Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52results about How to "Reduced Radar Cross Section" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
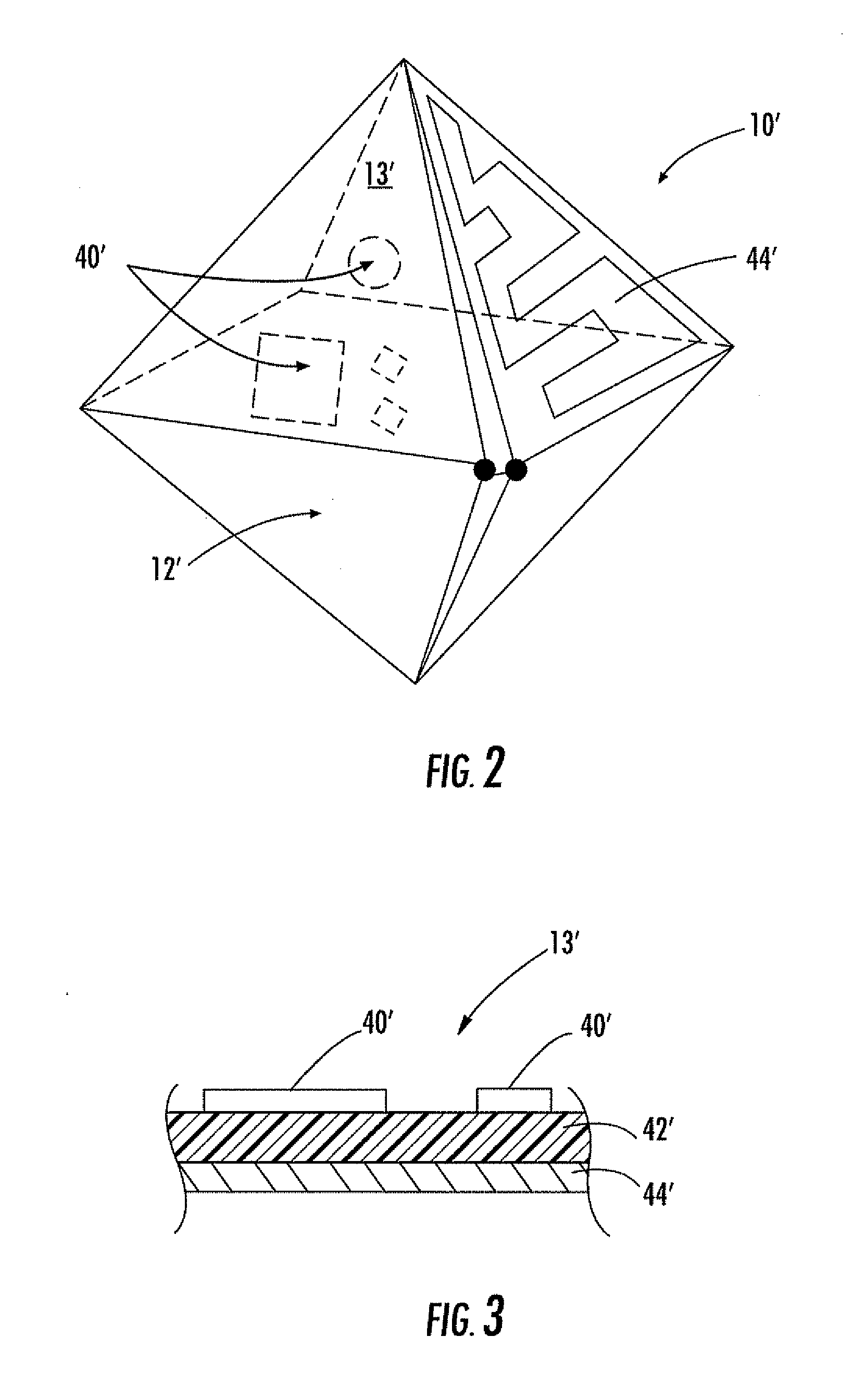
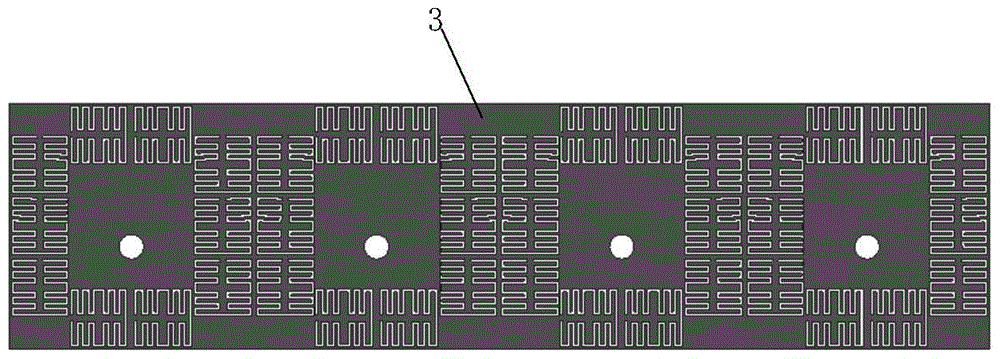
Electromagnetic shielding conformal optical window with longitude and latitude-shaped mesh structure
InactiveCN101917837AHigh electromagnetic shieldingReduced Radar Cross SectionMagnetic/electric field screeningAviationLongitude
The invention provides an electromagnetic shielding conformal optical window with a longitude and latitude-shaped mesh structure, which belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic shielding of optical transparent pieces. The electromagnetic shielding conformal optical window comprises a conformal optical window and is characterized in that: (1) a longitude and latitude-shaped metal mesh is manufactured on the inner side surface of the conformal optical window shell; and the longitude and latitude-shaped metal mesh covers the whole inner side surface of the conformal optical window shell; or (2) a longitude and latitude-shaped metal mesh and a conformal optical window inner shell are manufactured on the inner surface of the conformal optical window shell from outside to inside in turn; the longitude and latitude-shaped metal mesh covers the whole inner surface of the conformal optical window shell and outer surface of the conformal optical window inner shell; the latitude-shaped metal mesh consists of metal longitudes and metal latitudes; the metal latitudes are uniformly arranged in an equivalent centre angle along a circumferential direction; the metal longitudes are arranged at equal intervals according to a metal mesh cycle along a generatrix direction; and the metal longitudes and the metal latitudes are electrically connected with one another. The electromagnetic shielding conformal optical window with the longitude and latitude-shaped mesh structure is suitable for electromagnetic shielding technology of military or civil conformal optical windows for remote measuring and sensing, medical diagnosis, secret communication, aerospace equipment and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
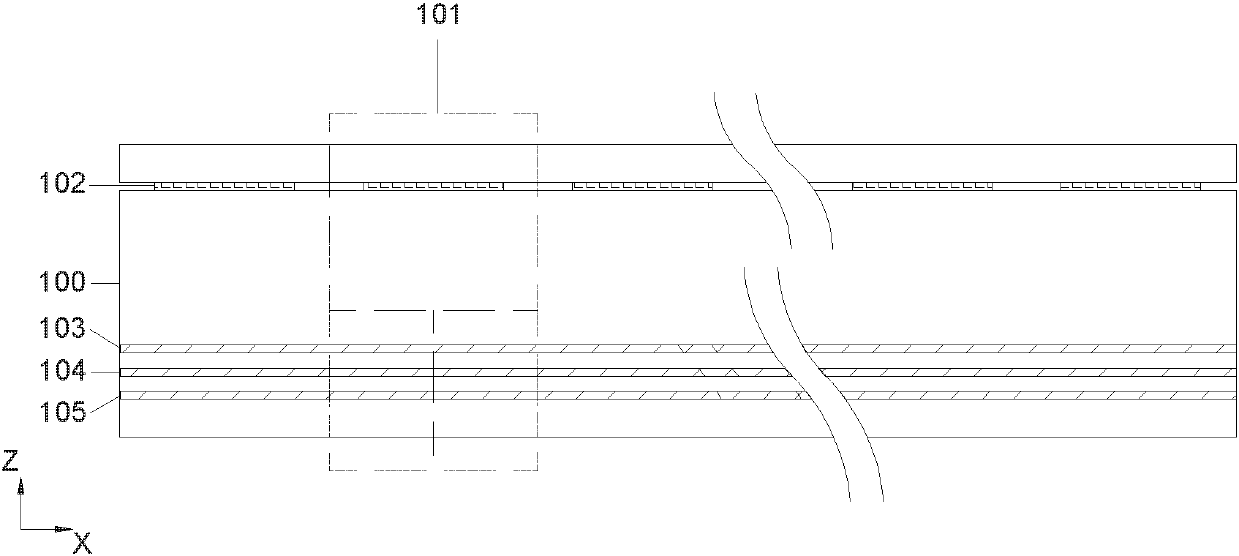
Single-passband bilateral wave-absorbing composite metamaterial and radome and antenna system including same
ActiveCN104993249AGood radiation characteristicsReduced Radar Cross SectionRadiating element housingsDielectric substrateConductive materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials and radomes, and specifically relates to a single-passband bilateral wave-absorbing composite metamaterial and a radome and an antenna system including the same. The single-passband bilateral wave-absorbing composite metamaterial comprises a dielectric substrate (100) made of a non-conductive material and four periodic metamaterial structure layers embedded into the dielectric substrate. The four periodic metamaterial structure layers are respectively a resistive film layer (102), a first metal patch layer (103), a second metal patch layer (104) and a third metal patch layer (105) in sequence from top to bottom. The metal patch layers for realizing frequency selection enable an array antenna to keep good radiation characteristic and communicate freely in an X band; and meanwhile, in the S band, Ku band and K band at the two sides of the passband of the X band, the resistive film layer with wave absorption characteristic and the metal patch layers in the composite metamaterial radome work together, and electromagnetic wave which is incident on the radome and then reflected back by the metal patch layers is well absorbed.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Broadband bionic yagi antenna with low radar cross section
InactiveCN102931481AEasy to hideAchieve stealthRadiating elements structural formsBroadbandWide band
The invention discloses a broadband bionic yagi antenna with a low radar cross section and mainly solves the problems of high radar cross section and relatively narrow band width in the traditional yagi antenna. The antenna simulates an opposite phyllotaxis plant leaf structure and comprises a director (2), a radiating element (3), a parallel strip line (4), a reflector (5) and a coaxial conversion joint (6). The radiating element (3) is of an oval structure, the director (2) simulates a feather-shaped leaf structure, and the reflector (4) is a rectangle patch with a tooth-shaped structure. The radiating element (3) is printed on a top layer and a bottom layer of a double-layer medium material plate (1) and respectively connected with an inner core and an outer core of the coaxial conversion joint (6) by the parallel strip line (4); the director (2) is printed on the top layer of the double-layer medium material plate (1); and the reflector (4) is printed between two layers of the double-layer medium material plate (1). The broadband bionic yagi antenna with the low radar cross section has the advantages of wide frequency band and good invisibility performance and can be used on an invisible target carrier.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
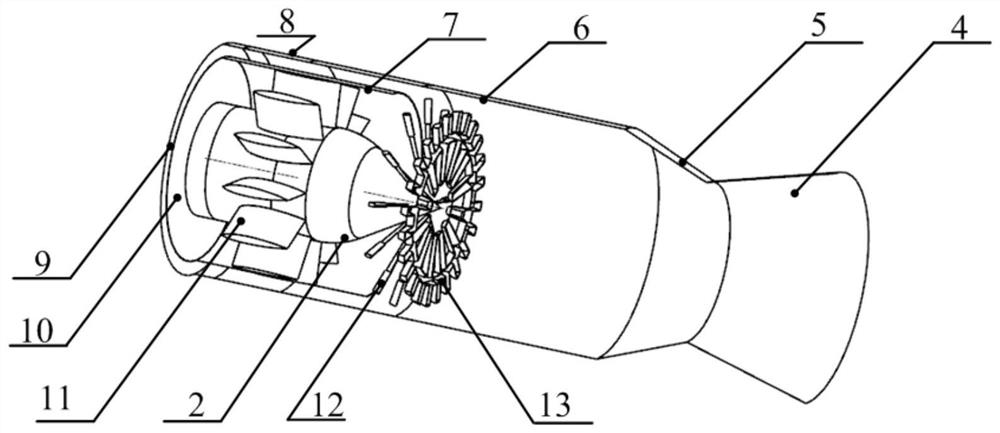
Radar and infrared comprehensive stealth structure of thrust augmentation type turbofan engine
PendingCN112228162ADoes not affect proper functionDoes not affect functionContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine coolingRadarEngineering
The invention provides a structure suitable for a thrust augmentation type turbofan engine and capable of realizing backward radar and infrared comprehensive stealth. The structure comprises a shielding support plate, an inner cone and a trailing edge blowing flame stabilizer, and is simple in structure, high in reliability, small in weight gain and small in aerodynamic loss, and the radar and infrared stealth performance can be remarkably improved only by virtue of the self structure.
Owner:AECC SICHUAN GAS TURBINE RES INST
Radar energy absorbing deformable low drag vortex generator
ActiveUS20150329200A1Easy to installReduce resistanceInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsCavity resonanceInstability
A family of Radar energy Absorbing Deformable Low Drag Vortex Generators (RAD-LDVG) is described herein. This family of devices are fabricated in such a way that it can conform to aircraft surface features while reducing radar returns from structural details. Vortex generators (VGs) are typically used to reattach or smooth gross flowfields over aircraft surfaces. By doing so, an airfoil or wing can maintain attached flow at higher angles of attack and / or higher lift coefficients than one without the VGs. These devices are also used to reattach and / or smooth flows that encounter crossflow-induced instabilities and / or adverse pressure gradients on the upper surfaces of wings or near aircraft boattails. Other uses include reduction of buffet, vibration, flutter, cavity resonance or general bluff-body pressure drag reduction. Although conventional rigid VGs do generate vortical aerodynamic structures, two major problems are often experienced: i.) the inability to conform to curved surfaces, ii.) the generation of radar cross-section spikes produced by the VGs themselves.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
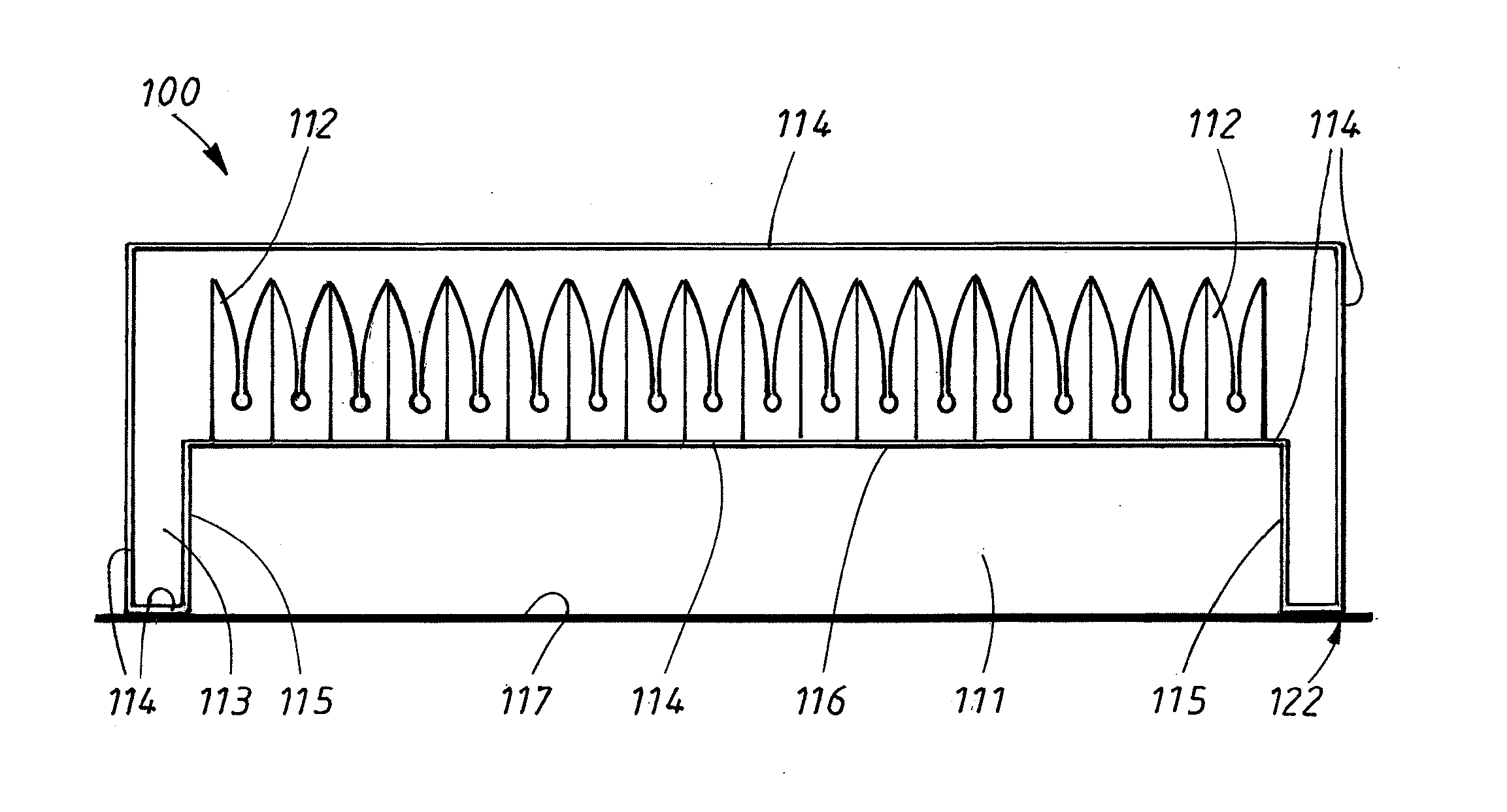
Reflecting plate based on frequency selection surface units
InactiveCN102904063AReduced Scattering Cross SectionAvoid couplingAntennasElectricityScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a reflecting plate based on frequency selection surface units. The reflecting plate is mainly used for solving the problems that an existing reflecting plate is relatively large in size, cannot be applied to antennae with smaller sizes and cannot reduce the antenna radar cross section in a multi-angle manner. The reflecting plate comprises Z frequency selection surface units (1) and a base plate (2), wherein Z is larger than or equal to 4; the Z frequency selection surface unit are uniformly distributed on the surface of the base plate in a rectangular array; each frequency selection surface unit consists of four pasters; each paster (11) comprises a rectangular trunk (111) and n arc-shaped branch knots (112), and the n arc-shaped knot are alternatively arranged on two sides of the rectangular trunk; and the four pasters respectively rotate 90 degrees, 180 degrees and 270 degrees by utilizing the bottom left corners of the pasters as centers, so as to form a crossed distribution structure of the four pasters. According to the reflecting plate, the electric size of each frequency selection surface unit is prolonged, the space is fully utilized, the resonant frequency is reduced, and the reflecting plate can be applied to the antennae with smaller sizes and can be used for reducing the antenna radar scattering cross section in a multi-angle manner.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
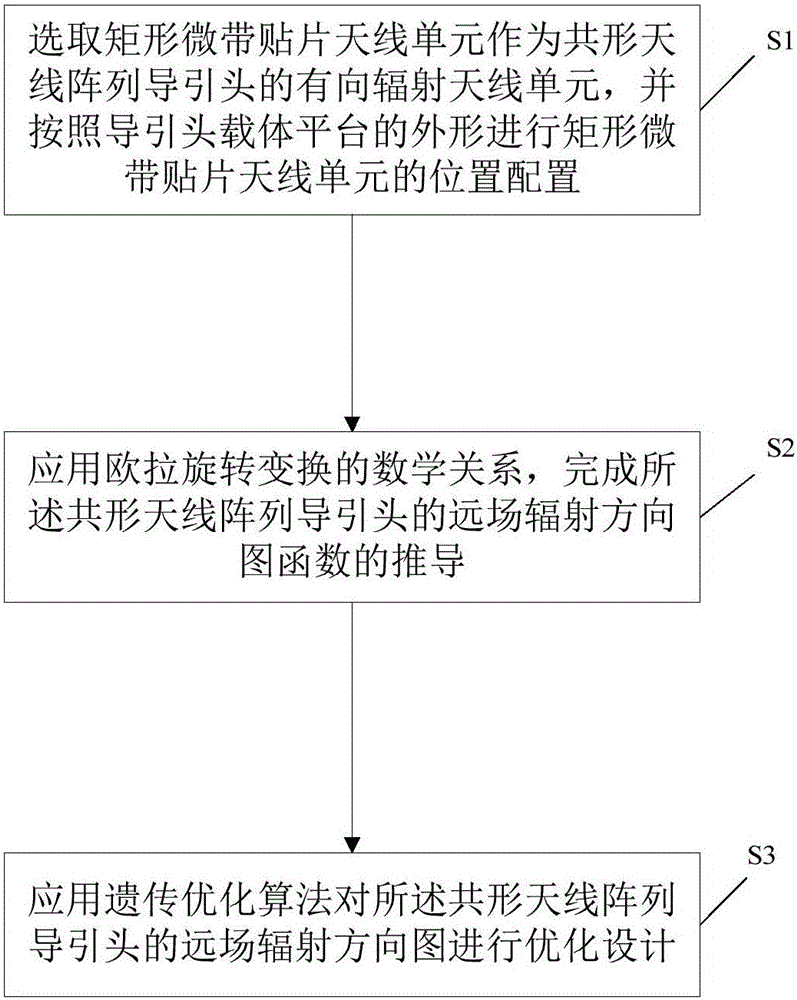
Conformal antenna array seeker modeling simulation method
InactiveCN105956258AReduced Radar Cross SectionGood electromagnetic stealth performanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMicrostrip patch antennaRadiation pattern
The present invention discloses a conformal antenna array seeker modeling simulation method. The method comprises: S1. selecting rectangular microstrip patch antenna elements as directed radiation antenna elements of a conformal antenna array seeker, and performing location configuration on the rectangular microstrip patch antenna elements according to a shape of a seeker carrier platform, wherein a plurality of rectangular microstrip patch antenna elements form an antenna array; S2. applying a mathematical relationship of Euler rotation transformation to complete derivation of a far-field radiation pattern function of the conformal antenna array seeker; and S3. applying a genetic optimization algorithm to optimally design a far-field radiation pattern of the conformal antenna array seeker. By use of the method disclosed by the present invention, a radar diffusion cross section of the seeker can be reduced, an excellent electromagnetism stealth property is achieved, and the highest sidelobe value of the far-field radiation pattern is significantly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENG
Compact low-RCS metasurface antenna array and design method thereof
PendingCN111585051AGood radiation characteristicsAchieve stealthRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysEngineeringBroadband
The invention discloses a compact low-RCS metasurface antenna array and a design method thereof. The antenna array comprises a metal patch layer, an intermediate dielectric layer, a metal backboard layer and a plurality of coaxial metal feed columns, and the metal patch layer, the intermediate dielectric layer and the metal backboard layer are seamlessly stacked in sequence from top to bottom; andthe plurality of coaxial metal feed columns respectively penetrate through the metal patch layer, the intermediate dielectric layer and the metal backboard layer. According to the invention, the tworadiation unit chessboards are arranged to realize coherent cancellation of the scattering field of the whole antenna, and the scattering field is dispersed to an angle without threat, so that the characteristic of low radar scattering cross section of the antenna broadband is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
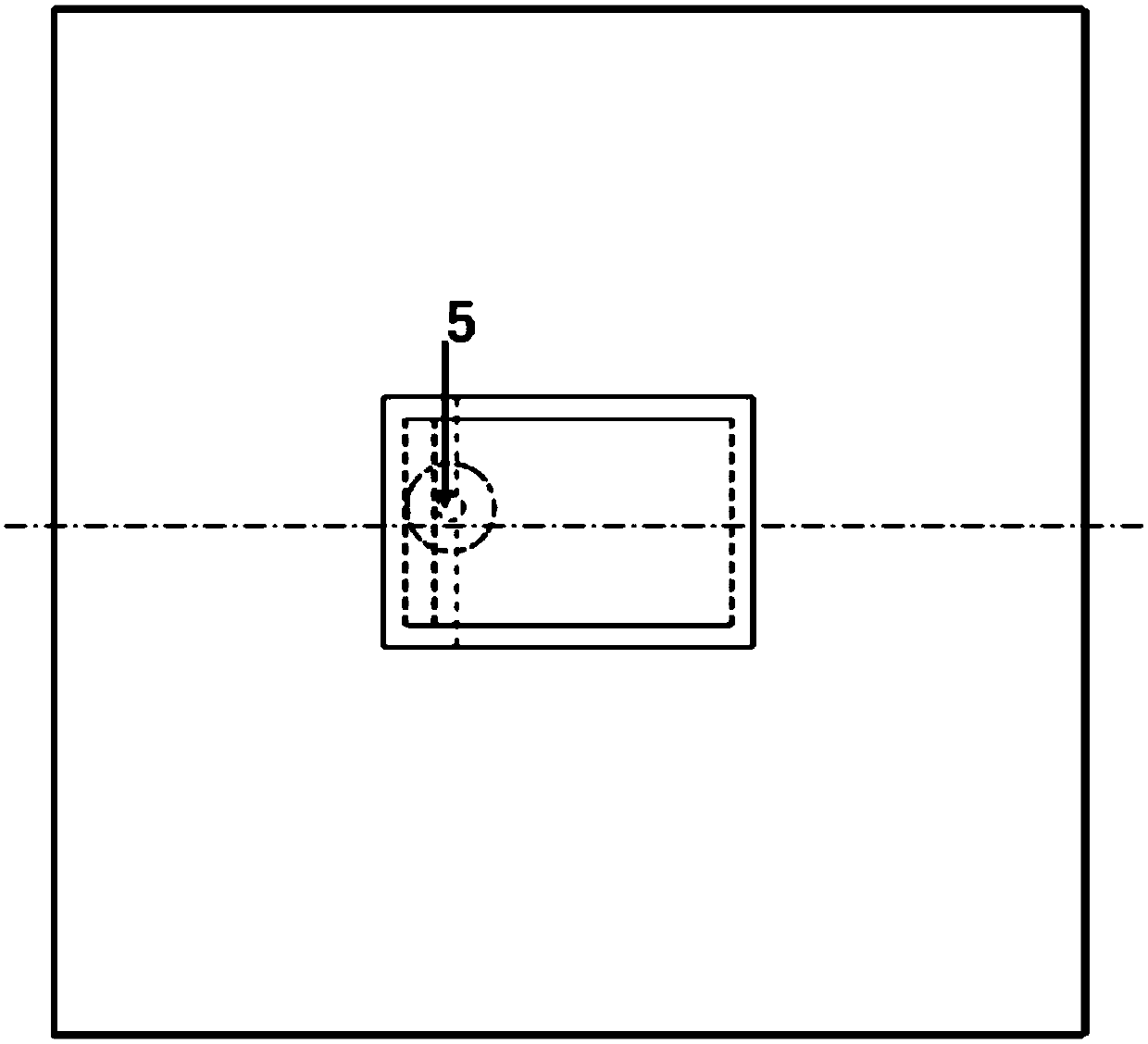
Low-RCS (radar cross section) microstrip patch antenna based on polarization conversion
InactiveCN104701613AReduced Radar Cross SectionGood scattering propertiesRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric slab
The invention discloses a low-RCS microstrip patch antenna based on polarization conversion. The low-RCS microstrip patch antenna based on polarization conversion is used for solving the defect of poor scattering performance of existing microstrip patch antennas. The low-RCS microstrip patch antenna based on polarization conversion comprises a radiating unit (1), a dielectric slab (2), a metal ground slab (3), a coaxial joint (4) and a polarization conversion surface (5). The upper surface and the lower surface of the dielectric slab (2) are printed with the radiating unit (1), and the polarization conversion surface (5) as well as the metal ground slab (3) respectively; the polarization conversion surface (5) is composed of four polarization conversion unit groups (51), and the center of the polarization conversion surface (5) is provided with a square area (6); every polarization conversion unit group (51) comprises a plurality of polarization conversion units (511) with the symmetric axises provided with square notches (512) which point to the same direction. The low-RCS microstrip patch antenna based on polarization conversion has the advantages of being stable in radiating performance and high in scattering performance and can serve as a communication antenna on a low-RCS device.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Convergent divergent nozzle with supported divergent seals
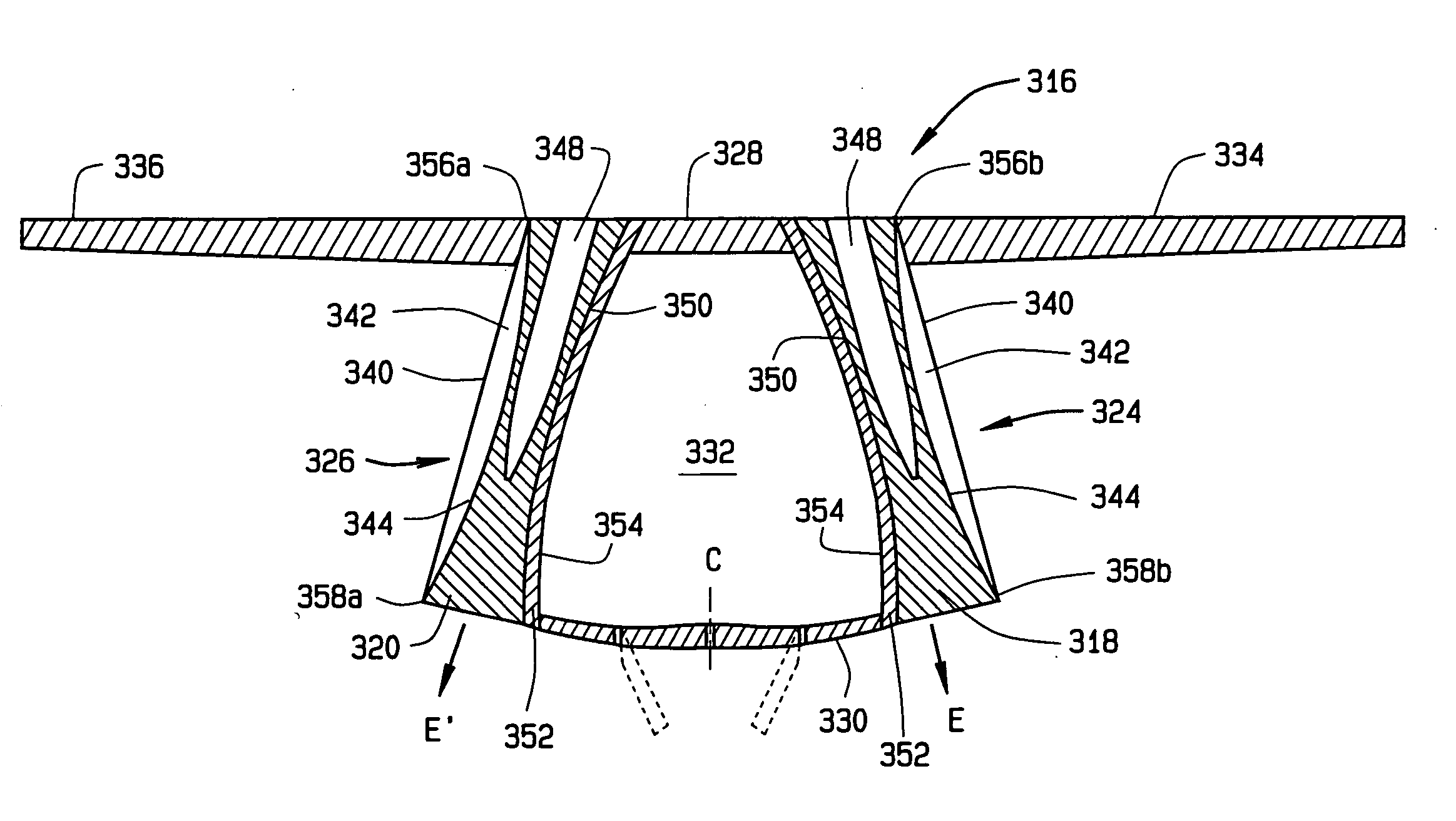
ActiveUS7624579B2Reduced Radar Cross SectionSpraying apparatusJet propulsion plantsEngineeringNozzle
A nozzle system includes a multitude of circumferentially distributed divergent seals that circumscribe an engine centerline. Each divergent seal includes an interface between a forward seal bridge bracket and an aft seal bridge bracket with a forward bridge support and an aft bridge support which provides axial and radial support for the divergent seals between adjacent divergent flaps. A divergent-convergent seal joint structure includes a horn and a fork. By having the forward bridge bracket retain the divergent seal in the axial direction, there is no need for axial sliding of the divergent seal relative to the divergent flap. The joint structure provides circumferential support as the axial and radial support are provided by the bridge-bracket interface. The joint interface permits the forward end section of the divergent seal and the forward end section of the divergent flap to include a radiused surface which provides a smooth interior interface between the convergent section and the divergent sections.
Owner:RTX CORP
Vertical takeoff and landing aircraft
InactiveUS20050109875A1Reduce vulnerabilityReduced Radar Cross SectionRocket type power plantsPower installationsFlight vehicleFixed wing
A method is provided for reducing vulnerability to hostile detection of and aggression towards an aircraft. The method includes adapting an aircraft fuselage to form an armored payload bay, wherein the armored payload bay includes a pair of sidewalls and a bottom. The method additionally includes adapting wings of the aircraft to allow the aircraft to be transported within a larger aircraft. For example, the wings could have a fixed wing span that allows the aircraft to transported within a larger aircraft or the wings could be adapted to fold so that the aircraft can transported within a larger aircraft. The method further includes disposing at least one pulse ejector thrust augmentor (PETA) bank within each sidewall. Each PETA bank is oriented such that a thrust exhaust produced is directed down and away from a centerline of the payload bay. Still further, the method includes adapting the bottom of payload bay to allow ingress and egress of cargo.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Wind turbine rotor blades with reduced radar cross sections
Wind turbine rotor blades with a reduced radar cross sections include a shell having a leading edge opposite a trailing edge, a structural support member that supports the shell and is disposed internal the wind turbine rotor blade between the leading edge and the trailing edge and extends for at least a portion of a rotor blade span length, wherein the structural support member comprises carbon fiber, one or more cavities internal the wind turbine rotor blade, and a lightweight broadband radar absorbing filler material disposed in at least one of the one or more cavities to provide the reduced radar cross section.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Polyhedral antenna and associated methods
ActiveUS20100066627A1Reduced Radar Cross SectionLoop antennasAntenna feed intermediatesCutoff frequencyPhysics
The antenna includes an electrically conductive antenna body having a polyhedral shape with opposing first and second ends and a medial portion therebetween. The medial portion of the electrically conductive antenna body is wider than the opposing first and second ends thereof, and the electrically conductive antenna body has a slot therein extending from at least adjacent the first end to at least adjacent the second end. The polyhedral antenna has an omnidirectional pattern, is horizontally polarized and broad in bandwidth above a lower cutoff frequency.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Method of passive reduction of radar cross-section using radar absorbing materials on composite structures
InactiveUS20180127599A1Improve survivabilityReduced Radar Cross SectionLiquid surface applicatorsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadar cross-sectionMaterials science
This invention relates to a system and method of enabling the passive reduction of radar cross-section of an object using radar absorbing materials on composite structures, such as an aircraft or unmanned aerial vehicle. The system includes a coating that is applied to a composite structure. The method includes a method of applying a coating to a composite structure.
Owner:WENTZ ROBERT LEE
Yagi antenna of electric-controlled plasma
InactiveCN101286587AIntelligent control of radiation directionReduced Radar Cross SectionAntenna supports/mountingsElectric controlDirectivity
The invention discloses an electrically-controlled plasma yagi-uda antenna, belonging to the technical field of antennae, which is characterized in that: the electrically-controlled plasma yagi-uda antenna comprises an active dipole at the center, and reflecting / director dipoles in ring shape and symmetrically arrayed at the periphery of the active dipole. The number of the reflecting / director dipoles is 2N (N represents a natural number that is more than or equal to 1). The reflecting / director dipoles can act as both reflecting dipoles and director dipoles, wherein, every two reflecting / director dipoles which are centrosymmetric with the active dipole are a pair of reflecting dipoles and a pair of director dipoles. Within a same period, only one pair of the reflecting dipoles and the director dipoles are in working states. The electronically-controlled plasma yagi-uda antenna is provided with flexible directionality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
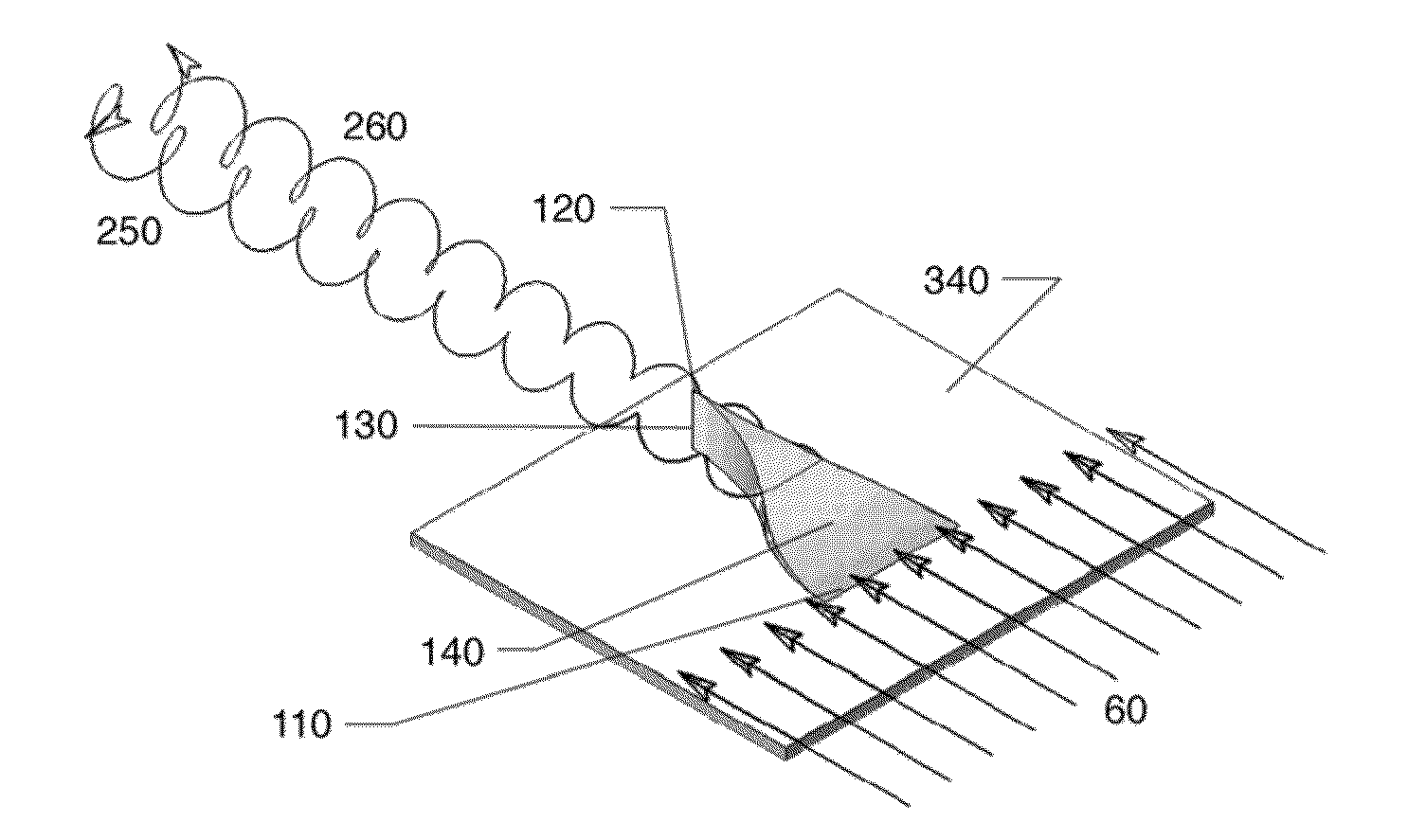
Method and arrangement for a low radar cross section antenna
ActiveUS20110291908A1Reduced Radar Cross SectionImprove handlingProtective material radiating elementsAntenna arrays manufactureElectromagnetic radiationAntenna element
A low-radar cross section antenna structure for an active electrically scanned antenna including an active electrically scanned antenna enclosure and at least two antenna elements. The antenna elements are arranged to be mounted on a front surface of the active electrically scanned antenna enclosure and embedded in a lightweight structure. The front surface and side surfaces of the active electrically scanned antenna enclosure and the antenna elements are arranged to be covered with the lightweight structure. A thin laminate is arranged to cover an outer top surface and an outer side surface of the lightweight structure. Parts of the lightweight structure are arranged to be doped with a lossy material having dielectric, magnetic and / or resistive losses, thus making these parts of the lightweight structure absorbing for electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:SAAB AB
Wind turbines and wind turbine rotor blades with reduced radar cross sections
ActiveUS20130177435A1Reduced Radar Cross SectionEngine fuctionsReaction enginesGlass fiberLeading edge
Wind turbine rotor blades with a reduced radar cross sections include a shell having a leading edge opposite a trailing edge, a structural support member that supports the shell and is disposed internal the wind turbine rotor blade between the leading edge and the trailing edge and extends for at least a portion of a rotor blade span length, wherein the structural support member comprises fiberglass, one or more cavities internal the wind turbine rotor blade, and a lightweight broadband radar absorbing filler material disposed in at least one of the one or more cavities to provide the reduced radar cross section.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radar apparatus for a ship
InactiveUS20160197399A1High strengthLight conductivityAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar cross-sectionTransmitter
A radar apparatus for a ship comprises a solid state transmitter and / or receiver enclosed within a housing, and an antenna coupled to the solid state transmitter and / or receiver. The external shape of the housing is substantially frusto-pyramidal. The frusto-pyramidal shape of the housing contributes to the robustness of the radar apparatus and allows the apparatus to have a low radar cross section.
Owner:KELVIN HUGHES
Ultra wide band low radar cross section microstrip antenna
ActiveCN107579346AEfficient conversionIncrease and decrease bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationElectromagnetic interferenceBroadband
The invention provides an ultra wide band low radar cross section microstrip antenna and aims to solve a technical problem of narrow bandwidth of a microstrip antenna reduction radar cross section inthe prior art. The microstrip antenna comprises a medium substrate, a metal floor, a polarized conversion surface, a radiation unit and a coaxial connector, wherein the metal floor is printed at a lower surface of the medium substrate, the polarized conversion surface is printed at an upper surface of the medium substrate, the center position of an upper side of the medium substrate is provided with a rectangular chamber, an upper portion of the chamber is provided with the radiation unit fixed with an output end of the coaxial connector, the polarized conversion surface is composed of four polarized conversion unit sets, each polarized conversion unit set comprises multiple decreasing fractal units, and arrangement direction difference of decreasing fractal units of the adjacent polarizedconversion unit sets is 900. The microstrip antenna is advantaged in that the ultra wide band decrement microstrip antenna radar cross section has stable performance, and the microstrip antenna can be applied to antenna systems with the complex electromagnetic environment to reduce electromagnetic interference among antennas in a wide band.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Radar energy absorbing deformable low drag vortex generator
ActiveUS9416802B2Easy to installReduce resistanceInfluencers by generating vorticesFluid dynamicsInstabilityCavity resonance
A family of Radar energy Absorbing Deformable Low Drag Vortex Generators (RAD-LDVG) is described herein. This family of devices are fabricated in such a way that it can conform to aircraft surface features while reducing radar returns from structural details. Vortex generators (VGs) are typically used to reattach or smooth gross flowfields over aircraft surfaces. By doing so, an airfoil or wing can maintain attached flow at higher angles of attack and / or higher lift coefficients than one without the VGs. These devices are also used to reattach and / or smooth flows that encounter crossflow-induced instabilities and / or adverse pressure gradients on the upper surfaces of wings or near aircraft boattails. Other uses include reduction of buffet, vibration, flutter, cavity resonance or general bluff-body pressure drag reduction. Although conventional rigid VGs do generate vortical aerodynamic structures, two major problems are often experienced: i.) the inability to conform to curved surfaces, ii.) the generation of radar cross-section spikes produced by the VGs themselves.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Composite materials comprising conductive nano-fillers
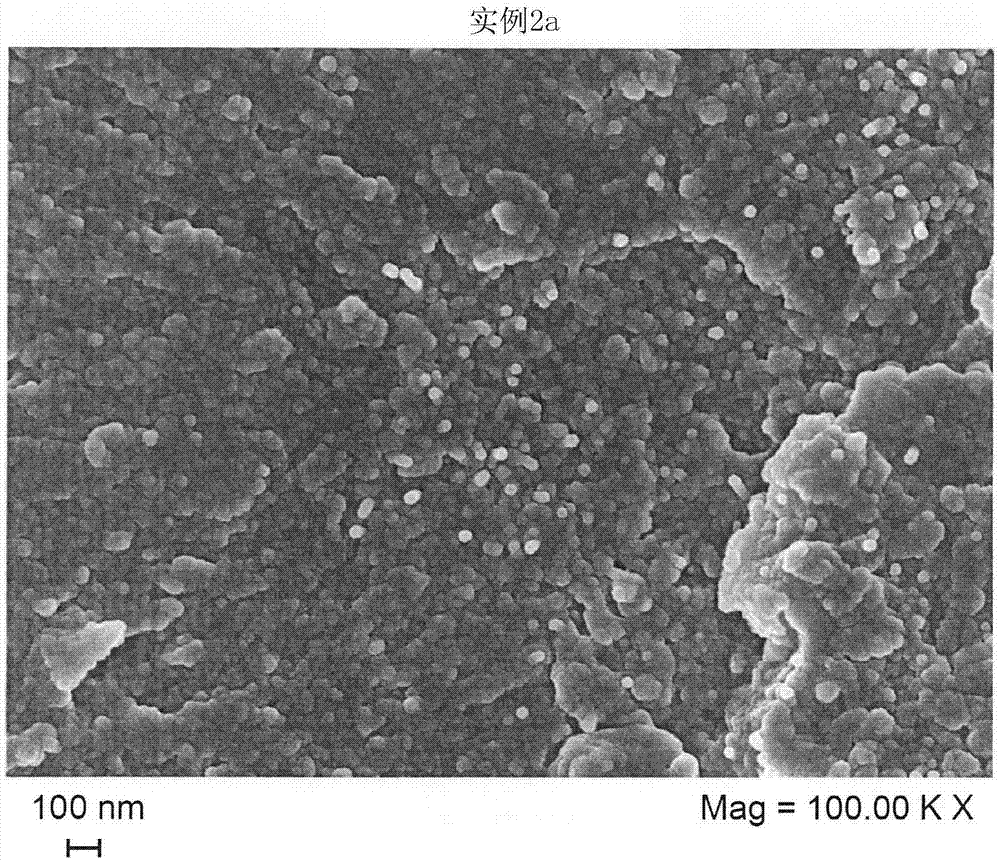
ActiveCN107254063AImprove conductivityHigh dielectric constantMaterial nanotechnologyShielding materialsComposite materialThermoplastic polymer
The invention relates to composite materials comprising conductive nano-fillers. A process for the production of a composition comprising one or more conductive nano- filler(s), one or more polyarylethersulphone thermoplastic polymer(s) (A), one or more uncured thermoset resin precursor(s) (P), and optionally one or more curing agent(s) therefor, wherein said process comprises mixing or dispersing a first composition comprising one or more conductive nano-filler(s) and one or more polyarylethersulphone thermoplastic polymer(s) (A) with or into one or more uncured thermoset resin precursor(s) (P), and optionally one or more curing agent(s) therefor.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Microstrip array antenna with low radar cross section
ActiveCN103840258AReduced Radar Cross SectionReduce areaAntenna arraysResonant antenna detailsMicrostrip array antennaMirror image
The invention discloses a microstrip array antenna with a low radar cross section. The microstrip array antenna mainly overcomes the defects that an existing microstrip array antenna is high in radar cross section, radiation and scattering characteristics can not be guaranteed at the same time. The antenna comprises a dielectric material plate (1), a radiation unit (2), a metal floor (3) and a coaxial connector (4). The radiation unit and the metal floor of the antenna are printed on the two sides of the dielectric material plate (1) respectively, the metal floor (3) is provided with n complementary split ring resonators (31) distributed around the metal floor under the radiation unit (2), each complementary split ring resonator is of a mirror image symmetric structure formed by an S-shaped bent groove line section, the outline of the periphery of each complementary split ring resonator is square, openings are reserved, and resonant frequency is the same as the work frequency of the array antenna. The antenna has the advantages of being stable in radiation performance, low in radar cross section, simple in structure and easy to process, and can serve as an array antenna on low-radar cross section equipment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Microstrip Array Antenna with Low Radar Cross Section
ActiveCN103840258BReduced Radar Cross SectionReduce areaAntenna arraysResonant antenna detailsMicrostrip array antennaSymmetric structure
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Coating for the concealment of objects from the electromagnetic radiation of antennas
ActiveUS20190334248A1Effective and economical solutionReduced Radar Cross SectionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsConductive coatingPhysics
An assembly comprising a device and an obstacle subjected to an incident electromagnetic wave of wavelength λ. The obstacle is formed from an electrically conductive material and has a substantially cylindrical shape of transverse dimensions r with respect to a longitudinal axis (O, ez). The longitudinal axis is substantially perpendicular to a propagation direction of the incident electromagnetic wave. The obstacle further has a maximum transverse dimension d such that the ration λ / d is less than 1. The device is placed on all or a part of a surface of the obstacle and comprises a sleeve with a dielectric coating of equivalent relative permittivity EREQ, of height hP along a longitudinal axis of the sleeve, substantially equal to formula A, and a sleeve with an electrically conductive coating placed on the periphery of the dielectric coating.
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
Liquid patch antenna
PendingCN107785652AReduced radar cross sectionExcellent concealment characteristicsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsDielectric substrateGain
The invention discloses a liquid patch antenna. The liquid patch antenna comprises a medium base plate which is provided with a metal floor, an exciting end port, a metal probe, a nonmetal radiation patch in which liquid is poured, and a nonmetal short circuit patch in which liquid is poured, wherein the nonmetal short circuit patch is vertically fixed to the metal floor; one end of the nonmetal short circuit patch is connected to the metal floor to form an earth short circuit, and the other end of the nonmetal short circuit patch is connected to the nonmetal radiation patch which is parallelto the metal floor; the nonmetal short circuit patch and the nonmetal radiation patch form an inverted L-shaped structure; liquid in the nonmetal short circuit patch is communicated with the liquid inthe nonmetal radiation patch; one end of the metal probe passes through the medium base plate and then extends into the nonmetal radiation patch, and the other end of the metal probe is equipped withthe exciting end port; and the metal probe is parallel with and close to the nonmetal short circuit patch without direct contact. The liquid patch antenna has the characteristics of being high in radiation efficiency, high in gain, high in impedance bandwidth and universal radiation, and the working frequency ranges from 2.26-3.24GHz.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Wind turbine rotor blades with reduced radar cross sections
Wind turbine rotor blades with a reduced radar cross sections include a shell having a leading edge opposite a trailing edge, a structural support member that supports the shell and is disposed internal the wind turbine rotor blade between the leading edge and the trailing edge and extends for at least a portion of a rotor blade span length, wherein the structural support member comprises carbon fiber, one or more cavities internal the wind turbine rotor blade, and a lightweight broadband radar absorbing filler material disposed in at least one of the one or more cavities to provide the reduced radar cross section.
Owner:LM WIND POWER US TECH APS
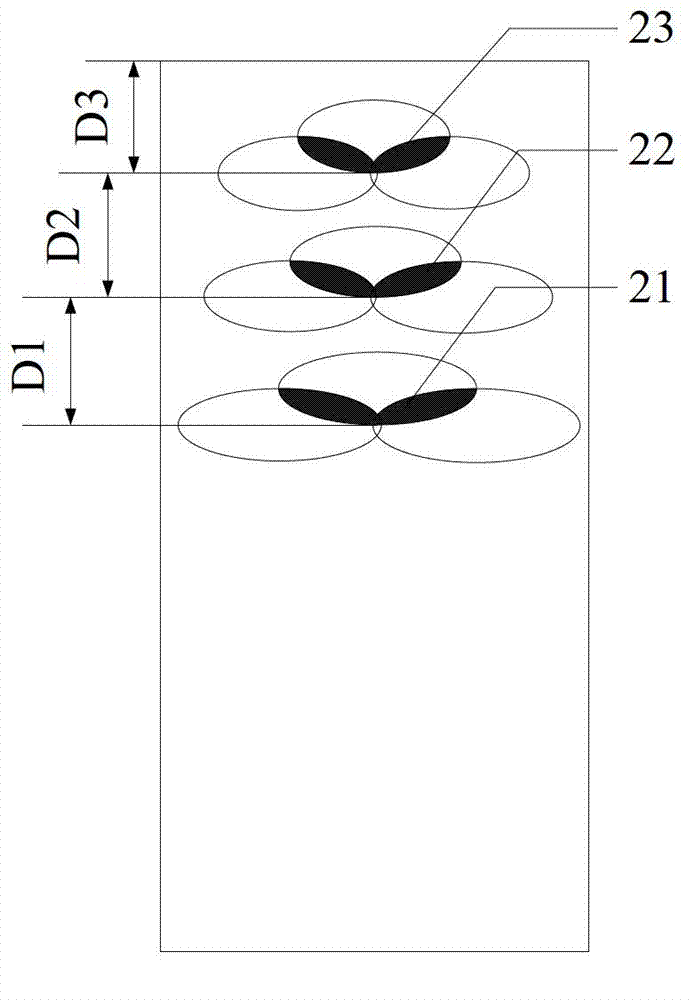
Ultra-wideband bionic antenna with low radar scattering cross section
ActiveCN101640310BEasy to hideAchieve stealthWave based measurement systemsRadiating elements structural formsUltra-widebandScattering cross-section
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband bionic antenna with a low radar scattering cross section, and mainly solves the problems that existing ultra-wideband antenna radar has high scattering cross section and can be easily found by radar. The ultra-wideband bionic antenna with the low radar scattering cross section comprises a radiation unit (2), a radiant floor (3) and an SMA coaxial adapter substitute. The antenna radiating unit and the antenna radiation floor are respectively printed on both sides of a medium material board (1), and are respectively connected with an inner core (4) and an outer core (5) of the SMA coaxial adapter substitute. The radiating unit is designed to be a sectoral structure comprising a rectangular column and a plurality of arc strips symmetrically arranged on the rectangular column in accordance with a design thinking similar to insect antennae, the degrees of the central angles of the arc strips are identical, and the sizes of semi-diameters are progressively increased according to equal intervals from the top to the bottom; and both sides of the radiant floor are rectangles with inversed 90-degree arc angles. The invention has the advantages of wide frequency band and good hiding performance, thereby being capable of being used as the ultra-wideband antenna on a hiding target vector.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
Ultra-wideband wave-absorbing structure for reducing RCS (radar cross section) of antenna
PendingCN114336086ASufficient mechanical stabilityImprove absorbing performanceAntennasUltra-widebandElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband wave-absorbing structure for reducing the RCS of an antenna. The ultra-wideband wave-absorbing structure comprises a surface skin dielectric layer, an impedance matching dielectric layer, an impedance type frequency selective surface, an impedance type frequency selective surface substrate, a dielectric layer and a conductive reflecting layer which are arranged from top to bottom, the impedance type frequency selective surface is composed of N * N conductive units, each conductive unit comprises a conductive outer circular ring and a conductive inner circular ring which are concentrically arranged, and each conductive circular ring is uniformly loaded with four resistors. According to the ultra-wideband wave-absorbing structure for reducing the RCS of the antenna, the resistance loading double circular rings are adopted as the impedance type frequency selective surface, so that the RCS of the antenna can be reduced, the purpose of hiding the antenna is achieved, and the ultra-wideband wave-absorbing structure is stable in performance and has a wide practical application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Radial multi-beam gap waveguide slot antenna array applied to microwave band
ActiveCN110061348ARealize independent controlEasy to integrateParticular array feeding systemsRadiating elements structural formsWaveguideMulti beam
The invention discloses a radial multi-beam gap waveguide slot antenna array applied to a microwave band. The radial multi-beam gap waveguide slot antenna array comprises three parts of a gap waveguide radial feeding network, a slot antenna array and a coaxial-gap waveguide conversion structure. By a design of a bottom-layer feeding network and each slot sub-array in a top layer in a radial direction, generation of random numbers of radial wave beams can be achieved, the size and the direction of each wave beam are independently adjustable, and a beam split phenomenon is proposed according toa certain radial asymmetric construction mode of the antenna.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Radar antenna
PendingCN113594679AReduced Radar Cross SectionImprove angle measurement accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntenna supports/mountingsRadar antennasMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a radar antenna, which is characterized in that a plurality of metal patches are arranged around an antenna unit, each metal patch comprises a first metal unit and a second metal unit, the first metal unit and the second metal unit are both L-shaped structures, and the first metal unit and the second metal unit form a square structure with gaps at opposite angles. The radar cross section of the radar antenna can be reduced, antenna surface waves are suppressed, the smoothness of an azimuth plane gain curve of the radar antenna is improved, and the angle measurement precision of the radar antenna is improved.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE INNOVATION CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com