Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Time domain multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multiplexing - Time Domain Multiplexing. In telecommunications and computer networks, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share an expensive resource.
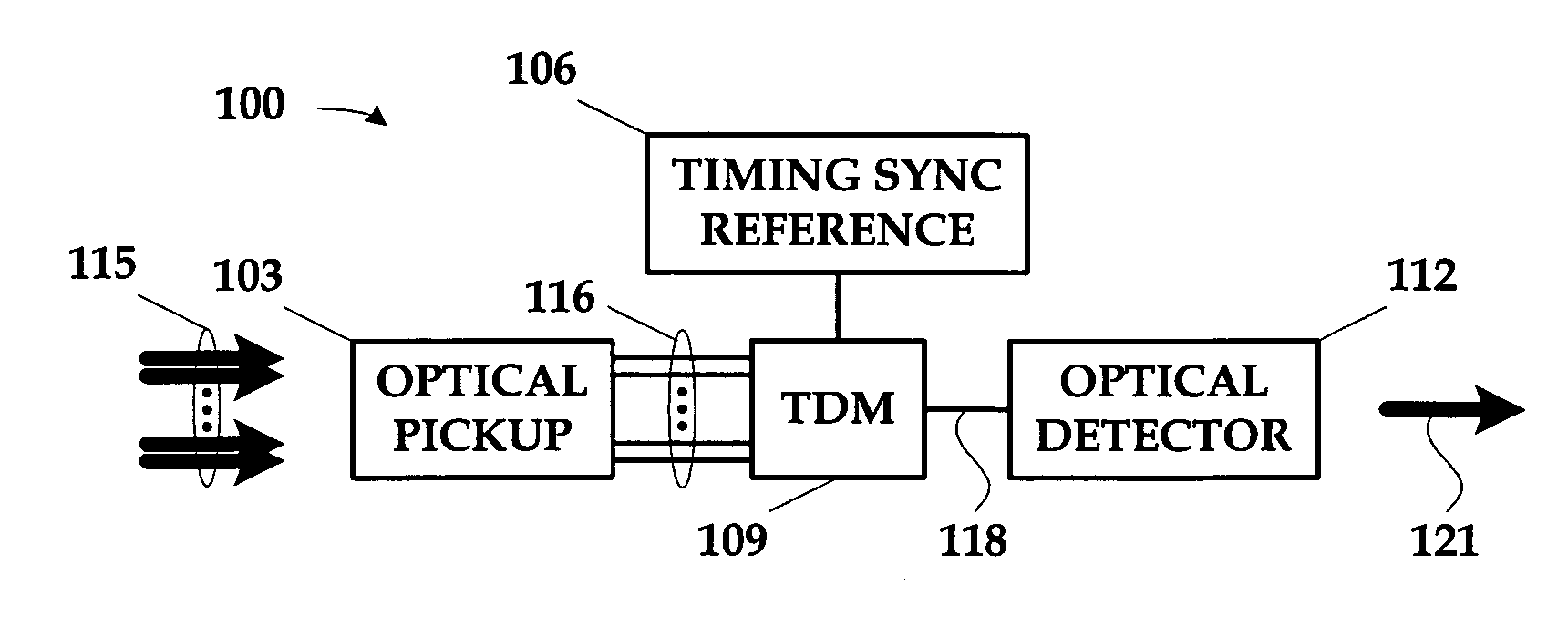
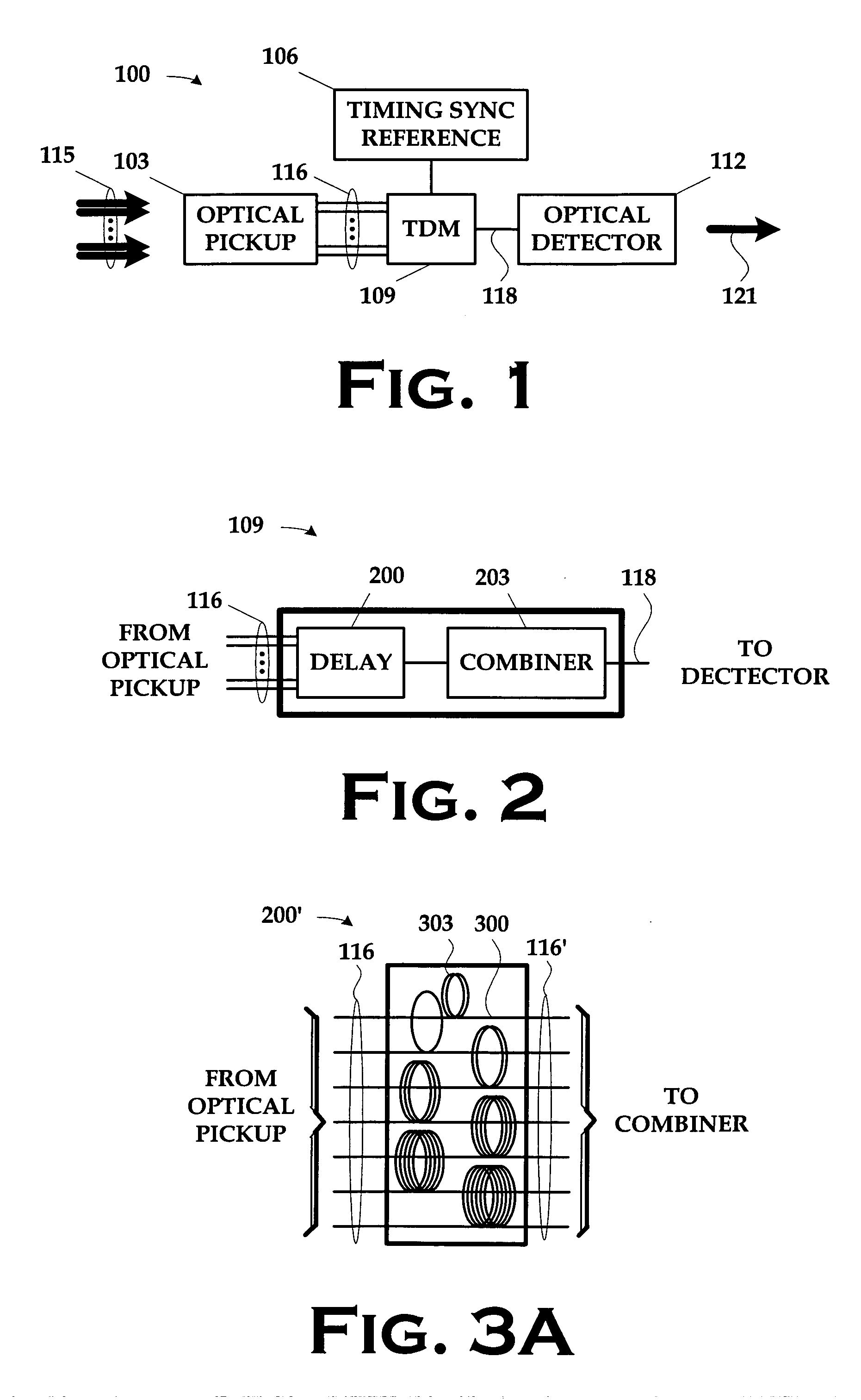
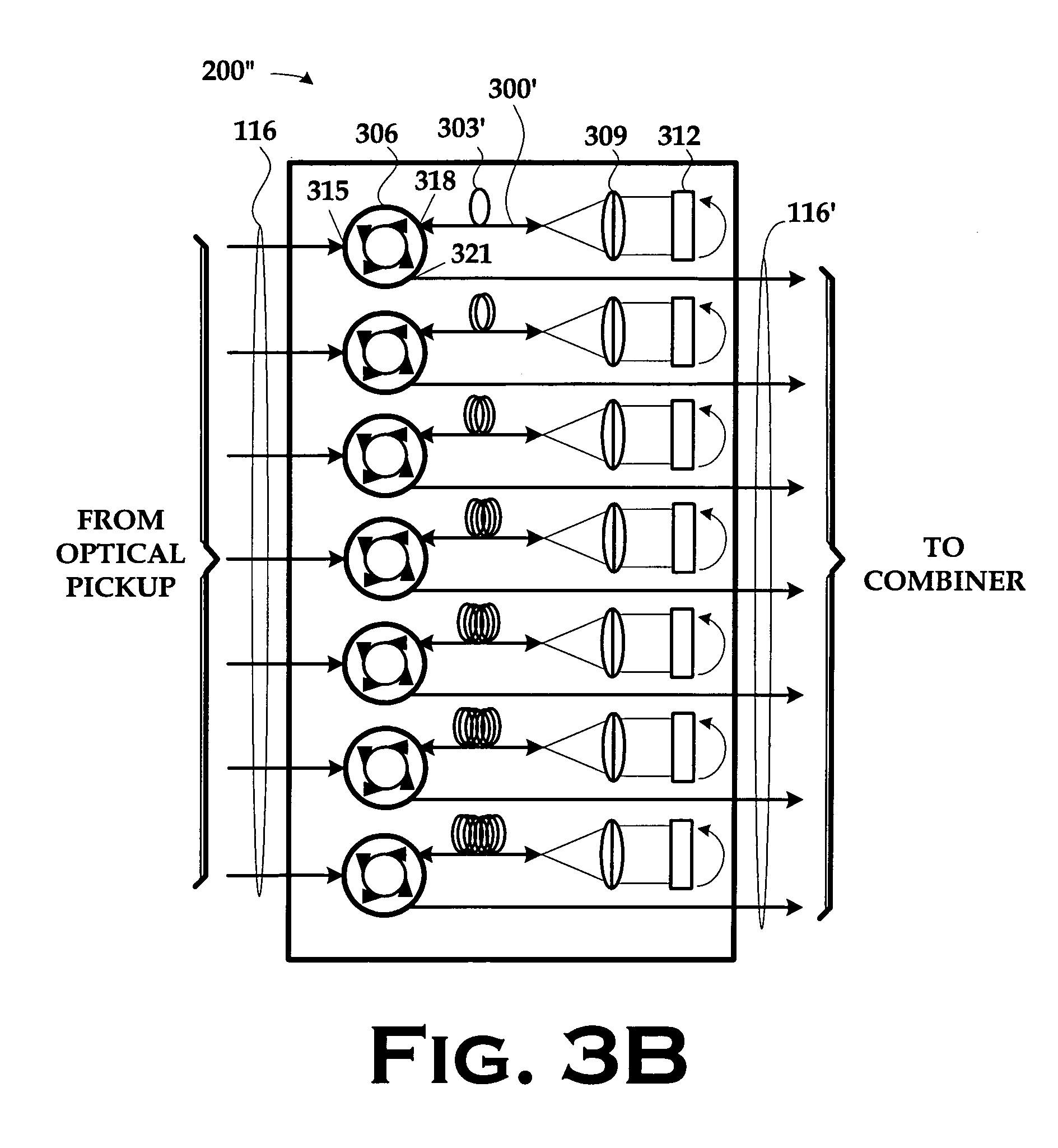
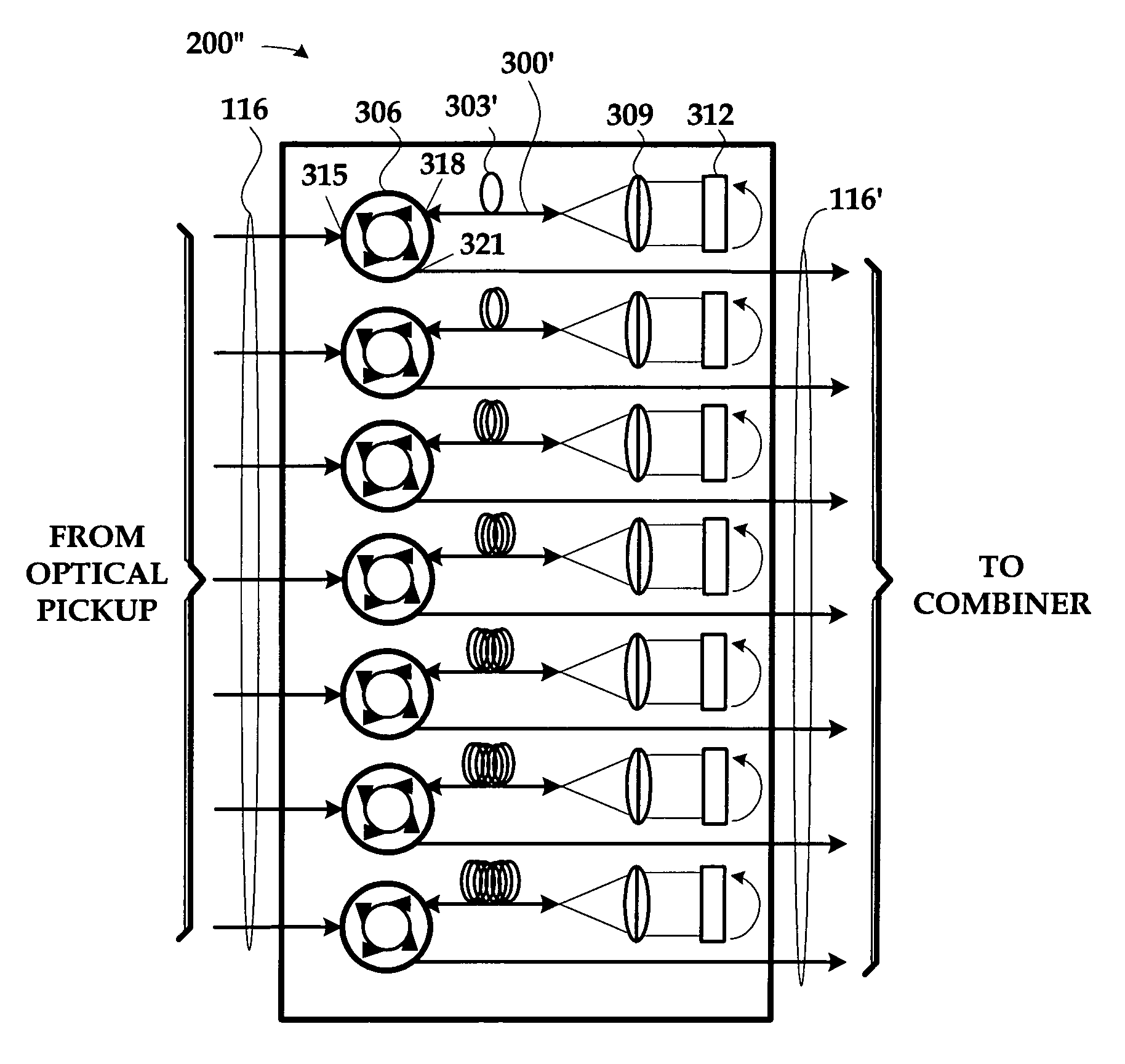
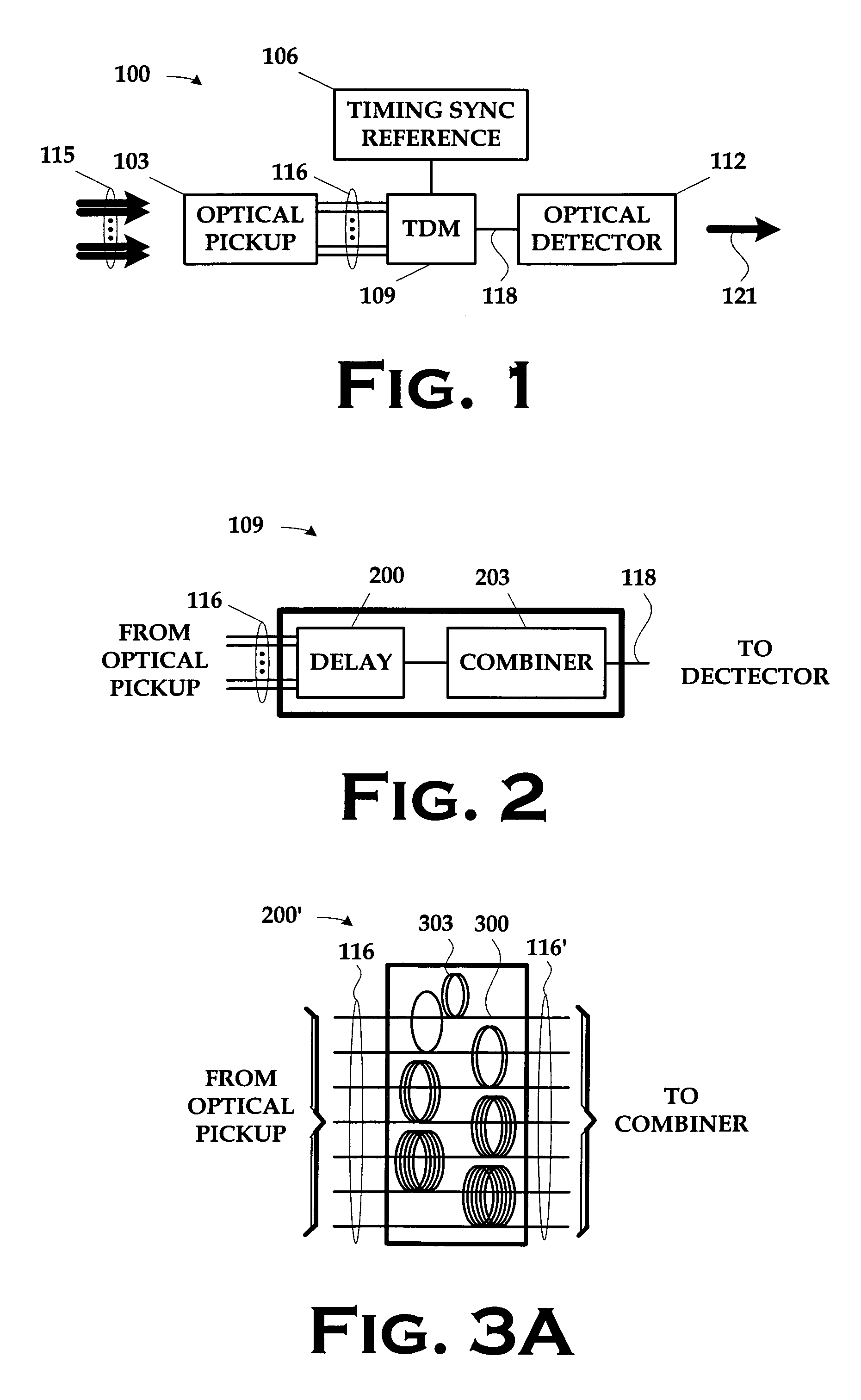
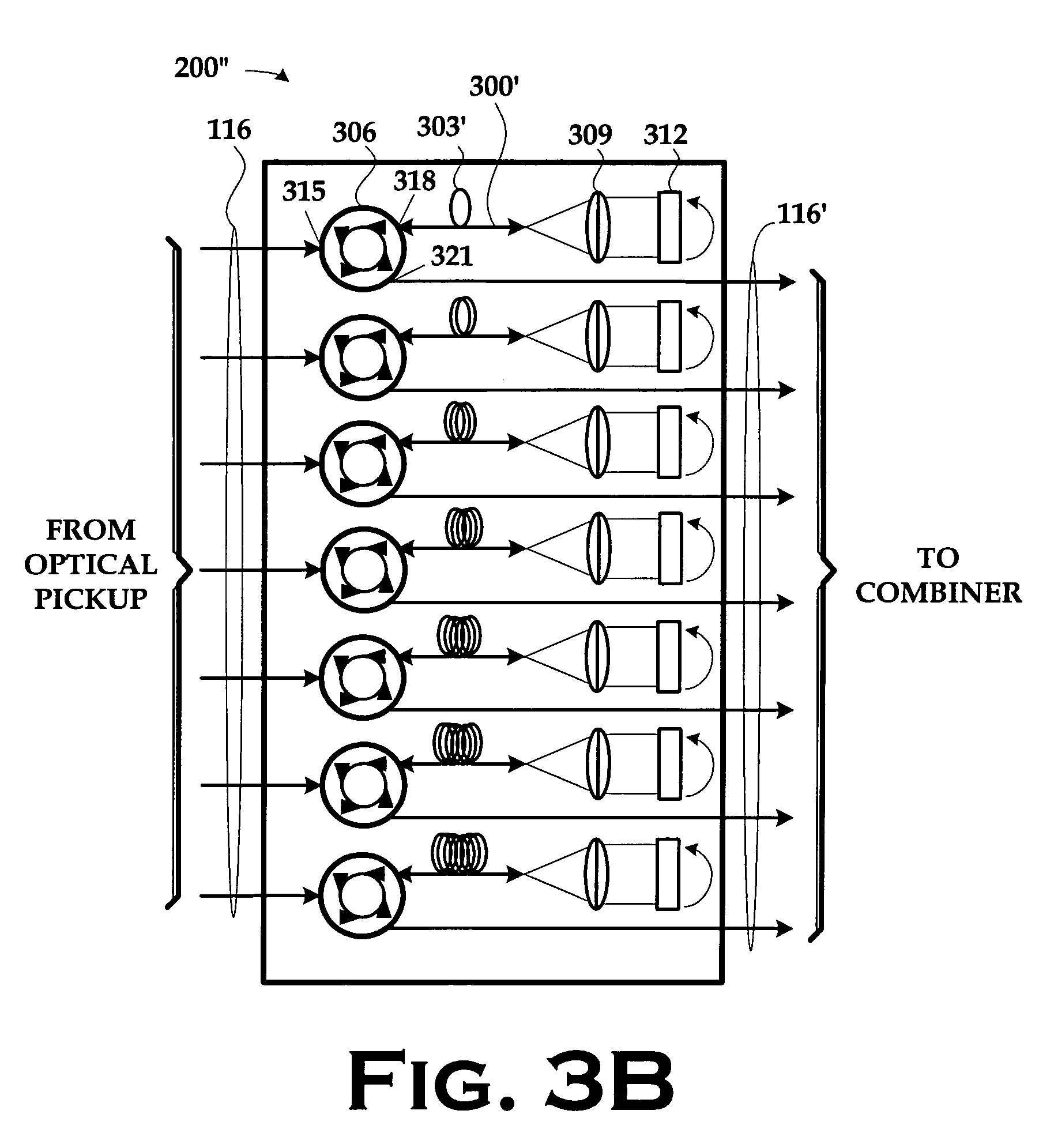
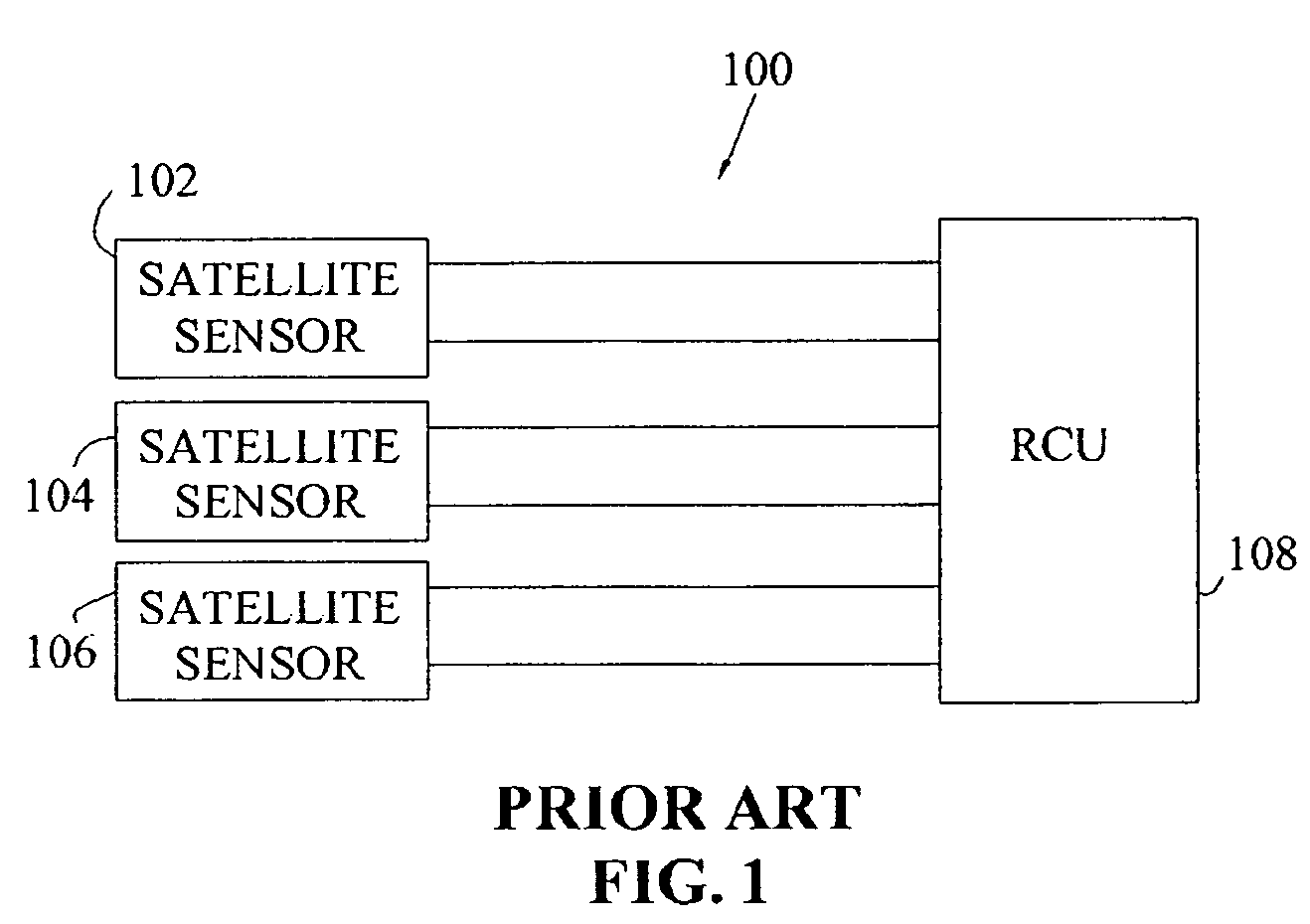
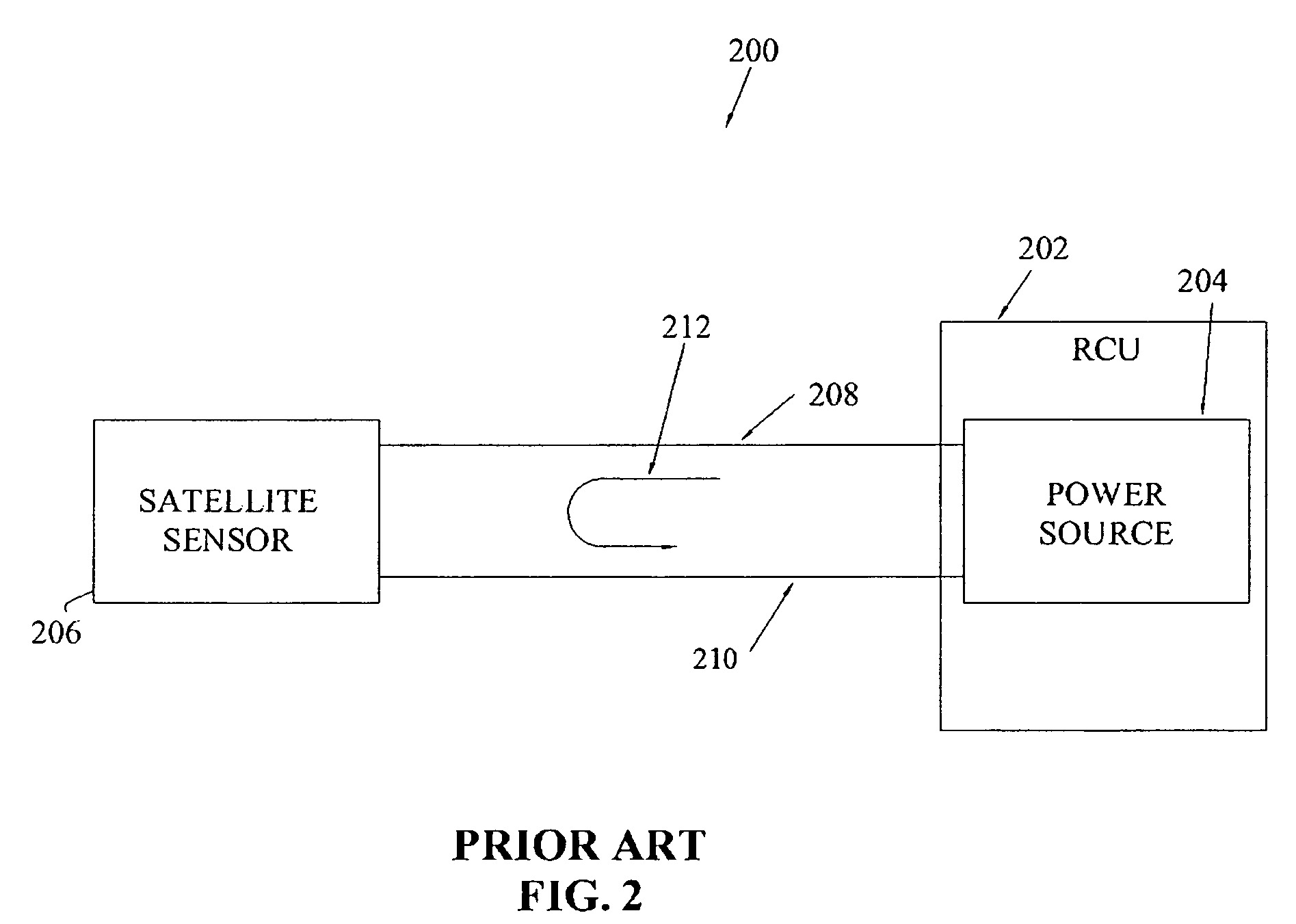
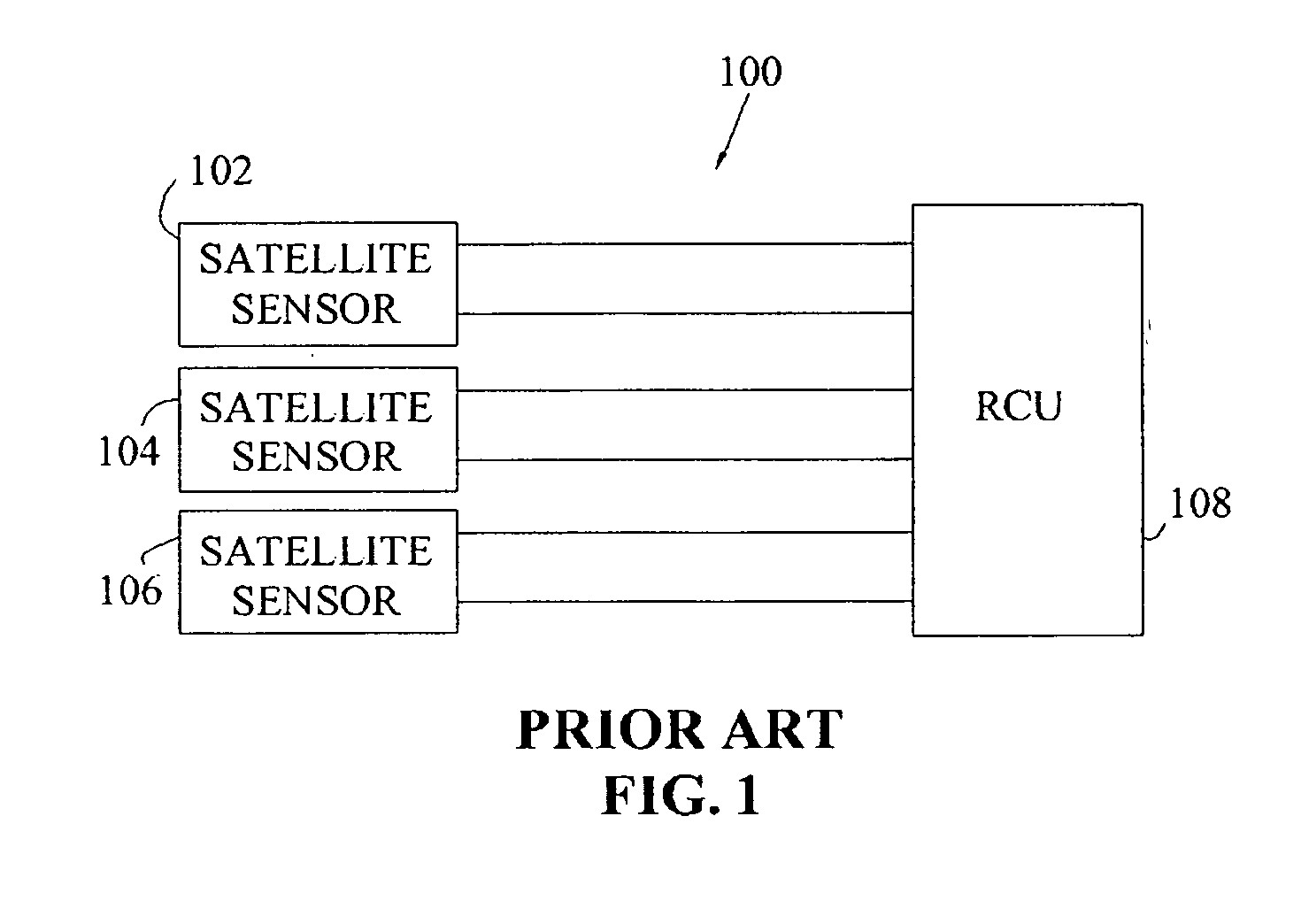
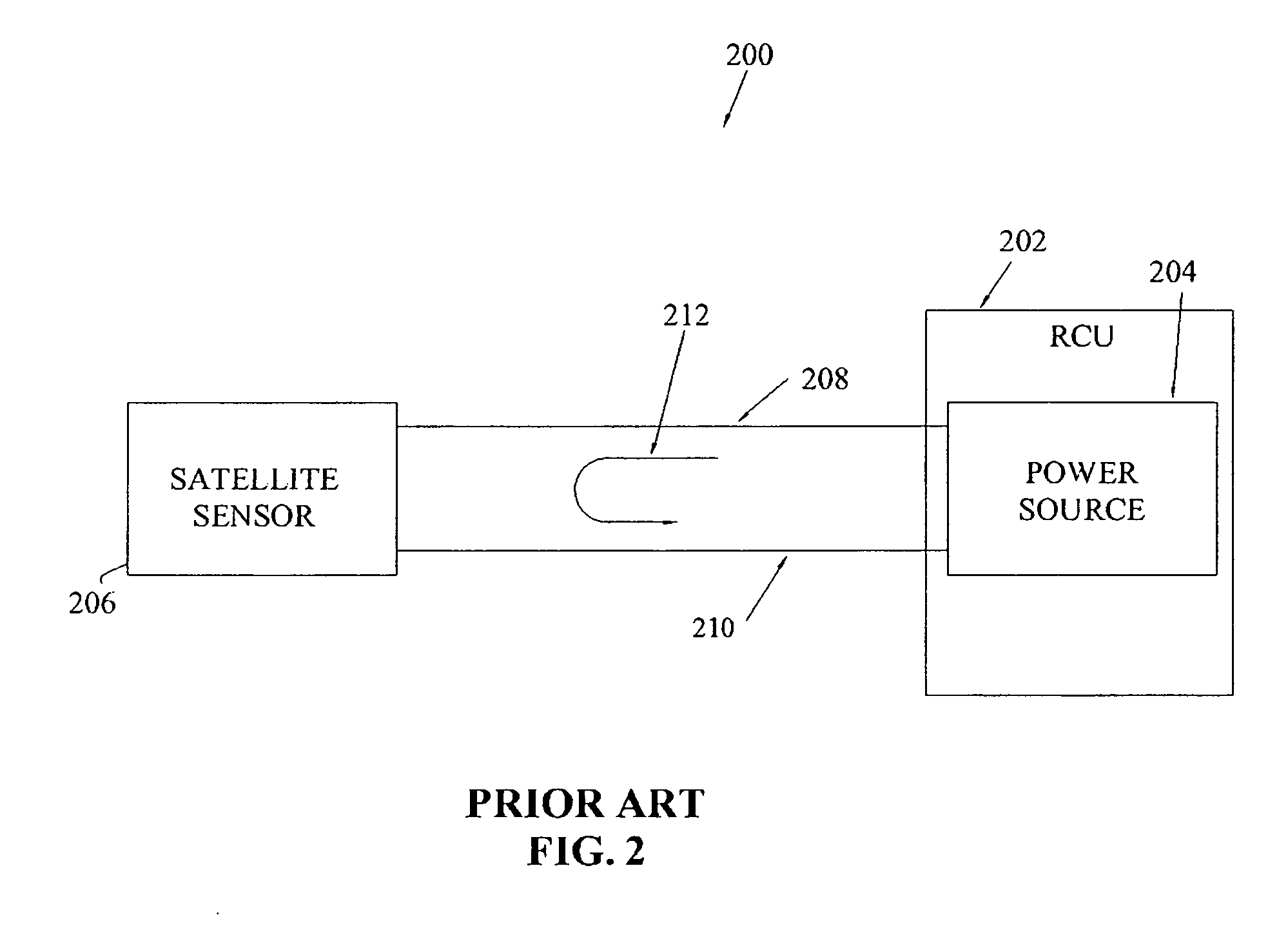
Single detector receiver for multi-beam LADAR systems
ActiveUS20060197936A1Optical rangefindersTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical pickupTime domain
A LADAR apparatus and a method for use in receiving a LADAR signal are disclosed. The apparatus includes an optical pickup capable of picking up a plurality of optical signals; a timing synchronization reference; a time domain multiplexer capable of multiplexing the optical signals into a multiplexed optical signal relative to the timing synchronization reference; and an optical detector capable of detecting the multiplexed optical signal. The method include time domain multiplexing a plurality of LADAR signals into multiplexed LADAR signal; detecting the multiplexed LADAR signal; and demultiplexing the detected LADAR signal.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Devices, systems and methods for time domain multiplexing of reagents
InactiveUS7276330B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTime domainReaction zone
Time dependent iterative reactions are carried out in microscale fluidic channels by configuring the channels such that reagents from different sources are delivered to a central reaction zone at different times during the analysis, allowing for the performance of a variety of time dependent, and / or iterative reactions in simplified microfluidic channels. Exemplary analyses include the determination of dose responses for biological and biochemical systems.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Method, apparatus and computer program product for interfacing a TDM link with a cell-switched network
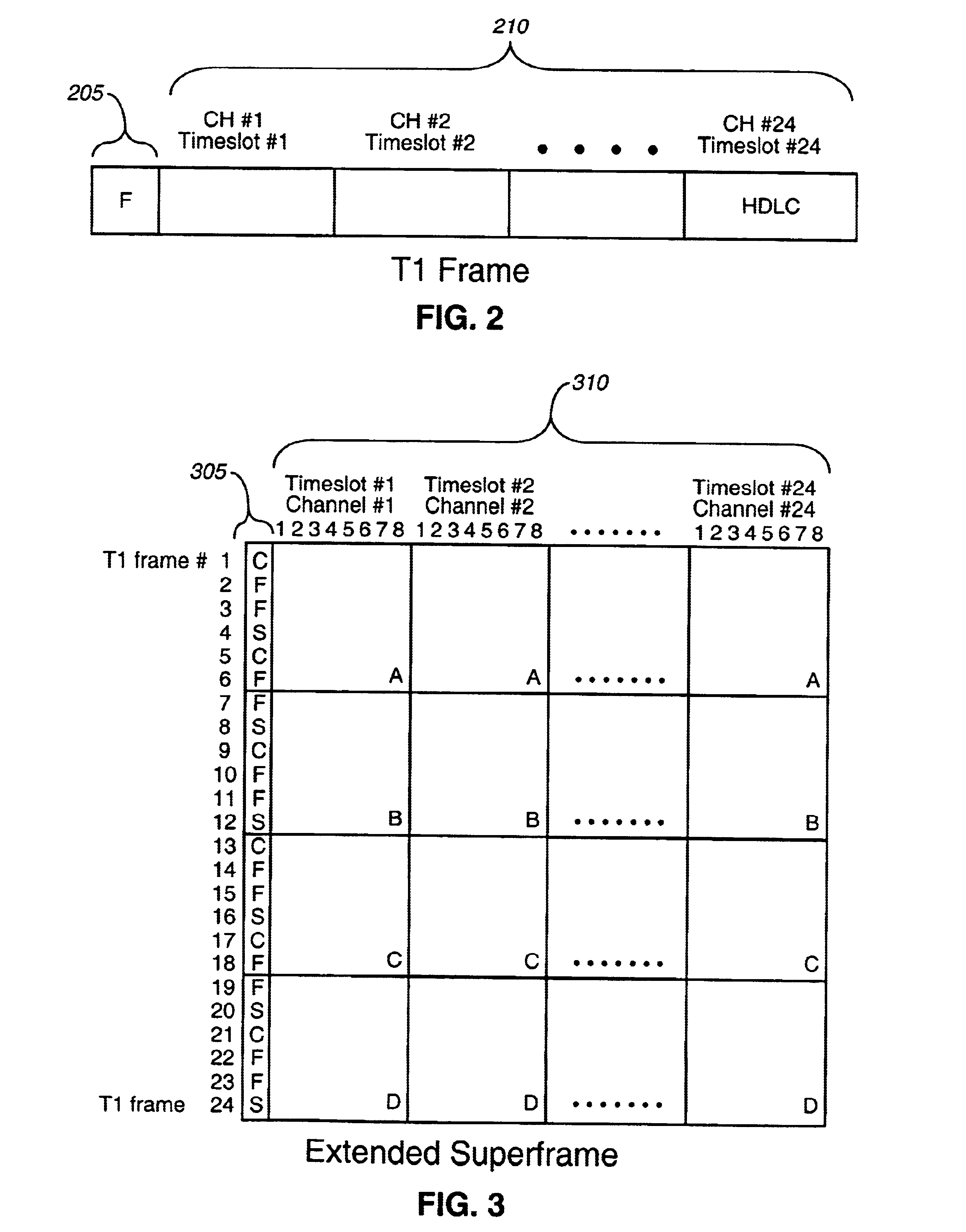
InactiveUS6633566B1Efficient use ofAvoid changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTime domainComputer network
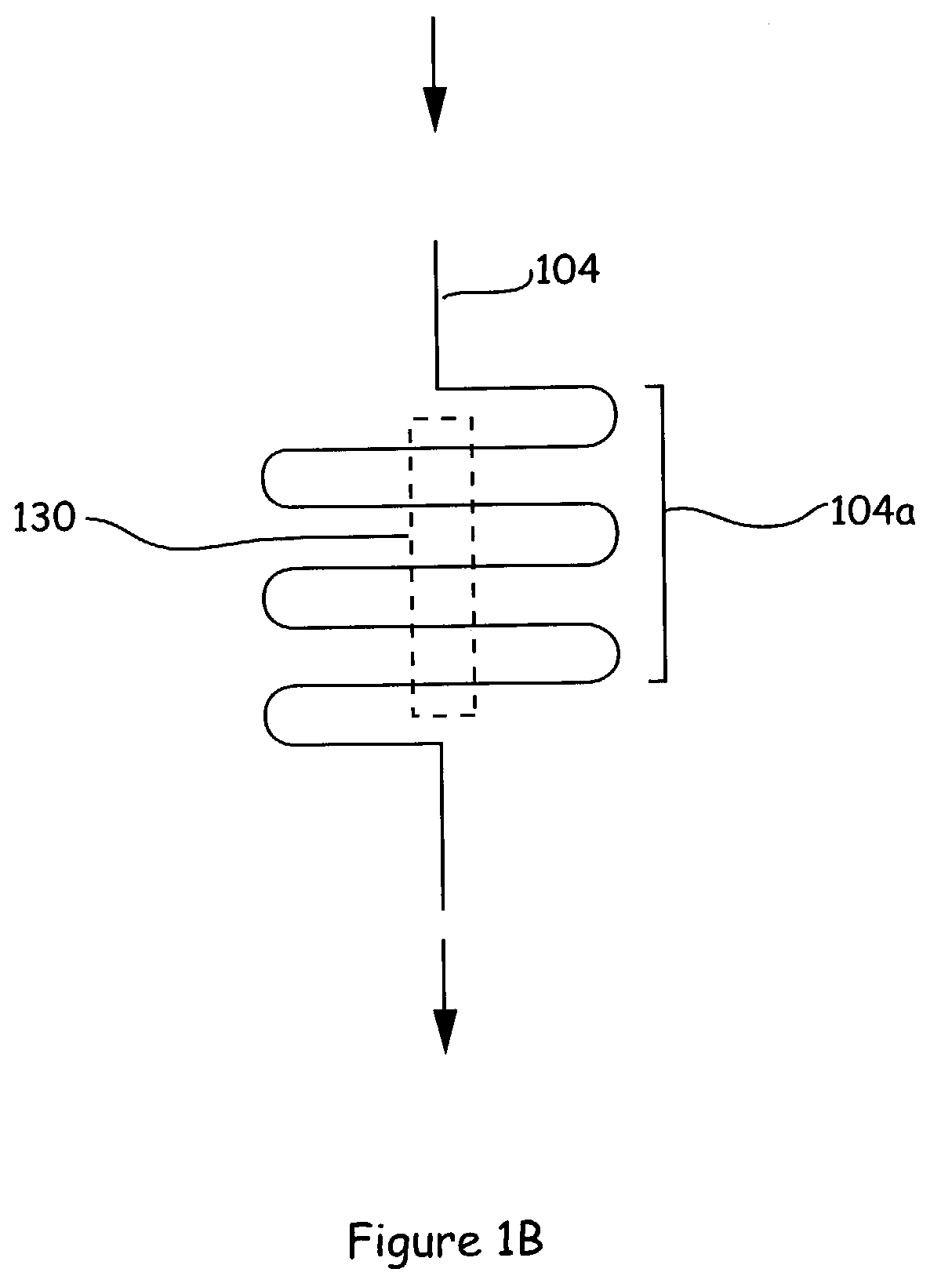
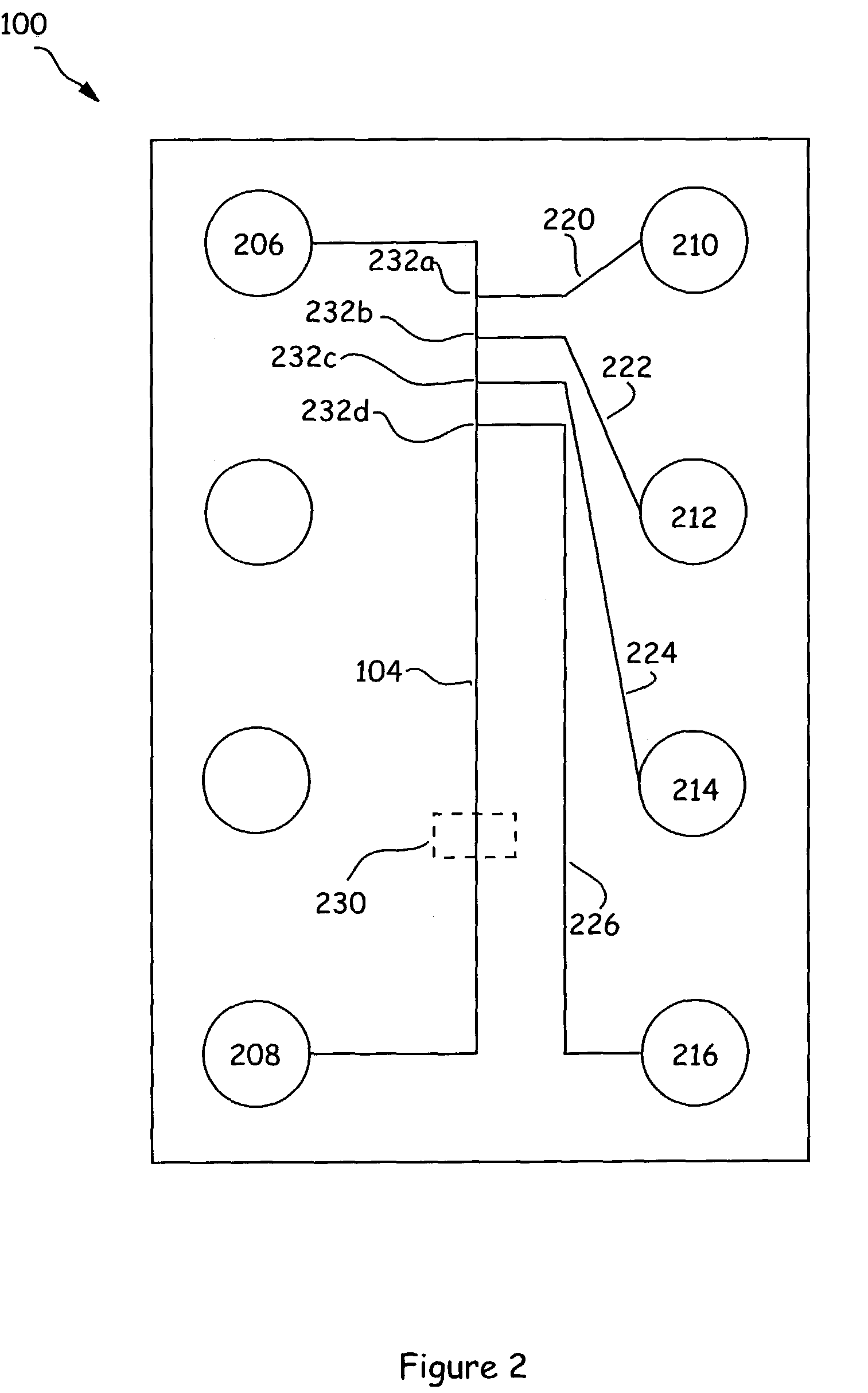
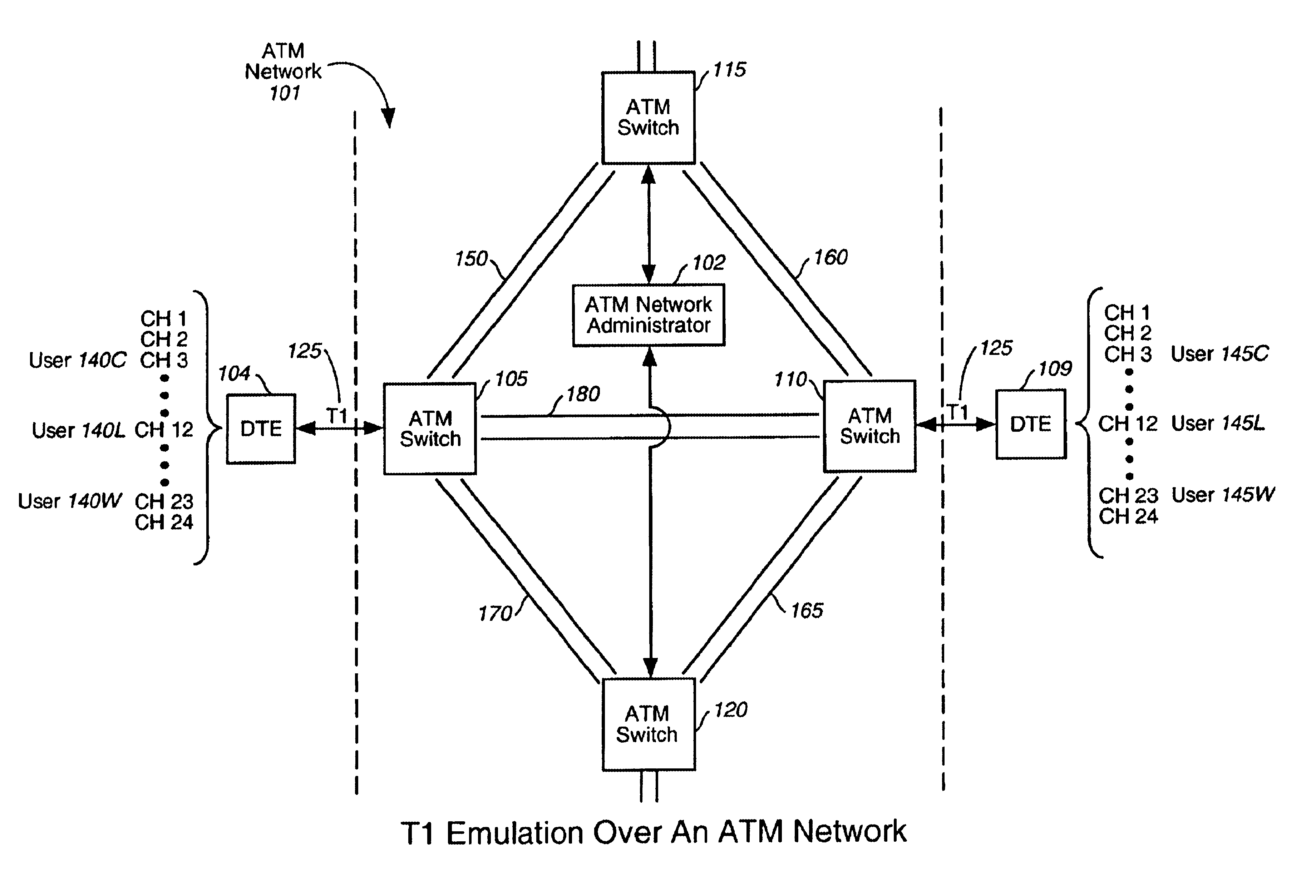
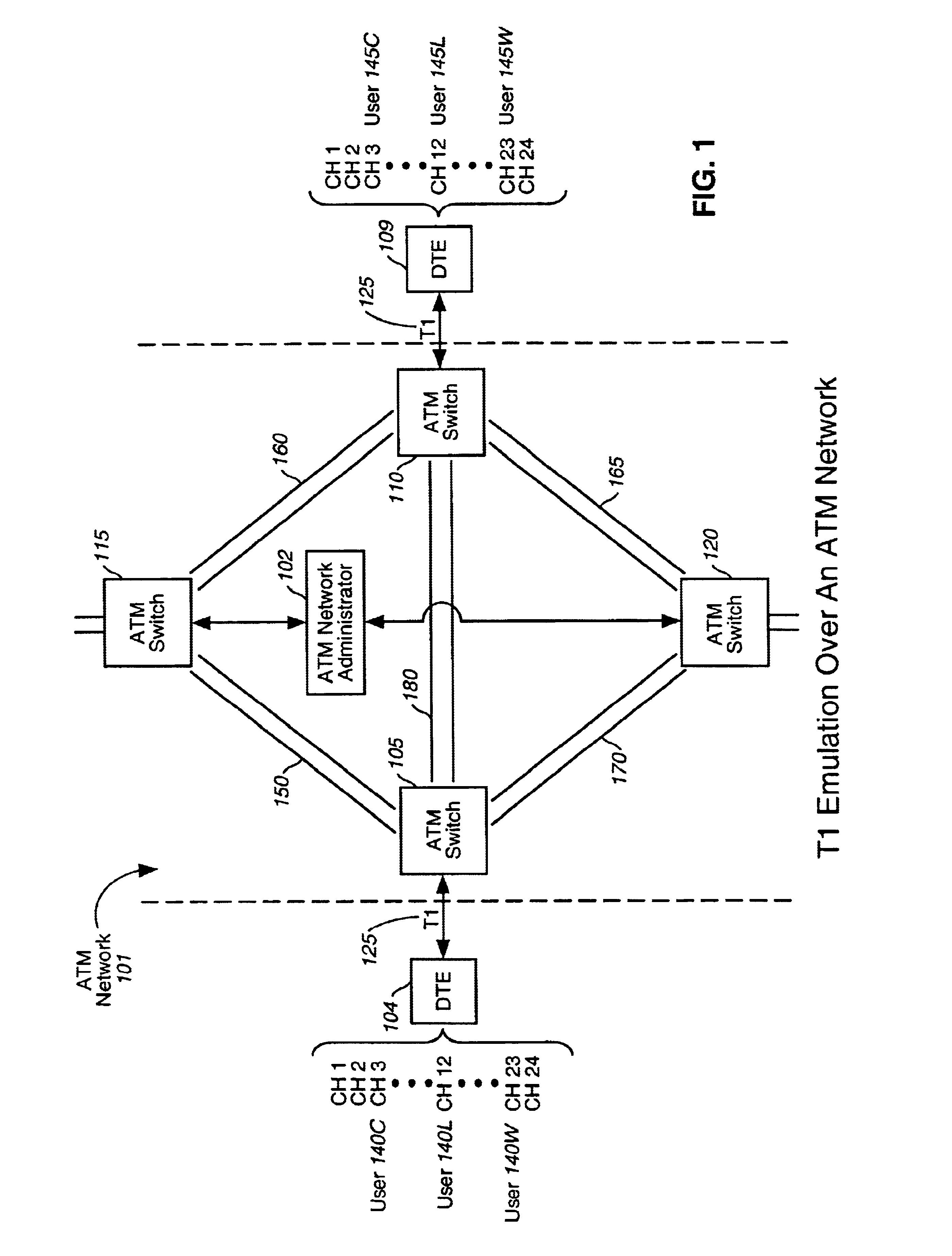
A method, apparatus, and computer program product of interfacing a time-domain multiplexed (TDM) link with a cell-switched network. The TDM link supports one or more active channels and one or more idle channels and supplies TDM frames with a sample of each channel in a dedicated timeslot. The TDM link is terminated at a first network node. One or more idle timeslots are removed from each TDM frame to create a compressed TDM frame, where each idle timeslot carries a sample of an idle channel. One or more compressed TDM frames are loaded in a cell that is sent over the cell-switched network to a second network node. The compressed TDM frames are unloaded from the cell. Idle timeslots are inserted in the compressed TDM frames to restore the compressed TDM frames to complete TDM frames. The bandwidth of the cell switched network is efficiently utilized because idle channel samples are not carried over the cell-switched network. In one embodiment, the TDM link is a T1 link that carries T1 frames, and the cell switched network is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network that carries ATM cells.< / PTEXT>
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
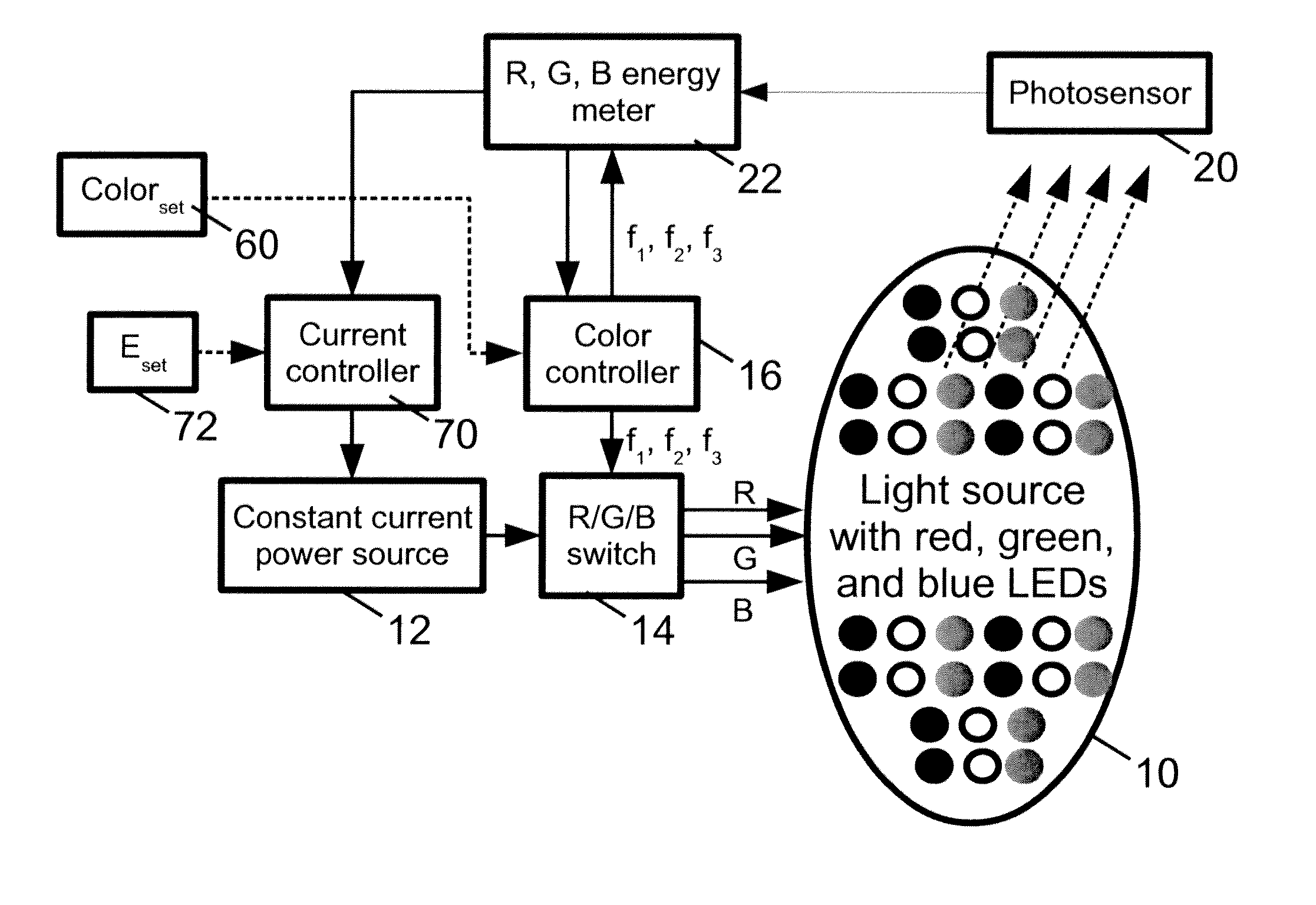
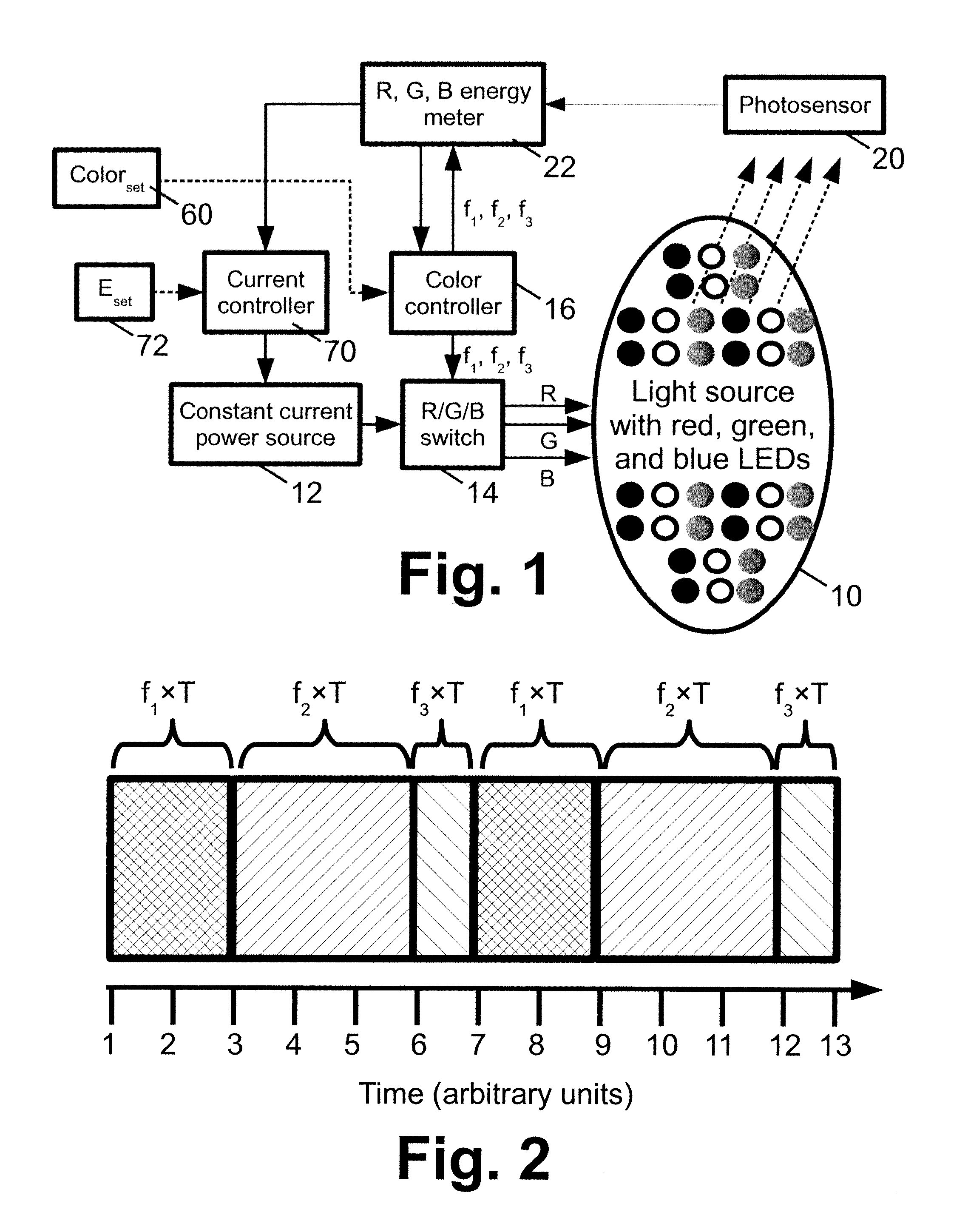
Configurable vehicle solid state lighting
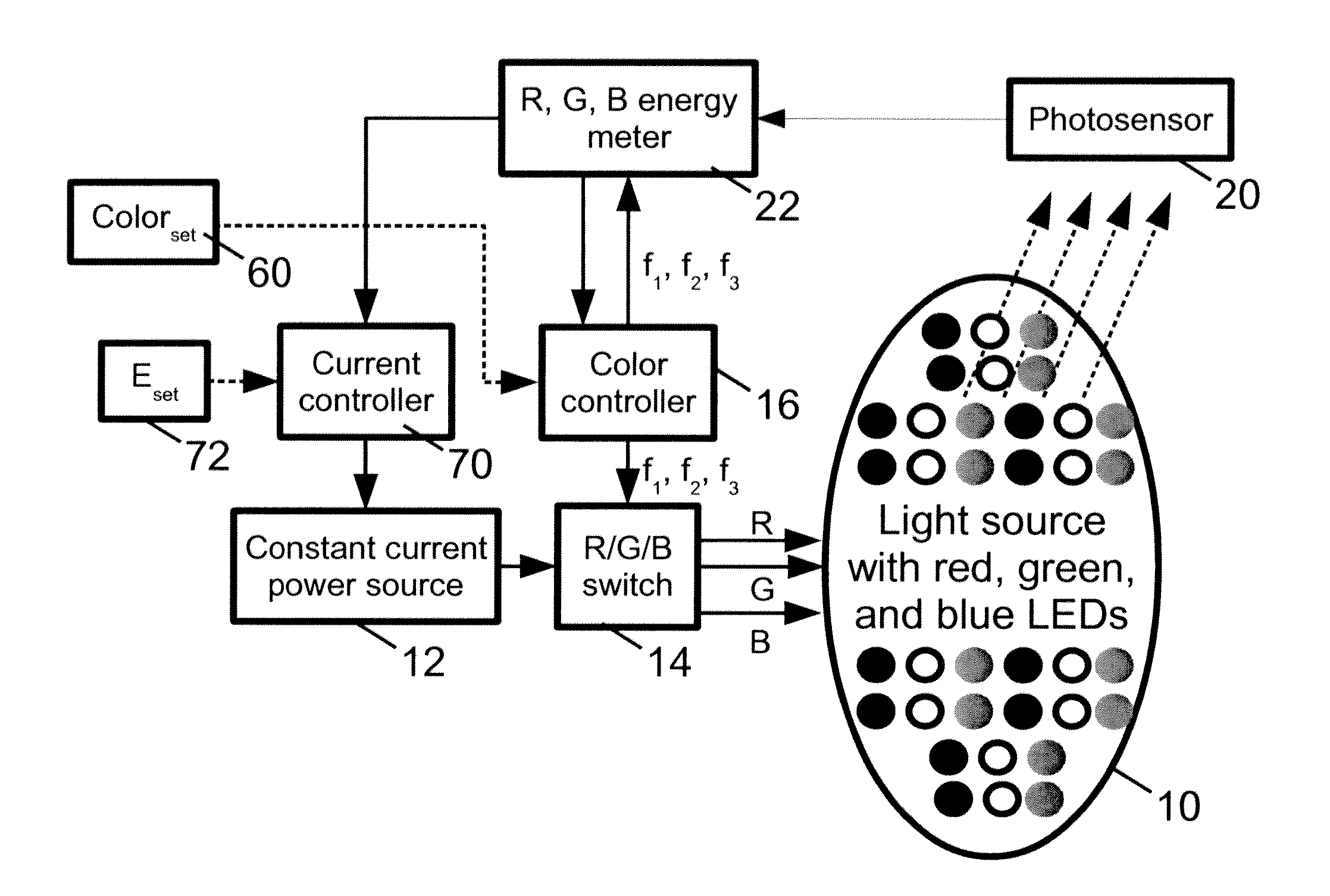
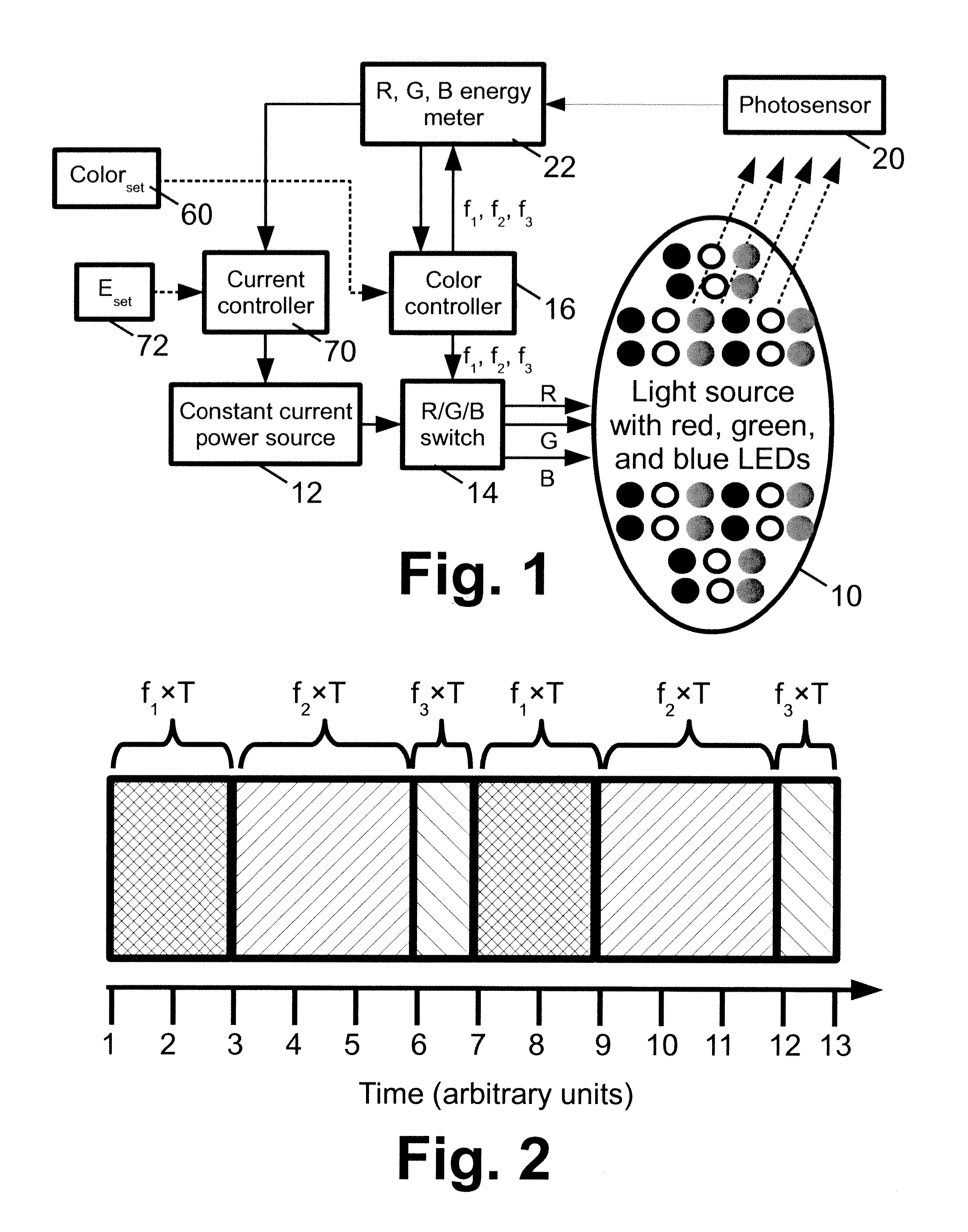
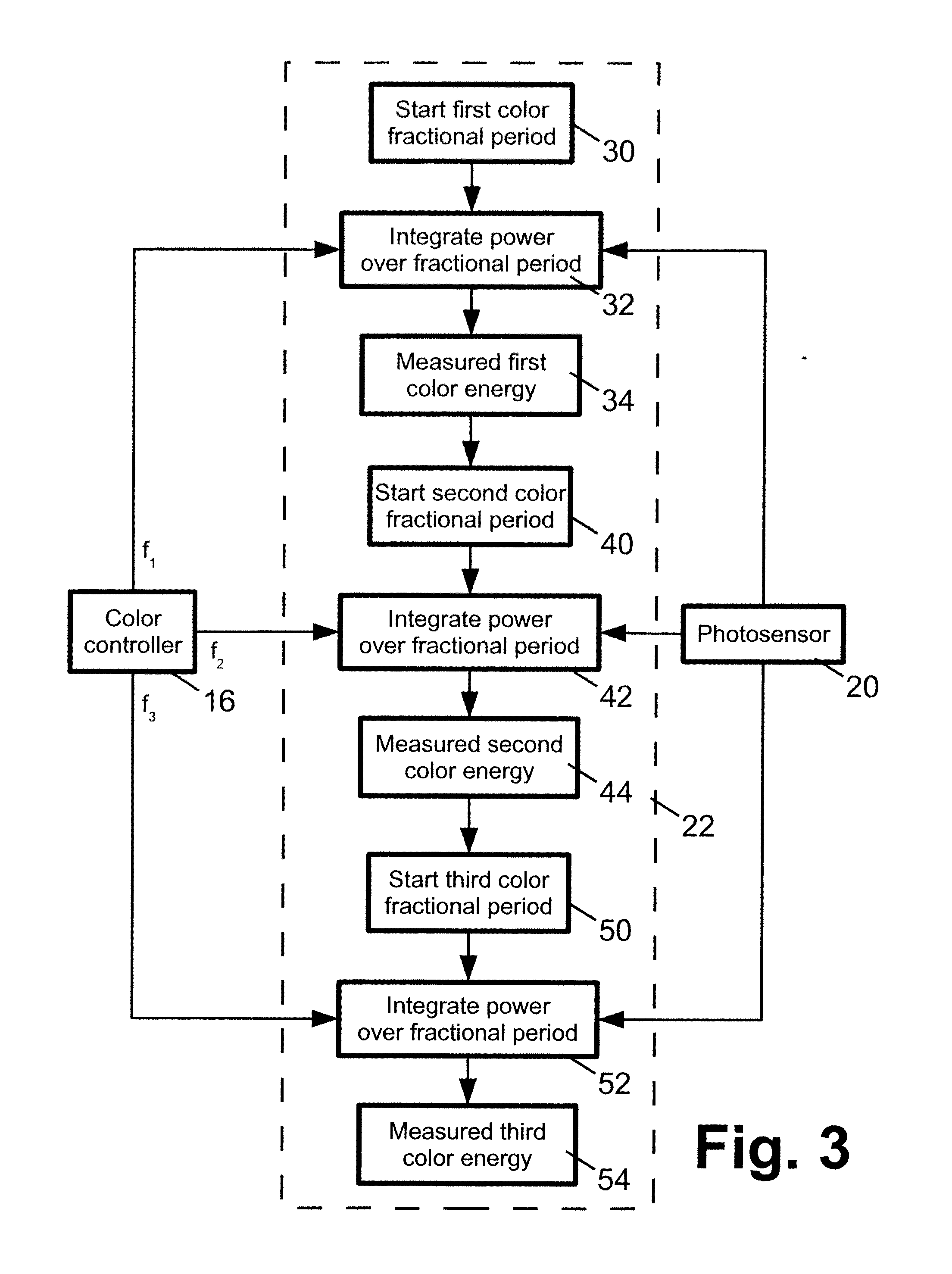
A vehicle signal light assembly includes: at least one color mixing light source; a support element configured to support the at least one color mixing light source on a vehicle as a signal light; and a controller configured to selectively drive each color mixing light source to generate light of a selected visually perceived color based on a received control signal. In some such embodiments, each color mixing light source of the vehicle signal light assembly comprises a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) of at least two constituent colors. In some such embodiments, the controller is configured to operate each color mixing light source of the vehicle signal light assembly using time domain multiplexing (TDM) to generate the light of the selected visually perceived color. In some such embodiments, the vehicle signal light assembly comprises a taillight assembly. In some of the embodiments, the vehicle light assembly comprises an ambient or auxiliary lighting, or a dashboard lighting assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS7426210B1Reduce complexityImprove data throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTime domainMicrowave
One embodiment of the present invention includes a router comprising an ingress edge unit with one or more ports and an egress edge unit with one or more ports connected by a switch fabric. The ingress edge unit can receive optical data and convert the optical data into a plurality of micro lambdas. The ingress edge unit can convert the incoming data to micro lambdas by generating a series of short-term parallel data bursts across multiple wavelengths. The ingress edge unit can also wavelength division multiplex and time domain multiplex each micro lambda for transmission to the switch fabric in a particular order. The switch fabric can receive the plurality of micro lambdas and route the plurality of micro lambdas to the plurality of egress edge units in a non-blocking manner.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Single detector receiver for multi-beam LADAR systems
ActiveUS7375804B2Optical rangefindersTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime domainOptical pickup
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
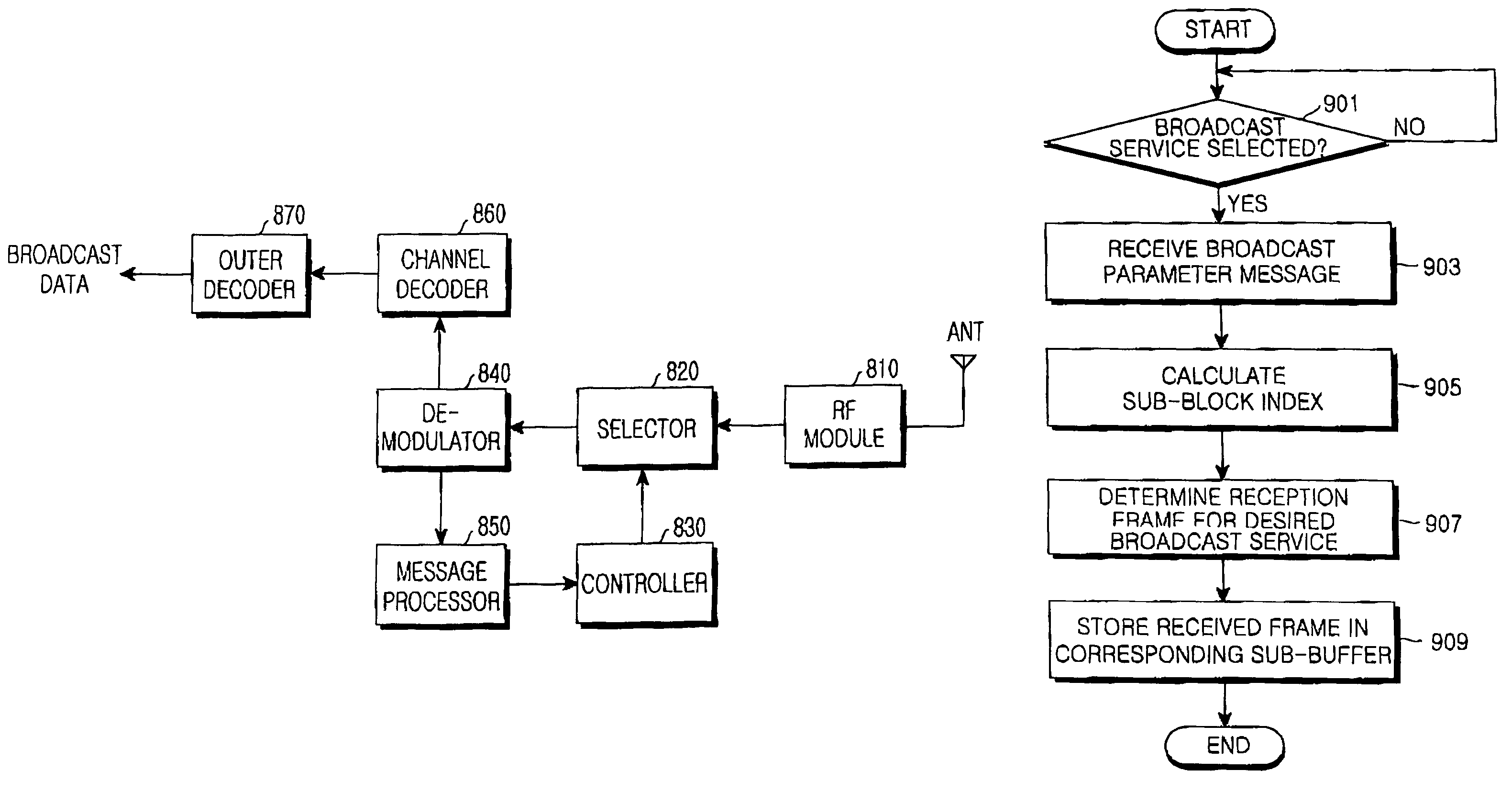
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving broadcast data using outer-coding
ActiveUS7359357B2Minimize the numberReduce complexityBroadcast specific applicationsTime-division multiplexTime domainBroadcast data
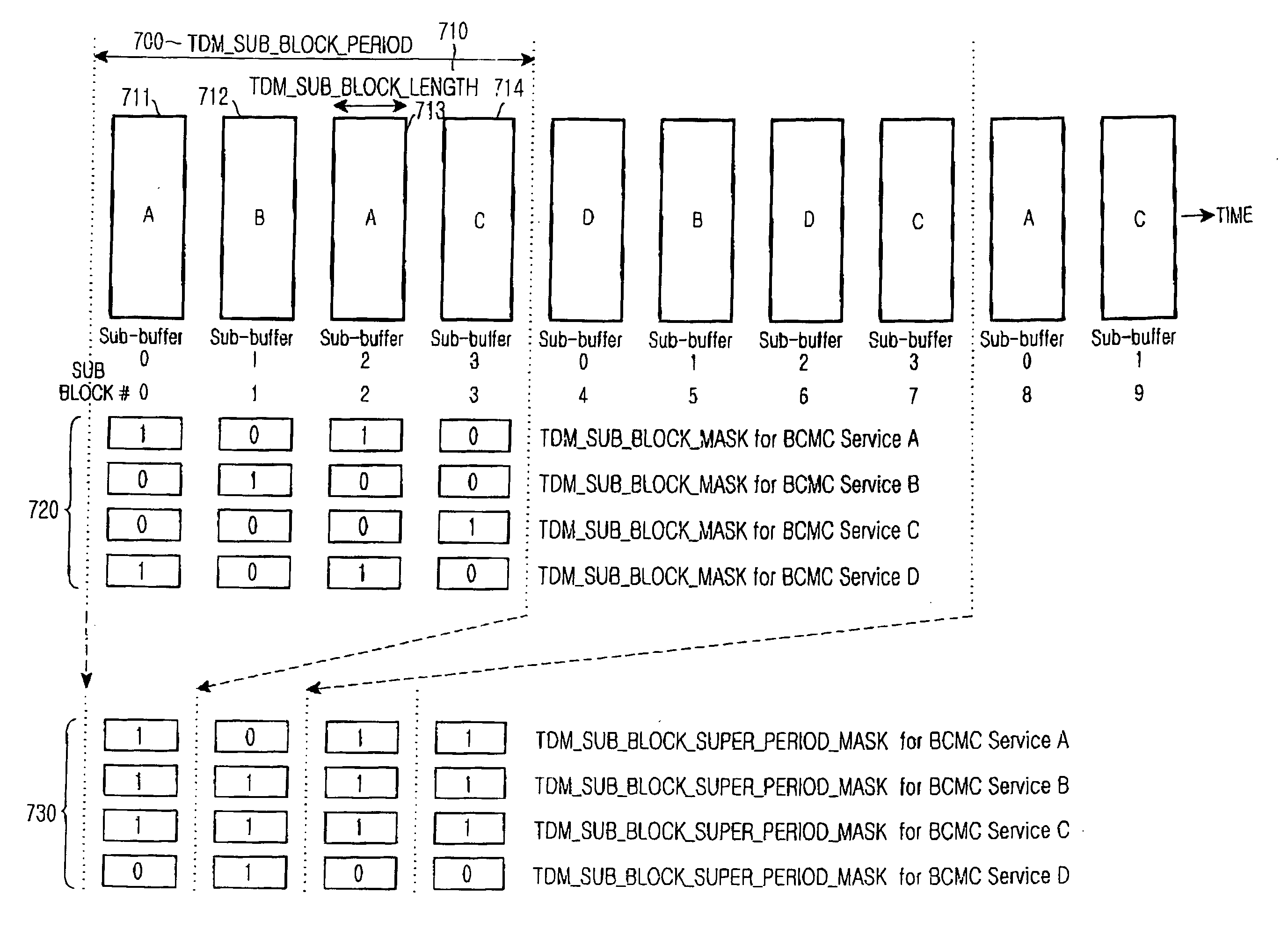
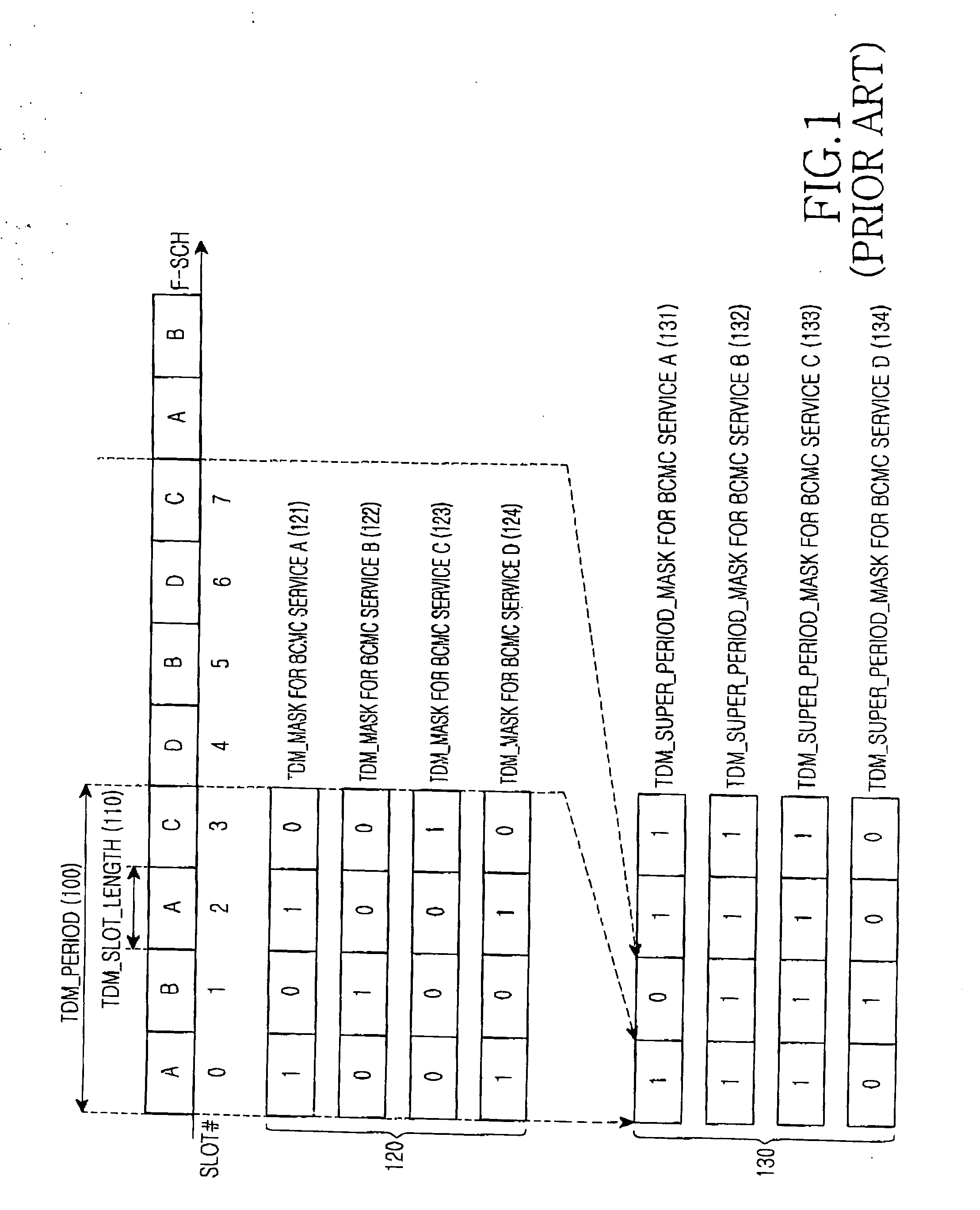
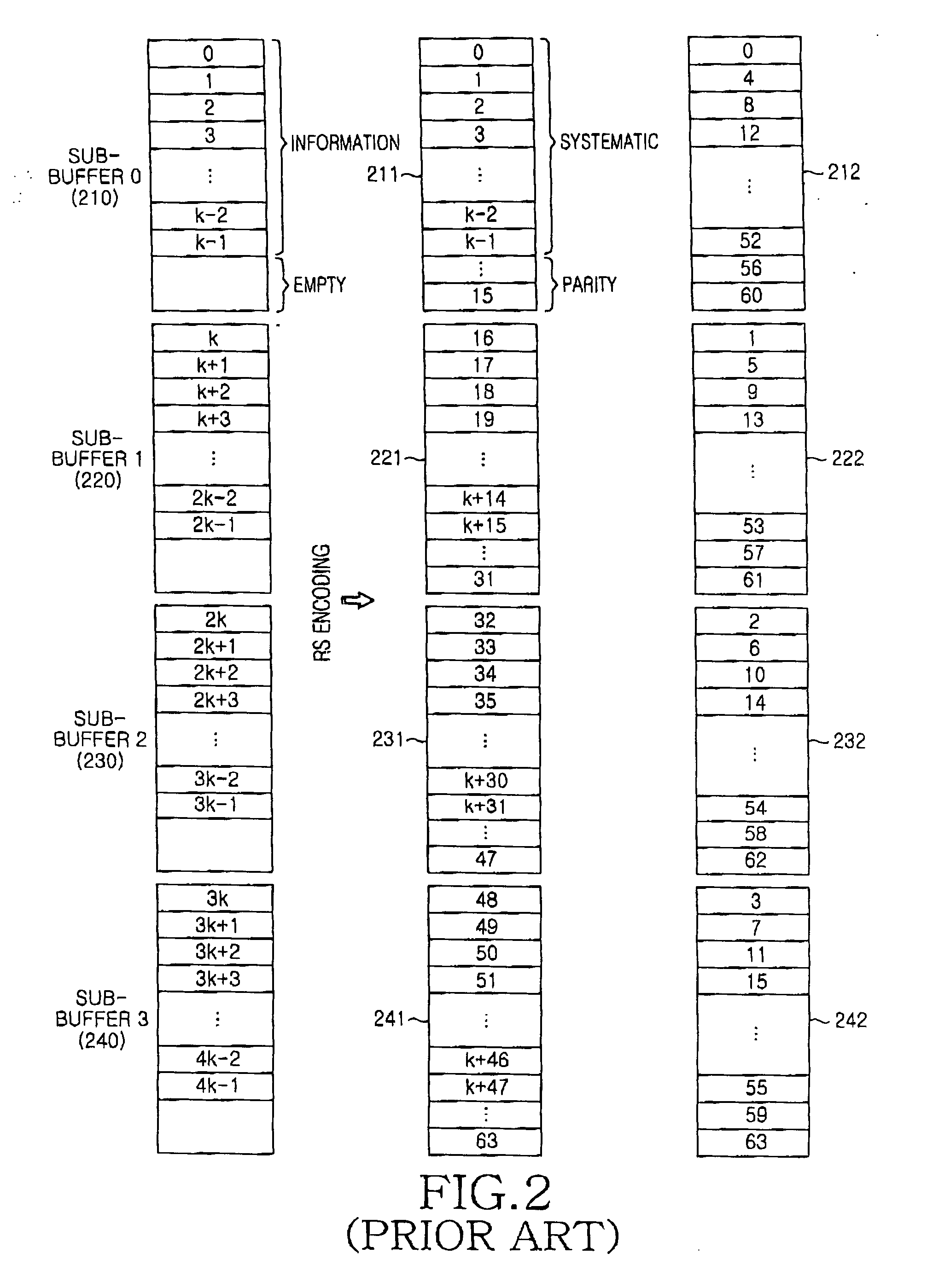
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a broadcast service in a mobile communication system which outer-codes frames for a plurality of broadcast services and Time Domain Multiplex (TDM)-transmits the outer-coded frames. A transmitter transmits a broadcast parameter message comprising information indicating a specific sub-buffer in which respective broadcast services are stored. A receiver for receiving the broadcast parameter message from the transmitter, and maps the sub-buffer to a corresponding sub-block mask based on the broadcast parameter message. The transmitter TDM-transmits the frames for the plurality of broadcast services per sub-block. The receiver selectively receives frames for a desired broadcast service using the sub-block mask and decodes the selectively received frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Configurable vehicle solid state lighting
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
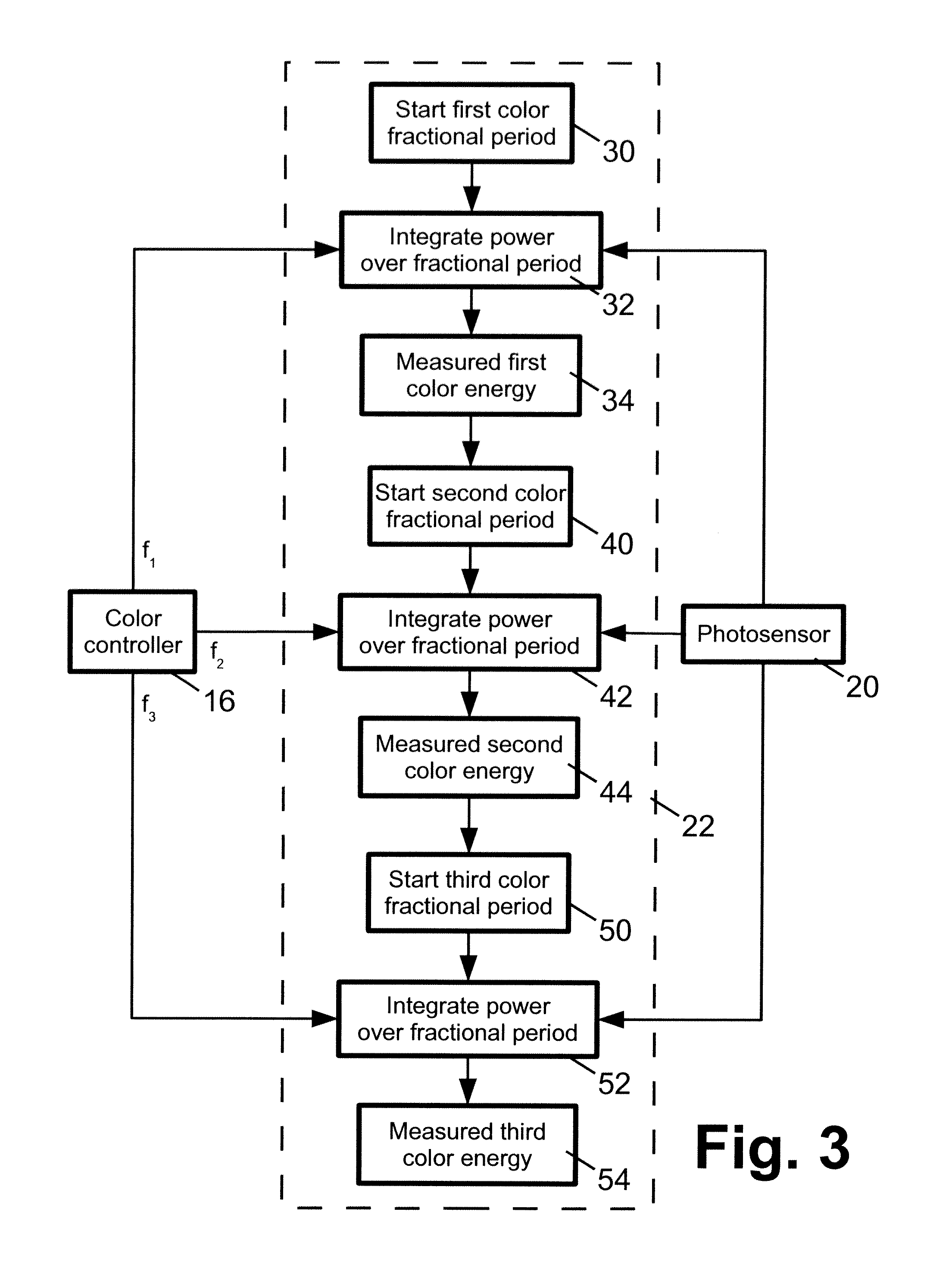
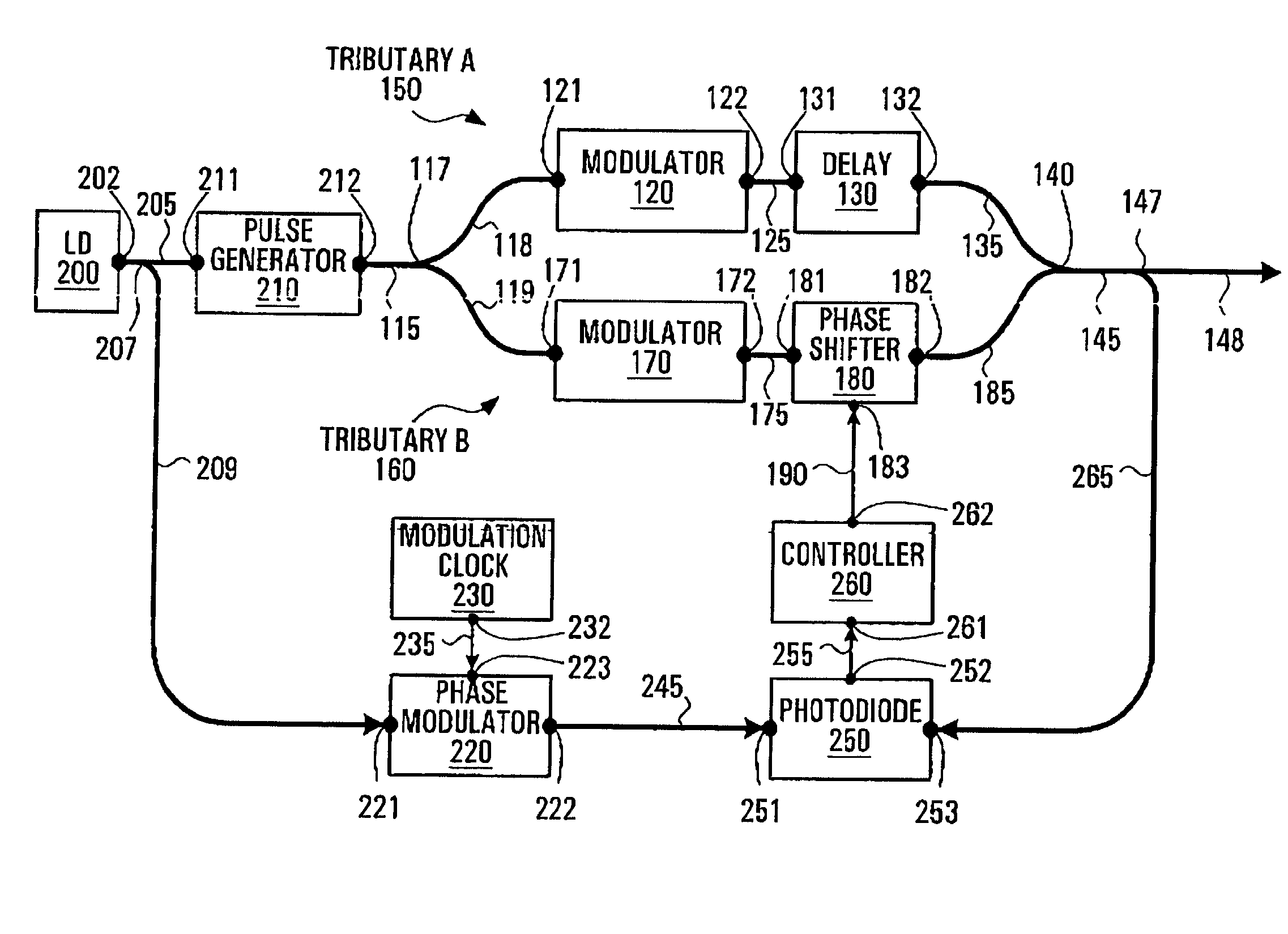
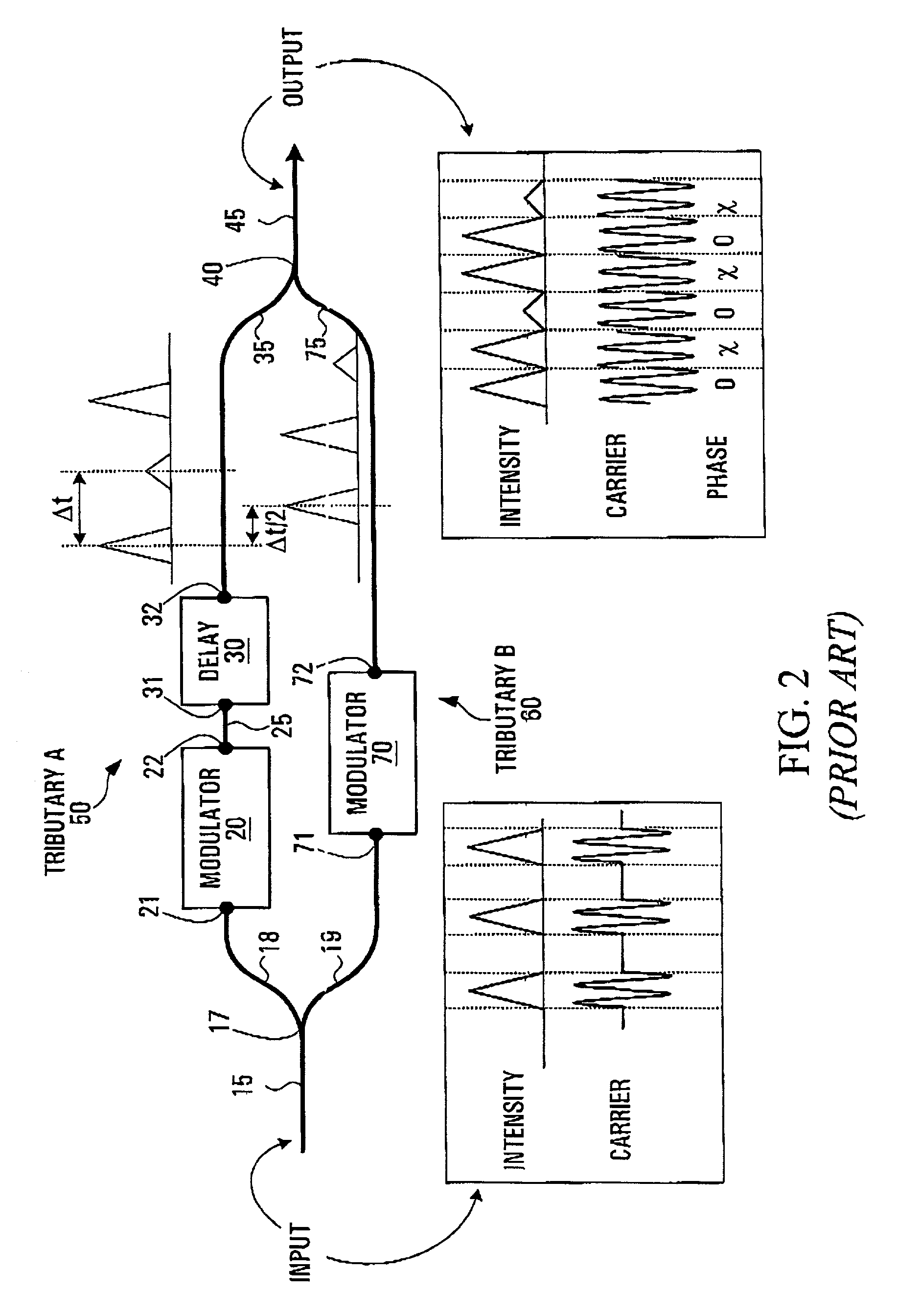
Carrier-suppressed optical time domain multiplexing
ActiveUS7574139B2Transmission control/equlisationTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime domainBandpass filtering
A method and an apparatus for implementing carrier suppressed data format on conventional OTDM modules is provided. Adaptive phase shifting of optical signals traversing one of the tributaries of an OTDM module is performed with feedback loop control. A tapped portion of the input carrier signal is phase modulated at a frequency fc, and is combined with a tapped portion of the output from the OTDM. A phase shifter controller fed with this combined signal photodetects and band-pass filters the signal around fc to extract the amplitude of the AC component of the envelope of the combined signal, which depends upon the phase difference between successive pulses of the OTDM output. This signal is used to control a phase shifter coupled along one of the tributaries of the OTDM to adjust the phase difference of the signals of the two tributaries so that carrier suppression results.
Owner:MOLEX INC
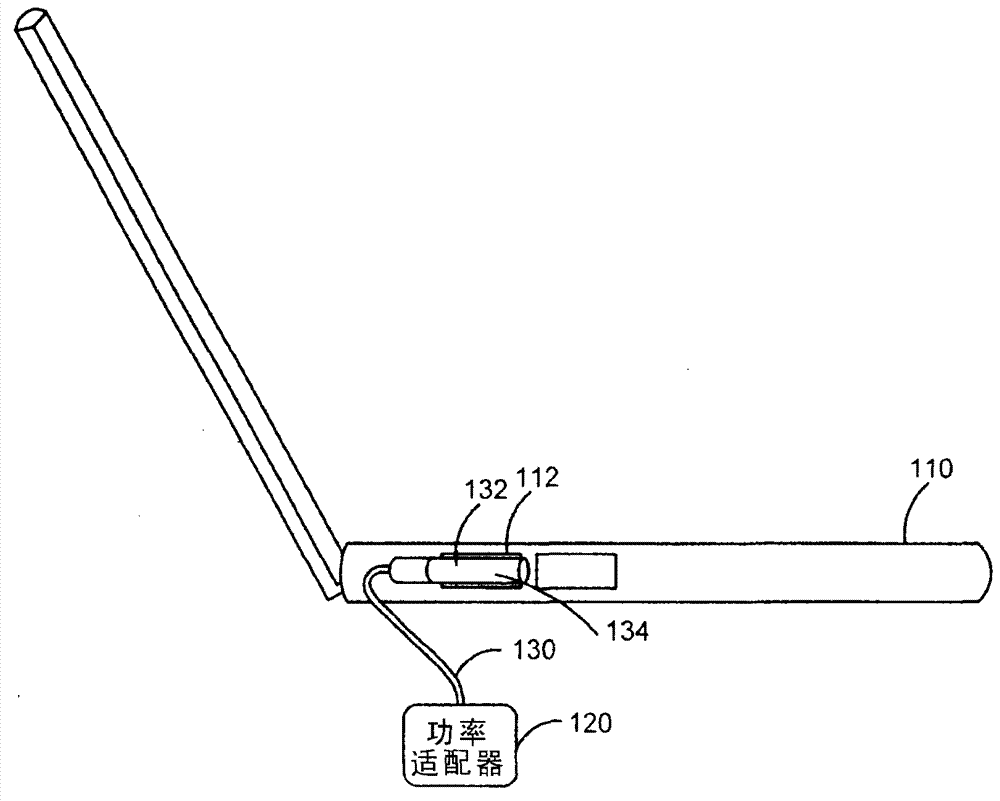
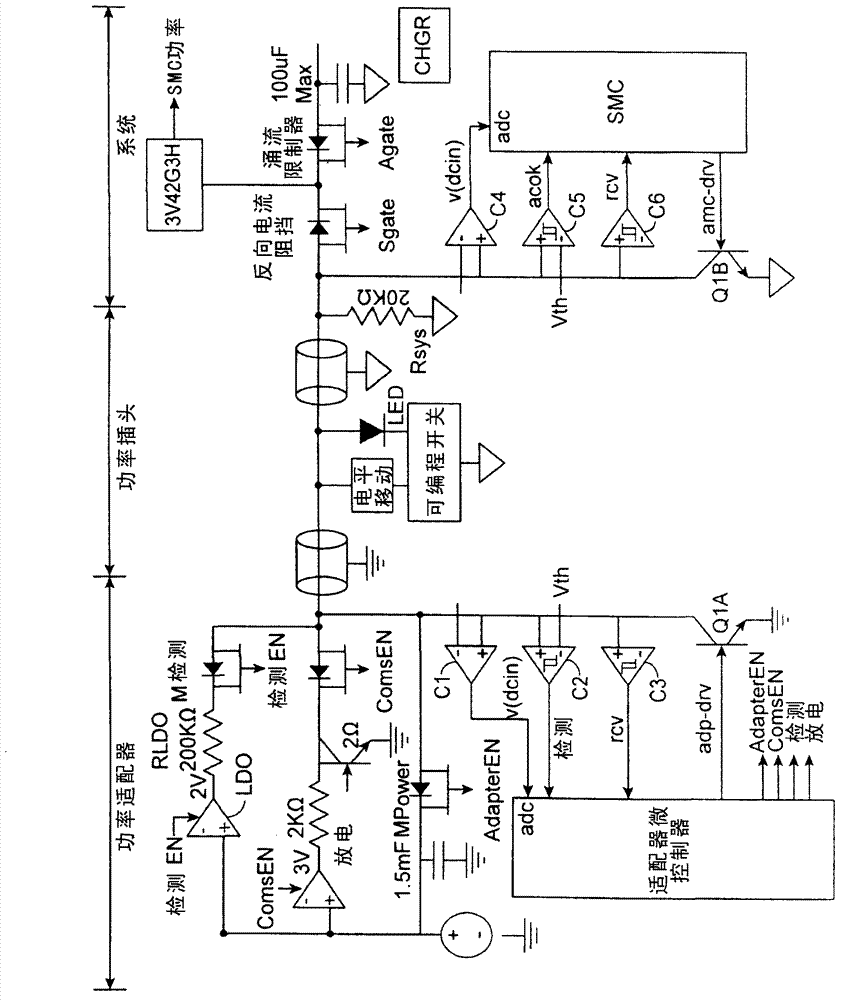
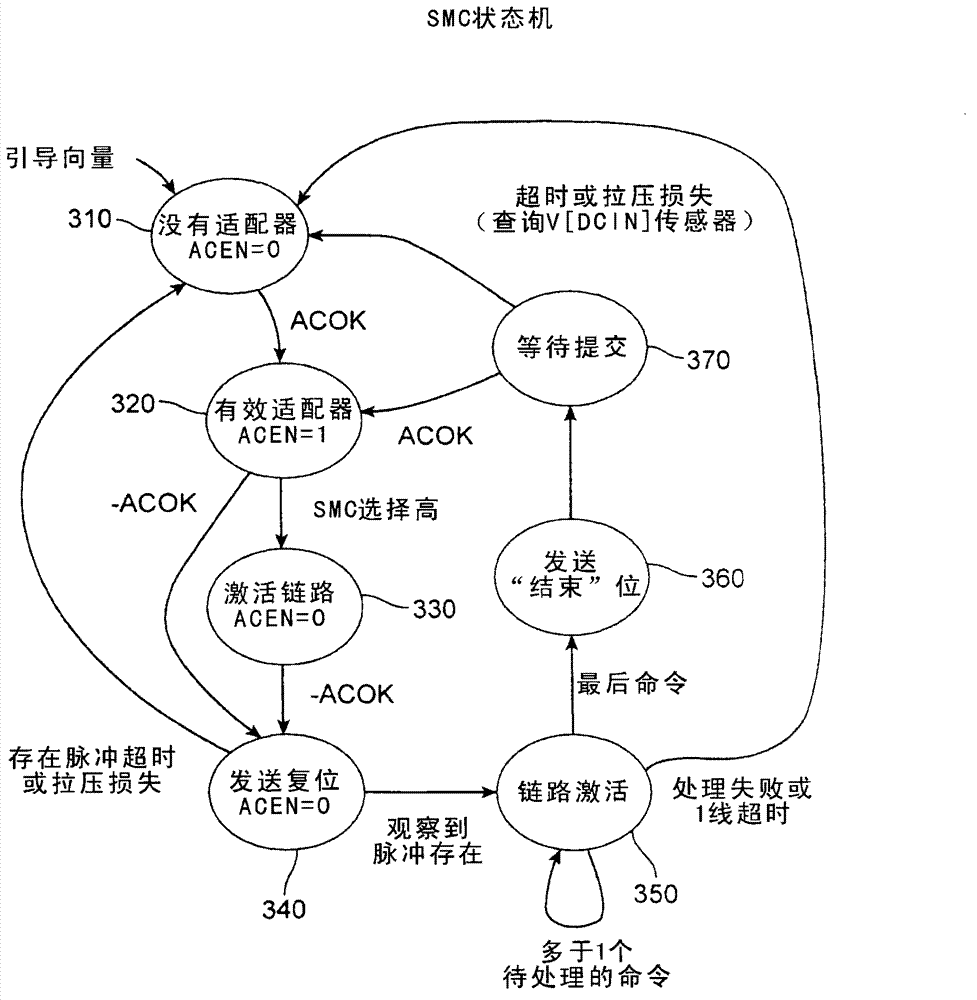
Time-domain multiplexing of power and data
ActiveCN102769312ABatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsTime domainElectronic systems
Circuits, methods, and apparatus that may allow an electronic device to control a power adapter. One example may provide an electronic system where an electronic device may control a power adapter through a communication channel. Data transferred in the communication channel may include the temperature of the power adapter, the charging capability of the adapter, and other types of data. In one example, power and data may share the same two wires, and the power and data may be time-division multiplexed. That is, the two wires may convey power and data at different times. Another example may include circuitry to detect a connection between the electronic device and the power adapter. Once a connection is detected, power may be transferred from the power adapter to the electronic device. This power transfer may be interrupted on occasion to transfer data between the power adapter to the electronic device.
Owner:APPLE INC
MR invasive device and method for active MR guidance of invasive devices with target navigation
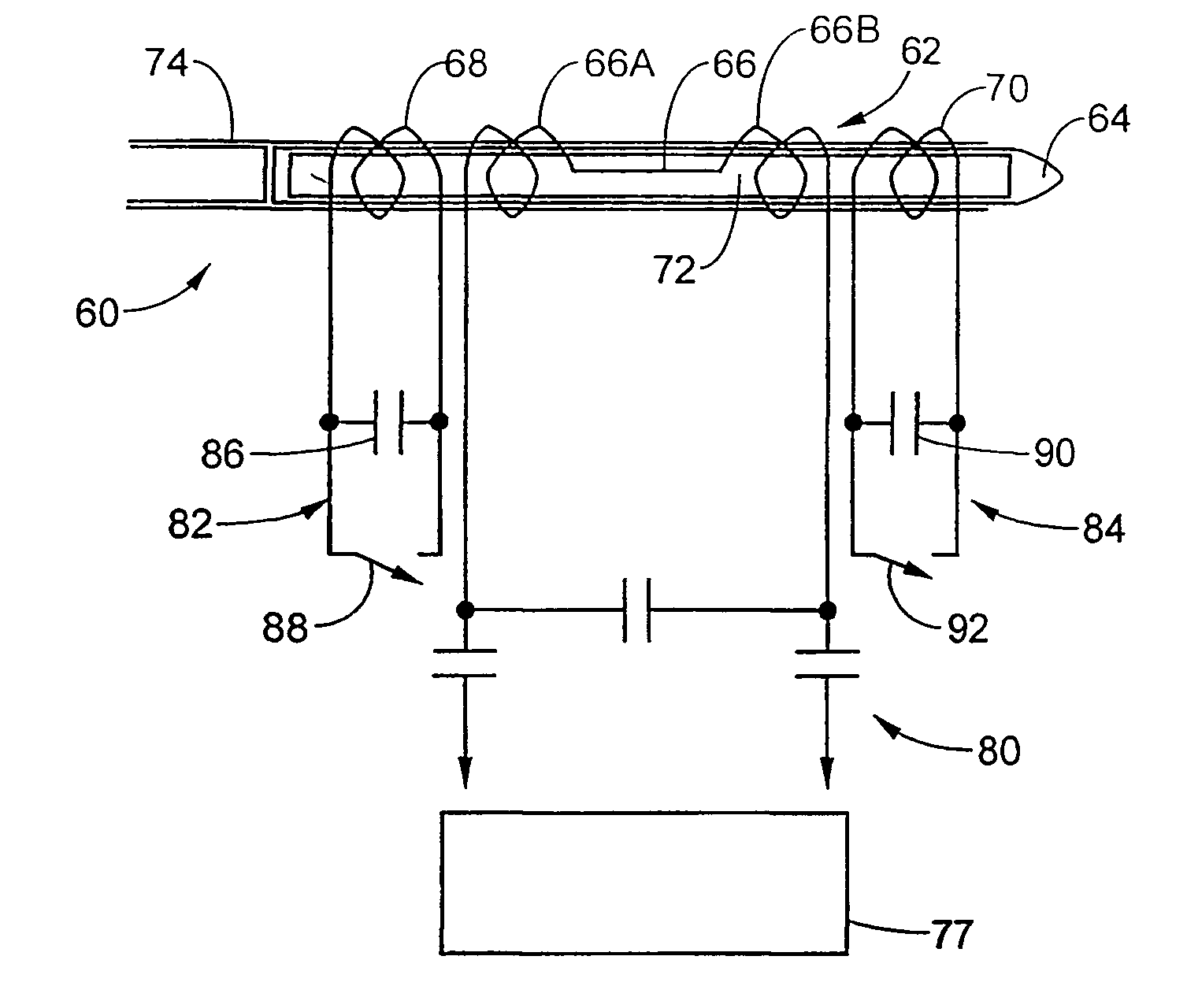
An invasive device having an inductive coupling element. One embodiment of the invasive device includes a plurality of receive coils inductively coupled to a communicating coil. The receive coils are selectively tuned and detuned to receive MR signals for providing coordinate information used for device tracking. A second embodiment of the invasive device includes a receive coil having a plurality of winding elements separated from each other by different distances. A method of rapidly acquiring both the invasive device orientation and position information to dynamically adapt MR scan planes to continuously follow the invasive device relative to a target is provided. The target-navigation technique automatically defines the MR scan plane and a time domain multiplexing technique is applied for MR imaging and device tracking. Using these techniques, the acquired MR images shows both the invasive device and the target tissue.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
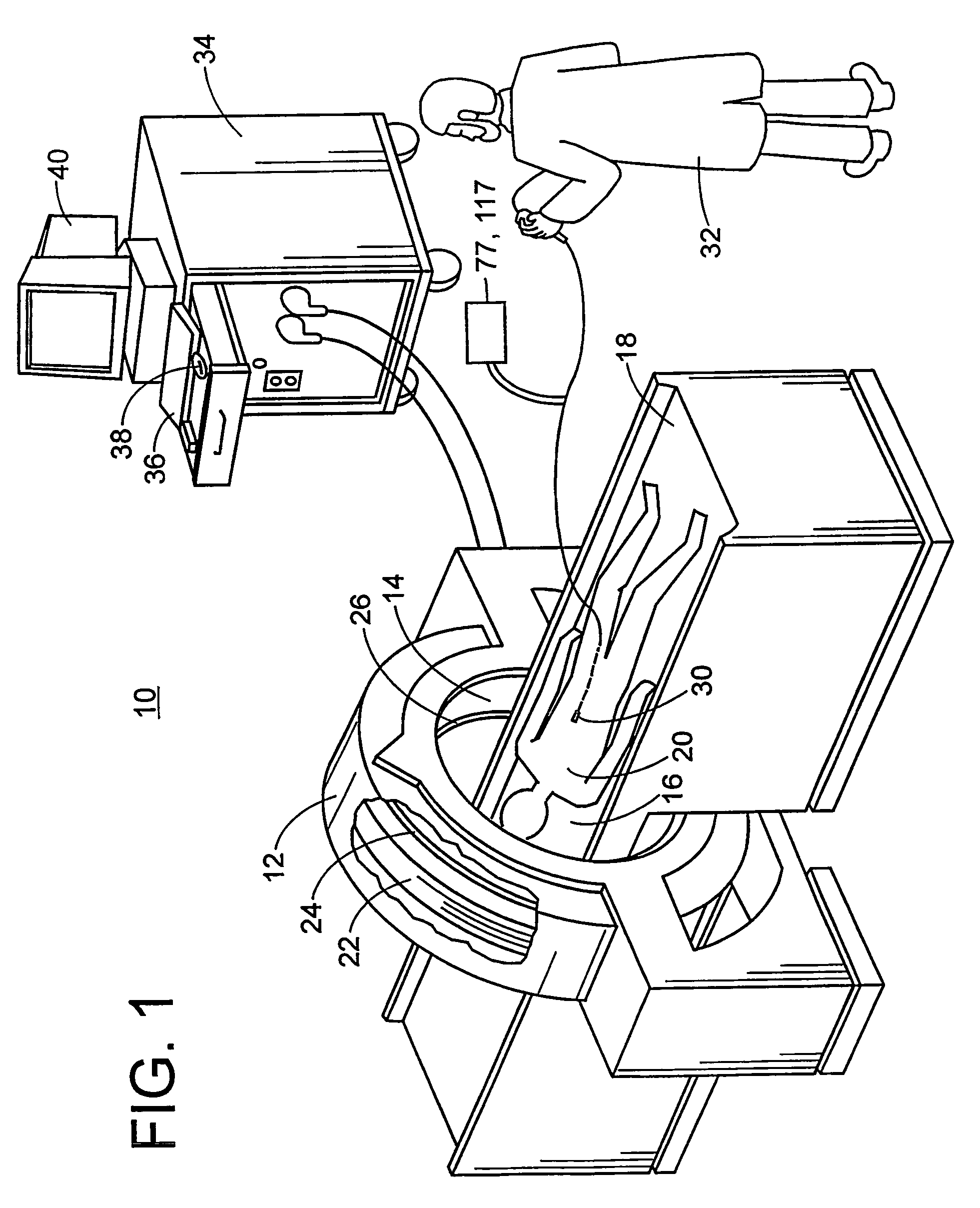
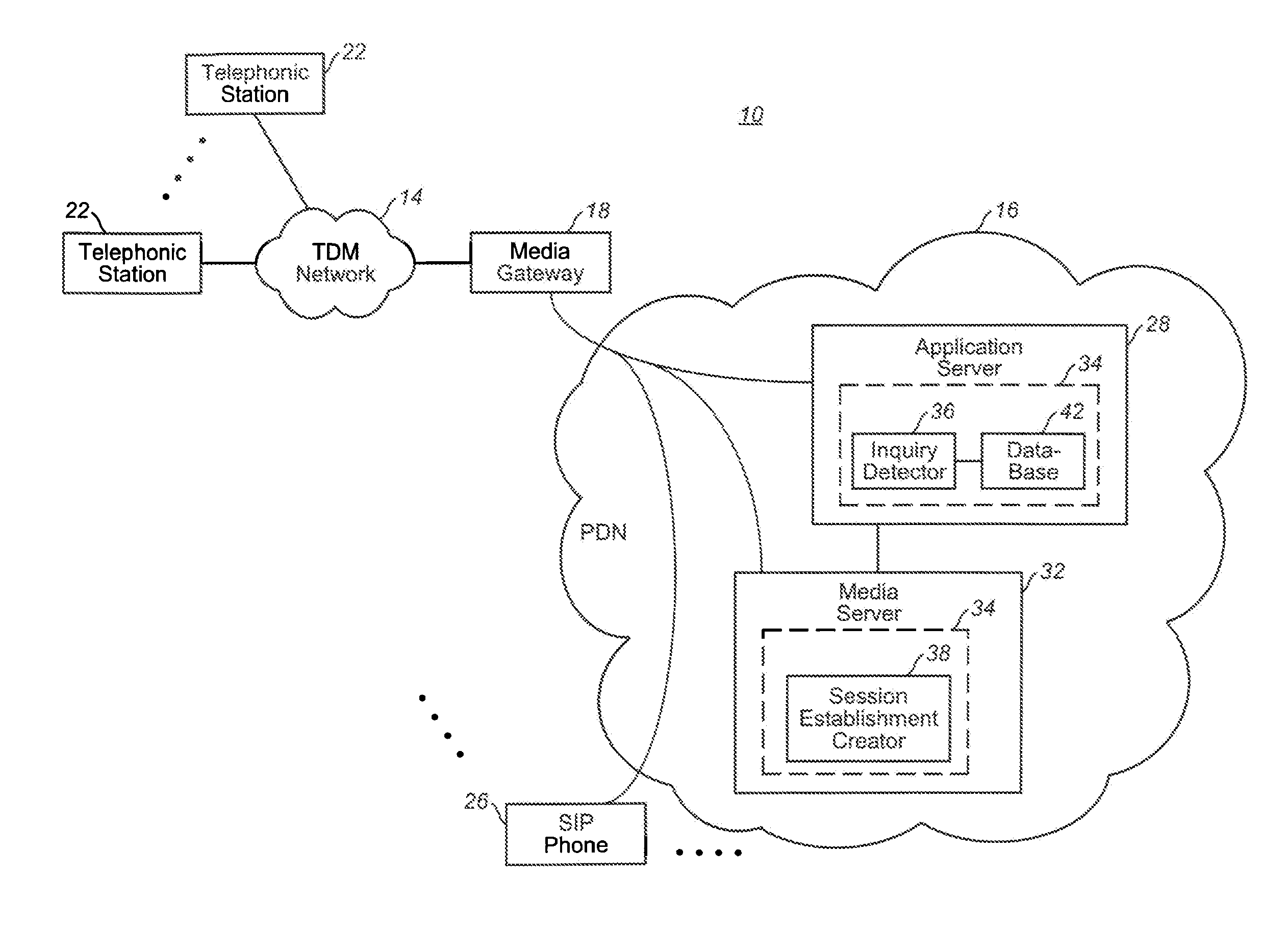
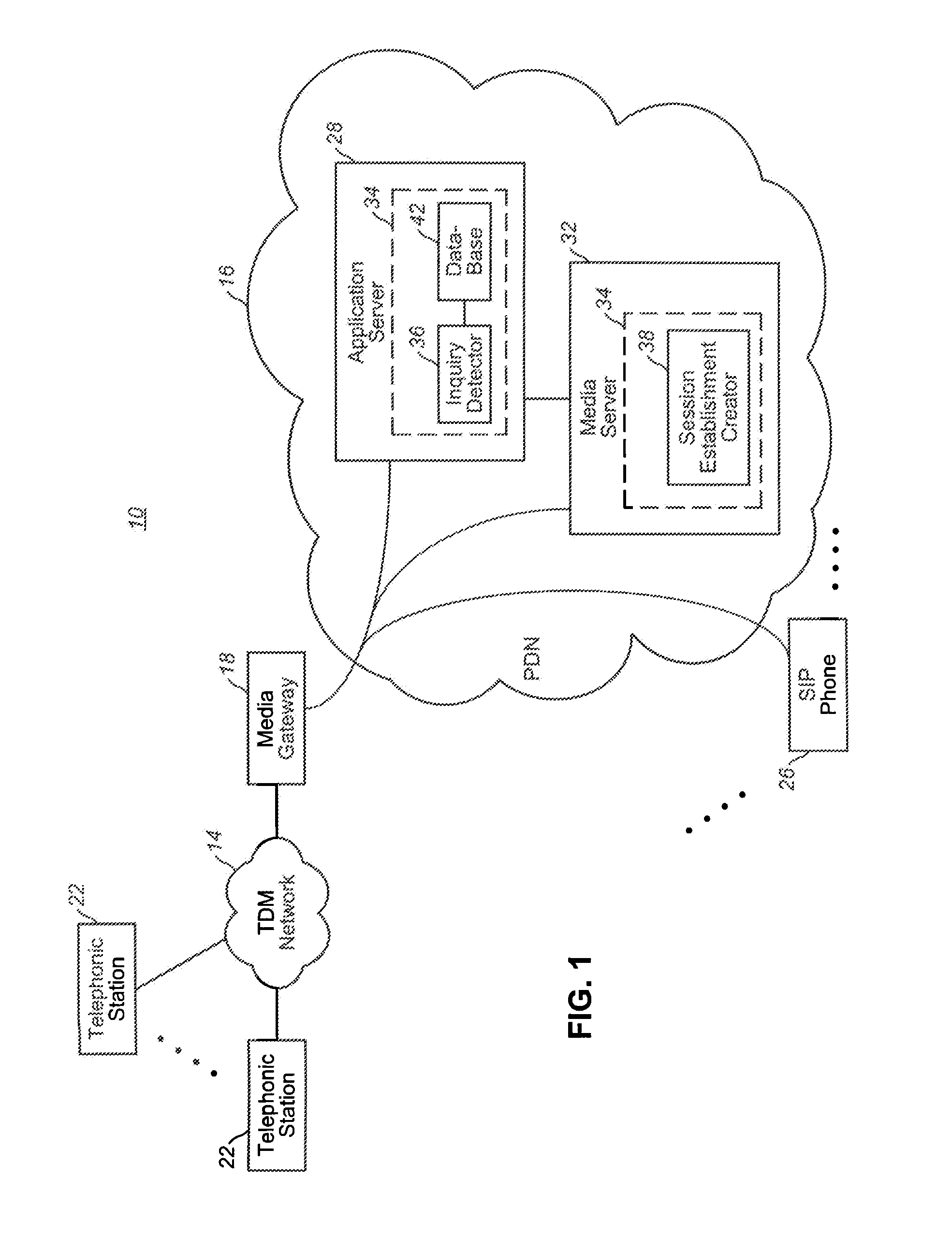
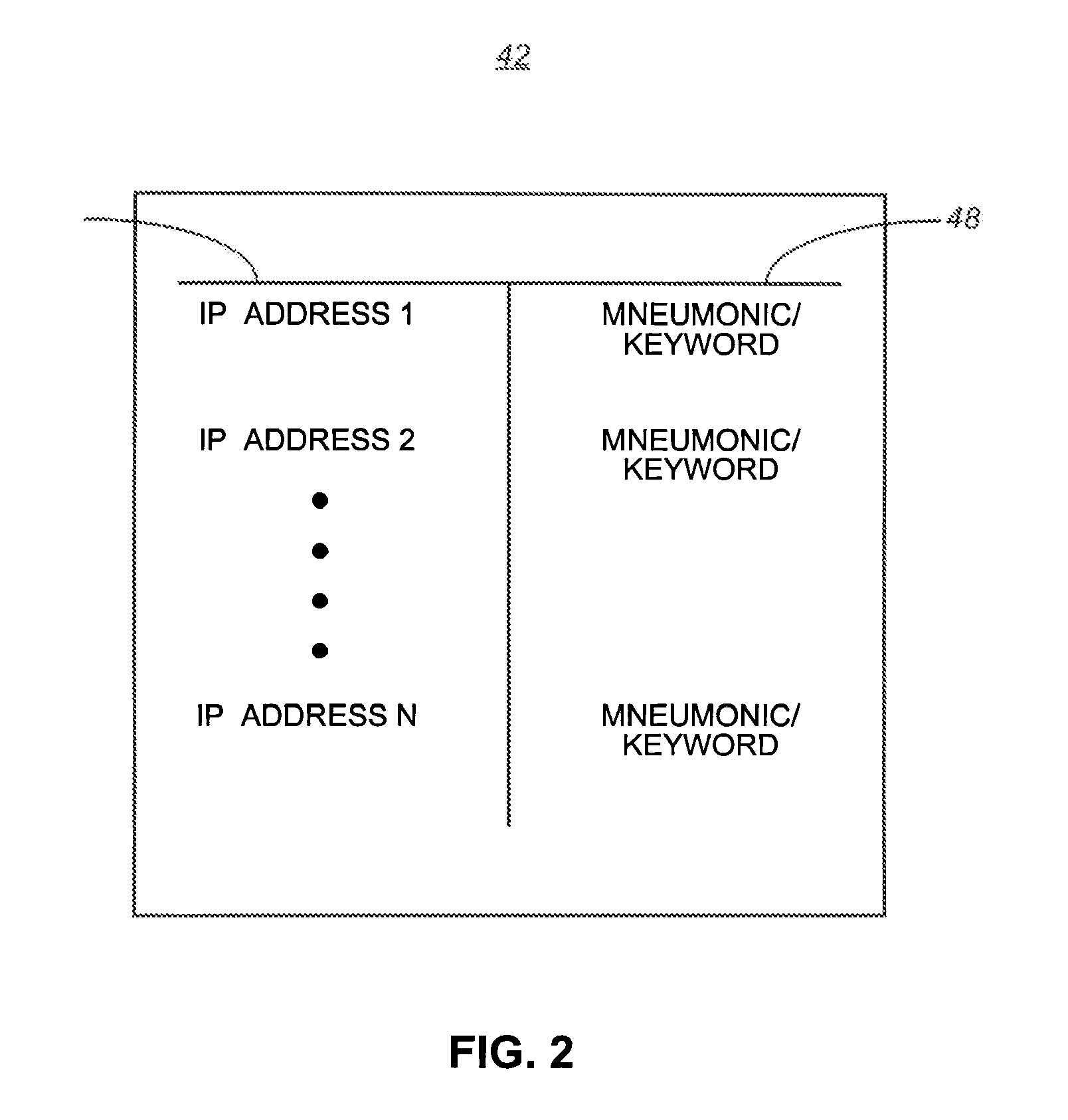
Apparatus, and associated method, for completing a call to a packet-network, telephonic station
Apparatus, and an associated method, for facilitating a call to a packet-network, telephonic station, such as an SIP phone. The call is originated at a originating station formed of a telephonic station of a time-domain-multiplexing network. A call establishment creator is embodied at a media server forming a portion of the packet data network. A call, originated at the originating station, is routed to the call establishment creator. Once the call is routed thereto, an interactive session is formed between the media server and the originating station. During the interactive session, the information needed to ascertain the identity of the terminating station is ascertained, and the call is routed thereto.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
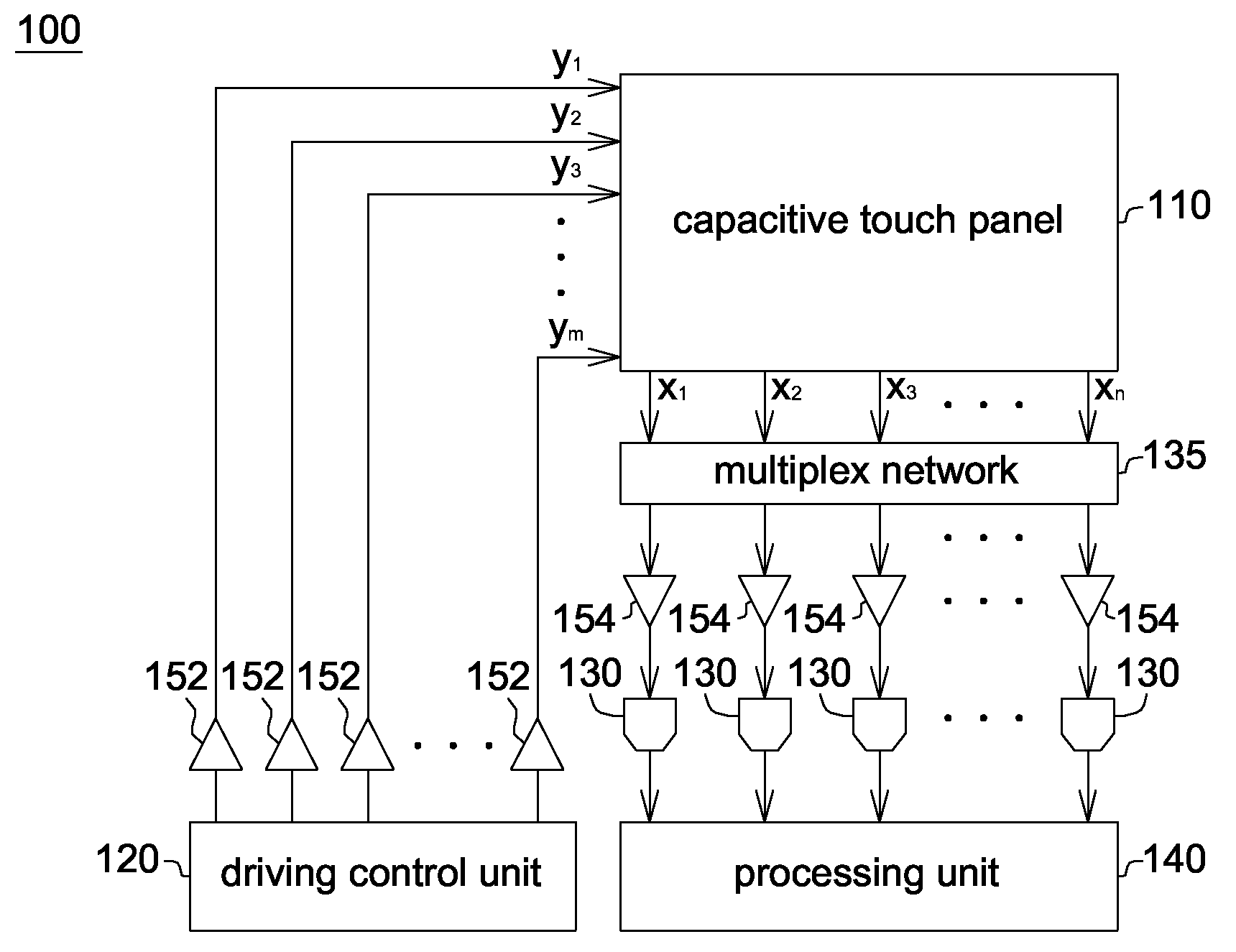
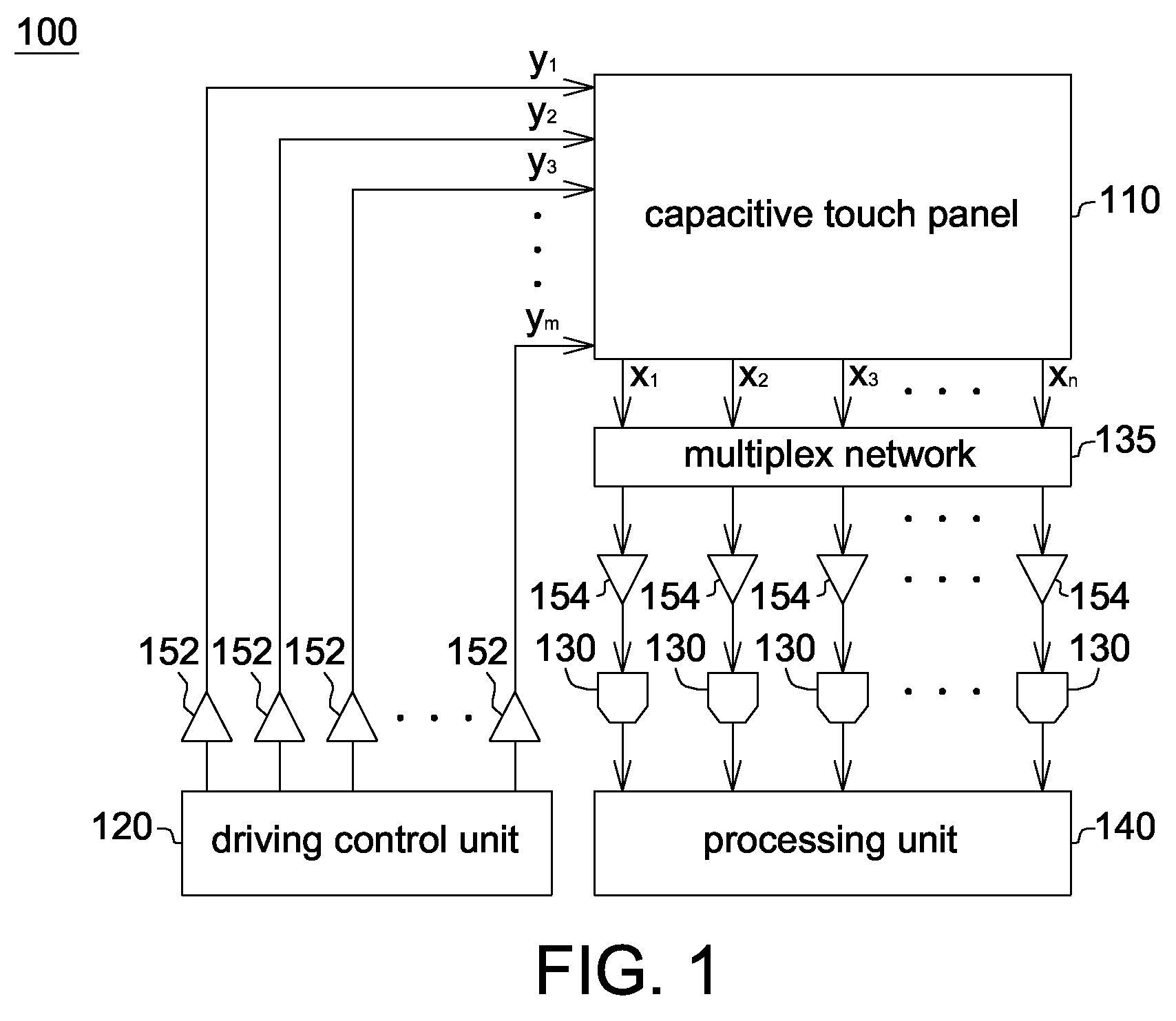
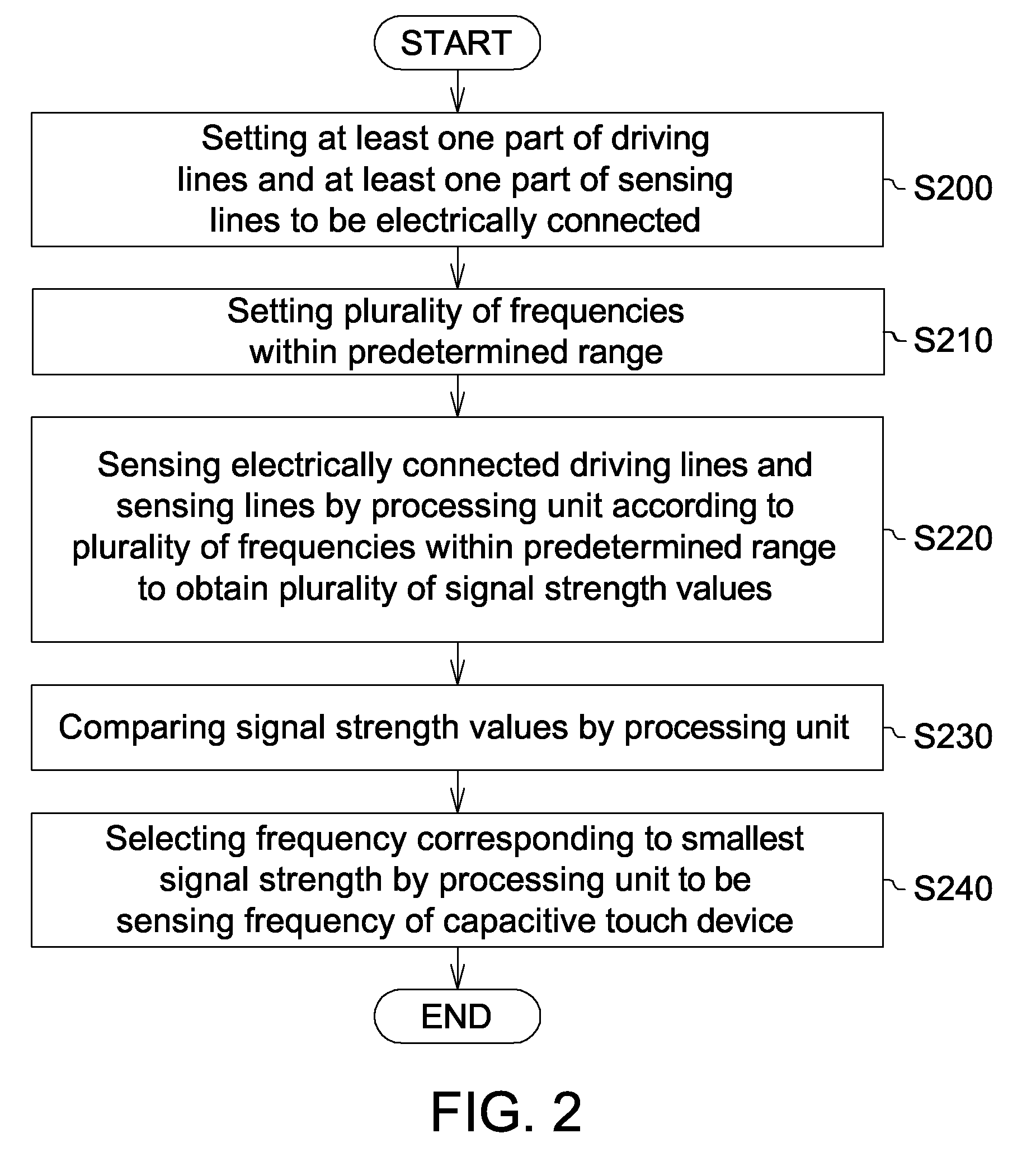
Capacitive touch device and sensing method thereof
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
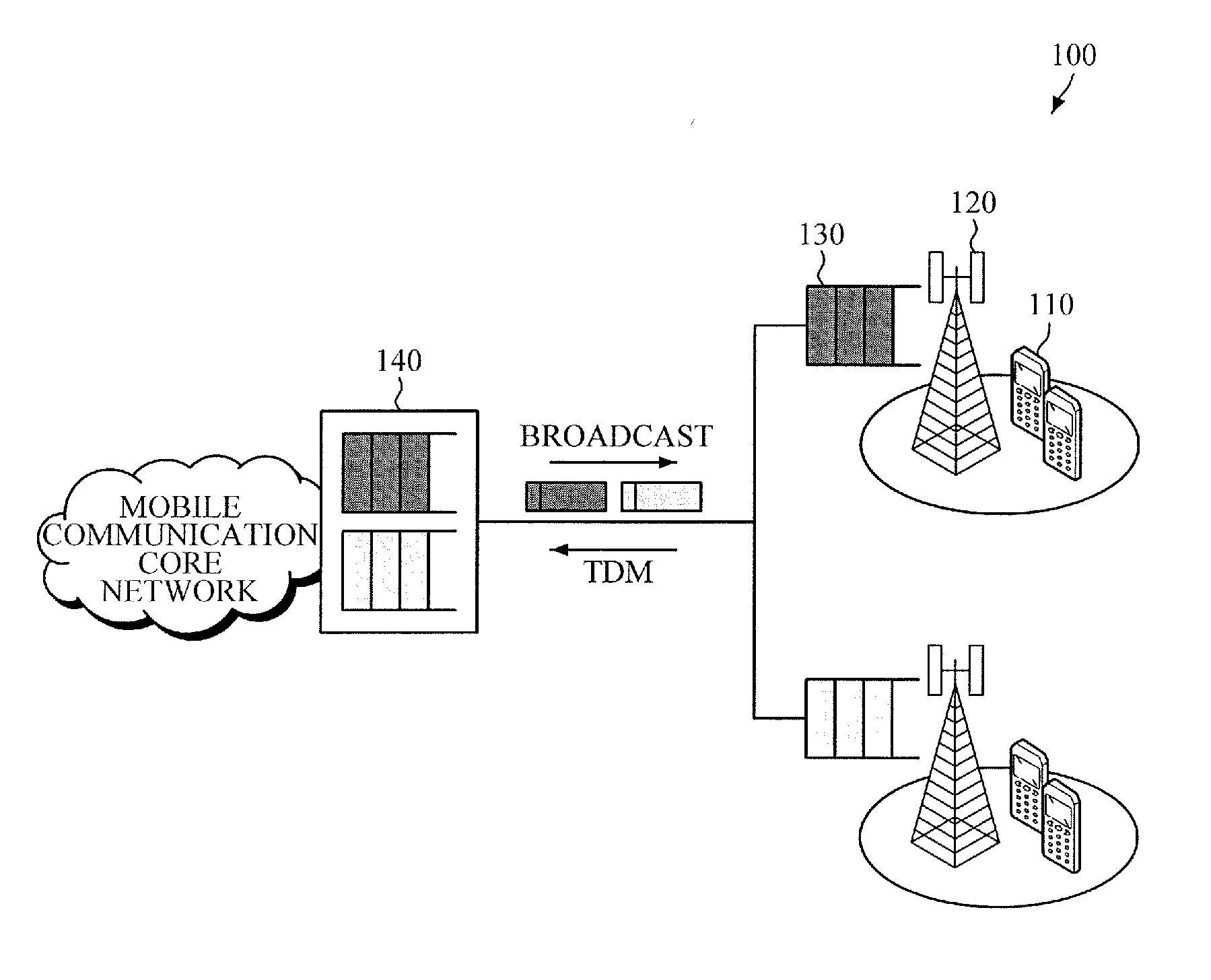
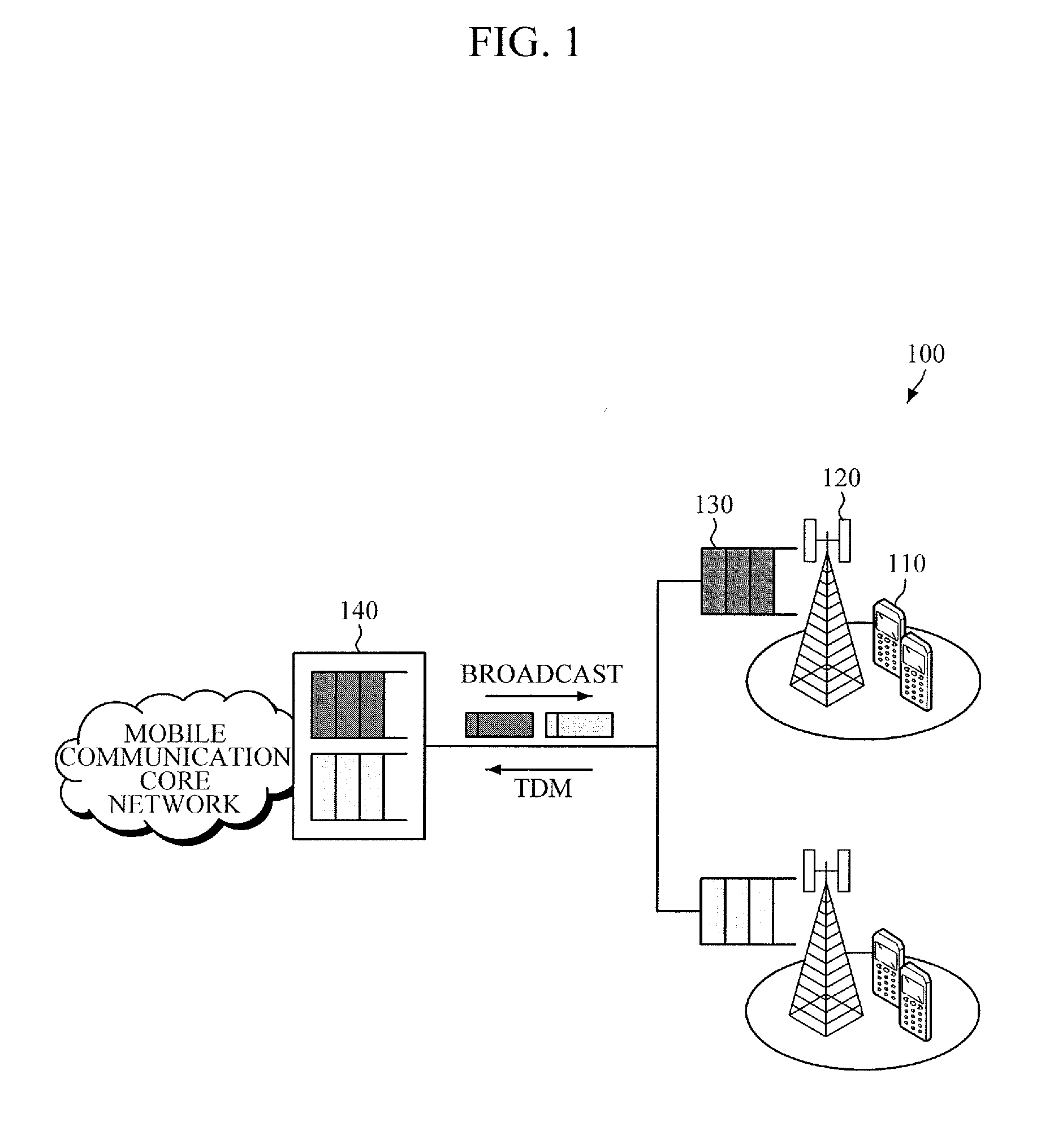
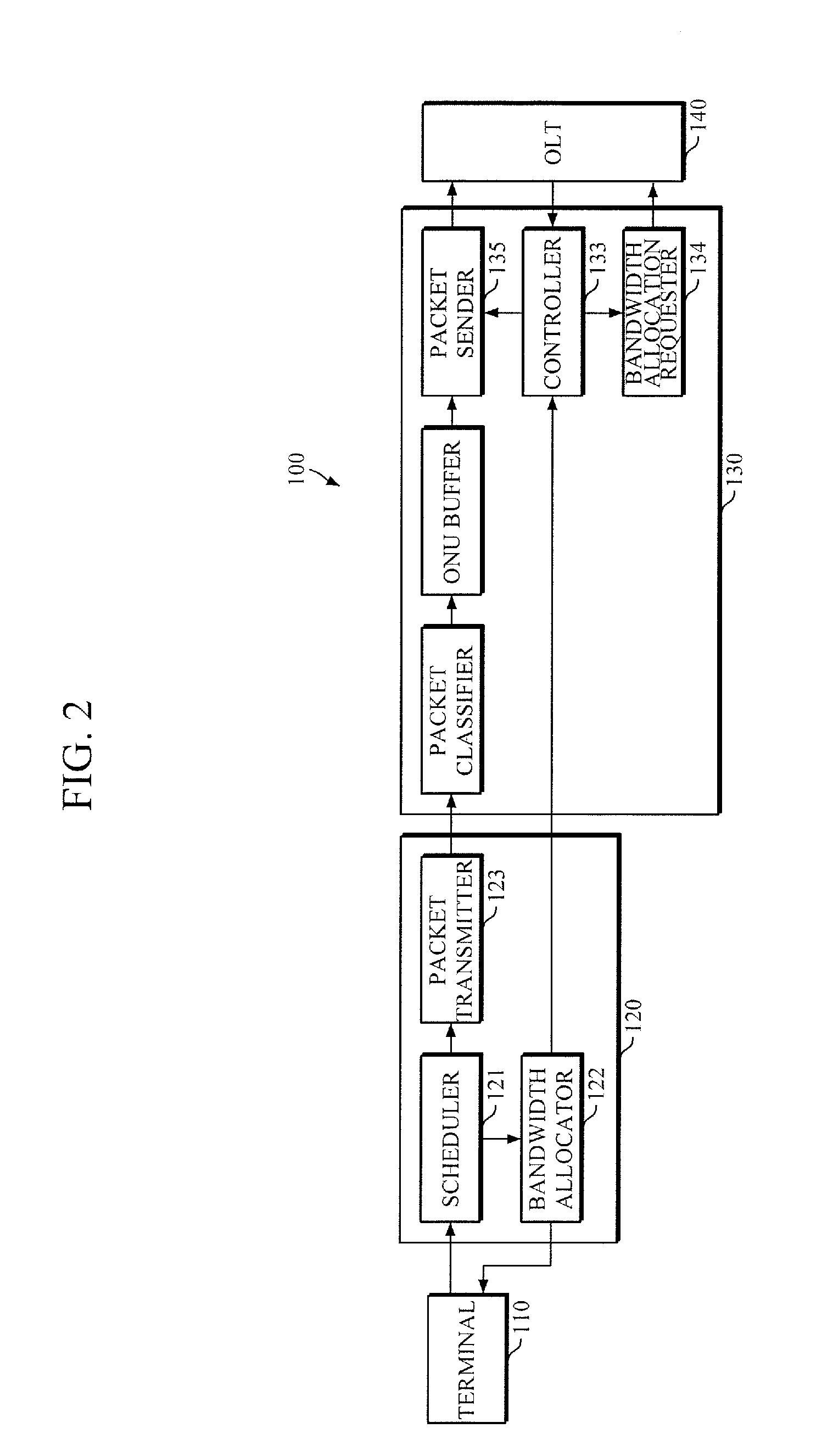
Optical network unit (ONU) for low latency packet transmission in time division multiplexing-passive optical network (tdm-pon), method of operating the same, and apparatus for controlling onu
ActiveUS20160277142A1Lower latencyDelay minimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsStatistical time division multiplexingFrequency-division multiplexing
Provided are an Optical Network Unit (ONU) for low latency packet transmission in a Time Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Network (TDM-PON), a method of operating the ONU, and an apparatus for controlling the ONU. The method includes: receiving, from a base station, first bandwidth allocation information regarding a bandwidth allocated by the base station to a terminal for uplink packet transmission; and transmitting a bandwidth allocation request, which is based on the received first bandwidth allocation information, to an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) before completing packet reception from the base station.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving broadcast data using outer-coding in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20050243775A1Minimize number of dataMinimize the numberBroadcast specific applicationsTime-division multiplexTime domainBroadcast data
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a broadcast service in a mobile communication system which outer-codes frames for a plurality of broadcast services and Time Domain Multiplex (TDM)-transmits the outer-coded frames. A transmitter transmits a broadcast parameter message comprising information indicating a specific sub-buffer in which respective broadcast services are stored. A receiver for receiving the broadcast parameter message from the transmitter, and maps the sub-buffer to a corresponding sub-block mask based on the broadcast parameter message. The transmitter TDM-transmits the frames for the plurality of broadcast services per sub-block. The receiver selectively receives frames for a desired broadcast service using the sub-block mask and decodes the selectively received frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Current multiplexing circuit for optical power monitoring
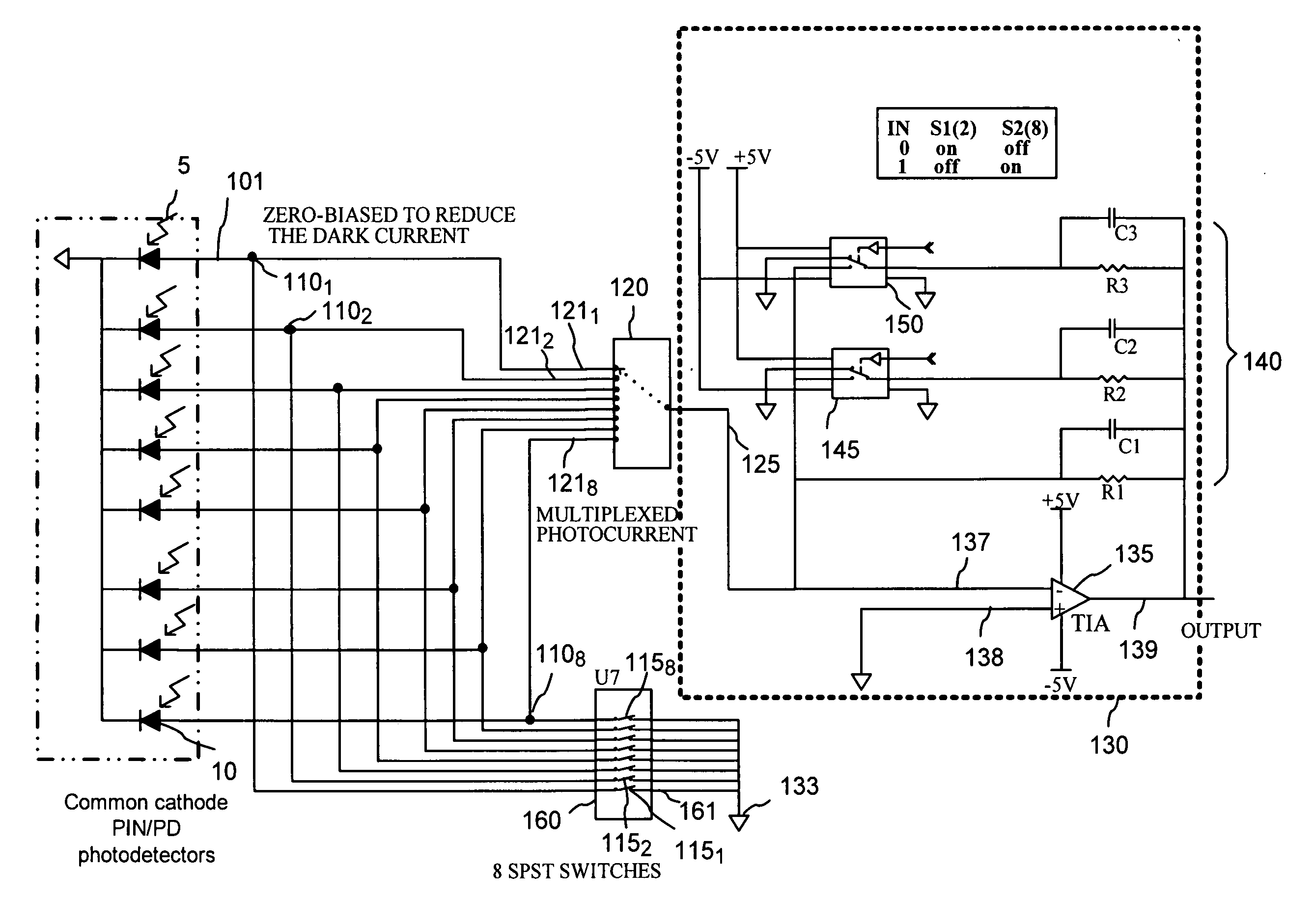
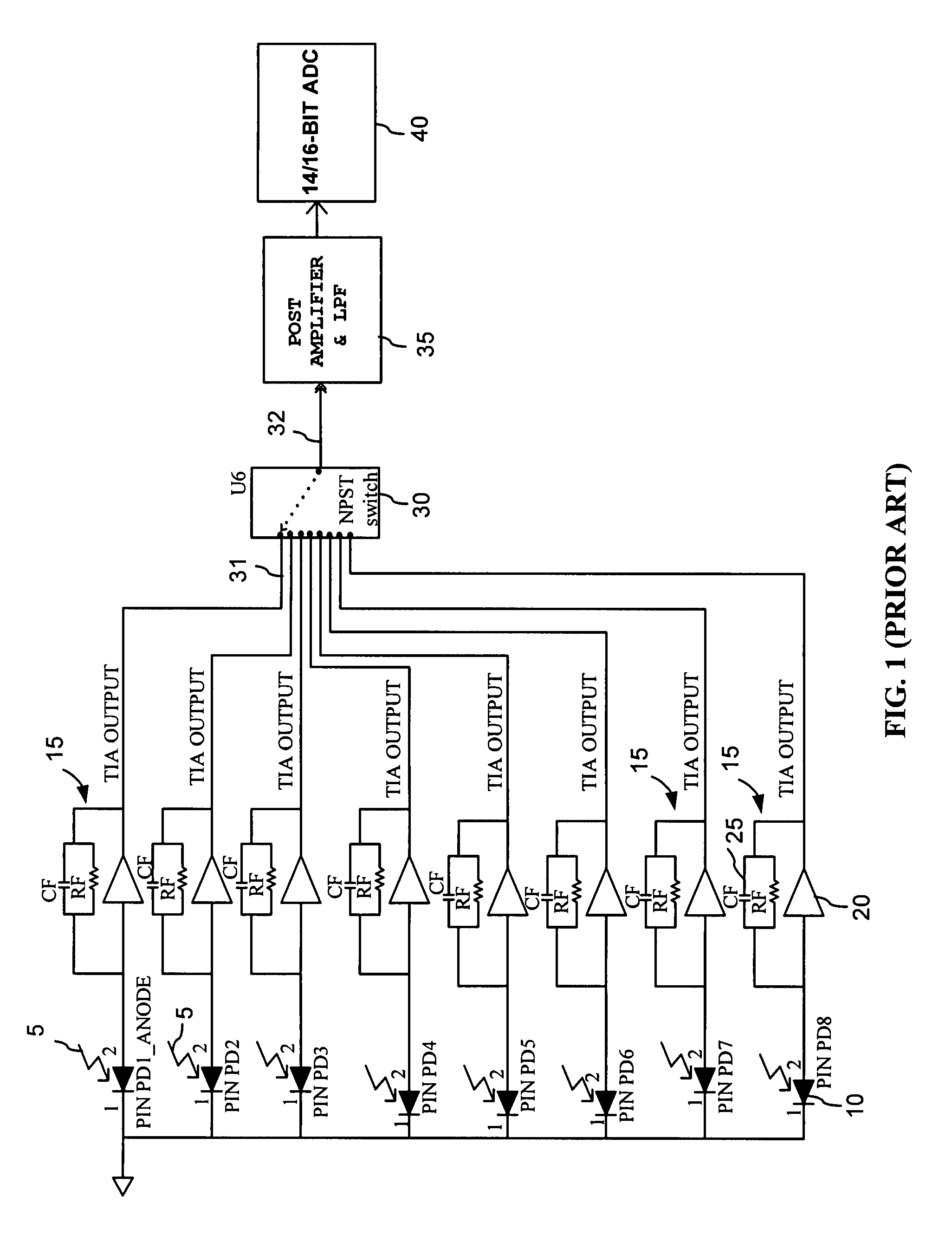
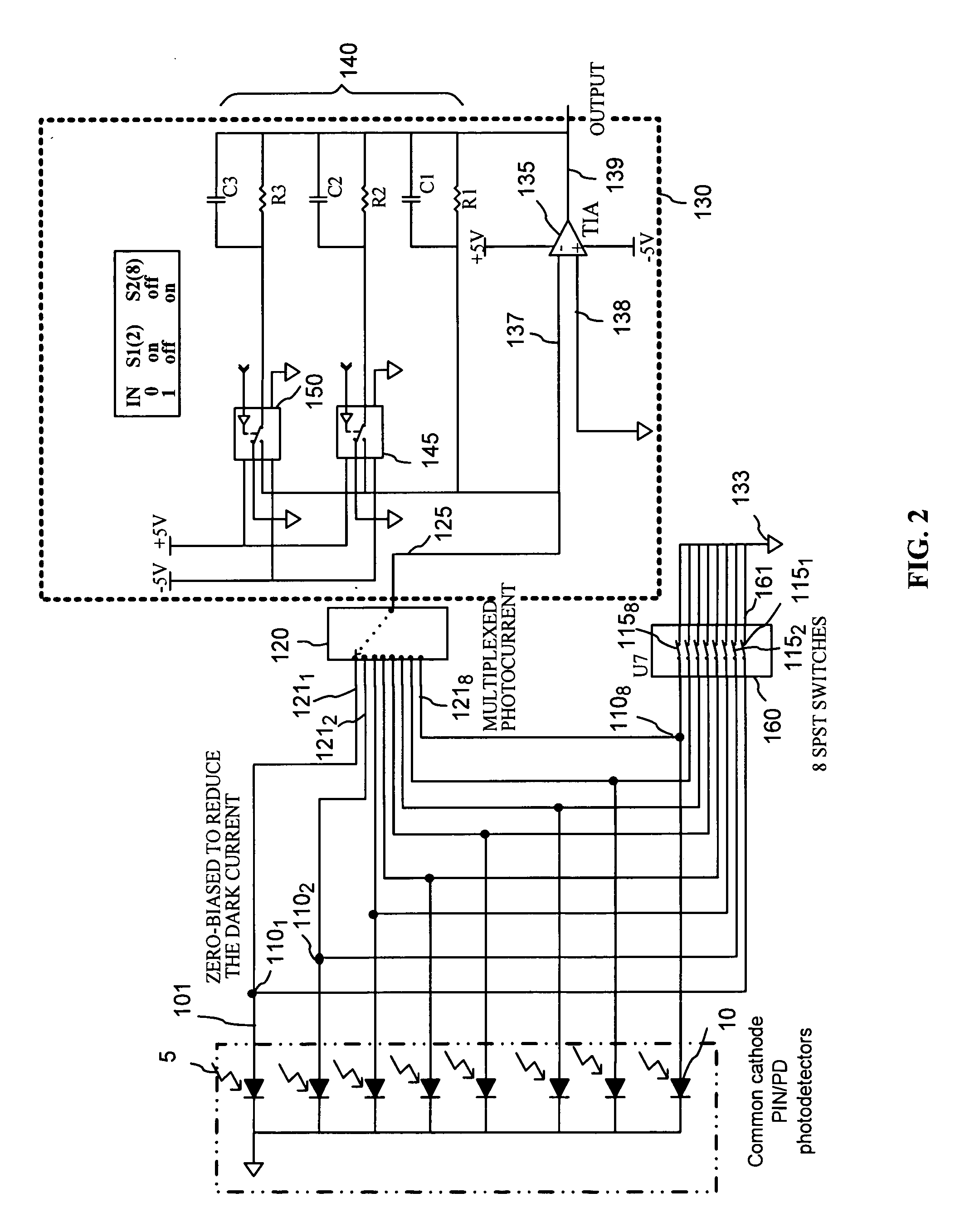
The invention provides a current multiplexing circuit for time-domain multiplexing a plurality of current signals such as photocurrents that are received in a plurality of input terminals. The current signals are multiplexed using one or more analog low-resistance switches operational to connect each of the input terminals to an output switch terminal at a time in a selected sequence, while coupling the other input terminals and the output switch terminal to a reference potential such as ground. The current multiplexing circuit can be used in an optical power monitor with auto-calibration functionality for monitoring a plurality of optical signals.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
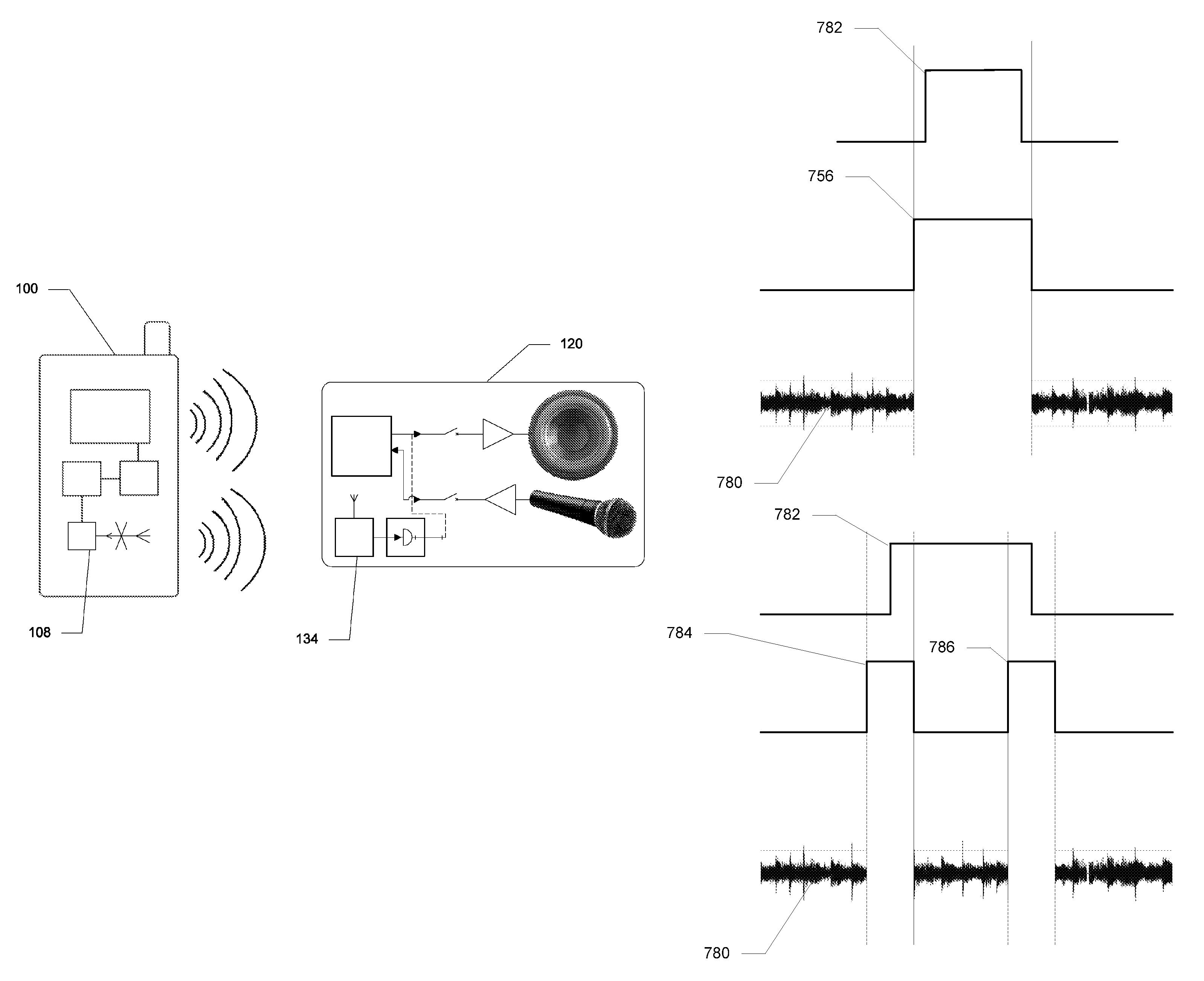
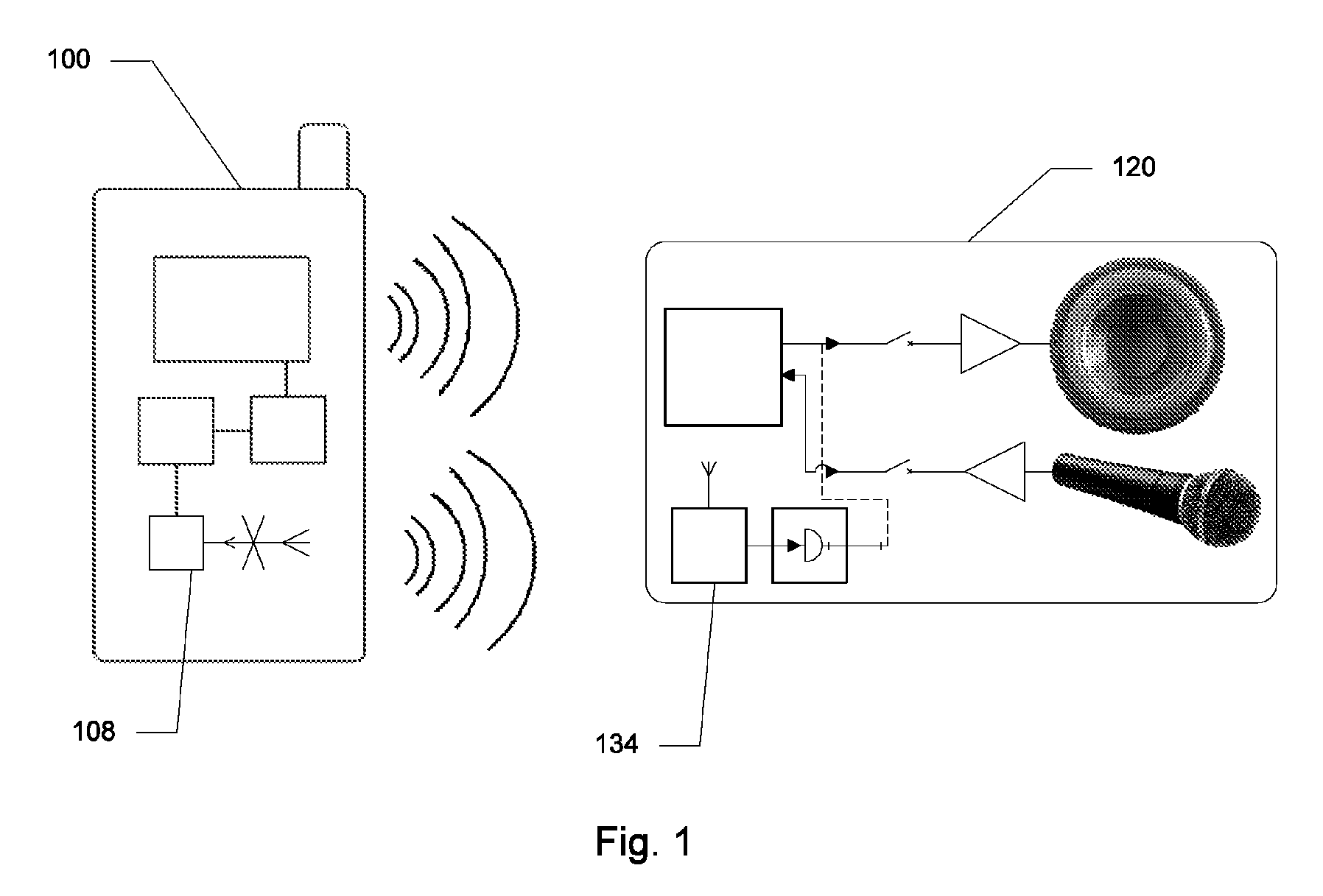
Systems and Methods for Dampening TDMA Interference
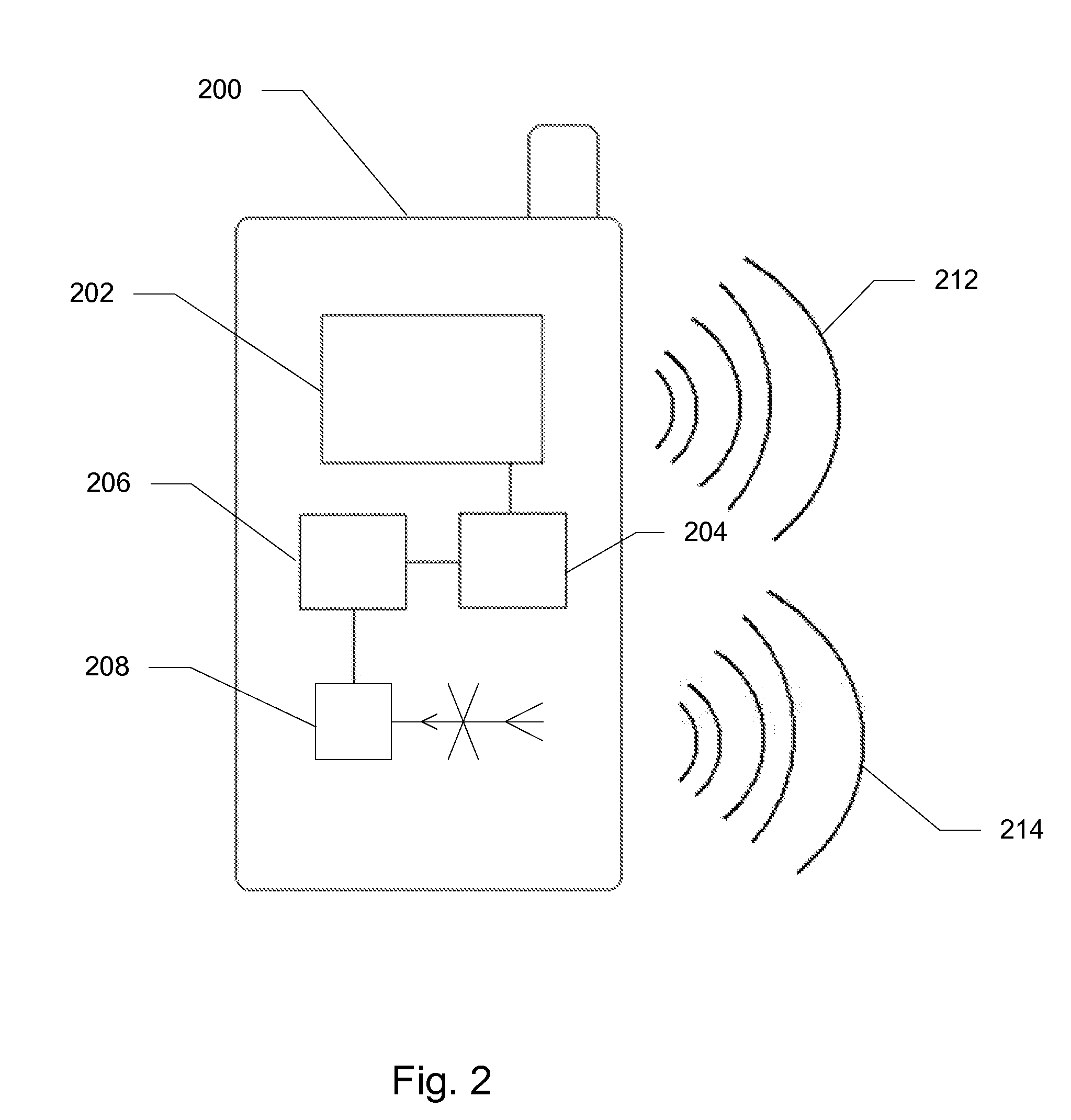
ActiveUS20100120382A1Minimize audible effectDifficult to noticeTransmissionShort range communication serviceTime domainActuator
Systems and methods are disclosed which relate to mitigating the detrimental effects of interference to electronic devices from mobile telephones utilizing any form of time-domain multiplexing technology. A wireless transmitter inside the mobile telephone broadcasts a warning transmission which can be received by affected devices. Once the warning transmission is received by an affected device, the device activates a blanking circuit comprising an actuator and a switch or switches. The switches open for the duration of the interference so that the user does not receive undesired output such as: noise through a speaker, noise through a microphone, or other interference with electrical signals.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
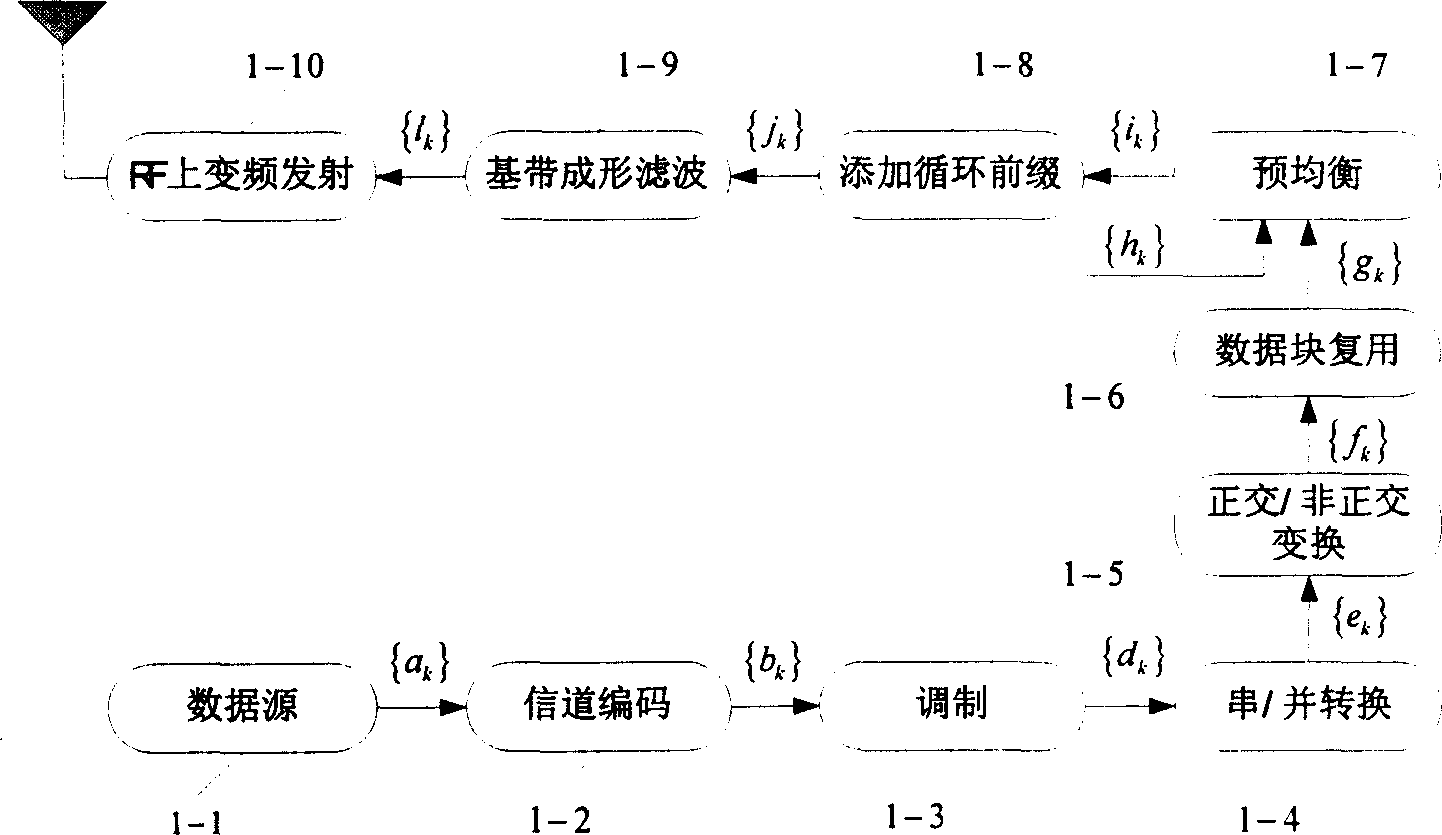
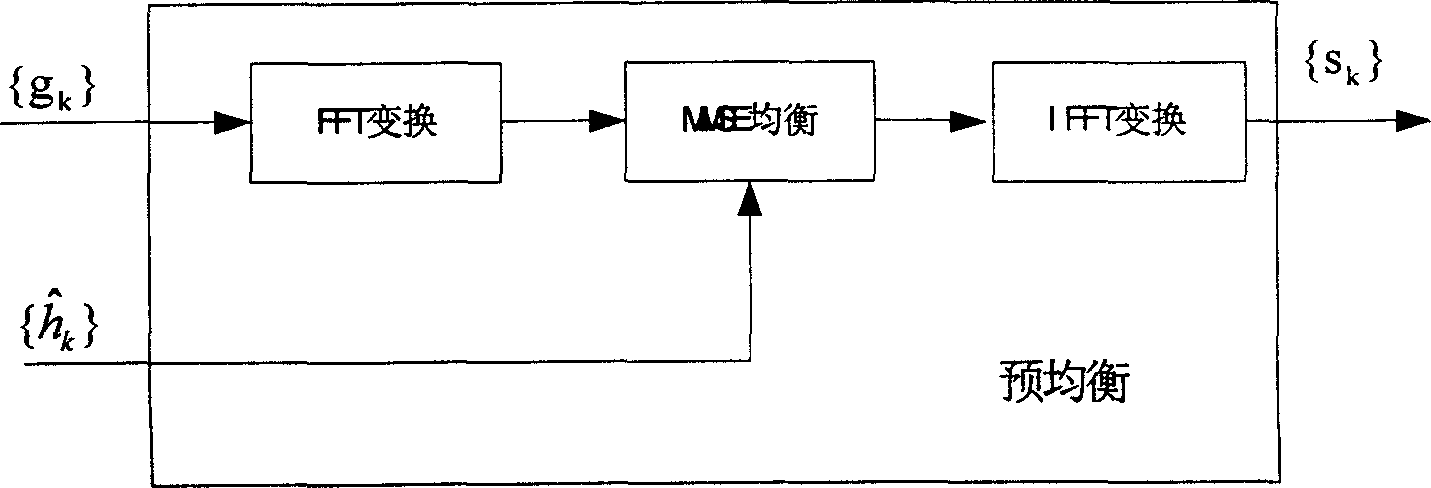
Signal transmitting method and apparatus based on cyclic prefix
InactiveCN1848828AOvercoming Phase Rotation EffectsImprove throughputTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputer hardwareTime domain
A method for transmitting signal based on cyclic prefix includes dividing modulated symbol stream to be data blocks in different size correspondingly based on emission end transform, multiplexing said blocks to be one large data block and adding two protective intervals known by receiving end at its two ends at emission end; dividing received symbol to be a numbers of data blocks according to multiplexed number of emission end by searching protective interval at reception end; finally carry out inverse transform corresponding to emission end separately on those data blocks for obtaining transmission data.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
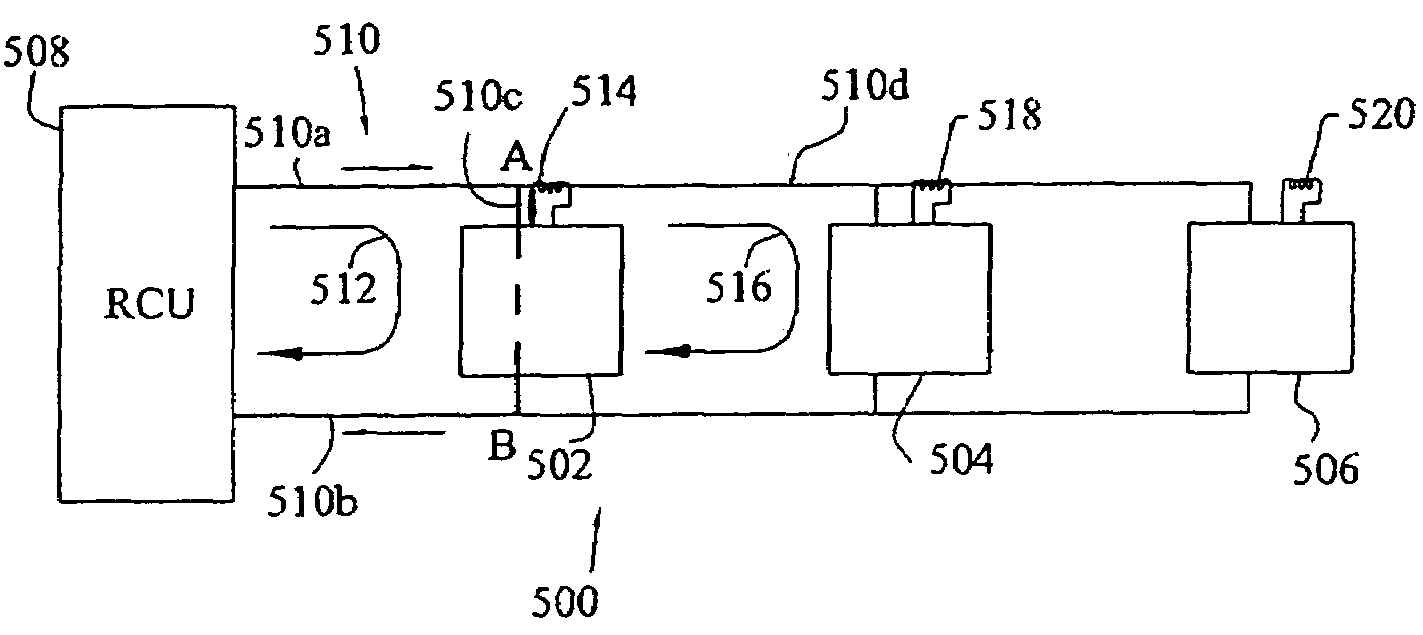
Method for multiple sensors to communicate on a uni-directional bus
ActiveUS7191269B2Low costRotary current collectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime domainCommunications system
The present invention provides a system of and a method for multiple transmitters to communicate data over a single uni-directional communication bus. In one form of the present invention, a data communication system using time-domain multiplexing includes a uni-directional current-modulated communication bus, a plurality of sensors coupled to the communication bus, at least one of the sensors capable of detecting the data transmission of a sensor outside of the current loop of the first sensor, the sensors also capable of transmitting data on the communication bus using current loop modulation. In another form of the present invention, a method of transmitting data on a uni-directional communication bus is provided. The method includes the steps of enabling a first device to transmit a data signal on the communication bus, the data transmission followed by an idle period, and the first device including a current sensor; enabling a second device to detect the first device's data transmission and the idle period; and enabling the first device to transmit data upon detecting the idle period, the first device positioned in a first current loop and the second device positioned in a second current loop outside of the first current loop, the second current loop passing through the current sensor of the first device.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
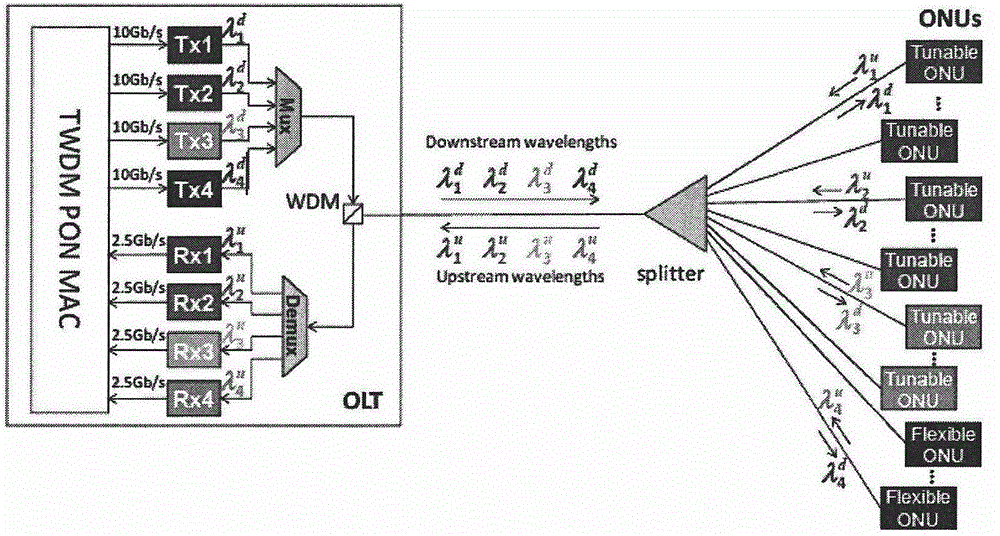
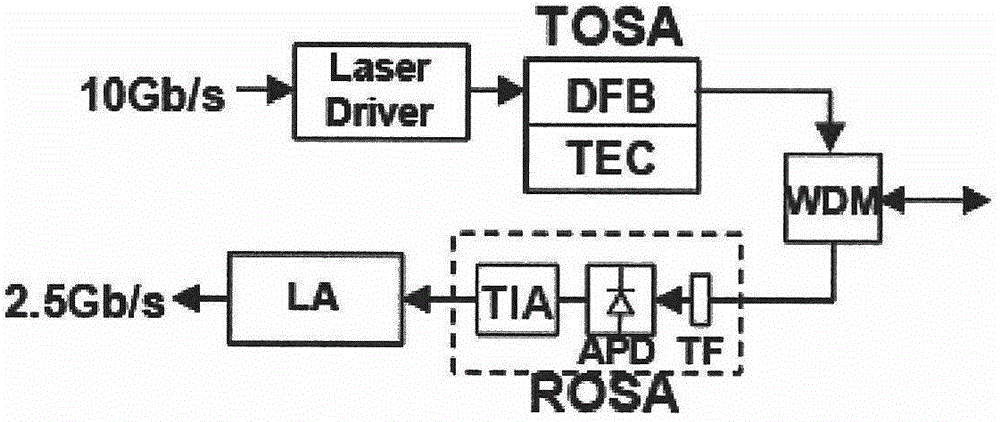
TWDM-PON (time division multiplexing-passive optical network) structure and TWDM-PON equipment for annular subnet extension and control method
ActiveCN104954898ALow costSimple structureMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionSignal qualityStructure of Management Information
At present, low-cost optical network units in TWDM-PON (time division multiplexing-passive optical network) and user amount expansion are key research issues in optical access networks. an embodiment of the invention provides a TWDM-PON optical access network structure for annular subnet extension and provides specific structures of certain devices in the network and a control method of the whole network and particularly provides a novel optical network unit structure supportive to subnet extension, an optical network unit side subnet structure and a structure of a subnet optical network unit. By adoption of the network structure and the equipment, users in subnets can share a tunable laser with the optical network units while receiving of downlink signals is unaffected; gains of uplink and downlink optical amplifiers can be tuned according to intensity of uplink and downlink optical signals, and accordingly quality of signals in the optical network units and optical network unit side subnets can be optimized; in addition, TWDM-PON user amount expansion can be carried out effectively while low terminal cost is kept.
Owner:桂林
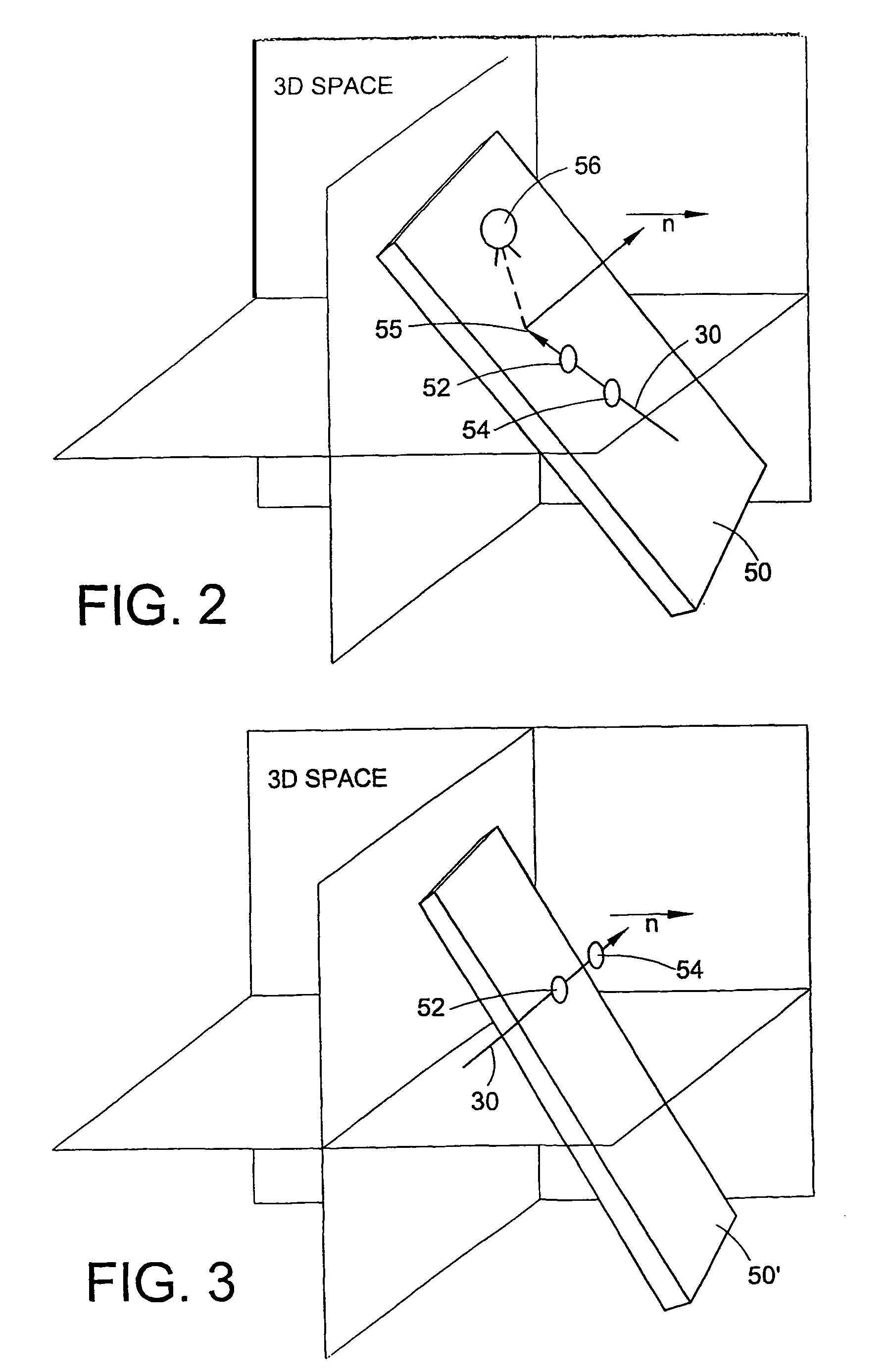
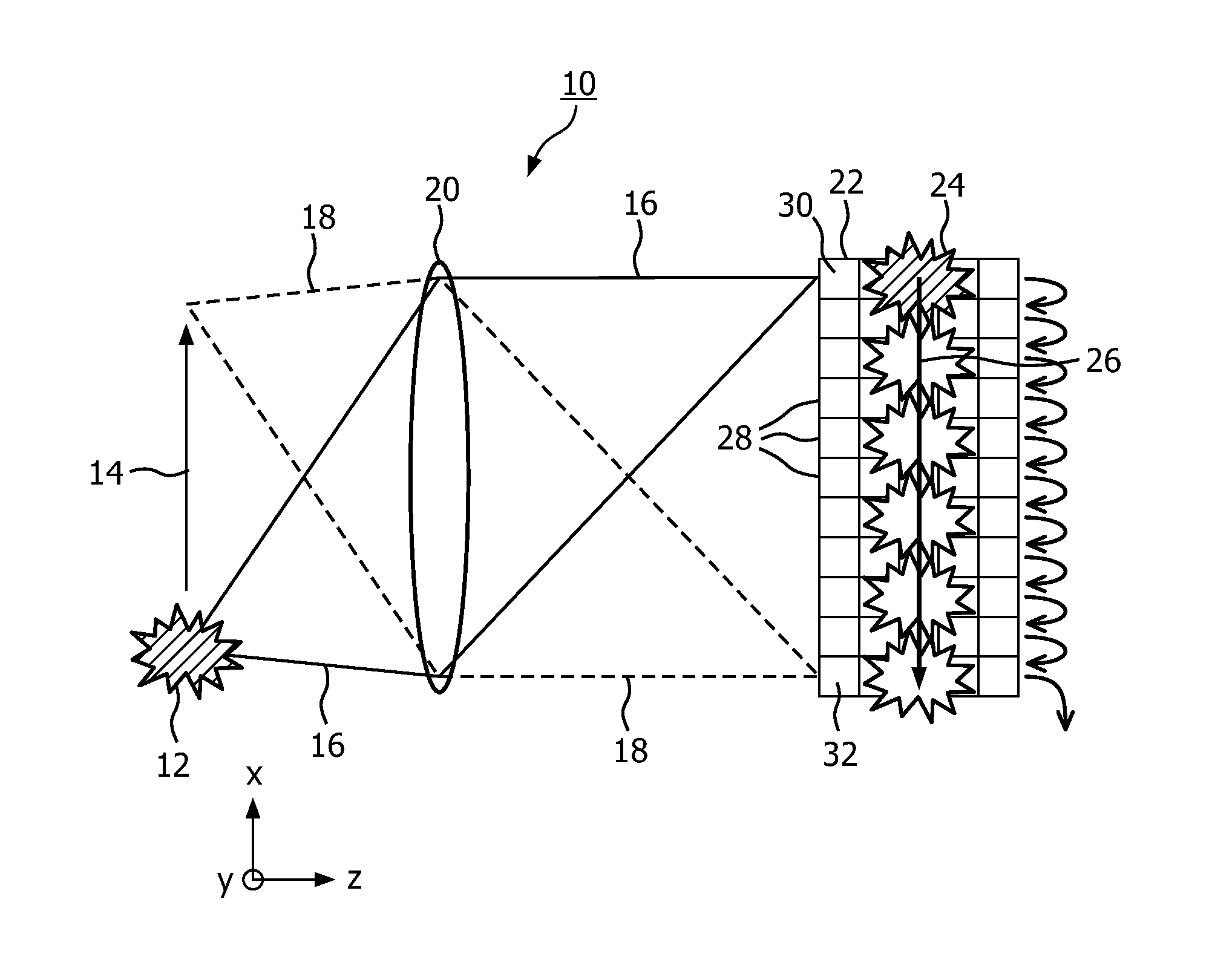
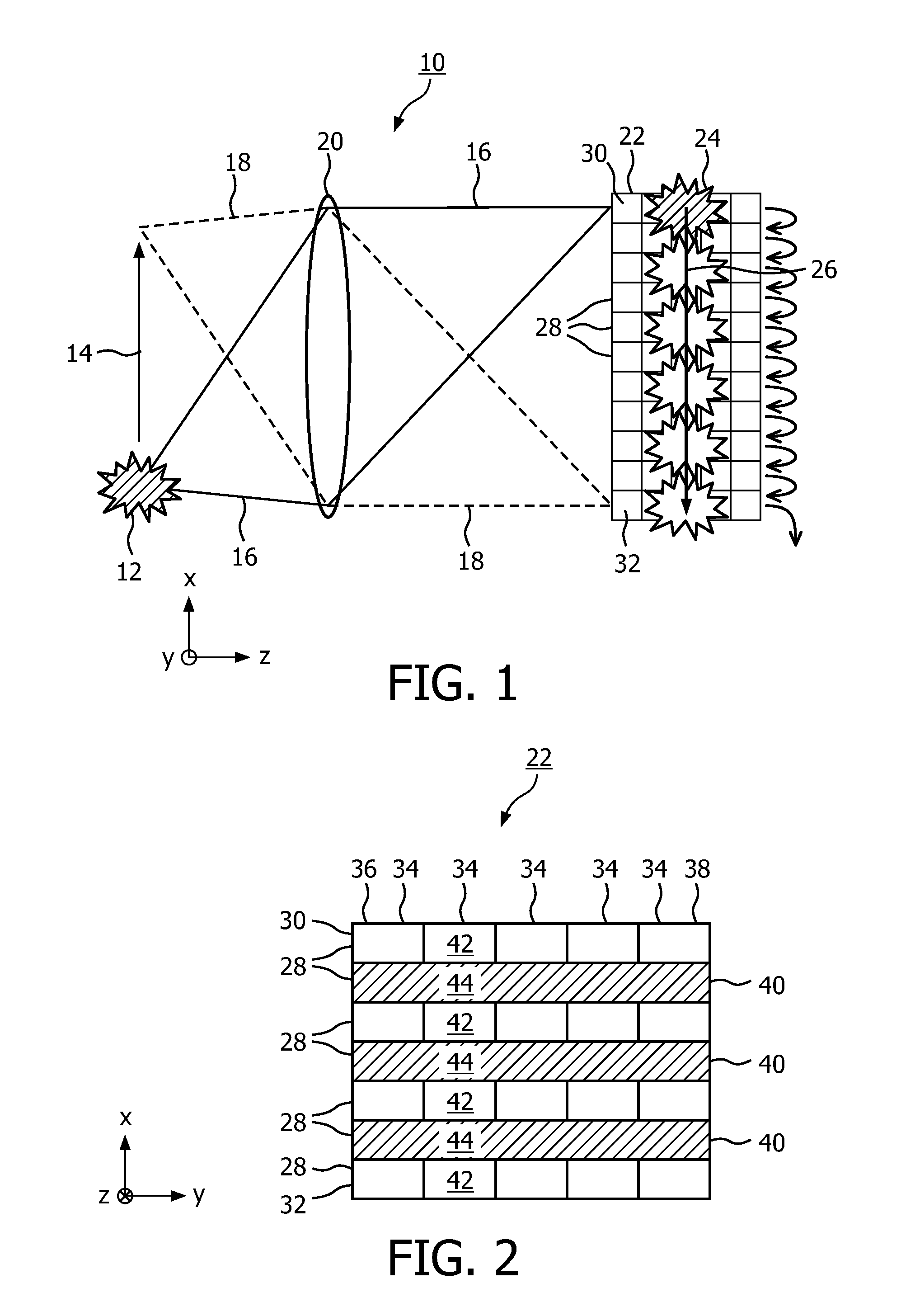
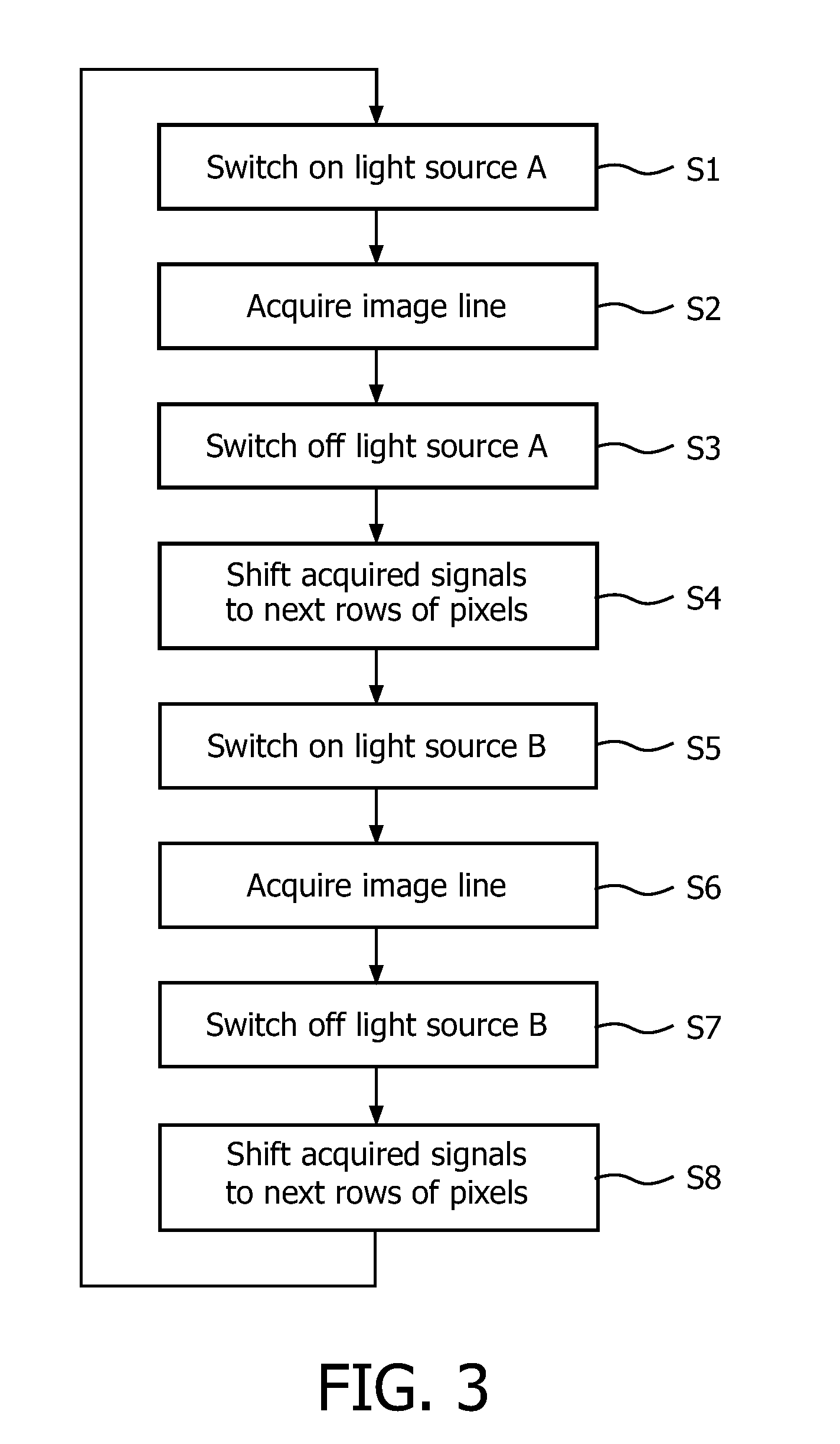
Time domain multiplexing for imaging using time delay and integration sensors
A time delay integration (TDI) sensor (22) comprises a sequence of cells (42, 44, 42, 44) numbered 1 to N. The TDI sensor is configured for transferring a charge from the cell numbered 1 via the cells numbered 2 to N-1 to the cell numbered N. Each cell (42; 44) in the sequence of cells is either sensitive or insensitive in the sense that when the TDI sensor (22) is evenly illuminated by light (46) incident on any of the insensitive cells (44) is at most 90% of the intensity of the light (46) incident on any of the sensitive cells (42). The sequence of cells (42, 44, 42, 44) comprises, in this order: a first sensitive cell (42), at least one insensitive cell (44), and a second sensitive cell (42). An imaging system comprising a TDI sensor and a method of imaging an object are also disclosed.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Virtual time-domain multiplexing for reference signals and data with modified cyclic prefix
Aspects of the disclosure relate to methods and apparatus of time-domain multiplexing (TDM) for reference signals (RS) and data using a modified cyclic prefix. A reference signal (RS) and data are multiplexed either in a single symbol or in two time consecutive symbols that respectively including the RS and data. The cyclic prefix (CP) is added to the single symbol using a portion of the RS or to a first symbol of the two time consecutive symbols using a portion of the RS. The CP may be copied from the RS or the end of the symbol, but not the data, in a manner that affords a virtual Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) of the RS and data before discrete Fourier transform (DFT) spreading is performed in a transceiver to provide lower peak to average power ratios and no Inter-symbol interference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for multiple sensors to communicate on a uni-directional bus
ActiveUS20050073403A1Low costRotary current collectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime domainCommunications system
The present invention provides a system of and a method for multiple transmitters to communicate data over a single uni-directional communication bus. In one form of the present invention, a data communication system using time-domain multiplexing includes a uni-directional current-modulated communication bus, a plurality of sensors coupled to the communication bus, at least one of the sensors capable of detecting the data transmission of a sensor outside of the current loop of the first sensor, the sensors also capable of transmitting data on the communication bus using current loop modulation. In another form of the present invention, a method of transmitting data on a uni-directional communication bus is provided. The method includes the steps of enabling a first device to transmit a data signal on the communication bus, the data transmission followed by an idle period, and the first device including a current sensor; enabling a second device to detect the first device's data transmission and the idle period; and enabling the first device to transmit data upon detecting the idle period, the first device positioned in a first current loop and the second device positioned in a second current loop outside of the first current loop, the second current loop passing through the current sensor of the first device.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
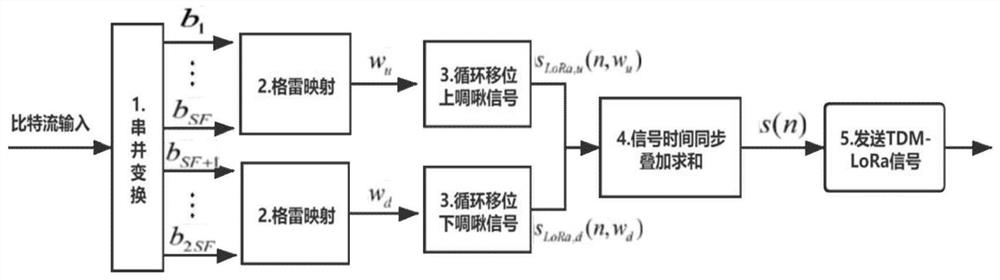
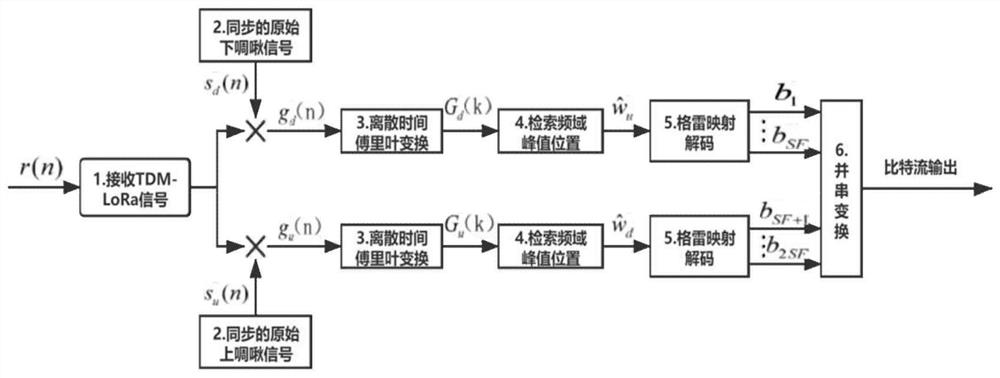
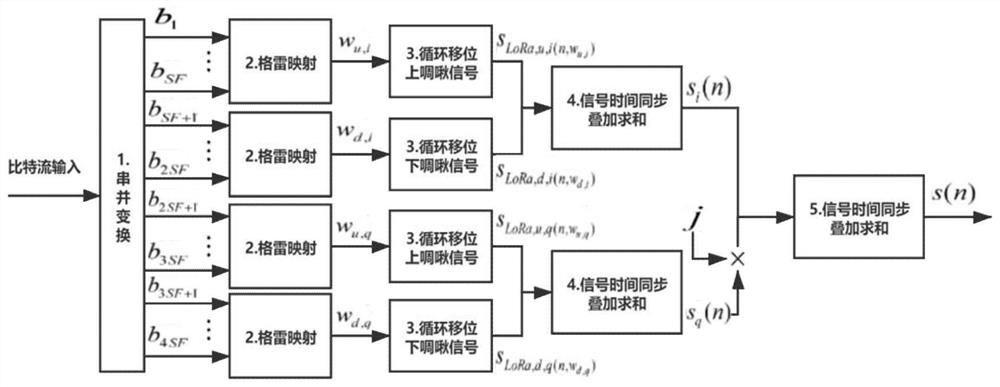
Time domain multiplexing frequency shift chirp keying modulation and quadrature modulation extension method thereof
The invention provides a time domain multiplexing frequency shift chirp keying modulation and quadrature modulation extension method thereof, which can improve the data transmission rate and the spectrum efficiency, ensure that the bit error rate performance is basically unchanged, and greatly improve the throughput rate. The method includes the following steps: grouping information bits input into a modulator by a sending end of a time domain multiplexing frequency shift chirp keying modulation system, performing serial-parallel conversion and Gray mapping on SF bits in one group, then selecting an upper chirp signal of periodic frequency shift, performing serial-parallel conversion and Gray mapping on SF bits in the other group, and adding and then transmitting the upper chirp signal and the lower chirp signal carrying the information; receiving, by a receiving end of the time domain multiplexing frequency shift chirp keying modulation system, the signals, and multiplying the received signals respectively by original lower chirp signals and upper chirp signals, performing discrete Fourier transform on the respectively multiplied received signals, and acquiring the position information of the highest peak from two frequency spectrums, and demodulating corresponding sending information bits.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
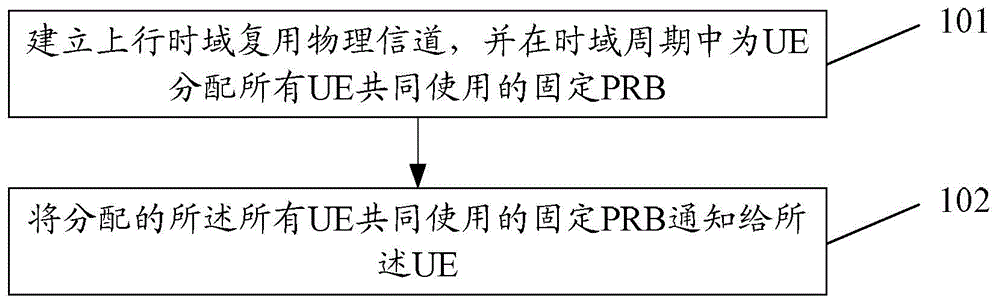
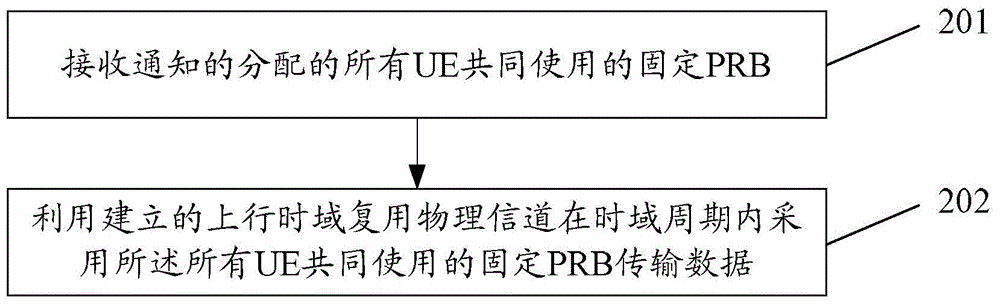
Data transmission method and system, base station and user equipment
The invention discloses a data transmission method, comprising the steps that: a base station establishes an uplink time domain multiplexing physical channel, allocates a fixed physical resource block (PRB) shared by all UE to user equipment (UE) within a time domain period and notifies the fixed physical resource block to the UE; and after receiving the notification, the UE uses the established uplink time domain multiplexing physical channel to transmit data within the time domain period by adopting the fixed PRB shared by all UE. The invention further discloses a base station, UE and a data transmission system.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
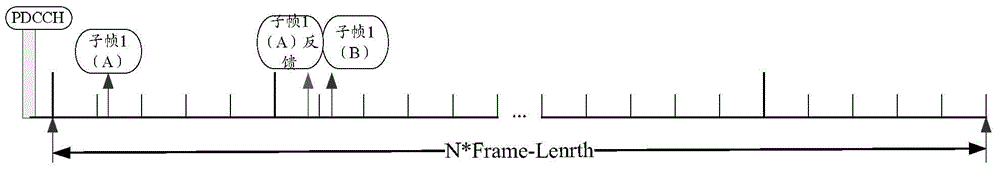
Method and device for downlink transmission
ActiveCN104144510ATransmission path multiple useWireless communicationTime domainInformation transmission
The invention provides a method and device for downlink transmission. According to an embodiment, the method is based on time domain multiplexing. According to the method, a physical resource block (PRB) pair used for transmitting scheduling information of one set of user equipment is selected from predetermined PRB pairs capable of being used for transmitting the scheduling information in available PRB pairs, and the scheduling information is transmitted to the user equipment on predetermined subcarriers of first two orthogonal frequency division multiplexing symbols of the selected PRB pair. In addition, the invention further provides a technical scheme based on frequency domain multiplexing. According to the embodiment, the technical scheme based on time domain multiplexing and frequency domain multiplexing is provided, so PMCH information transmission on new types of carriers can be achieved in LTE-A, and meanwhile the influence on regulations of an RAN1 is limited.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SHANGHAI BELL CO LTD
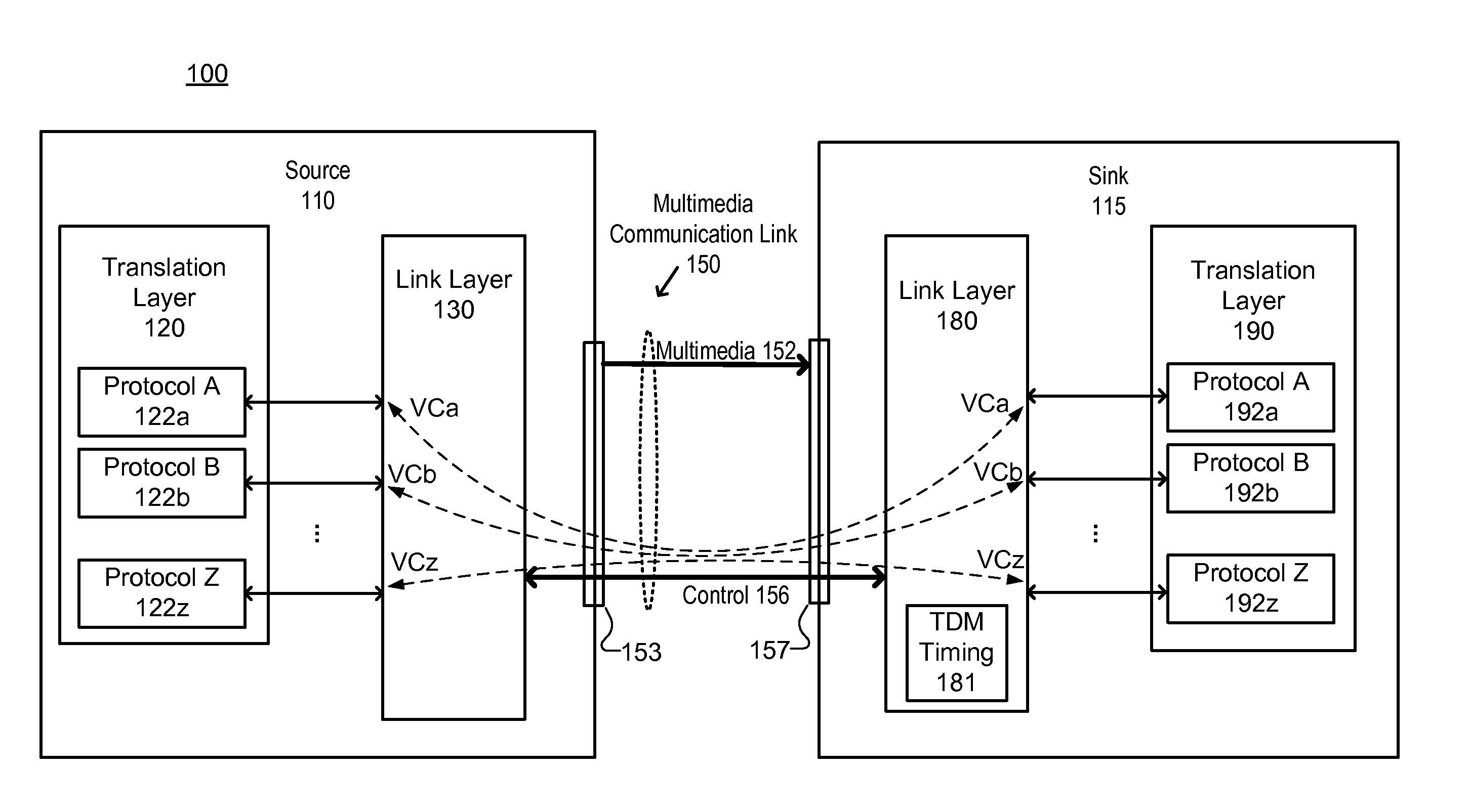
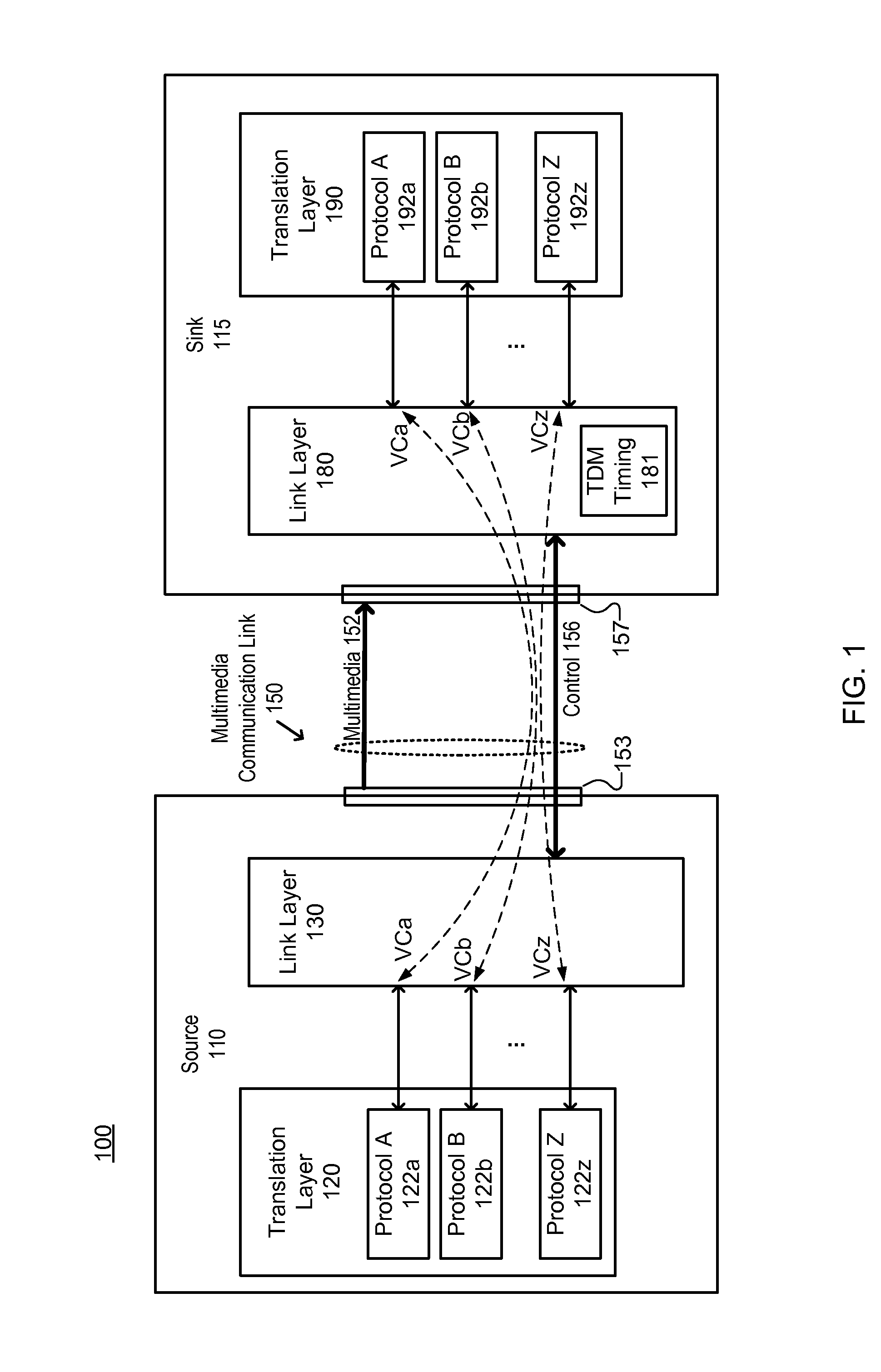
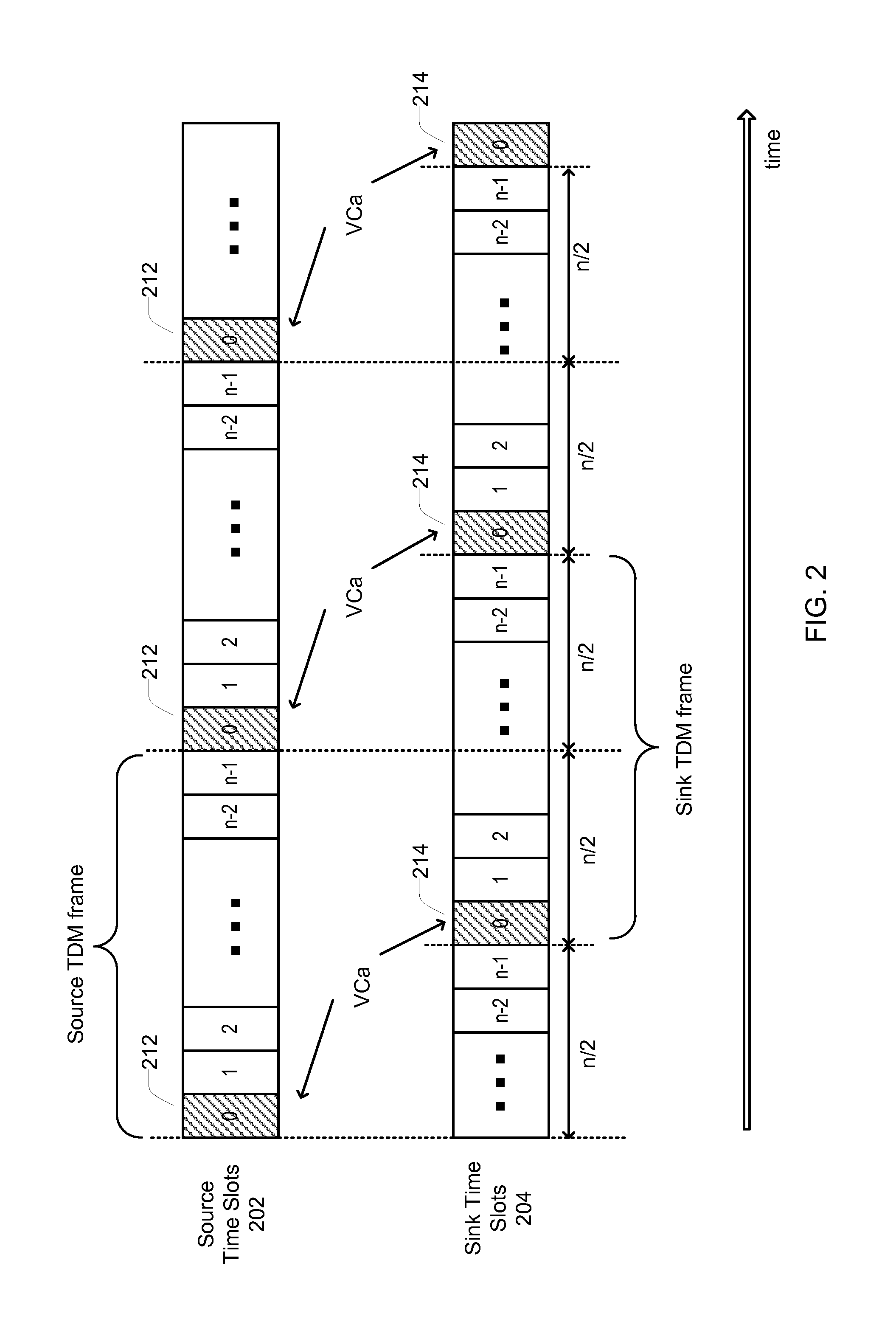
Phase Relationship Control for Control Channel of a Multimedia Communication Link
ActiveUS20160065353A1Time-division multiplexElectric digital data processingTime domainControl channel
A multimedia system for data communications. A source device communicates over a full duplex control channel of a multimedia communication link using time domain multiplexed (TDM) frames having n time slots per frame. The source device allocates a first time slot position to a virtual channel for data transmission by the source device over the full duplex control channel. A sink device communicates over the full duplex control channel of the multimedia communication link. The sink device allocates a second time slot position to the virtual channel for data transmission by the sink device over the full duplex control channel. A timing of the second time slot position is offset from a timing of the first time slot position by substantially n / 2 time slots.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
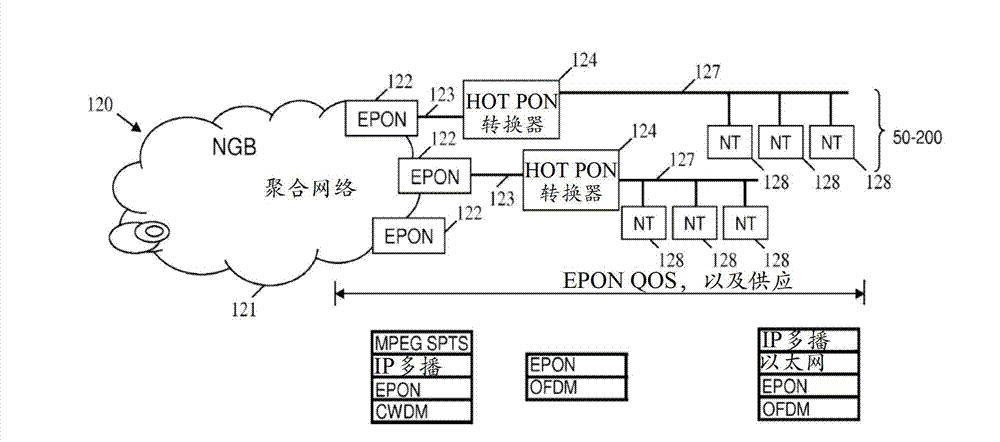
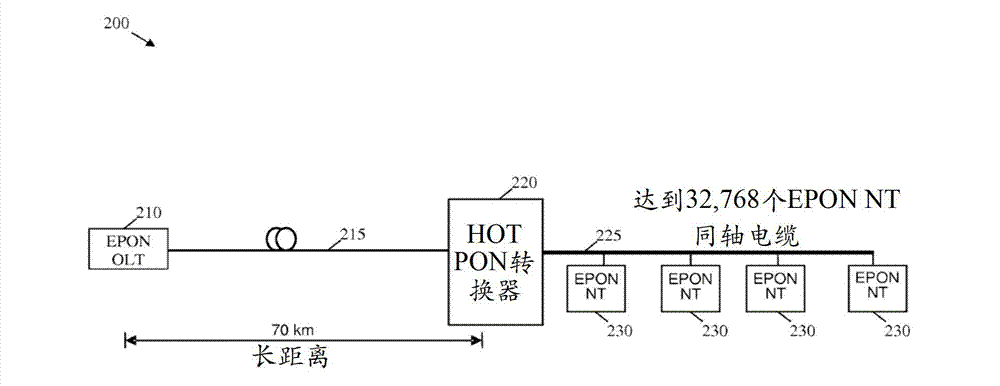
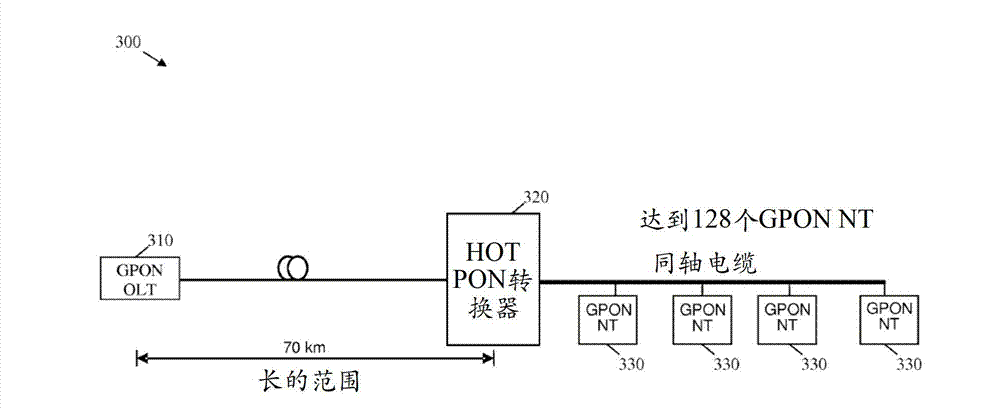
Hybrid orthogonal frequency division multiplexing time domain multiplexing passive optical network
InactiveCN103026678AMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexQuality of serviceNetwork termination
An apparatus comprising a time domain multiplexing (TDM) to Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) or bounded Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) channels HOT PON converter configured to couple to an optical line terminal (OLT) via an optical fiber and to a plurality of network terminals (NTs) via a point-to-multipoint coaxial cable and configured to transmit TDM data from the OLT using OFDM or bounded QAM channels to the corresponding NTs, wherein the OFDM or bounded QAM channels transmission of TDM data maintains End-to-End (E2E) TDM passive optical network (PON) protocols, service provisioning, and quality of service (QoS).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for dampening TDMA interference
ActiveUS8913961B2Minimize audible effectDifficult to noticeUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsTime domainActuator
Systems and methods are disclosed which relate to mitigating the detrimental effects of interference to electronic devices from mobile telephones utilizing any form of time-domain multiplexing technology. A wireless transmitter inside the mobile telephone broadcasts a warning transmission which can be received by affected devices. Once the warning transmission is received by an affected device, the device activates a blanking circuit comprising an actuator and a switch or switches. The switches open for the duration of the interference so that the user does not receive undesired output such as: noise through a speaker, noise through a microphone, or other interference with electrical signals.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com