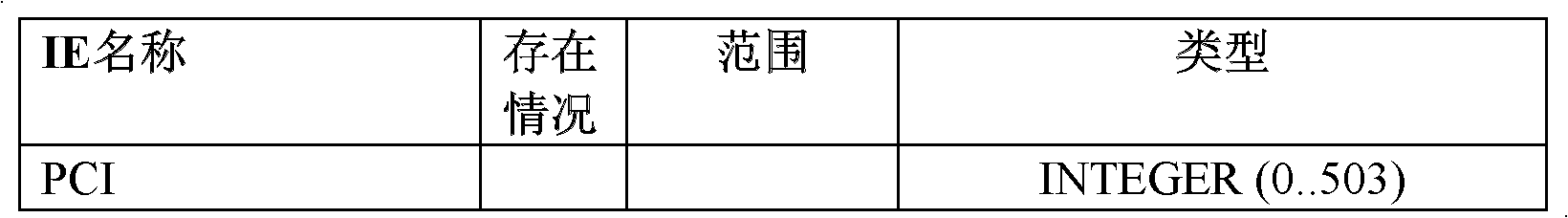
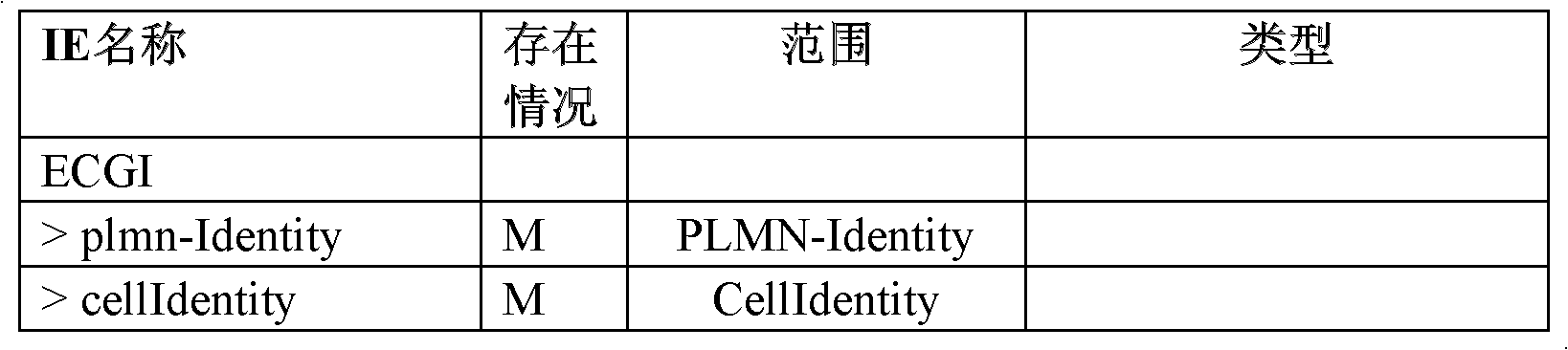
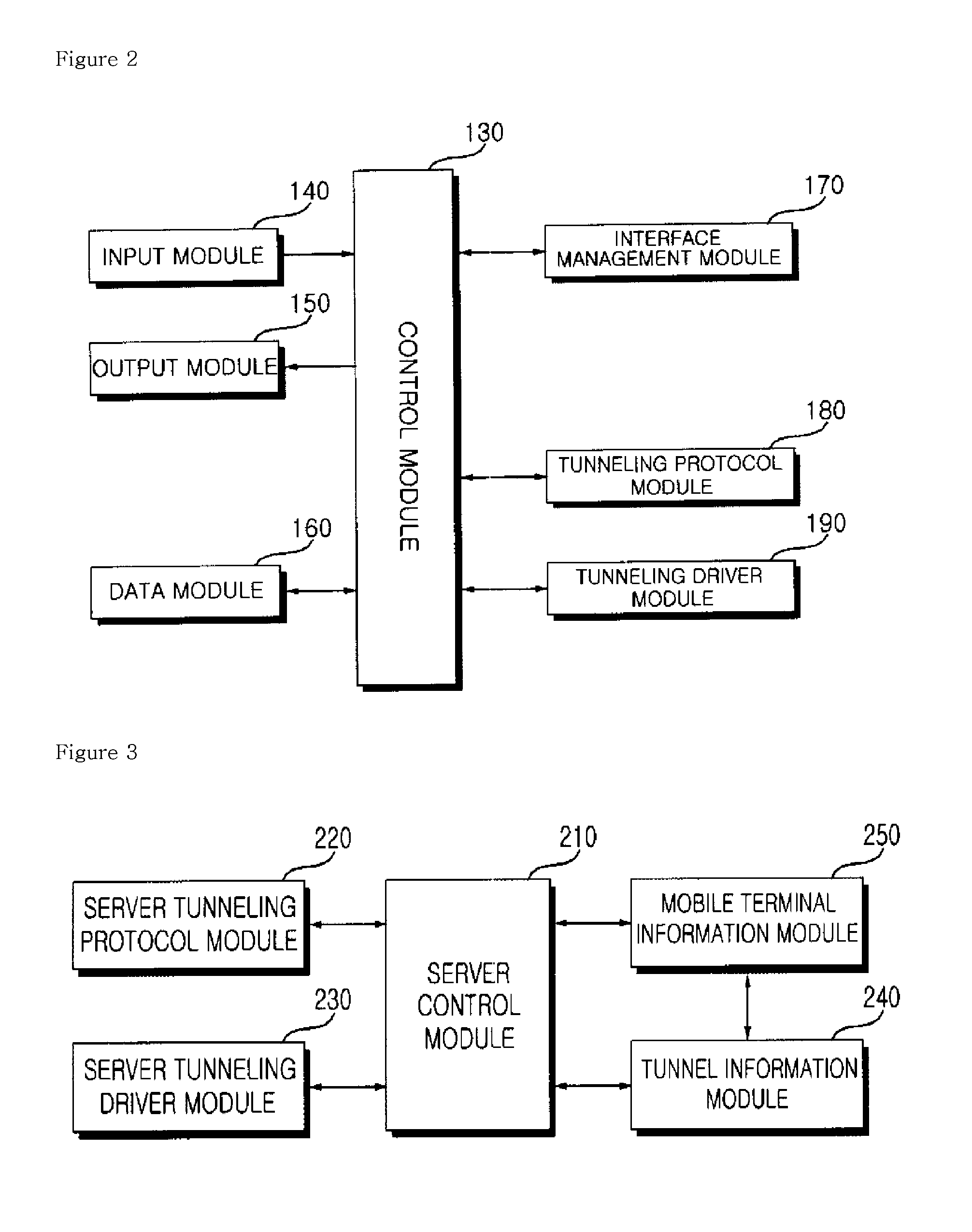
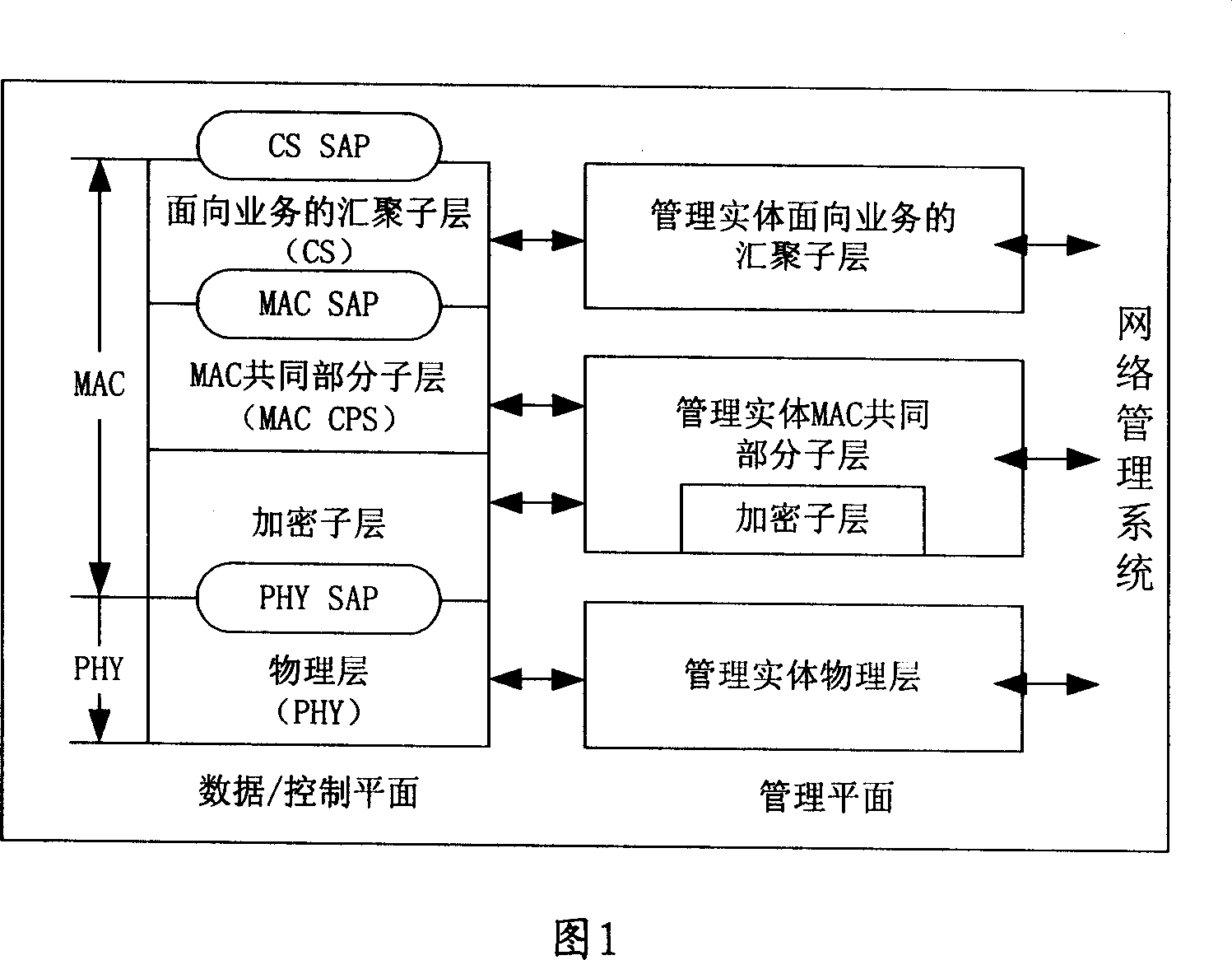
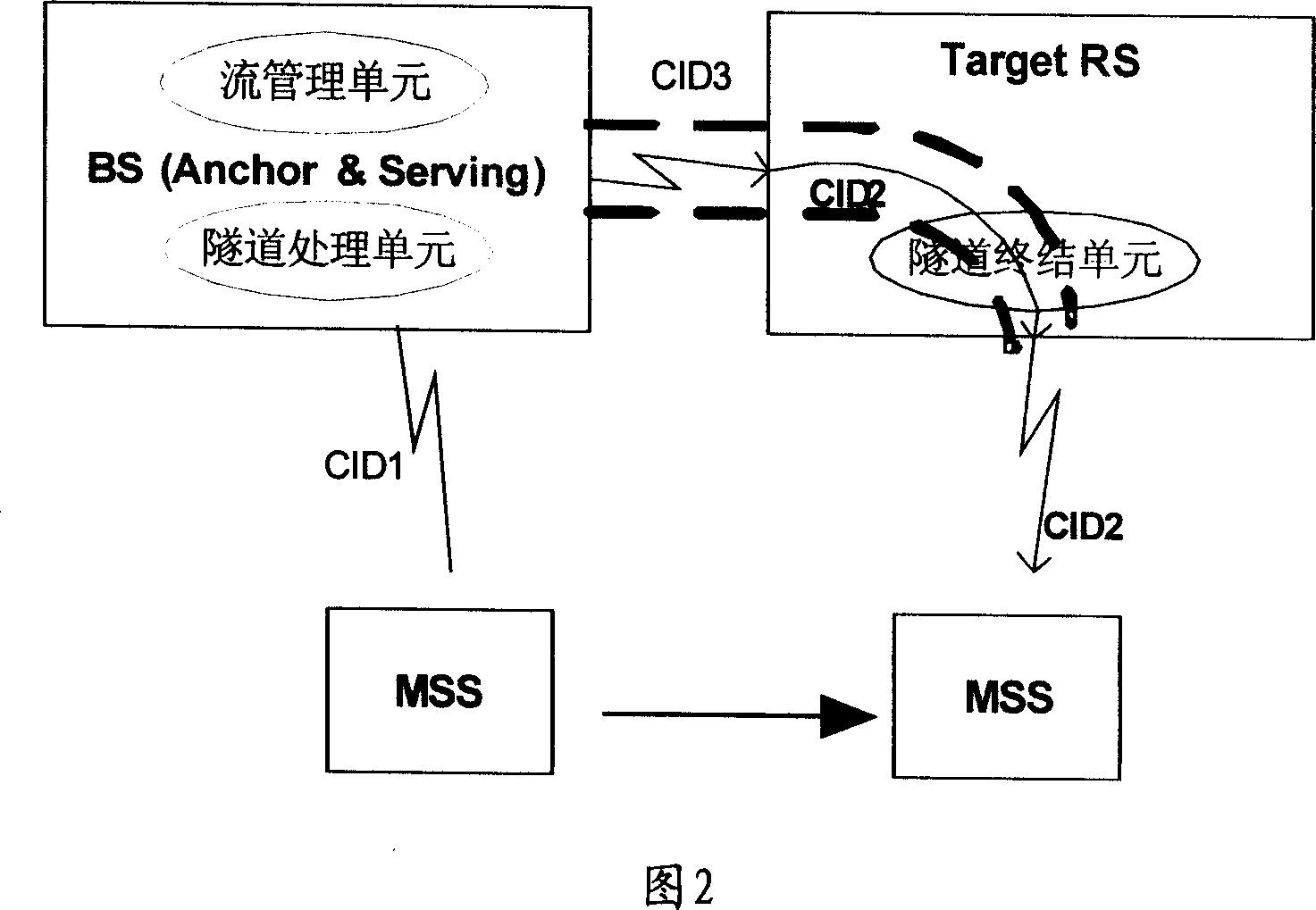
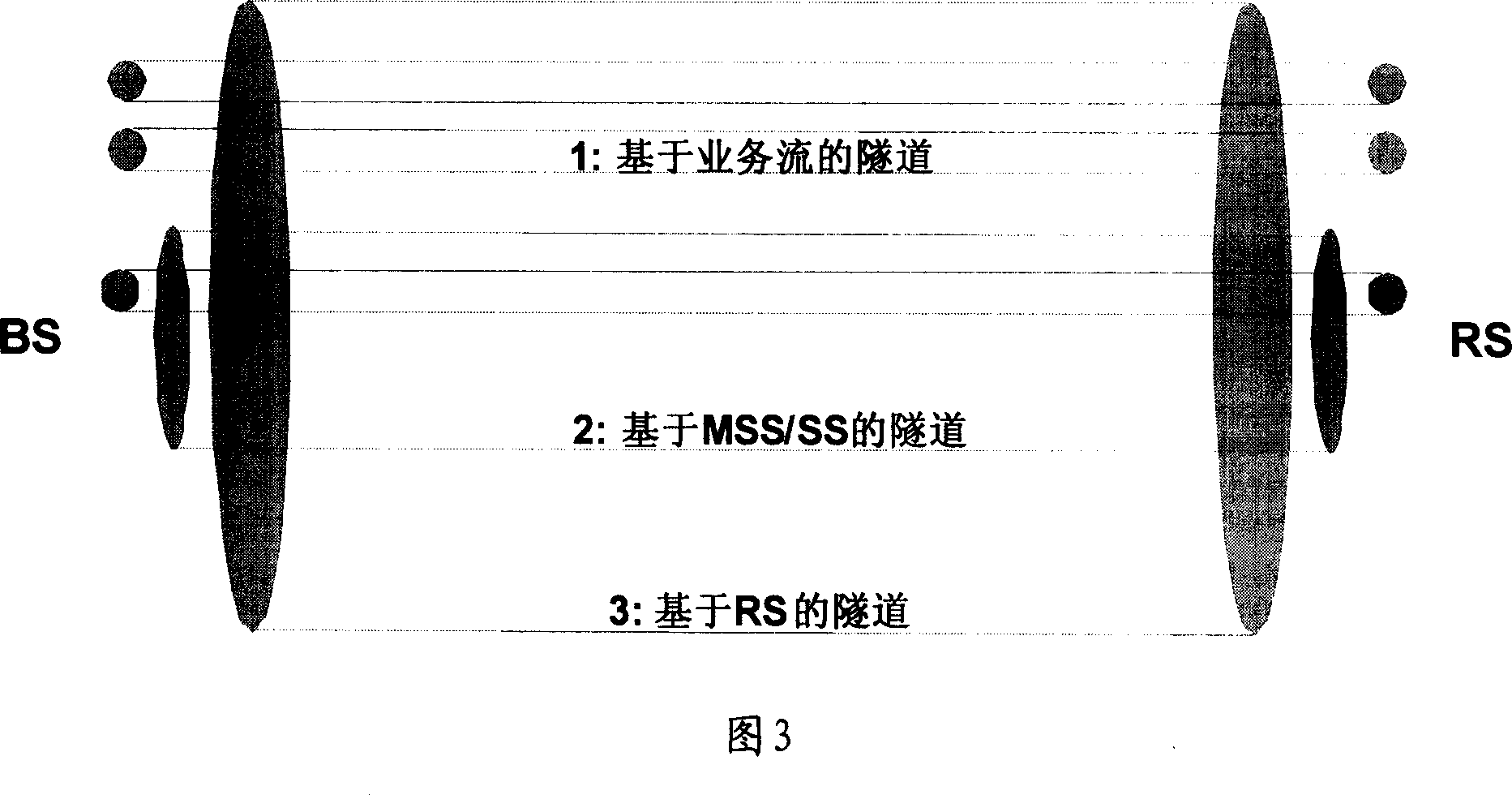
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Guarantee service continuity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
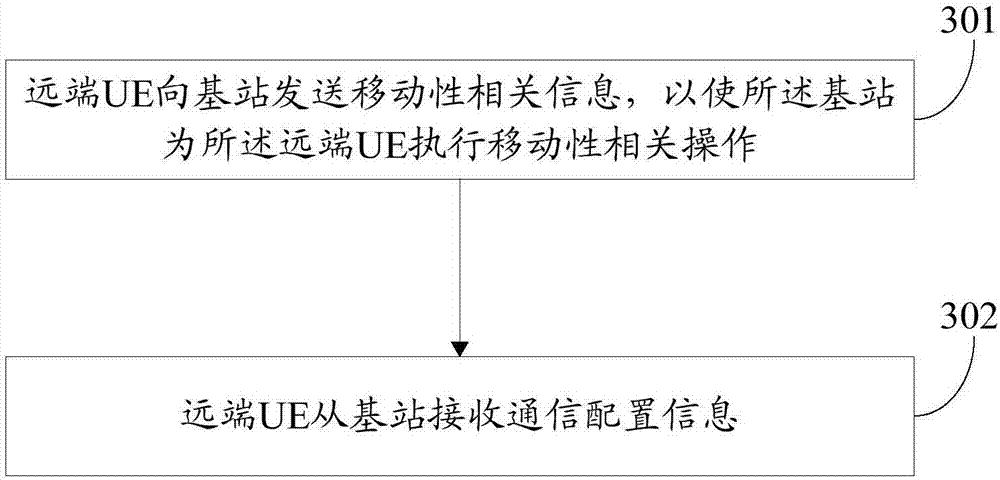
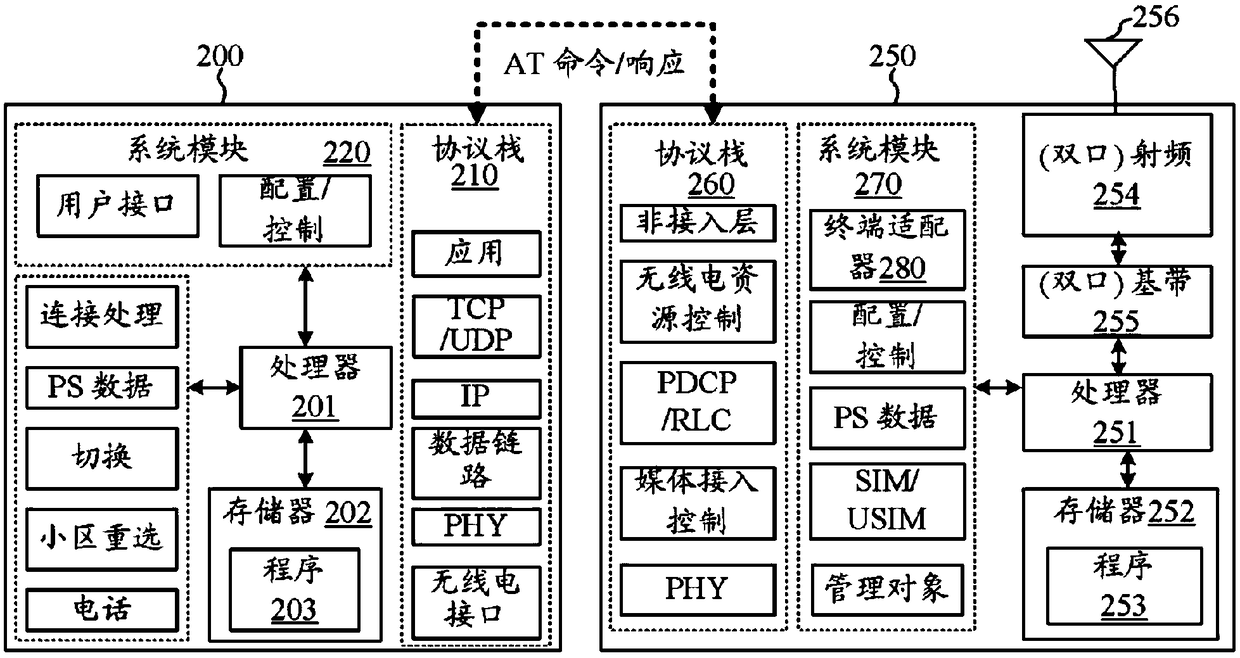
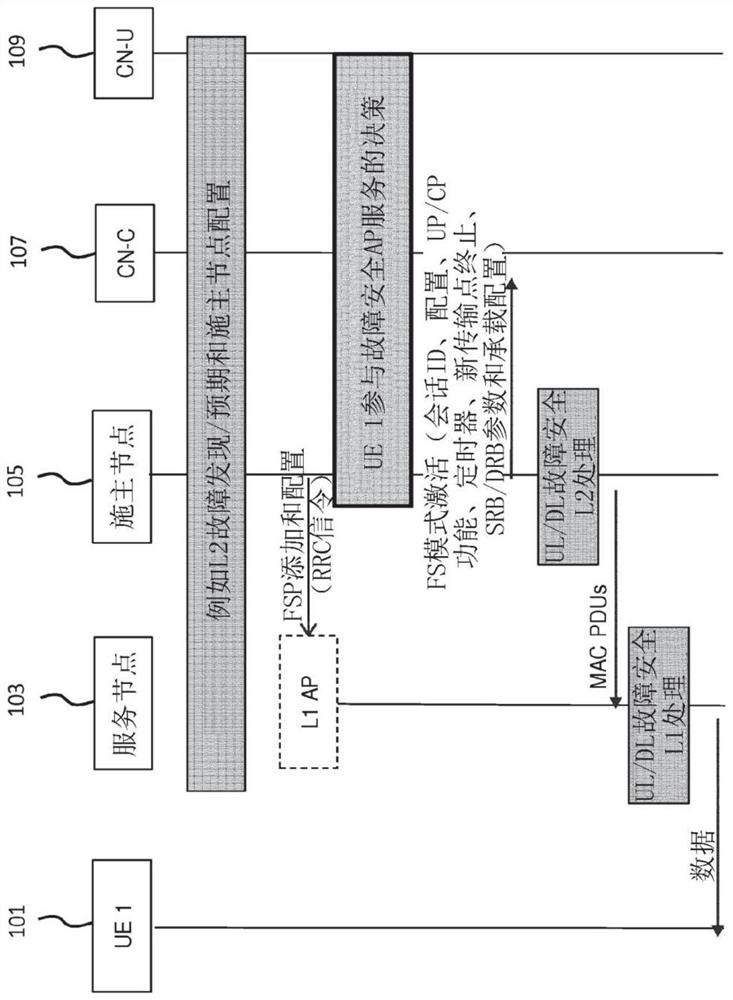
Method and apparatus for supporting mobility of remote UE (User Equipment)
ActiveCN107889080AGuarantee service continuityMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceUser equipmentComputer science
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for supporting mobility of a remote UE (User Equipment). The method comprises the following steps: the remote UE sends mobility related information toa base station such that the base station executes a mobility related operation for the remote UE; and the remote UE receives communication configuration information from the base station.
Owner:ZTE CORP
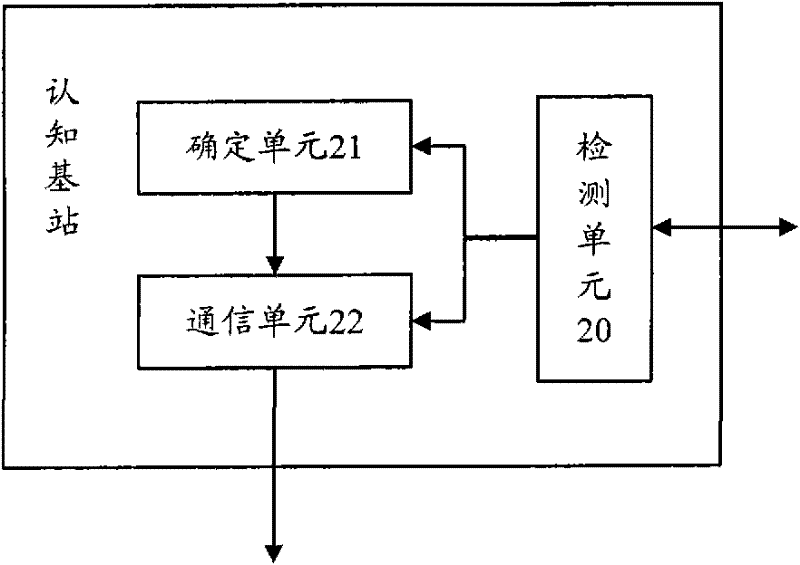
Method, device and system for realizing cell switch based on CR (Cognitive Radio)
InactiveCN102457863AAvoid interferenceMeet performance indication requirementsConnection managementCurrent cellQuality of service
The invention relates to the field of communication and discloses a method, a device and a system for realizing cell switch based on CR (Cognitive Radio). In the method, when the access of an authorized user to a working frequency point of a current cell is determined, a target working frequency point determined according to a frequency spectrum detection result is transmitted to UE (User Equipment) resided in the current cell by a cognitive base station through an RRC (Radio Resource Controller) connection reconfiguration message, so that the UE can quickly and accurately exit from the current cell and is switched to a target cell using the target working frequency point, further the interference of the UE on the authorized user is avoided, the service continuousness of the system is ensured, the performance indication requirement of a mobile communication system during adoption of a CR technology is met and the service quality of the system is improved. The invention also discloses the corresponding device and the corresponding system.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
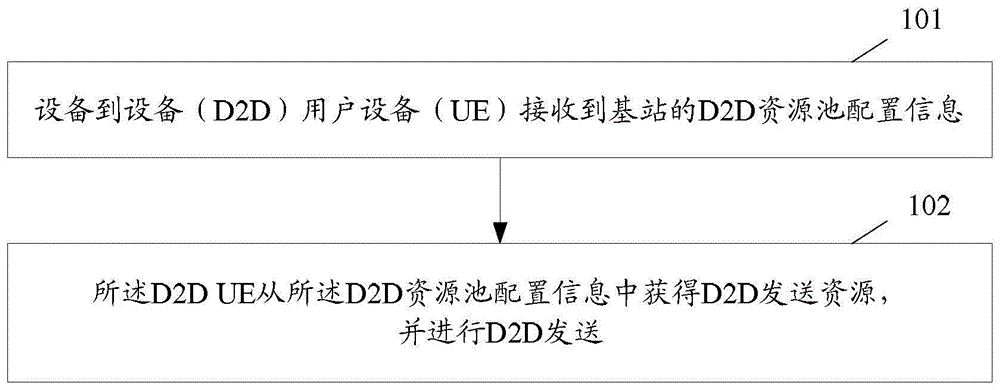
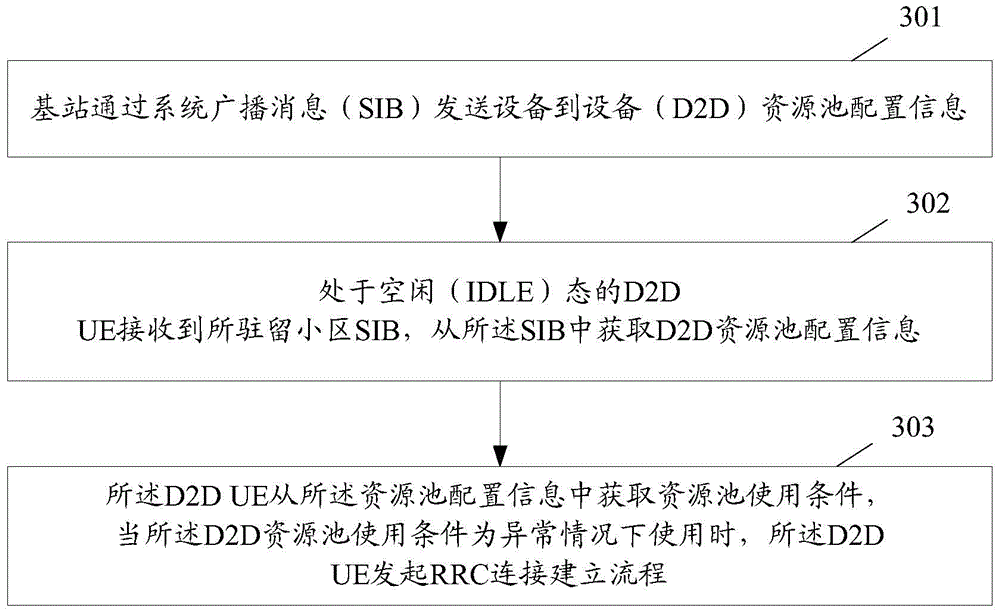
Device-to-device resource pool configuration method, device and system
InactiveCN105338548AGuarantee service continuityImprove service qualityConnection managementHigh level techniquesResource poolUser equipment
The invention discloses a device-to-device D2D resource pool configuration method, device and system. The method comprises the following steps: receiving D2D resource pool configuration information of a base station by a D2D UE (User Equipment); and acquiring a D2D sending resource from the D2D resource pool configuration information by the D2D UE, and performing D2D transmission.
Owner:ZTE CORP
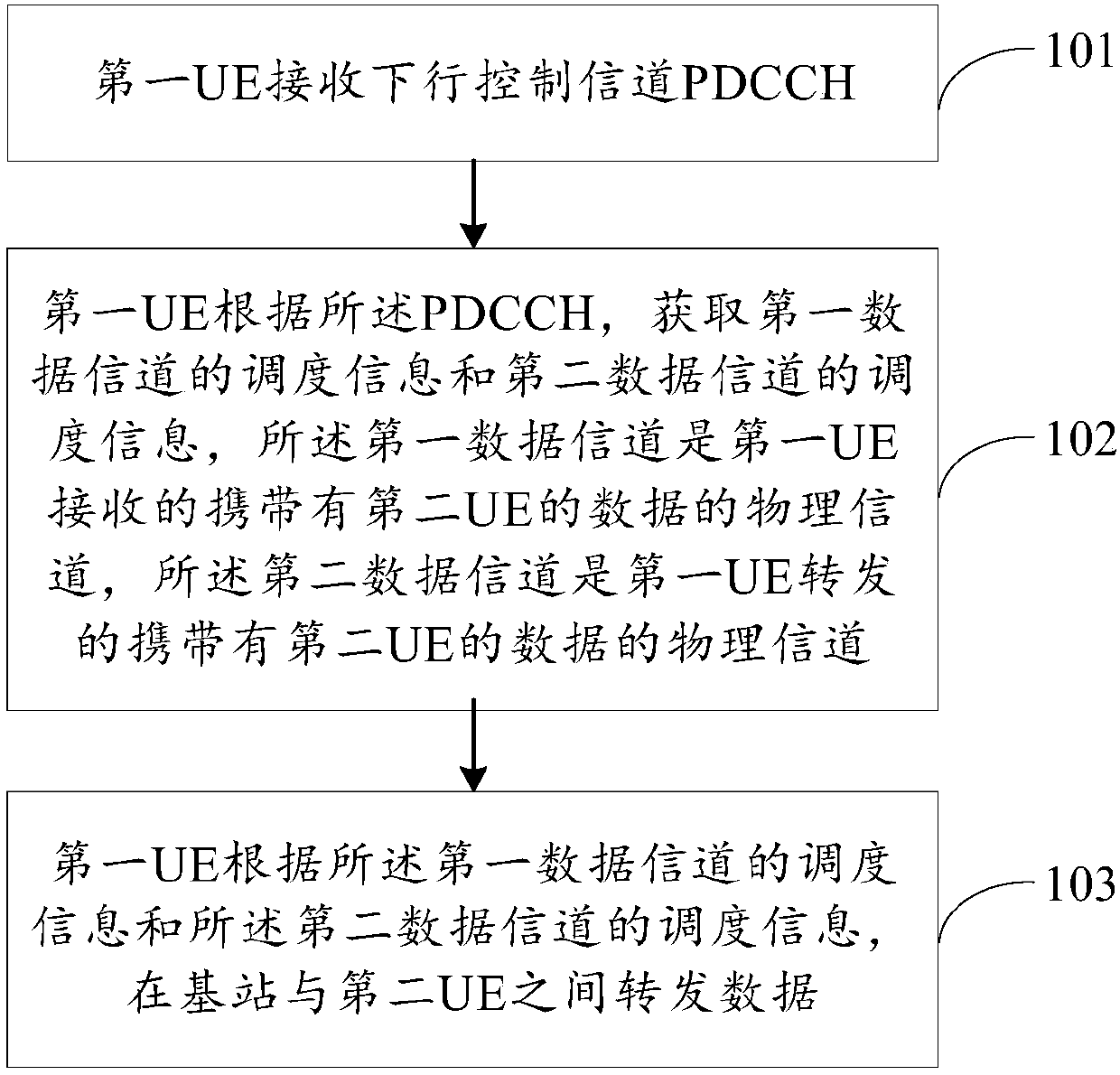
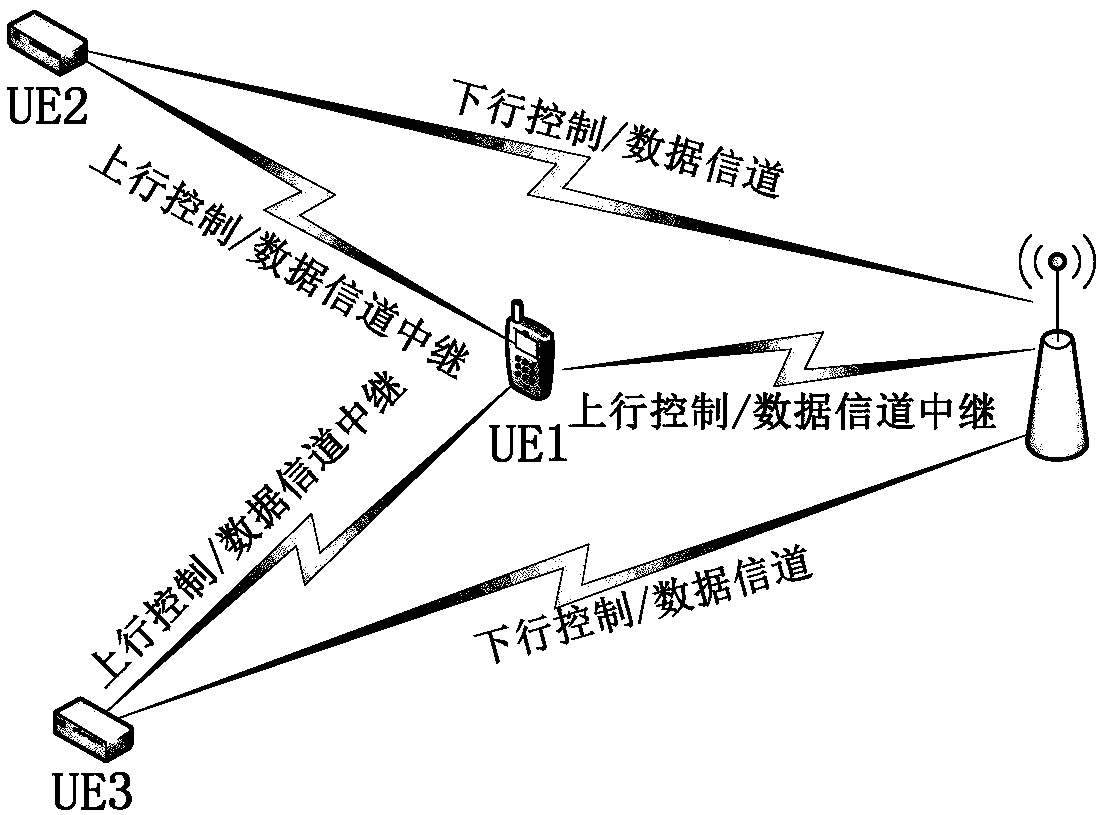
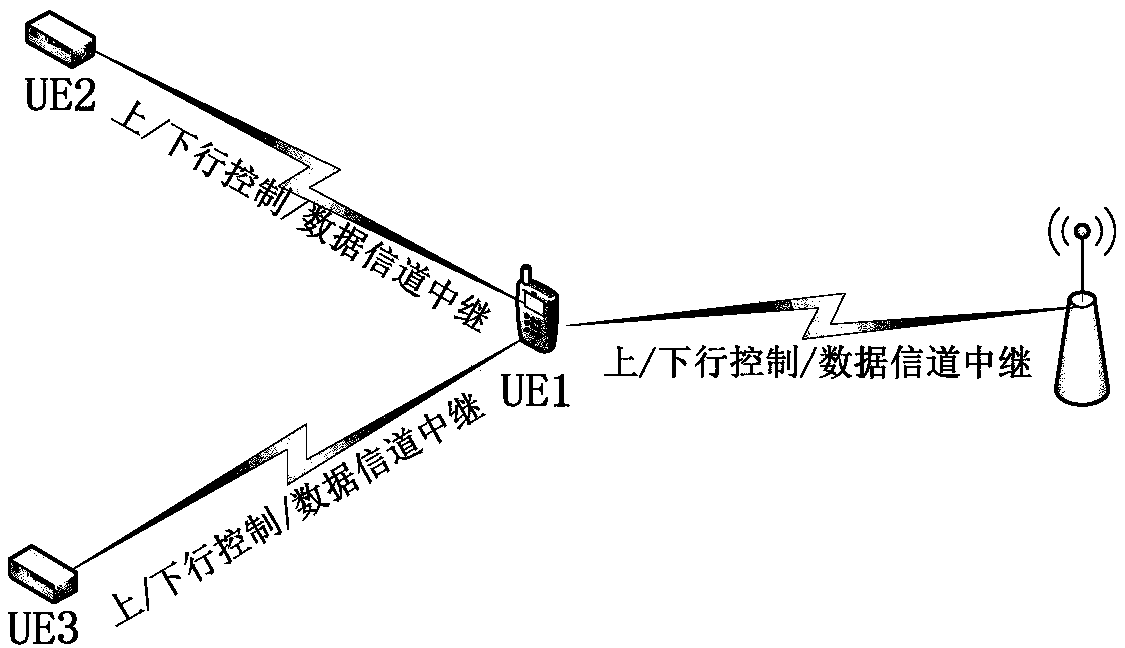
Relay transmission method and user equipment
PendingCN110290592AGuarantee service continuityIncrease success rateError prevention/detection by using return channelSignalling characterisationControl channelData transmission
The invention discloses a relay transmission method. The method comprises the following steps: first UE receives a downlink control channel PDCCH; the first UE acquires scheduling information of a first data channel and scheduling information of a second data channel according to the PDCCH, the first data channel being a physical channel which is received by the first UE and carries data of the second UE, and the second data channel being a physical channel which is forwarded by the first UE and carries data of the second UE; and the first UE forwards data between the base station and the second UE according to the scheduling information of the first data channel and the scheduling information of the second data channel. Compared with the prior art, the relay transmission service is provided for the remote node of the mobile communication network through the relay node in the first layer / the second layer, the service continuity of the remote node is guaranteed, and the success rate of remote node data transmission is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
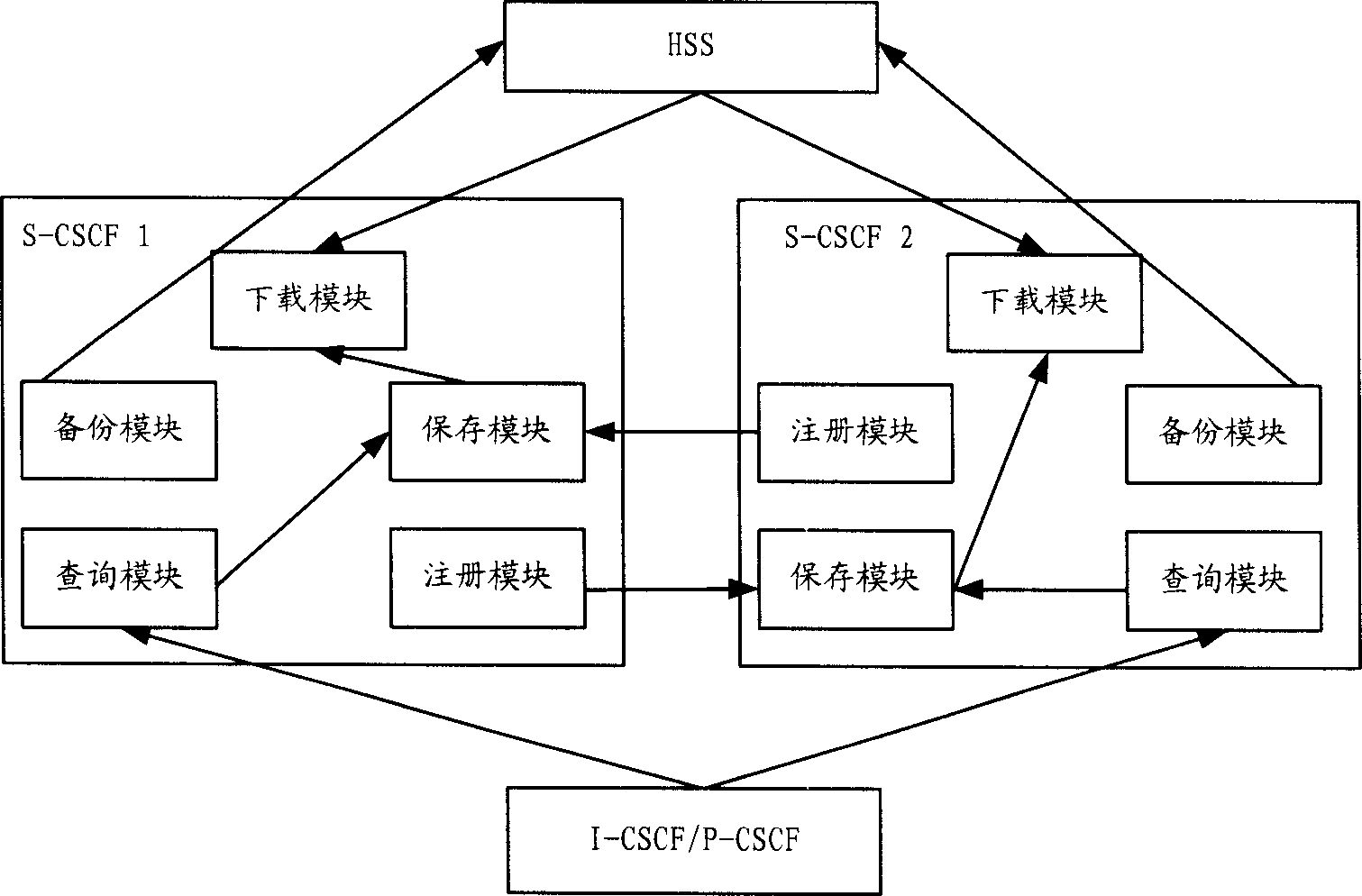
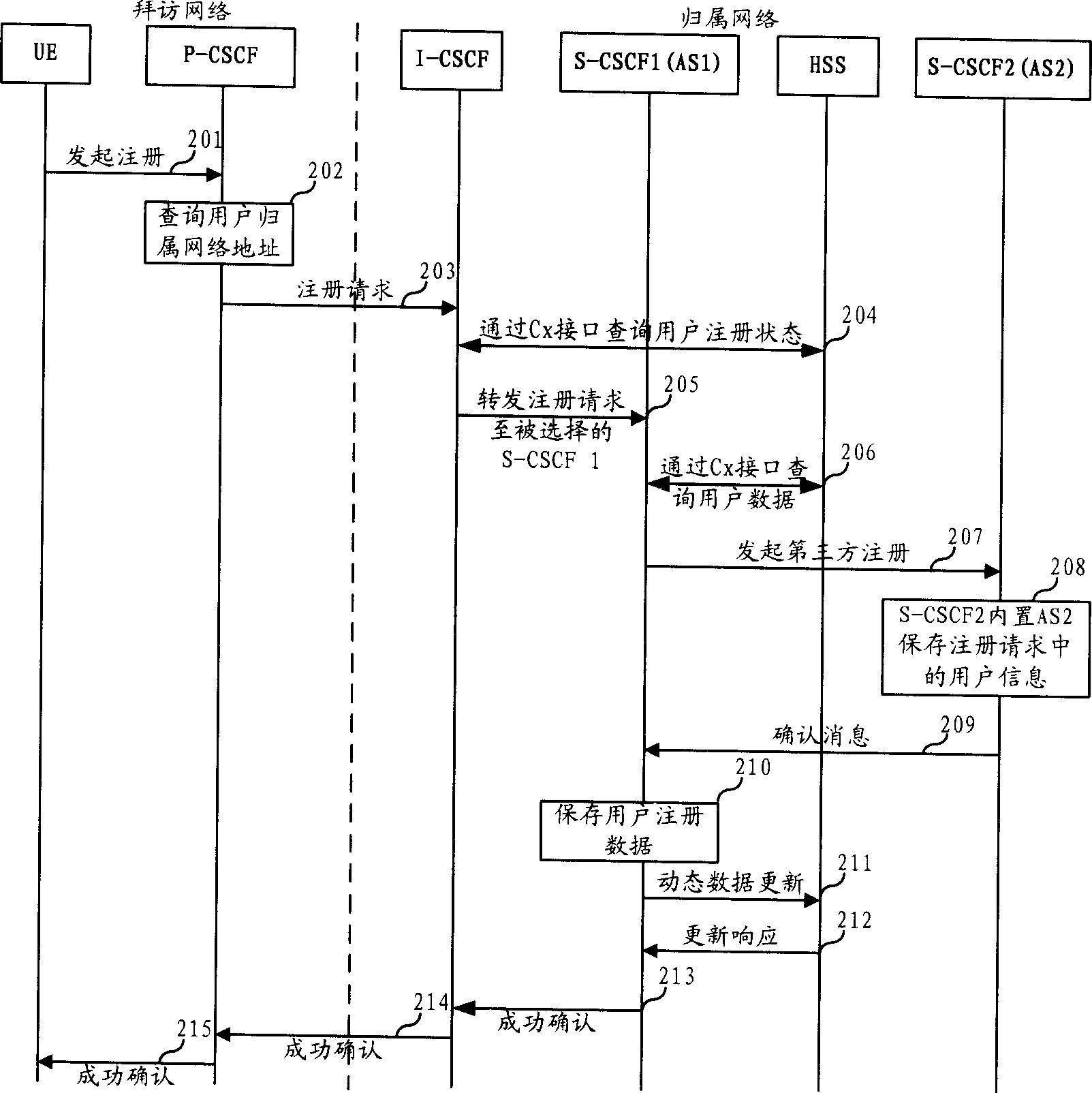
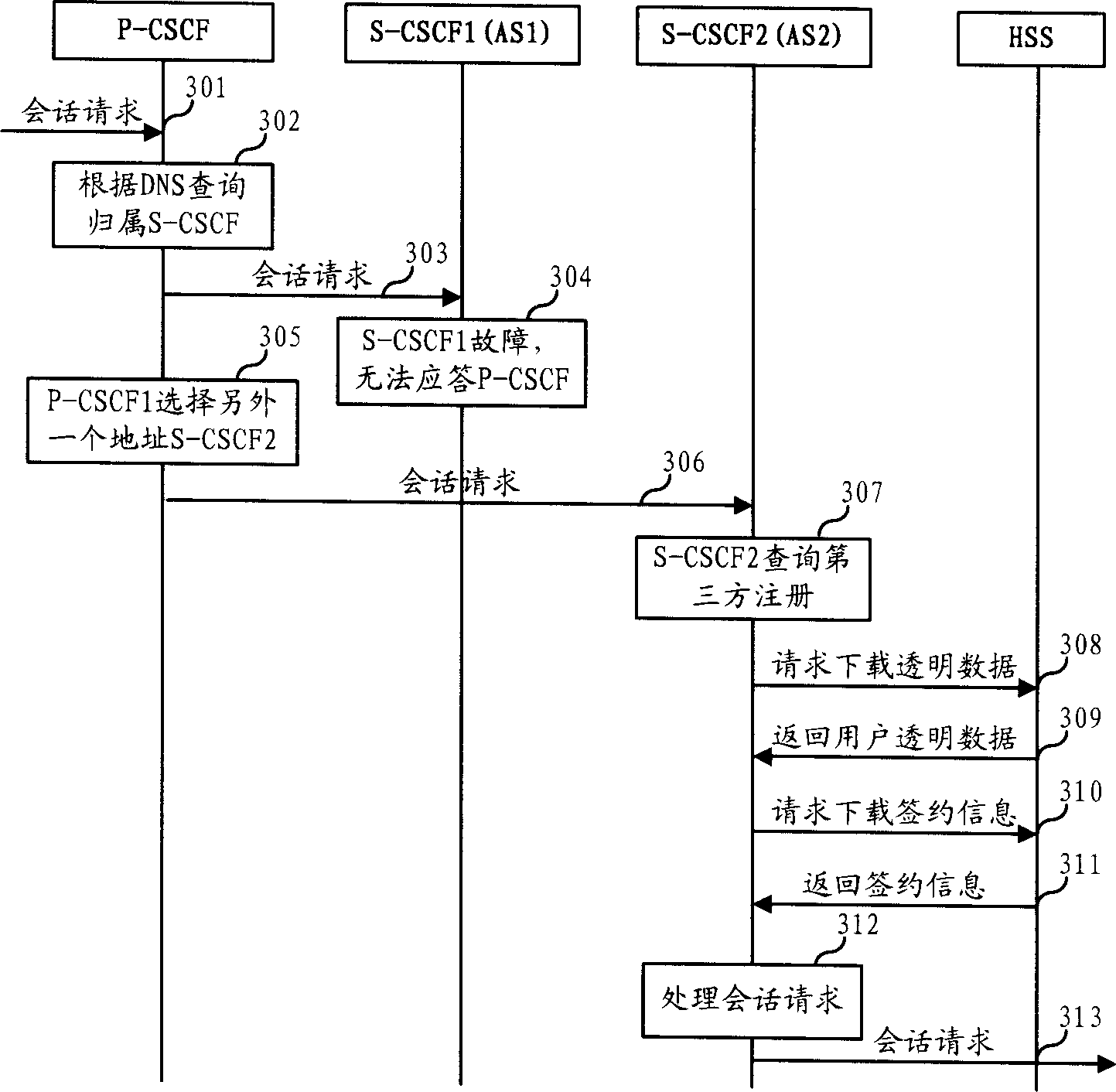
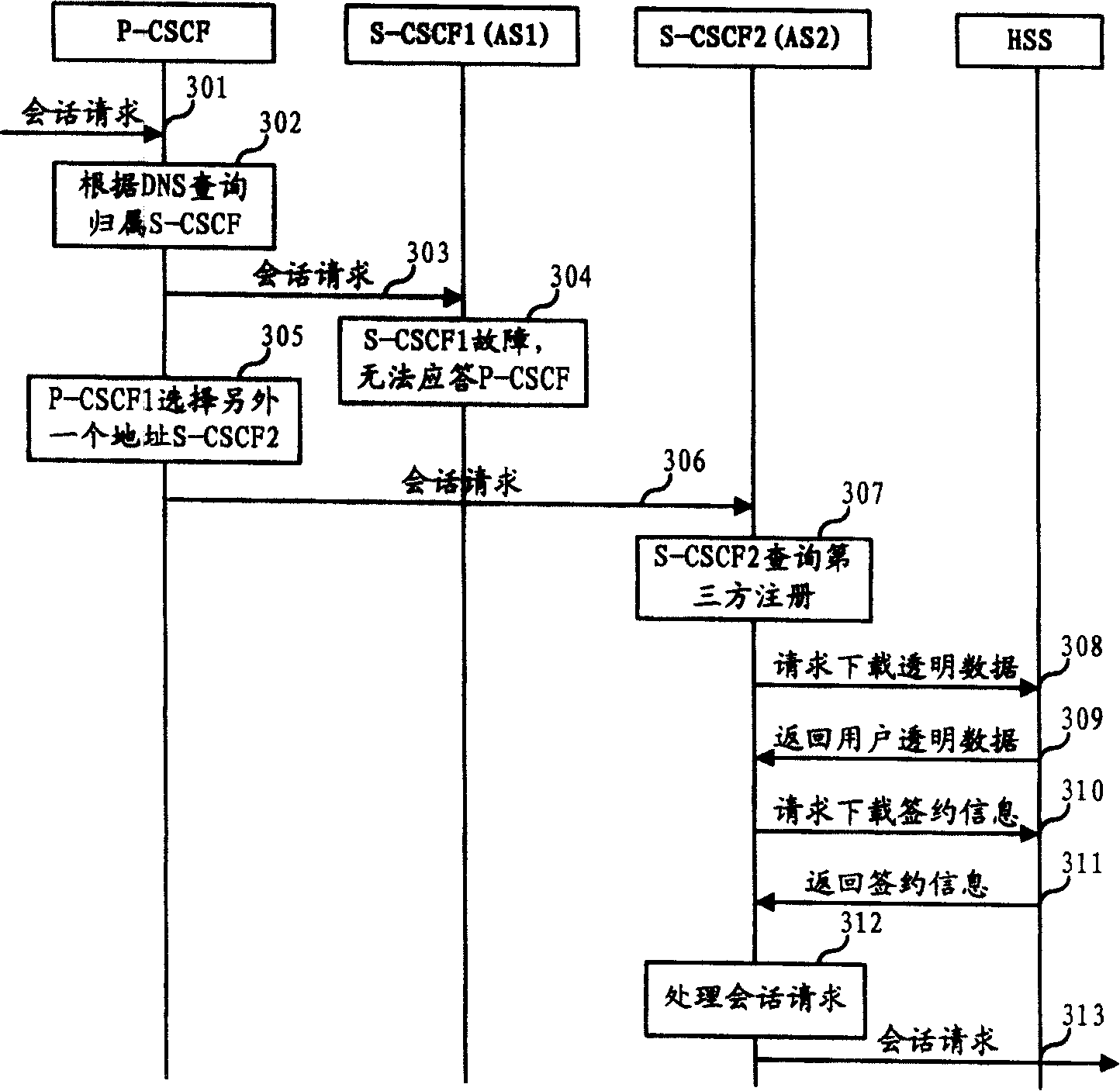
Service call session control function entity backup method and system thereof
ActiveCN1878087AGuarantee service continuityImprove experienceData switching networksSession controlDynamic data
The invention discloses an S-CSCF alternate method and system, which is characterized by the following: building AS in the S-CSCF; sending user information to other S-CSCF working with S-CSCF at load share pattern at successful registering time; reserving other S-CSCF in the user information to realize the third registering for user; duplicating the needed dynamic data of S-CSCF in the HSS; transferring the business request of accident S-CSCF at network side to other S-CSCF at S-CSCF accident time; downloading the dynamic data and practice information from HSS according to the third registering information if S-CSCF receives the business request of the third part registered user; providing service for user continually.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
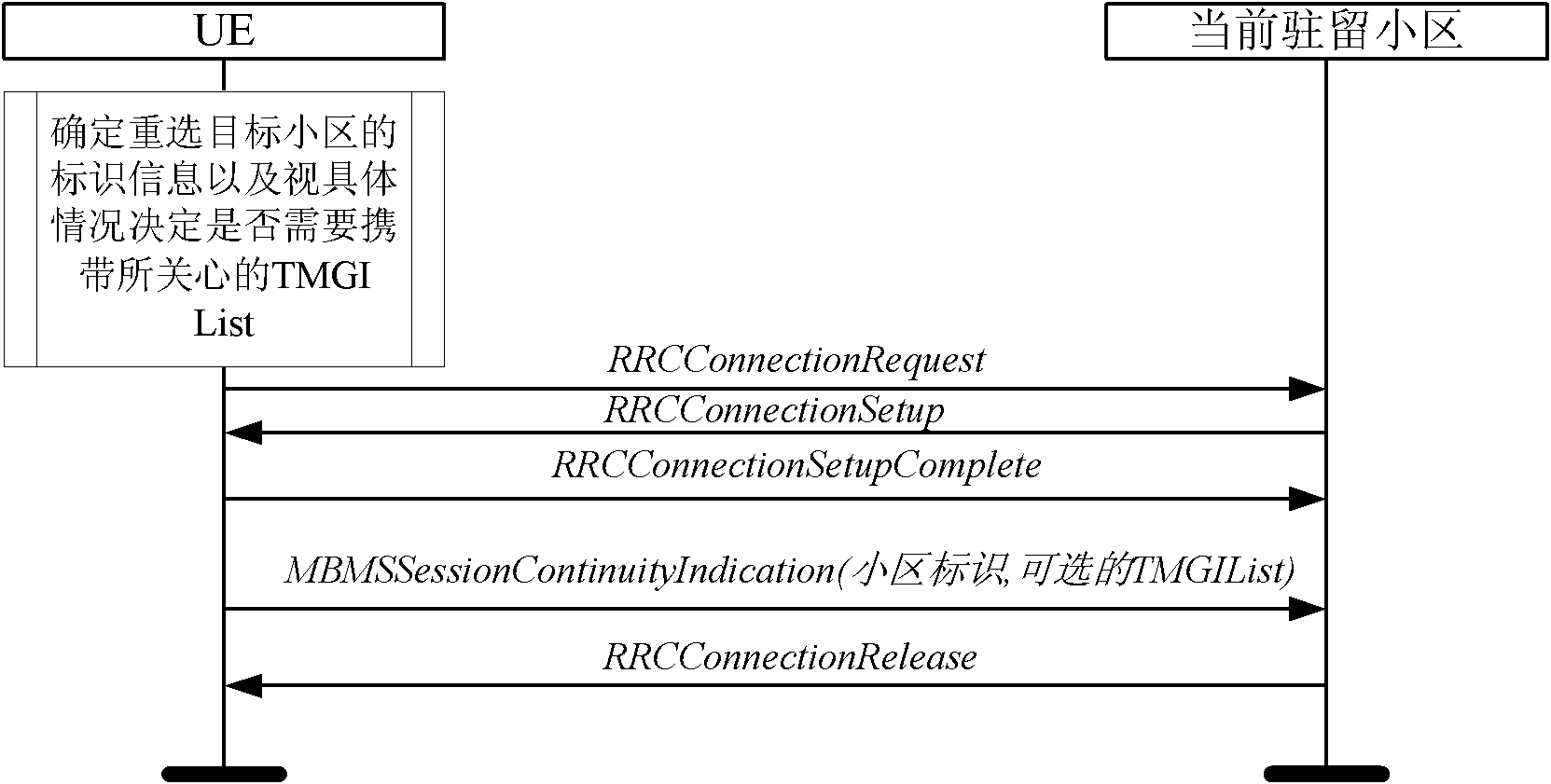
Method for ensuring eMBMS service continuity for community reselection
InactiveCN102761828AGuarantee service continuityConnection managementBroadcast service distributionCommunity supportControl channel
The invention discloses a method for ensuring eMBMS service continuity for community reselection. The method comprises the steps that in the situation of meeting the triggering condition of community reselection, if UE in an RRC_IDLE state currently has eMBMS service which is being received, the US needs to determine whether the target reselection community supports the current eMBMS service continuity or not according to configuration information on a multicast control channel of a target reselection community in community reselection; if not, the UE initiates an RRC connection establishment request to a current residence community / base station; and after RRC connection establishment, the UE reports the identification information of the target reselection community through an added RRC message and hopes the target reselection community to provide an eMBMS service list in an MBSFN mode. The method of the invention can better ensure the eMBMS service continuity of UE in an RRC_IDLE state through the mechanism, thereby positively improving service quality experience of users.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
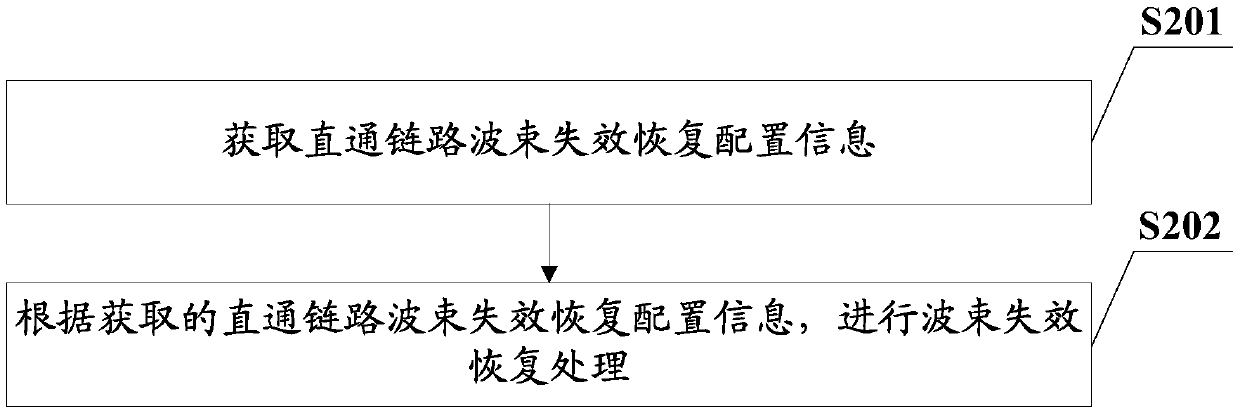
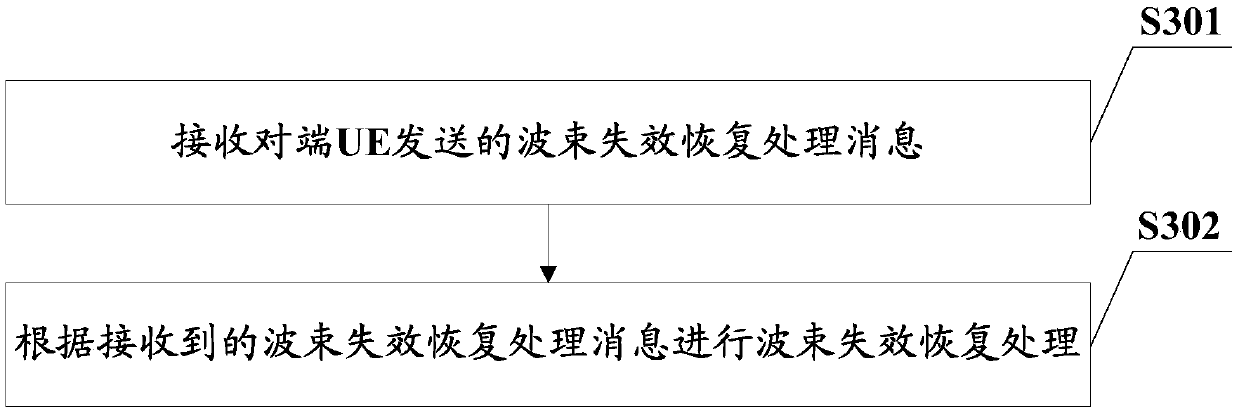
Straight-through link beam management method, device, equipment and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110536429AGuarantee service continuityImprove reliabilityConnection managementReliability engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a straight-through link beam management method, a device, equipment and a readable storage medium. Firstly, beam failure recovery configuration information ofa straight-through link is obtained; and then according to the obtained straight-through link beam failure recovery configuration information, beam failure recovery processing is carried out, so thatwhen straight-through link beam failure occurs in a straight-through link unicast communication process or other communication processes, recovery of a straight-through link beam can be carried out intime to ensure service continuity, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
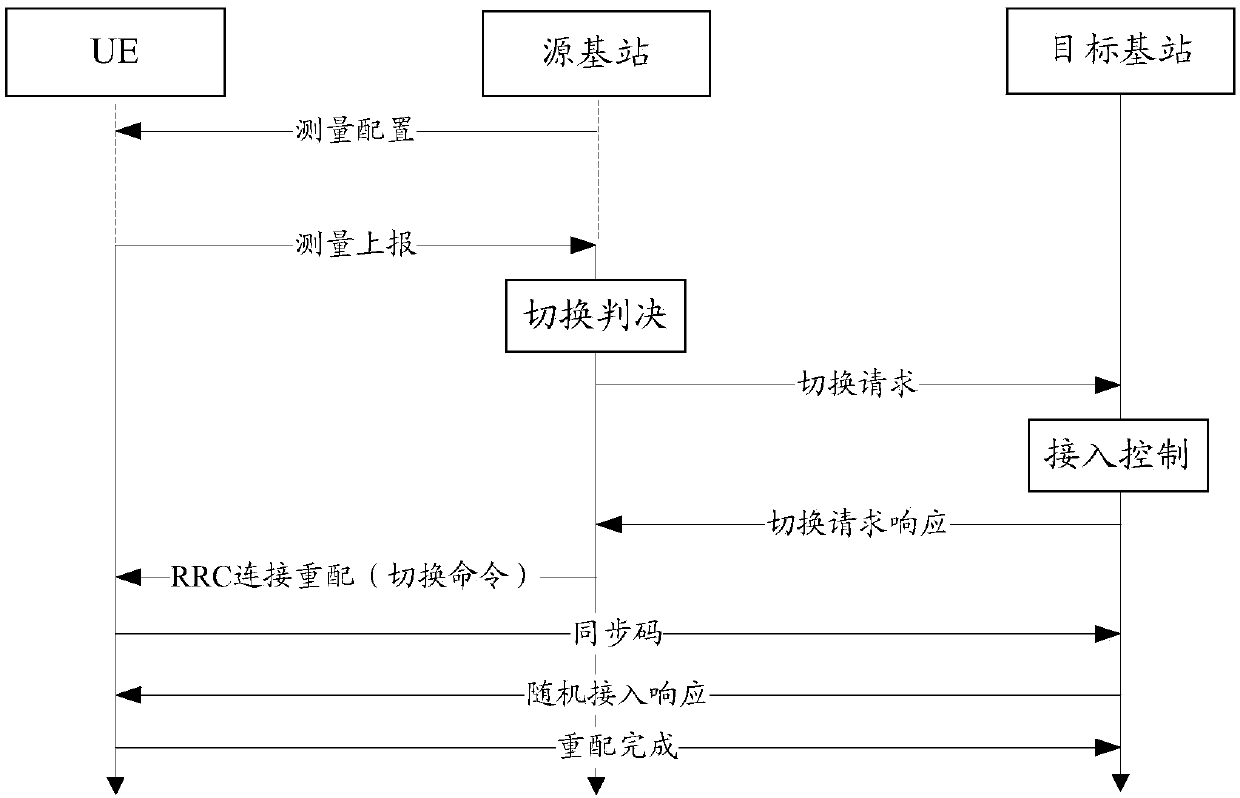
Mobility measurement methods, mobility measurement devices and mobility measurement system
ActiveCN109474951AGuarantee service continuityAccurate measurementTransmission monitoringWireless communicationMeasurement deviceSignal quality
The embodiment of the application provides mobility measurement methods, mobility measurement devices and a mobility measurement system, and relates to the field of communication. Service continuity in a terminal movement process is guaranteed. The method specifically includes: receiving, by a terminal, measurement configuration information which is sent by the network equipment and is of a neighboring area of a service cell where the terminal is currently located, wherein the measurement configuration information includes frequency point information of at least one Anchor sub-band of the neighboring area; measuring, by the terminal, signal strength and / or signal quality of at least one Anchor sub-band in Anchor sub-bands corresponding to the frequency point information included in the measurement configuration information, and acquiring a measurement result of each Anchor sub-band measured by the terminal; and sending a measurement report by the terminal to the network equipment, wherein the measurement report includes identifiers of Anchor sub-bands which are in the Anchor sub-bands measured by the terminal and correspond to measurement results meeting a preset condition.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
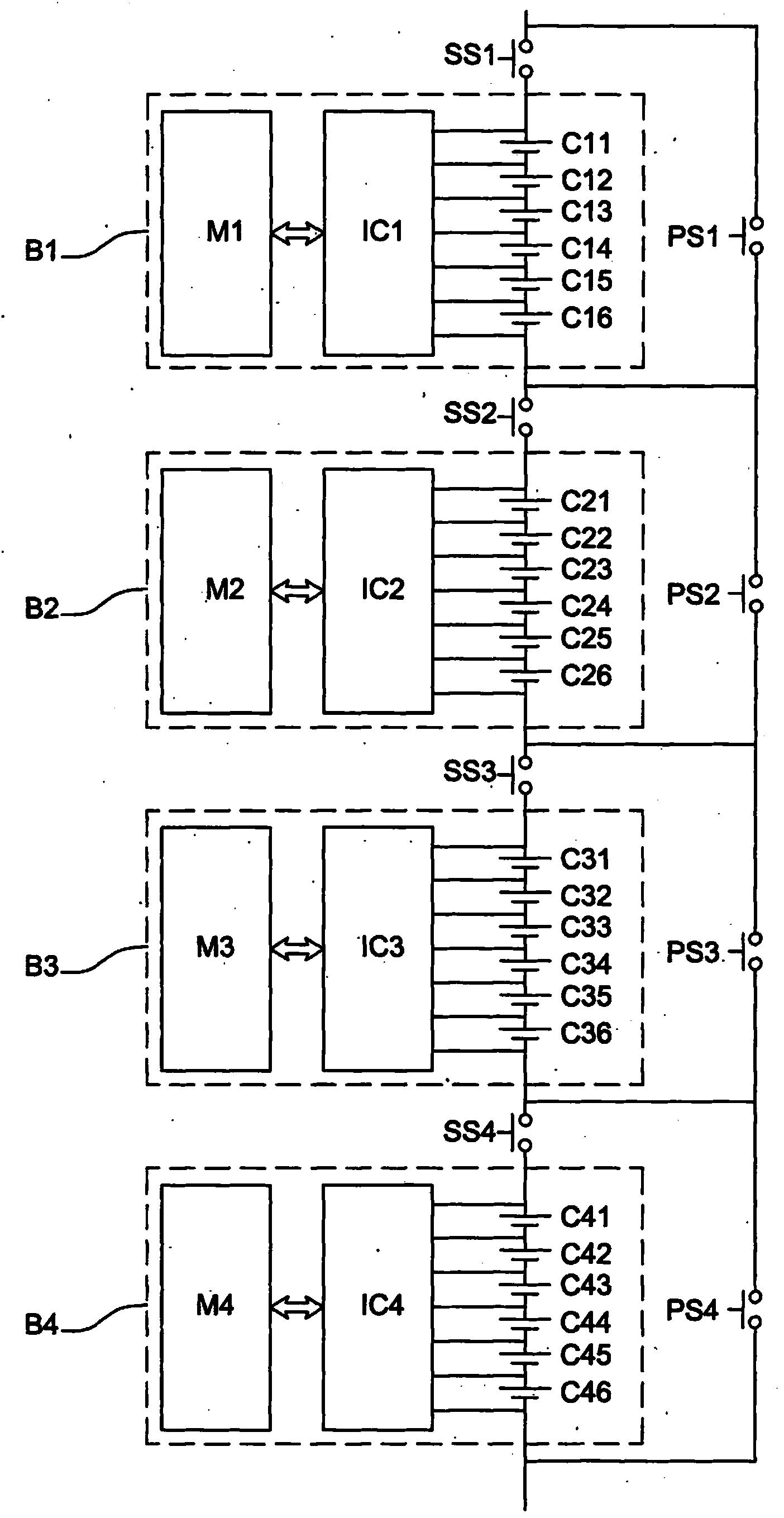
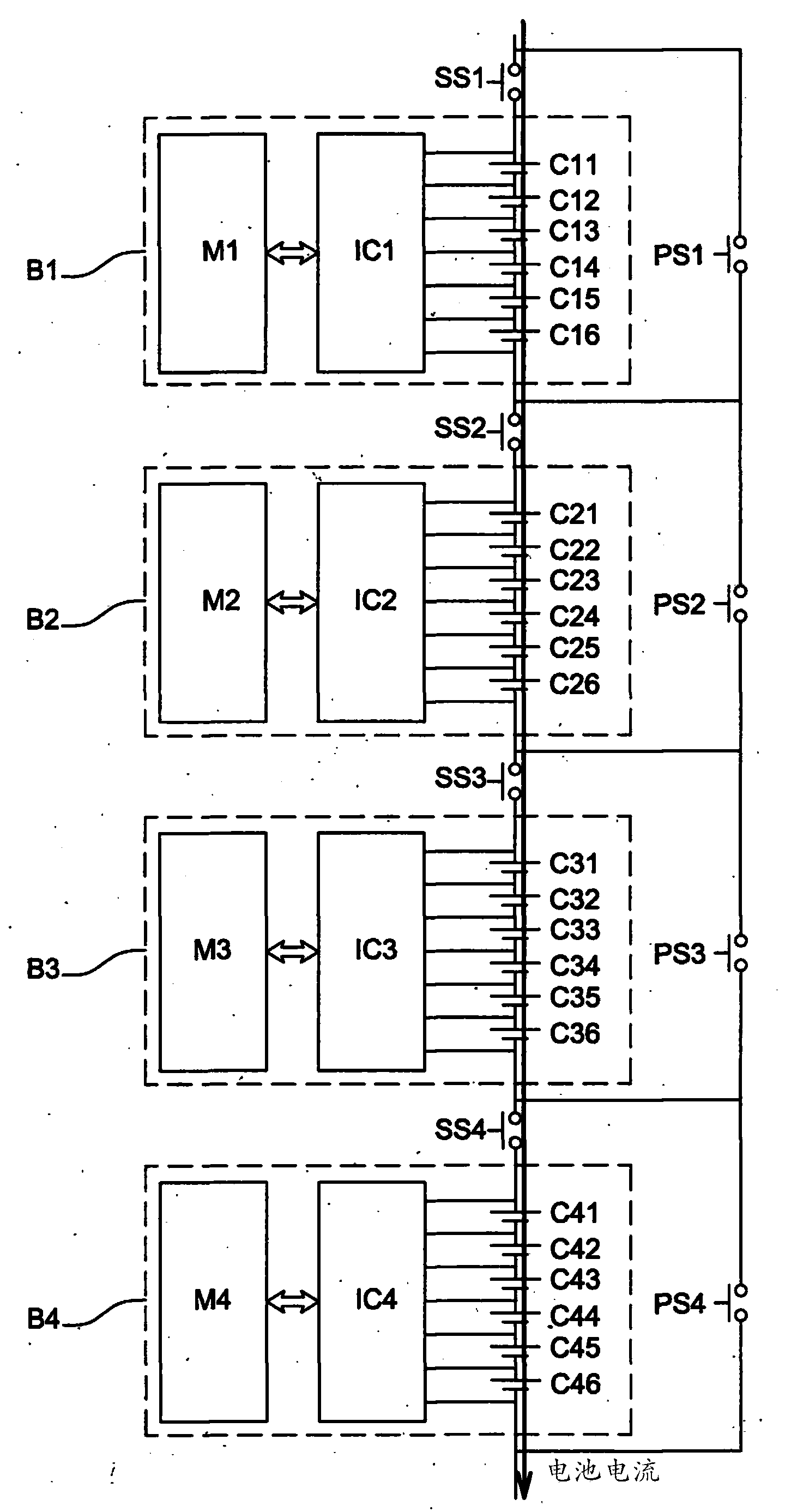
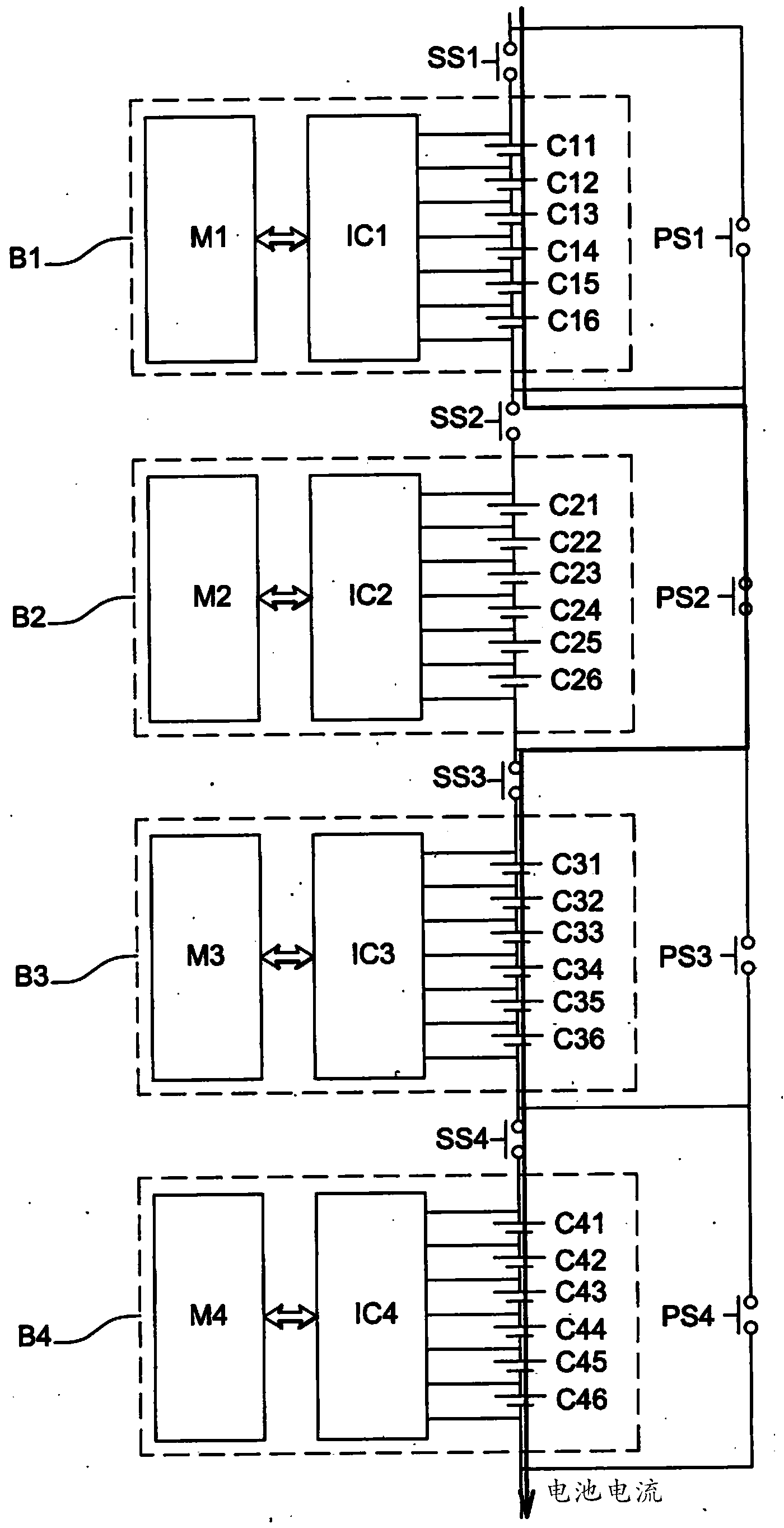
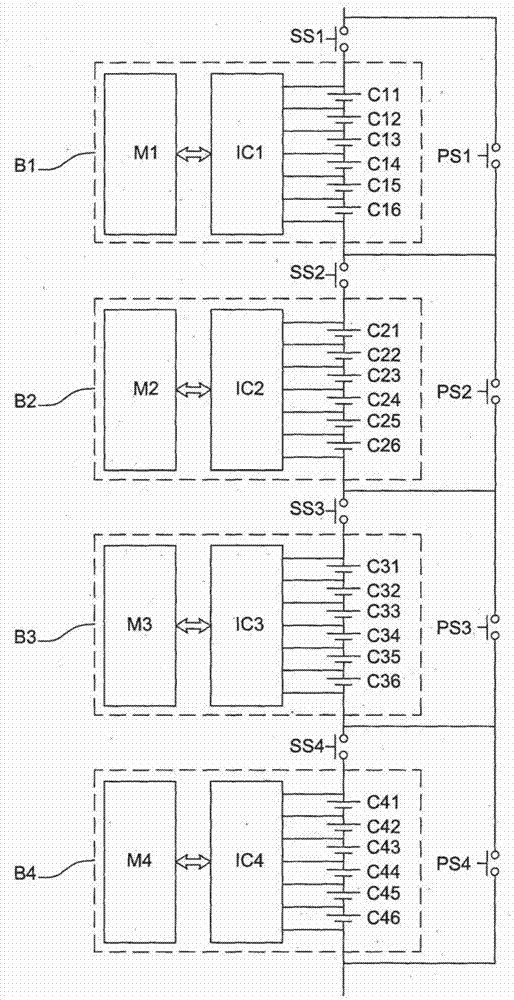
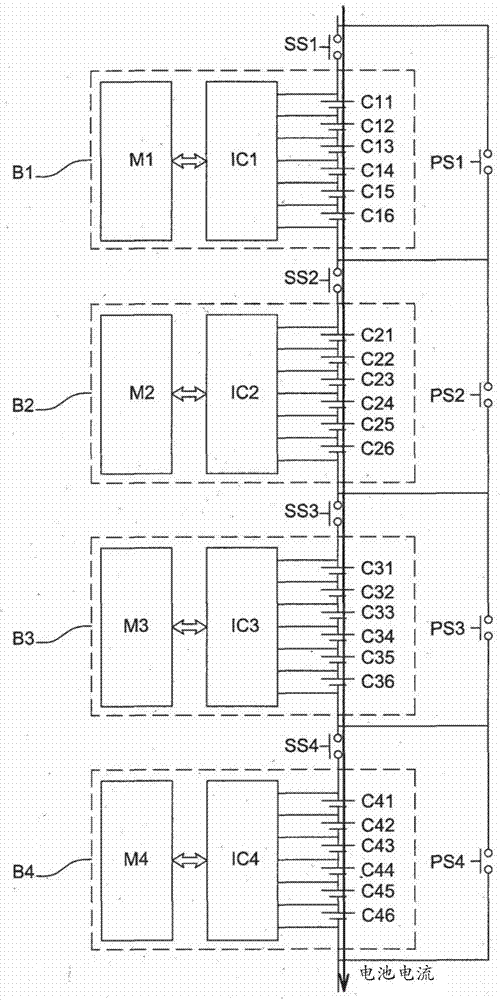
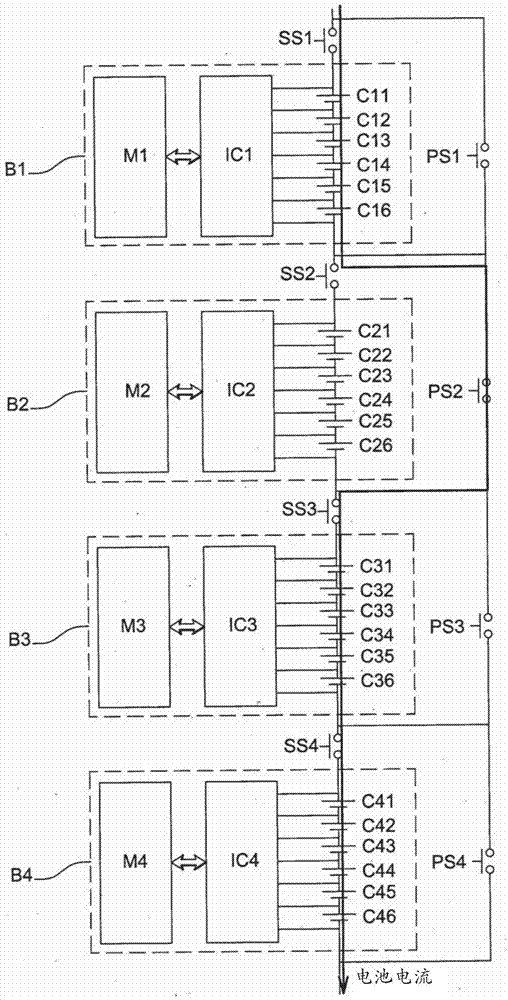
Method for balancing the charge and discharge level of a battery by switching its blocks of cells
ActiveCN104221244AQuickly balance battery levelsImprove energy efficiencyCharge equalisation circuitElectrical testingElectrical batteryCharge and discharge
The present invention relates to a device for balancing the overall levels of electrical charge in a plurality of blocks of cells in a battery. The blocks are able to be connected in a circuit during a charging phase during which the cells of the connected blocks accumulate charge, and during a discharging phase during which the cells of the connected blocks give back the charge in the form of an electrical current. The device comprises at least one series switch and one parallel switch. The series switch is able, when it is closed and the parallel switch is open, to connect a block to the circuit, in series with the other blocks, so that said block is connected during the charging and discharging phases.; The parallel switch is able, when it is closed and the series switch is open, to disconnect said block from the circuit, so that said block is disconnected if discharging disconnection conditions are met during the discharging phase or if charging disconnection conditions are met during the charging phase, said block furthermore comprising means for balancing locally the charge levels of its cells when it is disconnected.
Owner:RENAULT SA
Method and system for business flow management based on transfer station
ActiveCN1929440AReduce complexityGuarantee service continuityNetwork topologiesConnection managementFlow managementComputer science
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
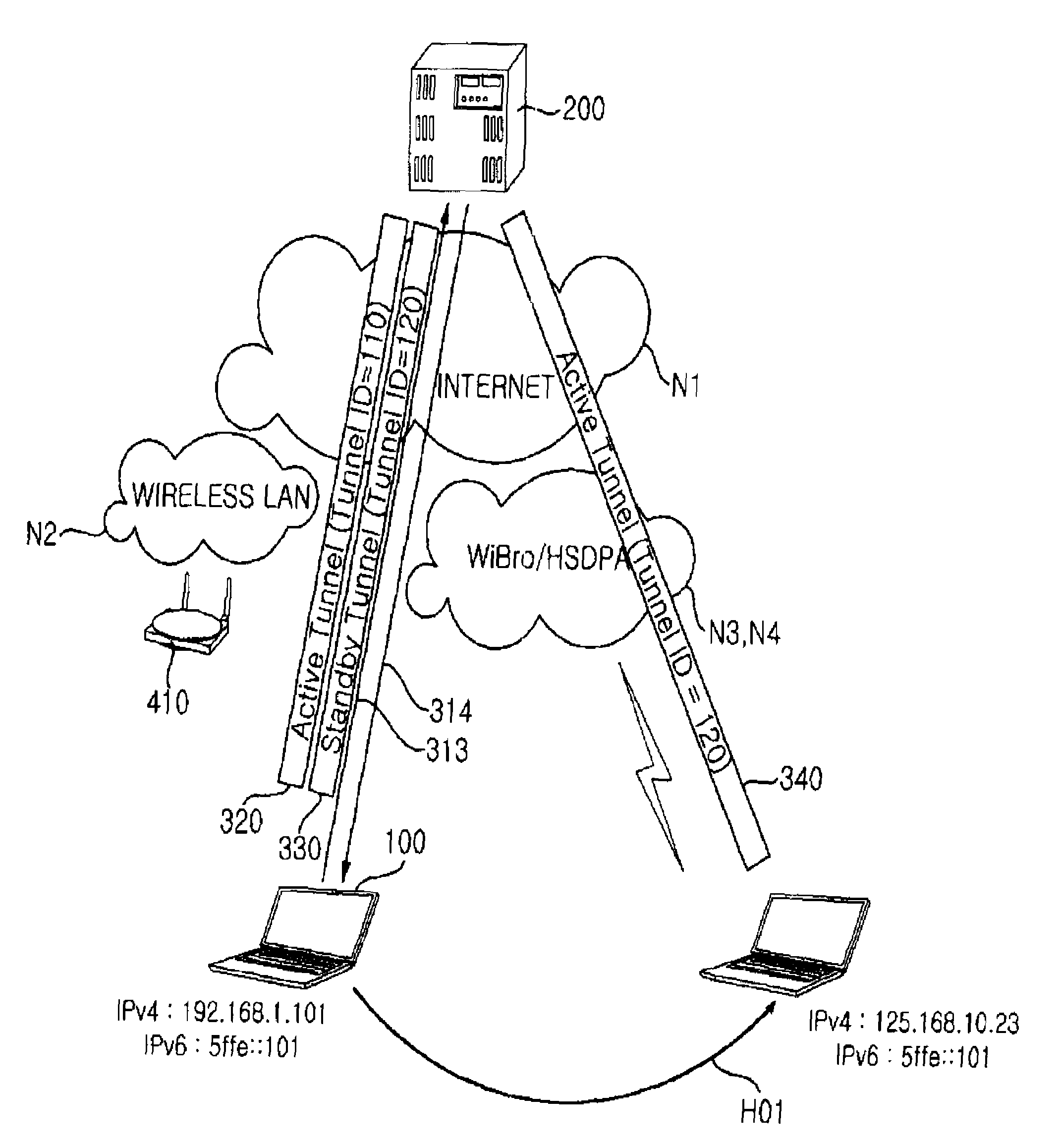
Apparatus and method of controlling seamless handover between heterogeneous networks based on IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling mechanism
InactiveUS8699466B2Low costGuarantee service continuityConnection managementWireless commuication servicesHeterogeneous networkData loss
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for controlling seamless handover between heterogeneous networks based on IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling. When IPv6 service is provided using tunneling in an IPv4 based network environment, handover of a mobile terminal between different networks is achieved through switching of an active tunnel and a standby tunnel, and thus handover between different networks is facilitated and data loss is prevented to secure continuity of service provided to the mobile terminal even when the mobile terminal hands over to a heterogeneous network.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
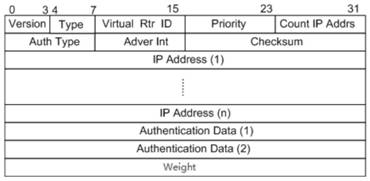
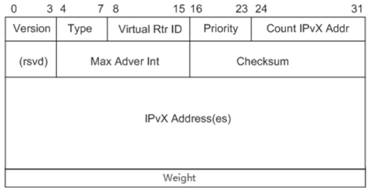
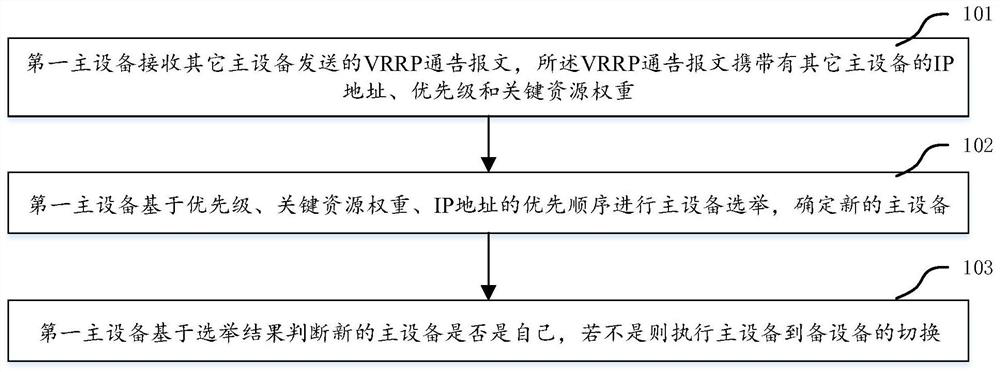
Main equipment election method and device and machine readable storage medium
ActiveCN111698158AReduce business impactGuarantee service continuityData switching networksEngineeringReal-time computing
The invention discloses a main equipment election method and device and a machine readable storage medium, which are used for reducing the influence of a VRRP protocol on service continuity in the main equipment election process. According to the invention, after the main equipment receives VRRP notification messages sent by other main equipment, the priorities, the key resource weights and the IPaddresses carried by the notification messages are compared, the main equipment election is carried out based on the priority sequence, and the new main equipment is determined. According to the method, the decision condition for judging the key resource weight on the main equipment is added in the main equipment election rule, and the main equipment state of the main equipment with the large keyresource weight is maintained preferentially, so that the influence on the current ongoing service is reduced, and the service continuity of client hosts or users is ensured as much as possible.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
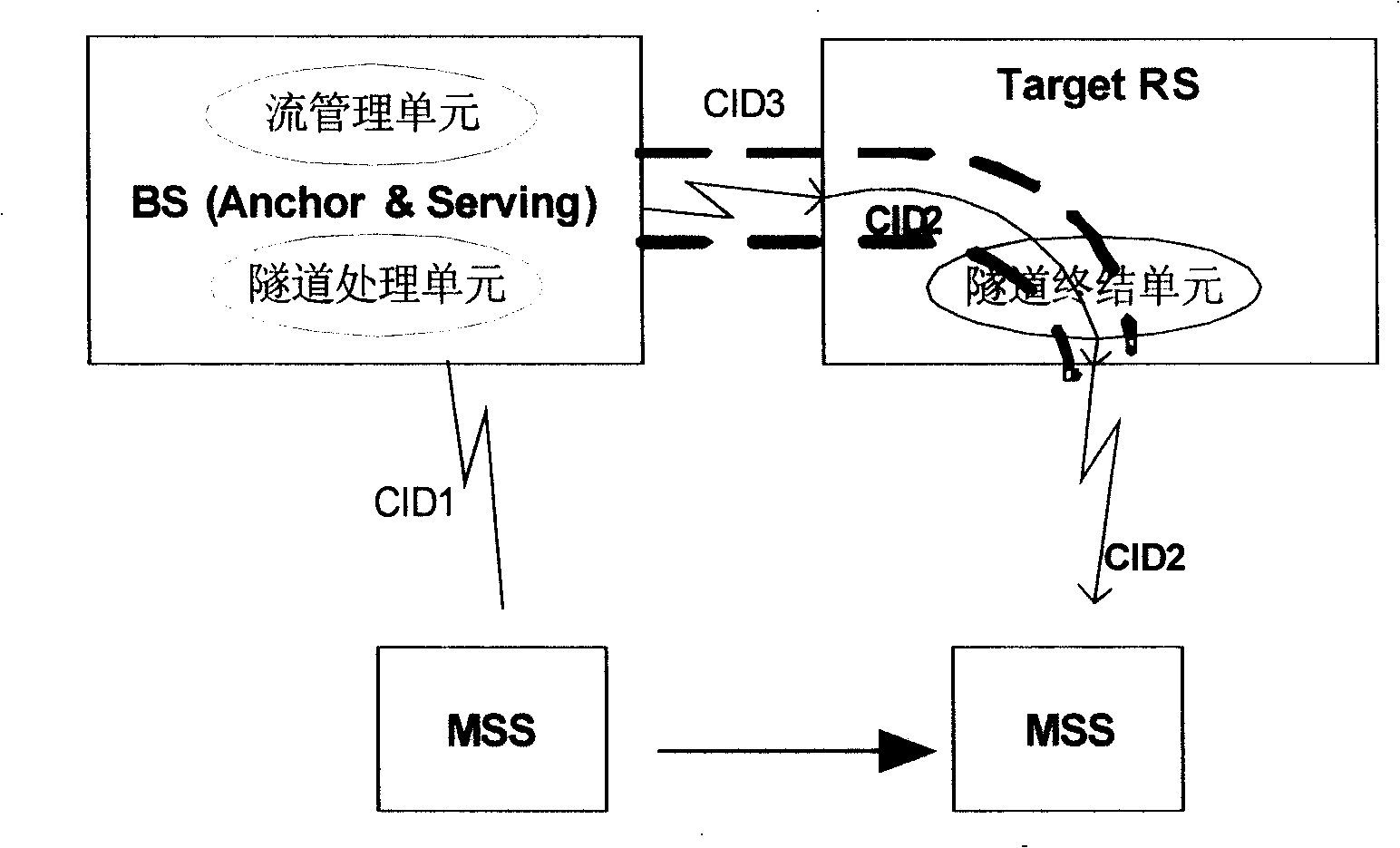
Method of based on tunnel proceed flow management and radio access relay system
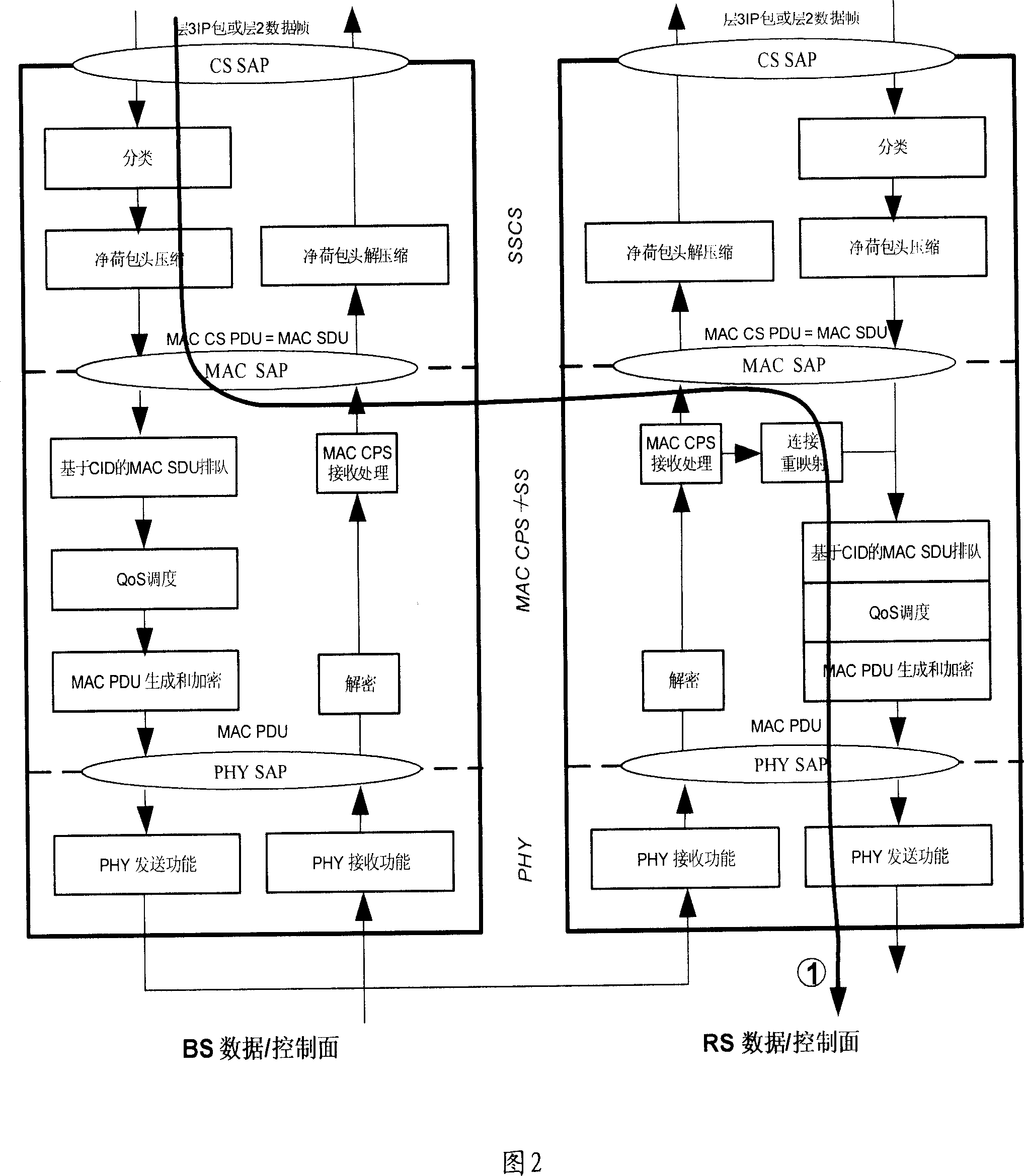
ActiveCN1956353ASimplify complexityReduce complexityRadio transmission for post communicationRadio relay systemsTransfer systemFlow management
This invention relates to a method for carrying out flow management based on tunnel and a radio access transfer system including: setting up layer communication path based on the tunnel between the data loading points of BS and those of RS belonging to MSS / SS, when BS determines that the received flow message needs the RS transfer and adds control information to it, it carries out tunnel package process and sends out the processed flow messages via said communication path, when said flow message arrives at the RS, which de-packages it and picks up said control information then to transmit it according to said control information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
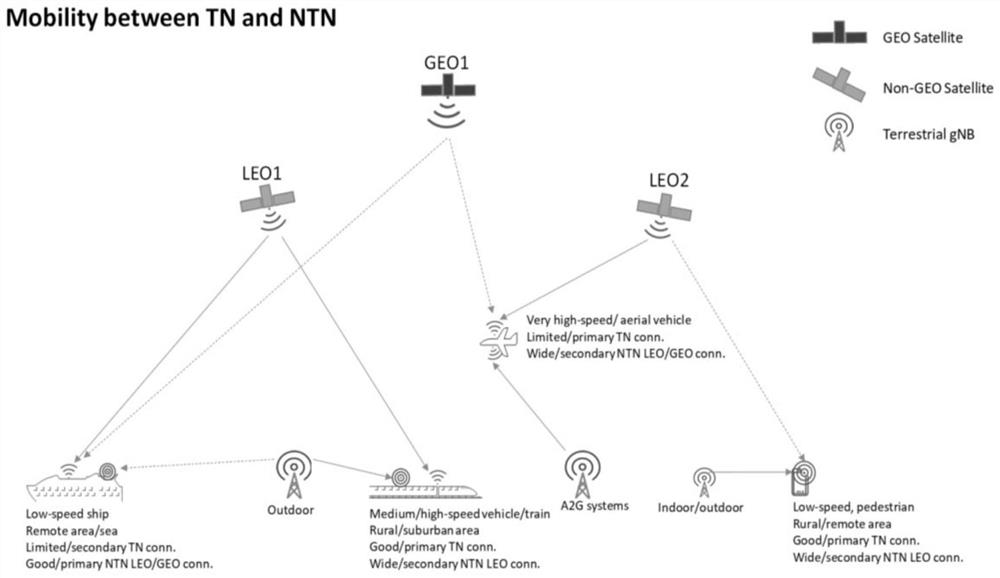
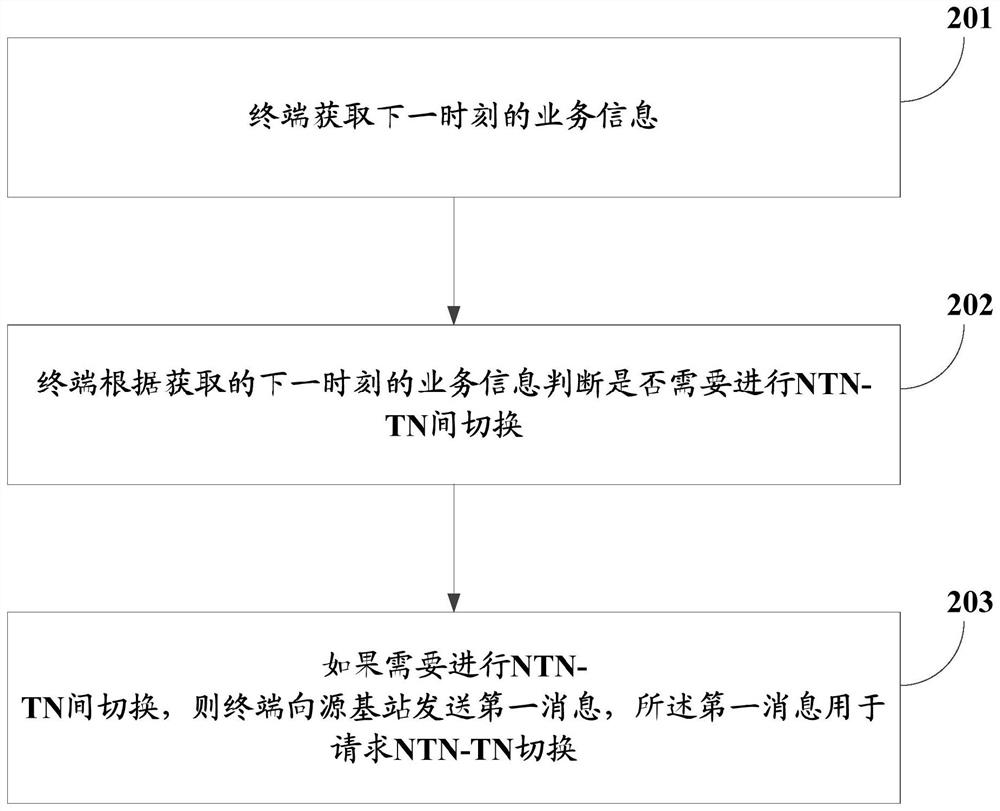
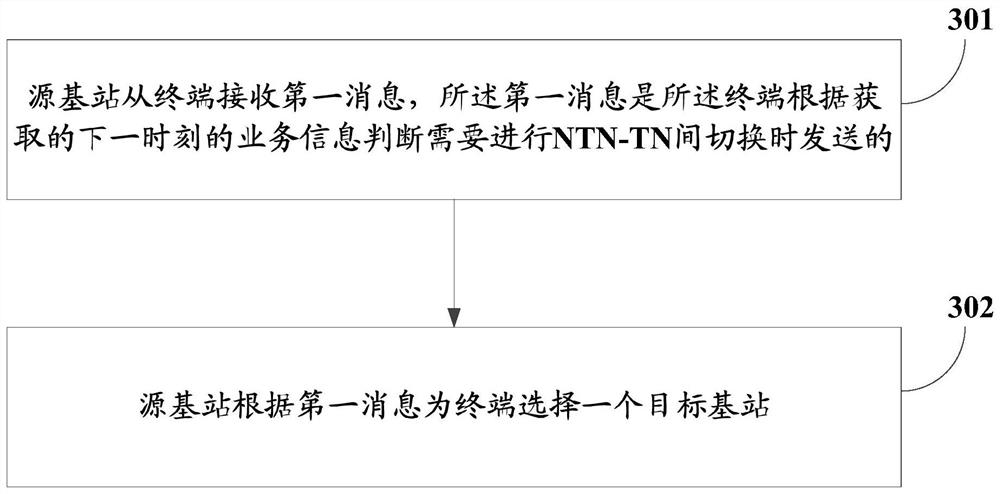
NTN-TN switching method, apparatus and device, and readable storage medium
PendingCN114245425AGuarantee service continuityWireless communicationRadio transmissionService informationProtocol Application
The embodiment of the invention provides an NTN-TN switching method and device, equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps that a terminal obtains service information of the next moment; the terminal judges whether switching between the NTN and the TN needs to be carried out or not according to the obtained service information at the next moment; and if the switching between the NTN and the TN needs to be carried out, the terminal sends a first message to a source base station, and the first message is used for requesting the switching between the NTN and the TN. In the embodiment of the invention, the switching process is no longer triggered only by the traditional RSRP or RSRQ measurement, and the NTN-TN switching is actively requested to the source base station through the service information of the next moment acquired by the terminal from the application layer; the source base station selects a target base station most suitable for switching for the terminal by comprehensively considering factors such as the moving speed and the moving direction of the terminal and the load condition, the moving speed and the moving direction of the candidate target base station, so that the service continuity of the switching process between the non-ground network and the ground network is ensured.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM LTD RES INST +1
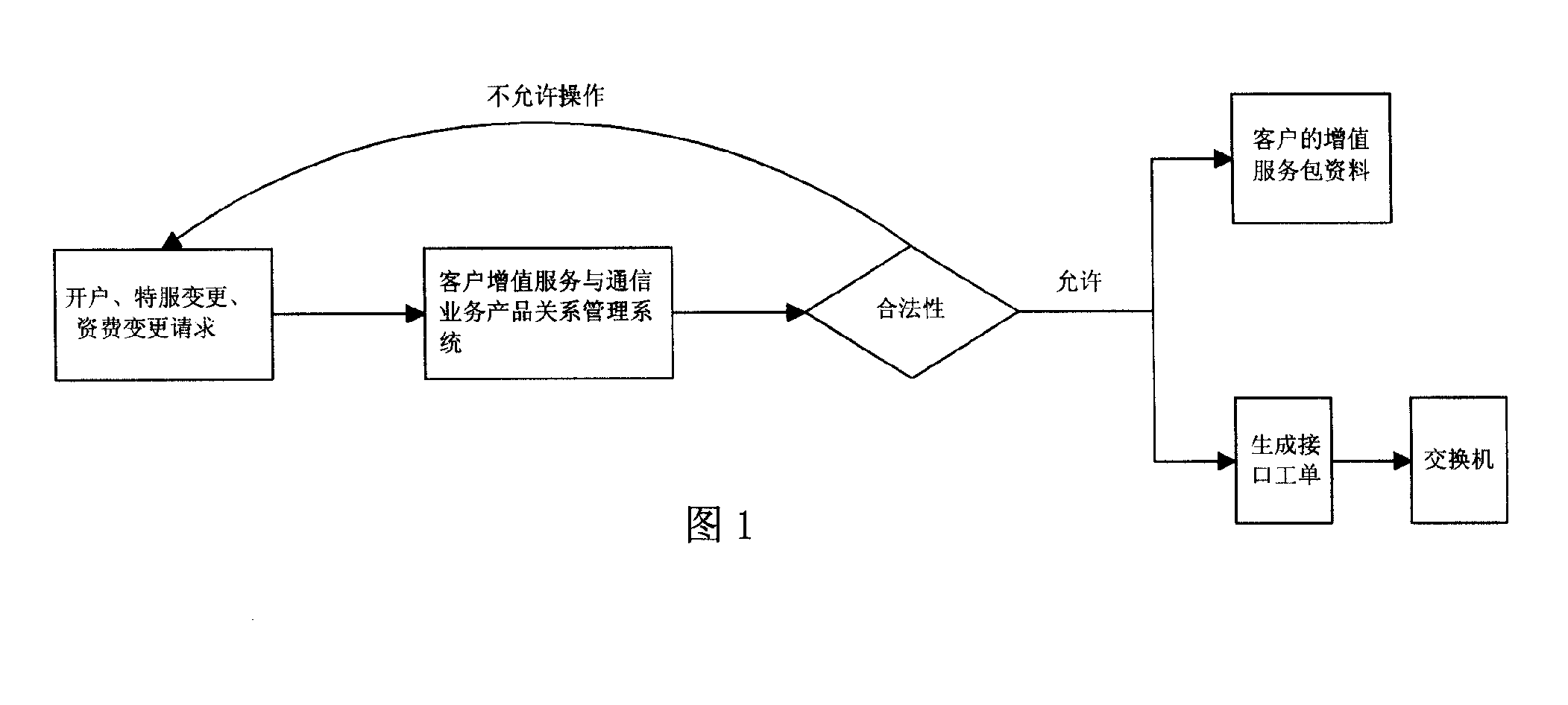
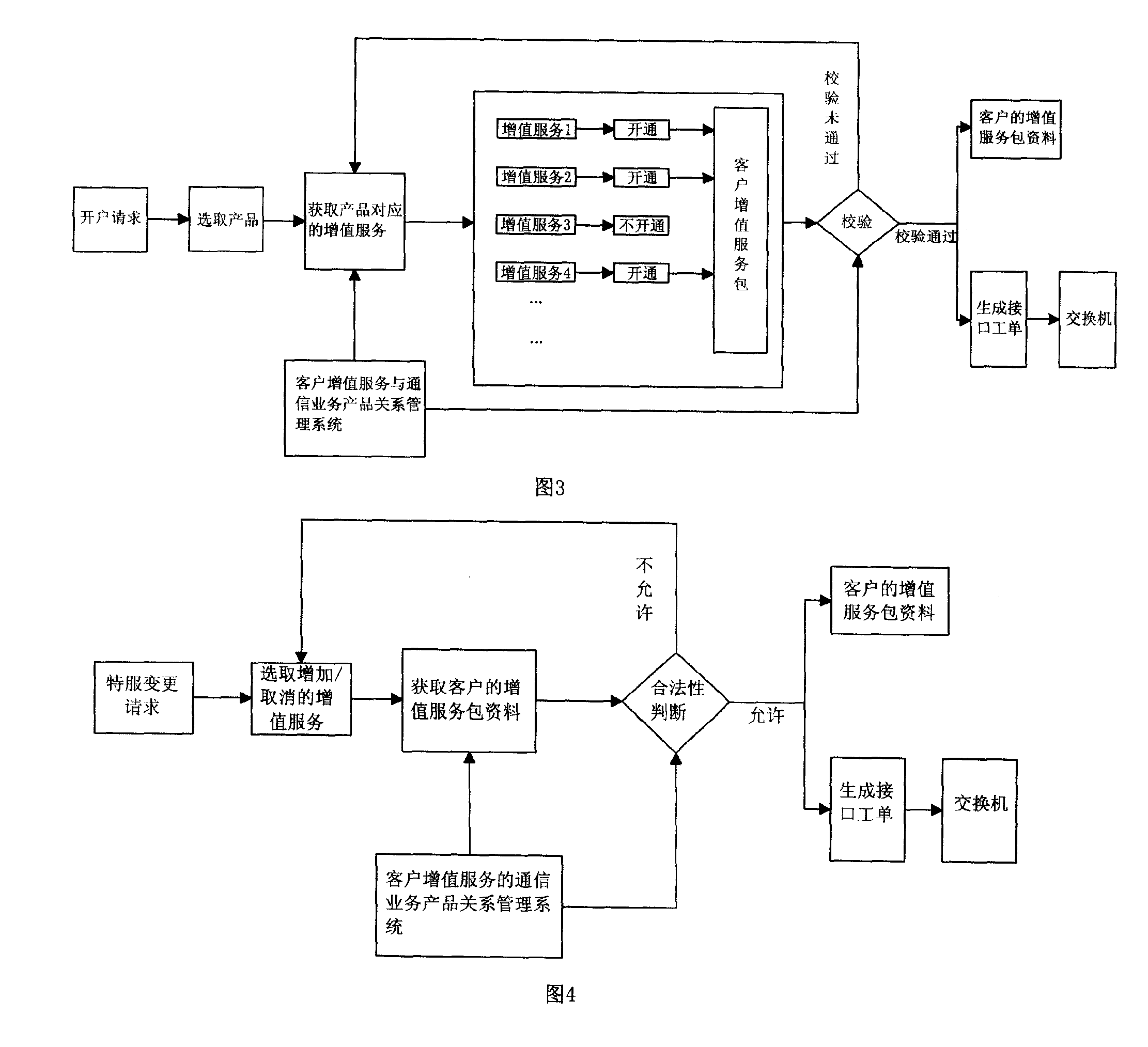
A method for guaranteeing service change continuity
ActiveCN101237606AGuarantee service continuityImprove satisfactionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSecurity arrangementCommunication industryDatabase
The invention discloses a method for ensuring the continuity in service change. The method is characterized in that: when a user applies for opening an account, special service change and tariff change, legitimacy verification of the application is carried out through a customer value-added service and communication service product relation management system; when the user application is legitimate, the user is allowed to change the corresponding value-added service packet data of a customer; when the user application is illegitimate, the user is forbidden. Through comparing the relation between a user change product and value-added service, the method ensures that customer communication service maintains continuous service relation with a use product before and after change, and realizes safe and effective safety management and customer service management of operating revenue capital in the communication industry; therefore, the method is particularly suitable to be used in customer service management of a communication enterprise.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SICHUAN
Device and method for simultaneous data transmission service in heterogeneous network
ActiveCN103493398AImprove data transfer speedGuarantee service continuityNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionData transmissionNetwork on
Disclosed is a method for simultaneous data transmission service in heterogeneous networks, comprising: a data splitting step in which a transmission device splits data into two or more partial data; a data transmission step in which the transmission device transmits, through two or more networks, the items of split partial data, each including access information for a virtual network; a data receiving step in which a receiving device receives each of items of the partial data through two or more networks; a first data generation step in which the receiving device generates data by combining the items of partial data on the basis of the virtual network access information accompanying each of the items of partial data received thereby; an abnormality occurrence confirmation step in which the transmission device confirms an occurrence of an abnormality in a particular network among the two or more networks; a data transmission switch step in which the transmission device transmits the partial data, which is transmitted through the particular network, and which includes the access information for the virtual network, is transmitted through another network among the two or more networks to which a switch has been made; a second data generation step in which the receiving device generates data by authenticating the virtual network access information for the partial data received after a switch has been made to another network. Thus, by enabling data transmission and reception through valid networks on the basis of the virtual network access information, even during disconnection from a particular network in a heterogeneous network, continuity of service is guaranteed, and consequently, an efficient and highly reliable simultaneous data transmission service in heterogeneous networks can be achieved.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
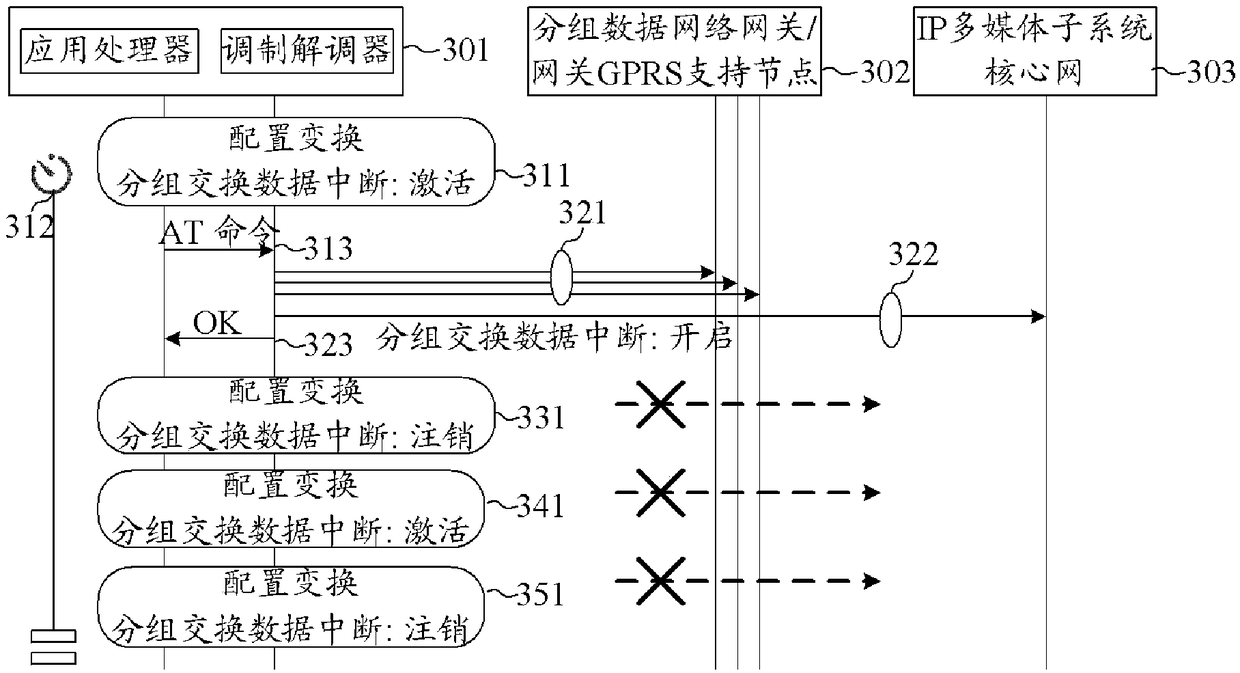
Enhanced ps domain data-off mechanism
ActiveCN109076089AAvoid transmissionBlocking can block transmissionAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesData packEngineering
Solutions are proposed to facilitate the support of 3GPP PS_Data_Off feature. The PS_Data_Off feature prevents transport via 3GPP access of all IP packets except those related to 3GPP PS_Data_Off Exempt Services. In one example, signaling storms due to frequent PS_Data_Off reconfiguration are prevented. In another example, for multi-SIM devices and for devices that supporting WiFi access, UE reconfigures the PS_Data_Off feature upon a triggering condition is satisfied. In yet another example, upon status change of PS_Data_Off feature, UE initiates RAT change to improve performance, to reduce power consumption and cost, and to maintain service continuity. Furthermore, new AT commands and parameters are introduced to enable the PS_Data_Off feature.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Enhanced ps domain data-off mechanism
ActiveCN109076333AAvoid transmissionBlocking can block transmissionAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesData packPacket switched
Solutions are proposed to facilitate the support of 3GPP PS_Data_Off feature. The PS_Data_Off feature prevents transport via 3GPP access of all IP packets except those related to 3GPP PS_Data_Off Exempt Services. In one example, signaling storms due to frequent PS_Data_Off reconfiguration are prevented. In another example, for multi-SIM devices and for devices that supporting WiFi access, UE reconfigures the PS_Data_Off feature upon a triggering condition is satisfied. In yet another example, upon status change of PS_Data_Off feature, UE initiates RAT change to improve performance, to reduce power consumption and cost, and to maintain service continuity. Furthermore, new AT commands and parameters are introduced to enable the PS_Data_Off feature.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
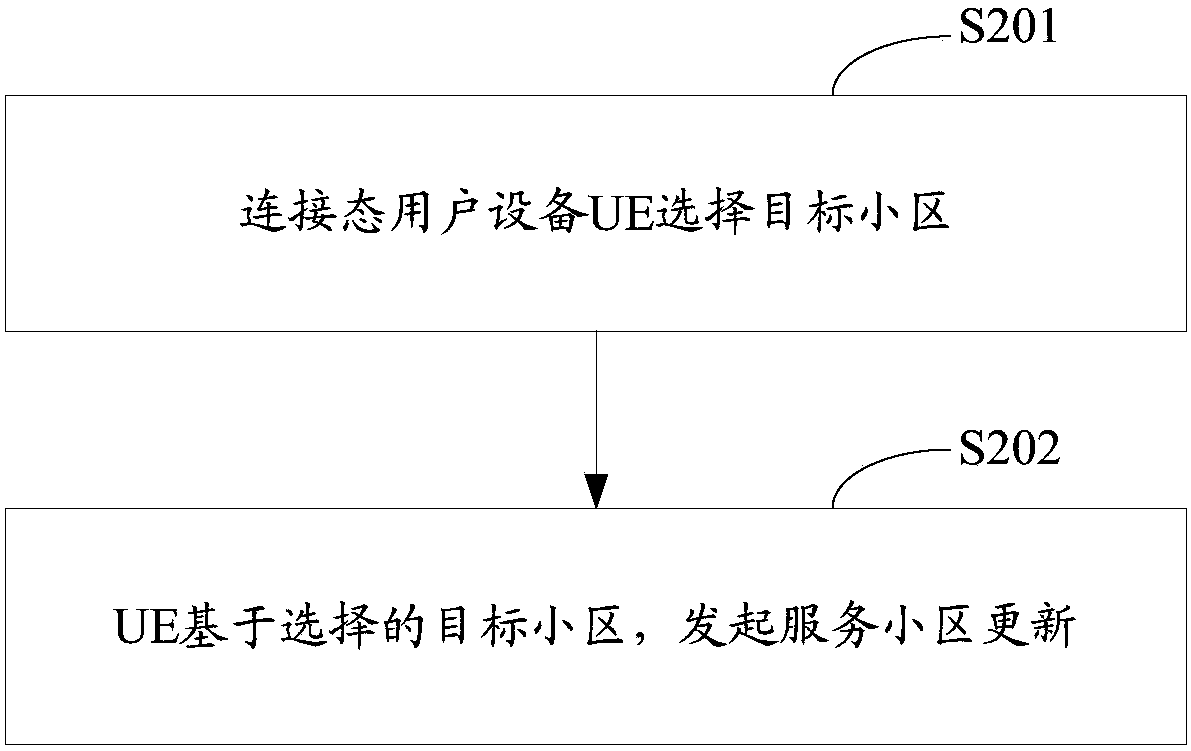
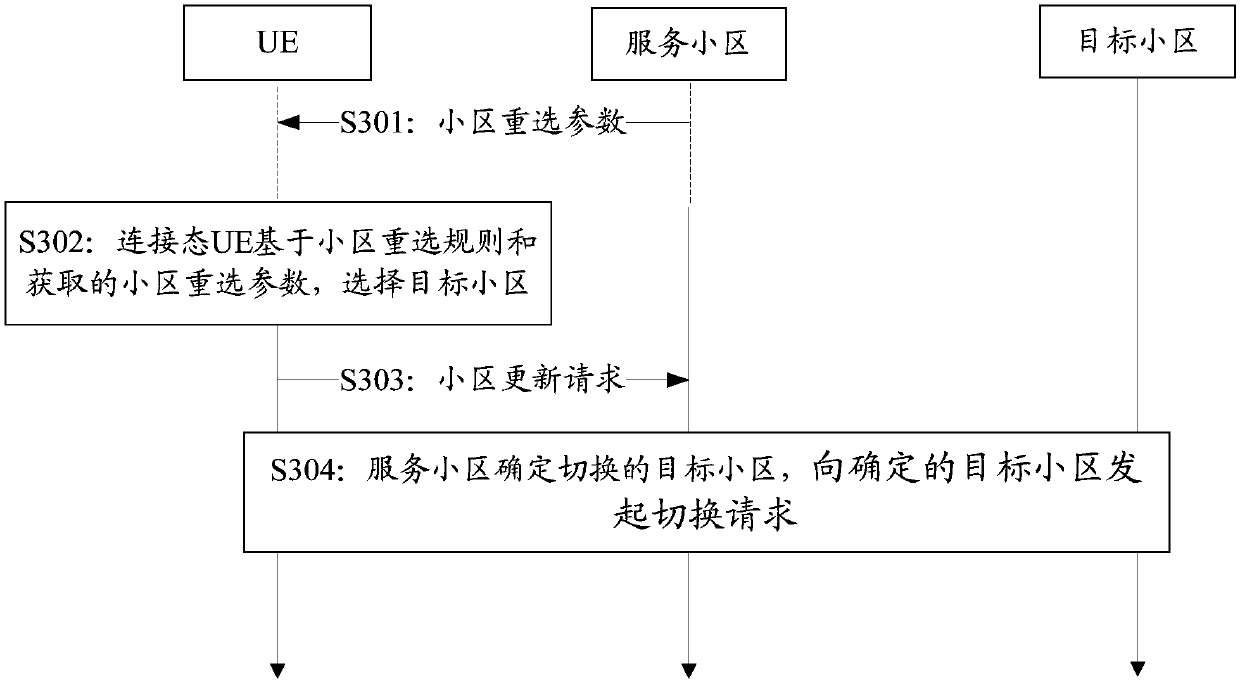
Serving cell updating method and device
ActiveCN107734542AReduce power consumptionGuarantee service continuityPower managementHigh level techniquesTelecommunicationsCell based
The invention relates to the technical field of communication, and particularly relates to a serving cell updating method and device. The method and device supports service continuity while UE moves,and lowers UE power consumption. The serving cell updating method comprises the steps that UE in a connection state selects a target cell; and the UE initiates updating of a serving cell based on theselected target cell. According to the method, the UE in the connection state selects the target cell independently, and initiates updating of the serving cell based on the selected target cell. The UE does not need to report measurement results for many times, so that the service continuity is maintained, and the UP power consumption is lowered.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
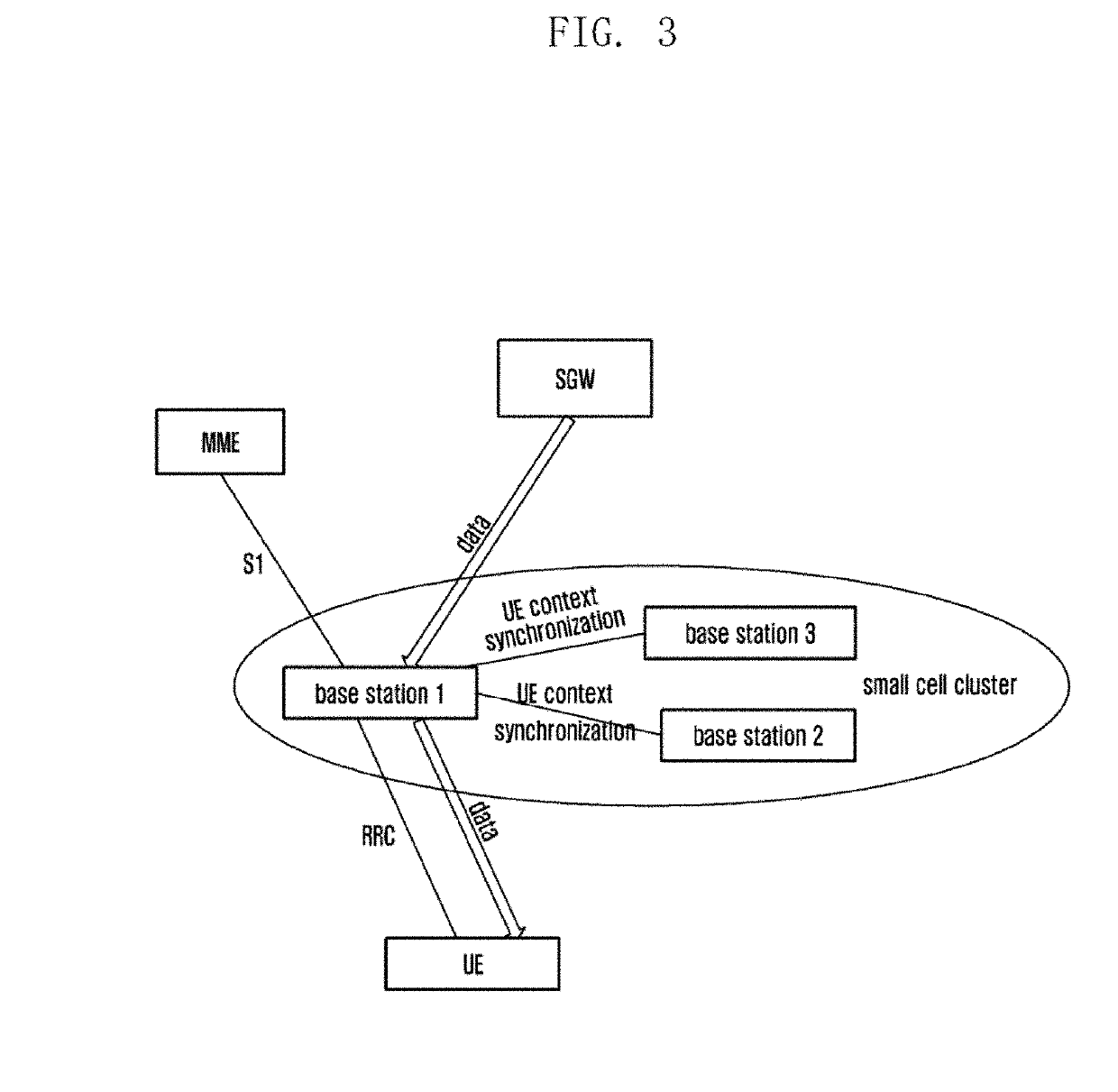
Method and system for supporting fast recovery of user equipment
ActiveUS20190159079A1Promote recoveryAvoid data lossNetwork topologiesConnection managementSmall cellData loss
A method for supporting fast recovery of a User Equipment (UE) includes performing, by a serving base station, UE context synchronization for one or more other base stations in a related small cell cluster when a UE accesses the serving base station, performing, by a base station that the UE performs a radio resource control (RRC) connection re-establishment, the RRC connection re-establishment for the UE according to UE context saved in a synchronization process. The present also discloses another method and system for supporting UE fast recovery. By applying the technical solution disclosed by the present disclosure, when the UE moves in a small cell scenario, the UE can be recovered quickly in the case of a failure, so as to avoid the UE returns to an idle mode, avoid data loss, guarantee business continuity, and improve UE experience.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
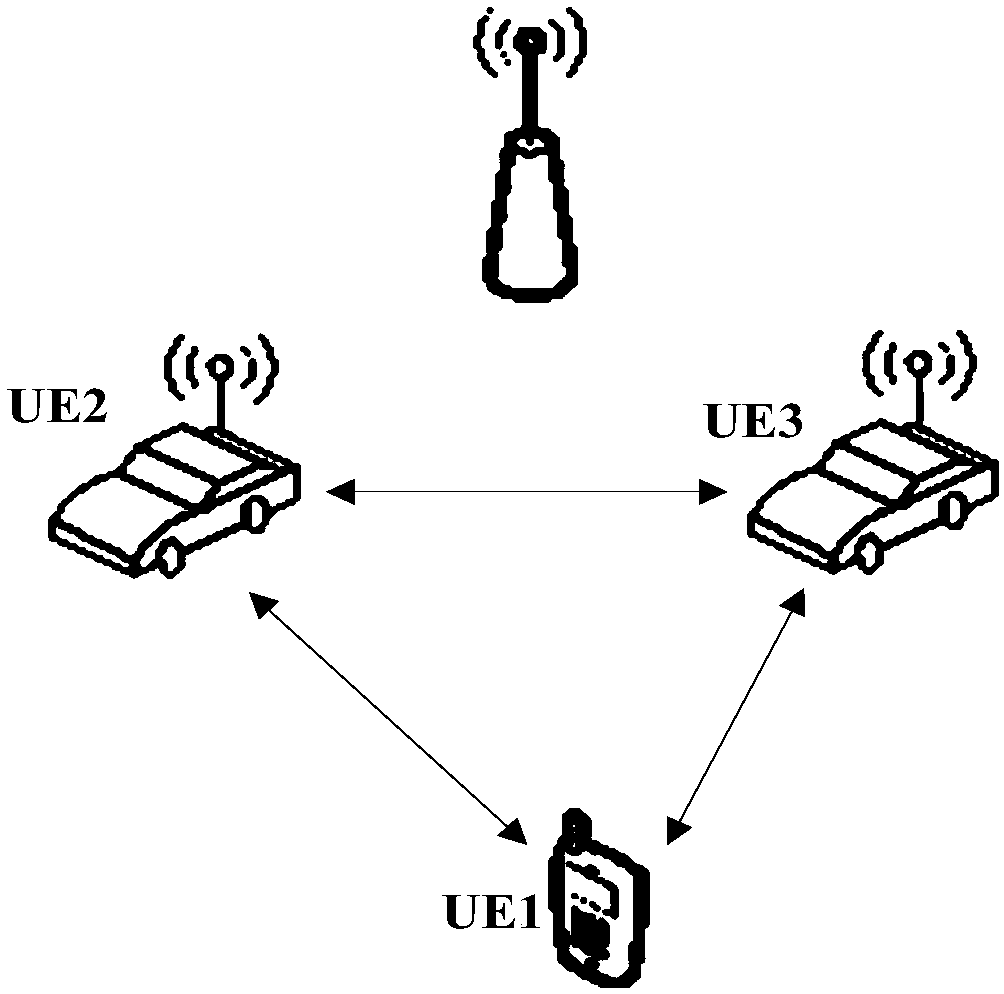
Method and apparatus for communication between user equipments
ActiveCN109804612BGuarantee service continuityNetwork traffic/resource managementParticular environment based servicesTelecommunicationsIp address
The present invention provides a method and device for inter-user equipment (user equipment, UE) communication. The method includes: receiving a data packet from a first UE, the data packet including data and an IP address of a second UE; obtaining a context record of the second UE, the context record including The IP address of the second user plane and the identifier of the second user plane; according to the identifier of the second user plane, the data packet is sent to the second user plane, so that the second user plane can send The data packet is sent to the second UE. By using the solution provided in the method, when a cross-UP communication scenario occurs, the UE can still communicate normally and maintain service continuity.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
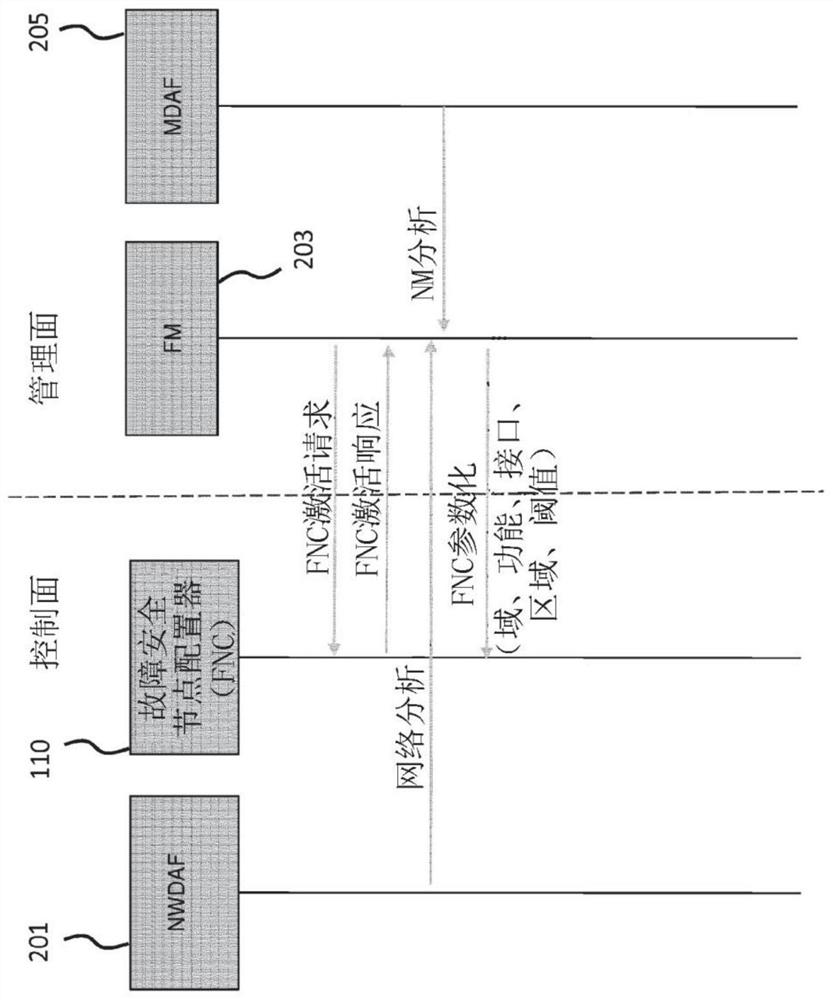
Devices and methods for service continuity in a 5g communication network
ActiveCN113169763AGuarantee service continuityFast and reliable failure recoverySite diversityNetwork controlEngineering
The invention relates to a network control entity for a wireless communication network, wherein the wireless communication network comprises a plurality of network nodes, in particular base stations, wherein each network node defines a set of functions, in particular protocol functions, to communicate with a user equipment (UE) of the wireless communication network. The network control entity is adapted to: select for a first network node, that communicates with the UE, a second network node; configure the second network node to concurrently process at least a subset of functions of the first network node (103) for communicating with the UE; and trigger the second network node to provide the subset of functions to the UE.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
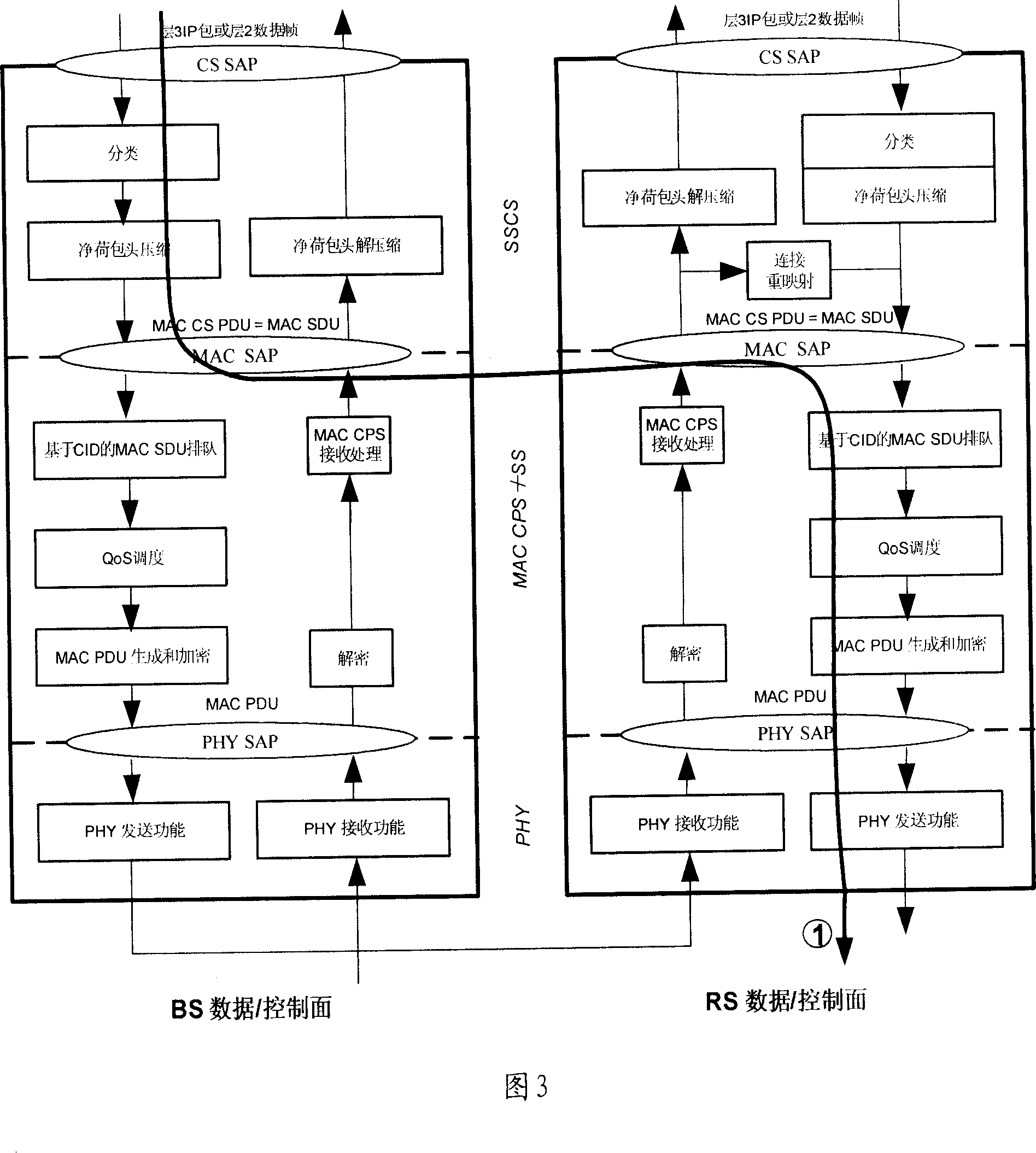
Method of flow management based on tunnel and radio access relay system
ActiveCN1956353BSimplify complexityReduce complexityRadio transmission for post communicationRadio relay systemsRound complexityTransfer system
This invention relates to a method for carrying out flow management based on tunnel and a radio access transfer system including: setting up layer communication path based on the tunnel between the data loading points of BS and those of RS belonging to MSS / SS, when BS determines that the received flow message needs the RS transfer and adds control information to it, it carries out tunnel package process and sends out the processed flow messages via said communication path, when said flow message arrives at the RS, which de-packages it and picks up said control information then to transmit it according to said control information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method of balancing charge and discharge levels of a battery by switching blocks of cells of the battery
ActiveCN104221244BQuickly balance battery levelsGuarantee service continuityCharge equalisation circuitElectrical testingElectrical batteryHemt circuits
The present invention relates to an apparatus for balancing the overall charge level among a plurality of battery cell blocks in a battery. The blocks can be connected to a circuit during a charging phase, during which the battery cells of the connected blocks accumulate charge and during a discharging phase, where the battery cells of the connected blocks The unit returns the charge in the form of current. The device includes at least one series switch and one parallel switch. This series switch is able to connect one block into the circuit in series with the other blocks when it is closed and when the parallel switch is open, so that the blocks are energized during the charging and discharging phases. connected. This parallel switch can remove the block from the circuit when it is closed and when the series switch is open, so that if the discharge disconnection condition is met during the discharge phase or if it is met during the charging process The bank is disconnected when a charging disconnect condition is met, and the bank further includes means for locally balancing the charge levels of its cells while being disconnected.
Owner:RENAULT SA
Method and apparatus for handing over device
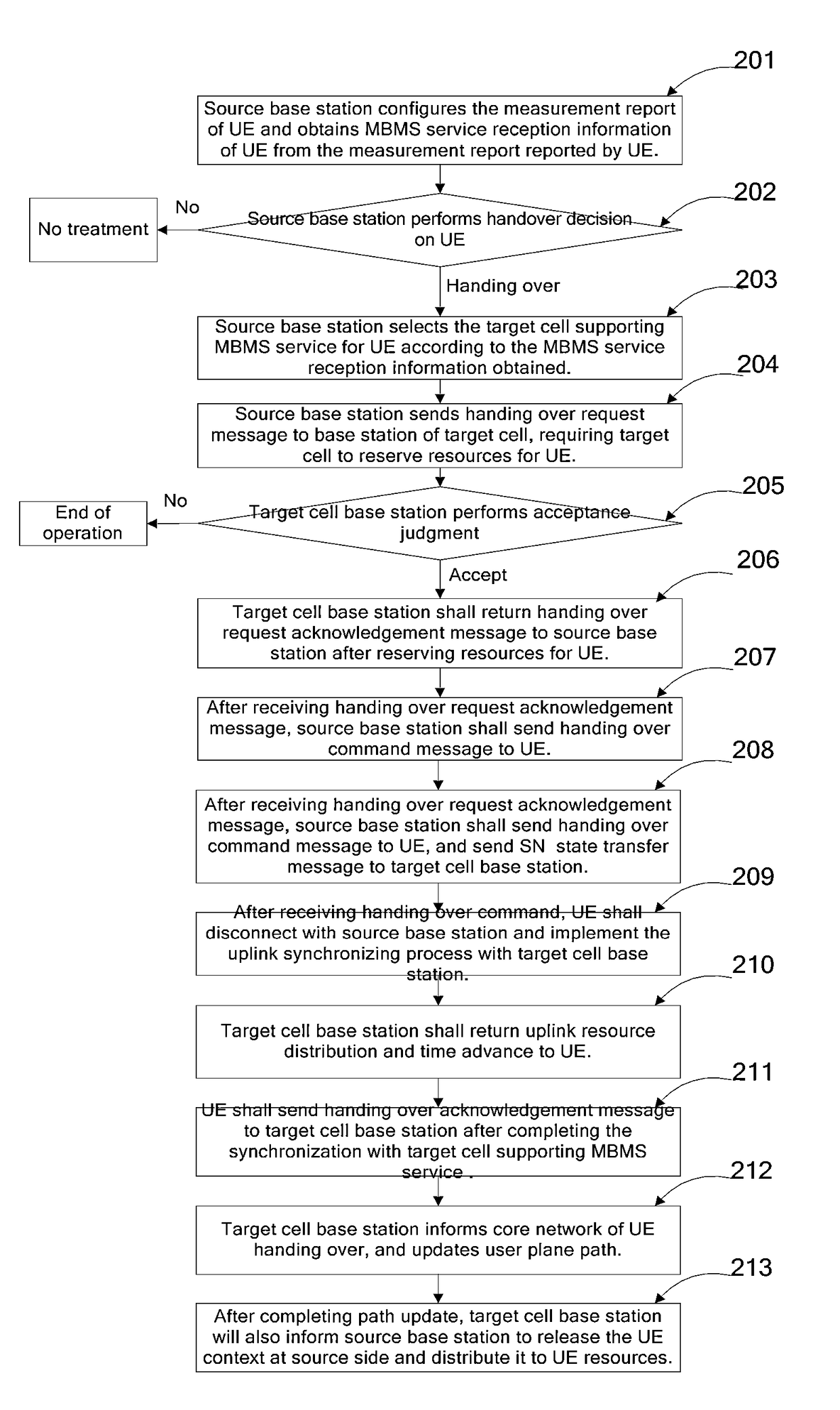
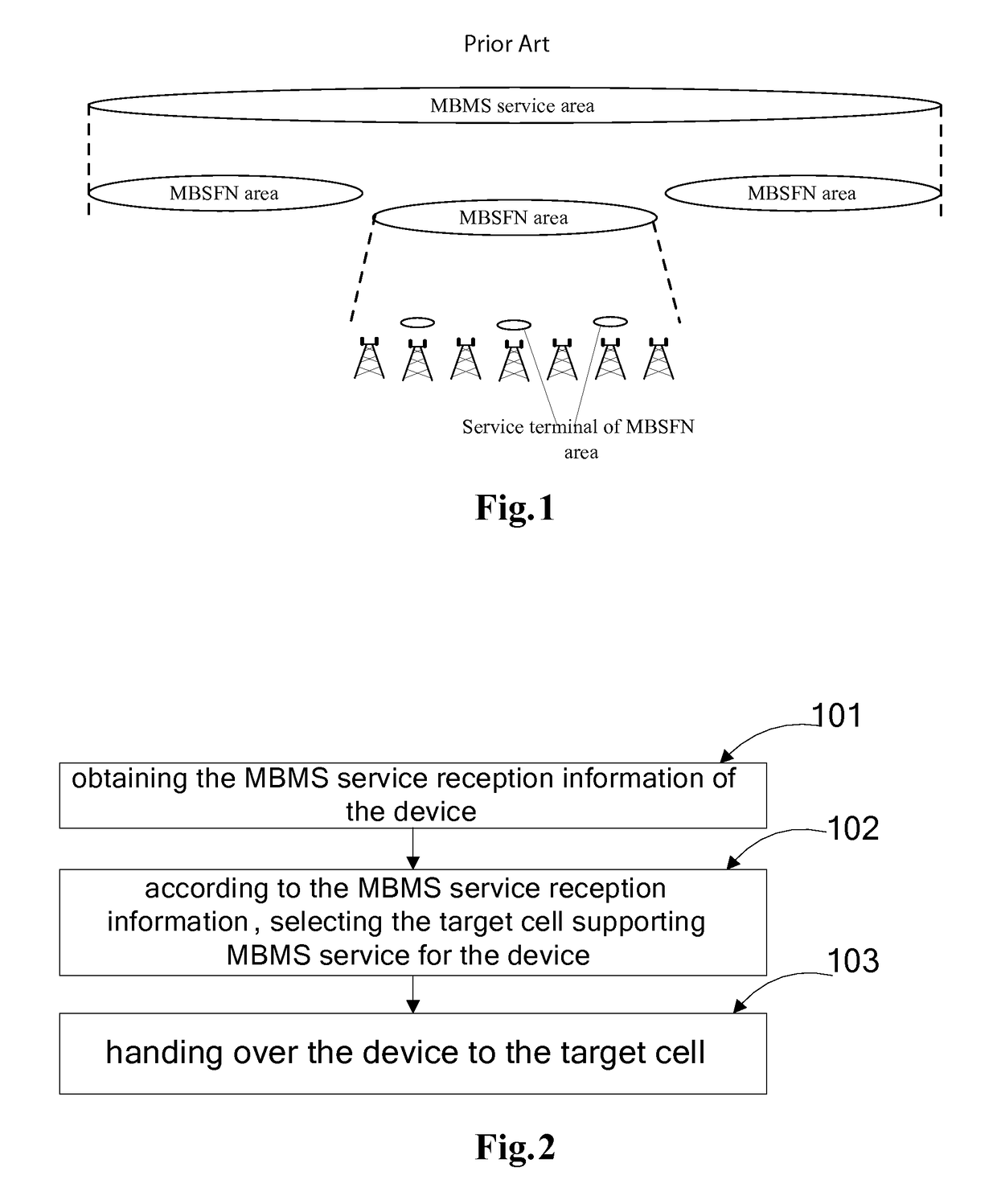
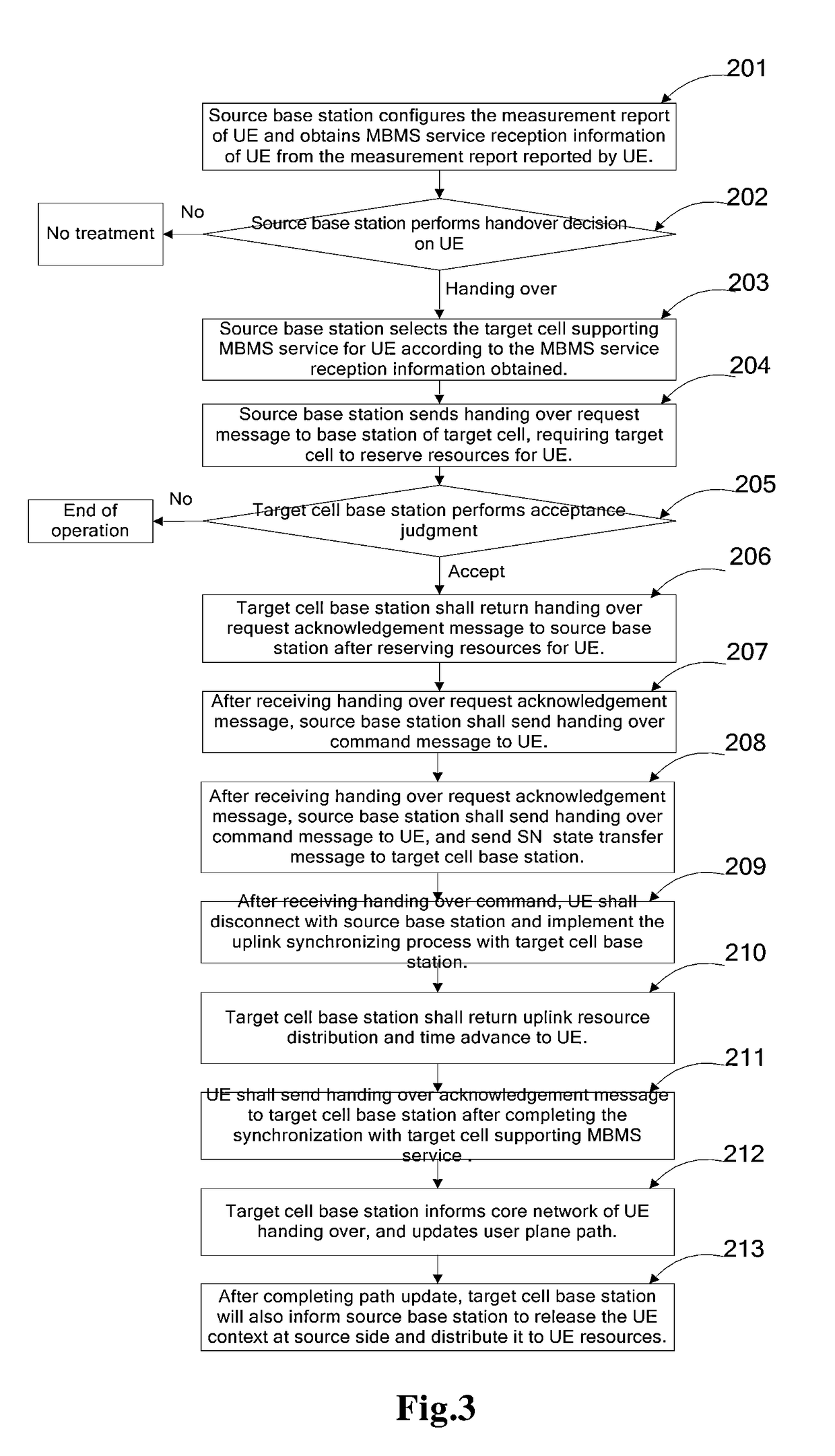
ActiveUS10057822B2Guarantee service continuityBroadcast service distributionRadio transmissionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceEngineering
Disclosed in the present invention are a method and apparatus for handing over device, and belongs to the field of mobile communication. The method comprises: obtaining the Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS) service reception information of the device; according to the MBMS service reception information, selecting a target cell supporting the MBMS service for the device; handing over the device to the target cell. The apparatus comprises: an acquiring module, for obtaining the MBMS service reception information of the device; a selection module, for selecting a target cell supporting the MBMS service for the device according to the MBMS service reception information; a handing over module, for handing over the device to the target cell. By the implementation of the technical solution that selecting a target cell supporting the MBMS service for the device according to the MBMS service reception information, and switching the device to the target cell, the present invention guarantees the continuity of the MBMS service during the handover process of the device.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Service call session control function entity backup method and system thereof
ActiveCN100391167CGuarantee service continuityImprove experienceData switching networksSession controlDynamic data
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
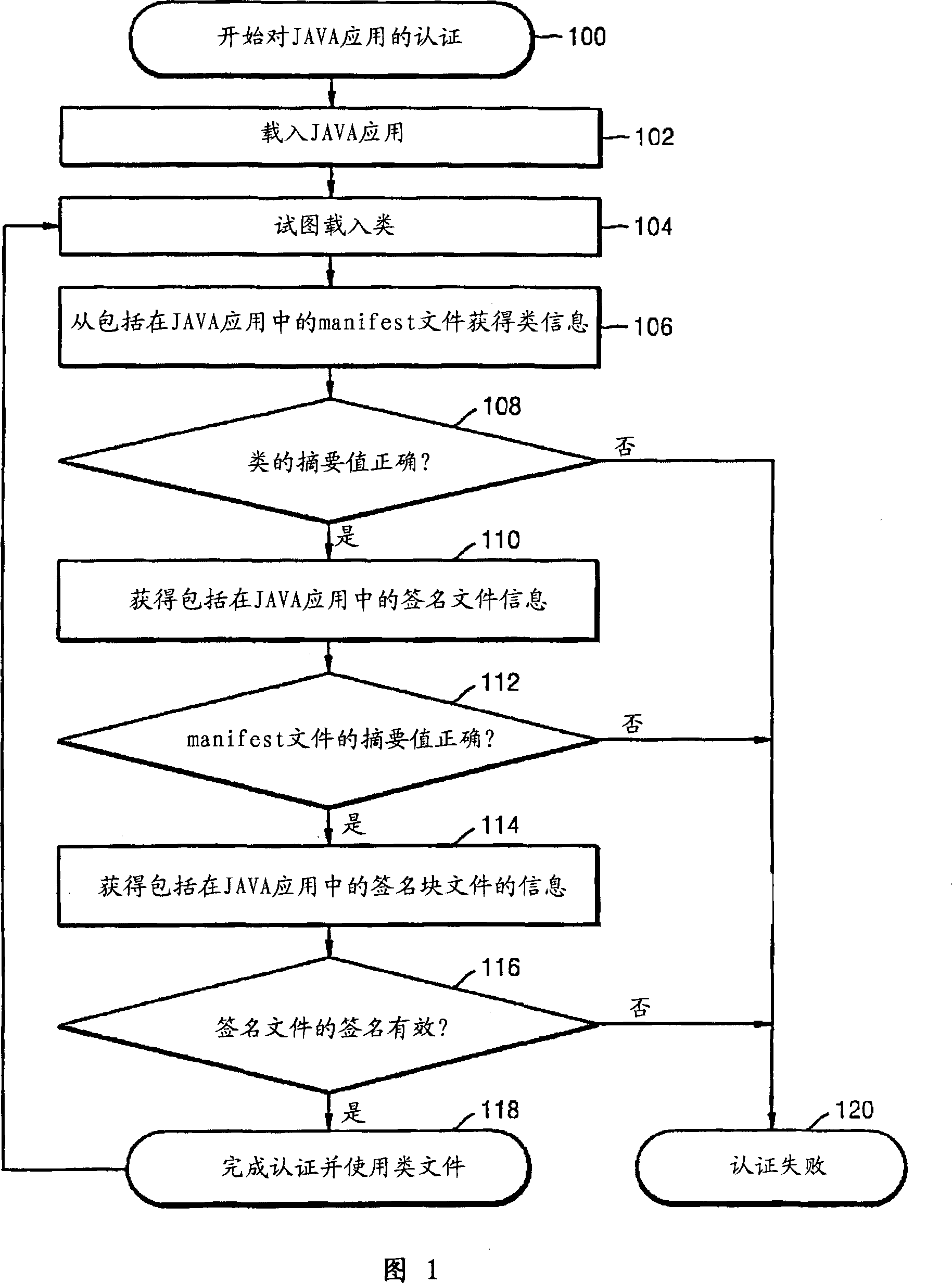
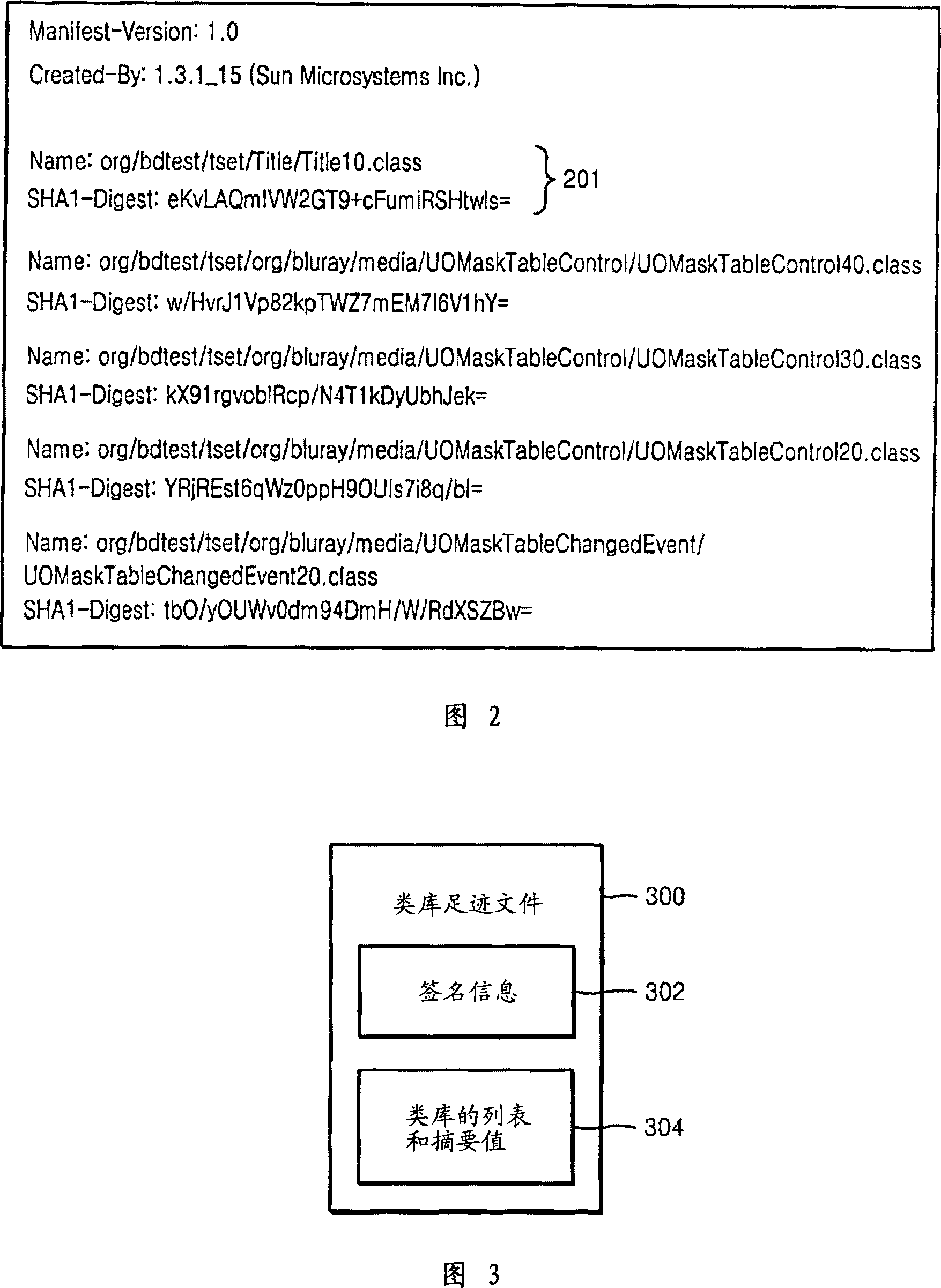
Class library footprint file and JAVA application authentication method using the same
InactiveCN101218564AImprove Feasible SecurityEnsure reliable certificationMultiprogramming arrangementsDigital data protectionAuthentication informationFootprint
A class library footprint file for authenticating a dynamically loaded class library during the execution of a JAVA application and a JAVA application authentication method using the class library footprint file are provided. The class library footprint file includes: authentication information for verifying the integrity of one or more class libraries used by the JAVA application before the JAVA application is executed. A list of class libraries to be authenticated is provided, in advance, to a JAVA application.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
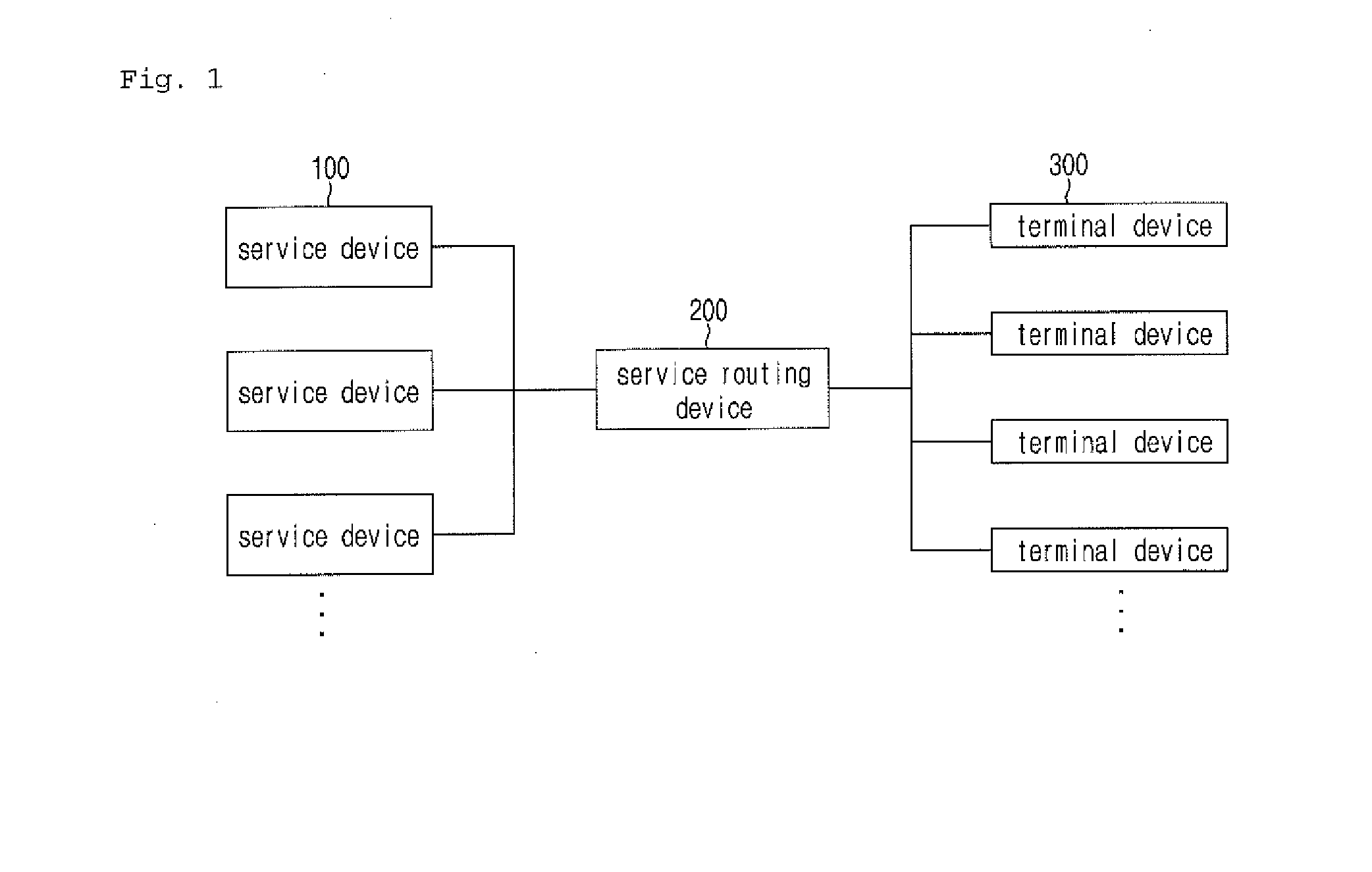
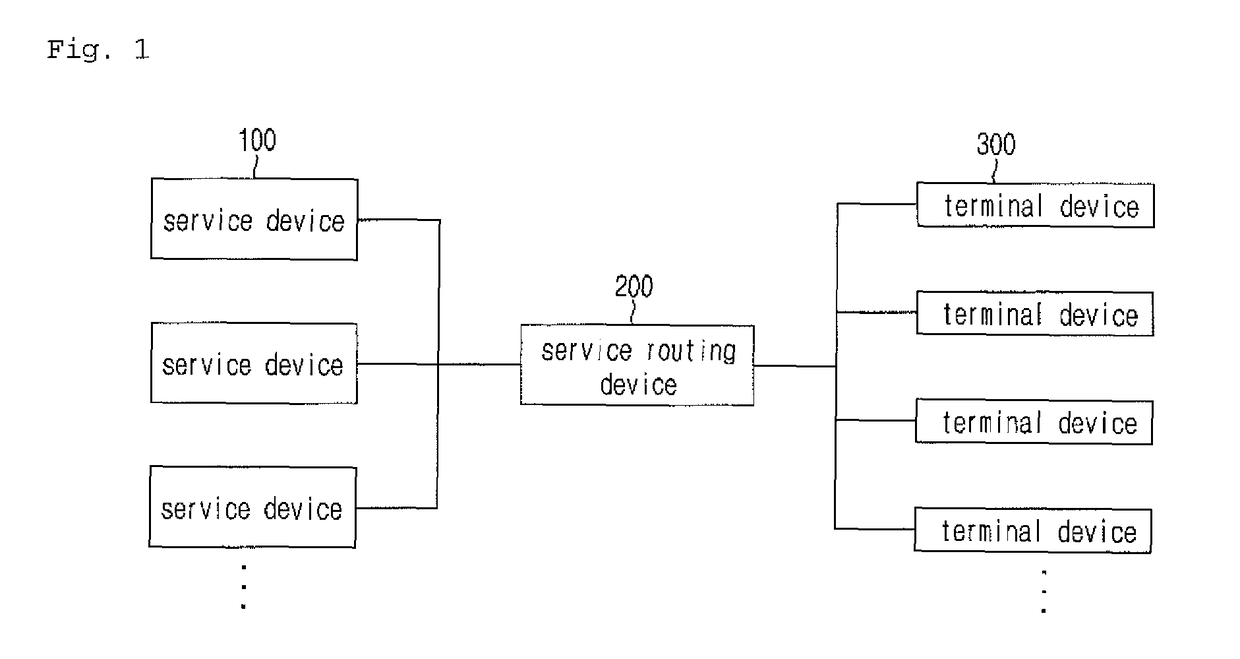
System for providing cloud streaming-based service menu and method for same
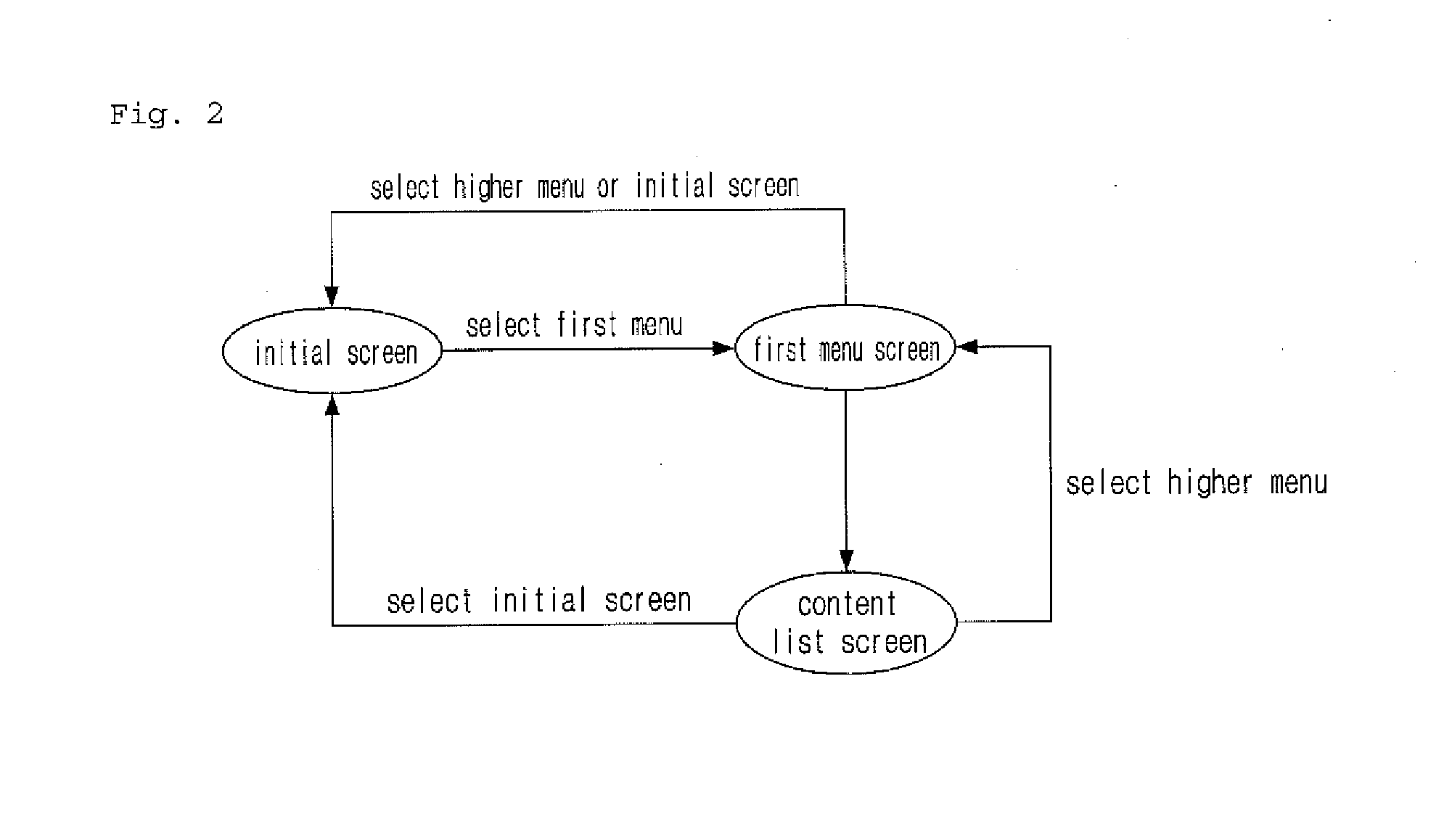
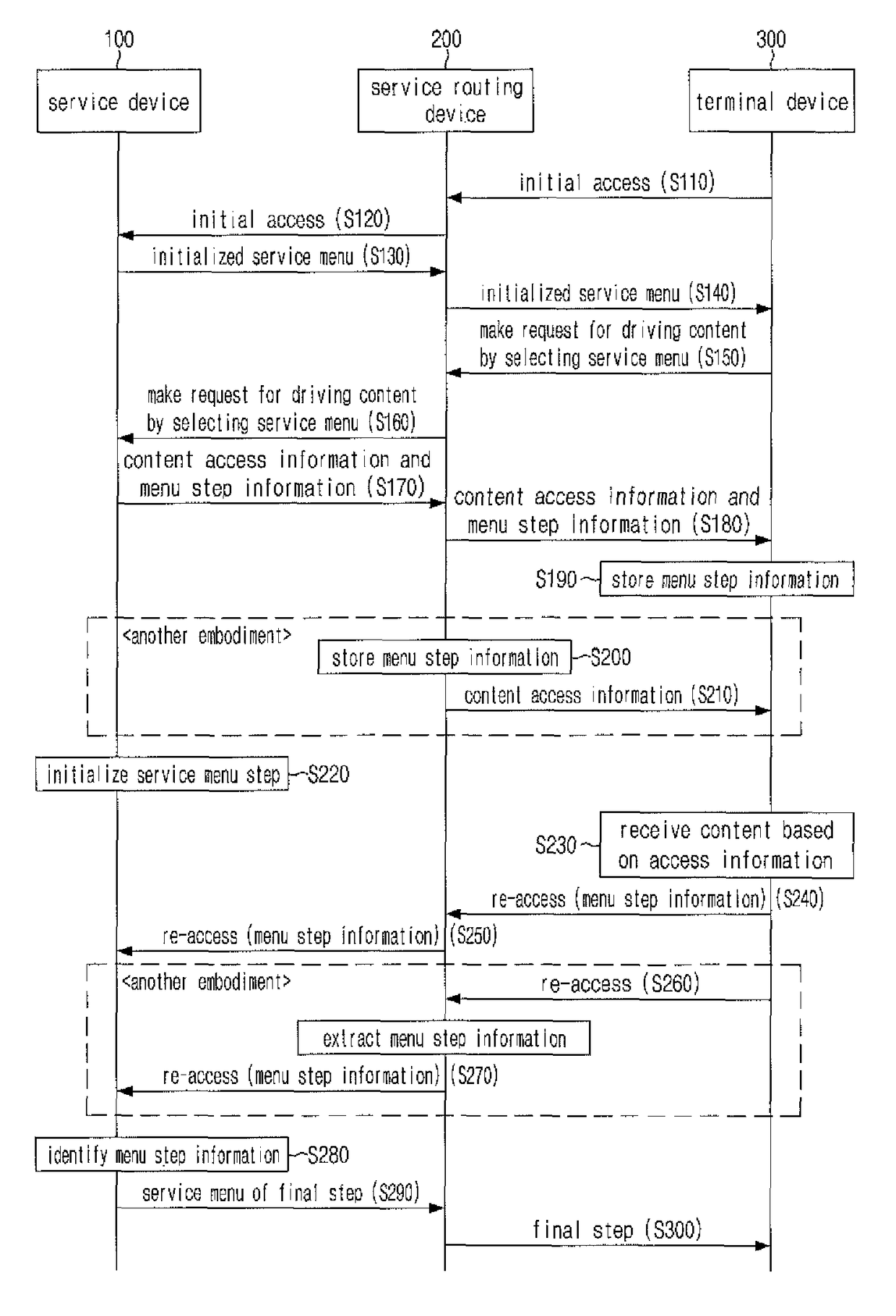
ActiveUS20150074537A1Guarantee service continuityData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsTerminal equipment
A system for providing a cloud streaming-based service menu, a method and a terminal device. The terminal device selects a particular step in a step-by-step service menu to make a request for driving a content and the service device, in response to the request, provides content access information and menu step information corresponding to the particular step selected and initializes a step in the step-by-step service menu provided to the terminal device for switching a state of the service menu to a state in which an additional access of another terminal device is possible, so as to provide the initialized step-by-step service menu to another initially accessed terminal device. When the terminal device re-accesses, the service device will provide the service menu of the particular step corresponding to the menu step information to another accessed terminal device.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
System for providing cloud streaming-based service menu and method for same
ActiveUS9817550B2Guarantee service continuityData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
A system for providing a cloud streaming-based service menu, a method and a terminal device. The terminal device selects a particular step in a step-by-step service menu to make a request for driving a content and the service device, in response to the request, provides content access information and menu step information corresponding to the particular step selected and initializes a step in the step-by-step service menu provided to the terminal device for switching a state of the service menu to a state in which an additional access of another terminal device is possible, so as to provide the initialized step-by-step service menu to another initially accessed terminal device. When the terminal device re-accesses, the service device will provide the service menu of the particular step corresponding to the menu step information to another accessed terminal device.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
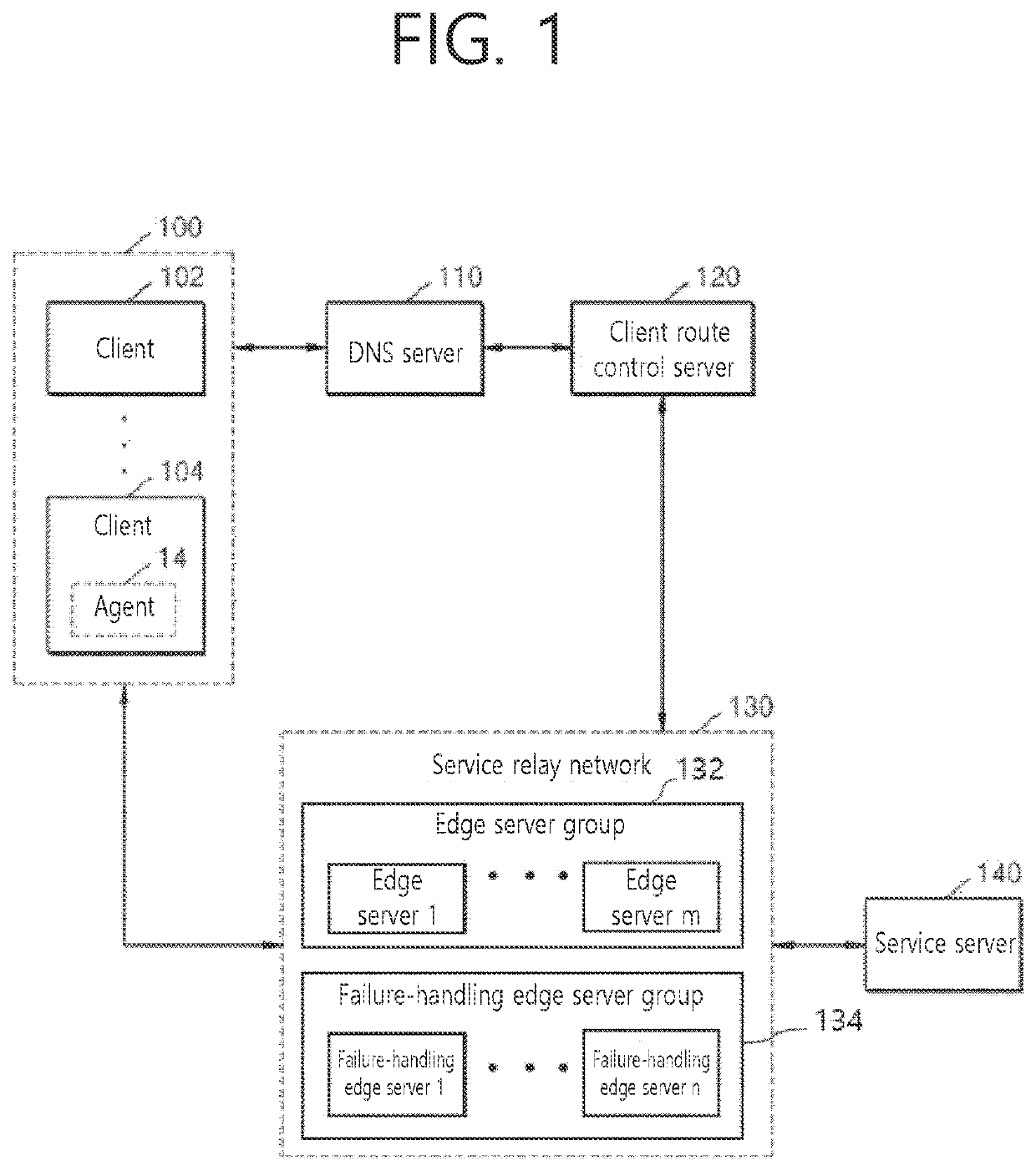
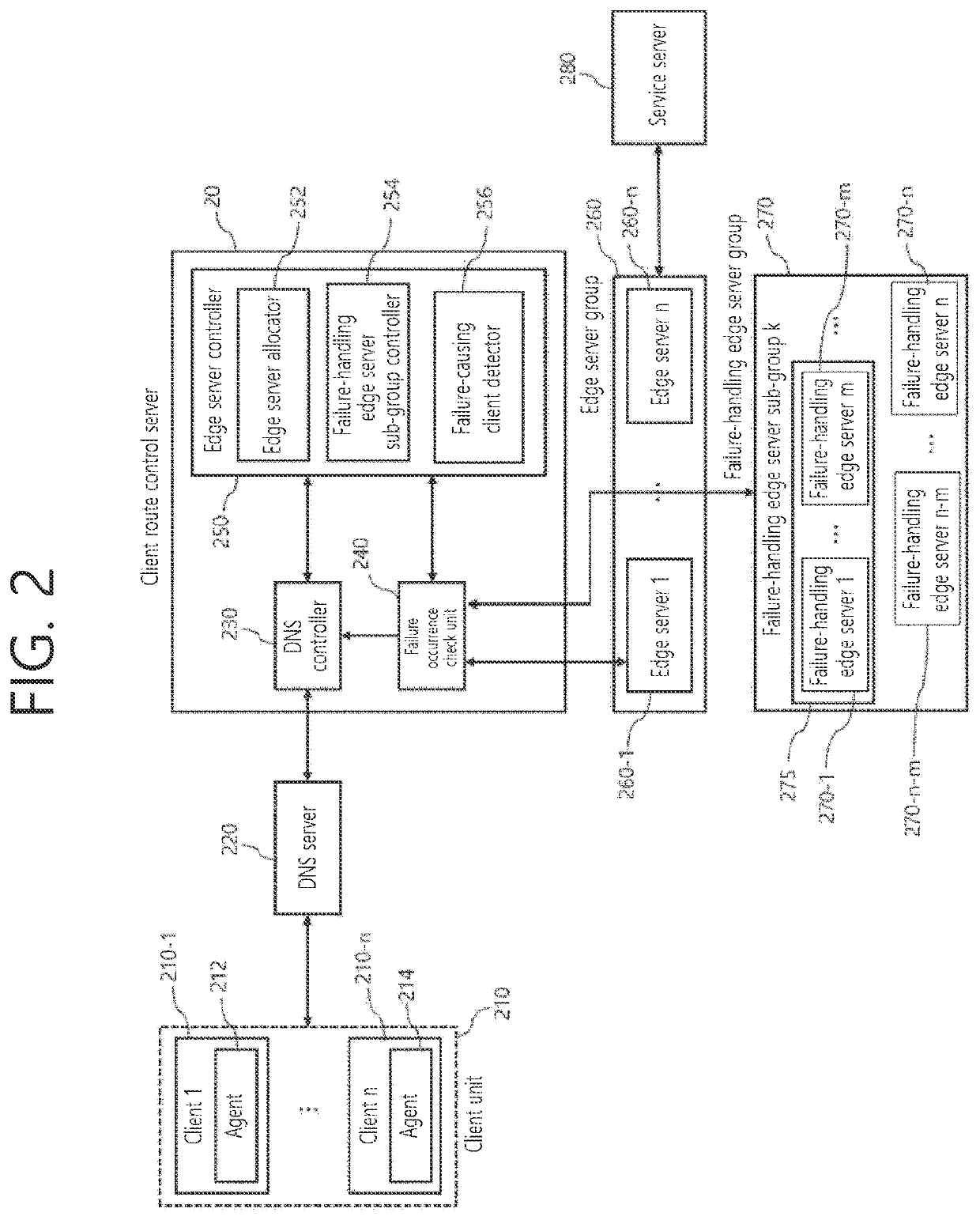
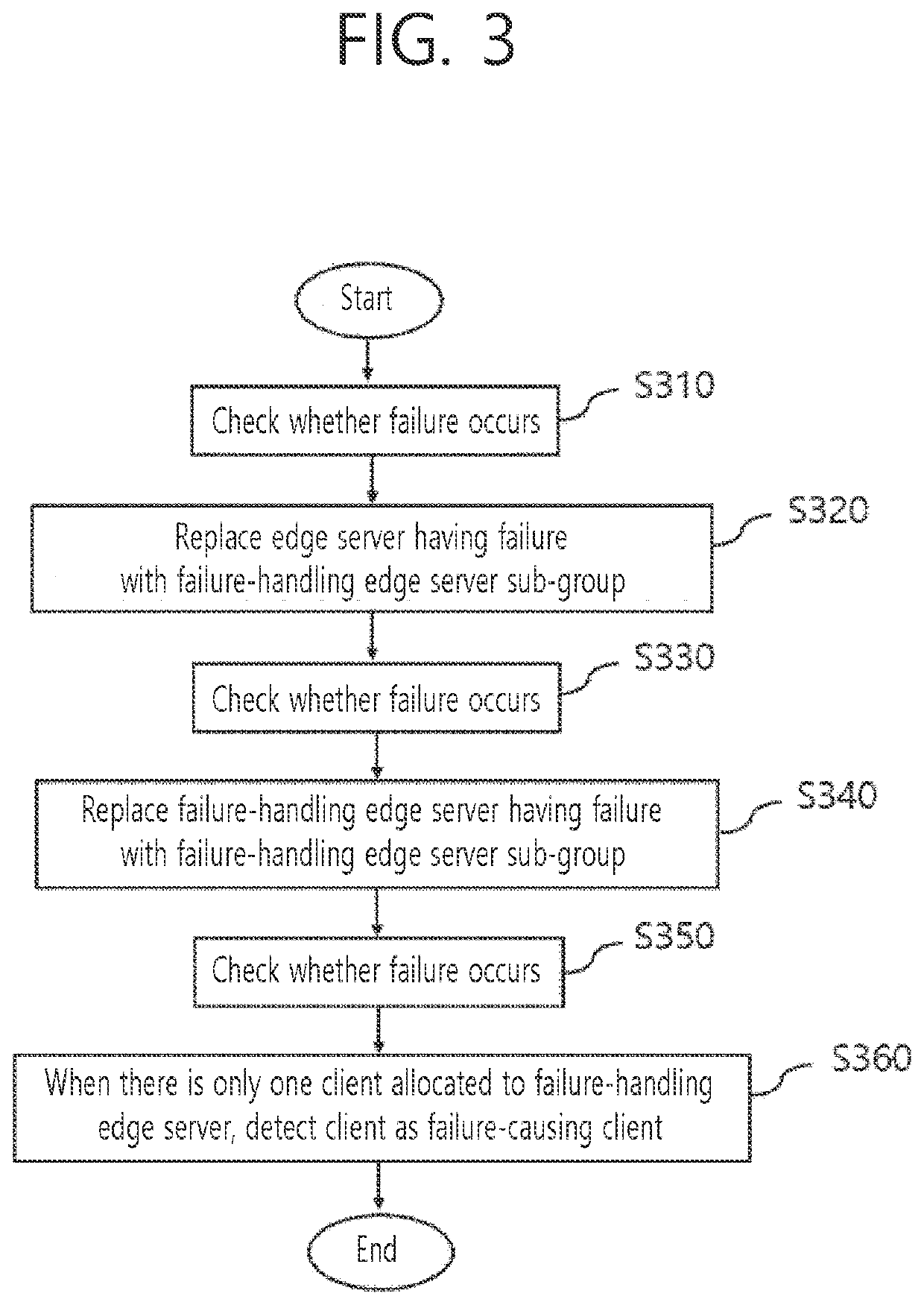
Method and system for detecting failure-causing client with failure handling edge server grouping
InactiveUS20220360485A1Guarantee service continuityGuaranteed continuityTransmissionEdge serverEngineering
Provided is a client terminal access control method, and the method includes: allocating a communication process of a first client group comprising a plurality of client terminals to an edge server; when a failure occurs in an operation of the edge server, allocating a communication process of a second client group comprising at least one client terminal belonging to the first client group to a failure-handling edge server; and determining whether a failure occurs in an operation of the failure-handling edge serve.
Owner:INNOGS KOREA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com