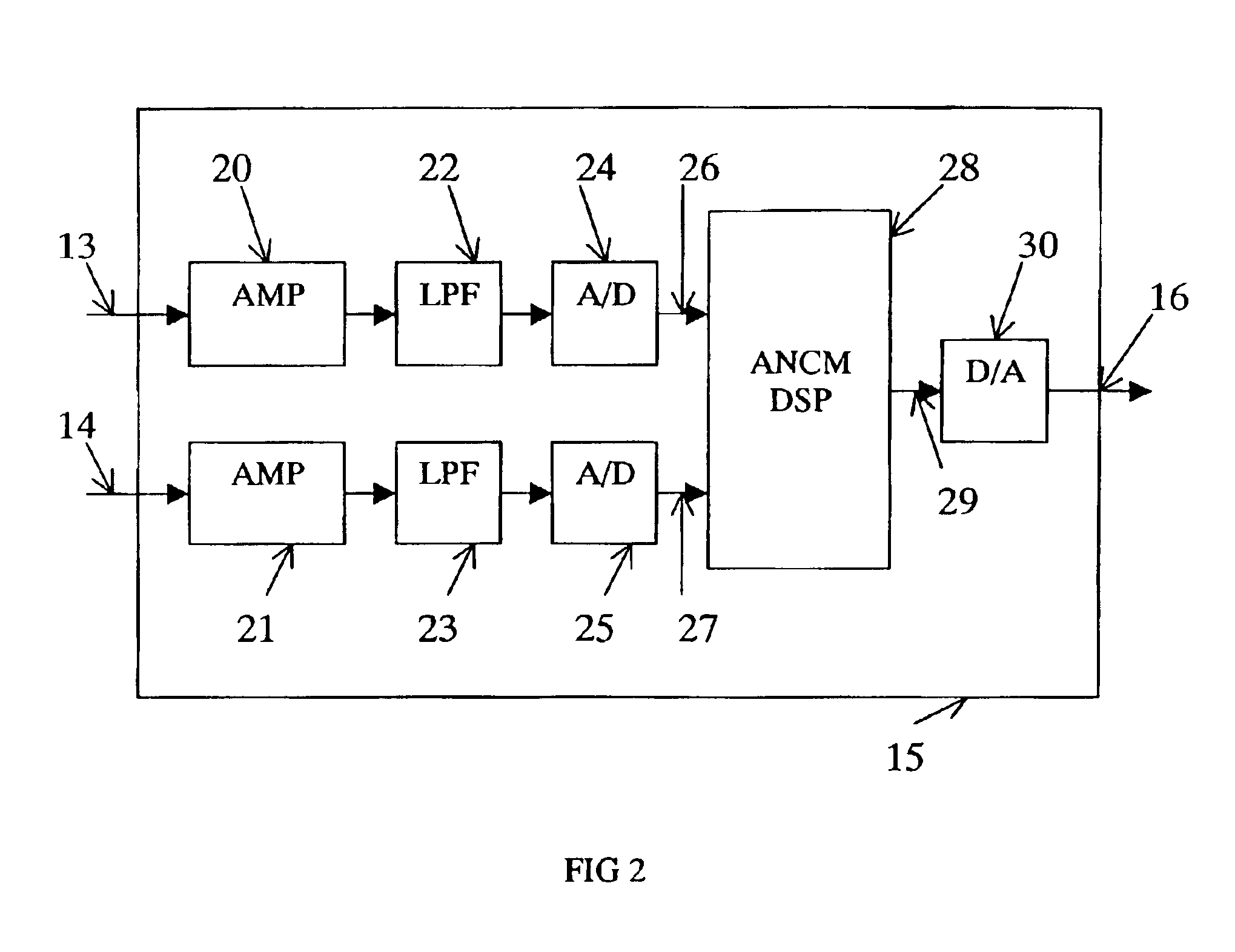
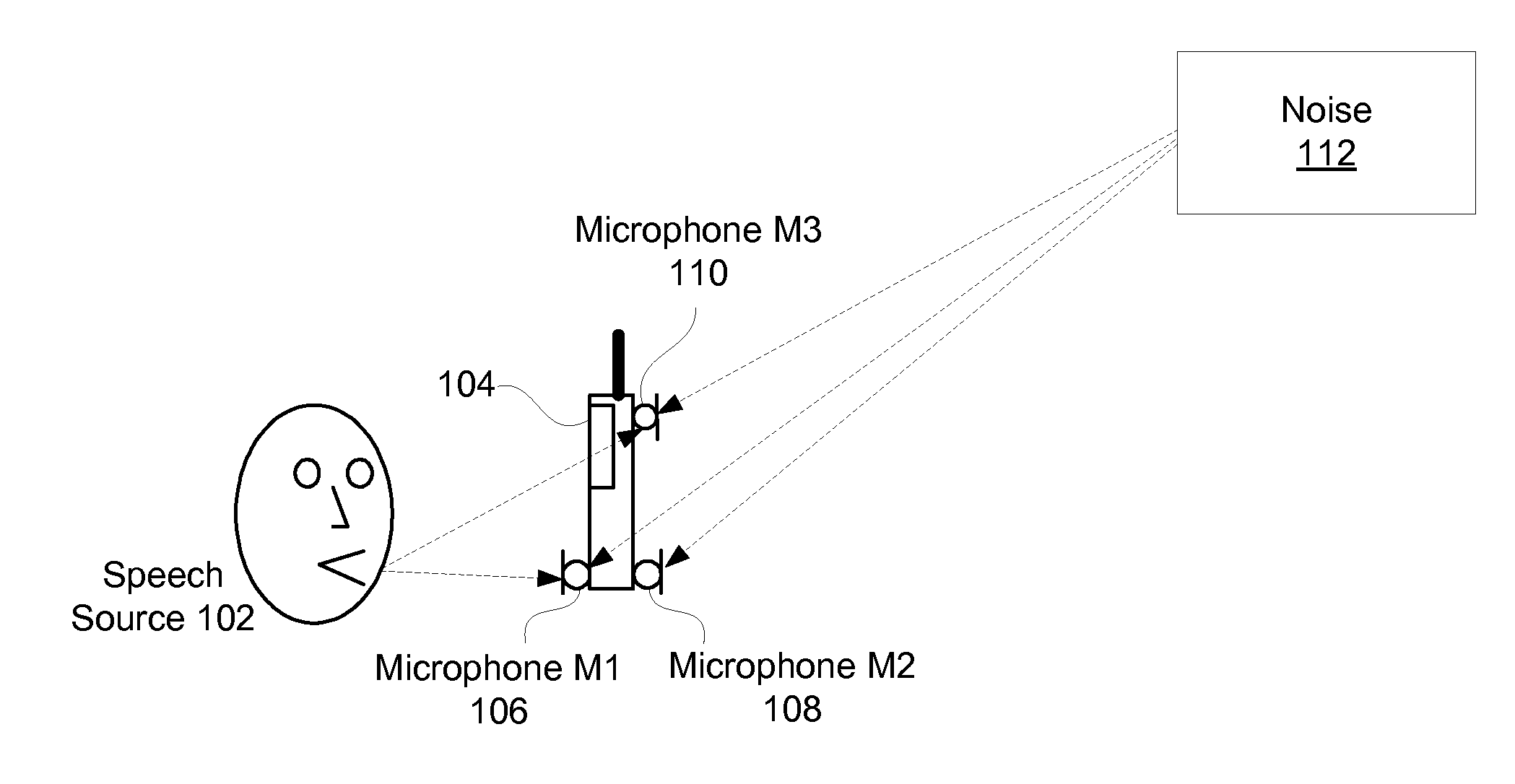
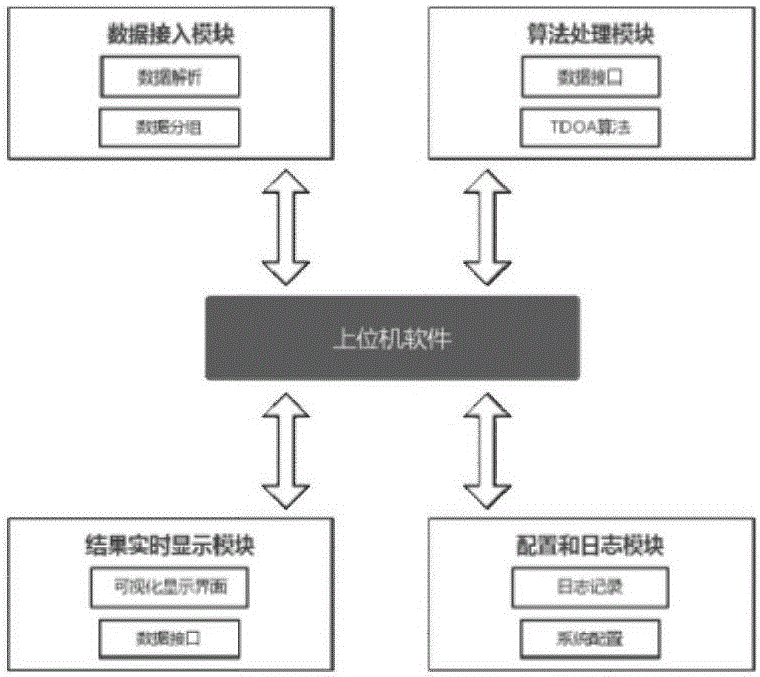
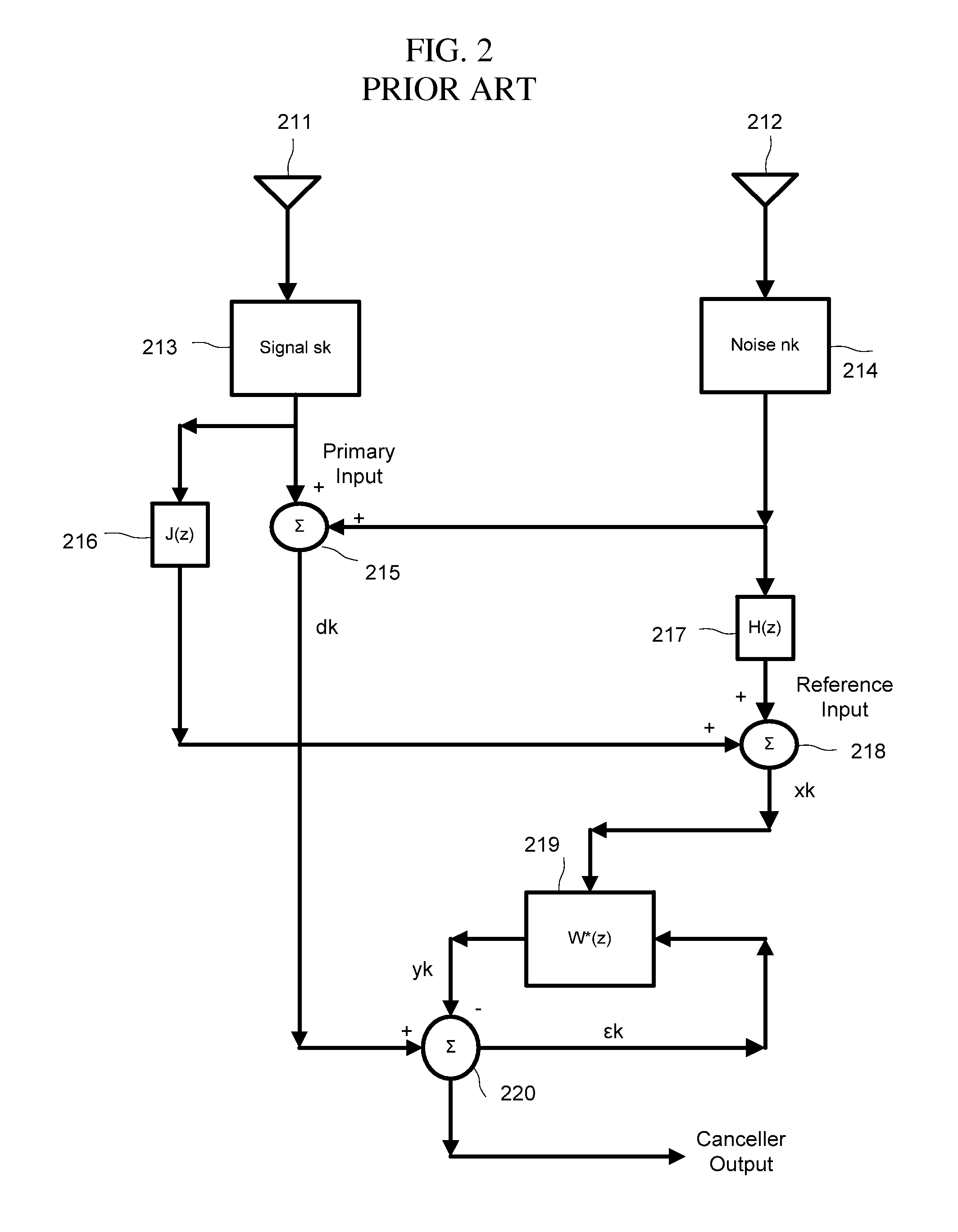
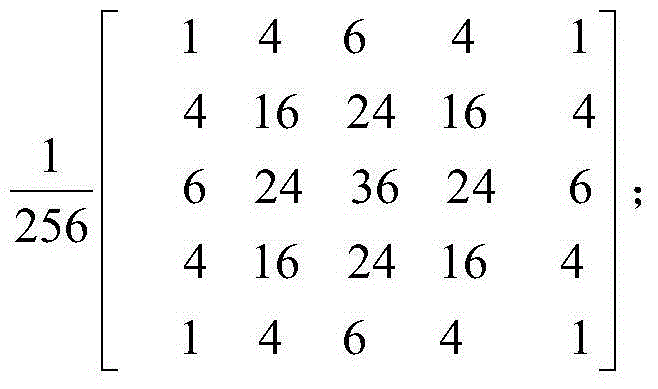
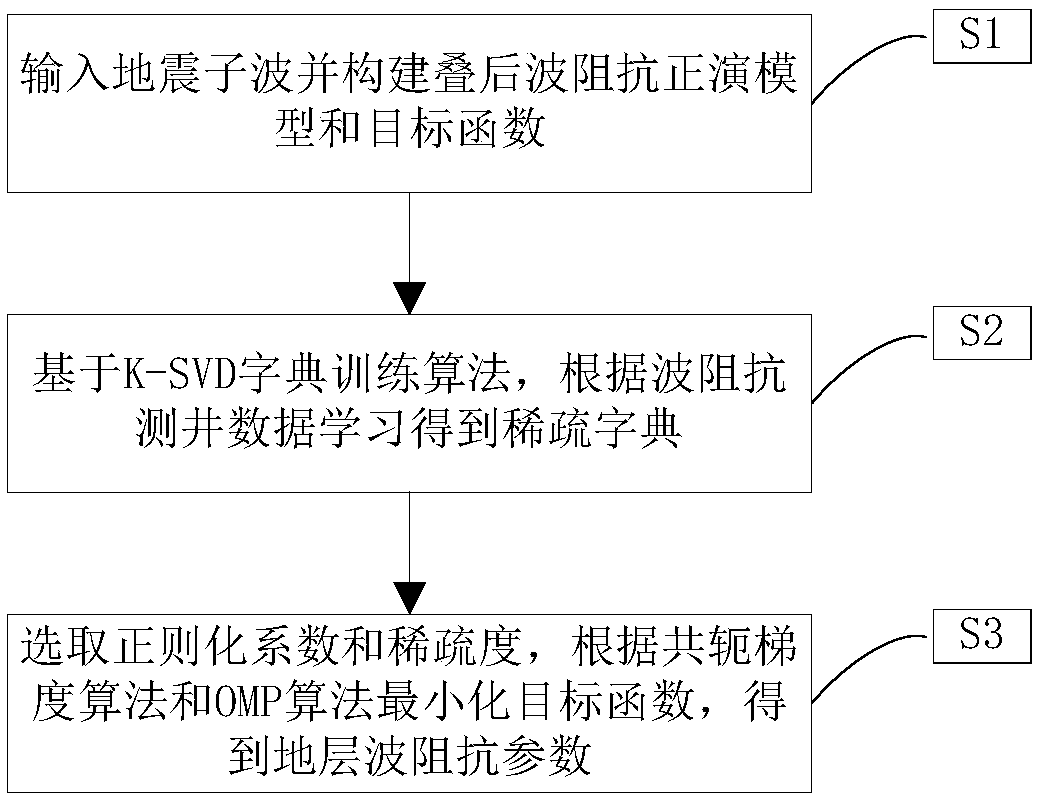
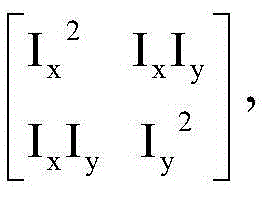Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Adaptive denoising" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
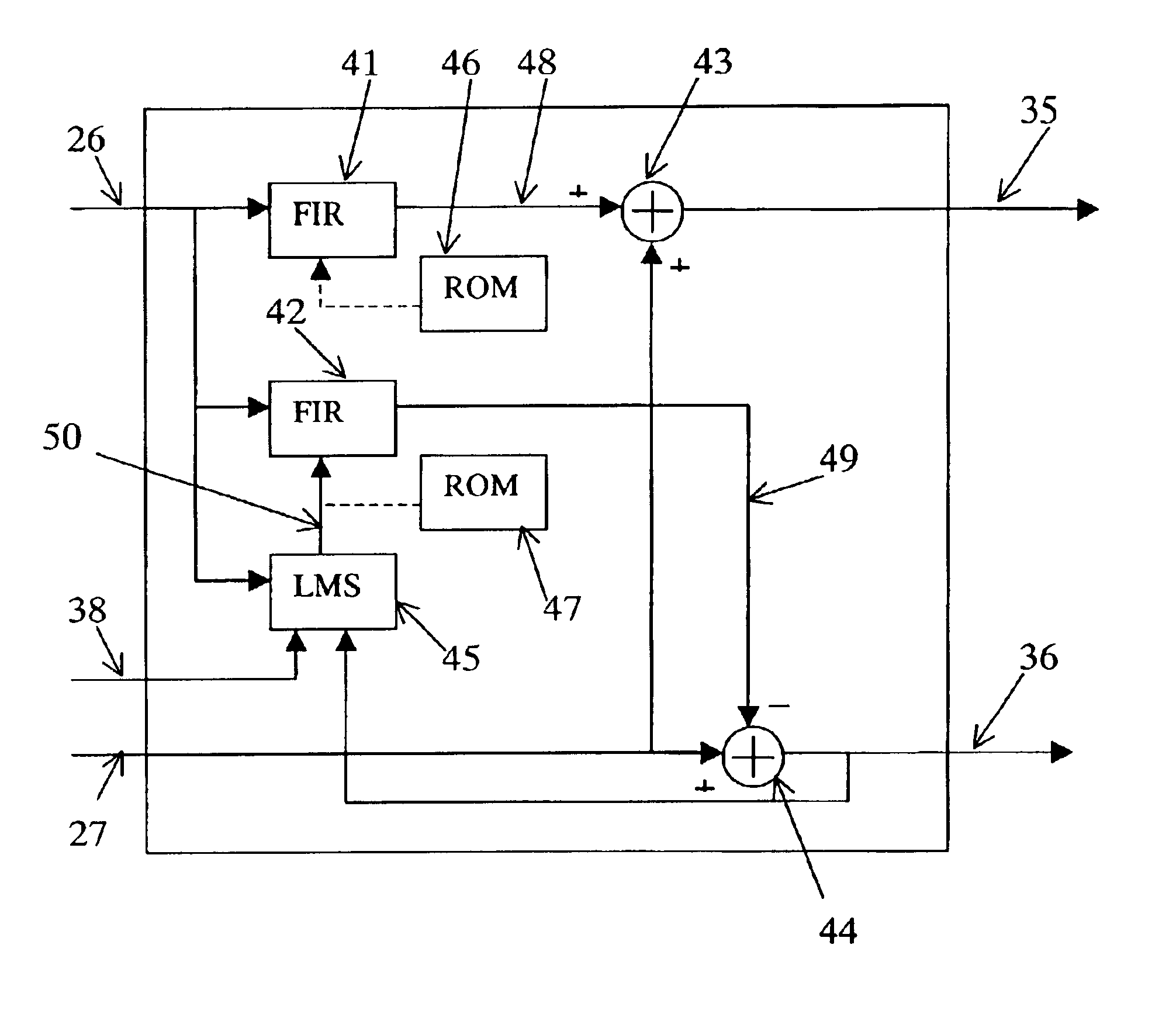
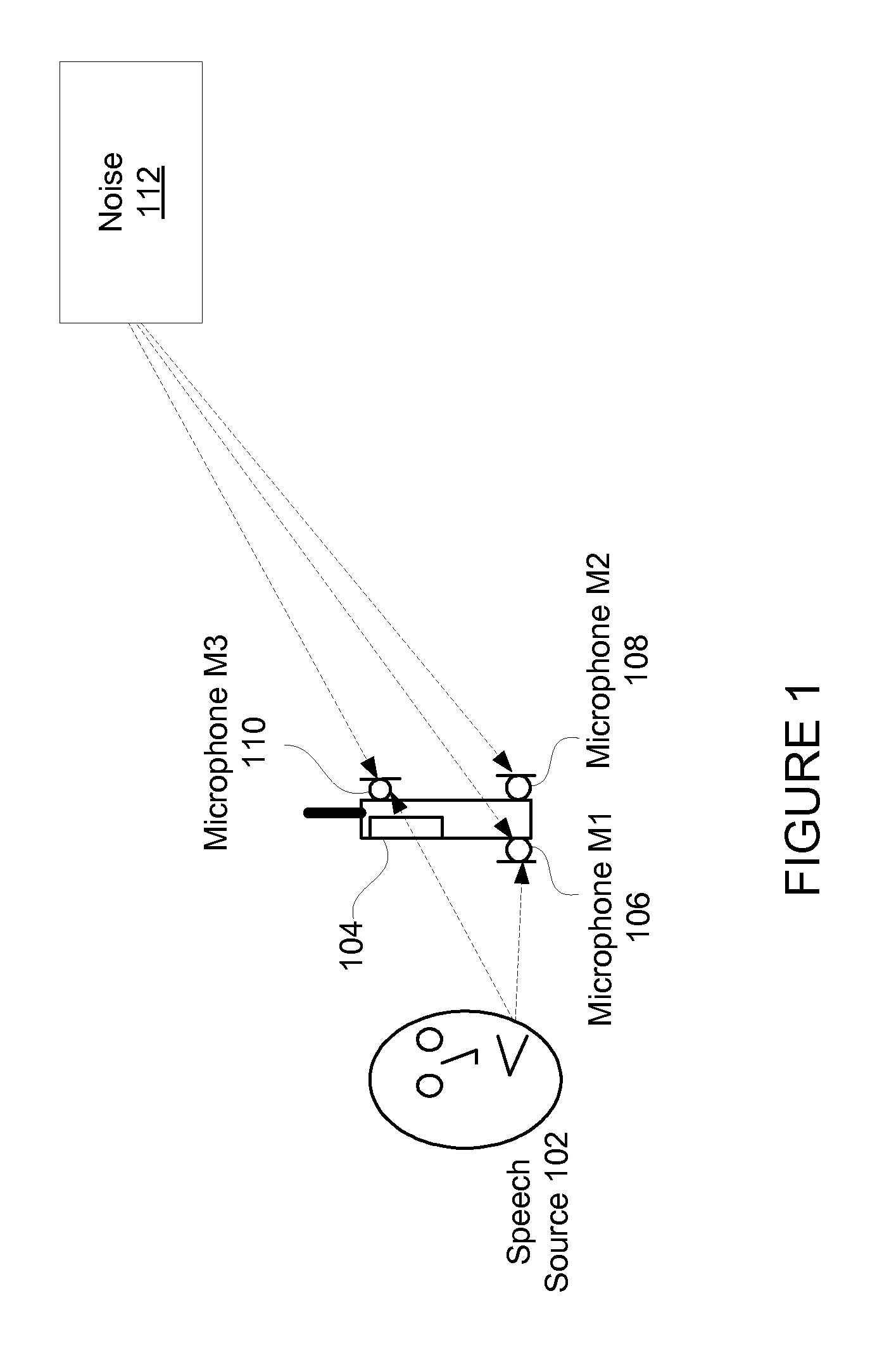
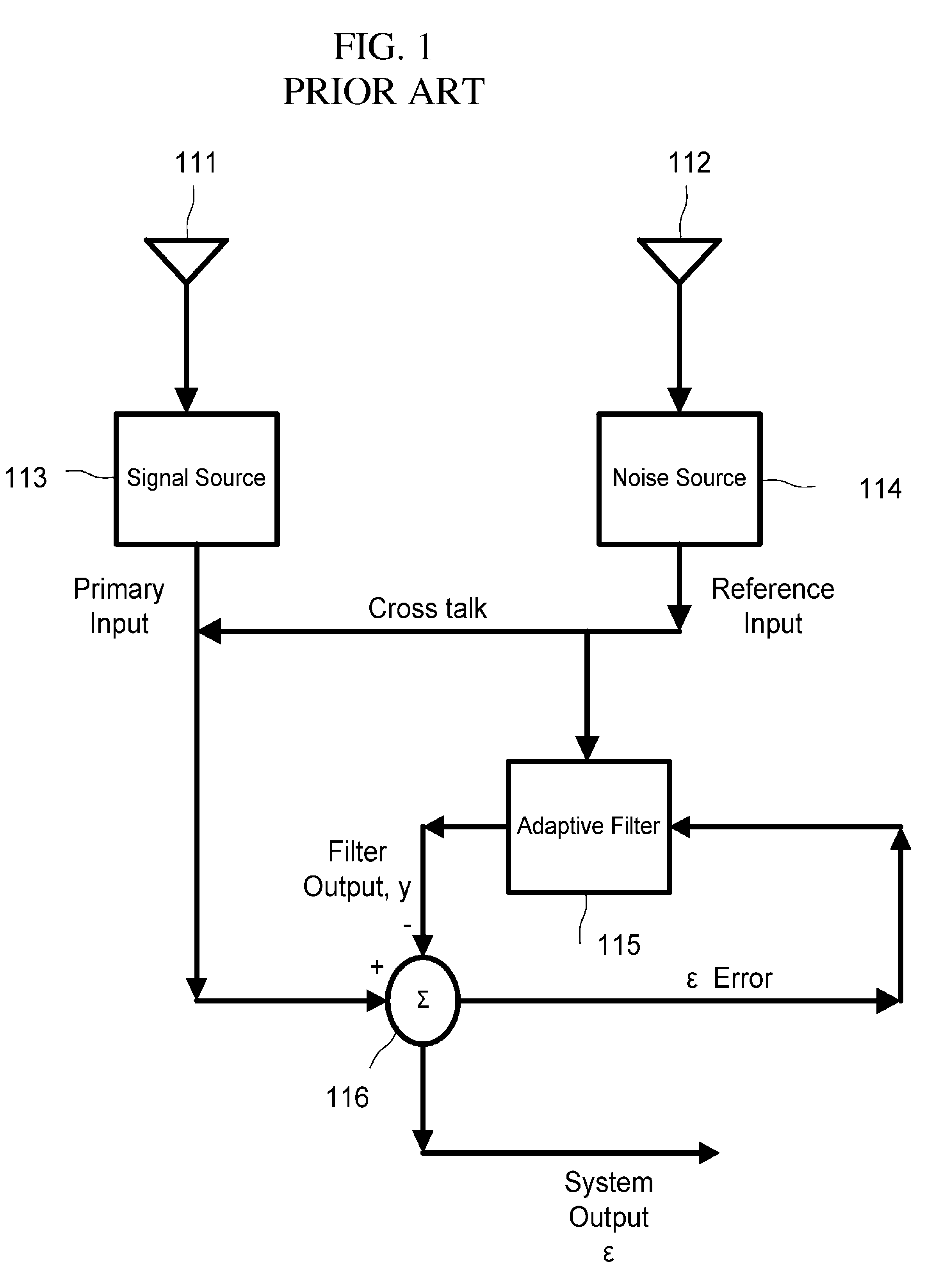
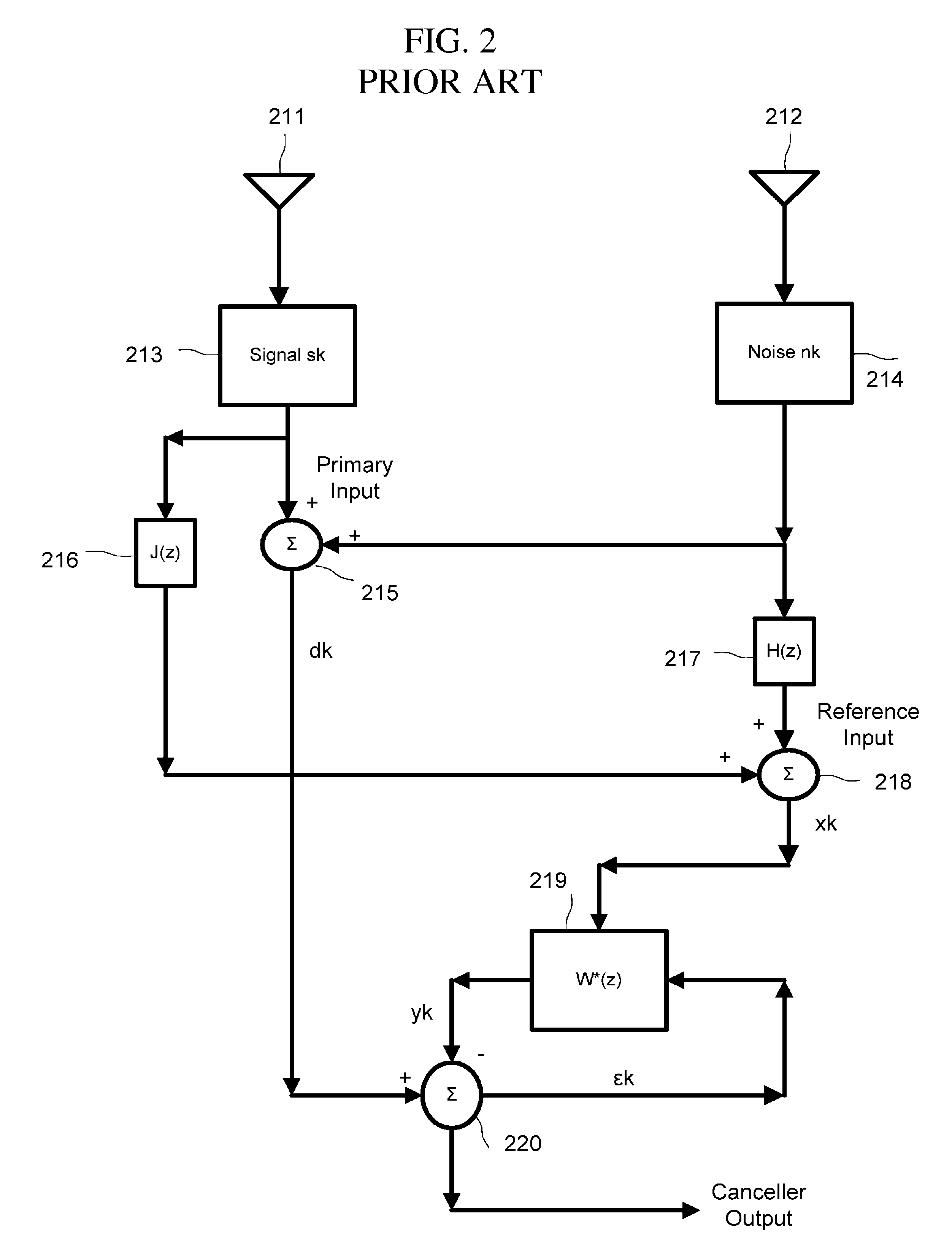
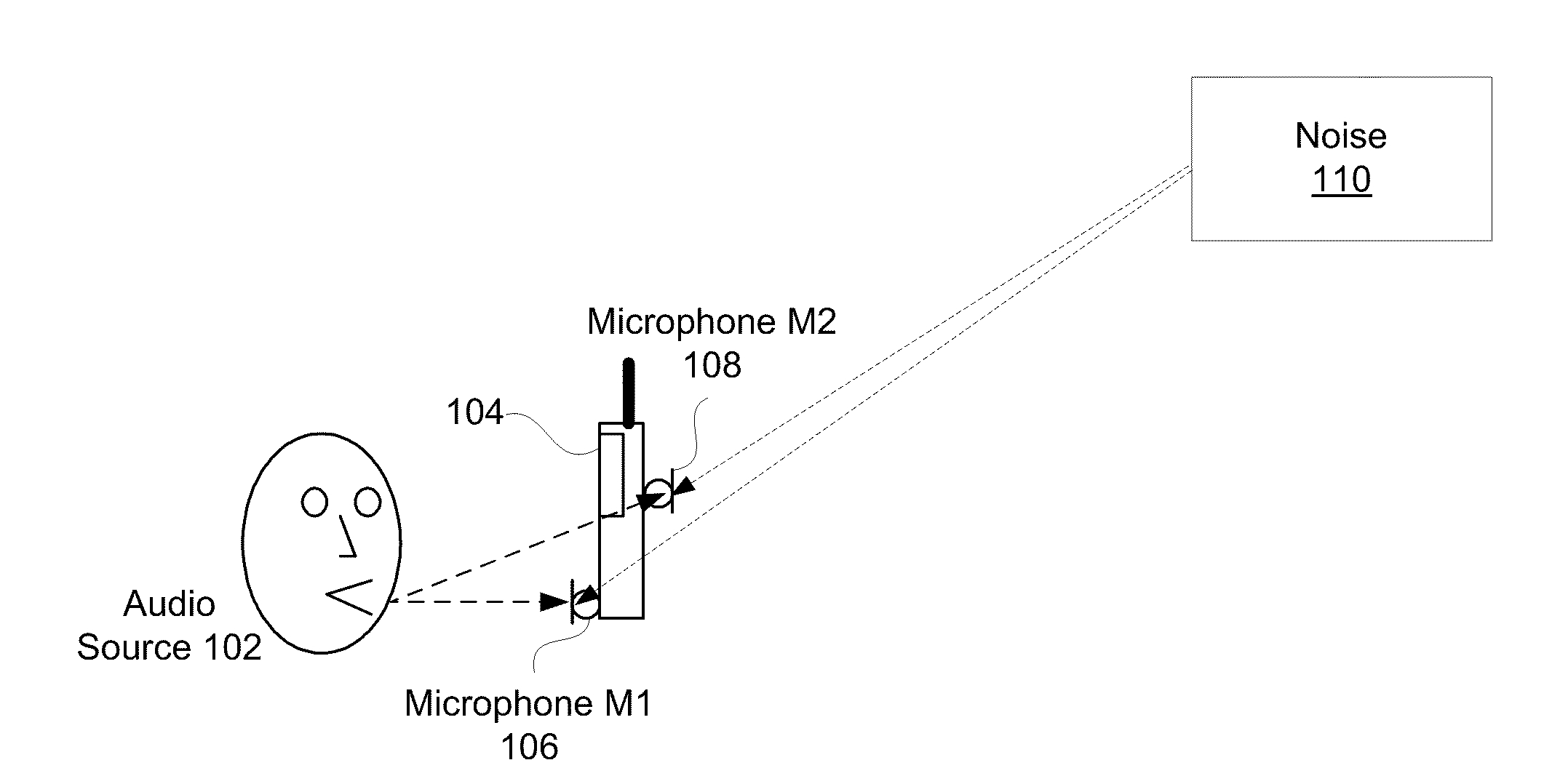
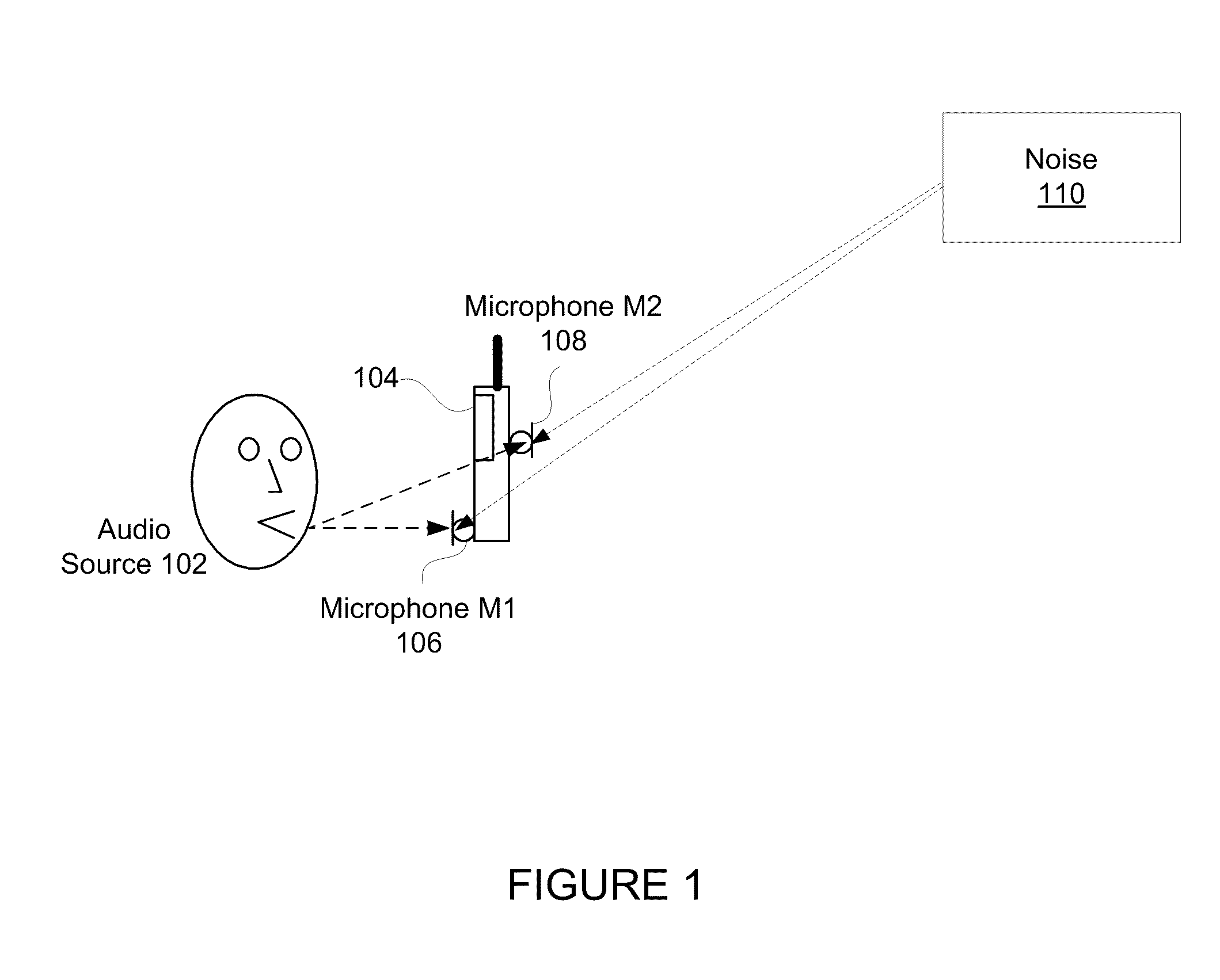
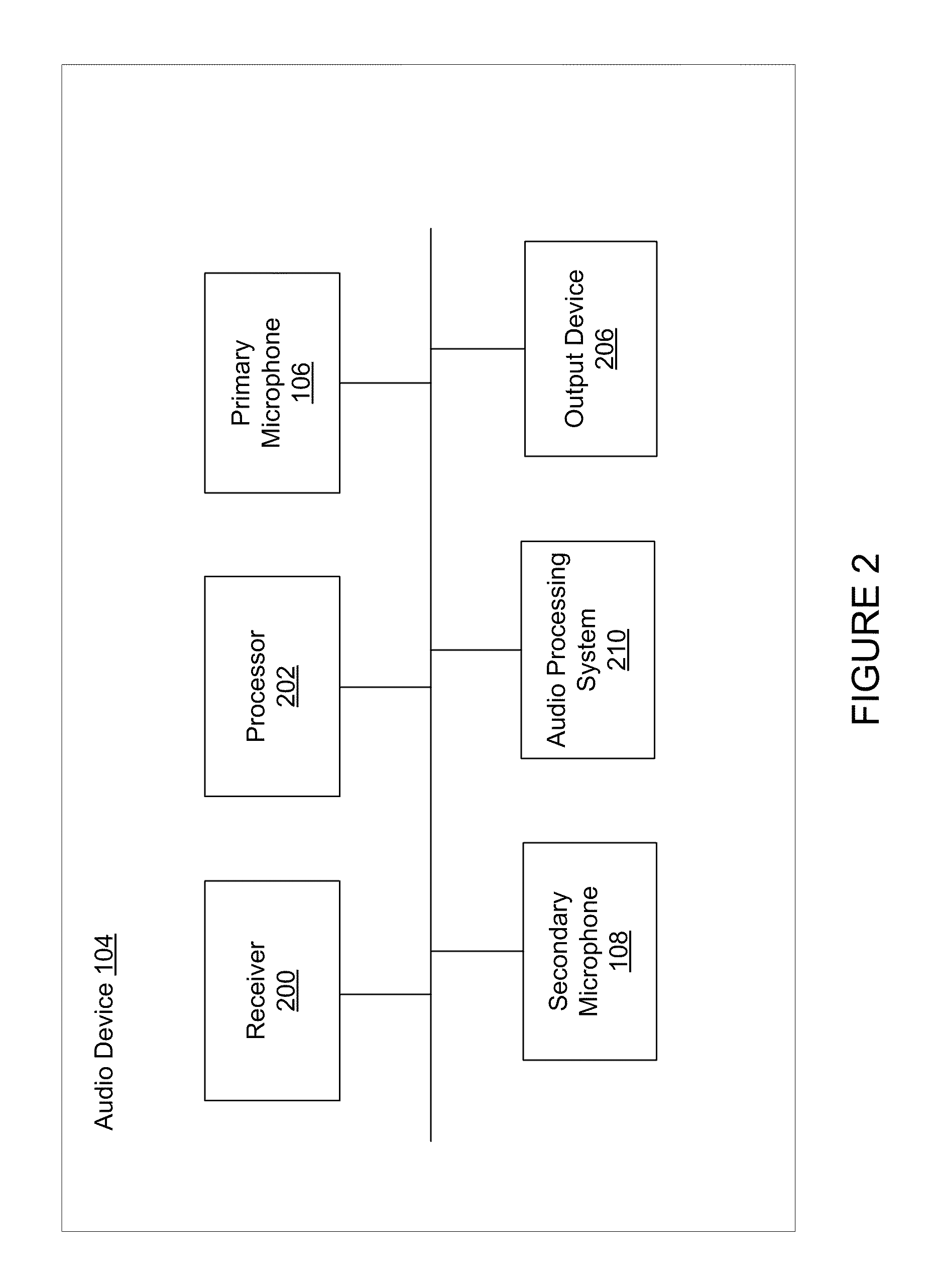
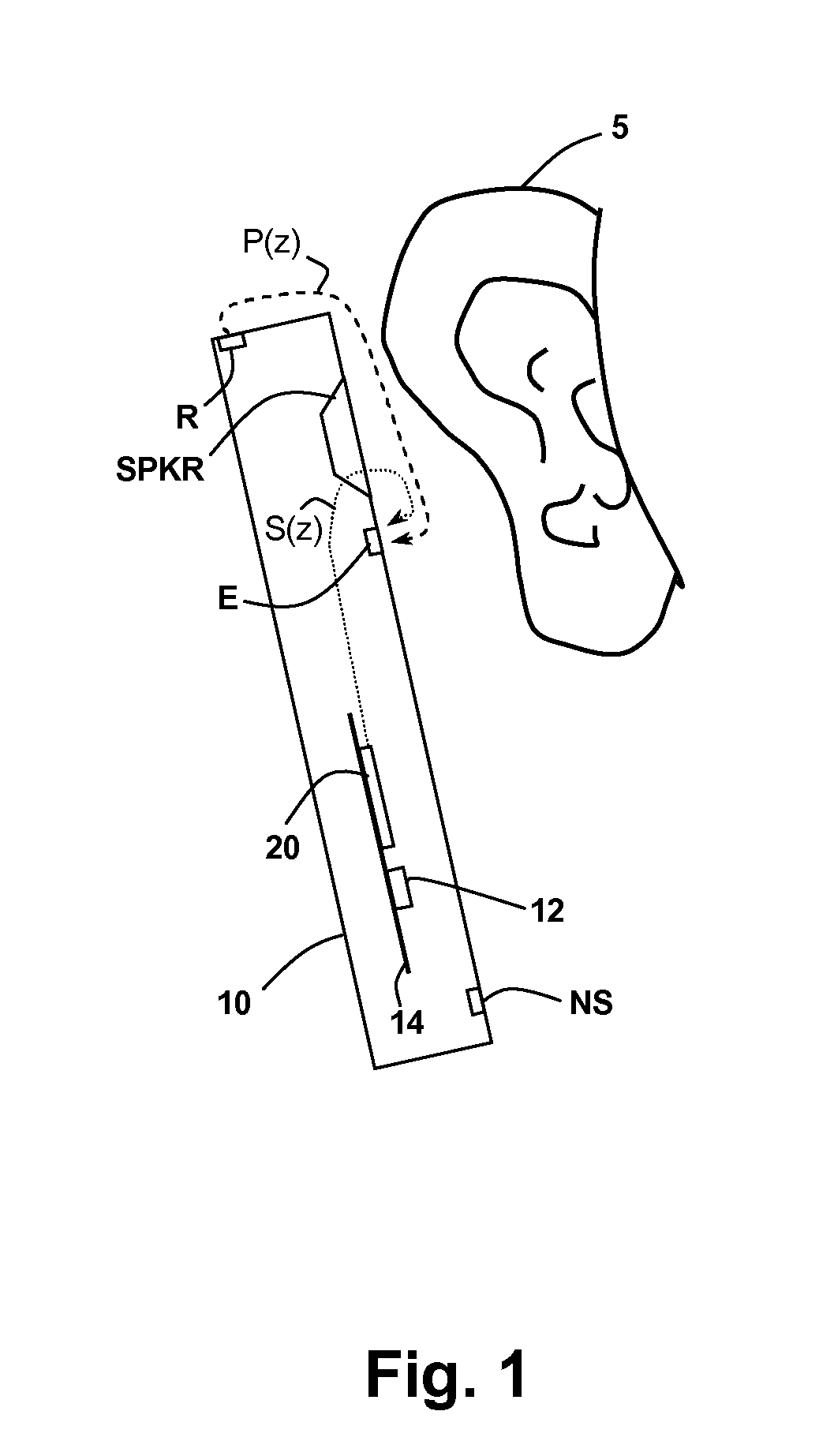
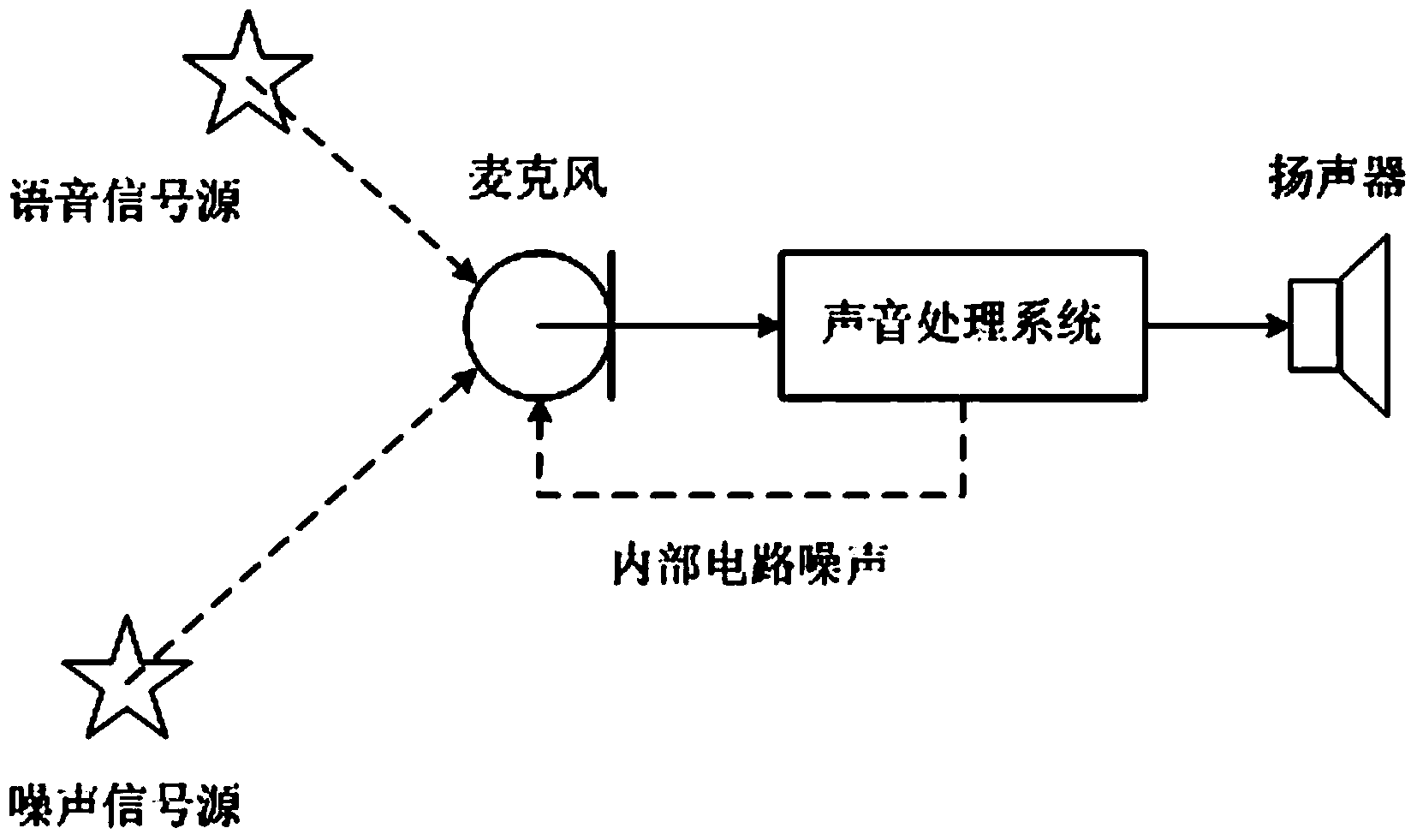
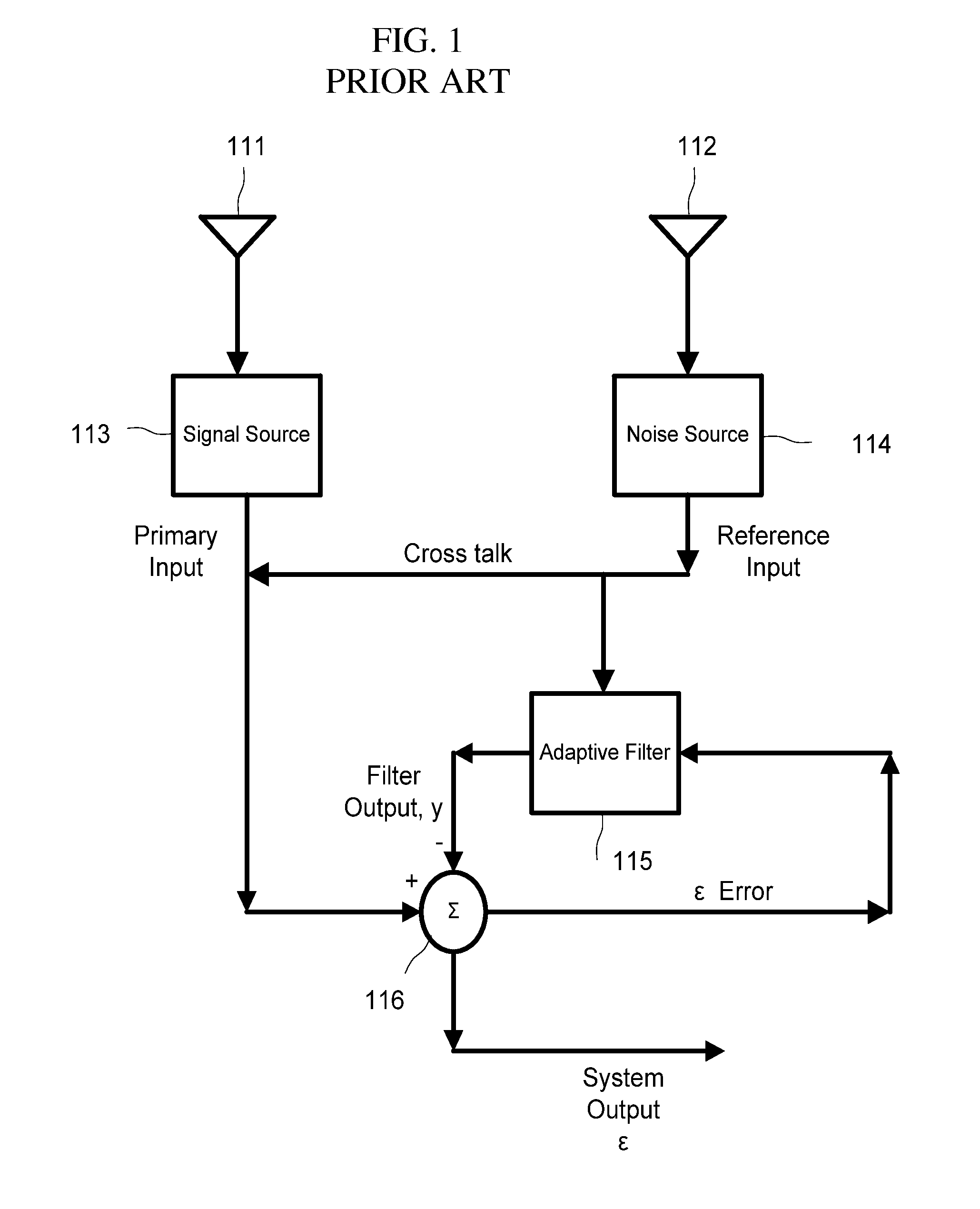
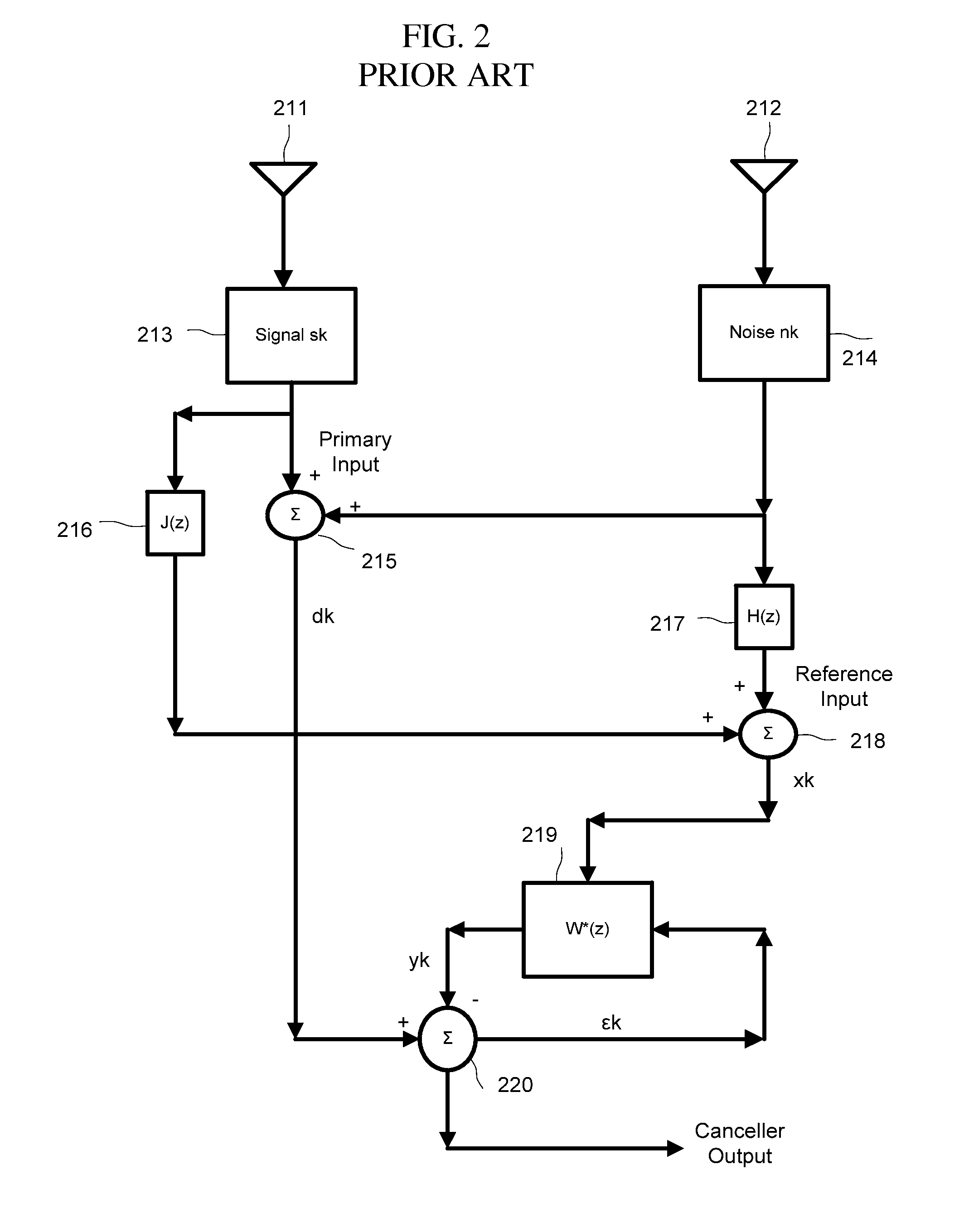
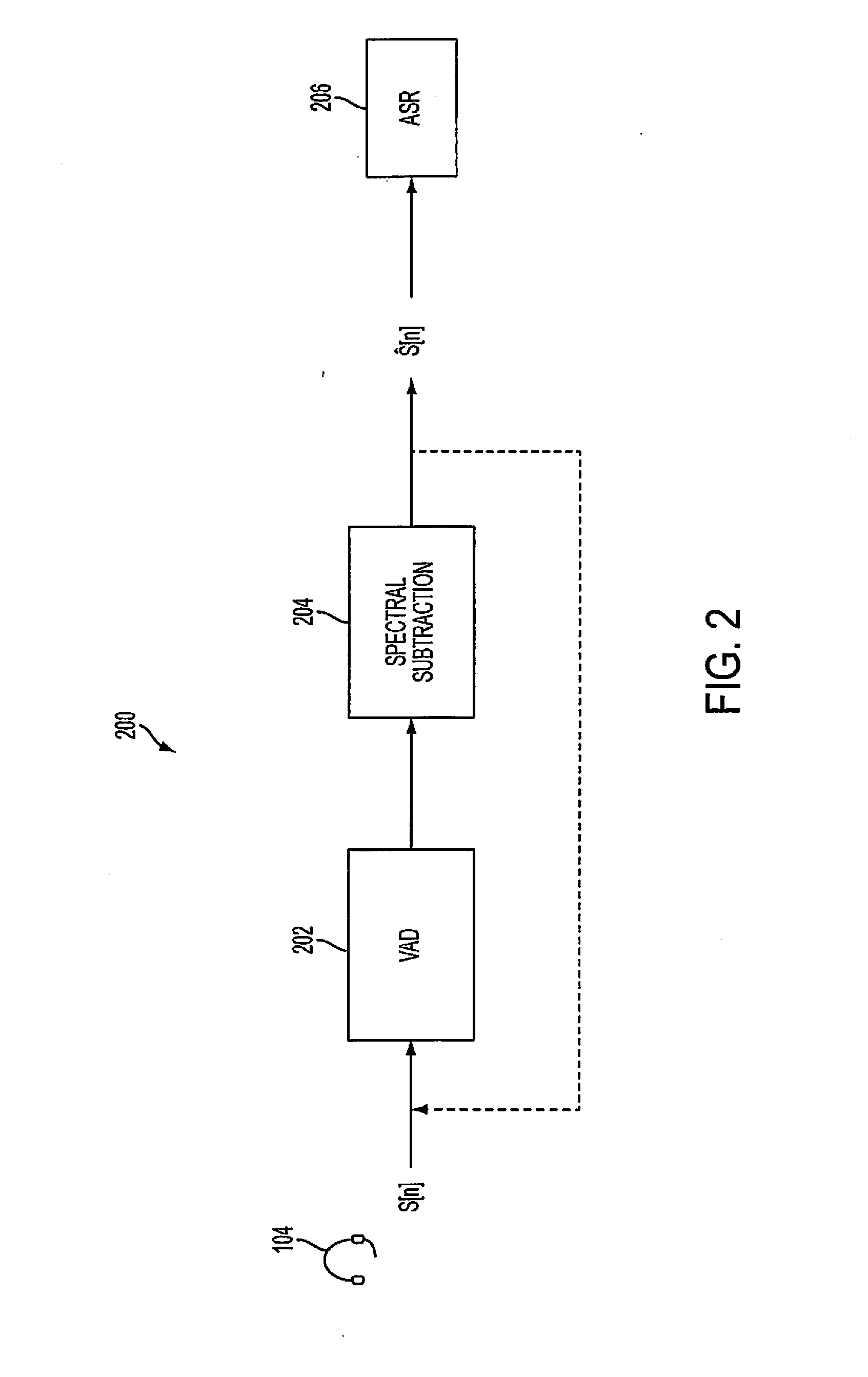
Adaptive noise cancelling microphone system
ActiveUS6917688B2Effectively cancel unwanted noiseIncrease flexibilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstation equipmentSound generationAdaptive denoising
An adaptive noise canceling microphone system for extracting a desired signal, in particular a desired speech signal, comprising two microphones being arranged at a predefined distance from each other; a signal forming system (SFS) being adapted to receive a first and second input signals resulting from sounds received by the two microphones wherein an acoustical signal component in the first input signal is determined, wherein an acoustical signal component in the second input signal is determined, wherein the acoustical signal component in the first input signal is enhanced to generate a speech enhanced signal, and wherein the acoustical signal component in the second input signal is suppressed to generate a speech nulled signal; an adaptive noise cancellation filtering circuit being adapted to receive the speech enhanced signal and the speech nulled signal, wherein the noise in the speech enhanced signal is cancelled using the speech nulled signal as reference, thereby generating an output filtered signal representing the desired signal.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Adaptive Noise Reduction Using Level Cues
ActiveUS20110182436A1Maximize noise reduction performanceOptimizationEar treatmentSpeech analysisControl signalAdaptive denoising
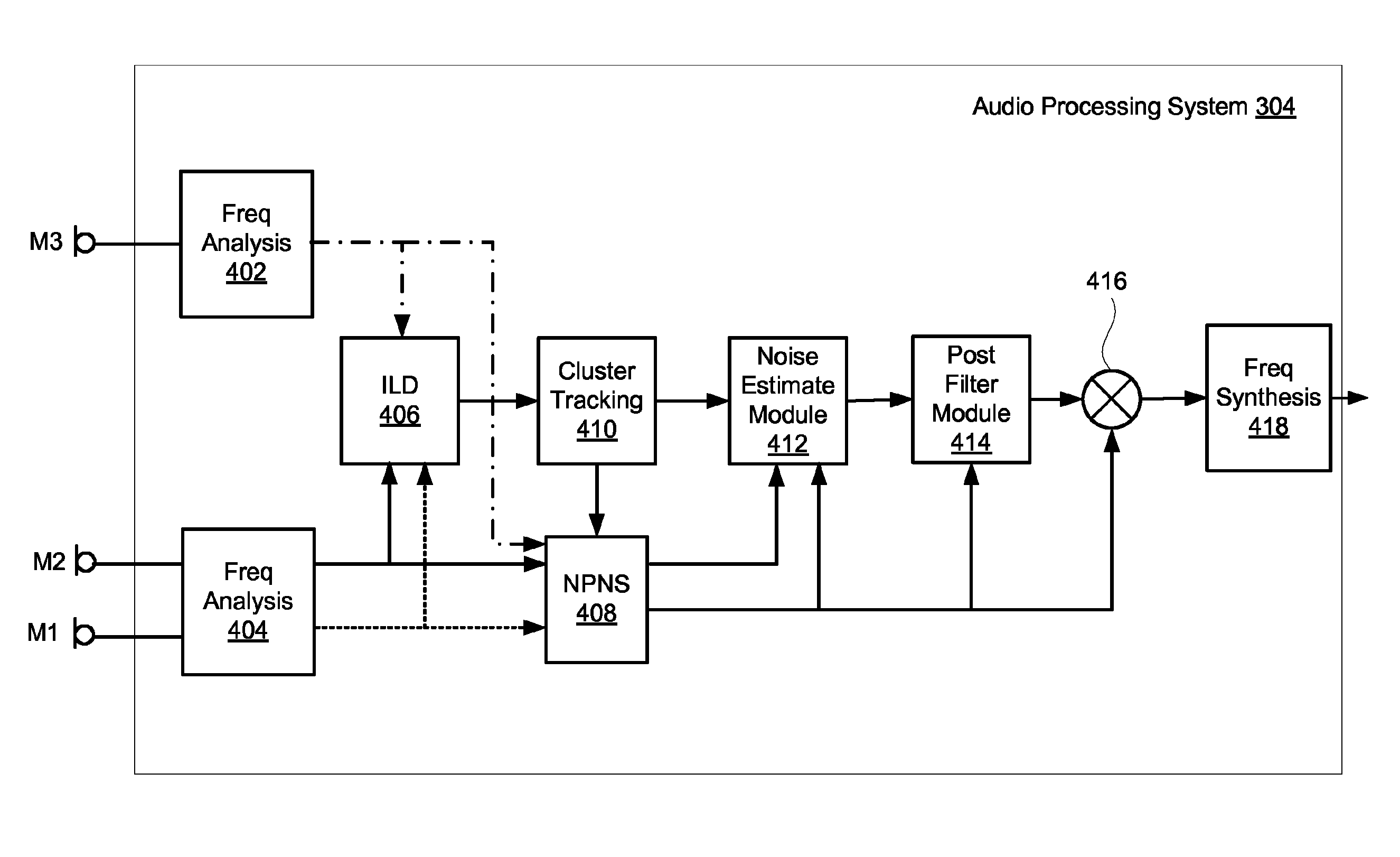
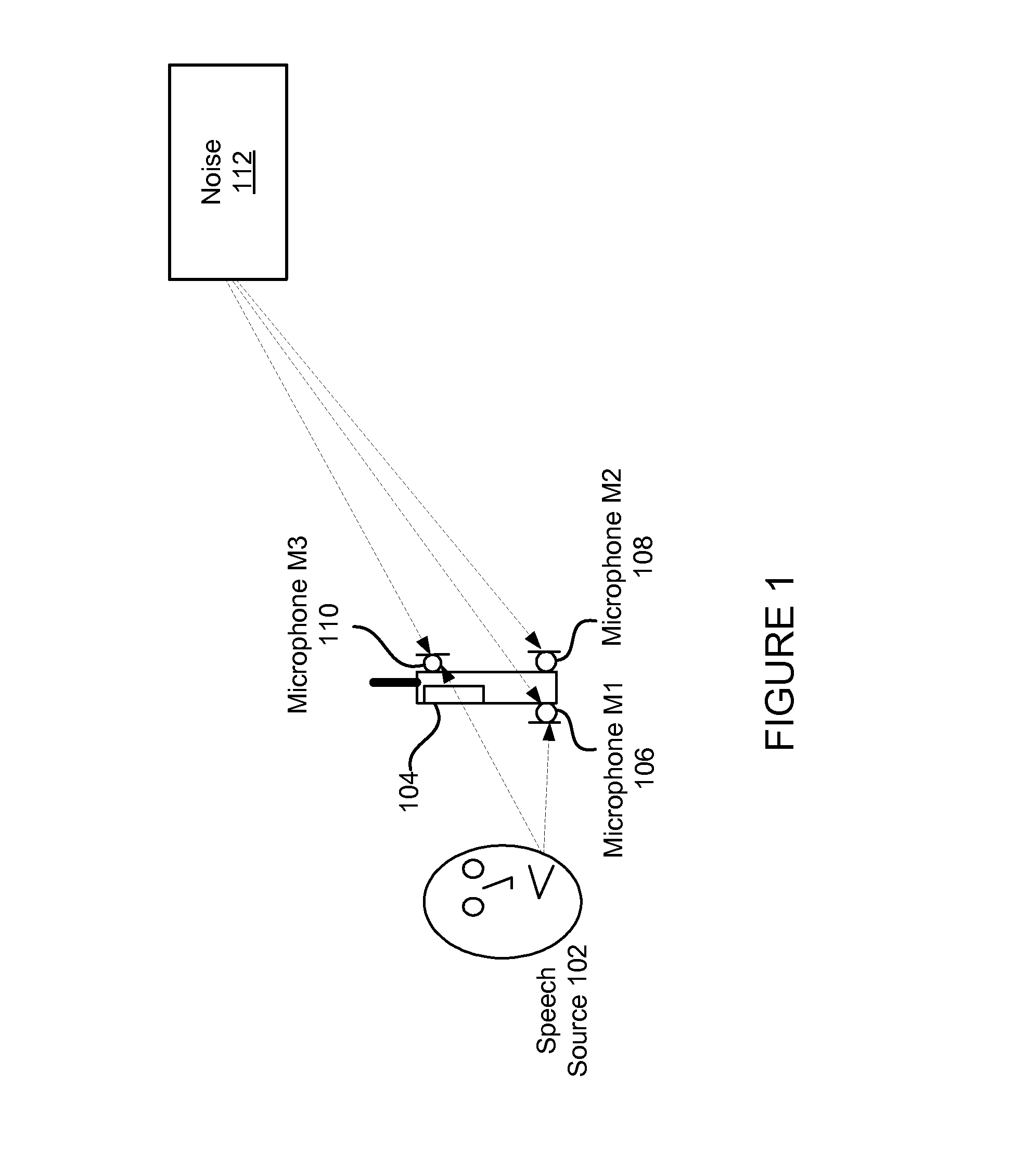
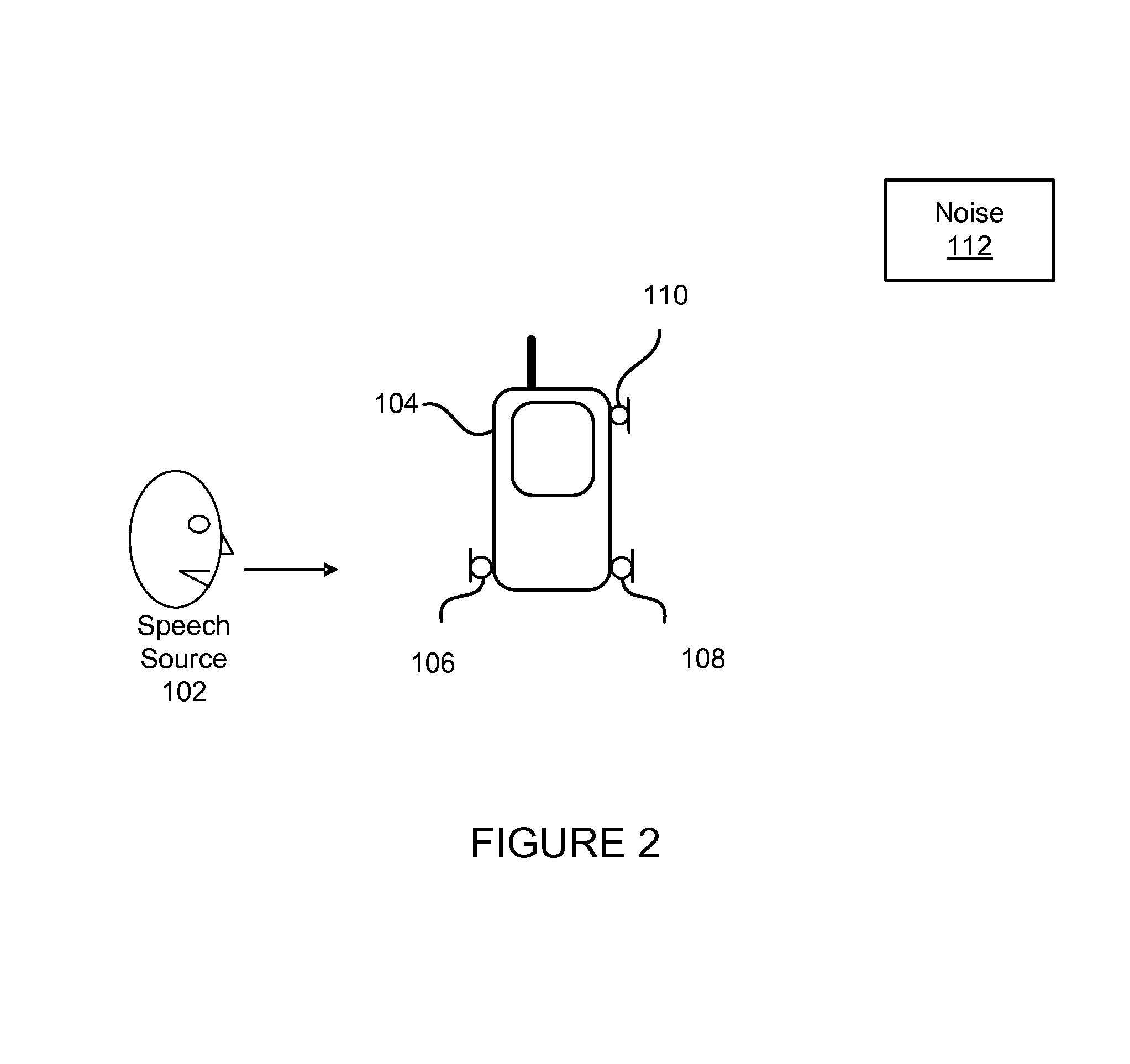
An array of microphones utilizes two sets of two microphones for noise suppression. A primary microphone and secondary microphone of the three microphones may be positioned closely spaced to each other to provide acoustic signals used to achieve noise cancellation. A tertiary microphone may be spaced with respect to either the primary microphone or the secondary microphone in a spread-microphone configuration for deriving level cues from audio signals provided by tertiary and the primary or secondary microphone. Signals from two microphones may be used rather than three microphones. The level cues are expressed via an inter-microphone level difference (ILD) which is used to determine one or more cluster tracking control signals. The ILD based cluster tracking signals are used to control the adaptation of null-processing noise cancellation modules. A noise cancelled primary acoustic signal and ILD based cluster tracking control signals are used during post filtering to adaptively generate a mask to be applied against a speech estimate signal.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
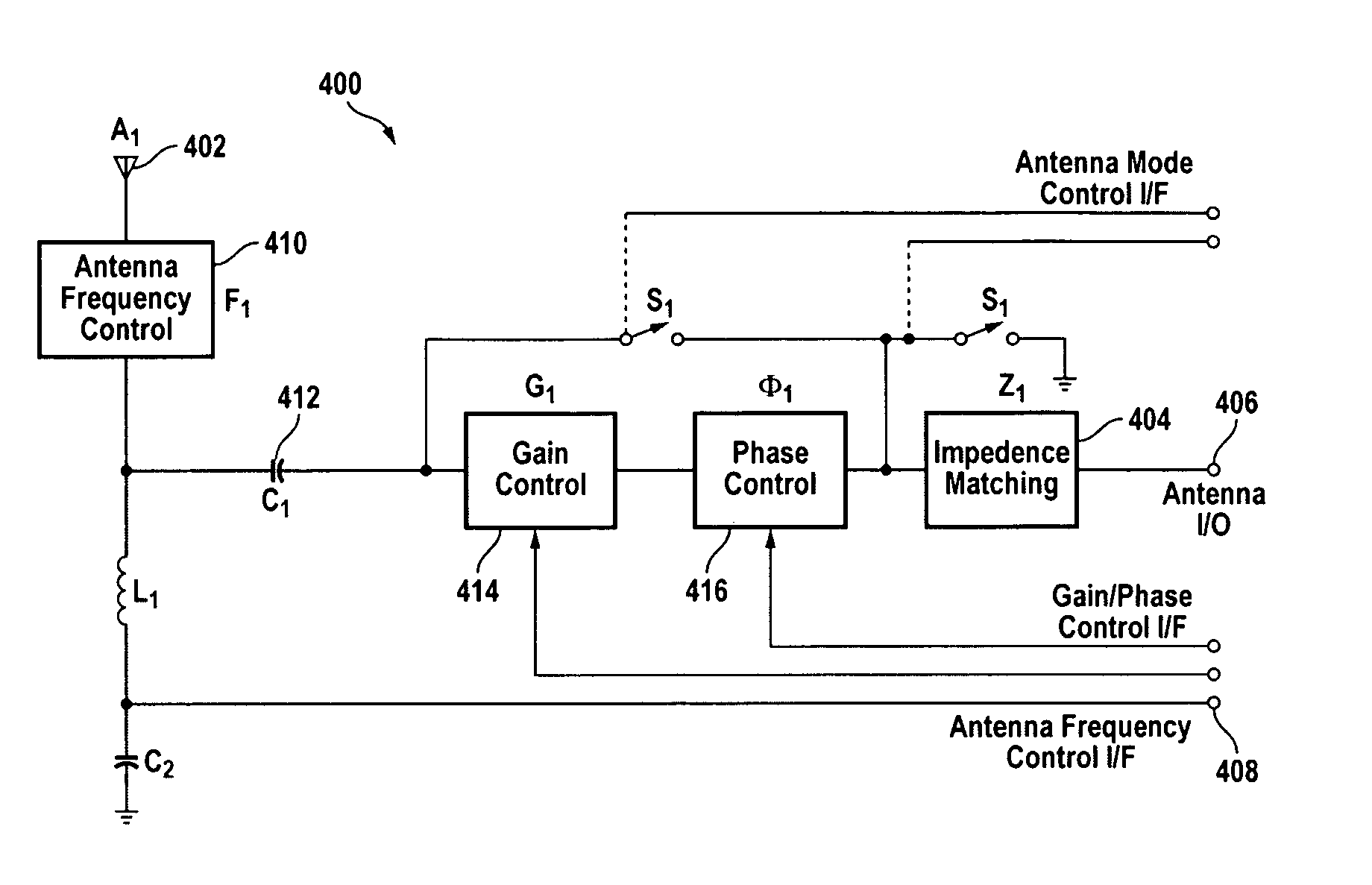
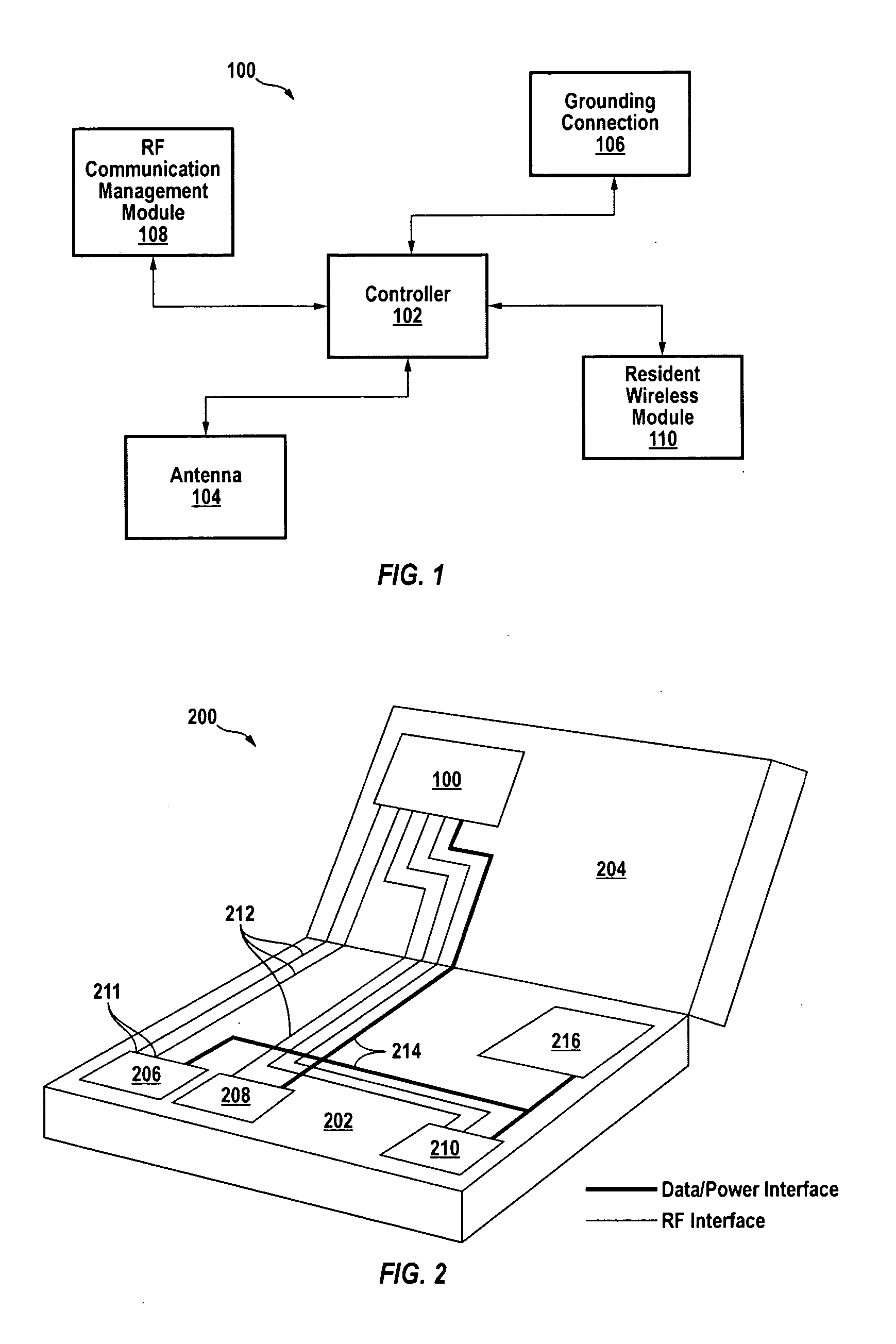
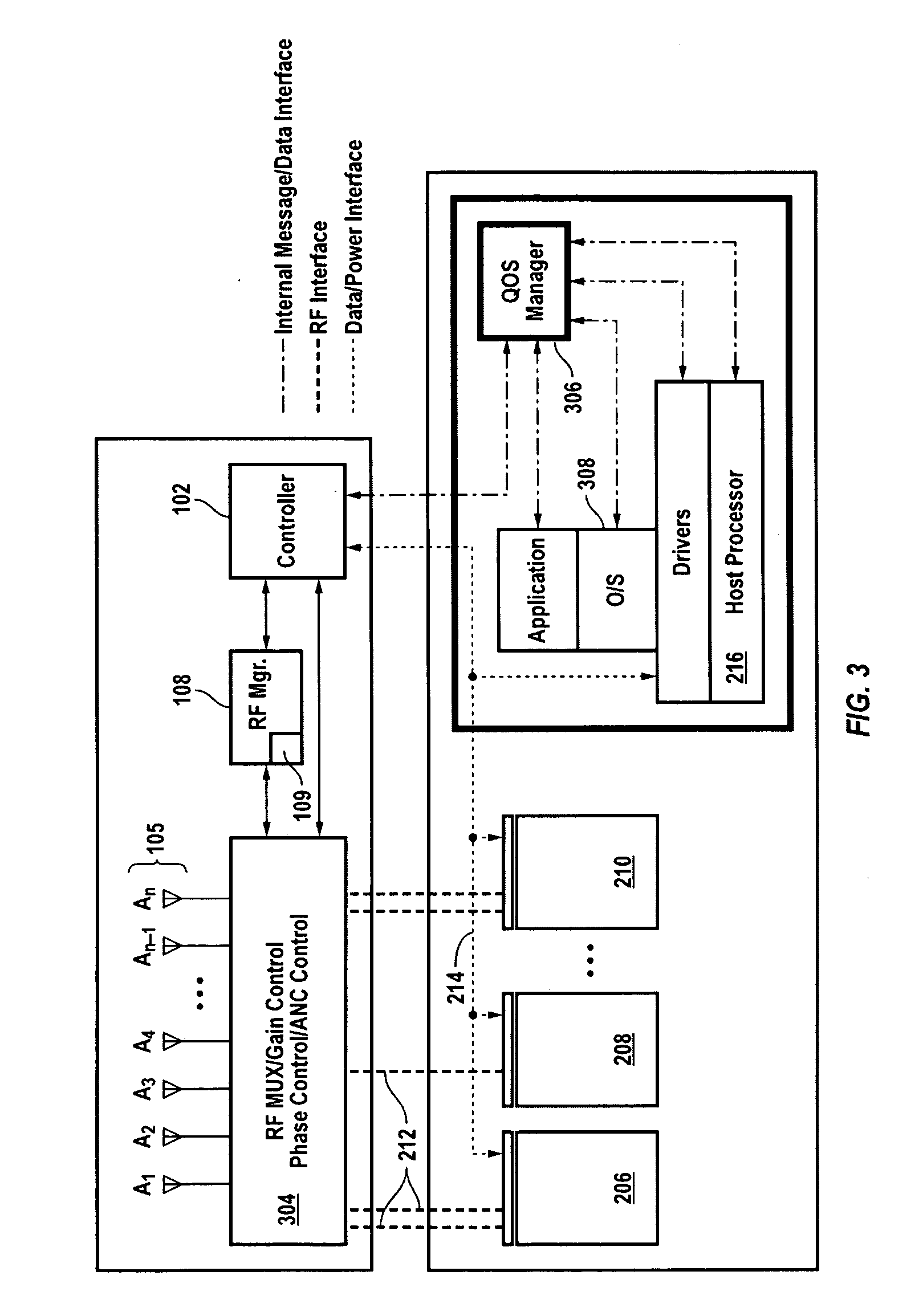
Centralized wireless communication system
InactiveUS20080102760A1Faster time to marketEngineering development riskRadio transmissionCommunications systemMultiplexer
A centralized wireless communication system for a host device having a host processor and one or more host wireless communication modules includes a controller, one or more antenna elements, and an RF multiplexer coupled to the one or more antenna elements. The RF multiplexer includes one or more ports and is configured to establish an RF communication path between one or more ports and one or more antenna elements based on instructions from the controller. The centralized wireless communication system can provide adaptive noise cancellation and / or operate antenna elements as part of an active phased array.
Owner:SIERRA WIRELESS
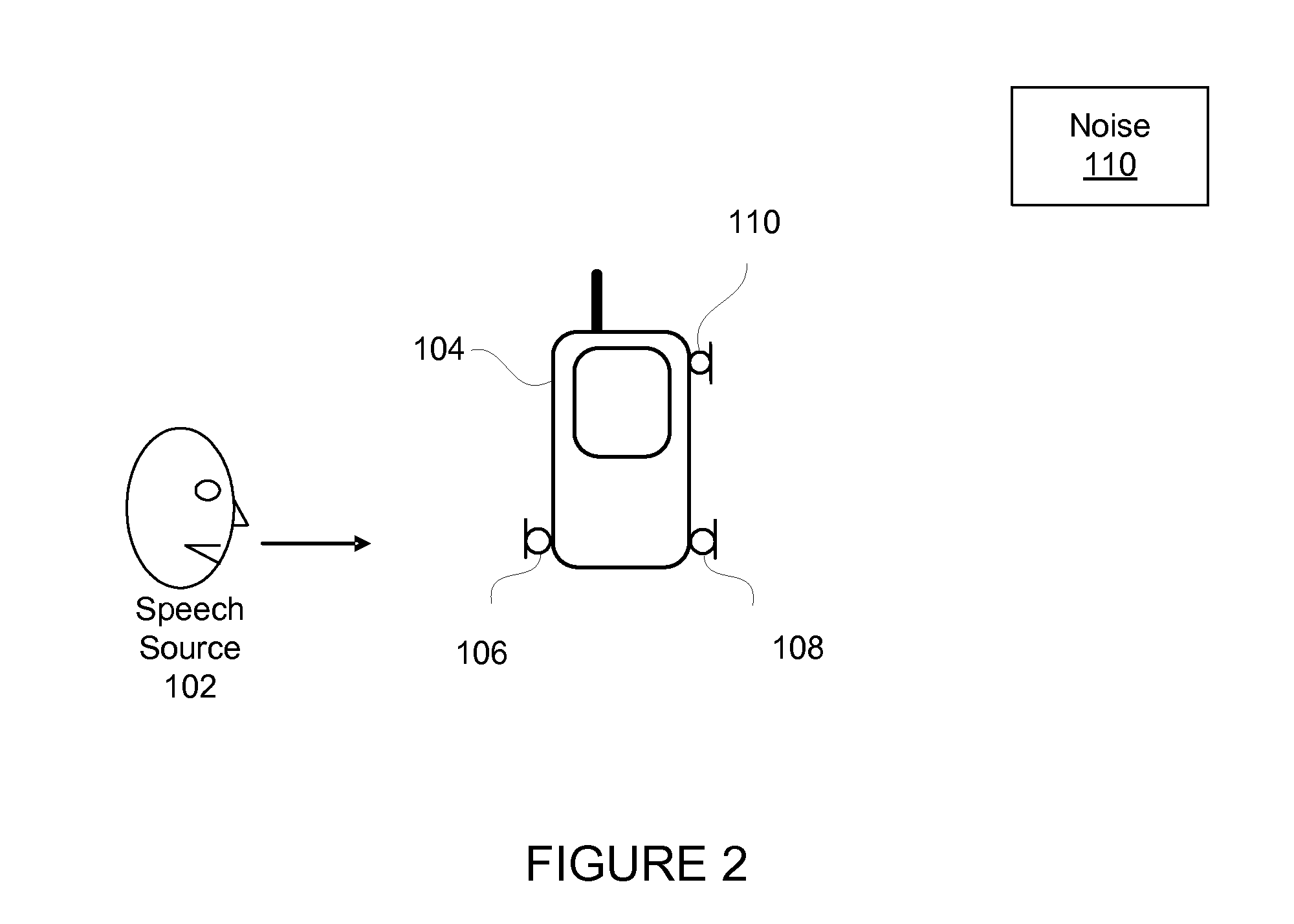
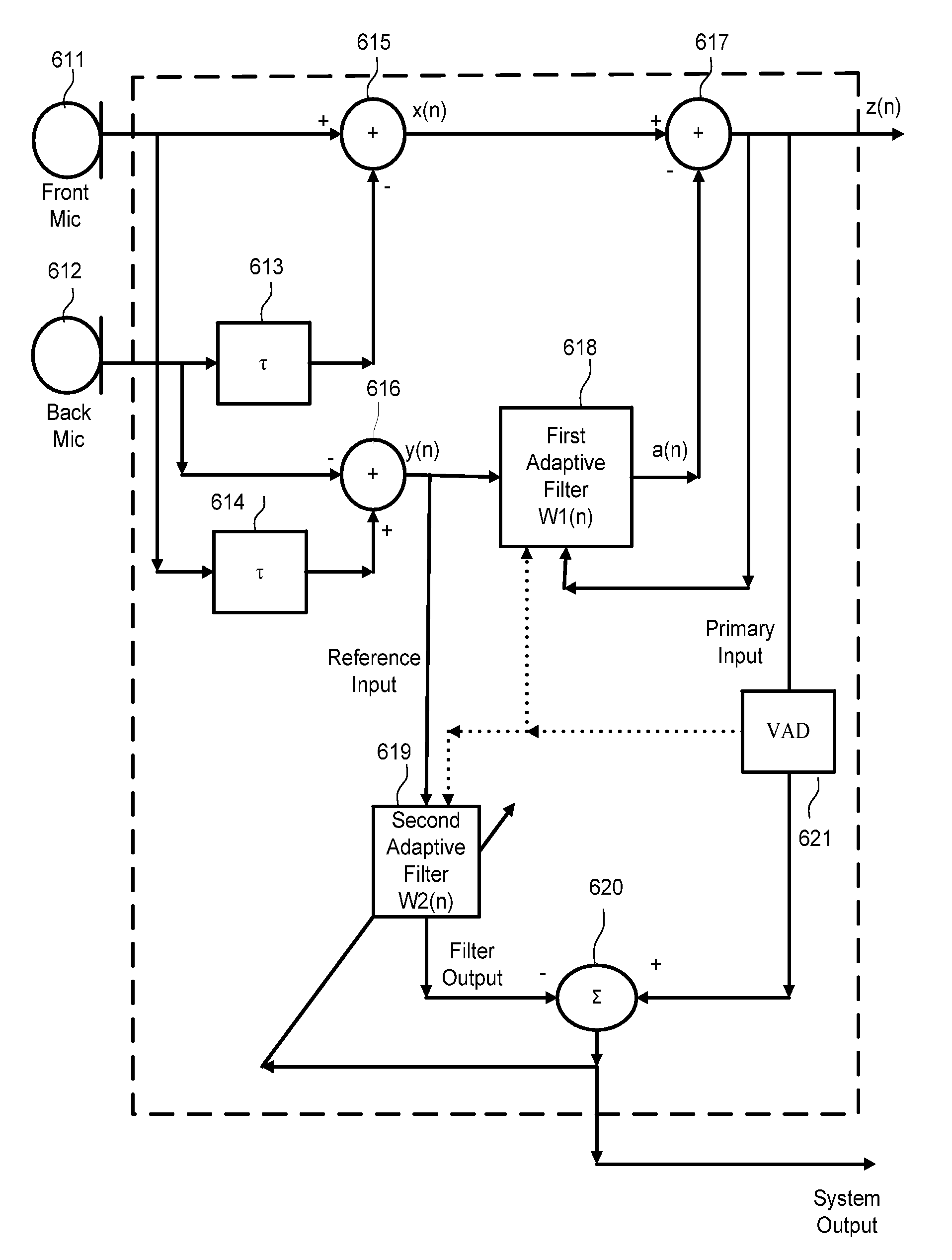
Dual adaptive structure for speech enhancement
InactiveUS7817808B2Easy to hearReduce noiseSignal processingEar treatmentSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Adaptive denoising
A clear, high quality voice signal with a high signal-to-noise ratio is achieved by use of an adaptive noise reduction scheme with two microphones in close proximity. The method includes the use of two omini directional microphones in a highly directional mode, and then applying an adaptive noise cancellation algorithm to reduce the noise.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
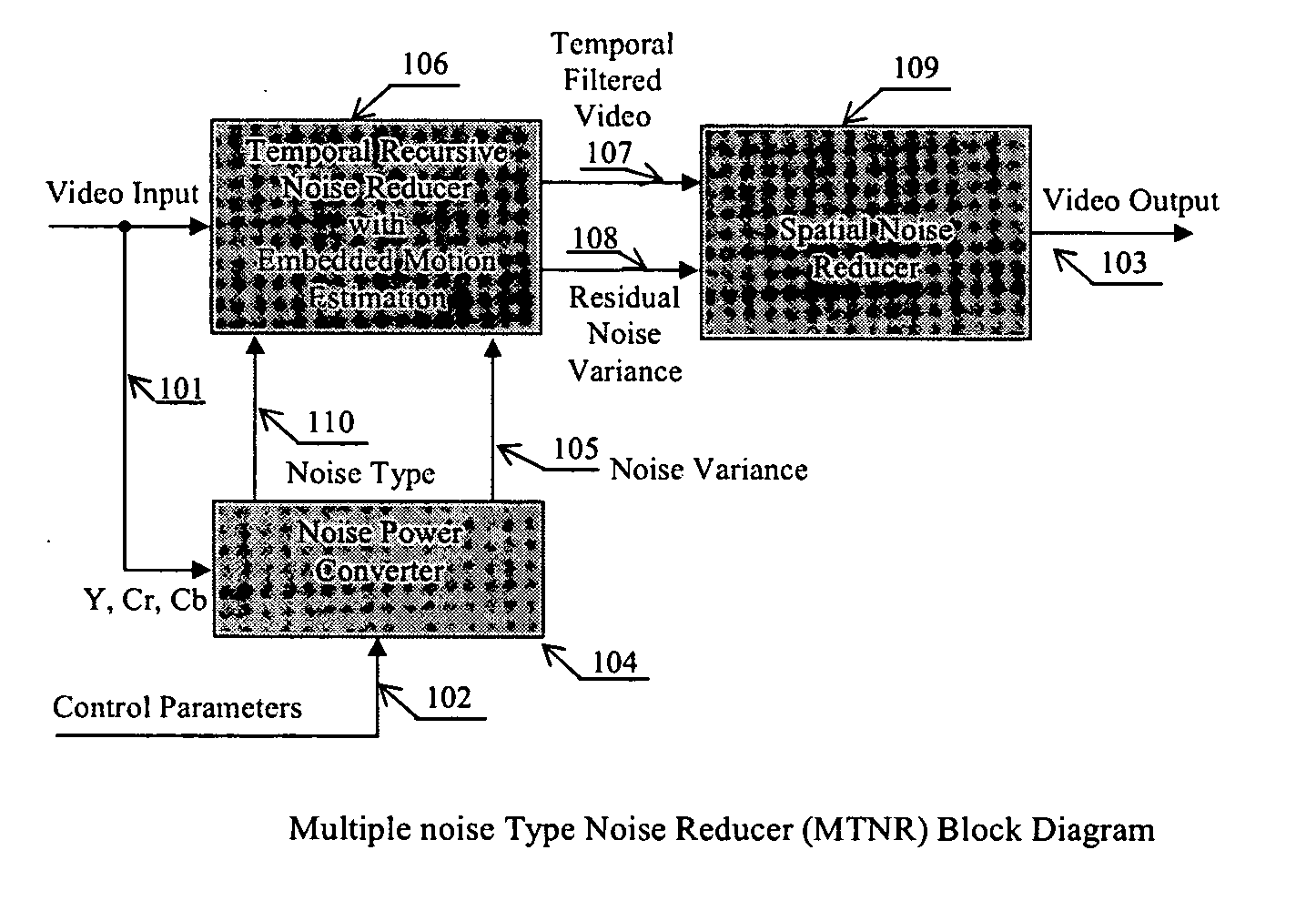
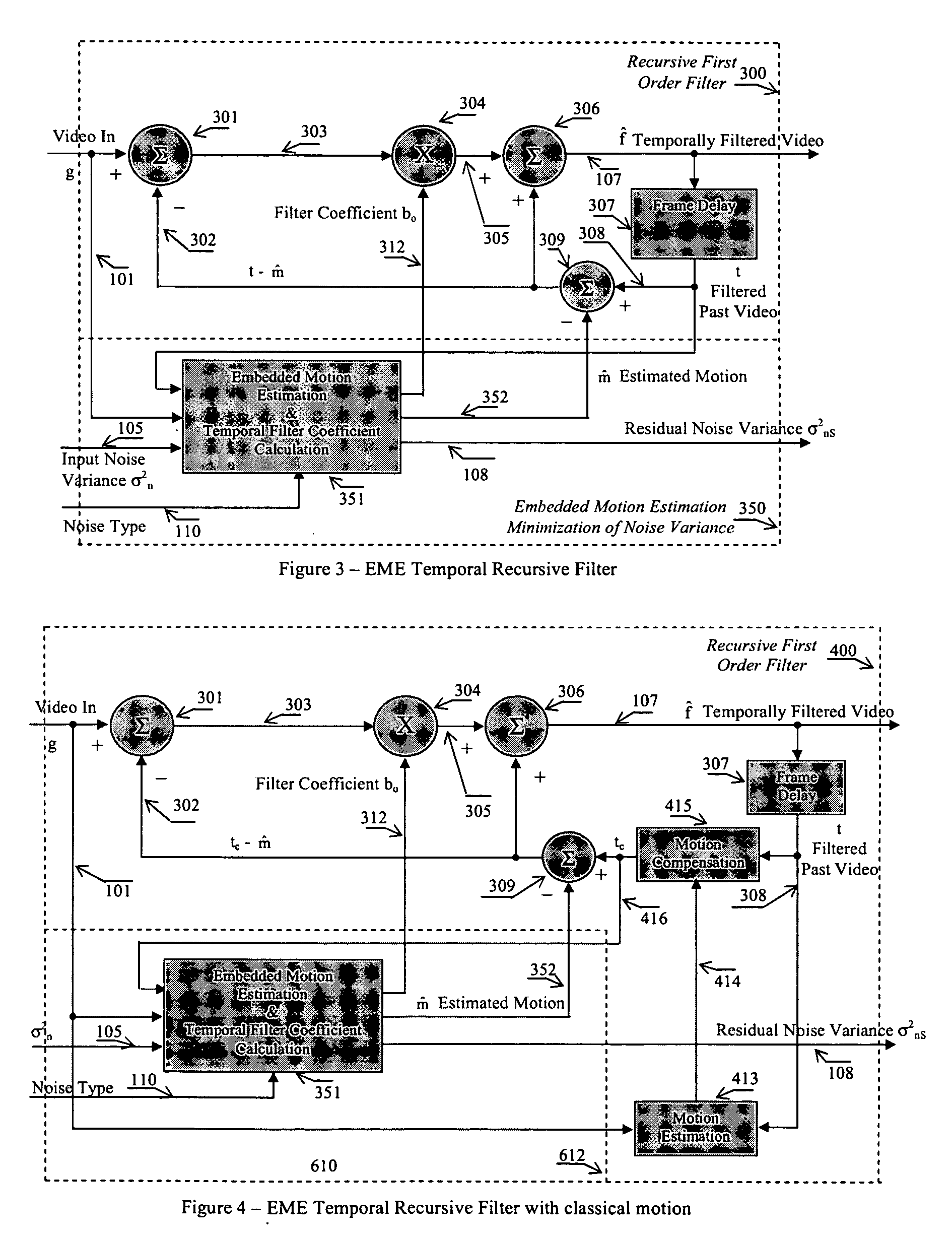
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D noise reduction
InactiveUS20060056724A1Reduce noiseType of reductionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
A non-iterative 3D processing method and system is disclosed for generic noise reduction. The 3D noise reducer is based on a simple conversion of the five types of noise to equivalent additive noise of varying statistics. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient temporal filtering technique which combines Minimization of Output Noise Variance (MNV) and Embedded Motion Estimation (EME). The proposed temporal filtering technique may be furthermore combined with classical motion estimation and motion compensation for more efficient noise reducer. The proposed technique comprises also a spatial noise reducer which combines Minimum Mean Squared Error (MMSE) with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing (SAW) is utilized for smoothing random noise in the whole image, particularly for edge regions. Another modification to MMSE is also introduced for handling banding effect for eventual excessive filtering in slowly varying regions.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
Method for Jointly Optimizing Noise Reduction and Voice Quality in a Mono or Multi-Microphone System
ActiveUS20110257967A1Reduce noiseDecreased energy levelSpeech analysisTransducer circuit dampingAdaptive denoisingEngineering
The present technology provides adaptive noise reduction of an acoustic signal using a sophisticated level of control to balance the tradeoff between speech loss distortion and noise reduction. The energy level of a noise component in a sub-band signal of the acoustic signal is reduced based on an estimated signal-to-noise ratio of the sub-band signal, and further on an estimated threshold level of speech distortion in the sub-band signal. In embodiments, the energy level of the noise component in the sub-band signal may be reduced to no less than a residual noise target level. Such a target level may be defined as a level at which the noise component ceases to be perceptible.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
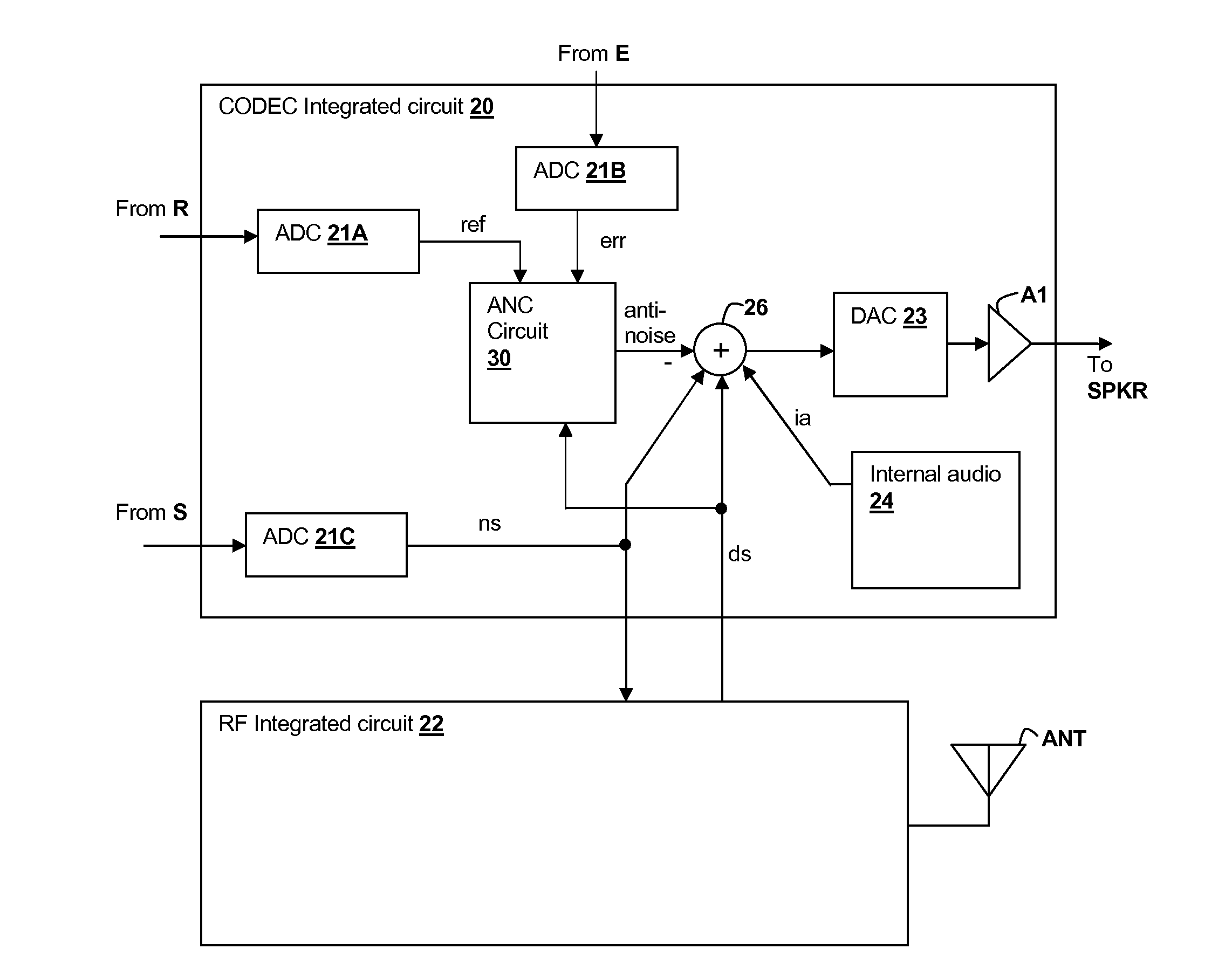
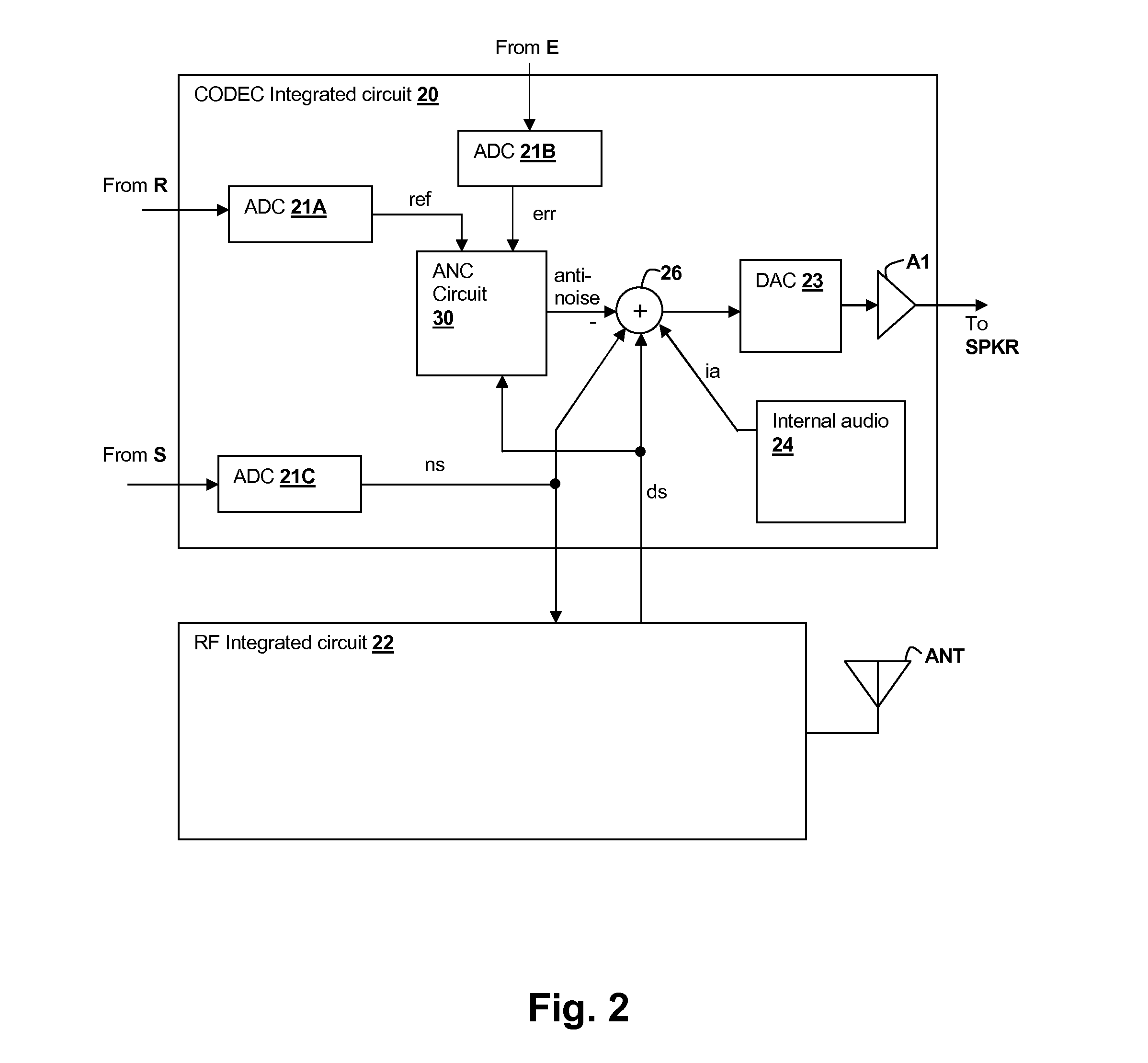
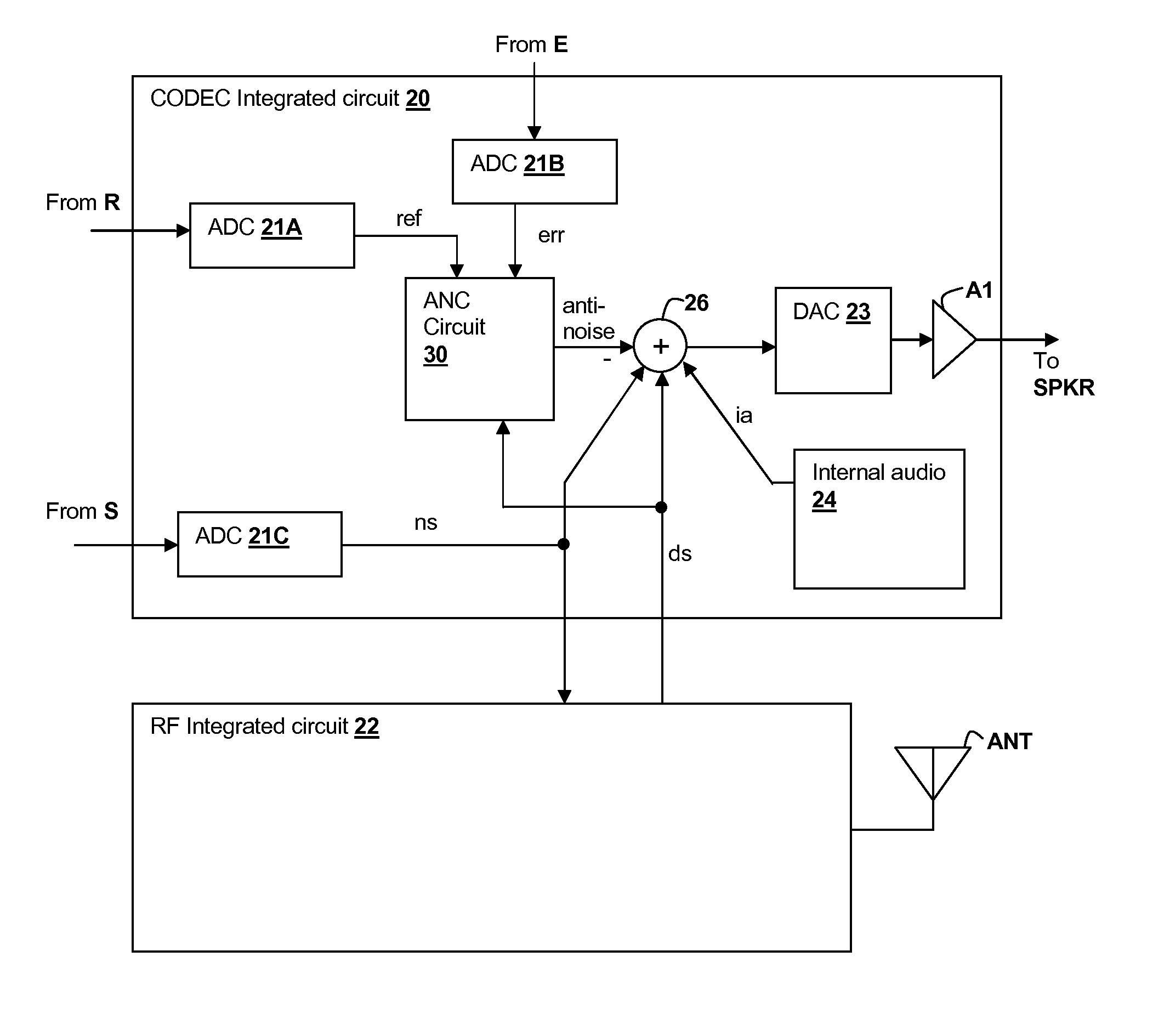
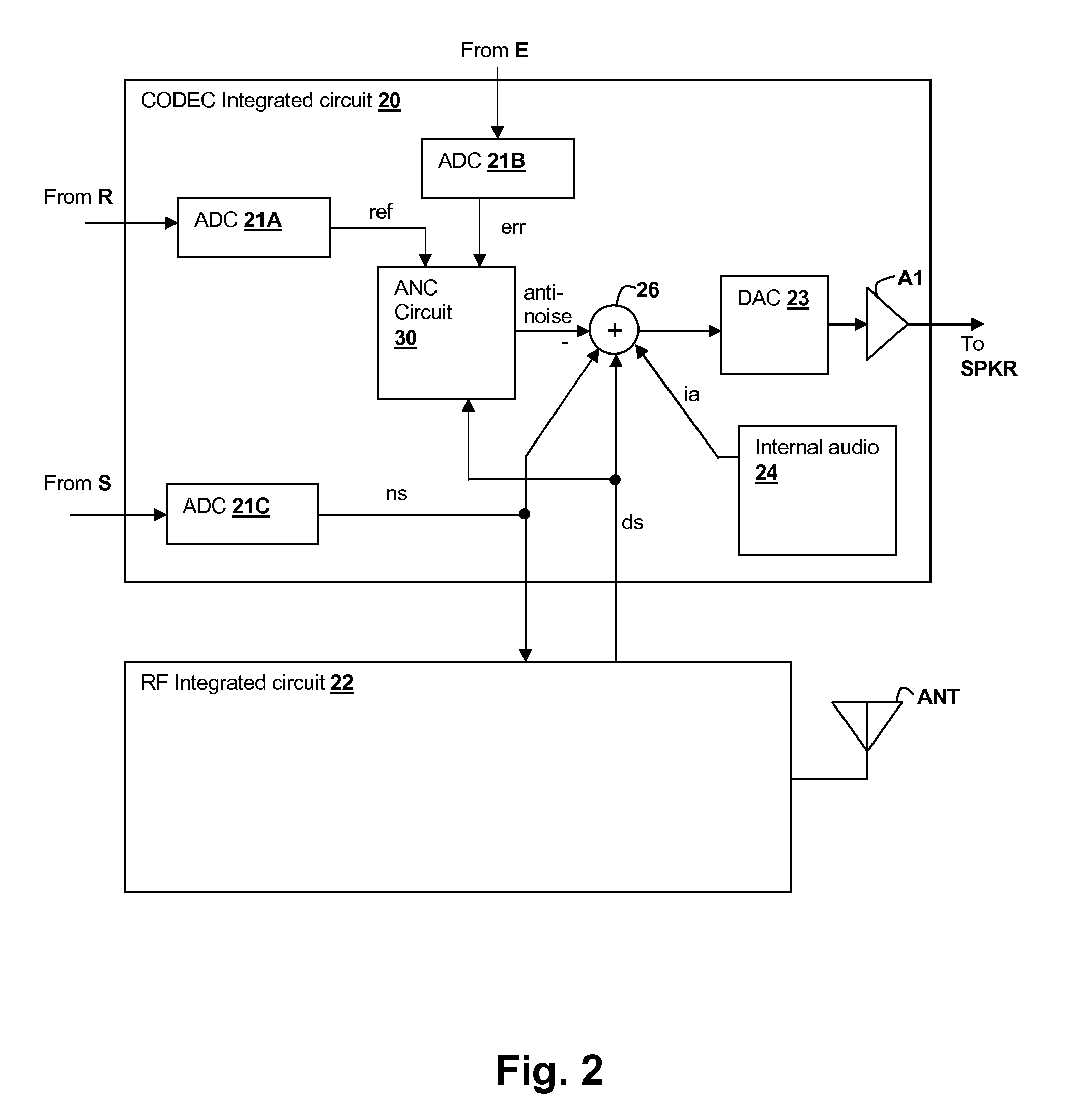
Speaker damage prevention in adaptive noise-canceling personal audio devices
ActiveUS20120308021A1Avoid damageMaximal cancellationEar treatmentNoise generationAdaptive denoisingTransducer
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes noise canceling circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. A processing circuit monitors a level of the anti-noise signal, determines that the anti-noise signal may cause damage to the transducer and adjusts the generation of the anti-noise signal such that damage to the transducer is prevented.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Cloth defect detection method based on image processing
InactiveCN107870172AMeet the needs of quality managementIncrease production capacityImage analysisOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSelf adaptiveImage based
The invention discloses a cloth defect detection method based on image processing. The method comprises steps as follows: a self-adaptive denoising algorithm is adopted according to the actual condition on site; (2) a denoised image is subjected to sharpening enhancement processing, so that texture details and edge contours of image defects are enhanced, and extraction of follow-up characteristicvalues is more reliable; (3) the image defects are subjected to segmentation, smoothing and circulation enhancement processing with a morphological algorithm and a circulation area marking method; (4)characteristic values of the cloth are extracted and normalized; (5) the cloth defects are recognized and classified. According to the cloth defect detection method based on image processing, an automatic cloth checking system based on image processing and information integration is researched and developed, and functions including automatic detection, finished product grading, quality statisticanalysis, information sharing, concentrated monitoring and management and the like of the cloth defects are completed, so that the common technical problems that the labor intensity is high, the production efficiency is low and the like when conventional manual cloth checking and manual counting are adopted in the textile dyeing and finishing industry are solved.
Owner:LIMING VOCATIONAL UNIV
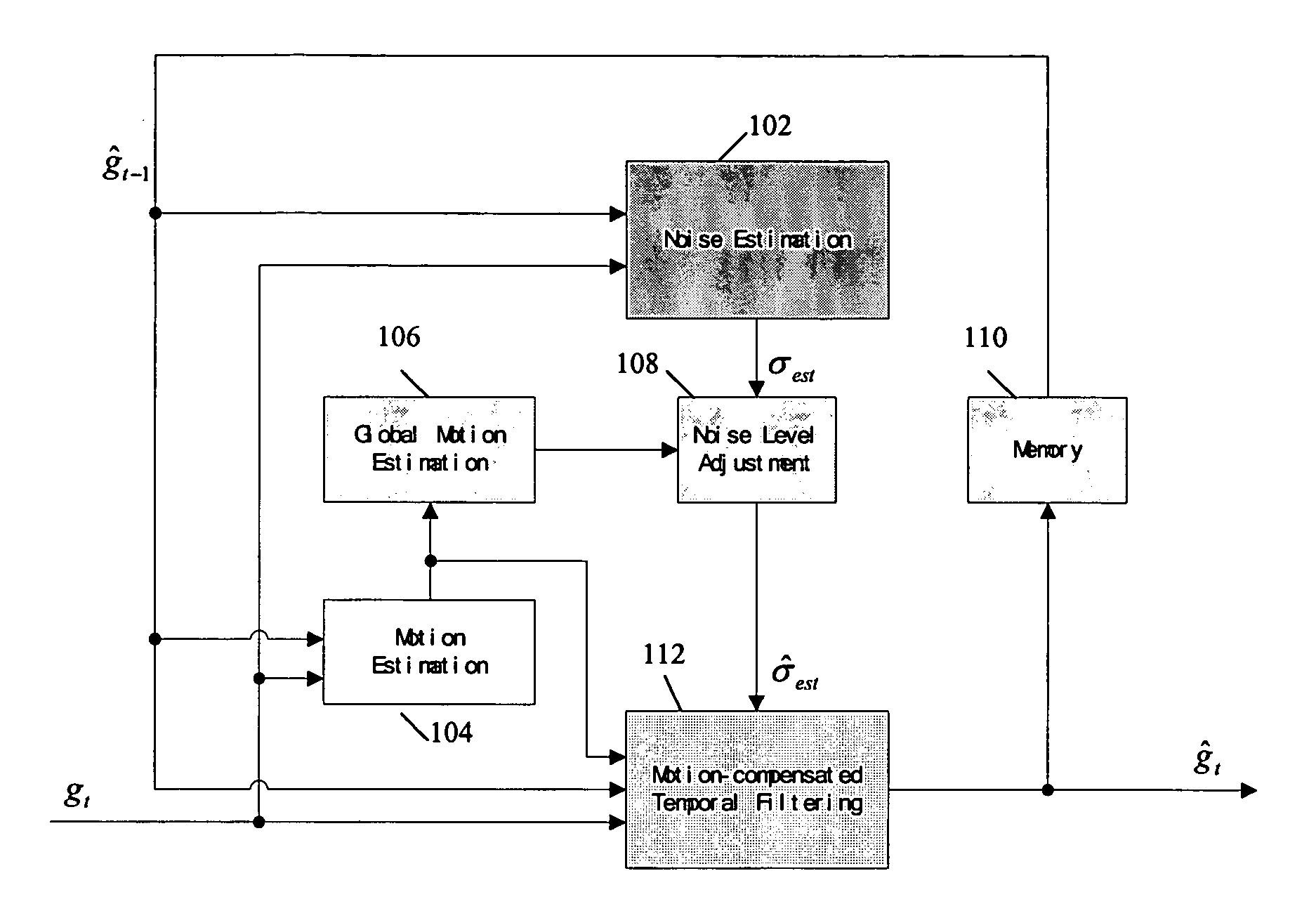
Methods for adaptive noise reduction based on global motion estimation
InactiveUS20070070250A1Reduce noiseEasy to adjustTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionMotion vector
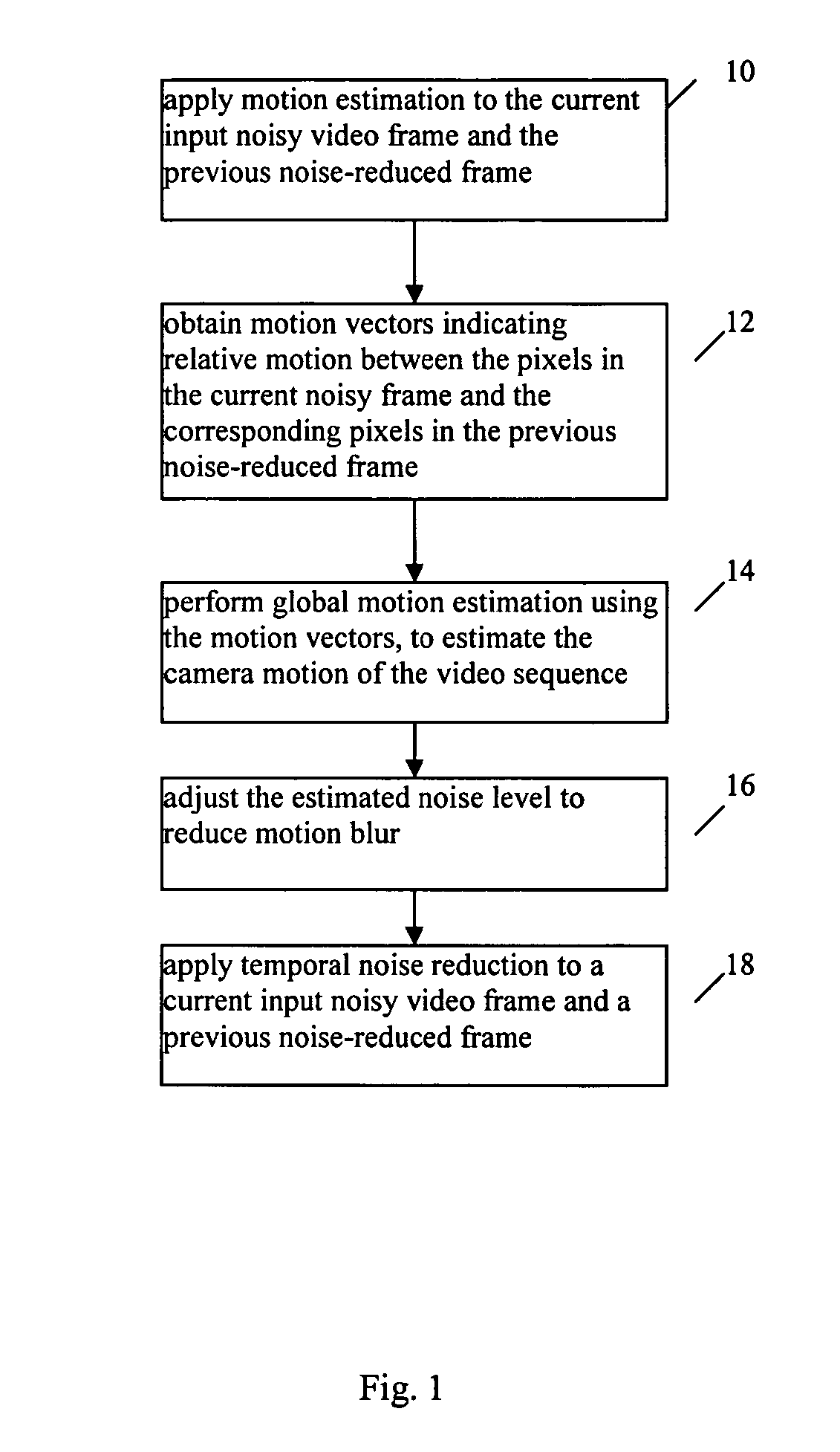
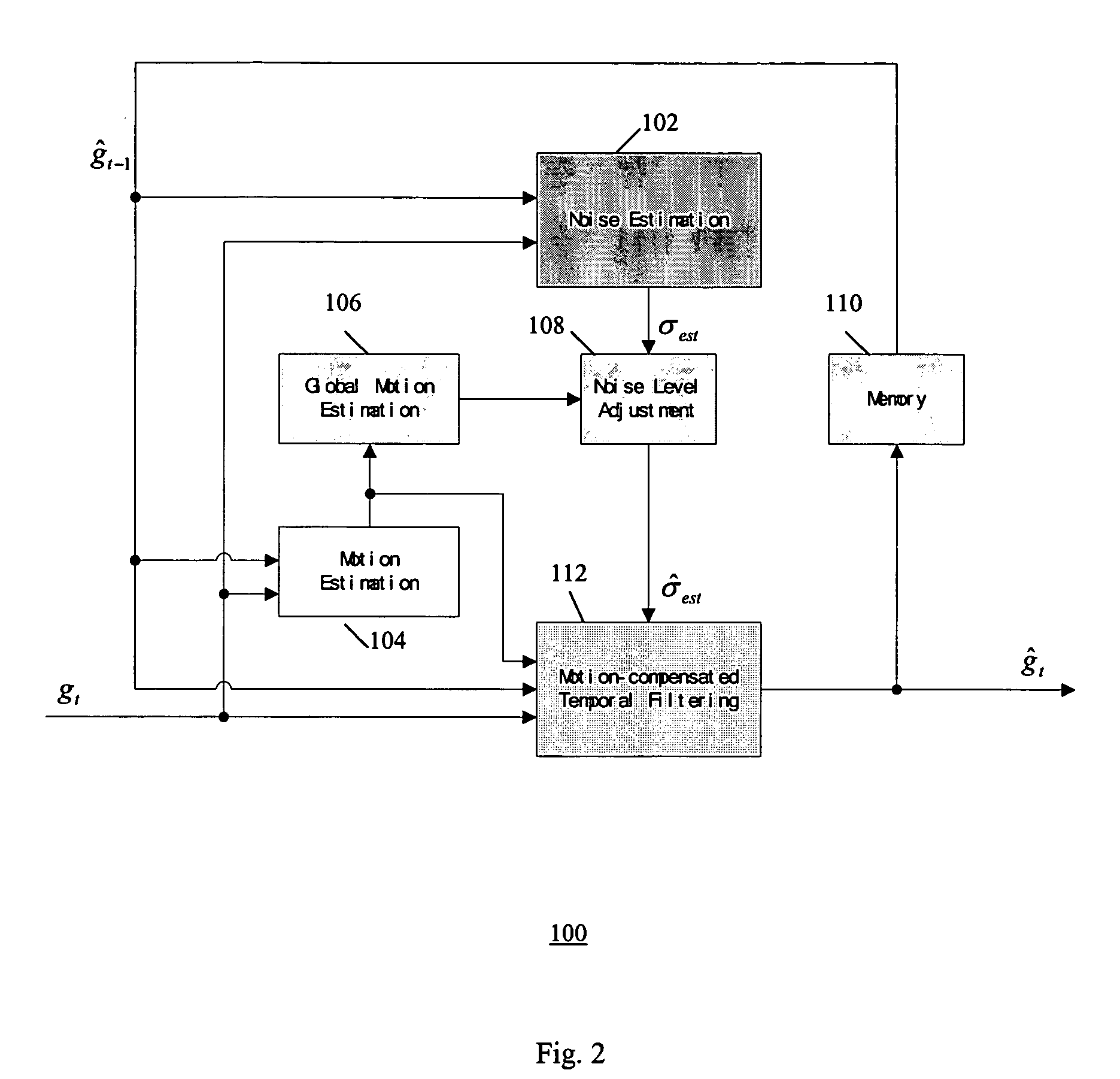
An improved temporal noise reduction method and system detects the global motion and adjusts the overall gain of the temporal filtering. Temporal noise reduction is applied to two video frames, wherein one video frame is the current input noisy frame, and the other video frame is a previous filtered frame stored in memory. In this method, noise estimation is first performed to estimate the noise variance / standard deviation in the input video sequence. Then, motion estimation is applied to obtain the motion vectors indicating relative motion between the pixels in the current noisy frame and the corresponding pixels in the previous noise-reduced frame. From such motion vectors, global motion estimation is applied to estimate the camera motion of the video sequence. If reliable global motion is obtained, the overall gain of the temporal filtering is reduced by adjusting the estimated noise level. Motion blur is thus prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
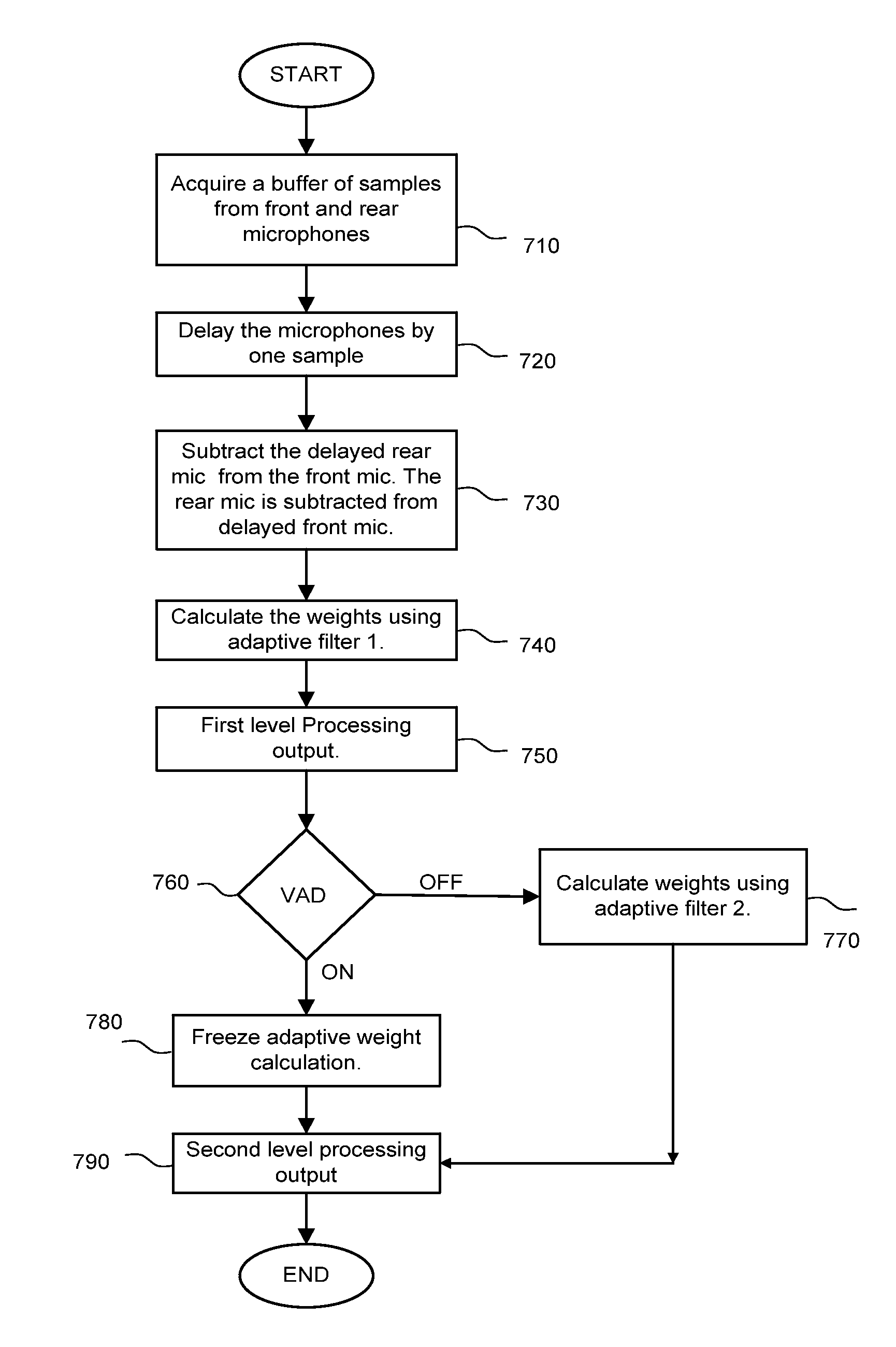
Method and device for reducing noise of two microphones of terminal
ActiveCN103079148AEliminate the disadvantages of declining effects and even affecting normal voice qualityOvercome limitationsSpeech analysisTransducer circuitsSound sourcesAdaptive denoising
The invention discloses a method and a device for reducing noise of two microphones of a terminal, and relates to the technical field of communications. The method comprises the following steps of collecting handheld gesture information of the terminal in a real-time way during terminal conversation; according to the handheld gesture information, obtaining a first actual distance between a primary microphone of the terminal and a sound source, and a second actual distance between a secondary microphone of the terminal and the sound source; according to the first actual distance and the second actual distance, adjusting initial noise-reduction parameters in the terminal in a real-time way, so as to obtain a self-adaptive noise-reduction parameter; and according to the self-adaptive noise-reduction parameter, reducing the noise of the conversation audio frequency.
Owner:ZTE CORP
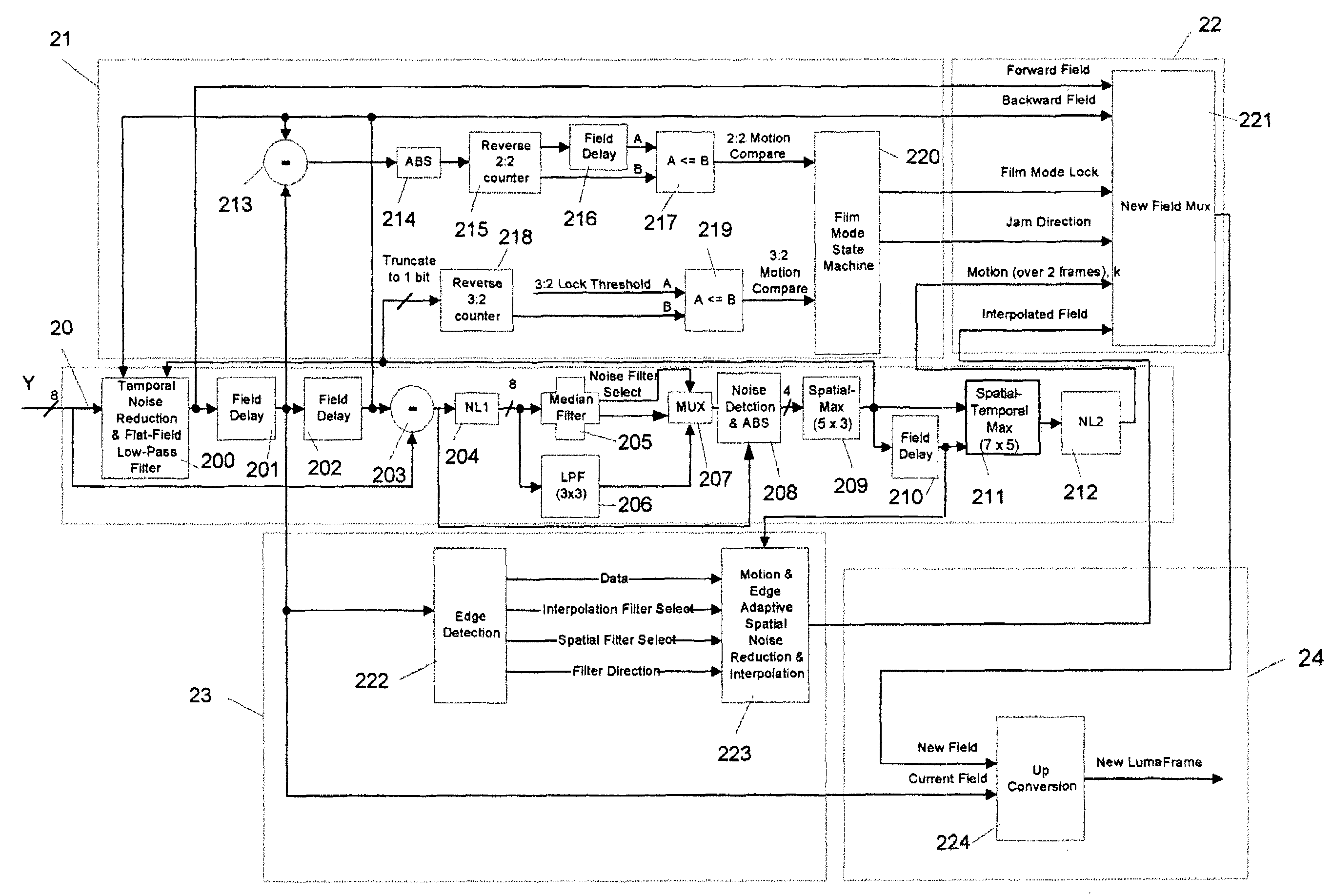
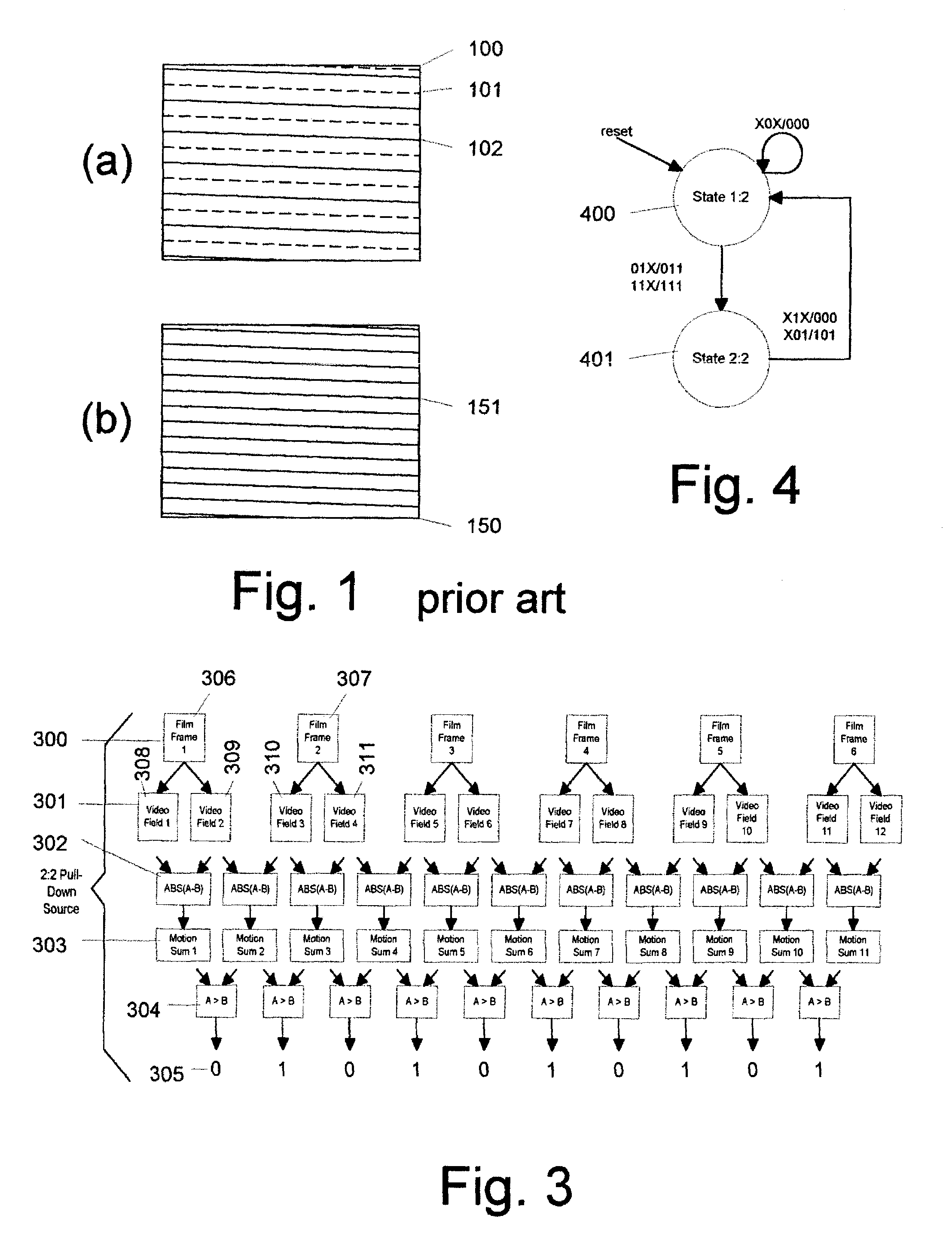
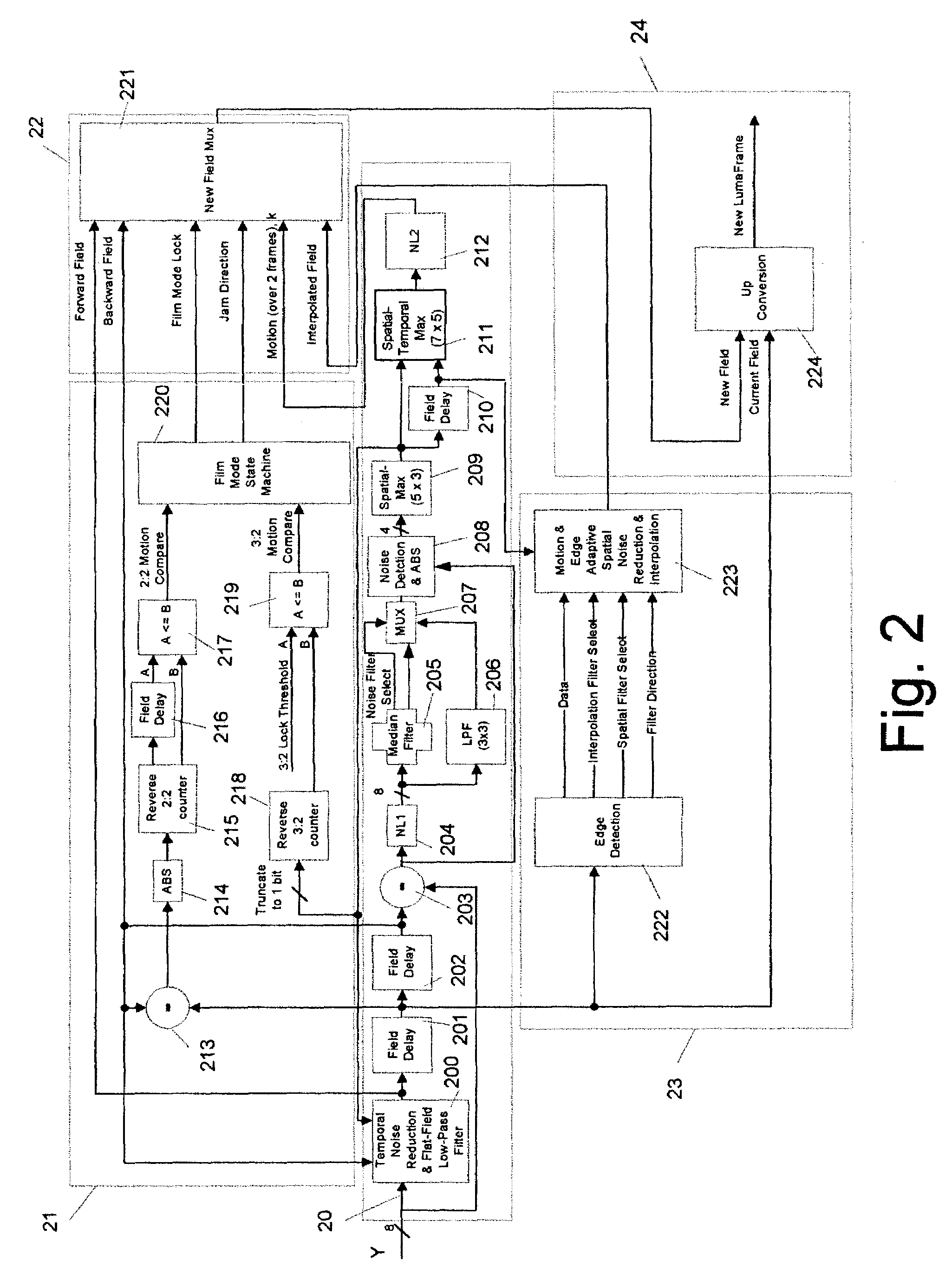
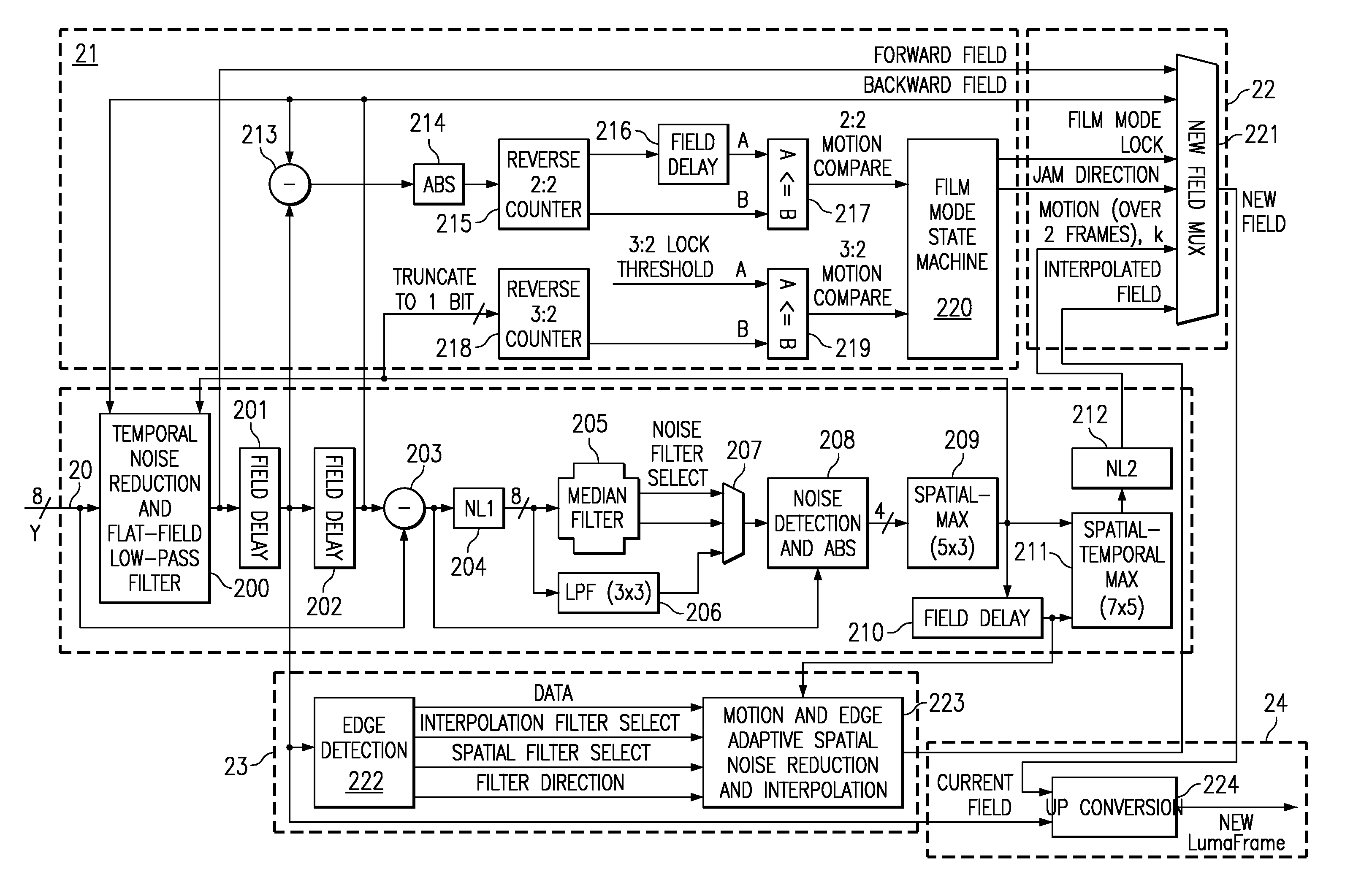
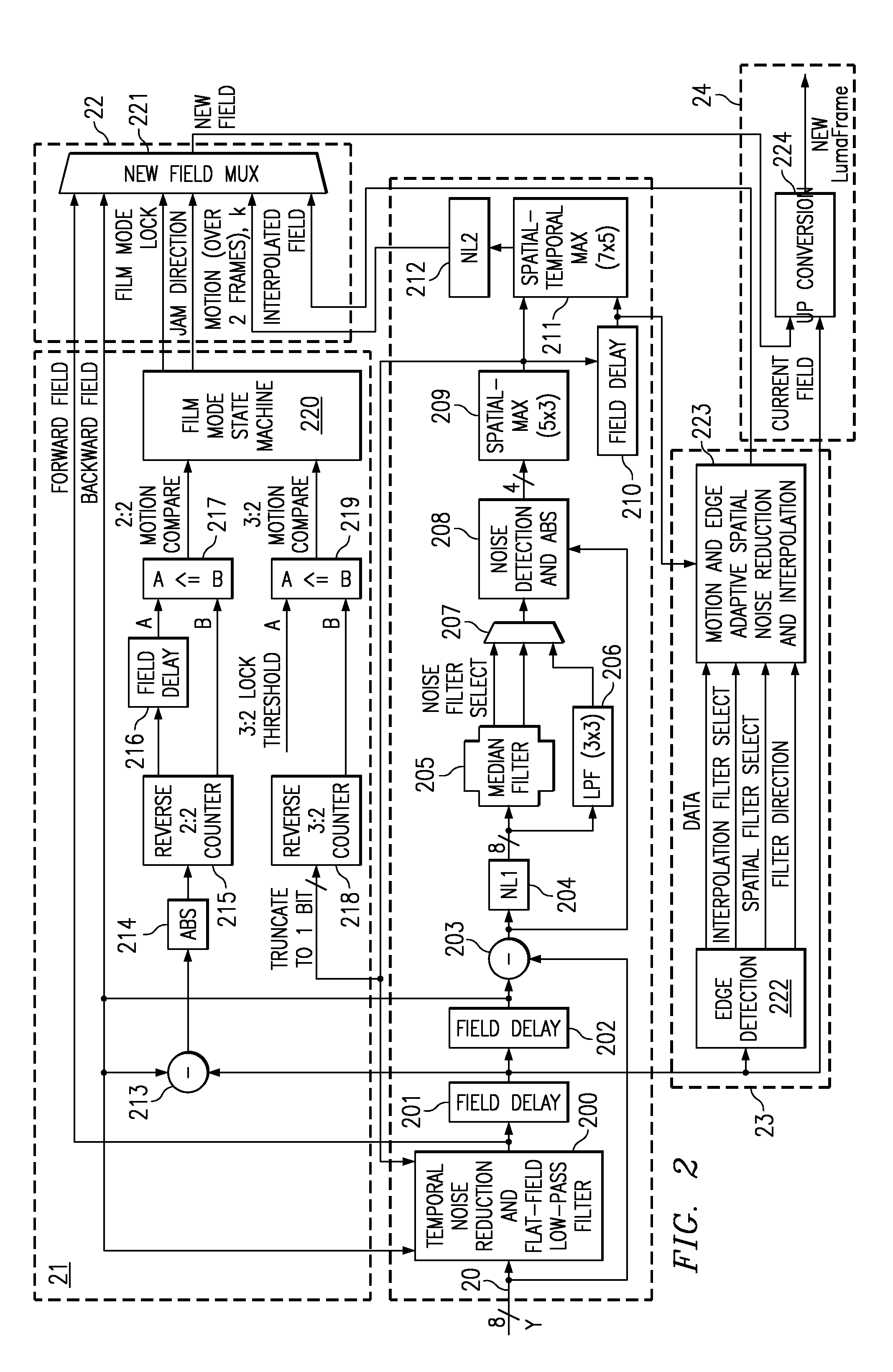
Content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction
ActiveUS7375760B2Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
A content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction that provides a highly integrated, implementation efficient de-interlacer. By identifying and using redundant information from the image (motion values and edge directions), this scan rate converter is able to perform the tasks of film-mode detection, motion-adaptive scan rate conversion, and content-dependent video noise reduction. Adaptive video noise reduction is incorporated in the process where temporal noise reduction is performed on the still parts of the image, thus preserving high detail spatial information, and data-adaptive spatial noise reduction is performed on the moving parts of the image. A low-pass filter is used in flat fields to smooth out Gaussian noise and a direction-dependent median filter is used in the presence of impulsive noise or an edge. Therefore, the selected spatial filter is optimized for the particular pixel that is being processed to maintain crisp edges.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Speaker damage prevention in adaptive noise-canceling personal audio devices
ActiveUS8848936B2Avoid damageMaximal cancellationEar treatmentNoise generationAdaptive denoisingTransducer
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes noise canceling circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. A processing circuit monitors a level of the anti-noise signal, determines that the anti-noise signal may cause damage to the transducer and adjusts the generation of the anti-noise signal such that damage to the transducer is prevented.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
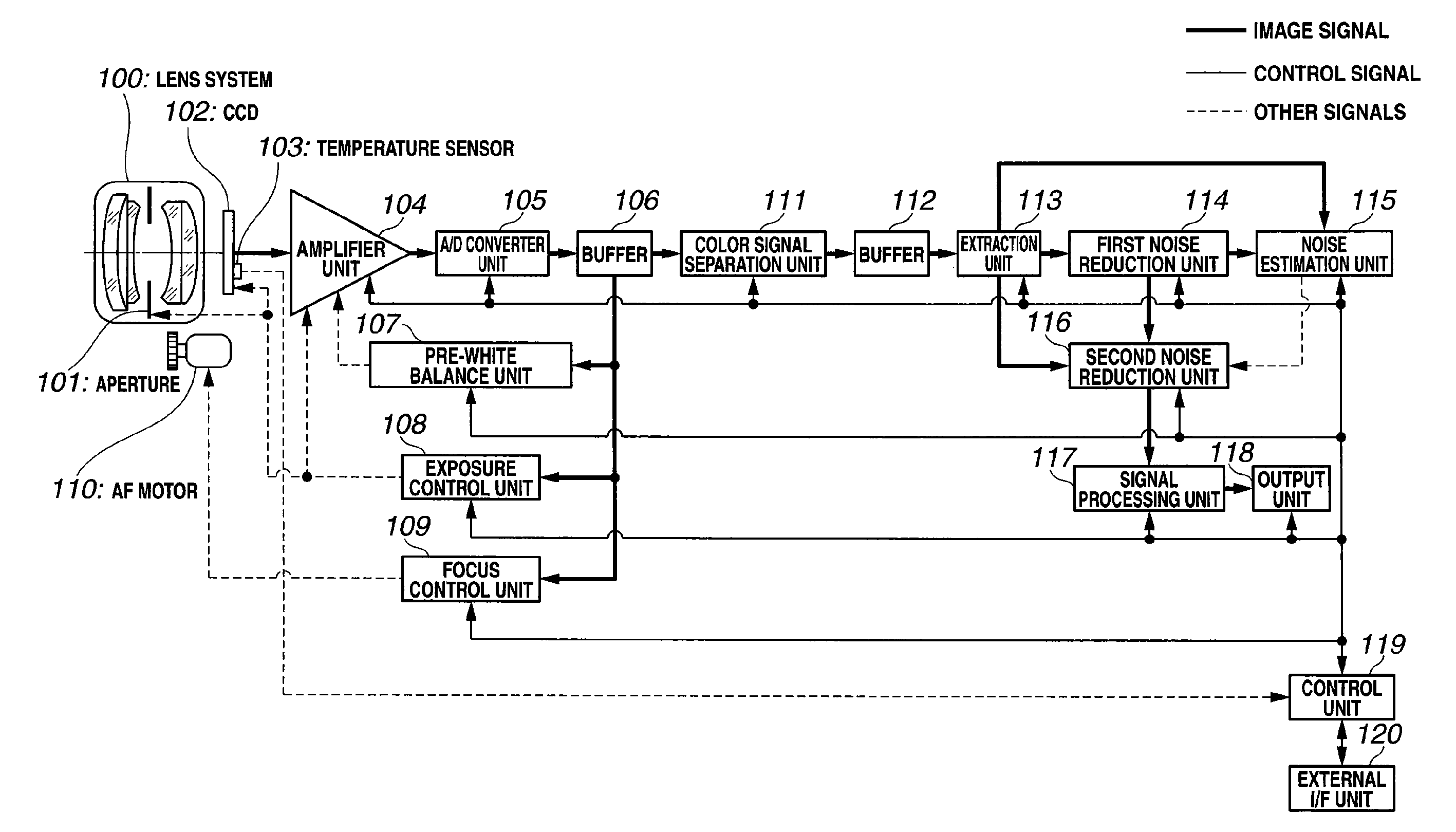
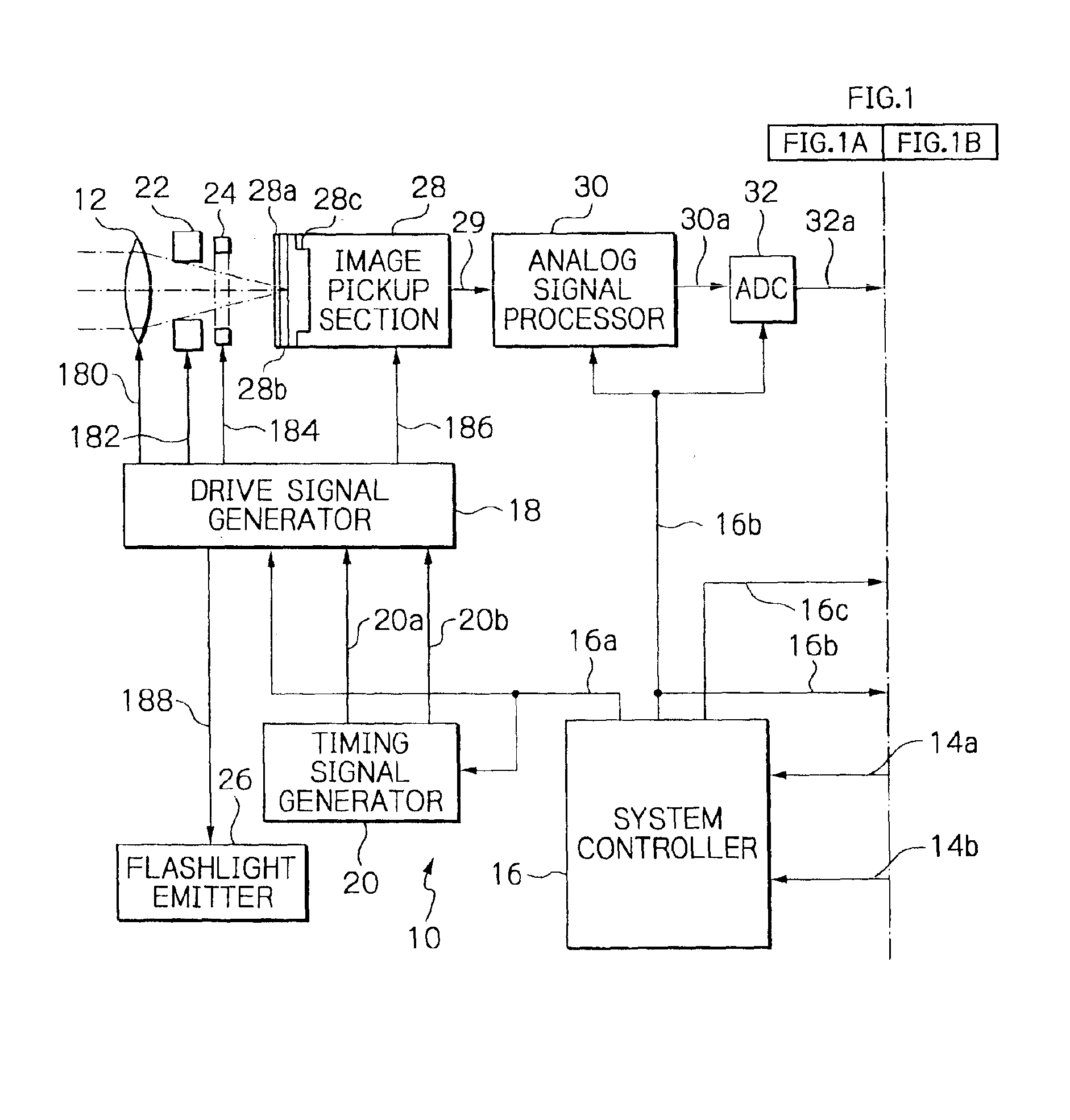
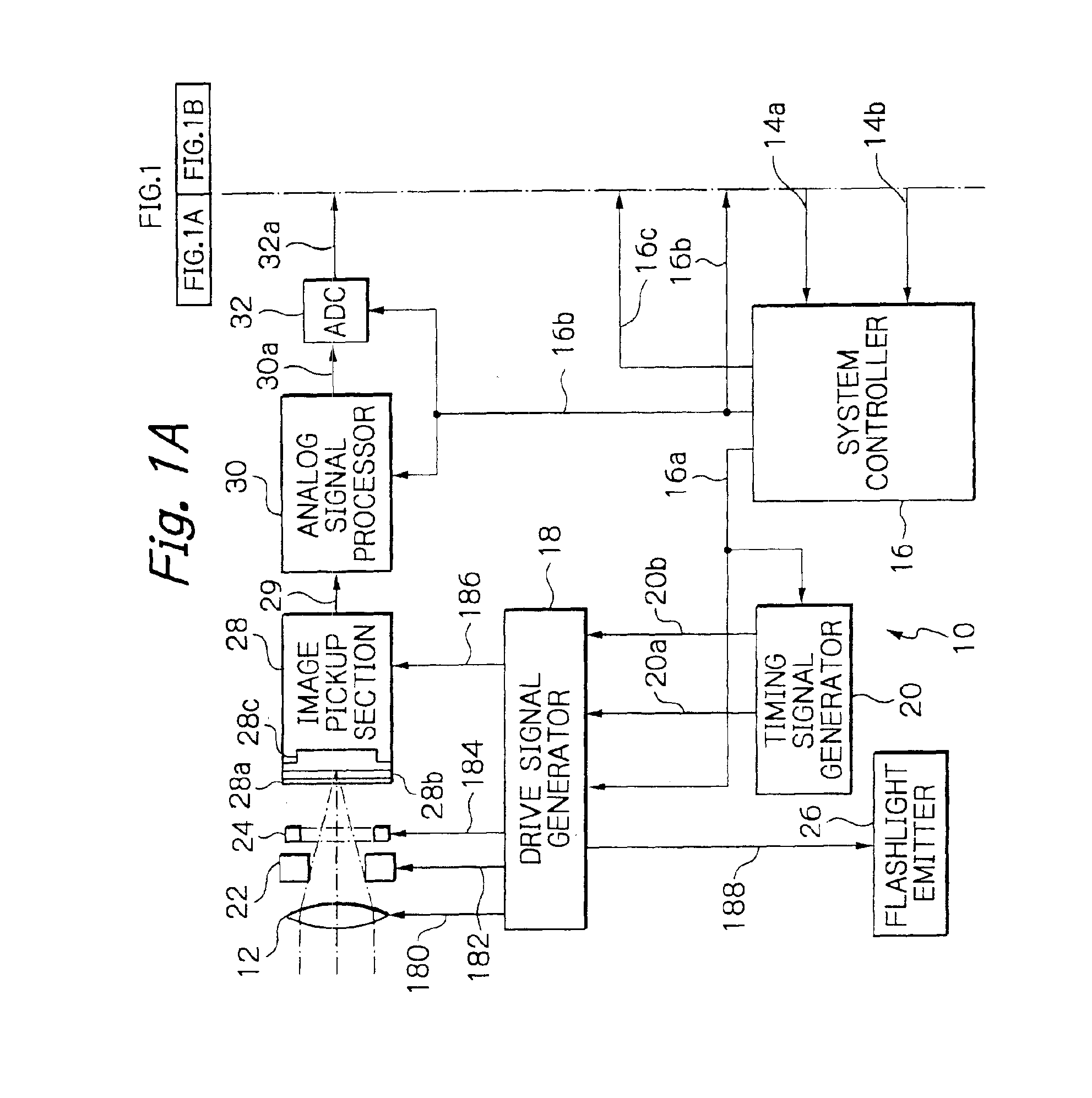
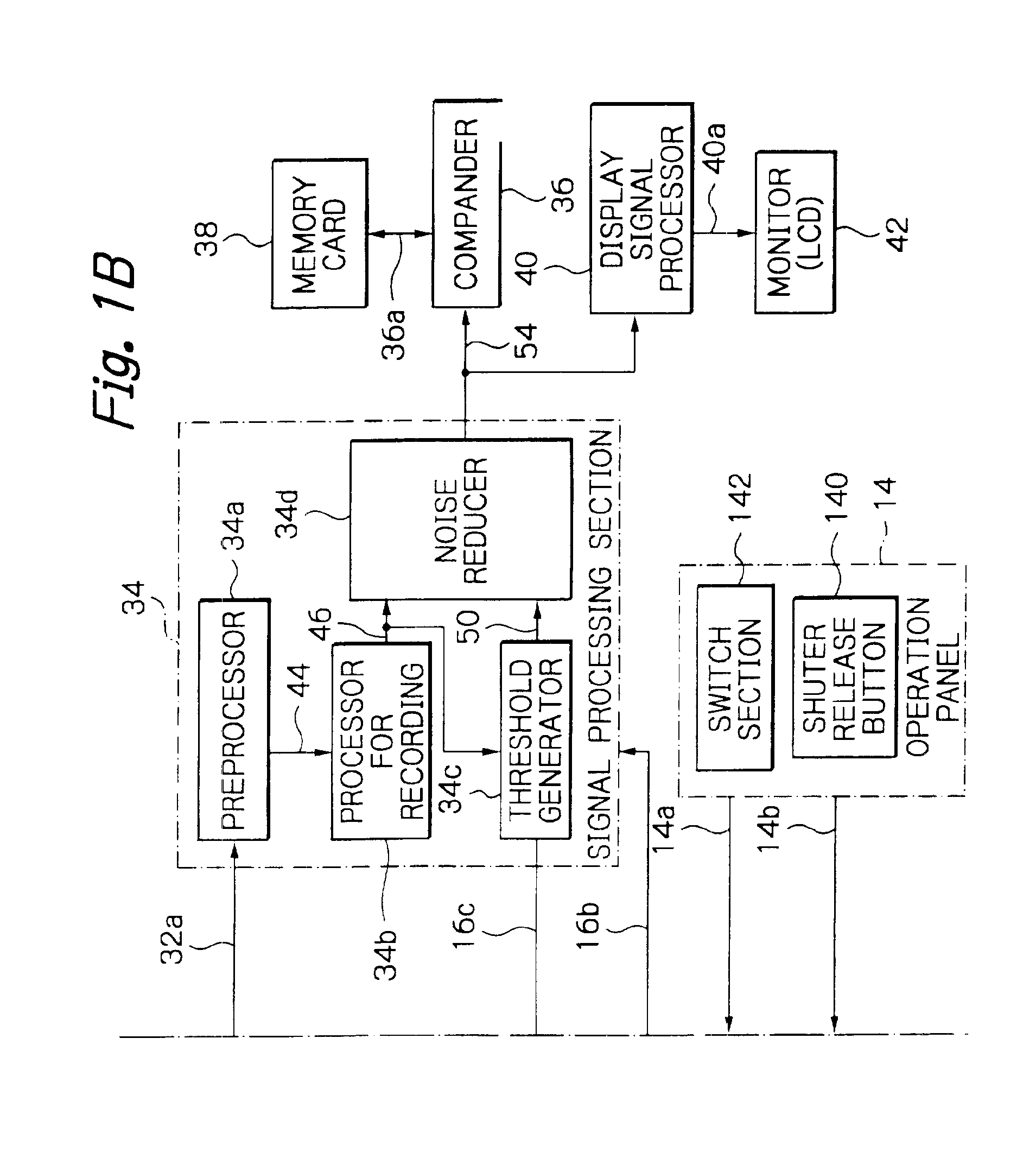
Image capturing system and computer readable recording medium for recording image processing program
ActiveUS20090219417A1Reduce processImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
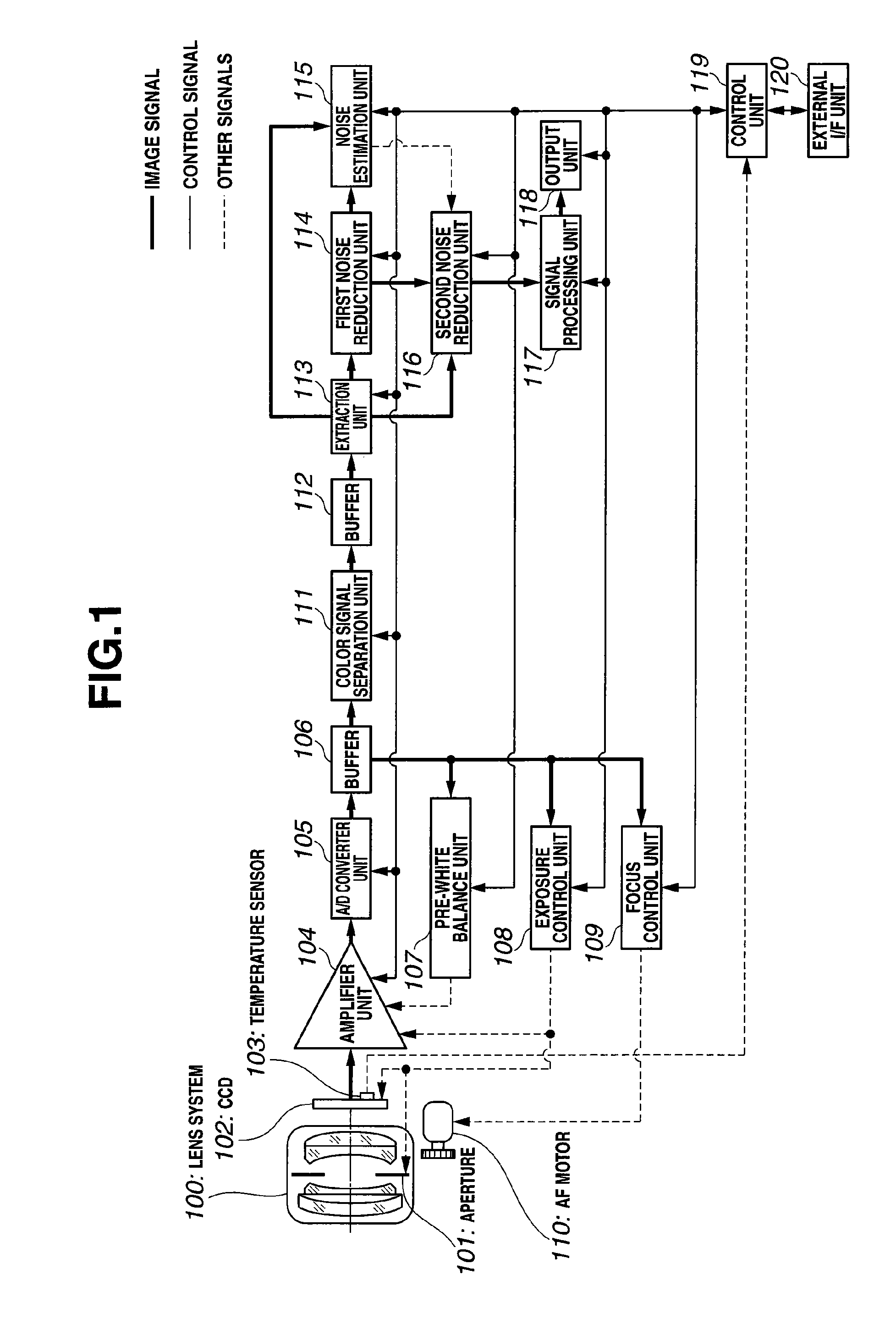
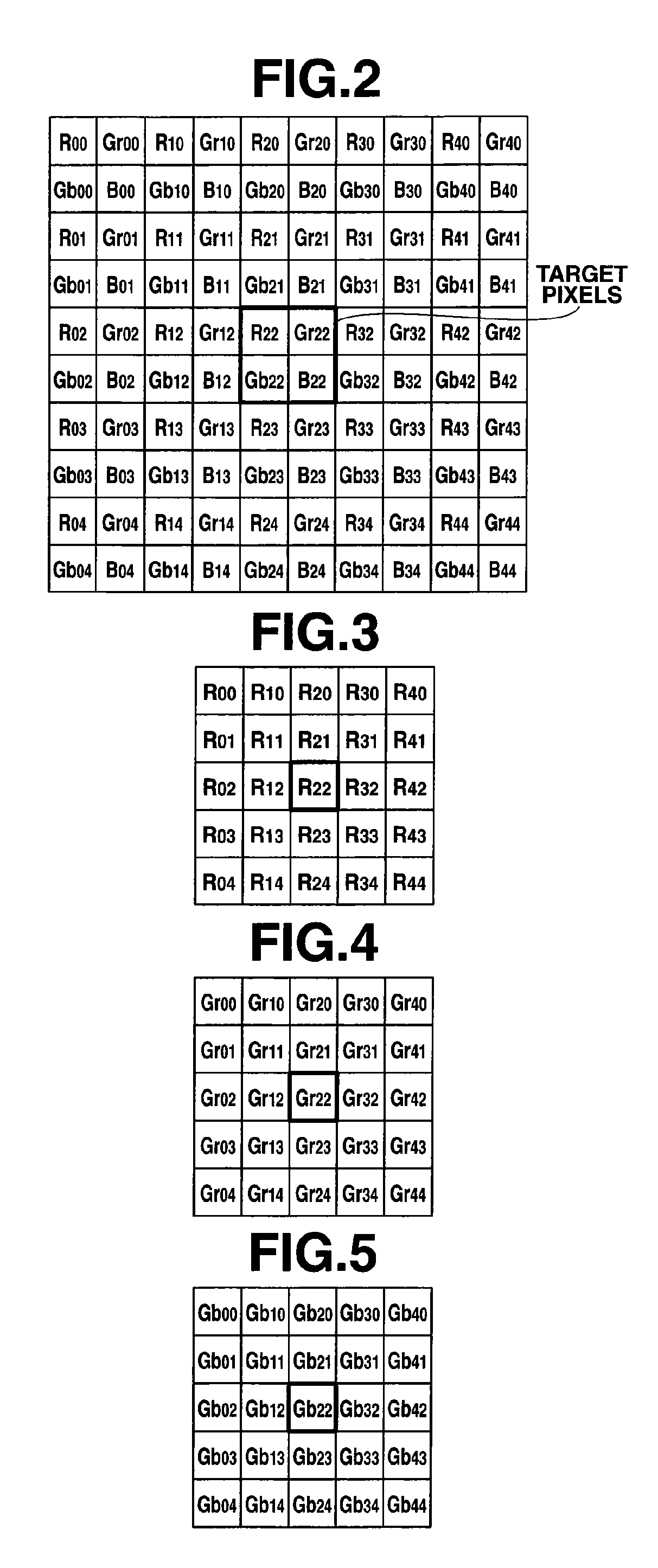
An image capturing system includes: a first noise reduction unit which roughly removes the effects of an edge component by performing edge-preserving adaptive noise reduction processing on a target pixel within a local region including the target pixel and the neighboring pixels extracted from an image signal acquired from a CCD; a noise estimation unit which dynamically estimates the noise amount with respect to the target pixel based upon the target pixel value thus subjected to the noise reduction processing by the first noise reduction unit; and a second noise reduction unit which performs noise reduction processing on the target pixel based upon the target pixel value thus subjected to the noise reduction processing by the first noise reduction unit and the noise amount thus estimated by the noise estimation unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Self-adaptive denoising method and system based on sub-band noise analysis
ActiveCN103871421ASignificant Gain DifferenceImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpeech analysisTarget signalAdaptive denoising
The invention relates to the field of voice technologies, in particular to a self-adaptive denoising method based on sub-band noise analysis. The method includes the steps that firstly, framing and short time frequency domain transformation are conducted on input time domain audio signals with noise, and then frequency domain audio signals with noise are generated; secondly, a noise energy spectrum of the frequency domain audio signals with noise is estimated through a minimum value tracking method; thirdly, the posterior signal to noise ratio and the prior signal to noise ratio of the noise energy spectrum are calculated; fourthly, through a nonlinear gain extension method, denoising gains of all time frequency units are calculated through the posterior signal to noise ratio and the prior signal to noise ratio; fifthly, smoothing filtering is conducted on the denoising gains of all the time frequency units to reduce tone quality distortion; sixthly, the denoising gains act on all the time frequency units of the audio signals with noise in the first step, and then denoised frequency domain audio signals are acquired; seventhly, short time frequency domain inverse transformation is conducted, and then the final denoised time frequency audio signals are acquired and output. According to the method and system, stable noise in target signals can be greatly lowered.
Owner:厦门莱亚特医疗器械有限公司
Content-Dependent Scan Rate Converter with Adaptive Noise Reduction
InactiveUS20080218630A1Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
A method and device for adaptively denoising video images
InactiveCN102281386AGood denoising effectEfficient removalTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTime domainMotion vector
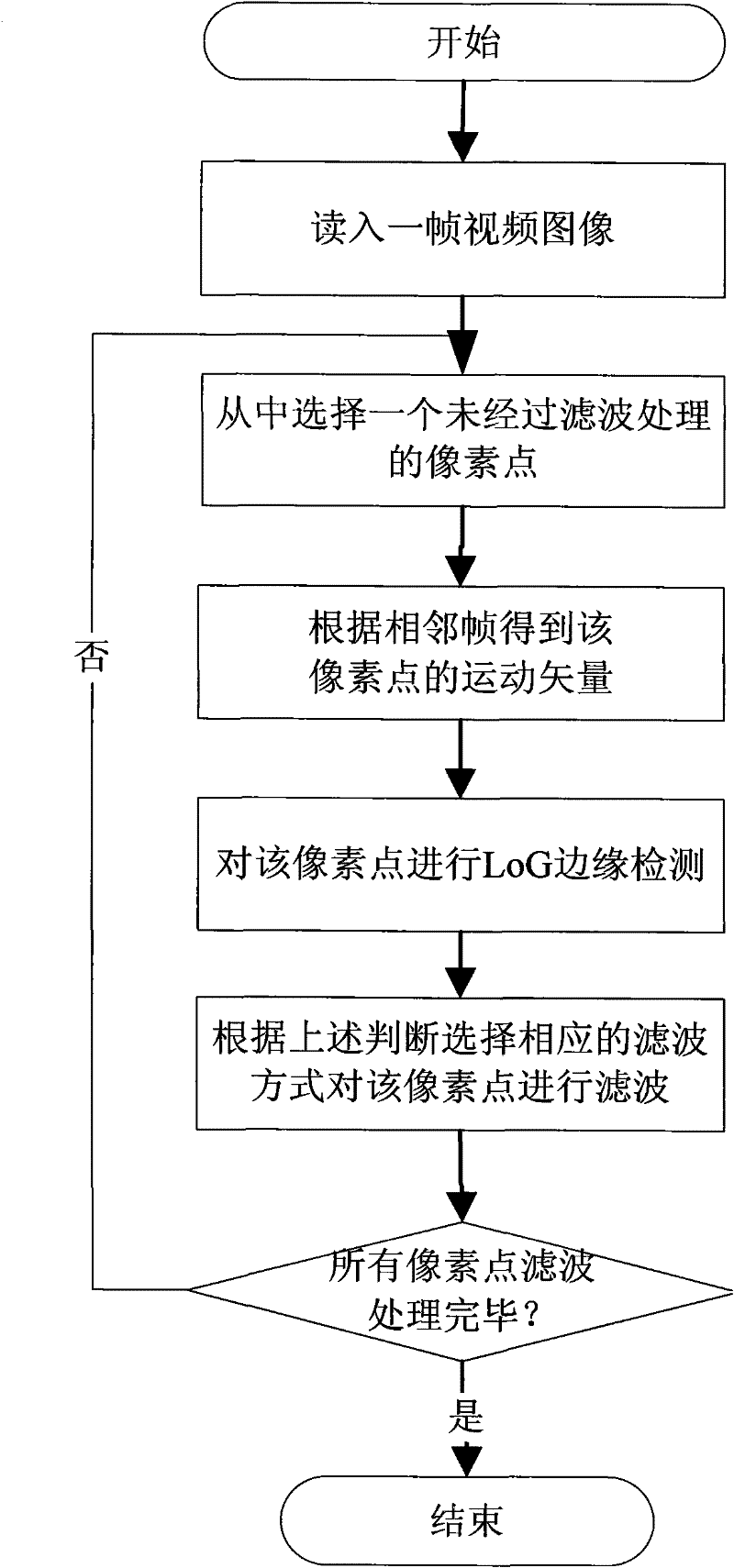
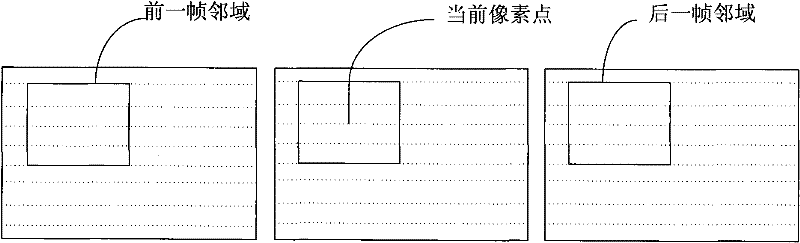
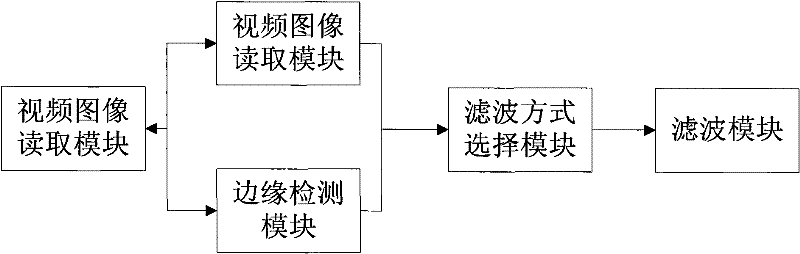
The invention discloses a method and device for performing adaptive denoising on a video image. The device comprises a video image reading module, an edge detection module, a filtering mode selection module and a filtering module; the method comprises the following steps of: reading in a frame of video image from a buffer zone, respectively calculating motion vectors between each pixel in the frame of image and the pixel at the same location in a neighboring frame, and respectively executing the edge detection on each pixel in the frame of image; respectively selecting the filtering mode having corresponding intensity for each pixel according to the edge detection result and the calculation result of the motion vector and of each pixel, and then, correspondingly filtering each pixel by a Gaussian similarity filter. The method and the device have obvious denoising effect on various noises of different scene sequences, and can effectively remove noises by combination of a time domain and a space domain.
Owner:ZTE CORP
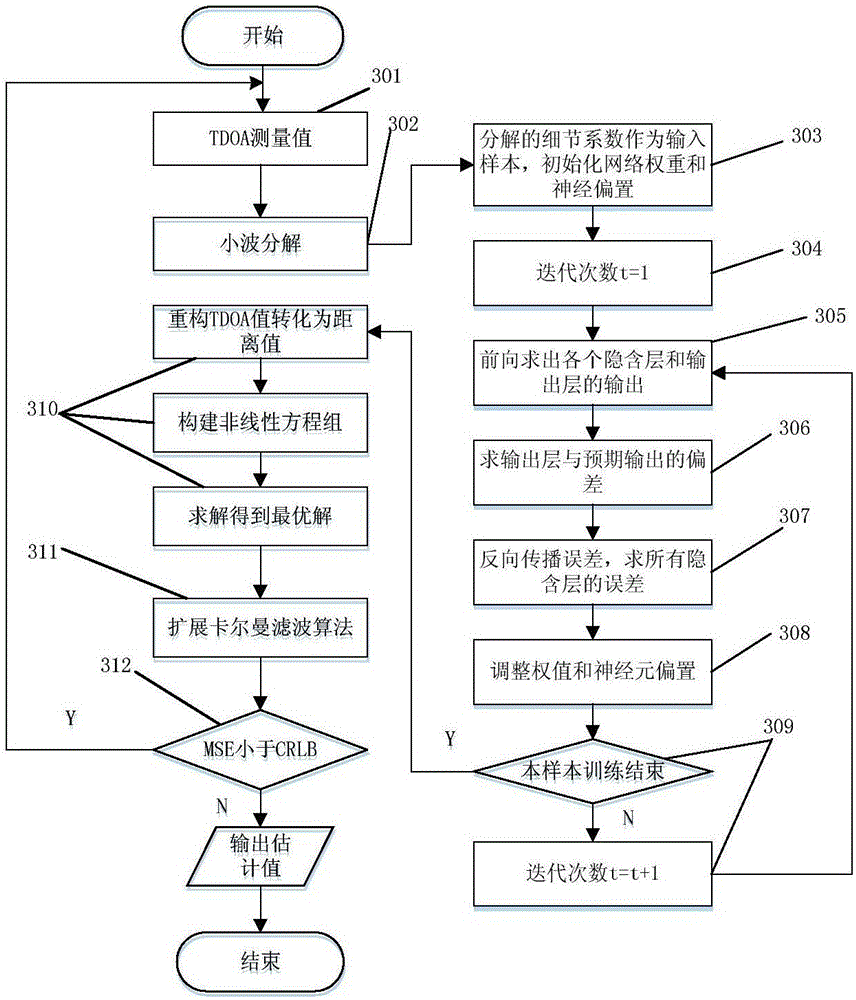
Adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning method and adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning system
ActiveCN106793077AAchieve positioningAchieve precise positioningPosition fixationWireless communicationNonlinear systems of equationsAdaptive denoising
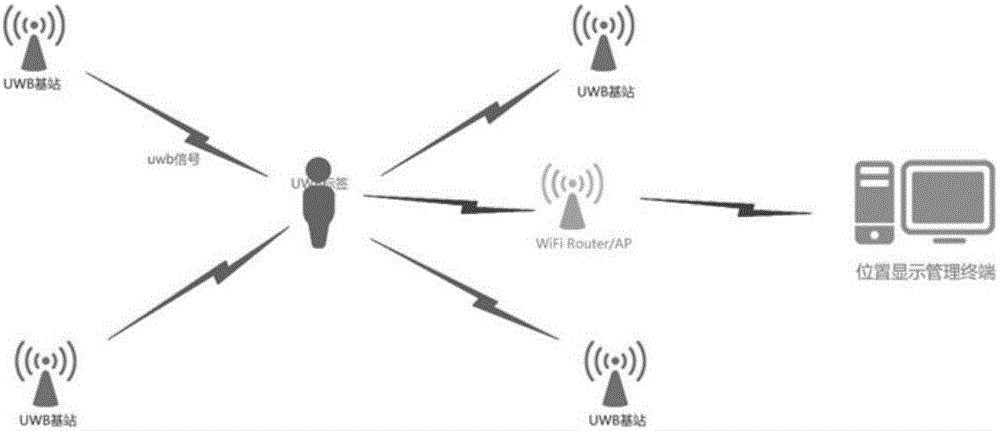
The invention discloses an adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly measuring a TDOA value by using a UWB positioning system; then, processing the measured TDOA value by using a wavelet analysis adaptive denoising method, outputting a reconstructed TDOA value, converting the reconstructed TDOA value into a distance difference, establishing a nonlinear equation set, and obtaining an optimal solution of the equation set; then using the optimal solution as an initial value, performing tracking and positioning on a dynamic target by using an extended Kalman filtering algorithm, and figuring out a final estimated value; and finally outputting the final estimated value. By virtue of the adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning method provided by the invention, a distance measuring error caused by the influence of multipath propagation (Multipath) and non-line-of-sight interference (NLOS) in a UWB signal propagation process can be weakened and even eliminated, the positioning precision is improved, and the accurate positioning of the dynamic target in a non-line-of-sight indoor environment can be realized. The ultra wide band positioning system verifies the validity of the positioning method and realizes the indoor positioning of the dynamic target.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dual Adaptive Structure for Speech Enhancement
InactiveUS20090022335A1Easy to hearEasy to determineSignal processingEar treatmentSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Adaptive denoising
A clear, high quality voice signal with a high signal-to-noise ratio is achieved by use of an adaptive noise reduction scheme with two microphones in close proximity. The method includes the use of two omini directional microphones in a highly directional mode, and then applying an adaptive noise cancellation algorithm to reduce the noise.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
Adaptive noise reduction using level cues
An audio device having two pairs of microphones for noise suppression. Primary and secondary microphones of the three microphones may be positioned closely spaced to each other to provide acoustic signals used to achieve noise cancellation / suppression. A tertiary microphone may be spaced with respect to either the primary microphone or the secondary microphone in a spread-microphone configuration for deriving level cues from audio signals provided by the tertiary and the primary or secondary microphone. Signals from two microphones may be used rather than three microphones. The level cues are expressed via an inter-microphone level difference (ILD) used to determine one or more cluster tracking control signal(s). The ILD based cluster tracking signals are used to control adaptation of null-processing noise suppression modules. A noise cancelled primary acoustic signal and ILD based cluster tracking control signals are used during post filtering to adaptively generate a mask to be applied against a speech estimate signal.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Image signal processor with adaptive noise reduction and an image signal processing method therefor
InactiveUS6882754B2Reduce noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSignal processing circuits
An image signal processing device includes a signal processing circuit for executing signal processing for correction and recording on image data representative of an input image. Also, the signal processing circuit executes noise reduction on the individual image data in accordance with image inputting conditions and / or a pixel level. In the signal processing circuit, a threshold generating circuit generates a threshold by taking account of the image inputting conditions and / or a pixel level. During noise reduction, a noise reducing circuit produces a difference in level between the subject pixel data whose noise is to be detected and the mean value of the subject pixel data and pixel data around the subject pixel. The noise reducing circuit then selects either one of the subject pixel data and mean value in accordance with the difference and threshold.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
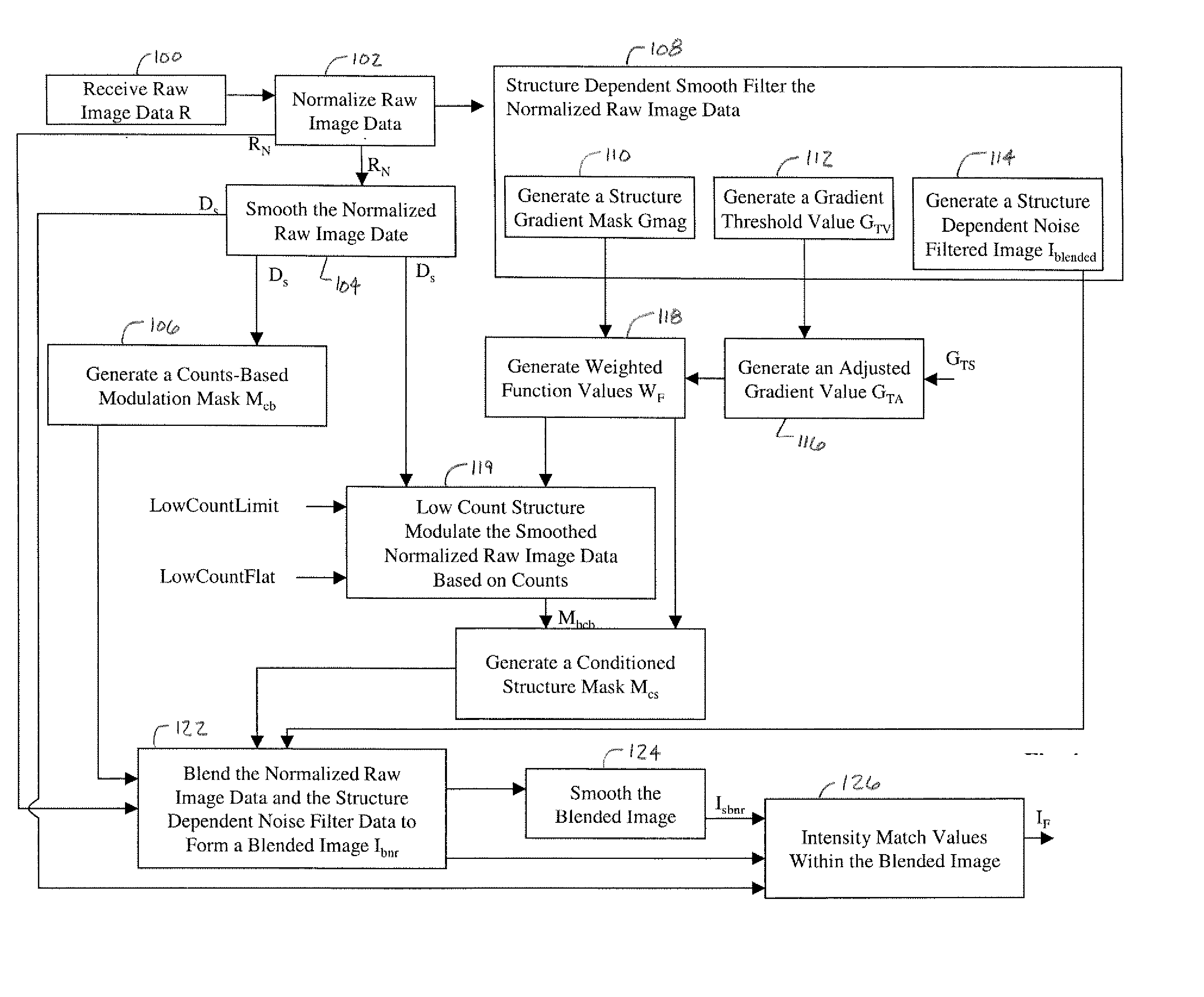
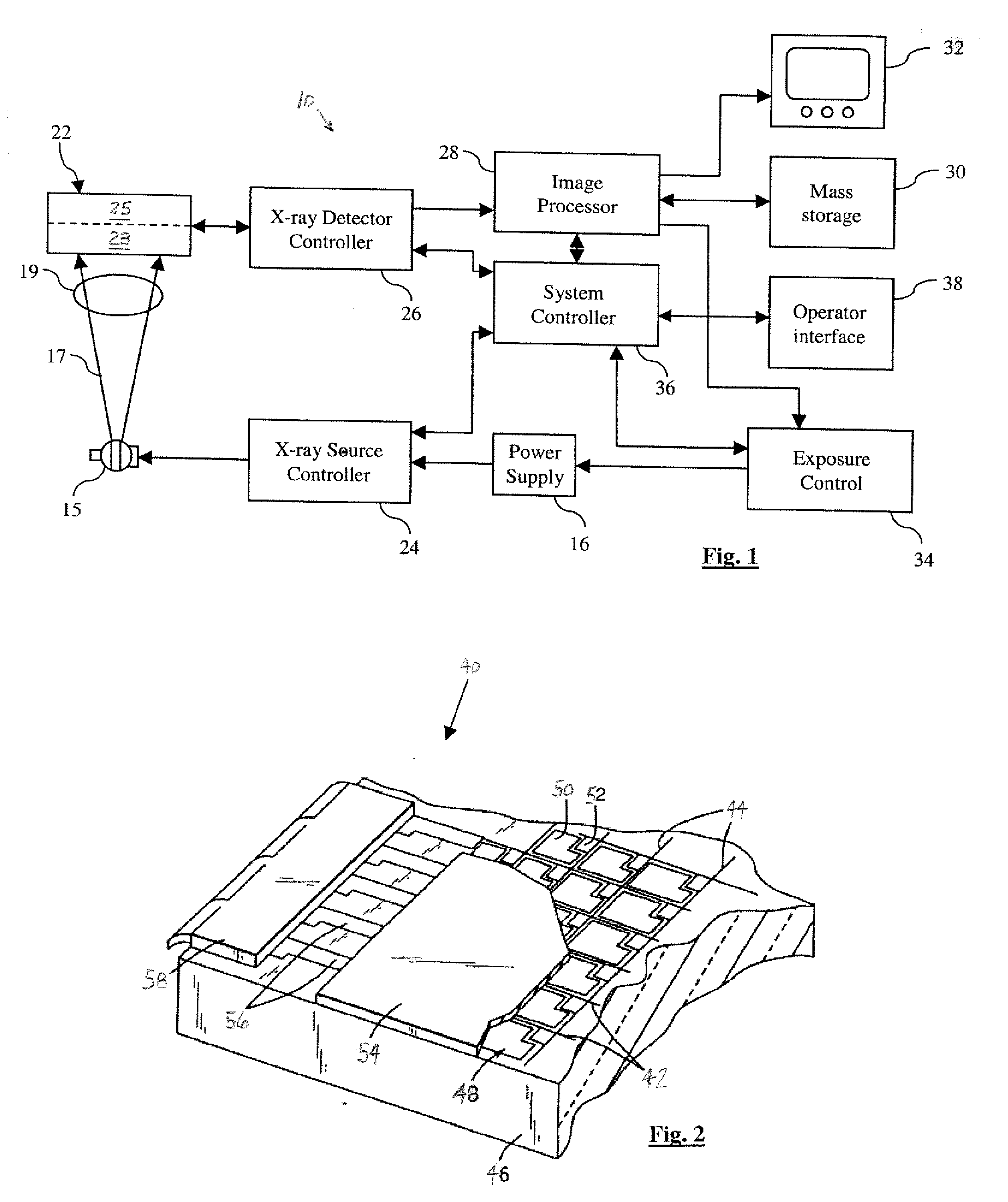
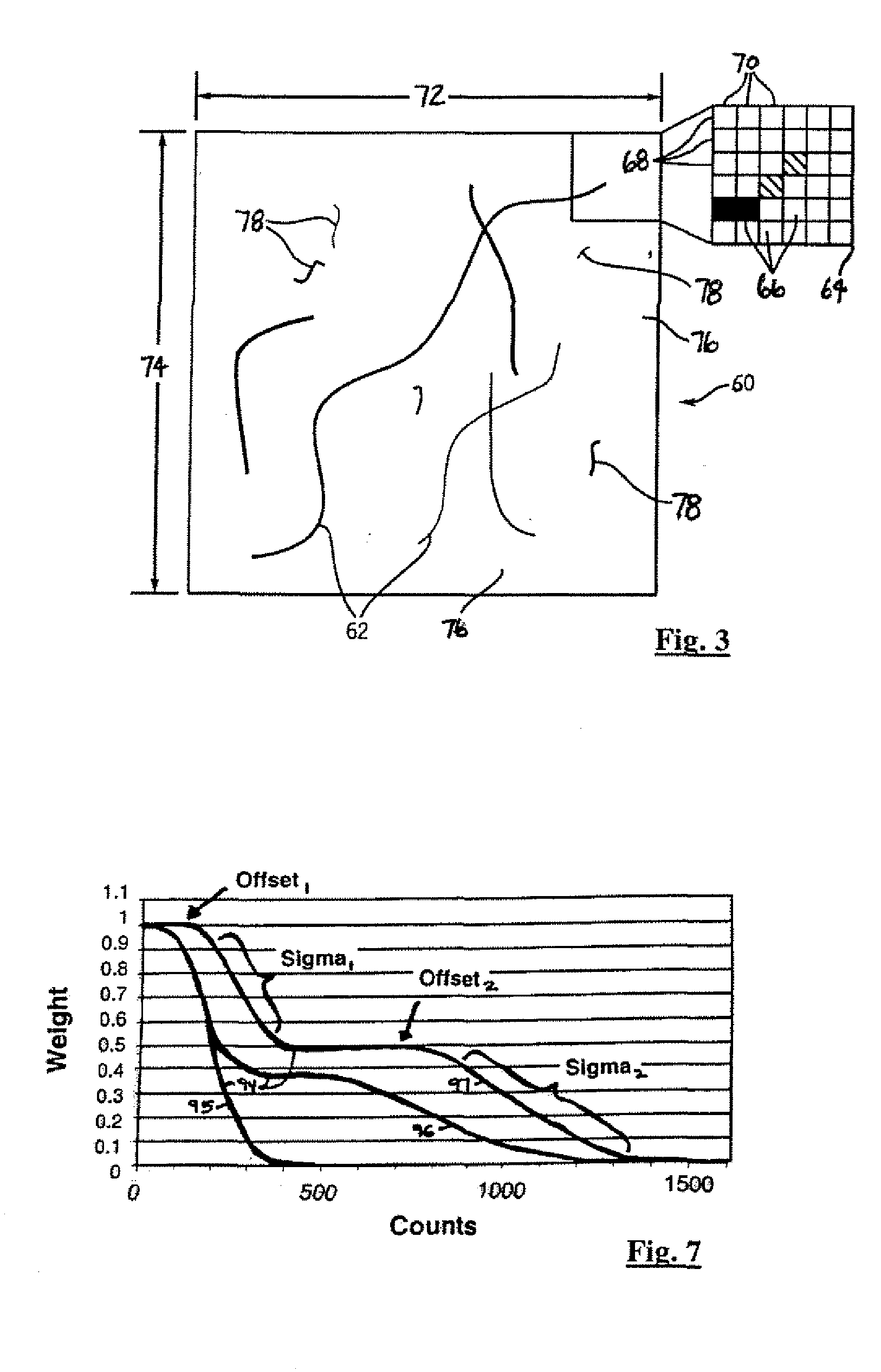
Count adaptive noise reduction method of x-ray images
InactiveUS20060008174A1Reduce noiseImage degradationImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayAdaptive denoising
A method of adaptively reducing noise within an x-ray image includes receiving raw data (R) representing a detected x-ray signal from an object. A counts-based modulation mask (Mcb) is generated in response to the raw data (R). In one embodiment, a structure dependent noise filtered image (Iblended) is generated in response to the raw data. A noise-reduced image (IF) is generated in response to the counts-based modulation mask (Mcb) and the structure dependent noise filtered image (Iblended). In another embodiment, a structure gradient mask (Mcs) is generated in response to the raw data (R). The noise-reduced image (IF) is generated in response to the counts-based modulation mask (Mcb) and the structure gradient mask (Mcs).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Dual Adaptive Structure for Speech Enhancement
InactiveUS20110135107A1Easily hear and determineAttenuate and even eliminate pre-selected portionSignal processingEar treatmentSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Adaptive denoising
A clear, high quality voice signal with a high signal-to-noise ratio is achieved by use of an adaptive noise reduction scheme with two microphones in close proximity. The method includes the use of two omini directional microphones in a highly directional mode, and then applying an adaptive noise cancellation algorithm to reduce the noise.
Owner:KONCHITSKY ALON
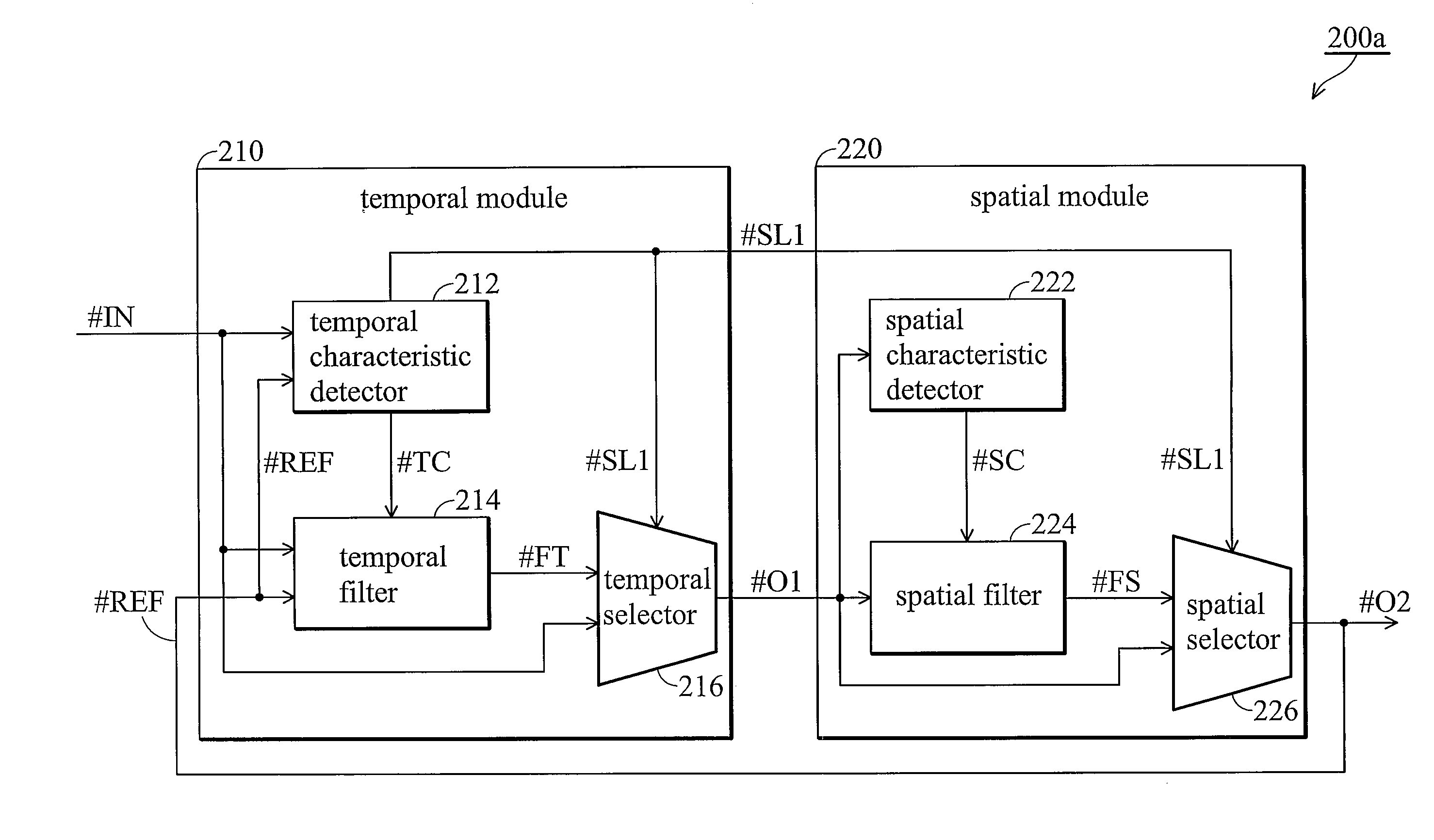
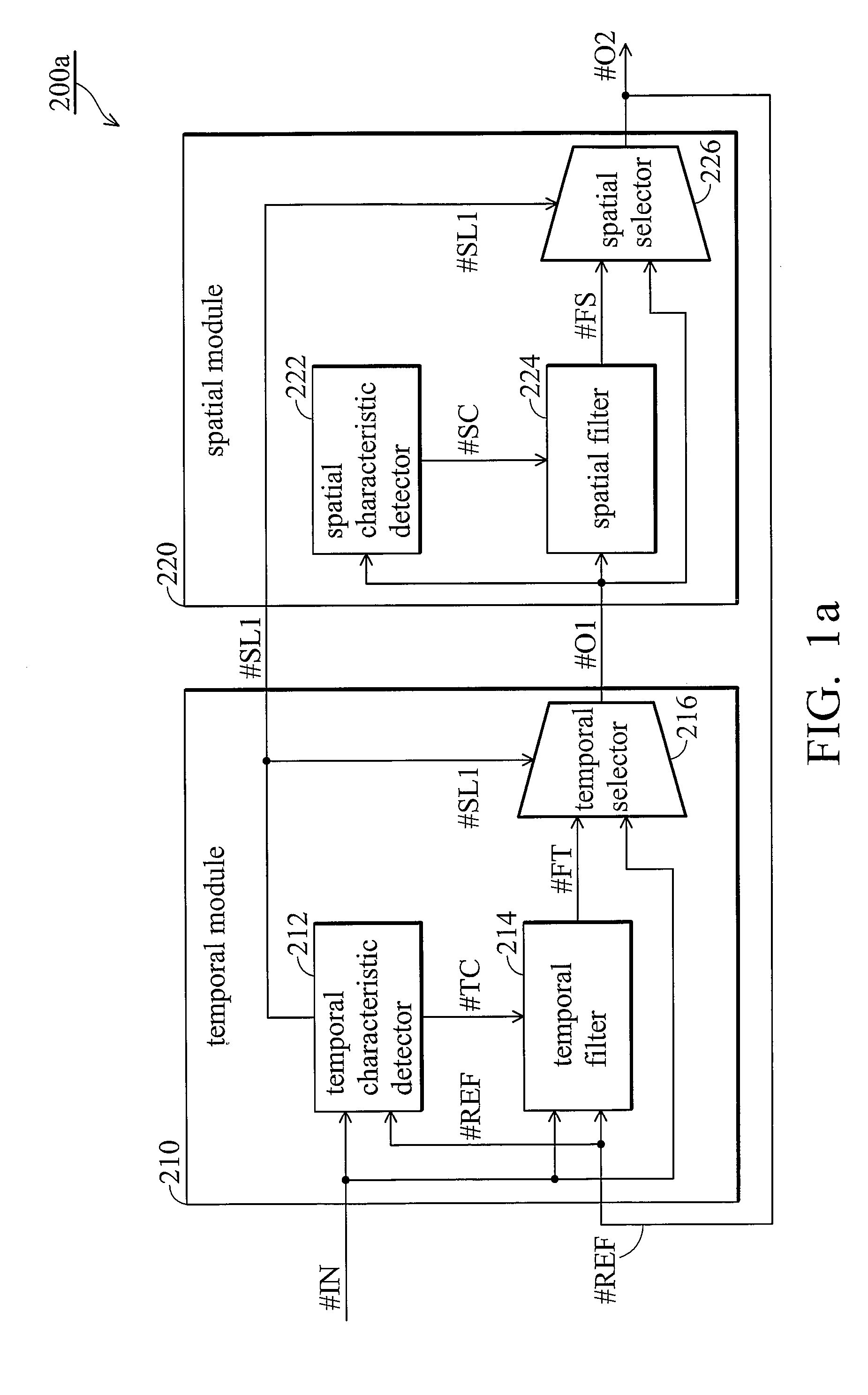
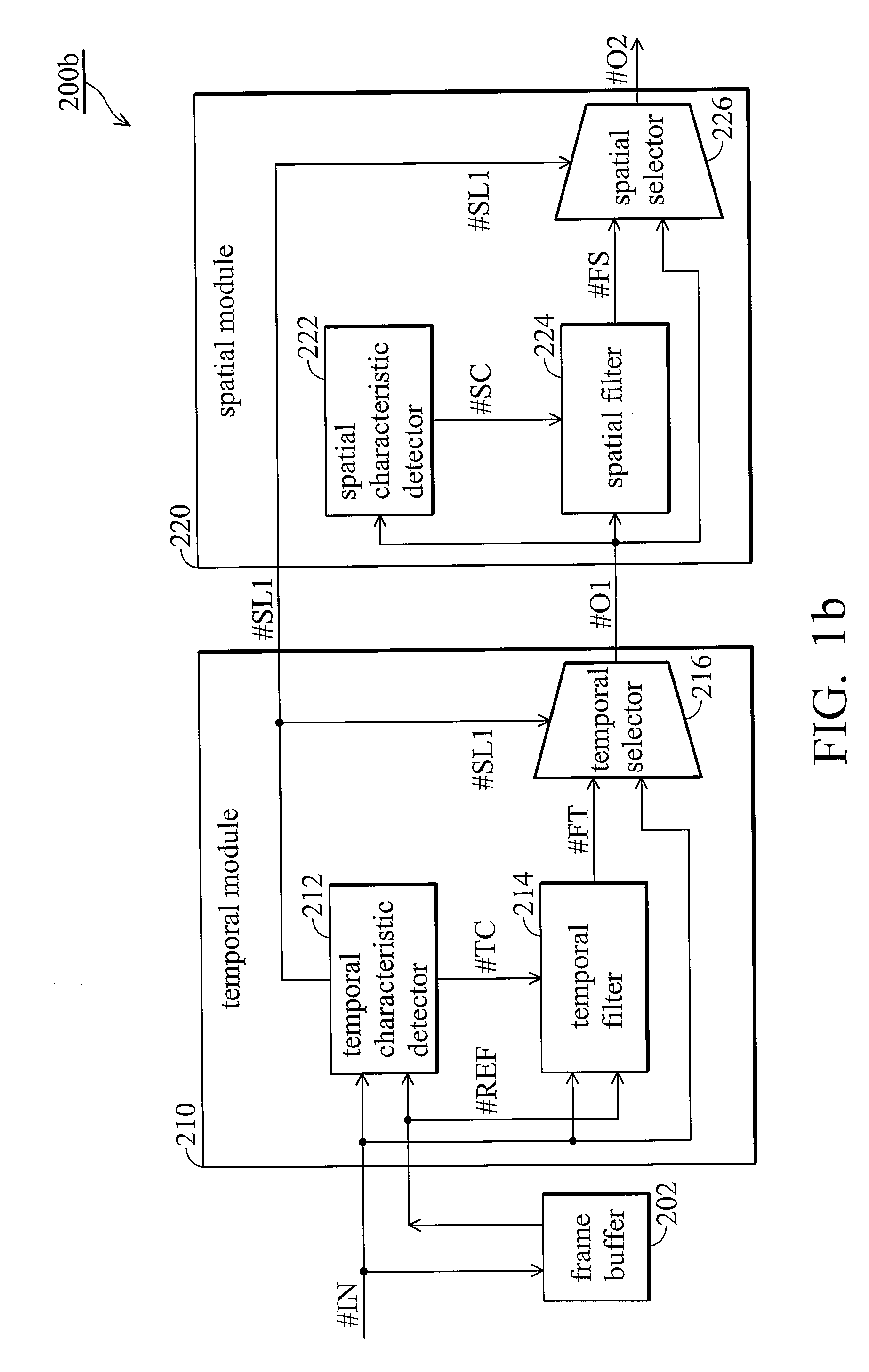
Adaptive noise reduction system
InactiveUS20100045870A1Temporal noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSpatial noiseAdaptive denoising
A noise reduction system is provided. In a temporal module, a temporal characteristic detector detects a temporal characteristic of the input image based on the input image and a reference image. A temporal filter performs temporal noise reduction on the input image based on the reference image and the temporal characteristic to generate a temporal filtered image. A temporal selector selects the temporal filtered image or the input image as a preliminary output accordingly. In a spatial module, a spatial characteristic of the input image is detected. A spatial filter performs spatial noise reduction on the input image based on the preliminary output and the spatial characteristic to generate a spatial filtered image. A spatial selector selects the spatial filtered image or the preliminary output as the output image based on the temporal or spatial characteristics.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Morphing resonators for adaptive noise reduction
Tunable perforate acoustic liners are disclosed using shape memory materials, which allow the acoustic liners to tune for multiple frequencies across a wide range, unlike current designs which are limited to specific frequencies or small ranges. The liner will be initiated through a sensor and feedback loop to monitor the current acoustic environment and initiate geometry change needed to more effectively attenuate engine noise.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
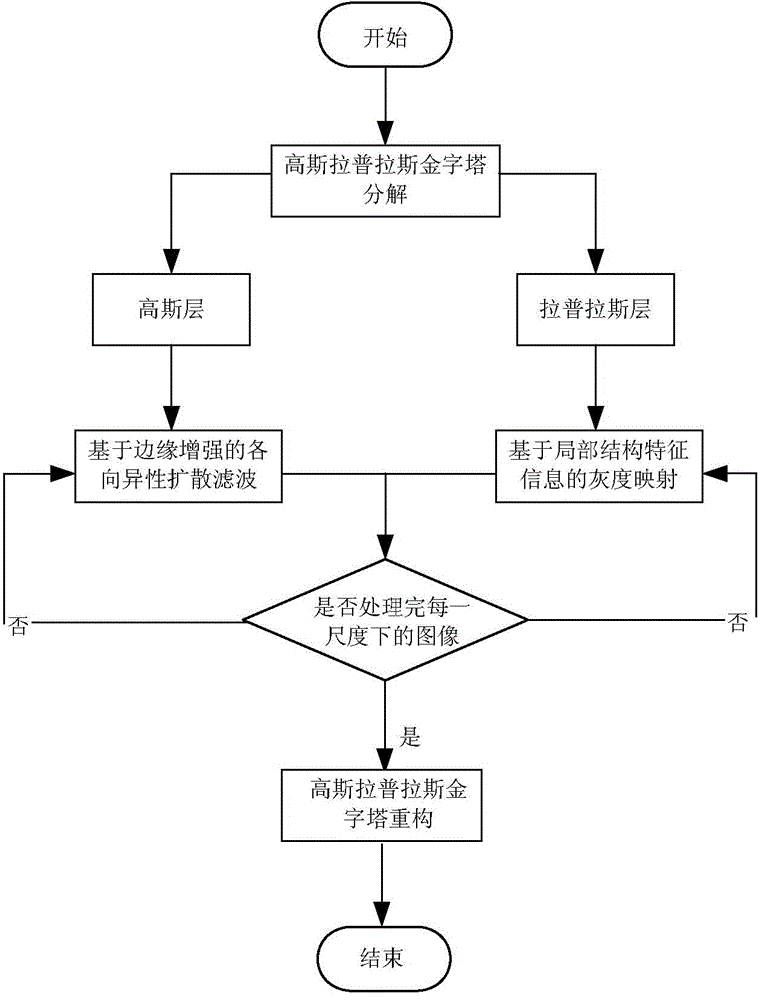
Adaptive denoising method for ultrasonic image
The invention discloses an adaptive denoising method for an ultrasonic image. The adaptive denoising method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the ultrasonic image; (2) performing Gaussian-Laplacian pyramid decomposition on the ultrasonic image and obtaining Gaussian layers and Laplacian layers at different scales; (3) calculating a structure tensor and a diffusion tensor of the Gaussian layer at each scale and performing anisotropic diffusion filtering treatment on the Gaussian layer at the scale; (4) according to a characteristic value of the structure tensor of the Gaussian layer, designing a grey mapping curve, and performing grey mapping on the Gaussian layer at the scale according to the grey mapping curve; (5) repeating the steps (3) and (4) for multiple times and performing the same treatment on the Gaussian layer and the Laplacian layer at each scale; (6) performing reverse reconstruction on the treated Gaussian layer and Laplacian layer and obtaining a denoised ultrasonic image; (7) outputting the denoised ultrasonic image. The adaptive denoising method can inhibit edge enhancement and spots of the image and is simple in algorithm and strong in adaptability.
Owner:WUHAN BEBEL HEALTH BIOTECH
Adaptive noise reduction for high noise environments
Systems, methods, and devices for providing noise reduction to an audio signal, such as a speech signal, to improve the accuracy of a speech recognition system. The various embodiments may be particularly useful for training and simulation systems.
Owner:ADVANCED SIMULATION TECH INC ASTI
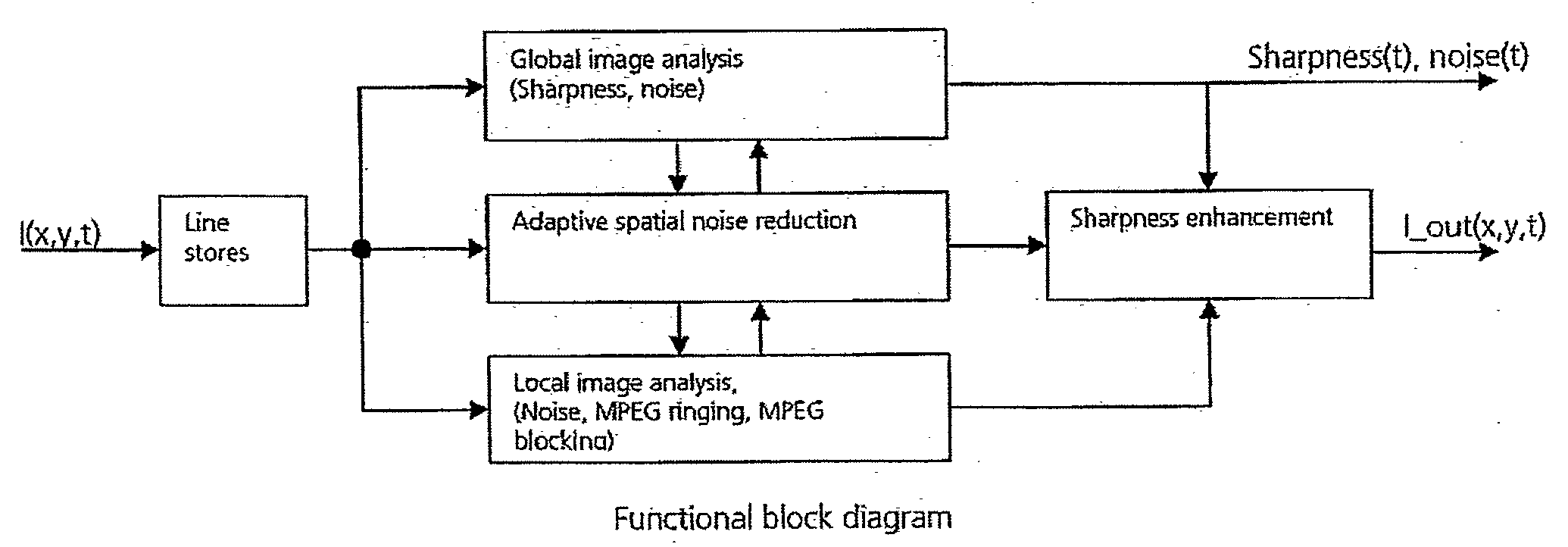
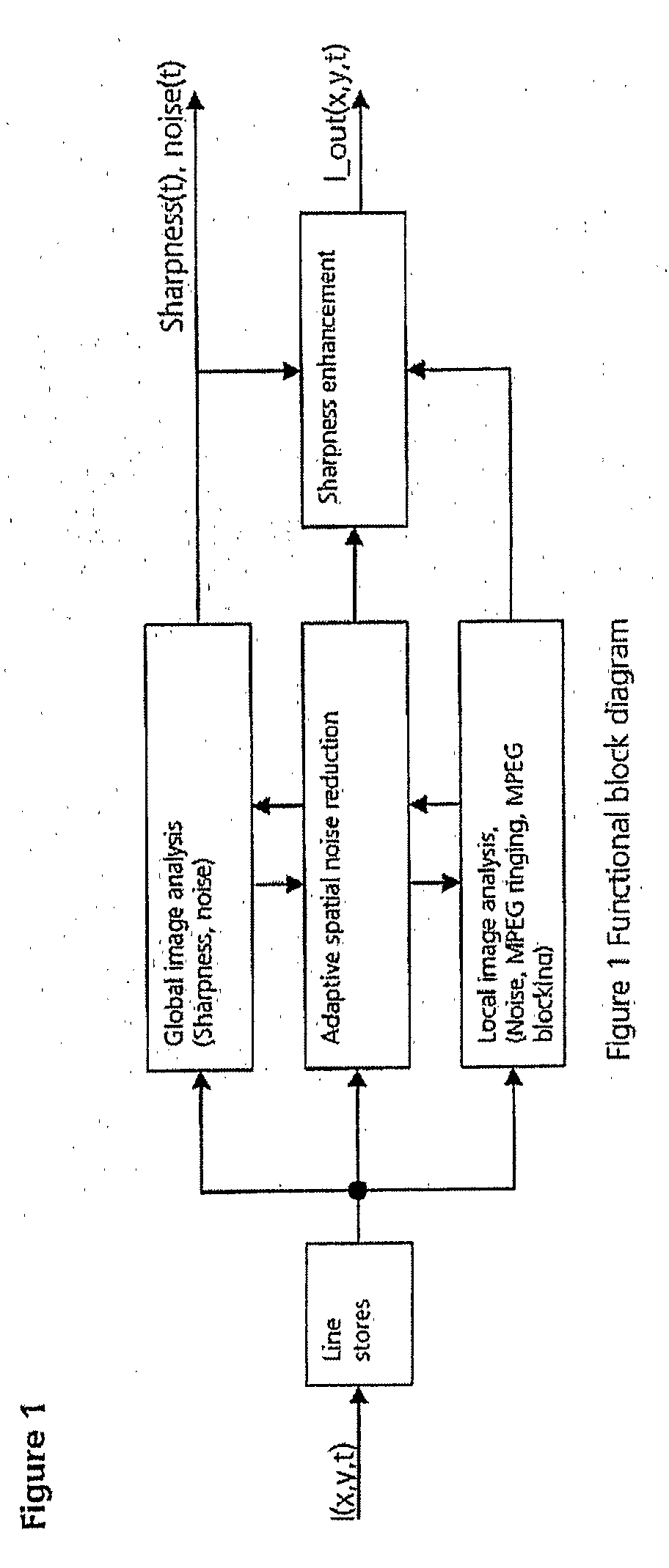
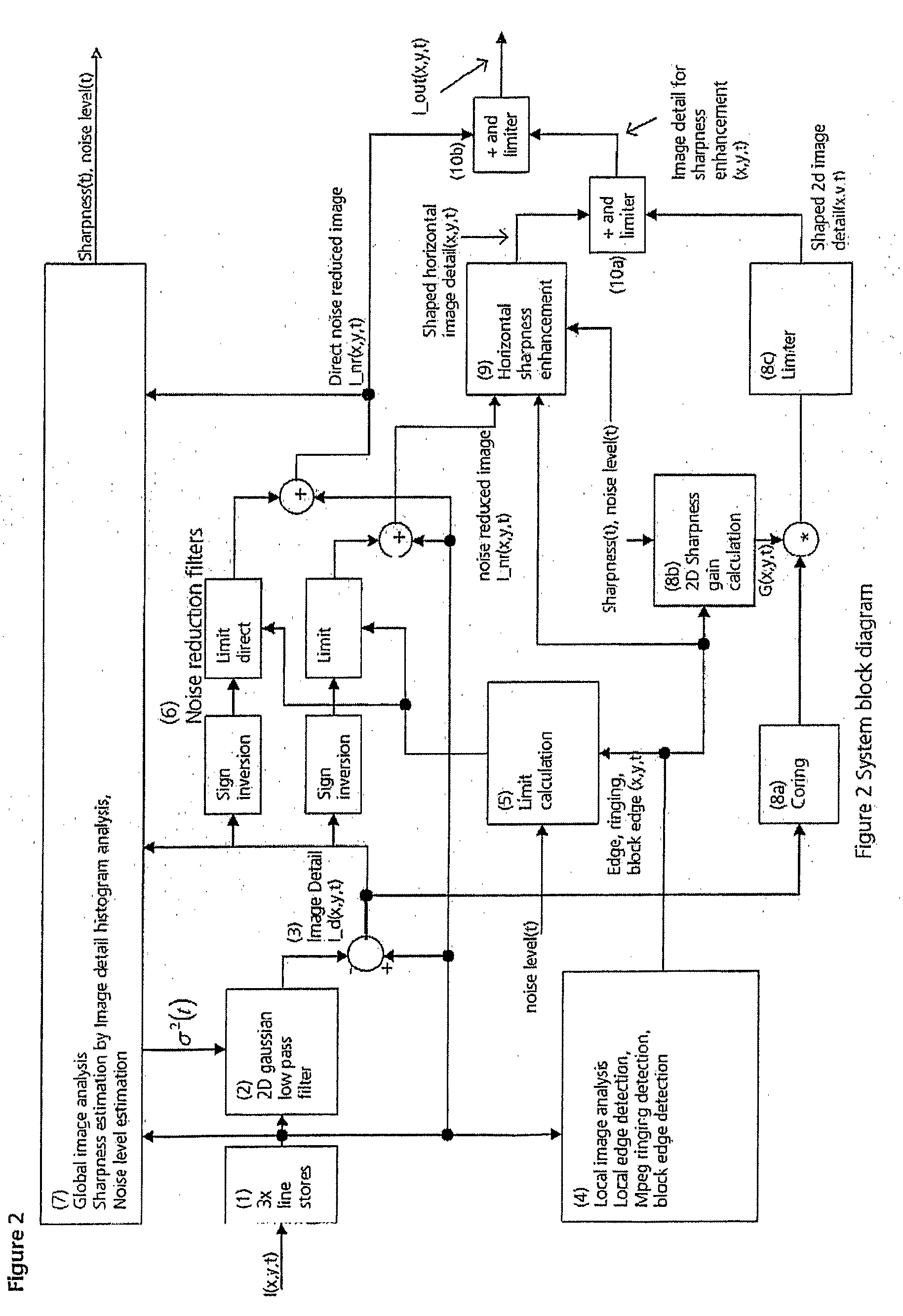
Filter for adaptive noise reduction and sharpness enhancement for electronically displayed pictures
ActiveUS20090060370A1Improve noiseReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging analysis
Electronic images that are degraded by noise and data reduction, such as MPEG encoding, display artifacts in the reproduced image, such as ringing (“ripples”) and blocks (“huge pixels”), and noise in the image may be apparent as graininess. By performing image analysis, both on a frame-by-frame and pixel-by-pixel basis it is possible to identify and separate edges in the image, ringing artifacts and the boundaries between block transitions. By applying noise reduction according to the analysis, followed by sharpness enhancement, it is possible to clean up the image for further utilization.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
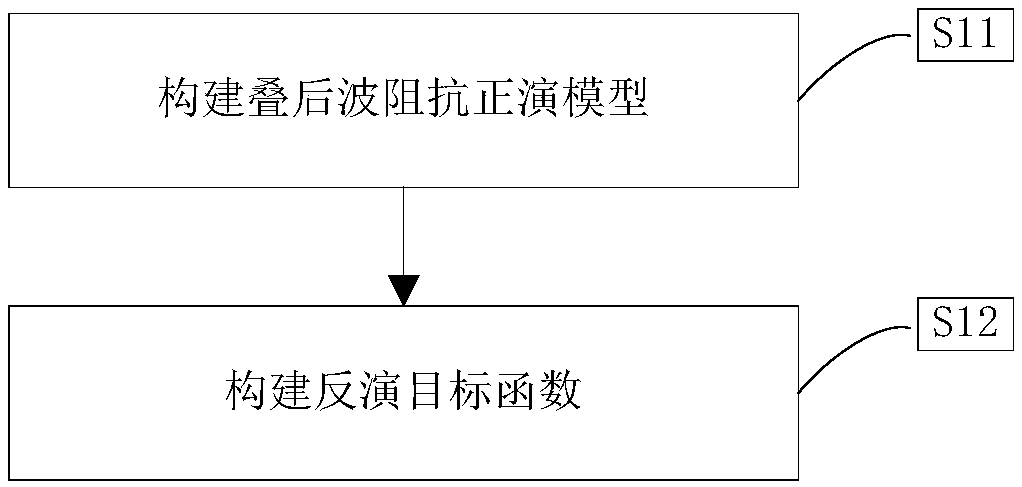
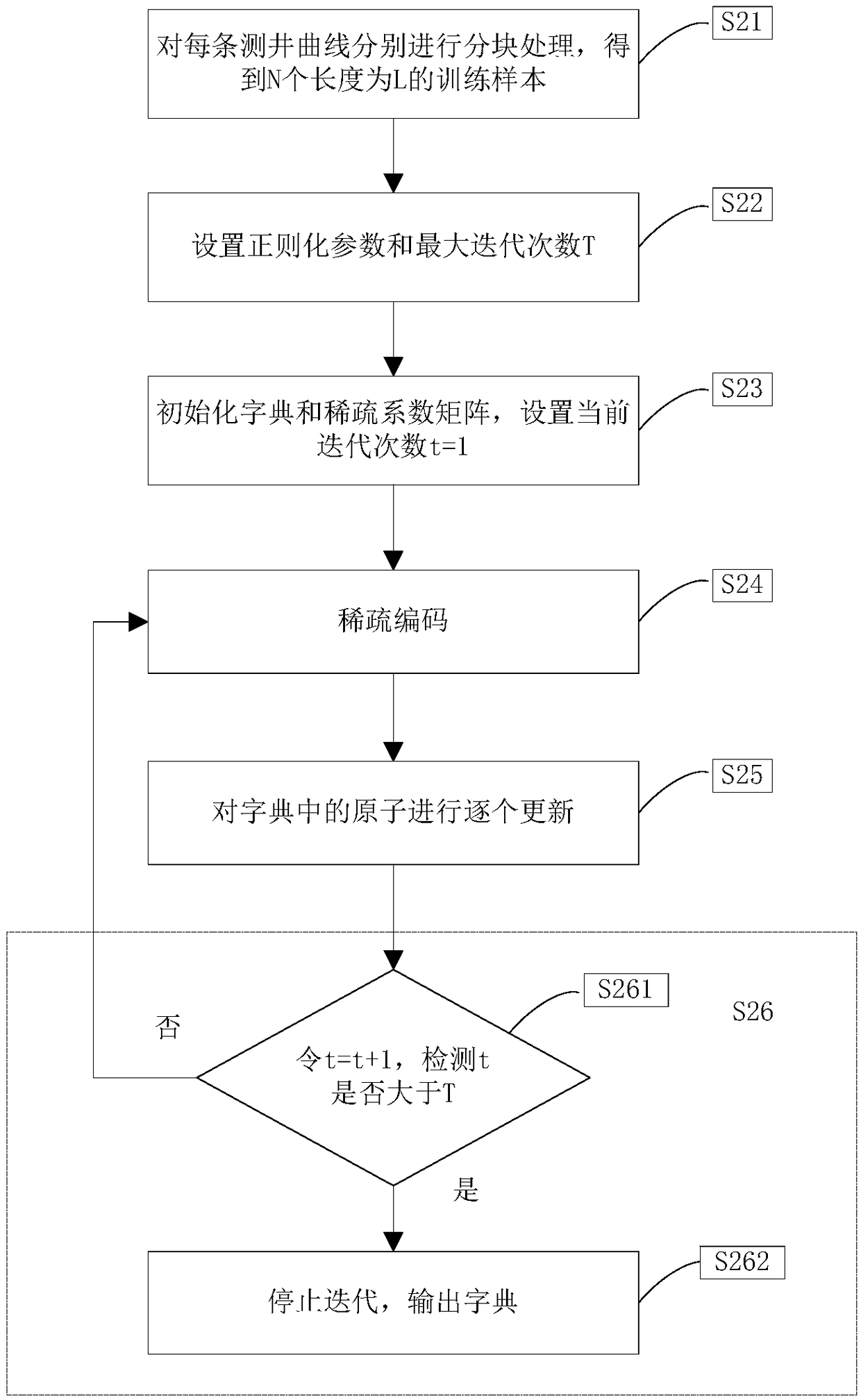
Adaptive hybrid norm dictionary learning seismic wave impedance inversion method
InactiveCN109143356AOvercoming non-Gaussian noiseAvoid influenceSeismic signal processingWell loggingAdaptive denoising
The invention provides an adaptive hybrid norm dictionary learning seismic wave impedance inversion method, and belongs to the field of seismic inversion. Through the combination of the post-stack wave impedance inversion in exploration geophysics with dictionary learning and denoising, the adaptive denoising and dictionary learning based post-stack wave impedance inversion method can be provided.The method adopts an adaptive hybrid norm objective function to replace an original 2-norm objective function, so that an objective function can better overcome non-gaussian noise; well logging information is introduced through a dictionary learning method, so that influences of different seismic noise can be effectively overcome, and the vertical resolution of inversion can be enhanced by fullyutilizing the well logging information; and compared with traditional methods of least squares, robustness can be stronger, the noise immunity and inversion result precision of the seismic wave impedance inversion can be enhanced, multiple solutions can be reduced, and convenient data processing in geological exploration can be achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
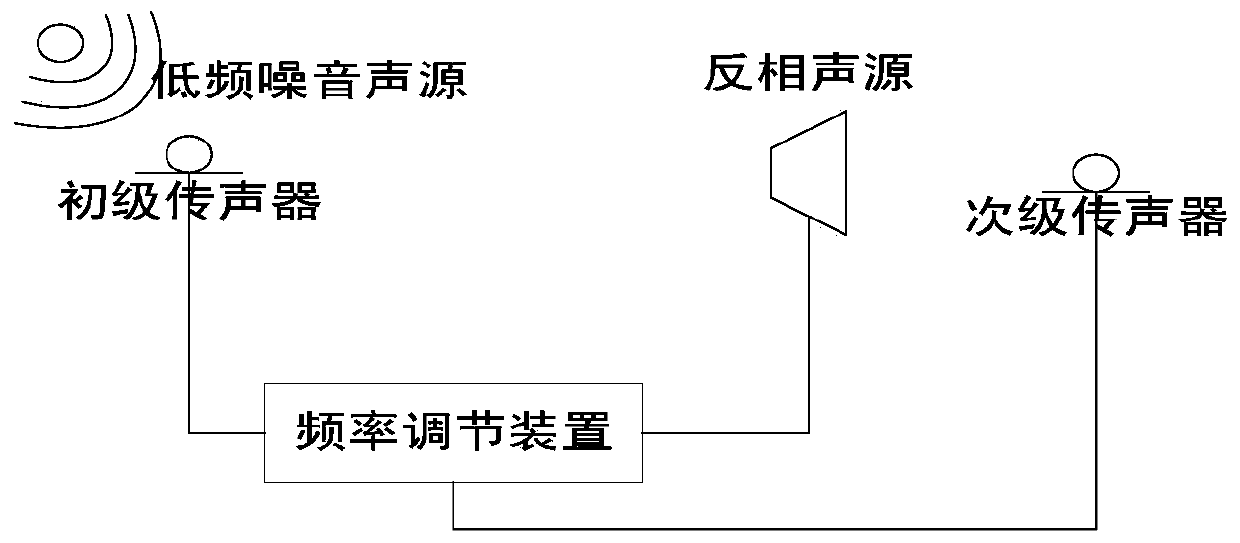
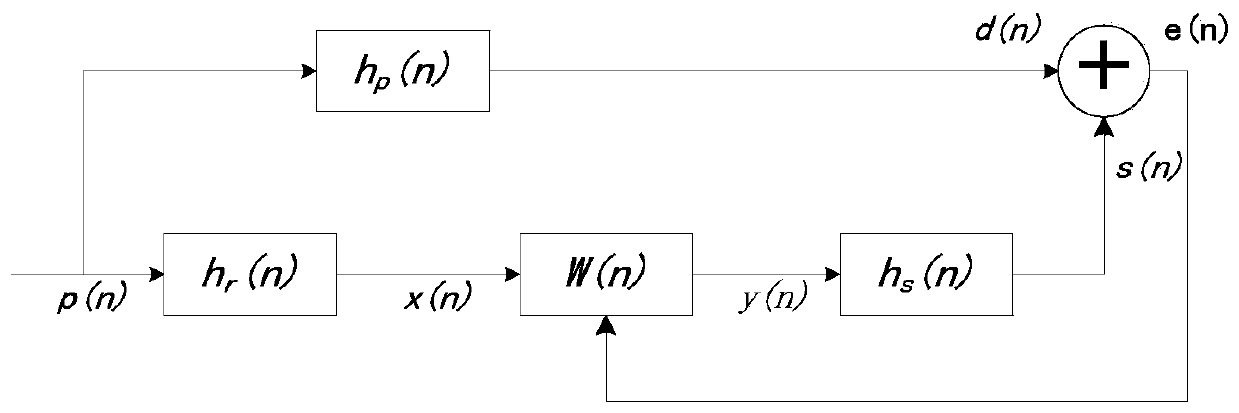
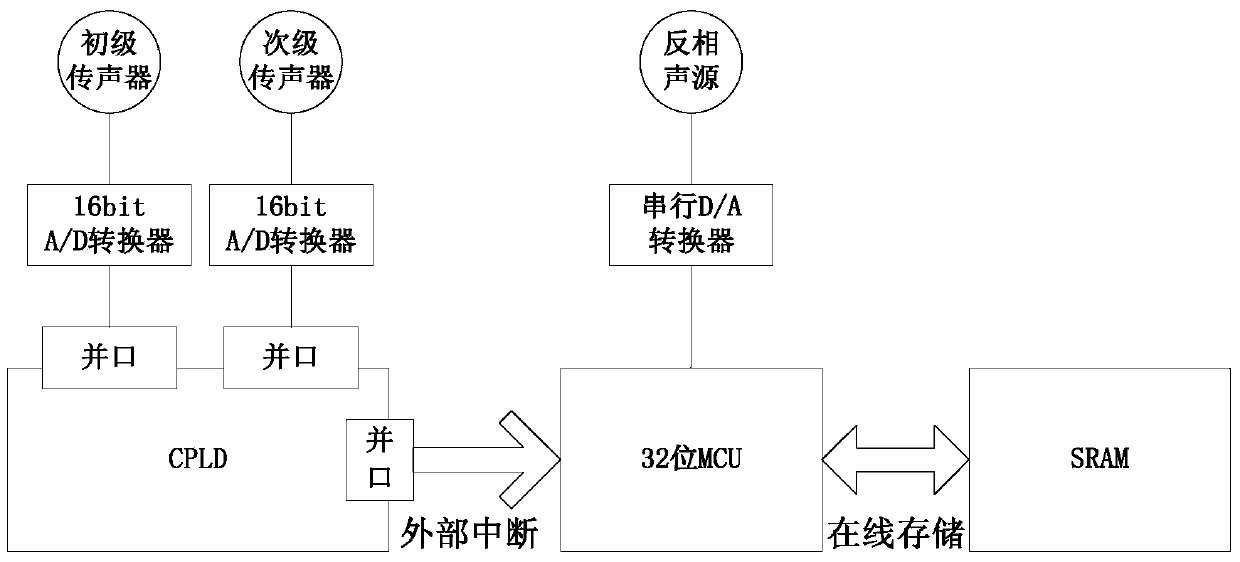
Self-adaption noise reduction device for low frequency noise in indoor environment
InactiveCN103440861AGuaranteed robustnessGuaranteed suitabilitySound producing devicesSound sourcesLife quality
The invention discloses a self-adaption noise reduction device for low frequency noise in an indoor environment. The self-adaption noise reduction device for low frequency noise in the indoor environment comprises a primary microphone, an inverse sound source, a frequency adjusting device and a secondary microphone. The secondary microphone is a high-sensitivity omnidirectional electret secondary microphone with the response frequency ranging from 20Hz to 20KHz. The primary microphone and the secondary microphone are connected through an audio cable and a 16-bit analog-to-digital converter respectively. The 16-bit analog-to-digital converter is connected with an I / O read-write parallel interface of the frequency adjusting device through a 16-pin parallel interface bus. The reverse sound source is connected with an MCU processor of the frequency adjusting device through a serial analog-to-digital converter. The self-adaption noise reduction device for low frequency noise in the indoor environment is particularly suitable for low frequency noise processing in a household environment, low frequency noise emitted by indoor electronic devices and electrical devices can be obviously reduced, the living environment is improved, and the living quality is improved. The self-adaption noise reduction device for low frequency noise in the indoor environment is small in size, capable of being used once a system is powered, free of a complex installation process, low in manufacturing cost and capable of being completely purchased and deployed by general users.
Owner:云南省科学技术情报研究院
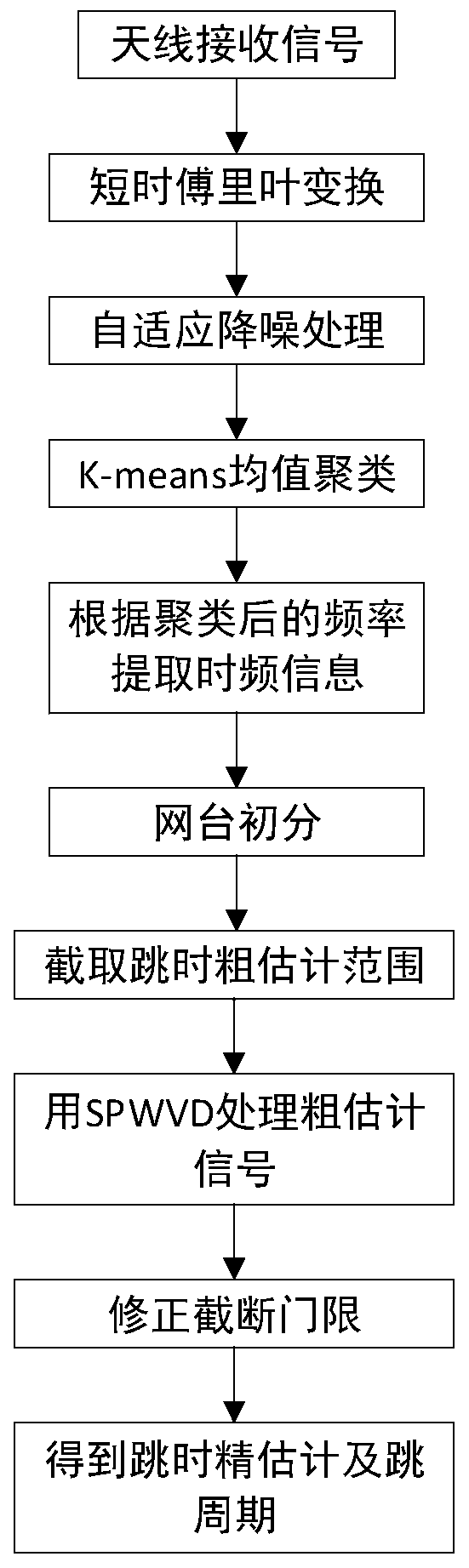
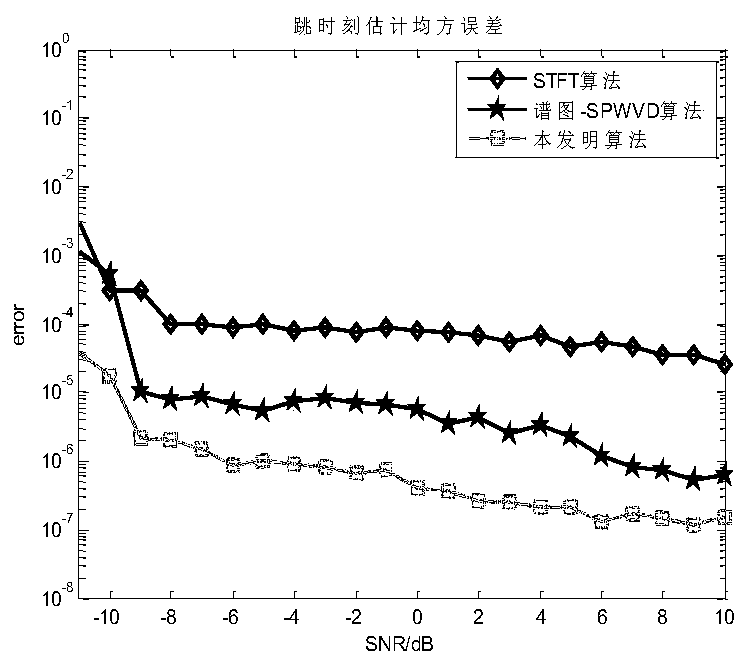
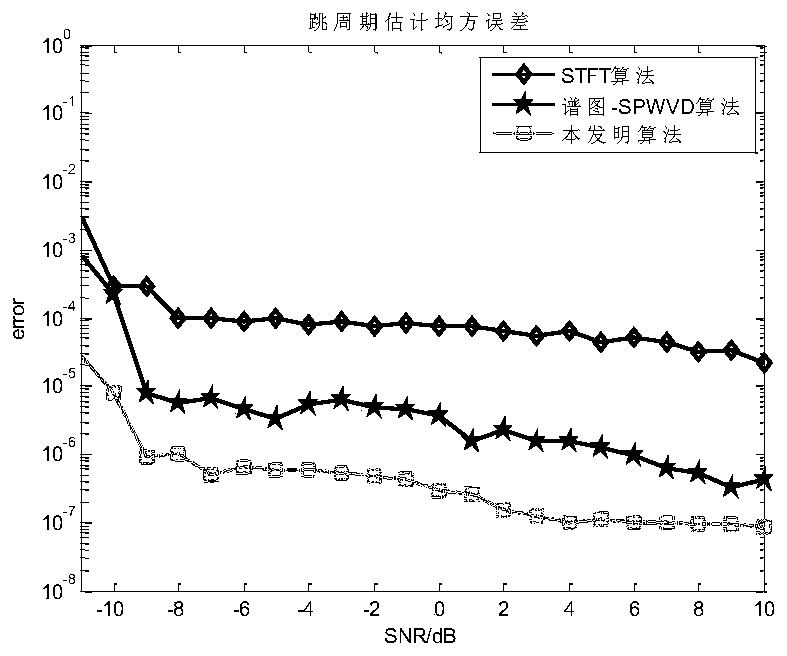
Hybrid network station frequency hopping parameter blind estimation method based on STFT-SPWVD
ActiveCN110113075AHigh-resolutionImproved noise immunityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAdaptive denoisingNoise reduction
The invention discloses a hybrid network station frequency hopping parameter blind estimation method based on short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and smooth pseudo Wigner distribution (SPWVD), which is used for solving the problems of low frequency hopping parameter estimation precision and high complexity under the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio in the prior art. According to the implementation scheme, the method comprises the following steps of firstly, transforming an antenna receiving signal into a time-frequency domain by using the short-time Fourier transform, and carrying out the adaptive noise reduction processing on the time-frequency signal so as to improve the anti-noise performance of a system; secondly, carrying out fine estimation on the frequency through a K-means mean value clustering algorithm; then extracting the time-frequency information according to the finely estimated frequency to obtain the time-hopping coarse estimation; and finally, carrying out fine estimation on a hopping moment by adopting the smooth pseudo Wigner transformation and a corrected truncation threshold. According to the method, the complexity is reduced, the frequency resolution isincreased, the estimation precision of the frequency hopping moment is improved, and the method can be used for the parameter estimation of the frequency hopping signal in a complex electromagnetic environment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com