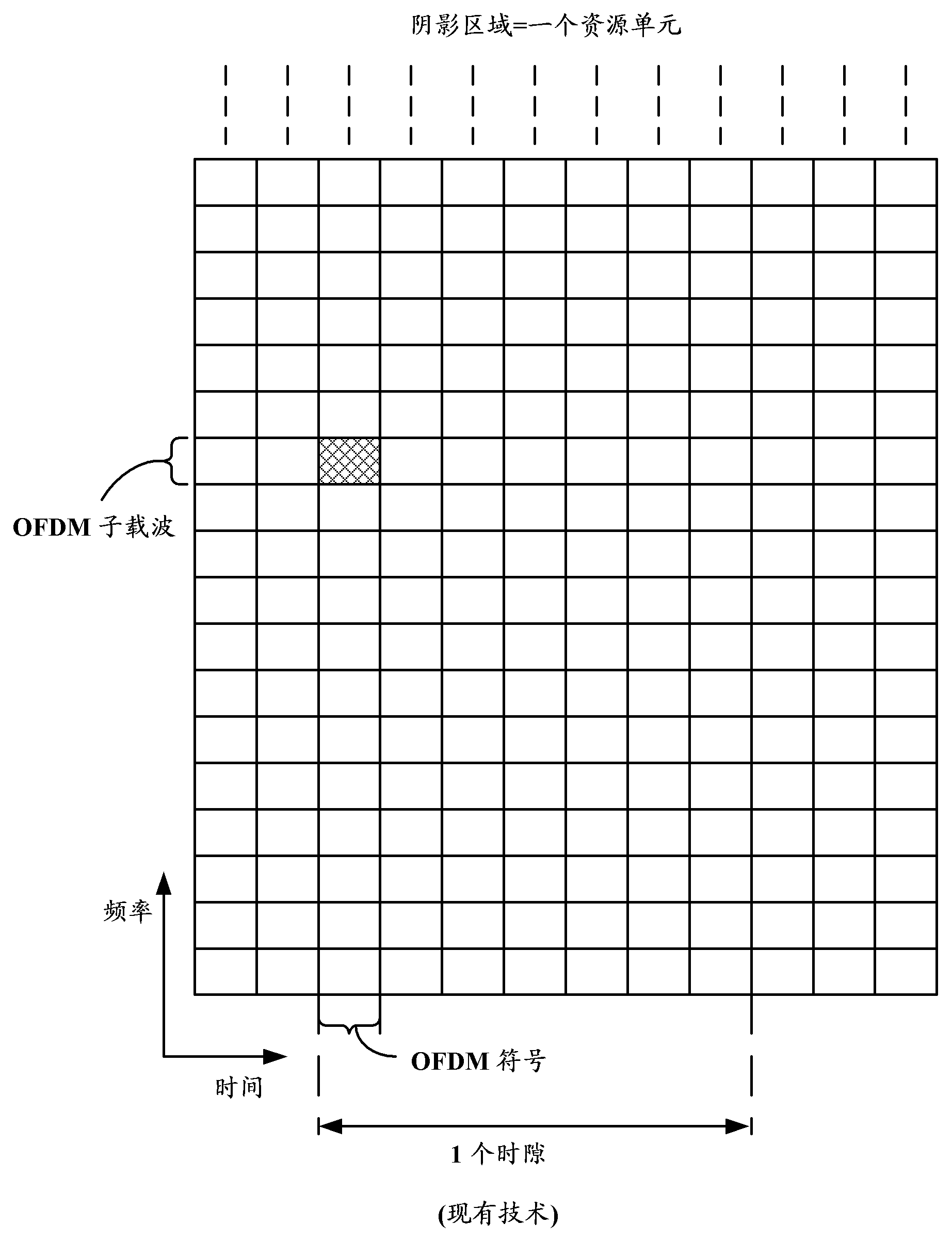
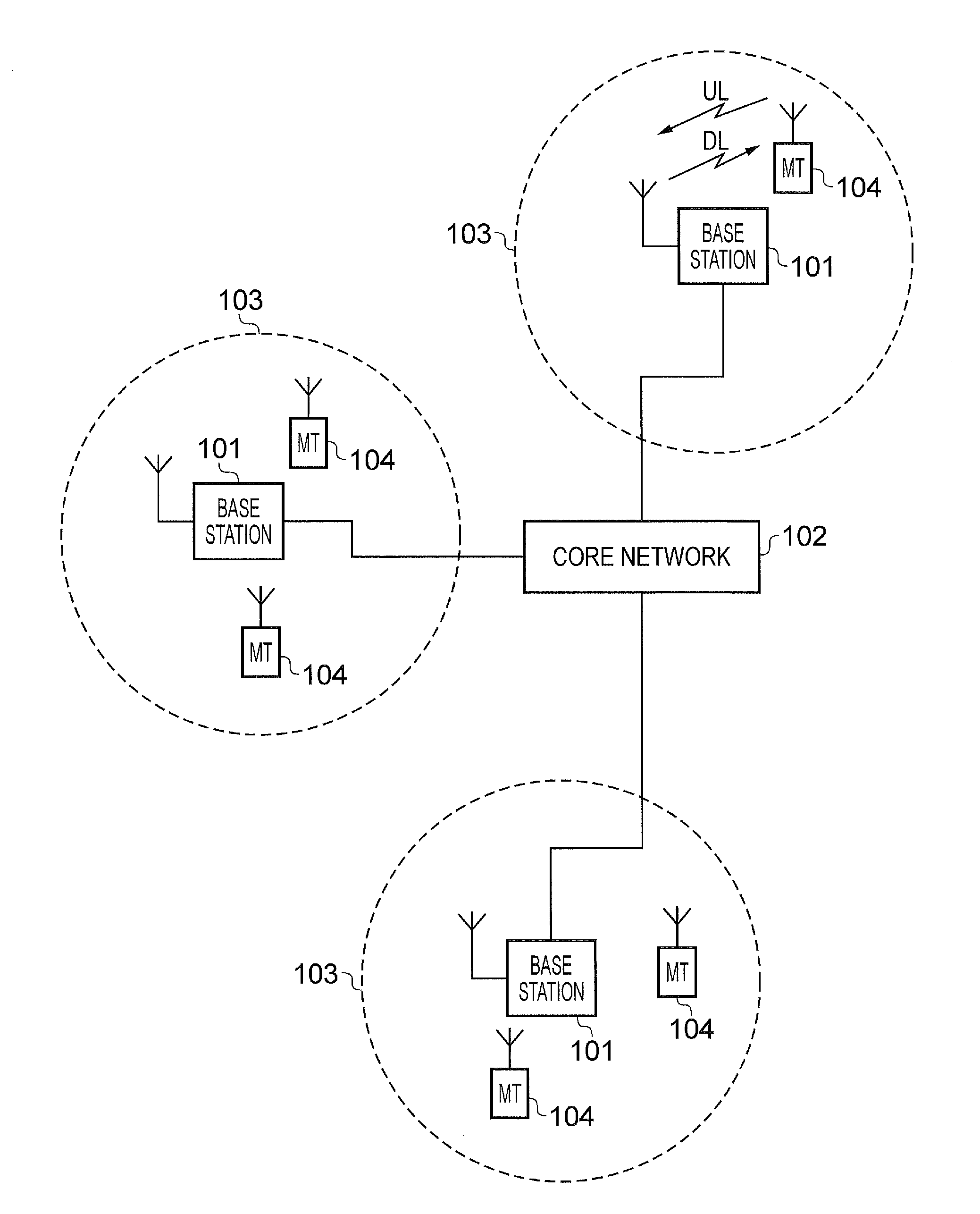
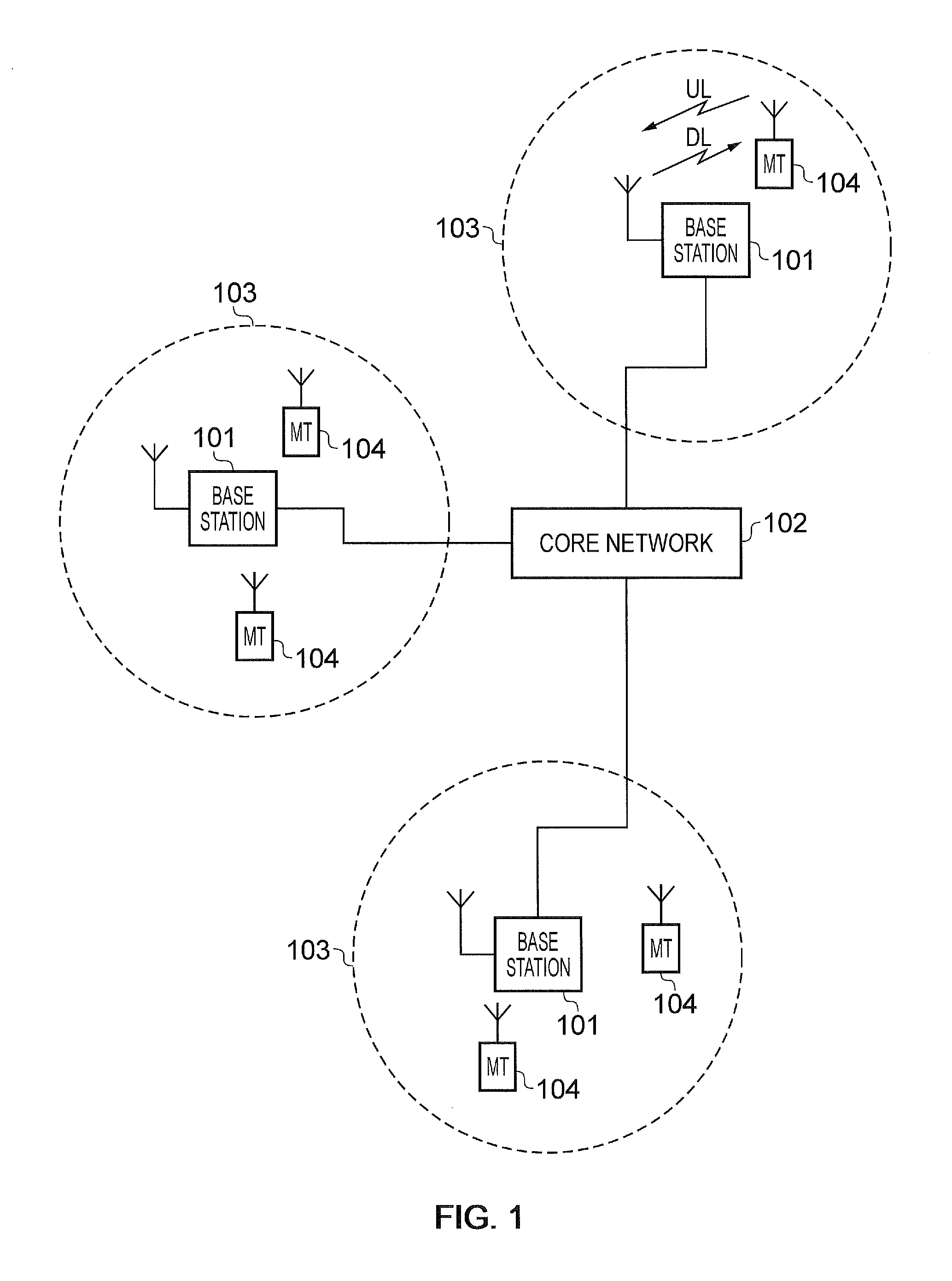
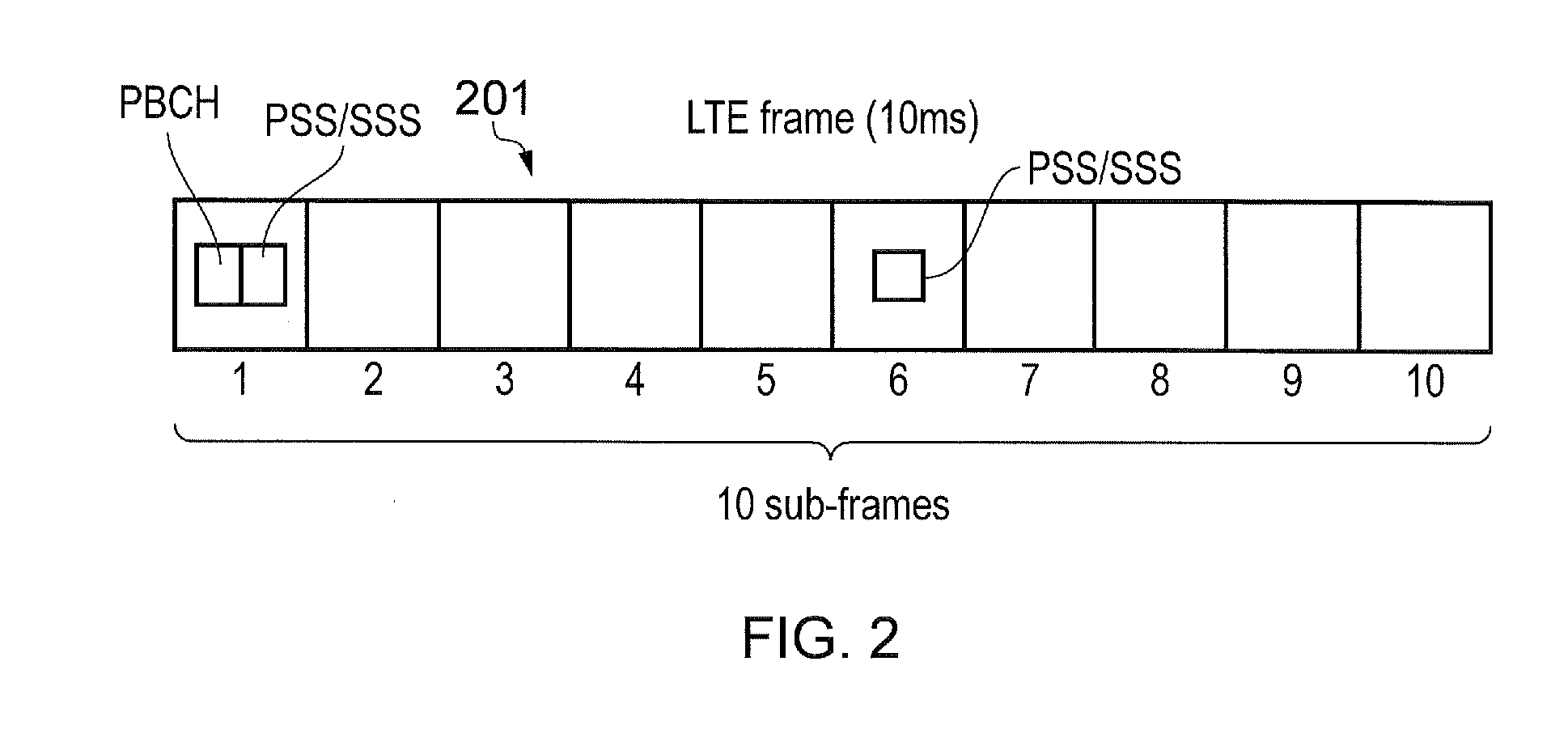
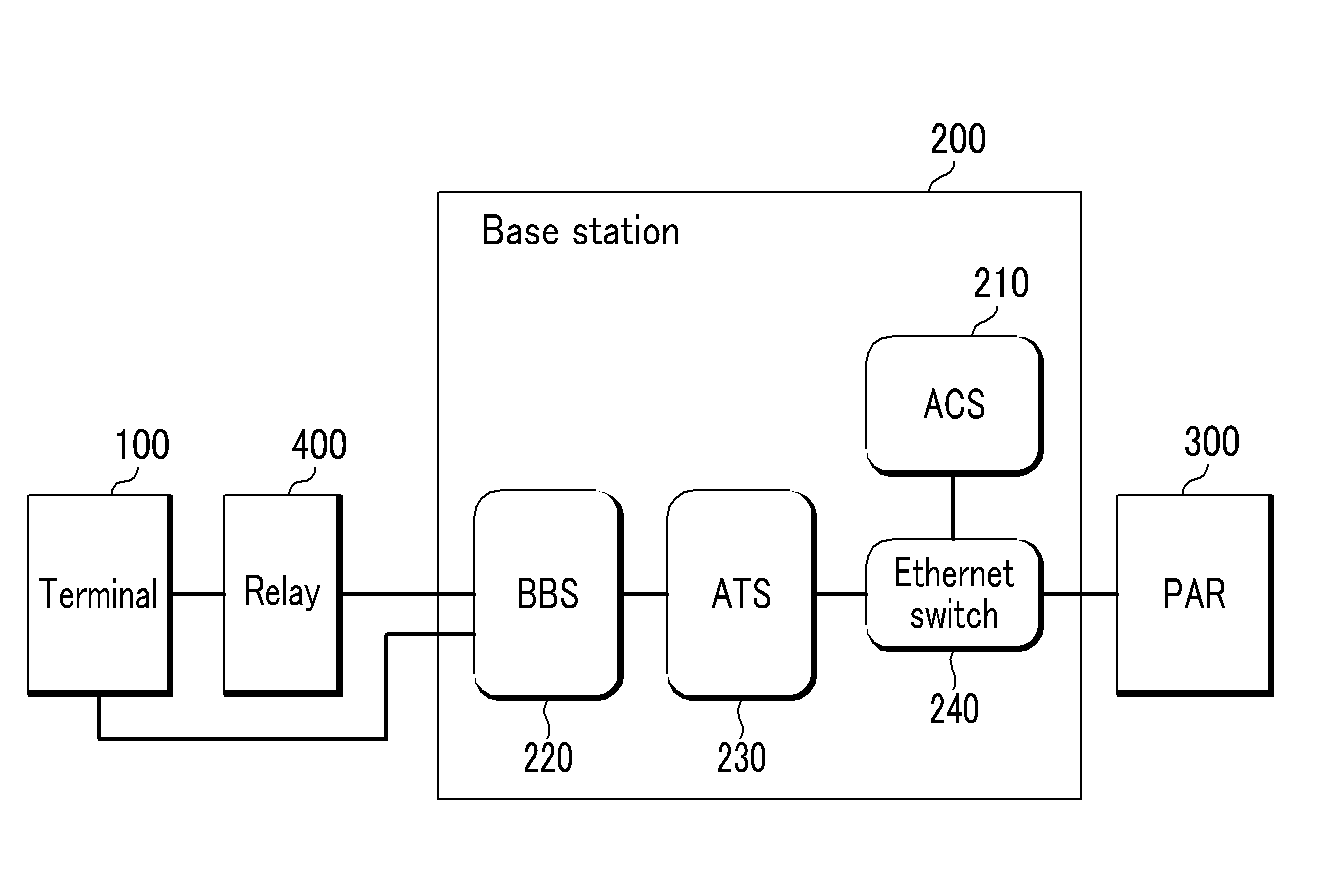
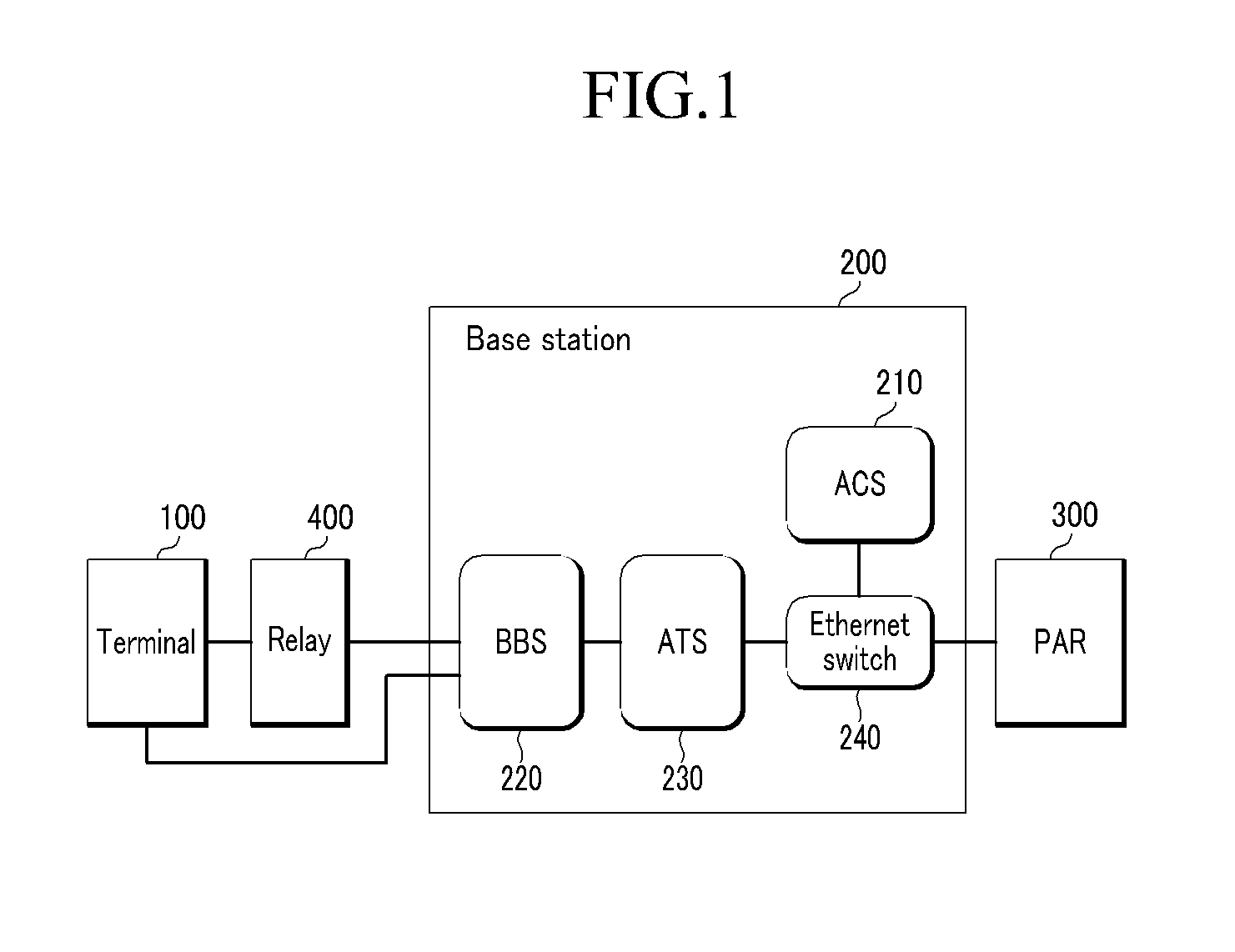
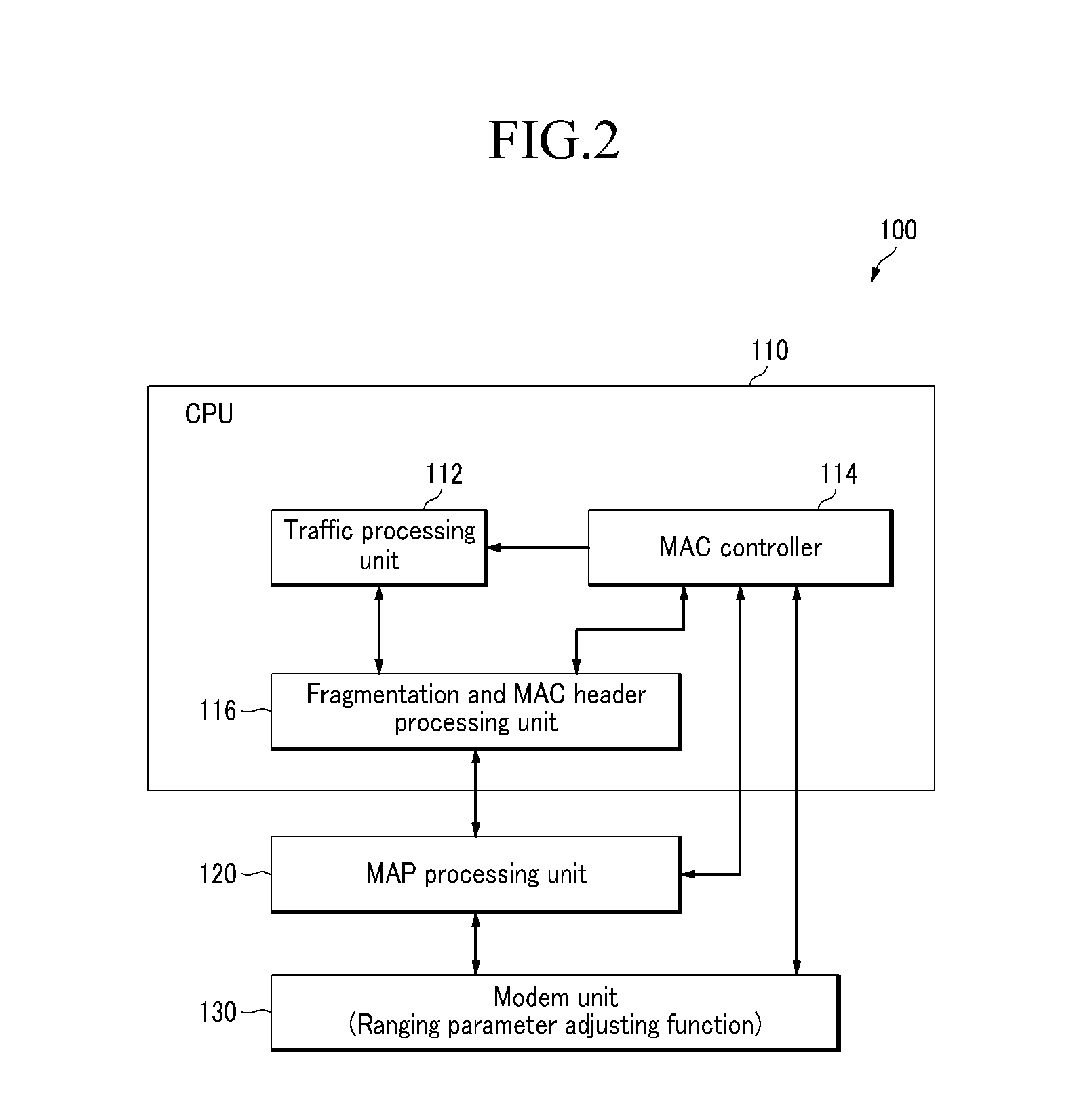
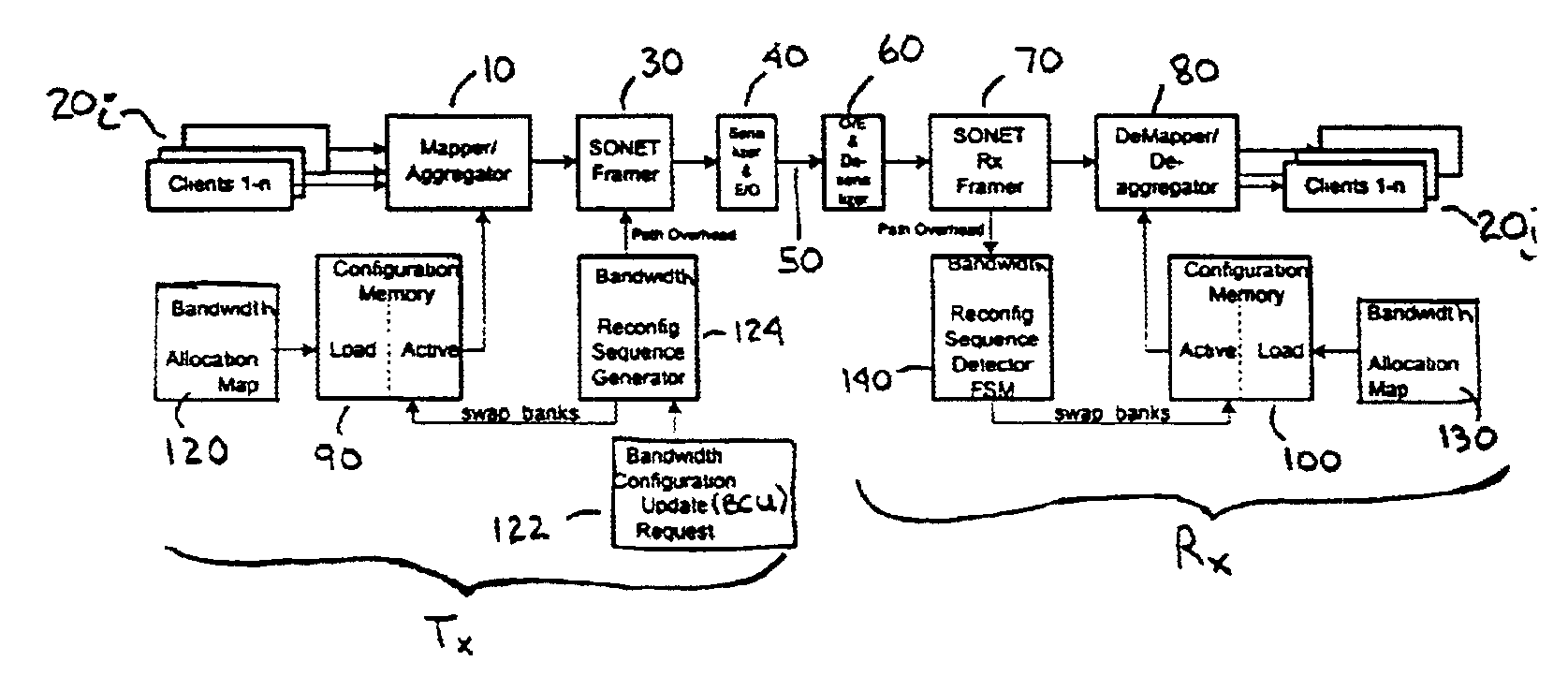
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
122 results about "Receiver Bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
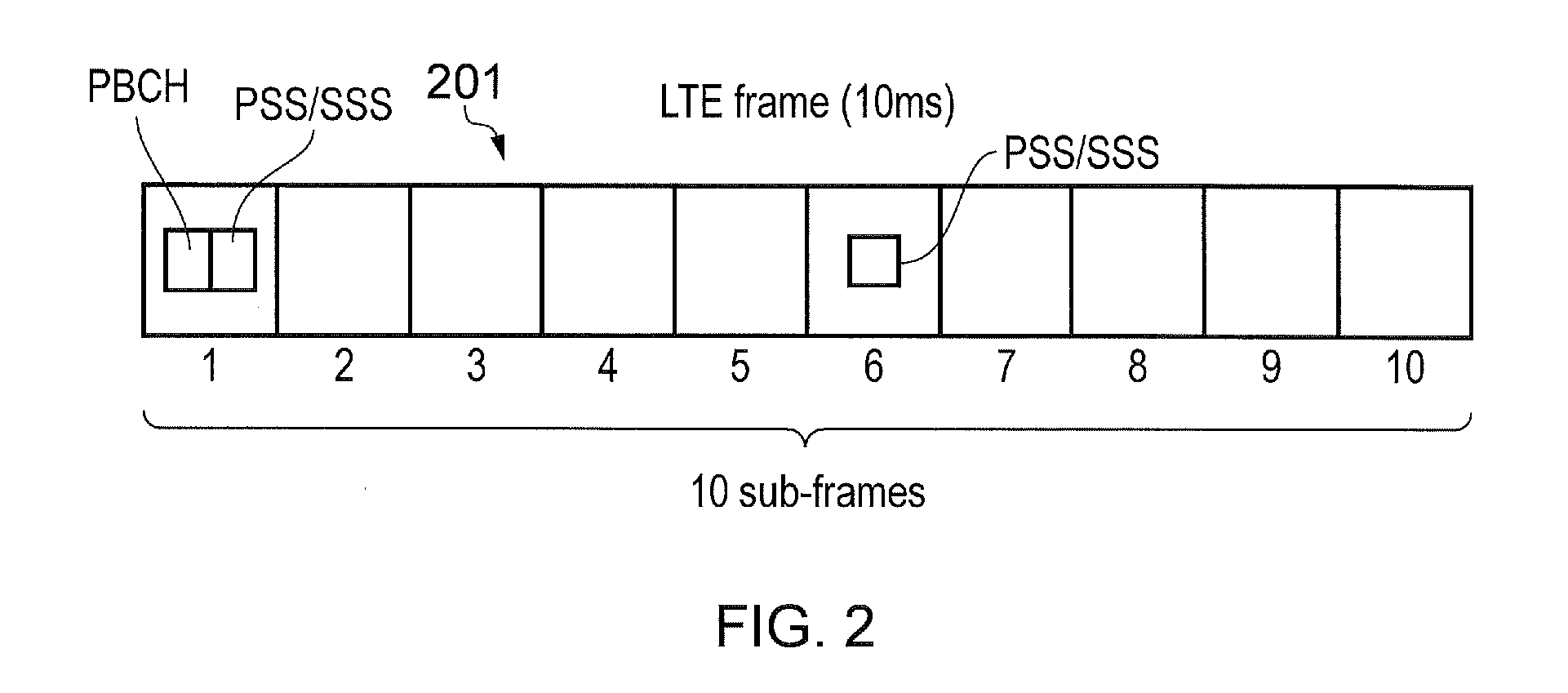
The range between the minimum and maximum cut-off frequencies for a particular receiver, commonly measured in Hertz. (NCI)
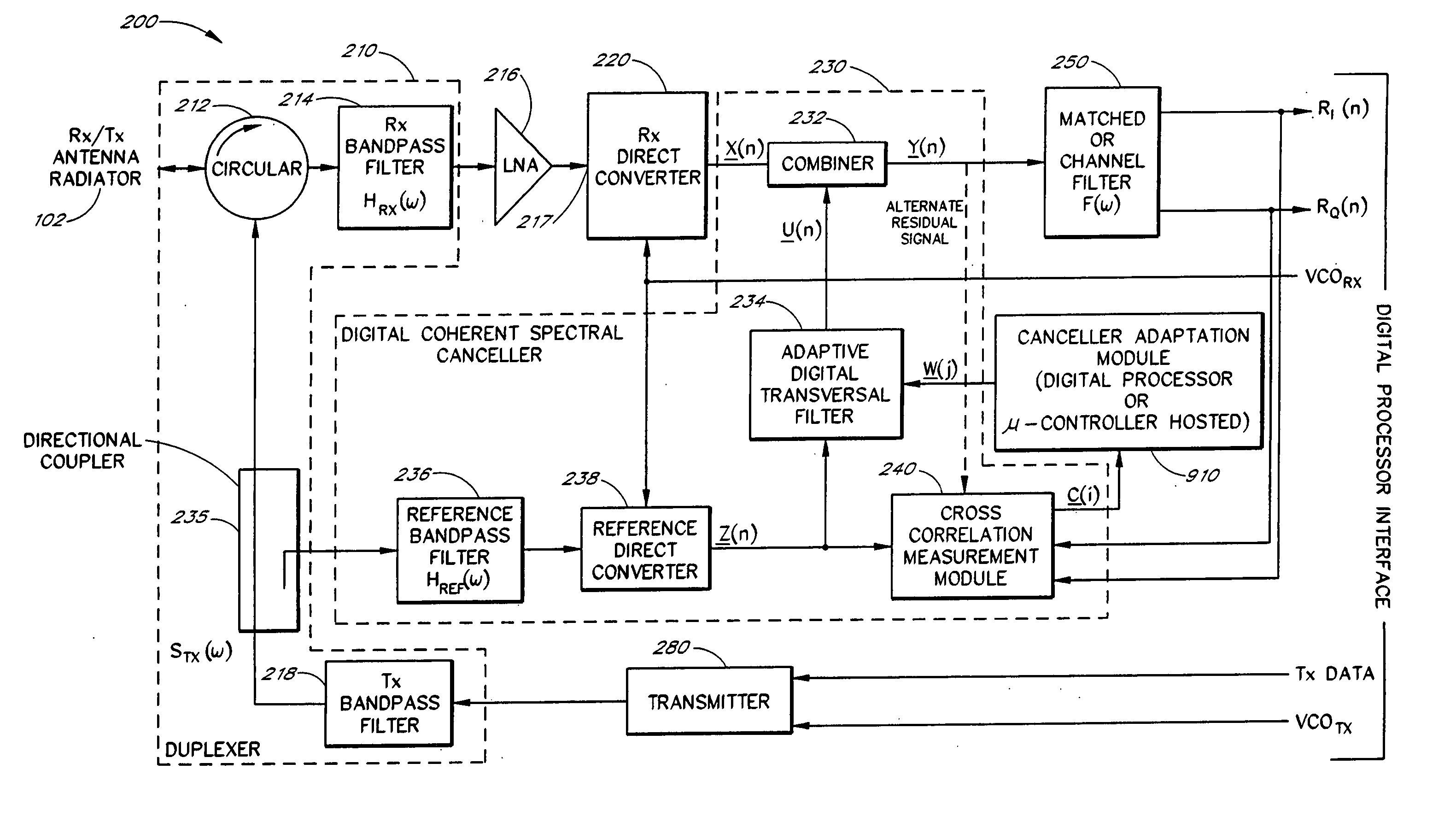
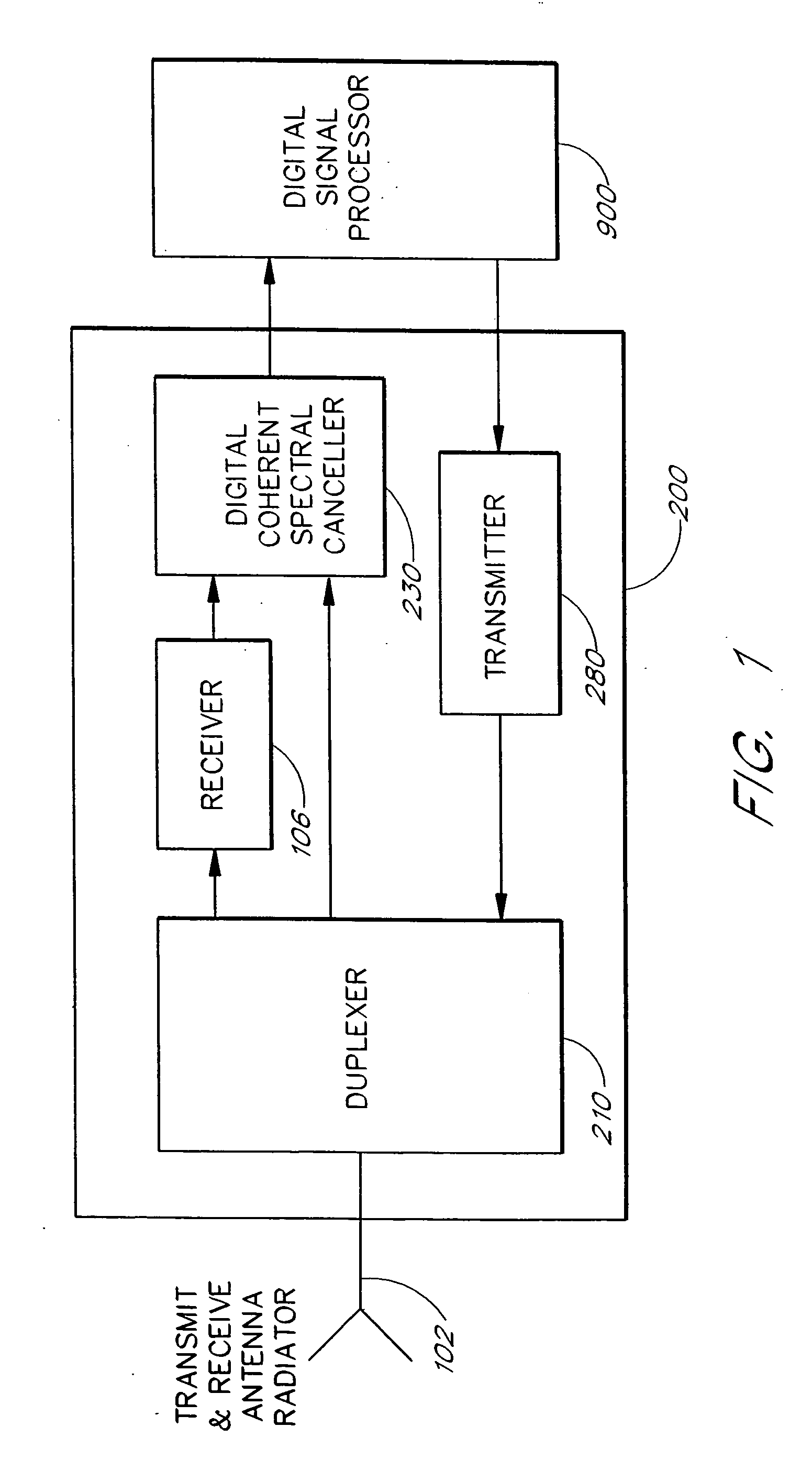
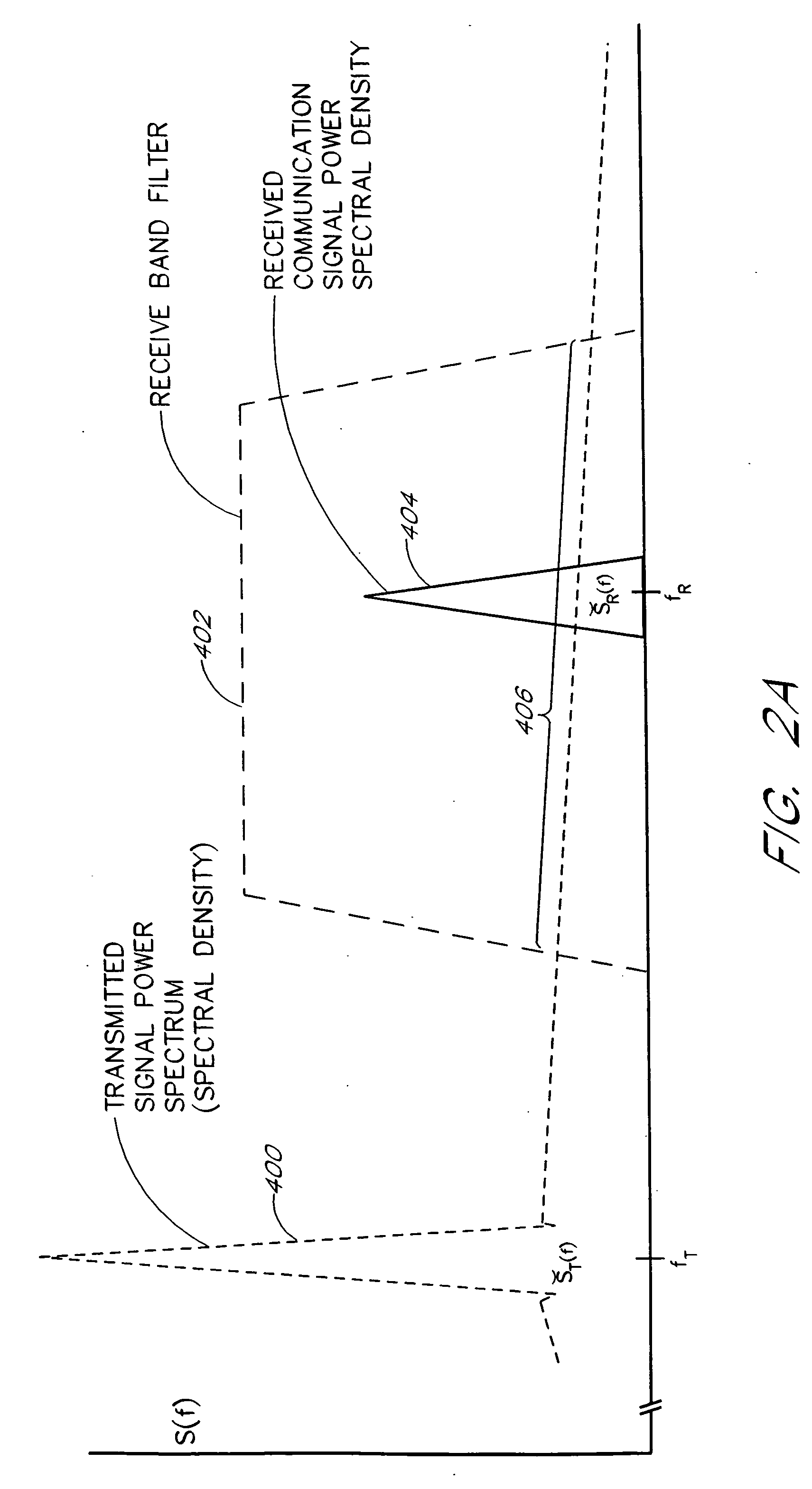
Method and apparatus for canceling a transmit signal spectrum in a receiver bandwidth
InactiveUS20040151238A1Transmission control/equalisingDuplex signal operationFrequency spectrumEngineering
Owner:DITRANS IP INC
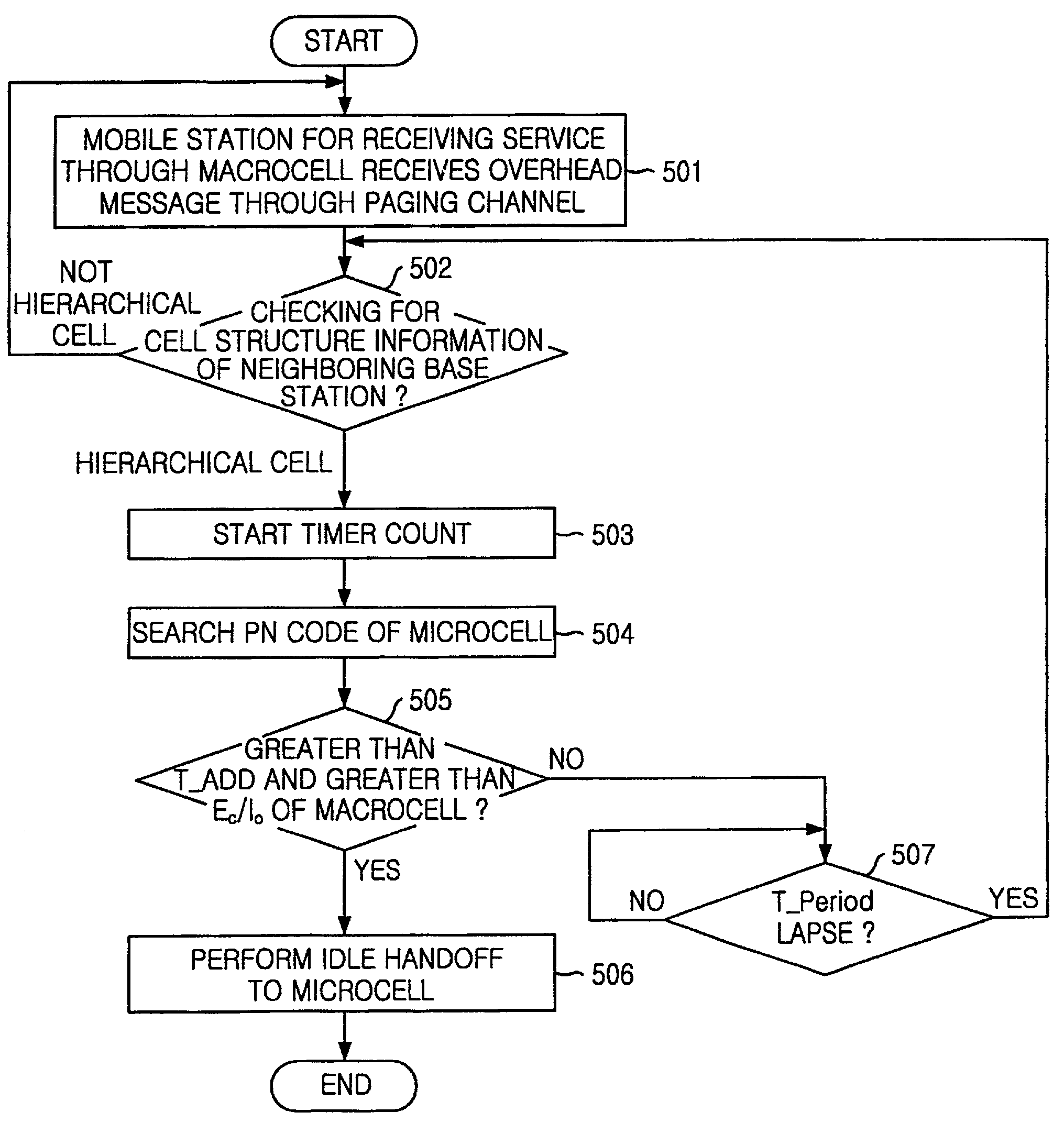
Method for carrying out handoff between macrocell and microcell in hierarchical cell structure
A method for carrying out an idle handoff from a macrocell to a microcell (picocell) in a hierarchical cell structure includes the steps of: a) allocating different frequency assignments (FA) to the macrocell and the microcell in a same service band, to construct the hierarchical cell structure; b) transmitting cell structure information of neighboring base stations and pseudo noise (PN) code from base station to mobile station; c) checking whether the mobile station is in the hierarchical cell by using the cell structure information of neighboring base station; and d) checking whether a value of the pseudo noise (PN) code is greater than T_ADD and greater than Ec / Io of the macrocell by periodically searching the pseudo noise (PN) code of the microcell, to carry out an idle handoff to the microcell, wherein the T_ADD represents a value of base station pilot strength required for the base station of neighboring set to be included in a candidate set, the Ec represents an pilot energy accumulated during one pseudo noise (PN) chip period, and the Io represents a total power spectrum density within a reception bandwidth.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
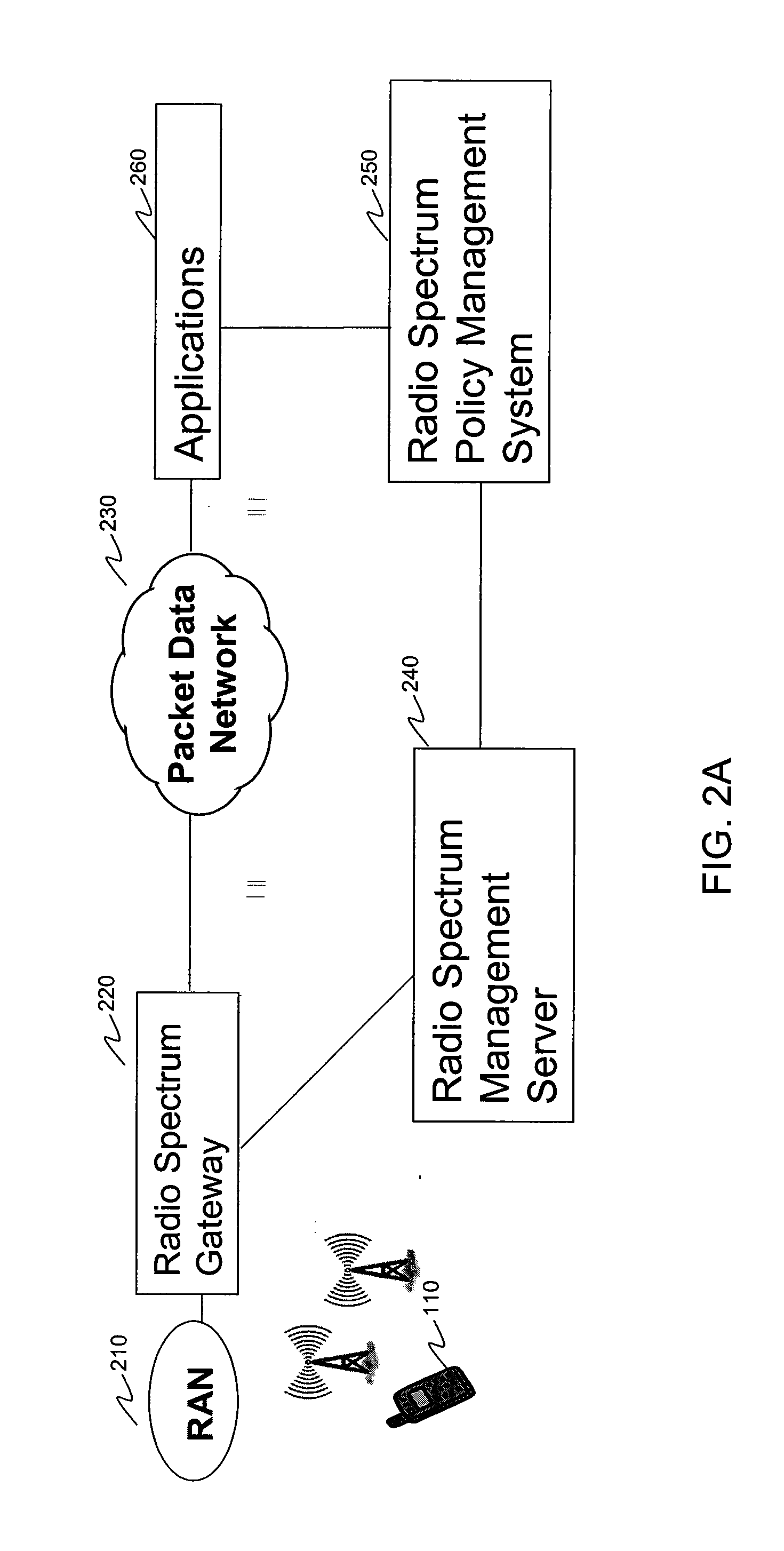
Systems and Methods for Subscriber-Centric Dynamic Spectrum Management
ActiveUS20080117869A1Promote generationReduce network operating costsError preventionTransmission systemsPolicy decisionFrequency spectrum
A radio spectrum management system is provided. In an embodiment, the radio spectrum management system includes a radio spectrum gateway, a radio spectrum management server and a radio spectrum policy decision server. The radio spectrum gateway is coupled to a radio access network that receives bandwidth requests from subscriber devices and provides bandwidth allocation decisions to the radio access network. The radio spectrum management server receives bandwidth requests from the radio spectrum gateway and provides bandwidth allocation decisions to the radio spectrum gateway based on radio resources and bandwidth policy decisions. The radio spectrum policy management server provides bandwidth policy decisions to the radio spectrum server. The bandwidth policy decisions are generated based on consideration of subscriber and / or application service provider characteristics. Methods for allocation of radio spectrum for a subscriber within a wireless network when the subscriber requests an application are also provided.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
Information transmission method and device
InactiveCN103716841AIncrease the scope of applicationSolve the problem of correctly receiving downlink informationModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementCarrier signalData transmission
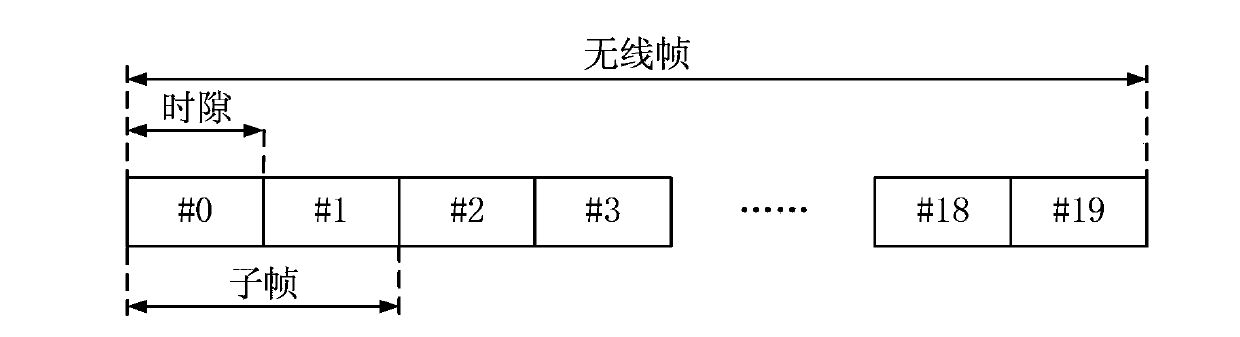
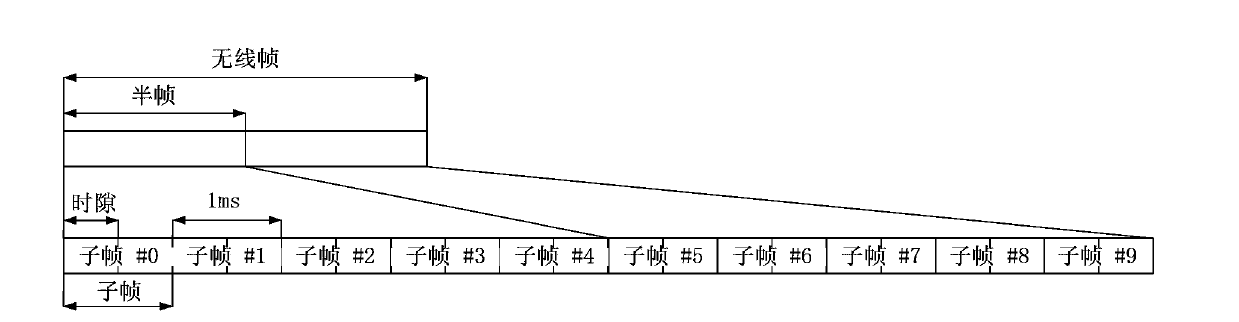
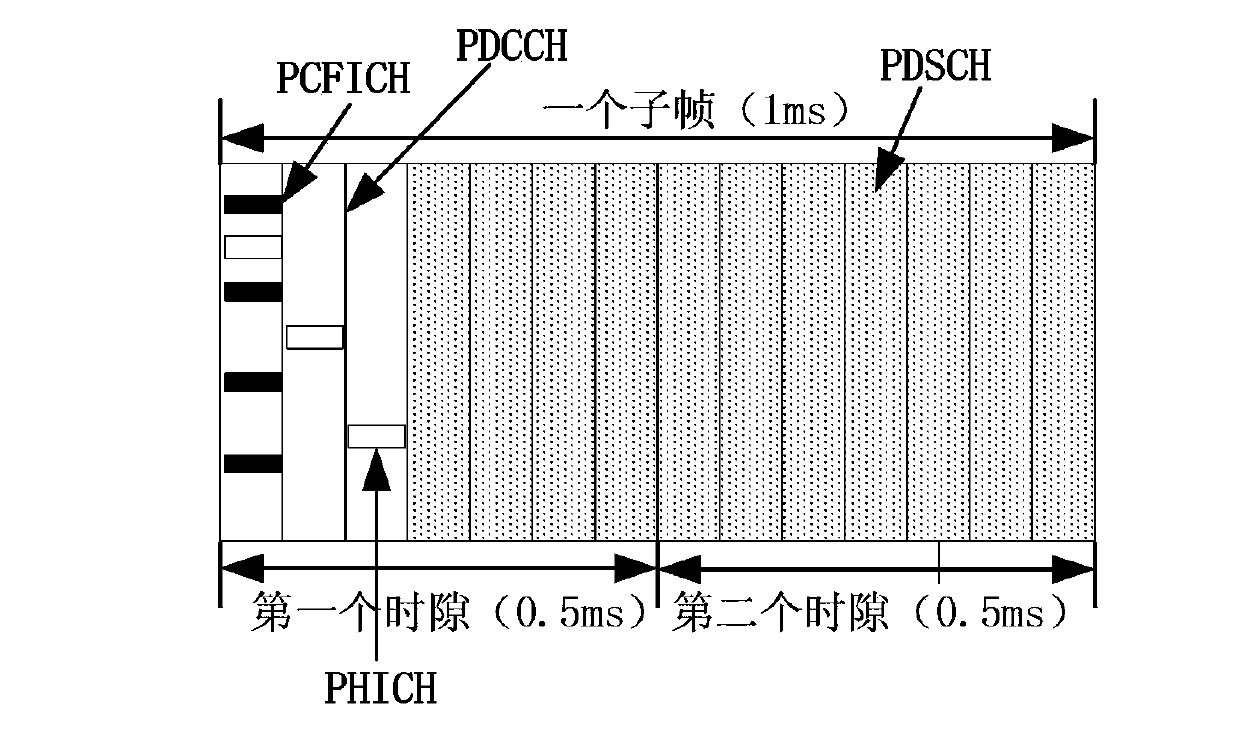
The invention discloses an information transmission method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a base station determining that a receiving bandwidth of a terminal is less than a system bandwidth or a component carrier accessed by the terminal is a new type component carrier; and the base station transmits downlink data to the terminal within the receiving bandwidth of the terminal according to preset radio frame, subframe, time domain and frequency domain resources. The method and device provided by the present invention solve the problem of how to receive downlink information correctly in case of a small downlink bandwidth in related arts and enable various types of terminals to exist in the system at the same time so as to increase the applicable scope of the system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
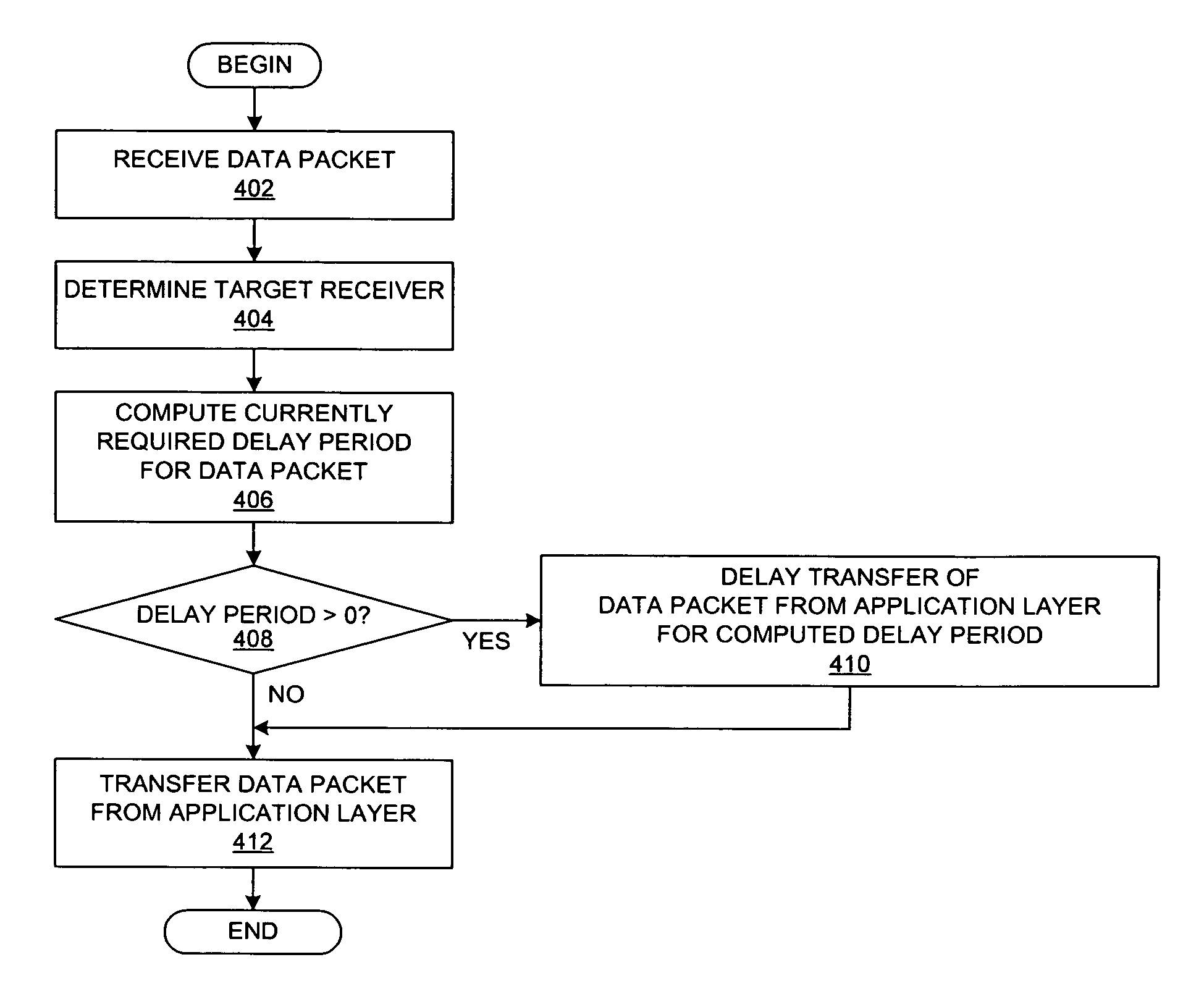
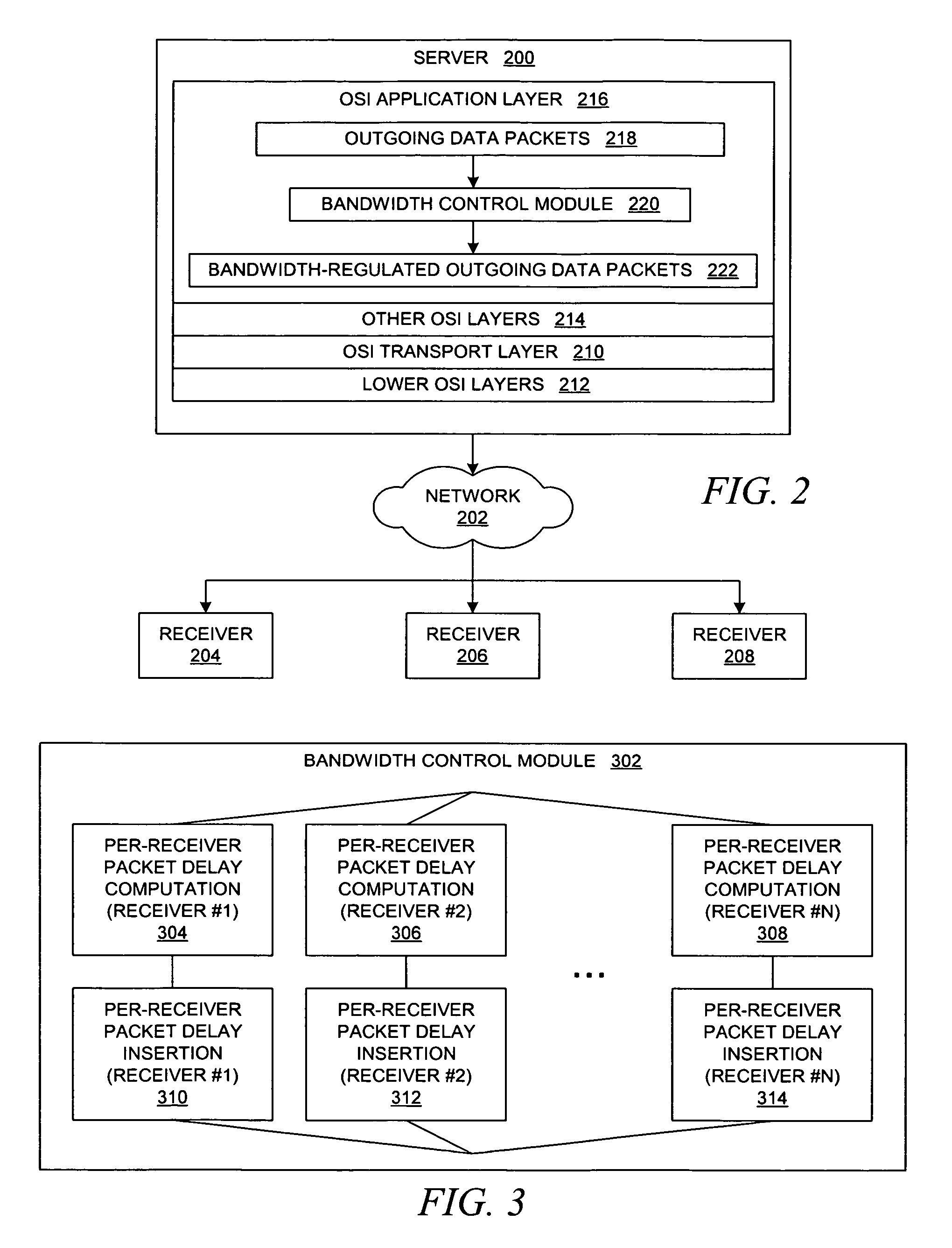
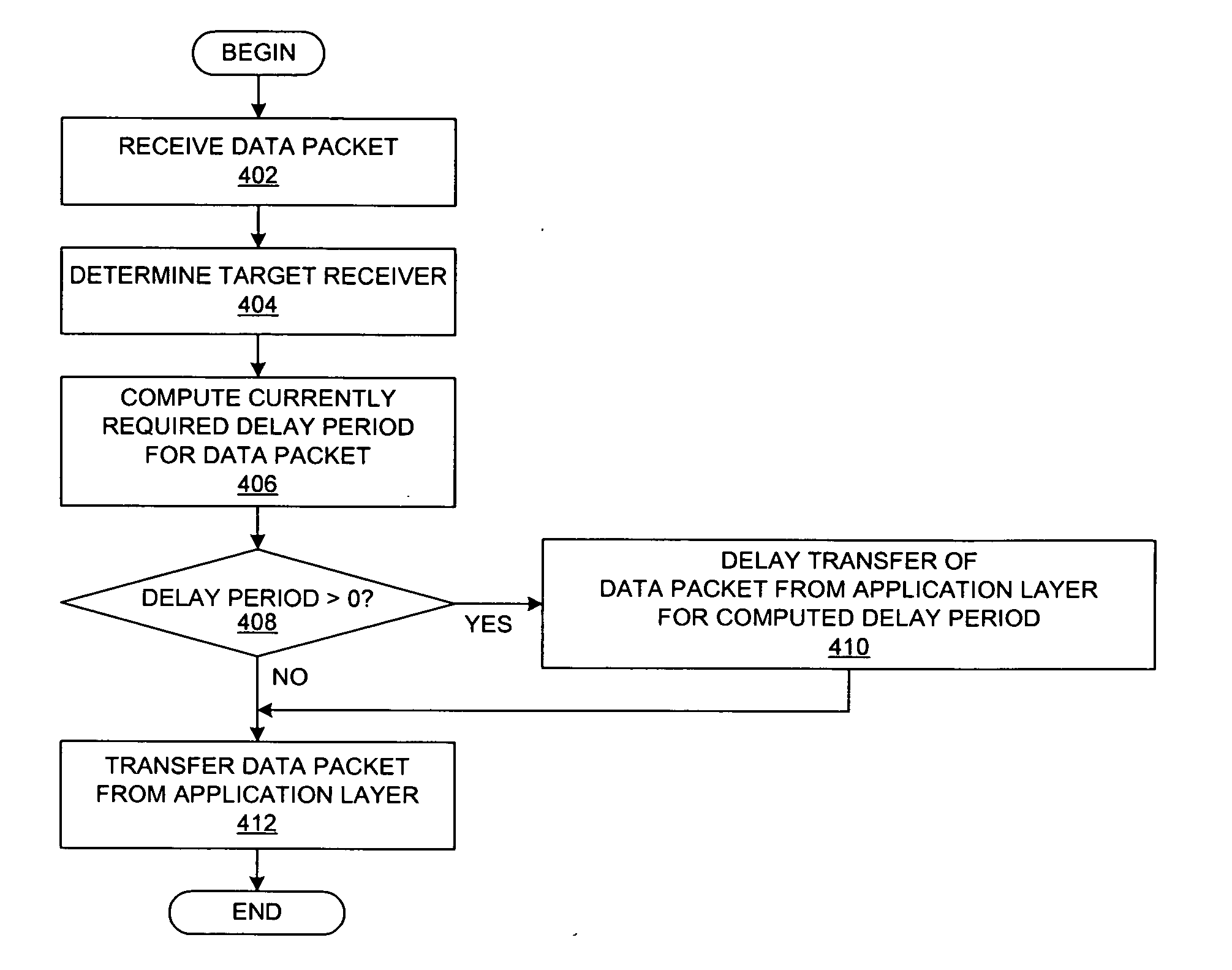
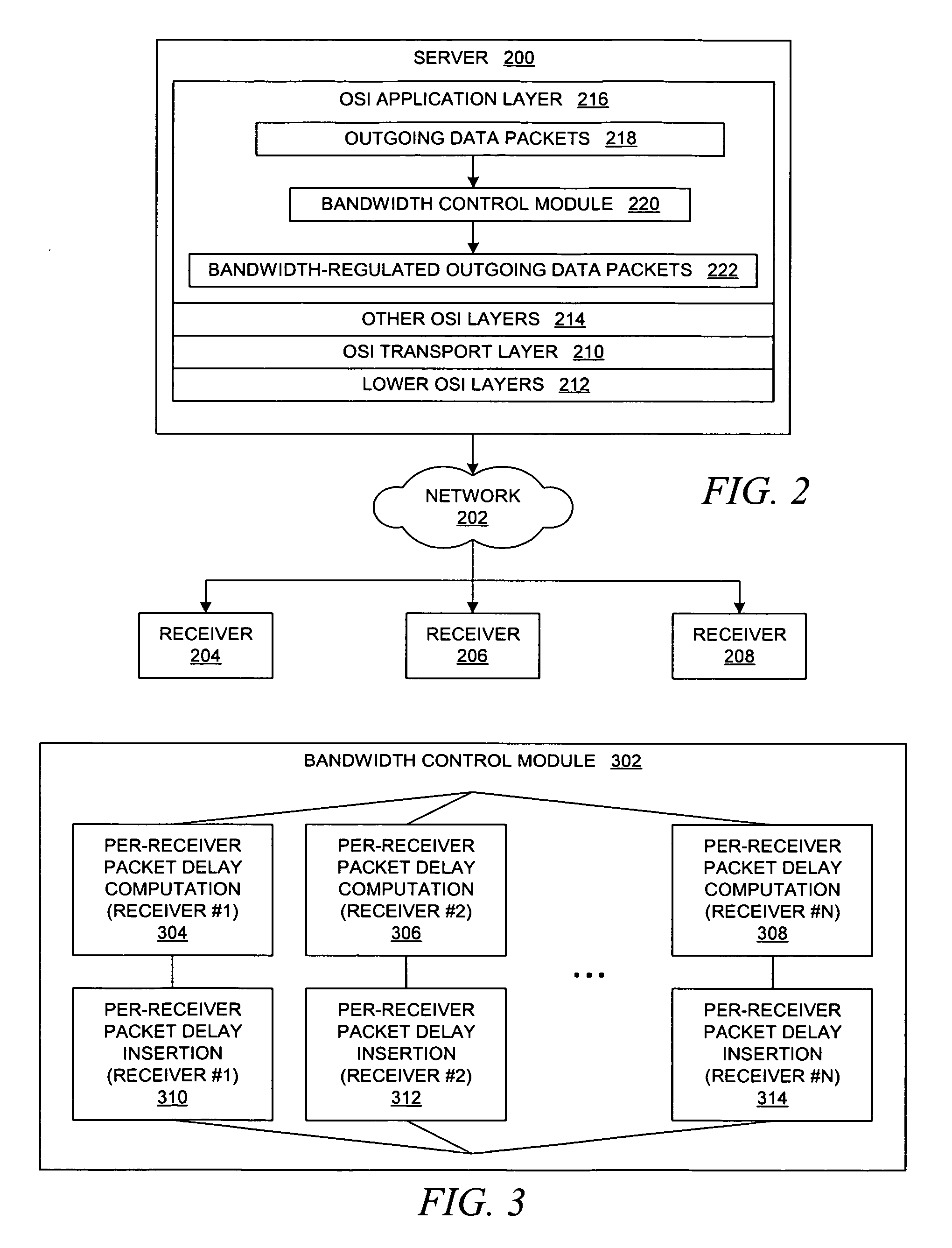
Method and system for throttling network transmissions using per-receiver bandwidth control at the application layer of the transmitting server
A method is presented for throttling data transmissions within a data processing system. Information about a data transfer from a server to a client is received within the application layer of a server, which stores the information about the data transfer along with information about a number of recent data transfers from the server to the client to create a sliding window of historical information about data transfers. The data transfer from the application layer of the server is delayed within the application layer of the server for an amount of time that is approximately equal to a computed delay time value in response to a determination that an average data transfer rate over the number of recent data transfers from the server to the client may exceed a data transfer rate threshold parameter.
Owner:IBM CORP
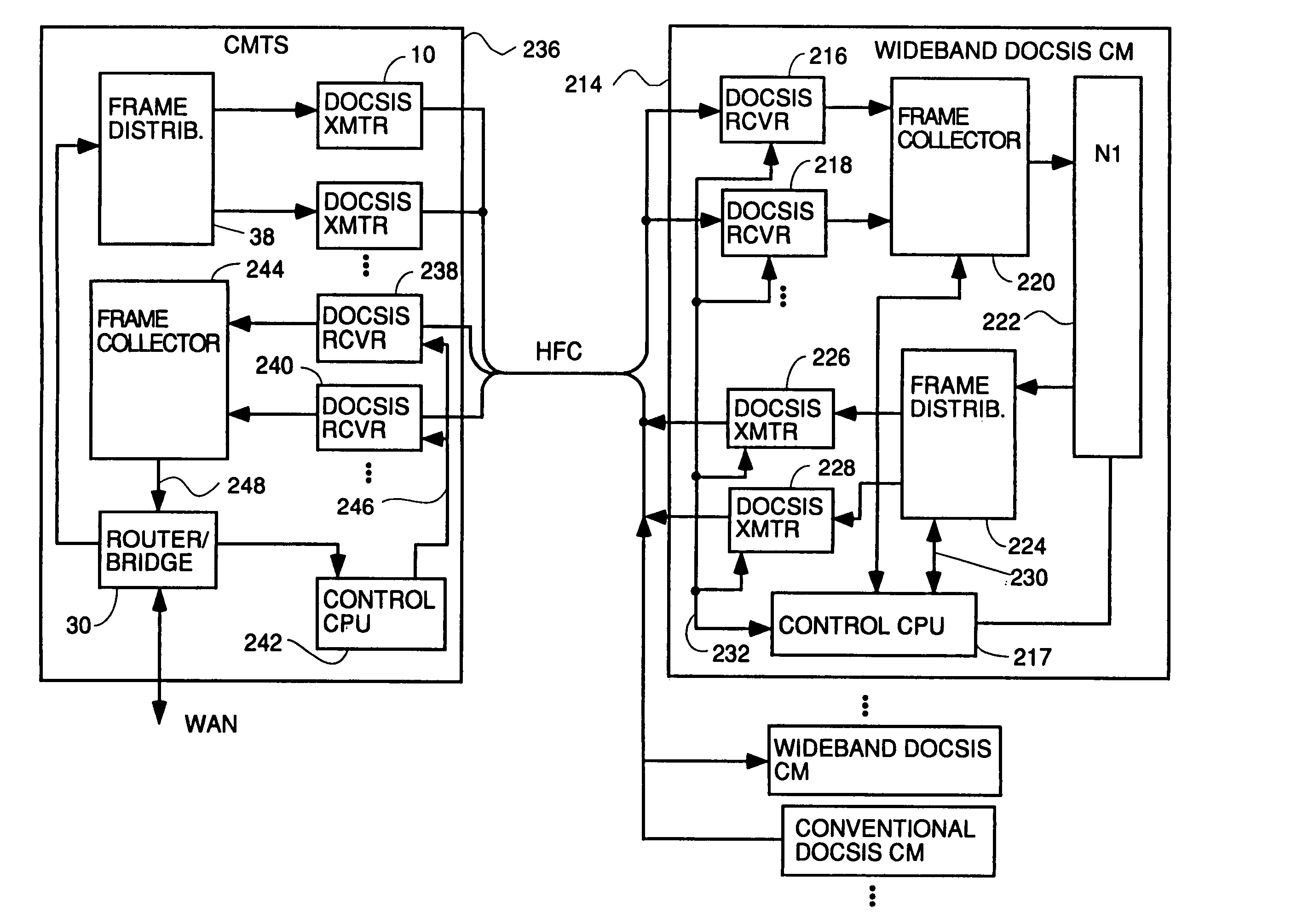
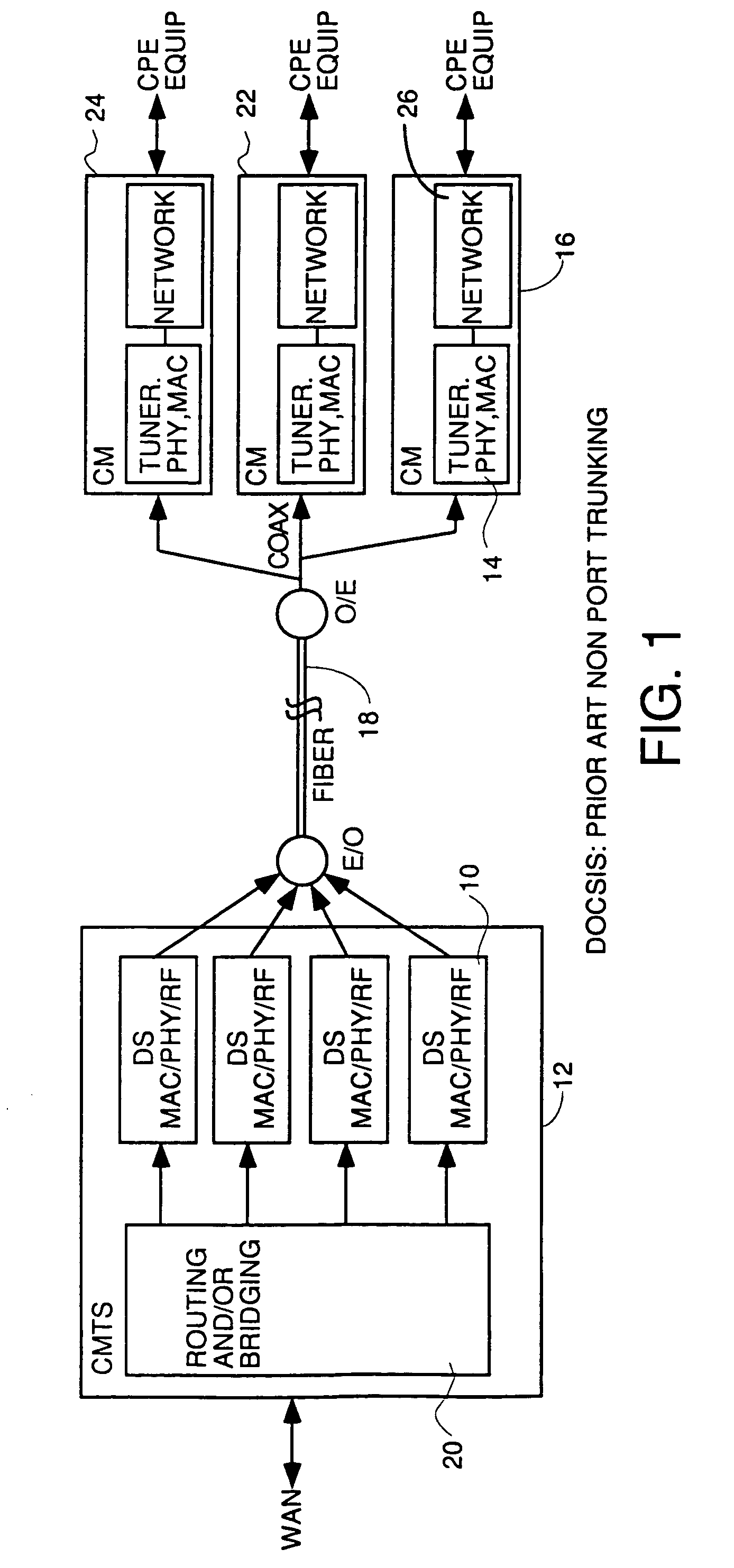
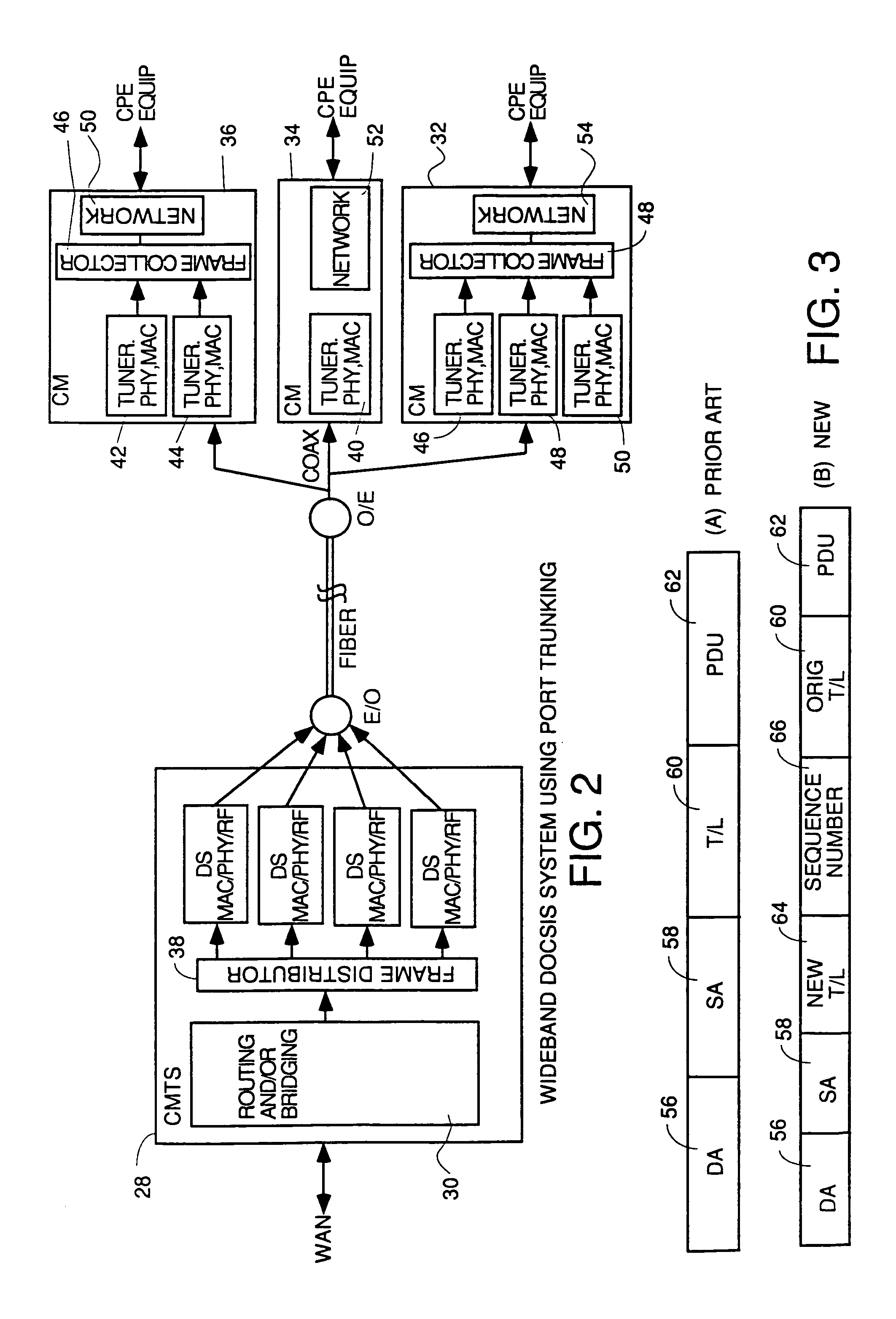
Wideband DOCSIS on catv systems using port-trunking
Method and apparatus to carry out wideband DOCSIS both upstream and downstream in a point-to-multipoint environment of an HFC system using port trunking concepts. For the downstream, each CMTS has a frame distributor which distributes frames to various transmitters transmitting on downstream channels to be used to transmit downstream data simultaneously to a CM using wideband DOCSIS. The frame distributor adds sequence numbers in some embodiments to guarantee proper order of frames can be restored at the CM, and schedules transmissions according to quality of service considerations to meet guaranteed and committed portions of constant bit rate and variable bit rate flows. The CMTS sends and Extended Channel Enable (ECE) message to wideband capable CMs telling them which downstreams to enable. Each CM has a frame collector to which all frames received on various downstream channels are sent. The frame collector makes sure they are all there, puts them into the proper order and delivers them to a NI. Upstream wideband DOCSIS works the same way with a frame distributor in each CM and a frame collector in the CMTS. The CMTS receives bandwidth requests and controls upstream wideband DOCSIS transmissions by sending downstream UCD and MAP and ECE messages to the CMs instructing them which upstream channels to use, describing the parameters of the channel and assigning times for transmission which are simultaneous on multiple channels for upstream wideband capable CMs.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
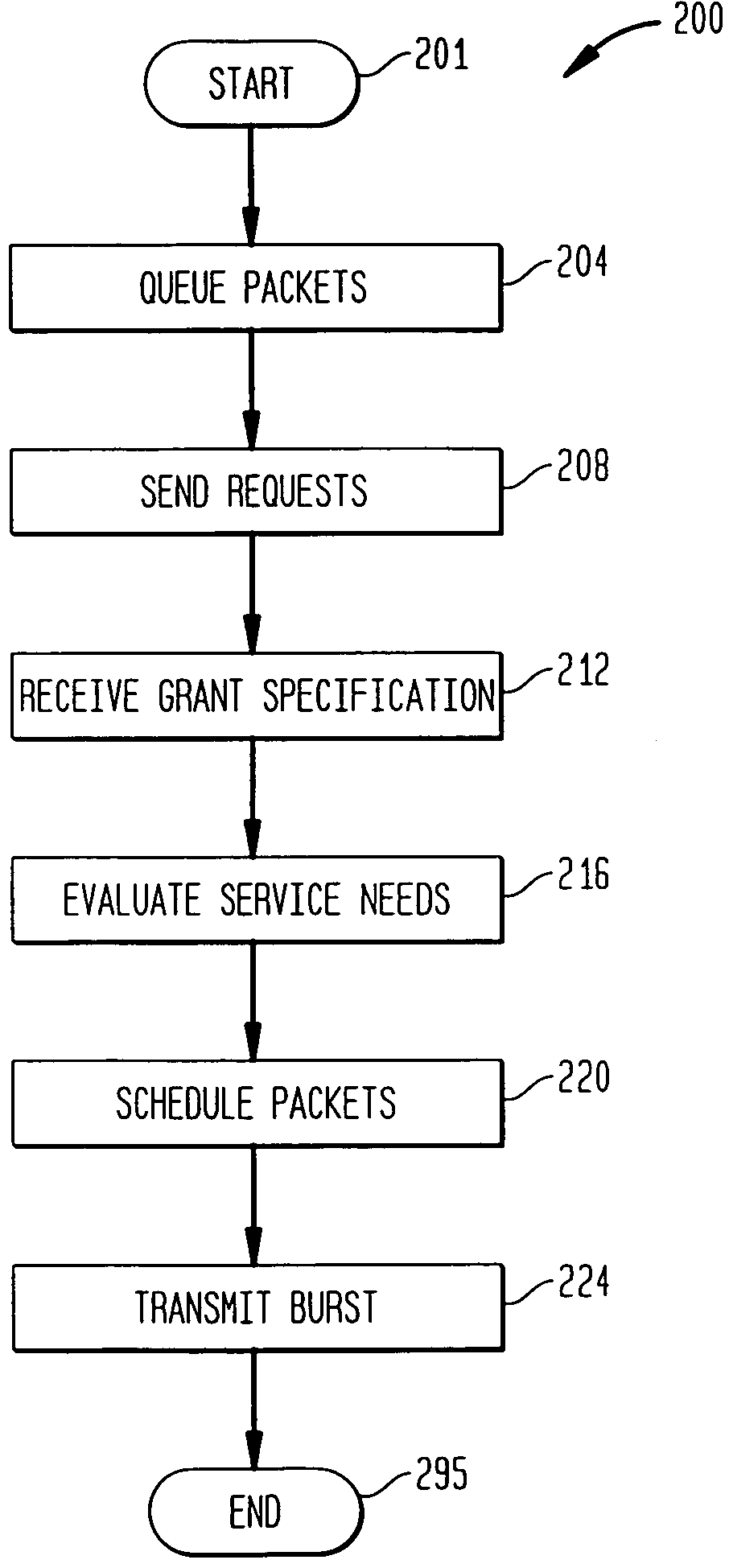
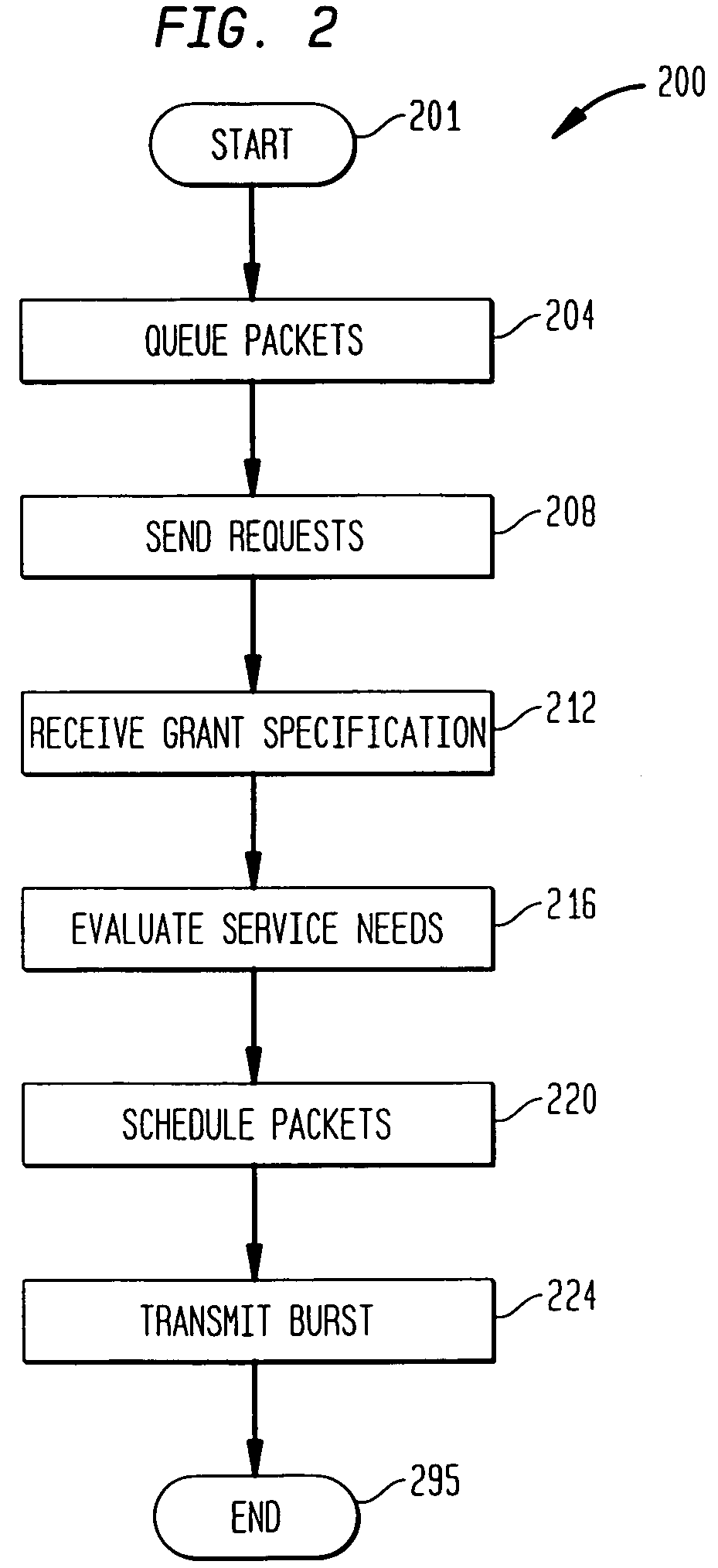
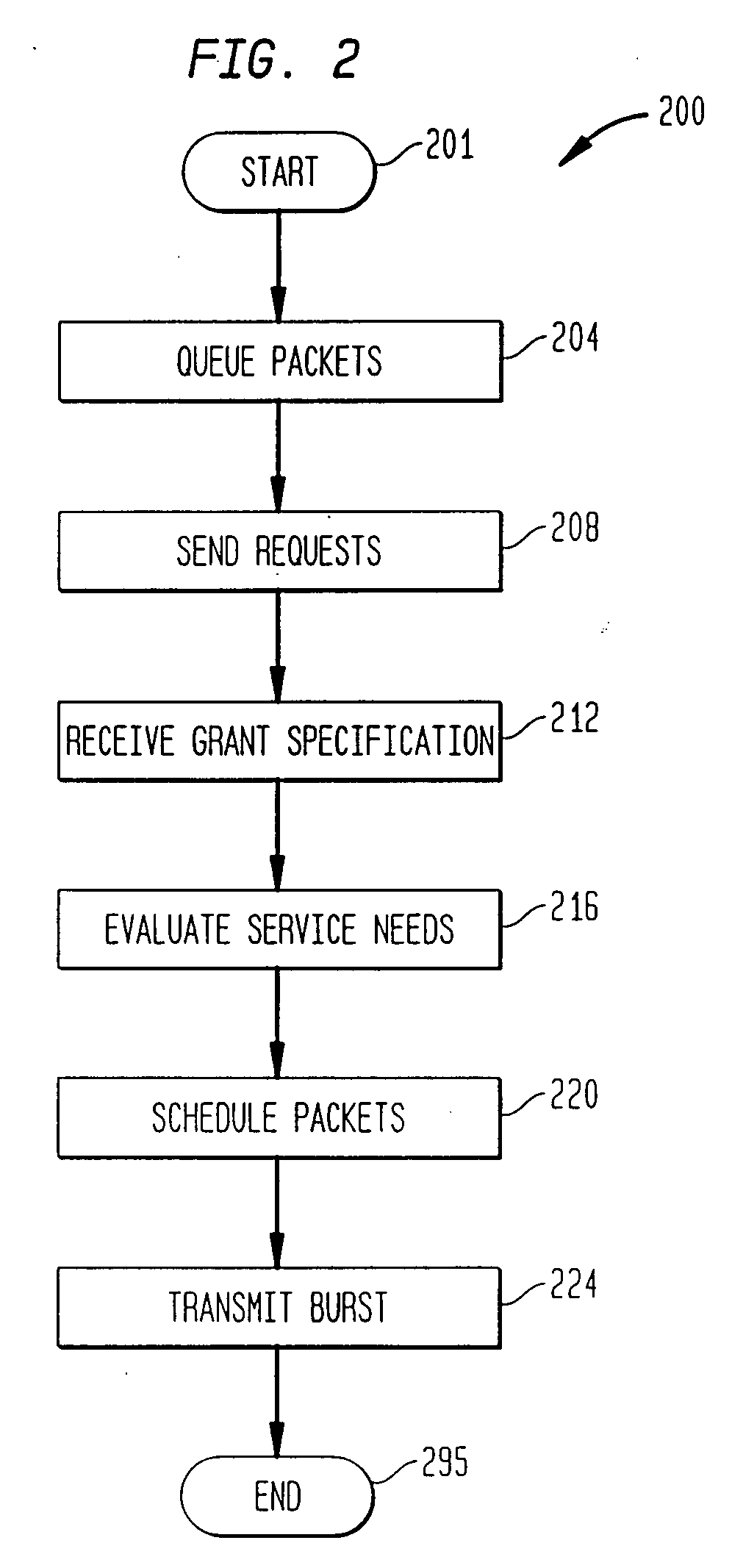
Method for scheduling upstream communications
InactiveUS7333495B2Broadband local area networksTime-division multiplexReceiver BandwidthCommunication device
A system and method is provided for scheduling transmissions from a plurality of services operating over a widely distributed communications network. A headend communications device (such as a cable modem termination system) arbitrates bandwidth among a plurality of cable modems configurable for bi-directional communications. The headend grants a bandwidth region to a specified cable modem or assigns contention regions for a group of cable modems. Each cable modem contains a local scheduler that sends requests for bandwidth according to local policies or rules. Upon receipt of a grant from the headend, the local scheduler selects packets to be transmitted to best serve the needs of the services associated with the cable modem. Accordingly, a service requesting bandwidth may not be the service utilizing the grant corresponding to bandwidth request. Nonetheless, the local scheduler manages bandwidth allocation among its local services such that all requesting services eventually receive bandwidth.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for throttling network transmissions using per-receiver bandwidth control at the application layer of the transmitting server
A method is presented for throttling data transmissions within a data processing system. Information about a data transfer from a server to a client is received within the application layer of a server, which stores the information about the data transfer along with information about a number of recent data transfers from the server to the client to create a sliding window of historical information about data transfers. The data transfer from the application layer of the server is delayed within the application layer of the server for an amount of time that is approximately equal to a computed delay time value in response to a determination that an average data transfer rate over the number of recent data transfers from the server to the client may exceed a data transfer rate threshold parameter.
Owner:IBM CORP
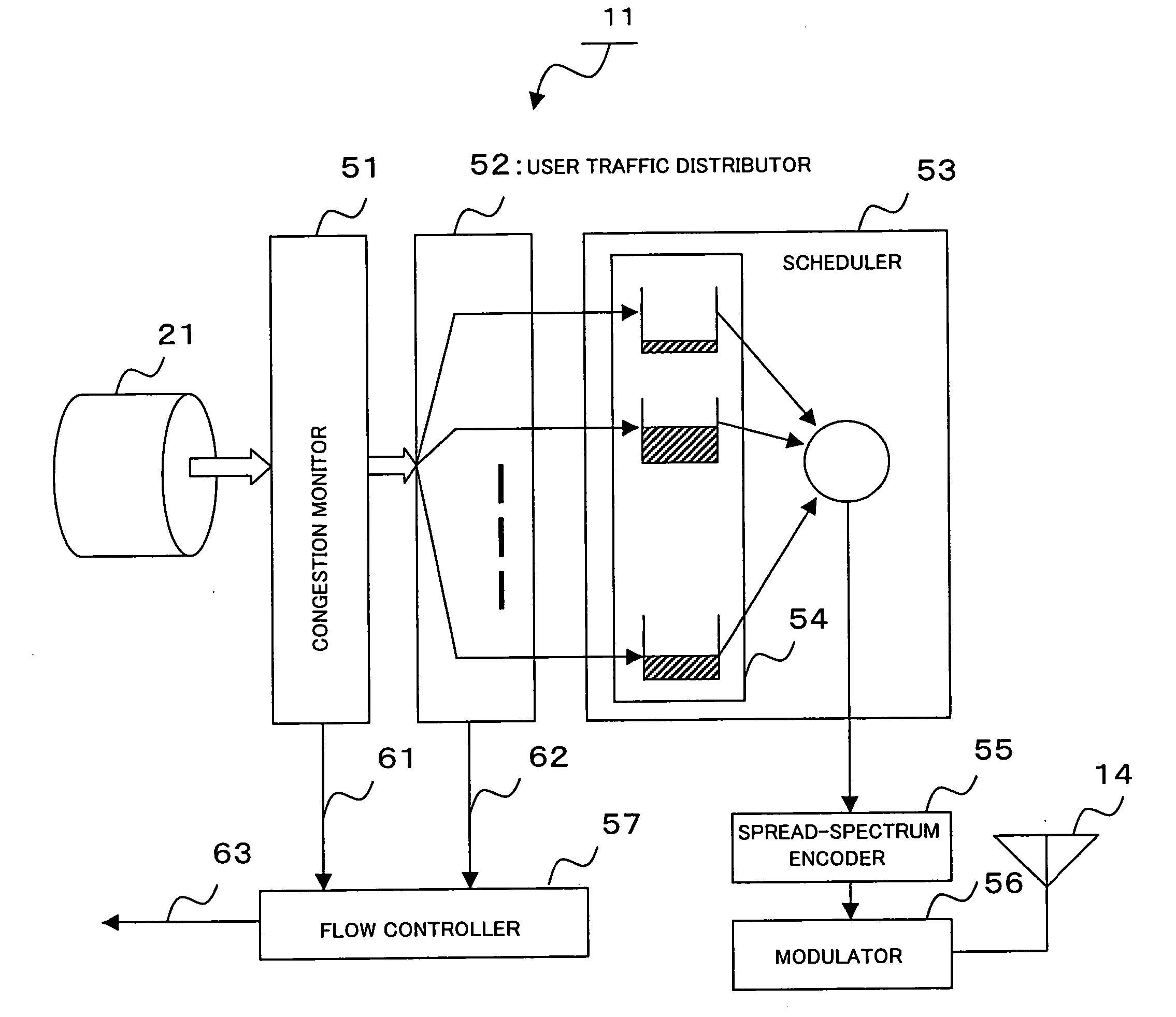
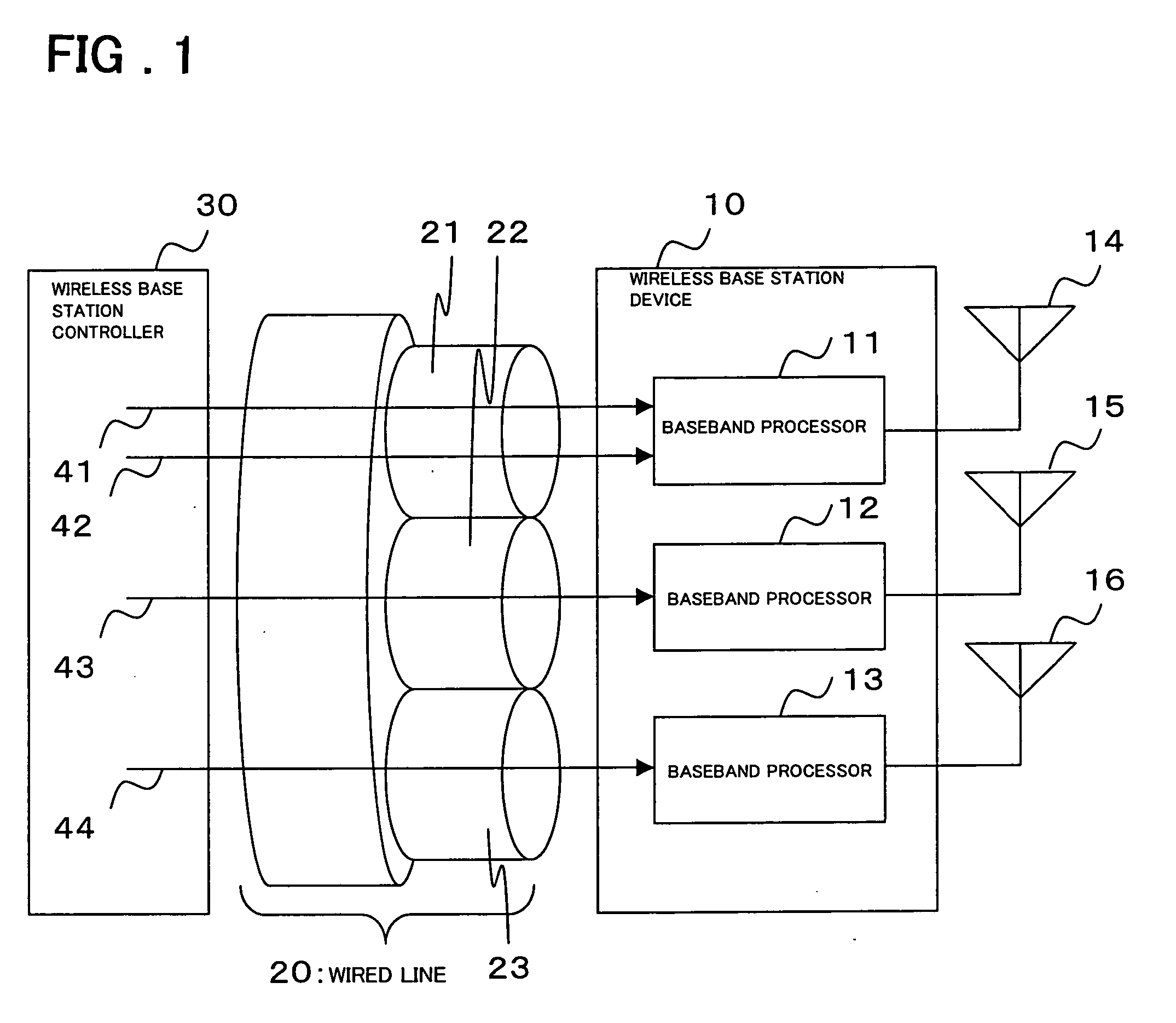
Wireless base station device and rate control method thereof
InactiveUS20060126507A1Increase profitLow costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamStation
A wireless base station device, connected to a higher-level station device via a wired line, comprises baseband processors 11, one for each virtual link 21 to which user data flows belong. In the baseband processor 11, a congestion monitor 51 monitors the reception bandwidth usage rate of a virtual link allocated to each cell for detecting congestion and, upon detecting congestion, sends a notification to a flow controller 57. A user traffic distributor 52 distributes a received user traffic into the traffic flow of each user and, at the same time, extracts, for each user data flow, the buffer holding amount in the higher-level station device where user data flows are multiplexed and sends a notification to the flow controller 57. The flow controller 57 manages the data flow of each user and, in response to a congestion notification from the congestion monitor 51, requests the higher-level station device to reduce the rate of a user data flow in descending order of rates beginning with a data flow with a highest rate.
Owner:NEC CORP
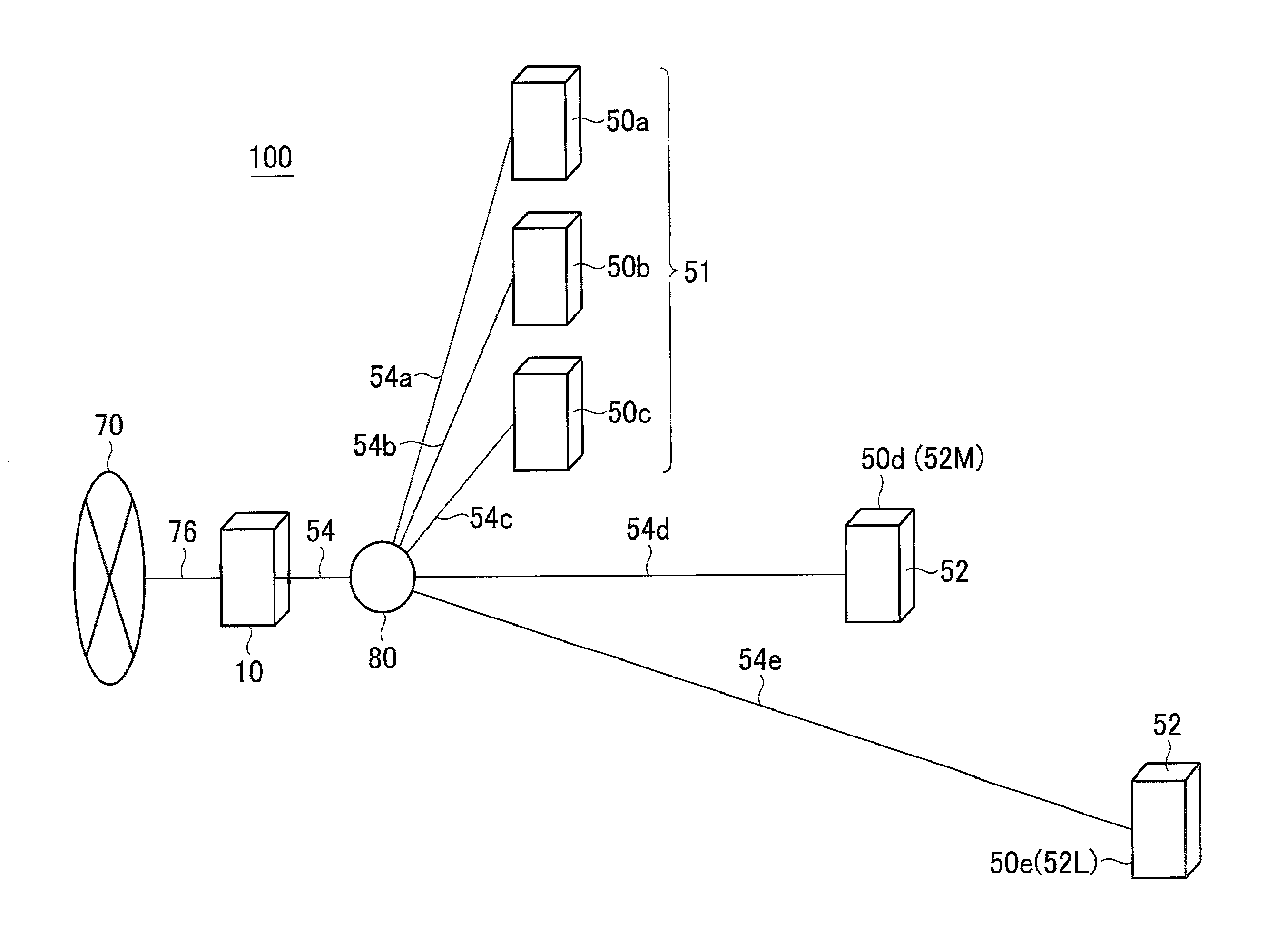
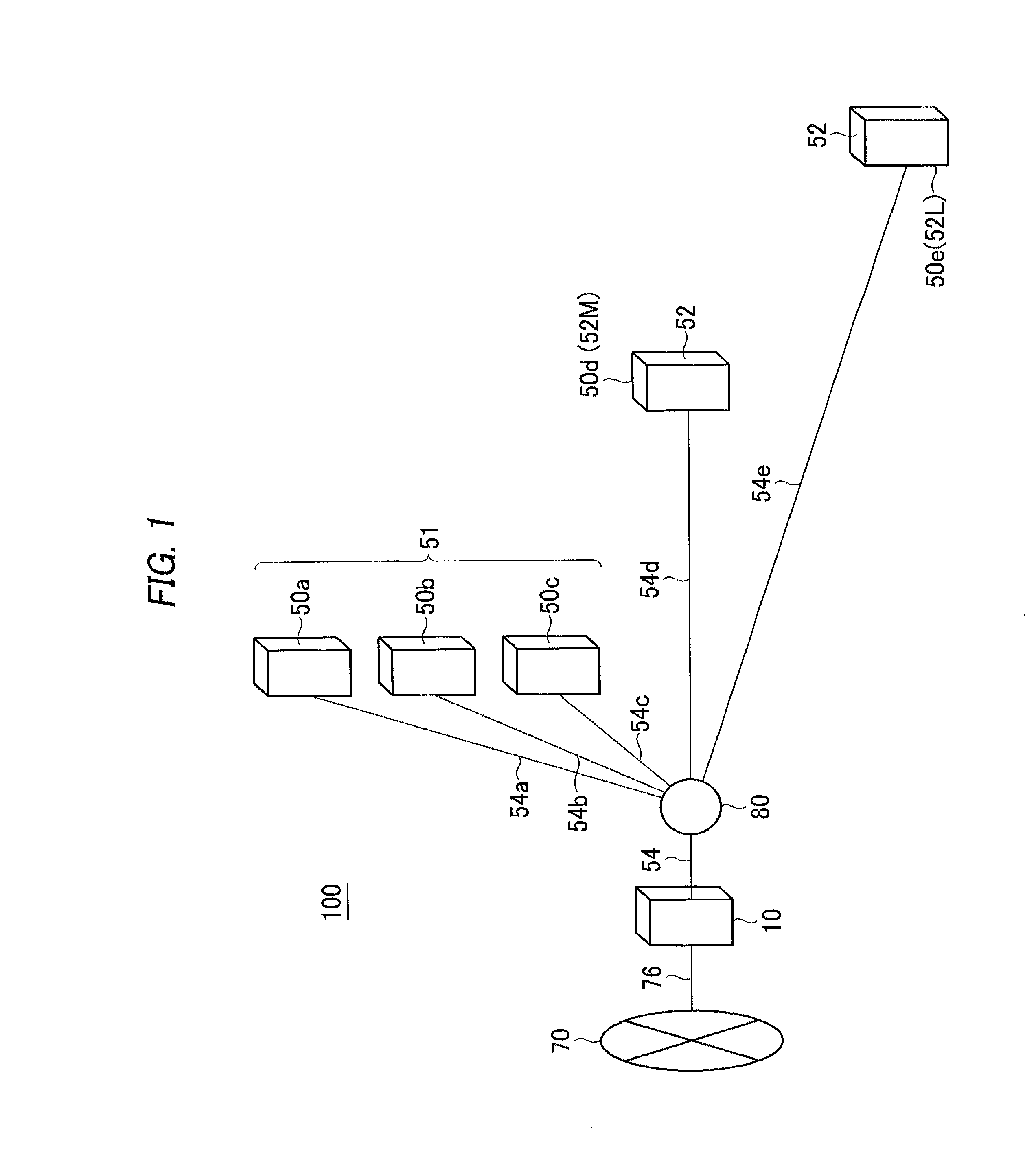
Optical line terminal, passive optical network system, and bandwidth assignment method
InactiveUS20100239255A1Maximize throughputAttenuation bandwidthTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexDynamic bandwidth assignmentBandwidth requirement
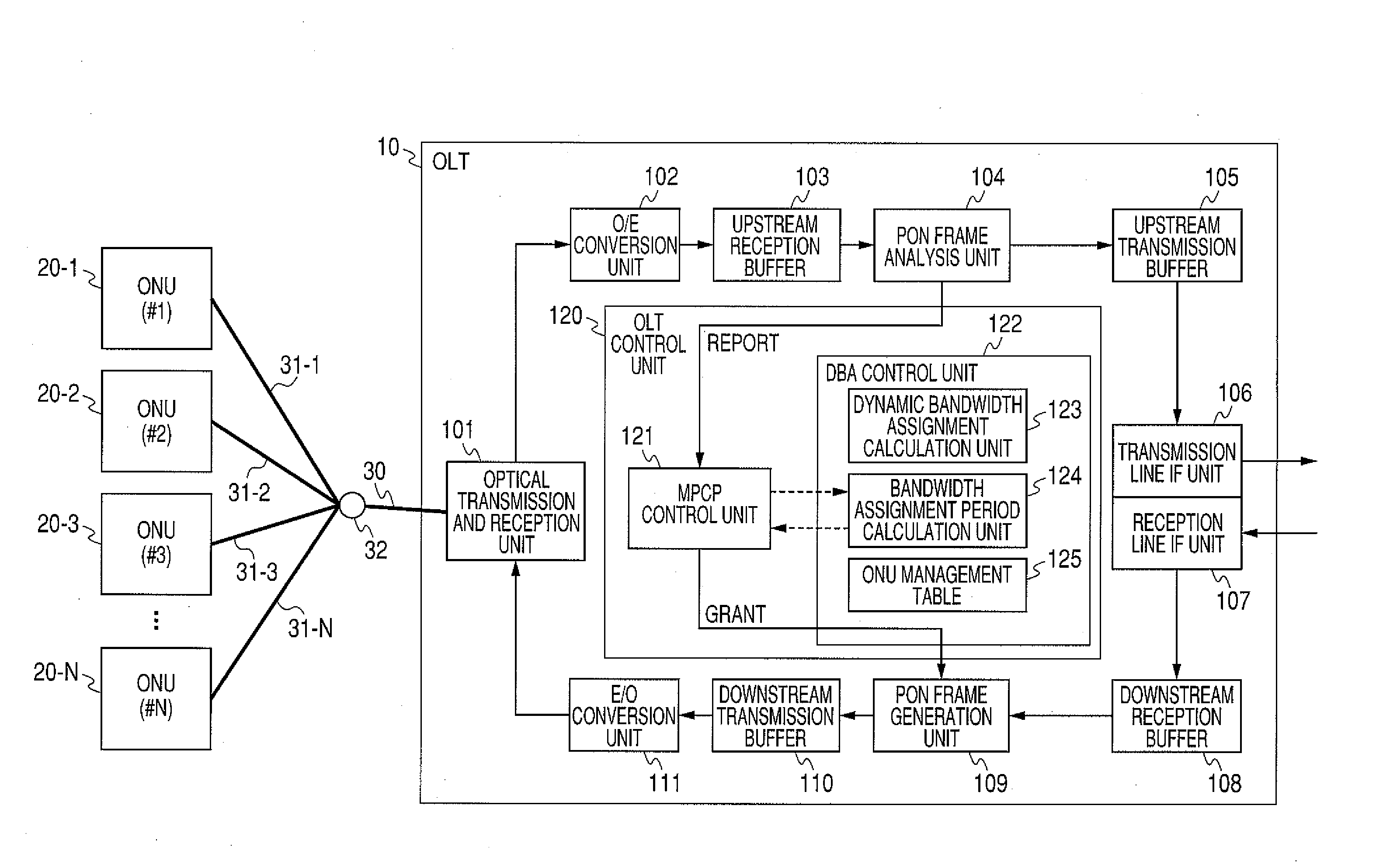
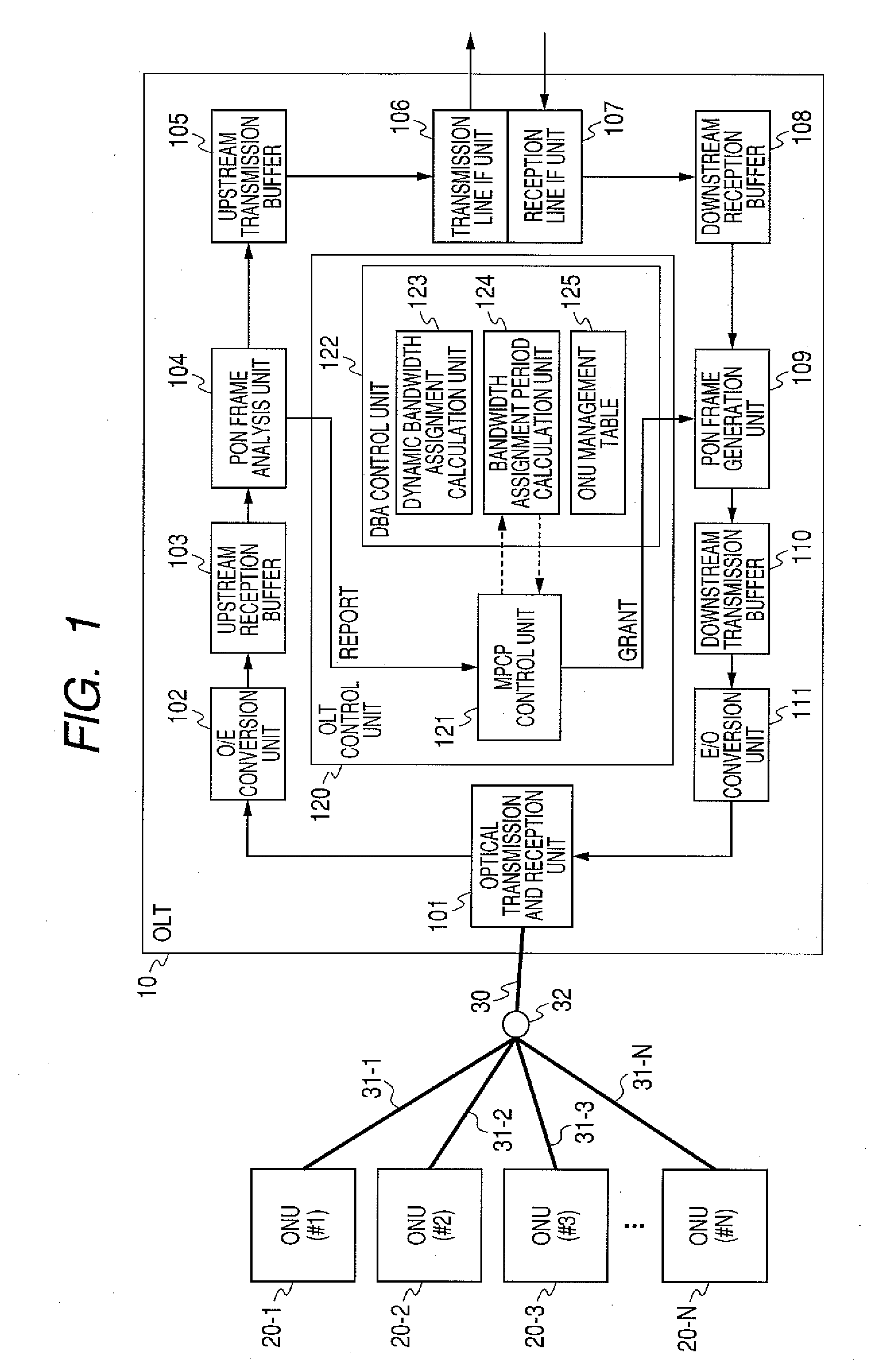
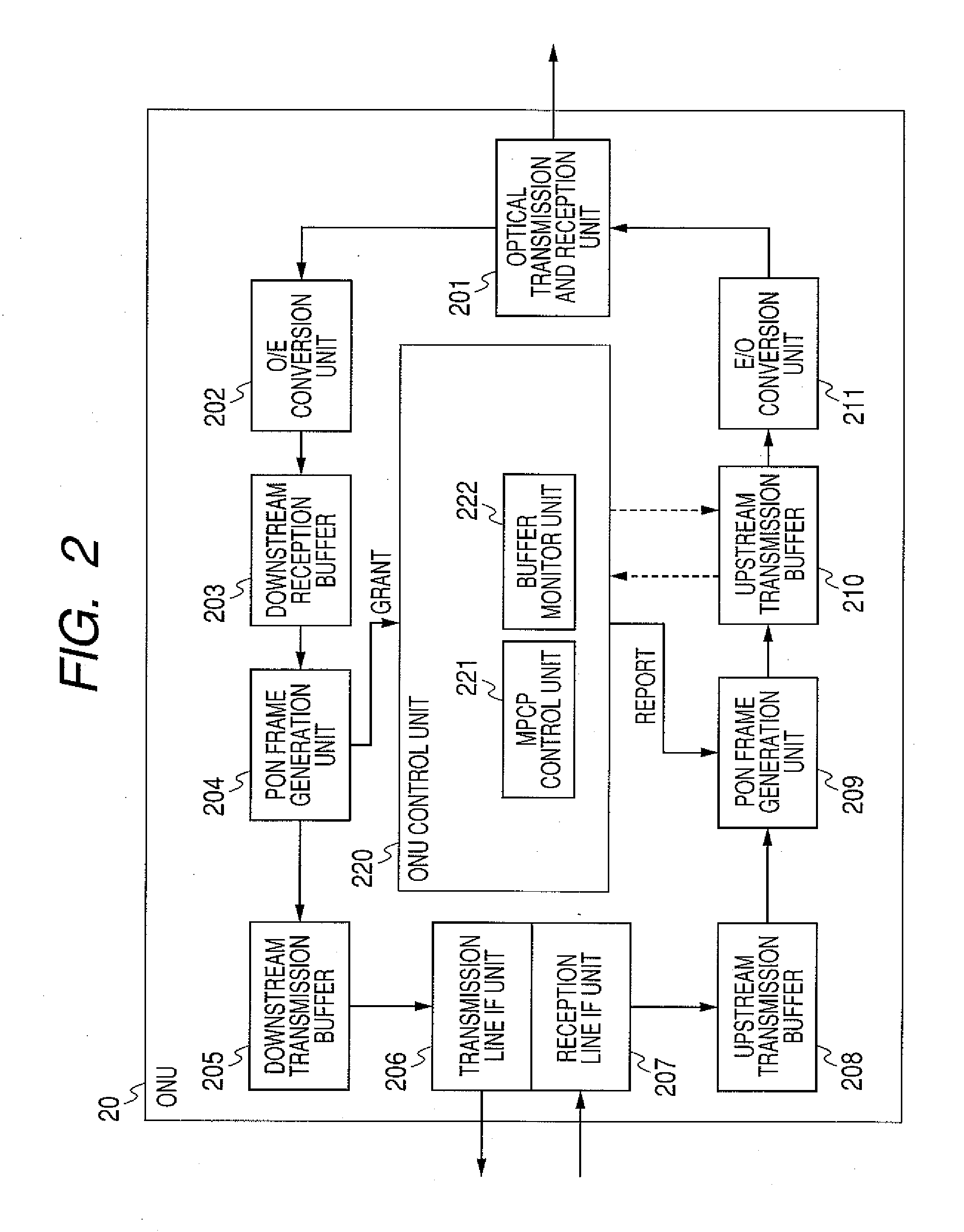
An OLT of a station-side device in a PON system, the OLT including: an MPCP control unit for receiving bandwidth requirements from each of a plurality of ONUs of home-side devices; a bandwidth assignment period calculation unit for calculating the following bandwidth assignment period for each request source based on the received bandwidth requirements for each request source; a dynamic bandwidth assignment calculation unit for calculating the following bandwidth assignment for each request source based on the received bandwidth requirements for each request source; and the MPCP control unit for transmitting transmission allowance based on the calculated bandwidth assignment to each of the plurality of ONUs.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
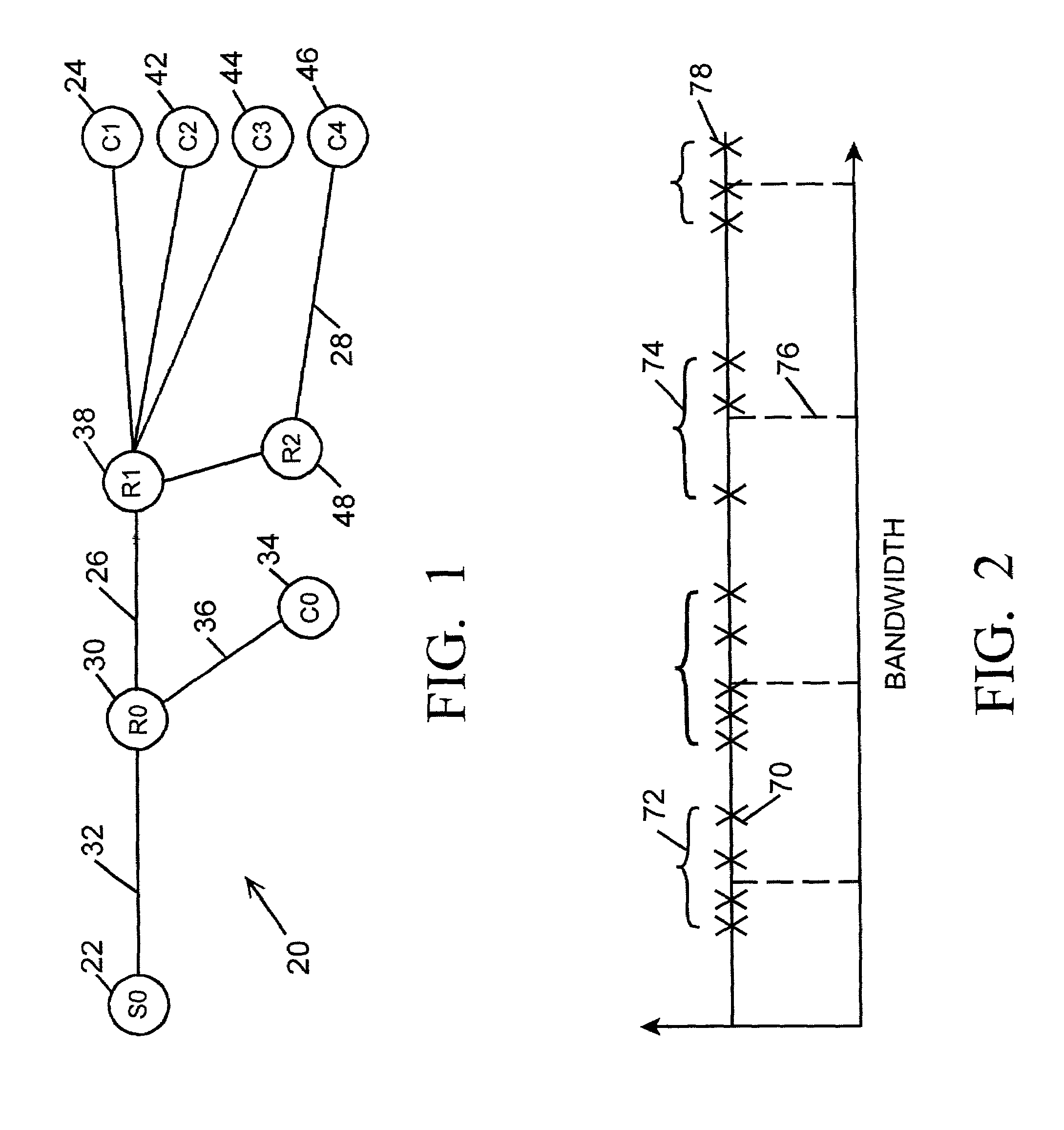
Transmission rate selection for a network of receivers having heterogenous reception bandwidth
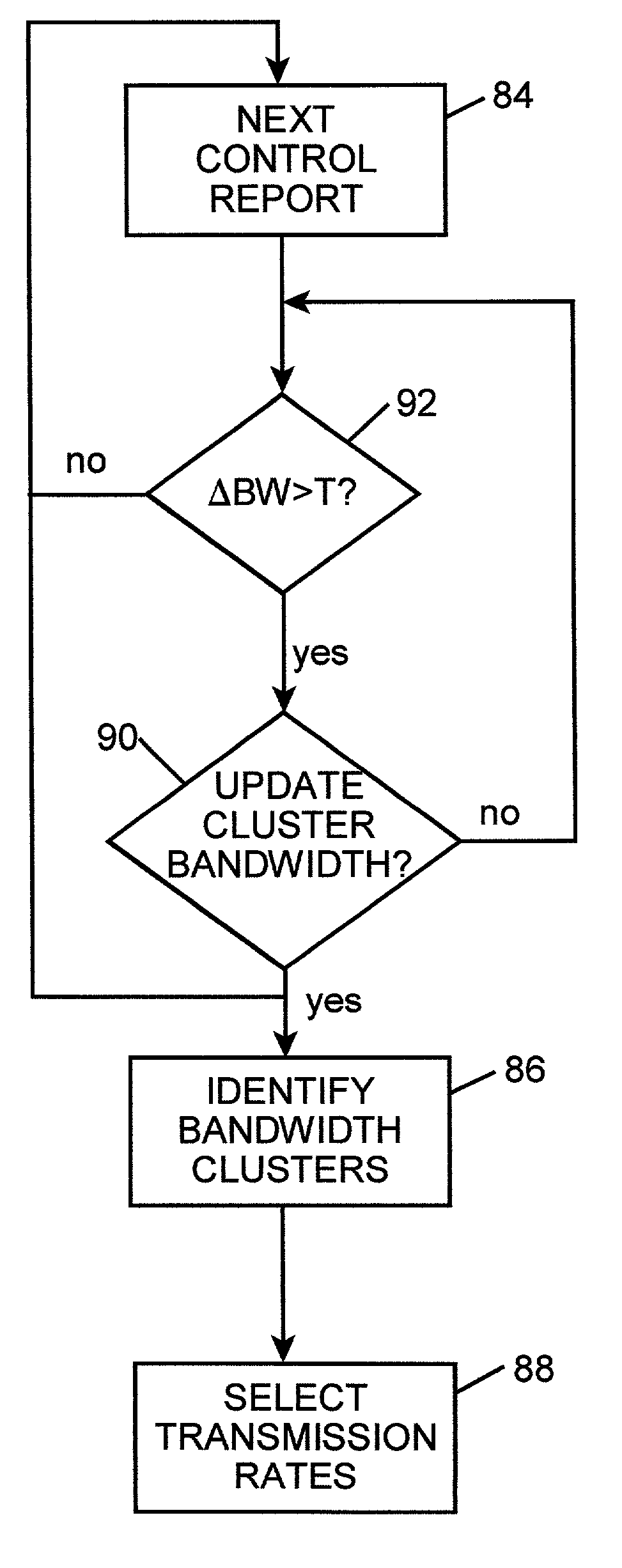
InactiveUS7191246B2Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistortionData transmission
A method of selecting a data transmission rate for a heterogeneous network clusters the results of reports of local reception bandwidth and determines an appropriate data transmission rate that either minimizes data loss or minimizes a cost function relating distortion and local bandwidth utilization for each cluster.
Owner:SHARP KK
Mobile communication base station and method for allocating resources outside of a virtual carrier based on ue capabilities
ActiveUS20150296514A1Reduce the amount requiredVirtual capacity can be increasedTransmission path divisionSignal allocationResource elementCarrier signal
A mobile communications network includes one or more network elements providing a wireless access interface for communications devices. The wireless access interface provides plural communications resource elements across a host frequency bandwidth, and includes, within the host frequency bandwidth, first communications resource elements within a first frequency bandwidth for allocation preferably to reduced capability devices to receive signals representing the data transmitted by the transmitter unit within the first bandwidth forming a first virtual carrier, the reduced capability devices each having a receiver bandwidth which is greater than or equal to the first frequency bandwidth but less than the host frequency bandwidth. Communications devices of different capabilities can be allocated communications resources within different frequency ranges according to their capability, which can relieve congestion on a centre frequency of communications resources in which communications devices with a minimum bandwidth capability must receive communications resources for receiving down link signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for a signal selective RF transceiver system
InactiveUS7245882B1Reducing communication system efficiencyIncrease costSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentTransceiverEngineering
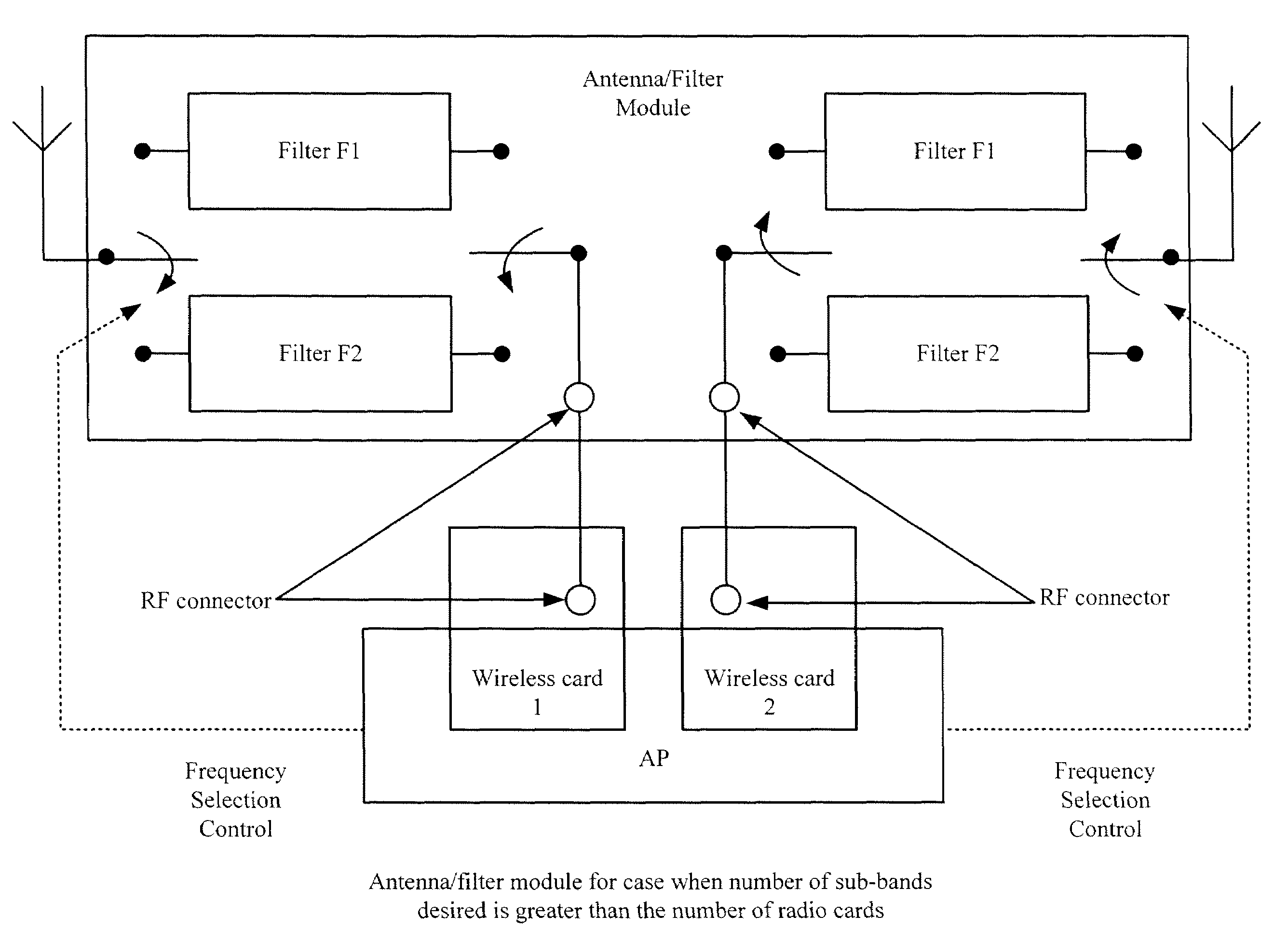
Method and apparatus to dynamically configure the signal reception selectivity of a plurality of transceivers is described. In one embodiment, a transceiver includes a receiver circuit having two or more filter circuits. Each of the filter circuits is configured to pass RF signals from a different portion of an overall receiver bandwidth. When two or more receivers in proximity to one another are simultaneously operating, the filter circuits of the respective receiver are dynamically configured to different RF frequency passbands to minimize interference and cross talk between receivers and transmitters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
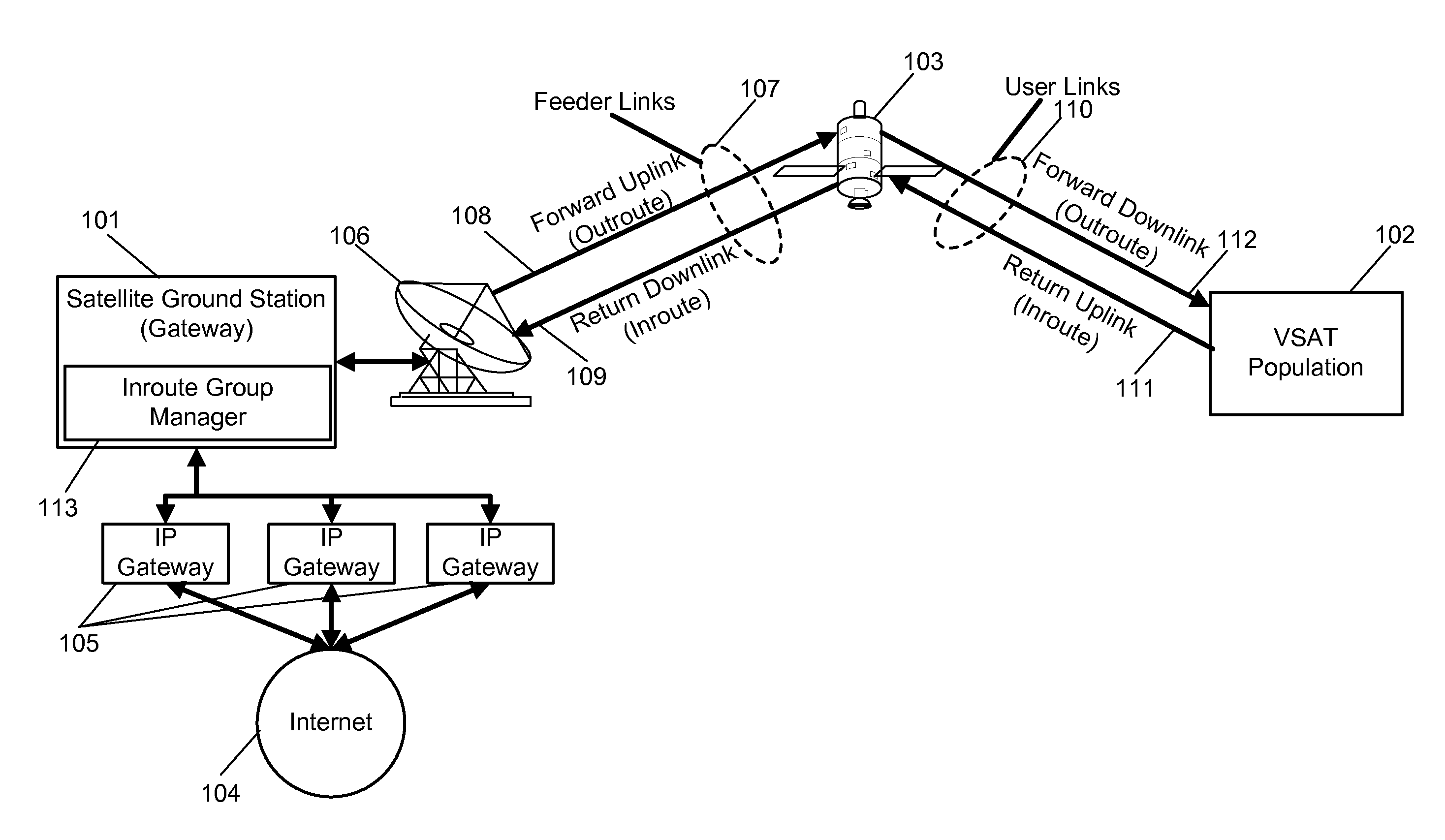
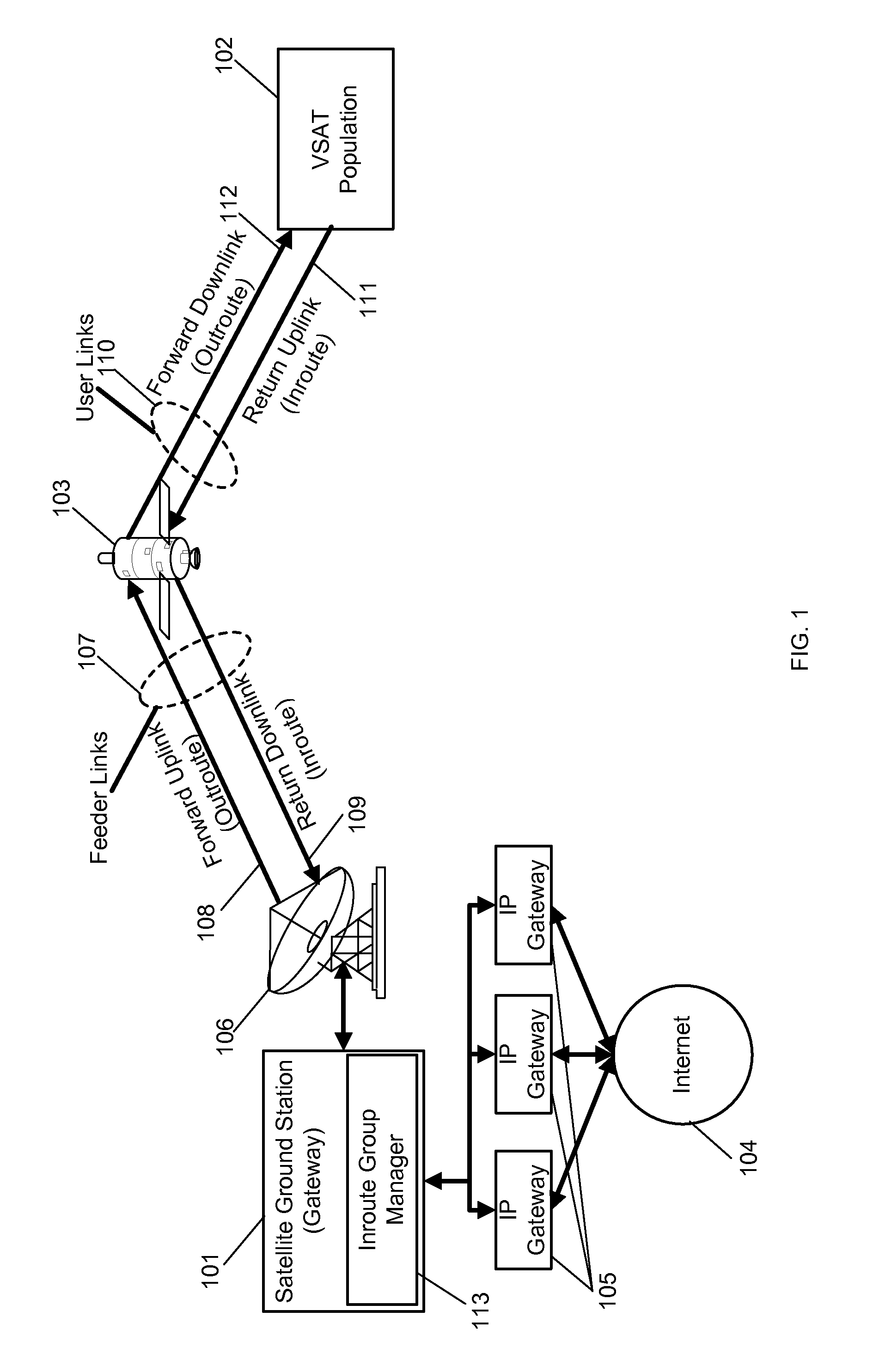
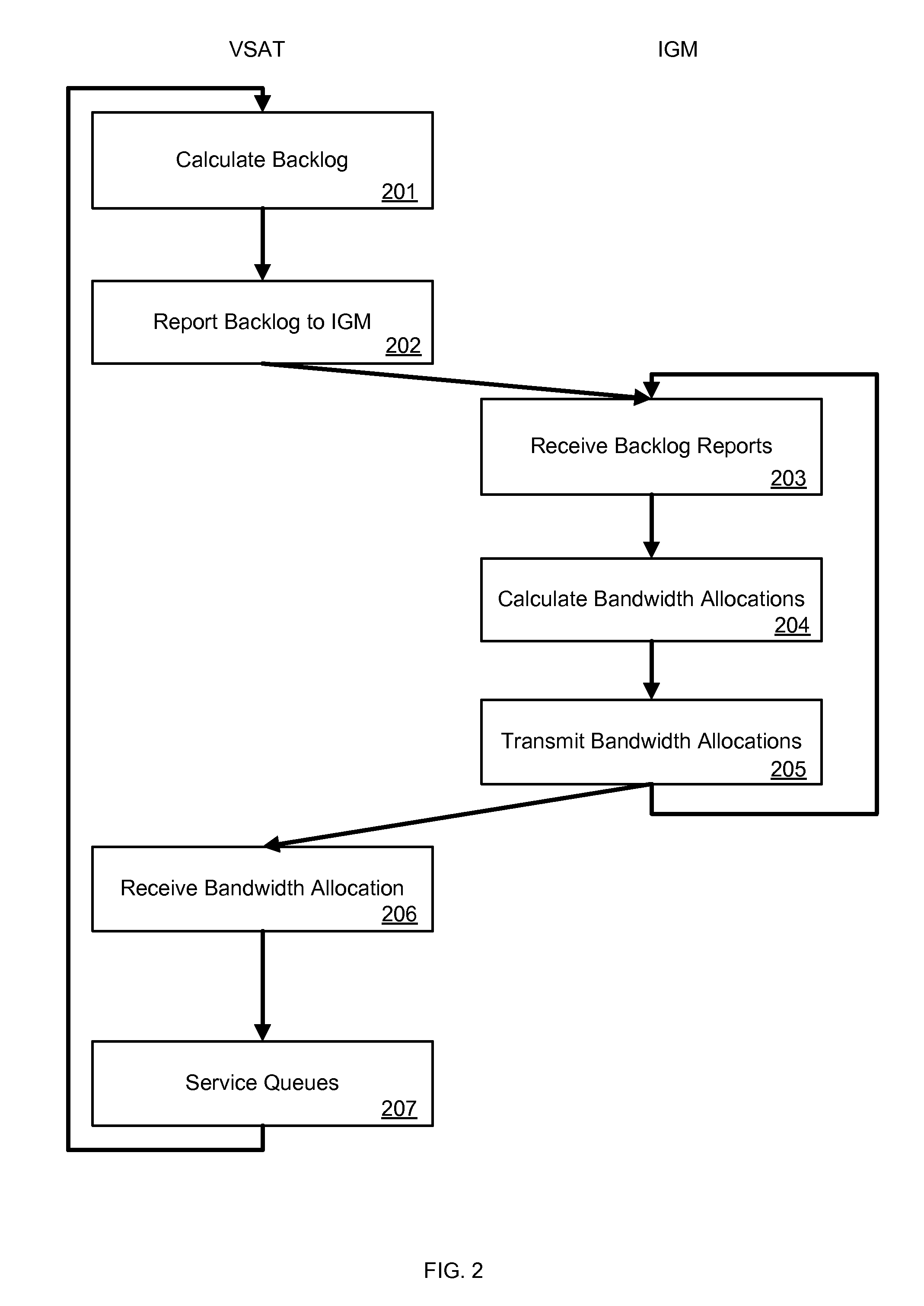
Method and system for inroute bandwidth allocation supporting multiple traffic priorities in a satellite network
A method for inroute bandwidth allocation supporting multiple traffic priorities in a satellite network including generating a backlog report, transmitting the backlog report to an inroute group manager, receiving a bandwidth allocation from the inroute group manager, and servicing priority queues and transmitting data to a satellite based on the bandwidth allocation from the inroute group manager.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
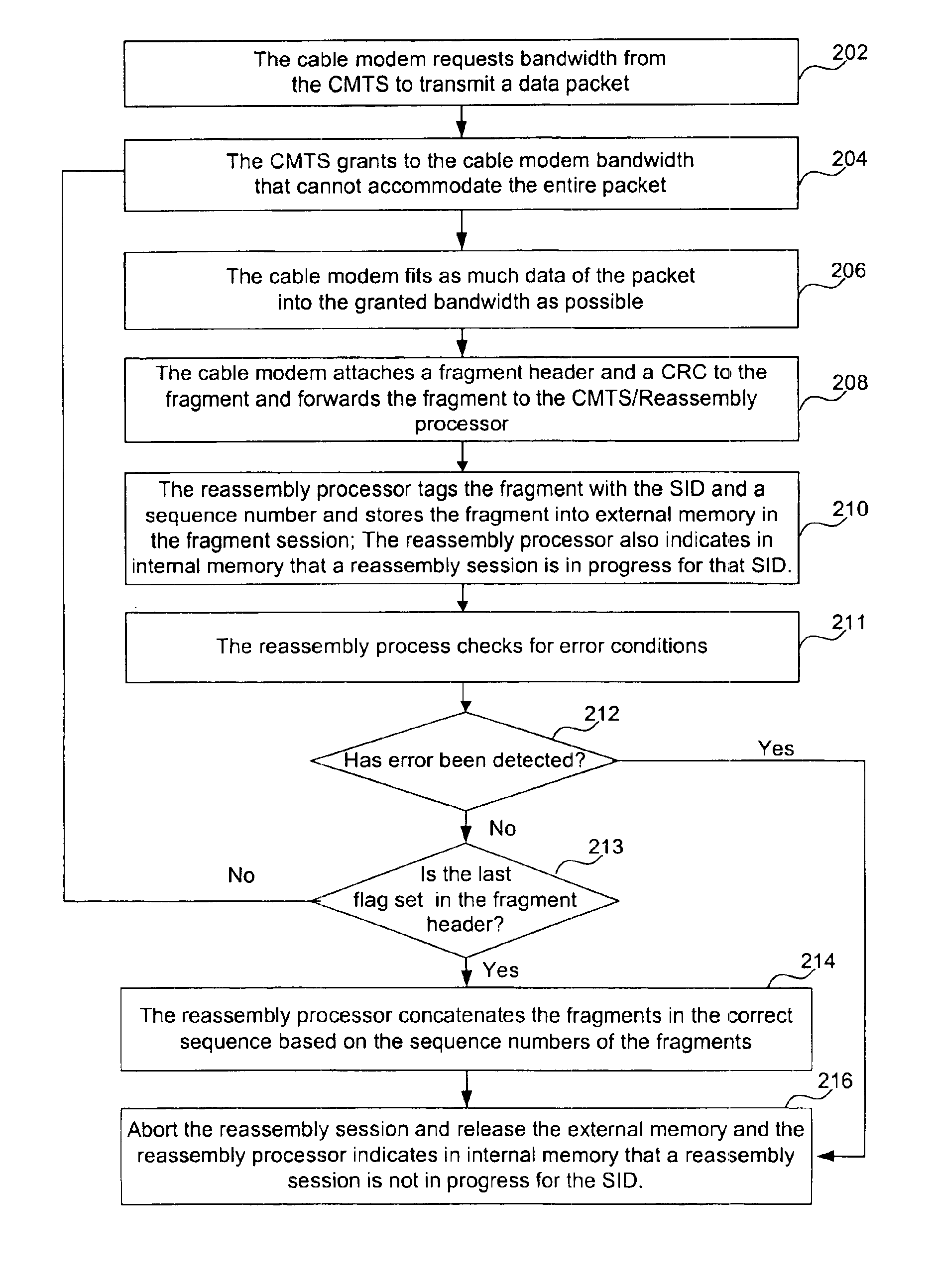
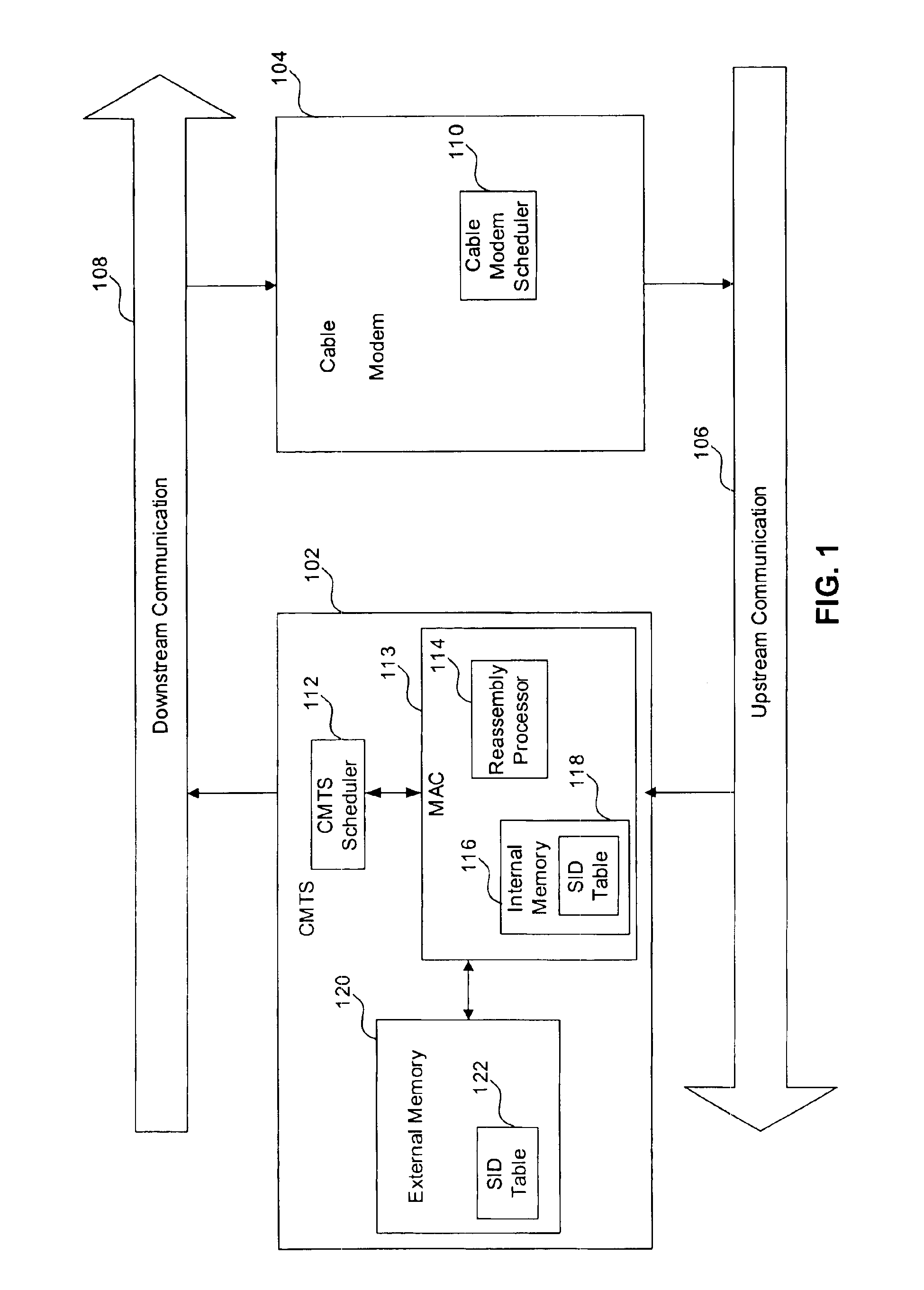
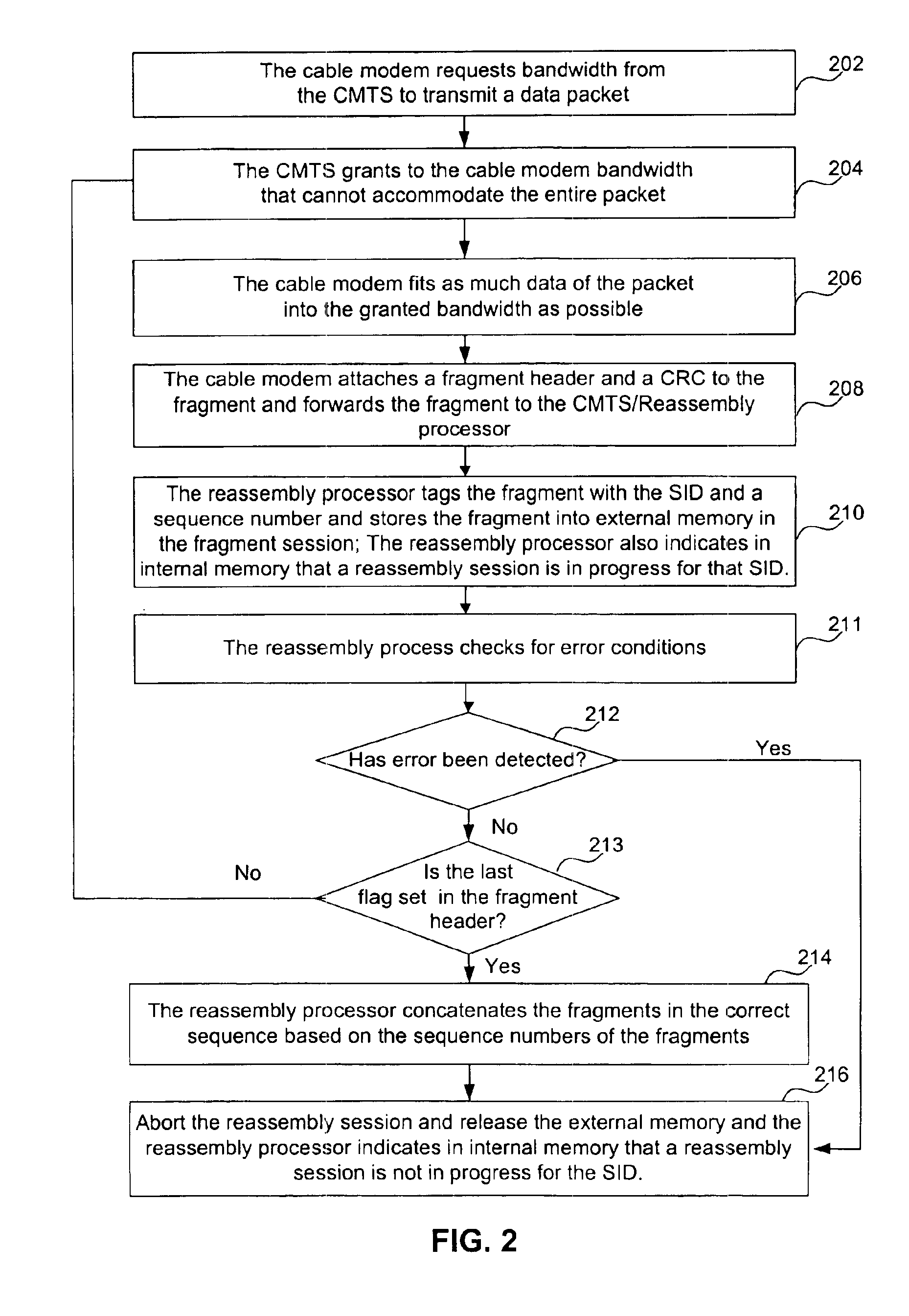
System and method for hardware based reassembly of a fragmented packet
InactiveUS6915358B2Significant savings in CPU cycles for the CMTS softwareBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexExternal storageNetwork packet
A system and method for hardware based reassembly of a fragmented packet is shown. The method includes receiving a bandwidth request to transfer a data packet from the data provider. Then, bandwidth is allocated to the data provider, where the allocated bandwidth is less than the requested bandwidth. Next, the present invention receives part of the data packet in the allocated bandwidth from the data provider, where the part of the data packet includes a fragment header, and the fragment header includes a sequence number for the part of the data packet. The part of the data packet is then stored in external memory. Finally, the data packet is reassembled by concatenating in the correct sequence the part of the data packet with other parts of the data packets to create the reassembled data packet.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
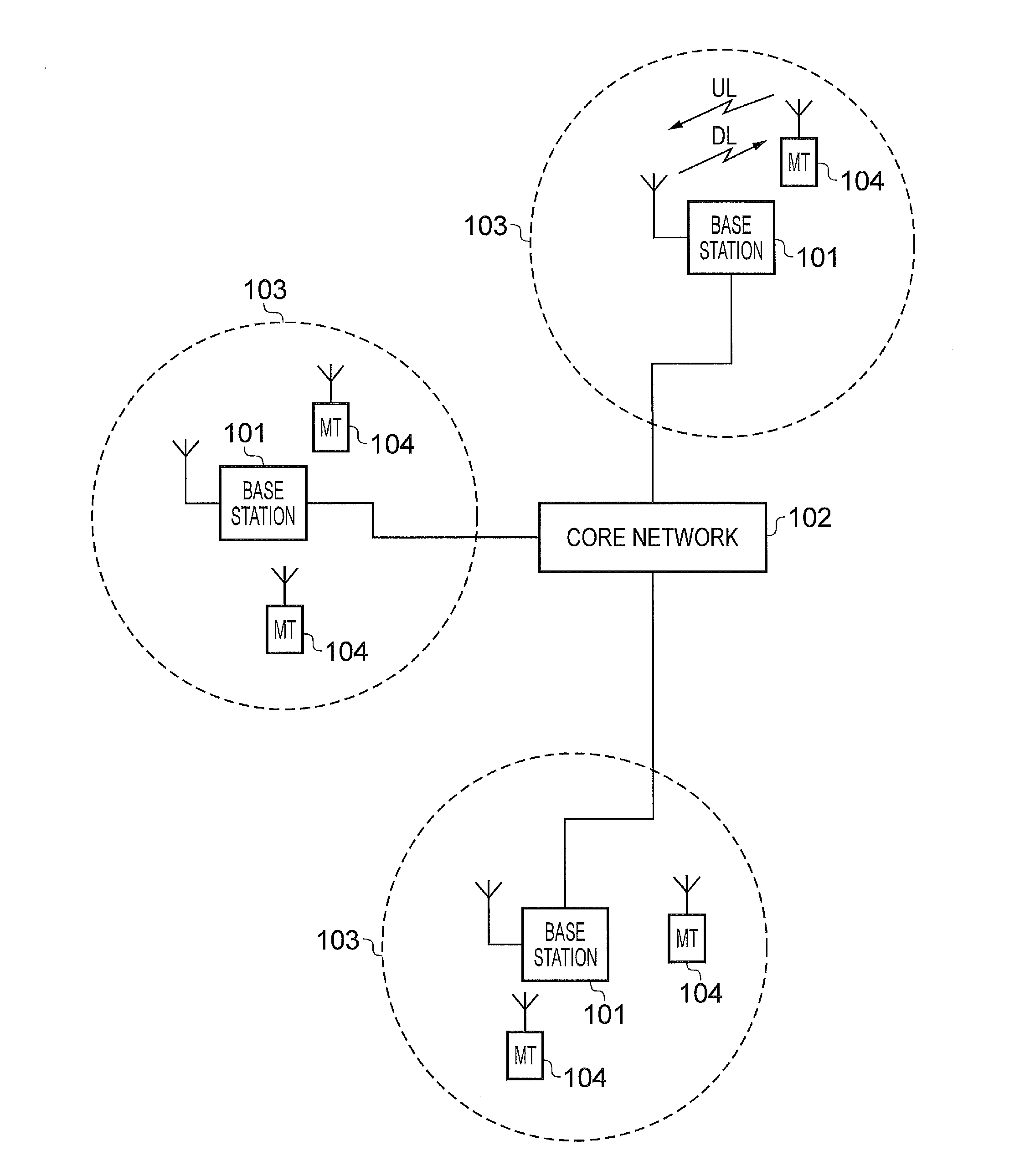
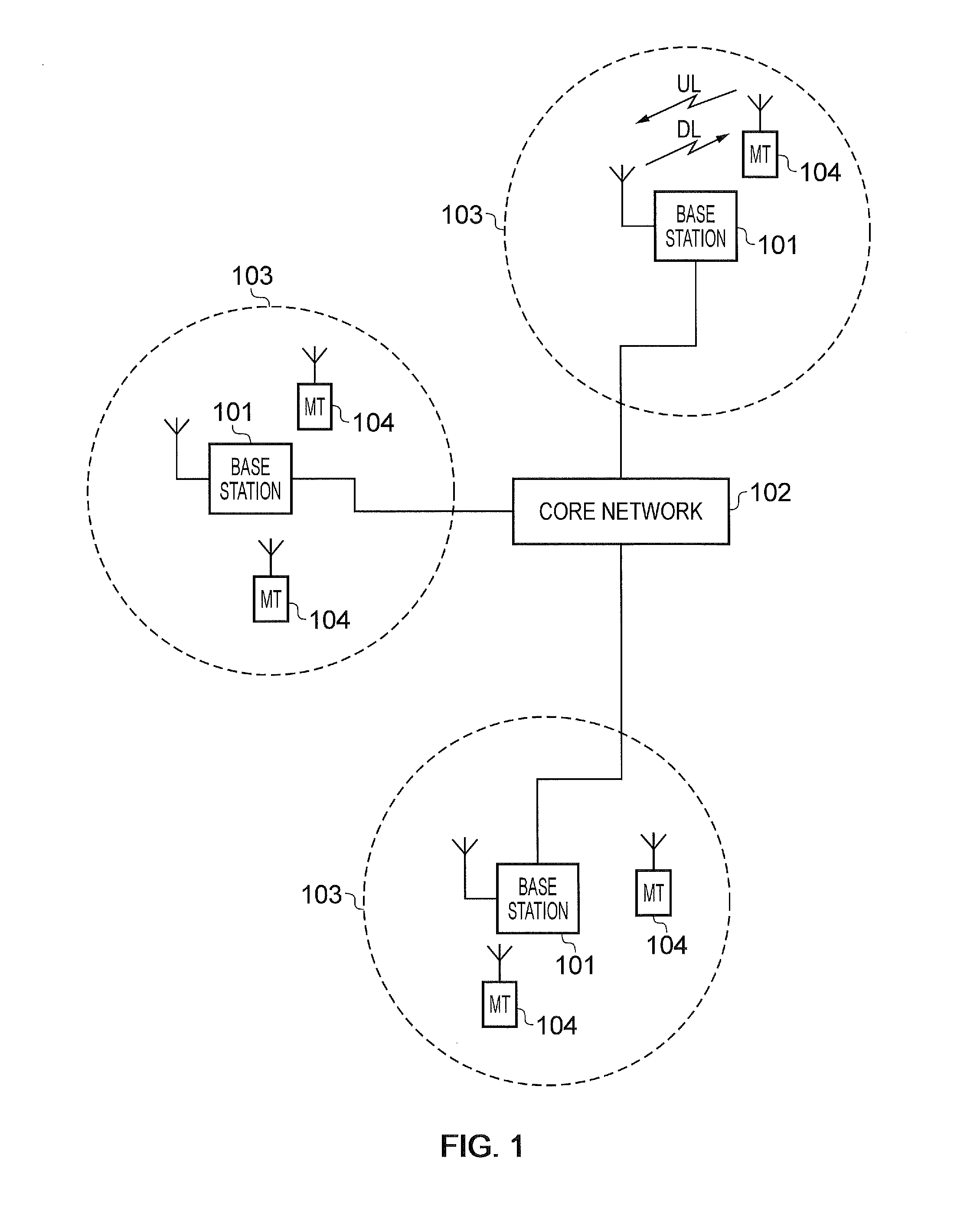
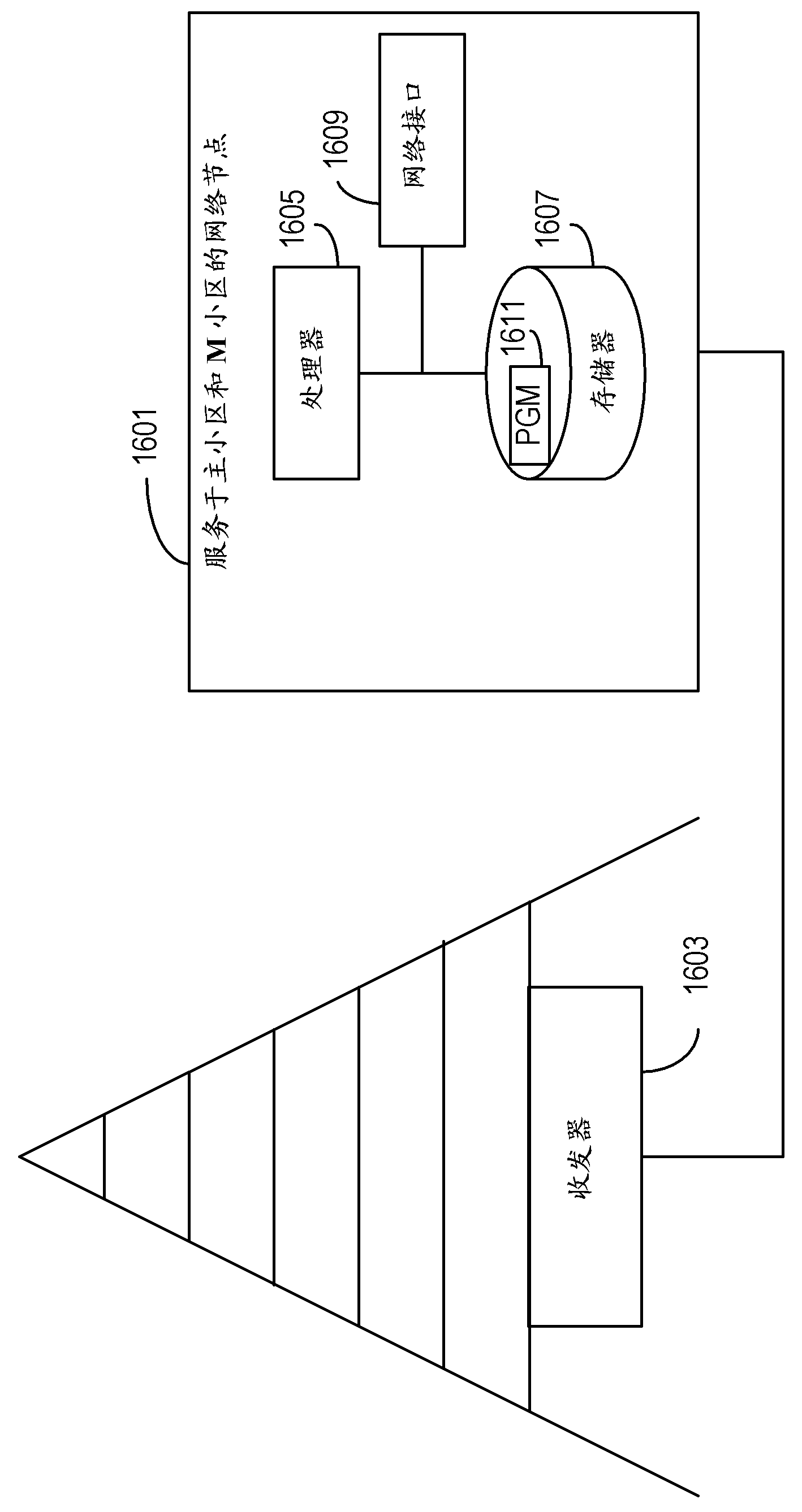
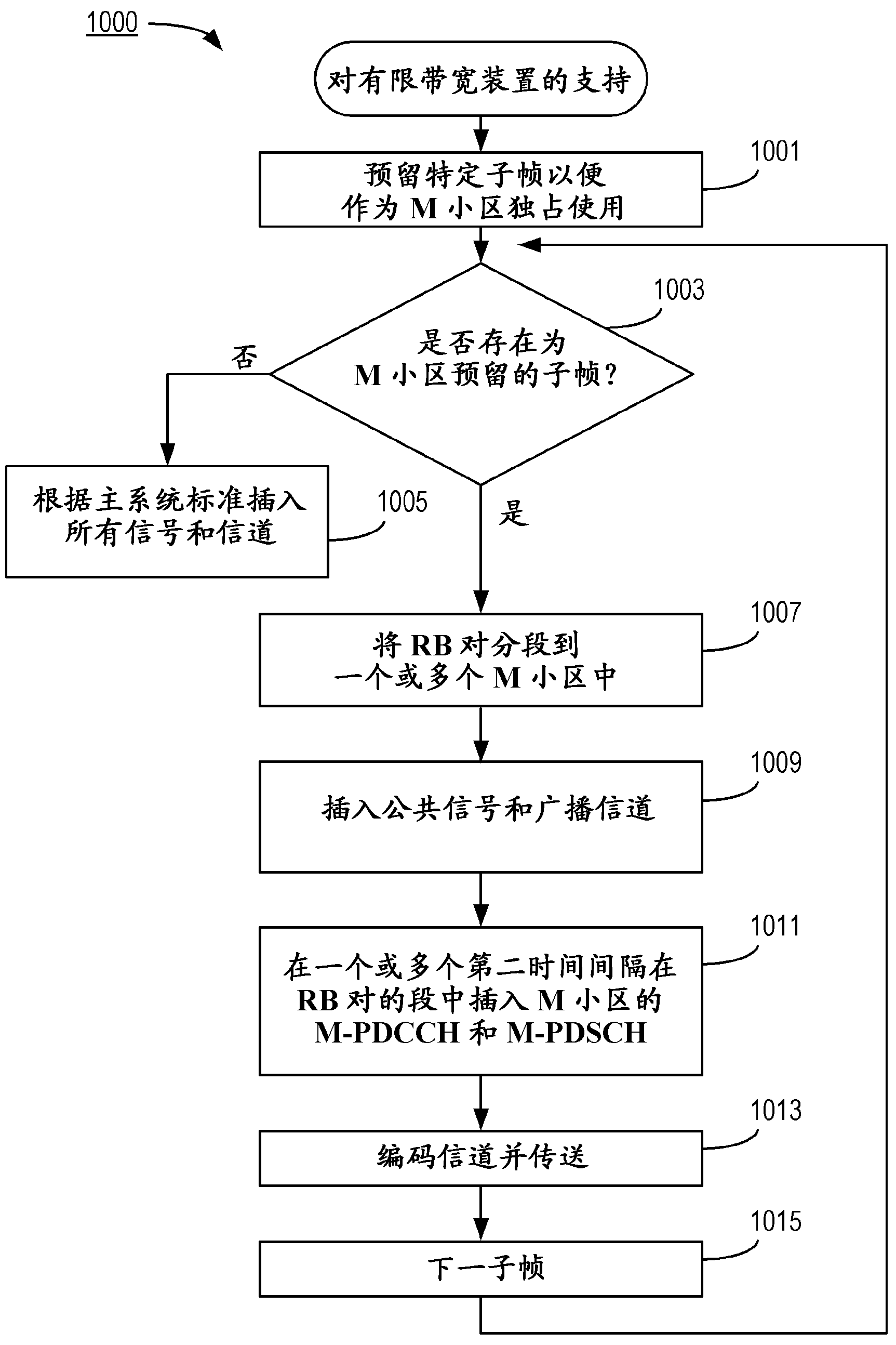
Cellular communication system support for limited bandwidth communication devices
A network node that serves a host cell in a cellular communication system transmits, at (a) first time interval(s), first control channel information on a control channel that extends over a first bandwidth of a radiofrequency spectrum. The first control channel communicates information necessary to enable a first type of communication device to receive data from the host cell. The first type of communication device can receive first bandwidth-wide signals. At (a) second time interval(s), second control channel information is transmitted on a second control channel of a first M-cell. The second control channel occupies a second bandwidth that is smaller than the first bandwidth. The second time interval(s) do(es) not coincide with any of the first time interval(s).; A second type of communication device having reduced receive bandwidth capabilities compared to those of the first type of communication device is thereby made capable of being served by the node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Mobile communication device and method for allocating resources outside of a virtual carrier based on ue capabilities
ActiveUS20150365945A1Reduce the amount requiredVirtual capacity can be increasedNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionResource elementCarrier signal
A communications device configured to receive data from a mobile communications network including one or more network elements providing a wireless access interface. The wireless access interface provides plural communications resource elements across a host frequency bandwidth, and includes, within the host frequency bandwidth, first communications resource elements within a first frequency bandwidth for allocation preferably to reduced capability devices to receive signals representing data transmitted by a transmitter within the first bandwidth forming a first virtual carrier, the reduced capability devices each having a receiver bandwidth greater than or equal to the first frequency bandwidth but less than the host frequency bandwidth. Communications devices of different capabilities can be allocated communications resources within different frequency ranges according to their capability, to relieve congestion on a center frequency of communications resources in which communications devices with a minimum bandwidth capability must receive communications resources for receiving down link signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
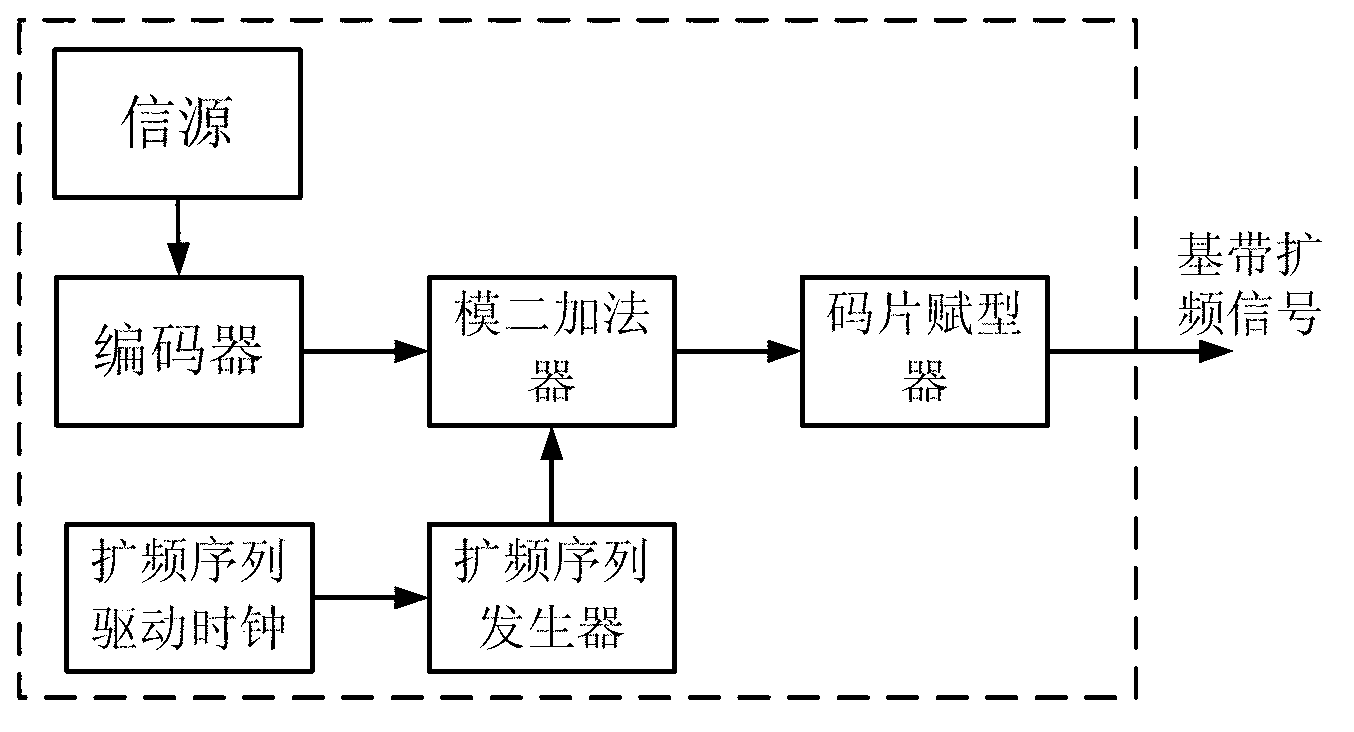
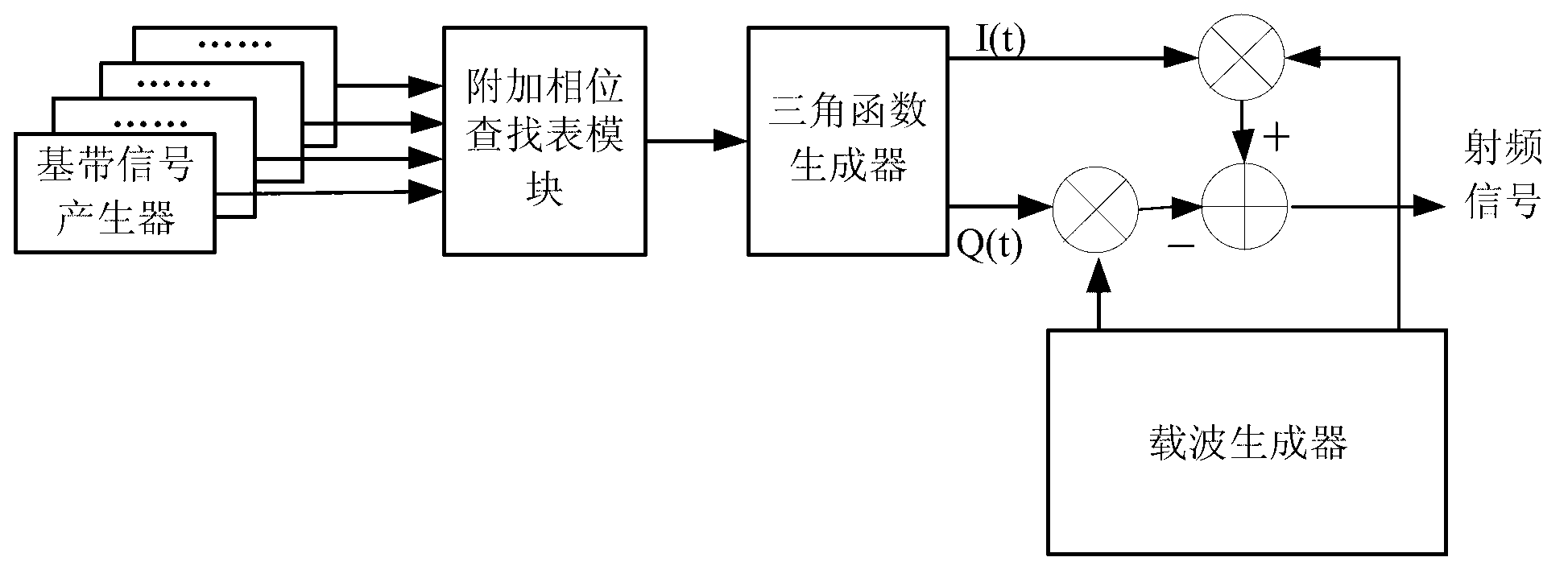
Constant envelope multiplexing method and of double-frequency four-component spread spectrum signals and receiving method of constant envelope multiplexed signal
ActiveCN103023598ABasic Ranging PerformanceRanging Performance ImprovementsBaseband system detailsMultiplex code generationMultiplexingCarrier signal
The invention discloses a constant envelope multiplexing method of double-frequency four-component spread spectrum signals. The method comprises the following steps of: generating four signal components as corresponding baseband spread spectrum signals, and obtaining corresponding additional phase according to the value combination state of the baseband spread spectrum signals within the current period of time; generating a pair of components, of which the phases are orthogonal to each other, by the additional phase through a trigonometric function generator; generating two paths of carriers, which are orthogonal to each other, by a carrier generator, respectively multiplying the carriers by the generated components, and executing subtraction on the products to get a radio frequency signal meeting the constant envelope condition. The invention also provides a generation device of the constant envelope multiplexed signal, and a receiving method of the constant envelope multiplexed signal. According to the constant envelope multiplexing method, four signal components of two frequency points are synthesized into one constant envelope signal, so that low-range and medium-range receivers can process the signal with narrower receiving bandwidth and lower baseband so as to obtain the basic ranging performance, high-range receivers can get better ranging accuracy by wider receiving bandwidth and higher processing complexity, and the ranging performance of the receivers during receiving each signal component respectively is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
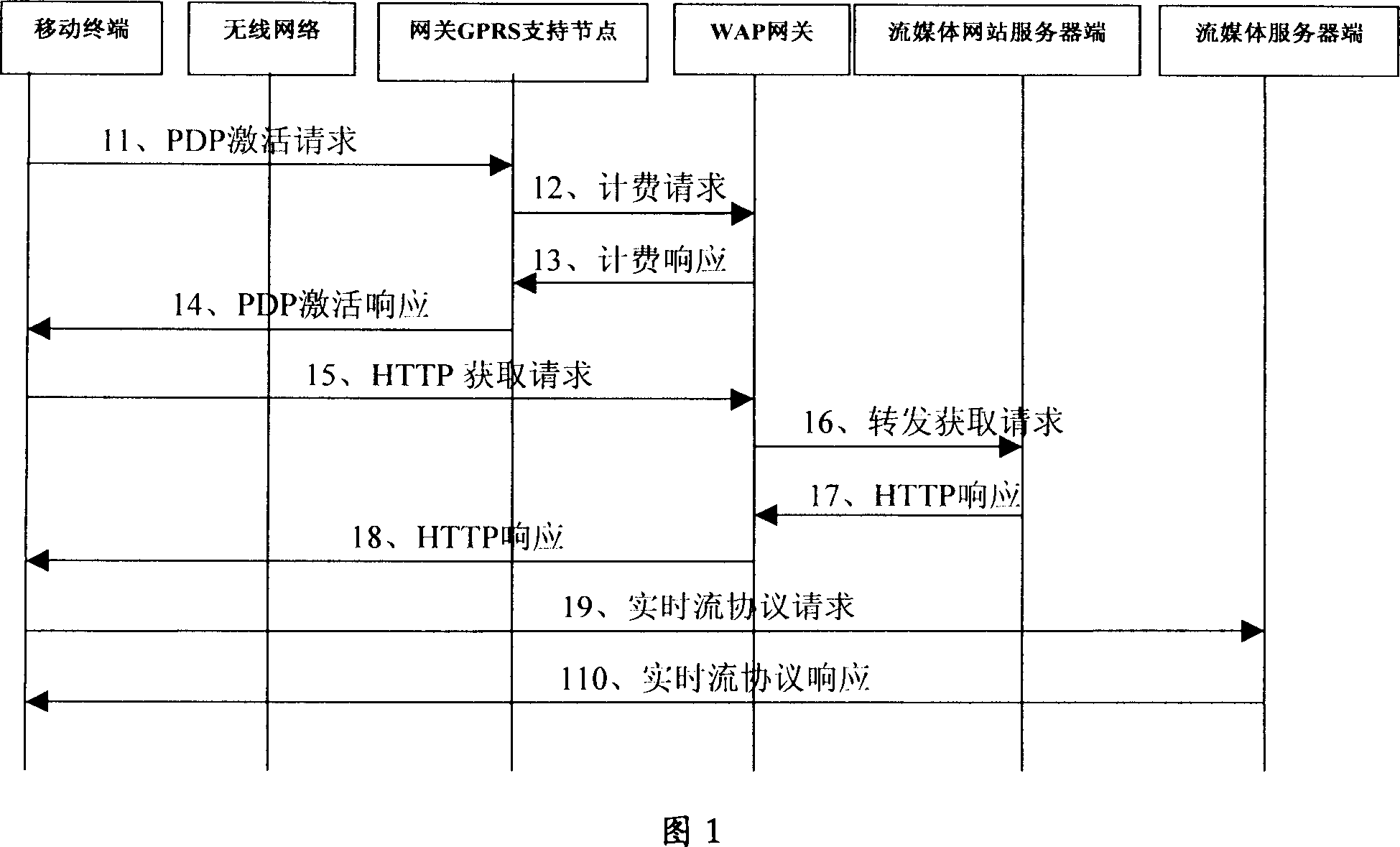
Data transmission method and system between movable terminal and server end
ActiveCN1946087AEasy to implementIncrease cost inputTransmissionWireless Application ProtocolRadio networks
This invention provides a data transmission method and a system between mobile terminals and server ends including: a WAPGW reports to the control end that the radio network negotiates with the mobile terminal to get the largest receiving bandwidth, the controller end determines data to be sent to the mobile terminal based on the maximum receiving bandwidth and the mobile terminal selects from the data to be sent to the mobile terminal and loads the necessary data.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
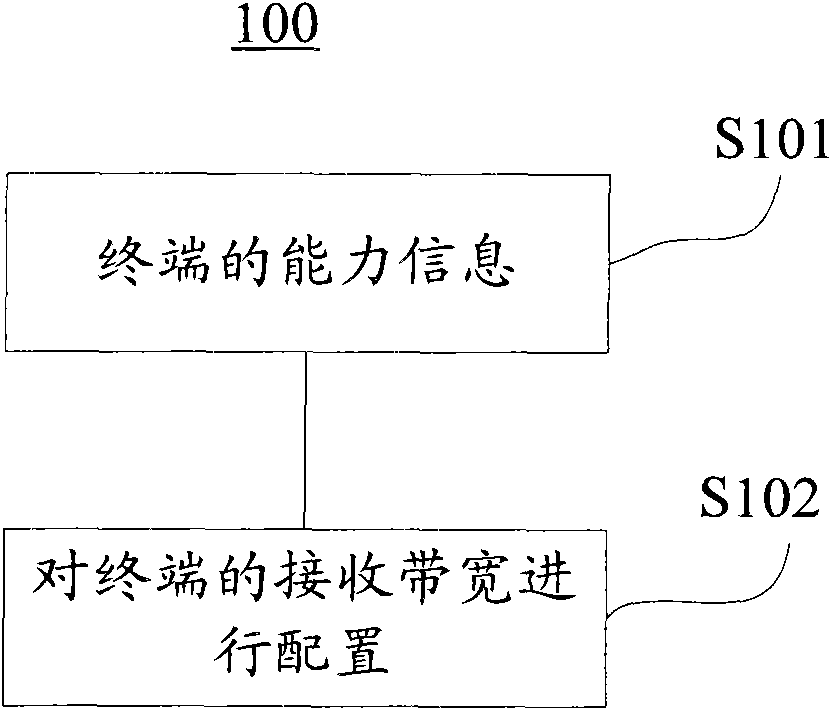
Resource scheduling method and resource scheduling device in multi-carrier communication system
ActiveCN102448176AAvoid positionAvoid the situationMulti-frequency code systemsWireless communicationCommunications systemCarrier signal
The invention provides a resource scheduling method and a resource scheduling device in a multi-carrier communication system. The resource scheduling method comprises the following steps: acquiring capability information of a terminal; and configuring receiving bandwidth of the terminal to enable the baseband direct current position in the receiving bandwidth to correspond to the empty sub-carrier position in transmitting bandwidth of a base station. According to the resource scheduling method and device disclosed by the application, the situation that the DC position of the terminal is aligned with a non-empty sub-carrier is avoided and the problem of data receiving in the position of local oscillation leakage interference direct current carrier of the terminal is effectively solved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Method for scheduling wireless communications
InactiveUS20070297436A1Broadband local area networksHybrid transportReceiver BandwidthCommunication device
A system and method is provided for scheduling transmissions from a plurality of services operating over a widely distributed communications network. A headend communications device (such as a cable modem termination system) arbitrates bandwidth among a plurality of cable modems configurable for bidirectional communications. The headend grants a bandwidth region to a specified cable modem or assigns contention regions for a group of cable modems. Each cable modem contains a local scheduler that sends requests for bandwidth according to local policies or rules. Upon receipt of a grant from the headend, the local scheduler selects packets to be transmitted to best serve the needs of the services associated with the cable modem. Accordingly, a service requesting bandwidth may not be the service utilizing the grant corresponding to bandwidth request. Nonetheless, the local scheduler manages bandwidth allocation among its local services such that all requesting services eventually receive bandwidth
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
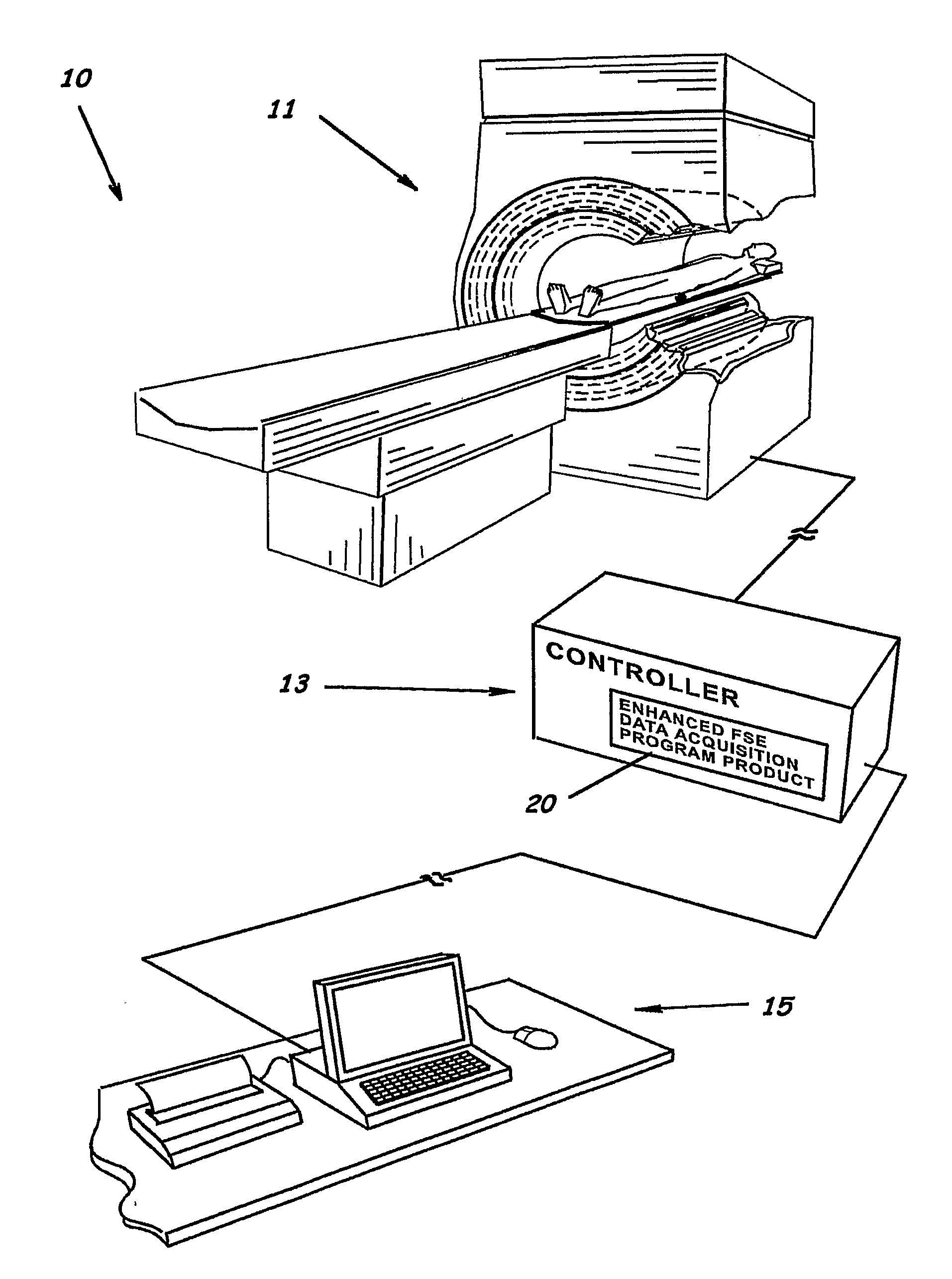
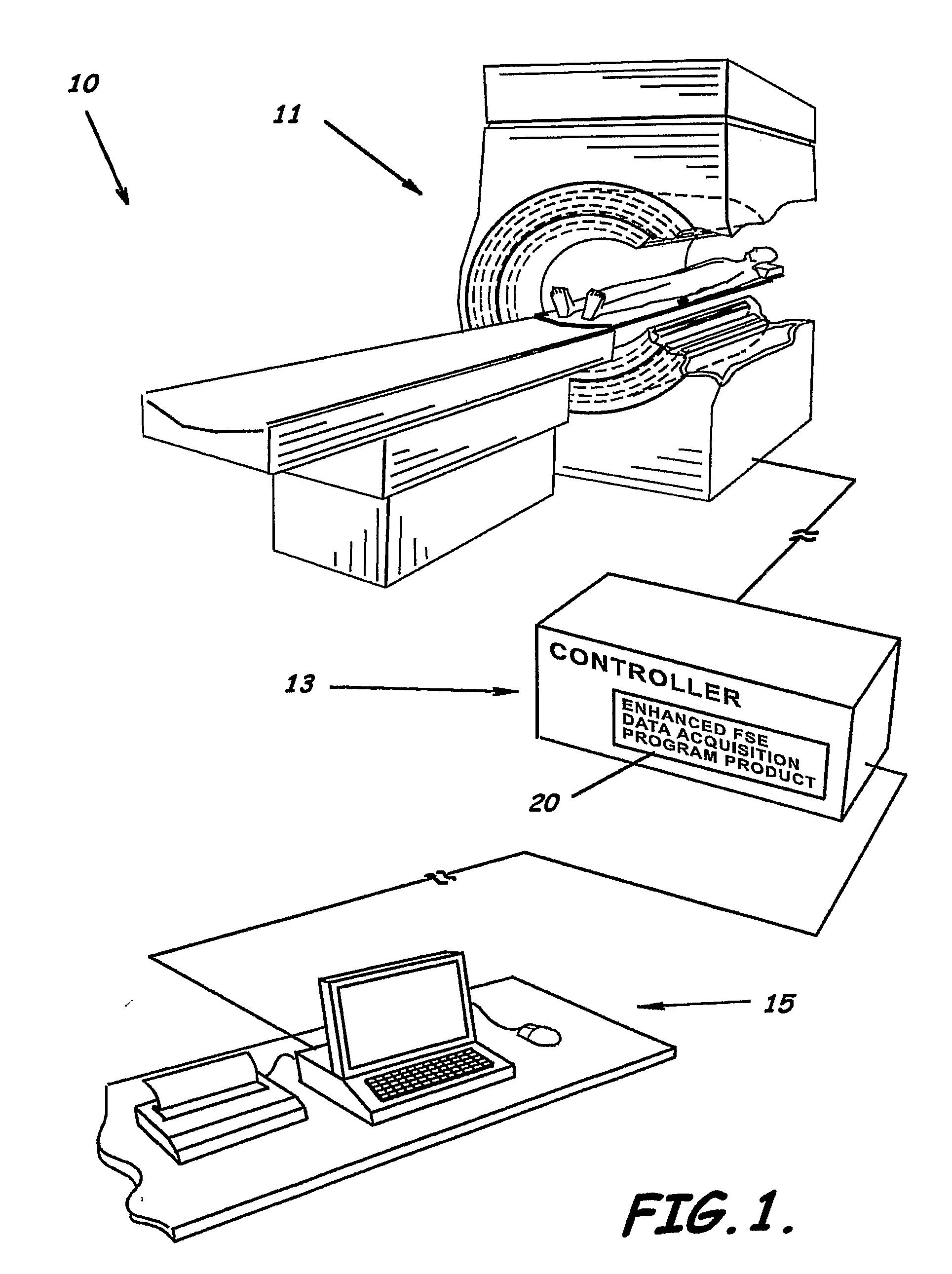
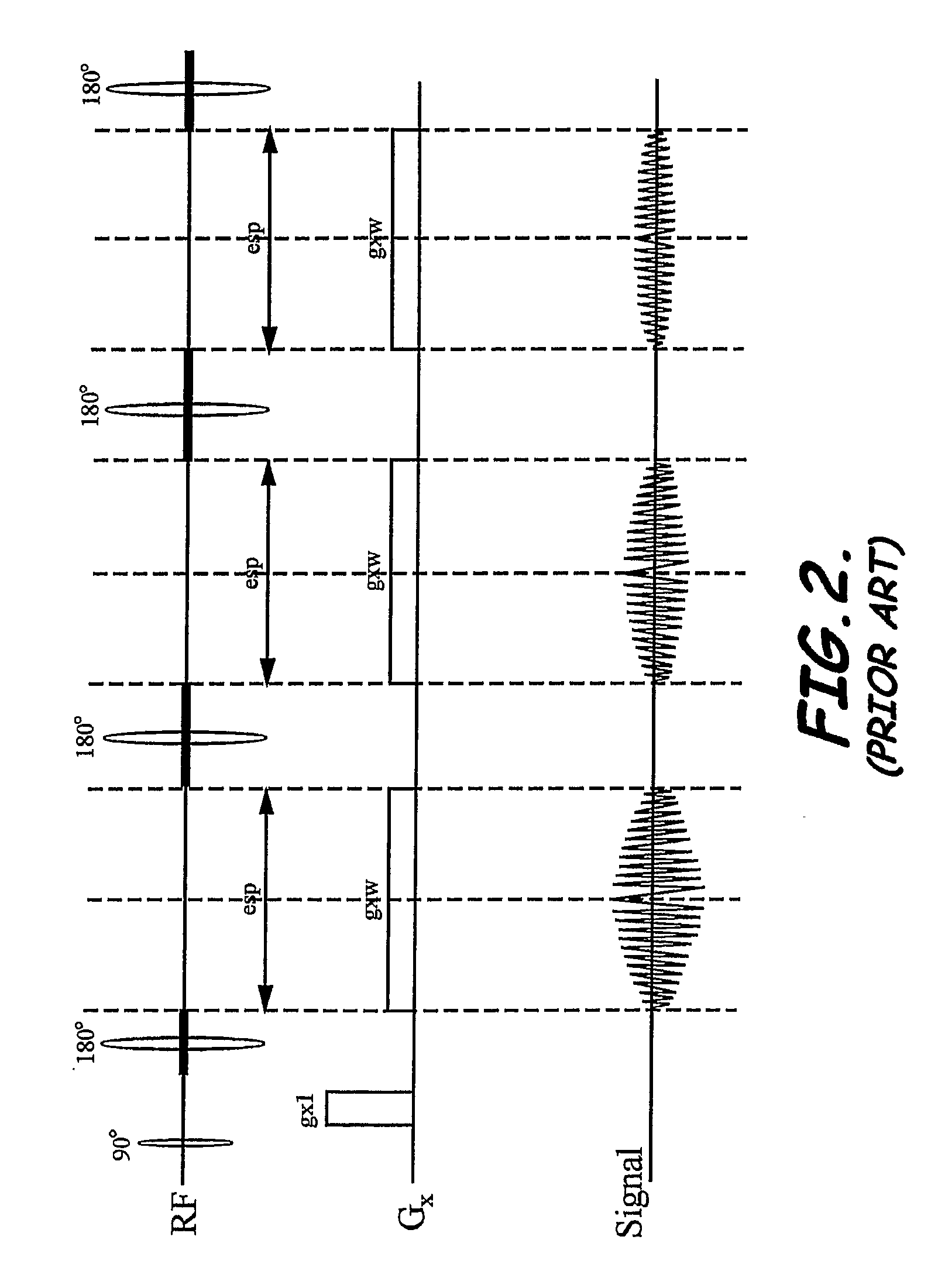
System, program product, and method of acquiring and processing MRI data for simultaneous determination of water, fat, and transverse relaxation time constants
ActiveUS20090093704A1Extension of timeEfficiently determine separateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSingle imageRelaxation time constant
A system, program product, and method to determine water, fat, and transverse relaxation time constants in MRI scanning are provided. A method includes initiating readout gradient pulses to collect echo signals with identical phase encoded gradients to thereby produce a plurality of images, instead of a single image with a single readout gradient. A receiver bandwidth used for collecting the echo signals can be determined responsive to an acquisition matrix size along the readout axis and a time duration for water and fat signals to evolve by a preselected phase angle. In a modified FSE implementation, for example, a method includes using readout gradient pulses that use substantially all of the echo spacing time periods between successive refocus RF pulses. By exploiting the phase and the amplitude relationship between the images, the method can include processing the images to generate separate water and fat images, as well as quantitative maps of transverse relaxation time constants.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Dynamic bandwidth allocating control apparatus with bandwidth usability improved
ActiveUS20120051371A1Improving bandwidth usabilityAttenuation bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexBandwidth allocationReceiver Bandwidth
A bandwidth allocating control apparatus for use in an optical communication base station has its reception bandwidth divided into a bandwidth for short distance and a bandwidth for long distance. A residual bandwidth calculator calculates a residual bandwidth remaining unallocated in the bandwidth for short distance after having allocated the reception bandwidth to short-distance subscriber terminal units. A middle-distance subscriber terminal classifier uses a middle-distance boundary calculation model representing the relationship between the residual bandwidth and a communication distance from the base station to the subscriber terminal units to further classify long-distance subscriber terminal units into a middle-distance subscriber terminal unit and a long-distance subscriber terminal unit. A middle-distance bandwidth allocator further allocates the residual bandwidth to the middle-distance subscriber terminal unit in addition to a predetermined bandwidth allocated thereto.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
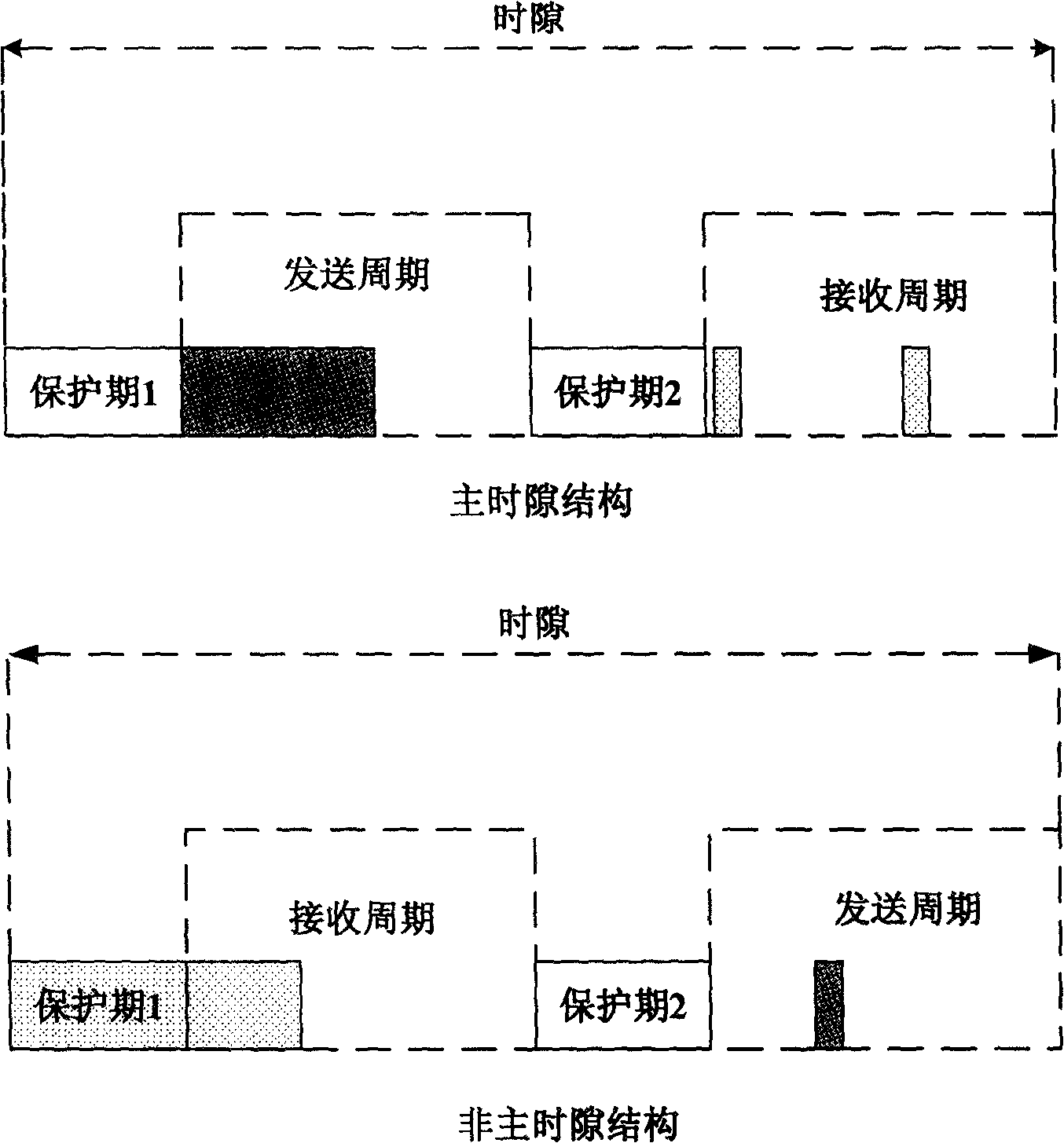
Synchronized cyclic scheduling technique for media access oriented to wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101291265AReduce latencySynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexScheduling functionControl layer
The invention provides a synchronizing cycle scheduling algorithm by accessing a wireless sensor network media to a control layer. The algorithm defines a characteristic frame structure and a time slot structure and has the characteristics of low node energy consumption, small transmission time lapse, easy realization, etc. The algorithm has the advantages that: 1) a time slot division method is adopted to avoid sending conflict between nodes and reduce the waiting time for receiving, thereby saving the node energy and having no strict need to node synchronization and easy realization. 2) The algorithm defines the characteristic frame structure and the processing flow in order that each node in a movable time slot (main time slot) has a scheduling function and can send data and receive data and information which is randomly accessed. 3) The node can freely adjust a sending and a receiving bandwidths with each adjacent node in the main time slot according to the needs. 4) Through setting a sending and a receiving cycles in a time slot, one node can acquire a plurality of chances to send the data in every frame cycle, thereby greatly reducing the network time lapse.
Owner:张宝贤 +1
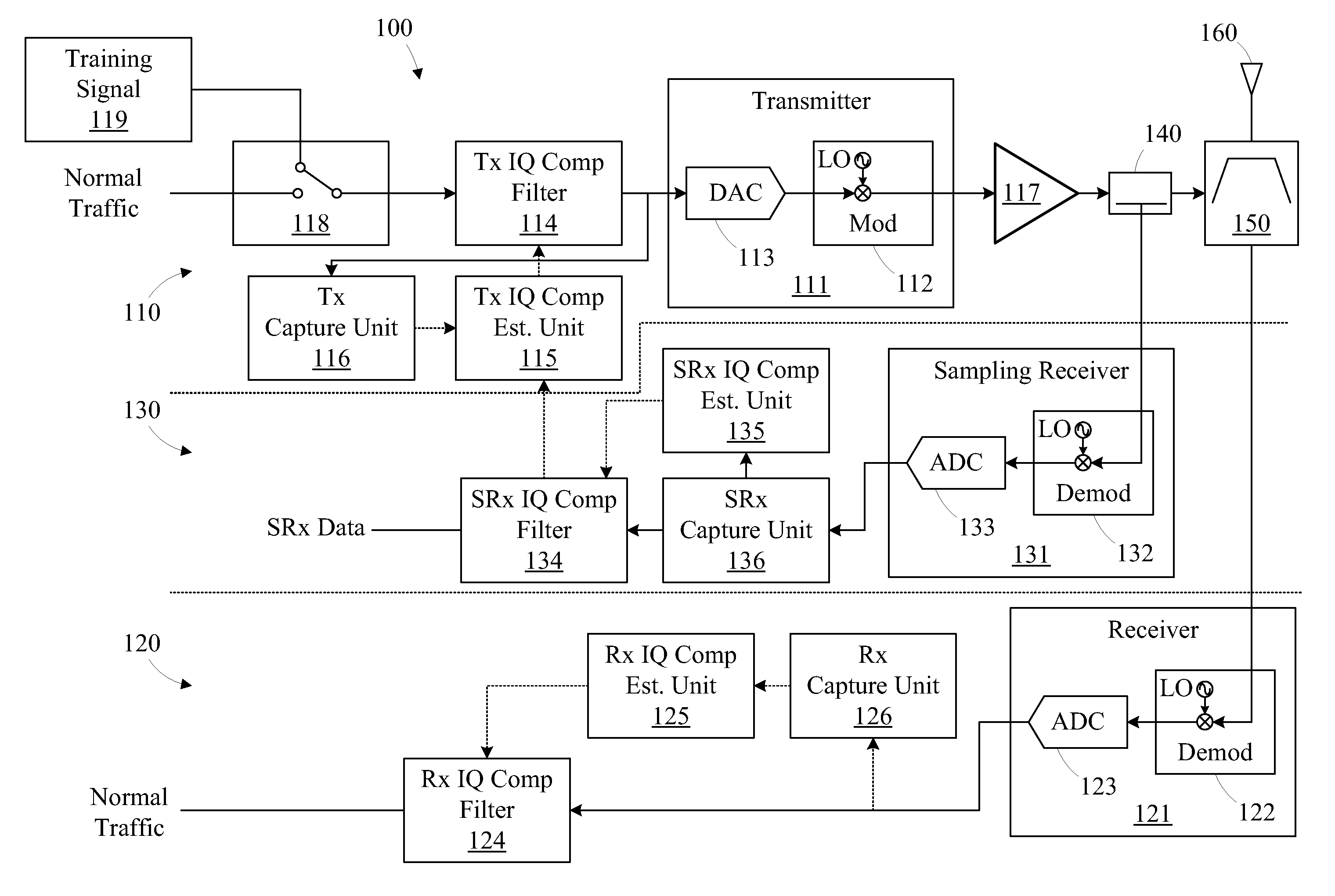
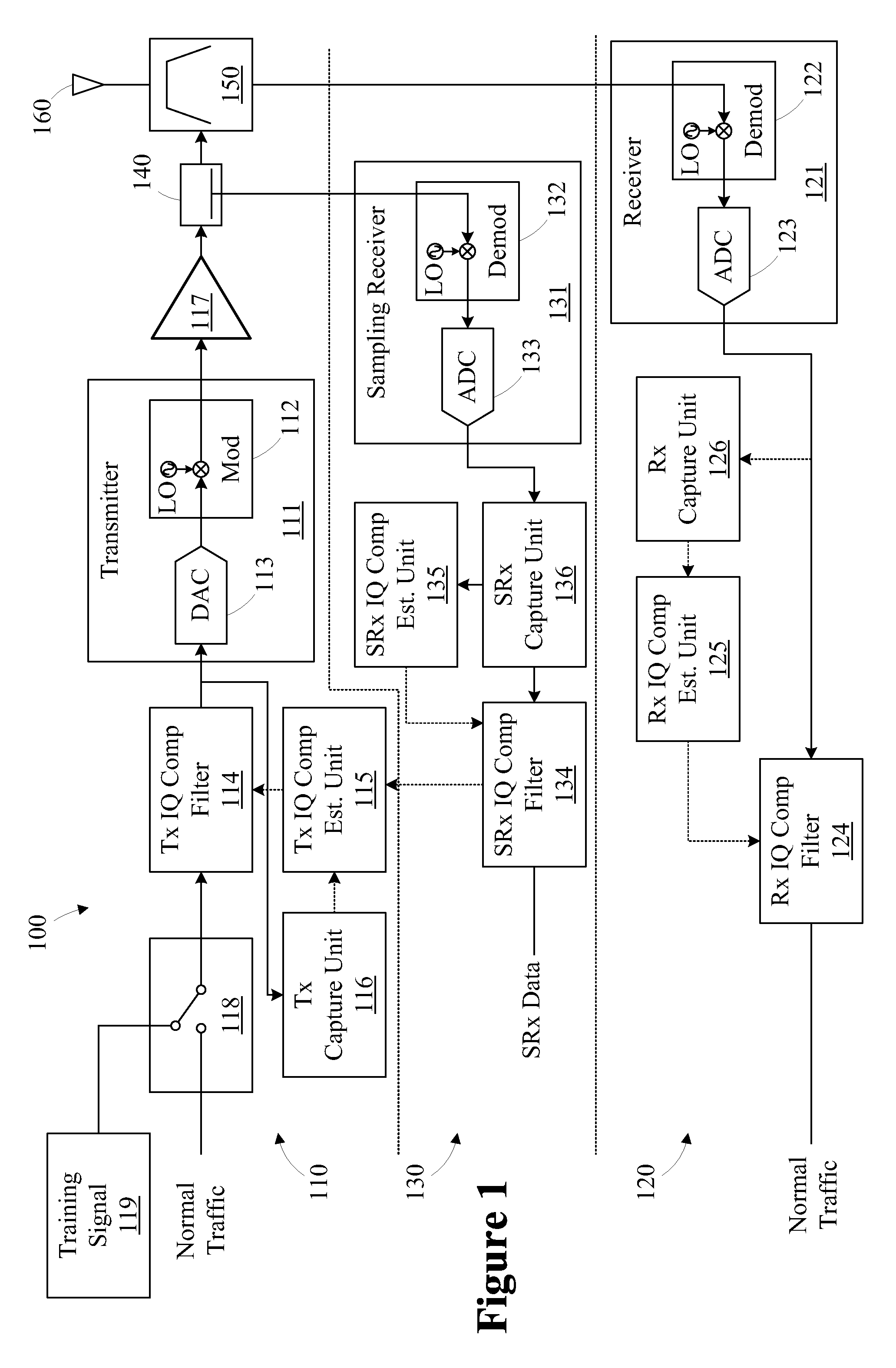
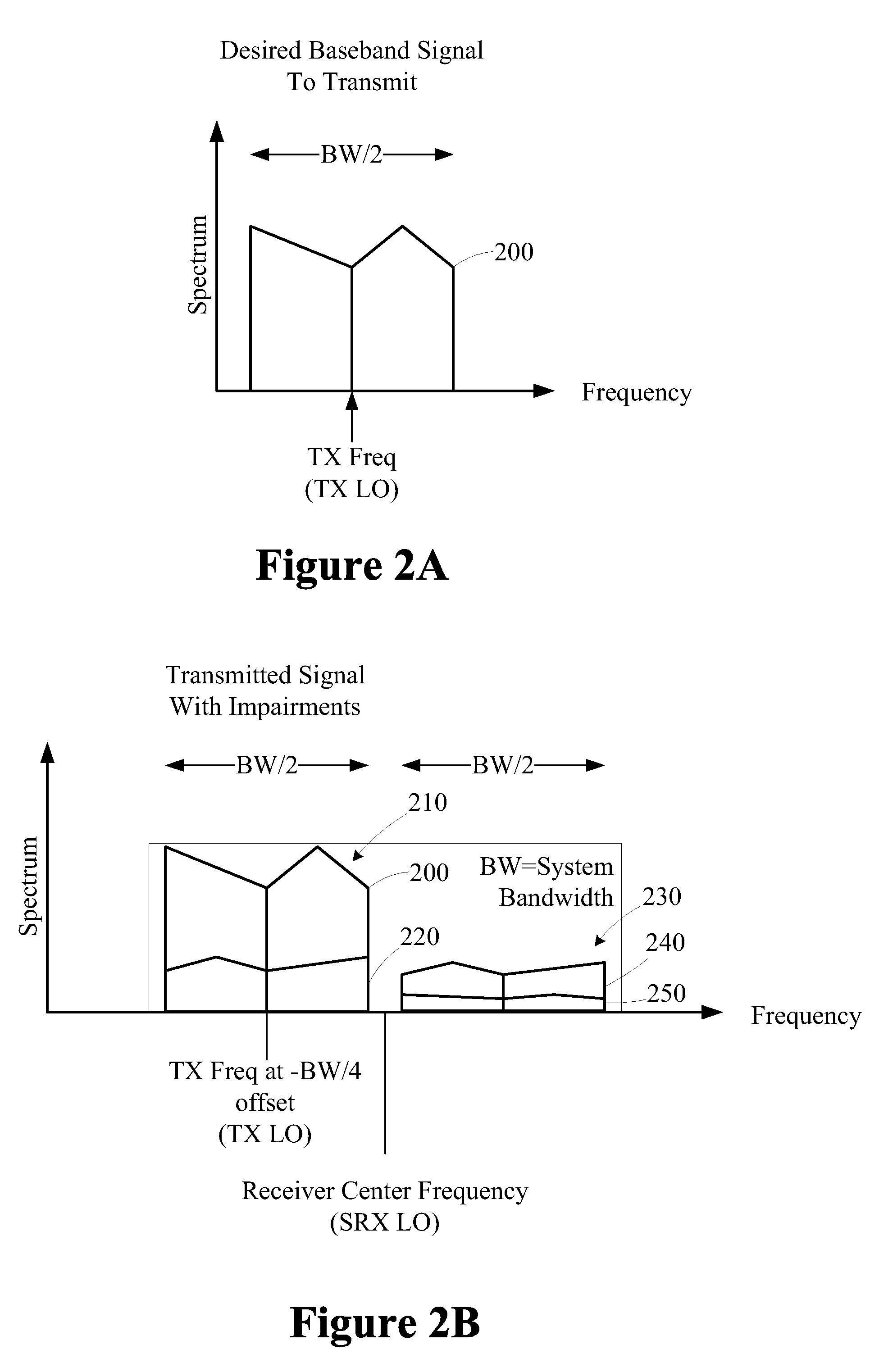
Method and apparatus for compensating for transceiver impairments
A method for compensating a transceiver for impairments includes transmitting a plurality of partial bandwidth training signals using a transmitter. A plurality of response signals of a receiver having a bandwidth and exhibiting receiver impairments is captured. Each response signal is associated with one of the partial bandwidth training signals. Each of the partial bandwidth training signals is associated with a portion of the receiver bandwidth. A plurality of partial compensation filters is generated based on the plurality of response signals. Each partial compensation filter is associated with one of the response signals. The partial compensation filters are combined to configure a receiver compensation filter operable to compensate for the receiver impairments.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Relay and method of allocating bandwidth in communication system
InactiveUS20080130550A1Efficiently allocate bandwidthEffective bandwidthFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemComputer science
To allocate a bandwidth to a terminal, a base station in a communication system including a relay receives a bandwidth request code from the relay, and determines whether a bandwidth request code that is the same as the received bandwidth request code has been received from the terminal. In addition, when the same bandwidth request code has been received from the terminal, the base station allocates the bandwidth to at least one among the relay and the terminal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Flexible multiplexer/demultiplexer and method for transport of optical line data to a wide/metro area link
InactiveUS6965619B2Time-division multiplexData switching networksData transmissionBandwidth allocation
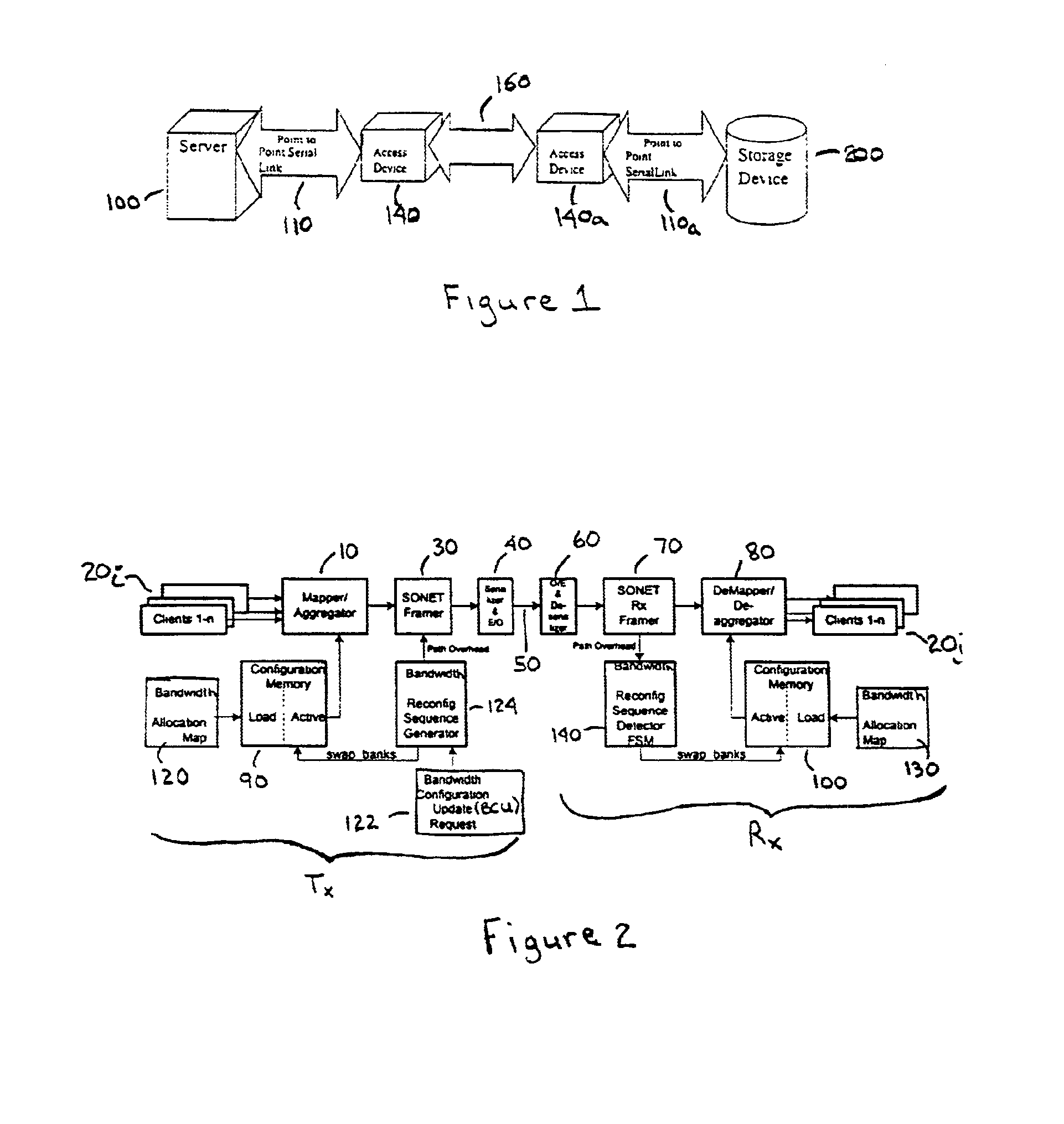
A method and apparatus are provided for flexible time-division multiplexing, and demultiplexing, of serial line data, from 1-n client lines, based on the SONET standard (e.g. OC-48 or OC-192) whereby a predetermined and reconfigurable number of STS-1s are allocated to each client. A multiplexer includes 1 to n mappers for mapping the data of 1 to n clients, according to a predetermined bandwidth allocation, to an N×STS-1 SONET payload, each mapper using y STS-1s where y is 0 to N, the y STS-1s being selected on a sequential or non-sequential concatenation basis from the N STS-1s. Each mapper maps the data of one client and each allocated STS-1 is allocated to one client and the total number of STS-1s allocated to the clients is less than or equal to N. An aggregator aggregates the mapped data into a composite STS payload comprising N STS-1s. A bandwidth allocation receiver receives the bandwidth allocation. The bandwidth allocation may be received from a source external to the multiplexer and the source may be a network controller. A demultiplexer includes a deaggregator for deaggregating the STS payload to provide the mapped data for the clients. 1 to n demappers demap the client data according to the predetermined bandwidth allocation. A bandwidth allocation receiver receives the bandwidth allocation.
Owner:CIENA
Method And Apparatus For A Signal Selective RF Transceiver System
ActiveUS20070238425A1Reducing communication system efficiencyIncreased complexitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentTransceiverReceiver Bandwidth
Method and apparatus to dynamically configure the signal reception selectivity of a plurality of transceivers is described. In one embodiment, a transceiver includes a receiver circuit having two or more filter circuits. Each of the filter circuits is configured to pass RF signals from a different portion of an overall receiver bandwidth. When two or more receivers in proximity to one another are simultaneously operating, the filter circuits of the respective receiver are dynamically configured to different RF frequency passbands to minimize interference and cross talk between receivers and transmitters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
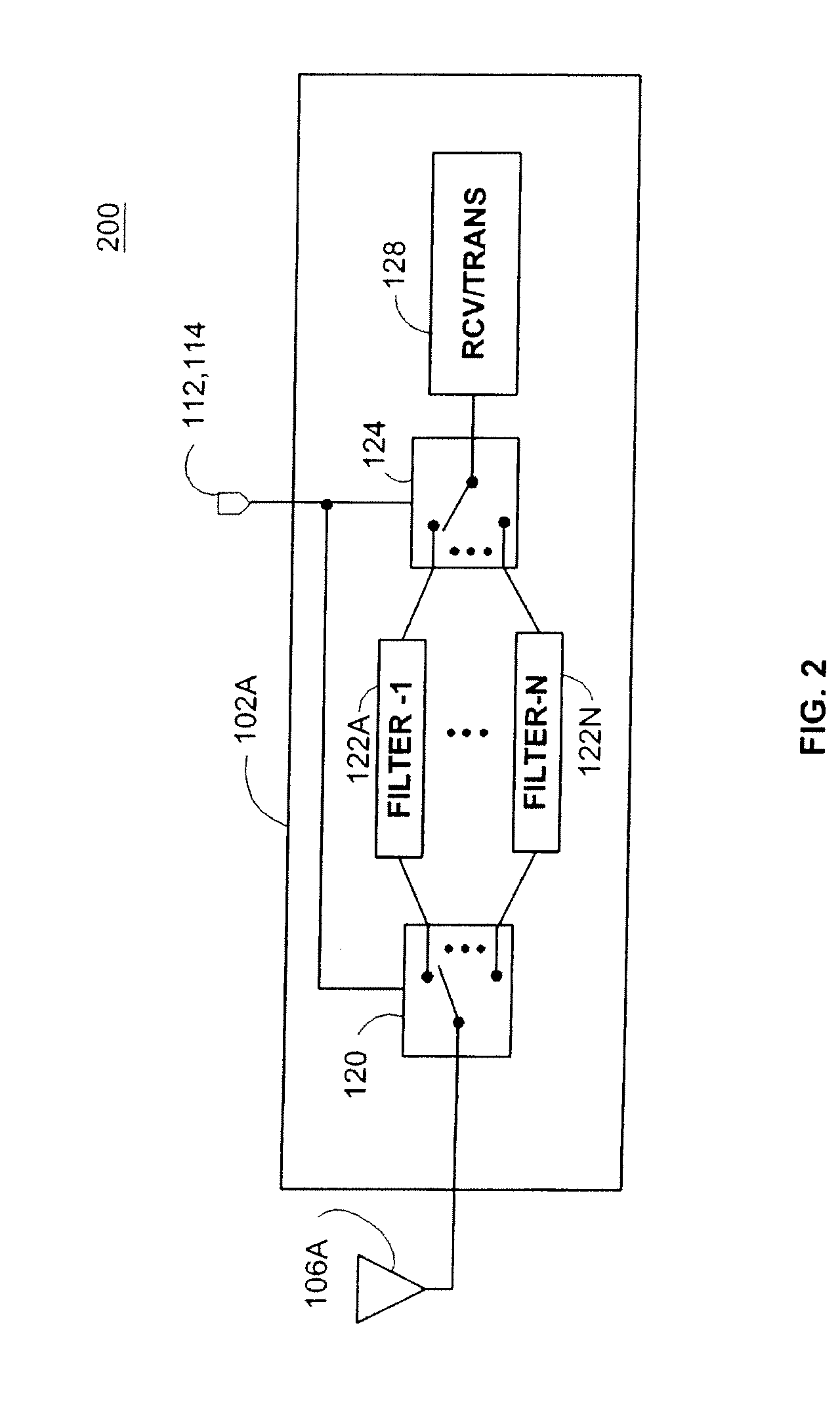
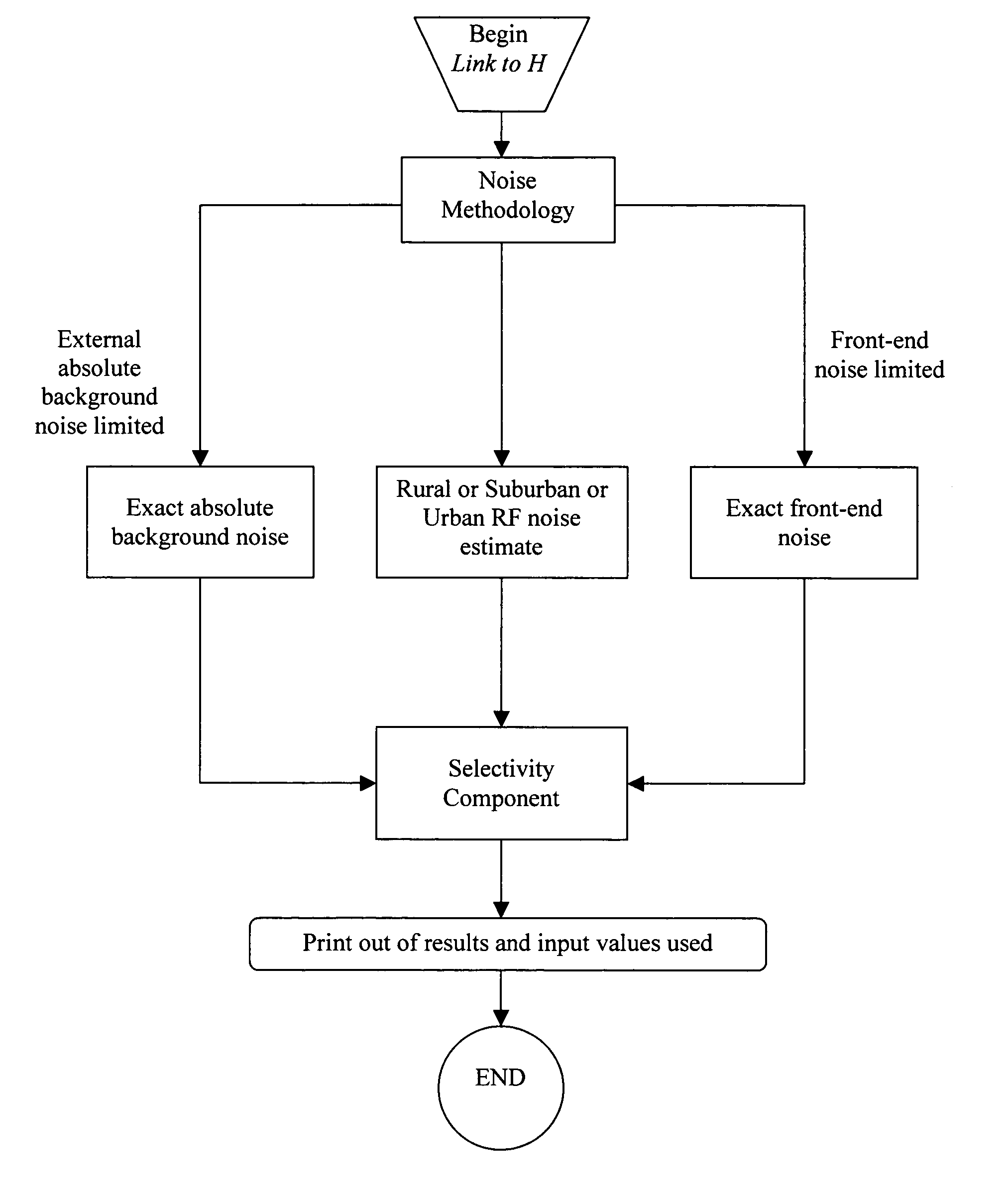
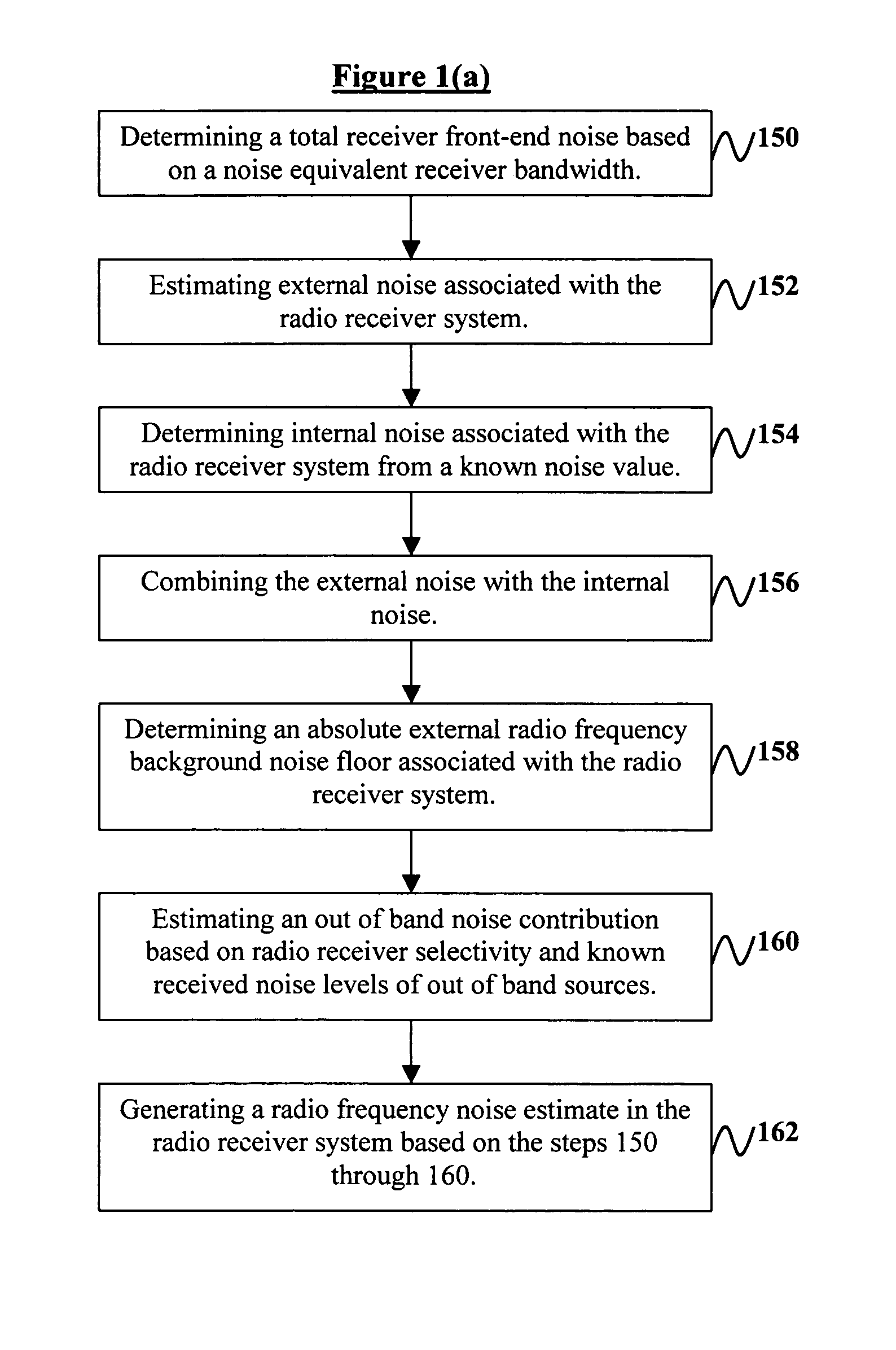
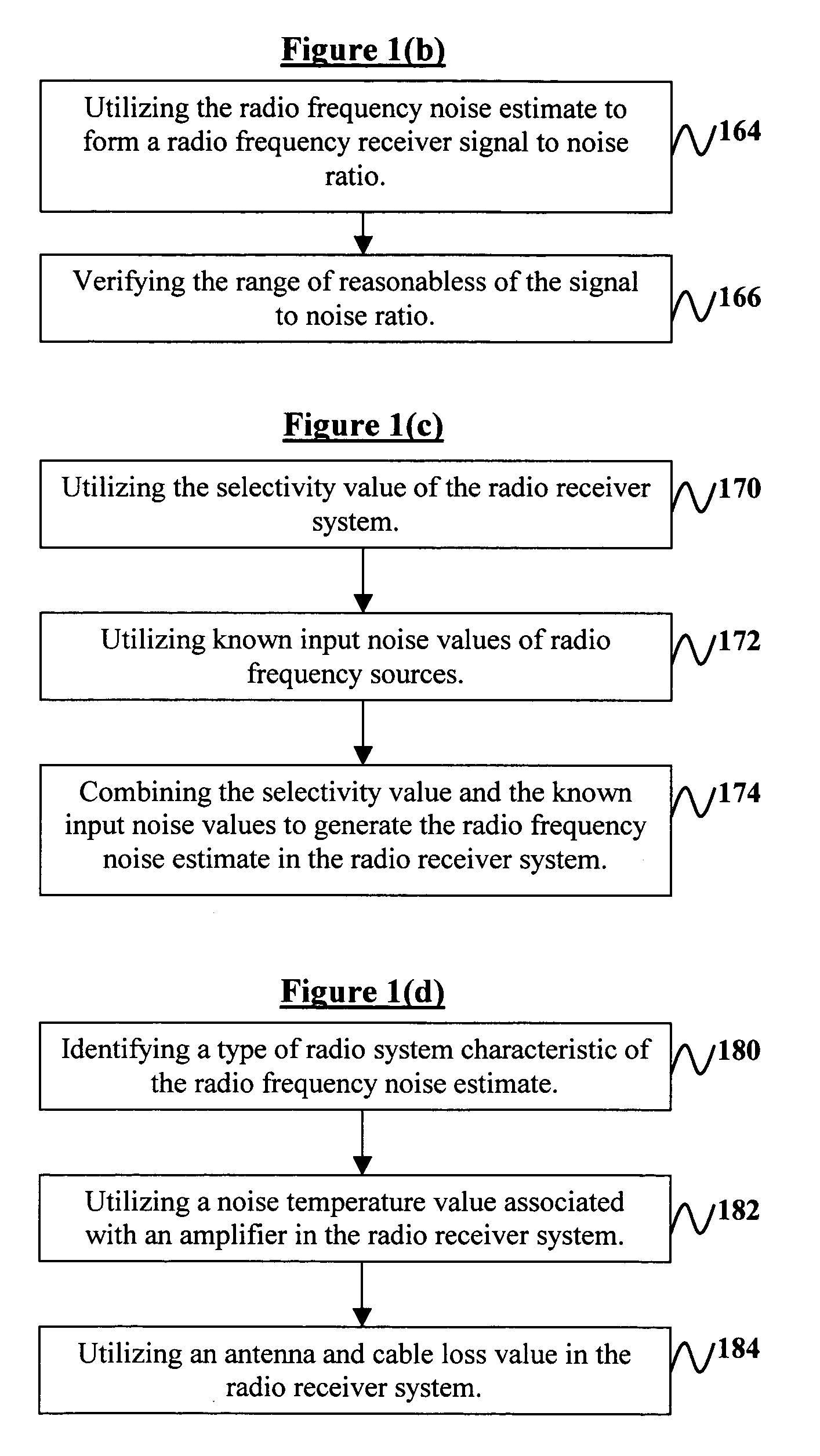
System and method for radio receiver RF background noise estimation
A system and method of estimating radio frequency (RF) background noise in a radio receiver system comprises determining a total receiver front-end noise based on a noise equivalent receiver bandwidth; estimating external noise associated with the radio receiver system; determining internal noise associated with the radio receiver system from a known noise value; combining the external noise with the internal noise; determining an absolute external (RF) background noise floor associated with the radio receiver system; estimating an out of band noise contribution based on radio receiver selectivity and known received noise levels of out of band sources; and generating a (RF) noise estimate in the radio receiver system based on the above steps. The invention utilizes the (RF) noise estimate to form a (RF) receiver signal to noise ratio enabling an estimate performance of (RF) radio links in the radio receiver system operating in a benign and hostile (RF) environment.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Reception method and apparatus
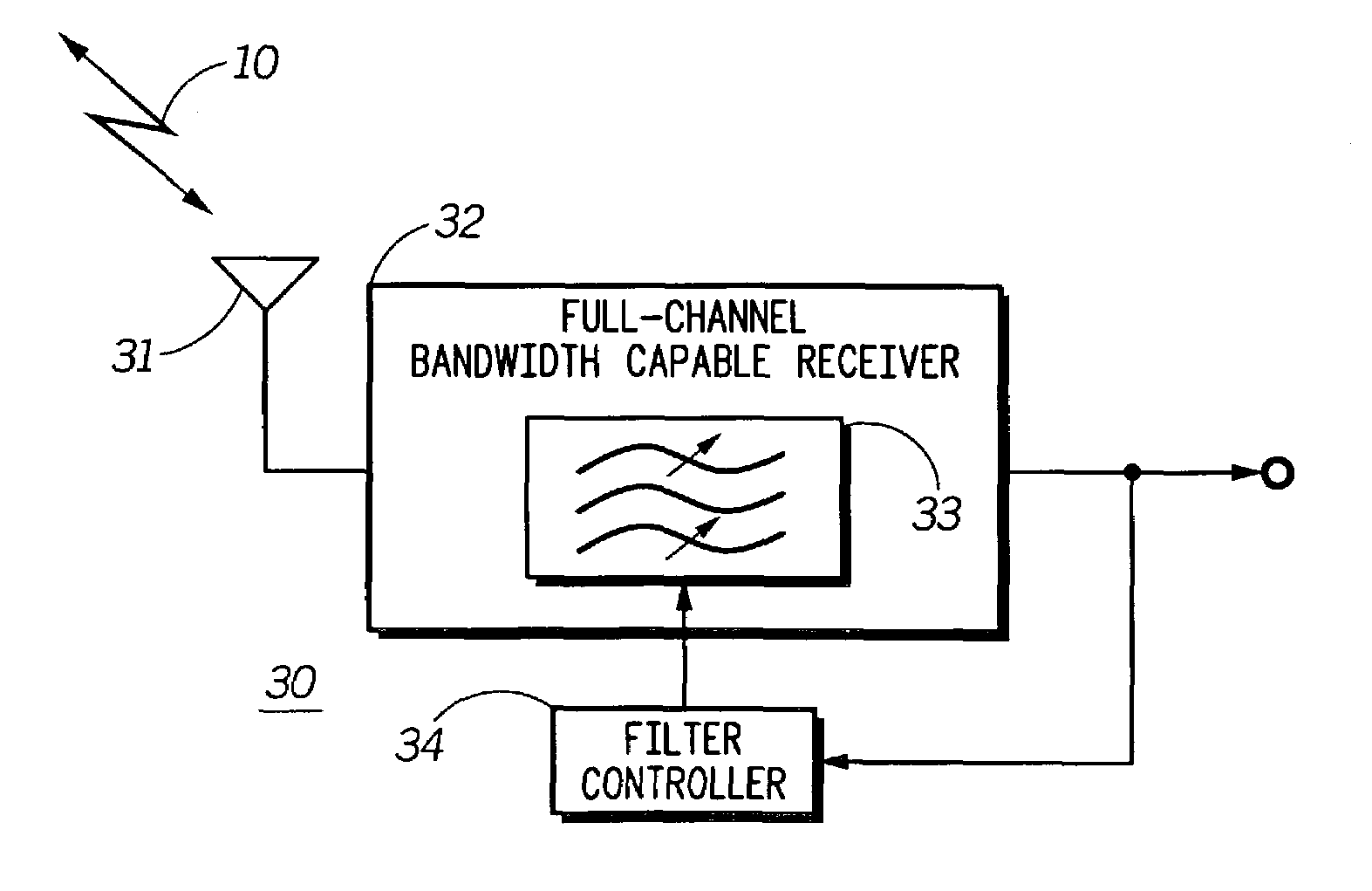
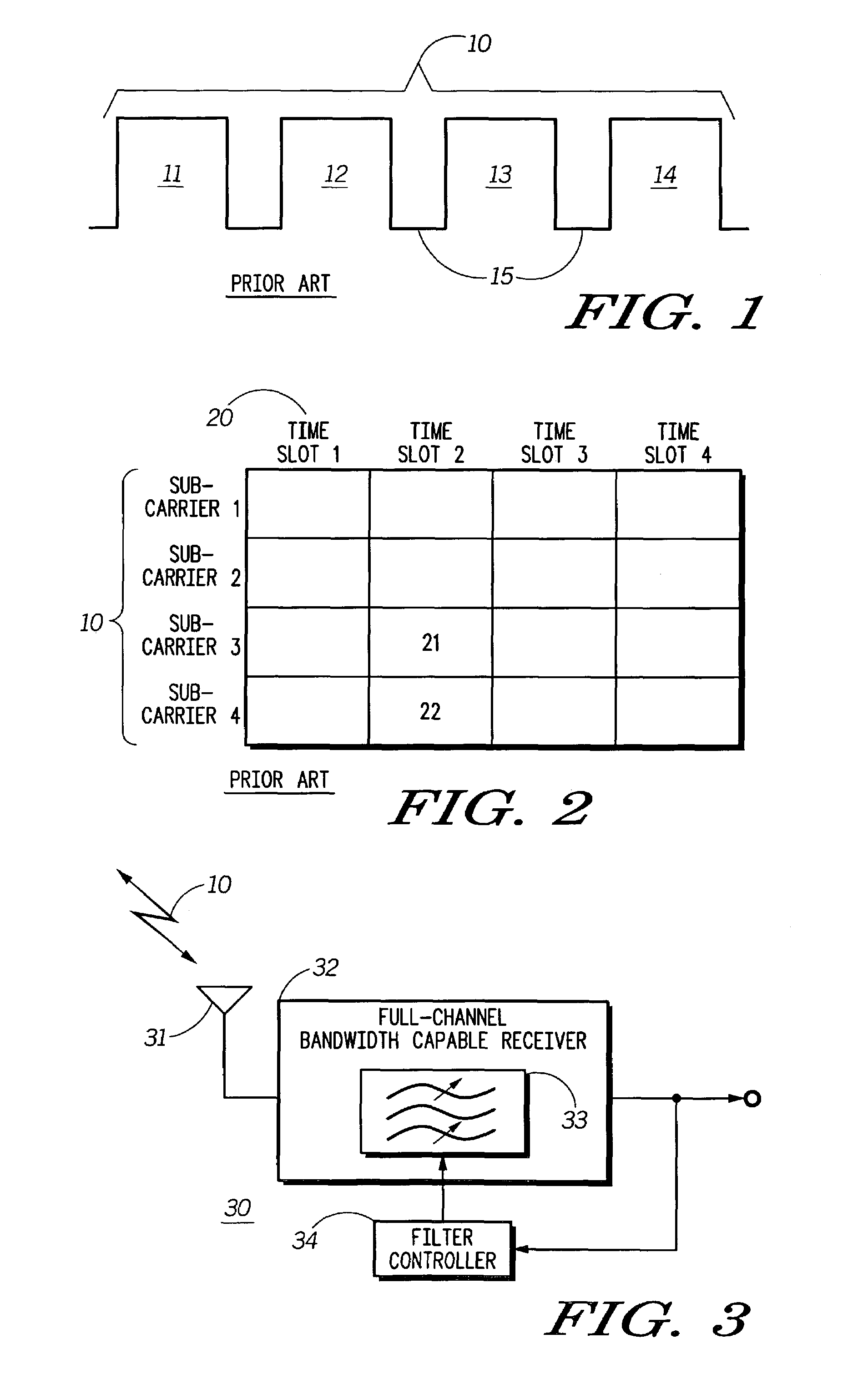
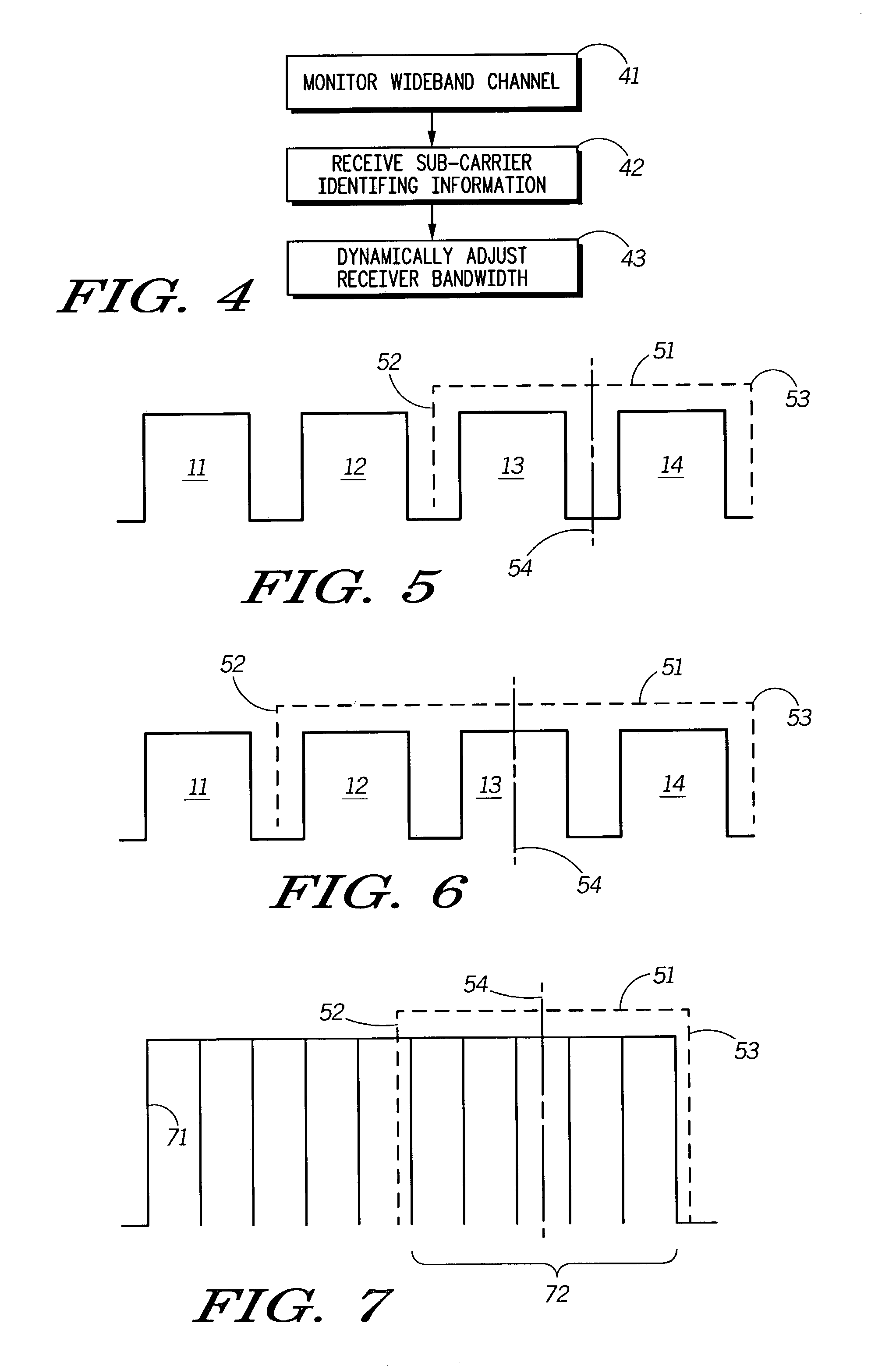
ActiveUS7263365B2Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionResource allocationCenter frequency
Receiver bandwidth is dynamically altered during operation (with respect to, for example, filter bandwidth and / or filter center frequency) as a function, at least in part, of communication resource allocation.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com