Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
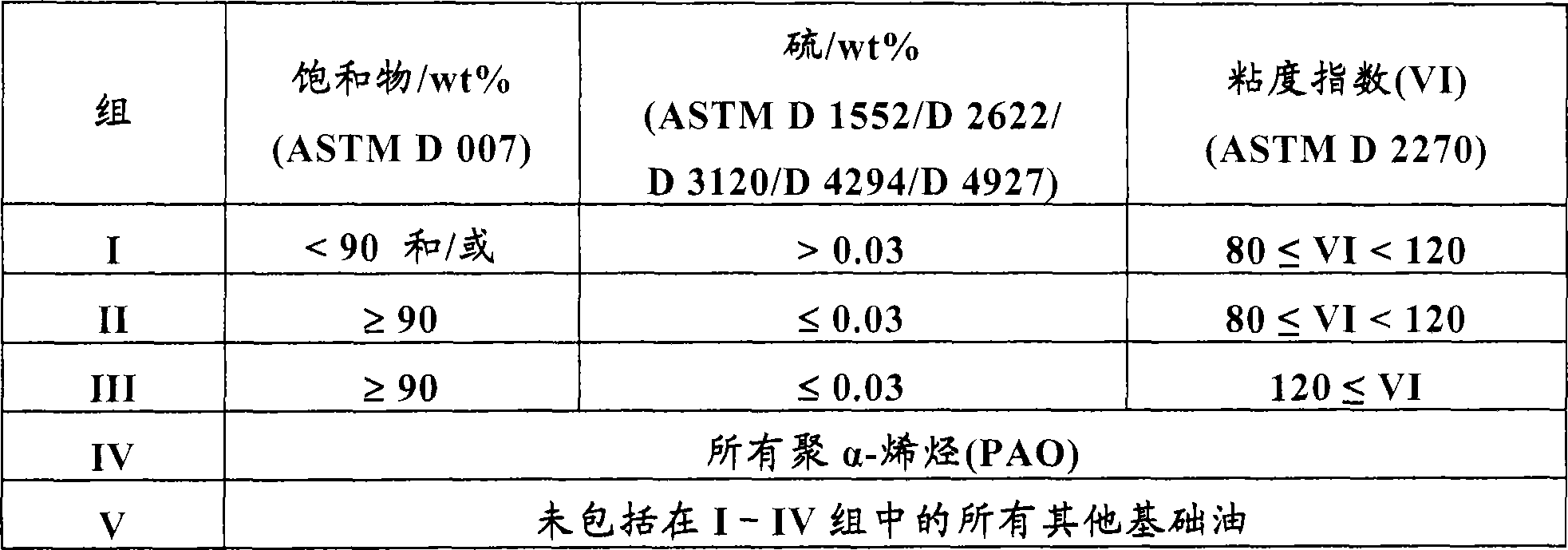
243results about "Hydrocarbon by addition and hydrogenation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydroalkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons
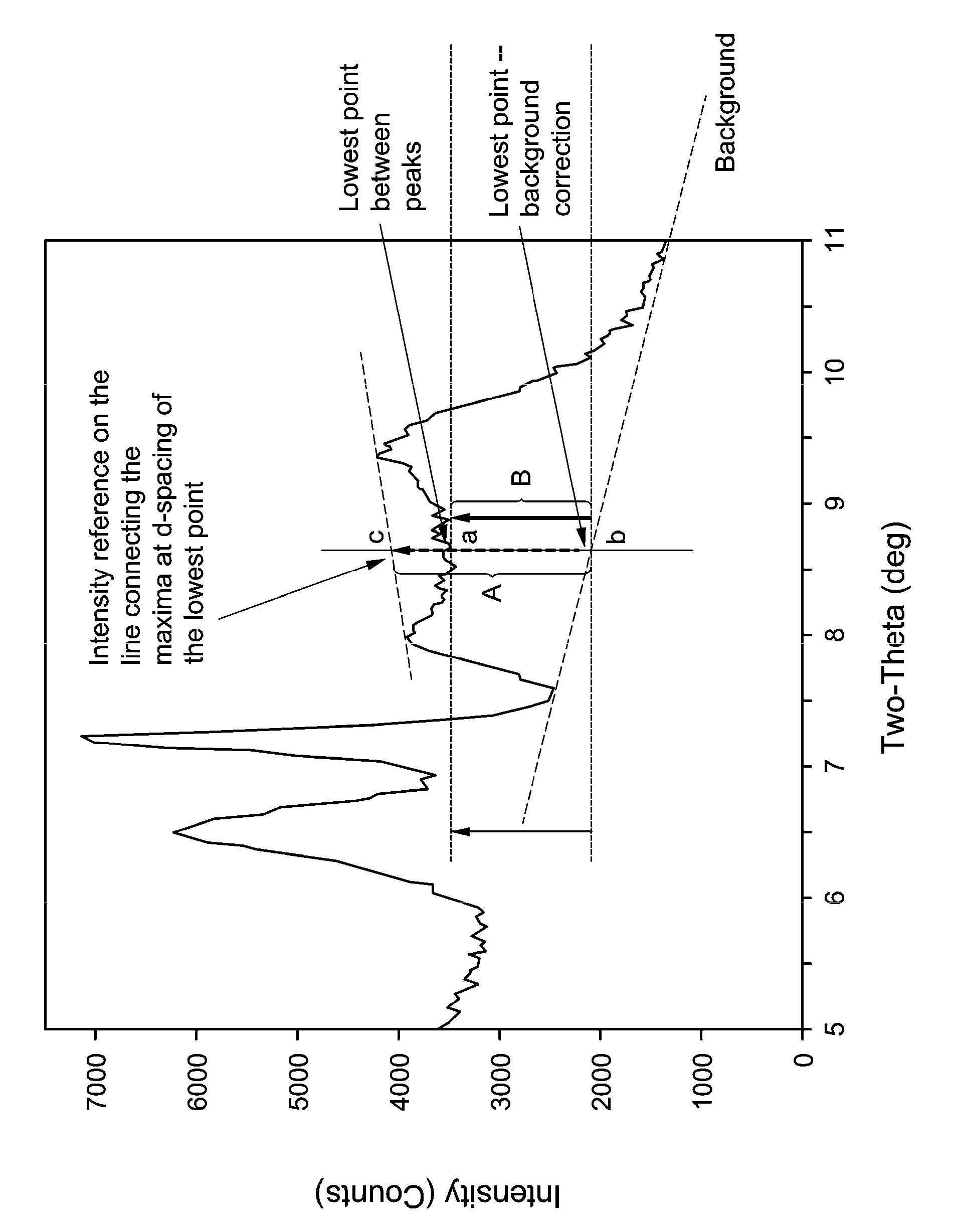
InactiveUS6037513AHigh activityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationBenzeneX-ray
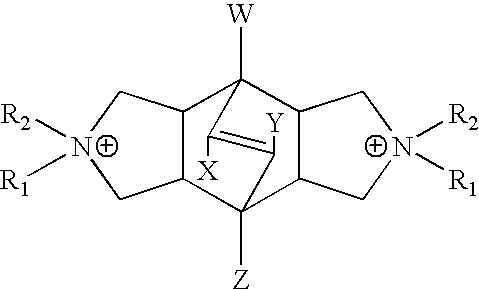
There is described a process and a catalyst for the hydroalkylation of an aromatic hydrocarbon, particularly benzene, wherein the catalyst comprises a first metal having hydrogenation activity and a crystalline inorganic oxide material having a X-ray diffraction pattern including the following d-spacing maxima 12.4+ / -0.25, 6.9+ / -0.15, 3.57+ / -0.07 and 3.42+ / -0.07.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Hydroalkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6730625B1High activityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystBenzeneX-ray
There is described a process and a catalyst for the hydroalkylation of an aromatic hydrocarbon, particularly benzene, wherein the catalyst comprises a first metal having hydrogenation activity and a crystalline inorganic oxide material having a X-ray diffraction pattern including the following d-spacing maxima 12.4±0.25, 6.9±0.15, 3.57±0.07 and 3.42±0.07.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
Oligomerization of alpha olefins using metallocene-ssa catalyst systems and use of the resultant polyalphaolefins to prepare lubricant blends
ActiveUS20100317904A1Improve productivityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationAdditivesOligomerViscosity index
This disclosure provides for alpha olefin oligomers and polyalphaolefins (or PAOs) and methods of making the alpha olefin oligomers and PAOs. This disclosure encompasses metallocene-based alpha olefin oligomerization catalyst systems, including those that include at least one metallocene and an activator comprising a solid oxide chemically-treated with an electron withdrawing anion. The alpha olefin oligomers and PAOs prepared with these catalyst systems can have a high viscosity index combined with a low pour point, making them particularly useful in lubricant compositions and as viscosity modifiers.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Synthesis of poly-alpha olefin and use thereof
InactiveUS7129197B2Improve oxidation stabilityImproved biodegradibilityOrganic chemistry methodsSolid fuelsHydrogenIsomerization
One or more oligomers of an olefin are prepared in the presence of a single-site catalyst. Preferably, the olefin is an α-olefin, and the oligomers are a poly-alpha-olefin (PAO). The PAO so prepared is completely or substantially free of tertiary hydrogen resulting from isomerization. Consequently, the PAO possesses improved biodegradability, improved oxidation resistance, and / or a relatively higher viscosity index. The PAO has many useful applications, such as a component of a lubricant.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
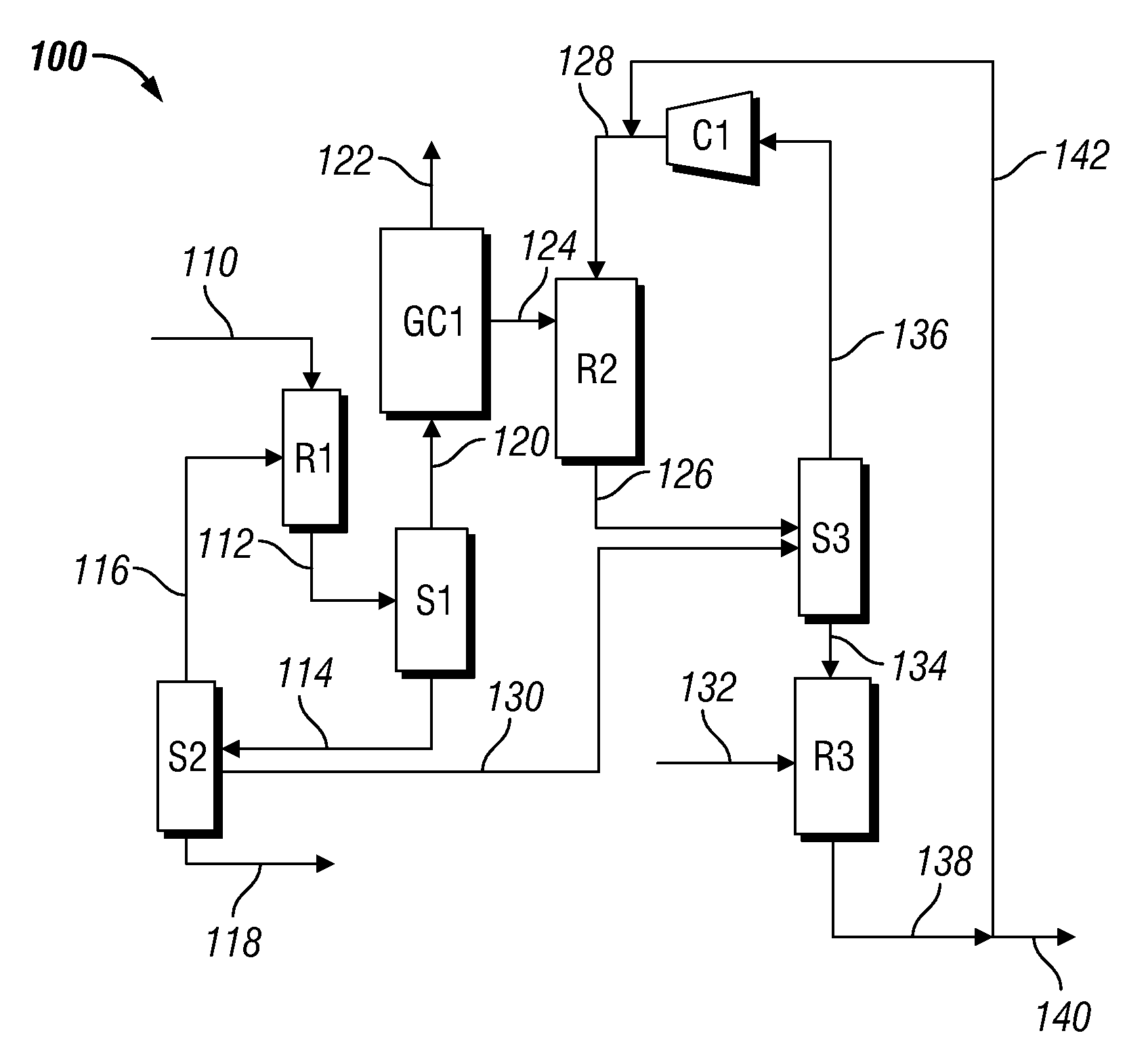
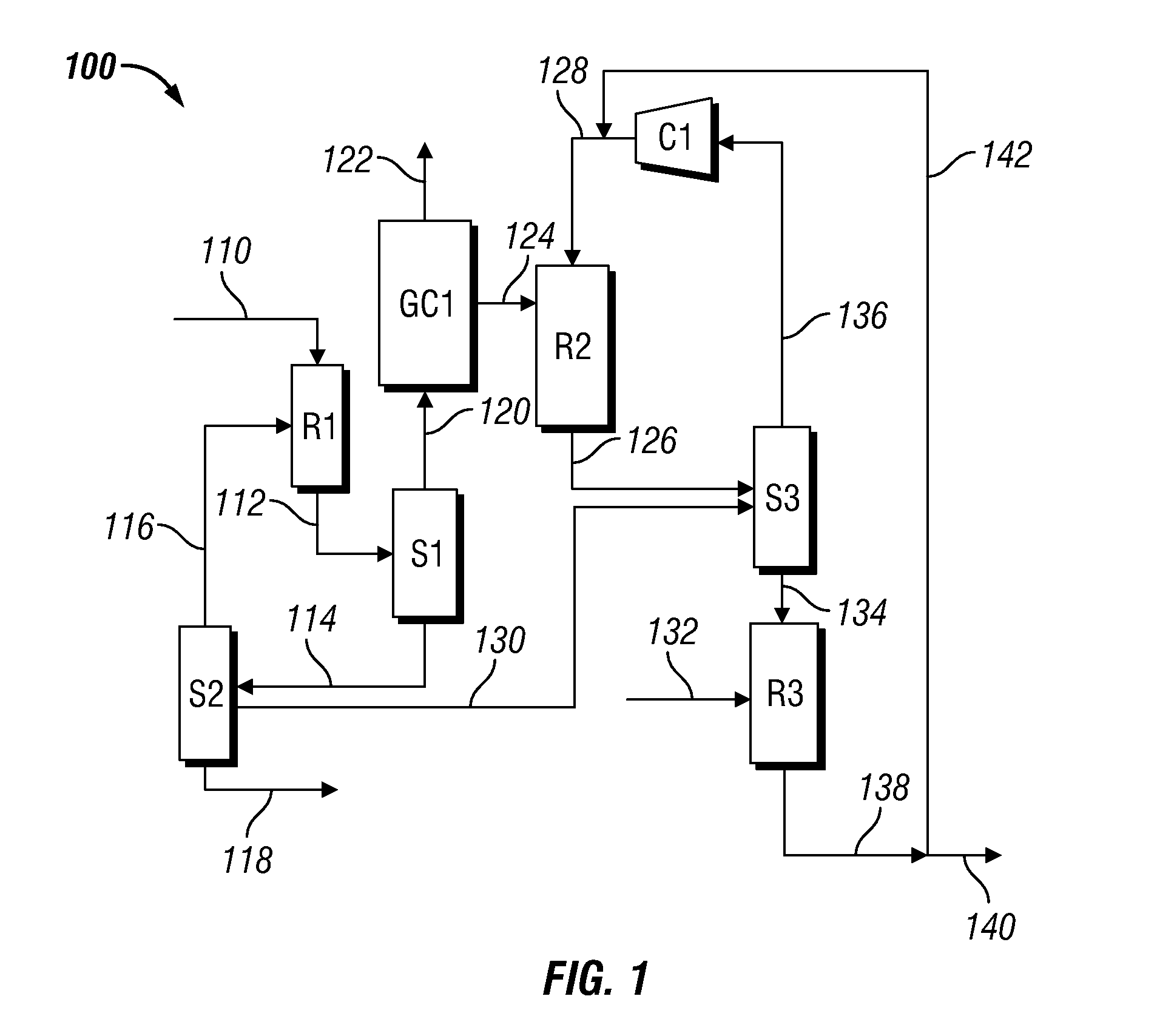
System and method for the production of liquid fuels
InactiveUS20120197053A1Readily apparentHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationOligomerLiquid state
A method of producing liquid fuels by providing an olefin feed containing at least one C2-C20 olefin, oligomerizing a part of the feed in the presence of a first catalyst to form a first product comprising oligomers of the at least one olefin, and oligomerizing a portion of the first product in the presence of a second catalyst to produce a second product. A system of producing liquid hydrocarbons, the system including a first reactor configured to provide a first product by oligomerizing, in the presence of a first catalyst, at least a portion of an olefin feed comprising at least one olefin, a separator configured to provide an unreacted olefin-reduced first product by separating unreacted olefin from the first product, and a second reactor configured to provide a second product by oligomerizing, in the presence of a second catalyst, at least a portion of the unreacted olefin-reduced first product.
Owner:SYNFUELS INT
Process to produce high viscosity fluids
ActiveUS20080177121A1Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbonsPolyolefinPtru catalyst
This invention relates to processes to produce liquid poly-alpha-olefins (PAOs) having a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of more than 20 cSt in the presence of a metallocene catalyst with a non-coordinating anion activator and hydrogen.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Oligomerization of alpha olefins using metallocene-SSA catalyst systems and use of the resultant polyalphaolefins to prepare lubricant blends
This disclosure provides for alpha olefin oligomers and polyalphaolefins (or PAOs) and methods of making the alpha olefin oligomers and PAOs. This disclosure encompasses metallocene-based alpha olefin oligomerization catalyst systems, including those that include at least one metallocene and an activator comprising a solid oxide chemically-treated with an electron withdrawing anion. The alpha olefin oligomers and PAOs prepared with these catalyst systems can have a high viscosity index combined with a low pour point, making them particularly useful in lubricant compositions and as viscosity modifiers.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Process for oligomerizing olefins
InactiveUS20110230690A1Easy to disassembleEmission reductionMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystReaction zoneSolvent
A process for oligomerizing olefinic, lower hydrocarbons. The process comprises the steps of feeding a fresh olefinic hydrocarbon feedstock to a reaction zone; contacting the olefinic hydrocarbons of the feedstock with an acidic catalyst in the reaction zone in order to dimerize at least a part of the olefinic hydrocarbons, withdrawing an effluent containing oligomerized olefins from the reaction zone; and conducting the effluent to a separation zone, wherein the oligomerization reaction product is separated from said effluent. According to the invention, the reaction is carried out in homogeneous phase comprising a solvent for olefinic hydrocarbons, maintained at supercritical conditions. By using supercritical carbon dioxide as a solvent deactivation rate of catalyst can be diminished. Carbon dioxide is easy to remove from the product mixture and spent reaction medium can be used for regeneration of the catalyst.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Process for reducing the toxicity of hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20050197256A1Low toxicityHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon distillationFractional distillationHydrocarbon
This invention relates to a method for reducing the toxicity of a mixture of hydrocarbons by means of fractional distillation, a distillate having a reduced toxicity and a composition including the distillate.
Owner:THE PETROLEUM OIL & GAS CORP OS SOUTH AFRICA PTY LTD
Synthetic lubricant composition and process
ActiveUS7022784B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationPolymer scienceAlpha-olefin
A liquid polymer suitable for use as a lubricant base oil is produced by polymerizing ethylene and at least one alpha-olefin using a metallocene catalyst to provide a polymer which is then isomerized and hydrogenated to produce the liquid polymer.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process to produce high viscosity fluids
ActiveUS7989670B2Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbonsHydrogenNon-coordinating anion
This invention relates to processes to produce liquid poly-alpha-olefins (PAOs) having a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of more than 20 cSt in the presence of a metallocene catalyst with a non-coordinating anion activator and hydrogen.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
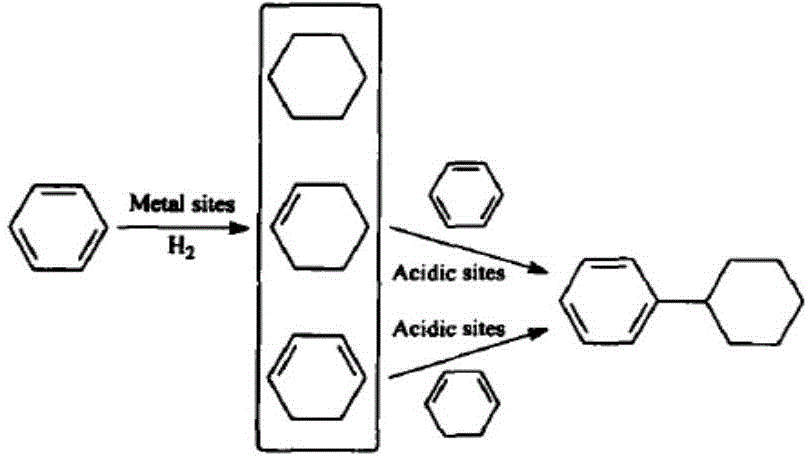
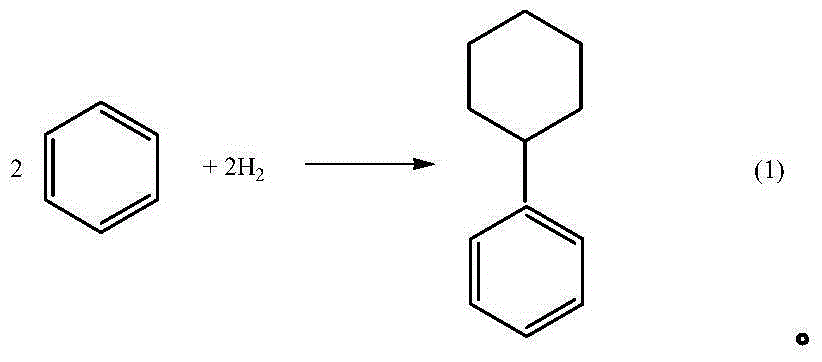
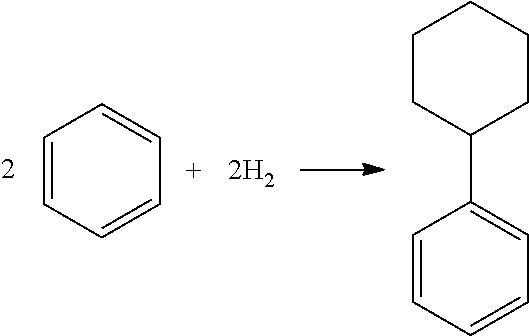
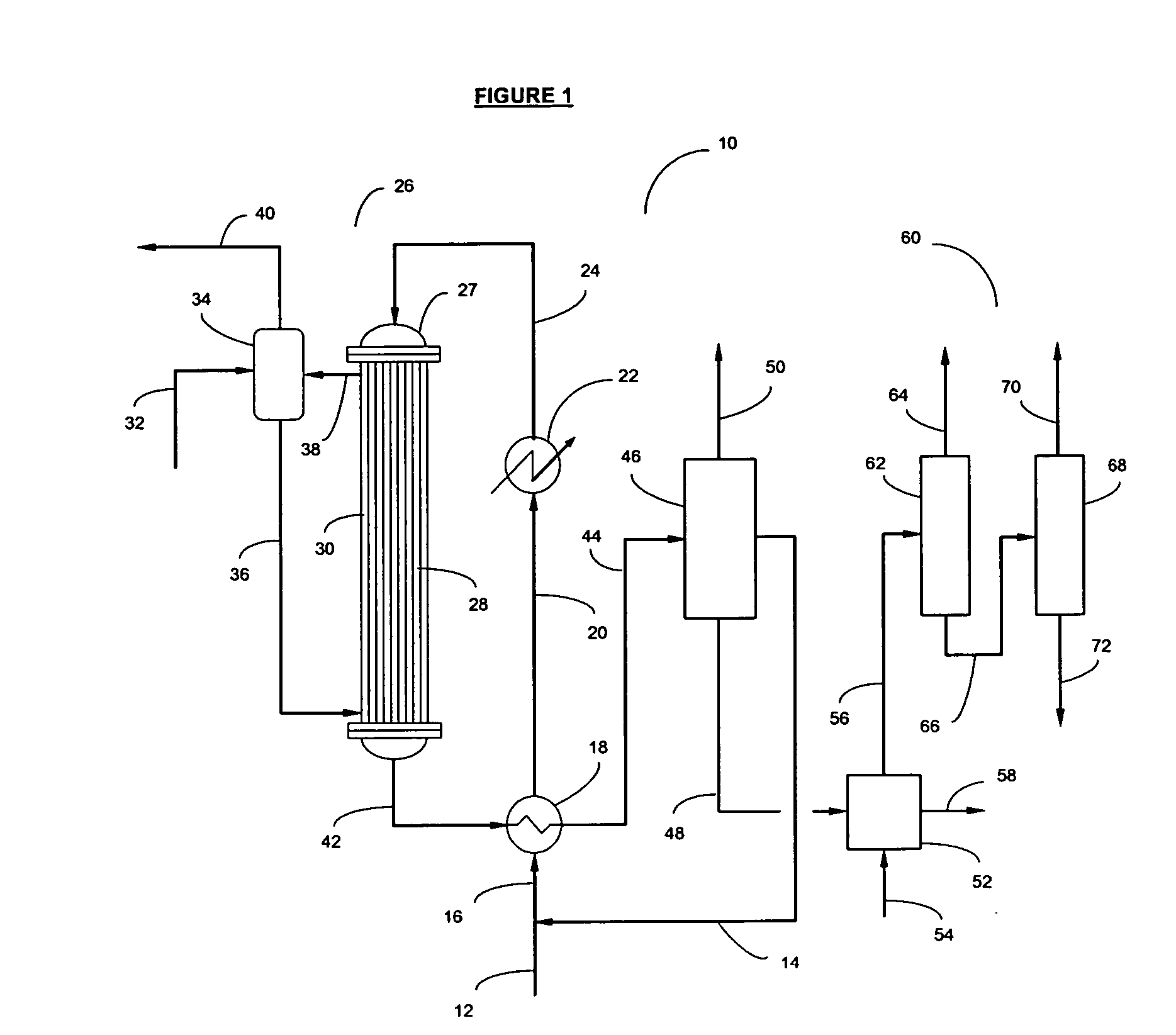
Process of producing cyclohexylbenzene
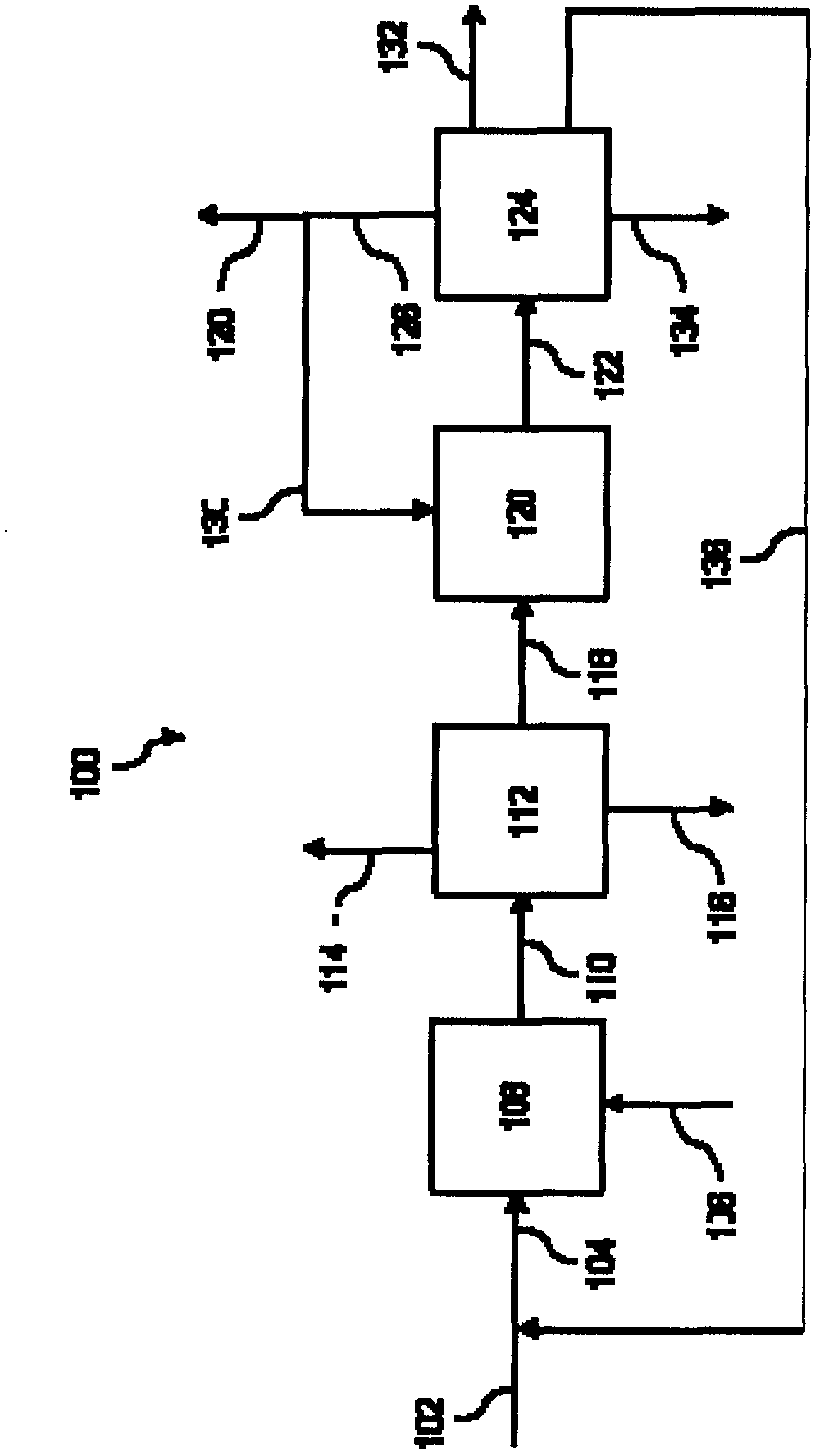
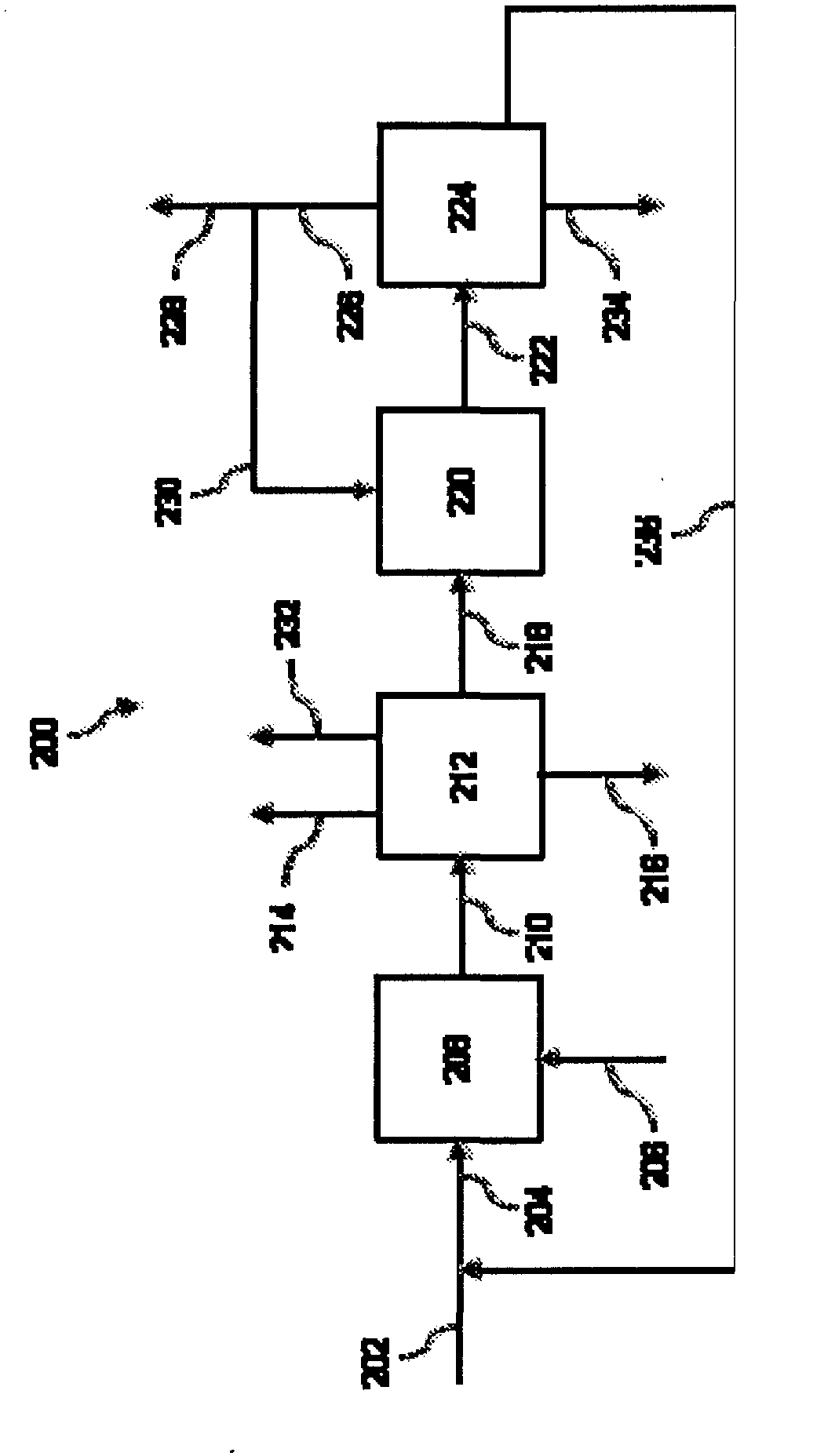
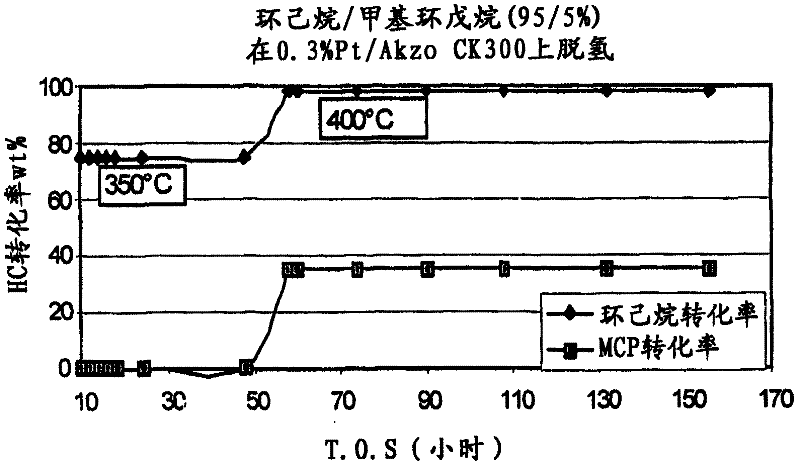
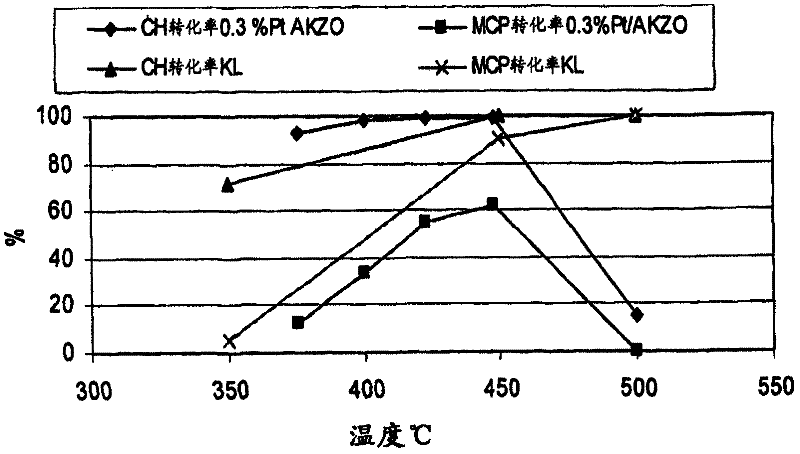
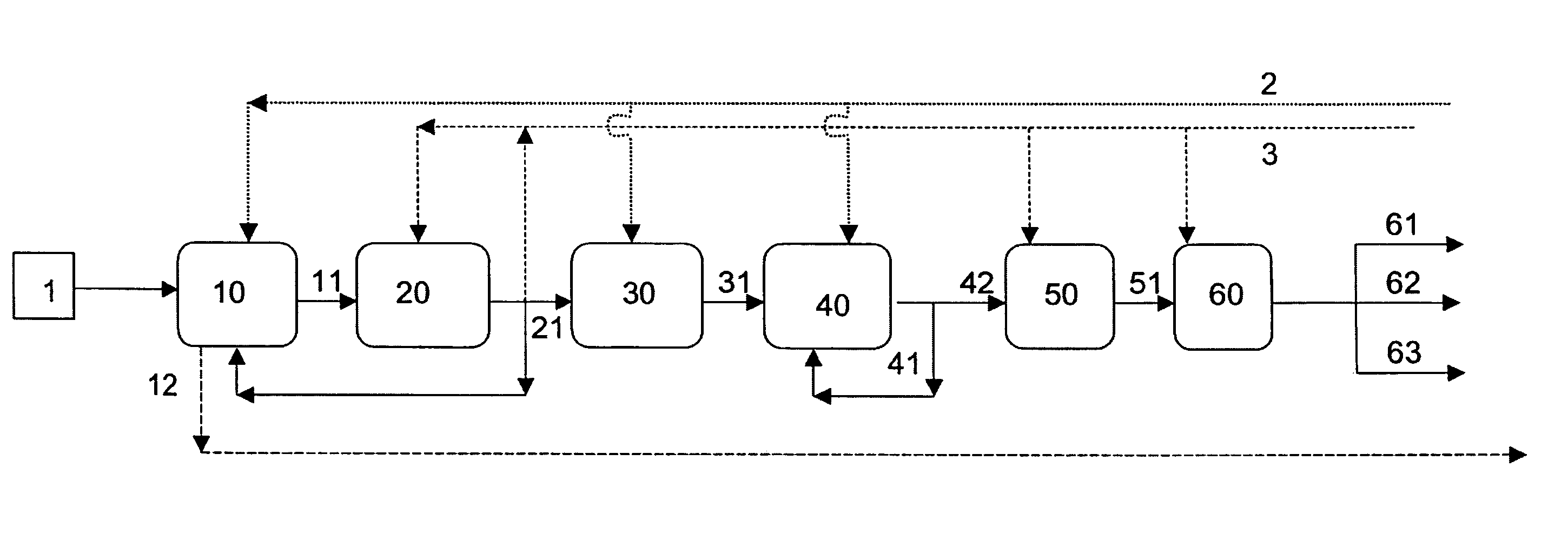
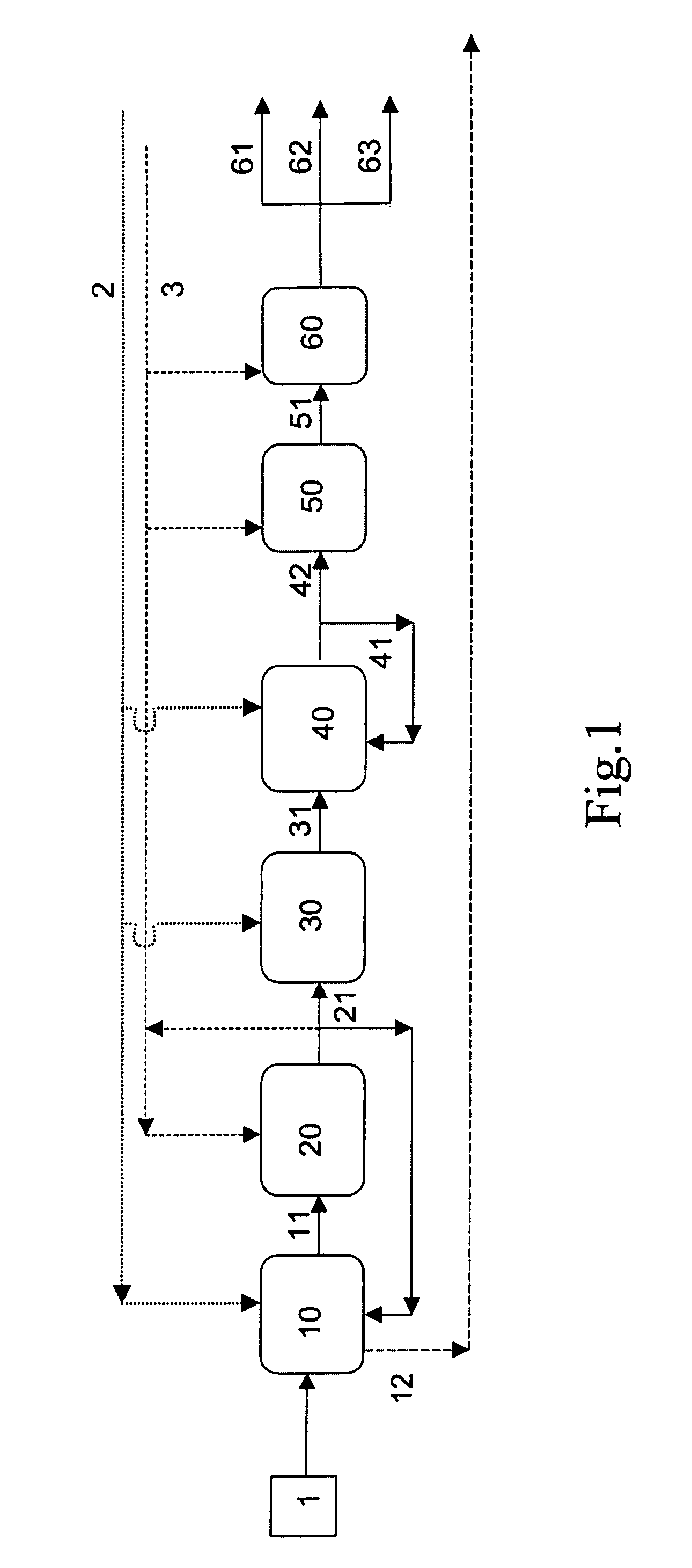
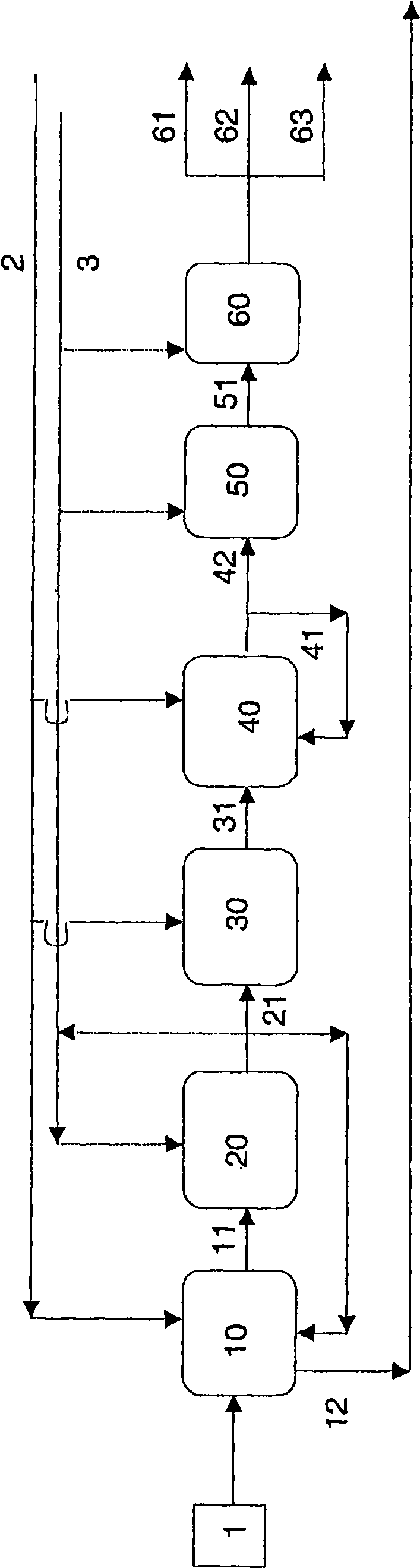
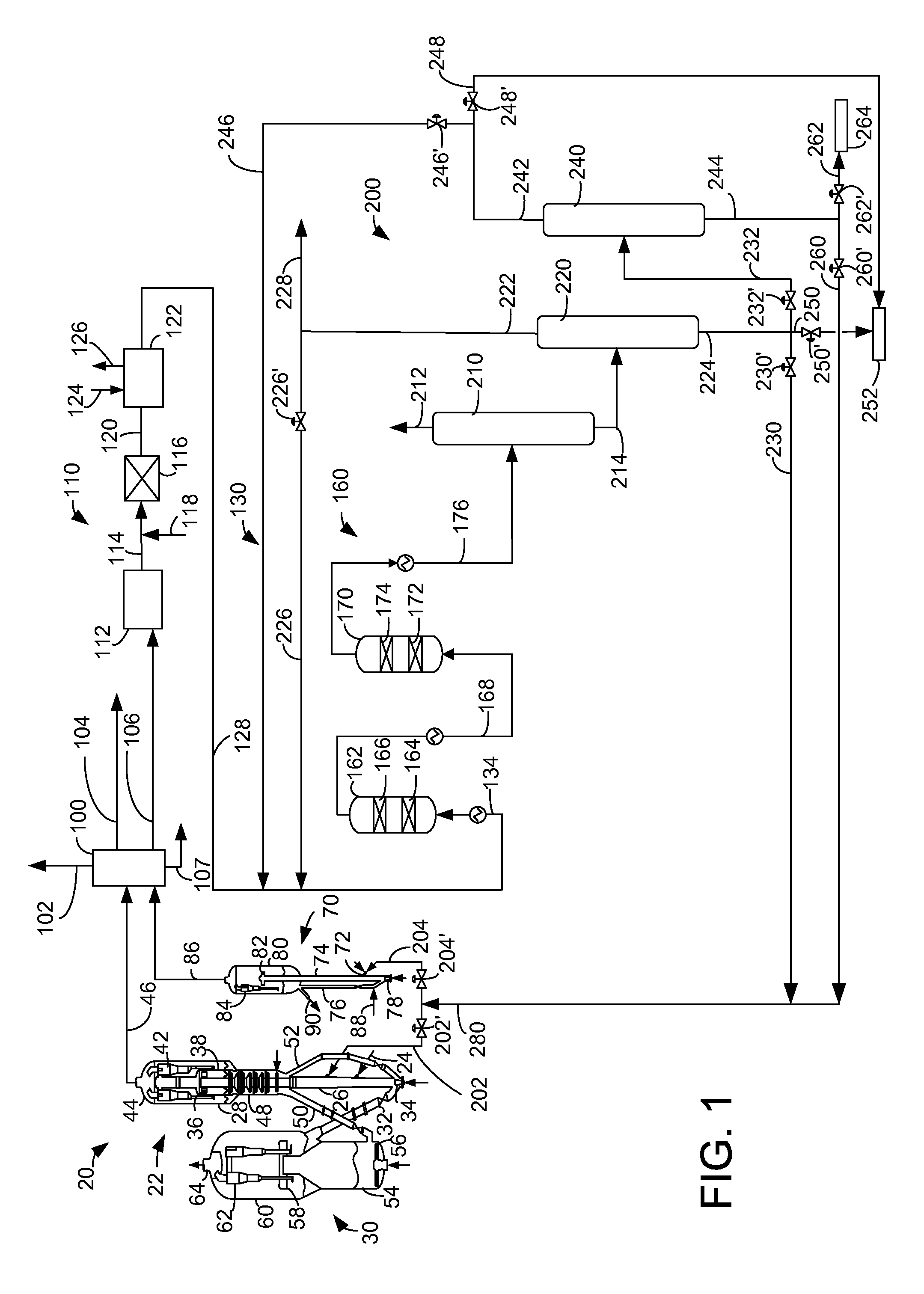
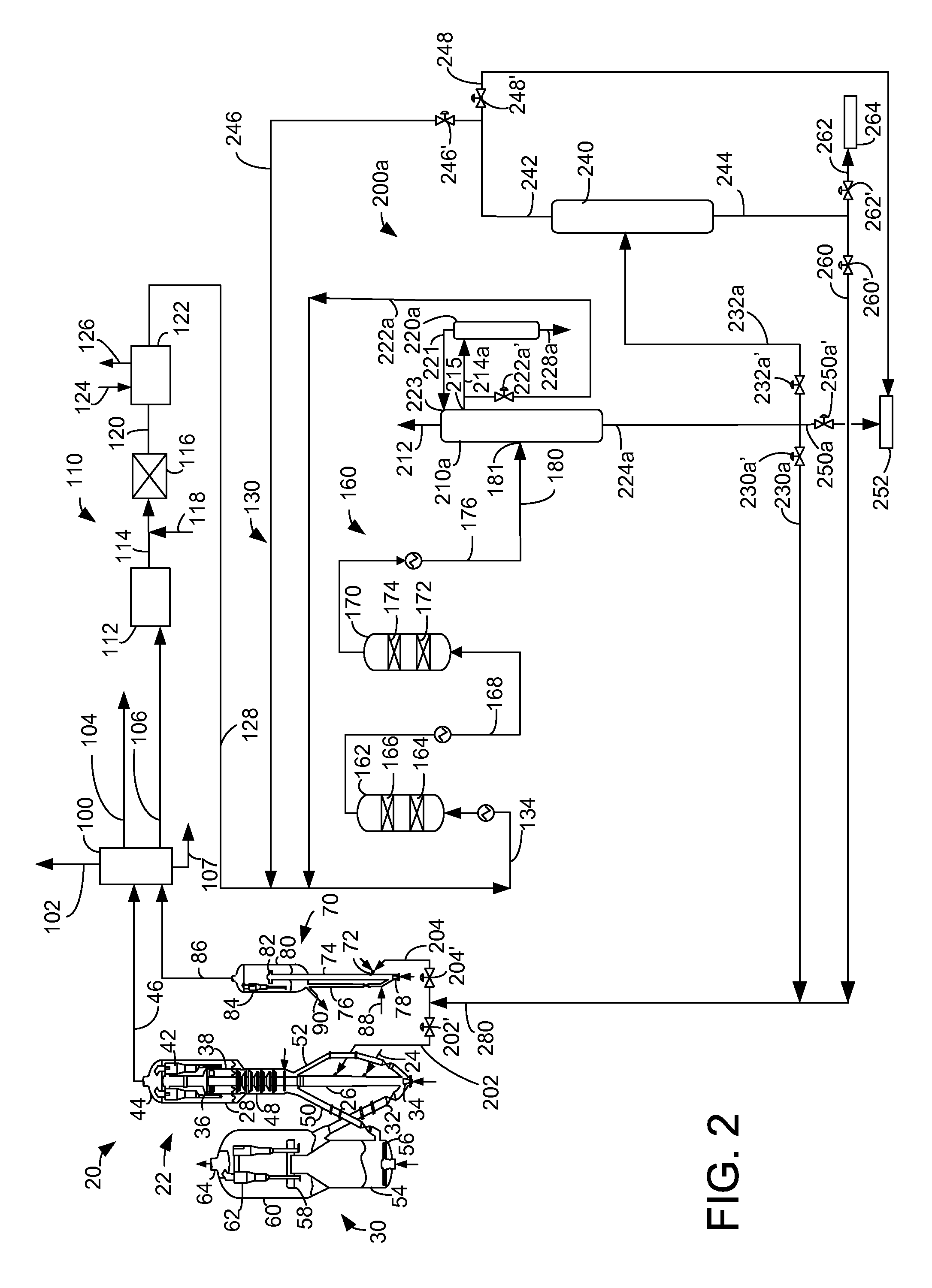
In a process for producing cyclohexylbenzene, benzene is contacted with hydrogen under hydroalkylation conditions effective to form a first effluent stream comprising cyclohexylbenzene, cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, and unreacted benzene. At least a portion of the first effluent stream is contacted with a dehydrogenation catalyst under dehydrogenation conditions to convert at least a portion of the cyclohexane to benzene thereby forming a second effluent stream. The amount of methylcyclopentane in the second effluent stream is different by no more than 65% of the total amount of the portion of the first effluent stream, said amounts being on a weight basis. A methylcyclopentane-containing stream is removed from either the first or the second effluent stream and at least a portion of the second effluent stream containing benzene is recycled to the hydroalkylation step.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Hydroalkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons
There is described a process the hydroalkylation of an aromatic hydrocarbon, particularly benzene, to produce a cycloalkyl-substituted aromatic compound, particularly cyclohexylbenzene, comprising the step of contacting the aromatic hydrocarbon with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst comprising MCM-68 and at least one metal having hydrogenation activity.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
Methods for producing jet-range hydrocarbons
A method for producing jet-range hydrocarbons includes passing a stream comprising renewable C4 olefins to an oligomerization reactor containing a zeolite catalyst to produce an oligomerized effluent, separating the oligomerized effluent to produce a jet range hydrocarbon stream and a recycle stream comprising C8 olefins, and passing at least a portion of the recycle stream to the oligomerization reactor. A first at least about 10% of the jet-range hydrocarbon stream hydrocarbons boil between n-octane and n-undecane and wherein a second at least about 10% of the jet-range hydrocarbon stream hydrocarbons boil between n-dodecane and n-pentadecane.
Owner:UOP LLC
Olefin upgrading process
A process for the use in the oligomerization of olefins is presented. The process produces a gasoline boiling range product having a high research octane number and almost no aromatics content. The process utilizes a solid catalyst comprising a zeolite that is treated with a phosphorous containing reagent to generate a catalyst having phosphorous content between 0.5 and 15 wt %.
Owner:UOP LLC
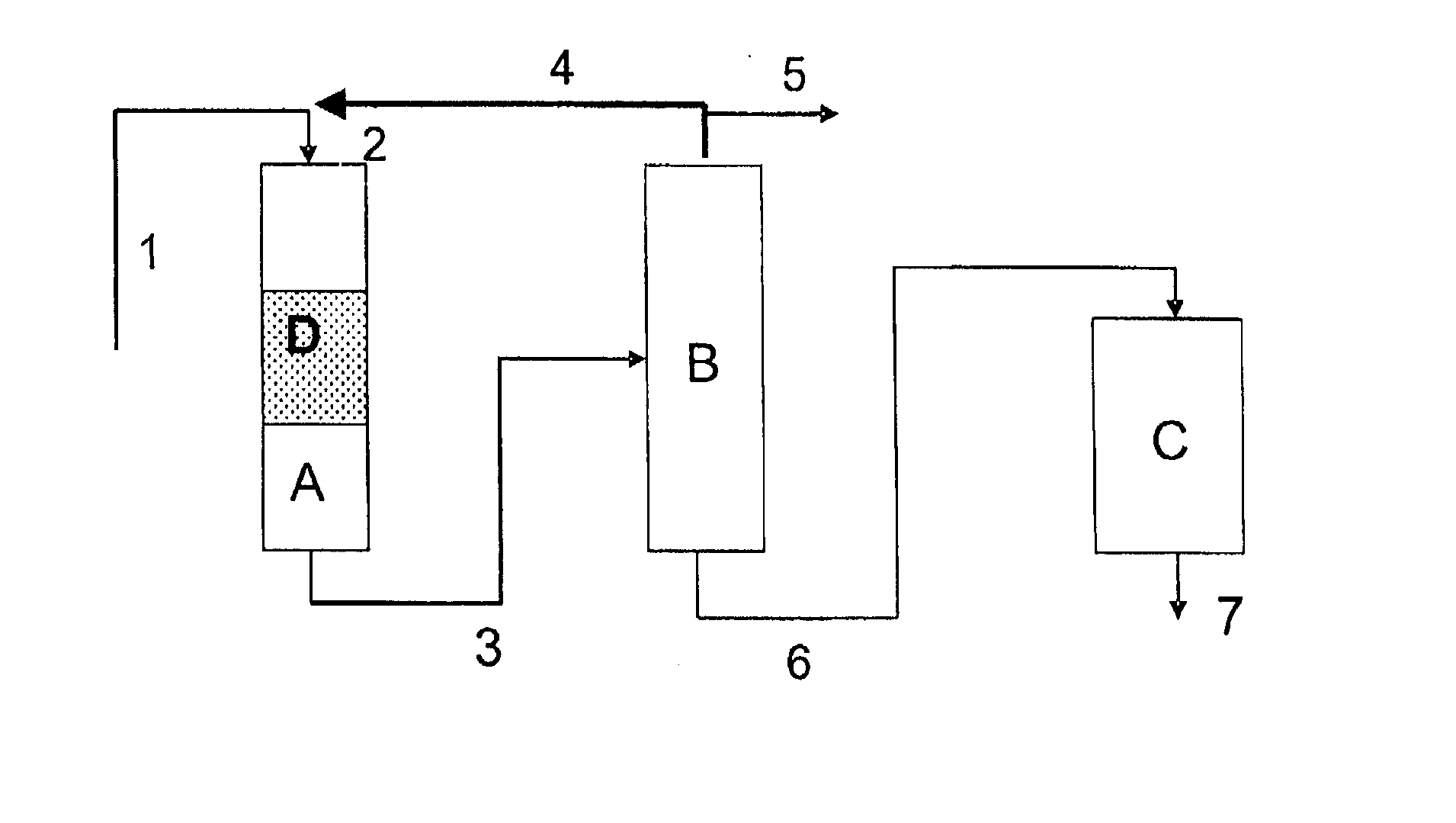
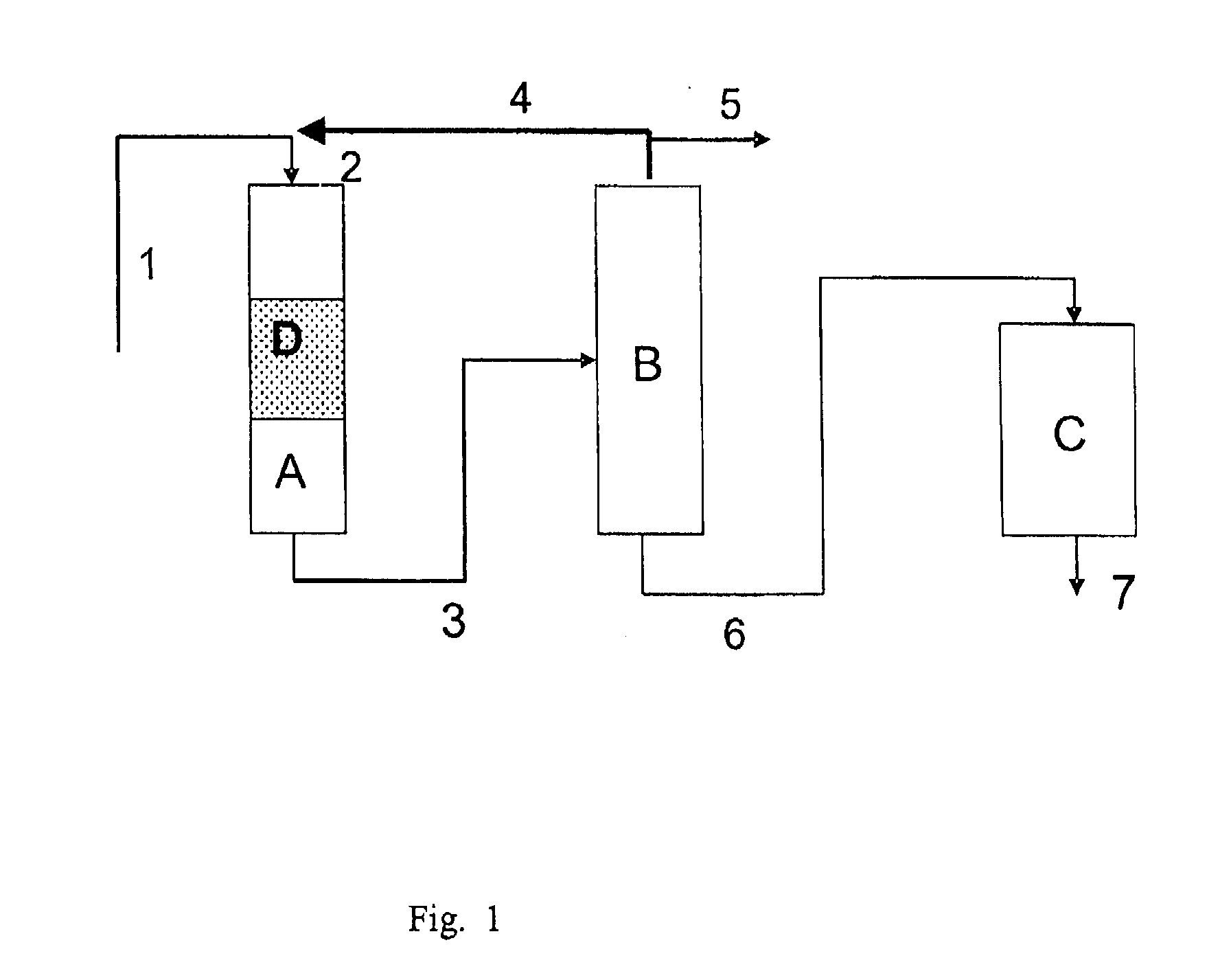
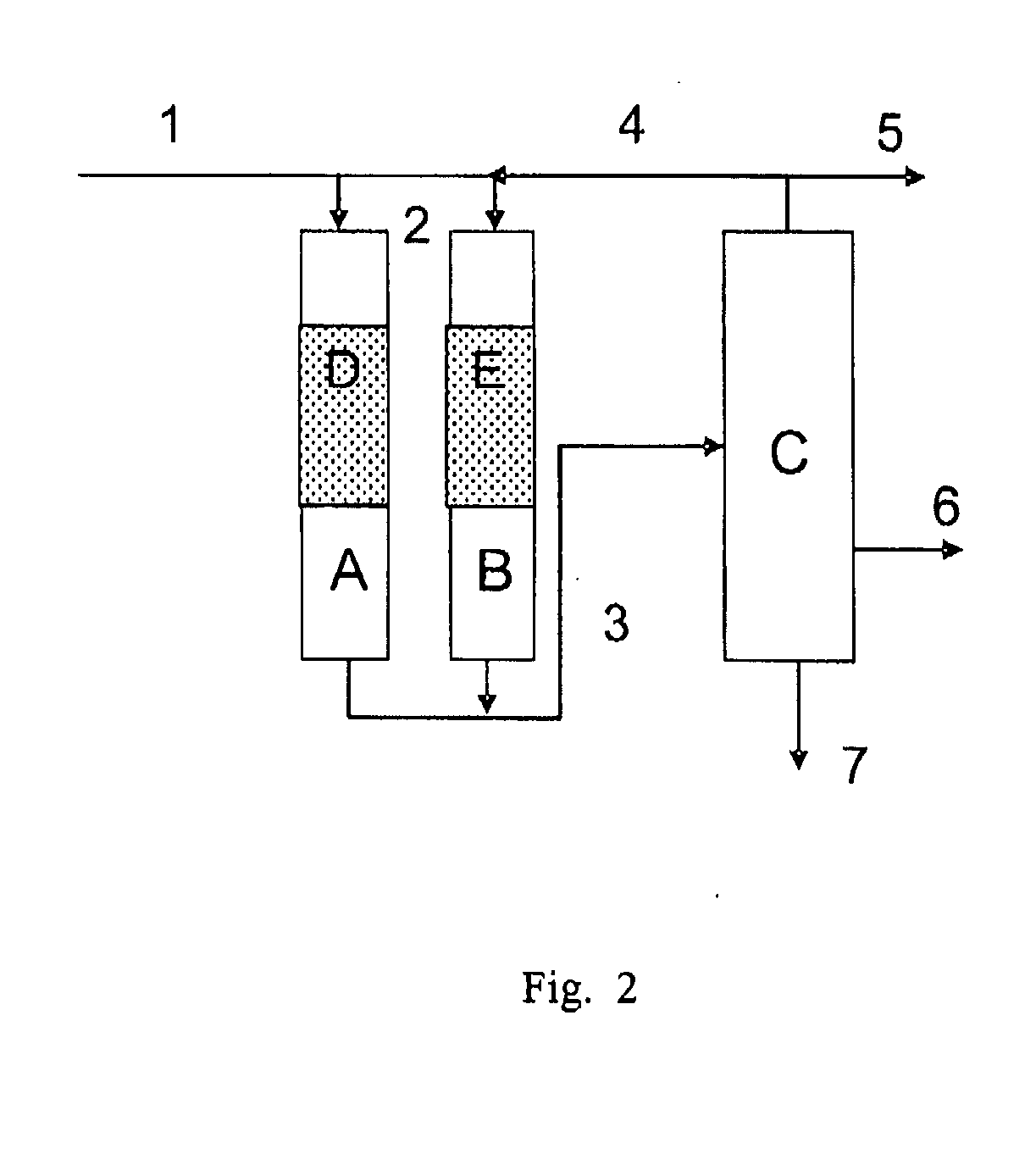
Process for making cyclohexylbenzene
A process for making cyclohexylbenzene includes (a) contacting benzene and hydrogen in the presence of a first catalyst under hydroalkylation conditions sufficient to form a first effluent stream having cyclohexylbenzene, cyclohexane, methyl cyclopentane, and unreacted benzene, (b) supplying a portion of the first effluent stream to a first separation system to divide the first effluent stream part into (i) a C6-rich stream comppsing benzene, cyclohexane, and methylcyclopentane and (II) a cyclohexylbenzene-rich stream, (c) contacting a portion of the C6-rich stream with a second catalyst that catalyzes dehydrogenation and exhibits low acidity under conditions sufficient to convert a portion of the cyclohexane to benzene and a portion of the methylcyclopentane to linear and / or branched paraffins to form a second effluent stream, and (d); recycling a portion of the second effluent stream to the contacting step (a).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for the preparation of phenol and cyclohexanone
InactiveUS20120157718A1EfficiencyGood choiceOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationCyclohexanoneCyclohexene
Process for the preparation of phenol and cyclohexanone which comprises:a. the synthesis of cyclohexylbenzene by the hydro-alkylation of benzene by contact with hydrogen or the alkylation of benzene with cyclohexene using Y zeolites;b. the selective aerobic oxidation of cyclohexylbenzene to the corresponding hydroperoxide catalyzed by N-hydroxy-derivatives in the presence of polar solvents; andc. the scission of the hydroperoxide of cyclohexylbenzene to phenol and cyclohexanone by homogeneous or heterogeneous acid catalysts;characterized in that the synthesis of cyclohexylbenzene takes place in the presence of a catalytic system comprising a Y zeolite and an inorganic ligand wherein the Y zeolite has a crystalline structure with openings consisting of 12 tetrahedra and the inorganic ligand is γ-alumina, and wherein said catalytic composition is characterized by a pore volume, obtained by adding the mesoporosity and macroporosity fractions, greater than or equal to 0.7 cm3 / g, wherein at least 30% of said volume consists of pores with a diameter greater than 100 nanometers.
Owner:POLIMERI EUROPA SPA
Process for the manufacture of base oil
ActiveUS7795484B2Significant environmental benefitsReduce impactHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationHeteroatom
A feedstock originating from renewable sources is converted to branched and saturated hydrocarbons without heteroatoms in the base oils distillation range by converting the fatty acids to olefins, which are subsequently oligomerised.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Process for the manufacture of base oil
ActiveCN101484552AGood environmental benefitsReduce positive impactHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationHeteroatom
A feedstock originating from renewable sources is converted to branched and saturated hydrocarbons without heteroatoms in the base oils distillation range by converting the fatty acids to olefins, which are subsequently oligomerised.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Catalyst for synthesizing cyclohexylbenzene
ActiveCN105582989ALow selectivityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by addition and hydrogenationMolecular sieveBenzene
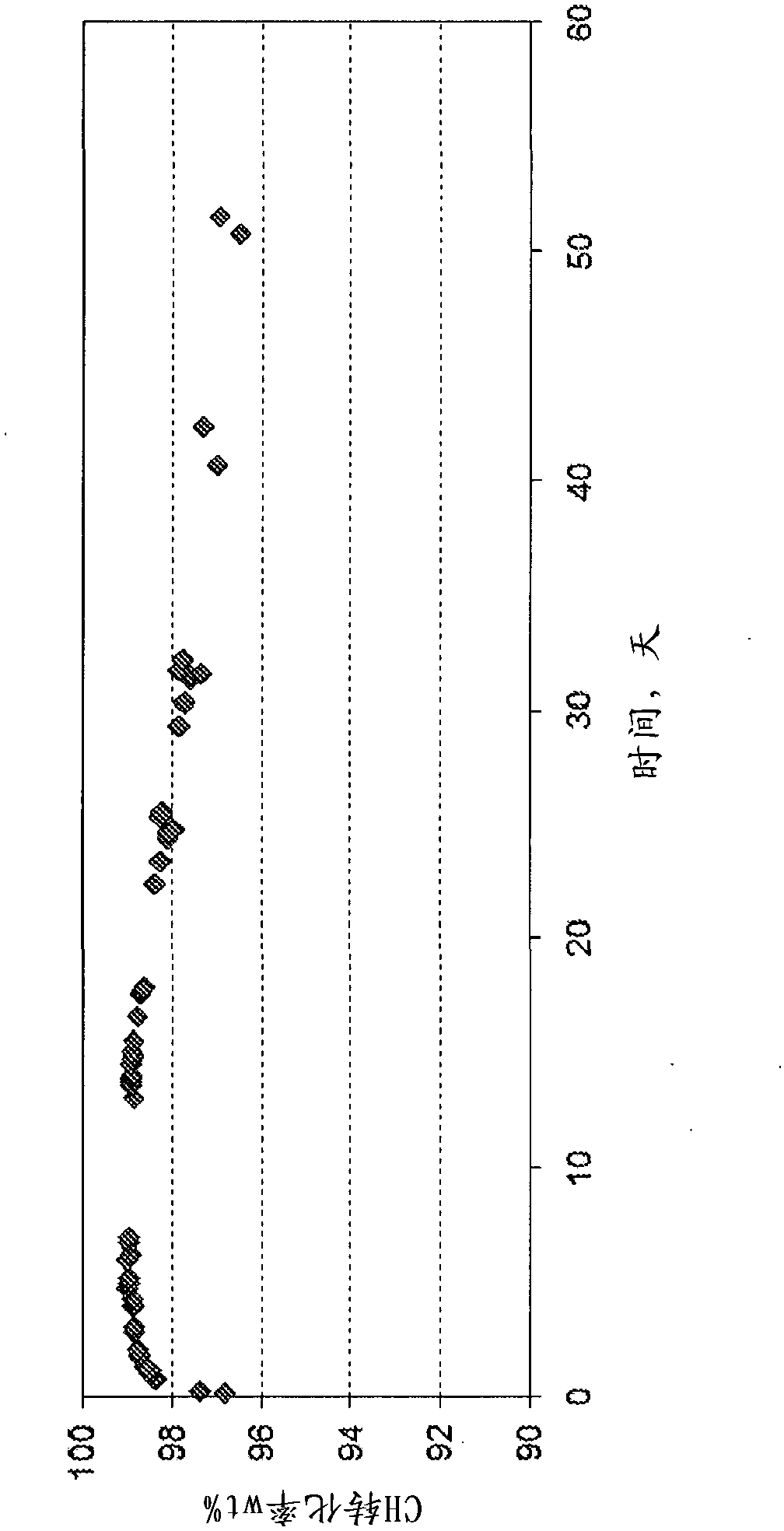
The invention relates to a catalyst for synthesizing cyclohexylbenzene and a method for synthesizing cyclohexylbenzene by a benzene-hydroalkylation one-step method. The catalyst is used for solving the technical problem in the prior art that the reaction is high in methyl cyclopentyl benzene selectivity and low in cyclohexylbenzene selectivity due to catalysts. Through adopting the technical scheme that the catalyst for synthesizing cyclohexylbenzene contains a carrier and the following ingredients in percentage by weight: (1) 0.05-2.0% of Pd; (2) 0-3.0% of at least one of lanthanide elements; and (3) 0-4.0% of at least one of ferrous elements, wherein the carrier is H-type zeolite molecular sieves, a better effect is obtained, and the catalyst can be applied to the preparation of cyclohexylbenzene by the benzene-hydroalkylation one-step method.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Polyolefins from non-conventional feeds
ActiveUS20070123659A1Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbonsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Polyolefins made in accordance with the present invention are produced by polymerizing an unsaturated olefin or combination of unsaturated olefins to produce an unsaturated polyolefin, isomerizing the unsaturated polyolefin in the presence of an acid catalyst under conditions to produce a substantially unsaturated-isomerized polyolefin, and hydrogenating the unsaturated-isomerized polyolefin to produce a saturated isomerized polyolefin. A lube oil comprising the inventive saturated isomerized polyolefin is also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Polyolefins from non-conventional feeds
ActiveUS7456329B2Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionLiquid carbonaceous fuelsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Polyolefins made in accordance with the present invention are produced by polymerizing an unsaturated olefin or combination of unsaturated olefins to produce an unsaturated polyolefin, isomerizing the unsaturated polyolefin in the presence of an acid catalyst under conditions to produce a substantially unsaturated-isomerized polyolefin, and hydrogenating the unsaturated-isomerized polyolefin to produce a saturated isomerized polyolefin. A lube oil comprising the inventive saturated isomerized polyolefin is also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
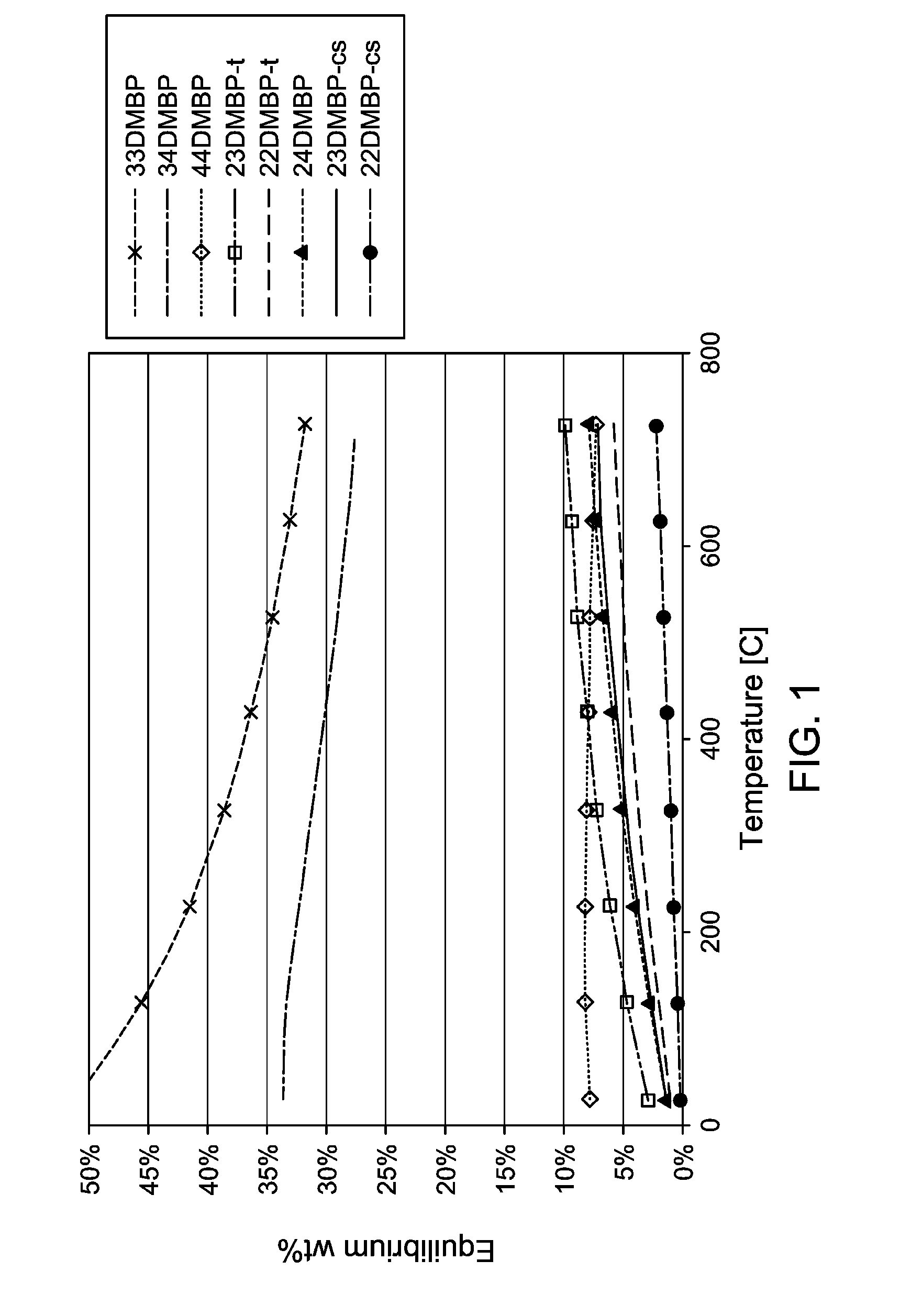
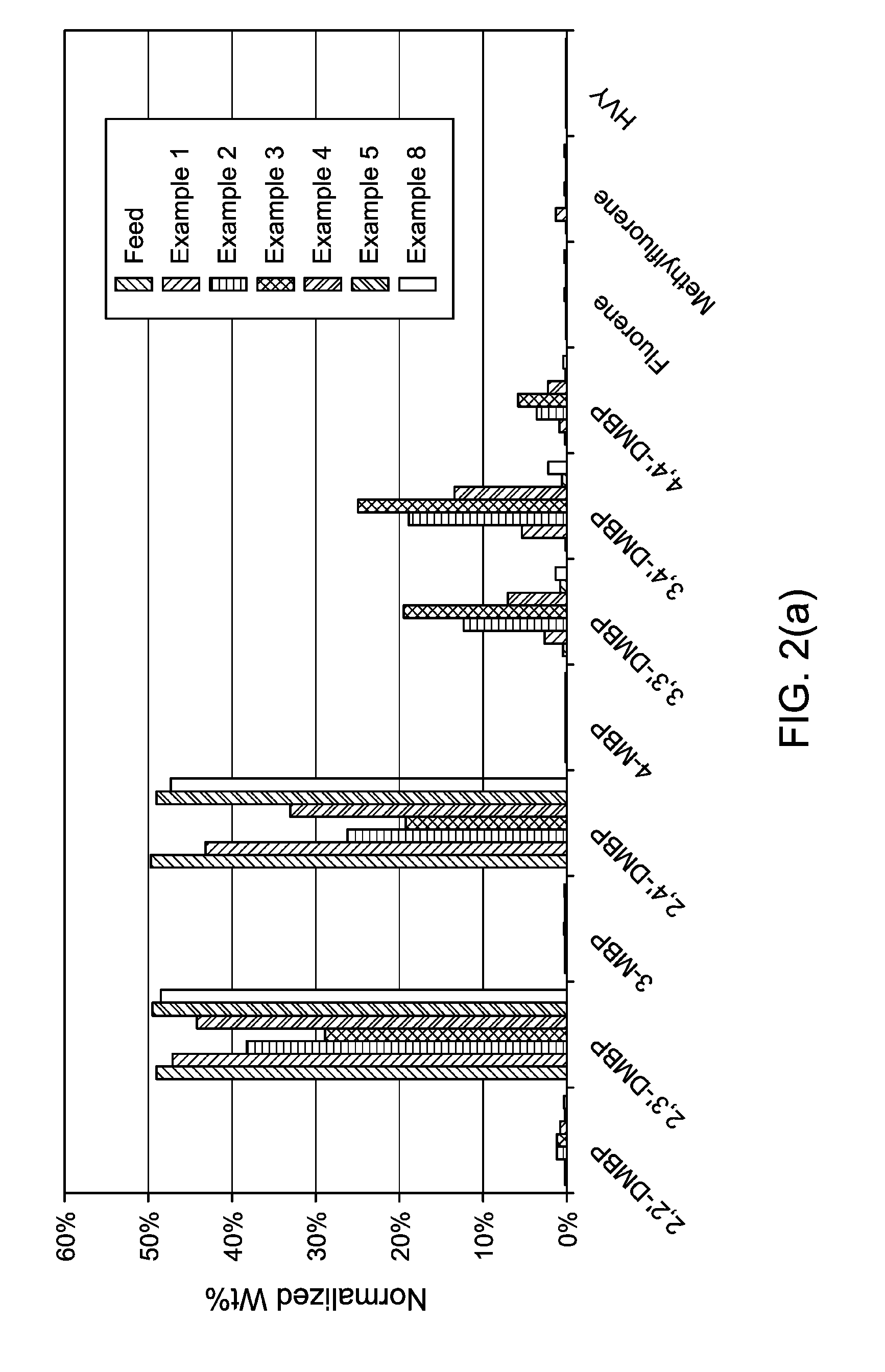
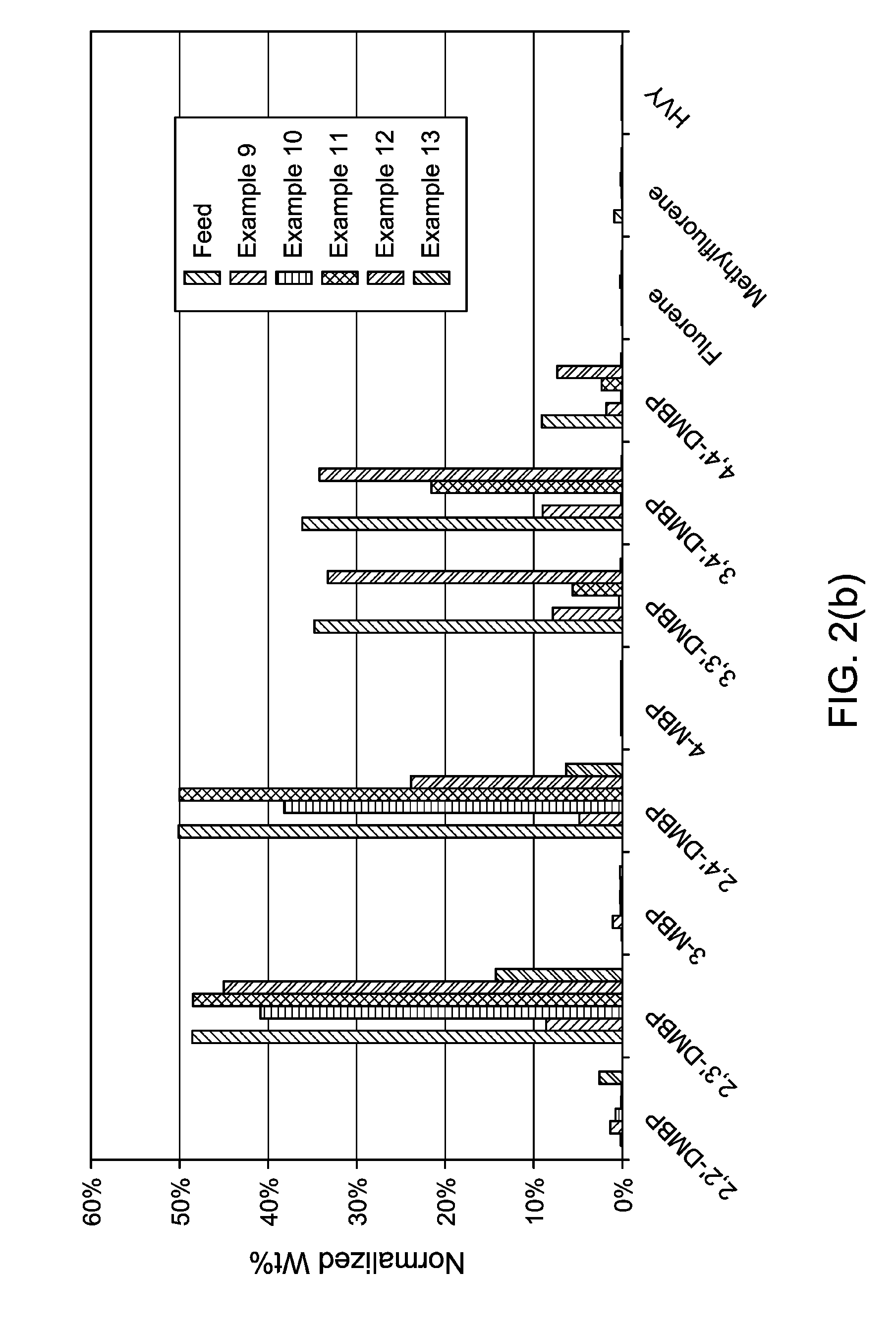
Production and Use of Dialkylbiphenyl Isomer Mixtures
ActiveUS20160176785A1Low conversionHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystIsomerizationOrganic chemistry
A process is described for converting at least one isomer of a dialkyl-substituted biphenyl compound, such as at least one 2,X′ dialkylbiphenyl isomer (where X′ is 2′, 3′ and / or 4′), into at least one different isomer, 3,3′, 3,4′ and / or 4,4′ dialkylbiphenyl isomer. The process comprises contacting a feed comprising the dialkyl-substituted biphenyl compound isomer with an acid catalyst under isomerization conditions.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
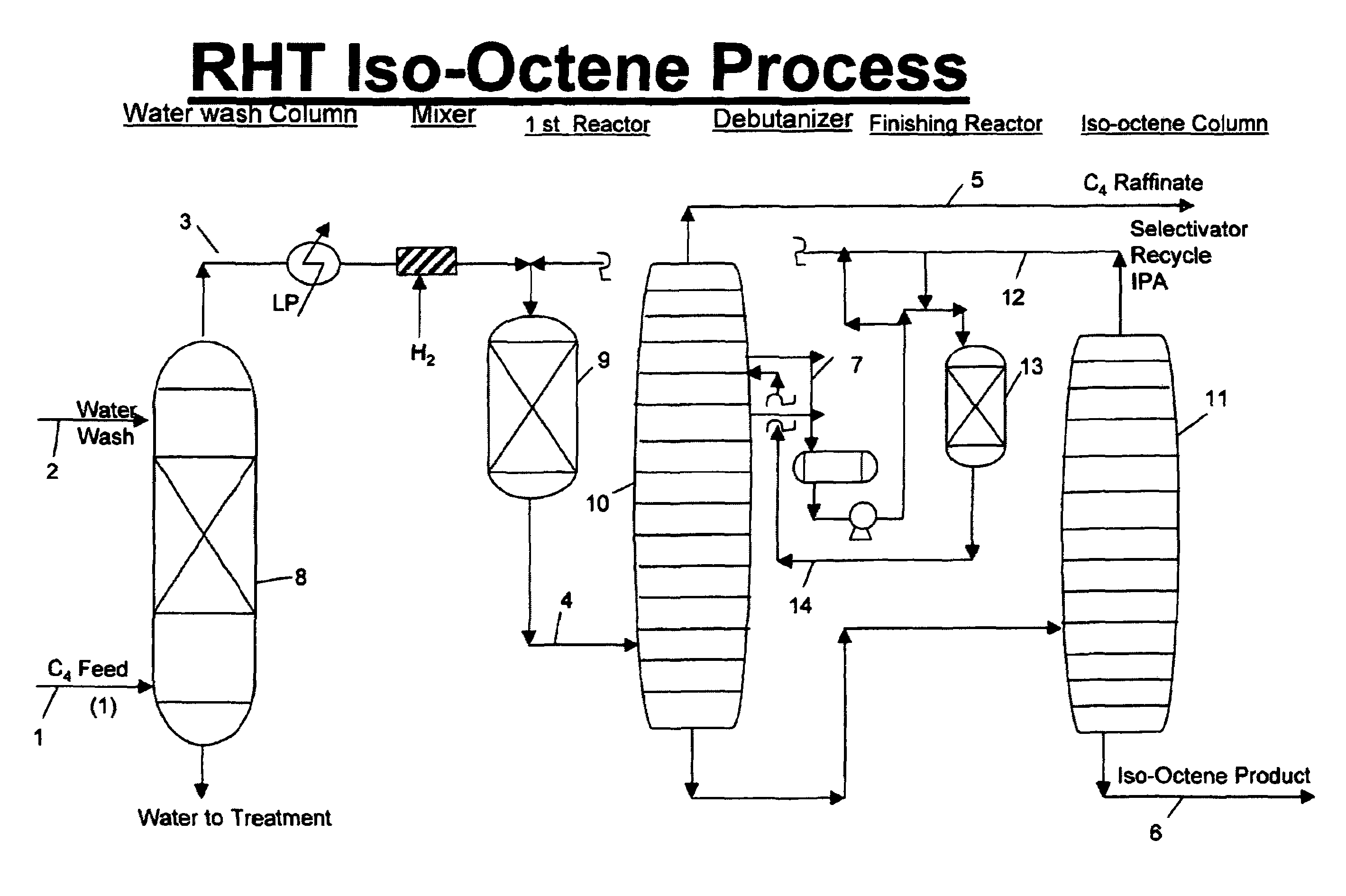
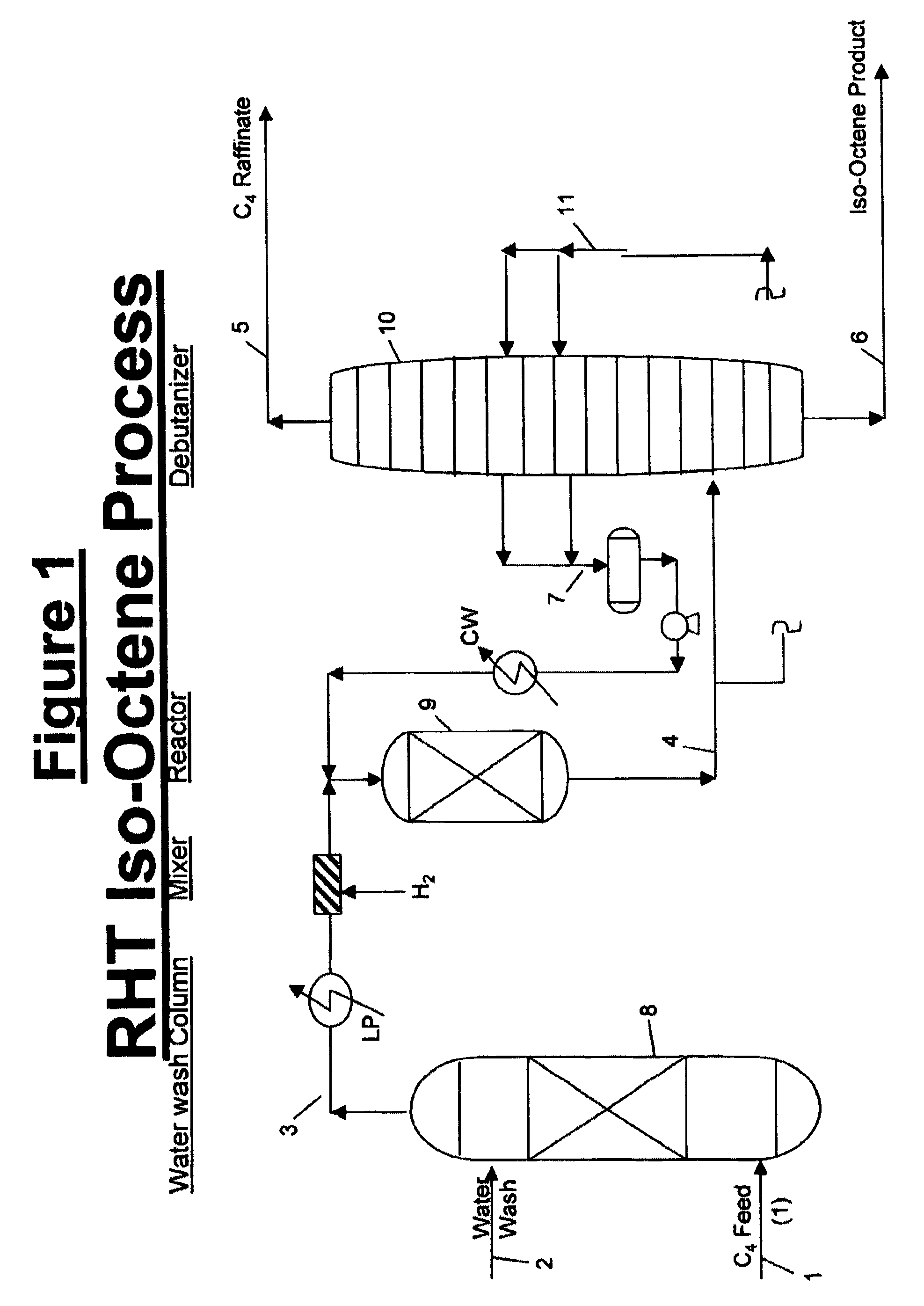
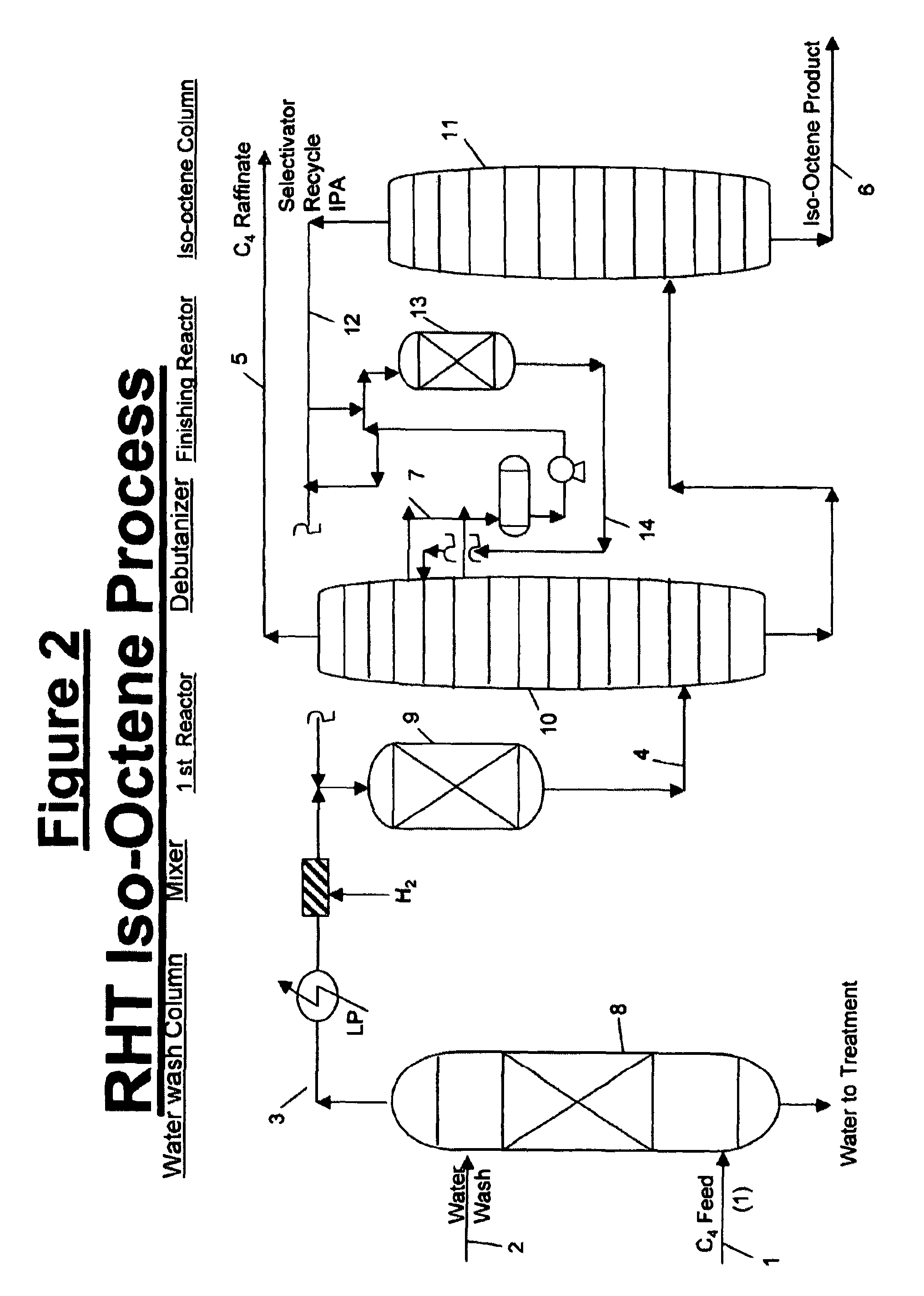
Isooctene/isooctane process
InactiveUS8188327B1Reduce concentrationGood choiceHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationOcteneAlkene
This invention covers a process for dimerizing of isobutylene to Iso-octene and unique configuration is being disclosed, where the Feed is diluted to low level with recycle which has essentially no Iso-octene, dual catalyst system, new selectivator (IPA) and successive catalyst stages if needed to enhance the conversion. The process is very selective and provides higher isobutylene conversion.Additionally the invention also covers the hydrogenation of olefins to Paraffin, Iso-octene to Iso-octane product under moderate conditions and with dual or single catalyst system.
Owner:BAKSHI AMARJIT S
Dehydrogenation method
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for the manufacture of polyolefins
ActiveUS20070293712A1Molecular sieve catalystHydrocarbon by hydrogenationPolyolefinCatalytic distillation
The present invention relates to a process for producing polyolefins wherein a feedstock comprising n-olefin or a mixture of n-olefins is dimerized in the presence of a solid acidic catalyst by passing the feedstock to a catalytic distillation apparatus comprising either a) a combination of a distillation column and a reactor comprising at least one catalyst bed, or b) a distillation column connected to one or more side reactors comprising at least one catalyst layer, recovering the unreacted n-olefin from the distillation column or the combination of the distillation column and the reactor at the upper part thereof as a side-stream to be combined with the feedstock, and the reaction product from the dimerization is hydrogenated.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Hydroalkylation of aromatic compounds using EMM-12
This disclosure relates to a process for manufacturing a mono-cycloalkyl-substituted aromatic compound, said process comprising contacting a feedstock comprising an aromatic compound and hydrogen under hydroalkylation reaction conditions with a catalyst system comprising a molecular sieve and at least one metal with hydrogenation activity, wherein said molecular sieve has, in its as-synthesized form and in calcined form, an X-ray diffraction pattern including peaks having a d-spacing maximum in the range of 14.17 to 12.57 Angstroms, a d-spacing maximum in the range of 12.1 to 12.56 Angstroms.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Olefin oligomerization and compositions therefrom
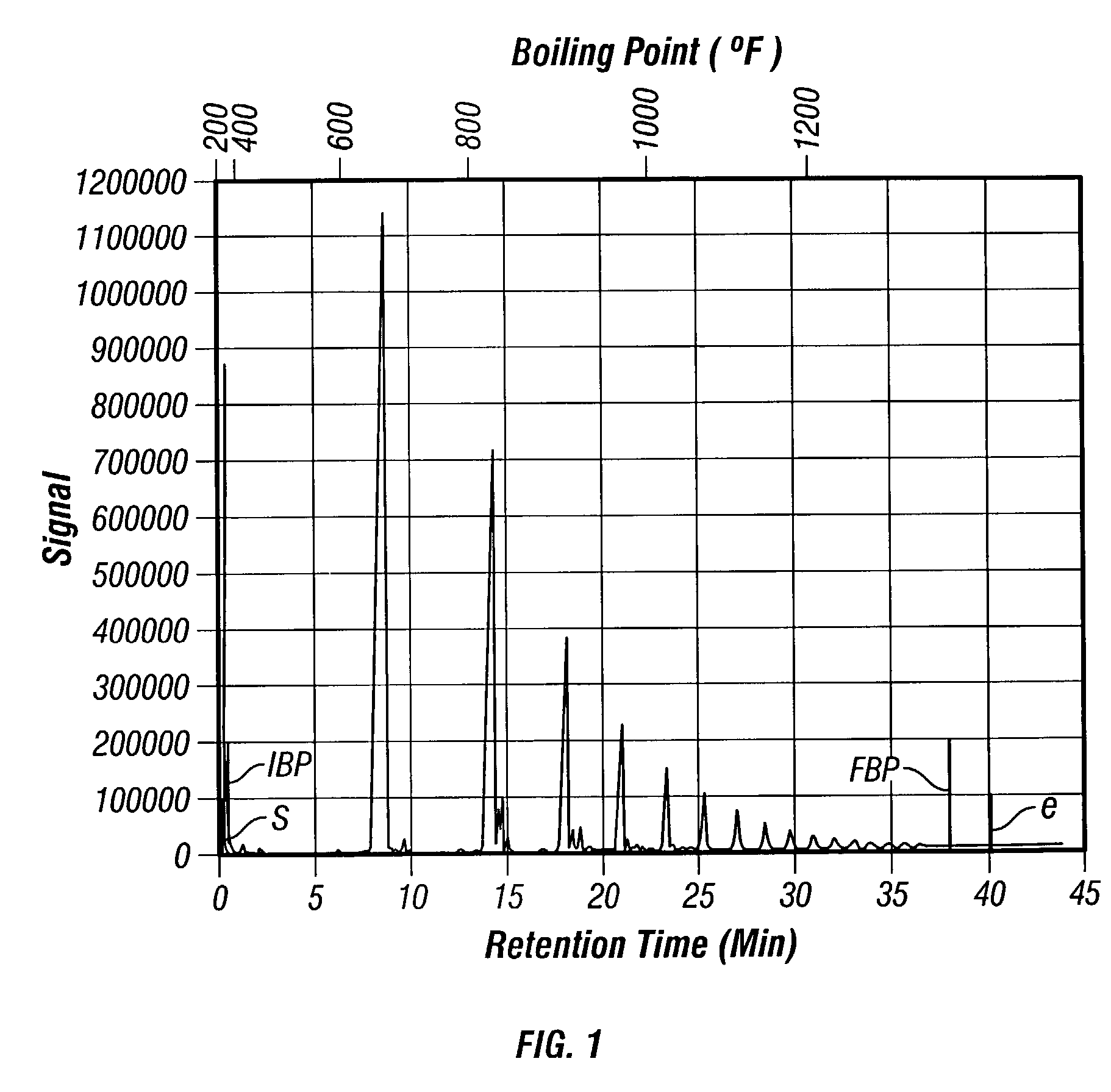
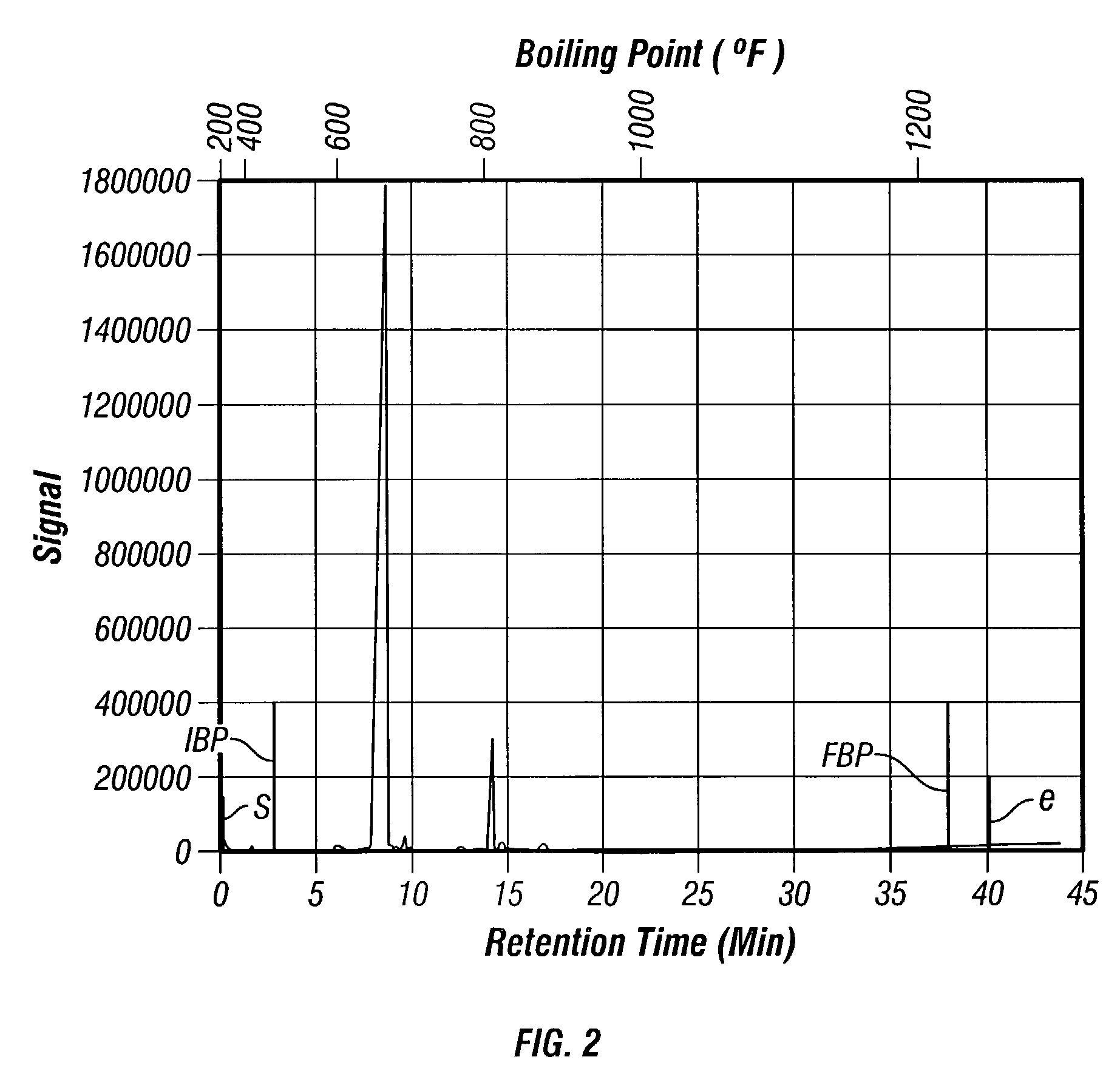
ActiveUS20060199985A1Hydrocarbon purification/separationLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionCarbon numberBoiling point
A hydrocarbon composition that comprises species of at least 3 different carbon numbers, at least about 95 wt % non-normal hydrocarbons, no greater than 1000 wppm aromatics, no greater than 10 wt % naphthenes, and also has a certain boiling point range; and a process for making the hydrocarbon composition.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
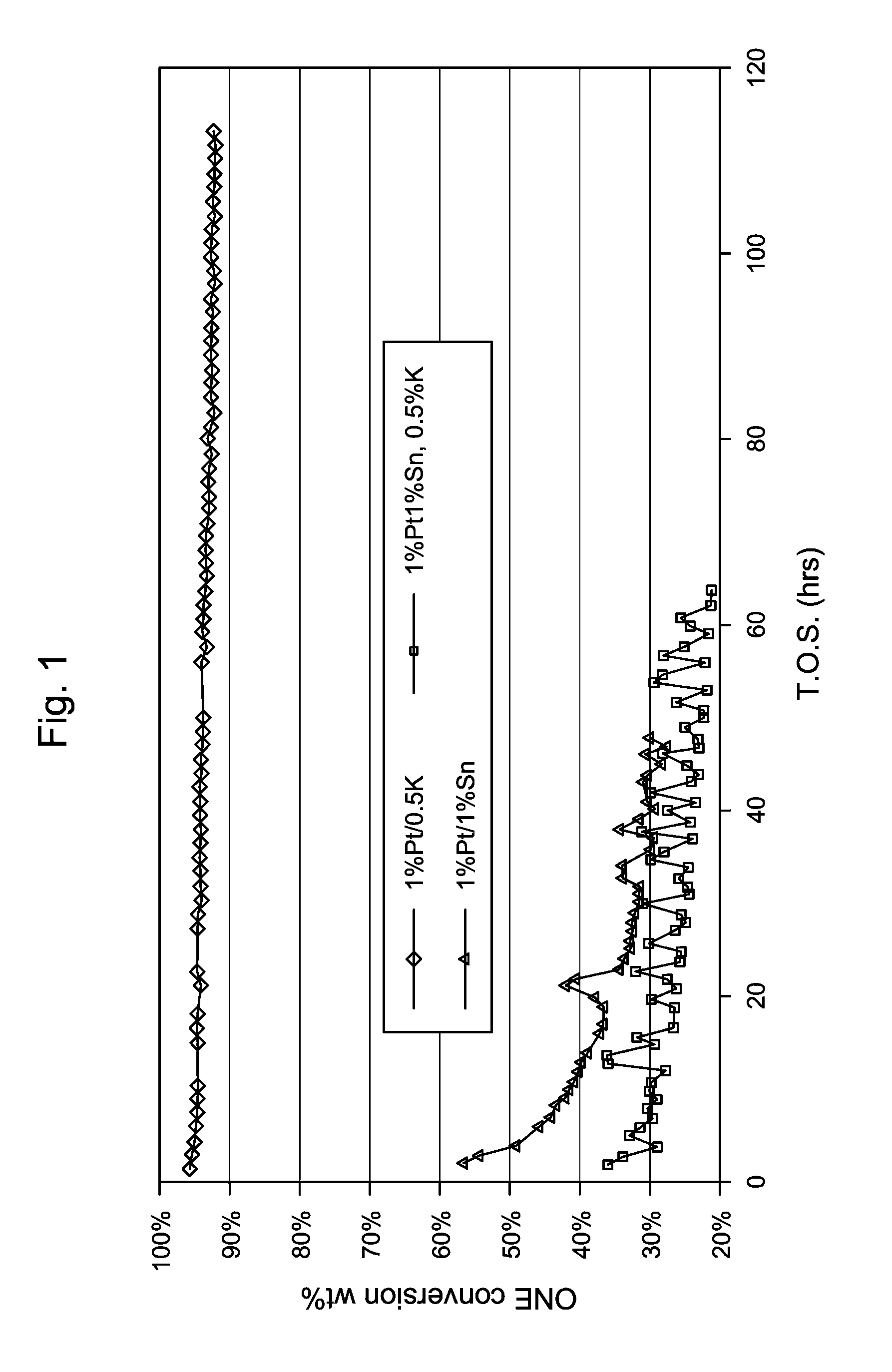
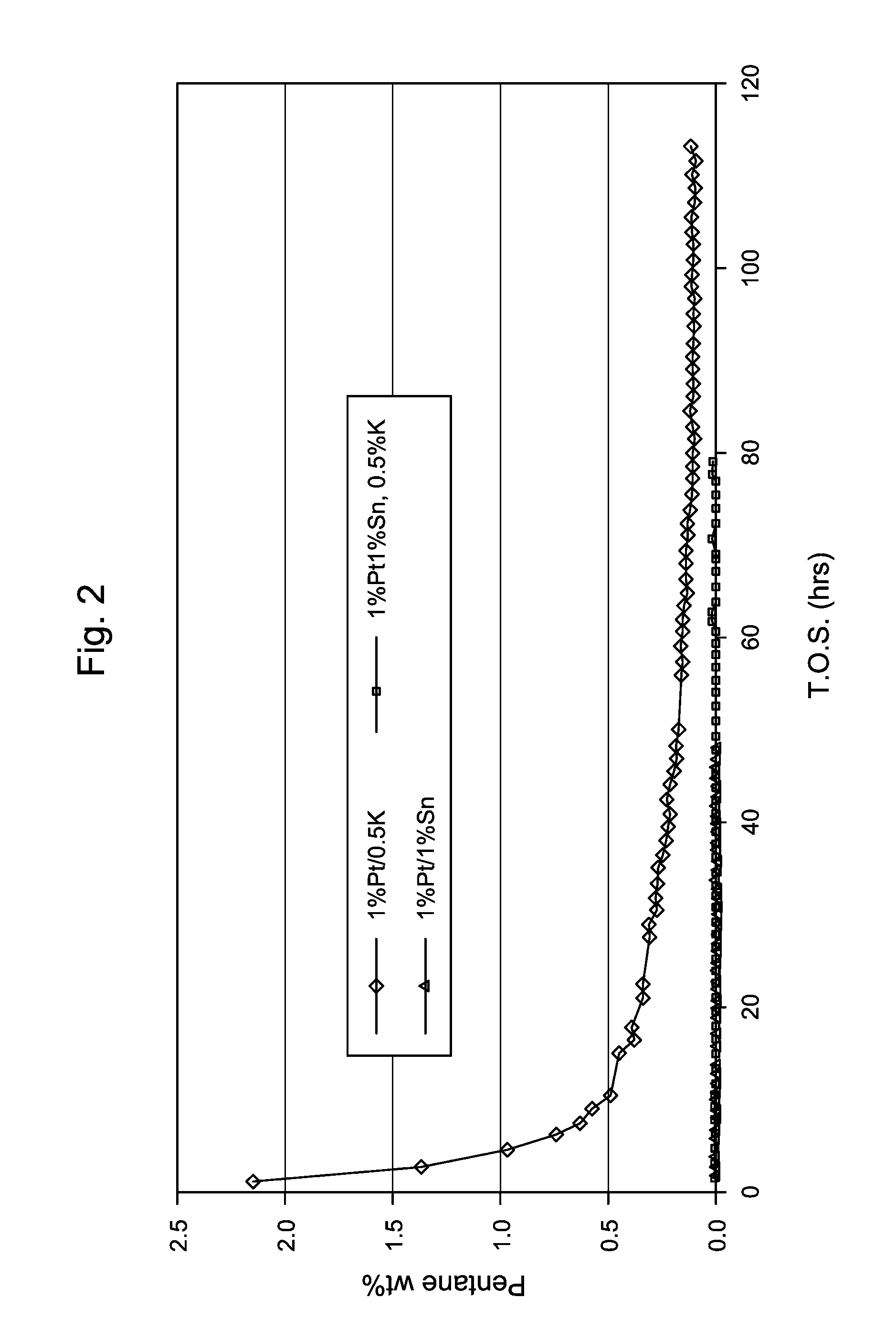
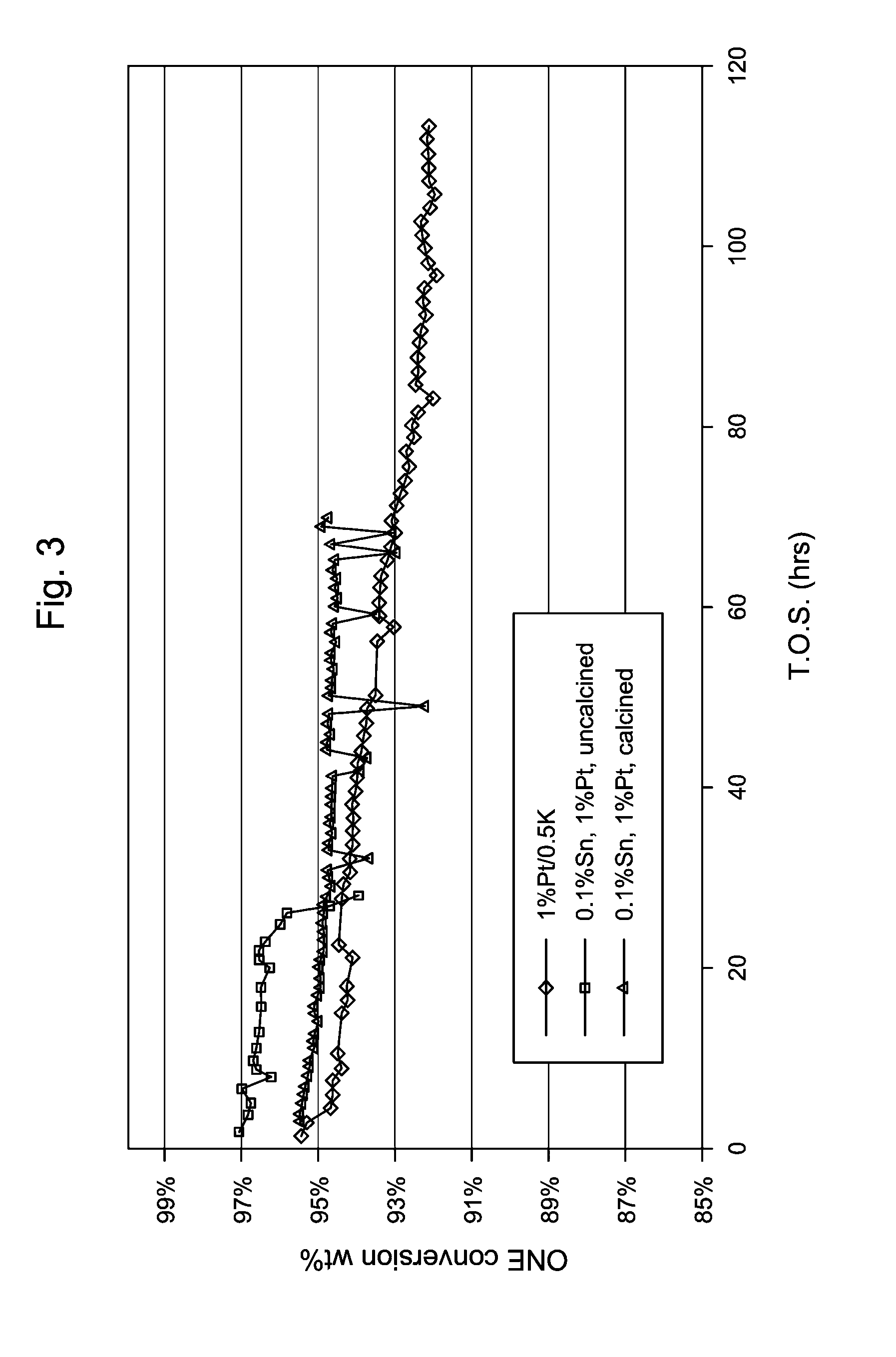
Dehydrogenation Catalyst and Process
InactiveUS20140066663A1Organic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationDehydrogenationTin
A catalyst composition comprises (i) a support; (ii) a dehydrogenation component comprising at least one metal or compound thereof selected from Groups 6 to 10 of the Periodic Table of Elements; and (iii) tin or a tin compound, wherein the tin is present in an amount of 0.01 wt % to about 0.25 wt %, the wt % based upon the total weight of the catalyst composition.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for oligomerizing gasoline without further upgrading
ActiveUS20140135541A1Readily used as gasolineMolecular sieve catalystHydrocarbon by hydrogenationGasoline
Owner:UOP LLC
Popular searches
Hydrocarbon from oxygen organic compounds Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensation Base-materials Bulk chemical production Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalysts Catalytic reactions Polishing compositions Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production Treatment with hydrotreatment processes
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com