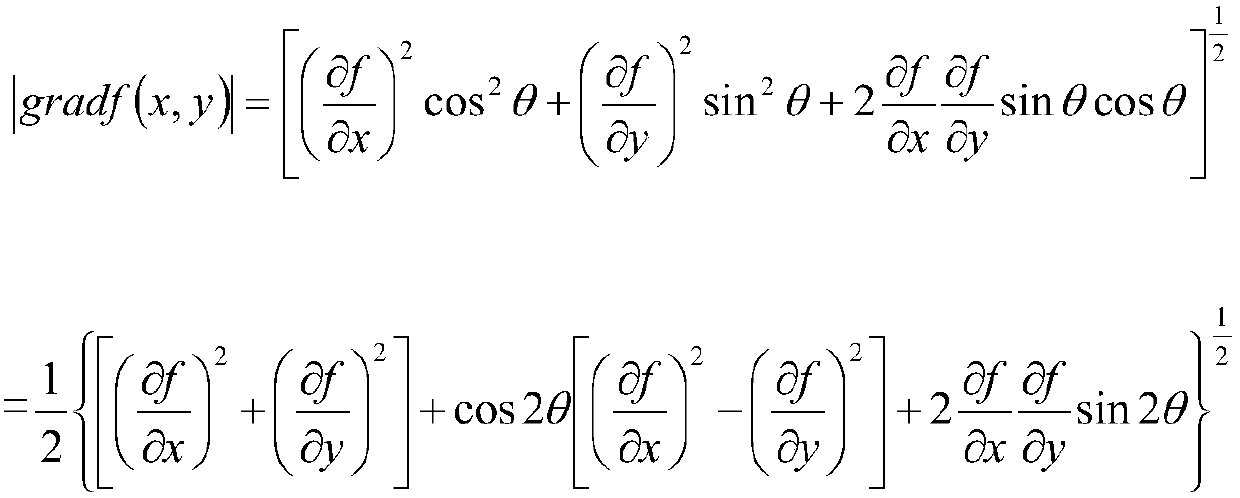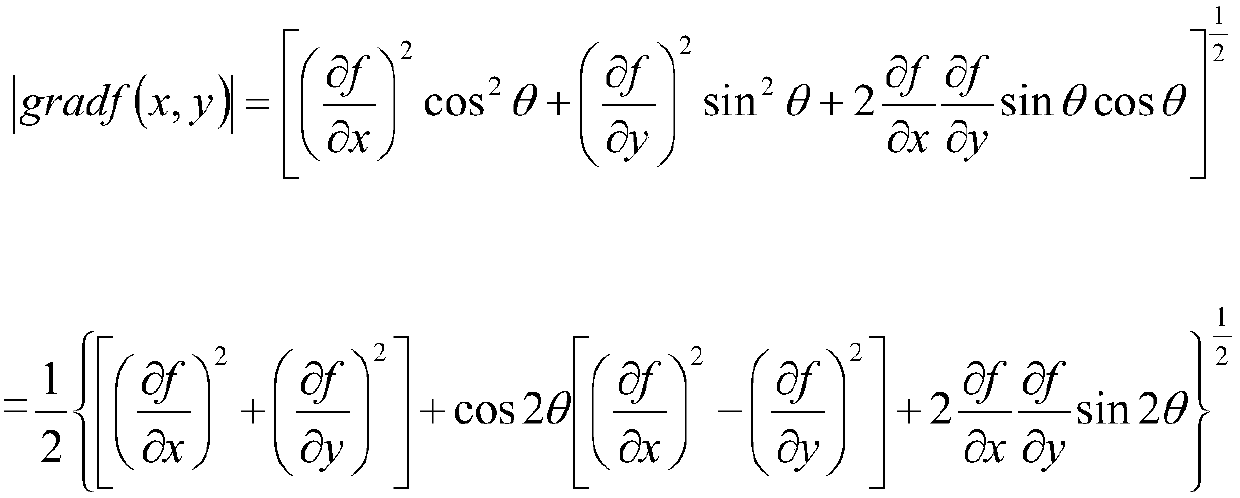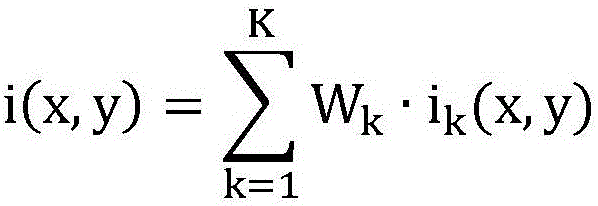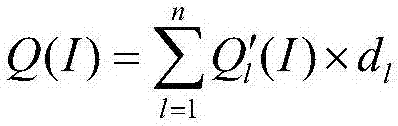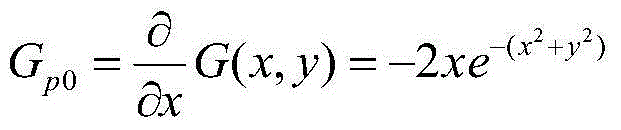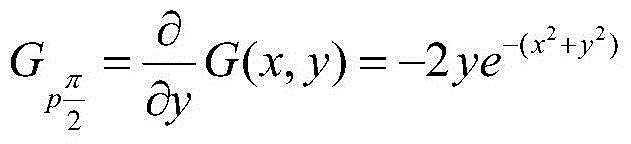Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Steerable filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In applied mathematics, a steerable filter is an orientation-selective convolution kernel used for image enhancement and feature extraction that can be expressed via a linear combination of a small set of rotated versions of itself. As an example, the oriented first derivative of a 2D Gaussian is a steerable filter. The oriented first order derivative can be obtained by taking the dot product of a unit vector oriented in a specific direction with the gradient.
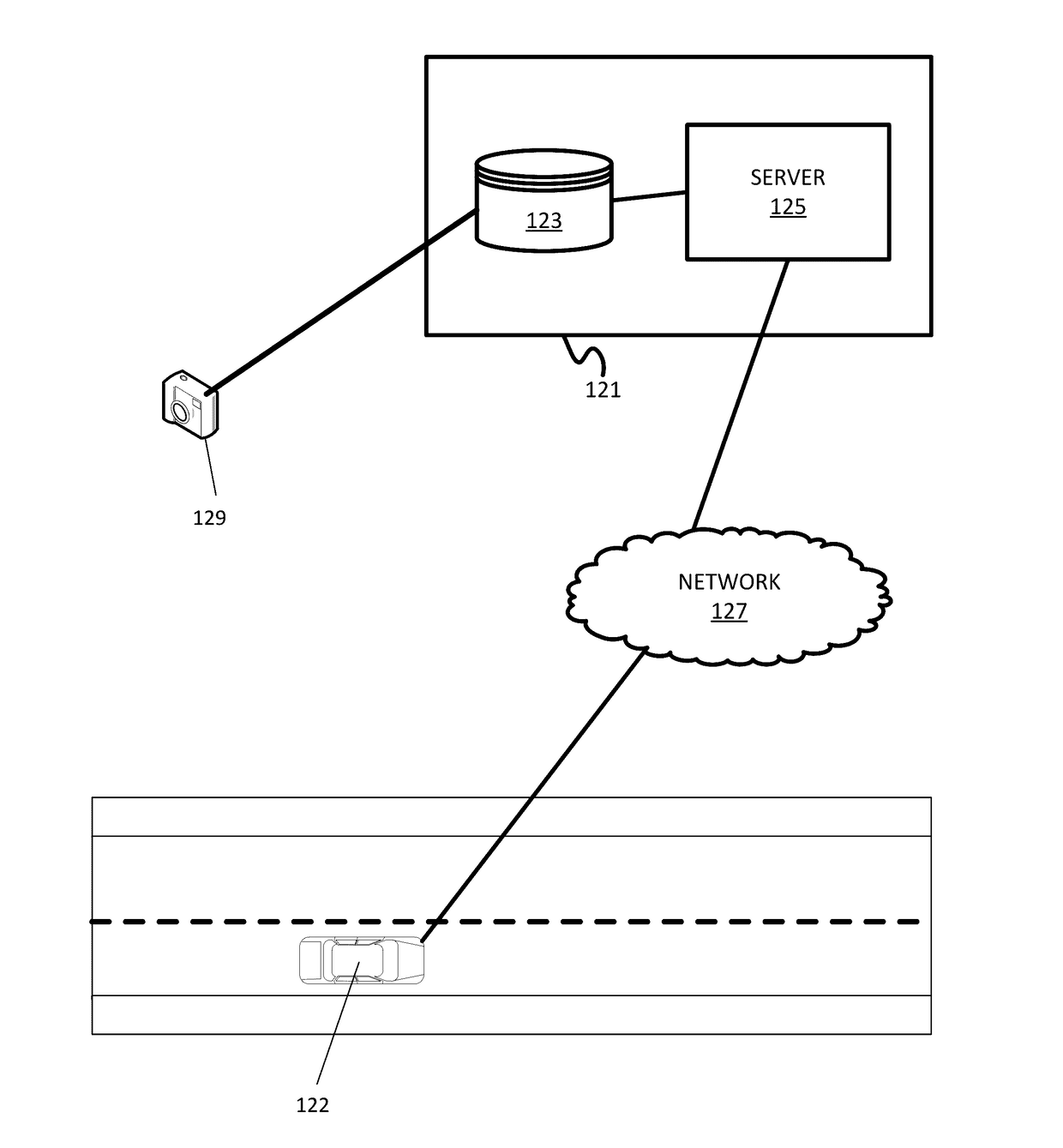
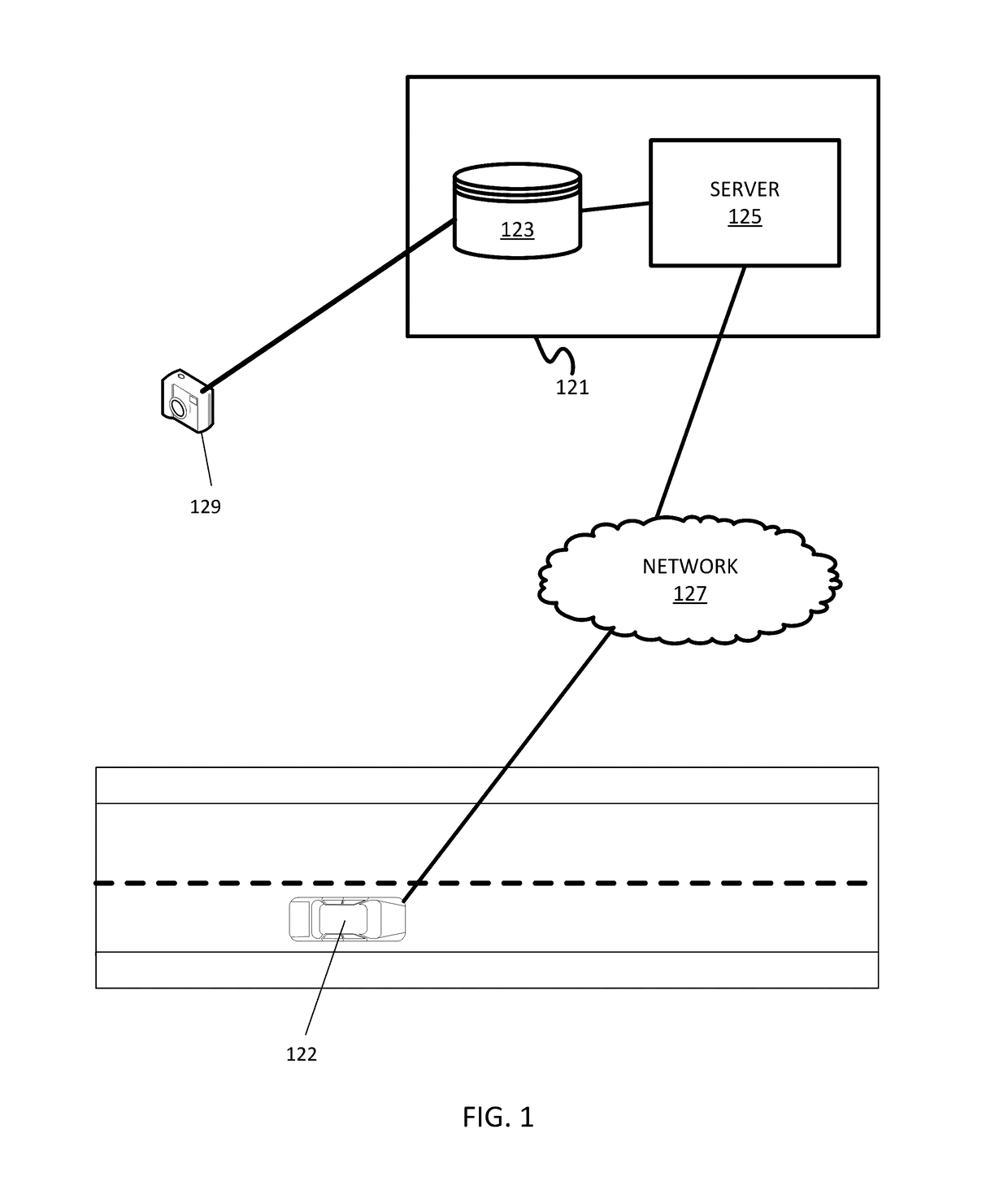
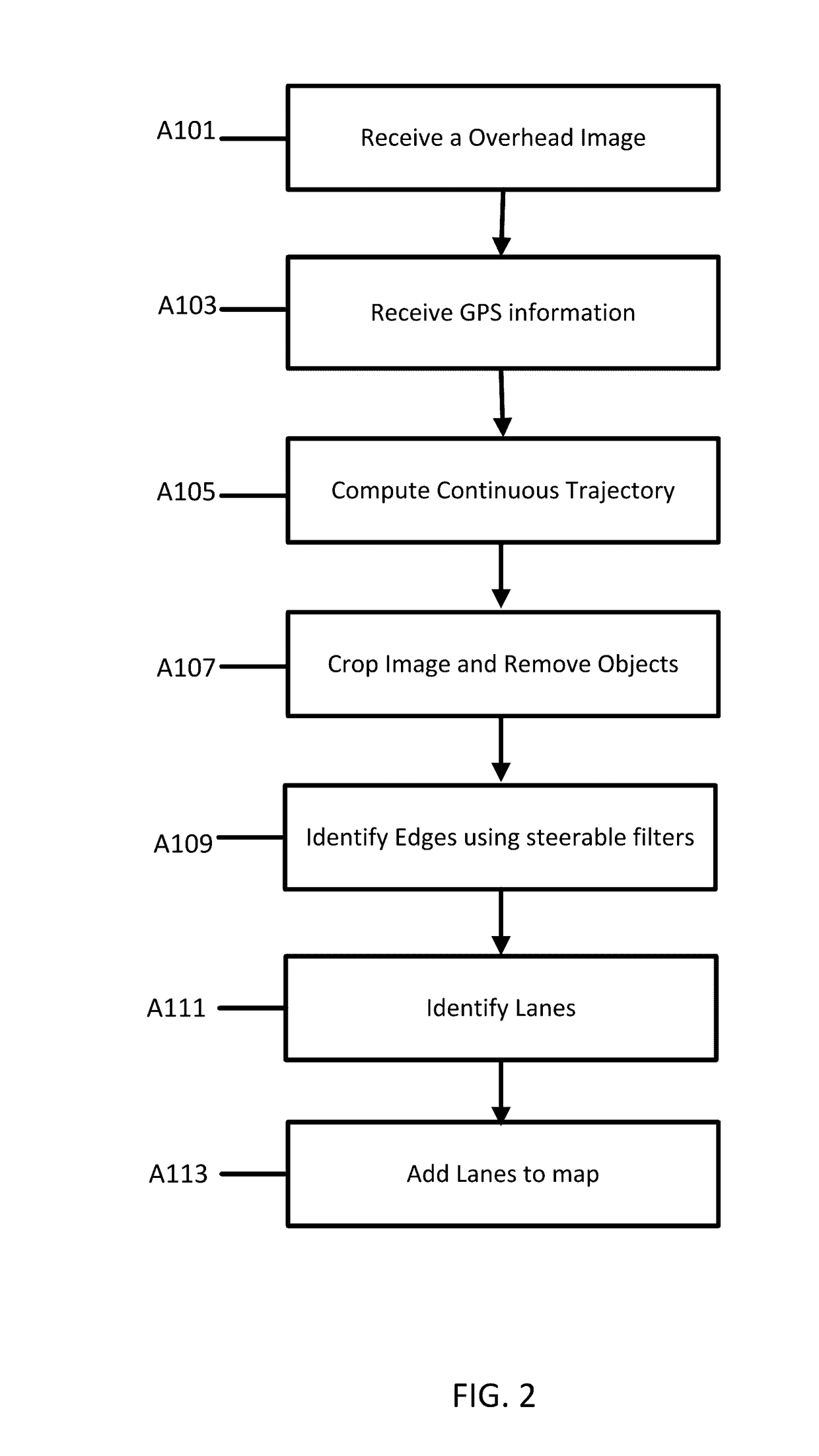
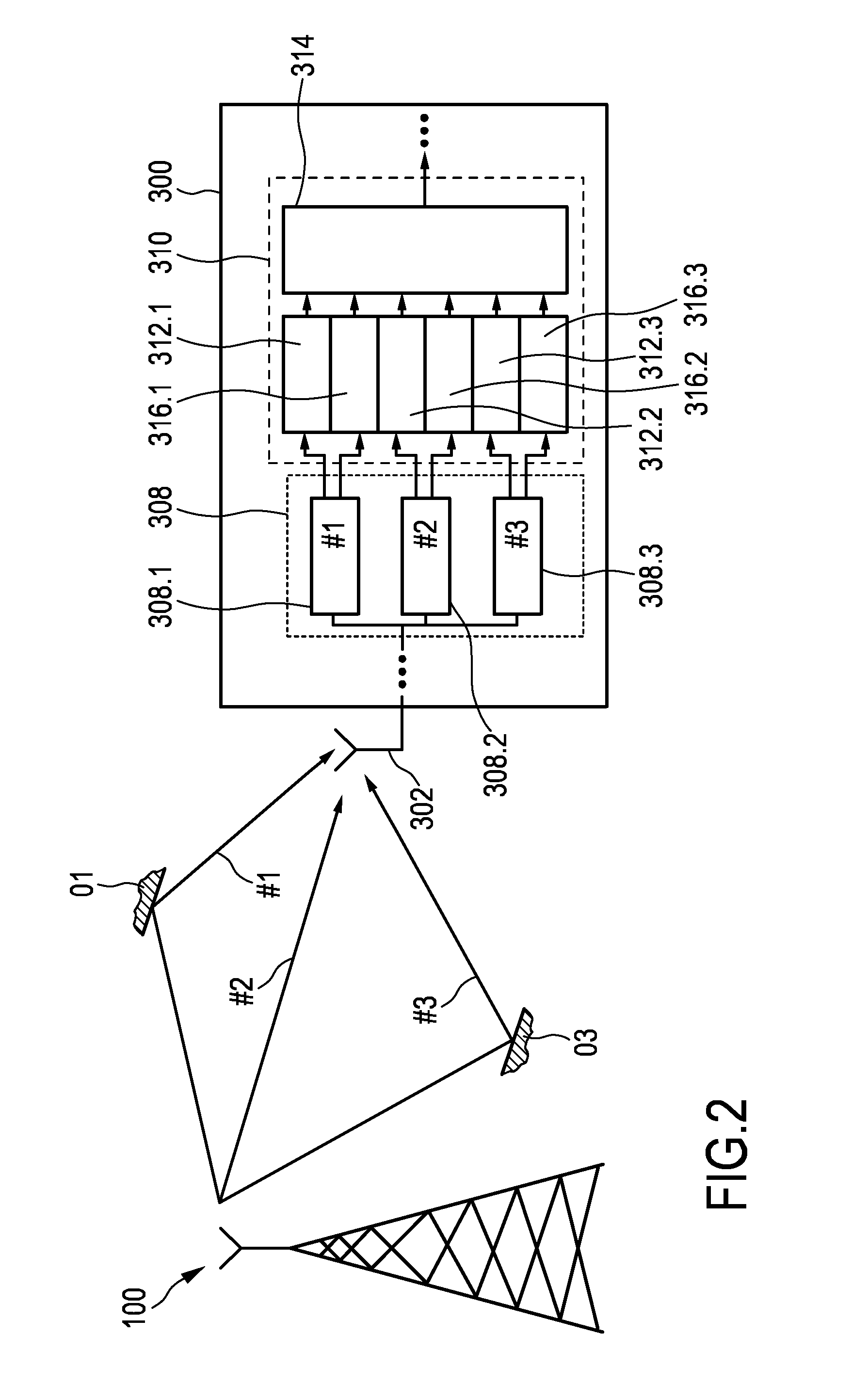
Integration of positional data and overhead images for lane identification
InactiveUS20170116477A1Image enhancementInstruments for road network navigationEdge filterSteerable filter
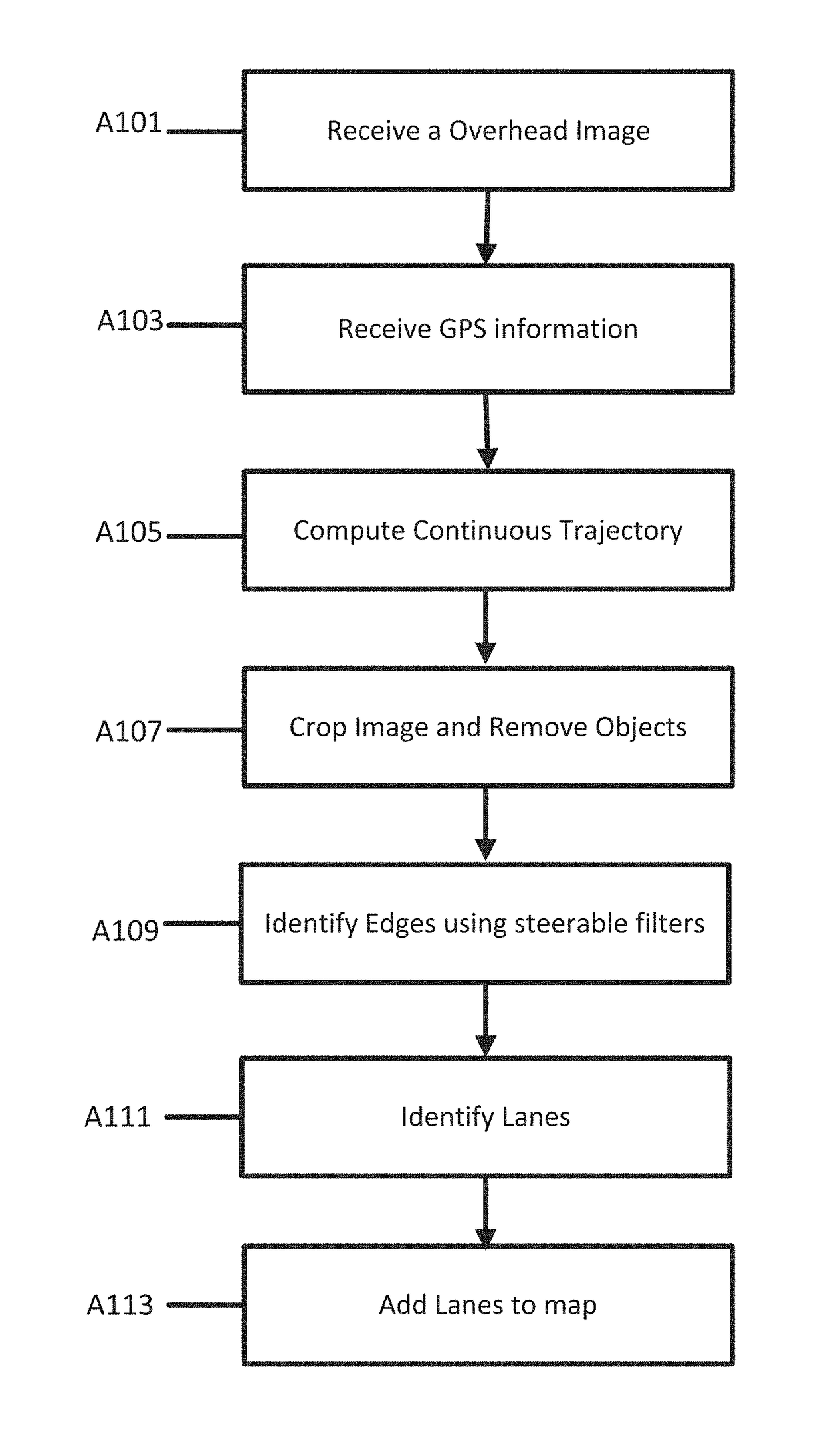
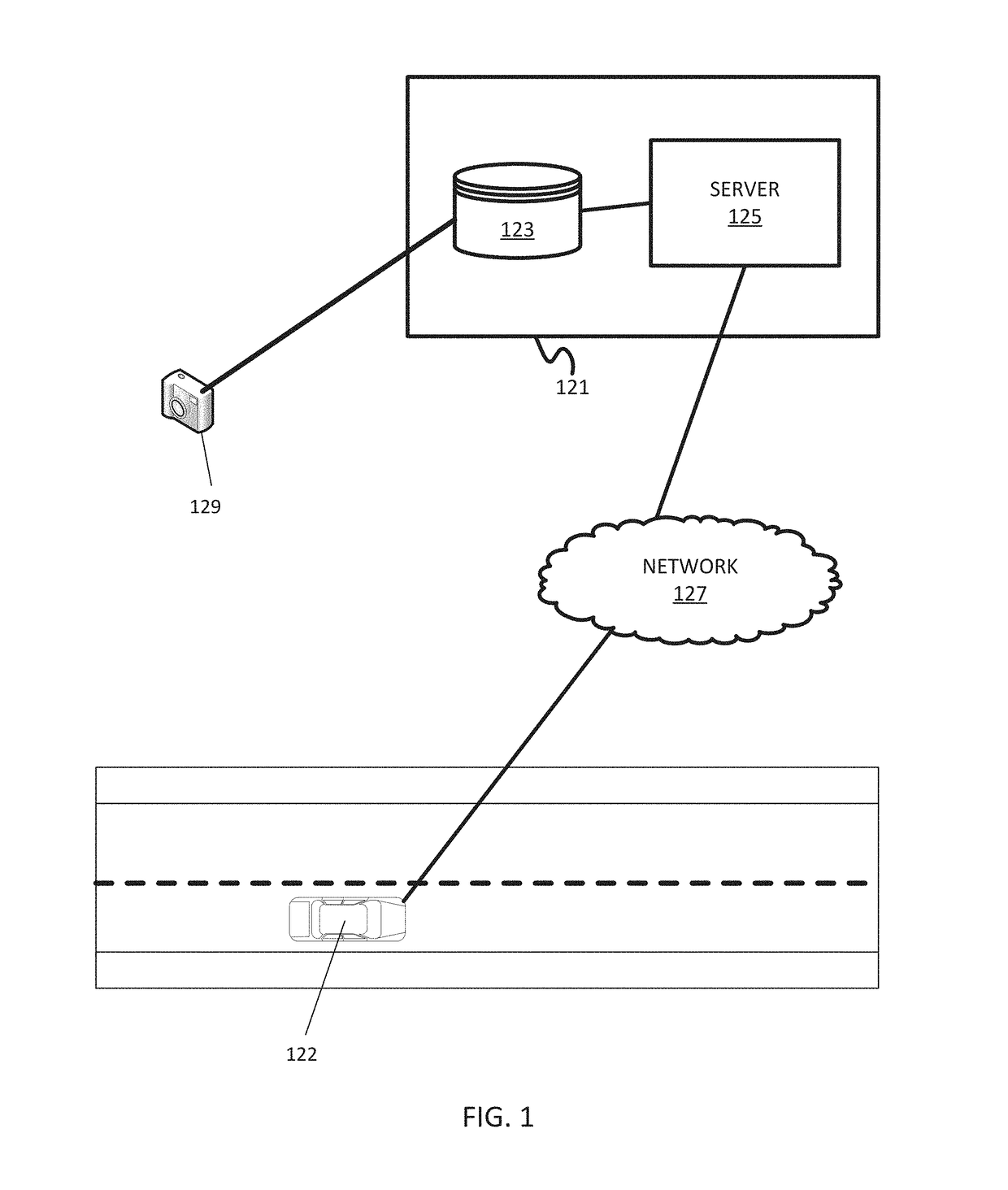
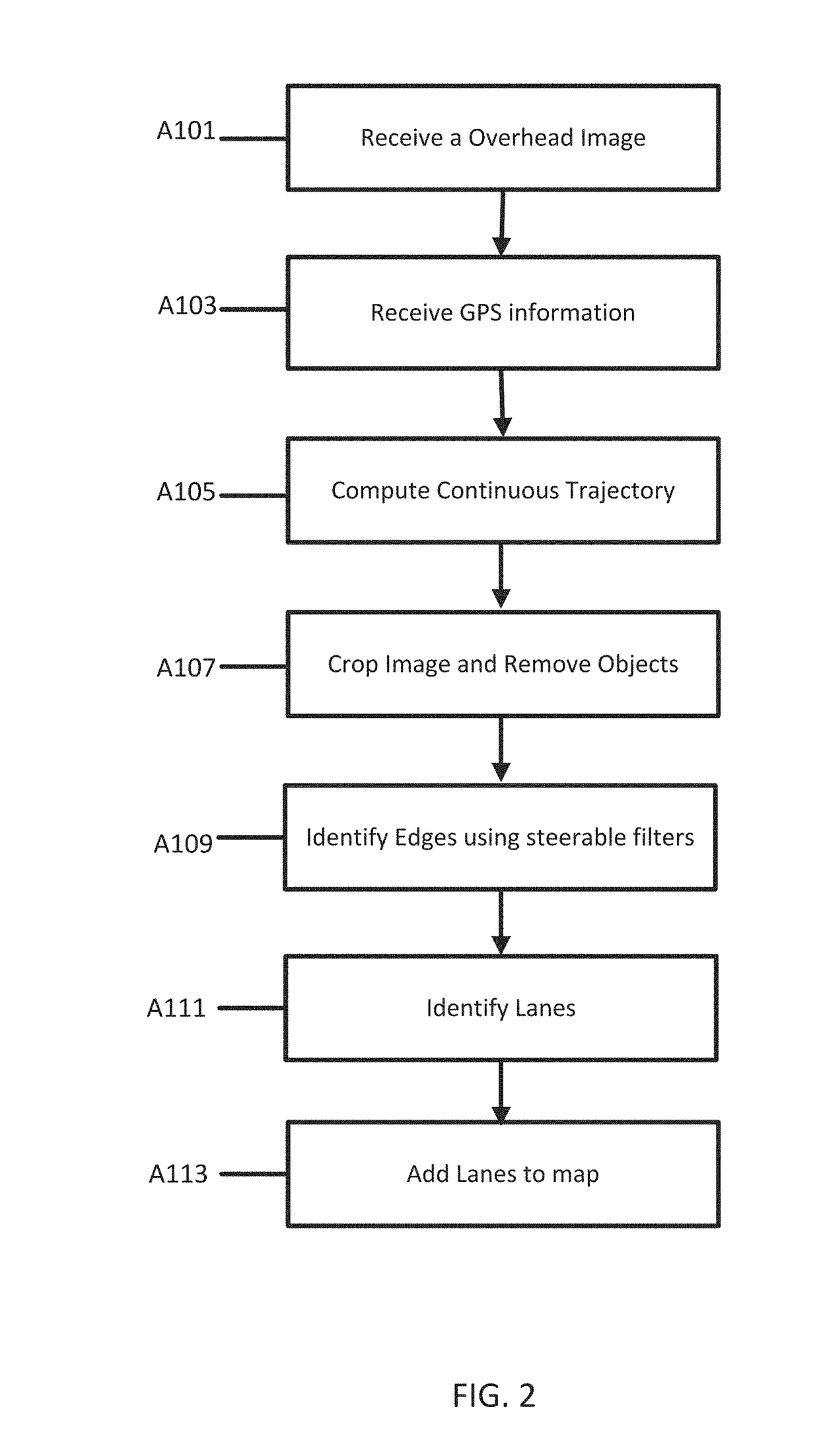
A method and apparatus for lane detection using overhead images and positional data. A server receives positional data from a vehicle and computes a continuous trajectory. The server receives an overhead image of a road section. The server crops and processes the overhead image to remove unwanted portions. The server identifies edge features using the continuous trajectory and steerable filters. The server identifies lanes in the overhead image using a maximization algorithm, the edge filters, and the continuous trajectory.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
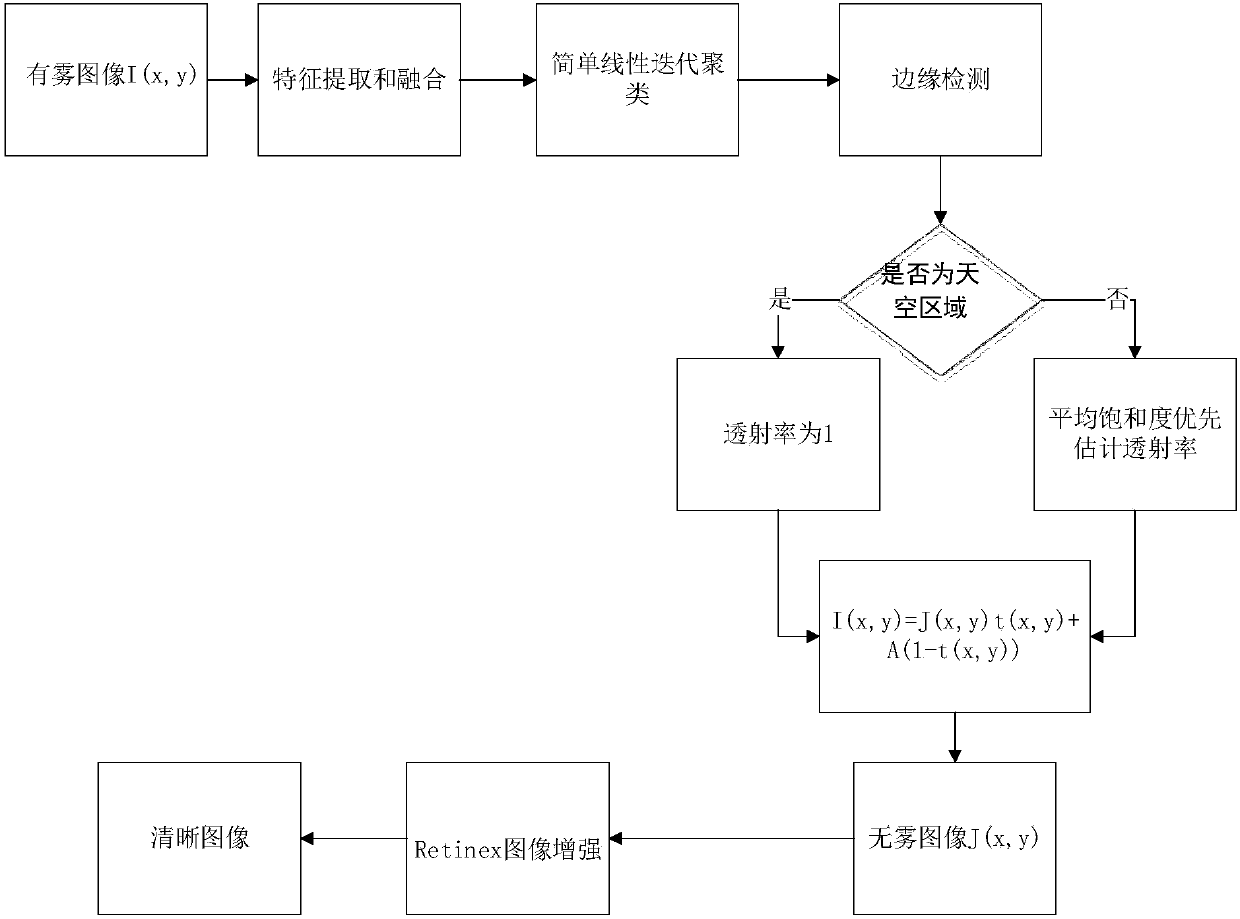
Sky region segmentation-based single image defogging method
ActiveCN108596849AImprove visual effectsAddresses the shortcoming of not working with sky areasImage enhancementImage analysisSkyCombined method
The invention discloses a sky region segmentation-based single image defogging method, and overcomes the shortcoming of a negative visual effect due to the fact that a conventional dark channel defogging algorithm is not adaptive to a sky region. By comprehensively utilizing visual features in an image, the sky region in the image is accurately segmented out by adopting a simple linear iterative clustering and edge detection combined method. Based on this, a non-sky region is subjected to independent transmissivity estimation according to average saturation priori, and the sky region is subjected to independent visual effect enhancement processing, so that the negative effects of over-enhancement, color cast and the like caused by performing conventional defogging processing on the sky region are eliminated. Finally, for the shortcoming that the defogged image is relatively dark, a steerable filter-based Retinex method is proposed for performing enhancement, so that the visual effect of the defogged image is further improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
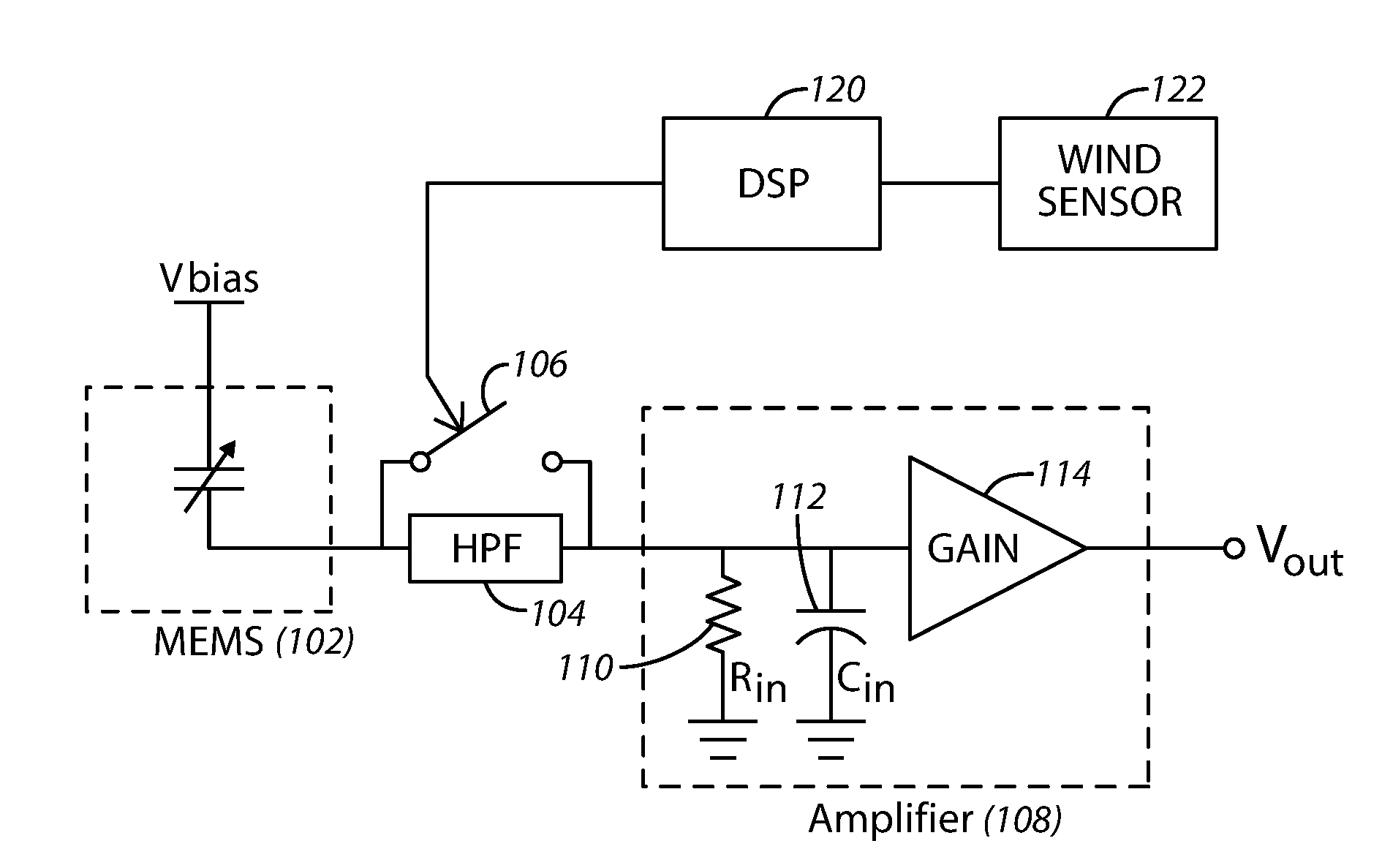
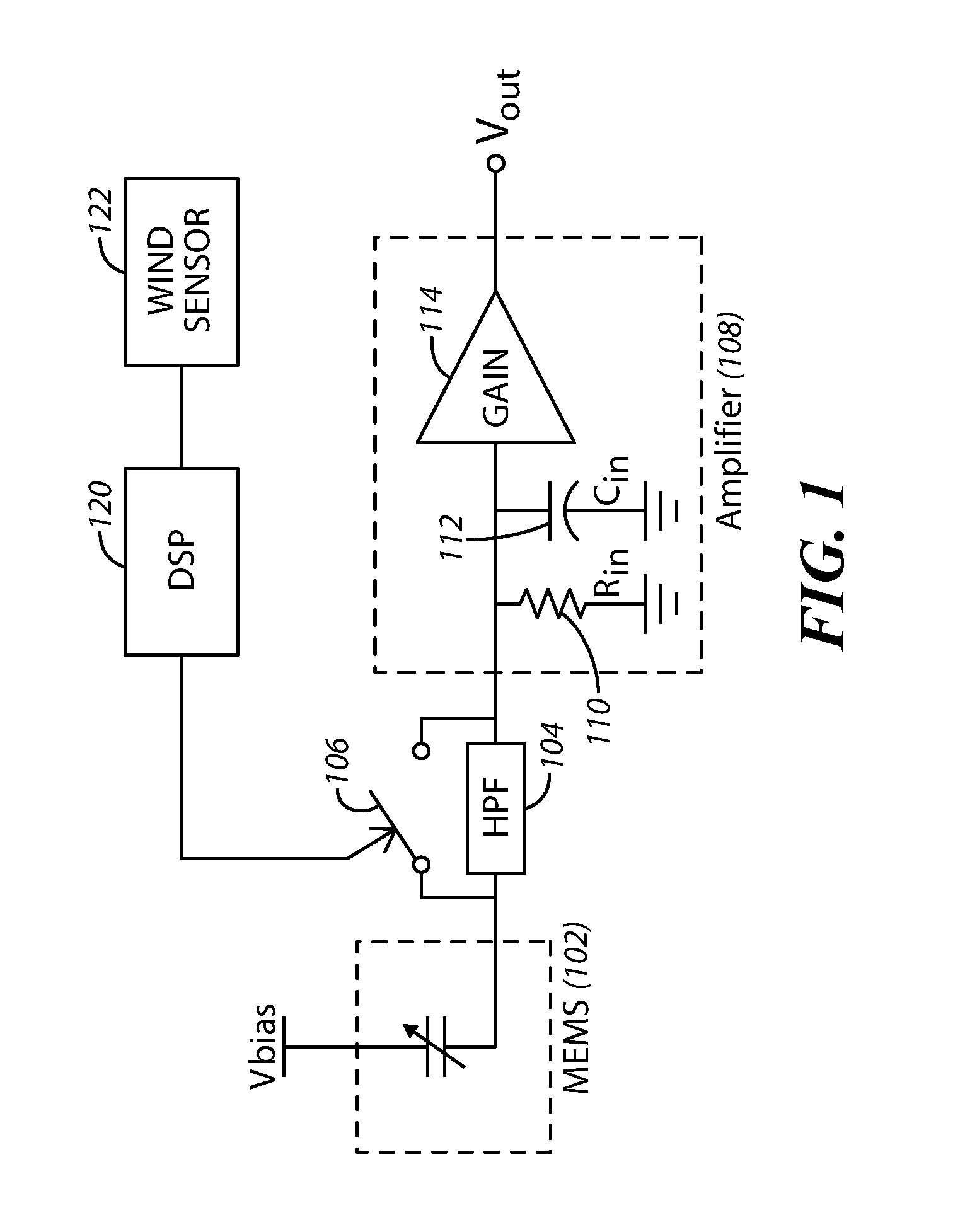
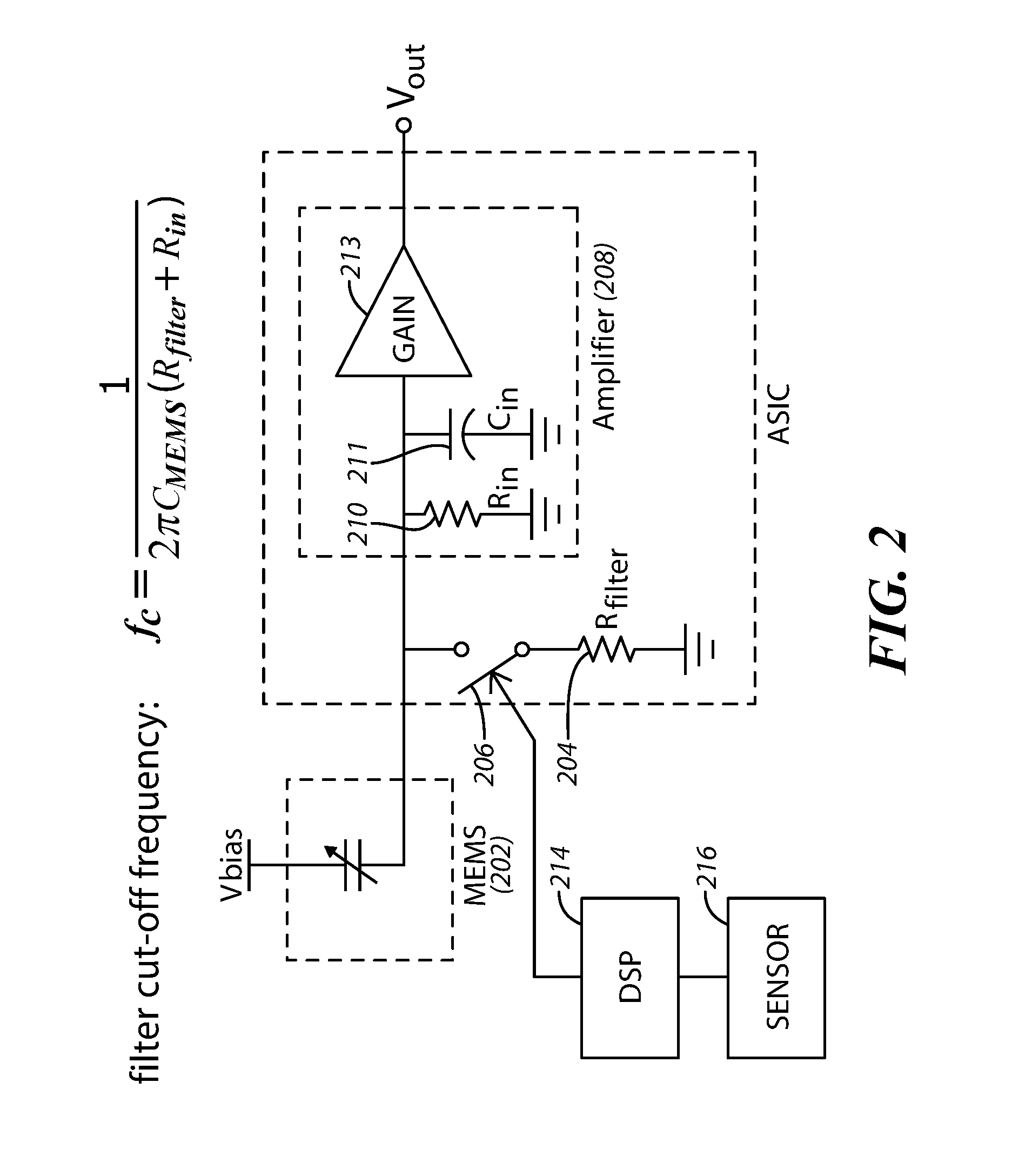
Microphone With Electronic Noise Filter
InactiveUS20160133271A1Semiconductor electrostatic transducersSpeech analysisAudio power amplifierMicroelectromechanical systems
An acoustic apparatus includes a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) device, a controlled filter coupled to the MEMS device, and an amplifier. The controllable filter and the amplifier are coupled together at a node. A cut-off frequency of the filter is selectable based upon reception or non-reception of a low frequency audio signal by the acoustic apparatus.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
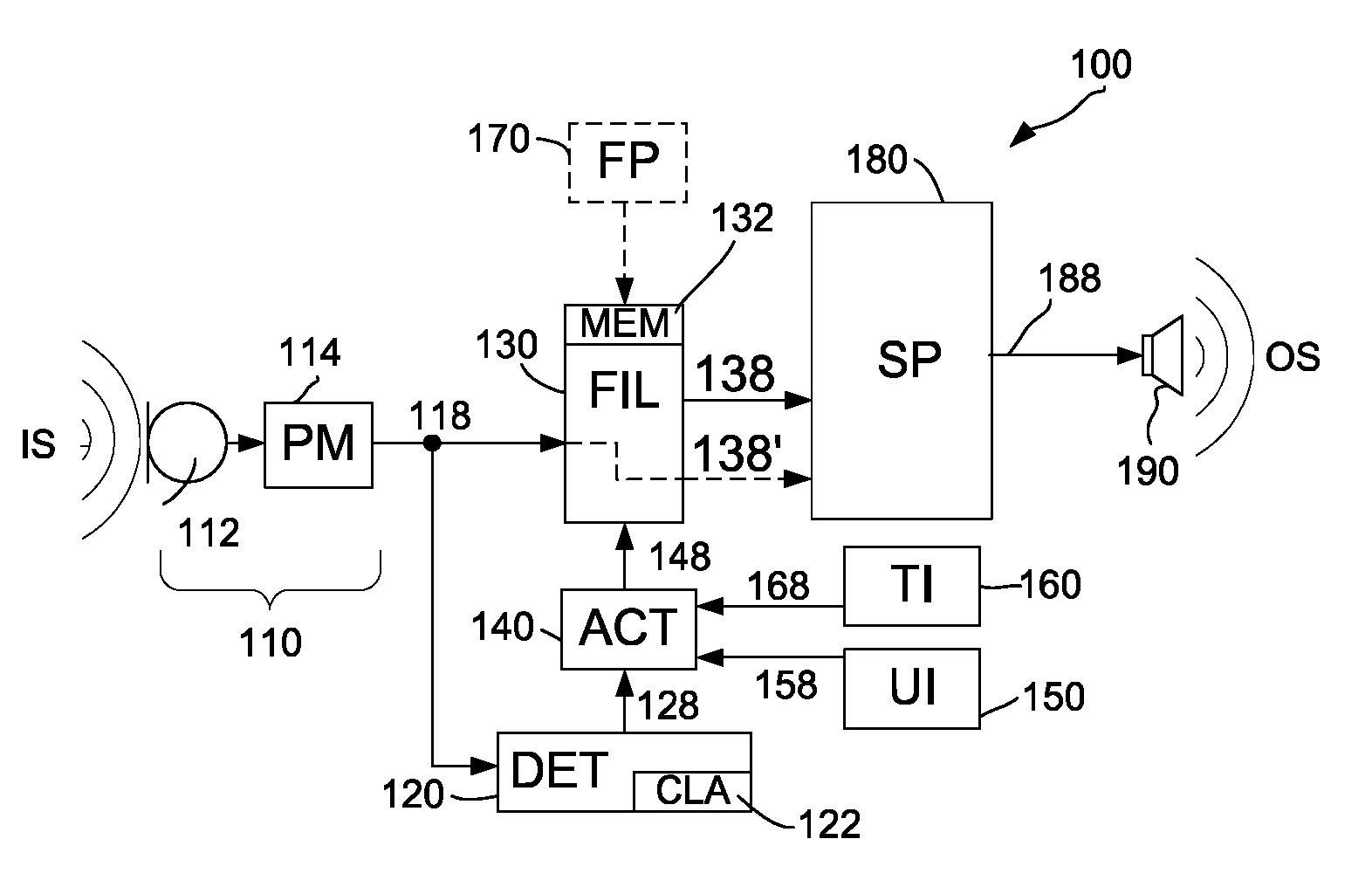
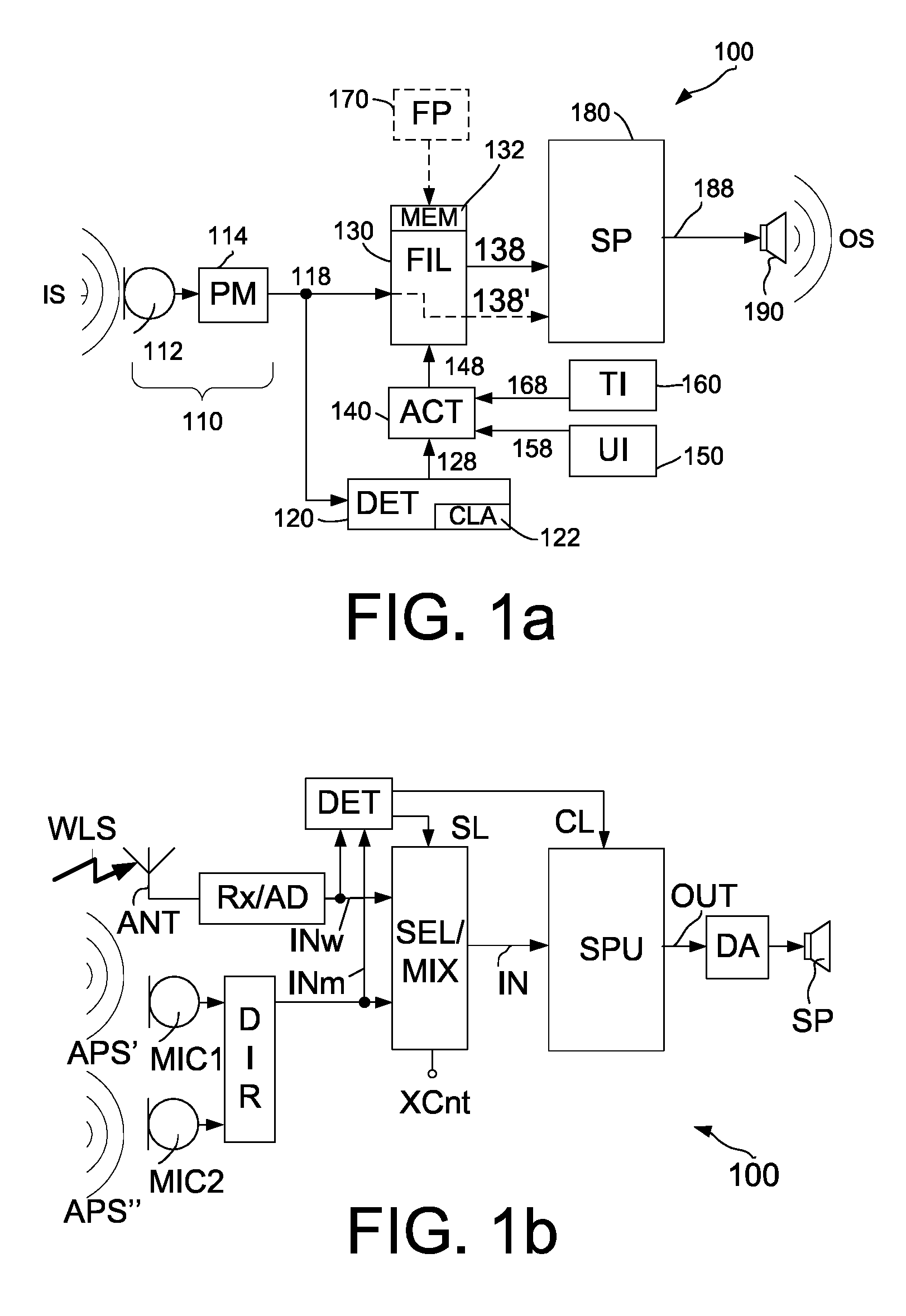
Diminishing tinnitus loudness by hearing instrument treatment
ActiveUS20120308060A1Reduce componentsHarm intelligibilityElectric tinnitus maskersTransducerBroadband
A listening device comprises an input transducer providing an electric input signal comprising audio and a detector coupled to the input transducer, for determining whether the electric input signal is a broadband signal or not and providing a detection signal in response. The listening device furthermore comprises a controllable filter for filtering the electric input signal being coupled to the detector and the input transducer and for outputting a filtered electric input signal such that a component of the electric input signal in the tinnitus frequency range is dampened, if the detection signal indicates that the electric input signal is a broadband signal, and outputting an unfiltered electric input signal such that a component of the electric input signal in the tinnitus frequency range is not dampened, if the detection signal indicates that the electric input signal is not a broadband signal.
Owner:OTICON
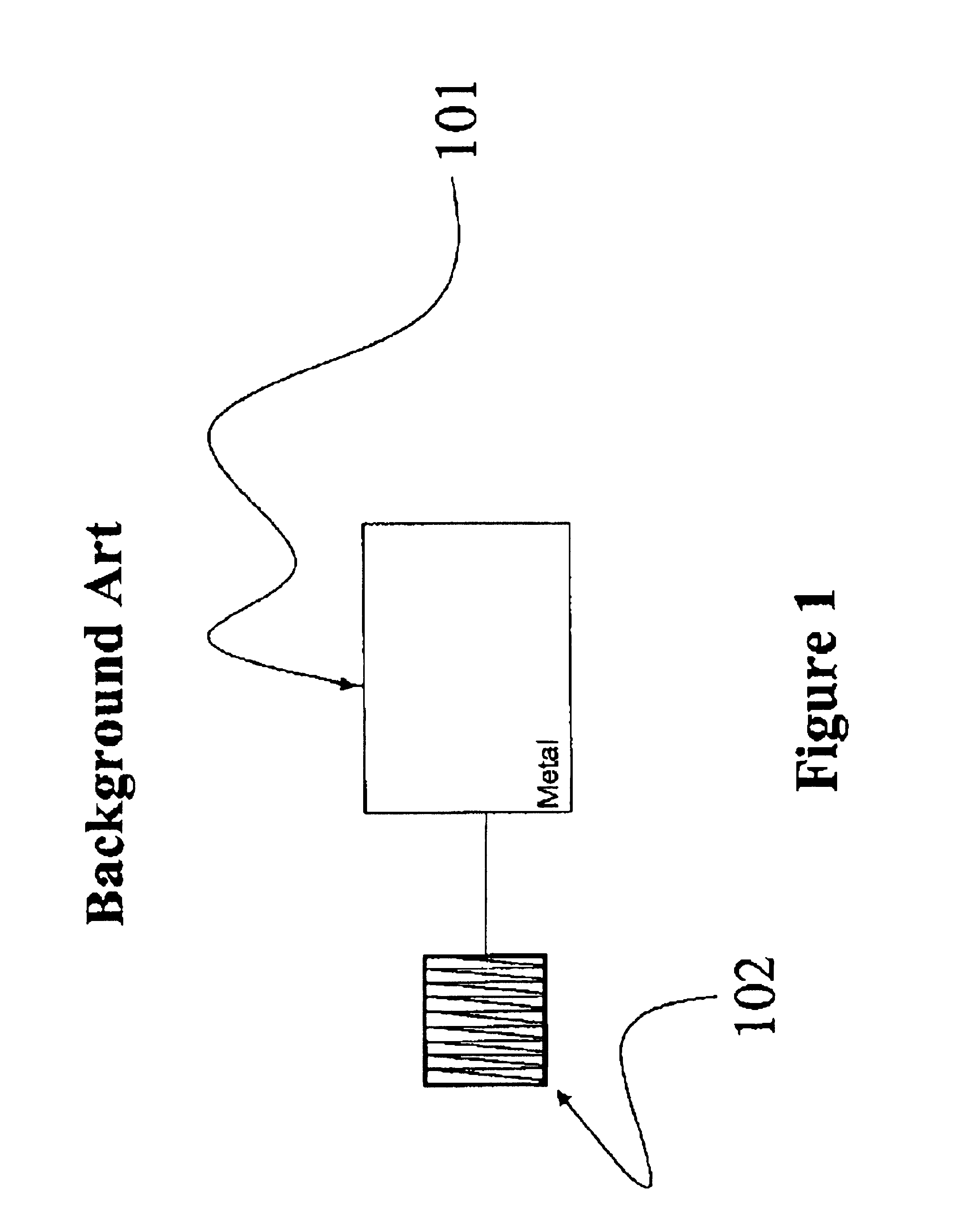
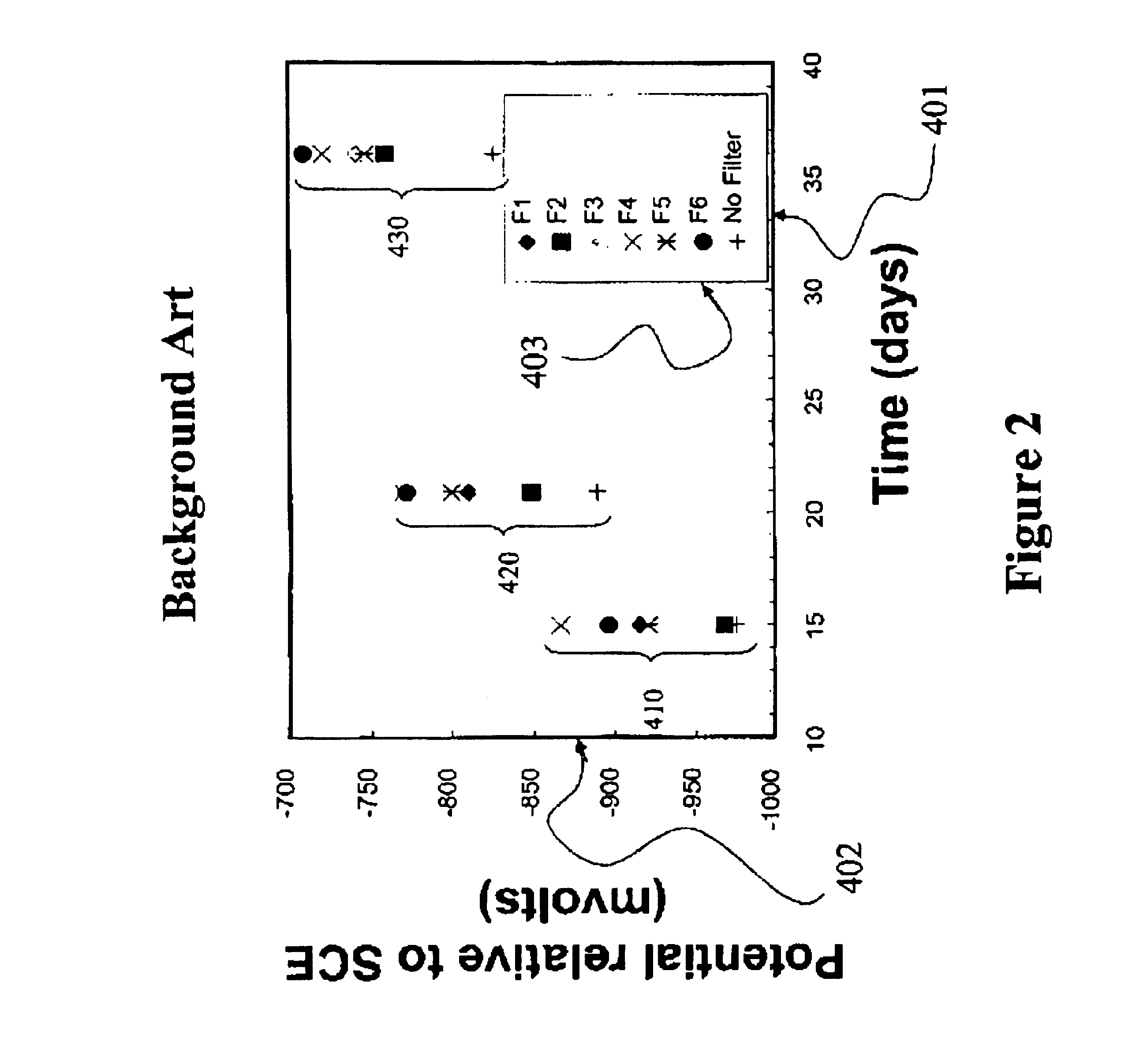
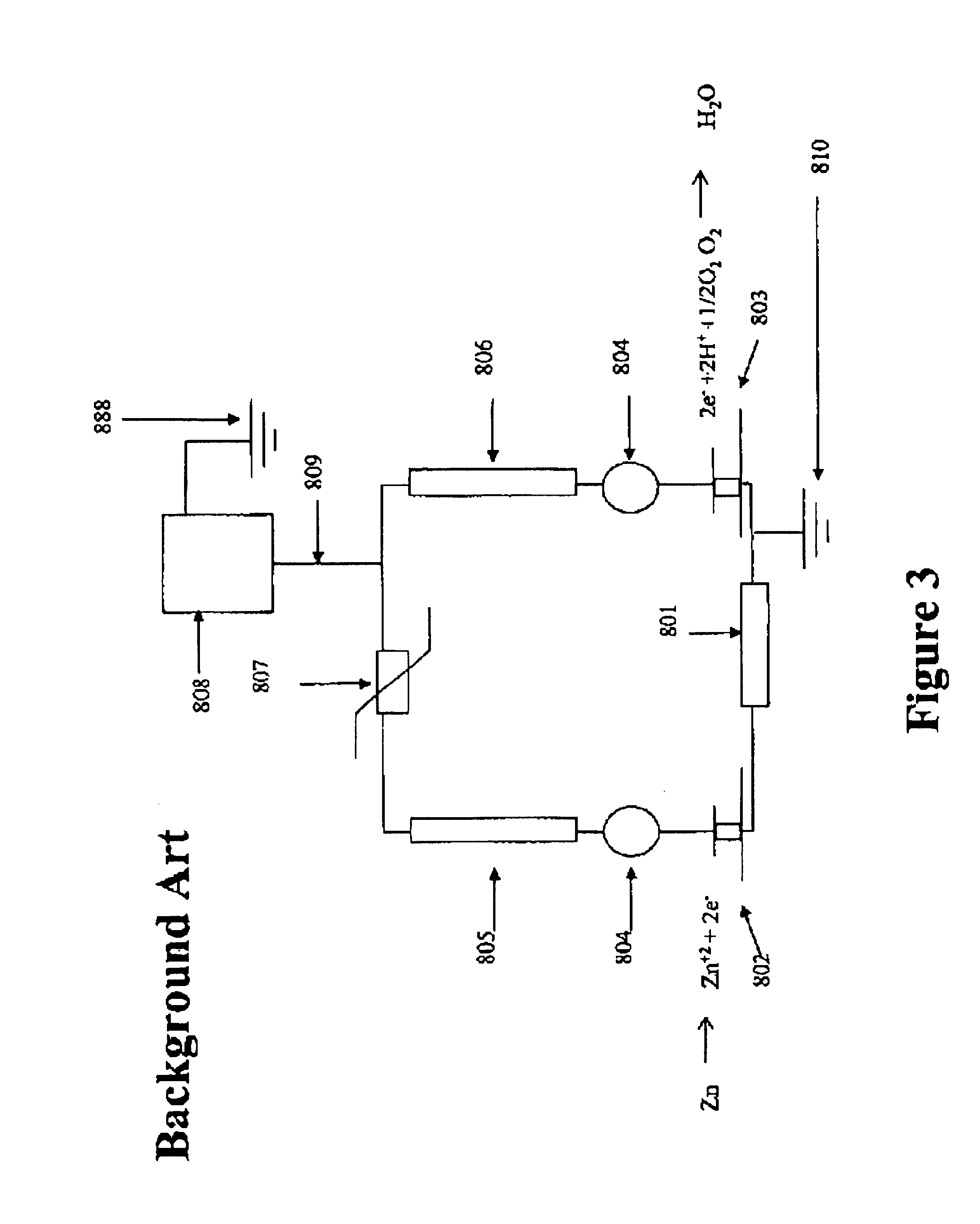
Apparatus, system and method for extending the life of sacrificial anodes on cathodic protection systems
InactiveUS20070023295A1Prolong lifePrevention of corrosion in aviation structures/craftWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectricityEngineering
An apparatus, system, method and computer program product directed to controlling corrosion of a conductive structure in contact with a corrosive environment and electrically connected to one or more anodes, wherein the anodes are less noble than the conductive structure, where the corrosion is controlled by a controllable filter and a corresponding electronic control unit configured to process at least one stored or measured parameter, and wherein the apparatus, system and method serve to prolong the lifetime of the one or more anodes by reducing, minimizing or substantially eliminating their sacrificial character.
Owner:APPLIED SEMICON INT
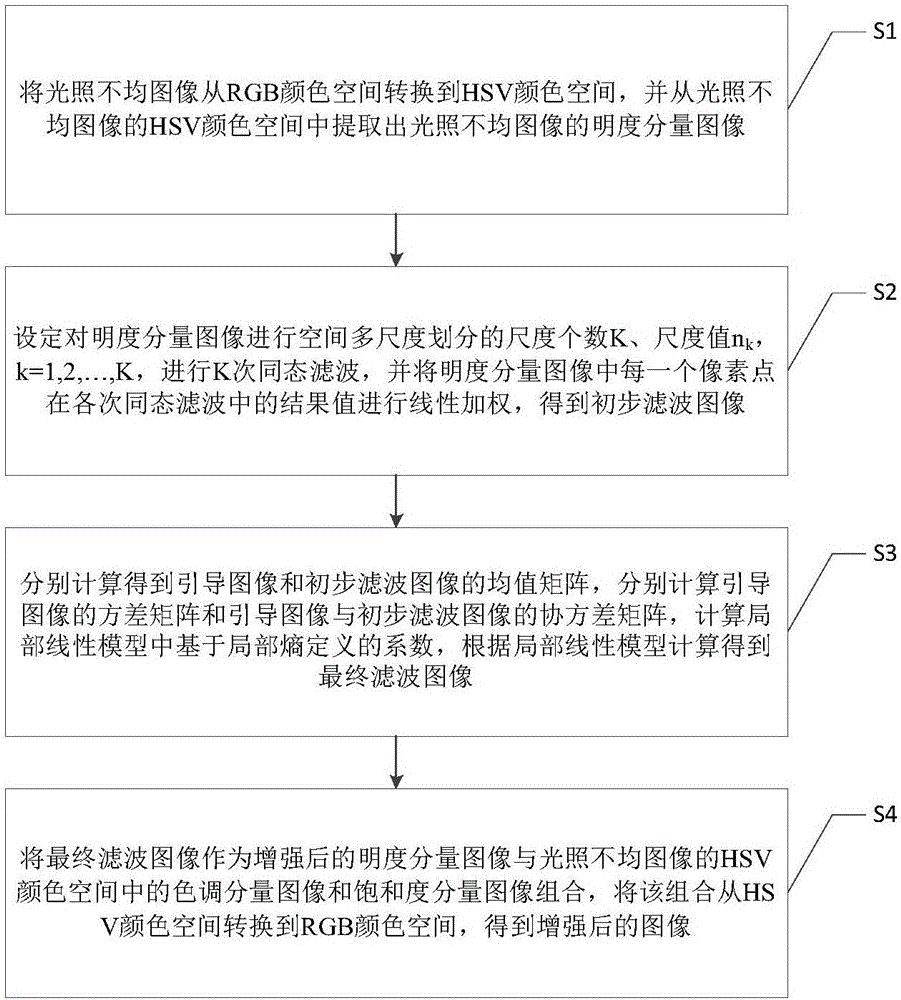
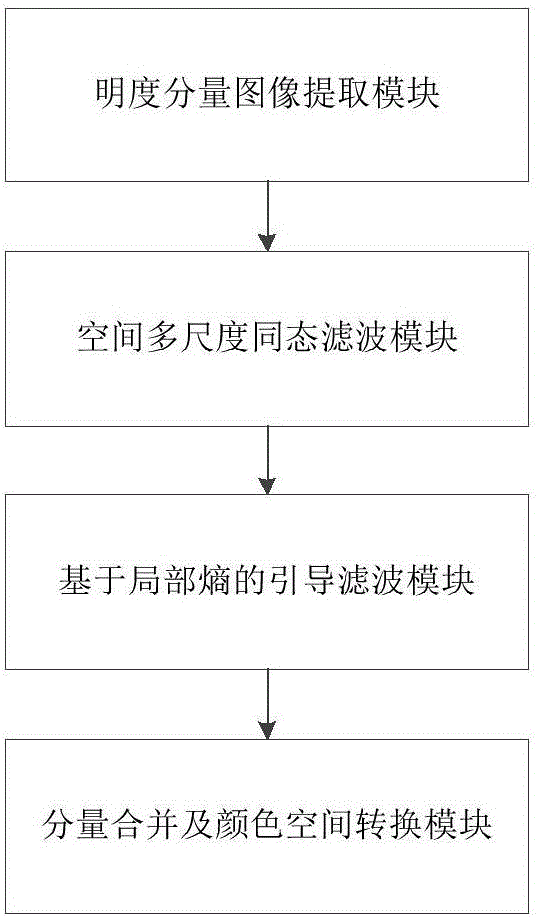
Illumination unevenness image enhancement method and system
The invention discloses an illumination unevenness image enhancement method and system. The method comprises the steps of S1, converting an illumination unevenness image to an HSV color space from an RGB color space, and extracting a brightness component image; S2, performing spatial multi-size homomorphic filtering on the brightness component image to obtain a primary filtered image; S3, performing local entropy-based steerable filtering on the primary filtered image to obtain a final filtered image; and S4, combining the final filtered image as an enhanced brightness component image with an original hue component image and an original saturation component image, and converting a combined image to the RGB color space from the HSV color space, thereby obtaining an enhanced image. According to the method and the system, the illumination unevenness image can be enhanced, so that the illumination is even, the details are rich, and the color is natural.
Owner:北交智轨(北京)科技有限公司
Non-positive-definite optical filtering from positive-definite transfer functions
Fractional Fourier transform properties of lenses or other optical environments are applied to one or more positive-definite optical transfer functions at locations outside the Fourier plane to realize or closely approximate arbitrary non-positive-definite transfer functions varying in both amplitude and phase. Controllable filter elements can be employed to create controllable optical processors which may be used for image filtering and optical computations using complex-valued arithmetic for monochromatic, color, and wide-spectrum optical signals. Applications include integrated optics, optical computing systems, particle beam systems, radiation accelerators, astronomical observation systems, and controllable lens systems.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Diminishing tinnitus loudness by hearing instrument treatment
A listening device for a hearing impaired person being subjected to a tinnitus at a tinnitus frequency range including a tinnitus frequency is disclosed. The device includes an input transducer for providing an electric input signal comprising audio and a controllable filter for filtering the electric input signal received from the input transducer. The filter outputs a filtered electric input signal such that signal energy of the electric input signal immediately surrounding the tinnitus frequency remain substantially unchanged and signal energy of the electric input signal at a distance to the tinnitus frequency is substantially reduced. The device further includes a processor connected downstream of the filter and processes the filtered electrical input signal and outputs a processed electric signal, and an output transducer connected downstream of the processor and converts the processed electric signal to an acoustic output signal to be presented to a hearing impaired person.
Owner:OTICON
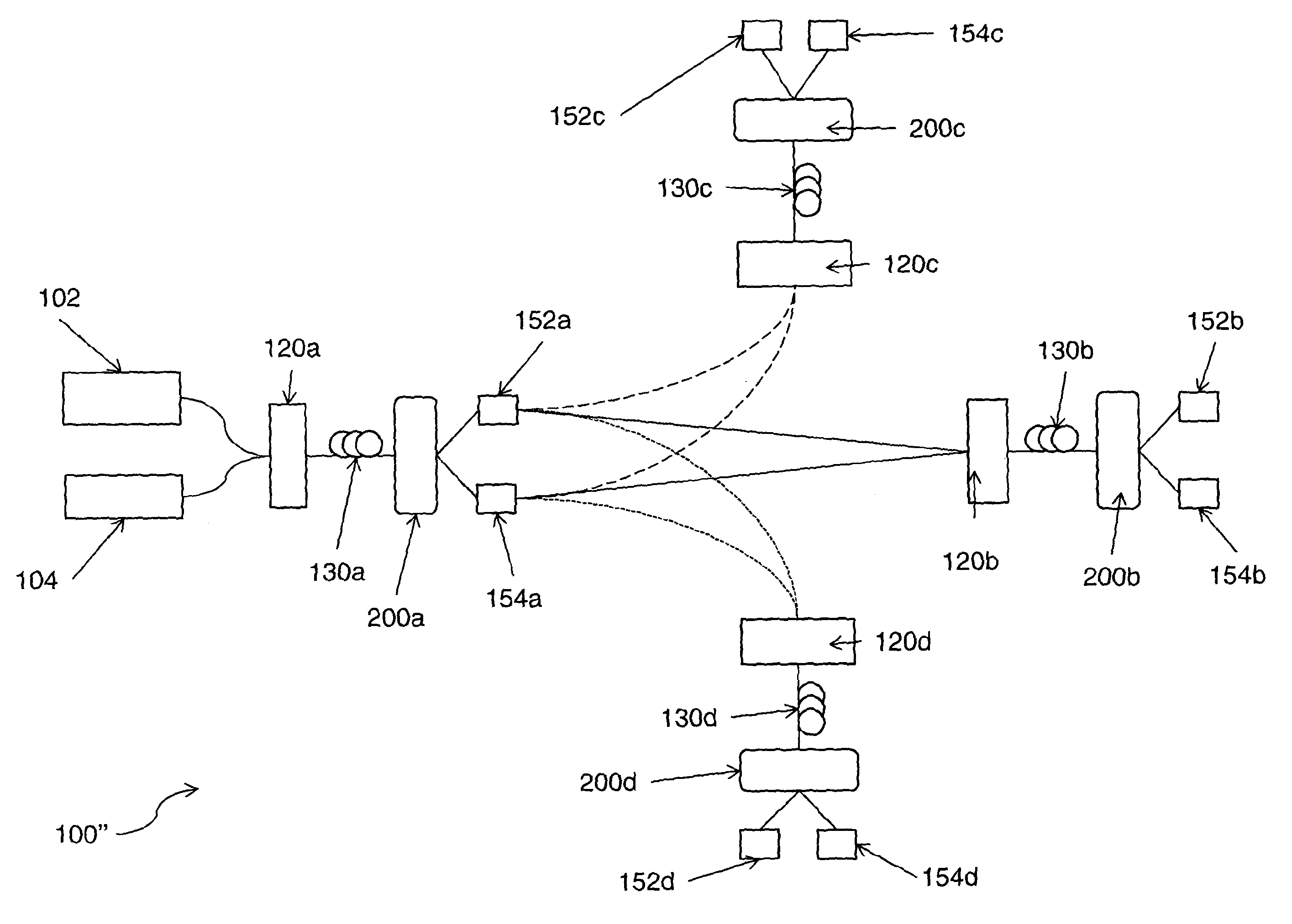
Communications network
ActiveUS9271058B2Information carrying capacity of can increasedImprove carrying capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical fiber cableSteerable filter
A communications network wherein first and second optical signals can be launched into an optical fiber in respective first and second regions of a transmission window such that controllable filters can be used to selectively recover the first and second optical signals. This partitioning of the transmission window allows two incompatible optical signals to coexist in the same optical fiber.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Underwater target detection image enhancement method adopting self-adaptive multi-scale dark channel prior
ActiveCN107203980AImprove visual qualityEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisColor imagePattern recognition
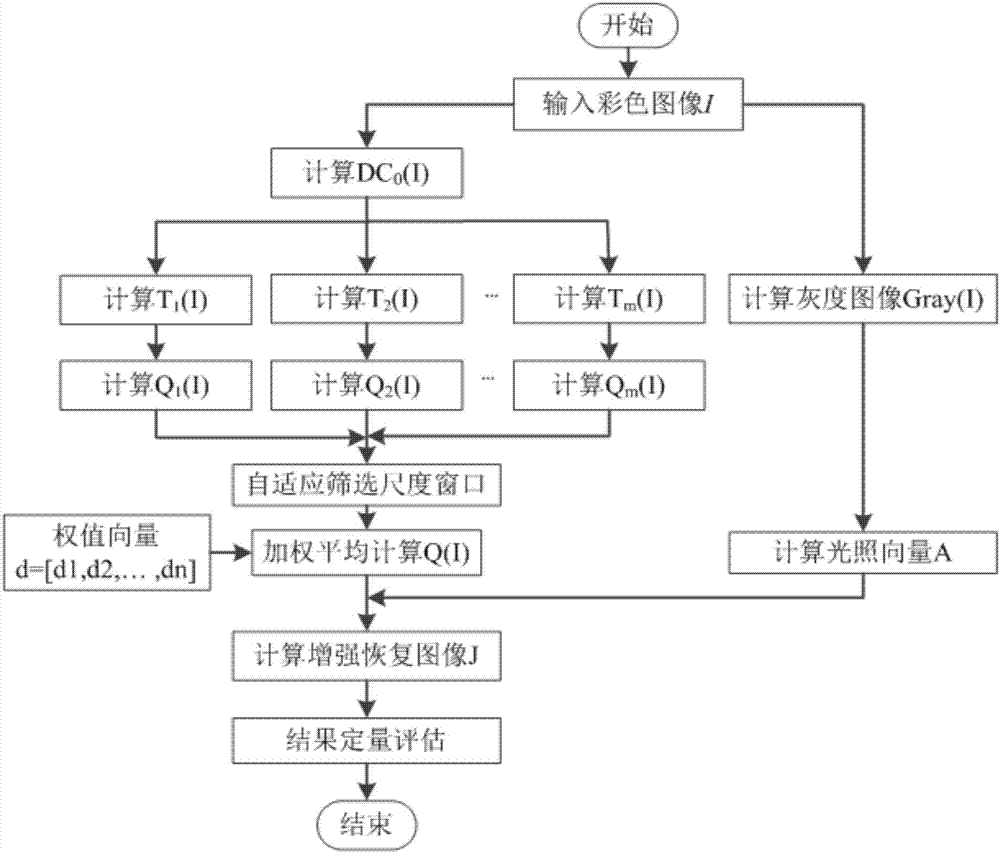
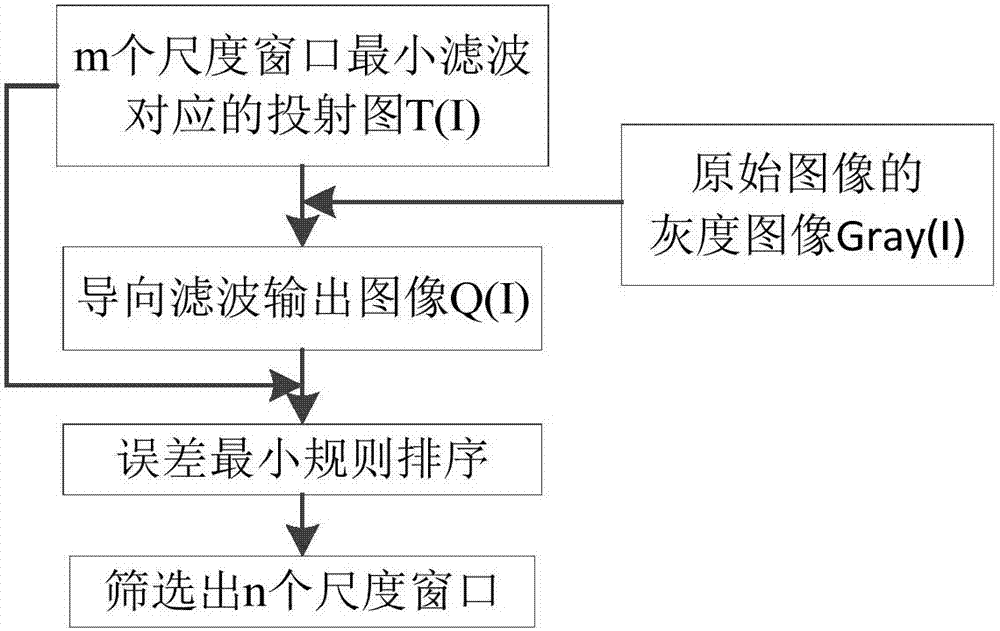
The invention discloses an underwater target detection image enhancement method adopting self-adaptive multi-scale dark channel prior. The method comprises steps as follows: acquiring an original color image of an underwater target; calculating a light vector of the original image; calculating a dark channel image of the original image; calculating transmission graphs corresponding to different-scale windows of the dark channel image; calculating steerable filter output images corresponding to the transmission graphs in different-scale windows of the original color image with a steerable filter method; primarily selecting several most appropriate windows in the minimum filter scale according to the condition that the error between each steerable filter output image and the corresponding transmission graph is minimum; performing weighted average on the screened-out steerable filter output images; calculating a restored and enhanced image of the original image according to the dark channel prior theory; performing quantitative evaluation on the restored image J in the mean value, the variance, the contrast ratio, the information entropy and other aspects. With the adoption of a steerable filter function applied in the method, texture and smoothness balancing processing on the image can be realized, so that the processed image has improved visual quality and rich texture information.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
Improved dark channel prior image defogging algorithm based on fast steerable filtering
InactiveCN108022225AGood fog removal effectOptimize processing timeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSky
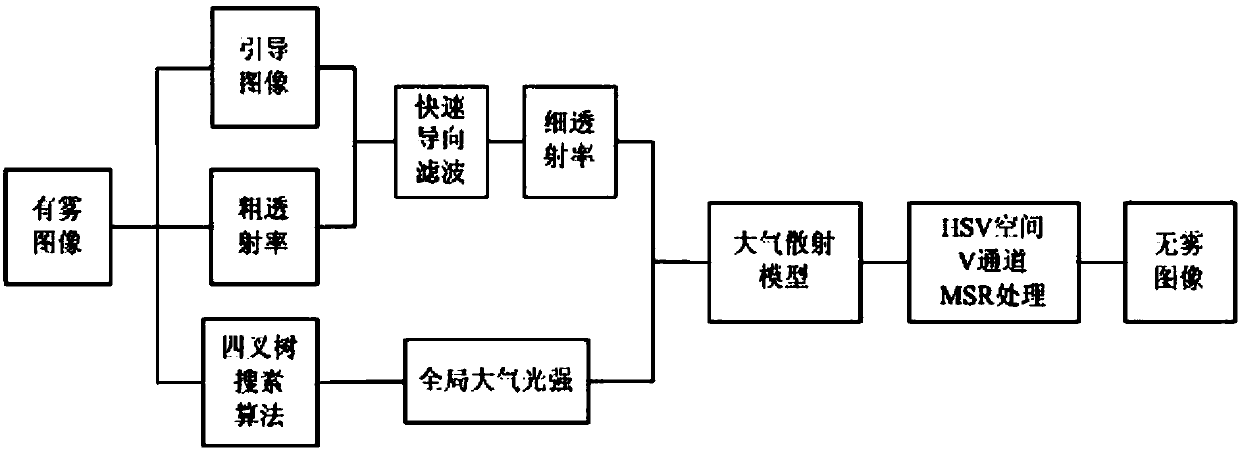
The invention discloses an improved dark channel prior image defogging algorithm based on fast steerable filtering, and belongs to the technical field of image defogging algorithms. The invention aimsat solving problems that the global atmosphere light intensity evaluation in a conventional dark channel single-image defogging algorithm is liable to be disturbed by a white object, the color of a sky region is distorted and the calculation is complex when a software image cutting method is used for optimizing transmissivity. According to the invention, the algorithm provided by the invention employs an improved quadtree search algorithm and the improved fast steerable filtering for refining the transmissivity, effectively improves the defogging effect, is bright in color of a recovered image, is clear and natural in visual effect, and improves the processing time to a certain degree.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
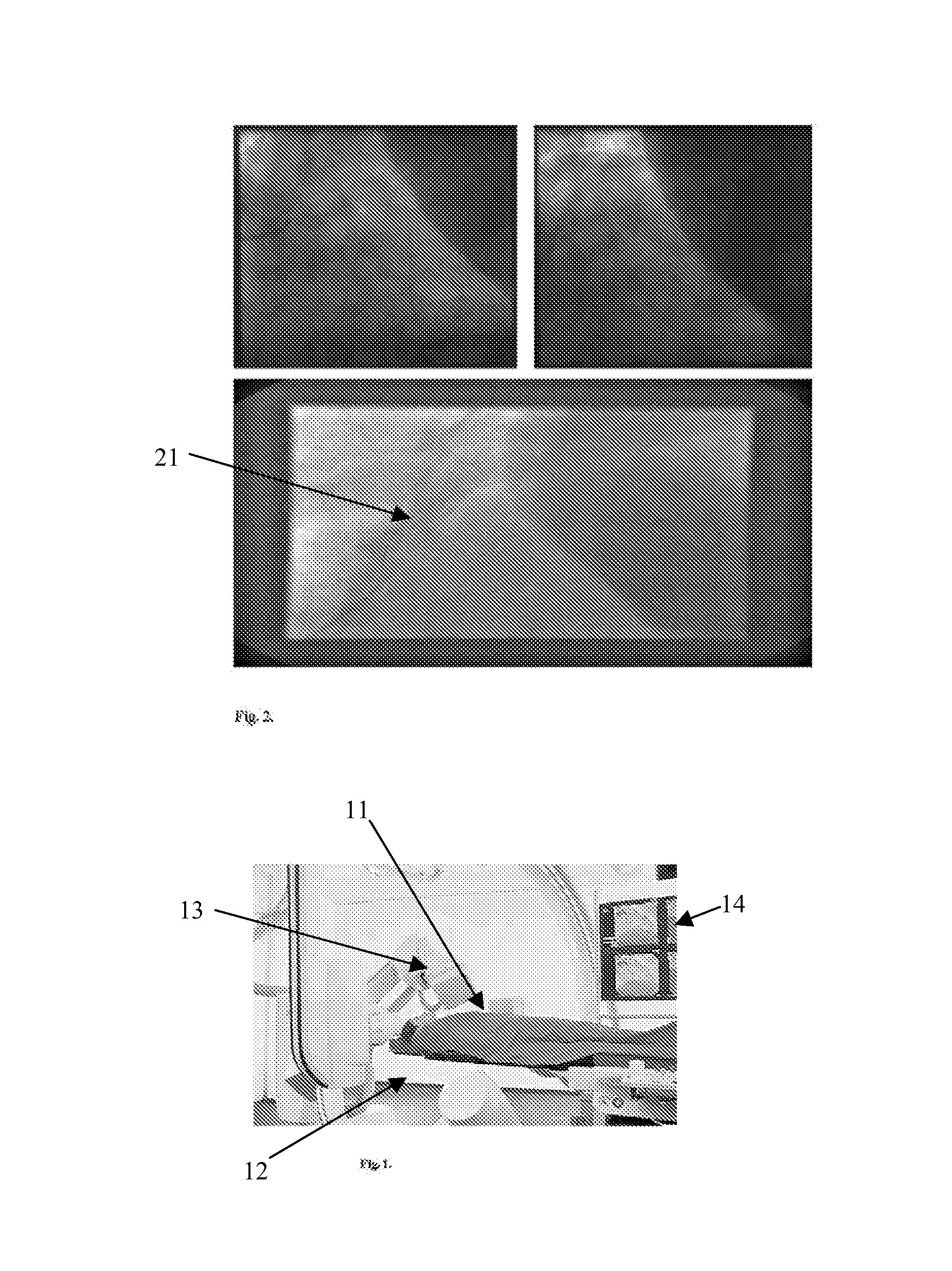
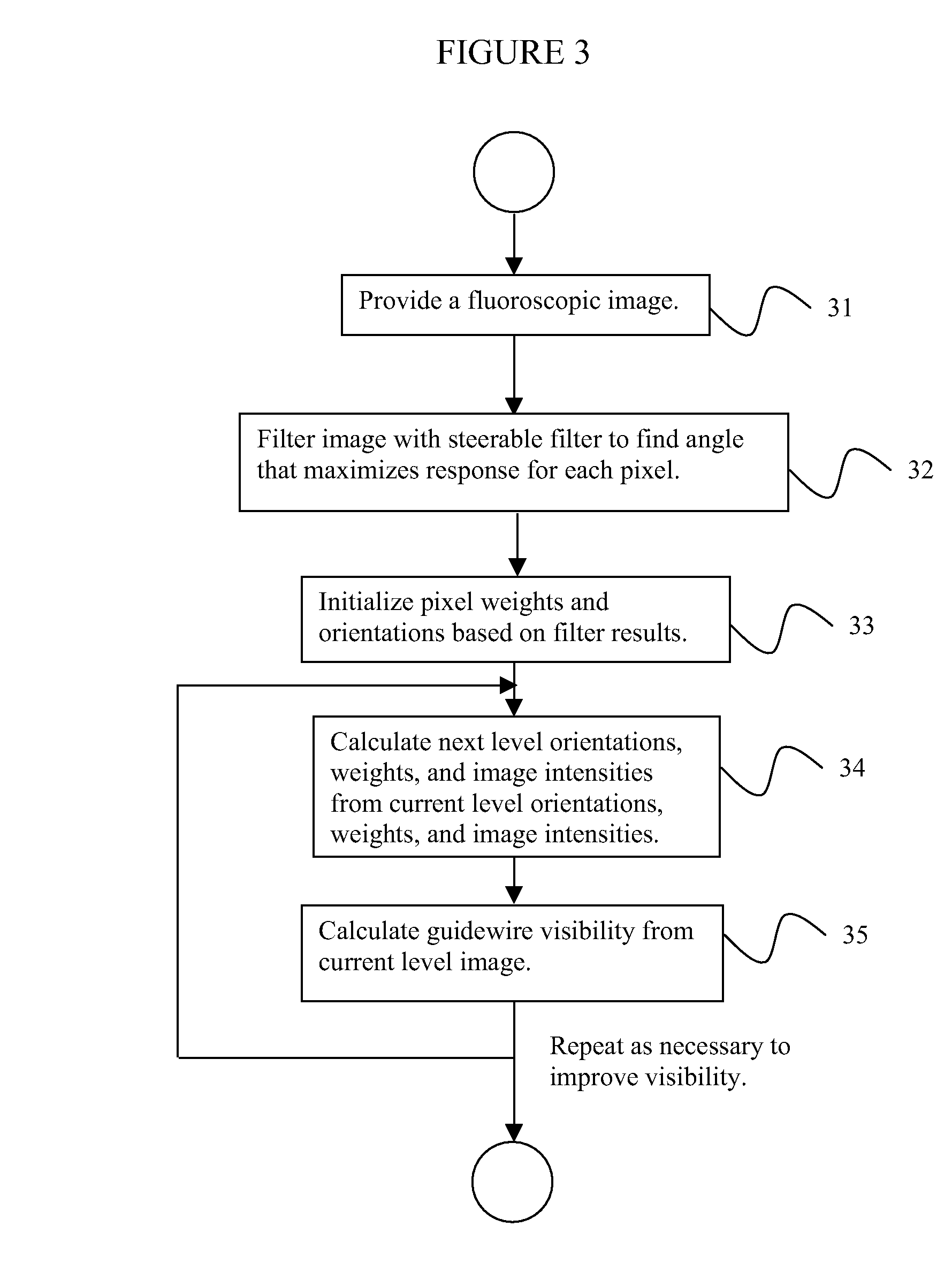
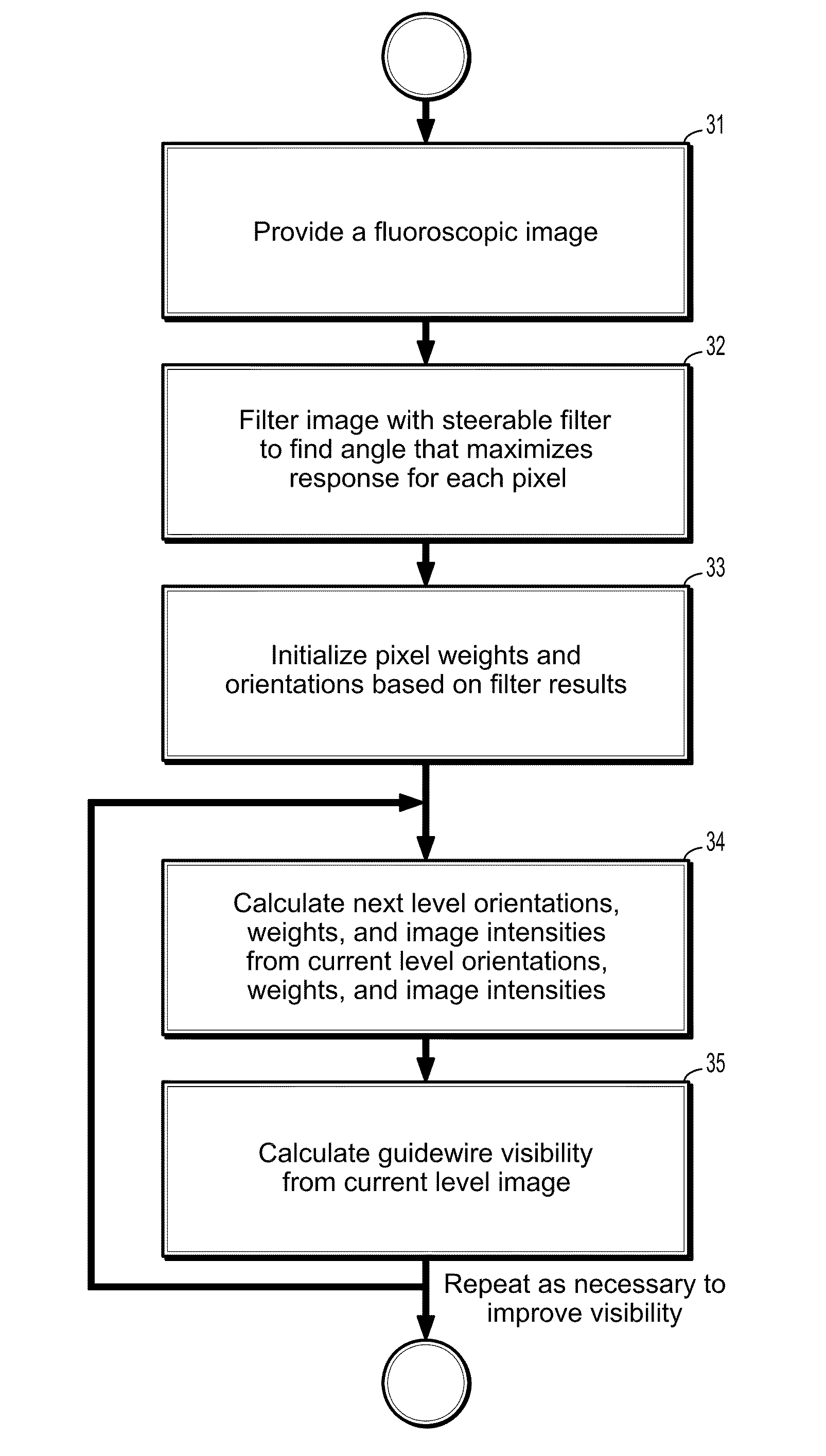
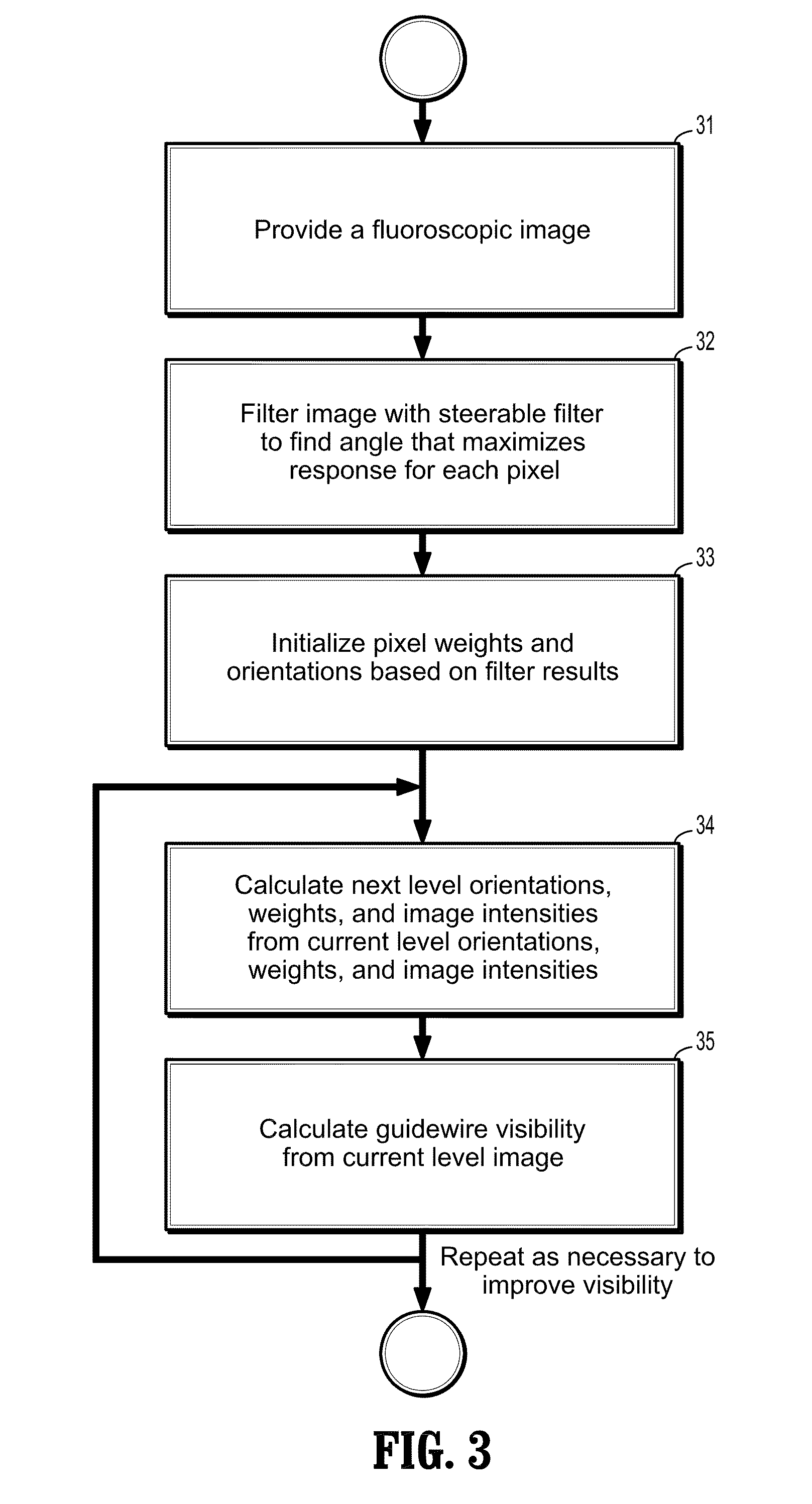
System and Method For Simultaneously Subsampling Fluoroscopic Images and Enhancing Guidewire Visibility
InactiveUS20080107314A1Enhancing guidewire visibilityReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityFluoroscopic image
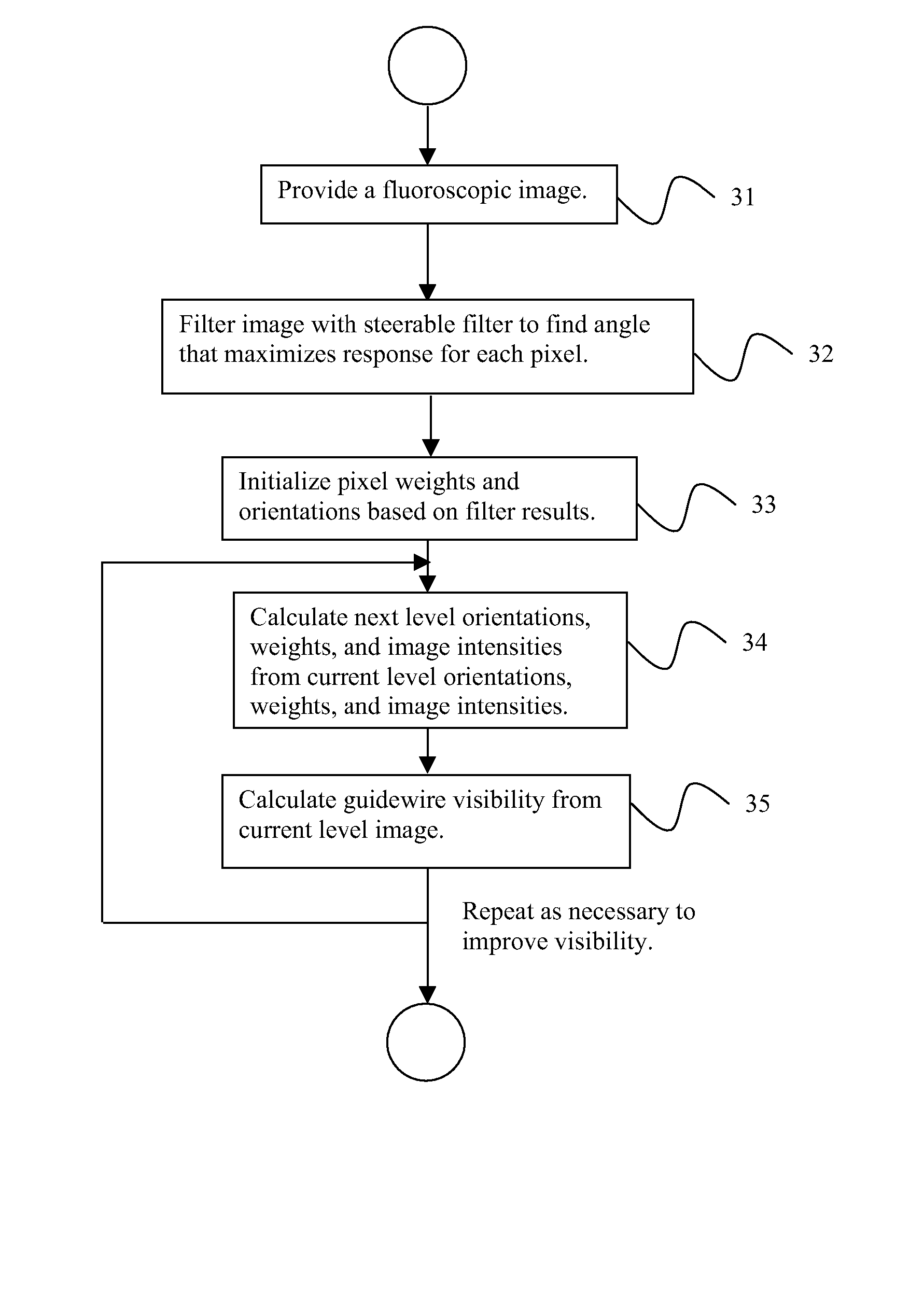
A method for downsampling fluoroscopic images and enhancing guidewire visibility during coronary angioplasty includes providing a first digitized image, filtering the image with one or more steerable filters of different angular orientations, assigning a weight W and orientation O for each pixel based on the filter response for each pixel, wherein each pixel weight is assigned to a function of a maximum filter response magnitude and the pixel orientation is calculated from the angle producing the maximum filter response if the magnitude is greater than zero, wherein guidewire pixels have a higher weight than non-guidewire pixels, and downsampling the orientation and weights to calculate a second image of half the resolution of the first image, wherein the downsampling accounts for the orientation and higher weight assigned to the guidewire pixels.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method and System for Filtering Elongated Features
InactiveUS20080317370A1Efficient solutionImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionComputer science
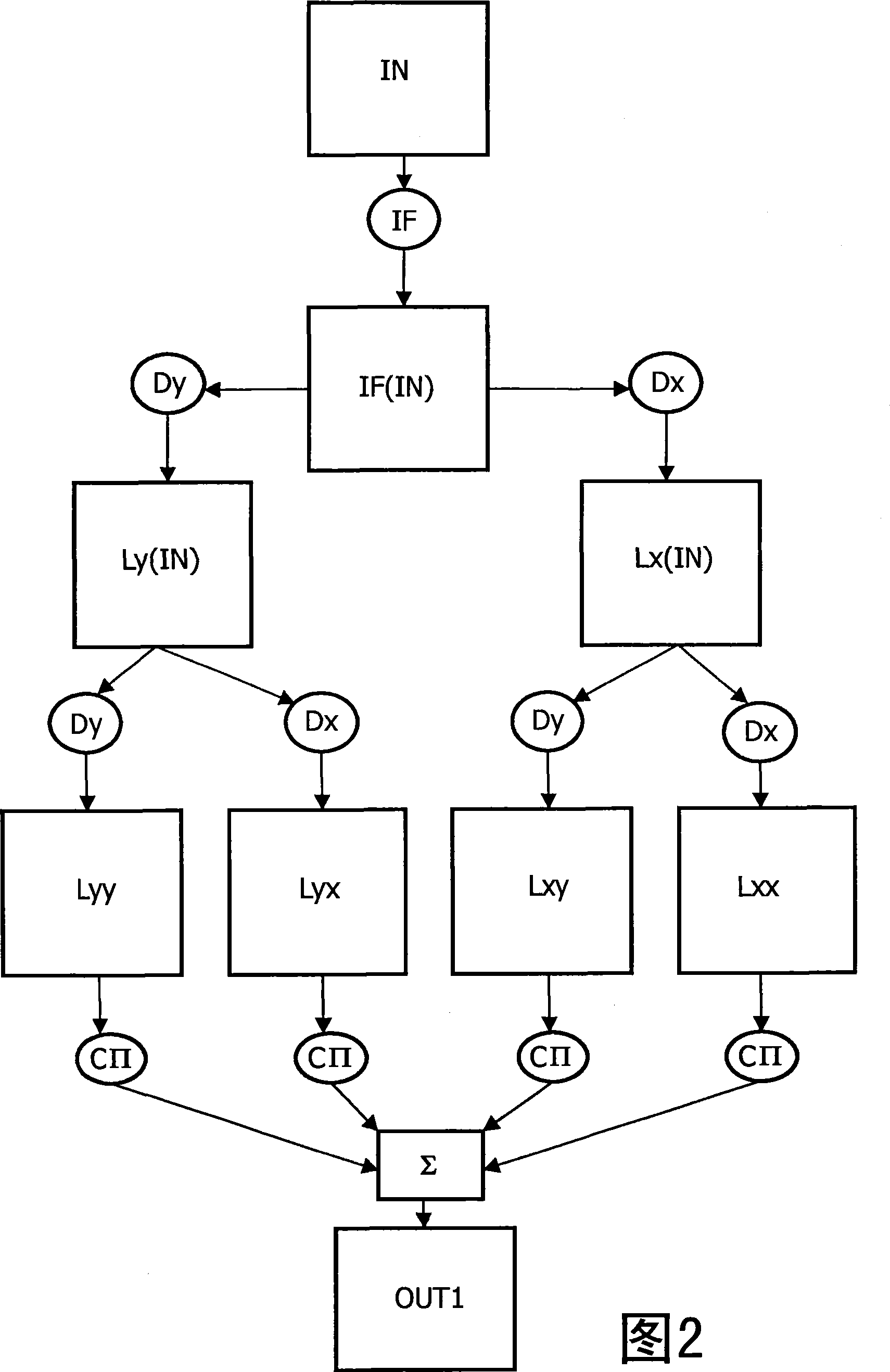
The present invention relates to a method of filtering an input image for producing an output image. The method comprising the steps of, for a first image point located at first spatial coordinates:—analysing intensity levels of the input image in a first vicinity of the first image point for calculating a first direction of filtering at said first image point;—computing an intensity level of a first output image point of a first output image by applying a first steerable filter kernel to the input image, which is centered at the first image point and oriented along the calculated first direction of filtering; selecting at least a second image point in a second vicinity of said first image point in the first output image;—computing an intensity level of at least one second output image point of a second output image by applying at least a second steerable filter kernel to the input image, which is centered at the at least second image point and oriented along a second direction of filtering;—calculating a linear combination of the first output image point and of the at least second output image point for providing an output intensity level;—applying said output intensity level to an output image point of said output image, said output image point having said first spatial coordinates.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Spatially selective detection using a dynamic mask in an image plane
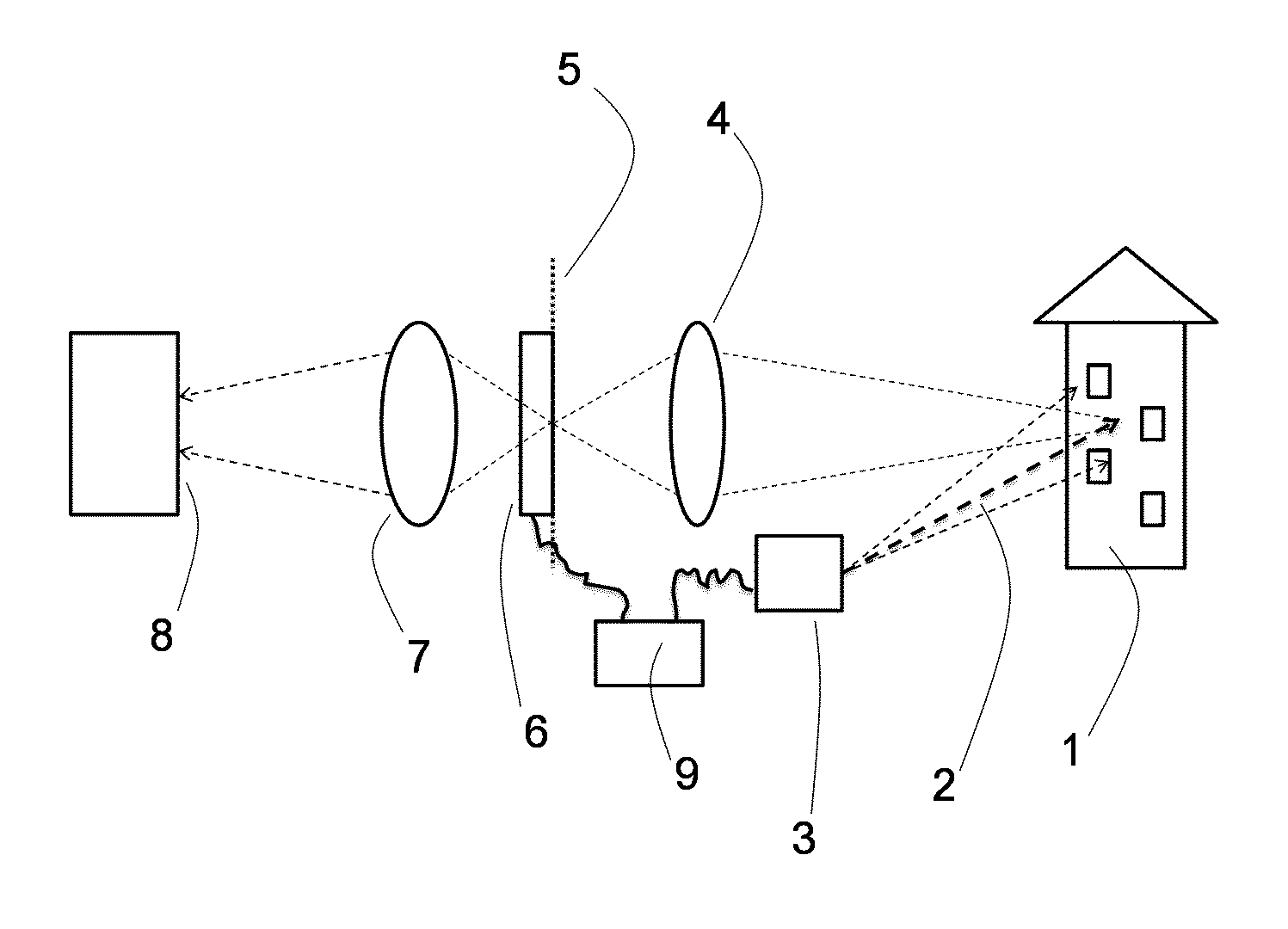
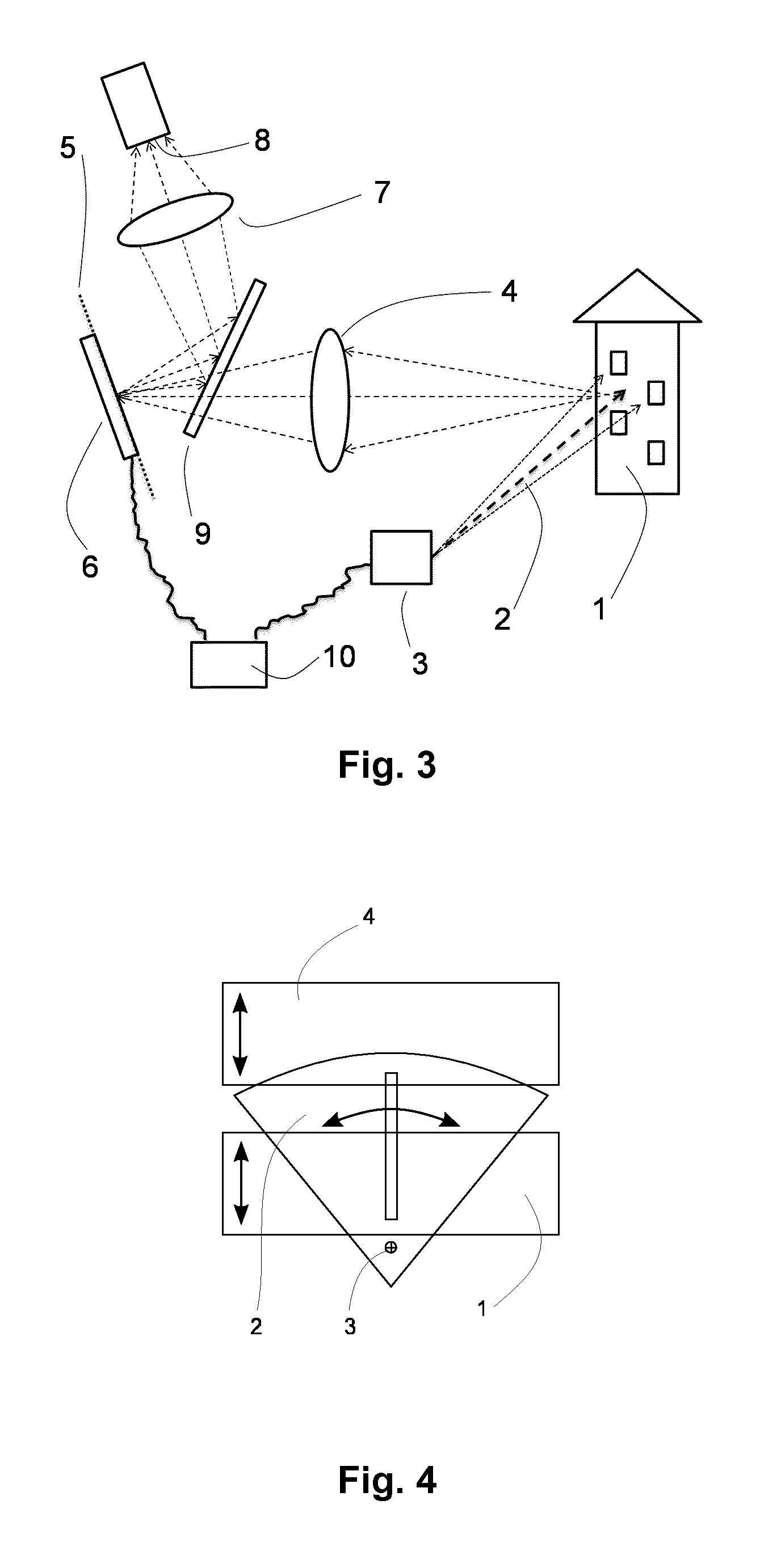
ActiveUS9528819B2Design of becomes criticalLarge freedom of designActive open surveying meansUsing optical meansLight beamLighting system
A three-dimensional laser scanner instrument for acquiring three-dimensional geometric data of a scene (1) comprises an illumination system (3) for generating a light beam (2) and for scanning an illumination point of said light beam (2) through said scene (1), a light detection system (6-9) comprising at least one light detector (8), said light detection system being arranged to receive light from said scene (1), and an optical system (4) for imaging light scattered in or reflected from said scene (1) onto said light detection system (6-9). The light detection system (6-9) further comprises a controllable filter element (6) for dynamically discriminating light impinging from selected regions of said scene (1) and a control unit (9) operatively connected to said controllable filter element (6) and to said illumination system (3), wherein in operation of said scanner instrument, said filter element (6) is controlled by said control unit (9) so as to guide only light impinging from a selected, spatially delimited region around said illumination point in said scene (1) onto said at least one light detector (8).
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Remote-sensing image building location detection method based on probability
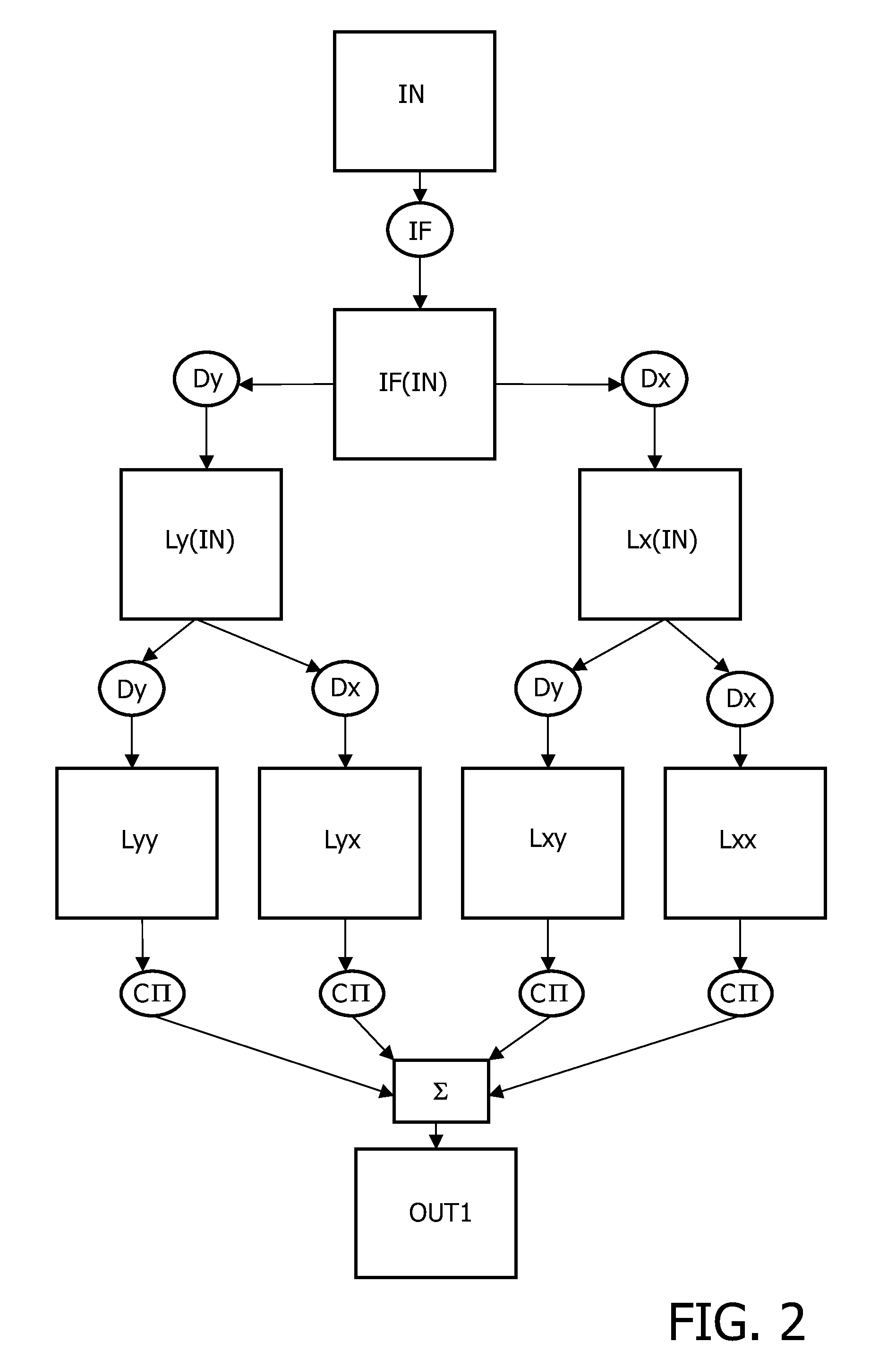
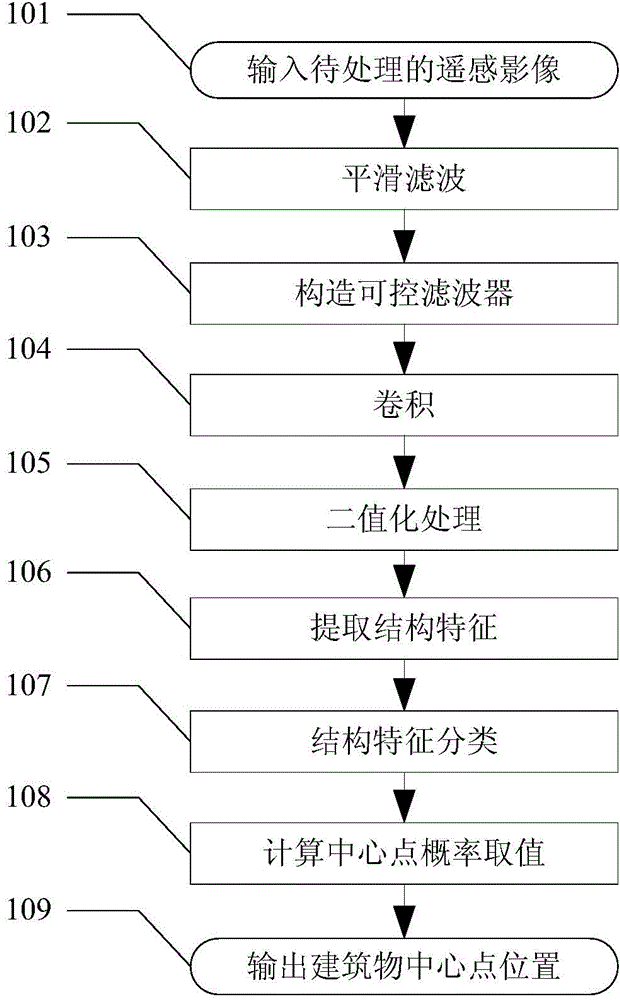
InactiveCN104794723ASolve the low detection efficiencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLocation detectionComputer vision
The invention relates to a remote-sensing image building location detection method based on probability. The remote-sensing image building location detection method includes the steps of (1) performing smoothing filter to acquire the image 2; (2) constructing a controllable filter; (3) convoluting; (4) binaryzating; (5) extracting structure features of twelve directions; (6) classifying straight lines and curves; (7) calculating probability of central points of candidate buildings by means of probability density functions; and (8) defining thresholds to determine location of the central points of the buildings. By determining the location of the central points of the buildings according to the probability density functions, the problem of low building-location detection efficiency caused by the conventional methods which adopt modeling and classifiers and the like is solved, accuracy and efficiency of building detection are both improved, and the effect of full automation is achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
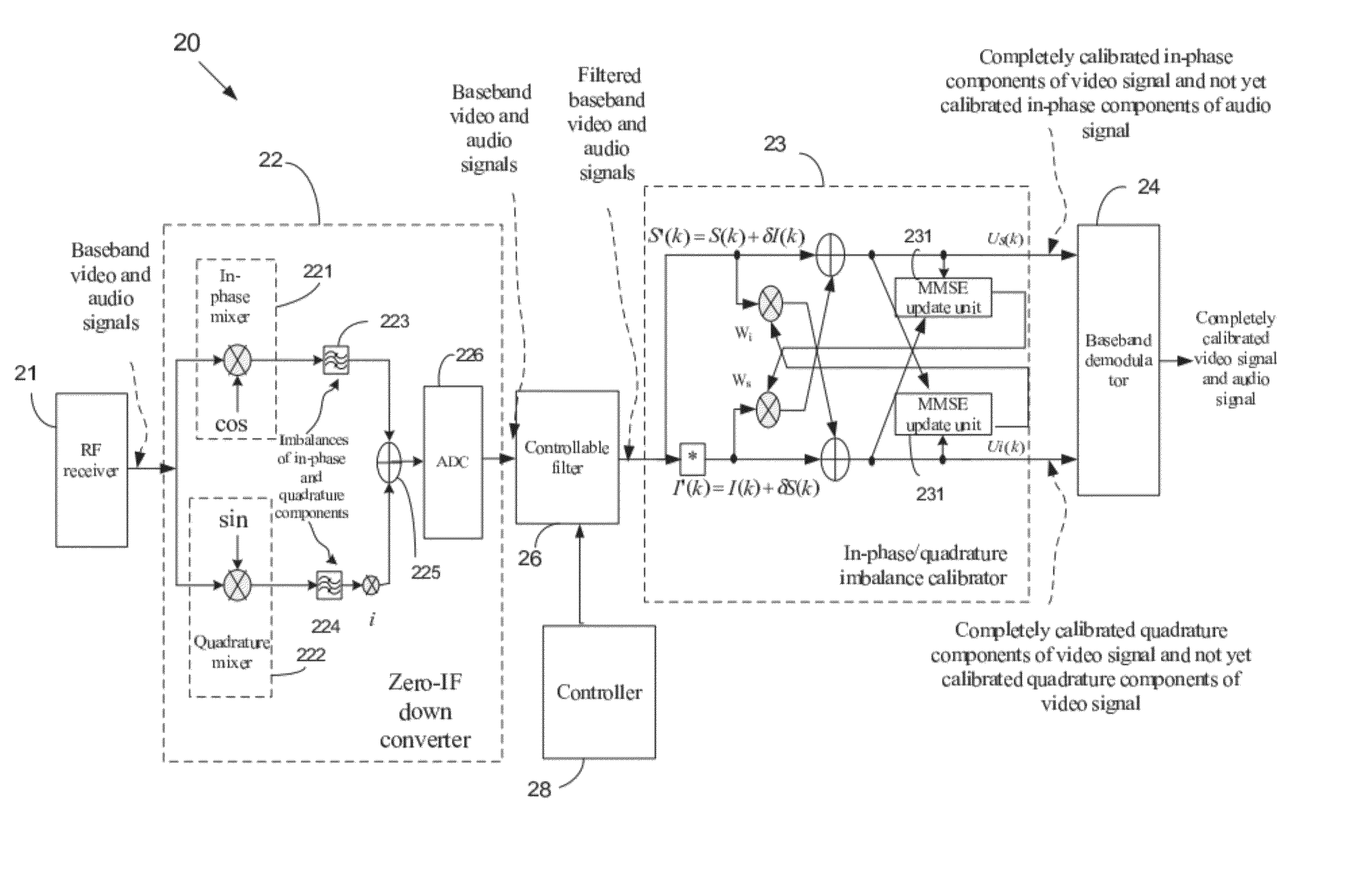
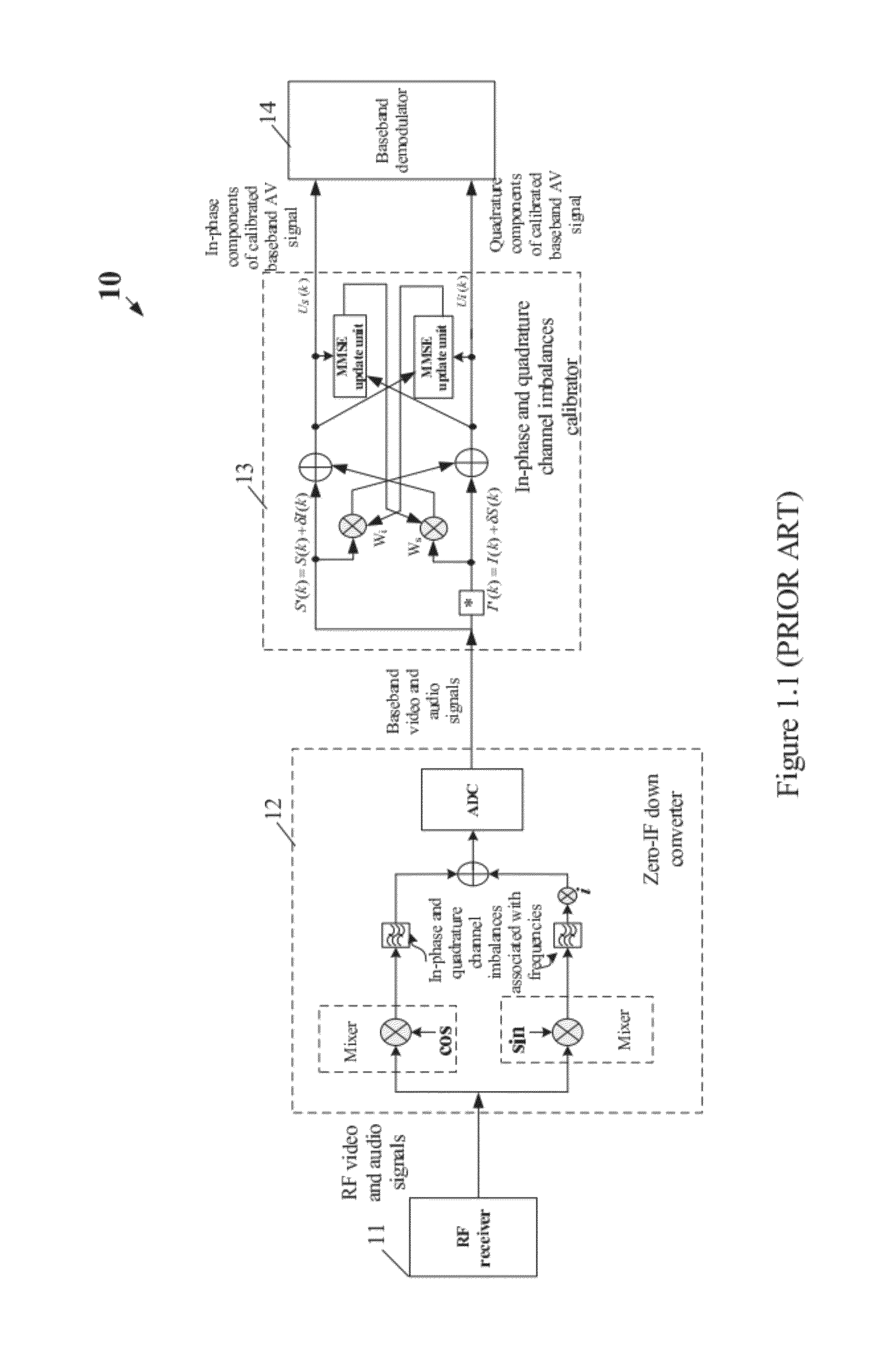
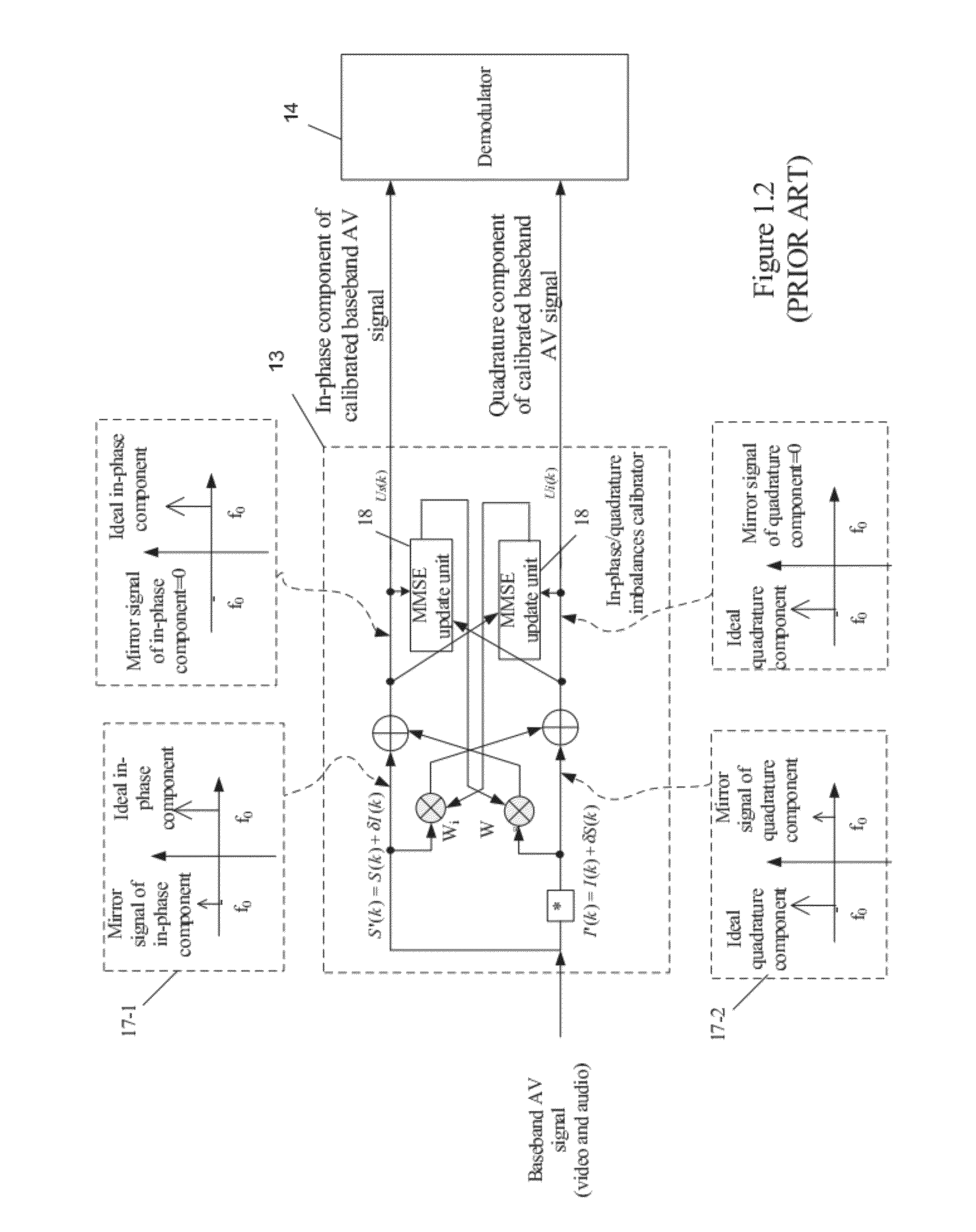
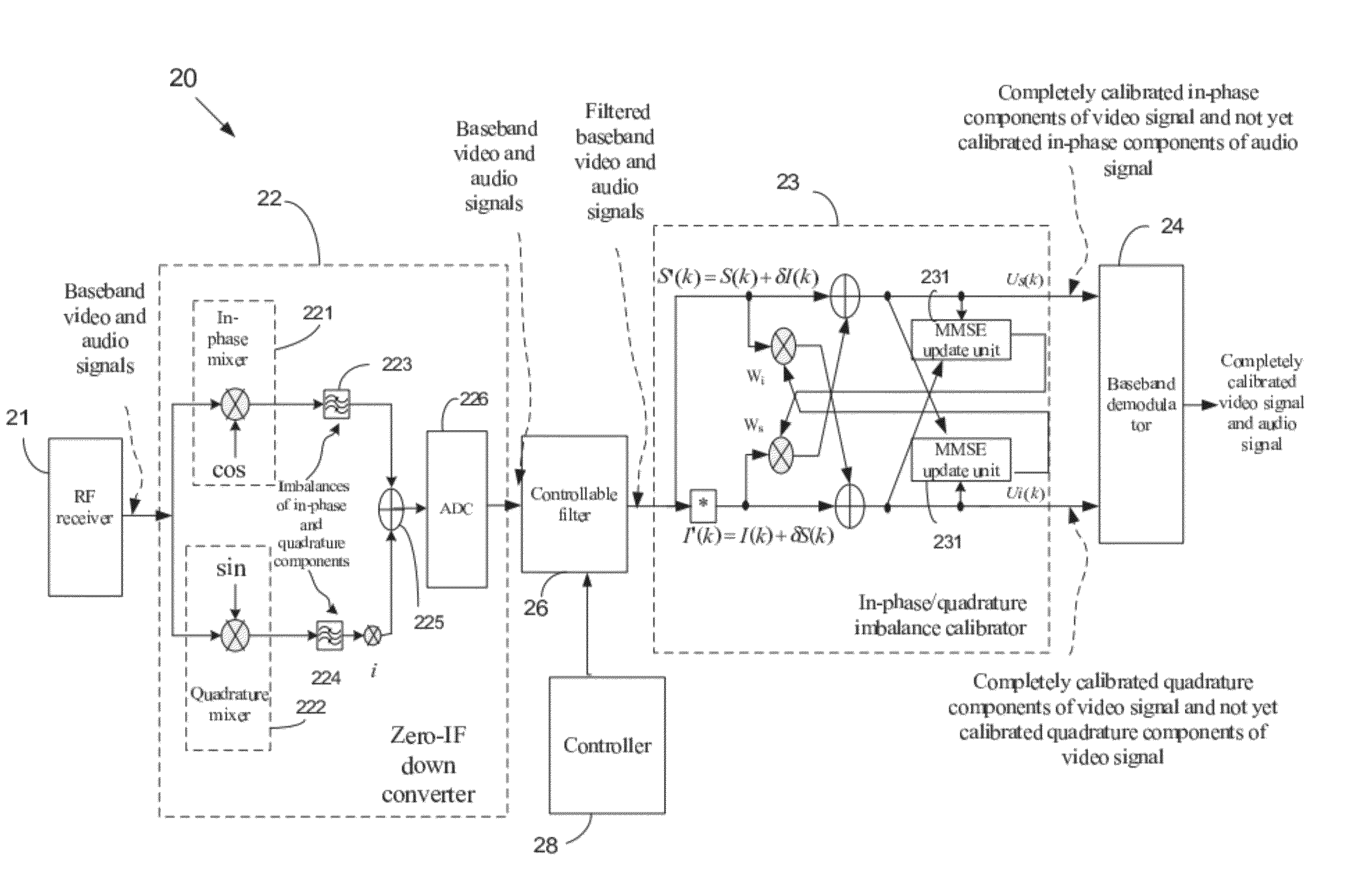
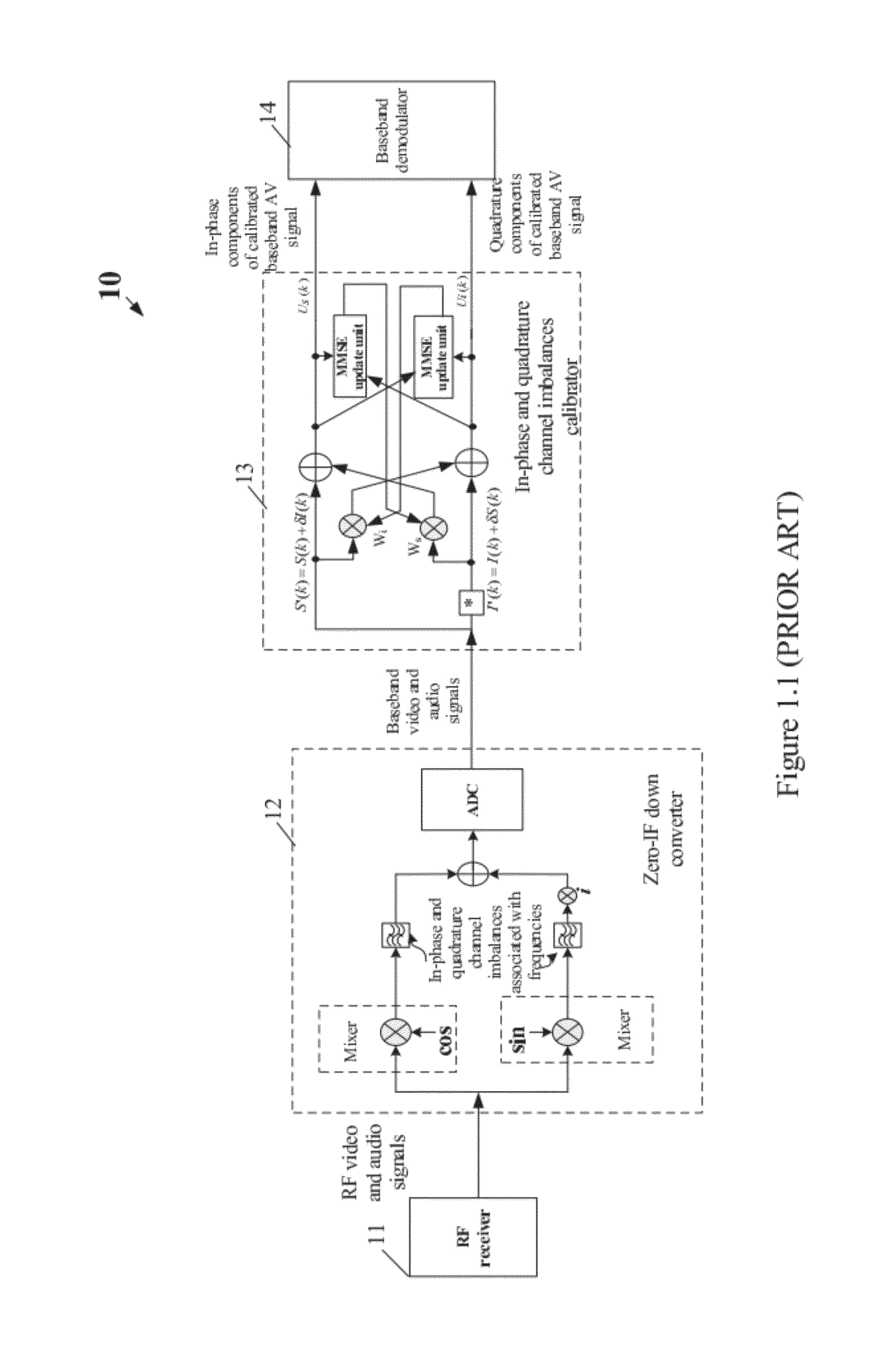
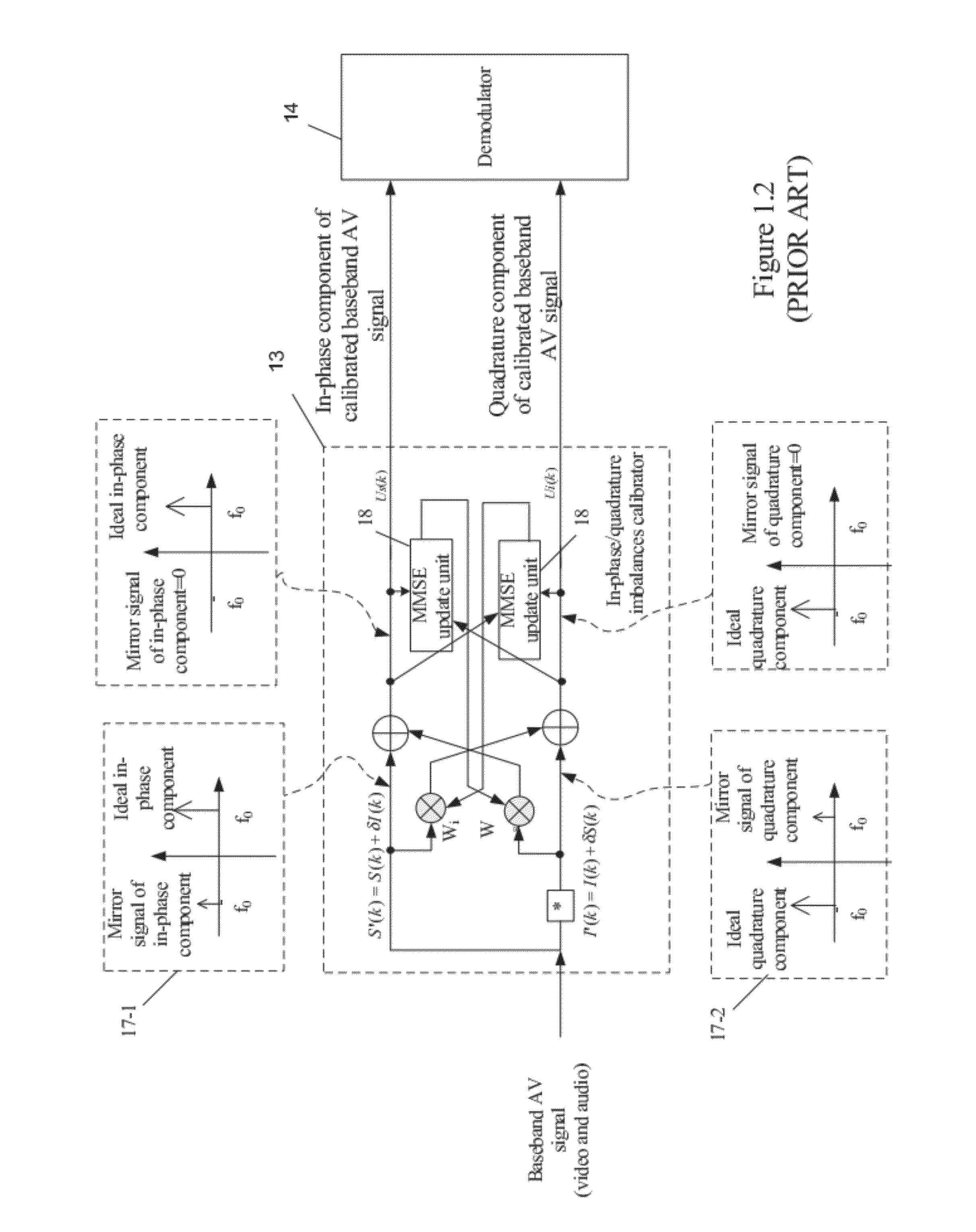
Apparatus and Method for Calibrating Audio-Visual Signal
An apparatus for calibrating an audio-visual (AV) signal includes a controller for generating a control signal, a controllable filter for selectively filtering the AV signal in response to the control signal to output either the AV signal or a filtered AV signal; and a calibrator for generating a group of calibrating coefficients according to the filtered AV signal and calibrating the AV signal according to the group of calibrating coefficients.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
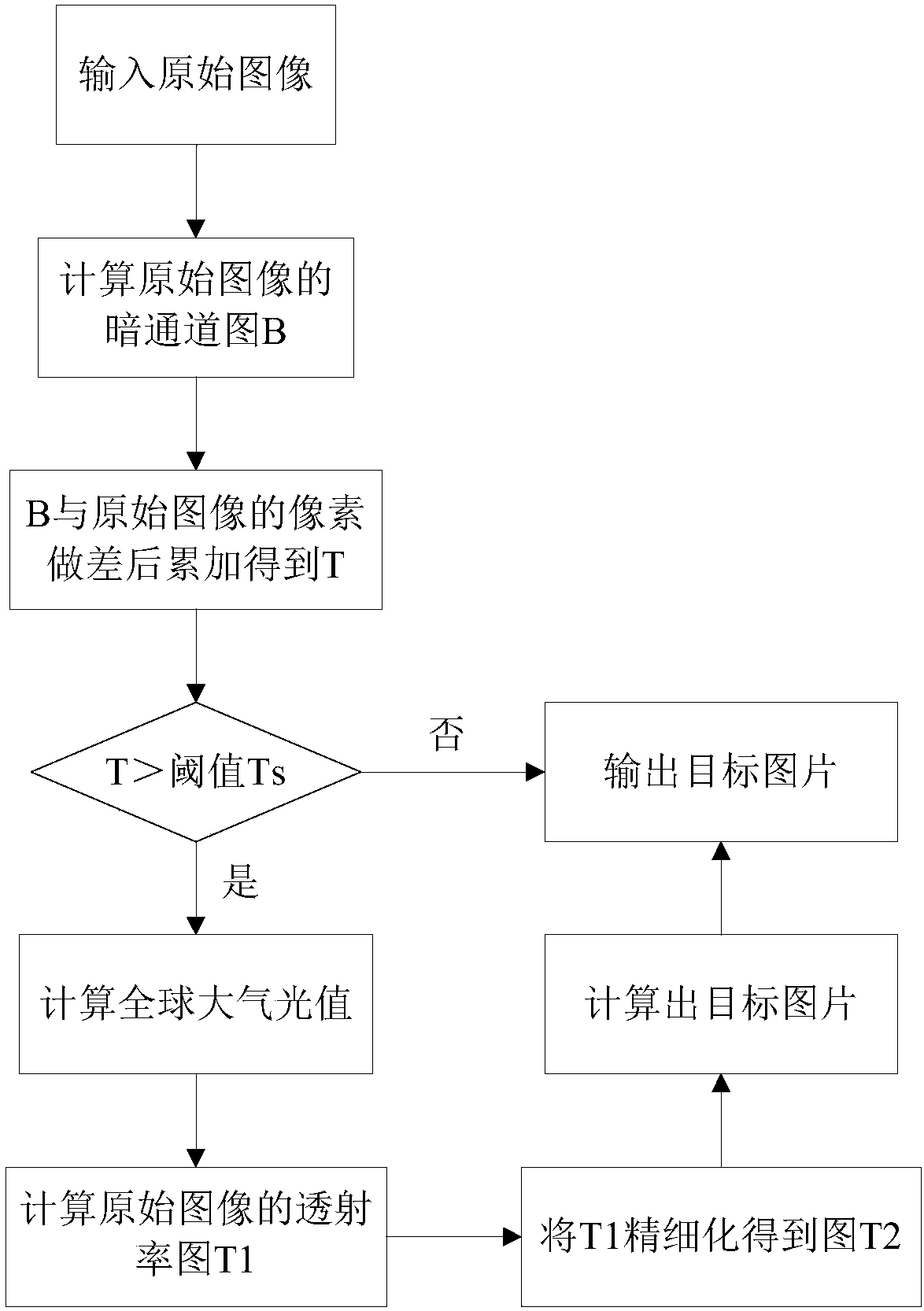
Image dehazing method
InactiveCN108230275AFast downloadCache processing pressureImage enhancementProcessor architectures/configurationPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention relates to an image dehazing method. The method comprises the steps that A, whether dehazing processing is needed or not is judged according to the accumulated value obtained after all pixel values of dark channel graphs D of original images and the original images are subtracted respectively, if not, the original images are output and the process ends, and otherwise, step B is started; B, a global atmospheric light value is acquired according to the dark channel graphs D and the original images; C, dark channel graphs D2 of new images are calculated after each pixel of the original images is divided by the global atmospheric light value, and a white picture and the pixel values of the dark channel graphs D2 are subtracted respectively to obtain a transmittance graph T1; D, the transmittance graph T1 is refined through steerable filtering to obtain a transmission rate graph T2; E, dehazed images are output through a haze graph formation model. The image dehazing method can effectively improve the image dehazing effect, simplify the dehazing processing process, greatly shorten image processing time and effectively improve the image processing efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus, system and method for extending the life of sacrificial anodes on cathodic protection systems
InactiveUS7318889B2Prolong lifePrevention of corrosion in aviation structures/craftWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectricityEngineering
An apparatus, system, method and computer program product directed to controlling corrosion of a conductive structure in contact with a corrosive environment and electrically connected to one or more anodes, wherein the anodes are less noble than the conductive structure, where the corrosion is controlled by a controllable filter and a corresponding electronic control unit configured to process at least one stored or measured parameter, and wherein the apparatus, system and method serve to prolong the lifetime of the one or more anodes by reducing, minimizing or substantially eliminating their sacrificial character.
Owner:APPLIED SEMICON INT
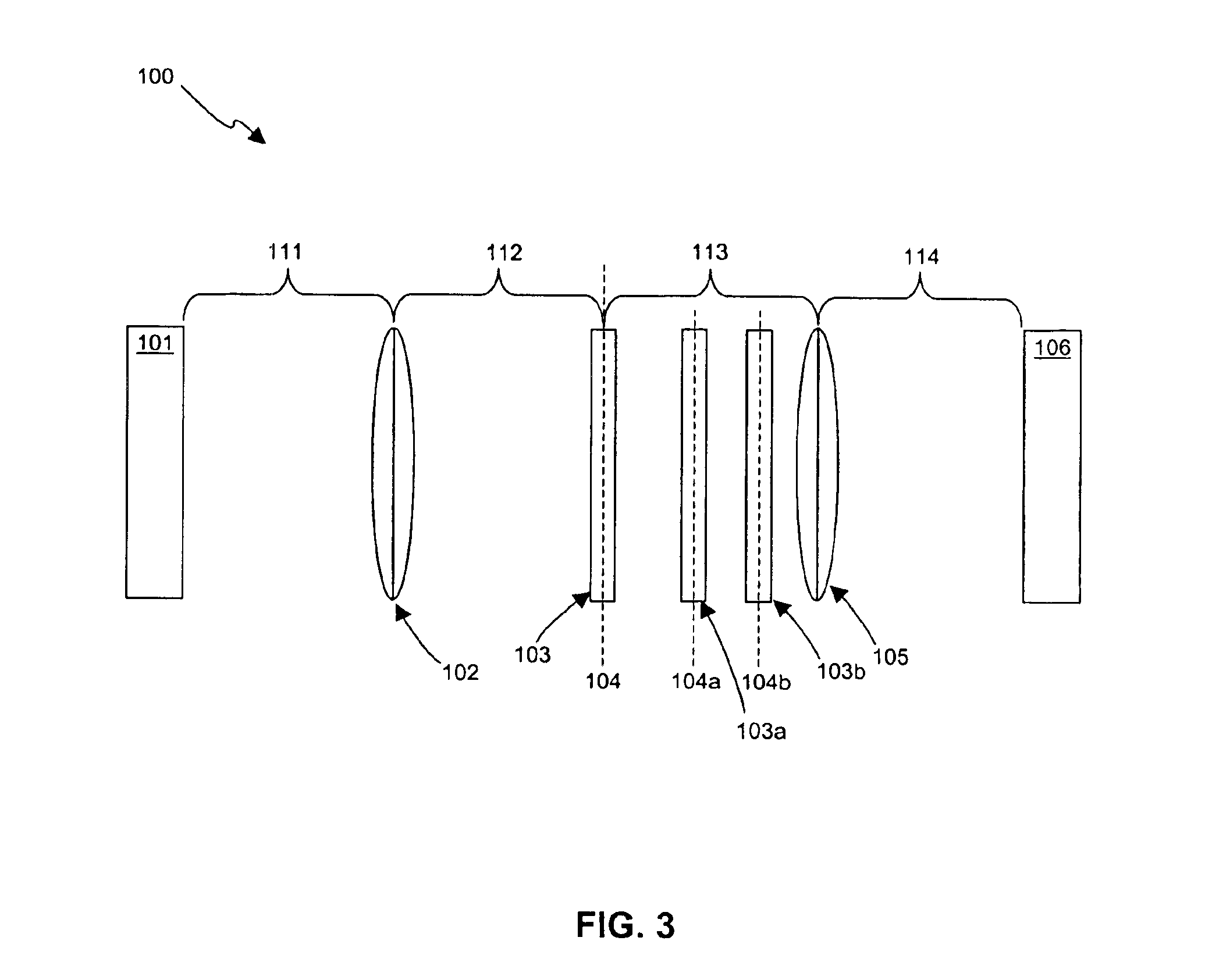
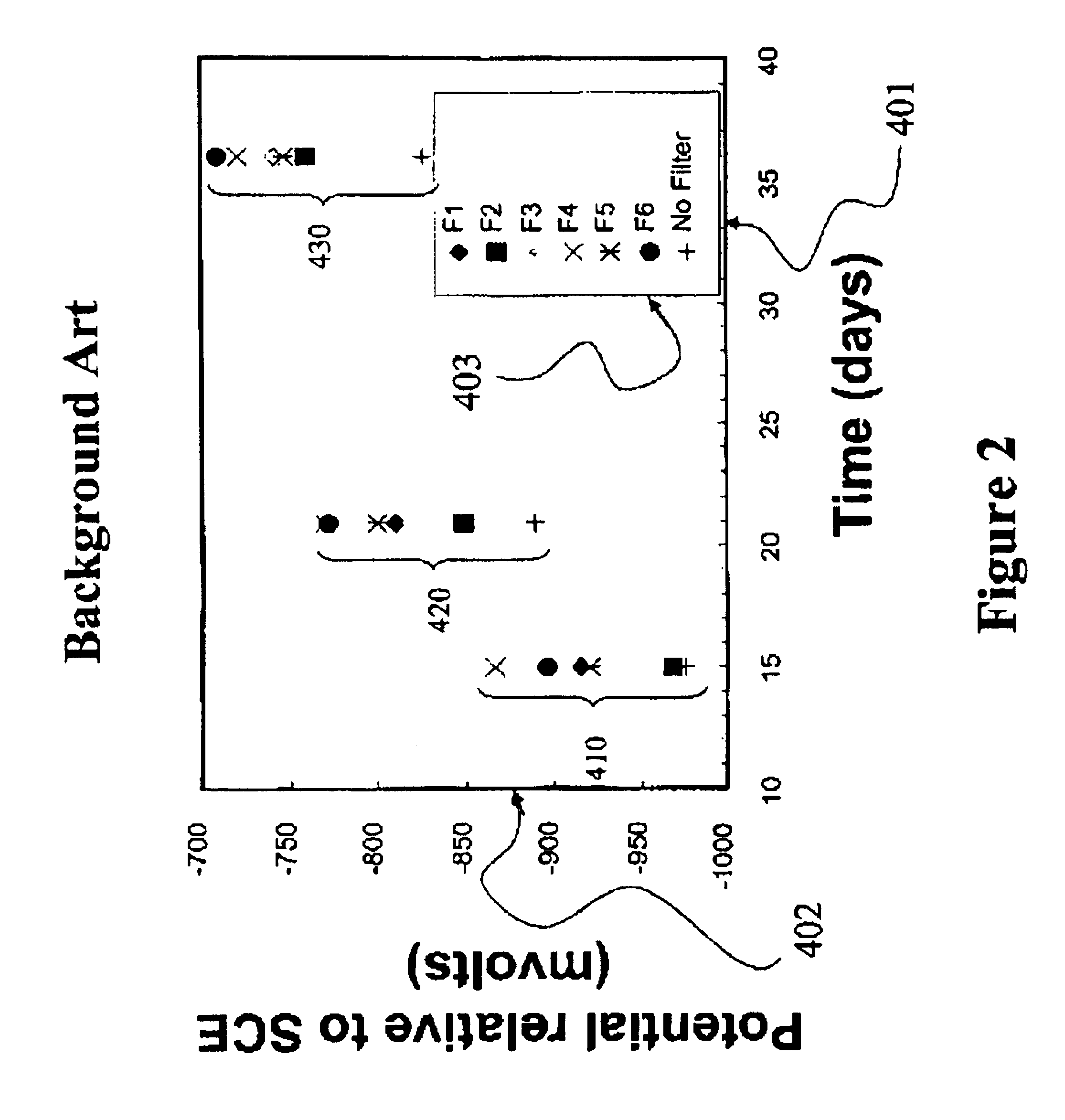
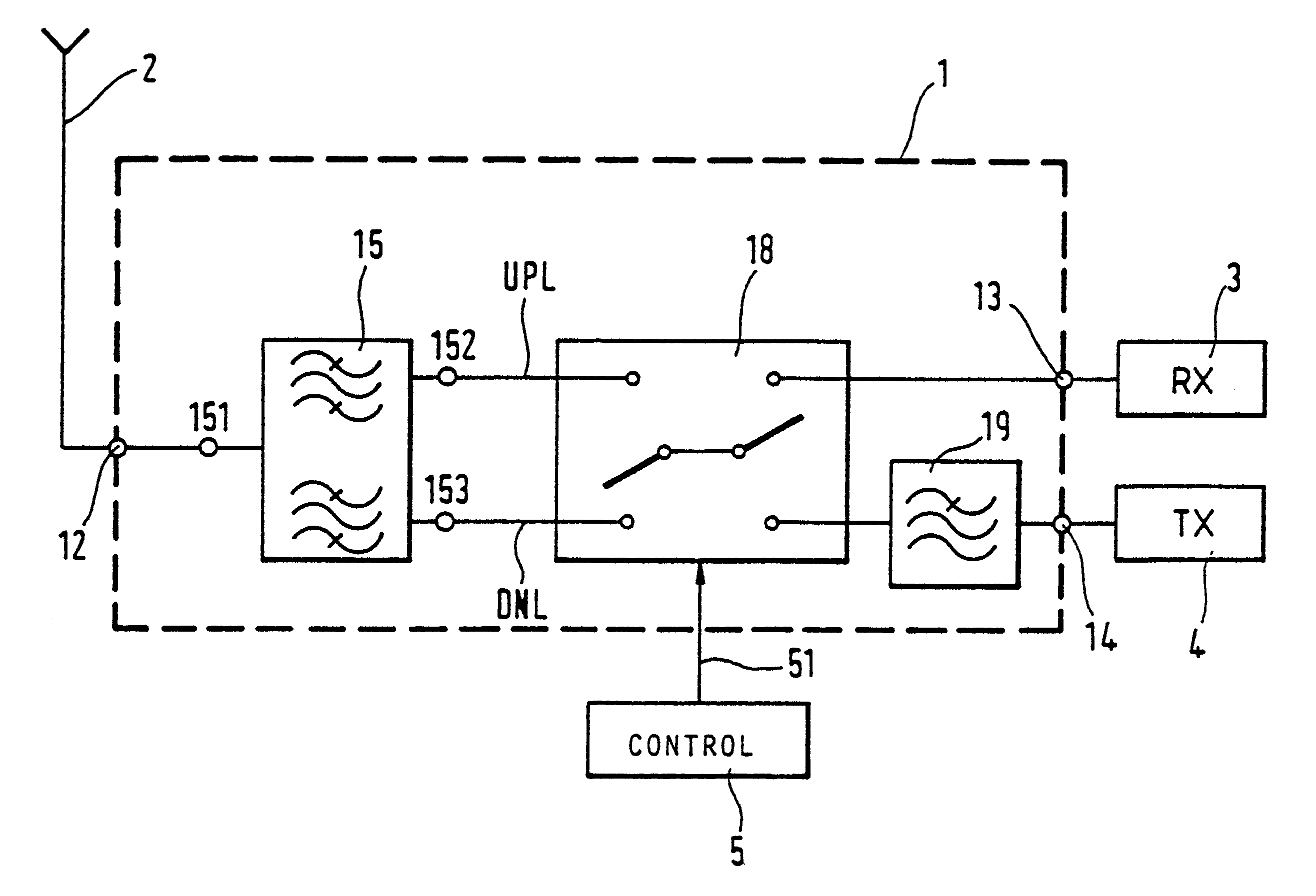
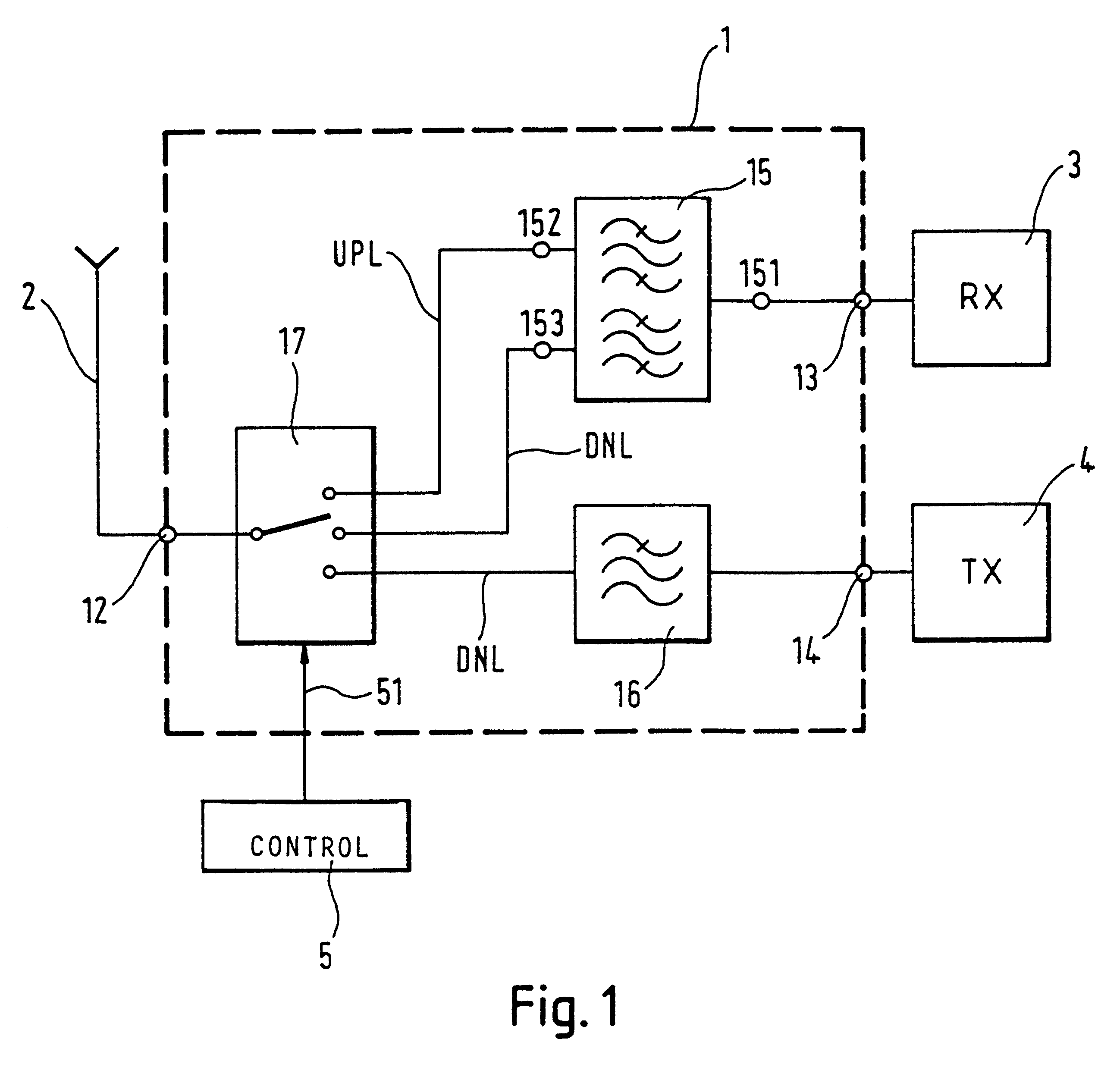
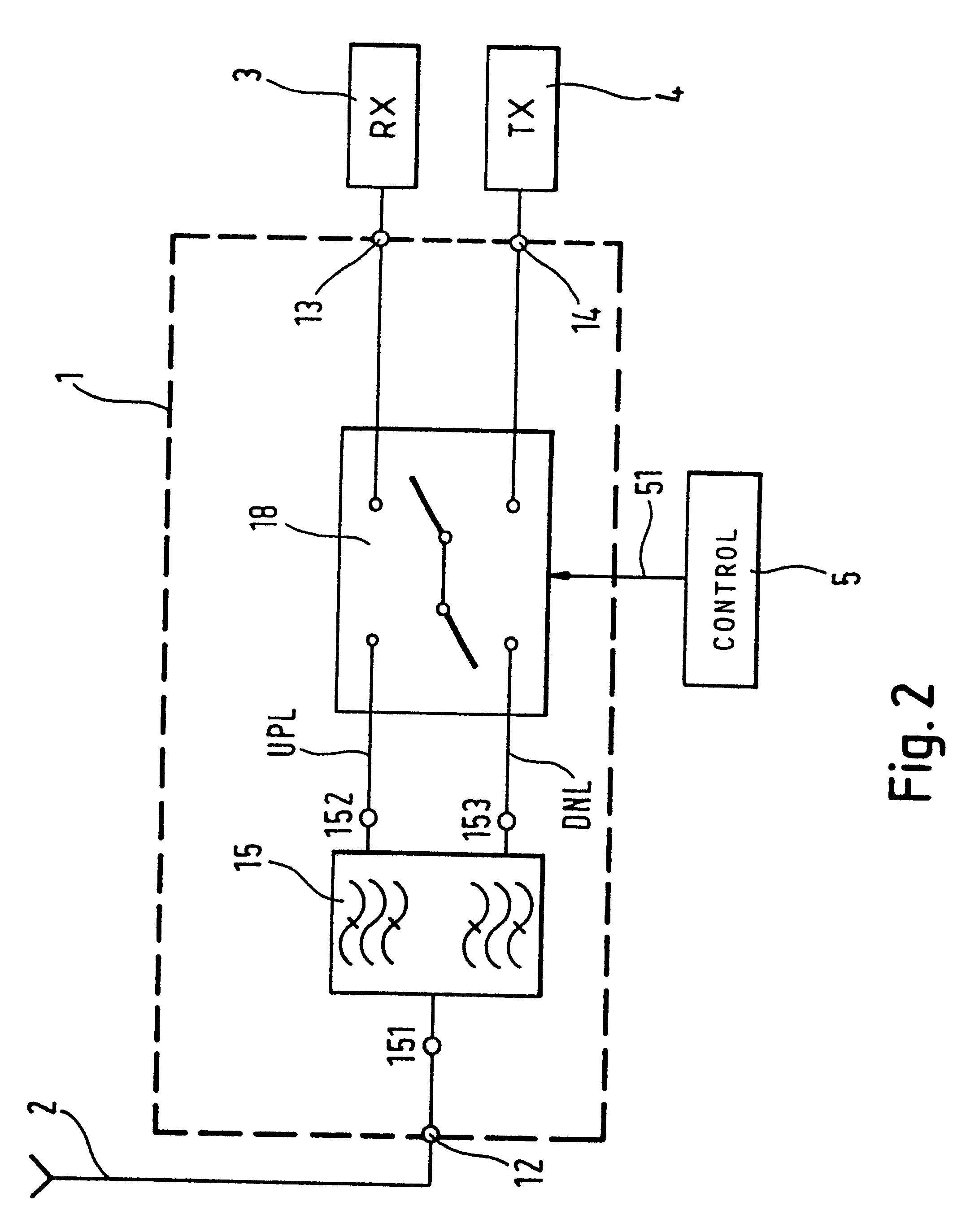
Controllable filter
InactiveUS6381446B1Low costMultiple-port networksMultiple-port active networksMobile stationWalkie-talkie
The application relates to a controllable filter (1) that is placed between an antenna on the one side and a receiver and transmitter on the other, where the receiver branch can be switched between two filter characteristics. In this way, a simple device for allowing simplex reception in the transmission band can be provided. This filter is preferably applied as a frontend filter (FP) in the fixed part of a cordless telephone system and / or in a mobile station to thereby provide said mobile station with walkie-talkie capabilities.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Integration of positional data and overhead images for lane identification
InactiveUS10013610B2Image enhancementInstruments for road network navigationEdge filterSteerable filter
A method and apparatus for lane detection using overhead images and positional data. A server receives positional data from a vehicle and computes a continuous trajectory. The server receives an overhead image of a road section. The server crops and processes the overhead image to remove unwanted portions. The server identifies edge features using the continuous trajectory and steerable filters. The server identifies lanes in the overhead image using a maximization algorithm, the edge filters, and the continuous trajectory.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Method and system for filtering elongated features
InactiveCN101443814AEffective filteringImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionSteerable filter
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Self-tracking filter
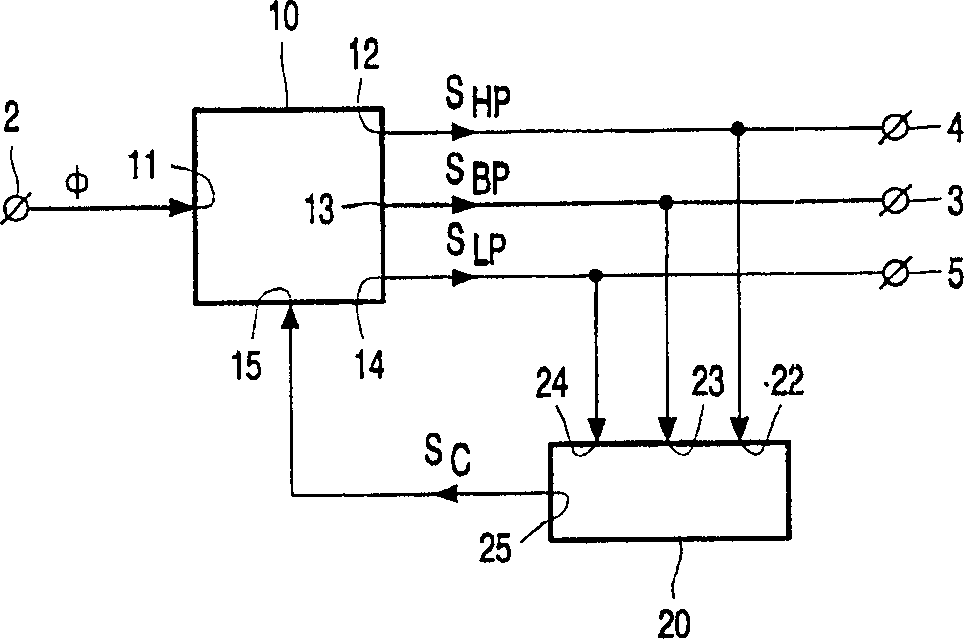
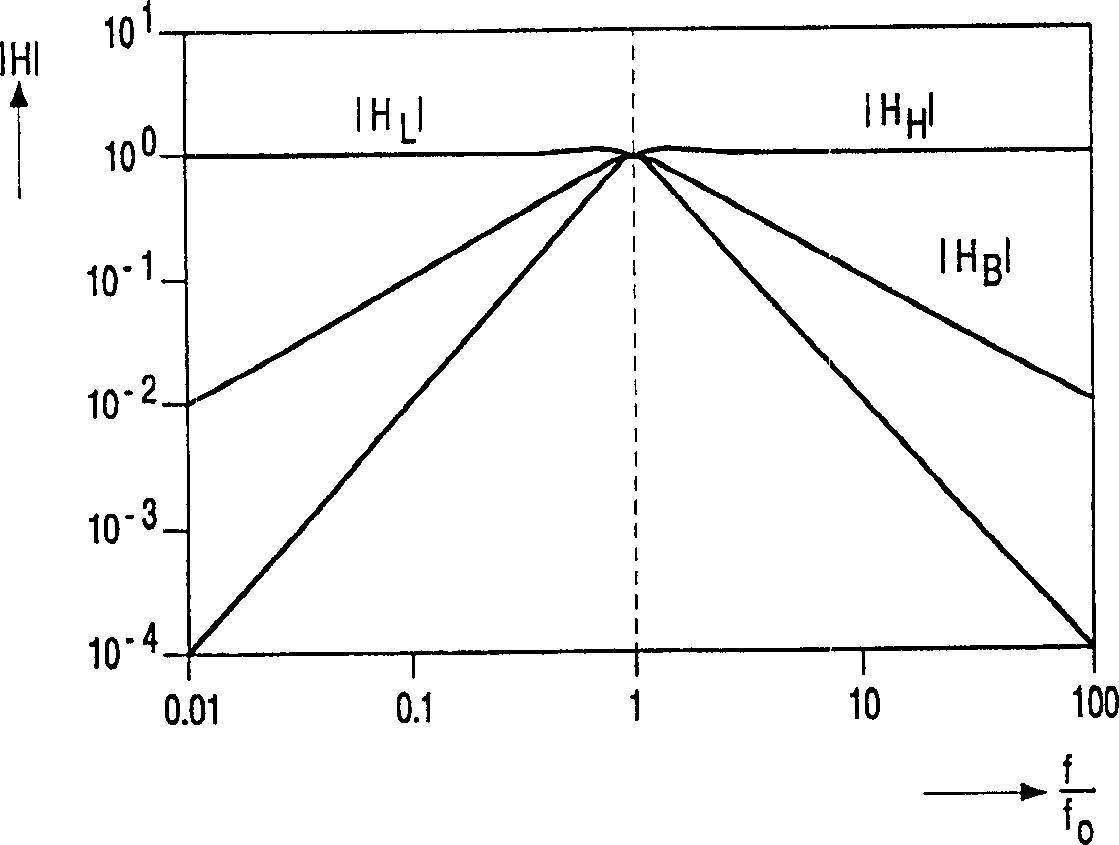
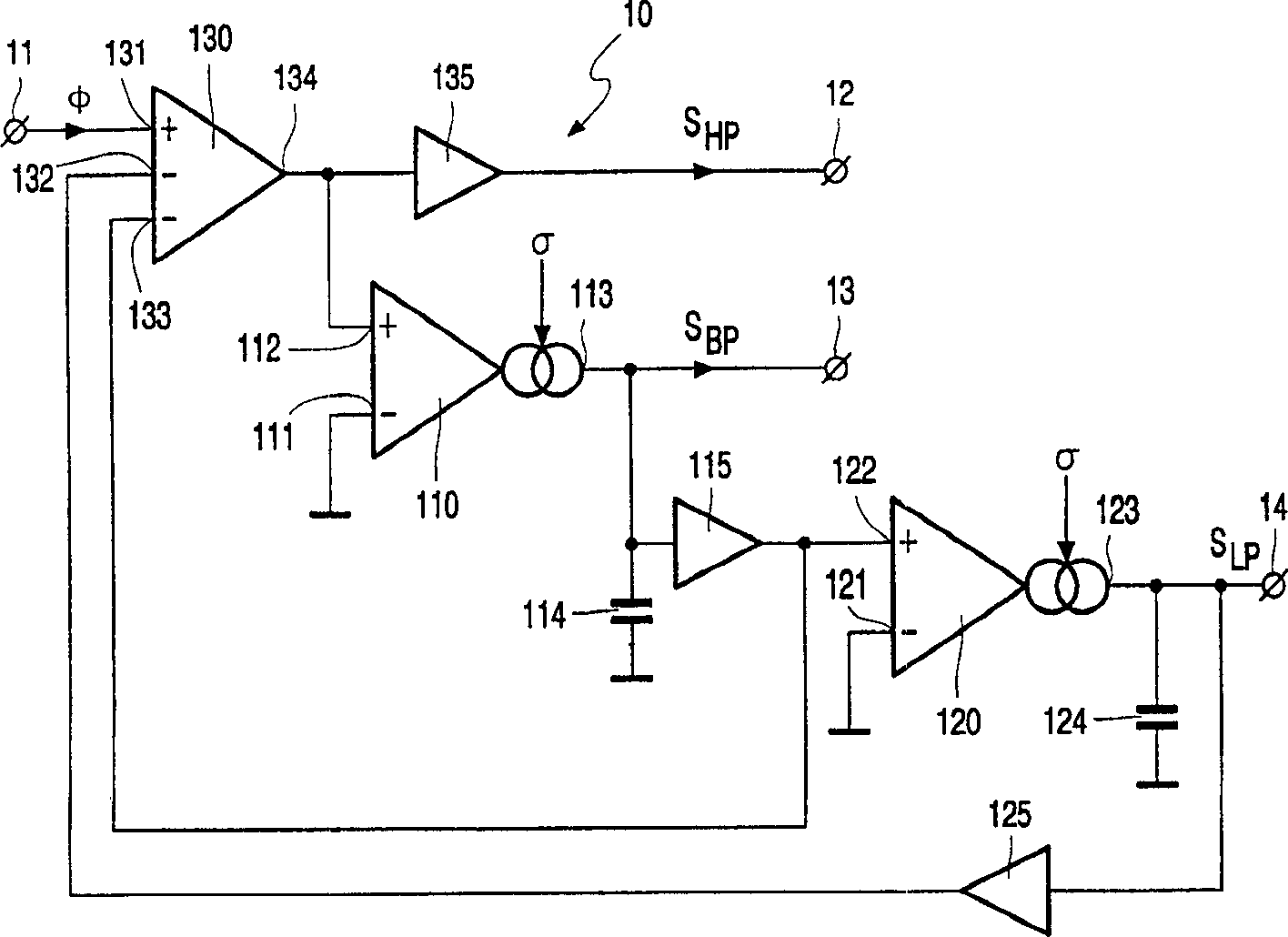
InactiveCN1372717ADigital technique networkFrequency selective two-port networksBandpass filteringControl signal
A self-tracking bandpass filter (1) comprising a controllable filter (10), the controllable filter (10) having a signal input (11) for receiving a signal (φ) to be filtered, for providing a bandpass output of a bandpass signal (SBP) at a center frequency (f0), and a control input (15) for receiving a control signal (SC); and a control input (15) coupled to a controllable filter (10) A control unit (20) for generating such a control signal (SC) that the center frequency (fO) of the bandpass characteristic (HB) of the controllable filter (10) is substantially equal to that of the input signal (φ) frequency (f).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
CW pulse narrow band tracking filter and its tracking filter method
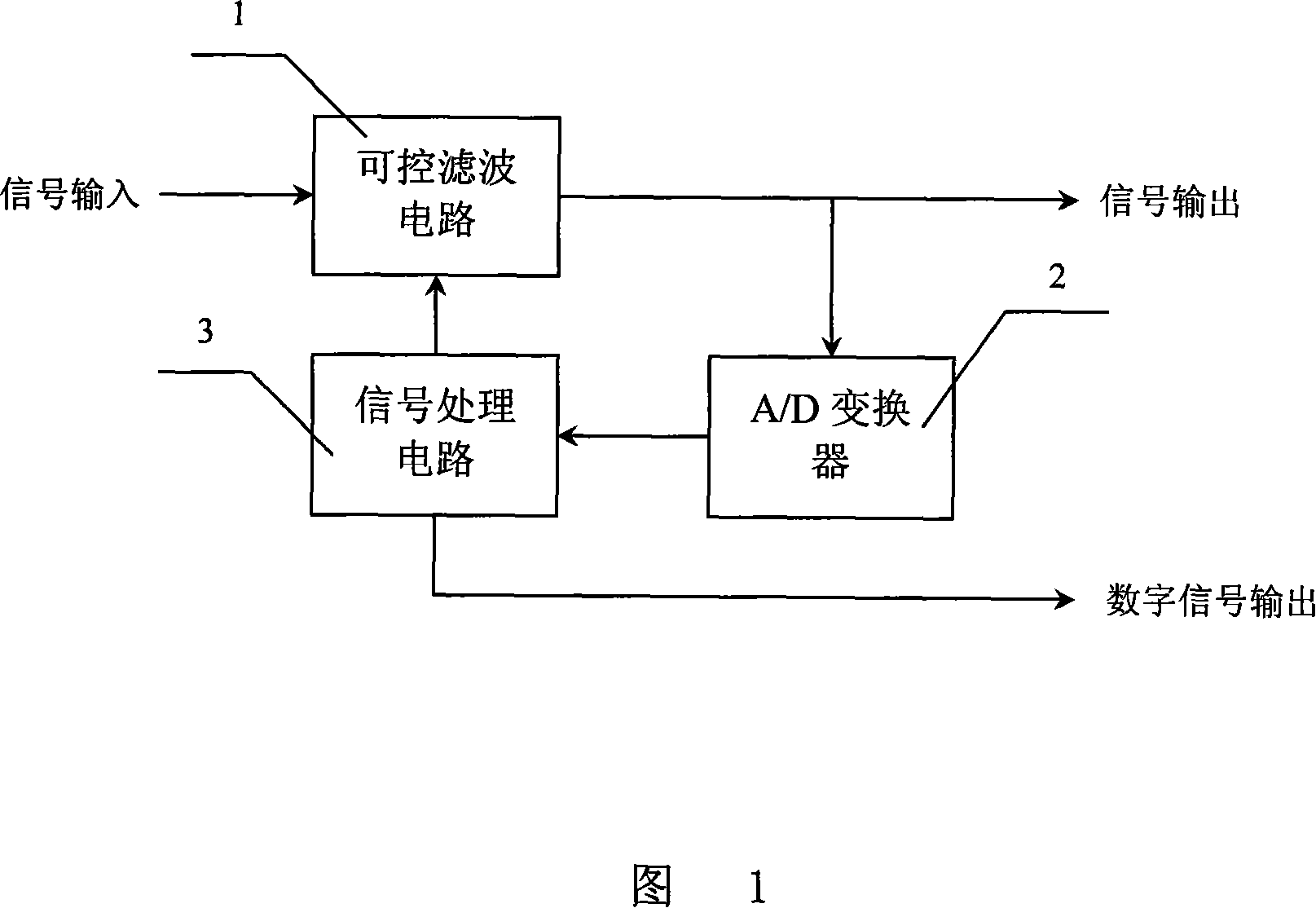
InactiveCN101046488AImplement narrowband tracking filteringReduce computationFrequency analysisSignal processing circuitsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The present invention is CW pulse narrow band tracking filter and its tracking filter method. The tracking filter includes one controllable filter circuit, one A / D converter and one signal processing circuit. In the signal processing circuit, signal is acquired, filtered digitally and resolved to obtain the frequency and period time of the signal; and resolved frequency is then used in controlling the central frequency and bandwidth of the controllable filter circuit, so as to realize the tracking filtering on CW pulse. The present invention is superior to traditional tracking filter, which tends to track noise automatically in the pulse signal interval to loss lock on signal. The present invention adopts variable bandwidth frequency hopping search mode and sampling based on echo time, and thus has reduced operation amount and capacity of performing tracking filter in low S / N ratio. The present invention is suitable for tracking filter on both CW pulse signal and continuous signal.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
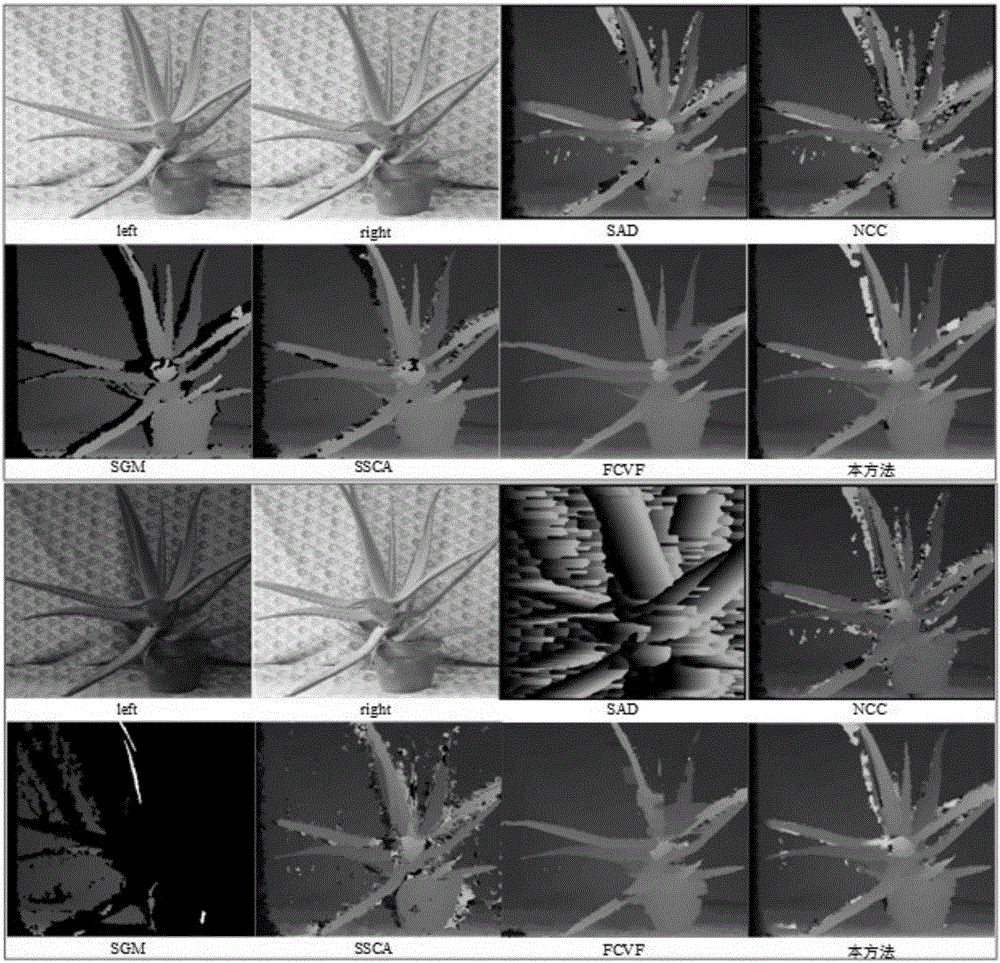
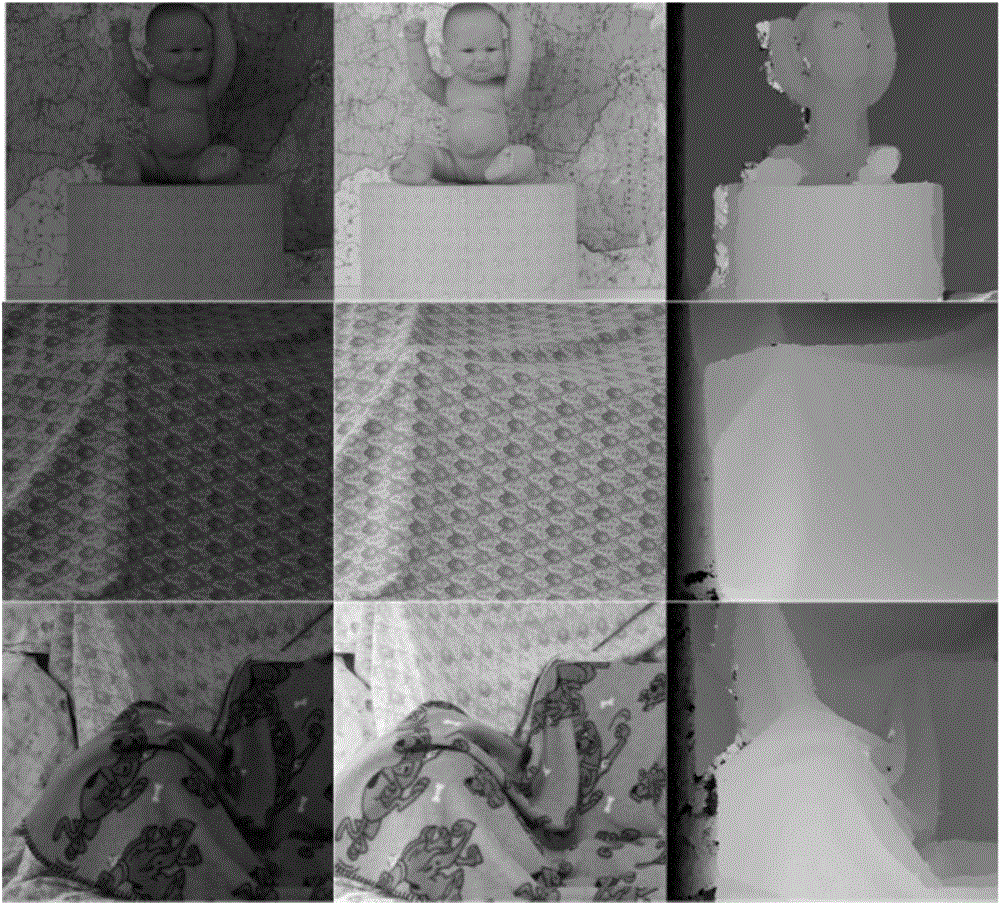
Illumination-insensitive fast stereo matching method based on local linear model
ActiveCN106548490AImprove robustnessQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxLab color space
The invention discloses an illumination-insensitive fast stereo matching method based on a local linear model. It is hard for a mainstream method in the prior art to realize accurate matching under the condition of illumination inconsistency; before matching, color correction of a stereo image is carried out first; and however, it is very difficult to obtain a color-consistent stereo image, and still no algorithm can finish accurate stereo image correction at present. The method is characterized by converting an RGB color space of an image into a CIE-Lab color space; based on the local linear model, eliminating influence of illumination inconsistency on stereo image left-right view matching; carrying out processing through an improved NCC matching algorithm based on steerable filtering; and finally, carrying out stereo disparity image solving on matching cost. The method can carry out matching no longer on dependence of the color information in stereo image left and right images in the stereo matching process, so that operating efficiency and matching accuracy are high, and the problem that it is hard for stereo matching to realize accurate matching under the condition of illumination inconsistency is effectively solved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Control apparatus, system, and method for reduction and/or prevention of space weather induced corrosion
InactiveUS20100025261A1Minimize corrosive noiseReduce corrosionCellsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceConductive coatingControl electronics
An apparatus, system, method and computer program product directed to controlling corrosion, particularly space weather induced corrosion, of a conductive structure in contact with a corrosive environment and coated with a semiconductive coating, where the corrosion is controlled by a controllable filter and a corresponding electronic control unit configured to process and adjust the controllable filter in response to at least one measured parameter associated with space weather effects on the conductive structure.
Owner:APPLIED SEMICON INT
Correlation-driven adaptation of frequency control for a RF receiver device
InactiveUS8081939B2Frequency errorCarrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsControl signalEngineering
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Apparatus and method for calibrating audio-visual signal
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
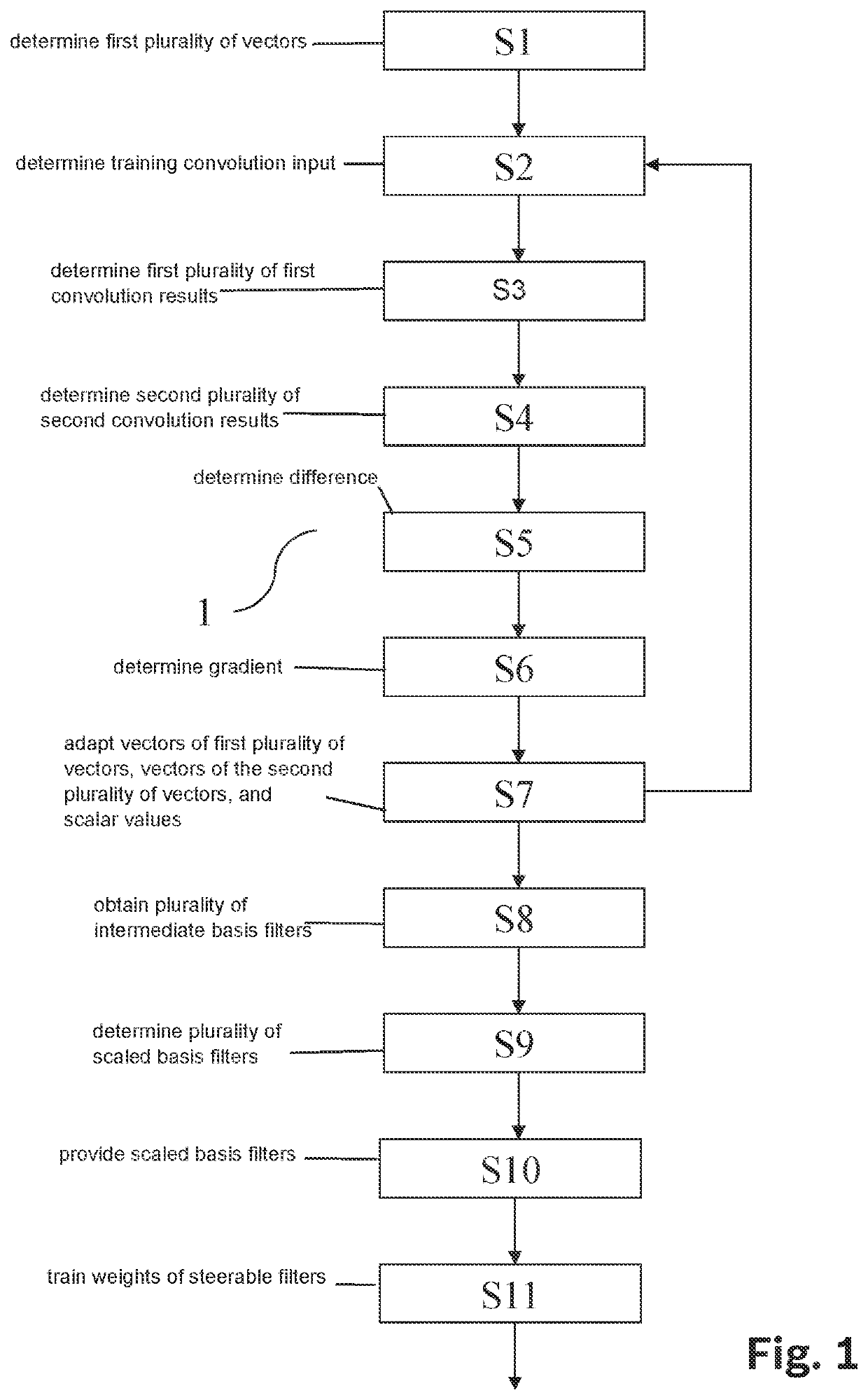
Device and method for training a scale-equivariant convolutional neural network
PendingUS20220076096A1Improve performanceSelf-equivariance error of the convolutional layer is minimizedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNeural network nnSteerable filter
A computer-implemented method for training a scale-equivariant convolutional neural network. The scale-equivariant convolutional neural network is configured to determine an output signal characterizing a classification of an input image of the scale-equivariant convolutional neural network. The scale-equivariant convolutional neural network includes a convolutional layer. The convolutional layer is configured to provide a convolution output based on a plurality of steerable filters of the convolutional layer and a convolution input. The convolution input is based on the input image and the steerable filters are determined based on a plurality of basis filters. The method for training includes training the plurality of basis filters.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
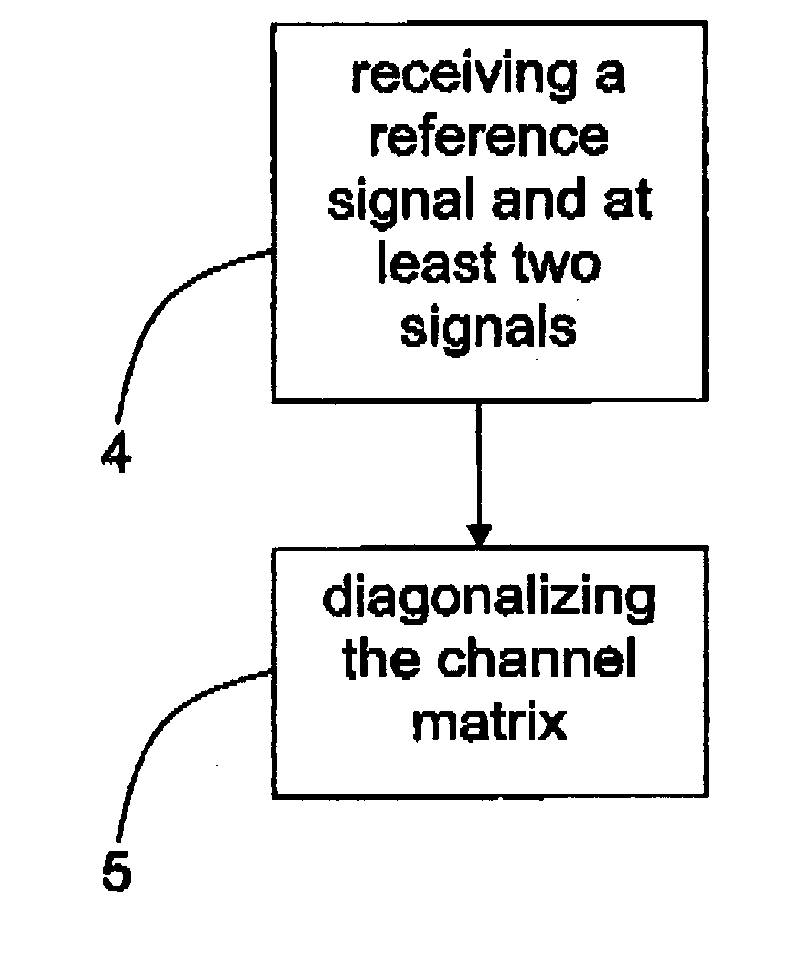
Controllable filter to diagonalize a transmission channel
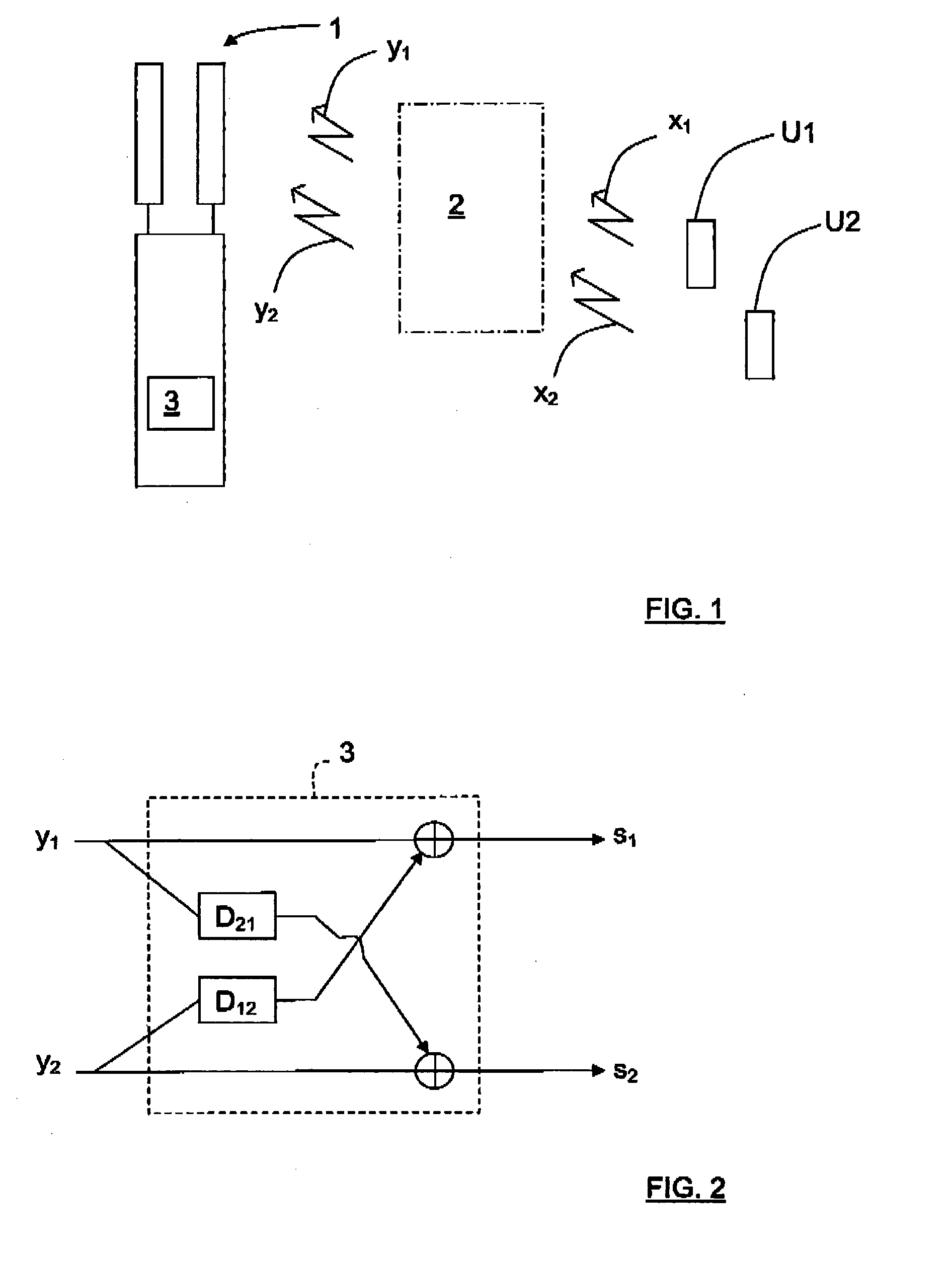
ActiveUS20120219098A1Good estimateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationTransmission channelEngineering
The present invention relates to a node (1) in a wireless communication network, where the node (1) is arranged to receive at least two signals (y1(n), y2(n)) which correspond to at least two transmitted uncorrelated signal streams (x1(n), X2(n)) which have been transmitted to the node via a channel. The channel (2) is signals represented by means of a channel matrix (H(q−1)). The node (1) comprises a controllable filter structure (3) that is arranged to diagonalize the channel matrix (H(q−1)) such that a channel matrix estimation (Ĥ(q−1)) may be obtained. The present invention also relates to a corresponding method.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for simultaneously subsampling fluoroscopic images and enhancing guidewire visibility
InactiveUS7970191B2Reduce resolutionIncrease awarenessImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityFluoroscopic image
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com