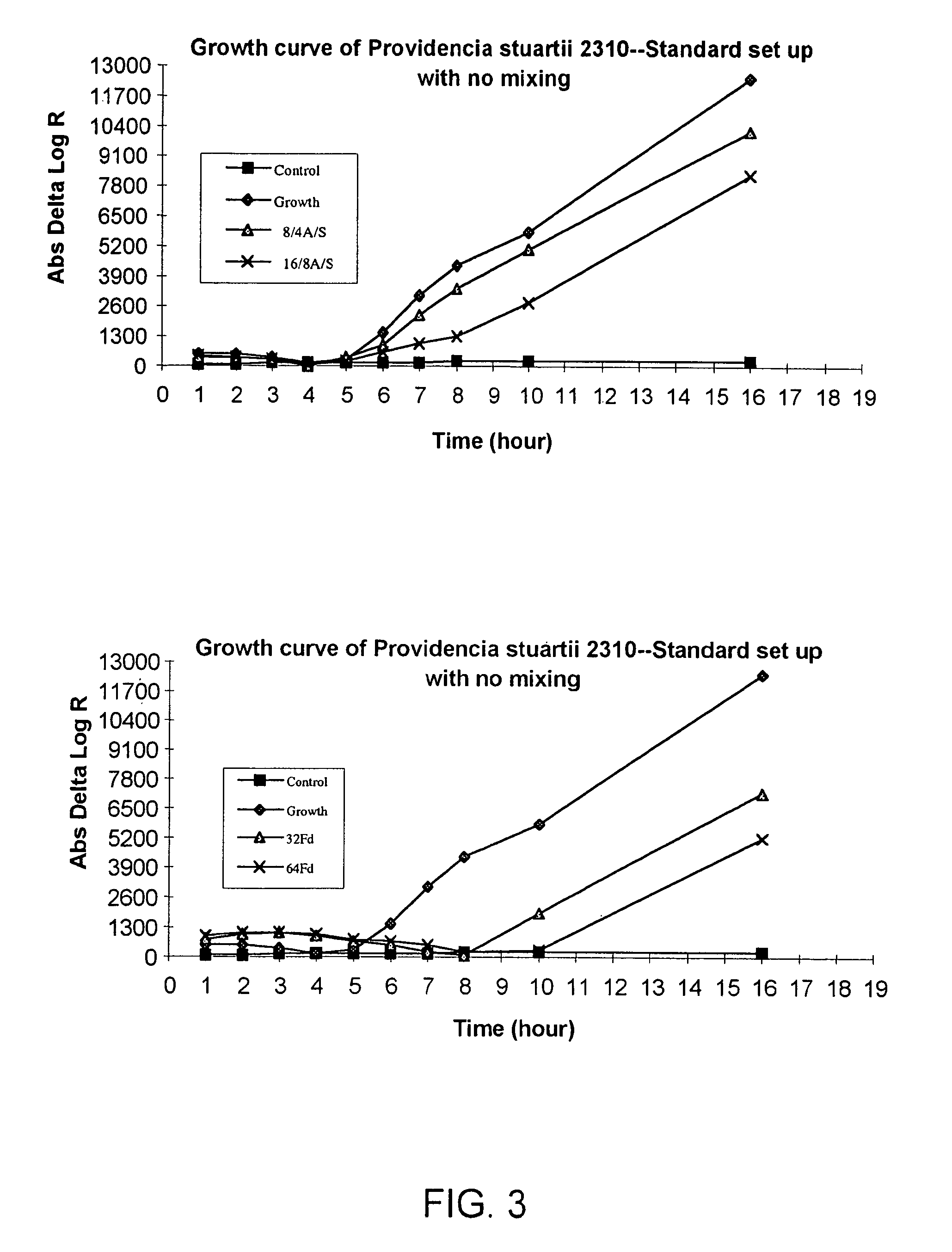
In response to the need for highly-sensitive antibiotic susceptibility assays and identification assays that do not require extensive incubation times, the present invention provides automated assay methods and systems that permit the determination of antibiotic susceptibilities and / or microorganism identification in a timeframe that is substantially shorter than has previously been attainable using a hybrid system that combines turbimetric and fluorescence determinations using a single, clear-plastic assay platform. Related devices, kits, and components thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
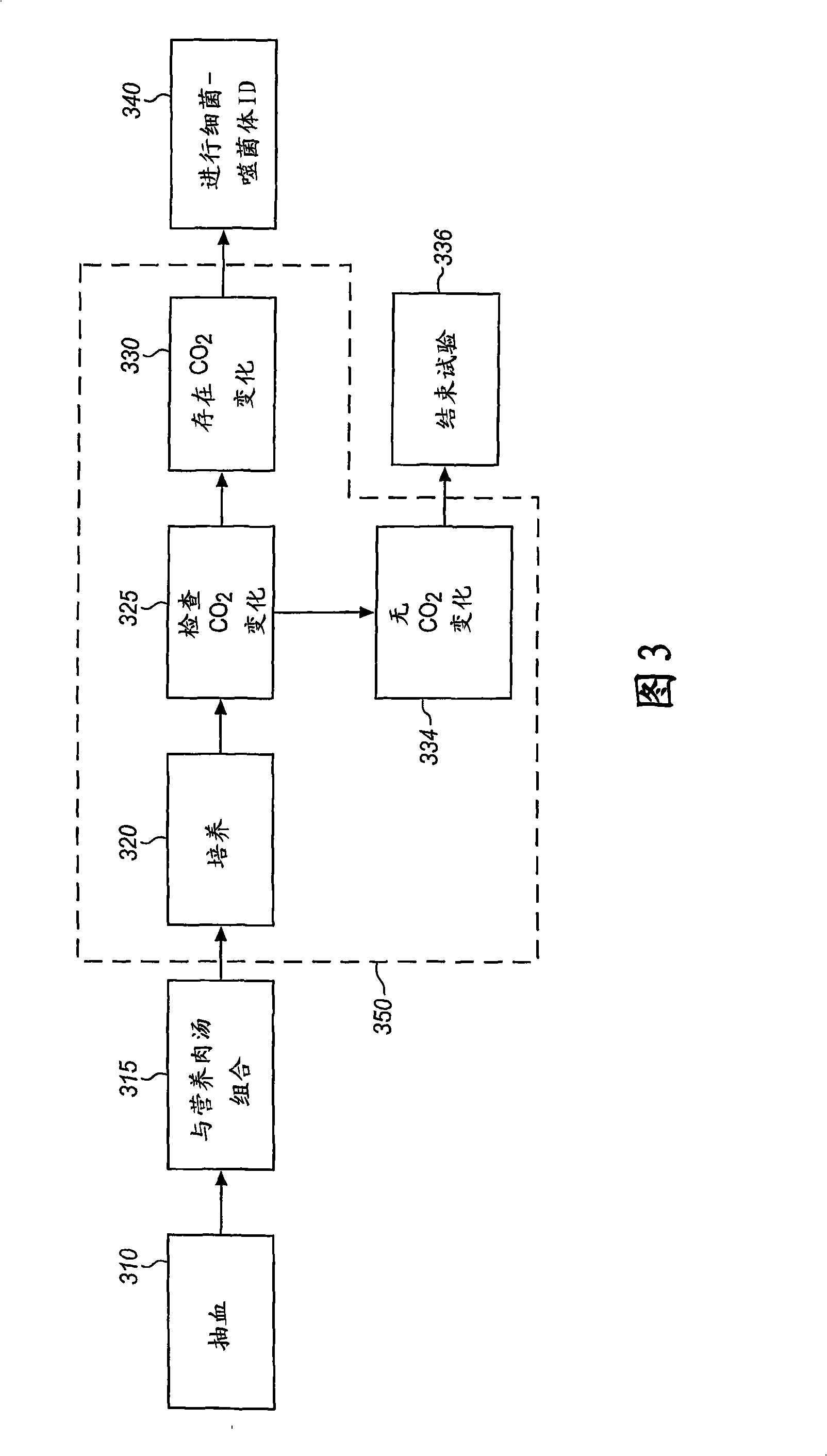
Method and Apparatus for Identification of Microorganisms Using Bacteriophage
InactiveUS20080286757A1Improve reliabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria identificationMicroorganism
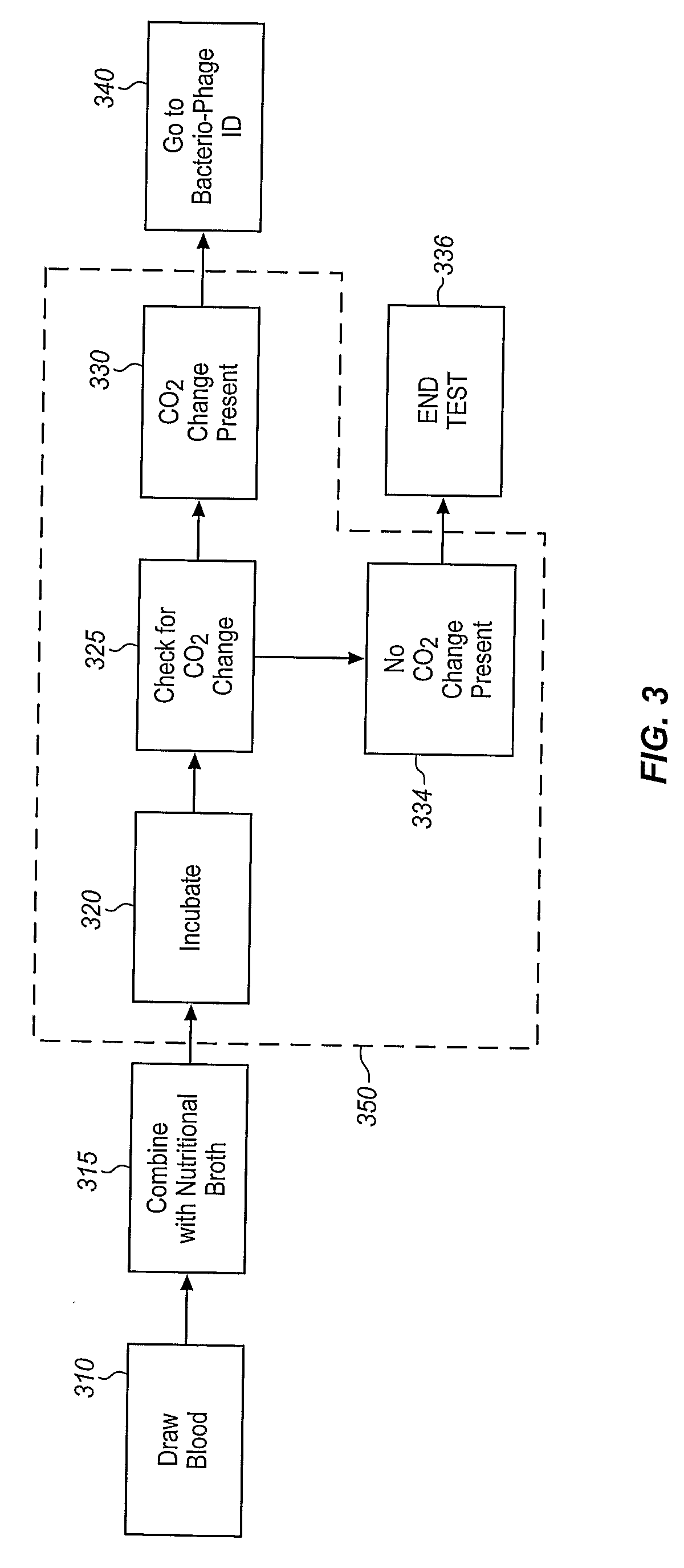
A sample is tested for the presence of bacteria, such as in an automatic blood culturing apparatus. If bacteria are determined to be present, a bacteriophage-based bacteria identification process is performed to identify the bacteria present. A plurality of bacteria detection processes, such as a blood culture test and Gram stain test may be carried out prior to the bacteria identification process. A bacteriophage-based antibiotic resistance test or antibiotic susceptibility test is also conducted on the sample.
Owner:MICROPHAGETM
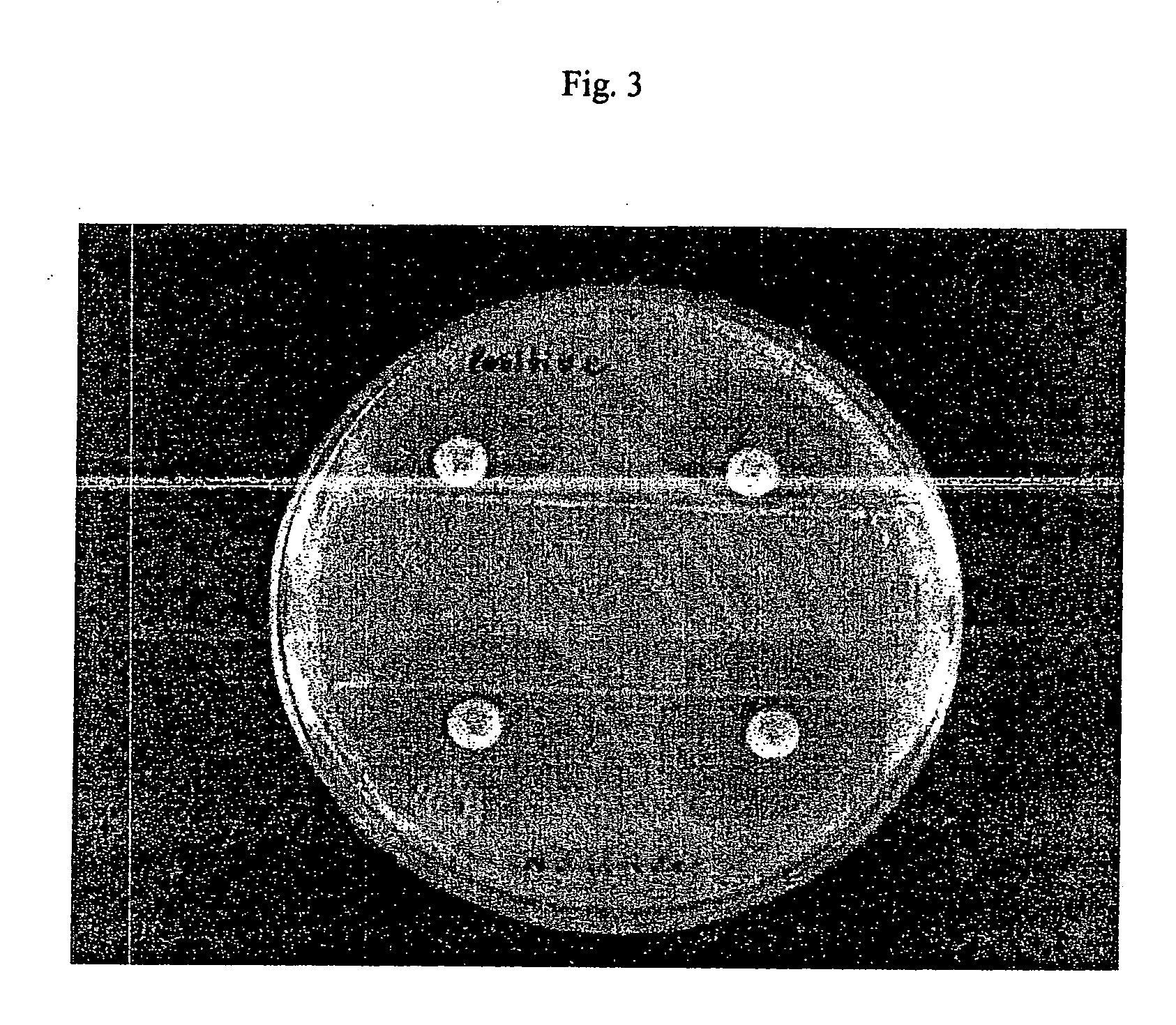
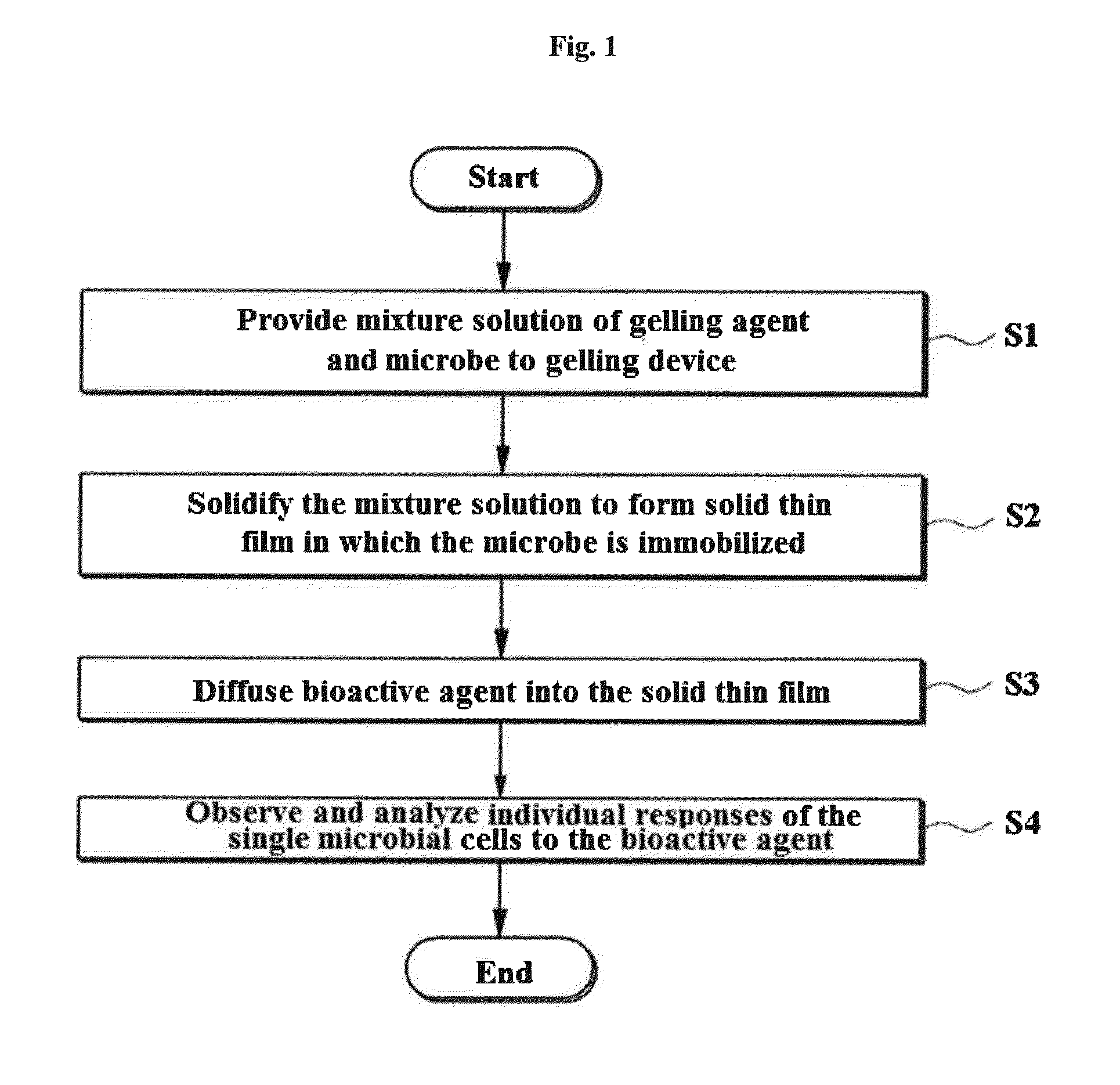
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing system based on bacterial immobilization using gelling agent, antibiotic diffusion and tracking of single bacterial cells
ActiveUS9133498B2Prevent burstBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage analysisDiffusionMinimum inhibitory concentration
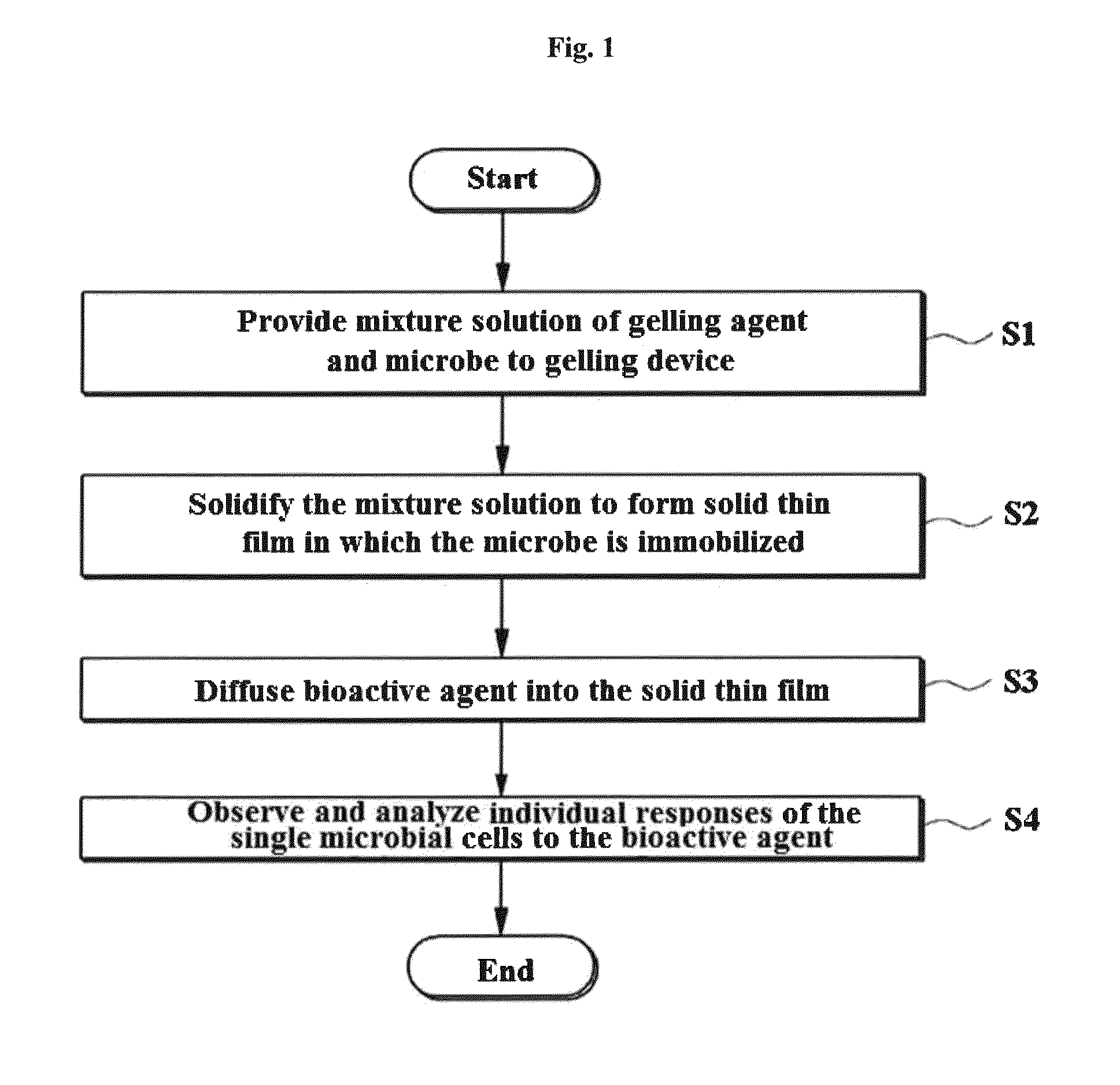
A testing method is disclosed. The testing method includes: providing a mixture solution of a gelling agent and a microbe to a gelling device; solidifying the mixture solution to form a solid thin film in which the microbe is immobilized; supplying a bioactive agent to the solid thin film and allowing the bioactive agent to diffuse into the solid thin film; and imaging the individual responses of the single microbial cells to the bioactive agent, and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the bioactive agent based on the analysis of the images to obtain AST results.
Owner:QUANTA MATRIX
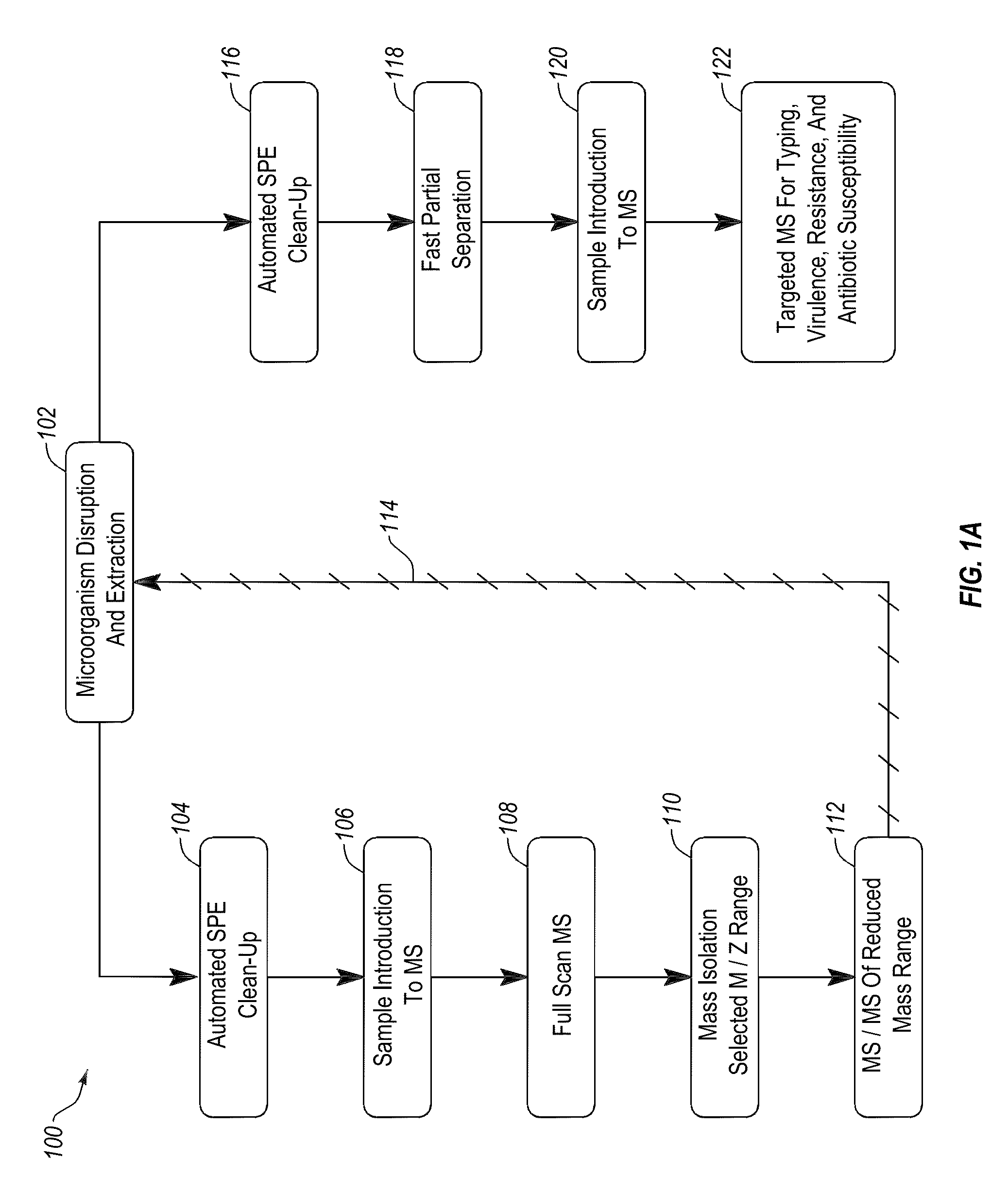
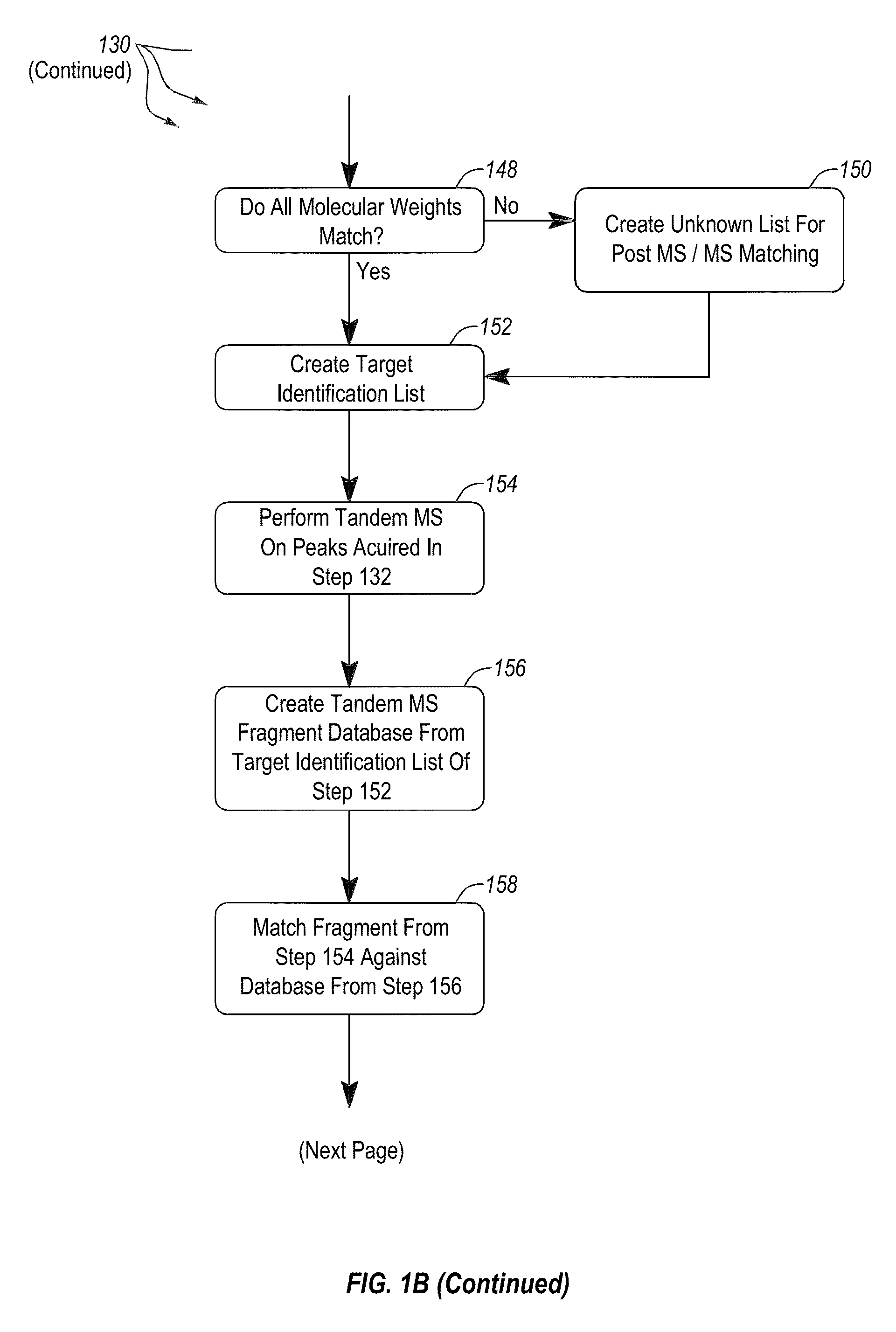
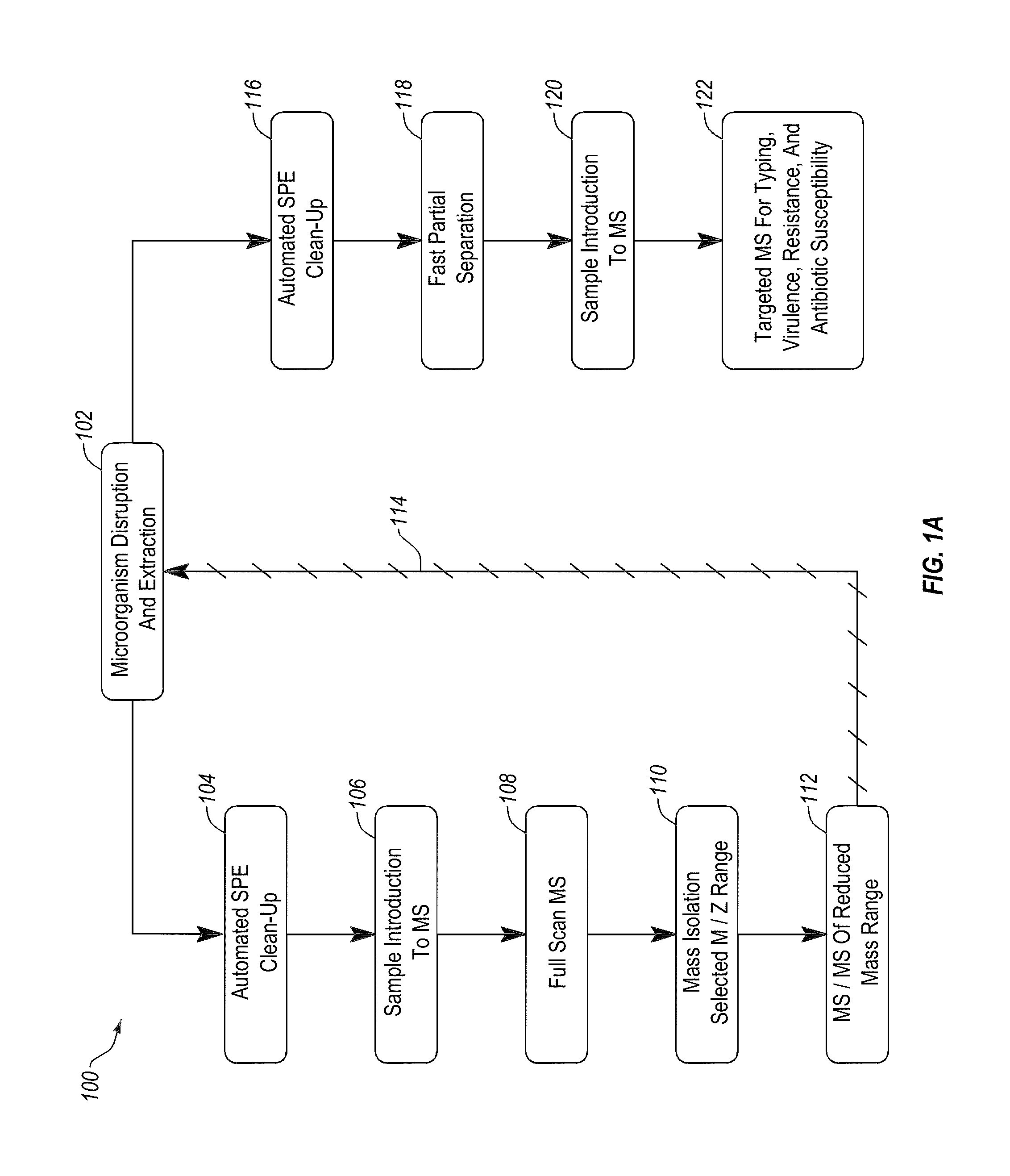
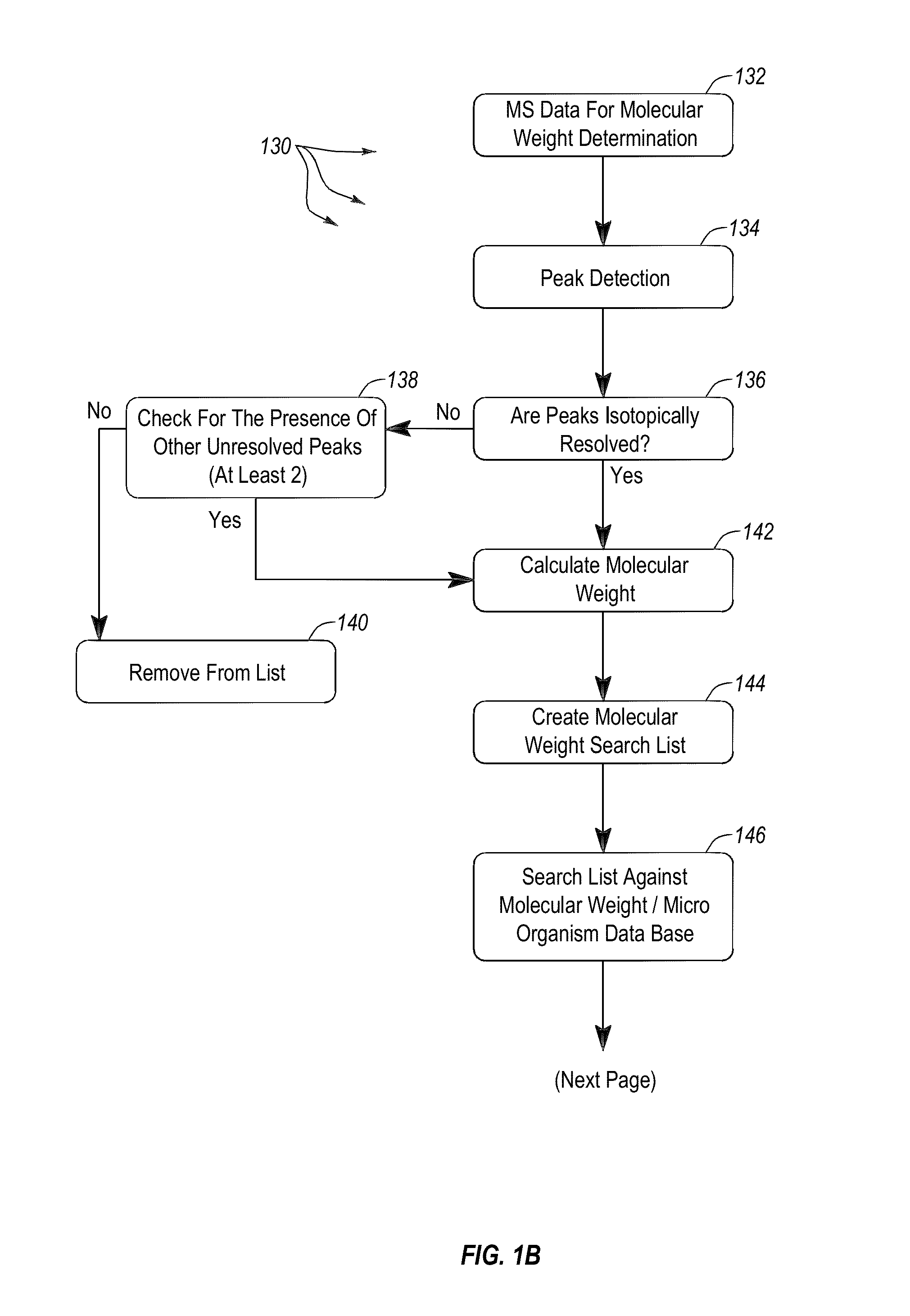
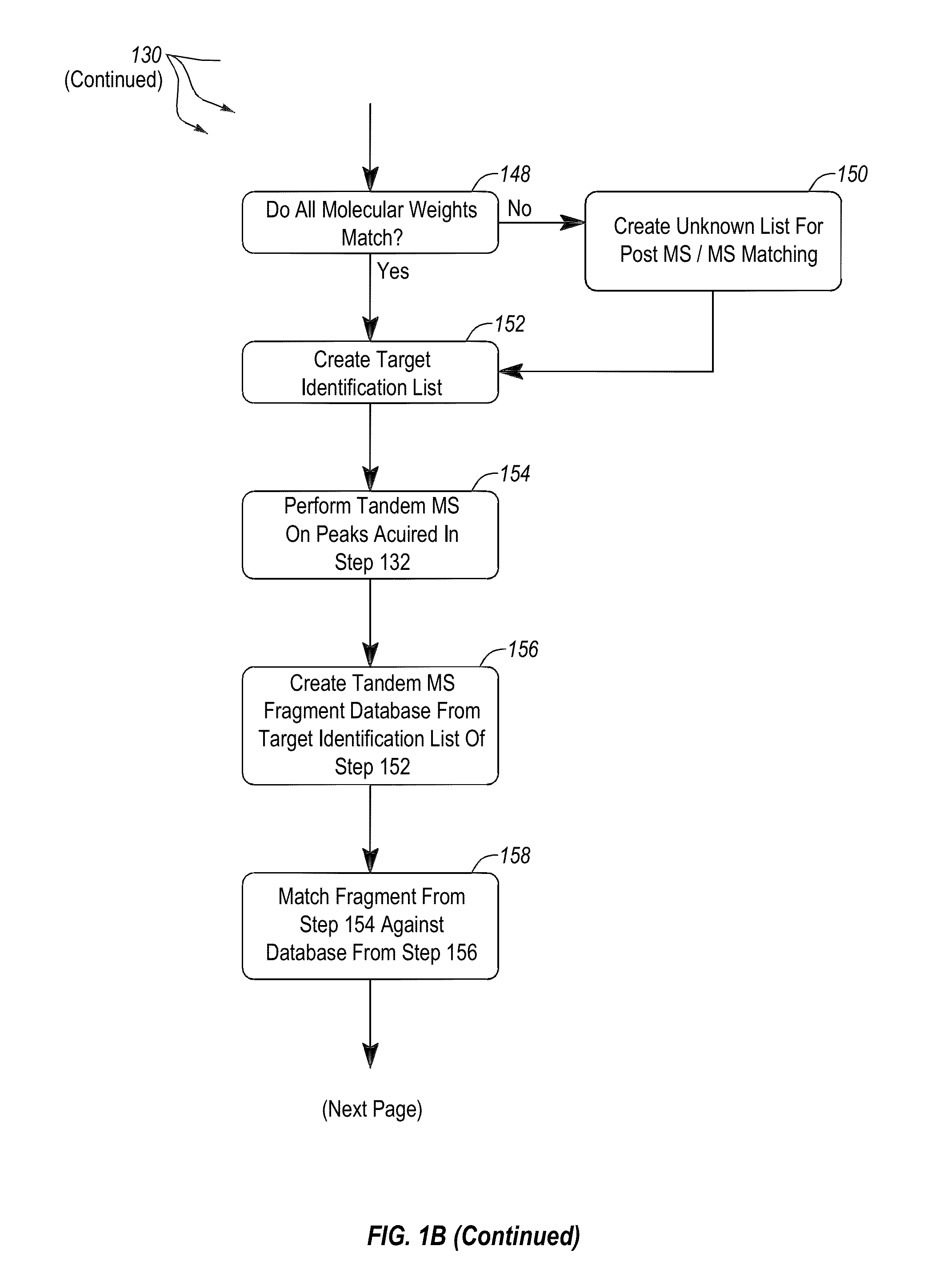
Apparatus and methods for microbial identification by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS9074236B2The process is simple and fastFacilitates epidemiological trackingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMass spectrometry imagingMass spectrometric
Methods and systems for identification of microorganisms either after isolation from a culture or directly from a sample. The methods and systems are configured to identify microorganisms based on the characterization of proteins of the microorganisms via high-resolution / mass accuracy single-stage (MS) or multi-stage (MSn) mass spectrometry. Included herein are also discussion of targeted detection and evaluation of virulence factors, antibiotic resistance markers, antibiotic susceptibility markers, typing, or other characteristics using a method applicable to substantially all microorganisms and high-resolution / mass accuracy single-stage (MS) or multi-stage (MSn) mass spectrometry.
Owner:OXOID
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Apparatus and methods for microbiological analysis
ActiveUS20140051113A1Facilitates epidemiological trackingThe process is simple and fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismSingle stage
Methods and systems for identification of microorganisms either after isolation from a culture or directly from a sample. The methods and systems are configured to identify microorganisms based on the characterization of proteins of the microorganisms via high-resolution / mass accuracy single-stage (MS) or multi-stage (MSn) mass spectrometry. Included herein are also discussion of targeted detection and evaluation of virulence factors, antibiotic resistance markers, antibiotic susceptibility markers, typing, or other characteristics using a method applicable to substantially all microorganisms and high-resolution / mass accuracy single-stage (MS) or multi-stage (MSn) mass spectrometry.
Owner:OXOID
Automated method and system for obtaining and preparing microorganism sample for both identification and antibiotic susceptibility tests
ActiveUS20180284146A1Undesired varianceUndesired mistakeMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMicroorganismDownstream processing
A method and automated apparatus for locating and selecting a colony of microorganisms on a culture dish and subjecting the obtained sample to a plurality of downstream tests including a test to identify the microorganism and a test to identify the susceptibility of the microorganism to antibiotics. The method includes the automated steps of locating and selecting a colony of microorganisms on a culture dish; obtaining a sample of the selected colony of microorganisms; preparing a suspension of a sample of microorganisms automatically by submerging the pick tool with the sample in a suspension, after which the pick tool is vibrated in at least the vertical direction to release the sample from the pick tool in the suspension. The turbidity of the suspension is monitored to ensure that the concentration of microorganism in suspension is sufficient so that the suspension is used a source for sample for both identification and antibiotic susceptibility of the microorganisms in the sample. The apparatus and system optionally provides for downstream processing of samples prepared for antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST). Such apparatus includes further processing after inoculation of an AST panel for the AST test. Such further processing includes capping and transferring inoculated panels to AST instrument.
Owner:BD KIESTRA BV
Capacitive biosensor for identifying a microorganism or determining antibiotic susceptibility
InactiveUS20180045725A1Effective treatmentQuick confirmationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAntibiotic sensitivityMicroorganism
An apparatus for inspecting an antibiotic and a method for determining antibiotic sensitivity using the same is provided. The antibiotic susceptibility inspection time which has conventionally taken longer than 24 hours is shortened to about 2 hours or less, the efficacy of the target substance is monitored in real time, the identification of the microorganism, the kind of the antibiotic capable of treating the microorganism, and the minimum dosage thereof are quickly confirmed. Microbial infections requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment can be effectively treated.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV +1
Methods and compositions for detecting pathogenic bacteria
ActiveUS20150218614A1Determining antibiotic susceptibilitySusceptibility to ciproMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBacteroidesSuperoxide radical
The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for detecting pathogenic bacteria. Additionally, the present invention encompasses methods and compositions for catalyzing the dismutation of superoxide radicals. Further, the present invention encompasses methods for determining the antibiotic susceptibility of pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Antibiotice Susceptibility Profiling Methods
InactiveUS20110269130A1Low costReduce the necessary timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMinimum inhibitory concentrationRapid identification
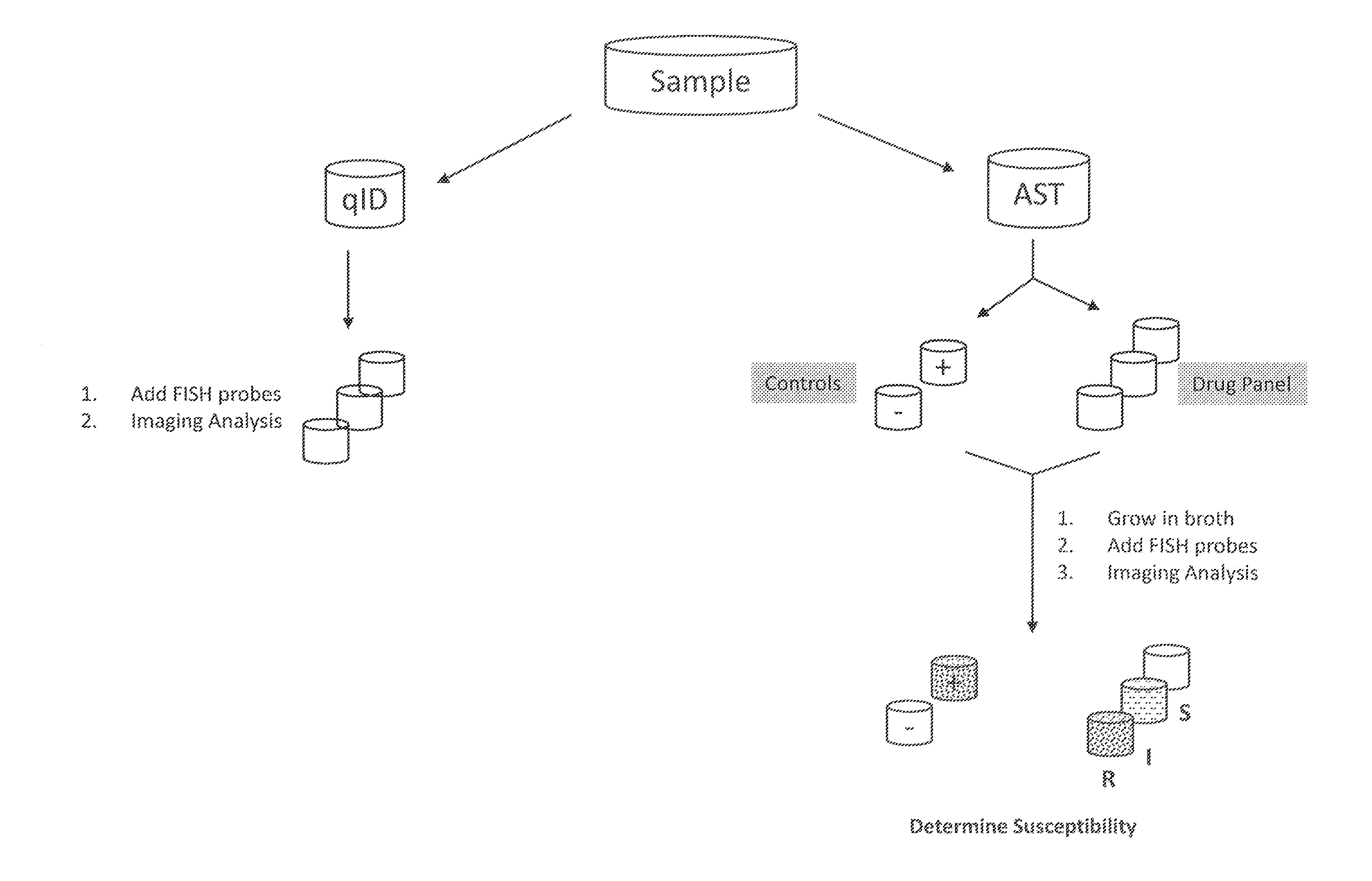
The invention provides methods for the rapid determination of the antibiotic susceptibility of a microorganism, such as, an infectious microorganism in a biological sample, using fluorescence in situ hybridization (“FISH”). Methods of the invention may be applied to the rapid identification, typing, antibiotic susceptibility determination, and / or antibiotic minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination for any infectious microorganism, such as a Gram positive bacteria, a Gram negative bacteria, or a yeast.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Combined rapid susceptibility assay and microorganism identification system
InactiveUS8828680B2Increased susceptibilityRapid and accurate and reproducible resultMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMicroorganismAssay
In response to the need for highly-sensitive antibiotic susceptibility assays and identification assays that do not require extensive incubation times, the present invention provides automated assay methods and systems that permit the determination of antibiotic susceptibilities and / or microorganism identification in a timeframe that is substantially shorter than has previously been attainable using a hybrid system that combines turbimetric and fluorescence determinations using a single, clear-plastic assay platform. Related devices, kits, and components thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Image analysis systems and devices for use therewith
InactiveUS7106889B1Decrease needEasy to adjustBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage analysisUnderline
An image analysis system for automated reading of printed multi-character codes, for example on antibiotic susceptibility testing disks, makes use of an orientation means, for example an underline printed beneath the code, to bring the code or its image into canonical alignment with an optimum reading direction for the code. Automated reading of the codes on randomly-orientated AST disks is therefore possible.
Owner:OXOID
Device and method for detecting antibiotic inactivating enzymes
The present invention provides a method of determining the antibiotic susceptibility of a microorganism comprising the following steps. First, a culture of the microorganism whose susceptibility is to be determined is admixed with an antibiotic to which susceptibility is to be assayed, and a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth-inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing effective amount to form an assay culture. Next, the assay culture is incubated under appropriate culture conditions and for a time sufficient to determine the susceptibility of the microorganism to the antibiotic. In another aspect, the present invention provides an improved method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of a microorganism in a culture by admixing the culture with an antibiotic to which susceptibility is to be assayed, and incubating the culture for a time sufficient to determine the susceptibility of the microorganism to the antibiotic, the improvement comprising admixing the culture with a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing effective amount.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing system based on bacterial immobilization using gelling agent, antibiotic diffusion and tracking of single bacterial cells
ActiveUS20130196364A1Prevent burstBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMinimum inhibitory concentrationDrug biological activity
A testing method is disclosed. The testing method includes: providing a mixture solution of a gelling agent and a microbe to a gelling device; solidifying the mixture solution to form a solid thin film in which the microbe is immobilized; supplying a bioactive agent to the solid thin film and allowing the bioactive agent to diffuse into the solid thin film; and imaging the individual responses of the single microbial cells to the bioactive agent, and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the bioactive agent based on the analysis of the images to obtain AST results.
Owner:QUANTA MATRIX
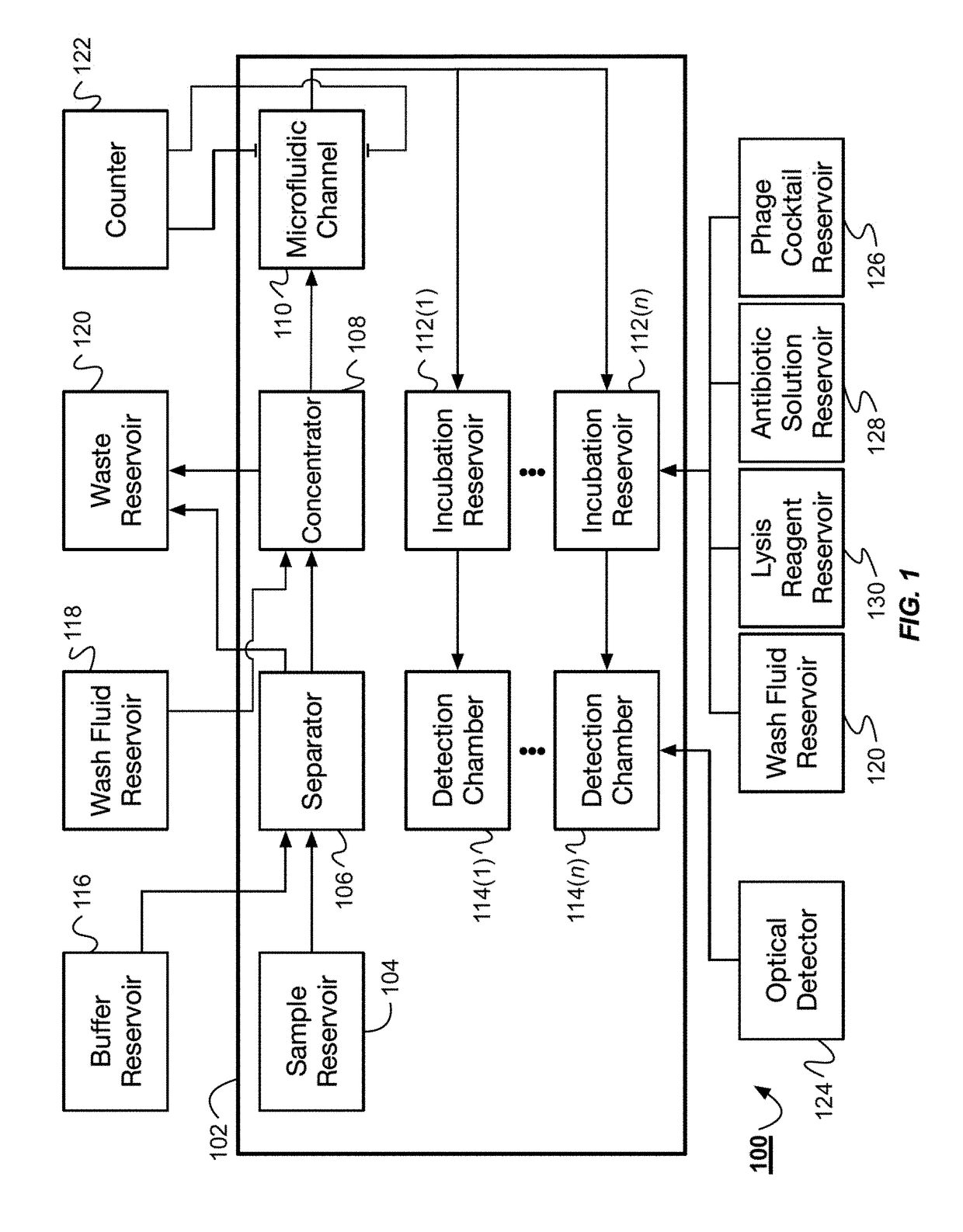
Bacteria identification and antibiotic susceptibility profiling device
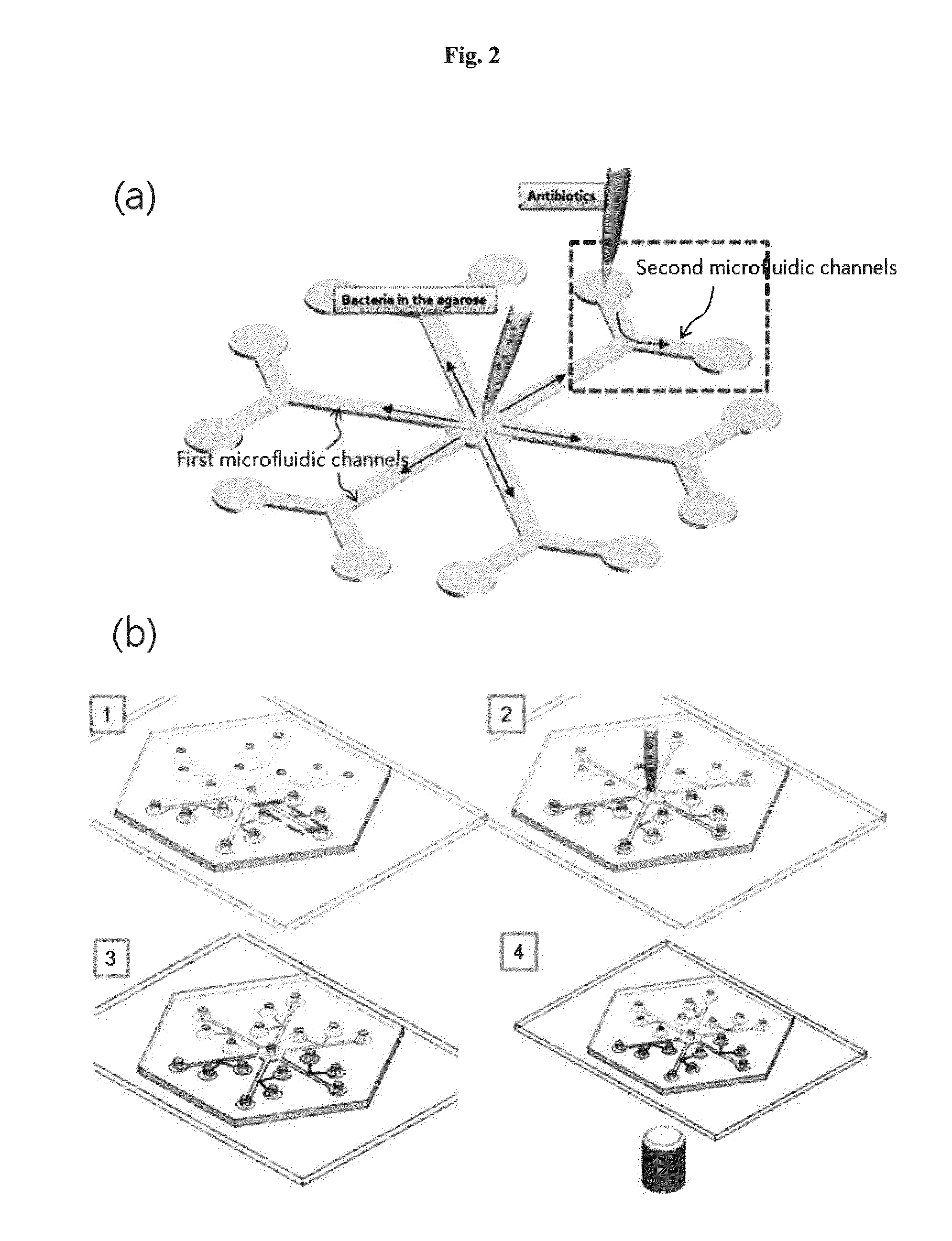
The system described herein for bacterial identification can be used as a point-of-care or lab-based diagnostic system. In some implementations, the system can be used to detect other foreign agents within blood or other samples. The system can include disposable microfluidic cartridges that are removable from the system. The microfluidic cartridges can receive a sample, such as a blood sample, that is suspected of containing bacterial cells and separate the bacterial cells from the blood sample. Once the bacterial cells are separated from the blood, the system can introduce the recombinant detector bacteriophages into the system that can infect the bacterial cells. The system can then detect the expression of reporter genes from the recombinant detector bacteriophages.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Combined rapid susceptibility assay and microorganism identification system
InactiveUS20120149599A1Increased susceptibilityRapid and accurate and reproducible resultMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMagnetic susceptibilityTime range
In response to the need for highly-sensitive antibiotic susceptibility assays and identification assays that do not require extensive incubation times, the present invention provides automated assay methods and systems that permit the determination of antibiotic susceptibilities and / or microorganism identification in a timeframe that is substantially shorter than has previously been attainable using a hybrid system that combines turbimetric and fluorescence determinations using a single, clear-plastic assay platform. Related devices, kits, and components thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Antibiotic resistance profile for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and use of same in diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhea
The present invention relates to an antibiotic resistance profile for Neisseria gonorrhoeae by assessing the presence of mutations (e.g., SNP) in antibiotic resistant genes that confer bacterial resistance against antibiotics such as penicillin, tetracycline, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporin, macrolides and spectinomycin. There is provided a method and a kit for generating an antibiotic resistance profile for Neisseria gonorrhoeae by utilizing a multiplex PCR to amplify segments of antibiotic-resistant genes, allele-specific primer extension to detect gene mutation, and detection of such gene mutations with gel electrophoresis, capillary electrophoresis, or DNA microarray. The present method provides useful information to physicians relating the antibiotic susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae against different classes of antibiotics. Relying on this personalized diagnostic tool, physicians can better inform about antibiotic susceptibility and thereby open up medical intervention avenues for treating Neisseria gonorrhoeae with antibiotics. There is provided a therapeutic application of the antibiotic resistance profile that has advantages of: (i) providing a more effective regime for gonorrhea treatment; and (ii) halting the evolutionary pressures towards antibiotic resistance in the Neisseria gonorrhoeae therapy.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Device and method for detecting antibiotic inactivating enzymes
InactiveUS20040115756A1Facilitated releaseRobust in vitro informationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismSufficient time
The present invention provides a method of determining the antibiotic susceptibility of a microorganism comprising the following steps. First, a culture of the microorganism whose susceptibility is to be determined is admixed with an antibiotic to which susceptibility is to be assayed, and a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth-inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing effective amount to form an assay culture. Next, the assay culture is incubated under appropriate culture conditions and for a time sufficient to determine the susceptibility of the microorganism to the antibiotic. In another aspect, the present invention provides an improved method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of a microorganism in a culture by admixing the culture with an antibiotic to which susceptibility is to be assayed, and incubating the culture for a time sufficient to determine the susceptibility of the microorganism to the antibiotic, the improvement comprising admixing the culture with a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing effective amount.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
Fish-ribosyn for antibiotic susceptibility testing
InactiveUS20110151455A1Rapid and inexpensive screening procedureMeasures the rate of ribosome synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismAntibiotic Y
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for evaluating the susceptibility of bacterial cells to an antibiotic or other antimicrobial compound or agent. In one embodiment, a sample comprising a microbial population is exposed to an antibiotic of interest. The sample is then processed using FISH-RiboSyn methods to determine the specific growth rate of the antibiotic-exposed microbes as compared to an untreated control. The subject invention also concerns materials and methods for determining the most suitable and / or effective antibacterial treatment for a person or animal having a bacterial infection.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Antibiotic susceptibility testing via plasmonic imaging and tracking
A rapid antibiotic susceptibility test (AST) based on the detection and quantification of the movement of single bacterial cells with a plasmonic imaging and tracking (PIT) technology. The PIT-based AST detects changes in the metabolic activity of the bacterial cells long before cell replication, and allows rapid AST for both cultivable and non-cultivable strains. PIT tracks 3D movement with sub-nanometer resolution and millisecond temporal resolution. PIT also allows simultaneous measurement of the binding kinetic constants of antibiotics and bacterial metabolic state after the introduction of antibiotics.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Device and method for detecting antibiotic inactivating enzymes
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
Device and method for detecting antibiotic inactivating enzymes
InactiveUS20070190592A1Susceptibility and resistanceGood choiceMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymeAntibiotic susceptibilities
The present invention provides a method of detecting production of antibiotic-inactivating factor and for determining the antibiotic susceptibility of a microorganism comprising the following steps. a culture of the microorganism suspected of producing inactivating factors and / or whose susceptibility is to be determined is admixed with an antibiotic to which susceptibility is to be assayed, and a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth-inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing effective amount to form an assay culture. The assay culture is incubated under appropriate culture conditions and for a time sufficient to determine production of antibiotic-inactivating factors and / or the susceptibility of the microorganism to the antibiotic. In another aspect, the present invention provides an improved method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of a microorganism in a culture by admixing the culture with an antibiotic to which susceptibility is to be assayed, and incubating the culture for a time sufficient to determine the susceptibility of the microorganism to the antibiotic, the improvement comprising admixing the culture with a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing effective amount.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
Automated method and system for obtaining and preparing microorganism sample for both identification and antibiotic susceptibility tests
ActiveUS10921336B2Cost lossLoss of timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:BD KIESTRA BV
Antibiotic susceptibility testing via plasmonic imaging and tracking
A rapid antibiotic susceptibility test (AST) based on the detection and quantification of the movement of single bacterial cells with a plasmonic imaging and tracking (PIT) technology. The PIT-based AST detects changes in the metabolic activity of the bacterial cells long before cell replication, and allows rapid AST for both cultivable and non-cultivable strains. PIT tracks 3D movement with sub-nanometer resolution and millisecond temporal resolution. PIT also allows simultaneous measurement of the binding kinetic constants of antibiotics and bacterial metabolic state after the introduction of antibiotics.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for identification of microorganisms using bacteriophage
InactiveCN101292043AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria identificationMicroorganism
Owner:MICROPHAGE
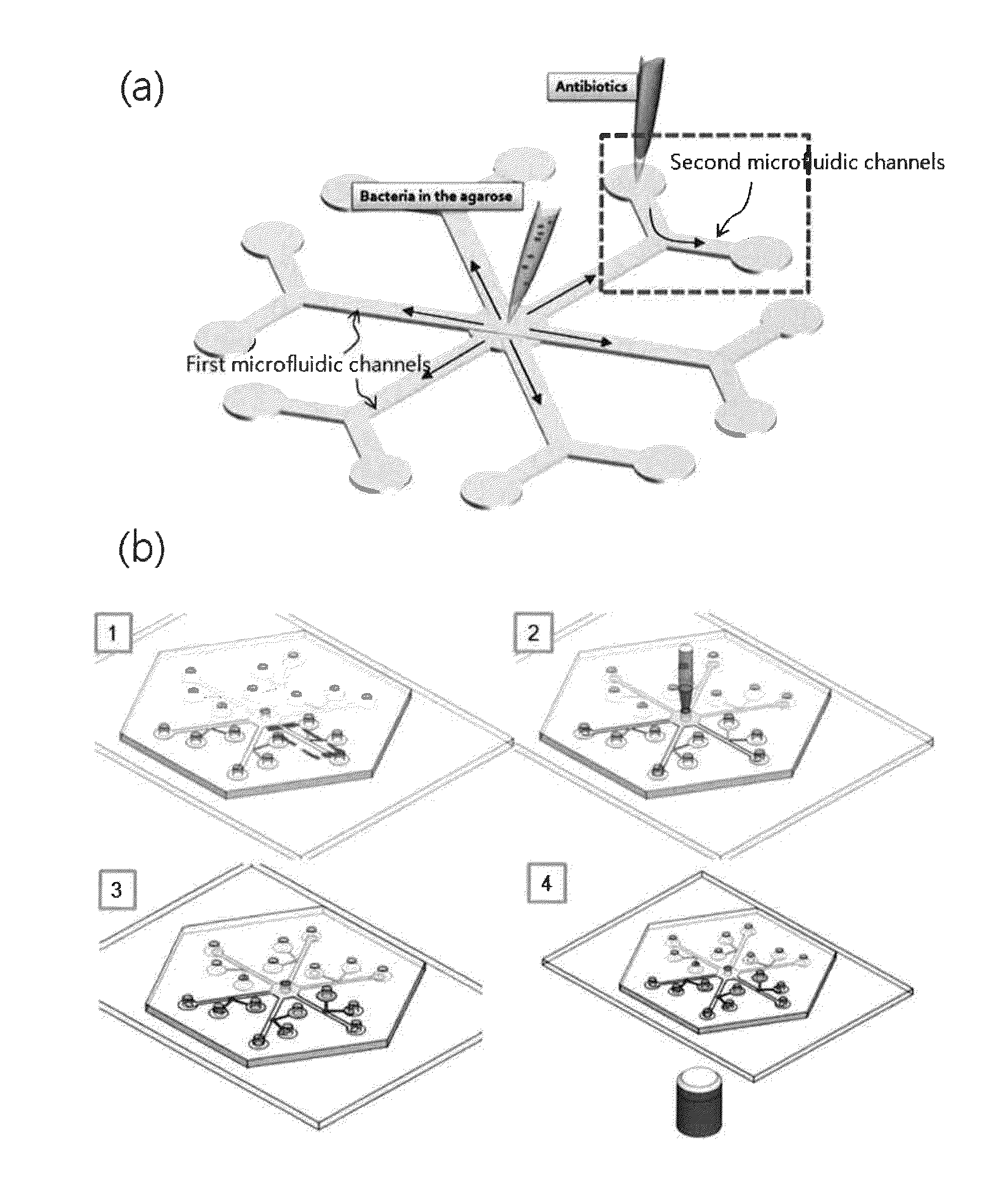
Automatic microfluidic system for antibiotic susceptibility testing and method of operating thereof
ActiveUS20180142279A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresAntibiotic susceptibilitiesStorage cell
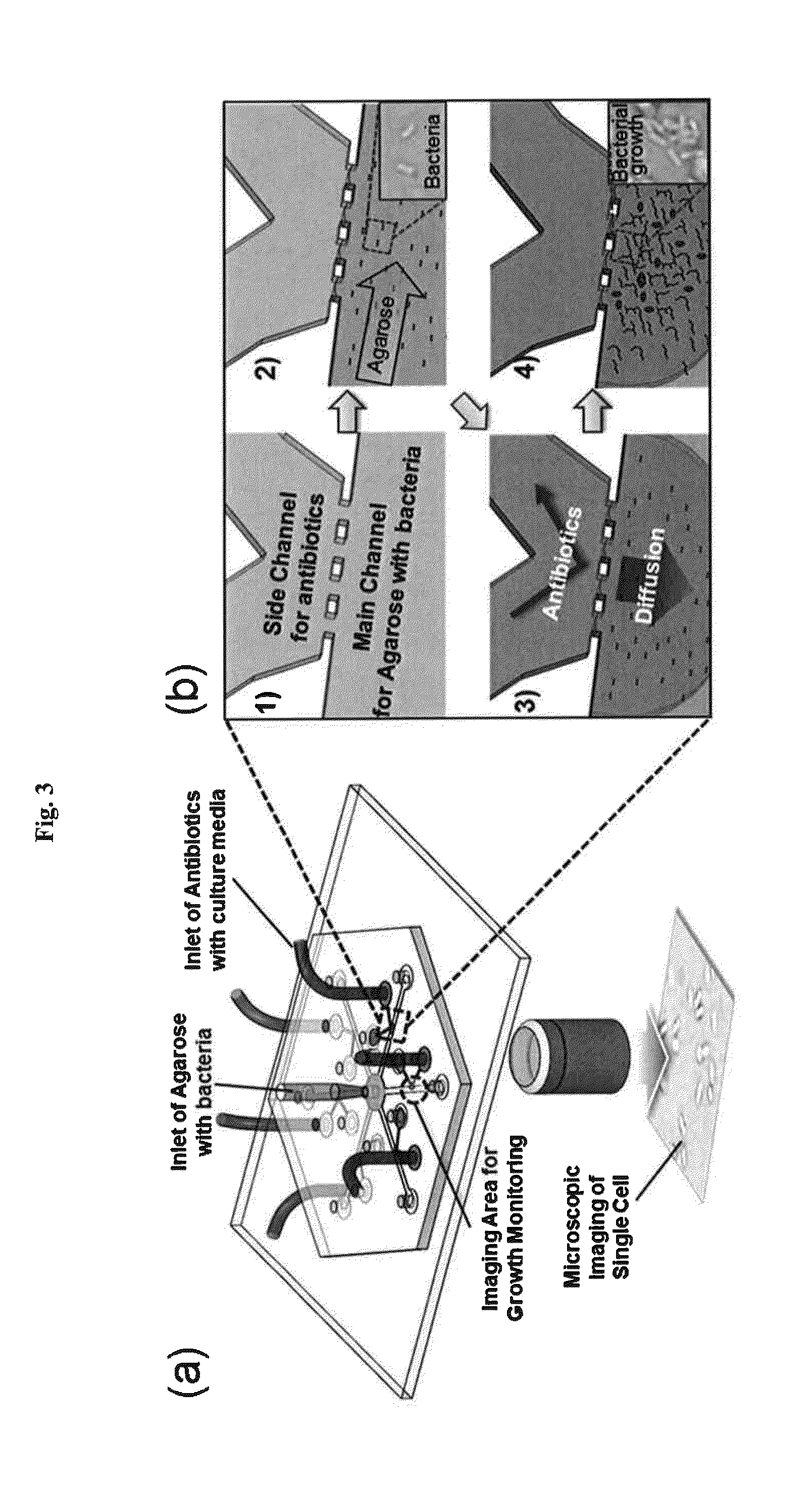
An automatic microfluidic system for antibiotic susceptibility testing of the present disclosure at least includes a microfluidic chip. The microfluidic chip includes a fluid storage unit, a reaction unit, a pneumatic micro-pumping unit and a plurality of valve units. The fluid storage unit is provided for storing a bacterial suspension, a broth and an antibiotic solution. The reaction unit includes a first reaction chamber and at least two second reaction chambers. The pneumatic micro-pumping unit is adjacently disposed to the fluid storage unit and the reaction unit for selectively, repeatedly and quantitatively transporting the broth, the bacterial suspension and the antibiotic solution to the reaction unit to form a first mixing solution and at least two second mixing solutions. The valve units include a plurality of pneumatic micro-valves and a plurality of valve control air holes for controlling the opening and closing of the pneumatic micro-valves.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Construction method of antibacterial cefquinome PK/PD model for livestock and application
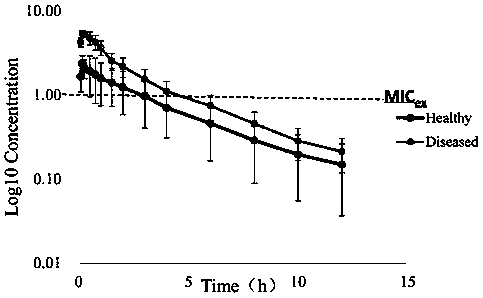
PendingCN110607344ADelay drug resistanceMolecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibacterial actionDrug administration
The invention discloses a construction method of an antibacterial cefquinome PK / PD model for livestock and an application. The specific contents of the construction method comprise detecting the drugsusceptibility of antibacterial cefquinome to haemophilus parasuis so as to obtain an MIC distribution range; determining the concentrations of free drugs in plasma samples of healthy model animals and disease model animals at different time points after drug administration to obtain drug-time curves by a liquid chromatography detection method; performing fitting on pharmacokinetics parameters ofdrugs by pharmacokinetics software to obtain PK parameters; researching the antibiotic action of the antibacterial on pathogenic bacteria under the condition of in vitro and half in vivo, and performing fitting on the time limitation relationship of the antibacterial to the pathogenic bacteria under the condition of in vitro and half in vivo to obtain PD parameters; establishing a half in vivo PK-PD model according to a Sigmoid Emax equation; and obtaining drug administration schemes under different drug administration objectives through a dosage calculating formula and Mlxplore software. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, an optimization method is provided for a drug resistance resistant medication scheme of the cefquinome clinically, and production and propagation of bacterial drug resistance are relieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for using (CNTs/PANI)n-ITO anode-based MFC (Microbial Fuel Cell) biosensors in antibiotic susceptibility tests
ActiveCN107271524AHigh detection sensitivityAvoid timeFinal product manufactureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCarbon nanotubeEngineering
The invention discloses a method for using (CNTs / PANI)n-ITO anode-based MFC (Microbial Fuel Cell) biosensors in antibiotic susceptibility tests. A layer-by-layer self-assembly method is adopted to prepare a carbon nanotube / polyaniline compound-modified IT anode, which is used for constructing single-chamber and double-chamber microbial fuel cell biosensors, and the single-chamber and double-chamber microbial fuel cell biosensors are applied in antibiotic susceptibility tests on drugs such as gentamicin. The invention proposes a new method for conventional antibiotic susceptibility test methods, the problems of long assay time, complex operation, poor repetitiveness and the like existing in the microbial plate method are solved, the constructed microbial fuel cell biosensors are easy to operate, and moreover, a quick, real-time and high-sensitivity antibiotic susceptibility test can be carried out.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com