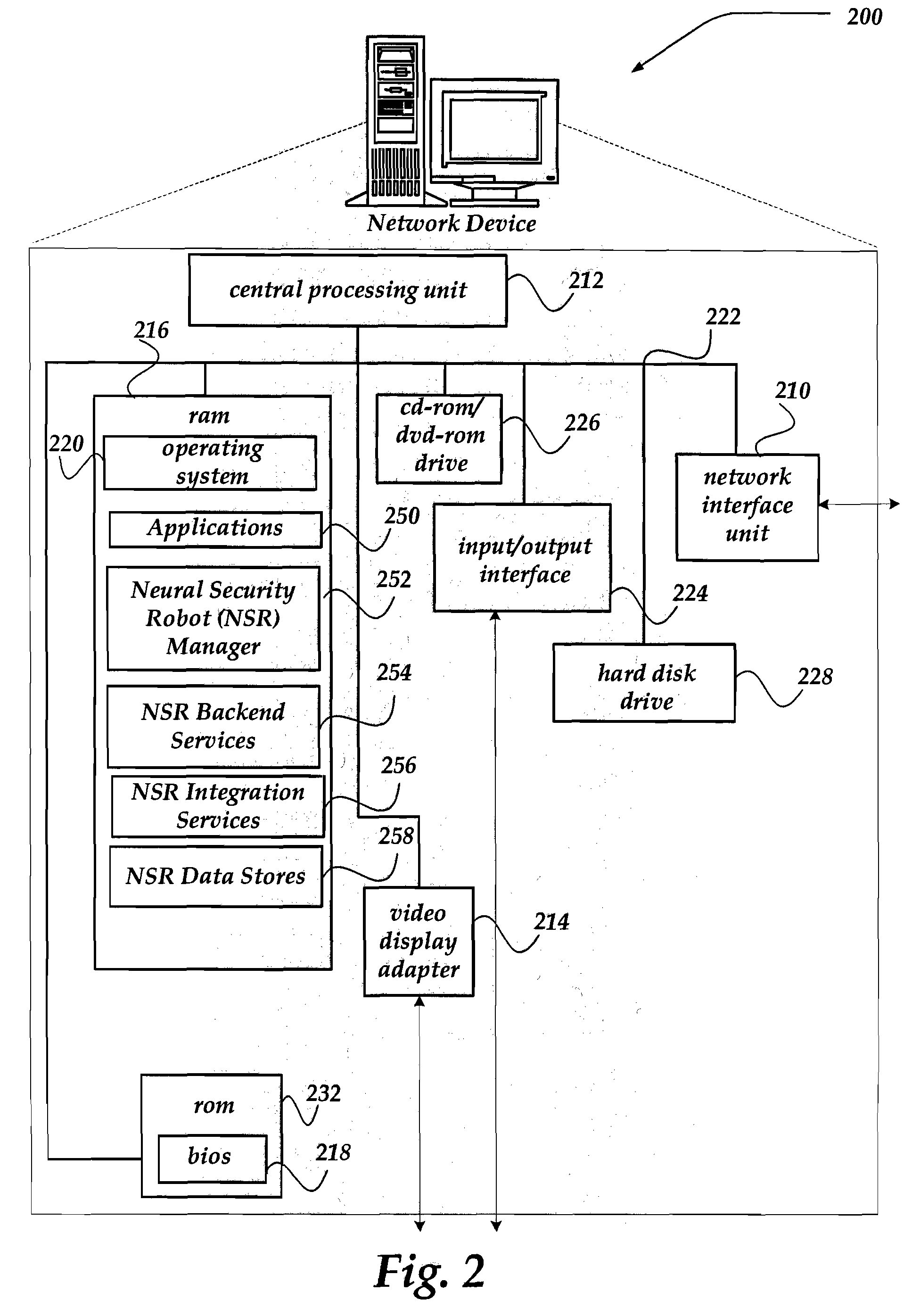
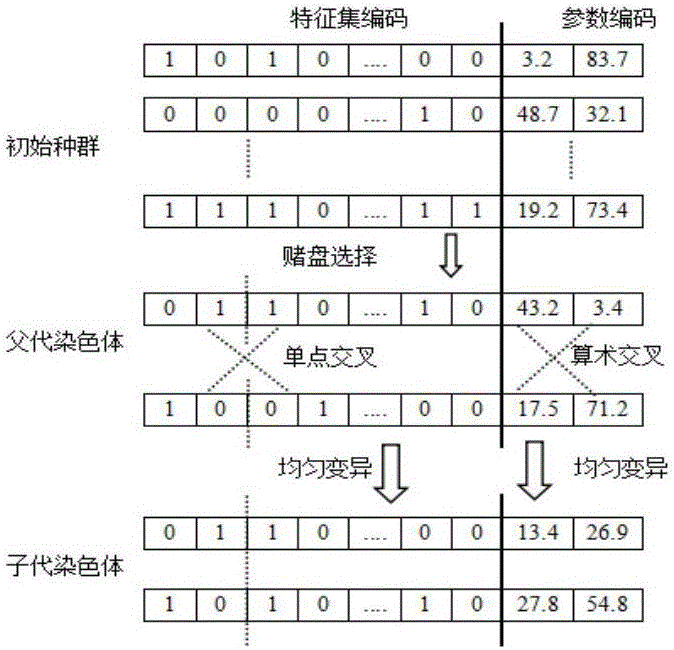
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
120 results about "Self training" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
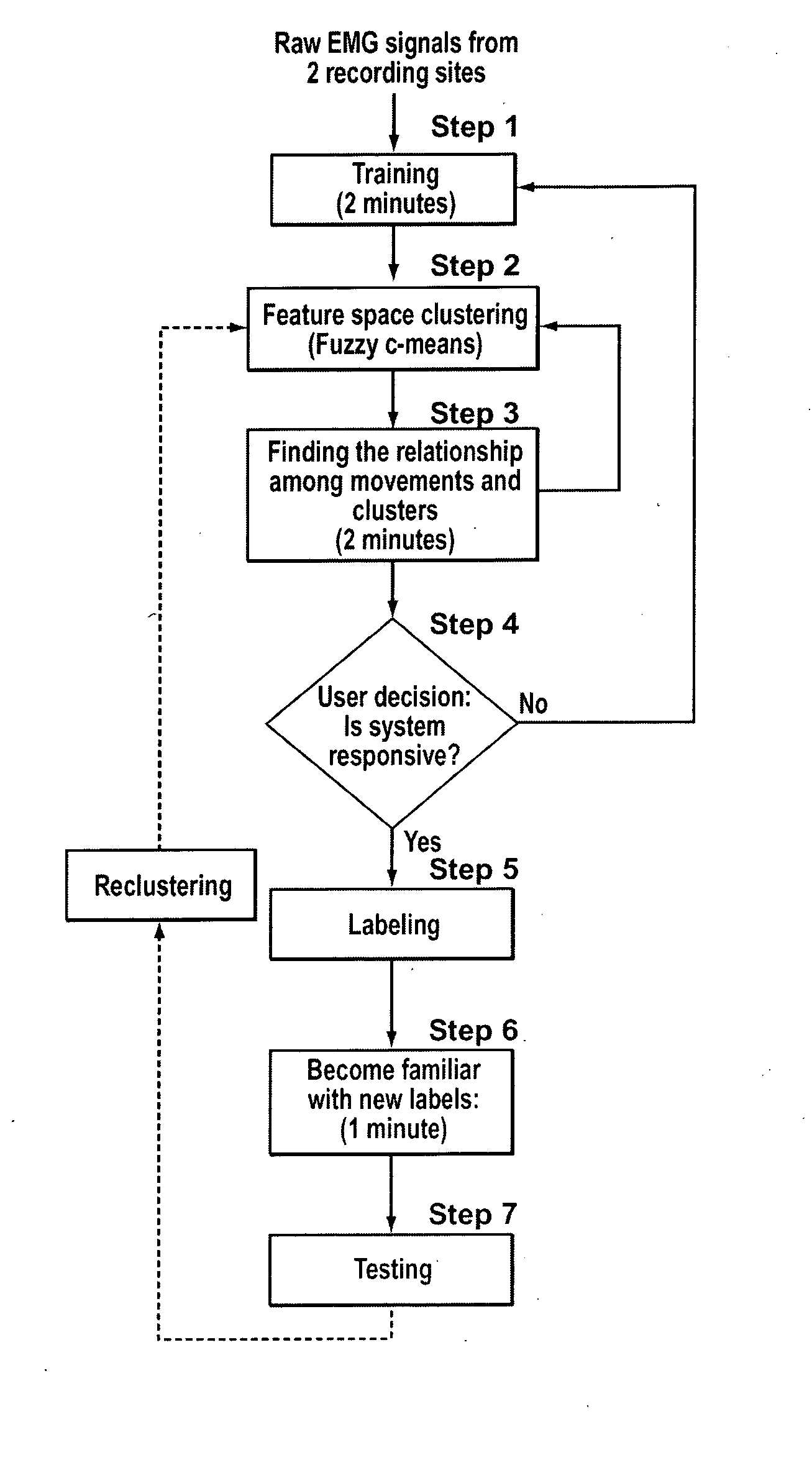
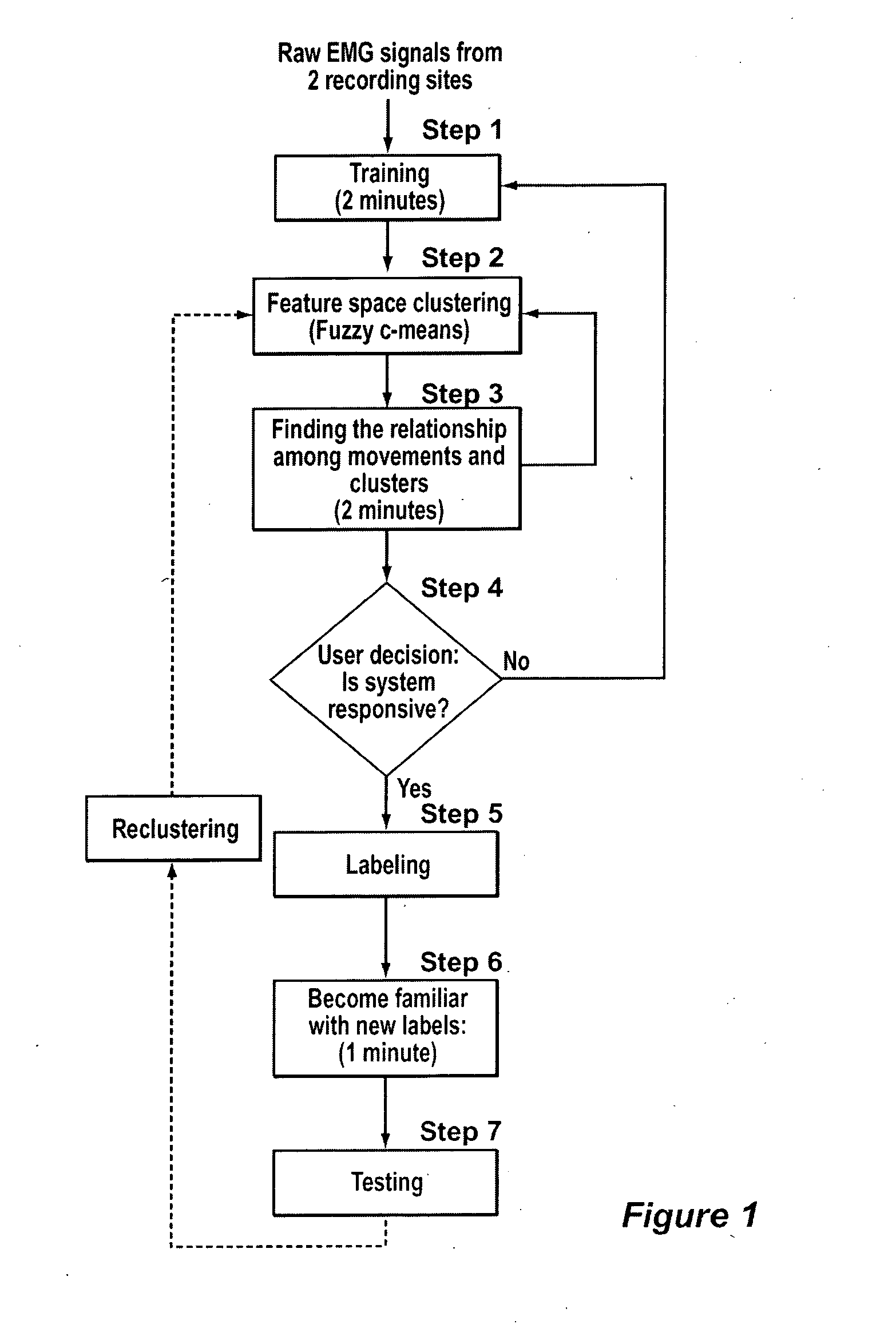
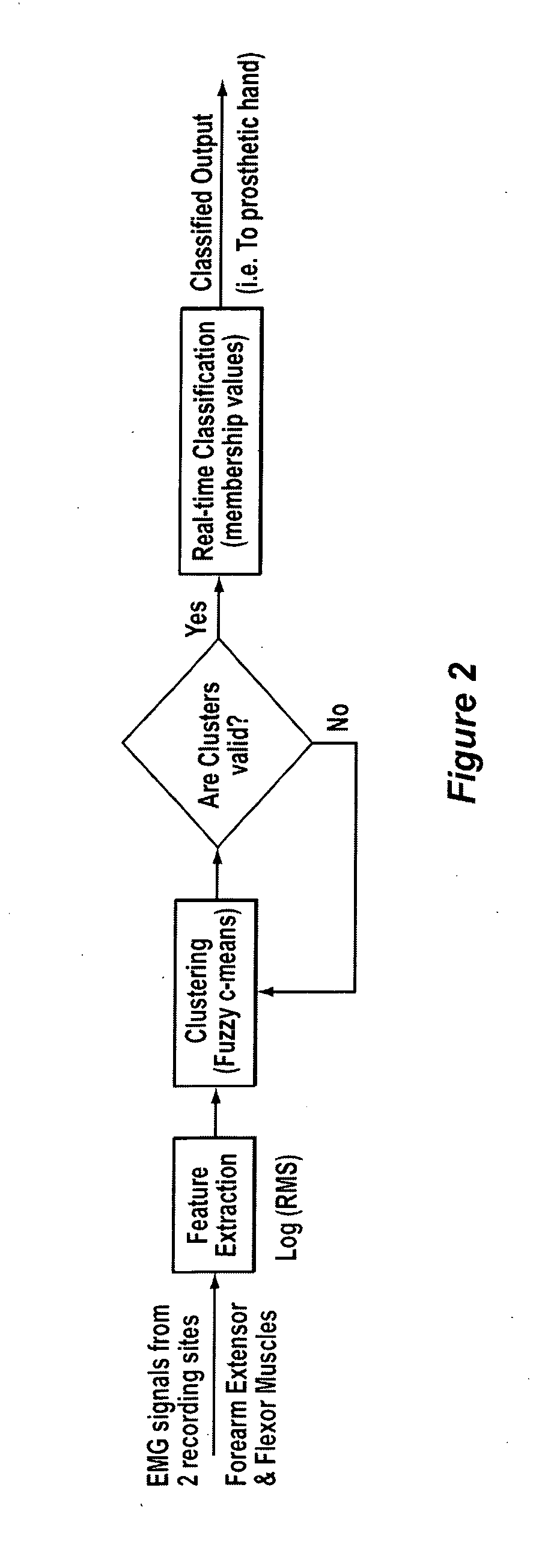
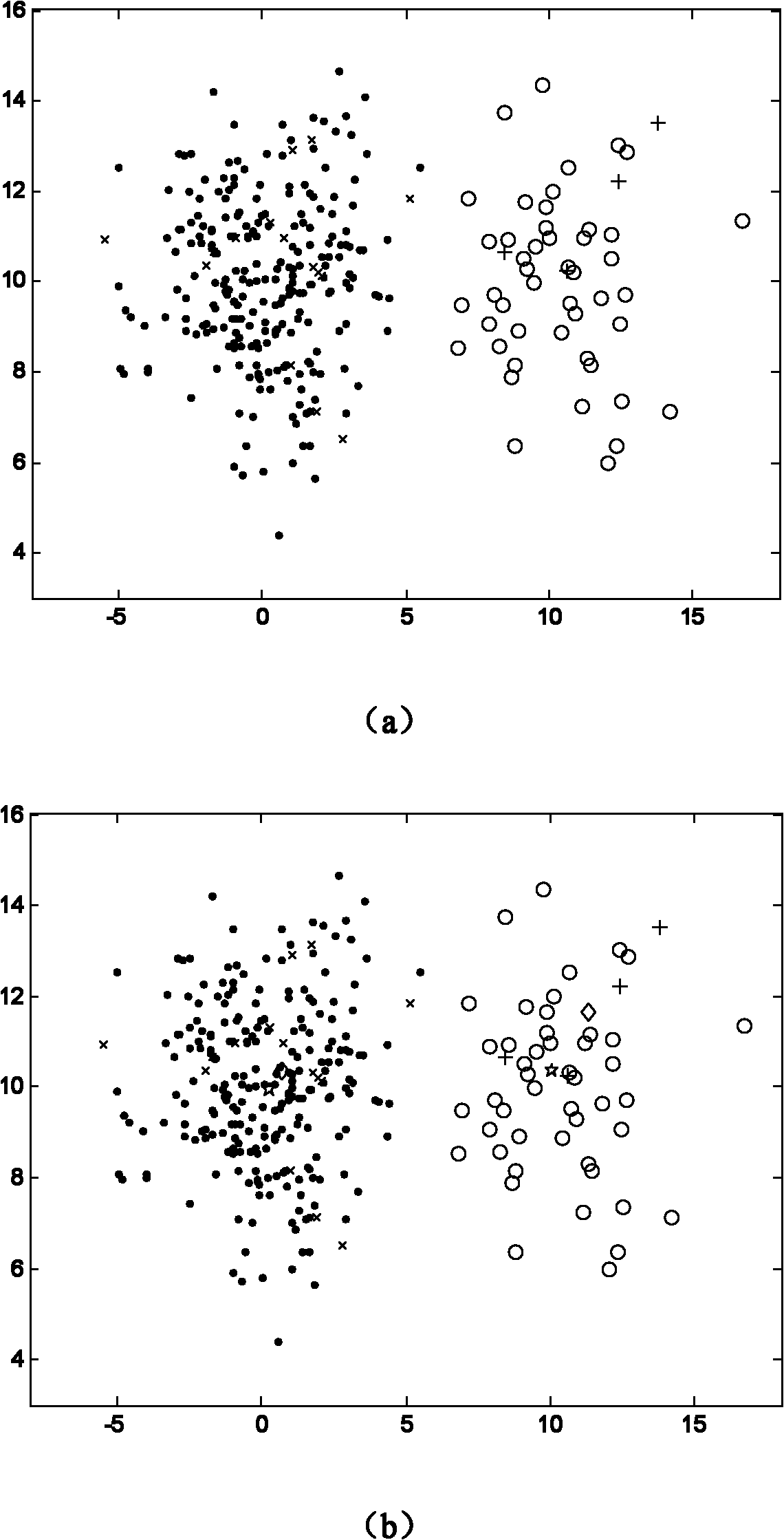
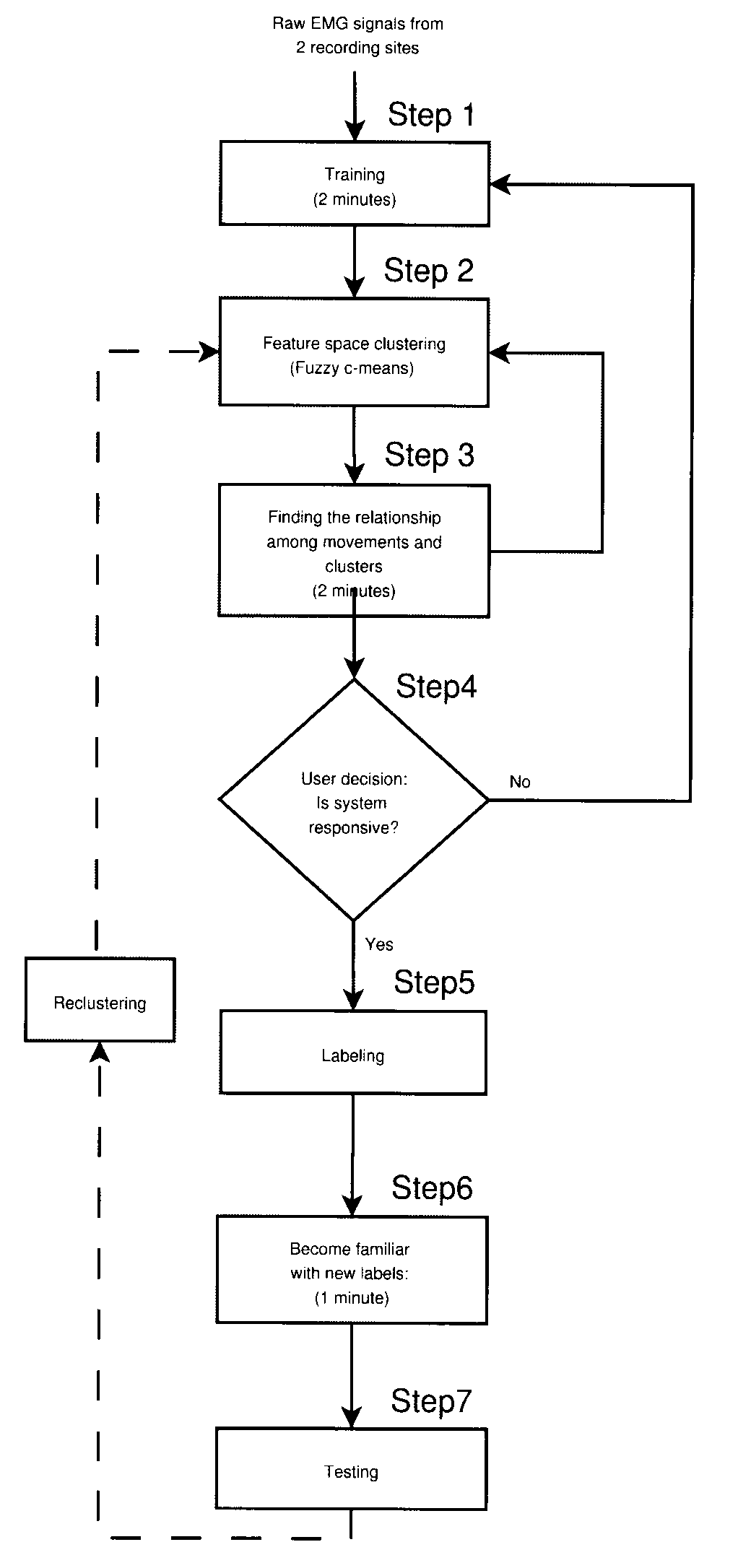
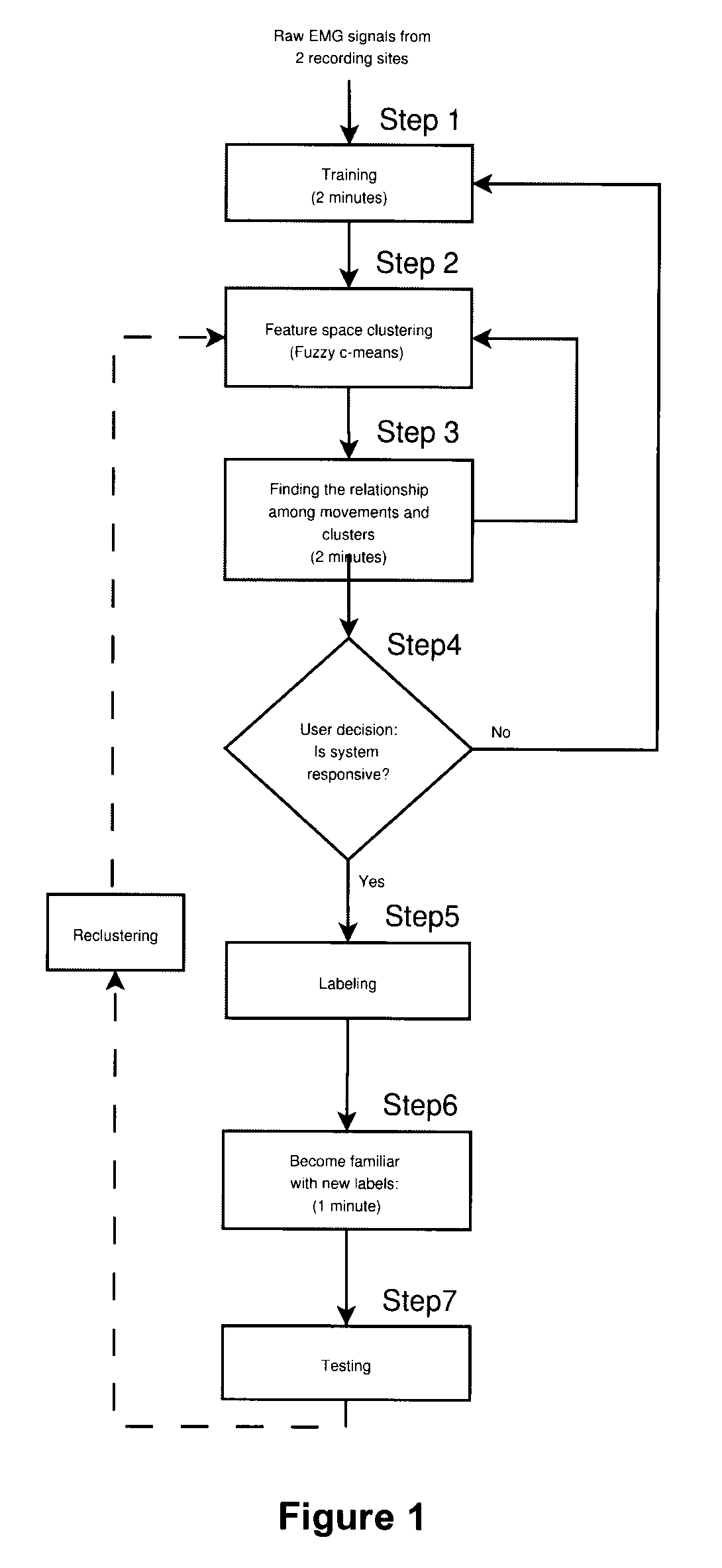
Method, system and apparatus for real-time classification of muscle signals from self-selected intentional movements
InactiveUS20080058668A1Improve abilitiesEasy to operateMedical data miningElectromyographyMuscle contractionSelf training
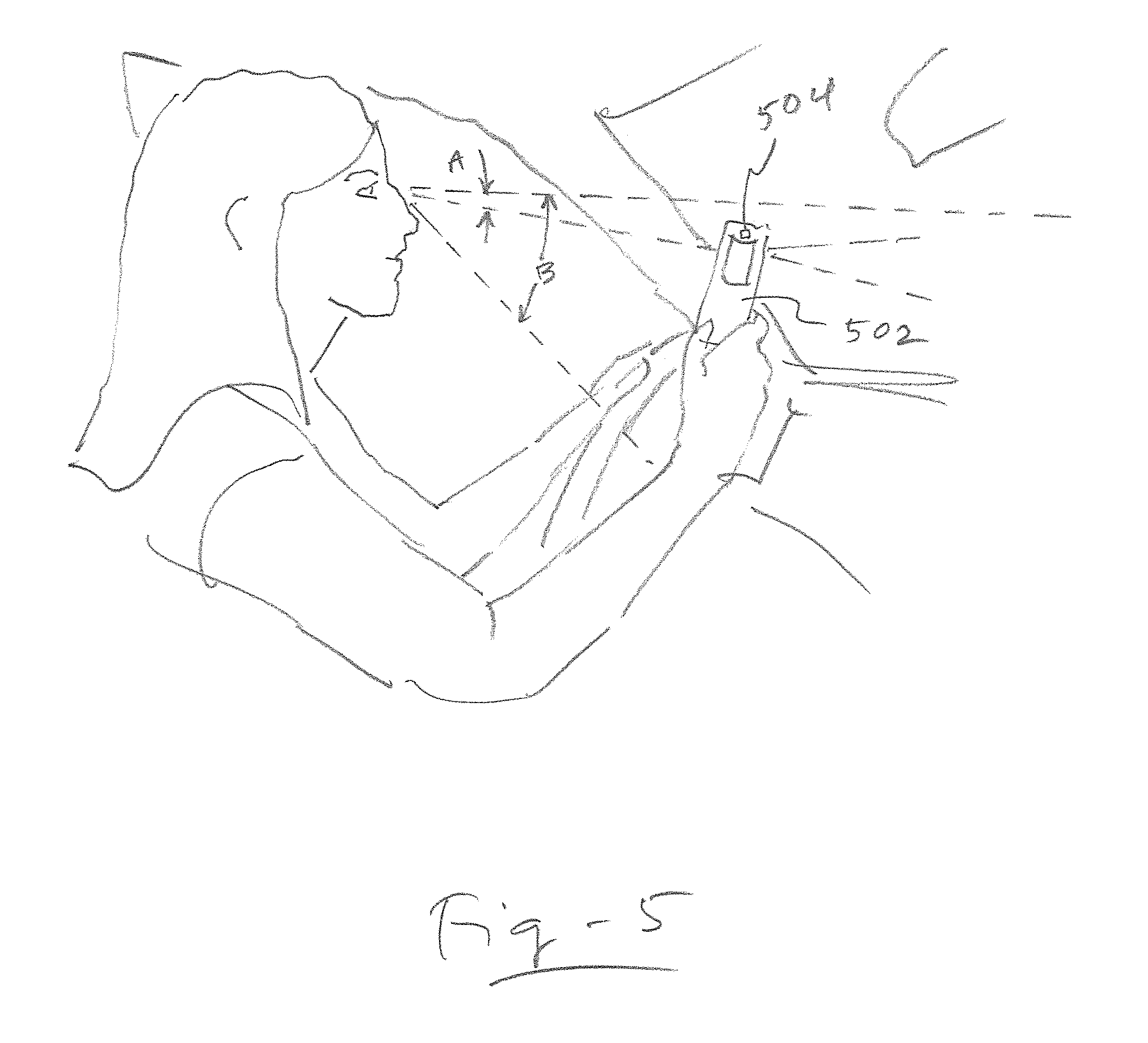
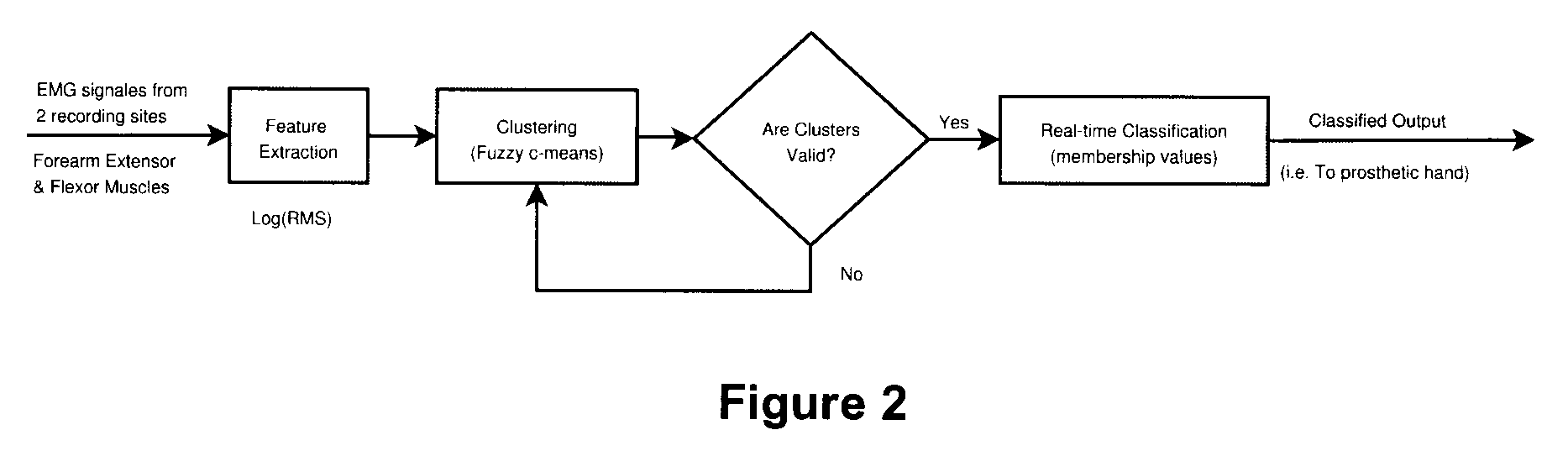
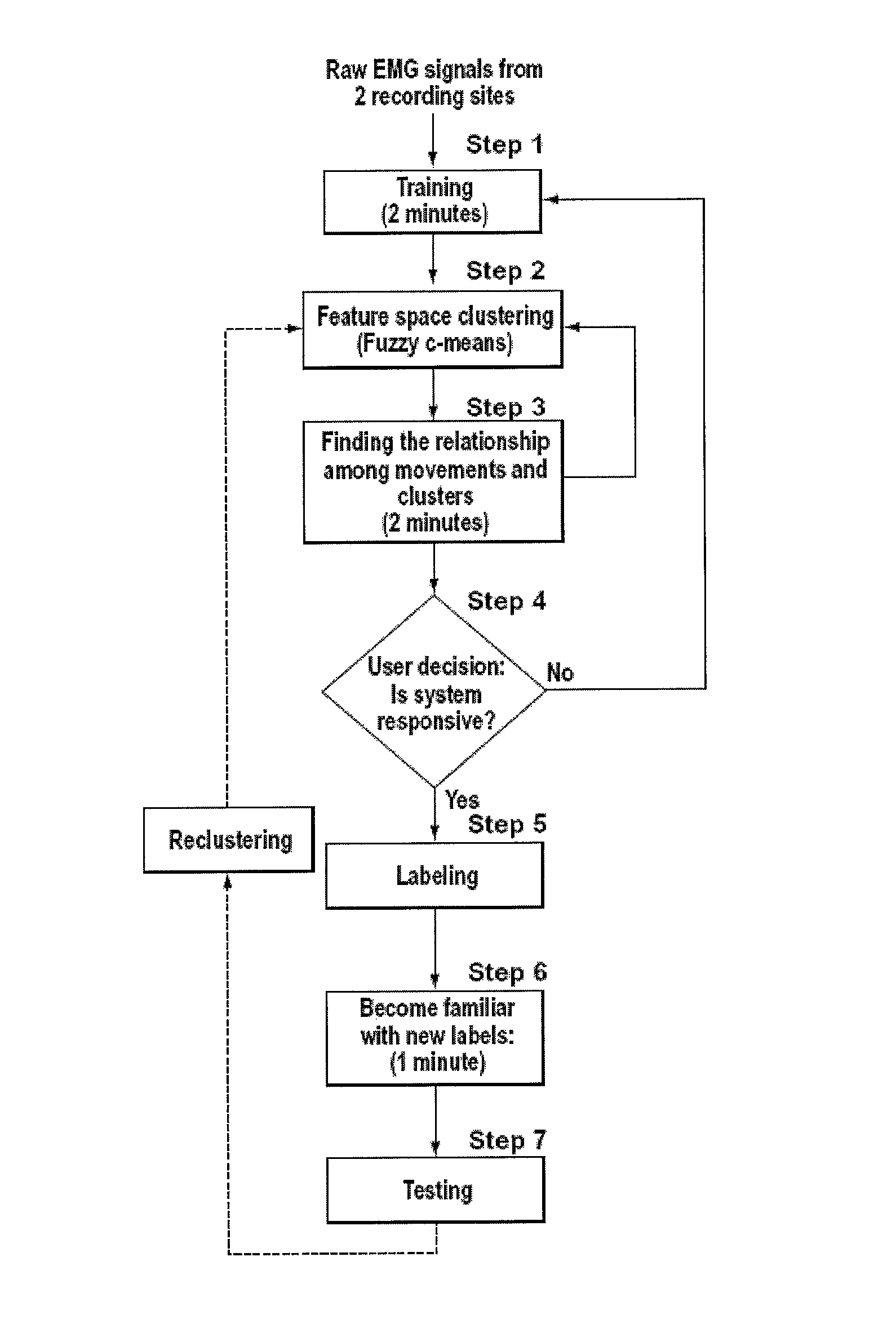
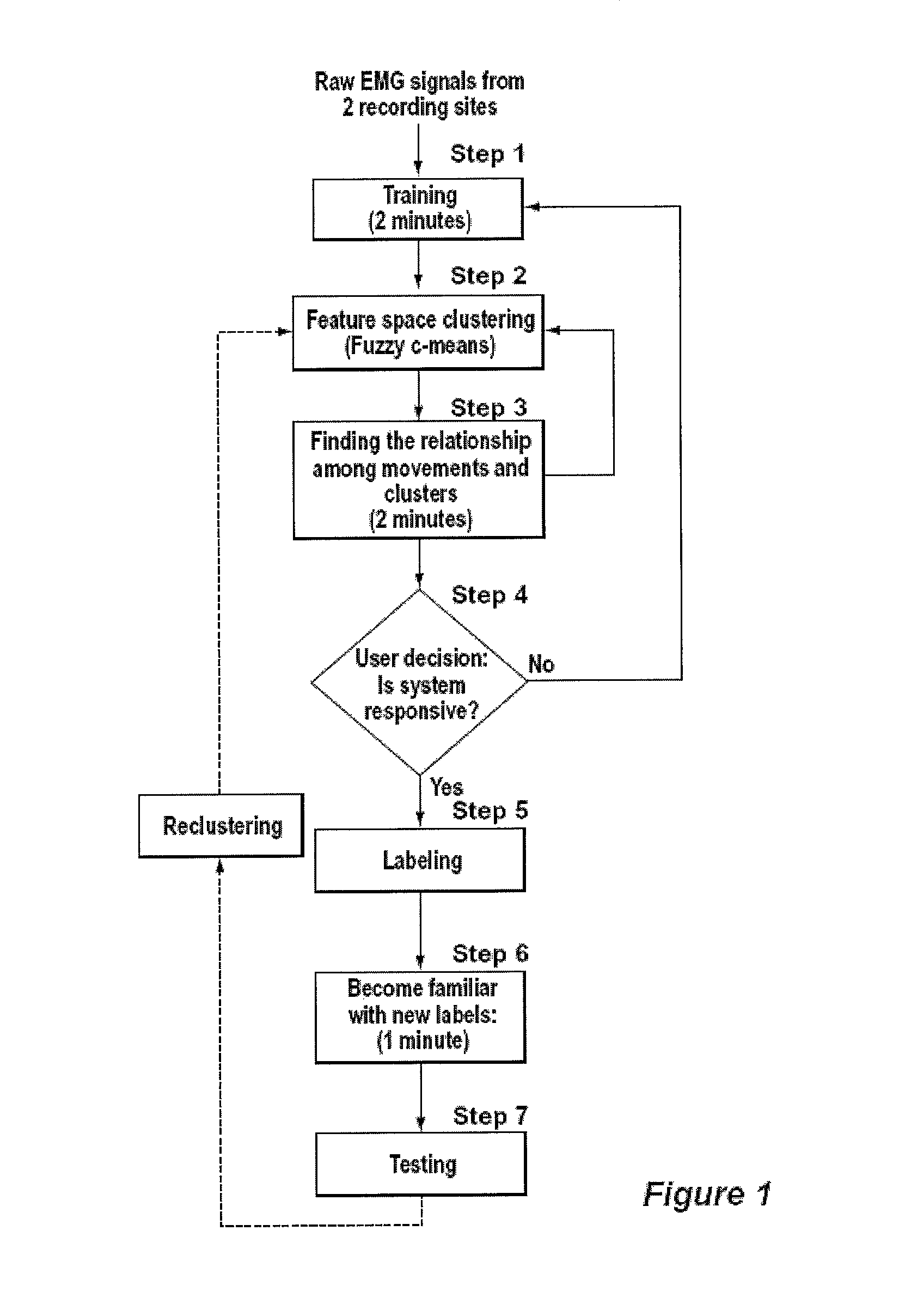
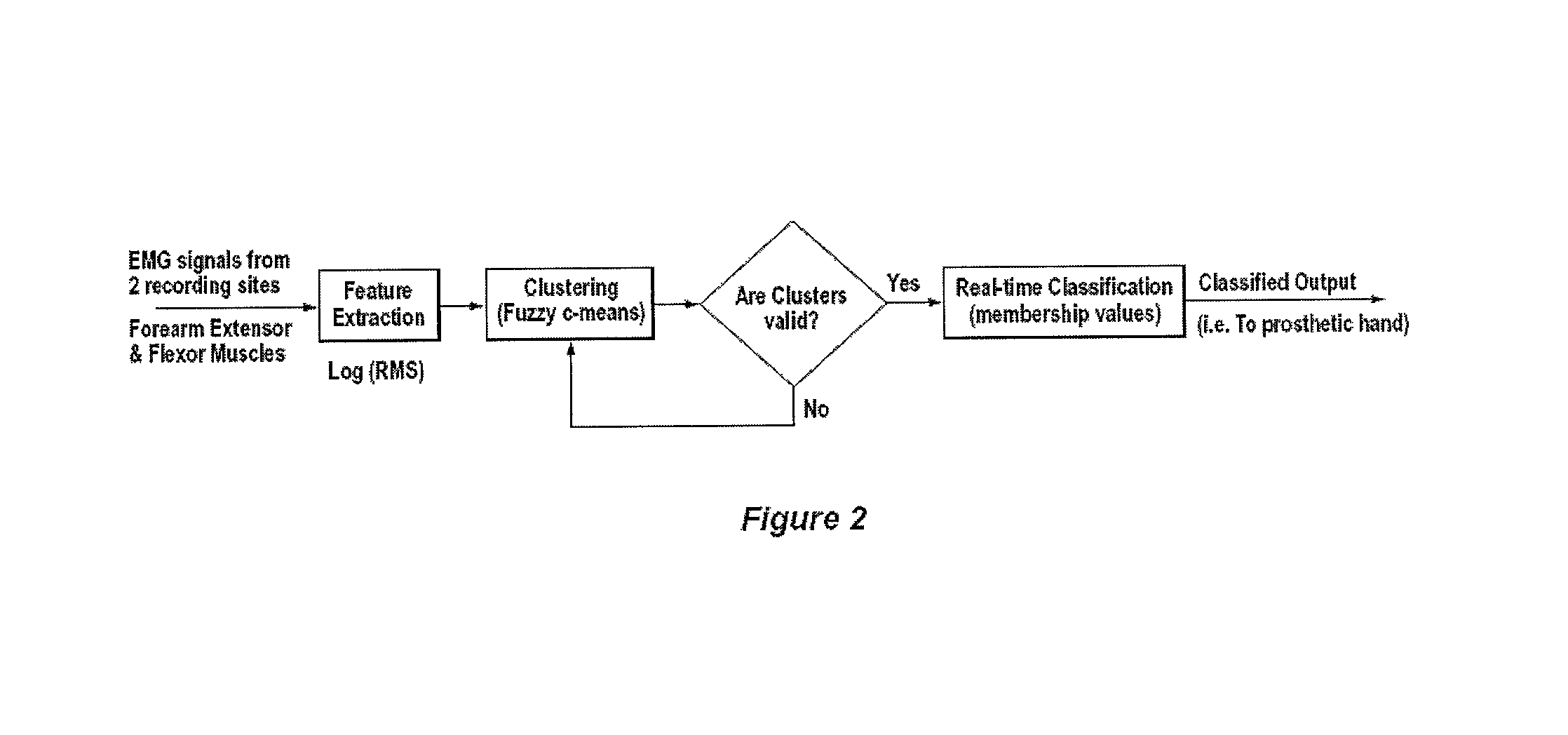
A new method, system and apparatus is provided that enables muscle signals that correspond to muscle contractions to be mapped to one or more functions of an electronic device such as a prosthetic device or gaming apparatus. Muscle signals are classified in real-time from self-selected intentional movements. A self-training protocol allows users to select and label their own muscle contractions, and is operable to automatically determine the discernible and repeatable muscle signals generated by the user. A visual display means is used to provide visual feedback to users illustrating the responsiveness of the system to muscle signals generated by the user.
Owner:HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL
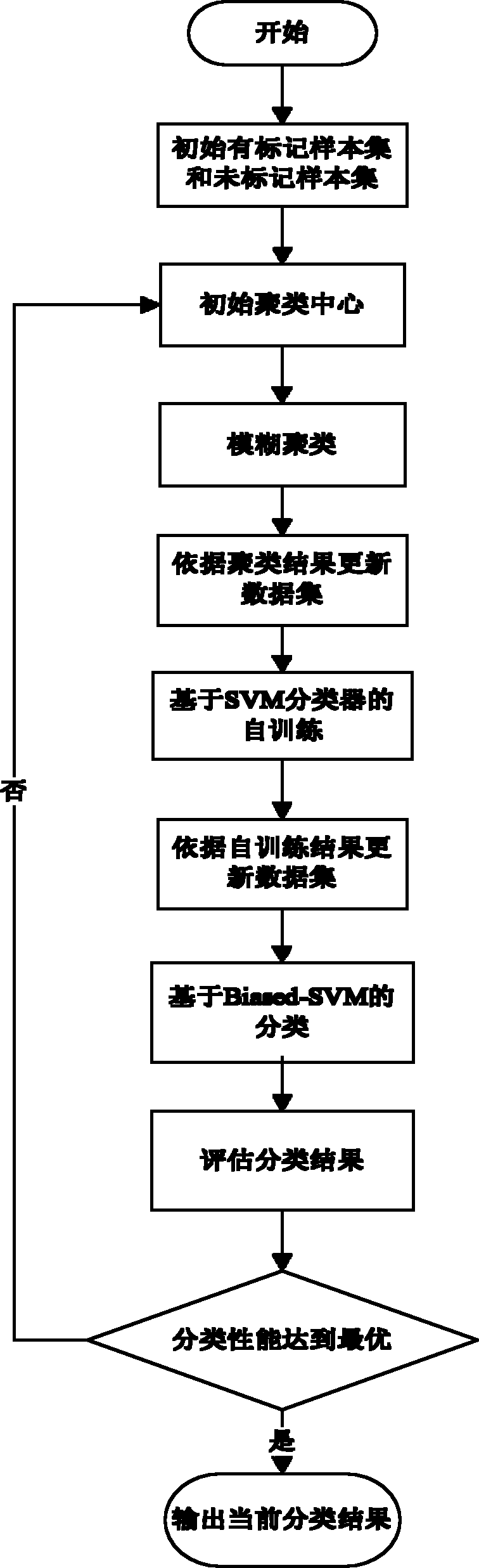
Semi-supervised classification method of unbalance data
InactiveCN101980202AImprove generalization abilityTedious and time-consuming labeling workSpecial data processing applicationsSelf trainingAlgorithm
The invention discloses a semi-supervised classification method of unbalance data, which is mainly used for solving the problem of low classification precision of a minority of data which have fewer marked samples and high degree of unbalance in the prior art. The method is implemented by the following steps: (1) initializing a marked sample set and an unmarked sample set; (2) initializing a cluster center; (3) implementing fuzzy clustering; (4) updating the marked sample set and unmarked sample set according to the result of the clustering; (5) performing the self-training based on a support vector machine (SVM) classifier; (6) updating the marked sample set and unmarked sample set according to the result of the self-training; (7) performing the classification of support vector machines Biased-SVM based on penalty parameters; and (8) estimating a classification result and outputting the result. For unbalance data which have fewer marked samples, the method improves the classification precision of a minority of data. And the method can be used for classifying and identifying unbalance data having few training samples.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method, system and apparatus for real-time classification of muscle signals from self -selected intentional movements
InactiveUS20100293115A1User training can be minimizedImprove performanceMedical data miningElectromyographyMuscle contractionSelf training
A new method, system and apparatus is provided that enables muscle signals that correspond to muscle contractions to be mapped to one or more functions of an electronic device such as a prosthetic device or gaming apparatus. Muscle signals are classified in real-time from self-selected intentional movements. A self-training protocol allows users to select and label their own muscle contractions, and is operable to automatically determine the discernible and repeatable muscle signals generated by the user. A visual display means is used to provide visual feedback to users illustrating the responsiveness of the system to muscle signals generated by the user.
Owner:HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL
Method, system and apparatus for real-time classification of muscle signals from self-selected intentional movements
InactiveUS8437844B2User training can be minimizedSimple designMedical data miningElectromyographyMuscle contractionSelf training
A new method, system and apparatus is provided that enables muscle signals that correspond to muscle contractions to be mapped to one or more functions of an electronic device such as a prosthetic device or gaming apparatus. Muscle signals are classified in real-time from self-selected intentional movements. A self-training protocol allows users to select and label their own muscle contractions, and is operable to automatically determine the discernible and repeatable muscle signals generated by the user. A visual display means is used to provide visual feedback to users illustrating the responsiveness of the system to muscle signals generated by the user.
Owner:HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL
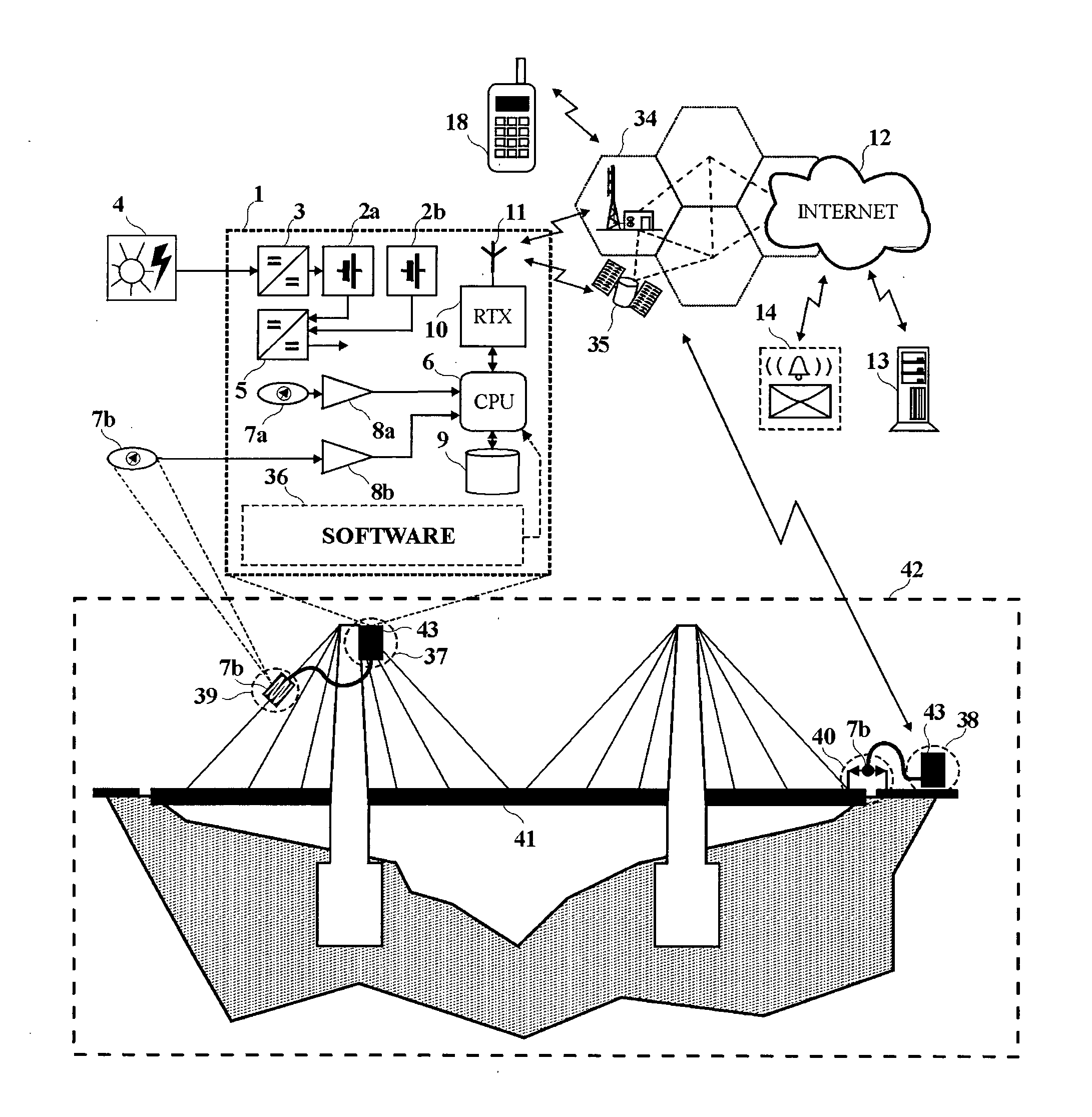
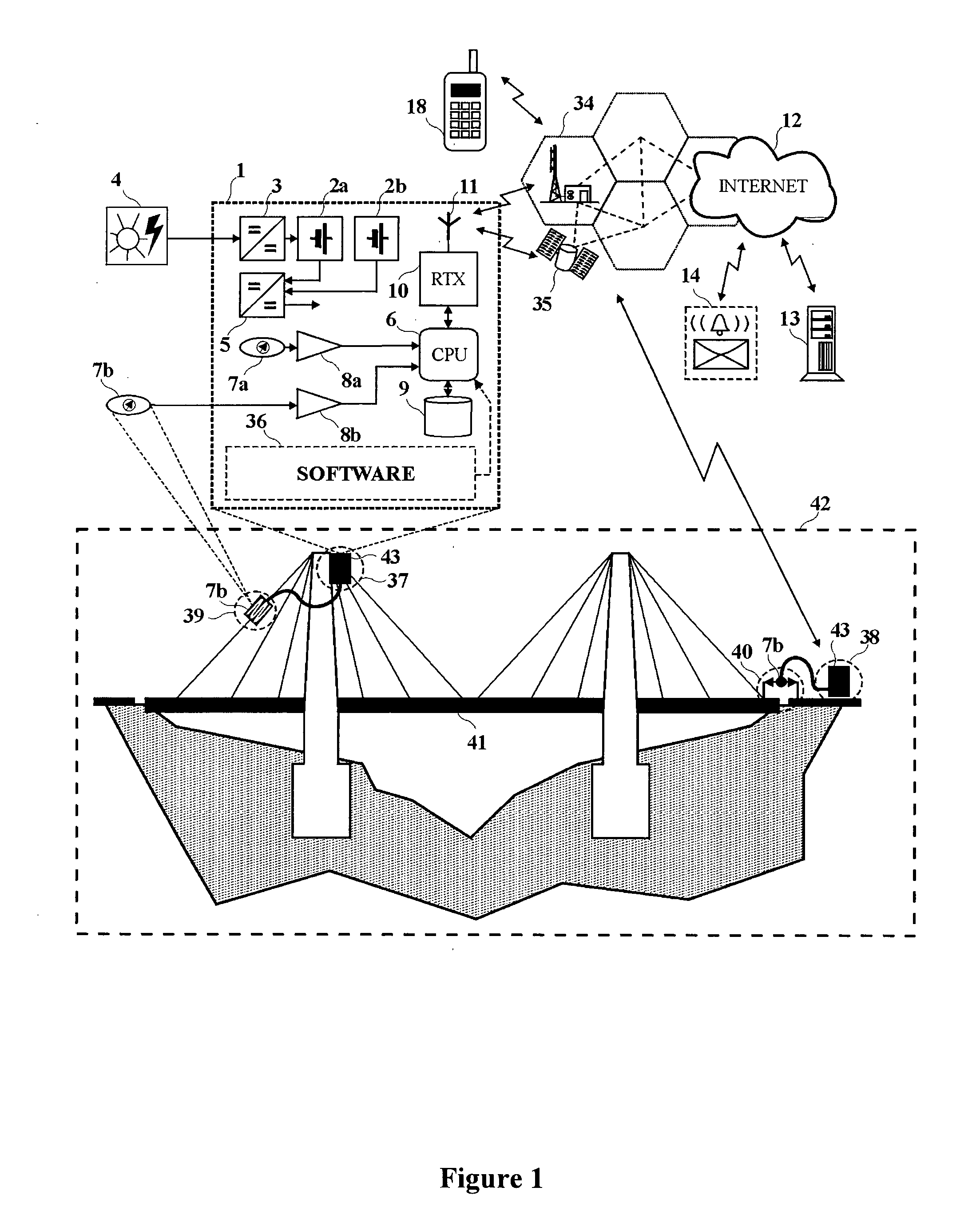
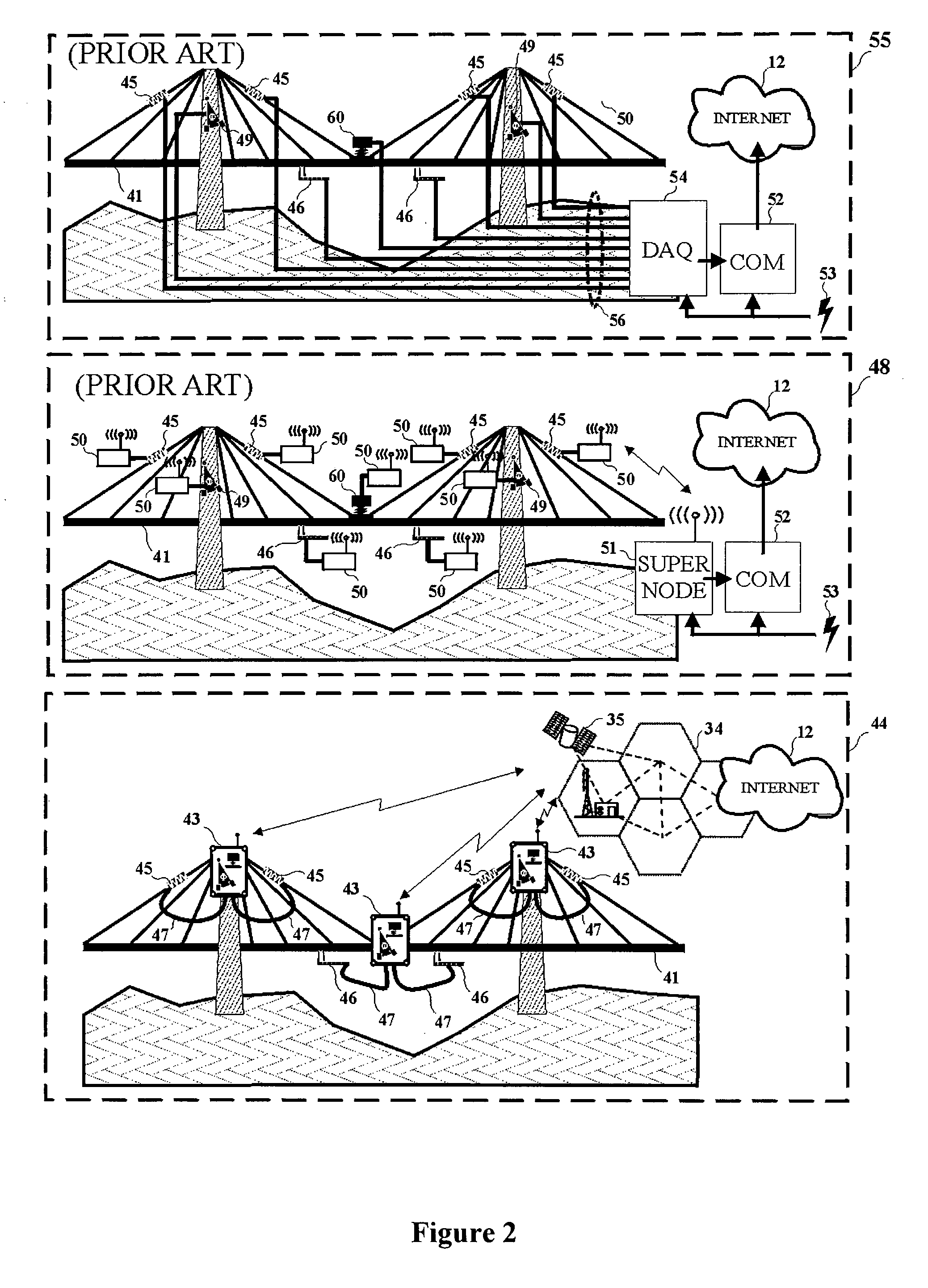
Device for monitoring the health status of structures
InactiveUS20100238027A1Fast and safe and easy to testHigh sensitivityPlug gaugesMobile data collection deviceData compressionTelecommunications network
Structural health monitoring device with improved reliability and performances that is applied in selected locations on a structure. The structural health monitoring device includes a data acquisition, process and storage media, a direct and independent wireless connection system to a standard and globally interconnected telecom network, is uninterruptedly powered by a power management system featuring at least two battery power sources. The structural health monitoring device further includes sensors specifically intended to remain permanently active and “asynchronously” trigger data acquisition sessions in occurrence of timely unpredictable phenomena having structural relevance and is moreover comprising data processing media for data compression and for automatic detection of possible structural anomalies using a self-training neural data processing algorithm.
Owner:BASTIANINI FILIPPO
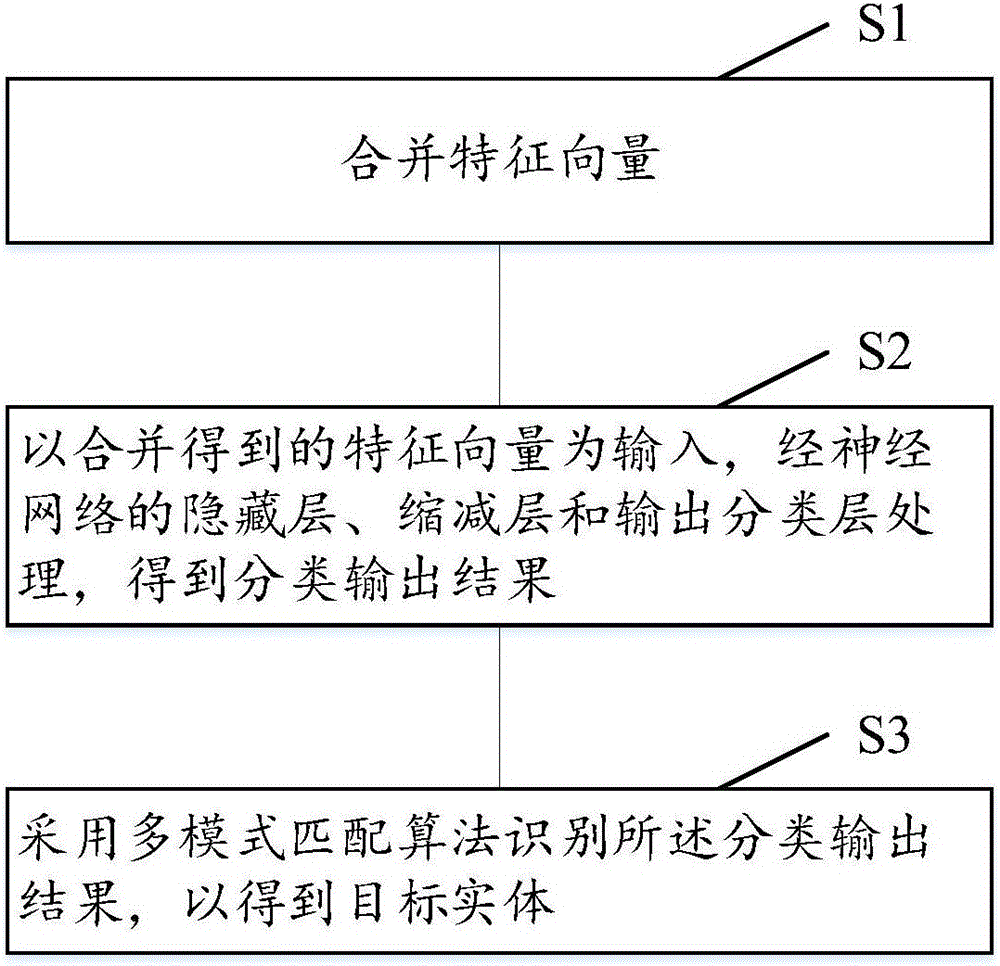
Method and system for identifying named entity
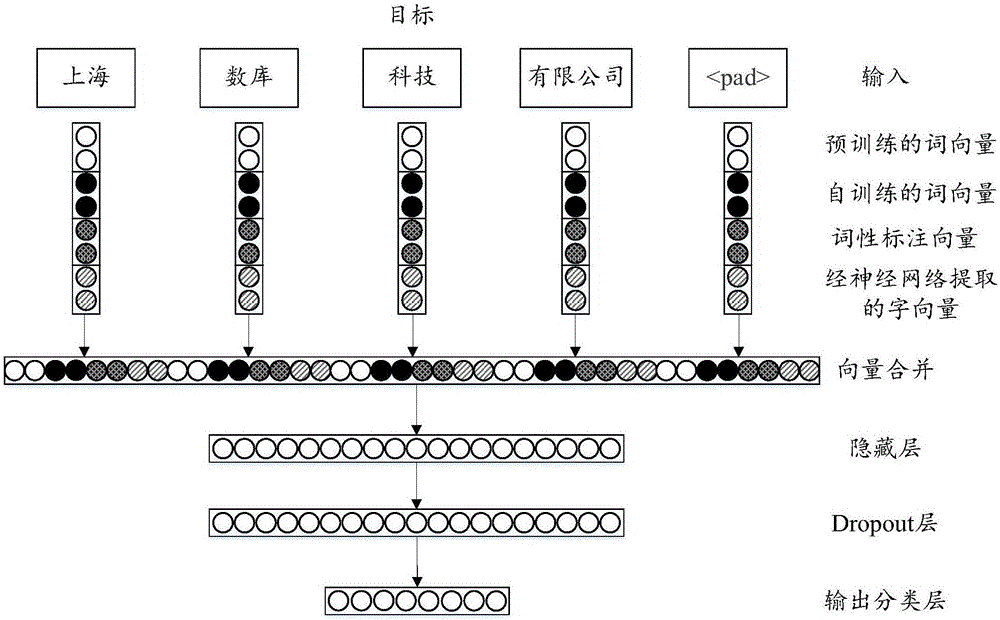
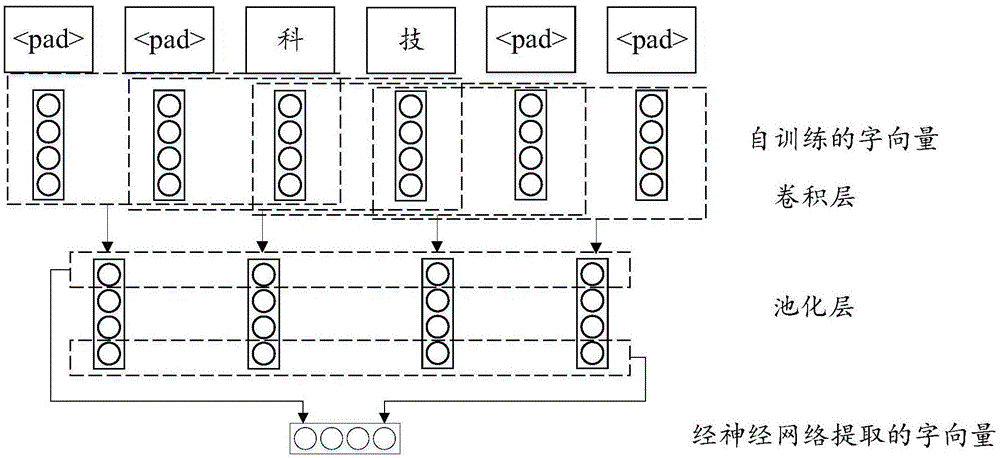
InactiveCN106557462AMake full use of "prior knowledgeSolve predictive powerBiological neural network modelsNatural language data processingHidden layerFeature vector
The technical scheme of the invention discloses a method and a system for identifying a named entity. The method for identifying the named entity comprises the following steps: merging feature vectors, wherein the feature vectors comprise pre-trained word vectors, self-training word vectors and part-of-speech tagging vectors, and a neural network is a convolutional neural network or a deep belief neural network; using the merged and obtained feature vectors as input, and obtaining a classified output result through treatment of a hidden layer, a reducing layer and an output classification layer of the neural network; and adopting a multi-mode matching algorithm to identify the classified output result so as to obtain the target entity. Through the technical scheme, the feature vectors are merged as input features of the neural network, so that the method can be well applied to specific classification scenes through treatment of the neural network and multi-mode matching.
Owner:数库(上海)科技有限公司
Musical Performance Self-Training Apparatus
Owner:KAWAI MUSICAL INSTR MFG CO
Semi-supervised anomaly intrusion detection method
InactiveCN101980480AReduce troubleImprove detection rateData switching networksSelf trainingFuzzy clustering
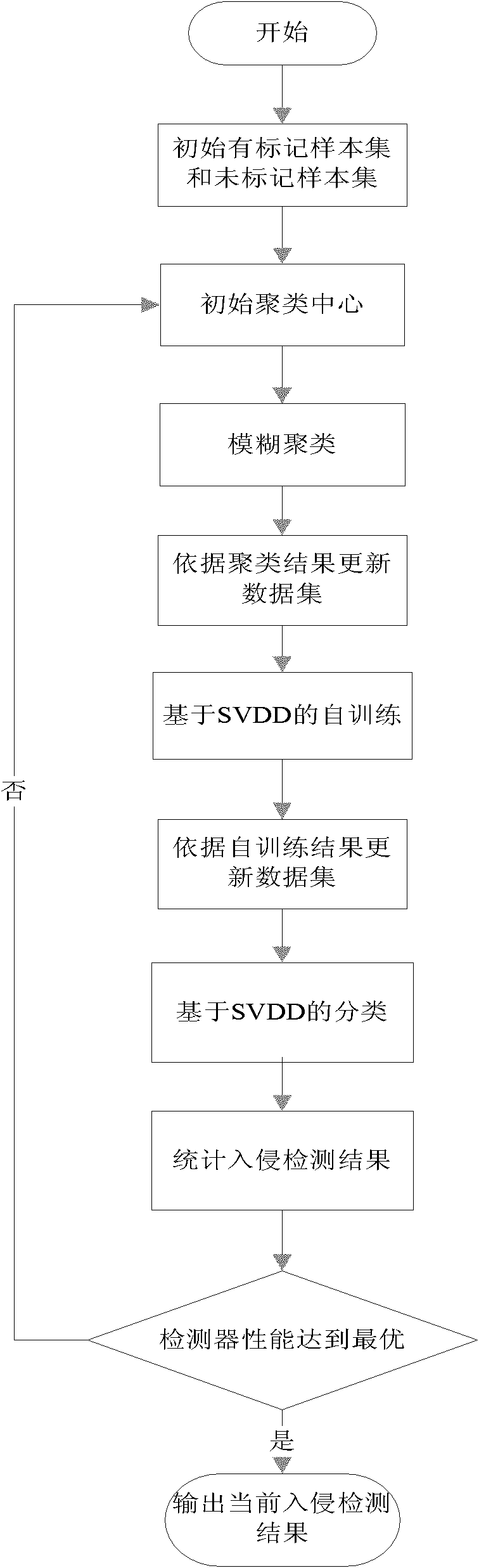
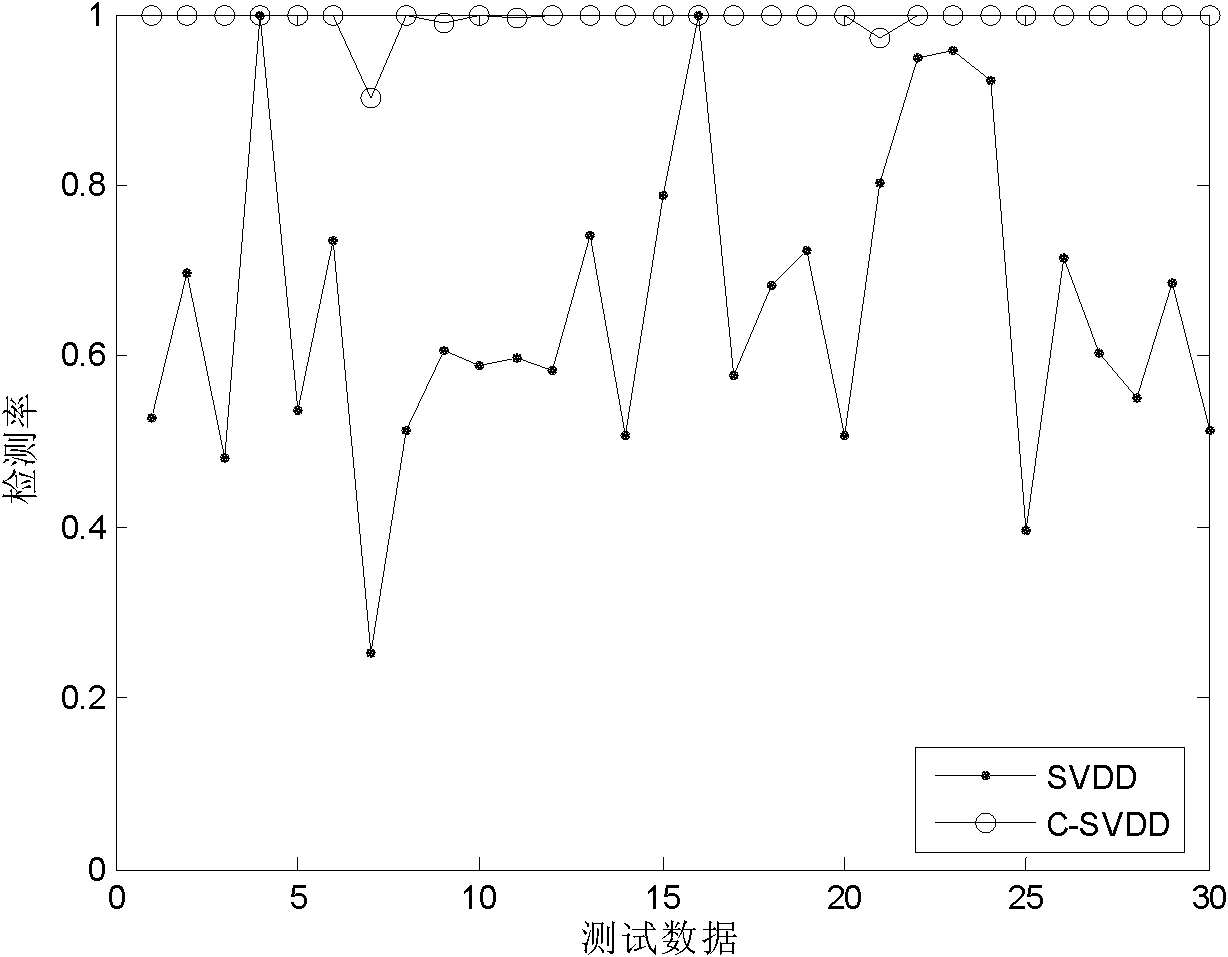
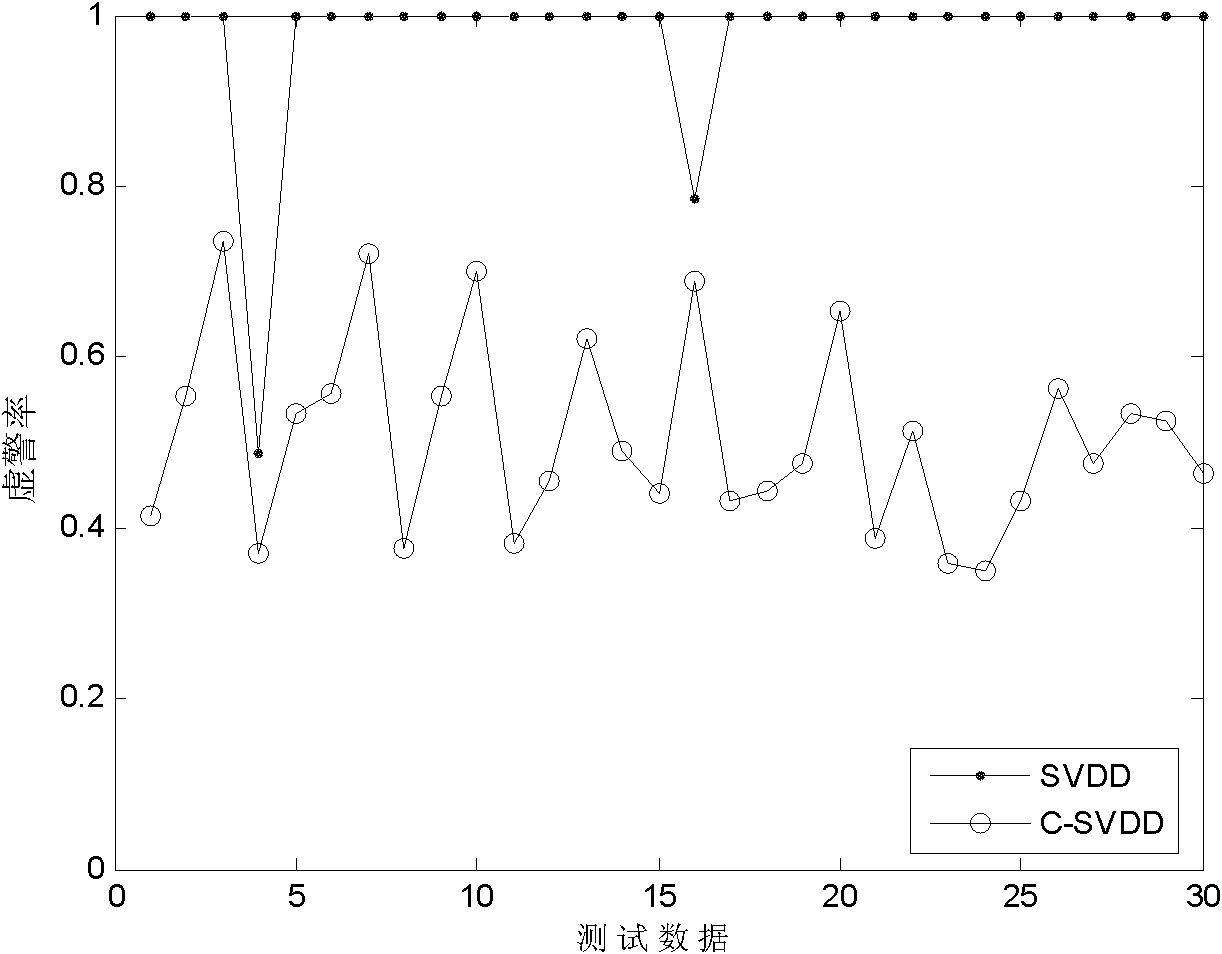
The invention discloses a fuzzy clustering and support vector domain description-based (SVDD) semi-supervised anomaly intrusion detection method, which is mainly used for solving the problems of low intrusion detection data detection rate and high false alarm rate in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) initializing a labeled sample set and an unlabeled sample set; (2) initializing a clustering center; (3) carrying out fuzzy C-mean clustering; (4) updating the labeled sample set and the unlabeled sample set according to a clustering result; (5) carrying out SVDD-based self-training; (6) updating the labeled sample set and the unlabeled sample set according to a self-training result; (7) carrying out SVVD-based classification; and (8) evaluating and outputting anintrusion detection result. The method improves the detection rate and reduces the false alarm rate at the same time, and can be used for a real-time intrusion detection system in which training dataonly contains less normal data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Pixel-level based micro-feature extraction
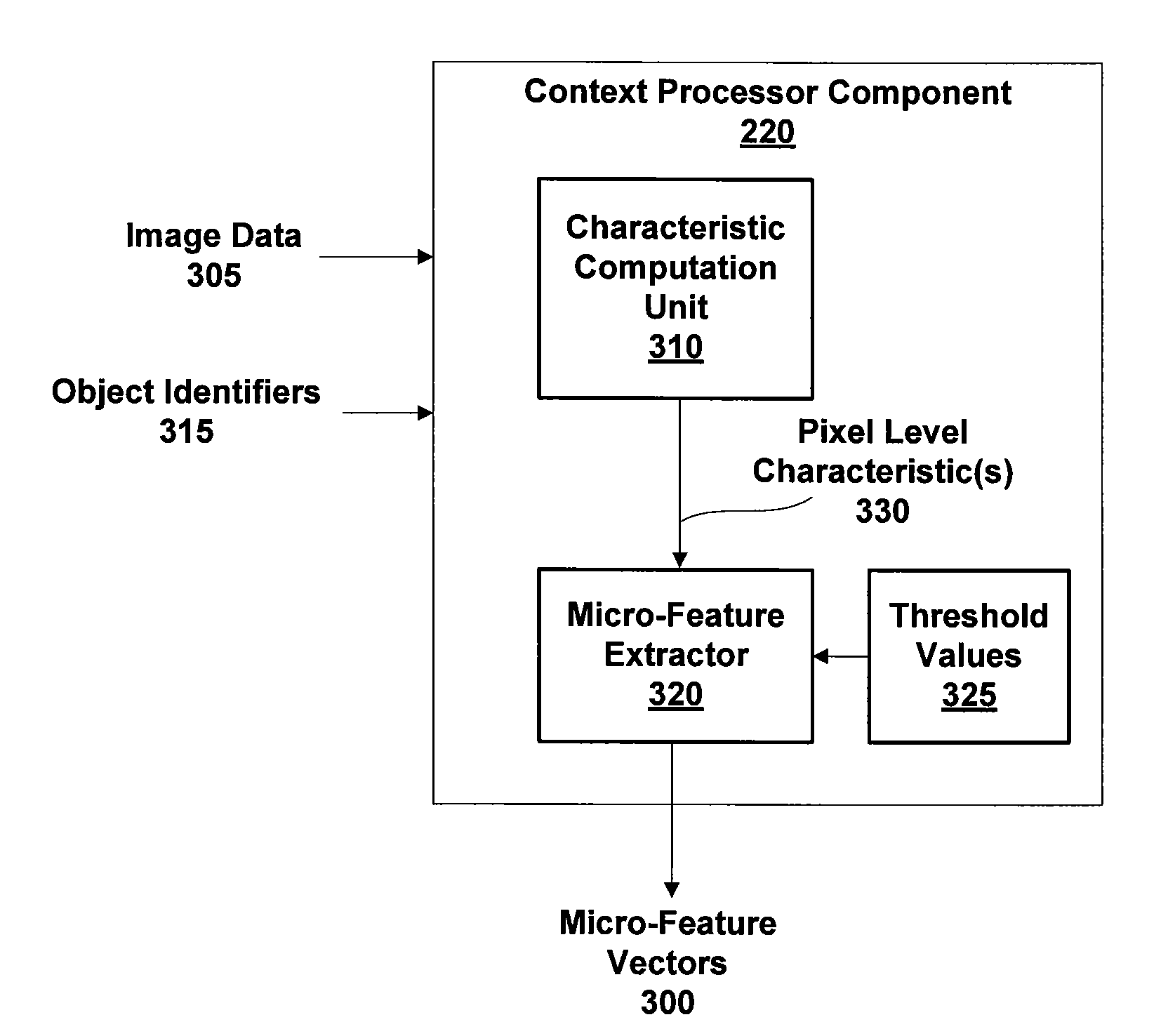
ActiveUS20110044536A1Character and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsFeature vectorTraining phase
Techniques are disclosed for extracting micro-features at a pixel-level based on characteristics of one or more images. Importantly, the extraction is unsupervised, i.e., performed independent of any training data that defines particular objects, allowing a behavior-recognition system to forgo a training phase and for object classification to proceed without being constrained by specific object definitions. A micro-feature extractor that does not require training data is adaptive and self-trains while performing the extraction. The extracted micro-features are represented as a micro-feature vector that may be input to a micro-classifier which groups objects into object type clusters based on the micro-feature vectors.
Owner:INTELLECTIVE AI INC
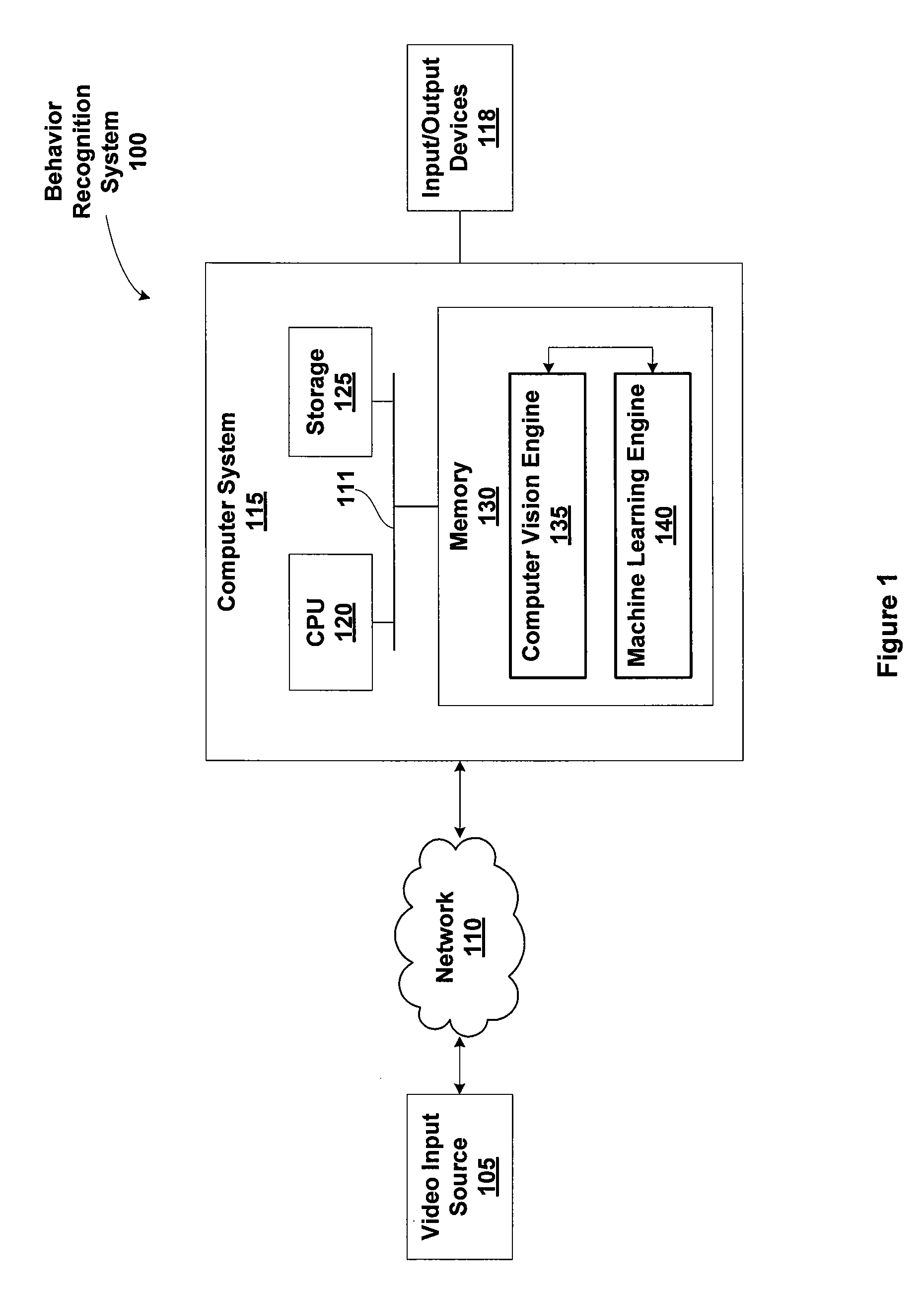
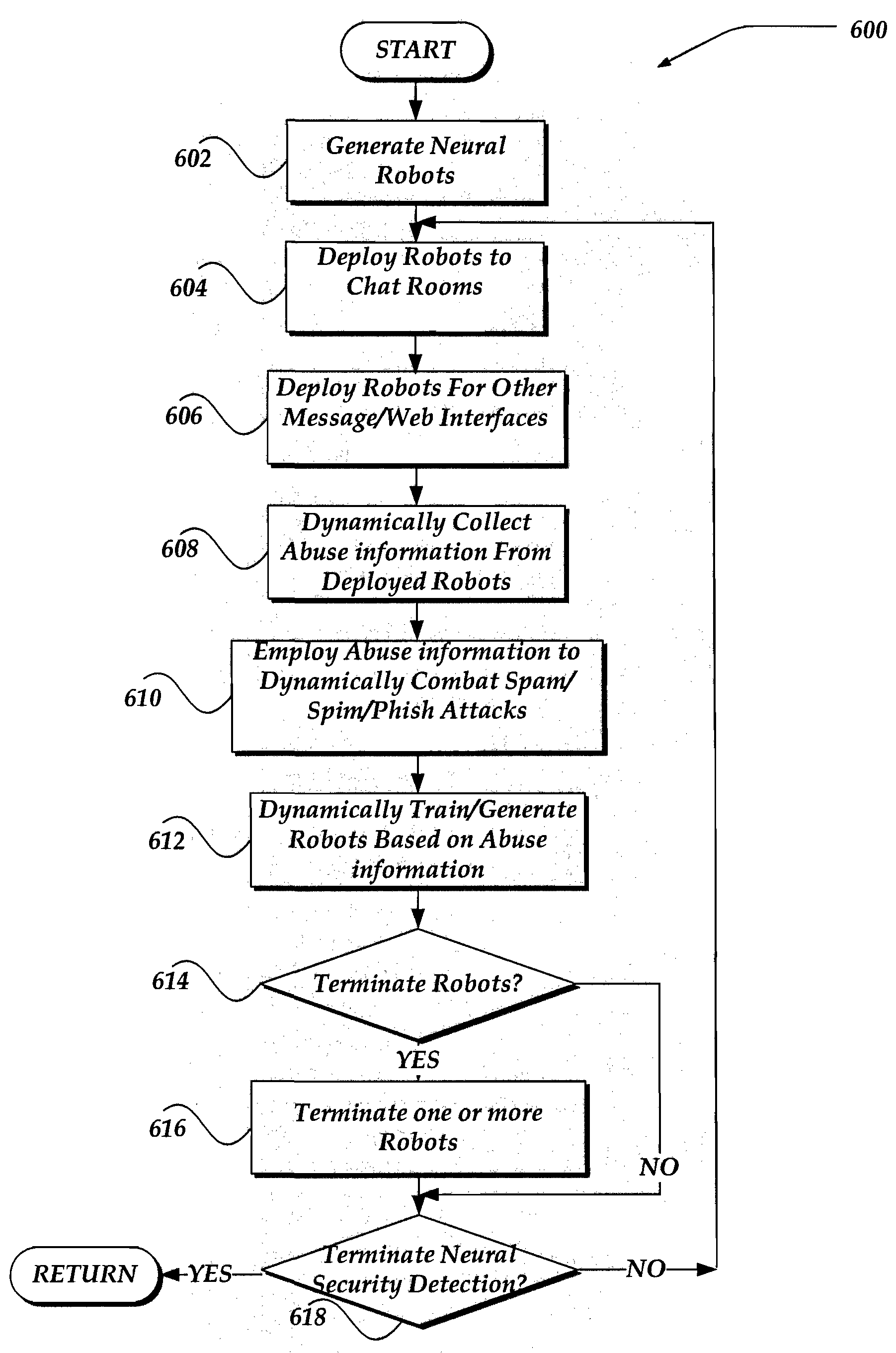
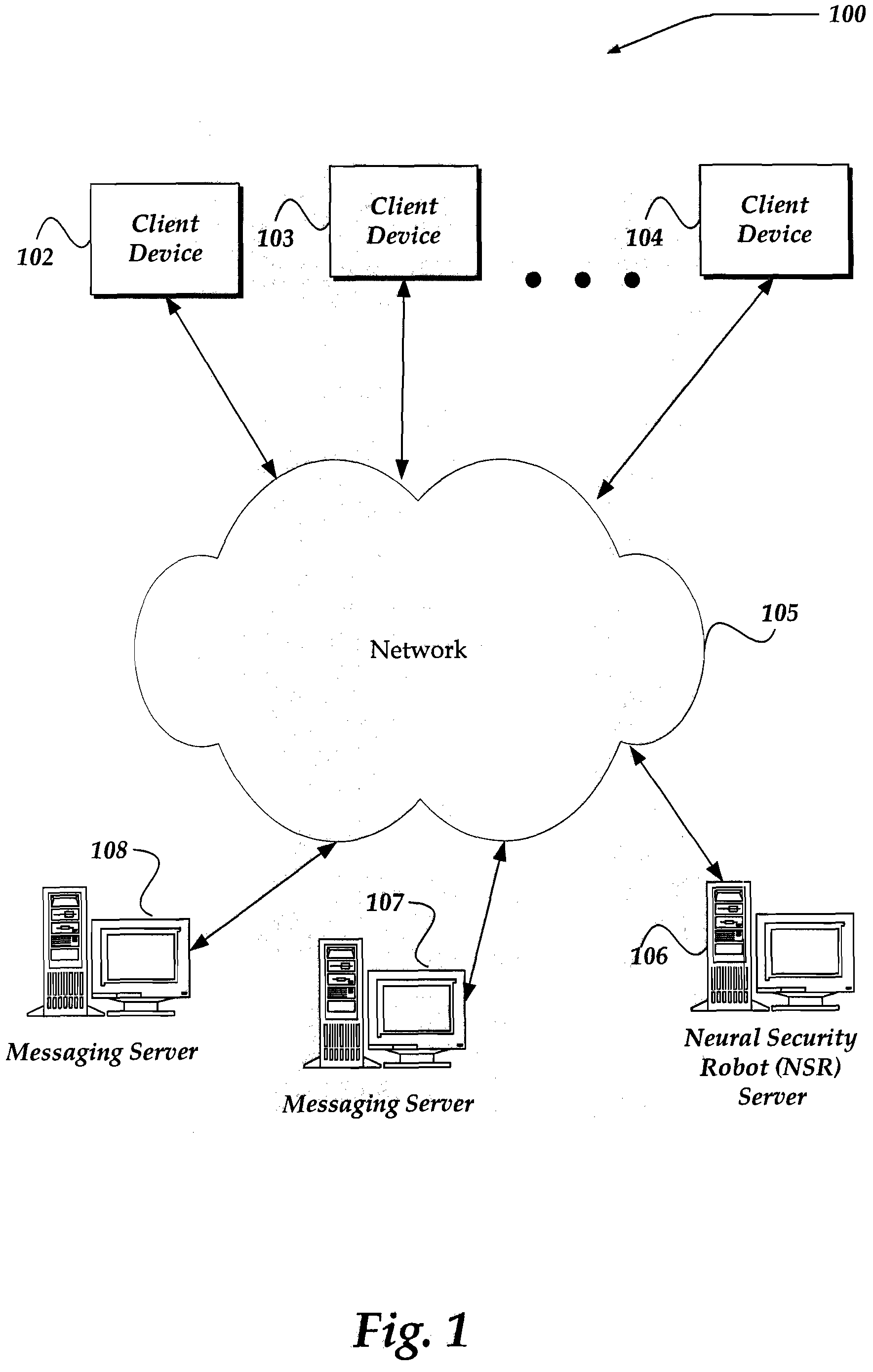
Dynamic combatting of SPAM and phishing attacks
A self training set of robots are configured to proactively search for selective communication abuses over a network. Robots may enter a chat room to proactively send messages. The robots then analyze patterns and / or content of a received message for potential abuse. Robots may also passively reside on / off line without publishing their network address. If a message is received, the message may be interpreted to be SPAM / SPIM. Robots may also perform a variety of other actions, such as access websites, and analyze received messages to determine if the messages indicate abuse. If abuse is detected, information may also be obtained to enable blocking or filtering of future messages from the sender, or access to / from an abusive website. The information also may be used to retrain robots, so that the robots may learn from and share their collective knowledge of abusive actions.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Dynamic combatting of spam and phishing attacks
A self training set of robots are configured to proactively search for selective communication abuses over a network. Robots may enter a chat room to proactively send messages. The robots then analyze patterns and / or content of a received message for potential abuse. Robots may also passively reside on / off line without publishing their network address. If a message is received, the message may be interpreted to be SPAM / SPIM. Robots may also perform a variety of other actions, such as access websites, and analyze received messages to determine if the messages indicate abuse. If abuse is detected, information may also be obtained to enable blocking or filtering of future messages from the sender, or access to / from an abusive website. The information also may be used to retrain robots, so that the robots may learn from and share their collective knowledge of abusive actions.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
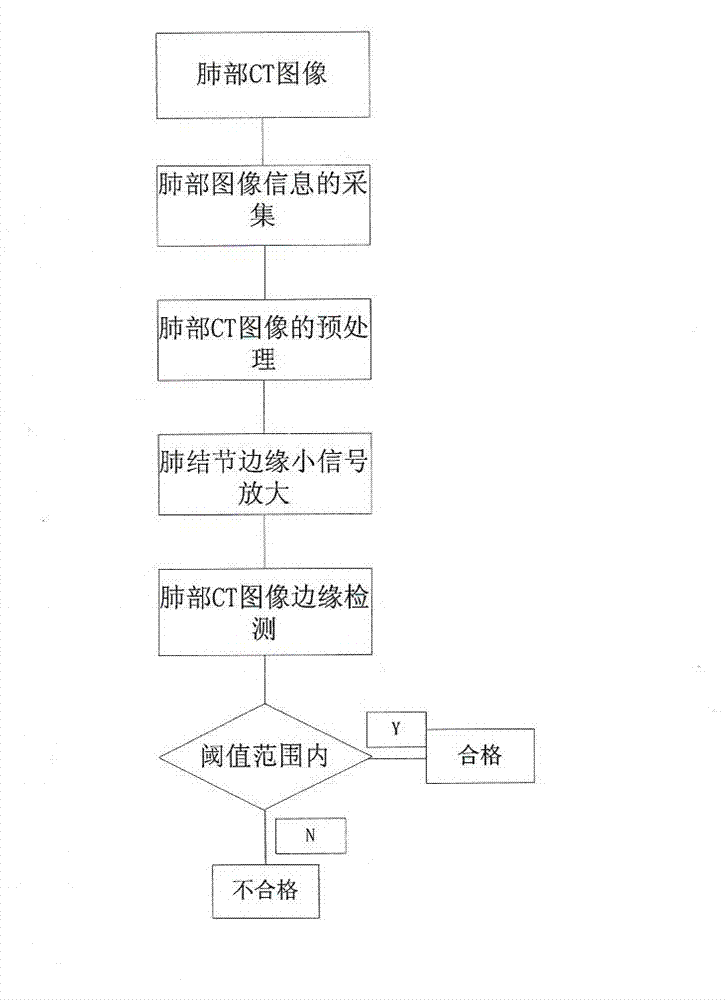
Pulmonary nodule edge rebuilding and partitioning method based on computed tomography (CT) image
InactiveCN103035009APreserve large energy conversion coefficientsGradient Feature EnhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleSelf training
The invention discloses a pulmonary nodule edge rebuilding and partitioning method based on a computed tomography (CT) image. According to the pulmonary nodule edge rebuilding and partitioning method, the image is subjected to spatial transformation by using a transformation method which has a sparse representation ability on gradient characteristics; a high energy transformation coefficient is reserved through shrinkage of a transformation domain; the image is rebuilt through inverse transformation to realize strengthening of the gradient characteristics; and amplification of small signals of the gradient characteristics is realized through multistage strengthening of the signals, a pulmonary nodule edge is rebuilt, and important edge information is provided for subsequent partitioning. The pulmonary nodule edge rebuilding and partitioning method provides a clustering-based pulmonary nodule partitioning algorithm, does not have the process of a training classifier, has a self-training ability, and can be used for strengthening edge detection, overcoming partitioning difficulty caused by uneven gray levels, and eliminating influence by speckle noise. The pulmonary nodule edge rebuilding and partitioning method can also be used for establishing a CT image partitioning algorithm evaluation system and combining contours drawn manually by different clinical medical experts into optimum partitioning standards so that the partitioning algorithm can be compared systematically, and the effectiveness of the partitioning algorithm can be revealed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
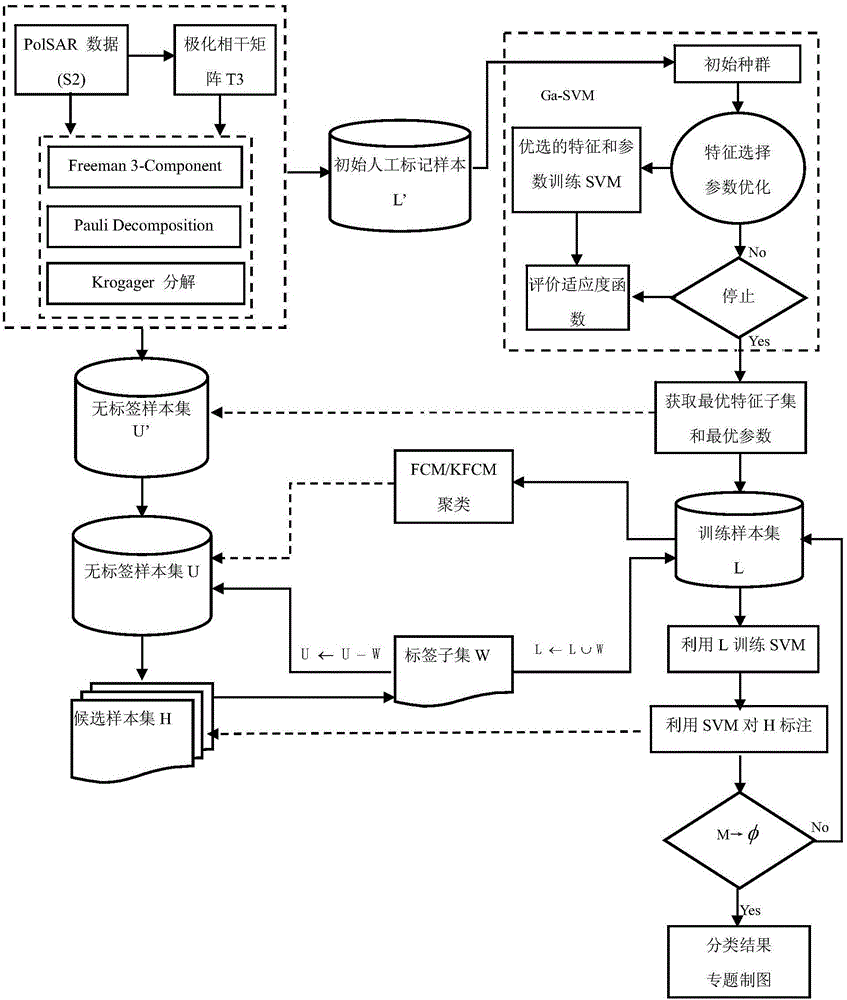
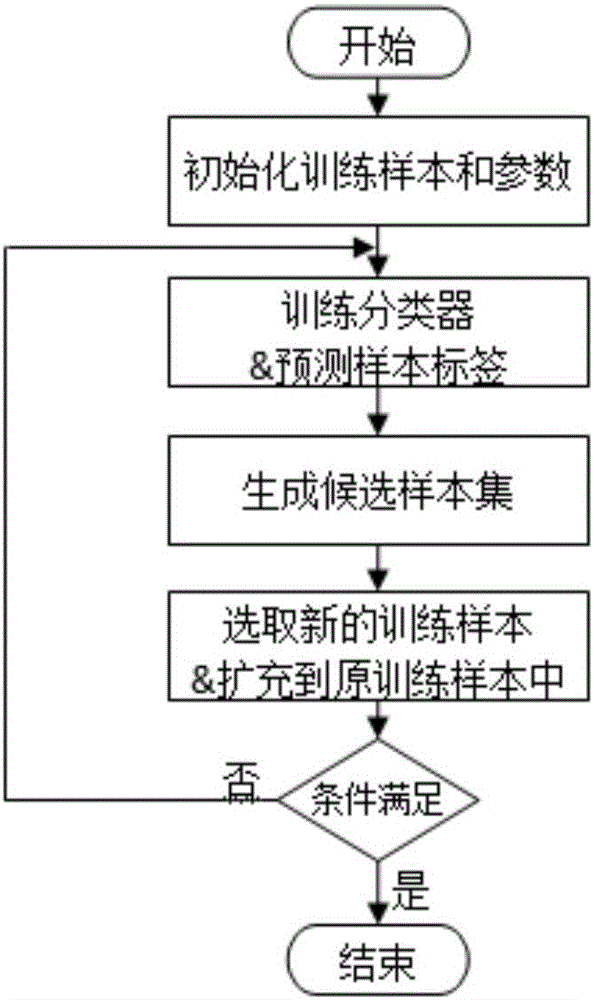
Polarized SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image semi-supervised classification method capable of considering characteristic optimization
InactiveCN106096627AOvercome limitationsImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsSelf trainingSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a polarized SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image semi-supervised classification method capable of considering characteristic optimization. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting a refined polarized LEE filtering method to carry out filtering, extracting polarization characteristics, carrying out combination to obtain an original characteristic set, and carrying out normalization processing; selecting an initial training sample set and a no-label set, and carrying out characteristic selection and classifier parameter optimization through a hybrid coding genetic algorithm under the initial training sample set; reconstructing the training sample set and a no-label sample set; training the classifier, and selecting a candidate set from the no-label sample set; utilizing a trained SVM (Support Vector Machine) classifier to label the candidate set, and selecting and expanding sample points with a high confidence coefficient into the training sample set; repeating the training of the classifier until learning is finished; and classifying the whole image by a finally trained SVM to obtain a classification thematic map. By use of the classification method, on one hand, effective characteristics can be adaptively extracted to improve a semi-supervised classification effect; and on the other hand, the efficiency of self-training learning can be improved, and error accumulation can be effectively avoided.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
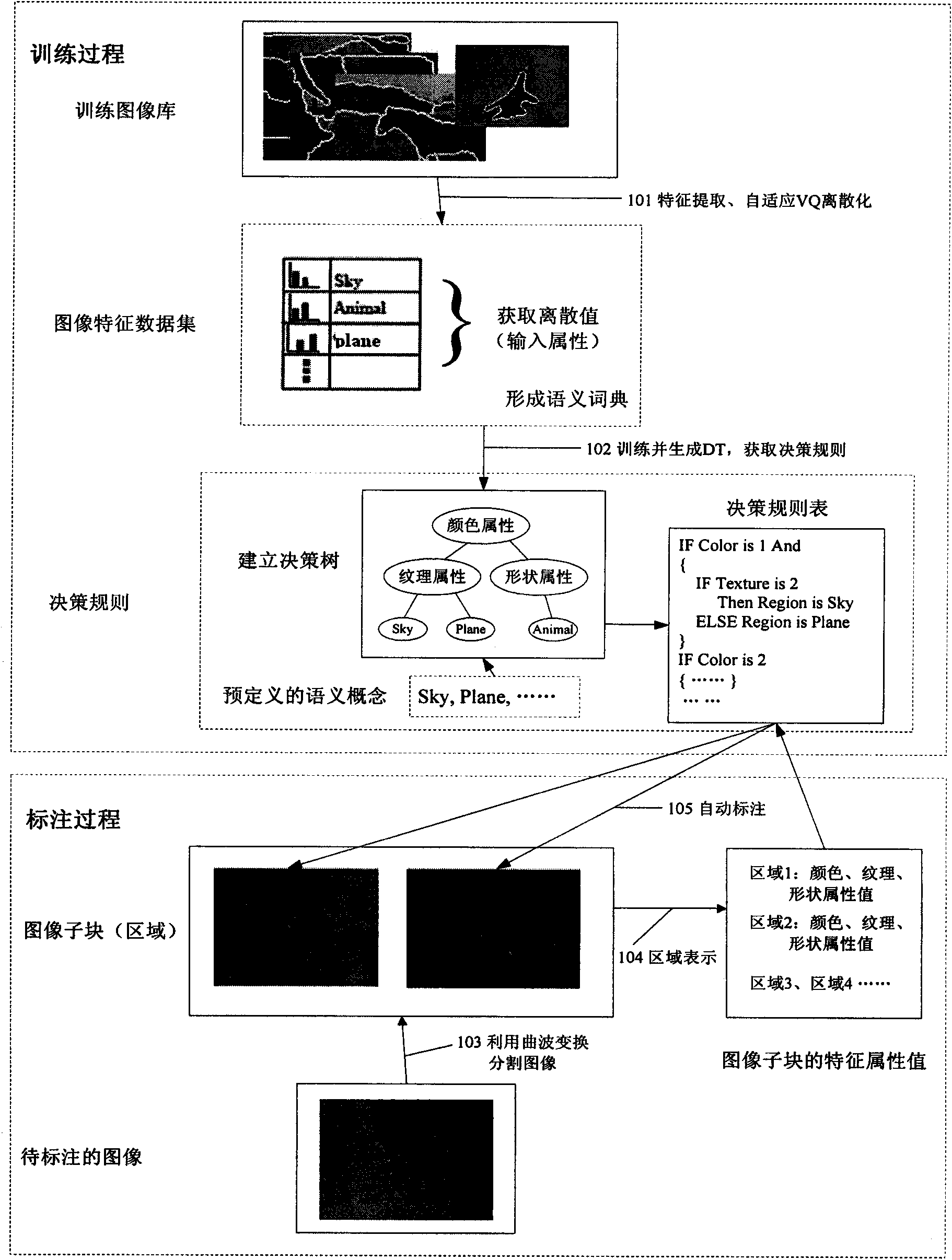
Automatic image annotation and translation method based on decision tree learning
InactiveCN101620615AImprove recallImprove precisionSpecial data processing applicationsWord listImage segmentation algorithm
The invention discloses an automatic image annotation and translation method based on decision tree learning. A new image is automatically annotated, and a text word list with a visualized content is translated by a machine so as to realize the machine retrieval of image data, comprising a training annotation image set and image automatic annotations, wherein the training annotation image set utilizes an image segmentation algorithm to segment a training image set into sub areas and extract low-level visual features of each sub area; the feature data is discretized, and then the training annotation image set is classified by a clustering algorithm based on a low-level feature discrete value to construct a semantic dictionary; the low-level feature discrete value is used as an input attribute of the decision tree learning; and self training learning is carried out on the constructed dictionary by a decision tree machine learning corresponding to preset semantic concepts so as to generate a decision tree and obtain a corresponding decision rule. The training annotation image set has expandability and robustness and can improve the recall ratio and the precision ratio of the retrieval when the training annotation image set is applied to semantic image retrievals.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
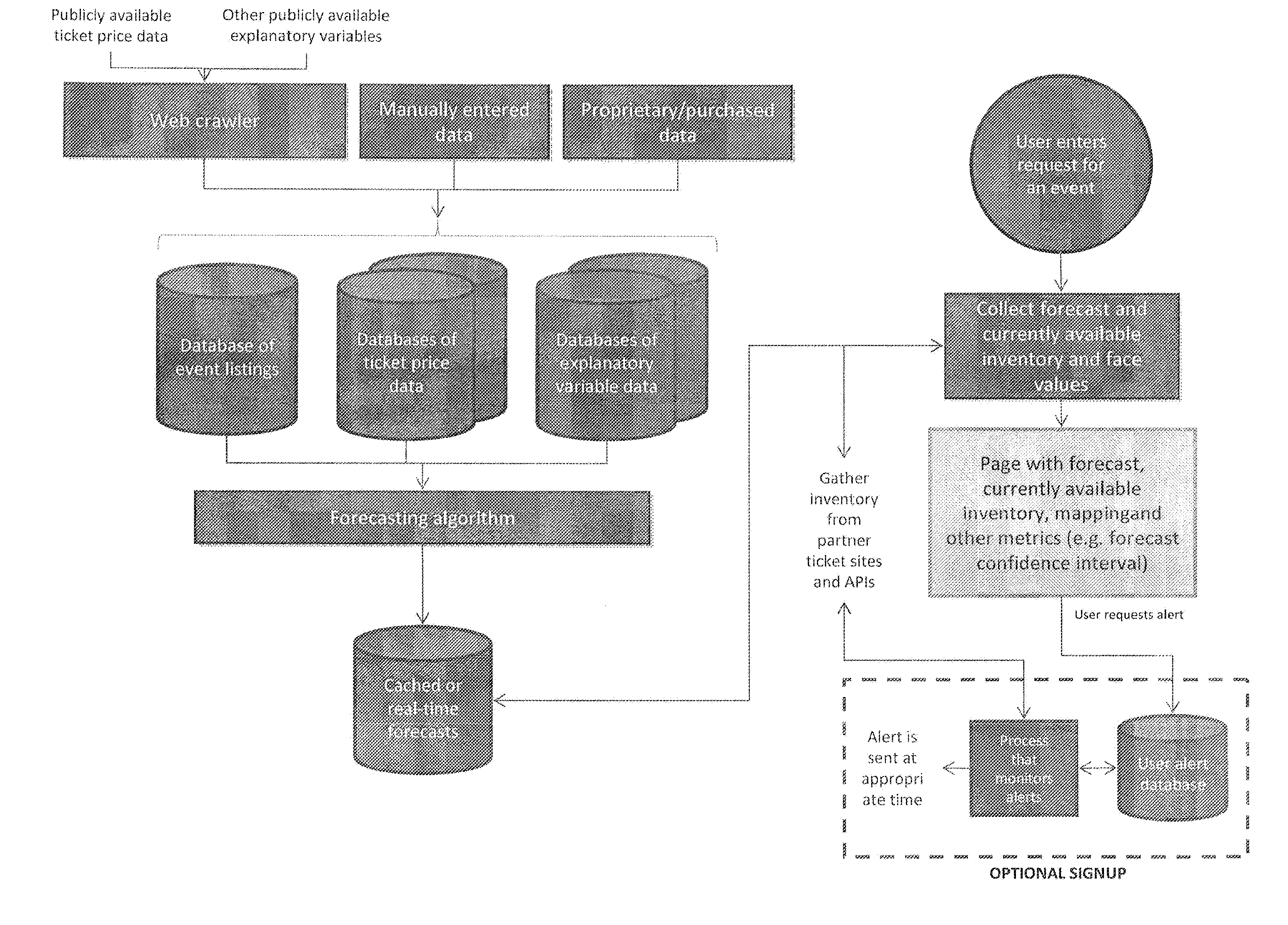
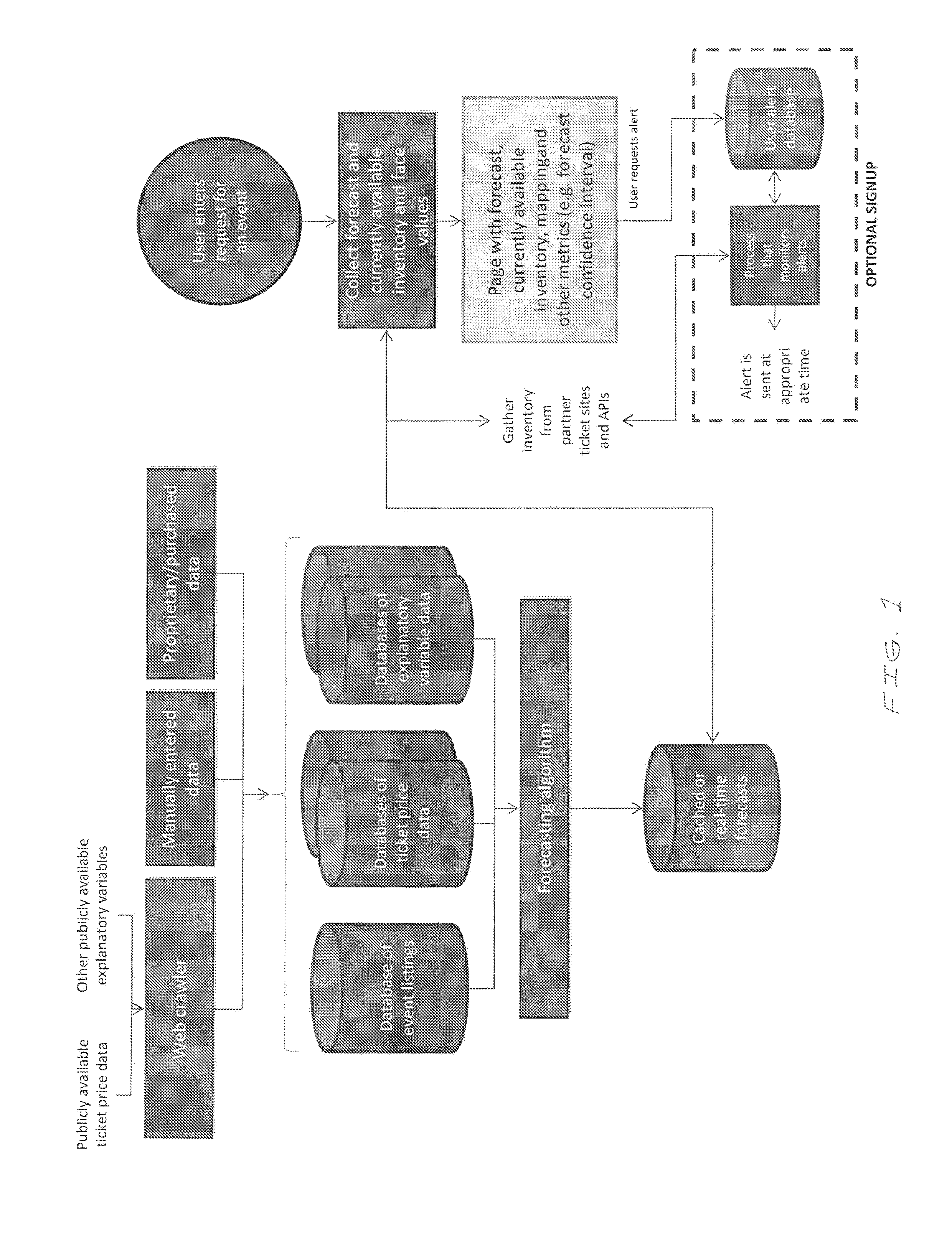
System and method for generating predictions of price and availability of event tickets on secondary markets
InactiveUS20110040656A1Purchase price is minimizedSelling price is maximizedProduct appraisalSelf trainingPrice prediction
A system and method is provided for predicting future price and availability of event tickets on the primary and secondary market and providing buyers with a recommendation as to when to purchase the event tickets at the lowest possible cost or, for sellers, when to sell the tickets at the highest possible price. Data is collected and used to generate statistics about the historical price and availability of event tickets. This data is further used to provide forecasts about the future price and availability of event tickets, including the probability of a sell out for events currently on sale and events not yet on sale. The system makes predictions by differentially weighing factors, both economic and non-economic, that influence the price trajectory and availability of event tickets. The system further includes a self-training mechanism that evolves behaviors based on previous price predictions thereby increasing the systems ability to accurately predict future event ticket prices.
Owner:SEATGEEK
Smart phone with self-training, lip-reading and eye-tracking capabilities
InactiveUS20130332160A1Raise the possibilityDevices with GPS signal receiverDevices with sensorSelf trainingDisplay device
Smartphones and other portable electronic devices include self-training, lip-reading, and / or eye-tracking capabilities. In one disclosed method, an eye-tracking application is operative to use the video camera of the device to track the eye movements of the user while text is being entered or read on the display. If it is determined that the user is moving at a rate of speed associated with motor vehicle travel, as though GPS or other methods, a determination is made if the user is engaged in a text-messaging session, and if the user is looking away from the device during the text-messaging session assumptions may be made about texting while driving, including corrective actions.
Owner:POSA JOHN G
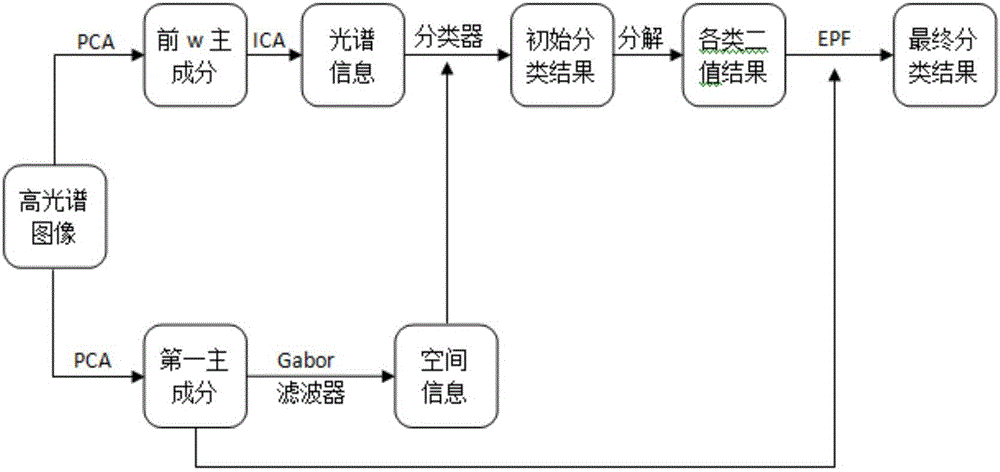
Hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification method based on space-spectral information
InactiveCN106056157AImprove classification resultsSolve classification problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleSelf training
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification method based on space-spectral information. The hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification method combines spectral information and spatial information in a hyperspectral image to act on a support vector machine classifier, adopts a self-training semi-supervised classification framework, utilizes an active learning method as a sample selecting strategy of semi-supervised classification, decomposes initial classification results obtained through semi-supervised classification according to classes so as to obtain various classes of binary images as input images of an edge preserving filter, regards a first principal component content as a reference image of the filter, utilizes the edge preserving filter to perform local smoothing, eliminates noise, and classifies image elements according to a class with maximum probability, thus the classification process is completed. The hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification method combines the spectral information and the spatial information to improve the classifiability of classes, utilizes the self-training semi-supervised classification framework to solve the classification problem of hyperspectral image small samples, can effectively eliminate spot-like errors in the initial classification results, and increases classification precision.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Data feature-based deep neural network self-training method
InactiveCN106779064AOvercome lack of adjustment experienceImprove test accuracyNeural learning methodsSelf trainingTechnical standard
The invention discloses a data feature-based deep neural network self-training method. The method comprises the following steps of extracting corresponding standard features from prepared different sample sets, wherein the standard features represent data distribution characteristics of the sample sets, and can be used for uniquely distinguishing the different sample sets; inputting the known sample sets and the corresponding standard features to a trainer, and searching for which parameter setting is needed by sample sets with different features to reach training precision as high as possible; and when a new sample set is introduced, automatically selecting a group of optimal deep neural network parameters according to features of the new sample set, thereby ensuring that prediction precision as high as possible can be obtained when the neural network is constructed by the parameters and new samples are trained. The method has the advantages that the parameters of the deep neural network are automatically adjusted according to features of sample data by utilizing a machine learning algorithm, a proper network model is built, and it can be ensured that relatively high test precision can be achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Domain adaptation via class-balanced self-training with spatial priors
InactiveUS20190130220A1Reducing target segmentation lossReduce segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisSelf trainingDomain adaptation
A vehicle, system and method of navigating a vehicle. The vehicle and system include a digital camera for capturing a target image of a target domain of the vehicle, and a processor. The processor is configured to: determine a target segmentation loss for training the neural network to perform semantic segmentation of a target image in a target domain, determine a value of a pseudo-label of the target image by reducing the target segmentation loss while providing aa supervision of the training over the target domain, perform semantic segmentation on the target image using the trained neural network to segment the target image and classify an object in the target image, and navigate the vehicle based on the classified object in the target image.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
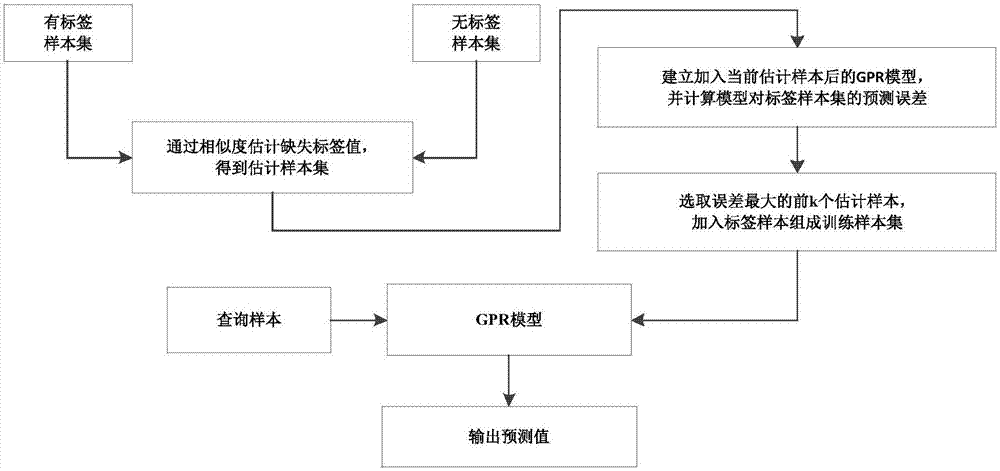
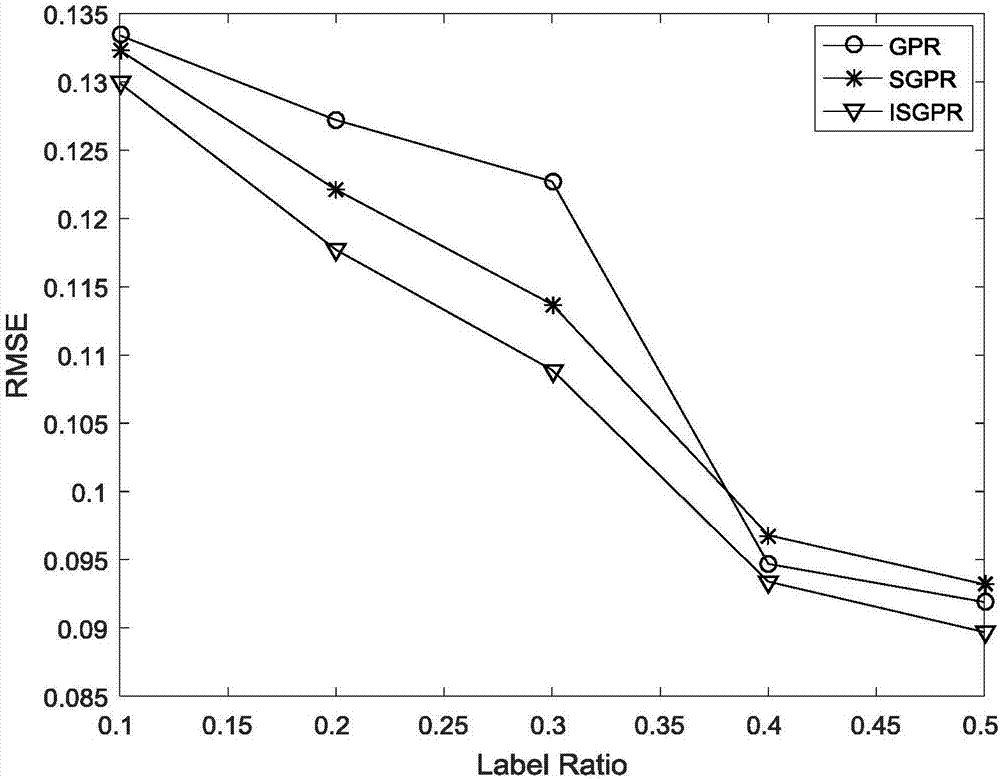
Semi-supervised Gaussian process regression soft measurement modeling method improving self-training algorithm
ActiveCN107451102ACharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsData setSelf training
The invention discloses a semi-supervised Gaussian process regression soft measurement modeling method on the basis of improving a self-training algorithm. The method is used for chemical process soft measurement modeling of a training dataset with a deletion primary variable. The method comprises the steps that deleted primary variable samples are estimated through the self-training algorithm, according to the influence of obtained estimation samples on original training data, samples high in generalization capacity are screened out and added into an original sample set, and then a new training sample set is formed to conduct modeling. By means of the method, on one hand, effective screening of estimation samples is achieved, and the semi-supervised model precision is improved; on the other hand, screening rules are simple, an entire data set does not need to be divided, and limitation of the model structure does not exist. Accordingly, the product quality can be improved, and the production cost can be lowered.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for updating gender classifier in image analysis and the gender classifier
InactiveCN101510254AImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method for updating a gender sorter in image analysis and comprises the following steps of: extracting the characters of a face image to be checked and obtaining the characteristic vector of the face image to be checked; identifying the gender corresponding to the characteristic vector through the gender sorter and determining that the gender identification result is satisfied with the characteristic vector required by the preset confidence coefficient; adding the characteristic vector with the gender identification result satisfying the preset confidence coefficient into a training sample set of the gender sorter, thus obtaining the updated training sample set; and obtaining an updated gender sorter by using the updated training sample set for training the gender sorter. The method for updating the gender sorter in image analysis raises the self-training capability of the gender sorter and raises the correctness and suitability of gender identification. The invention also discloses a gender sorter.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Data-driven self-training system and technique
InactiveUS20010034730A1Improve performanceDigital data processing detailsElectrical appliancesPersonalizationSystems analysis
An automated training system and method for providing personalized instruction or advice to a plurality of users or students in a simple, easy-to-use manner to improve their performance in their respective domain, i.e., specific filed of human activity such as sports, stock trading, gardening, etc. The system analyzes the user's performance data to determine domain-specific performance metrics and generates advice / instruction based on the performance metrics.
Owner:VIRTUAL GOLD
Self-training method and system
InactiveCN106176134AImprove subjective initiativeAdd funElectrotherapyDiagnosticsSelf trainingExercise state
The invention discloses a self-training method and system. The method comprises steps as follows: acquiring motion state information about a distal joint on the uninjured side of a hemiplegic patient and an electromyographic signal of key muscles at the distal joint; controlling the distal joint on the affected side of the hemiplegic patient to conduct corresponding rehabilitation exercises according to the motion state information and the electromyographic signal; controlling motion of a controlled object in a preset virtual scene according to the rehabilitation exercises. The affected side is controlled to conduct the corresponding rehabilitation exercises according to the motion state information on the uninjured side of the hemiplegic patient, and the patient is allowed to participate in rehabilitation training actively, therefore, the subjective initiative of the patient is improved, the rehabilitation exercise interestingness is increased, the operation is simple, and the training effect is improved.
Owner:王春宝
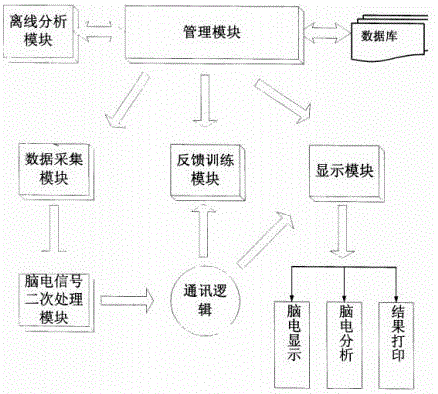
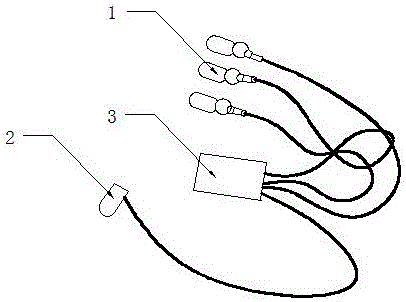
Biologic information feedback system based on virtual reality
InactiveCN106377252AAccurate collectionExact pressure levelSensorsPsychotechnic devicesDiseaseSelf training
The invention discloses a biological information feedback system based on virtual reality, which comprises an acquisition system S1 and a virtual reality feedback system S2; the acquisition system S1 comprises a plurality of scalp electrodes, an electroencephalogram (EEG) signal extraction module and an EEG signal processing module; and the virtual reality feedback system S2 comprises a management module, a database, a feedback training module, a display module, an off-line analysis module, a communication logic module and an EEG secondary processing module. The biological information feedback system of the invention accurately collects the biological electric signals, processes and extracts the pure EEG signals, processes signal characteristics, and compares with the database and analyzes to obtain an accuracy pressure level; an intervention system can be configured for different diseases to achieve a targeted intervention system; real-time operation realizes a real-time feedback system, so that the current state of a subject can be visually observed, thus achieving self-training and adjustment; and good virtual reality system and the new design of interactive scenes and interactive means can enhance the sense of interaction and immersion and operability.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
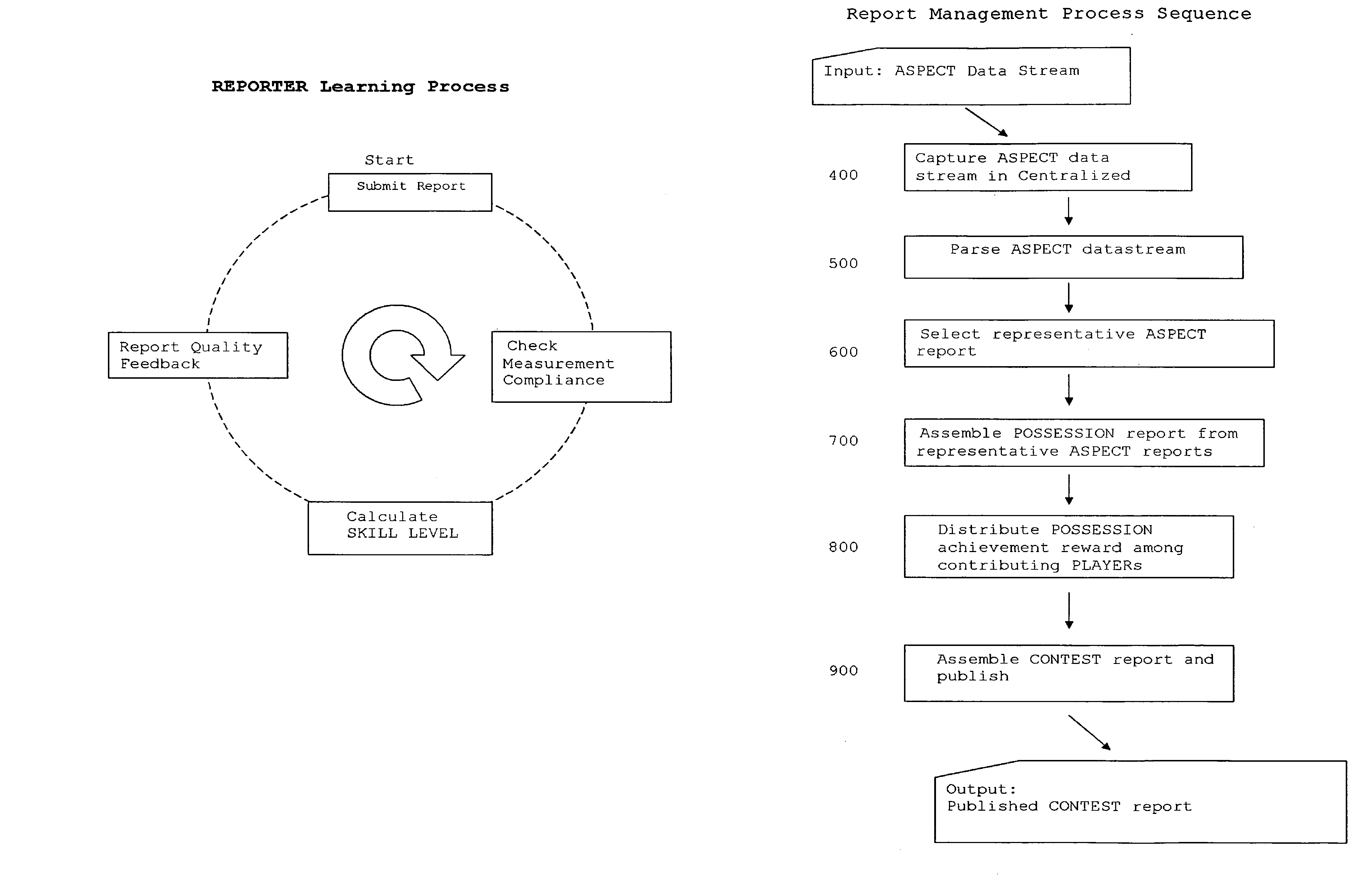
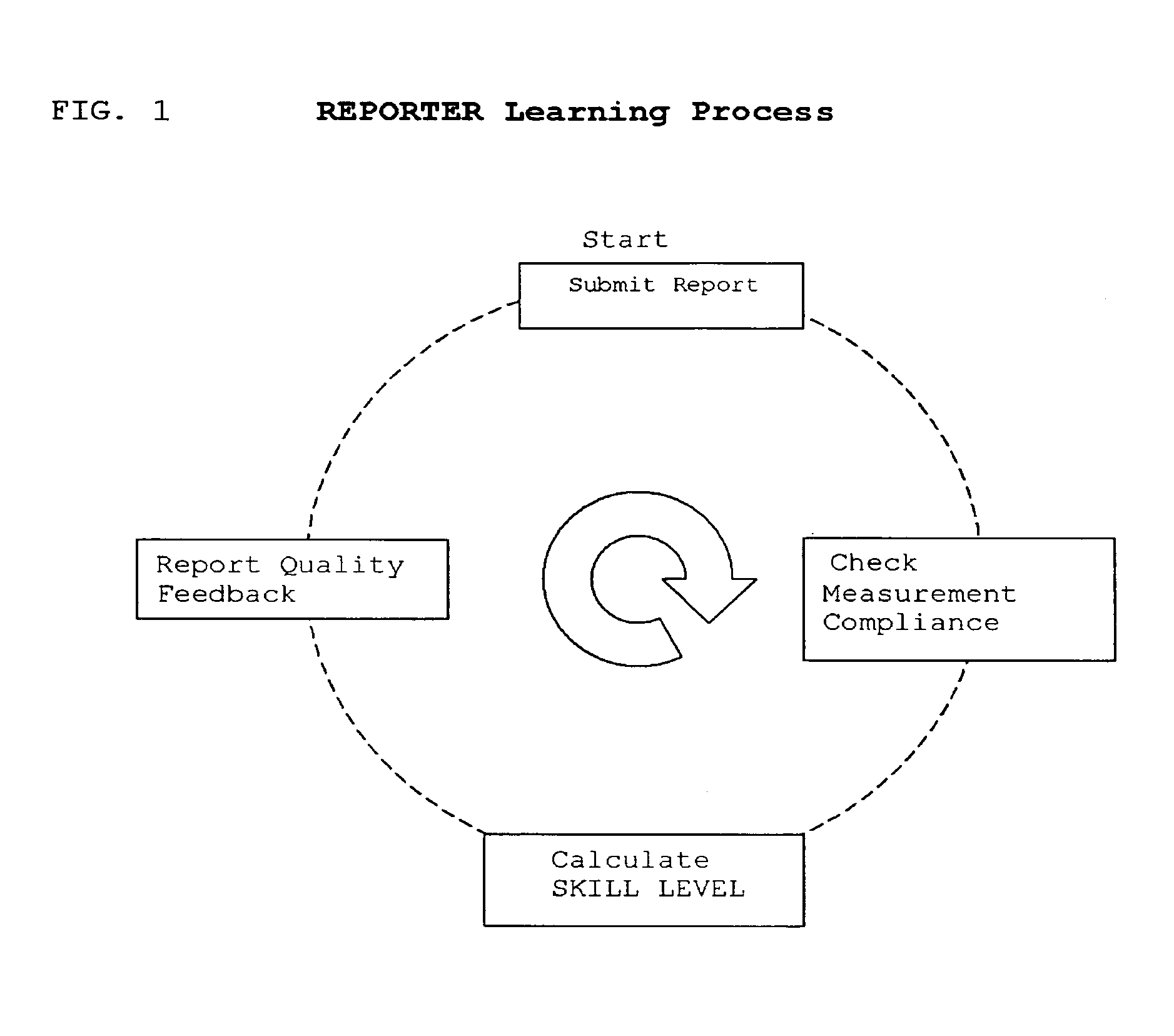
Method and system to optimize group achievement employing group members' collective intelligence
InactiveUS7153211B2Enhance their reporting skillsEliminate needOffice automationVideo gamesSelf trainingThe Internet
A method and system for a plurality of reporters to collectively self-organize, for the purpose of identifying, measuring and recording team-member activity that is causal to team achievement. The method includes steps of role selection, information discovery, information reporting and information aggregation of team-member activity that is causal to team achievement. It includes means for creating a common perspective among reporters, a common means to judge the value of team-members' contributions, means for collective self-organizing and self-training by reporters, and means for valuing reporters' contributions to the reporting process. One preferred embodiment is a game that enables a large group of humans to determine the critical few actions and collaborations that lead to winning a basketball game viewed live, via TV or internet broadcast. Another preferred embodiment is a game for maximizing the selling activity of a commercial sales group.
Owner:OBJECT POWER
A radar emitter signal modulation identification method combined with multi-dimensional feature migration fusion
ActiveCN109446877AGood effectConvenient timeCharacter and pattern recognitionSelf trainingSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention belongs to the field of electronic reconnaissance identification, in particular to a radar emitter signal modulation identification method combined with multi-dimensional feature migration fusion, comprising the following steps of generating nine kinds of radar signals to form a radar signal set; transforming the radar signal into time-frequency image by time-frequency transform; transforming the time-frequency image so as to meet the input requirements of the pre-trained large-scale network; sending the pre-processed time-frequency image to LeNet 5 network for feature extraction, and using the feature extraction module from input layer to form C5 convolution layer to output the feature extraction module; selecting a dimensionality reduction mode for the data obtained from the extracting feature step and processing the dimensionality reduction mode. The invention adopts the method of time-frequency analysis, maps the one-dimensional time-domain signal to the two-dimensional time-frequency domain, analyzes and processes the radar signal in the time-frequency domain, and has better effect for the non-stationary radar signal. The self-training network adopted by the invention has simple structure, and can improve the reliability of the system under the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Senile dementia preventing method
InactiveCN1521683AHigh degree of automationDegree of controlSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationOlder people
A method for preventing senile dementia, wherein the learning and exercise under the help of the exercise equipment can stimulate the brain to work fully, the exercise content and intensity can be designed in a personalized way according to the previous exercise data of the trained elderly people, thus effectively preventing the brain degeneration for the elderly people.
Owner:浙江亚卫通科技有限公司
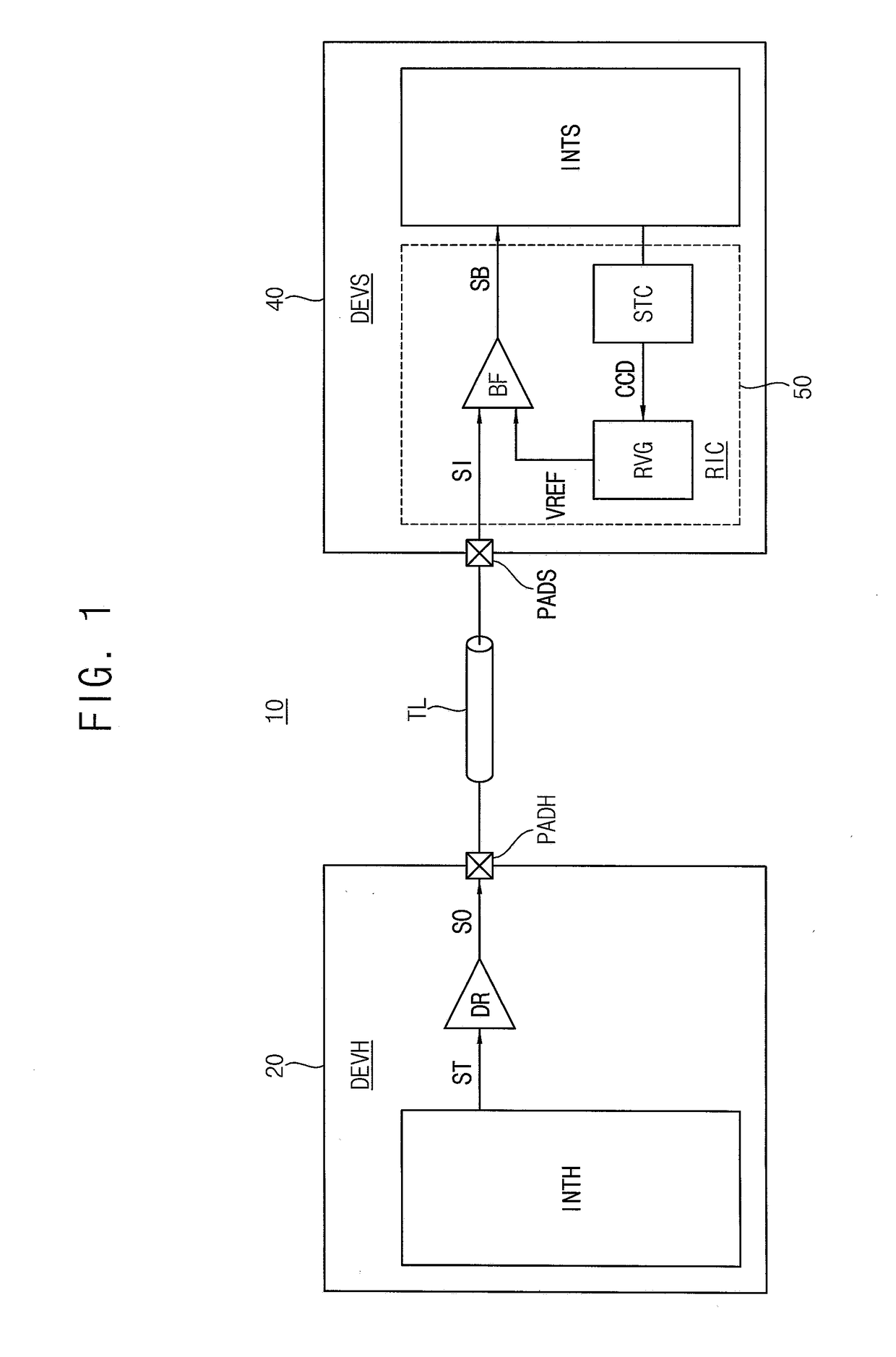
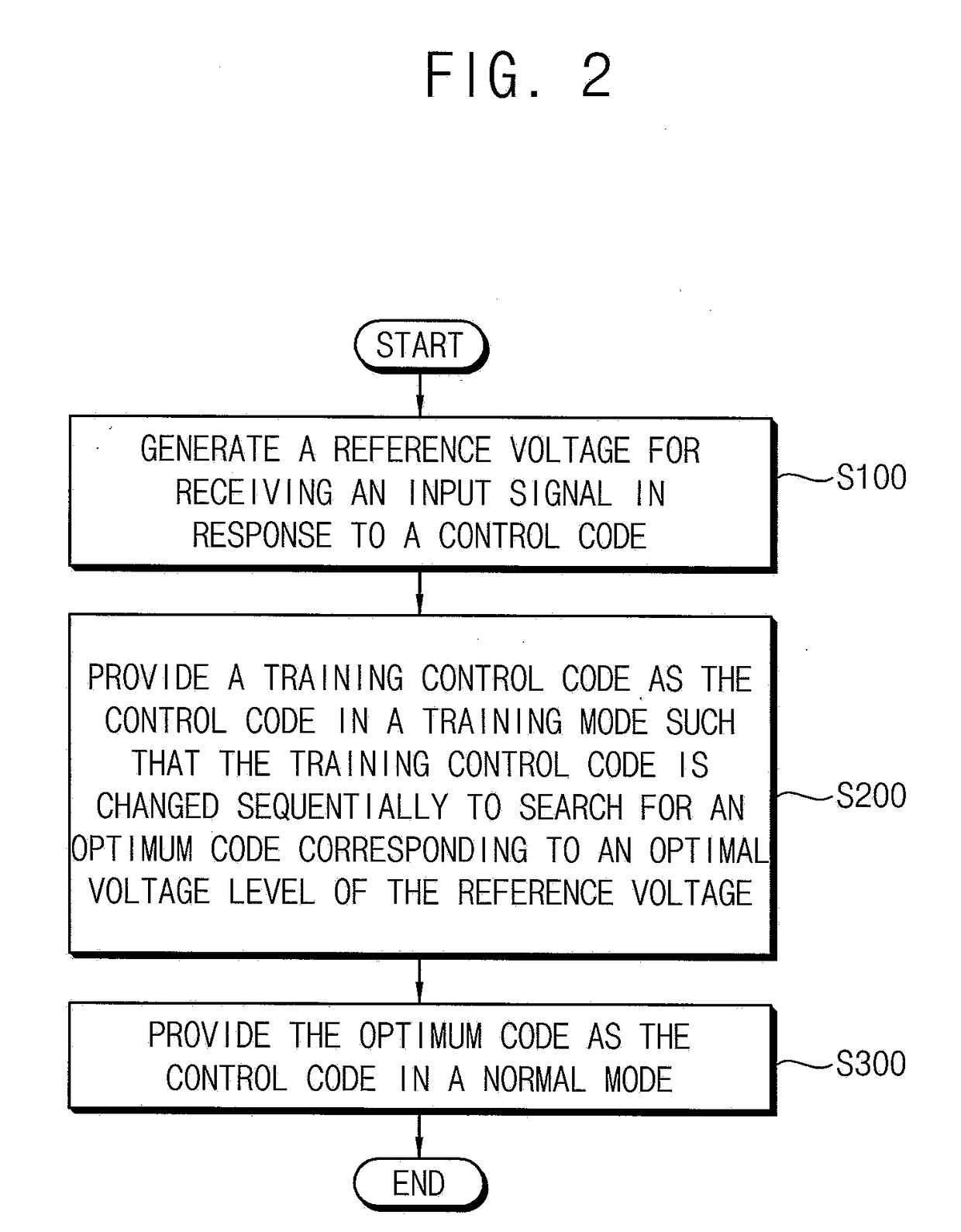
Method and circuit for self-training of a reference voltage and memory system including the same
A semiconductor device, includes at least a first memory chip, which includes at least a first buffer connected to receive an input signal and a reference voltage; at least a first reference voltage generator configured to output a reference voltage based on a first control code; and at least a first self-training circuit for determining an operational reference voltage to use during a normal mode of operation of the semiconductor device. An output from the first buffer is input to the first self-training circuit, the first control code is output from the first self-training circuit into the first reference voltage generator, and the first buffer, the first self-training circuit, and the first reference voltage generator form a loop.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Football training device and control method for football device
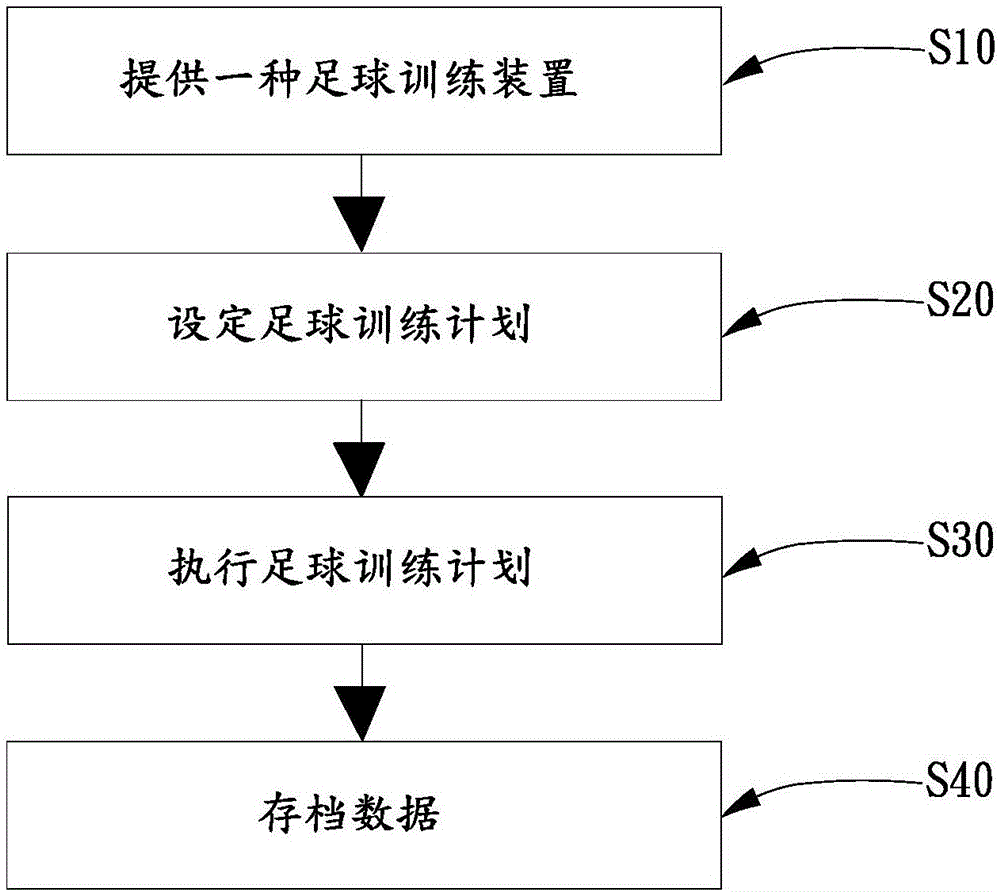
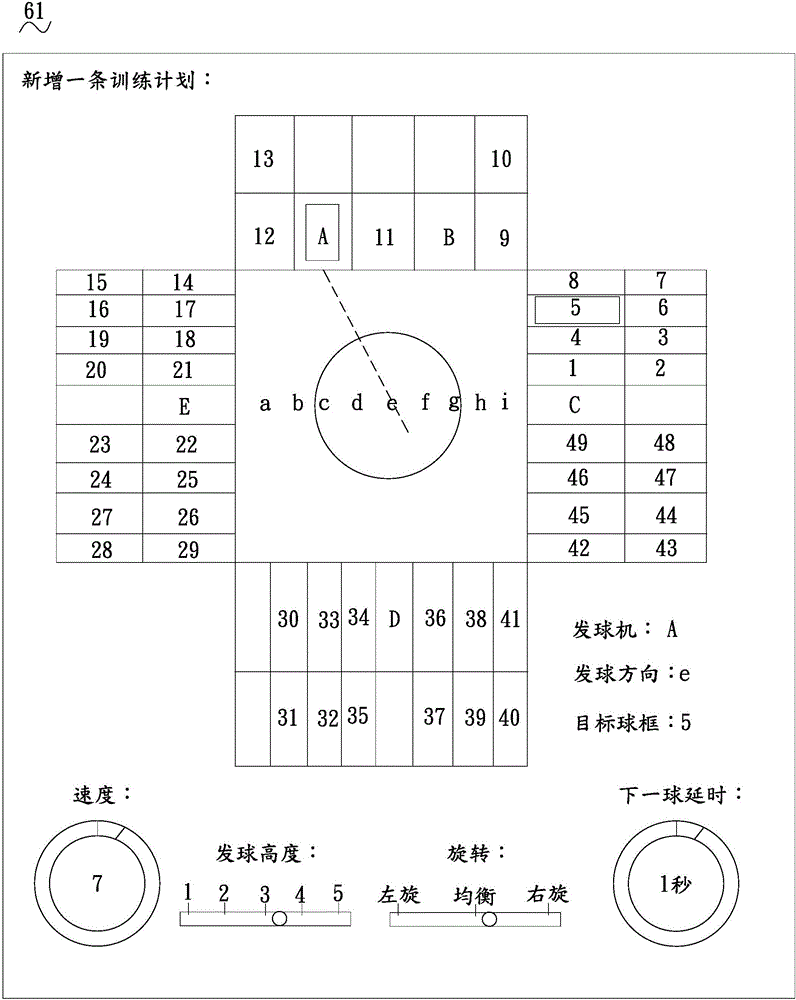
InactiveCN106237601AImprove responseIncrease physical strengthSki bindingsBall sportsElectricityTraining plan
The invention relates to a football training device which comprises a training field, a scoring rail, a guard bar, a plurality of pitching devices and a control console, wherein the scoring rail is encircled on the periphery of the training field; the guard bar is encircled on the exterior of the scoring rail; the pitching devices are arranged between the scoring rail and the guard bar; the control console is arranged on the outer side of the guard bar; the scoring rail comprises a plurality of target ball frames; a sensor and an indicator are respectively arranged on each of the target ball frames; a recycling conveyor belt is arranged on the inner side of the guard rail; the recycling conveyor belt is connected with the pitching devices; a display screen is arranged on the guard bar; shooting openings of the pitching devices are faced to the training field; each of the pitching devices is electrically connected with the control console and is equipped with a prompt tone player. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a control method for the football training device. The football training device and control method have the beneficial effects that the athletes can make various football training plans according to self-training requirements, such as, shooting training, throwing training, and the like; various functions are provided; the urgent and various game scenes can be truly simulated; the football training device is beneficial to the promotion of the quick reaction capability and physical power of the players.
Owner:东莞市斯波阿斯体育用品科技有限公司
Gastric cancer image recognition system and device and application thereof
InactiveCN109671053AImprove the detection rateImprove recognition accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSelf trainingGastric carcinoma
The invention relates to a gastric cancer image recognition system and device and application thereof. The system comprises a data input module, a data preprocessing module, an image recognition modelconstruction module and a lesion recognition module. And meanwhile, the system can realize self-training, so that the lesion part in the gastric cancer image can be accurately identified.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com