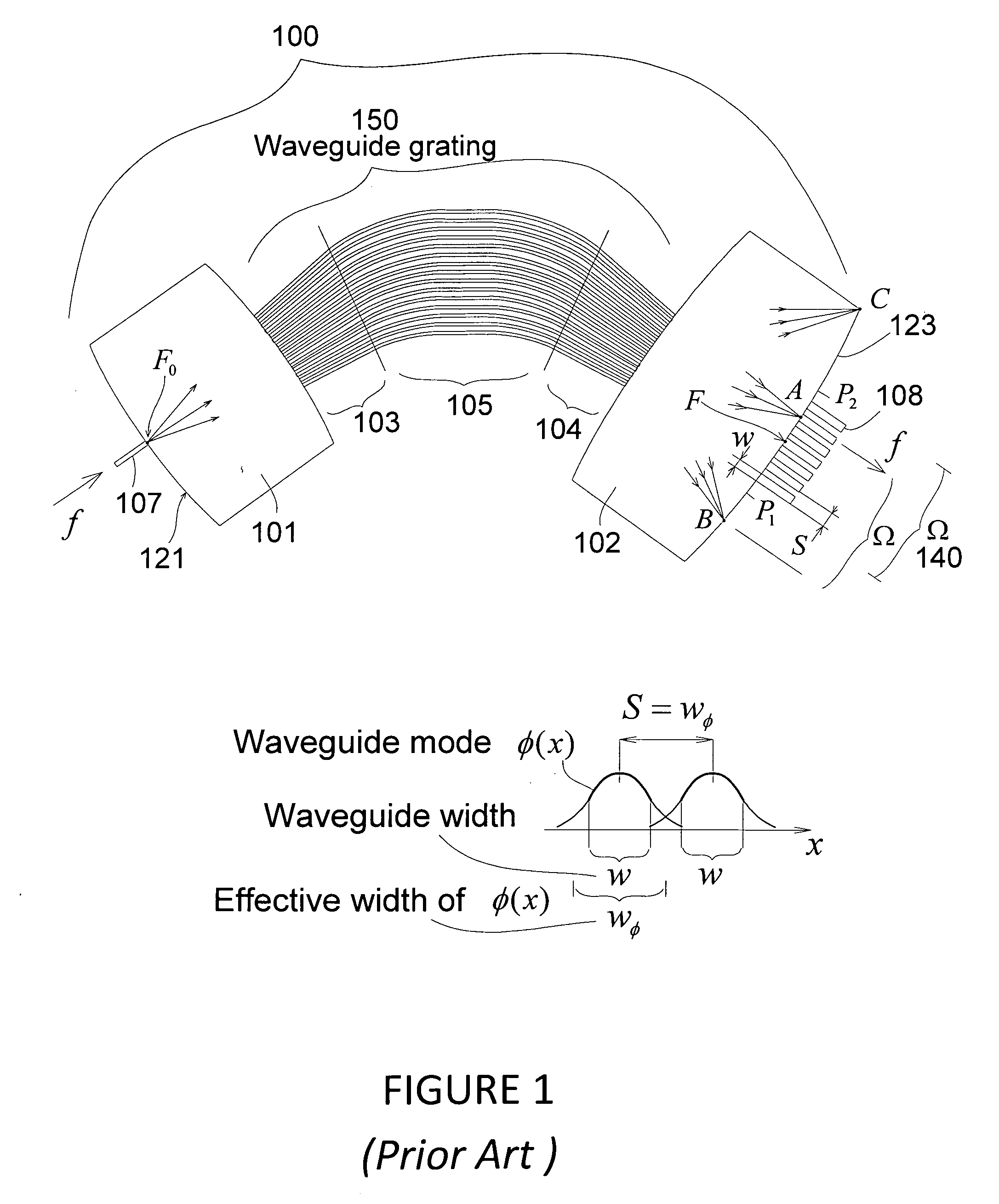
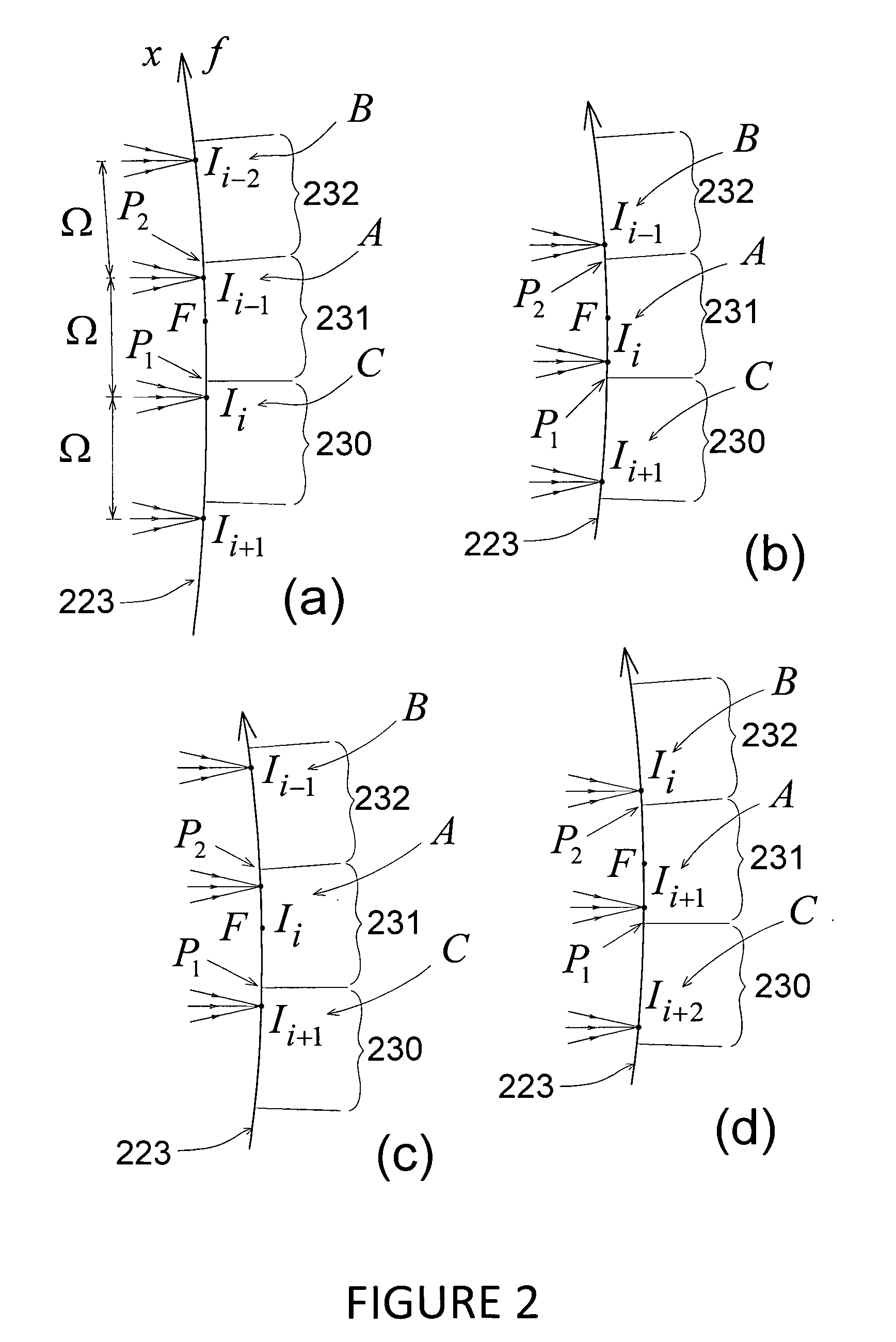
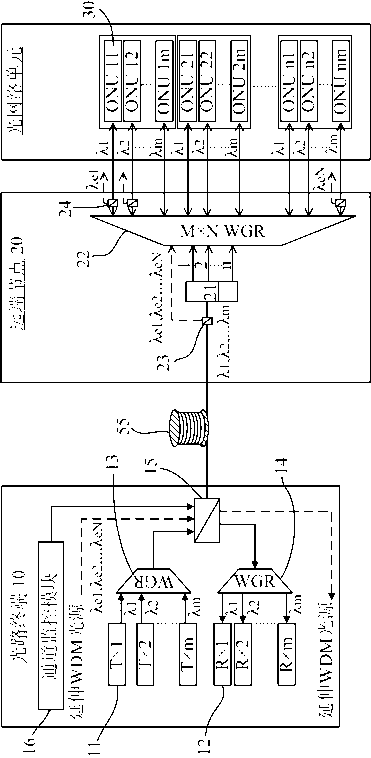
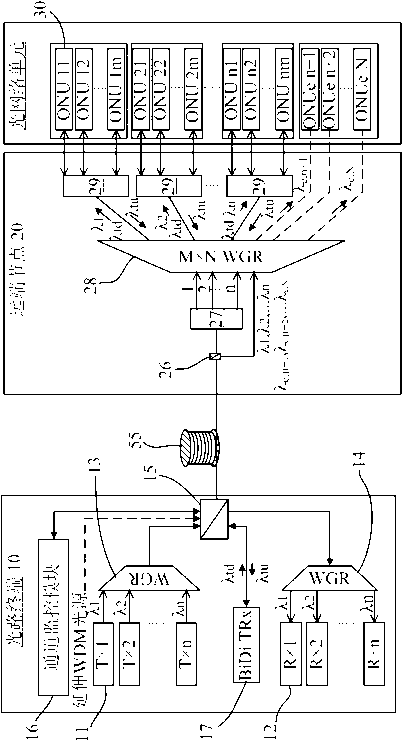
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Waveguide grating router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
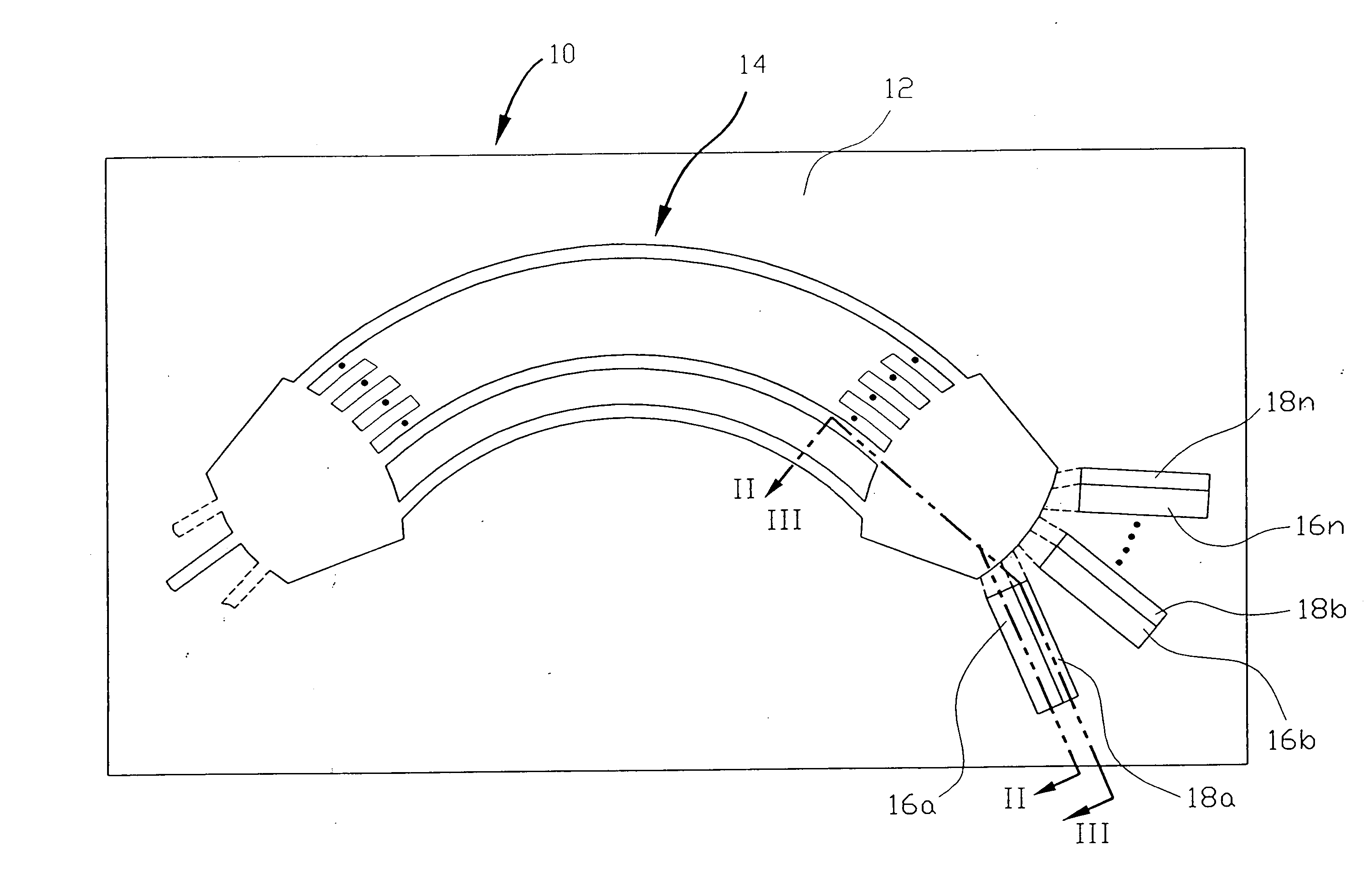
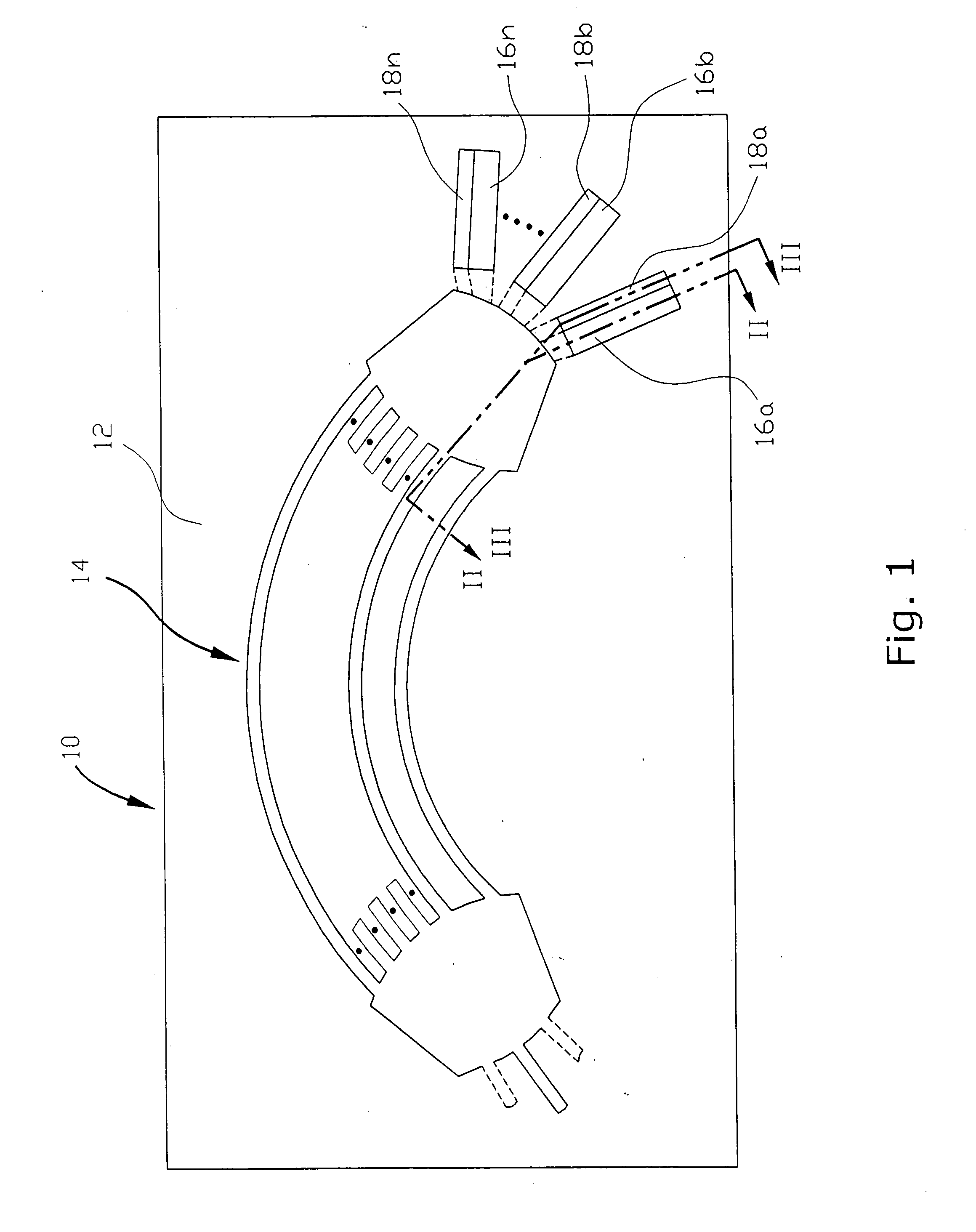
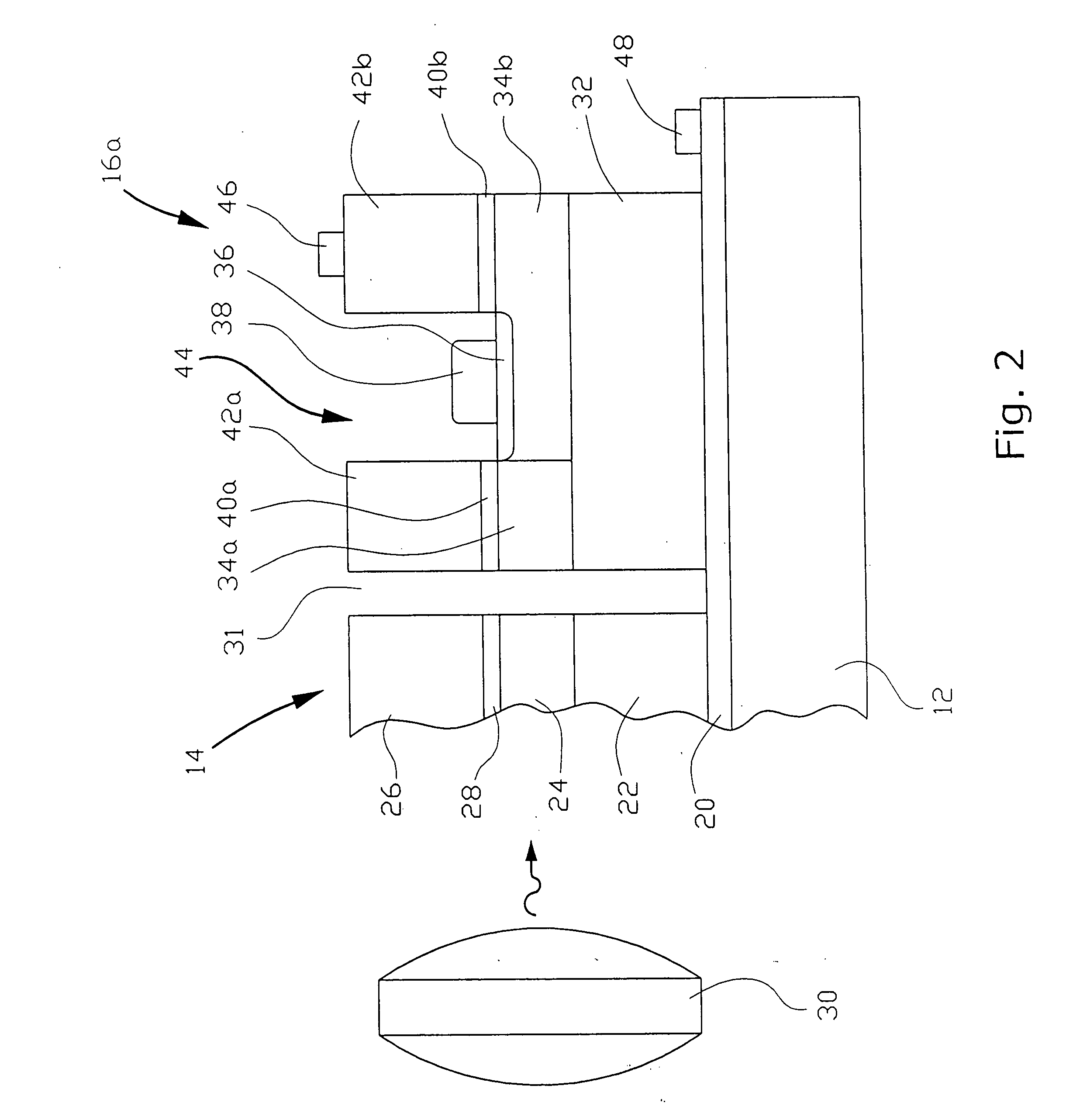
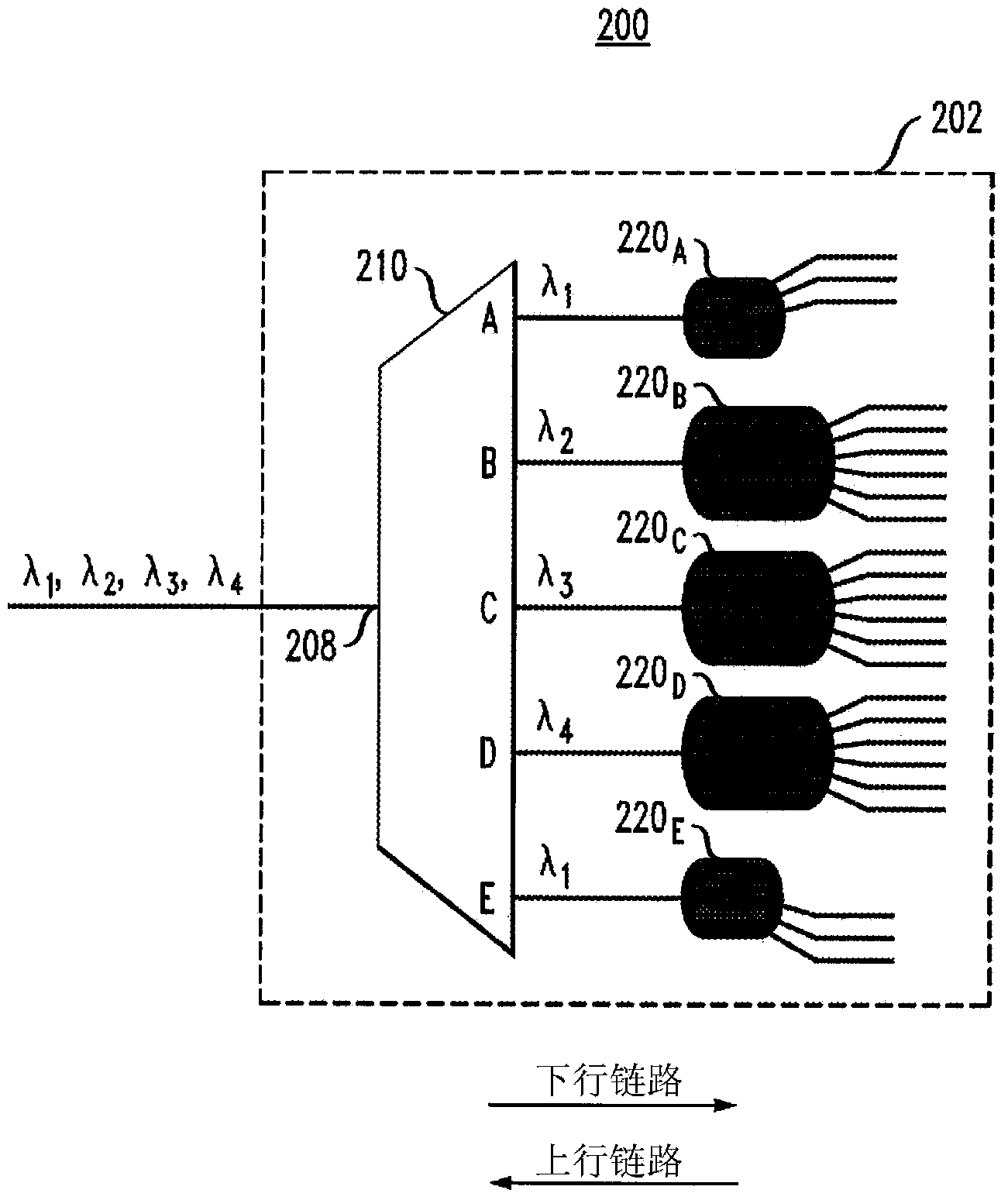
Integrated demultiplexer/photoreceiver for optical networks and method of controlling transparency of optical signal transmission layer
InactiveUS20050100272A1Low costSimple designCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic receiversHeterojunctionPhotodetector
An integrated demultiplexer / photoreceiver (IDP) for optical networks and optical interconnection devices has a common substrate which supports three sequentially arranged basic components: a waveguide grating router, an array of photodetectors, and an array of heterojunction transistors. Basic layers of all three components are grown together in a common epitaxial process, and then each of the components is individually patterned in accordance with its function. Such structure of IDP makes it possible to reduce the cost, simplify the design, improve conditions for optical alignment, and reduce optical losses. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, transparency of the optical signal transmission layer of the WGR is controlled by selectively doping the layers of the multiple-layer waveguide structure, while in another embodiment such control is achieved by changing the width of the energy gap in the optical signal transmission layer of the WGR. Such a change is achieved by utilizing electrical bias and optical pumping from an external light source operating on a predetermined wavelength. The invention also provides a method for controlling transparency of the layer that transmits optical signals through the waveguide units in optoelectronic devices, such as an integrated demultiplexer / photoreceiver for optical network, by utilizing optical pumping and electrical bias.
Owner:XONPHU LINE LIMITED LIABILITY
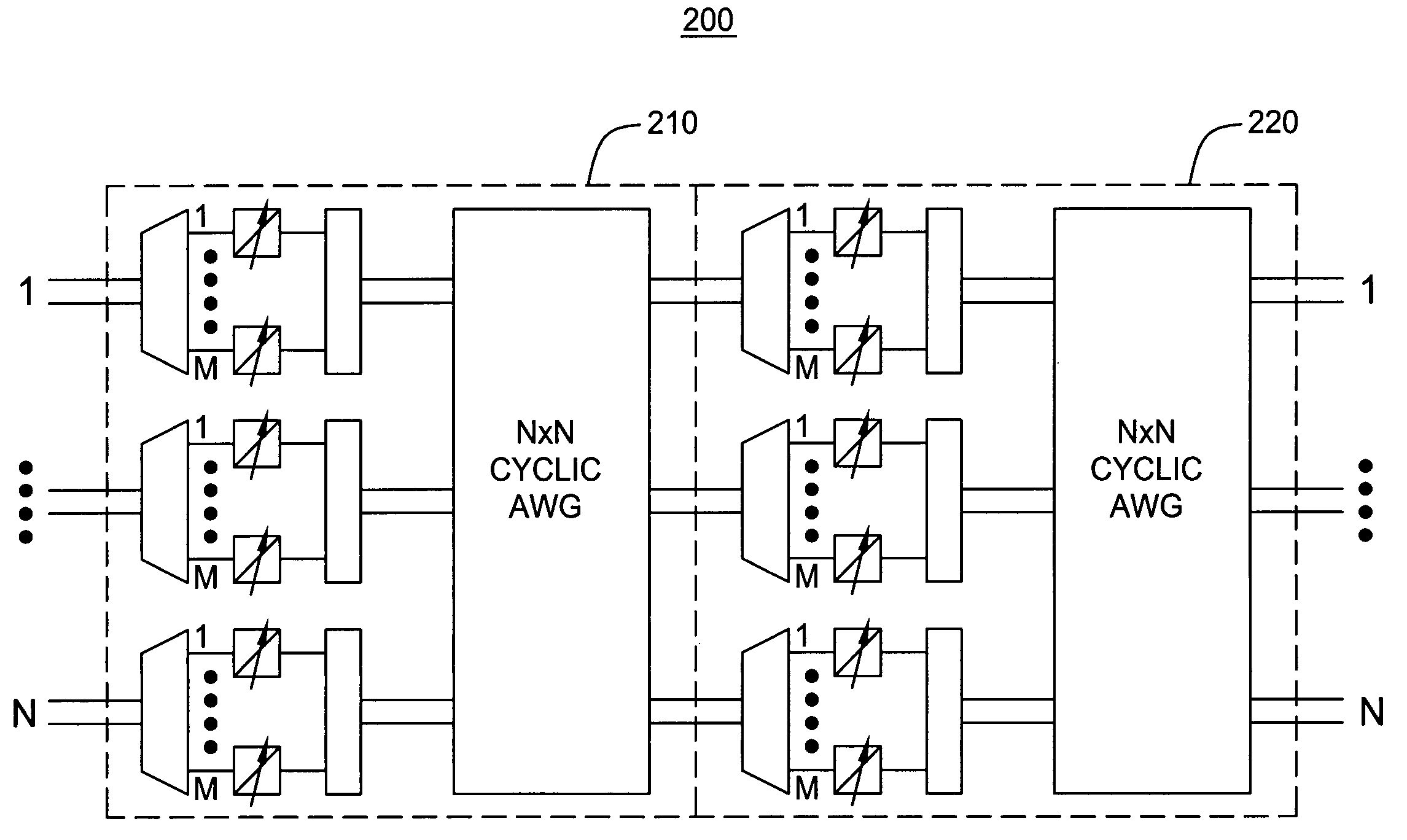
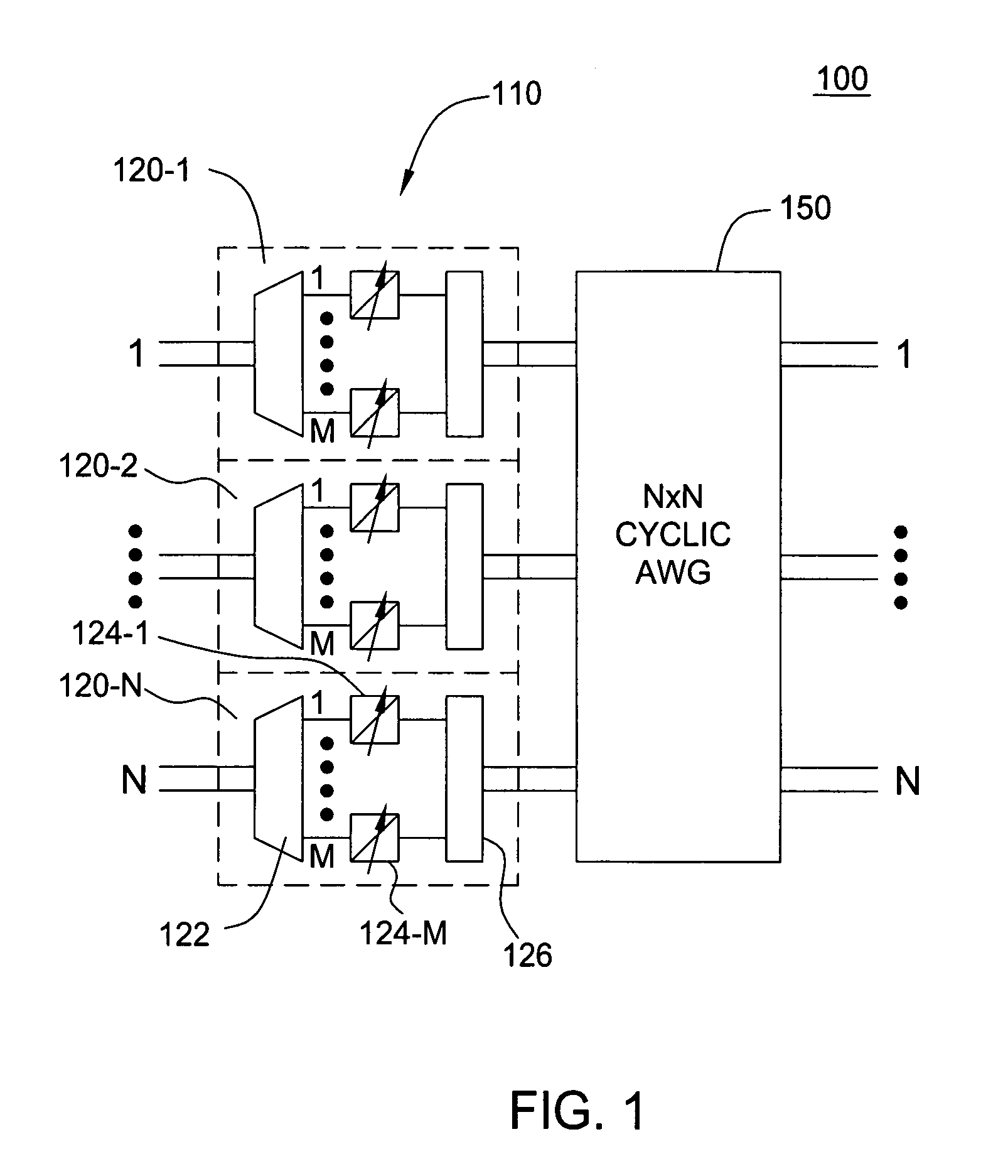
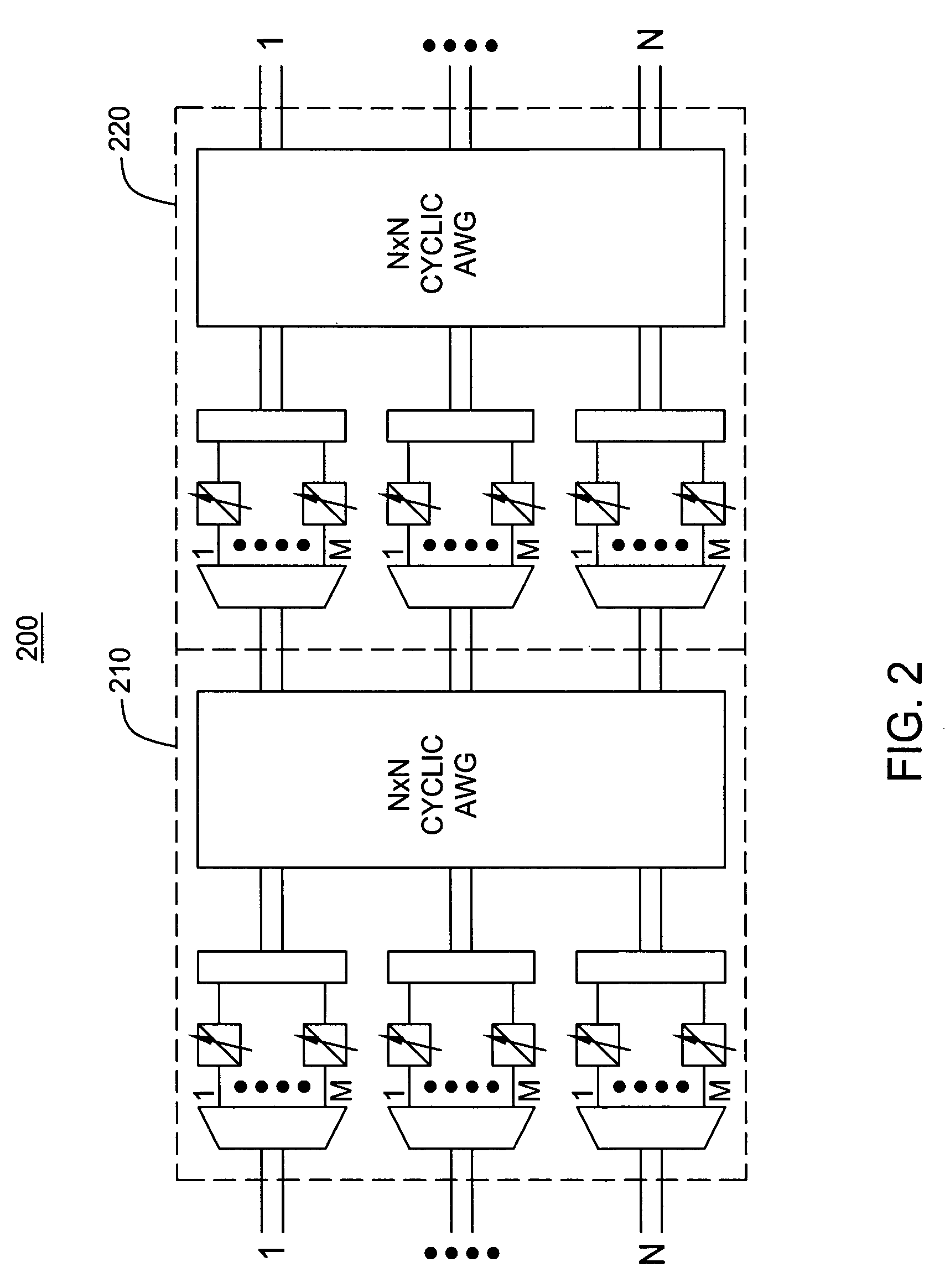
Non-blocking cyclic AWG-based node architectures
InactiveUS20070098319A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesGratingLength wave
An optical switching architecture utilizing a multiple stage configuration of wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) component wavelength converters and cyclic arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) routers.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
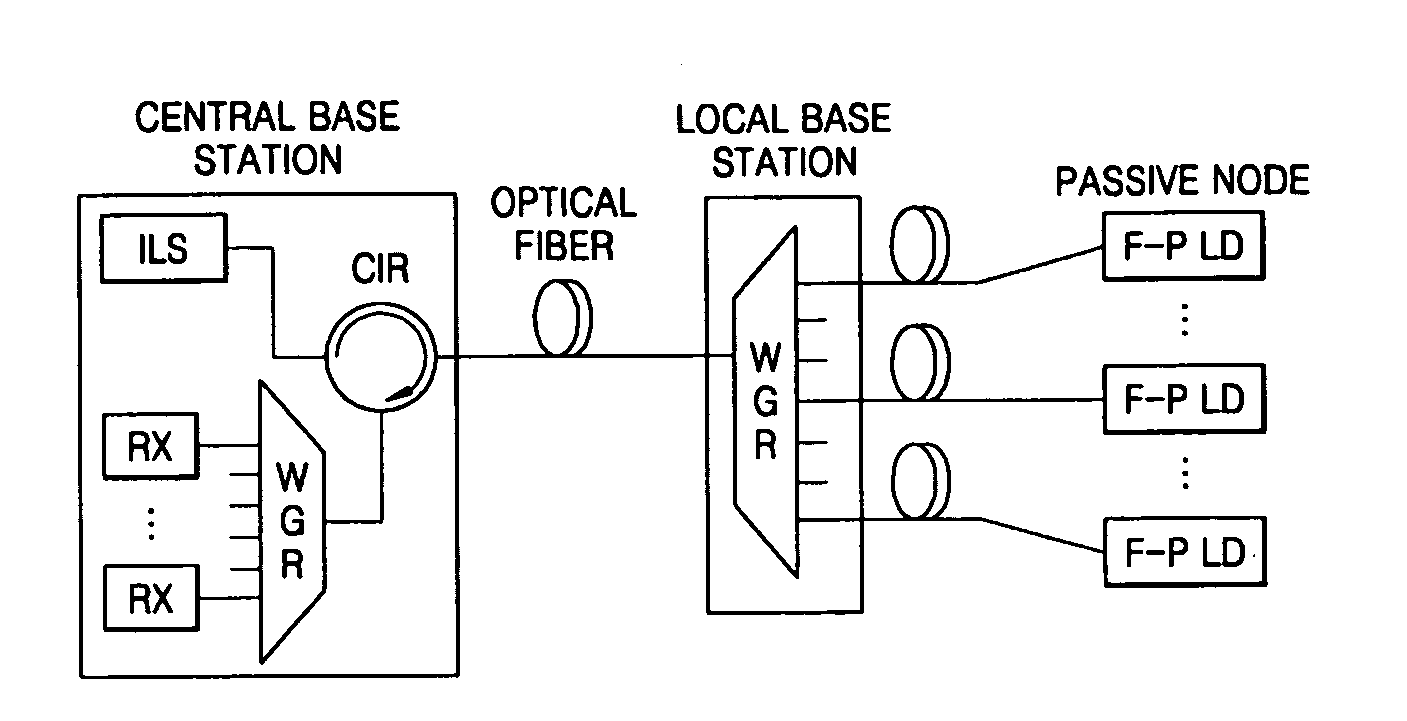
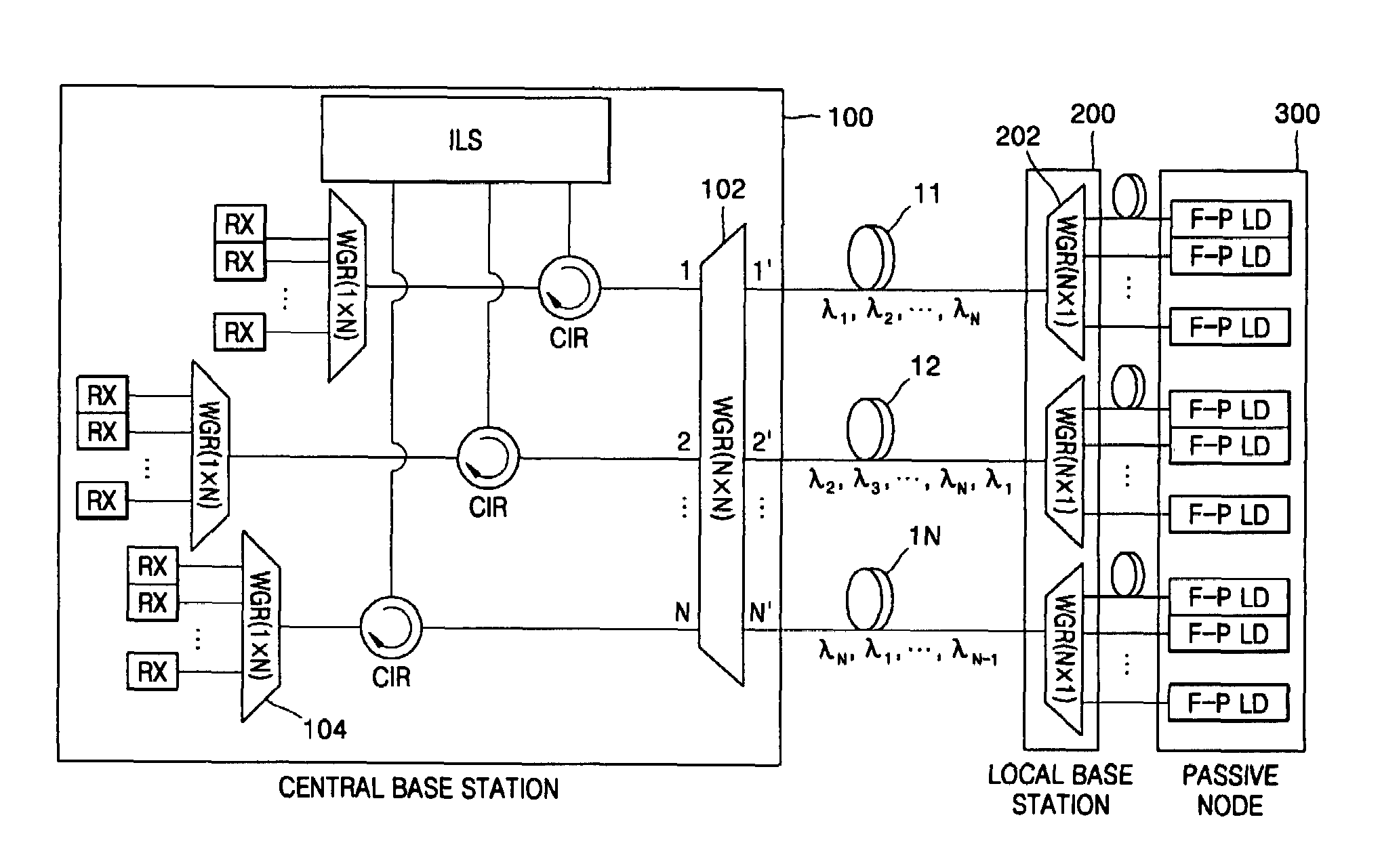
Optical transmission apparatus and method
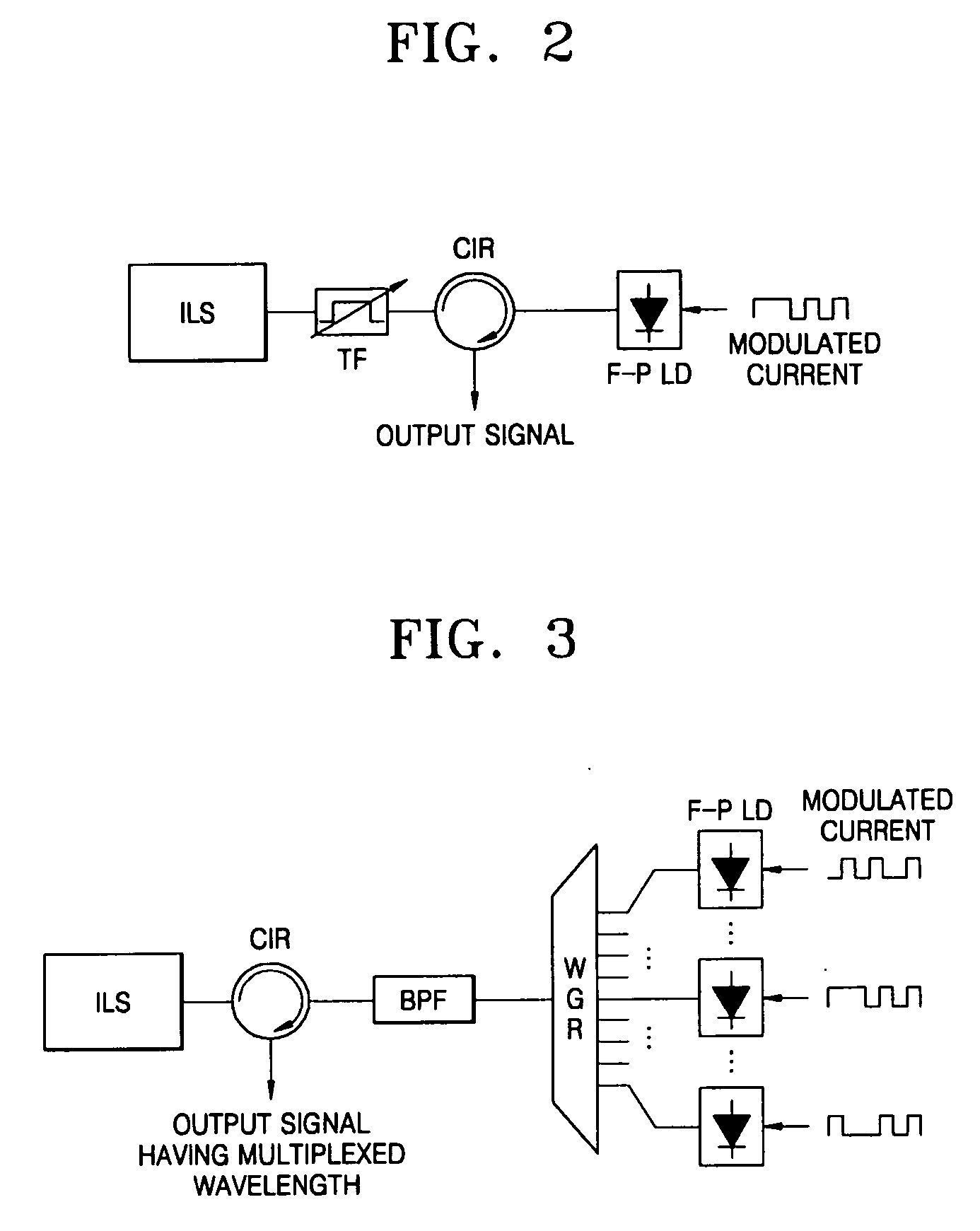
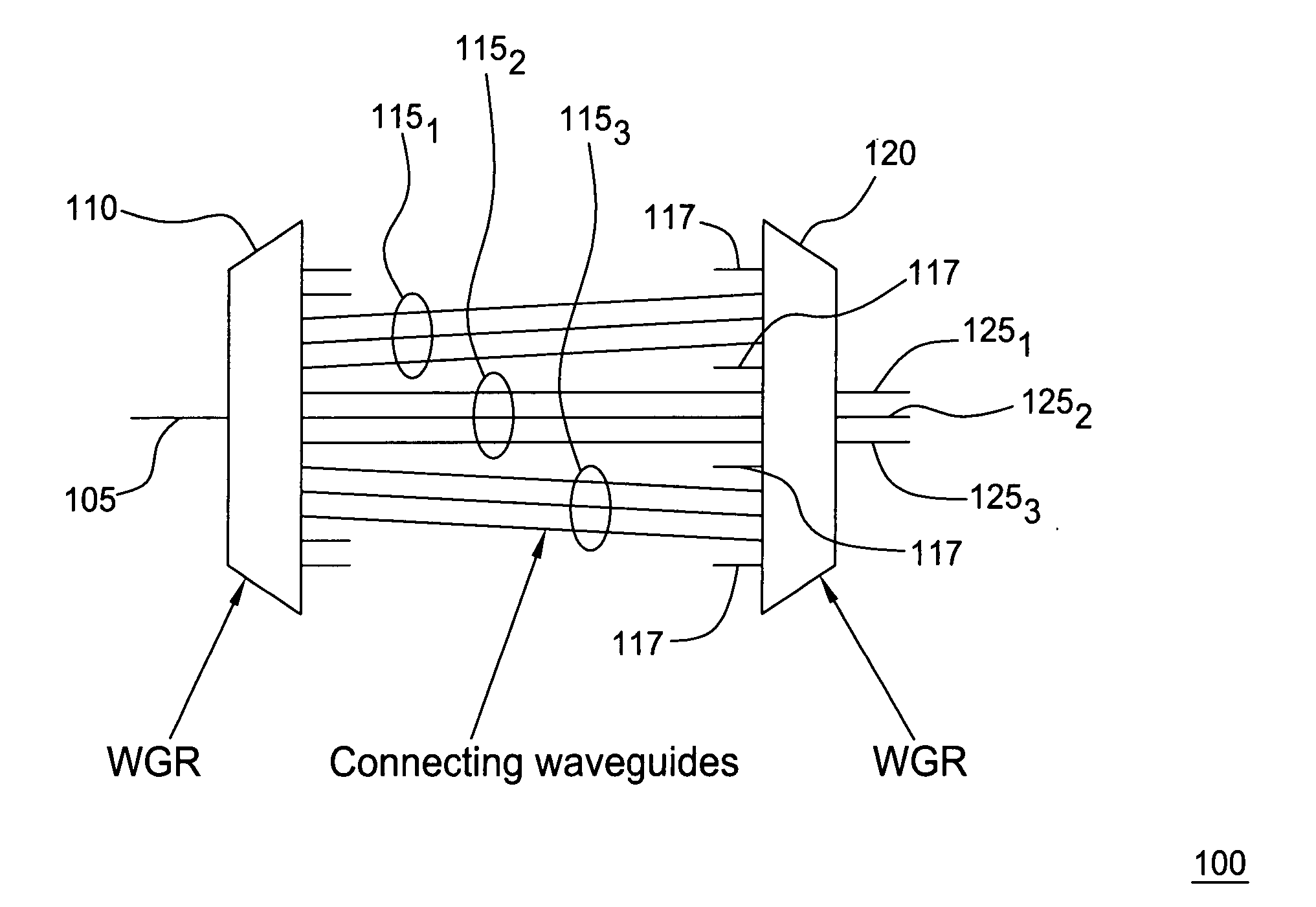
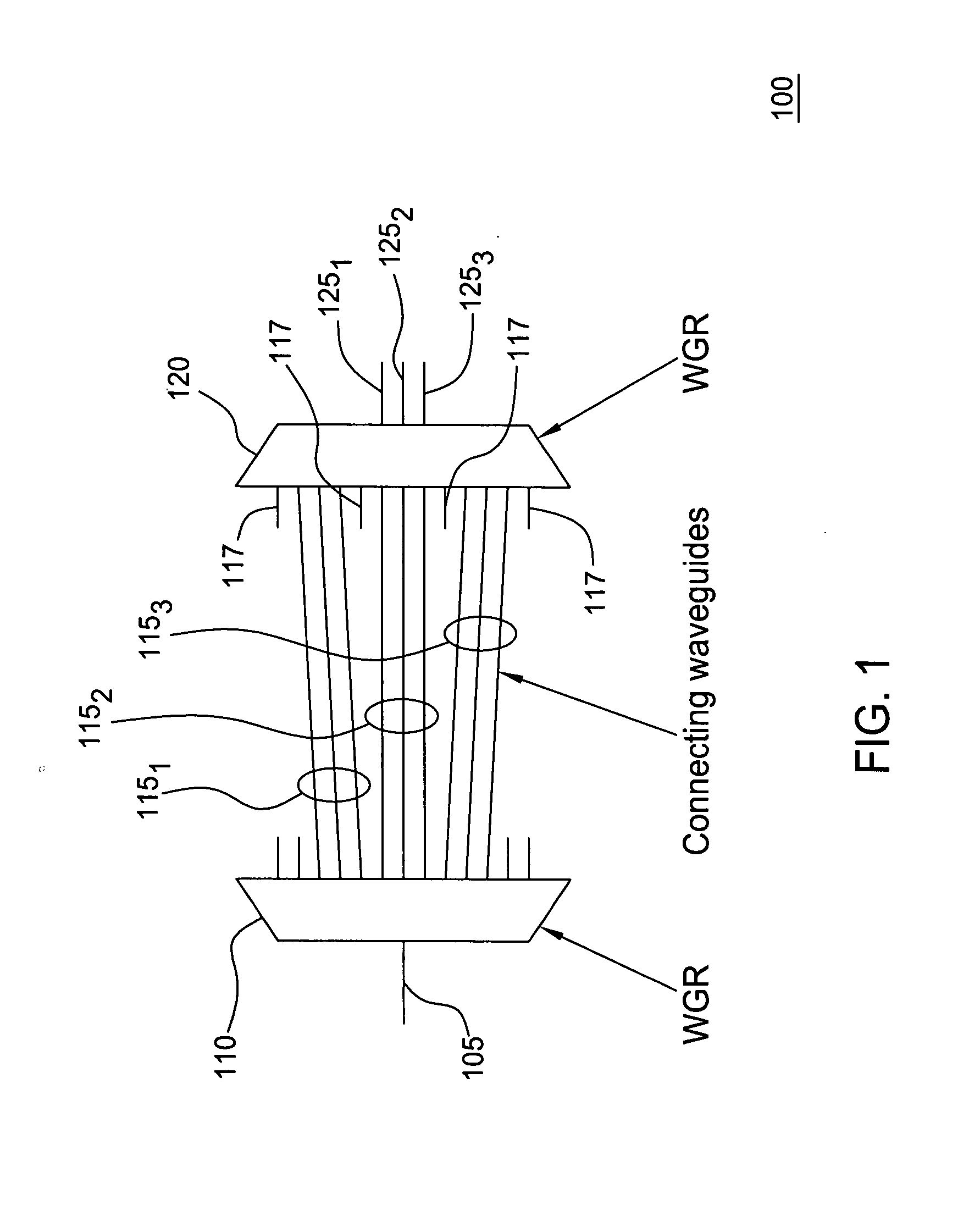
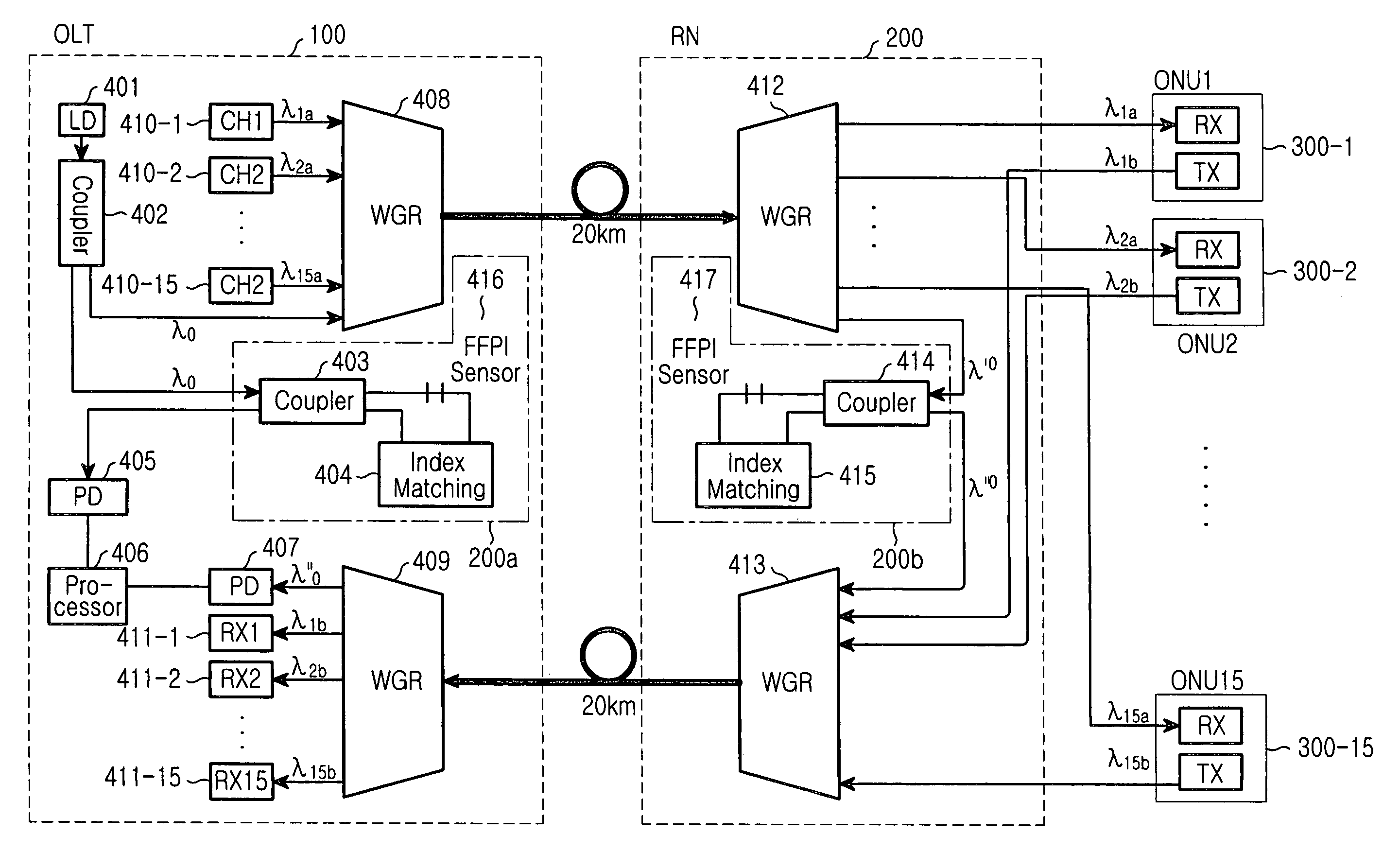
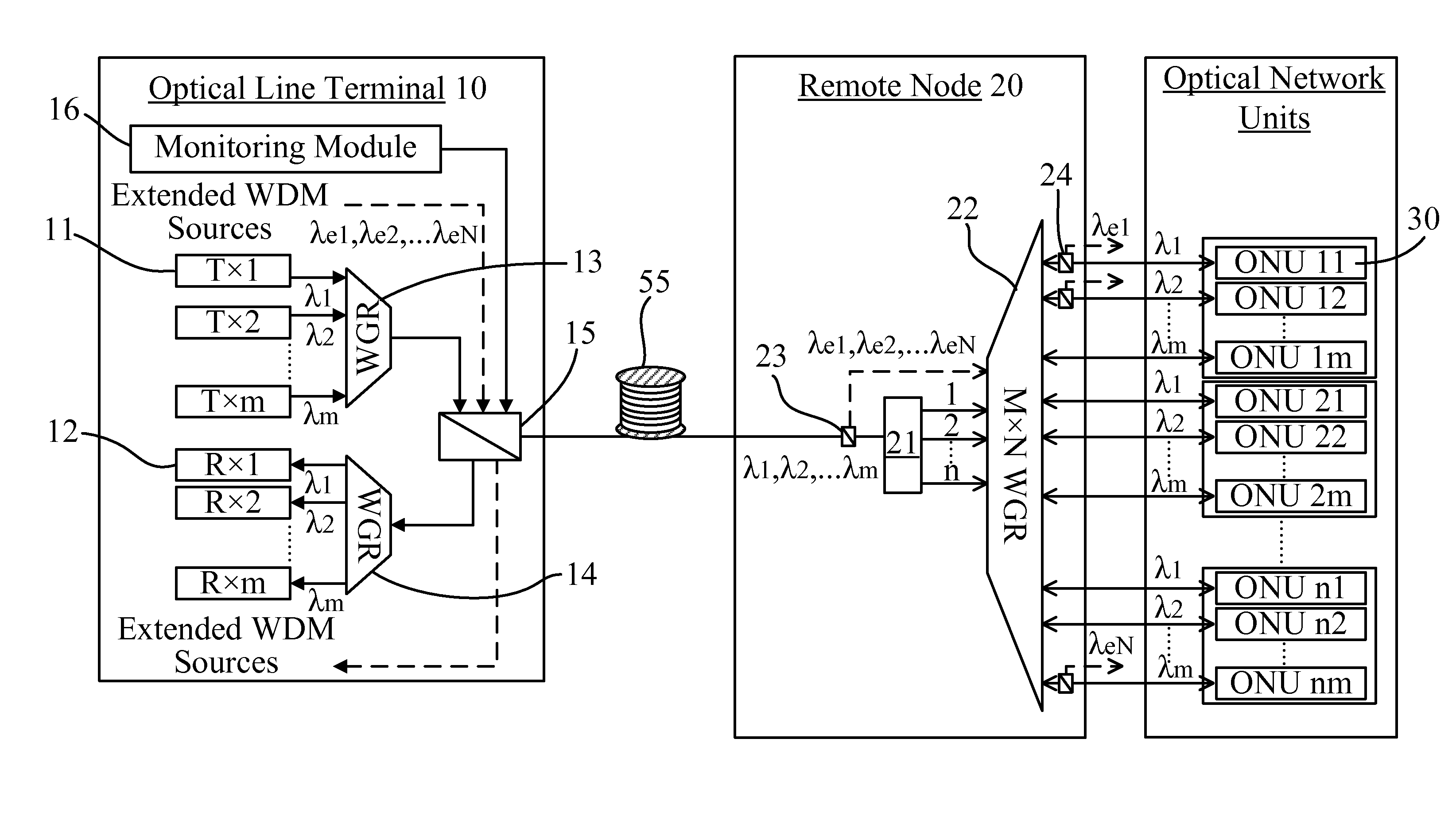
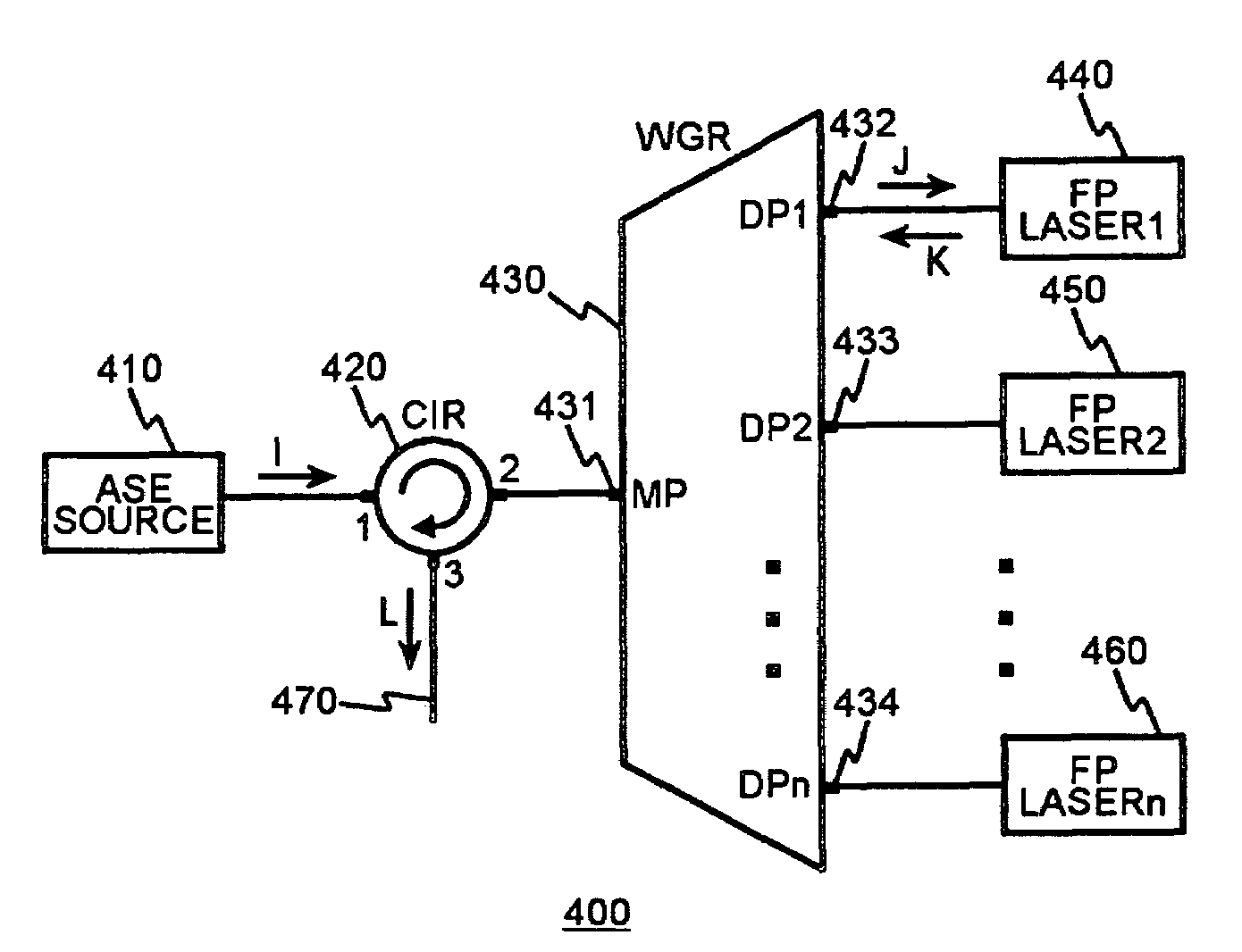
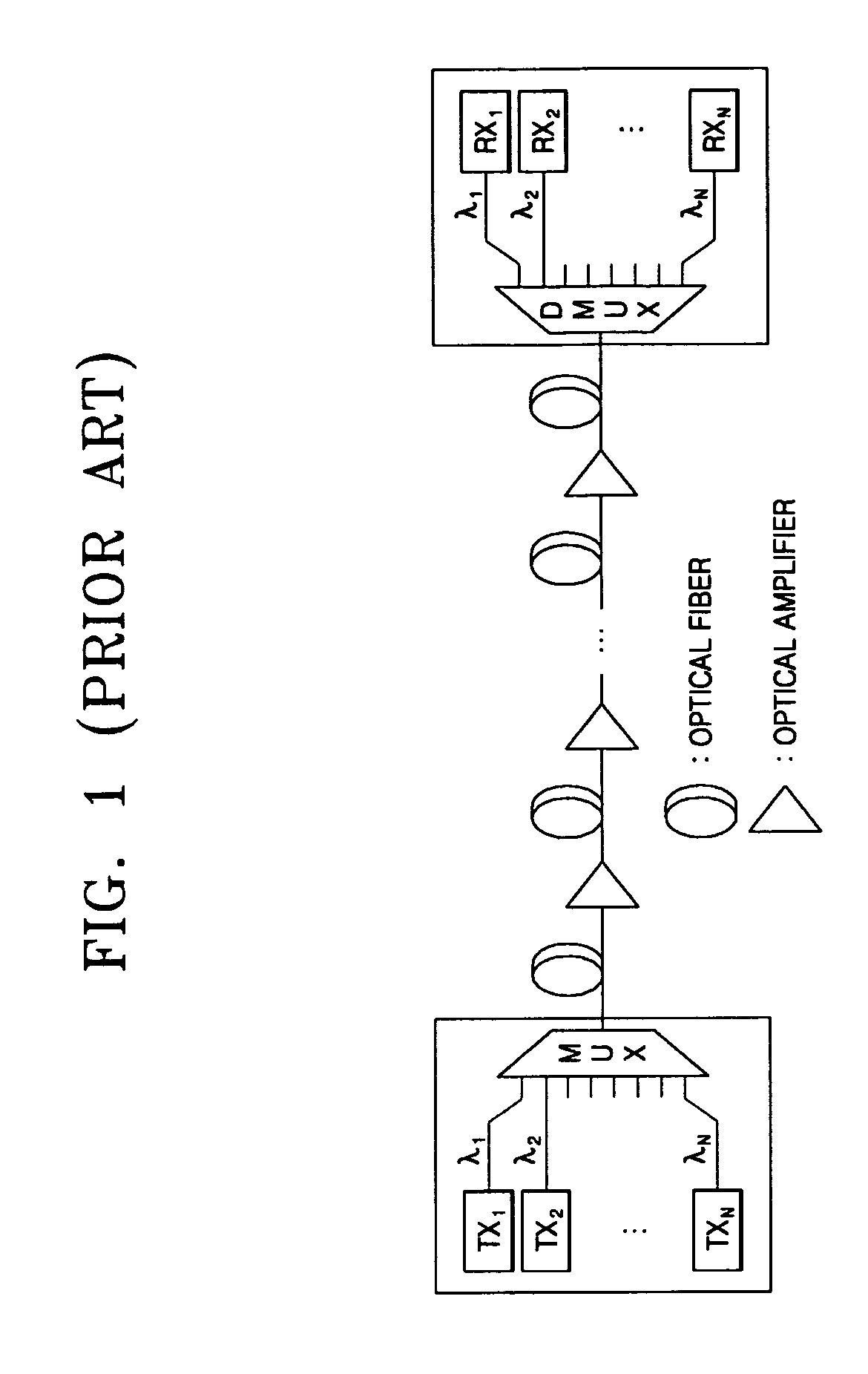
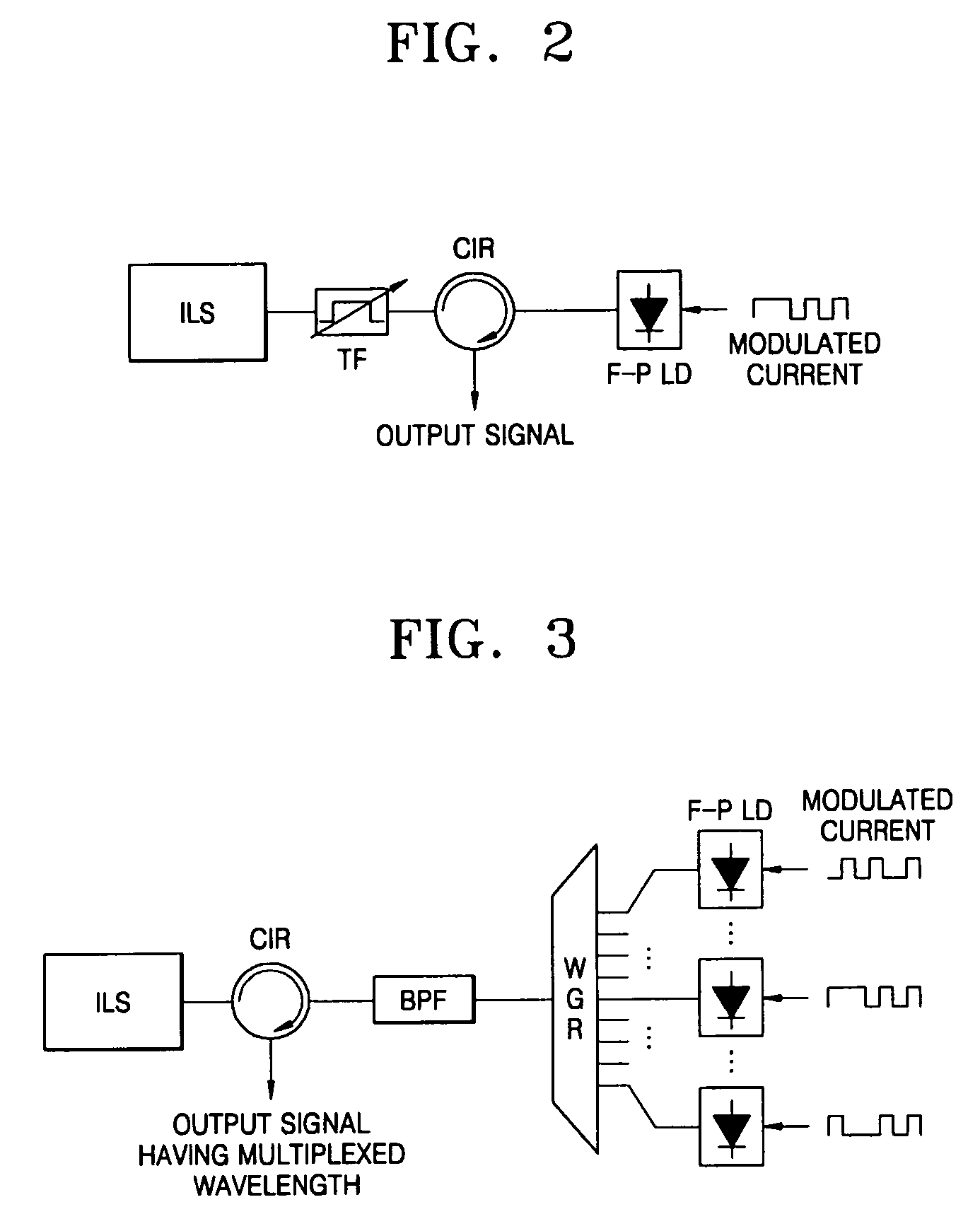
Provided are an optical transmission apparatus and method using a light source for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication that employs a Fabry-Perot laser diode (F-P LD) whose output wavelength is locked by an externally injected incoherent light, a multifiber, and a waveguide grating router. The light transmission apparatus includes: an incoherent light source (ILS) outputting incoherent light; a plurality of circulators (CIRs) connected to the ILS, receiving the incoherent light from the ILS, and outputting first optical signals; a first waveguide grating router (WGR) outputting the first optical signals output from each of the CIRs to optical fibers corresponding to each of the CIRs, and outputting second optical signals input from the optical fibers to the corresponding CIRs; a plurality of second WGRs corresponding to each of the CIRs, and demodulating the second optical signals output from each of the plurality of CIRs; and a plurality of receivers connected to the plurality of the second WGRs, and inputting the demultiplexed optical signals output from the plurality of second WGRs. A plurality of light sources for WDM optical communication whose output wavelength is locked can increase size and economical efficiency of a light transmission system (subscriber). The N×N WGR can produce a conventional light transmission system and accommodate many subscribers.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optically controlled phased array radar system based on wavelength routing
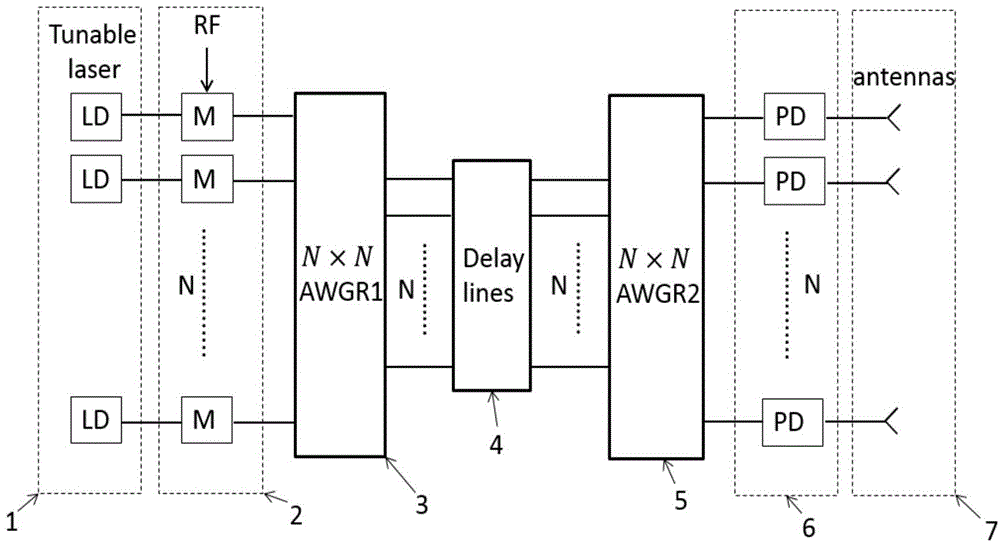
The invention discloses an optically controlled phased array radar system based on wavelength routing. N tunable semiconductor lasers emit multiple paths of optical wave signals different in wavelength; microwave signals are loaded and modulated through respective modulators, transmitted to a first array waveguide grating router, transmitted to a second array waveguide grating router through a delayed linear array and transmitted to N semiconductor detectors for demodulation; the semiconductor detectors emit the demodulated microwave signals through an antenna. The tunable semiconductor lasers are used to change the wavelengths for switching the delayed linear array, so that the use of a large amount of optical switches is avoided; with an integrated optics method, an overlapping problem of fiber Bragg gratings is solved, the two array waveguide grating routers and the delayed linear array are integrated on the same substrate, and the precision of the delay line length is guaranteed, so that the stability of the system is improved, the cost is reduced, and the system has the advantages of small size, low loss, light mass, high precision, electromagnetic interference resistance and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dynamic gain equalization arrangement for optical signals
InactiveUS6892021B2Maximizes DGEF spectral resolutionMinimize rippleCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationNegative phase
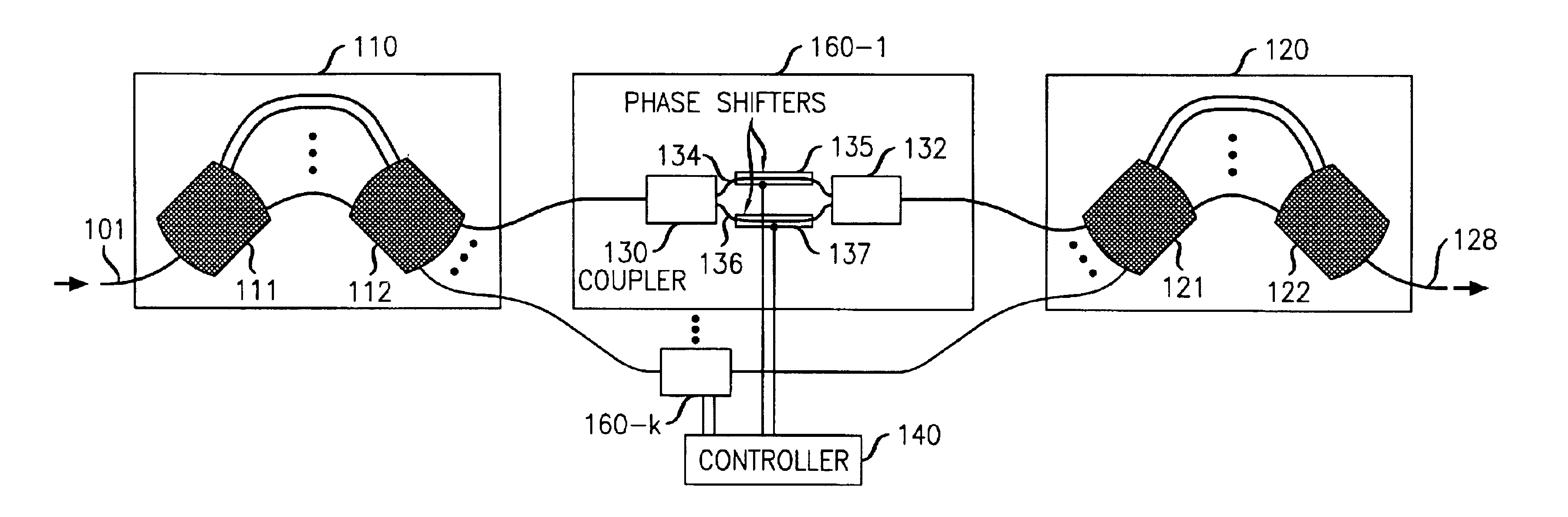
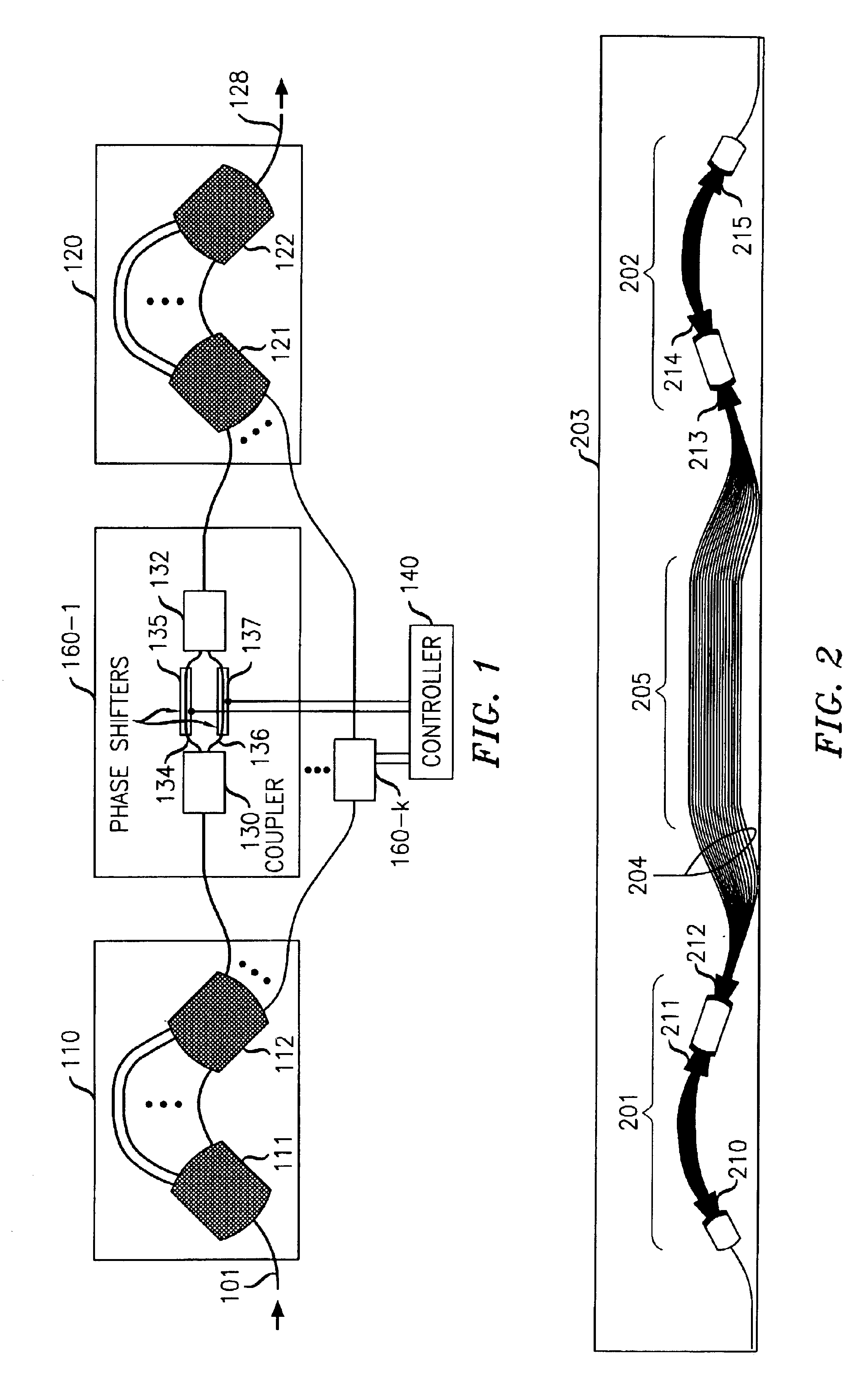
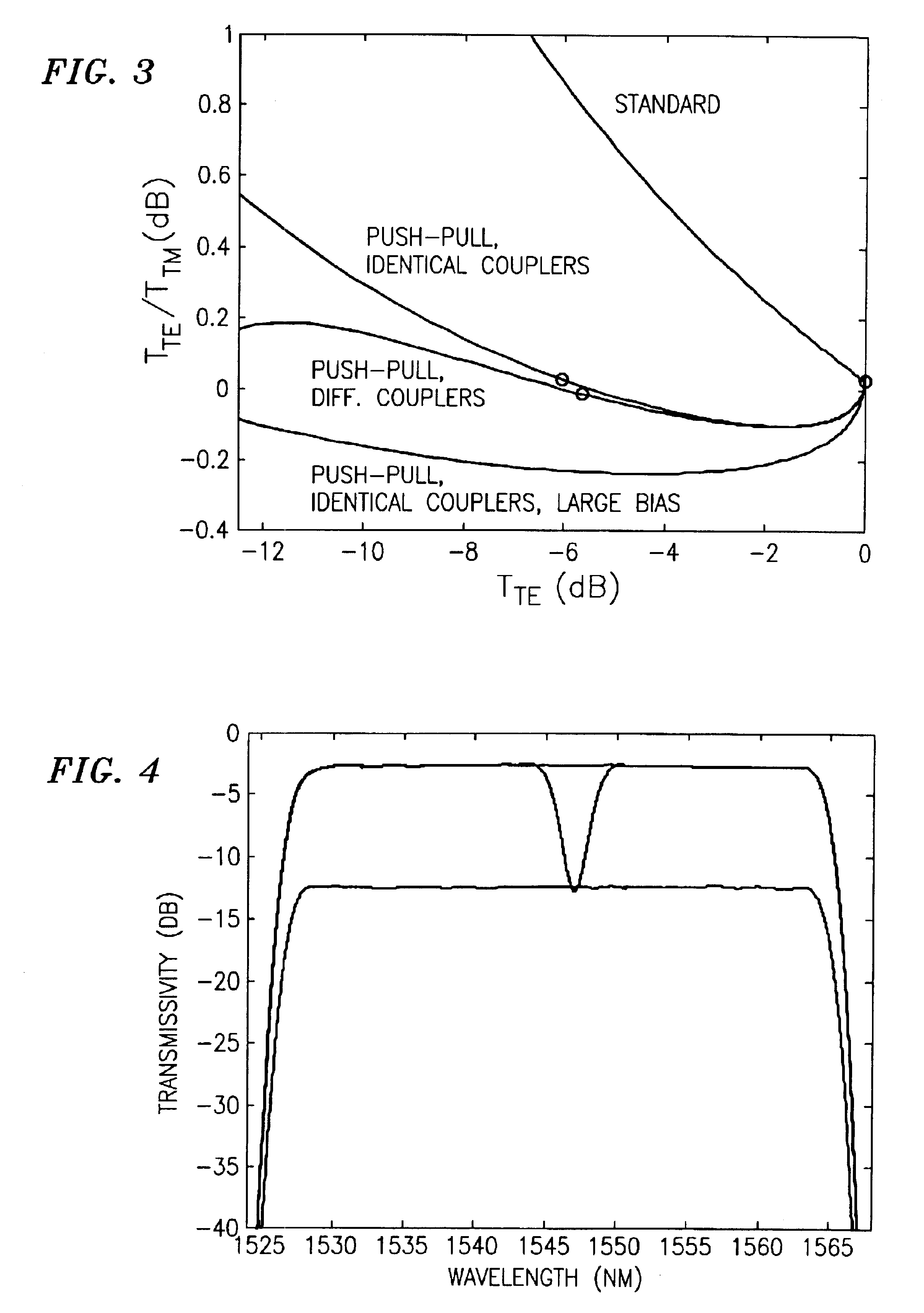
An optical dynamic gain equalization filter (DGEF) comprises a planar arrangement of preferably “perfectly sampled” (or alternatively oversampled) waveguide grating routers (WGR's) connected by individual optical paths each containing a Mach-Zehnder interferometer operated in a push-pull fashion so that a positive phase change in one interferometer arm and a corresponding negative phase change in the other interferometer arm produces a desired change in attenuation while, at the same time, the overall phase of the optical signals after passing through the Mach-Zehnder interferometer is kept constant with respect to the adjacent paths. Alternatively, the above-described arrangement is effectively “cut in half”, and its size effectively also reduced accordingly, using a mirror placed at the midpoint of the device and an appropriate circulator to separate the input and output optical signals.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
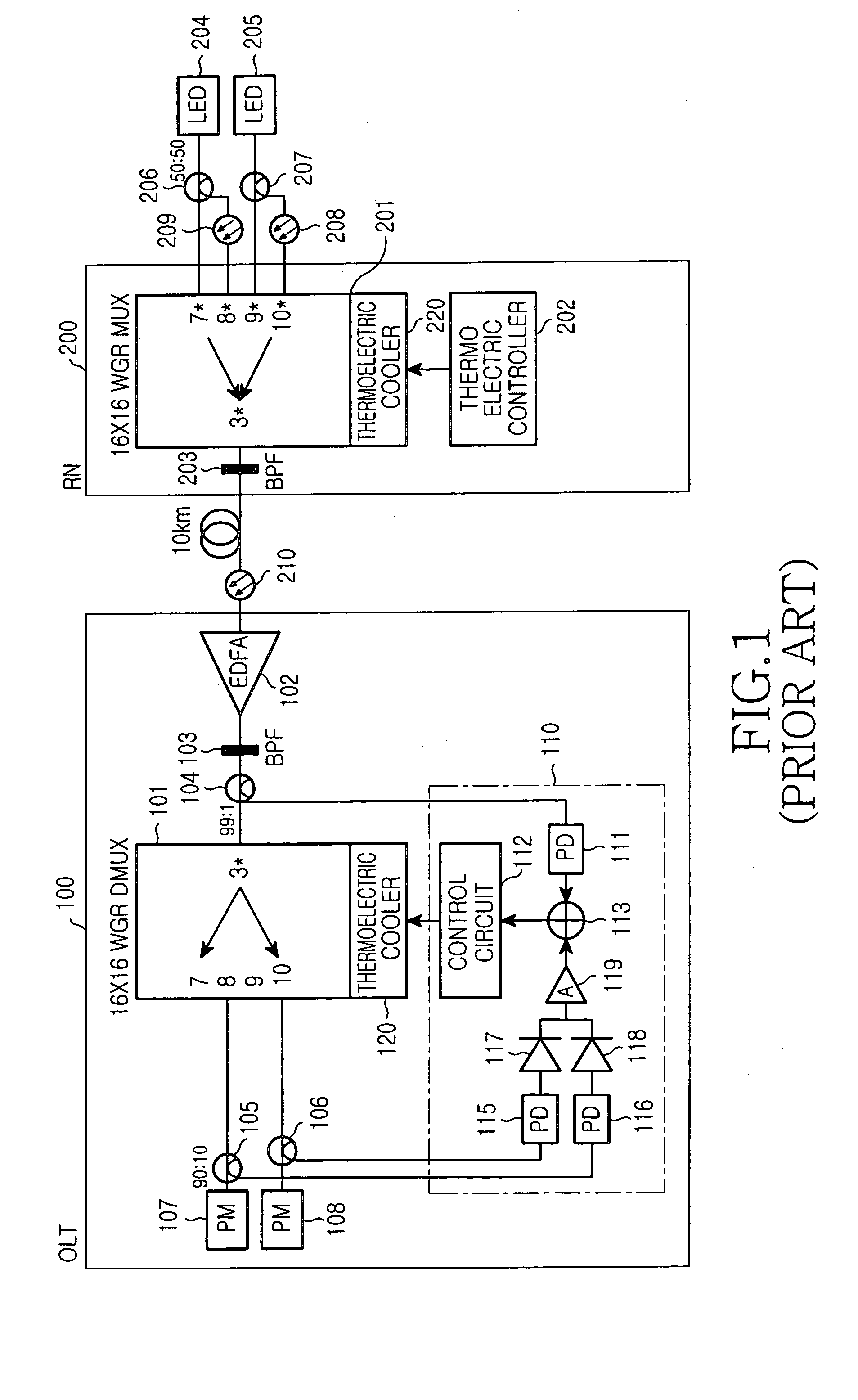
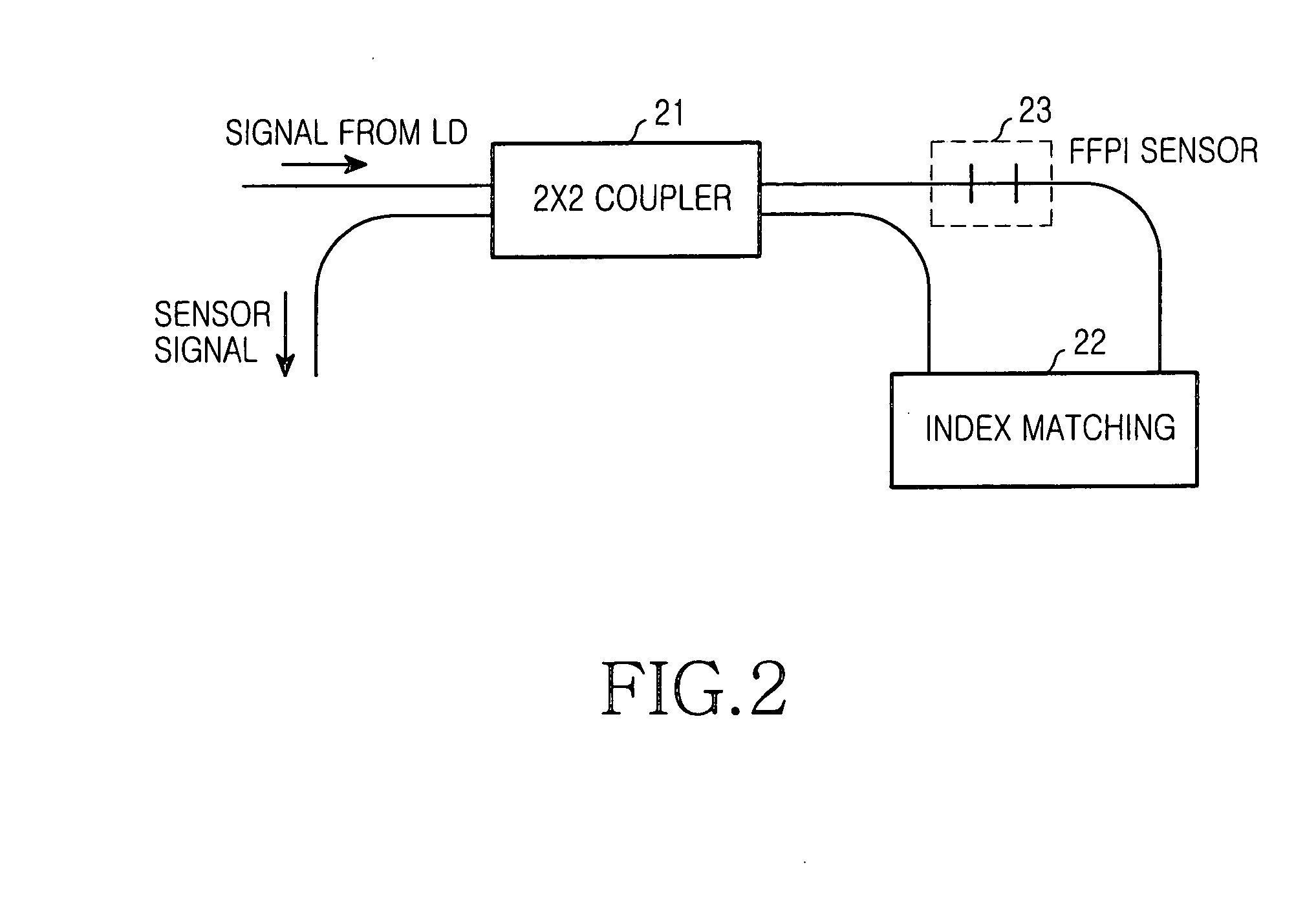
WDM optical communication system capable of monitoring temperature
InactiveUS20050078356A1Avoid disagreementReduce crosstalkLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberGrating
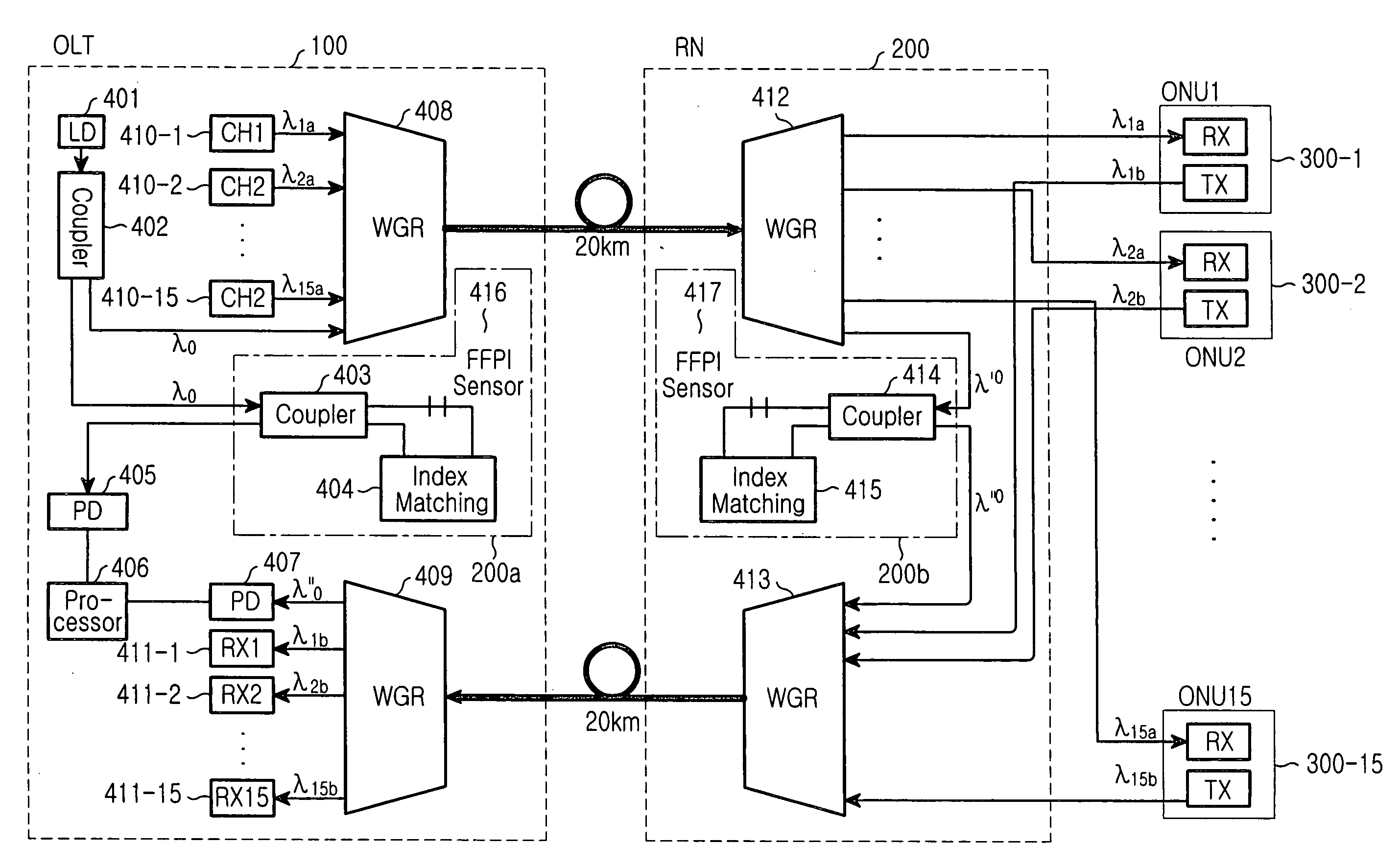
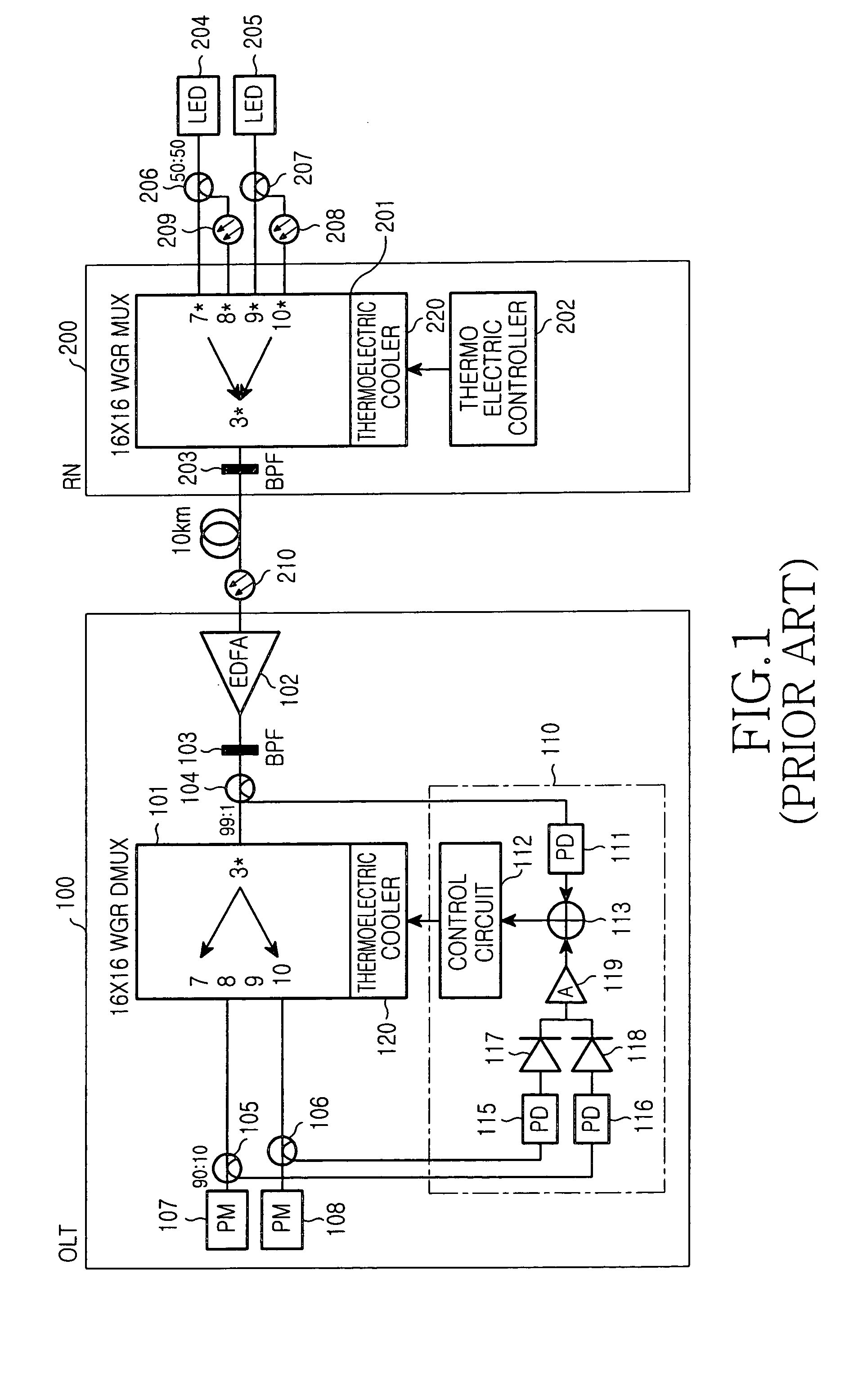
A device and method to monitor and temperature compensate change in wavelength within a WDM optical communication system is disclosed. The device includes a laser diode for generating an optical signal for temperature monitoring, a first fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer sensor unit for generating a first sensor signal according to temperature by means of the optical signal, and a processor for monitoring temperature by means of the first sensor signal and an externally provided second sensor signal and equalizing waveforms of the two sensor signals with each other. The externally provided second sensor signal is provided by a remote node that includes a second fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer sensor unit for receiving the optical signal for temperature monitoring to generate the second sensor signal according to temperature, and a waveguide grating router unit for transmitting the second sensor signal to the optical line terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
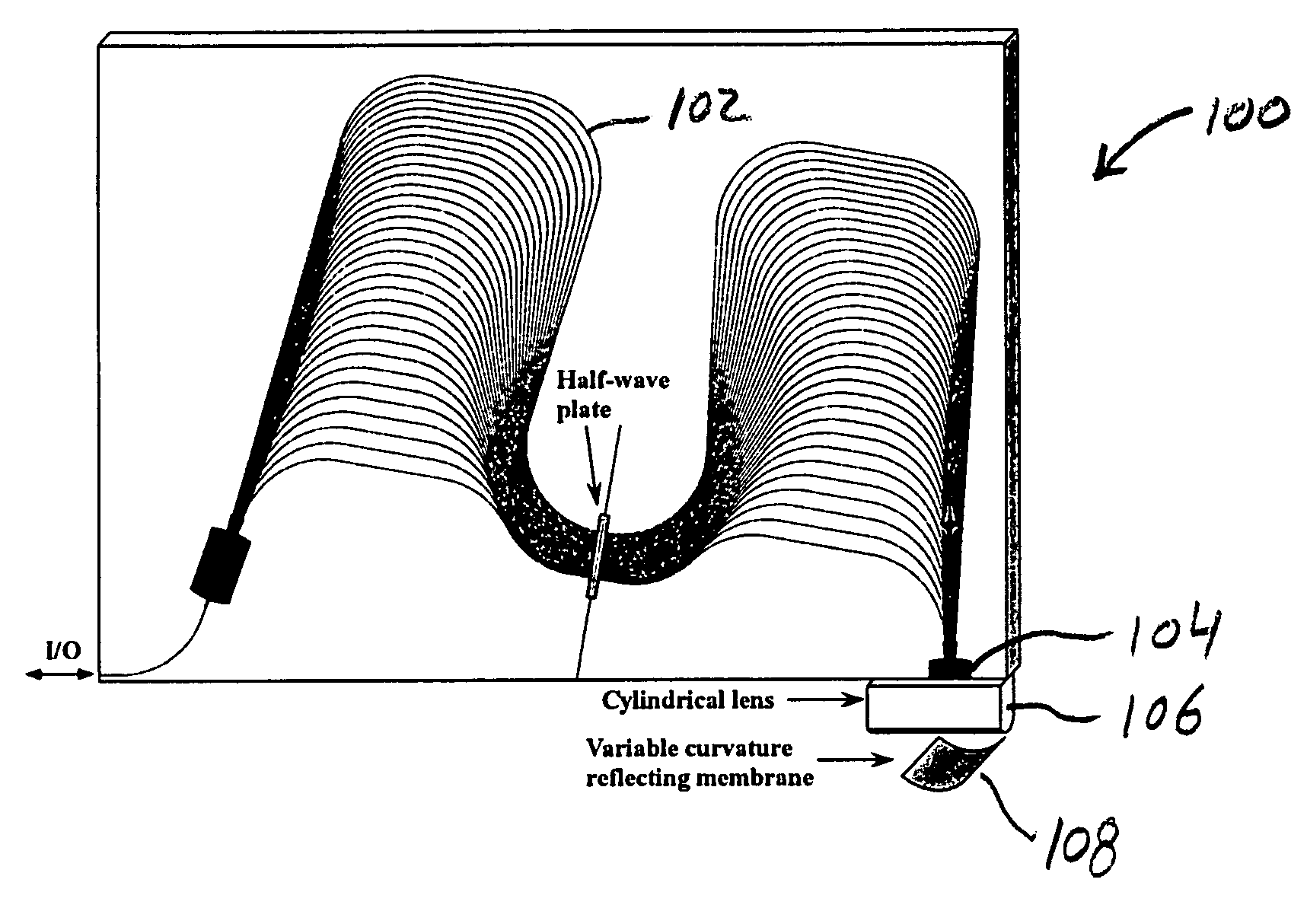
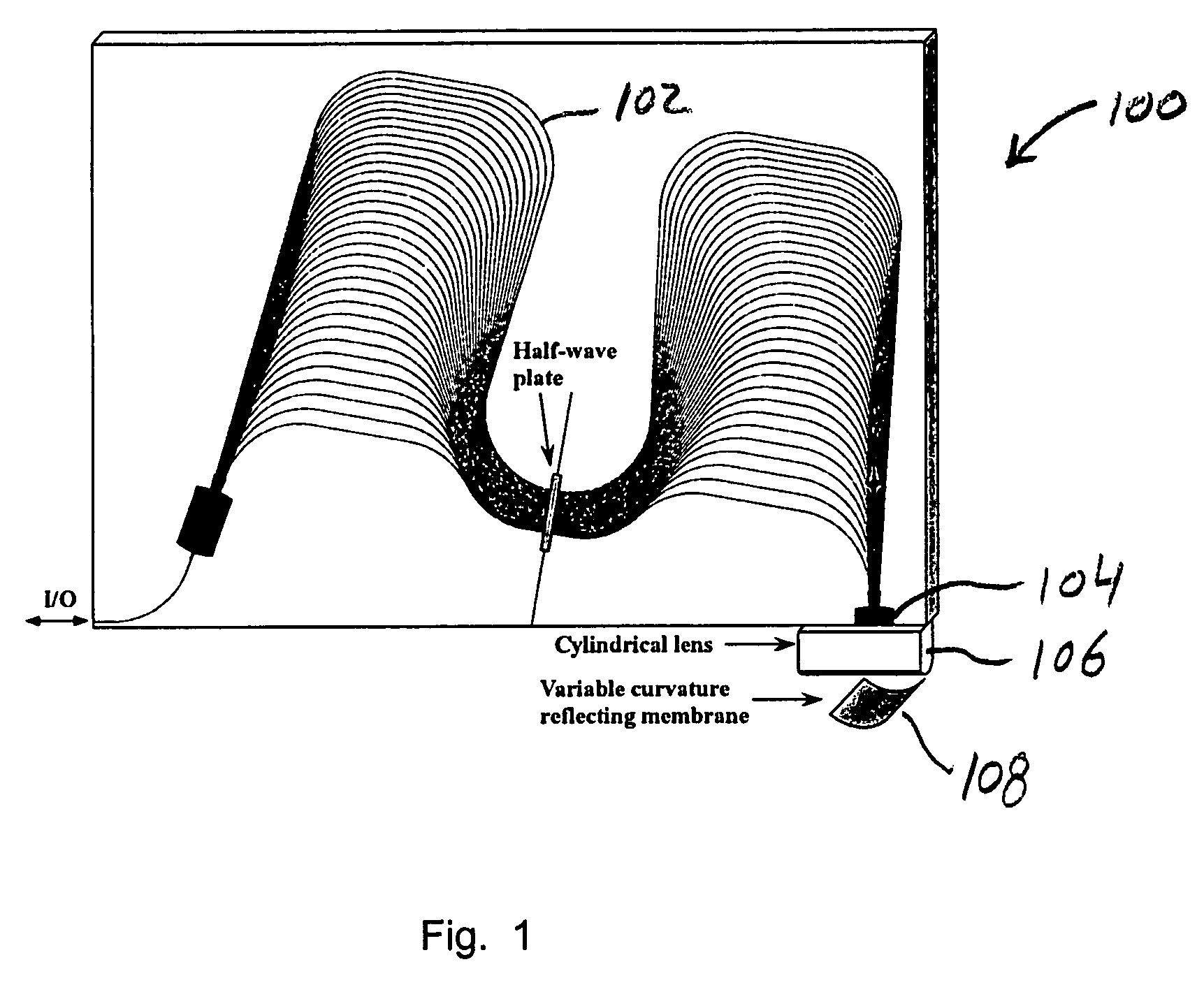
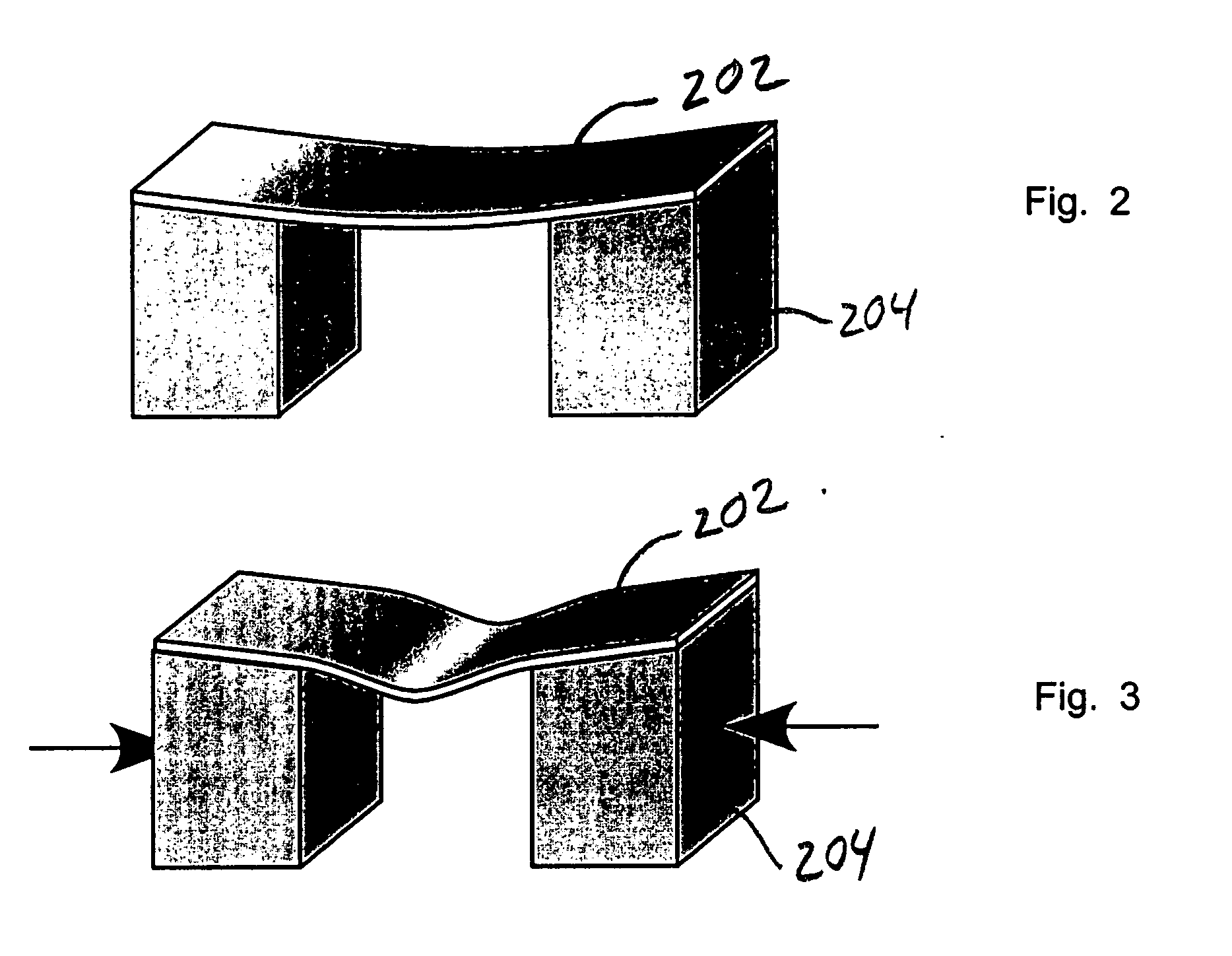
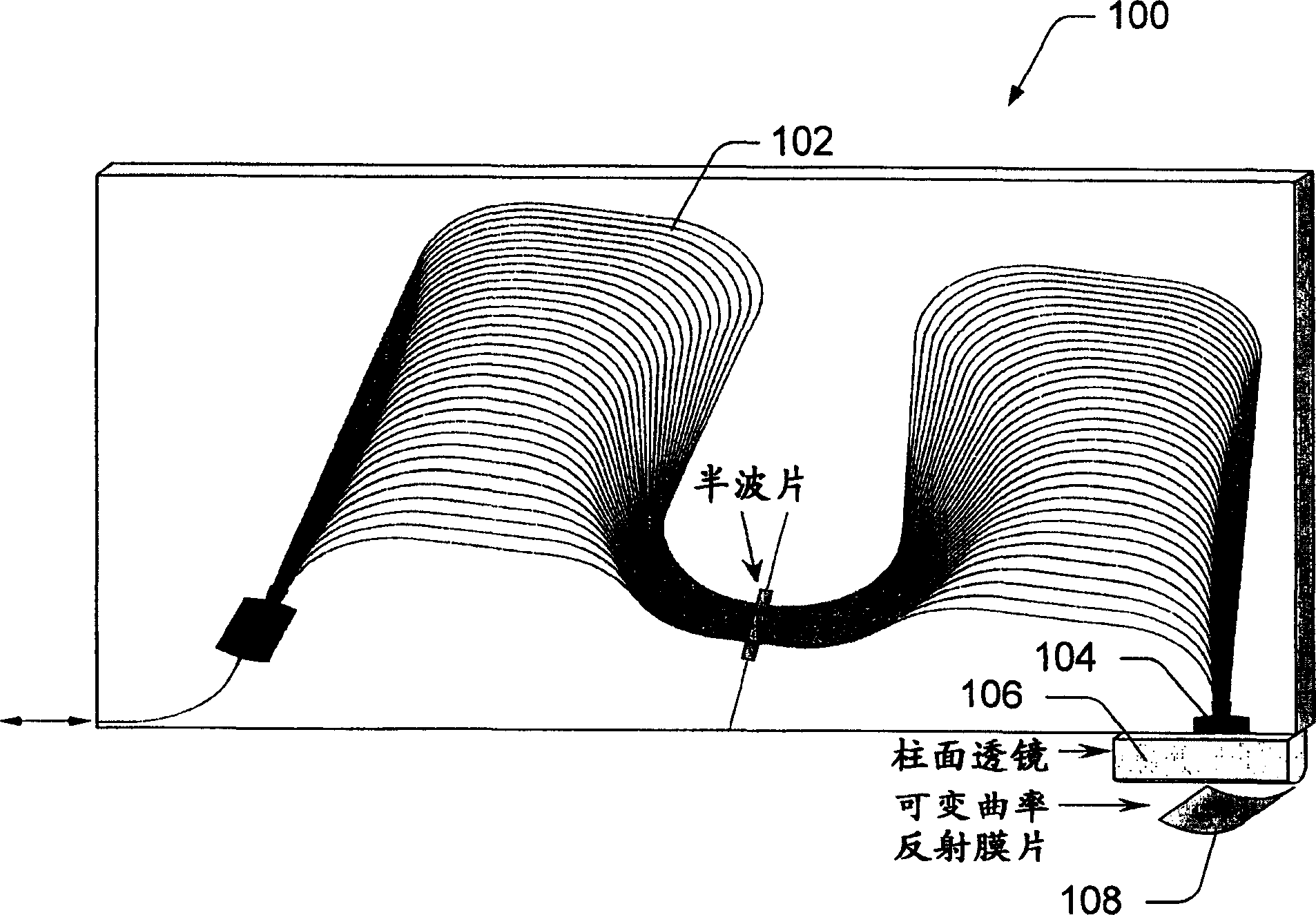
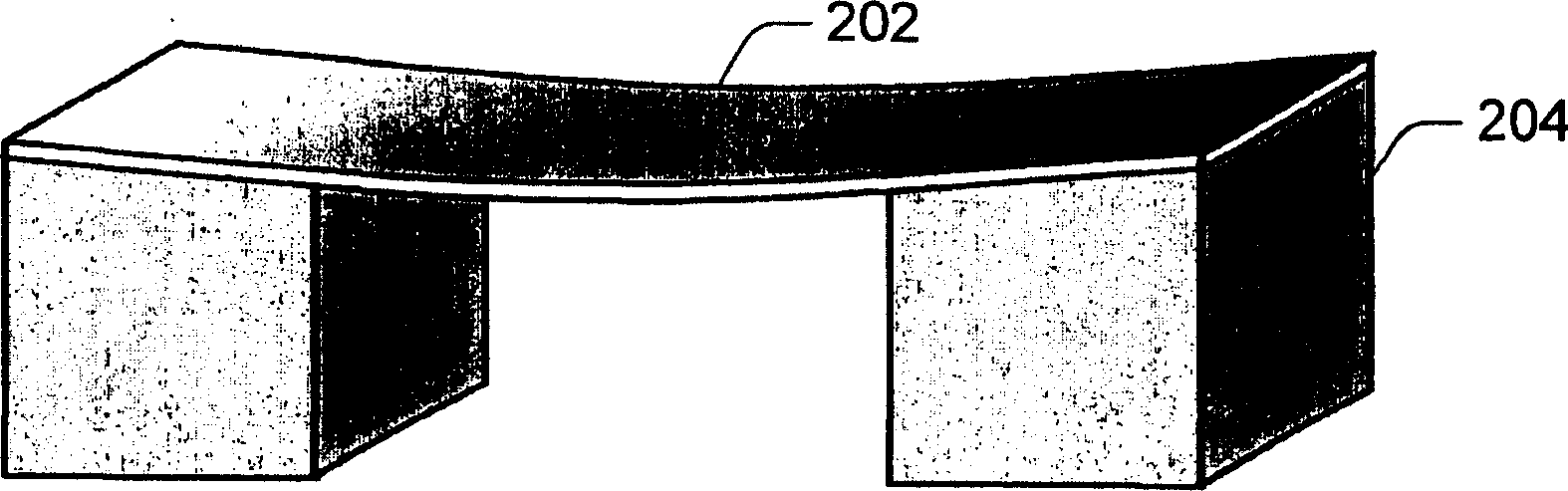
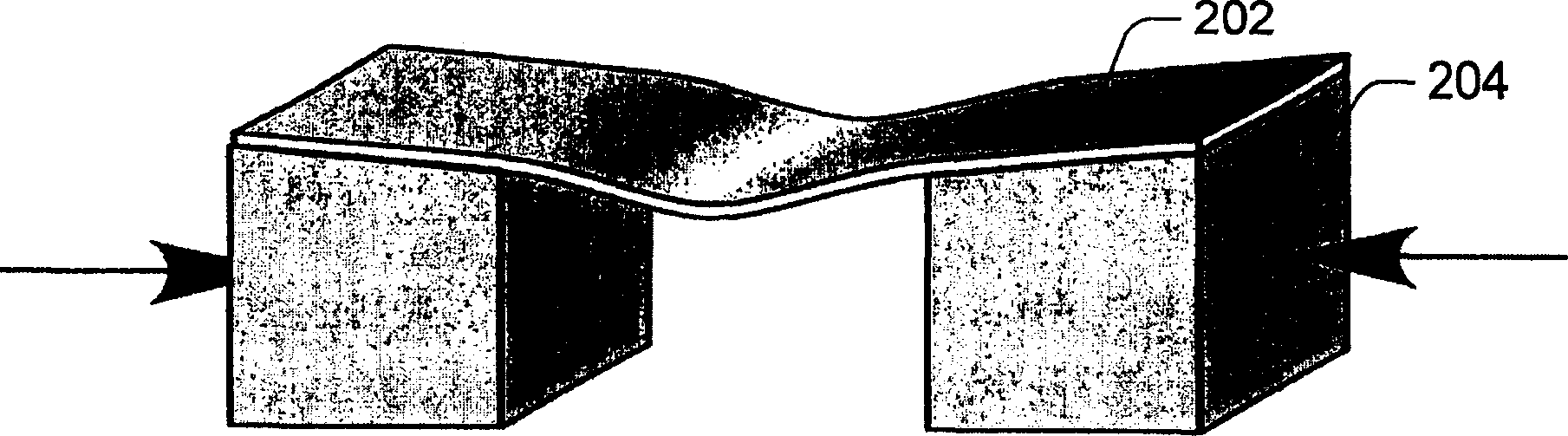
Colorless tunable dispersion compensator employing a planar lightwave circuit and a deformable mirror
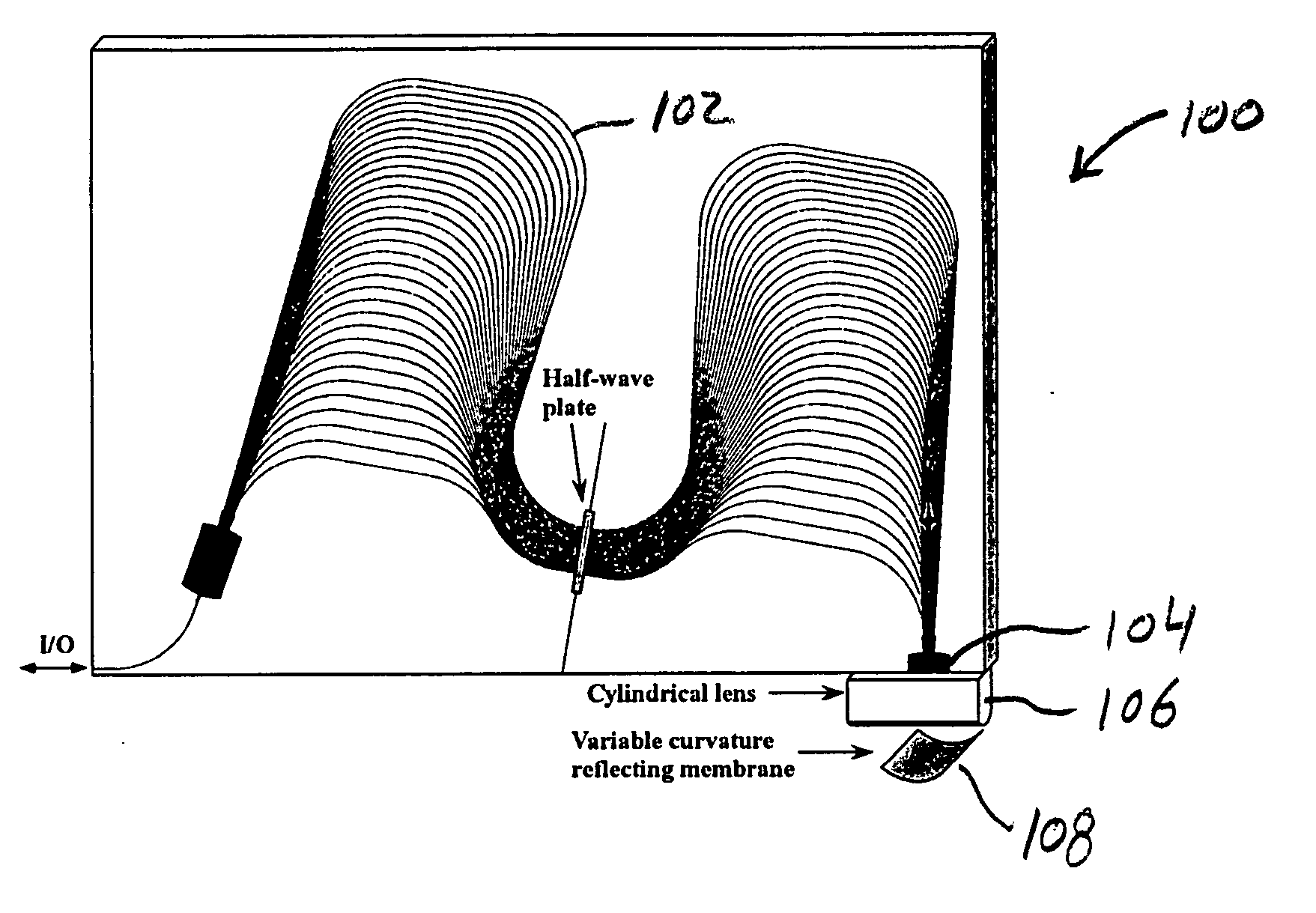
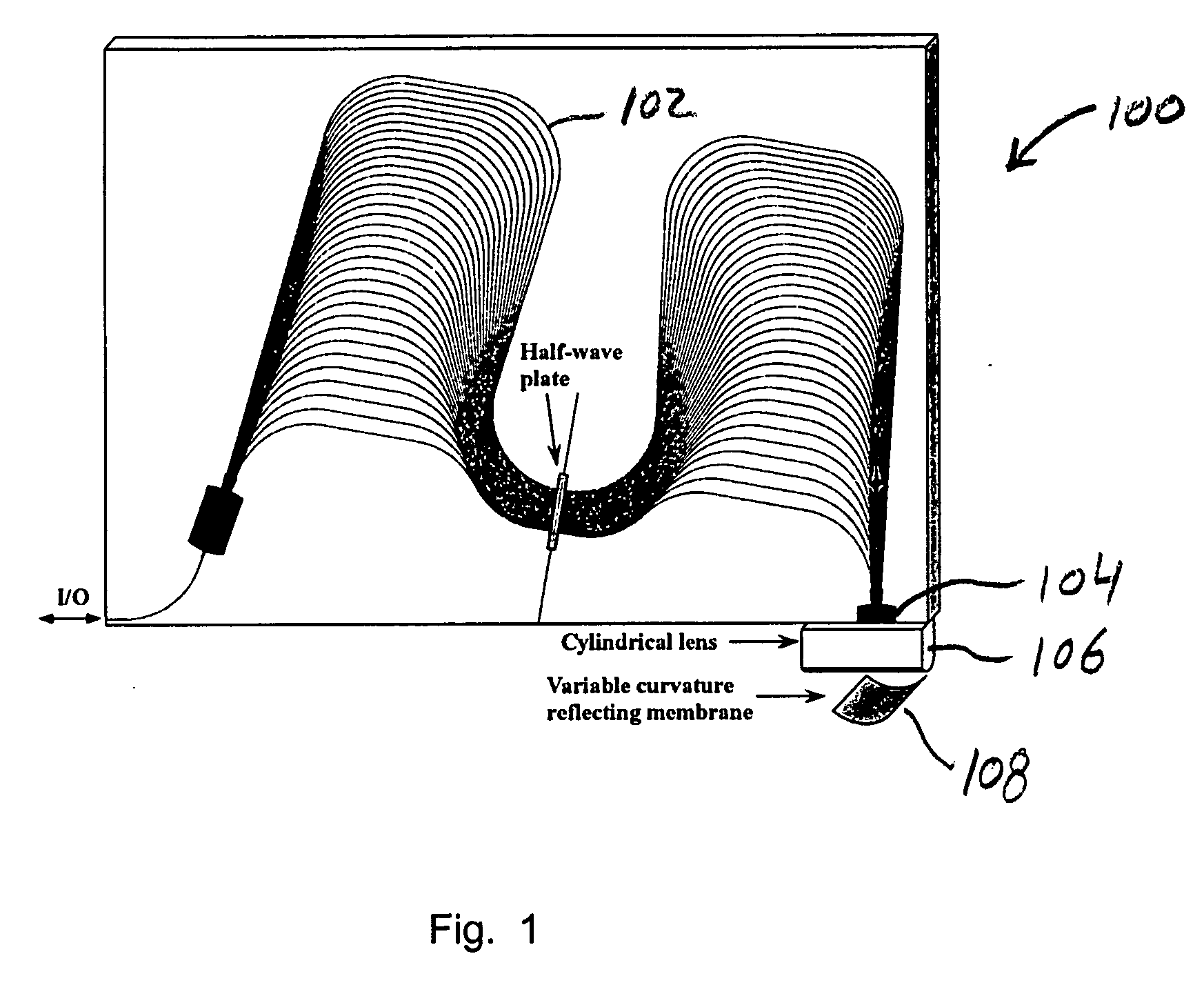
A colorless, waveguide-grating-router-based tunable dispersion compensator includes a planar lightwave circuit and a deformable mirror, optically coupled to each other by a plano-cylindrical glass lens such that a fast tuning speed and single-knob dispersion adjustment are obtained. In a further aspect of the present invention, the waveguide-grating router is pinched, symmetrical about its center line, and has a half-wave plate inserted therein to provide polarization independence. In a still further aspect of the present invention, the deformable mirror includes, reflective film attached to opposing piezo-electric actuators.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Integrateable band filter using waveguide grating routers
ActiveUS20050053332A1Easy to makeReduce rippleCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsThird wavePath length
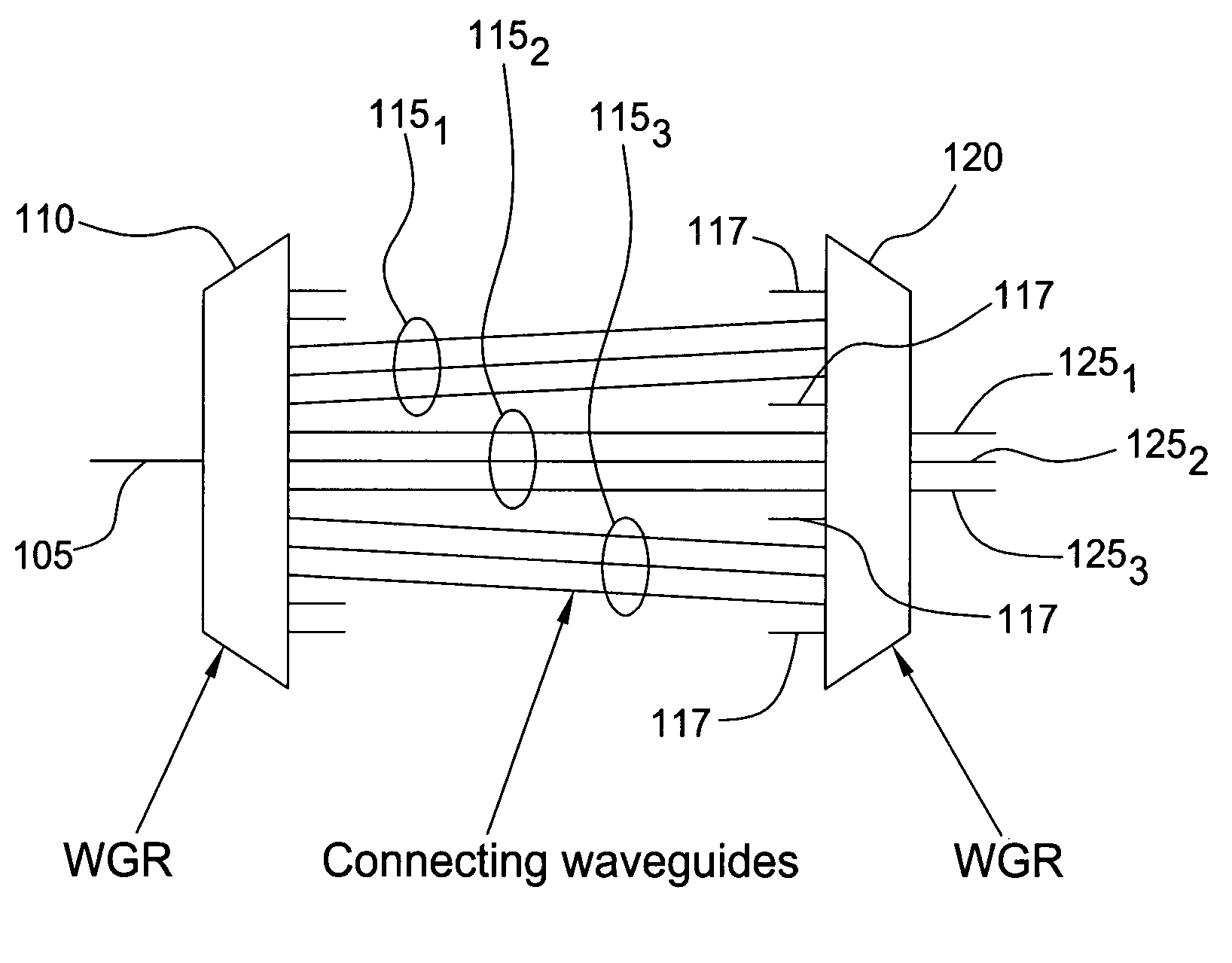
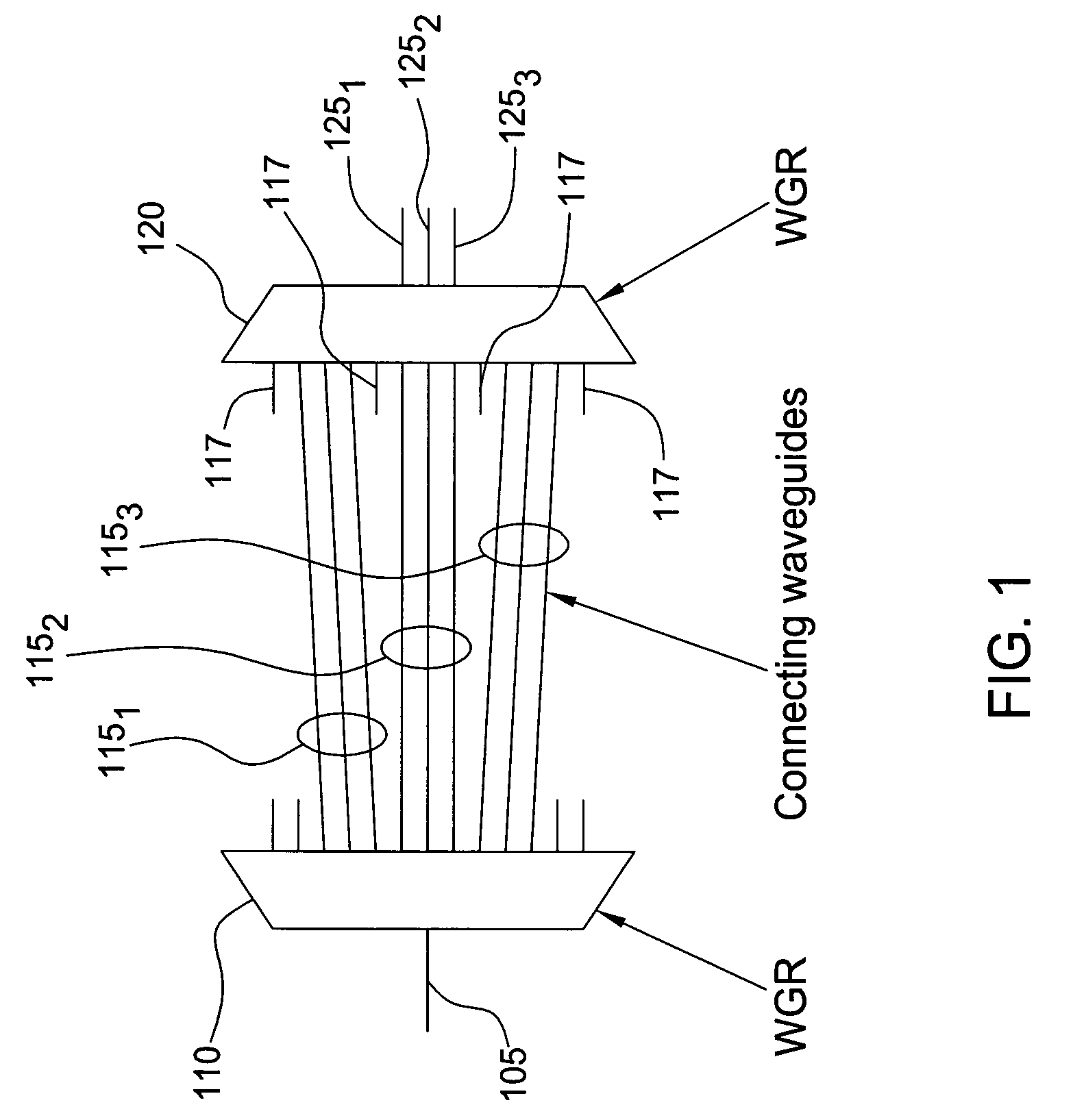
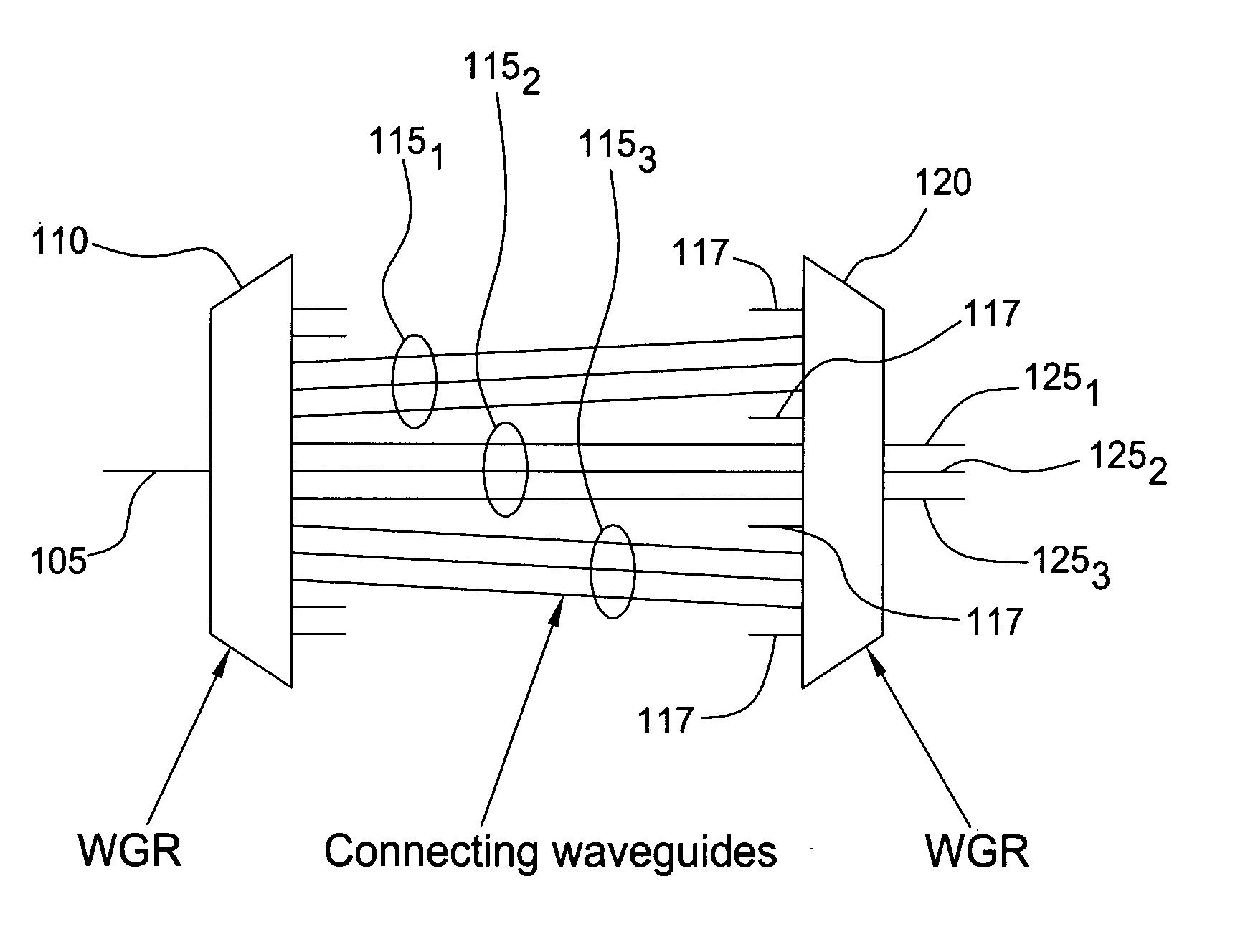
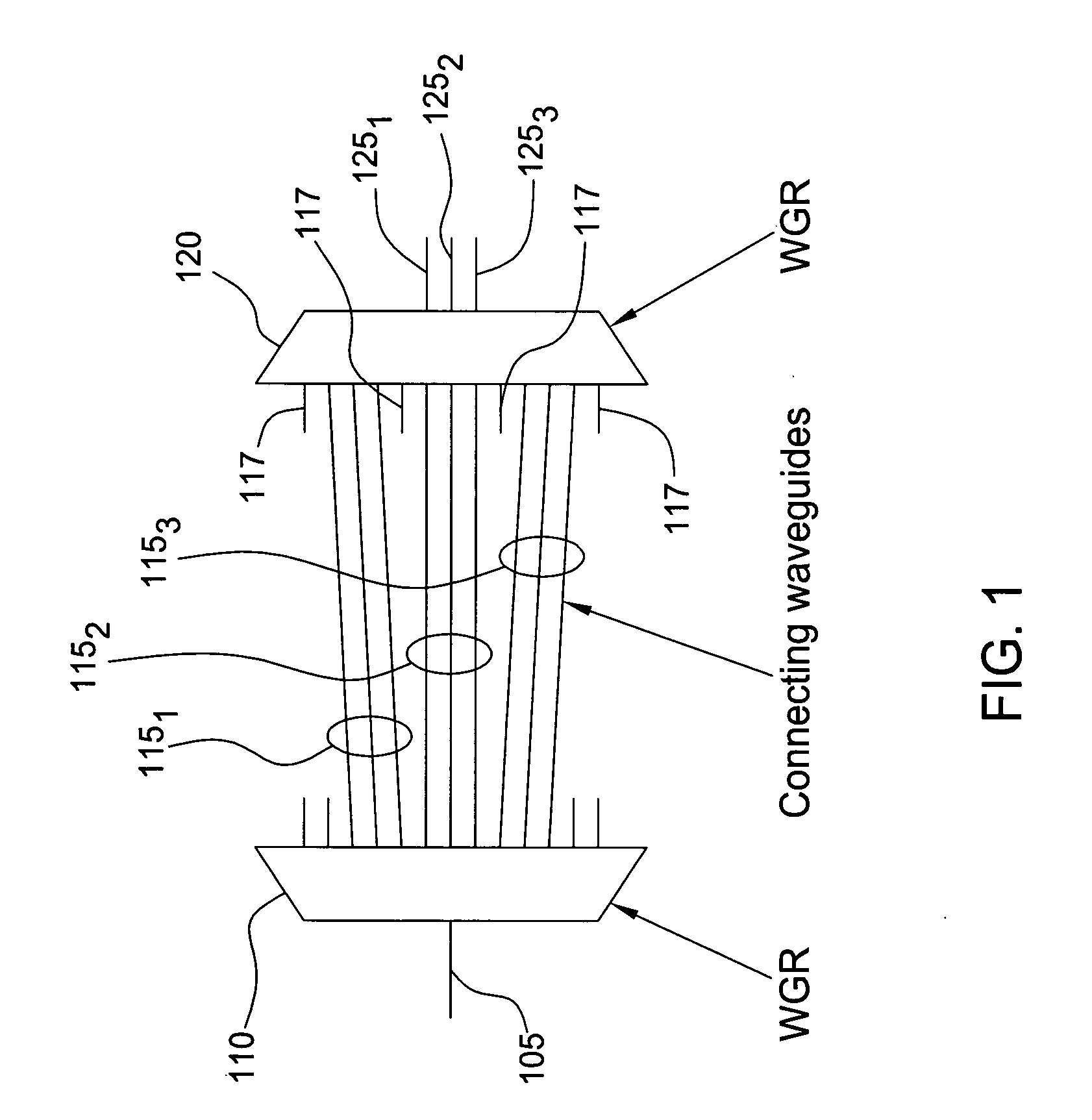
The inventors propose herein a novel band filter design for planar lightwave circuits. In one embodiment of the present invention, the band filter includes two waveguide grating routers interconnected by a third waveguide grating, wherein waveguides comprising the third waveguide grating have unequal path lengths. In addition, the waveguides in the third grating are partitioned into sets of adjacent waveguides wherein each set corresponds to a particular wavelength band for the filter. The individual sets of waveguides are spaced at their connection to the second waveguide grating router such that optical signals within predetermined, different optical wavelength bands are routed to different output ports of the band filter. Some of the advantages of this novel band filter include compactness, sharp passband corners, low spectral ripple, and a lack of chromatic dispersion.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
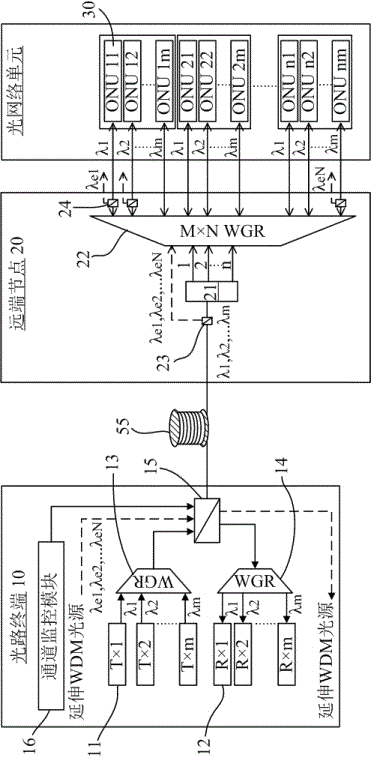
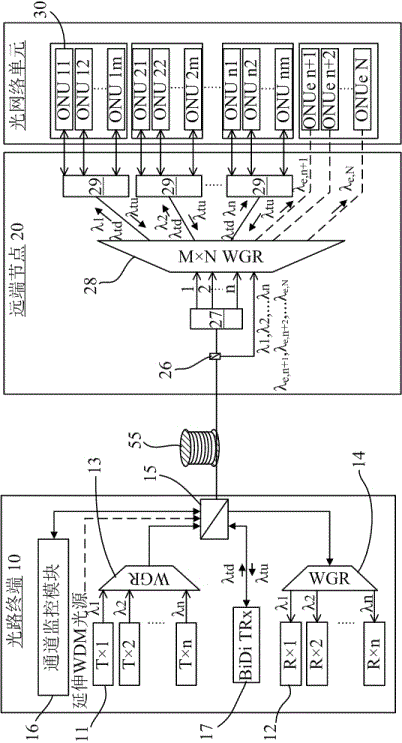
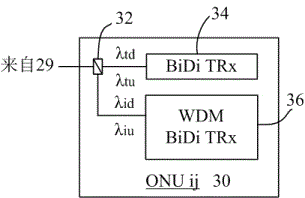
System and method for online updating of bandwidth of optical network unit in wavelength division multiplexing optical access network
ActiveCN101521836AIncrease profitLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAccess networkGrating
The invention relates to a system and a method for achieving the online updating of the bandwidth of an optical network unit in a wavelength division multiplexing optical access network. The system is formed by adopting a mode that one optical line terminal is connected with one remote node which is connected with 40 optical network units, wherein the remote node adopts a mode that a waveguide grating router is combined with a microelectronic mechanical optical switch to achieve the dynamic scheduling with any specified wavelength. Based on the system, the method applies the wavelength dynamic scheduling mode to performing the online updating of the bandwidth of the optical network unit. The system and the method have the characteristics of low cost for network construction and bandwidth updating, no influence on the running of the original static network by the online updating of the bandwidth of the optical network unit, and high utilization rate of the wavelength of the whole network.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Rectangular-passband multiplexer
ActiveUS20070086699A1Easy constructionCompact and easy constructionCoupling light guidesPath lengthGrating
A low-loss rectangular-passband multiplexer including a three-arm interferometer coherently connected to a waveguide grating router (WGR), resulting in a passband substantially of type N=3, without intrinsic loss. The three-arm interferometer has a free-spectral range (FSR) substantially equal to the channel spacing and is connected to an M-arm interferometer having a much larger FSR. The three-arm interferometer includes three waveguides each exhibiting a linearly increasing path length optically connected to a 1×3 coupler and a 3×3 coupler. The 1×3 coupler may be constructed from a series of Y-branch couplers.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
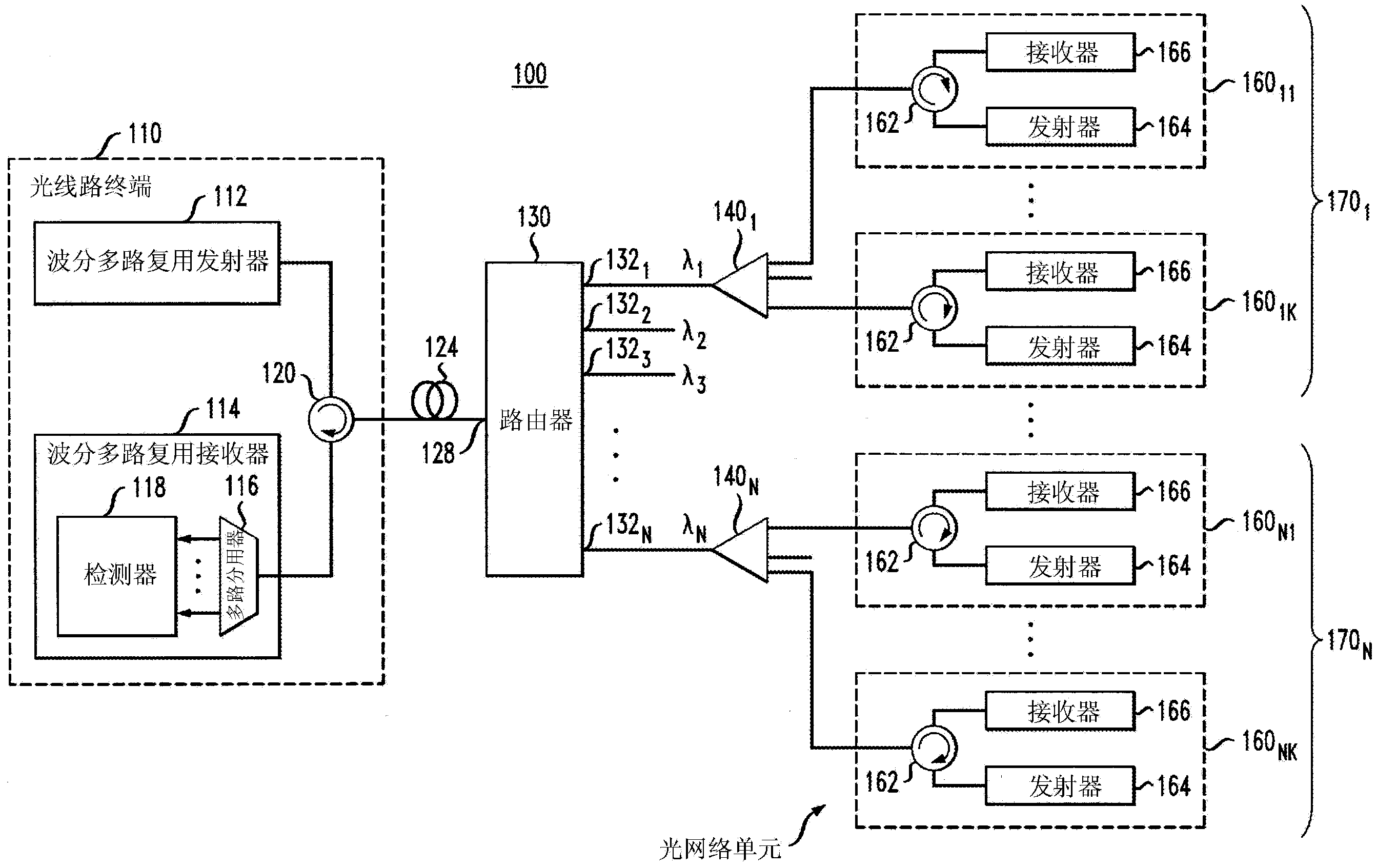
Optical router using stationary imaging
ActiveUS7283700B2Reduce crosstalkImprove efficiencyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical routerCrosstalk
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
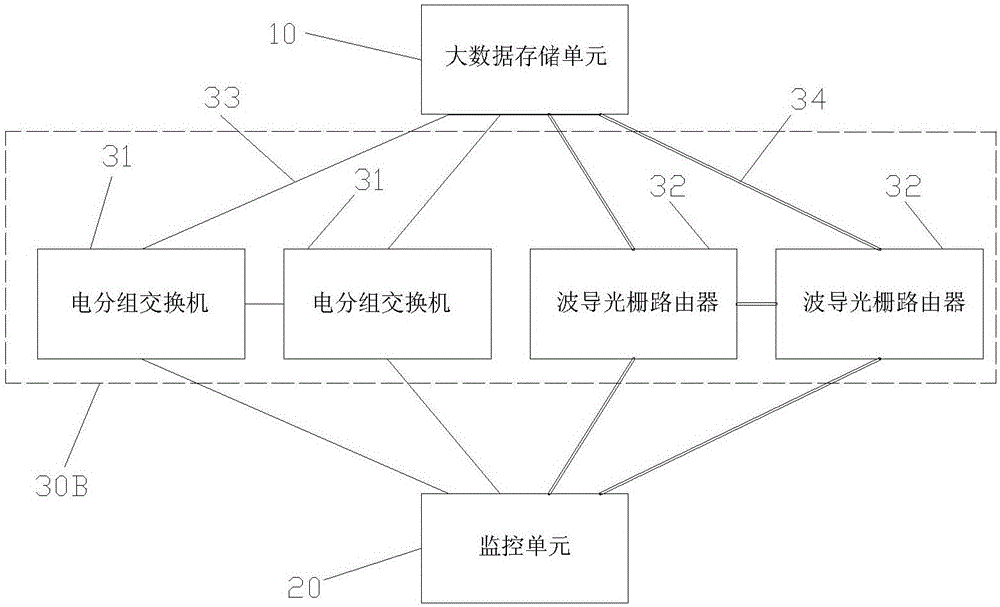
Big data exchange platform network architecture
InactiveCN106160864AReduce demandHigh bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionNetwork architectureData interchange
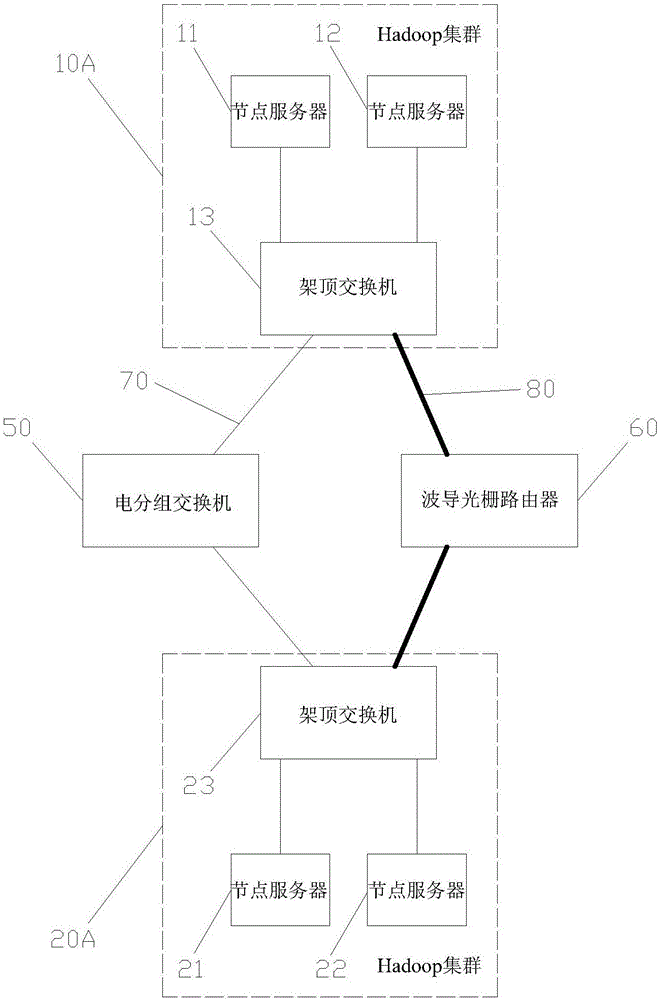
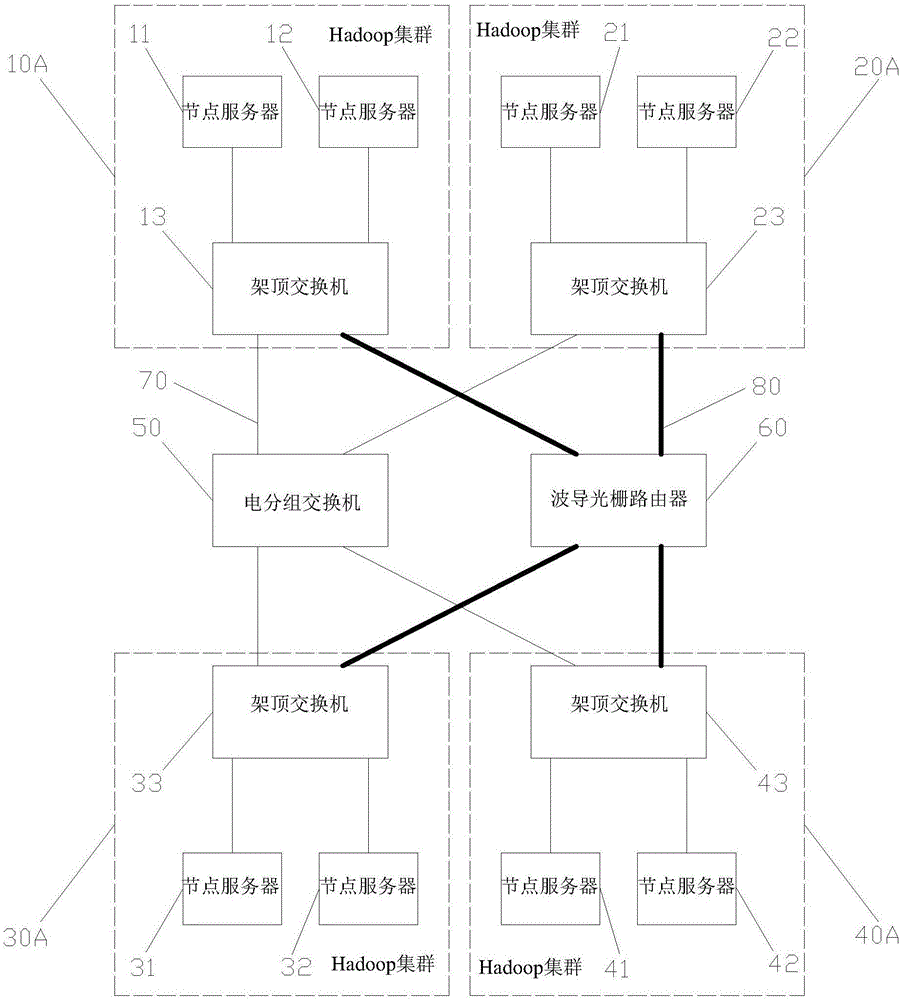
The invention discloses a big data exchange platform network architecture, and relate to the technical field of big data exchange. The big data exchange platform network architecture comprises at least two Hadoop clusters and an electric packet-switched exchange and a waveguide grating router which are connected with the Hadoop clusters respectively, each Hadoop cluster comprises top-of-rack switches and at least one node server, and the node servers are connected with the electric packet-switched exchange and the waveguide grating router through the corresponding top-of-rack switches respectively. According to the big data exchange platform network architecture, by means of cooperative communication of the electric packet-switched exchange and the waveguide grating router, the advantages of being high in bandwidth and transmission efficiency and the like for an optical network are fully utilized, the network capacity and bandwidth are increased, and the single point failure problem is avoided.
Owner:王楚
WDM optical communication system capable of monitoring temperature
InactiveUS7340177B2Avoid disagreementReduce crosstalkLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberGrating
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Array waveguide grating router with uniform loss
ActiveCN108469651AUniform lossSmall sizeOptical waveguide light guideHigh level techniquesGratingWaveguide
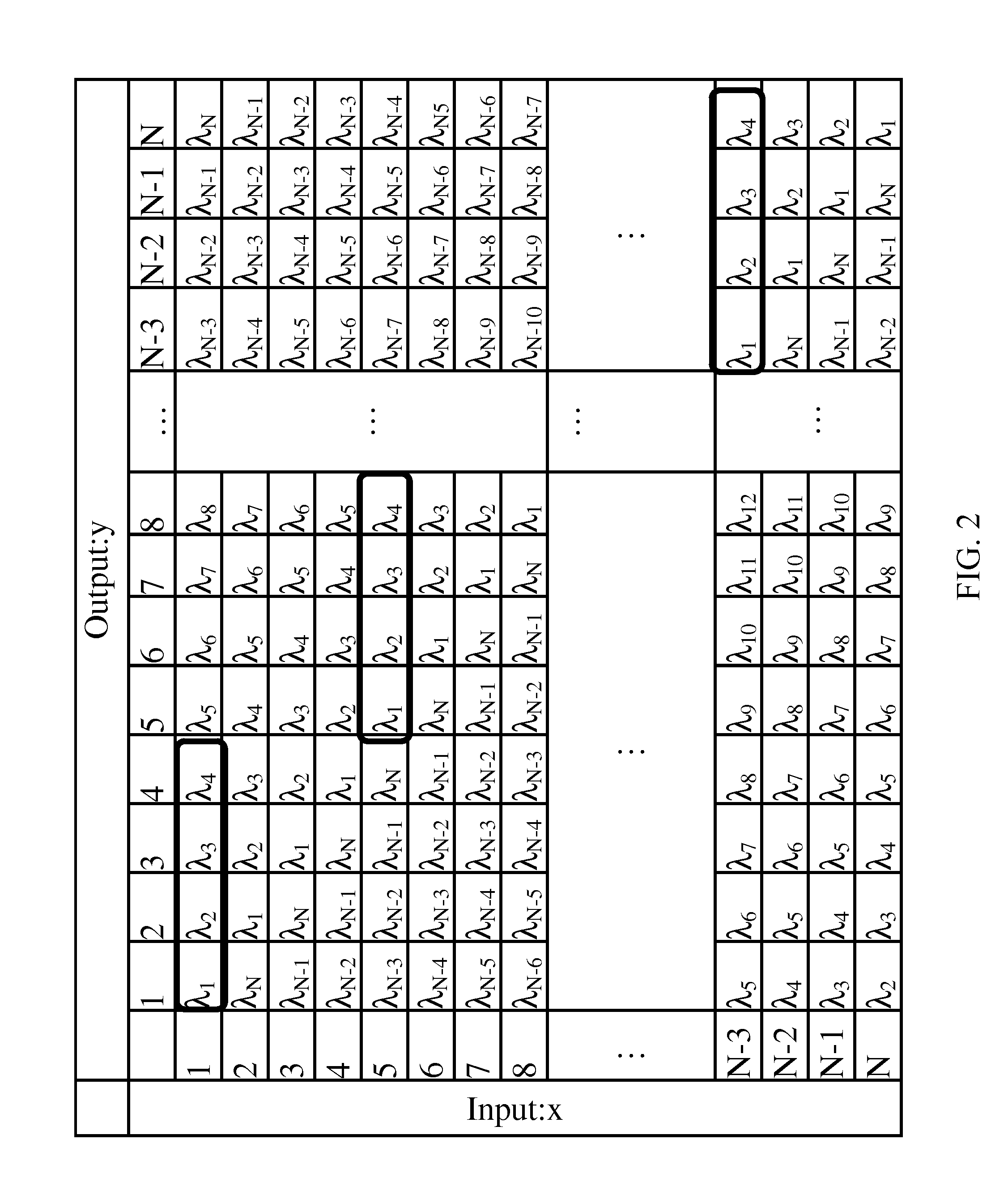
The invention discloses an arrayed waveguide grating router with uniform loss. Light is input from input waveguide to an input star coupler. Due to the Kirchhoff diffraction phenomenon, the optical field is expanded in the input star coupler and is received by the array waveguide. Then the received light of the array waveguide passes through the Sinc function coupling zone and forms focused imaging in an output star coupler. The Sinc function coupling region transforms the Gaussian optical field transmitted by the array waveguide into the Sinc function type optical field, so that the rectangular optical field is output from the output star coupler to achieve the function of uniform loss of the arrayed waveguide grating router. The arrayed waveguide grating router solves the problem of non-uniformity of loss inherent in the arrayed waveguide grating router. It has the advantages of large volume difference, low cost, small serial interference and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Integrateable band filter using waveguide grating routers
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
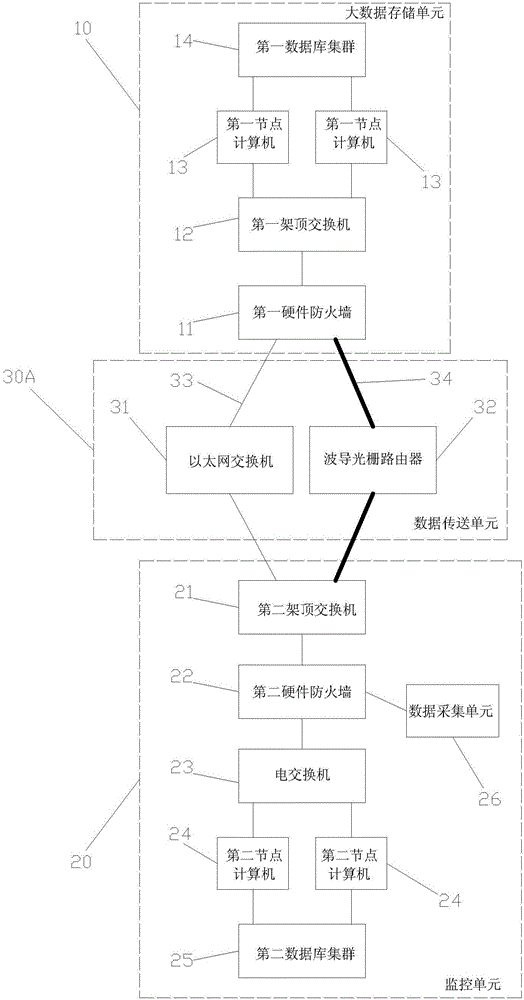
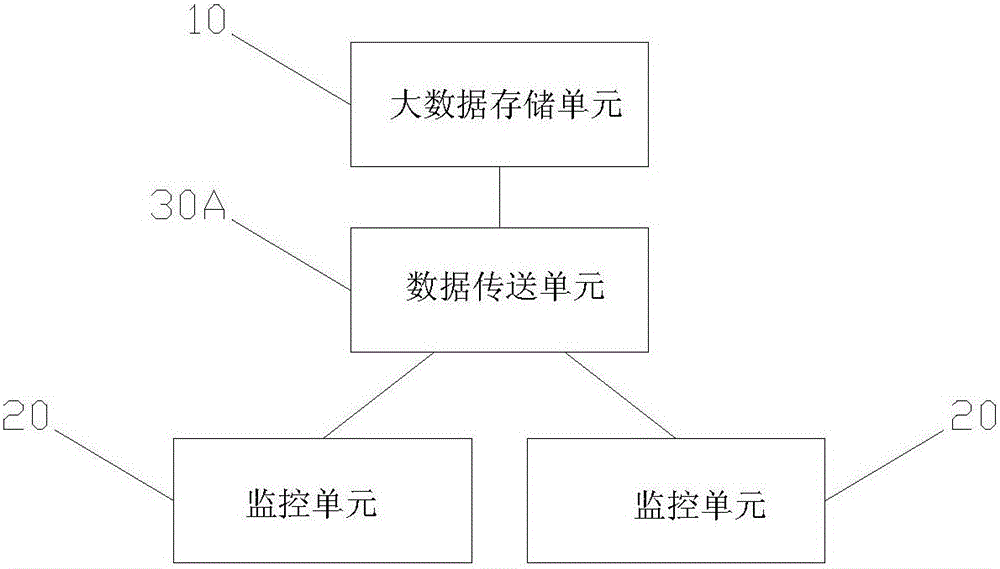
Monitoring big data storage platform network architecture
InactiveCN106230952AReduce energy consumptionReduce demandError preventionNetwork architectureDatabase clustering
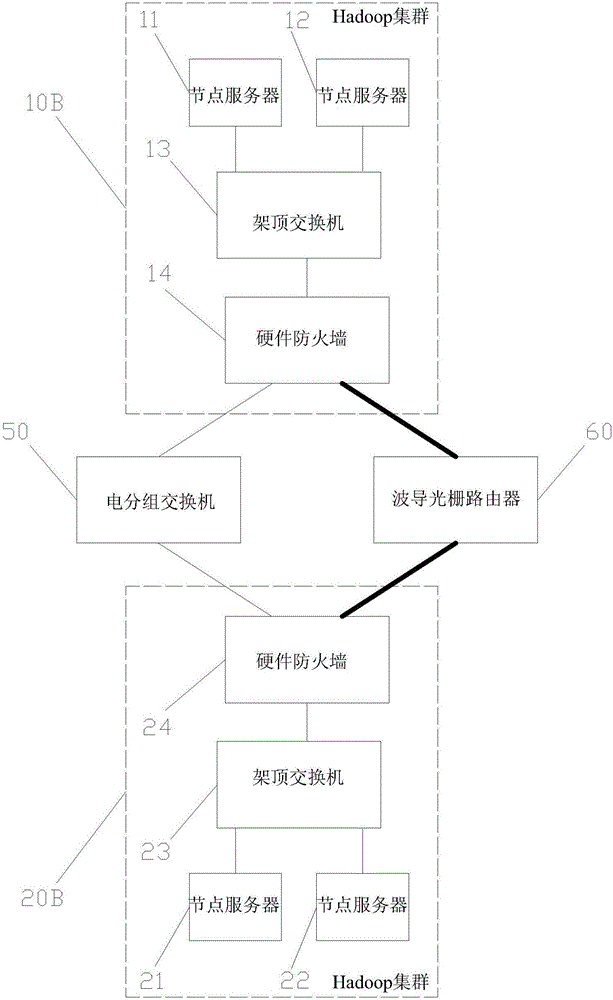
The invention discloses a monitoring big data storage platform network architecture, relating to the technical field of big data storage. The monitoring big data storage platform network architecture comprises a big data storage unit and at least one monitoring unit; each monitoring unit transmits the monitoring data to the big data storage unit via a data transfer unit; the big data storage unit comprises a first hardware firewall, a first top-of-rack switch, a first database cluster and at least one first node computer; the monitoring unit comprises a second top-of-rack switch, a second hardware firewall, at least one data collection unit, an electrical switch, at least one second node computer and a second database cluster; and the data transfer unit comprises an Ethernet switch and a waveguide grating router. According to the monitoring big data storage platform network architecture disclosed by the invention, external storage of collected data of the monitoring unit is realized via cooperative communication between the Ethernet switch and the waveguide grating router, the advantages of high bandwidth, high transmission efficiency and the like of an optical network are fully utilized, and the network capacity and bandwidth are increased.
Owner:王楚
Time/wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network (TWPON)
ActiveUS20150163011A1Avoid less flexibilityIncrease capacityTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberGrating
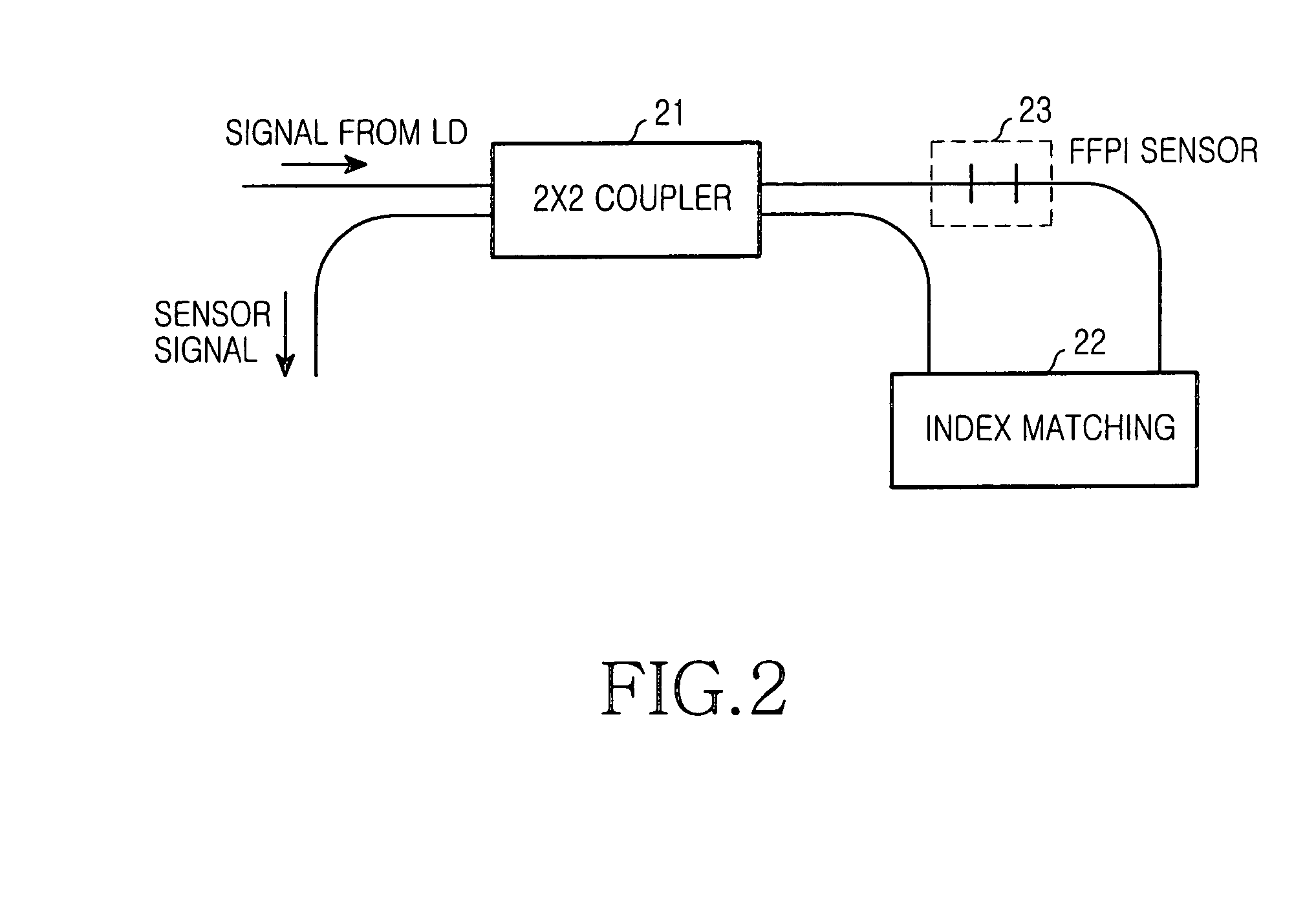
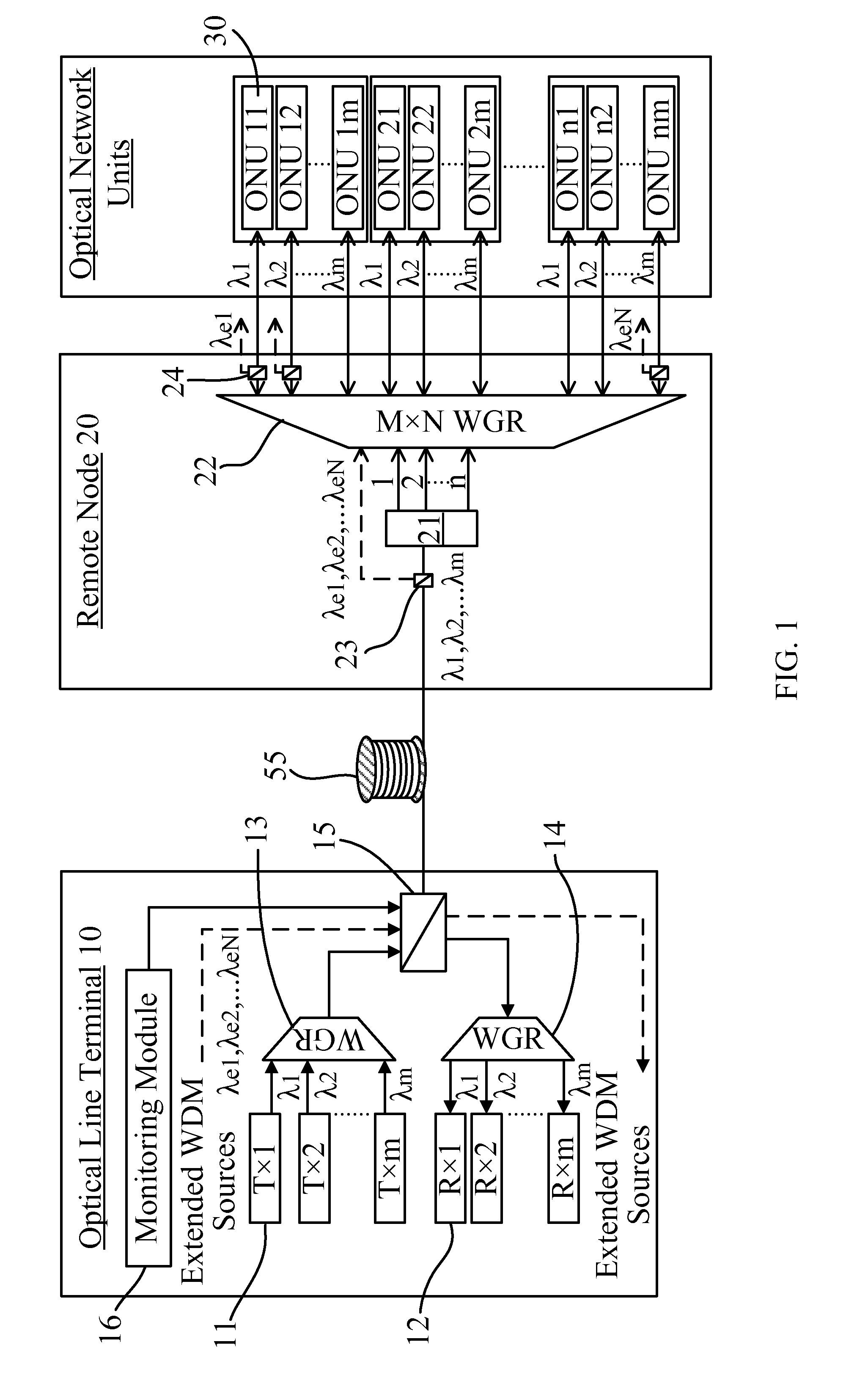
The present invention discloses a time / wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network (TWPON), which has an optical splitter (21) and a waveguide grating router (WGR) (22) disposed at a remote node (RN) (20). The optical splitter (21) and the WGR (22) can be connected in a cascade or in a parallel such that the present invention can use less number of wavelengths to increase transmission capacity or increase the number of users. A channel fault monitoring (CFM) module provided at an optical line terminal (OLT) is utilized to locate fiber breaks among distribution fibers. The TWPON of the present invention can provide TDM-PON, WDM-PON, and Hybrid PON co-existing platform with less wavelengths channel fault monitoring mechanism.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Colorless tunable dispersion compensator employing a planar lightwave circuit and a deformable mirror
InactiveUS20060198577A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideGratingPiezoelectric actuators
A colorless, waveguide-grating-router-based tunable dispersion compensator includes a planar lightwave circuit and a deformable mirror, optically coupled to each other by a plano-cylindrical glass lens such that a fast tuning speed and single-knob dispersion adjustment are obtained. In a further aspect of the present invention, the waveguide-grating router is pinched, symmetrical about its center line, and has a half-wave plate inserted therein to provide polarization independence. In a still further aspect of the present invention, the deformable mirror includes, reflective film attached to opposing piezo-electric actuators.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Colorless tunable dispersion compensator employing a planar lightwave circuit and a deformable mirror
InactiveCN1828352AQuick tuneReduce power consumptionCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionElectricityGrating
A colorless, waveguide-grating-router-based tunable dispersion compensator includes a planar lightwave circuit and a deformable mirror, optically coupled to each other by a plano-cylindrical glass lens such that a fast tuning speed and single-knob dispersion adjustment are obtained. In a further aspect of the present invention, the waveguide-grating router is pinched, symmetrical about its center line, and has a half-wave plate inserted therein to provide polarization independence. In a still further aspect of the present invention, the deformable mirror includes, reflective film attached to opposing piezo-electric actuators.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
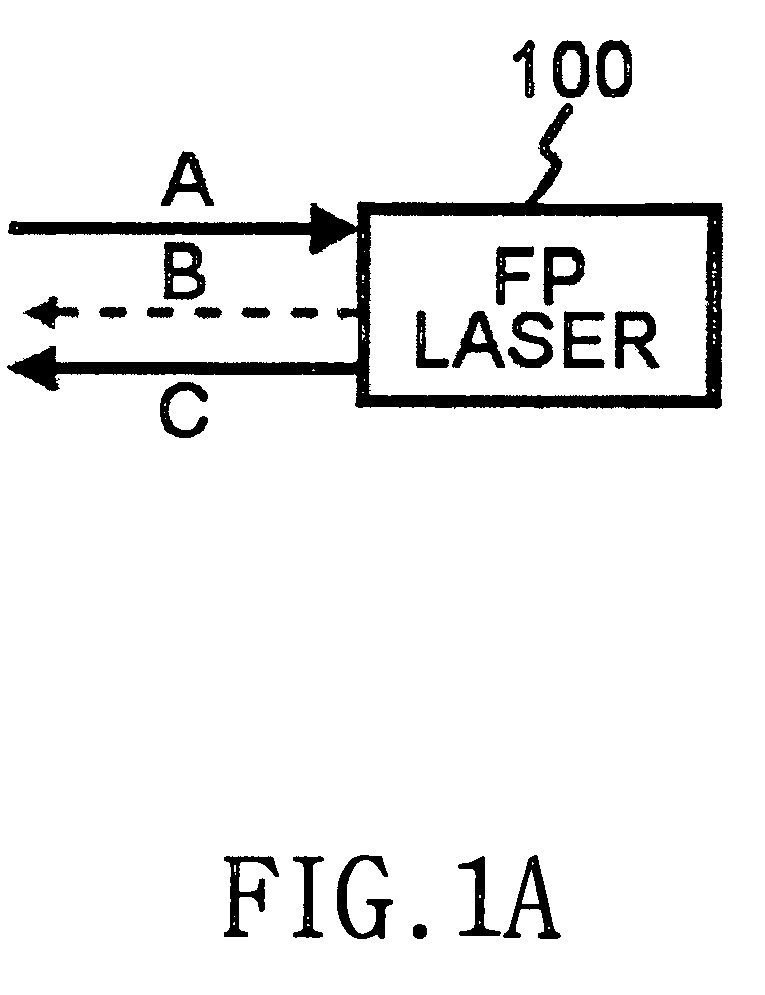
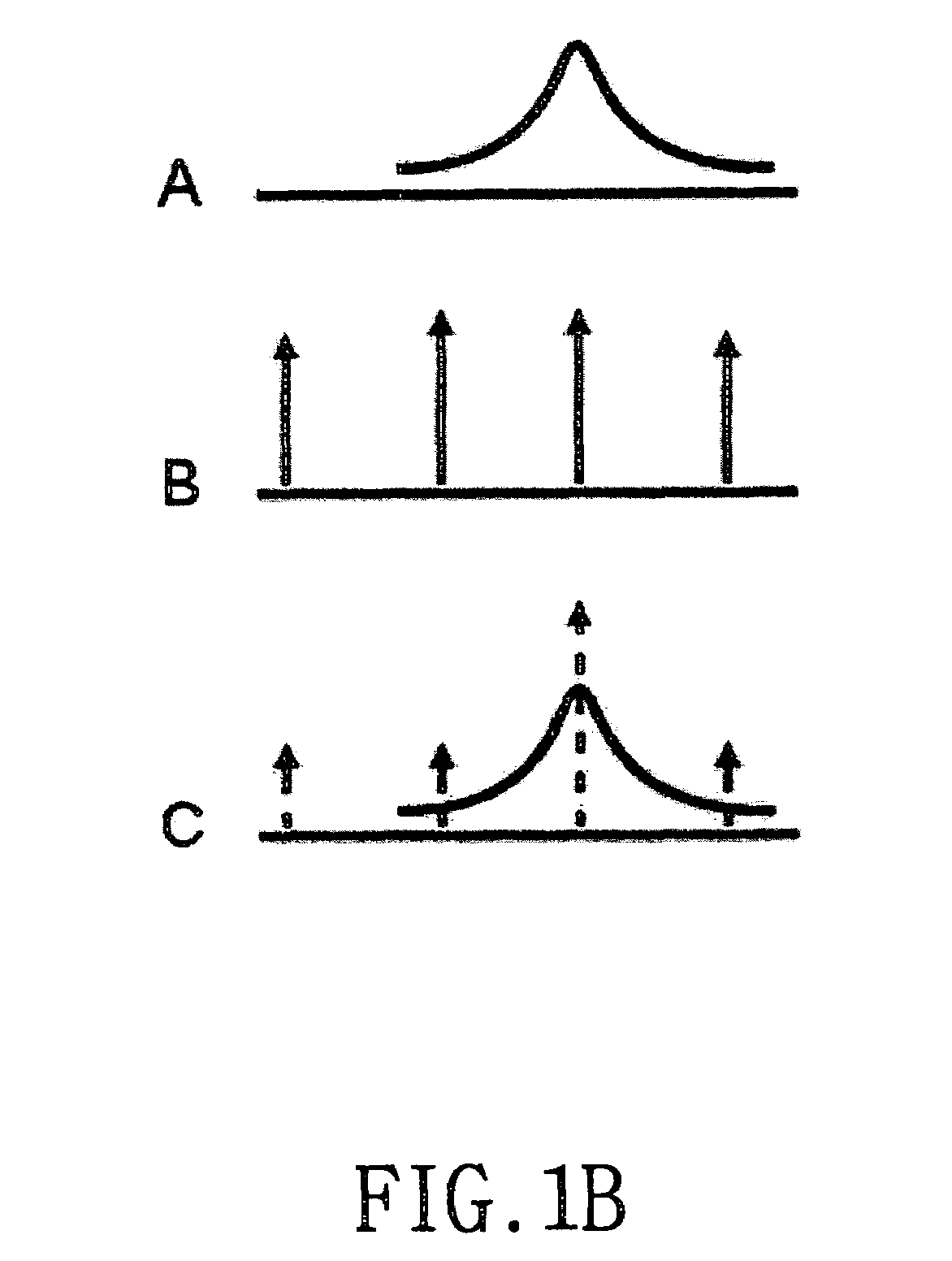
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmitter using Fabry-Perot laser
InactiveUS7340173B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingGrating
A WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) optical transmitter using a Fabry-Perot laser is disclosed. The WDM optical transmitter includes a light source for outputting incoherent light of a prescribed wavelength bandwidth, a circulator having the first to the third ports, for outputting the incoherent light received at the first port coupled to the light source to the second port, and outputting an optical signal received at the second port to the third port coupled to the external waveguide, a WGR (Waveguide Grating Router) having a multiplexing port (MP) coupled to the second port of the circulator and a plurality of demultiplexing ports (DPs), for performing WD (Wavelength Division) demultiplexing on the incoherent light received at the MP to output WD-demultiplexed signals to the plurality of DPs, and performing WD multiplexing on a plurality of channel signals received at the plurality of DPs to output WD-multiplexed signals to the MP, and a plurality of FB (Fabry-Perot) lasers respectively connected to the DPs of the WGR, each FP laser is comprised of a laser cavity, an antireflection coating layer deposited at one end of the laser cavity facing a corresponding DP, and a high reflection coating layer deposited at the other end of the laser cavity, whereby an optical injection efficiency increases and an influence of reflected light is reduced, resulting in facilitation of a wavelength-locked phenomenon.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
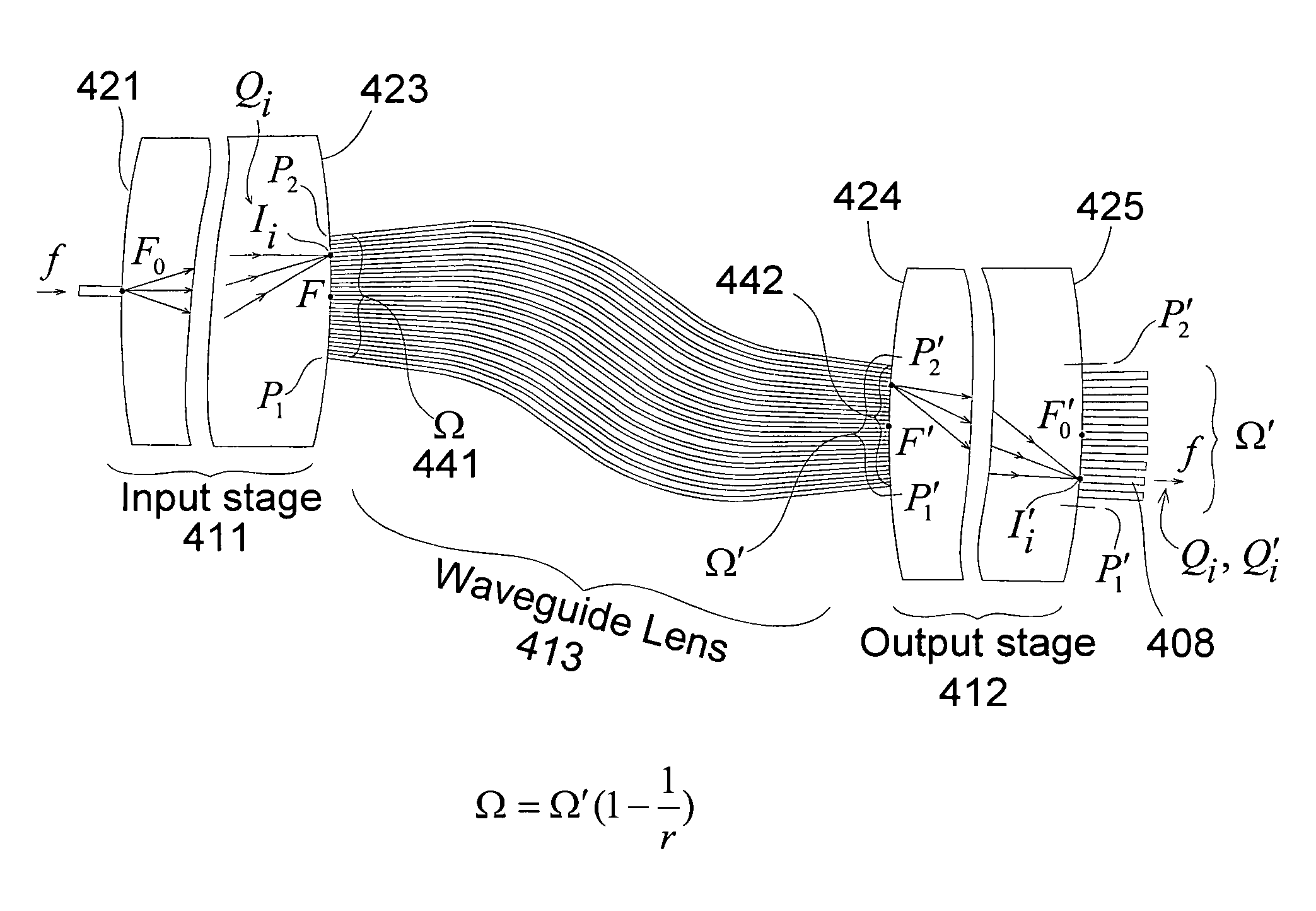
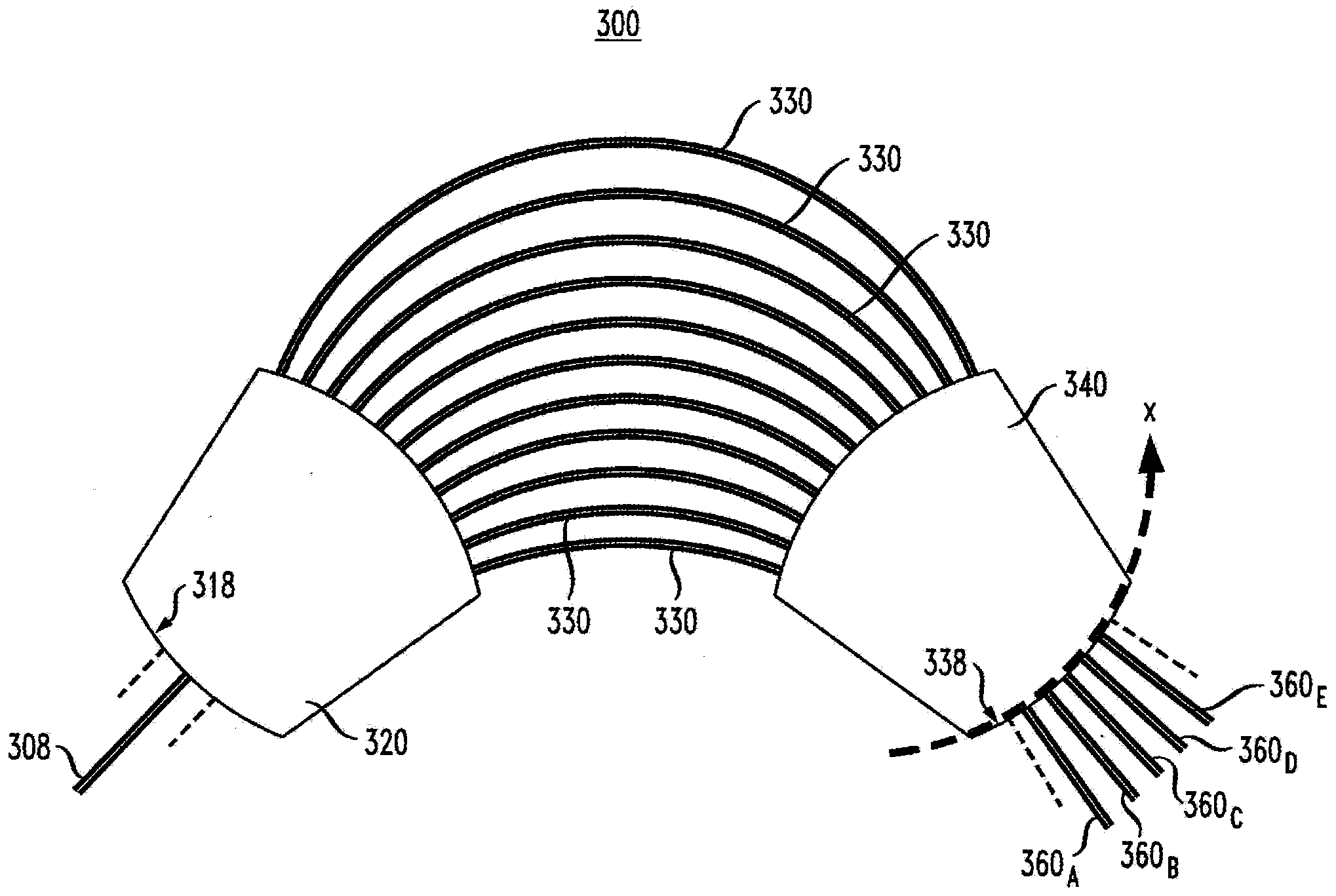
Optical router with nearly ideal performance
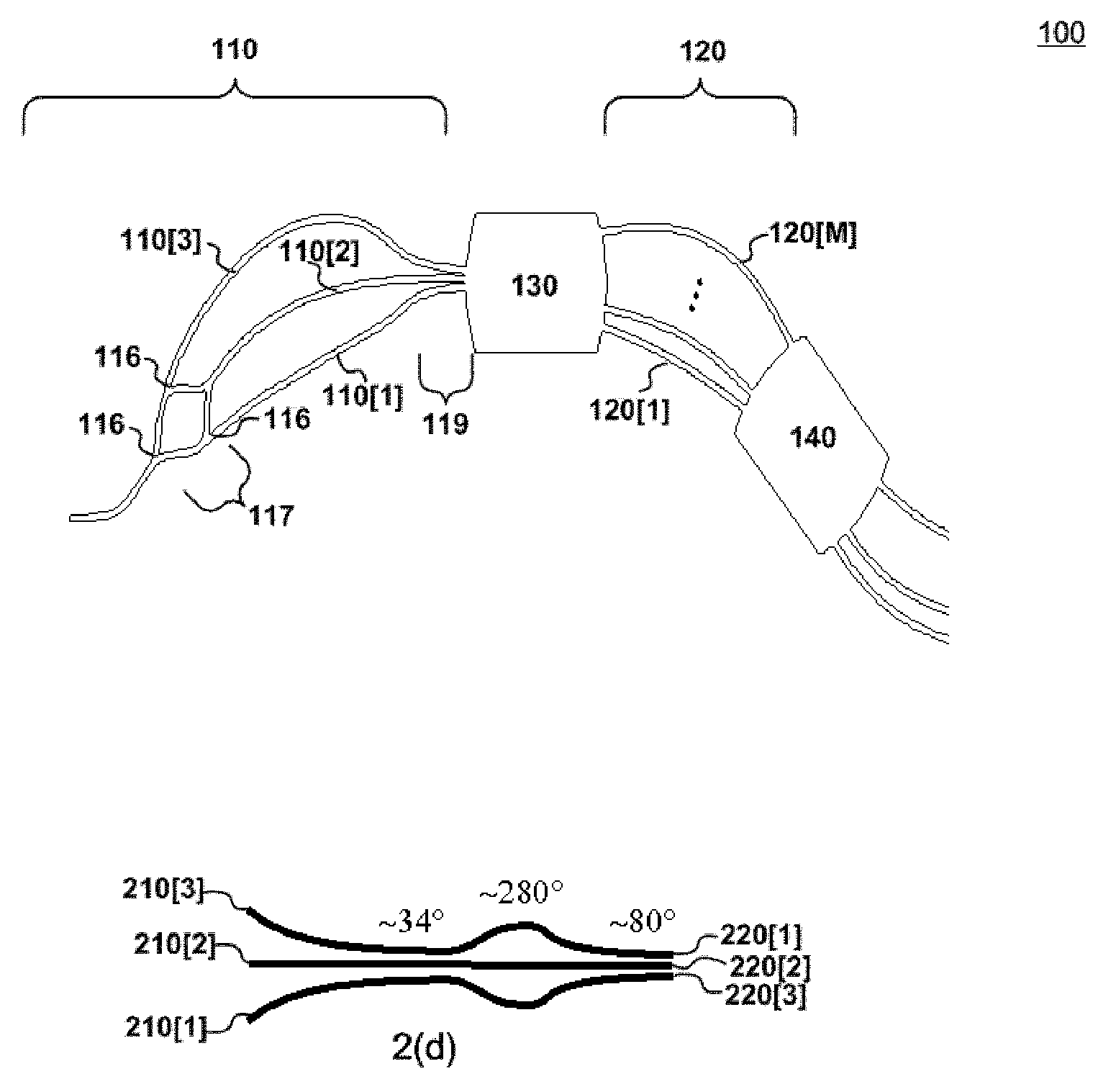
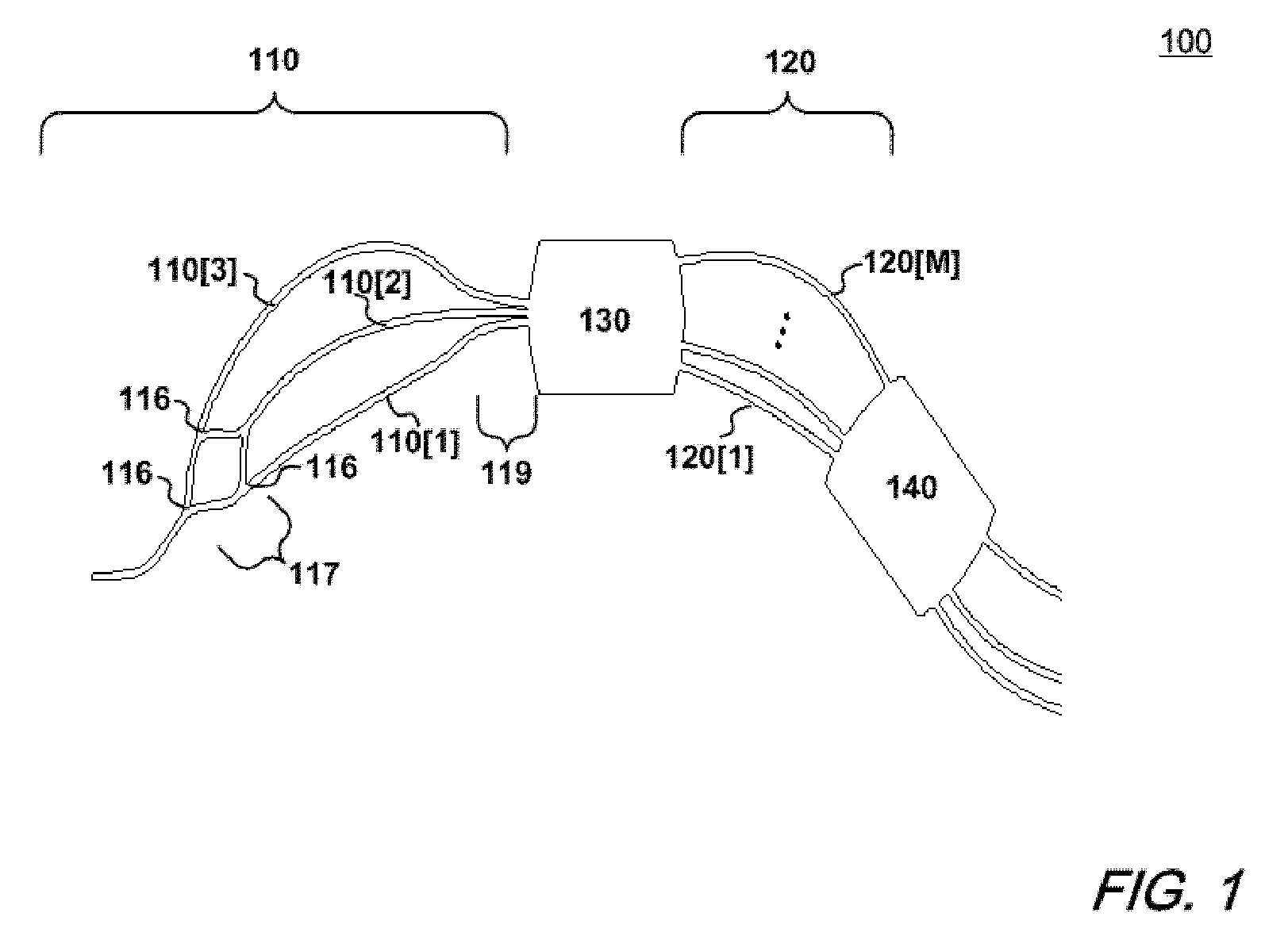
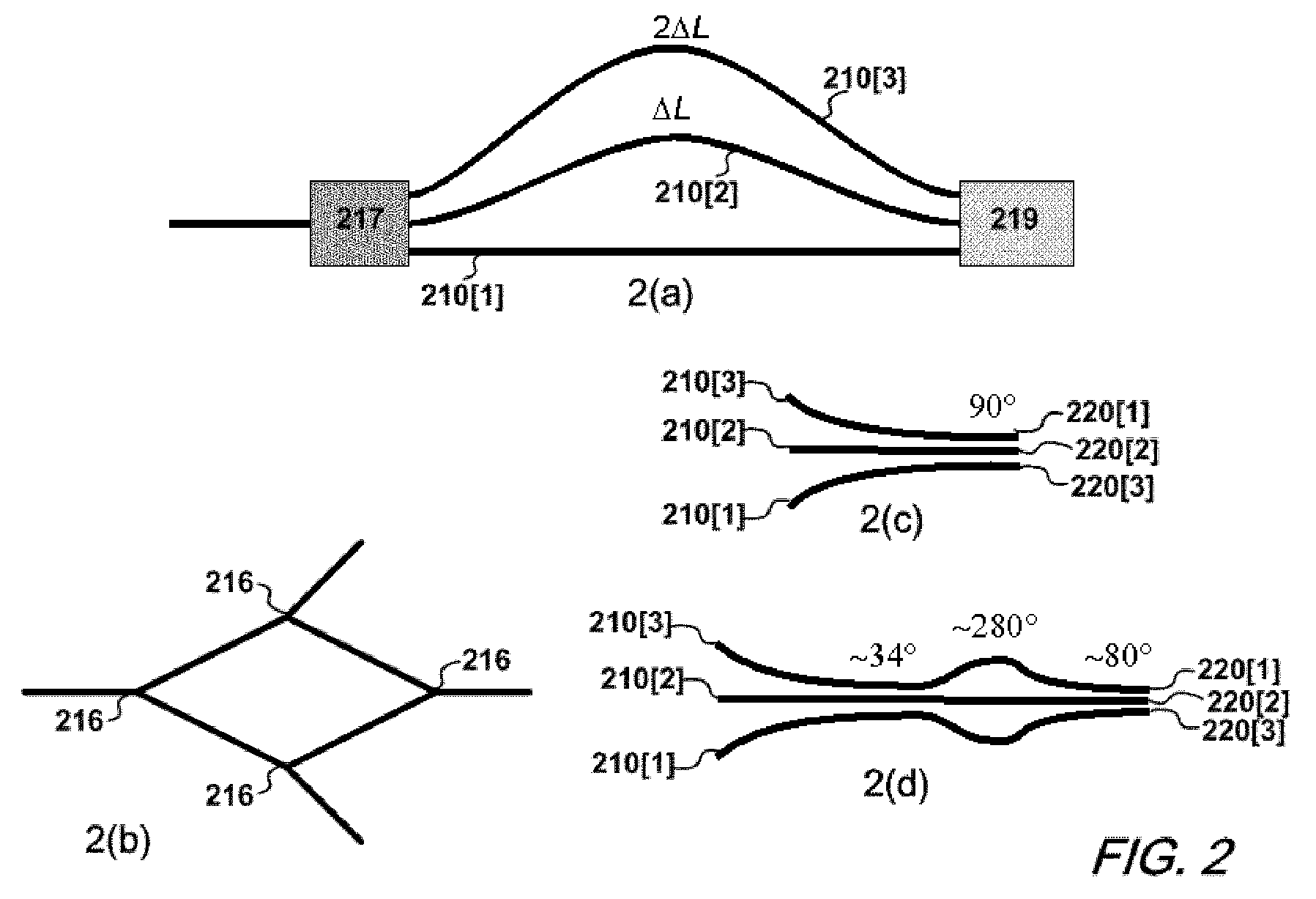
ActiveUS20110123148A1Improve transmission performanceSmall sizeCoupling light guidesDiffraction orderGrating
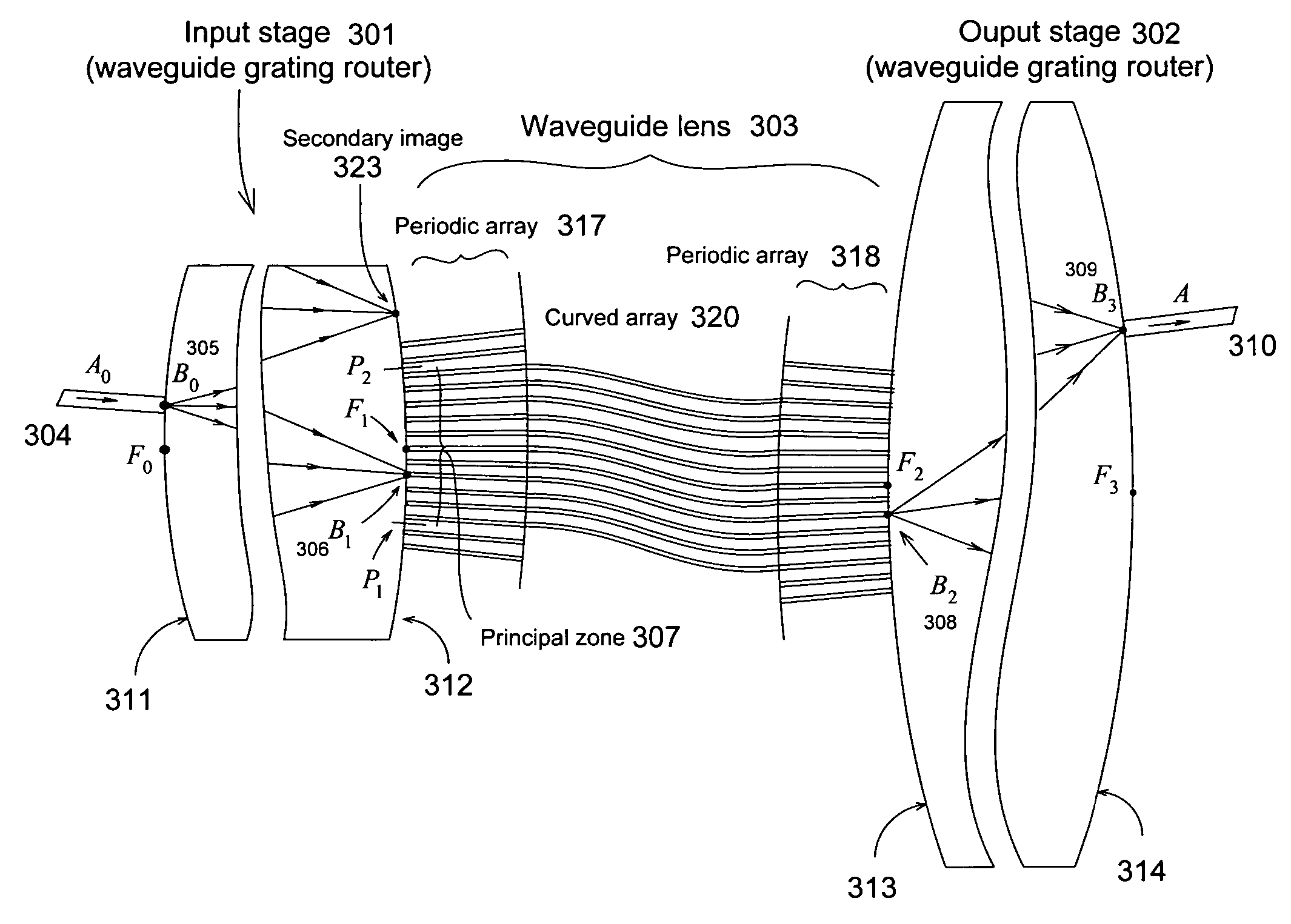
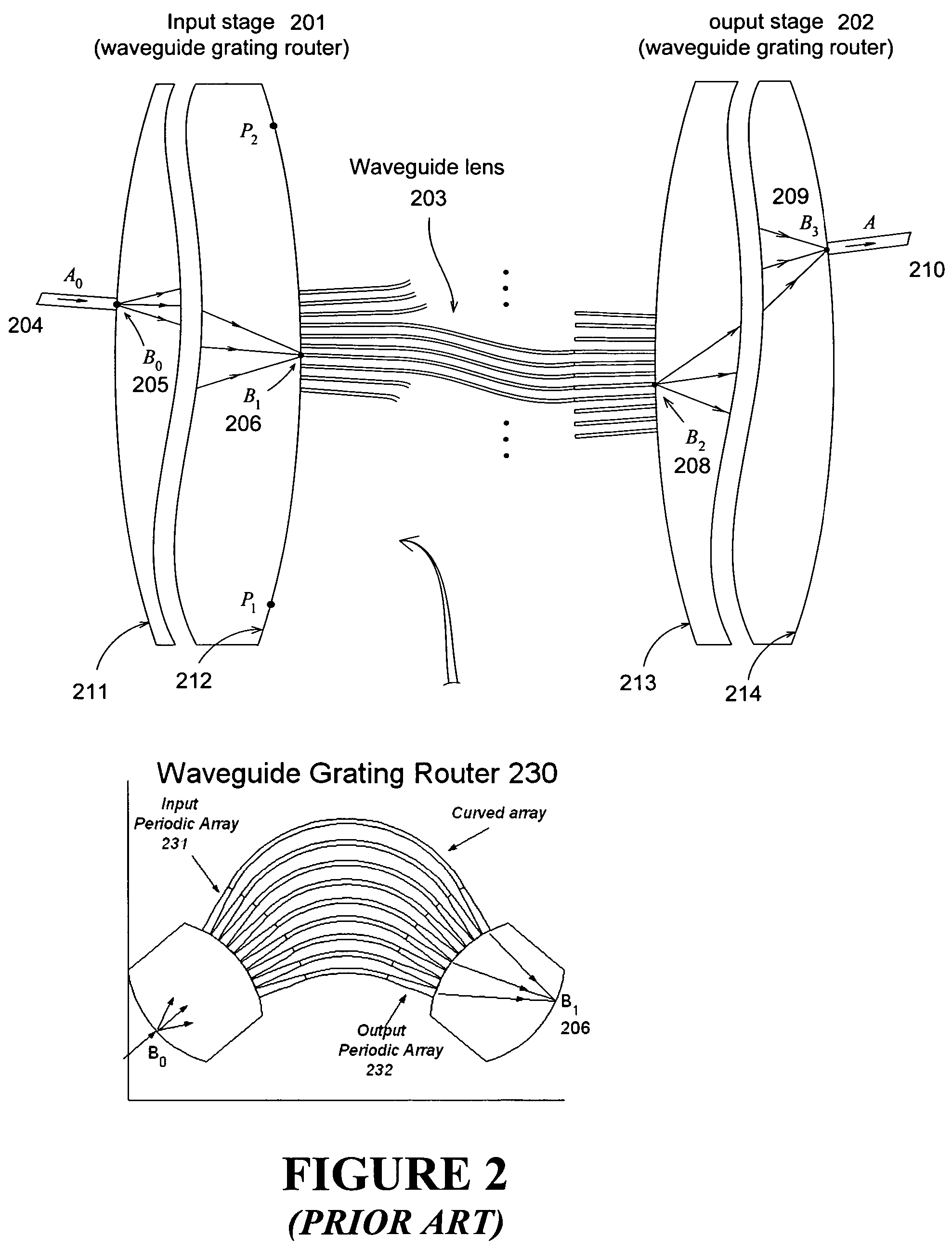
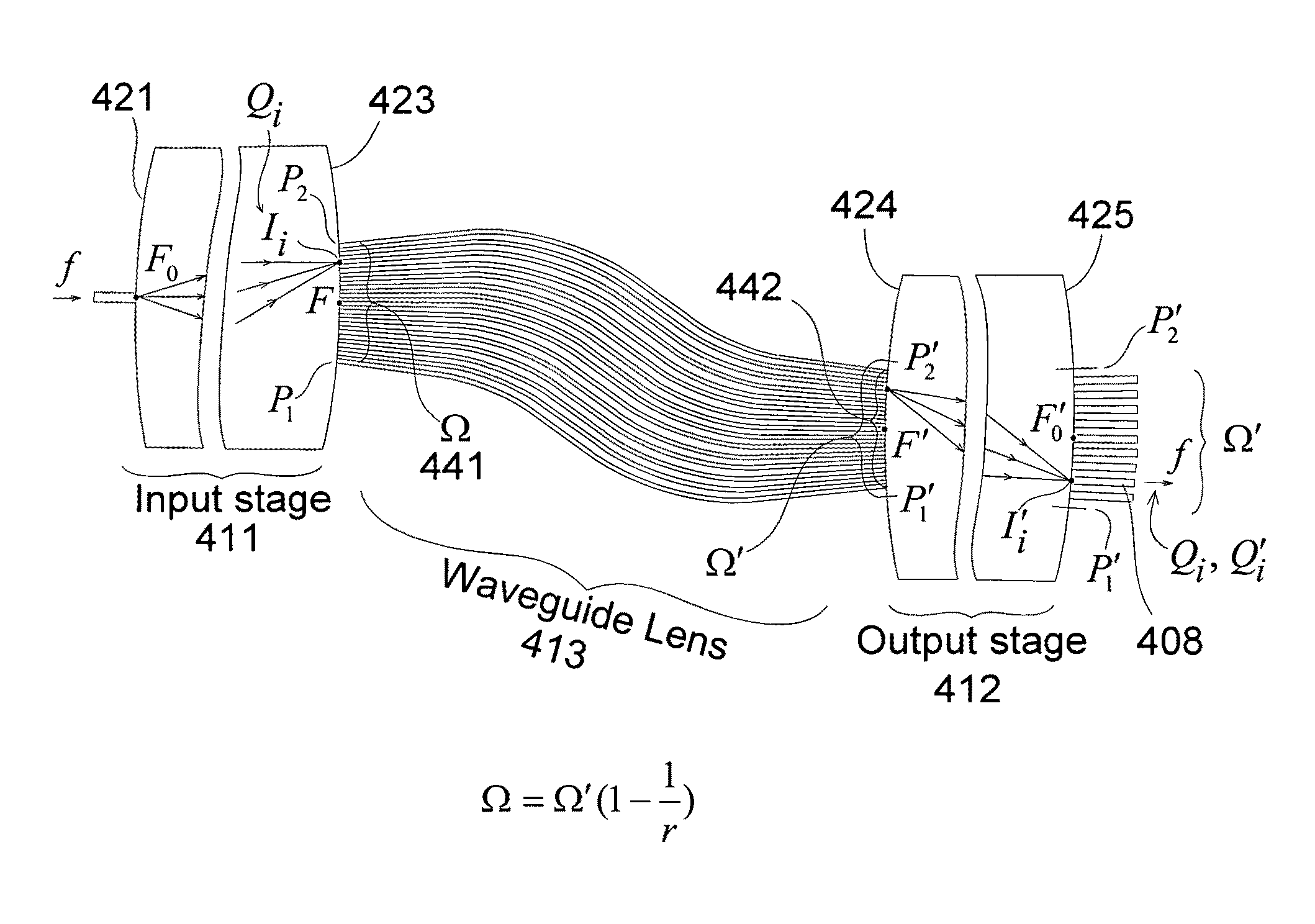
An optimized planar optical router consisting of two stages performing stationary imaging between an input waveguide and a set of output waveguides has advantages of reduced size, larger number of channels and minimal loss variation in each passband. Each stage is a waveguide grating router, the two stages are characterized by nearly equal free-spectral ranges, and a waveguide lens is connected between the two stages. In one embodiment, the lens is connected between the central zones of the two stages, and the diffraction orders of the two stages vary monotonically from each passband to the next. In another embodiment, the loss caused by secondary images is substantially reduced by using a composite lens providing efficient transmission of both principal and secondary images.
Owner:DRAGONE CORRADO PIETRO
Time/wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network
InactiveCN103297867ALow costLow cost to achieve high capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLength waveElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a TWPON, an optical splitter (21) and a WGR (22) are arranged on a RN (20), the optical splitter (21) and the WGR (22) can be in cascade connection or parallel connection to be implemented, and therefore the purpose of promoting transmission capacity or increasing user quantities can be realized by means of smaller wavelength; the invention further provides a platform where a time-division multiplexed passive optical network, a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network and a hybrid passive optical network exist simultaneously, and a channel barrier monitoring mechanism of the smaller wavelength.
Owner:李三良
Rectangular-passband multiplexer
ActiveUS7433560B2Easy constructionCompact and easy constructionCoupling light guidesGratingPath length
A low-loss rectangular-passband multiplexer including a three-arm interferometer coherently connected to a waveguide grating router (WGR), resulting in a passband substantially of type N=3, without intrinsic loss. The three-arm interferometer has a free-spectral range (FSR) substantially equal to the channel spacing and is connected to an M-arm interferometer having a much larger FSR. The three-arm interferometer includes three waveguides each exhibiting a linearly increasing path length optically connected to a 1×3 coupler and a 3×3 coupler. The 1×3 coupler may be constructed from a series of Y-branch couplers.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Time Division Wavelength Multiplexing Passive Optical Network
InactiveCN103297867BLow costLow cost to achieve high capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLength waveElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a TWPON, an optical splitter (21) and a WGR (22) are arranged on a RN (20), the optical splitter (21) and the WGR (22) can be in cascade connection or parallel connection to be implemented, and therefore the purpose of promoting transmission capacity or increasing user quantities can be realized by means of smaller wavelength; the invention further provides a platform where a time-division multiplexed passive optical network, a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network and a hybrid passive optical network exist simultaneously, and a channel barrier monitoring mechanism of the smaller wavelength.
Owner:李三良
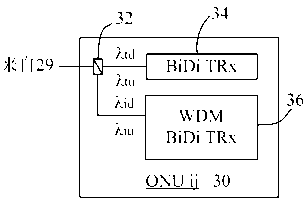
Wavelength router for a passive optical network
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and method for online updating of bandwidth of optical network unit in wavelength division multiplexing optical access network
ActiveCN101521836BIncrease profitLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAccess networkGrating
The invention relates to a system and a method for achieving the online updating of the bandwidth of an optical network unit in a wavelength division multiplexing optical access network. The system isThe invention relates to a system and a method for achieving the online updating of the bandwidth of an optical network unit in a wavelength division multiplexing optical access network. The system isformed by adopting a mode that one optical line terminal is connected with one remote node which is connected with 40 optical network units, wherein the remote node adopts a mode that a waveguide gra formed by adopting a mode that one optical line terminal is connected with one remote node which is connected with 40 optical network units, wherein the remote node adopts a mode that a waveguide grating router is combined with a microelectronic mechanical optical switch to achieve the dynamic scheduling with any specified wavelength. Based on the system, the method applies the wavelength dynamicting router is combined with a microelectronic mechanical optical switch to achieve the dynamic scheduling with any specified wavelength. Based on the system, the method applies the wavelength dynamicscheduling mode to performing the online updating of the bandwidth of the optical network unit. The system and the method have the characteristics of low cost for network construction and bandwidth u scheduling mode to performing the online updating of the bandwidth of the optical network unit. The system and the method have the characteristics of low cost for network construction and bandwidth updating, no influence on the running of the original static network by the online updating of the bandwidth of the optical network unit, and high utilization rate of the wavelength of the whole networpdating, no influence on the running of the original static network by the online updating of the bandwidth of the optical network unit, and high utilization rate of the wavelength of the whole network.k.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Optical router with nearly ideal performance
ActiveUS8204346B2Improve transmission performanceSmall sizeCoupling light guidesDiffraction orderGrating
An optimized planar optical router consisting of two stages performing stationary imaging between an input waveguide and a set of output waveguides has advantages of reduced size, larger number of channels and minimal loss variation in each passband. Each stage is a waveguide grating router, the two stages are characterized by nearly equal free-spectral ranges, and a waveguide lens is connected between the two stages. In one embodiment, the lens is connected between the central zones of the two stages, and the diffraction orders of the two stages vary monotonically from each passband to the next. In another embodiment, the loss caused by secondary images is substantially reduced by using a composite lens providing efficient transmission of both principal and secondary images.
Owner:DRAGONE CORRADO PIETRO
Optical transmission apparatus and method
Provided are an optical transmission apparatus and method using a light source for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication that employs a Fabry-Perot laser diode (F-P LD) whose output wavelength is locked by an externally injected incoherent light, a multifiber, and a waveguide grating router. The light transmission apparatus includes: an incoherent light source (ILS) outputting incoherent light; a plurality of circulators (CIRs) connected to the ILS, receiving the incoherent light from the ILS, and outputting first optical signals; a first waveguide grating router (WGR) outputting the first optical signals output from each of the CIRs to optical fibers corresponding to each of the CIRs, and outputting second optical signals input from the optical fibers to the corresponding CIRs; a plurality of second WGRs corresponding to each of the CIRs, and demodulating the second optical signals output from each of the plurality of CIRs; and a plurality of receivers connected to the plurality of the second WGRs, and inputting the demultiplexed optical signals output from the plurality of second WGRs. A plurality of light sources for WDM optical communication whose output wavelength is locked can increase size and economical efficiency of a light transmission system (subscriber). The N×N WGR can produce a conventional light transmission system and accommodate many subscribers.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Integrateable band filter using waveguide grating routers
The inventors propose herein a novel band filter design for planar lightwave circuits. In one embodiment of the present invention, the band filter includes two waveguide grating routers connected by sets of substantially equal path length waveguides within each set separated on one side, wherein the waveguides of each set are formed such that optical signals having overlapping frequency ranges are propagated through adjacent waveguides. In addition, the waveguides of each set are spaced at their connection to the second waveguide grating router such that optical signals with predetermined optical frequency ranges are routed to selected, respective output ports. Some of the advantages of this novel band filter include compactness, sharp passband corners, and a lack of chromatic dispersion.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Integrated demultiplexer/photoreceiver for optical networks and method of controlling transparency of optical signal transmission layer
InactiveUS7035517B2Low costSimple designCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic receiversHeterojunctionGrating
An integrated demultiplexer / photoreceiver (IDP) for optical networks and optical interconnection devices has a common substrate which supports three sequentially arranged basic components: a waveguide grating router, an array of photodetectors, and an array of heterojunction transistors. Basic layers of all three components are grown together in a common epitaxial process, and then each of the components is individually patterned in accordance with its function. Such structure of IDP makes it possible to reduce the cost, simplify the design, improve conditions for optical alignment, and reduce optical losses. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, transparency of the optical signal transmission layer of the WGR is controlled by selectively doping the layers of the multiple-layer waveguide structure, while in another embodiment such control is achieved by changing the width of the energy gap in the optical signal transmission layer of the WGR. Such a change is achieved by utilizing electrical bias and optical pumping from an external light source operating on a predetermined wavelength. The invention also provides a method for controlling transparency of the layer that transmits optical signals through the waveguide units in optoelectronic devices, such as an integrated demultiplexer / photoreceiver for optical network, by utilizing optical pumping and electrical bias.
Owner:XONPHU LINE LIMITED LIABILITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com