Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Surveillance monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
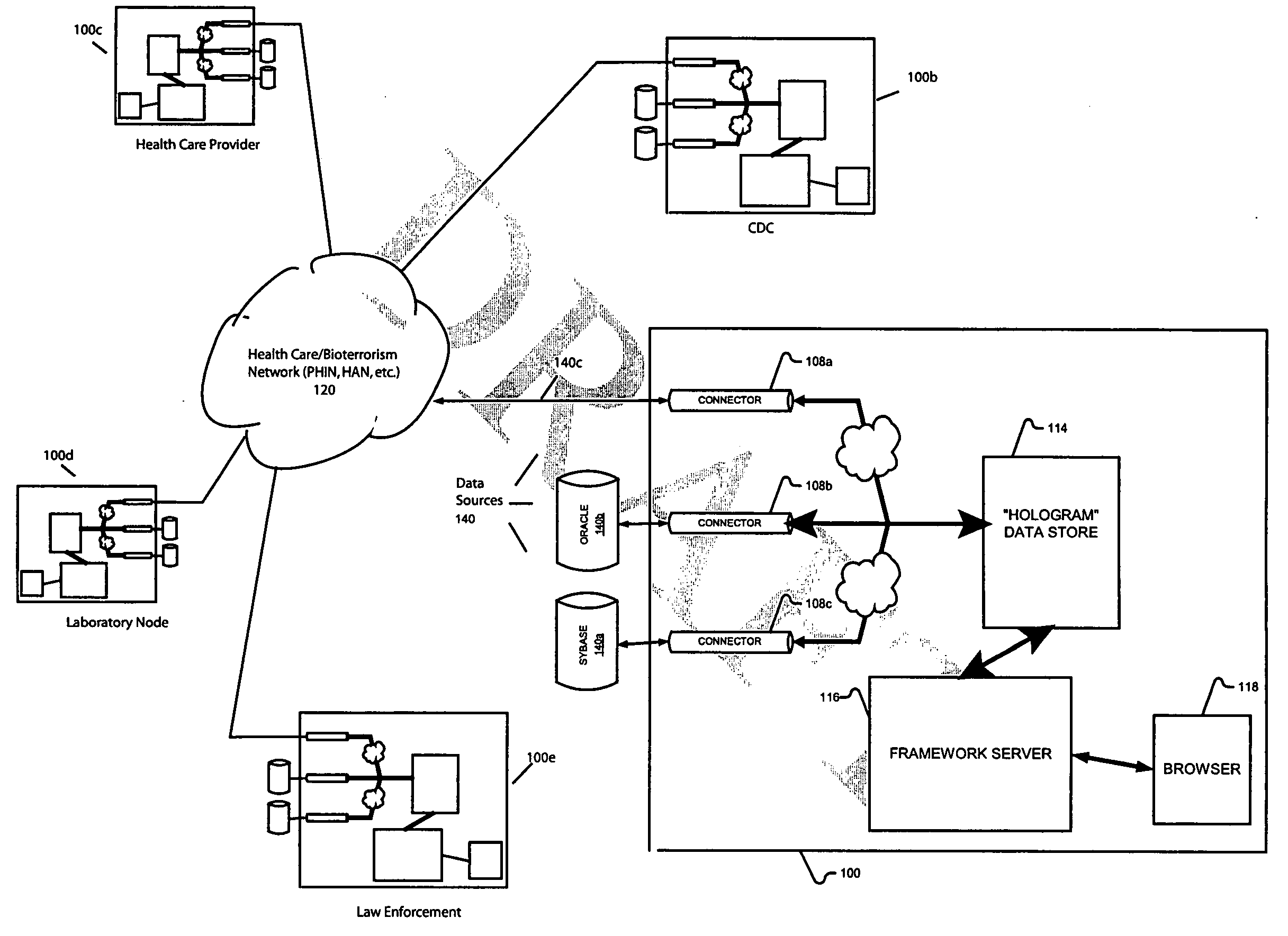
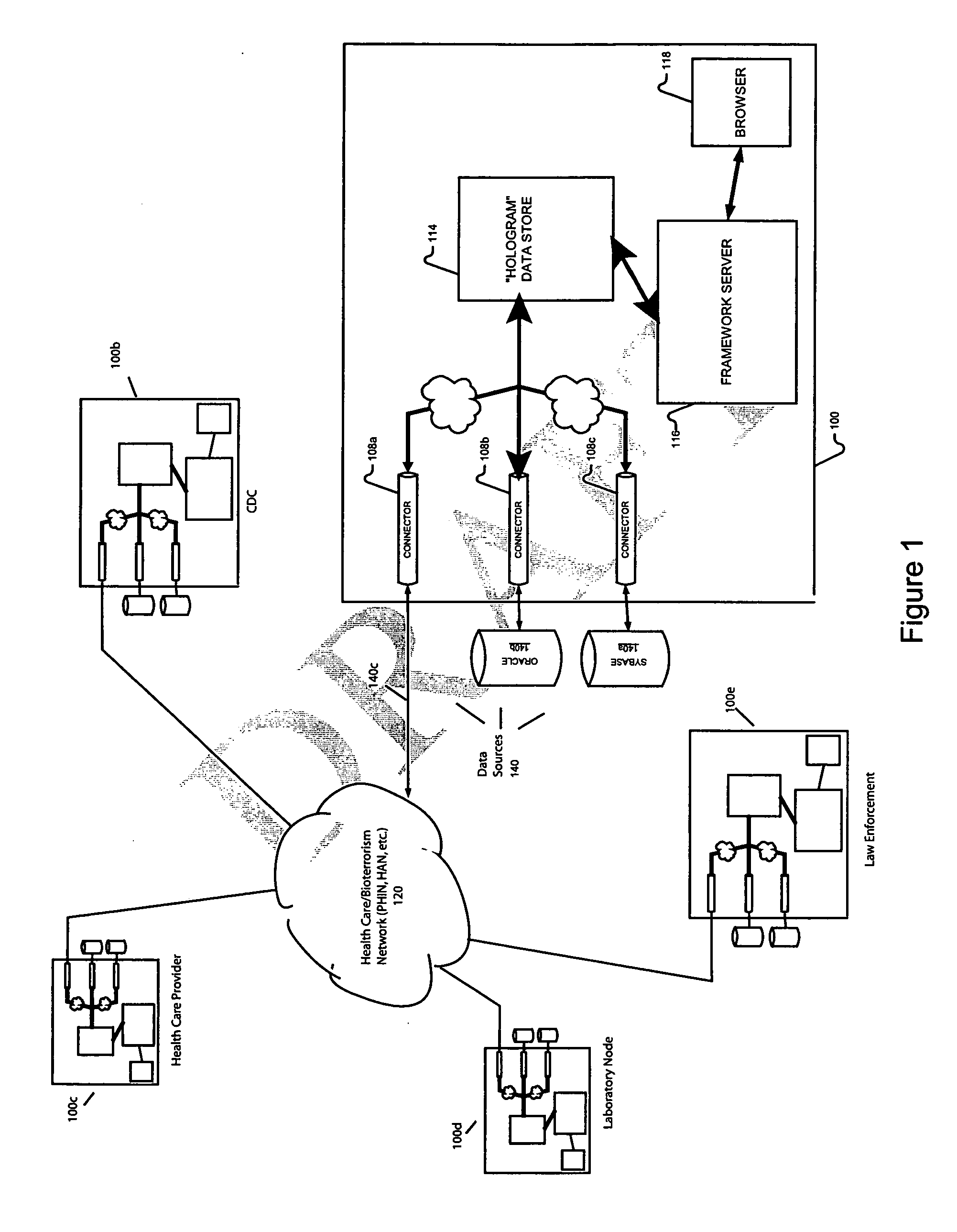
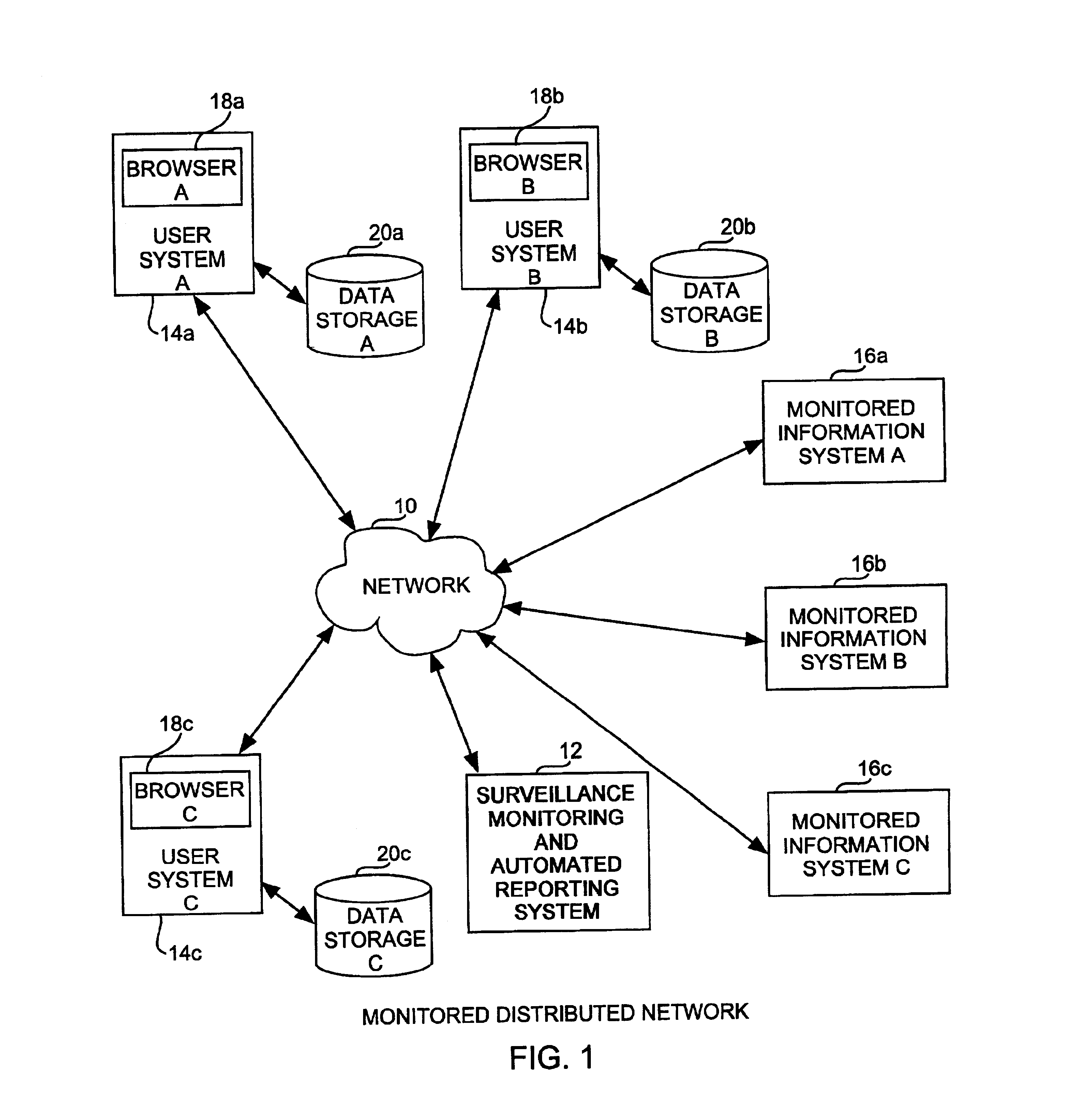
Surveillance, monitoring and real-time events platform
InactiveUS20050055330A1Highly flexibleHighly scaleableDigital data processing detailsEpidemiological alert systemsData sourceCommunity setting
Systems and methods according to the invention provide a surveillance, monitoring and real-time events platform to (i) enable the integration and communication of information between government agencies and organizations specifically tasked with ensuring the security and safety of our nation and its communities, (ii) to integrate information systems from federal, state and / or local agencies (from disparate data sources if necessary) in order to obtain a single, real-time view of the entire organization, and (iii) to extract more complete, actionable information from their existing systems, thereby dramatically improving decision making speed and accuracy.
Owner:OBJECT STORE INC
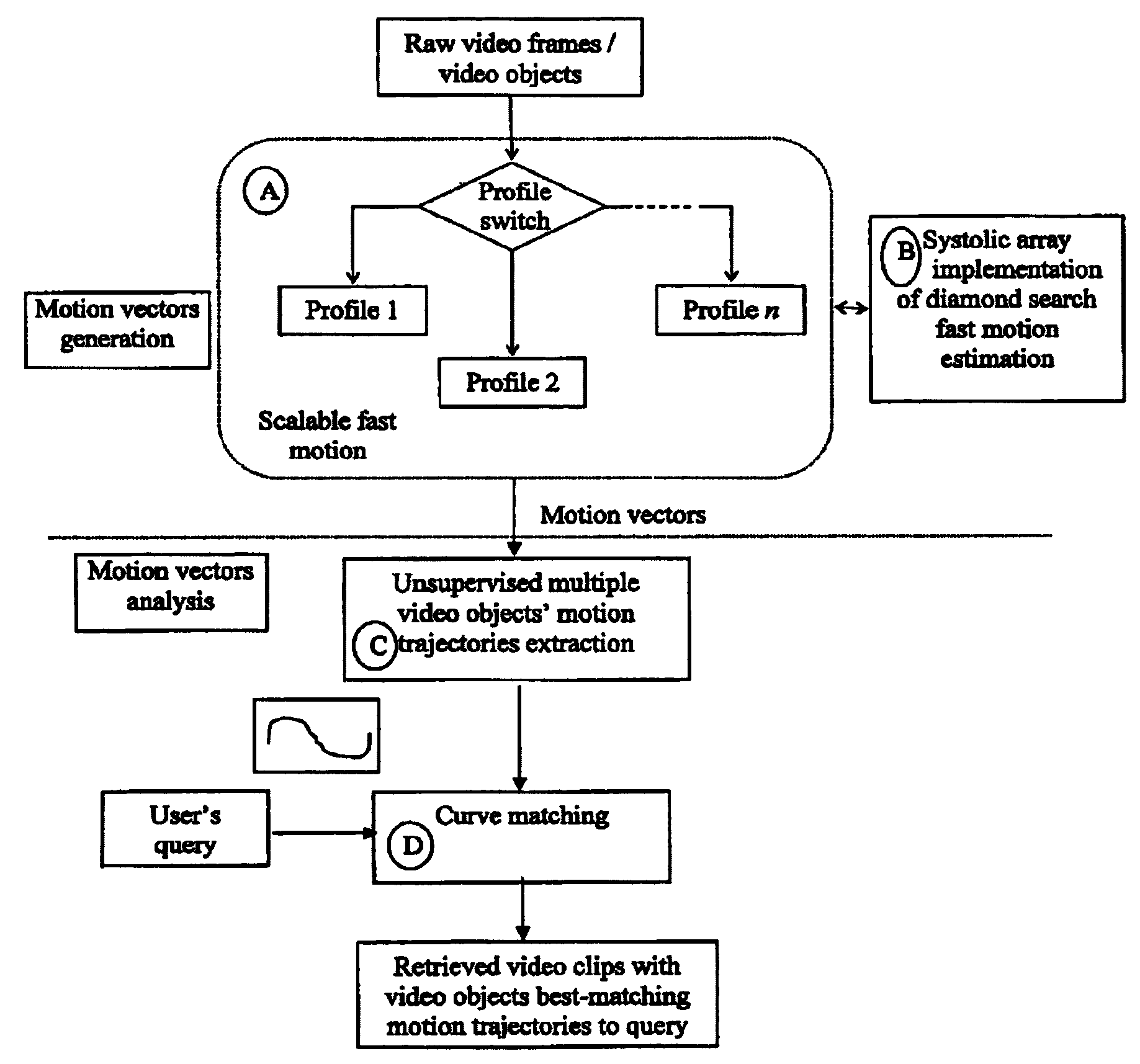
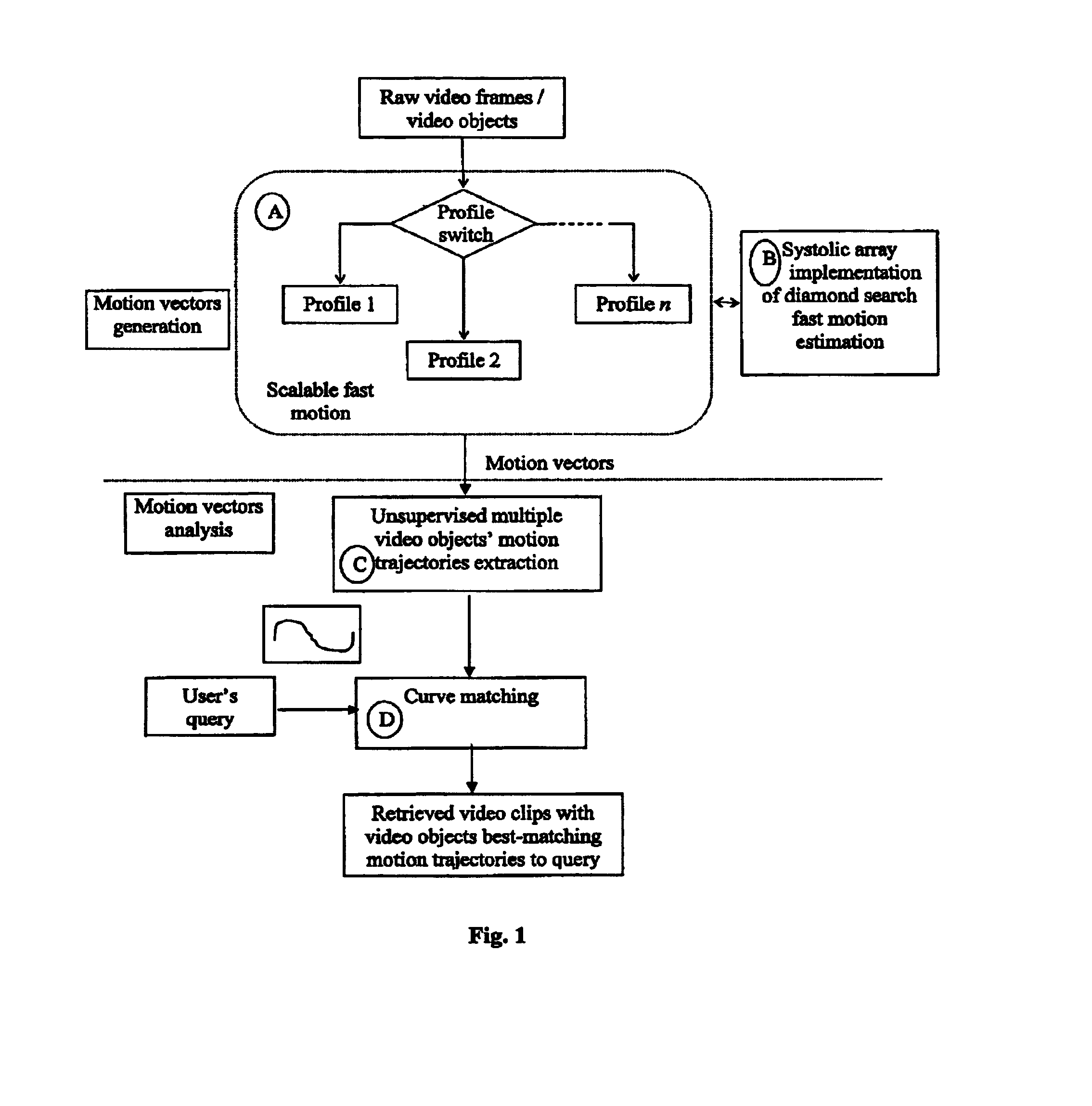
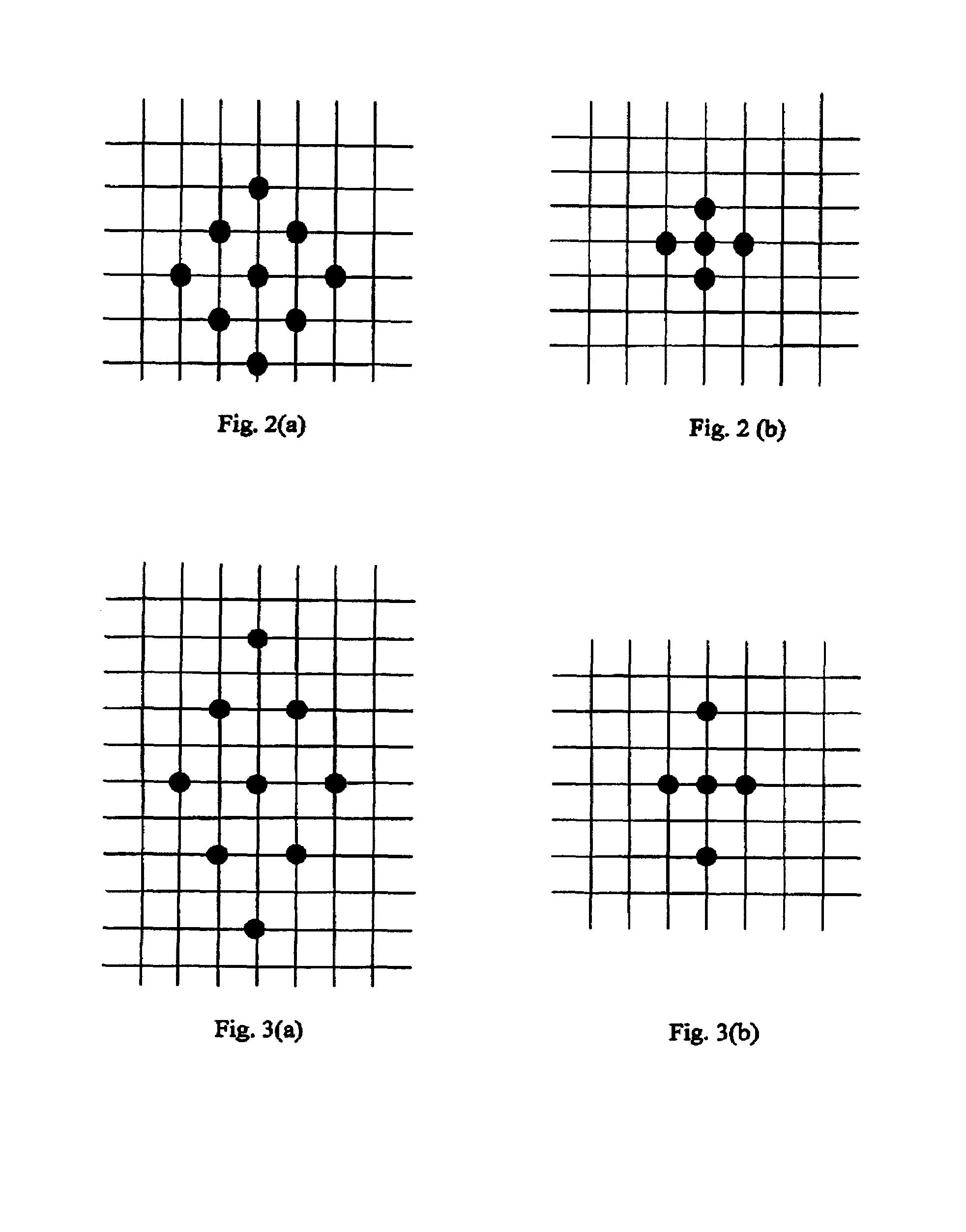
System and method for motion vector generation and analysis of digital video clips
InactiveUS7072398B2Convenience needsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMotion vector
Given a digital video clip, this invention describes how to efficiently compute the motion vectors and motion trajectory of each identified video object for facilitating various commonly encountered visual applications, such as video compression for transmission and archiving, security and surveillance monitoring, and search-by-query required in the Internet search engine or digital library.
Owner:MA KAI KUANG
Surveillance monitoring and automated reporting method for detecting data changes
A surveillance monitoring and automated reporting method is used for detecting observable changes in data sources over a network, such as the internet, for accessing changing data, such as world wide web content data, and for providing scheduled change detection notifications and results through user defined search criteria for automated monitored search criteria matches on a recurring basis by user defined scheduling. The method extracts content data from the data sources and updates a master database, then detects changes in the content data within the search criteria. Upon detection, the user is notified using graphical interfaces, electronic mail messages, pager messages, or personal data assistant messages.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
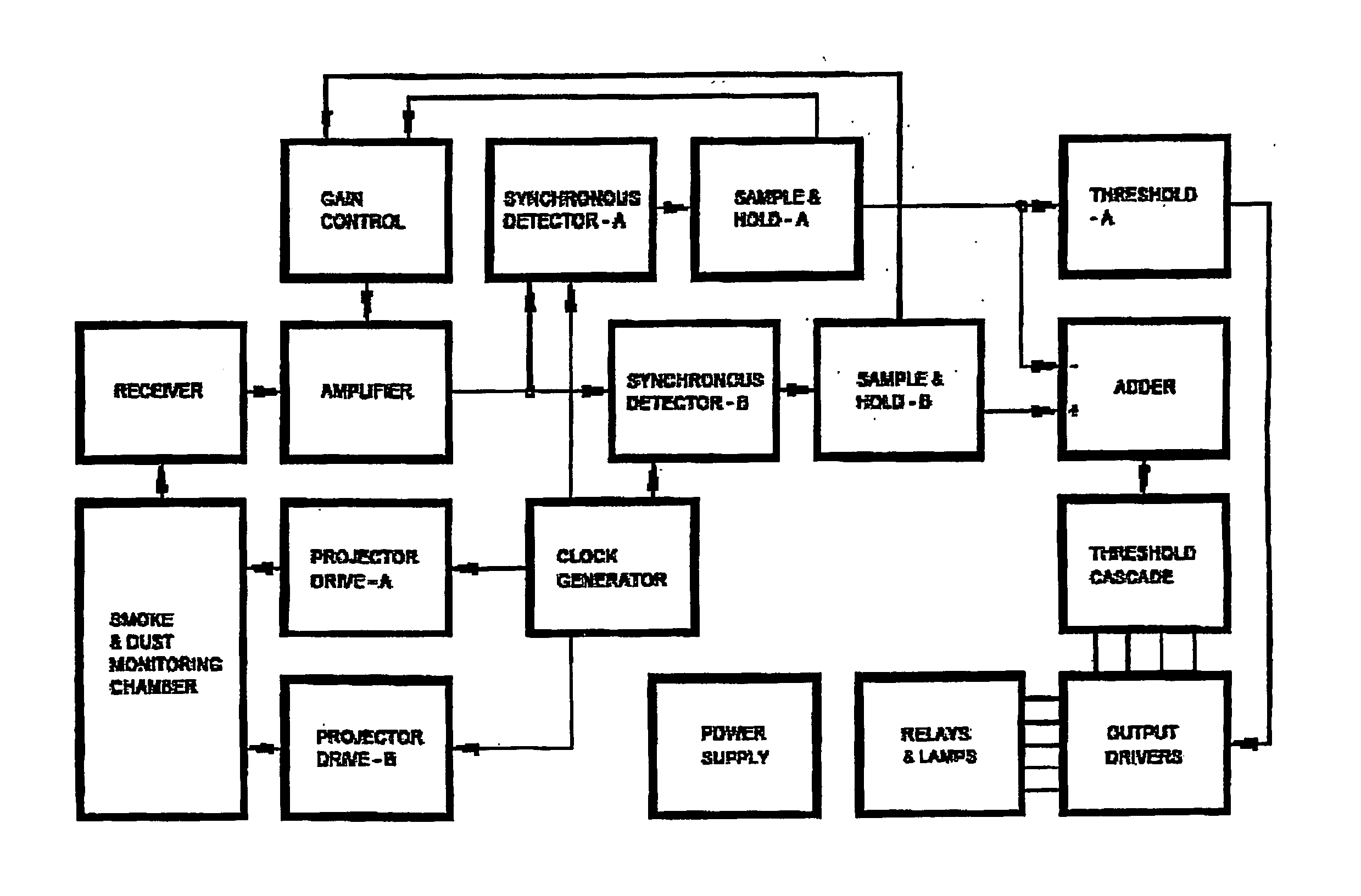
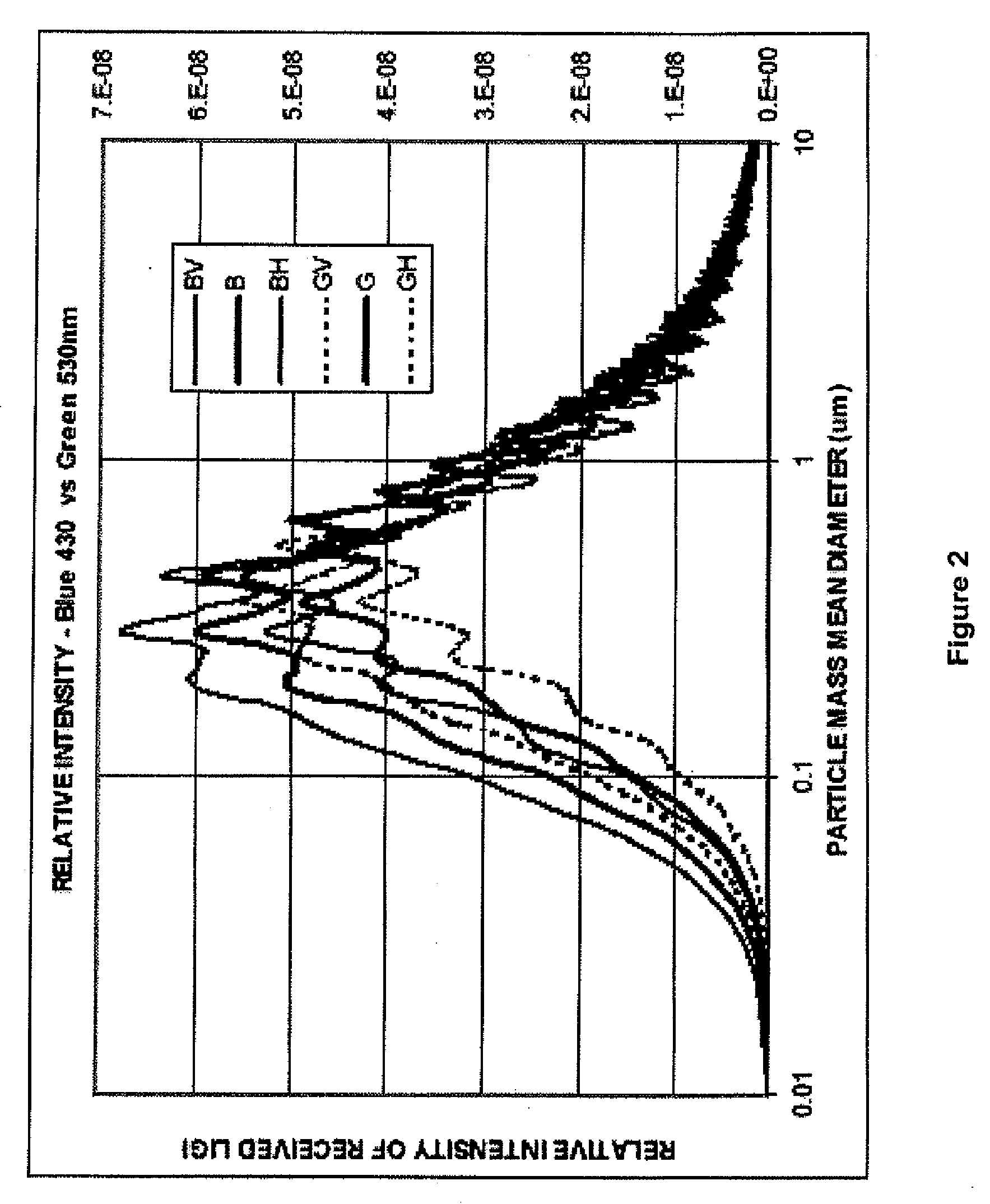
Particle monitors and method(s) therefor
InactiveUS20070024459A1Low costWeaken energyVolume/mass flow measurementScattering properties measurementsSmoke detectorsCombustion
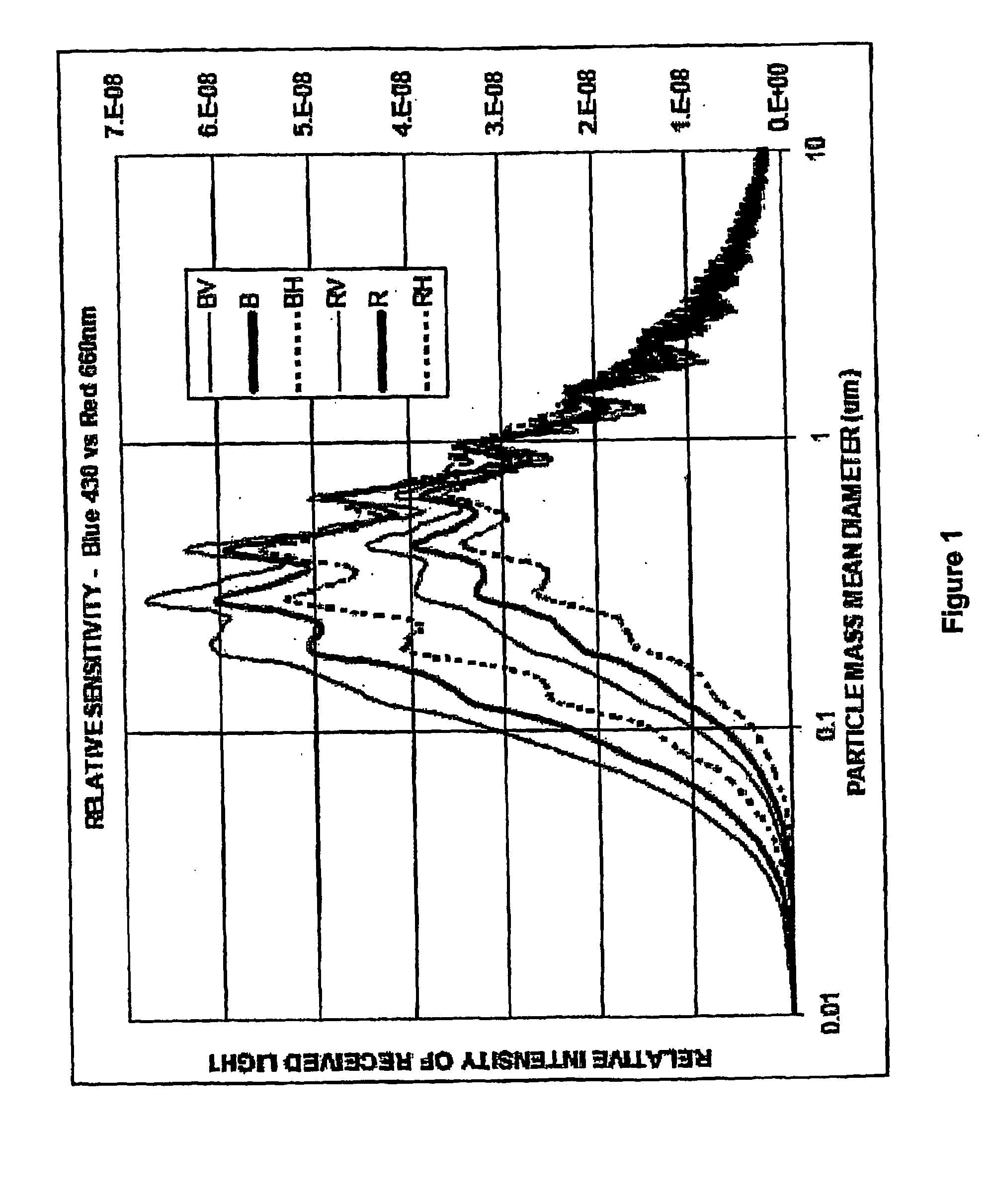
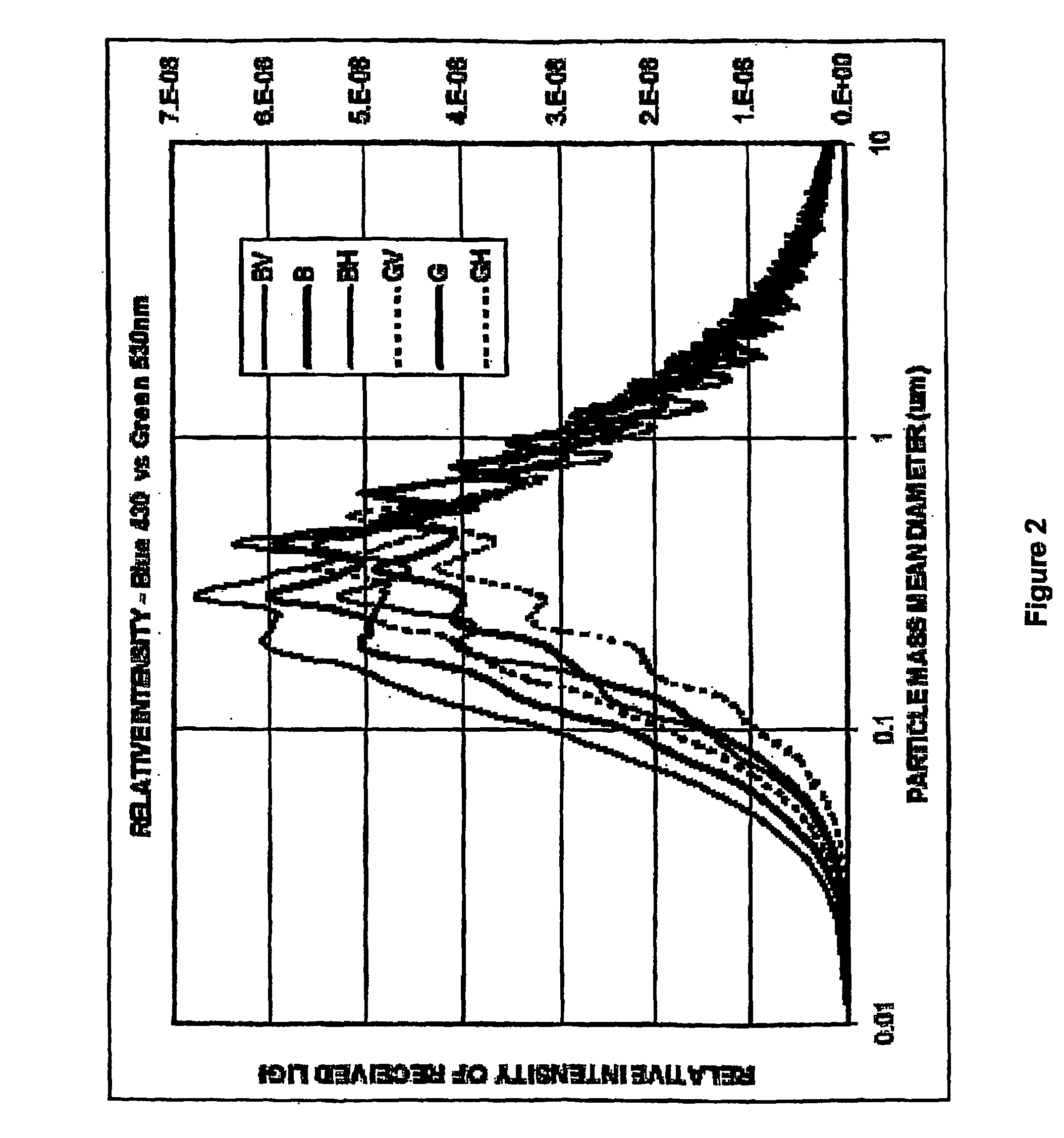
The present invention relates to the field of the detection, analysis and / or determination of matter or particles suspended in fluid. In one particular form, the present invention relates to smoke detectors, which detect unwanted pyrolysis or combustion of material. In another form, the present Invention relates to smoke detectors of the early detection type, and which may be applied to ventilation, air-conditioning or duct monitoring of a particular area. In yet another form, the present invention relates to surveillance monitoring, such as building, fire or security monitoring. in still another form, the present invention relates to environment monitoring, such as monitoring, detection and / or analysis of a fluid, zone, area and / or ambient environment, including commercial and Industrial environments.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
Unattended surveillance device and associated methods
ActiveUS20100079594A1Reduce data volumeReliable classificationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGHz frequency transmissionTransceiverSurveillance monitoring
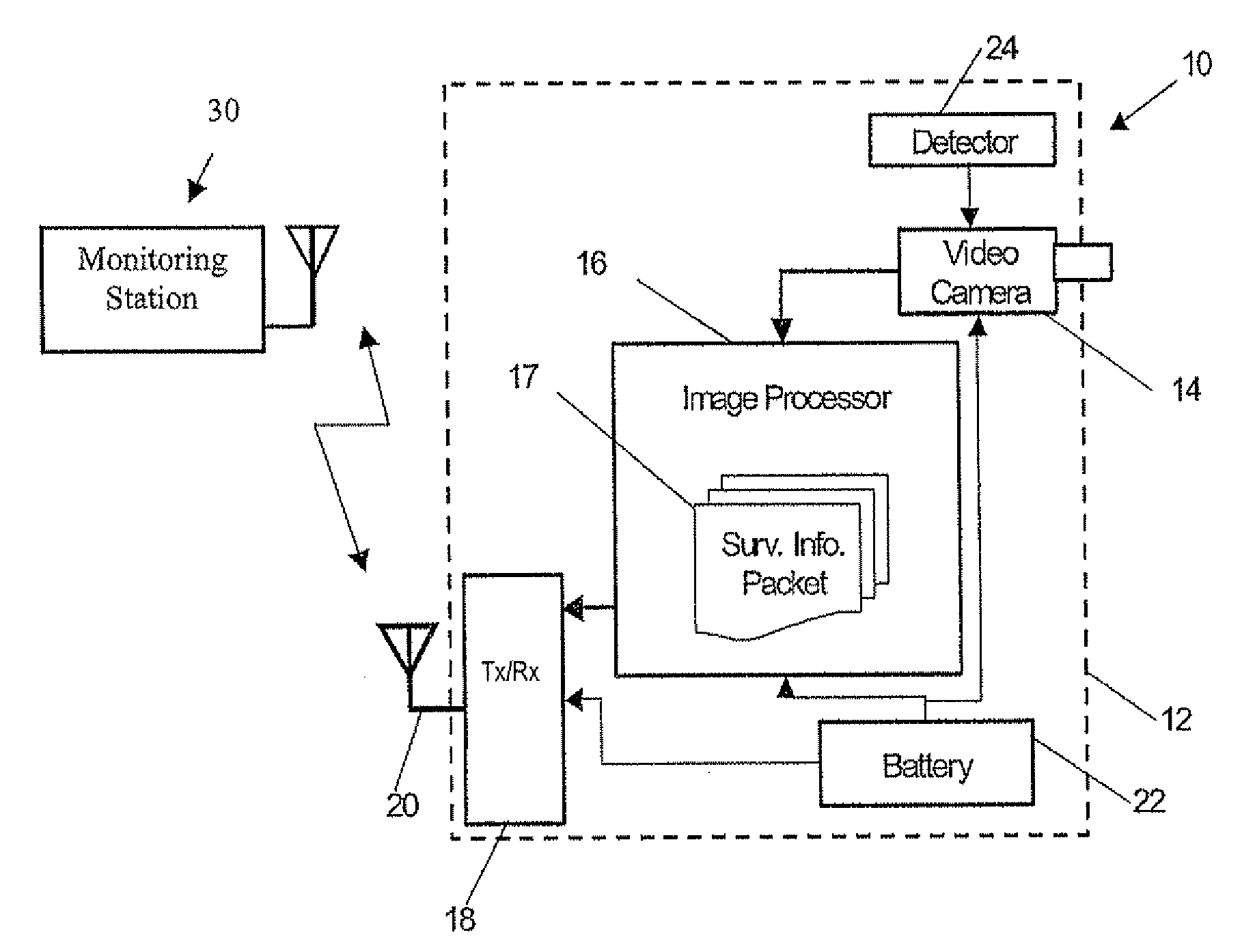
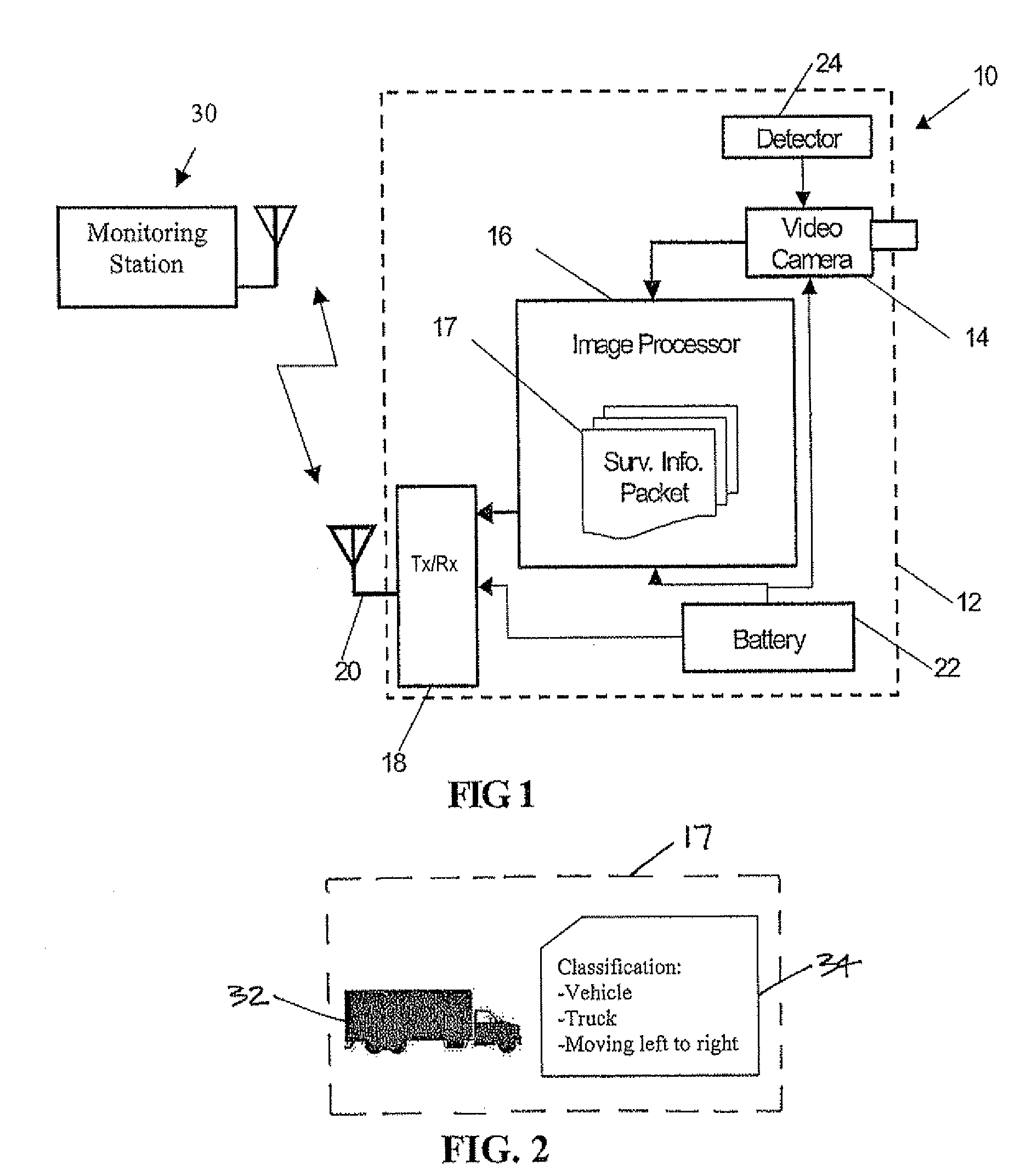
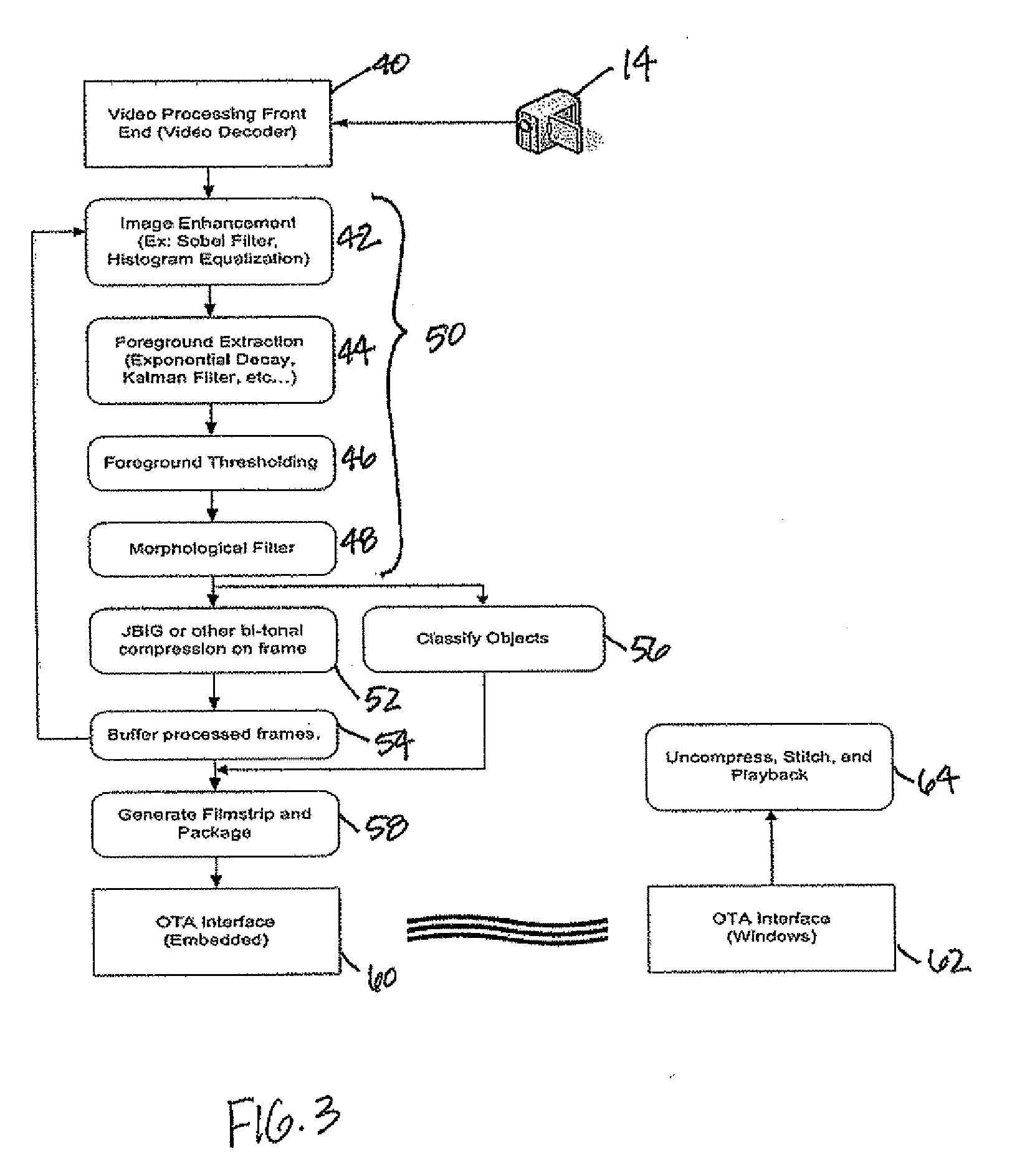
The unattended surveillance device may include a housing to be positioned for unattended surveillance, a video camera associated with or carried by the housing to capture video, and an image processor carried by the housing and cooperating with the video camera. The image processor extracts moving objects in the foreground of the captured video, generates a profile image or sequence of profile images of the extracted moving objects, compresses the sequence of profile images, and generates a surveillance information packet based upon the compressed sequence of profile images. Also, a wireless transmitter or transceiver may be associated with the image processor to transmit the surveillance information packet to a surveillance monitoring station.
Owner:OLLNOVA TECH LTD
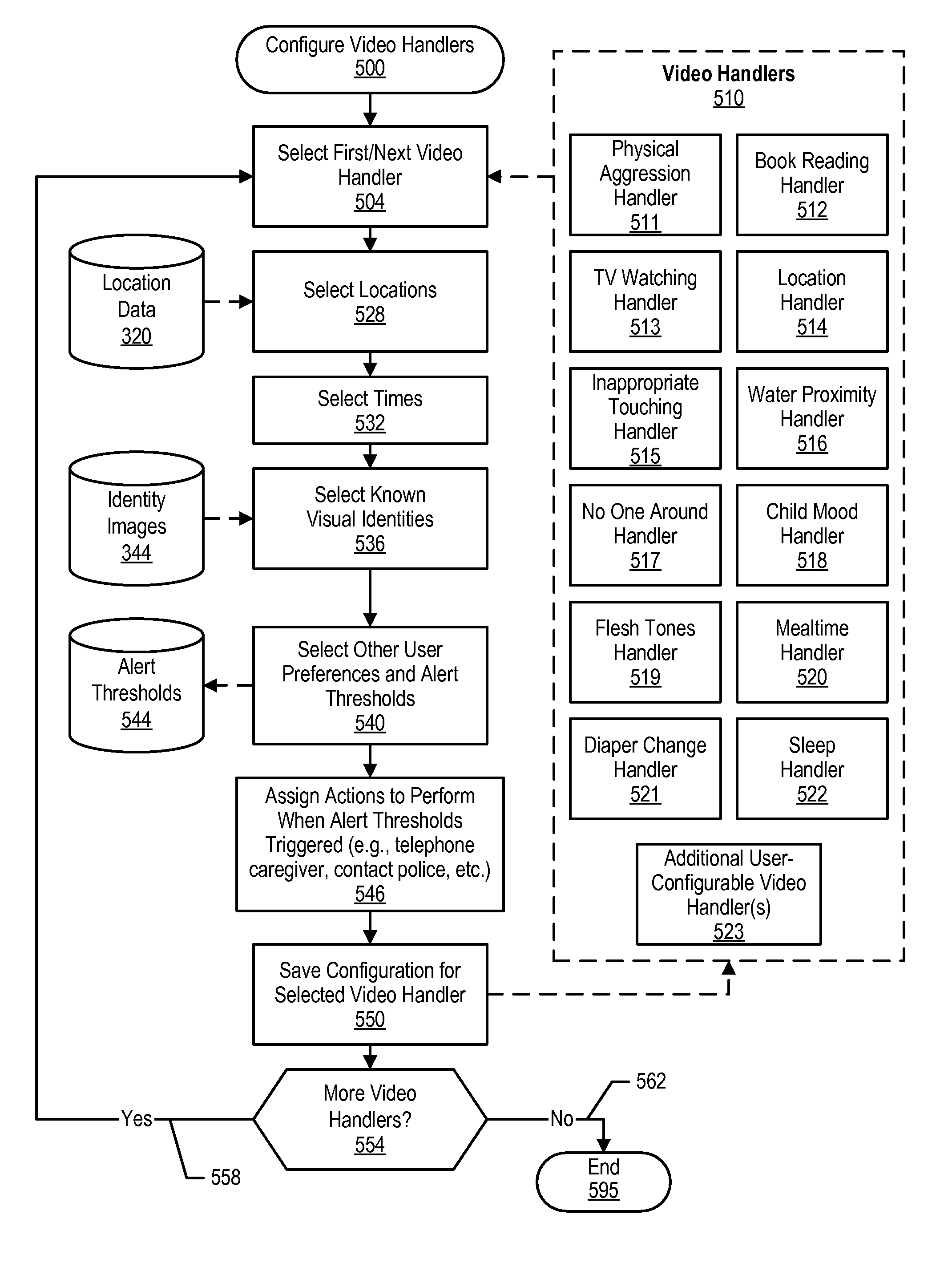
System and method for pattern based thresholding applied to video surveillance monitoring
InactiveUS20090189983A1Closed circuit television systemsBurglar alarmVideo monitoringPattern recognition
A system, method, and program product is provided that configures video handlers pertaining to a dependent individual. Configuring includes setting alert thresholds. Visual locations are configured. Visual images that pertain to caregivers of the dependent individual are configured. Video streams are received from video sources. Video streams are compared to configured locations to classify the dependent individual's location. Video stream is analyzed to determine whether the dependent individual is alone or with others. If with others, a list of known persons is determined by comparing the video streams with the configured visual images. The configured video handlers are initiated based on the inputs of the location and the people present with the dependent individual. Video handlers trigger alerts when thresholds are reached. Alerts include performing actions to protect the dependent individual from harm.
Owner:IBM CORP
Video monitoring system and method for agricultural diseases and insect pests
InactiveCN102300079AClosed circuit television systemsDigital video signal modificationVideo monitoringSurveillance monitoring
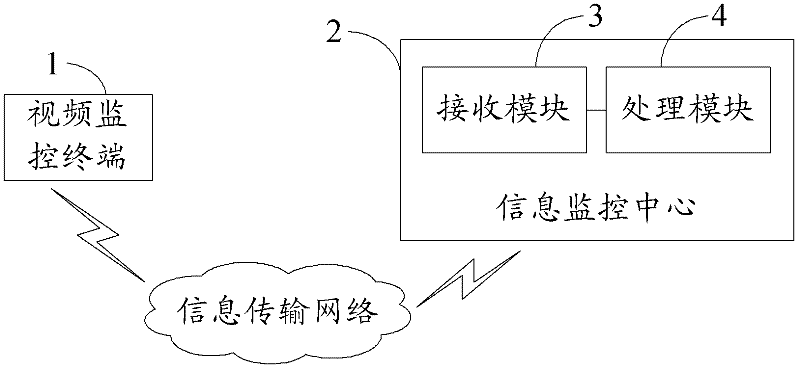
The invention provides a video monitoring system for agricultural diseases and insect pests and a method thereof. Wherein, the video monitoring system for agricultural diseases and insect pests includes a video monitoring terminal and an information monitoring center, the video monitoring terminal and the information monitoring center are connected through an information transmission network; the information monitoring center includes a receiving module and a processing module connected to each other. The agricultural disease and insect pest video monitoring system provided by the present invention collects field disease and insect pest information in real time through the video monitoring terminal, and transmits it to the information monitoring center through the information transmission network, so that the information monitoring center can process the obtained field real-time video and image information, Analysis provides intuitive image data for professional technicians to judge the development trend and severity of field diseases and insect pests, so that they can formulate corresponding control or management plans.
Owner:全国农业技术推广服务中心 +1
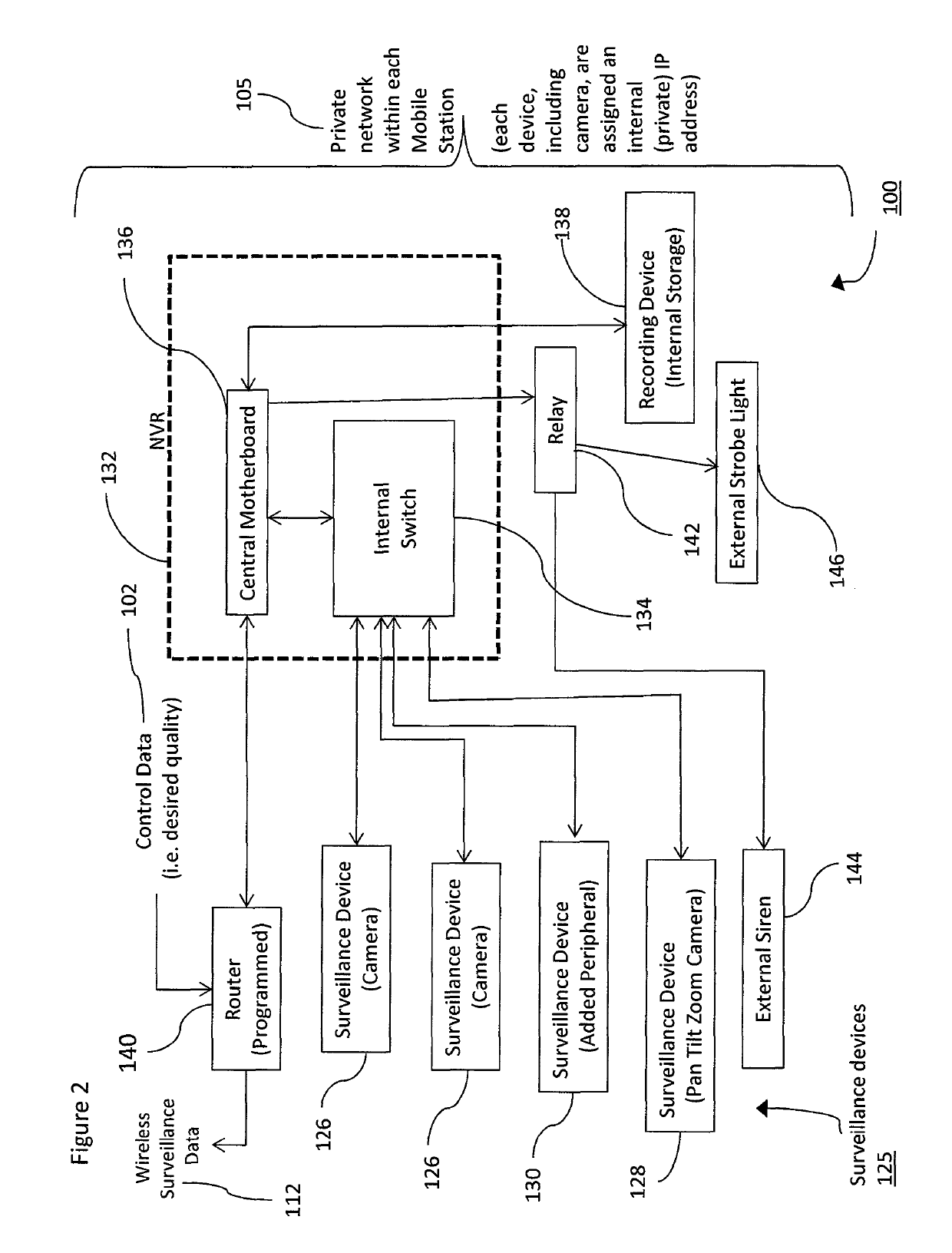
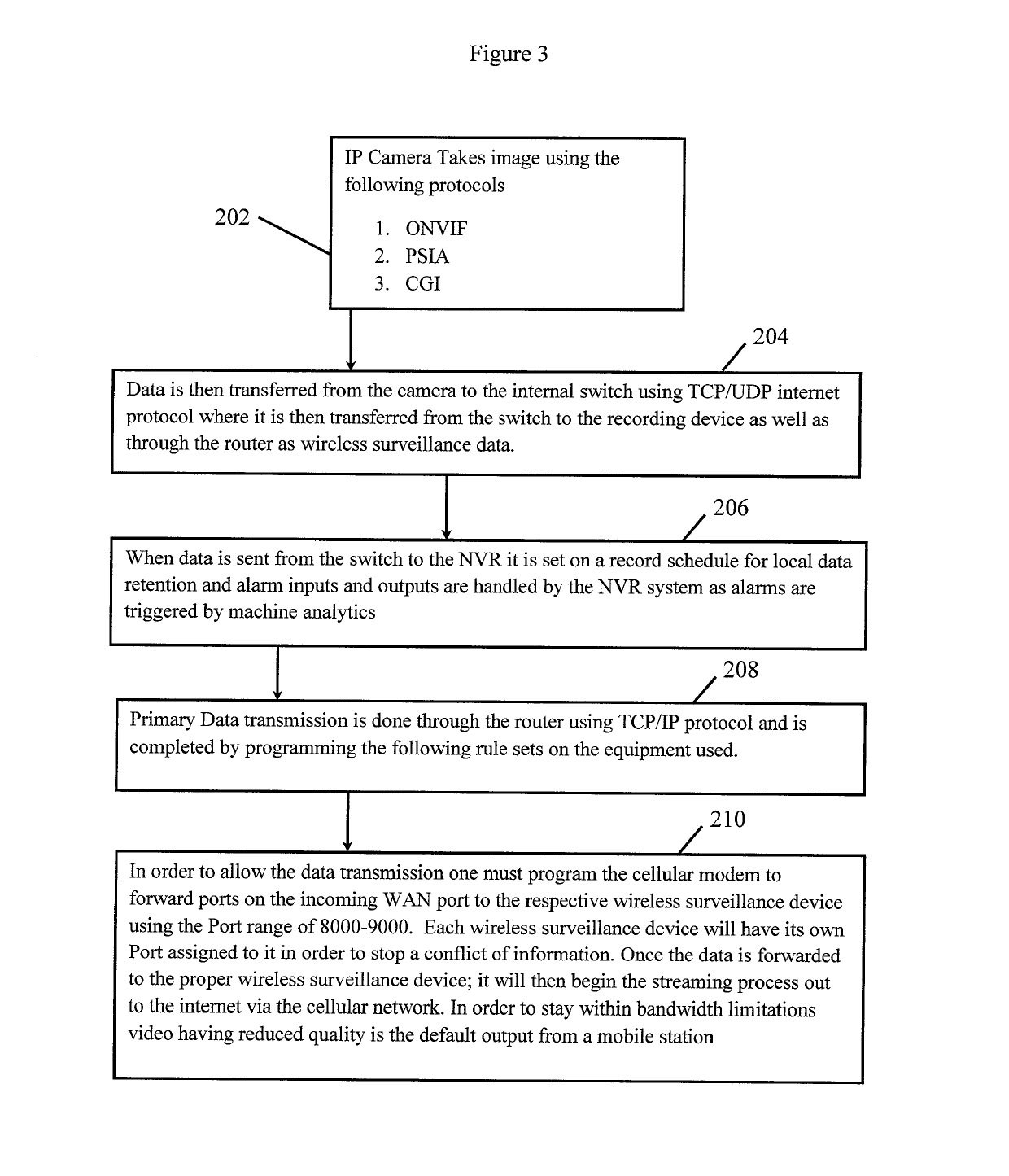
Method of video surveillance using cellular communication
ActiveUS20160044283A1Minimal electrical powerEasy to useNetwork topologiesColor television detailsTransceiverWireless transceiver
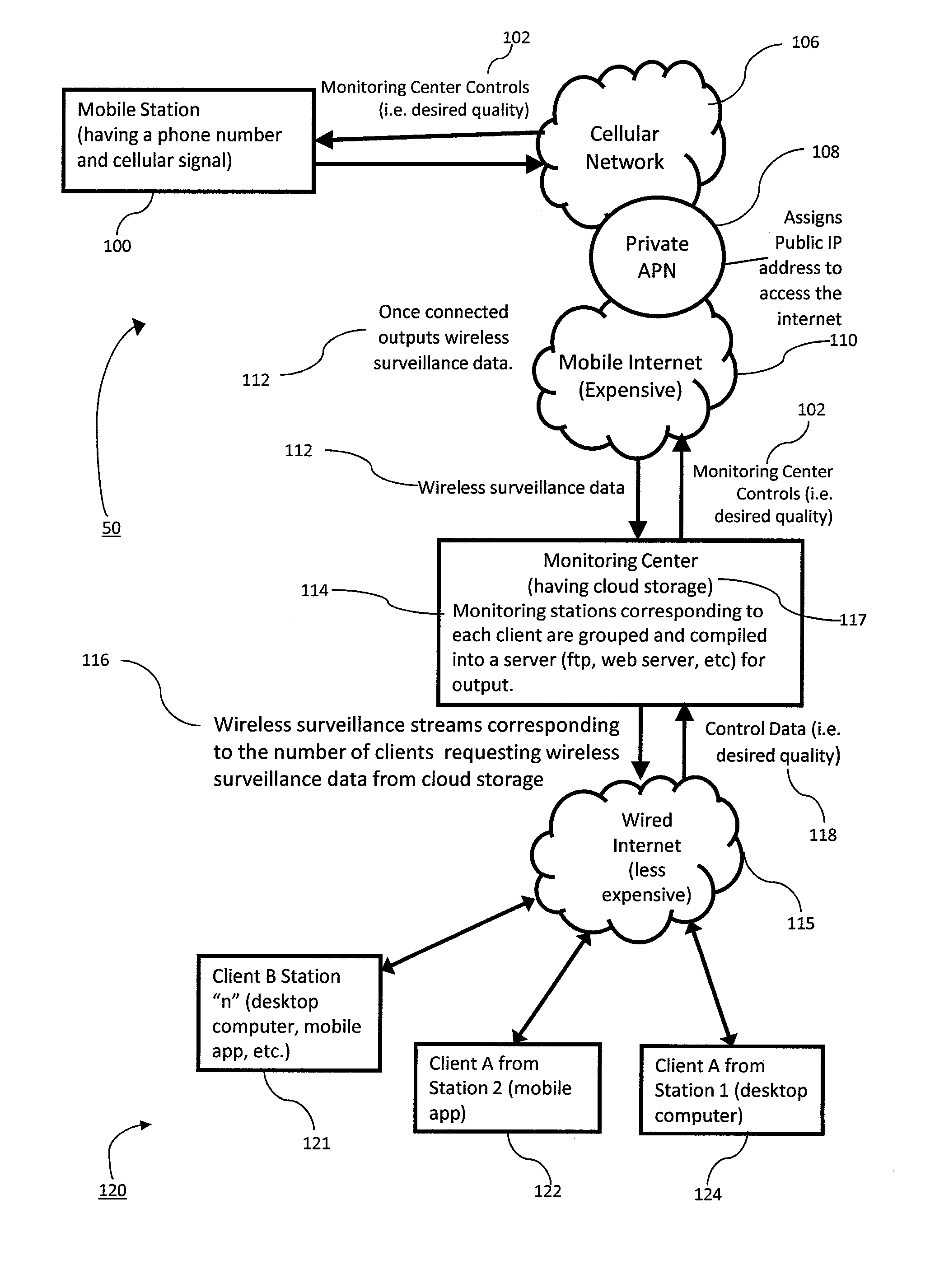
A method of video surveillance with a mobile station using cellular communication including the steps of: a) applying power to a mobile station which includes a router in communication with a wireless transceiver for transmitting data wirelessly; b) the router in communication with an private network in the mobile station; c) the private network in communication with surveillance devices attached to the mobile station; d) the router in communication with a private APN via the wireless transceiver over a cellular network and the mobile internet to a monitoring center; and e) the monitoring center receiving wireless surveillance data from the surveillance devices and transmitting control data wirelessly to the devices such that surveillance monitoring and device control is completed wirelessly over a series of networks.
Owner:CALIBER COMM INC
Particle monitors and method(s) therefor
ActiveUS20080001767A1Low costWeaken energyVolume/mass flow measurementScattering properties measurementsSmoke detectorsCombustion
The present invention relates to the field of the detection, analysis and / or determination of matter or particles suspended in fluid. In one particular form, the present invention relates to smoke detectors, which detect unwanted pyrolysis or combustion of material. In another form, the present invention relates to smoke detectors of the early detection type, and which may be applied to ventilation, air-conditioning or duct monitoring of a particular area. In yet another form, the present invention relates to surveillance monitoring, such as building, fire or security monitoring. In still another form, the present invention relates to environment monitoring, such as monitoring, detection and / or analysis of a fluid, zone, area and / or ambient environment, including commercial and industrial environments.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
Particle monitors and method(s) therefor
ActiveUS20080001768A1Low costWeaken energyVolume/mass flow measurementScattering properties measurementsSmoke detectorsCombustion
The present invention relates to the field of the detection, analysis and / or determination of matter or particles suspended in fluid. In one particular form, the present invention relates to smoke detectors, which detect unwanted pyrolysis or combustion of material. In another form, the present invention relates to smoke detectors of the early detection type, and which may be applied to ventilation, air-conditioning or duct monitoring of a particular area. In yet another form, the present invention relates to surveillance monitoring, such as building, fire or security monitoring. In still another form, the present invention relates to environment monitoring, such as monitoring, detection and / or analysis of a fluid, zone, area and / or ambient environment, including commercial and industrial environments.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
Video surveillance system and method with display advertising
InactiveUS20120013738A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringControl communications
A system for communicating content and monitoring a specified area, and method providing the same, includes a communications module including communication devices. The communication devices may include a display, a camera, and a microphone. The communications module also includes a first computer. A remote operations module includes an operations computer. The remote operations module communicates with the communications module using the operations computer. The operations computer communicates with the communication devices of the communications module and is configured to control the communications module. A plurality of operation modes may include: a first mode including the display being configured to display specified uploaded or streaming multimedia content, while providing a remote operator with real time video from a video camera for surveillance monitoring; and a second mode including the display being configured to display a remote operator of the remote operations module in two way communication with the communications module.
Owner:SDR SOLUTIONS
System and method for pattern based thresholding applied to video surveillance monitoring
InactiveUS8659657B2Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsPattern recognitionVideo monitoring
A system, method, and program product is provided that configures video handlers pertaining to a dependent individual. Configuring includes setting alert thresholds. Visual locations are configured. Visual images that pertain to caregivers of the dependent individual are configured. Video streams are received from video sources. Video streams are compared to configured locations to classify the dependent individual's location. Video stream is analyzed to determine whether the dependent individual is alone or with others. If with others, a list of known persons is determined by comparing the video streams with the configured visual images. The configured video handlers are initiated based on the inputs of the location and the people present with the dependent individual. Video handlers trigger alerts when thresholds are reached. Alerts include performing actions to protect the dependent individual from harm.
Owner:IBM CORP
Monitoring method for CT measurement winding disconnection and three-phase current imbalance operation
InactiveCN110927627AGood effectSolve runnabilityCurrent/voltage measurementElectric winding testingElectric power equipmentPower equipment
The invention discloses a monitoring method for CT measurement winding disconnection and three-phase current imbalance operation. The monitoring method comprises the following steps that (1) adding aCT current disconnection and three-phase imbalance monitoring program to a dispatching automation system; (2) judging the starting conditions of the CT current disconnection and three-phase imbalancejudgment program, and starting the corresponding judgment programs; (3) if the starting conditions of the CT current disconnection and three-phase imbalance judgment program are met, judging whether the following alarm logic judgment conditions are met or not, and if the corresponding alarm logic judgment conditions are met, sending out a CT current disconnection alarm or a CT current imbalance alarm. A regulation and control watch keeper can immediately discover the abnormal operation state of the power equipment by dispatching the CT current disconnection alarm or the CT current imbalance alarm sent by the automatic system, monitoring of CT measurement winding disconnection and three-phase current imbalance operation is achieved, and monitoring is convenient.
Owner:广西电网有限责任公司防城港供电局
Method for locating phase faults in a microgrid
ActiveUS20200041561A1Emergency protection detectionFault location by conductor typesCurrent analysisBusbar
A method for locating and clearing phase faults in a micro-grid in off-mode. The method includes determining a surveillance area of a microgrid having at least two busbars to monitor; determining all source feeders and load feeders of the surveillance area; acquiring measurement data comprising current magnitude for all source feeders and load feeders; and monitoring the at least two busbars in the surveillance area for a voltage dip in one of phase-to-phase or phase-to-neutral voltages. The method further includes, on detecting a voltage dip on the monitored busbars, determining a defect phase having a minimum phase-to-neutral voltage; and performing current analysis for the defect phase.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Expiration type alcohol detection and fatigue driving reminding device
InactiveCN111572457AMonitor mental state at all timesGood effectAlarmsTractorsAlcohol contentDriver/operator
The invention discloses an expiration type alcohol detection and fatigue driving reminding device. A flexible sucker is included. A sucker bracket is fixedly arranged on the flexible sucker; the sucker bracket is fixedly connected with a working box and a detection box; and sucker cavities are formed between the flexible sucker and the working box and between the flexible sucker and the detectionbox. When a vehicle door is opened by driver, a lifting mechanism is enabled to receive signals of a pressure sensor through a door connecting line connected with a driving position exit door; an expiration funnel can be taken out from a front notch by when an ascending state is started, after an alcohol content is detected, the exhalation funnel can be inserted back to an original position, and convenience and rapidness are achieved; and meanwhile, an eyeball tracking mechanism can monitor a mental state of a monitor all the time, a deflation mechanism can remind the driver by releasing an irritant gas, an effect is good, and driving safety is guaranteed.
Owner:金华阳学汽车科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for controlling an elevator system
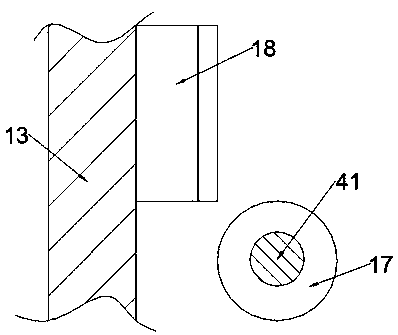
The method and the apparatus are used for securely controlling an elevator system (3) comprising a drive unit (38) which allows an elevator car (36) located in an elevator shaft (35) to move and whichis controlled in a secured manner by a control device (100) in such a way that during normal operation, the elevator car (36) can move to at least two access points to the elevator shaft (35) at which doors (30A, 30B) are provided. The elevator car (36) does not move or moves only to a limited extent if an individual is in the elevator shaft (35). A monitoring unit (10A; 10B) and a monitoring sensor (11A; 11B) that allow changes in state to be detected are associated with at least one of the doors (30A, 30B). The monitoring unit (10A; 10B) is equipped with a battery (14) and can be switched to an autonomous mode when the elevator system (3) is entirely or partially out of order. The monitoring unit (10A; 10B) is connected to the monitoring sensor (11A; 11B) and, in the autonomous mode, monitors the state of the monitoring sensor (11A; 11B) and records state data; furthermore, the monitoring unit (10A; 10B) is connected to a securing unit (1) which reads the recorded state data from all connected monitoring units (10A; 10B), evaluates said state data and prevents the elevator system (3) from being put into the normal mode of operation if a change in the state of one of the monitored doors (30A; 30B) has been detected. The monitoring sensor (11A, 11B) is a switching contact which is coupled to the associated door lock (31A; 31B) and via which a monitoring signal is transmitted from an output to an input of the monitoring unit (10A; 10B). According to the invention, the monitoring signal is in the form of a sequence of pulses.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
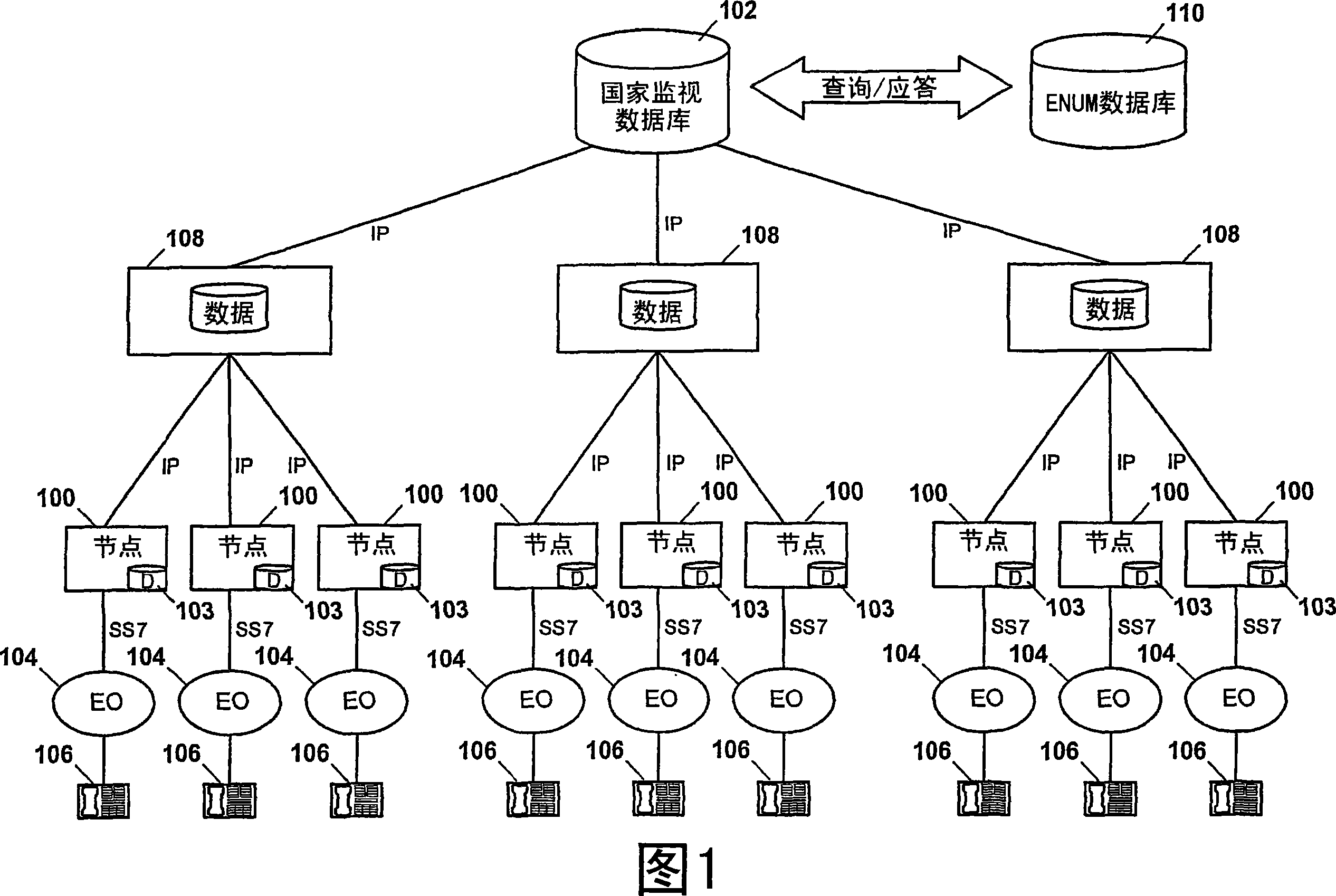
Methods, systems, and computer program products for surveillance monitoring in a communication network based on a national surveillance database
InactiveCN101208670AUnauthorized memory use protectionAutomatic exchangesRelevant informationComputer science
Methods, systems, and computer program products are disclosed for providing surveillance monitoring in a communication network based on a national surveillance database. Communication-related information is received from a national surveillance database that includes communication-related information relating to individuals under surveillance. The received communication-related information is used to screen signaling messages relating to communications associated with the individuals.
Owner:TEKELEC
Data compression apparatus, model generation apparatus, data compression method, model generation method and program recording medium
ActiveUS20210203840A1Precise compressionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData compressionEngineering
A data compression apparatus includes: a compression unit that performs a compression process on output data that is sequentially outputted as time series data by a monitoring apparatus for monitoring a monitoring target range; an output unit that outputs the output data on which the compression process is performed, to a data processing apparatus that performs an object detection process for detecting an object that exists in the monitoring target range by using the output data; and a setting unit that sets a compression ratio used in the compression unit, on the basis of an accuracy information indicating a relationship between a compression ratio at which the output data is compressed and a detection accuracy of the object by the object detection process performed by using the output data compressed at the compression ratio.
Owner:NEC CORP
Comprehensive management system for examination room monitoring
InactiveCN107341746AReduce labor intensityImprove efficiencyData processing applicationsClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringEXAMINATION ROOM
The invention discloses an examination room monitoring comprehensive management system, comprising a central processor, one side of the central processor is connected to a network transmission module, one side of the network transmission module is connected to an examination room monitoring system, and the examination room monitoring system is connected to a video monitoring system Module, voice monitoring module and electronic shielding instrument, the other side of the central processing unit is connected to the network transmission module, one side of the network transmission module is connected to the background monitoring module, and the background monitoring module is connected to a voice broadcast unit, a display unit and a data storage unit. The present invention comprehensively monitors the conditions of each examination room through the real-time video and voice control system of the test site, real-time and dynamic support of the test site conditions, greatly reduces the labor intensity of test staff, enhances efficiency, and maintains the fairness, justice, safety and order of the test .
Owner:安徽源行信息科技有限公司
Direct drinking water membrane purification processing unit control system
InactiveCN104731034AEasy to operateEasy to manageWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentAutomatic controlWater quality
The invention discloses a direct drinking water membrane purification processing unit control system. The system comprises a central controller, the central controller is connected with an original water tank control module, an original water pump control module, a water quality preprocessing control module, a membrane processing control module, a washing pump control module, a water purifying tank control module, a water purifying pump frequency conversion water supply control module, a network camera, an alarm output module, a monitoring module and a touch screen which are used for achieving functions of information collecting, automatic control, surveillance monitoring, alarming and displaying, and the central controller is further connected with a power interface and a communication interface which are used for connecting a power supply, supplying power and externally communicating. The direct drinking water membrane purification processing unit control system has the advantages of being beneficial for operating and managing a drinking water membrane purification processing unit by adopting a modular centralized control mode, good in maintainability, convenient to manage, high in automation degree and complete in function and capable of improving the reliability, and having remote network monitoring, supervisory controlling and supervising functions.
Owner:QINGDAO WANLI TECH
A panoramic monitoring device, system and method for an airport run-slip area
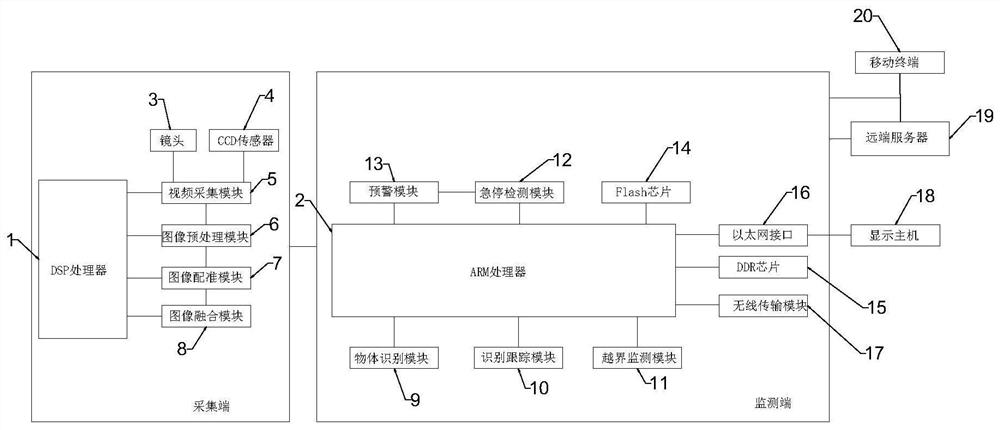
InactiveCN108184096BRealize panoramic monitoringImprove securityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsData streamFeature extraction
The invention relates to a panoramic monitoring device, system and method of an airport skid area. The method uses a plurality of monitoring devices to obtain the space scene light of the airport skid area through a camera lens, and converts the light into electric charge through a CCD sensor and passes it through an analog-to-digital converter chip. converted into a digital signal; the image acquisition module collects the real-time video image data stream of the airport run-and-skid area; the image preprocessing module performs feature extraction and segmentation processing on the input video image data stream, and then through the image registration module, several acquired The images are matched and superimposed, and then several acquired images are spliced and fused through the image fusion module to form a panoramic image of the airport run-slip area; the object recognition module recognizes the moving objects on the panoramic image of the airport run-slip area, Moving objects are tracked. The invention realizes the panoramic monitoring of the slipping area of the airport, can perform real-time identification, tracking and early warning, and improves the safety of the slipping area of the airport.
Owner:北京艾恩斯网络科技有限公司
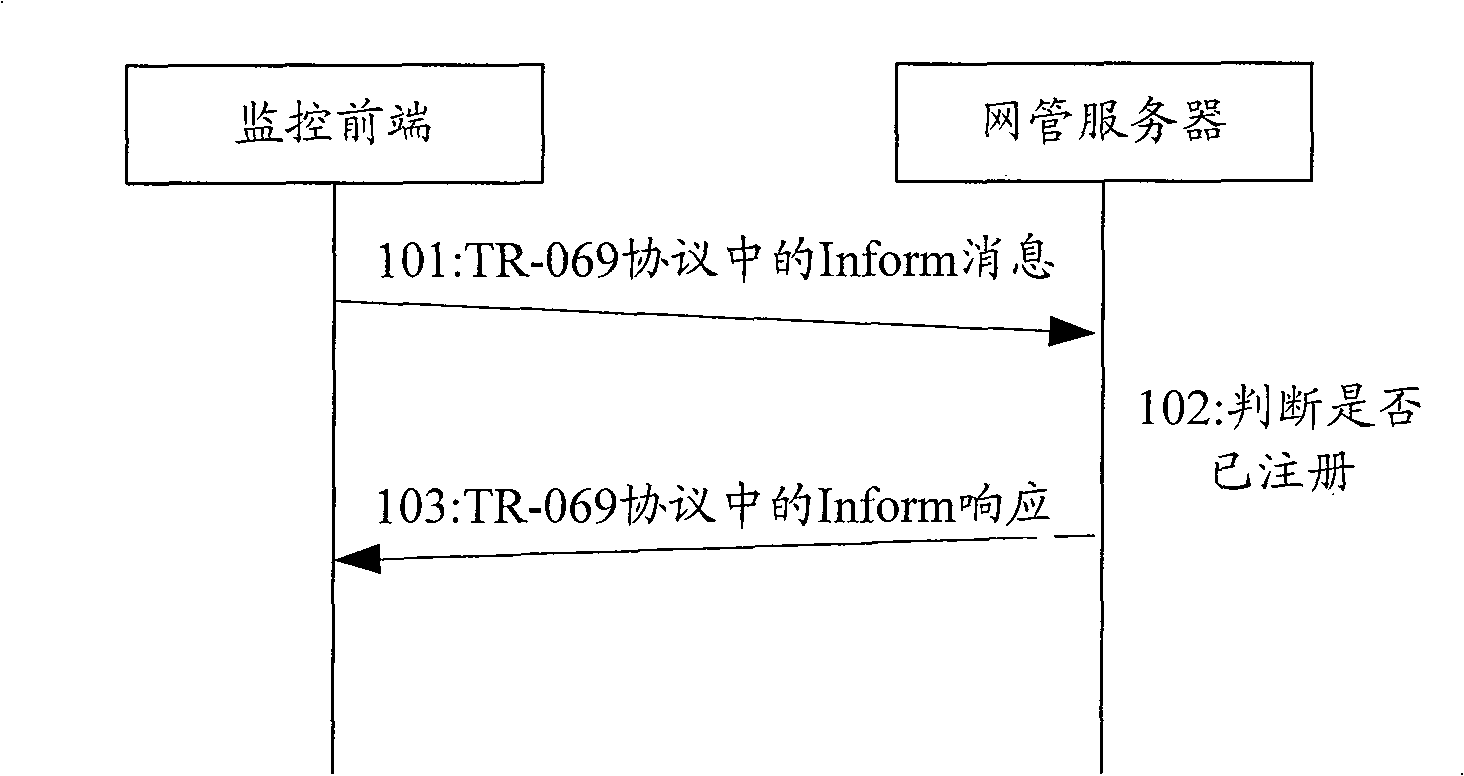
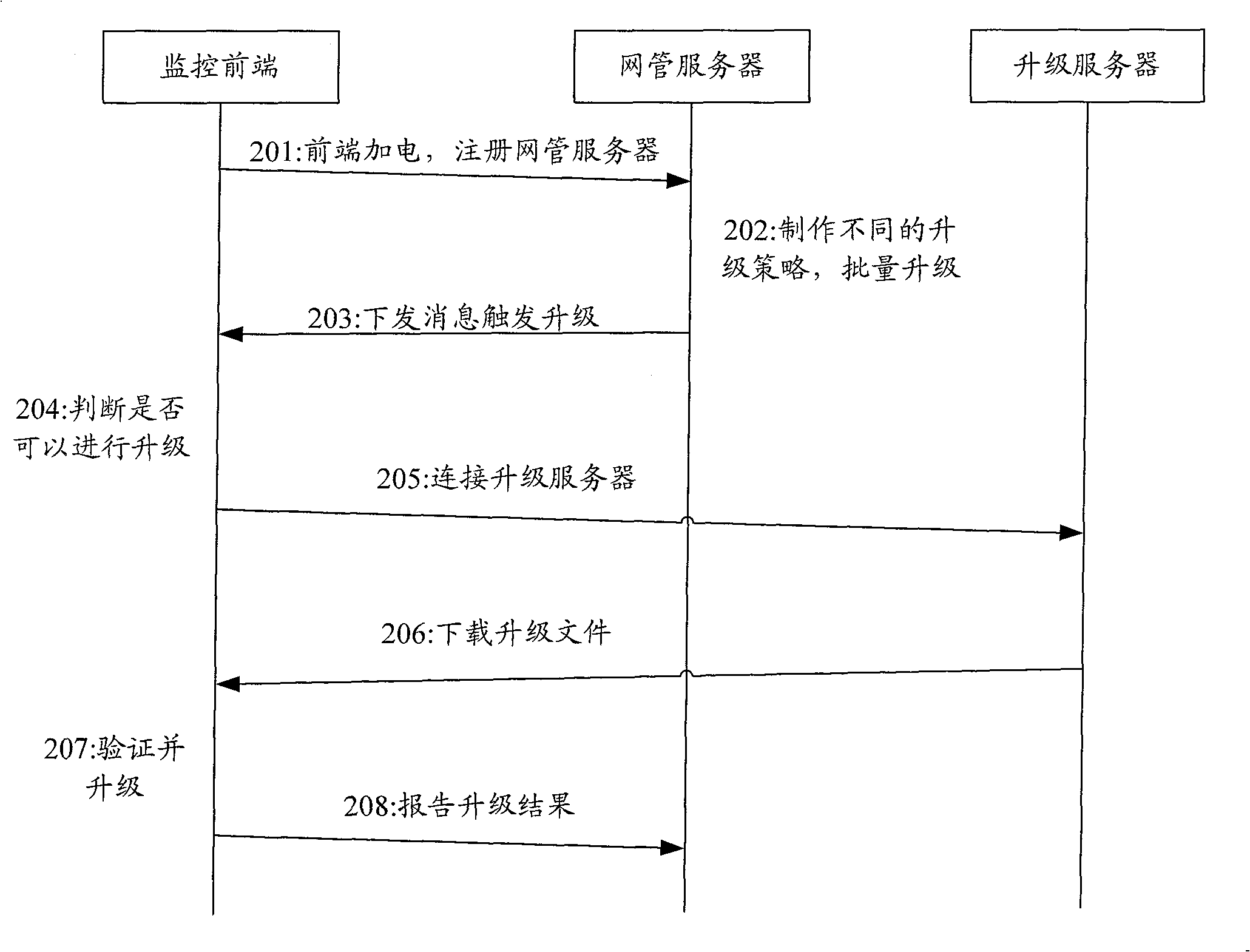
Method to update monitoring front end of video monitoring system
InactiveCN100551049CReduce maintenance costsThe upgrade process is fast and efficientClosed circuit television systemsData switching networksVideo monitoringNetwork management
The invention discloses a method for upgrading the monitoring front end of a video monitoring system. By building a network management protocol module in the monitoring front end, the protocol module is consistent with the protocol of the network management server. When the monitoring front end is powered on and started, the built-in protocol module registers with the network management server For the front-end information, if the monitoring front-end registration is successful or has been registered before, the network management server will make different upgrade strategies according to the information carried by the monitoring front-end registration, and the network management server will find the corresponding monitoring front-end according to the corresponding strategy, and issue a unified resource Locator (URL) message, the monitoring front end receives the message and makes a judgment, if it needs to be upgraded, it is linked to the upgrade server to download the upgrade package according to the URL message and upgrades. By adopting the method to upgrade the monitoring front end in batches, the maintenance cost of the monitoring front end is greatly reduced, and the upgrading process becomes fast and effective.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method of video surveillance using cellular communication
ActiveUS10356368B2Easy to useUltra low power consumptionMultiple digital computer combinationsClosed circuit television systemsWireless transceiverTransceiver
A method of video surveillance with a mobile station using cellular communication including the steps of: a) applying power to a mobile station which includes a router in communication with a wireless transceiver for transmitting data wirelessly; b) the router in communication with an private network in the mobile station; c) the private network in communication with surveillance devices attached to the mobile station; d) the router in communication with a private APN via the wireless transceiver over a cellular network and the mobile internet to a monitoring center; and e) the monitoring center receiving wireless surveillance data from the surveillance devices and transmitting control data wirelessly to the devices such that surveillance monitoring and device control is completed wirelessly over a series of networks.
Owner:CALIBER COMM INC
Remote video monitoring system and method
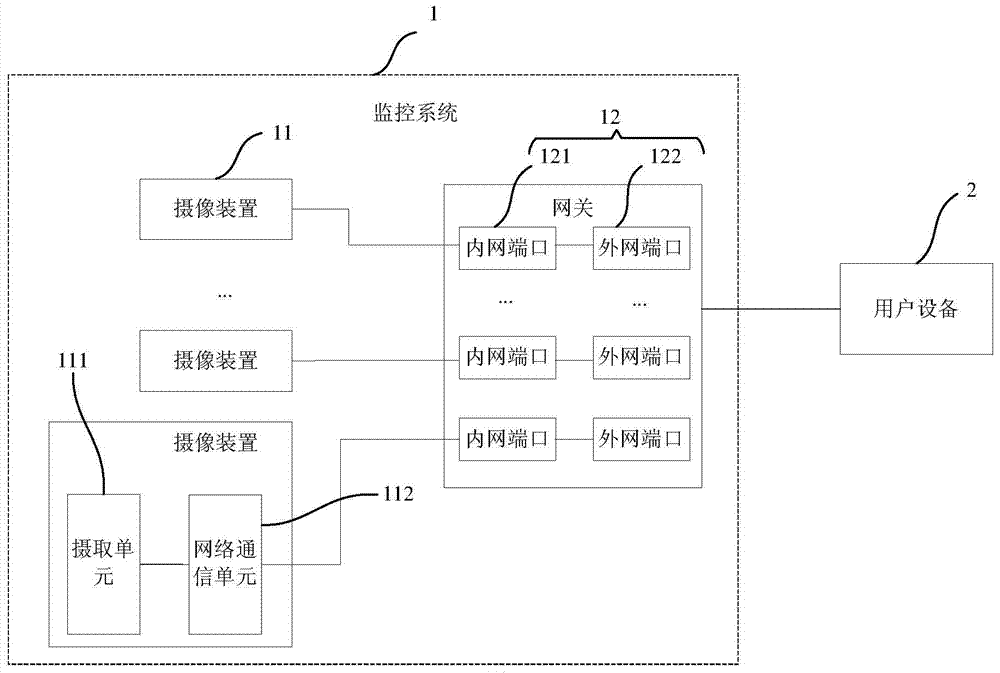
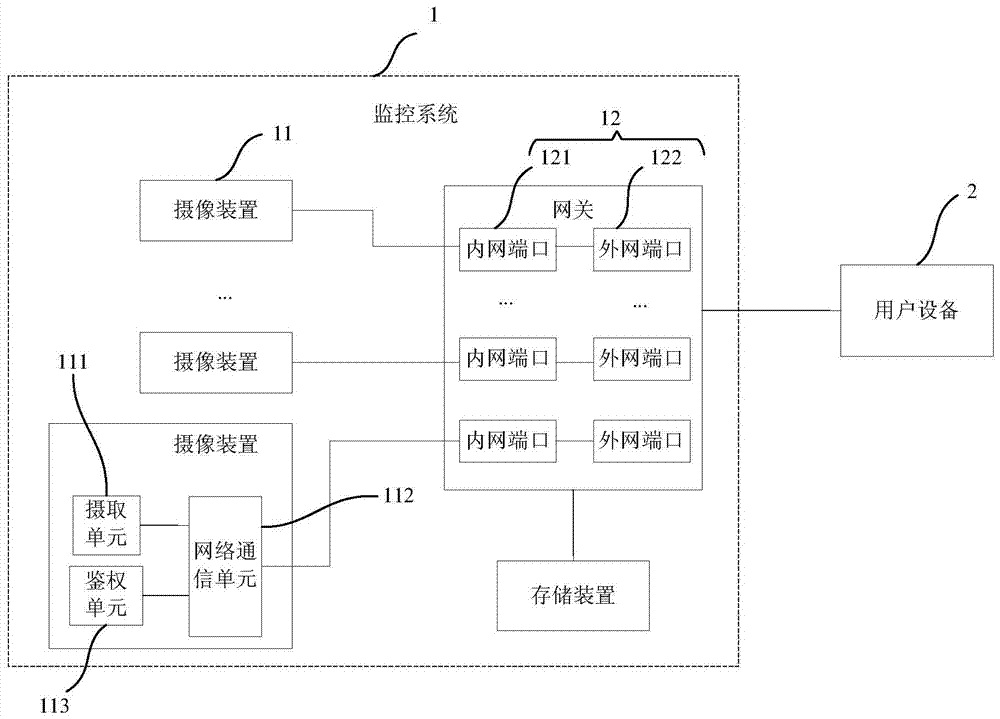
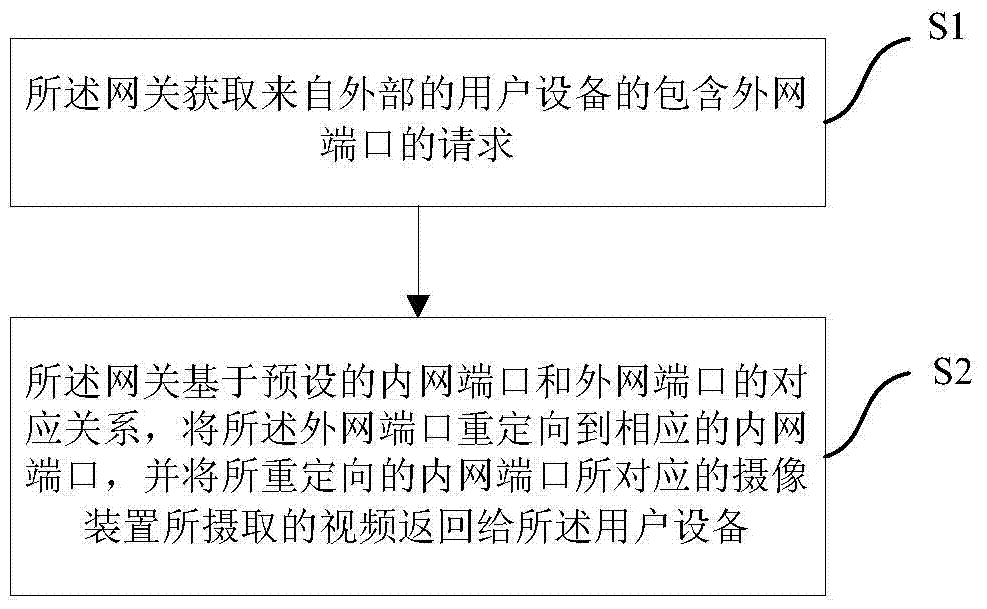
ActiveCN103501426BEasy to installSolve the troubleClosed circuit television systemsTransmissionVideo monitoringThe Internet
The invention provides a remote video monitoring system and method. According to the monitoring method of the present invention, the gateway obtains a request from an external user equipment that includes an external network port; then, the gateway sends the external network port to the Redirect to the corresponding intranet port, and return the video captured by the camera in the monitoring system corresponding to the redirected intranet port to the user equipment. The monitoring system is simple to install and easy to configure. At the same time, there is no need to use a home computer to process the video stream captured by the camera device, which avoids the annoyance of the user having to turn on the computer all the time. At the same time, the monitoring method can use the monitoring system to perform remote video monitoring.
Owner:DMS CORP
A method for optimizing the layout of monitoring points for emergency monitoring of sudden air pollution accidents
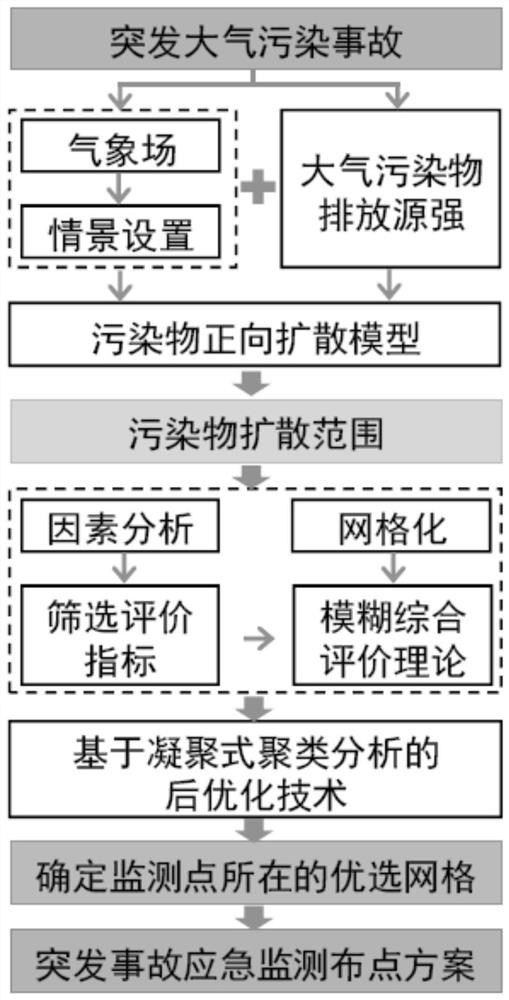
ActiveCN110084418BScientific acquisitionEasy accessForecastingICT adaptationMonitoring siteEnvironmental resource management
The invention relates to an optimal layout method of monitoring points for emergency monitoring of sudden air pollution accidents, which belongs to the technical field of early warning and evaluation of environmental risks. The invention uses a pollutant diffusion model to determine the diffusion range and concentration distribution characteristics of pollutants after the accident, and grids the distribution range based on the distribution characteristics of environmentally sensitive points in the downwind direction; quantitatively handles geographical and environmental sensitivity through fuzzy evaluation theory According to the uncertainty among the factors affecting the distribution of emergency monitoring points such as source distribution, different grids are screened by combining post-optimization technology based on cluster analysis, and the location and quantity of emergency monitoring points are determined according to the amount of monitoring resources. The optimal distribution method quantitatively converts the uncertainties in the optimal distribution, characterizes the influence of different factors on the monitoring distribution, and makes up for the defect that the emergency monitoring distribution of sudden air pollution accidents can only refer to the monitoring specifications and historical work experience of conventional pollutants. .
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A Crack Monitoring Device for Cement Pavement After an Earthquake
ActiveCN112681056BReduce widthReduce crack widthMeasurement devicesPaving gutters/kerbsStructural engineeringRoad surface
Owner:山西省地震局
Controllable power supply monitoring system and method
InactiveCN103235544BGuaranteed continuityEnsure safetyProgramme controlComputer controlMonitoring systemEngineering
The invention provides a method for monitoring a controllable power supply. In this method, a power control device is set between the monitoring terminal and the power output terminal to control the power output from the power output terminal to the monitoring terminal. When the monitoring terminal is in a power-off state, the power control device is used to detect the alarm situation of the controlled terminal. When an alarm occurs at the controlled end, the power supply control device is used to control the output end of the power supply to output power for the monitoring end, which ensures the continuity and safety of monitoring the controlled end when the monitoring end is powered off and shuts down, and effectively saves the cost of the monitoring end. Monitor the electrical energy required. The invention also provides a controllable power supply monitoring system.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW-TECH CO LTD
Method for locating phase faults in a microgrid
ActiveUS11209474B2Emergency protection detectionFault location by conductor typesCurrent analysisBusbar
A method for locating and clearing phase faults in a micro-grid in off-mode. The method includes determining a surveillance area of a microgrid having at least two busbars to monitor; determining all source feeders and load feeders of the surveillance area; acquiring measurement data comprising current magnitude for all source feeders and load feeders; and monitoring the at least two busbars in the surveillance area for a voltage dip in one of phase-to-phase or phase-to-neutral voltages. The method further includes, on detecting a voltage dip on the monitored busbars, determining a defect phase having a minimum phase-to-neutral voltage; and performing current analysis for the defect phase.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Unattended surveillance device and associated methods
ActiveUS9141862B2Reduce data volumeReliable classificationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGHz frequency transmissionTransceiverComputer science
The unattended surveillance device may include a housing to be positioned for unattended surveillance, a video camera associated with or carried by the housing to capture video, and an image processor carried by the housing and cooperating with the video camera. The image processor extracts moving objects in the foreground of the captured video, generates a profile image or sequence of profile images of the extracted moving objects, compresses the sequence of profile images, and generates a surveillance information packet based upon the compressed sequence of profile images. Also, a wireless transmitter or transceiver may be associated with the image processor to transmit the surveillance information packet to a surveillance monitoring station.
Owner:OLLNOVA TECH LTD
Automatic control system for tunnel temperature simulating and smoke controlling in mine rescue
PendingCN107703999AReduce power consumptionReduce output powerSimultaneous control of multiple variablesAutomatic controlControl signal
The invention provides an automatic control system for tunnel temperature simulating and smoke controlling in mine rescue. The invention relates to the automatic control system for tunnel temperaturesimulating and smoke controlling in mine rescue. A high-temperature drill smoke tunnel middle control system comprises a tunnel monitoring system, a data processing system and a tunnel control system.A comprehensive monitoring system comprises a tunnel smoke monitoring part, a tunnel temperature monitoring part, a video monitoring part and a tunnel audio monitoring part. The tunnel control systemcomprises a console, a real-time monitoring part, a data report part and an information management part. The console, the real-time monitoring part, the data report part and the information management part perform bidirectional signal transmission with video monitoring equipment. The console, the real-time monitoring part, the data report part and the information management part perform bidirectional signal transmission with an audio control system. The video monitoring equipment transmits a video signal to a large-screen monitor. The automatic control system is used for rescue simulation ofthe mine.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com