Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
178results about "Carrier tracks/pits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
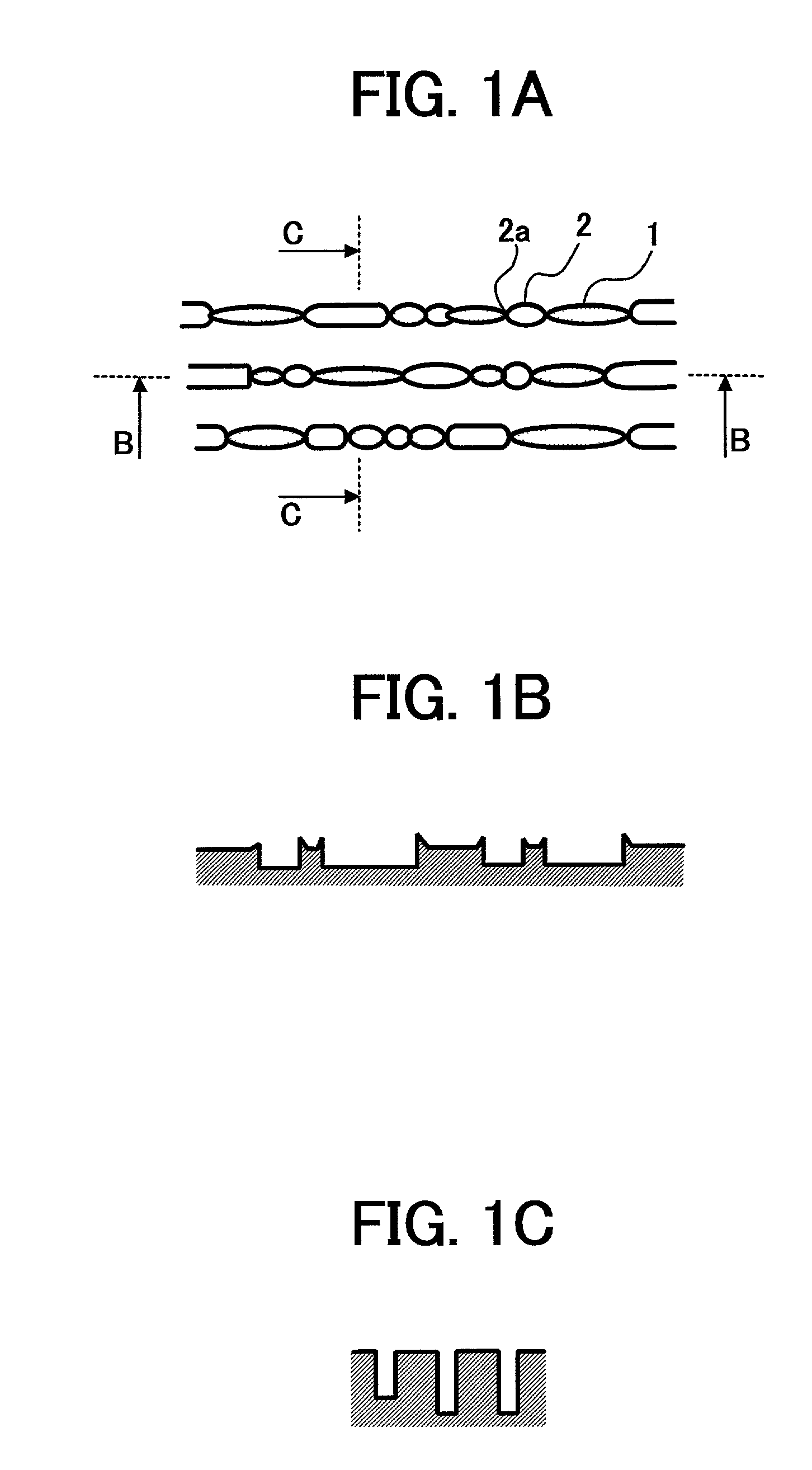
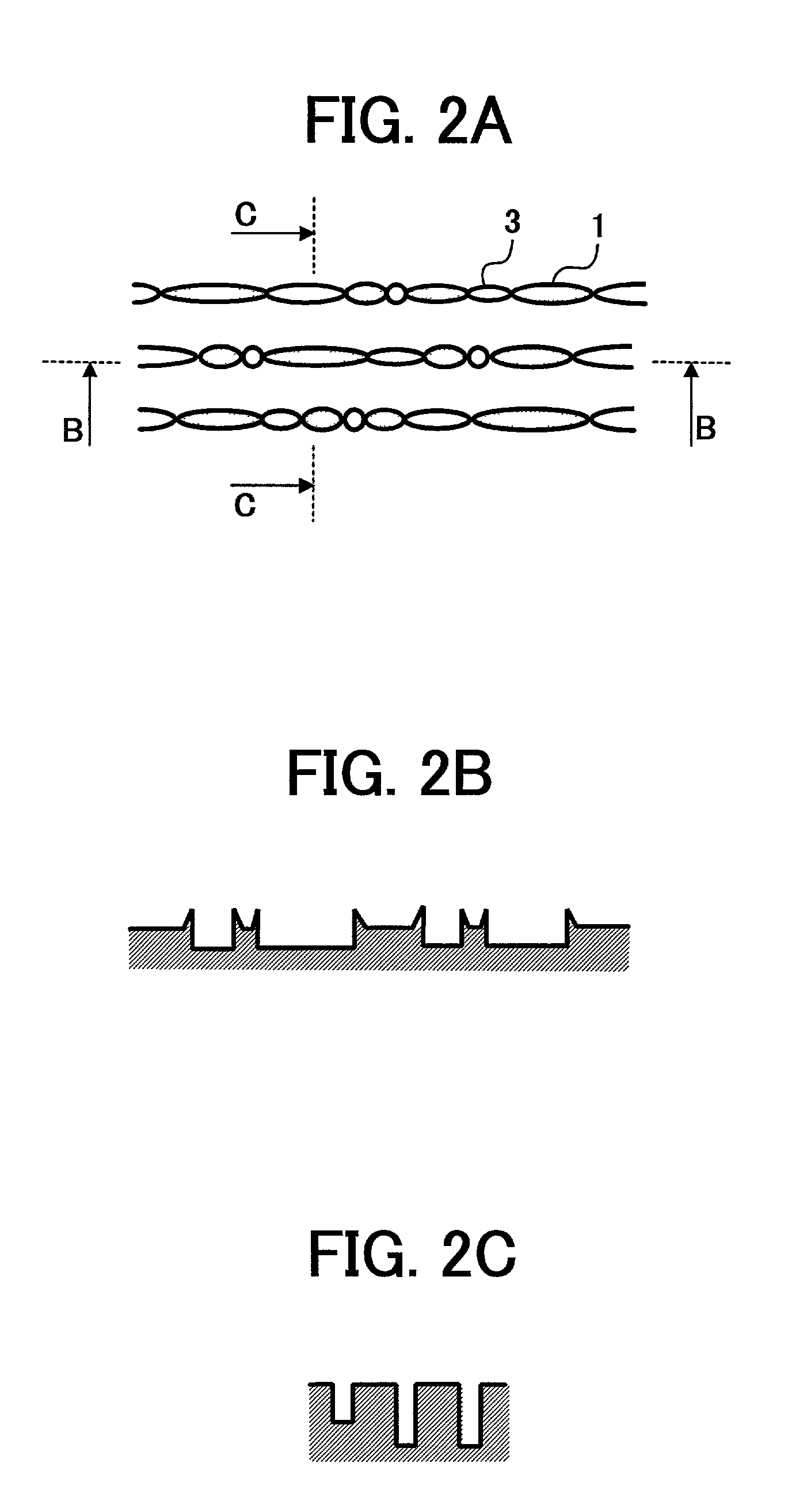
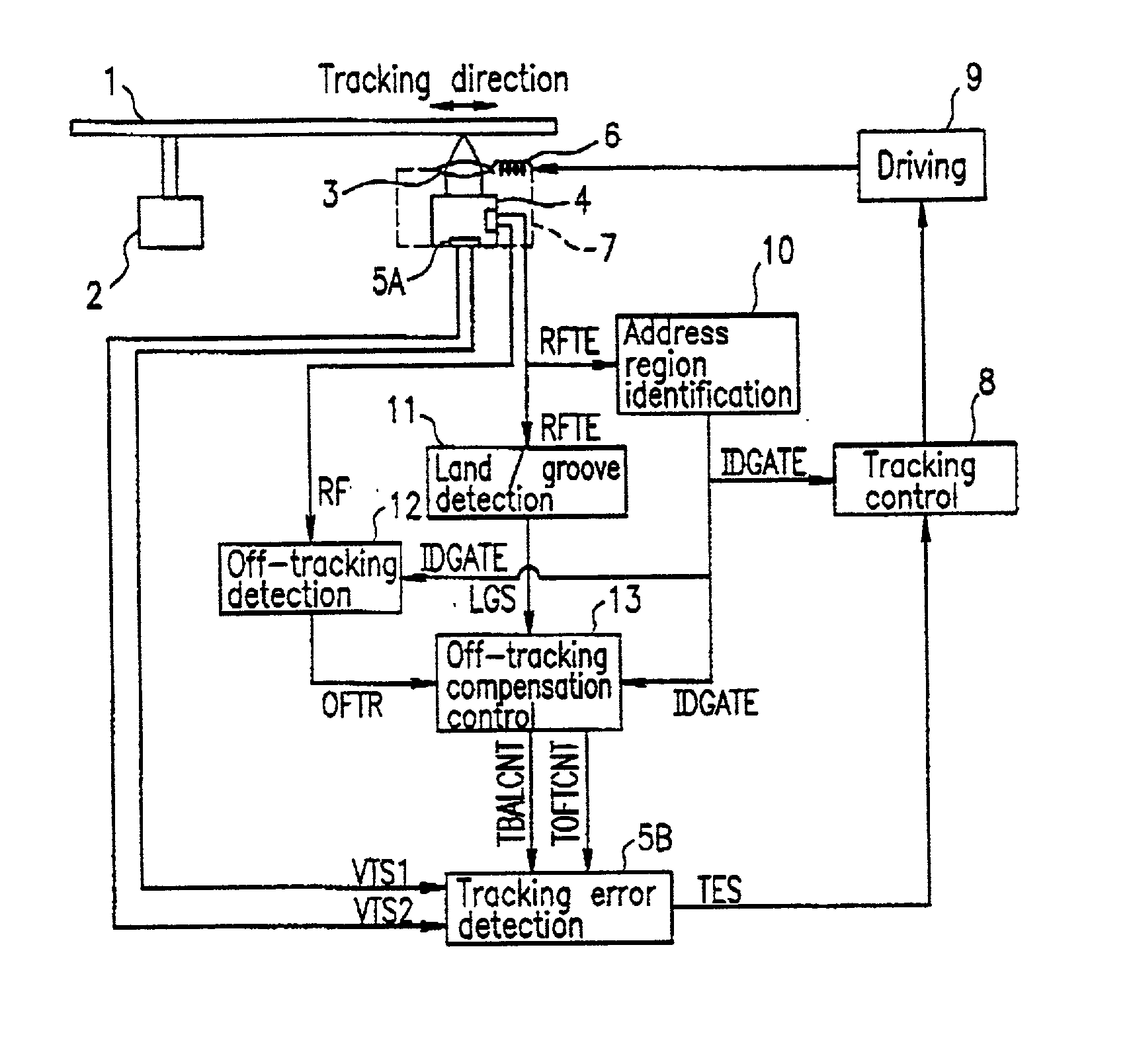
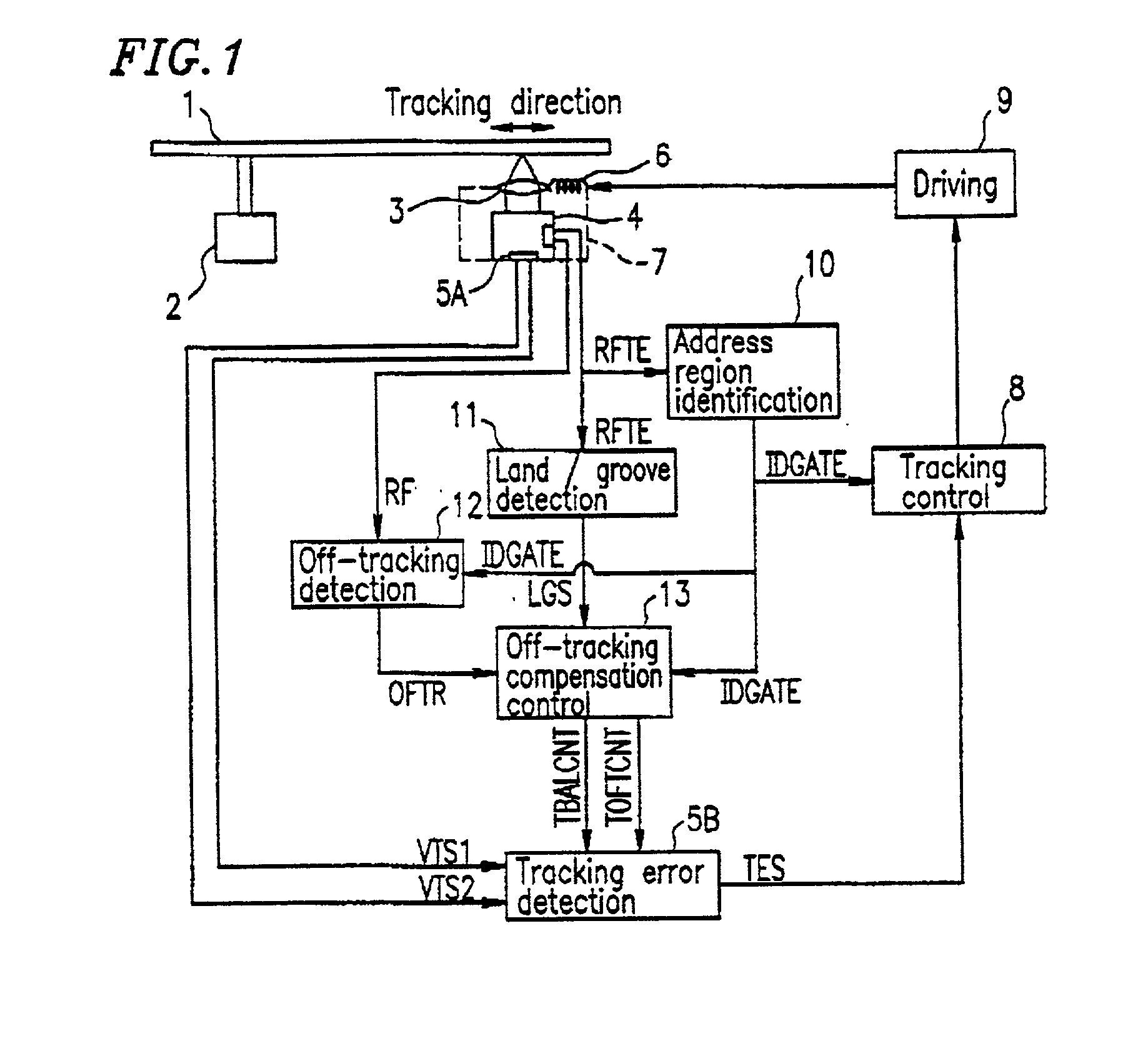
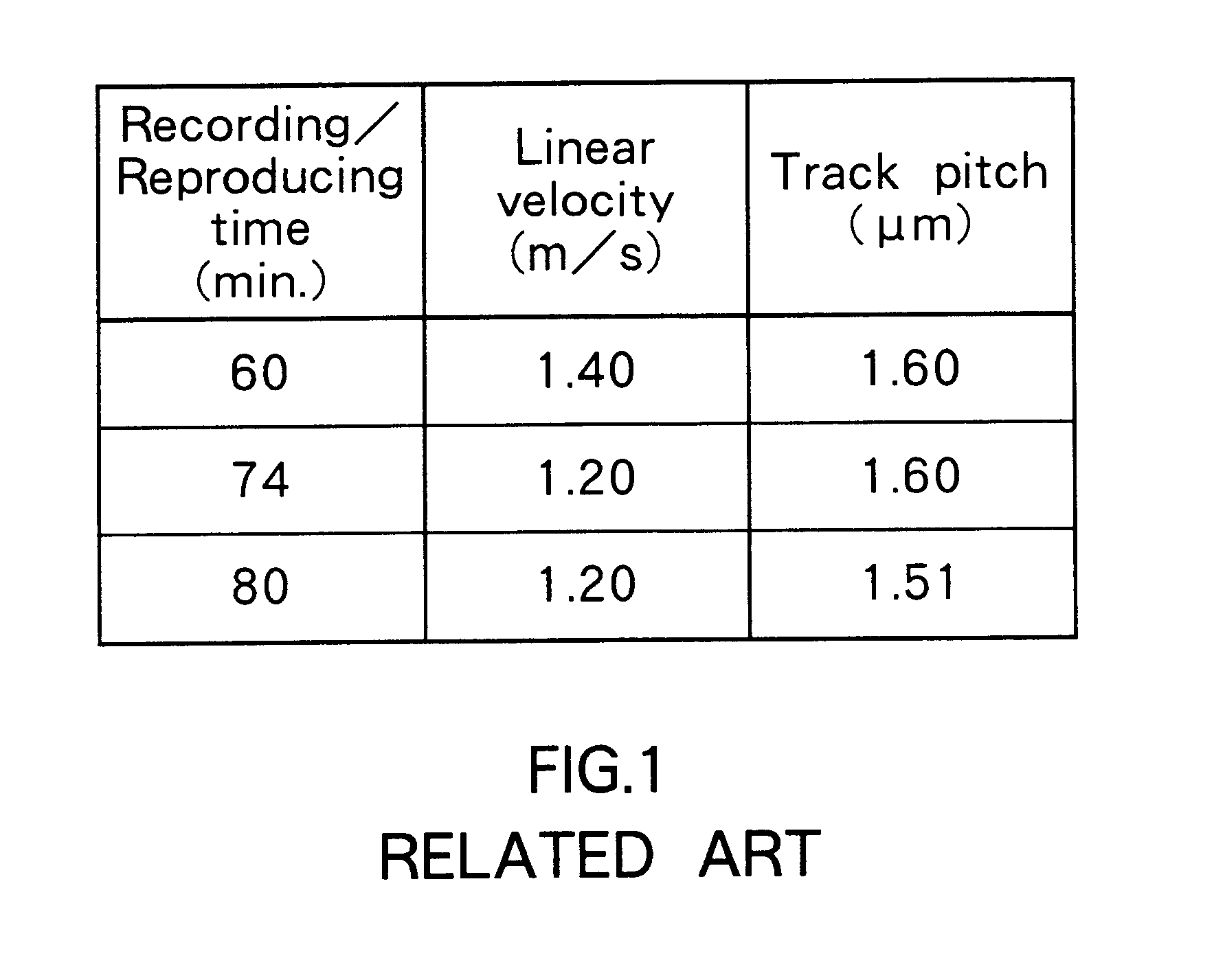
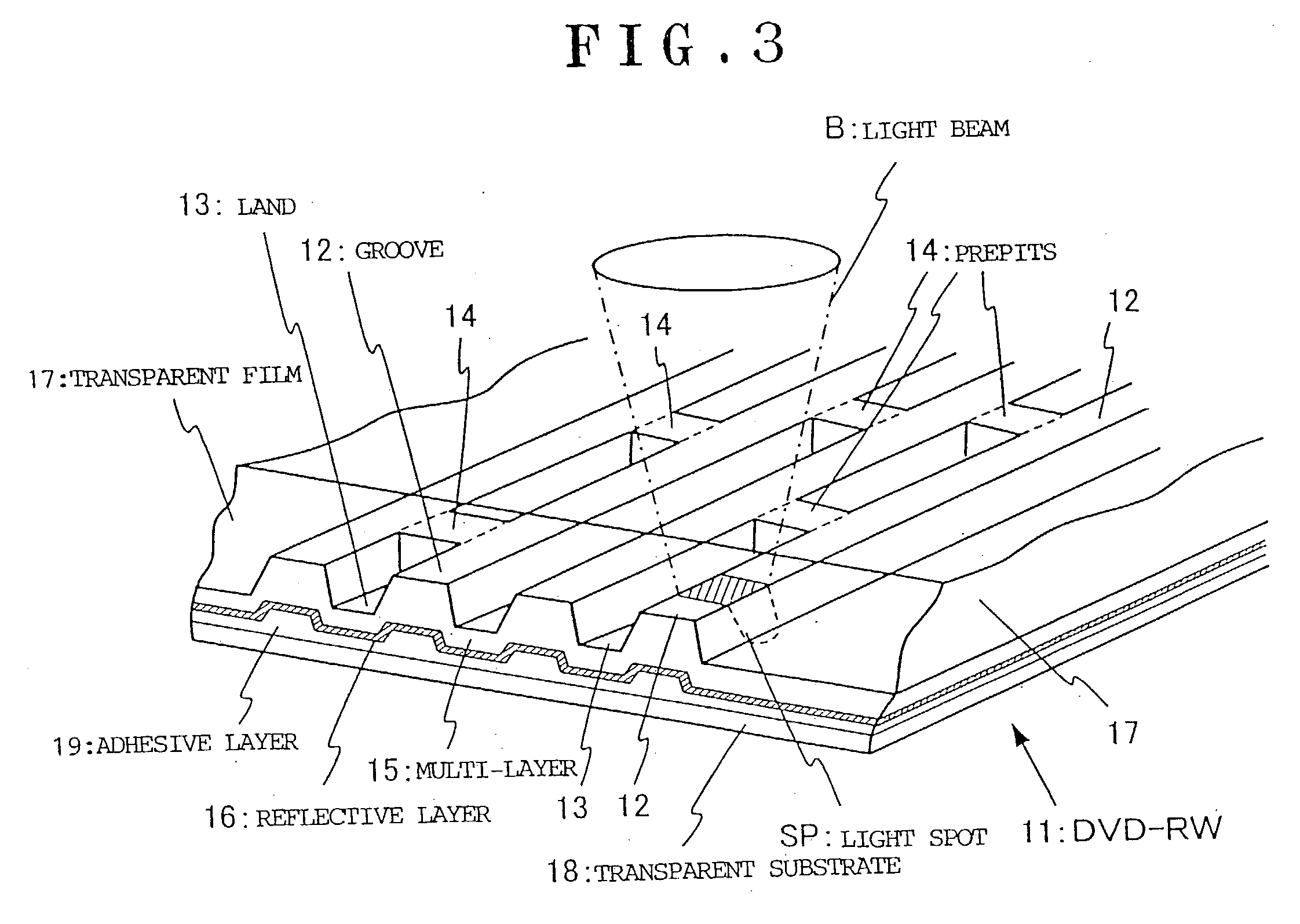
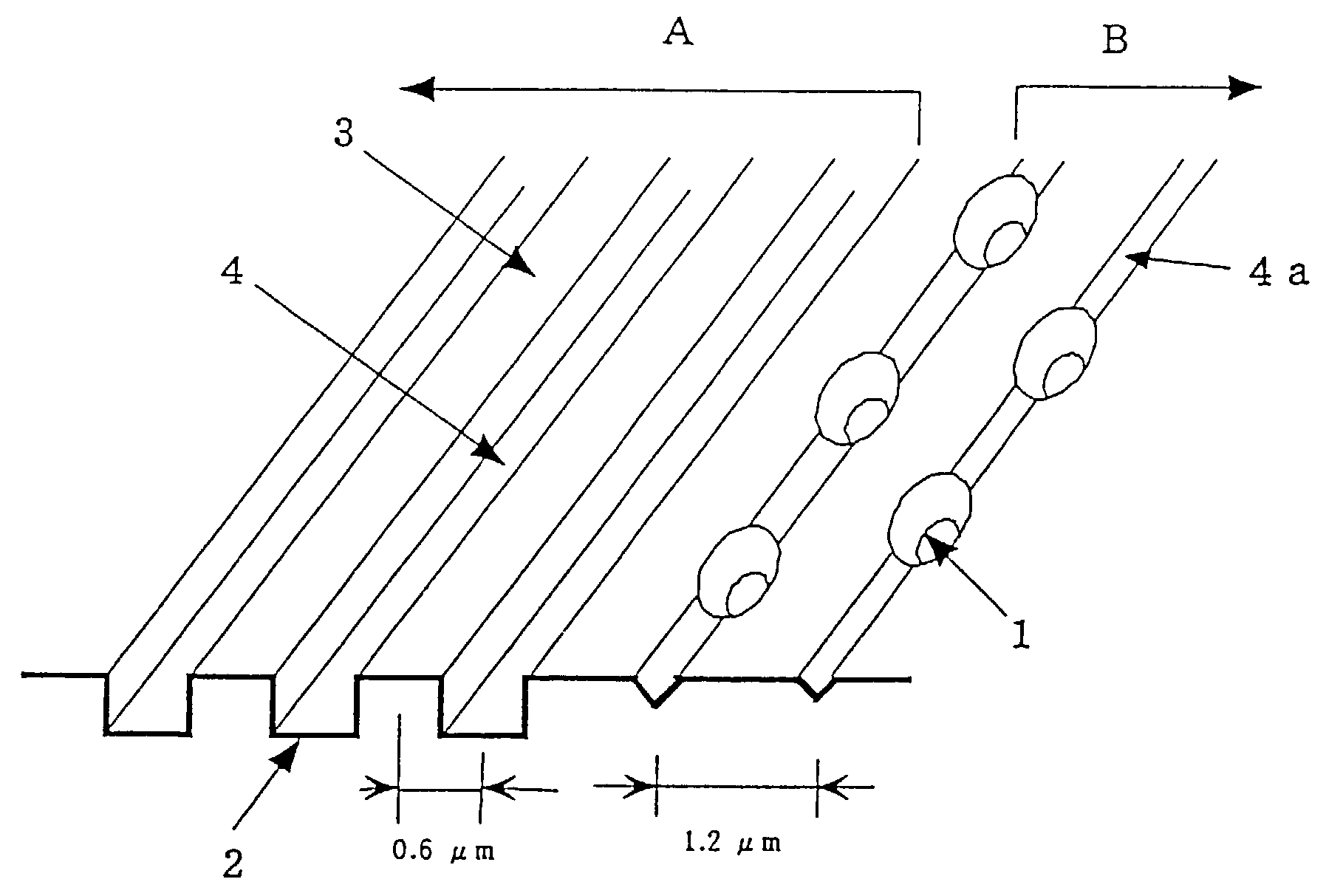
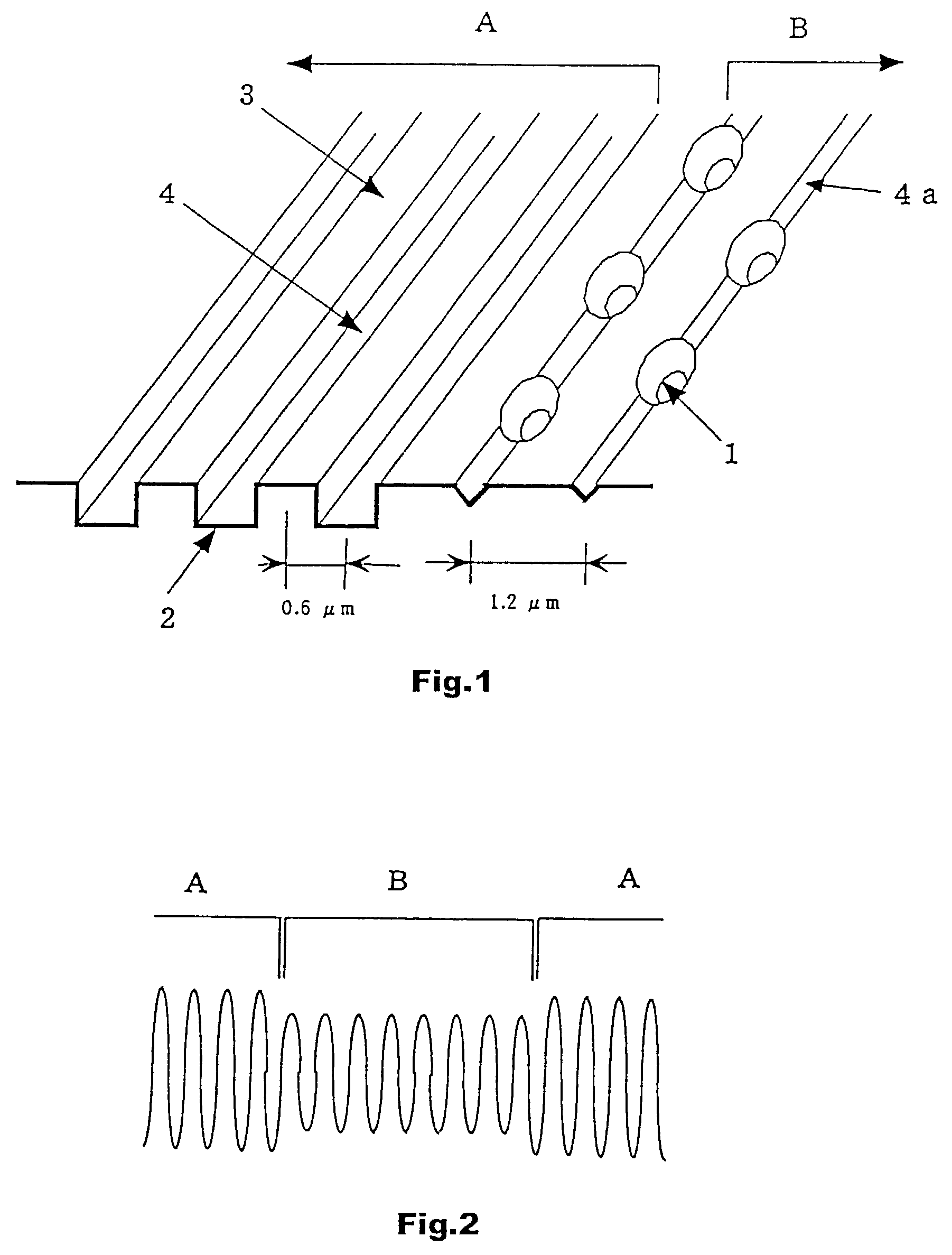
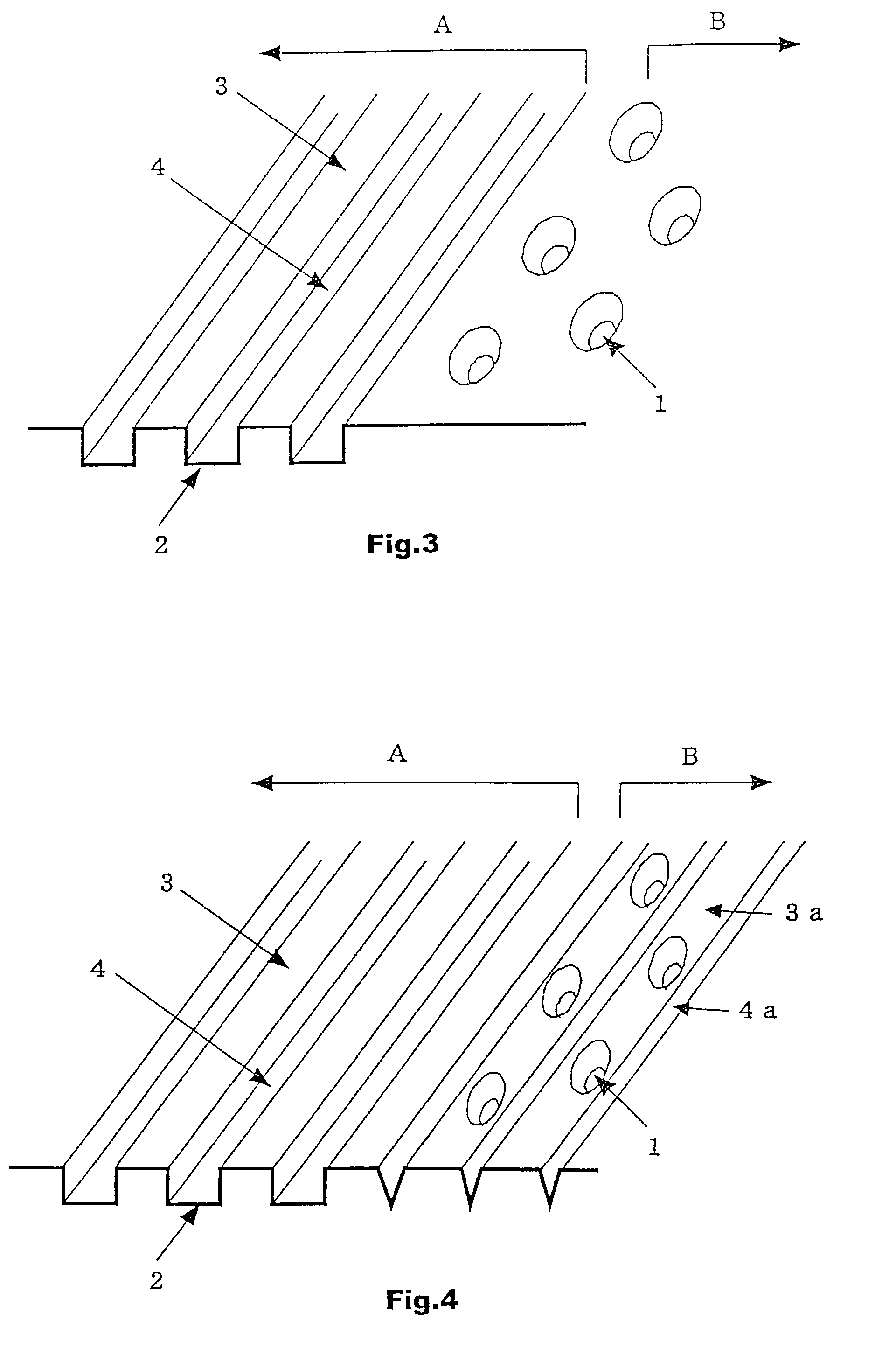
Optical recording medium having groove and land tracks, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6535477B1Quality improvementEasy to provideMechanical record carriersRecord information storageEngineeringOptical recording
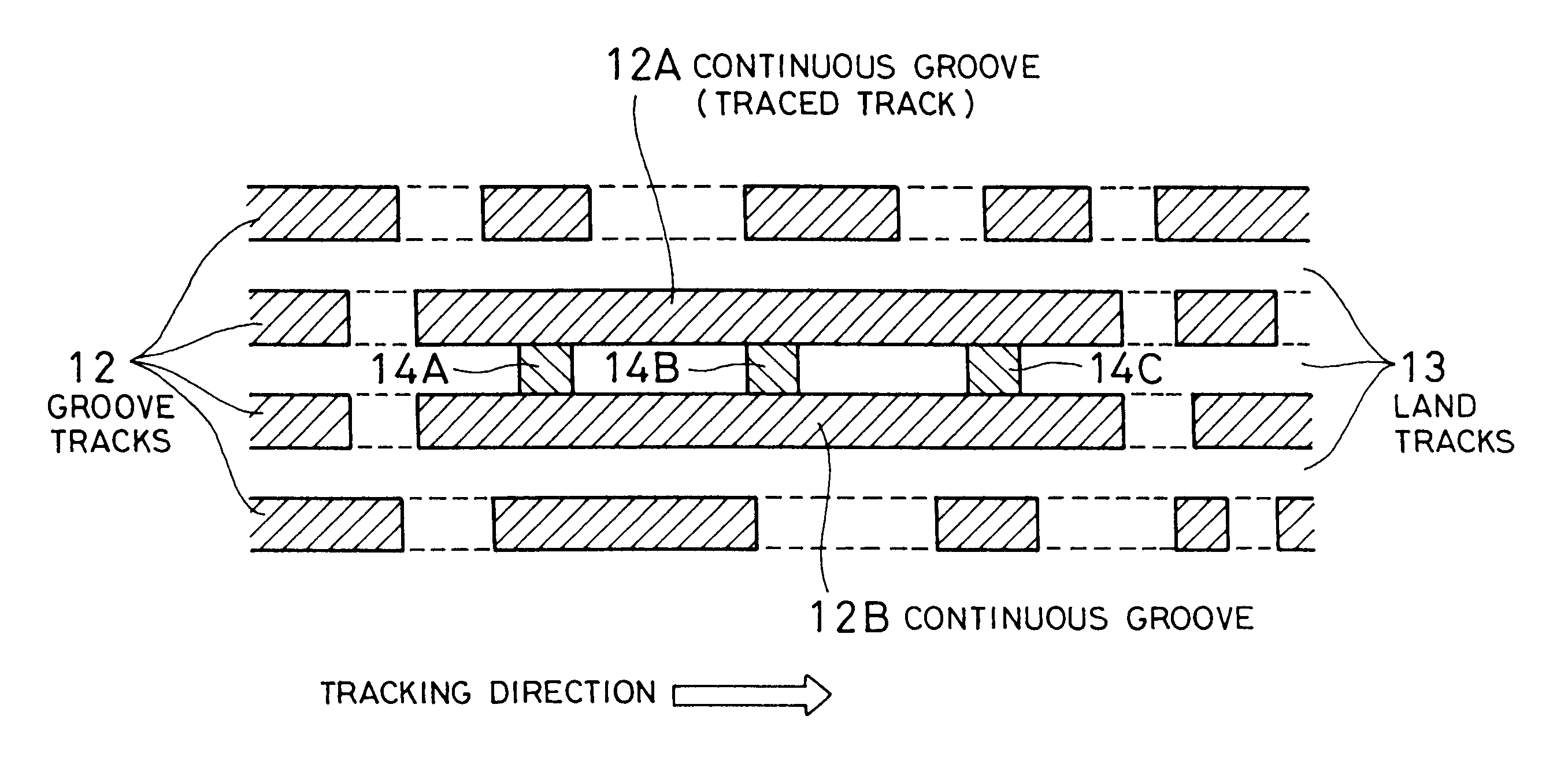
At least a portion of groove tracks in a information-data recording region of an optical recording medium comprises a plurality of groove portions separated by groove-absent portions in a rotational direction of the optical recording medium, each of the mark portions or each of the space portions includes one of the groove-absent portions. At least one of two groove tracks adjacent to prepit train, which is formed in land tracks, has a continuous groove portion or a groove-absent portion extending at least from a leading end to a trailing end of at least one prepit included in the prepit train in a rotational direction of the optical recording medium. The frequency band for separation of the groove tracks includes at least a portion of a frequency band of a modulated recording signal for recording information data on the optical recording medium.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Optical information recording medium
Owner:RICOH KK
Information recording medium
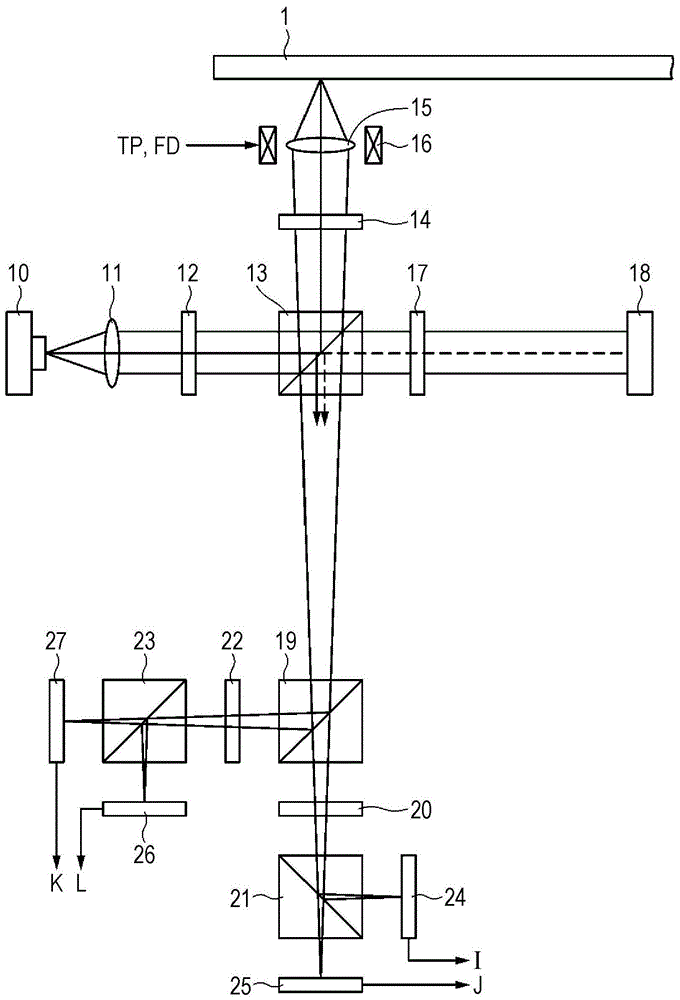
In an information recording medium comprising at least a substrate, a recording layer, and a resin layer, the substrate is formed with at least a pit corresponding to a read only area 31 and a groove corresponding to a recording / reproducing area 32 without overlapping with each other. A reflectivity of the recording layer is specified to be more than 10%. The recording layer and the resin layer are continuously adhered over both the read only and recording / reproducing areas 31 and 32. The information recording medium is characterized in that both push-pull signal outputs T1 and T2, which are reproduced from the read only area 31 and the recording / reproducing area 32 respectively, are more than 0.1 and satisfy an inequality 1.5≧T1 / T2≧0.5.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Mastering device, disc manufacturing method, disc-shaped recording medium, disc reproduction device, and disc reproduction method
InactiveUS20050122889A1Stably and reliably readReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useComputer hardwareRecording media
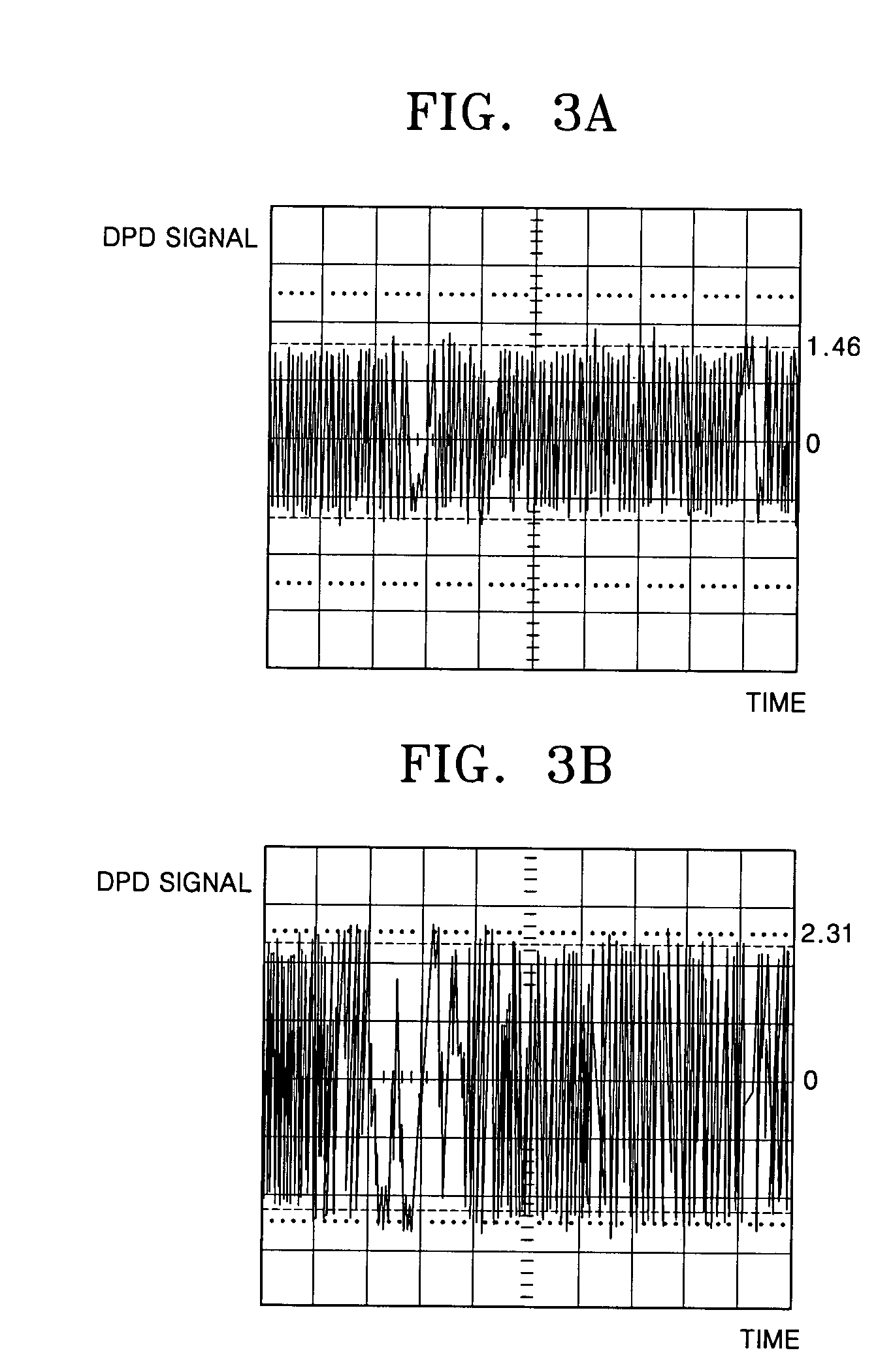
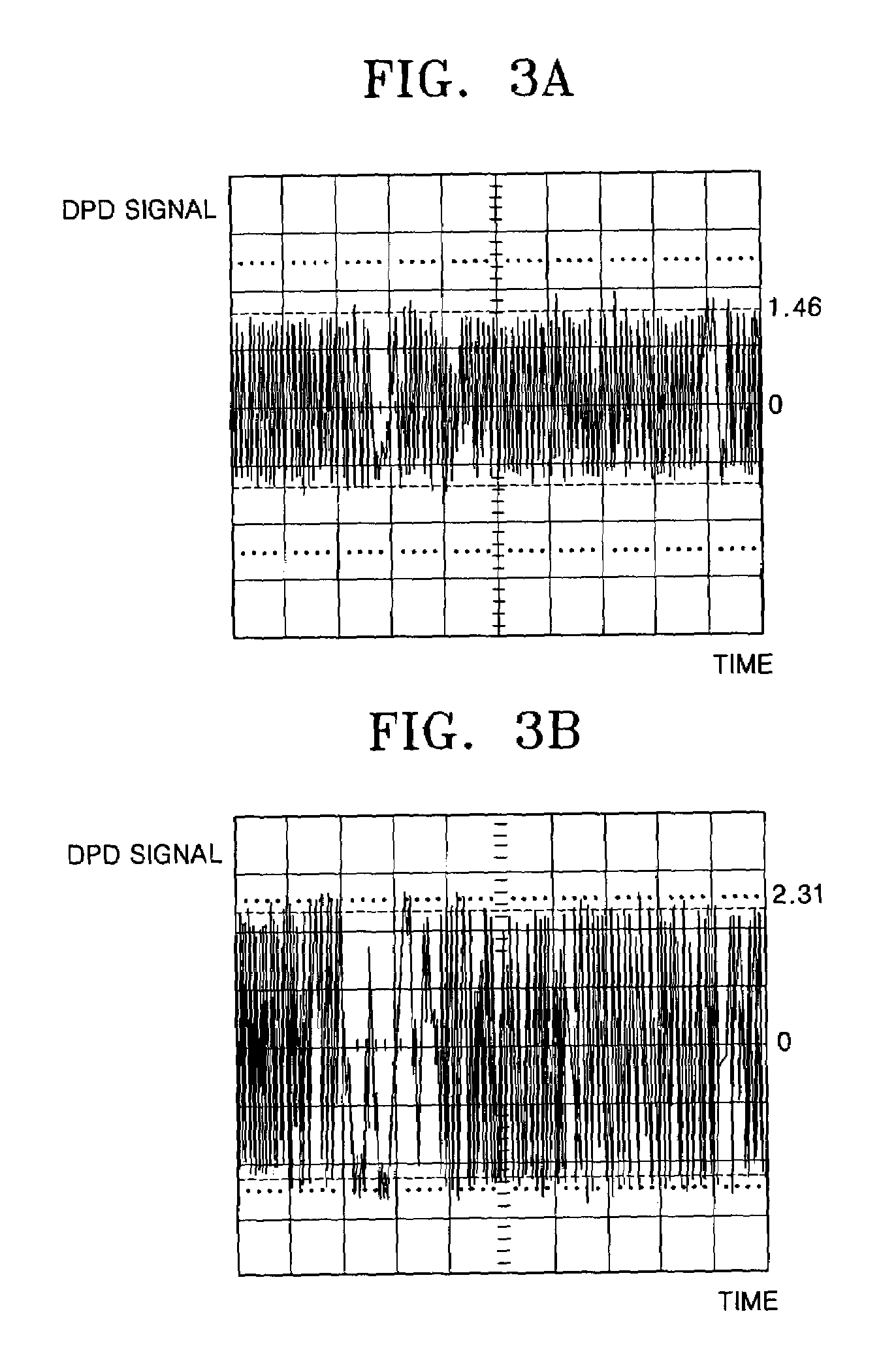
Second digital information serving as copyright protection information can be stably and reliably read without any effect of a defect or pit missing on a disk-shaped recording medium. The second digital information is recorded onto a disk-shaped recording medium by wobbling a pit sequence recorded as a first signal. The second digital information is recorded so that a plurality of bits constituting the second digital information are allocated in a unit period of an identical sync signal contained in the first signal. During playback, the plurality of bits constituting the recorded second digital information are read a plurality of times every unit period of the sync signal, and information of the read bits is then integrated. Thus, information from a large number of wobbled pits across unit periods of a plurality of sync signals can be integrated to determine the bit values.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recording medium with restricted playback feature and apparatus and methods for forming, recording, and reproducing the recording medium
InactiveUS20040233809A1Avoid repetitionFilamentary/web record carriersAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useComputer hardwareData stream
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Mastering device, disc manufacturing method, disc-shaped recording medium, disc reproduction device, and disc reproduction method
InactiveUS7248558B2Reduce the amount requiredStably and reliably readTelevision system detailsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useComputer hardwareRecording media
Second digital information serving as copyright protection information can be stably and reliably read without any effect of a defect or pit missing on a disk-shaped recording medium. The second digital information is recorded onto a disk-shaped recording medium by wobbling a pit sequence recorded as a first signal. The second digital information is recorded so that a plurality of bits constituting the second digital information are allocated in a unit period of an identical sync signal contained in the first signal. During playback, the plurality of bits constituting the recorded second digital information are read a plurality of times every unit period of the sync signal, and information of the read bits is then integrated. Thus, information from a large number of wobbled pits across unit periods of a plurality of sync signals can be integrated to determine the bit values.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical disc, information recording method, information reproducing method, and disc drive
InactiveUS20070280095A1High sensitivityAccessories for auxillary signalsRecording involving bubble/bump formingLong wavelengthBarcode
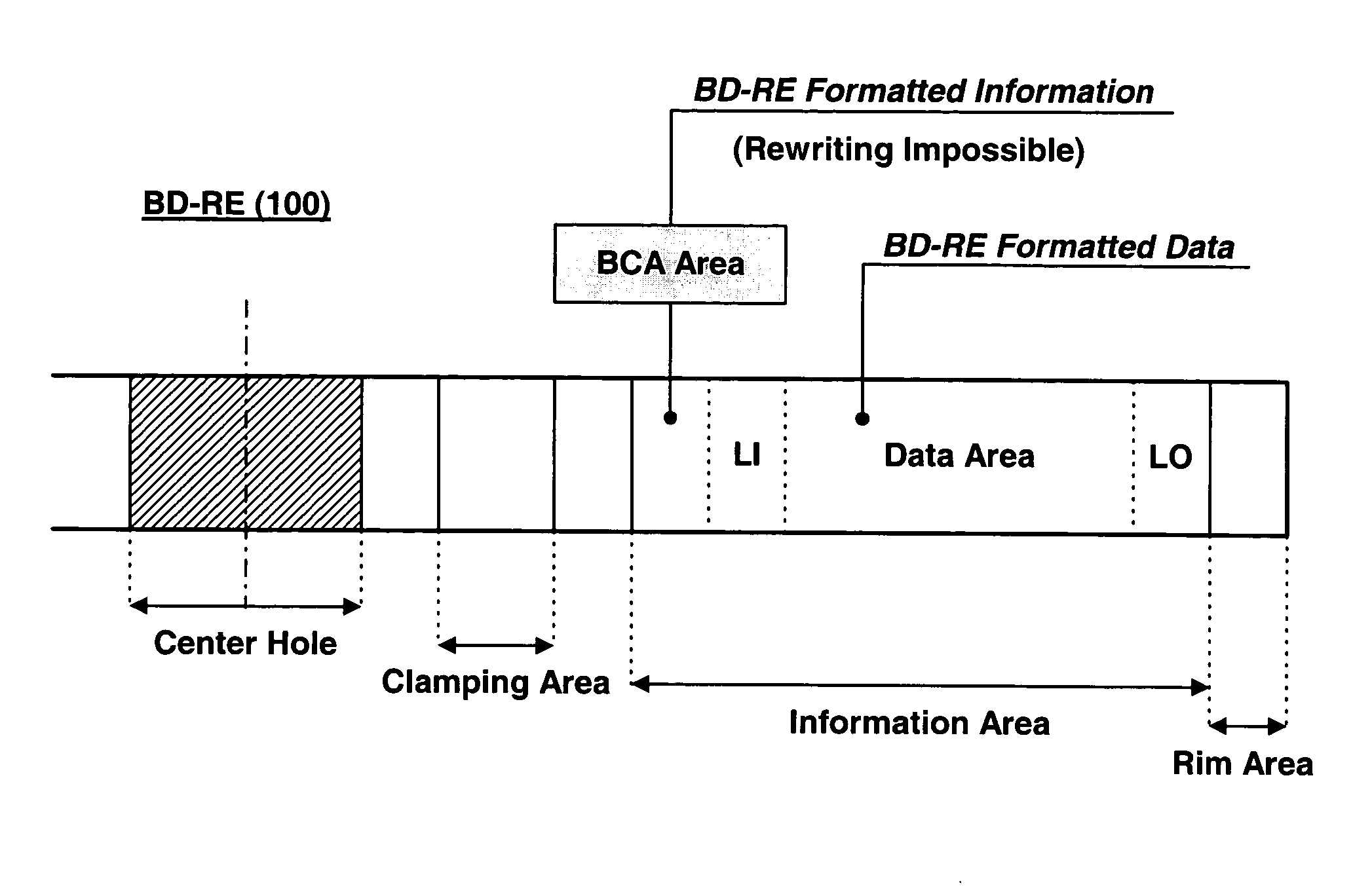
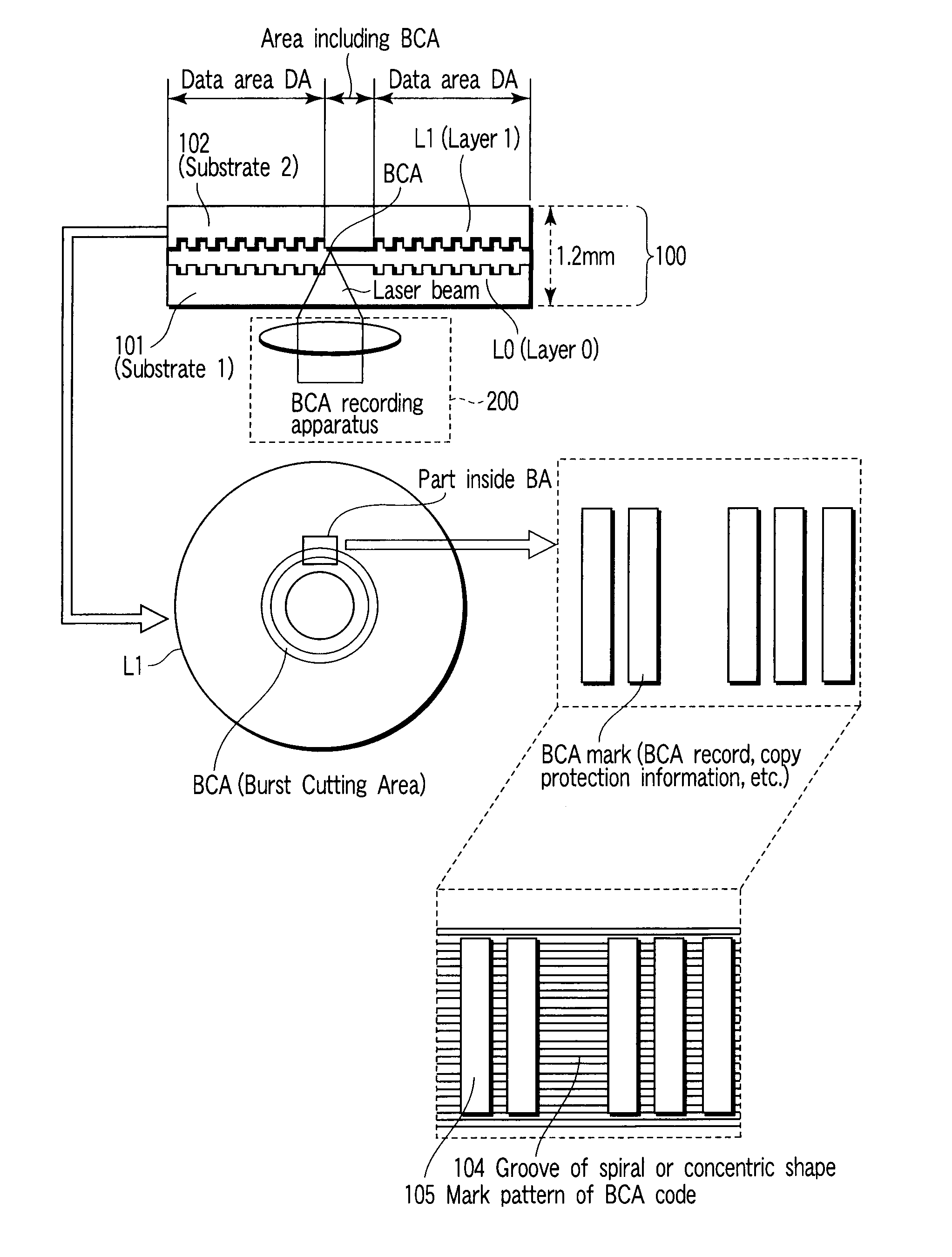
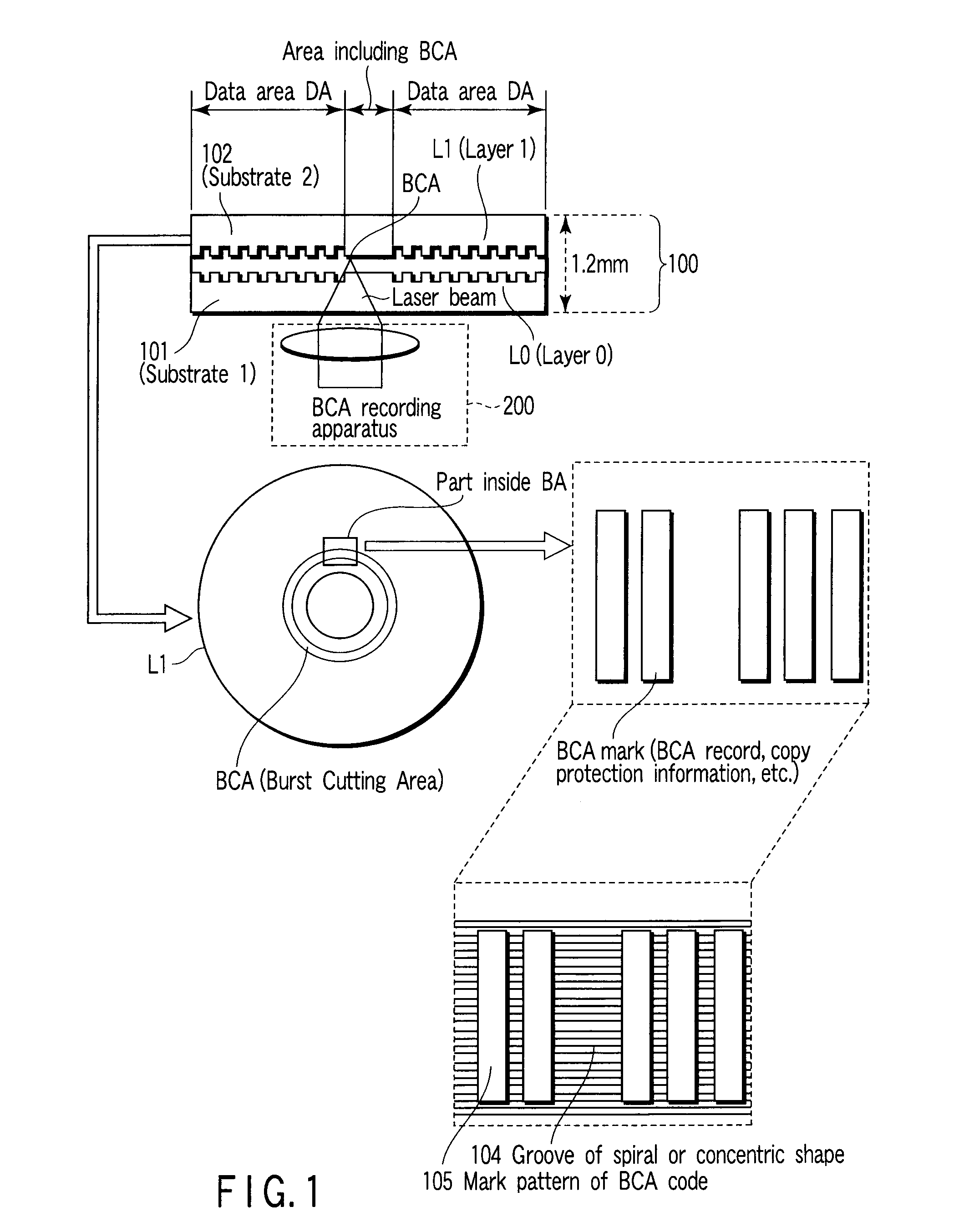
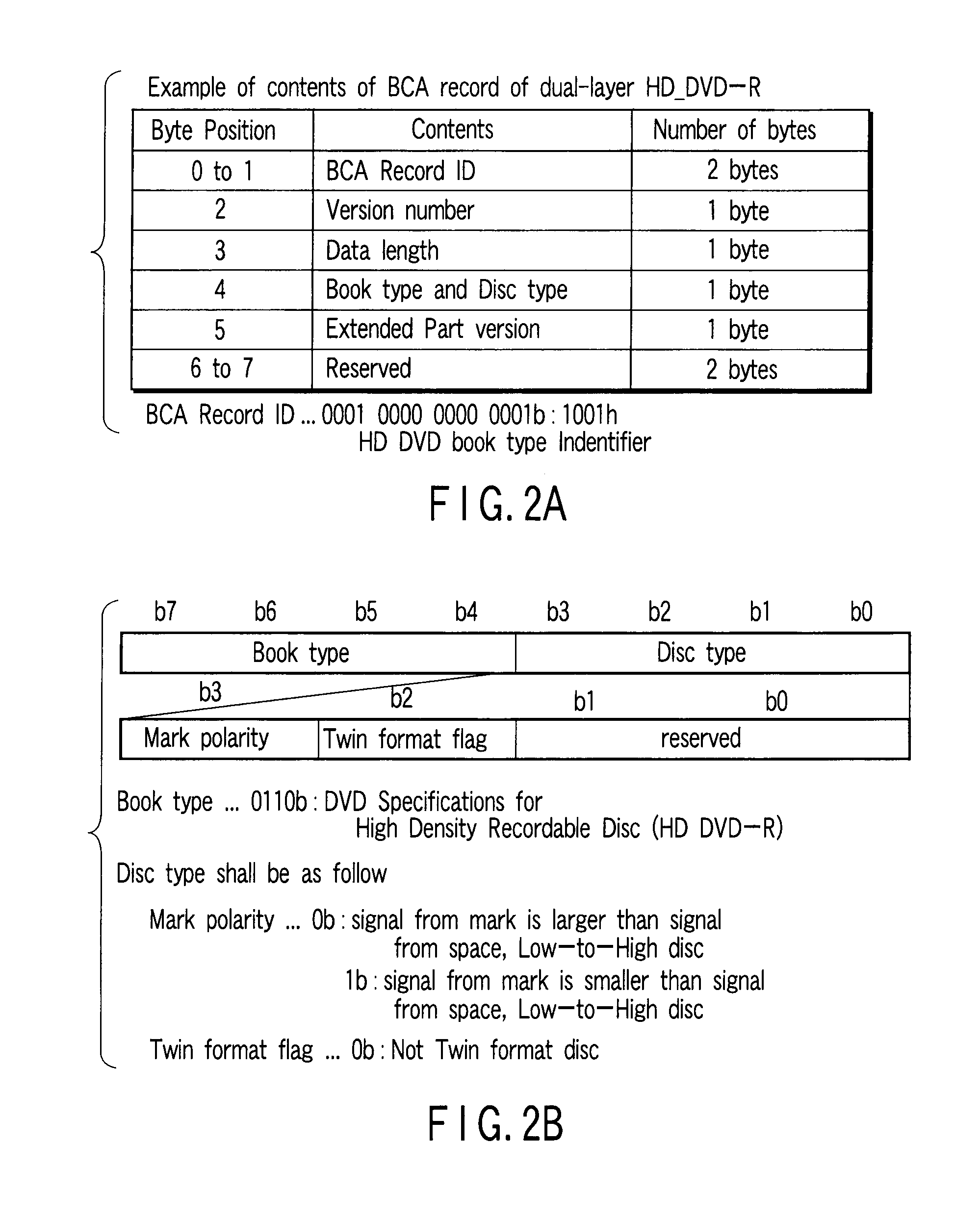
According to one embodiment, a write-once optical disc which uses a short-wavelength laser allows BCA information recording even using a long-wavelength laser. To this end, a groove is cut in advance on a BCA part on a molded substrate of the optical disc to store a dye. In this way, the sensitivity of the dye in the BCA increases, to allow a laser having a wavelength other than the wavelength corresponding to information recording of the dye to record a barcode pattern on the BCA.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
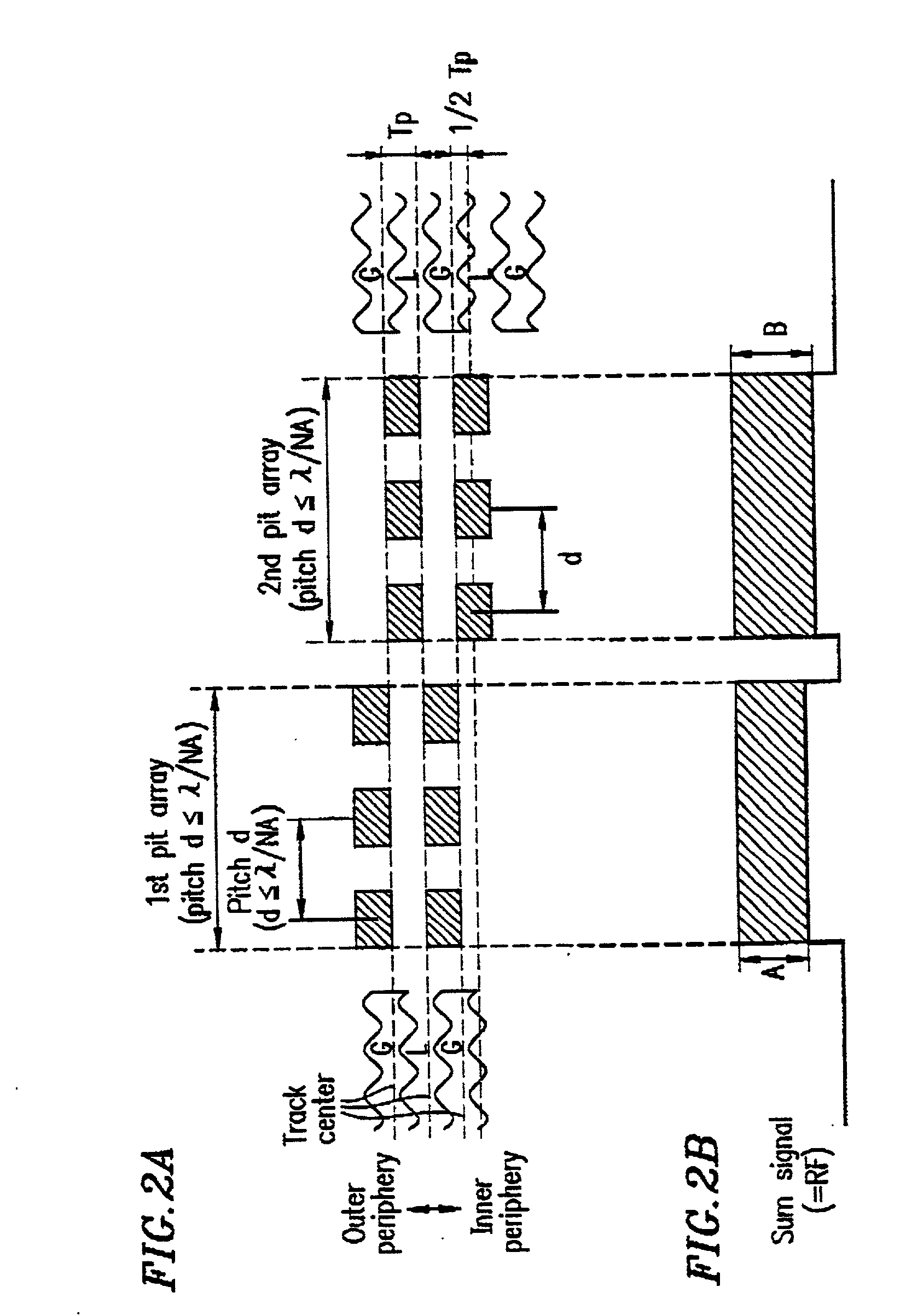
An optical disk and optical disk apparatus with tracks and grooves
InactiveUS20020126591A1Accurate trackingRecord information storageUsing detectable carrier informationLight beamEngineering
An optical disk includes tracks and grooves, the grooves being formed with a pitch equal to or greater than about .lambda. / NA. A first array of pits is provided at a position which is shifted by a predetermined amount with respect to each track in one of two directions substantially perpendicular to the tracks, the first array of pits being formed with a predetermined pitch, where the predetermined pitch is a function of a pitch of the grooves taking a value within a range from about 0 to about .lambda. / NA. A second array of pits is provided at a position which is shifted by a predetermined amount with respect to the track in the other one of the two directions substantially perpendicular to the tracks, the second array of pits being formed with a predetermined pitch, where the predetermined pitch is a function of the pitch of the grooves taking a value within the range from about 0 to about .lambda. / NA. .lambda. is a wavelength of a light beam which is radiated on the optical disk, and NA to a numerical aperture of a lens.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
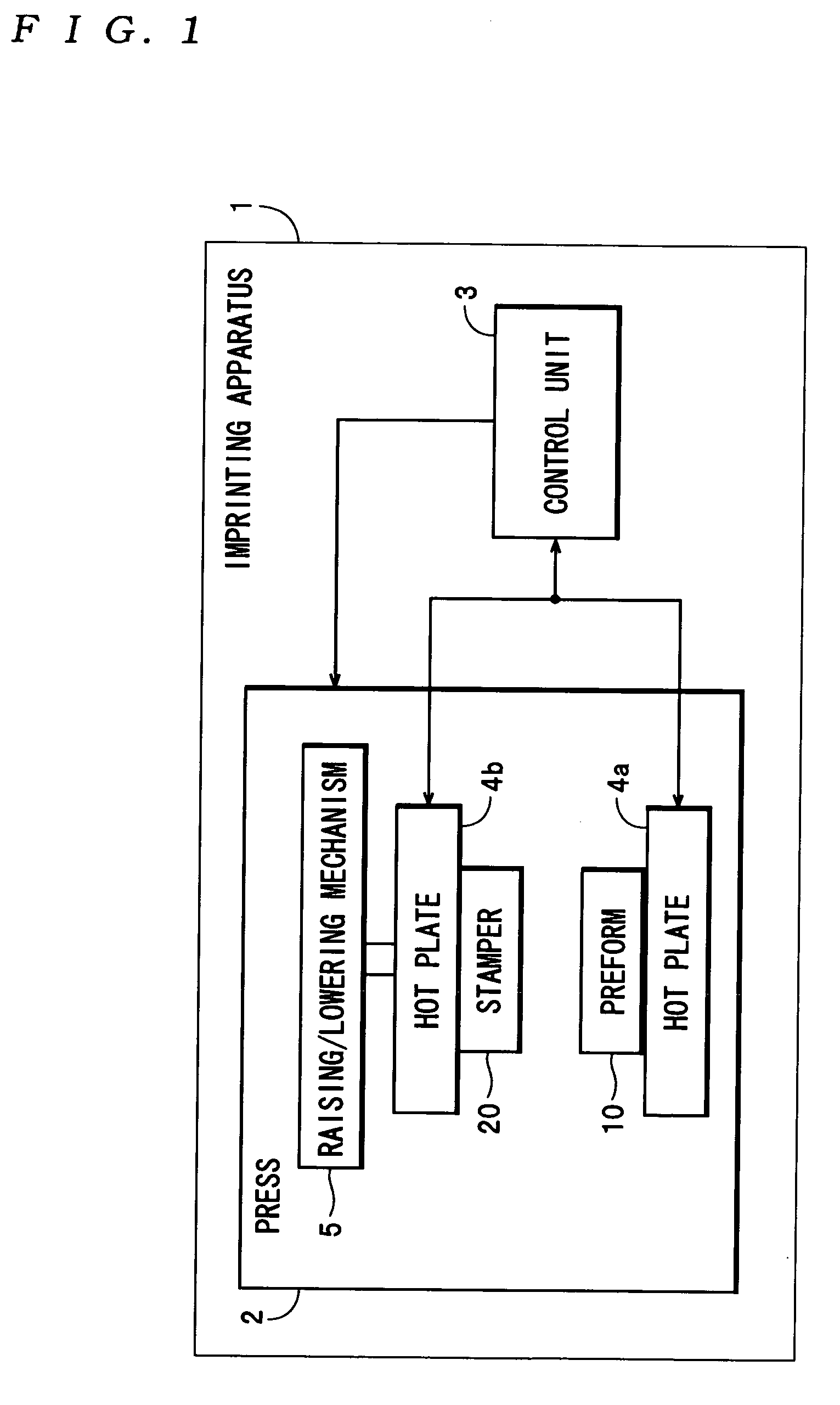
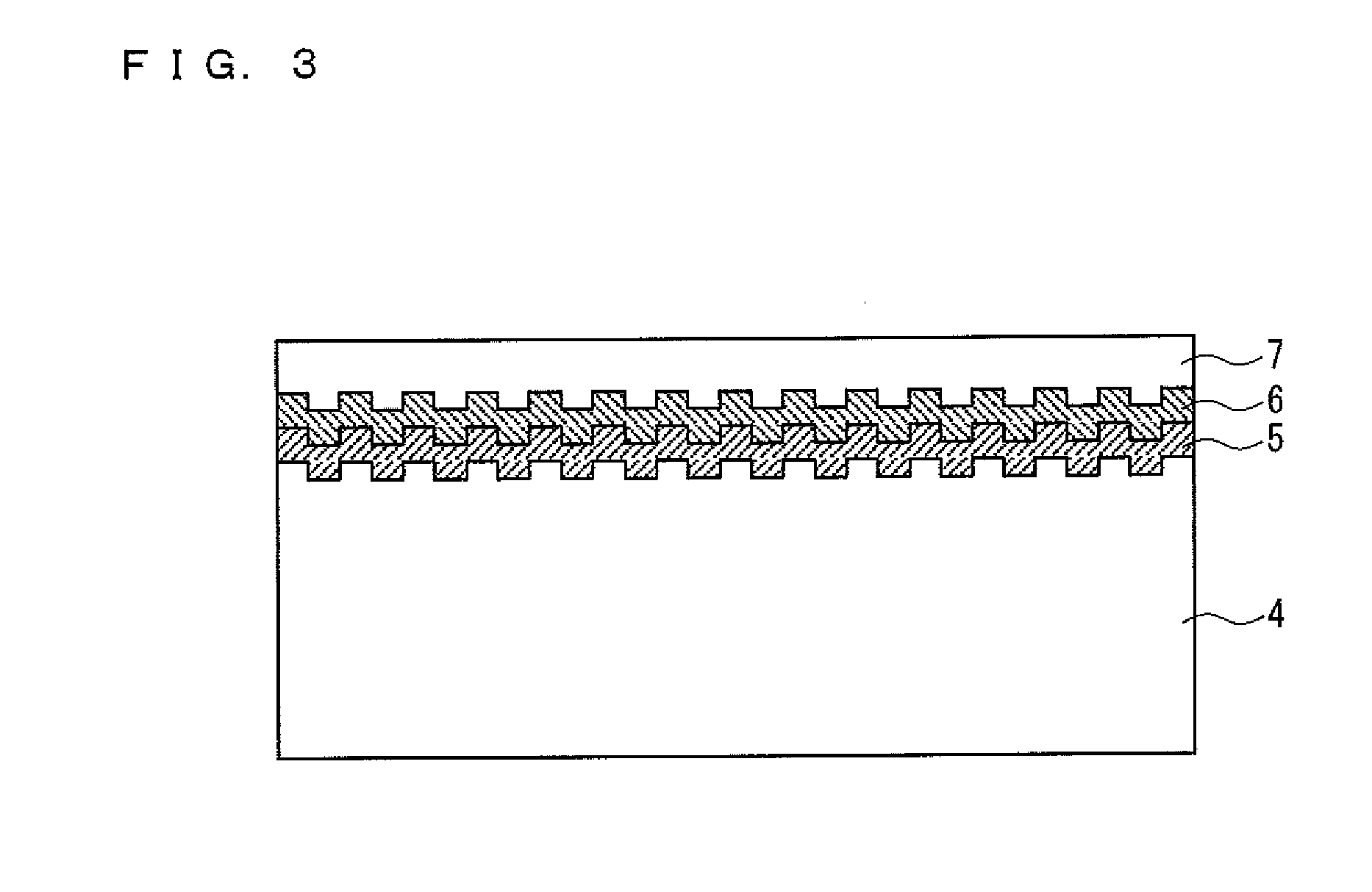
Stamper, imprinting method, and method of manufacturing an information recording medium
InactiveUS20050285308A1Long distanceUniform thicknessDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsEngineeringRecording media
There is provided a stamper for imprinting on which a concave / convex pattern is formed with a plurality of convex parts of different widths protruding from a surface. In the concave / convex pattern, the respective convex parts are formed so that a distance between a top of a convex part and a reference plane defined in a range between the surface and a rear surface of the stamper is longer for convex parts with wide widths than for convex parts with narrow widths. An imprinting method transfers the concave / convex form of the stamper to a resin layer on the surface of a substrate. A method of manufacturing an information recording medium uses the concave / convex form transferred by the imprinting method to manufacture an information recording medium.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
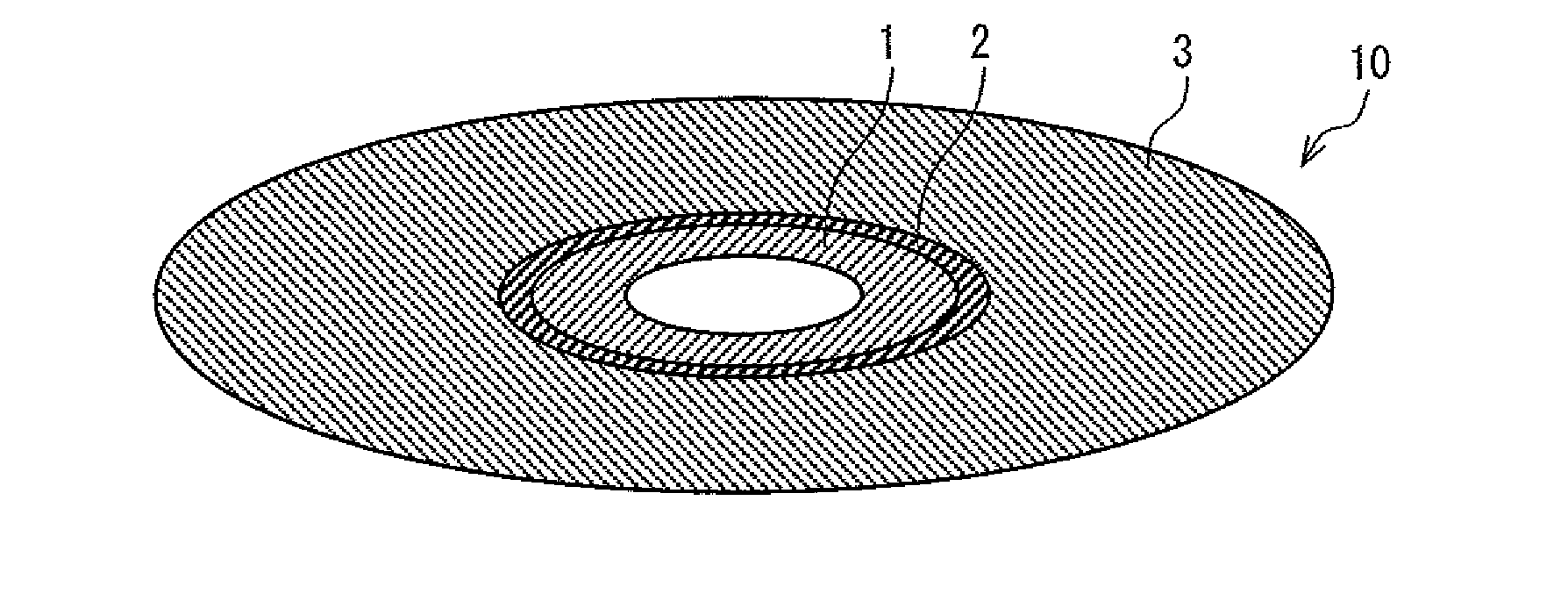
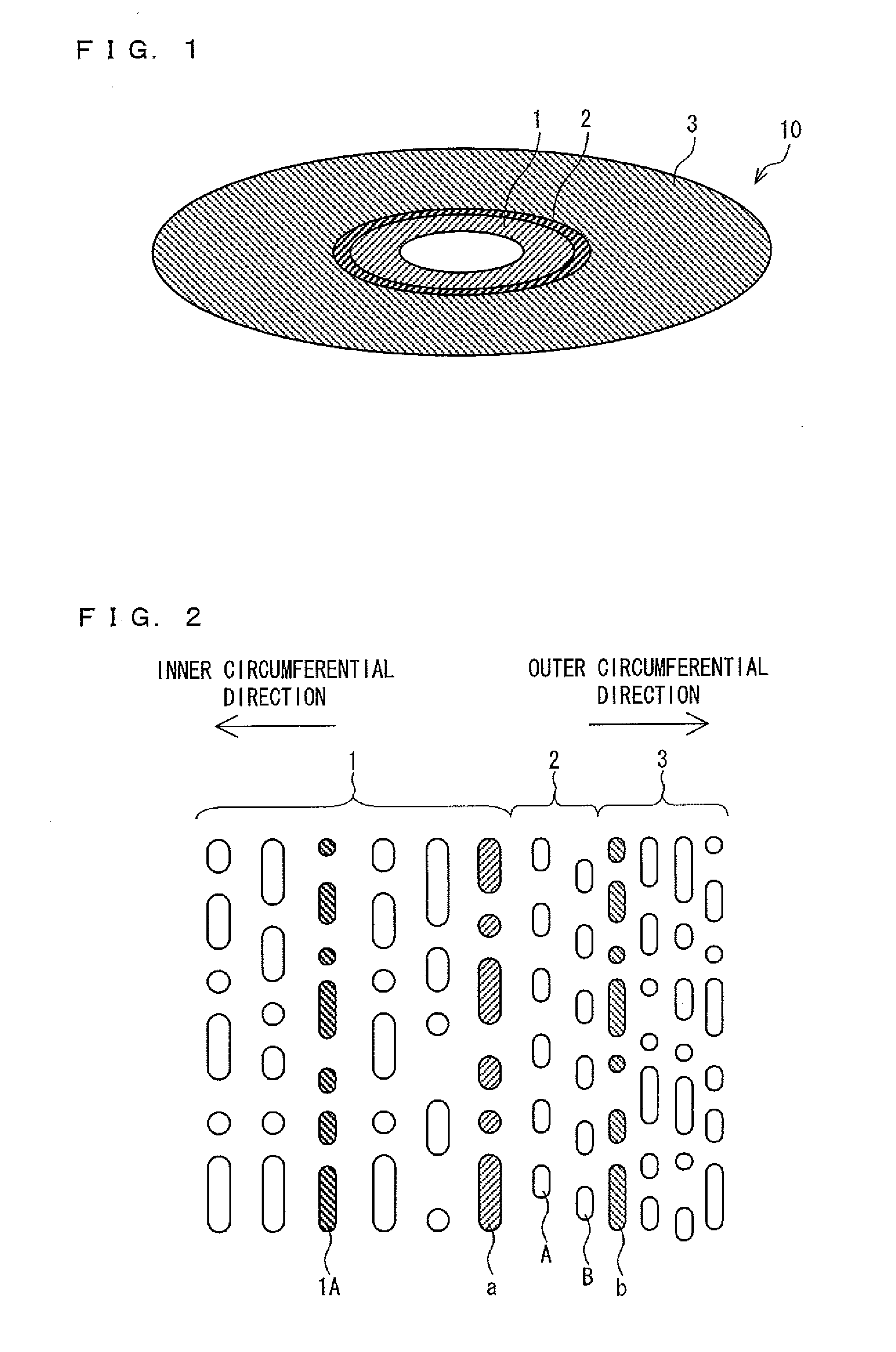
Super-resolution optical recording medium, optical recording medium reproduction device, control method of optical recording medium reproduction device, control program for optical recording medium reproduction device, and computer-readable recording medium for storing the program
ActiveUS20100208558A1Increase powerInformation arrangementFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareOptical recording
A super-resolution optical recording medium (10) of the present invention includes: a medium information region (1) on which medium identification information is recorded; a content region (3) on which content information is recorded; and a blank region (2) provided between the medium information region (1) and the content region (3) and in which at least two tracks are provided so as to connect a train of prepits in the medium information region (1) and a train of prepits in the content region (3). No information is recorded on the blank region (2). With this arrangement, the present invention provides a super-resolution optical recording medium in which a region on which medium identification information is recorded and a region on which content information is recorded are different in track pitch and in which a reproduction error hardly occurs when reproduction shifts from the region on which the medium identification information is recorded to the region on which the content information is recorded.
Owner:SHARP KK
Information Recording Medium
InactiveUS20080049933A1Easy maintenanceImprove confidentialityRecord information storageDigital signal formattingComputer hardwareRecording media
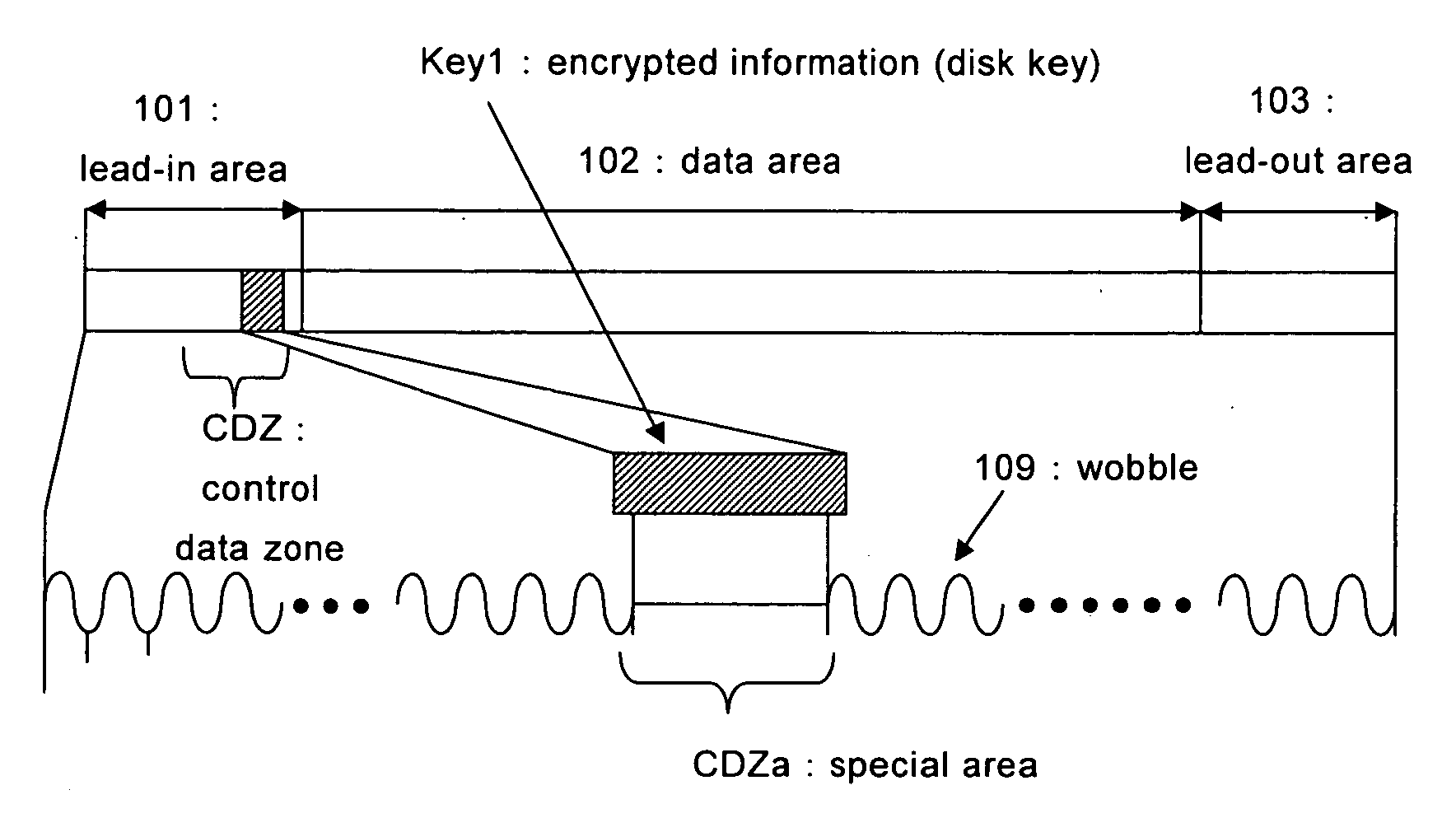
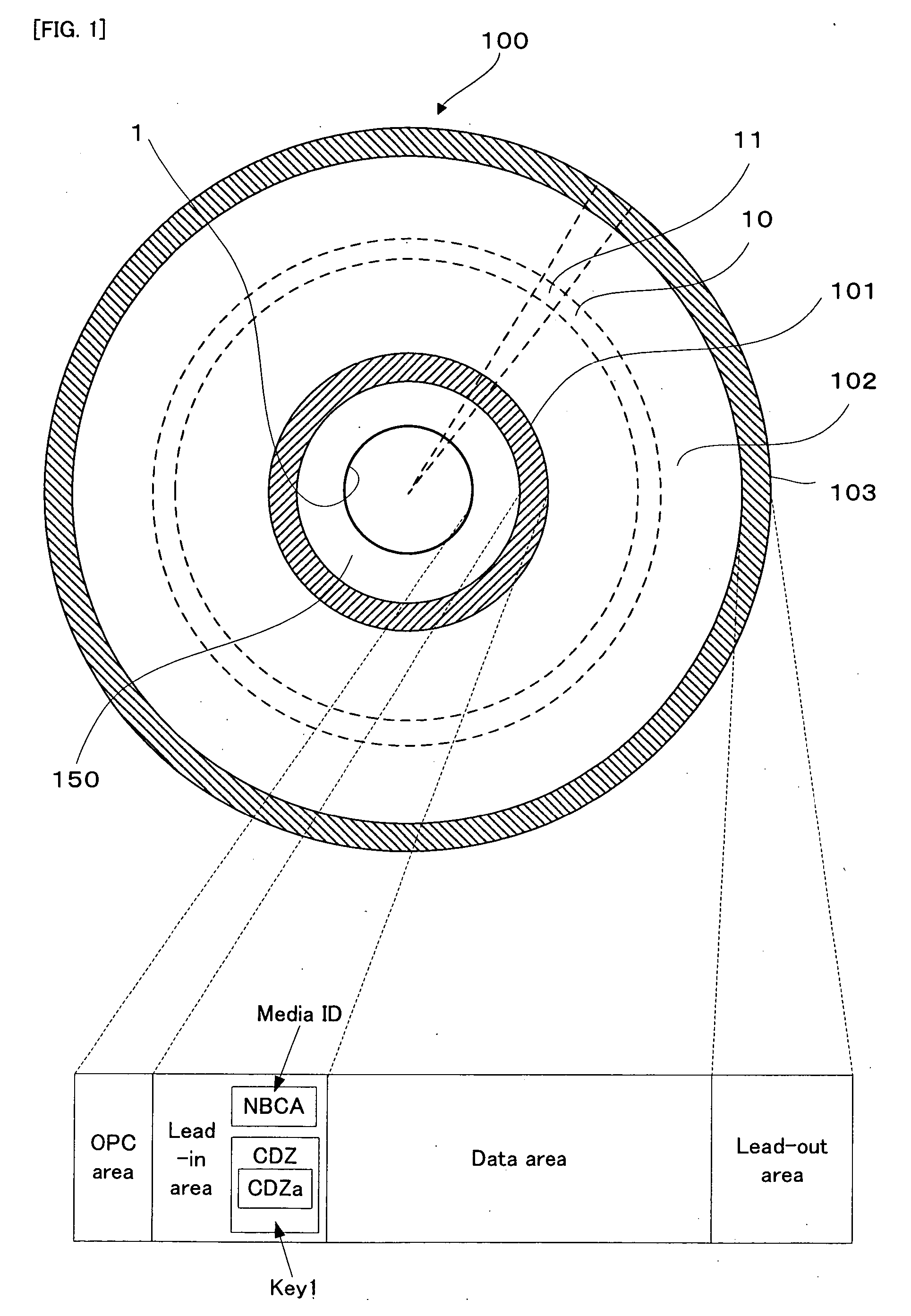
An information recording medium is provided with a recording information recording area (102) wherein recording information can be recorded, and an encrypting information recorded area (CDZ) wherein encrypting information (Key1) for encrypting the recording information is previously recorded. The encrypting information recorded area includes a special area (CDZa) having a physical structure different from that of the recording information recording area at least on one part.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Reverse optical mastering for data storage disks
InactiveUS6890704B2Large information capacityRecord carriersPhotomechanical apparatusOperating systemSurface relief
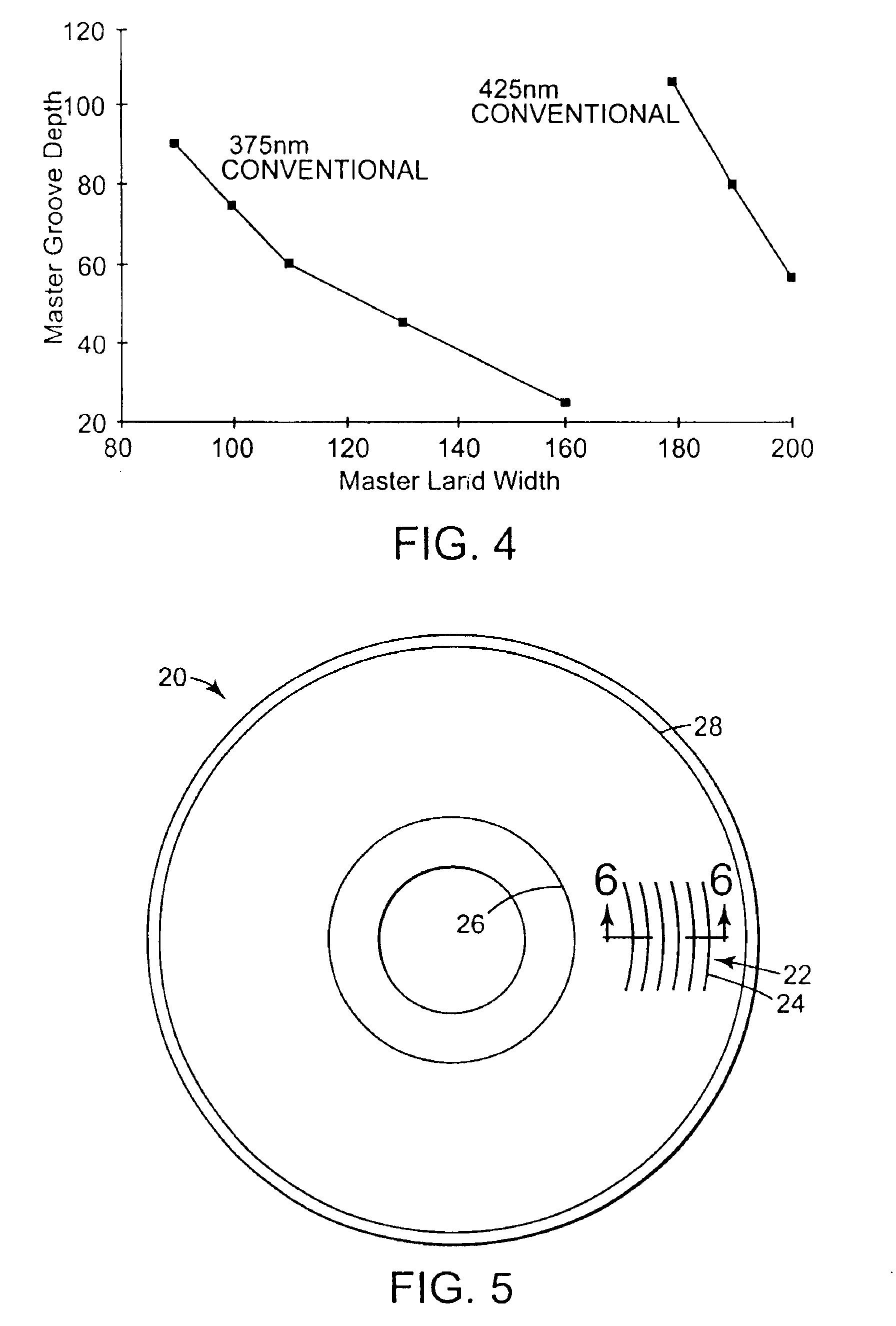
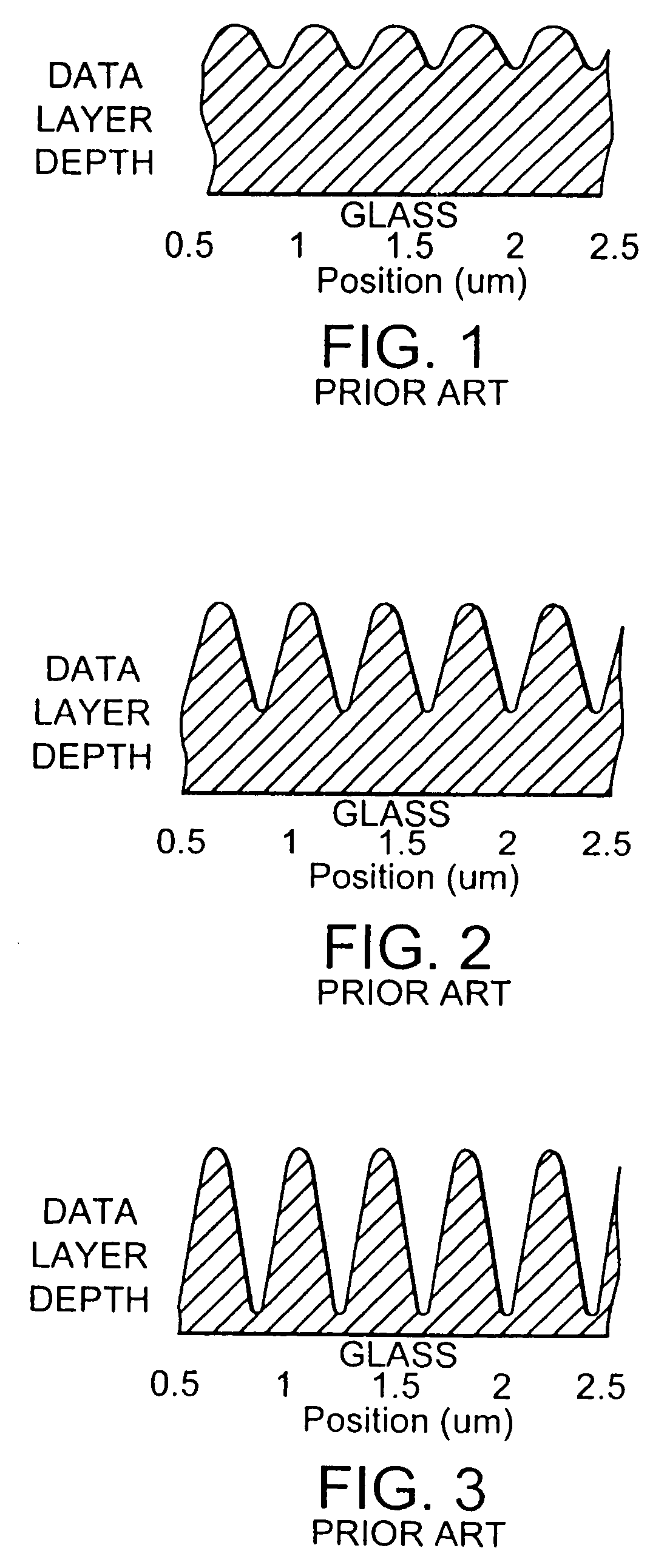
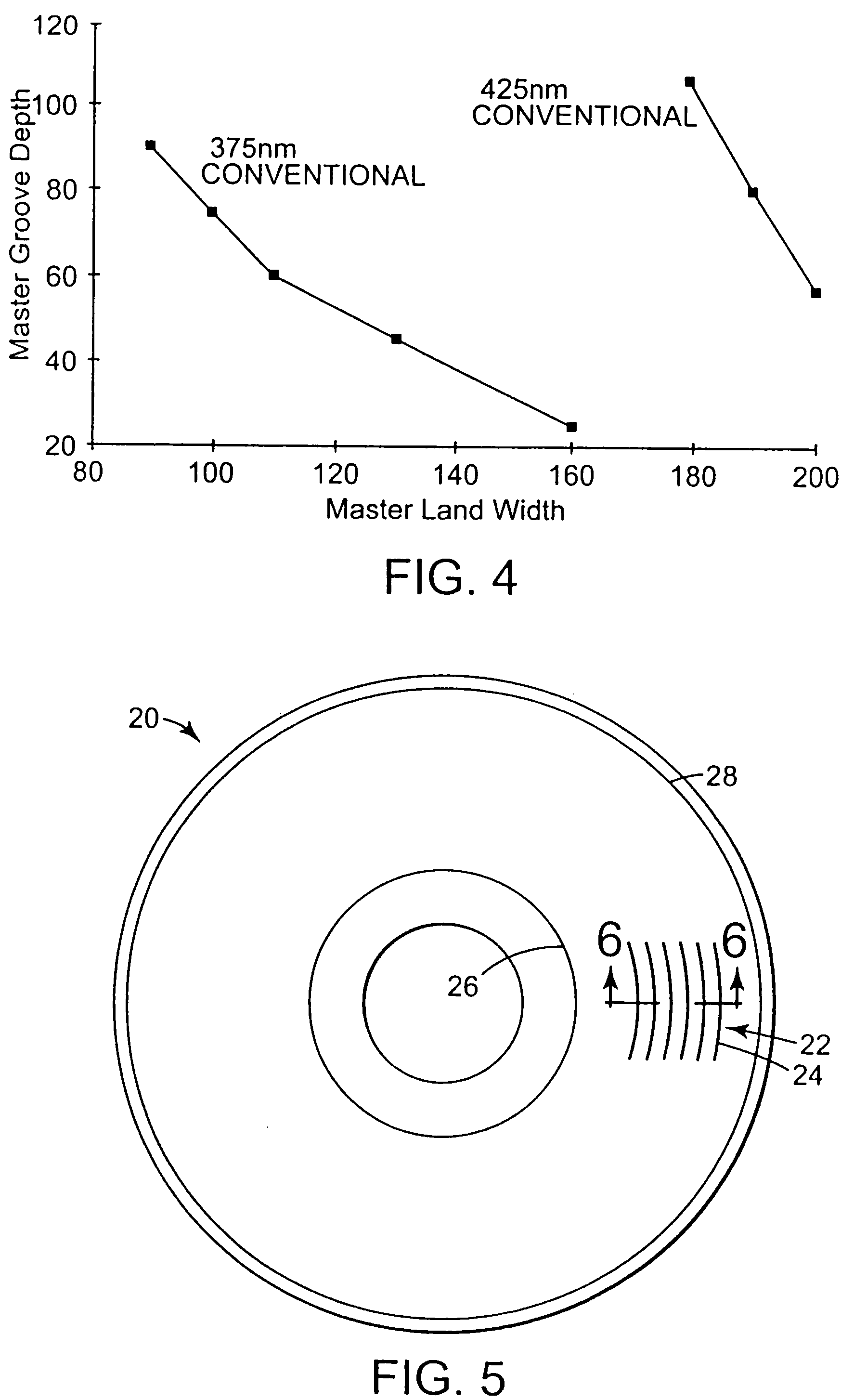
A data storage master disk and method of making a data storage master disk. The data storage disk master is for use in a data storage disk replication process. The data storage disk molding processes produces replica disks having a surface relief pattern with replica lands and replica grooves. The method includes providing a master substrate. The master substrate is at least partially covered with a layer of photosensitive material. A surface relief pattern having master lands and master grooves is recorded in the data storage disk master, including the steps of exposing and developing the photosensitive material. The exposing and developing of a specified thickness of photosensitive material is controlled to form master grooves extending down to a substrate interface between the master substrate and the layer of photosensitive material, such that the width of the master grooves at the substrate interface corresponds to a desired width of the replica lands.
Owner:MAX BLU TECH
Magneto-optical recording medium having pit pitch greater than groove pitch
A recording medium and a recoding medium master, and a method of manufacturing the recording medium which comply with the standard of recording / reproducing characteristic established in the MD standard while enabling precise discrimination of the pit track and groove track and optical detection of the pits by optical pickup and the like are provided. Pits and grooves are arranged on a surface of a disc-shaped substrate so as to form a grooves and the ratio is from 1.00 exclusive to 1.13 inclusive. It is preferable that the track pitch of the grooves is from 1.50 mum inclusive to 1.70 mum exclusive. The width of the pits and grooves in the radial direction of the substrate is the same.
Owner:SONY CORP
Disc-shaped optical recording medium and reproduction limit method thereof
InactiveUS20050018555A1Preventing illegal copyingControlled reproductionUnauthorized memory use protectionRecord information storageOptical pickupLow speed
A disk type optical recording medium that can limit the reproduction by a disk drive connected to a computer without drastically changing the specifications of recorded information on the medium conventionally processed by a dedicated player, thereby preventing illegal copying or the like. The disk type optical recording medium has information tracks formed by a pit train, and the information tracks have a read limiting region formed by a modified pit train including a special wobble or lateral displacement as modified from the pit train. In this read limiting region, the modified pit train can be followed by the tracking control of an optical pickup during low-speed rotation of the medium, thereby allowing proper reproduction. However, the modified pit train cannot be followed by the tracking control of the optical pickup during high-speed rotation of the medium, thereby disallowing the reproduction.
Owner:SONY CORP
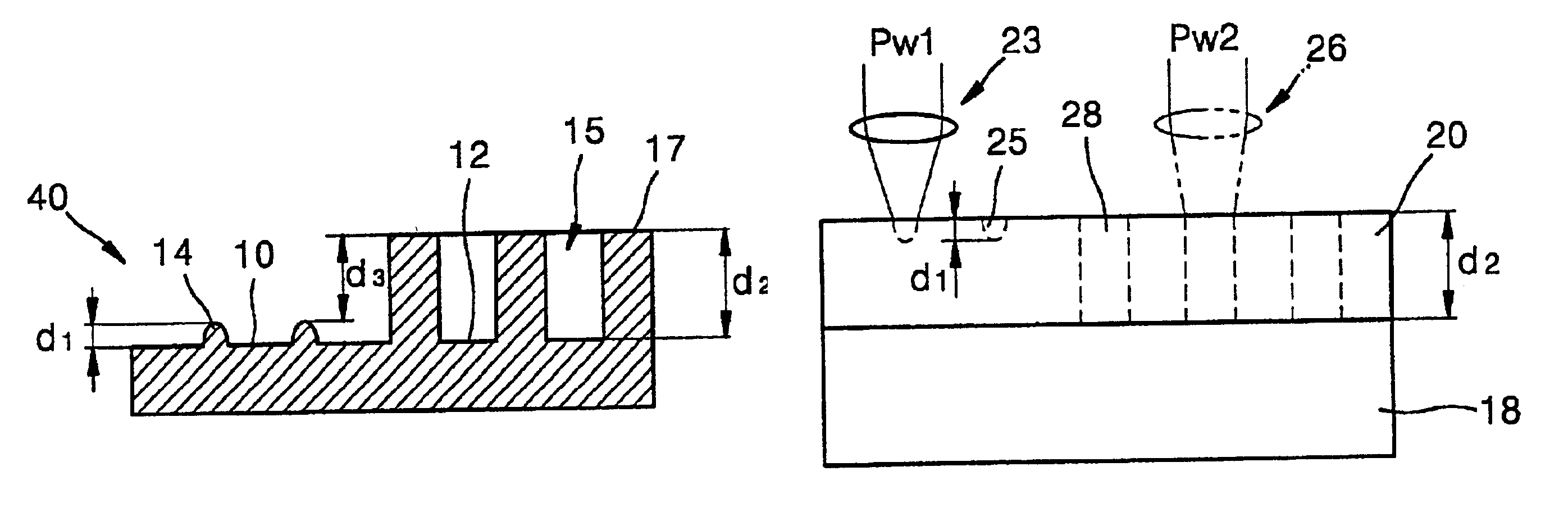
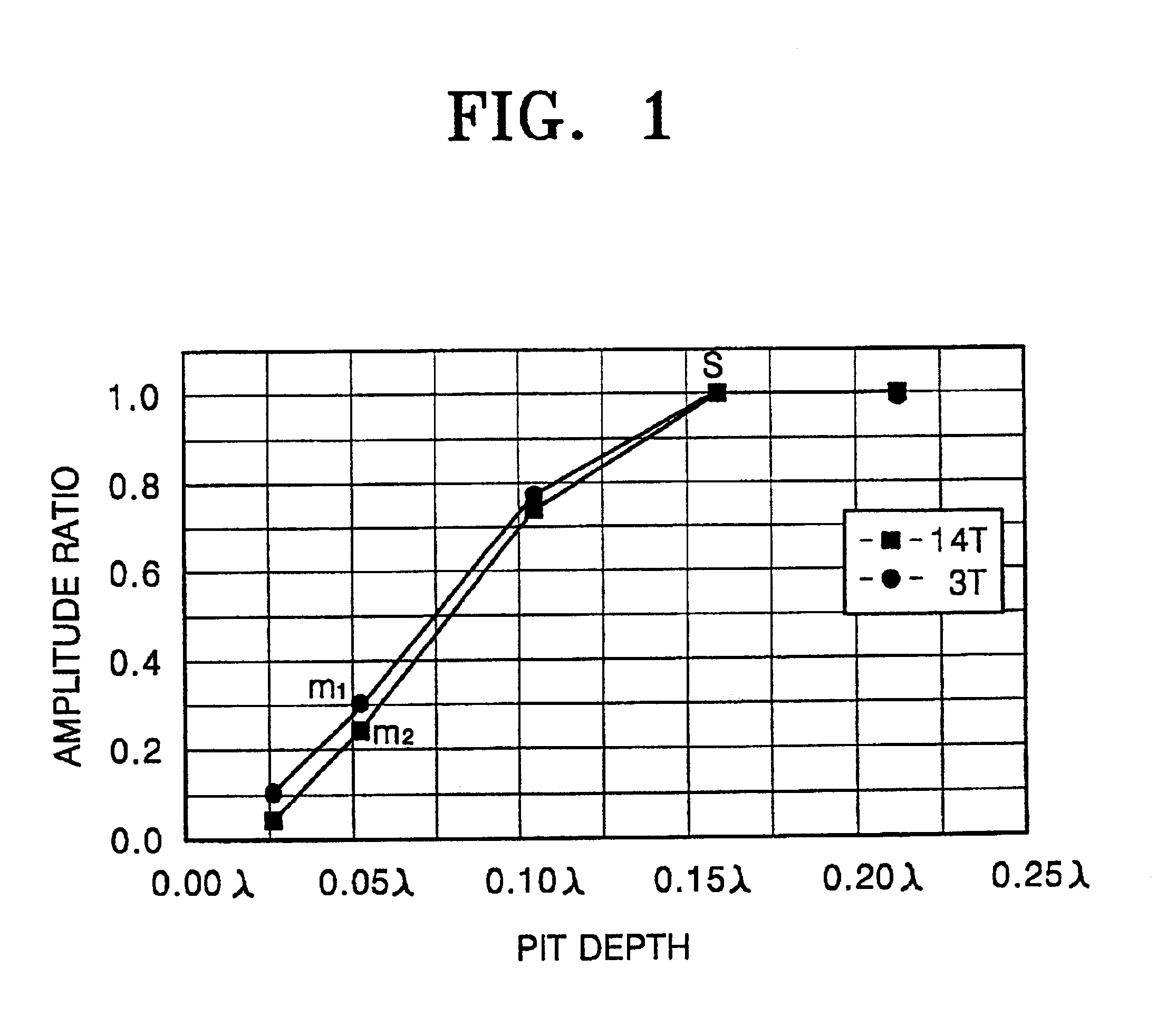
Disc having grooves and pits with different depths, and method for manufacturing the disc
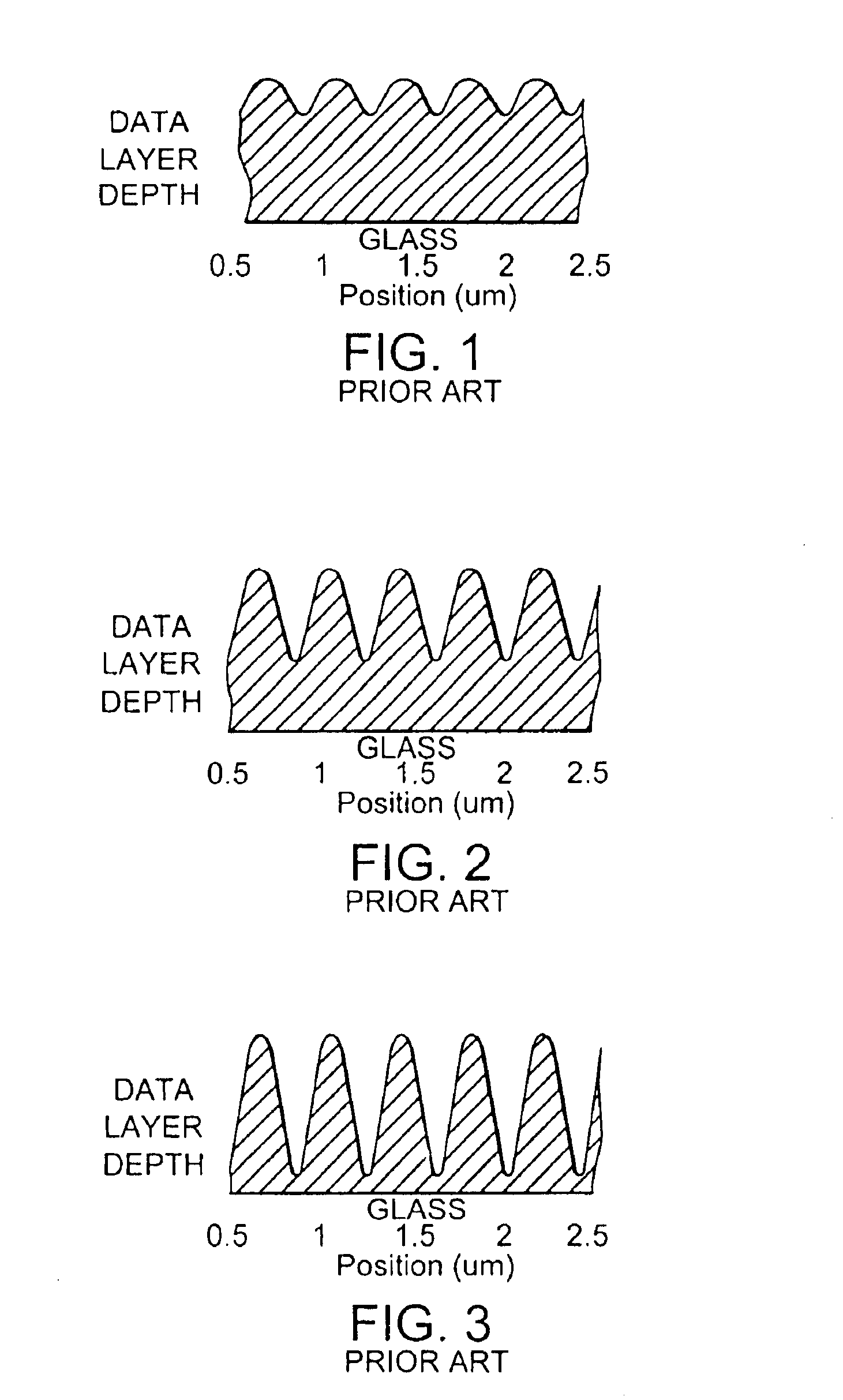
InactiveUS6906994B2Improving reproduction signal levelLayered productsRecord information storageRefractive indexLaser cutting
A disc having grooves and pits with different depths according toλ / 8n≦d3≦λ / 5nwhere d3 is a difference in depths between the grooves and the pits, λ is the wavelength of a light source, and n is the refractive index of the disc. A disc having grooves and pits with different depths can be manufactured without etching by using at least two stampers. Manufacturing a master by depositing photoresist over a glass master, forming a first land region and a second land region having different depths by laser cutting with laser beams having different power levels. Stamping a father stamper having a groove region and a pit region from the master, the shape of the father stamper inverse of the master. Stamping a mother stamper from the father stamper, the shape of the mother stamper inverse of the father stamper. Manufacturing the disc with the mother stamper.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical recording medium and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20030112736A1Record information storageDigital signal formattingEngineeringOptical recording
At least a portion of groove tracks in a information-data recording region of an optical recording medium comprises a plurality of groove portions separated by groove-absent portions in a rotational direction of the optical recording medium, each of the mark portions or each of the space portions includes one of the groove-absent portions. At least one of two groove tracks adjacent to prepit train, which is formed in land tracks, has a continuous groove portion or a groove-absent portion extending at least from a leading end to a trailing end of at least one prepit included in the prepit train in a rotational direction of the optical recording medium. The frequency band for separation of the groove tracks includes at least a portion of a frequency band of a modulated recording signal for recording information data on the optical recording medium.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Medium, apparatus, and method of recording optical-information
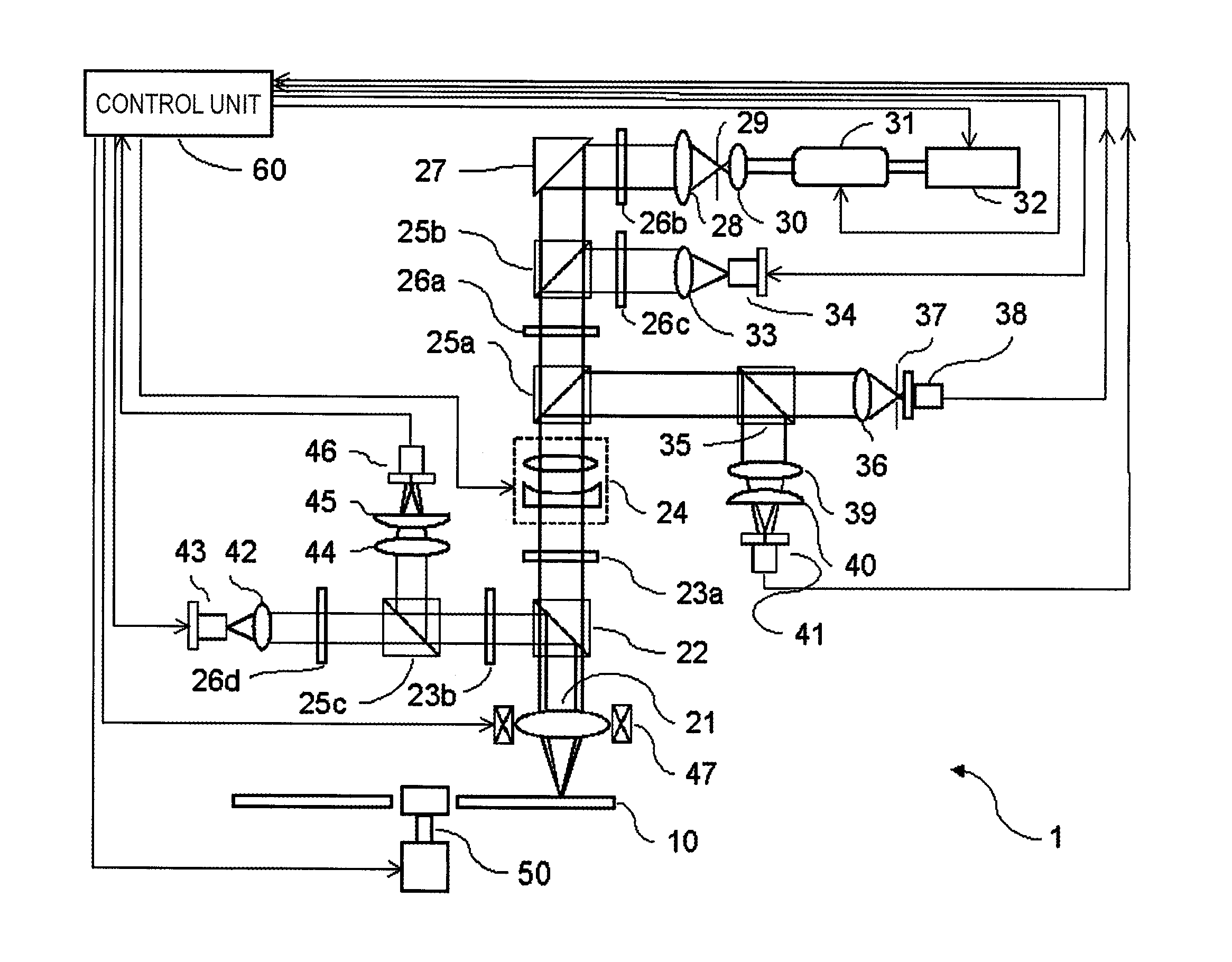
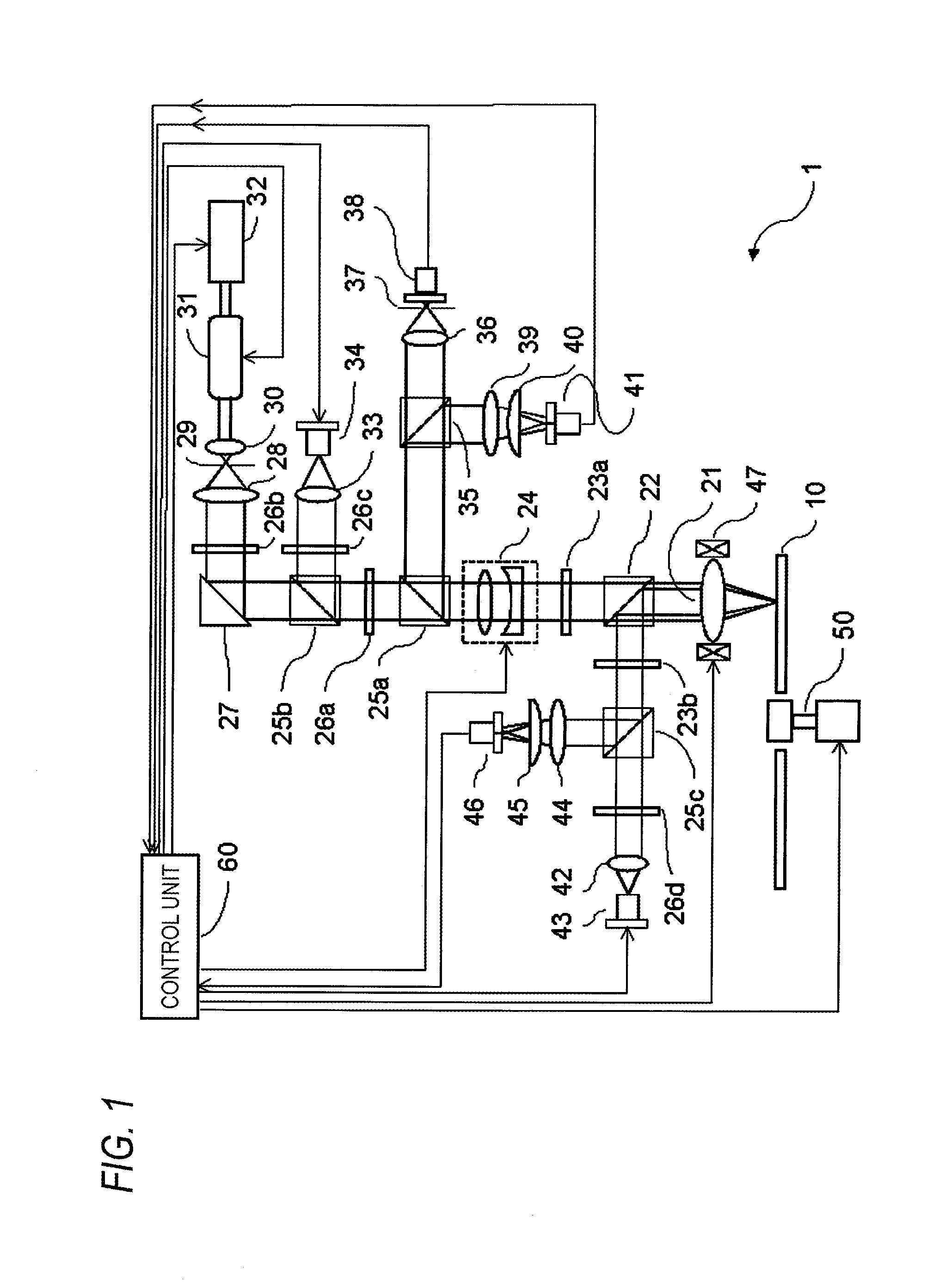
An optical-information recording medium includes a substrate that includes a servo surface having a servo pattern thereon; an information recording layer laminated on the servo surface of the substrate capable of recording information as a hologram produced by interference between an information beam containing the information and a reference beam; an address servo area that is formed as a part of the servo pattern, and that records therein address information and clock information for aligning a beam, emitted from an optical-information recording apparatus for recording information in the information recording layer, to a target position in the information recording layer; and a following up servo area that is formed as a part of the servo pattern, and that is to be irradiated by the beam to make the beam follow a rotation of the optical-information recording medium.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical recording medium
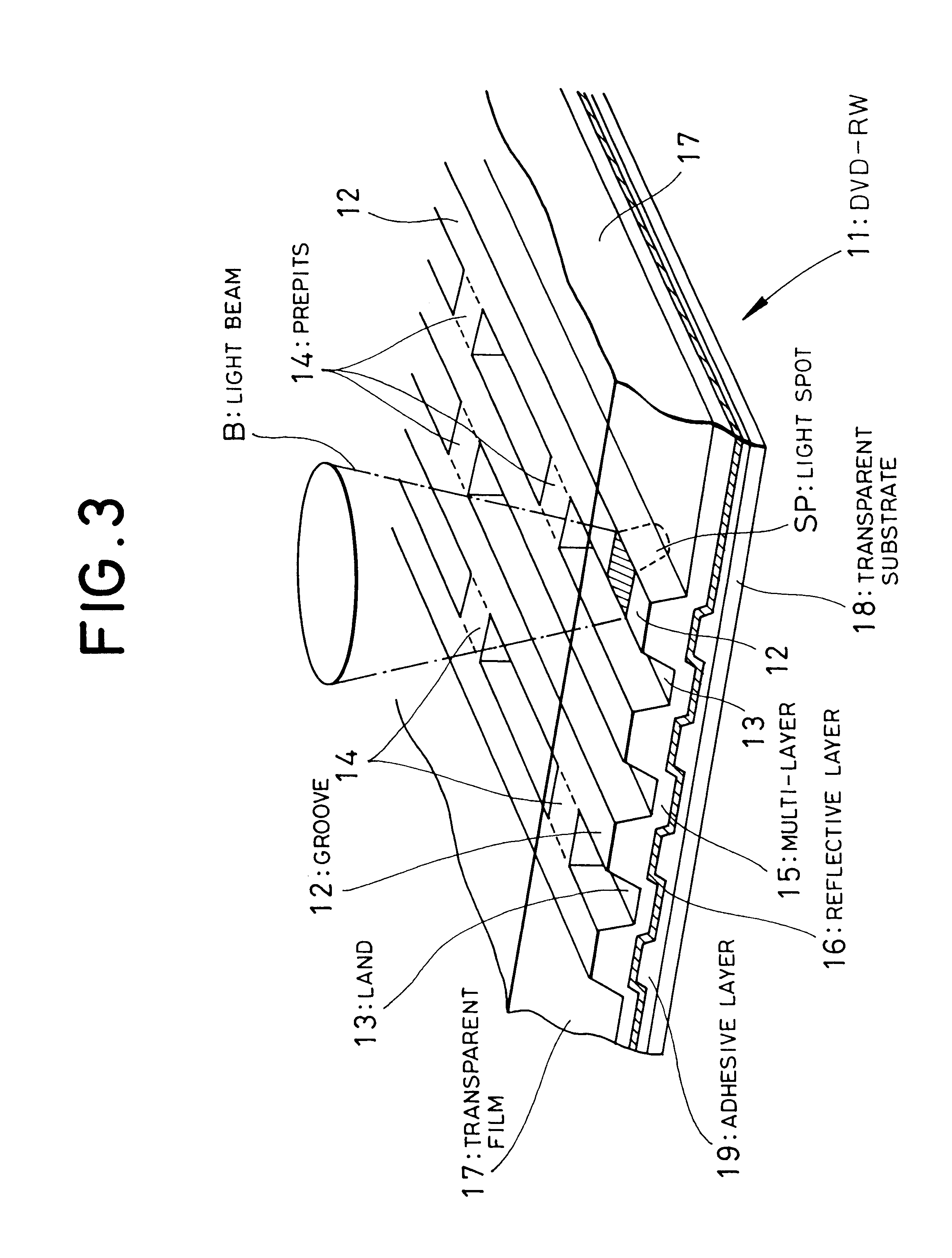
InactiveUS6673411B2Maintain good propertiesProvide satisfactoryLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusOrganic dyeRefractive index
A recordable optical recording medium comprising a recording layer containing an organic dye which can absorb a laser beam and a metal reflective layer directly or via another layer on a transparent supporting substrate having a pre-groove and a pre-pit, wherein the organic dye has a refractive index nk of 2.2 or more at a reproduction wavelength lambda2; in relation to the reproduction wavelength lambda2, the depths of the pre-groove and the pre-pit on the substrates are more than lambda2 / 4; and the following equations are satisfied:wherein r is a recording laser beam diameter represented by lambda1 / NA where lambda1 is a recording wavelength [mum] and NA is a numerical aperture for an object lens; wg [mum] and thetagr are a half value width and a cross-section tilting angle in a substrate radial direction for the pre-groove, respectively; and wp [mum], thetapr and thetapt are a half value width, a cross-section tilting angle in a substrate radial direction and a cross-section tilting angle in a tangential direction for the pre-pit, respectively.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Recording medium and recording medium master, and method of manufacturing recording medium
A recording medium and a recoding medium master, and a method of manufacturing the recording medium which comply with the standard of recording / reproducing characteristic established in the MD standard while enabling precise discrimination of the pit track and groove track and optical detection of the pits by optical pickup and the like are provided. Pits and grooves are arranged on a surface of a disc-shaped substrate so as to form a grooves and the ratio is from 1.00 exclusive to 1.13 inclusive. It is preferable that the track pitch of the grooves is from 1.50 mum inclusive to 1.70 mum exclusive. The width of the pits and grooves in the radial direction of the substrate is the same.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical disk
InactiveUS7102986B2Small widthRecord information storageDigital signal formattingControl dataComputer science
The present invention provides an optical disk comprising: at least a rewritable region and a read-only data region, wherein the rewritable region includes a plurality of groove tracks and a plurality of land tracks, the read-only data region includes a plurality of groove tracks and a plurality of land tracks, read-only data comprising control data are written as concavo-convex pits to the groove tracks and / or the land tracks in the read-only data region, and the width of each groove in the read-only data region is smaller than that of each groove in the rewritable region. According to the first optical disk of the present invention, the area of rewritable regions for users can be ensured as broadly as possible failing to deteriorate the high-speed performance of the system.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
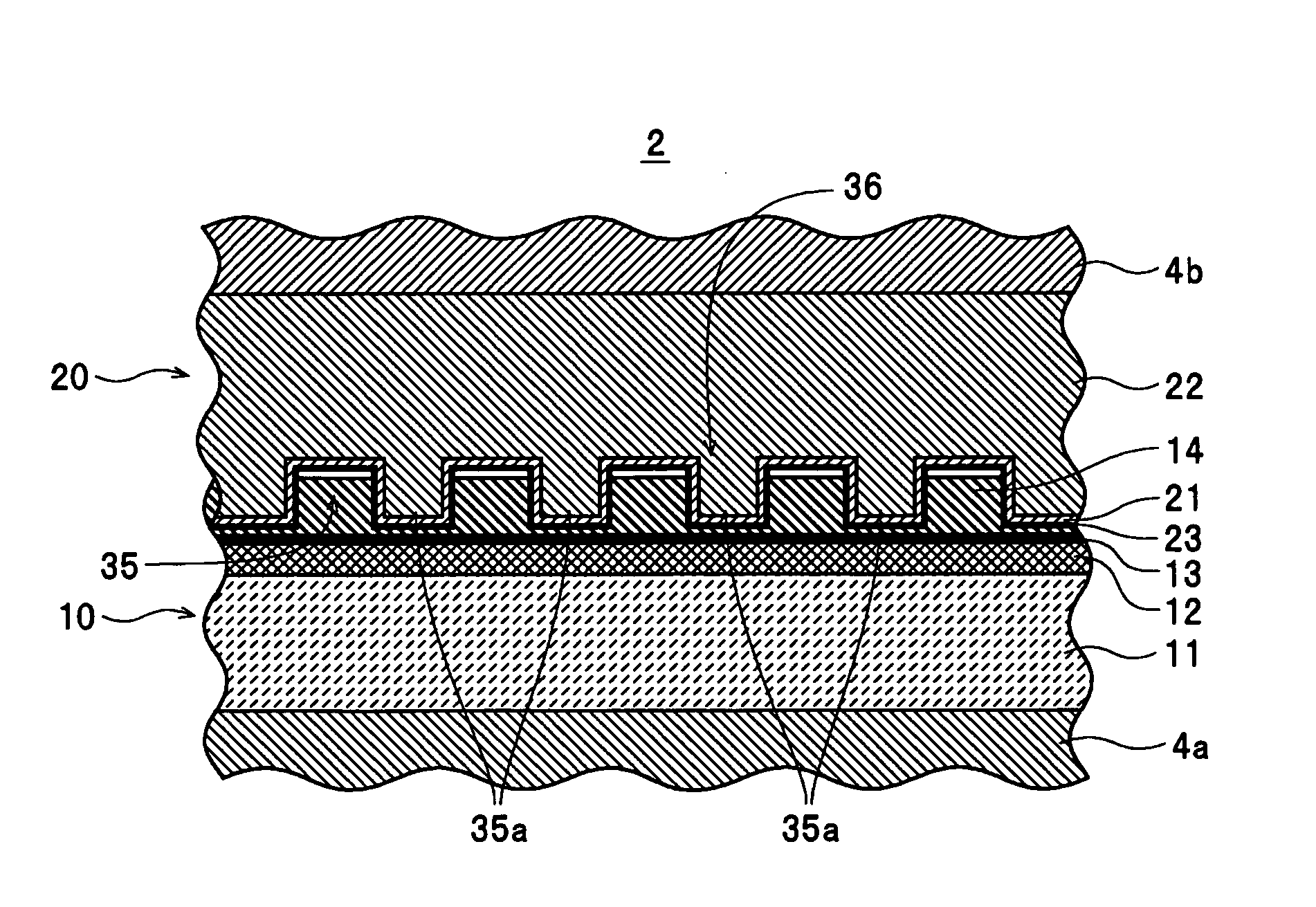
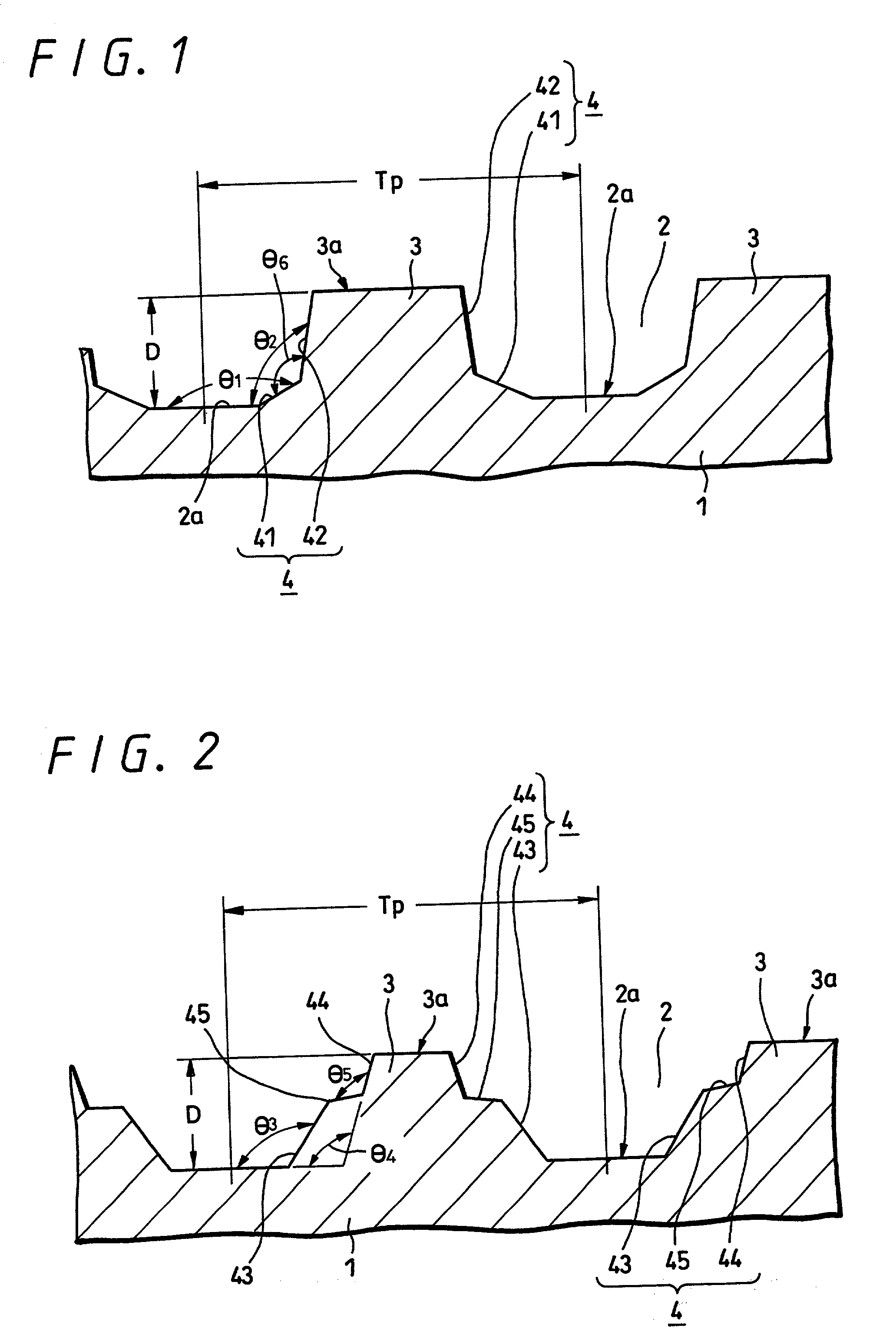
Substrate for optical recording media, optical recording medium, manufacturing process for optical recording media, and optical recording/reproducing method
InactiveUS20010030937A1Mechanical record carriersRecord information storageEngineeringCrosstalk minimization
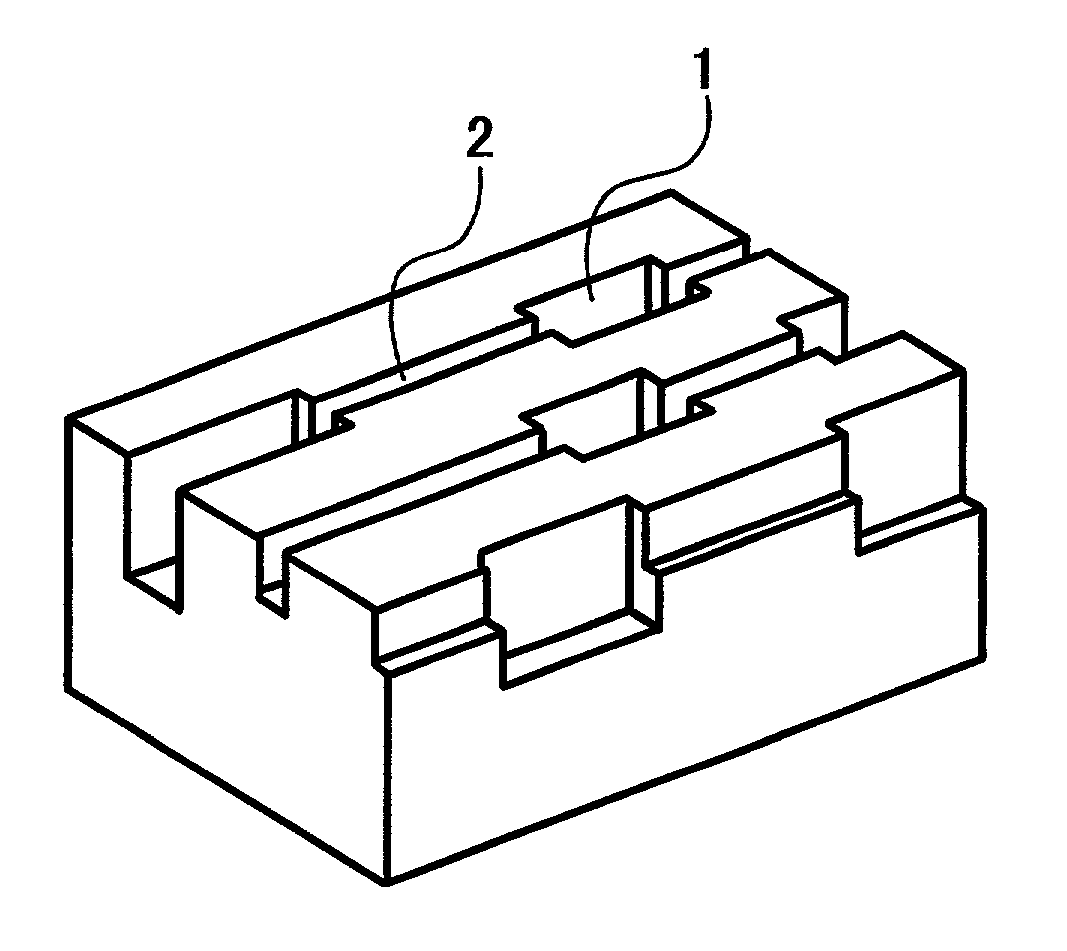
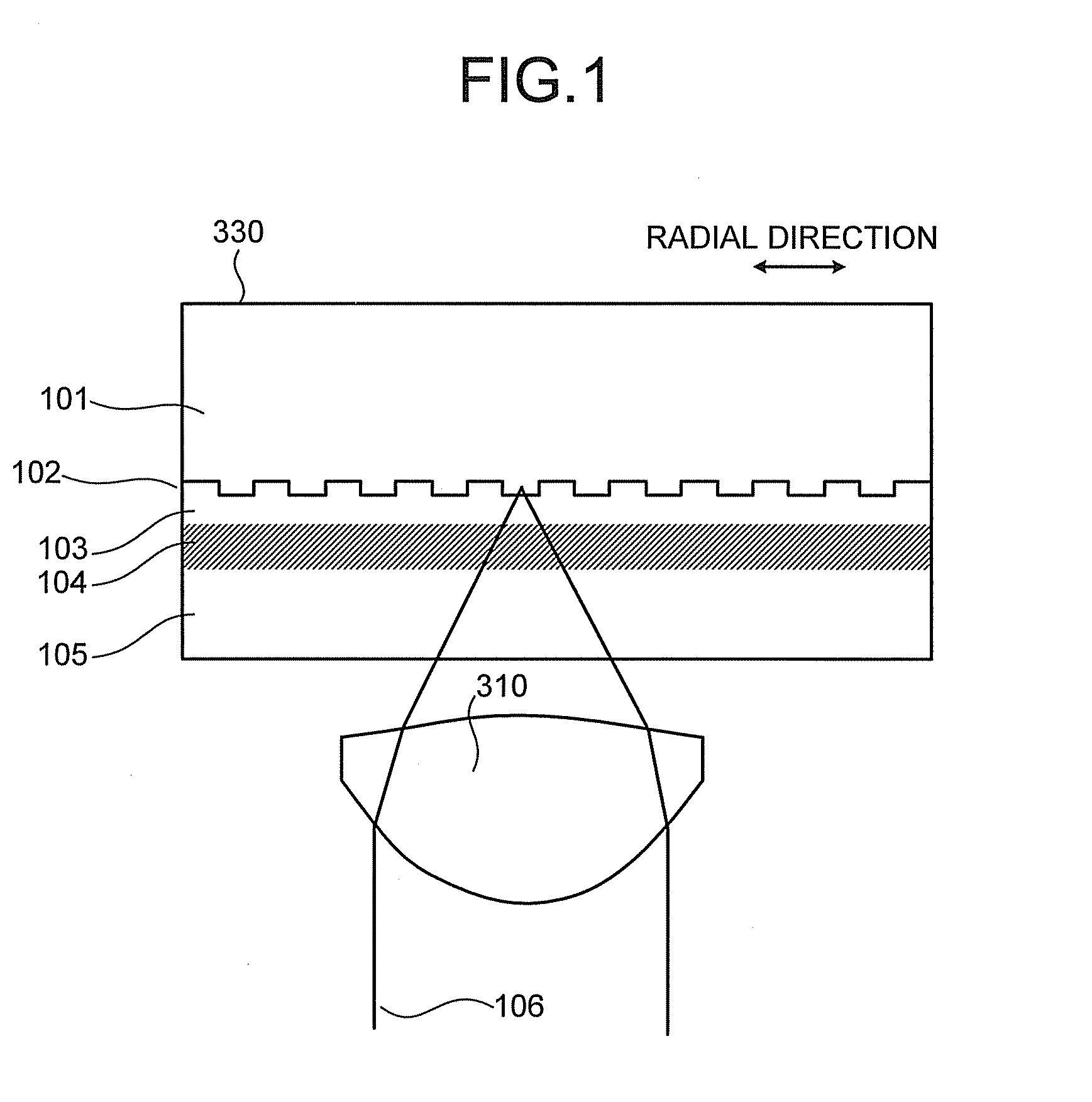
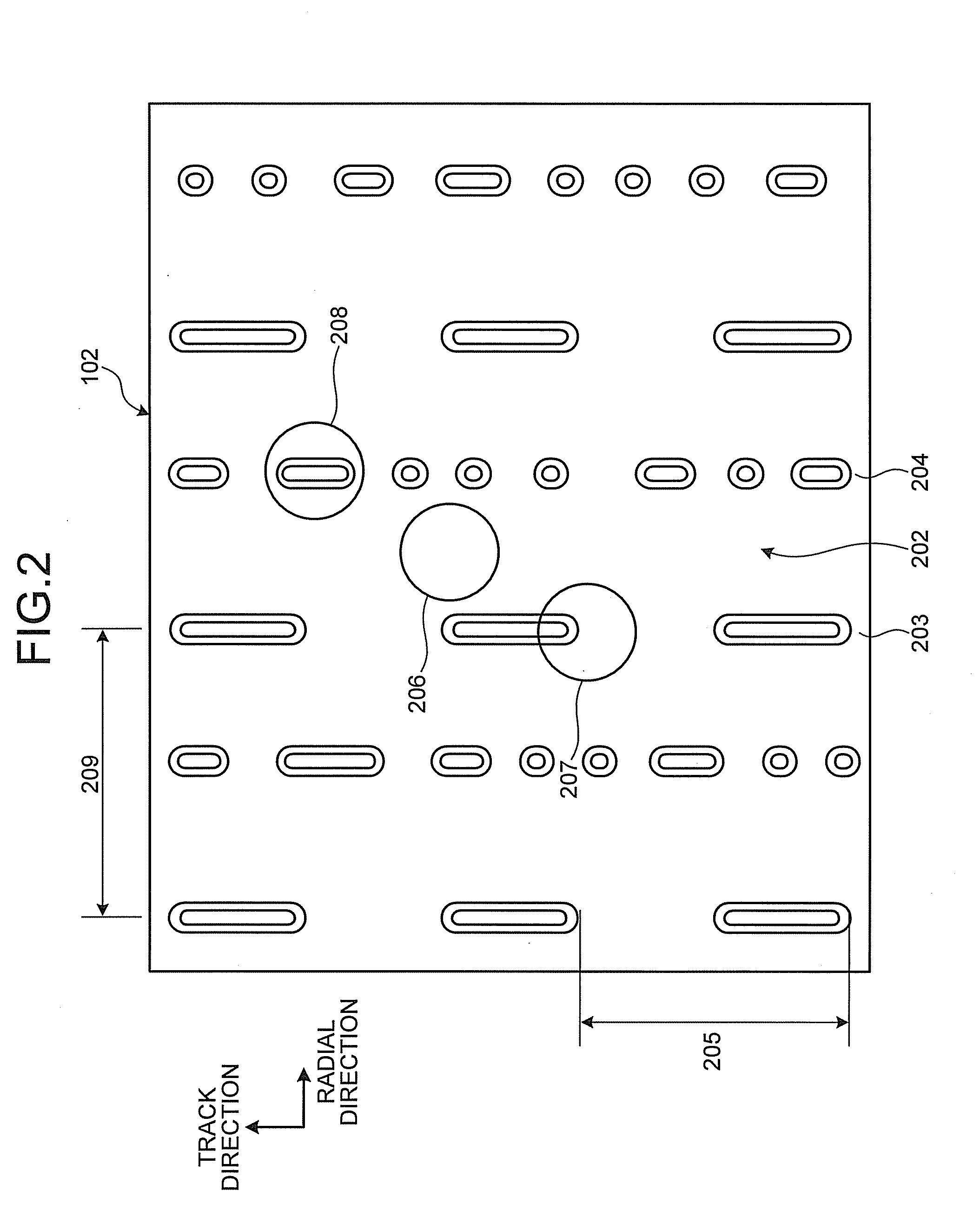
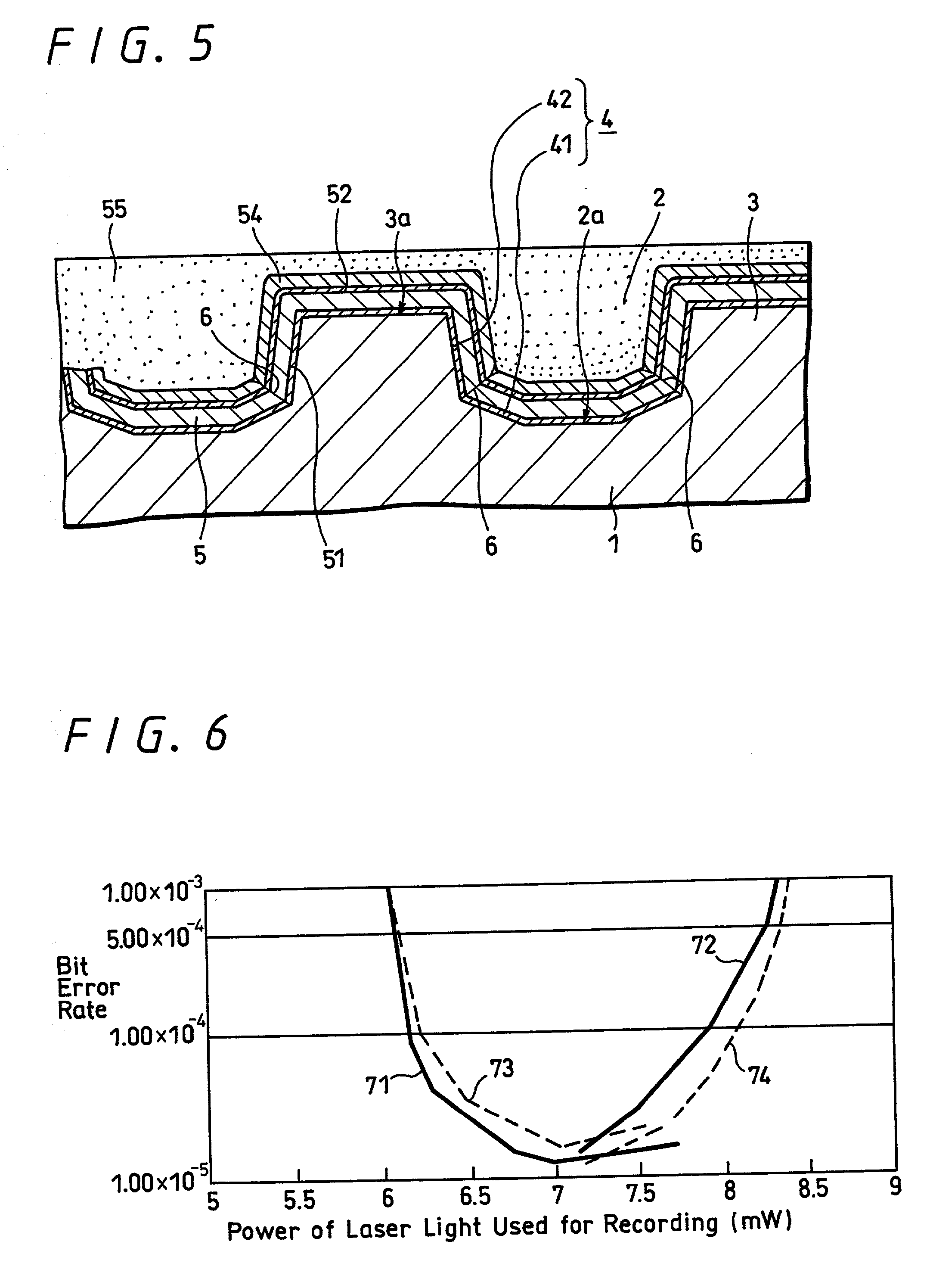
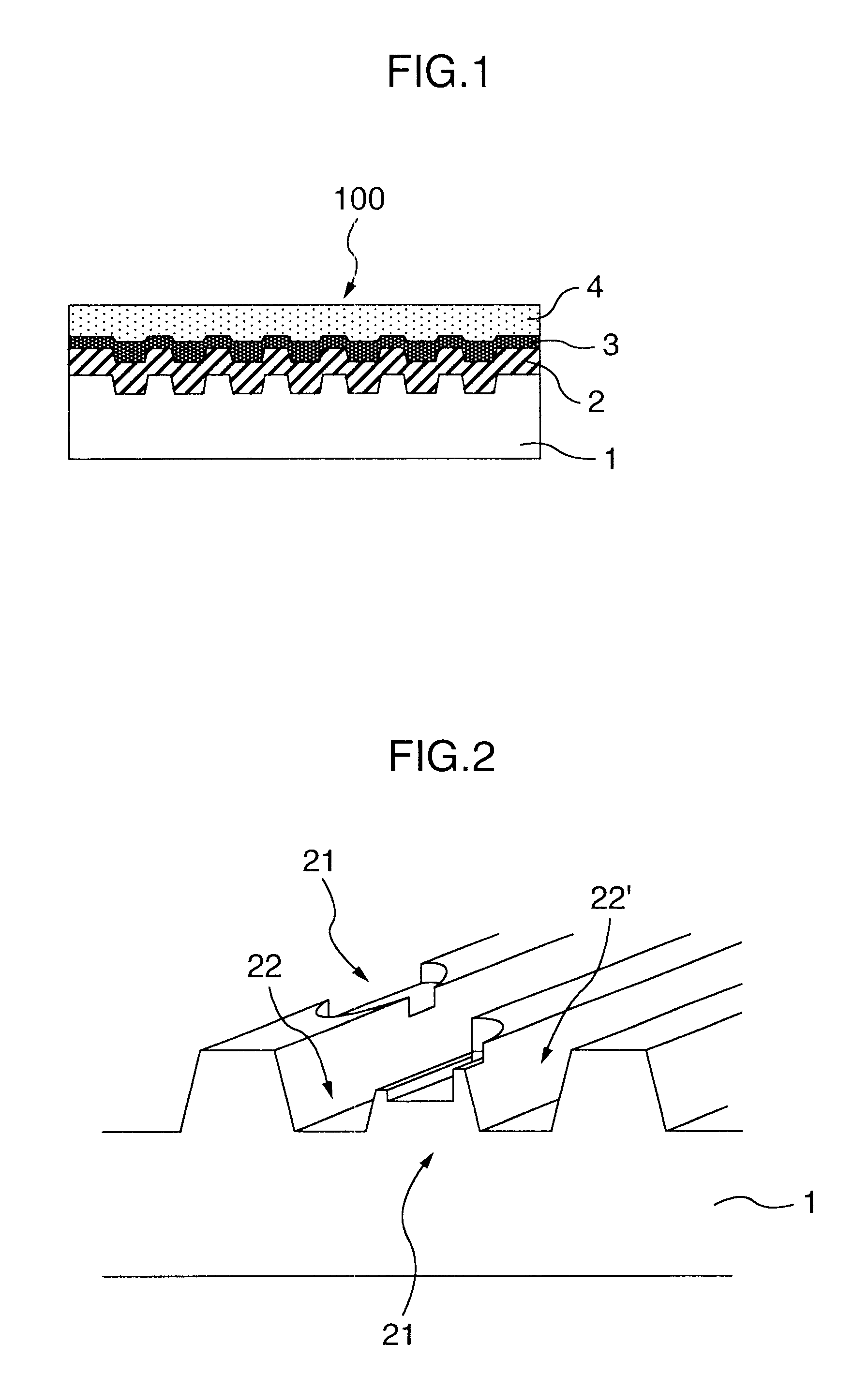
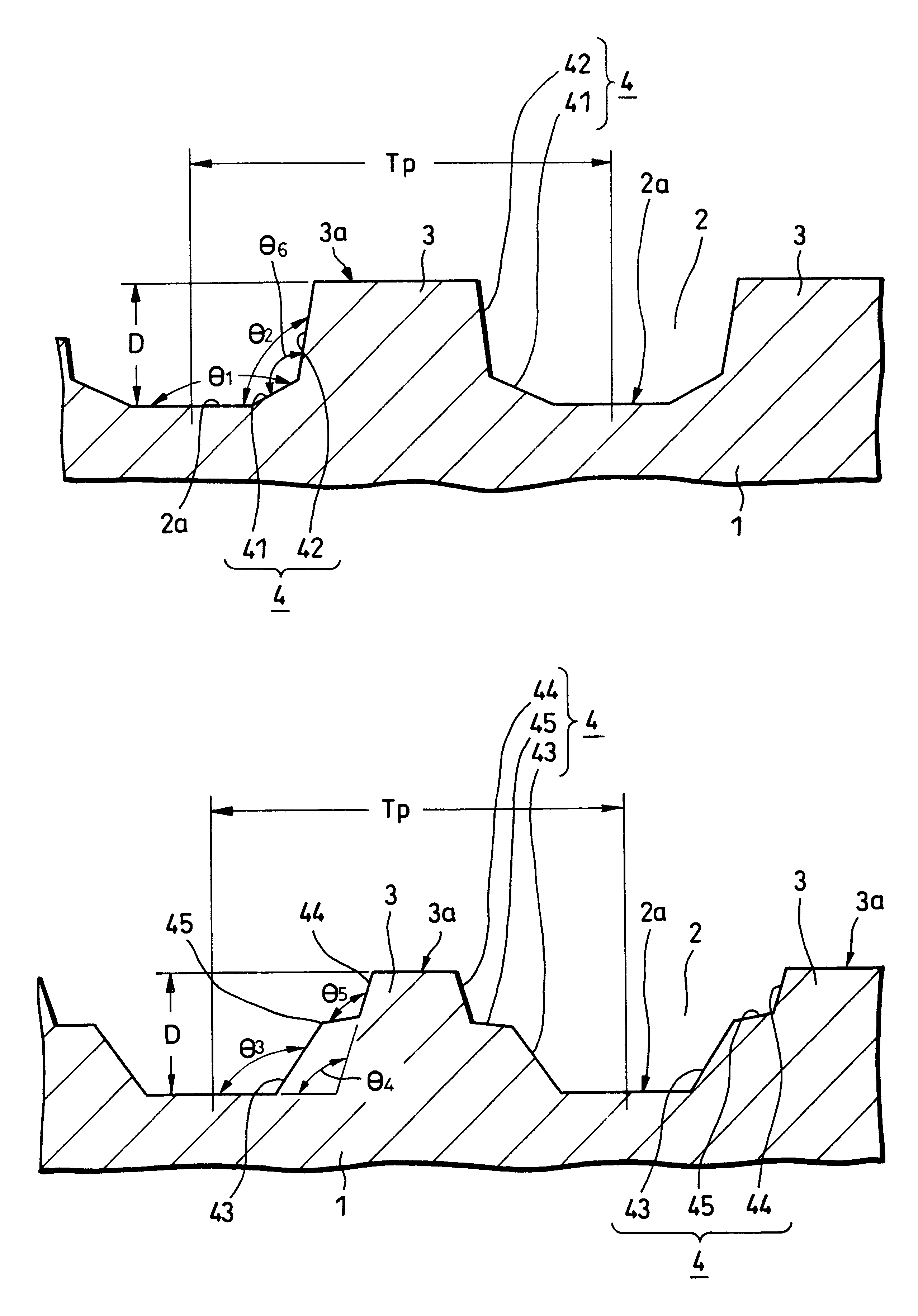
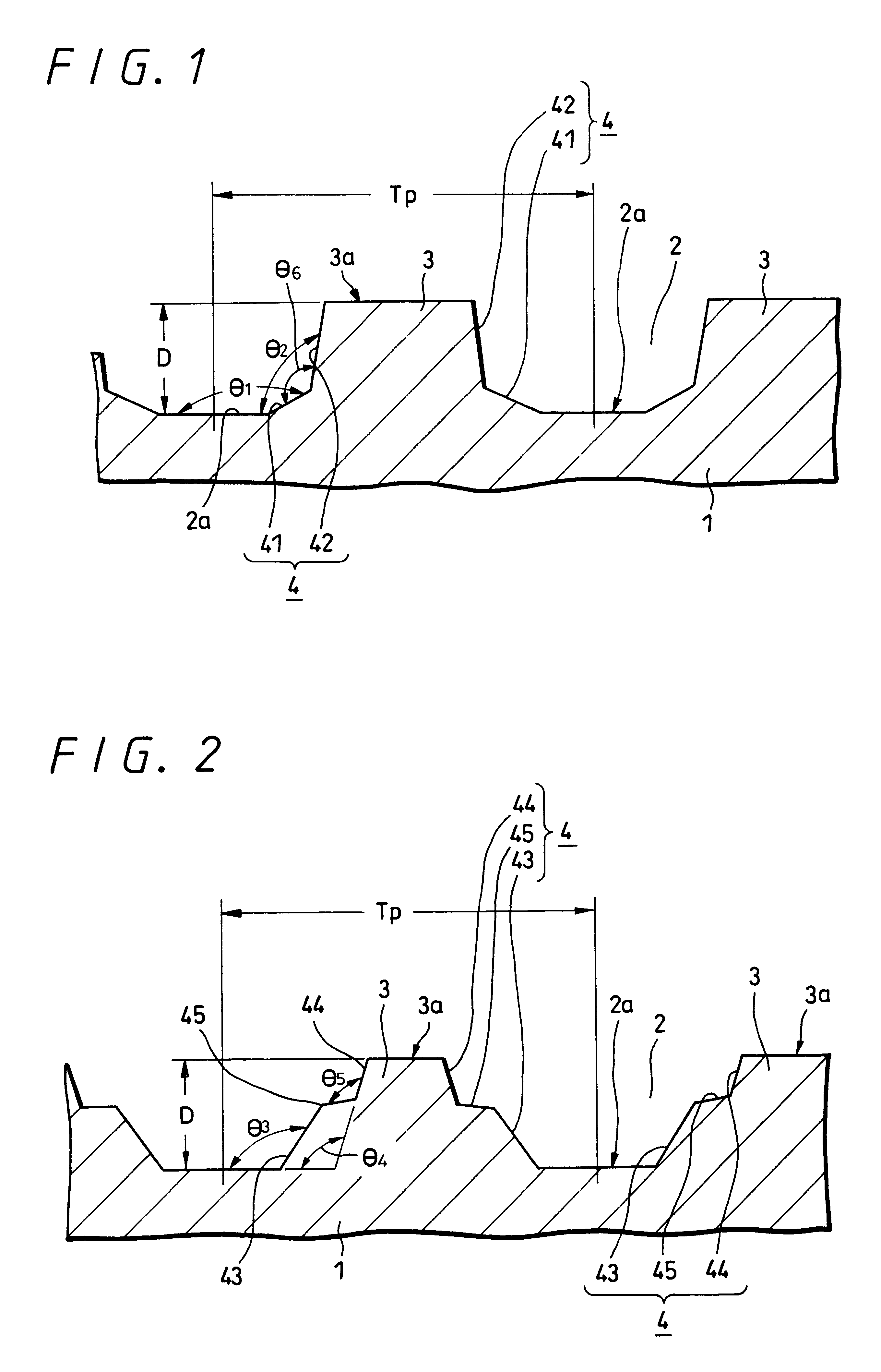
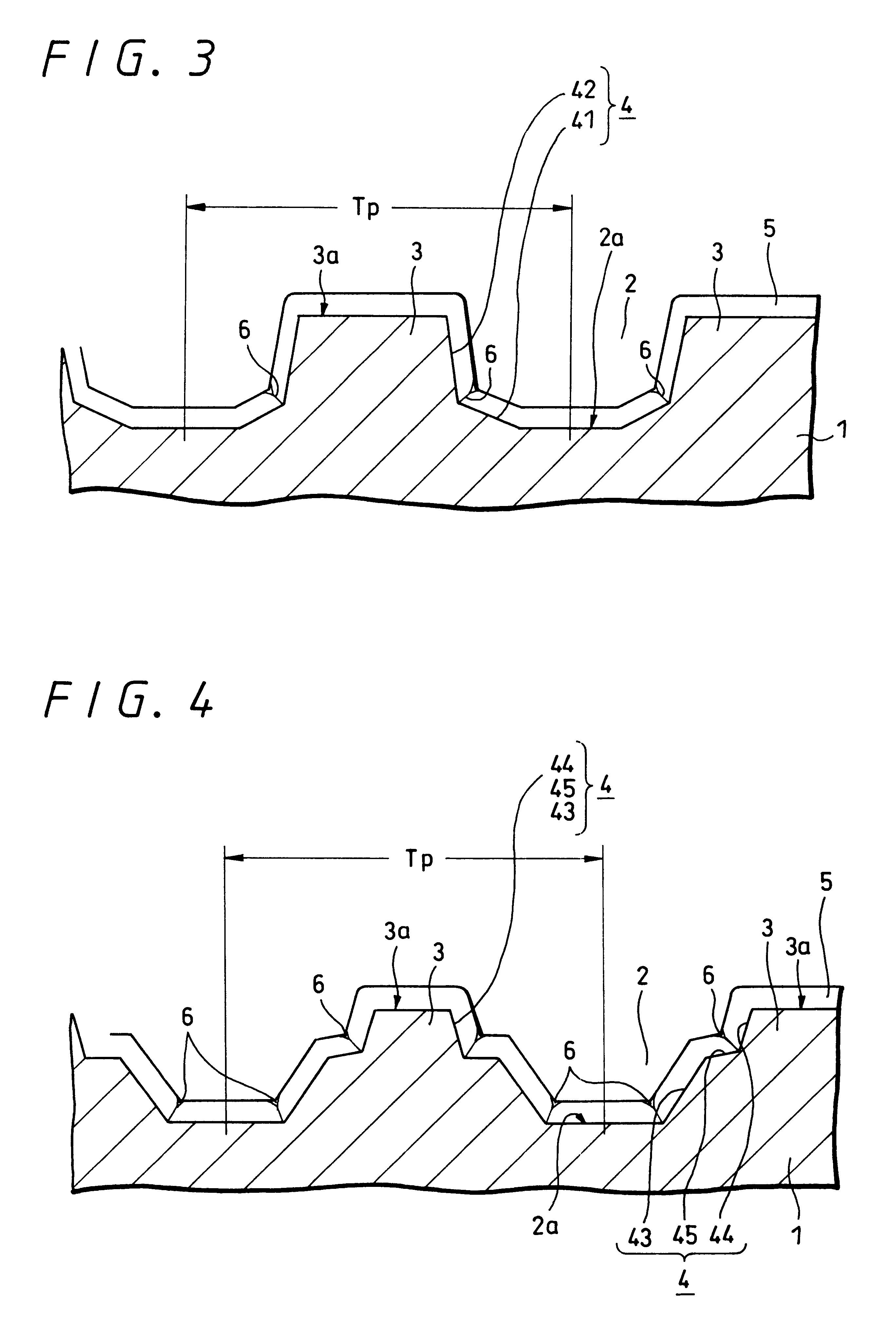
According to the present invention, when a land-groove recording method is adopted, thermal crosstalk between a land and an adjoining groove is suppressed effectively. Inhomogeneity of a recording layer between the land and groove is suppressed effectively. A substrate for optical recording media comprises groove-like concave parts (2) and convex parts each created between adjoining concave parts. A border sidewall (4) between a concave part and an adjoining convex part (2) has a plurality of sidewall planes, that is, at least a first sidewall plane (41) that leads to the bed of the concave part and a second sidewall plane (42) that leads to the apical plane of the convex part. The first sidewall plane meets the bed of the concave part at an angle ranging from 120° to less than 180°. The second sidewall plane meets the bed of the concave part at an angle ranging from 90° to 110°. A discontinuous part (6) is produced at least along a borderline between the first sidewall plane and second sidewall plane. The presence of the discontinuous part (6) is effective in minimizing thermal crosstalk between the concave part (2) and convex part (3) and suppressing inhomogeneity of a recording layer between a land and an adjoining groove.
Owner:SONY CORP
Reverse optical mastering for data storage disks
A data storage master disk and method of making a data storage master disk. The data storage disk master is for use in a data storage disk replication process. The data storage disk molding processes produces replica disks having a surface relief pattern with replica lands and replica grooves. The method includes providing a master substrate. The master substrate is at least partially covered with a layer of photosensitive material. A surface relief pattern having master lands and master grooves is recorded in the data storage disk master, including the steps of exposing and developing the photosensitive material. The exposing and developing of a specified thickness of photosensitive material is controlled to form master grooves extending down to a substrate interface between the master substrate and the layer of photosensitive material, such that the width of the master grooves at the substrate interface corresponds to a desired width of the replica lands.
Owner:MAX BLU TECH
Optical disc and physical address format
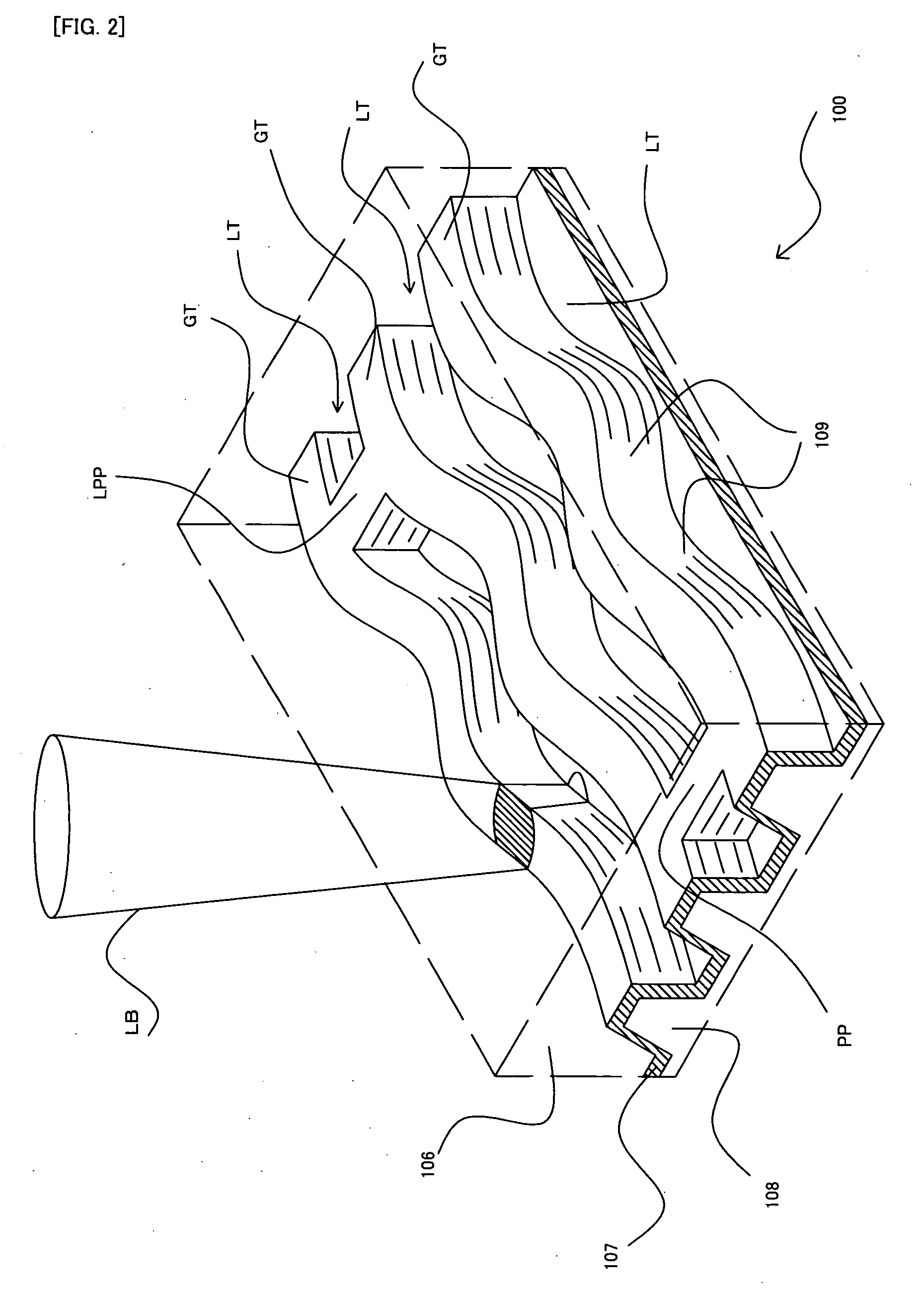
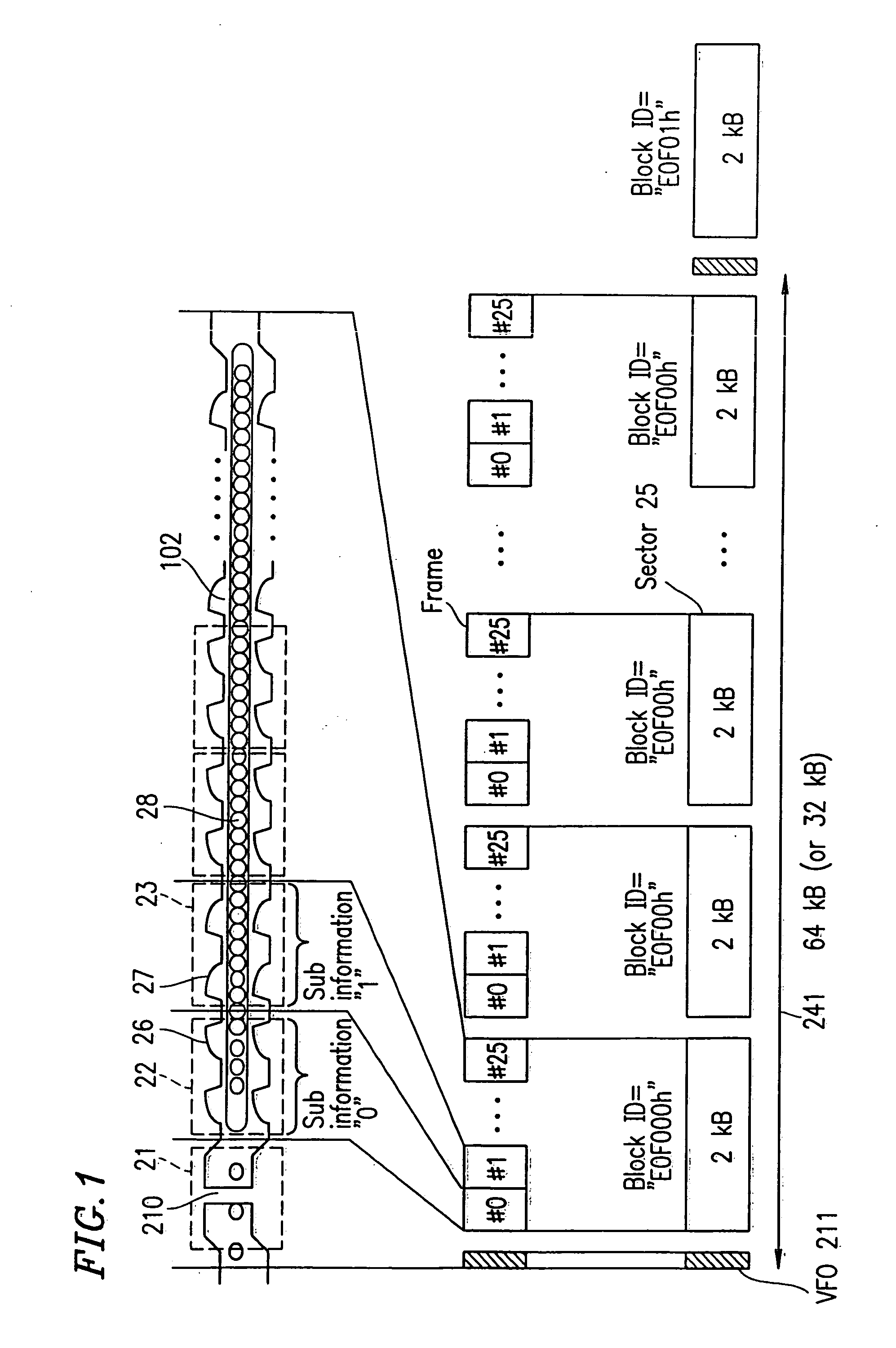
An optical disc medium compares a track groove, along which main information is recorded. The track groove is divided into a plurality of blocks. The plurality of blocks each include a plurality of frames. The plurality of frames each include one shape of wobbles indicating sub information, among a plurality of prescribed shapes of wobbles. The plurality of blocks each have address information. The address information is represented by a string of at least one piece of sub information represented by the shape of wobbles of at least one of the plurality of frames.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS6477136B2Record information storageUsing detectable carrier informationMaximum depthOptical recording
An optical recording medium which can precisely reproduce recording pits formed in pregrooves having width narrower than the diameter of a reproducing beam spot, and which can reduce the jitter and the block error rate, wherein the following unequal equation is satisfied:where Dg is a maximum depth of the pregrooves, Dp is a maximum depth of the prepits, a is a depth of edge parts between the pregrooves and the prepits on the inner peripheral side of the prepits, and b is a depth of the edge parts on the outer peripheral side of the prepits.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Reproducing apparatus and reproducing method
ActiveCN104347090AIncrease recording capacityModification of read/write signalsOptical beam sourcesDifferential signalingLight beam
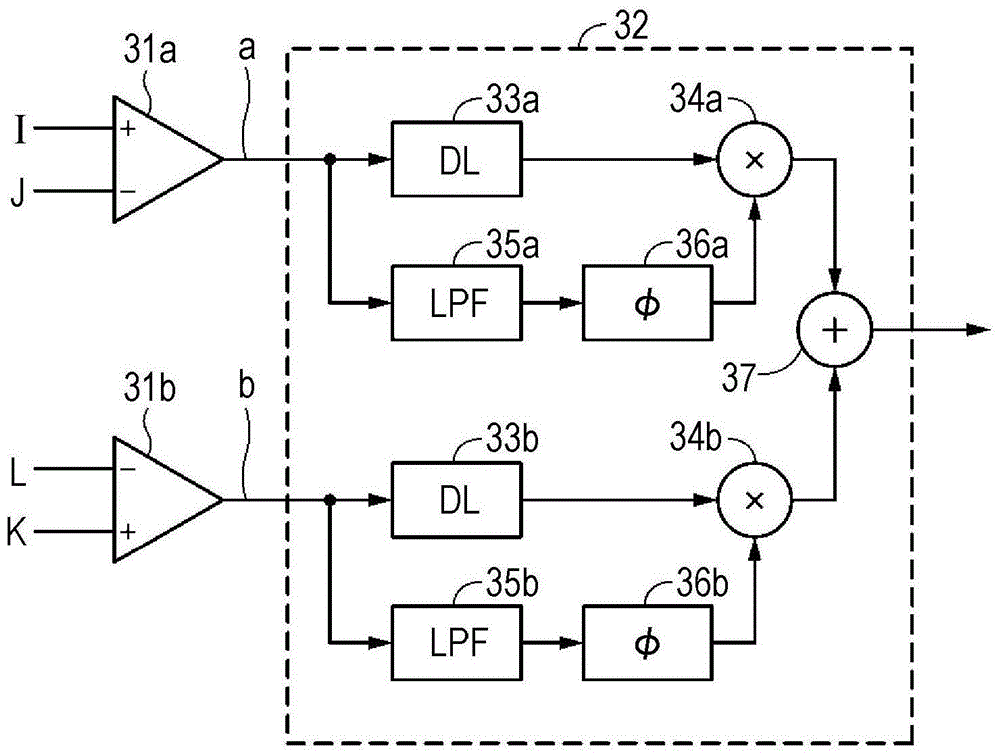
Provided is a reproducing apparatus including: an optical system that obtains a signal light by radiating light emitted from a light source and generates a reference light from the light emitted from the light source, with respect to a recording medium, and that generates first to fourth groups of the signal light beams and the reference light beams, with respect to the superposed light in which the signal light and the reference light are superposed onto each other; a light receiving unit that receives light beams of the first to fourth groups of the signal light beams and the reference light beams respectively through first to fourth light receiving elements; and a reproduction signal generation circuit that calculates a first differential signal and a second differential signal, and that generates a reproduction signal by performing an arithmetic operation using the first and second differential signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical information storage medium
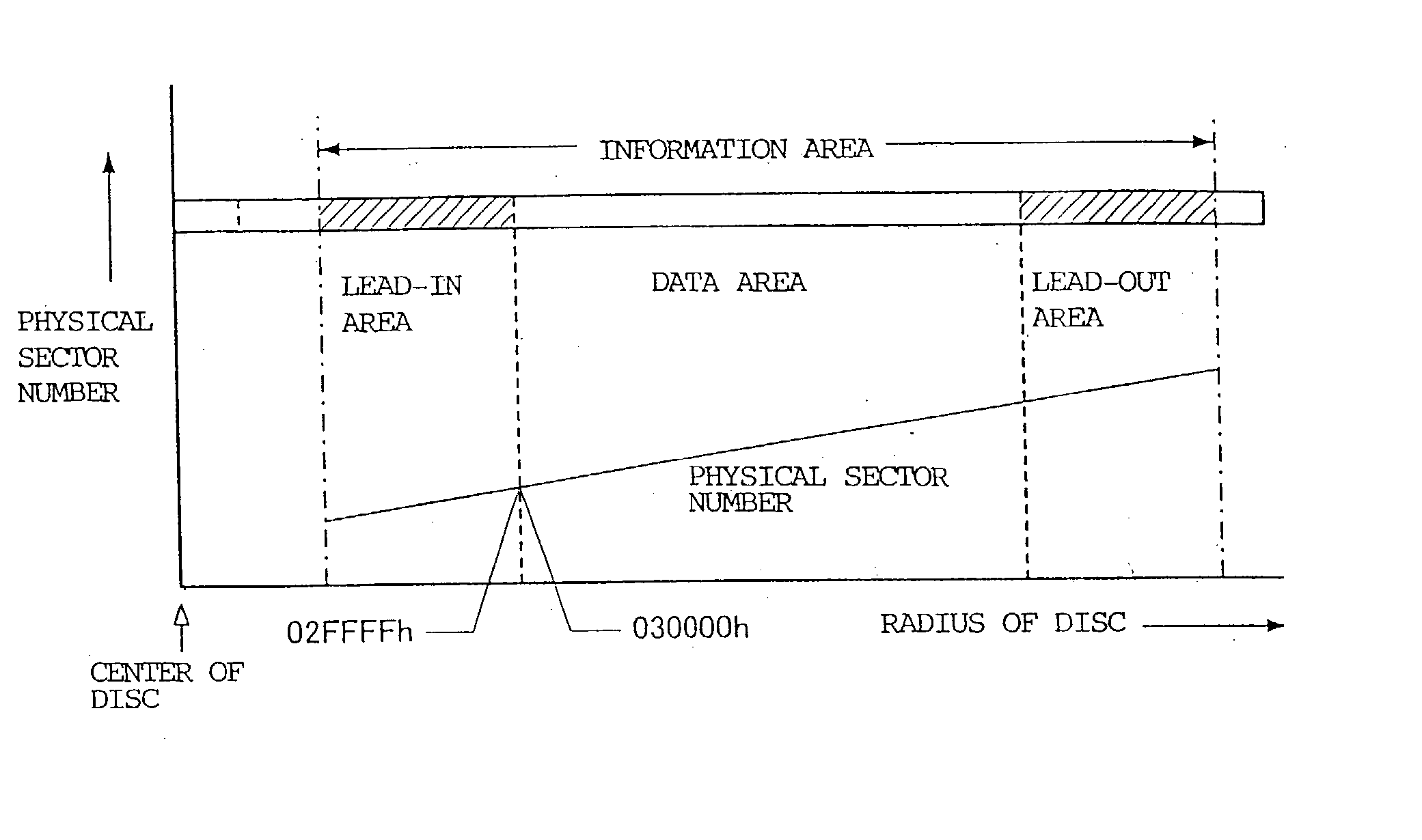
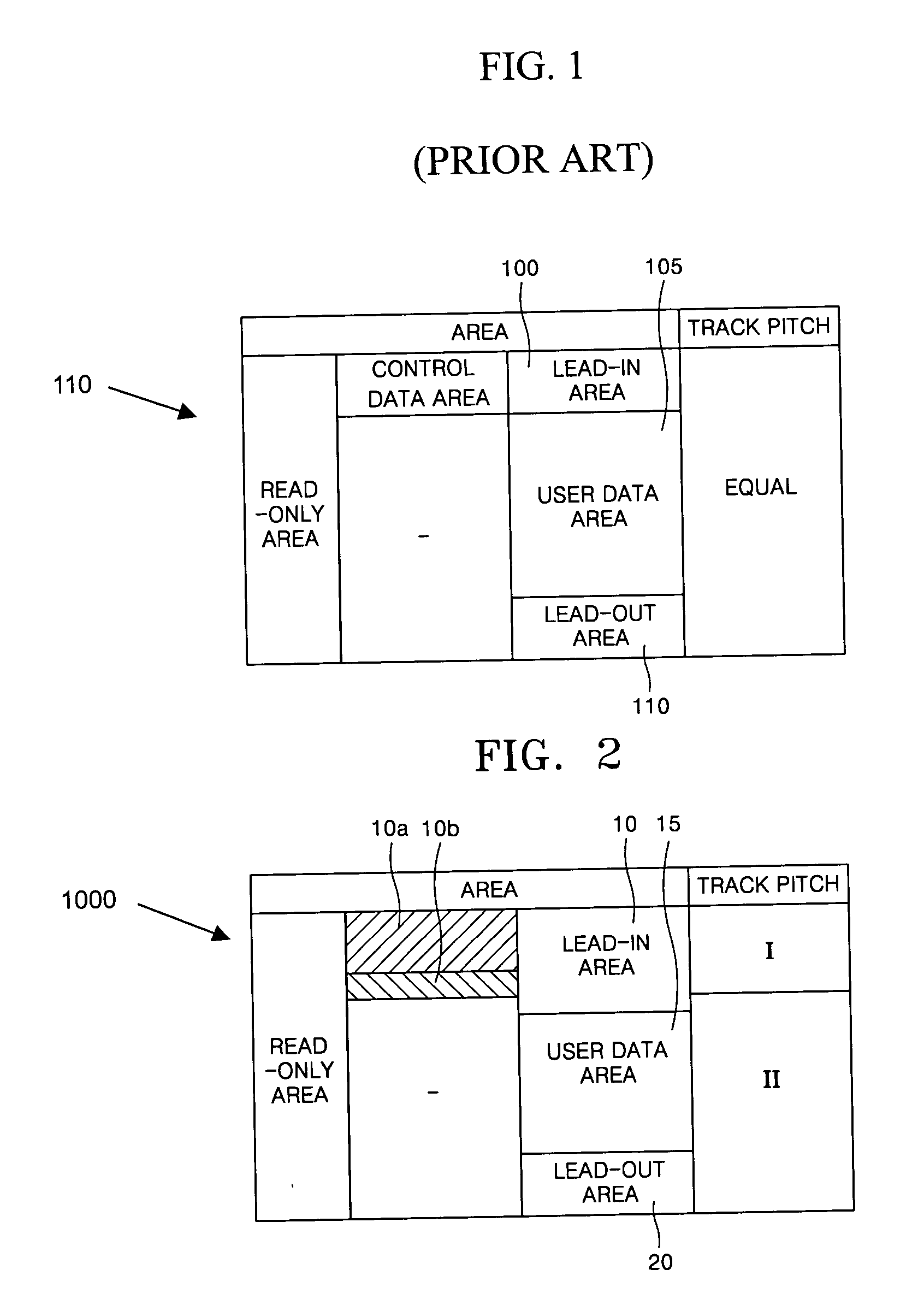
ActiveUS20040047249A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityRecord information storageCarrier tracks/pitsComputer scienceInformation storage
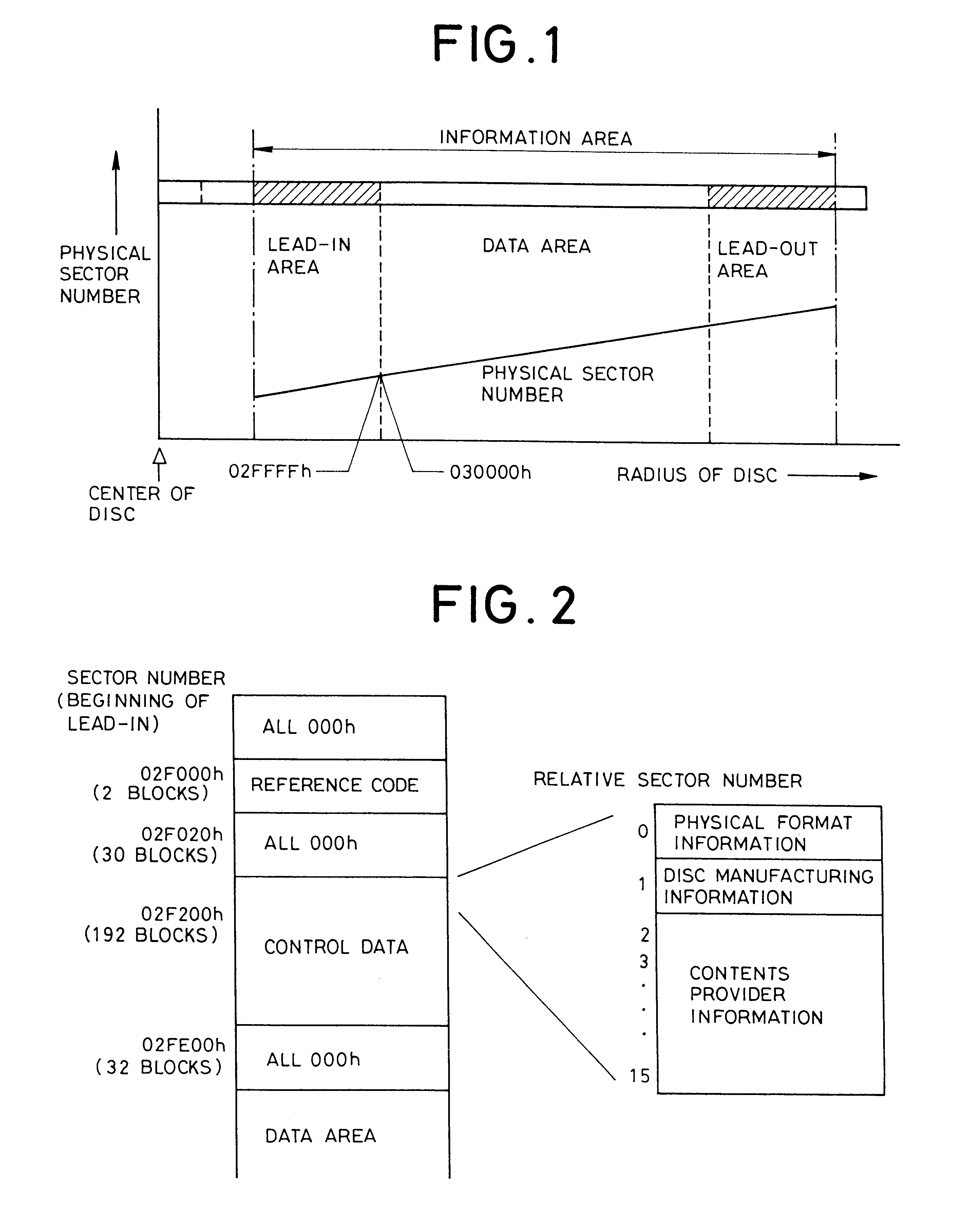
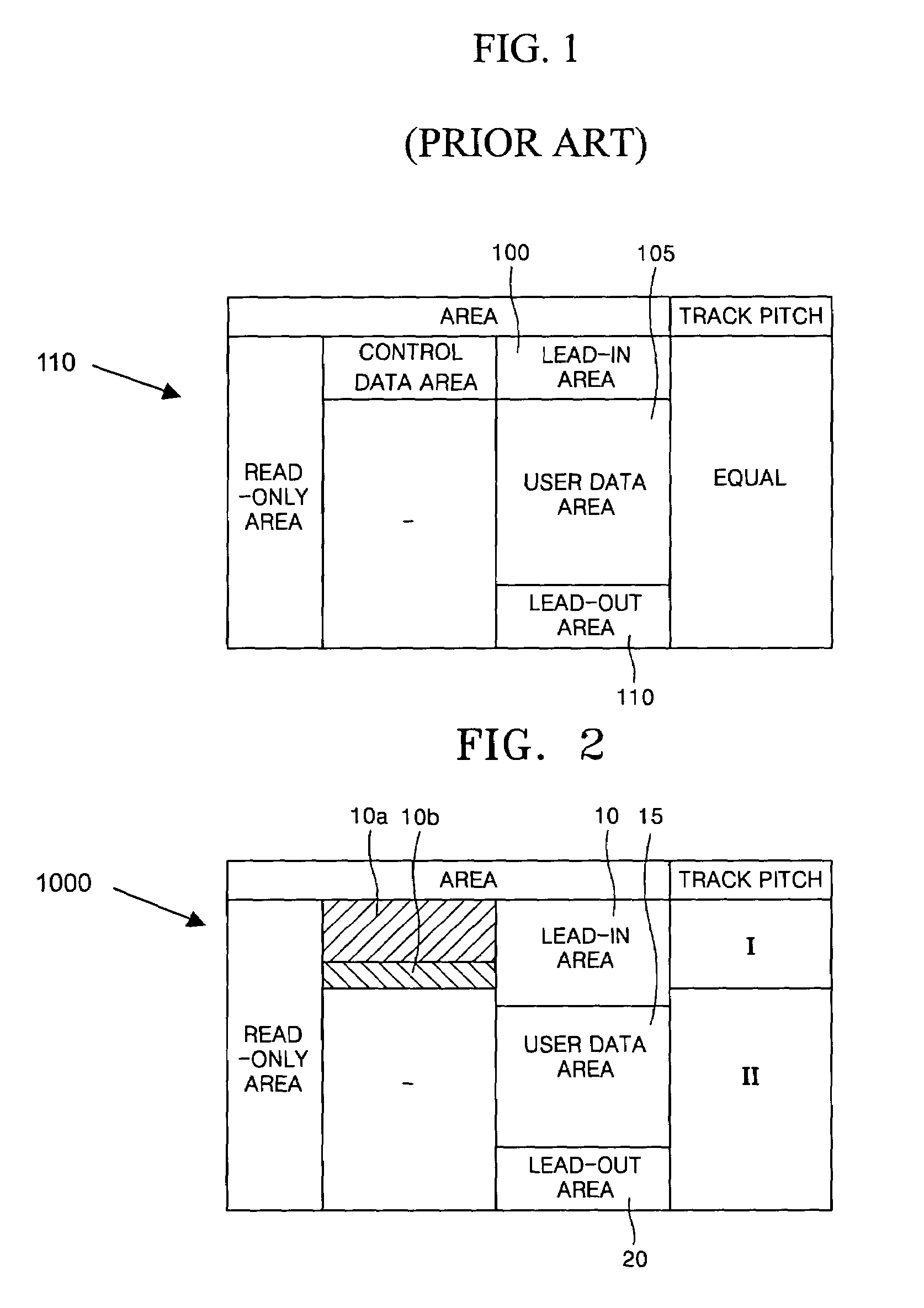
An optical information storage medium includes a lead-in area, a lead-out area, and a user data area between the lead-in and lead-out areas and in which user data is recorded. Pits are formed in the lead-in area, the user data area, and the lead-out area, and a track pitch in all or a portion of the lead-in area is different from a track pitch in the remaining area of the optical information storage medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical information storage medium
ActiveUS7272106B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityRecord information storageCarrier tracks/pitsComputer scienceInformation storage
An optical information storage medium includes a lead-in area, a lead-out area, and a user data area between the lead-in and lead-out areas and in which user data is recorded. Pits are formed in the lead-in area, the user data area, and the lead-out area, and a track pitch in all or a portion of the lead-in area is different from a track pitch in the remaining area of the optical information storage medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Non-resonant two-photon absorption recording material, non-resonant polymer two-photon absorption optical information recording medium, and recording/reproducing method
The present invention provides a non-resonant two-photon absorption recording material containing a non-resonant polymer two-photon absorption compound, and the non-resonant two-photon absorption recording material wherein the main chain of the non-resonant polymer two-photon absorption compound contains at least one member selected from polystyrene, polyacrylate, polymethacrylate, polyester, polyurethane, polyether and polyimide, and also provides an optical information recording medium having a recording layer containing the recording material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Substrate for optical recording media, optical recording medium, manufacturing process for optical recording media, and optical recording/reproducing method
According to the present invention, when a land-groove recording method is adopted, thermal crosstalk between a land and an adjoining groove is suppressed effectively. Inhomogeneity of a recording layer between the land and groove is suppressed effectively. A substrate for optical recording media comprises groove-like concave parts (2) and convex parts each created between adjoining concave parts. A border sidewall (4) between a concave part and an adjoining convex part (2) has a plurality of sidewall planes, that is, at least a first sidewall plane (41) that leads to the bed of the concave part and a second sidewall plane (42) that leads to the apical plane of the convex part. The first sidewall plane meets the bed of the concave part at an angle ranging from 120° to less than 180°. The second sidewall plane meets the bed of the concave part at an angle ranging from 90° to 110°. A discontinuous part (6) is produced at least along a borderline between the first sidewall plane and second sidewall plane. The presence of the discontinuous part (6) is effective in minimizing thermal crosstalk between the concave part (2) and convex part (3) and suppressing inhomogeneity of a recording layer between a land and an adjoining groove.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical recording medium and its information recording method, and recorder
InactiveUS20060120263A1Accurate detectionAvoid interferenceRecord information storageGroove/land recordingBit-lengthElectrical and Electronics engineering
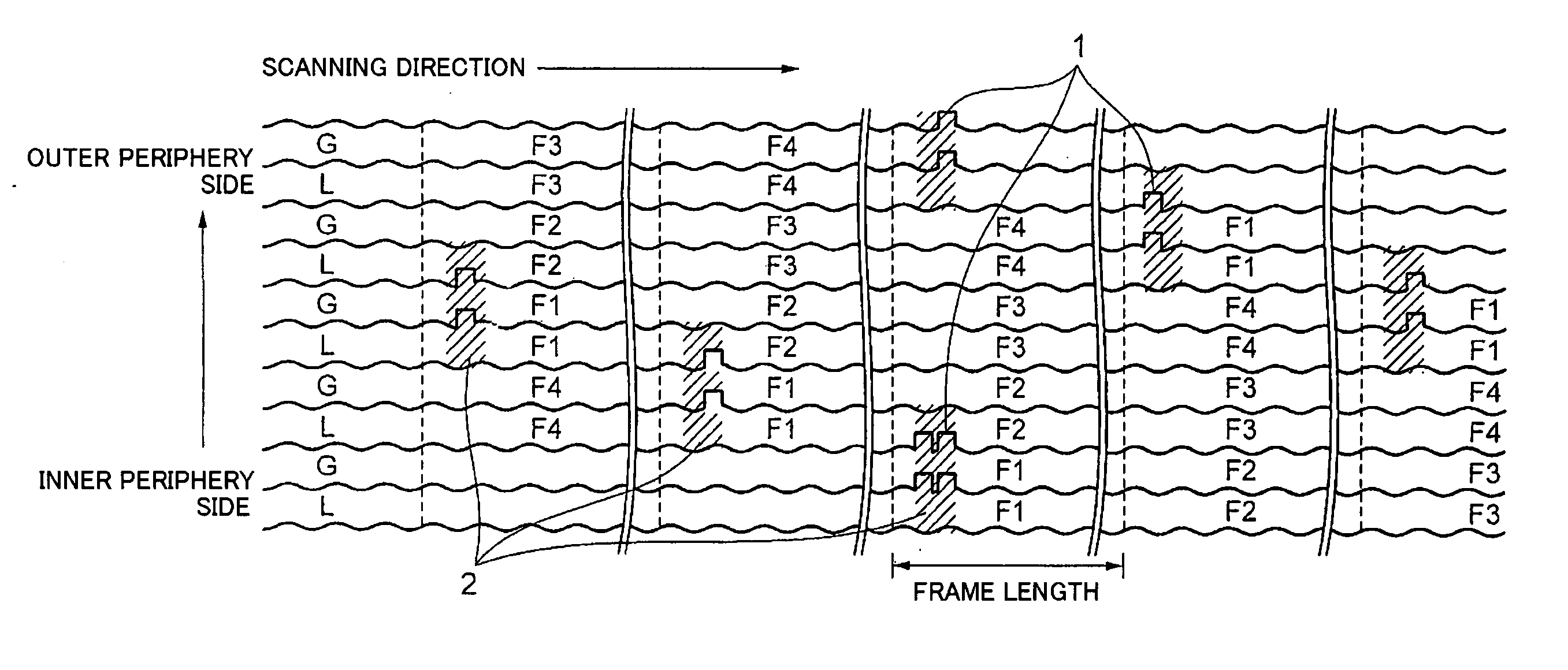
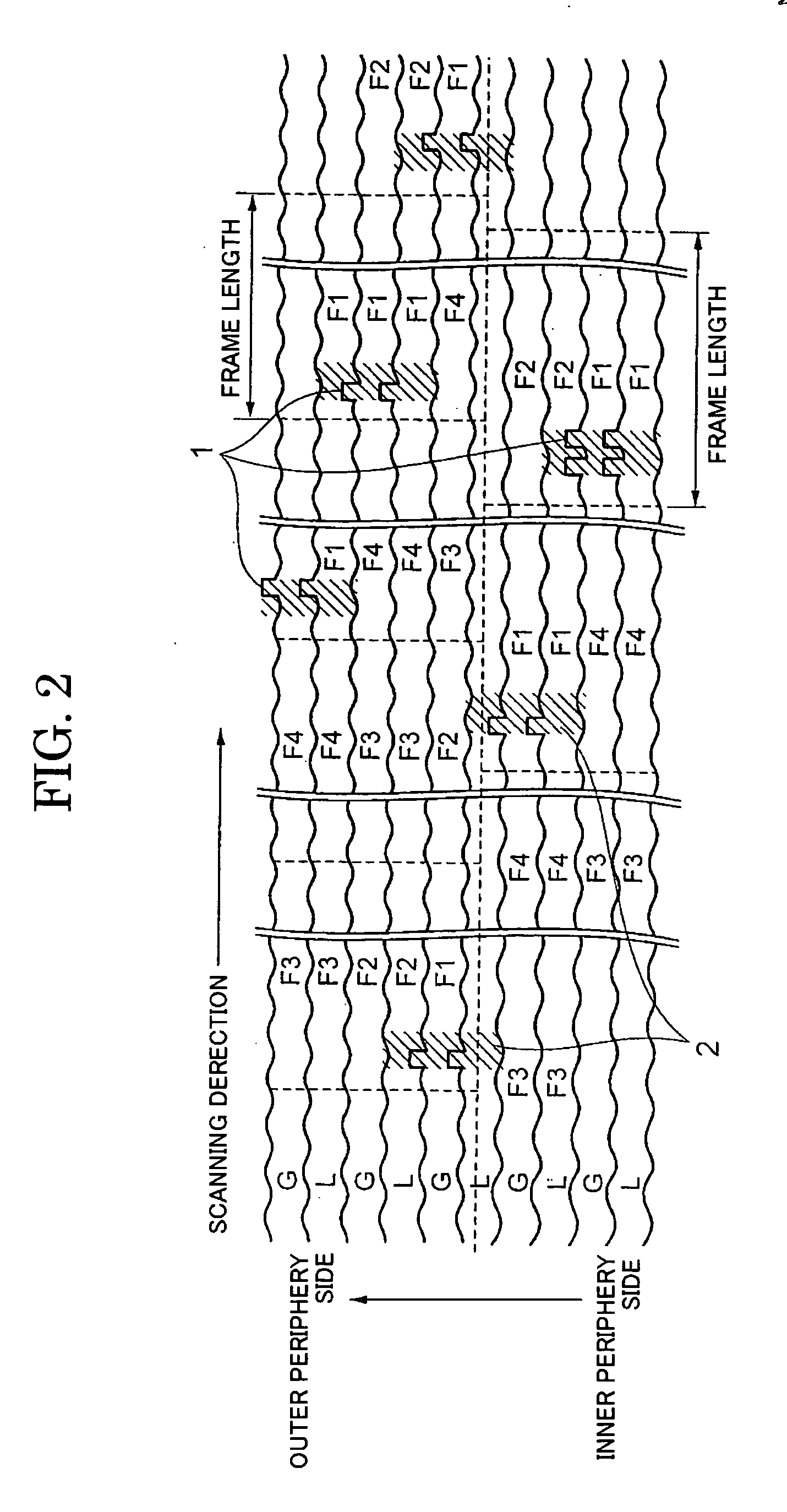
An optical disk includes grooves (G) formed concentrically or spirally from an inner periphery to an output periphery of a disk, wherein prepit (1) are formed on the lands (L) each sandwiched between grooves and grooves (G). The prepit forming region (2) is assigned as a region in which a single or a plurality of prepits (1) are formed. Th prepit forming regions (2) have a fixed length 36 or less times the recording channel length along the recording track, and are arranged apart from on another by 300 or more times the recording channel bit length along the recording track. On the prepit forming region (2), a pattern including a long mark or a long space having a length ten or more times the recording channel bit length so that the long mark or long space covers the prepit (1) on the recording track.
Owner:NEC CORP
Popular searches
Record carriers manufacture Optical record carrier manufacture Disposition/mounting of heads Arrangement for discrete information storage Recording involving reflectivity/absorption/color-change Record carrier types Recording signal processing Thin material handling Record carrier accessories Zoned data area
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com