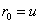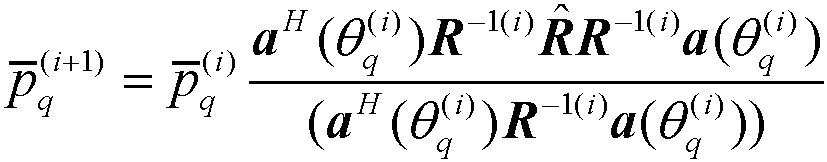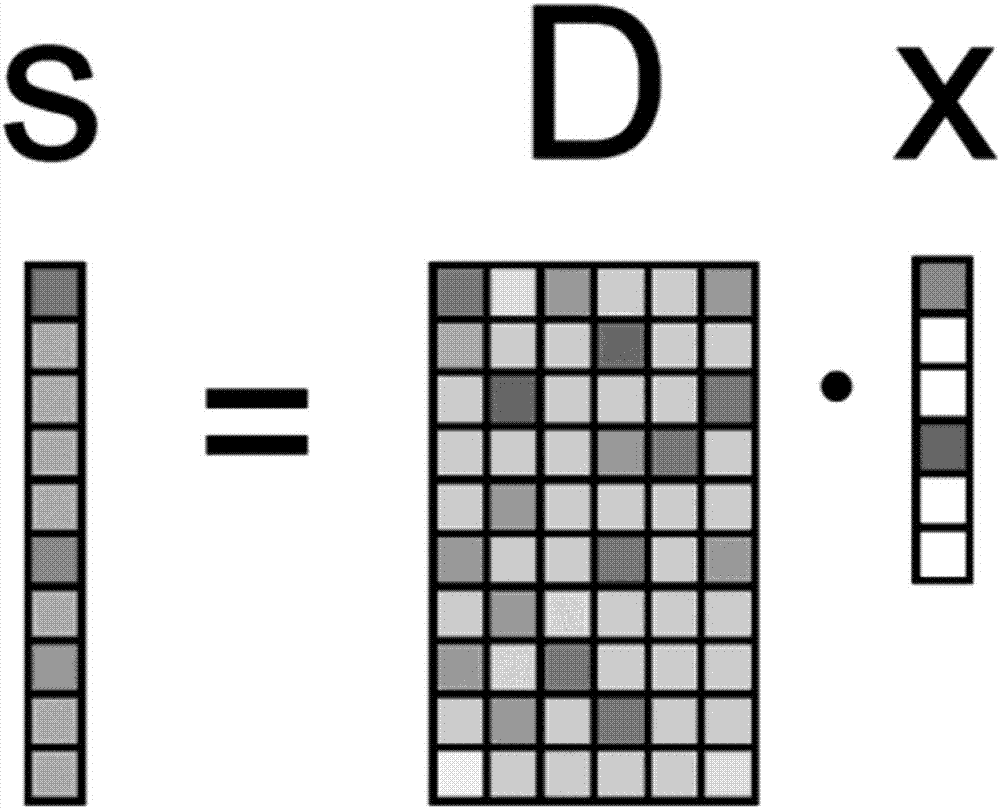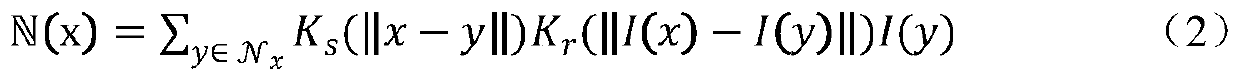Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Sparse approximation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
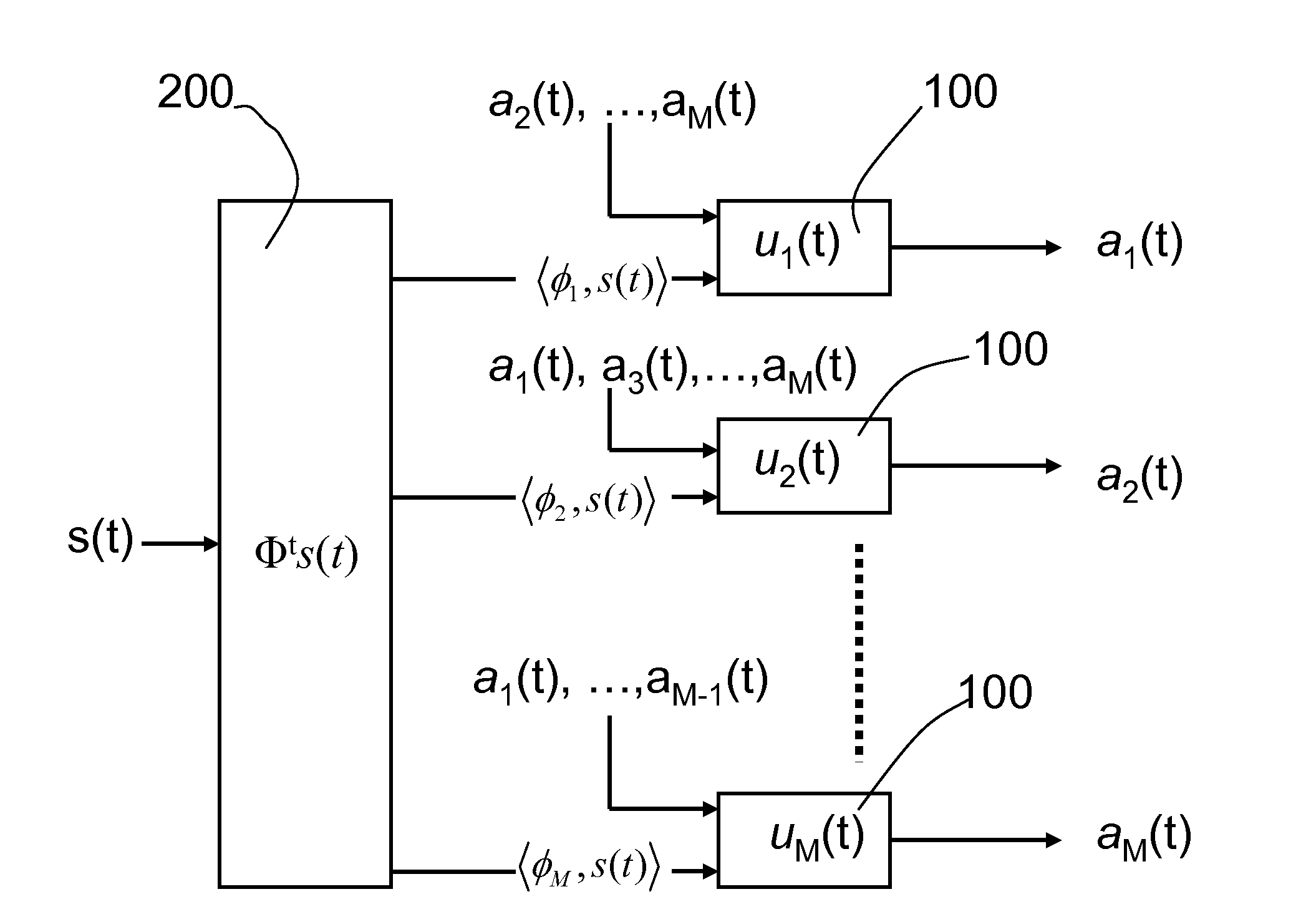
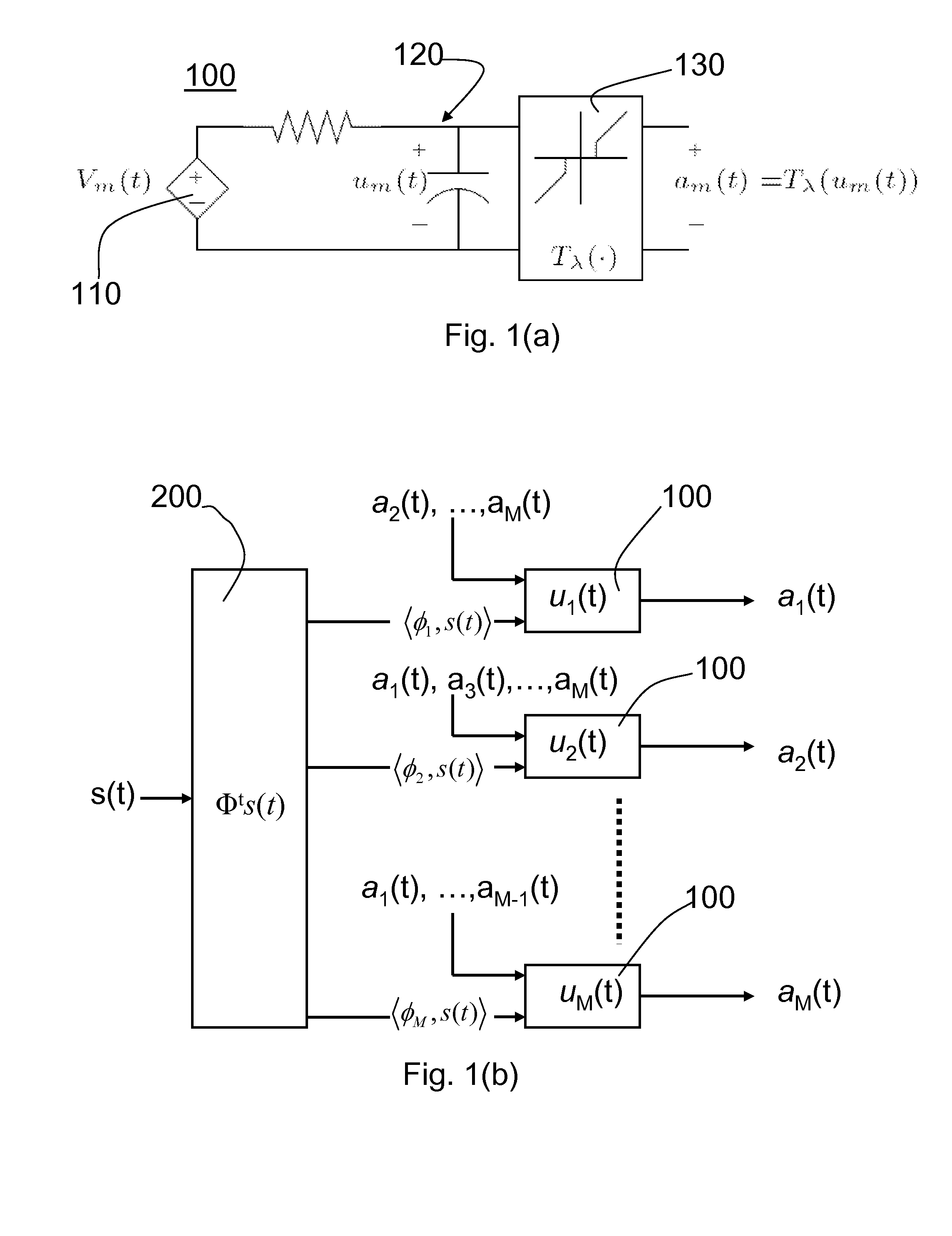
Sparse Approximation (also known as Sparse Representation) theory deals with sparse solutions for systems of linear equations. Techniques for finding these solutions and exploiting them in applications have found wide use in image processing, signal processing, machine learning, medical imaging, and more.
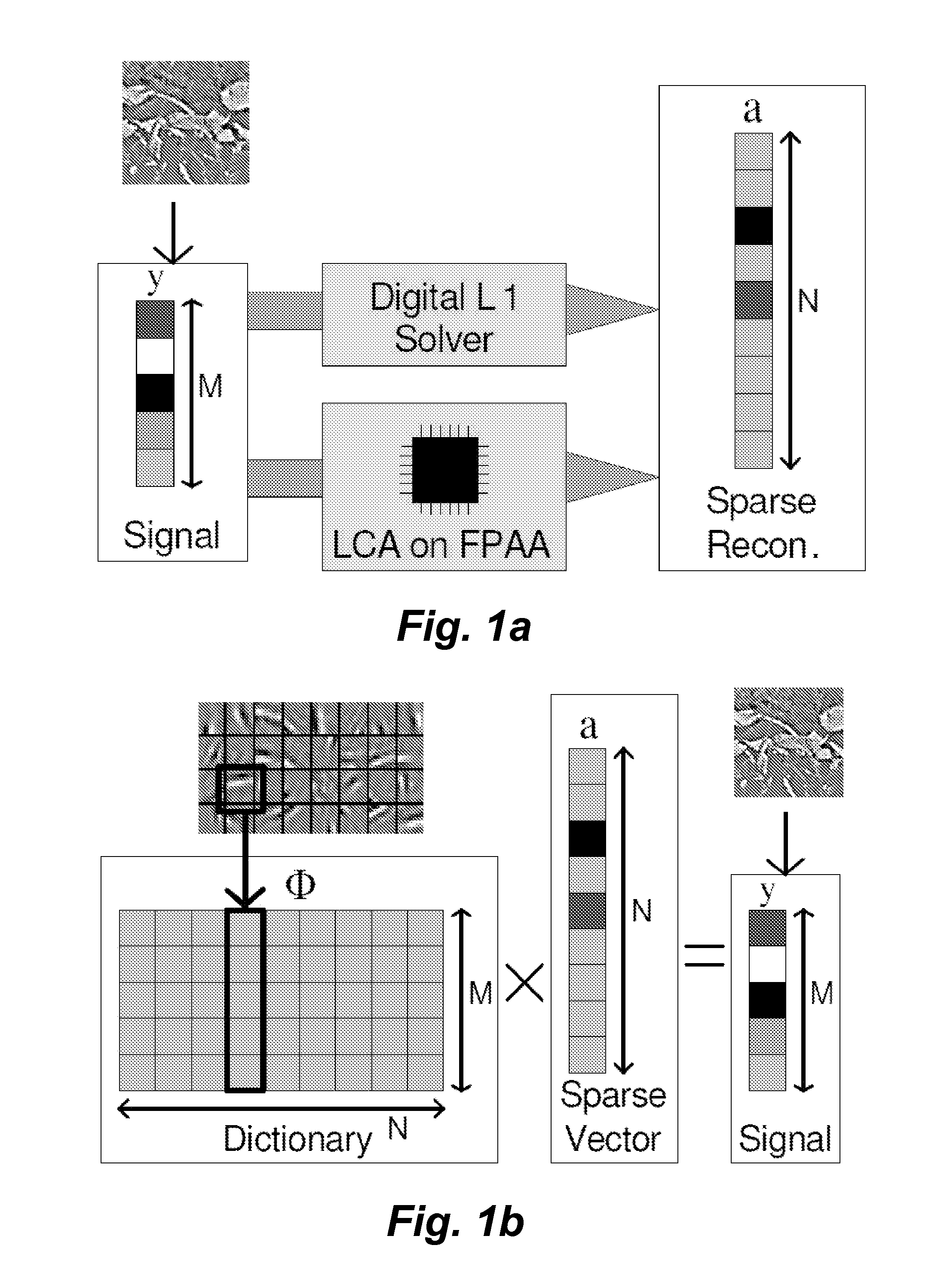
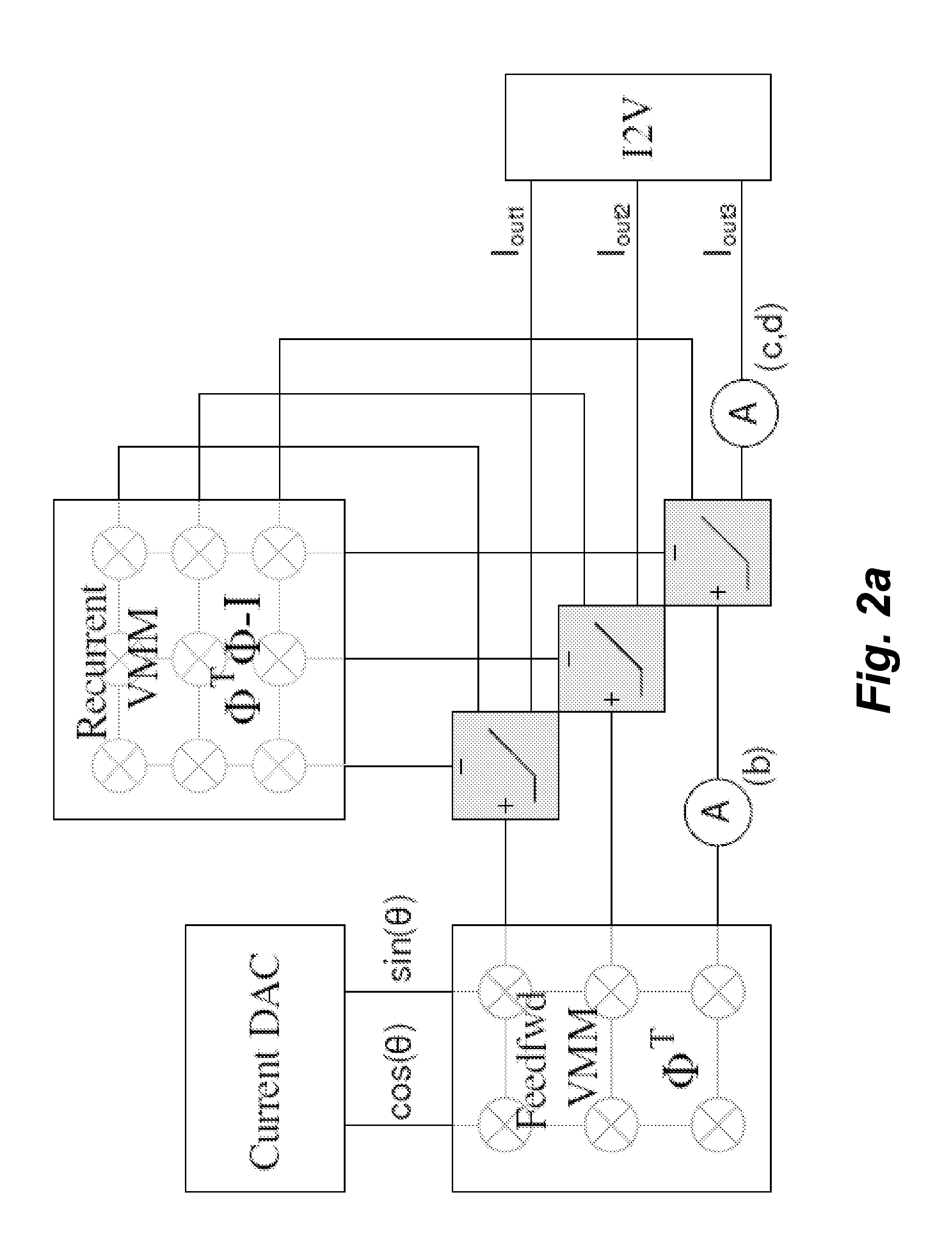
Analog system for computing sparse codes
ActiveUS20080270055A1Smoother in timeEasy to identifyNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementError preventionLateral inhibitionCoded element
A parallel dynamical system for computing sparse representations of data, i.e., where the data can be fully represented in terms of a small number of non-zero code elements, and for reconstructing compressively sensed images. The system is based on the principles of thresholding and local competition that solves a family of sparse approximation problems corresponding to various sparsity metrics. The system utilizes Locally Competitive Algorithms (LCAs), nodes in a population continually compete with neighboring units using (usually one-way) lateral inhibition to calculate coefficients representing an input in an over complete dictionary.
Owner:RICE UNIV +1
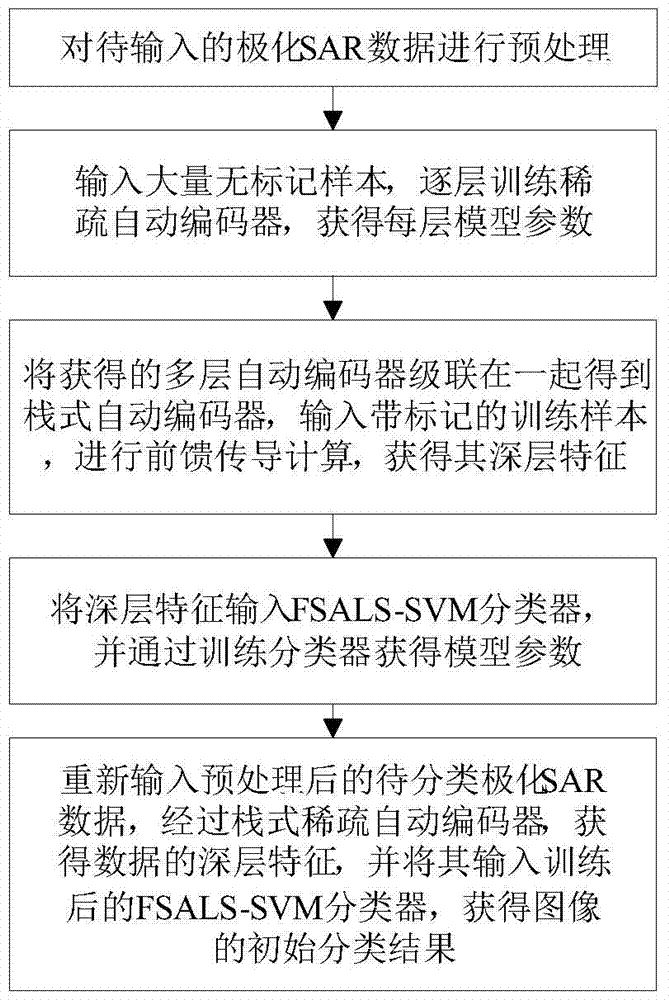
Polarization SAR image classification based on SSAE and FSALS-SVM
ActiveCN104166859AEssence portrayalStrong learning abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionOriginal dataLeast squares support vector machine
The invention aims to provide a polarization SAR image classification method based on an SSAE and an FSALS-SVM. According to the polarization SAR image classification method, a multi-implicit-strata structure of the stacked sparse automatic encoder (SSAE) is used for obtaining depth features which have the capacity for describing original data more intrinsically and are more suitable for classification, the fast sparse approximation least square-support vector machine (FSALS-SVM) which can obtain sparse solutions is used for replacing the Softmax commonly used in traditional deep learning and being combined with the SSAE, the classification accuracy of polarization SAR images is improved, the defect that a traditional polarization SAR image classification method based on pixels is greatly affected by speckle noise is overcome to a certain degree, and therefore coherence of homogeneous areas in classification result images is ensured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Analog system for computing sparse codes
ActiveUS7783459B2Smoother in timeEasy to identifyNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementError preventionLateral inhibitionCoded element
Owner:RICE UNIV +1
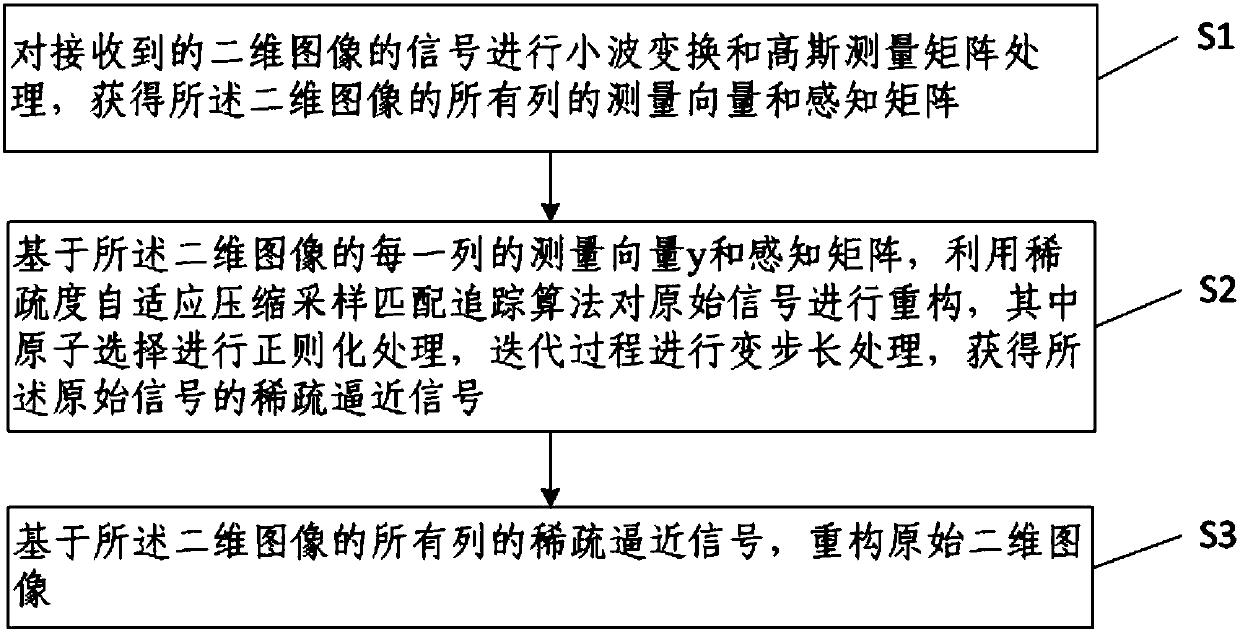
Compressive sensing based image processing method and device
InactiveCN107330946AImprove efficiencyReduce the number of iterationsImage codingIteration processSparse approximation
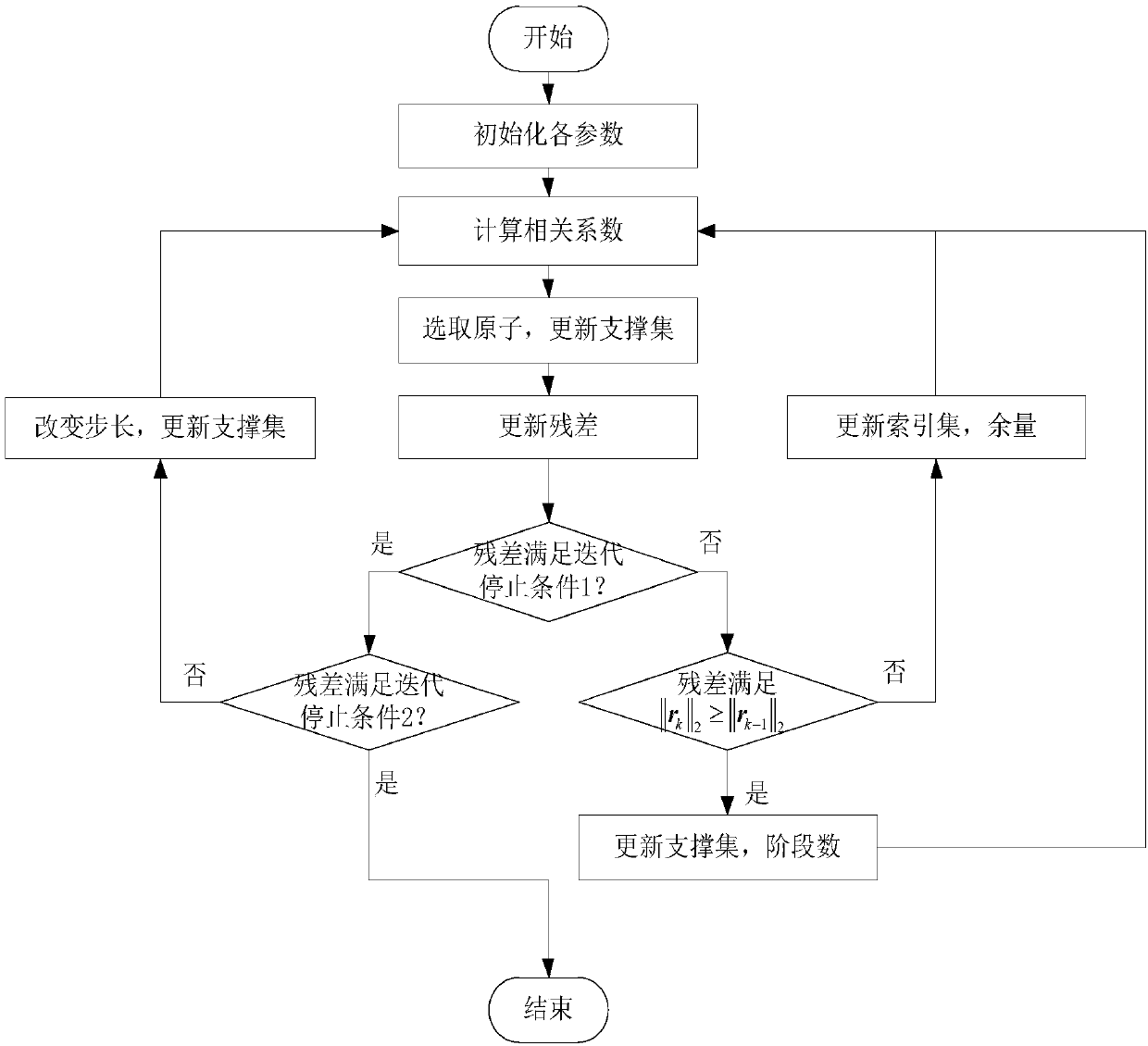
The invention provides a compressive sensing based image processing method and device. The compressive sensing based image processing method comprises the steps of S1, performing wavelet transform and Gaussian measurement matrix processing on received signals of a two-dimensional image to obtain measurement vectors of all columns of the two-dimensional image and a sensing matrix [Theta]; S2, reconstructing an original signal by using a sparsity adaptive compressive sampling matching pursuit algorithm based on the measurement vector y of each column of the two-dimensional image and the sensing matrix [Theta], wherein regularization processing is performed on atom selection, variable step processing is performed on the iteration process, and a sparse approximation signal x^ of the original signal is acquired; S3, reconstructing the original two-dimensional image based on the sparse approximation signals of all columns of the two-dimensional image. Compared with the prior art, the compressive sensing based image processing method is higher in efficiency and further reduces the number of iterations based on the variable step processing, thereby being capable of acquiring the most approximate sparsity signal, and solving problems of long time consumption of signal reconstruction and inaccurate sparsity estimation.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
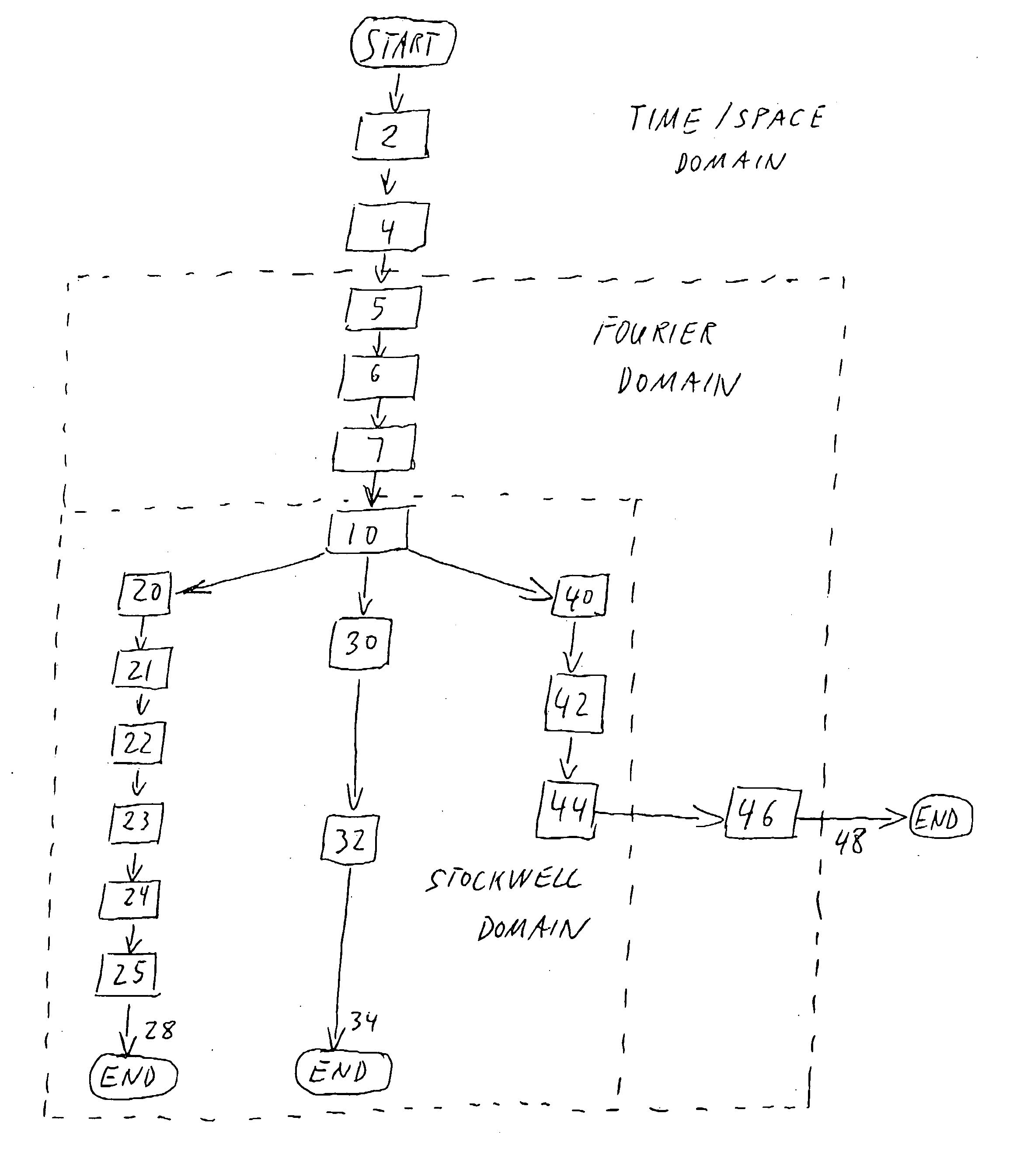
Method and system for signal processing using a sparse approximation of the S-transform
ActiveUS20070027657A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringS transformWorkstation
The present invention relates to a method and system for processing time series signal data or image signal data indicative of a characteristic of an object. Received signal data are transformed into second signal data within a Stockwell domain based upon a sparse approximation of a S-transform of the signal data. The second signal data are then processed within the Stockwell domain to extract features therefrom. The processing includes determination of local spectra at predetermined locations; determination of voices at predetermined frequencies; and filtering of the signal data using a filter function in dependence upon frequency and time or space. The signal processing method and system according to the invention enables signal processing based on the S-transform using a desktop computer or workstation.
Owner:CALGARY SCIENTIFIC INC
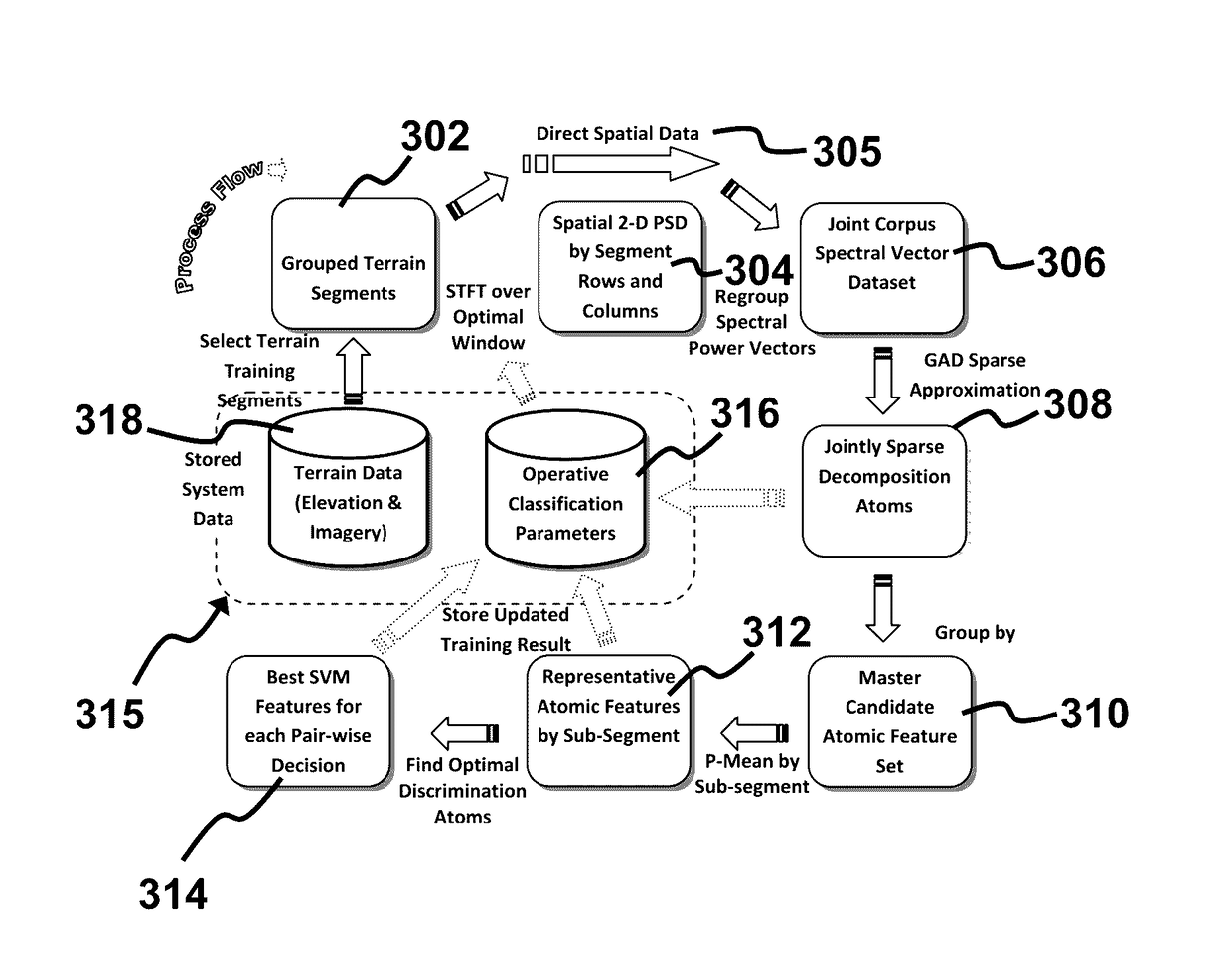
System and method for taxonomically distinguishing unconstrained signal data segments
ActiveUS9691395B1Automatically and accurately distinguishingSpeech recognitionData segmentSelf adaptive
A system and method are provided for taxonomically distinguishing grouped segments of signal data captured in unconstrained manner for a plurality of sources. The system comprises a vector unit constructing for each of the grouped signal data segments at least one vector of predetermined form. A sparse decomposition unit selectively executes in at least a training system mode a simultaneous sparse approximation upon a joint corpus of vectors for a plurality of signal segments of distinct sources. The sparse decomposition unit adaptively generates at least one sparse decomposition for each vector with respect to a representative set of decomposition atoms. A discriminant reduction unit executes during the training system mode to derive an optimal combination of atoms from the representative set. A classification unit executes in a classification system mode to discover for an input signal segment a degree of correlation relative to each of the distinct sources.
Owner:REALITY ANALYTICS INC
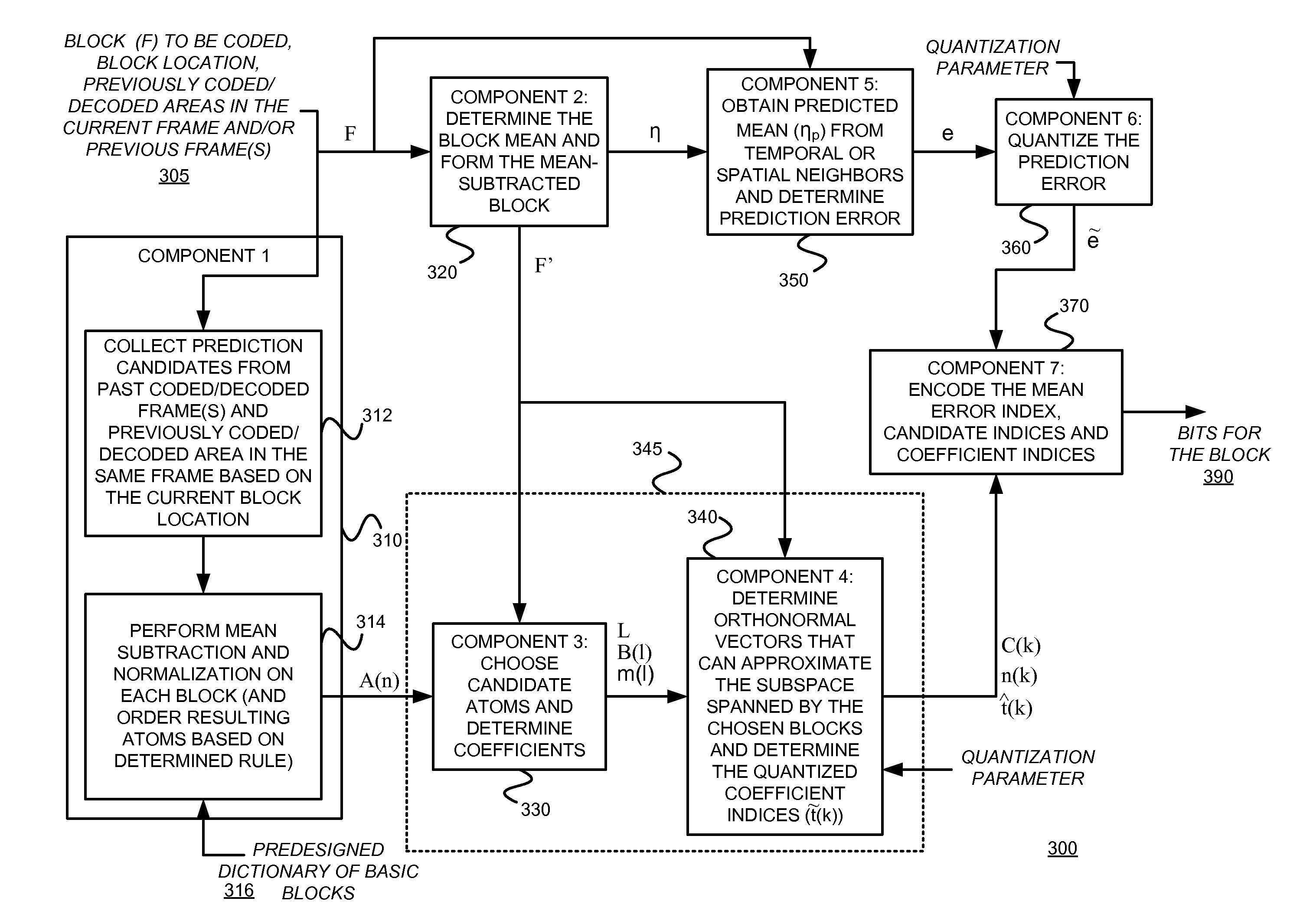
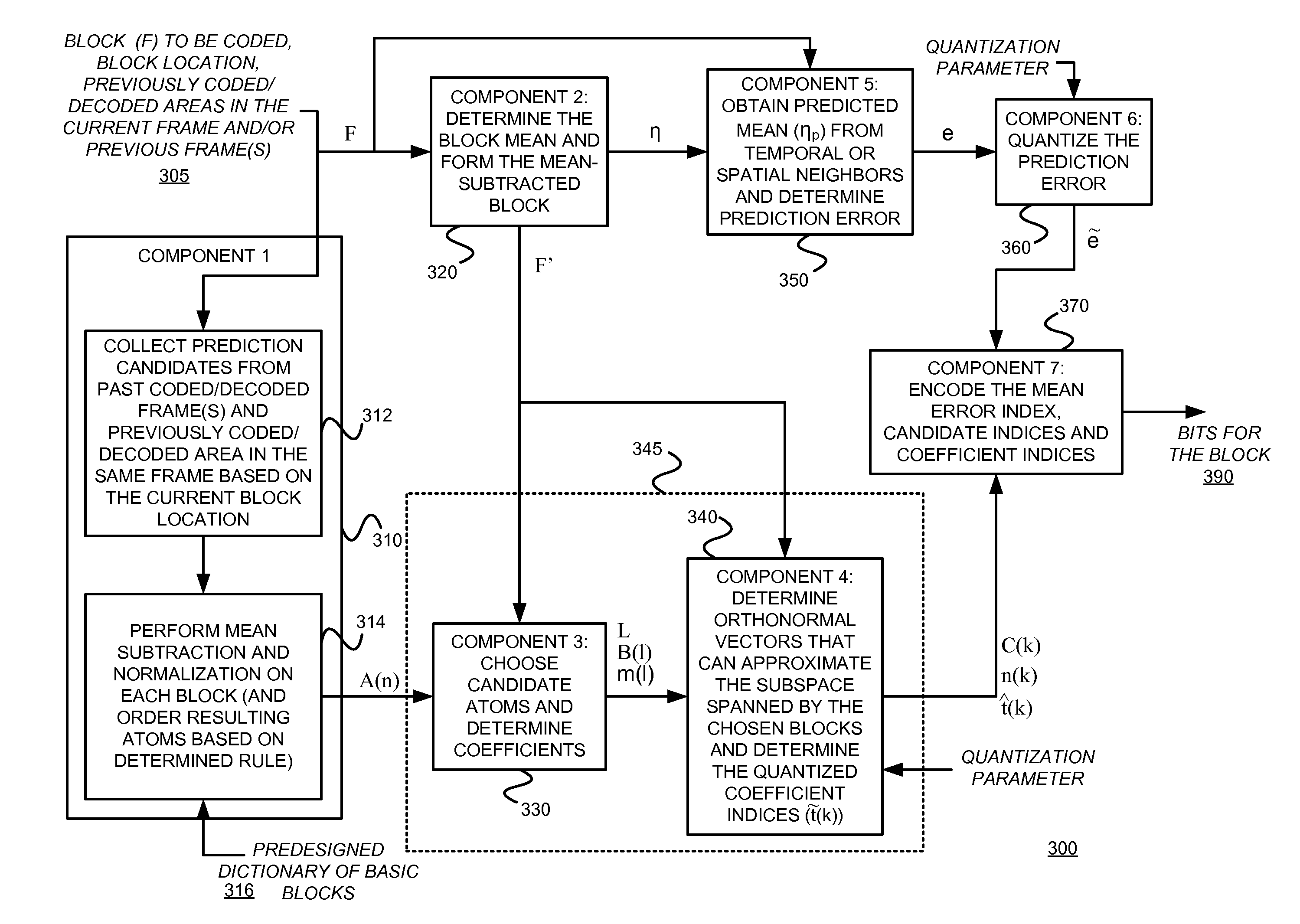
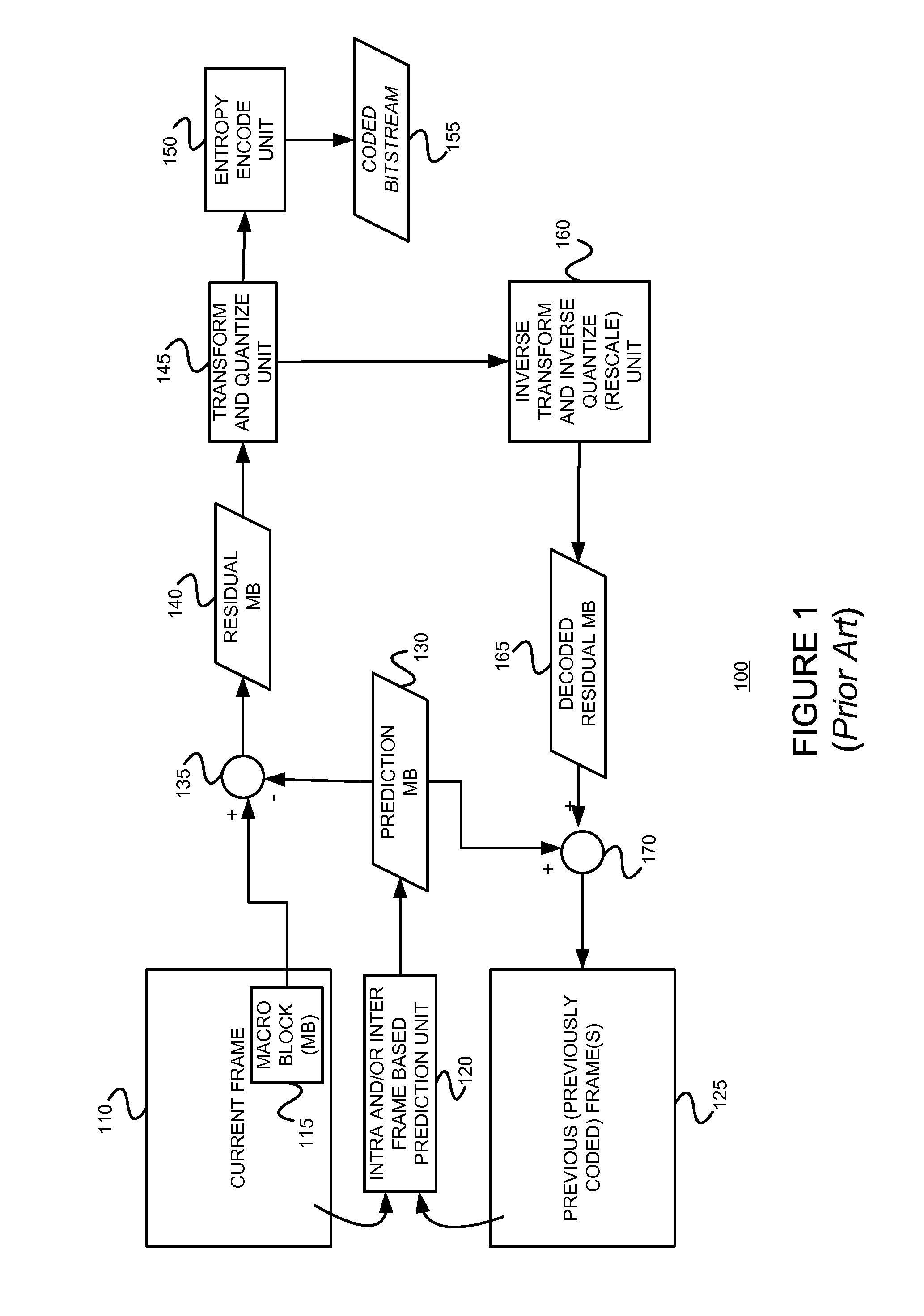
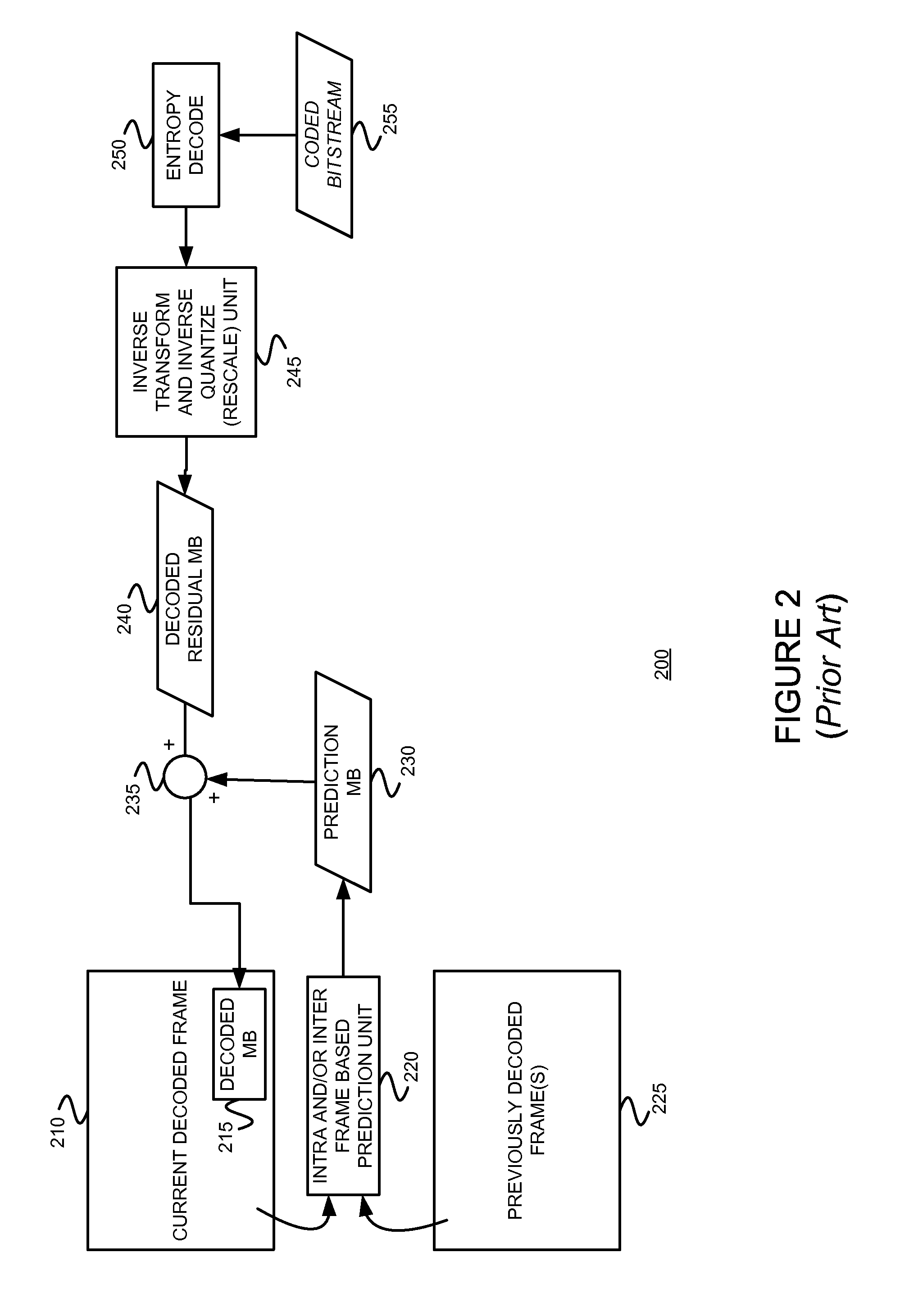
Coding using a redundant dictionary, such as video coding using a self-adaptive redundant dictionary including spatial and/or temporal prediction candidte atoms
InactiveUS20150189283A1Large gainSimilar performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNonzero coefficientsMotion vector
An example video encoder uses a self-adaptive dictionary that only depends on the block location, without requiring real time design / redesign of the dictionary. A mean-removed block may be directly represented using a redundant dictionary including all possible inter-prediction candidates with integer motion vectors (mean-removed). In general the dictionary may also contain some intra-prediction candidates and some pre-designed fixed dictionary atoms. The coefficients may be determined by minimizing the L0 norm of the coefficients subject to a constraint on the sparse approximation error. Using such a self-adaptive dictionary can lead to a very sparse representation, with significantly fewer non-zero coefficients than using the DCT transform on the prediction error. Some example embodiments consistent with the present invention use a modified orthogonal matching pursuit (“OMP”) algorithm to orthonormalize each new chosen atom with respect to all previously chosen and orthonormalized atoms. Each image block is represented by the quantized coefficients corresponding to the orthonormalized atoms.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
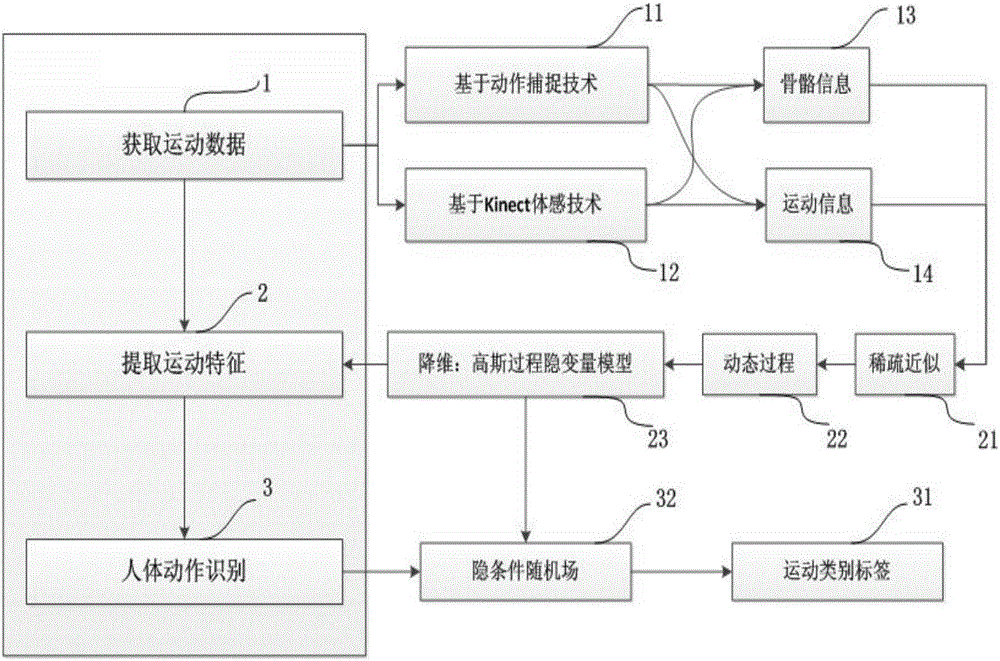
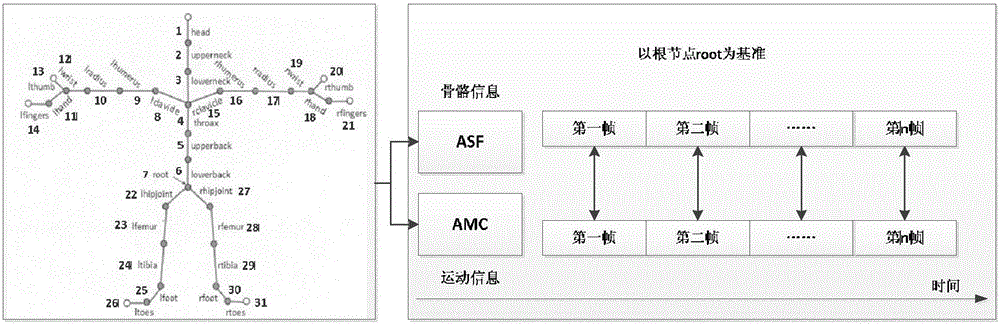
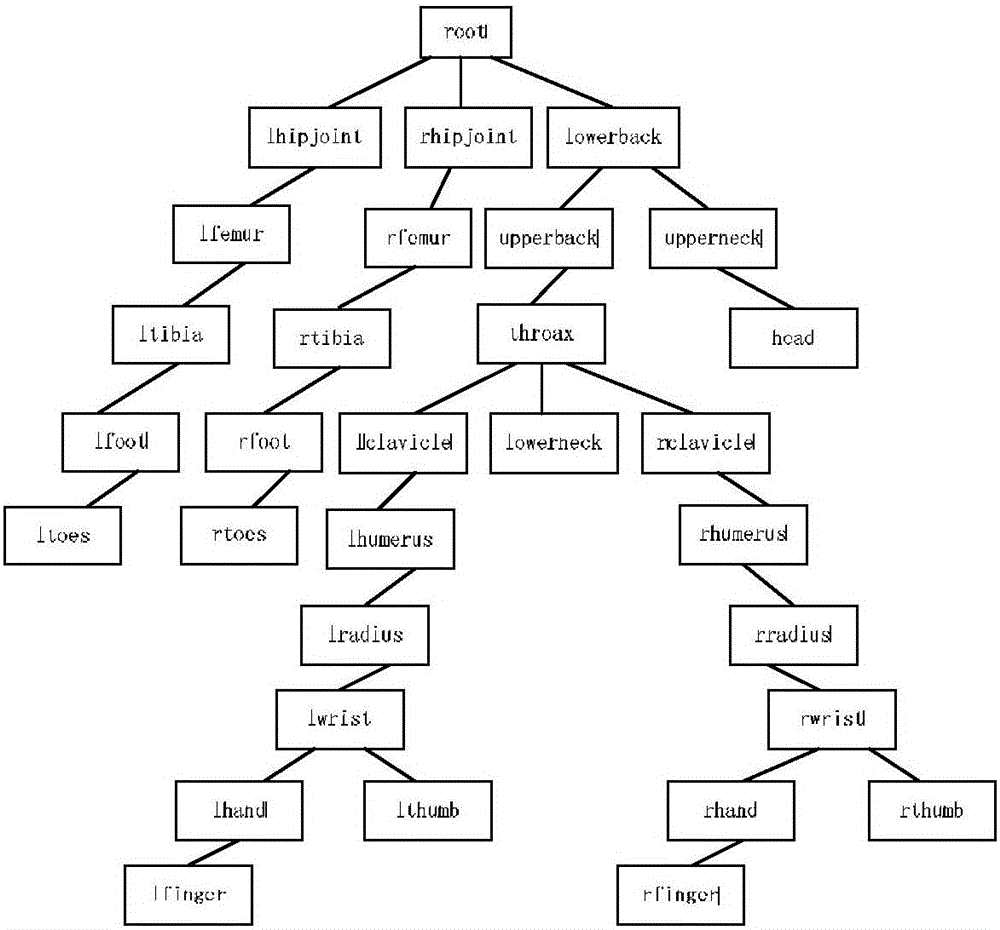
Human motion identification method based on Gaussian process latent variable model
ActiveCN105930770AImplement classificationRealize visualizationCharacter and pattern recognitionConditional random fieldHuman body
The invention provides a discriminant human motion identification method based on a Gaussian process latent variable model and a hidden condition random field. The method mainly comprises that skeletal structure and motion information of the human body are obtained via motion capturing technology or Kinect motion sensing technology when motion data is obtained; when motion characteristics are extracted, the Gaussian process latent variable model added with a dynamic process and sparse approximation is used to obtain structure of high-dimension motion information in low-dimension hidden space and further to represent the motion characteristic; and when the human motion is identified, the discriminant hidden condition random field is used to model characteristics of sequential motion data, and motions are classified. According to the invention, characteristics of the human motions can be visualized, information among the sequential motion data can be used effectively, the human motions can be identified in high precision, and the method is suitable for the field of real-time human motion identification.
Owner:北京陟锋科技有限公司
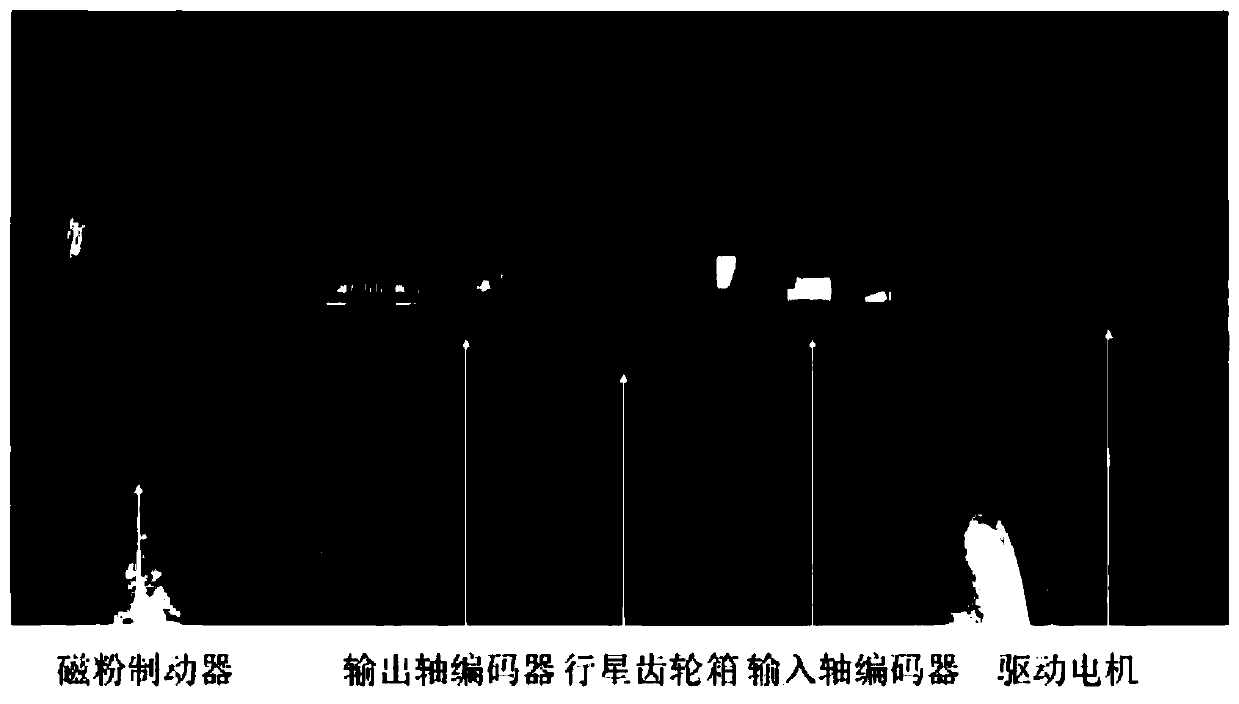
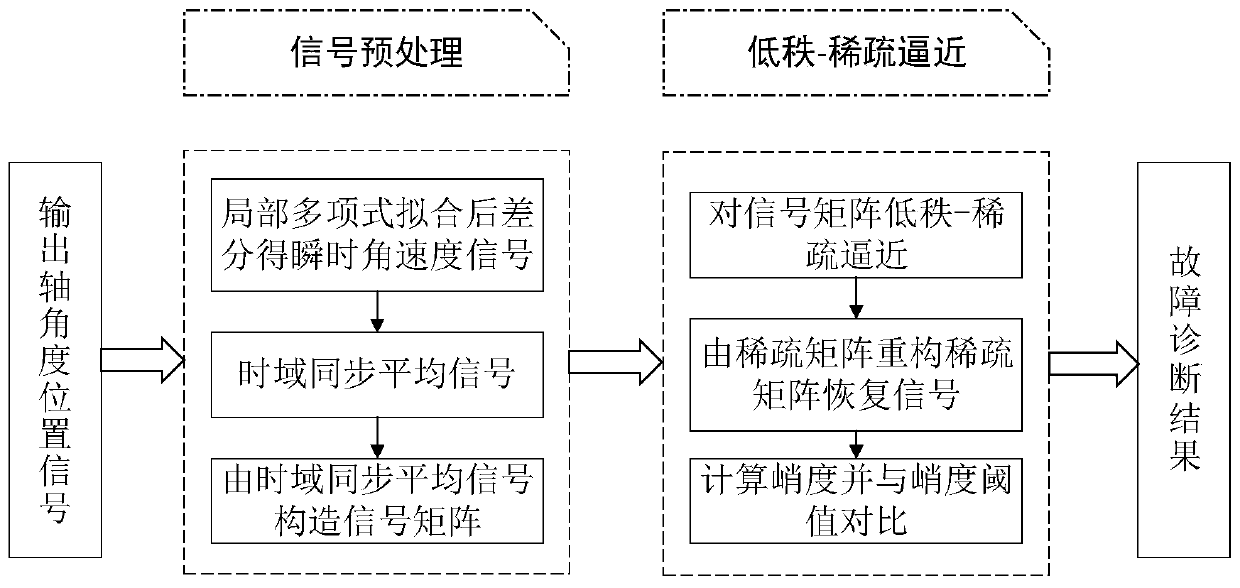
Planetary gear box fault diagnosis method based on low-rank sparse approximation
ActiveCN109883693ASimplify the analysis processSave computing resourcesMachine part testingTime domainMean square
The invention relates to a planetary gear box fault diagnosis method based on low-rank sparse approximation. The planetary gear box fault diagnosis method based on low-rank sparse approximation comprises the steps of: acquiring output shaft angle position signals by utilizing a built-in coder at first, then, fitting and differentiating the output shaft angle position signals by taking the mean square error as a loss function, so that instantaneous angle speed signals are obtained, on the basis of the instantaneous angle speed signals, respectively performing time-domain synchronous averaging on a planet wheel, a sun wheel and a gear ring, then, performing low-rank sparse approximation on respective time-domain synchronous averaging signals, so that sparse recovery signals of the planet wheel, the sun wheel and the gear ring are obtained, furthermore, calculating each kurtosis, and judging that the signal, the kurtosis of which is greater than a kurtosis threshold value, fails. According to the planetary gear box fault diagnosis method based on low-rank sparse approximation in the invention, by utilization of the characteristics of a low-rank sparse approximation method, acquired compound signals are decoupled; normal meshing information and fault information of a planetary gear box are separated; fault characteristics are prominent; and early weak fault diagnosis of the planetary gear box is easily realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
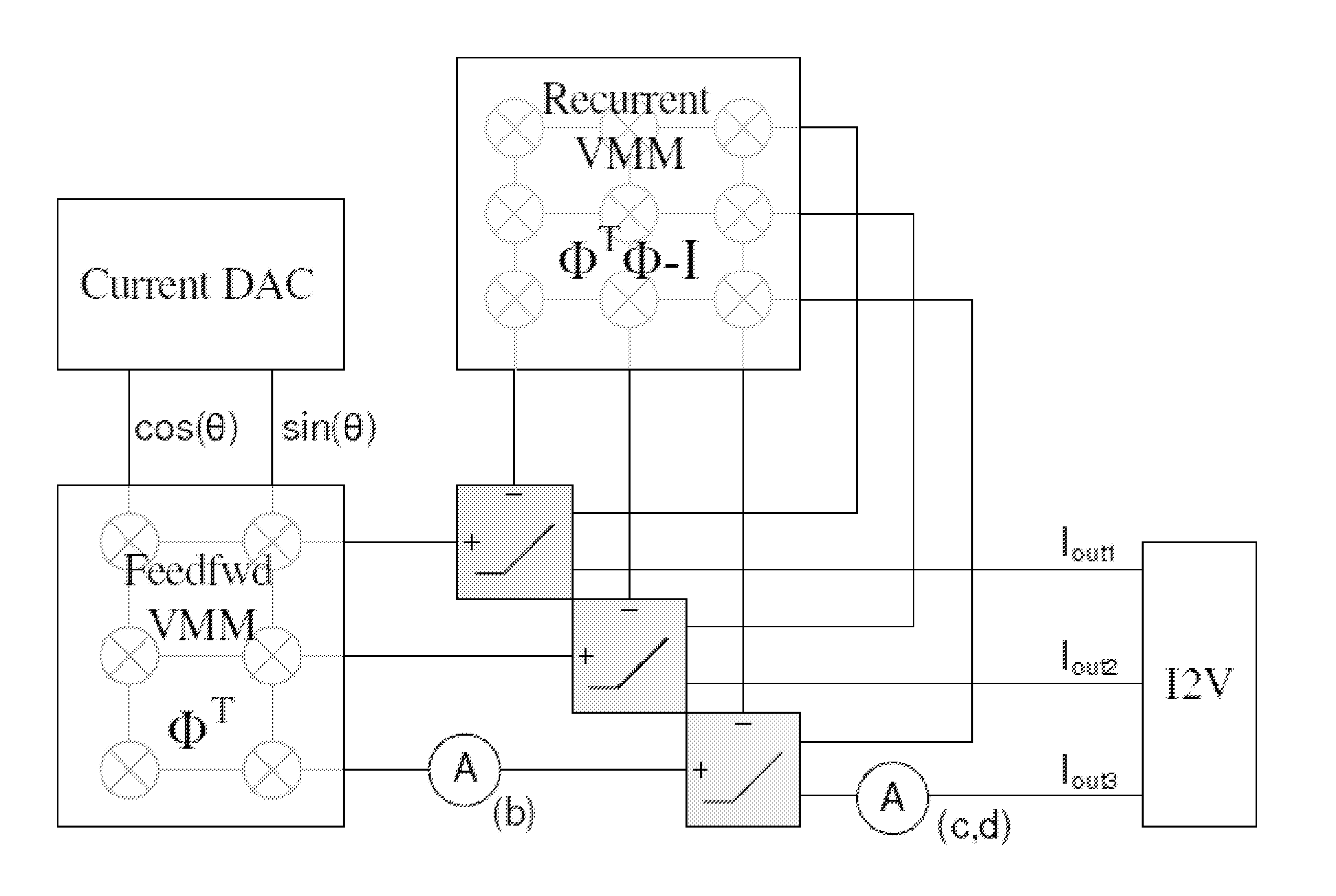
Analog programmable sparse approximation system
InactiveUS20130318020A1Reduce energy consumptionLower computational expenseDigital computer detailsDigital dataSub thresholdAnalog chip
A system and device for solving sparse algorithms using hardware solutions is described. The hardware solution can comprise one or more analog devices for providing fast, energy efficient solutions to small, medium, and large sparse approximation problems. The system can comprise sub-threshold current mode circuits on a Field Programmable Analog Array (FPAA) or on a custom analog chip. The system can comprise a plurality of floating gates for solving linear portions of a sparse signal. The system can also comprise one or more analog devices for solving non-linear portions of sparse signal.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Data reconfiguration and decompression method of power system based on projection pursuit
The invention discloses a data reconfiguration and decompression method of a power system based on projection pursuit. A signal can be sampled at frequency far below Nyquist frequency on the basis of a compressive sensing theory. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing an over-complete atom dictionary to ensure that atoms in the atom dictionary are redundant; secondly, searching an optimally-matched atom, updating signal residuals, and re-acquiring sparse vector elements; and finally, acquiring a sparse vector. According to the method, in an iteration process at each time, the atom which is optimally matched with the signal is selected from a sensing matrix to construct sparse approximation, signal residual representation is obtained, and the signal is linearly represented by a certain number of atoms by certain iteration frequency. According to the conventional data compression method, sampling and compression are required to be performed in sequence. According to the data reconfiguration and decompression method, the sampling and the compression are performed concurrently, and an original electric energy quality signal can be well restored by low sampling frequency.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
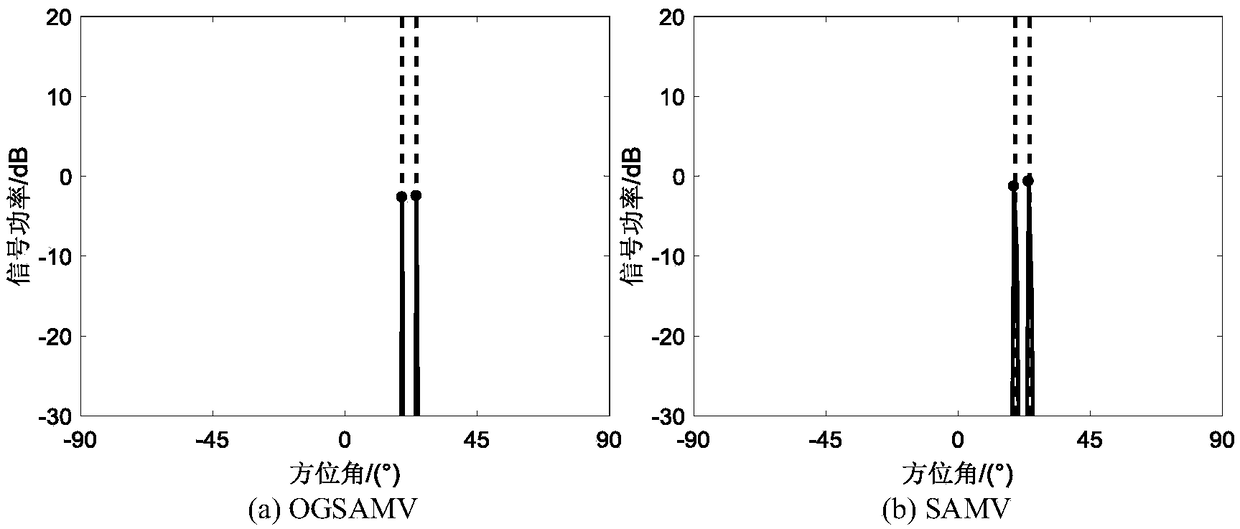
Matrix-filtering-based sparse asymptotic minimum variance direction-of-arrival estimation method
ActiveCN109116337AAvoid choiceAffect positioning accuracyWave based measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Target signal
The invention relates to a matrix-filtering-based sparse asymptotic minimum variance direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation method. A matrix filter is used as a preprocessor to process an array receiving signal, so that a strong interference signal is suppressed and thus a phenomenon that a weak target is shielded by the strong interference signal or the positioning precision of the weak target bythe subsequent DOA estimation algorithm is affected by the strong interference signal is avoided. DOA estimation is carried out base on a sparse asymptotic minimum variance (SAMV) algorithm, so that the high-resolution performance is kept under the circumstances of small snapshot and low signal-to-noise ratio and a direction-of-arrival estimation problem of a coherent signal is solved. Meanwhile,the algorithm only needs to provide a threshold value eta of iterative stopping, thereby avoiding selection of regular parameters and enhancing the practicability of the algorithm. Besides, while thearray manifold change of the interference destroys the structure of the covariance matrix, the DOA estimation of the weak target signal still can be realized by the SAMV algorithm.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
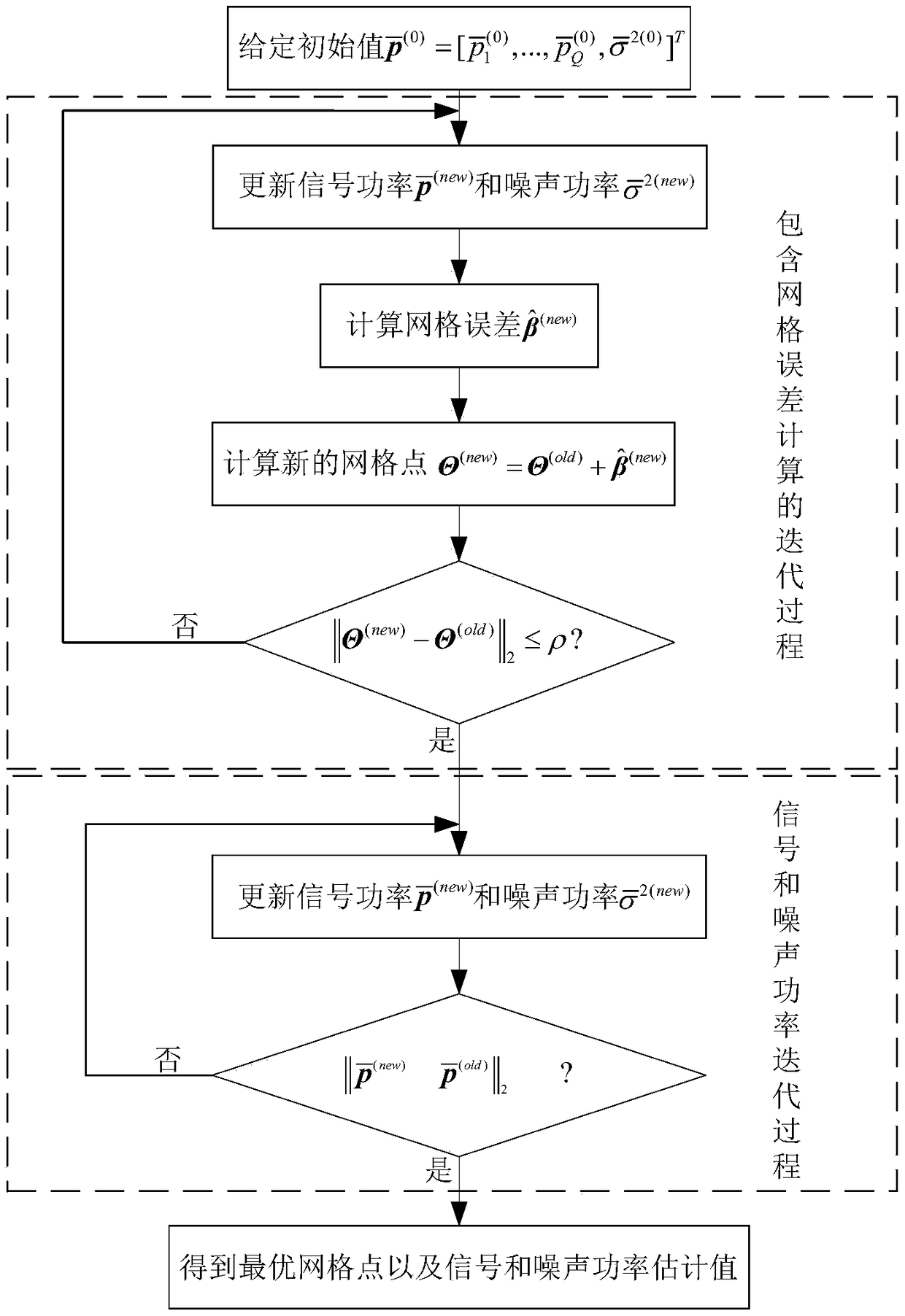
Lattice error model-based mesh-free sparse approximate minimum variance direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method
ActiveCN109307855AHigh positioning accuracyHigh precisionRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsEstimation methodsTarget signal
The invention relates to a lattice error model-based mesh-free sparse approximate minimum variance direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method. A lattice error model-based array receiving signal model is built, a signal, a noise power and a lattice error are sequentially and iteratively solved according to the model, so that the positioning accuracy of the sparse approximate minimum variance DOAestimation method is free from the limitation of space lattice division accuracy, and relatively high DOA estimation accuracy still can be achieved when DOA of a target signal is not matched with a lattice point.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
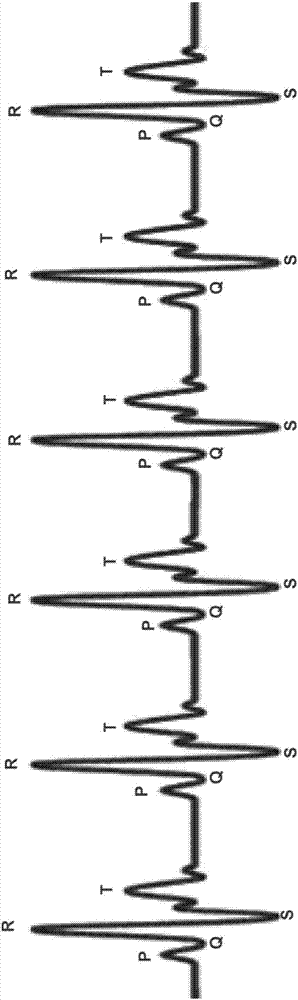
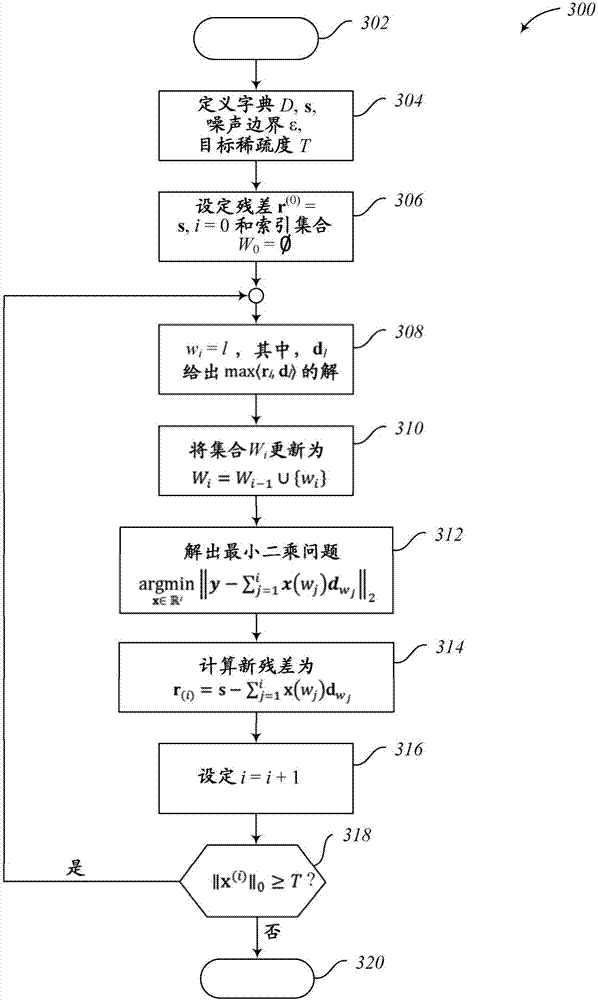
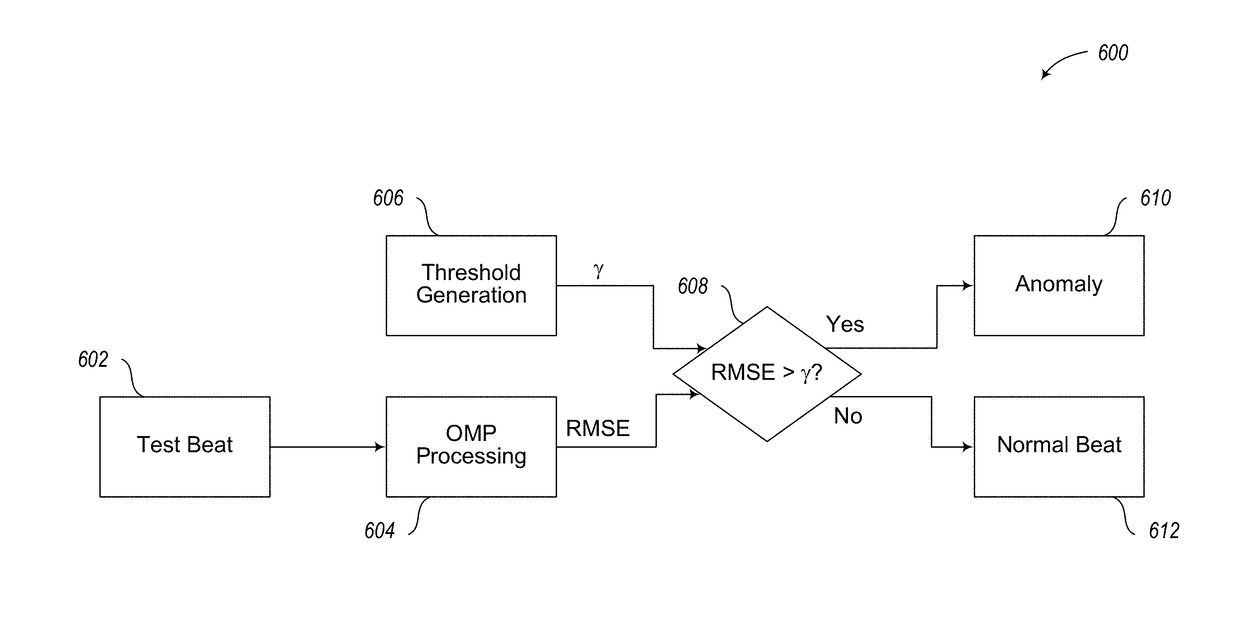
Method For The Detecting Electrocardiogram Anomalies And Corresponding System
A heart-rate associated with a heartbeat signal is determined. A transform is selected based on the determined heart-rate associated with the heartbeat signal and a reference heart-rate associated with a dictionary of a sparse approximation model. The transform is selected independent of other factors associated with generation of the heartbeat signal. The selected transform is applied to the dictionary of the sparse approximation model, generating an adjusted dictionary of the sparse approximation model. Anomalous heartbeats in the heartbeat signal are detected using the adjusted dictionary of the sparse approximation model.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method for the detecting electrocardiogram anomalies and corresponding system
A heartrate monitor detects heartbeats in a test signal. A local heartrate and an energy of acceleration are associated with the detected heartbeats. Detected heartbeats are included or excluded from a test set of heartbeats based on the local heartrate and energy of acceleration associated with the respective heartbeats. Anomalous heartbeats in the test set of heartbeats are detected using a sparse approximation model. The heartrate monitor may detect heartbeats in a training heartbeat signal. A reference heart rate and an energy of acceleration are associated with detected beats of the training heartbeat signal and selectively included in a set of training data based on the heart rate and energy of acceleration associated with the detected beat in the training heartbeat signal. A dictionary of the sparse representation model may be generated using the set of training data.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method and system for signal processing using a sparse approximation of the S-transform
ActiveUS7401006B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsS transformWorkstation
The present invention relates to a method and system for processing time series signal data or image signal data indicative of a characteristic of an object. Received signal data are transformed into second signal data within a Stockwell domain based upon a sparse approximation of a S-transform of the signal data. The second signal data are then processed within the Stockwell domain to extract features therefrom. The processing includes determination of local spectra at predetermined locations; determination of voices at predetermined frequencies; and filtering of the signal data using a filter function in dependence upon frequency and time or space. The signal processing method and system according to the invention enables signal processing based on the S-transform using a desktop computer or workstation.
Owner:CALGARY SCIENTIFIC INC
Sparse microwave imaging method based on online observation
InactiveCN103760559AReduce complexitySmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsBackscatter coefficient
The invention provides a sparse microwave imaging method based on online observation. The method comprises the following steps that S1, according to the radar observation imaging principle, a sparse microwave imaging module based on the sparse approximation theory is constructed; S2, a value estimated for the nth time of a backscatter coefficient of a target scene is set to be x(n); S3, a value x(n+1) estimated for the n+1th time of the backscatter coefficient of the target scene is obtained online by means of observation based on the homotopy algorithm through the backscatter coefficient x(n) of the target scene and newly-added radar observation echo data yn+1; the steps are repeated continuously until a stopping condition is satisfied, so that sparse microwave imaging is achieved. According to the sparse microwave imaging method based on online observation, the smallest sampling number can be determined in a self-adaptive mode according to the characteristics of the scene, an original result can be directly corrected by newly-added sampling data, and therefore recalculation is avoided and the calculated amount is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for MDCT domain signal energy and phase compensation
InactiveCN101521012AReduce complexityCompensate for energy jitterSpeech analysisAudio frequencyComputer science
The invention provides a method and a device for MDCT domain signal energy and phase compensation. By analyzing the relationship between an MDCT transform radix and an MDST transform radix and by using the sparse approximation matrix, the transformation matrix of the MDCT to the MDST is extracted and simplified; the transformation of an MDCT spectrum to an MDST spectrum is realized by using the transformation matrix, and an MDFT spectrum with constant energy and linear phase is formed by combining the MDCT spectrum and the MDST spectrum; and the spatial parameters are extracted according to the MDCT spectrum. The invention effectively solves the problems of field wobbling and phase deletion of the signal in the MDCT domain and realizes the extraction and synthesis of the spatial parameters in the MDCT domain with low complexity in the spatial audio coding system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Sparse array method for vector hydrophones based on compressed sensing theory
ActiveCN109557526AAccurate Sparse Array ResultsPrecise Control of ComplexityWave based measurement systemsTarget arrayControl system
The invention provides a sparse array method for vector hydrophones based on the compressed sensing theory. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining functions of the directivity ofa vector hydrophone combination and the directivity of a composite array; (2) constructing a target directional beam of a vector hydrophone array; (3) constructing an array problem model of a sparsevector hydrophone; and (4) reconstructing the vector hydrophone array sparsely. The method is based on the sparse array mechanism of the vector hydrophone array, combines with the convex optimizationand the compressed sensing theory, uses the sensing relationship between the sparse array position and the target array beam, and uses the non-uniform spacing array to reconstruct the target beam, toobtain accurate sparse array results. According to the sparse array method for the vector hydrophones based on the compressed sensing theory, the method can set the number of hydrophones in the desired sparse vector array independently according to the requirements of the system performance, and can control the complexity of the system accurately. The vector sparse array method adopts the orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm; the obtained sparse approximation result is fixed; and the method does not need to be debugged for multiple times, thereby saving a lot of algorithm adjustment time; andthe method is more aligned with the practical application of the engineering.
Owner:NAT INNOVATION INST OF DEFENSE TECH PLA ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
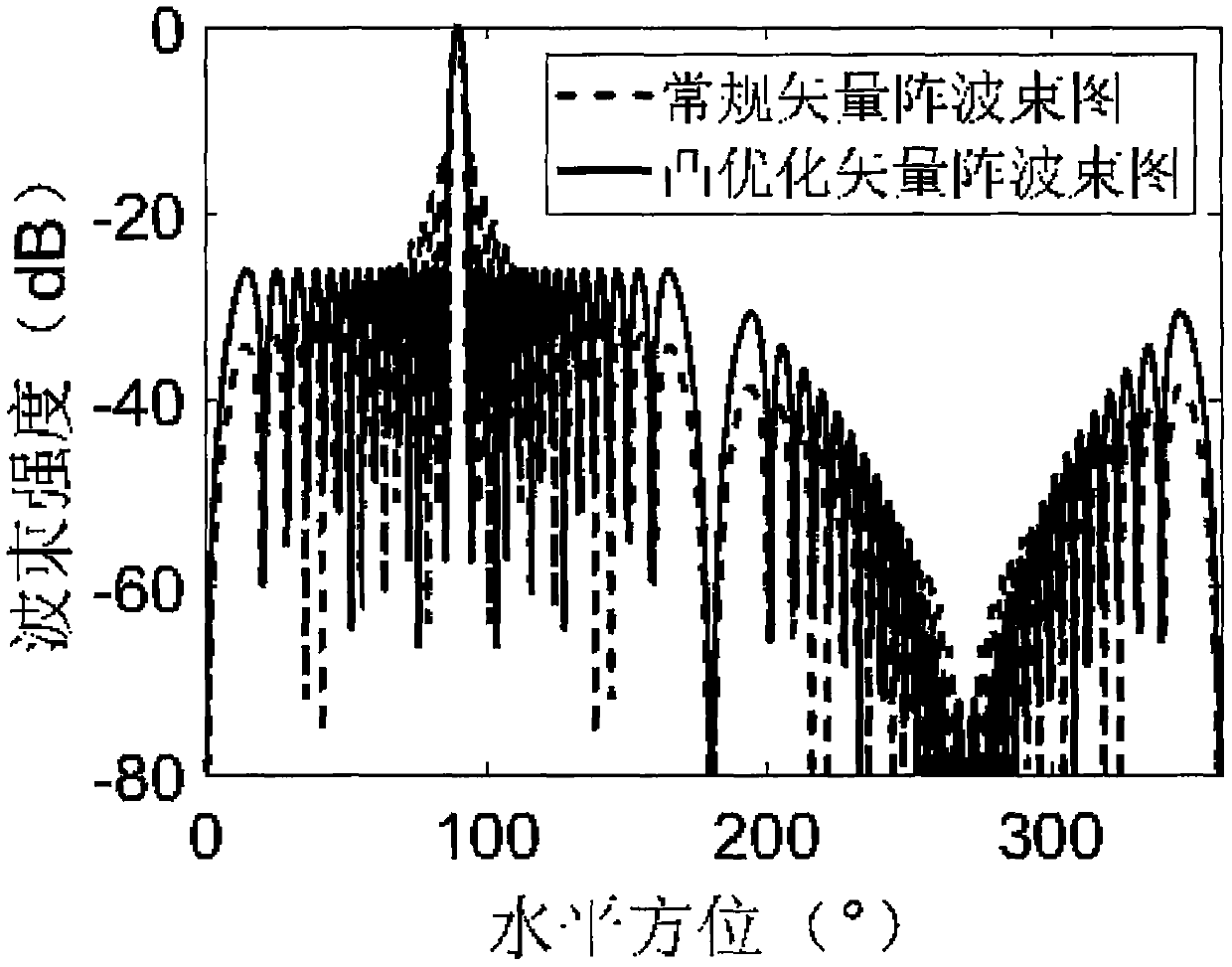
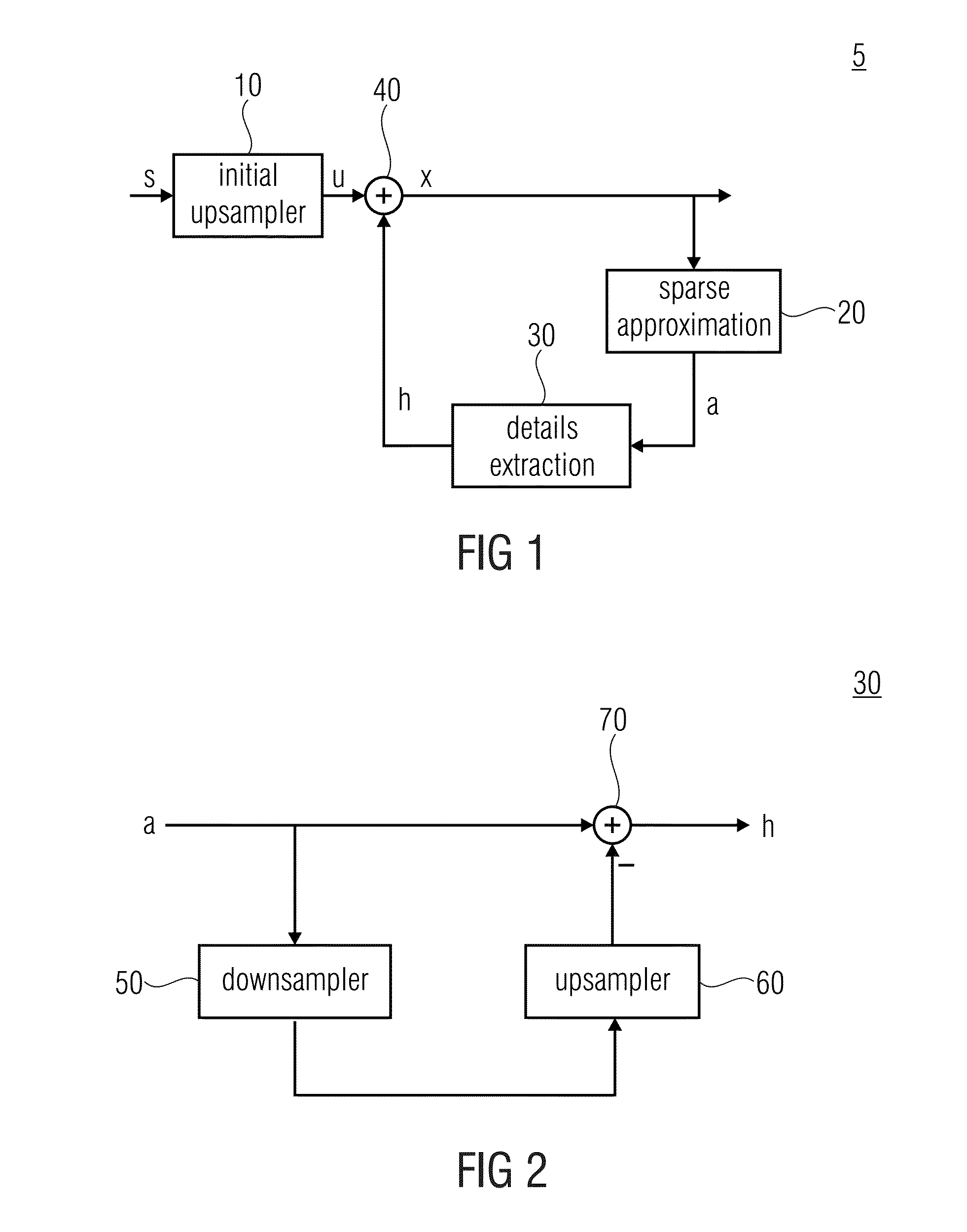
Upsampling and signal enhancement
ActiveUS20160048947A1Reduce quality problemsHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisSparse approximationSignal enhancement
A signal which is to be quality-improved often suffers from the quality degradation in the spatial high frequency region more than compared to the spatial low frequency region. Accordingly a quality improvement is performed efficiently by combining the signal to be quality improved with a high frequency portion extracted from a sparse approximation of the signal to be quality improved.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
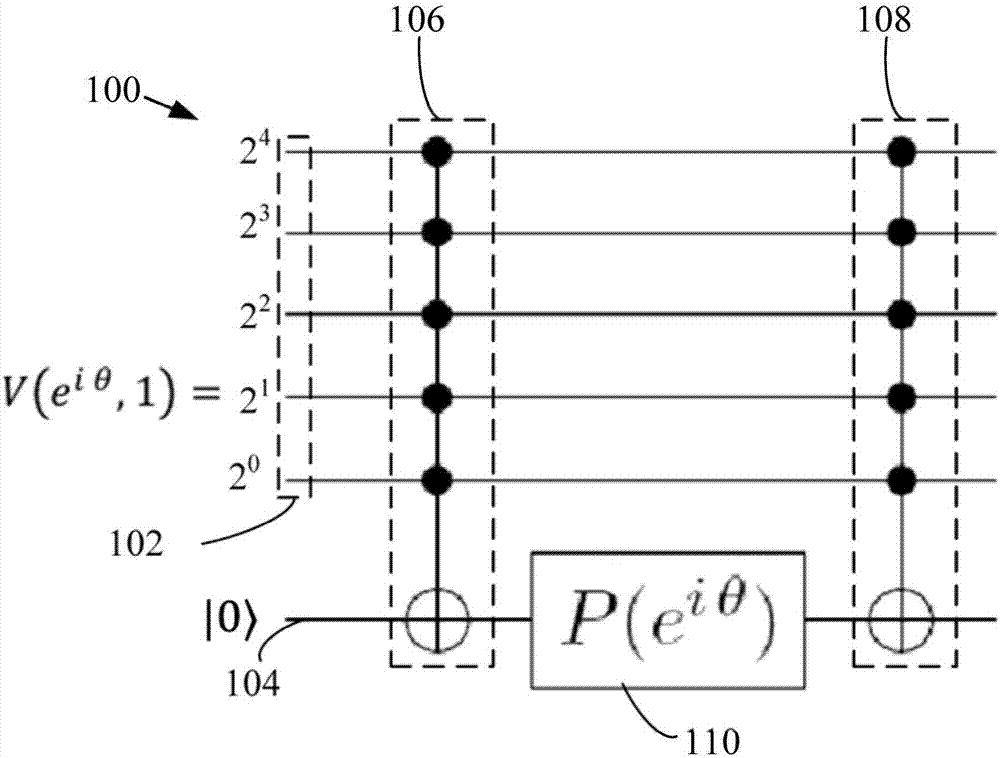
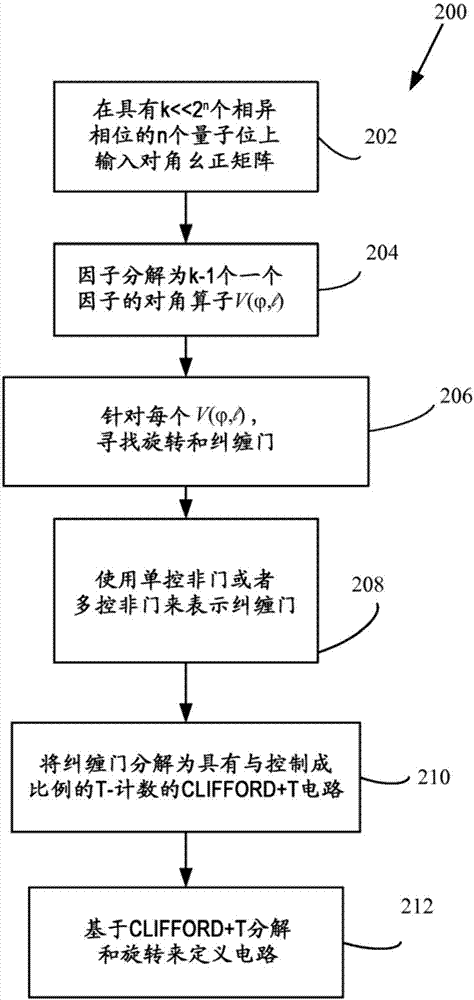
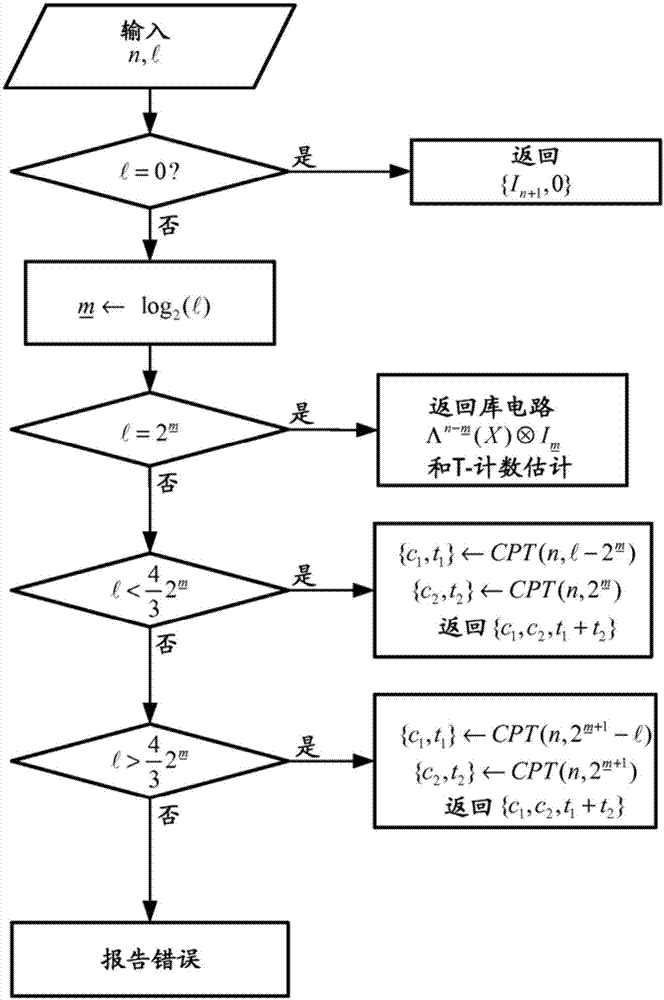
Method for efficient implementation of diagonal operators over CLIFFORD+T basis
ActiveCN107004161AQuantum computersSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureQuantum circuit
Quantum circuits and circuit designs are based on factorizations of diagonal unitaries using a phase context. The cost / complexity of phase sparse / phase dense approximations is compared, and a suitable implementation is selected. For phase sparse implementations in the Clifford+T basis, required entangling circuits are defined based on a number of occurrences of a phase in the phase context in a factor of the diagonal unitary.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
A fast video inference method based on cyclic residual module
InactiveCN109272035AReduce operational complexityAvoid time costCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesVision processingTime changes
The invention provides a fast video inference method based on a cyclic residual module, a cyclic residual module, which reduces the complexity of neural network operation, improves the sparsity of intermediate feature mapping, and synthesizes efficient inference engine, is used in the method. The process is as follows: firstly, frame similarity is utilized in cyclic residual module to reduce theredundant calculation in frame-by-frame video convolutional neural network inference; then, by improving the sparse approximation output of the intermediate feature map, the inference speed is accelerated and the inference precision is ensured by the error control mechanism. Finally, the synthesis of efficient inference engine, that is, the use of matrix vector multiplication in the dynamic sparsity of the accelerator, so that the cycle residual module is in efficient operation. Compared with the traditional method, the invention can remarkably improve the running speed of the vision processing system, and enhance the understanding ability of the network to the real-time changing video fragments, thereby realizing the acceleration of the video inference process on the premise of ensuring the identification accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
System and method for taxonomically distinguishing unconstrained signal data segments
ActiveUS10699719B1Automatically and accurately distinguishingSpeech recognitionData segmentEngineering
A system and method are provided for taxonomically distinguishing grouped segments of signal data captured in unconstrained manner for a plurality of sources. The system comprises a vector unit constructing for each of the grouped signal data segments at least one vector of predetermined form. A sparse decomposition unit selectively executes in at least a training system mode a simultaneous sparse approximation upon a joint corpus of vectors for a plurality of signal segments of distinct sources. The sparse decomposition unit adaptively generates at least one sparse decomposition for each vector with respect to a representative set of decomposition atoms. A discriminant reduction unit executes during the training system mode to derive an optimal combination of atoms from the representative set. A classification unit executes in a classification system mode to discover for an input signal segment a degree of correlation relative to each of the distinct sources.
Owner:REALITY ANALYTICS INC
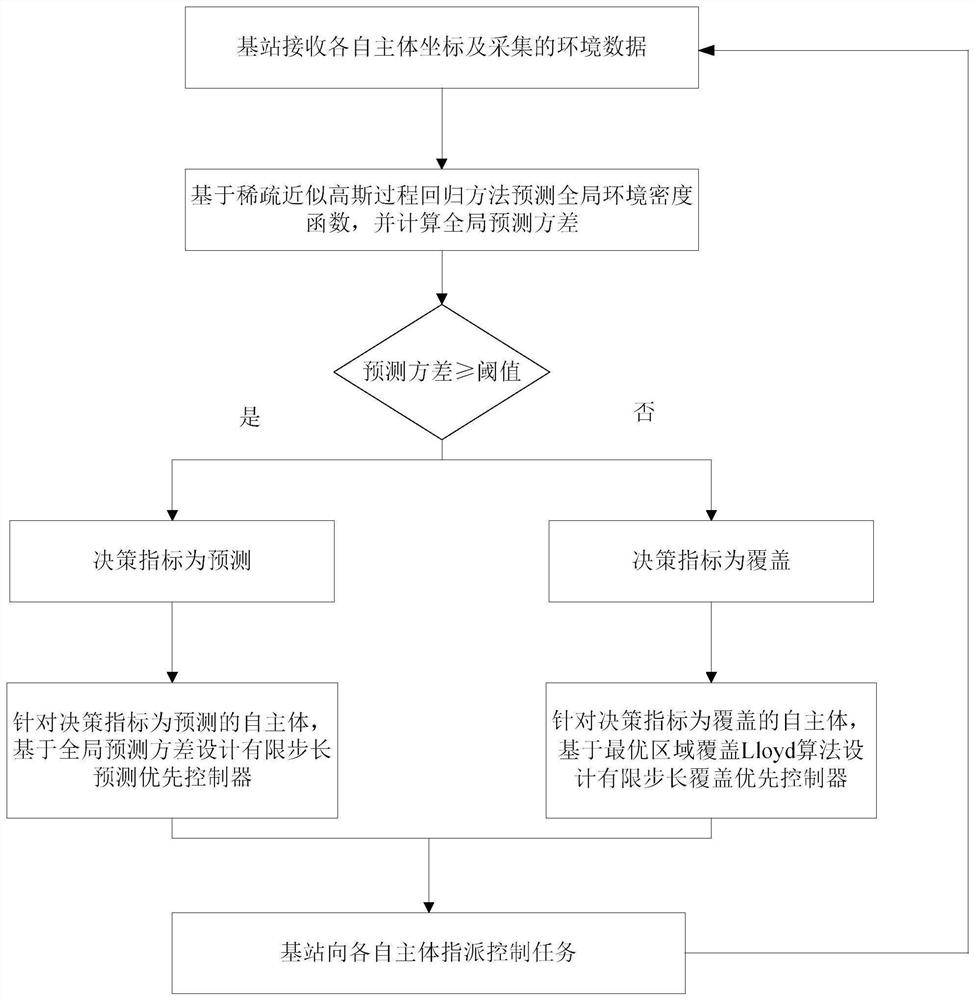
Multi-agent centralized region coverage method and system based on global environment prediction
The invention discloses a multi-agent centralized region coverage method and system based on global environment prediction. In the method, base stations receive respective main body positions and environment data, predict a global environment density function based on a sparse approximate Gaussian process regression method, and give a global prediction variance; the base station designs an autologous control scheme decision model based on the global prediction variance, assigns tasks to respective subjects through the decision model, designs a finite step prediction priority controller based on the global prediction variance by taking a decision index as a predicted autologous, designing a finite step length coverage priority controller based on an optimal region coverage Lloyd algorithm; and realizing the optimal coverage control through continuous interaction of the self-agent and the base station. According to the method, the base station-multi-autologous system can autonomously capture the environment density function model with high accuracy and high performance. Meanwhile, the multi-autologous system can quickly realize ideal optimal region coverage under the limitation of finite step length.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Target detection method based on non-convex motion assistance
The invention discloses a target detection method based on non-convex motion assistance. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, inputting to-be-processed video data into a constructed low-rank sparse decomposition model; 2, solving the constructed low-rank sparse decomposition model by adopting an alternating direction multiplier method to obtain a moving target in the input video data;according to the method, a non-convex gamma norm is adopted to replace a rank function in a traditional low-rank sparse decomposition model to approximately represent a low-rank part of a video background; meanwhile, by considering that the background still has sparsity in the transform domain, the l1 norm is adopted to carry out sparse approximation on the background of the transform domain, andthe l1 norm representing the sparse prior of the moving target is still adopted as the foreground. Moreover, a motion auxiliary information matrix is introduced into the model, so that the motion auxiliary information matrix is fused into foreground motion information, and the motion target detection of the video is better realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sparse approximation acceleration bilateral filtering method based on learning cosine dictionary
The invention provides a sparse approximation acceleration bilateral filtering method based on a learning cosine dictionary, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, enabling a bilateral filter to be converted into spatial convolution through the one-dimensional cosine approximation of a range kernel; and 2, utilizing two-dimensional cosine approximation of the space kernel to solve the space volume integral into a box type filtering result with the computational complexity of O(1).
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coding using a redundant dictionary, such as video coding using a self-adaptive redundant dictionary including spatial and/or temporal prediction candidate atoms
InactiveUS9591322B2Similar performanceLarge gainCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingMotion vector
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Moving target detection method in slowly-changing moving background
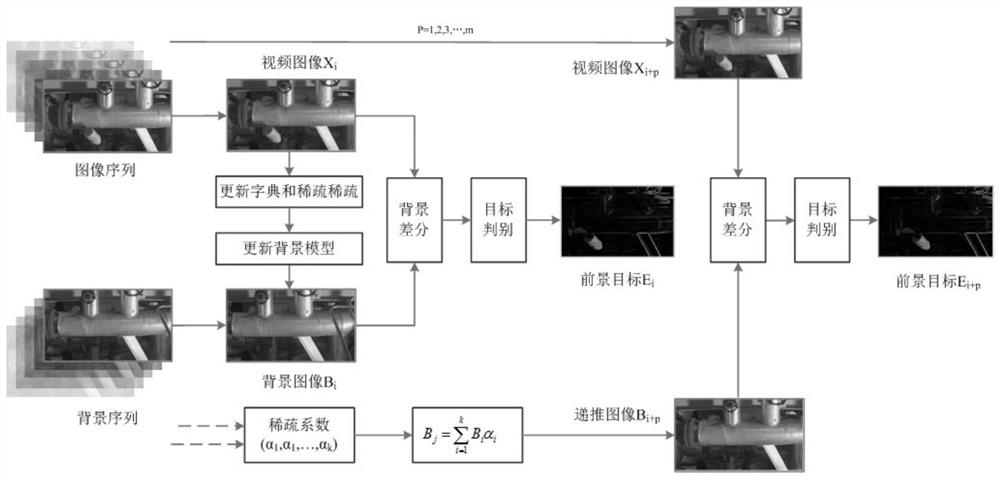
PendingCN112150502ALow real-time requirementsReduce operational complexityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse approximationImage resolution
The invention relates to the technical field of moving target detection in the field of pattern recognition, and discloses a moving target detection method in a slowly changing moving background, in acamera video, each frame of image can be segmented into a foreground target and a background, and supposing that the resolution of the camera video is p * q, the moving background sequence is B1, B2,..., Bk, and the image sequence is X1, X2,..., Xm. The method for detecting the moving target in the slowly-varying moving background comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing data dimension reduction by using low-rank sparse decomposition, taking a video sequence as a subspace set, proposing a calculation model by using sparse approximation recursive representation in combination withdictionary sparse representation, and then calculating a moving target object by using a background difference method; therefore, the operation complexity is effectively reduced, and the operation time is shortened; secondly, according to a sparse code migration idea, the operations are carried out in a down-sampling space, so that the operand and the requirement on memory storage are further reduced, and meanwhile, the method is suitable for multi-scale target objects and can overcome the influence caused by a very large abnormal region.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method for designing strong interference suppression beamformer under multi-target condition
PendingCN112630760AClean dataImprove signal-to-noise ratioDirection/deviation determination systemsSystems with undesired wave eliminationMeasurement testData verification
The invention belongs to the technical field of underwater acoustic equipment design and manufacturing and relates to a method for designing a strong interference suppression beamformer under a multi-target condition. The method comprises the following steps that: S1, a filtering matrix G belonging to CM*M is designed, the output y (t) of a filter is equal to Gx (t) has a spatial filtering characteristic, wherein t is equal to 1,..., N, and a matrix spatial filtering principle should satisfy one of conditions described in the descriptions of the invention; S2, a sparse super-resolution azimuth estimation algorithm is adopted; S3, spatial matrix filtering-based sparse super-resolution azimuth estimation is performed, namely, super-resolution azimuth estimation of a weak target in a strong interference environment can be realized by using spatial matrix filtering and a 1- type sparse approximate minimum variance algorithm; and S4, computer simulation and actual measurement test data verification of the algorithm are performed. The matrix filter with spatial filtering characteristics of the passband and the stop band is designed; a high-resolution sparse azimuth estimation algorithm is adopted, so that interference is effectively suppressed to the greatest extent in a signal processing process, the detection capability of a sonar on the weak target is improved, the output signal-to-noise ratio of the matrix is improved, and the remote detection capability of the sonar is enhanced.
Owner:HAIYING ENTERPRISE GROUP
Classification of polarimetric SAR images based on SSae and FSALS‑SVM
ActiveCN104166859BEssence portrayalImprove learning abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionOriginal dataLeast squares support vector machine
The invention aims to provide a polarization SAR image classification method based on an SSAE and an FSALS-SVM. According to the polarization SAR image classification method, a multi-implicit-strata structure of the stacked sparse automatic encoder (SSAE) is used for obtaining depth features which have the capacity for describing original data more intrinsically and are more suitable for classification, the fast sparse approximation least square-support vector machine (FSALS-SVM) which can obtain sparse solutions is used for replacing the Softmax commonly used in traditional deep learning and being combined with the SSAE, the classification accuracy of polarization SAR images is improved, the defect that a traditional polarization SAR image classification method based on pixels is greatly affected by speckle noise is overcome to a certain degree, and therefore coherence of homogeneous areas in classification result images is ensured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com