Laterally diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of oxide semiconductors and transistors, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as unstable device performance, increased cost, and increased photolithography processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
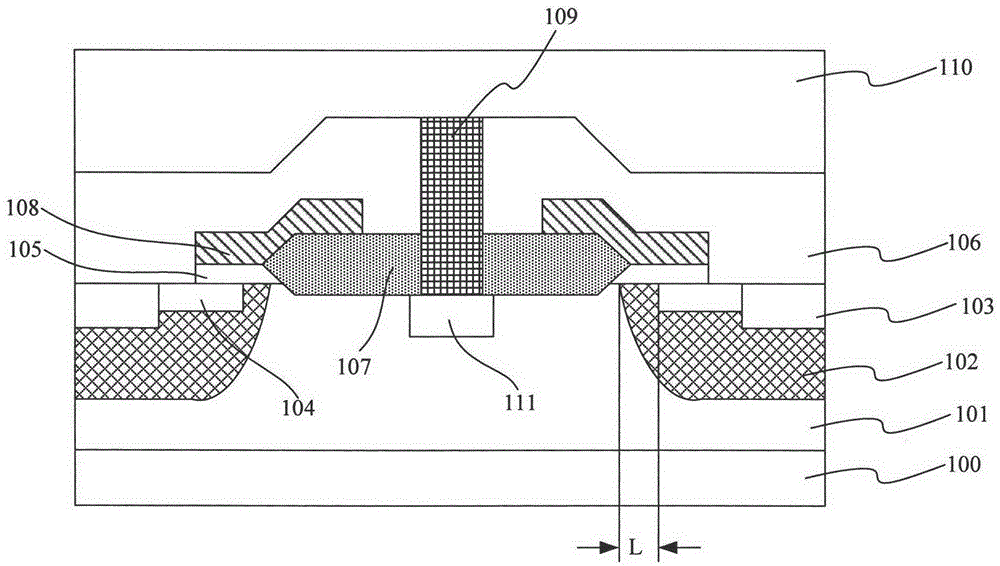
[0112] refer to Figure 4First, an N-type epitaxial layer 201 is formed on the surface of a P-type substrate 200 through an epitaxial process. Wherein, the P-type substrate 200 is a high-concentration doped raw silicon wafer, the resistivity of the P-type substrate is 0.001ohm·cm, the N-type epitaxial layer 201 is formed by an epitaxial process, and the N-type epitaxial layer 201 is used as the drain of the LDMOS, which will withstand a relatively high source-drain voltage. In this embodiment, the resistivity of the N-type epitaxial layer is 0.3 ohm·cm, and the thickness is 3 μm. The specific epitaxial growth process conditions are as follows: silane pyrolysis method is used for vapor phase epitaxy, the reactant is silane, N-type dopant phosphine, the epitaxy temperature is 1100° C., and the time is 20 minutes. The epitaxial thickness is determined according to the LDMOS operating voltage, that is, the source-drain voltage. The higher the voltage, the higher the thickness.
...
Embodiment 2
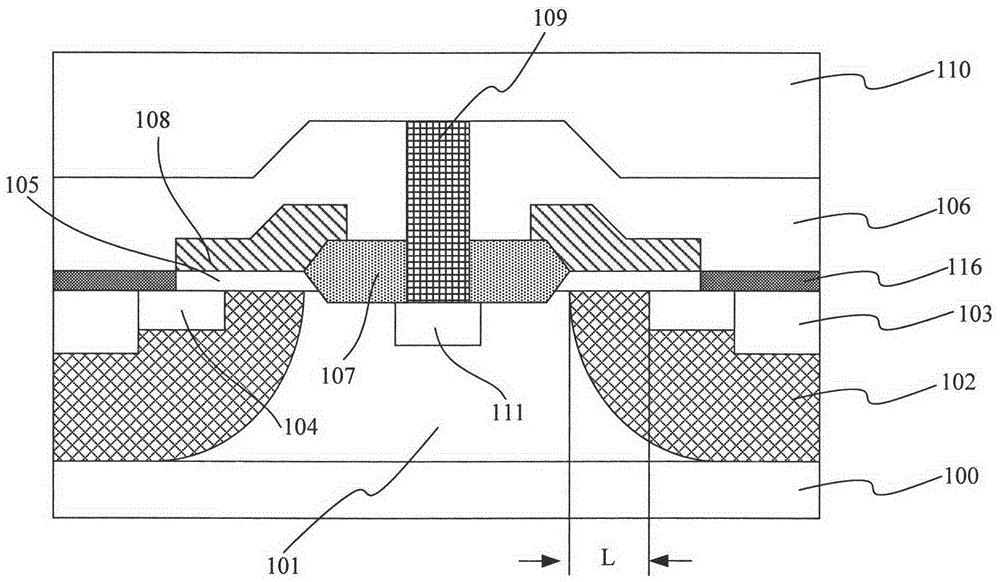
[0138] The principle of embodiment 2 is the same as embodiment 1, and its main steps are also the same, and the difference only lies in the selection of the following process parameters:
[0139] The resistivity of the P-type substrate is 0.01 ohm·cm, the resistivity of the N-type epitaxial layer is 1.0 ohm·cm, and the thickness is 5 μm, and the epitaxy temperature for forming the N-type epitaxial layer is 1200° C. for 40 minutes.
[0140] First grown by thermal oxidation process thickness of The lining oxide layer, and then deposit silicon nitride by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition process, wherein the thickness of silicon nitride is The thickness of the field oxide layer 207 grown by the thermal oxidation process is
[0141] The formation condition of the P-type doped region 202 is: the dopant dose is 1e14cm -2 The boron ions are accelerated to 200keV for P-type ion implantation to form a P-type doped region 202 in the N-type epitaxial layer.
[0142] The ion i...
Embodiment 3
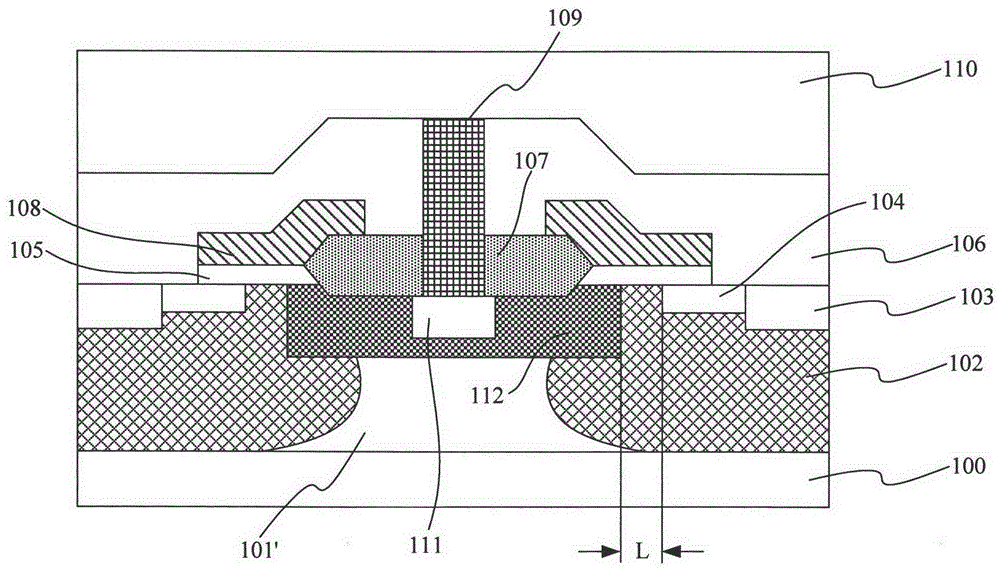
[0154] The principle of embodiment 3 is the same as embodiment 1, and its main steps are also the same, and the difference only lies in the selection of the following process parameters:
[0155] The resistivity of the P-type substrate is 0.005 ohm·cm, the resistivity of the N-type epitaxial layer is 0.8 ohm·cm, and the thickness is 7 μm, and the epitaxy temperature for forming the N-type epitaxial layer is 1150° C. for 45 minutes.
[0156] The formation condition of the P-type doped region 202 is: the dopant dose is 5e14cm -2 The boron ions are accelerated to 150keV for P-type ion implantation to form a P-type doped region 202 in the N-type epitaxial layer.
[0157] The ion implantation conditions of arsenic ions are: energy: 50keV; doping dose: 5e16cm -2 .
[0158] The thermal driving conditions for forming the P well are: the thermal driving temperature is 1050° C., the thermal driving time is 100 minutes, and the channel length L is 1.5 μm.
[0159] The thickness of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com