Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Known method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sonochemical leaching of polycrystalline diamond
InactiveUS20070169419A1Reduce generationKnown methodOther chemical processesAbrasion apparatusMetallurgyPolycrystalline diamond
A method for accelerated leaching of binder-catalyst material from the polycrystalline diamond structure of a PDC is disclosed. The PDC is sonochemically leached. Also disclosed are fixture, equipment and a system for sonochemically leaching the polycrystalline diamond structure of a PDC.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL
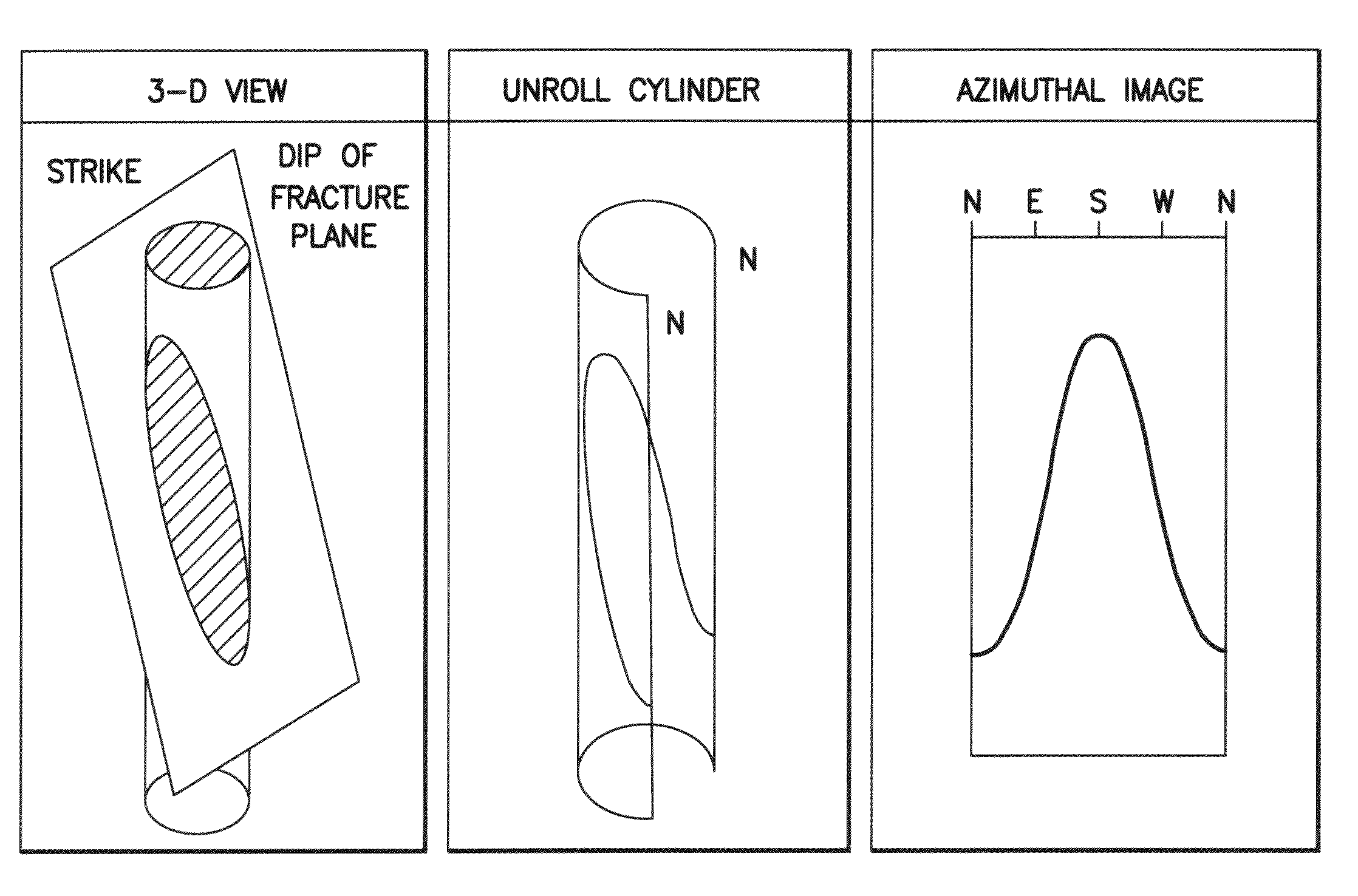
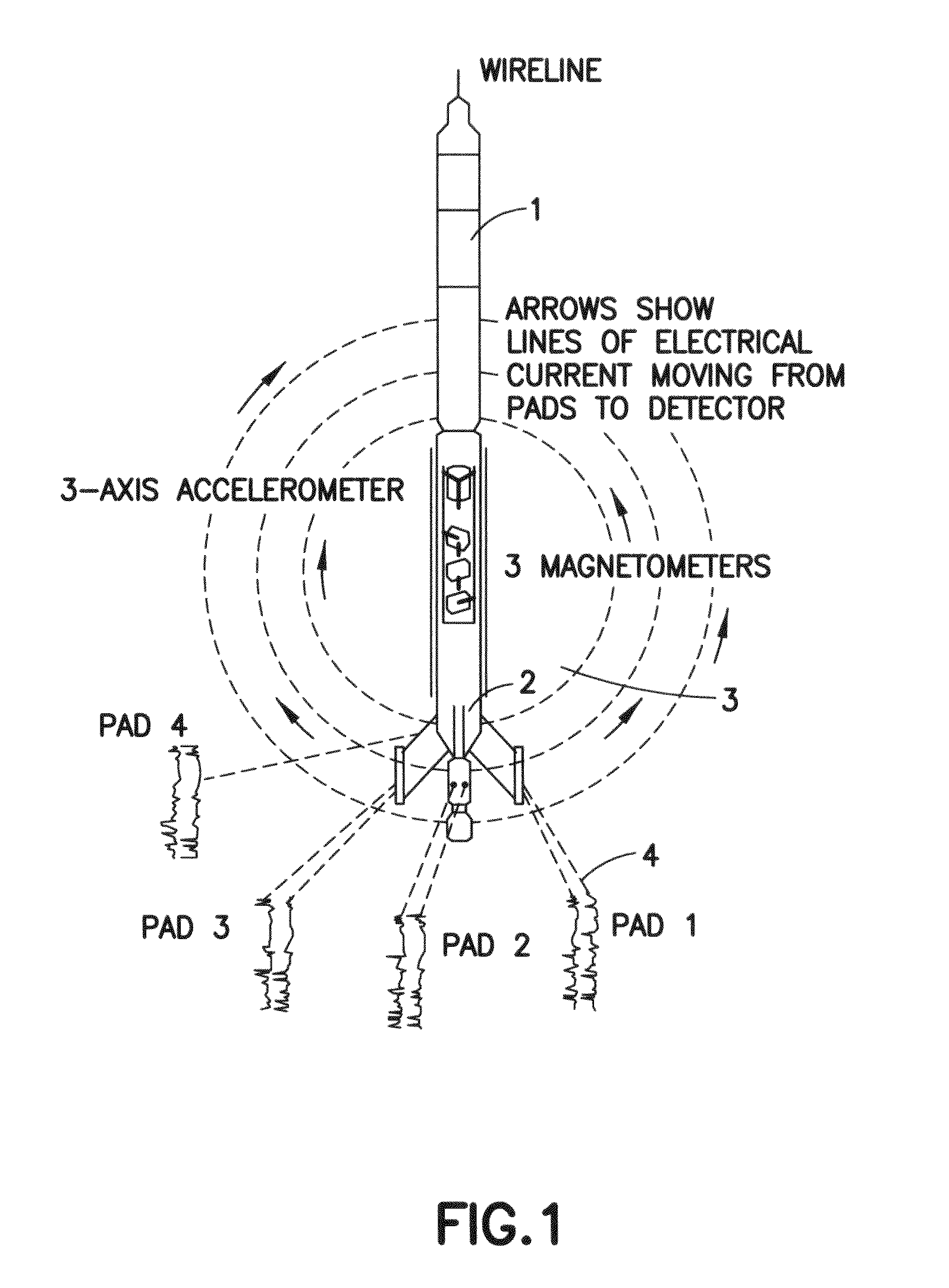
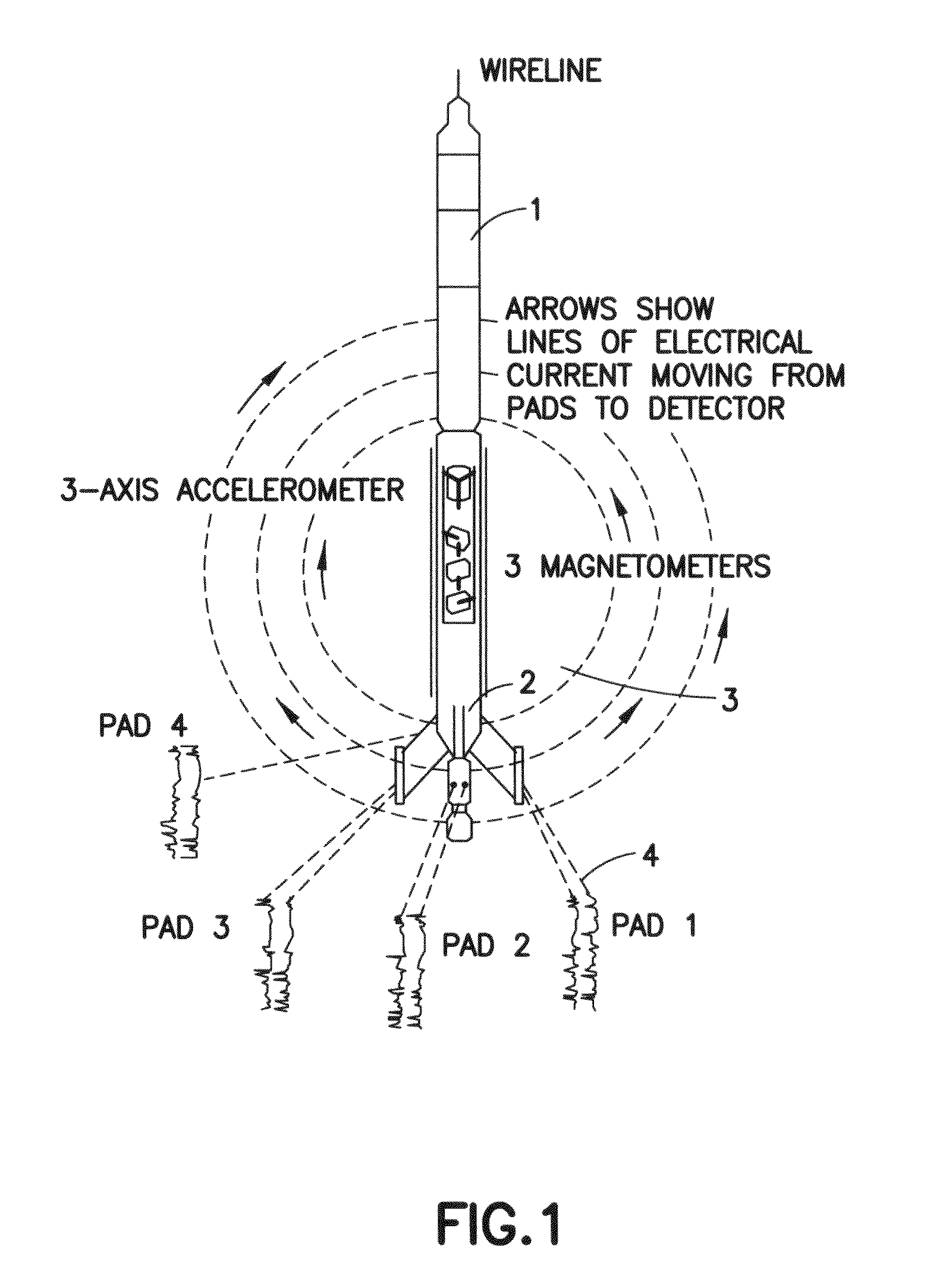
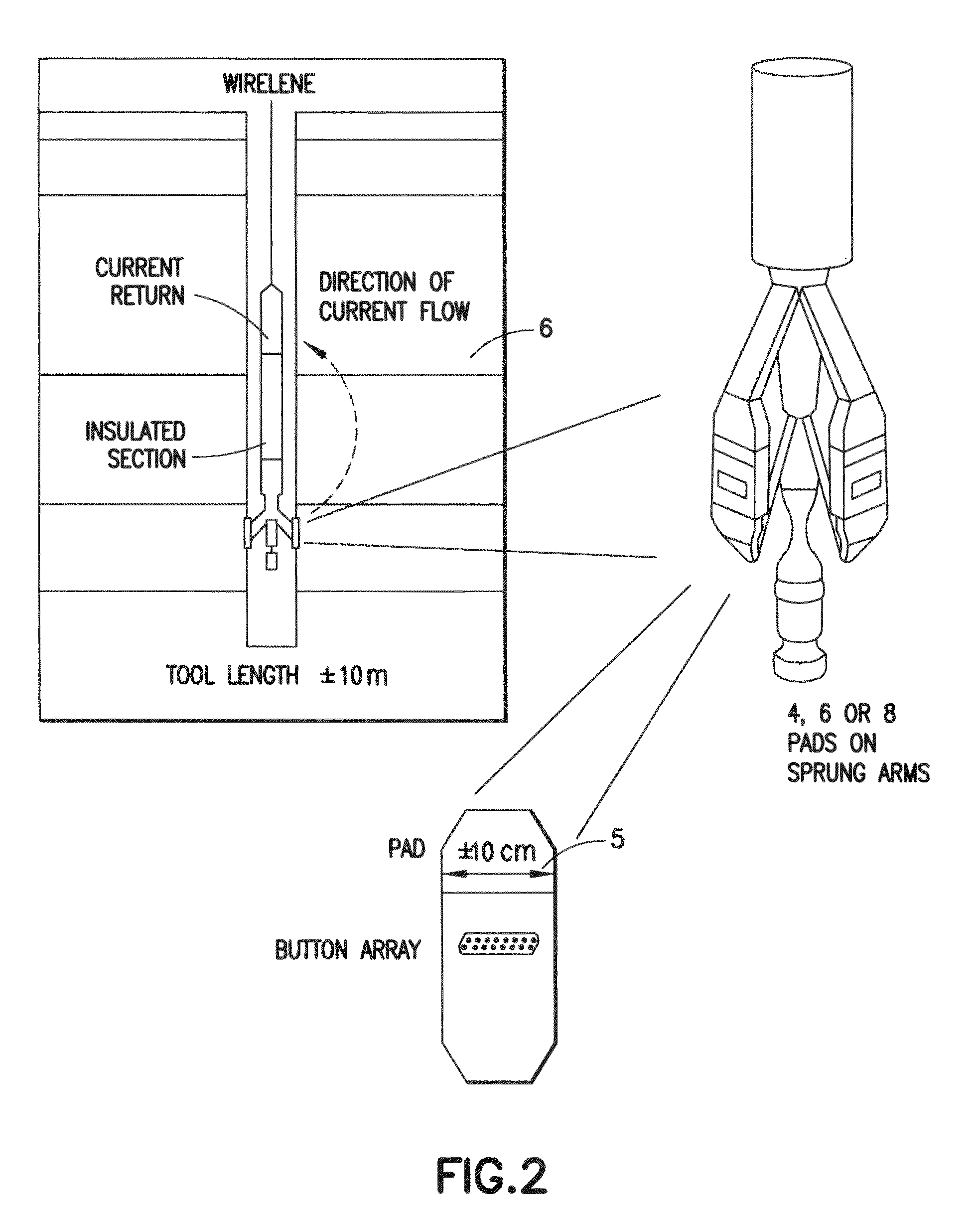
Method for characterizing a geological formation traversed by a borehole
InactiveUS20090262603A1Known methodElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingImage modeEnvironmental geology
Methods for characterizing a geological formation, the methods include retrieving measured data provided by a measuring tool along one or more logged borehole length for a borehole, another borehole or both in order to produce a borehole imaging log. Selecting depth-defined intervals of the borehole imaging log as training images for inputting in a multi-point geostatistical model. Determining pattern based simulations for each training image using a pixel-based template of the multi-point geostatistical model so as to obtain training image patterns. Using the pattern based simulation of each training image to assign to each of the training image a corresponding training image pattern. Constructing from the training image patterns one or more fullbore image log of a borehole wall of the borehole. Repeat the second to fourth steps through the one or more logged borehole length in order to construct fullbore images from successive, adjacent training images.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
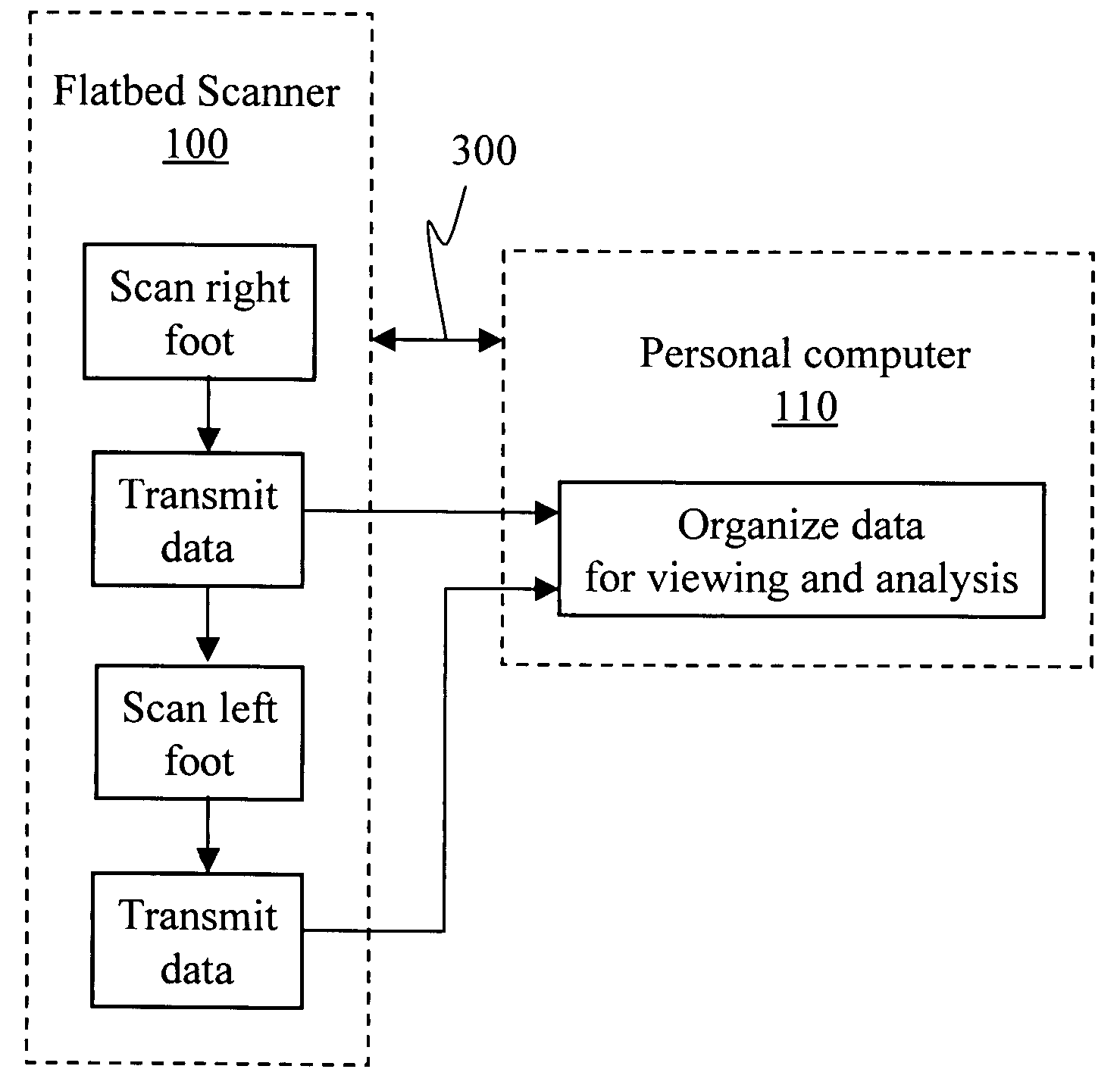
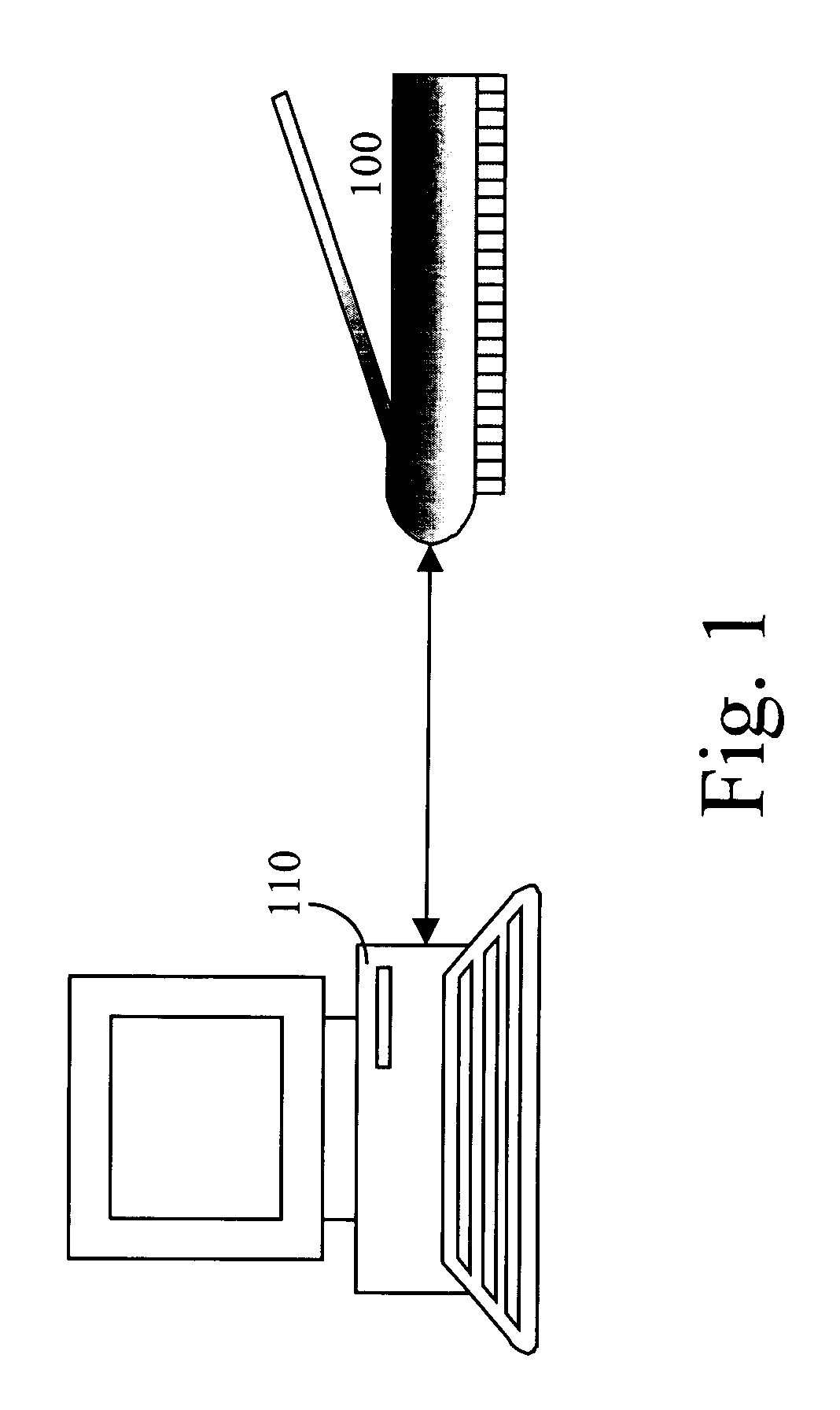
Method and apparatus for scanning feet for the purpose of manufacturing orthotics and other footwear
InactiveUS20050061332A1Ease of storage and transmittalRestore balanceFoot measurement devicesRestraining devicesKnee orthosisEngineering
Measurements for corrective footwear, orthopedics, and orthotics have traditionally been obtained through three-dimensional casts of a foot. Digital technology opens an avenue of utilizing a digital image in place of the cast. Using a single or dual flatbed scanner and a computer, all the data required to construct a corrective device may be obtained from a scan or scans of the foot. Observed features and color variations, as well as physical measurements are used to overcome imperfections of a patient's foot.
Owner:FOOT LEVELERS
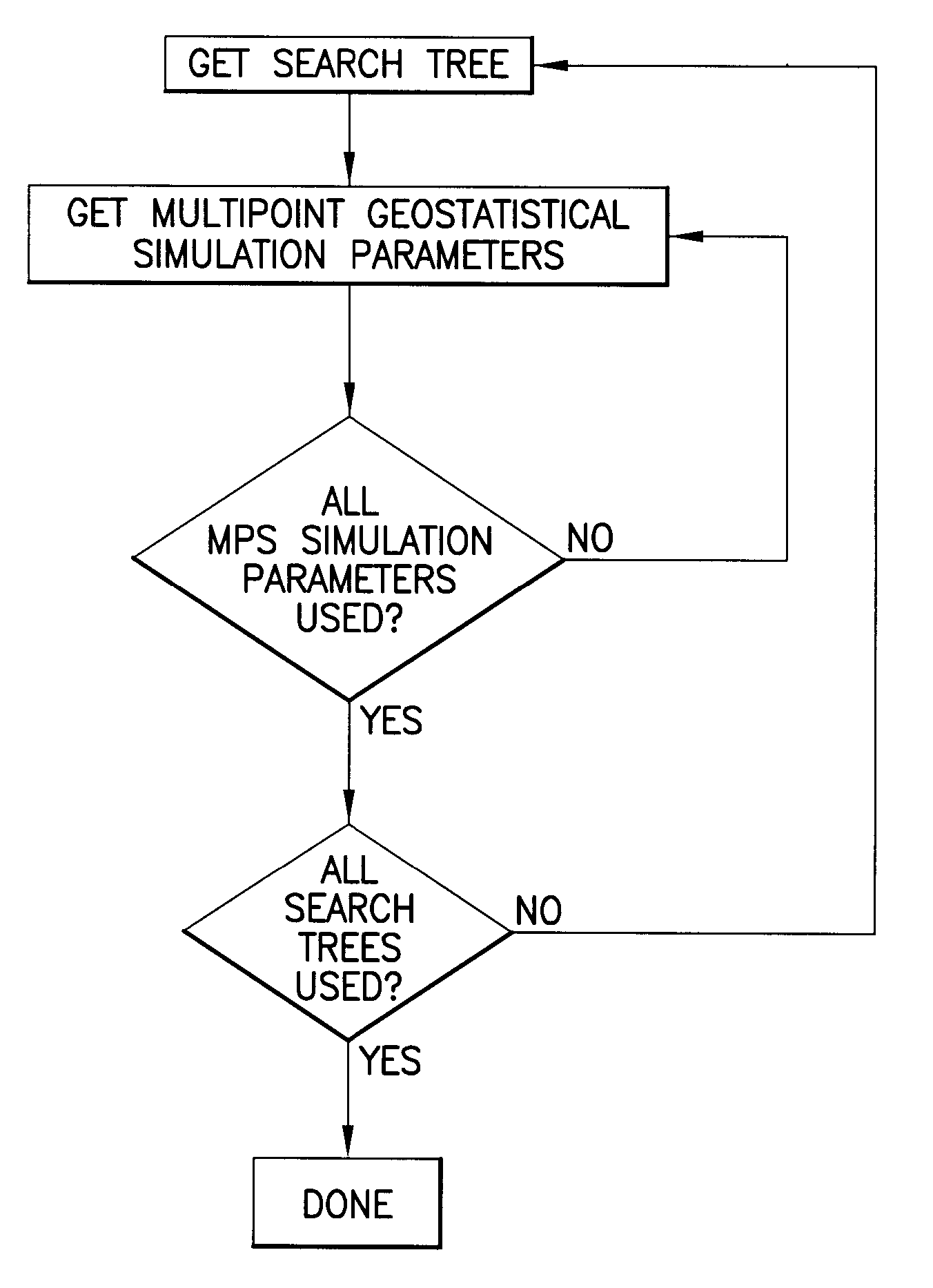
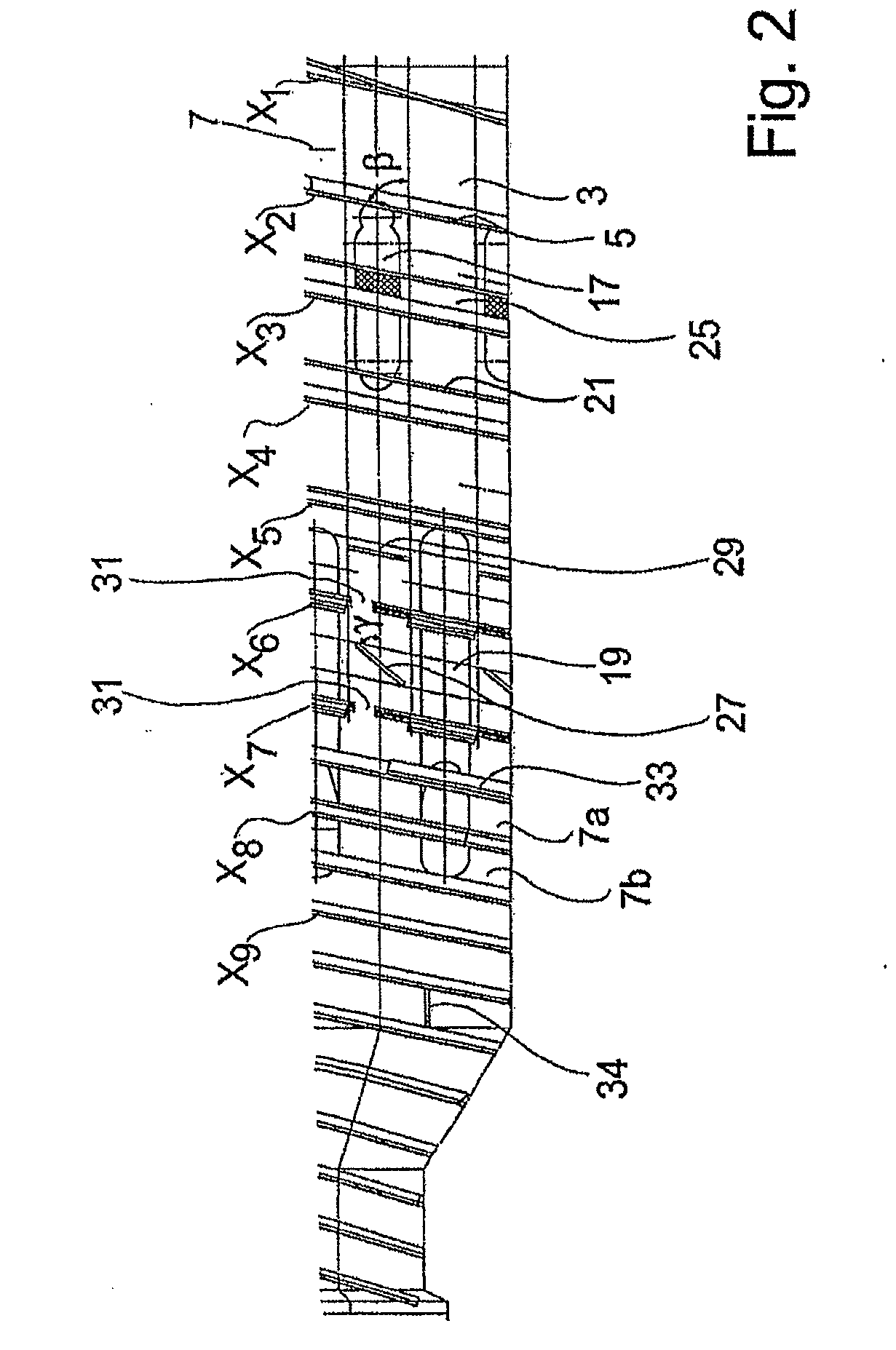
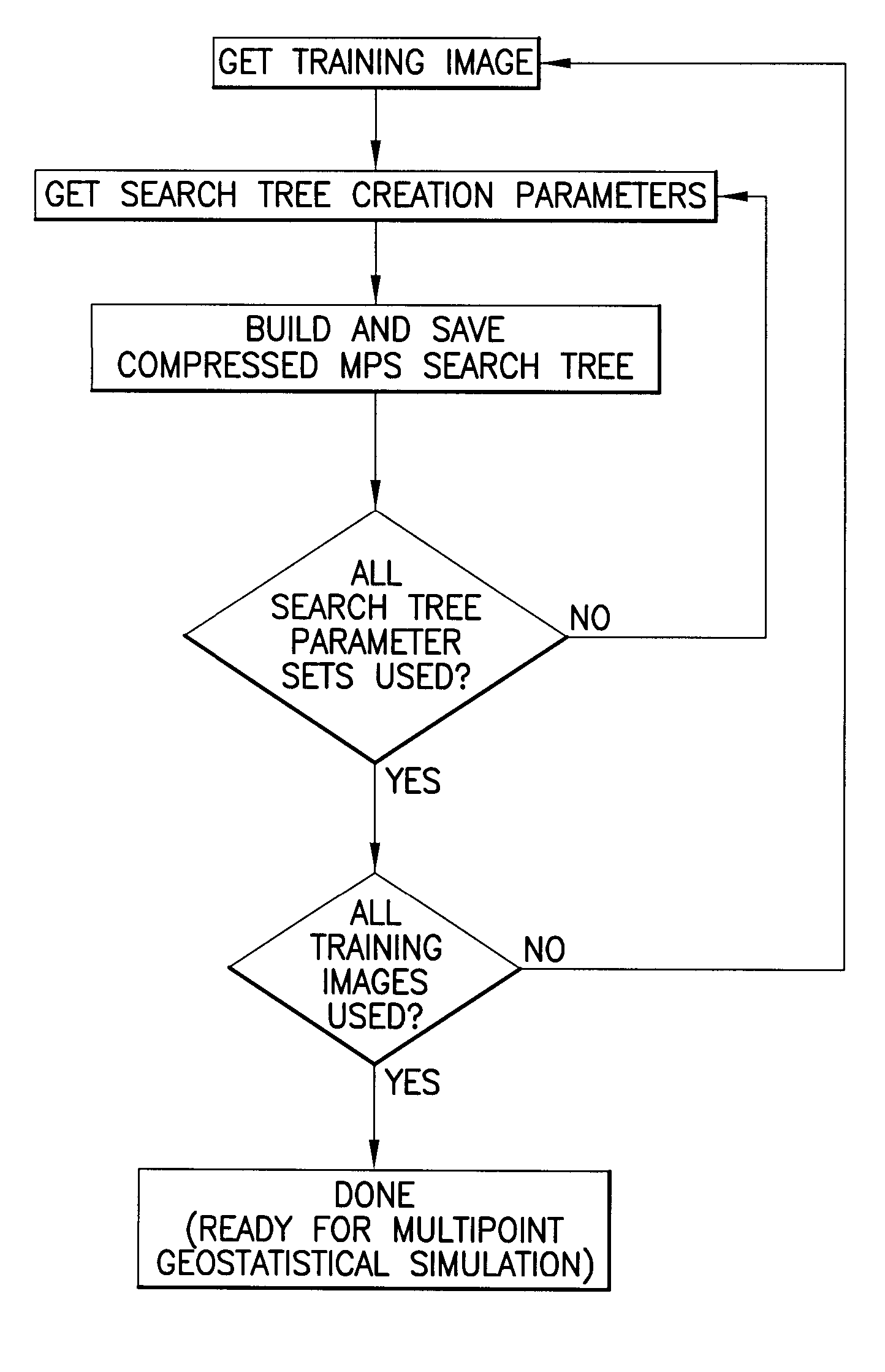
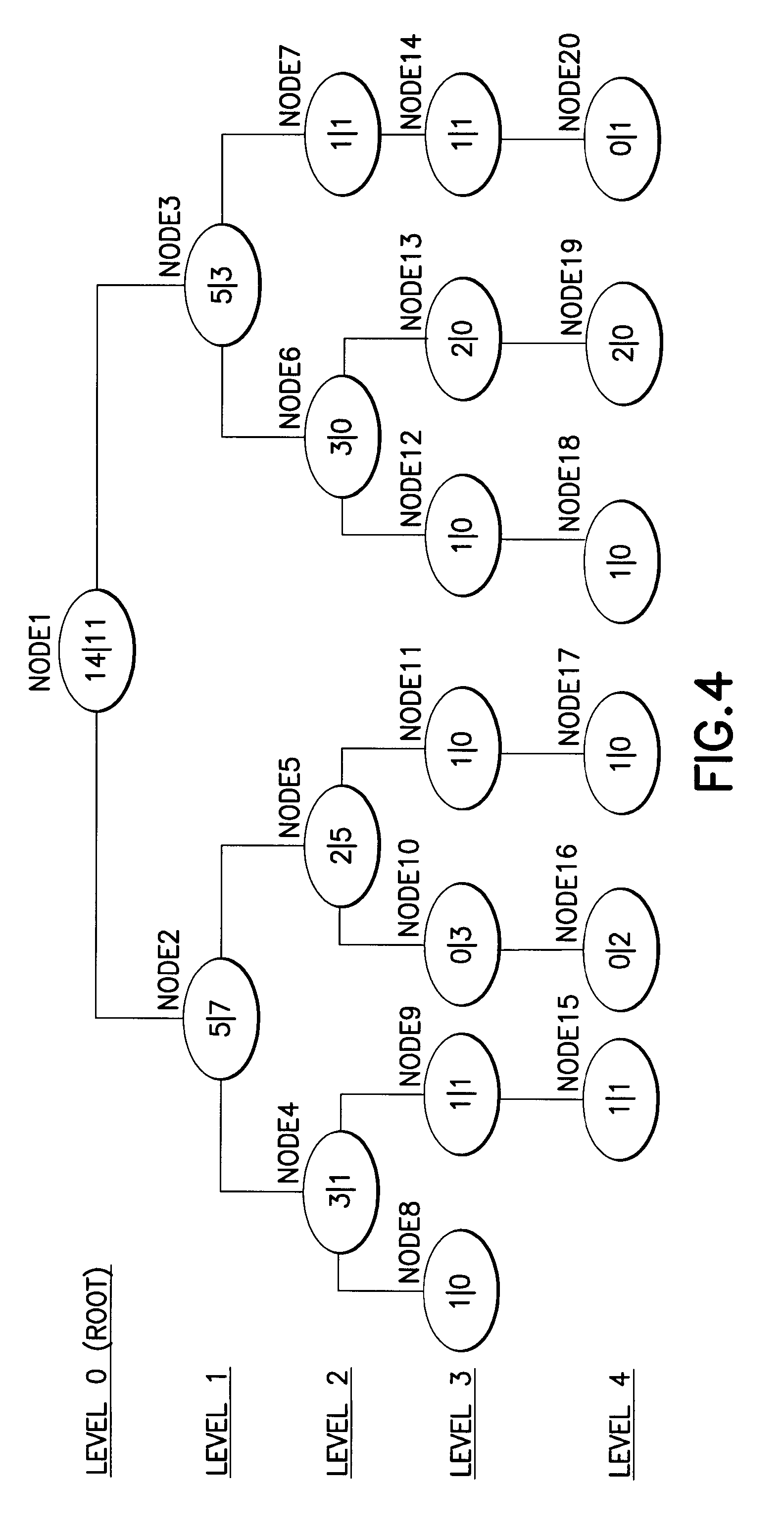
Multipoint geostatistics method using branch runlength compression
ActiveUS20090164182A1Improves known multipoint geostatistics method shortcomingShort timeDigital computer detailsSeismologyRelevant informationAlgorithm
A multipoint geostatistics computer-implemented method for modeling of discrete properties, comprising acquiring by a computer software program a training image made from at least one dimensional array of discrete property values, the values depicting the spatial relationship and variability considered to be typical of a n-dimensional surface to be modeled; constructing a search tree, the tree representing the probability of occurrence of combinations of values of a discrete property value, the construction being performed by counting these occurrences in the training image. The non-branching sequences of the search tree are compressed to what essentially amounts to a single node, by keeping only the relevant information the sequences contain.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
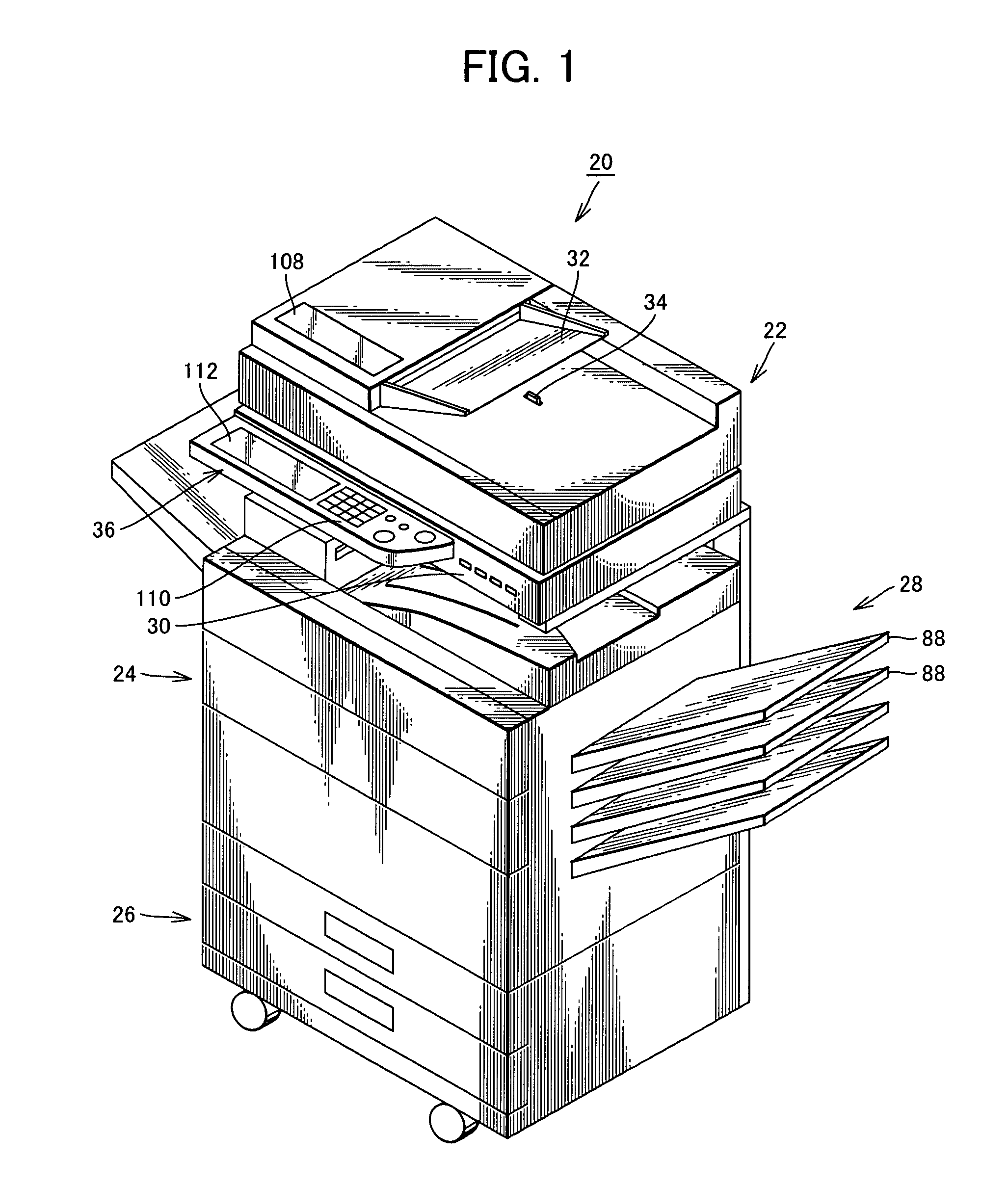
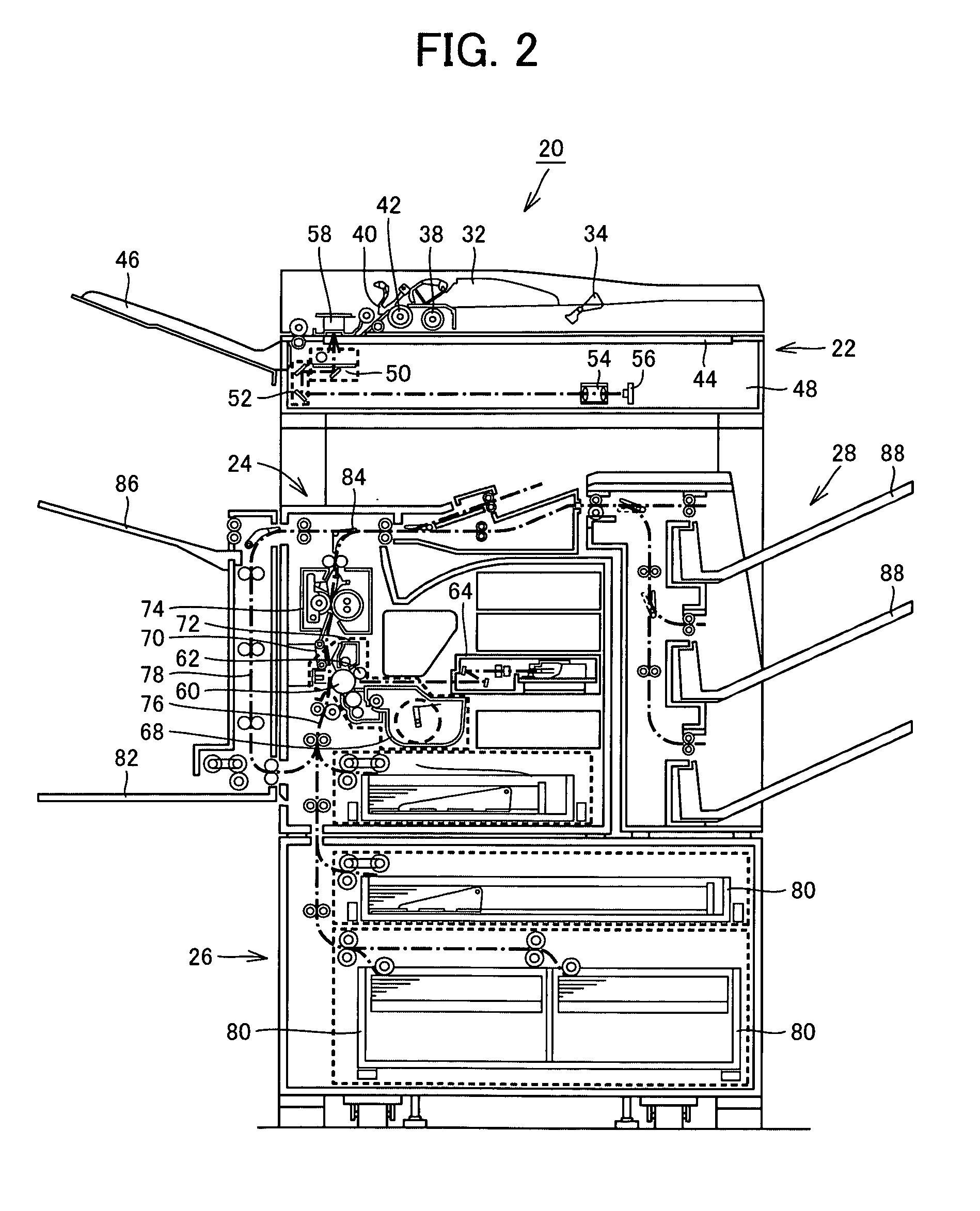
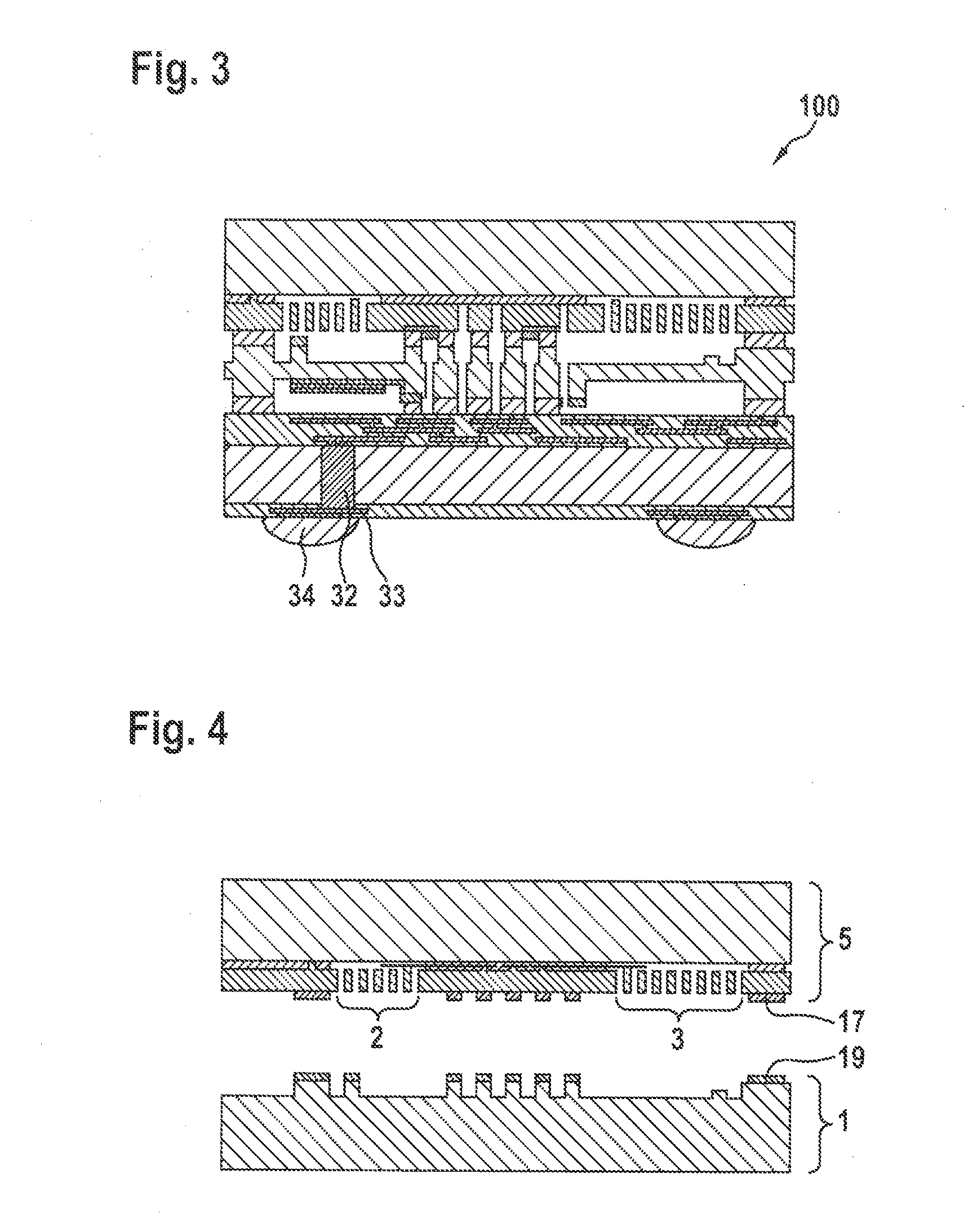
Image forming apparatus providing user support in sleep mode
ActiveUS20090262379A1Known methodFunction increaseMultiple digital computer combinationsElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
An image forming apparatus that can support the user in sleep mode is provided. When the apparatus enters sleep mode, guidance information is displayed on an electronic paper. The electronic paper maintains displayed contents even when power is not supplied and, therefore, even when power is not supplied to a display panel in the sleep mode, the display for the user is continuously given, thereby supporting the user.
Owner:SHARP KK
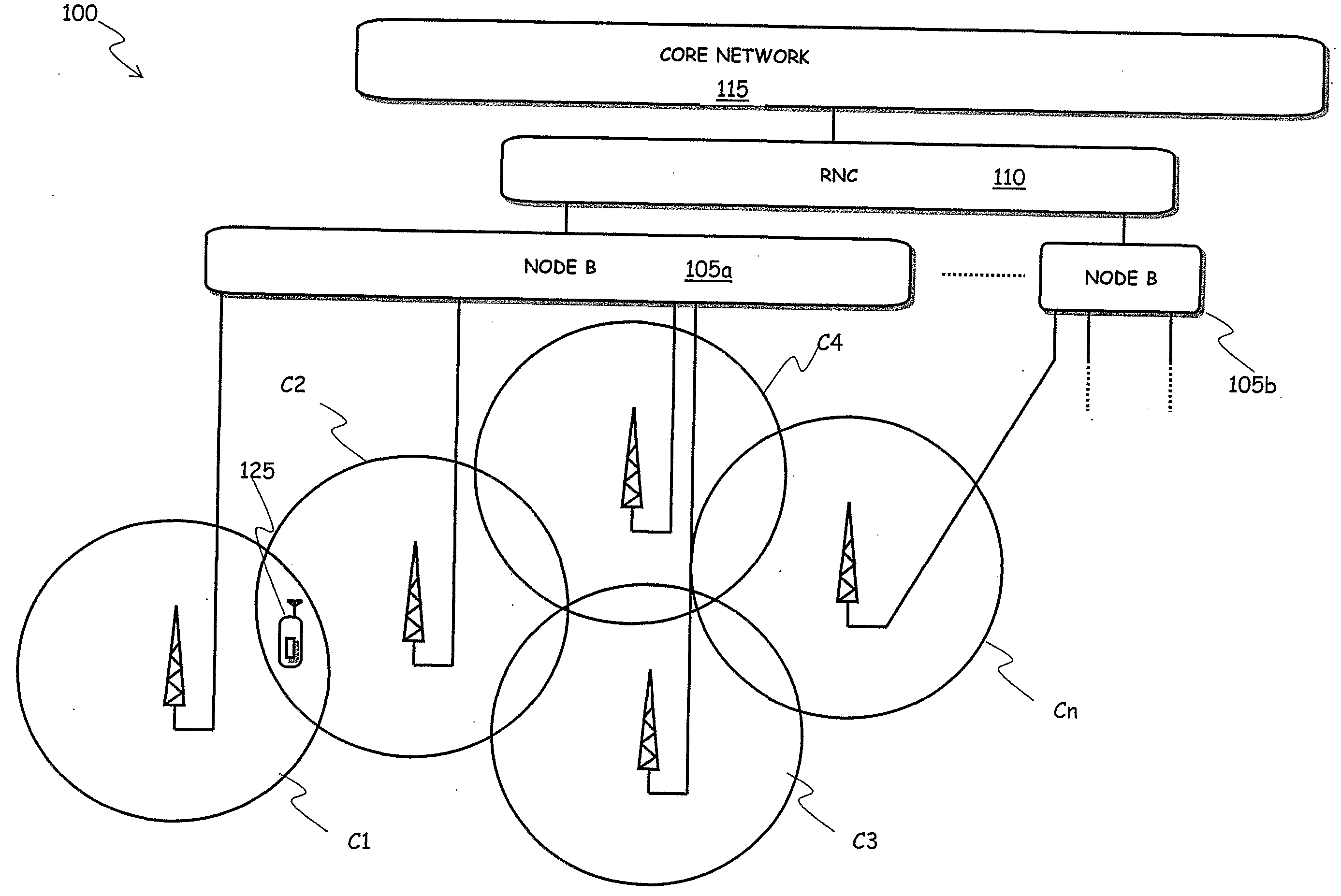
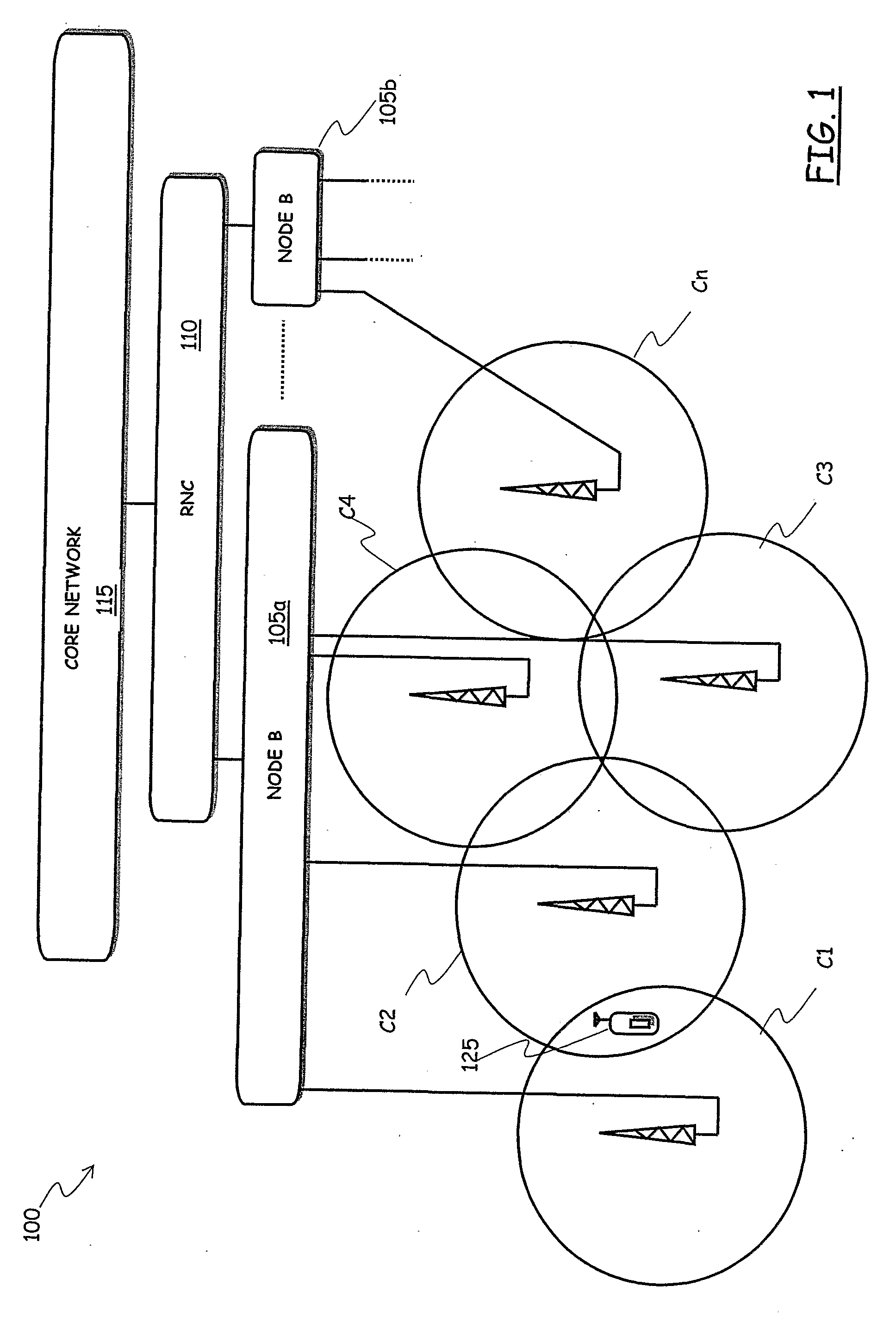
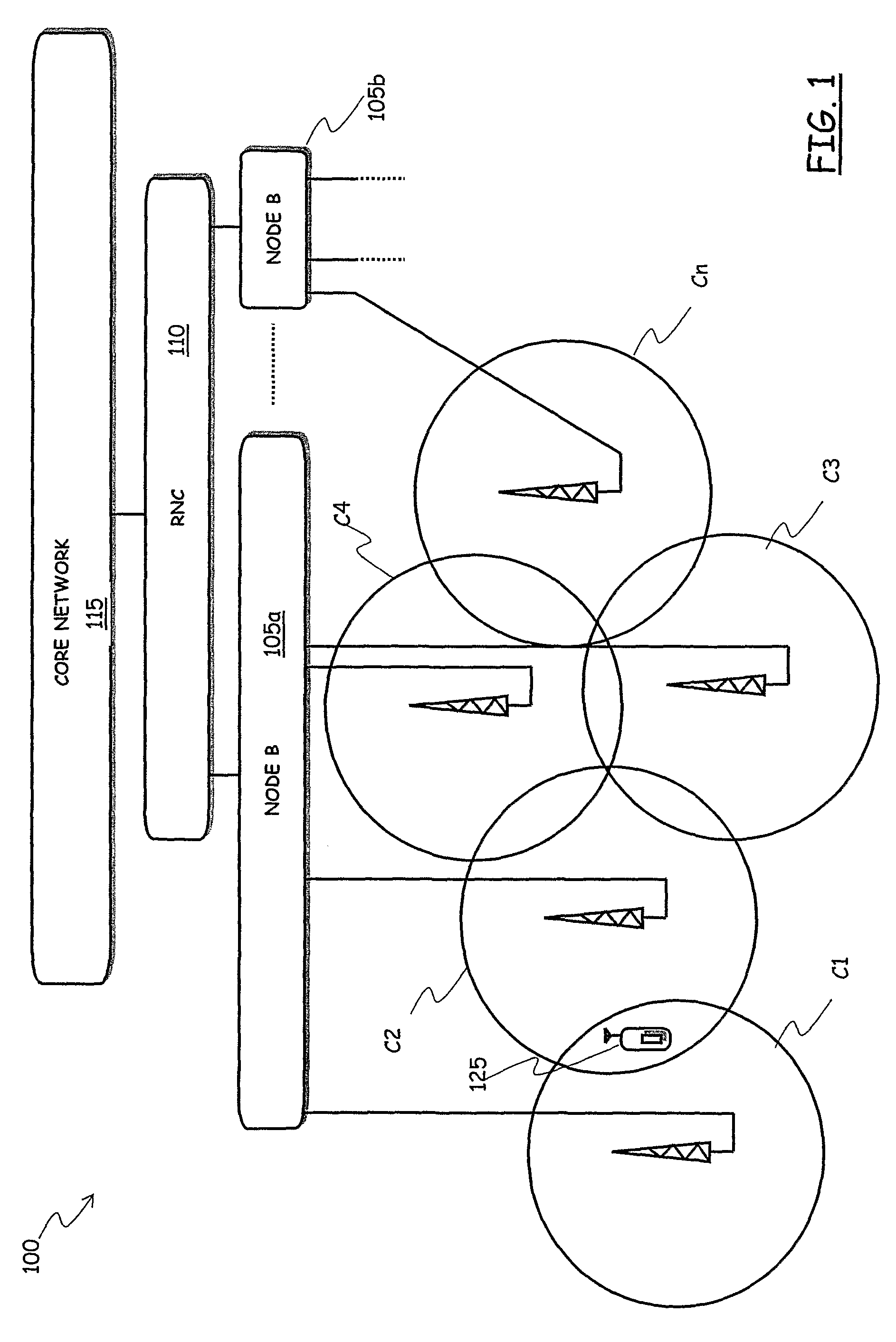
Method for Planning a Cellular Mobile Telecommunications Network
ActiveUS20090176500A1Impact efficiencyKnown methodTransmission monitoringRadio transmission for post communicationQuality of serviceTelecommunications network
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Method and device for lining a pipe conduit or a channel
ActiveUS20060254711A1Downtime be shortenDowntime caused by the renovation can be considerably shortenedLiquid surface applicatorsSpraying apparatusEngineeringBiomedical engineering
Owner:SCHWERT SIEGFRIED
Multilayer label and method of making the same
InactiveUS6948743B1Increase spaceProvide informationStampsOther printing matterComputer scienceMultiple layer
A multiple layer label and a method of making the same are provided. Specifically, a label having a base layer for adhering to a container is provided wherein the label has an overcoat layer having an end that is removably adhered to the container. Moreover, the end that is removably adhered to the container is grasped by a user of the label and pulled, thereby removing the end of the overcoat layer from the container and swinging the layer away from the remainder of the label and exposing sublayers beneath the overcoat layer. The overcoat layer is adhered directly to the base layer, and at least portions of the sublayers. Each of the overcoat layer, sublayers, and the base layer may have indicia printed thereon for communicating information.
Owner:WEBER MARKING SYST
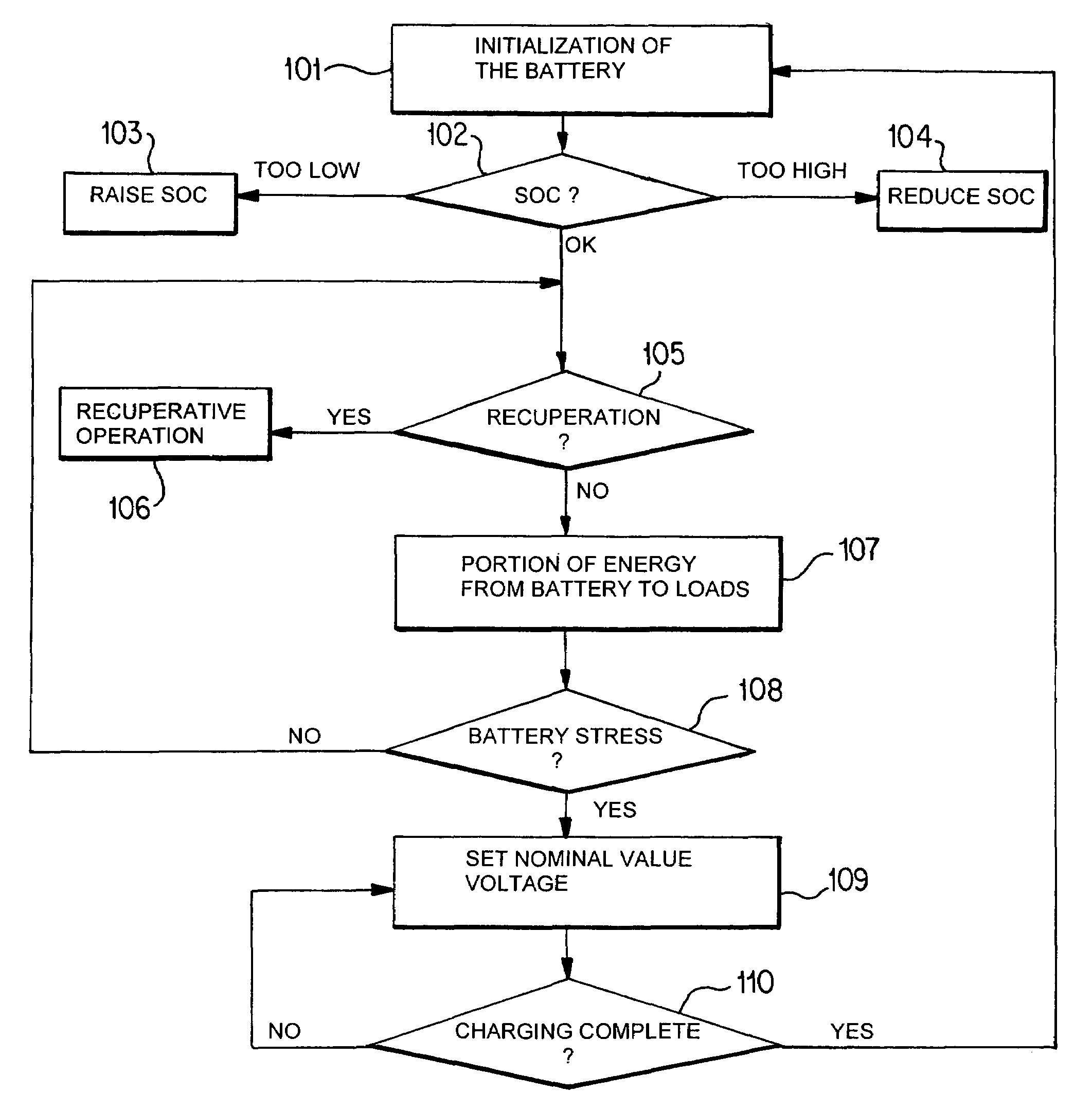
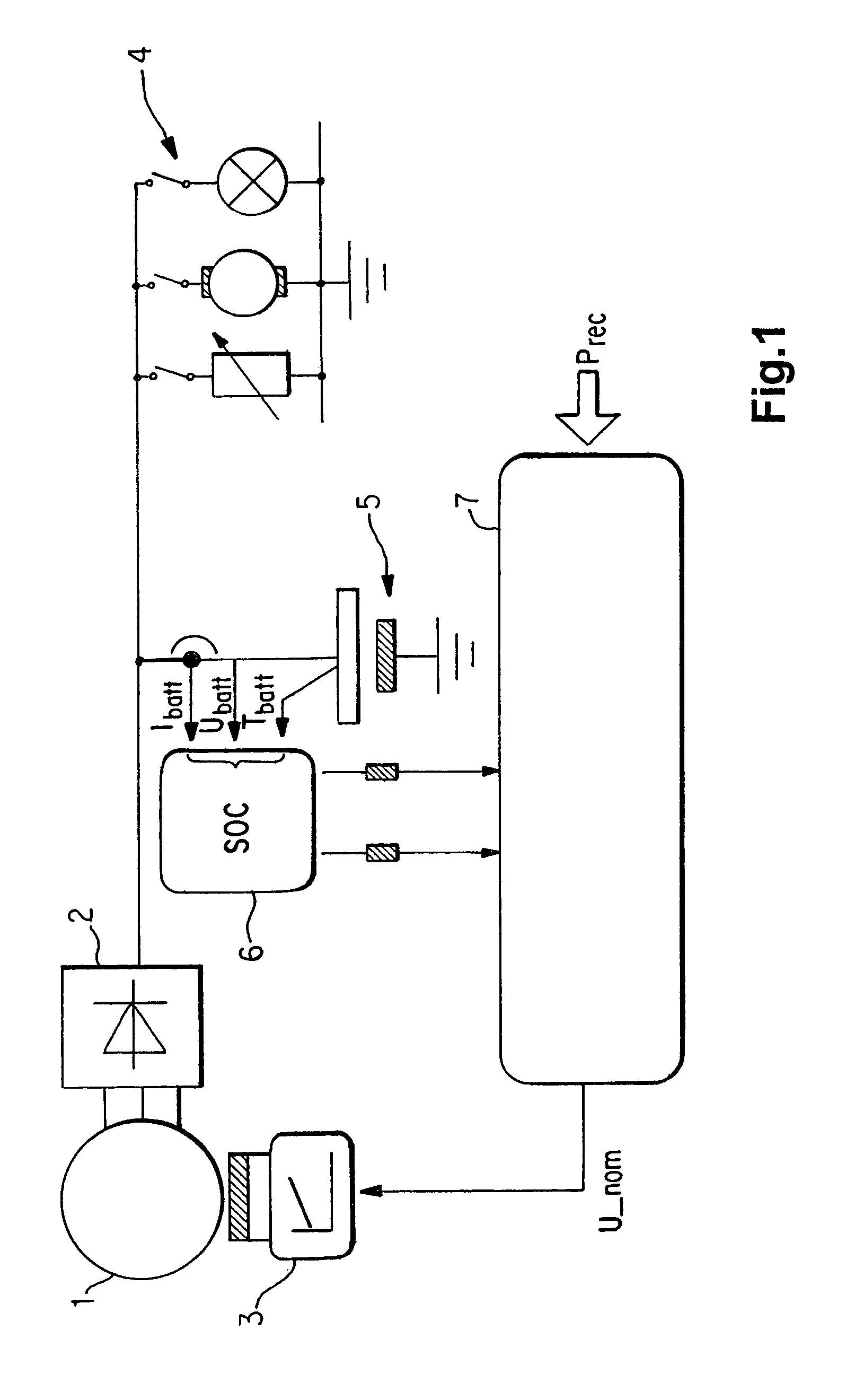
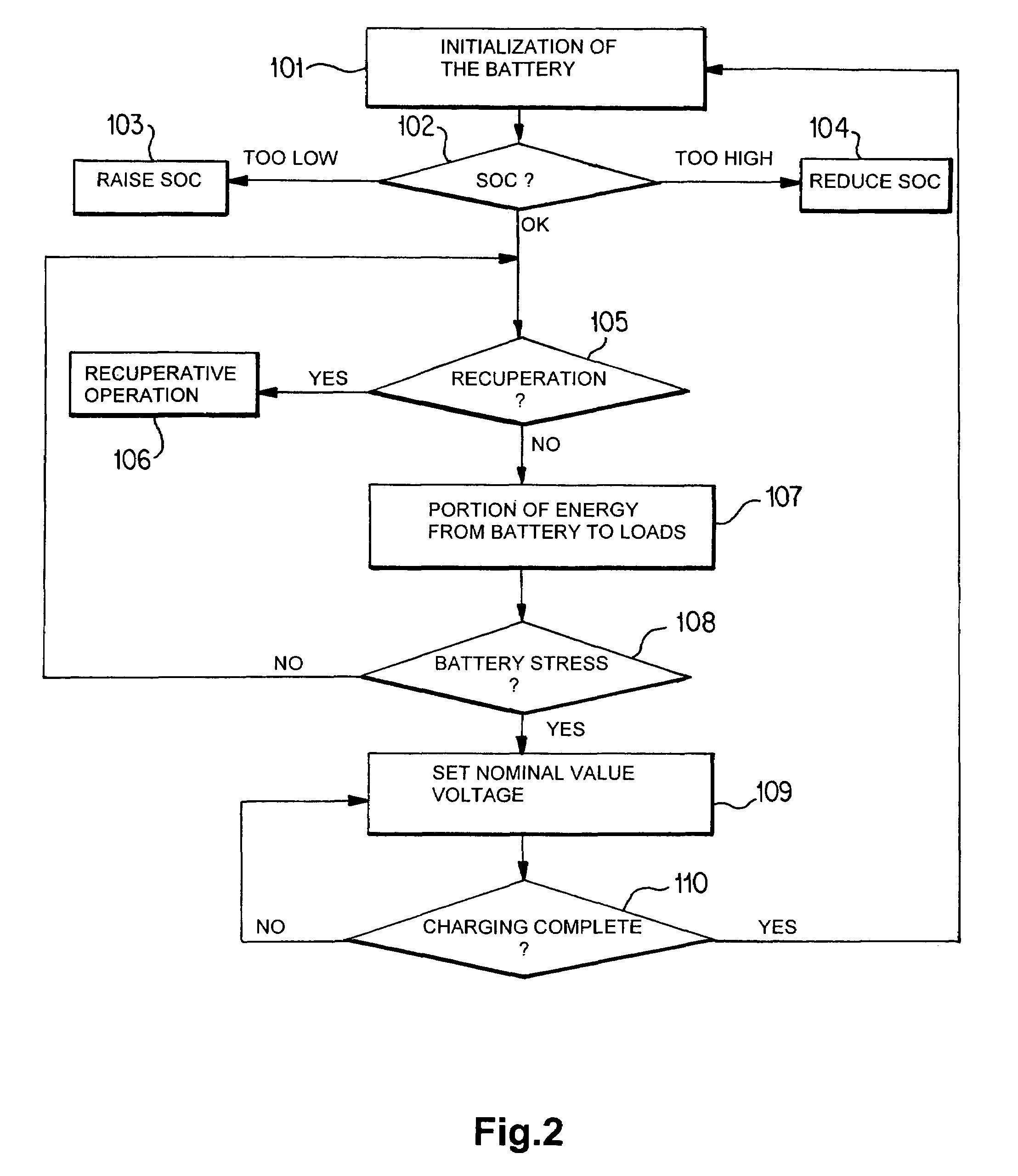
Method for regulating the generator voltage in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS7091626B2Reduce fuel consumptionIncrease pressureEngine controllersMachines/enginesMobile vehicleElectrical battery
A method for regulating a generator in a motor vehicle, in which the generator feeds a vehicle power supply system having loads and having at least one battery, with a regulator regulating the generator output voltage at the value of a nominal value voltage. In a recuperation readiness mode, the nominal value voltage is preset as a function of the driving state variables such that, during braking or when the vehicle is overrunning, electrical power is fed into the vehicle power supply system. Switching takes place between the recuperation readiness mode and a recovery mode as a function of predetermined switching conditions, with the nominal value voltage in the recovery mode being preset such that the battery is regenerated.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
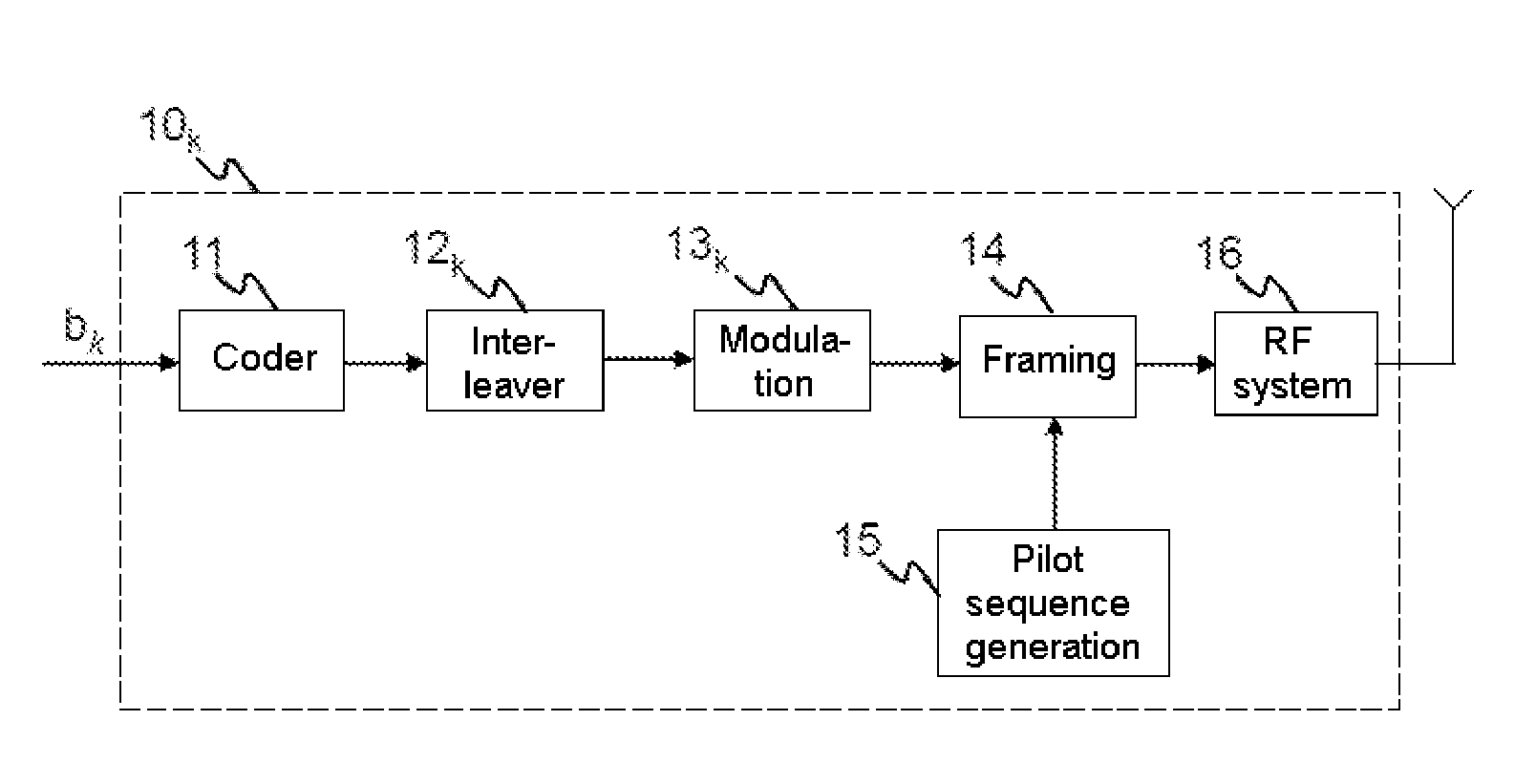
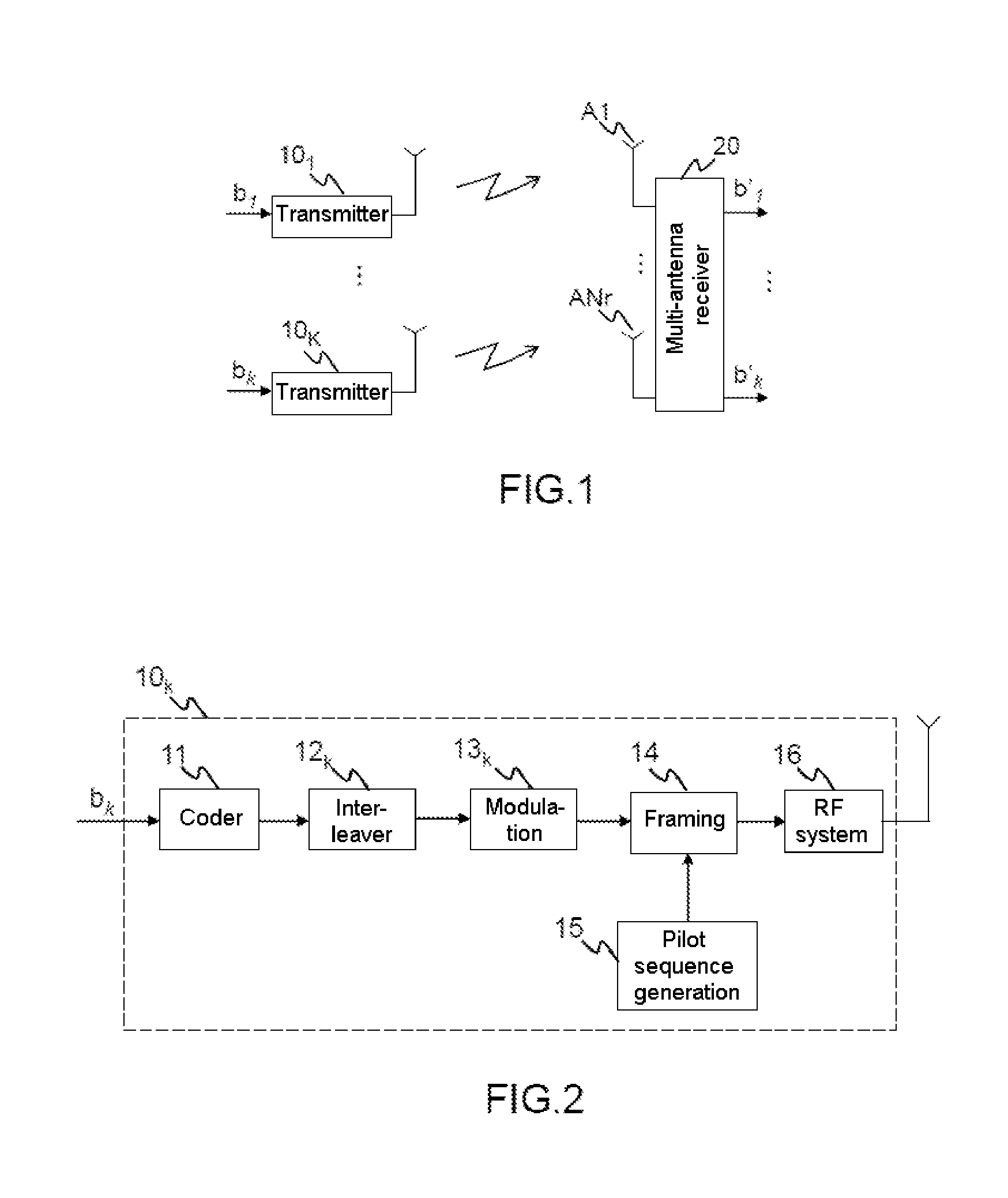
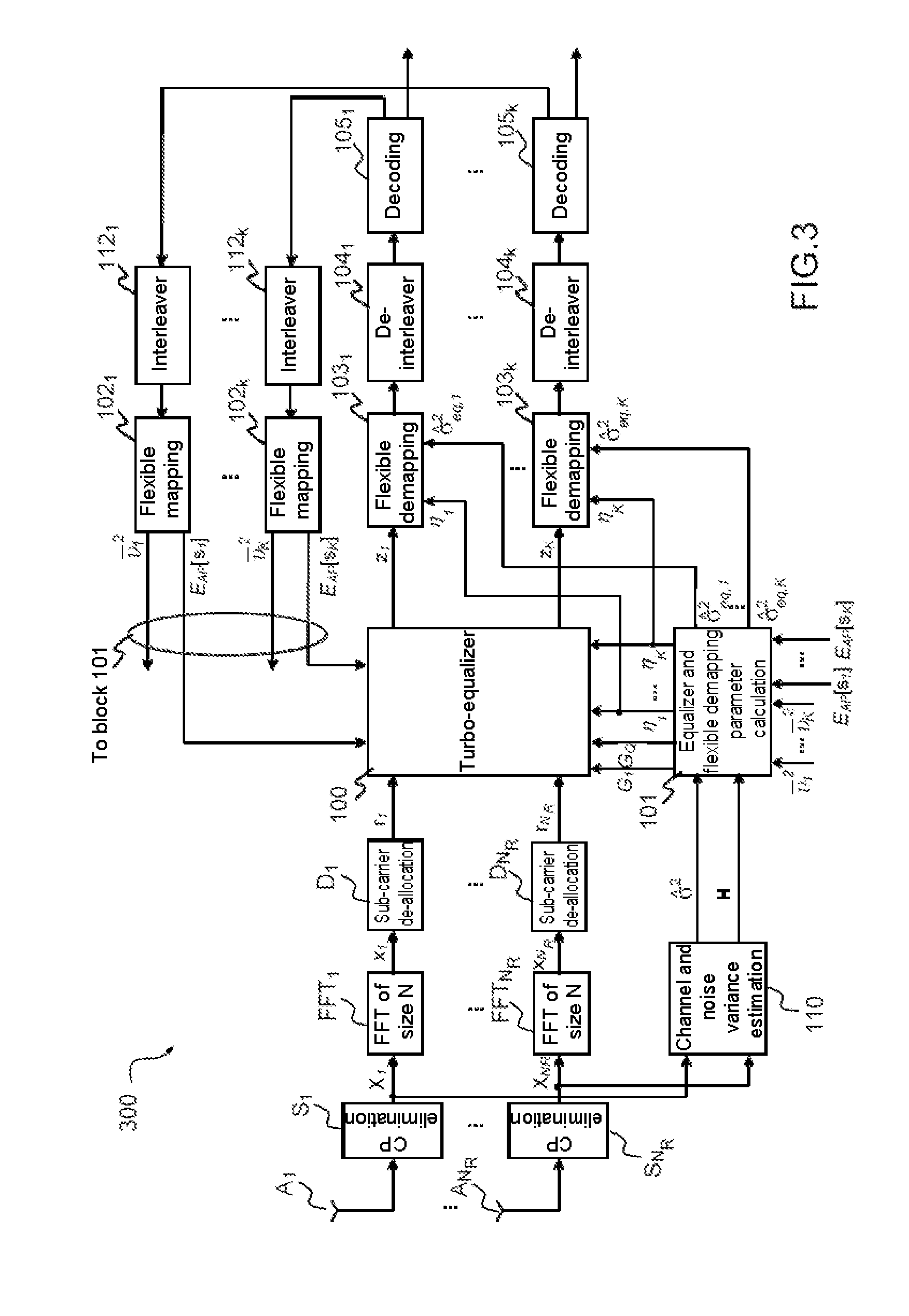
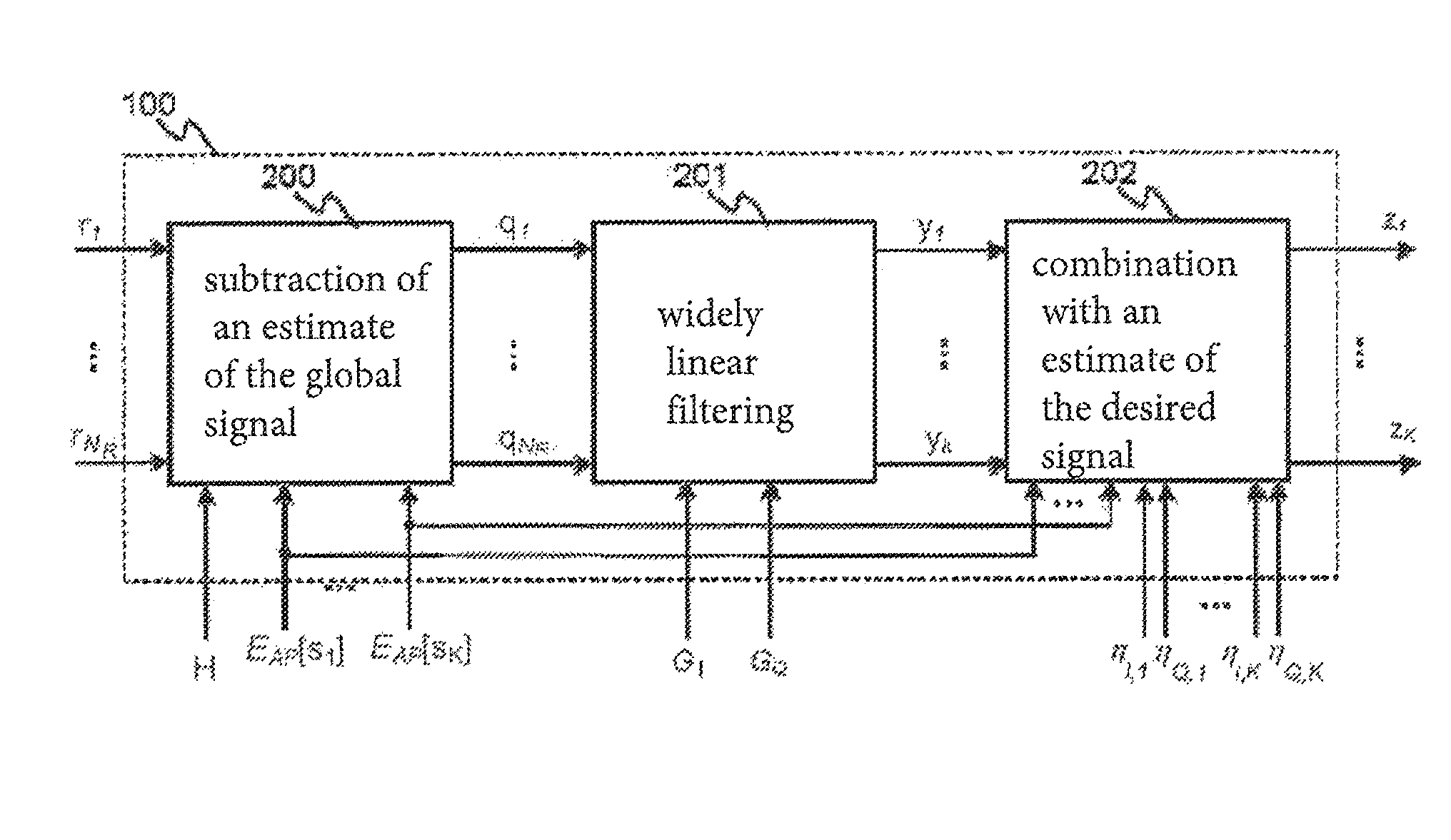
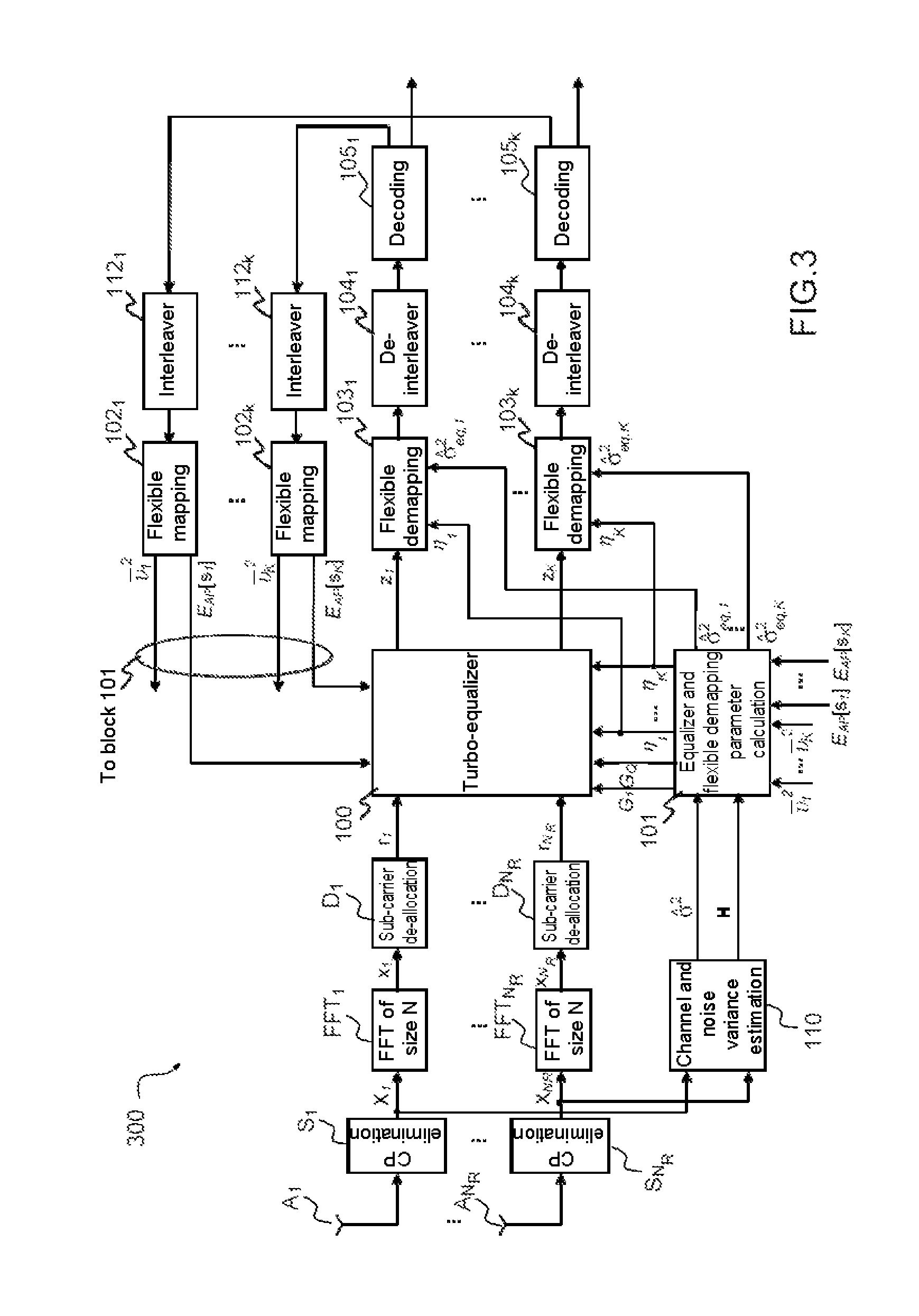
Method of widely linear turbo-equalization in a multi-user context and for a multi-channel multi-antenna receiver
InactiveUS20150341190A1Eliminate distractionsImprove equalization filterMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringEqualization
A method of equalizing a signal received by a plurality of antenna elements, the received signal being produced by the transmission of signals by a plurality of transmitters, includes: a step of converting the received signal into the frequency domain; a step of subtracting from the signal an estimate of the intersymbol interference and the interference between users so as to obtain a complex corrective signal; a step of conjoint widely linear filtering of the complex corrective signal and the conjugate complex corrective signal to obtain an equalized signal; a step of converting the equalized corrective signal into the time domain; a step of calculating coefficients of the at least one equalizer filter from the covariance matrix and the pseudo-covariance matrix of the received signal.
Owner:THALES SA
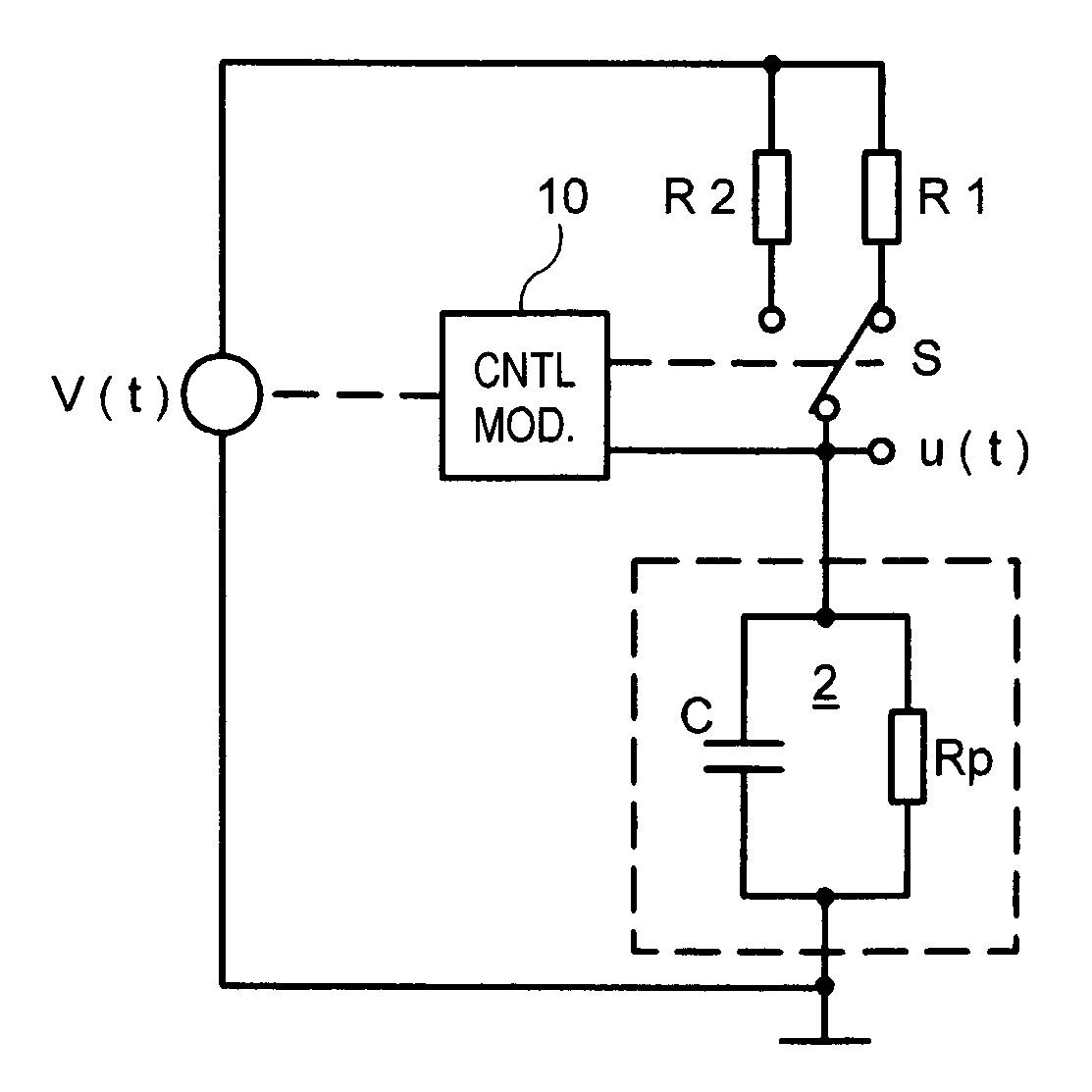
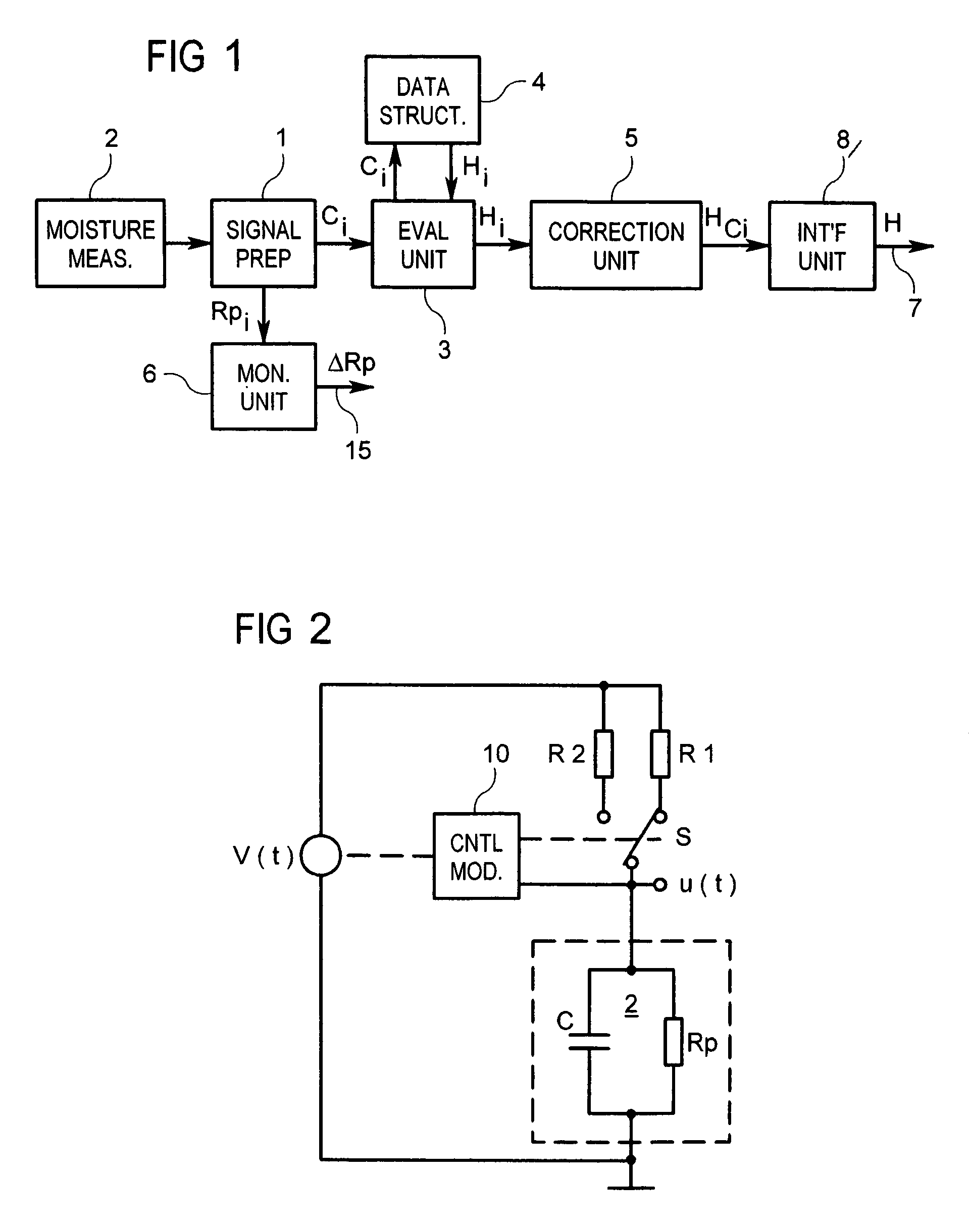
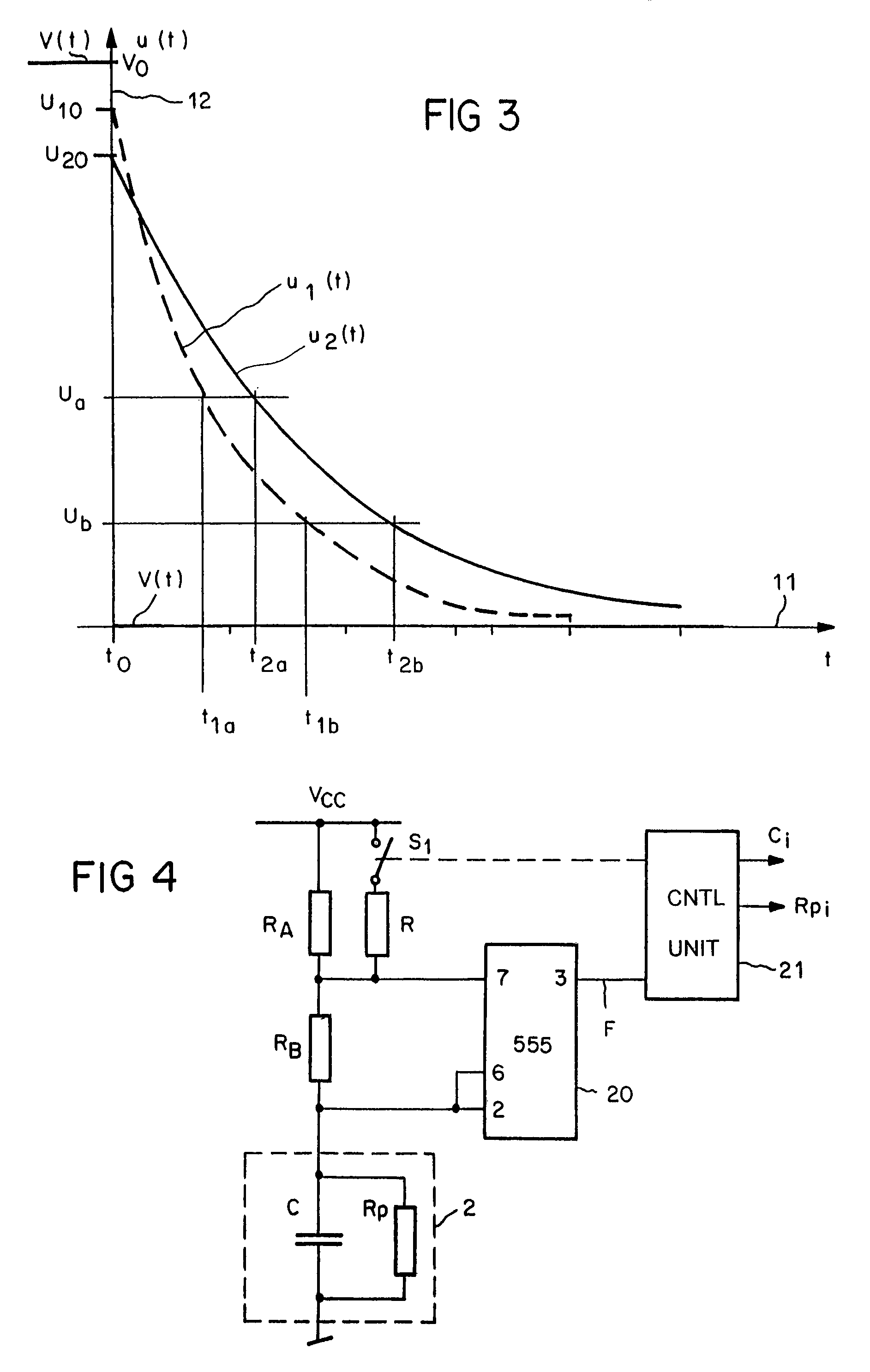
Moisture sensor with capacitive moisture measuring element and method of determining air humidity
ActiveUS7030630B2Improve the level ofKnown methodResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial capacitanceCapacitanceEngineering
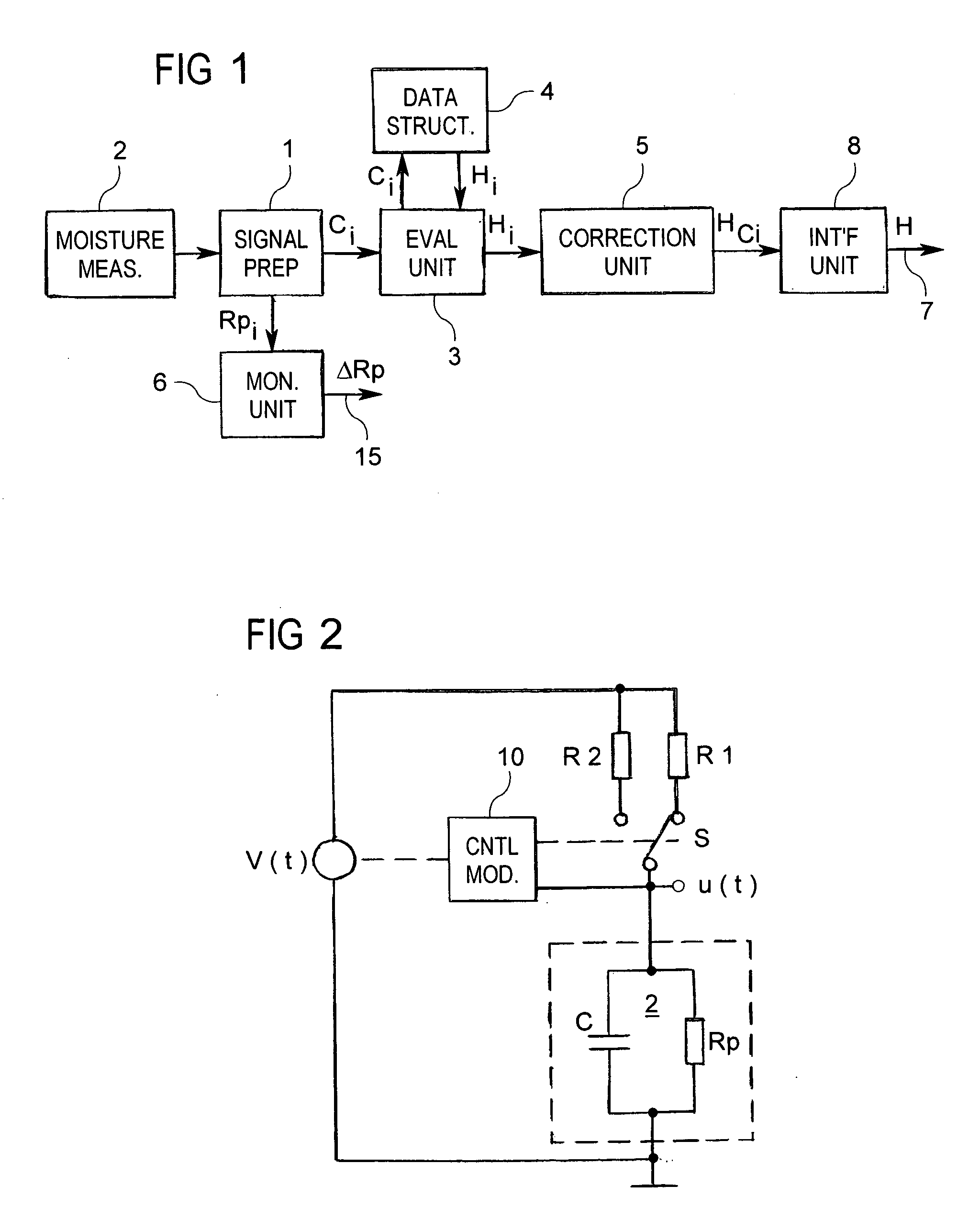
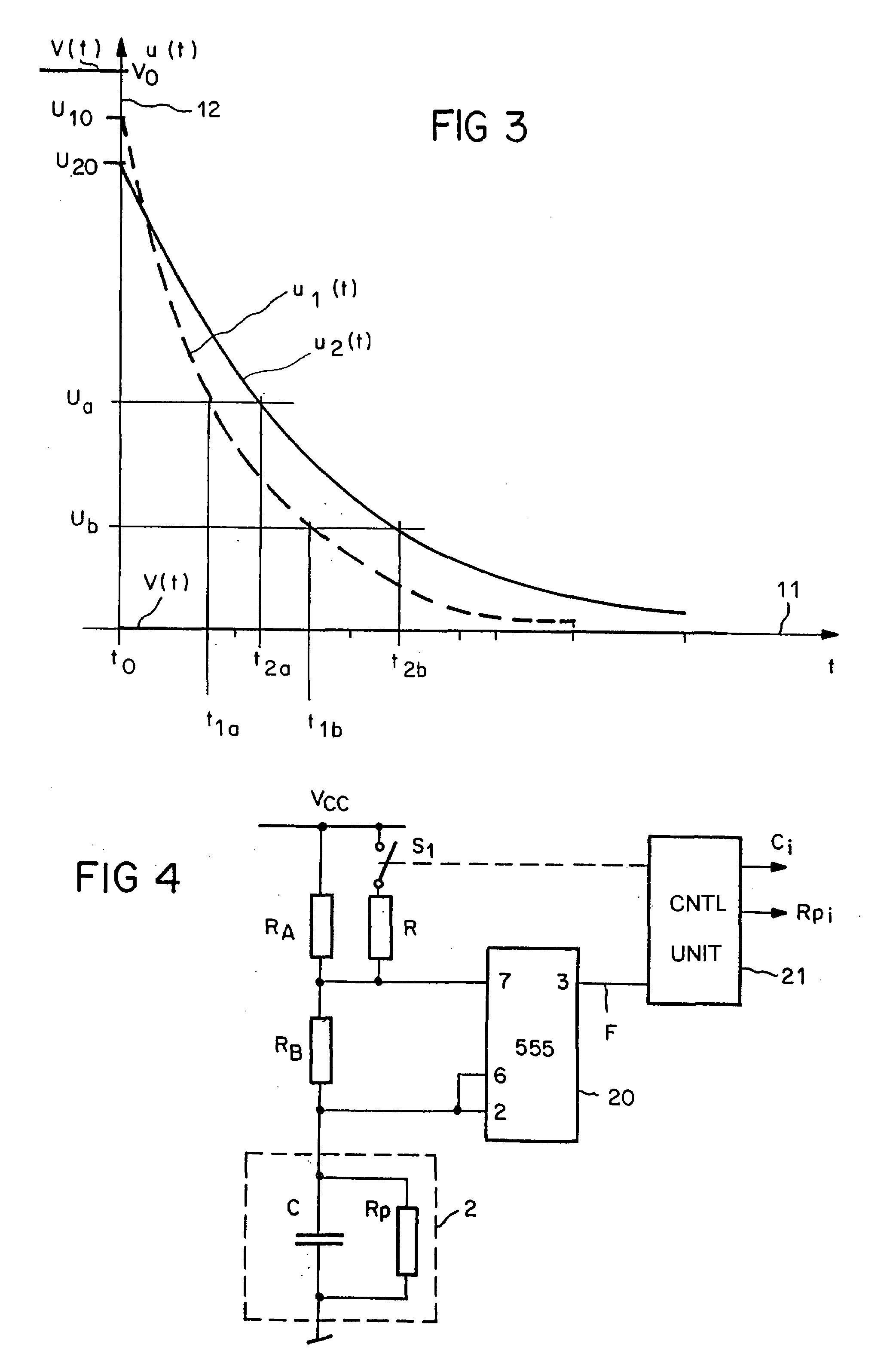
In a method of determining air humidity, a capacitive moisture measuring element (2) used in a moisture sensor for calculation operations is modelled by a parallel circuit of an ideal capacitor (C) and an ohmic resistance (Rp). Charging and / or discharging of the capacitive moisture measuring element (2) by way of a first measuring resistor (R1; RA) provides for ascertaining a first time constant or a first period duration of the charging and / or discharging operation, and charging and / or discharging of the moisture measuring element (2) by way of a second measuring resistor (R2; RA / / R) provides for ascertaining a second one. The capacitance (C) of the moisture measuring element (2) is then calculated from the two time constants or the two period durations, a value for the moisture level finally being ascertained from the capacitance. This method achieves a higher level of measuring accuracy on the part of the moisture sensor.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
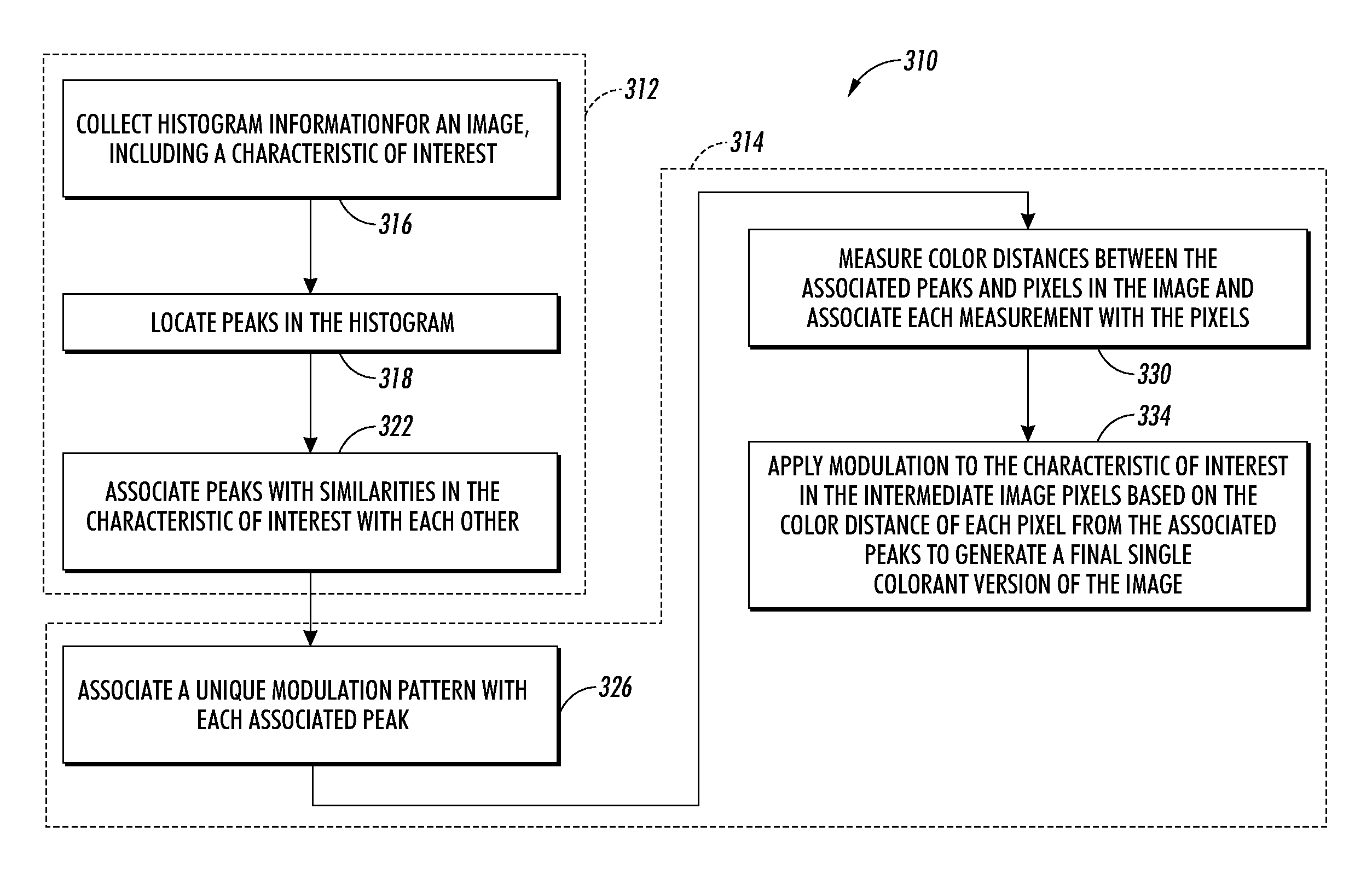
Intelligent color to texture converter
InactiveUS7453468B2Improve textureMinimal distortionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageGray level
A method for preserving color information in a black and white version of a color image includes the analysis of the color image. The analysis comprises a search for conflicting colors. Conflicting colors are colors that are normally transformed to the same gray level in a black and white version of the image. One embodiment, working in a CIELAB color space includes the use of a three dimensional histogram for detecting predominant colors having the same luminance. Such colors are classified as conflicting colors. Modulations are added to the gray scale versions of conflicting colors in order to make them distinguishable. Modulation is only applied to conflicting colors thereby minimizing any deleterious effect and allowing the method to be applied in a “walk up mode” of an image processor. An image processor operative to perform the method includes an image analyzer operative to find and classify conflicting colors in the color image, and a gray scale modulator operative to add modulations to gray scale versions of only the conflicting colors within a gray scale version of the color image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for characterizing a geological formation traversed by a borehole
InactiveUS9581723B2Known methodElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingPixel basedImage pattern
Methods for characterizing a geological formation, the methods include retrieving measured data provided by a measuring tool along one or more logged borehole length for a borehole, another borehole or both in order to produce a borehole imaging log. Selecting depth-defined intervals of the borehole imaging log as training images for inputting in a multi-point geostatistical model. Determining pattern based simulations for each training image using a pixel-based template of the multi-point geostatistical model so as to obtain training image patterns. Using the pattern based simulation of each training image to assign to each of the training image a corresponding training image pattern. Constructing from the training image patterns one or more fullbore image log of a borehole wall of the borehole. Repeat the second to fourth steps through the one or more logged borehole length in order to construct fullbore images from successive, adjacent training images.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Screw-Type Solid Bowl Centrifuge
InactiveUS20080312060A1Meet the requirementsIncrease oil extractionRotary centrifugesSeparation devicesHelical bladeEngineering
A screw-type solid-bowl centrifuge including a rotatable drum having a tapering portion and a cylindrical portion. The rotatable screw includes a screw body, at least one main screw blade surrounding the screw body and forming a plurality of screw flights. The plurality of screw flights forms a conveying path configured to transport a material to be processed in the centrifuge. Two blade segments are arranged in the conveying path in portions of the plurality of screw flights. The at least one main screw blade is provided in a region of the blade segments that includes clearances configured to allow a throughflow of the material to be processed to flow between adjacent screw flights.
Owner:GEA MECHANICAL EQUIP
Multipoint geostatistics method using branch runlength compression and local grid transformation
ActiveUS8311779B2Known methodShort timeSeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationRelevant informationAlgorithm
A multipoint geostatistics computer-implemented method for modeling of discrete properties, comprising acquiring by a computer software program a training image made from at least one dimensional array of discrete property values, the values depicting the spatial relationship and variability considered to be typical of a n-dimensional surface to be modeled; constructing a search tree, the tree representing the probability of occurrence of combinations of values of a discrete property value, the construction being performed by counting these occurrences in the training image. The non-branching sequences of the search tree are compressed to what essentially amounts to a single node, by keeping only the relevant information the sequences contain.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Moisture sensor with capacitive moisture measuring element and method of determining air humidity
ActiveUS7049829B2Improve the level ofKnown methodResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing mechanical meansEngineeringRelative air humidity
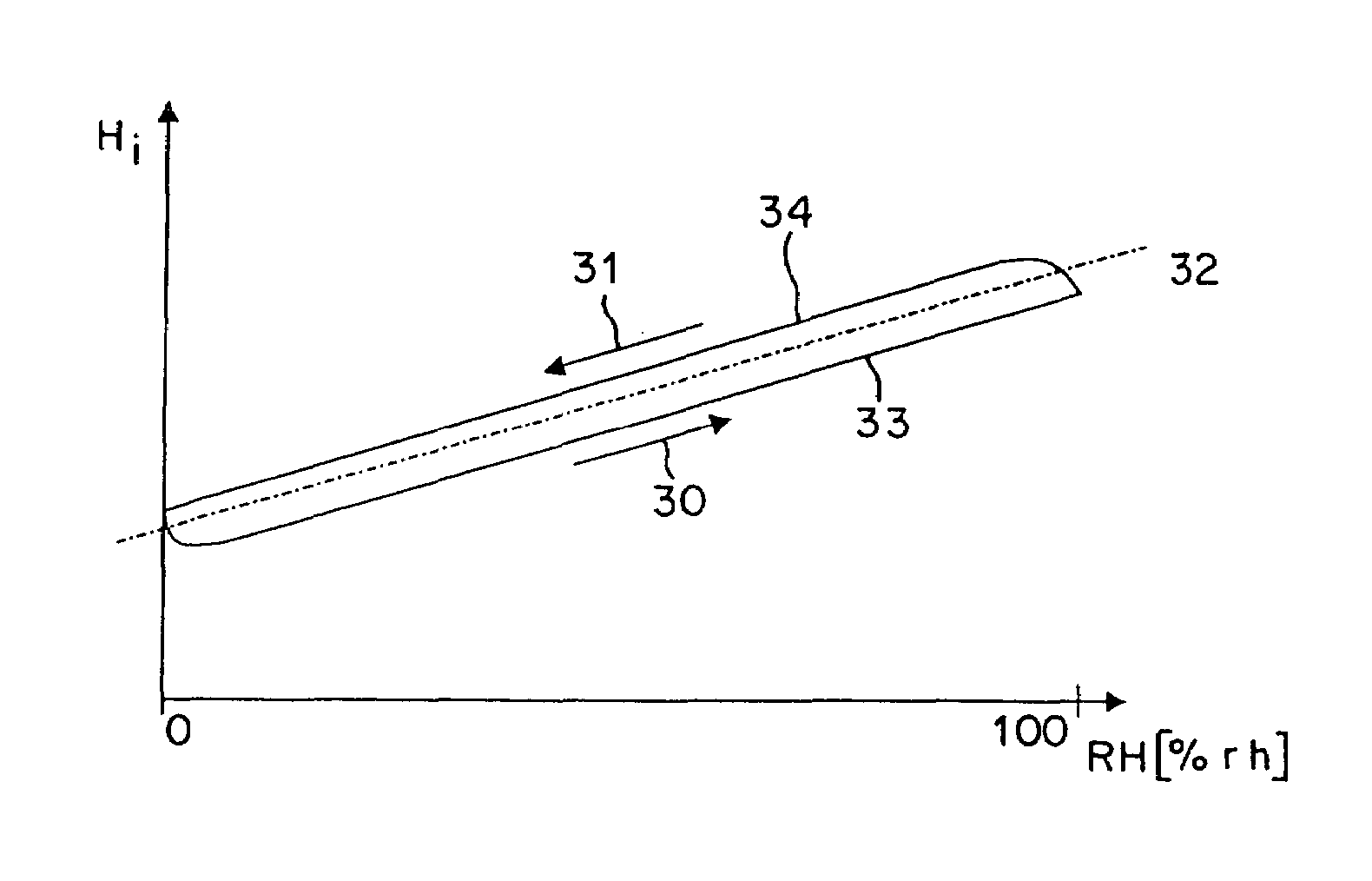
In a method of determining air humidity, a corrected moisture signal is calculated for a moisture signal (Hi) ascertained from electrical properties of a capacitive moisture measuring element. In a measuring phase (30) with rising relative air humidity (RH), the corrected moisture signal is the current moisture signal (Hi) increased by a correction value, whereas in a measuring phase (31) with falling relative air humidity (RH) the corrected moisture signal is the current moisture signal (Hi) reduced by a correction value. Depending on the respective properties of the moisture measuring element and the required degree of measuring accuracy, the correction value is constant or is taken into consideration in dependence on the relative air humidity RH. This method provides a higher level of measuring accuracy with a moisture sensor equipped with the moisture measuring element.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
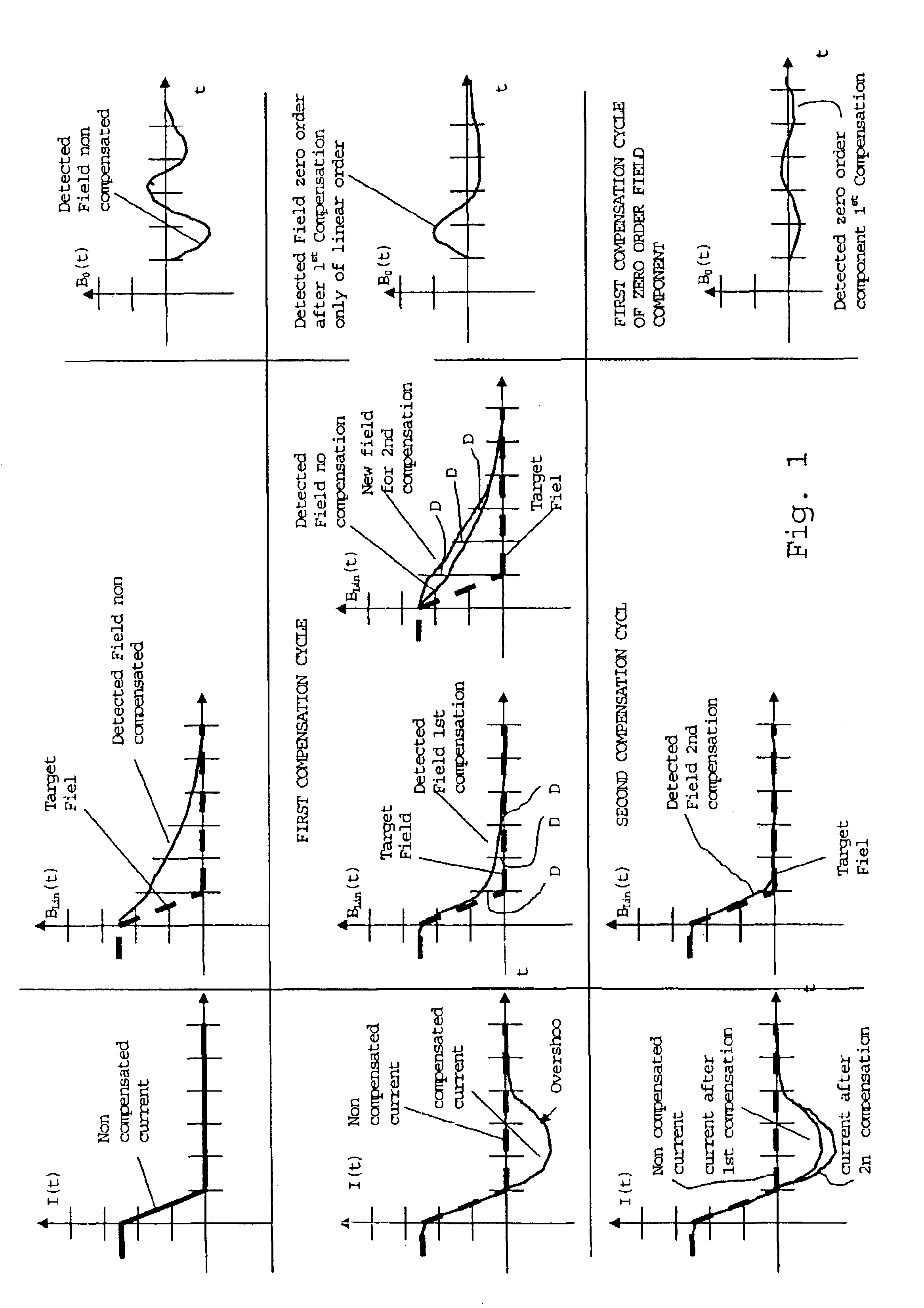
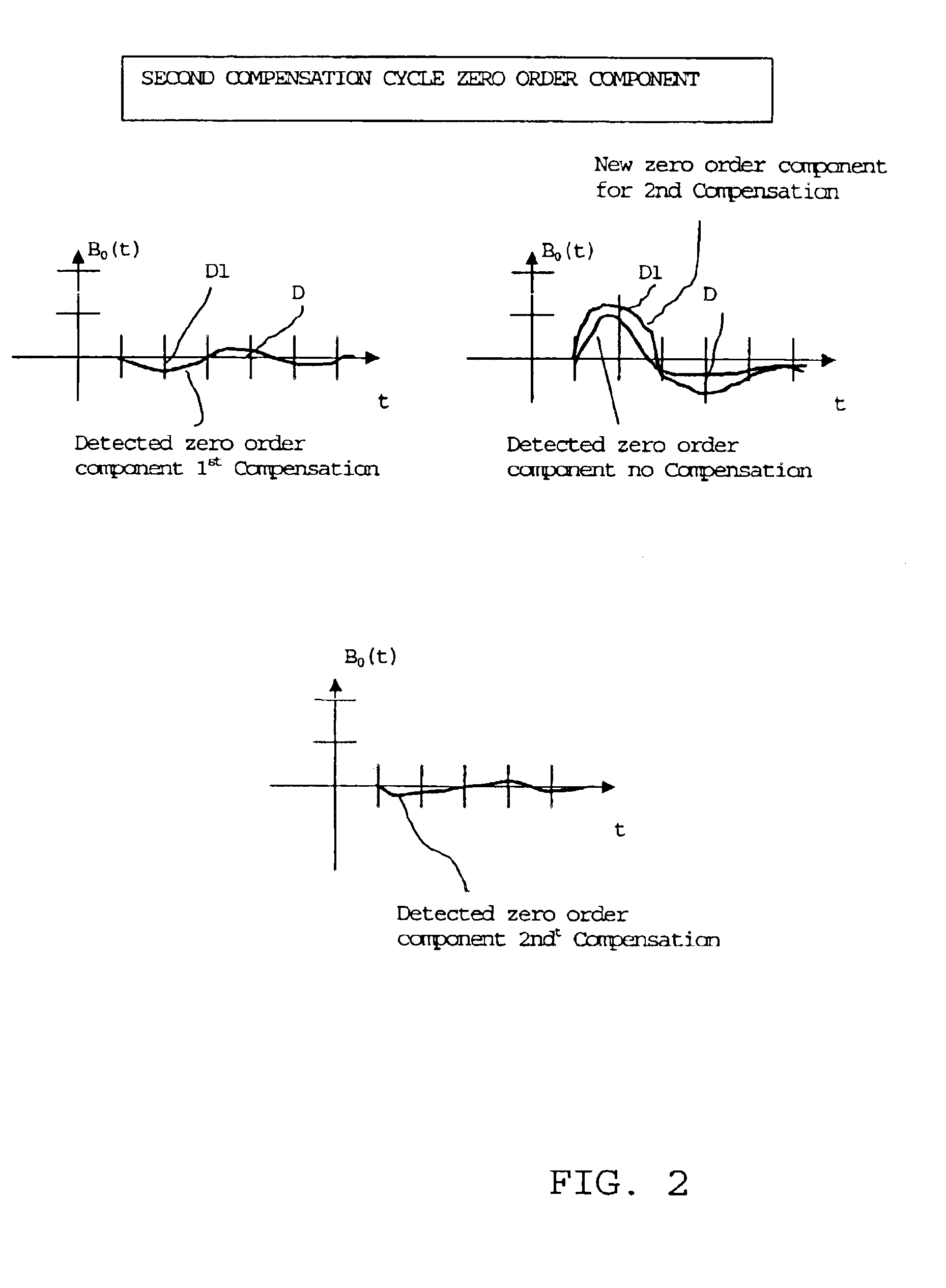
Method of compensating for gradient induced eddy currents in NMR imaging apparatuses
InactiveUS6867590B2Shorten the timeKnown methodMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionExcitation currentEddy current effect
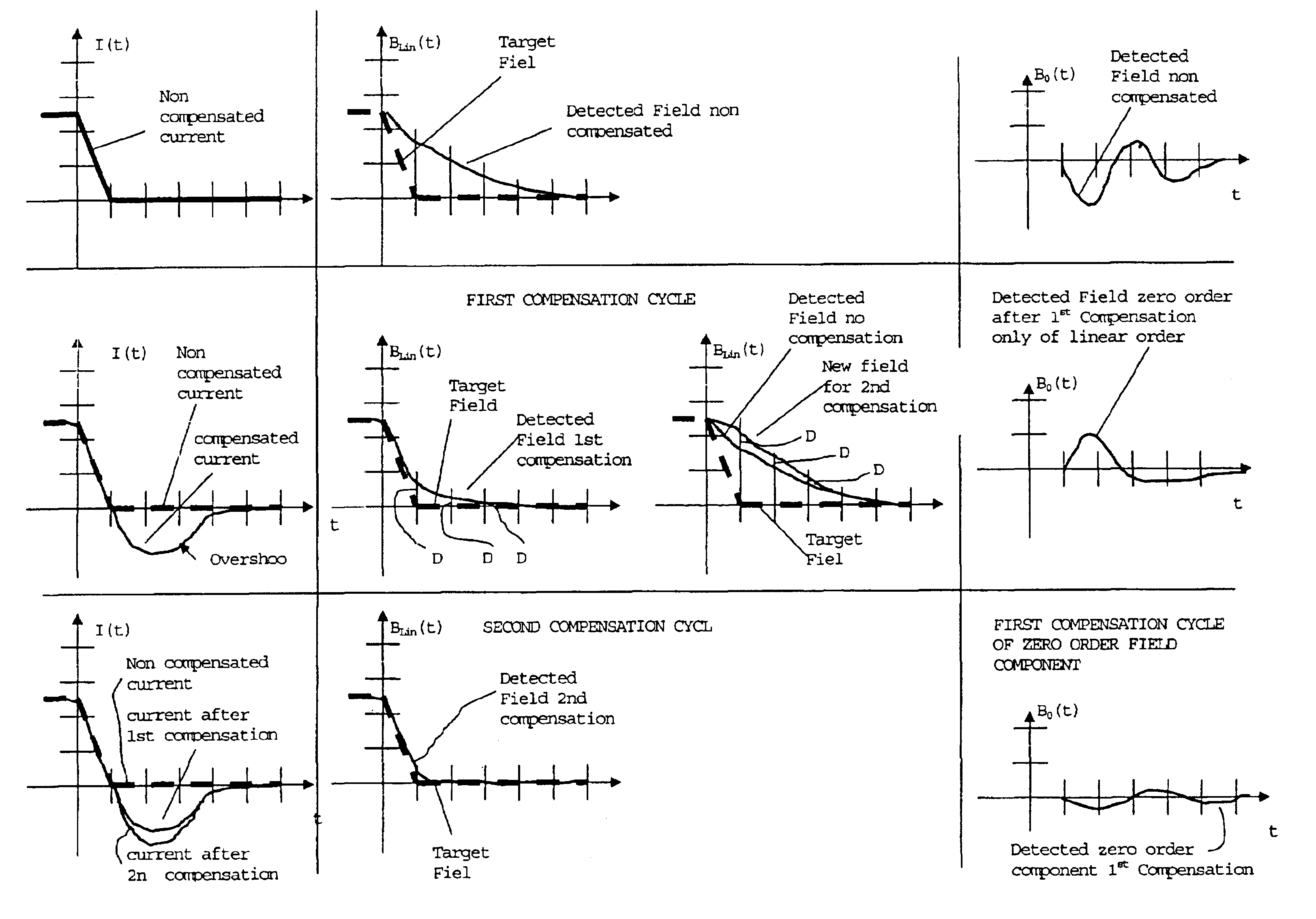
A method of compensating for eddy currents induced by the switching on and off magnetic fields in gradient coils in NMR imaging apparatuses, which method includes at least one compensation cycle including the steps of performing at least one detection of the magnetic field generated by the current flowing in a gradient coil, i.e., a gradient field; extrapolating the course of the effectively generated gradient field from the data of said at least one detection; generating a gradient fields excitation current compensating the eddy current effects on the gradient fields on the basis of the comparison of the effectively generated gradient fields and of the target gradient field.
Owner:ESAOTE
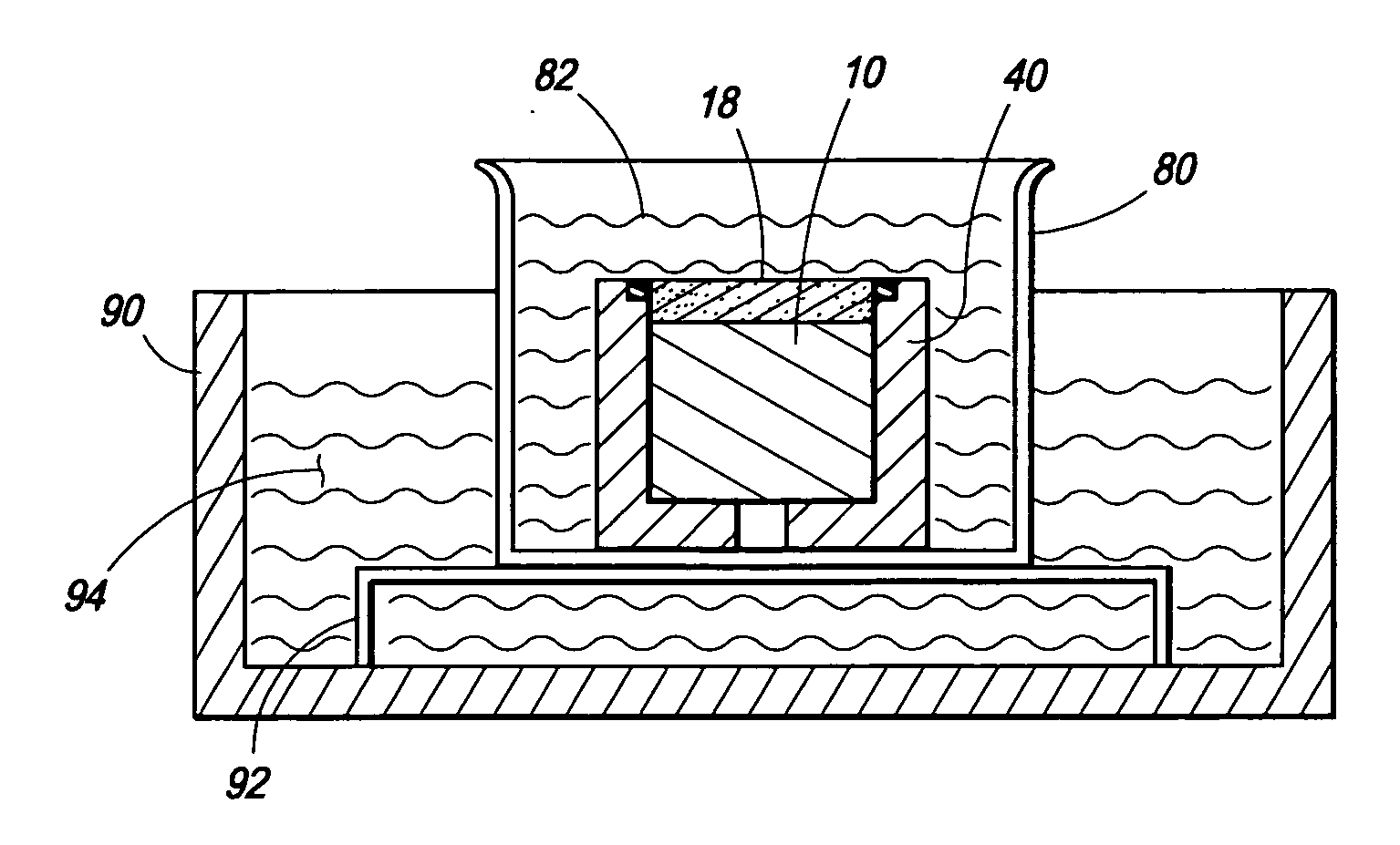
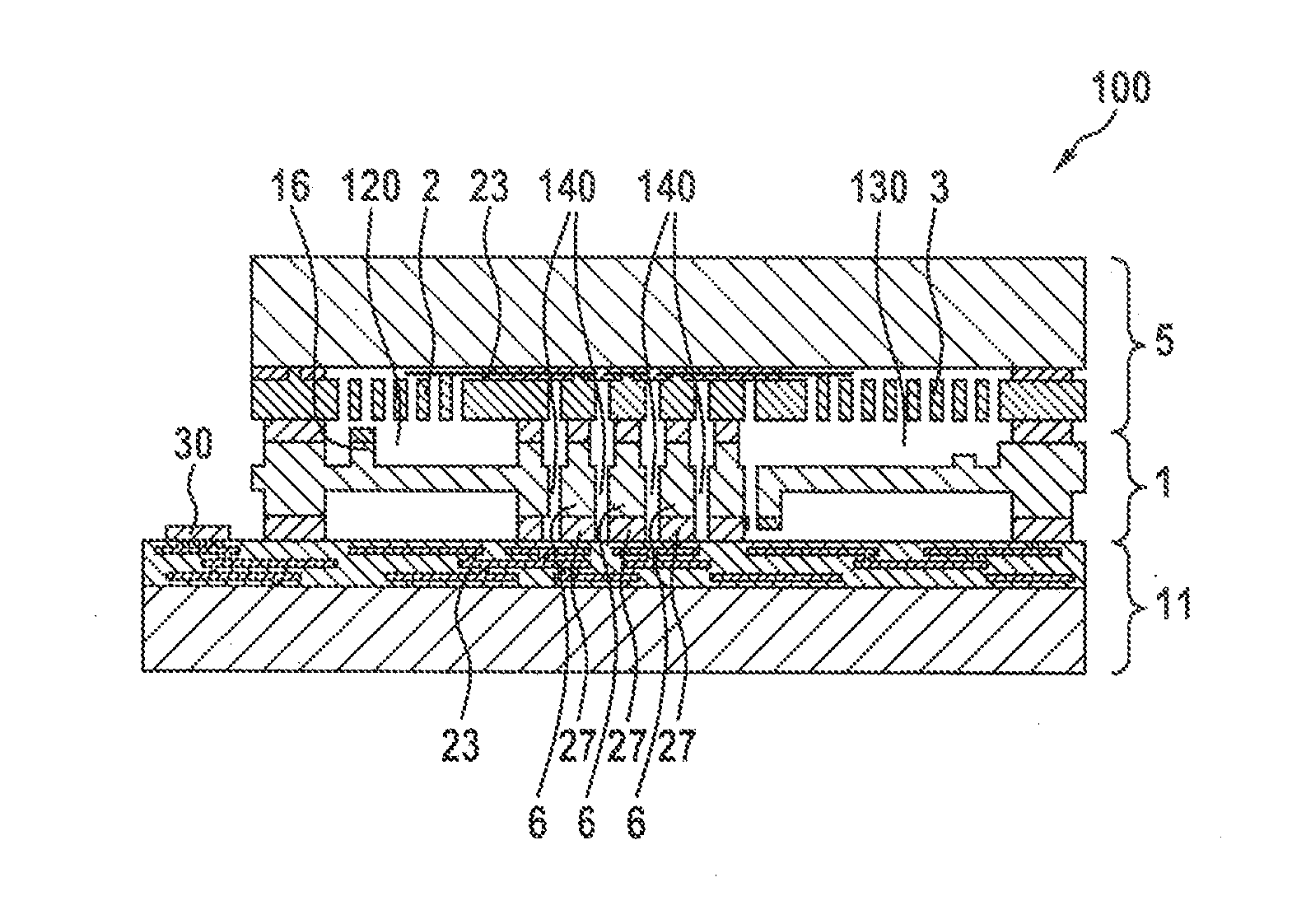
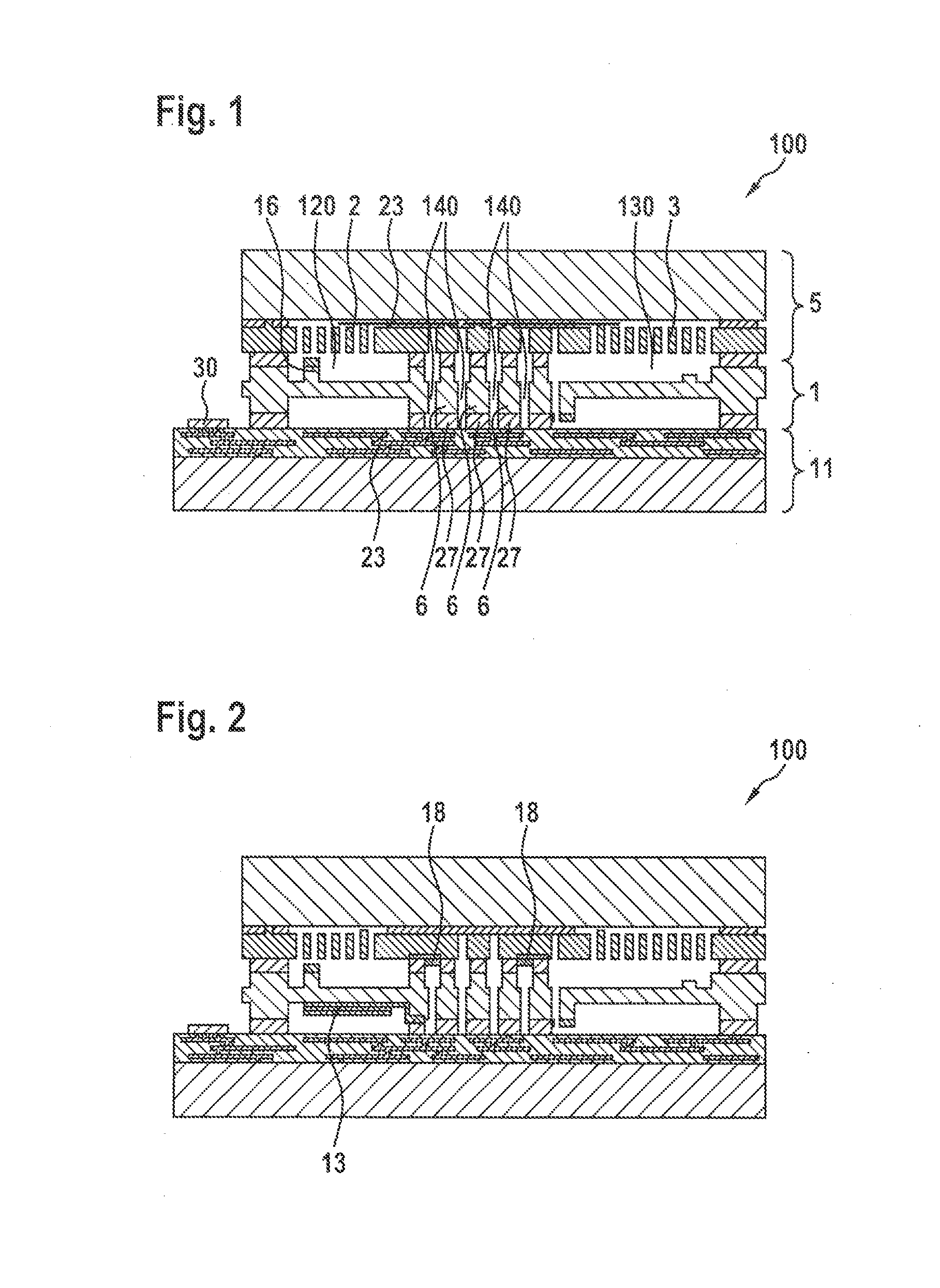
Integrated rotation rate and acceleration sensor and method for manufacturing an integrated rotation rate and acceleration sensor
InactiveUS20160084865A1Improved connection propertyHigh melting temperatureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsApplication-specific integrated circuitIntegrated circuit
A micromechanical device having a main plane of extension includes a sensor wafer, an evaluation wafer, and an intermediate wafer situated between the sensor wafer and the evaluation wafer, the evaluation wafer having at least one application-specific integrated circuit. The sensor wafer and / or the intermediate wafer includes a first sensor element and a second sensor element spatially separated from the first sensor element, the first and second sensor elements being respectively located in a first cavity and a second cavity each formed by the intermediate wafer and the sensor wafer, a first gas pressure in the first cavity differing from a second gas pressure in the second cavity, and the intermediate wafer having an opening at a point in a direction perpendicular to the main plane of extension.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Image forming apparatus providing user support in sleep mode
ActiveUS8203729B2Known methodFunction increaseMultiple digital computer combinationsElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
An image forming apparatus that can support the user in sleep mode is provided. When the apparatus enters sleep mode, guidance information is displayed on an electronic paper. The electronic paper maintains displayed contents even when power is not supplied and, therefore, even when power is not supplied to a display panel in the sleep mode, the display for the user is continuously given, thereby supporting the user.
Owner:SHARP KK
Screw-type solid bowl centrifuge
InactiveUS7549957B2Known methodImprove efficiencyRotary centrifugesSeparation devicesHelical bladeScrew thread
A screw-type solid-bowl centrifuge including a rotatable drum having a tapering portion and a cylindrical portion. The rotatable screw includes a screw body, at least one main screw blade surrounding the screw body and forming a plurality of screw flights. The plurality of screw flights forms a conveying path configured to transport a material to be processed in the centrifuge. Two blade segments are arranged in the conveying path in portions of the plurality of screw flights. The at least one main screw blade is provided in a region of the blade segments that includes clearances configured to allow a throughflow of the material to be processed to flow between adjacent screw flights.
Owner:GEA MECHANICAL EQUIP
Method for planning a cellular mobile telecommunications network
ActiveUS8150402B2Known methodPower managementTime-division multiplexQuality of serviceTelecommunications network
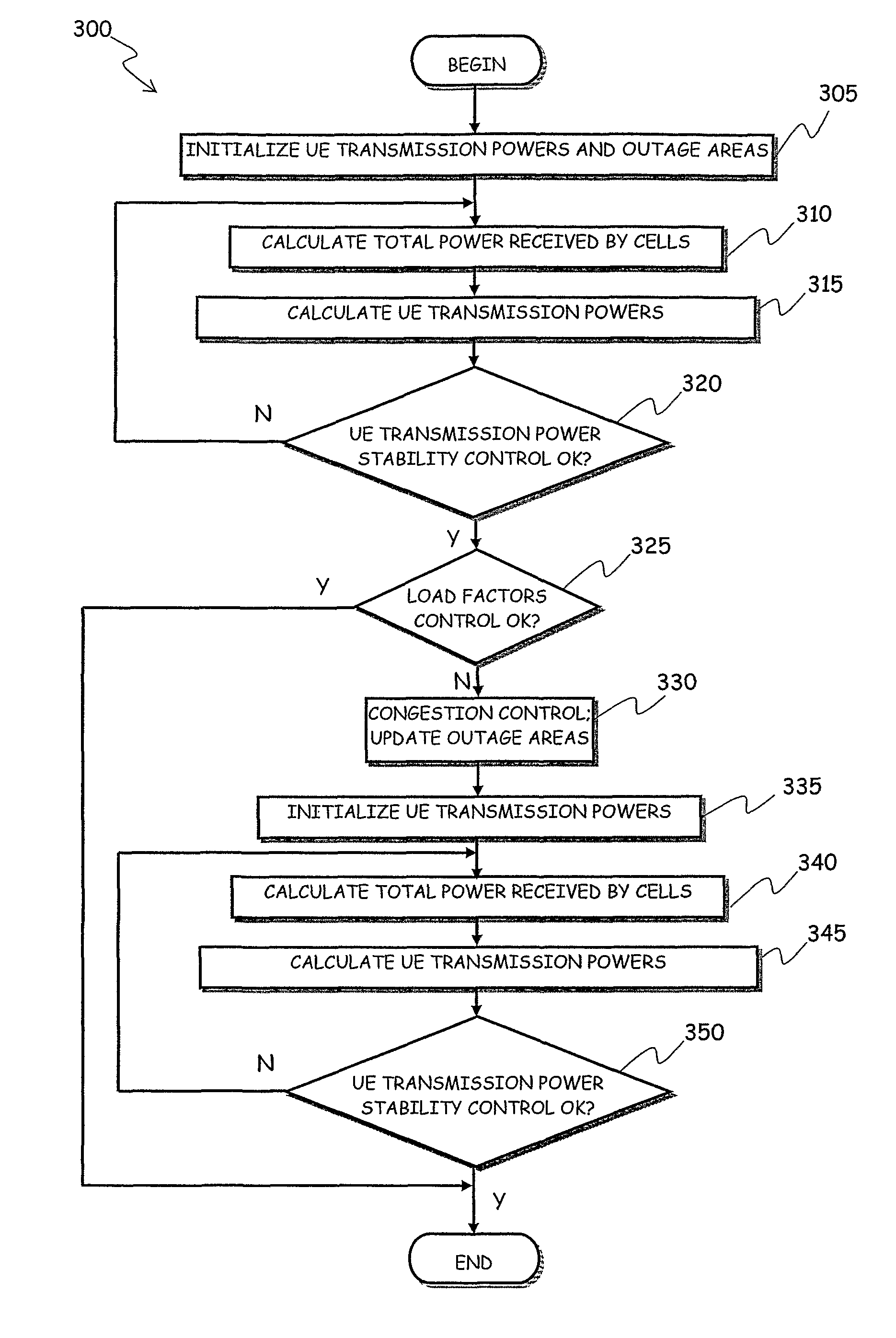
A method for planning a cellular mobile telecommunications network includes at least one network cell and is intended to provide network services to users located in the network cell. The method includes: a) initializing, for the at least one network cell, a service area and a transmission power for each user equipment; b) estimating a total power received by the at least one network cell from user equipment located in the service area and using the at least one network service; c) based on the estimated total received power, varying the transmission powers required to user equipment located in the service area in order to reach a target quality of service constraint for the at least one network service; d) iterating the steps b) and c) until a stability condition is reached wherein the transmission power variation for at least a predetermined fraction of the user equipment is lower than a predetermined threshold; e) calculating a total received power corresponding to the transmission powers at the end of step d); f) calculating an uplink load factor corresponding to the total received power calculated in step e); g) ascertaining whether the calculated uplink load factor is lower than a maximum uplink load factor, and, in the negative case: h) restricting said service area; and i) repeating the steps from b) to g).
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Target indentification method using cepstral coefficients
InactiveUS7180442B1Known methodSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency spectrumTime spectrum
A method of identifying an unknown target comprising creating a density function of cepstral coefficients for a known target; receiving a signal from the unknown target; transforming the signal from a time spectrum to a frequency spectrum using a Fourier transform; transforming the frequency spectrum to a cepstrum; creating a density function of cepstral coefficients for the unknown target; and comparing the density function of the unknown target with the density function of the known target.
Owner:NAVY U S OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
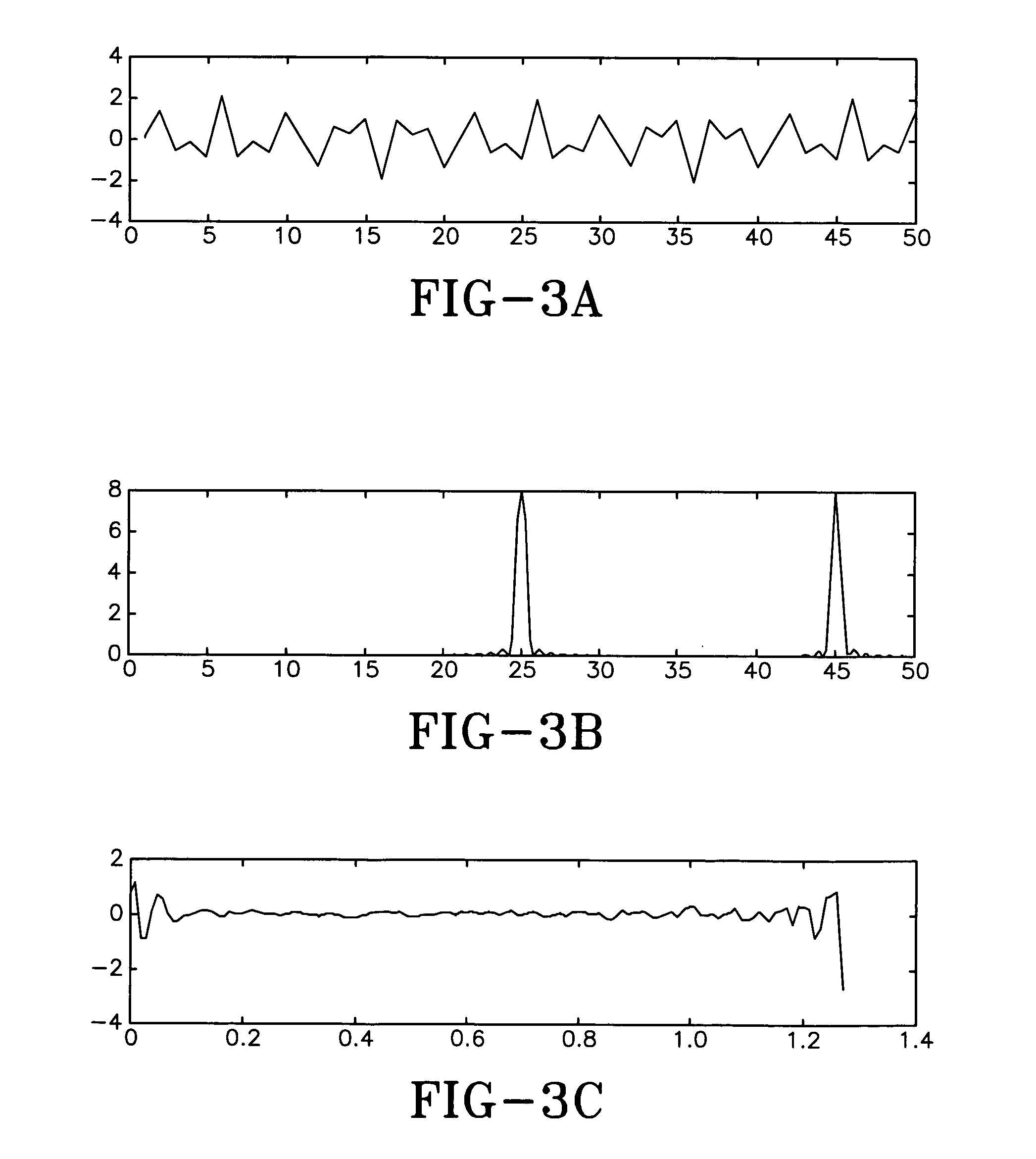
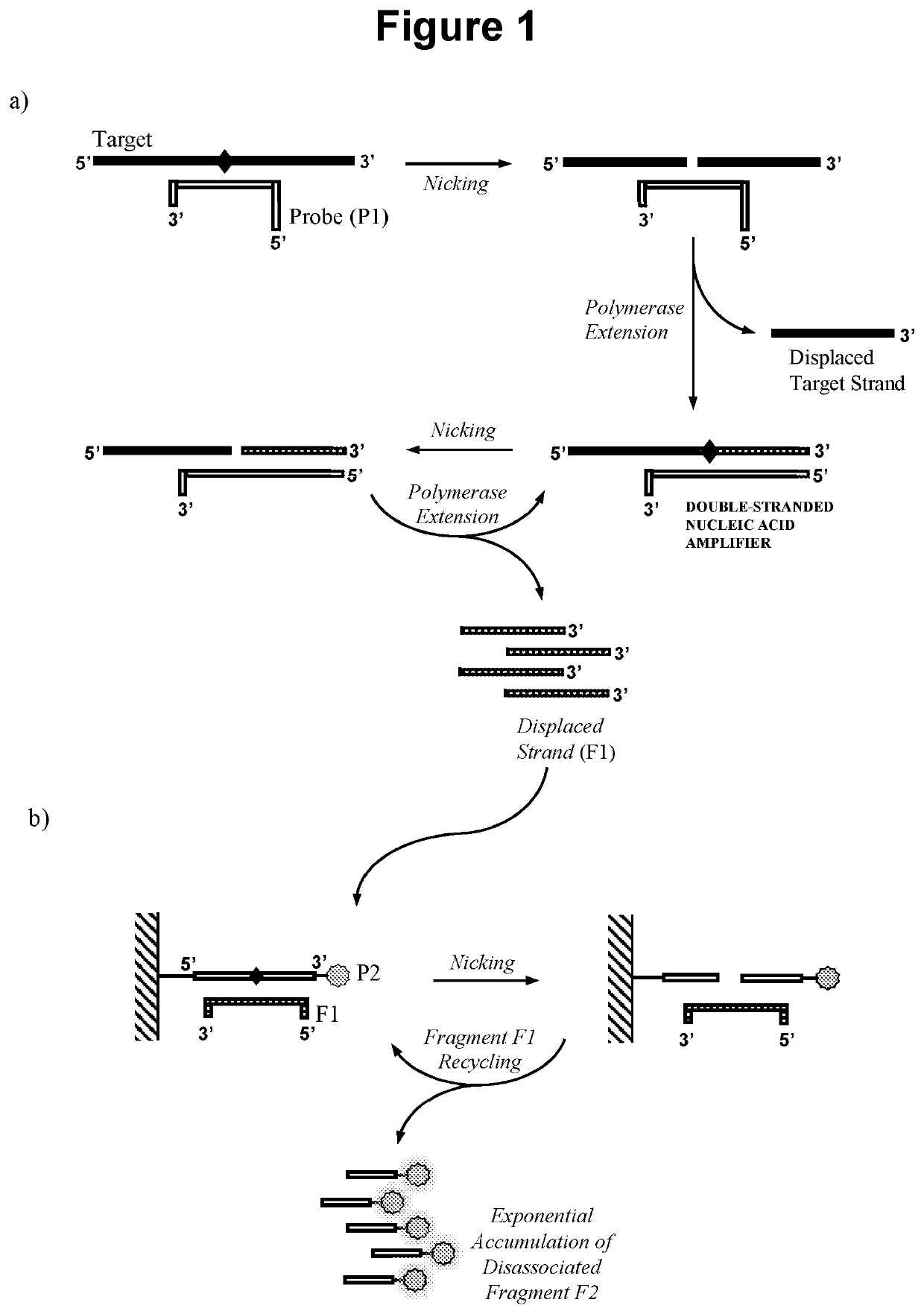
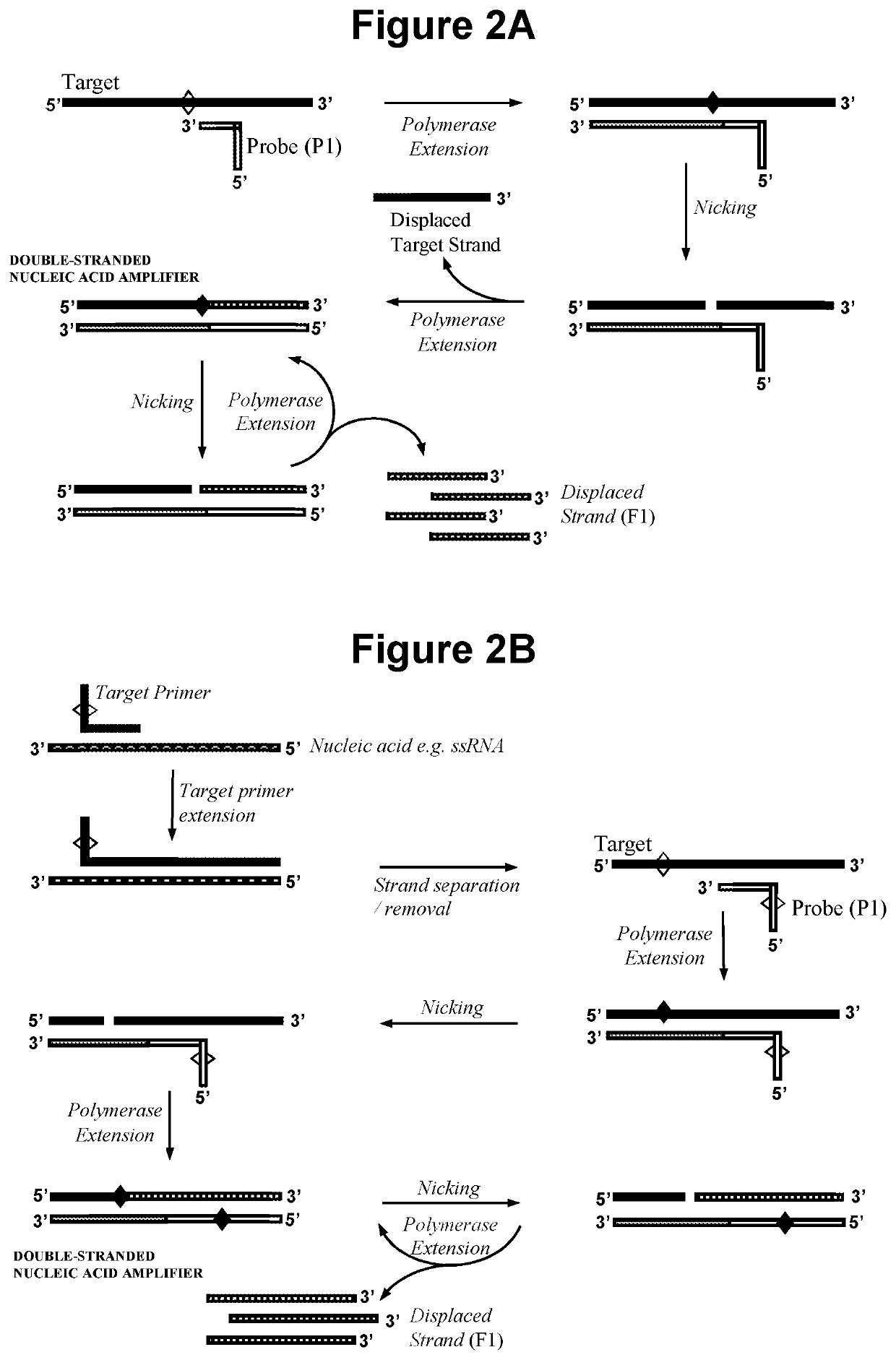
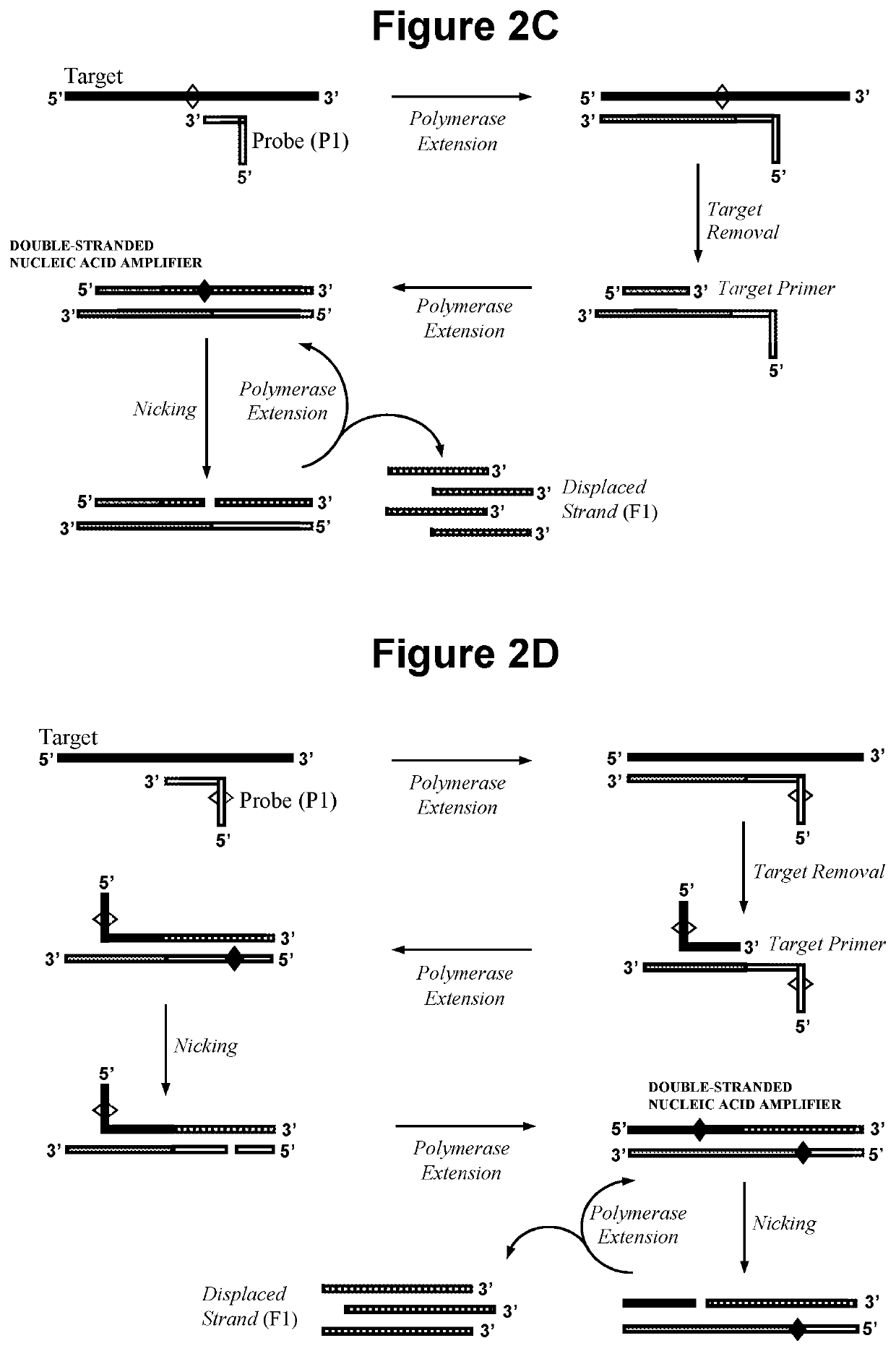
Nucleic acid detection method
ActiveUS20200002756A1Improve potentialImprove amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideMolecular biology
The present invention relates to methods for the detection of nucleic acids of defined sequence and kits for use in said methods. The methods employ nicking agent(s), polymerase and oligonucleotide probes to produce probe fragments in the presence of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:SENSE BIODETECTION
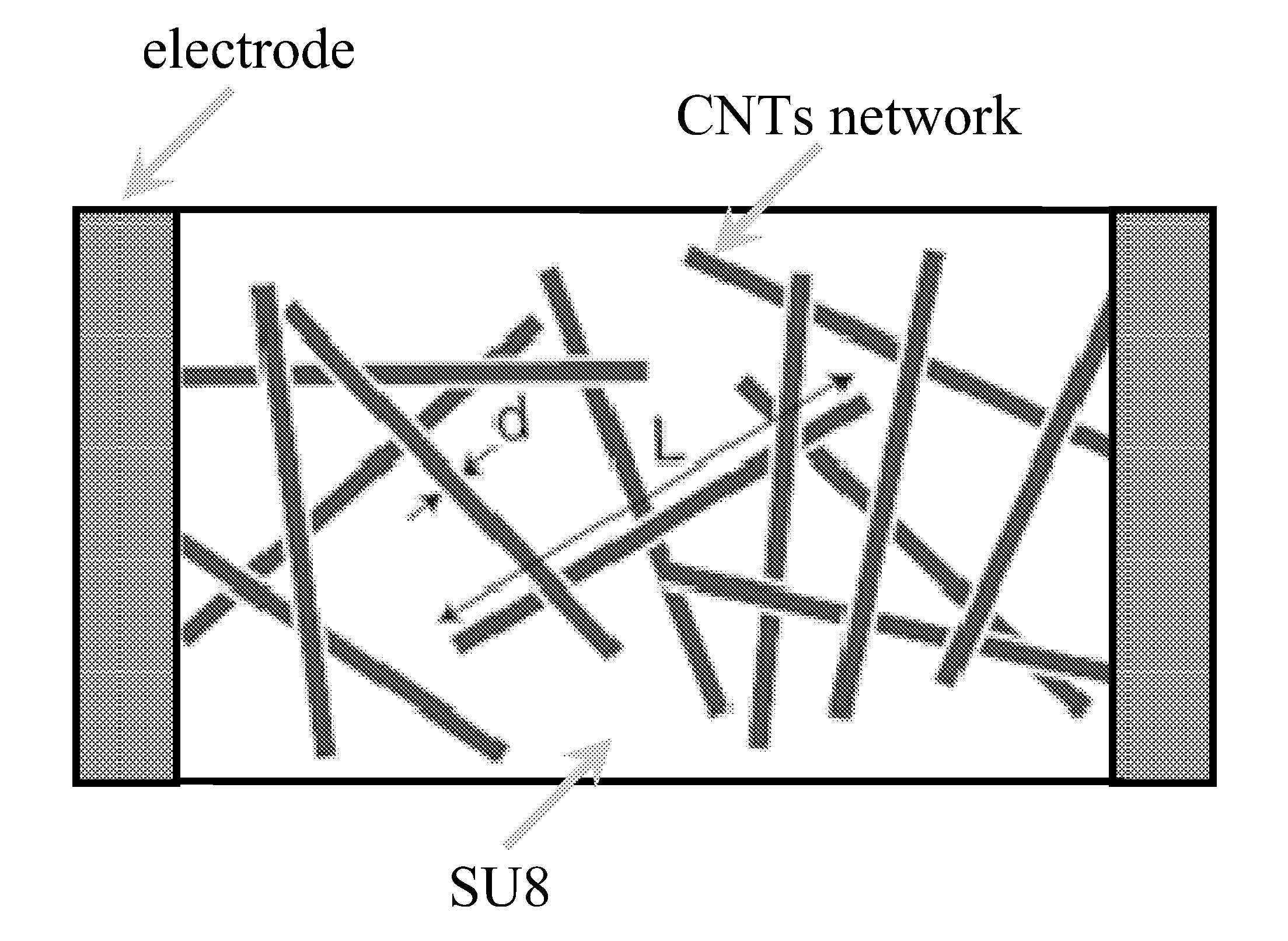
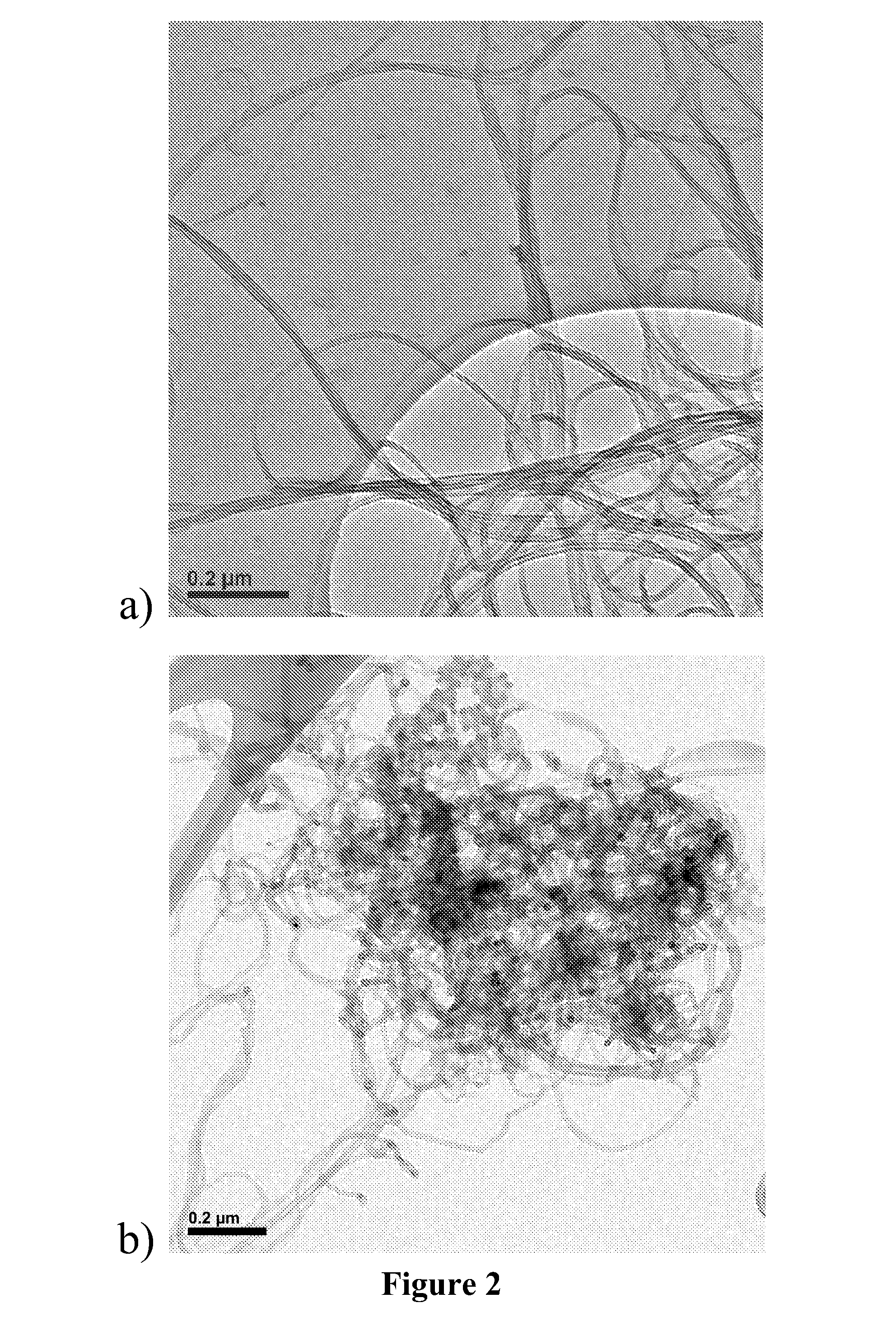
Carbon nanotubes nanocomposites for microfabrication applications
InactiveUS20130017374A1Known methodImprove known methodMaterial nanotechnologyPhotosensitive materialsEpoxyElectricity
A composite epoxy resin consisting in a SU-8 epoxy resin, a solvent, with or without photoinitiator and carbon nanotubes in powder. When the resin is combined with the carbon nanotubes, the mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of the nanocomposite are enhanced. That offers a wide range of composites which can be used with different micro-fabrication techniques, such as: lamination, spin-coating, spraying and screening for assembly, interconnect and packaging applications.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
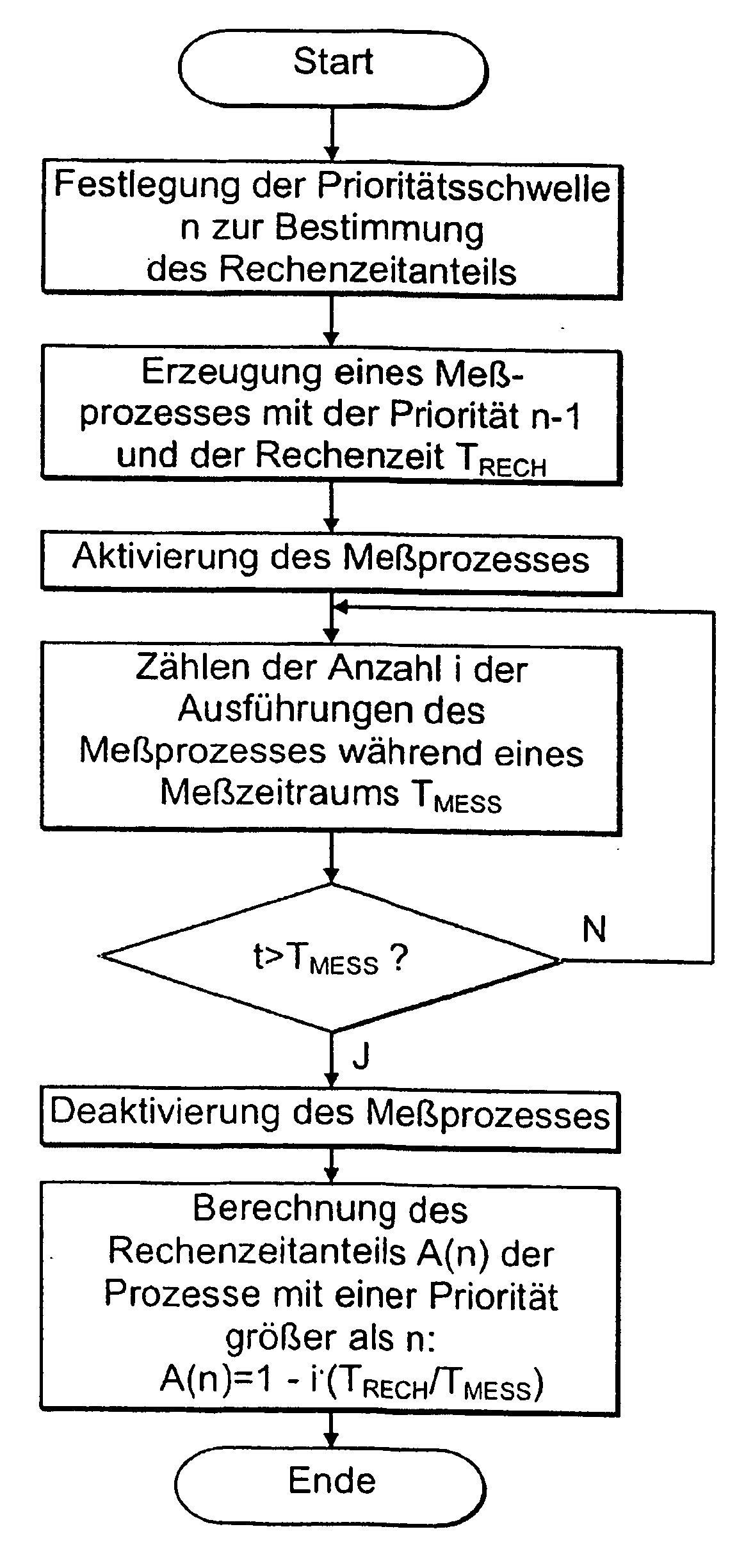
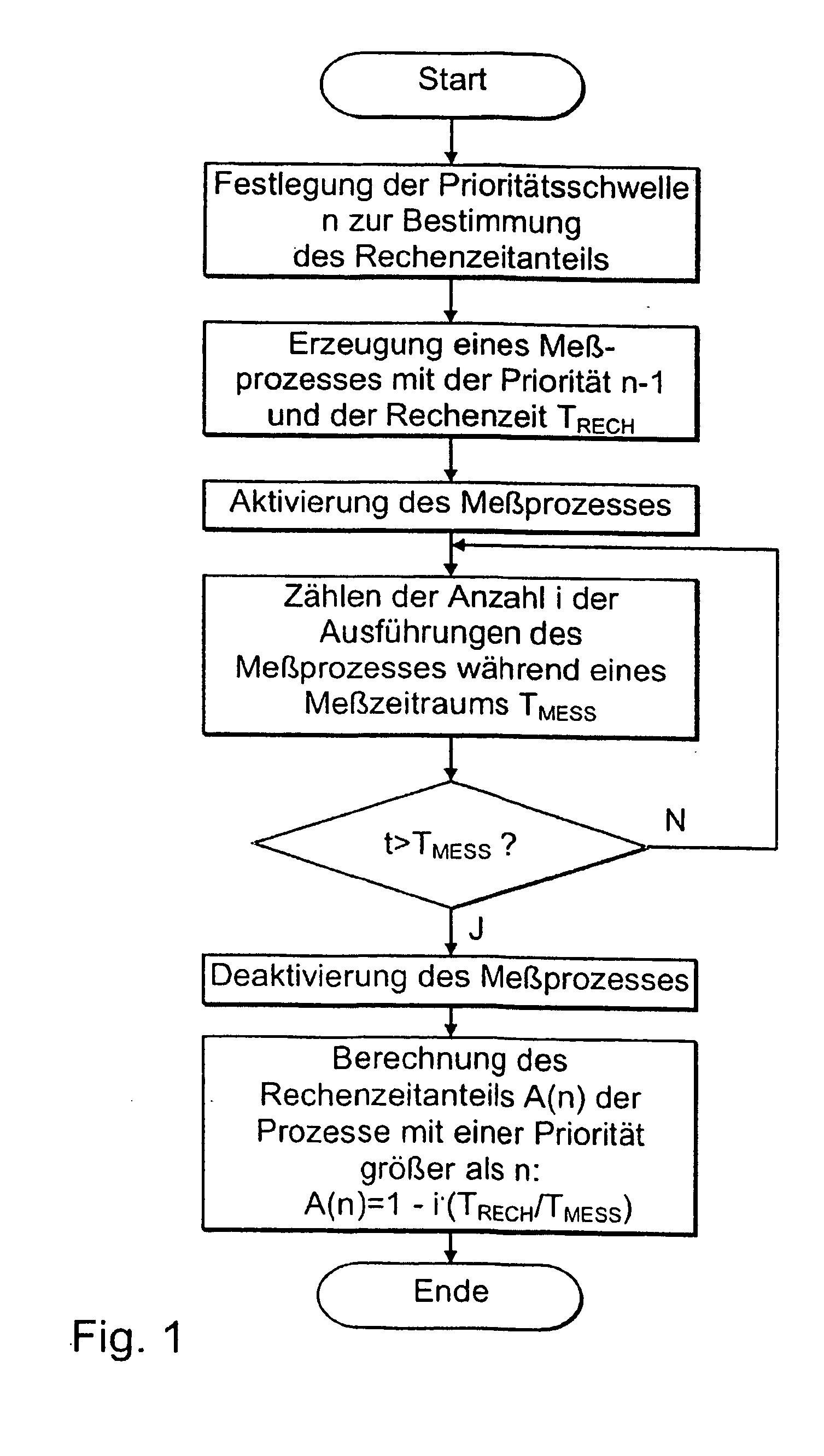
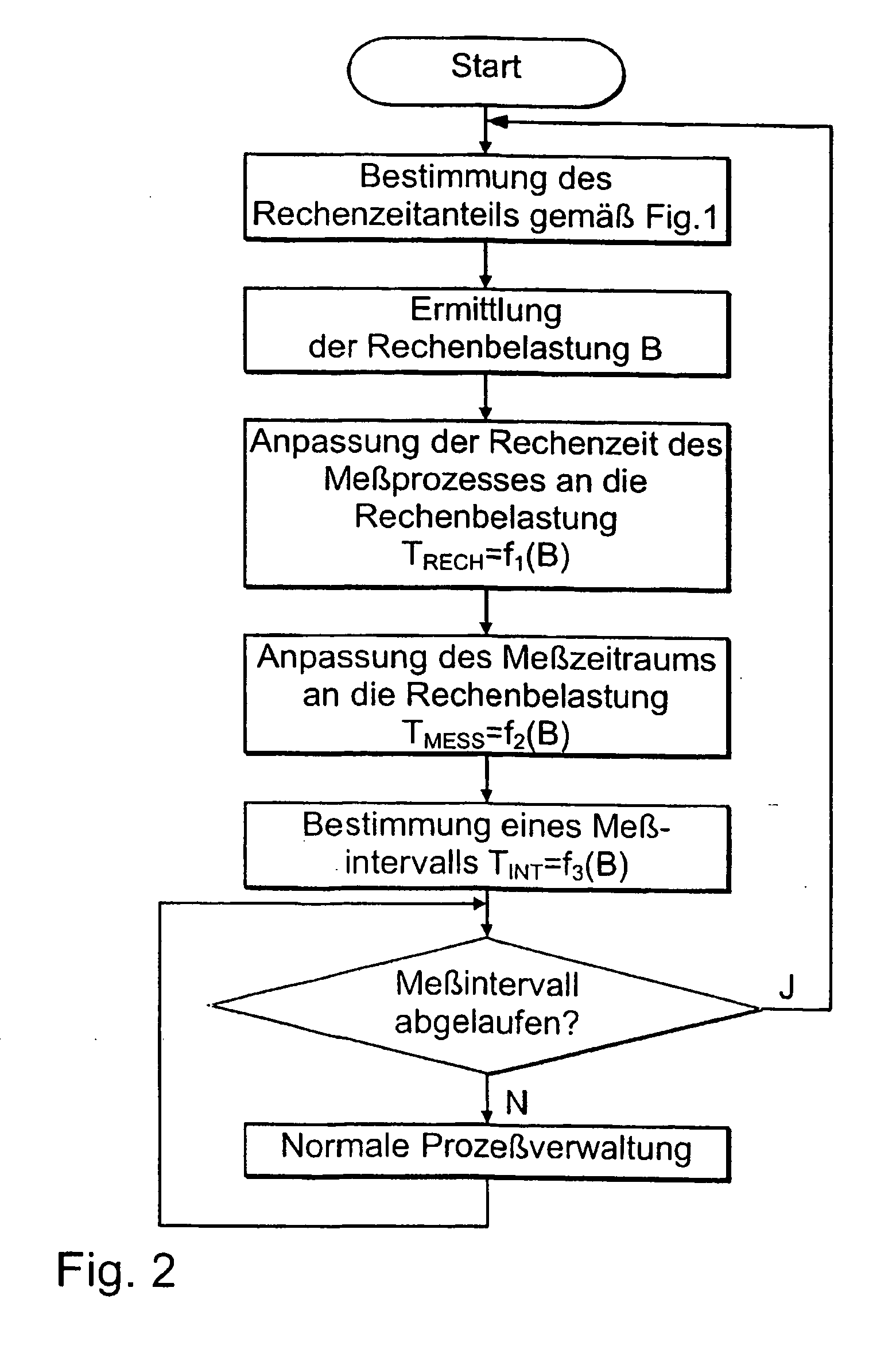
Method for determining priority-dependent computing-time distribution in a priority-controlled multiprocess computing system
InactiveUS20050066329A1Known methodResource allocationHardware monitoringTime distributionReal-time computing
A method for determining priority-dependent computing time distribution in a priority-controlled multiprocess computing system, comprising the following steps: creation of a measuring process with a given computing time and a given priority; repeated execution of said measuring process during a given measuring time period; determination of the number of executions of said measuring process within the measuring time period and determination of the priority-dependent computing time distribution according to the number of executions of the measuring process during the measuring time period and the given computing time of the measuring process.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for manufacturing a functional laminate, functional laminate and its use for security documents
InactiveUS20120038141A1Reduce widthReduce riskOther printing matterLamination ancillary operationsEngineering
Owner:HID GLOBAL GMBH
Method of widely linear turbo-equalization in a multi-user context and for a multi-channel multi-antenna receiver
InactiveUS9432223B2Eliminate distractionsKnown methodDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionEqualisersEqualizationLinearity
A method of equalizing a signal received by a plurality of antenna elements, the received signal being produced by the transmission of signals by a plurality of transmitters, includes: a step of converting the received signal into the frequency domain; a step of subtracting from the signal an estimate of the intersymbol interference and the interference between users so as to obtain a complex corrective signal; a step of conjoint widely linear filtering of the complex corrective signal and the conjugate complex corrective signal to obtain an equalized signal; a step of converting the equalized corrective signal into the time domain; a step of calculating coefficients of the at least one equalizer filter from the covariance matrix and the pseudo-covariance matrix of the received signal.
Owner:THALES SA
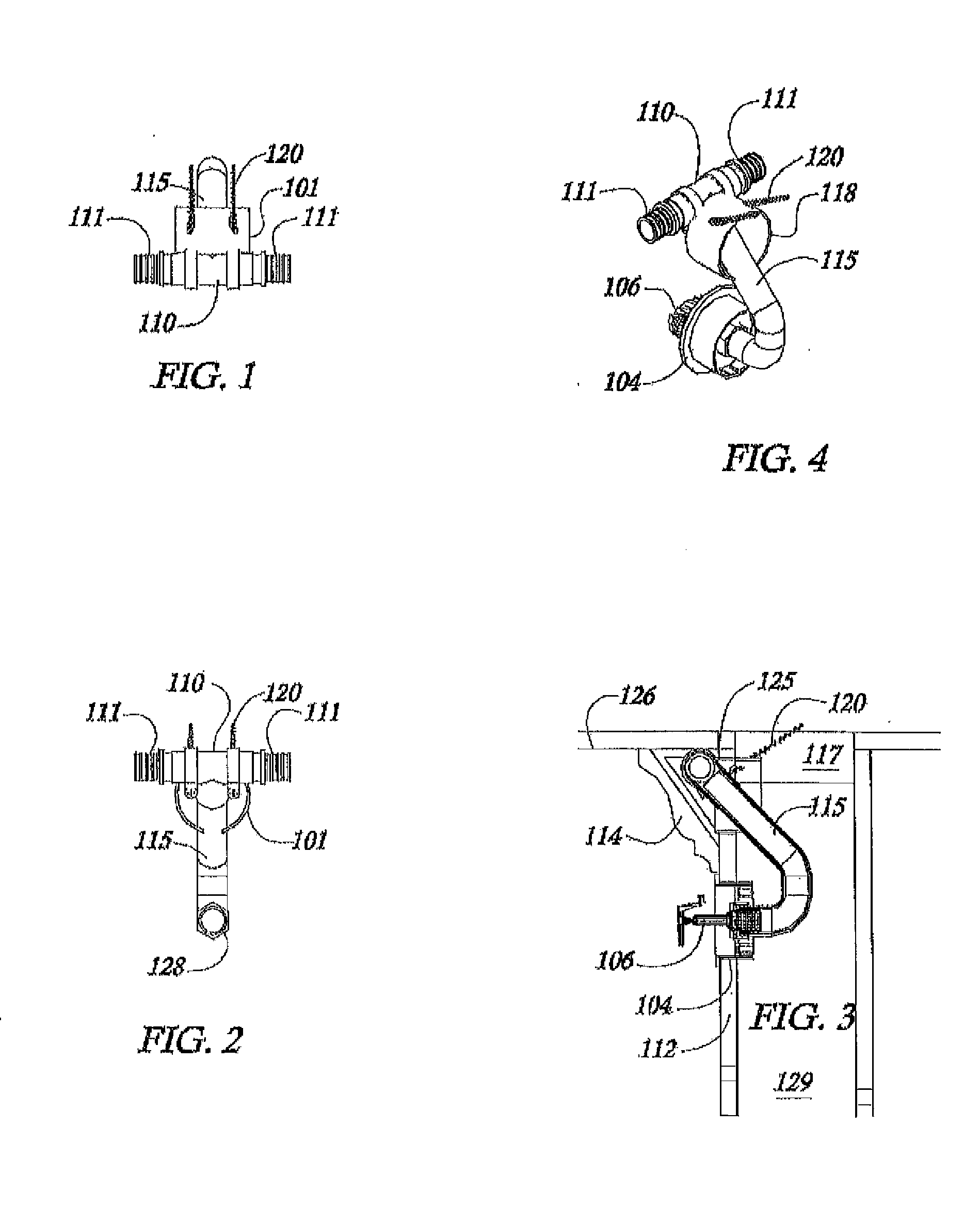
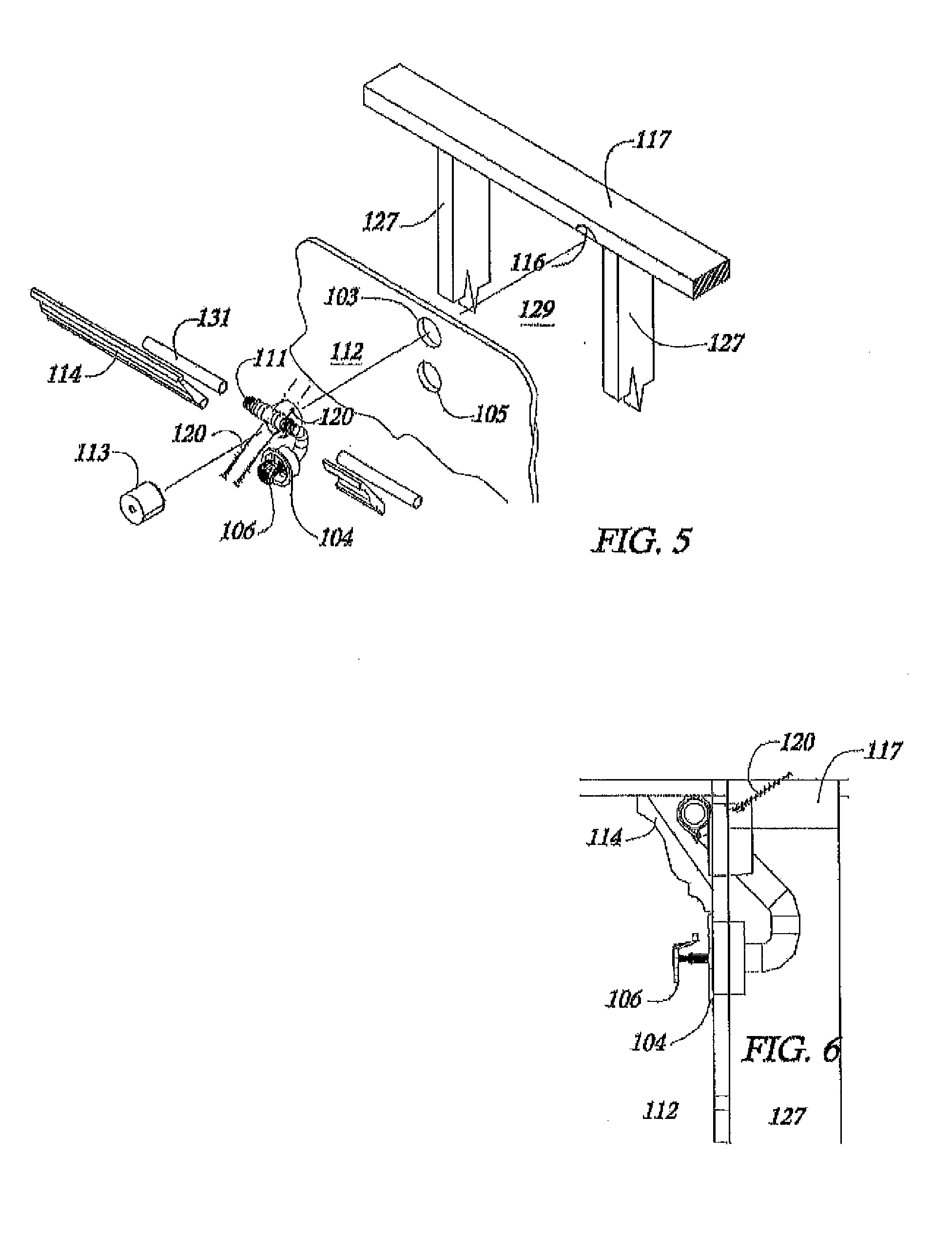
Sprinkler fitting attachment device
Apparatus and methods for attachment of a fire protection sprinkler fitting to the wall-ceiling junction of existing buildings. In a J-fitting assembly of a sprinkler system is coupled to a water supply and has an exposed sprinkler head connected to it, the attachment apparatus includes a guide channel coupled to the J-fitting to facilitate fastening the fitting to the internal structure of the wall.
Owner:THE WANDA GROUP
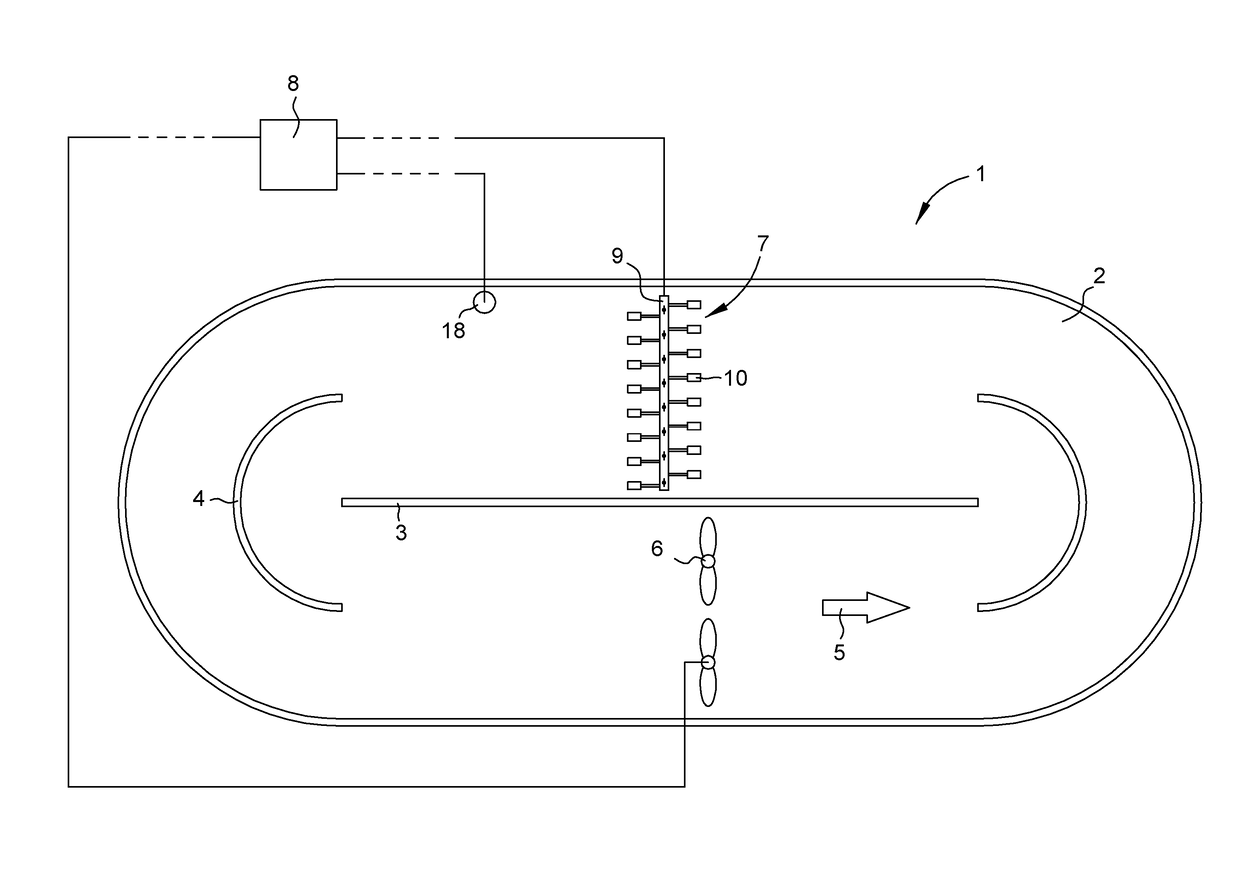
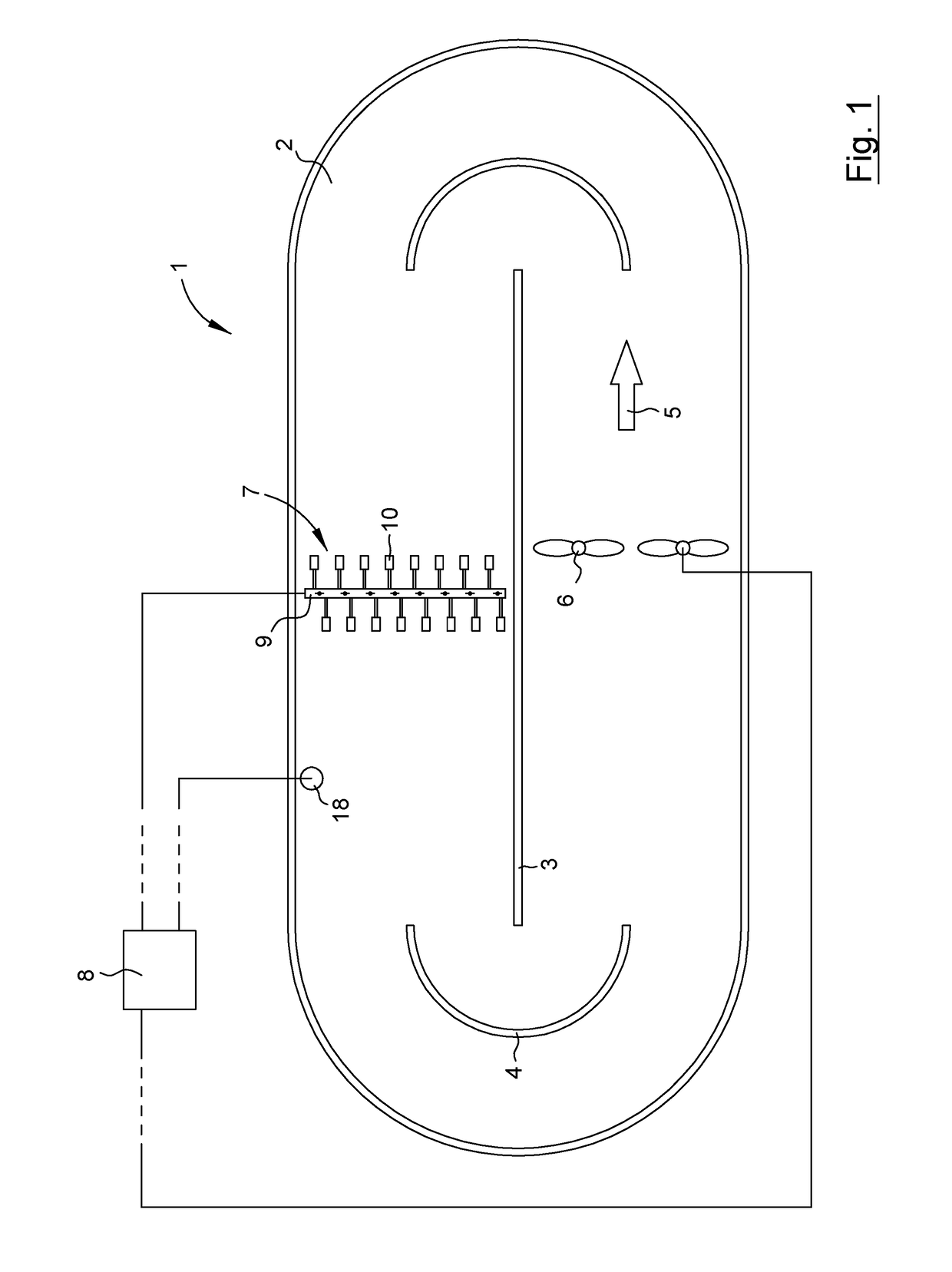
Plant for treatment of liquid as well as method for controlling such a plant
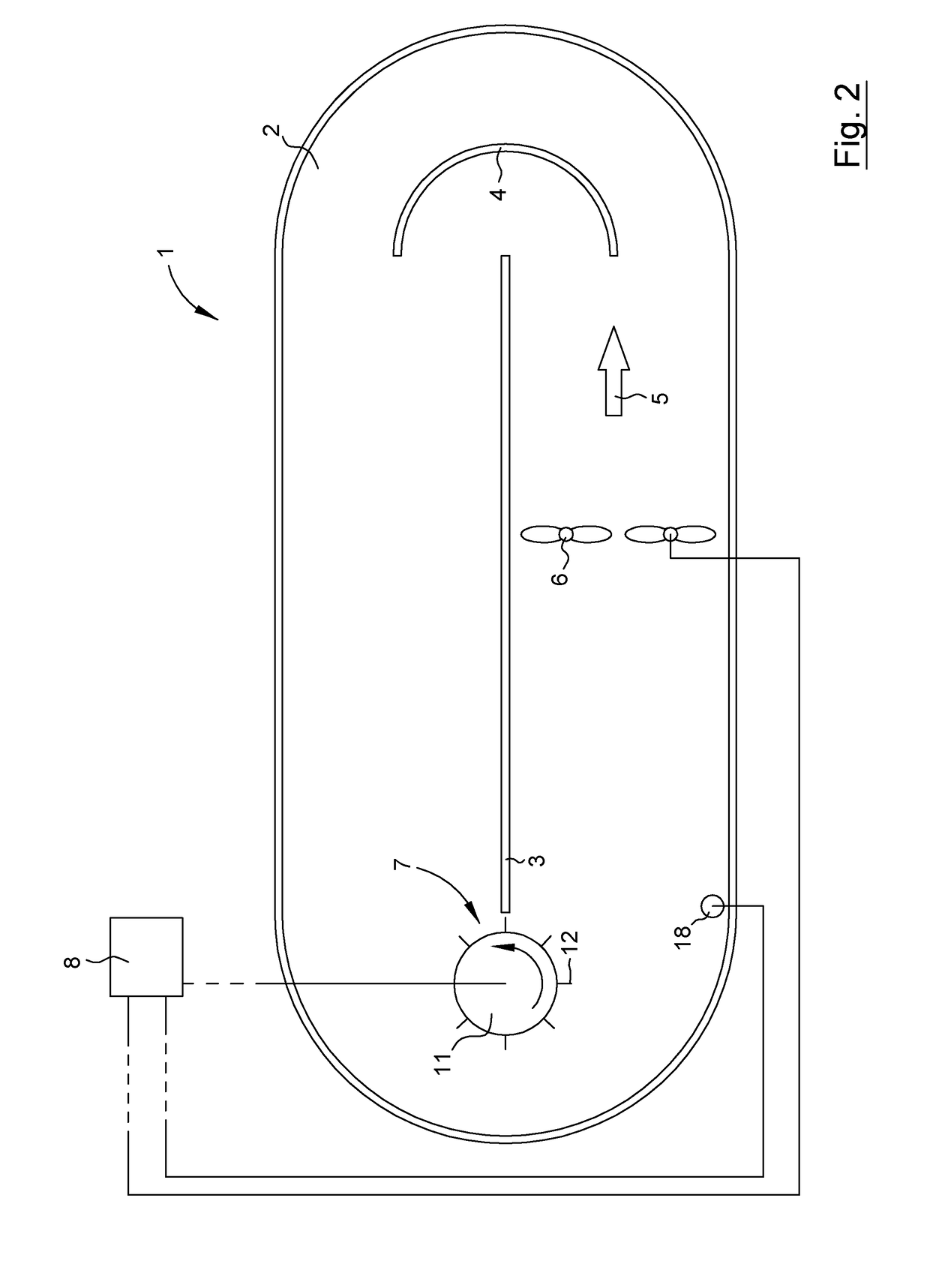
ActiveUS20170144909A1Low costKnown methodWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesMomentumWater flow
A plant and method for controlling such a plant suitable for treatment of waste water. The plant includes a basin, a flow generating machine adapted to generate a liquid flow in the basin, equipment in the basin that effects the momentum of the liquid flow, and a control unit. The method includes the steps of: storing a predetermined relationship between the operational speed N of the flow generating machine and an operational parameter P from which the torque M of the flow generating machine may be derived, determining the operational speed N, determining a set value of the operational parameter P of the flow generating machine, determining a real value of the operational parameter P of the flow generating machine, and adjusting the operational speed N if the real value of the operational parameter P is different than the set value of the operational parameter P.
Owner:XYLEM EURO GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com